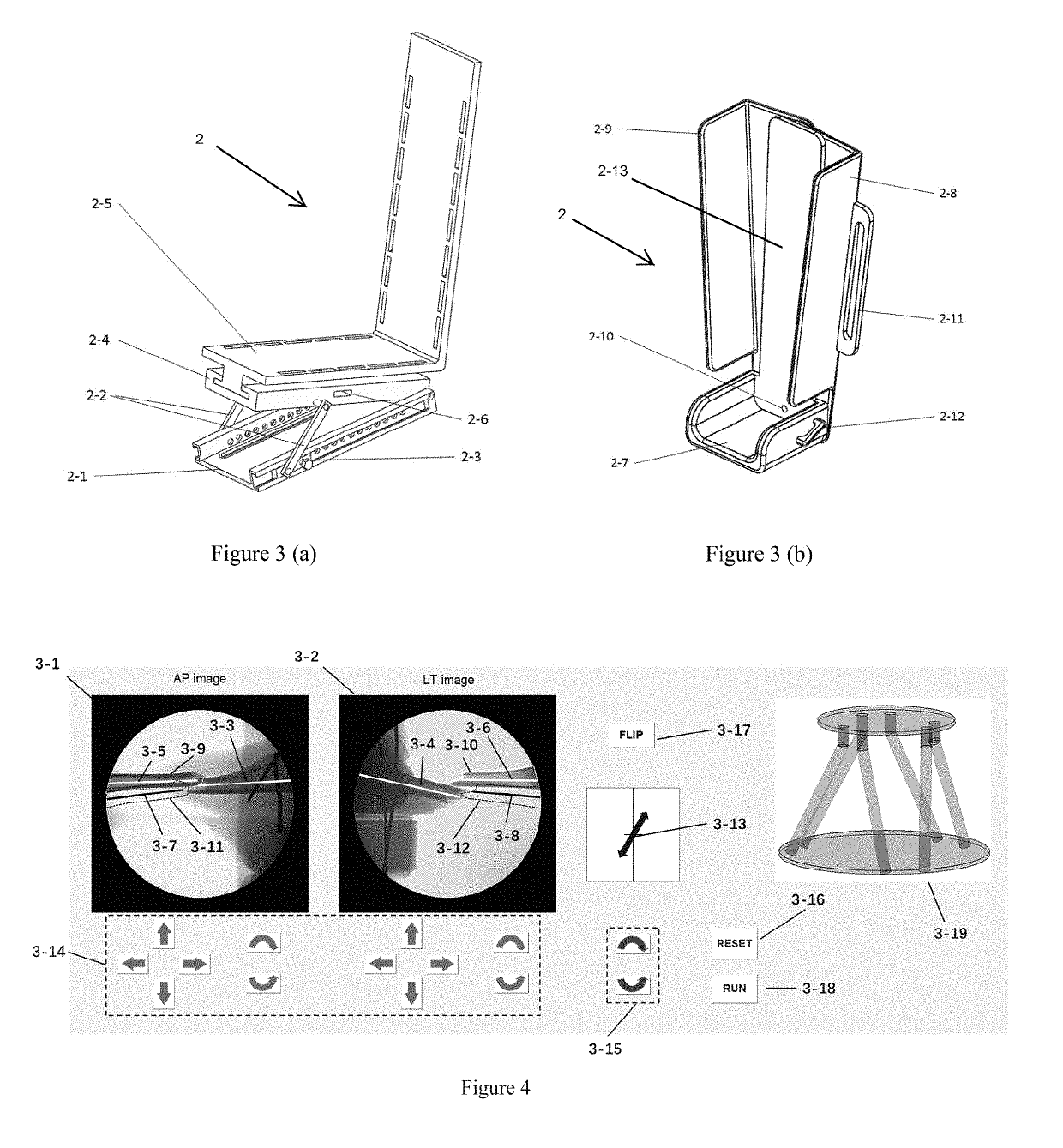
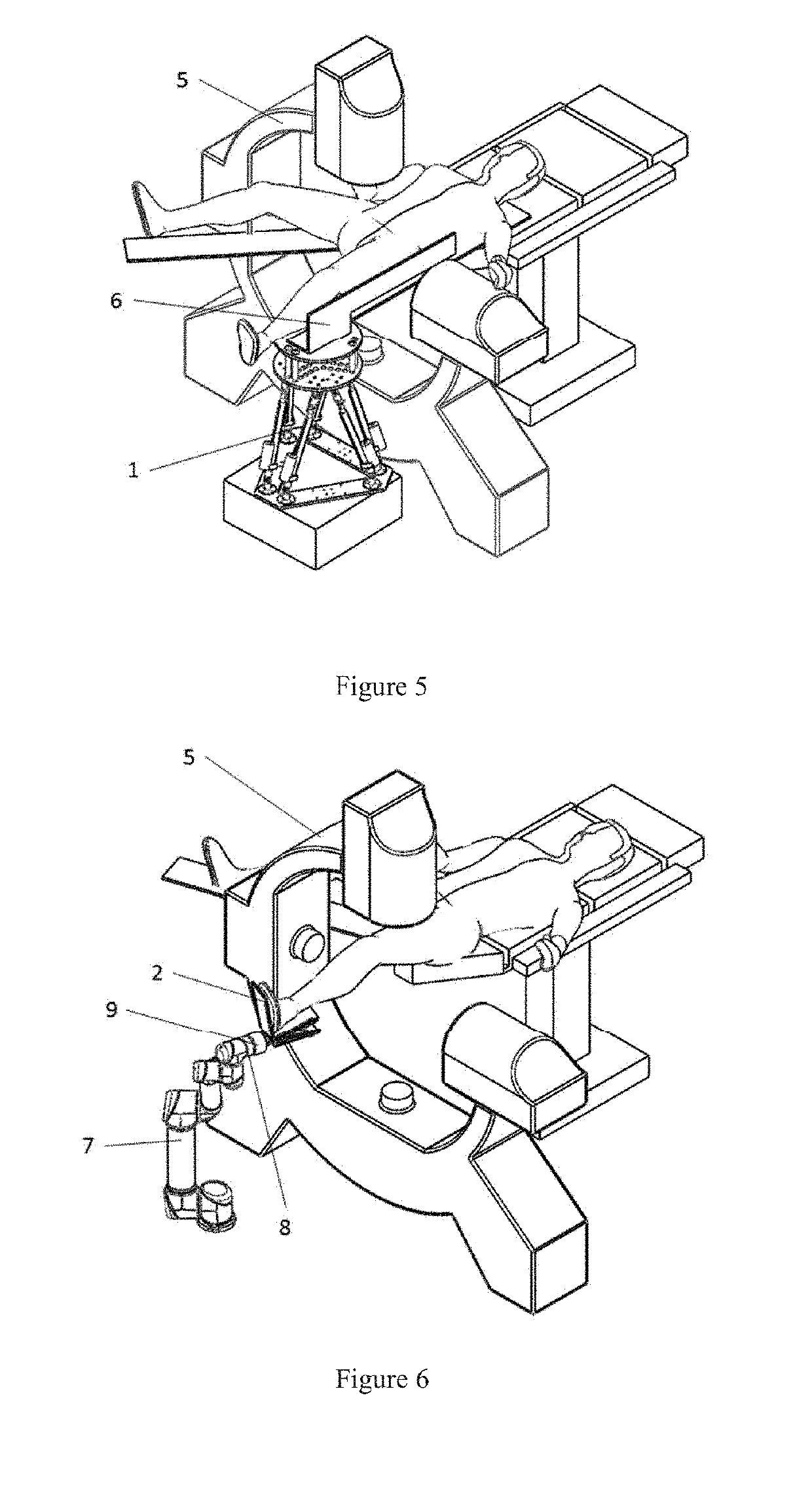
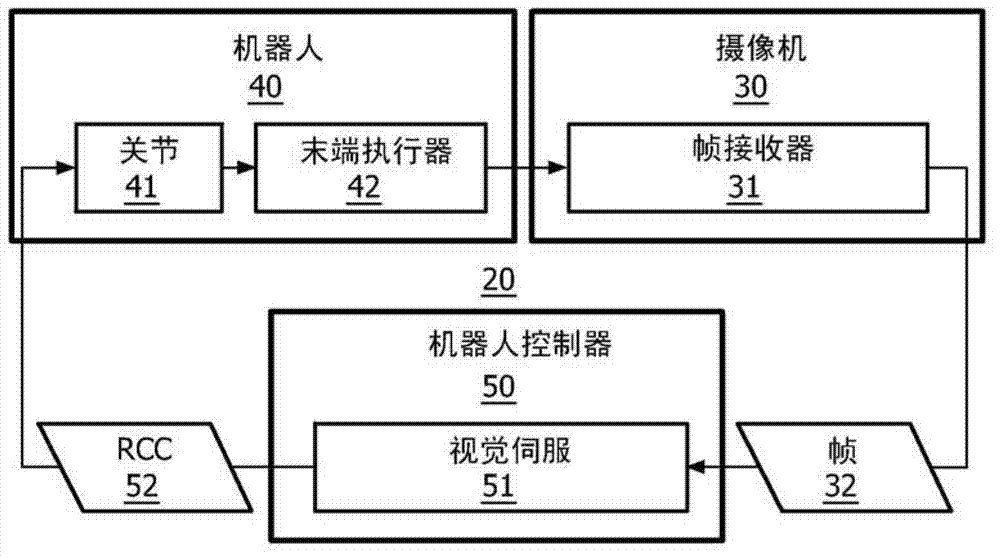
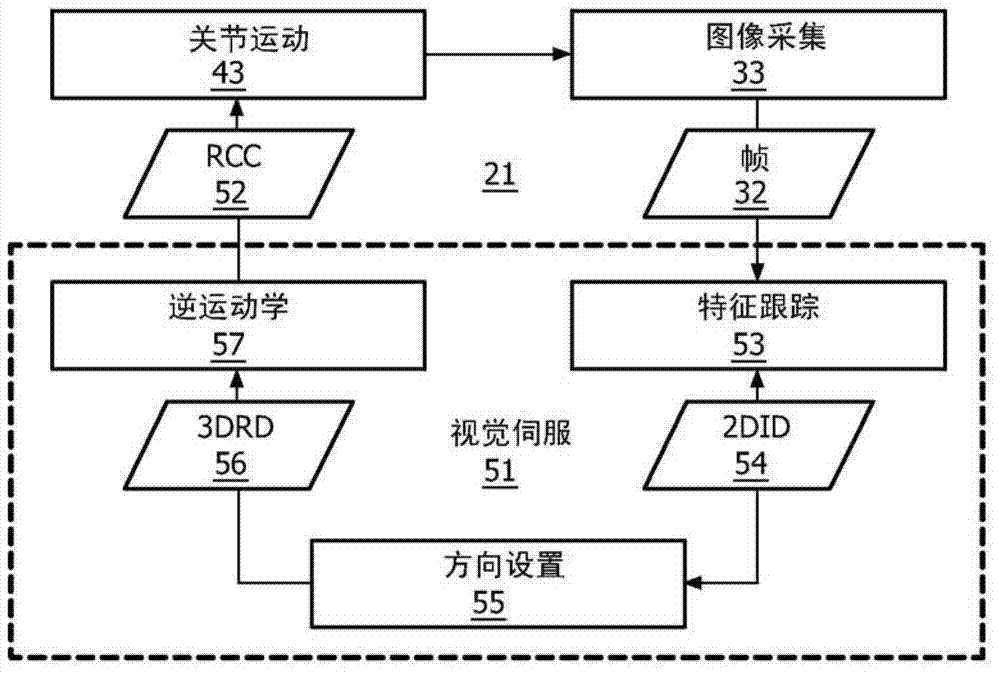
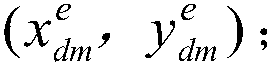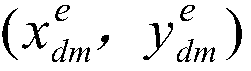Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
234 results about "Visual servoing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
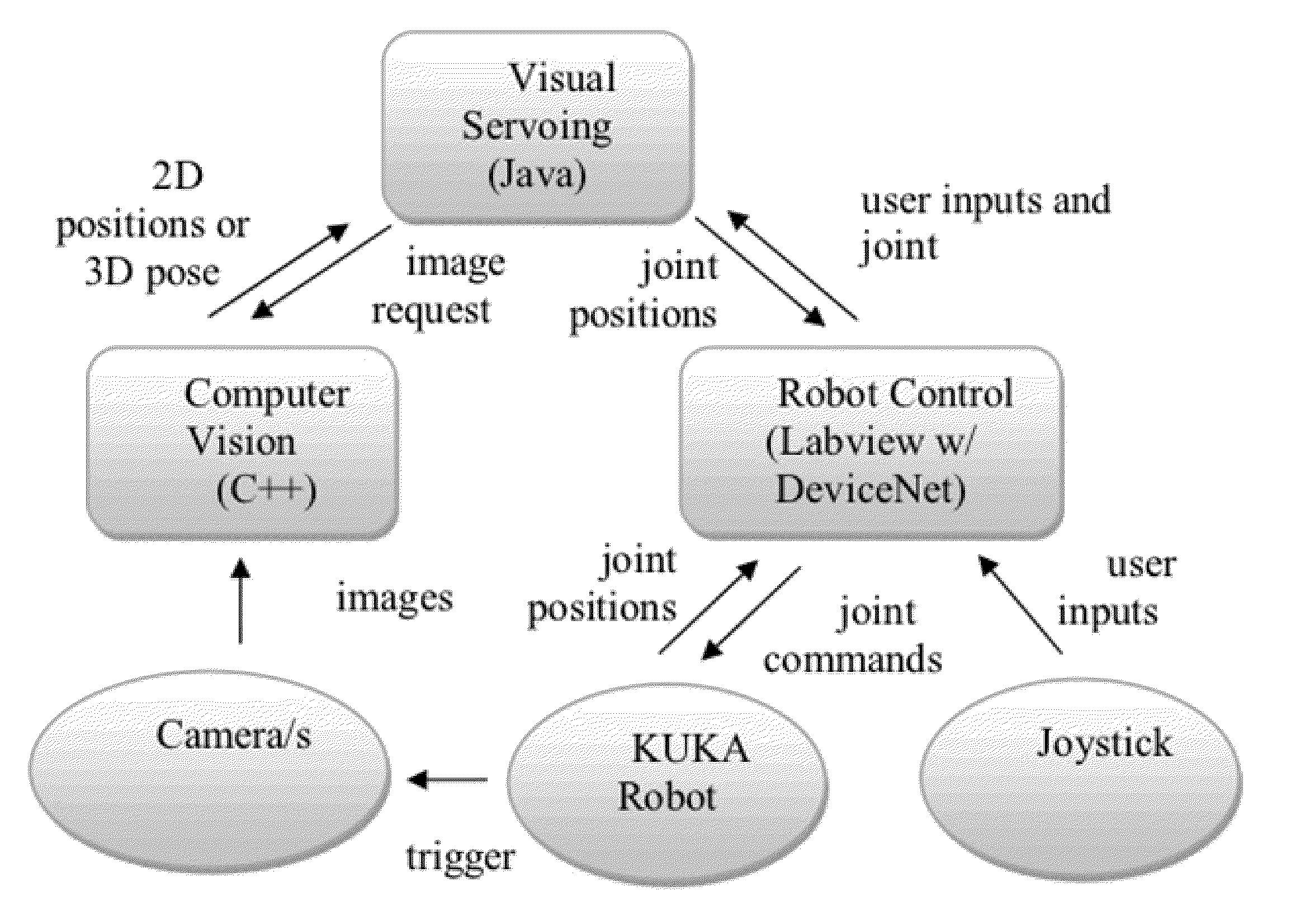
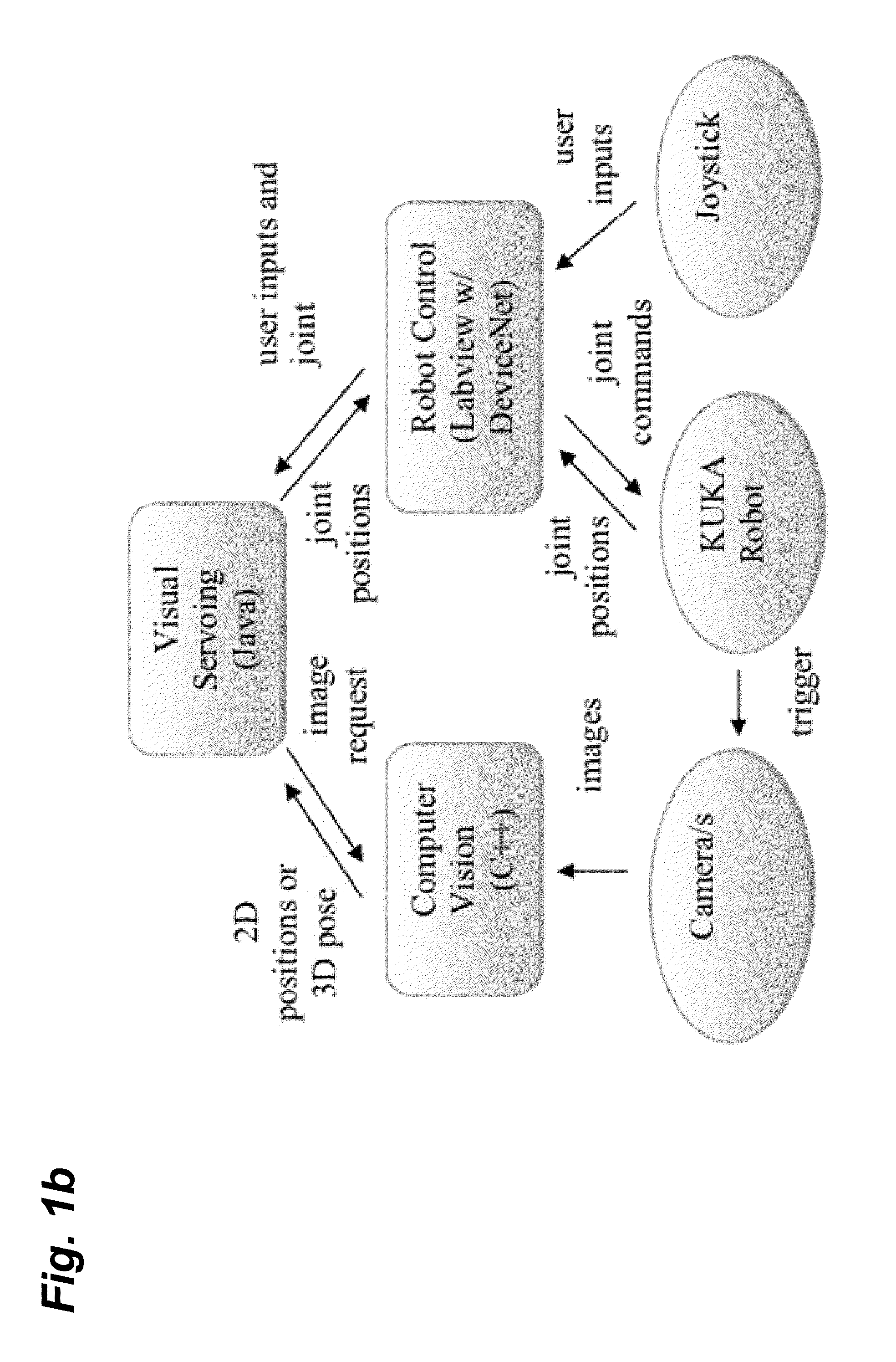
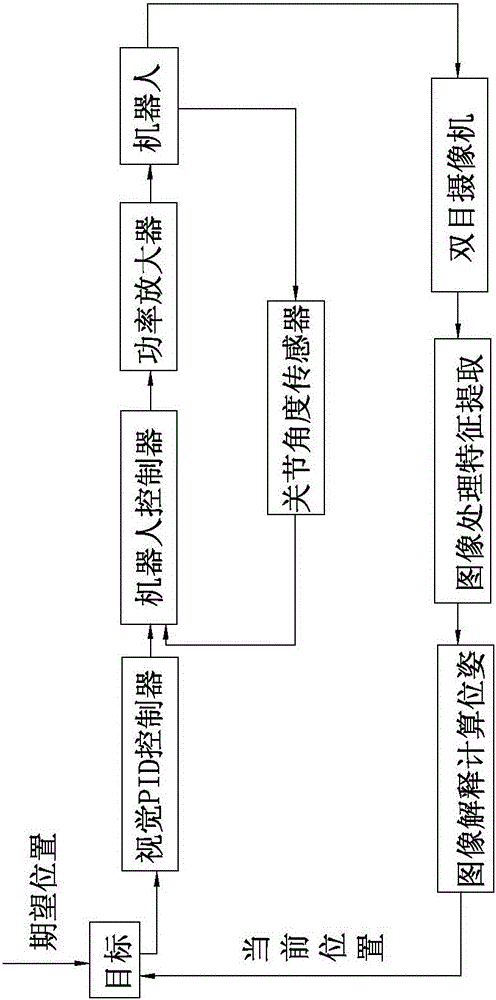
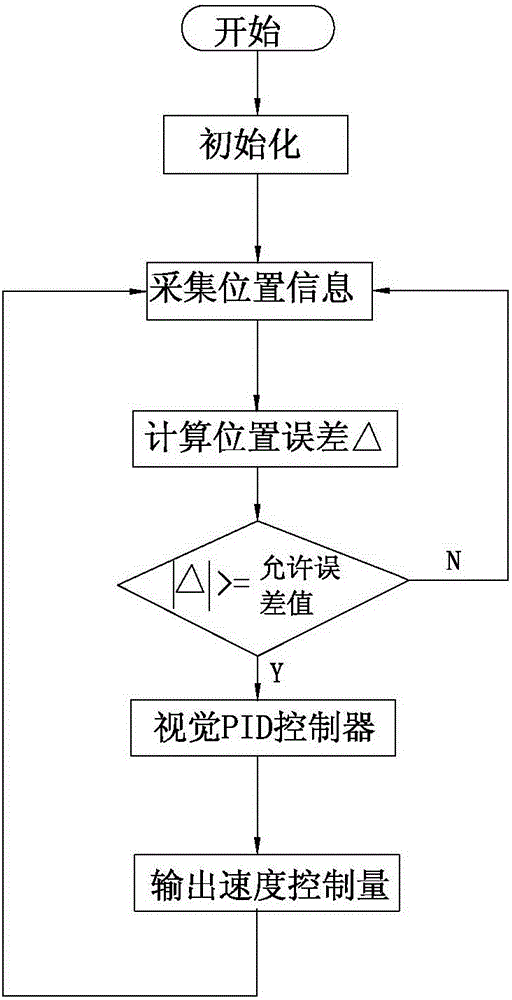
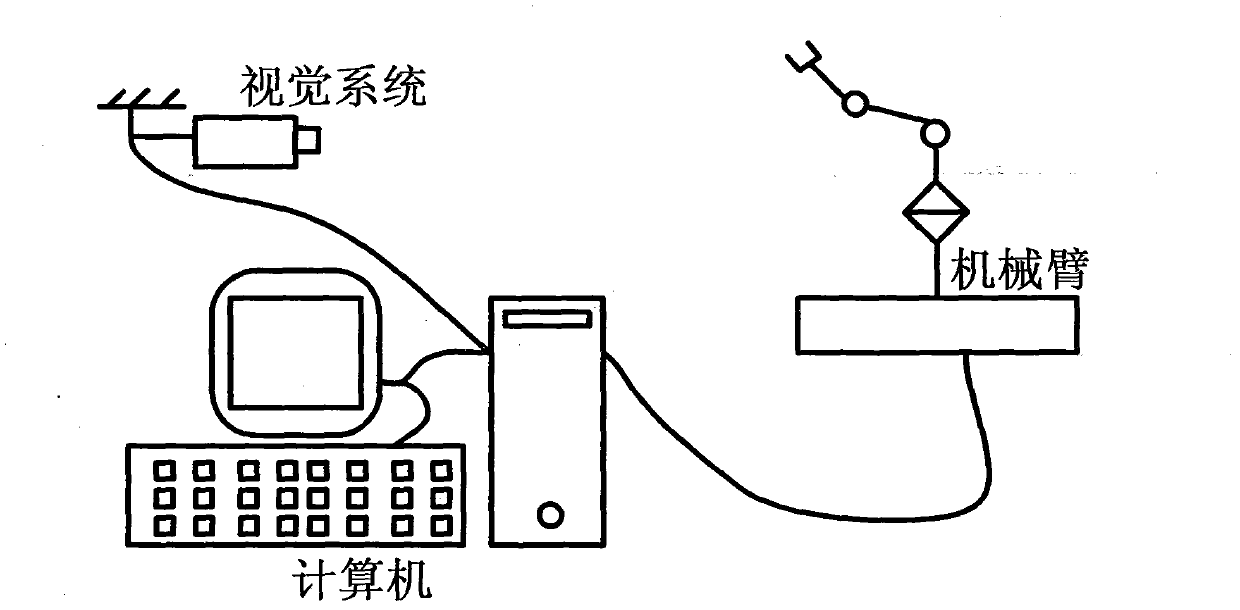
Visual servoing, also known as vision-based robot control and abbreviated VS, is a technique which uses feedback information extracted from a vision sensor (visual feedback) to control the motion of a robot. One of the earliest papers that talks about visual servoing was from the SRI International Labs in 1979.
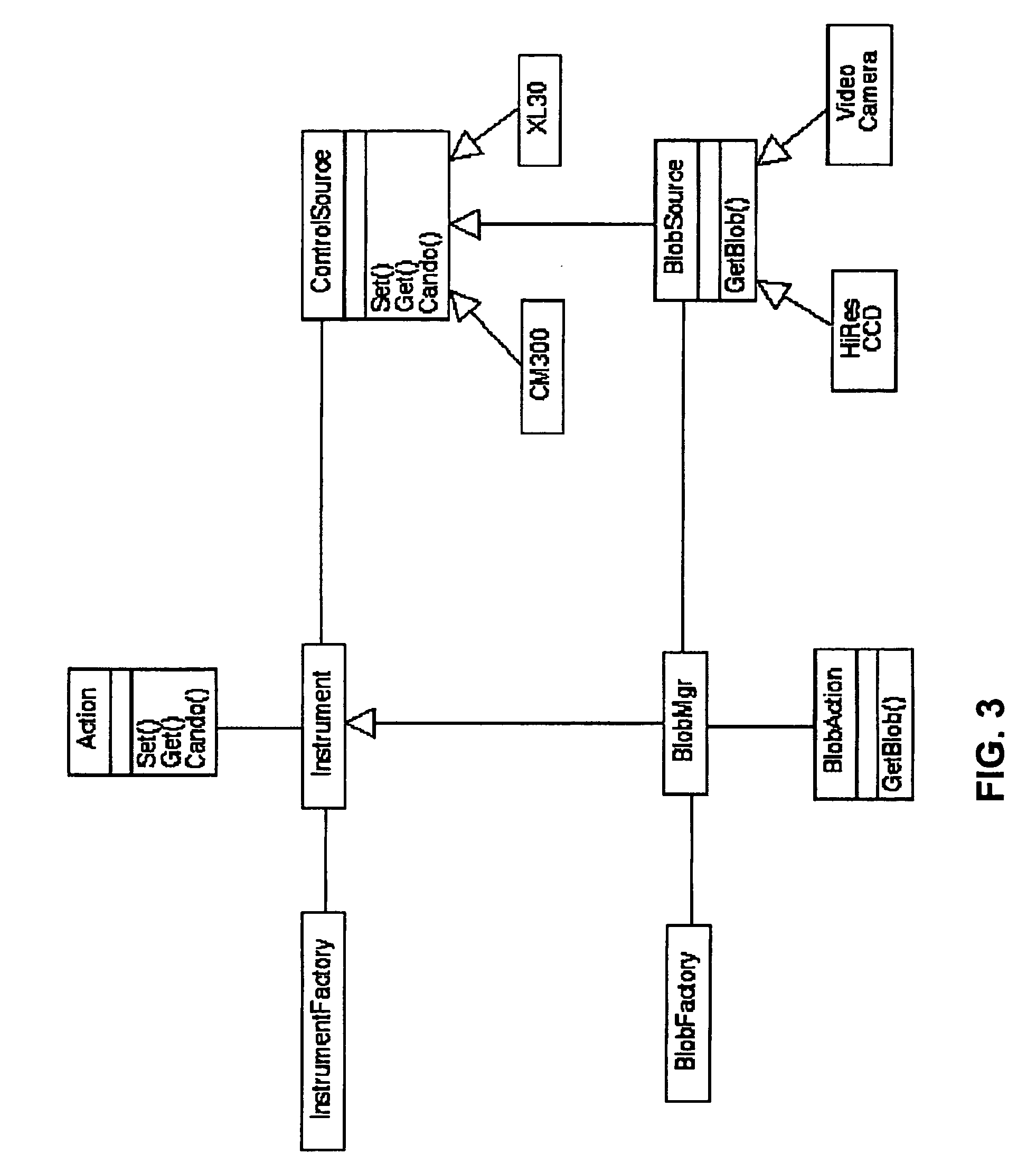
Systems and methods for operating robots using visual servoing
InactiveUS20130041508A1Easy to controlConsistent controlProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorVisual servoingOperating point
A system and method for providing intuitive, visual based remote control is disclosed. The system can comprise one or more cameras disposed on a remote vehicle. A visual servoing algorithm can be used to interpret the images from the one or more cameras to enable the user to provide visual based inputs. The visual servoing algorithm can then translate that commanded motion into the desired motion at the vehicle level. The system can provide correct output regardless of the relative position between the user and the vehicle and does not require any previous knowledge of the target location or vehicle kinematics.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
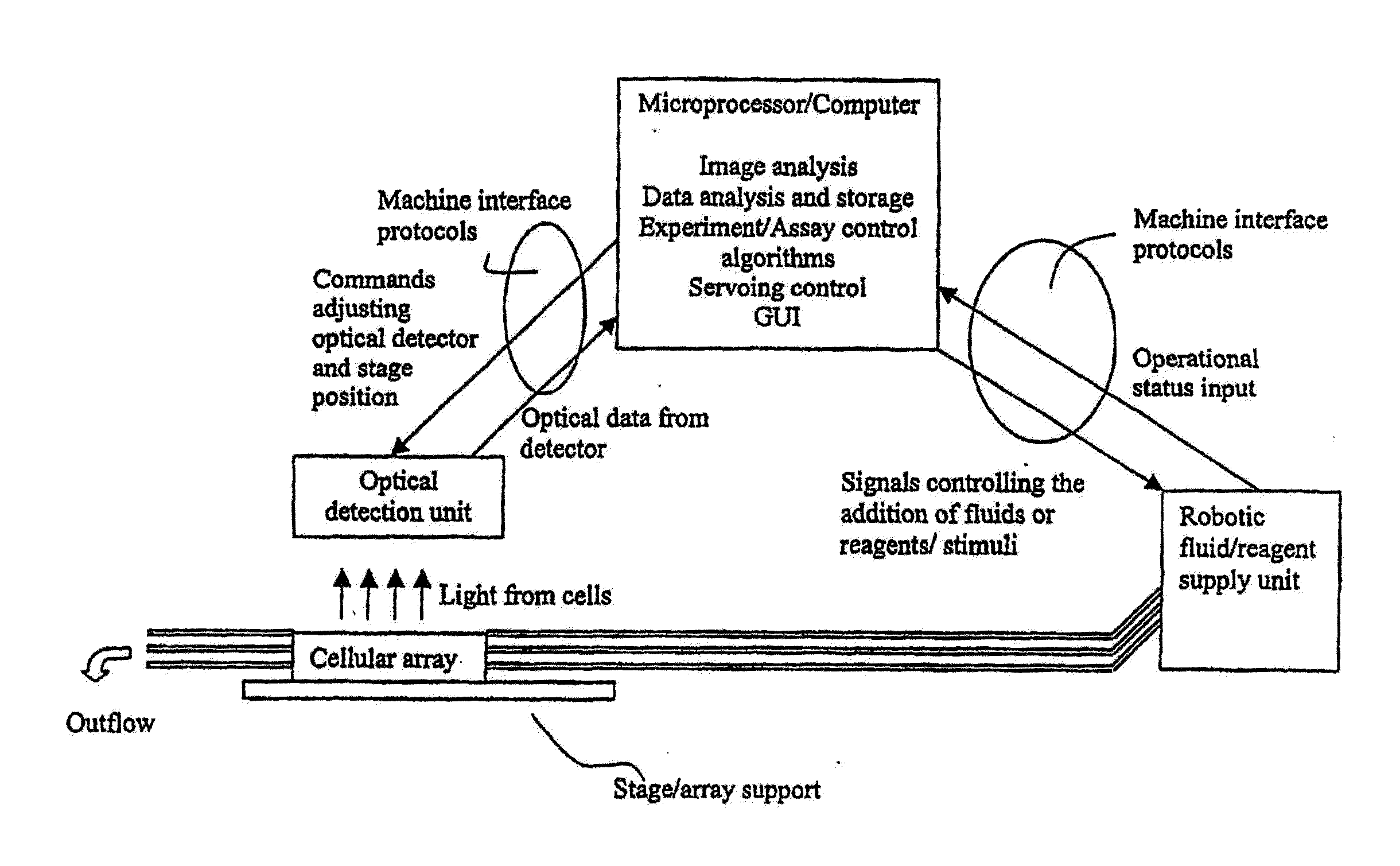
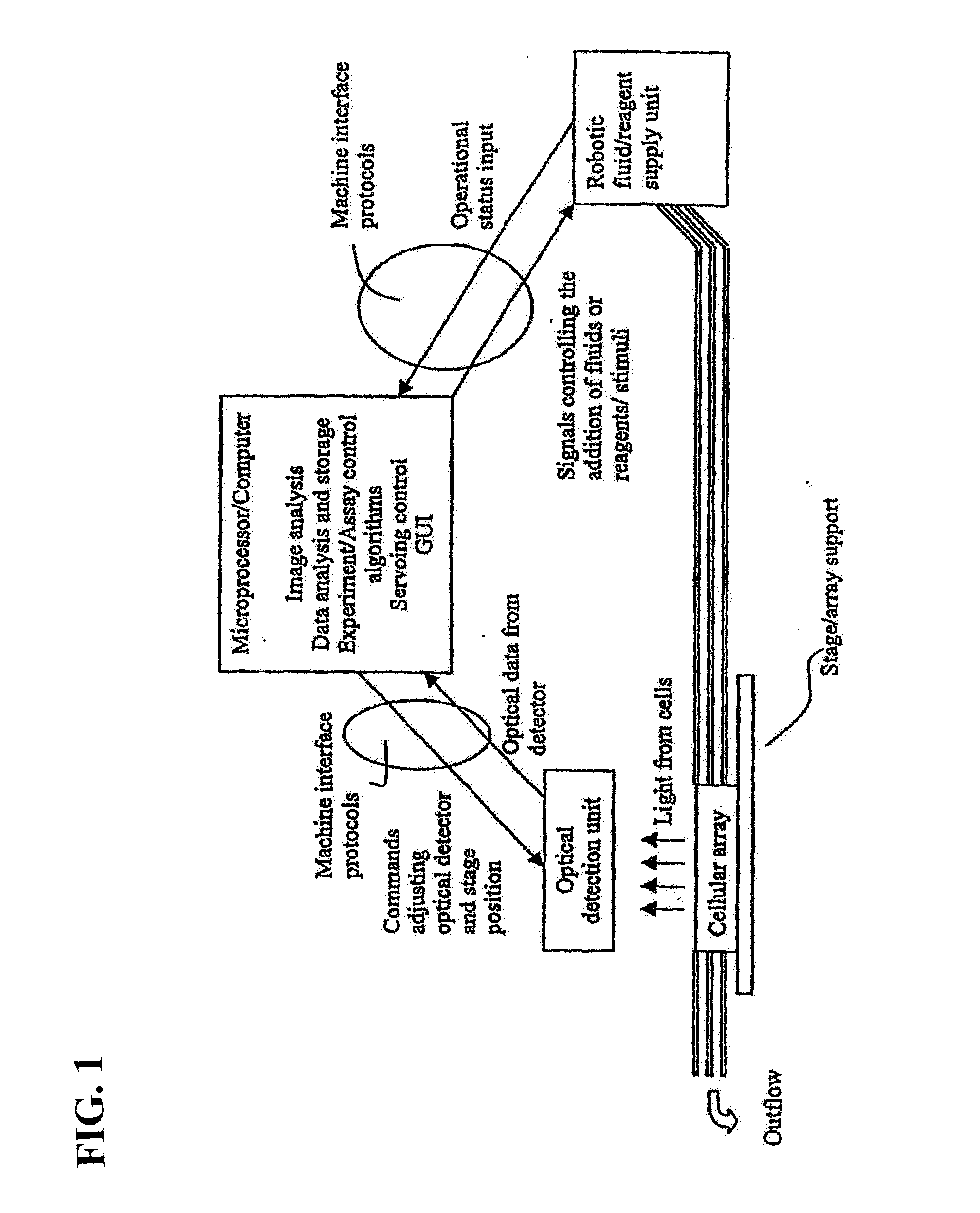
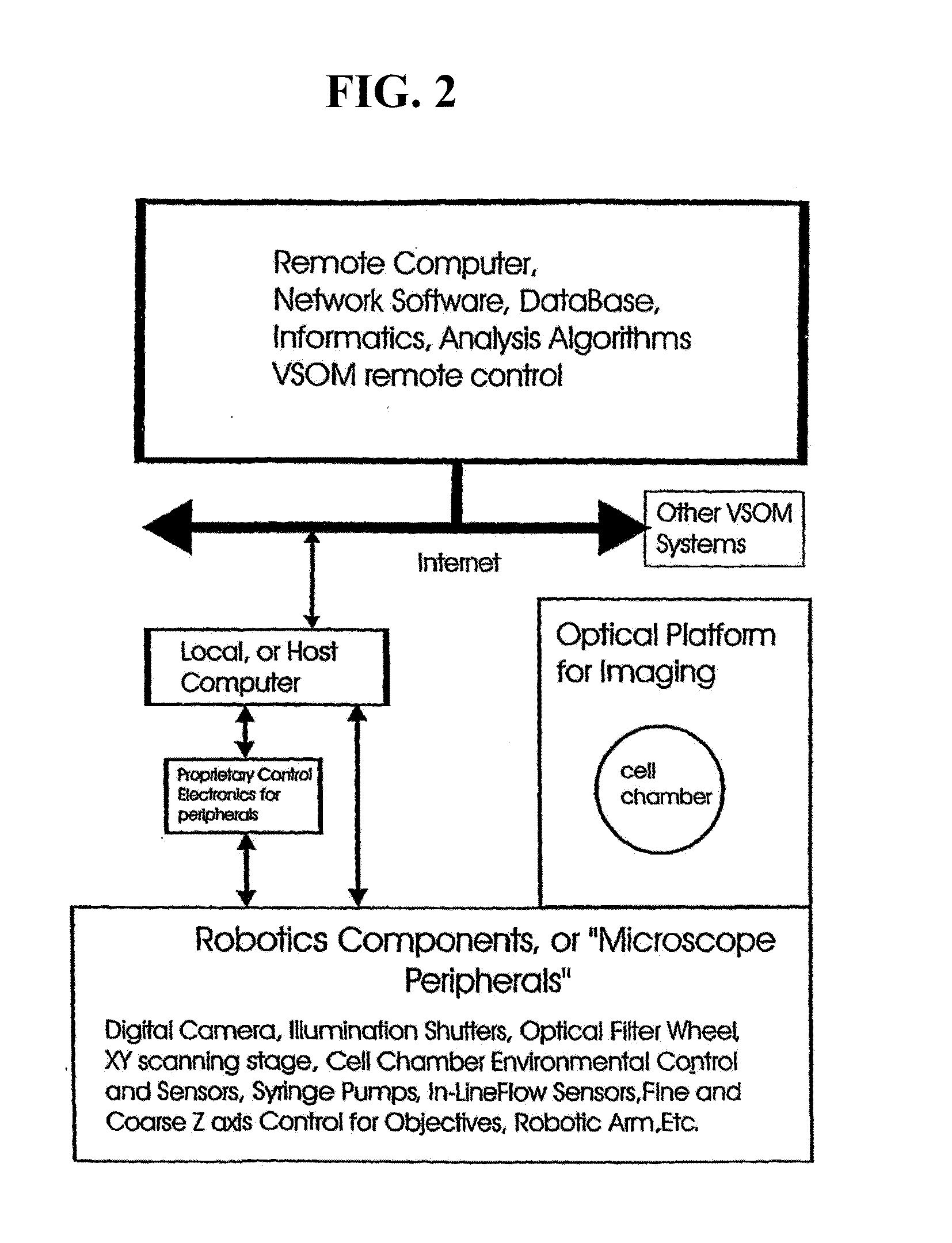
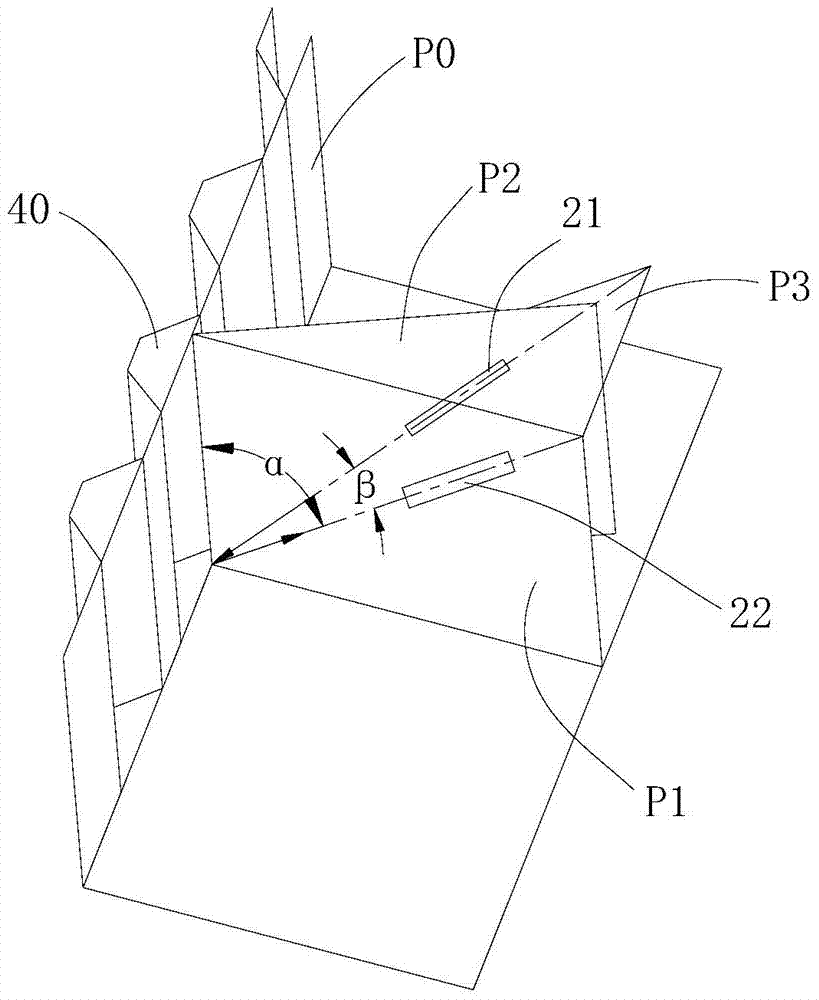
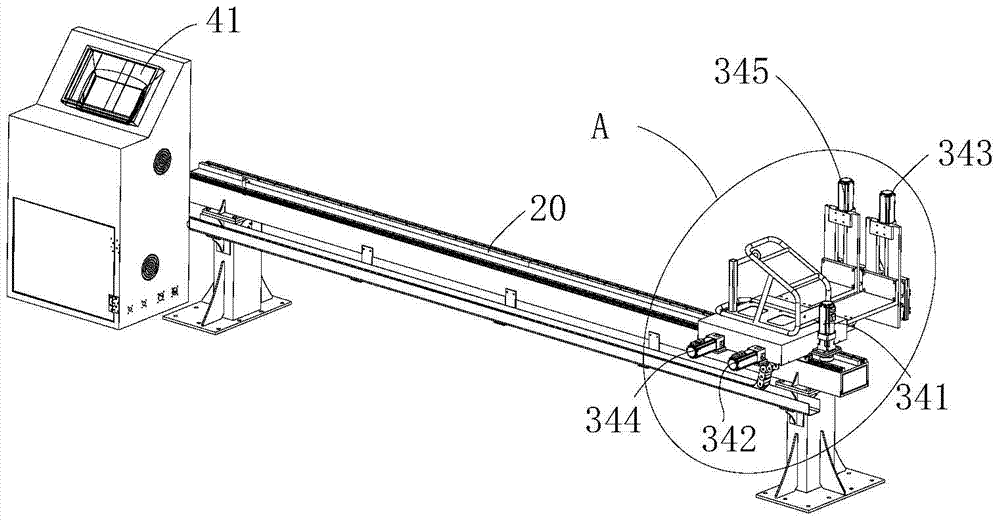
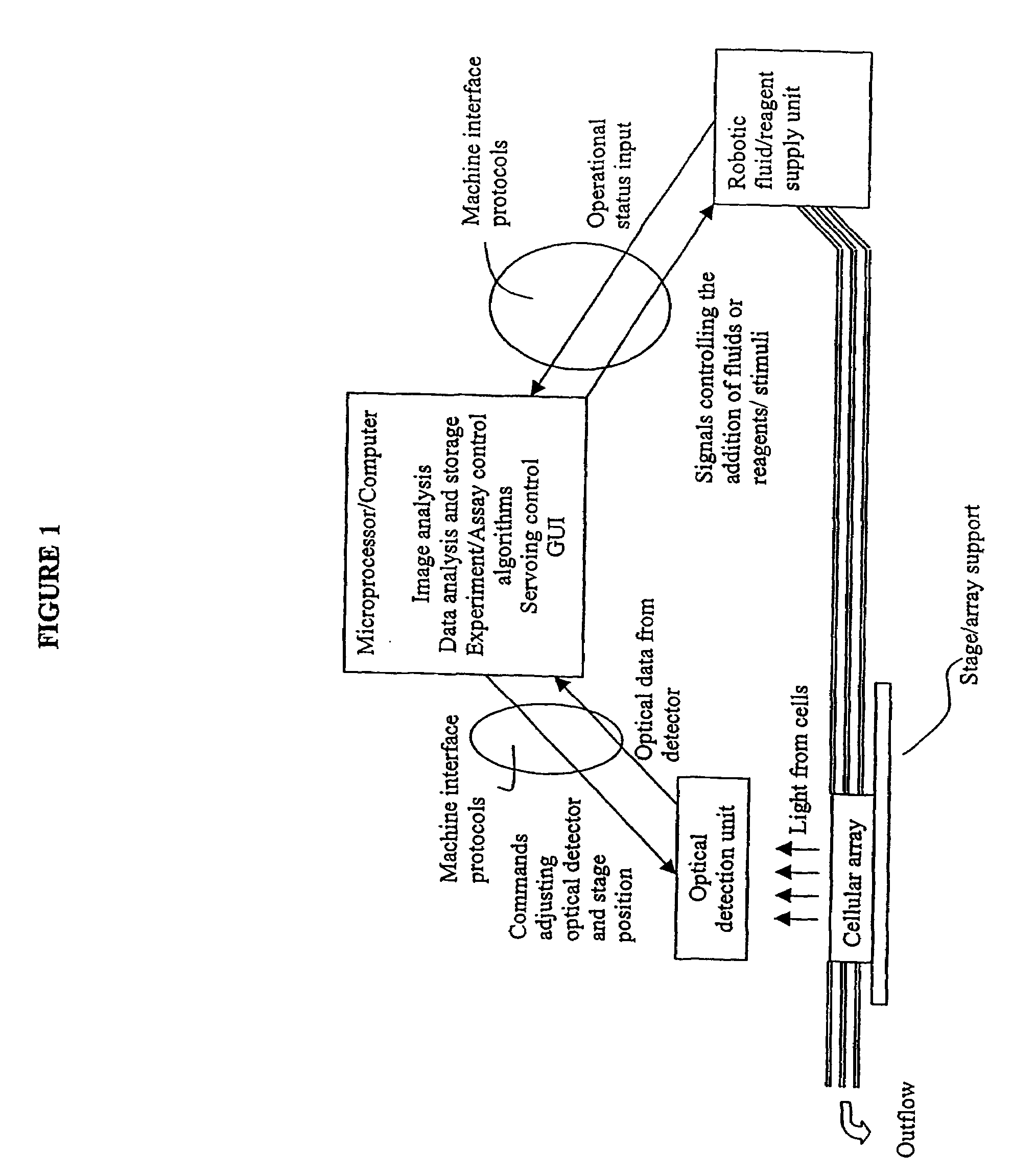
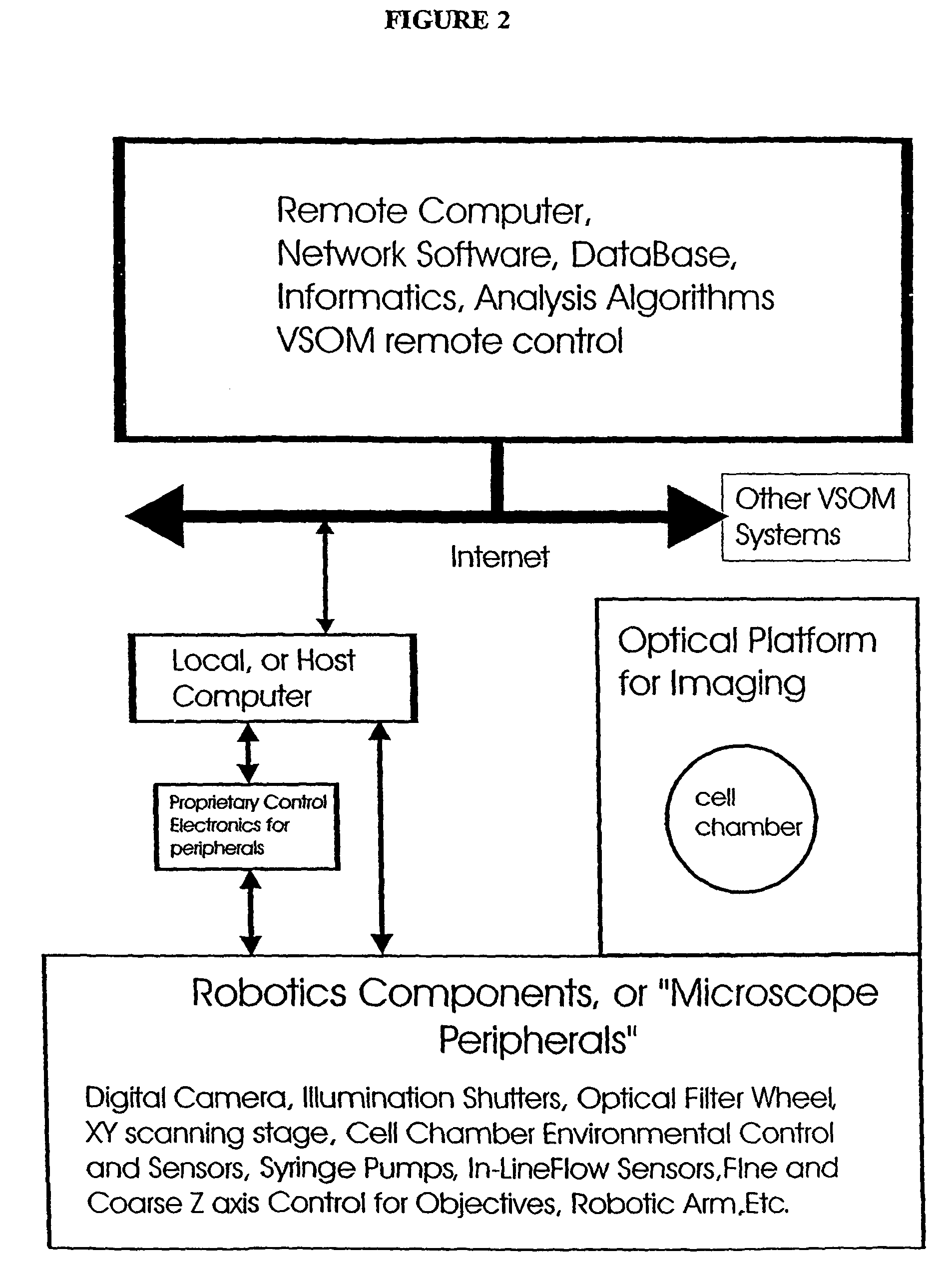
Visual-servoing optical microscopy
InactiveUS20110216953A1Close monitoringOptimize culture conditionsMicrobiological testing/measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionVisual perceptionCell stress
The present invention provides methods and devices for the knowledge-based discovery and optimization of differences between cell types. In particular, the present invention provides visual servoing optical microscopy, as well as analysis methods. The present invention provides means for the close monitoring of hundreds of individual, living cells over time; quantification of dynamic physiological responses in multiple channels; real-time digital image segmentation and analysis; intelligent, repetitive computer-applied cell stress and cell stimulation; and the ability to return to the same field of cells for long-term studies and observation. The present invention further provides means to optimize culture conditions for specific subpopulations of cells.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Robot system with visual servo and detection functions
ActiveCN103406905ARealize functionImprove motion control efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorAutomatic controlControl signal
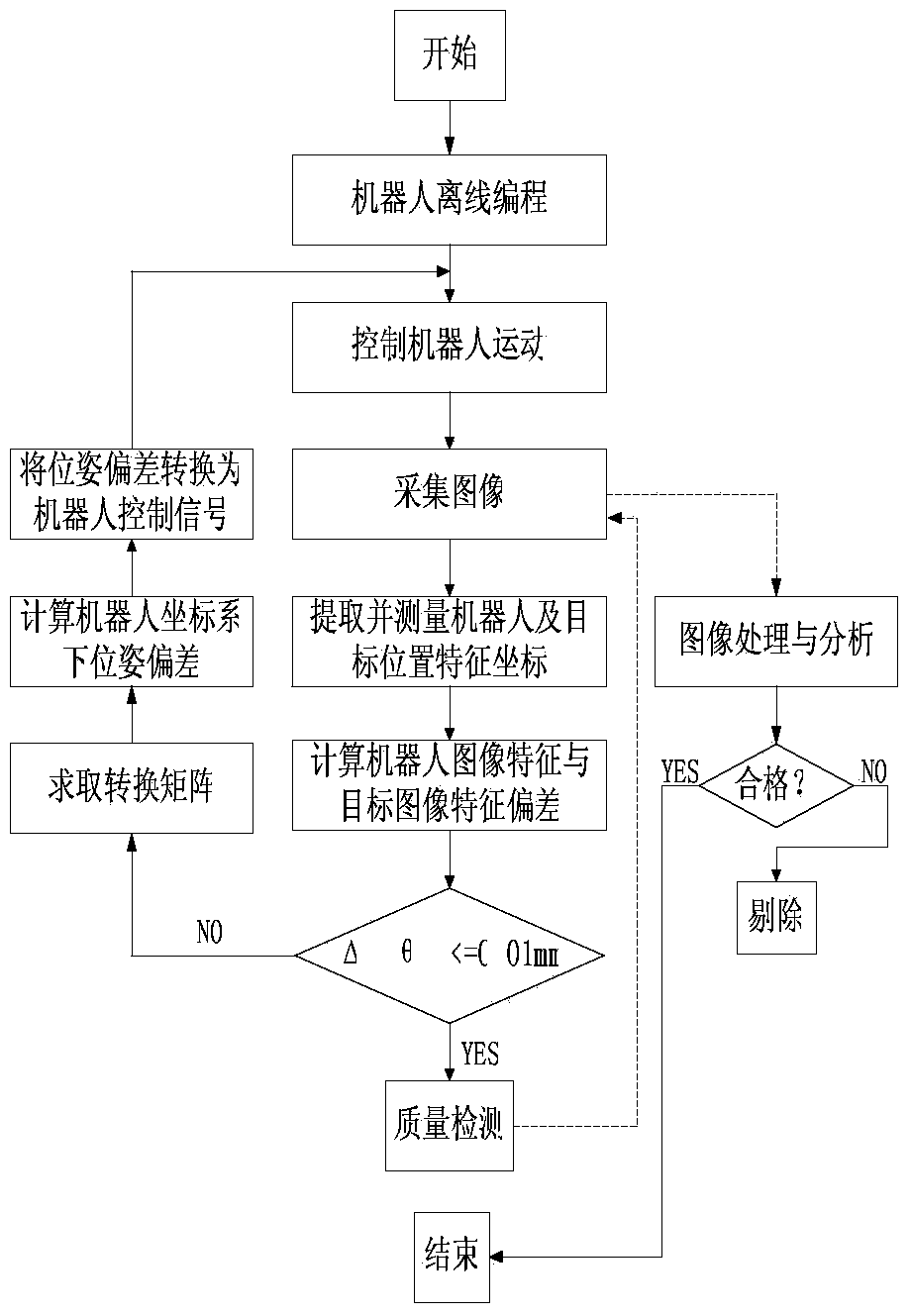
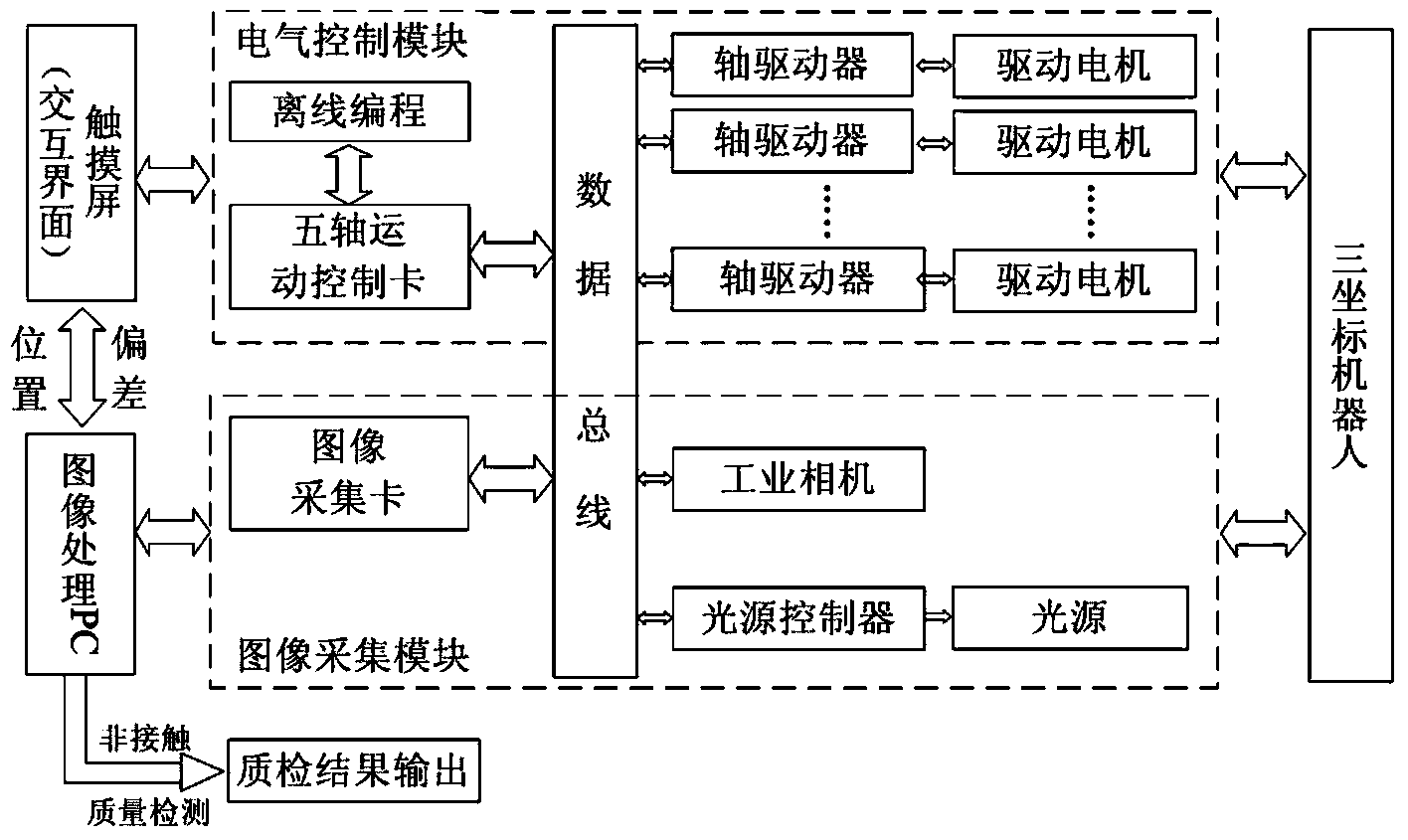
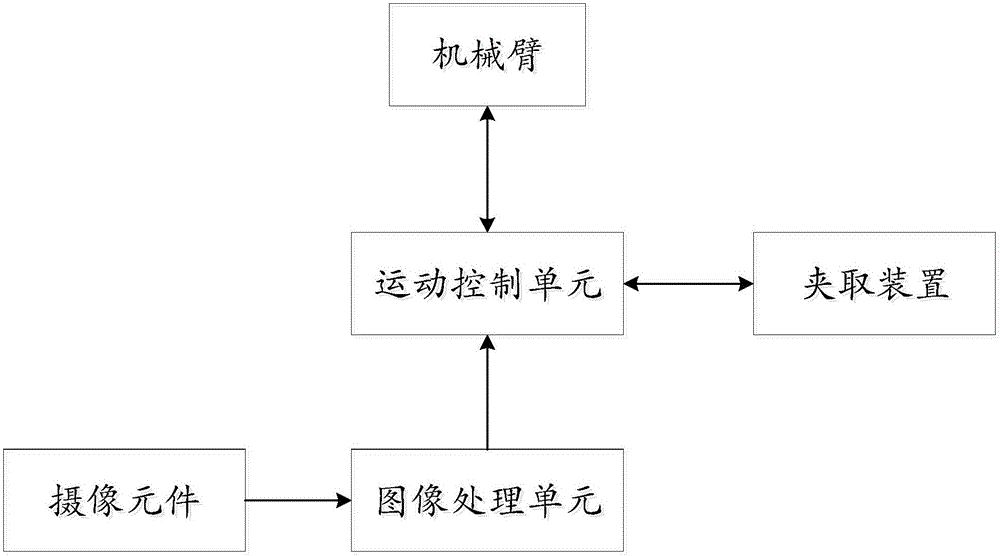
The invention discloses a robot system with visual servo and detection functions. The robot system comprises a robot, an image acquisition and image processing unit, a robot vision servo control unit and a communication network unit for connecting all the modules, wherein data and signal transmission among all the units is realized by the communication network unit; the robot vision servo control unit sends or receives a control signal of the robot by the communication network unit, rapidly understands the surrounding and constructs a vision feedback control model at the same time, so as to realize vision identification and movement control functions of the robot. The movement control of the robot adopts a method of combining offline programming with robot vision servo control to carry out automatic control on the robot and a tail end executer, so that the movement control efficiency of the robot and the repeated positioning precision and flexibility of the robot are improved; the robot system has higher intelligence. Robot control has a non-contact quality detection function based on robot vision; the robot system is simple in structure and convenient to operate.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
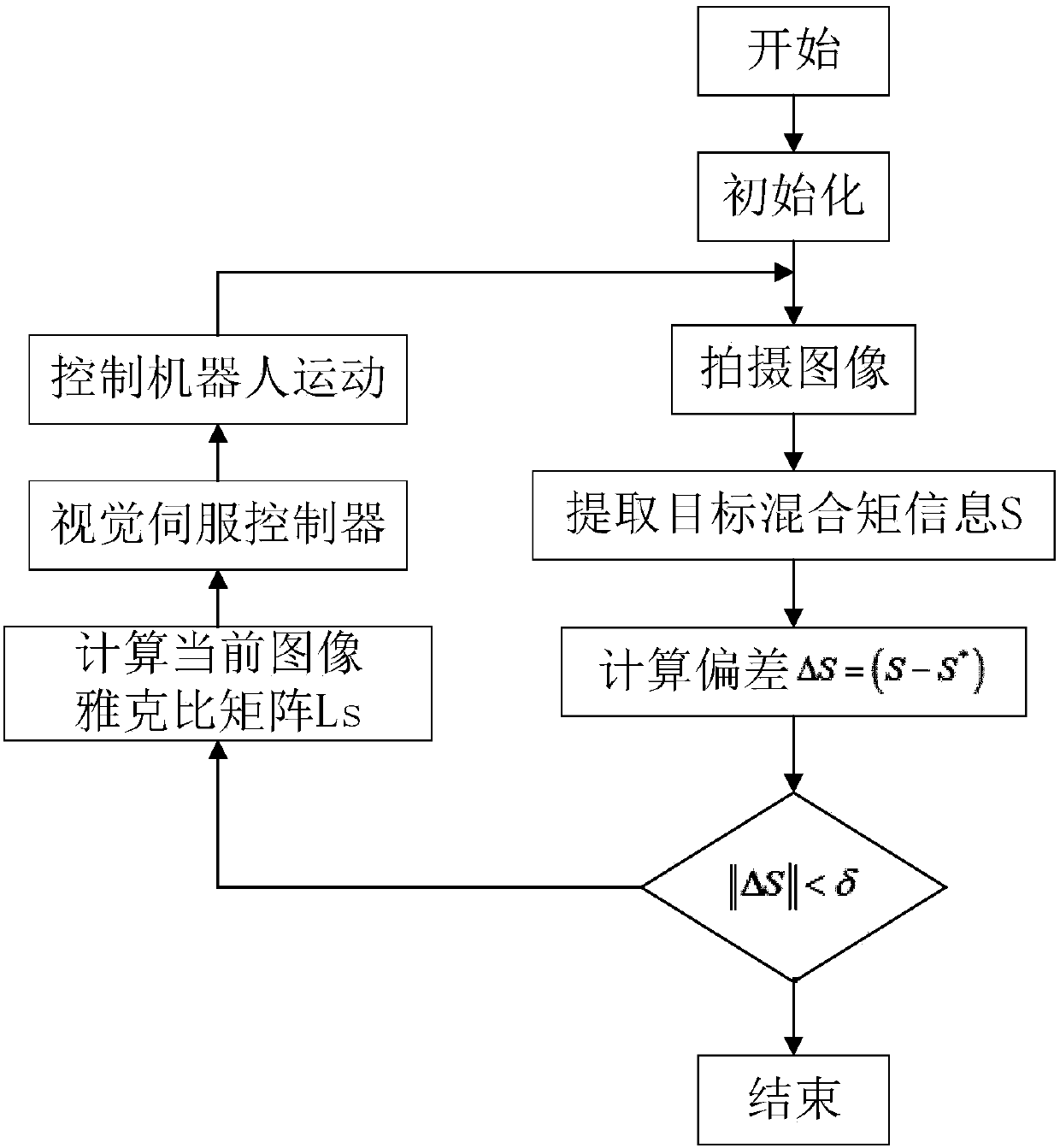
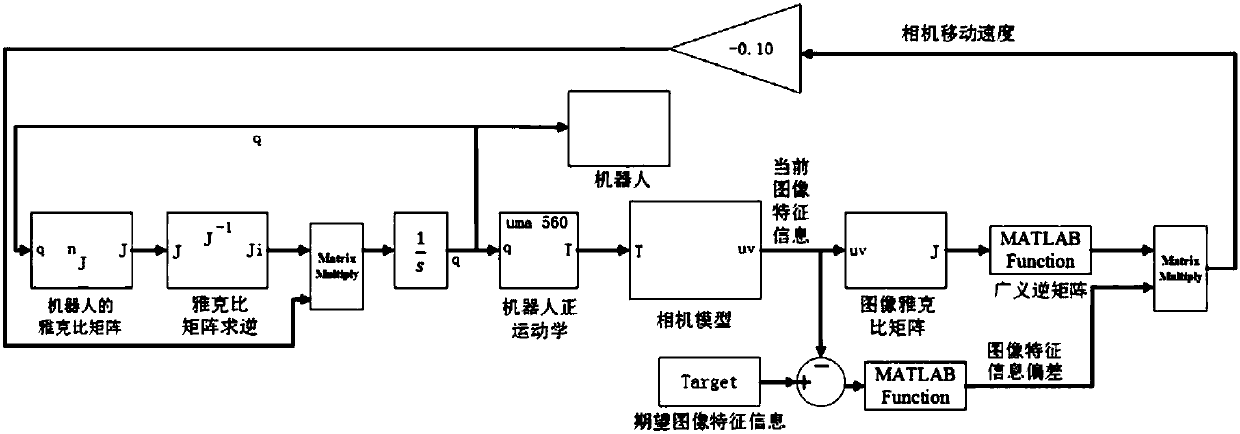
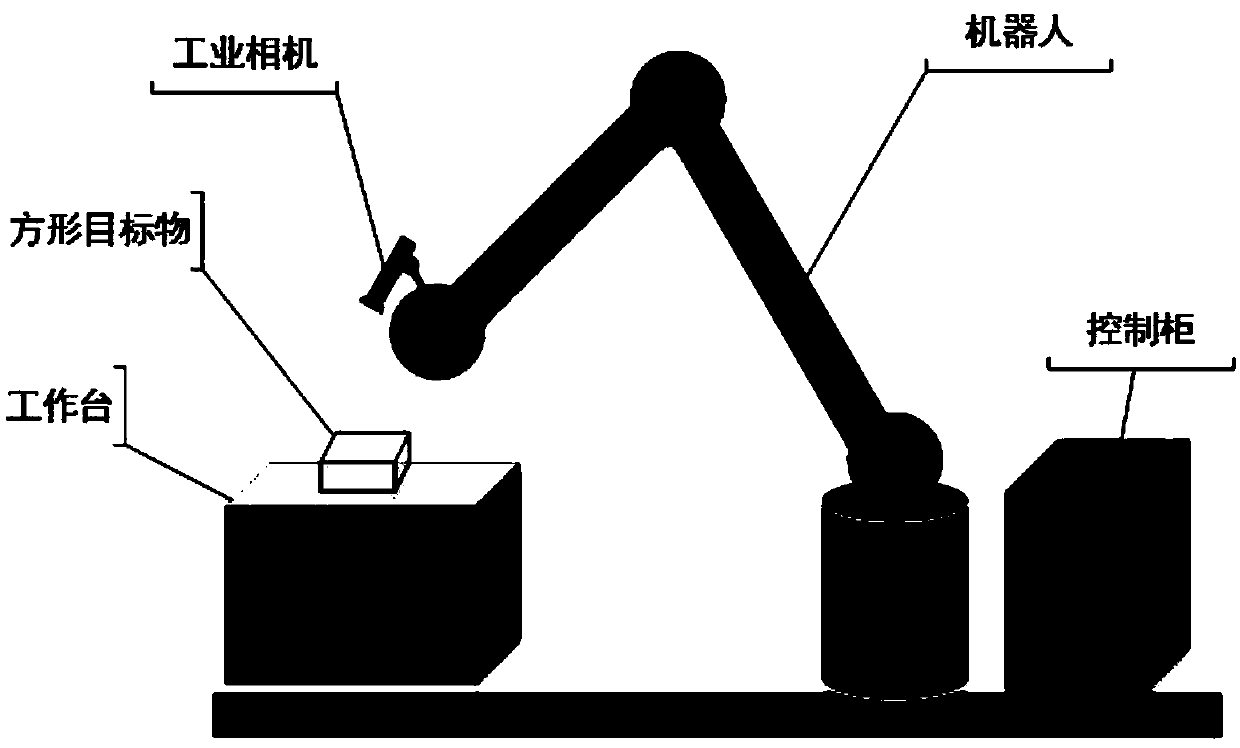
Robot vision servo control method based on image mixing moment
ActiveCN107901041AImprove work efficiencyAdaptableProgramme-controlled manipulatorVisual perceptionWork space
The invention discloses a robot vision servo control method based on the image mixing moment. Firstly, construction of mixing moment features in one-to-one correspondence with space attitudes after target object imaging under the robot expected pose is given; and then a target object image is obtained under any attitude, the current mixing moment feature information value is calculated, the deviation of the mixing moment feature value is calculated according to information of an expected image and information of the current image, if the deviation is smaller than the preset threshold value, itis shown that the robot achieves the expected pose, if the deviation is not smaller than the threshold value, an image jacobian matrix relevant to the mixing moment features is deducted, a vision servo robot is used so that the robot can move towards the expected pose till the feather deviation is smaller than the preset threshold value, and the control process is over. By means of the robot vision servo control method, the image field mixing moment feature corresponding to the space movement track of the robot is introduced in to serve as the control input, vision servo control of a eye-in-hand robot system under the working space model unknown circumstance is completed, and the method can be widely applied to robot intelligent control based on machine vision.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
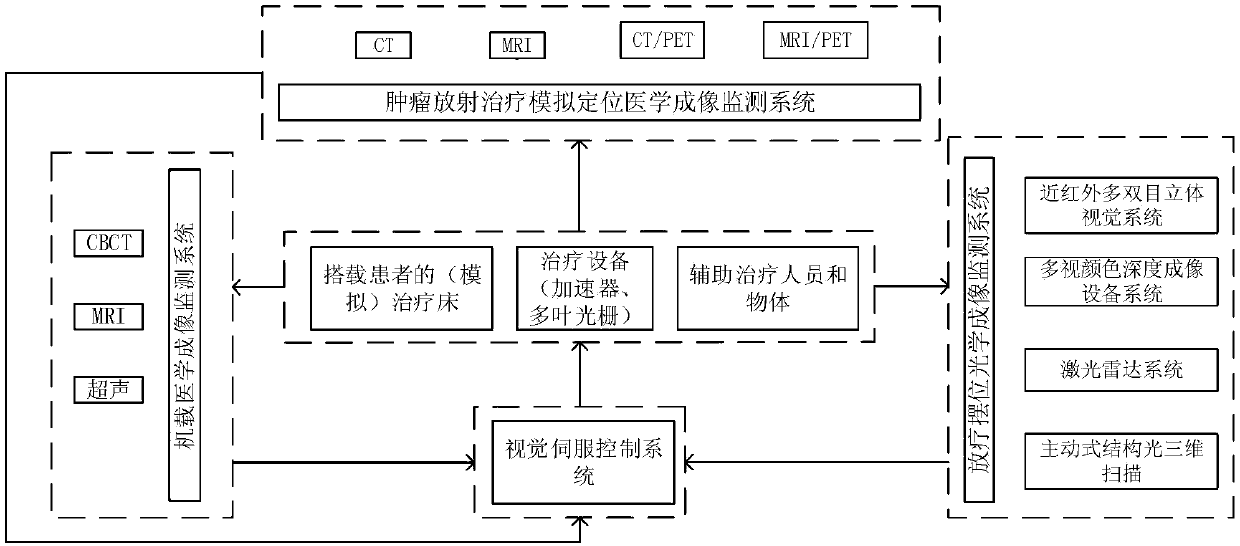
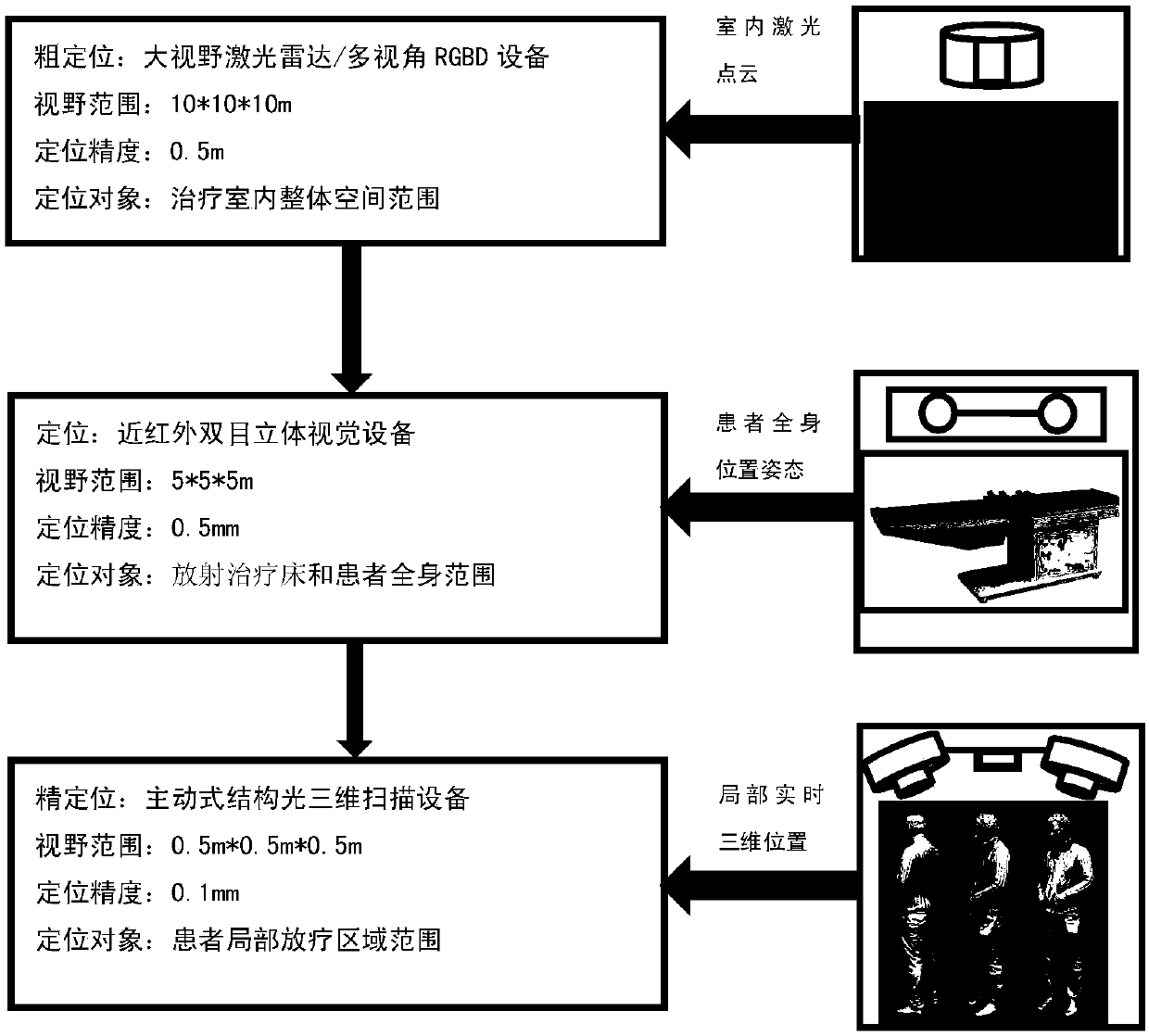
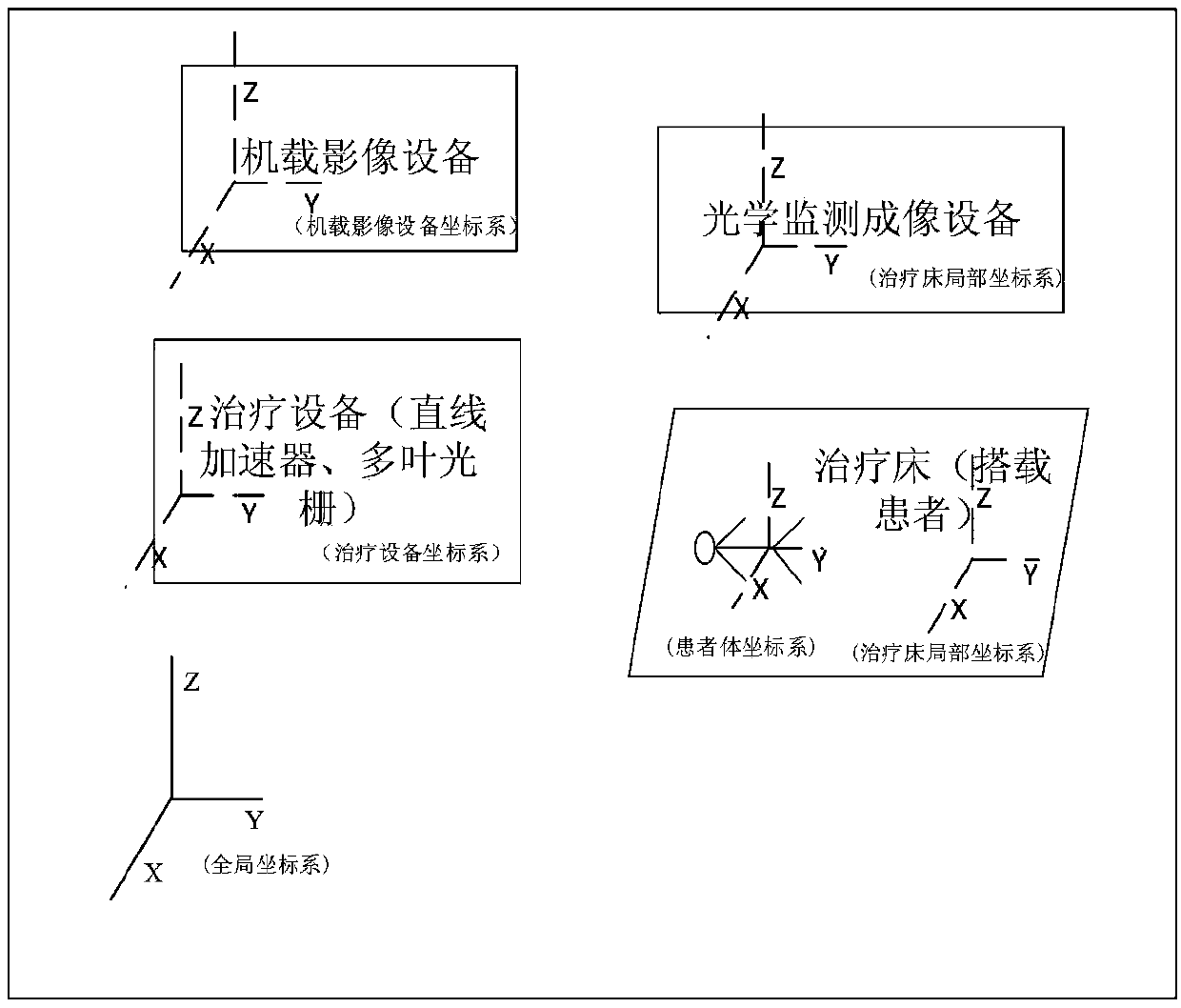
Intelligent control method of visual monitoring and visual servo of tumor radiation therapy
InactiveCN107358607AQuality assuranceAccurate positioningImage enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic Radiology ModalityTherapeutic Devices
The invention relates to an intelligent control method of visual monitoring and visual servo of tumor radiation therapy. The method comprises: (1) according to multi-mode medical images and multi-vision optical images collected by a radiation-oncology-plan-stage simulation and positioning medical imaging system, a radiation-oncology-positioning-stage treatment room internal optical imaging system, and a radiation-oncology-plan-execution-stage onboard medical imaging system and the like, intelligent analysis processing is carried out to monitor, identify and localize a tumor radiotherapy target and an organ at risk, radiotherapy beds with patients, radiotherapy equipment, and the auxiliary treatment staff and objects in a treatment room during the whole radiotherapy process; and (2), on the basis of optical images and / or medical images collected at different stages of the tumor radiotherapy process as well as the quality guaranteeing requirement of the clinical radiotherapy process, a multi-stage multi-vision servo intelligent control system (algorithm) is used for carrying out intelligent, automatic, high-precision, high-robust visual servo control on the radiotherapy beds, radiotherapy equipment, the onboard medical image system, and the optical imaging system in the treatment room during the tumor radiotherapy process.
Owner:强深智能医疗科技(昆山)有限公司
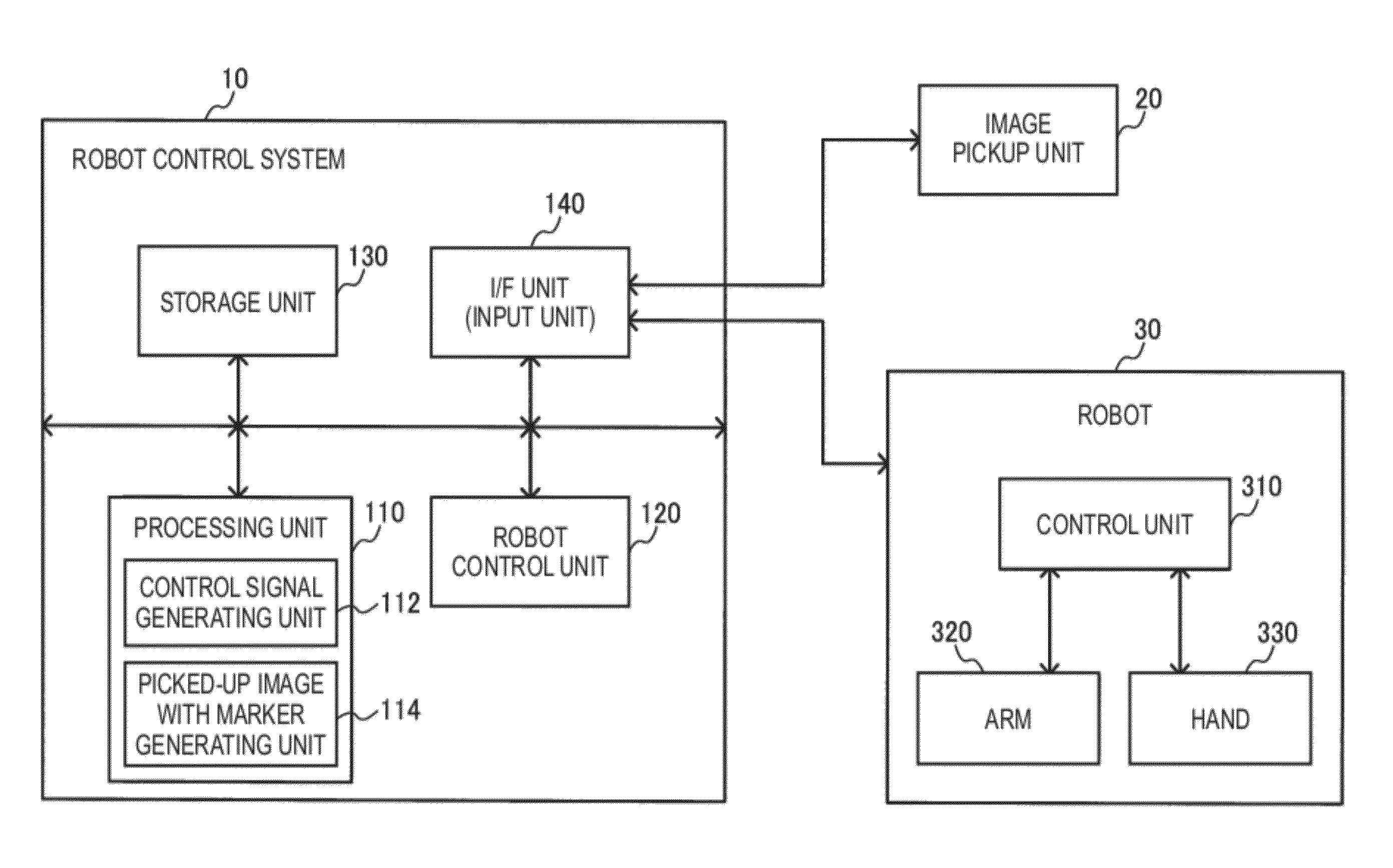
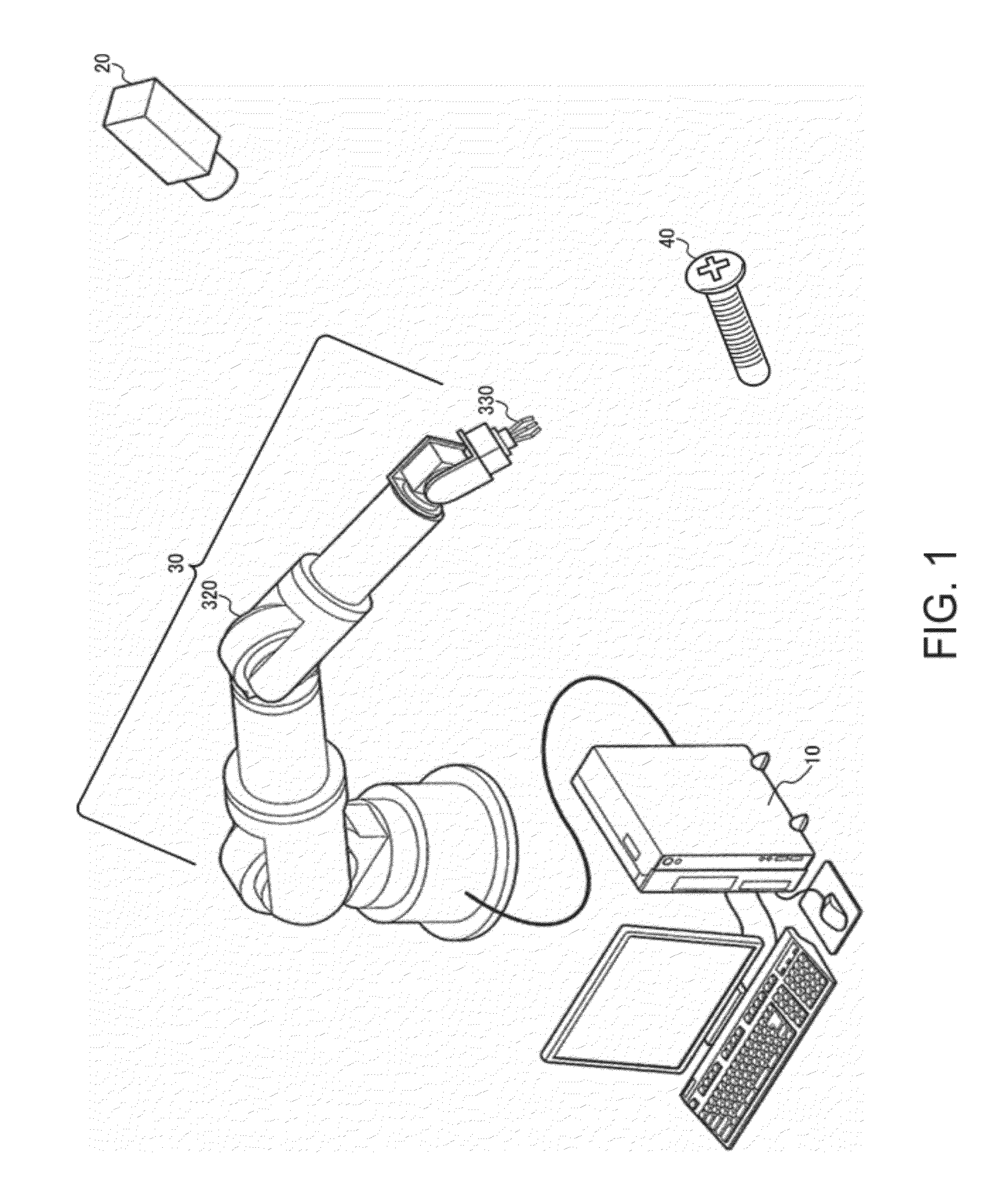
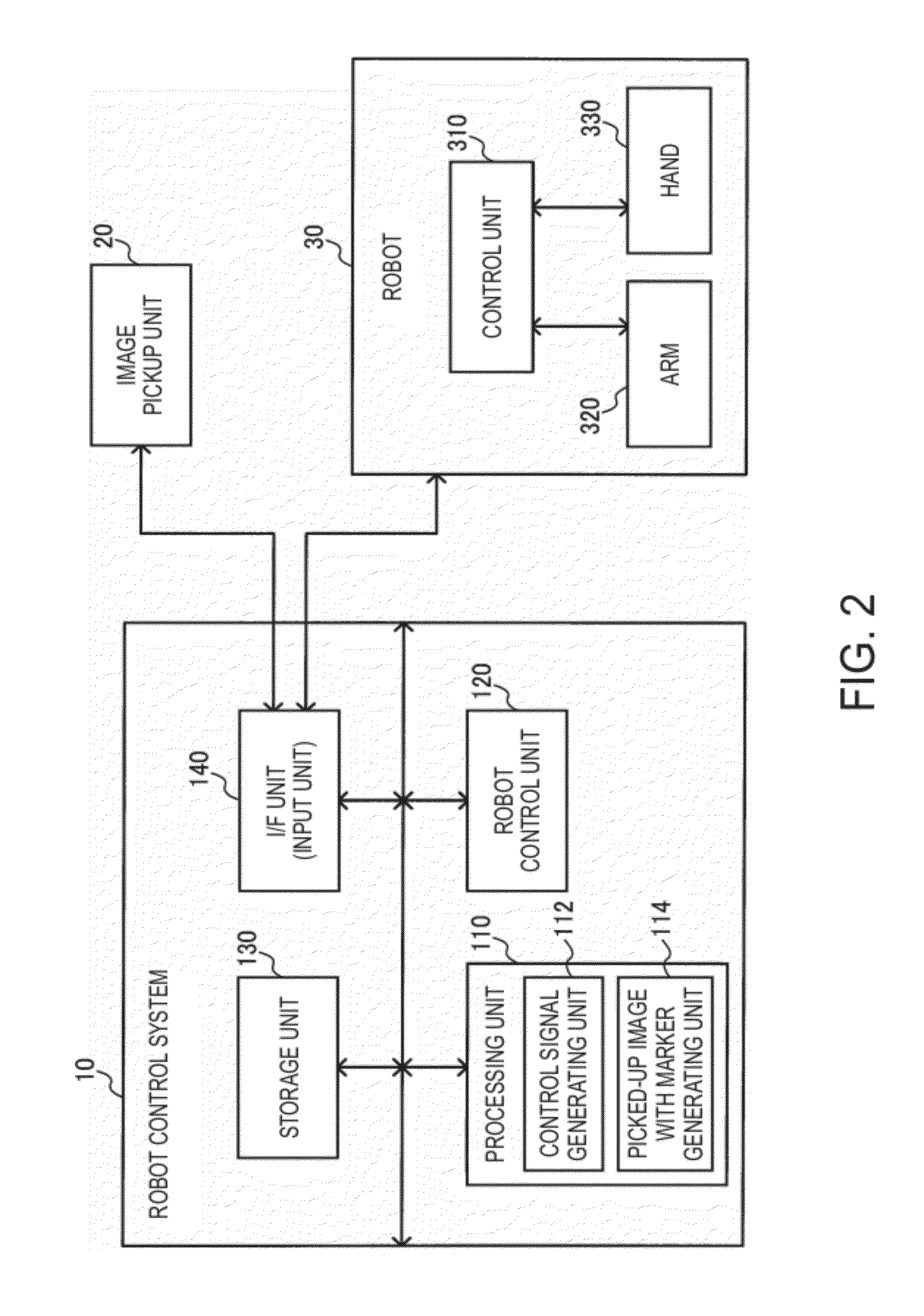
Robot control system, robot system and program
InactiveUS20120294509A1Low costAvoid processing loadProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobotic systemsVisual servoing
A robot control system includes a processing unit which performs visual servoing based on a reference image and a picked-up image, a robot control unit which controls a robot based on a control signal, and a storage unit which stores the reference image and a marker. The storage unit stores, as the reference image, a reference image with marker in which the marker is set in an area of a workpiece or a hand of the robot. The processing unit generates, based on the picked-up image, a picked-up image with marker in which the marker is set in an area of the workpiece or the hand of the robot, performs visual servoing based on the reference image with marker and the picked-up image with marker, generates the control signal, and outputs the control signal to the robot control unit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
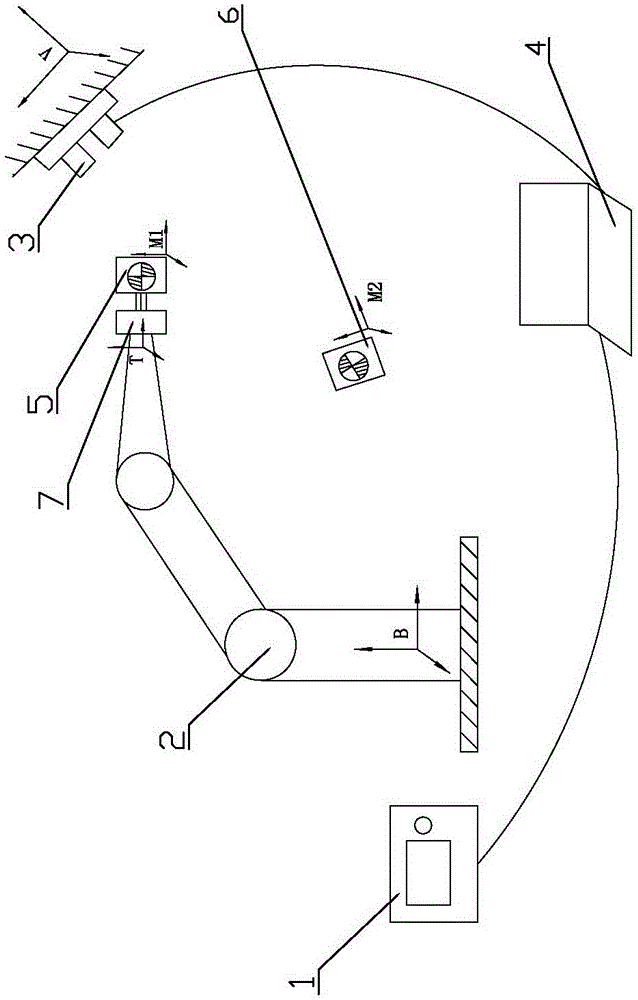
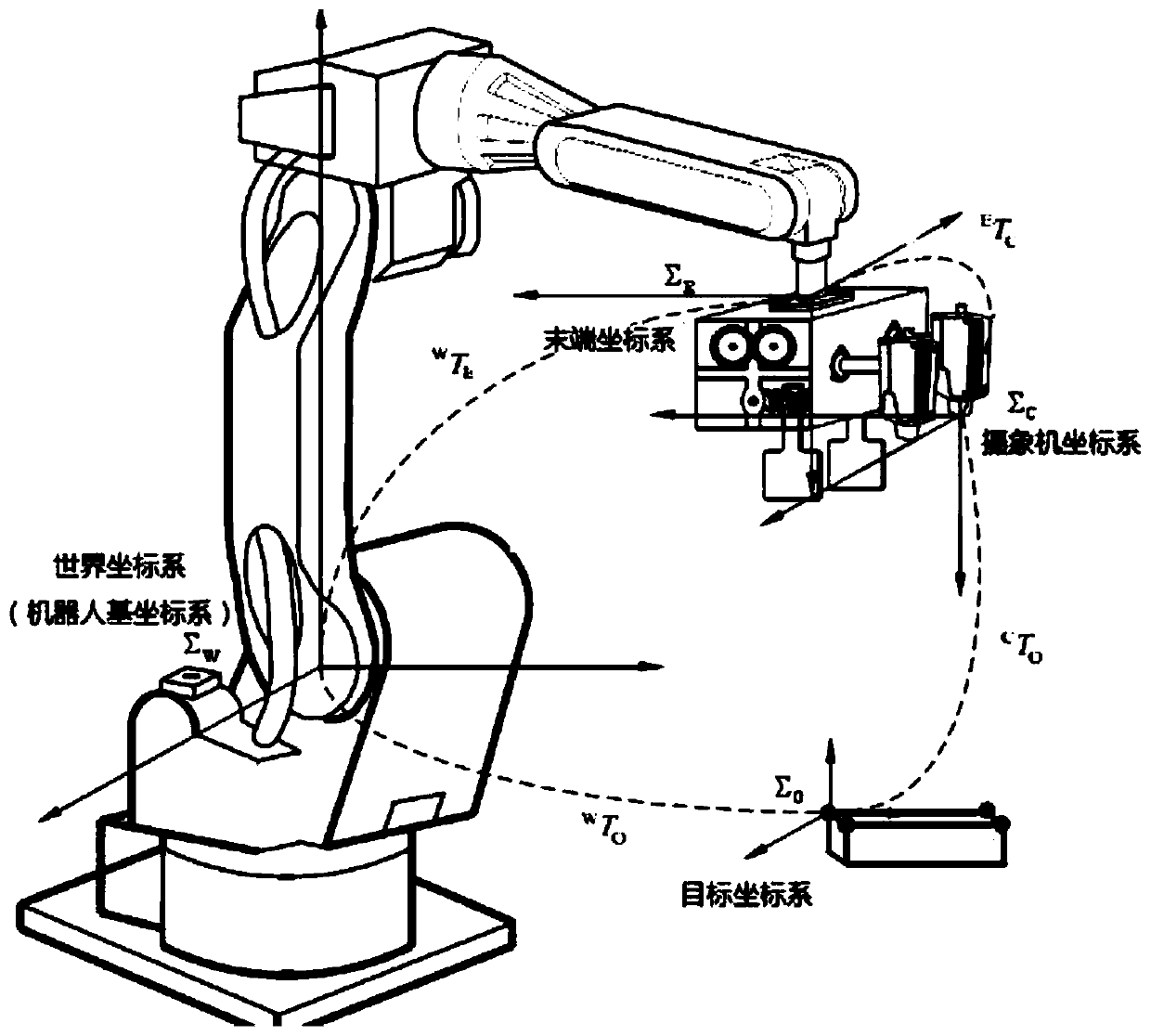
Robot vision servo control device of binocular three-dimensional video camera and application method of robot vision servo control device
The invention relates to the technical field of medical robots, in particular to a robot vision servo control device of a binocular three-dimensional video camera and an application method of the robot vision servo control device. The robot vision servo control device comprises a robot subsystem and a vision control subsystem. The robot subsystem comprises a robot controller and a knuckle type six-freedom-degree robot. The vision control subsystem comprises the binocular three-dimensional video camera and a vision controller. The output end of the robot controller is electrically connected with the input end of the knuckle type six-freedom-degree robot. The robot controller and the vision controller are connected through both-way communication. The output end of the binocular three-dimensional video camera is electrically connected with the input end of the vision controller. The relative position of the robot and a target is detected in real time through the fixed type binocular three-dimensional video camera, the position error is calculated, and following rapidness and accuracy of the robot are guaranteed. Collisions are avoided, the target tracking accuracy of the robot in the medical surgery is effectively improved, the surgery safety is ensured, and the risk coefficient of the surgery is lowered.
Owner:THE FIRST TEACHING HOSPITAL OF XINJIANG MEDICAL UNIVERCITY
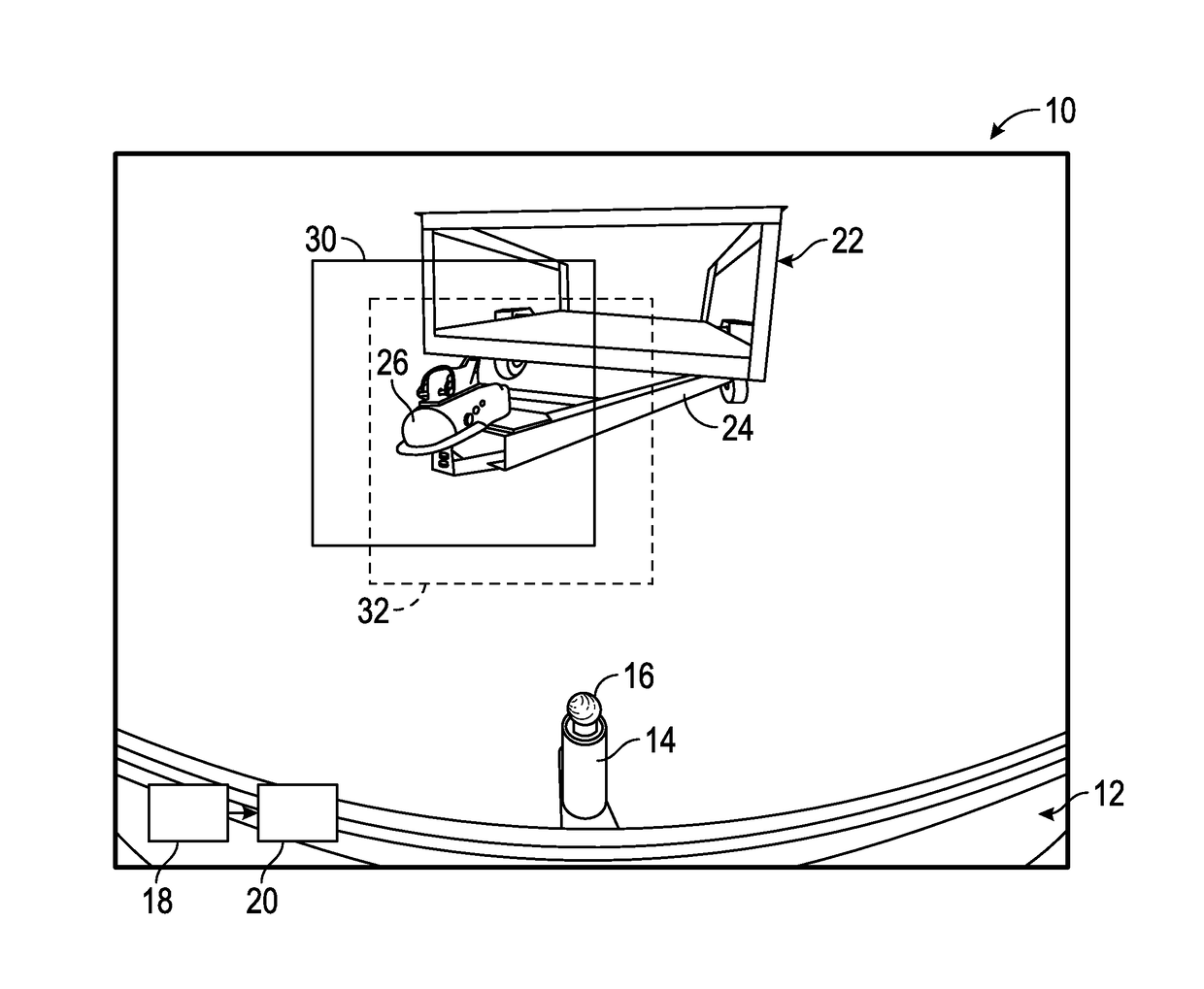
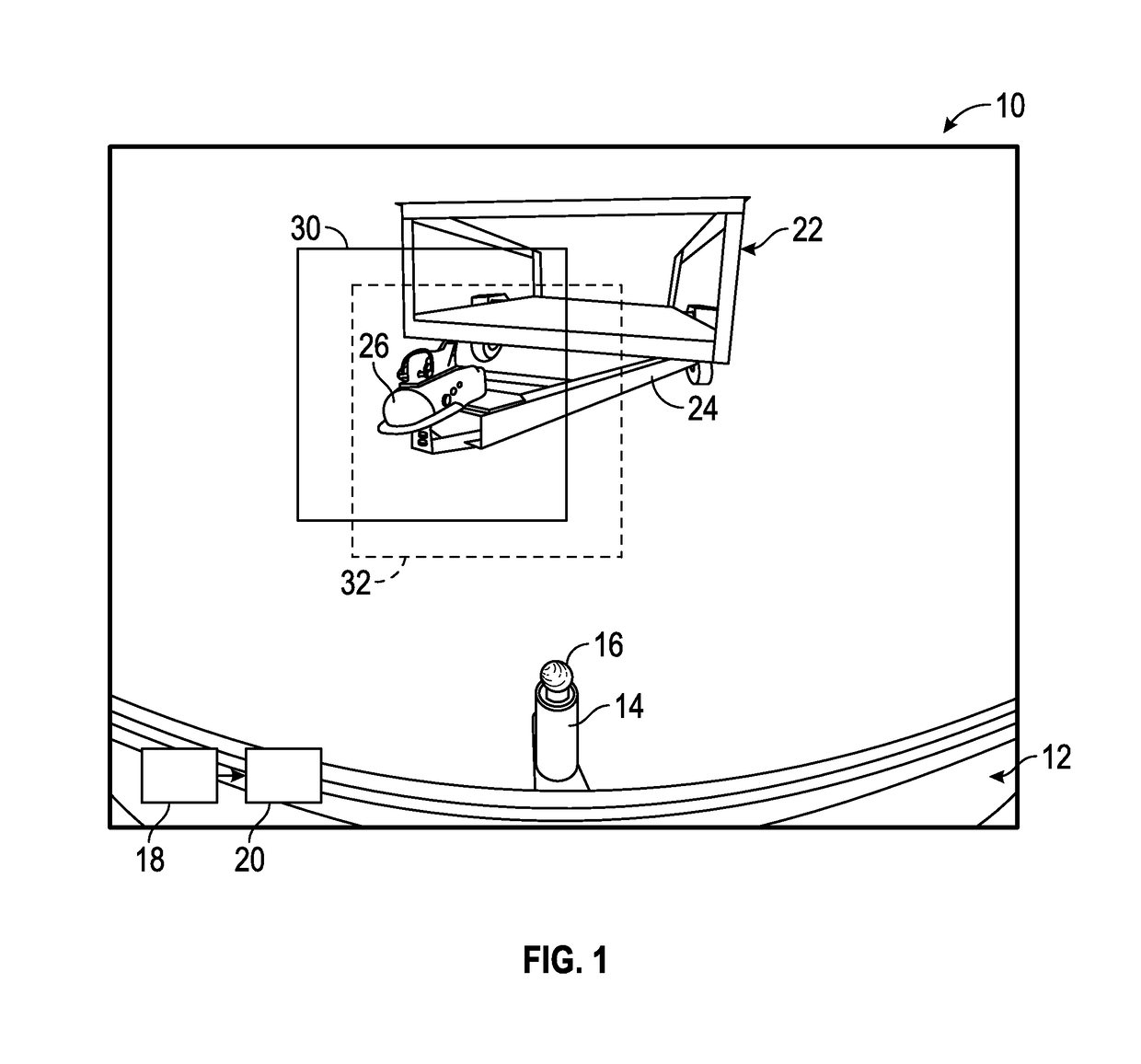
Smart trailer hitch control using HMI assisted visual servoing
A method for autonomously aligning a tow hitch ball on a towing vehicle and a trailer drawbar on a trailer through a human-machine interface (HMI) assisted visual servoing process. The method includes providing rearview images from a rearview camera. The method includes touching the tow ball on a display to register a location of the tow ball in the image and touching the drawbar on the display to register a location of a target where the tow ball will be properly aligned with the drawbar. The method provides a template pattern around the target on the image and autonomously moves the vehicle so that the tow ball moves towards the target. The method predicts a new location of the target as the vehicle moves and identifies the target in new images as the vehicle moves by comparing the previous template pattern with an image patch around the predicted location.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
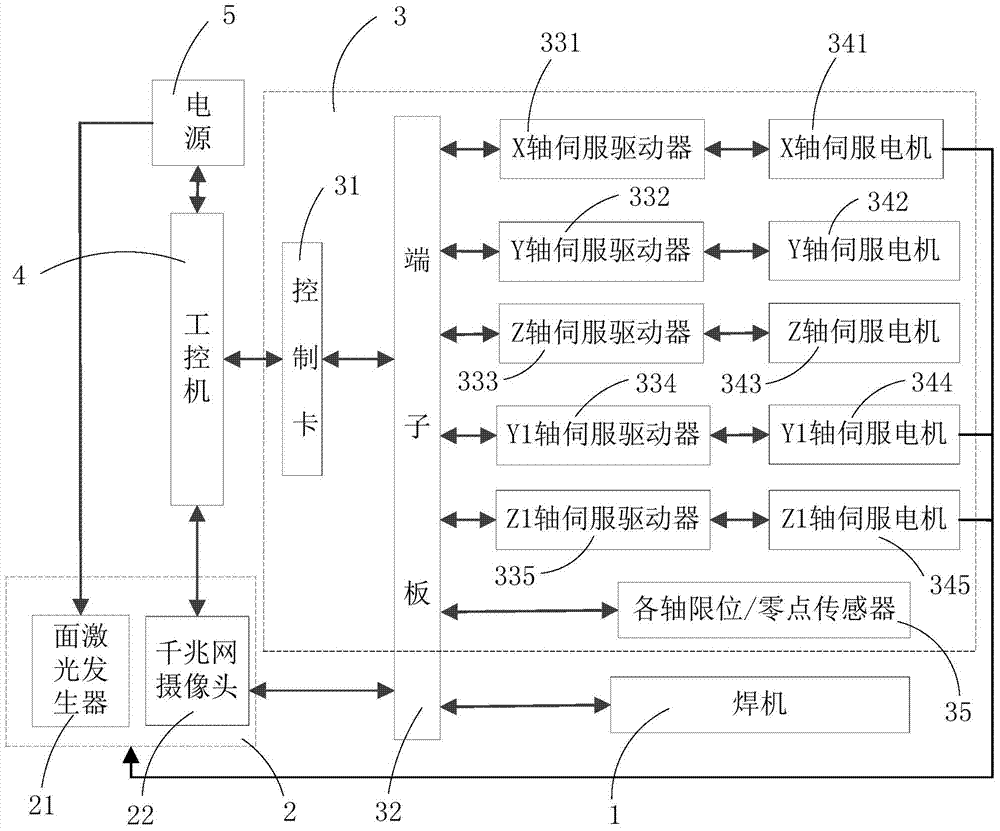
Container corrugated plate welding robot and visual servo control system thereof
ActiveCN104759736AAccurate Seam Tracking WeldingImprove welding efficiencyWelding/cutting auxillary devicesArc welding apparatusNetwork communicationTwo-way communication
The invention discloses a container corrugated plate welding robot and a visual servo control system thereof. The visual servo control system comprises an industrial personal computer, a visual sampling mechanism and a motion control mechanism, wherein the visual sampling mechanism comprises a surface laser generator, a network camera, and an optical filter arranged in front of the network camera; the network camera is connected with the industrial personnel computer in a network communication manner; the motion control mechanism comprises a control card connected with the industrial personnel computer, five servo drivers in two-way communication connection with the control card, five servo motors correspondingly driven by the five servo drivers, and limit / zero-point sensors connected with the control card; the five servo motors respectively and correspondingly drive the motions of a welding gun and the visual sampling mechanism; the limit / zero-point sensors are respectively arranged in five motion directions controlled by the five servo motors; and the control card is further connection with the network camera. The visual servo control system controls based on visual servo, can accurately perform the tracking welding of welding lines, and is high in welding efficiency and excellent in welding quality.
Owner:SHENZHEN CIMC SECURITY & SMART TECH
Visual-servoing optical microscopy
InactiveUS7546210B2Close monitoringOptimize culture conditionsImage enhancementImage analysisVisual perceptionCell stress
The present invention provides methods and devices for the knowledge-based discovery and optimization of differences between cell types. In particular, the present invention provides visual servoing optical microscopy, as well as analysis methods. The present invention provides means for the close monitoring of hundreds of individual, living cells over time: quantification of dynamic physiological responses in multiple channels; real-time digital image segmentation and analysis; intelligent, repetitive computer-applied cell stress and cell stimulation; and the ability to return to the same field of cells for long-term studies and observation. The present invention further provides means to optimize culture conditions for specific subpopulations of cells.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Robot dynamic capture method and system
PendingCN107992881AEfficient extractionAccurate extractionProgramme-controlled manipulatorImage enhancementTemplate matchingHigh frame rate
The invention discloses a robot dynamic capture method and system. The method comprises the steps that S1, a collected image transmitted from an industrial camera is received in real time, and the obtained image is preprocessed; S2, a template tracking algorithm based on multiple clues is utilized to determine a foreground target region; S3, a template matching algorithm based on an edge gradientis adopted to precisely recognize a foreground target; S4, a random sampling consensus algorithm is adopted to perform modeling on motion information of an object in a view field; and S5, the information is fed back to a robot in real time for dynamic capture in combination with camera calibration and hand-eye calibration parameters. According to the robot dynamic capture method and system, by theadoption of a target tracking algorithm based on multiple clues, the motion target foreground region can be extracted efficiently and accurately; and under the application scene of robot sorting, therunning speed of a visual motion target tracking algorithm can be effectively increased, high-frame-rate real-time recognition is realized, and therefore the precision of visual servo is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN CAS DERUI INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
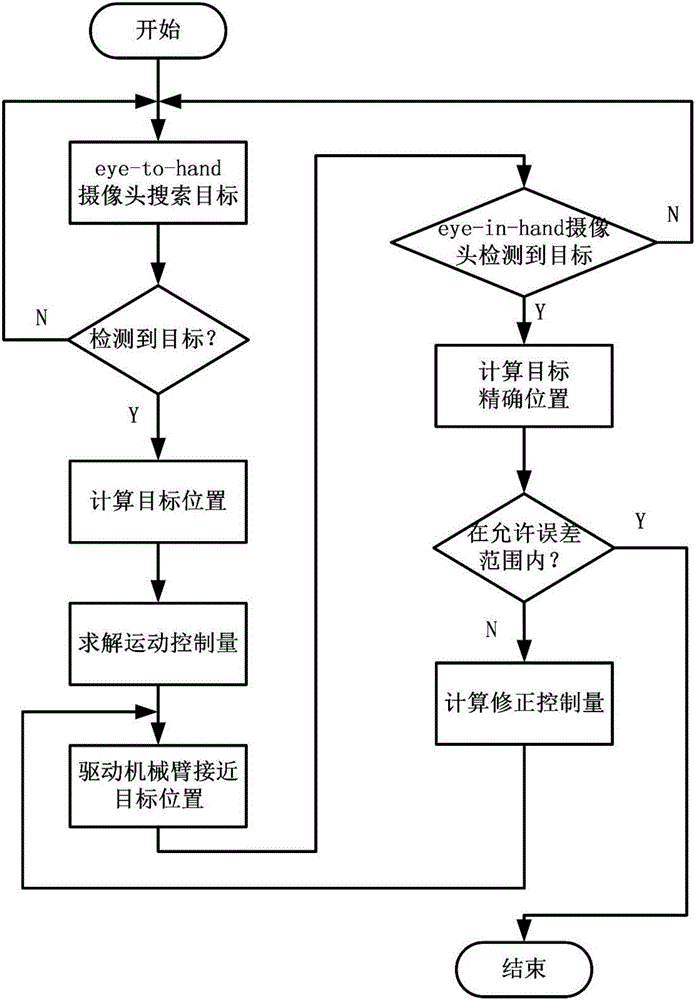
Hybrid vision servo system and method combining eye-to-hand and eye-in-hand structures
InactiveCN106041927AHigh positioning accuracyIncrease flexibilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorVisual servoingEngineering
The invention discloses a hybrid vision servo system and method combining eye-to-hand and eye-in-hand structures. According to the hybrid vision servo system and method, information of a to-be-identified target is acquired through an eye-to-hand camera and an eye-in-hand camera; position calculation is performed through a computer; and a driver is controlled to drive a mechanical arm to drive the eye-in-hand camera for precisely positioning the to-be-identified target. Compared with traditional vision servo based only on position and vision servo based on images, the hybrid vision servo system and method have higher positioning precision and flexibility; the characteristics that an overall vision field is large in range and a local vision field is high in precision are realized; the cost is low; the applicability is high; the application range is wide; great convenience can be brought to application in scientific research, target searching and positioning and the like; and the hybrid vision servo system and method have very important research value and practical significance.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
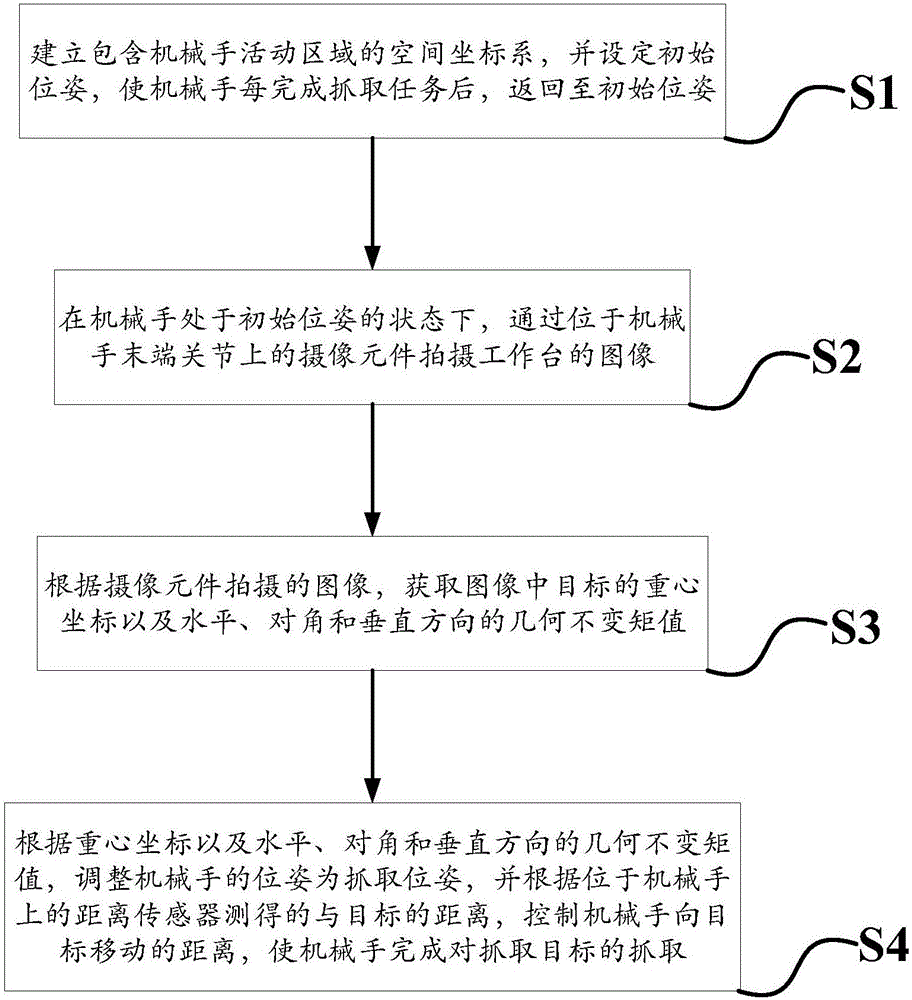
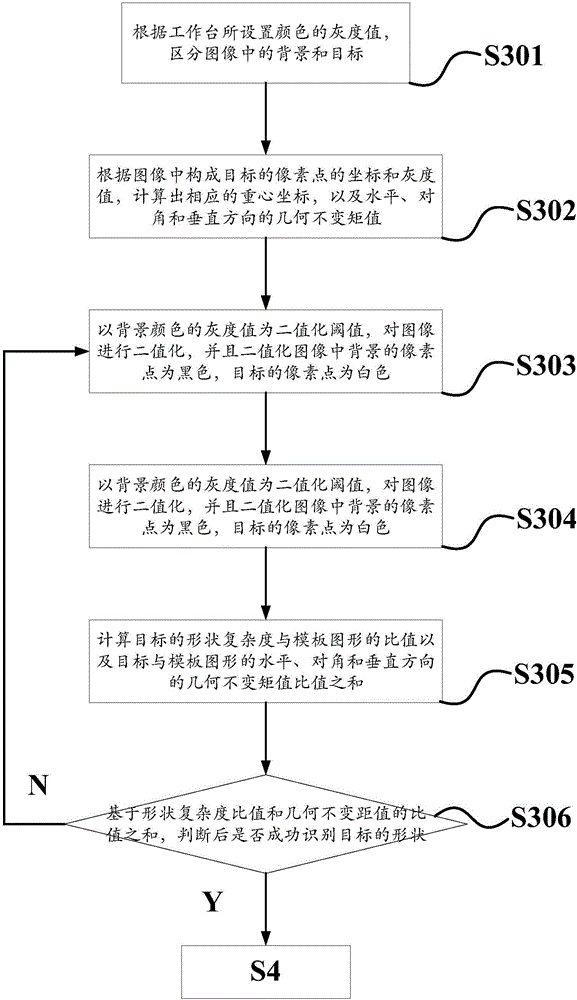
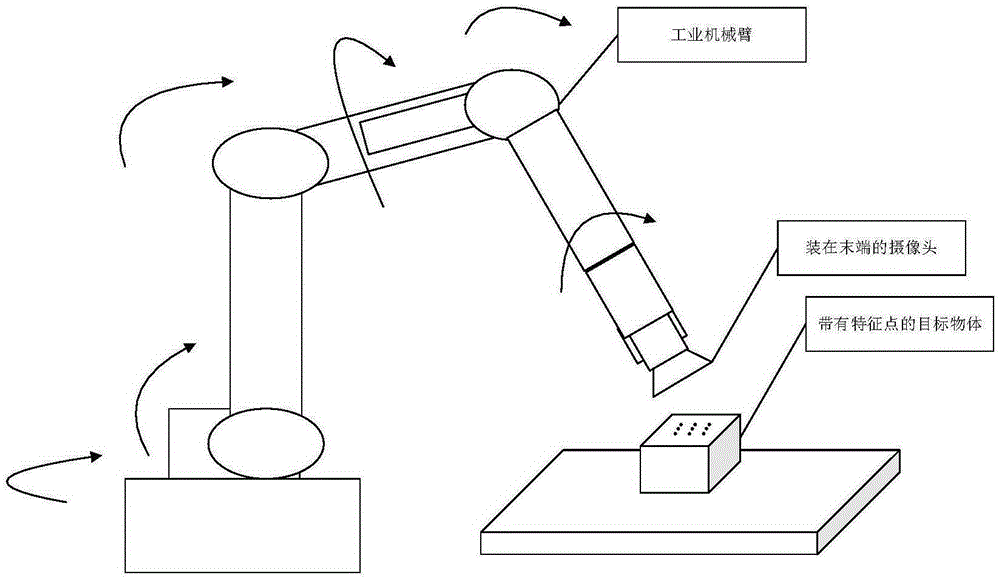
Image-based uncalibrated visual servo manipulator and control method thereof
InactiveCN106485746AImprove work efficiencyAdaptableProgramme-controlled manipulatorImage enhancementVisual servoingEngineering
The invention discloses an image-based uncalibrated visual servo manipulator and a control method thereof. The shape feature of a target and the position at which a manipulator should grab the target are acquired directly according to an image shot at an initial pose; the pose of the manipulator is adjusted to a grabbing pose according to the shape feature of the target; and the target is grabbed according to the distance between the manipulator and the target measured by a distance sensor. Thus, the manipulator has higher work efficiency and better adaptability to the environment.
Owner:GUANGDONG POLYTECHNIC NORMAL UNIV
Method for simultaneous performing visual servo and adaptive depth identification through robot
InactiveCN106774309ASolve the problem of identifying depth informationSolve the global stability problemPosition/course control in two dimensionsStabilization controlSimulation
A method for simultaneous performing visual servo and adaptive depth identification through a robot belongs to the computer vision and mobile robot technology field. The method comprises: obtaining an open loop kinematical equation with stable error according to a robot pose position polar coordinate representation method; and designing an adaptive updating rule capable of identifying depth information according to a concurrence learning strategy, and constructing a vision stabilization control rule of a mobile robot. The parameter adaptive updating rule designed by the invention can perform learning at the initial stage of the robot performing stabilization motion and perform online identification of the depth information in the robot motion process. The method for simultaneous performing visual servo and adaptive depth identification through the robot can prove the simultaneous convergence of the pose posture errors and the depth identification errors according to a Lyapunov method and a LaSalle invariance principle. The method for simultaneous performing visual servo and adaptive depth identification through the robot can accurately and reliability identify the depth information while the mobile robot completes the vision stabilization control so as to prove the simultaneous convergence of the controller and the identification module.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Screw hole positioning and screw locking-and-dismounting device based on visual servo
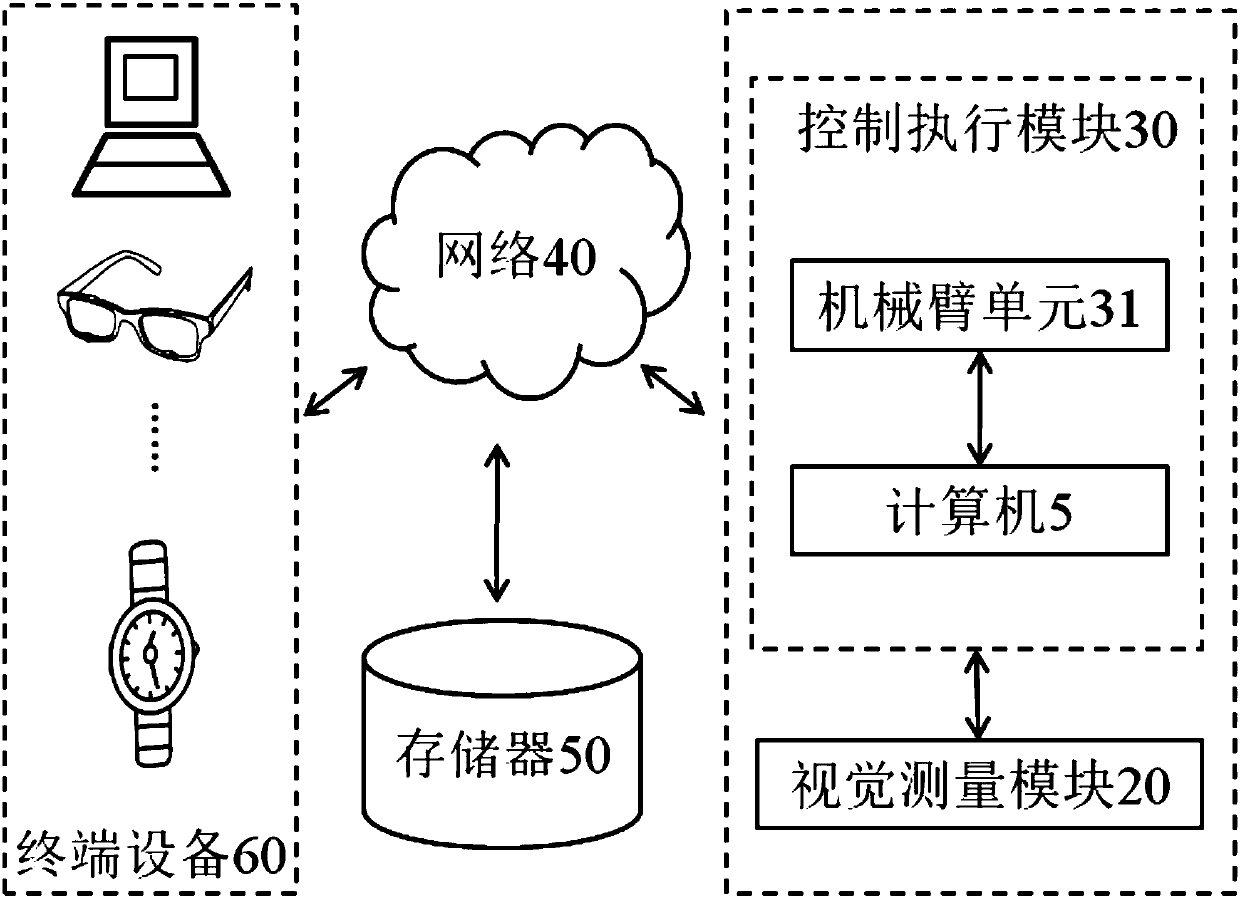
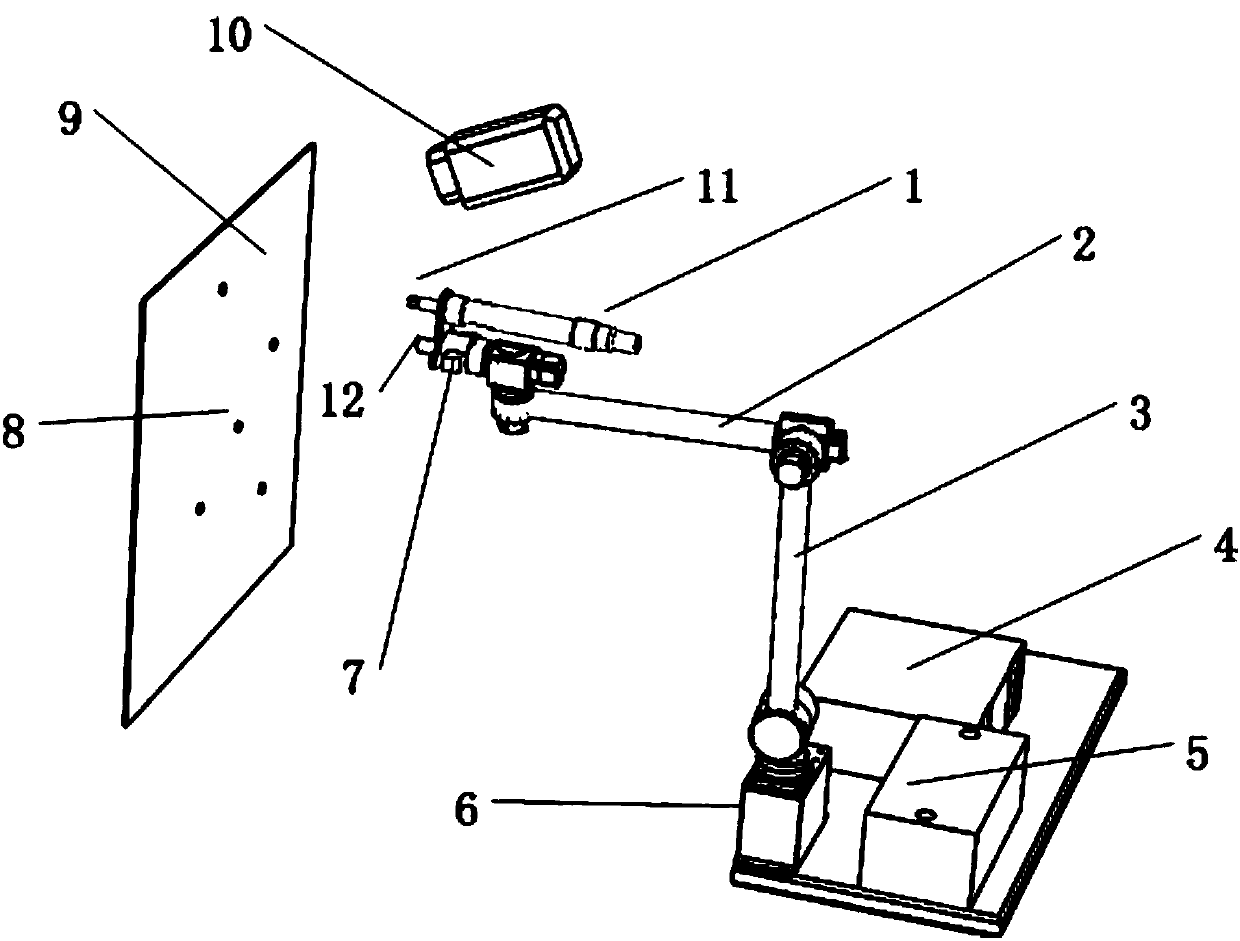
ActiveCN107825125AHigh precisionImprove efficiencyWork holdersMetal working apparatusVisual servoingEngineering
The invention relates to a screw hole positioning and screw locking-and-dismounting device based on visual servo and provides a point-to-face screw or screw hole positioning method. The screw hole positioning and screw locking-and-dismounting device is used for positioning a screw hole and locking and dismounting a screw and comprises a visual measuring module and a control executing module whichare in data transmission and communication with each other through a network. The visual measuring module comprises a binocular camera, a coarse positioning camera and a laser dotting device, and thecontrol executing module comprises a mechanical arm unit and a computer. The mechanical arm unit comprises a large-torque tightening gun, a mechanical arm small arm body, a mechanical arm large arm body, a mechanical arm control box, a base and a screw sleeve. The large-torque tightening gun, the screw sleeve, the binocular camera and the laser dotting device are located at the tail end of the mechanical arm unit. According to the screw hole positioning and screw locking-and-dismounting device based on visual servo, the positioning accuracy of the screw can be improved to a large extent, a mechanical arm is utilized as a moving carrier, thus the work range is increased, and screw locking and dismounting can also be conducted in the environment which workers inconveniently go to.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
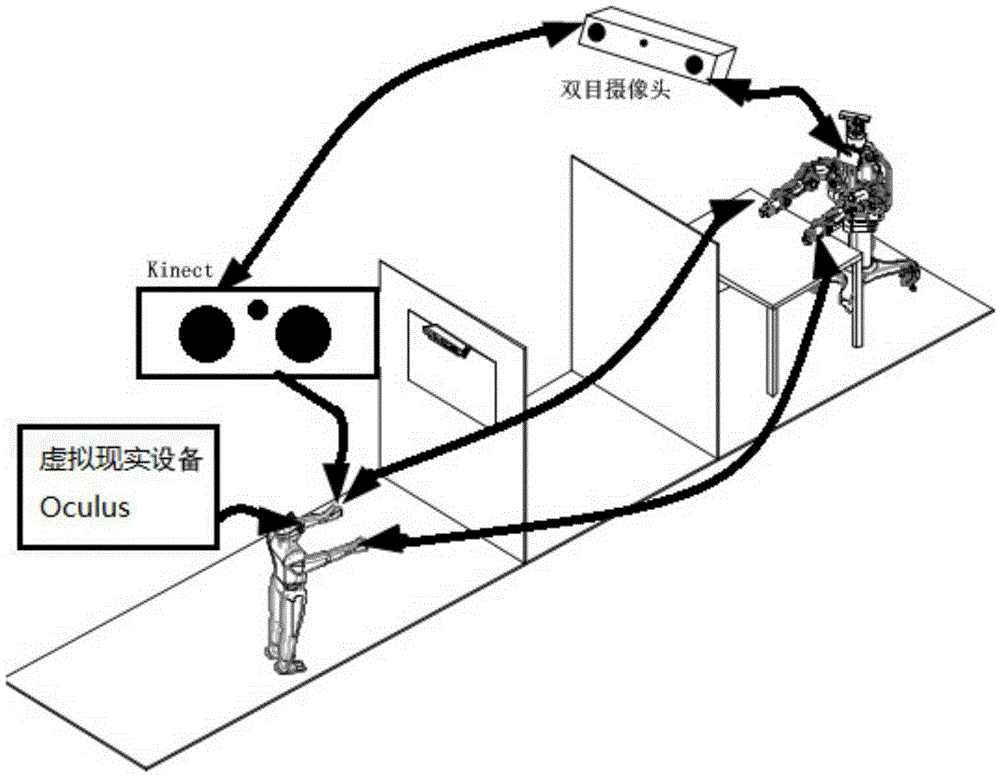
Visual feedback platform improving virtual reality immersion degree
ActiveCN105291138ASolve the problem of limited work spaceAchieve intuitive controlManipulatorVisual servoingEnvironmental modelling
The invention discloses a visual feedback platform improving the virtual reality immersion degree. The visual feedback platform is characterized by comprising a robot, a visual servo tracking control unit and an immersion type visual feedback unit and forms a closed presence sense system with users; the visual servo tracking control unit is used for tracking movement behaviors of the users and carrying out environment modeling; the immersion type visual feedback unit receives the information of the movement behaviors of the users and environment modeling and then mixes the information with limb models of the robot into a 3D virtual reality interface, and the users wear virtual reality equipment to achieve man-machine interaction. The visual feedback platform has the advantages that the immersion degree of man-machine interaction is high, the hardware investment is small, the system is simple and the integration level is high, thereby being suitable for constructing man-machine interaction systems of robots of different functions.
Owner:创泽智能机器人集团股份有限公司
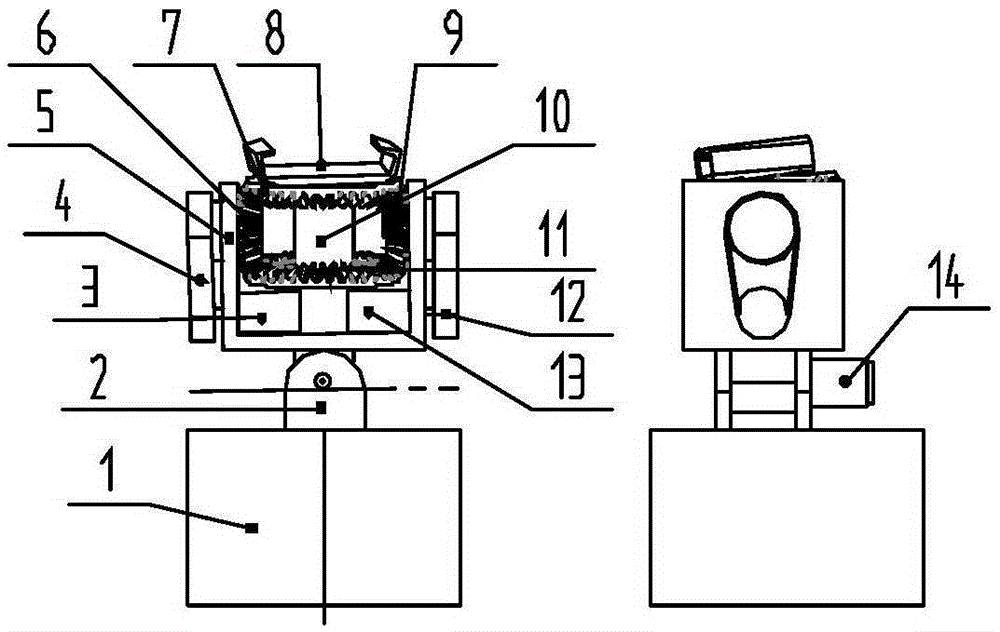
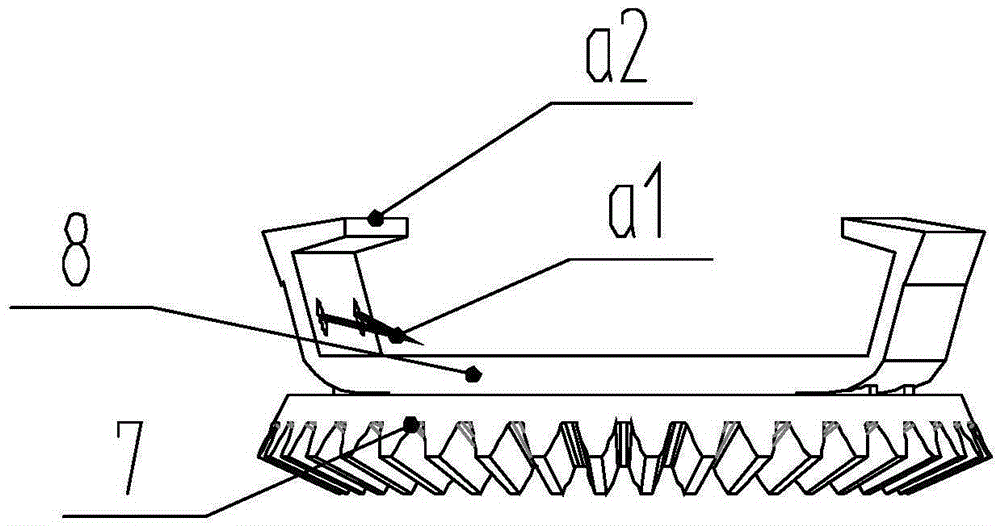
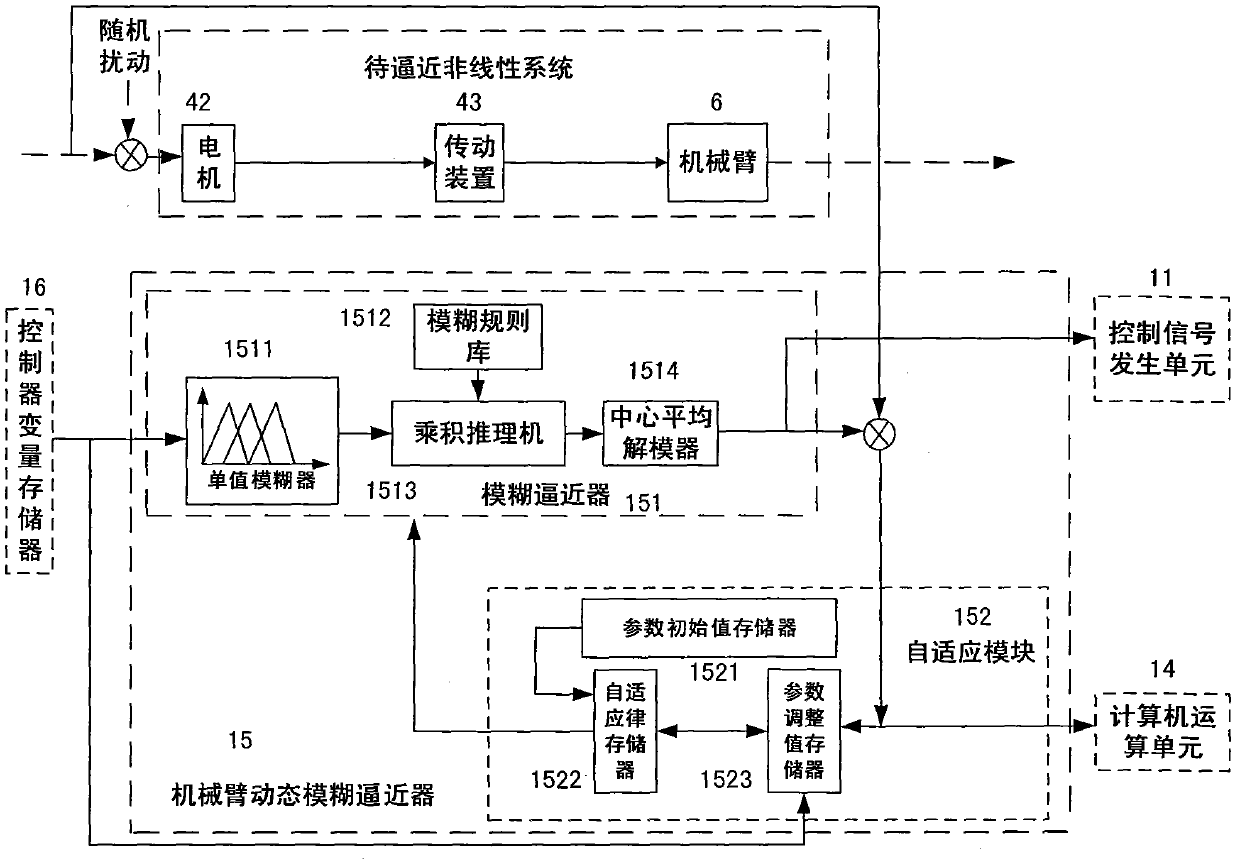
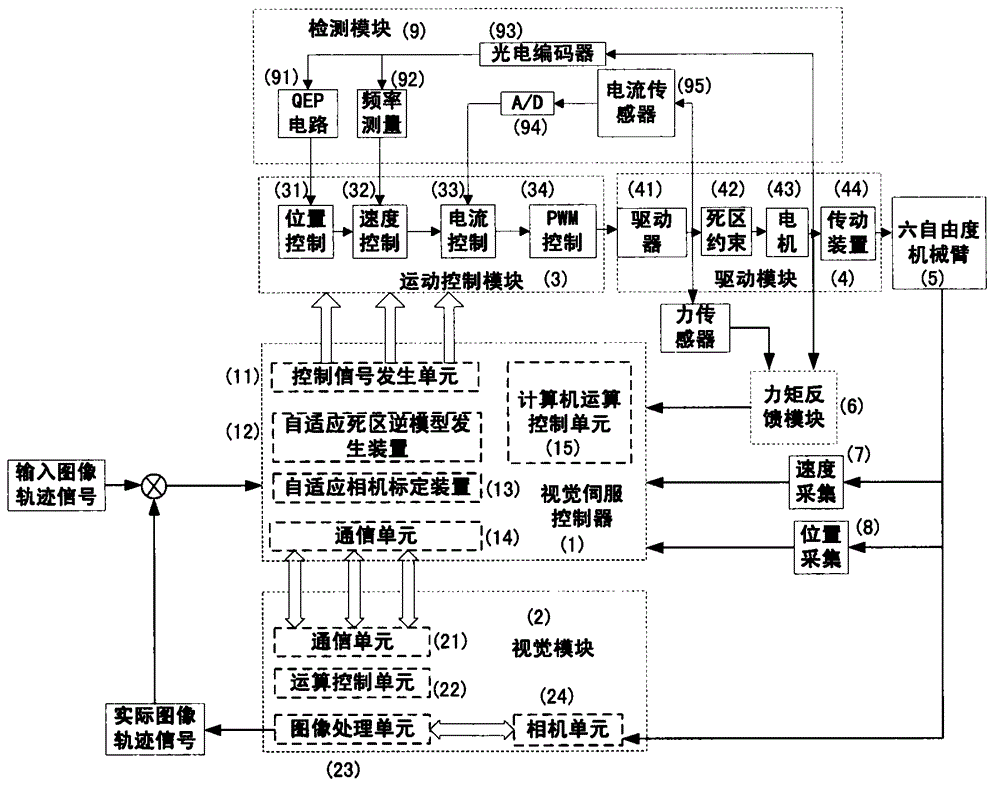
Mechanical arm dynamic fuzzy approximator based on visual servo system
InactiveCN104942809AGuaranteed performanceEffective approximationProgramme-controlled manipulatorAdaptive controlVisual servoingVision based
The invention relates to a mechanical arm dynamic fuzzy approximator based on a visual servo system. The visual servo mechanical arm system is composed of a visual servo controller, a visual module, a motion control module, a driving module, a mechanical arm module, a speed and position collecting module and a detecting module; the mechanical arm dynamic fuzzy approximator in the visual servo controller is used for approximating the unknown mechanical arm dynamic state which is subjected to random disturbance; the approximator comprises a fuzzy approximator body and a self-adaption module, the self-adaption module regulates parameters in the fuzzy approximator body on line to enable the error between the output of the fuzzy approximator body and the mechanical arm system to be approximated to always keep within the bounded errors, and the error tends to zero along with time; on the condition that the mechanical arm dynamic characteristics are unknown and are subjected to random disturbance, the stability of the system is guaranteed, and the trajectory tracking precision on an image plane is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and visual servo control method and device thereof
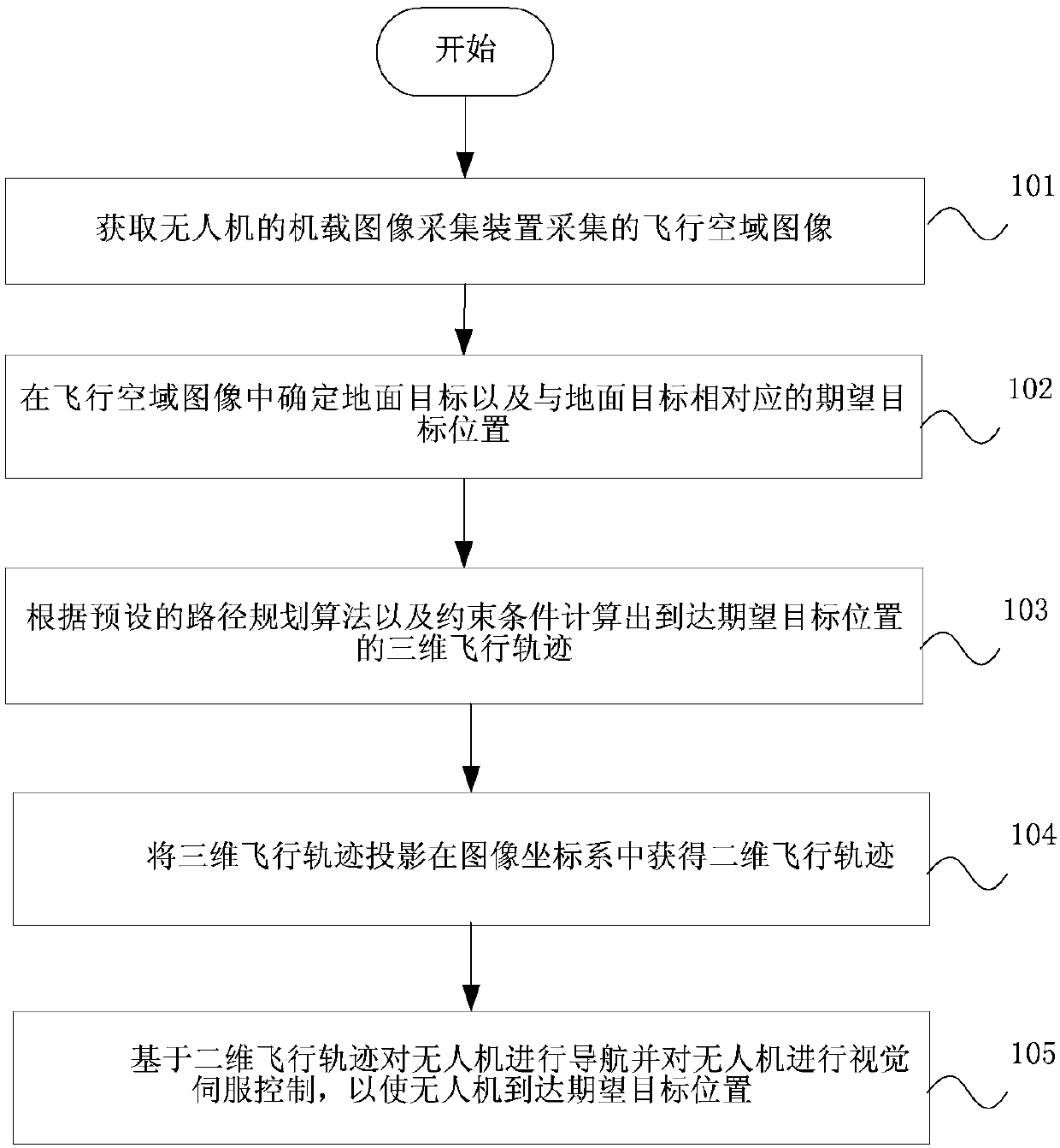
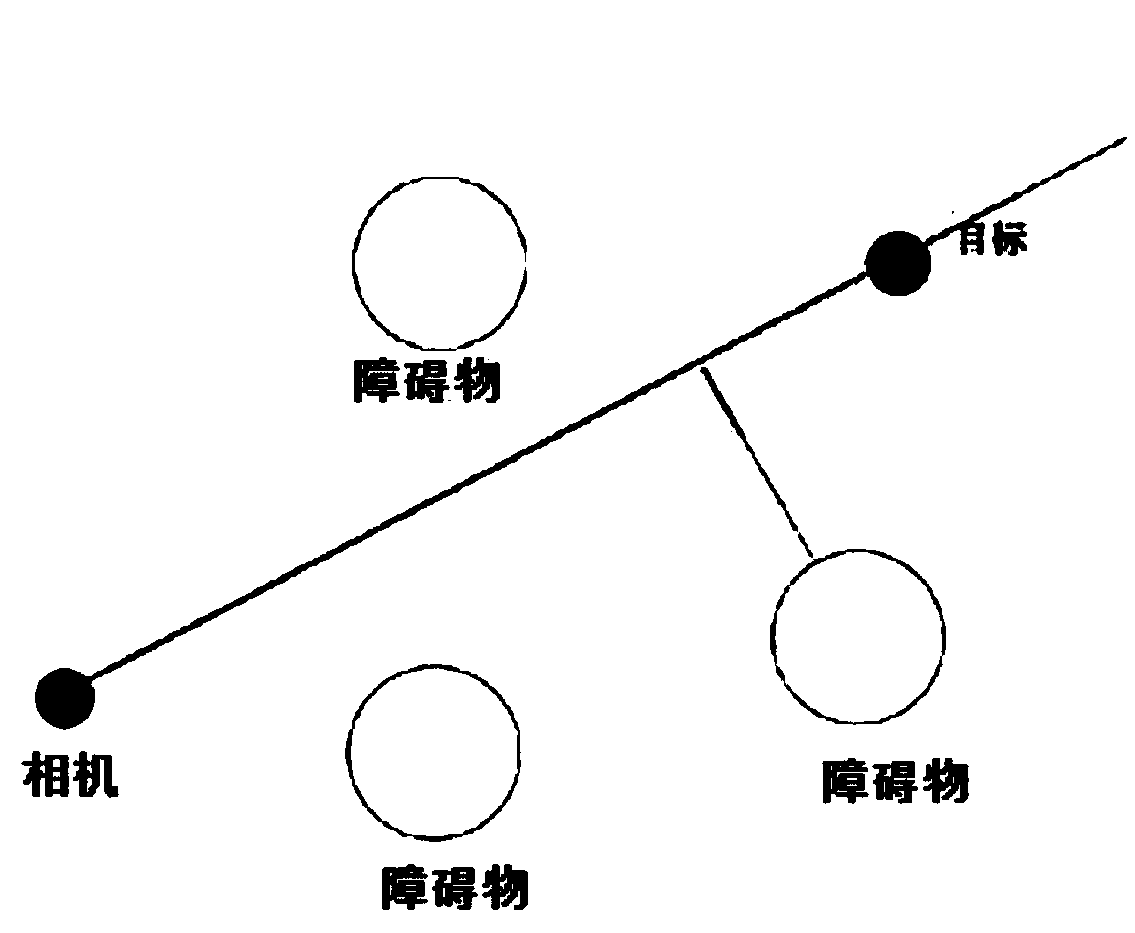
ActiveCN110362098AImprove securityReduce complexityAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsWalking around obstaclesVisual servoing
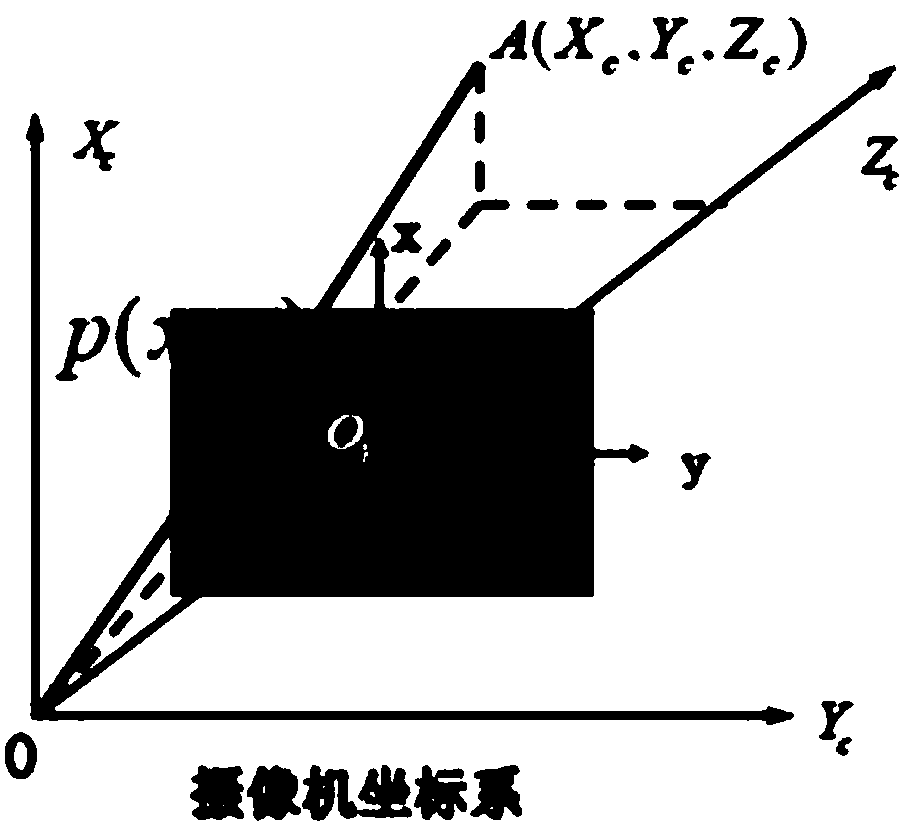
The invention provides a UAV and a visual servo control method and device thereof. The method comprises that a ground target and an expected target position corresponding to the ground target are determined in a flight spatial domain image, a three-dimensional (3D) flight trajectory to reach the expected target position is calculated according to a path planning algorithm and different constrainedconditions, the 3D flight trajectory is projected into an image coordinate system to obtain a two-dimensional (2D) flight trajectory, and navigation and visual servo control care carried out on the UAV based on the 2D flight trajectory. According to the method, device and UAV, the different constraints are integrated in path planning, navigation and visual servo control care carried out on the UAV based on the 2D flight trajectory, an obstacle can be avoided, and image characteristic information collected by a camera is directly used for feedback and servo control, it is not required to estimate the 3D attitude of the UAV, the visual servo control method is less complex, and the flight safety of the UAV is improved.
Owner:BEIJING JINGDONG SHANGKE INFORMATION TECH CO LTD +1
Robot trajectory tracking control method based on visual guidance
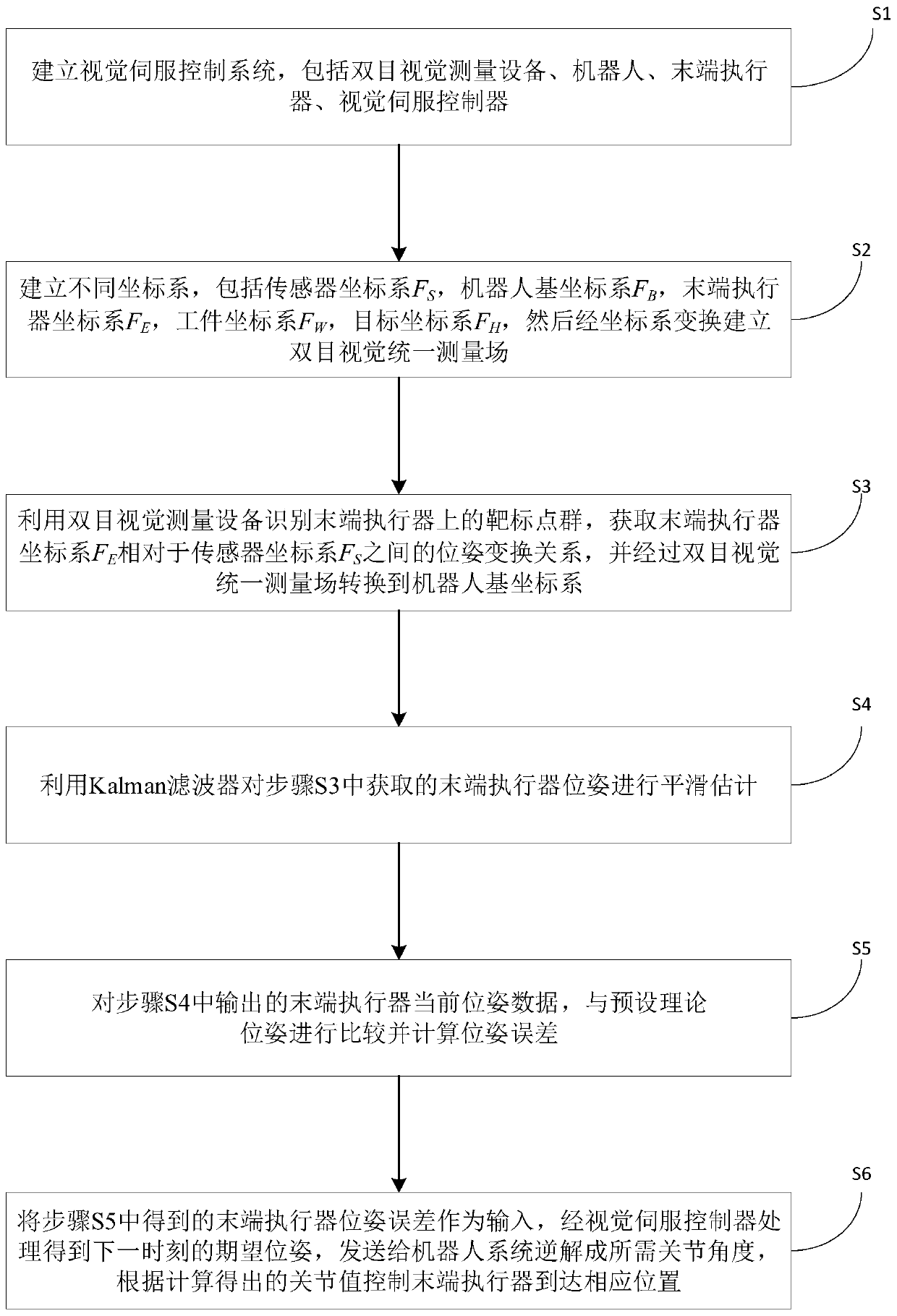
ActiveCN111590594ASolve poor trajectory accuracyOptimize layoutProgramme-controlled manipulatorVision basedVision sensor
The invention relates to a robot trajectory tracking control method based on visual guidance. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a robot visual servo control system; establishing abinocular vision unified measurement field; carrying out observing by using a binocular vision device to obtain a pose transformation relationship between an end effector coordinate system and a measurement coordinate system, and converting the pose transformation relationship to a robot base coordinate system through the binocular vision measurement field; carrying out smooth estimation on the observed pose of an end effector by utilizing a Kalman filter; calculating the pose error of the end effector; and designing a visual servo controller based on fuzzy PID, processing the pose error to obtain an expected pose at the next moment, and sending the expected pose to a robot system to control the end effector to move. The technical scheme is oriented to the field of flexible machining of aerospace large parts and the application requirements of robot high-precision machining equipment, the pose of the end effector is sensed in real time through a visual sensor, so that a closed-loop feedback system is formed, and the trajectory motion precision of a six-degree-of-freedom series robot is greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Self-adaptive dead zone inverse model generating device of visual servo mechanical arm system
InactiveCN104476544AReduce complicated workloadGood effectProgramme-controlled manipulatorDead zone nonlinearityControl system
The invention discloses a self-adaptive dead zone inverse model generating device of a visual servo mechanical arm system. The visual servo mechanical arm system is composed of a visual servo controller, a visual module, a motion control module, a driving module, a six-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm, a torque feedback module, a speed and position collecting module and a detecting module. The self-adaptive dead zone inverse model generating device of the visual servo controller is used for eliminating dead zone non-linear constraint and comprises a dead zone inverse model module, a self-adapting module and an operating module, wherein the dead zone inverse model module is used for structuring a smooth dead zone nonlinear inverse model; the self-adapting module adjusts estimated dead zone parameters through self-adaptive laws and transmits the parameters into the dead zone inverse model module to change the parameters of the inverse model; by means of the signal communication of the modules, a closed-loop control system can be formed inside the visual servo mechanical arm system. The self-adaptive dead zone inverse model generating device of the visual servo mechanical arm system can effectively eliminate the influence of the dead zone nonlinear restraint and achieve high image tracing precision.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Visual servo switching control method and system
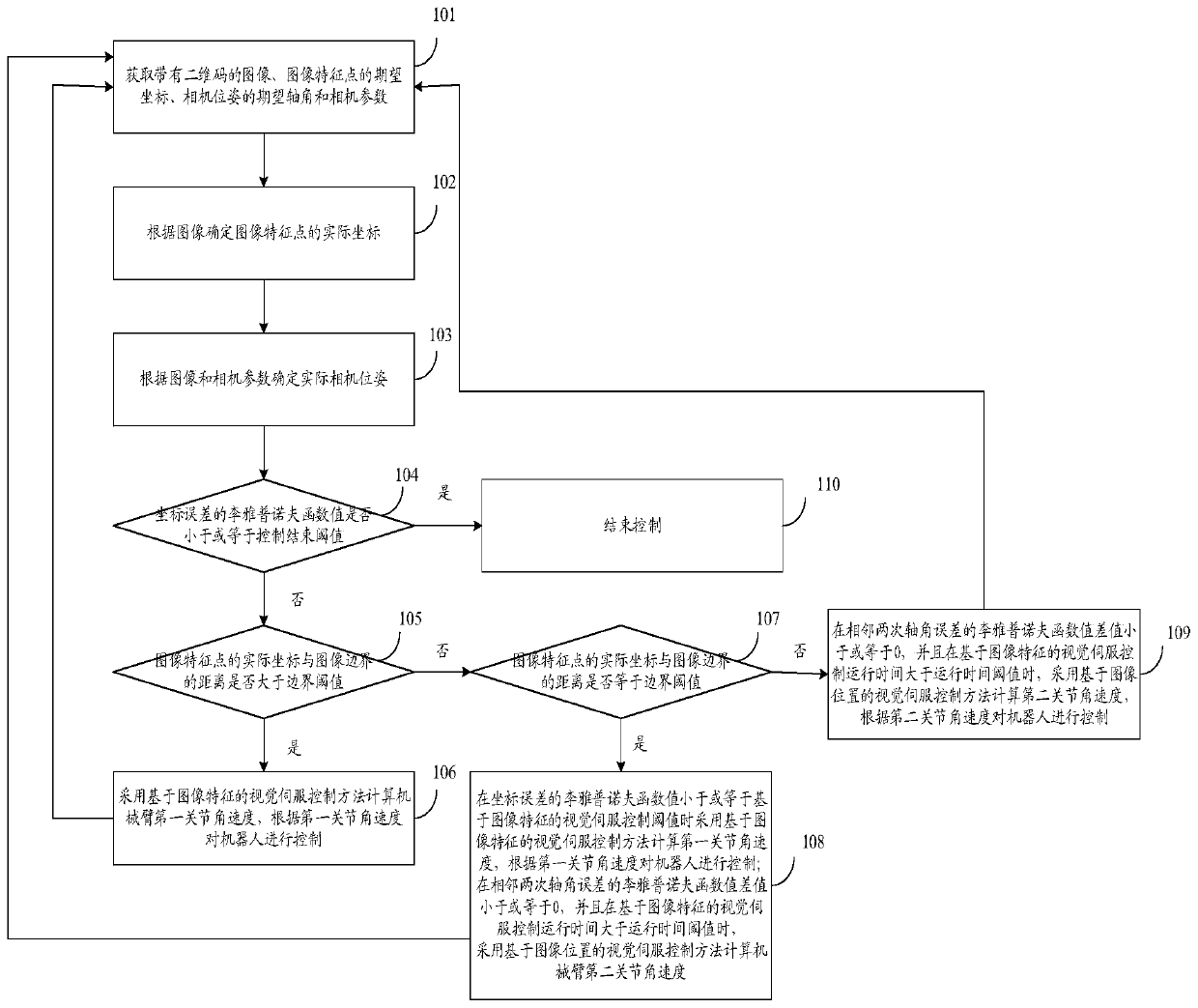
ActiveCN111360827AHigh precisionImprove stabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorVisual servoingControl system
The invention discloses a visual servo switching control method and system. The method comprises the following steps: determining actual coordinates and actual camera poses of image feature points with two-dimensional codes; if a distance between the actual coordinates of the image feature points and an image boundary is greater than a boundary threshold value, adopting the visual servo control method based on image features to calculate first joint angular velocity of a mechanical arm, and controlling a robot according to the first joint angular velocity; judging whether the distance betweenthe actual coordinates of the image feature points and the image boundary is equal to the boundary threshold value or not, distinguishing and calculating the joint angular velocity; and adopting the visual servo control method based on the image positions to calculate second joint angular velocity if a difference value of Lyapunov function values of adjacent twice axle angle errors is smaller thanor equal to 0, and operation time of the visual servo control based on the image features is greater than an operation time threshold value. The method and the system disclosed by the invention havethe advantages of being capable of strengthening stability of a robot control system, and improving the visual servo effect.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Calibration method suitable for visual servo plug-pull operation
ActiveCN109318234AIncreased durabilityGood Visual Servo EffectProgramme-controlled manipulatorVisual servoingImaging Feature
The invention relates to a calibration method suitable for a visual servo plug-pull operation, and belongs to the field of image identification. The problems that servo alignment control precision based on the visual servo is low, and the effect of the plug-pull operation controlled by an open loop is poor in a plug-pull stage are solved; the calibration method suitable for the visual servo plug-pull operation is provided, an image containing pins, a socket and a plug clamping device is collected by using a camera; a depth learning algorithm is utilized to obtain a center point of each pin inthe socket and the center point of each calibration board on the plug clamping device; then a socket middle point coordinate, a socket deflection angle, a plug clamping device middle point and a plugclamping device deflection angle are calculated; the point coordinate is transferred into a joint coordinate system at the tail end of a mechanical arm of a robot; the socket middle point coordinatesin a tail end coordinate system of the robot is obtained; a visual servo image feature error is calculated in the tail end coordinate system; and a visual servo feature is sent to a robot visual servoalgorithm, and the robot is controlled to move. According to the method, the operation precision in visual servo plug-pull operation is improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Vision-based pose stabilization control method of moving trolley
InactiveCN102736626AObvious advantageGood effectPosition/course control in two dimensionsKinematic controllerVisual servoing
The invention discloses a vision-based pose stabilization control method of a moving trolley, which fully considers about a kinematics model and a dynamics model of a trolley and a camera model. The vision-based pose stabilization control method comprises the following steps of: respectively obtaining an initial image and an expected image at a starting pose position and an expected pose position through a camera, and obtaining an existing image in a movement process in real time; by utilizing an antipode geometric relation and a trilinear restrain relation among shot images, designing three independent ordered kinematics controllers based on Epipolar geometry and 1D trifocal tensor by utilizing a three-step conversion control policy; finally designing a dynamic conversion control rule by taking outputs of the kinematics controllers as the inputs of the kinematics controllers by utilizing an retrieval method so that the trolley quickly and stably reaches an expected pose along a shortest path. The invention solves problems in the traditional vision servo method that the dynamics characteristic of the trolley is not considered during pose stability control and slow servo speed is slow, and the vision-based pose stabilization control method is practical and can enable the trolley to quickly and stably reach the expected pose.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Remotely Operated Orthopedic Surgical Robot System for Fracture Reduction with Visual-servo Control Method
ActiveUS20190125461A1Overcome deficienciesSimple compositionPhysical therapies and activitiesMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesFracture reductionEngineering
A remotely operated orthopedic surgical robot system for performing a fracture reduction operation using a visual-servo control method is provided. The system includes the surgical image acquisition equipment, the fracture reduction robot and the remote operation workstation. The fracture reduction robot has a plurality of types. The remote operation workstation includes a graphical user interface for doctors to examine the fracture reduction path planning result made by an artificial intelligence algorithm and to manually perform the path planning The remote operation workstation calculates the robot control quantity using the visual servo control method according to the path planning result and sends it to the robot.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
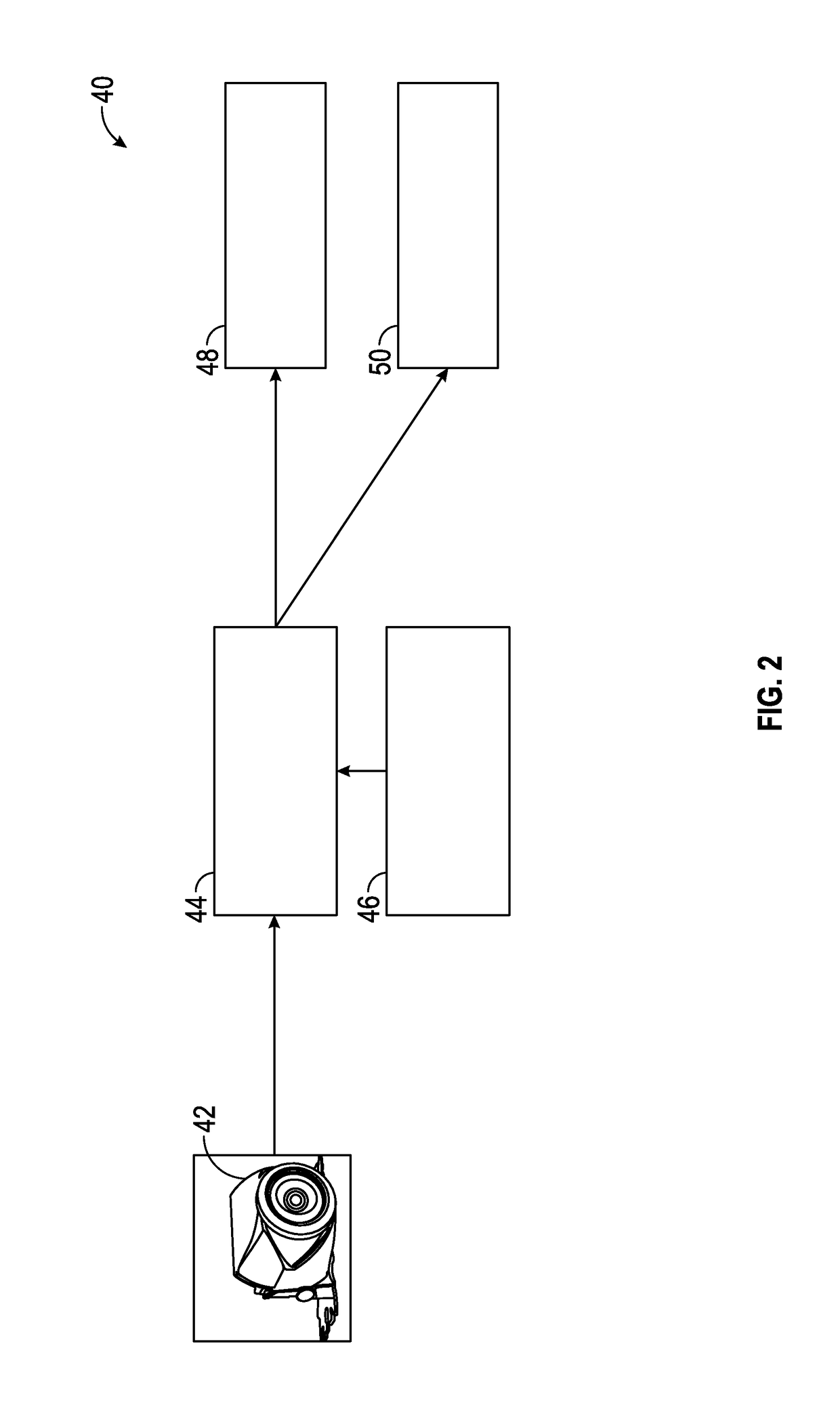
Uncalibrated visual servoing using real-time velocity optimization
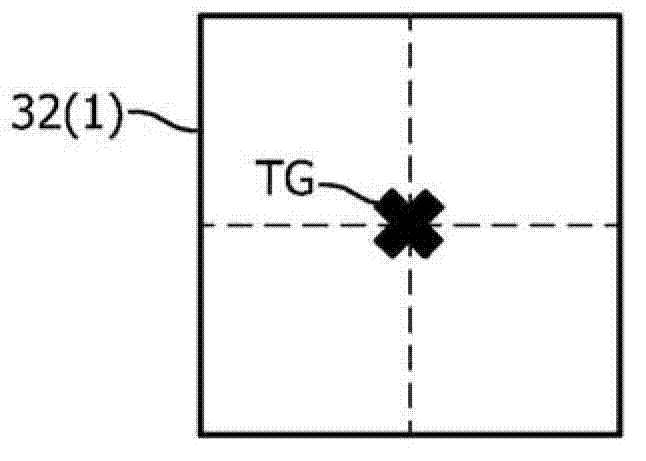
A robotic control method for a camera (30) having an optical view and a robot (40) having an end-effector (42) and one or more joints (41) for maneuvering end-effector (42). The robotic control method involves an acquisition of a digital video frame (32) illustrating an image as optically viewed by the camera (30), and an execution of a visual servoing for controlling a pose of end-effector (42) relative to an image feature within the digital video frame (32). The visual servoing involves an identification of a tracking vector (vtrk) within an image coordinate system (80) of the digital video frame (32) extending from a tracking point (TR) to a target point (TG) associated with the image feature, a mapping of the tracking vector within a configuration space (100) constructed from a robotic coordinate system (90) associated with the end-effector (42), and a derivation of a pose of the end-effector (42) within the robotic coordinate system (90) from the mapping of the tracking vector (vtrk) within the configuration space (100).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Laser mark automatic tracking extensometer control method based on uncalibrated visual servo
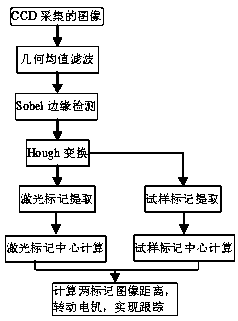
InactiveCN103439981AAvoid calibrationAvoid measurement errorsUsing optical meansControl using feedbackObservational errorVisual servoing
The invention discloses a laser mark automatic tracking extensometer control method based on uncalibrated visual servo. An image Jacobian matrix on-line identification method is adopted, the mapping relation between the actual distance between a laser mark and a sample mark, namely, the tracking displacement of the laser mark and image space tracking displacement is built, a controlled quantity is calculated by identifying the pixel distance difference between a Jacobian matrix and the central points of the two marks through a Karman filter, a servo motor is controlled to drive a pentaprism to rotate, the automatic tracking of the laser mark on the sample mark is achieved, and the laser mark displacement in the extending process is a sample deformation quantity. The method not only avoids the camera calibration step of an existing video extensometer and measuring errors introduced from the step, but also achieves the precise whole-process tracking of the laser mark on the sample mark, and is strong in environmental disturbance resistance capacity and high in tracking precision.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
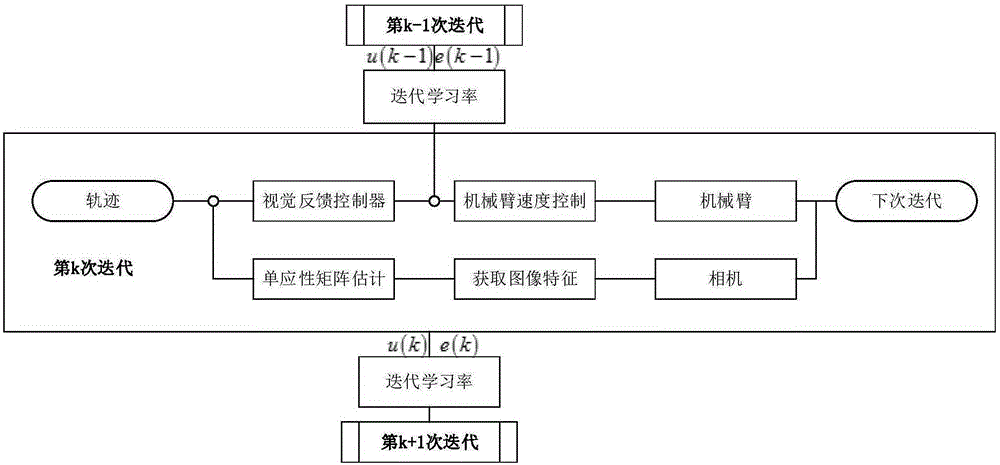
Visual servo control method based on iterative duration variation
InactiveCN105196292AAvoid instabilityOvercome field of view constraintsProgramme-controlled manipulatorRelational modelVisual servoing
The invention discloses a mechanical arm visual servo control method based on iterative duration variation. The method includes the steps that 1, a series of images are acquired in a demonstration mode; 2, the relation between the current image and the tracking image is acquired to define image features which express the movement condition of a mechanical arm; 3, a mutual relation model of a visual control system is established based on a mechanical arm kinematics model and a camera model, and an iterative feedforward and feedback control scheme is adopted; 4, if the phenomenon that a target object is beyond a visual range in the operation process of the mechanical arm, current iteration is ended. According to the method, it is not required that the target is continuously visual in the movement process, and meanwhile it is guaranteed that the mechanical arm can track the target image accurately to some degree.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Fast expansion random tree and potential field method based visual servo path planning method
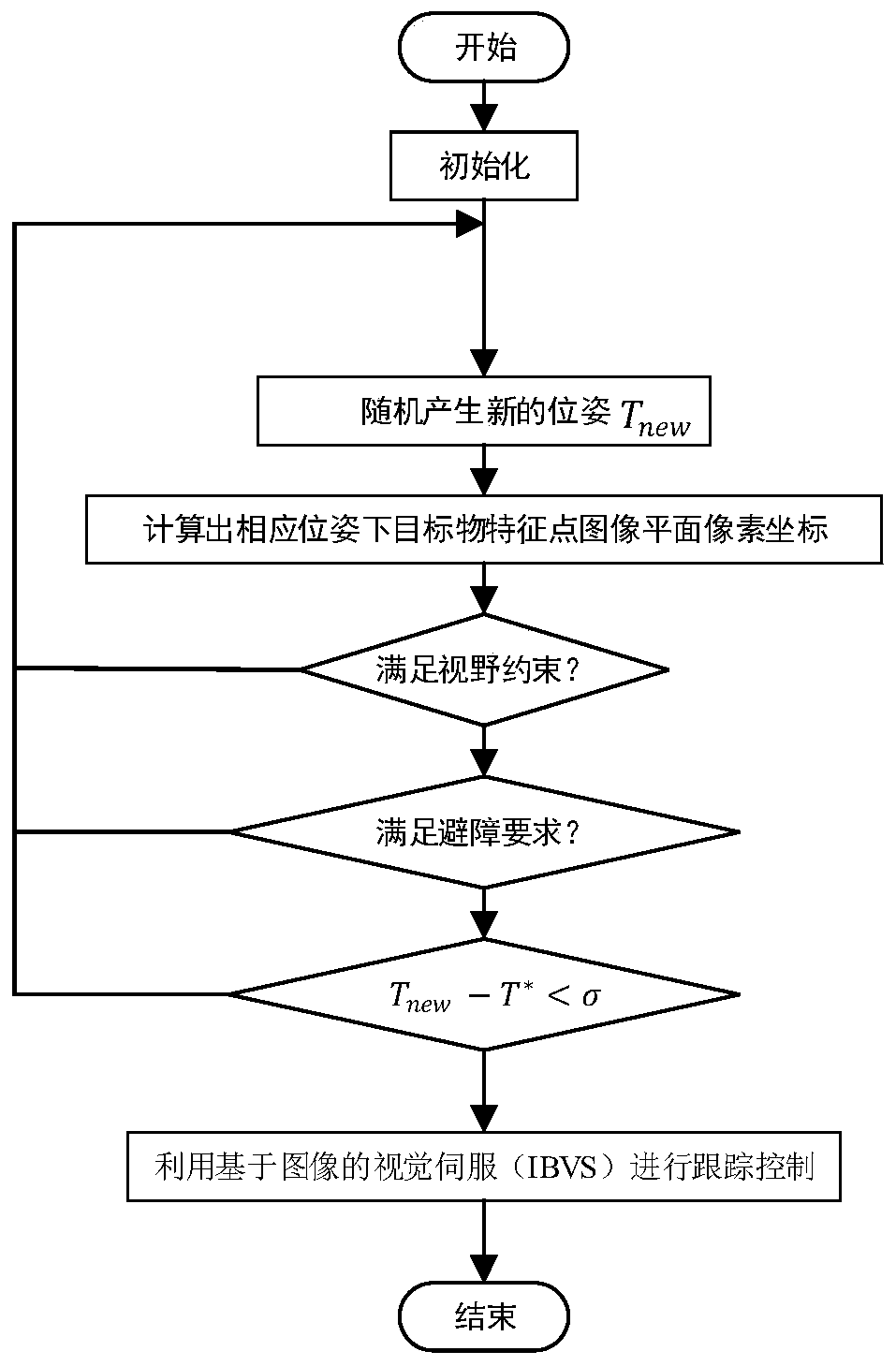
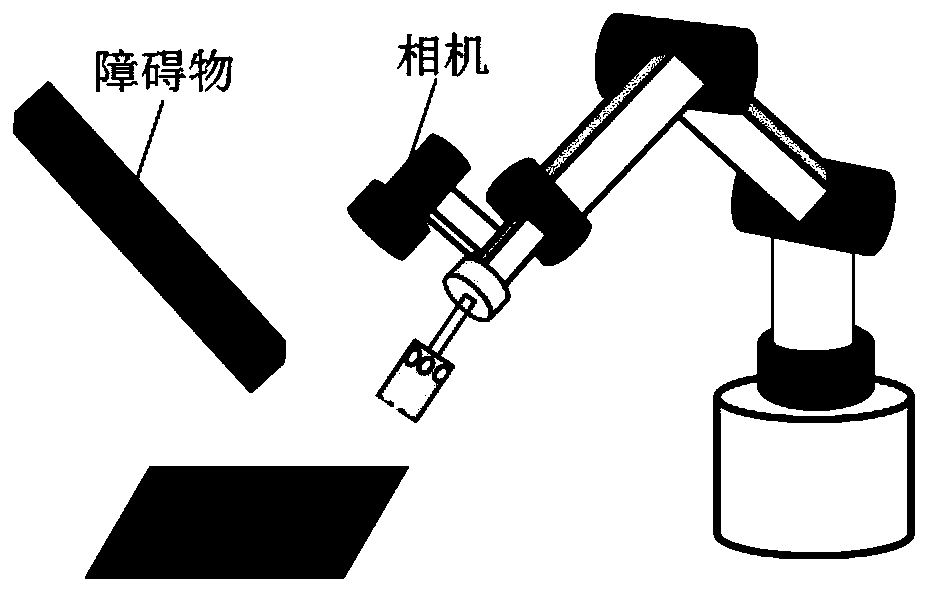
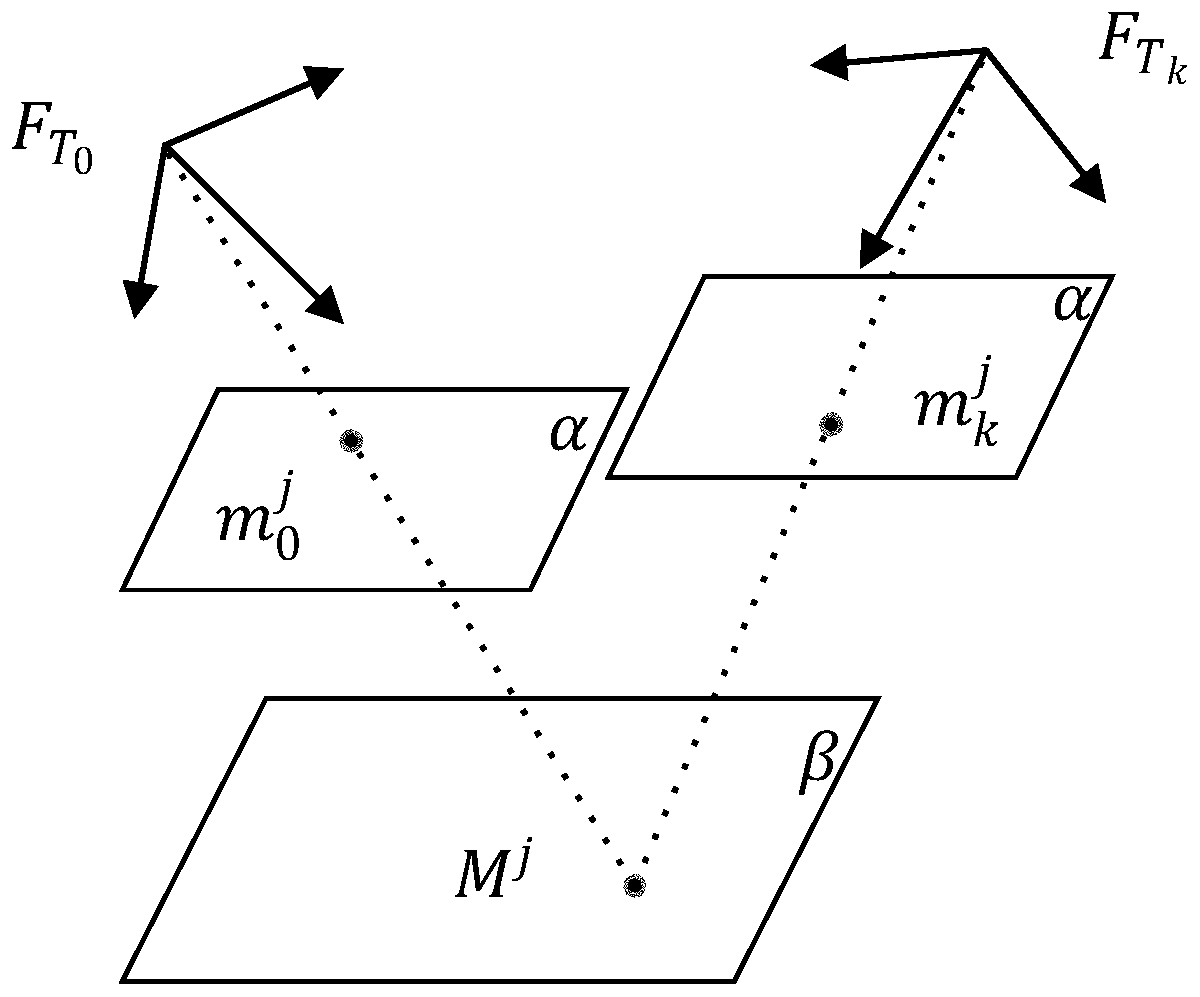
PendingCN109976347AEfficient searchMeet the problem of anti-collisionPosition/course control in two dimensionsVisibilityVisual field loss
The invention discloses a fast expansion random tree and potential field method based visual servo path planning method. The method includes giving mapping relation between task space coordinates andimage plane pixel coordinates of target feature points of a robot under any pose; and randomly producing new poses in task space, no obstacles between the new poses and the closest original pose beingguaranteed, and calculating the image plane pixel coordinates of the target feature points under the corresponding poses so as to maintain the image plane pixel coordinates in camera visual field scope. The method searches feasible camera paths in the task space to obtain corresponding image plane feature trajectories, and utilizes an image based visual servo (IBVS) to perform tracking control sothat the robot can realize the obstacle avoidance from an initial pose to an expected pose, and visual field constrained motion can be met. Through the introduction of a path planning technology in the visual servo of the robot, the problems of obstacle avoidance and feature visibility in the visual servo of the robot can be solved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
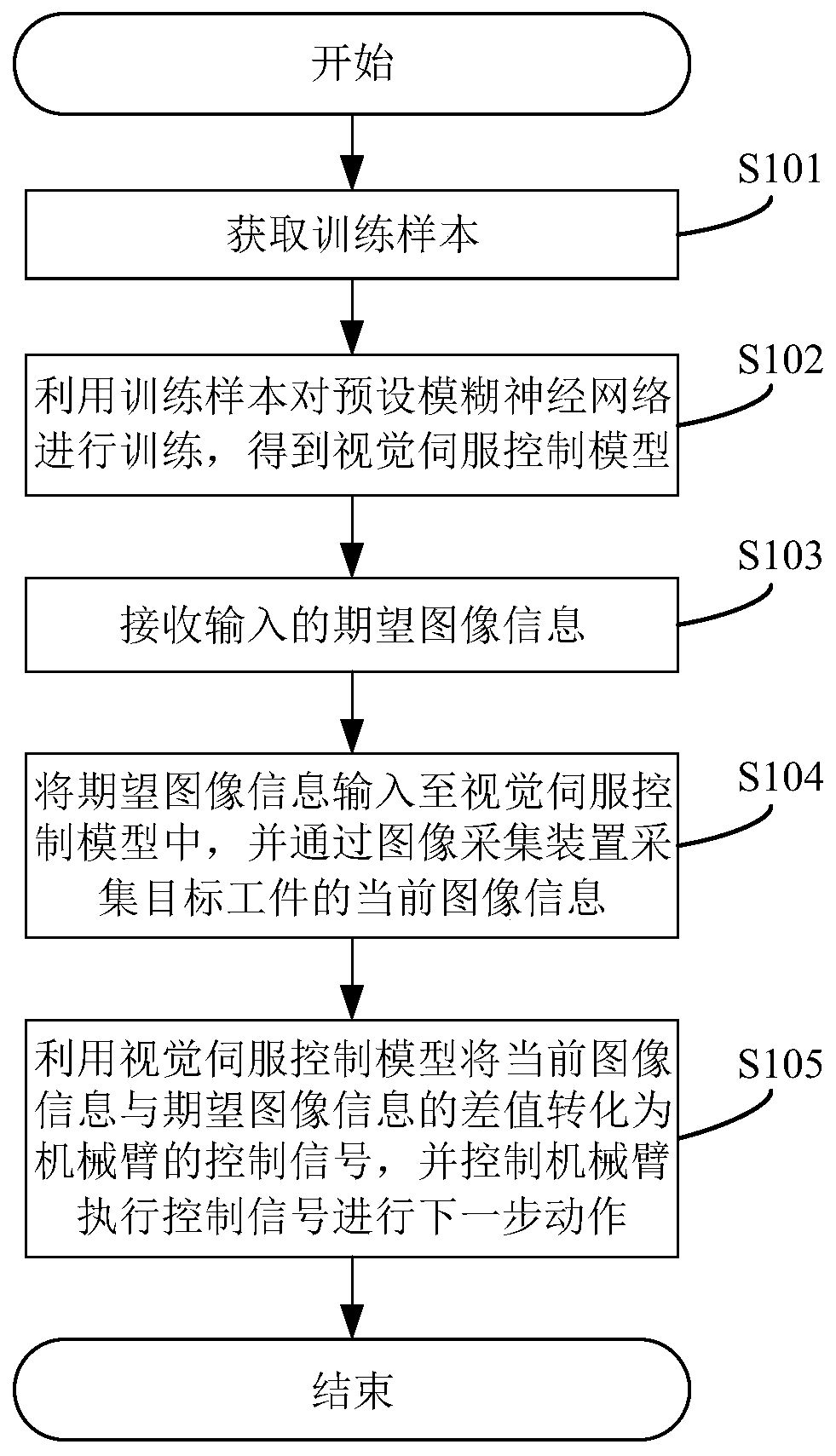
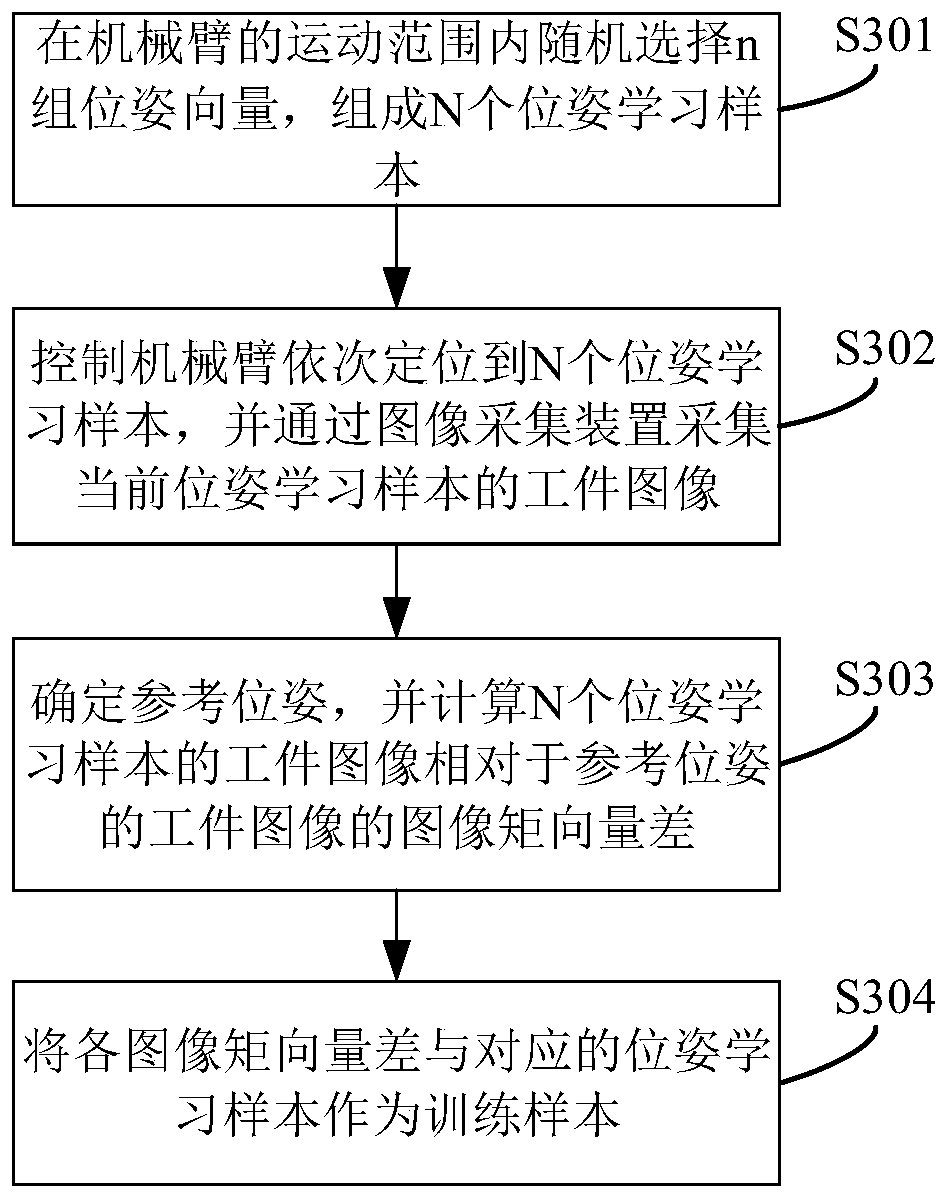
Method and system for visual servo controlling and equipment
PendingCN110000795AHigh speedHigh precisionProgramme-controlled manipulatorVisual servoingControl signal
The invention discloses a method for visual servo controlling. The method comprises the steps that a training sample is obtained, a preset fuzzy neural network is trained by using the training sampleto obtain a visual servo controlling model; input expecting image information is received; the expecting image information is input to the visual servo controlling model, and current image informationof a target work piece is collected through an image collecting device; the difference of the current image information and the expecting image information is converted into a controlling signal of amanipulator, and the manipulator is controlled to execute the controlling signal to perform the next movement. According to the method, Jacobian matrix inversion is omitted to greatly improve the speed of visual servo controlling, complicated marking is not needed, the precision of visual servo controlling is effectively improved, and the motion controlling of a robot on automatically grabbing and transporting casting pieces is achieved. The invention further provides a visual servo controlling system, equipment and a computer storage medium which can achieve the above advantages.
Owner:SUZHOU VOCATIONAL UNIV
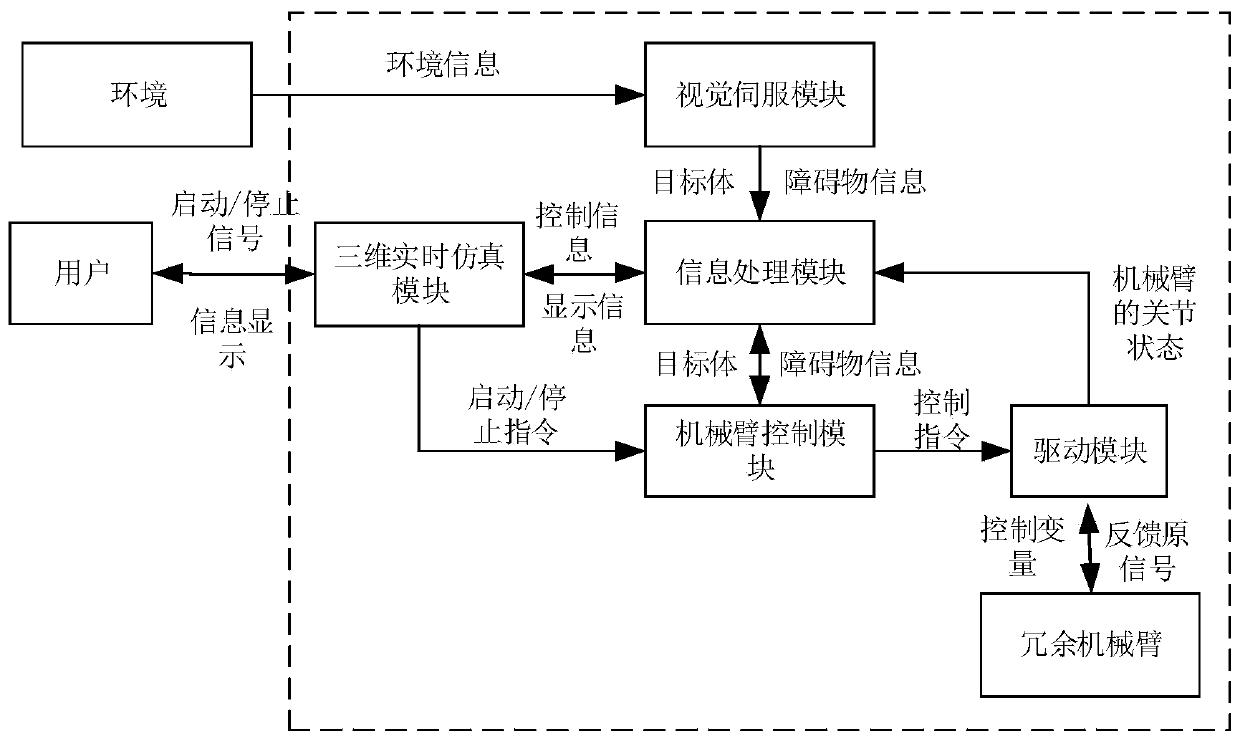
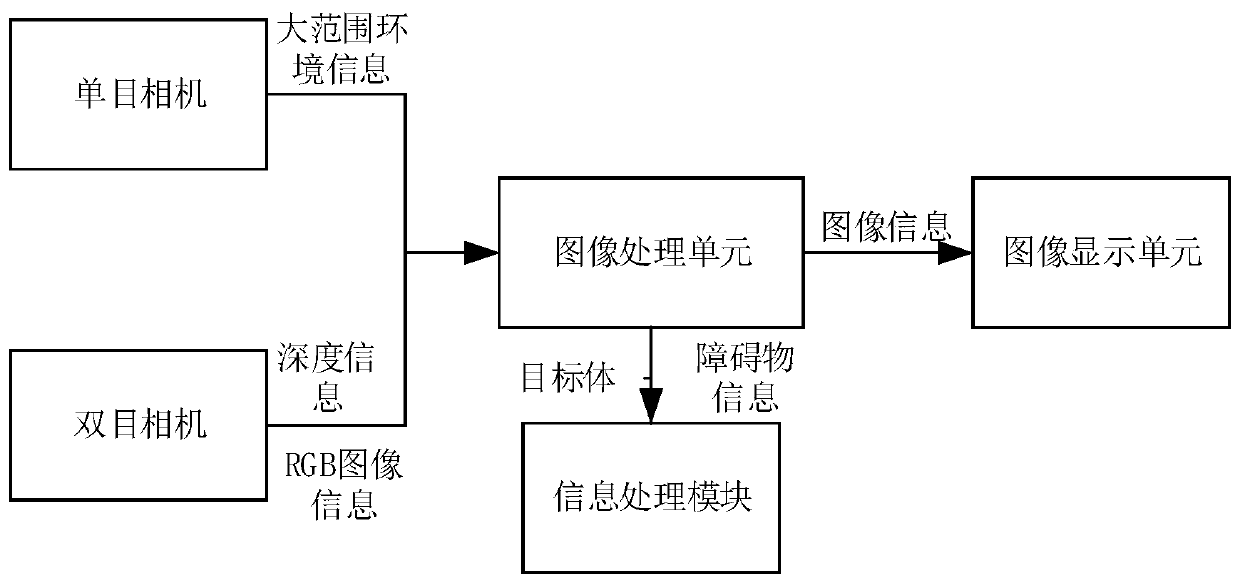
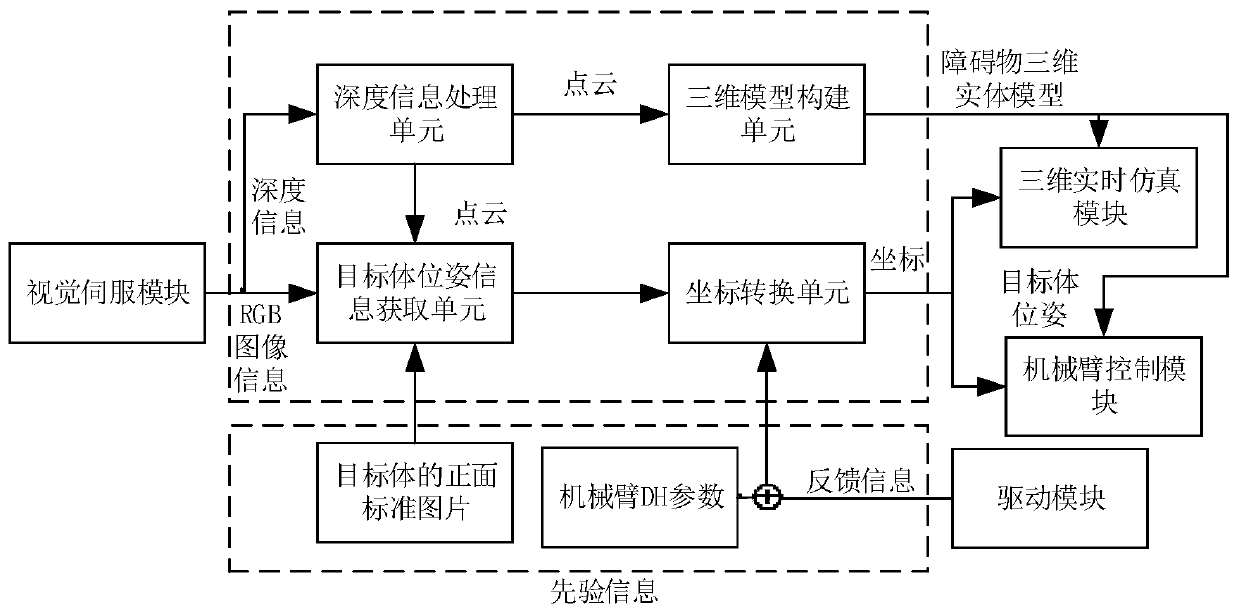
Redundancy-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm visual servo obstacle avoiding system
The invention provides a redundancy-degree-of-freedom mechanical arm visual servo obstacle avoiding system. The system comprises a visual servo module, an information processing module, a mechanical arm control module, a driving module and a three-dimensional real-time simulating module; the driving module realizes communication between the mechanical arm control module and a redundancy mechanicalarm; the visual servo module acquires environment information of working space, and identifies target body and obstacle information; the information processing module builds three-dimensional solid models of obstacles according to the target body and obstacle information to obtain pose information of target bodies; and the mechanical arm control module converts targets in the working space to control instructions of joint space according to user operation instructions from the three-dimensional real-time simulating module, the three-dimensional solid models of the obstacles and the pose information of the target bodies, and sends the control instructions to the driving module to control mechanical arm terminals to move to the target bodies. The system integrates the advantages of visual servo and the objective function requirements of obstacle avoidance, can be verified offline, and can be connected with solid mechanical arms to achieve broad application prospect.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com