Acidic heat-resisting isoamylase genetic engineering bacterium and application thereof
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and isoamylase, applied in the field of enzyme engineering, can solve the problems of too expensive raw materials, substrate concentration, long reaction cycle, and difficulty in industrialized production, and achieve the effect of high enzyme activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Embodiment 1: the construction of genetically engineered bacteria
[0021] 1. According to the gene sequence of Tfu_1891 registered on NCBI (Genbank No. NC_007333.1), the thermostable isoamylase gene sequence was synthesized by chemical total synthesis method, cloned into the pMD18-T simple vector (commercial tool vector), and the ligated product was transformed Escherichia coli JM109, the transformation product was spread on LB plates containing 100 mg / L ampicillin. After culturing overnight at 37°C, colonies were selected and inserted into LB liquid medium. After 8-10 hours, the plasmid was extracted and named as Tfu_1891 / pMD18-T simple. The plasmid was sequenced. The results showed that the inserted fragment was a 2124bp DNA fragment encoding a protein with 708 amino acids.
[0022] 2. The plasmid used to construct the expression vector in Escherichia coli is pT7-7 with a T7 promoter. The pT7-7 plasmid and Tfu_1891 / pMD18-T simple were digested with Nde I and HindII...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Embodiment 2: fermentation produces isoamylase
[0025] Transfer the glycerol tube strain to LB medium for 37°C liquid culture overnight, and then insert TB (glycerol 5g / L, peptone 12g / L, yeast extract 24g / L, K 2 HPO 4 12.54g / L, KH 2 PO 4 2.31g / L) fermentation liquid medium, cultured at 30°C until OD reached 0.6, then induced with a final concentration of 0.01μM isopropylthio-β-D-galactoside, and cultured at constant temperature or lowered to 25°C for 36 to 48 hours, Centrifuge the bacteria, suspend the cells with pH5.50.1M phosphate-citrate buffer, ultrasonically disrupt, measure the activity of isoamylase in the supernatant after centrifugation, and the fermentation activity of recombinant isoamylase reaches 3185U / mL.
Embodiment 3
[0026] Example 3: Purification and Enzymatic Properties of Recombinant Isoamylase
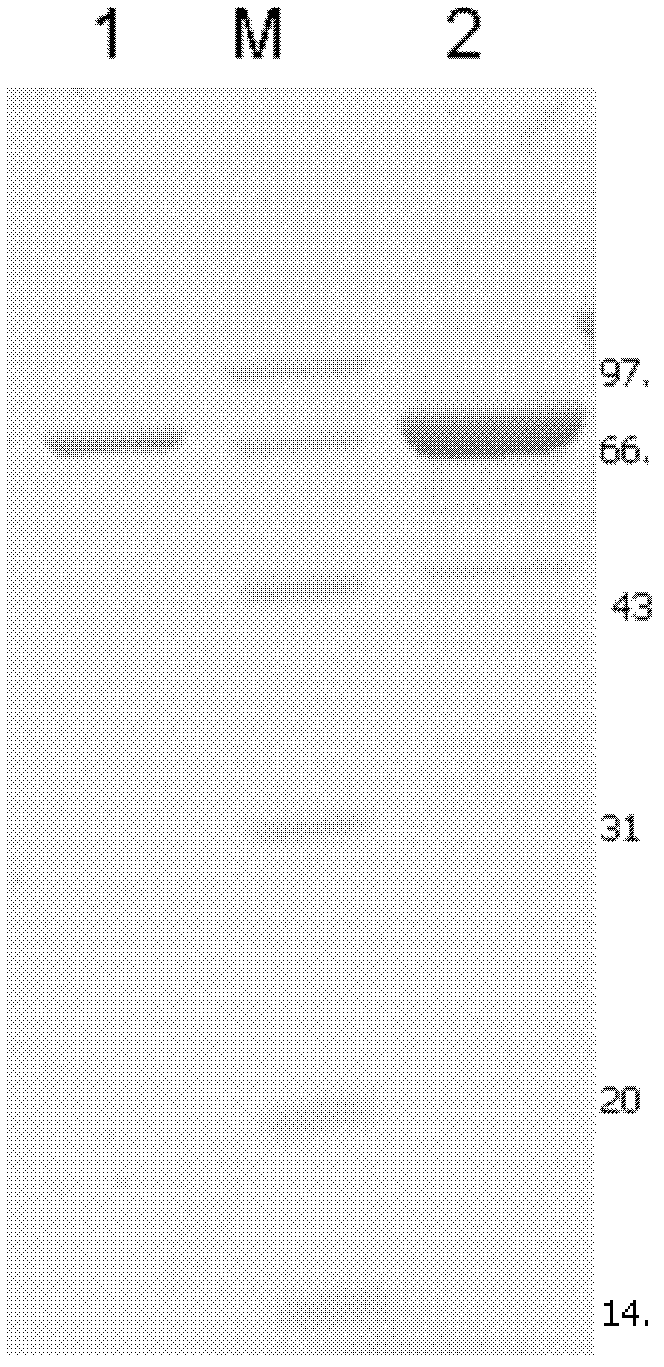
[0027] The sonicated supernatant was centrifuged at 40,000×g for 20 min at 4°C to remove cell debris. Add 20% solid ammonium sulfate to the supernatant for salting out overnight, centrifuge at 40,000×g for 20 minutes at 4°C, dissolve the precipitate with an appropriate amount of pH 5.5, 20mM phosphoric acid-citric acid buffer, and filter it through a 0.4μm membrane to make a sample sample. After purified by DEAE-Sepharose anion exchange resin, the sample was added to Sephadex G50 for purification to obtain electrophoretic pure isoamylase. figure 1 .
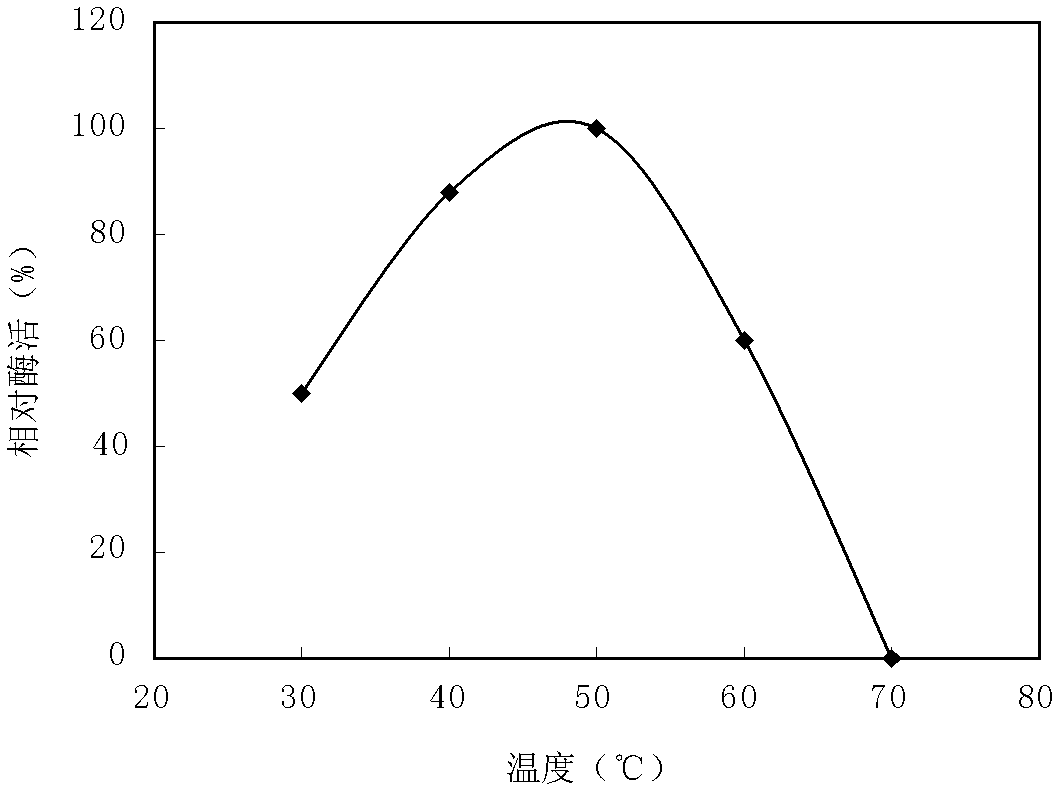
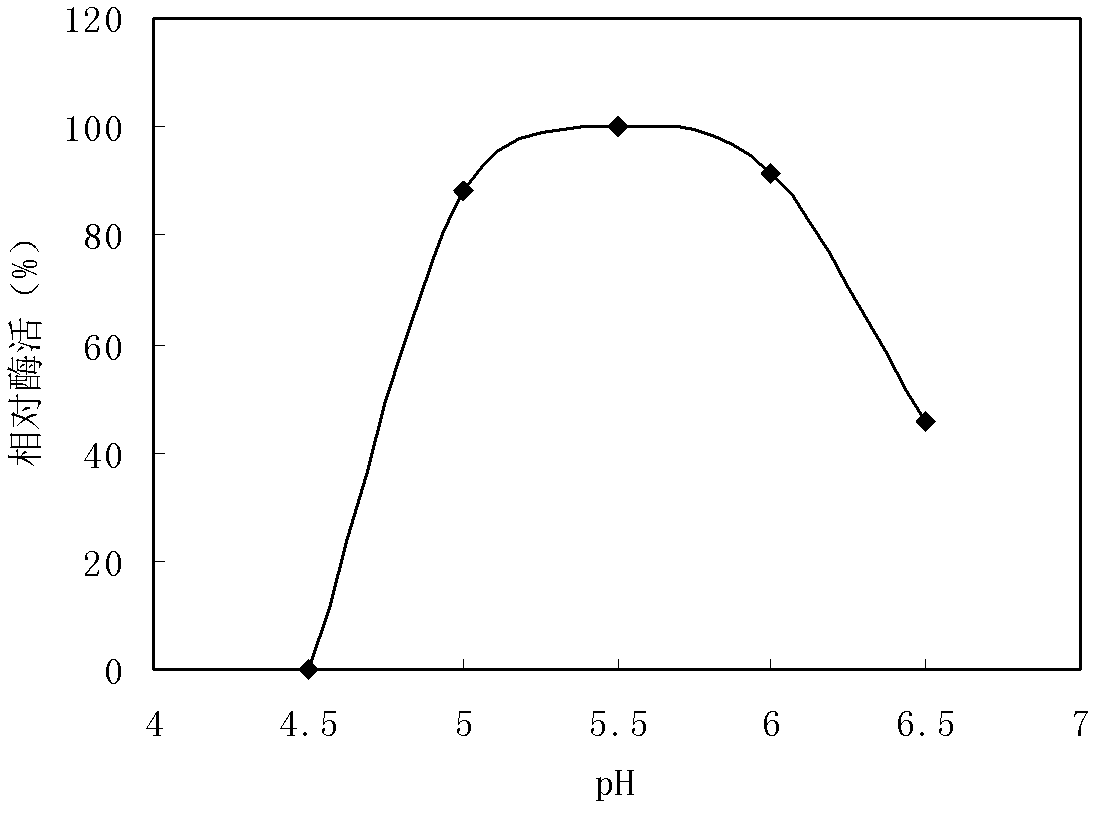
[0028]The recombinant isoamylase was tested for hydrolysis of different substrates, and it was found that it could hydrolyze waxy corn amylopectin, but not glycogen and pullulan. The results showed that the gene encoding recombinant isoamylase was highly expressed. The optimum temperature for acid thermostable isoamylase is 50°C ( figure 2 ),...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com