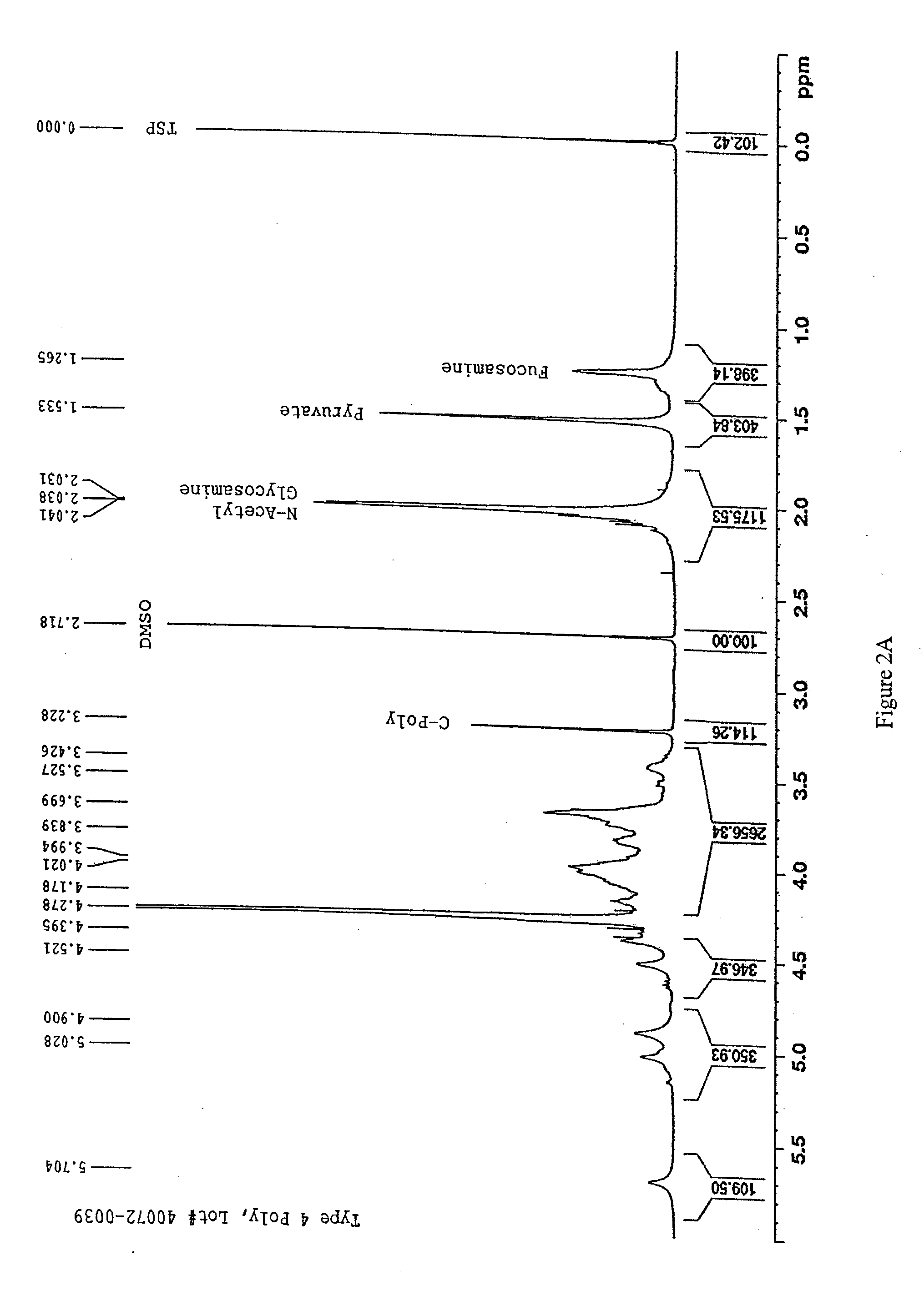
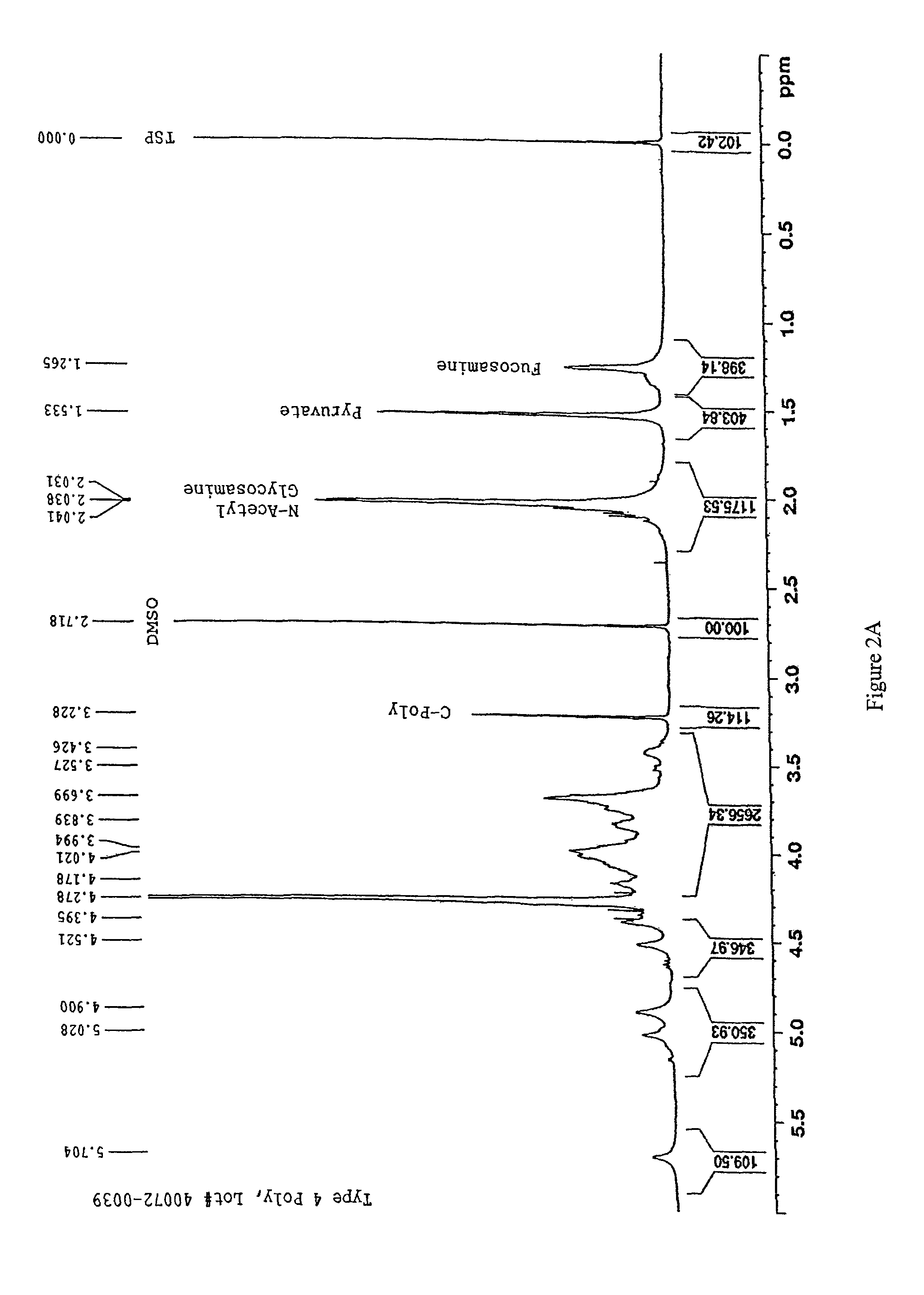
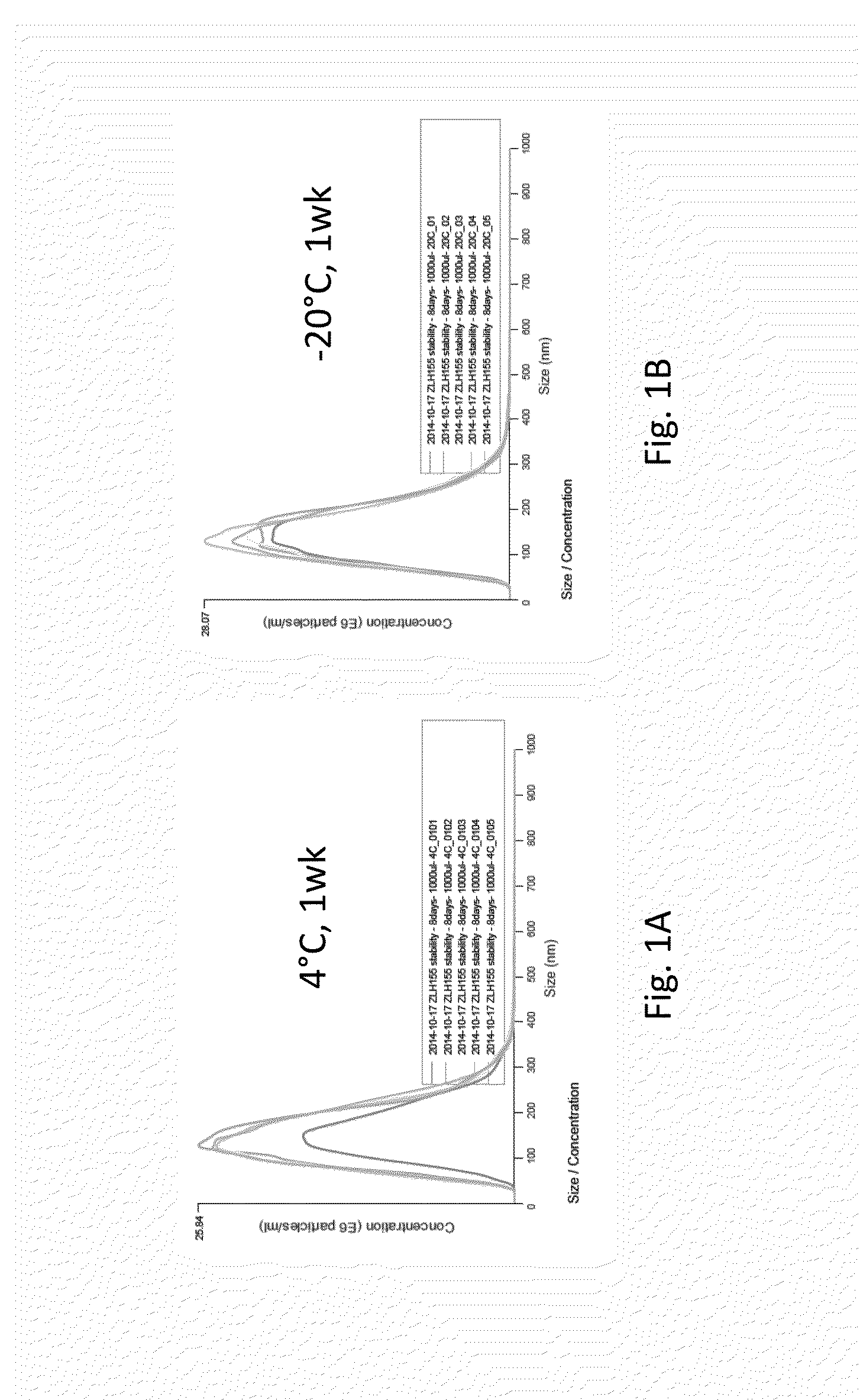
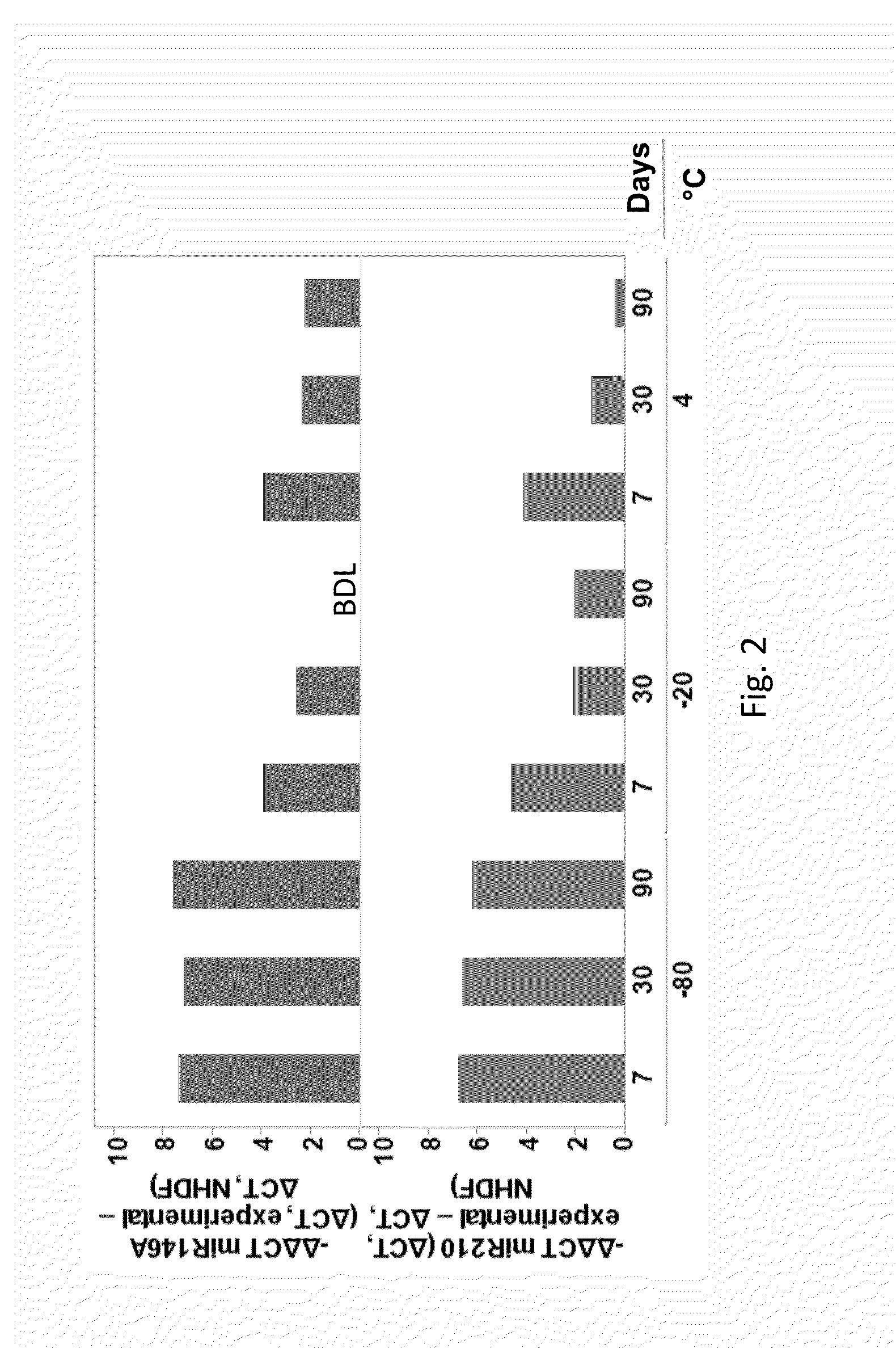
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
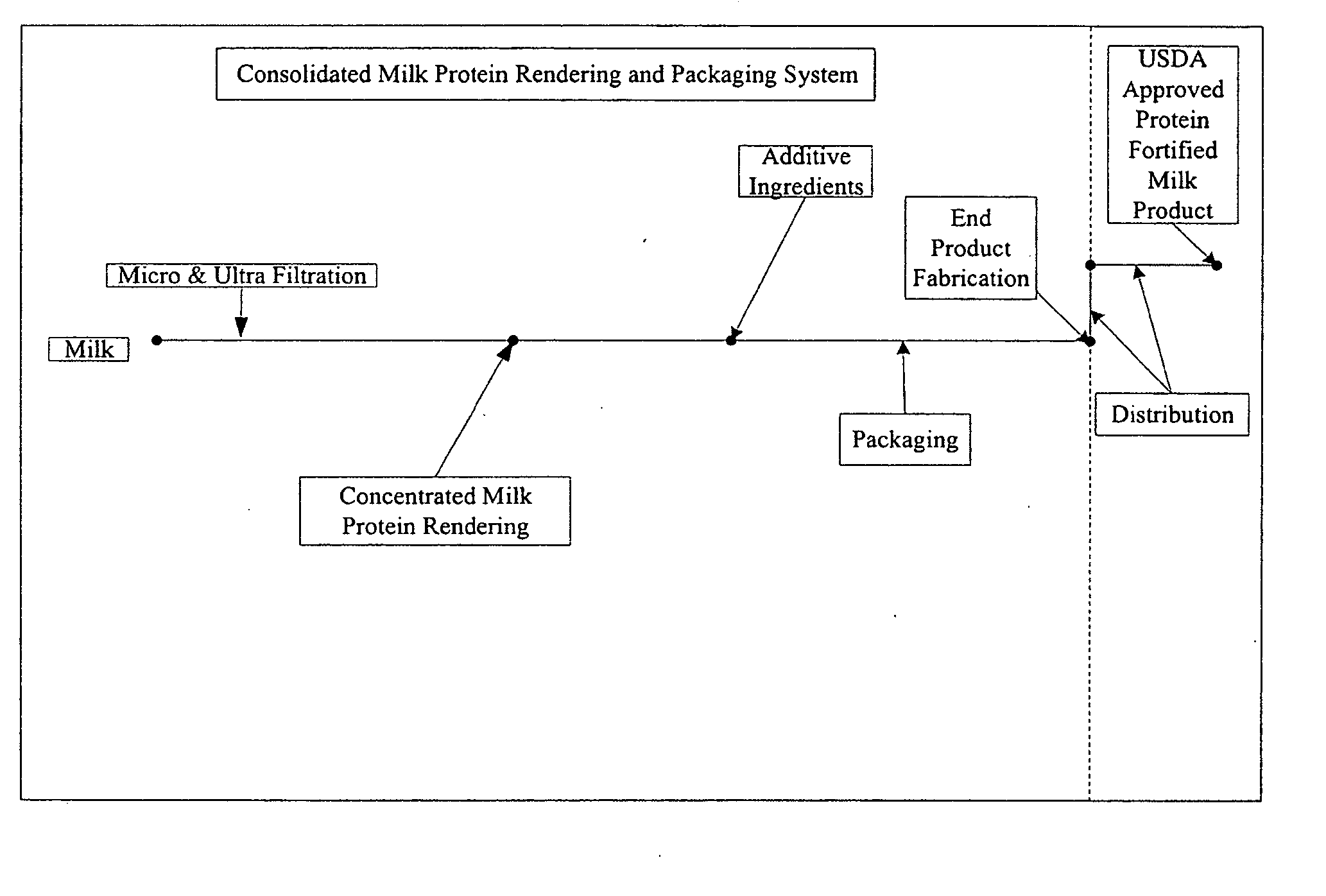
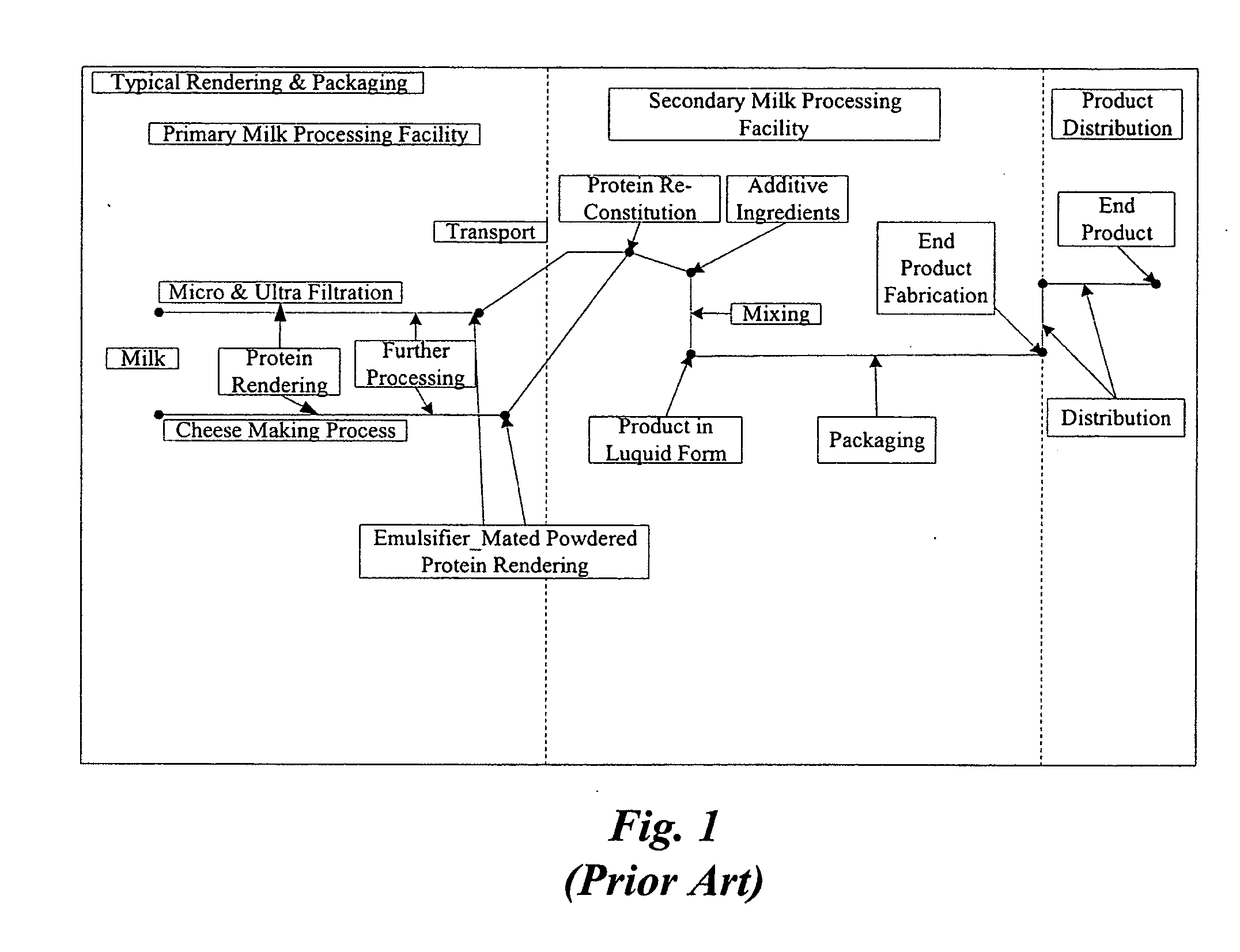
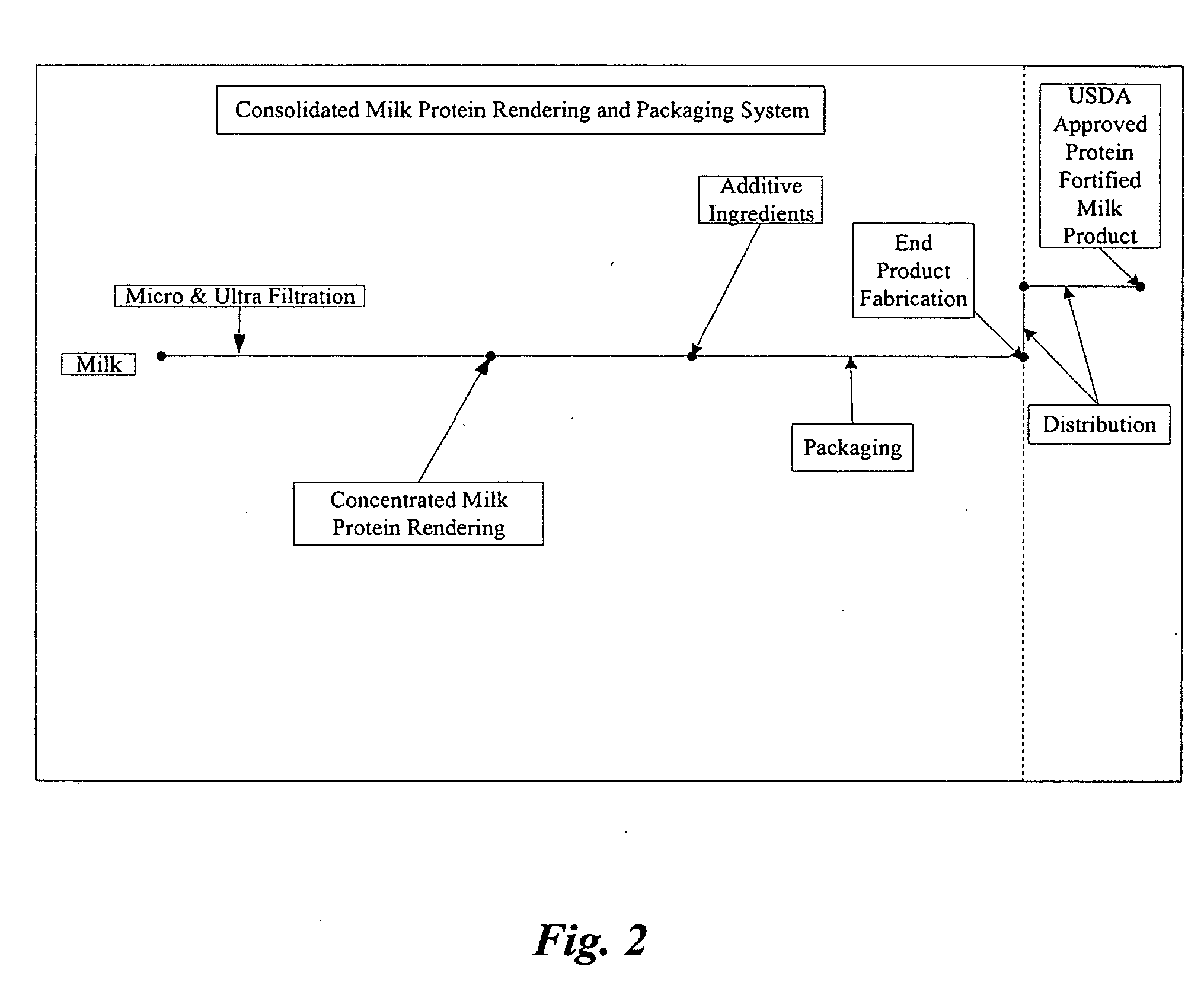
211 results about "Diafiltration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
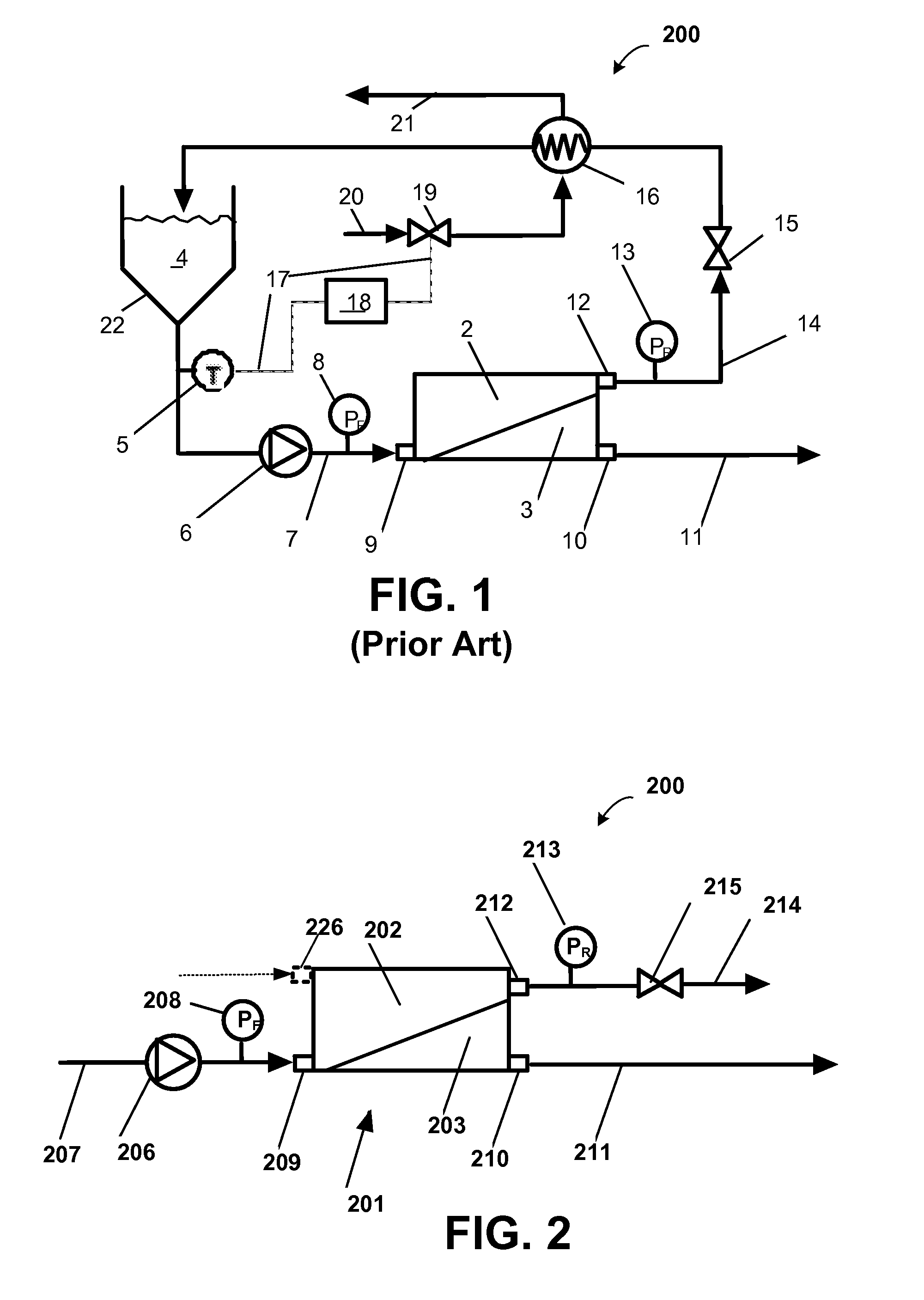
Diafiltration is a dilution process that involves removal or separation of components (permeable molecules like salts, small proteins, solvents etc.,) of a solution based on their molecular size by using micro-molecule permeable filters in order to obtain pure solution.
Electro-optic assemblies, and adhesives and binders for use therein
InactiveUS20090122389A1Lower volume resistivityLayered productsPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesOrganic matterAdhesive materials
An electro-optic assembly comprises an adhesive layer and a layer of electro-optic material. The adhesive layer comprises a polymeric adhesive material and an ionic material having either its cation or its anion fixed to the polymeric adhesive material. The ionic material reduces the volume resistivity of the polymeric adhesive material and is not removed upon heating to 50° C. In a similar electro-optic assembly comprising an adhesive layer and a layer of electro-optic material, the adhesive layer comprises a polymeric adhesive material which has been subjected to dialysis or diafiltration to remove organic species having a molecular weight less than about 3,500, so that the adhesive material has a content of N-methylpyrrolidone not exceeding 500 ppm based upon the total weight of the adhesive layer and layer of electro-optic material.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Production of Soluble Protein Solutions from Soy ("S701")
ActiveUS20100098818A1Prevent oxidationMilk preparationProtein composition from vegetable seedsProtein solutionSports drink
A soy protein product, which may be an isolate, produces transparent heat-stable solutions at low pH values and is useful for the fortification of soft drinks and sports drinks without precipitation of protein. The soy protein product is obtained by extracting a soy protein source material with an aqueous calcium salt solution to form an aqueous soy protein solution, separating the aqueous soy protein solution from residual soy protein source, adjusting the pH of the aqueous soy protein solution to a pH of about 1.5 to about 4.4 to produce an acidified clear soy protein solution, which may be dried, following optional concentration and diafiltration, to provide the soy protein product.
Owner:BURCON NUTRASCI MB
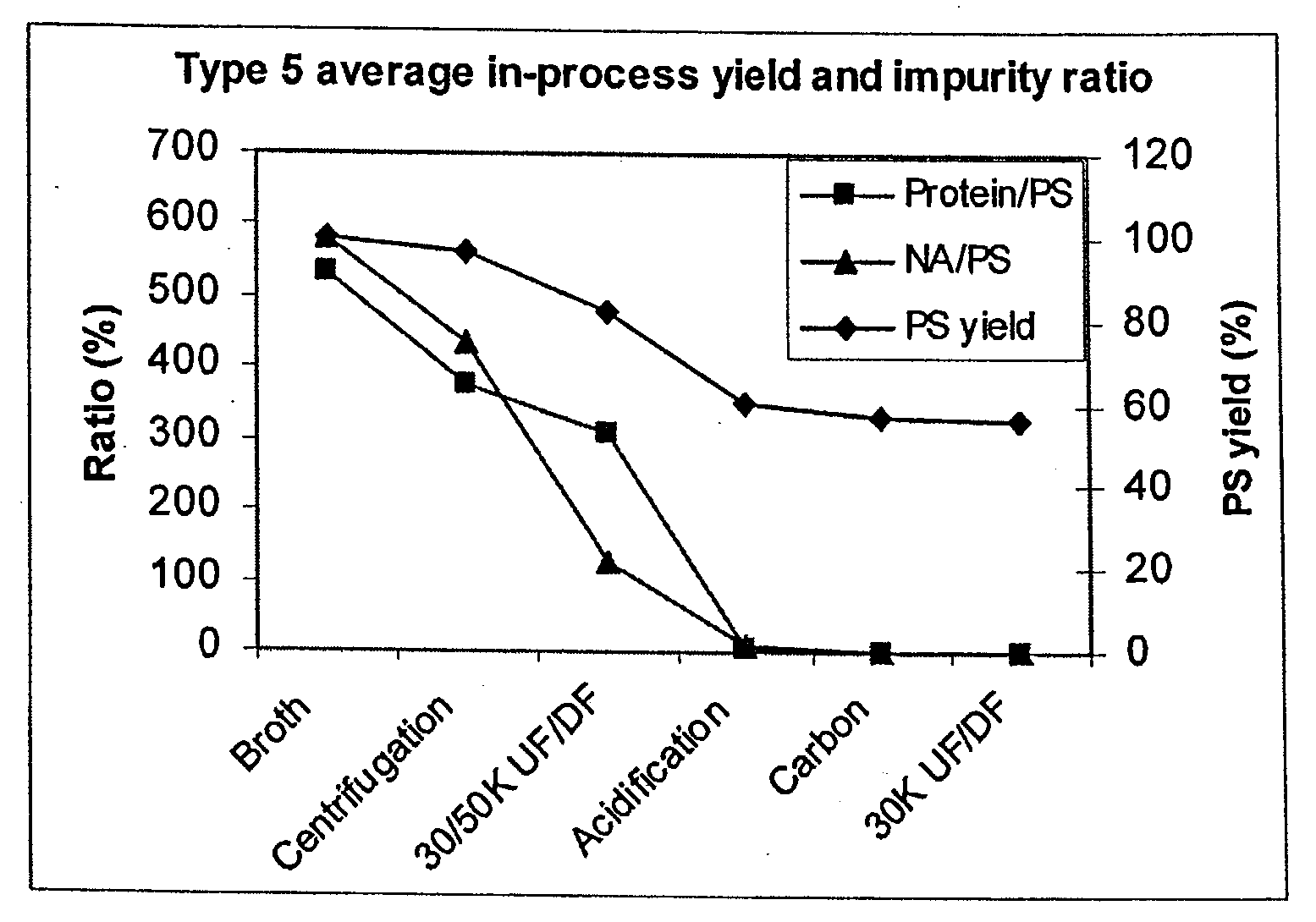
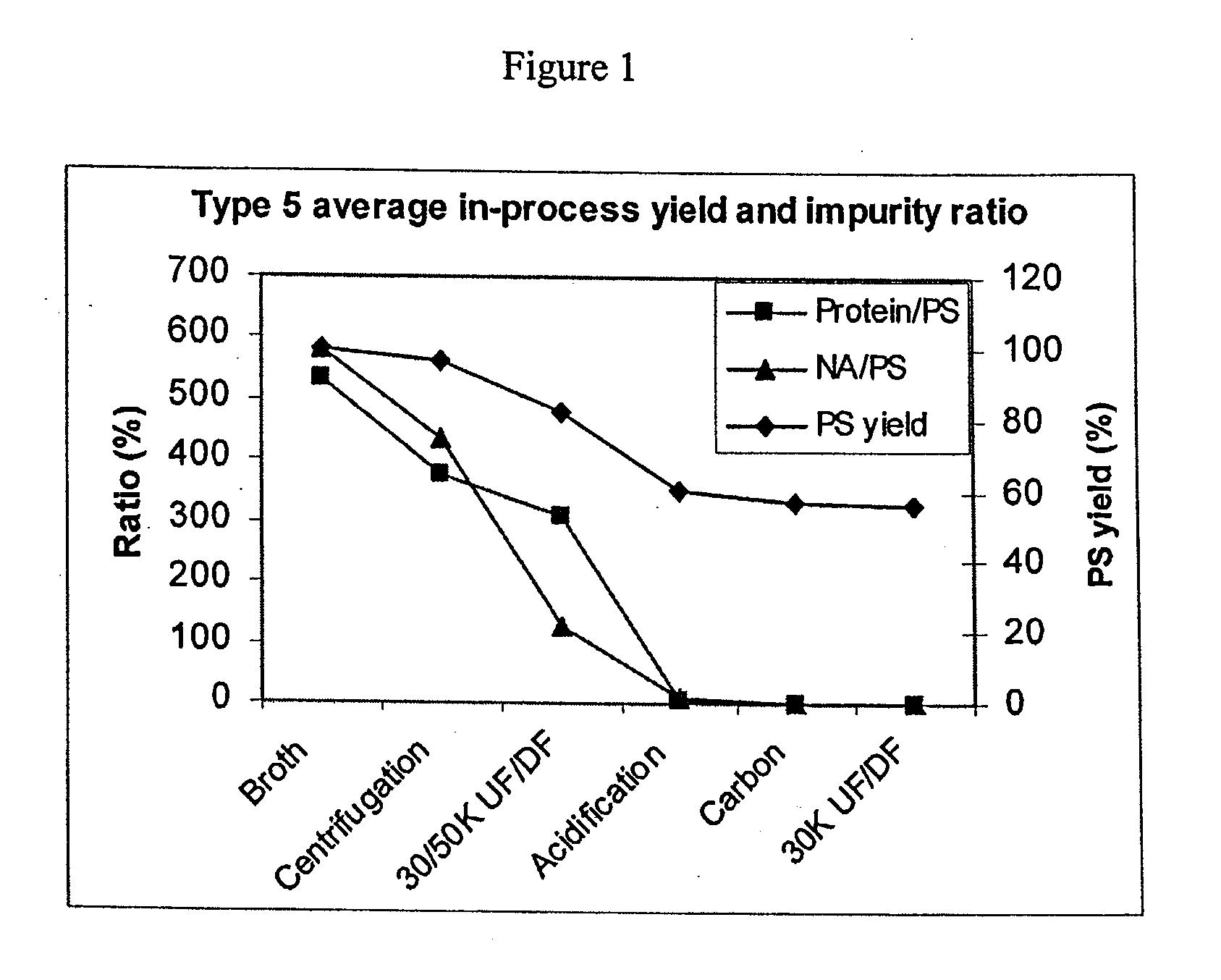
Shortened purification process for the production of capsular streptococcus pneumoniae polysaccharides
ActiveUS20080286838A1Increase polysaccharide concentrationReduce the presence of impuritiesAntibacterial agentsSugar derivativesPurification methodsActivated carbon filtration
A shortened process for producing a solution containing substantially purified capsular polysaccharides from a cellular Streptococcus pneumoniae lysate broth is described. Ultrafiltering and diafiltering a clarified S. pneumoniae lysate followed by pH adjustment to less than 4.5, preferably about 3.5, precipitated at least 98% of the protein in the solution without seriously affecting polysaccharide yield. Furthermore, following ultrafiltration and diafiltration and acidification to a pH of less than 4.5, filtration using activated carbon precipitated at least 90% of remaining protein without seriously affecting polysaccharide yield. Exemplary, non-limiting S. pneumoniae serotypes that can be purified using the shortened process of the invention are 1, 4, 5, 6A, 6B, 7F, 9V, 14, 18C, 19A, 19F, and 23F. In one embodiment, the Streptococcus pneumoniae cells are lysed using deoxycholate sodium (DOC), while in another embodiment the lytic agent is a non-animal derived lytic agent such as N-lauryl sarcosine sodium (NLS).
Owner:WYETH LLC
Ultrafiltration and diafiltration formulation methods for protein processing
InactiveUS20130195888A1Speed up the processAffecting qualityDepsipeptidesAntibody ingredientsProtein processingChemistry
Disclosed herein are methods of purifying proteins using ultrafiltration and diafiltration processes.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Isolation and purification of antibodies using protein a affinity chromatography
ActiveUS20100135987A1Easy to disassembleReduce or inactivate pH-sensitive virusesAntipyreticAnalgesicsIon exchangeAntibody Affinity Chromatography
Disclosed herein are methods for the isolation and purification of antibodies wherein the use of an affinity chromatographic step results in an antibody composition sufficiently pure for pharmaceutical uses. The methods described herein comprise pH viral reduction / inactivation, ultrafiltration / diafiltration, affinity chromatography, preferably Protein A affinity, ion exchange chromatography, and hydrophobic chromatography. Further, the present invention is directed toward pharmaceutical compositions comprising one or more antibodies of the present invention.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Process for concentration of macromolecules
ActiveUS20060149042A1Reduce conductivityHigh final concentrationDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsCell culture supernatantOragene
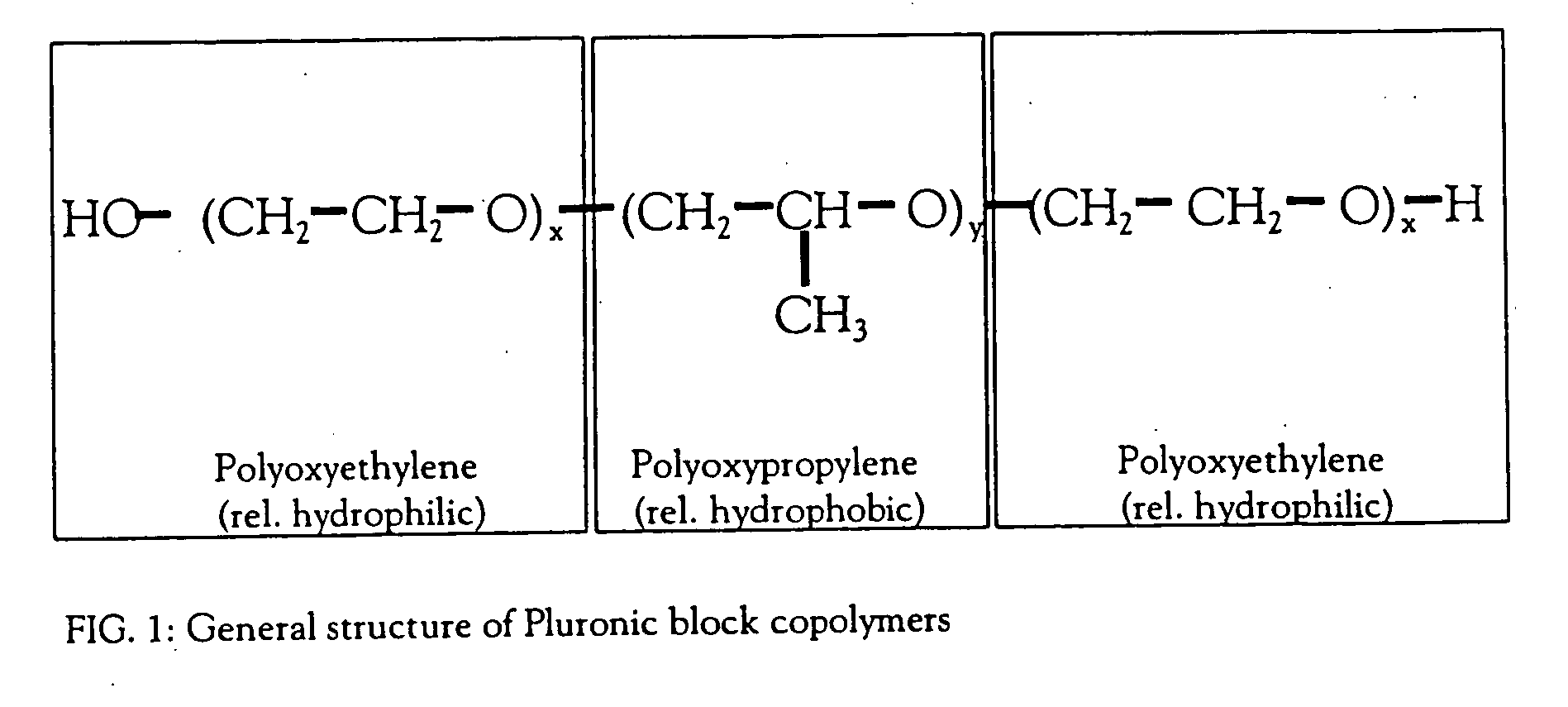
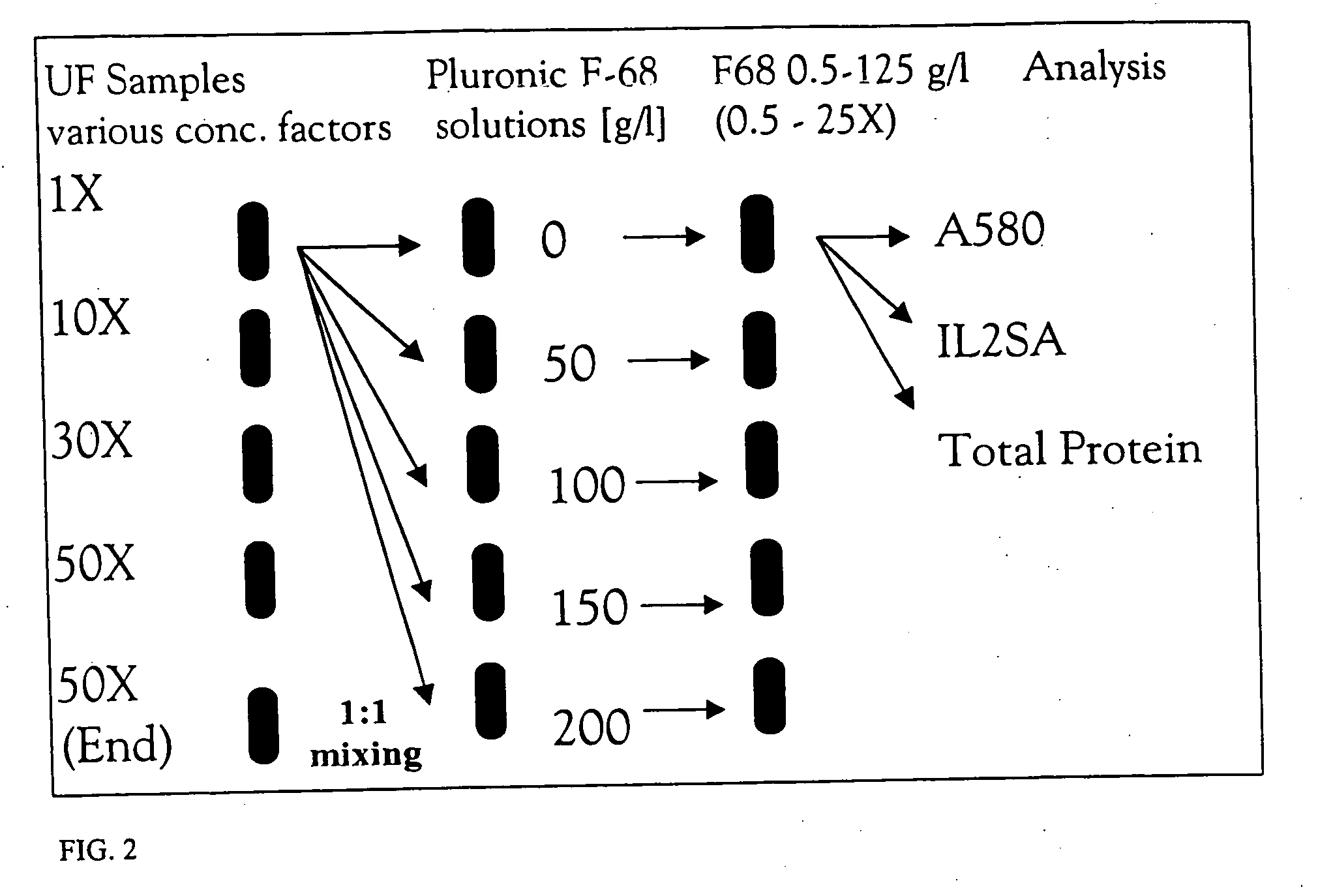
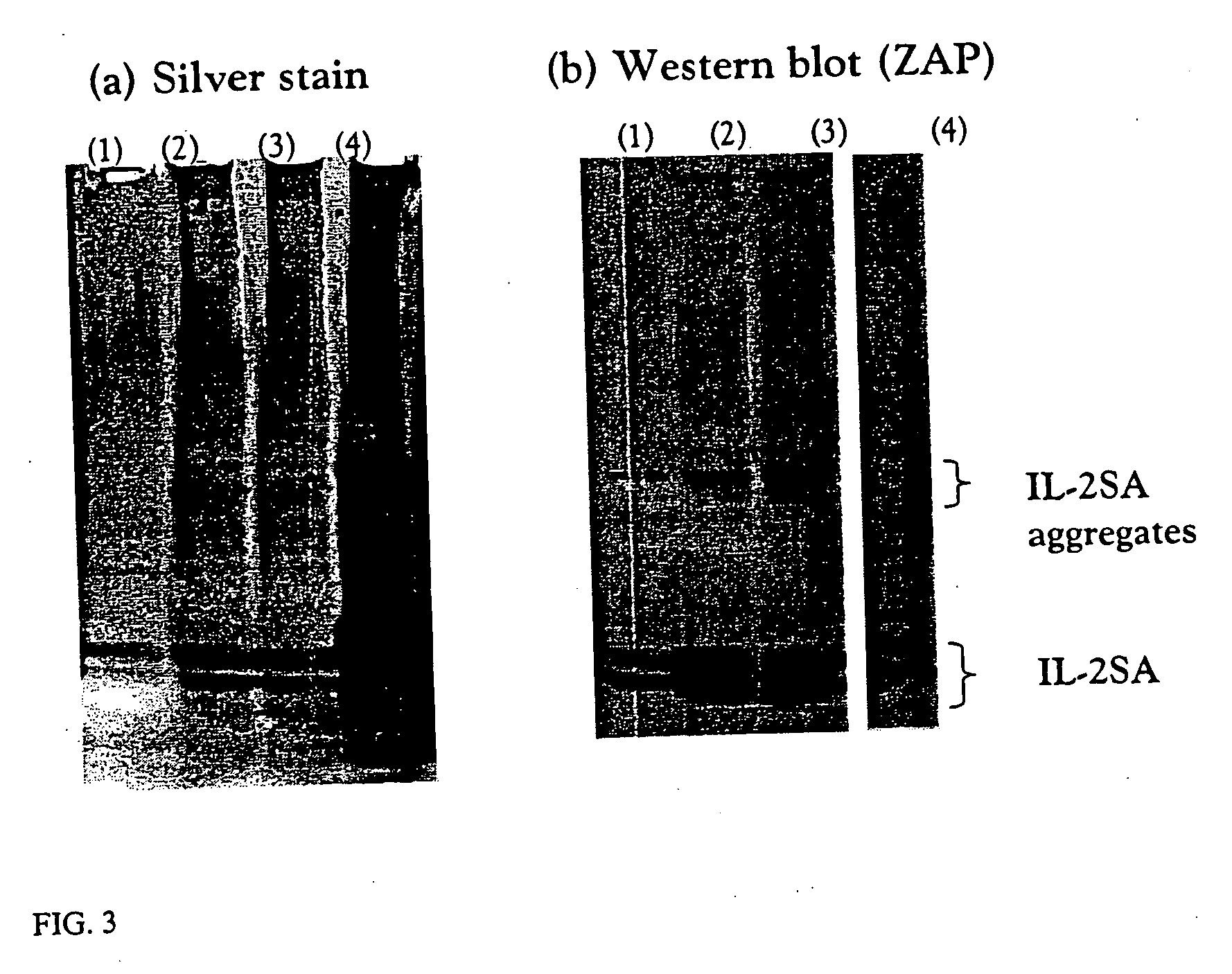
The invention provides methods for concentrating a macromolecule from a solution comprising the macromolecule and an organic polymer by first subjecting the solution to ultrafiltration to produce a first retentate solution, then adjusting the conductivity of the first retentate solution such that any protein precipitation induced by the organic polymer is essentially prevented to produce a second retentate solution, and then subjecting the second retentate solution to ultrafiltration. In a preferred embodiment, the conductivity is adjusted by diafiltration against water, suitable diluent or buffer. Preferably, the invention pertains to the concentration of solutions of native or recombinant proteins. The invention further pertains preferably to methods for the concentration of cell culture supernatant comprising a product protein and organic polymers of the Pluronic family of block co-polymers, and more preferably comprising Pluronic F-68 block co-polymer.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
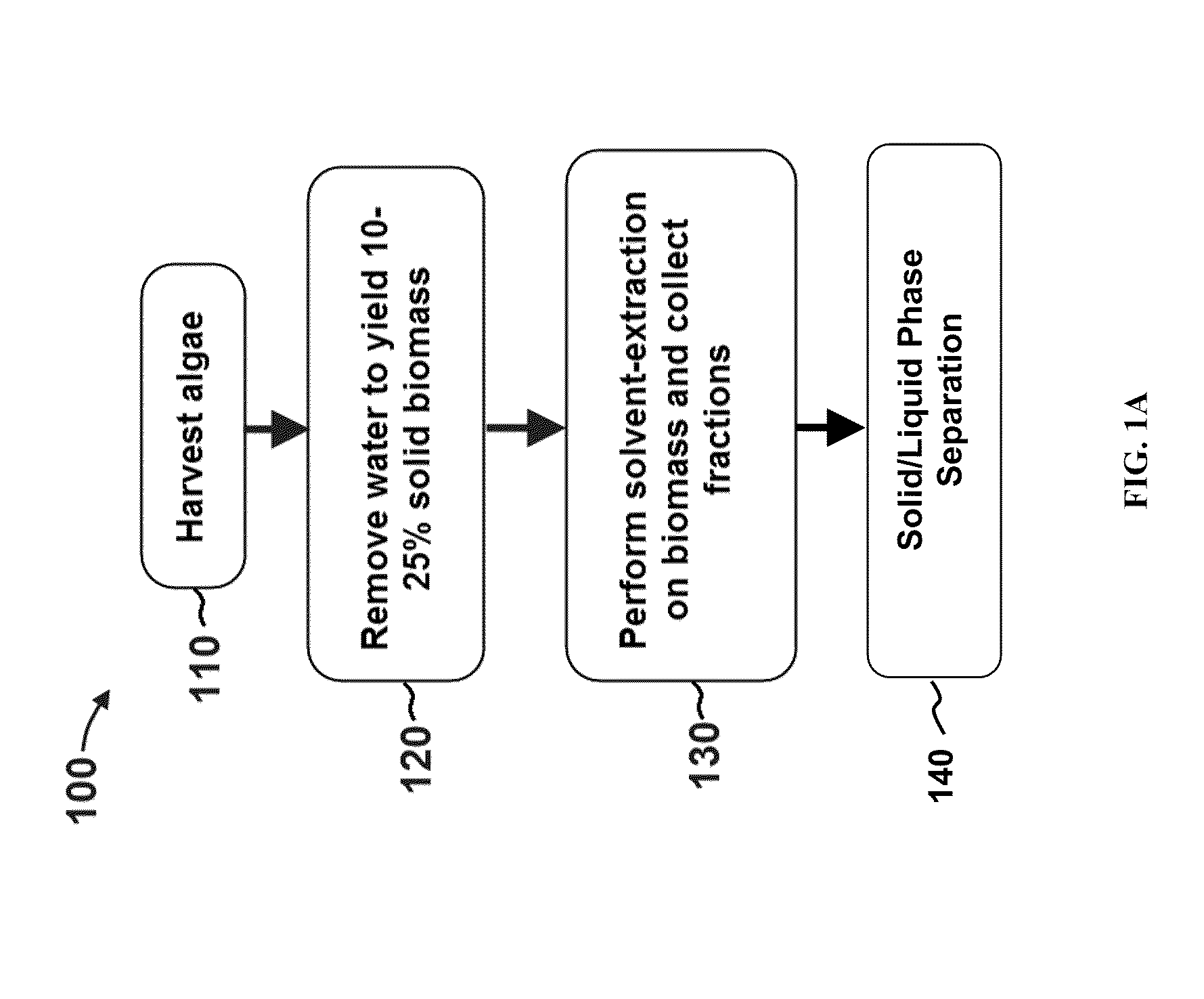
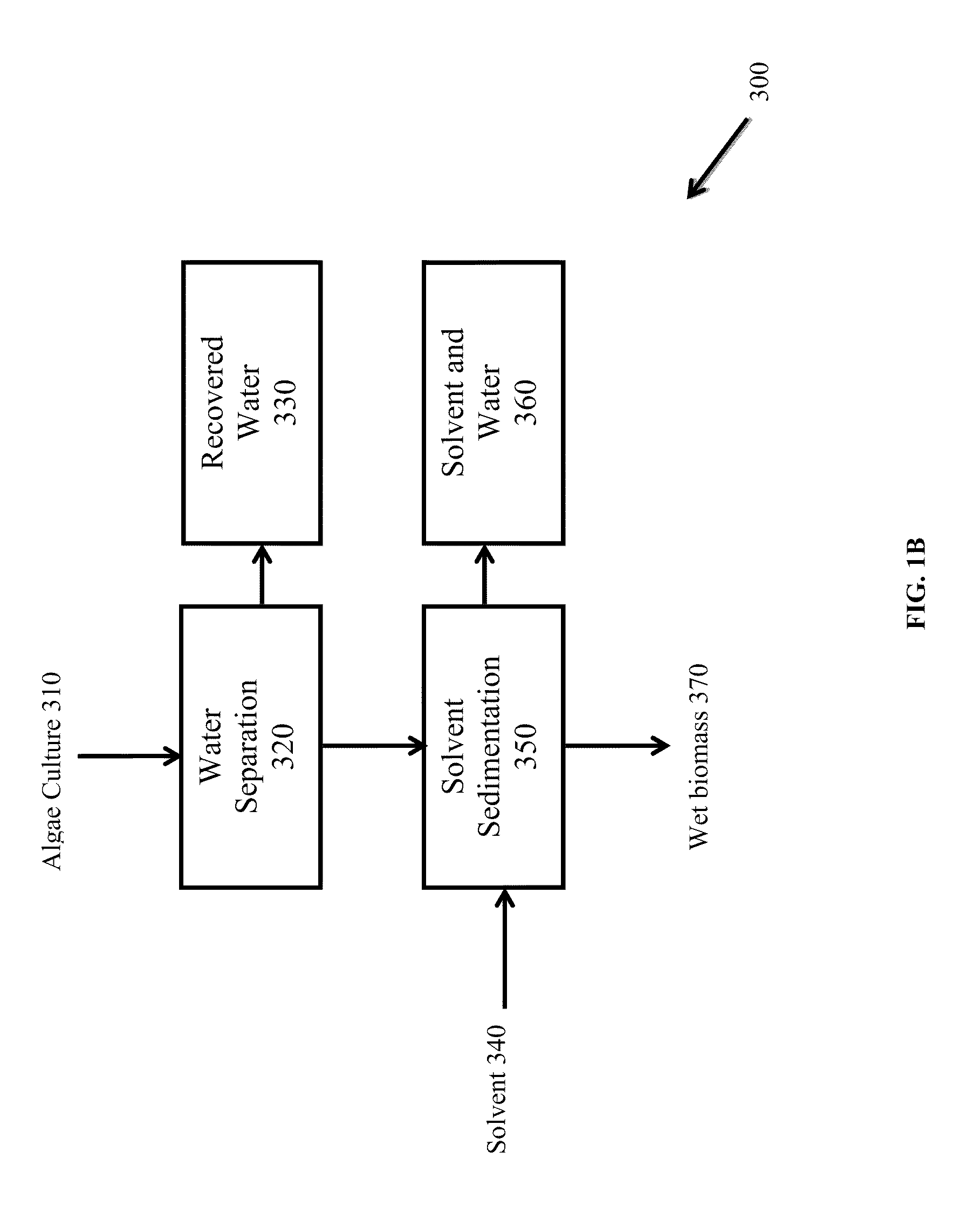
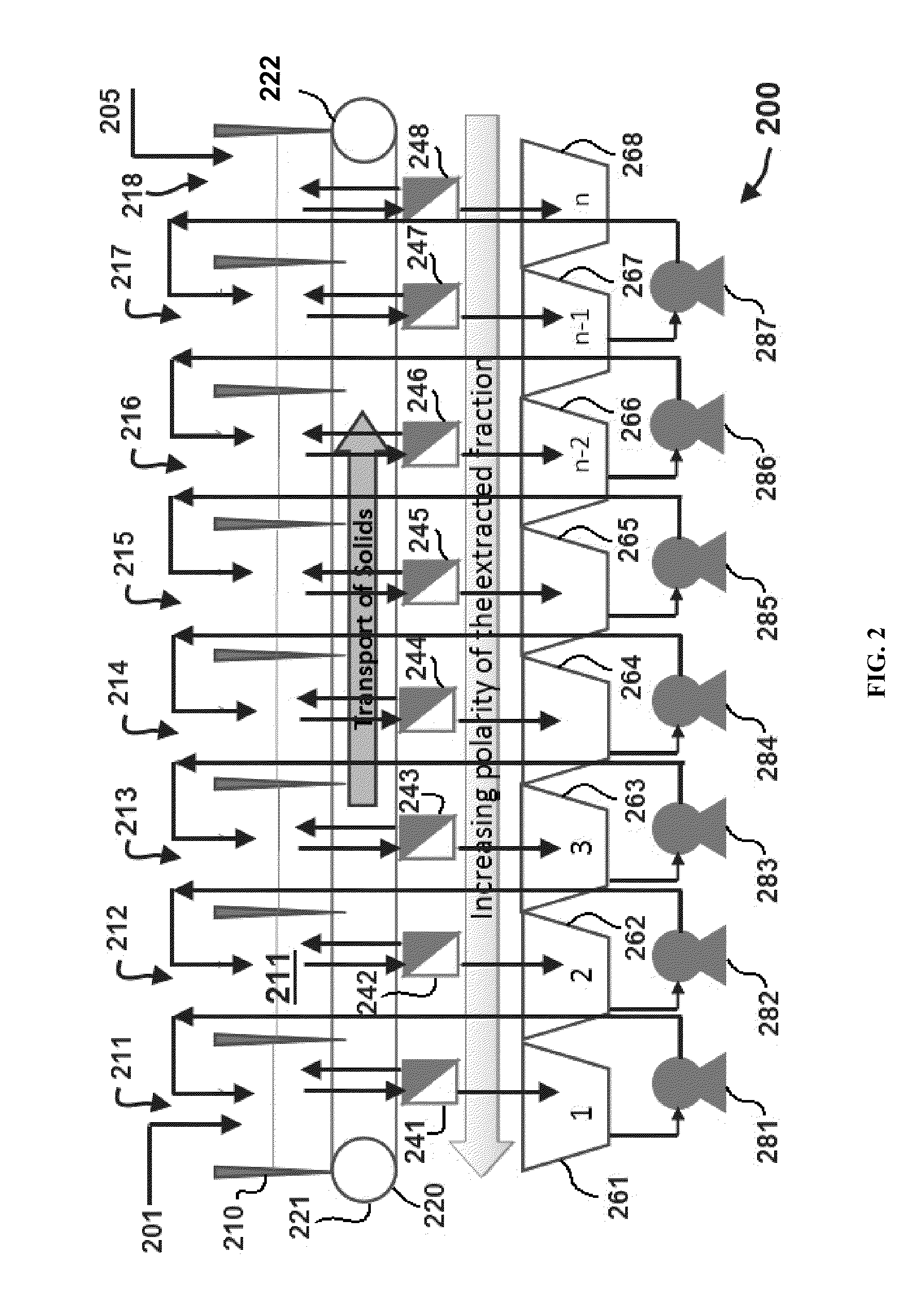
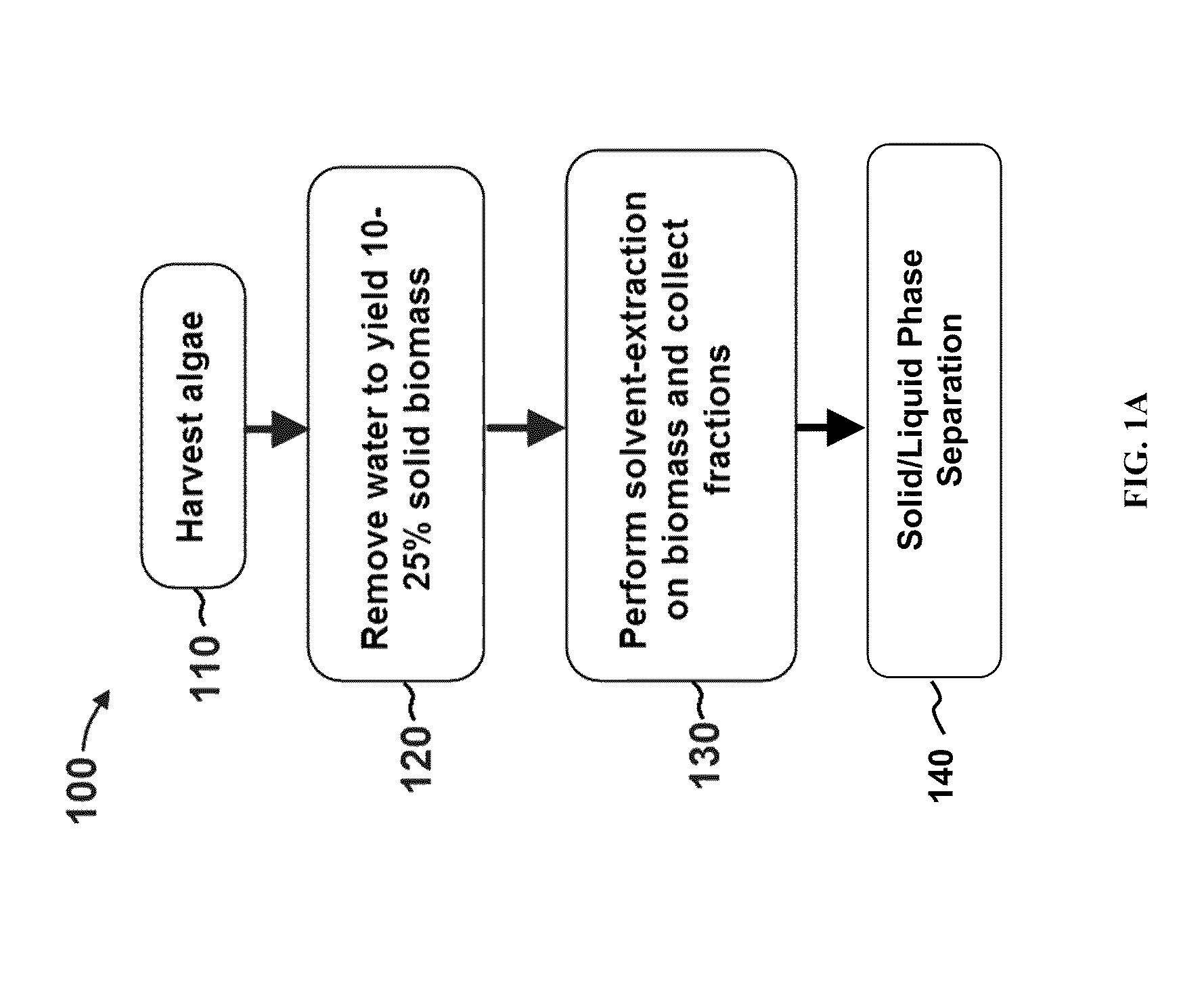
Methods of producing biofuels, chlorophylls and carotenoids
InactiveUS20110263886A1Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationWater insolubleBiofuel
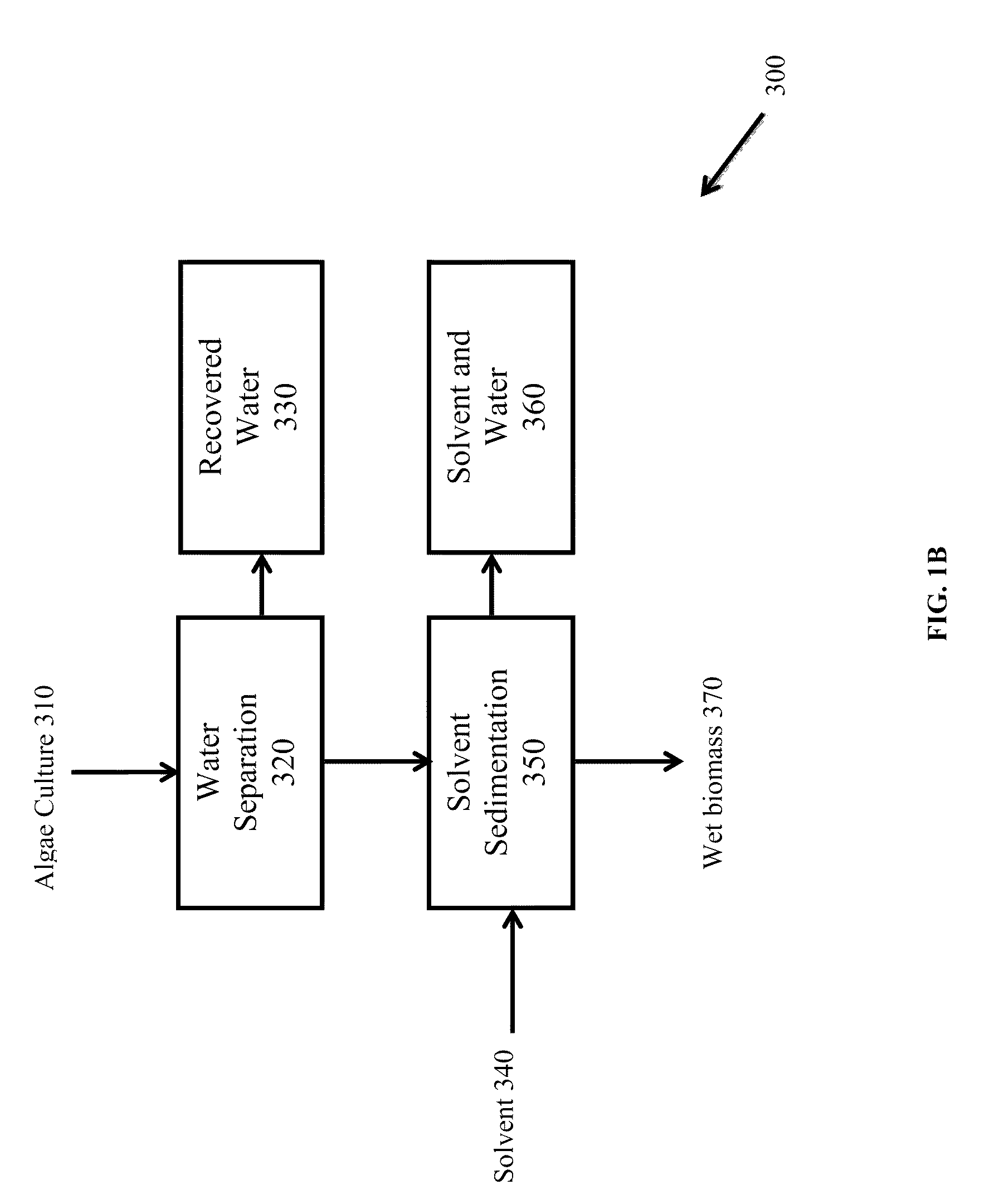
A method for producing biofuels along with valuable food and neutraceutical products is provided. A method of making biofuels includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass, extracting neutral lipids along with carotenoids and chlorophylls from the algal biomass, and separation of the carotenoids and chlorophylls using adsorption or membrane diafiltration or other methods. The remaining neutral lipids are esterified with a catalyst in the presence of an alcohol. The method also includes separating a water soluble fraction comprising glycerin from a water insoluble fraction comprising fuel esters and distilling the fuel esters under vacuum to obtain a C16 or shorter fuel esters fraction, a C16 or longer fuel ester fraction, and a residue comprising omega-3 fatty acids esters and remaining carotenoids. The method further includes hydrogenating and deoxygenating at least one of (i) the C16 or shorter fuel esters to obtain a jet fuel blend stock and (ii) the C16 or longer fuel esters to obtain a diesel blend stock.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Production of soluble protein solutions from soy ("S701" CIP)
ActiveUS20110038993A1Prevent oxidationProtein composition from vegetable seedsFood ingredient as solubility improving agentProtein solutionSports drink
A soy protein product, which may be an isolate, produces transparent heat-stable solutions at low pH values and is useful for the fortification of soft drinks and sports drinks without precipitation of protein. The soy protein product is obtained by extracting a soy protein source material with an aqueous calcium salt solution to form an aqueous soy protein solution, separating the aqueous soy protein solution from residual soy protein source, adjusting the pH of the aqueous soy protein solution to a pH of about 1.5 to about 4.4 to produce an acidified clear soy protein solution, which may be dried, following optional concentration and diafiltration, to provide the soy protein product.
Owner:BURCON NUTRASCI MB
Methods of producing biofuels, chlorophylls and carotenoids
InactiveUS8115022B2Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationWater insolubleBiofuel
A method for producing biofuels along with valuable food and neutraceutical products is provided. A method of making biofuels includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass, extracting neutral lipids along with carotenoids and chlorophylls from the algal biomass, and separation of the carotenoids and chlorophylls using adsorption or membrane diafiltration or other methods. The remaining neutral lipids are esterified with a catalyst in the presence of an alcohol. The method also includes separating a water soluble fraction comprising glycerin from a water insoluble fraction comprising fuel esters and distilling the fuel esters under vacuum to obtain a C16 or shorter fuel esters fraction, a C16 or longer fuel ester fraction, and a residue comprising omega-3 fatty acids esters and remaining carotenoids. The method further includes hydrogenating and deoxygenating at least one of (i) the C16 or shorter fuel esters to obtain a jet fuel blend stock and (ii) the C16 or longer fuel esters to obtain a diesel blend stock.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Methods for the production of non-covalently complexed and multivalent proteosome sub-unit vaccines
InactiveUS6476201B1Shorten the timeIncrease temperatureAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsContinuous monitoringContamination
A continuous method for preparing proteosome-amphiphilic determinant vaccines for parenteral or mucosal administration using diafiltration or ultrafiltration technology. The amphiphilic determinants include lipopolysaccharides from gram negative bacteria, e.g. S. flexneri, P. shigelloides and S. sonnei. Proteosomes are obtained from group B type 2b meningococci. The active proteosome-amphiphilic determinant complexes (non-covalent complexes) of the vaccine are formed using diafiltration or ultrafiltration to remove the detergent under non-static conditions. The use of diafiltration or ultrafiltration decreases processing time and the opportunity for contamination and further permits the use of ambient temperature and efficient scale-up. In addition, the process permits the reliable and continuous monitoring of the dializate which enhances the efficiency of the entire process. The time of dialysis for the production of a lot of vaccine is reduced from 7-10 days to less than 72 hours and usually less than 48 or 24 hours. The use of the process optimizes the presence of each antigenic component in the preparation of multivalent vaccines.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY +1
Method and apparatus for the filtration of biological solutions
ActiveUS20070151925A1Easy to makeReduces bio-processing system costLiquid separation auxillary apparatusMembranesFiltrationProcess engineering
A system, method and device are disclosed for bio-processing a feed stream and providing a constant output by operating a continuous single-pass tangential-flow process. The single-pass process provides high conversion concentration while operating at relatively low feed flow rates, and the process can also be used to provide constant output diafiltration.
Owner:SPF INNOVATIONS
Method for producing medical and commercial grade poly-gamma-glutamic acid of high molecular weight
ActiveUS20050095679A1Reduce molecular weightHigh molecular weightBacteriaFermentationFiltrationHigh molecular mass
Methods for producing high molecular weight poly-gamma-glutamic acid (PGA). The PGA is produced by fermentation, and purified by use of tangential flow filtration, followed by diafiltration, as necessary, to yield a product of the desired purity. Product obtained may be of very high purity using all the prescribed purification steps. Product of this purity is suitable for in vivo medical applications. Other applications, such as food or agricultural, may utilize lower purity levels, and hence do not require all the purification steps specified.
Owner:CRESCENT INNOVATIONS
Isolation and purification of antibodies using protein A affinity chromatography
ActiveUS8895709B2Easy to disassembleReduce or inactivate pH-sensitive virusesAntipyreticAnalgesicsIon exchangeAntibody Affinity Chromatography
Disclosed herein are methods for the isolation and purification of antibodies wherein the use of an affinity chromatographic step results in an antibody composition sufficiently pure for pharmaceutical uses. The methods described herein comprise pH viral reduction / inactivation, ultrafiltration / diafiltration, affinity chromatography, preferably Protein A affinity, ion exchange chromatography, and hydrophobic chromatography. Further, the present invention is directed toward pharmaceutical compositions comprising one or more antibodies of the present invention.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
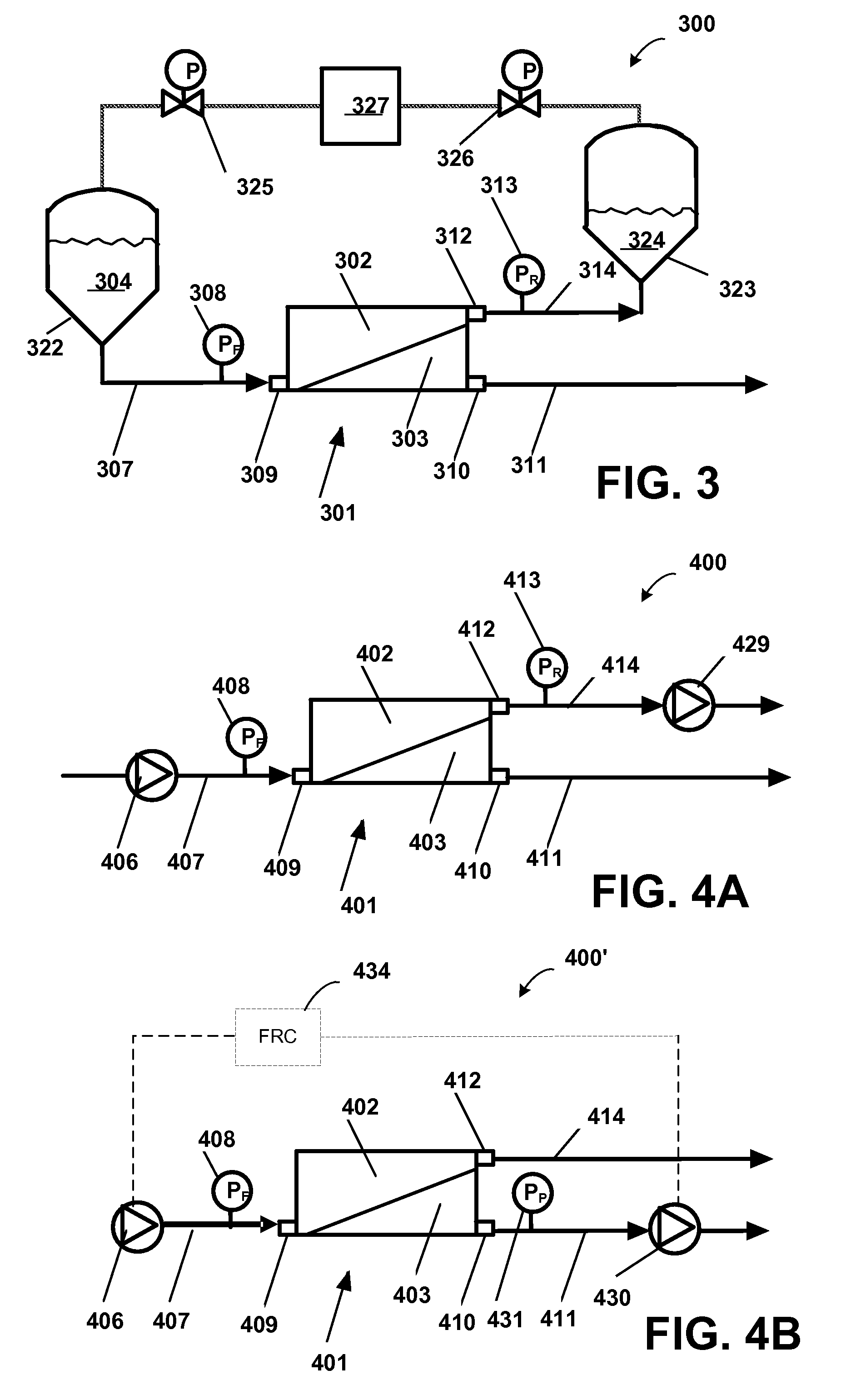
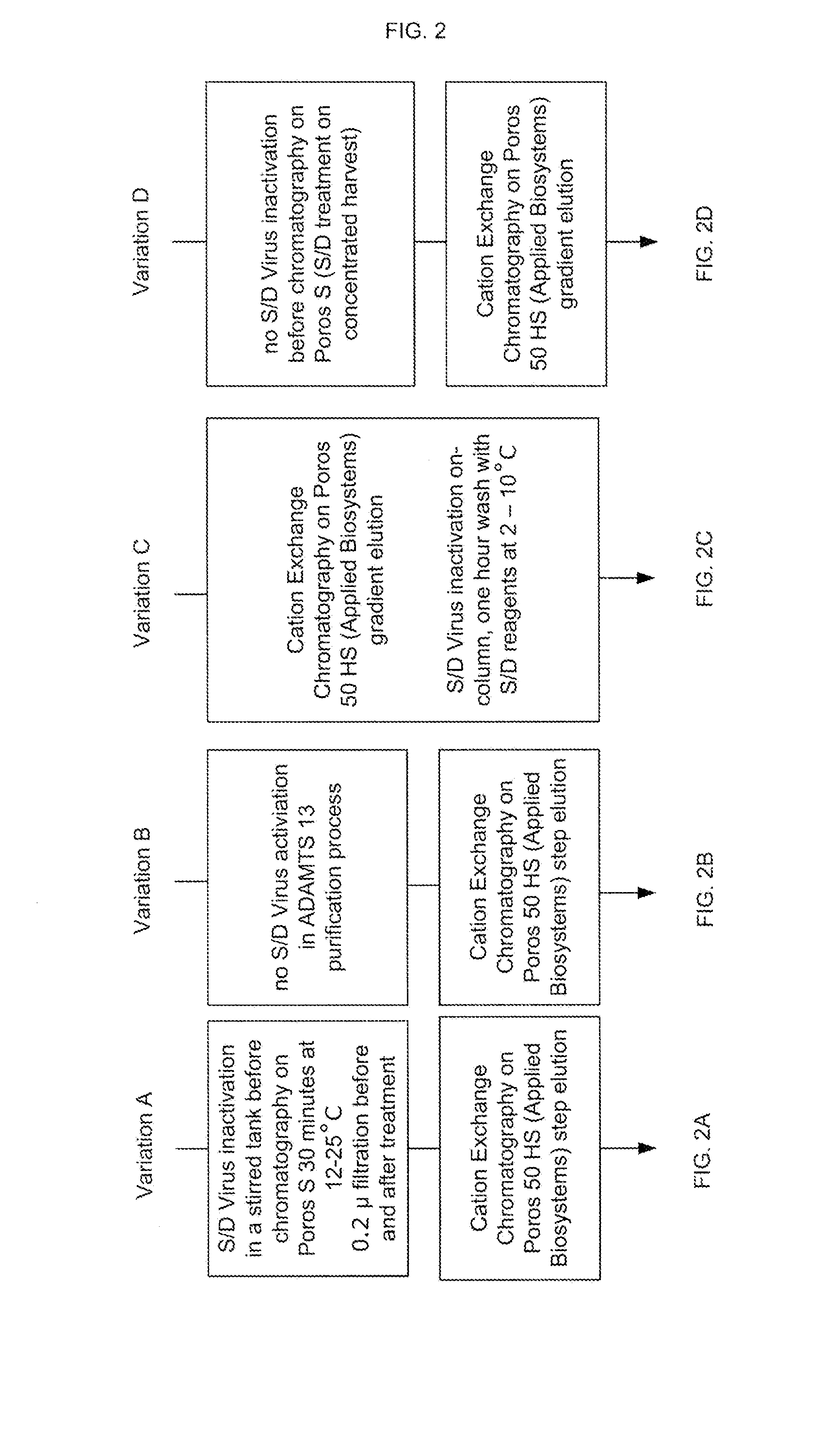
Methods of Purifying Recombinant Adamts13 and Other Proteins and Compositions Thereof
ActiveUS20110081700A1Reduce formationExtension of timeInactivation/attenuationBiomass after-treatmentHydroxylapatiteAnion-exchange chromatography
Provided herein are methods for purifying recombinant A Disintegrin-like and Metallopeptidase with Thrombospondin Type 1 Motif 13 (ADAMTS13) protein from a sample. The method comprises enriching for ADAMTS13 protein by chromatographically contacting the sample with hydroxyapatite under conditions that allow ADAMTS13 protein to appear in the eluate or supernatant from the hydroxylapatite. The methods may further comprise tandem chromatography with a mixed mode cation exchange / hydrophobic interaction resin that binds ADAMTS13 protein. Additional optional steps involve ultrafiltration / diafiltration, anion exchange chromatography, cation exchange chromatography, and viral inactivation. Also provided herein are methods for inactivating virus contaminants in protein samples, where the protein is immobilized on a support. Also provided herein are compositions of ADAMTS13 prepared according to said methods.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
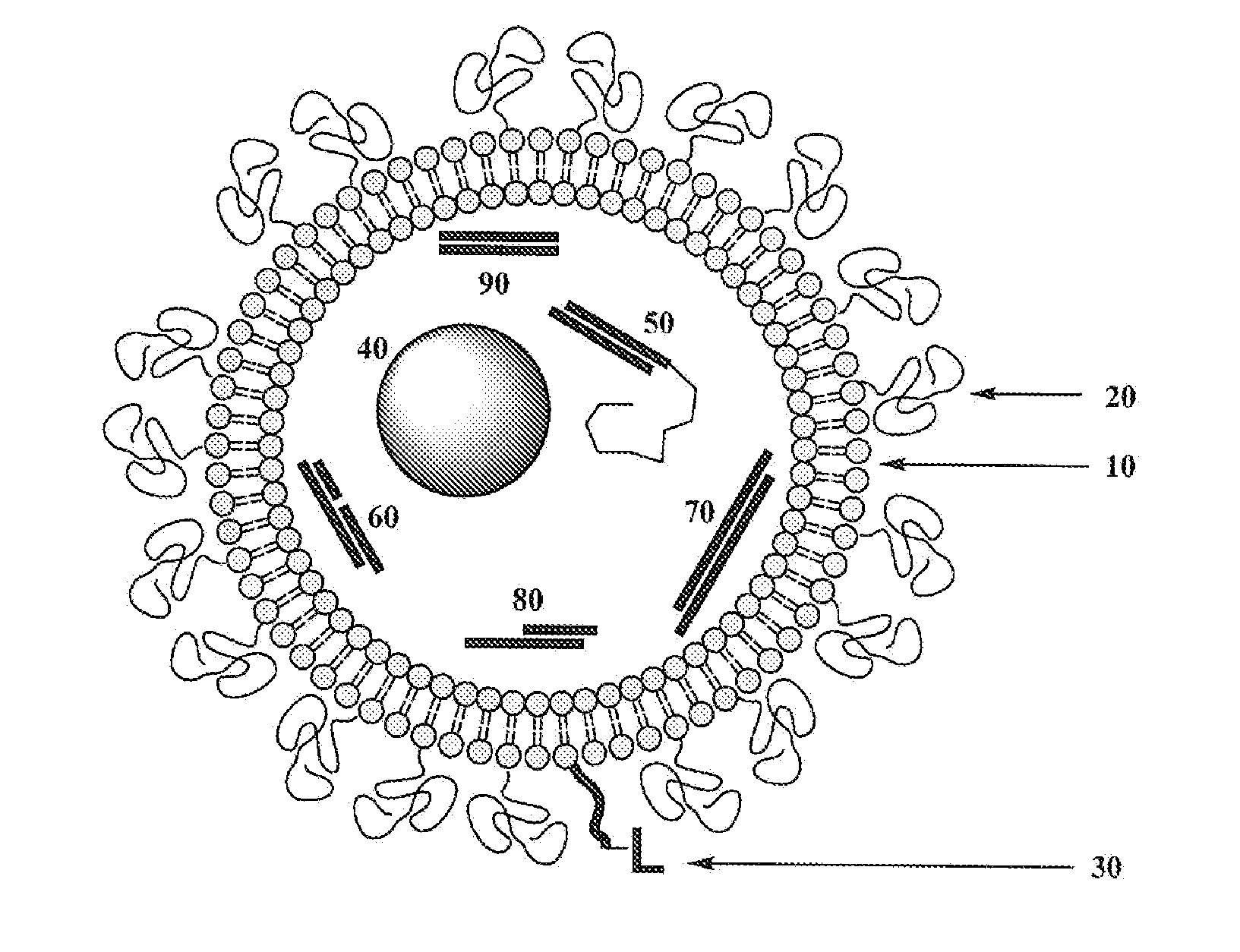
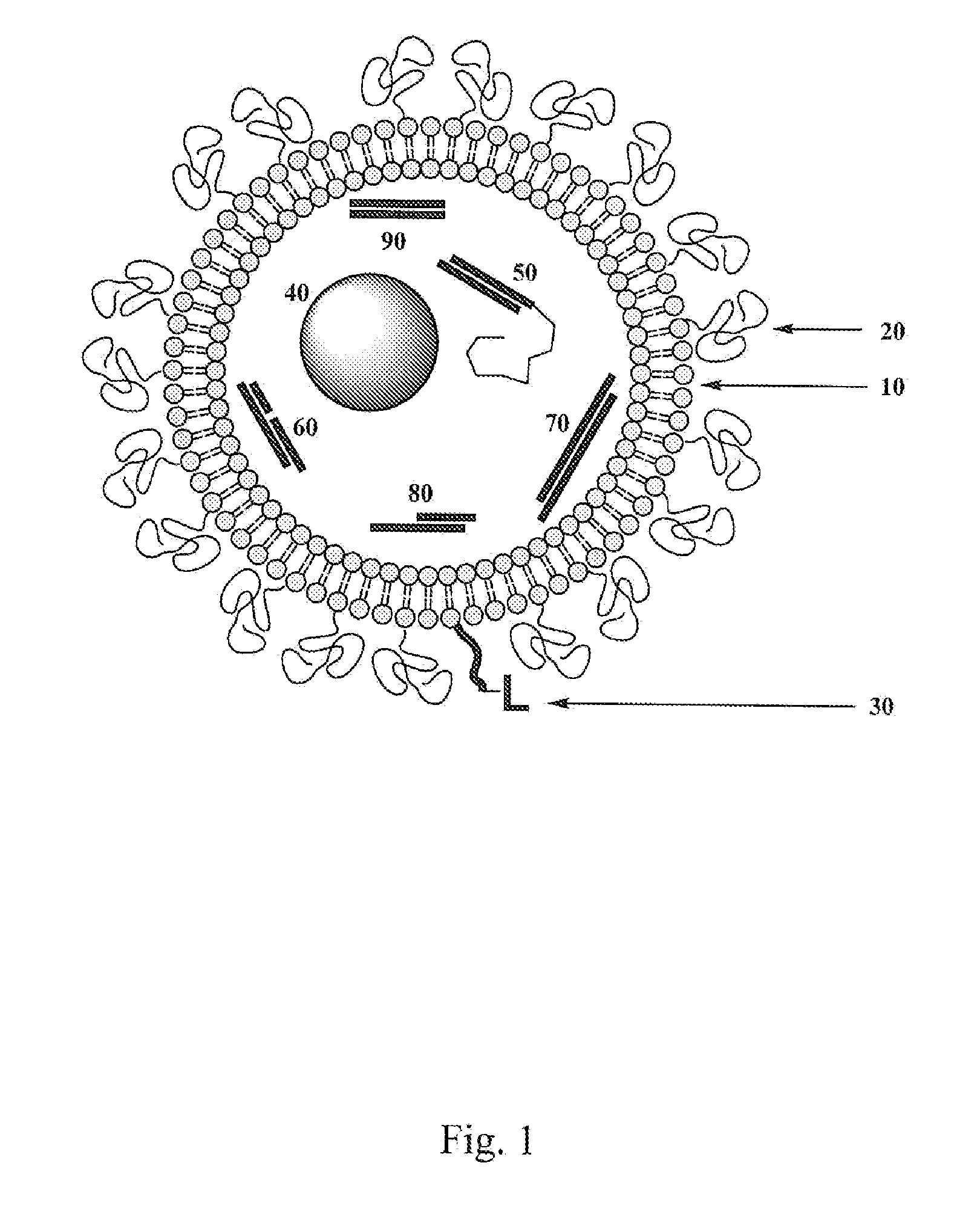
Processes and Compositions for Liposomal and Efficient Delivery of Gene Silencing Therapeutics
InactiveUS20100112042A1Low toxicityModulate activityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderLipid formationActive agent
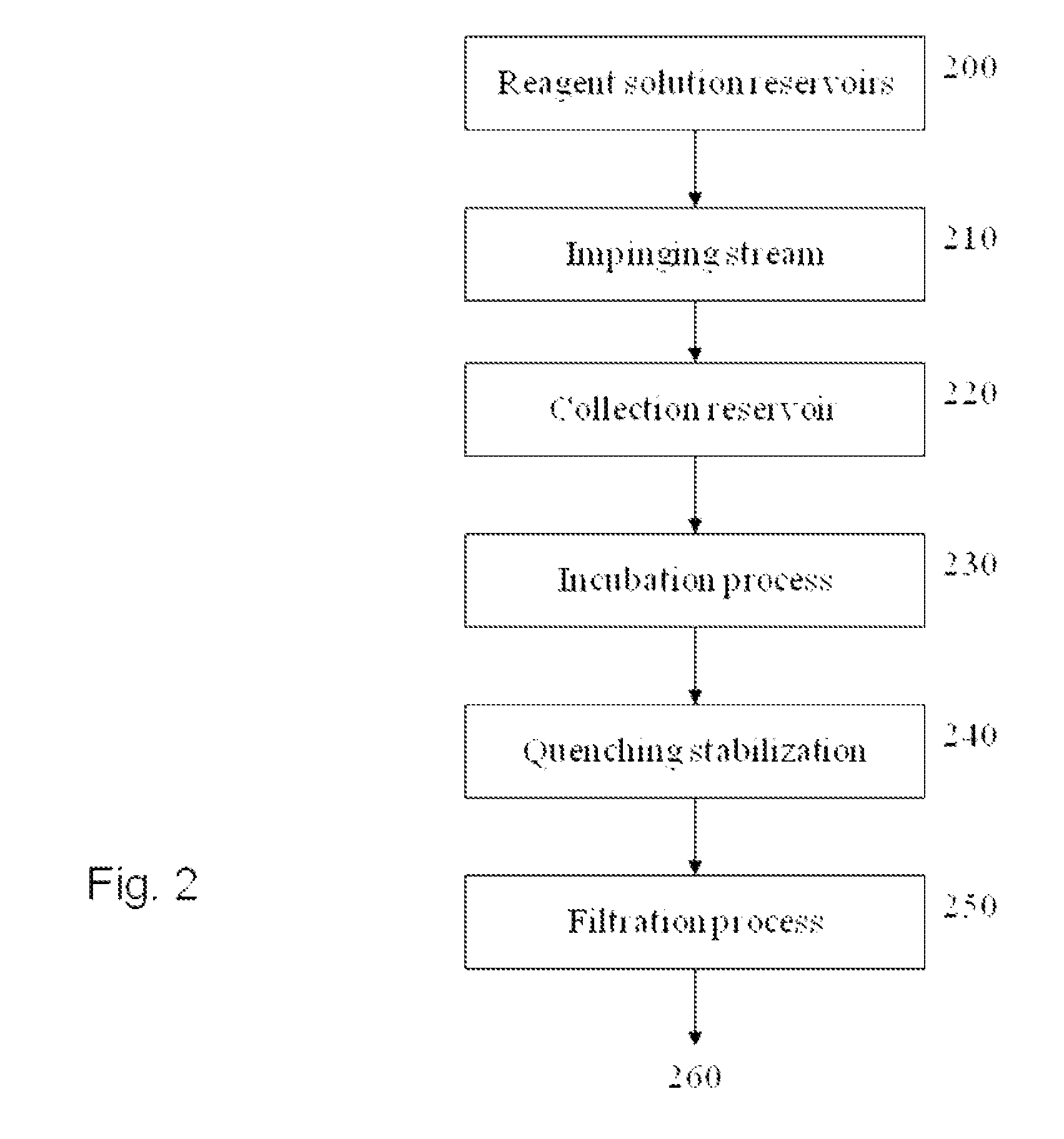
Processes and compositions for liposomal delivery of therapeuticals prepared by contacting an aqueous solution of an active agent with a solution of liposome-forming components containing one or more DILA2 amino acid compounds or lipids in organic solvent to form an impinging stream. A protocol including flow rates, pH, and an incubation period are used to control formation of liposomal components for therapeutic applications. The impinging stream may be collected and incubated to prepare a liposomal formulation which encapsulates the active agent. The composition can be quenched with buffer and filtered by tangential flow and diafiltration and other means for finishing as a pharmaceutical composition. An efficiency for delivering a drug cargo is provided. Compositions can include a liposome containing one or more carrier particles, each carrier particle having an active agent and a peptide, wherein the ratio of the mass of the peptide plus the mass of the liposome to the mass of the active agent is less than about 15.
Owner:MDRNA
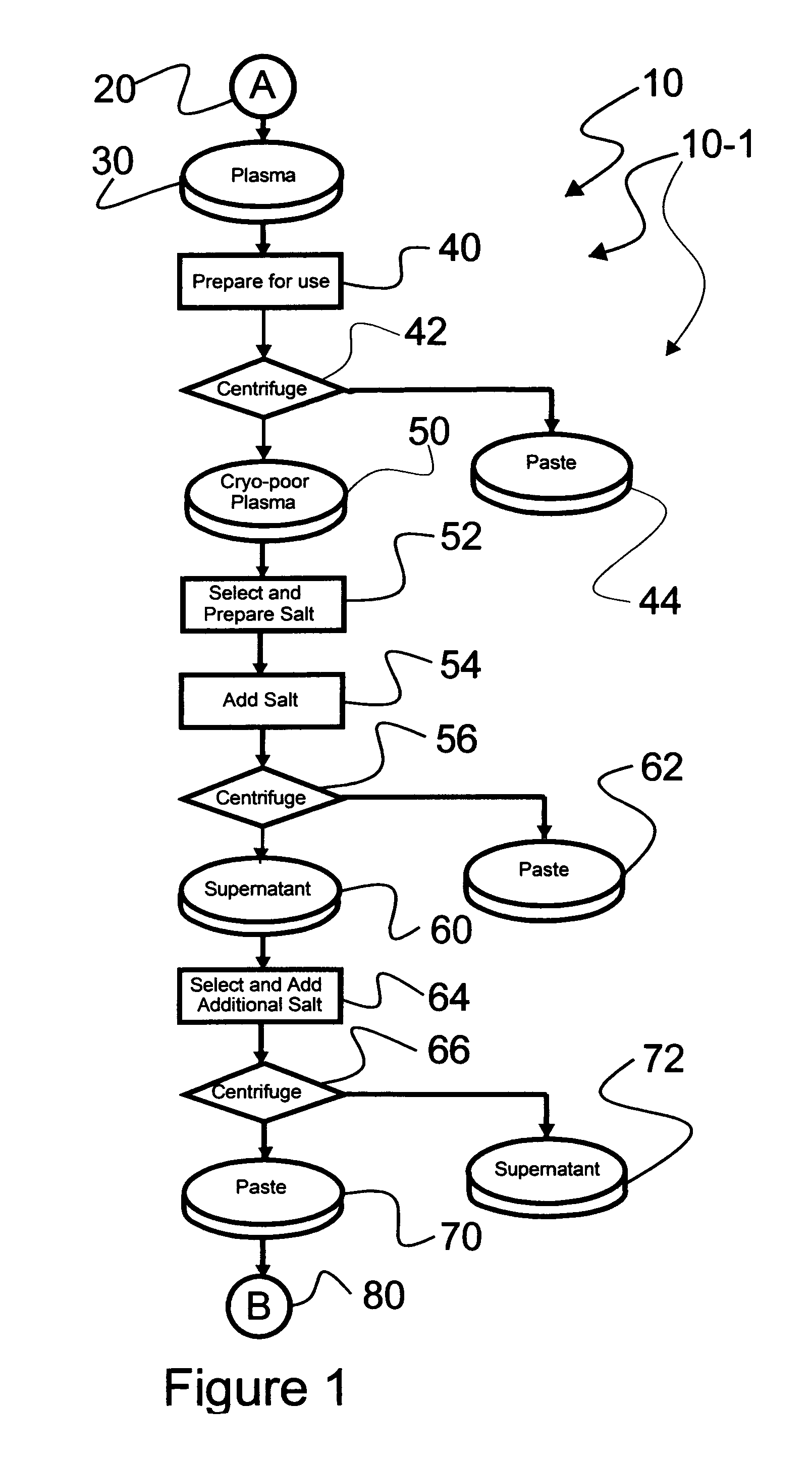
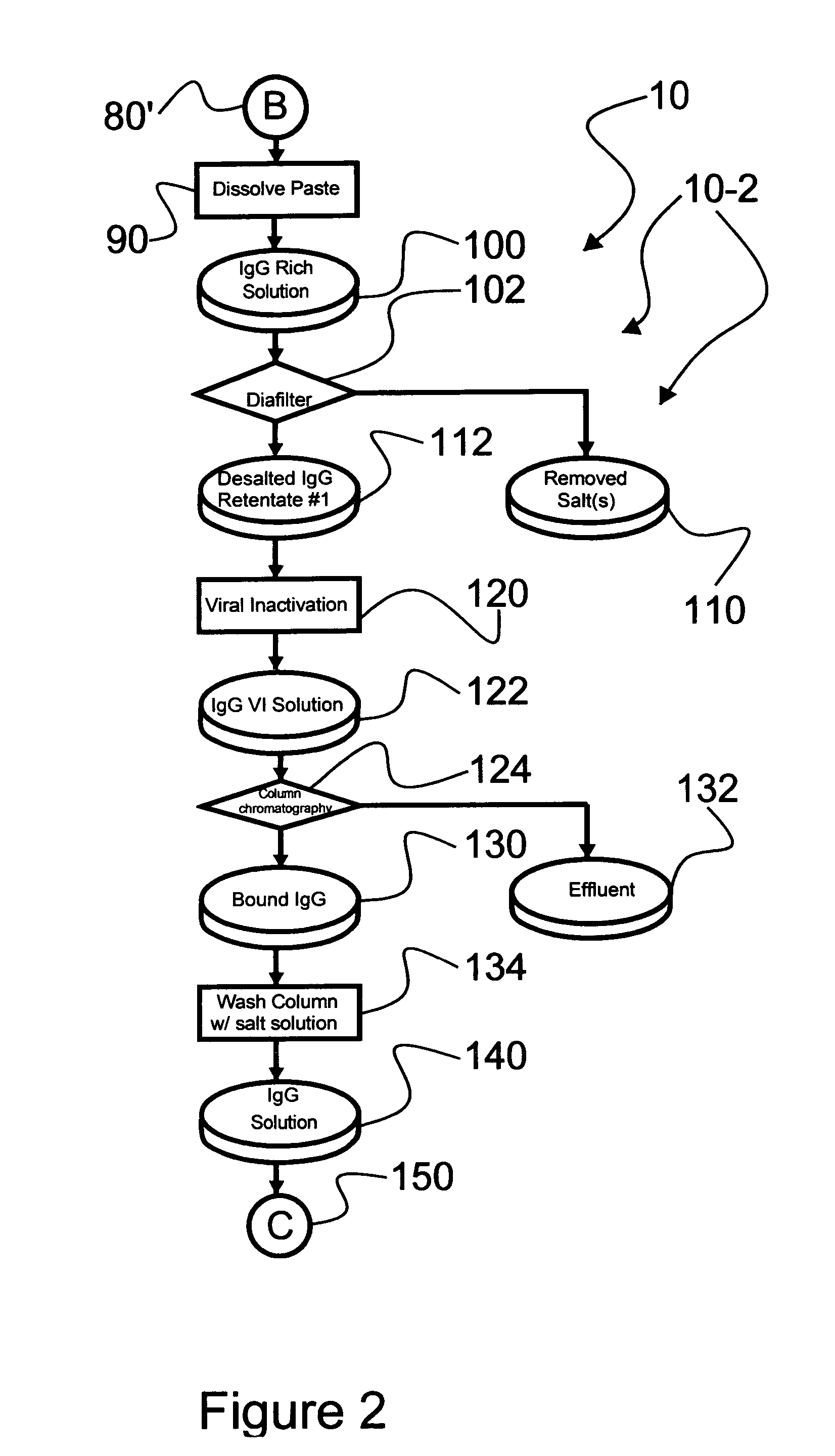
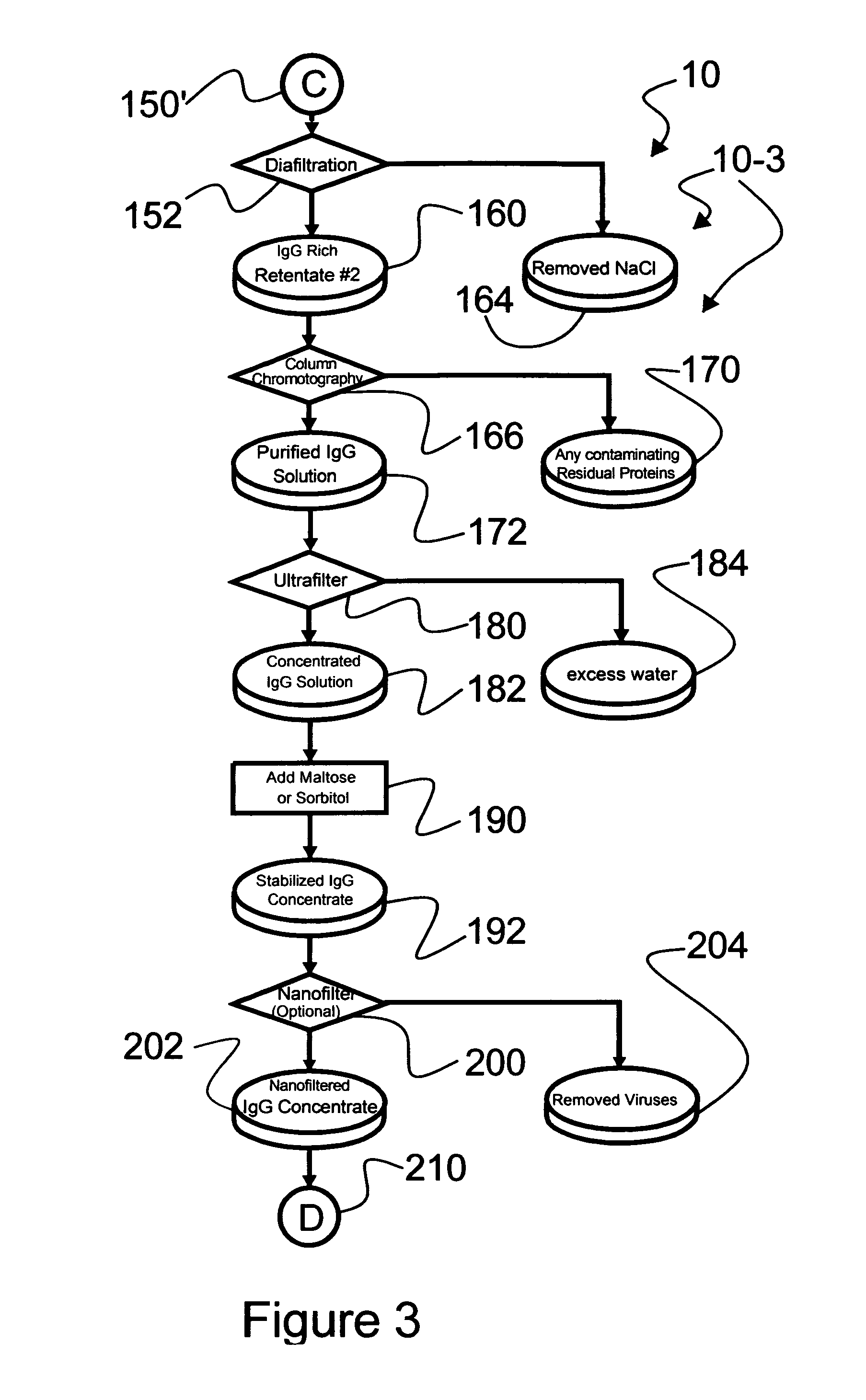
Ultra-high yield intravenous immune globulin preparation
ActiveUS7879332B2Quick restoration of the internal water moleculeReduce formationBiocideMedical devicesSodium acetateAlcohol free
An efficacious large-scale alcohol-free plasma fractionation production process which produces a high-yielding, non-denatured, double viral-inactivated intravenous human immune gamma globulin (IgG) product. The process employs one or more salts from a group of salts comprising sodium citrate, sodium acetate, sodium gluconate, ammonium sulfate, sodium chloride, sodium sulfate and ammonium chloride in two initial fractionation steps, followed by diafiltration to remove those salts employed. A process which employs alcohol via the process of the disclosed inventive method is also disclosed.
Owner:PLASMA TECH LLC
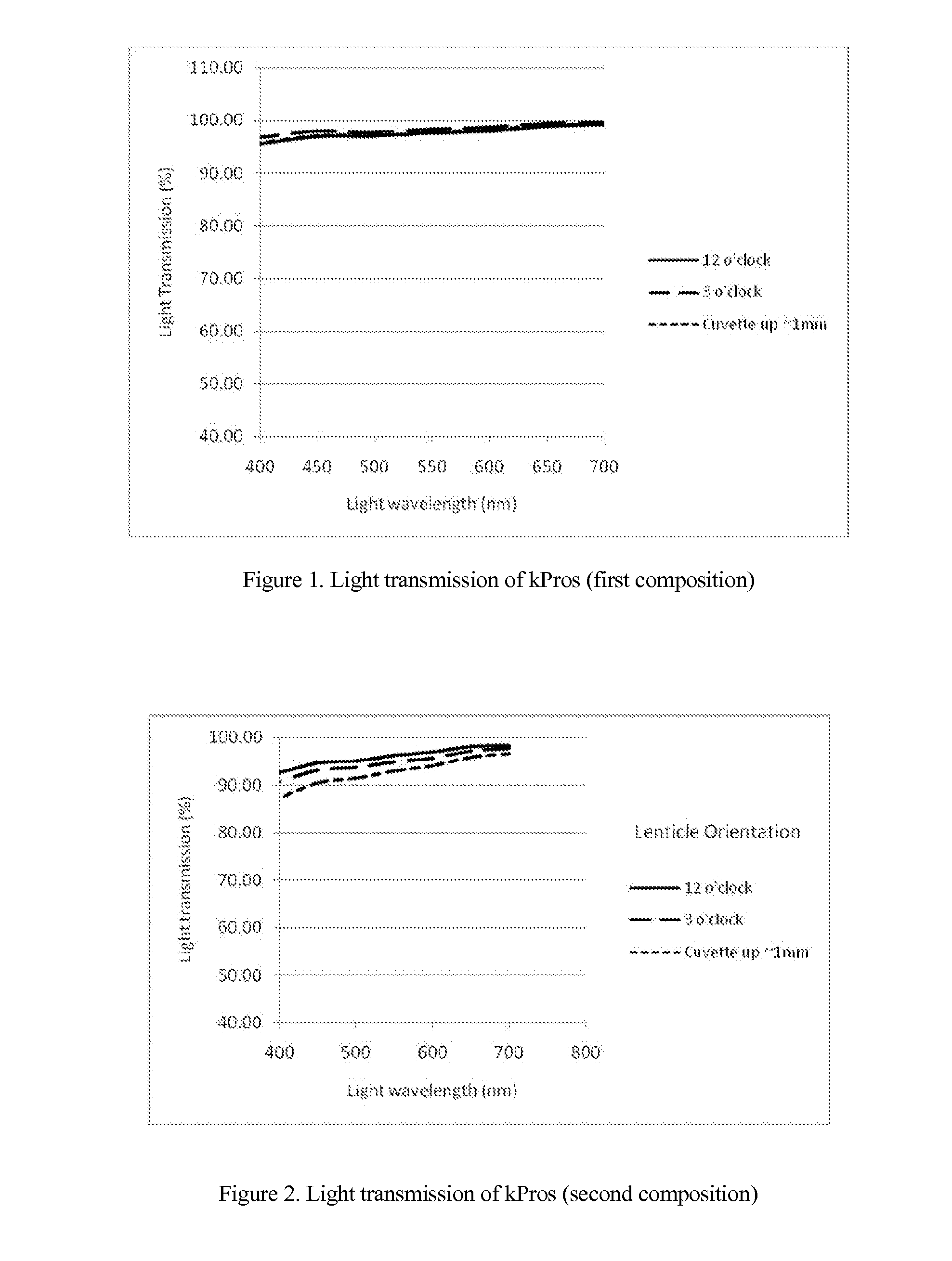
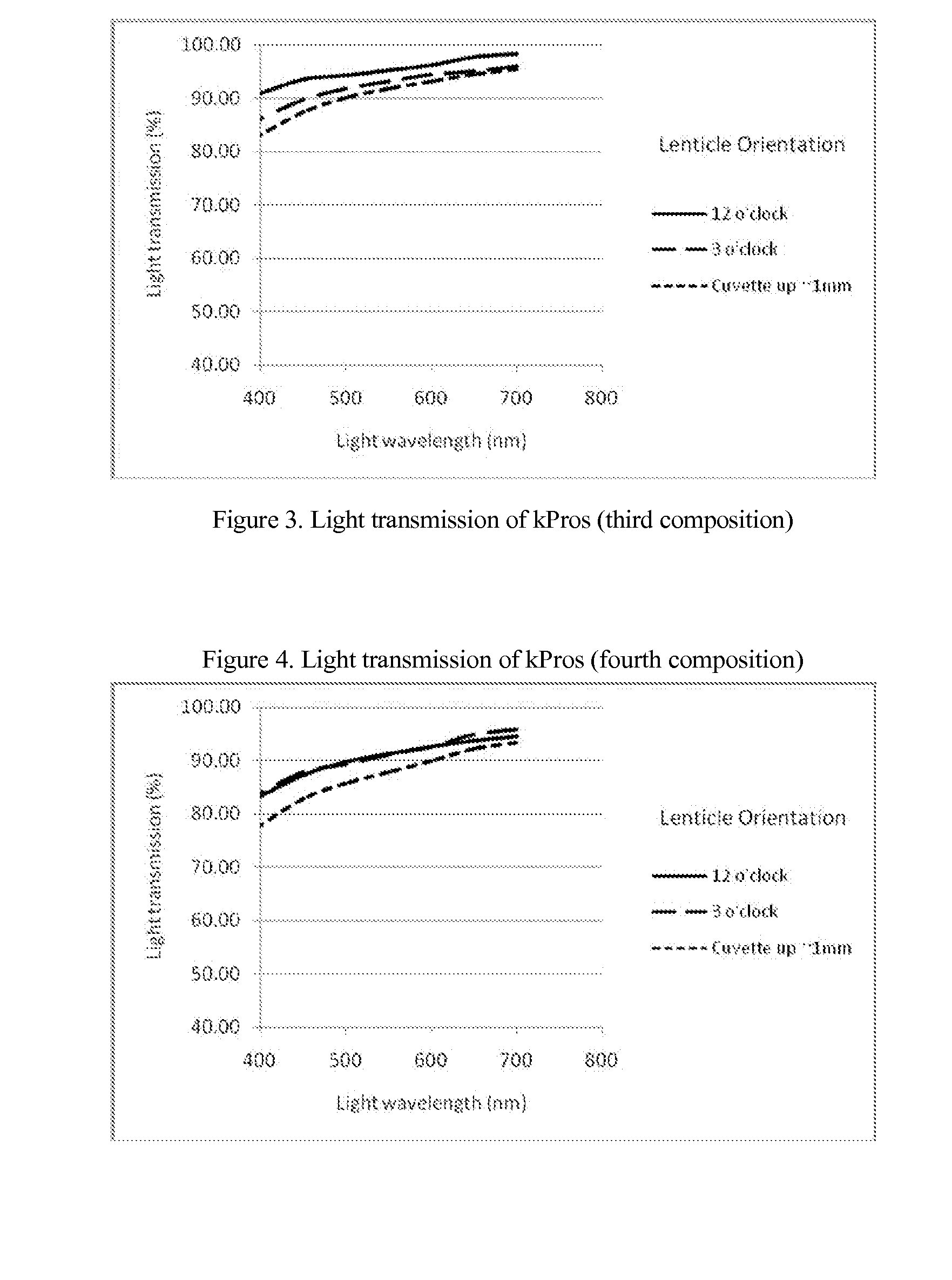
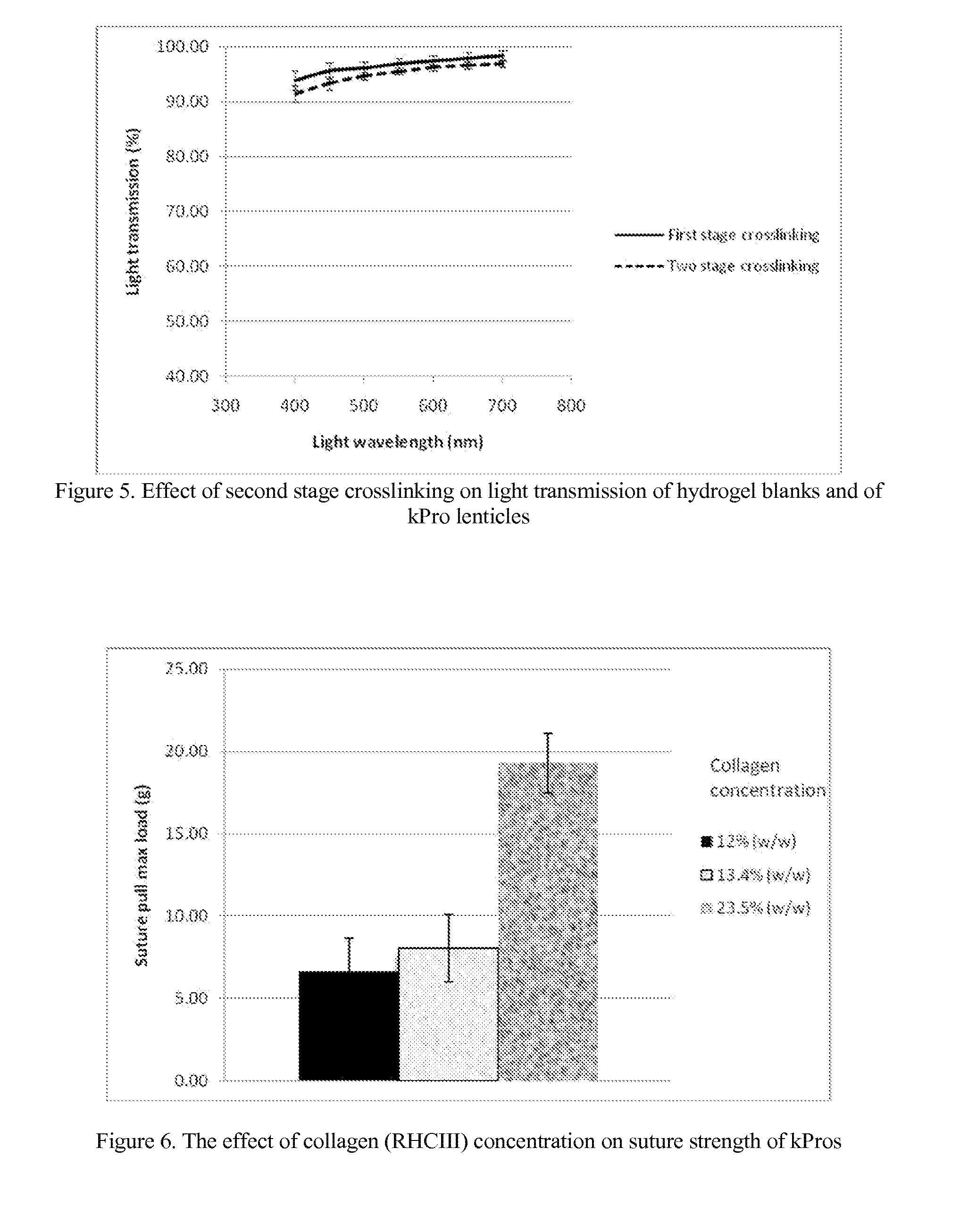
Keratoprosthesis
InactiveUS20140142200A1Easy to controlImprove consistent qualityBiocideAbsorbent padsWound dressingArtificial cornea
The invention comprises a method of making molded, double-crosslinked (i.e., two stages of crosslinking), transparent, collagen materials using a novel combination of diafiltration, lyophilization, and homogenization. The collagen material can be used not only as an ophthalmic device, but also as a tissue scaffold, drug delivery device, wound dressing, or other collagen hydrogel based device.
Owner:EYEGENIX
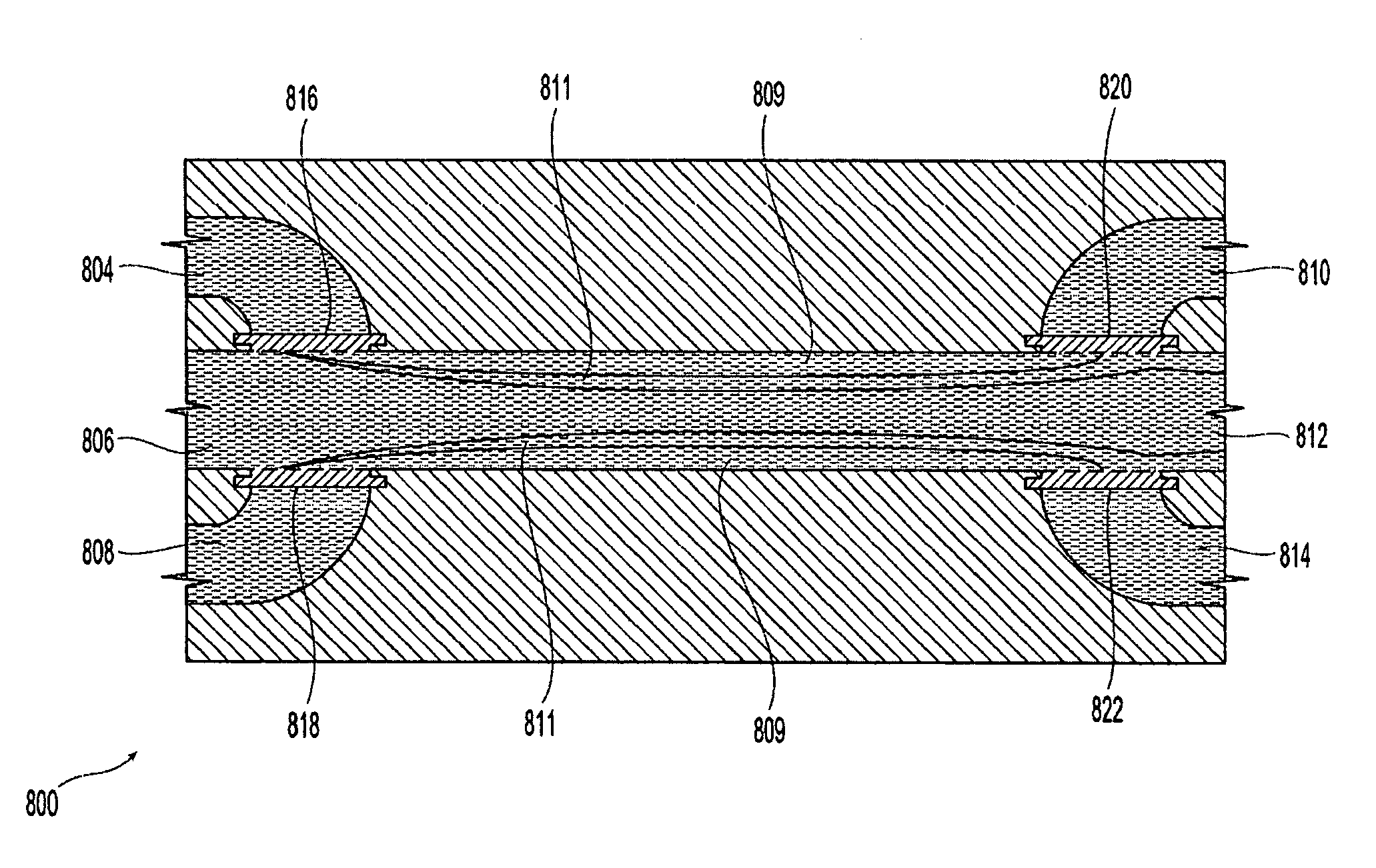
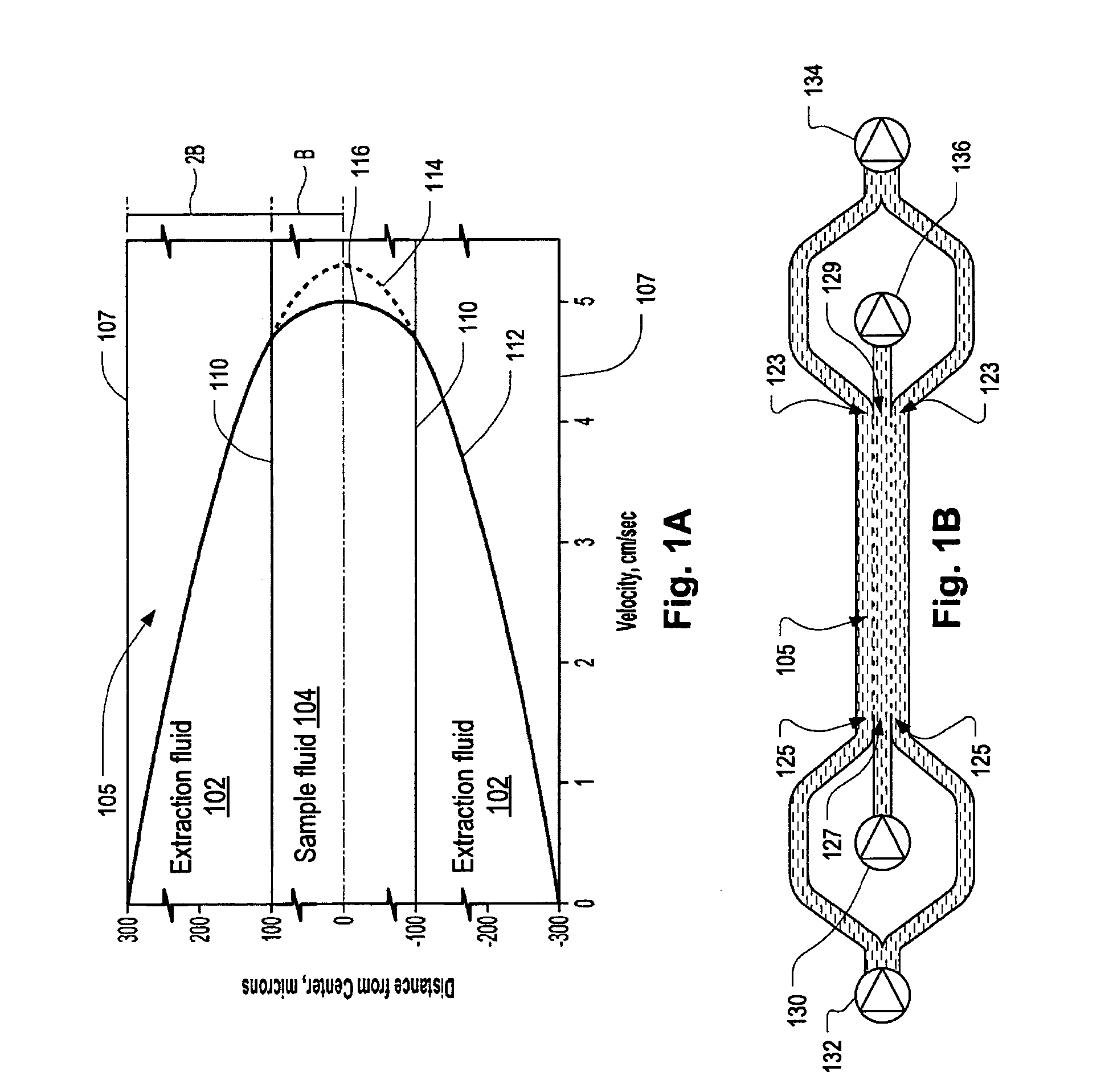
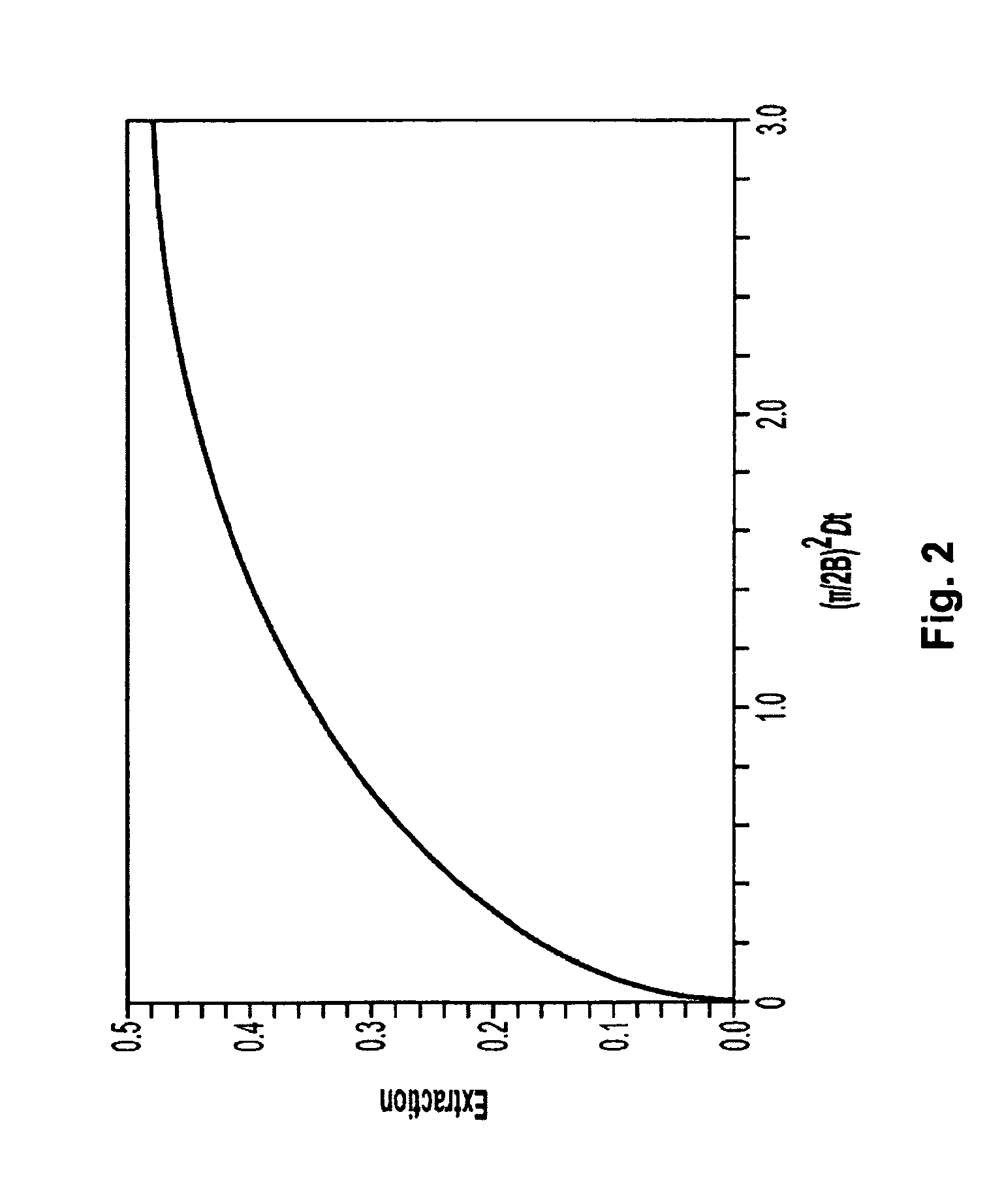
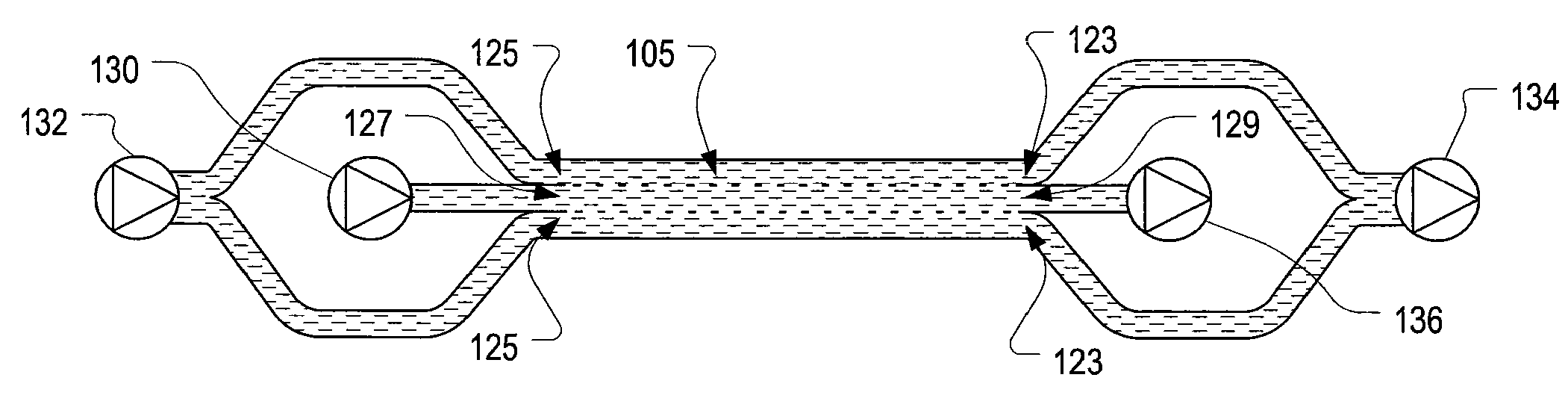
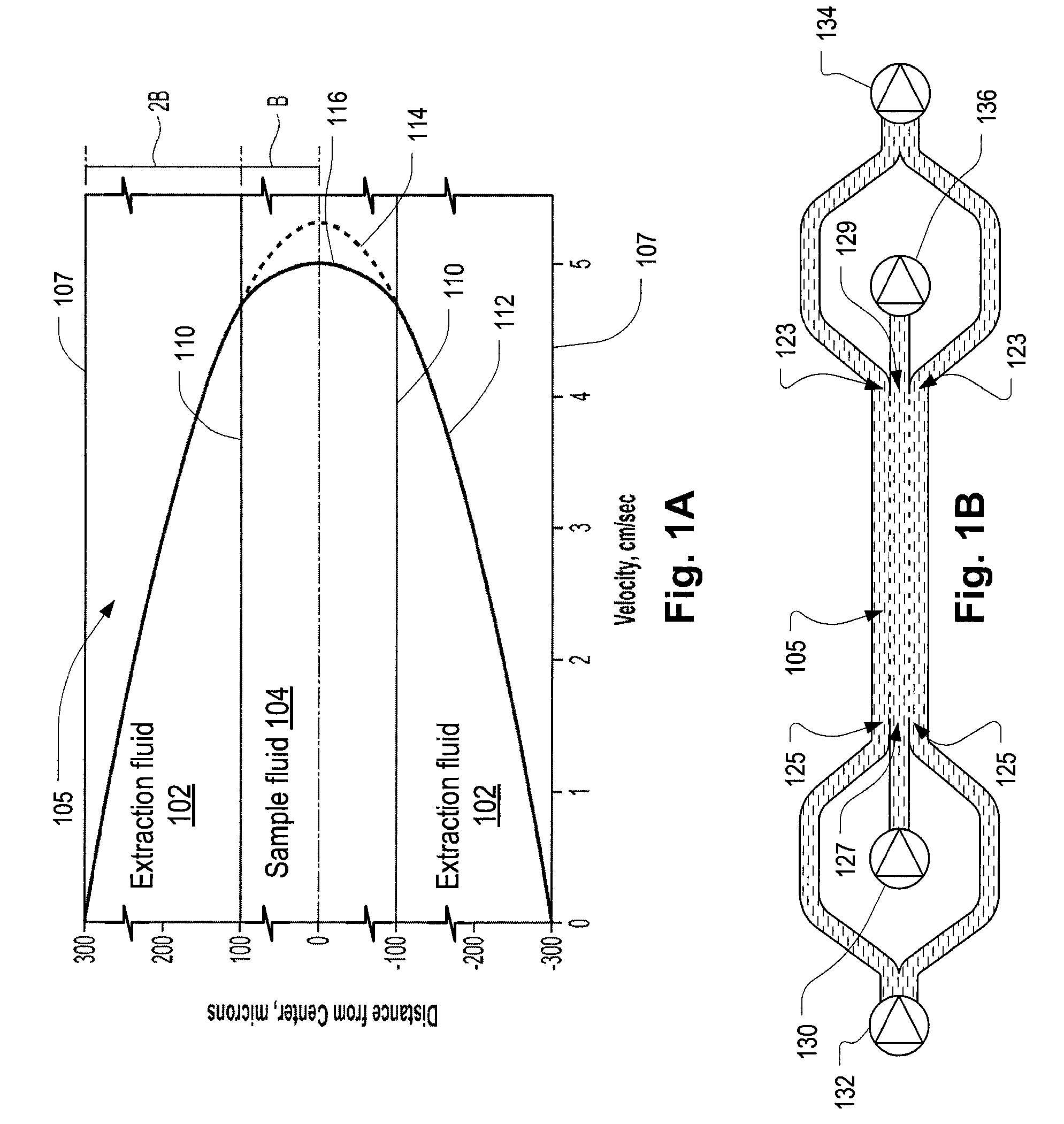
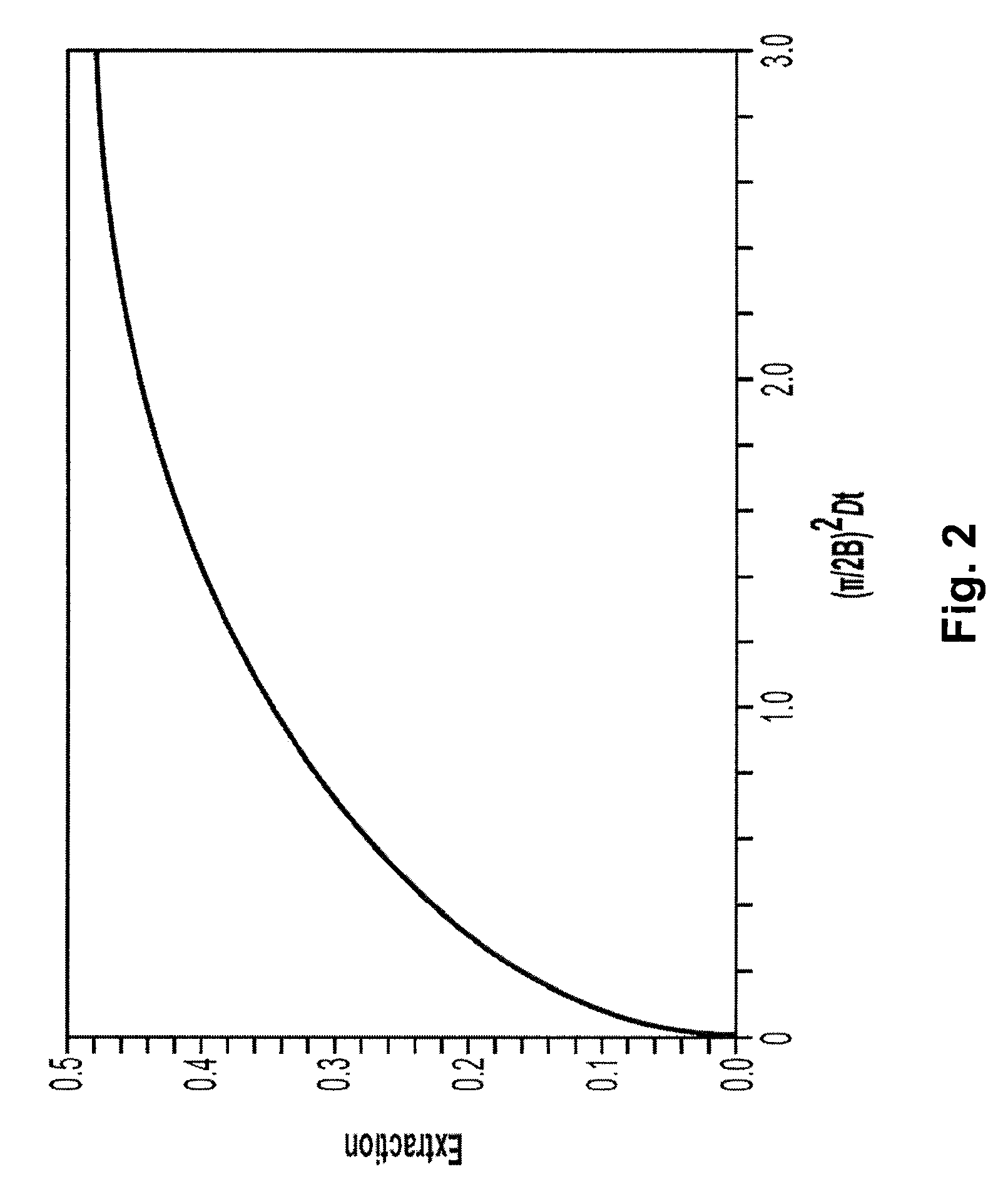
Systems and methods of microfluidic membraneless exchange using filtration of extraction outlet streams
InactiveUS7727399B2Reduce activationReducing bio-incompatibilitiesComponent separationHaemofiltrationFiltrationThin layer
A device, system and method for exchanging components between first and second fluids by direct contact in a microfluidic channel. The fluids flow as thin layers in the channel. One of the fluids is passed through a filter upon exiting the channel and is recycled through a secondary processor which changes the fluid's properties. The recycled fluid is reused for further exchange. The filter excludes blood cells from the recycled fluid and prevents or limits clogging of the filter. The secondary processor removes metabolic waste and water by diafiltration.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Systems and methods of microfluidic membraneless exchange using filtration of extraction outlet streams
InactiveUS20090139931A1Reduce activationReducing bio-incompatibilitiesComponent separationSolvent extractionMetabolic wasteFiltration
A device, system and method for exchanging components between first and second fluids by direct contact in a microfluidic channel. The fluids flow as thin layers in the channel. One of the fluids is passed through a filter upon exiting the channel and is recycled through a secondary processor which changes the fluid's properties. The recycled fluid is reused for further exchange. The filter excludes blood cells from the recycled fluid and prevents or limits clogging of the filter. The secondary processor removes metabolic waste and water by diafiltration.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
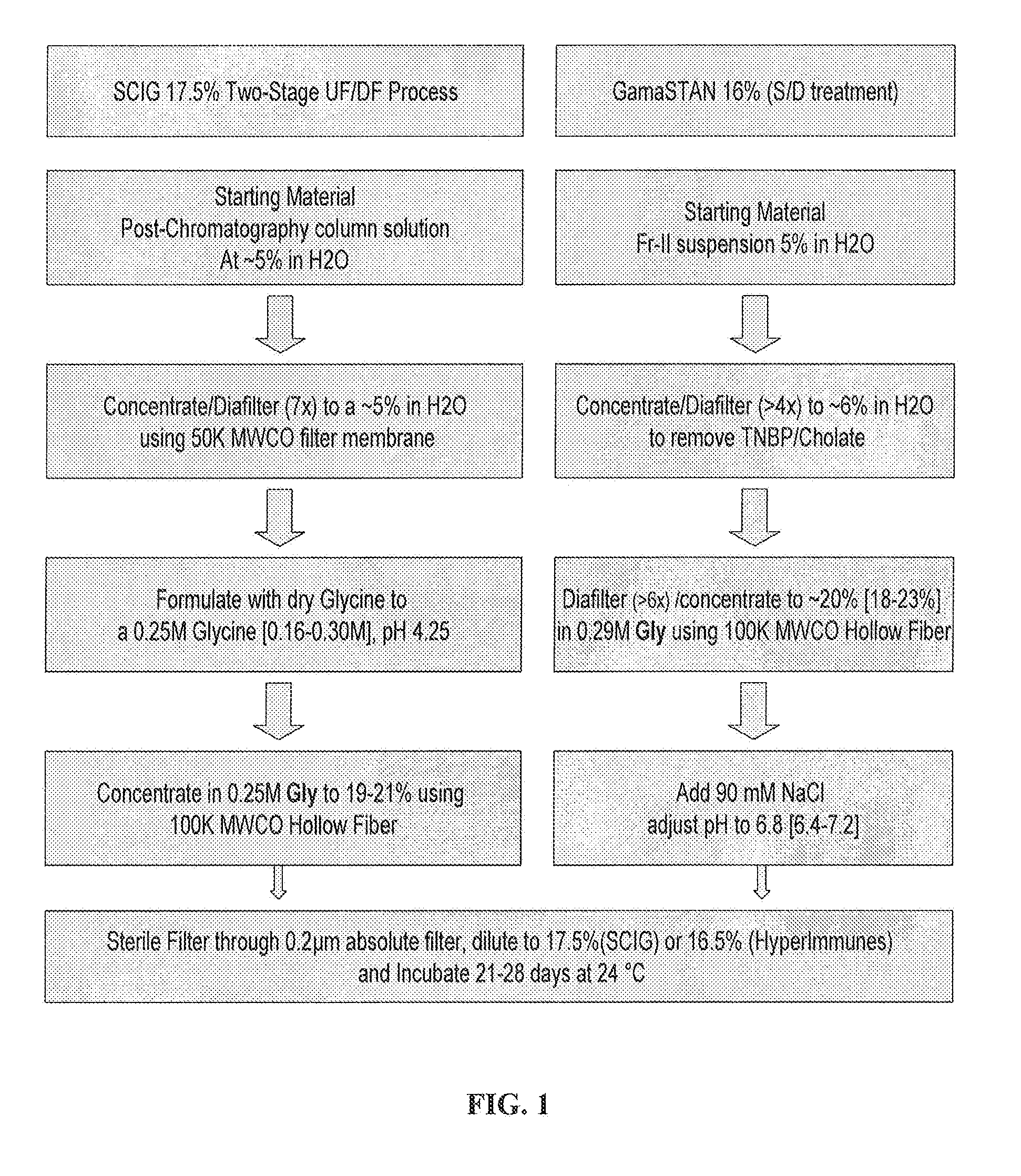
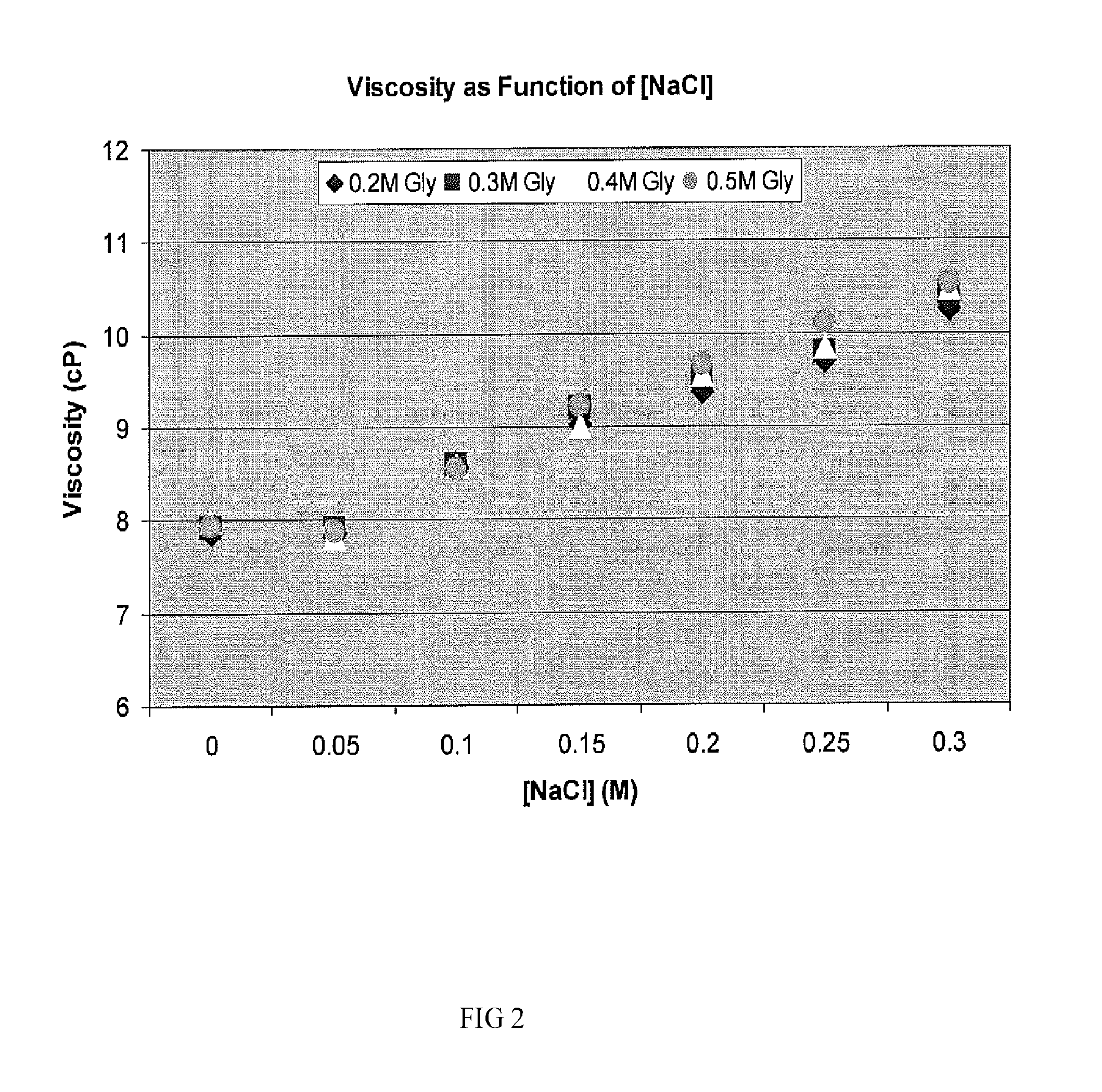
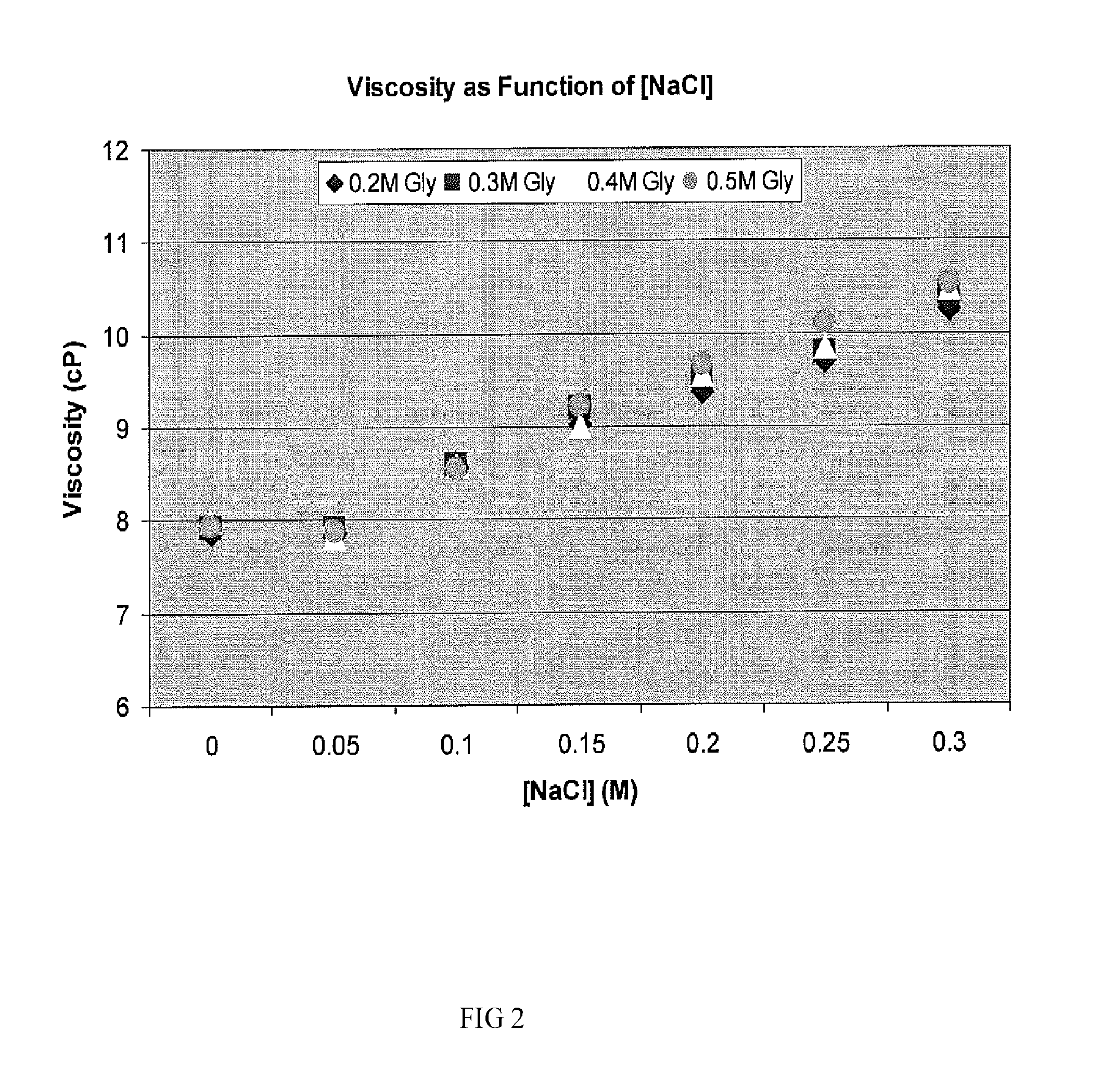
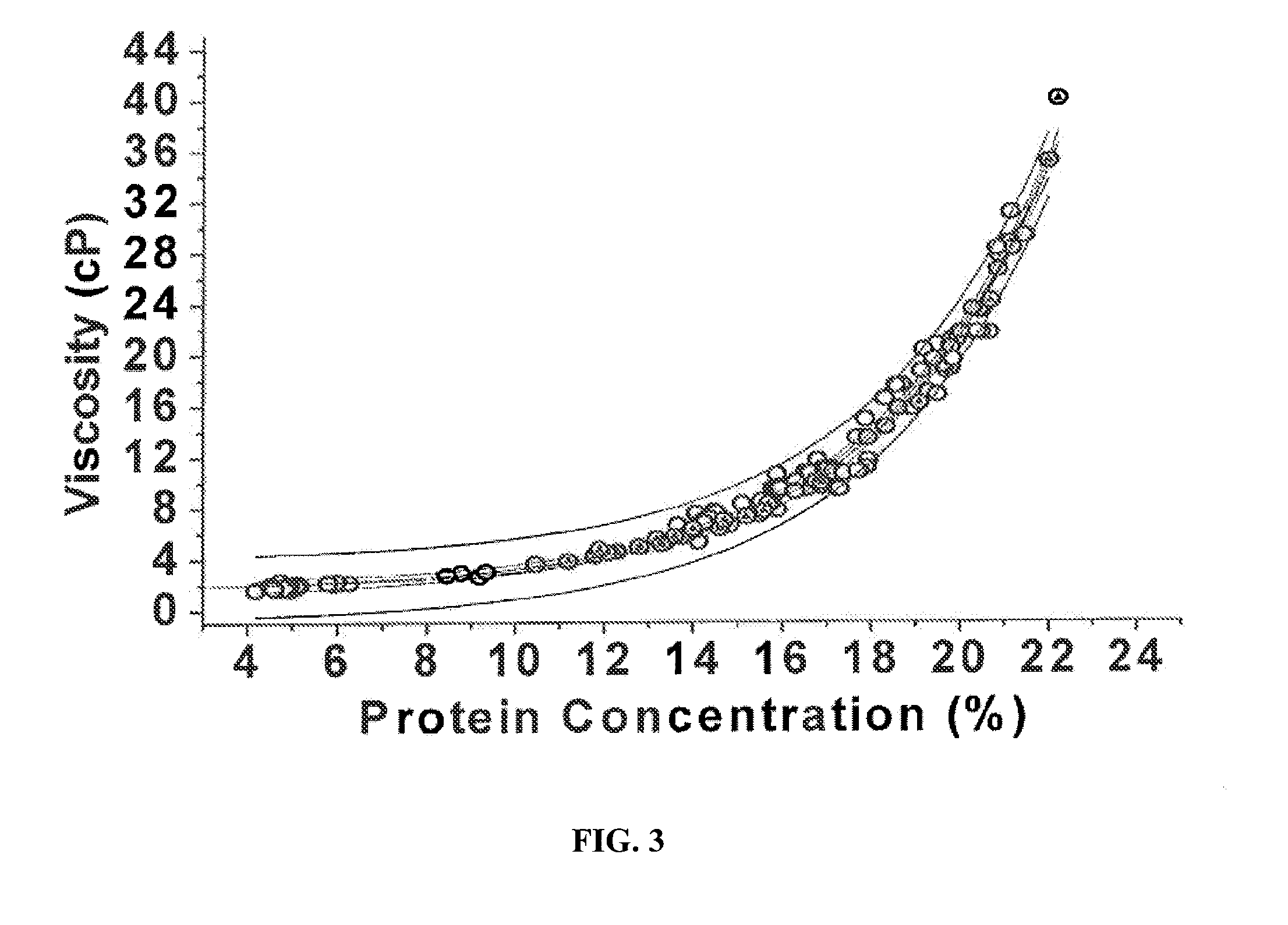
Two-stage ultrafiltration/diafiltration
The present invention provides a method for concentrating a protein, in particular a method for concentrating a plasma product, in particular IgG, using glycine in a (two-stage ultrafiltration / diafiltration approach.
Owner:GRIFOLS THERAPEUTICS LLC
Bioprocess for the production of recombinant anti-botulinum toxin antibody
A process for producing recombinant anti-botulinum toxin antibody comprising the steps of fermenting recombinant E. Coli cells in broth, concentrating the cells by removing the broth, crushing the concentrated cells, separating a permeate derived from the crushed cells from cell debris, purifying a recombinant antibotulinum antibody (Fab) from said permeate, and separating said Fab from impurities by diafiltration.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Concentrated-protein food product and process
InactiveUS20060172058A1Protein composition from fishMilk preparationConcentration proteinMicrofiltration
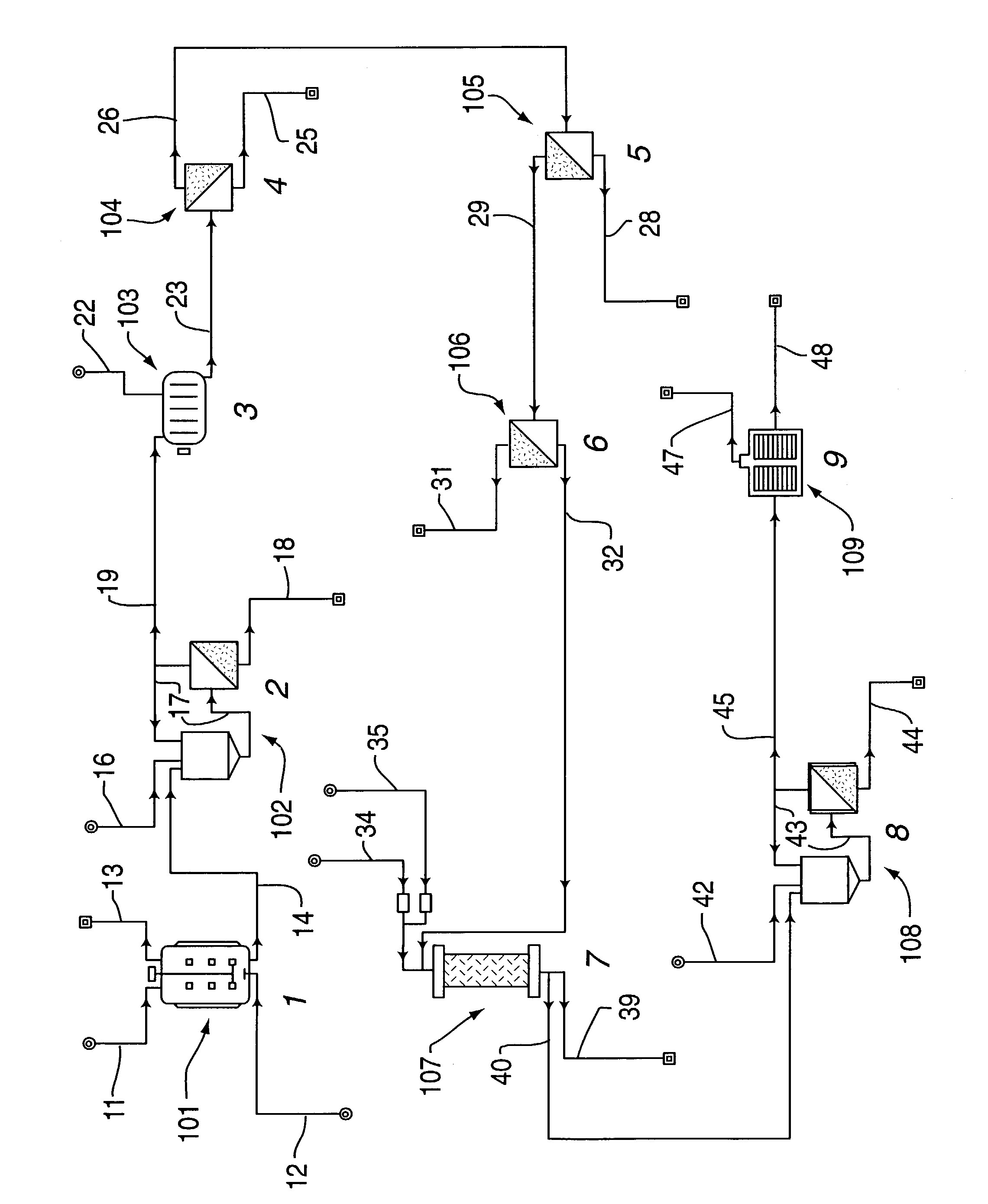
A system, processes, and milk-based food products made from the system and processes, in which cream is separated from milk to produce an ultra-low fat milk product. The milk product is microfiltered to produce a retentate that is ready to drink and is high in protein and has no or substantially no fat. The permeate from the microfiltration process is ultrafiltered to produce a retentate that is high in protein with few other solids. The permeate of the ultrafiltration step, or other milk salt containing fluid may be used to perform diafiltration on the retentate of the microfiltration process. The permeate may also be used to provide protein fortification to other food and beverage products, and is especially useful in its liquid form for such fortification.
Owner:DOMINION NUTRITION
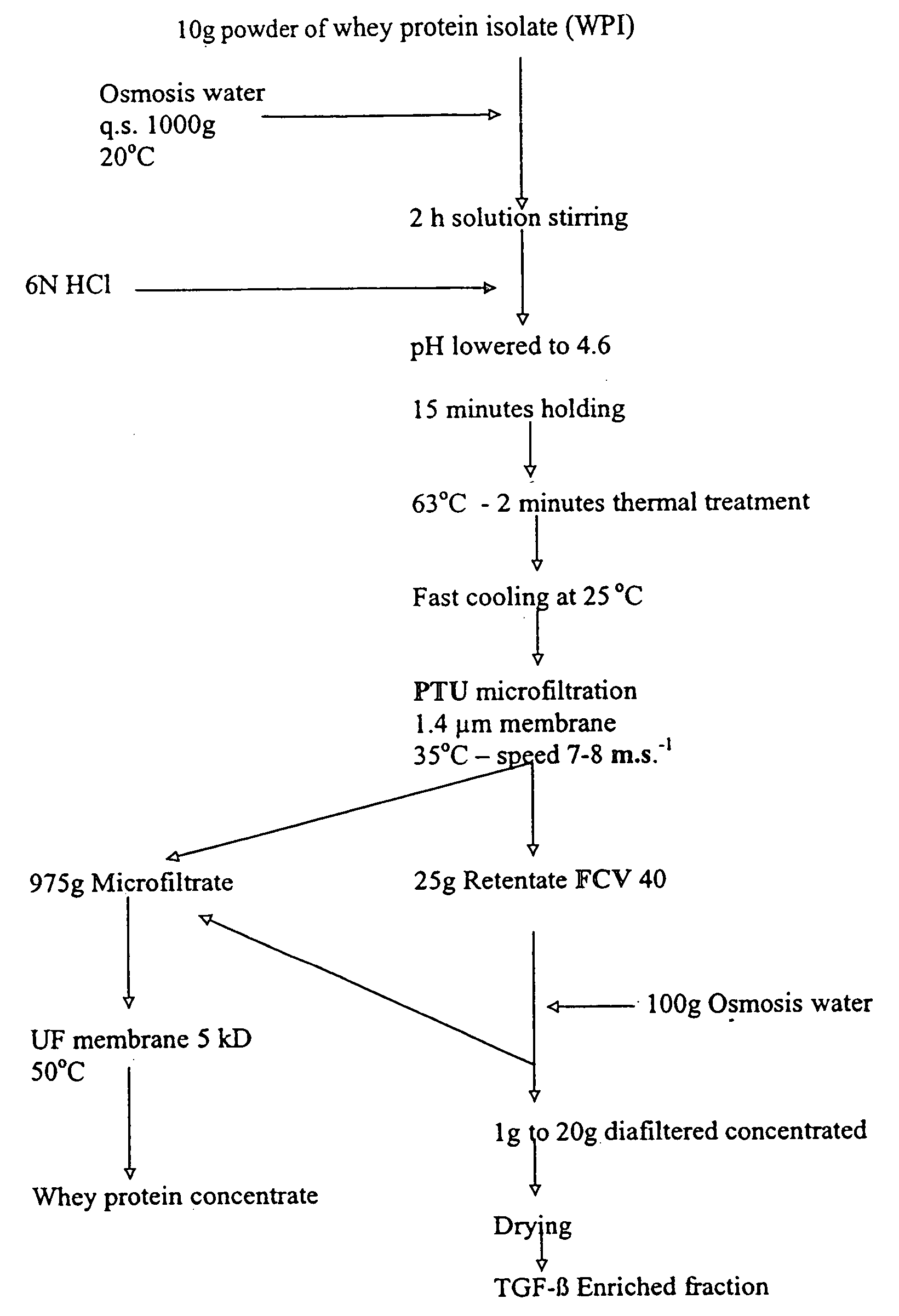
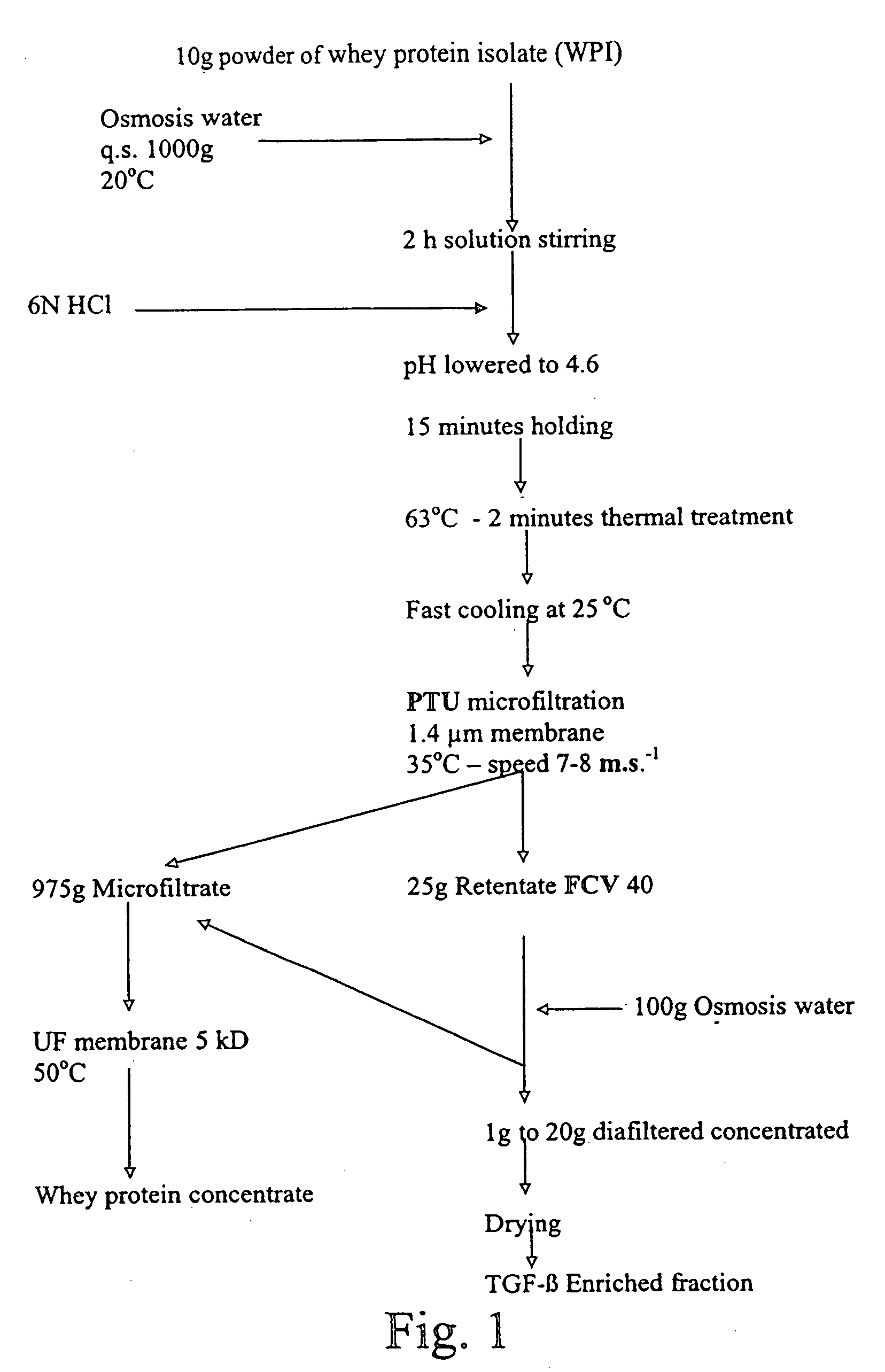
Method for obtaining a TGF-beta enriched protein fraction in activated form, protein fraction and therapeutic applications
The invention concerns a method for obtaining a highly enriched TGF-beta protein fraction in activated form, from a liquid solution rich in proteins said to be soluble in the aqueous phase of milk and / or of whey, said method comprising the following steps; a) adjusting soluble proteins purified at a concentration between 5 and 30 g / liter of solution; b) precipitating part of the whey proteins by acidic treatment of the solution thus obtained to a pH ranging between 4 and 5.5 and at a temperature ranging between 55° C. and 68° C.; c) carrying out a microfiltration of the treated solution by diafiltration, so as to obtain respectively a microfiltration retentate and a microfiltrate; d) recuperating the microfiltration retentate containing the protein fraction highly enriched in TGF-beta; e) drying the microfiltration retentate which has been subjected to diafiltration to obtain a powder highly enriched in TGF-beta.
Owner:PIERRE JOUAN BIOTECH
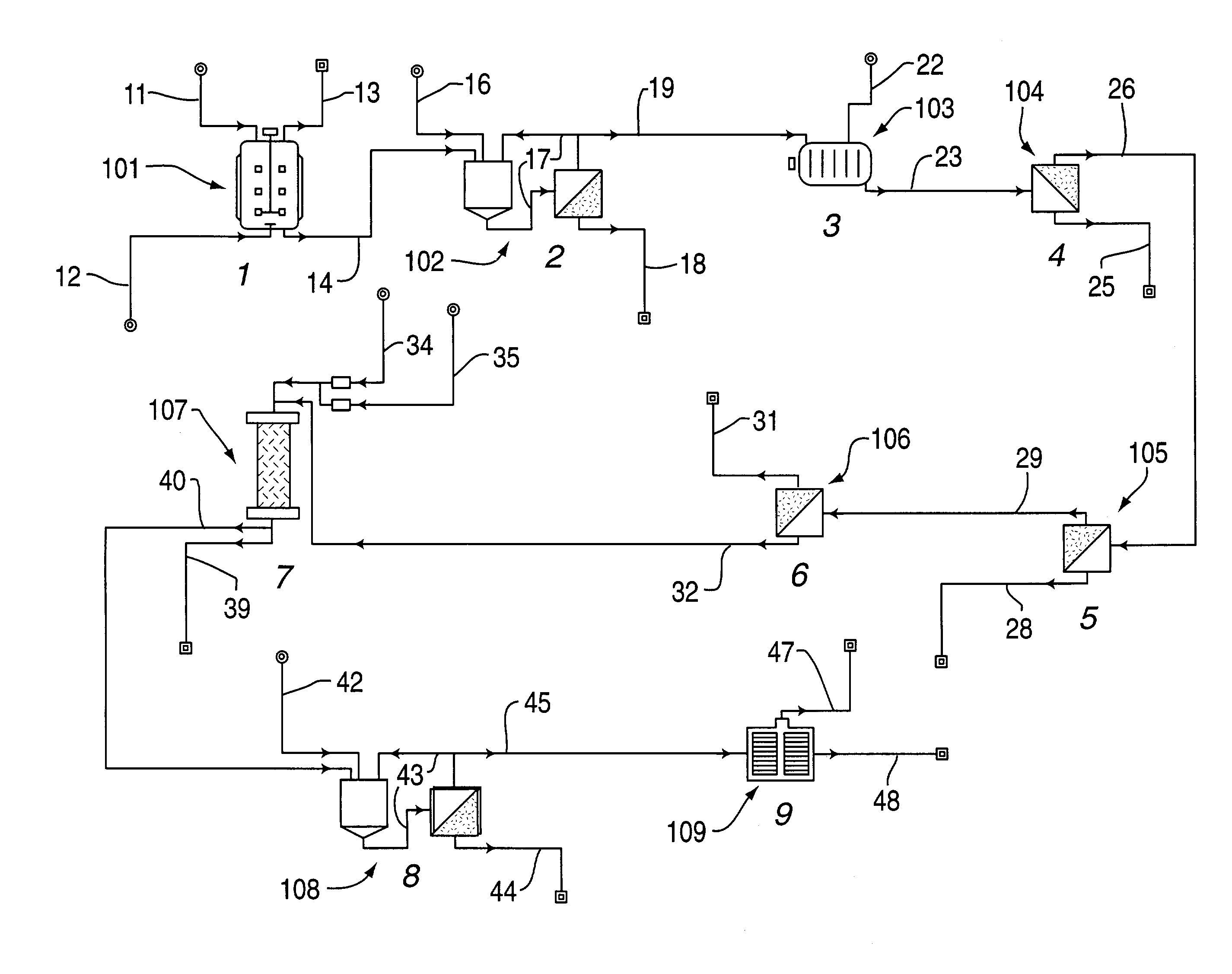
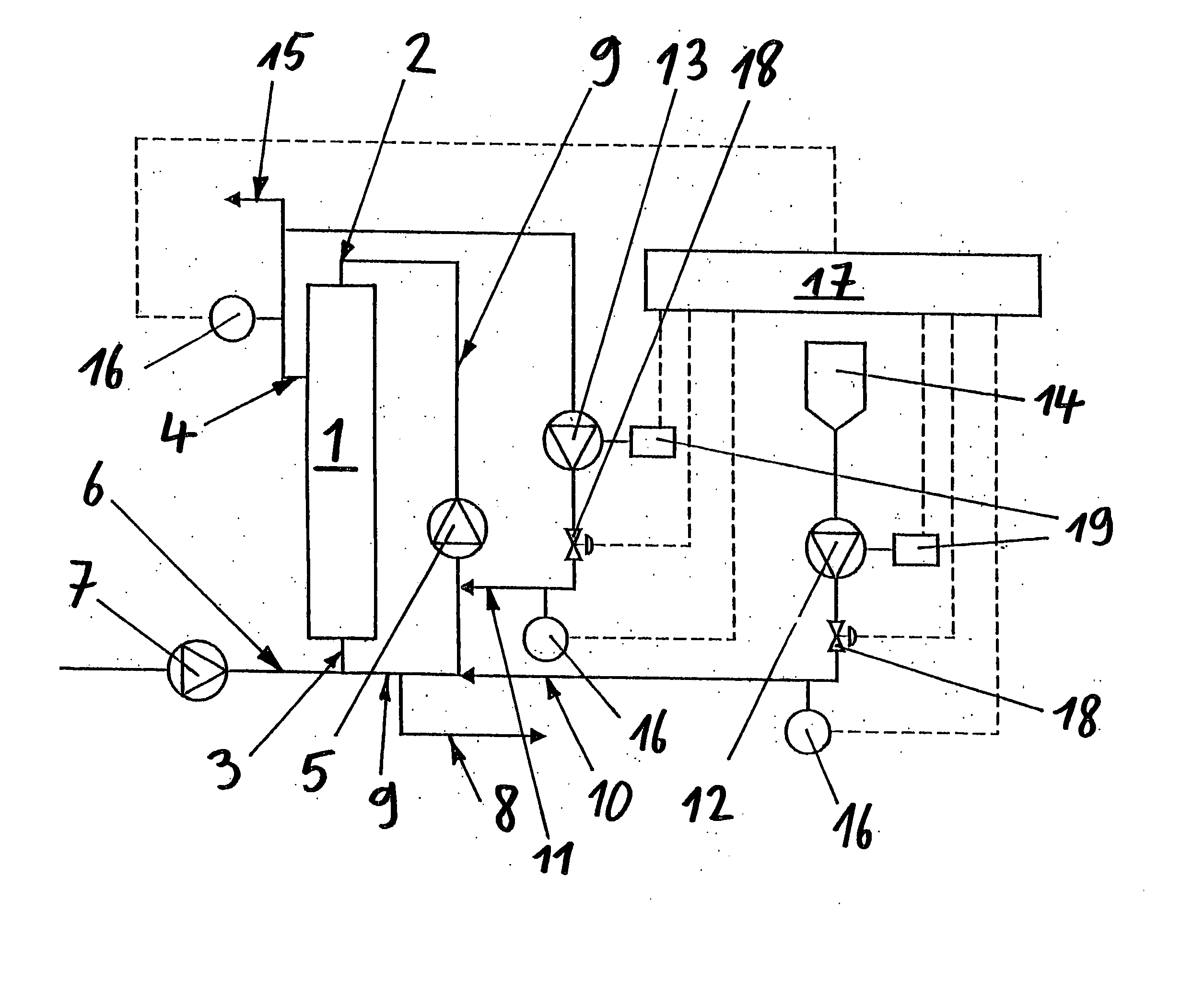
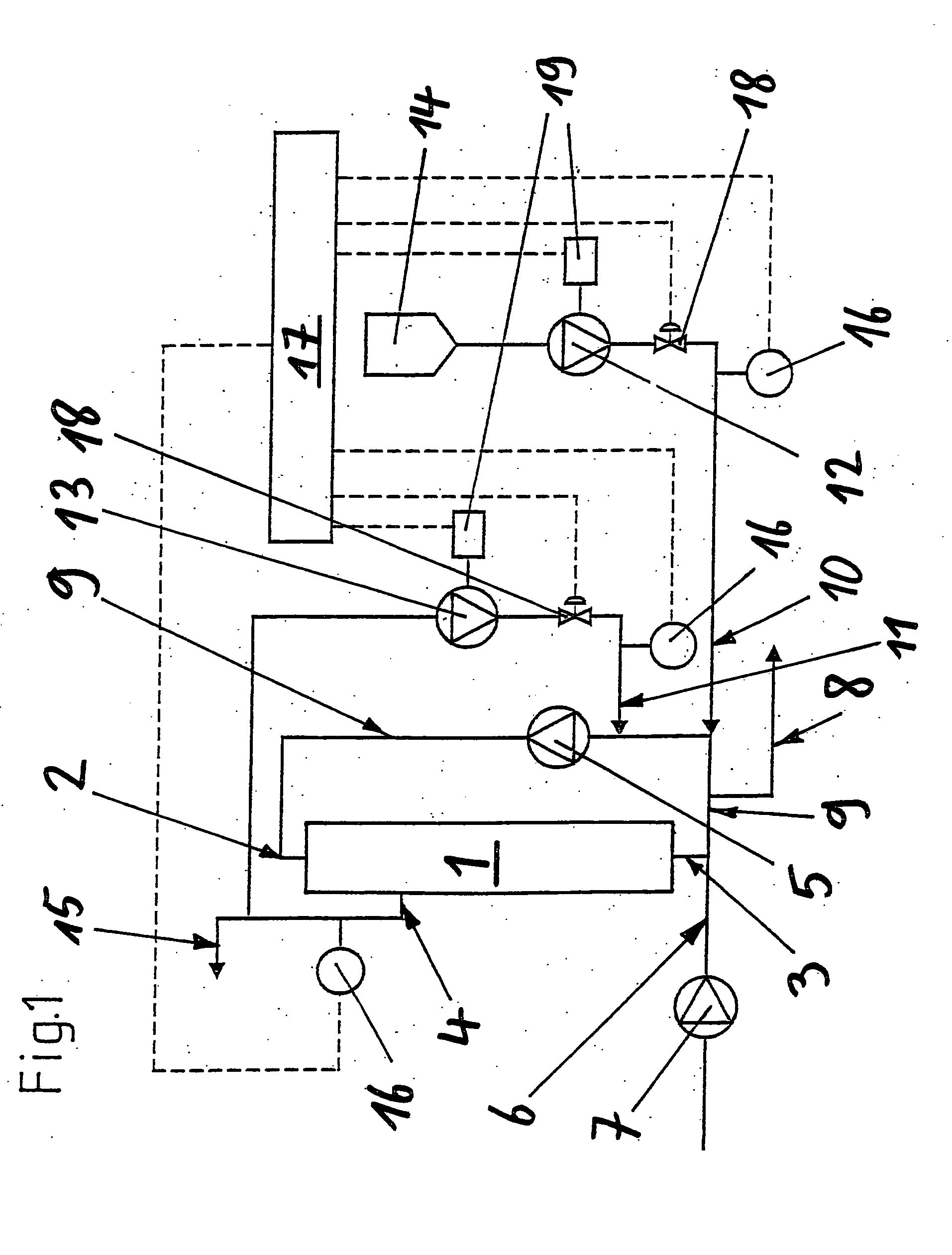
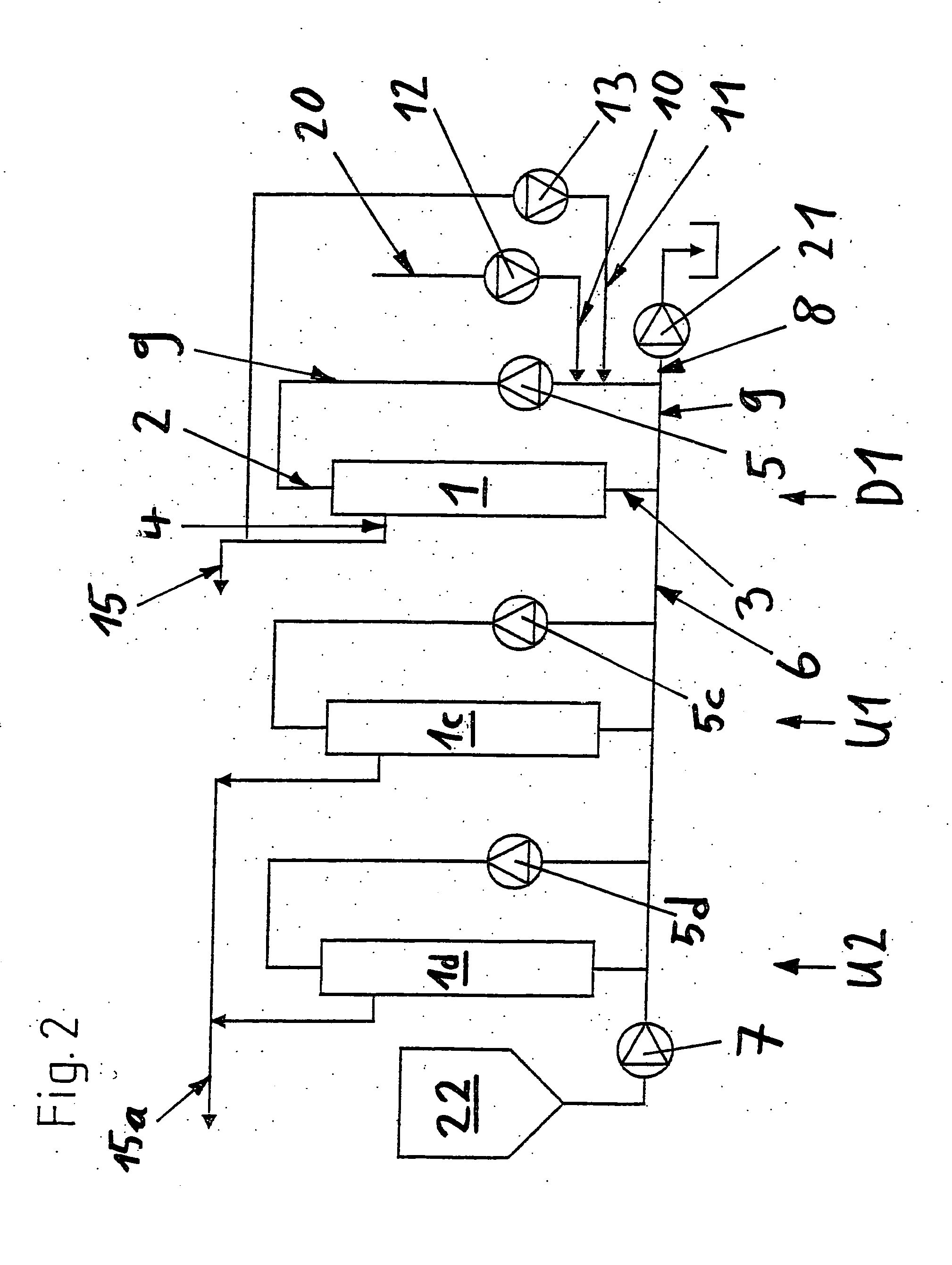
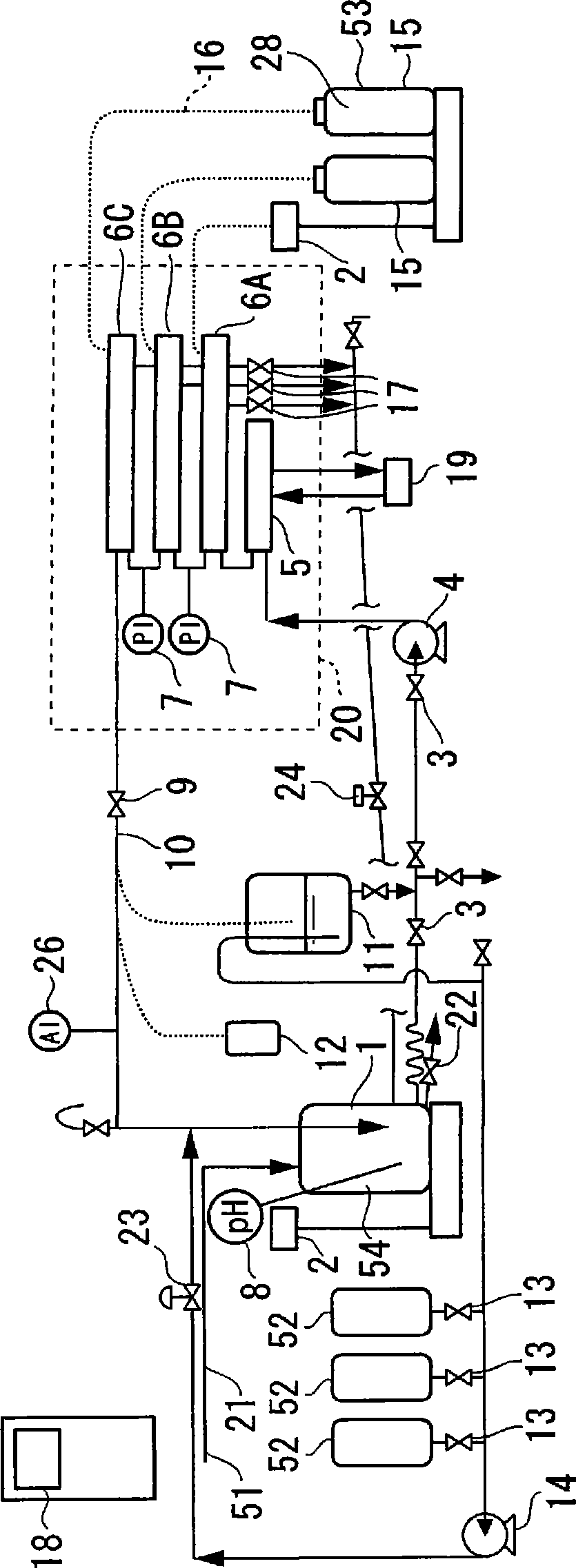
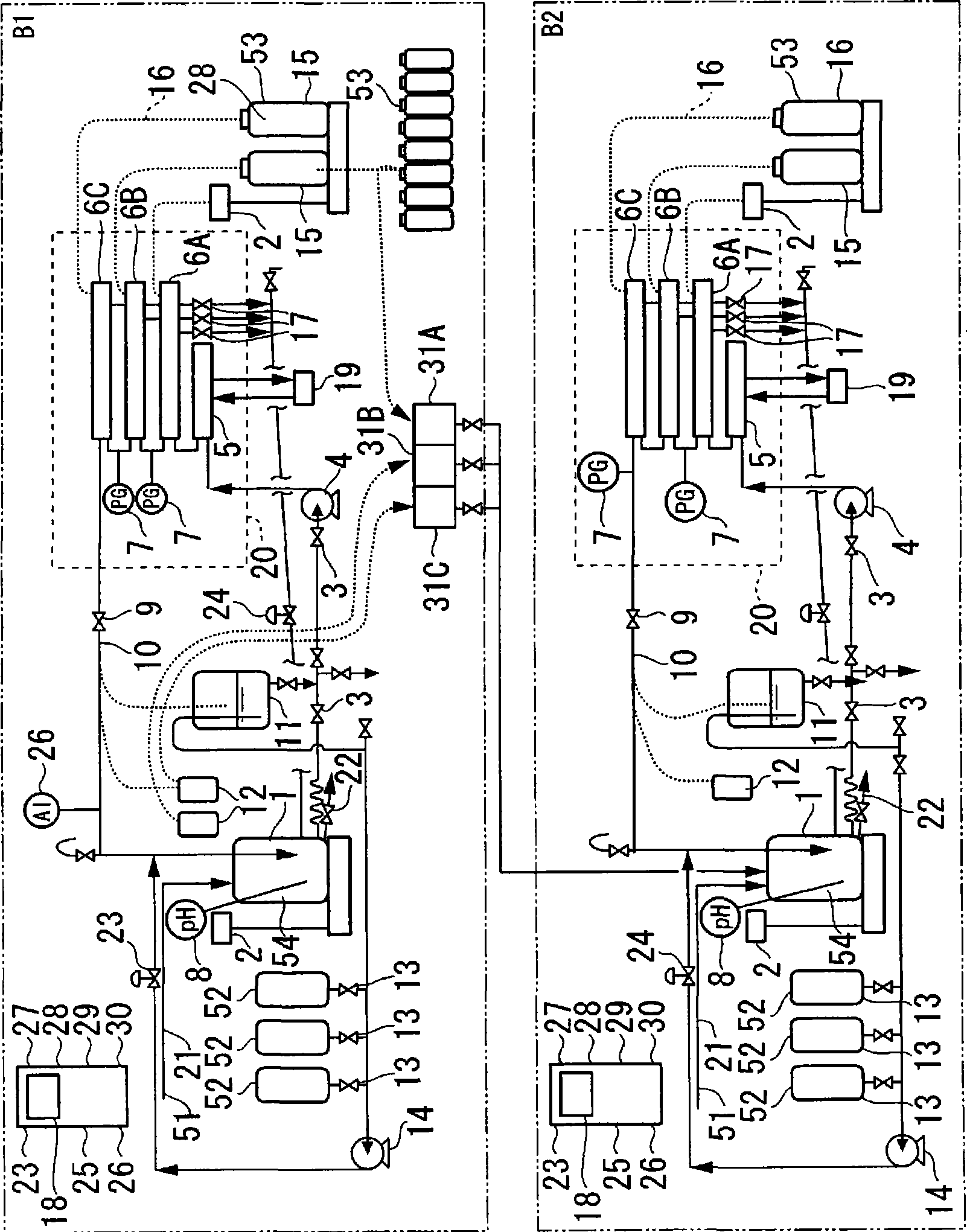
Method for diafiltration of a product and device for carrying out this method
The invention relates to a diafiltration stage for concentrated fruit juices, comprising a cross-flow filtration element (1). The product inlet (2) and the product outlet (3) of the filtration element (1) are united via a circulation pump (5) to form a product circuit, to which product is continuously supplied via a product supply line (6) and from which product can be continuously removed via a product discharge line (8). The permeate outlet (4) of the filtration element (1) is connected to the product circuit via a return line (1) comprising a permeate pump (13), enabling a desired amount of permeate to be returned to the product circuit. In addition, the stage comprises a wash-fluid supply line (10) that is equipped with a wash-fluid pump (12), which is used to supply a desired amount of water to the product circuit as wash fluid. The supplied amounts of permeate and water can be set independently of one another. Said diafiltration stage permits both the degree of washing of the product and the quality and amount of the product retentate and the permeate that is produced to be set and regulated within a wide range, even for fixed operating conditions, such as those required in continuous multi-stage large-scale installations.
Owner:BUCHER GUYER MASCHFAB
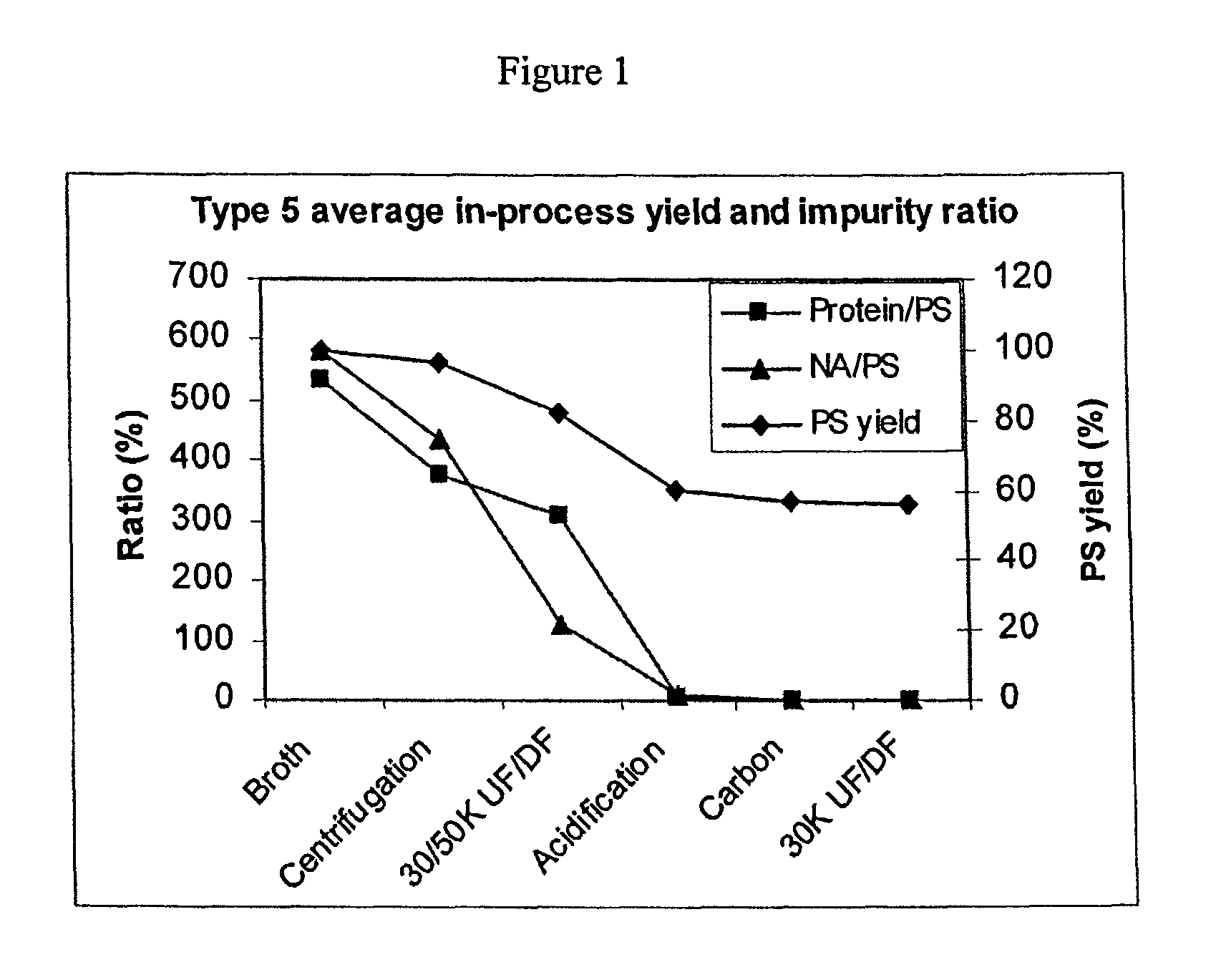
Shortened purification process for the production of capsular Streptococcus pneumoniae polysaccharides
ActiveUS8652480B2Reduce molecular weightImprove concentrationAntibacterial agentsBiocideActivated carbon filtrationSarcosine
A shortened process for producing a solution containing substantially purified capsular polysaccharides from a cellular Streptococcus pneumoniae lysate broth is described. Ultrafiltering and diafiltering a clarified S. pneumoniae lysate followed by pH adjustment to less than 4.5, preferably about 3.5, precipitated at least 98% of the protein in the solution without seriously affecting polysaccharide yield. Furthermore, following ultrafiltration and diafiltration and acidification to a pH of less than 4.5, filtration using activated carbon precipitated at least 90% of remaining protein without seriously affecting polysaccharide yield. Exemplary, non-limiting S. pneumoniae serotypes that can be purified using the shortened process of the invention are 1, 4, 5, 6A, 6B, 7F, 9V, 14, 18C, 19A, 19F, and 23F. In one embodiment, the Streptococcus pneumoniae cells are lysed using deoxycholate sodium (DOC), while in another embodiment the lytic agent is a non-animal derived lytic agent such as N-lauryl sarcosine sodium (NLS).
Owner:WYETH LLC
Processes for producing stable exosome formulations
The invention encompasses methods for generating stable exosome formulations and encompasses stable exosome formulations. The exosome formulations encompass stable liquid exosome formulations and stable lyophilized exosome formulations. In some embodiments, the exosome formulations can be generated by ultrafiltration and diafiltration. The exosome formulations can be suitable for administration to a human.
Owner:CAPRICOR
Method for obtaining a TGF-beta enriched protein fraction in activated form, protein fraction and therapeutic applications
The invention concerns a method for obtaining a highly enriched TGF-beta protein fraction in activated form, from a liquid solution rich in proteins said to be soluble in the aqueous phase of milk and / or of whey, said method comprising the following steps; a) adjusting soluble proteins purified at a concentration between 5 and 30 g / liter of solution; b) precipitating part of the whey proteins by acidic treatment of the solution thus obtained to a pH ranging between 4 and 5.5 and at a temperature ranging between 55° C. and 68° C.; c) carrying out a microfiltration of the treated solution by diafiltration, so as to obtain respectively a microfiltration retentate and a microfiltrate; d) recuperating the microfiltration retentate containing the protein fraction highly enriched in TGF-beta; e) drying the microfiltration retentate which has been subjected to diafiltration to obtain a powder highly enriched in TGF-beta.
Owner:PIERRE JOUAN BIOTECH
Two-stage ultrafiltration/diafiltration
The present invention provides a method for concentrating a protein, in particular a method for concentrating a plasma product, in particular IgG, using glycine in a (two-stage ultrafiltration / diafiltration approach.
Owner:GRIFOLS THERAPEUTICS LLC
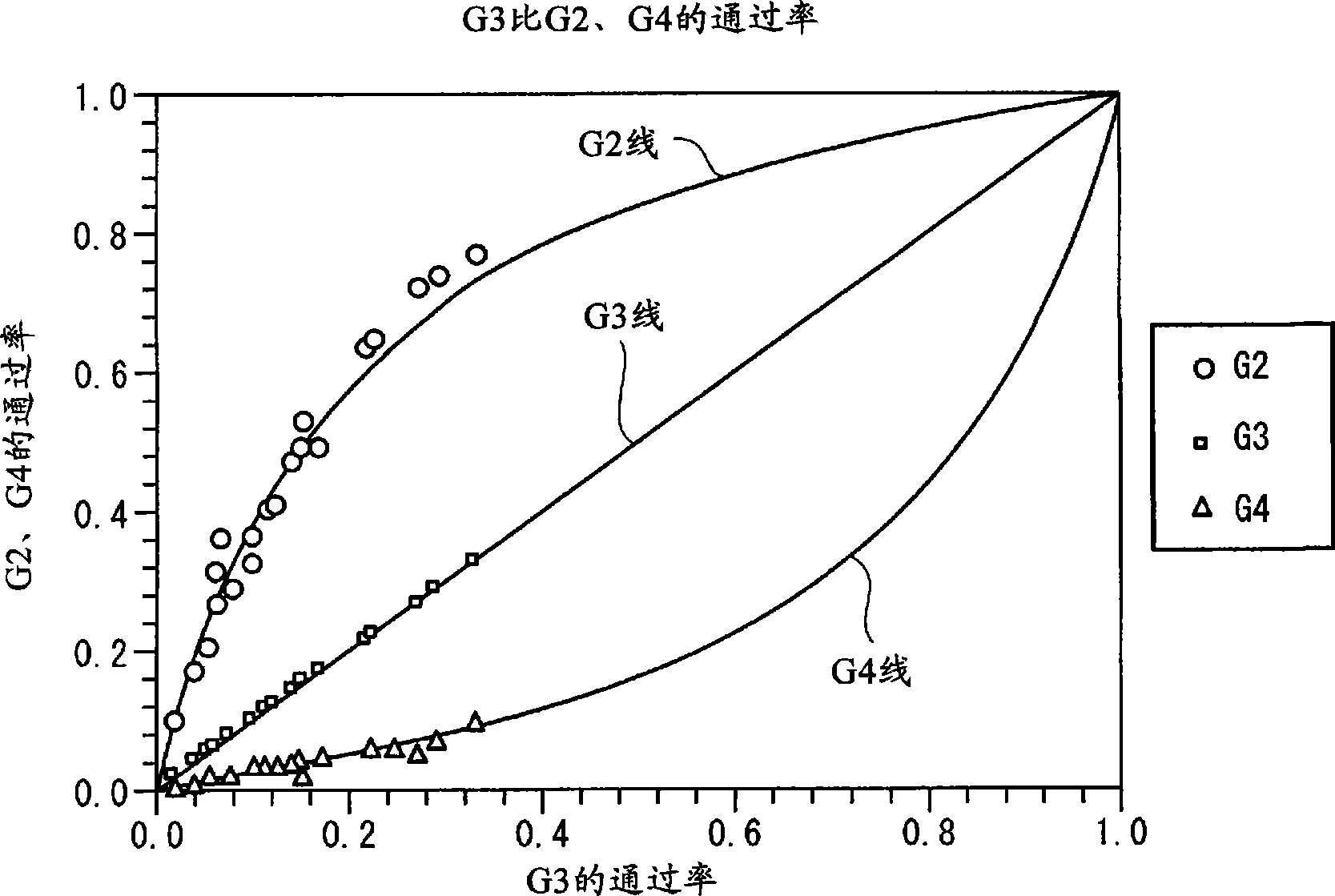
Method of separating target substance according to membrane separation and apparatus therefor
ActiveCN101547735APrecision SeparationNot easy to thermal decompositionOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationMembranesPermeationOperating temperature
A separation apparatus with which, in the event of diafiltration using a membrane, accurate separation of a target substance can be carried out by conducting monitoring / regulation of the tendency of permeation of the target substance with the use of analytical values and measurement values indicating the status of separation by the membrane apparatus, such as the physical values and concentrations of permeate liquid and circulating liquid / internal circulating liquid. In a diafiltration in which a washing liquid is added to a raw liquid containing multiple target substances and a target substance is drawn out into a permeate liquid obtained from the membrane separation apparatus so as to isolate the same from the other target substances remaining in the residue liquid, the tendency of target substance permeation is controlled by carrying out regulation or control within a preset region of at least one operating item selected from among permeate liquid flow rate and with respect to the membrane separation apparatus, operating pressure, operating temperature, circulating liquid concentration and circulating liquid amount with the use of the separation status index and / or progress course index for separating operation.
Owner:TSUKISHIMA KANKYO ENG
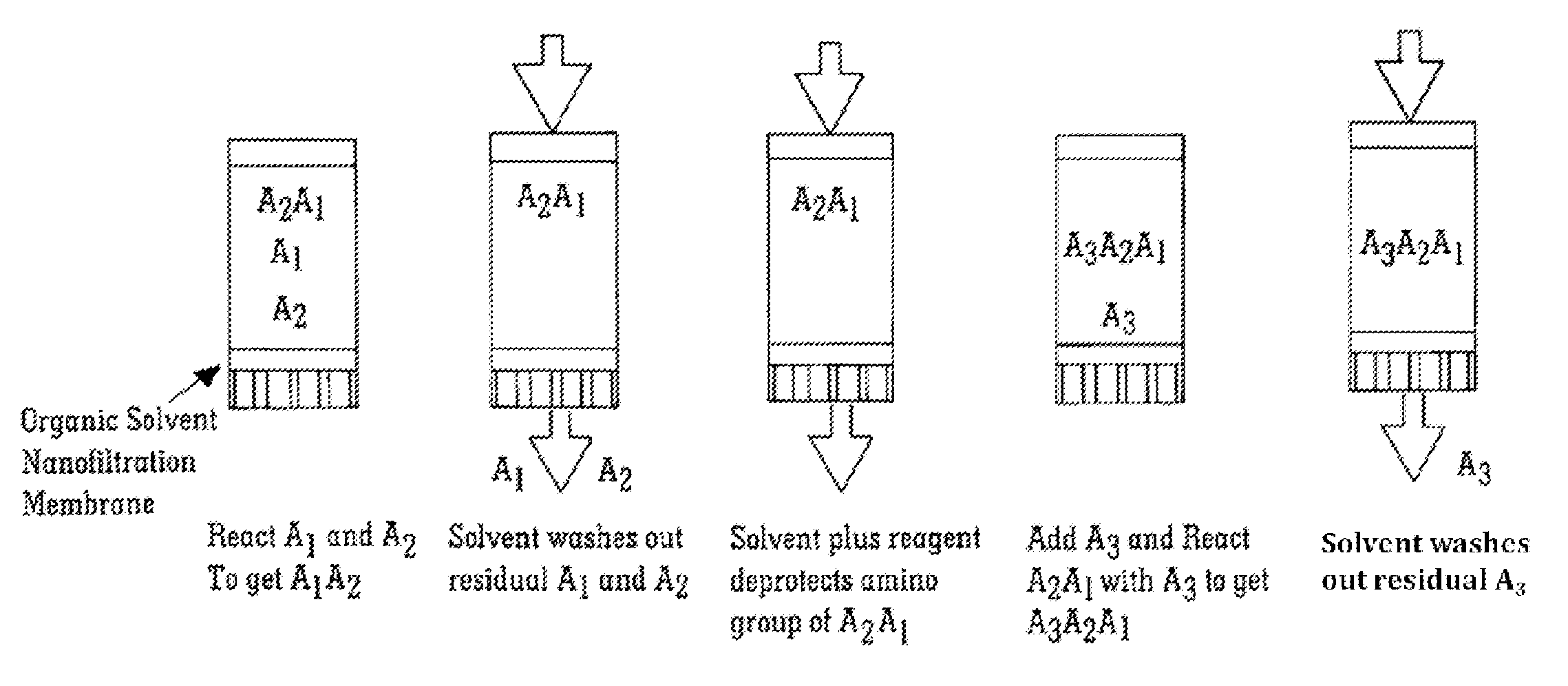
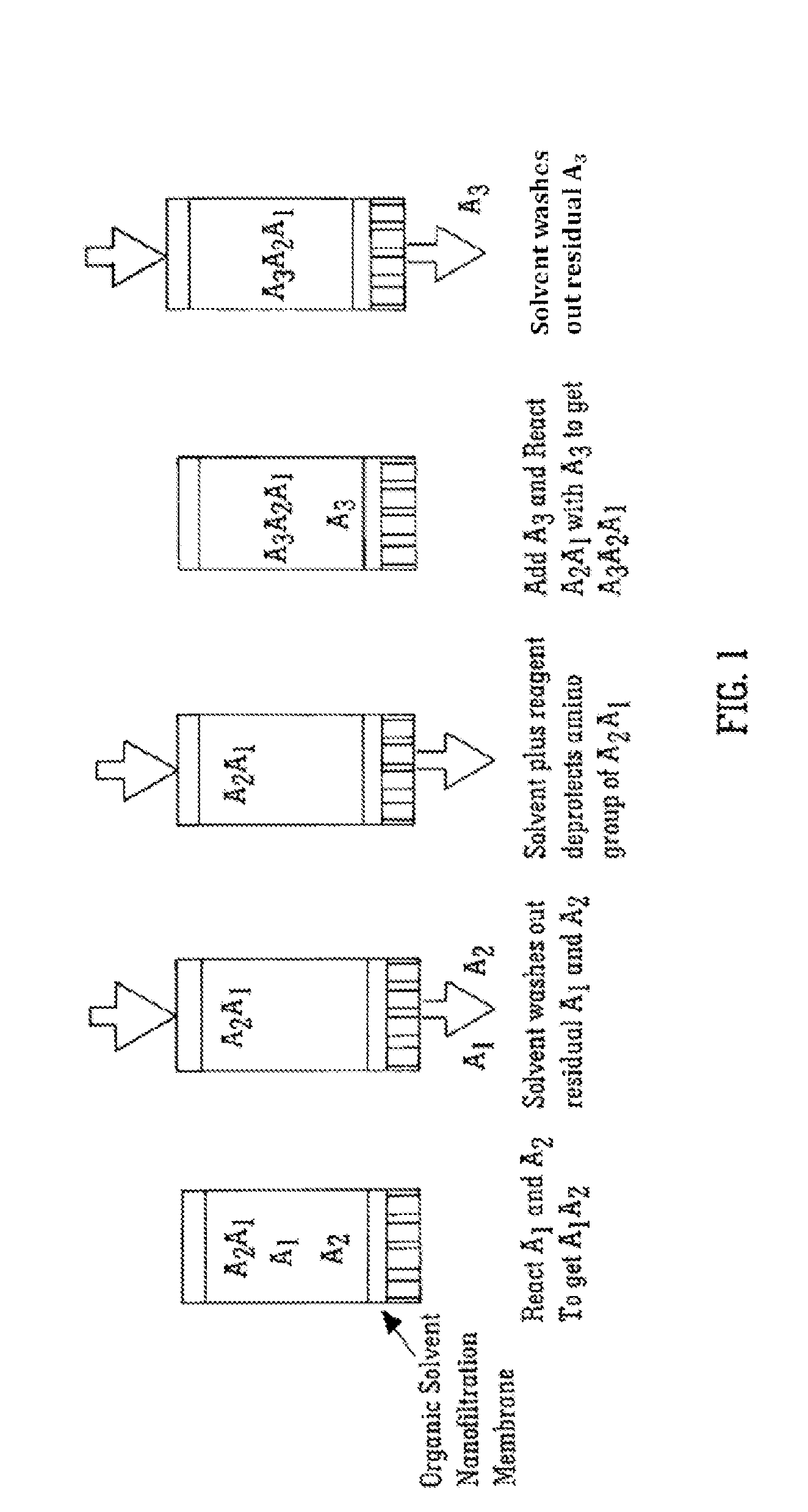
Solvent resistant diafiltration of peptides, PNA or oligonucleotides
According to the present invention, there is provided a process for the preparation of a first compound selected from peptides, oligonucleotides and peptide nucleic acids. The process comprises synthesizing the first compound and then separating the first compound formed in step (i) from a second compound, which is a reaction by-product of the synthesis of the first compound and / or an excess of a reagent used for the synthesis of a first compound by a process of diafiltration. The membrane used for the diafiltration process is stable in organic solvents and provides a rejection for the first compound which is greater than the rejection for the second compound.
Owner:IP2IPO INNOVATIONS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com