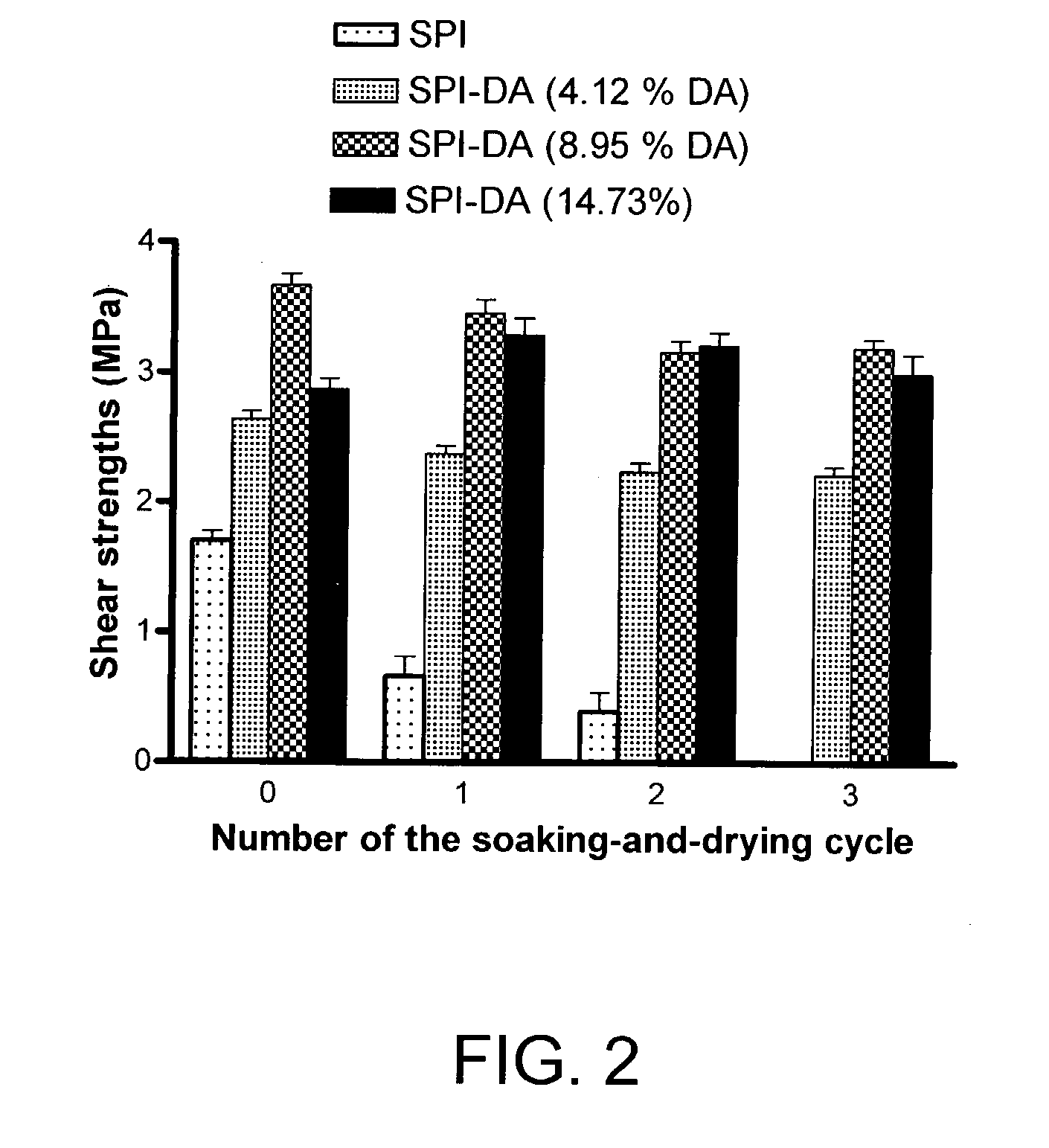
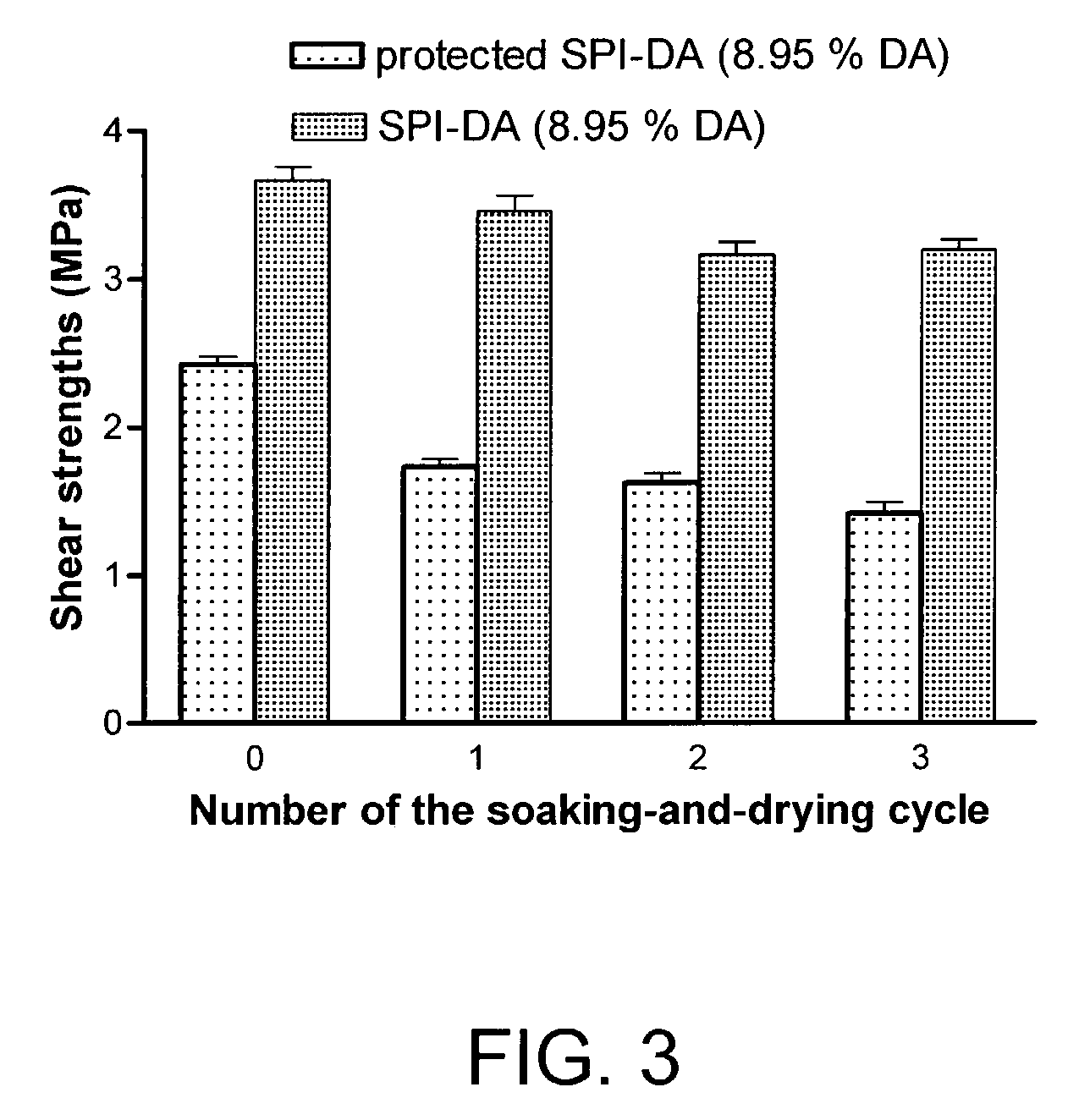
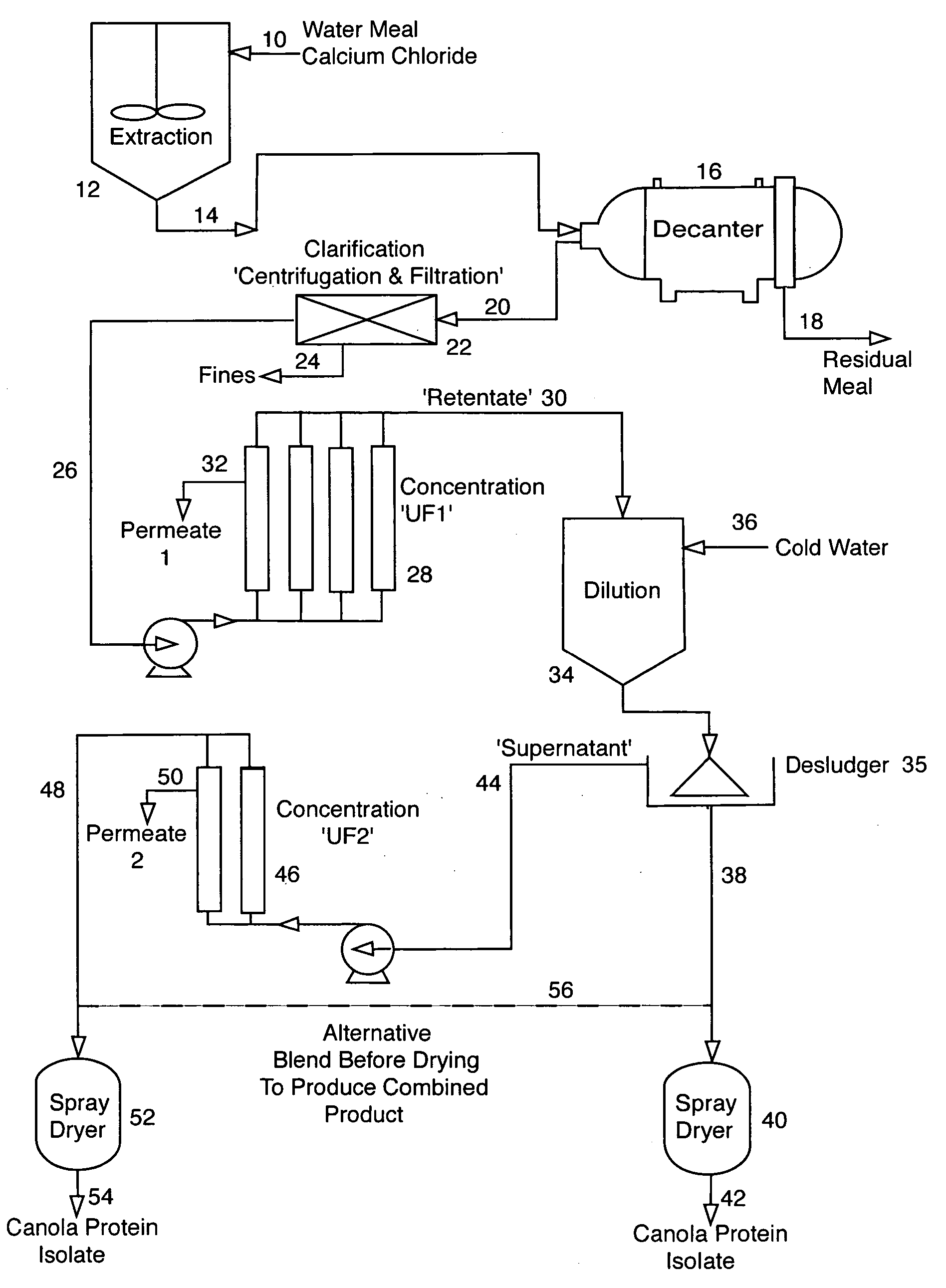
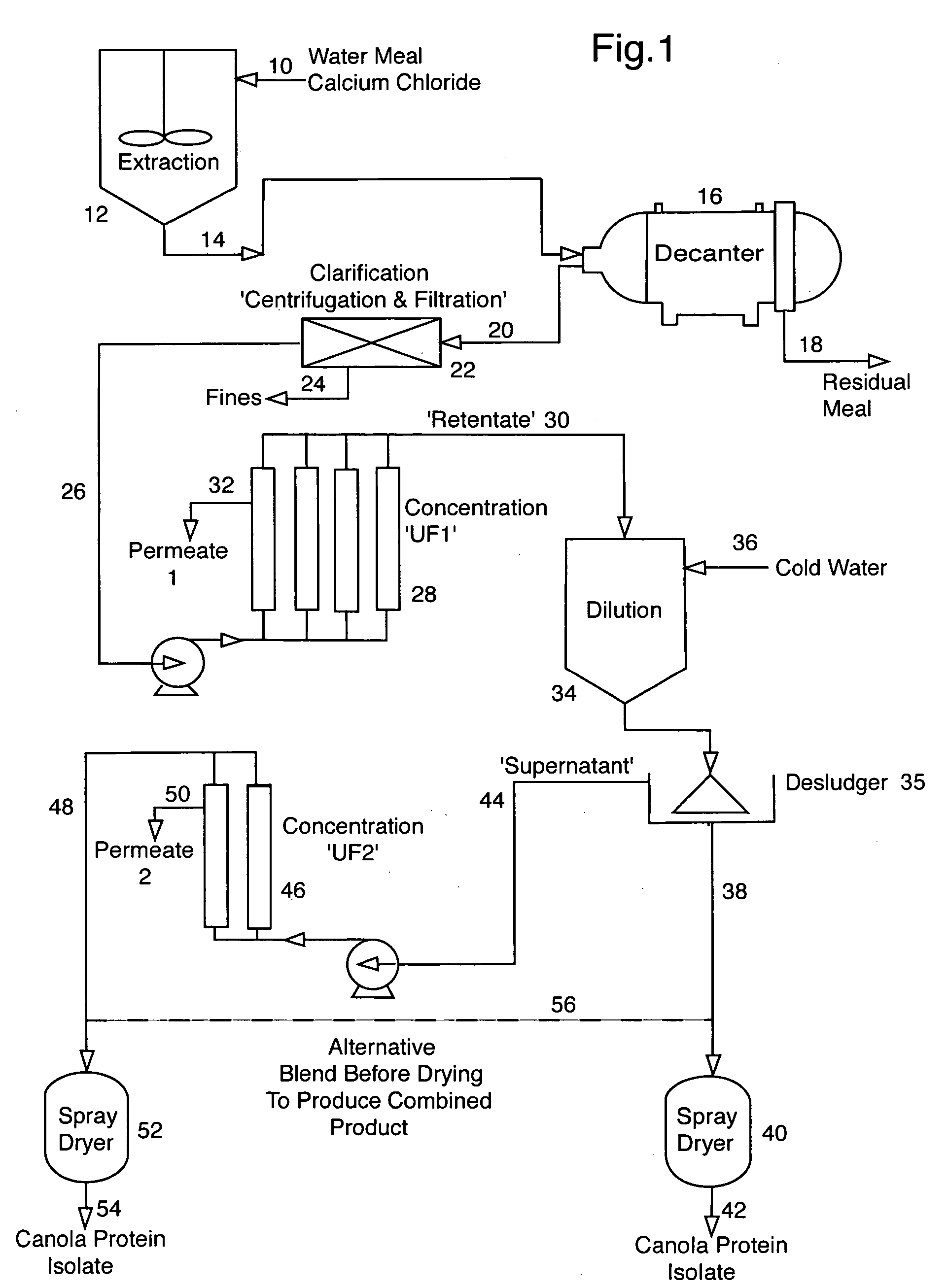
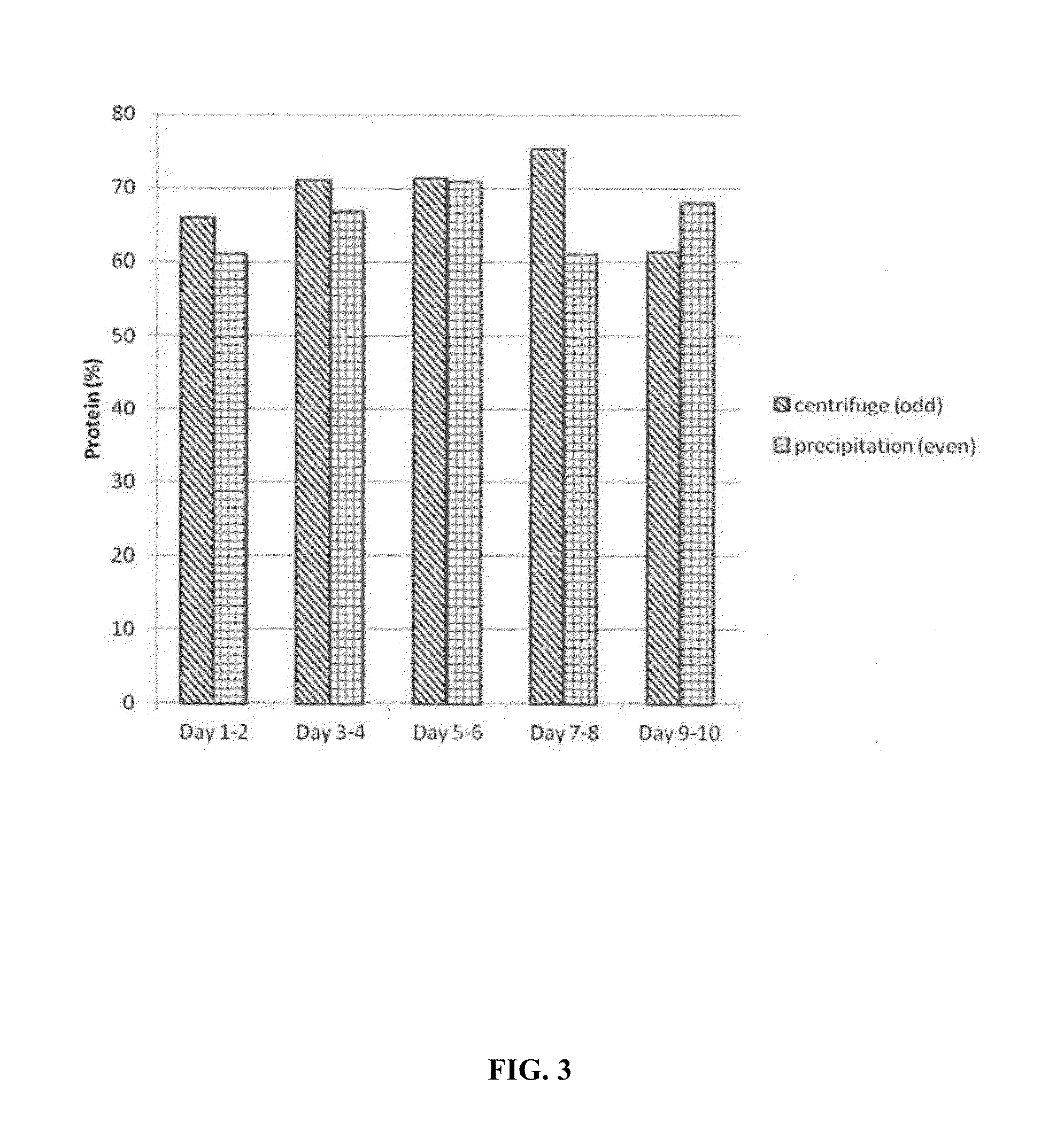
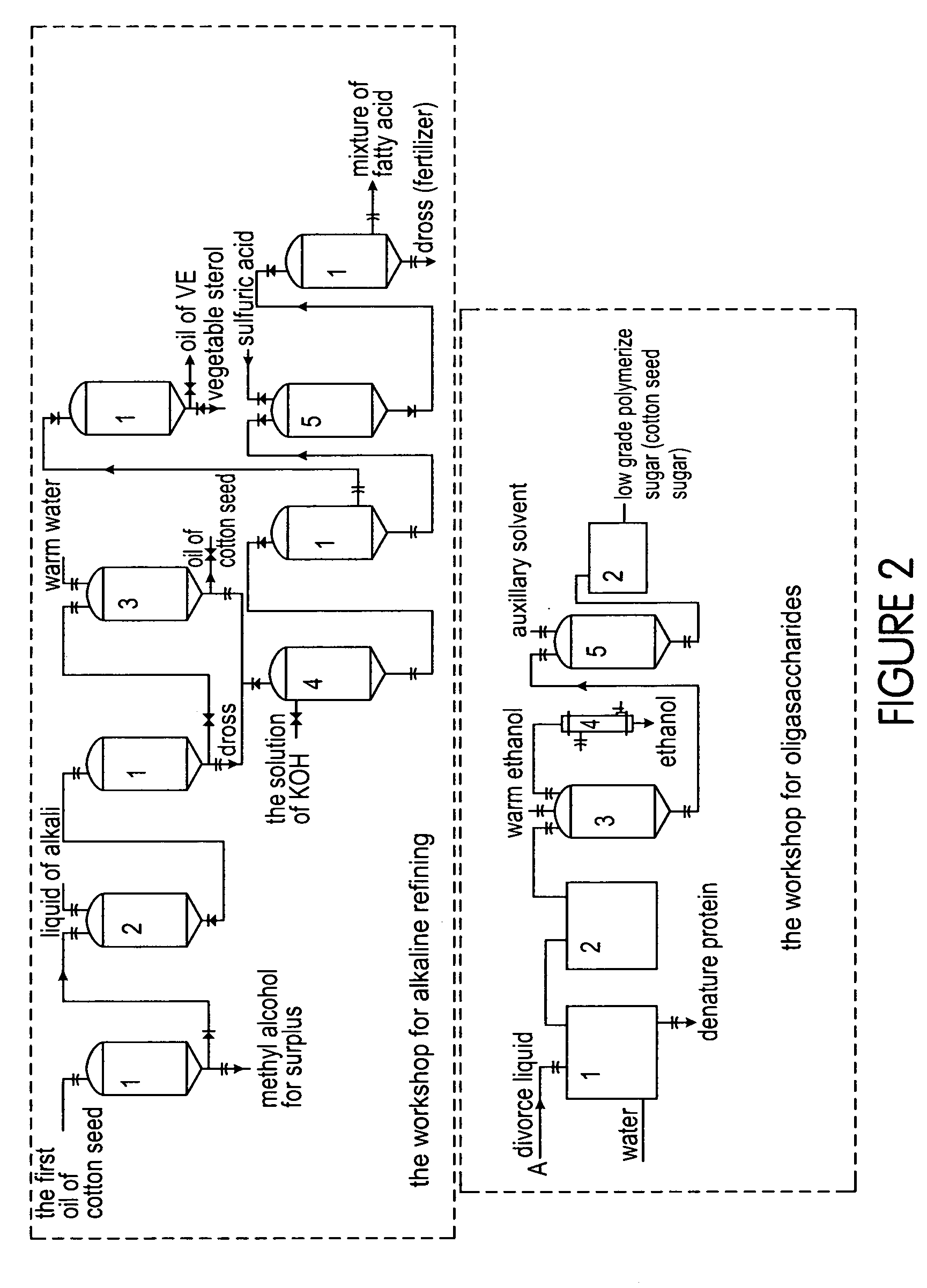
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1714results about "Protein composition from vegetable seeds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
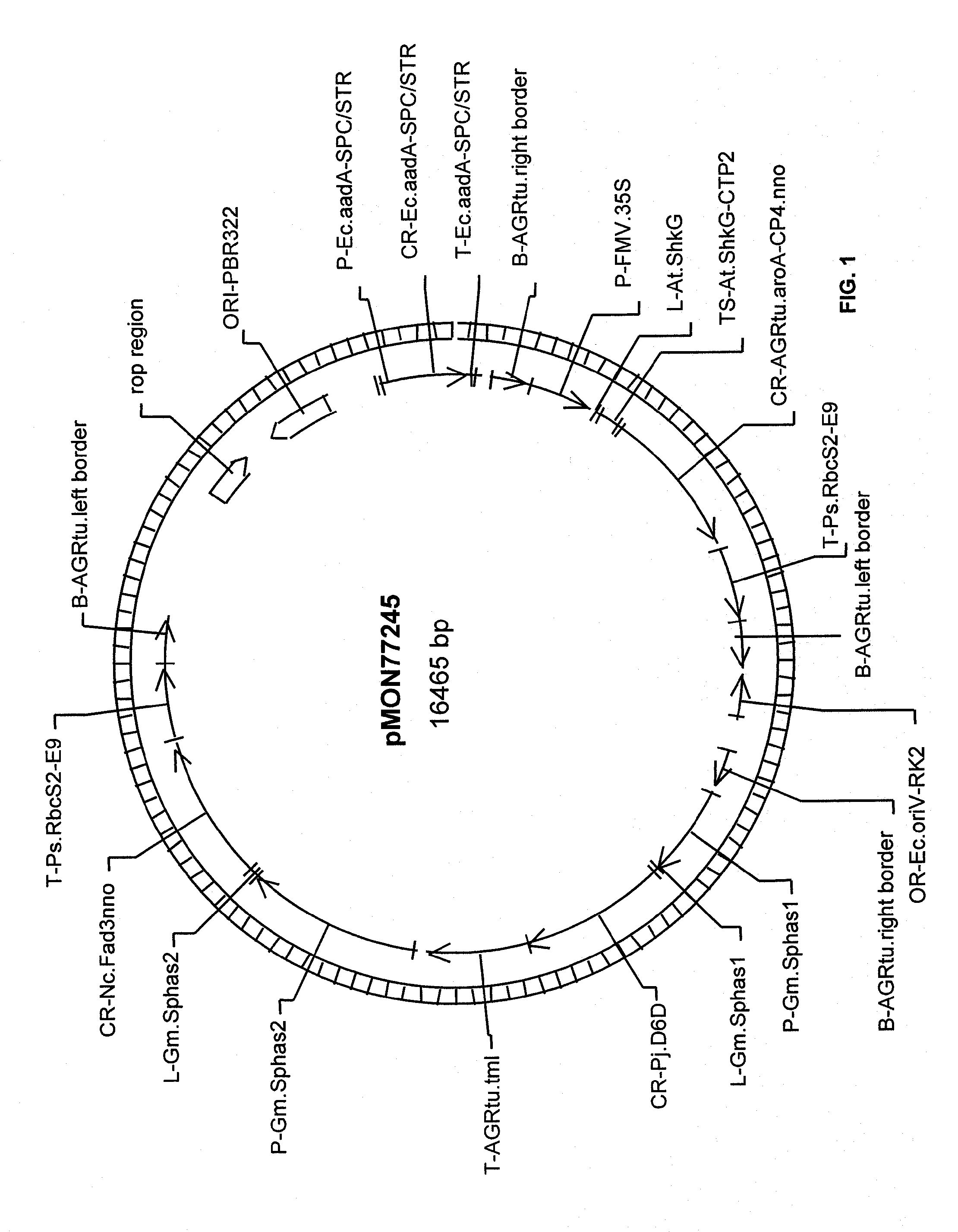
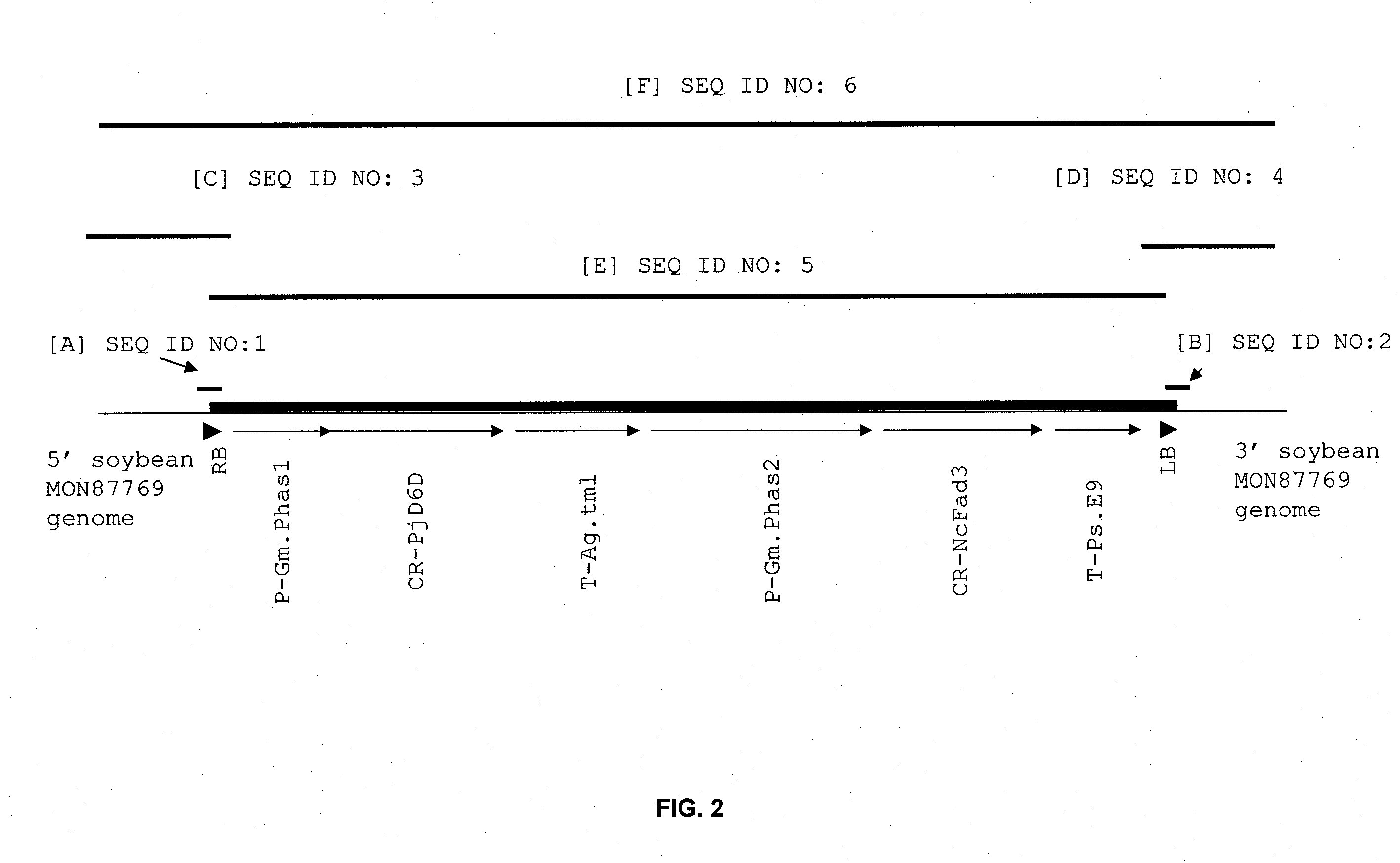
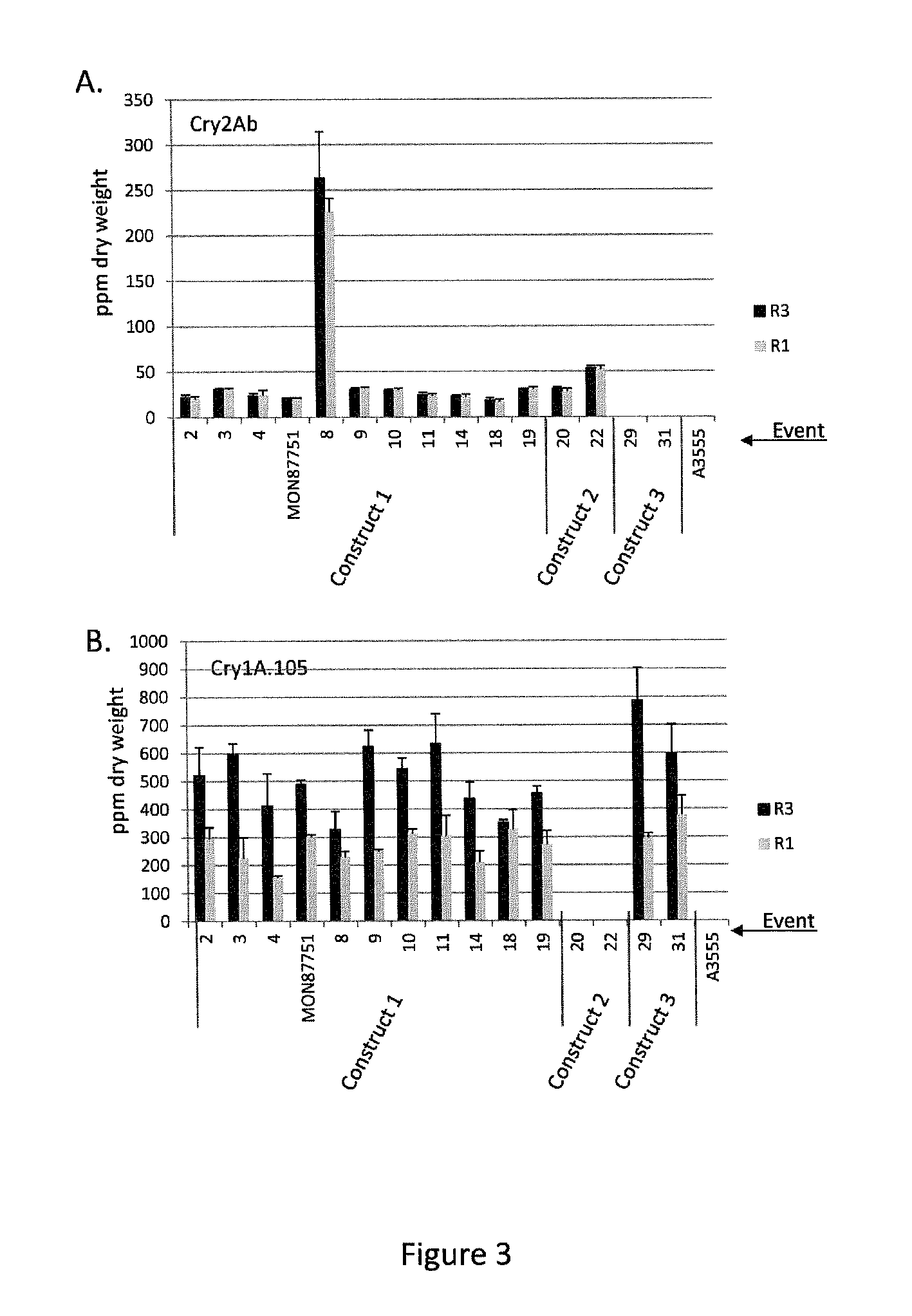
Soybean plant and seed corresponding to transgenic event mon87769 and methods for detection thereof
The present invention provides transgenic soybean event MON87769, and cells, seeds, and plants comprising DNA diagnostic for the soybean event. The invention also provides compositions comprising nucleotide sequences that are diagnostic for said soybean event in a sample, methods for detecting the presence of said soybean event nucleotide sequences in a sample, probes and primers for use in detecting nucleotide sequences that are diagnostic for the presence of said soybean event in a sample, growing the seeds of such soybean event into soybean plants, and breeding to produce soybean plants comprising DNA diagnostic for the soybean event.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
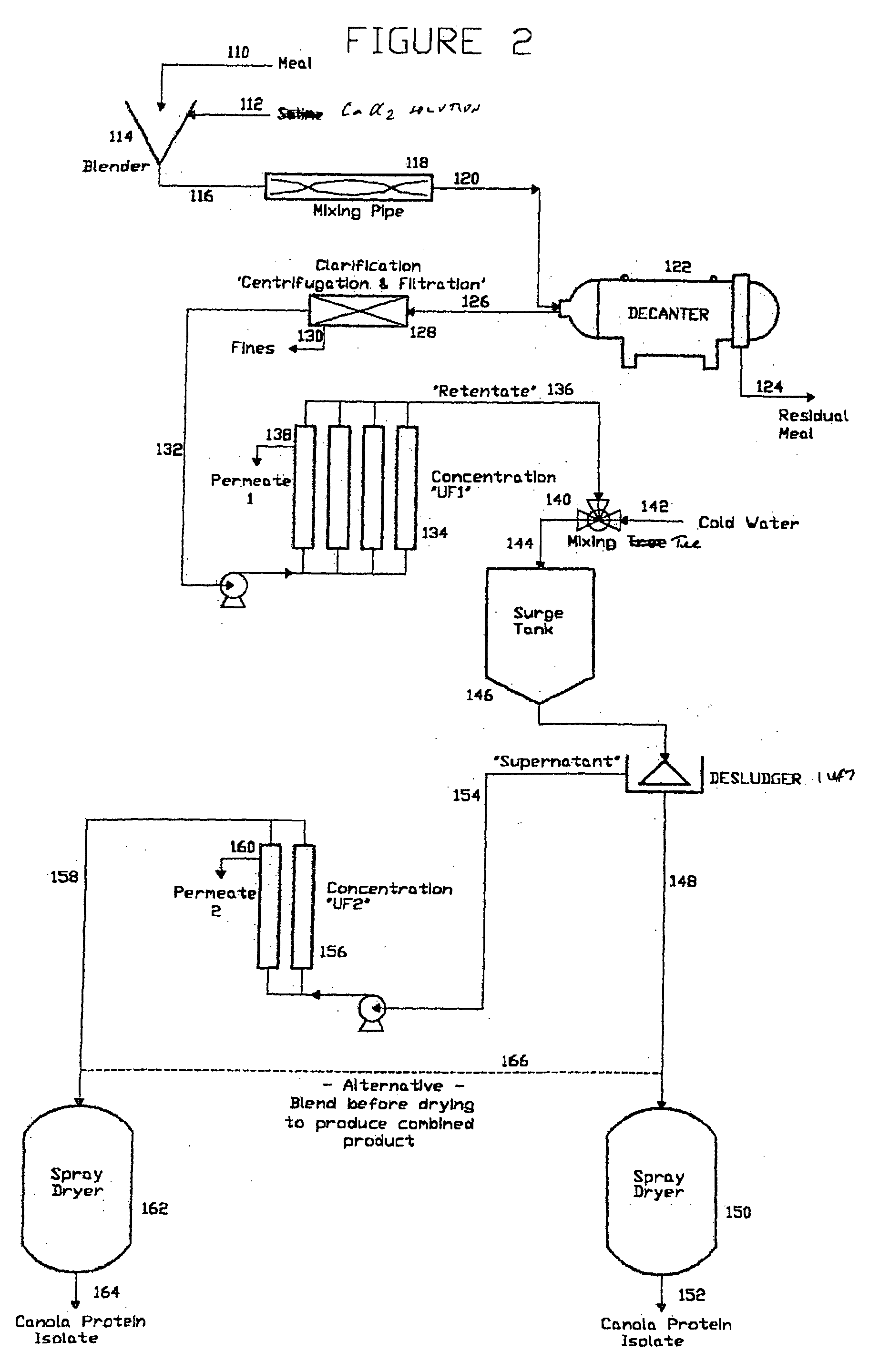
Production of Soluble Protein Solutions from Soy ("S701")
ActiveUS20100098818A1Prevent oxidationMilk preparationProtein composition from vegetable seedsProtein solutionSports drink
A soy protein product, which may be an isolate, produces transparent heat-stable solutions at low pH values and is useful for the fortification of soft drinks and sports drinks without precipitation of protein. The soy protein product is obtained by extracting a soy protein source material with an aqueous calcium salt solution to form an aqueous soy protein solution, separating the aqueous soy protein solution from residual soy protein source, adjusting the pH of the aqueous soy protein solution to a pH of about 1.5 to about 4.4 to produce an acidified clear soy protein solution, which may be dried, following optional concentration and diafiltration, to provide the soy protein product.
Owner:BURCON NUTRASCI MB
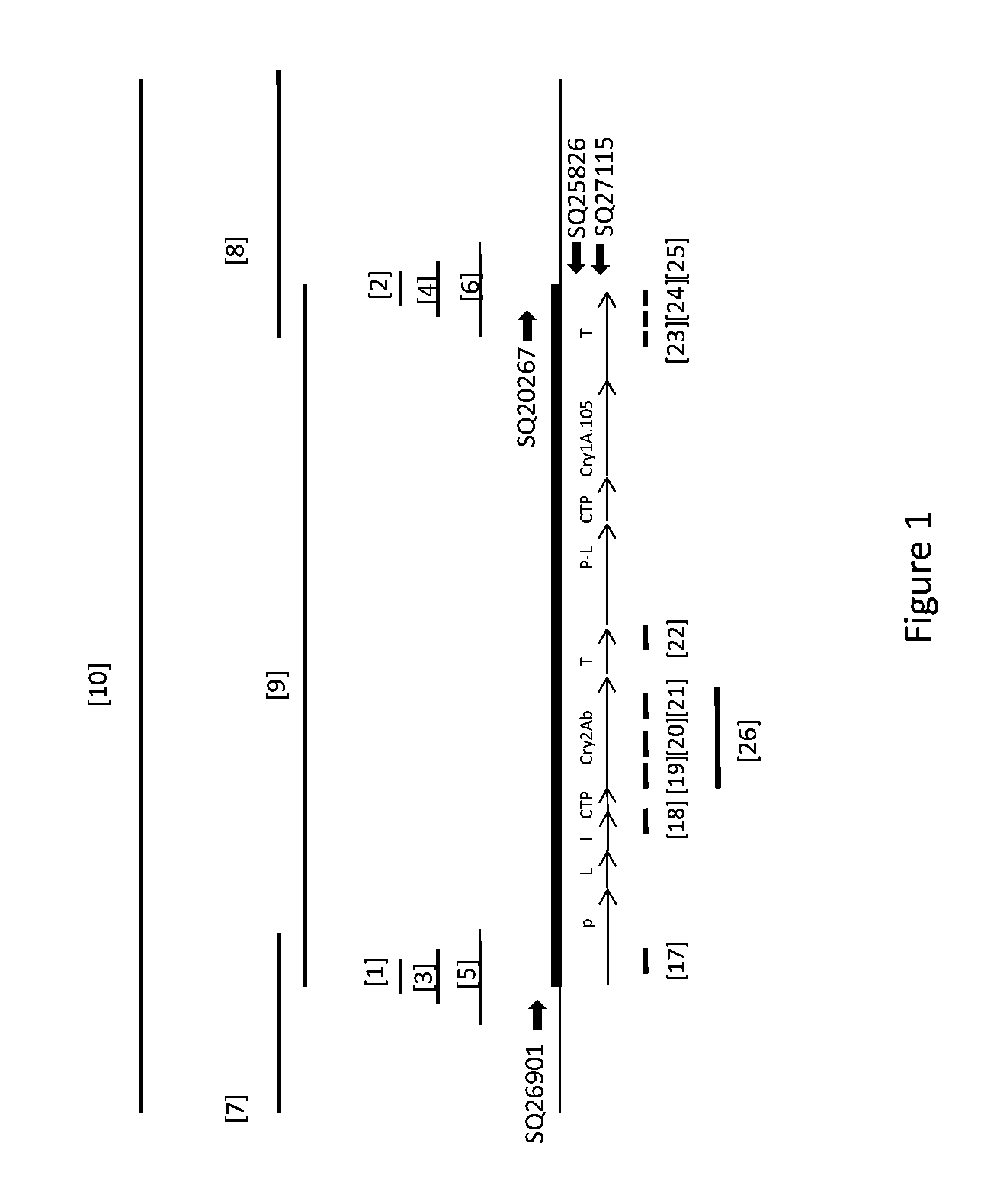
Soybean transgenic event mon87751 and methods for detection and use thereof
ActiveUS20140373191A1Maintain good propertiesImprove performanceCheese manufactureVector-based foreign material introductionGlycinePlant cell
The invention provides a transgenic Glycine max event MON87751, plants, plant cells, seeds, plant parts, progeny plants, and commodity products comprising event MON87751. The invention also provides polynucleotides specific for event MON87751, plants, plant cells, seeds, plant parts, and commodity products comprising polynucleotides for event MON87751. The invention also provides methods related to event MON87751.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
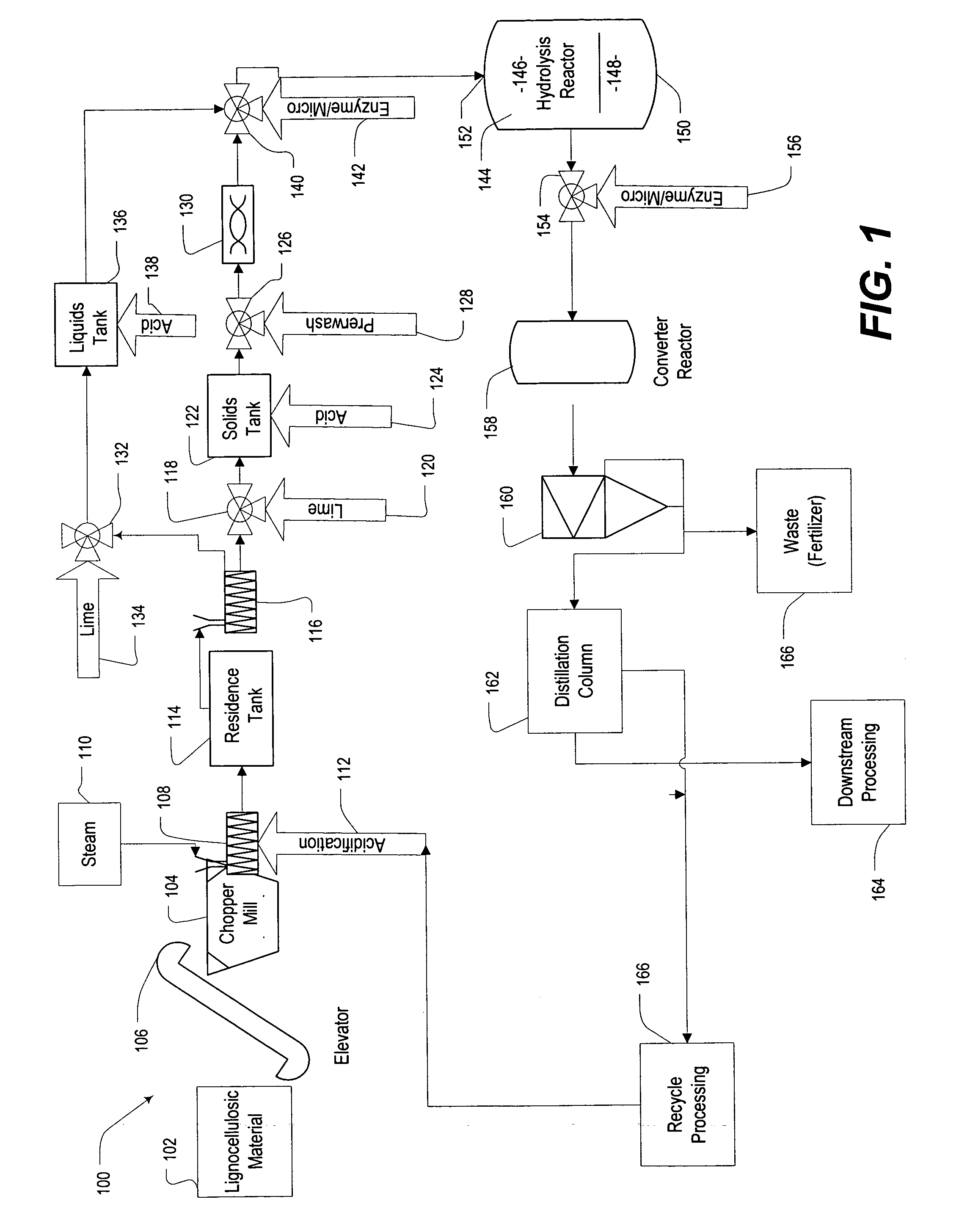
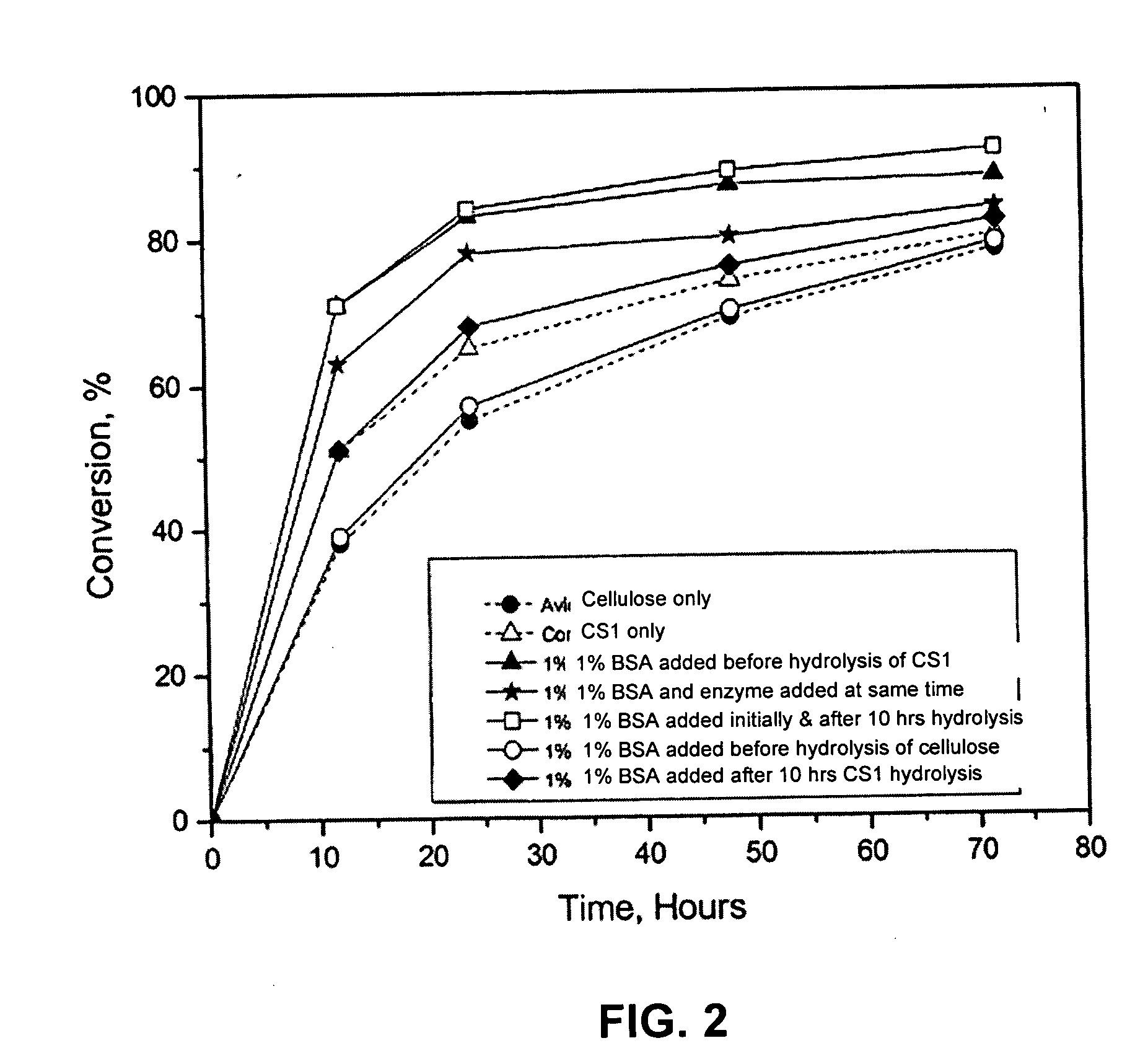
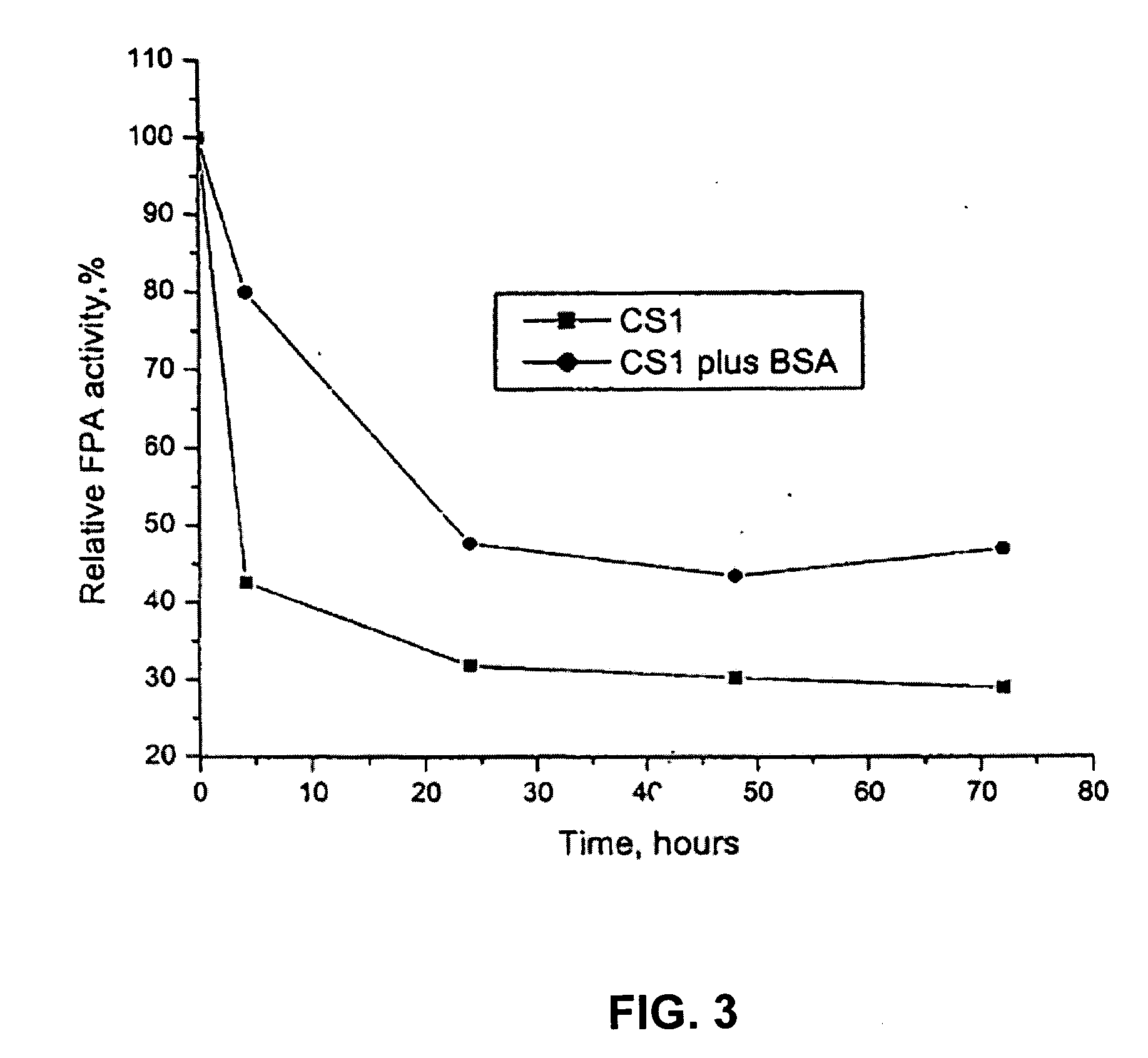
Lignin blockers and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060088922A1High efficiency in cellulose conversionLess of advantageProtein composition from vegetable seedsBiofuelsLignin degradationLignocellulosic biomass
Disclosed is a method for converting cellulose in a lignocellulosic biomass. The method provides for a lignin-blocking polypeptide and / or protein treatment of high lignin solids. The treatment enhances cellulase availability in cellulose conversion and allows for the determination of optimized pretreatment conditions. Additionally, ethanol yields from a Simultaneous Saccharification and Fermentation process are improved 5-25% by treatment with a lignin-blocking polypeptide and / or protein. Thus, a more efficient and economical method of processing lignin containing biomass materials utilizes a polypeptide / protein treatment step that effectively blocks lignin binding of cellulase.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Fractionation of protein containing mixtures
InactiveUS7812138B2Easy to operatePeptide/protein ingredientsIon-exchanger regenerationHigh densitySorbent
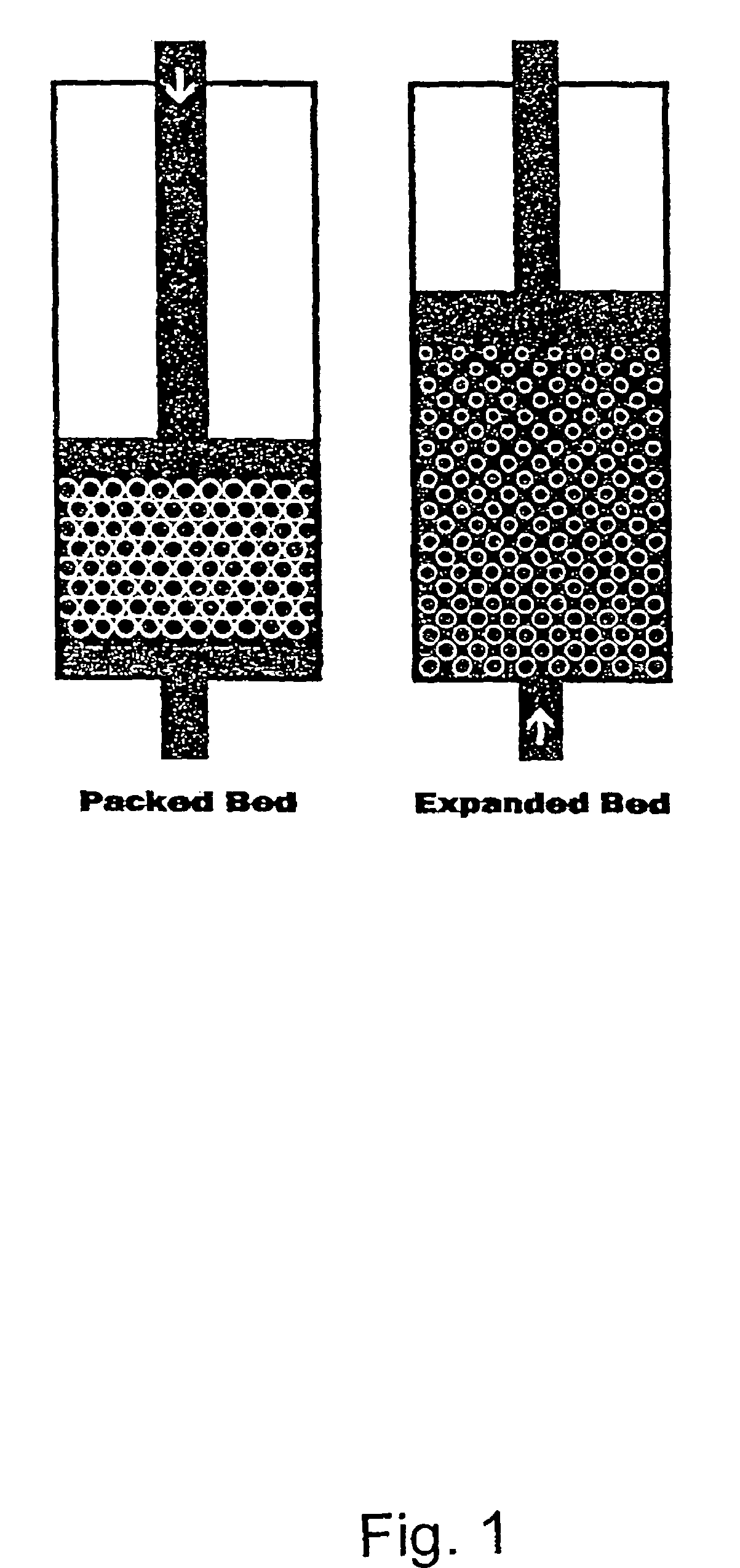
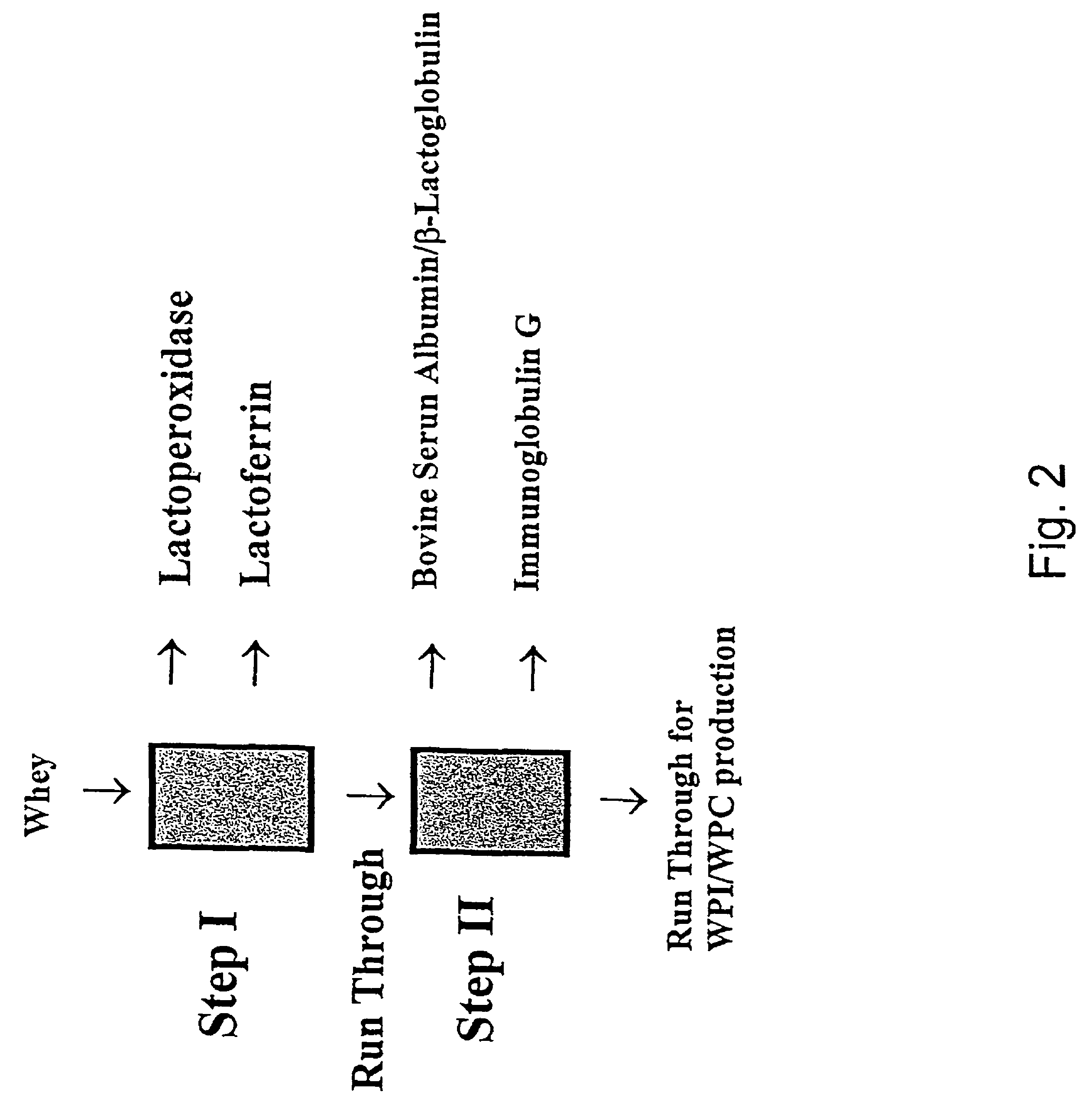
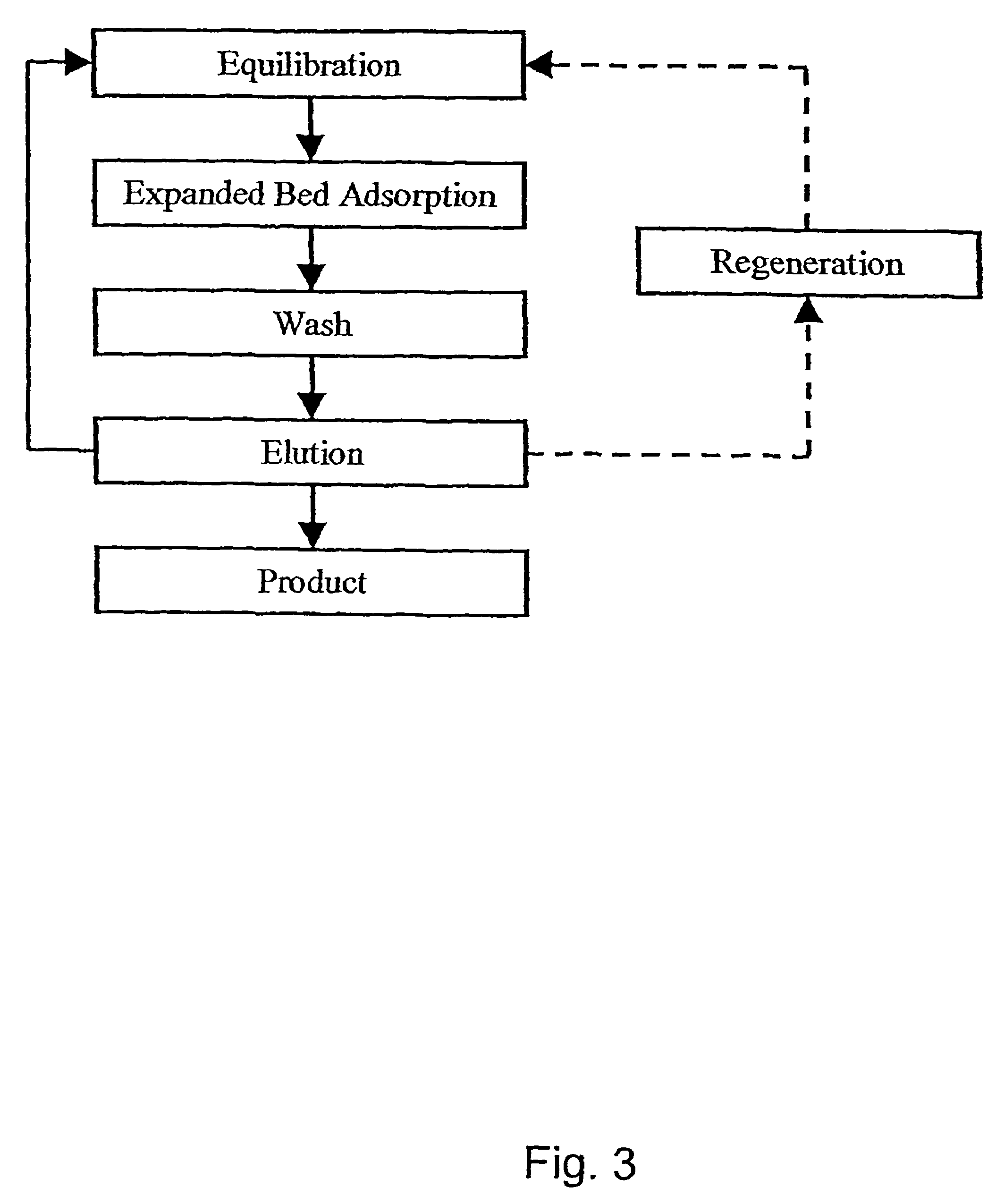
Thus, a primary aspect of the present invention relates to a method for the fractionation of a protein-containing mixture wherein the protein-containing mixture is selected from the group consisting of milk, milk derived products, milk derived raw materials, vegetable derived products, vegetable derived extracts, fruit derived products, fruit derived extracts, fish derived products, and fish derived extracts, the method comprising the steps of: a) optionally adjusting the pH of the mixture; b) applying the mixture to an adsorption column comprising an adsorbent, the adsorbent comprises a particle with at least one high density non-porous core, surrounded by a porous material, the adsorbent having a particle density of at least 1.5 g / ml and a mean particle size of at most 150 μm; c) optionally washing the column; d) eluting at least one protein from the adsorbent.
Owner:UPFRONT CHROMATOGRAPHY
Modified protein adhesives and lignocellulosic composites made from the adhesives
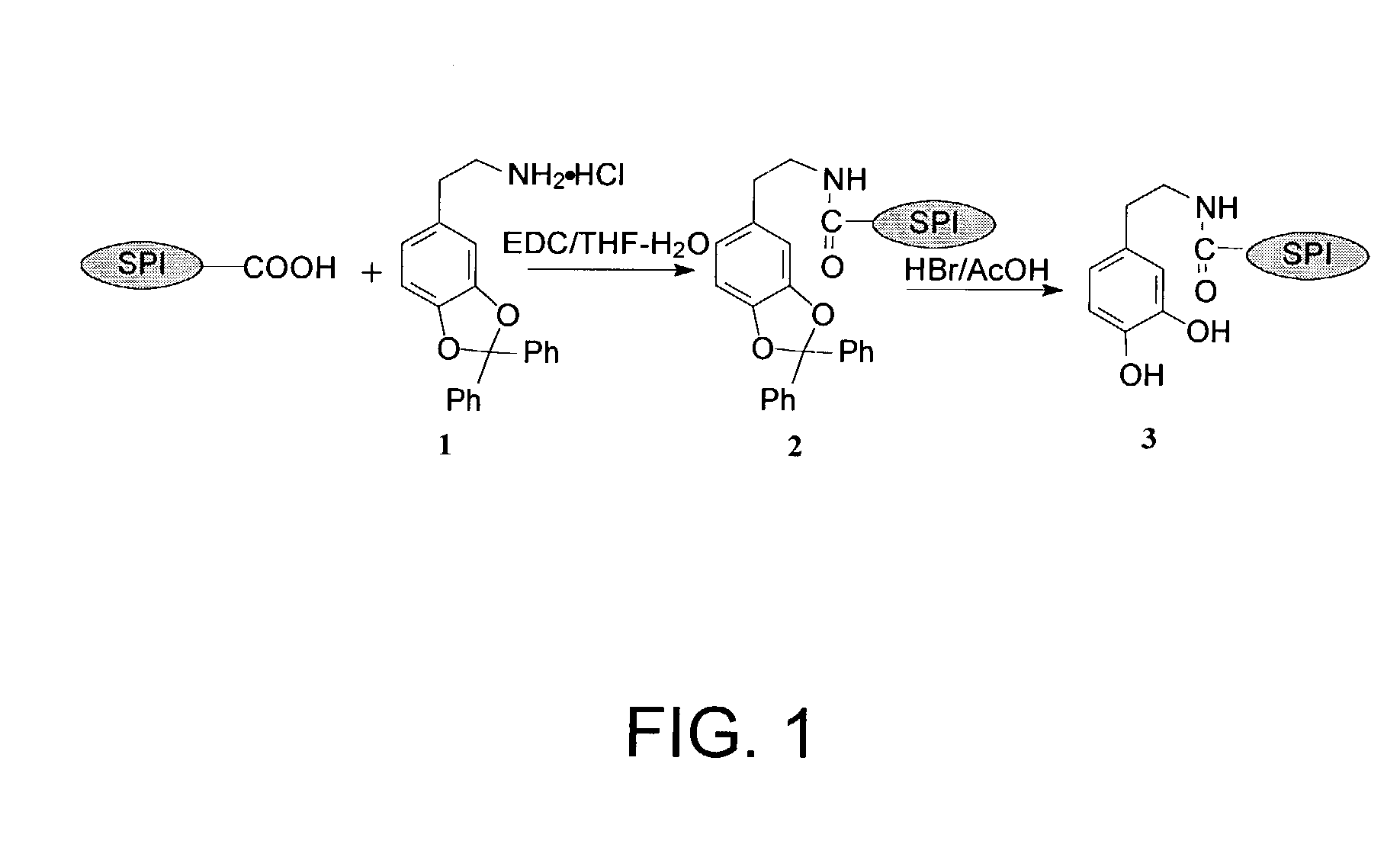
An adhesive composition made by reacting a soy protein with at least one compound under conditions sufficient for introducing additional phenolic hydroxyl functional groups, amine functional groups, and / or thiol functional groups into the soy protein structure.
Owner:THE STATE OF OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE OREGON STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF OREGON STATE UNIV
Protein isolation procedures for reducing phytic acid
ActiveUS20050255226A1Reduced phytic acid contentHigh nutritional valueBiocideProtein composition from vegetable seedsIsolation proceduresProtein isolate
Owner:BURCON NUTRASCI MB
Process for the fractionation of cereal brans
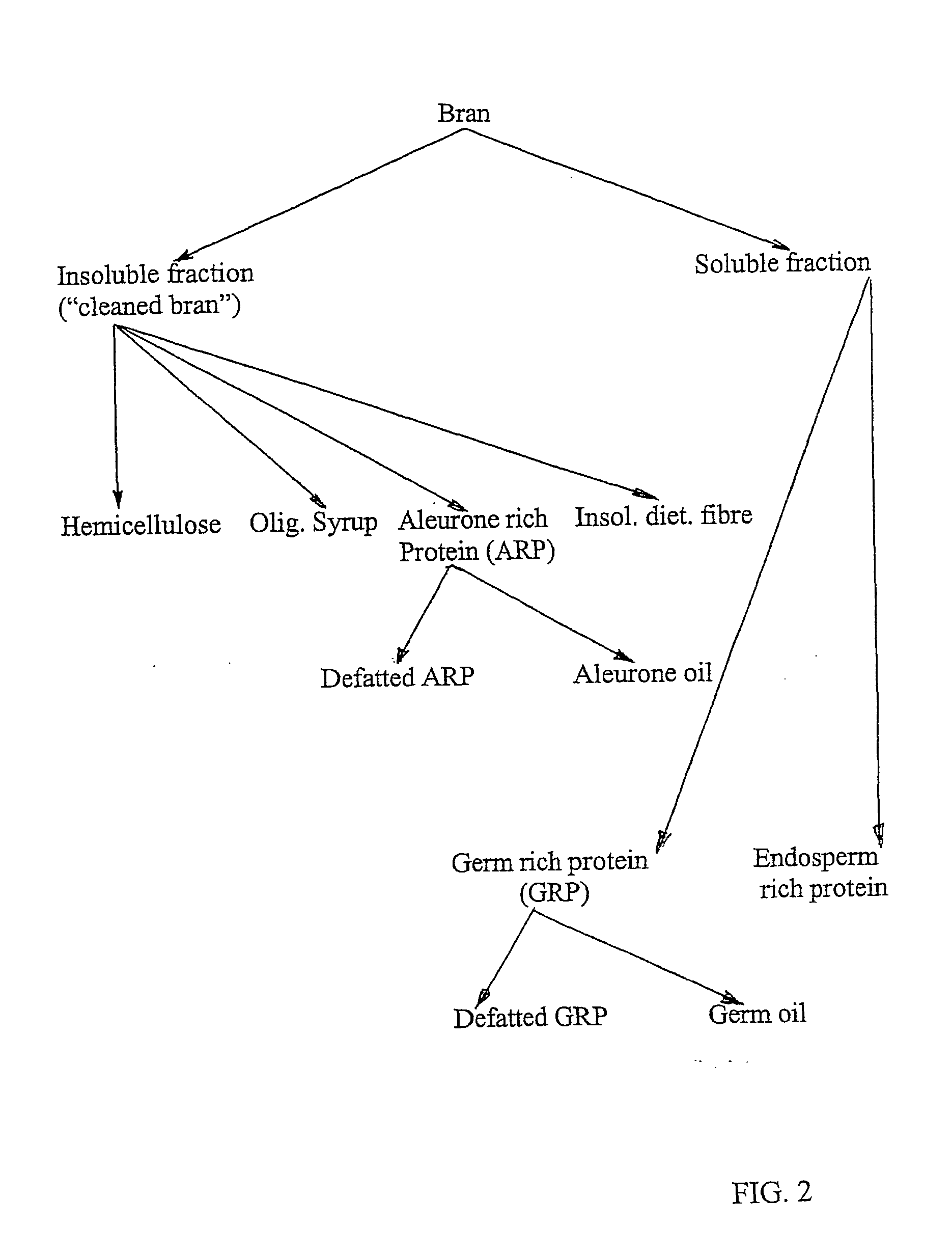
InactiveUS20050089602A1Minimal contaminationImprove efficiencyTea extractionProtein composition from vegetable seedsUltrafiltrationHordeum vulgare
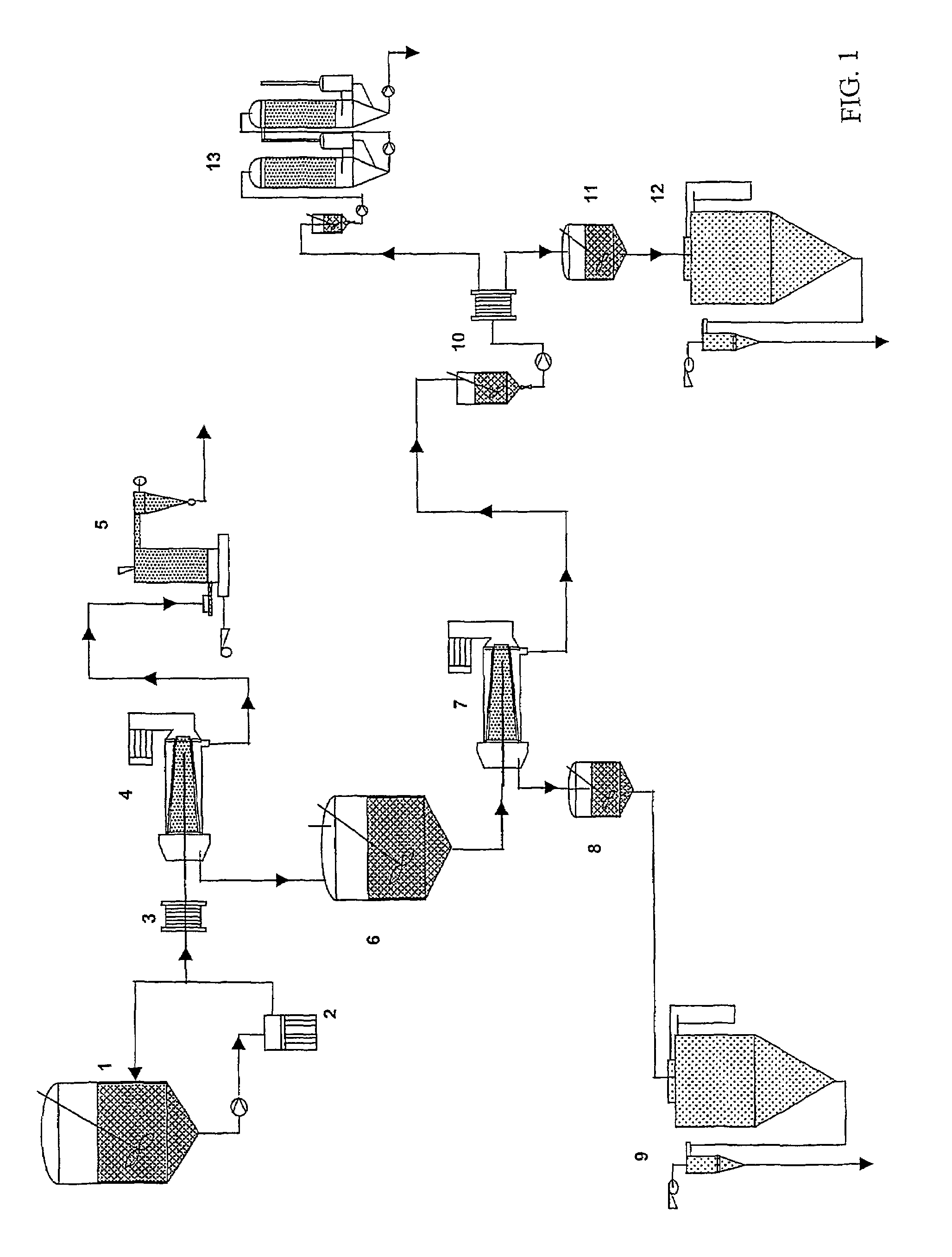
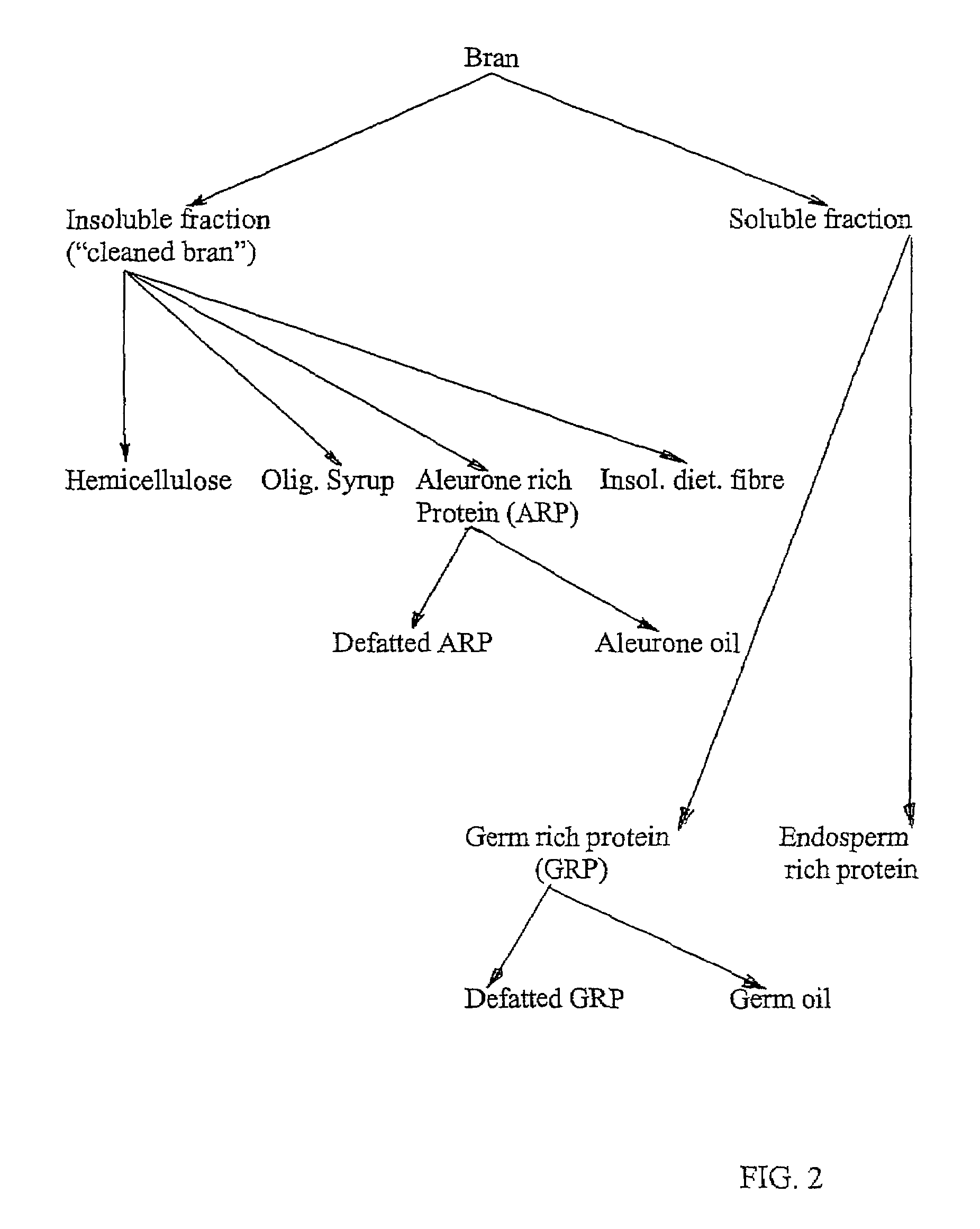
A process for the fractionation of valuable fractions from cereal brans (e.g. wheat, barley and oat brans, and rice polish) is described. In particular, this invention describes a two step process, in which the said bran is first subjected to a combination of enzymatic treatment and wet milling, followed by sequential centrifugation and ultrafiltration, which aims at physically separating the main bran factions, i.e. insoluble phase (pericarp and aleurone layer), germ-rich fraction, residual endosperm fraction and soluble sugars. A second step consists of fractionating cereal brans substantially free of soluble compounds, hence insoluble phase from the above-mentioned first step, by enzymatic treatment with xylanases and / or beta-glucanase and wet milling, followed by sequential centrifugation and ultrafiltration, which aims at physically separating the main fractions, i.e. insoluble phase (remaining cell wall components), protein-rich fraction, soluble hemicellulose and oligosaccharide, and therefore maximizes the extraction rate of valuable cell wall components and aleurone cells from previously cleaned bran.
Owner:LANTMANNEN OATS AB
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with transcription in plants and uses thereof for plant improvement
InactiveUS20080229439A1Improvement of oneImprovement of more important propertyImmunoglobulinsFermentationBiotechnologyPlant Sources
Polynucleotides useful for improvement of plants are provided. In particular, polynucleotide sequences are provided from plant sources. Polypeptides encoded by the polynucleotide sequences are also provided. The disclosed polynucleotides and polypeptides find use in production of transgenic plants to produce plants having improved properties.
Owner:LA ROSA THOMAS J +8
Aqueous process for preparing protein isolate and hydrolyzed protein from an oilseed
InactiveUS20120252065A1Peptide/protein ingredientsProtein composition from vegetable seedsProtein solutionPhytase
The present disclosure relates to an aqueous process for the preparation of a protein isolate and a hydrolyzed protein concentrate from an oilseed meal, optionally comprising:mixing an oilseed meal with an aqueous solvent to form a slurry;optionally treating the slurry with phytase y;separating the slurry with a solid / liquid separation to form:a liquid phase, comprising the aqueous solvent, soluble protein and oil; anda solid phase comprising insoluble protein;separating the liquid phase to form:an oil phase; andan aqueous protein phase;subjecting the aqueous protein phase to membrane filtration to obtain a protein solution; and drying the protein solution to obtain the protein isolatesubjecting the insoluble protein to enzymatic hydrolysis, andsubjecting the hydrolyzed protein to membrane filtration to obtain an amino acid and peptide solution; and drying the amino acid and peptide solution to obtain the hydrolyzed protein concentrate.
Owner:POS PILOT PLANT CORP +1
Production of soluble protein solutions from soy ("S701" CIP)
ActiveUS20110038993A1Prevent oxidationProtein composition from vegetable seedsFood ingredient as solubility improving agentProtein solutionSports drink
A soy protein product, which may be an isolate, produces transparent heat-stable solutions at low pH values and is useful for the fortification of soft drinks and sports drinks without precipitation of protein. The soy protein product is obtained by extracting a soy protein source material with an aqueous calcium salt solution to form an aqueous soy protein solution, separating the aqueous soy protein solution from residual soy protein source, adjusting the pH of the aqueous soy protein solution to a pH of about 1.5 to about 4.4 to produce an acidified clear soy protein solution, which may be dried, following optional concentration and diafiltration, to provide the soy protein product.
Owner:BURCON NUTRASCI MB
Method for treating and processing lupine seeds containing alkaloid, oil and protein
InactiveUS7074449B1Water being largely excludedAvoid heatProtein composition from vegetable seedsFood preparationFractionationPlanting seed
A method of treating and processing alkaloid, oil and protein-containing lupine seeds for the extraction of products from the lupine seeds by means of targeted fractionation is described, whereby the comminuted lupine seed is de-oiled by introducing a solvent and the residue is depleted of substances soluble in the acid range, preferably of alkaloids, by adding acids. The invention is characterized by the provisions that the lupine seeds are comminuted and / or shaped to form discoid flakes in such a way that after pre-crushing of the shelled or non-shelled seed containing the plant seeds the comminution of the plant seeds is carried out by means of a cooled flocculating roller, and the seed is heated by indirect supply of heat, largely with exclusion of water, and that after de-oiling the depletion of the flakes of substances soluble in the acid range, preferably of alkaloids, is performed by aqueous extraction, with a refined product of reduced alkaloid level and an aqueous extract being obtained.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Modified protein adhesives and lignocellulosic composites made from the adhesives
An adhesive composition made by reacting a soy protein with at least one compound under conditions sufficient for introducing additional phenolic hydroxyl functional groups, amine functional groups, and / or thiol functional groups into the soy protein structure.
Owner:THE STATE OF OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE OREGON STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF OREGON STATE UNIV
Granulated powder containing vegetable proteins and maltodextrins, process for producing same, and uses thereof
The present invention concerns a granulated powder comprising at least one vegetable protein and at least one starch hydrolyzate, characterized in that it has a laser volume average diameter D4,3 of between 10 μm and 500 μm, preferably between 50 μm and 350 μm, and even more preferably between 70 μm and 250 μm, and a dry matter content, determined after stoving at 130° C. for 2 hours, of greater than 80%, preferably greater than 85%, and even more preferably greater than 90%.The present invention also concerns process for manufacturing this granulated powder its use in various industrial field, and more particularly in the food-processing field, where it is used as a functional agent such as an emulsifying, overrun, stabilizing, thickening and / or gelling agent, in particular for totally or partially replacing certain animal proteins in the preparation of food products.
Owner:ROQUETTE FRERES SA
Enhancement of accessibility of cellulose by expansins
InactiveUS6326470B1Protein composition from vegetable seedsClimate change adaptationCellulosePlant cell
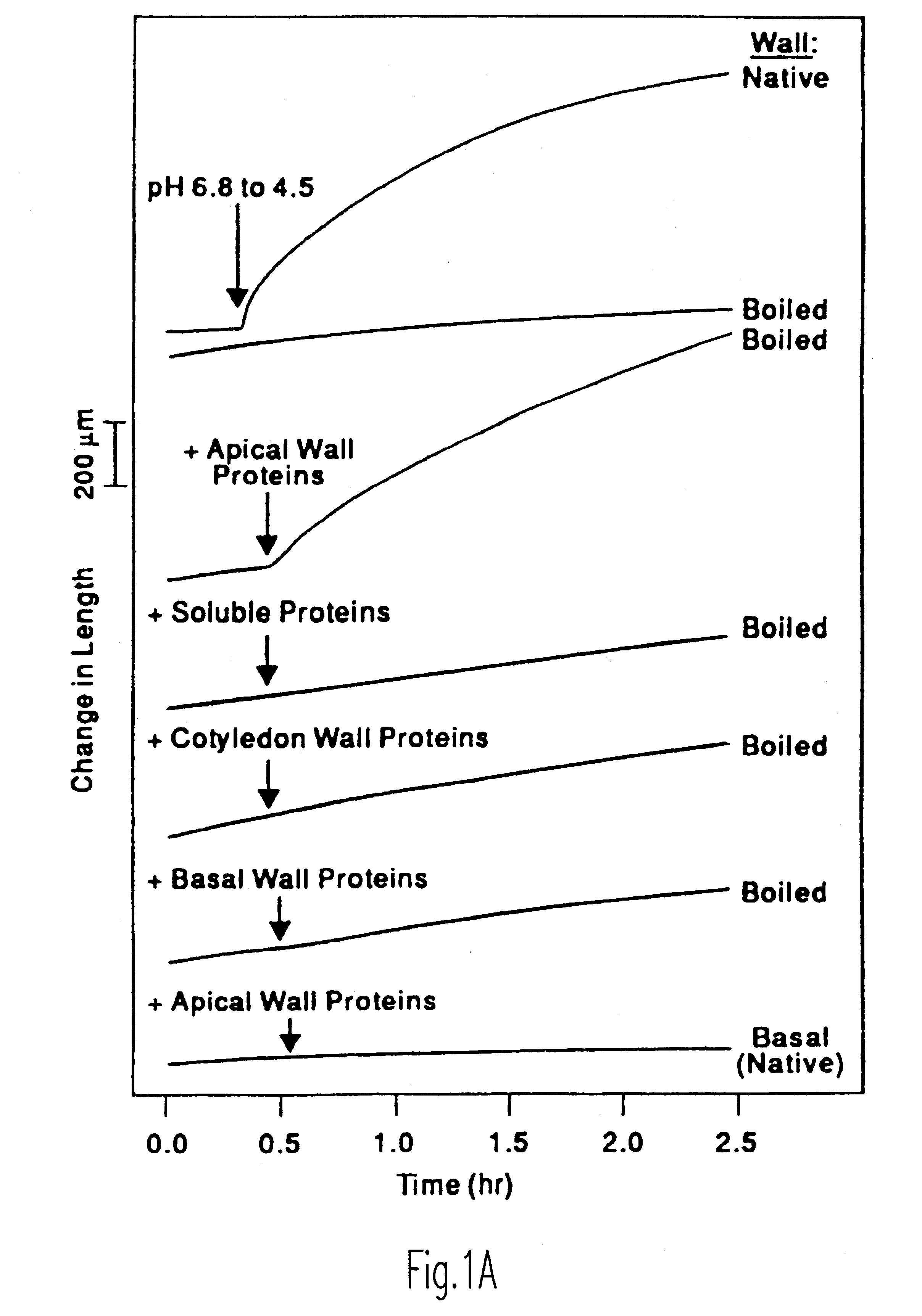
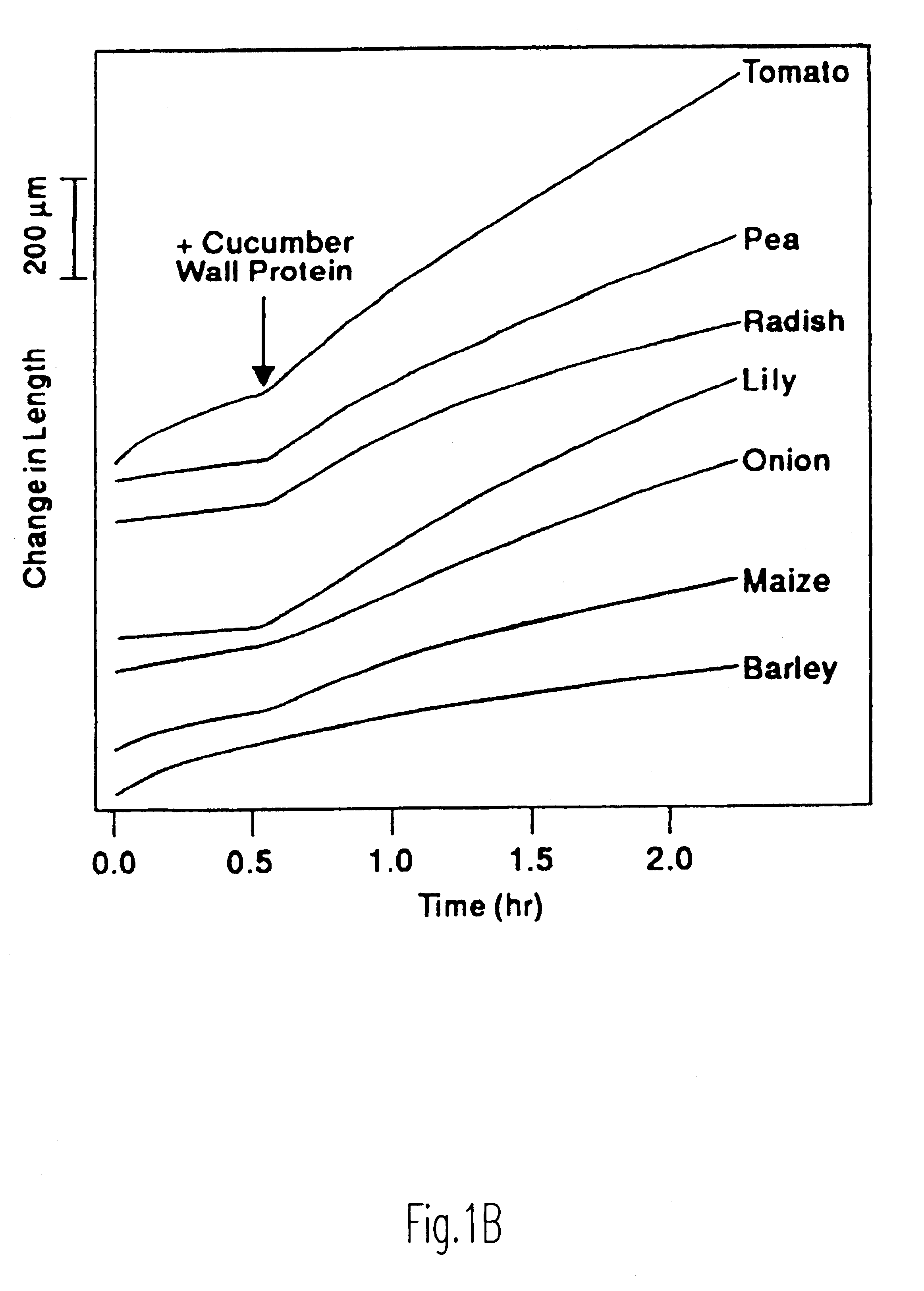
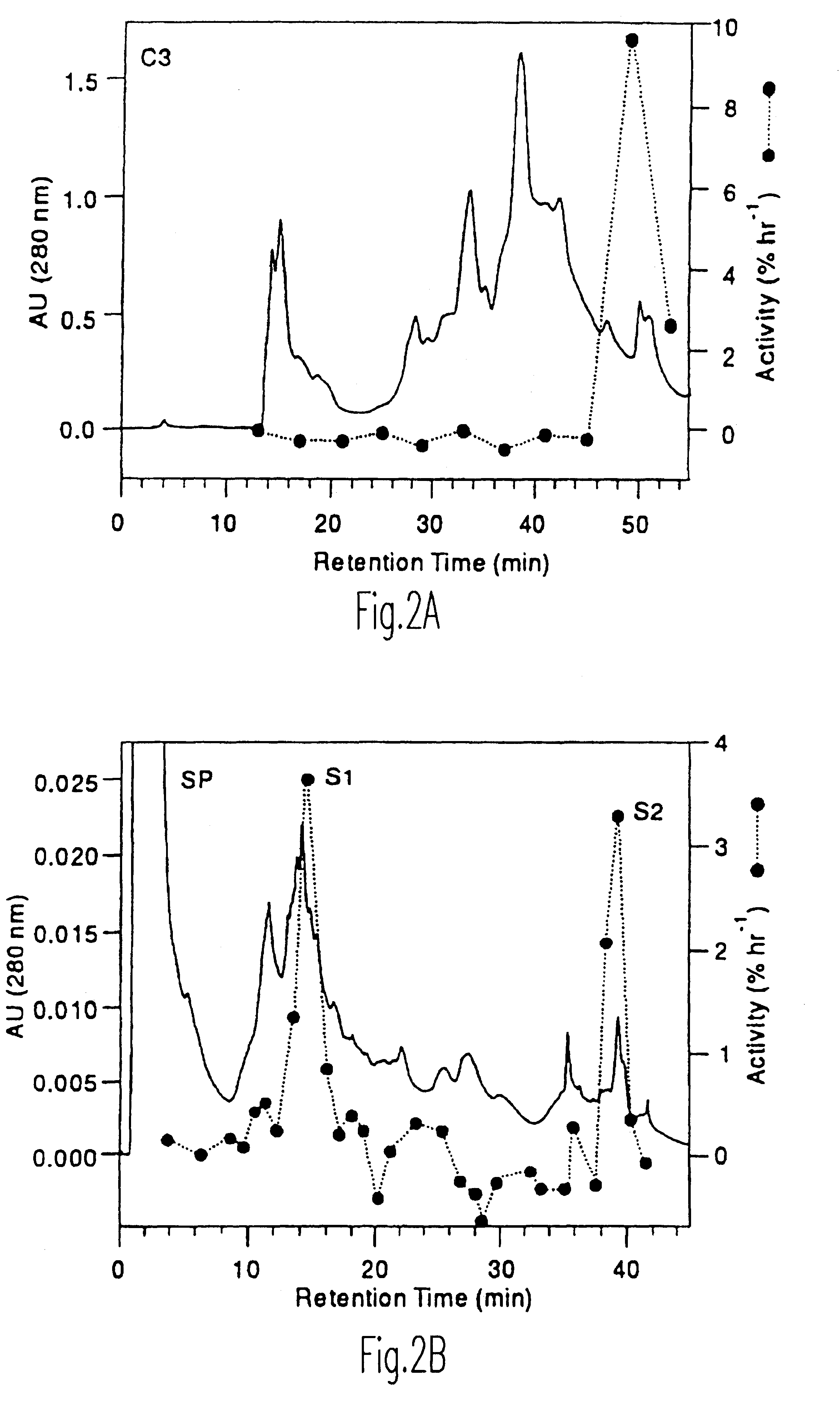
Plant cell expansion is regulated by wall relaxation and yielding, which is thought to be catalyzed by elusive "wall loosening" enzymes. By employing a reconstitution approach, we initially found that a crude protein extract from the cell walls of growing cucumber seedlings possessed the ability to induce the extension of isolated cell walls. This activity was restricted to the growing region of the stem and could induce the extension of isolated cell walls from various dicots and monocots, but was less effective on grass coleoptile walls. Sequential HPLC fractionation of the active wall extract revealed two proteins with molecular masses of 29 and 30 kD, as measured by SDS-PAGE, associated with such activity. Each protein, by itself, could induce wall extension without detectable hydrolytic breakdown of the wall. We proposed the name "expansins" for this class of proteins. Expansins have been isolated from various plant sources including oat, cucumber, broccoli, celery, tomato, cotton, cabbage, and corn, and also from snail and its feces. These proteins weaken the intermolecular bonds between plant wall polysaccharides. They decrease the mechanical strength of commercial products made from polysaccharides, such as paper, and therefore present a novel approach in developing new technologies in industries which make use of such polysaccharides, such as in the paper industry, in the applications of polysaccharide gums and related products. These proteins moreover present a novel approach in the control of plant growth.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Method of preparing walnut polypeptide powder
InactiveCN101228918ALess impuritiesAnti-fatigueMetabolism disorderProtein composition from vegetable seedsEnzymatic hydrolysisCentrifugation
The invention relates to a preparation method of a walnut peptide powder, which effectively embodies a plurality of biological functional properties of the walnut peptide powder, reserves a plurality of nutritional components of walnuts. The polypeptide content in the walnut peptide powder is 60-80 percent, while the walnut peptide powder is light yellow or yellow-white color and has functions of anti-fatigue and antioxidation, etc. The invention comprises the following operation steps: crushing the walnut cakes before extracting the walnut protein, then carrying out enzymatic hydrolysis and centrifugation to the crude walnut protein to acquire the supernatant, dialyzing the supernatant and removing impurities and macromolecular compounds, and then concentrating the acquired dialysate, and at last vacuum drying to prepare the walnut peptide powder and packing into finished products.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV +1
Colour reduction in canola protein isolate
InactiveUS20040077838A1Prevent oxidationHigh protein concentrationBiocidePharmaceutical delivery mechanismBiotechnologyProtein isolate
Owner:BURCON NUTRASCI MB
Protein Hydrolysate Compositions Having Improved Sensory Characteristics and Physical Properties
InactiveUS20080305212A1Fatty substance preservation using additivesCocoaArginineProtein hydrolysates
The present invention provides protein hydrolysate compositions, processes for making protein hydrolysate compositions, and food products comprising protein hydrolysate compositions. The protein hydrolysate compositions generally comprise polypeptide fragments having primarily either an arginine residue or a lysine residue at each carboxyl terminus.
Owner:SOLAE LLC
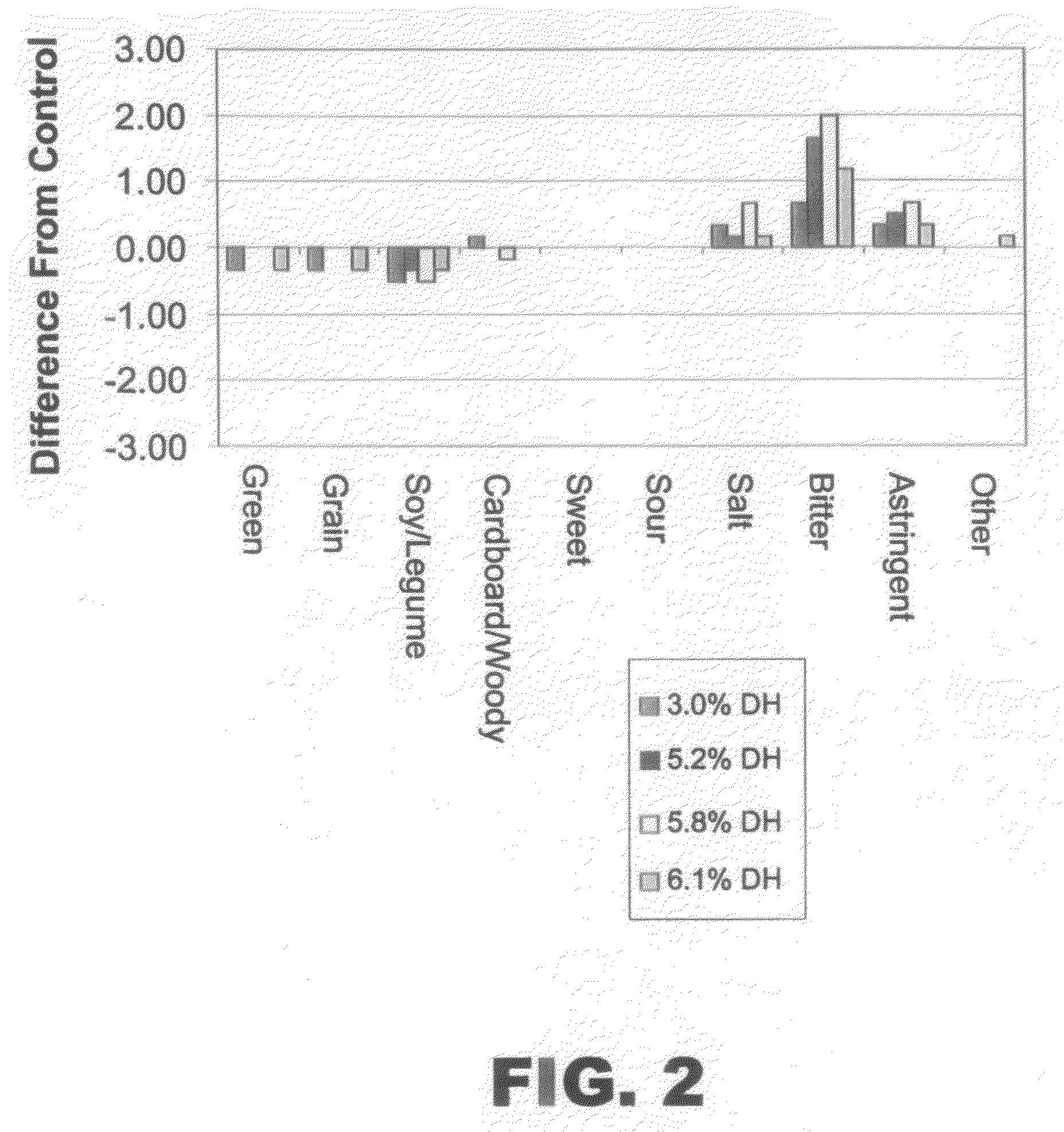
Medium test method for extracting oil and protolysate from peanut with water-enzyme method
InactiveCN101401658AHas a physiologically active functionProtein composition from vegetable seedsEdible oils/fatsHydrolysateInsoluble residue
The invention provides an intermediate test method for extracting oil and hydrolyzed protein from peanut by a water enzyme method, which belongs to the technical field of the application of biological technique in food industry. In the method, the peanut is used as a raw material, single alkali protease is used for enzymolysis, a three-phase separator is used to separate oil, oil-water mixture and insoluble residue simultaneously, a disc-type centrifuge is used to further separate the oil-water mixture so as to obtain emulsion and hydrolysate, wherein the emulsion is subjected to freezing, thawing and emulsion breaking to obtain emulsion breaking oil, and the hydrolysate is subjected to spray drying to obtain peanut hydrolyzed protein powder. The invention provides a better process for industrializing the method of extracting oil and hydrolyzed protein by the water enzyme method, and has the advantages of simple technological line and high utilization rate of products.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Dispersible pharmaceutical compositions
ActiveUS7842791B2Good dispersionEfficacious level of antibacterialAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseMicrocrystalline wax
A pharmaceutical composition is provided comprising a vehicle that comprises (a) an amphipathic oil that is water dispersible and ethanol insoluble, (b) microcrystalline wax, and (c) a pharmaceutically acceptable non-aqueous carrier; and having an antibacterial substance in an antibacterially effective amount stably dispersed in the vehicle. The composition is suitable for administration by intramammary infusion to a milk producing animal for treatment and / or prevention of mastitis or other diseases of the udder, as well as for otic administration for treatment and / or prevention of an ear infection.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Method of producing fermentation-based products from corn
InactiveUS7083954B2Excellent extractabilityIncrease usable surface areaProtein composition from vegetable seedsClimate change adaptationCorn mealFermentation
Corn oil and corn meal obtained from corn are included in useful products. A method for producing fermentation-based products comprises combining corn meal with water and an enzyme, and mixing the combination with a micro-organism capable of fermenting a carbon source to produce a fermentation-based product. The corn meal is produced by cracking whole corn, conditioning the whole corn and extracting the whole corn to produce corn meal without flaking the corn during processing. The corn grain process generally includes the steps of cracking corn grain having a total oil content of from about 3% by weight to about 30% by weight and extracting a corn oil from the cracked corn grain.
Owner:RENESSEN
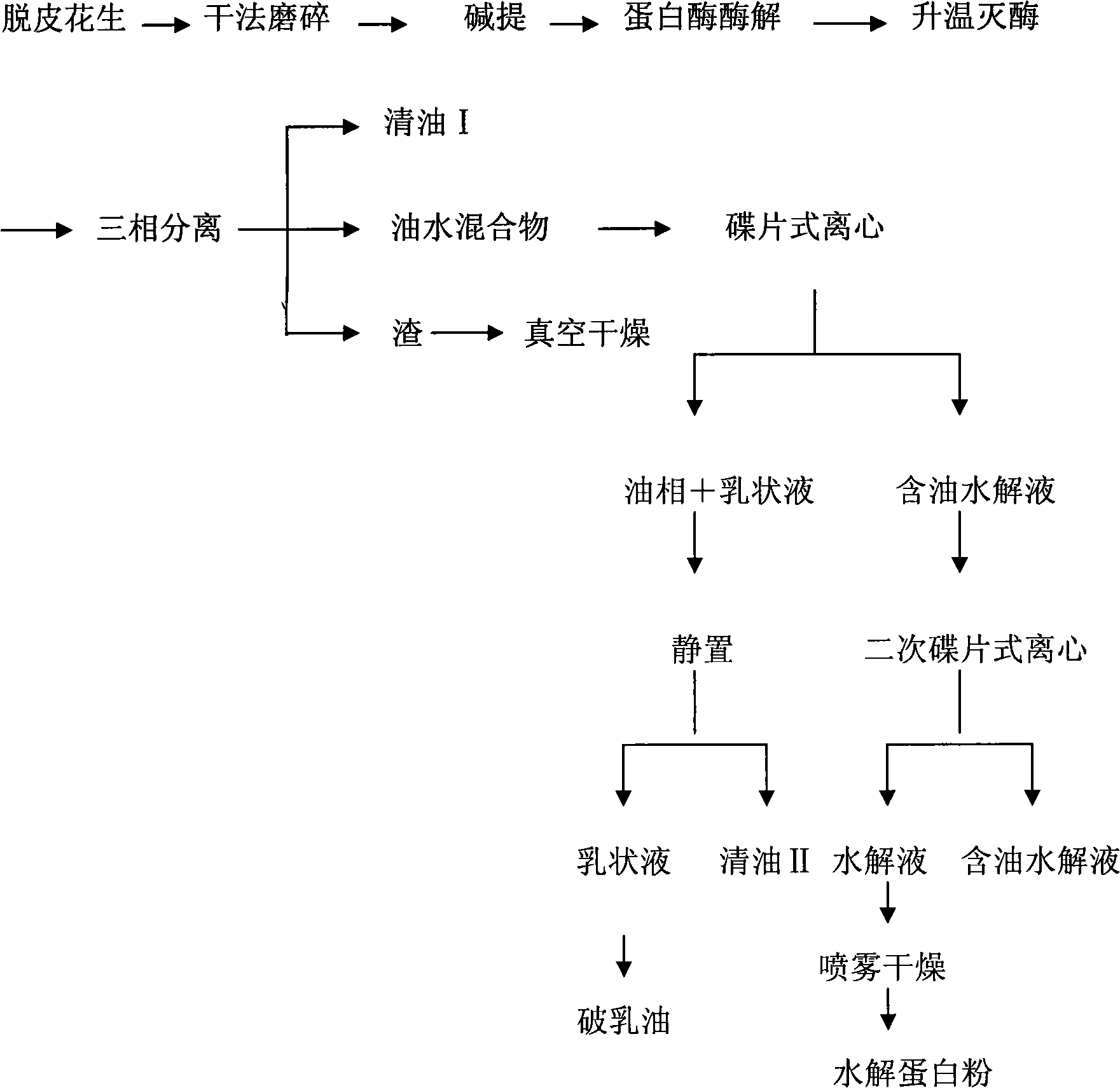
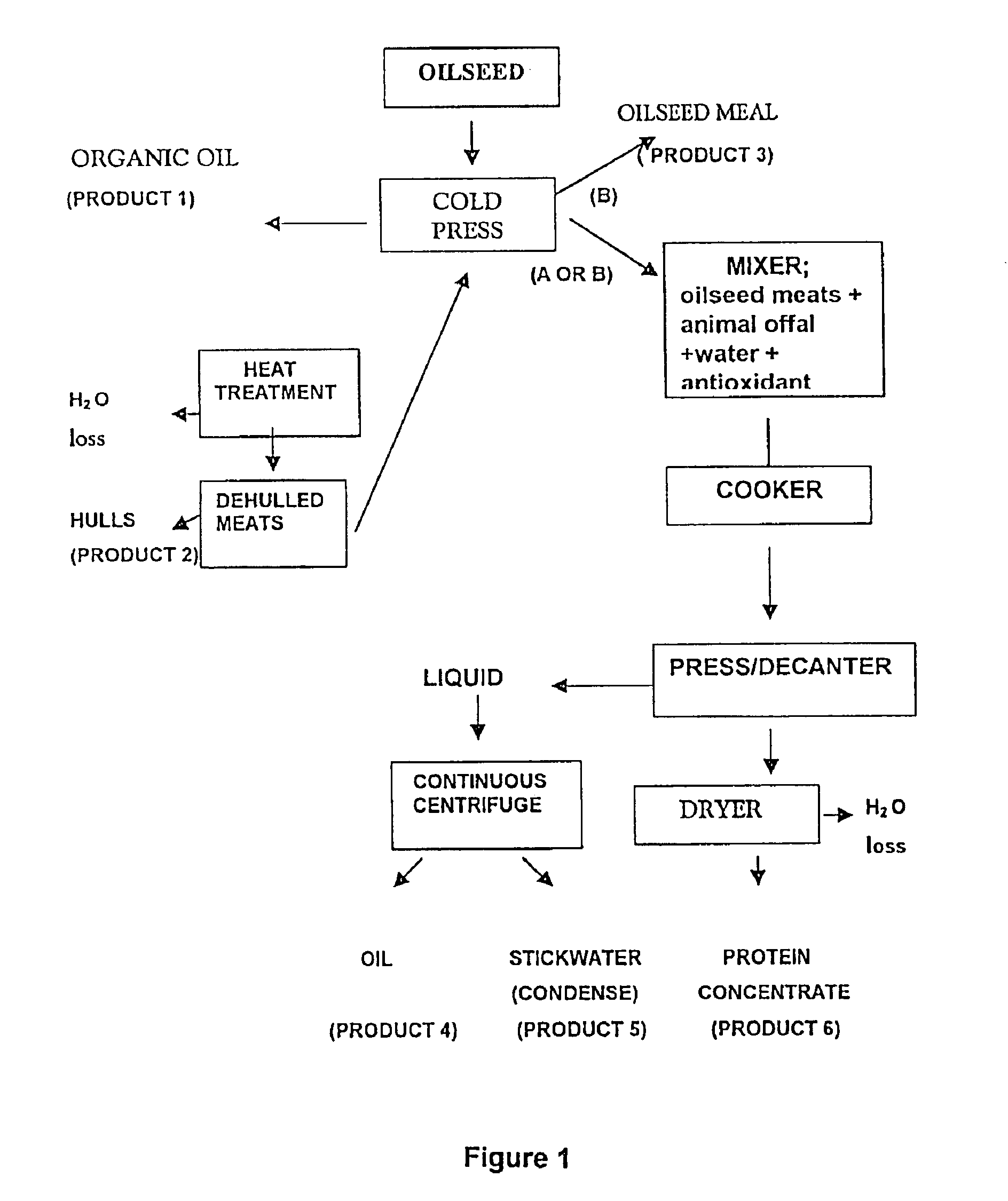
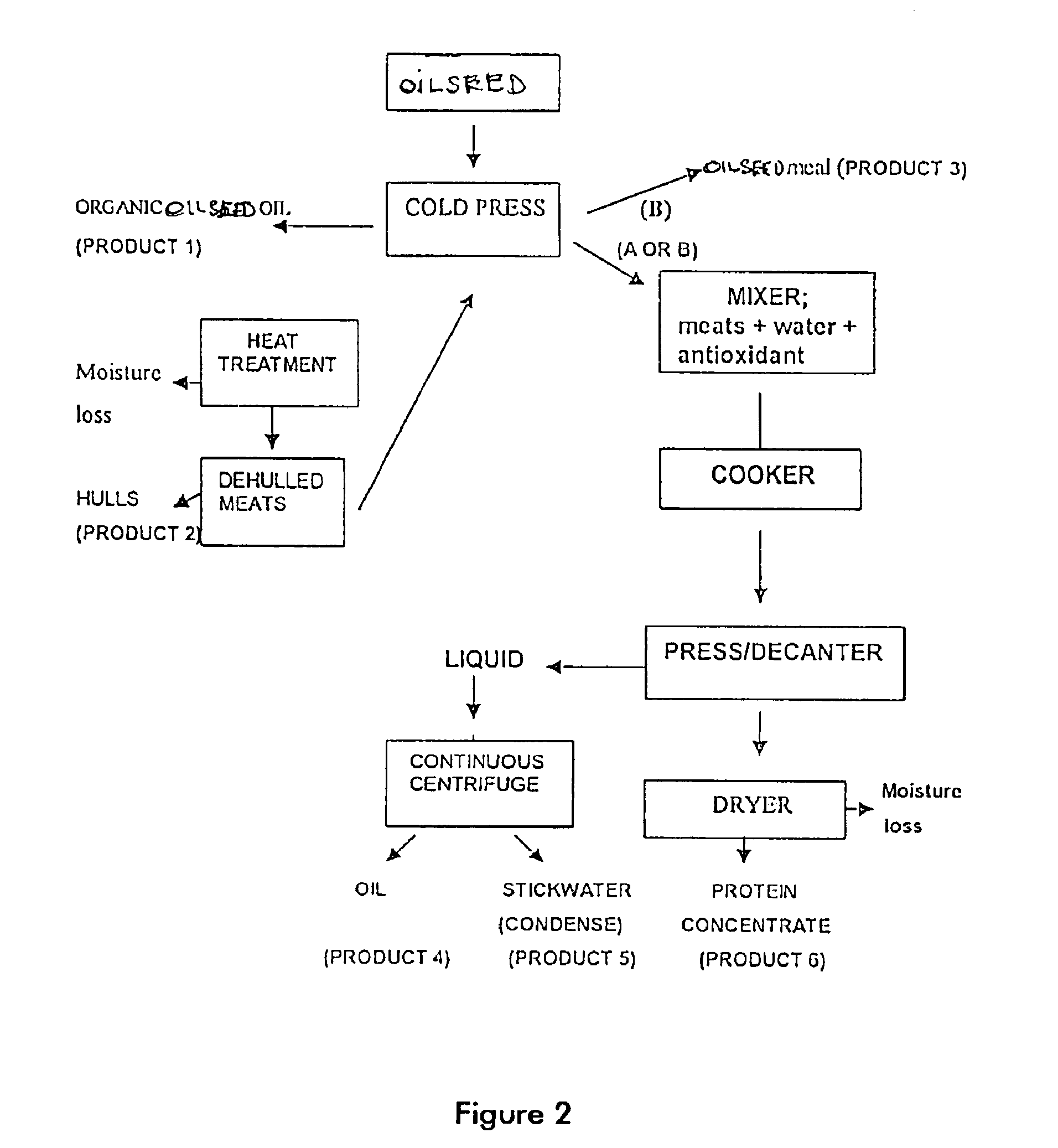
Protein and lipid sources for use in aquafeeds and animal feeds and a process for their preparation
InactiveUS6955831B2Increased digestible energy contentAdditional componentBioloigcal waste fertilisersEdible oils/fatsFiberHuman animal
A process for preparation of nutritionally upgraded oilseed meals which are protein and lipid-rich and have a reduced fiber content, and plant oils from oilseeds for use in fish or other non-human animal diets or human foods comprising the steps of: providing a source of oilseed; subjecting the oilseed to heat treatment to substantially reduce the concentration of at least some antinutritional components normally present in the oilseed to obtain heat-treated seed; dehulling the heat-treated seed to produce a meat fraction, a hull fraction or a mixture thereof; and cold pressing the meat fraction or the mixture to yeild the plant oils and the protein and lipid-rich meals.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN IN RIGHT OF CANADA AS REPRRESENTED BY THE MINIST OF FISHERIES & OCEANS
Protein concentrates and isolates, and processes for the production thereof
InactiveUS20090286961A1Protein composition from vegetable seedsDepsipeptidesInsoluble proteinProtein isolate
Protein concentrates and protein isolates, in addition to processes for the production of protein concentrates and protein isolates, are disclosed. In particular, the disclosure relates to a process for removing fiber from an oilseed meal, comprising:i) mixing an oilseed meal with a blending solvent, optionally water, saline solution, polysaccharide solution or protein containing solution, to form a mixture;ii) optionally adjusting the pH of the protein slurry to a pH of about 2 to about 10; andiii) separating the mixture to form a protein slurry comprising soluble and insoluble proteins and an insoluble fiber fraction.
Owner:SIEBTE PMI VERW
Production of high-quality protein isolates from defatted meals of Brassica seeds
The present invention provides a method for processing defatted oil seeds, comprising the steps of: (a) solubilizing at least a portion of the protein contained in the oil seeds to produce suspended residual solids and a first solution comprising protein, phenolic-protein complexes, and free phenolic compounds; (b) separating at least a portion of the free phenolic compounds from the first solution and recovering a free phenolic reduced solution; and (c) treating the free phenolic reduced solution to precipitate at least a portion of the protein as a precipitated protein isolate and recovering a treated solution containing a soluble protein isolate. Novel protein products are also disclosed. Food and drink products containing the novel protein products are also disclosed.
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO
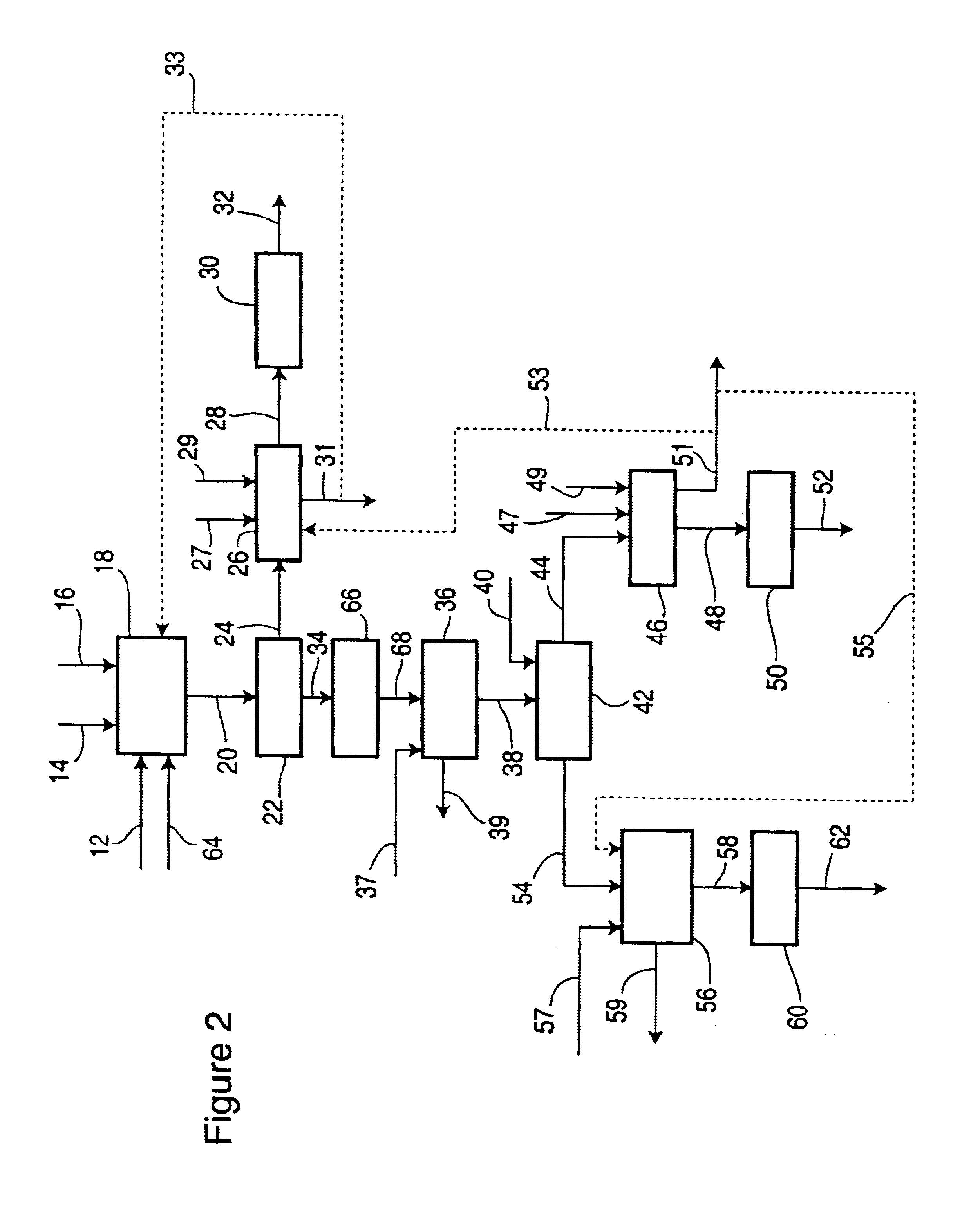
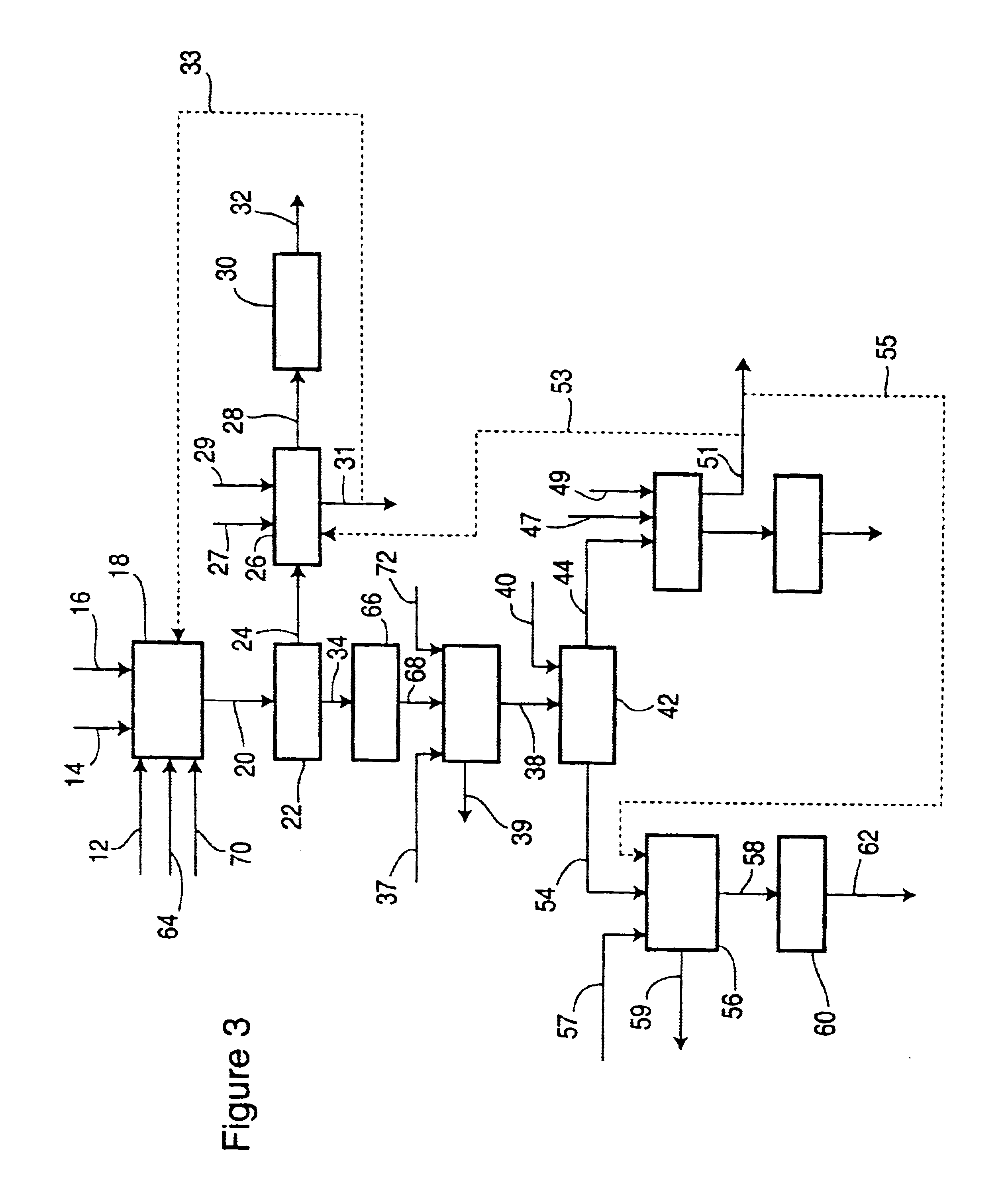
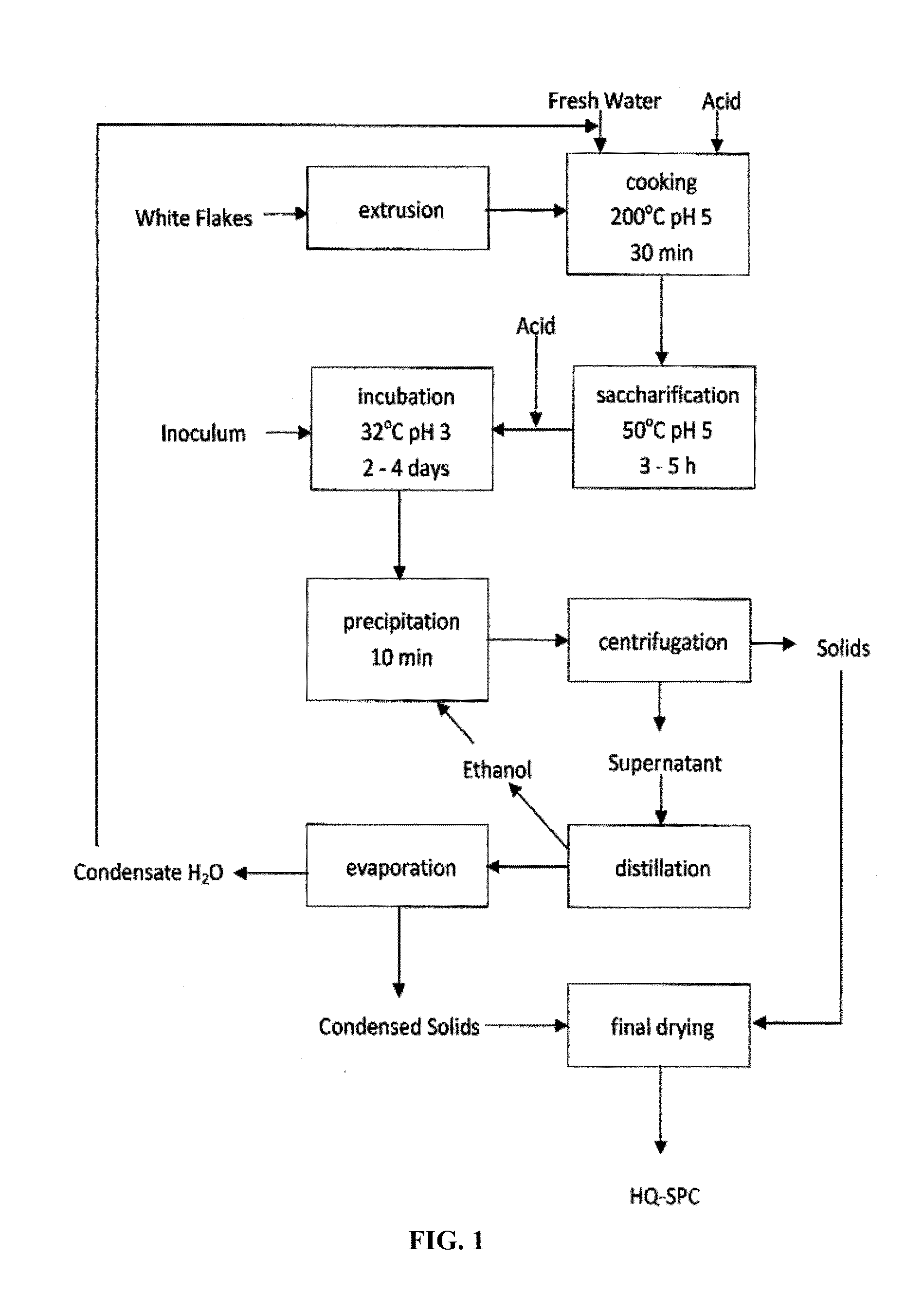
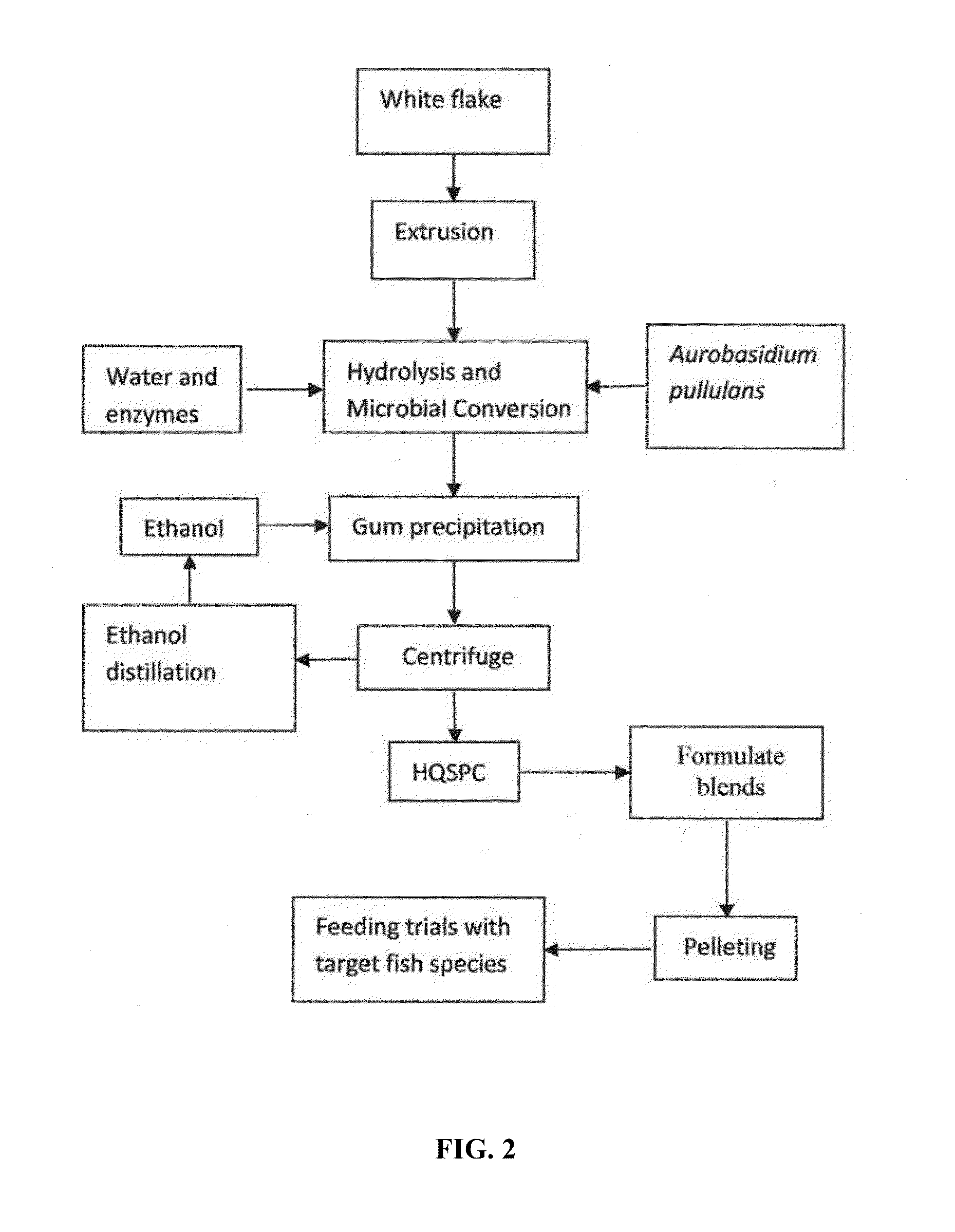
Microbial-Based Process For High-Quality Protein Concentrate
The present invention describes a bio-based process to produce high quality protein concentrate (HQPC) by converting plant derived celluloses into bioavailable protein via aerobic incubation, including the use of such HQPC so produced as a nutrient, including use as a fish meal replacement in aquaculture diets.
Owner:PRAIRIE AQUA TECH LLC +2
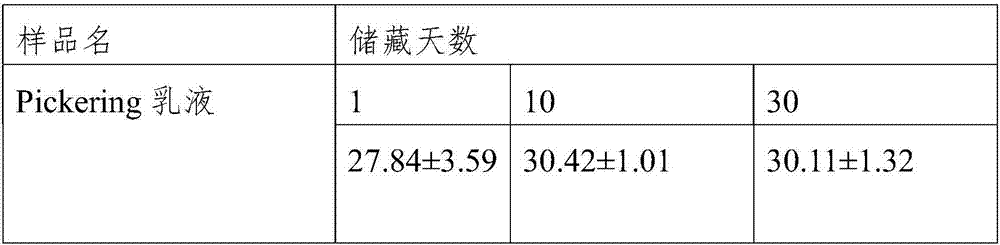
Pickering emulsion prepared from peanut protein isolate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107455550ALow costSimple and fast operationProtein composition from vegetable seedsVegetable proteins working-upProtein isolatePickering emulsion
The invention relates to a method for preparing a Pickering emulsion from peanut protein isolate, and the method comprises the following steps: preparing a peanut protein dispersion solution by taking a peanut protein isolate solution as a raw material; preparing a proteoglycan mixed dispersion solution from a polysaccharide solution and the peanut protein isolate dispersion solution; adding transglutaminase to the proteoglycan mixed dispersion solution, and preparing gel blocks by crosslinking reaction; preparing a microgel particle dispersion solution by taking the gel blocks as raw materials; and then adding the microgel particle dispersion solution to edible oil for preparing the Pickering emulsion. The method disclosed by the invention adopts high-speed shearing equipment, high-pressure homogenizing equipment and other common equipment for conducting granulation, and the Pickering emulsion prepared by high-speed shearing is not added with any inorganic materials in the preparation process, and has good biosafety and strong biocompatibility. The prepared Pickering can be stable at room temperature for more than 30 days, and can be used as a delivery system of fat-soluble and photosensitive active substances.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
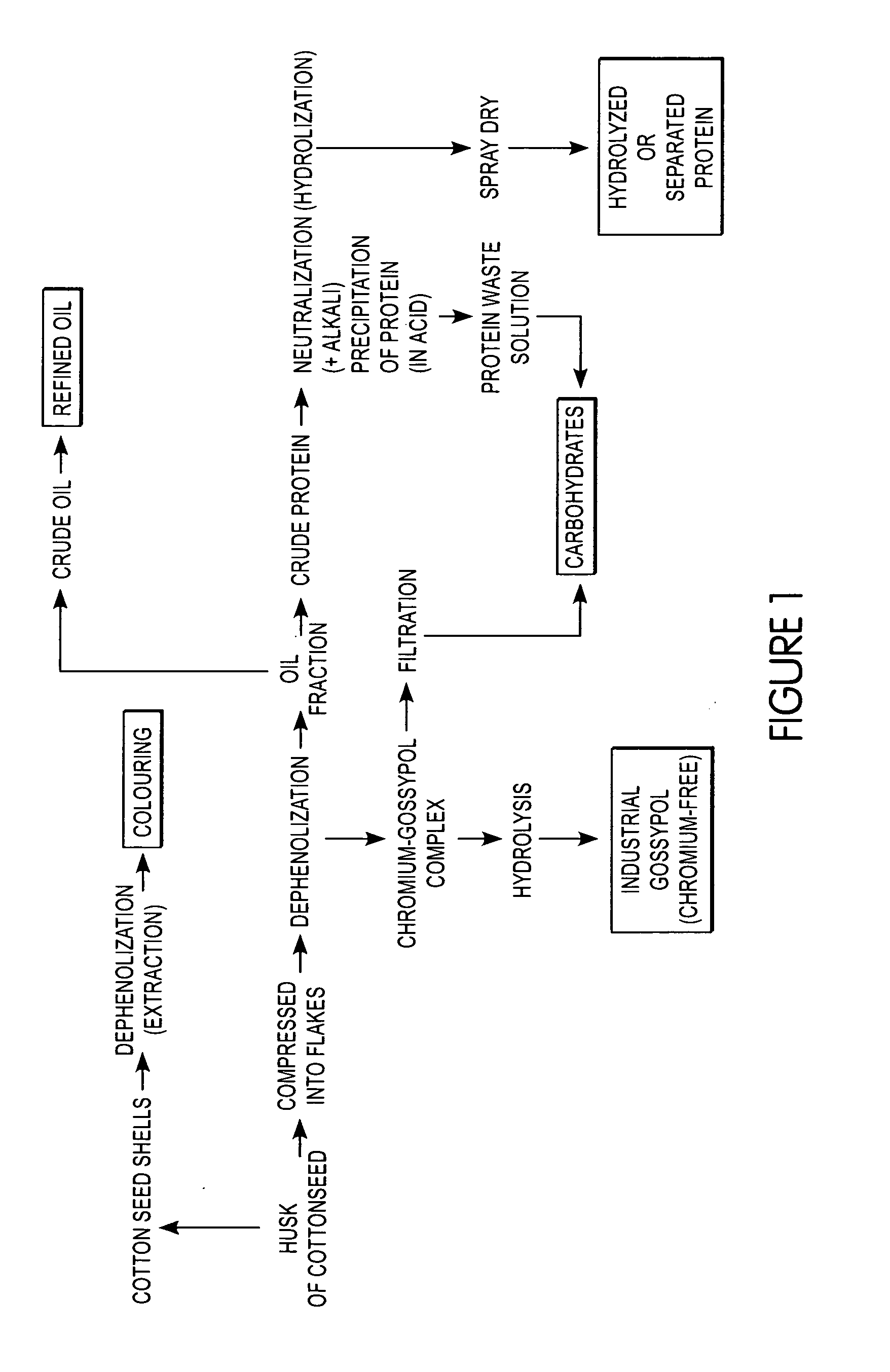
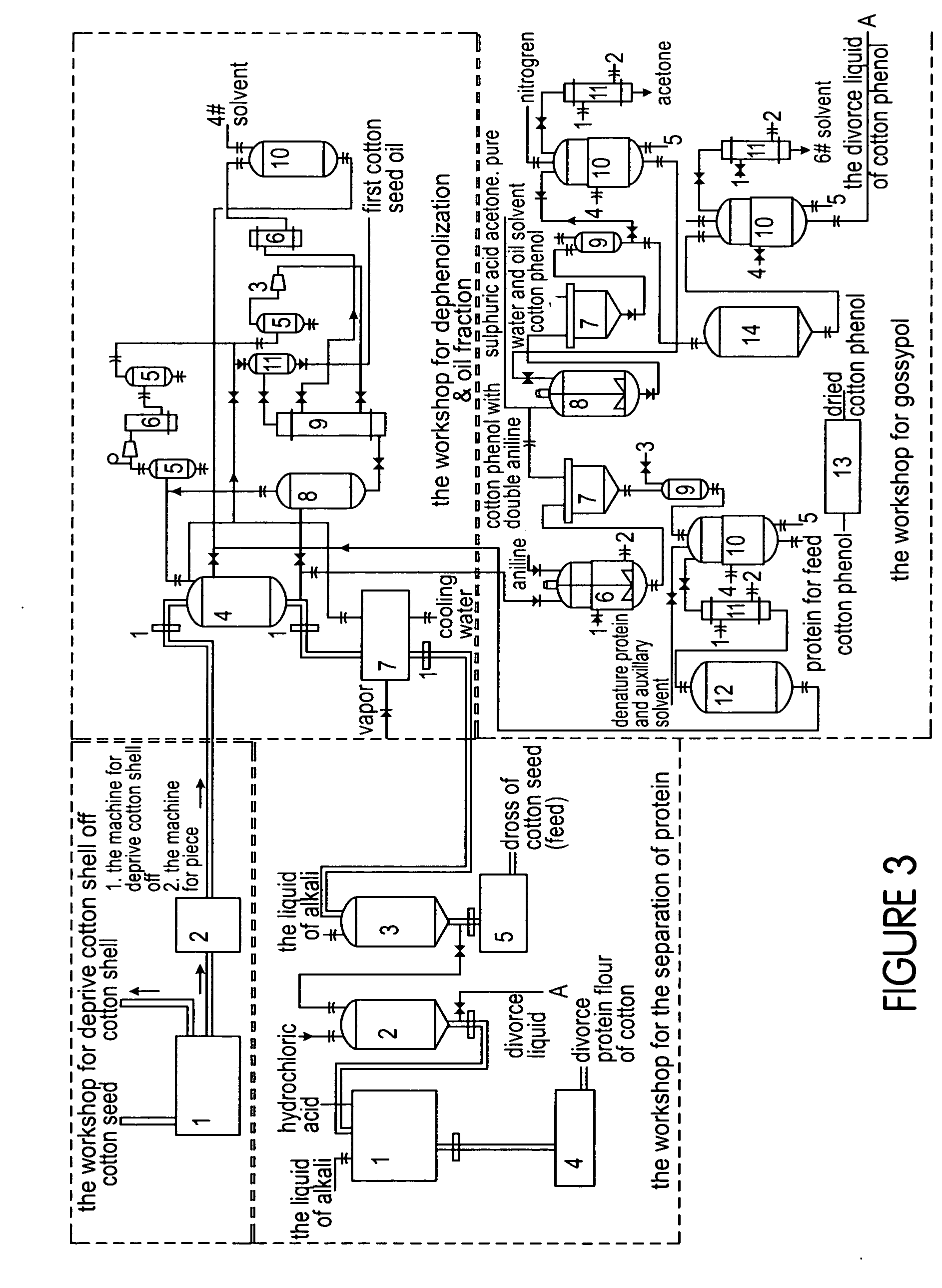
Integrated process for separation of oil, protein, carbohydrates, shell and minor toxic components from seeds
InactiveUS20050147722A1Protein composition from vegetable seedsDispersed particle separationAdemetionineHydrolyzed protein
This invention relates to a method for the separation of oil, protein, carbohydrates, shell, and minor toxic components from seeds. The oil seed is subjected to a dehulling process to separate out the hull and kernel and the dehulled oil seed is then compressed into flakes under low temperature. The oil seed is then dephenolized and undergo low temperature delintion. In addition, direct hydrolyzation of the oil-complex is carried out. This technology can be used to produce high quality oil and obtain hydrolyzed protein, thereby comprehensively utilizing the oil seed.
Owner:GAO SHEN
Walnut low molecular weight polypeptide and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102406050ASimple compositionRaise the ratioProtein composition from vegetable seedsFood additiveFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a walnut low molecular weight polypeptide and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: hydrolyzing walnut albumen powder through a high static pressure technique combined with a biological enzyme; decoloring and adsorbing to remove bitter substances in the walnut low molecular weight polypeptide, and then preparing the walnut low molecular weight polypeptide with high purity, good quality and high low molecular weight peptide proportion; and directly packaging or carrying out freeze drying to obtain the finished walnut low molecular weight polypeptide product. The walnut low molecular weight polypeptide disclosed by the invention can be widely applied to medicine raw materials, medicaments, food, health care products, foodadditives and the like. By using the method disclosed by the invention, the hydrolysis degree of protein is improved so that the proportion of the walnut low molecular weight polypeptide is improved,thereby being more beneficial to the absorption and utilization of walnut polypeptide, enhancing the nutrition and health care effects of walnut and improving the product additional value of walnut. Thus, the walnut low molecular weight polypeptide has a good market application prospect.
Owner:厦门元之道生物科技有限公司
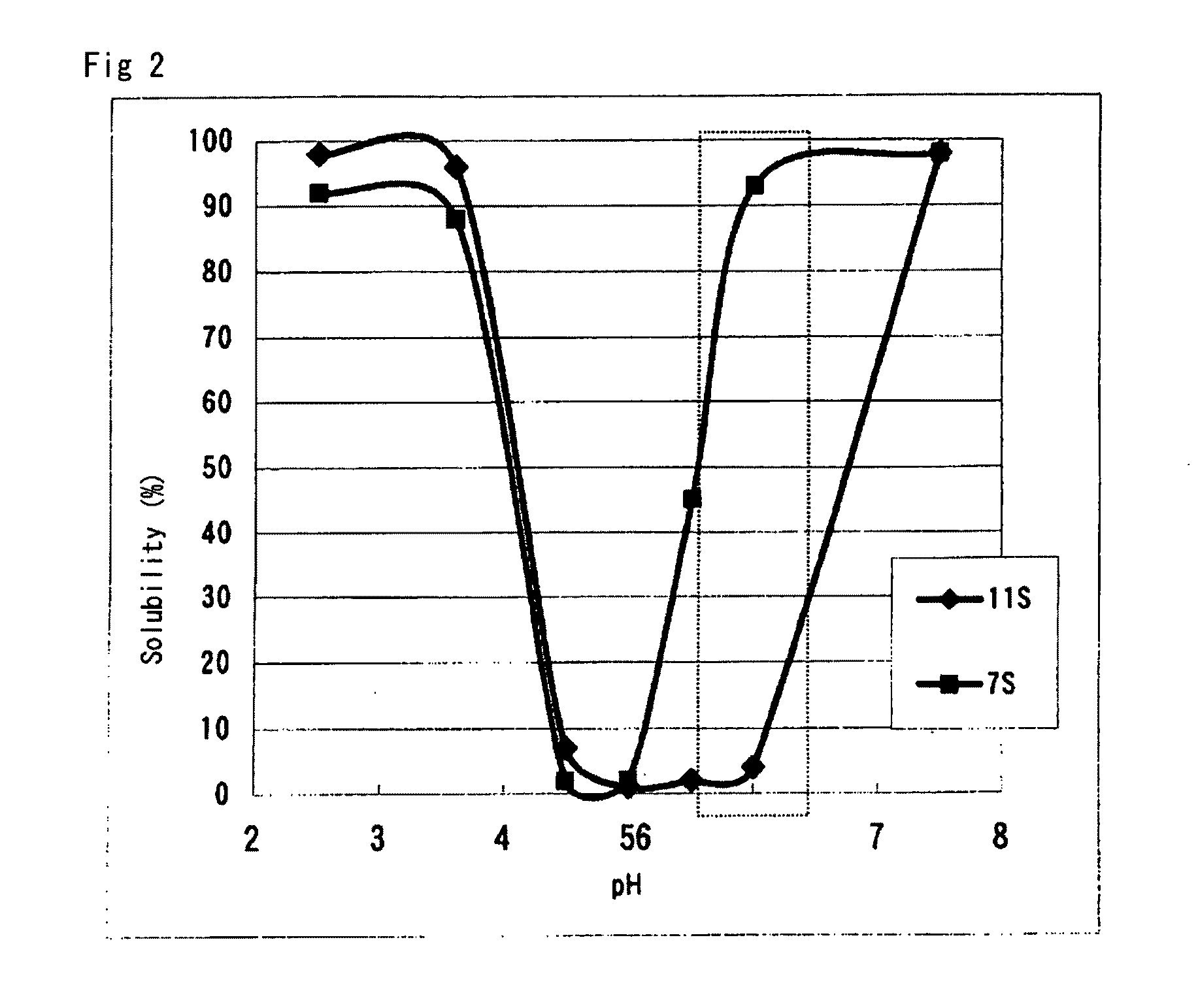
Fractionated soybean protein material, processed soybean suitable for the material , and processes for production of the soybean protein material and the processed soybean
ActiveUS20090232958A1Efficient production and processingHigh purityMetabolism disorderWort preparationFractionation7s globulin
Disclosed is a process for fractionating soybean protein into 7S globulin, 11S globulin or a lipophilic protein at a high purity with good efficiency, which relates to a fractionation technique for soybean protein into proteins having characteristic properties (7S globulin, 11S globulin and a lipophilic protein) and which is a process practicable at a food industrial level. It is found that soybean protein can be fractionated into 7S globulin, 11S globulin or a lipophilic protein at a high purity with good efficiency by extracting soybean milk from processed soybean which has been subjected to a water-insolubilization treatment specific to a desired protein and fractionating the resulting soybean milk or soybean curd refuse into the desired protein.
Owner:FUJI OIL CO LTD
Process for the fractionation of cereal brans
InactiveUS7709033B2Improve efficiencyEasy to separateTea extractionProtein composition from vegetable seedsUltrafiltrationFractionation
A process for the fractionation of valuable fractions from cereal brans (e.g. wheat, barley and oat brans, and rice polish) is described. In particular, this invention describes a two step process, in which the said bran is first subjected to a combination of enzymatic treatment and wet milling, followed by sequential centrifugation and ultrafiltration, which aims at physically separating the main bran factions, i.e. insoluble phase (pericarp and aleurone layer), germ-rich fraction, residual endosperm fraction and soluble sugars. A second step consists of fractionating cereal brans substantially free of soluble compounds, hence insoluble phase from the above-mentioned first step, by enzymatic treatment with xylanases and / or beta-glucanase and wet milling, followed by sequential centrifugation and ultrafiltration, which aims at physically separating the main fractions, i.e. insoluble phase (remaining cell wall components), protein-rich fraction, soluble hemicellulose and oligosaccharide, and therefore maximizes the extraction rate of valuable cell wall components and aleurone cells from previously cleaned bran.
Owner:LANTMANNEN OATS AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com