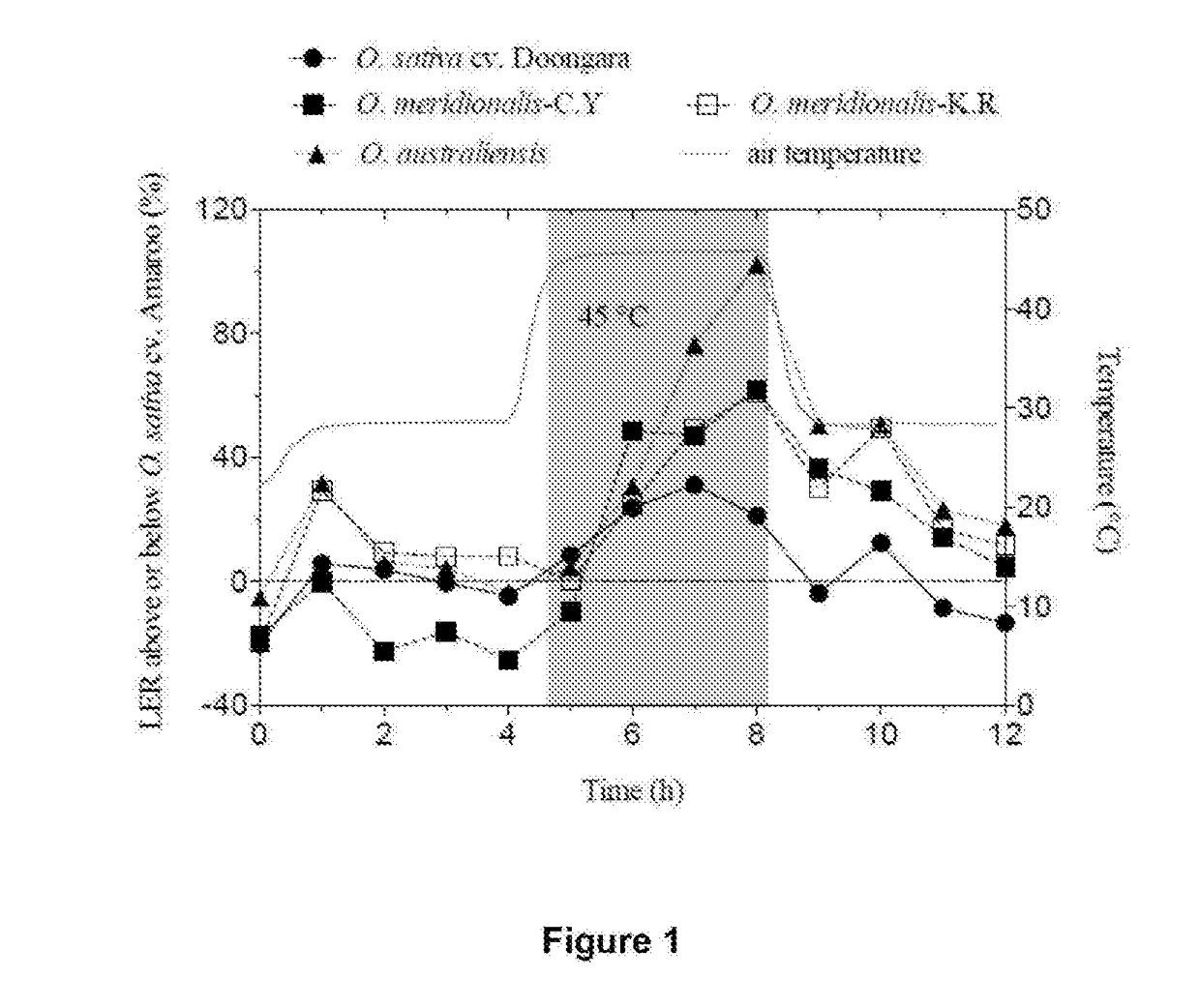
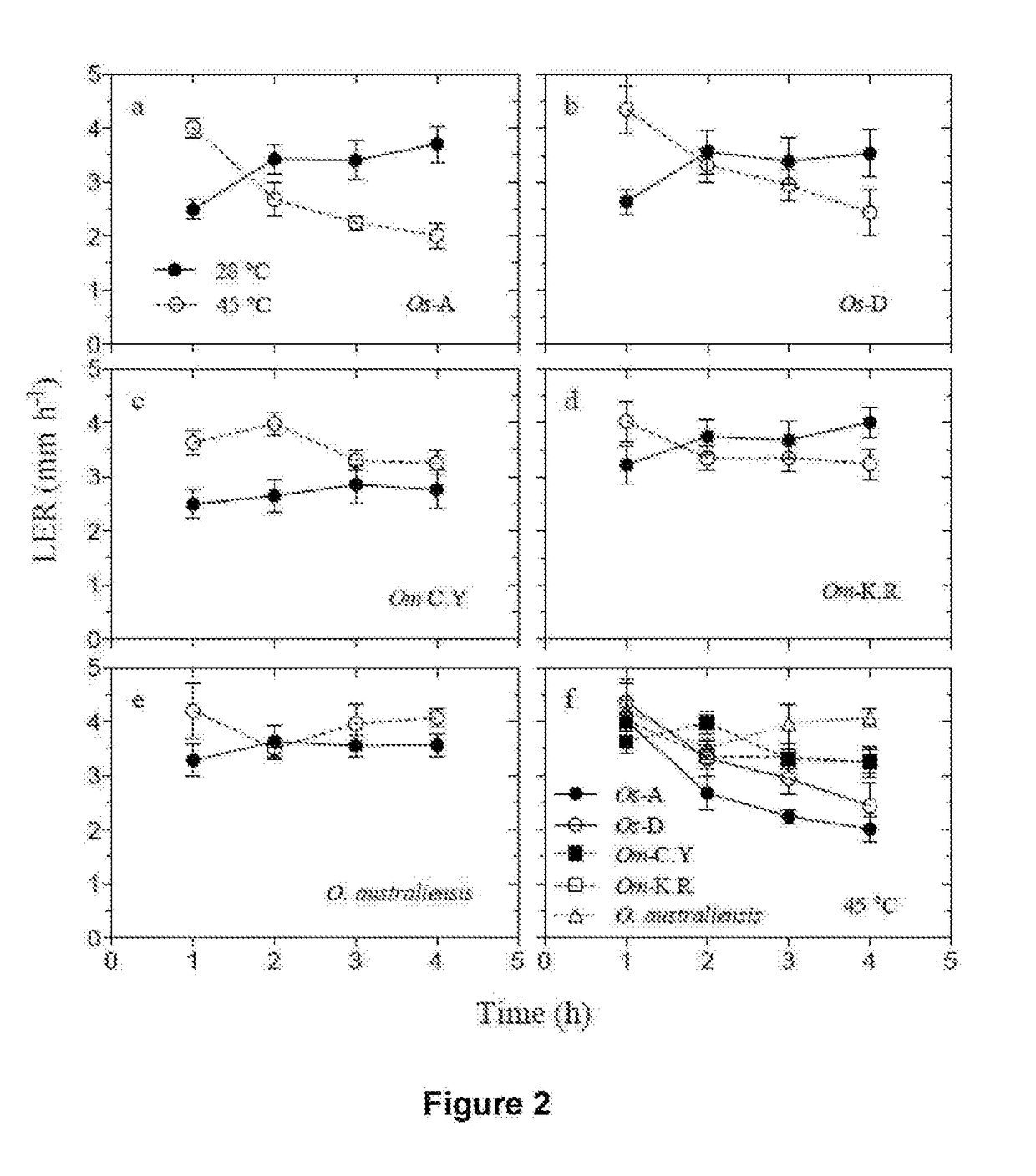
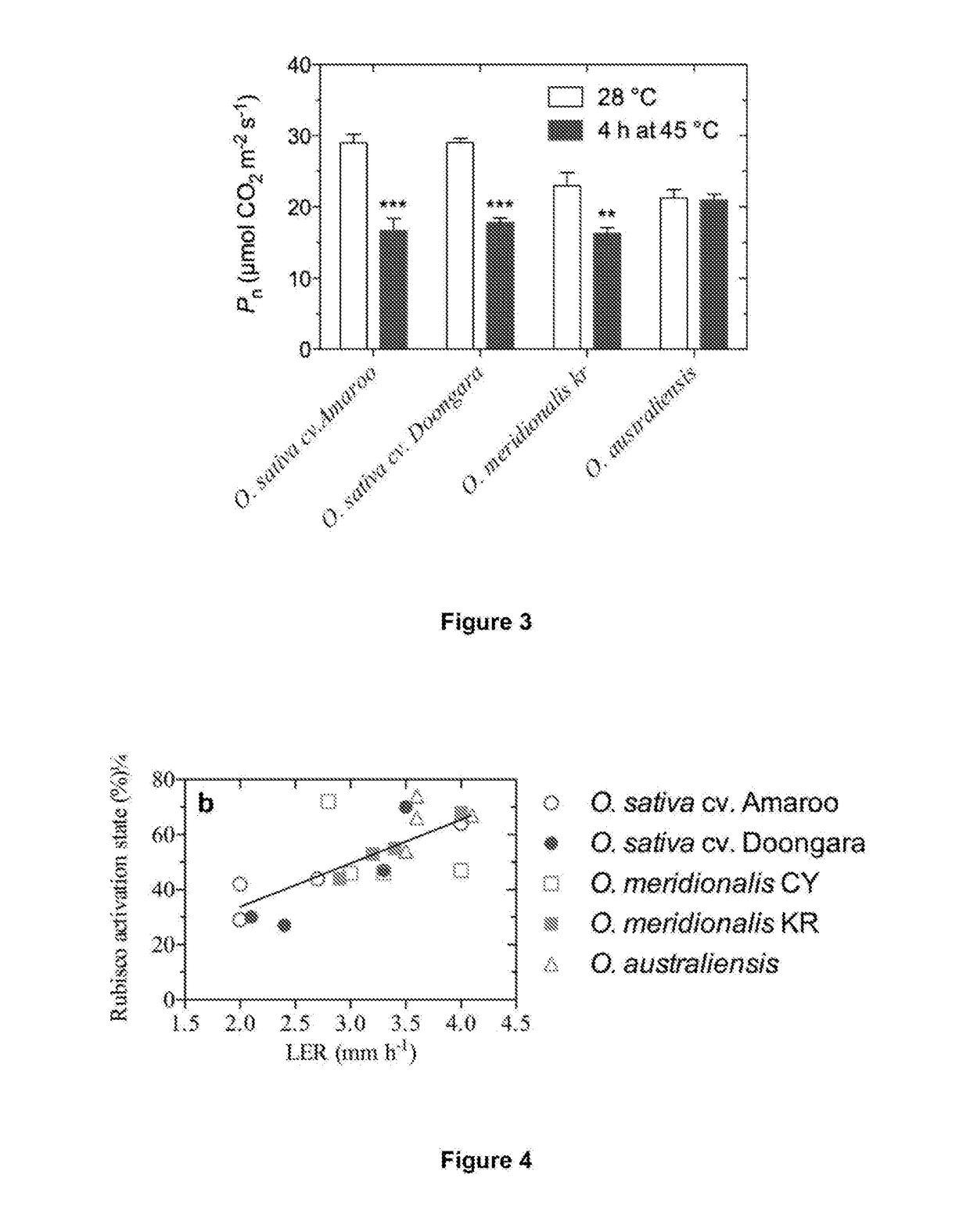
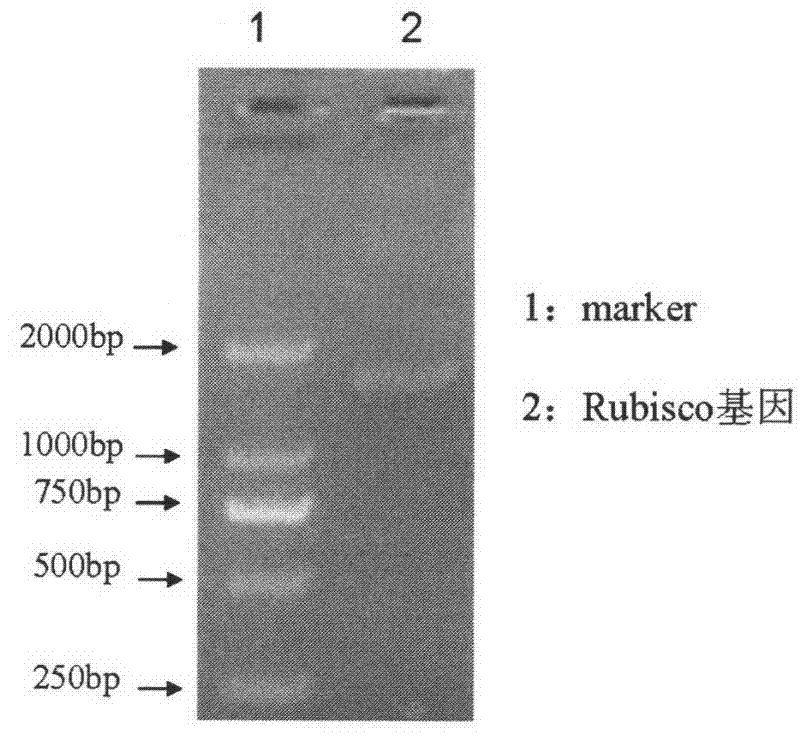
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
59 results about "RuBisCO" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase, commonly known by the abbreviations Rubisco, rubisco, RuBPCase, or RuBPco, is an enzyme involved in the first major step of carbon fixation, a process by which atmospheric carbon dioxide is converted by plants and other photosynthetic organisms to energy-rich molecules such as glucose. In chemical terms, it catalyzes the carboxylation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (also known as RuBP). It is probably the most abundant enzyme on Earth.
High-potency sweetener compositon with rubisco protein, rubiscolin, rubiscolin derivatives, ace inhibitory peptides, and combinations thereof, and compositions sweetened therewith
ActiveUS20080107775A1Improve flavor profileImproving temporal profile profileNervous disorderTobacco treatmentRubiscolinAdditive ingredient
The present invention relates generally to functional sweetener compositions comprising non-caloric or low-caloric natural and / or synthetic high-potency sweeteners and methods for making and using them. In particular, the present invention relates to different functional sweetener compositions comprising at least one non-caloric or low-caloric natural and / or synthetic high potency sweetener, at least one sweet taste improving composition, and at least one functional ingredient, such as rubisco protein, rubiscolin, rubiscolin derivatives, ACE inhibitory peptide, and combinations thereof. The present invention also relates to functional sweetener compositions and methods that can improve the tastes of non-caloric or low-caloric high-potency sweeteners by imparting a more sugar-like taste or characteristic. In particular, the functional sweetener compositions and methods provide a more sugar-like temporal profile, including sweetness onset and sweetness linger, and / or a more sugar-like flavor profile.
Owner:THE COCA-COLA CO
Plants with Increased Yield
InactiveUS20120227134A1MicroorganismsVector-based foreign material introductionUbiquitin-Protein LigasesSerine hydroxymethyltransferase
A method for producing a plant with increased yield as compared to a corresponding wild type plant whereby the method comprises at least the following step: increasing or generating in a plant or a part thereof one or more activities of a polypeptide selected from the group consisting of 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase, 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase, 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphate phosphatase, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase, 5OS chloroplast ribosomal protein L21, 57972199. R01.1-protein, 60952769. R01.1-protein, 60S ribosomal protein, ABC transporter family protein, AP2 domain-containing transcription factor, argonaute protein, AT1 G29250.1-protein, AT1 G53885-protein, AT2G35300-protein, AT3G04620-protein, AT4G01870-protein, AT5G42380-protein, AT5G47440-protein, CDS5394-protein, CDS5401_TRUNCATED-protein, cold response protein, cullin, Cytochrome P450, delta-8 sphingolipid desaturase, galactinol synthase, glutathione-S-transferase, GTPase, haspin-related protein, heat shock protein, heat shock transcription factor, histone H2B, jasmonate-zim-domain protein, mitochondrial asparaginyl-tRNA synthetase, Oligosaccharyltransferase, OS02G44730-protein, Oxygen-evolving enhancer protein, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase family protein, plastid lipid-associated protein, Polypyrimidine tract binding protein, PRLI-interacting factor, protein kinase, protein kinase family protein, rubisco subunit binding-protein beta subunit, serine acetyltransferase, serine hydroxymethyltransferase, small heat shock protein, S-ribosylhomocysteinase, sugar transporter, Thioredoxin H-type, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, ubiquitin-protein ligase, universal stress protein family protein, and Vacuolar protein.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
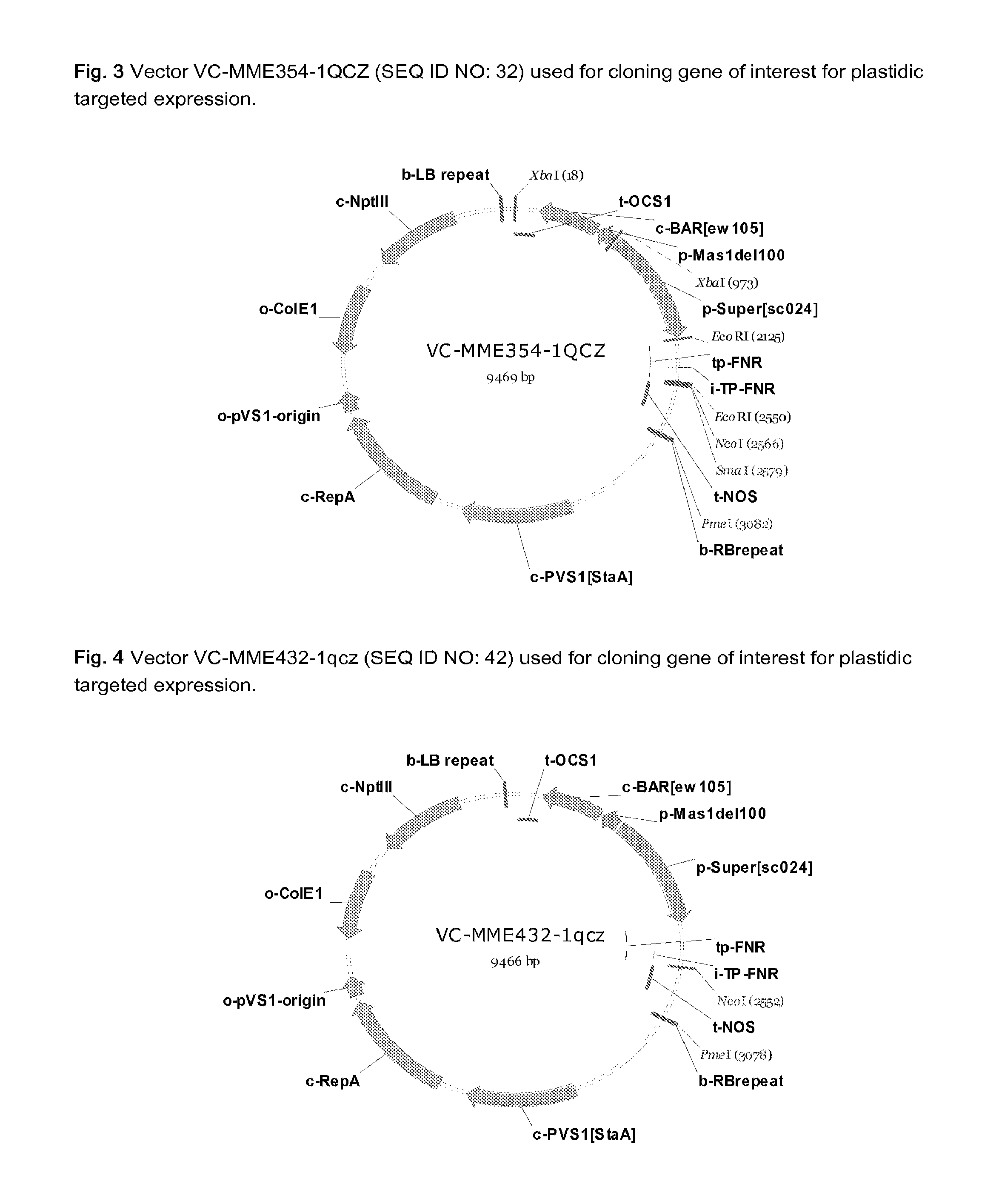
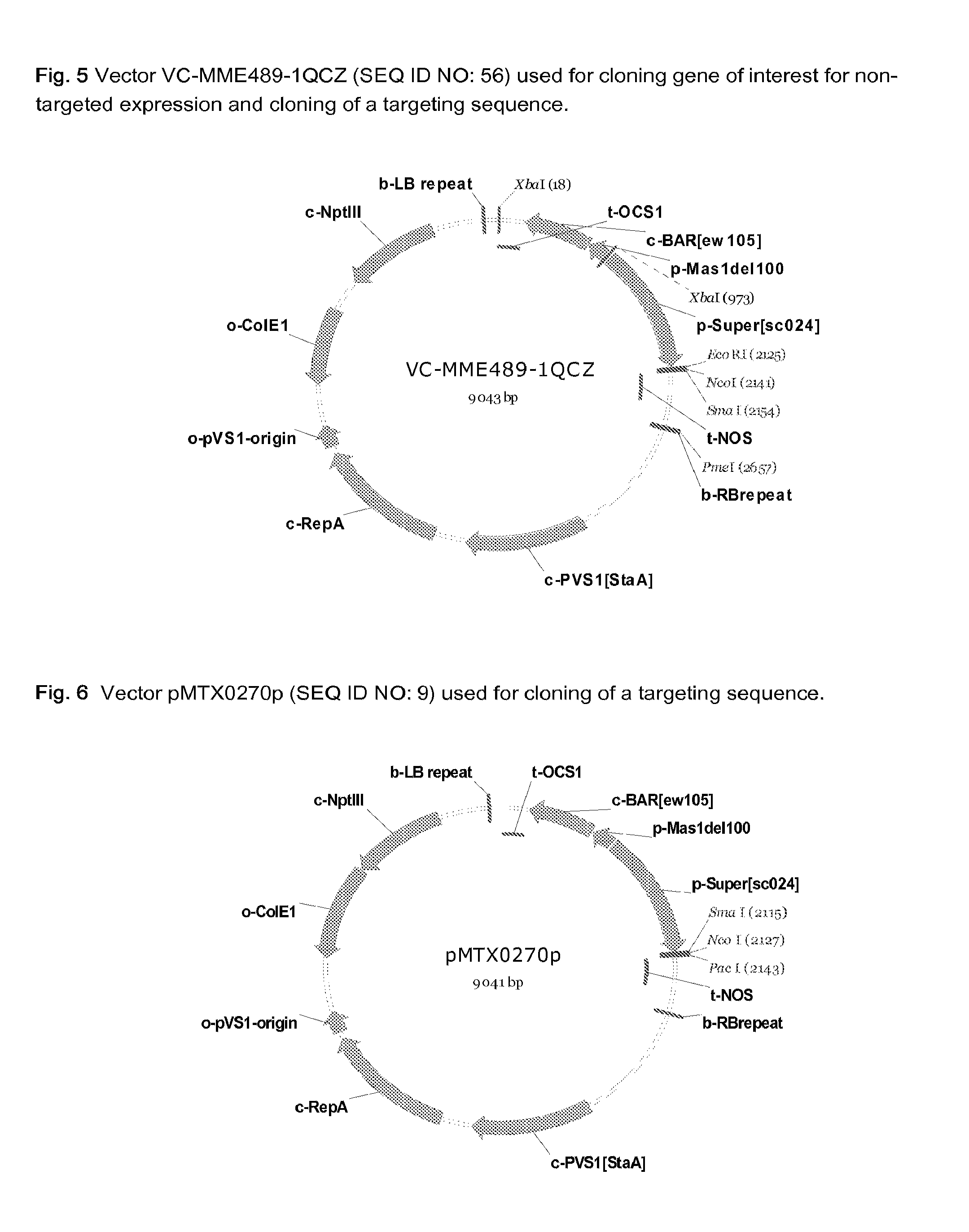
Gateway cloning entry vector, construction method and use thereof
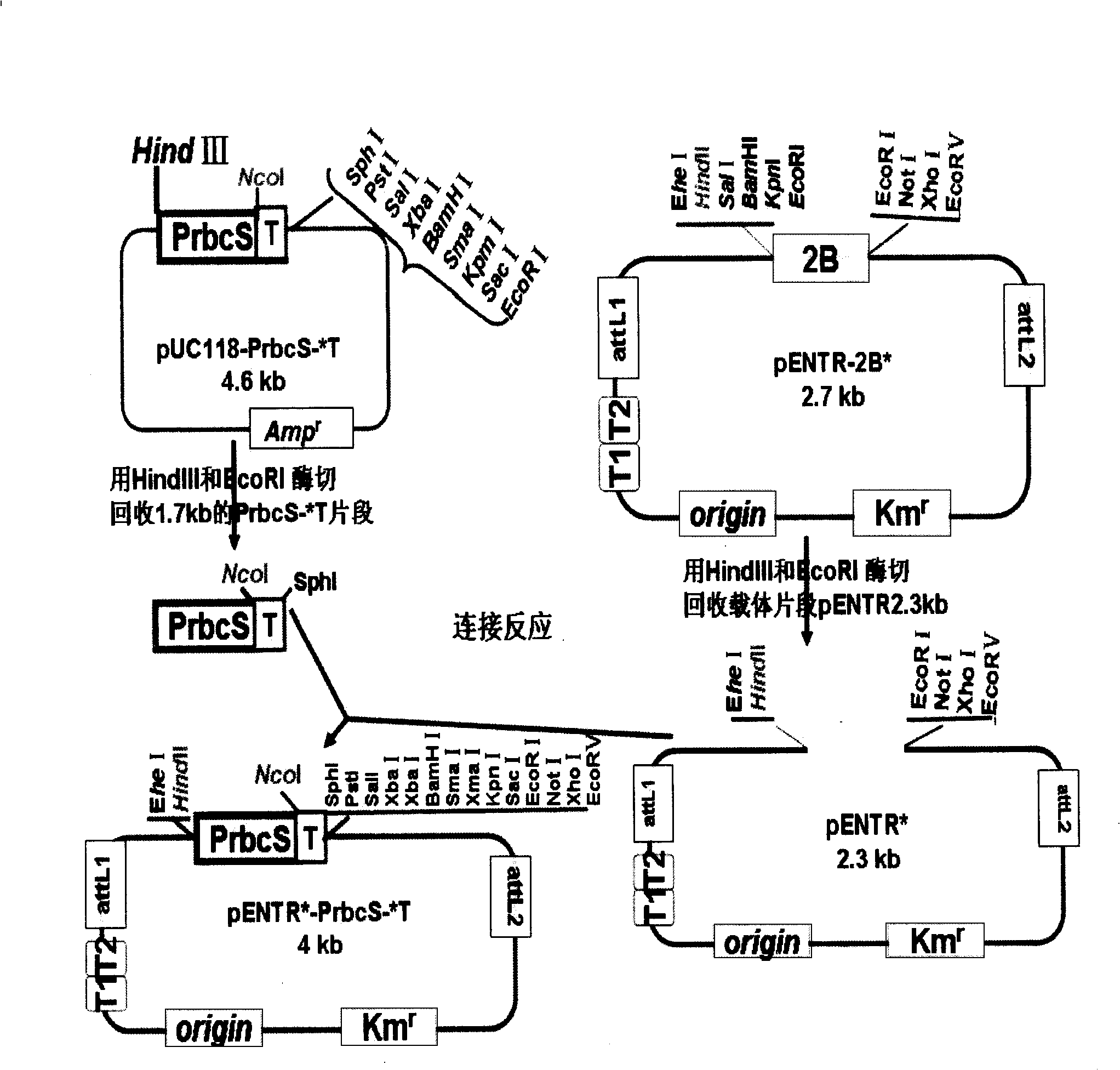
The invention discloses a gateway cloning technology entry plasmid vector. The vector contains a photoinducible promoter (Prbcs) of a small subunit gene of 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase (Rubisco) and a green fluorescent protein (GFP) reporter gene. The invention also discloses a construction method and application of the vector. Through the vector, the gateway cloning technology can be utilized to quickly construct a photoinducible plant expression vector of a target gene to realize the high level expression of the target gene in plant leaves, the expression of the target gene is adjusted by light intensity, and expressed target protein can be positioned into chloroplast or cytoplasm.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Rubisco promoters and uses thereof
The present invention is related to a family of novel spatiotemporally active Rubisco promoters (SEQ ID NO: 1, 2, 3) obtainable from light grown Brassica seedlings. Furthermore the invention is related to transgene expression in specific plant organs or at specific stages of plant development. DNA constructs and expression cassettes comprising at least one of the promoter sequences functionally fused in frame with genes encoding desired gene products are disclosed. Seeds from transformed homologous and herterologous plants and from subsequent generation of the transformed plants are collected and used for efficient production of desired gene products, especially in contained conditions.
Owner:UNICROP LTD
High-potency sweetener composition with rubisco protein, rubiscolin, rubiscolin derivatives, ace inhibitory peptides, and combinations thereof, and compositions sweetened therewith
InactiveUS8017168B2Improved profileAdd flavorNervous disorderTobacco treatmentAdditive ingredientRubiscolin
The present invention relates generally to functional sweetener compositions comprising non-caloric or low-caloric natural and / or synthetic high-potency sweeteners and methods for making and using them. In particular, the present invention relates to different functional sweetener compositions comprising at least one non-caloric or low-caloric natural and / or synthetic high potency sweetener, at least one sweet taste improving composition, and at least one functional ingredient, such as rubisco protein, rubiscolin, rubiscolin derivatives, ACE inhibitory peptide, and combinations thereof. The present invention also relates to functional sweetener compositions and methods that can improve the tastes of non-caloric or low-caloric high-potency sweeteners by imparting a more sugar-like taste or characteristic. In particular, the functional sweetener compositions and methods provide a more sugar-like temporal profile, including sweetness onset and sweetness linger, and / or a more sugar-like flavor profile.
Owner:THE COCA-COLA CO
Active enzyme biological resuming agent (fertilizer) and preparation method thereof
The invention provides an organized enzyme biologic restorer (fertilizer), which can remove toxin in crops and toxin in fruits organizations. The polluted noxious crops can be restored to an original innoxious status, and the soil which comprises noxious substances can also be restored to the original innoxiuos status. Meanwhile, the invention also has the functions of increasing yield of crops and killing pests. The restorer mainly comprises urease and peroxydase generated by bacteria one, two, three, laccase generated by fungi one and two, and tyrosinase generated by ray fungi one and two. An active bacterium and organized enzyme cenobium agent is formed, which can effectively degrade noxious polluted substances; chitinase (chitinase) acts as insecticidal action, and rubisco enzyme can improve yield of the crops. The formulation of the restorer (fertilizer) consists of bio organic liquid or sorbent (accounts for 25 percent), active enzyme revulsant I and II preparation (accounts for 9 percent), acylase nitrogen source (accounts for 25 percent), organized enzyme auxiliary and amplifier (accounts for 16 percent) and inorganic fertilizer and accessories (accounts for 25 percent).
Owner:段一皋 +1
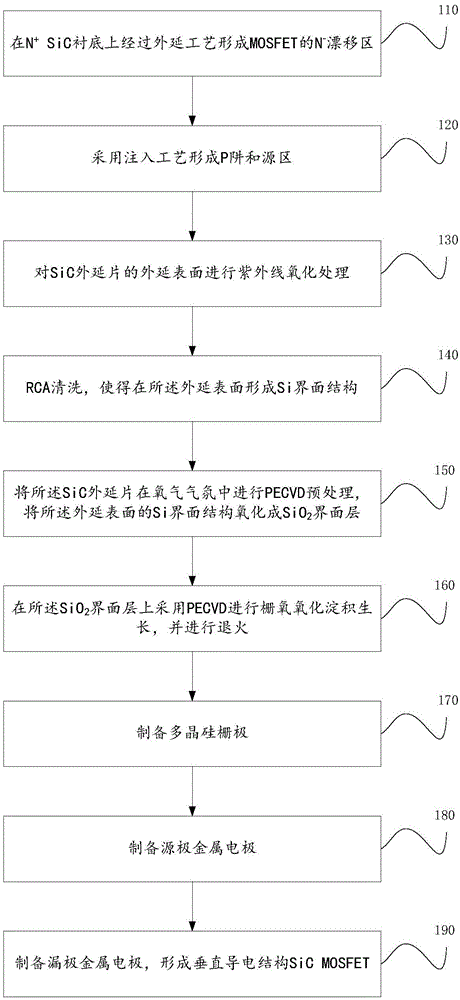
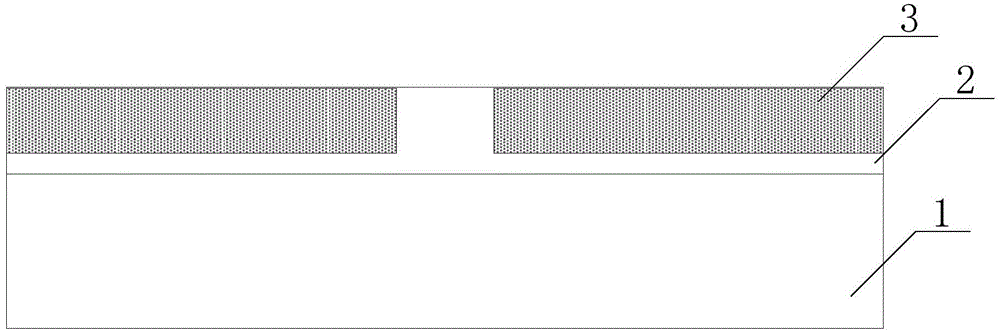
Method for improving channel mobility of SiC metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET)
ActiveCN105047539AImprove mobilityImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETGas phase
The embodiment of the invention relates to a method for improving the channel mobility of a SiC metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET). The method comprises the following steps: before gate-oxide is carried out, carrying out ultraviolet oxidation treatment on the epitaxy surface of SiC epitaxial wafer; carrying out rubisco activase (RCA) cleaning, and forming an Si interface structure on the epitaxy surface; carrying out plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) pretreatment on the SiC epitaxial wafer in oxygen atmosphere, and oxidizing the Si interface structure of the epitaxy surface into an SiO2 interface layer; carrying out gate-oxide oxidizing deposition growth on the SiO2 interface layer by PECVD, and carrying out annealing; and preparing a polycrystalline silicon gate and source and drain metal electrodes, so as to form the SiC MOSFET.
Owner:瑶芯微电子科技(上海)有限公司
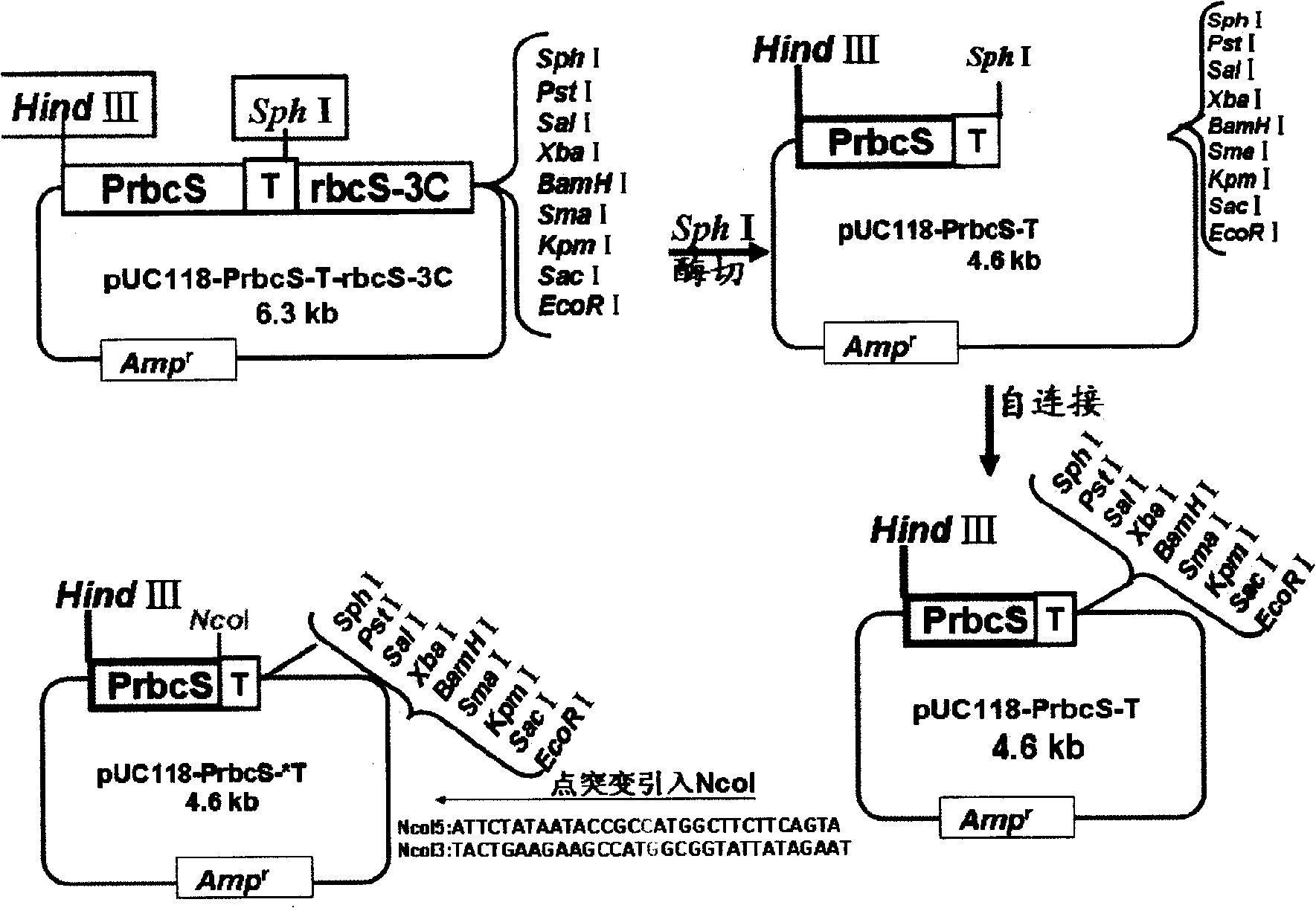
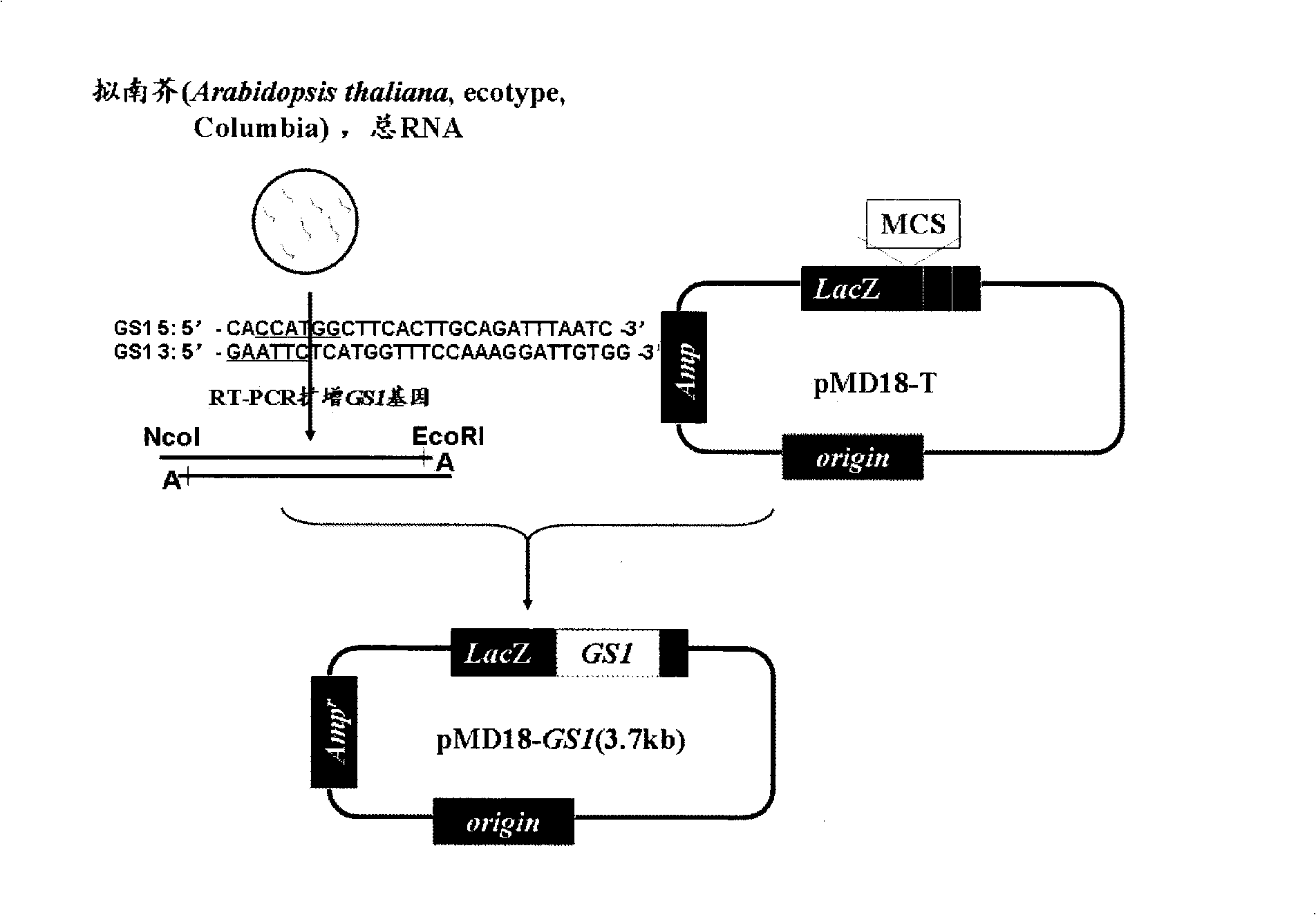
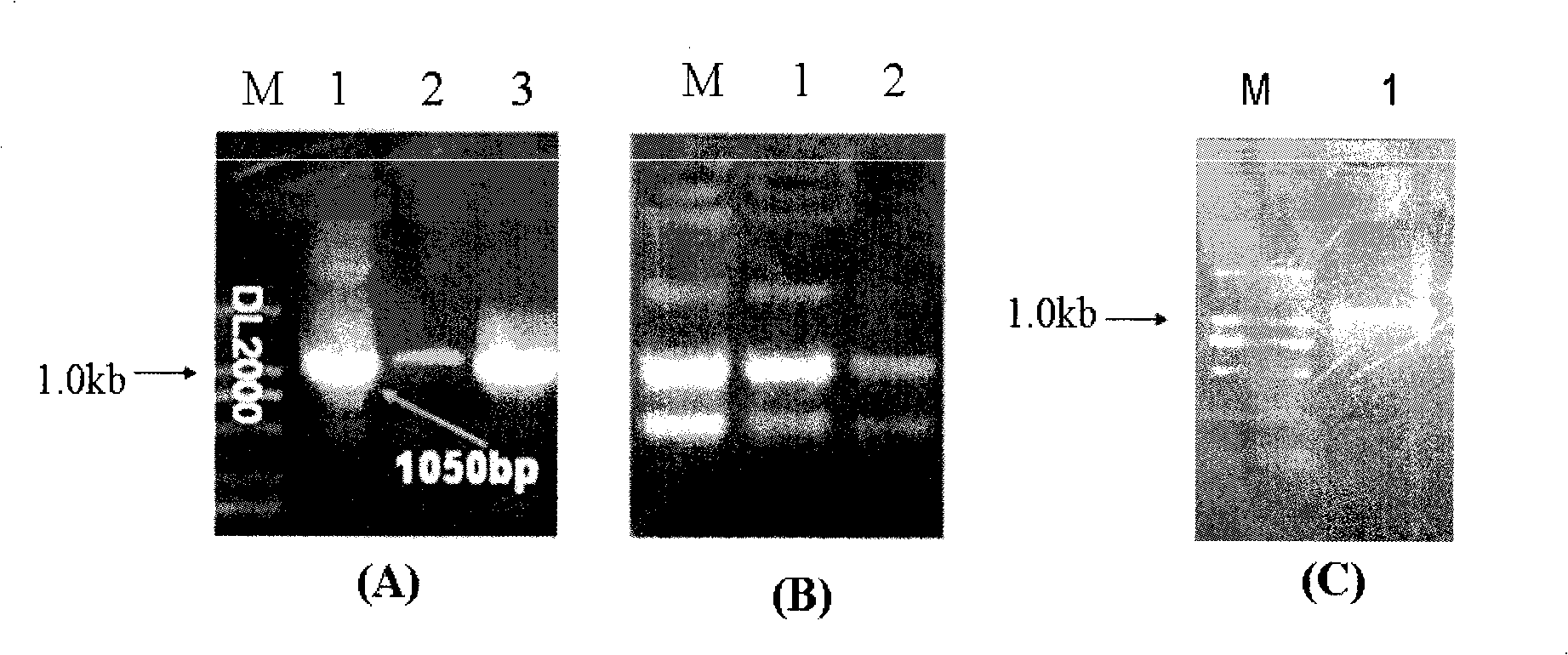
Construction and use of plant expression vector of Arabidopsis thaliana cytoplasm type glutamine synthetase gene
InactiveCN101407824AImprove nitrogen use efficiencyIncreased reassimilation capacityPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsNicotiana tabacumLow nitrogen
The invention relates to a special plant expression vector pH2-35S-PrbcS-GS1 which comprises an arabidopsis thaliana cytoplasm glutamine synthetase gene GS1 and can improve the utilization rate of a plant nitrogen element. A method of RT-PCR is used for cloning the GS1 gene from the arabidopsis thaliana of a model plant, a photoinduction type promotor (the promotor of a a small subunit Rubisco) is used for controlling the excessive expression of the GS1 gene in a plant leaf and a leaf disc conversion method is used for transferring the GS1 gene into a pPZP221-PrbcS-Dof1 type transgene tobacco. An experiment result shows that the GS1 gene can be normally transferred in the transgene tobacco; under the nutrition condition of low nitrogen and the growing conditions of indoor irradiation for 24 hours of 2000LUX and 25 DEG C, the growing situation of the plant transferred with the single gene of Dof1 is (the expression of the gene is controlled by the photoinduction type promotor Prbcs) is a little better than that of a contrast tobacco (a wild type without transgene); after being transferred under the natural growing condition of a green house, the growing situation of the tobacco which is simultaneously transferred with the GS1 gene and the Dof1 gene shows remarkable growing advantages than that of the contrast plant; and therefore, simultaneously and excessively expressing the GS1 gene and the Dof1 gene, can improve the efficiency of the GS / GOGAT (glutamine synthetase / glutamic acid synthetase) approaches in the leaf more extensively, thereby improving the utilization rate of the plant nitrogen element. The vector can be broadly applied to the molecule breeding of crops, improving the utilization rate of the plant nitrogen element thereof and the durability to the nutrition condition of low nitrogen and being capable of obtaining a higher yield under the conditions of applying less fertilizers and even not applying the fertilizers.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Rice Rubisco large-subunit antigen epitope, large-subunit antibody and applications of antibody
InactiveCN103952389AHigh potencyHigh affinitySerum immunoglobulinsBiological material analysisEpitopeOxygenase
The invention rice photosynthesis key enzyme-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase / oxygenase (Rubisco) large-subunit antigen epitope, a polyclonal antibody resisting rice Rubisco large-subunit, and a preparation method and applications of the antibody. The amino acid sequence of the rice Rubisco large-subunit specific antigen epitope is as shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The preparation method comprises the following steps: synthesizing a polypeptide; coupling the polypeptide with carrier protein; preparing antiserum from an immune animal; and performing affinity chromatography for purification, thereby obtaining the polyclonal antibody resisting rice Rubisco large-subunit. The polyclonal antibody is high in titer, remarkable in affinity, excellent in specificity, low in preparation cost and high in yield, and can generate specific binding reaction with rice Rubisco large-subunit; an important tool is supplied for the fundamental research on the rice Rubisco large-subunit as well as the research on the relevant physiological functions of the rice Rubisco large-subunit.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Plant expression vector of arabidopsis thaliana cytosolic malate dehydrogenase gene and application thereof
InactiveCN101586116ADetoxifyImprove the ability to resist aluminum poisoningFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionNicotiana tabacumWild type
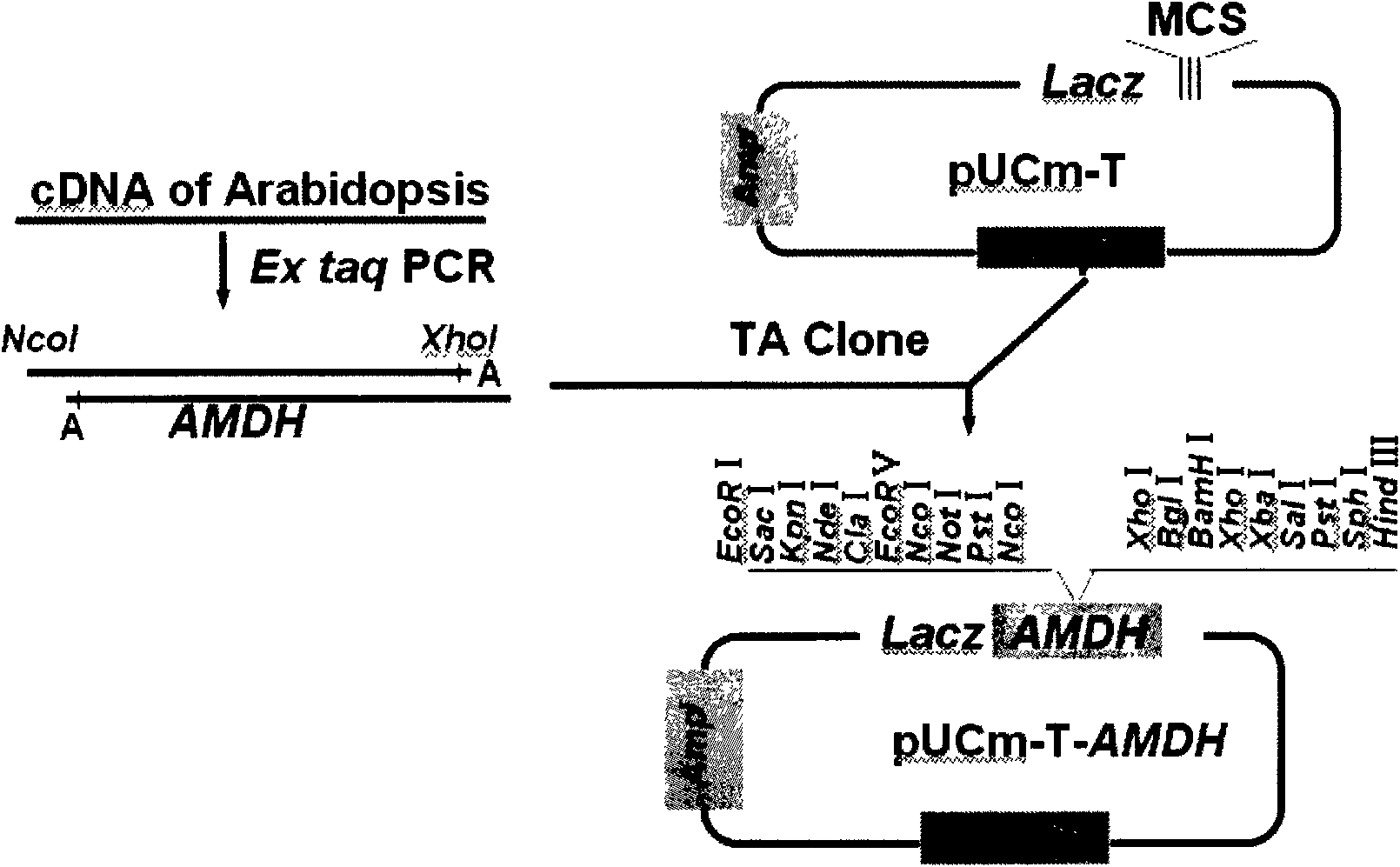
The invention in particular relates to a plant expression vector pH2-35S-PrbcS-AMDH for improving the aluminum toxicity resistance of plants, a construction method and application thereof, which belong to the field of plant gene engineering. The special vector pH2-35S-PrbcS-AMDH for improving the aluminum toxicity resistance of the plants is the plant expression vector containing a photoinducible promoter (PrbcS) of a rubulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase (RubIsco) small subunit gene and an arabidopsis thaliana cytosolic malate dehydrogenase gene (AMDH). The AMDH gene is cloned from arabidopsis thaliana, the photoinducible promoter is used to control the overexpression of the AMDH gene in tobacco, malic acid is synthesized, and the malic acid is secreted out of cells so as to strengthen the resistance of the plants on aluminum toxicity in acid soil. Experimental results show that the activity of malate dehydrogenase of trans-AMDH genic tobacco leaves is 1.4 times of that of wild tobacco. Under the stress of 30 mu M of aluminum toxicity, trans-AMDH genic tobacco can secrete more organic acid, and has better root system growth; and the growth condition under the stress of the aluminum toxicity shows that the plant height and the green leaf number of the trans-AMDH genic tobacco are higher than those of the wild tobacco.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for improving resistance of rice plant to cnaphalocrocis medinalis by transgenic technology
InactiveCN101280289AImprove securityTo achieve the goal of high resistance to rice leaf rollerBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetically modified riceRice plants
The invention discloses a method for improving the resistance of rice plants to rice case worms by applying the transgenic technology, and belongs to the technical field of the plant gene engineering breeding. The method comprises the following steps: Rubisco specific promoters RubS and insect-resistant genes Cry1A(b) are constructed to a pPZP201 expression plasmid carrier; the Cry1A(b) genes are integrated into a rice genome by using the method of co-transformation mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens; the homomycin resistance genes in the self-bred progenies are rejected. The Cry1A(b) insect-resistant genes in the transgenic rice present specific high-expression, present low-expression in seeds, and have no expression in roots, thus obviously improving the resistance of the rice plants to the rice case worms, greatly reducing the pesticide application amount, reducing the production cost and improving the plant profit; simultaneously, the expression of the insect-resistant protein in rice seeds, pollen and roots is decreased, and the worry of people to the rice security is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Regulated gene expression systems and constructs thereof
InactiveCN104039964AVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationBinding siteRuBisCO
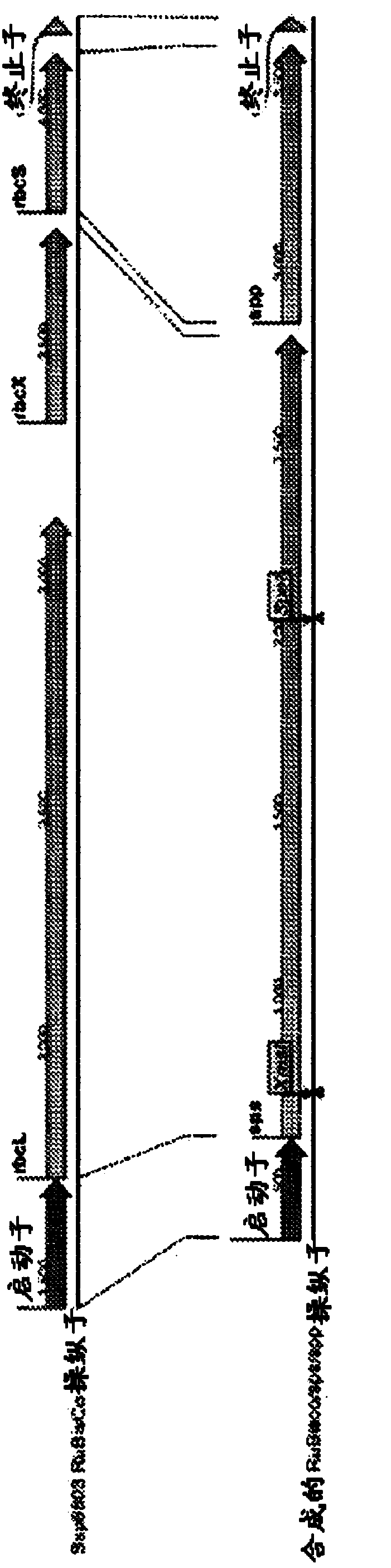
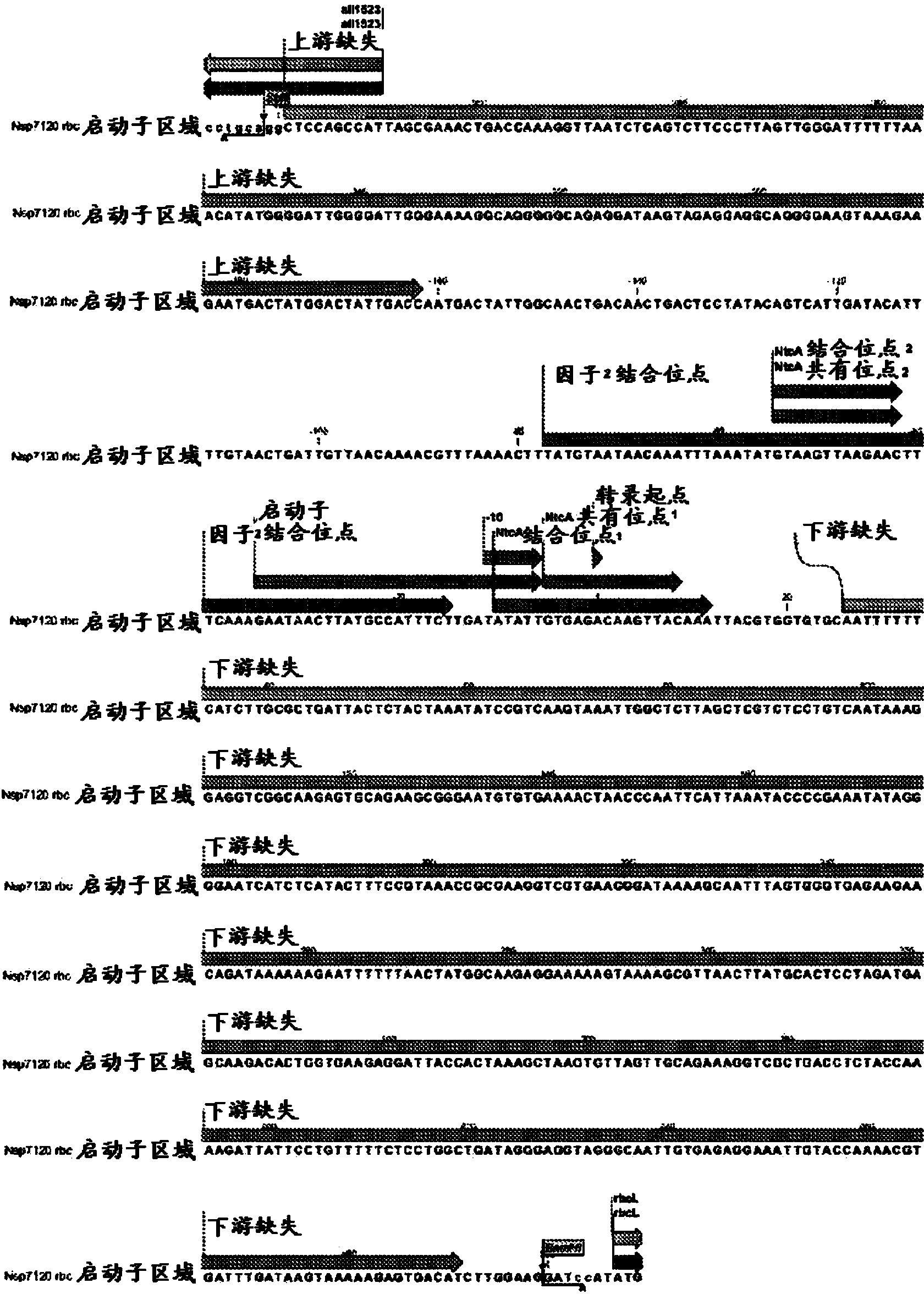
The present disclosure is directed to compositions and methods for nitrogen sensitive regulation of expression of a transcribable nucleic acid molecule. One aspect provides a nitrogen-sensitive expression system that includes a transcription factor region comprising an NtcA binding site and a core promoter region comprising a RuBisCo promoter or a variant or a functional fragment thereof. Another aspect provides a method of transforming a host cell with an expression system. Also provided are expression cassettes, transformed host cells, and kits.
Owner:PROTERRO INC
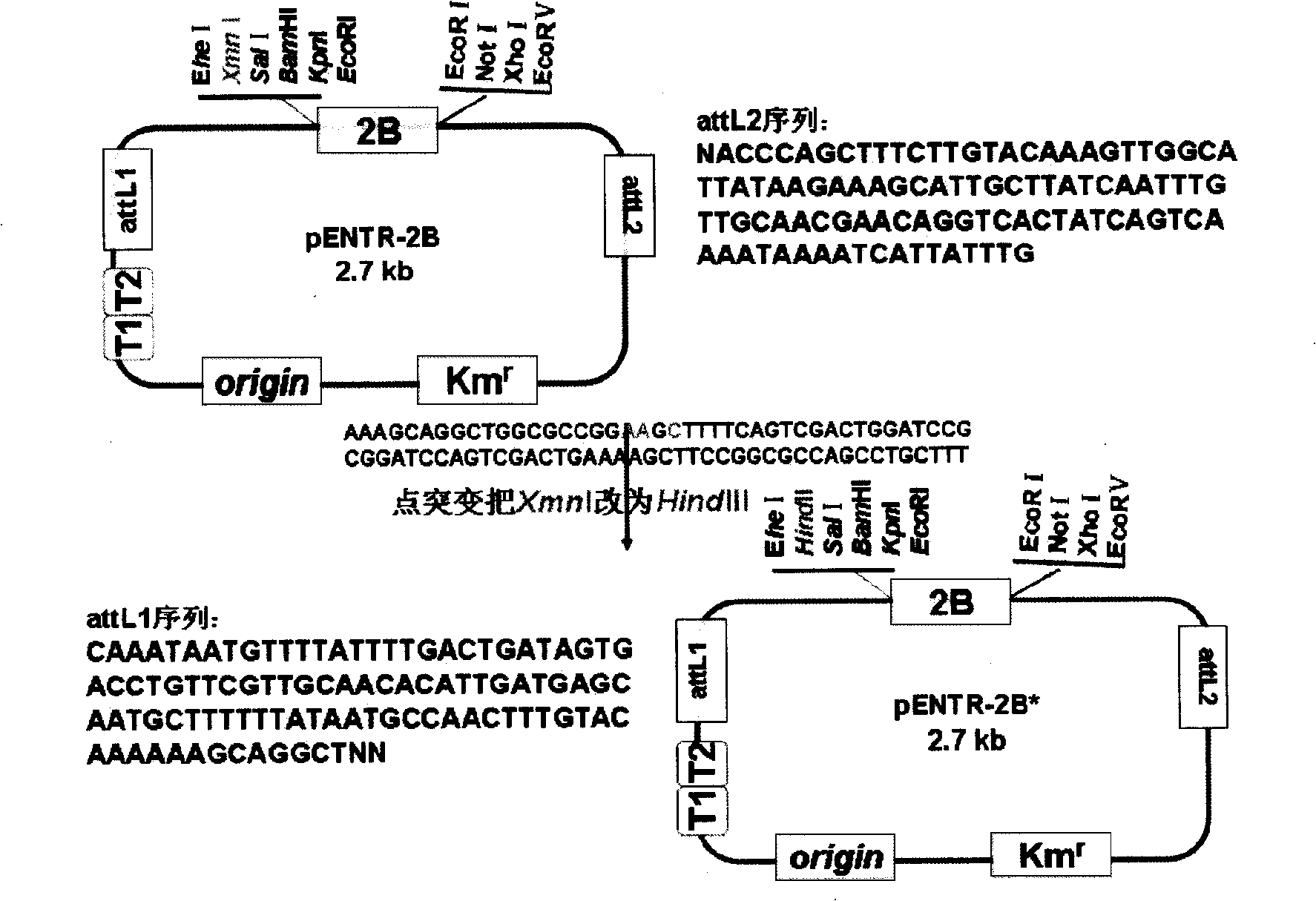
Gateway inlet vector pEn-L4*-PrbcS-*T-GFP-L3*, construction method thereof and application thereof
The invention relates to a gateway inlet vector for the gateway technology, and in particular to a gateway inlet plasmid vector (pEn-L4*-PrbcS-*T-GFP-L3*). The vector comprises sequences L4 and L3, rubisco, a small subunit gene photo-inductive promoter (PrbcS), a chloroplast stroma positioning sequence (T*) and a green fluorescent protein (GFP) reporter gene, which are required for the LR recombination reaction in the gateway technology. A construction method and application of the vector are that: one plant expression vector connected in series with two target gene expression boxes can be quickly constructed by using the vector and another gateway inlet vector containing L1 and L2 sequences through the LR recombination reaction so as to realize conversion operation of two target genes through one conversion event. The expression of the target gene can be controlled with the PrbcS promoter in the vector and high-level expression of the target gene in the leaves of a plant can be realized by substituting the GFP gene in the vector with the target gene.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Tobacco-derived protein compositions
The disclosure describes methods for the purification of protein-enriched extracts to provide concentrates and isolates and methods for incorporation of such materials into products. The purification methods are adapted for removal of one or more of ash, metal salts, alkaloids, particulates, heavy metals, and other impurities and / or contaminants from extracts, as well as modifying the sensory characteristics (e.g., odor, color, and / or taste characteristics) of extracts. The methods generally include diafiltration, treatment with functionalized resins, and supercritical extraction. A protein composition in the form of a concentrate or isolate is provided, the protein composition including RuBisCO, F2 fraction proteins, or combination thereof extracted from a plant of the Nicotiana species, wherein the protein composition is characterized by one or more of: an ash content of less than about 15% by weight; a nicotine content of less than about 10 [mu]g / g; and a heavy metal content of less than about 60 [mu]g / g.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
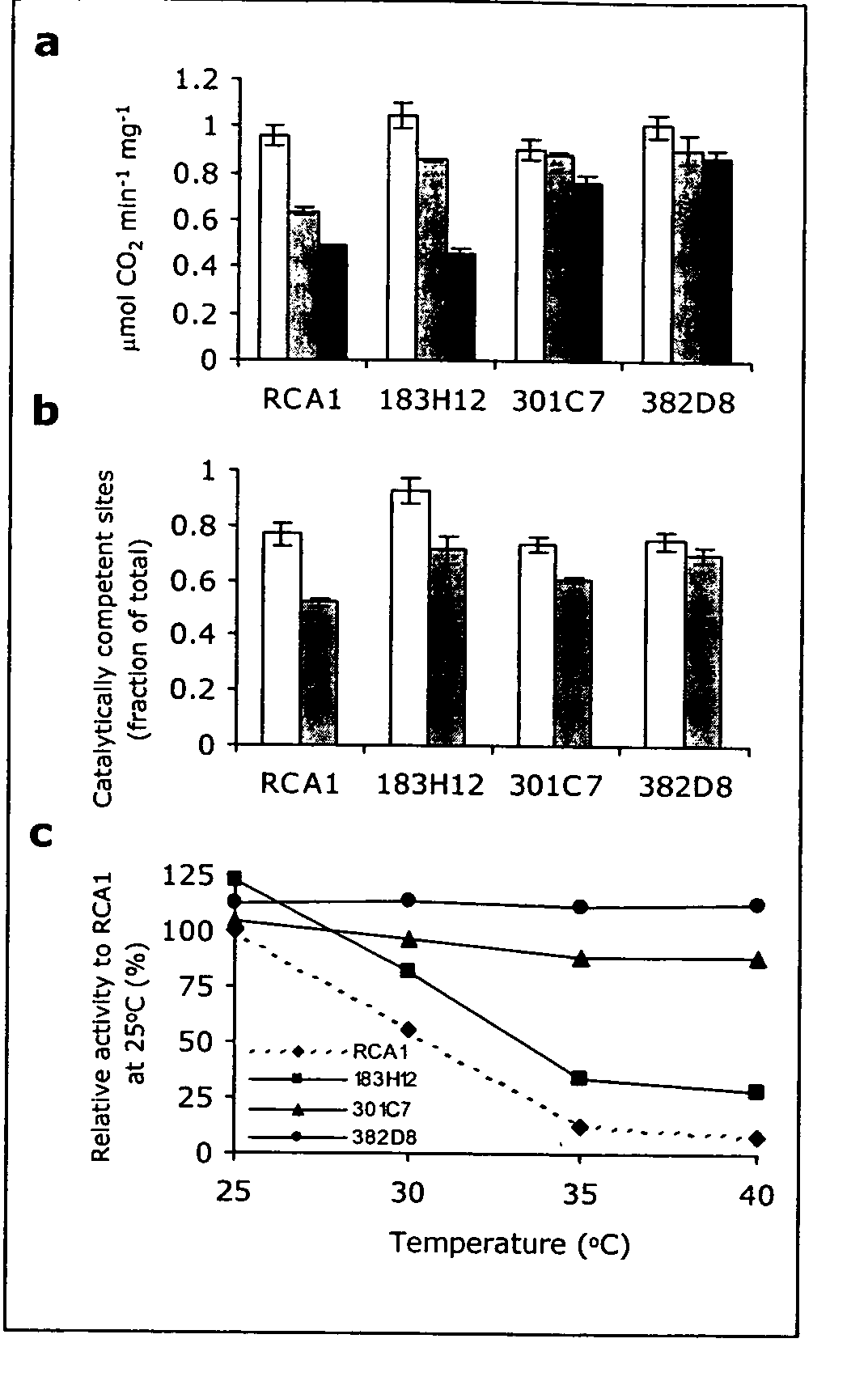
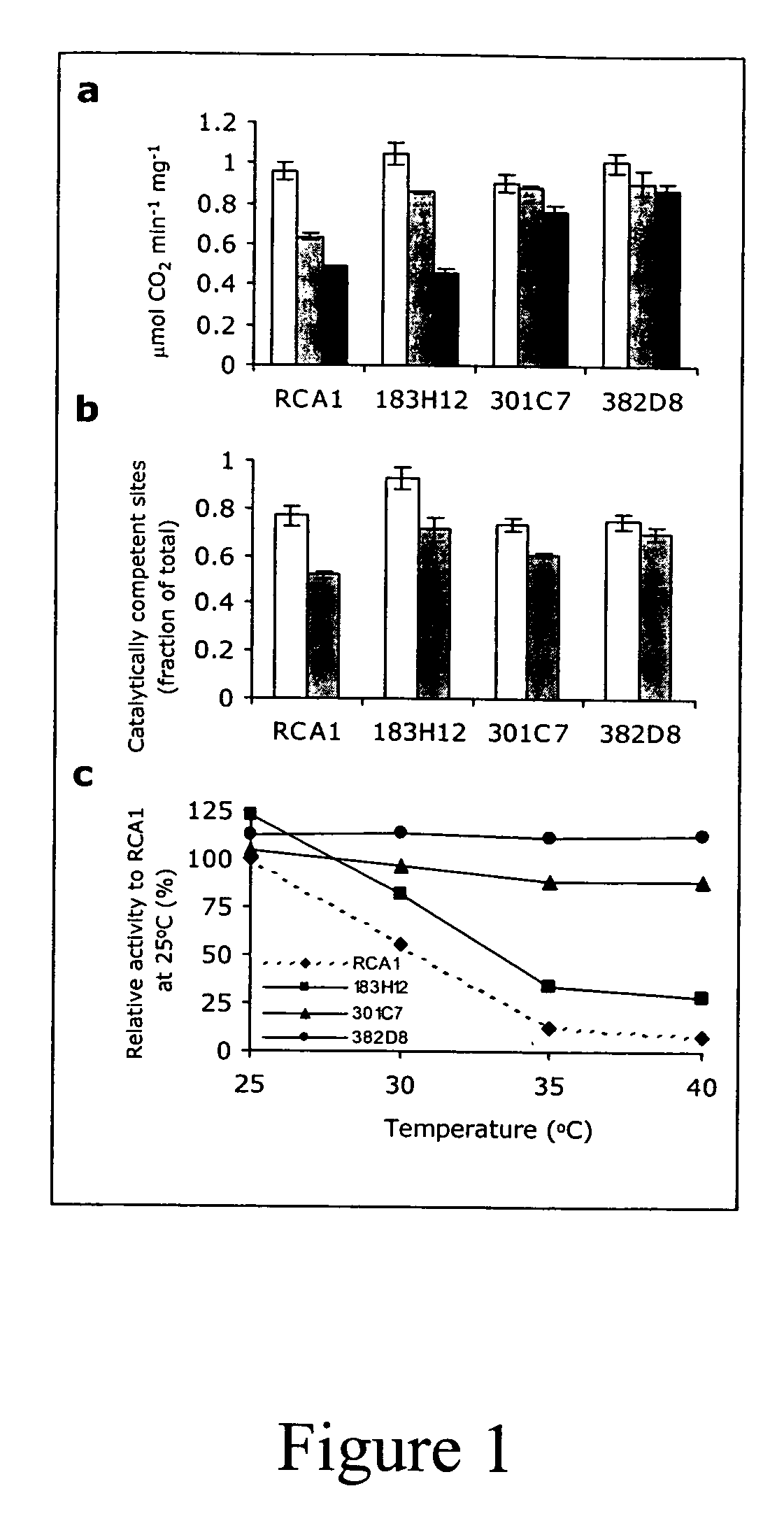
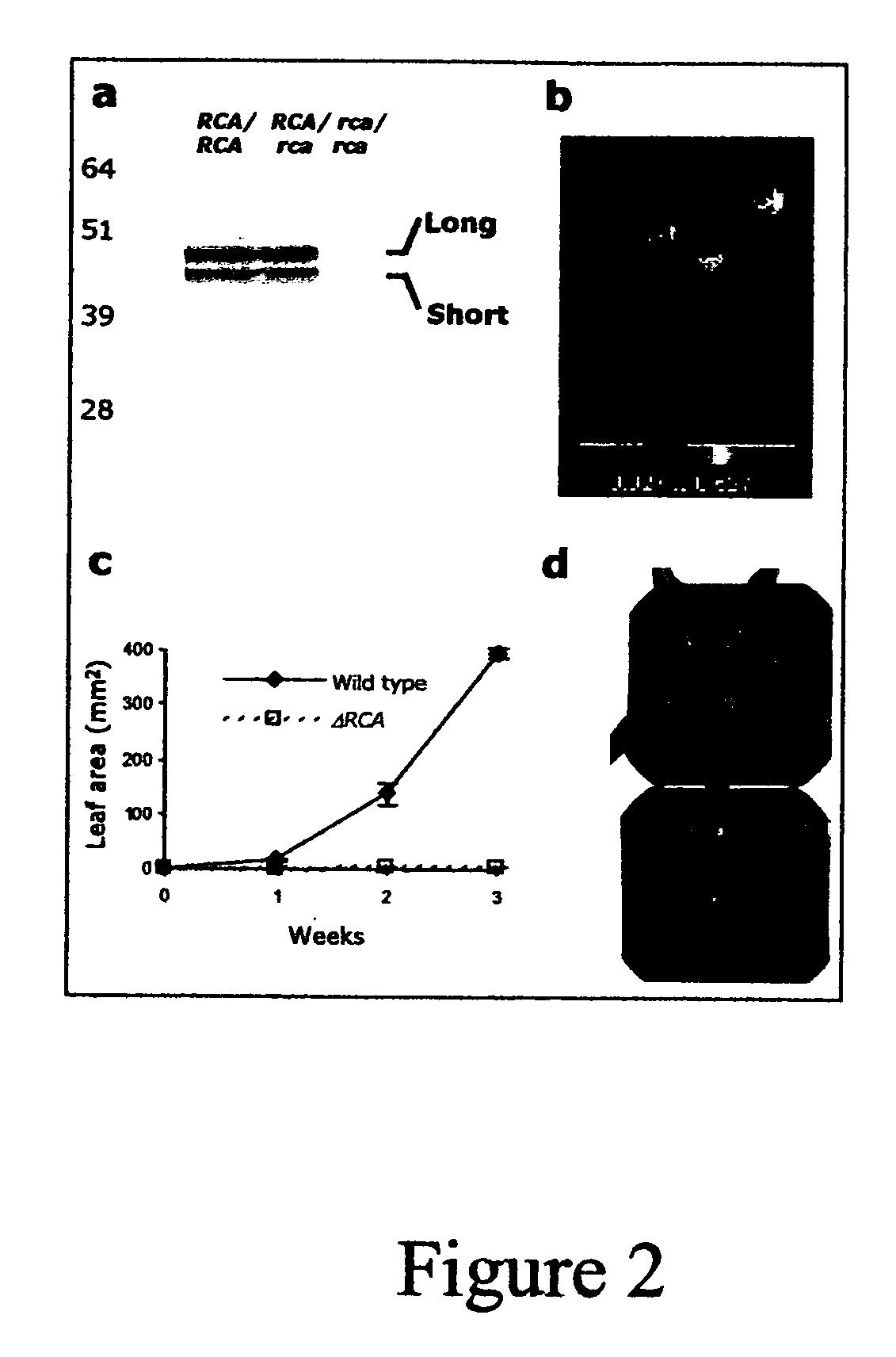
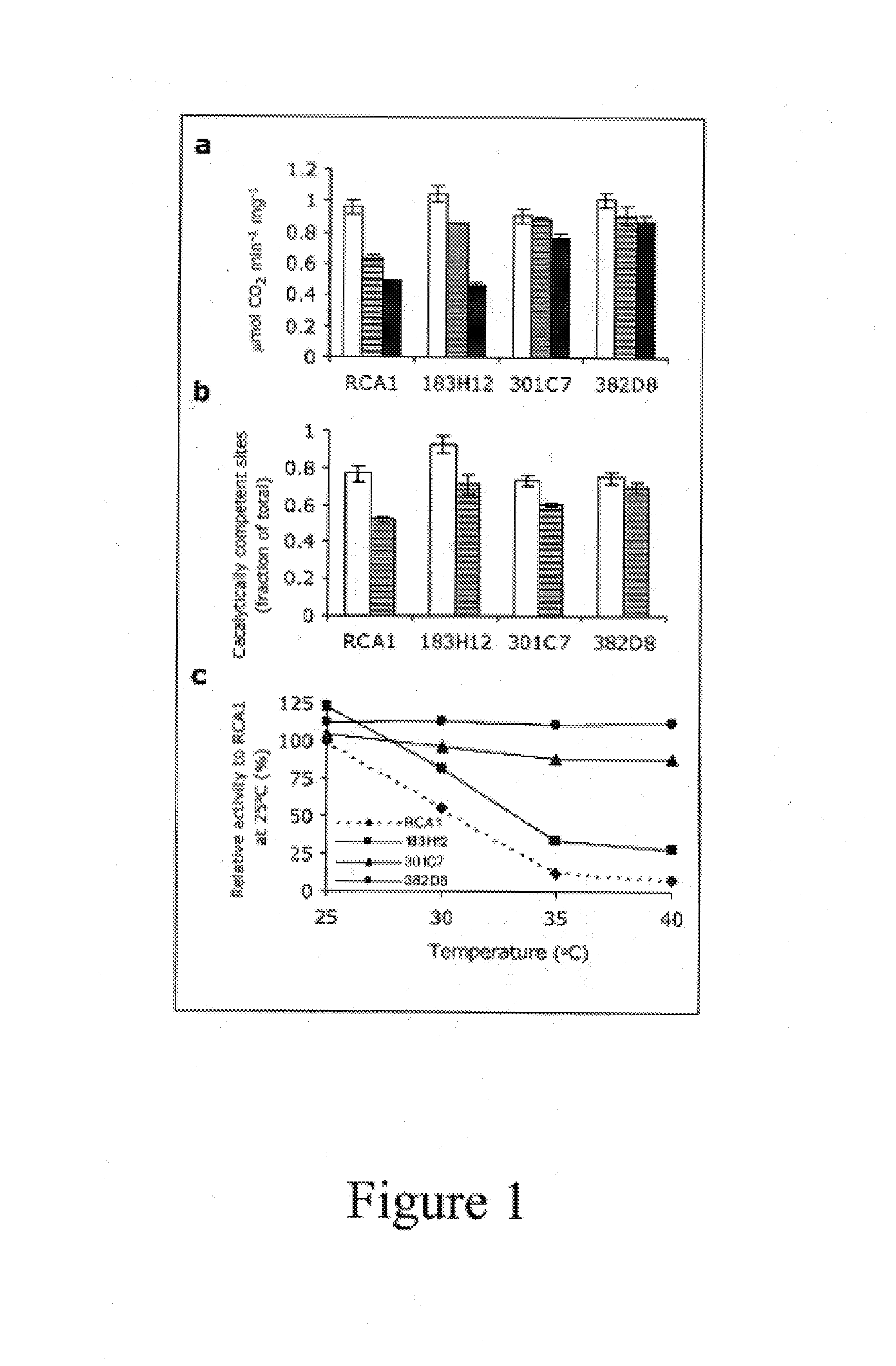
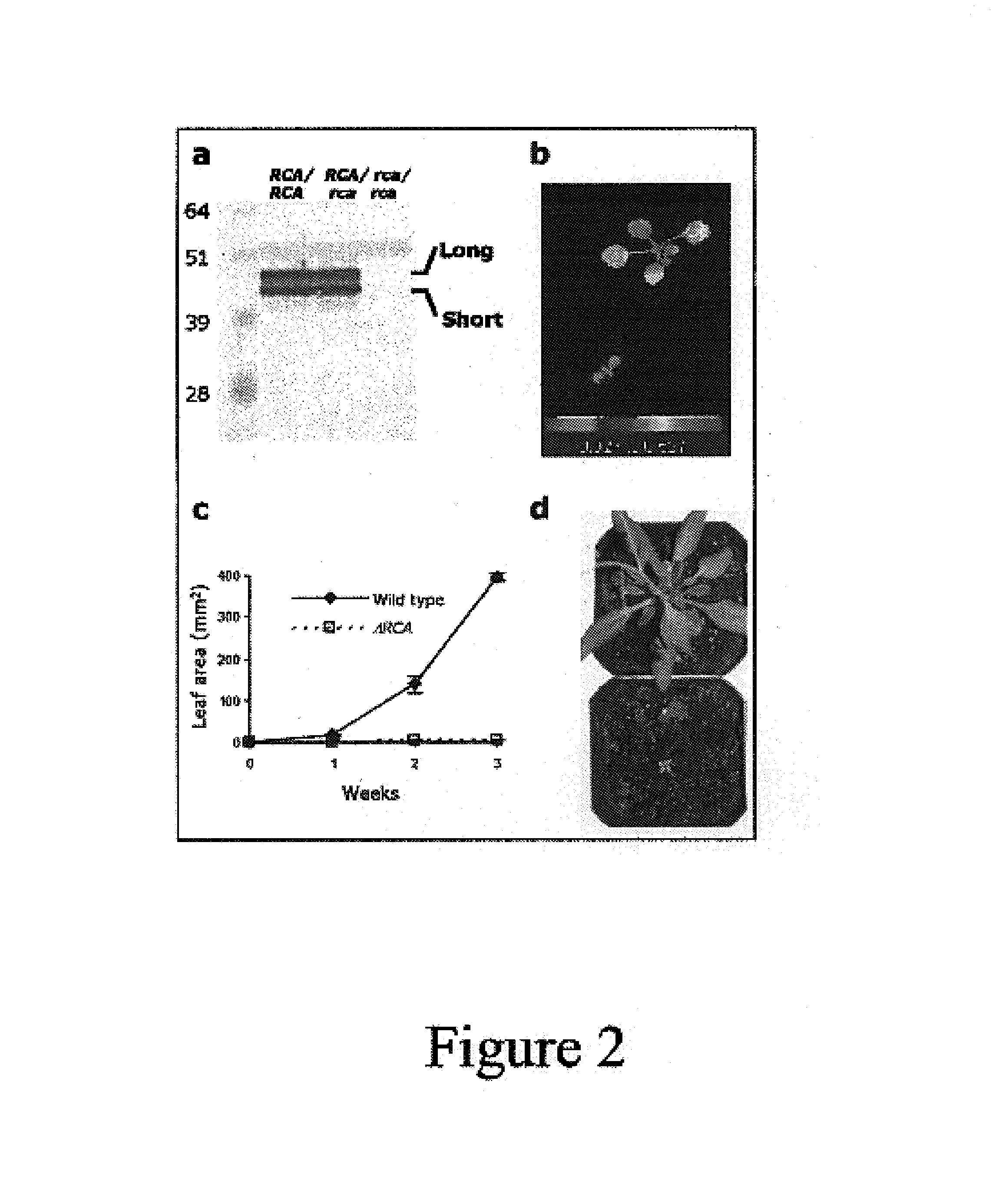
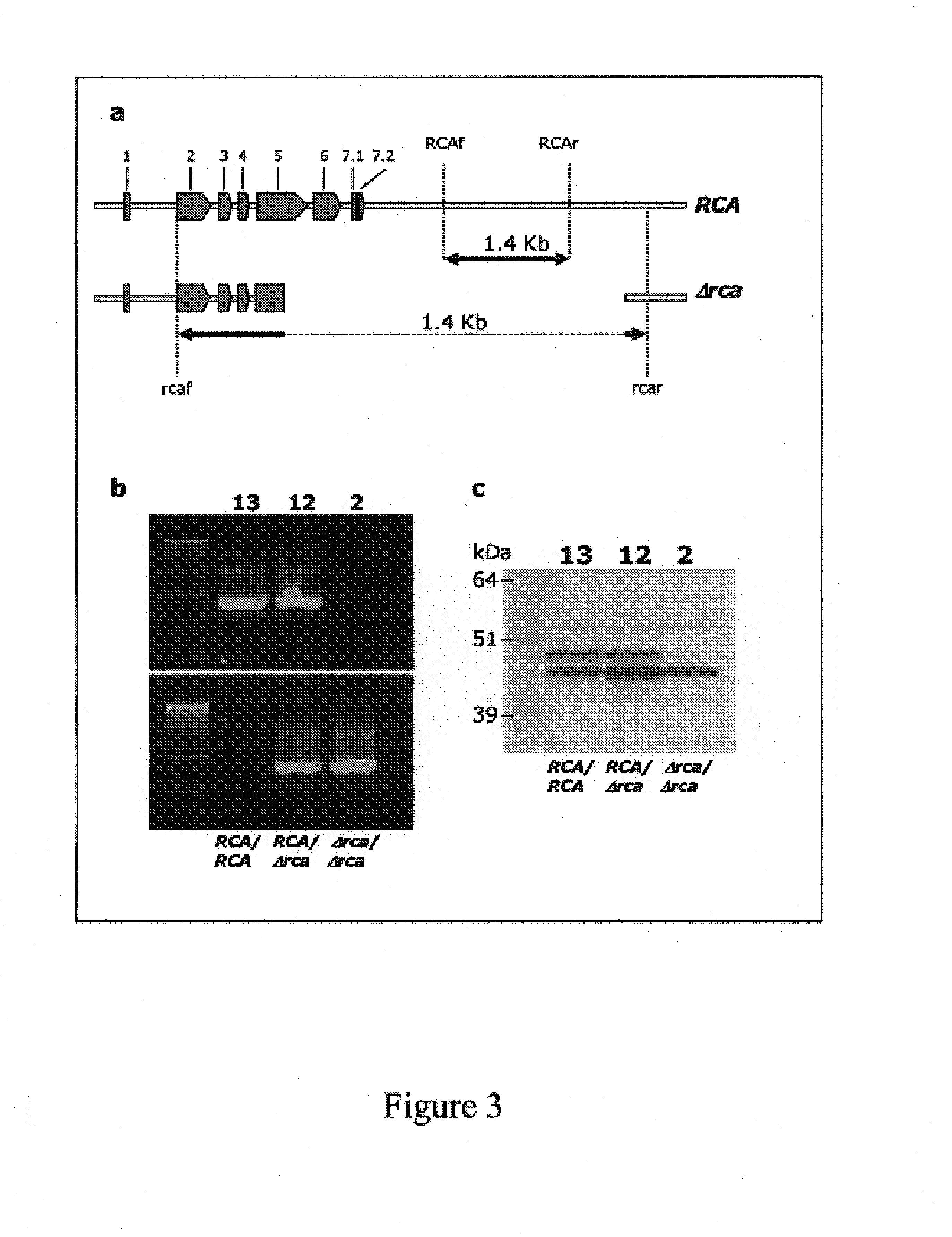
Rubisco activase with increased thermostability and methods of use thereof
The present invention provides thermostable polypeptides related to Arabidopsis Rubisco Activase polypeptides. Nucleic acids encoding the polypeptides of the invention are also provided. Methods for using the polypeptides and nuclei acids of the invention to enhance resistance of plants to heat stress are encompassed.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
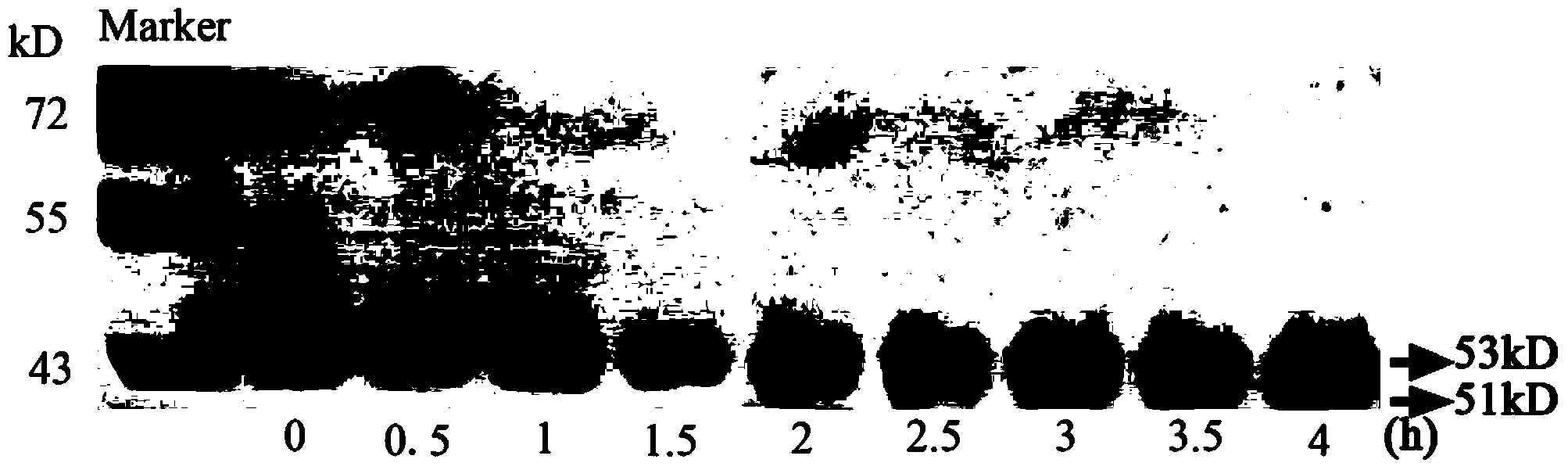
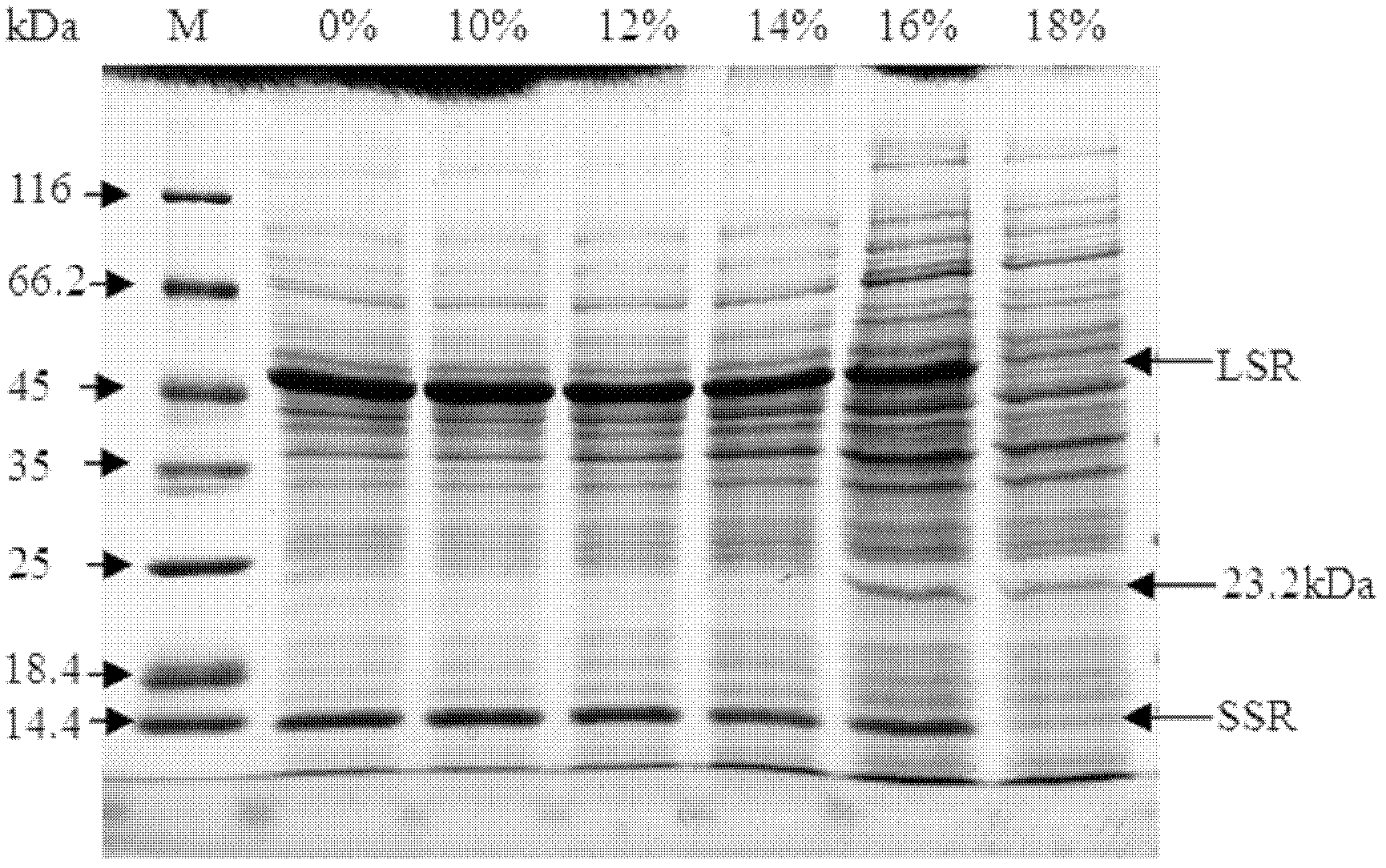
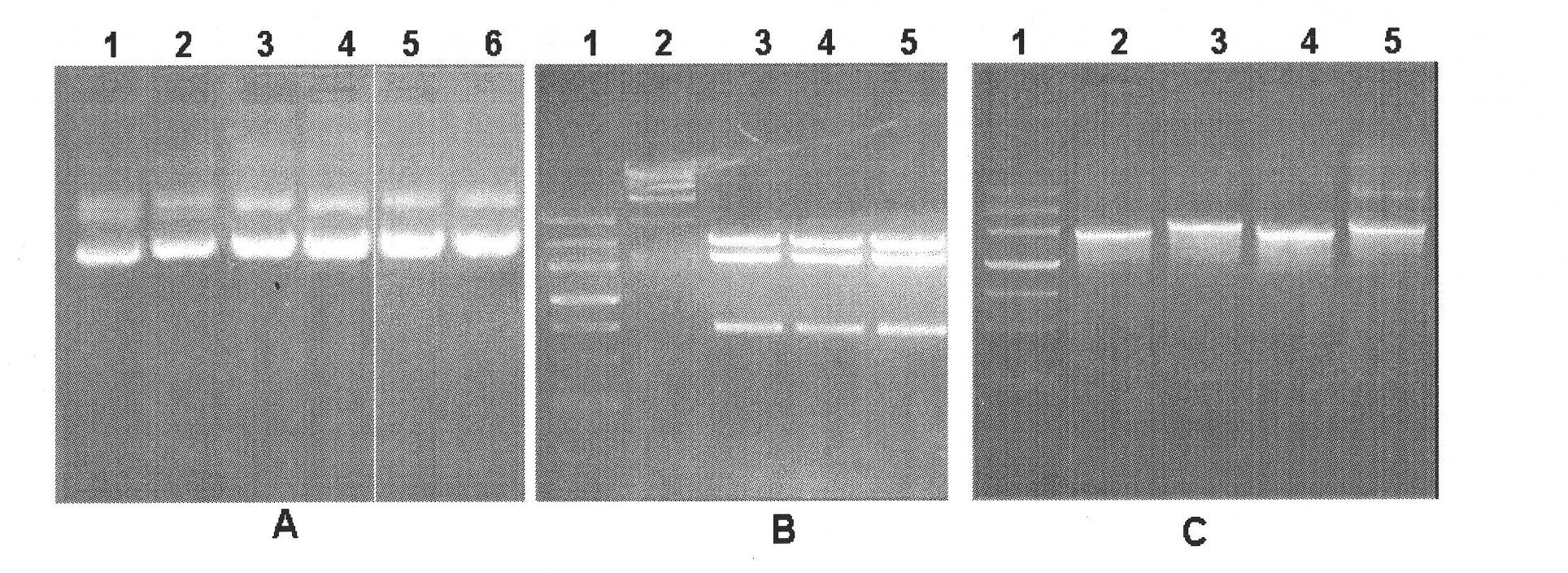
Electrophoresis method for removing Rubisco enzyme interference of watermelon leaves and separating residual low-abundance proteins
InactiveCN102584972AEfficient removalQuick removalPeptide preparation methodsPlant peptidesProtein spotSmall subunit
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and discloses an electrophoresis method for removing Rubisco from plant leaves and enriching and separating residual proteins. The method comprises the following steps of: removing Rubisco from watermelon leaves by using 18 percent PEG-4000; leaching residual proteins through a TCA-acetone precipitation method; and performing two-dimensional electrophoresis to separate residual proteins from watermelon leaves. Compared with a holoprotein two-dimensional electrophoretogram, the method has the advantages that: after Rubisco in watermelon leaves is precipitated by adopting the 18 percent PEG, most large and small subunits of Rubisco disappear, the expression levels of most residual proteins are raised, the quantity of proteins obtained by separating is increased by 48.4 percent, and a large quantity of new protein spots (65+ / -15) appear in a region of which the molecular weight is smaller than 25.0kDa. As proved by repeated experiments, the electrophoresis method has the advantages of high repeatability, clear spectra and reliable result.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Rubisco Activase with increased thermostability and methods of use thereof
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Plant expression vector for improving capability of assimilating and formaldehyde absorption of plant and application thereof
InactiveCN101629185AEnhanced efficiency of formaldehyde assimilationPromote absorptionVector-based foreign material introductionHigh concentrationWild type
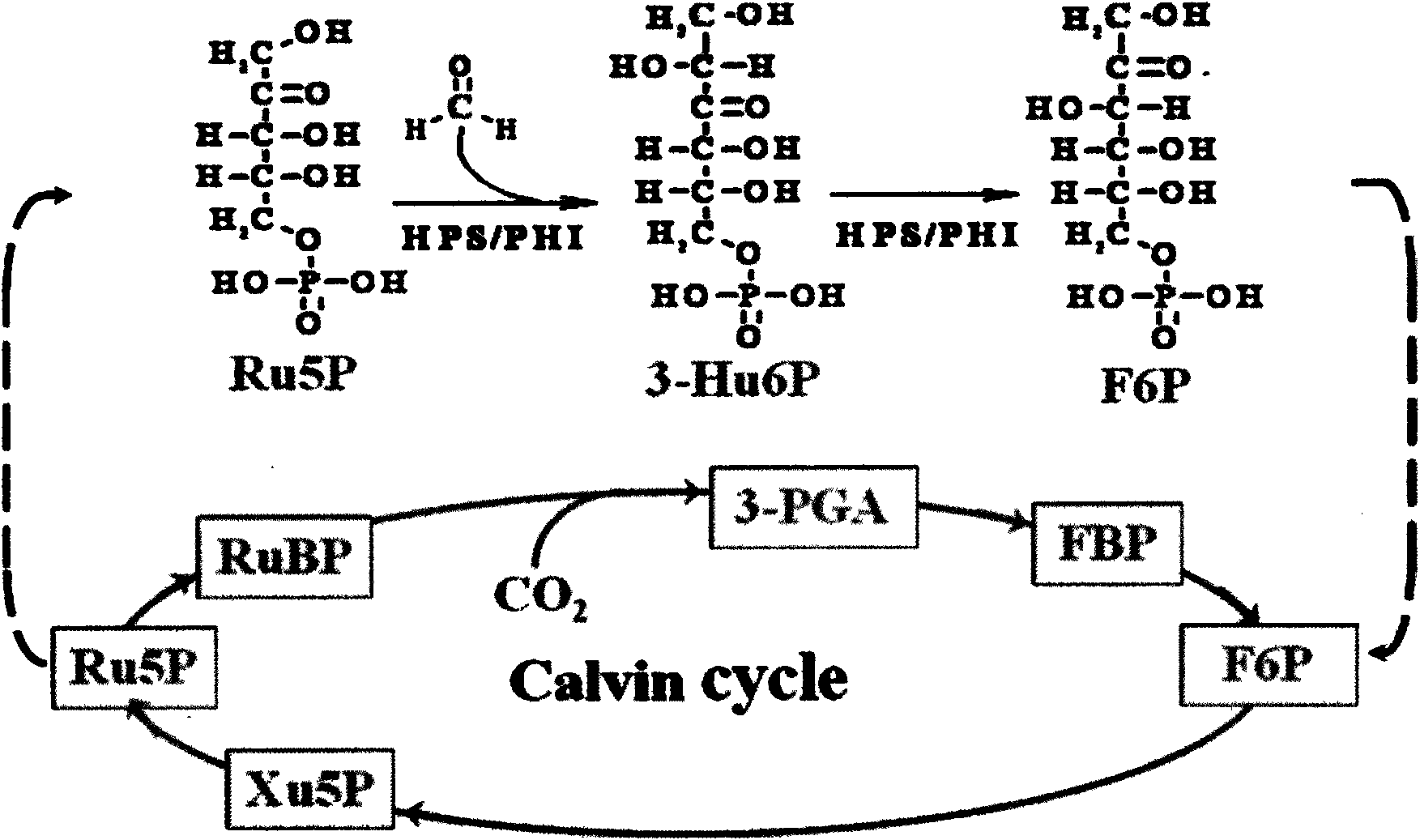
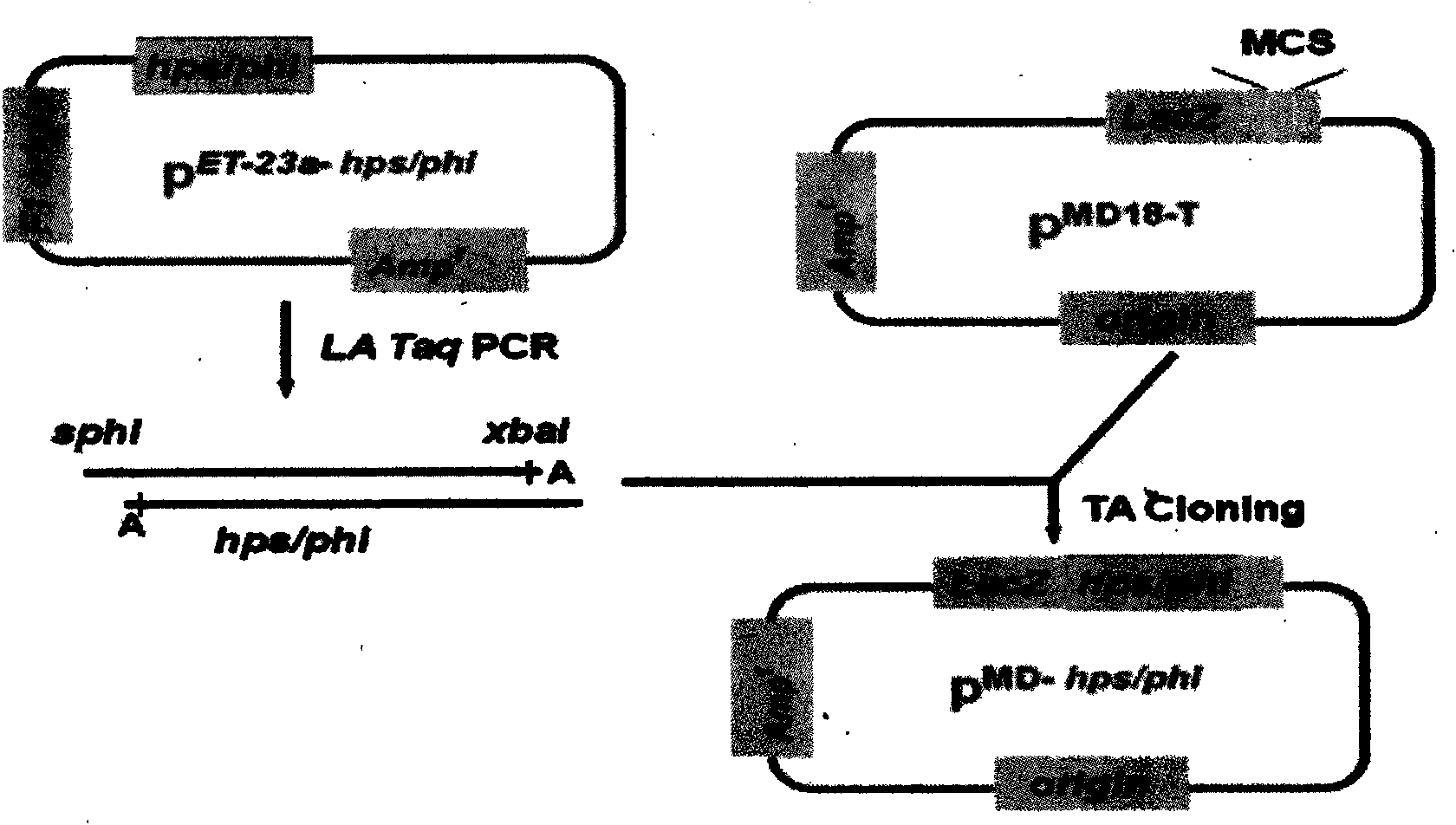
The invention discloses a plant expression vector pK2-35S-PrbcS-*T-hps / phi for improving the metabolic capability of assimilating and formaldehyde absorption of plants, and the plant expression vector is a plant expression vector of a bifunctional enzyme HPS / PHI gene formed by integrating a PrbcS containing a Rubisco 3C small subunit gene and a transfer peptide sequence thereof as well as 6-phosphonate hexulose synthetase and 6-osphofructose isomerase of Mycobacteriumgastri MB19. A procaryon expression vector pET-23a-hps / phi plasmid of HPS / PHI is used as a template and is amplified to acquire an hps / phi gene, and the PrbcS and a chloroplast transfer peptide are used for controlling the expression of the hps / phi gene in the chloroplast of plant leaves, thereby improving the capability of assimilating and formaldehyde absorption of the plants. An experiment indicates that the growing condition of transgenic plants is better than that of wild plants, and the transgenic plants have a lighter phenomenon of leaf chlorosis when the transgenic plants grow in the environments of high-concentration extrinsic gas and liquid formaldehyde. Transgenic plant leaves can completely eliminate the formaldehyde in 4mM of formaldehyde treatment fluid within 90 hours, but wild leaves have slower absorption efficiency, and 17 percent of formaldehyde still remains.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
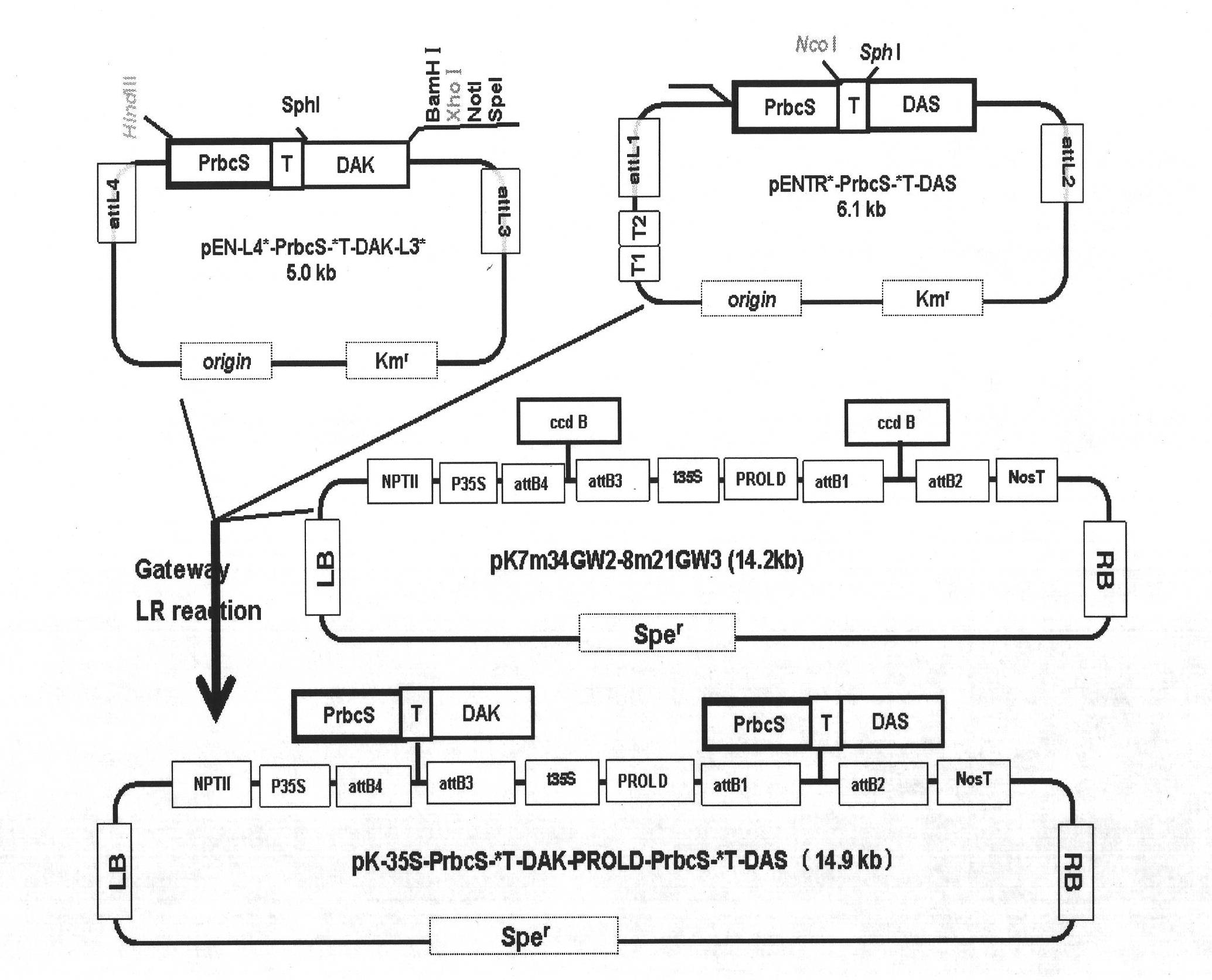
Plant expression vector constructed by dihydroxy acetone synthetase and dihydroxy acetone kinase gene expression cassette in series as well as construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN101838666AEnhanced efficiency of formaldehyde assimilationPromote absorptionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPichia pastorisDihydroxyacetone kinase
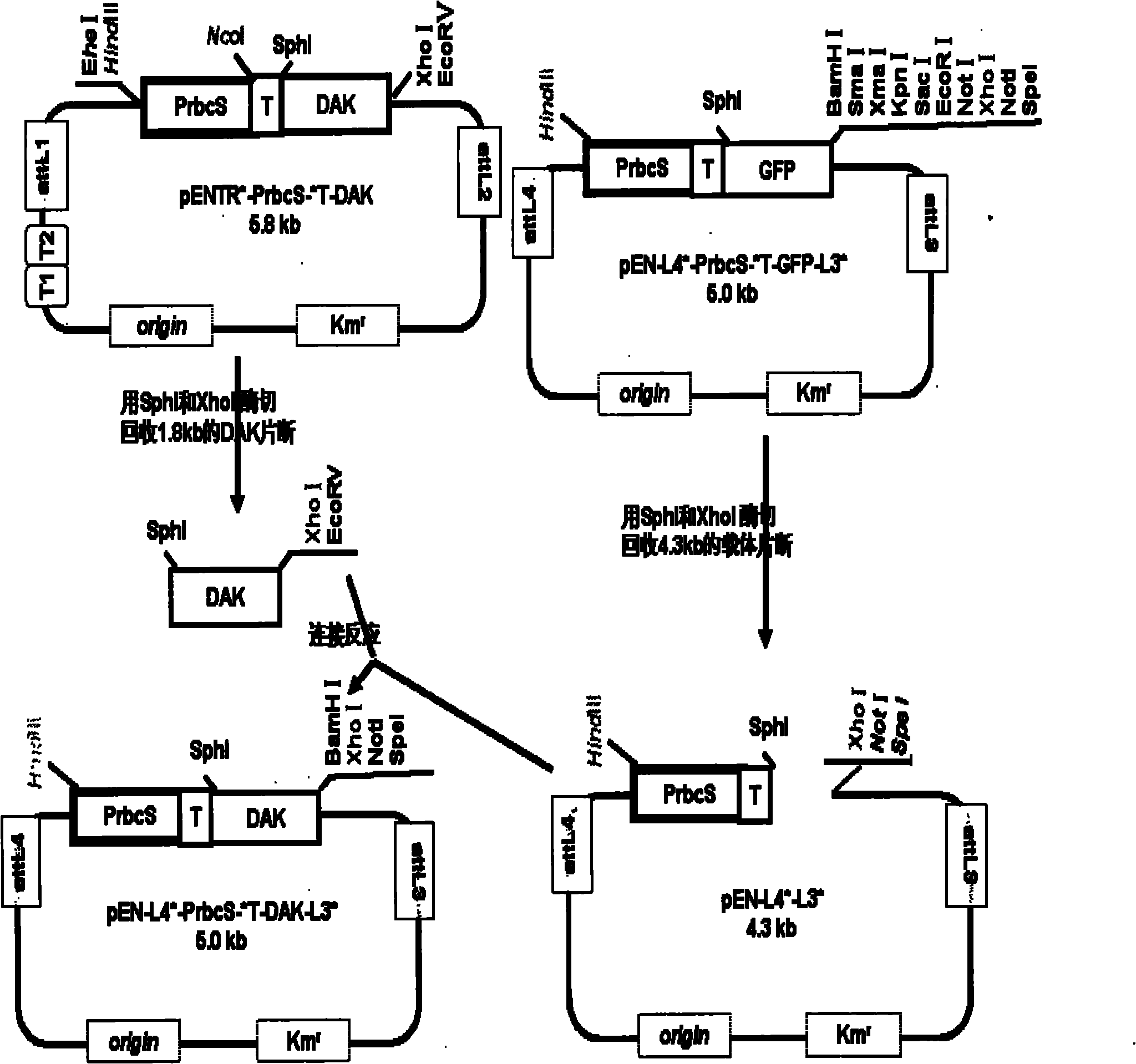
The invention particularly relates to a plant expression vector, namely pK-35S-PrbcS-*T-DAK-PROLD-PrbcS-*T-DAS, for improving the capability of assimilating and formaldehyde absorption of plants, as well as a construction method thereof and application thereof in improving the capability of absorbing and resisting exogenous formaldehyde of plants. The plant expression vector, namely pK-35S-PrbcS-*T-DAK-PROLD-PrbcS-*T-DAS, for improving the capability of assimilating and formaldehyde absorption of plants is formed by an optical inducible promoter (PrbcS) containing a tomato 1,5 ribulose diphosphate carboxylase (Rubisco) 3C small subunit gene and a transfer peptide sequence (*T) thereof, a dihydroxy acetone synthetase (DAS) gene of candida boidinii and a dihydroxy acetone kinase (DAK) gene (two genes) of Pichia pastoris. The conversion operation of both the DAS gene and the DAK gene can be completed by performing a conversion test by using the vector for one time.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Enhanced carbon fixation in photosynthetic hosts
InactiveUS20130145495A1Increase growth rateIncrease biomassAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFermentationBiotechnologyBiochemistry
This invention provides genetically modified photosynthetic organisms and methods and constructs for enhancing inorganic carbon fixation. A photosynthetic organism of the present invention comprises a RUBISCO fusion protein operatively coupled to a protein-protein interaction domain to enable the functional association of RUBISCO and carbonic anhydrase.
Owner:DONALD DANFORTH PLANT SCI CENT
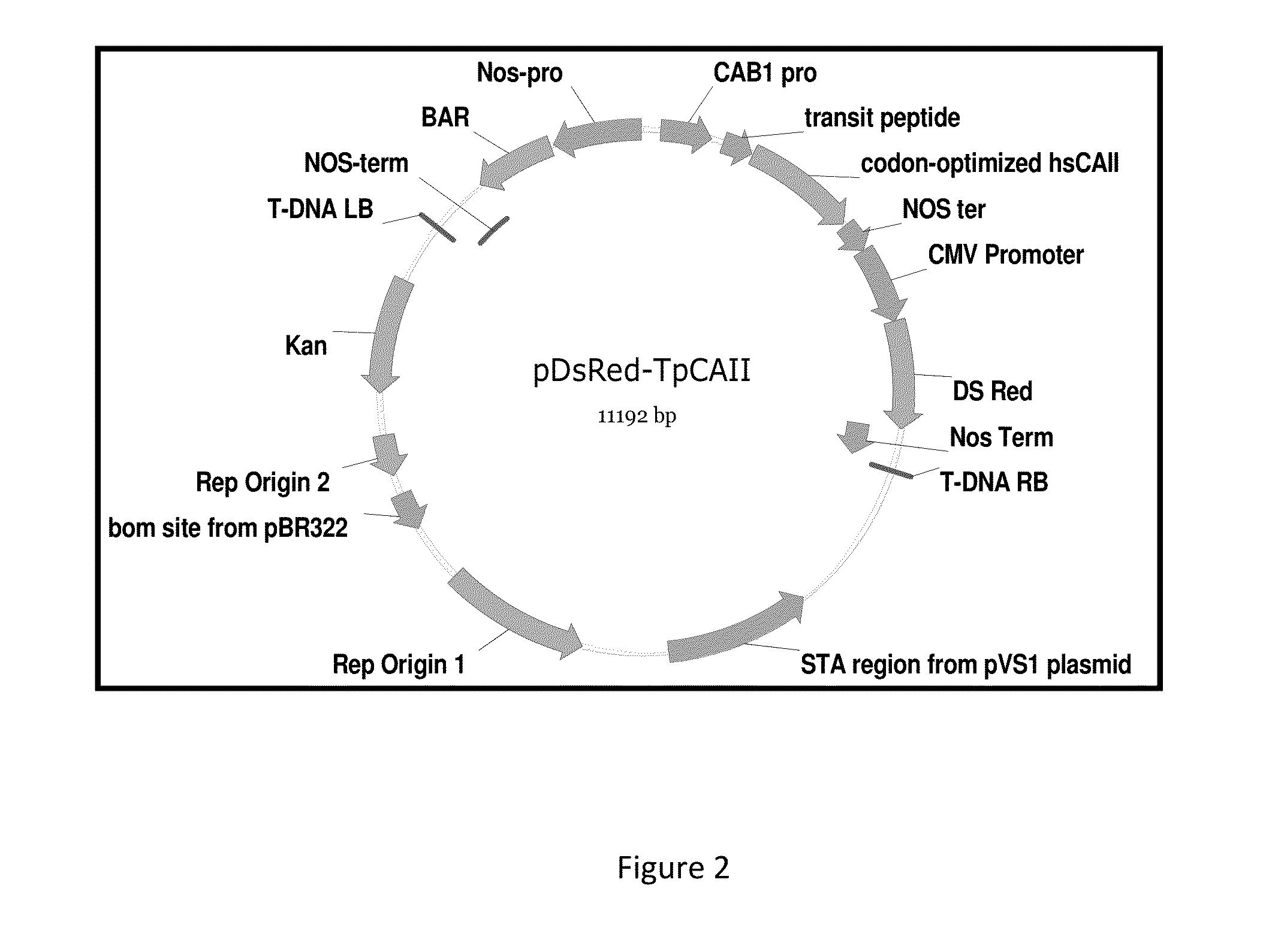
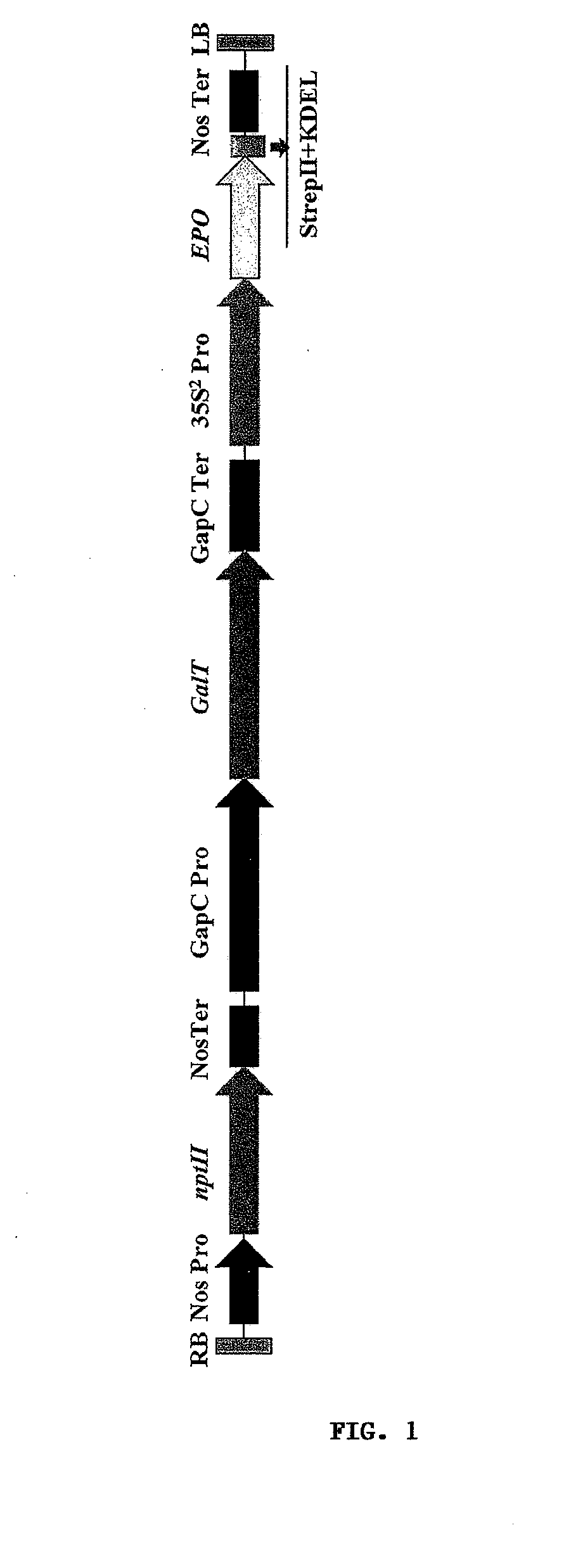
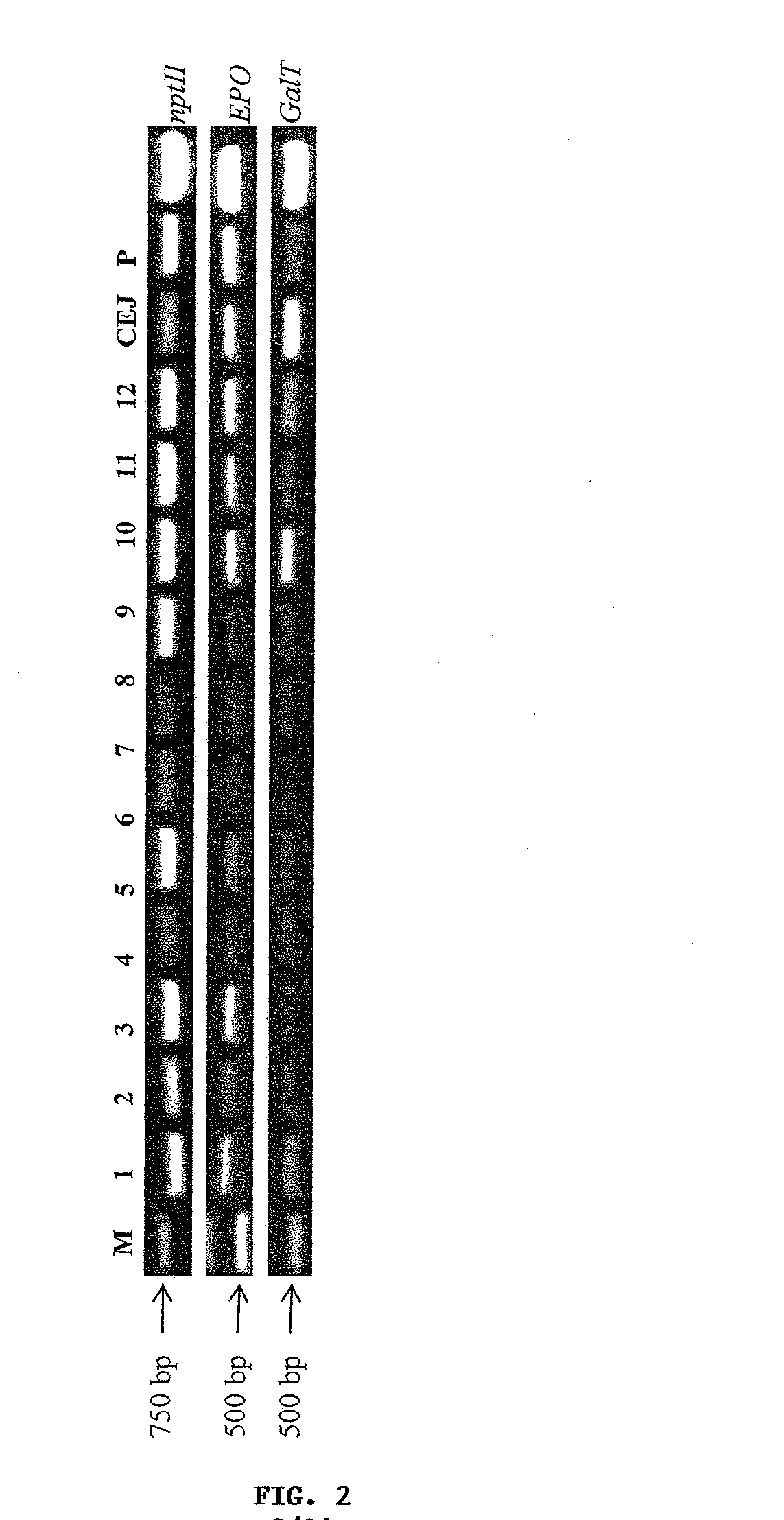
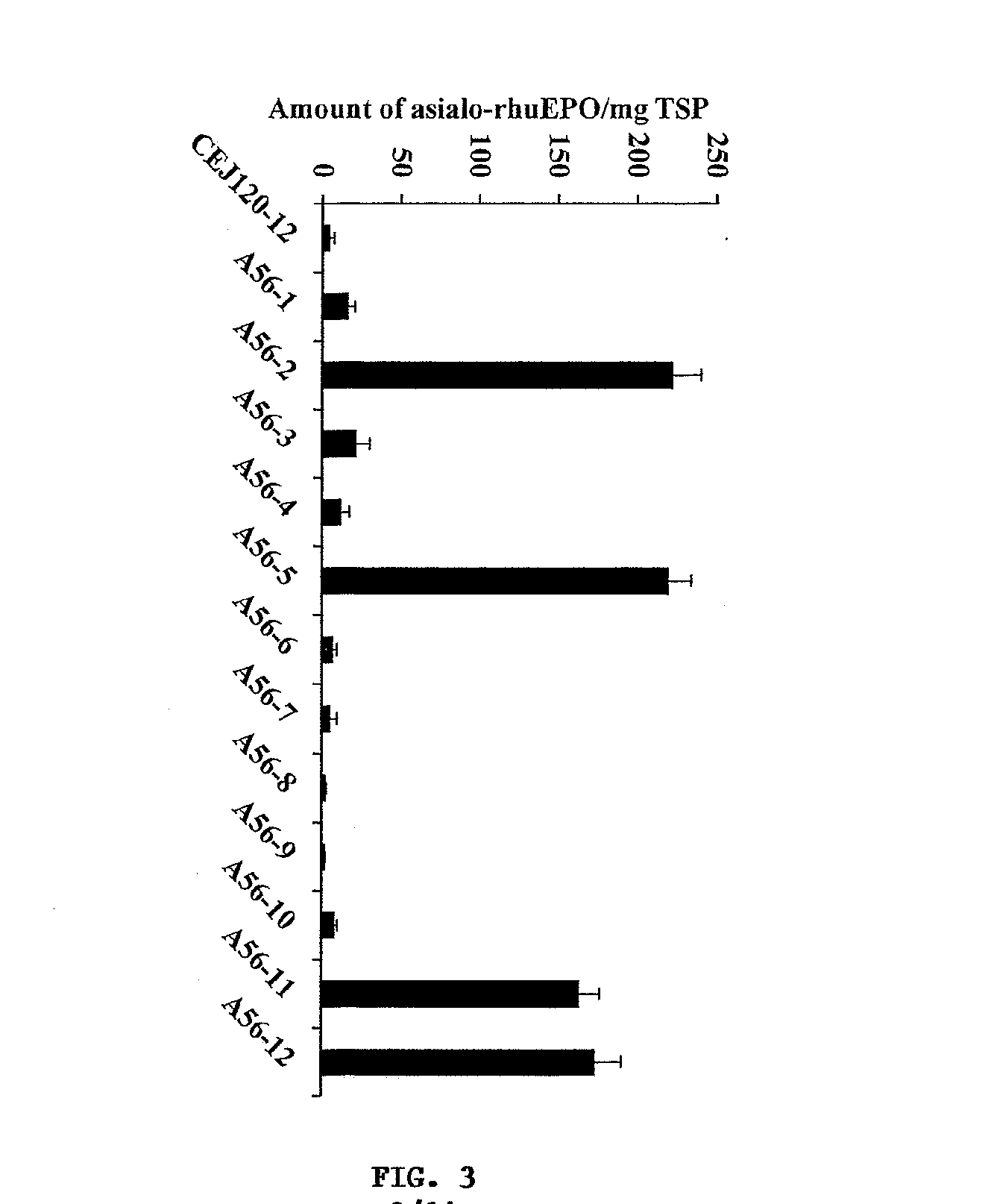
Methods for the production of cytoprotective asialo-erythropoietin in plants and its purification from plant tissues
PendingUS20150119325A1Improve the level ofEasy to producePeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsNucleotidePlant cell
The present invention provides methods for the high-level production of recombinant human erythropoietin (rhuEPO) derivative, asialoerythropoietin (asialo-rhuEPO), in plants. The methods for producing asialo-rhuEPO comprise making a plant or at least one plant cell that comprises a promoter that drives expression in a plant cell operably linked to a polynucleotide encoding a human erythropoieting fusion protein and a promoter that drives expression in a plant cell operably linked to a polynucleotide encoding N-glycosylation modification enzyme, particularly a mammalian β1,4-galactosyltransferase. The present invention further provides plants, plant cells, and seeds that have been genetically modified to produce high levels of asialo-rhuEPO. Additionally, provided are methods for purifying asialo-rhuEPO from plant tissues. Such methods comprise removing chlorophyll and / or RuBisCO protein from an aqueous extract of plant tissue comprising asialo-rhuEPO, binding the asialo-rhuEPO in the extract to an immune affinity column, and eluting the bound asialo-rhuEPO from immune affinity column.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA CENTRAL UNIVERSITY
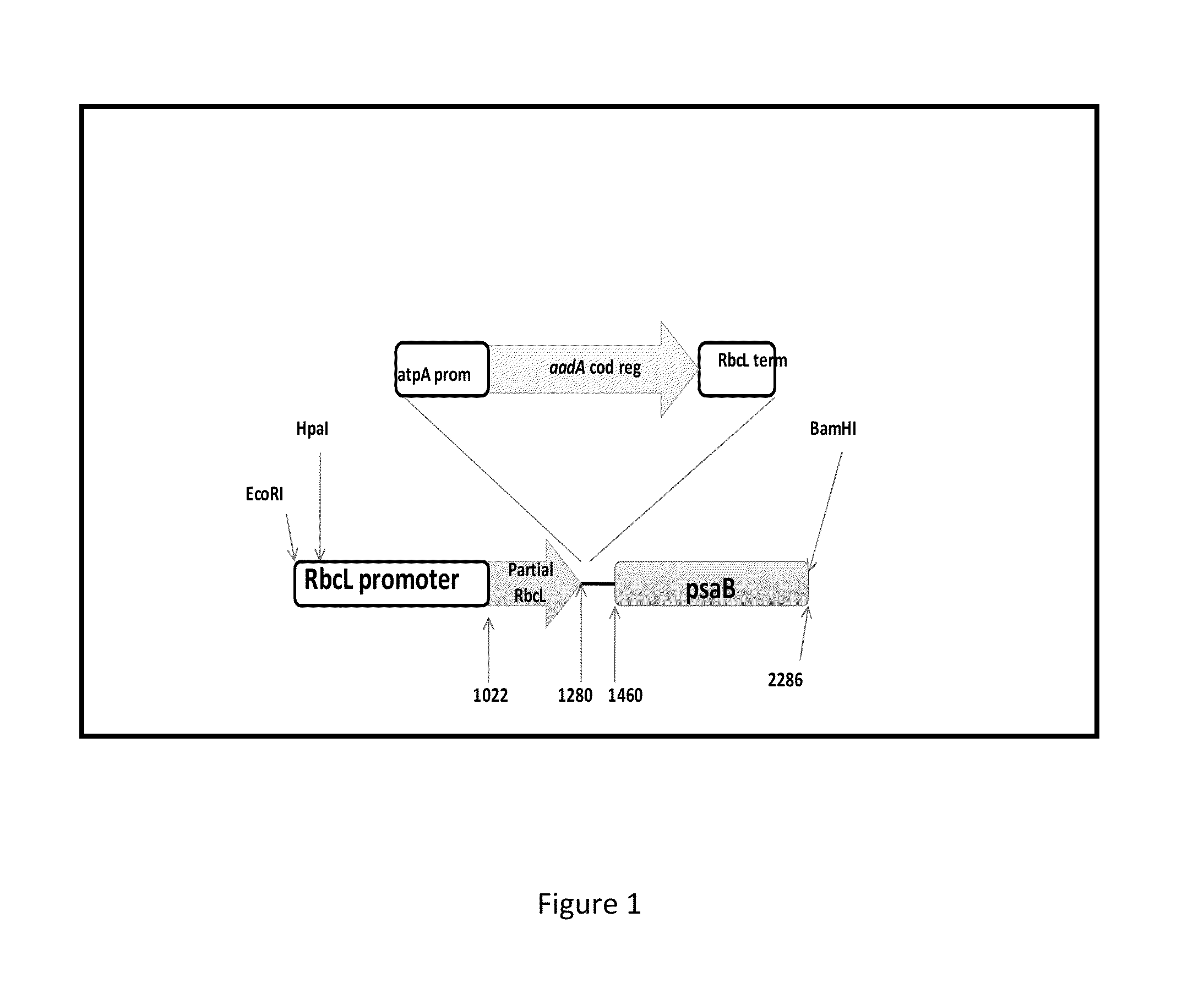
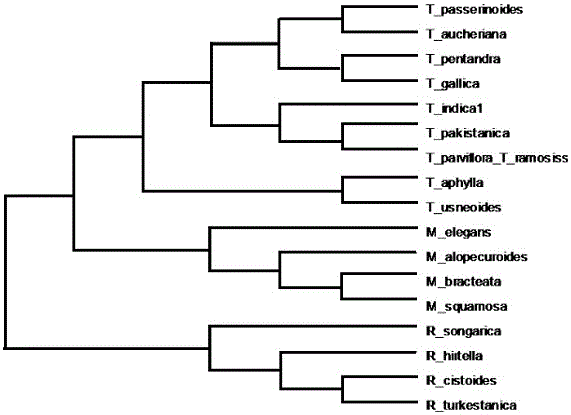
Method for detecting adaptive evolution and structural modeling of rbcL genes of tamaricaceae plants
InactiveCN106021976AReduce hydrophobicityReduce entropySystems biologySpecial data processing applicationsPositive selectionBranch site
A method for detecting adaptive evolution and structural modeling of rbcL genes of tamaricaceae plants comprises steps as follows: acquisition of rbcL gene sequences of the tamaricaceae plants; pedigree analysis and adaptive site detection of 17 species of the tamaricaceae plants; Rubisco structural simulation and selective site analysis of the tamaricaceae plants. The rbcl genes of tamaricaceae covering three genera and 17 species are taken as objects, a branch-site model is taken as a model, the genes have three positive selection sites in the amino acid level according to detection, and the selective sits are remarkably related with hydrophobicity and entropy for maintaining protein and are also related with the concentration of global CO2. Besides, the adaptability of tamaricaceae plants to the drought environment is related with adaptive evolution of the rbcL genes.
Owner:COLD & ARID REGIONS ENVIRONMENTAL & ENG RES INST CHINESE
Method, primer and probe for quantitative detection of transgenic maize IE034 in fodder based on ddPCR and application
InactiveCN107937595AAchieve specific amplificationImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenomic DNARuBisCO
The invention discloses a method, a primer and a probe for quantitative detection of transgenic maize IE034 in a fodder based on ddPCR and application and relates to the technical fields of molecularbiology and transgenic test. The primer comprises exogenous gene Cry1Ie primers, and the probe comprises reference gene rubisco probes. The method comprises the following steps: (1) extracting genomicDNA of a fodder sample; (2) utilizing the specific primers and probes of exogenous genes Cry1Ie and reference genes to perform ddPCR amplification on the diluted genomic DNA; and (3) detecting and analyzing a PCR product. The method does not depend on a standard curve, is not influenced by a PCR inhibitor or the PCR amplification efficiency, has higher sensitivity and stability compared with conventional PCR, can accurately and quantitatively detect the copy number concentration of a transgene in the fodder, and can quantitatively analyze the transgenic maize IE034 in the fodder.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MINIST OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT OF THE PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA
Construction method and applications of carrier with chlamydomonas endogenous gene knocked out and exogenous gene expressed
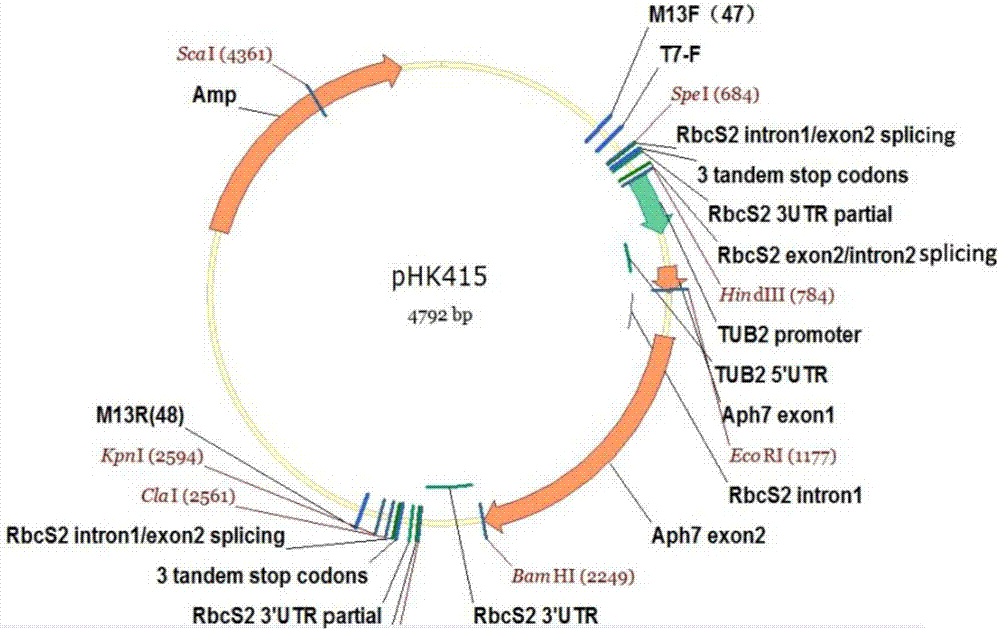
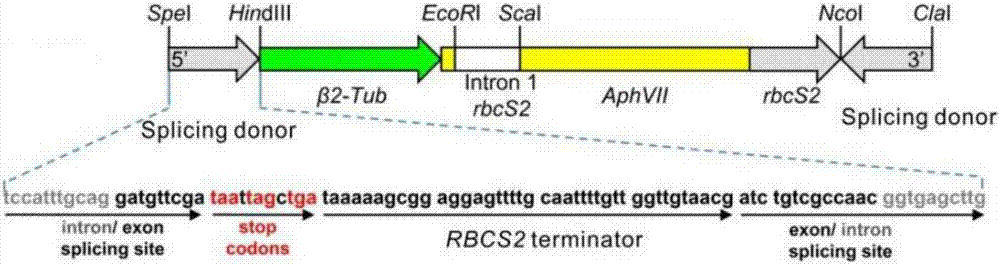
The invention provides a construction method and applications of a carrier with a chlamydomonas endogenous gene knocked out and an exogenous gene expressed. The carrier comprises a hygromycin resistance maker gene, wherein a splicing donor sequence (TCCATTTGCAG / GATGTTCGA) from the RubisCO gene, three termination codons in tandem duplication, and one transcription terminator are arranged at each of two ends of the maker gene. For the carrier, a 1.9kb fragment generated by Spel I and Cla I double digestion is adopted for carrying out electric shock for transforming chlamydomonas reinhardtii cells, an insertion carrier becomes one part of mRNA even if the carrier is inserted into the chlamydomonas gene intron, and genetic transcription stops at the three termination codons in tandem duplication and the transcription terminator. Compared with the 2.6kb AphVIII insertion carrier without SIS, the newly constructed carrier has the improved mutant transcription termination efficiency.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA +1
Nutrient solution for improving photosynthesis of oil peony
InactiveCN105399492APromote growthPromotes morphogenesisFertilizer mixturesSalicylic acidAlpha-amylase
The invention discloses a nutrient solution for improving photosynthesis of oil peony. The nutrient solution is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 3-5 parts of salicylic acid, 120-140 parts of rice bran, 4-6 parts of humic acid, 1.1-1.3 parts of trypsase, 37-43 parts of peanut cake powder, 40-45 parts of vinegar residues, 0.8-1.0 part of alpha amylase, 12-15 parts of water glass, 5-6 parts of sodium borate, 150-170 parts of bred maggots and an appropriate amount of water. The nutrient solution disclosed by the invention is used for performing treatments of irrigating, spraying or soaking plant and oil peony tissues and seeds, and can effectively promote the growth and morphogenesis of the oil peony and accelerate germination of the seeds, and meanwhile, the added salicylic acid, humic acid and water glass act together to change ultra microstructures of leaves of the oil peony, increase the content of chlorophyll and enhance the activity of Rubisco carboxylase, thereby improving the photosynthesis of the oil peony and achieving significant promotion effect on the growth of plants.
Owner:ANHUI YUMIN ECOLOGICAL AGRI
Novel rubisco promoters and uses thereof
The present invention is related to a family of novel spatiotemporally active Rubisco promoters (SEQ ID NO: 1, 2, 3) obtainable from light grown Brassica seedlings. Furthermore the invention is related to transgene expression in specific plant organs or at specific stages of plant development. DNA constructs and expression cassettes comprising at least one of the promoter sequences functionally fused in frame with genes encoding desired gene products are disclosed. Seeds from transformed homologous and herterologous plants and from subsequent generation of the transformed plants are collected and used for efficient production of desired gene products, especially in contained conditions.
Owner:UNICROP LTD
Thermostable rubisco activase complexes
ActiveUS20180037904A1Improve heat resistanceIncrease ratingsMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseOxygenase
Owner:MACQUARIE UNIV
Reagent for removing nonspecific hybridization of western blot
The invention relates to a reagent for removing nonspecific hybridization of western blot. The invention discloses a method for removing a background of the western blot, belonging to an innovative experiment technology of the field of biological scientific research. The method mainly utilizes a competitive antergic principle to remove or weaken the deep background or the nonspecific hybridization of the western blot due to high-abundance protein in the experimental process of the western blot, and the deep background or the nonspecific hybridization of the western blot can cause the phenomenon that an experimental result has deviation or the expression difference of a target gene in protein levels cannot be really reflected. A recombinant protein is utilized to build a RuBisCo-out kit, the experimental background can be significantly removed or weakened, and therefore the protein expression profiling of the target gene in the different growth stages and different organizational structures of plants can be reflected well.
Owner:BEIJING PROTEIN INNOVATION
Multifunctional and broad-spectrum active enzyme biological leaf fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105080026ABroad spectrum functionNot easy to loseBiocidePlant growth regulatorsActive enzymePeroxidase
The invention discloses active enzyme biological leaf fertilizer. The active enzyme biological leaf fertilizer is mainly composed of first bacteria (Arthrobacter sclerromae Huang et al.ACCC02953) generating peroxidase, second bacteria (Aurantimonas altamirensis juradoet al.ACCC01098) generating peroxidase, first fungi (moniliforme Sheldon ACCC30175) generating laccase, second fungi (Penicillium citrinum Thom penicillium citrinum ACCC30485) generating laccase, first actinomycetes (Streptomyces laurentii Trejo et al with the original number of CAH3.NAECC1210) generating tyrosinase, second actinomycetes ('Streptomyces jingyangensis'Tao et al.ACCC40021) generating tyrosinase, and enzymes Rubisco. By means of the leaf fertilizer, hazardous chemical substances on the surfaces of crops can be eliminated, toxin transferred into human bodies and fruit tissue can be blocked, contaminated crops containing toxin can be restored to the original non-toxic state, and soil containing toxic substances can be restored to the original non-toxic state. Meanwhile, the effect of increasing the yield of the crops is achieved.
Owner:段一皋 +1
Application of Escherichia coli molecular chaperone GroEL/ES in synergic synthesis of plant Rubisco
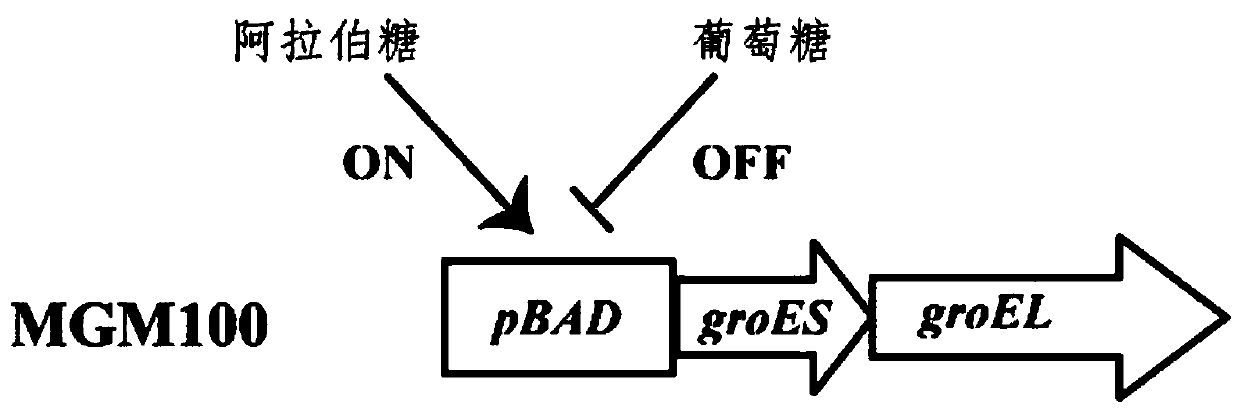
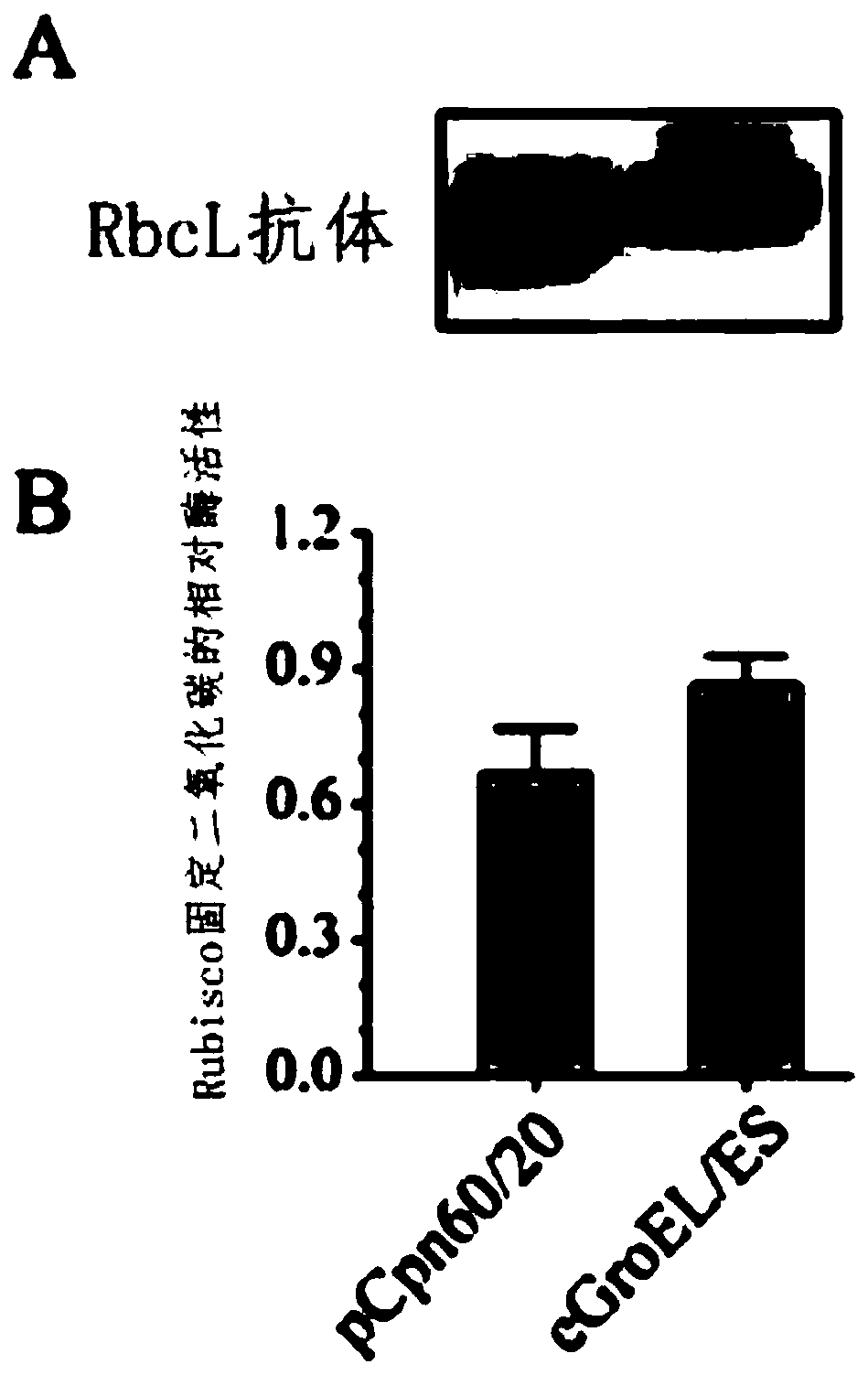
ActiveCN110734480ASimplified in vitro synthesis systemAvoid dependenceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnterobacterialesRuBisCO
The invention discloses application of Escherichia coli molecular chaperone GroEL / ES in synergic synthesis of plant Rubisco. The invention firstly discloses application of relevant biological materials of the Escherichia coli molecular chaperone GroEL / ES in biosynthesis of the plant Rubisco; and the Escherichia coli molecular chaperone GroEL / ES consists of GroEL protein and GroES protein. The invention further discloses a method for biologically synthesizing the plant Rubisco. A system for synthesizing arabidopsis Rubisco in an Escherichia coli MGM100 strain by using the Escherichia coli molecular chaperone GroES / EL and a plant molecular chaperone as a molecular chaperone system is constructed, the arabidopsis Rubisco can be effectively synthesized, the synthesis system of the arabidopsisRubisco is simplified, and convenience is provided for subsequent modification of Rubisco.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com