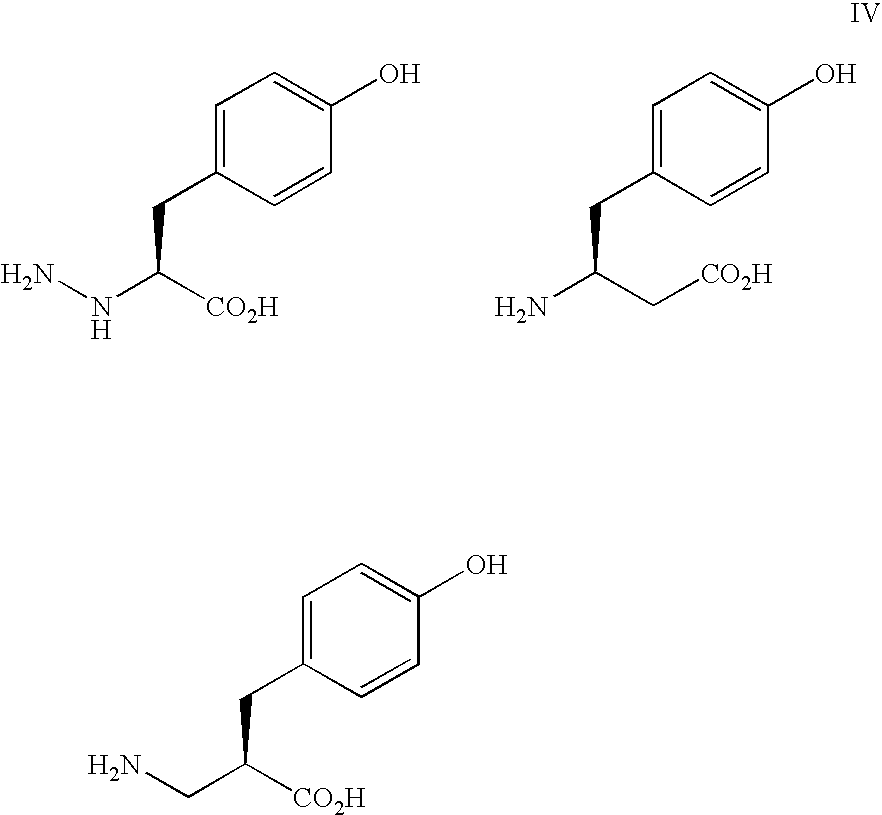
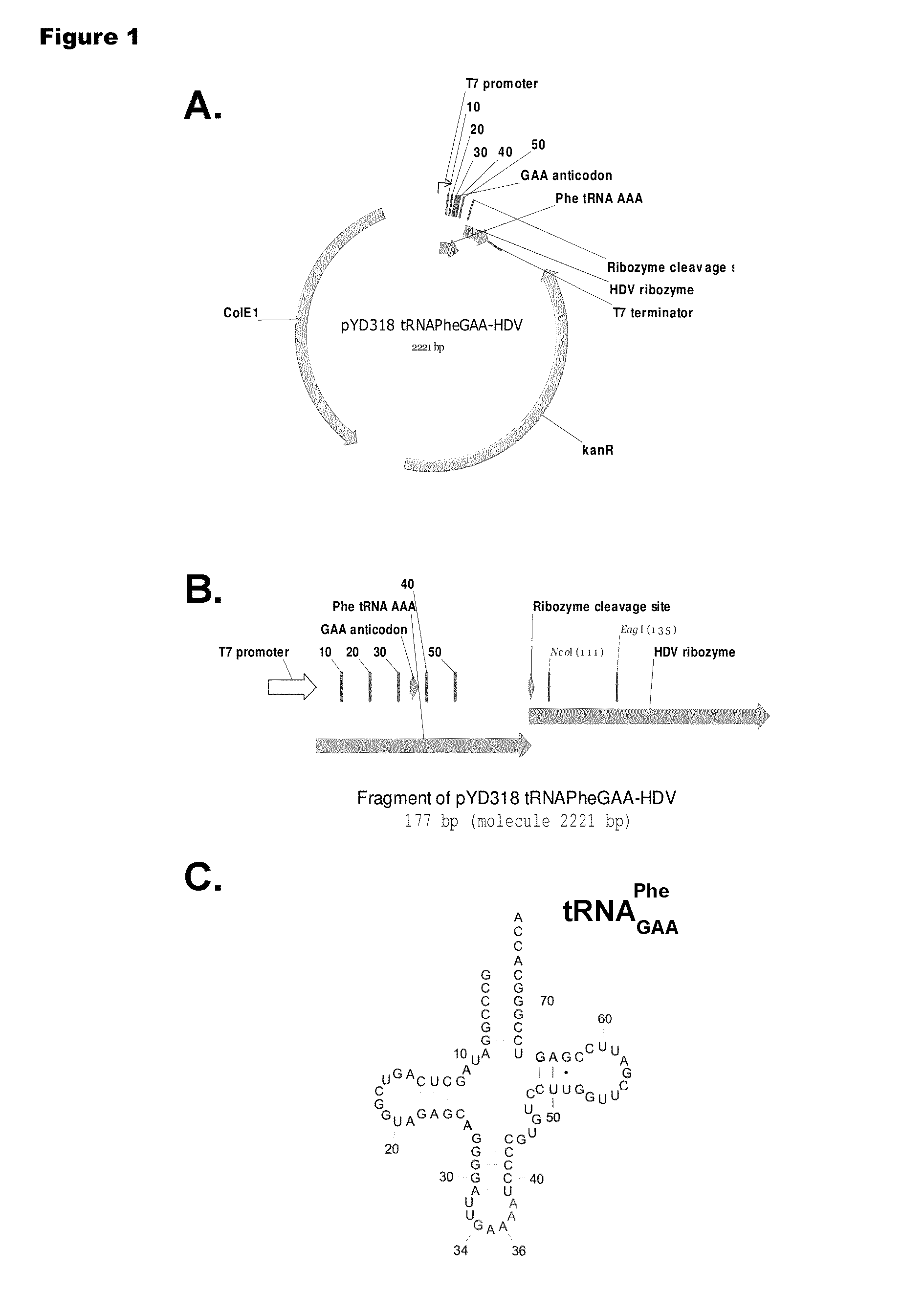
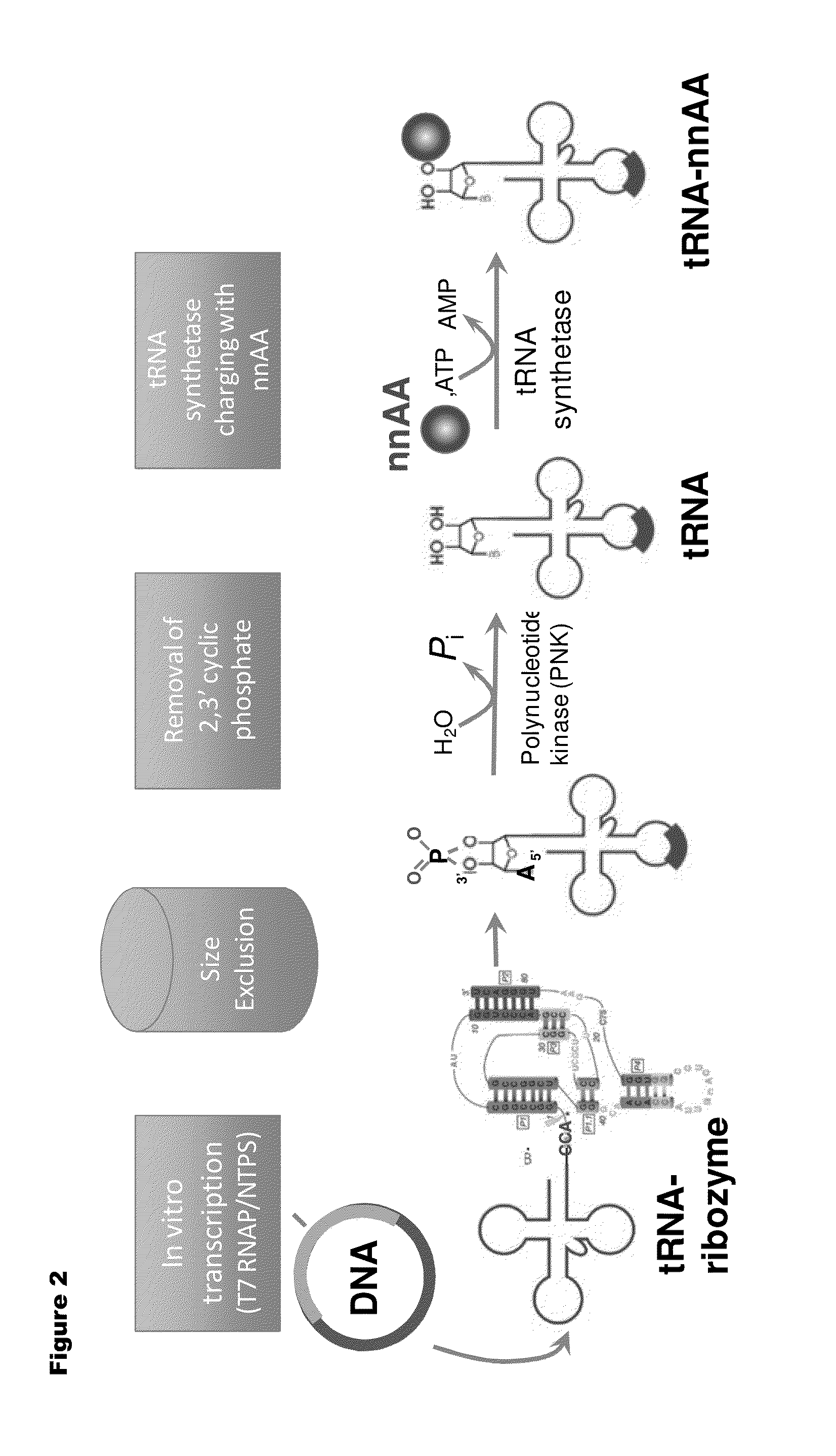
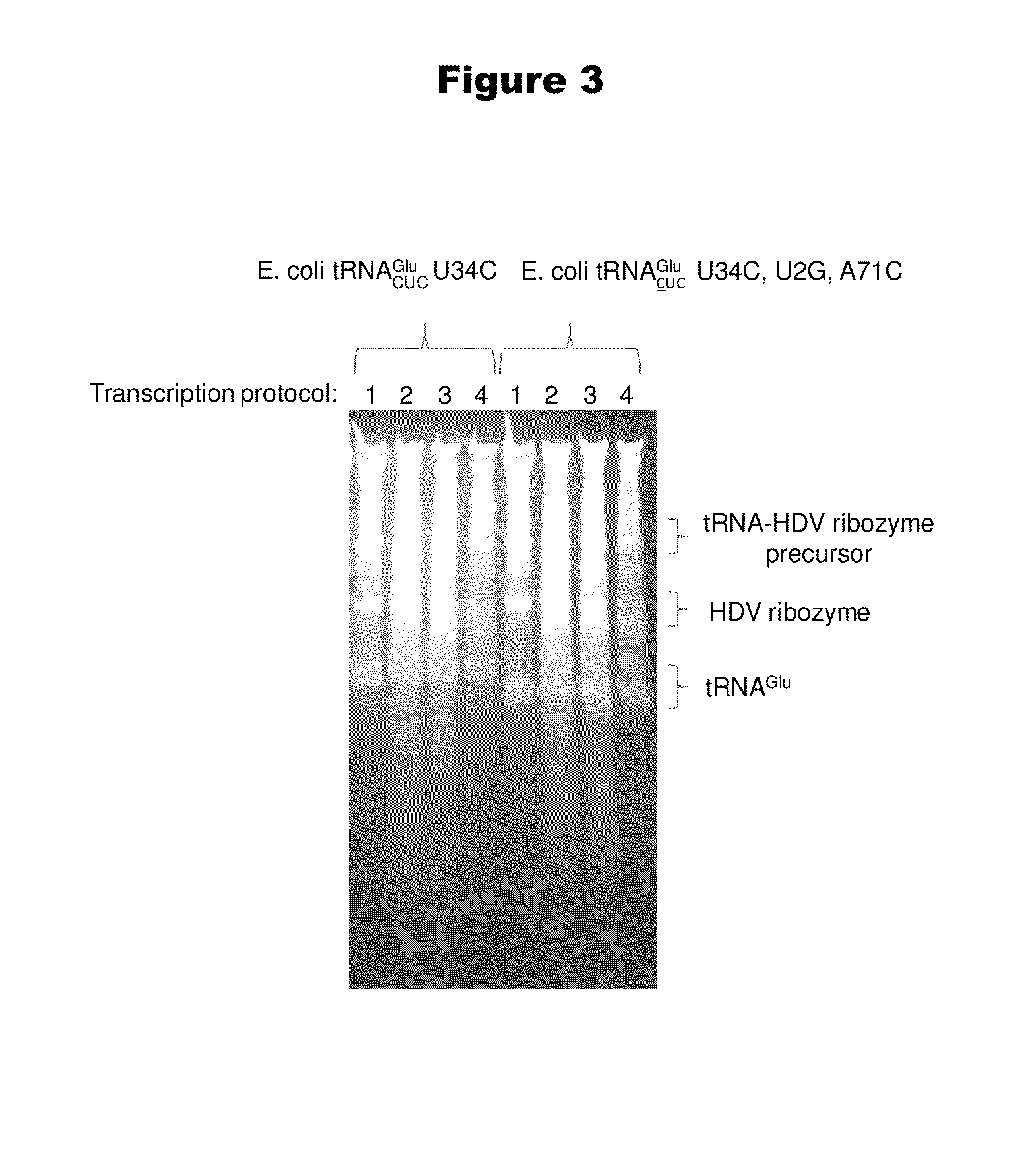
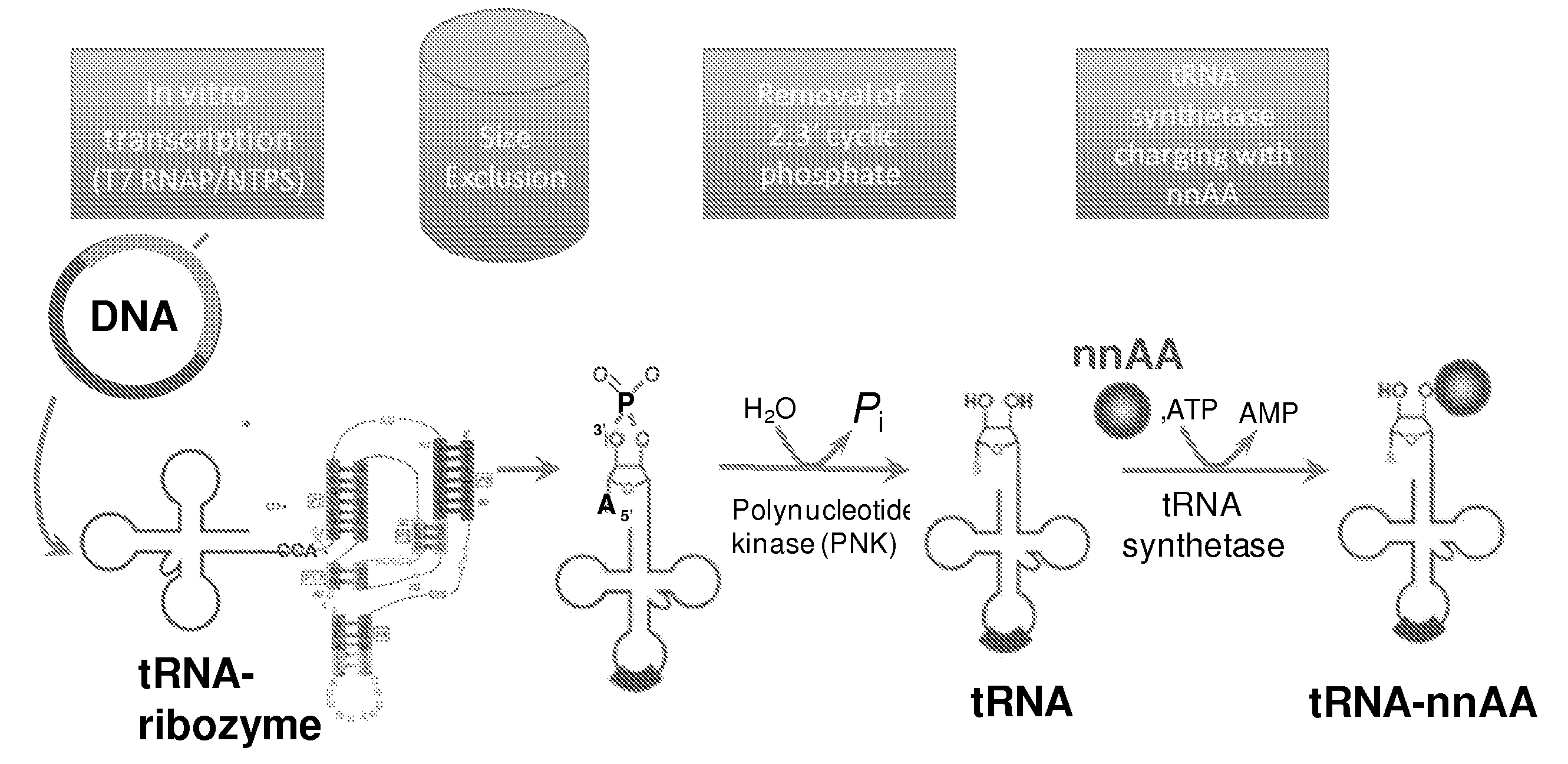
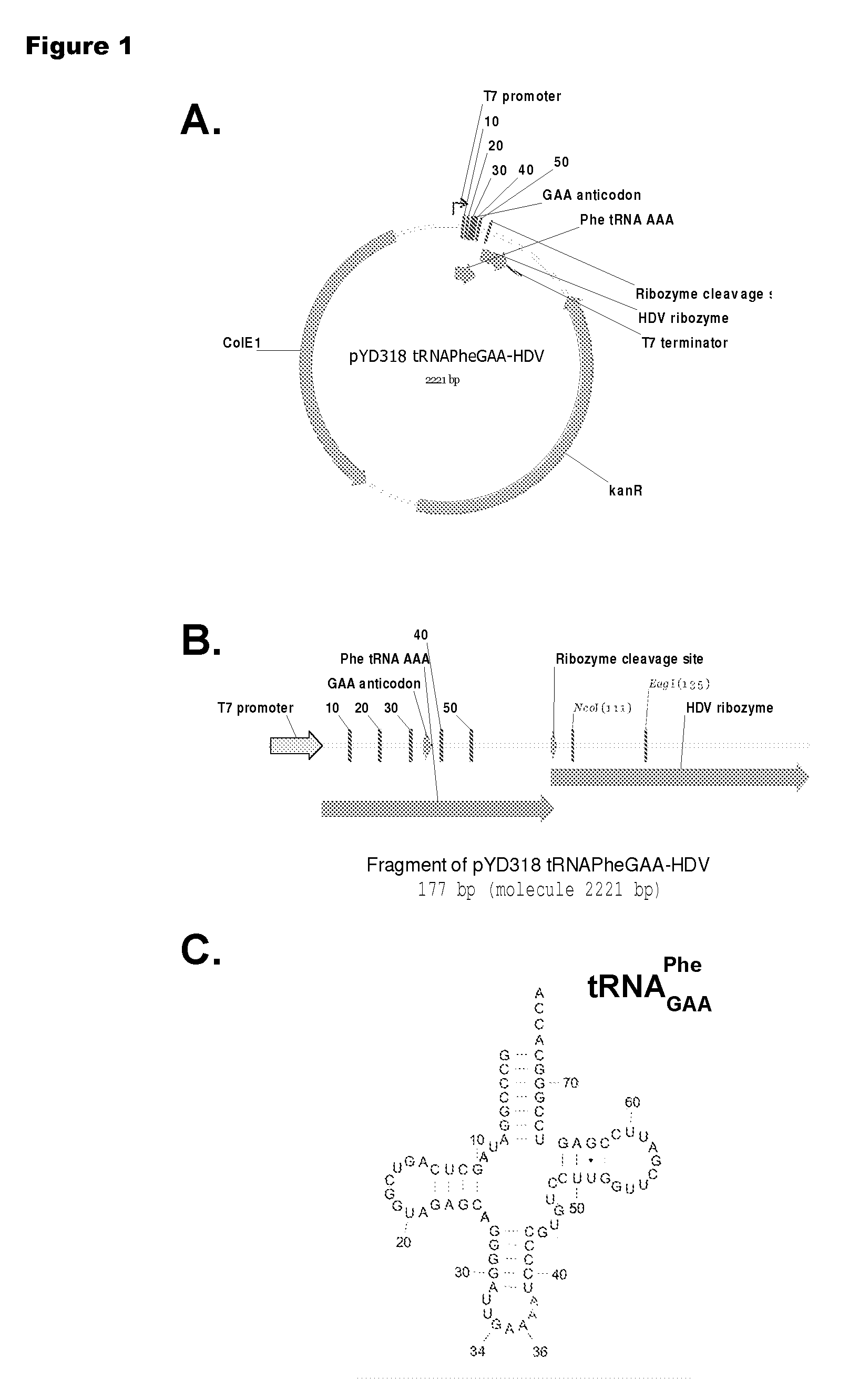
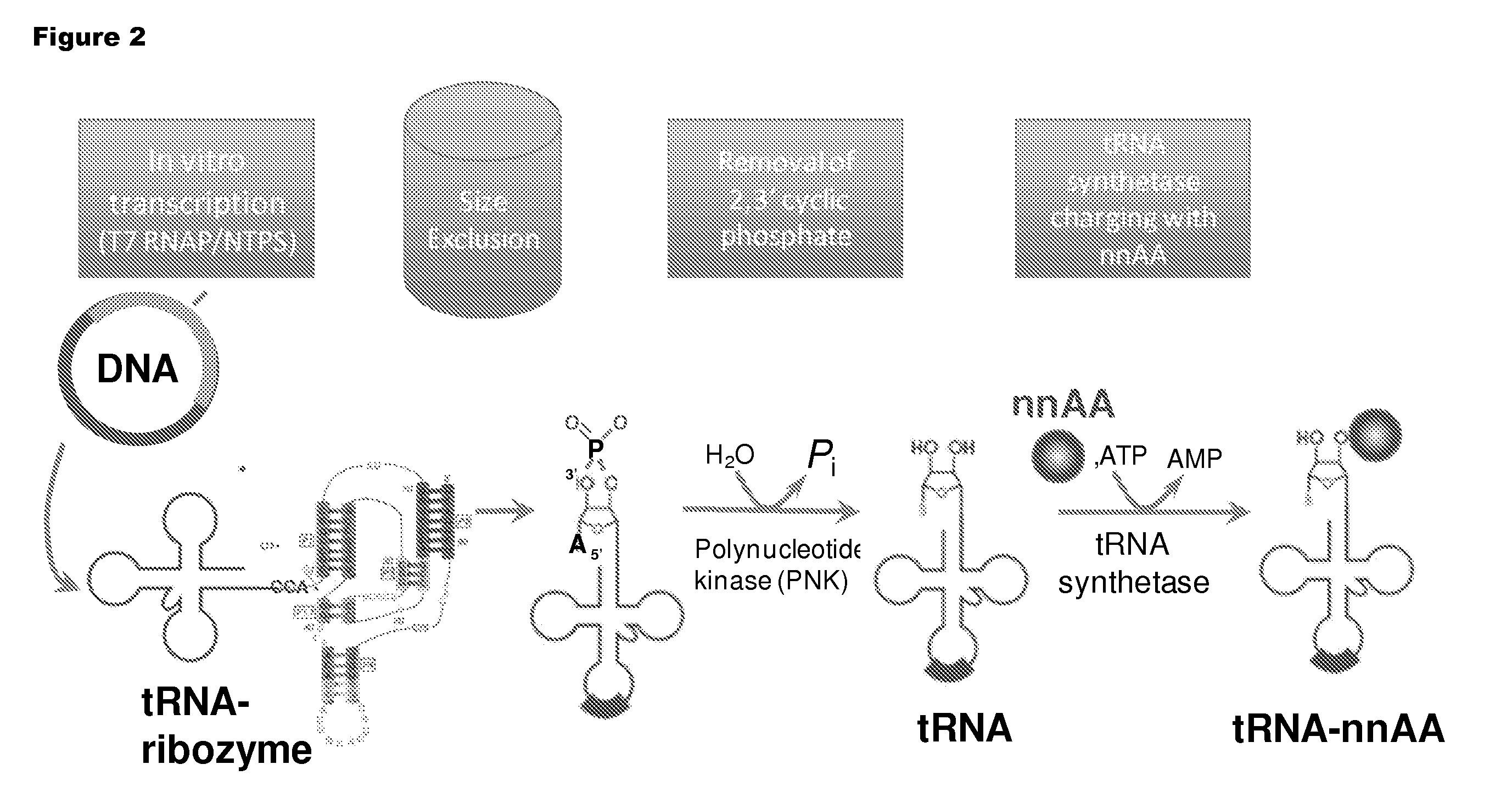
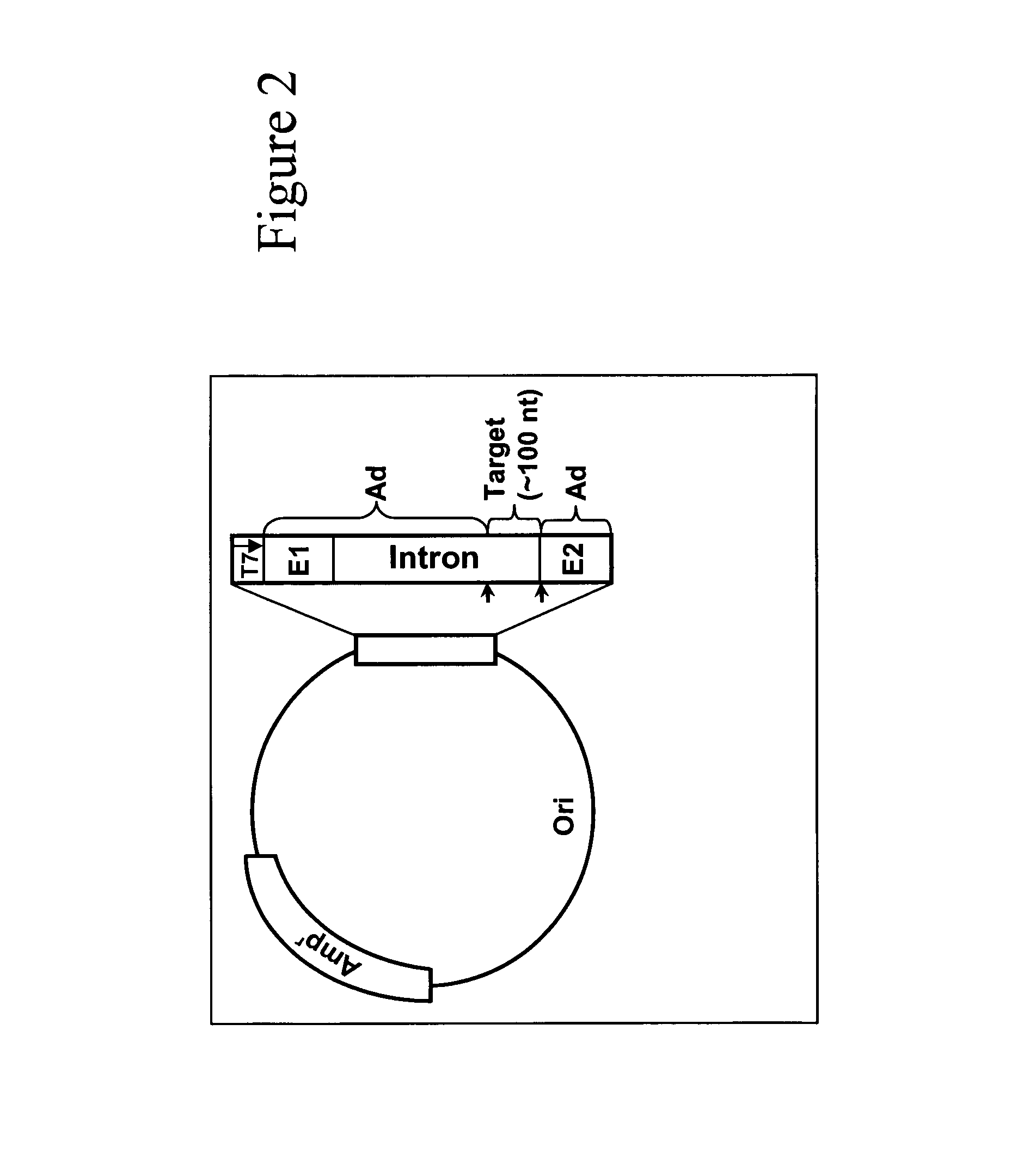
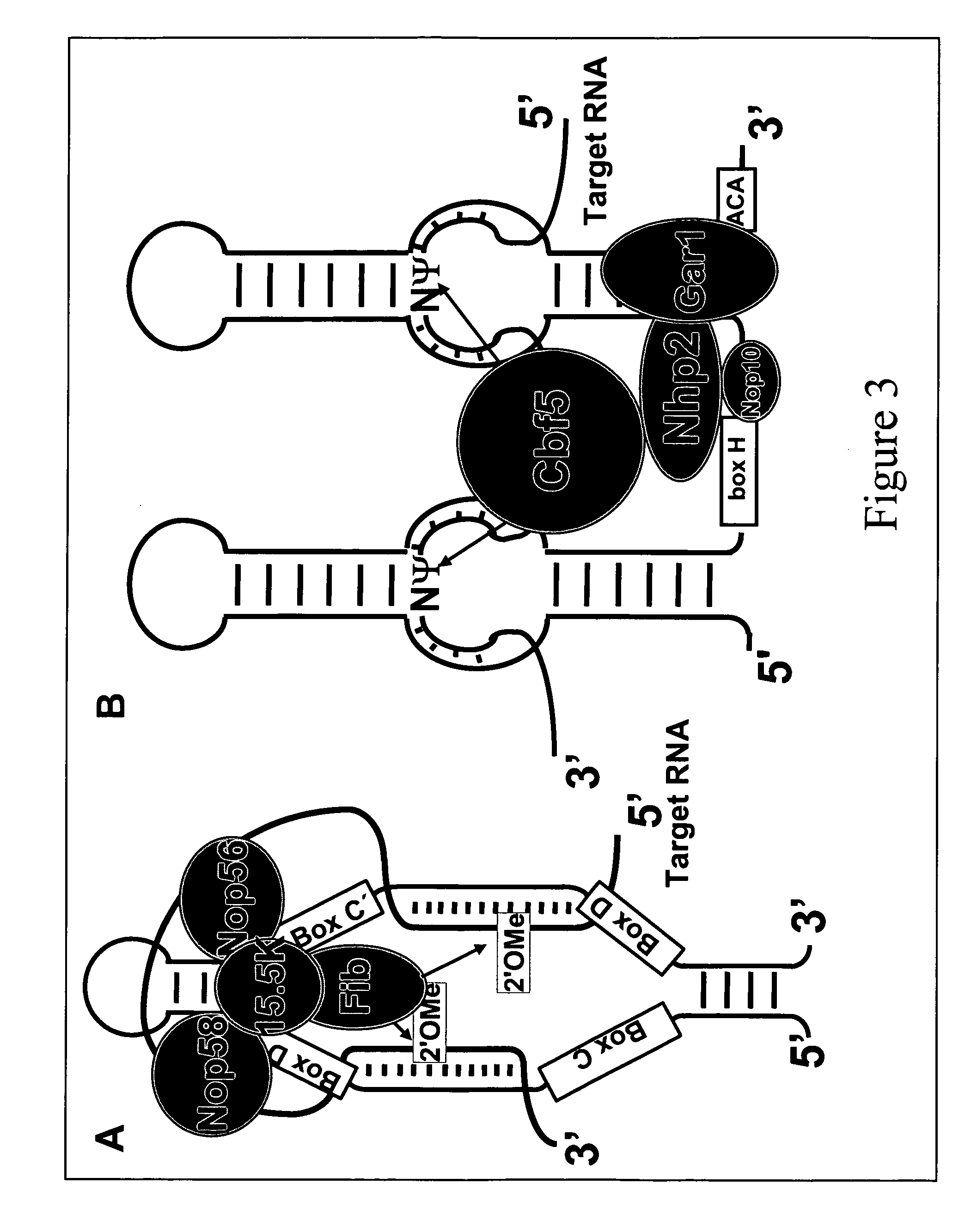
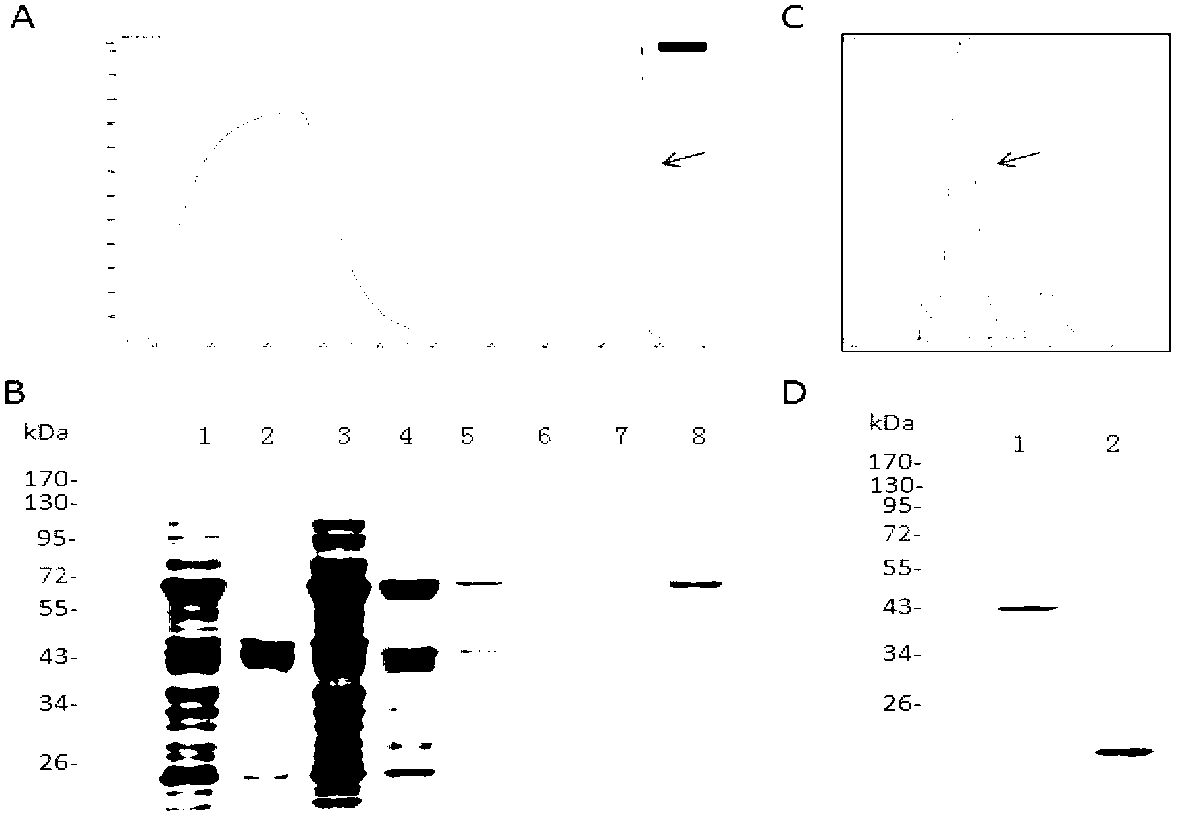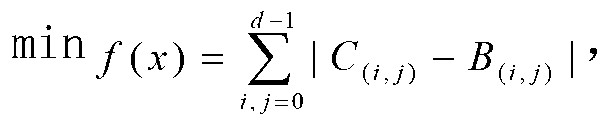Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
154 results about "Genetic code" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) into proteins. Translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by messenger RNA (mRNA), using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.
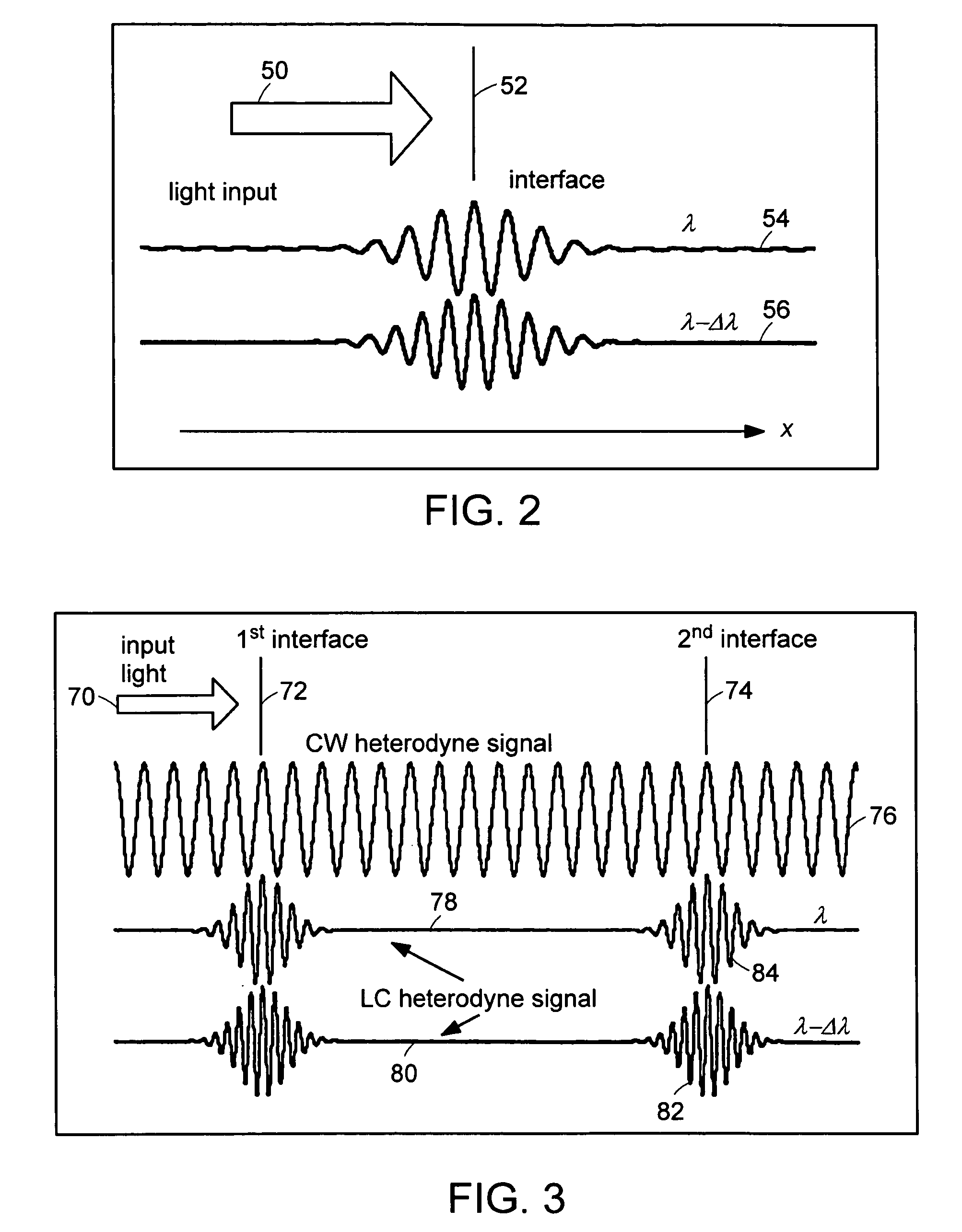
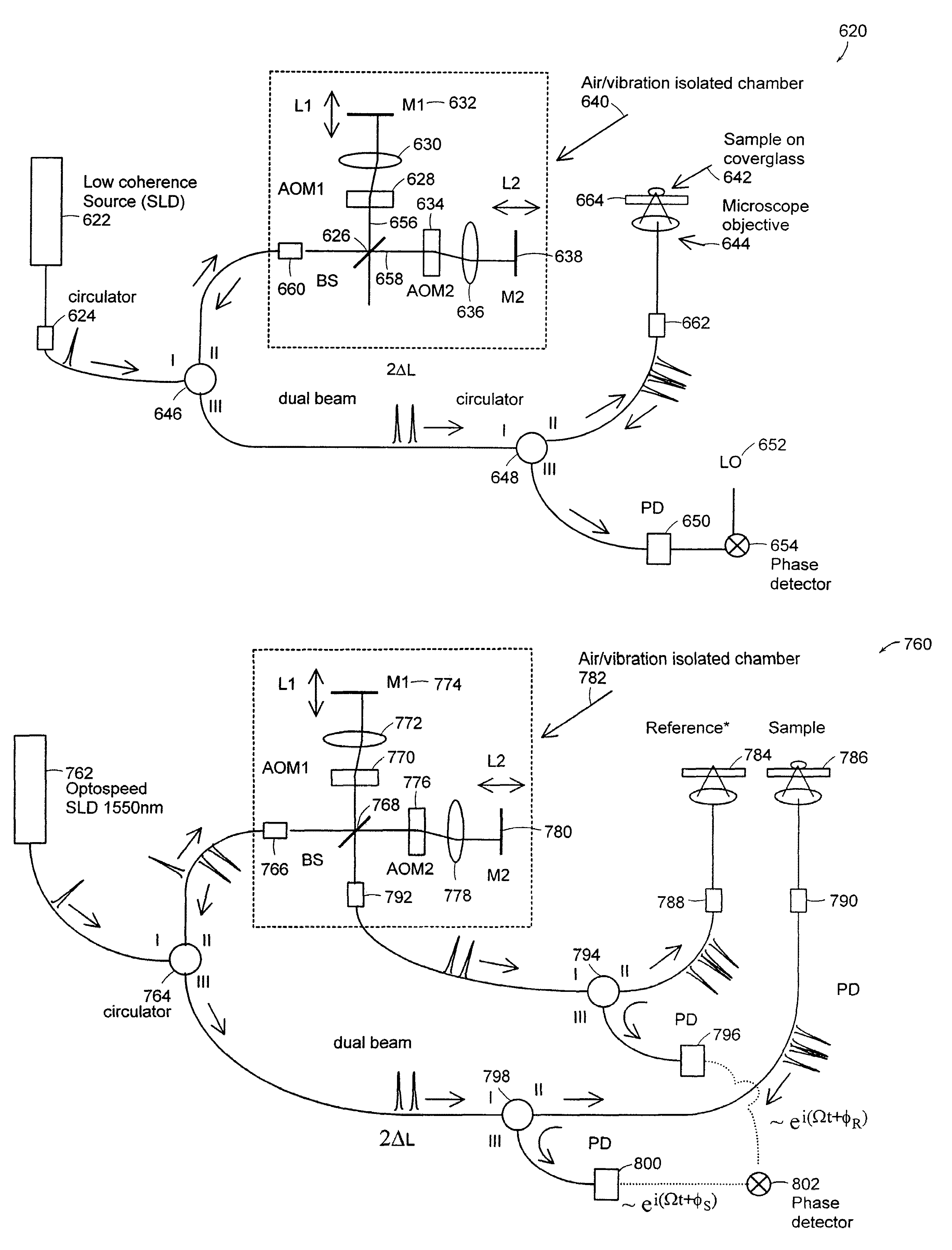
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS20050057756A1Efficient collectionNo loss of precisionOptical measurementsPhase-affecting property measurementsCellular componentPhase noise
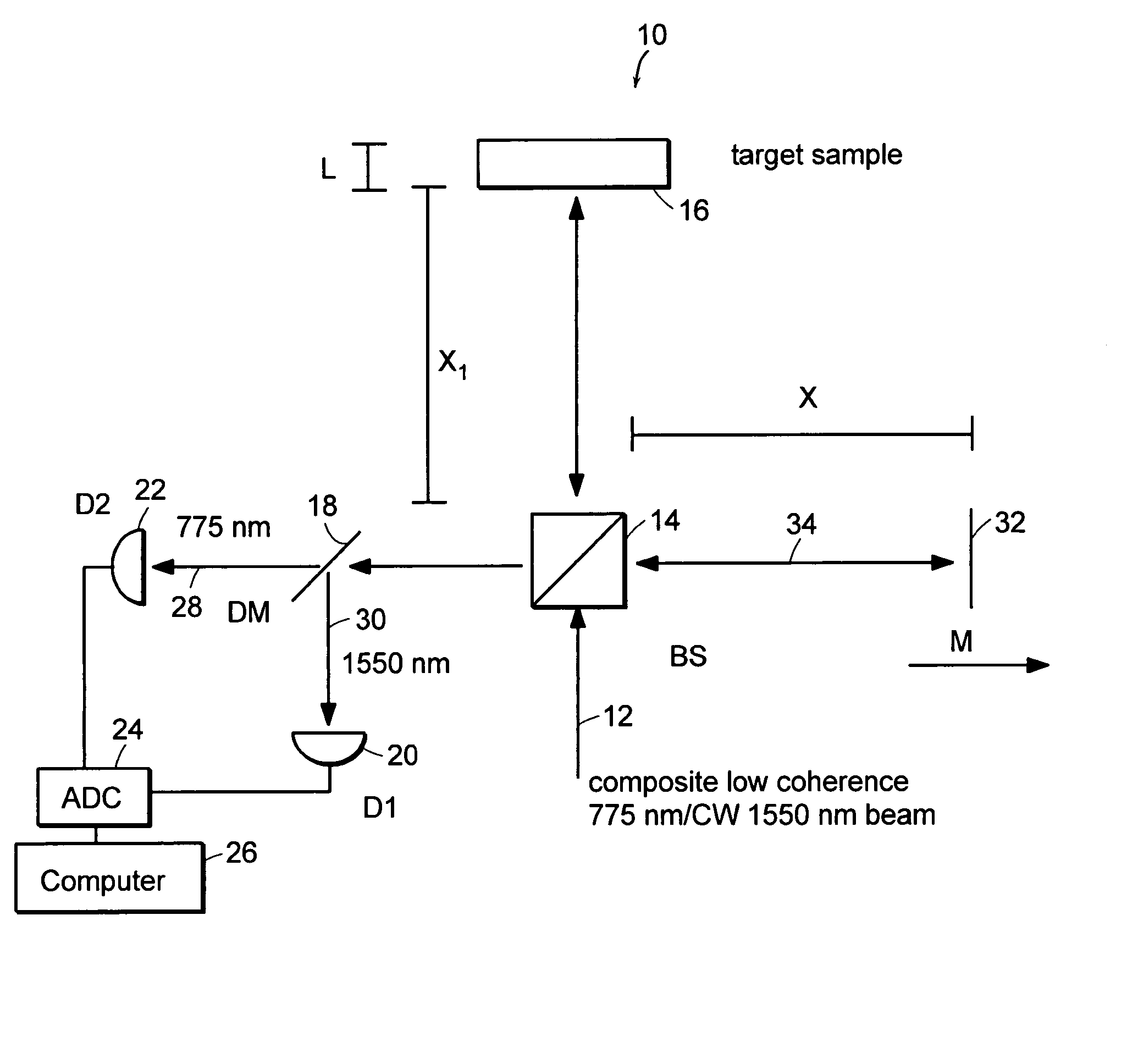
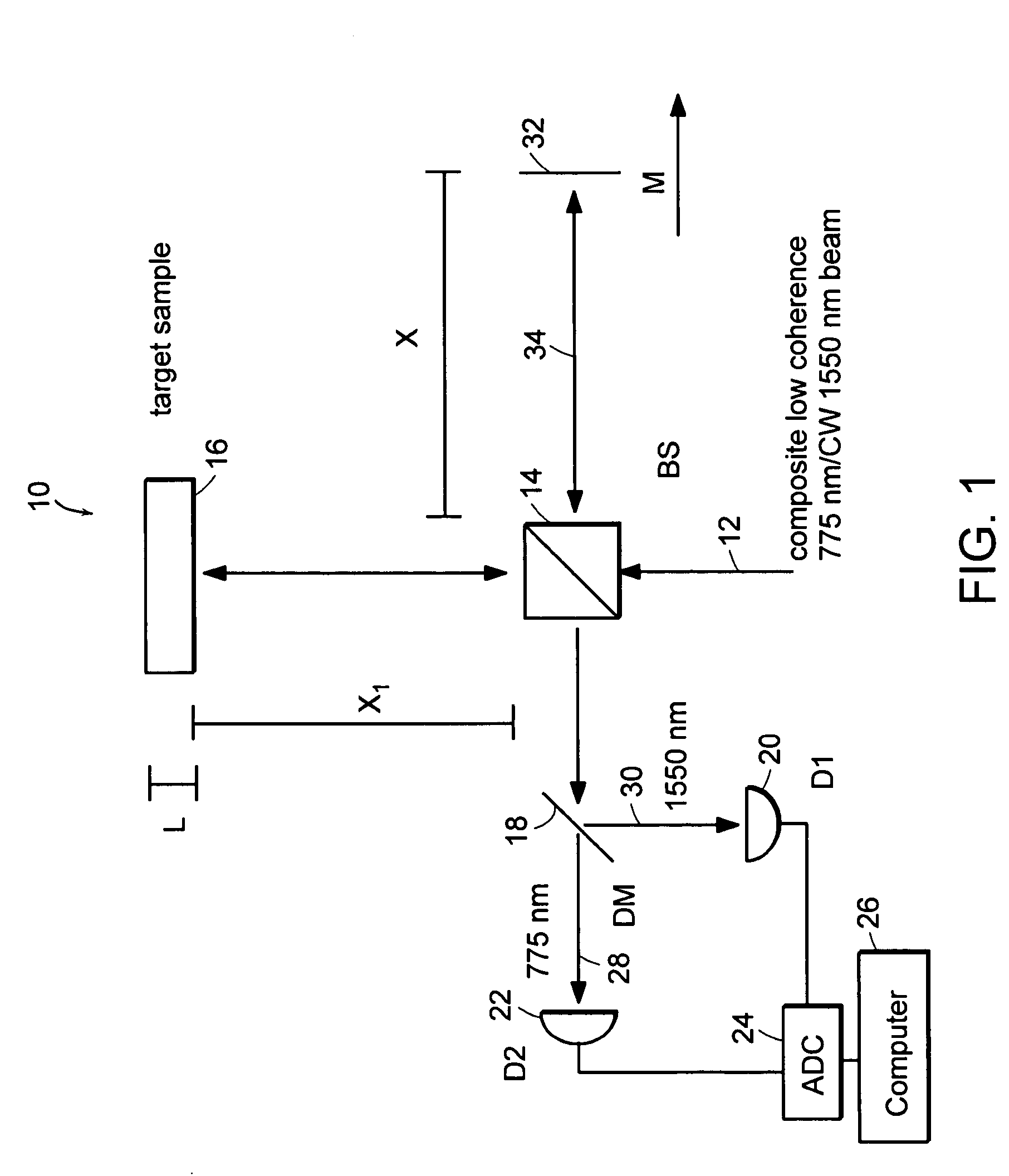
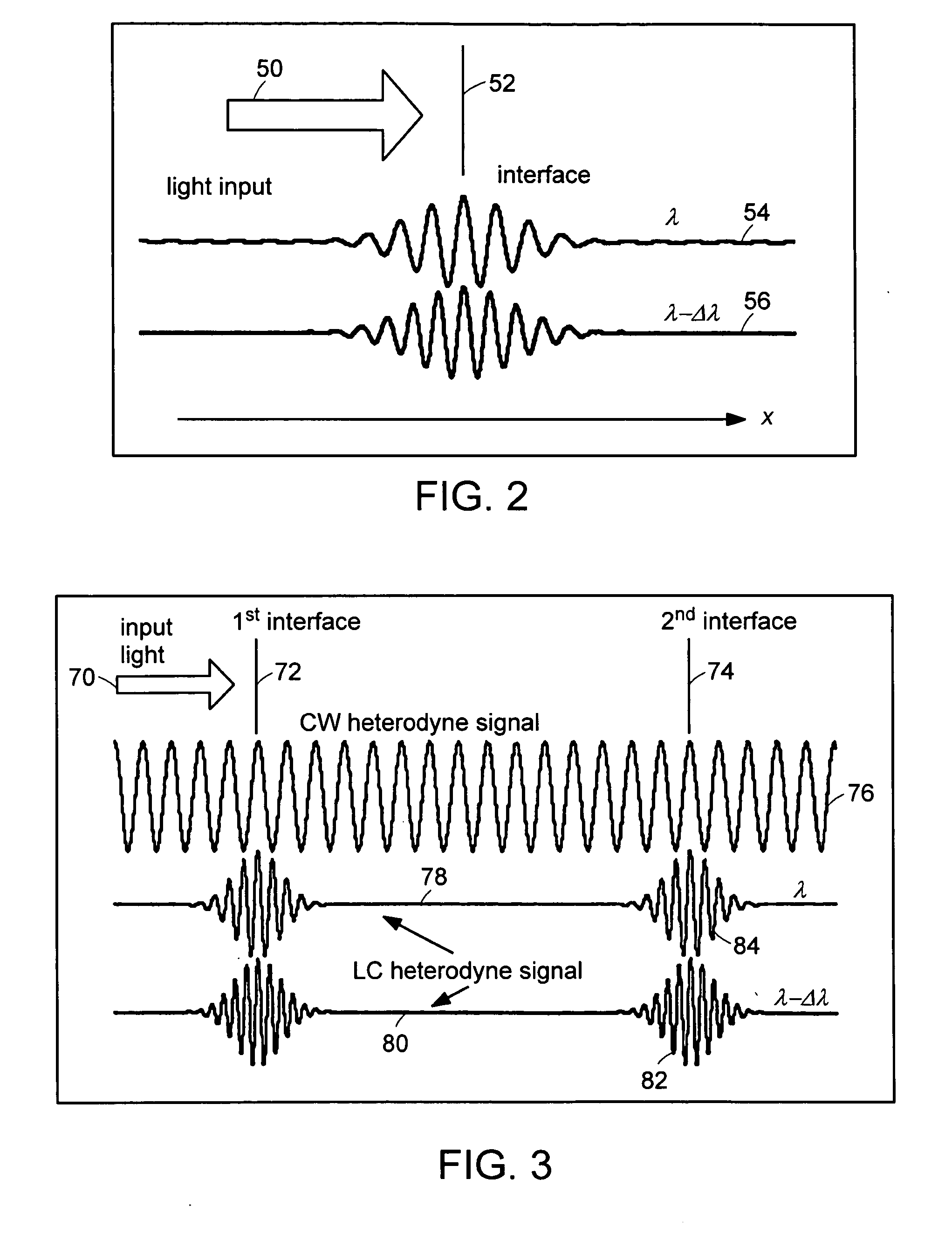
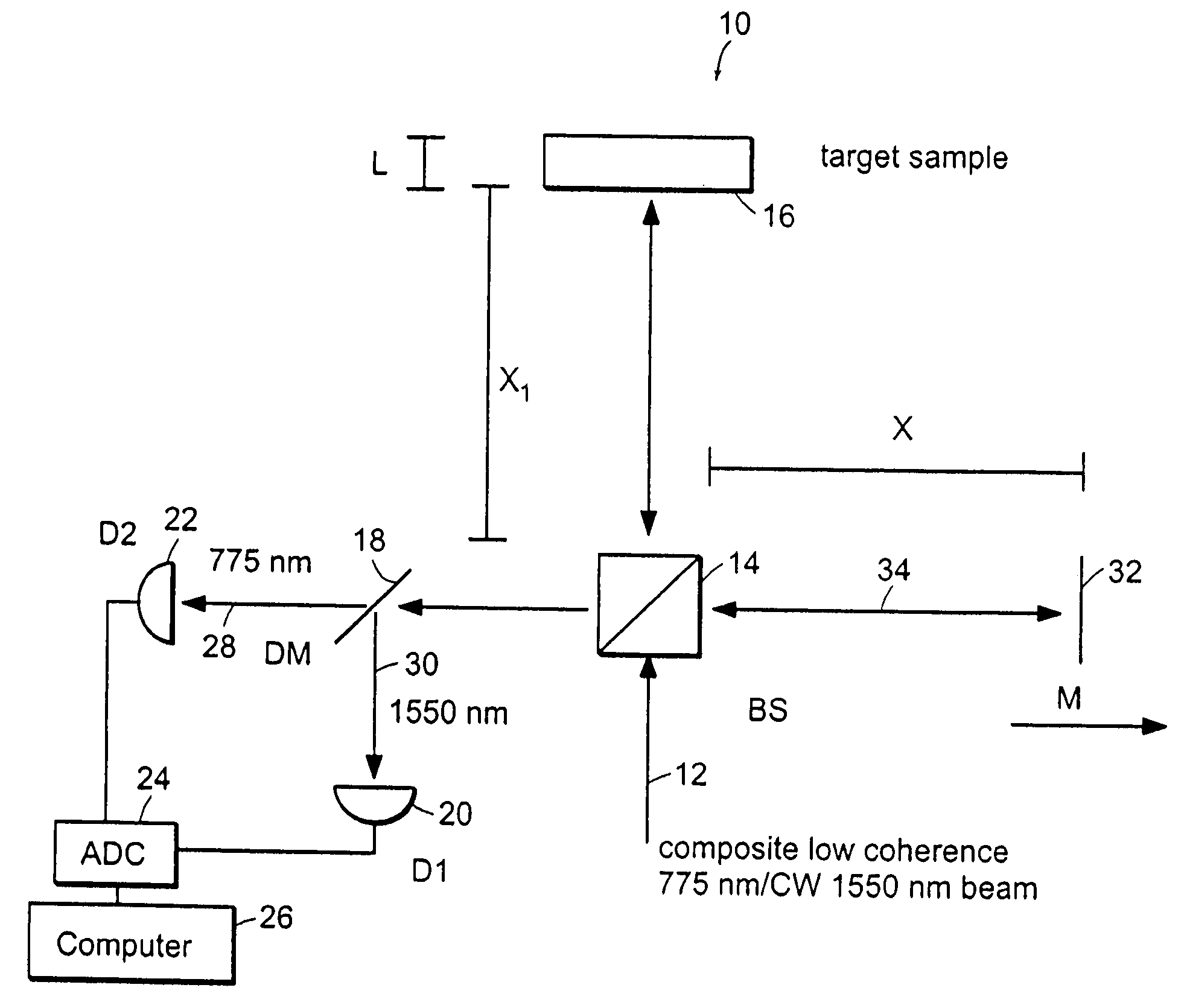
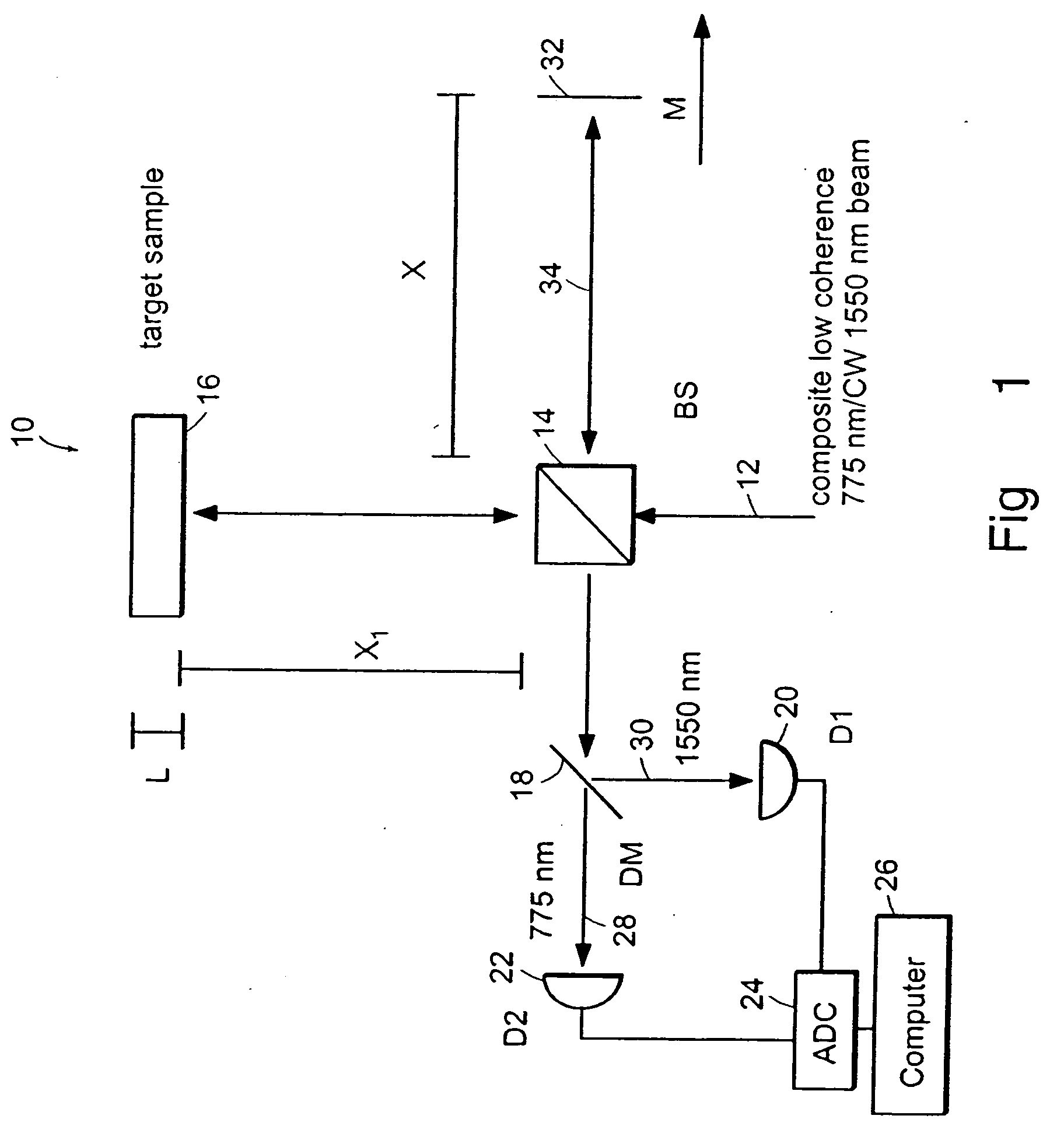
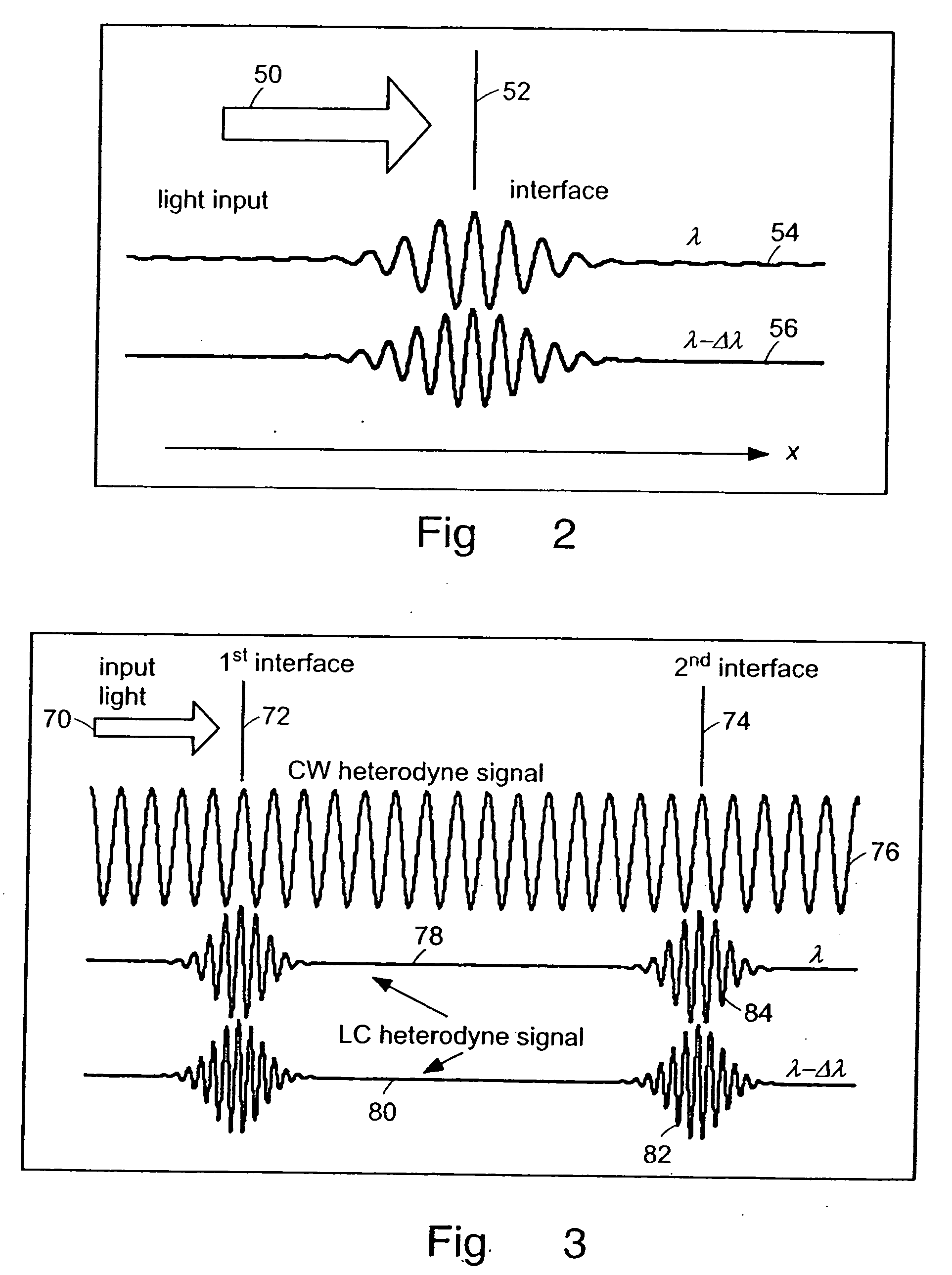
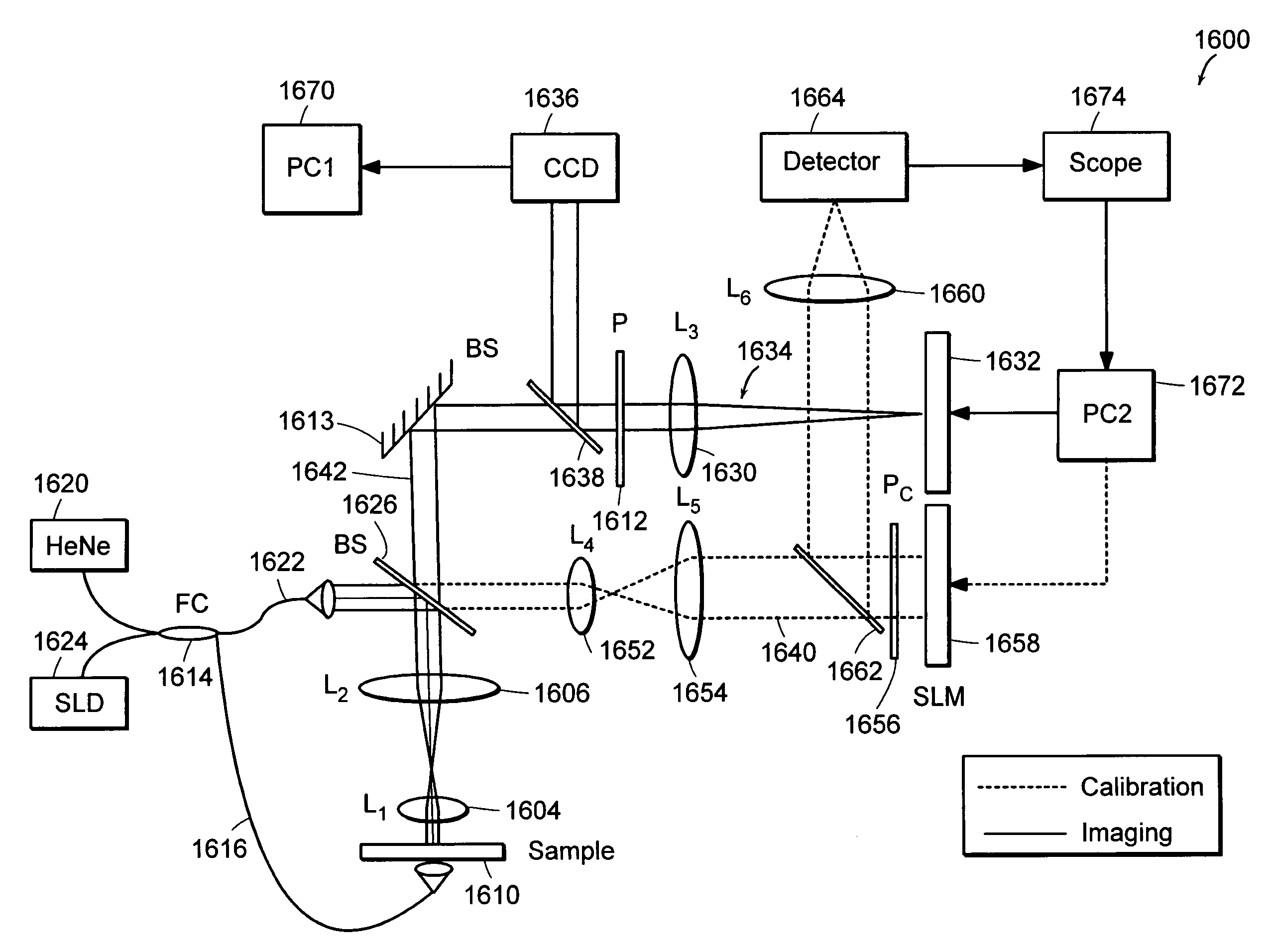
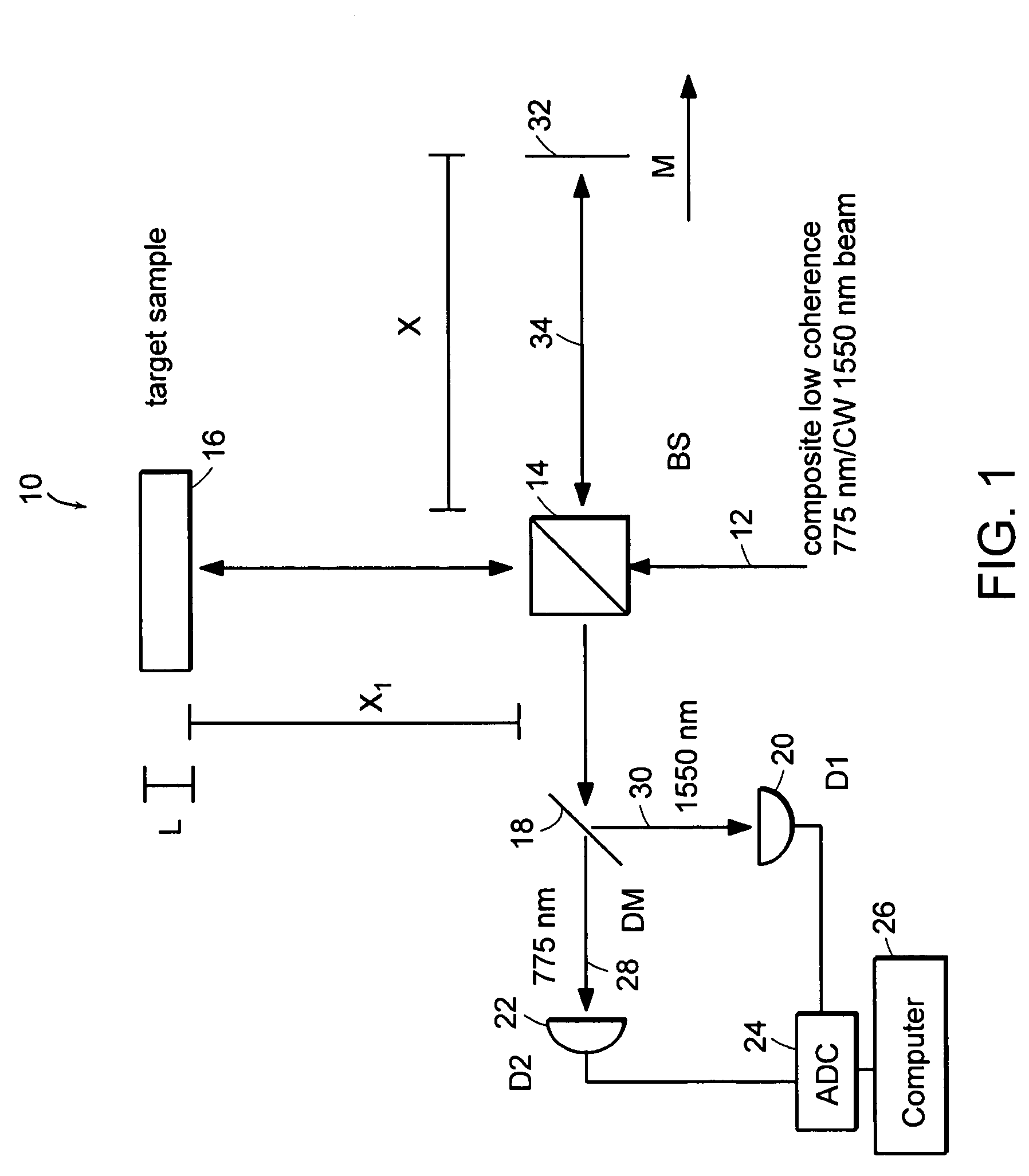
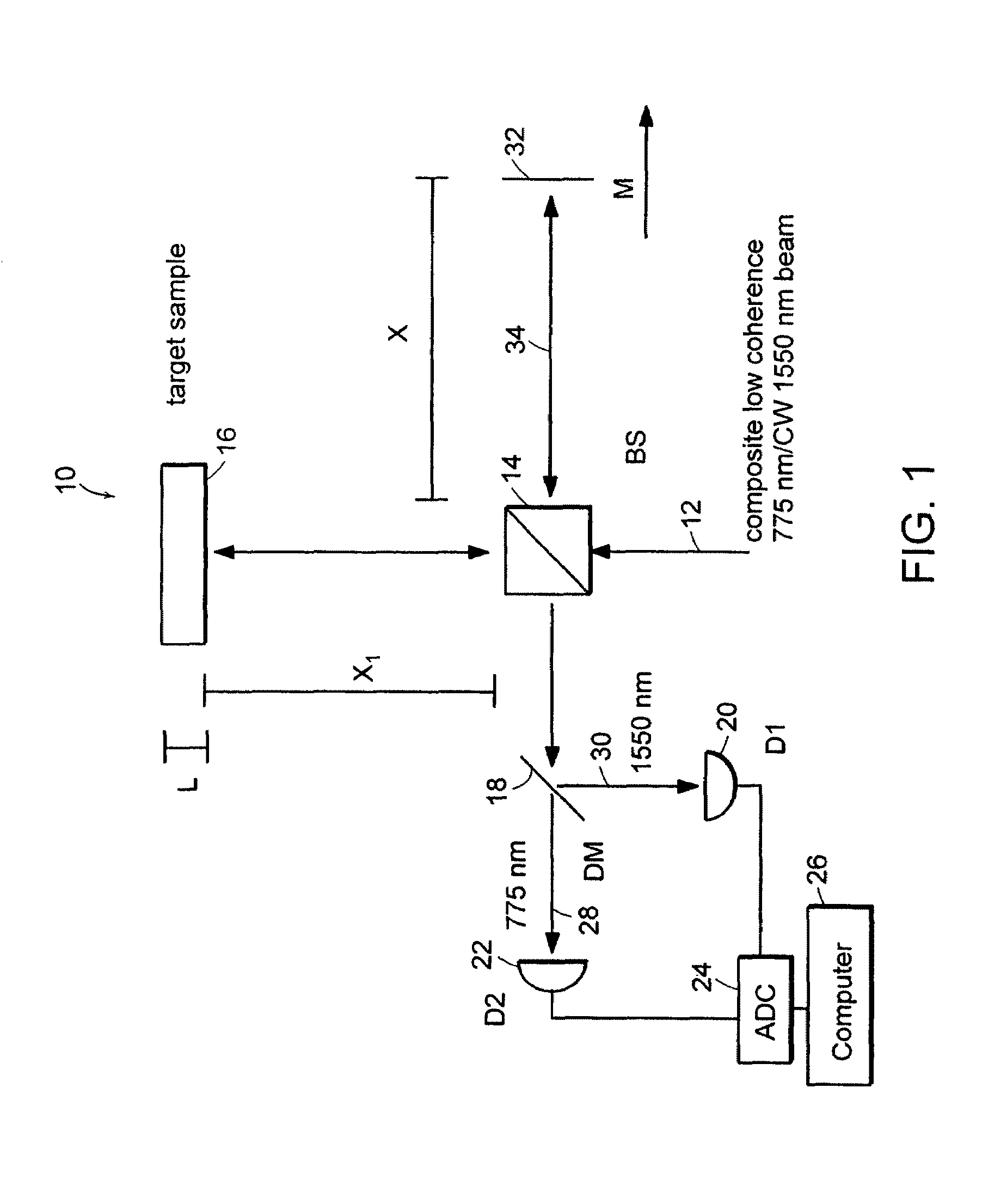
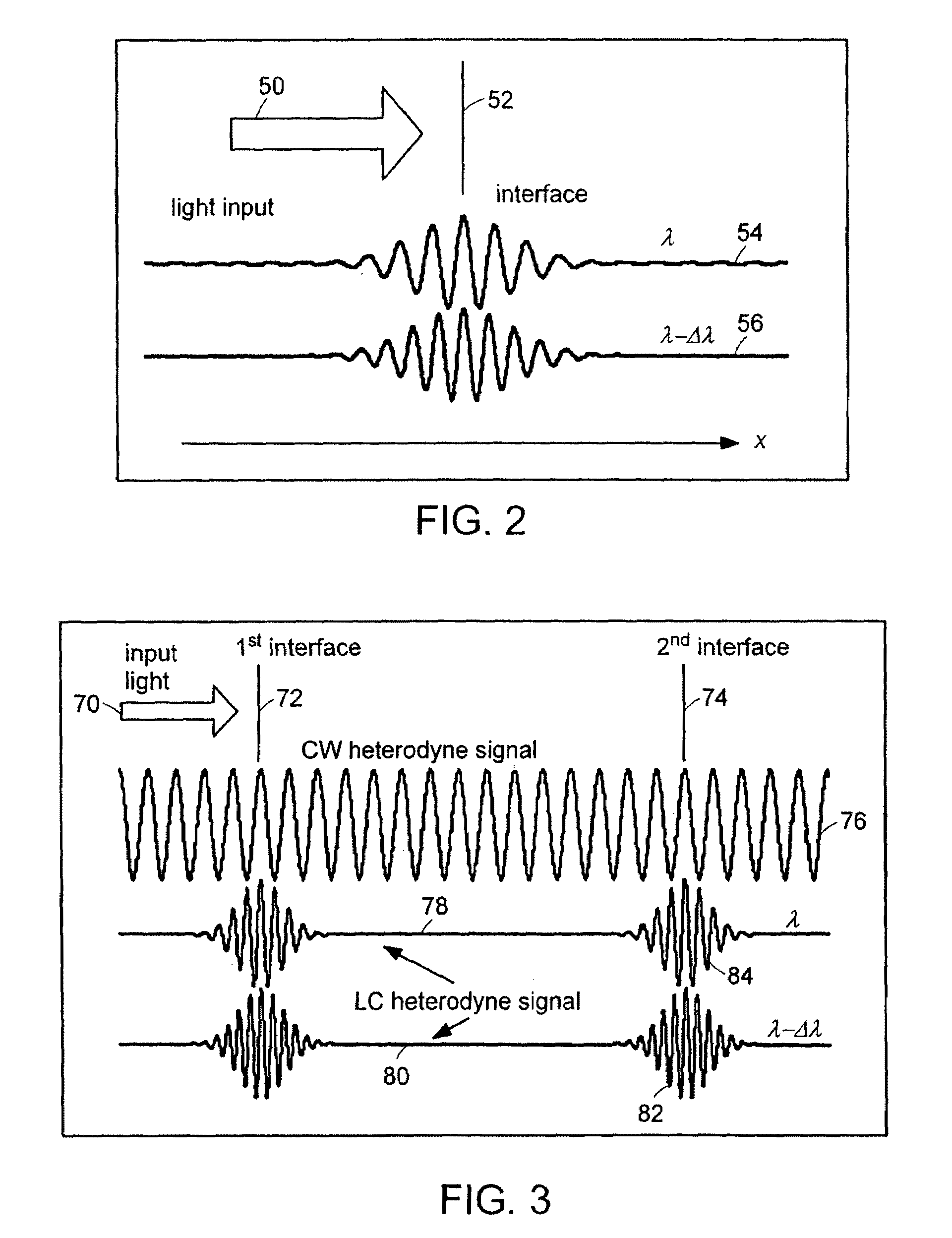
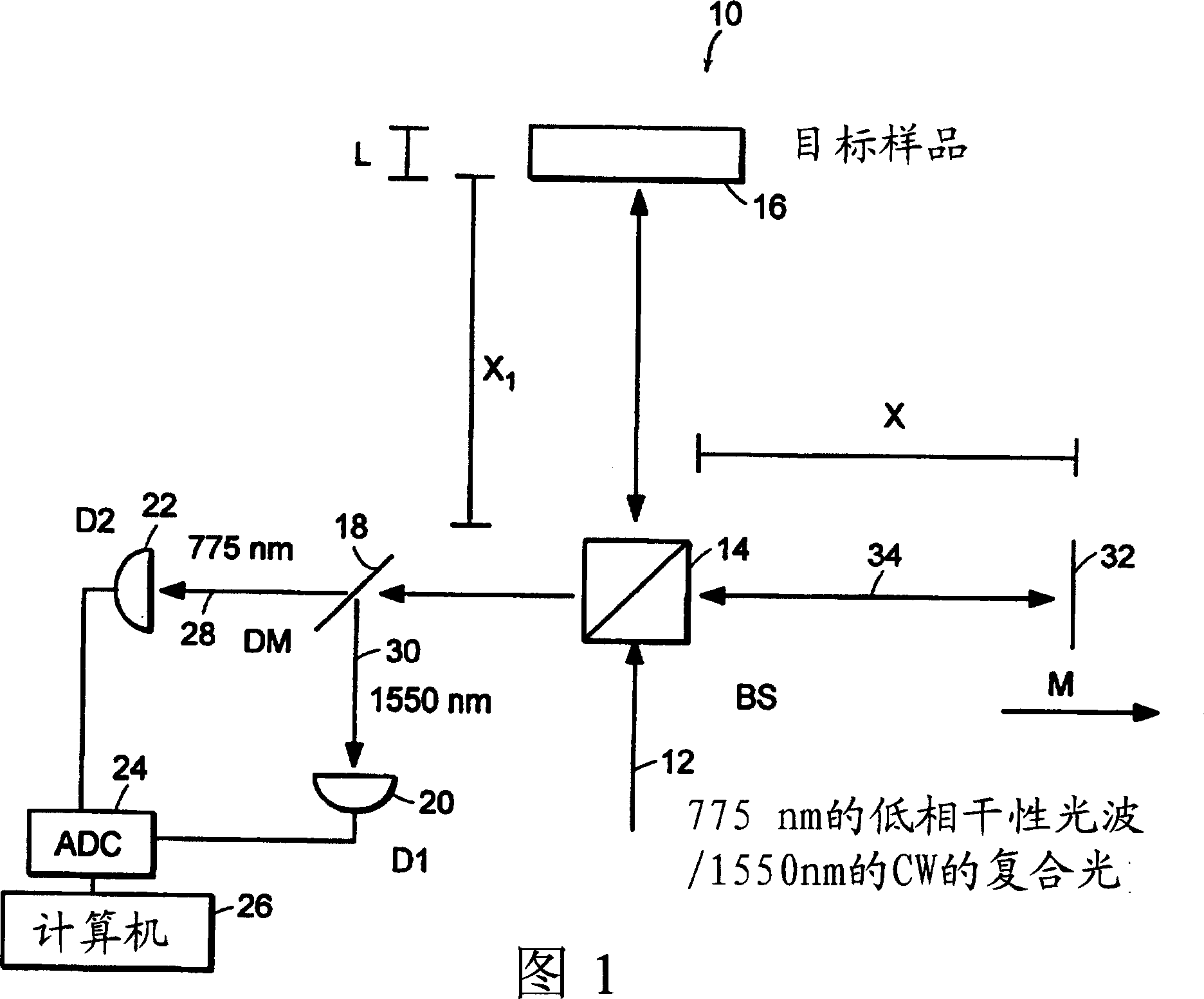
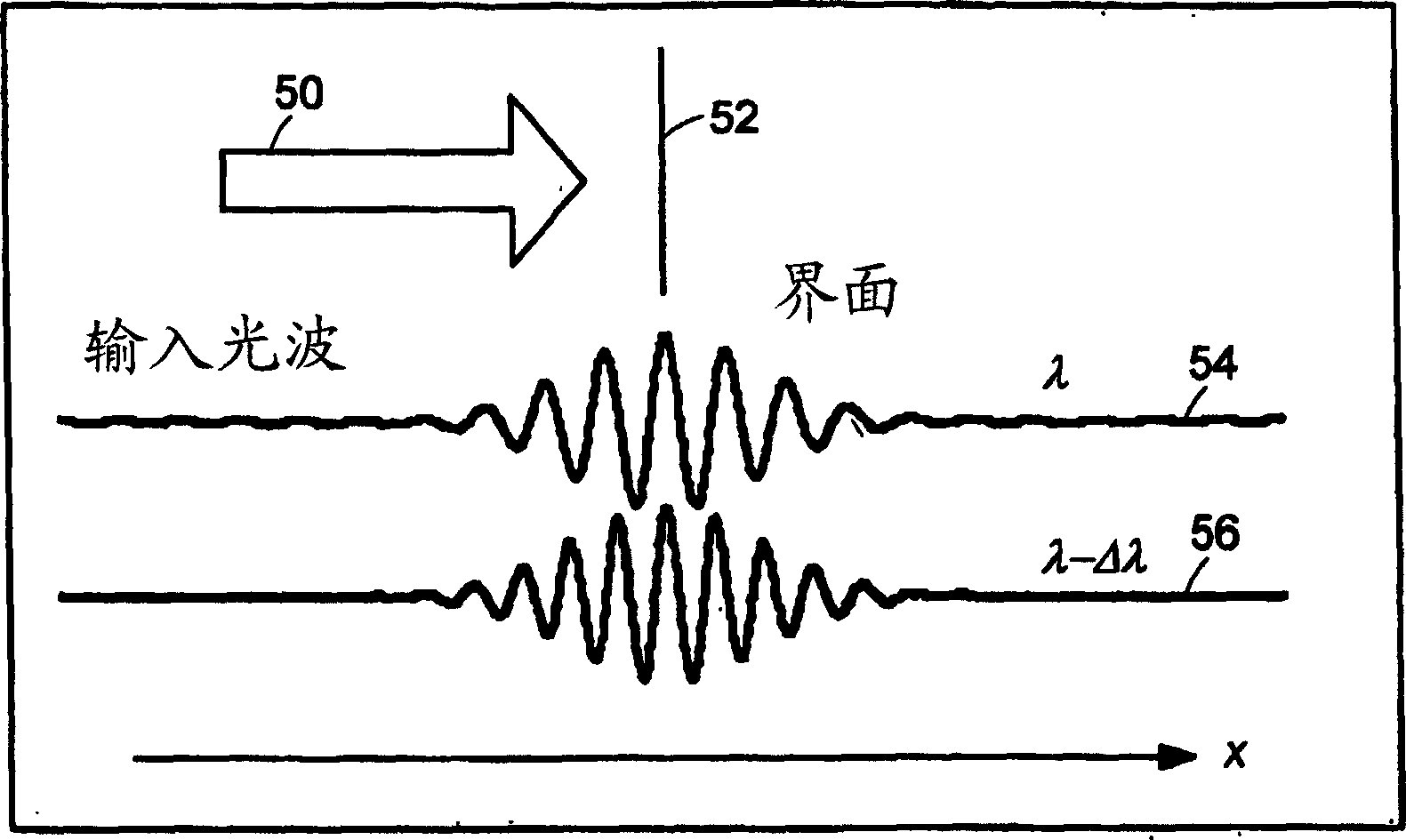
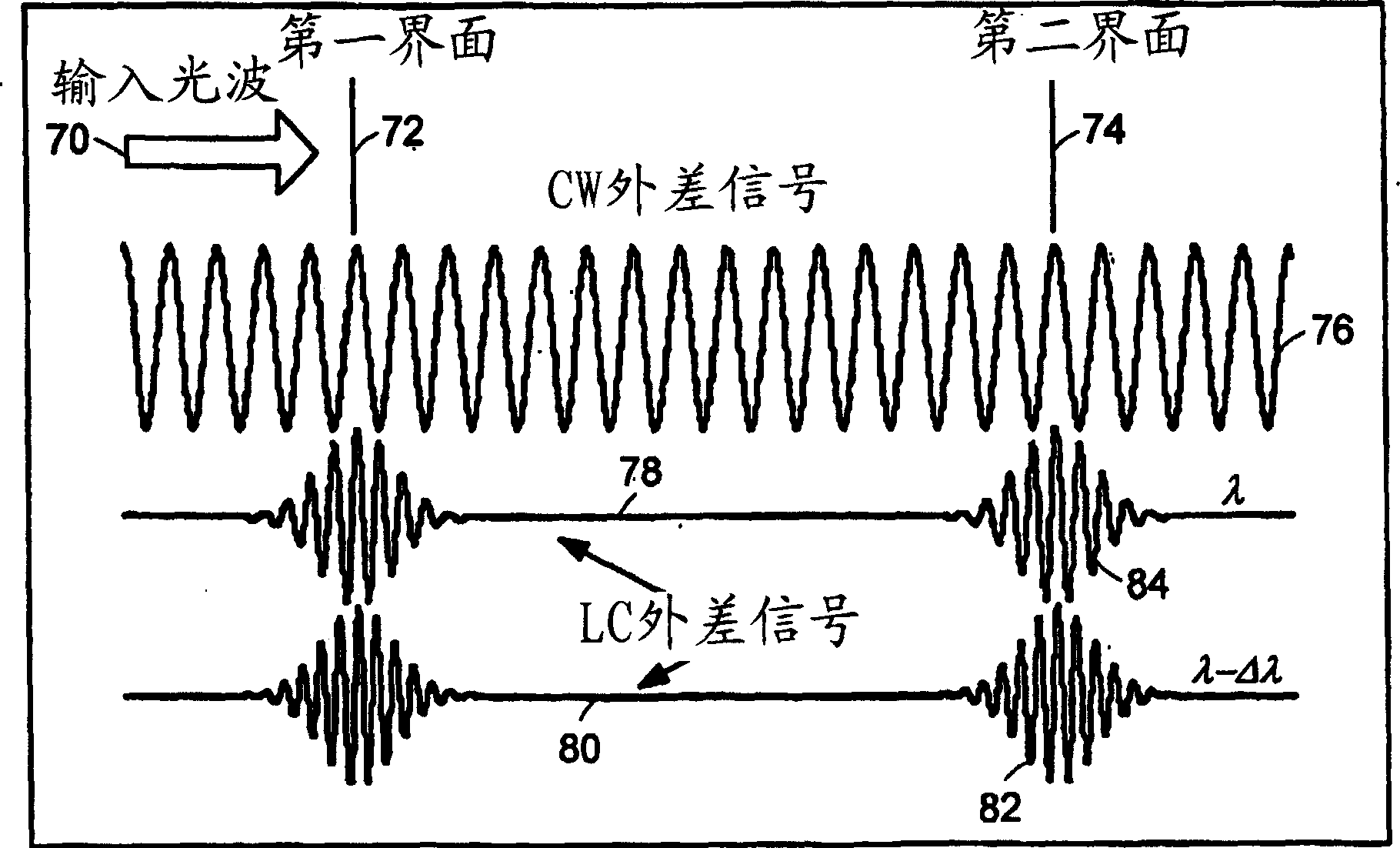
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS20050105097A1Efficient collectionNo loss of precisionOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS7365858B2No loss of precisionReduce coherenceOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Unnatural reactive amino acid genetic code additions
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
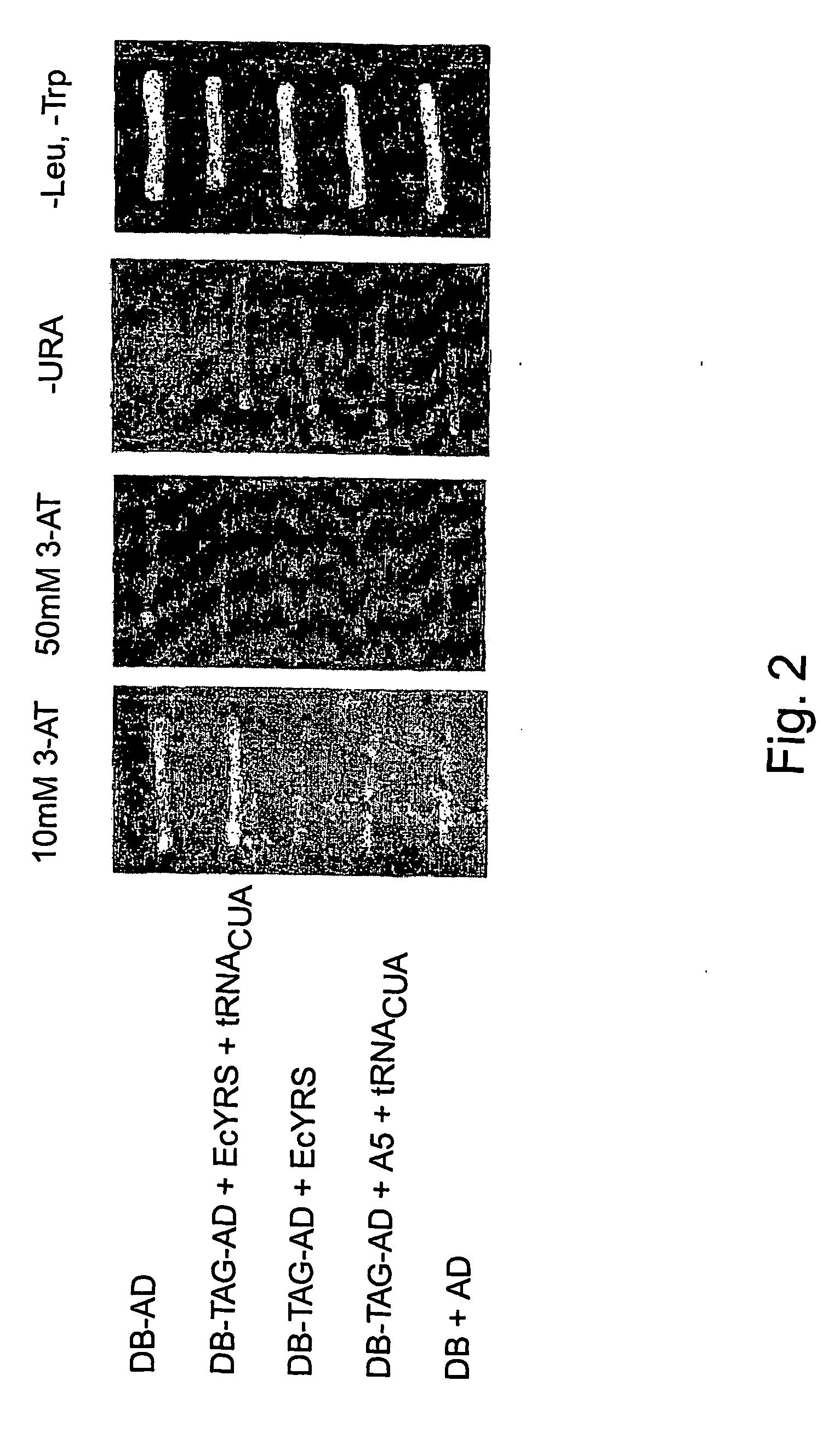
Adding photoregulated amino acids to the genetic code
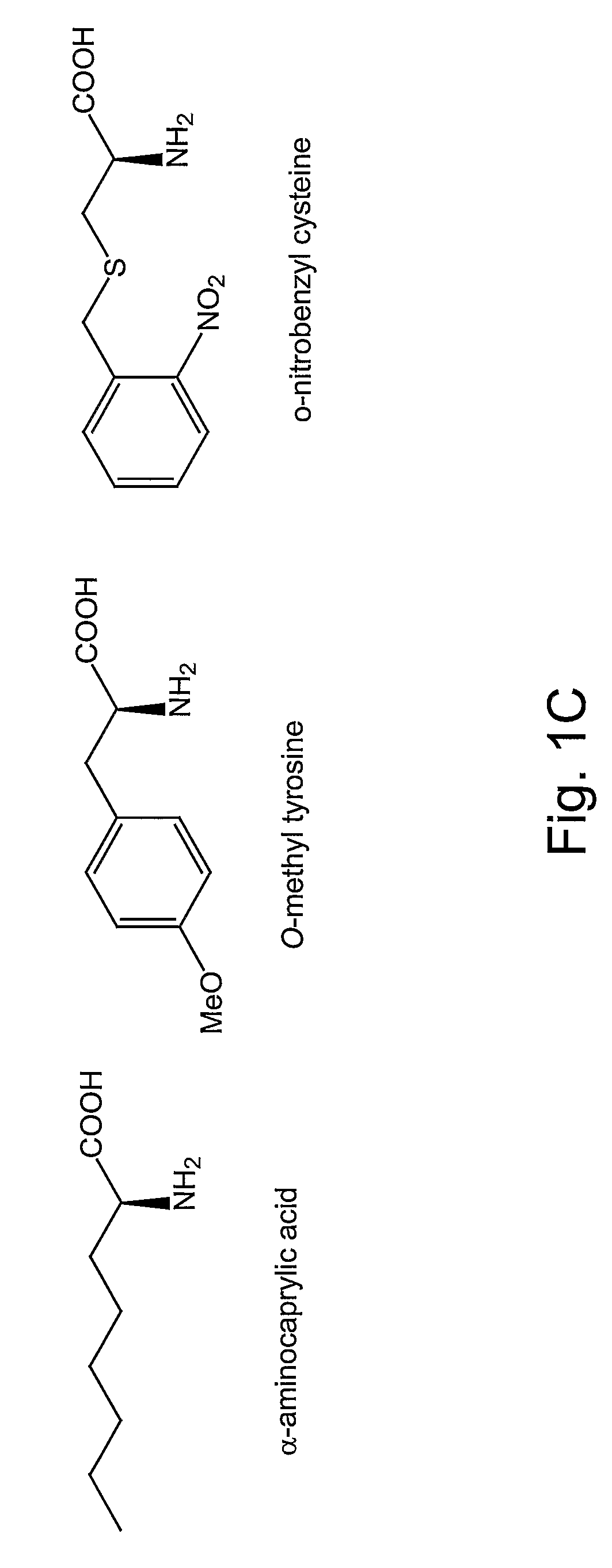
Compositions and methods of producing components of protein biosynthetic machinery that include orthogonal leucyl-tRNAs, orthogonal leucyl-aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, and orthogonal pairs of leucyl-tRNAs / synthetases, which incorporate photoregulated amino acids, OMe-L-tyrosine, α-aminocaprylic acid, or o-nitrobenzyl cysteine into proteins are provided in response to an amber selector codon. Methods for identifying these orthogonal pairs are also provided along with methods of producing proteins with a photoregulated amino acid, OMe-L-tyrosine, α-aminocaprylic acid, or o-nitrobenzyl cysteine using these orthogonal pairs.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Mono charging system for selectively introducing non-native amino acids into proteins using an in vitro protein synthesis system
Owner:SUTRO BIOPHARMA
Mono charging system for selectively introducing non-native amino acids into proteins using an in vitro protein synthesis system
This invention provides for a novel means of incorporating non-native amino acids into preselected positions of a protein using a cell-free synthesis system. The methods involve the use of non-orthogonal, native isoaccepting sense tRNAs that are encoded by the genetic code. Such methods allow for numerous non-native amino acids to be incorporated through the use of sense codons without having to rely upon orthogonal tRNA-synthetase pairs.
Owner:SUTRO BIOPHARMA
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS7557929B2No loss of precisionReduce coherenceOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
System and method for measuring phase
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
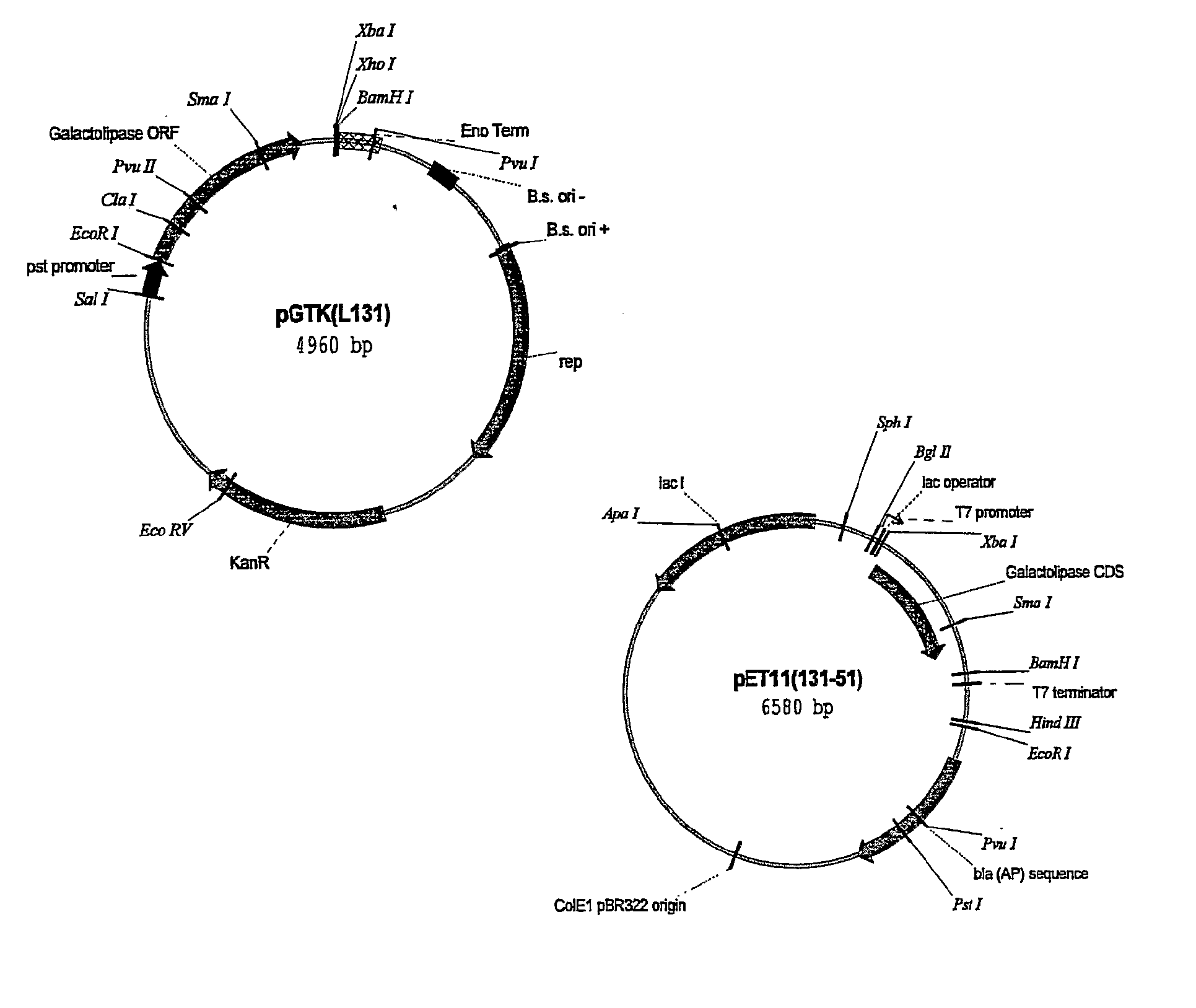
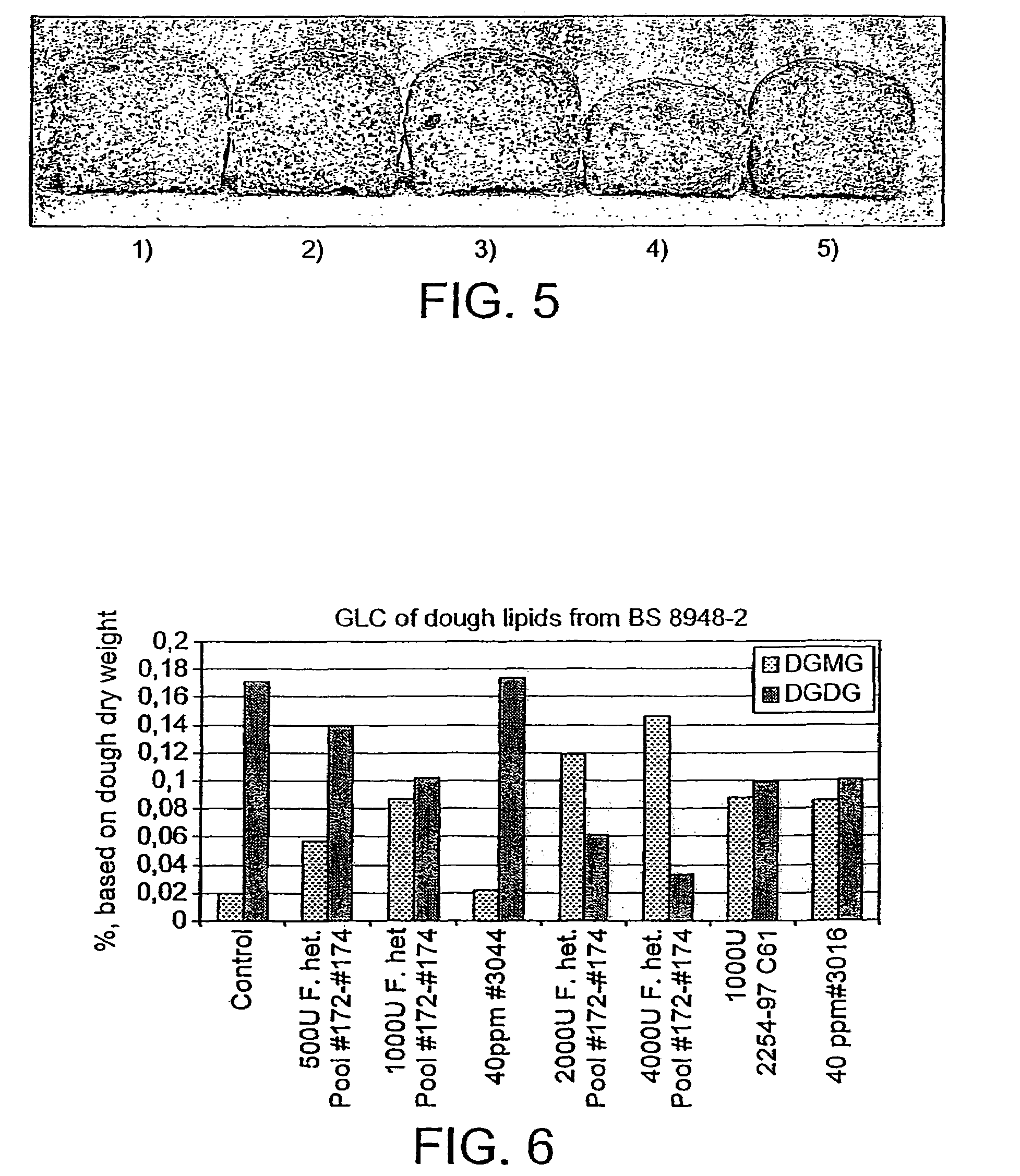
Lipolytic enzyme: uses thereof in the food industry
The invention encompasses the use of a lipolytic enzyme obtainable from one of the following genera: Streptomyces, Corynebacterium and Thermobifida in various methods and uses, wherein said lipolytic enzyme is capable of hydrolysing a glycolipid or a phospholipid or transferring an acyl group from a glycolipid or phospholipids to an acyl acceptor. Preferably, the lipolytic enzyme for use in these methods and uses comprises an amino acid sequence as shown in any one of SEQ ID NOs: 4, 5, 7, 8, 12, 14 or 16 or an amino acid sequence having at least 70% identity therewith or comprises a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 3, 6, 9, 13, 15 or 17 or a nucleotide sequence which has at least 70% identity therewith. The present invention also relates to a lipolytic enzyme capable of hydrolysing at least a galactolipid or capable of transferring an acyl group from a galactolipid to one or more acyl acceptor substrates, wherein the enzyme is obtainable from Streptomyces species and includes a lipolytic enzyme comprising an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 4 or an amino acid sequence which has at least 60% identity thereto. The enzyme may be encoded by a nucleic acid selected from the group consisting of: a) a nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence show in SEQ ID NO: 3; b) a nucleic acid which is related to the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO: 3 by the degeneration of the genetic code; and c) a nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence which has at least 70% identity with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 3.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Fungal lipolytic enzymes, nucleic acids encoding, and uses thereof
A fungal wild-type lipolytic enzyme having a higher ratio of activity on polar lipids compared with triglycerides, wherein the enzyme preferably has a phospholipid:triglyceride activity ratio of at least 4. Preferably, the lipolytic enzyme according to the present invention has a glycolipid:triglyceride hydrolyzing activity ratio of at least 1.5. In one embodiment, the fungal lipolytic enzyme according to the present invention comprises an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 or SEQ ID No. 2 or SEQ ID No. 4 or SEQ ID No. 6 or an amino acid sequence which has at least 90% identity thereto. The present invention further encompasses a nucleic acid encoding a fungal lipolytic enzyme, which nucleic acid is selected from the group consisting of: (a) a nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide shown in SEQ ID No. 3, SEQ ID No. 5 or SEQ ID No. 7; (b) a nucleic acid which is related to the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID No. 3, SEQ ID No. 5 or SEQ ID No. 7 by the degeneration of the genetic code; and (c) nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence which has at least 90% identity with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 3, SEQ ID No. 5 or SEQ ID No. 7.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
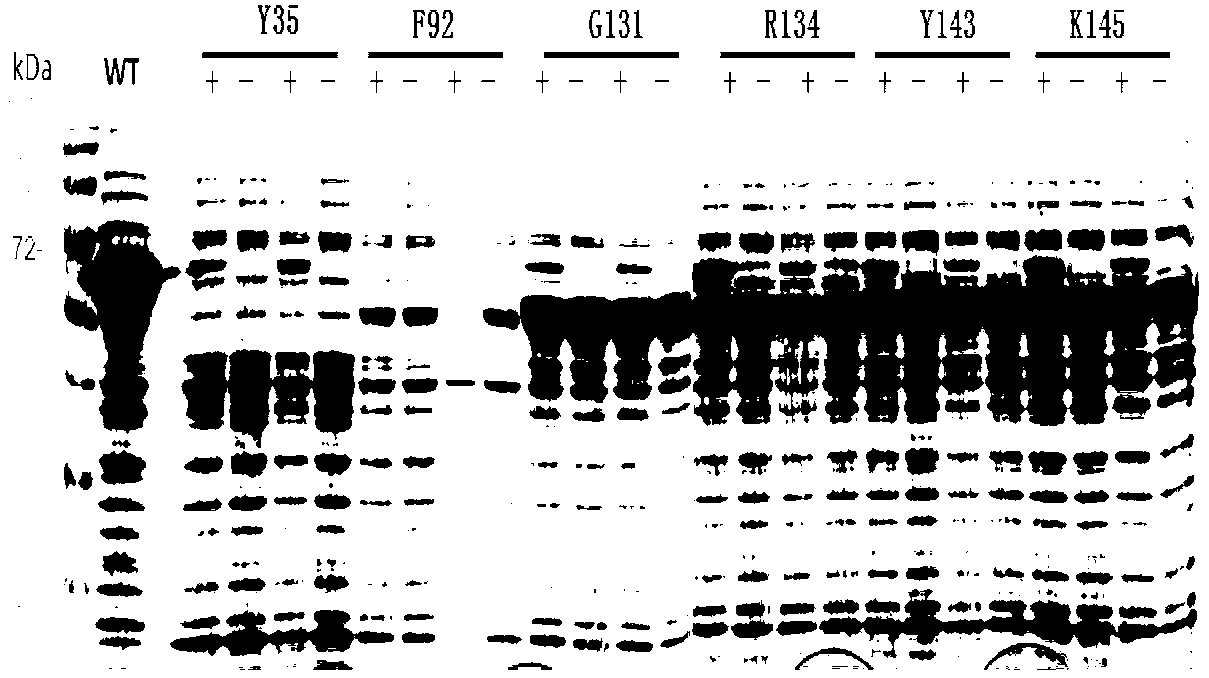
Growth hormone with site-specific mutagenesis and site-specific decoration, preparation method and applications of growth hormone
The invention relates to growth hormone with site-specific mutagenesis and site-specific decoration. The growth hormone derives from human or other animals. The invention also relates to a method of the growth hormone with site-specific mutagenesis and site-specific decoration. The method comprises the steps that unnatural amino acid fixed points are introduced into genes of the growth hormone by using a genetic code extension technology, and unnatural amino acid and a modifier are utilized, such as the fixed point connection of polyethylene glycol and the growth hormone. The invention further relates to applications of the growth hormone with site-specific mutagenesis and site-specific decoration, such as the applications of stable and long-acting growth hormone.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Adding photoregulated amino acids to the genetic code
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
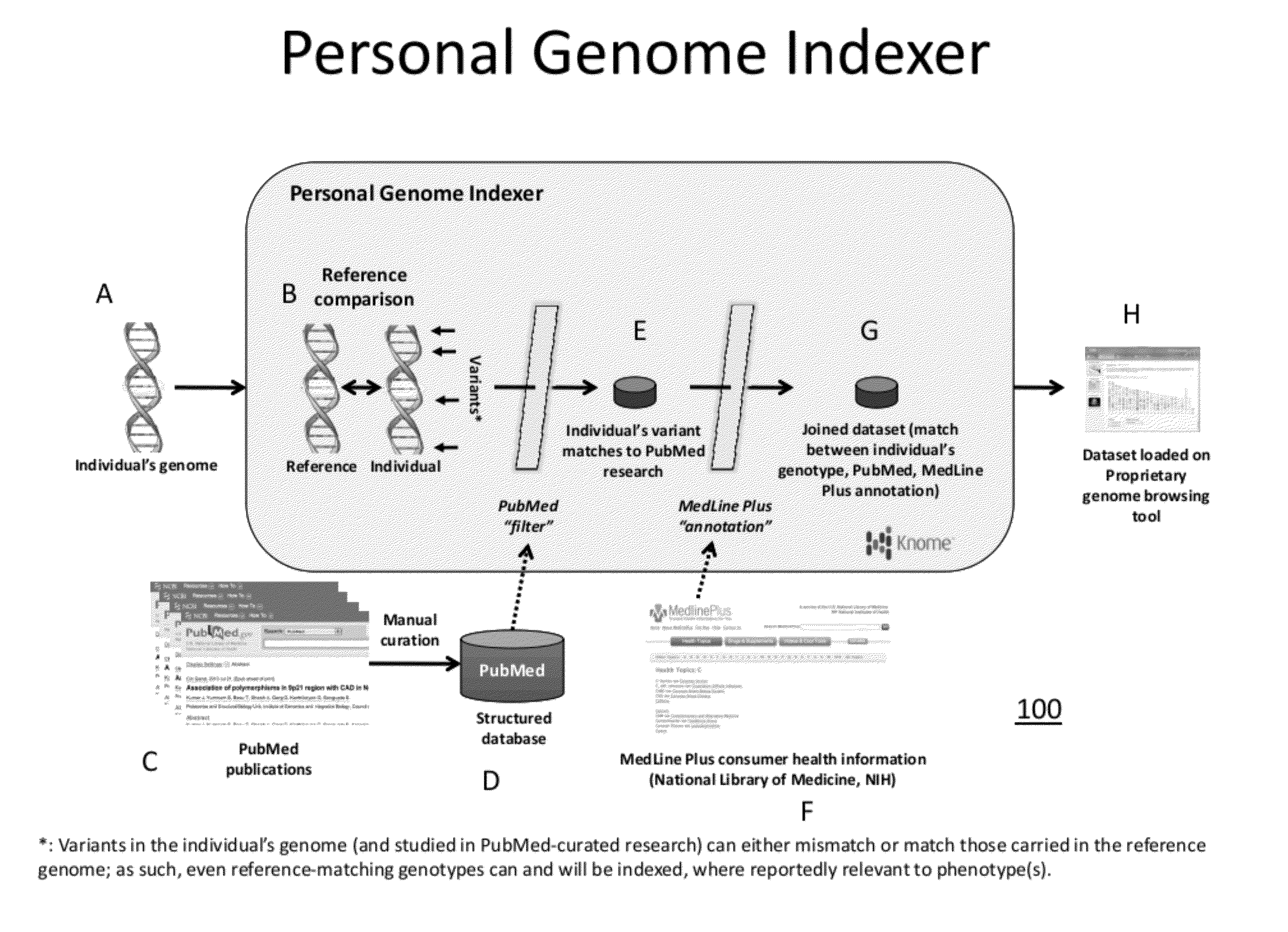
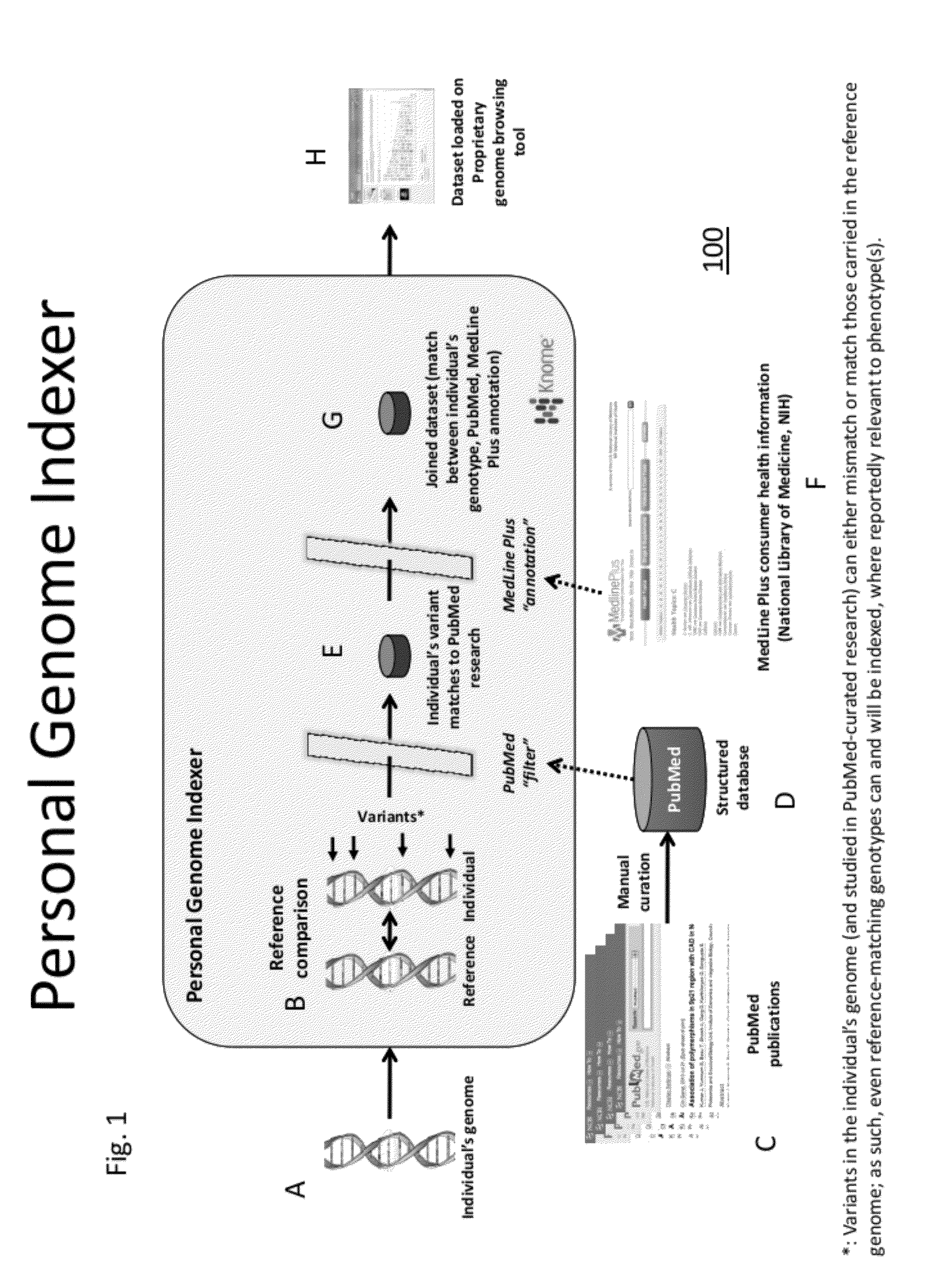
Personal Genome Indexer
InactiveUS20120078901A1Better presentDigital data processing detailsData visualisationRisk alleleComputerized system
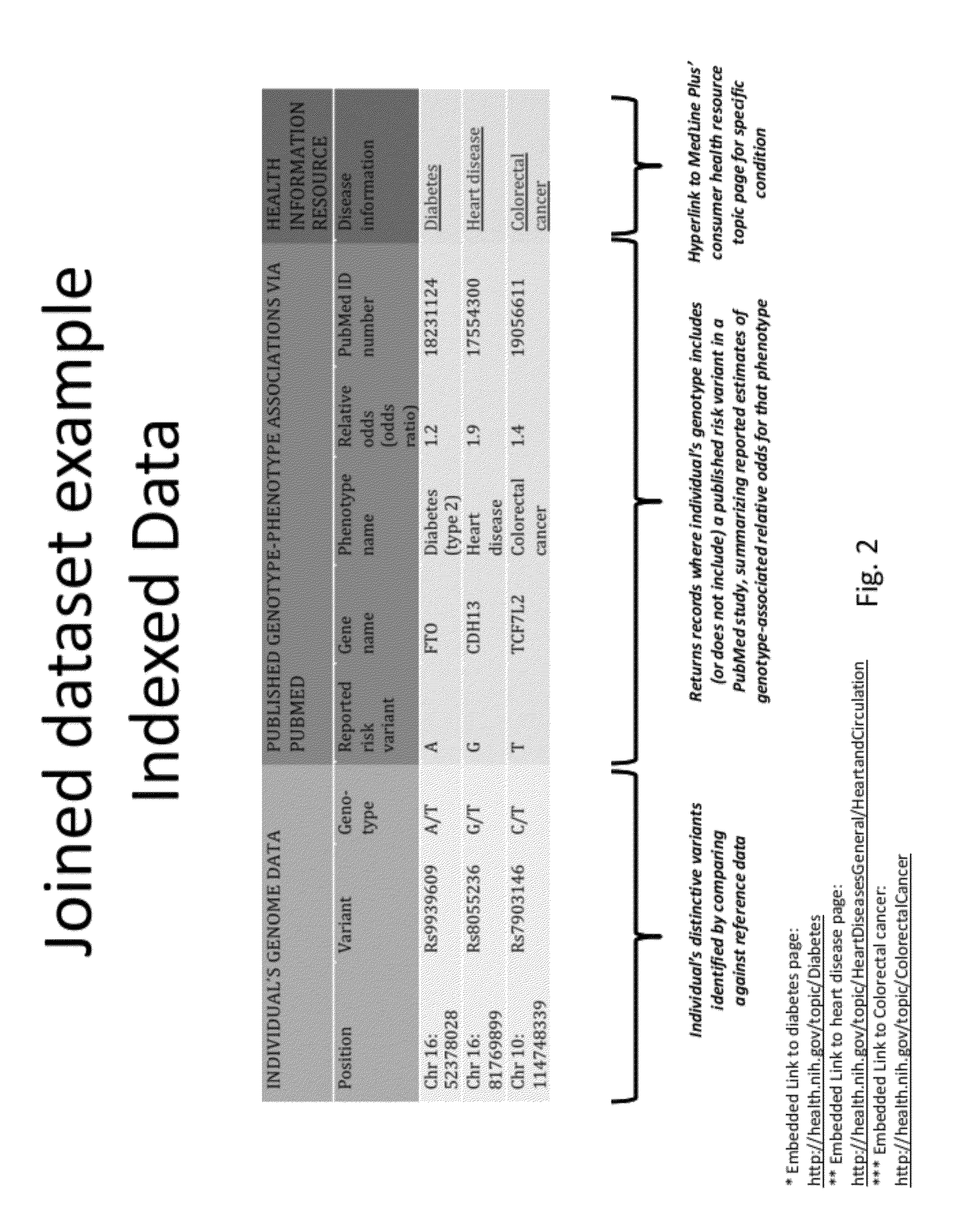
The present invention relates to method and computer systems that provide a personal genome indexer. The present invention provides an output that allows individuals to access publically available scientific resources through the “prism” of their unique genetic code. Individual genetic information is indexed with information from public databases (e.g., PubMed database) that contain genetic information about the condition and the risk allele, and public databases (e.g., MedLinePlus database) that provide information about the condition. In an aspect, the present invention provides an output display that correlates an individual's specific risk alleles with genetic information and associated phenotypic condition based on one or more references from a publically accessible database, and / or a link to consumer health information about the phenotypic condition.
Owner:KNOME
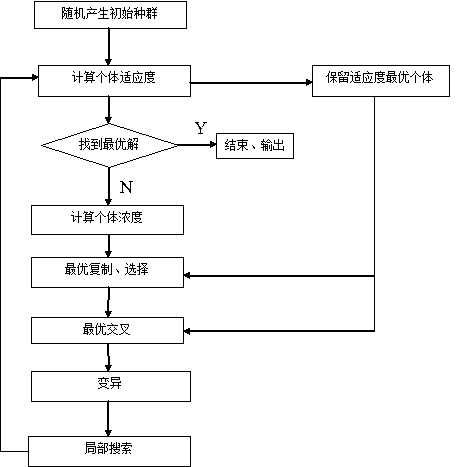
Mechanism kinematic link isomorphism identification method based on immunity genetic hybrid algorithm
InactiveCN103324983AOvercome the disadvantage of easy convergence to local optimumDiversity guaranteedGenetic modelsSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmGenetic code
The inventiondiscloses a mechanism kinematic link isomorphism identification method based on the immunity genetic hybrid algorithm. The mechanism kinematic link isomorphism identification method includes the steps of (1) forming a topological graph corresponding to a mechanism kinematic link according to the structural mode of the mechanism kinematic link, (2) setting a genetic code of an adjacent matrix according to the topological graph, (3) taking adjacent matrixes, to be determined, of the two topological graphs, determining an objective function, (4) generating the initial antibody population at random, calculating adaptability of each individual, sequencing the individuals according to the adaptability, (5) taking the optimal saving strategy on the initial antibody population, (6) calculating the concentration of each individual, enabling the each individual concentration to be equal to a value obtained by dividing the total individual number in a population by the adjacent individual sum, (7) taking the optimal interaction strategy on the antibody population obtained in the step (5), (8) conducting the mutation operation, adopting the inverse operator to achieve the mutation operation, (9) combining the local search operator and the genetic algorithm, (10) forming the immunity genetic hybrid algorithm, and conducting the isomorphism identification operation on the mechanism kinematic link. The mechanism kinematic link isomorphism identification method overcomes the shortcoming that the immunity genetic hybrid algorithm can be easily restrained to local optimum.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
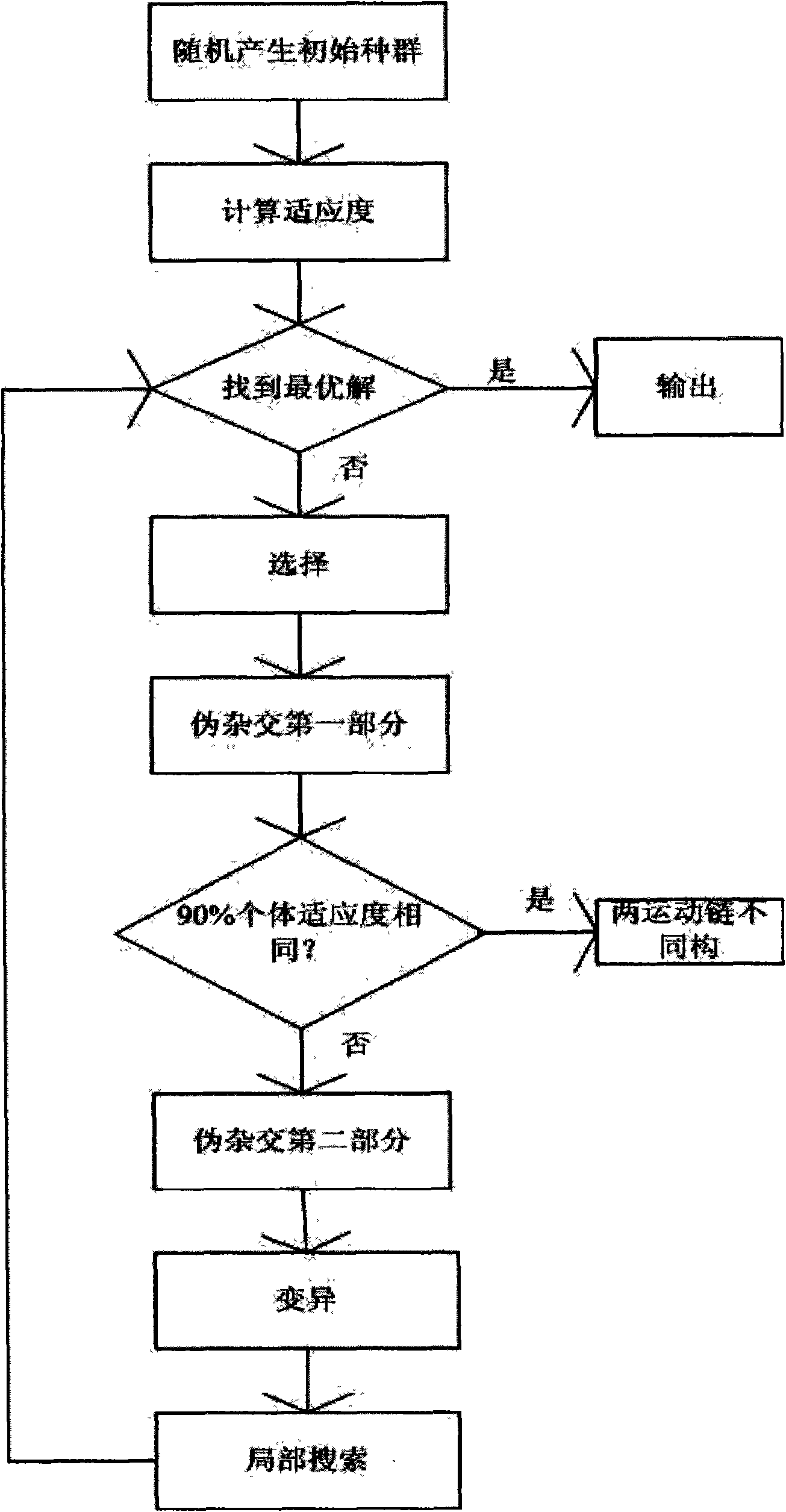
Isomorphism identification method of mechanism kinematics chain based on pseudo-hybridization hybrid genetic algorithm
InactiveCN101655928ASimple codingAvoid disadvantagesGenetic modelsSpecial data processing applicationsLocal search operatorAlgorithm
The invention discloses an isomorphism identification method of a mechanism kinematics chain based on a pseudo-crossover hybrid genetic algorithm, comprising the following steps: forming a corresponding mechanism topological graph according to a structure of the mechanism kinematics chain; setting genetic codes of an adjacent matrix; taking adjacent matrices of two mechanism topological graphs tobe judged to determine a target function and calculating a target function value and the fitness of each individual; then adopting a pseudo-crossover operator, randomly selecting two individuals froma population which is randomly generated, and randomly generating two crossover points to carry out air extension; selecting two individuals from an intermediate population which is generated by the extension to carry out primary local optimization; and finally, combining with a local searching operator to form the pseudo-crossover hybrid genetic algorithm. The invention can carry out operation and simulation on isomorphism identification of the mechanism kinematics chain so as to accurately carry out the isomorphism identification on the kinematics chain with high efficiency.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
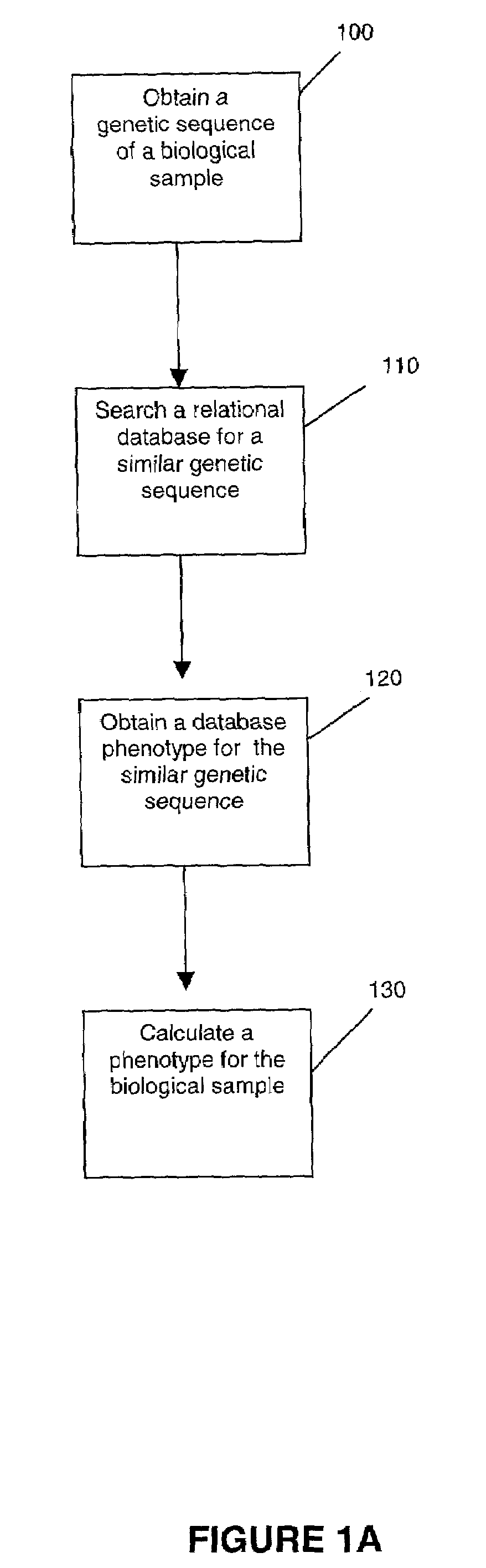
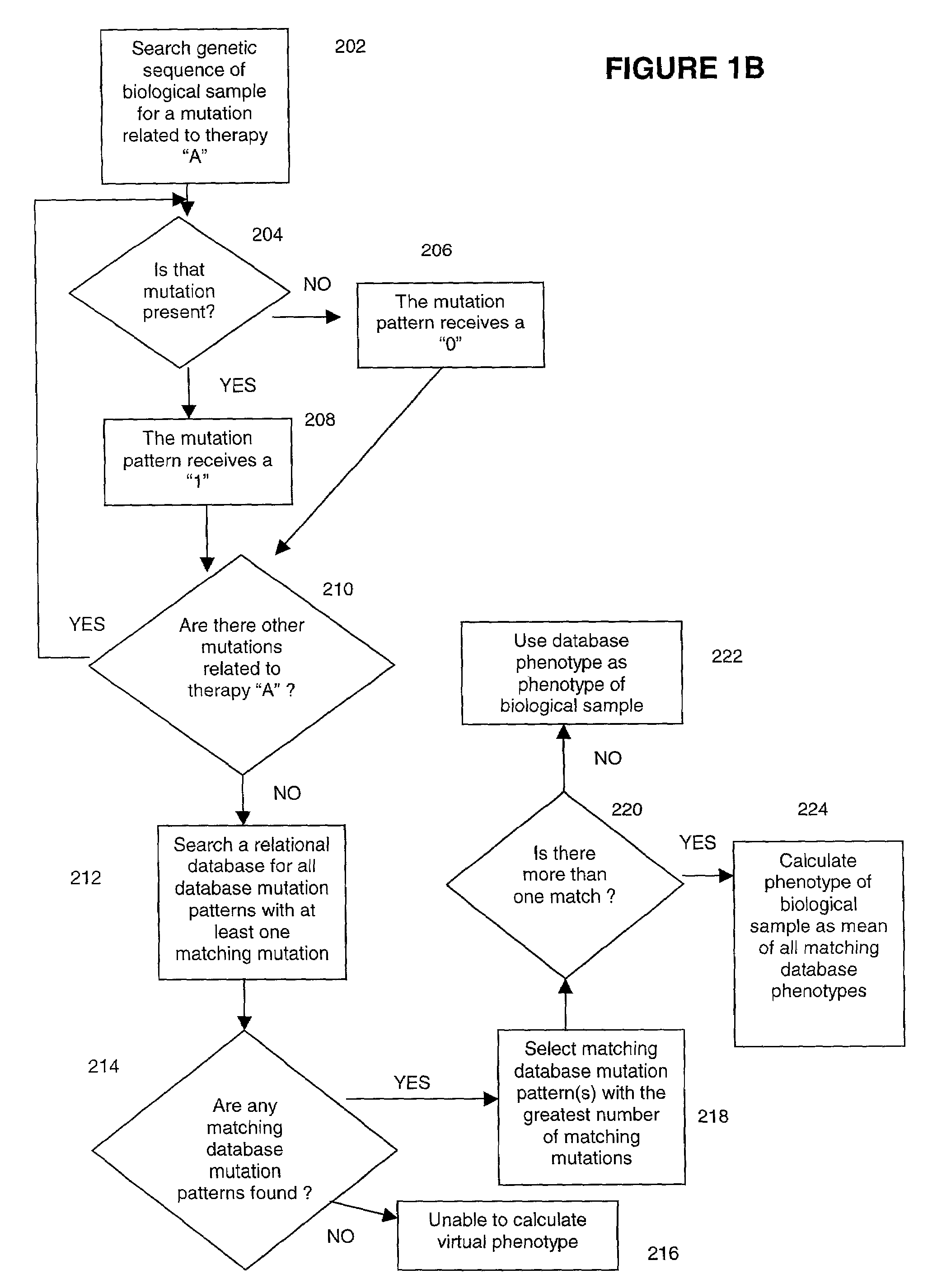
Methods for measuring therapy resistance
InactiveUS7206699B2Microbiological testing/measurementDigital data processing detailsGenotypeDrug resistance
The present invention concerns methods for measuring drug resistance by correlating genotypic information with phenotypic profiles. In one embodiment, a method for interpreting genotypic information is described wherein a genetic code is generated from a patient sample, a list of mutations known or suspect to play a role in the development of resistance to one or more drugs is obtained from the generated genetic code, a genotype database is interrogated for previous samples with similar mutations relating to said one or more drugs, a phenotype for said sample is located in a phenotype database, the mean change in inhibition is determined based on all the examples located in said phenotype database, a distribution of sensitivities of one or more drugs suitable for treating a specific indication is determined.
Owner:VIRCO BVBA
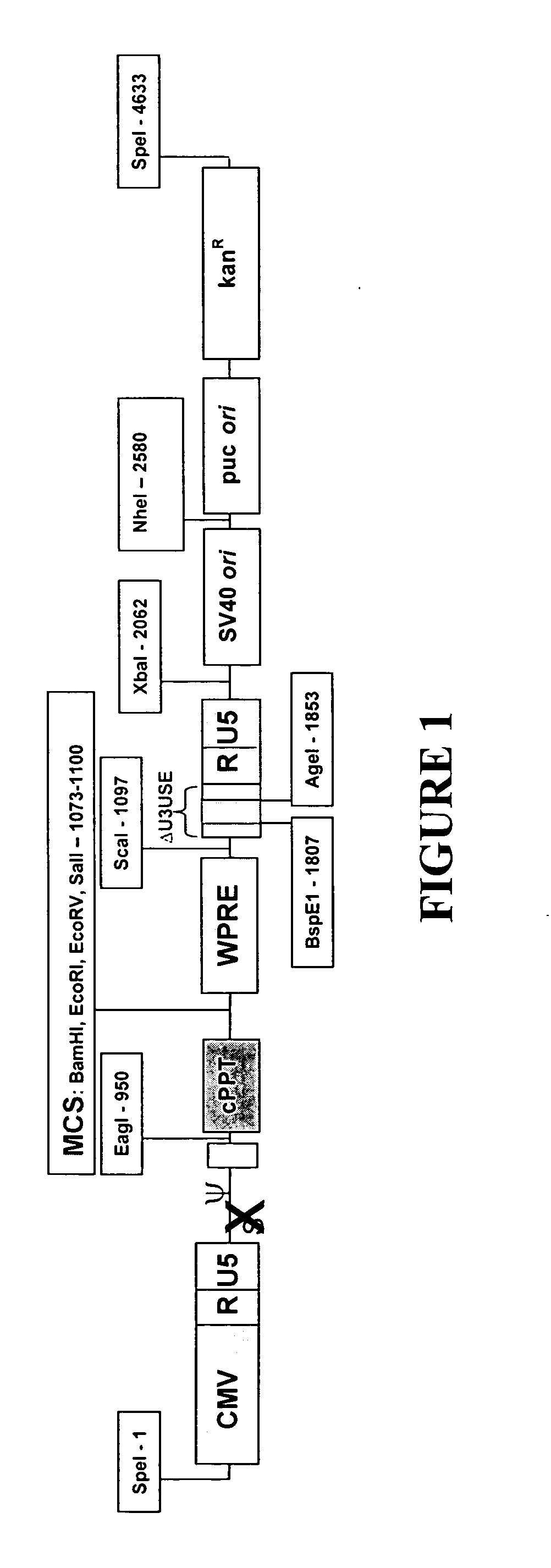
Minimal lentiviral vector system
InactiveUS20060019393A1High potencyMaximize preferenceGenetic material ingredientsVirus peptidesPoly-A RNAUpstream Enhancer
A lentiviral vector system is described. The system comprises a lentiviral transfer vector and a packaging construct. The transfer vector comprises (a) a 5′ LTR; (b) a 3′ LTR comprising a polyadenylation signal; (c) a minimal packaging signal, (d) (i) at least one heterologous upstream enhancer (UE) sequences, and / or (ii) at least one additional copy of endogenous UE sequences operatively associated with said polyadenylation signal; and (e) a PRE. The packaging construct comprises a nucleic acid encoding and expressing a lentiviral Gag nucleic acid (preferably Gag and Pol). Preferably the lentiviral Gag nucleic acid is a mutated Gag nucleic acid containing one or more substitution mutations, wherein said mutated Gag nucleic acid encodes the same amino acid sequence as the corresponding unmutated Gag nucleic acid, but differs from the nucleic acid sequence of said corresponding unmutated Gag nucleic acid sequence due to the degeneracy of the genetic code. Preferably the packaging construct further comprises a heterologous nucleic acid encoding and expressing an adenovirus VA RNA. The transfer vector and packaging construct can be used together in a producer cell to produce viral particles.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF LOS ANGELES
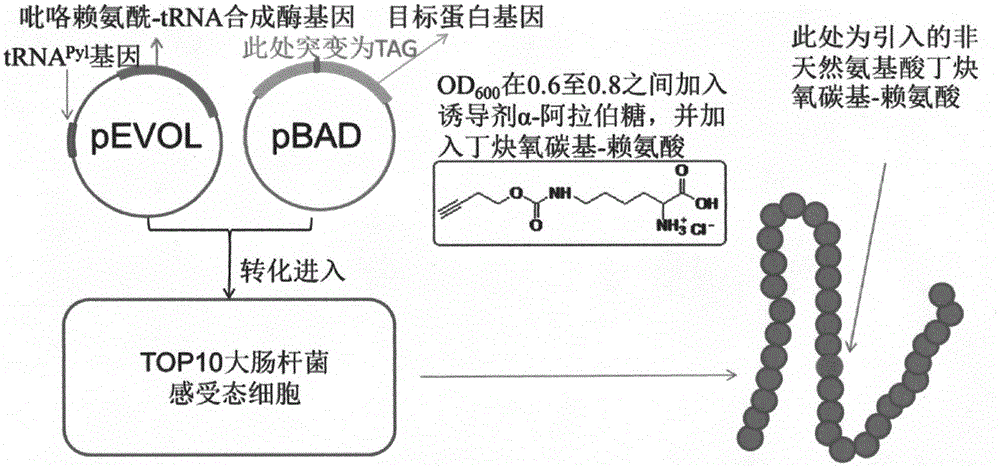
Method for fixed-point introduction of non-natural amino acid to protein
The invention relates to a method for fixed-point introduction of non-natural amino acid to protein. More specifically, the invention discloses a method for specifically guiding a non-natural amino acid Ne-butineoxycarbonyl-lysine site into expected protein. The invention also provides a system for fixed-point introduction of non-natural amino acid Ne-butineoxycarbonyl to genetic coding expression of protein. The system comprises a DNA for expressing a wild pyrrole lysyl-tRNA synthetase, a homologous related tRNA and a gene sequence of which the site needing introduction of the non-natural amino acid Ne-butineoxycarbonyl-lysine is mutated into TAG.
Owner:武汉佰福泰制药有限公司
Bacterial spores
InactiveUS20050232947A1Easy to produceLow costAntibacterial agentsPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAntigenFusion Protein Expression
The invention provides a spore genetically modified with genetic code comprising at least one genetic construct encoding an antigen and a spore coat protein as a chimeric gene, said genetically modified spore having said antigen expressed as a fusion protein with said spore coat protein.
Owner:ROYAL HOLLOWAY & BEDFORD NEW COLLEGE
Fire resistant xylanase XynA1, gene for encoding the enzyme and uses thereof
InactiveCN101402963AImprove thermal stabilityHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliReaction temperature
The invention discloses a xylanase XynA1 which is obtained by the PCR amplification of Geobacillus thermodenitrificans NG80-2 genome DNA and a recombinant xylanase for constructing an expression vector to express the genetic code in Escherichia coil. The optimal reaction temperature of the xylanase is 70 DEG C, the optimum reaction pH is 7.6, and the thermal stability is good in neutral and weak alkaline environments. The xylanase is applicable to decomposing xylan in hemicellulose to produce functional xylooligosaccharides.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Mono charging system for selectively introducing non-native amino acids into proteins using an in vitro protein synthesis system
This invention provides for a novel means of incorporating non-native amino acids into preselected positions of a protein using a cell-free synthesis system. The methods involve the use of non-orthogonal, native isoaccepting sense tRNAs that are encoded by the genetic code. Such methods allow for numerous non-native amino acids to be incorporated through the use of sense codons without having to rely upon orthogonal tRNA-synthetase pairs.
Owner:SUTRO BIOPHARMA INC
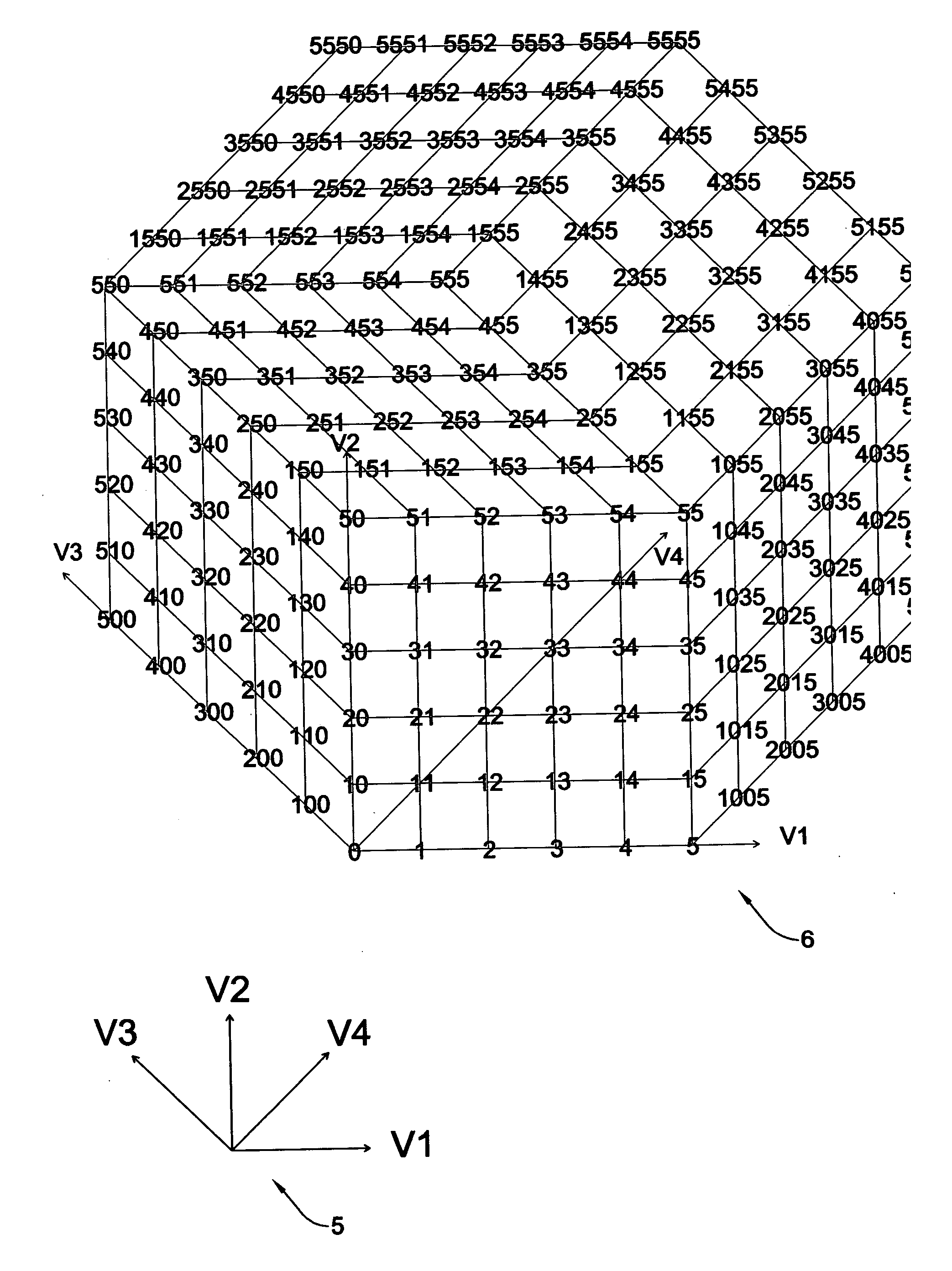
Morphological genome for design applications
ActiveUS20070188489A1Increased Design PossibilitiesGenetic modelsDigital computer detailsInteractive modelingCo ordinate
This invention deals with an integrated morphological system, herein called a morphological genome (morph genome), for design applications. This is the genome that encodes all form and is similar in intent to the biological genome that encodes all living things by its genetic code. The morph genome comprises a finite set of morphological genes, each gene specifies a distinct group of morphological transformations, each group of transformations is defined by a group of independent topological, geometric or other parameters. The morph genes and their parameters are mapped within an integrated higher-dimensional framework, with each parameter being represented along a vector in higher-dimensional Euclidean space. Each distinct number associated with a parameter or a group of parameters is represented by a distinct point in this space and is referenced by the higher-dimensional Cartesian co-ordinates of that point. This space uses a combination of discrete and continuous values for these parameters. The specific co-ordinates of any point in the space represent a genetic code for the specific form being mapped at that point. The entire space is a map of the morph genome and encodes all possible morphologies. The morph genome can be used as a design tool to generate known and new forms for applications in all fields of design including architecture, product design, environments and spaces, building or engineering structures, graphics, art, sculpture, technological devices, etc. The underlying method for the model for the morph genome applies to other fields of knowledge for systematically organizing and creating new concepts, structures, designs, information and taxonomies. The morph genome can also provide a basis for an integrated, interactive modeling environment for computers. It is a pedagogical tool for discovery and invention as well. Other applications include a graphic code for encryption as an alternative to numeric codes, and a system for representing numbers as integers, rational numbers and real numbers.
Owner:LALVANI HARESH
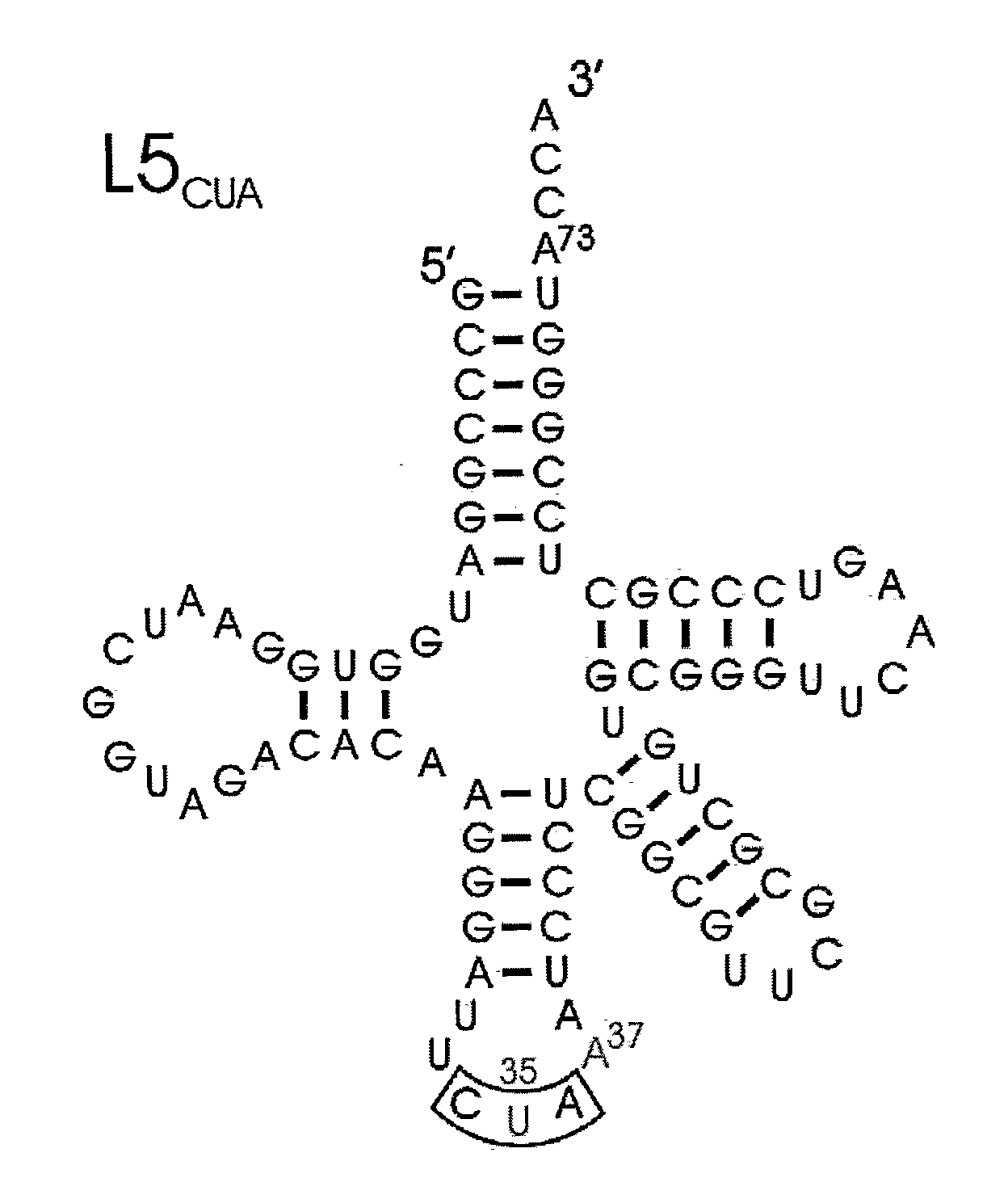
Nonsense suppression and genetic codon alteration by targeted modification
ActiveUS8603457B2Easy to identifyLarge productionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAdenosineGenetics
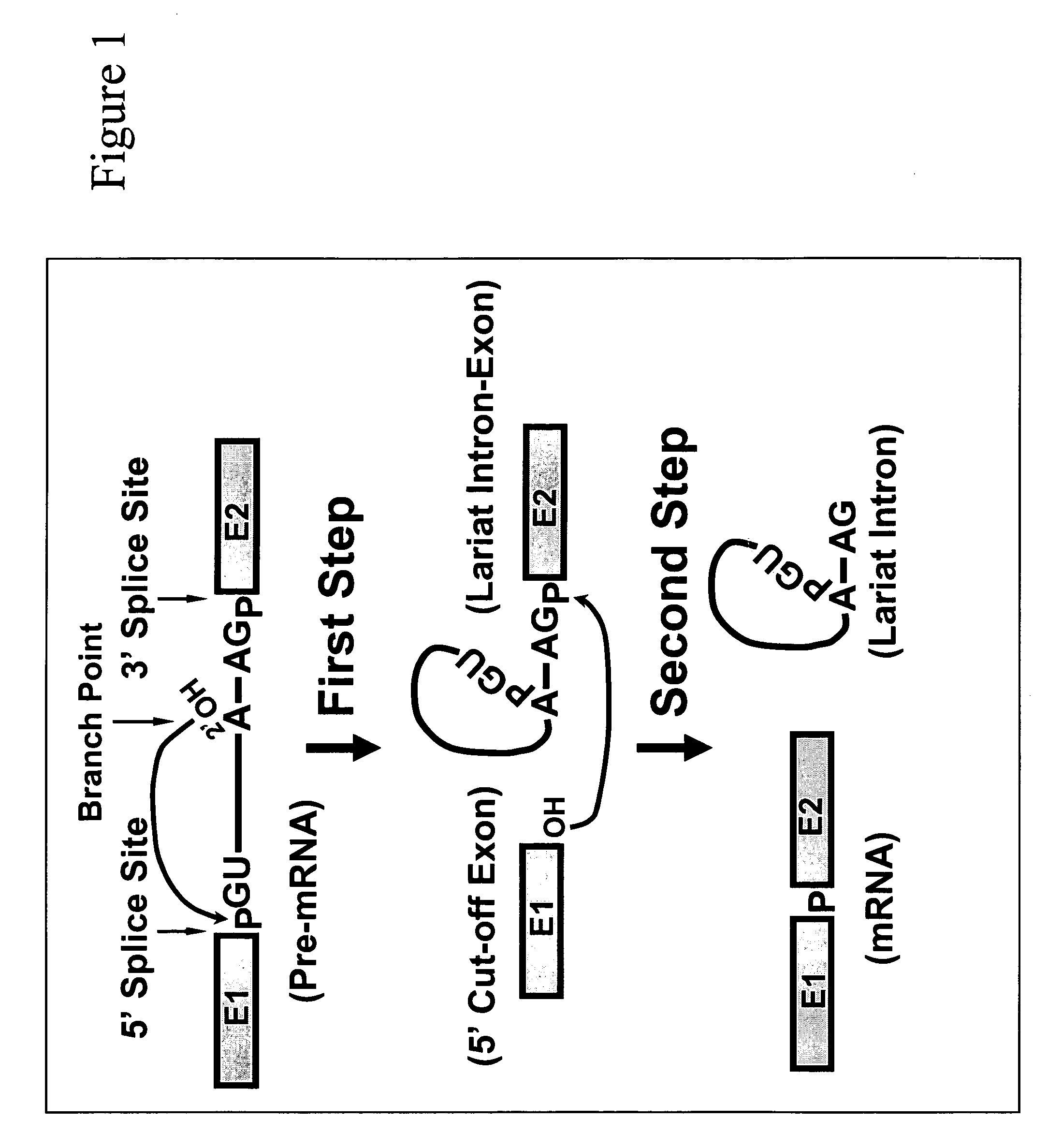
Methods for affecting mRNA expression or translation through the modification of pre-mRNA or mRNA transcripts are described. In one embodiment of the methods of the present invention, the branch point adenosine of a pre-mRNA transcript is 2′-O-methylated to block splicing and subsequent expression of the protein encoded by the transcript. In another embodiment, a uridine residue in a nonsense stop codon may be modified to pseudouridine, causing the translation machinery to read through the nonsense stop codon and translate a full length protein.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
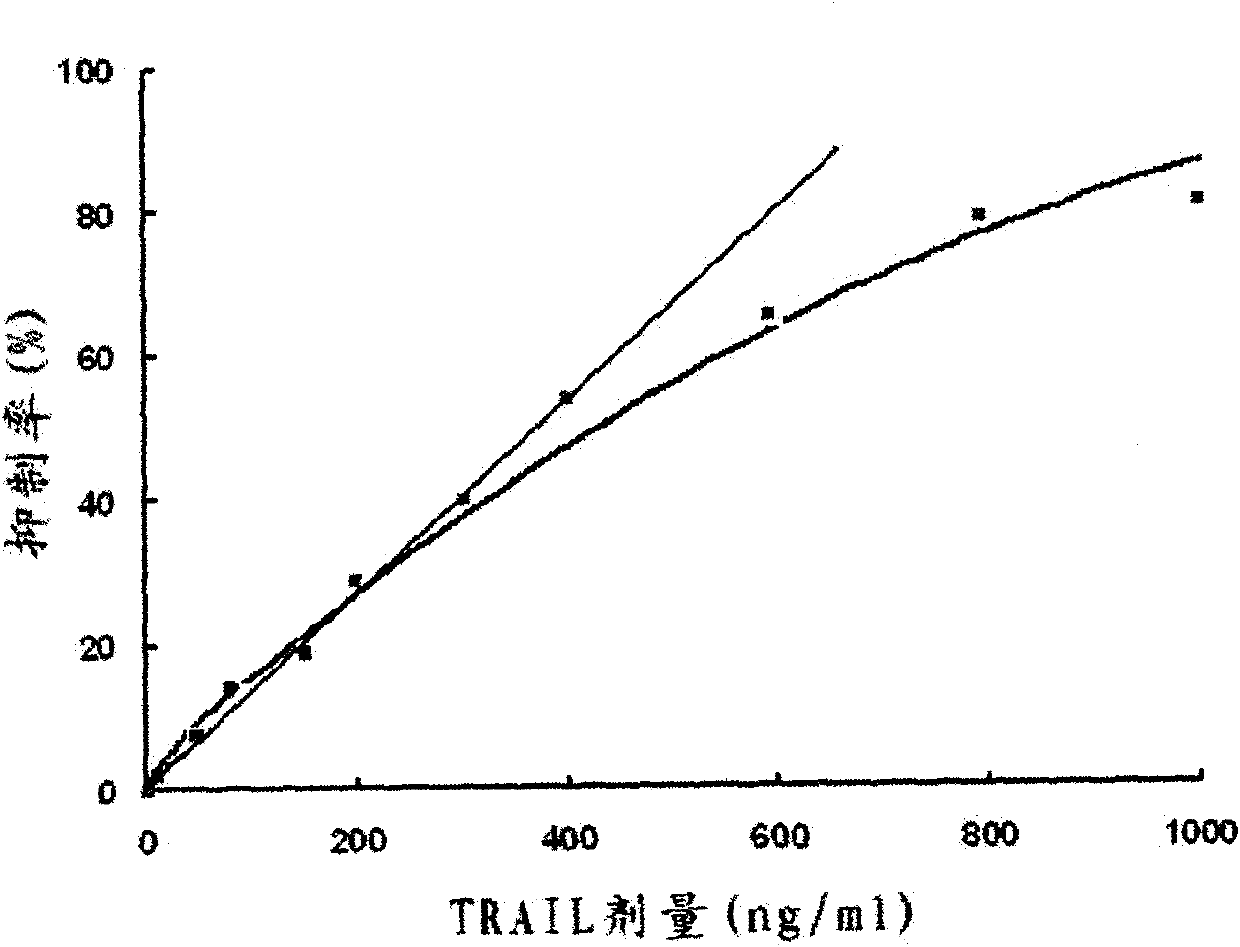
Preparation method for soluble truncated human tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) active protein
InactiveCN102021173ATruncated soluble expressionShort fermentation timeCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide preparation methodsHumaninInclusion bodies
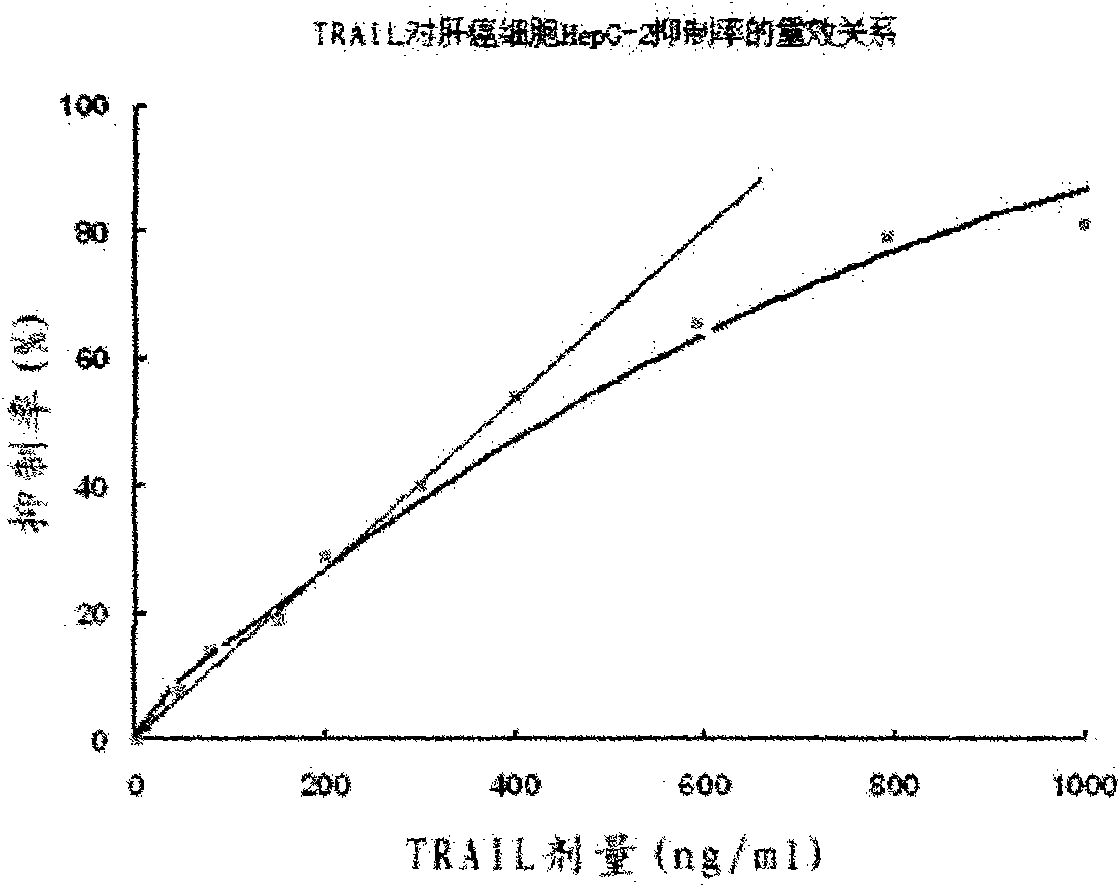
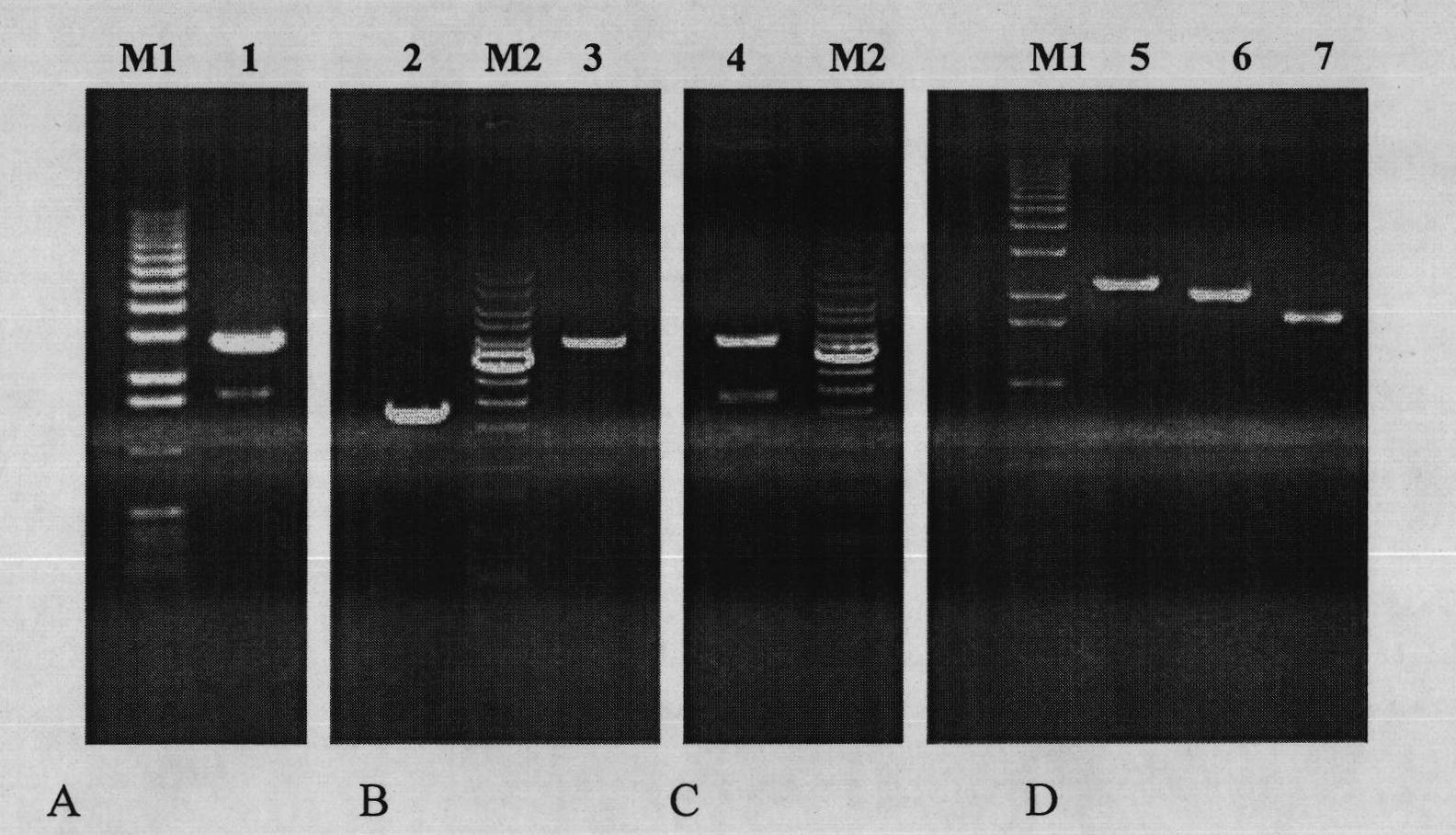
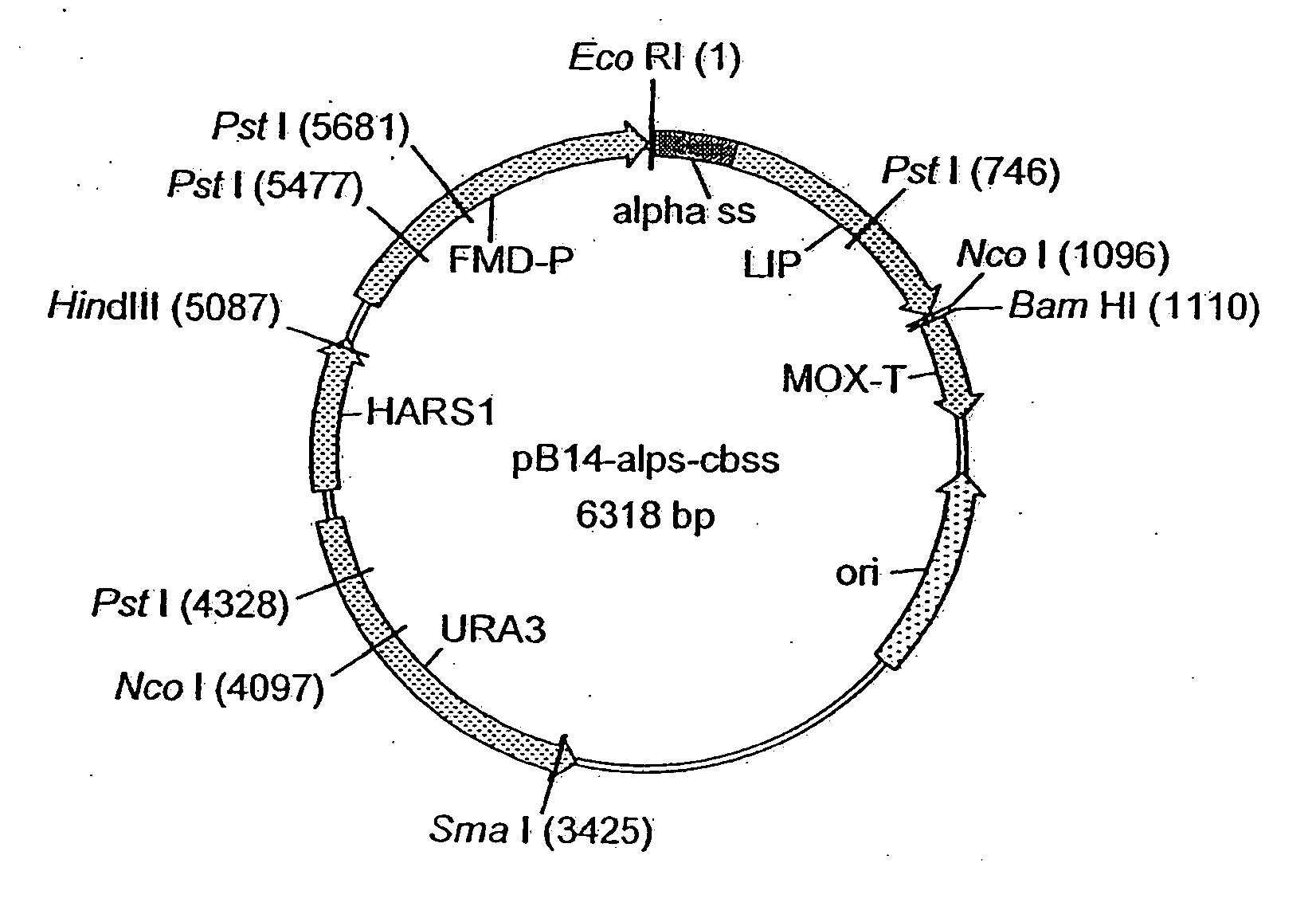
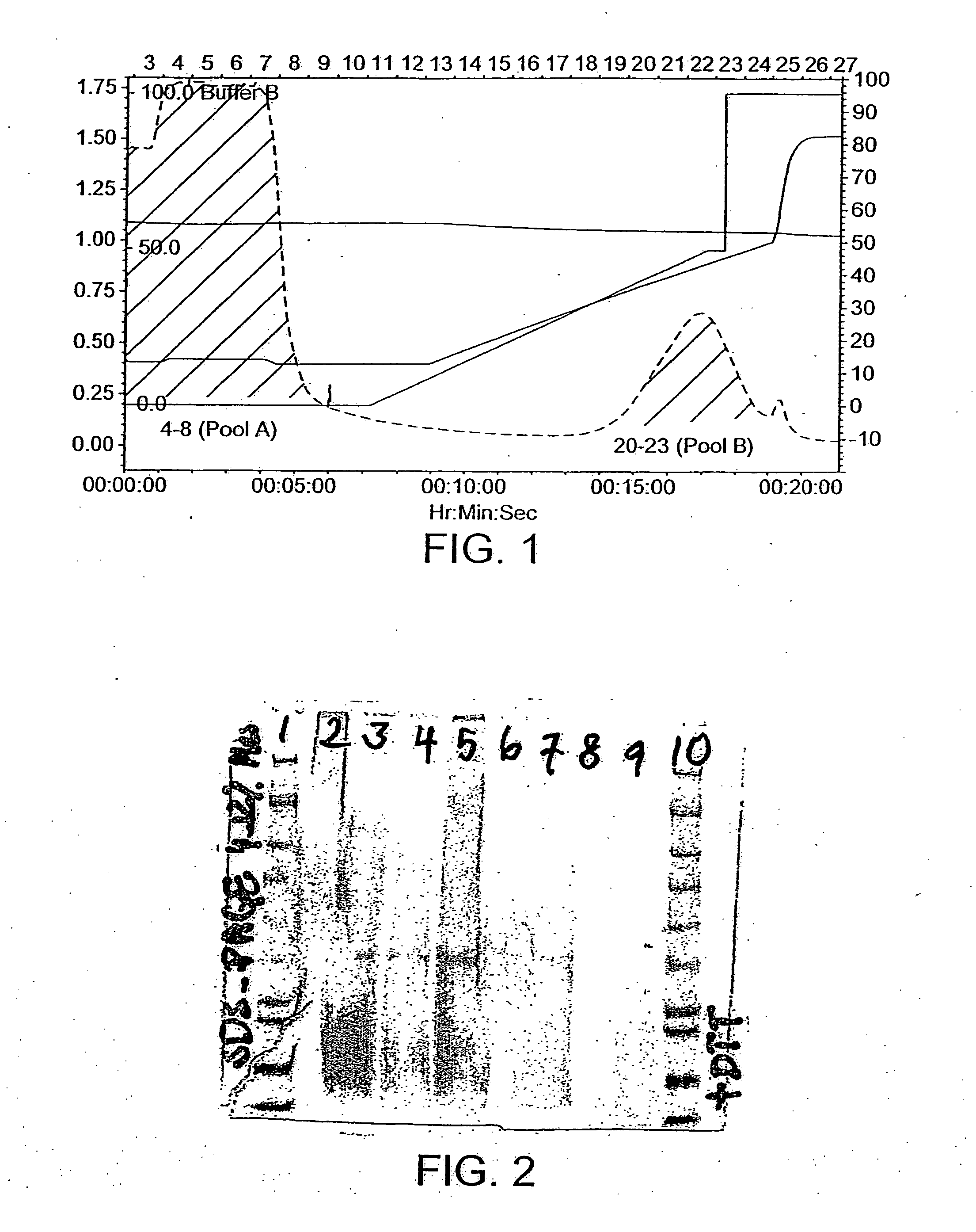
The invention provides a preparation method for a soluble truncated human tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) active protein, comprising the following steps of: (A) designing and synthetizing an oligomerization deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) single-stranded segment according to the amino acid sequence of the human TRAIL protein issued by a Genebank by the preference of a bacterium genetic code; (B) synthetizing a complete double stranded DNA by three-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR); (C) carrying out amplification by utilizing a T-carrier, and inserting the amplified double stranded DNA segment into an expression carrier and screening a positive transformant; (D) expressing the truncated human TRAIL protein in escherichia coli at low temperature; (E) purifying the protein by using a three-step method; and (F) determining the truncated TRAIL protein. The invention realizes that the truncated human TRAIL protein is efficiently expressed in an escherichia coli cell and a purification preparation technique thereof and overcomes the problem that an infusible inclusion body is easy to form in the prior art. The method has the advantages of simple operation, short fermentation time and easy purification, and moreover, the protein is ensured not to have any modification, and the protein reaches electrophoretically pure. The invention can be directly used for the research work of biochemistry and molecular biology and the oncology and the preclinical stage of tumor treatment or the development of clinical drugs.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Preparation method of maltooligosyltrehalose hydrolase gene sequence and recombinant protein thereof
The preparation method of the invention comprises the following steps: the genetic codon of maltooligosyltrehalose hydrolase (MTHase) gene is modified artificially, yeast preferred codon is synthesized and the A / T content of the genetic codon is modified, a MTHase gene sequence of which structure of genetic codon is optimized and A / T content is reduced is obtained; then the complete MTHase gene is cloned to the yeast expression vector pPICZ alpha A, recombinant vector is screened out and introduced in Pichia Pastoris cell to perform recombinant expression; and a yeast strain which can efficiently and stably express MTHase can be obtained. The enzyme activity of MTHase which is secreted by the yeast strain in the supernate of expression culture medium is more than 800mg / L, thus the preparation method of the invention lays a foundation for the industrial production of trehalose which adopts enzyme process and uses starch as raw material.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV
Protein
A fungal wild-type lipolytic enzyme having a higher ratio of activity on polar lipids compared with triglycerides, wherein the enzyme preferably has a phospholipid:triglyceride activity ratio of at least 4. Preferably, the lipolytic enzyme according to the present invention has a glycolipid:triglyceride hydrolyzing activity ratio of at least 1.5. In one embodiment, the fungal lipolytic enzyme according to the present invention comprises an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 or SEQ ID No. 2 or SEQ ID No. 4 or SEQ ID No. 6 or an amino acid sequence which has at least 90% identity thereto. The present invention further encompasses a nucleic acid encoding a fungal lipolytic enzyme, which nucleic acid is selected from the group consisting of: (a) a nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide shown in SEQ ID No. 3, SEQ ID No. 5 or SEQ ID No. 7; (b) a nucleic acid which is related to the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID No. 3, SEQ ID No. 5 or SEQ ID No. 7 by the degeneration of the genetic code; and (c) nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence which has at least 90% identity with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 3, SEQ ID No. 5 or SEQ ID No. 7.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
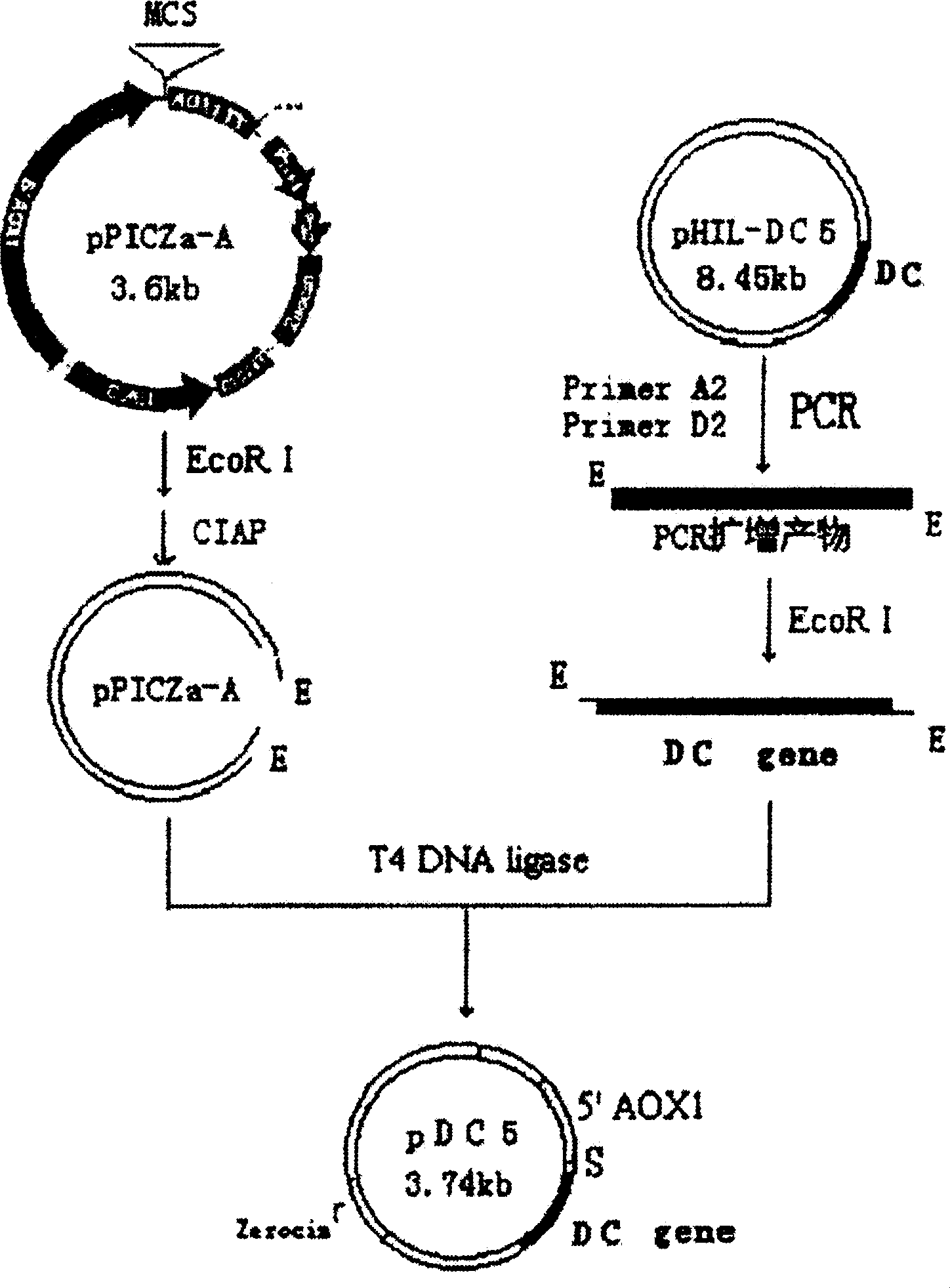
Antibacterial peptide DC and its preparing process and use
InactiveCN1702083AGood antibacterial effectHigh bactericidal potencyAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsProtozoaCandida famata
The invention discloses an antibiotic peptide and its preparation and application. According to sequence of natural antibiotic peptide, gene of antibiotic peptide is designed and synthesized in DNA synthesizer by choosing genetic code preferred by yeast. The invention selects dispense of culture medium and optimizes condition of fermentation. The antibiotic peptide can kill many pathogenic microorganisms such as Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacterium and so on.
Owner:GUANGDONG COOWAY BIOTECH CO LTD
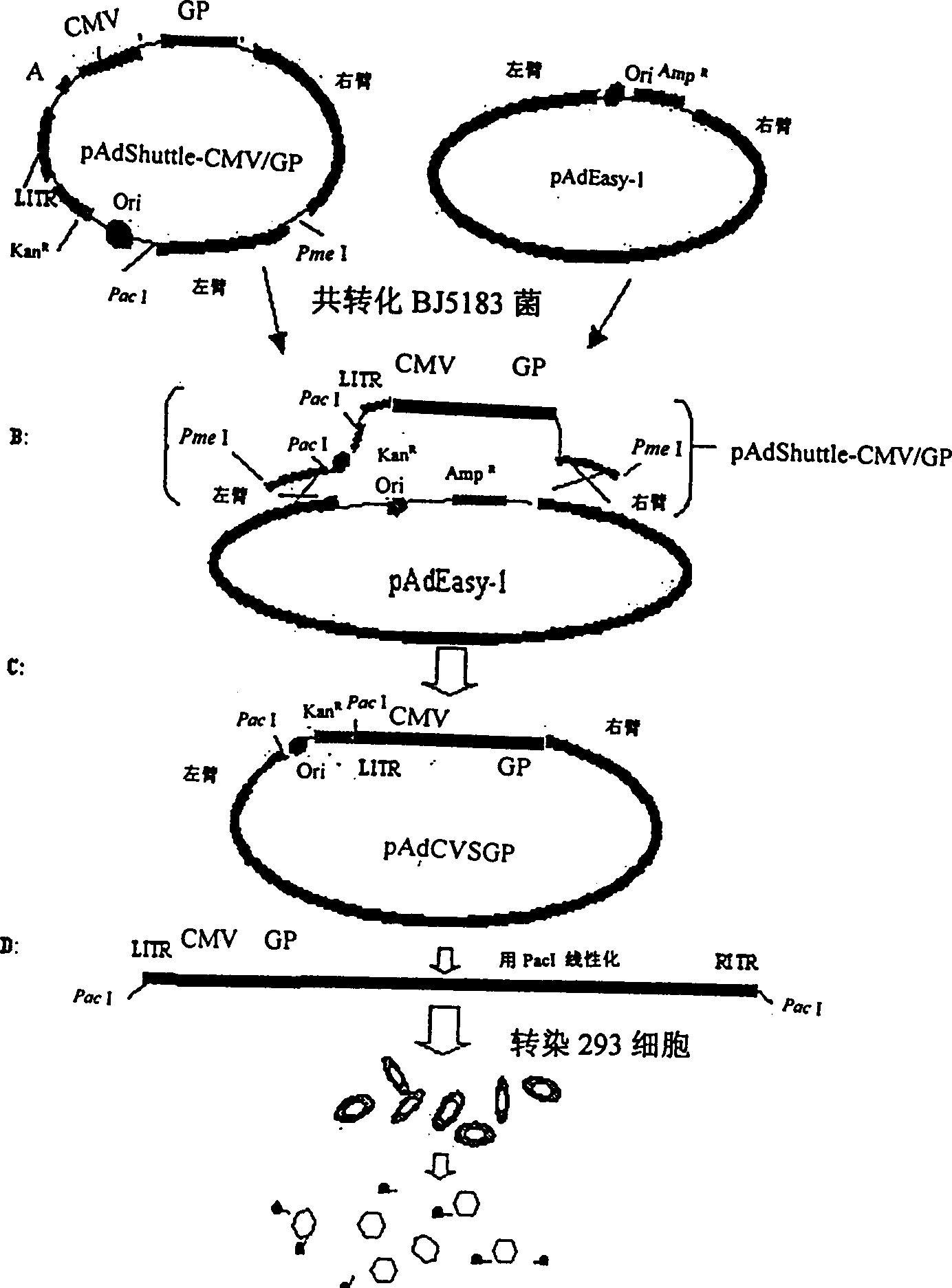
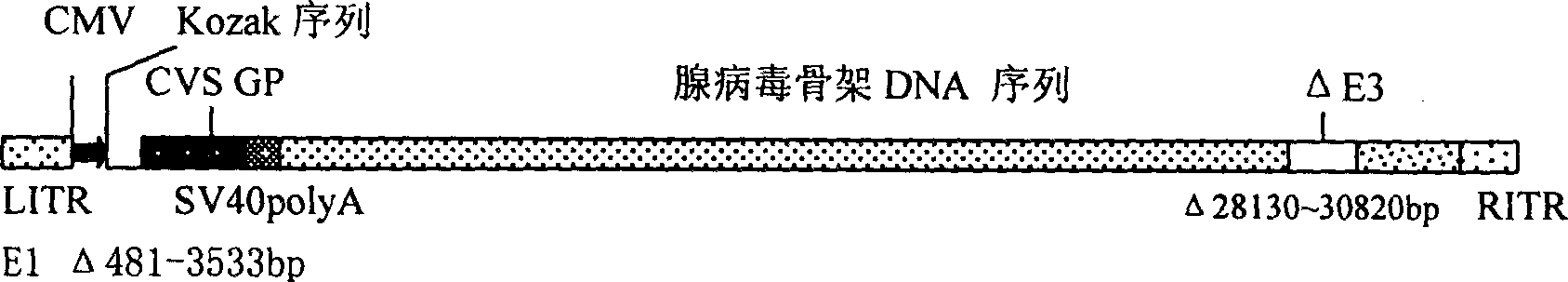
Genetically engineered rabies virus vaccine with recombination-defective adenovirus carrier
A genetically engineered rabies virus vaccine with the E1 and E3 deficient recombinant defective human adenovirus as carrier is disclosed. The rabies virus coated glucoprotein encoding gene and the element to regulate it for efficient expression are carried in the E1 region. The said encoding gene comes from the rabies virus CVS-N2C with strong neurovirulence.
Owner:THE INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Rice stress resistance related gene OsPP2C44 and coded protein and application thereof
InactiveCN102943084AImprove resistance to osmotic stressResponsive to stressHydrolasesFermentationBiotechnologyAbscisic acid
The invention discloses an OcPP2C44 gene separated and cloned from rice deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) fragments and related to rice stress resistance. The protein of the genetic code contains protein phosphatase family conservative catalytic structural domain and is a member of a PP2C type of the gene family. The OsPP2C44 gene is performed with inducible expression of high salinity, low temperature, high temperature and abscisic acid (ABA), and overexpression OsPP2C44 can improve osmotic stress resistance capability of rice during seedling stage and is related to rice stress resistance. The rice gene of the OcPP2C44 gene has obvious response to adverse situation, can be applied to plant stress resistance breeding, and improves stress resistance of plants.
Owner:SHANGHAI AGROBIOLOGICAL GENE CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com