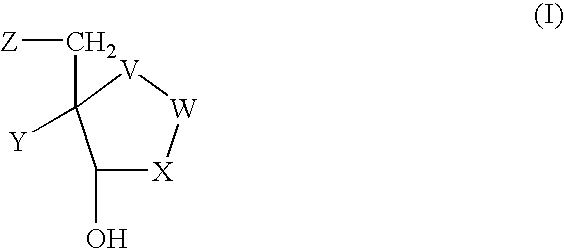Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
504 results about "Protozoa" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Protozoa (also protozoan, plural protozoans) is an informal term for single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, which feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Historically, the protozoa were regarded as "one-celled animals", because they often possess animal-like behaviors, such as motility and predation, and lack a cell wall, as found in plants and many algae. Although the traditional practice of grouping protozoa with animals is no longer considered valid, the term continues to be used in a loose way to identify single-celled organisms that can move independently and feed by heterotrophy.
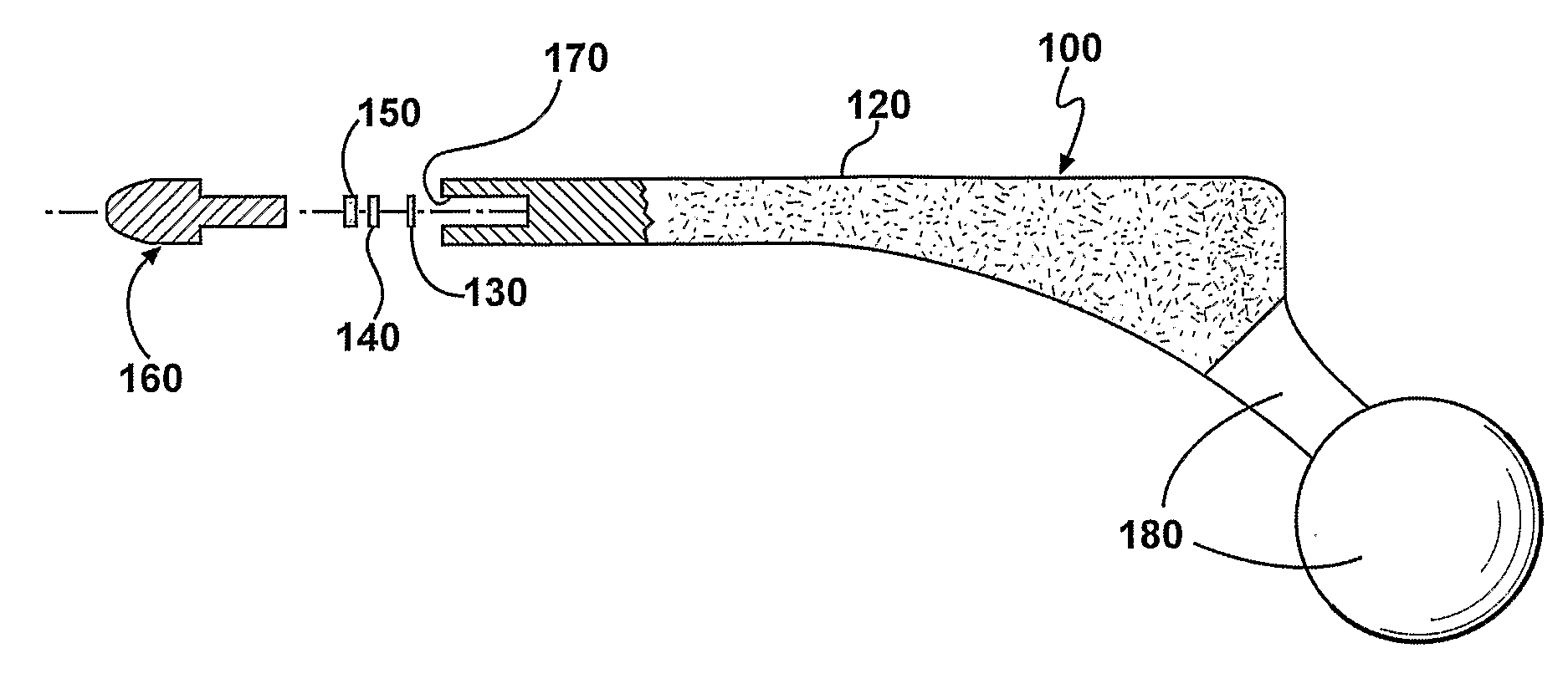
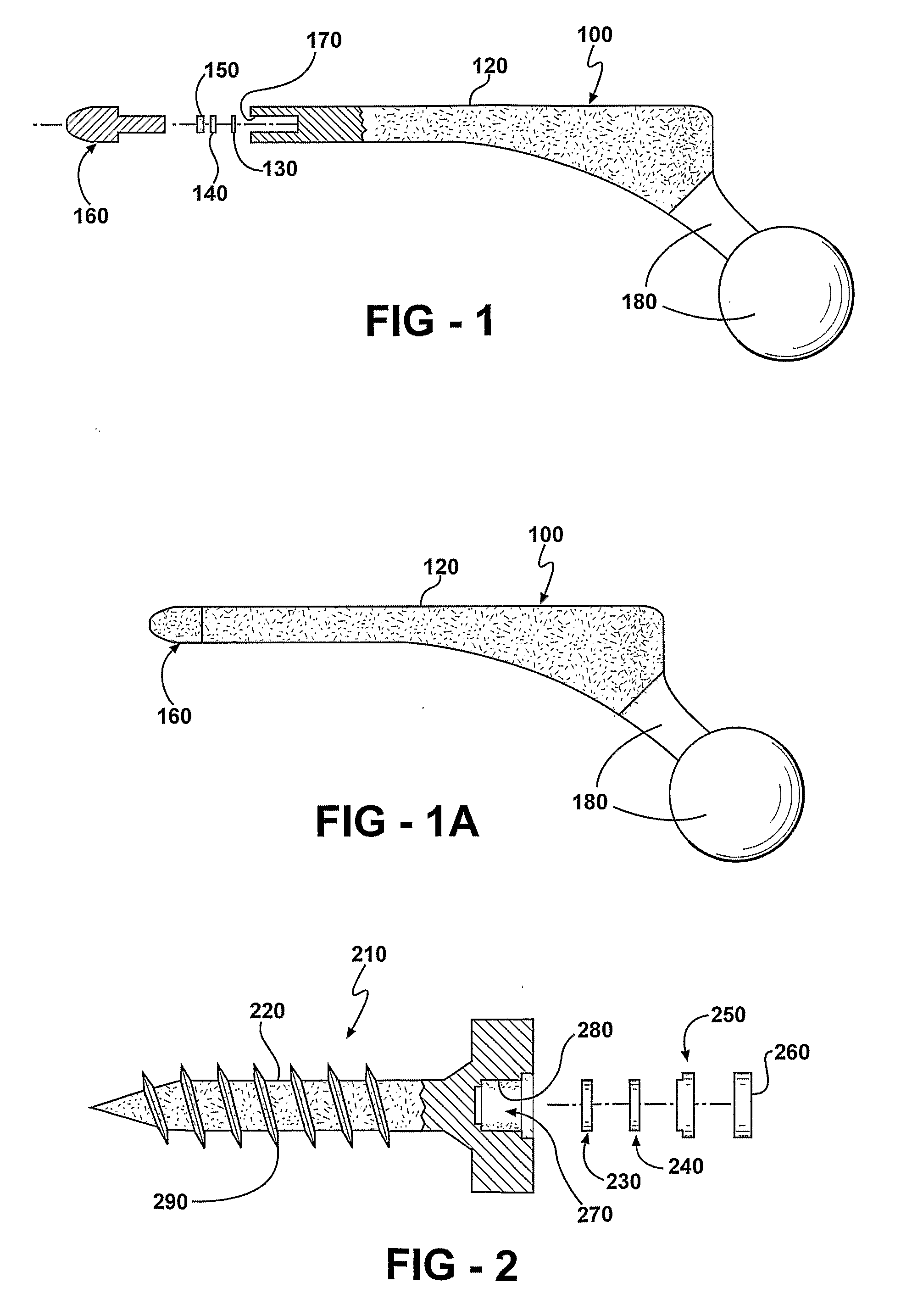
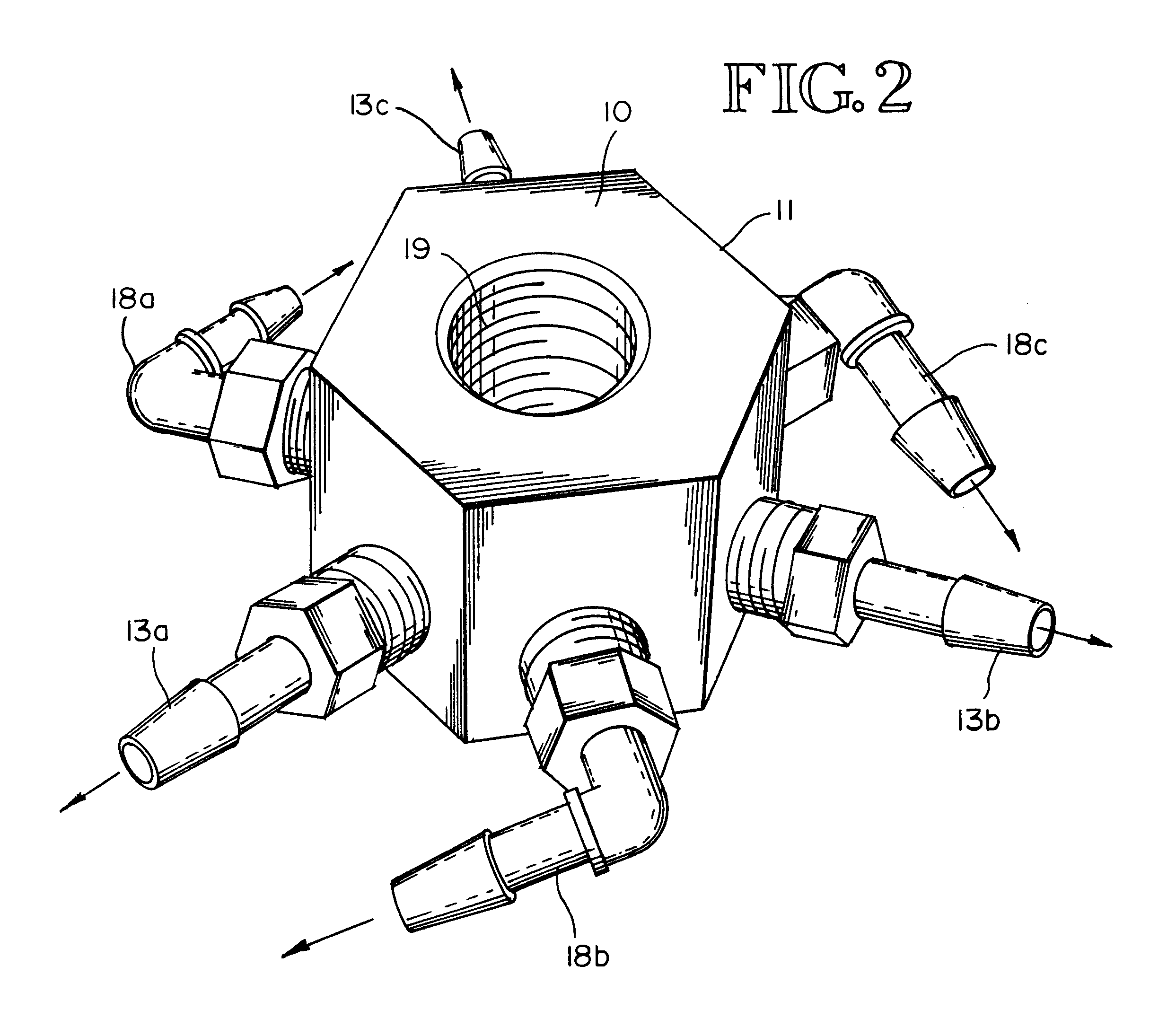
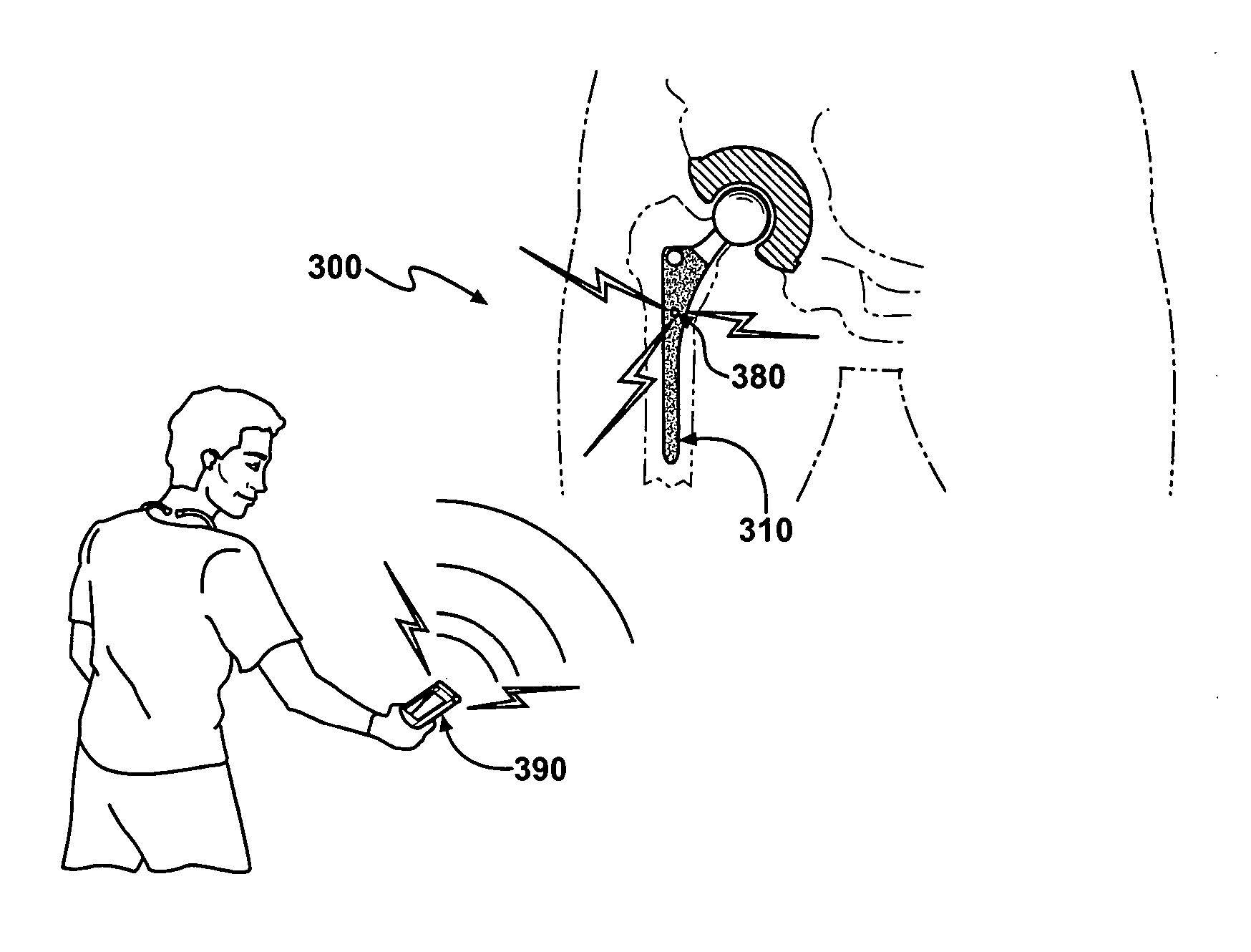
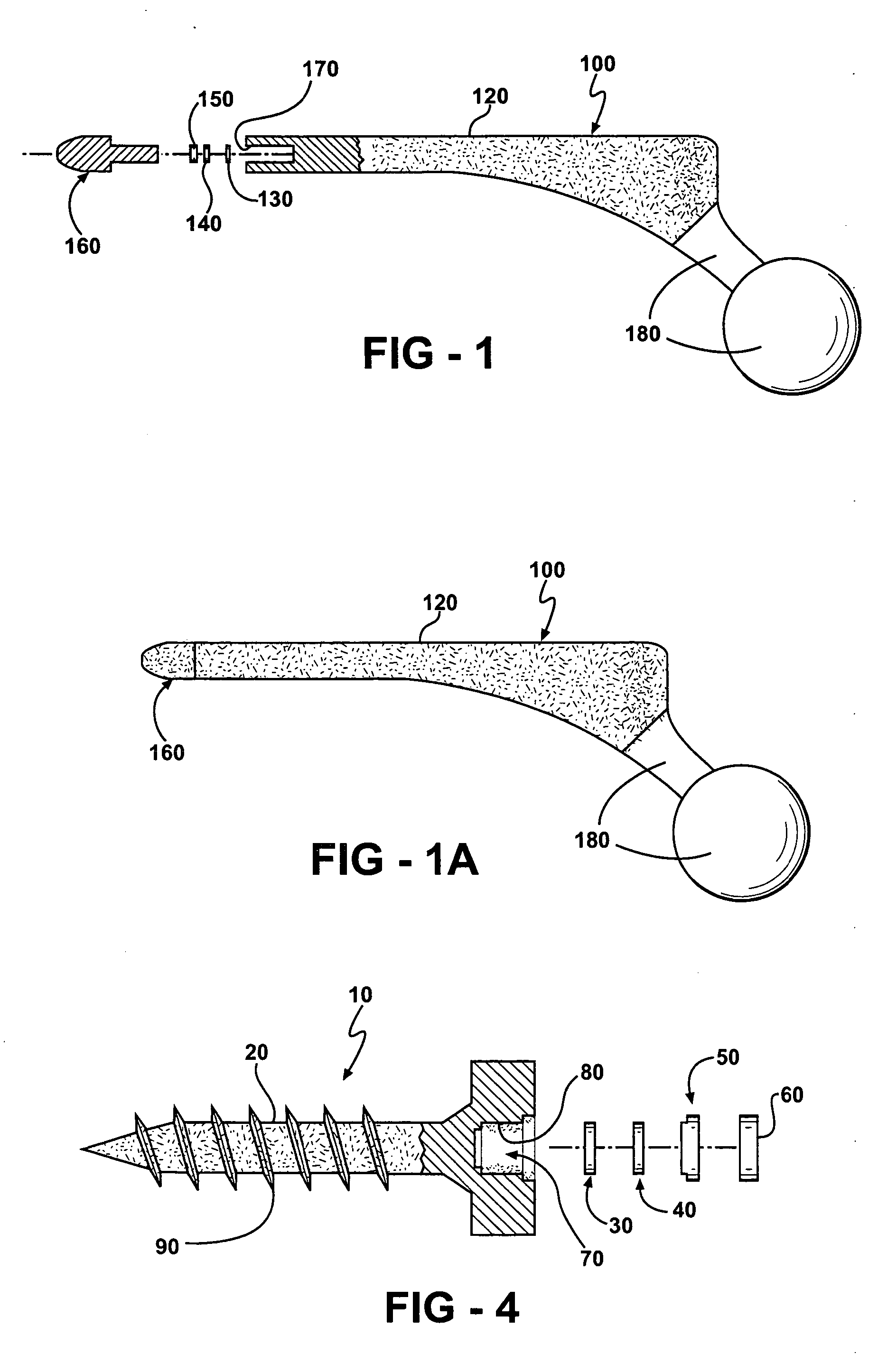
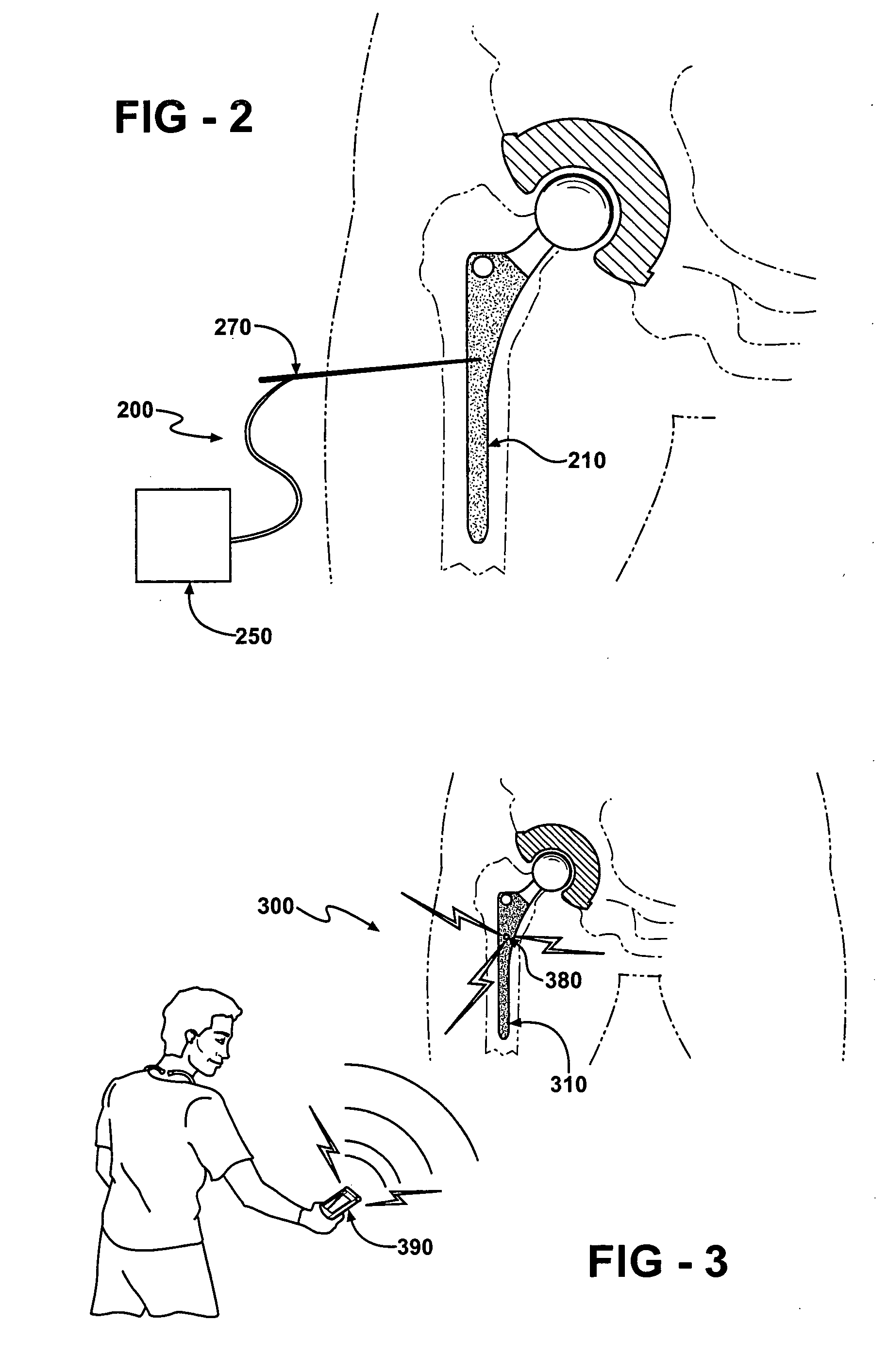
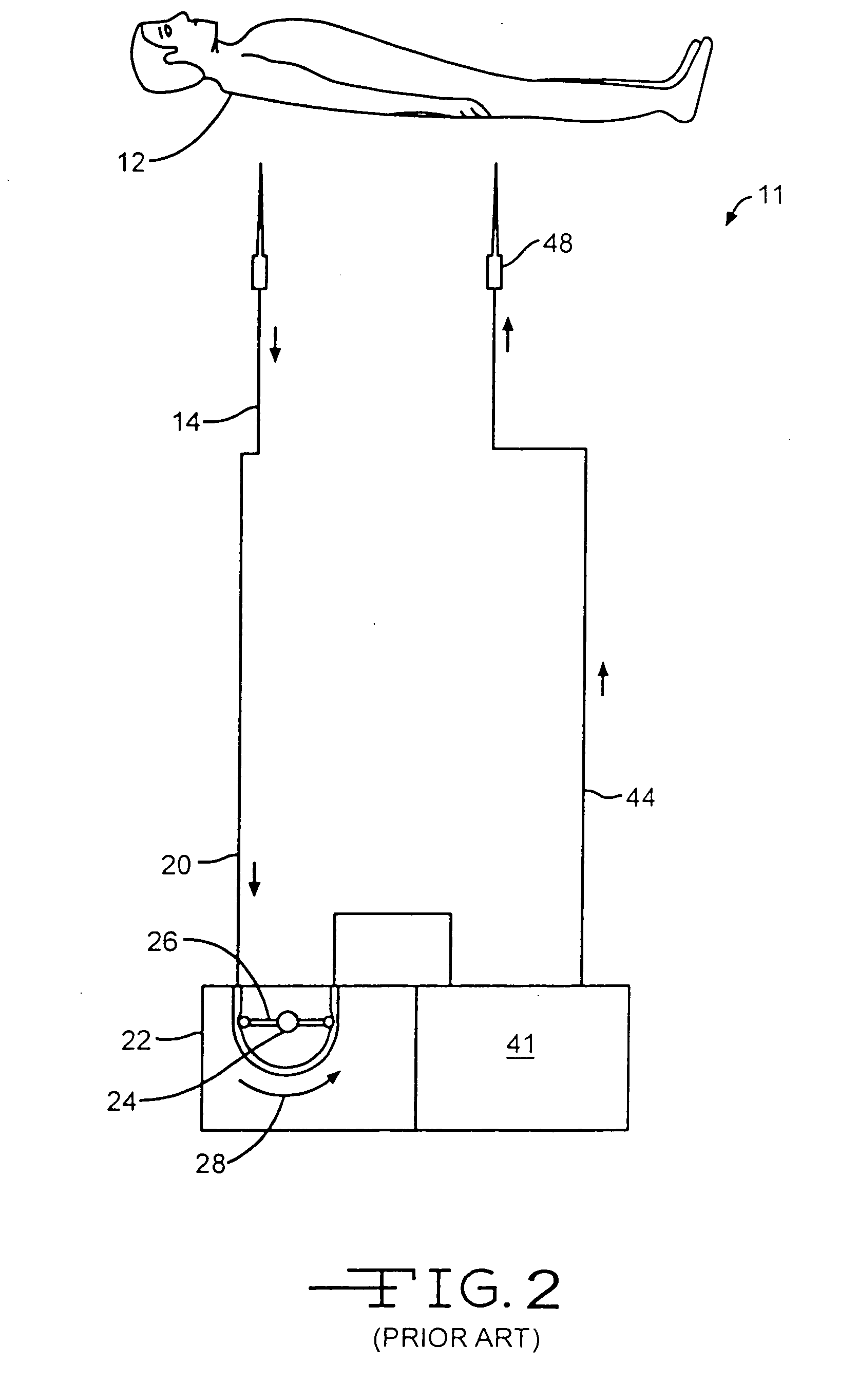
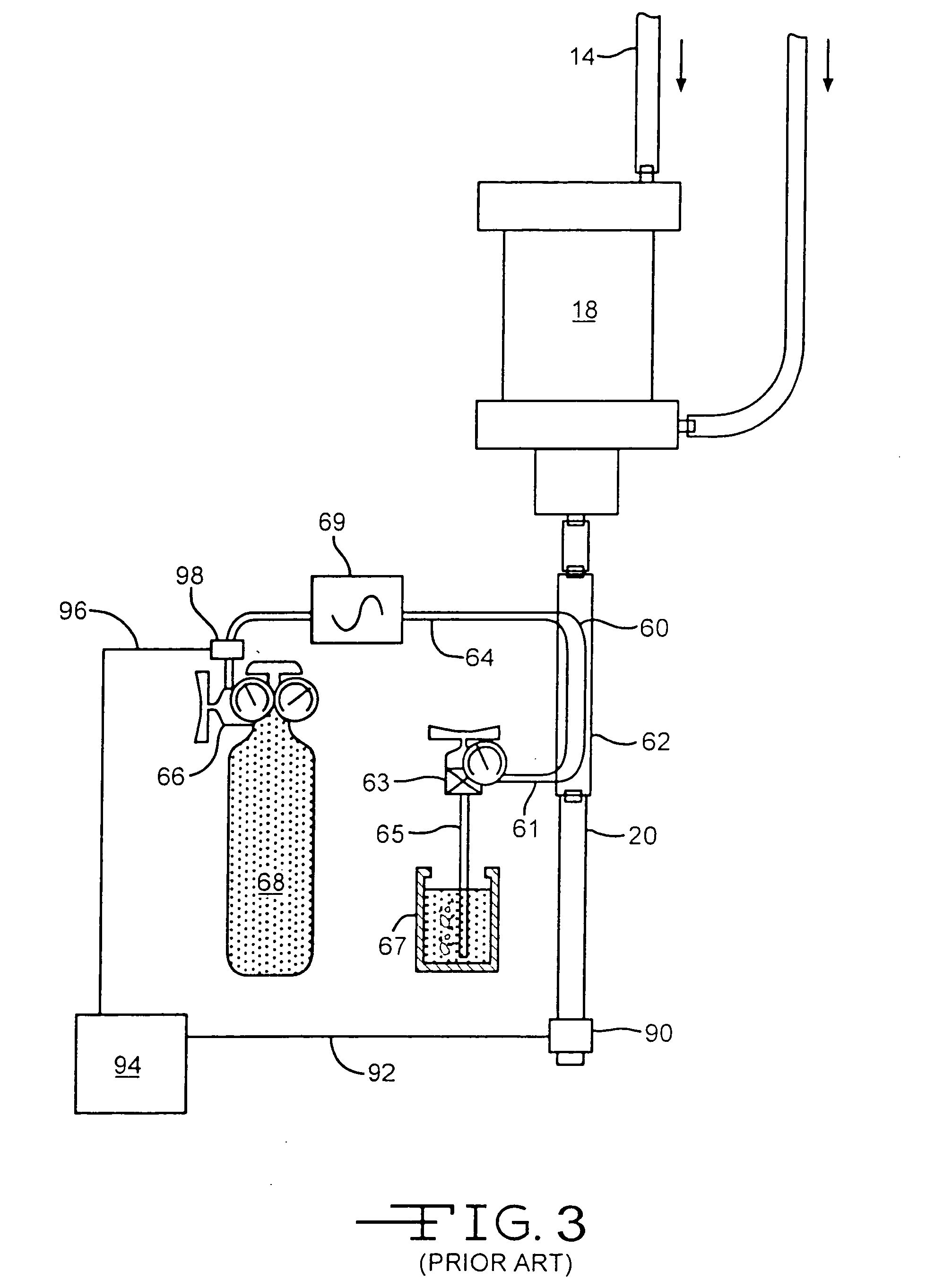
Prophylactic bactericidal implant
InactiveUS20060004431A1Prevent microbial infectionSuture equipmentsElectrotherapyProtozoaSurgical operation
A medical implant system is described for inhibiting infection associated with a joint prosthesis implant. An inventive system includes an implant body made of a biocompatible material which has a metal component disposed on an external surface of the implant body. A current is allowed to flow to the metal component, stimulating release of metal ions toxic to microbes, such as bacteria, protozoa, fungi, and viruses. One detailed system is completely surgically implantable in the patient such that no part of the system is external to the patient while the system is in use. In addition, externally controlled devices are provided which allow for modulation of implanted components.
Owner:AIONX ANTIMICROBIAL TECH INC
Vectors for the diagnosis and treatment of solid tumors including melanoma
The present invention is directed to the isolation and use of super-infective, tumor-specific vectors that are strains of parasites including, but not limited to bacteria, fungi and protists. In certain embodiments the parasites include, but are not limited to, the bacterium Salmonella spp., such as Salmonella typhimurium, the bacterium Mycobacterium avium and the protozoan Leishmania amazonensis. In other embodiments, the present invention is concerned with the isolation of super-infective, tumor-specific, suicide gene-containing strains of parasites for use in treatment of solid tumors.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Systems and methods for enrichment of analytes
The present invention relates to methods for detecting and concentrating minute amounts of biohazard analytes, including but not limited to bacteria, protozoa, viral pathogens, and toxins, in environmental and other samples. These analytes can be substantially enriched by the methods of the invention, and further, a second analyte can be removed from the sample.
Owner:ARTEMIS HEALTH INC +2
Vectors for the diagnosis and treatment of solid tumors including melanoma
The present invention is directed to the isolation and use of super-infective, tumor-specific vectors that are strains of parasites including, but not limited to bacteria, fungi and protists. In certain embodiments the parasites include, but are not limited to, the bacterium Salmonella spp., such as Salmonella typhimurium, the bacterium Mycobacterium avium and the protozoan Leishmania amazonensis. In other embodiments, the present invention is concerned with the isolation of super-infective, tumor-specific, suicide gene-containing strains of parasites for use in treatment of solid tumors.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Ultrasensitive sensor and rapid detection of analytes
The present invention relates to systems and methods for real time, rapid detection, identification, and enumeration of a wide variety of analytes, which include but are not limited to, cells (Eukarya, Eubacteria, Archaea), microorganisms, organelles, viruses, proteins (recombinant or natural proteins), nucleic acids, prionss, and any chemical, metabolites, or biological markers. The systems and methods, which include the laser / optic / electronic units, the analytic software, the assay methods and reagents, and the high throughput automation, are particularly adapted to detection, identification, and enumeration of pathogens and non-pathogens in contaminated foods, clinical samples, and environmental samples. Other microorganisms that can be detected with the present invention include clinical pathogens, protozoa and, viruses.
Owner:KIM LAB INC
Aspartyl protease inhibitors
Disclosed are compounds of the formula I or a stereoisomer, tautomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, wherein W, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, and R7 are as defined in the specification; and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I. Also disclosed is the method of inhibiting aspartyl protease, and in particular, the methods of treating cardiovascular diseases, cognitive and neurodegenerative diseases, and the methods of inhibiting of Human Immunodeficiency Virus, plasmepins, cathepsin D and protozoal enzymes. Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases using the compounds of formula I in combination with a cholinesterase inhibitor or a muscarinic antagonist.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Methods of promoting immunopotentiation and preparing antibodies with anti-CD3 antibodies
Disclosed are immunopotentiating agents, and vaccines thereof, which enhance and / or otherwise modify immune responses, and method for their preparation and use in vivo. Immunopotentiating agents can be single agents that act directly, adjuvants added concurrently with the agents, or heteroconjugates wherein the immunopotentiating agent is chemically coupled to the compound against which an immune response is desired. Examples of immunopotentiating agents include monoclonal antibodies, such as anti-CD3, anti-CD2) and anti-CD5 antibodies, and proteins derived from microorganisms (e.g., enterotoxins) which activate T cells. The compounds against which an immune response can be generated, which may be the second component in a heteroconjugate, include compound from abnormal or diseased tissues such as tumors, or infectious agents, such as viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoal or metozoal parasites, and can be obtained by natural or recombinant means. Methods of using the invention to prepare monoclonal antibodies are particularly disclosed.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
Monoclonal antibodies to Sarcocystis neurona and uses therefor
The present invention is directed to particular monoclonal antibodies that find use in the identification and purification of Sarcocystis neurona and related antigens. In particular, these antibodies permit the diagnosis of Sarcocystis related diseases such as equine protozoal myeloencephalitis (EPM).
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Vaccines against cancer and infectious diseases
InactiveUS6440416B1Promote antibody productionPromote productionOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansProtozoaPrimate
A method of stimulating an immune response in a human against malignant cells or an infectious agent comprises the step of administering to the human an immunogenic amount of a primate anti-idiotype antibody or antibody fragment that acts as an immunogenic functional mimic of an antigen produced by or associated with a malignant cell or an infectious agent. Sub-human primate anti-idiotype antisera, especially from baboons, are preferred. Such anti-idiotype antibodies are used to make vaccines for inducing preventive immunity or a therapeutic immune response against tumors, viruses, bacteria, rickettsia, mycoplasma, protozoa, fungi and multicellular parasites.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Dioxanes and uses thereof
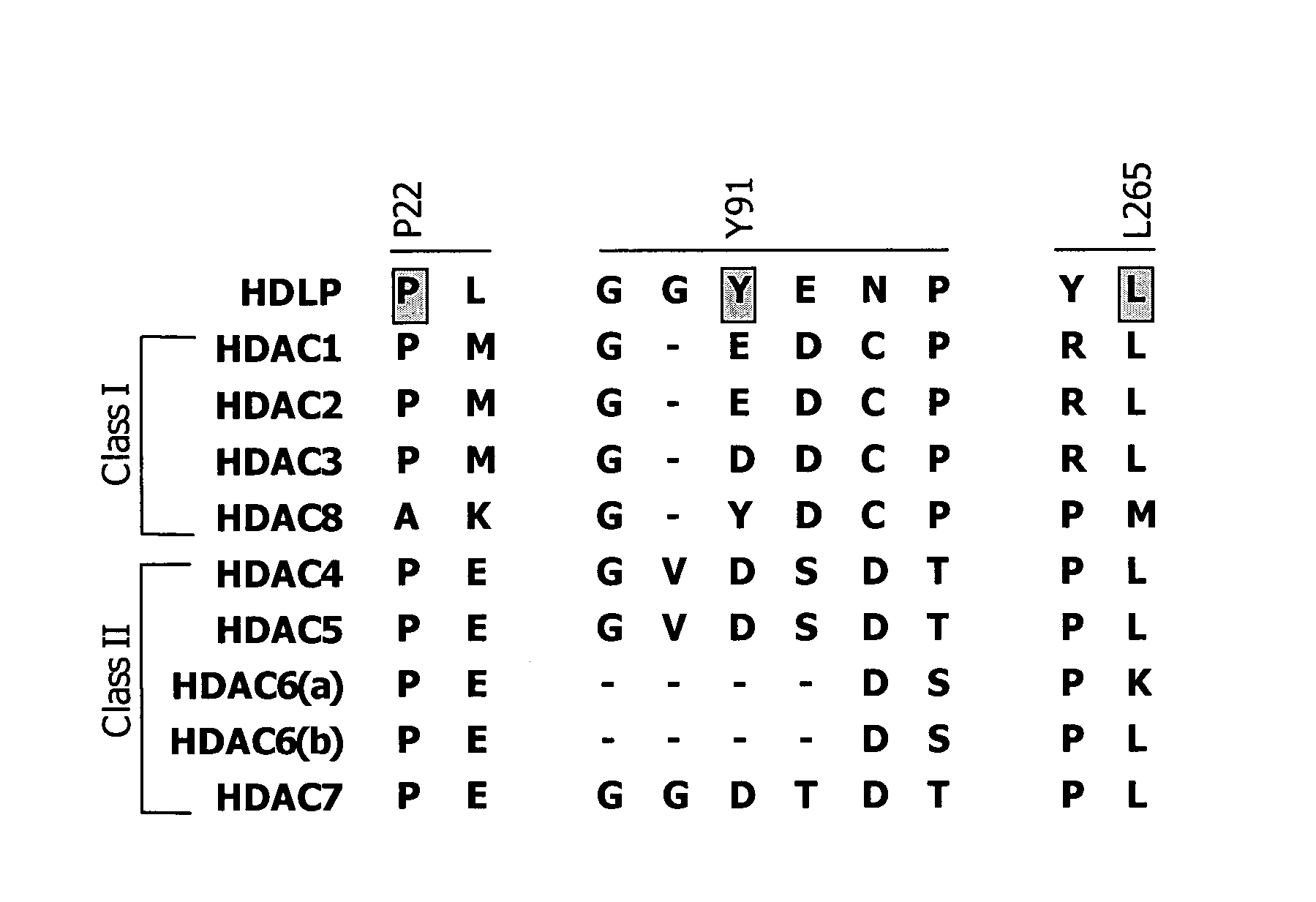
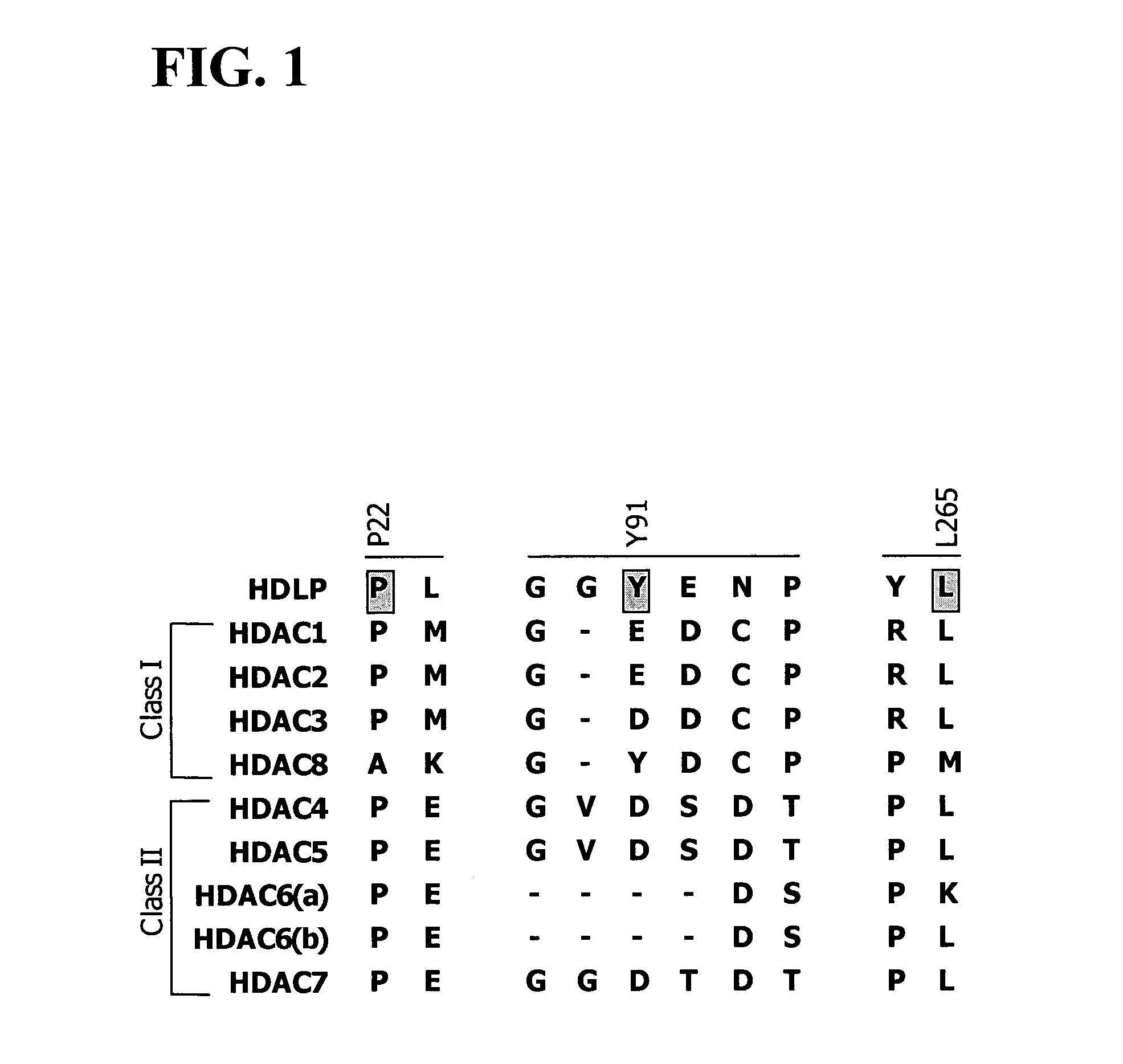
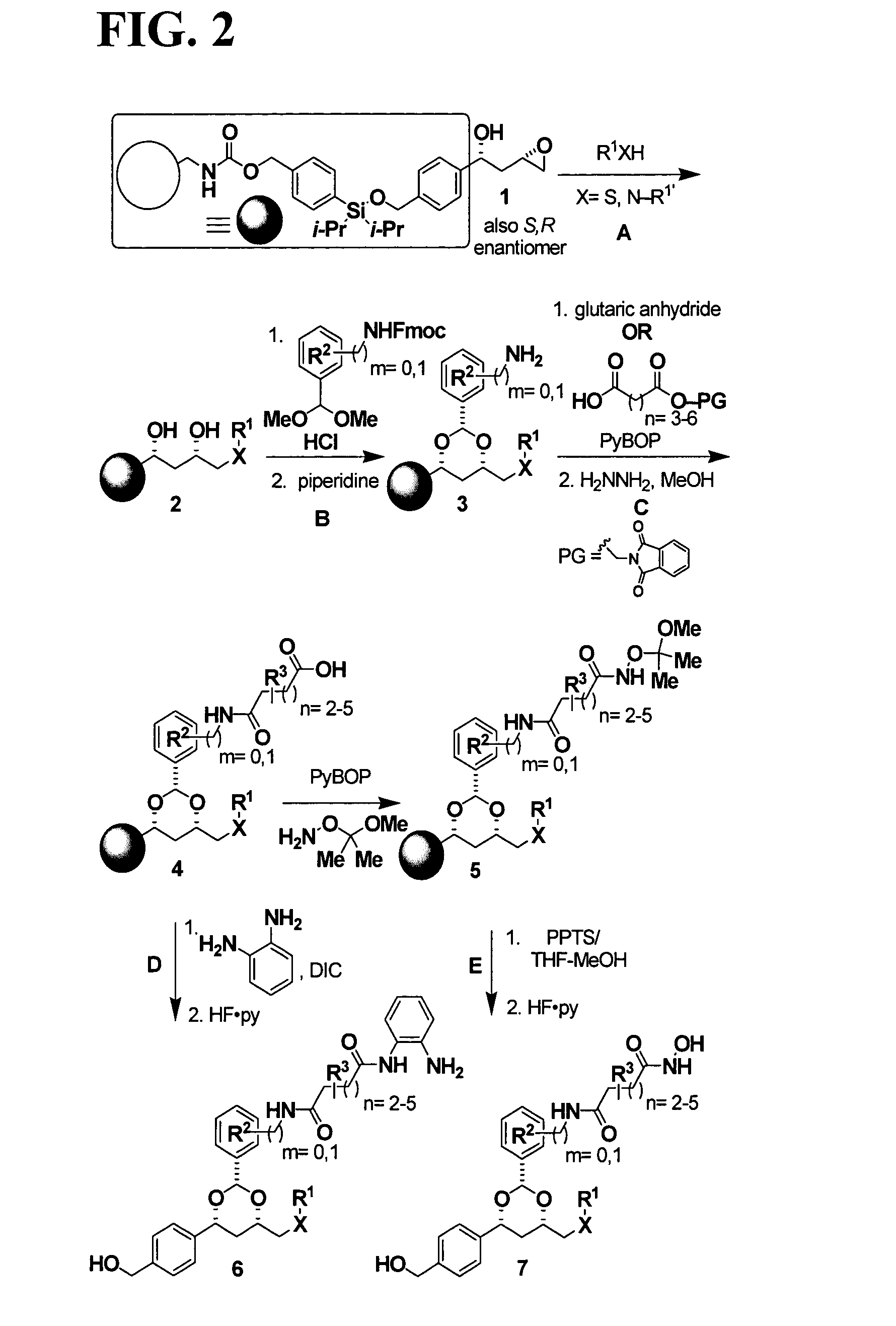
In recognition of the need to develop novel therapeutic agents and efficient methods for the synthesis thereof, the present invention provides novel compounds of general formula (I):and pharmaceutically acceptable derivatives thereof, wherein R1, R2, R3, n, X and Y are as defined herein. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising a compound of formula (I) and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention further provides compounds capable of inhibiting histone deacetylatase activity and methods for treating disorders regulated by histone deacetylase activity (e.g., cancer and protozoal infections) comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I) to a subject in need thereof. The present invention additionally provides methods for modulating the glucose-sensitive subset of genes downstream of Ure2p. The present invention also provides methods for preparing compounds of the invention.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Practical serological assay for the clinical diagnosis of leishmaniasis
InactiveUS7008774B2Improve purification effectPurification is easy and lessBiocideProtozoa antigen ingredientsProtozoaAntigen capture
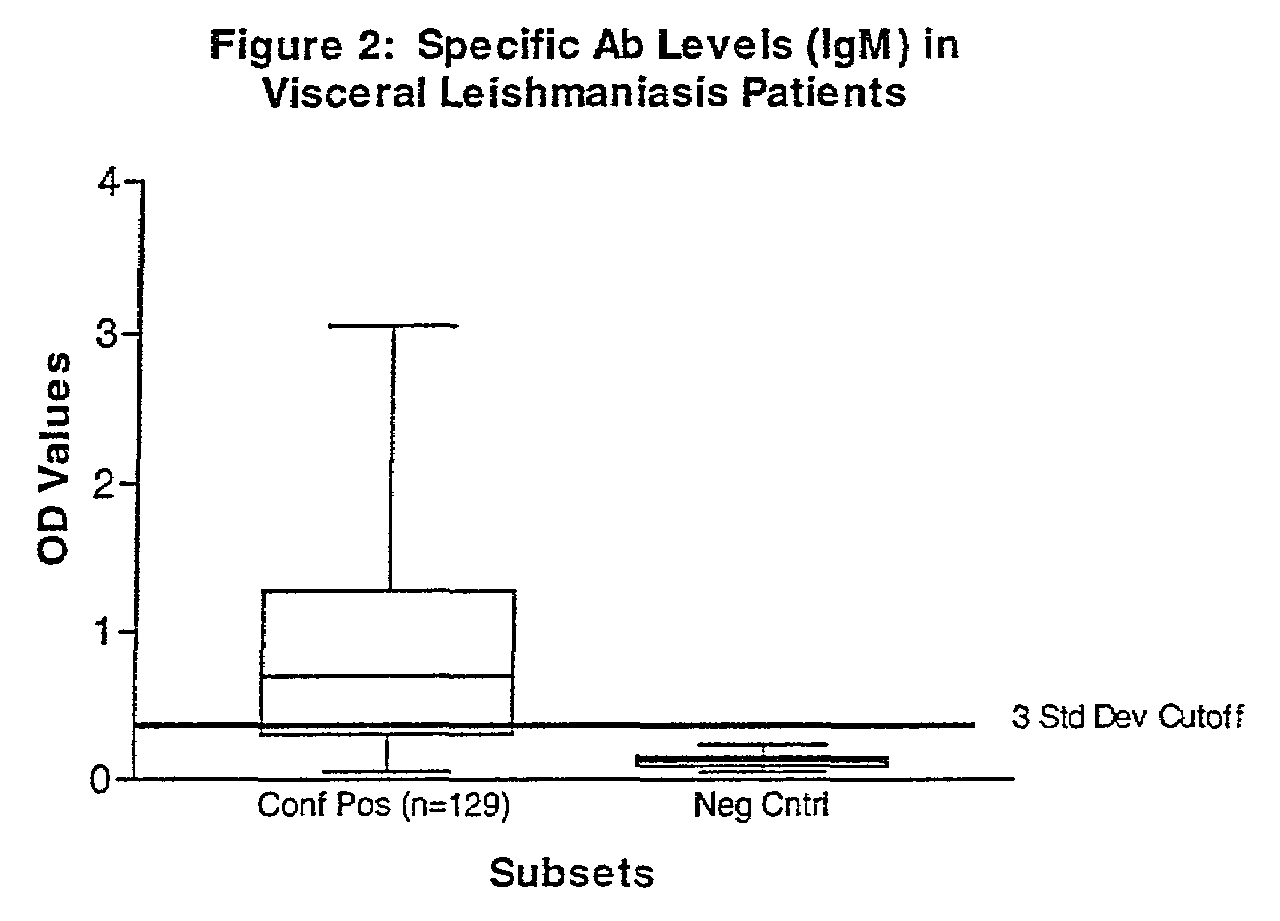
Methods for the diagnosis of visceral, cutaneous and canine leishmaniasis in a subject suspected of being infected with the parasitic protozoa Leishmania is disclosed. Disclosed are antibody-capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) for the detection of antibodies to Leishmania parasite soluble antigens and antigen-capture ELISAs for the detection of Leishmania parasite soluble antigens in host samples. Also disclosed are immunodiagnostic kits for the detection of Leishmania parasite circulating antigens or IgM and IgG antibodies in a sample from subject having visceral, cutaneous or canine leishmaniasis. In these methods and kits, detection may be done photometrically or visually. The methods and kits also allow the visualization of Leishmania amastigotes or promastigotes in a sample.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Use of exogenous gasoues nitric oxide in the treatment and disinfection of biofilms
ActiveUS20060068031A1Eliminates pump starvationBiocideInorganic active ingredientsProtozoaNitric oxide gas
Owner:BEYOND AIR LTD
Method and technical embodiment for the cleaning of surfaces by means of a high-pressure cleaning device using electrolyzed water by using oxidative free radicals
A method and technical execution, for the chemical and residue-free cleaning, hygienization, disinfection and odor neutralization of surfaces, materials, and objects by means of a high-pressure cleaning device and an electrolysis generators using electrolyzed cold or warm water, with the aid of oxidative groups, characterized in that the method, in combination with high pressure and oxidative radicals produced by electrolysis from salt ion-containing water, in total group concentrations of at least 35 ppm and higher, is able to not only clean surfaces, materials, and objects, but also to disinfect them, and is able to, by means of cold oxidation, in the form of ultrafast superoxidation, to eliminate 99.9% of microorganisms such as viruses, gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, yeasts, fungi, algae and protozoa organisms and the like, without forming resistances in the microorganisms or pathogens.
Owner:STEFFEN HANSPETER
Use of nitric oxide in the treatment and disinfection of biofilms
The administration of gaseous nitric oxide as a biocidal moiety is proffered as a de novo treatment in the control and eradication of biofilms. The present invention relates to the use or methods of application of exogenous nitric oxide gas (gNO) as a stand alone biocidal agent or in cohort with any or all adjunct vehicles in the control of biofilms generated by microbial organisms, i.e., bacteria, protozoa, amoeba, fungi etc. Further, the present invention introduces the concept of utilization and methods of application of gaseous nitric oxide in control and eradication of biofilm forming microorganisms. Other embodiments include the use of a nitric oxide releasing material to eradicate and-control the growth of biofilms. Another embodiment includes the use of a gaseous nitric oxide releasing material packaged in an air-tight container with a medical device to prevent the growth of biofilm on the medical device.
Owner:PULMONOX TECH
Method for treating systemic bacterial, fungal and protozoan infection
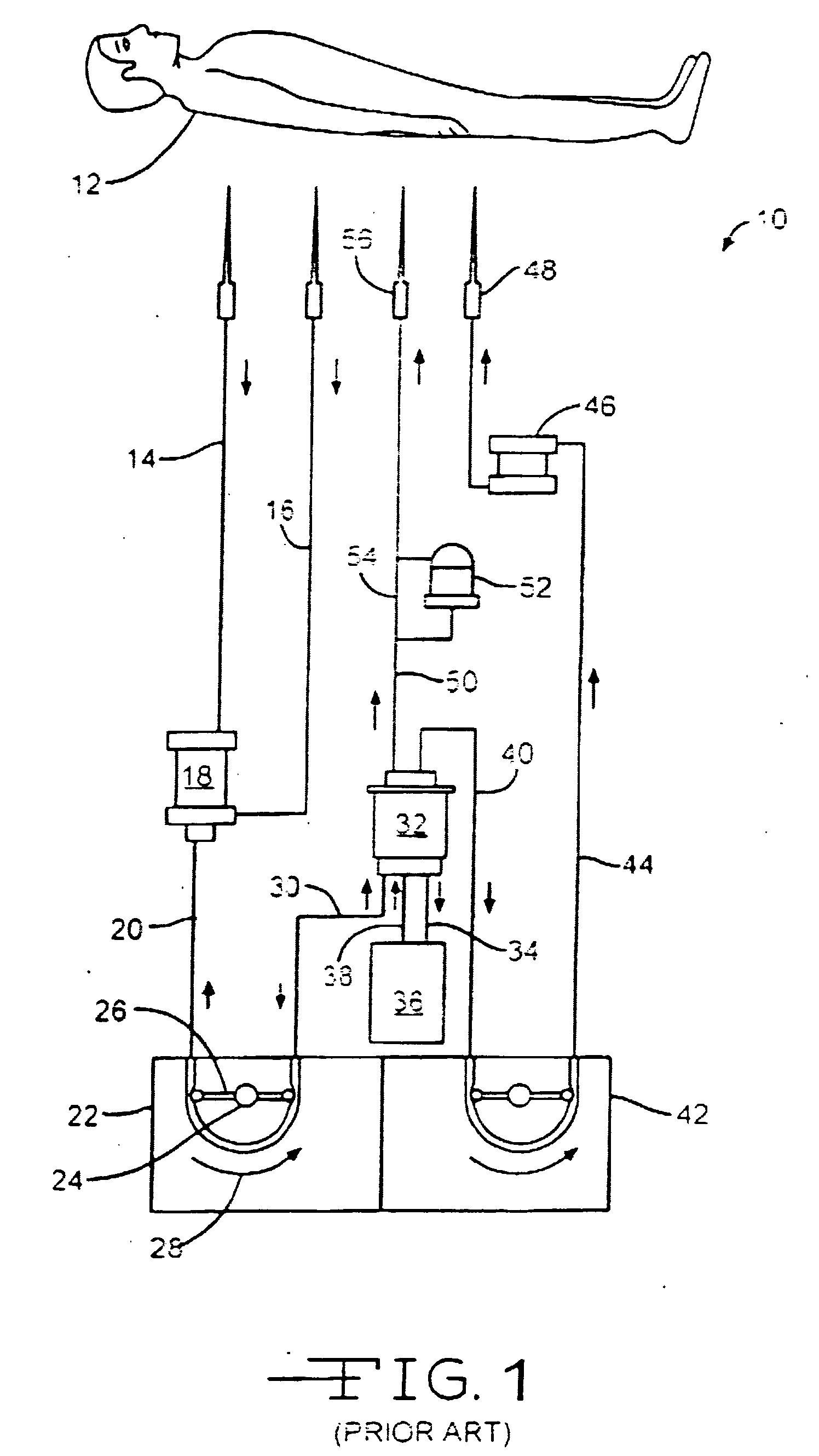
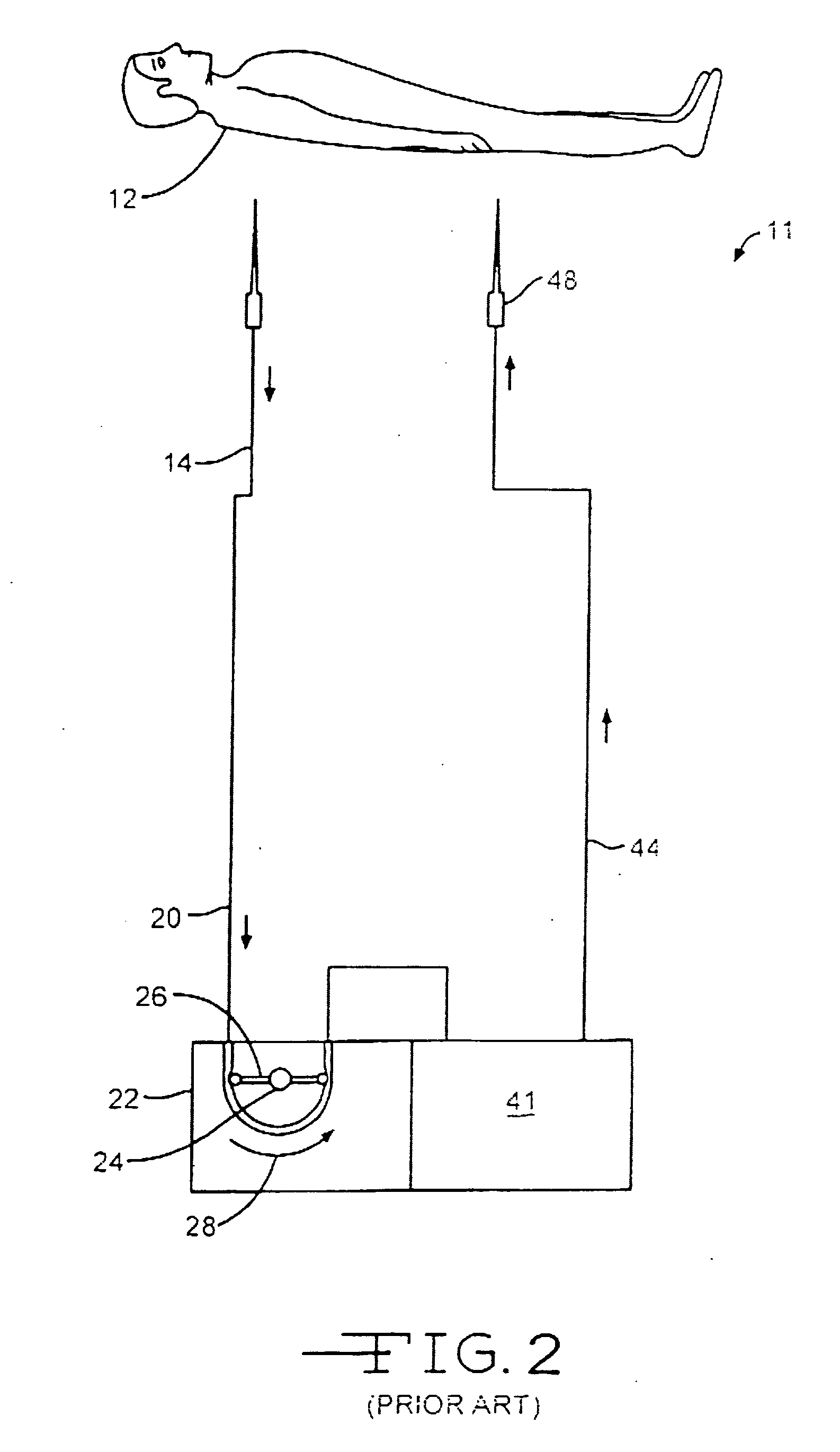
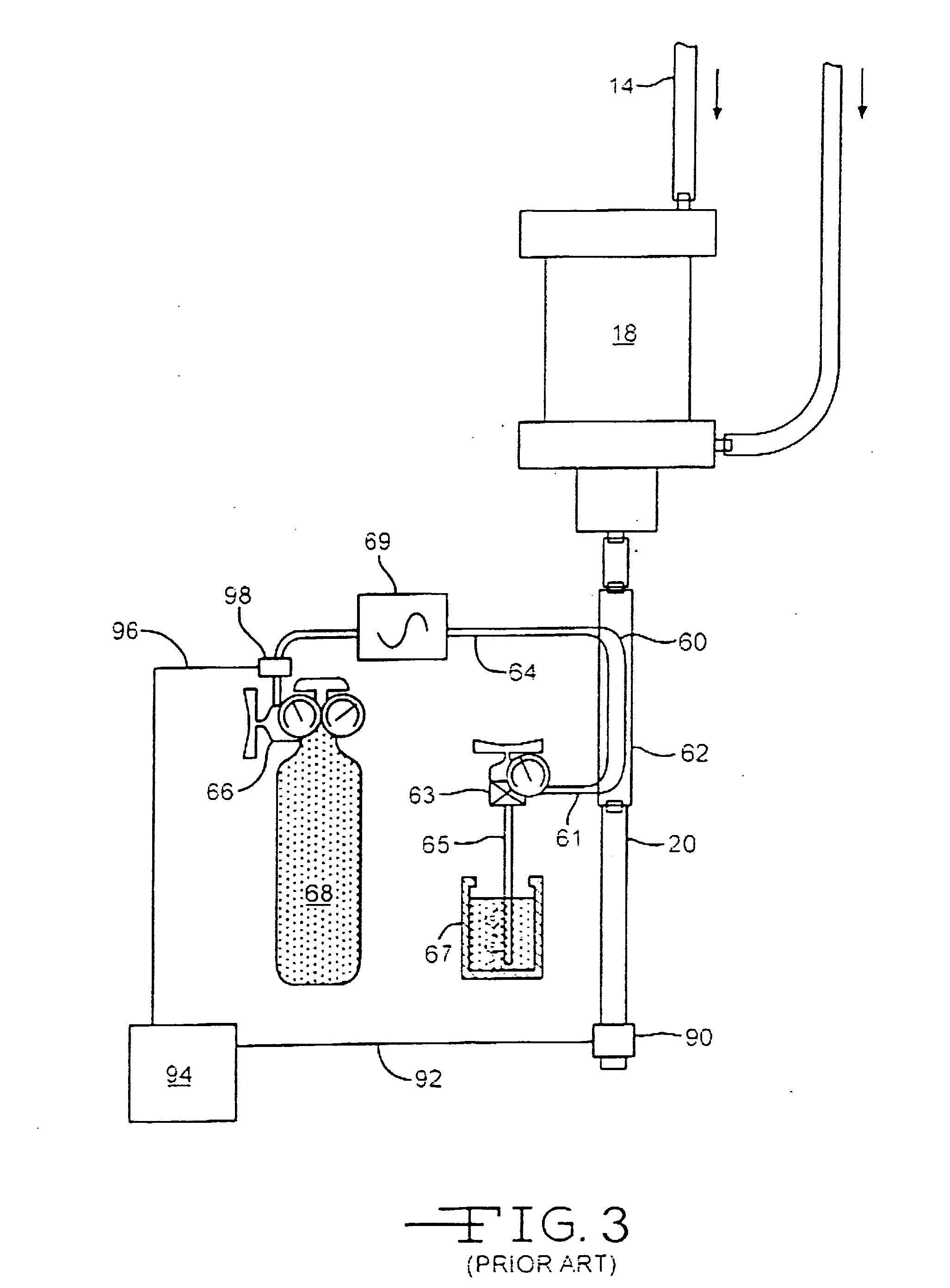
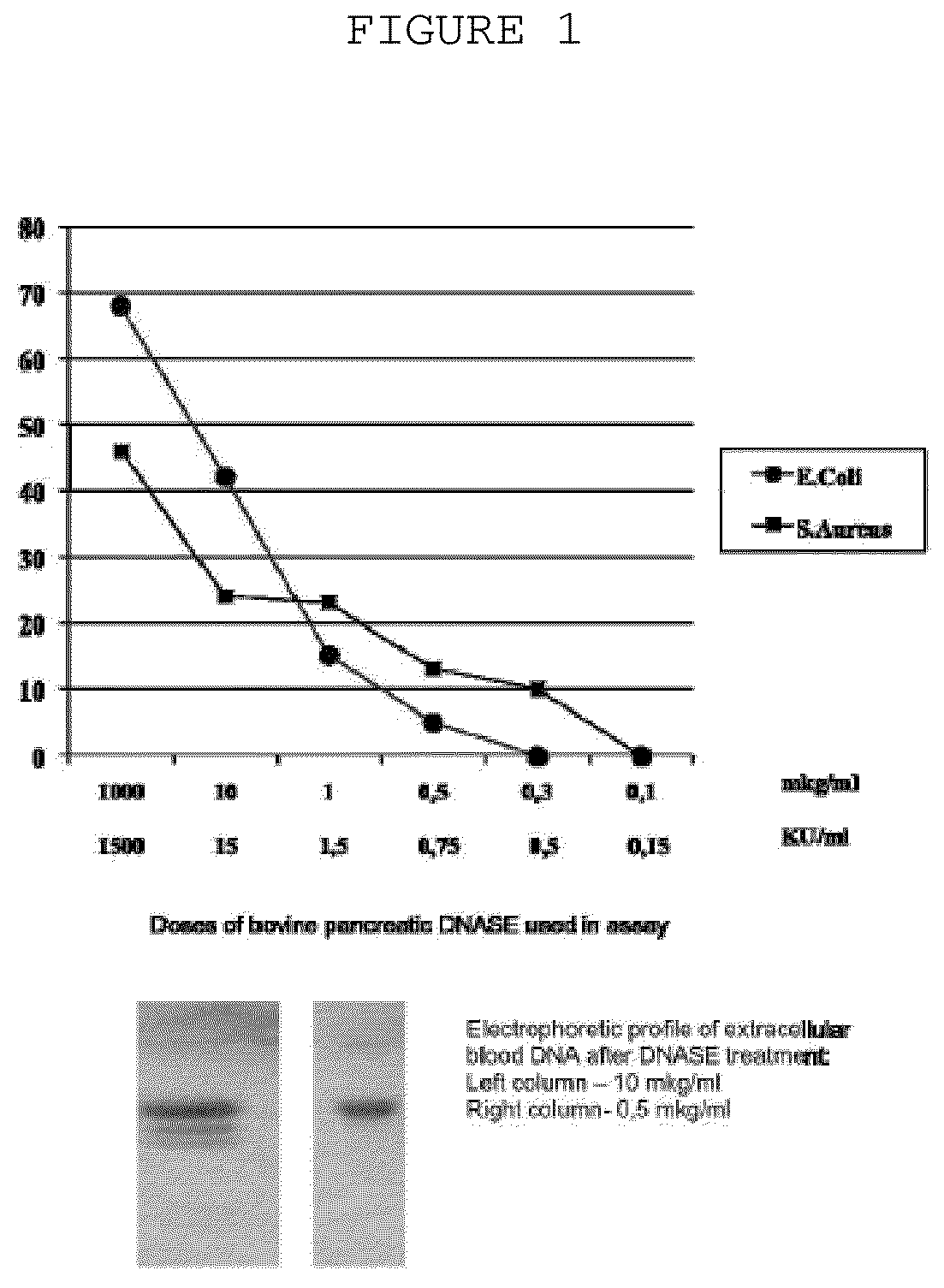
ActiveUS8431123B2Low-toxicLower Level RequirementsHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsBacteroidesProtozoa
The invention is directed to a treatment of diseases that are accompanied by quantitative and / or qualitative changes of blood extracellular DNA and, more particularly, to a treatment of systemic bacterial, fungal and protozoan infections. The inventive method comprises introducing a treatment agent into a circulating blood system of a patient diagnosed with systemic infection caused by bacteria, fungi or protozoa, wherein said treatment agent destroys extracellular DNA in said blood of said patient and wherein said treatment agent used to destroy said extracellular DNA is a DNase enzyme: said agent being administered in doses and regimens which are sufficient to decrease the average molecular weight of circulating extracellular blood DNA in the blood of said patient; such decrease in the average molecular weight can be measured by gel electrophoresis of extracellular blood DNA fraction from the blood of said patient. A DNase enzyme may be applied in a dose and regimen that provide a DNase DNA hydrolytic activity measured in blood plasma that exceeds 1.5 Kunitz units per 1 ml of blood plasma for more than 12 hours within a period of 24 hours.
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
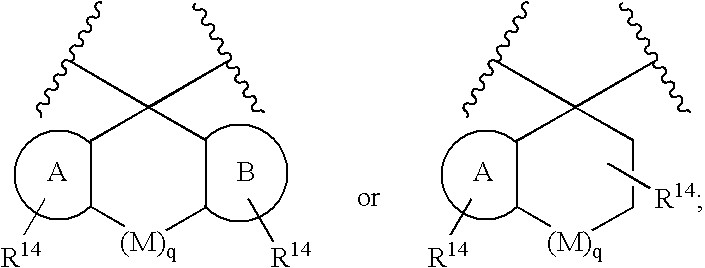
Heterocyclic aspartyl protease inhibitors
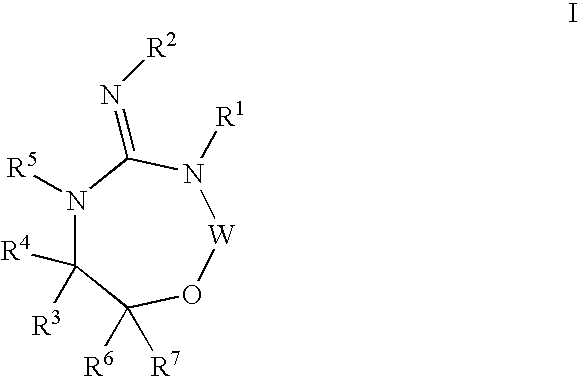
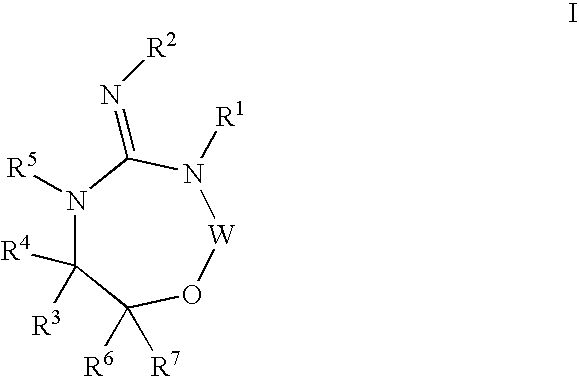
Disclosed are compounds of the formula Ior a stereoisomer, tautomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, whereinW is a bond, —C(═S)—, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(═O)—, —O—, —C(R6)(R7)—, —N(R5)— or —C(═N(R5))—;X is —O—, —N(R5)— or —C(R6)(R7)—; provided that when X is —O—, U is not —O—, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(═O)— or —C(═NR5)—;U is a bond, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(O)—, —O—, —P(O)(OR15)—, —C(═NR5)—, —(C(R6)(R7))b— or —N(R5)—; wherein b is 1 or 2; provided that when W is —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—, U is not —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—; provided that when X is —N(R5)— and W is —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—, then U is not a bond;and R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, and R7 are as defined in the specification; and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I.Also disclosed is the method of inhibiting aspartyl protease, and in particular, the methods of treating cardiovascular diseases, cognitive and neurodegenerative diseases, and the methods of inhibiting of Human Immunodeficiency Virus, plasmepins, cathepsin D and protozoal enzymes.Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases using the compounds of formula I in combination with a cholinesterase inhibitor or a muscarinic m1 agonist or m2 antagonist.
Owner:PHARMACOPEIA INC +1
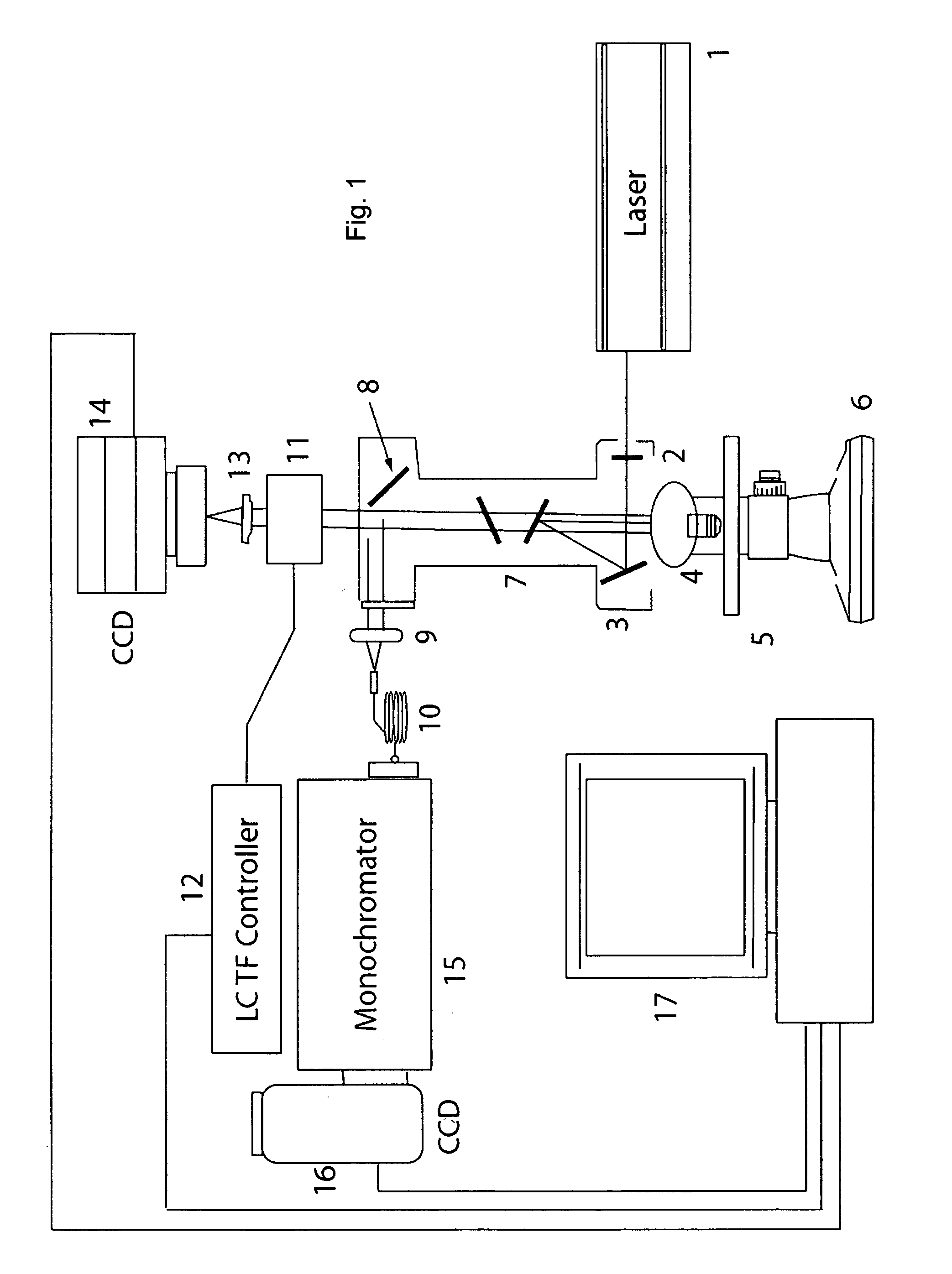
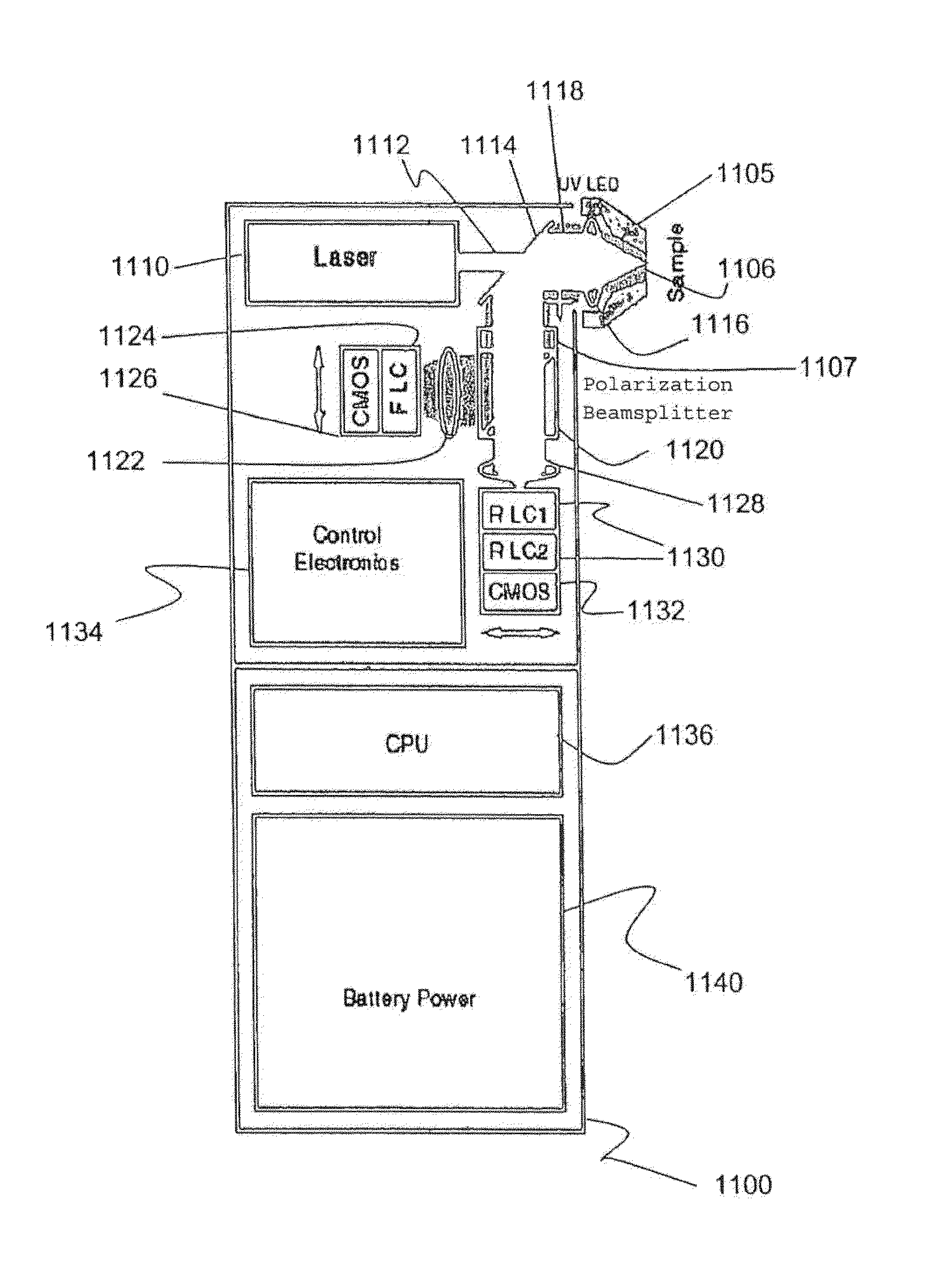
Method and apparatus for compact spectrometer for multipoint sampling of an object
A method and a portable device for assessing the occurrence of an agent in a sample. A sample is illuminated with photons emanating from a portable device to produce photons reflected, emitted, or absorbed from a set of multiple points in the sample having a defined geometric relationship. The portable device is used to simultaneously illuminate the sample and analyze the photons reflected, emitted, or absorbed from the set of multiple points using spectroscopic methods, including infrared, fluorescence, and UV / visible. The agent assessed may include a hazardous agent, a chemical agent, a biological agent, a microorganism, a bacterium, a protozoan, a virus, and combinations thereof.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE CORP
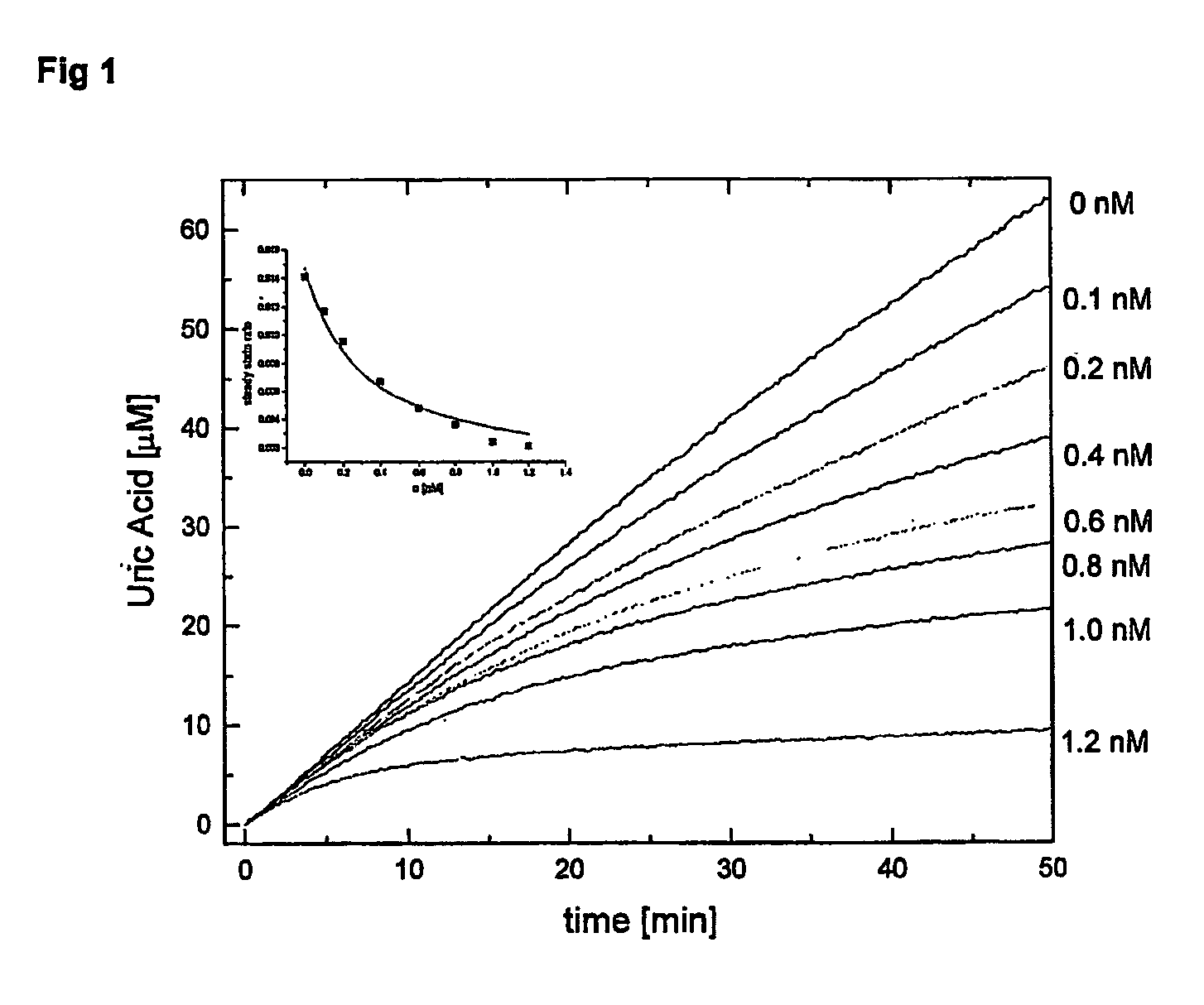
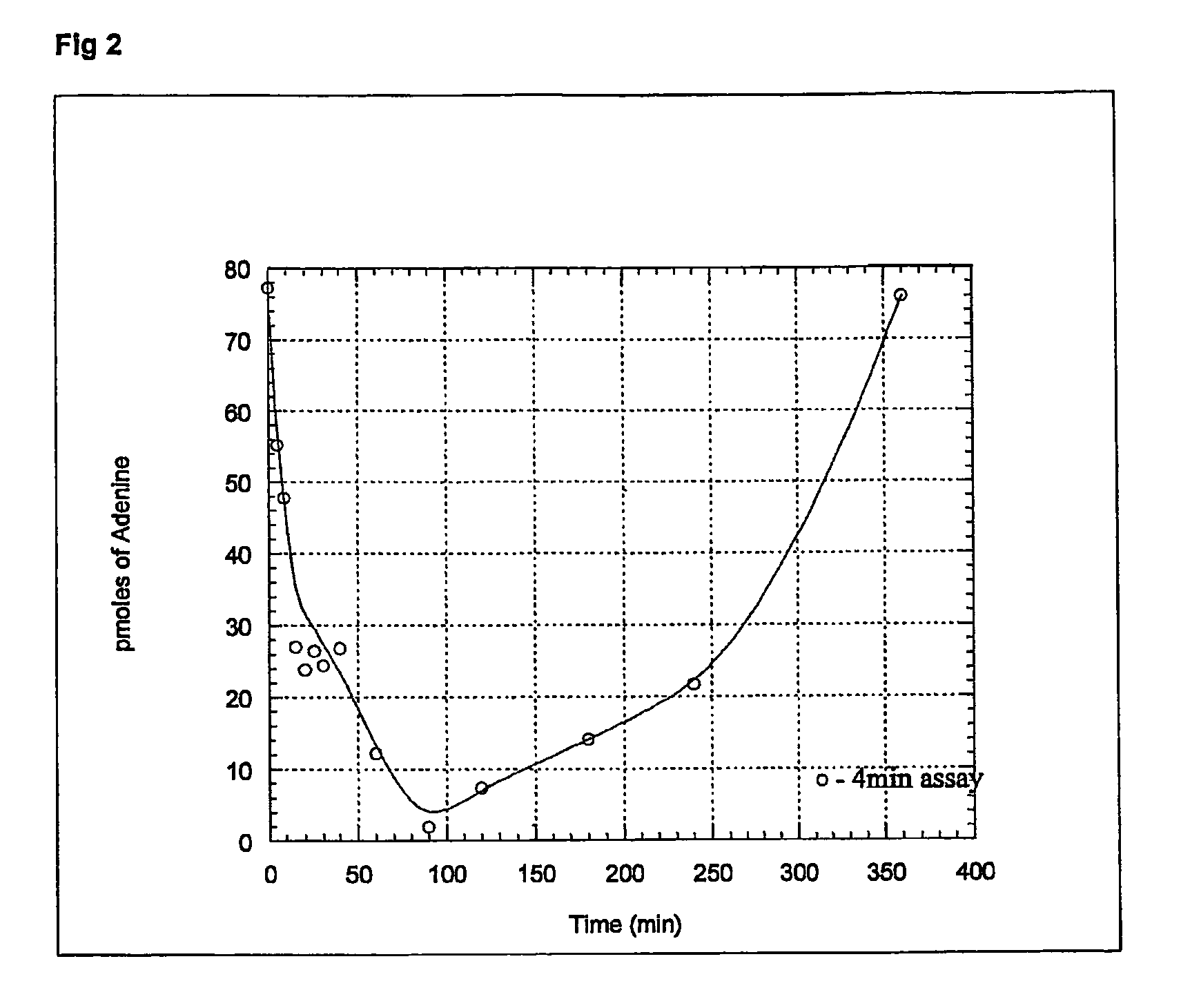
5h-pyrrolo[3,2-D] pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases
The present invention relates to compounds of the general formula (I) which are inhibitors of purine muclioside phosphorylases (PNP), purine phosphoribosyltransferases (PPRT), 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylases (MTAP), 5′-methylthioadenosine mucliosidases (MTAN) and / or nucleoside hydrolases (NH). The invention also relates to the use of these compounds in the treatment of diseases and infections including cancer, bacterial infections, protozoal infections, and T-cell mediated disease and to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds.
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
Enrichment culture method of salt-tolerant nitrifying bacterium communities
InactiveCN102382767AEasy to trainWide range of substrates availableMicroorganismsBiological water/sewage treatmentProtozoaActivated sludge
The invention discloses an enrichment culture method of salt-tolerant nitrifying bacterium communities, which comprises the steps that: activated sludge is inoculated, and the culture mode is the sequencing batch type enrichment culture; the enrichment culture is carried out in simulated wastewater, the main ingredient of nutritive salt of the enrichment culture is inorganic salt, the substrate is externally added ammonium salt, and a carbon source is inorganic carbonate; the pH value in an aeration tank in the enrichment culture process is regulated and controlled through sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate, and the dissolved oxygen value is regulated through the aeration quantity; a method for gradually increasing the salinity is adopted for domesticating the nitrifying bacterium communities; and when no filamentous bacterium is observed in the sludge and the number and the variety of protozoans are few, the enrichment culture of the nitrifying bacterium communities is finished. The enrichment culture method has the advantages that the available matrix range is wide, the culture is easy, the concentration of the cultured salt-tolerant nitrifying bacterium communities is high, the activity is good, the biochemical treatment removal rate of high-salt ammonia-nitrogen wastewater can be obviously improved, the enrichment culture method is suitable for the treatment of various ammonia-nitrogen industrial wastewater and is suitable for the scale production, the wastewater treatment cost is reduced, and good economic benefits and environmental benefits are realized.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
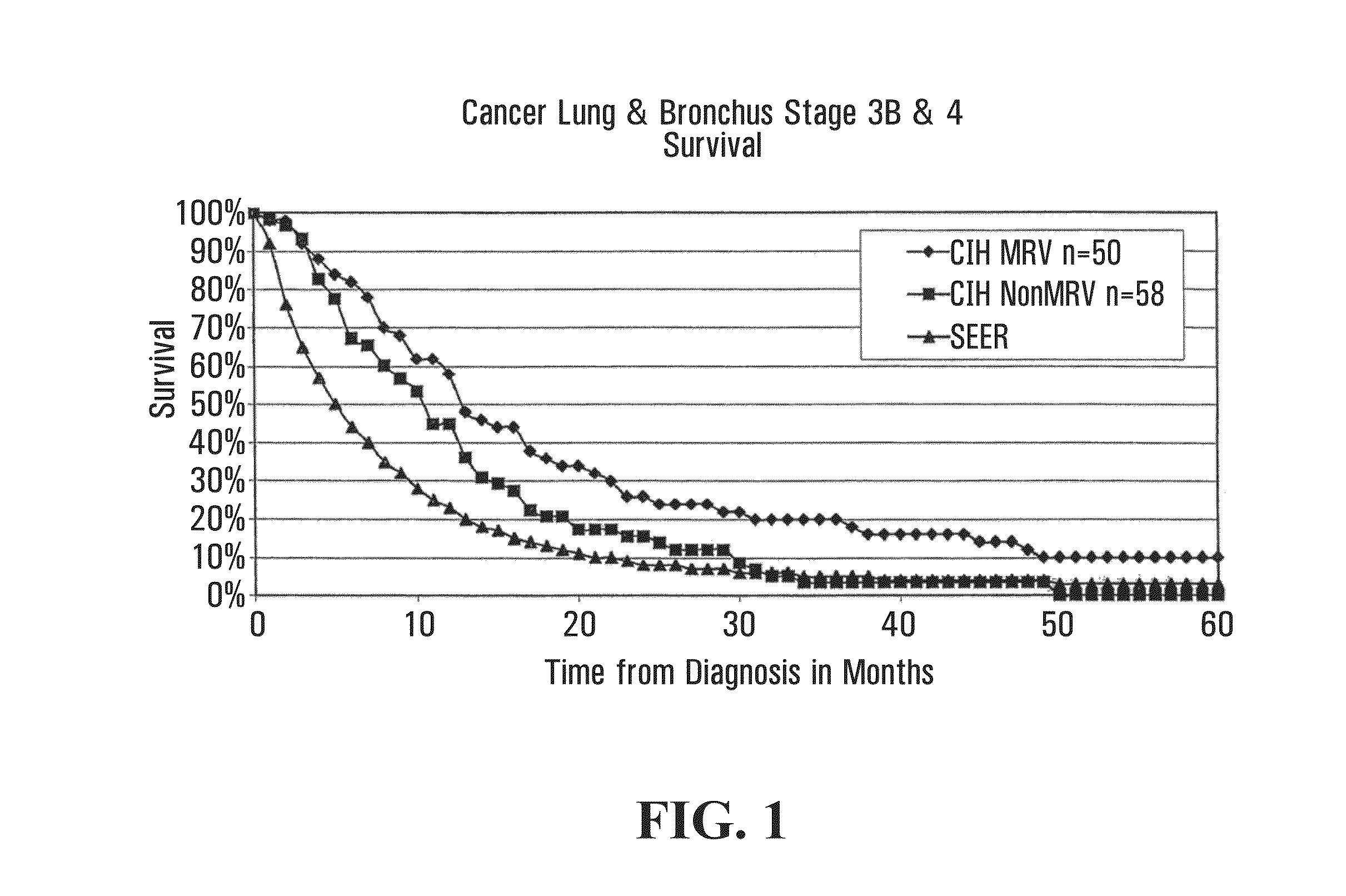
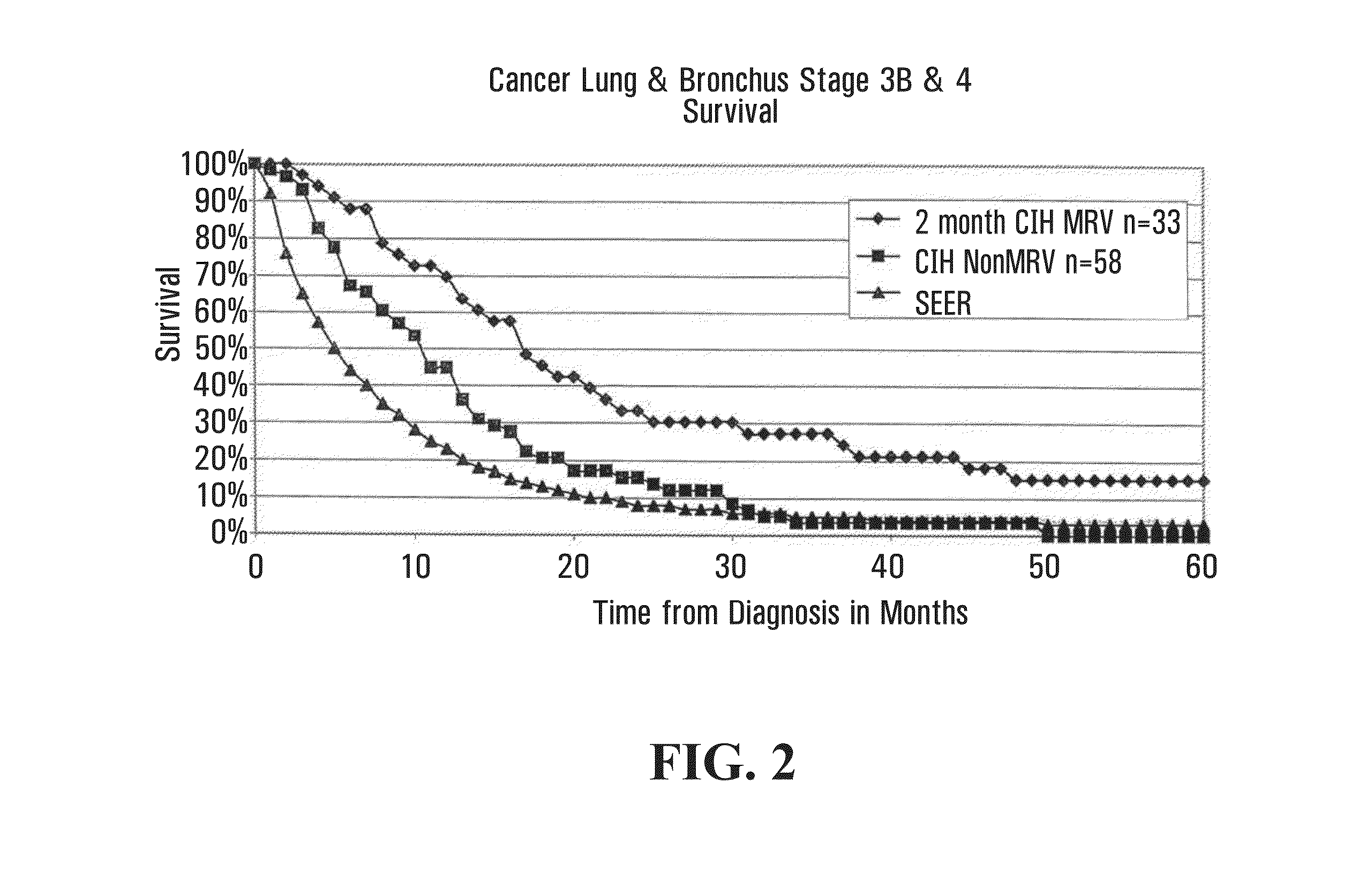
Method for Treating Oncological, Virulent and Somatic Diseases, Method for Controlling Treatment Efficiency, Pharmaceutical Agents and Composition for Carrying Out Said Treatment
The invention relates to medicine and veterinary science and discloses a novel method for treating oncological, virulent and somatic diseases whose main target for therapeutic action is embodied in the form of DNA which freely circulates in blood plasma (and other liquid media) and originates from tumoral and mutant cells or cells infected by bacteria, fungi or protozoan and from different microorganisms which reside in the organism thereof. Said invention also relates to novel pharmaceutical compositions and to the use thereof for treating oncological diseases and infectious states provoked by bacteria, fungi and protozoa and non-infectious somatic diseases and states produced by accumulation of somatic mutations in cells of organism. Medicinal and immunological compositions, sorption and physico-chemical engineering and the method for using them in order to treat malignant tumors and other diseases are also disclosed.
Owner:GENKIN DMITRY DMITRIEVICH +1
Prophylactic Bactericidal Implant
A medical implant system is described for inhibiting infection associated with a joint prosthesis implant. An inventive system includes an implant body made of a biocompatible material which has a metal component disposed on an external surface of the implant body. A current is allowed to flow to the metal component, stimulating release of metal ions toxic to microbes, such as bacteria, protozoa, fungi, and viruses. One detailed system is completely surgically implantable in the patient such that no part of the system is external to the patient while the system is in use. In addition, externally controlled devices are provided which allow for modulation of implanted components.
Owner:AIONX ANTIMICROBIAL TECH INC
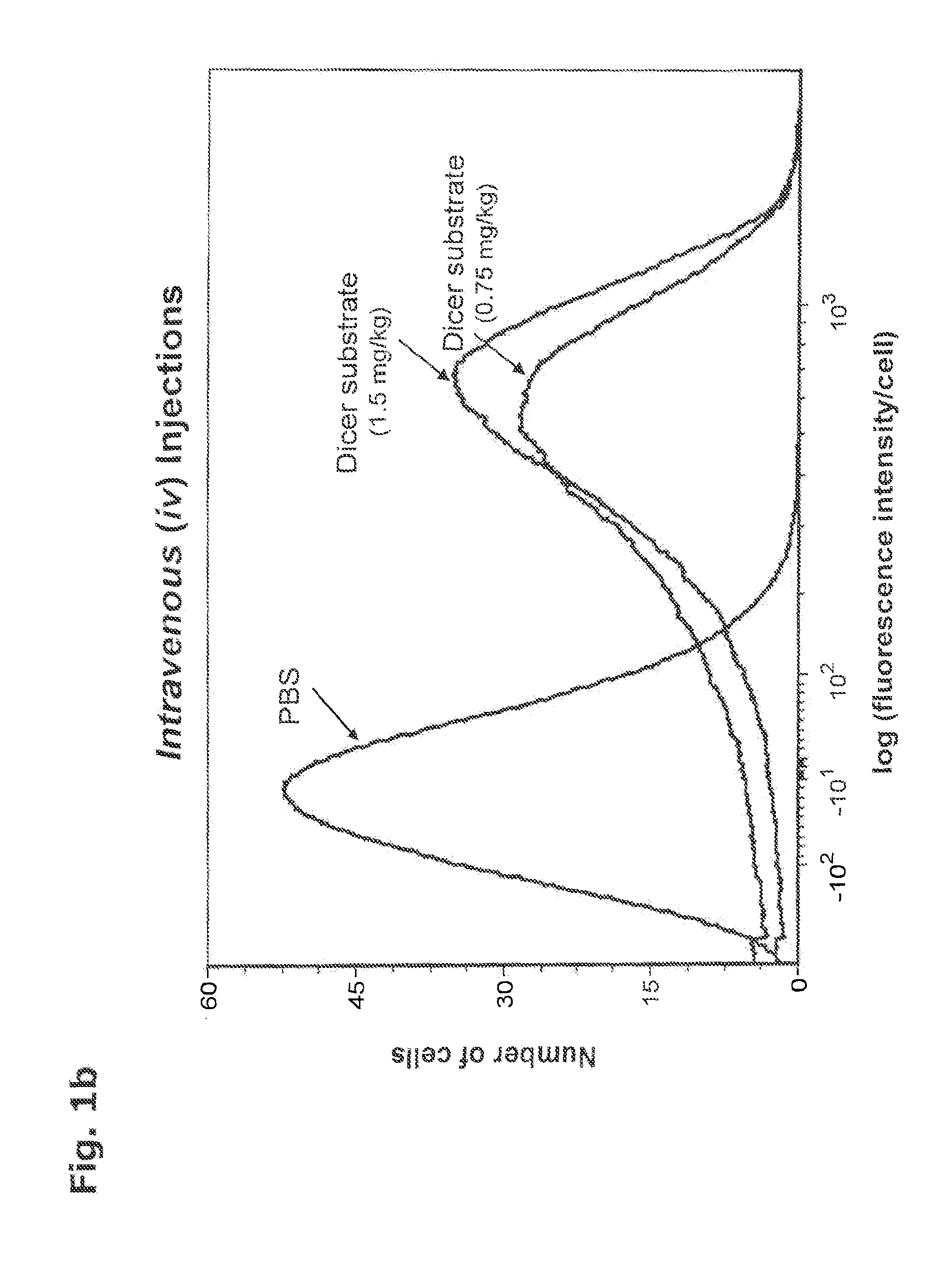
In Vivo Delivery of Oligonucleotides
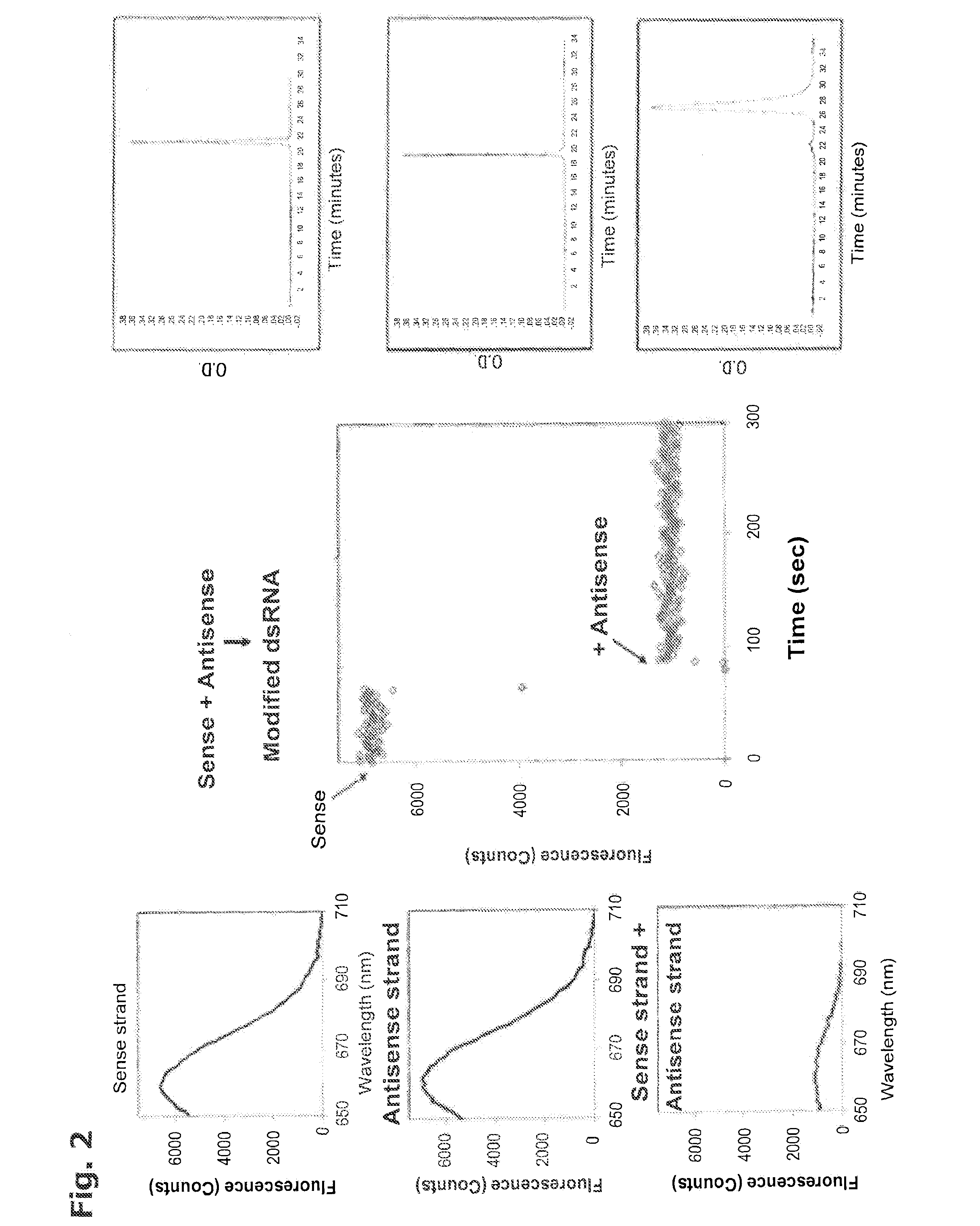
ActiveUS20160040161A1Reduce deliveryEfficient deliveryOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderProtozoaBacteroides
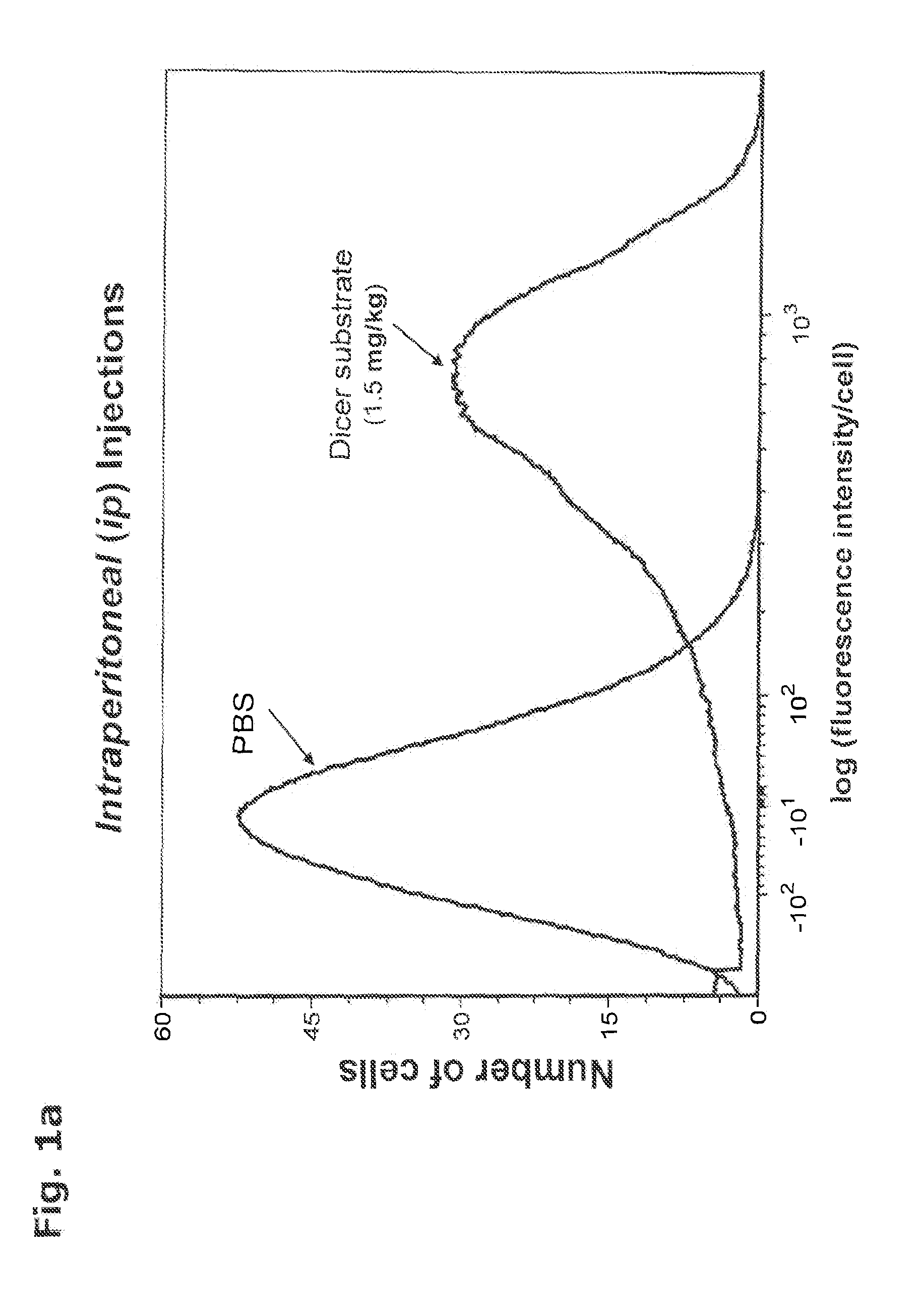
This invention provides a method for the in vivo delivery of oligonucleotides. The invention utilizes the presence of one or plurality of HES linked to an oligonucleotide to deliver a nucleic acid sequence of interest into the cytoplasm of cells and tissues of live organisms. The delivery vehicle is nontoxic to cells and organisms. Since delivery is sequence-independent and crosses membranes in a receptor-independent manner, the delivered oligonucleotide can target complementary sequences in the cytoplasm as well as in the nucleus of live cells. Sequences of bacterial or viral origin can also be targeted. The method can be used for delivery of genes coding for expression of specific proteins, antisense oligonucleotides, siRNAs, shRNAs, Dicer substrates, miRNAs, anti-miRNAs or any nucleic acid sequence in a living organism. The latter include mammals, plants, and microorganisms such as bacteria, protozoa, and viruses.
Owner:ONCOIMMUNIN
Disinfestation and disinfection of food, perishables and other commodities
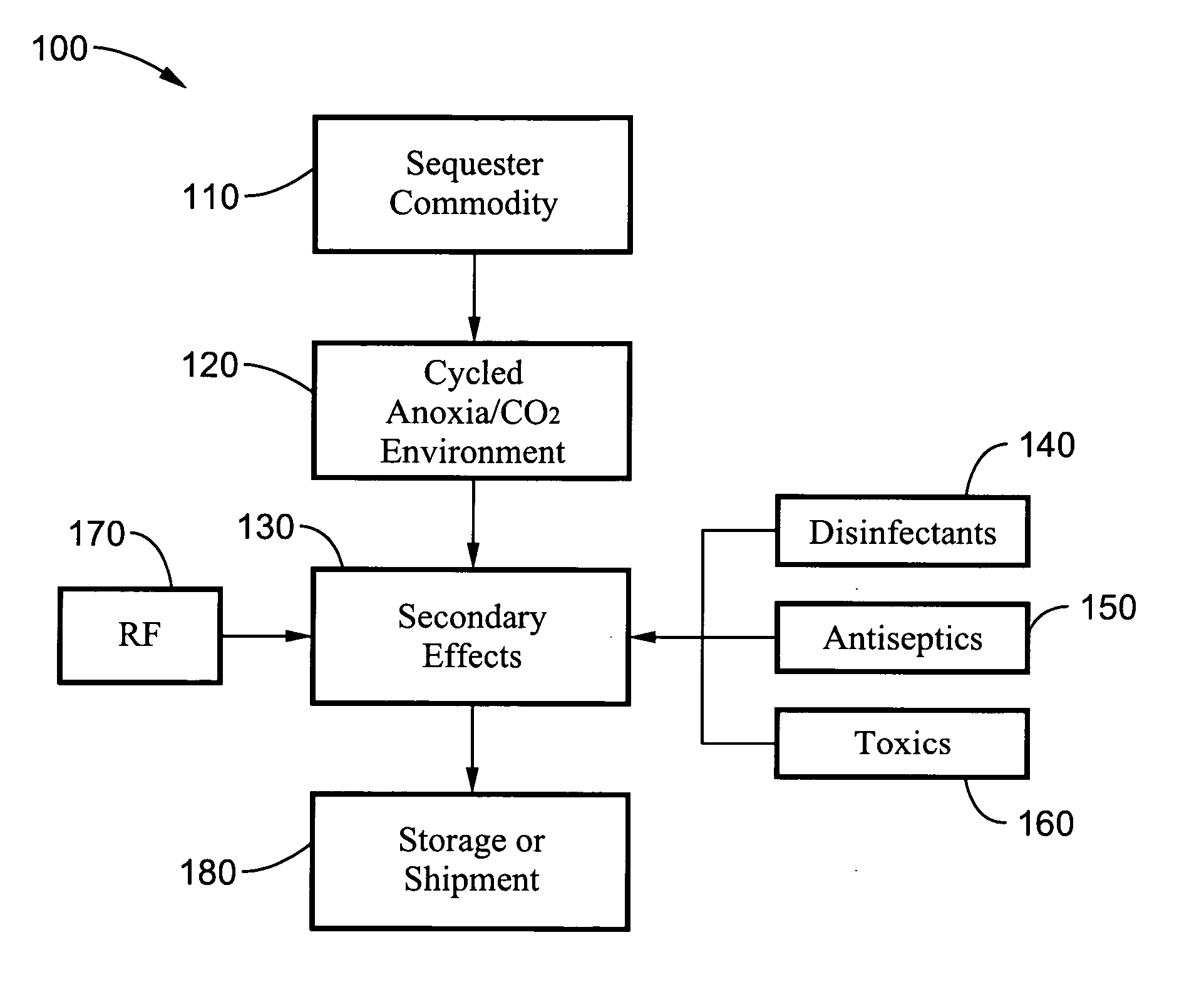
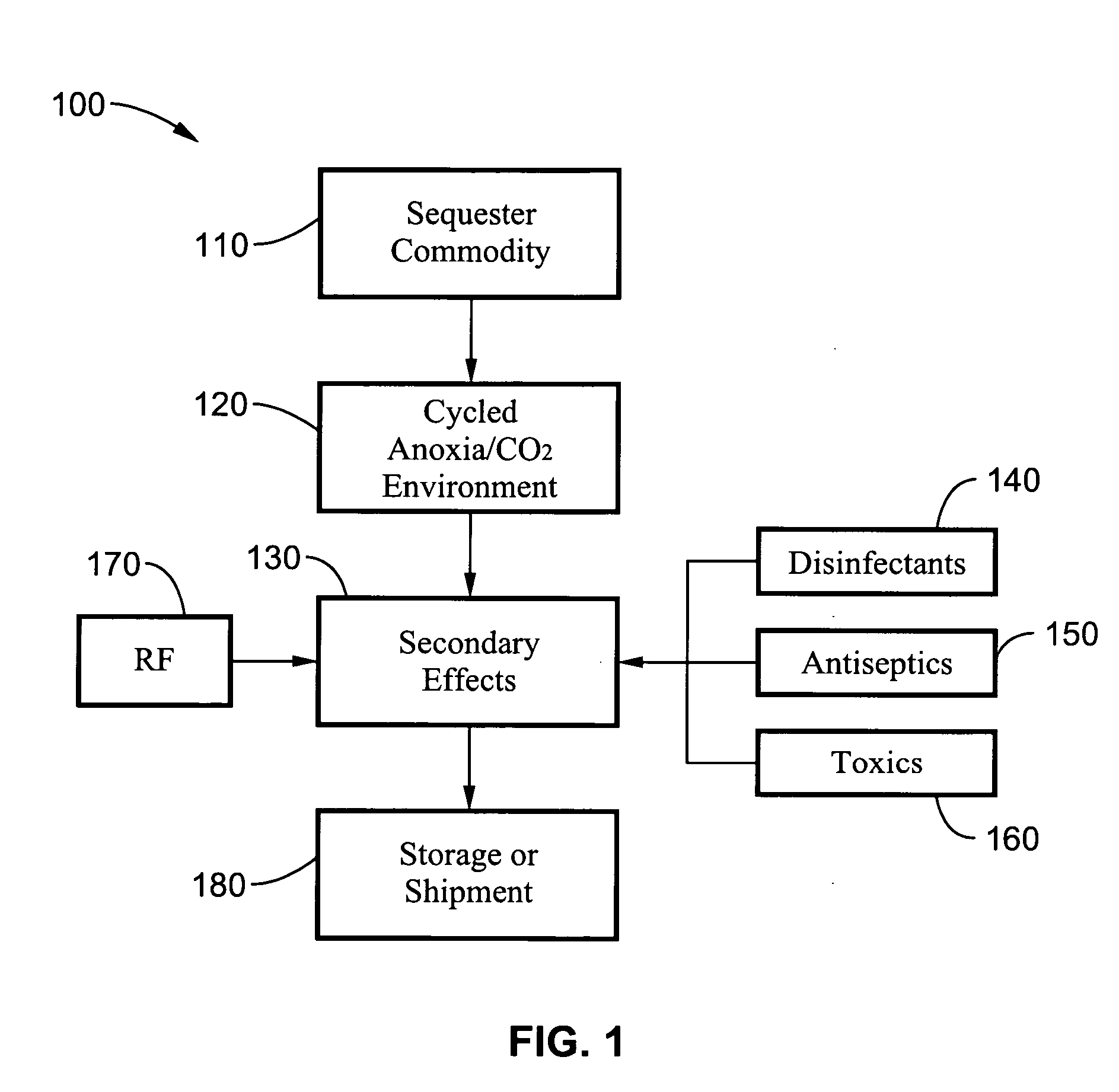
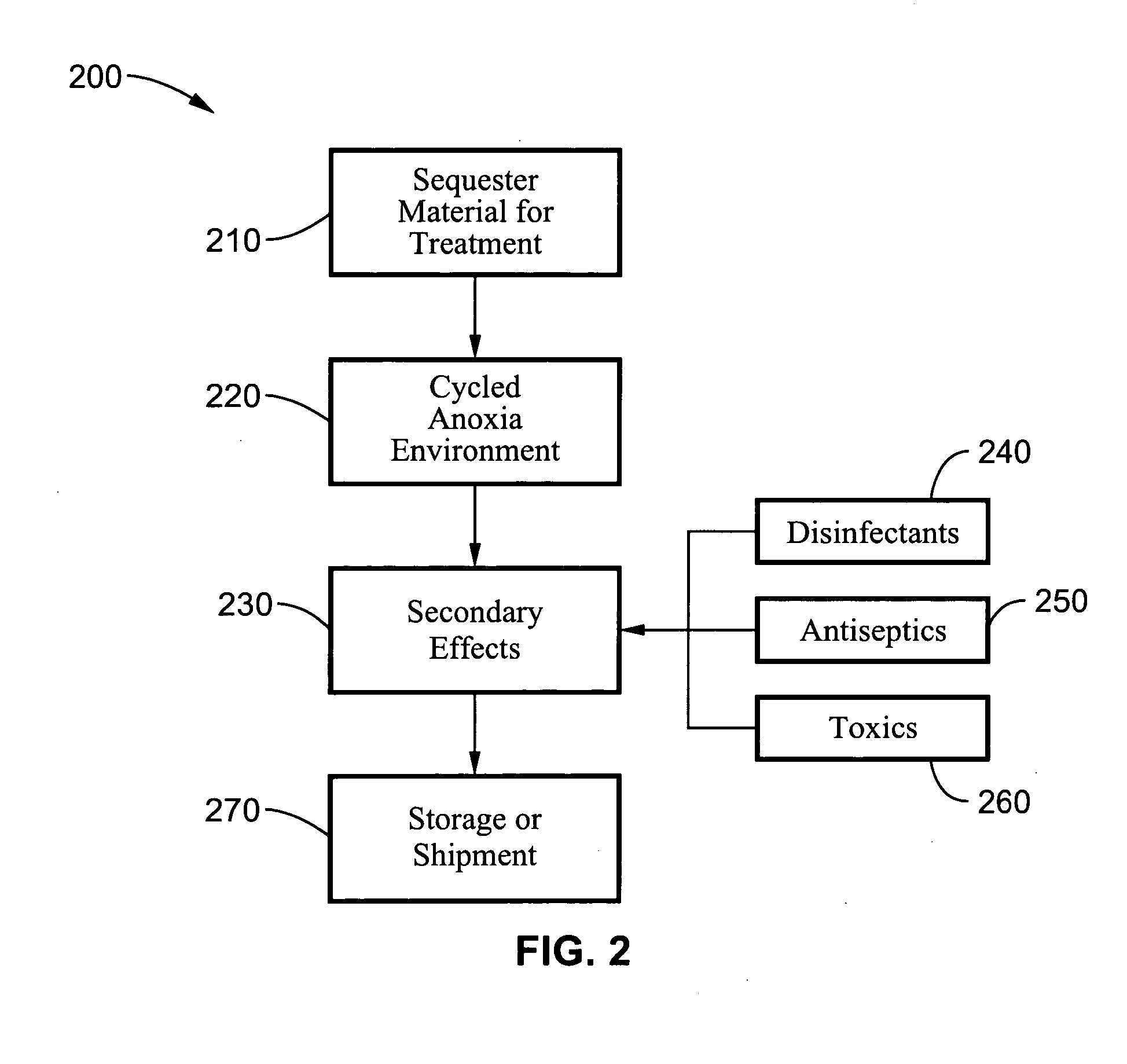
InactiveUS20060269438A1Rapid and quarantine level disinfestationExtended shelf lifeFruit and vegetables preservationEdible seed preservationProtozoaDisinfectant
A method and system for disinfecting and disinfesting a commodity, such as a perishable agricultural commodity, by treatment with an environment of low oxygen / high ballast gas with cycled pressure changes that overwhelm and damage the respiratory system of the insect without damaging the host commodity. The system and method may also include the introduction of disinfectants, antiseptics and other toxic chemicals or the exposure to radio frequencies with intense electric fields that may increase the metabolic activity of the pest or decrease the fitness of the pest within the low oxygen environment. Treatments according to the methods can also increase the shelf life of agricultural commodities by eradicating or delaying the growth of bacteria, fungi, protozoa and other microbial pests.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Inhibitors of nucleoside phoshorylases and nucleosidases
The present invention relates to compounds of the general formula (I) which are inhibitors of purine nucleoside phosphorylases (PNP), purine phosphoribosyltransferases (PPRT), 5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylases (MTAP), 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidases (MTAN) and / or nucleoside hydrolases (NH). The invention also relates to the use of these compounds in the treatment of diseases and infections including cancer, bacterial infections, protozoal infections, and T-cell mediated disease and to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds.
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
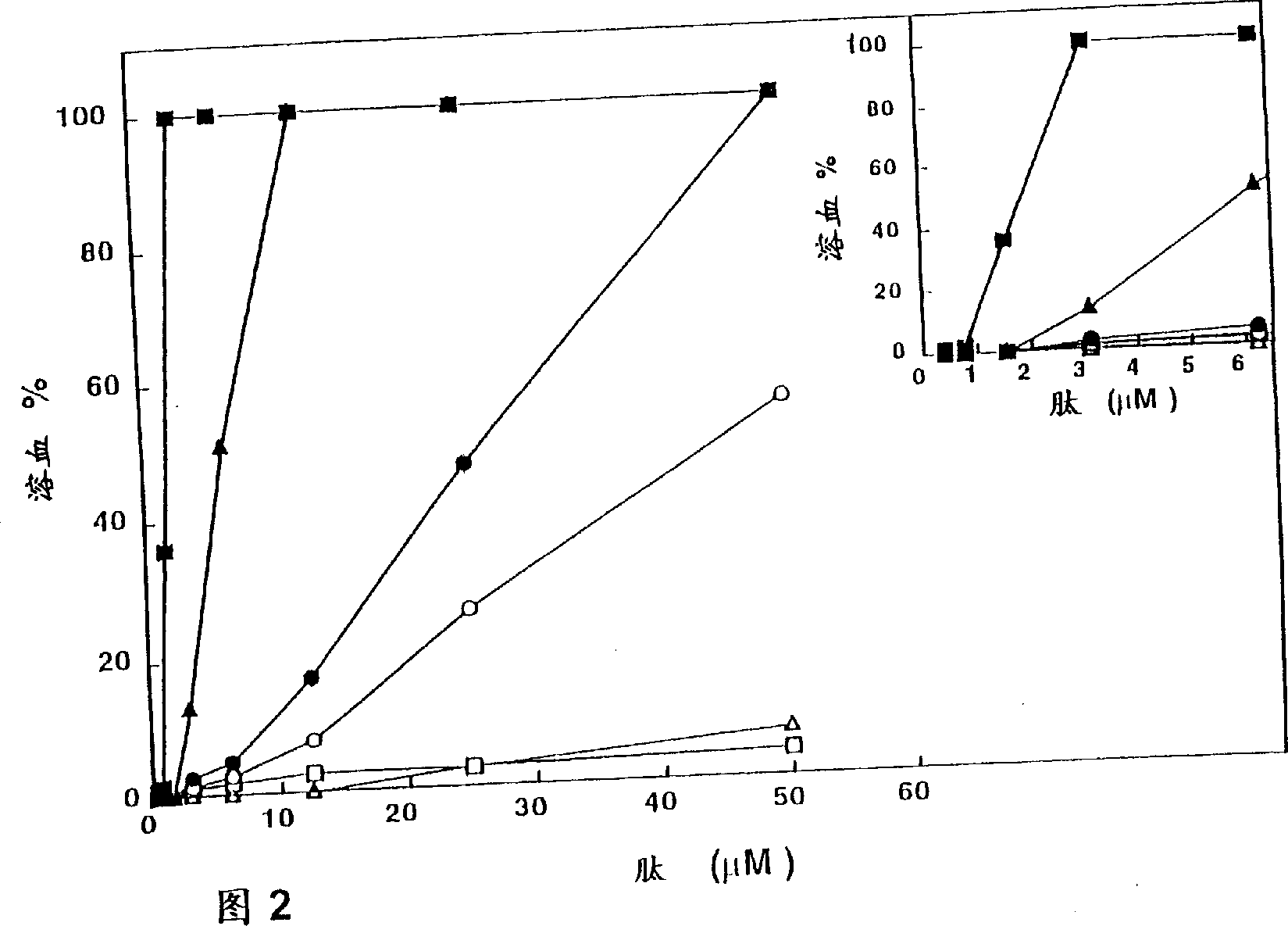
Antipathogenic synthetic piptides and compositions comprising them
Non-hemolytic cytolytic agents selected from peptides, complexes of bundled peptides, mixtures of peptides or random peptide copolymers have a selective cytolytic activity manifested in that they have a cytolytic activity on pathogenic cells, being cells which are non-naturally occurring within the body consisting of microbial pathogenic organisms and malignant cells; and are non-hemolytic, having no cytolytic effect on red blood cells. The peptides may be cyclic derivatives of natural peptides such as pardaxin and mellitin and fragments thereof in which L-amino acid residues are replaced by corresponding D-amino acid residues, or are diastereomers of linear peptides composed of varying ratios of at least one positively charged amino acid and at least one hydrophobic amino acid, and in which at least one of the amino acid residues is a D-amino acid. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the non-hemolytic cytolytic agents can be used for the treatment of several diseases caused by pathogens including antibacterial, fungal, viral, mycoplasma and protozoan infections and for the treatment of cancer.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Personalized site-specific immunomodulation
ActiveUS20130177593A1Inhibit growthPrevent proliferationBacterial antigen ingredientsCancer antigen ingredientsAntigenPersonalization
The invention provides methods of treating inflammation in a specific organ or tissue of an individual. The method involves determining whether the individual has previously been infected with at least one pathogen that is pathogenic in the specific organ or tissue; and administering to the individual an anti-inflammatory composition comprising antigenic determinants, the antigenic determinants selected or formulated so that together they are specific for the at least one pathogen. The pathogen may be an endogenous or exogenous pathogen, and may further be a bacterial pathogen, a viral pathogen, a fungal pathogen, a protozoan pathogen, or a helminth pathogen.
Owner:QU BIOLOGICS INC
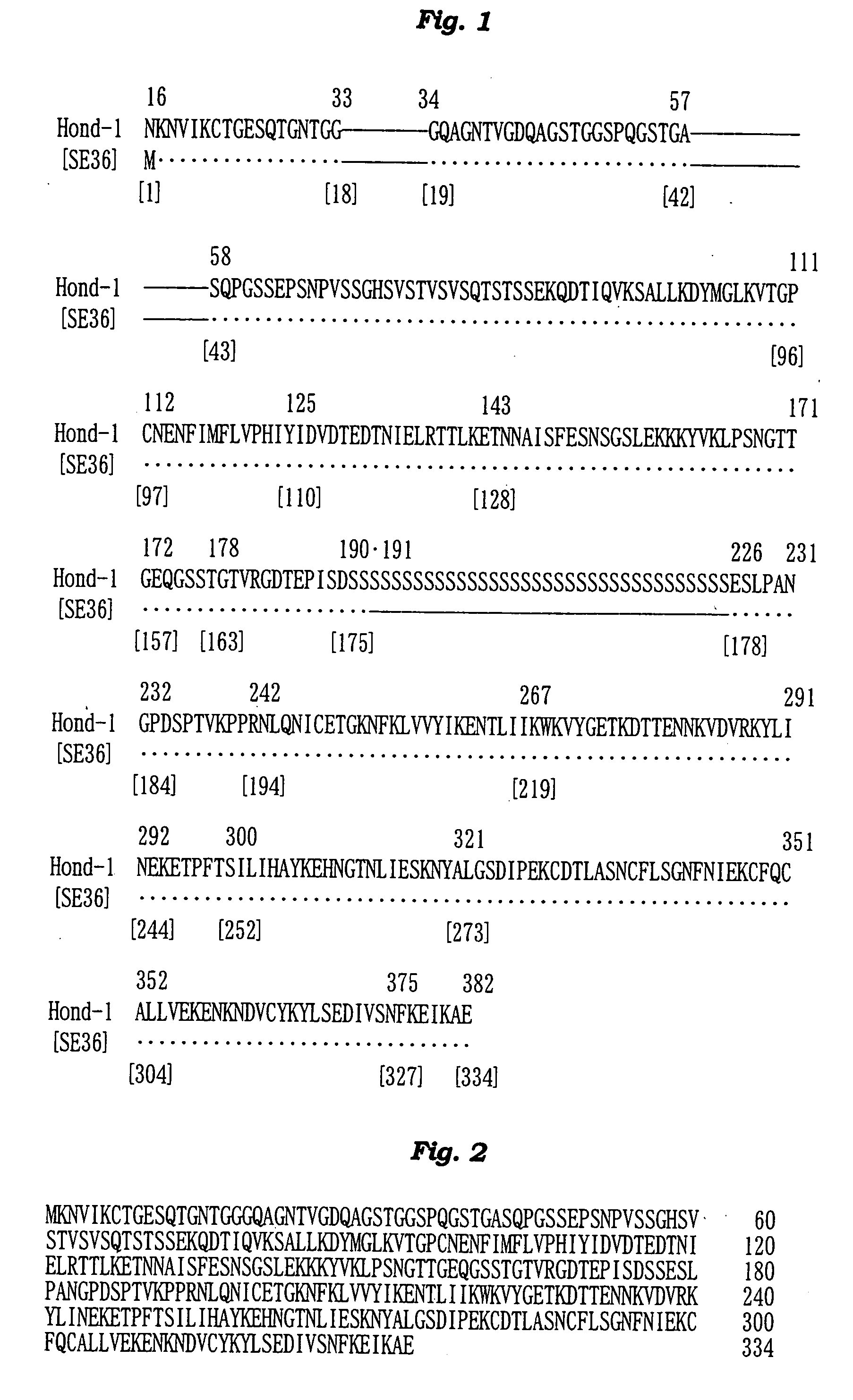
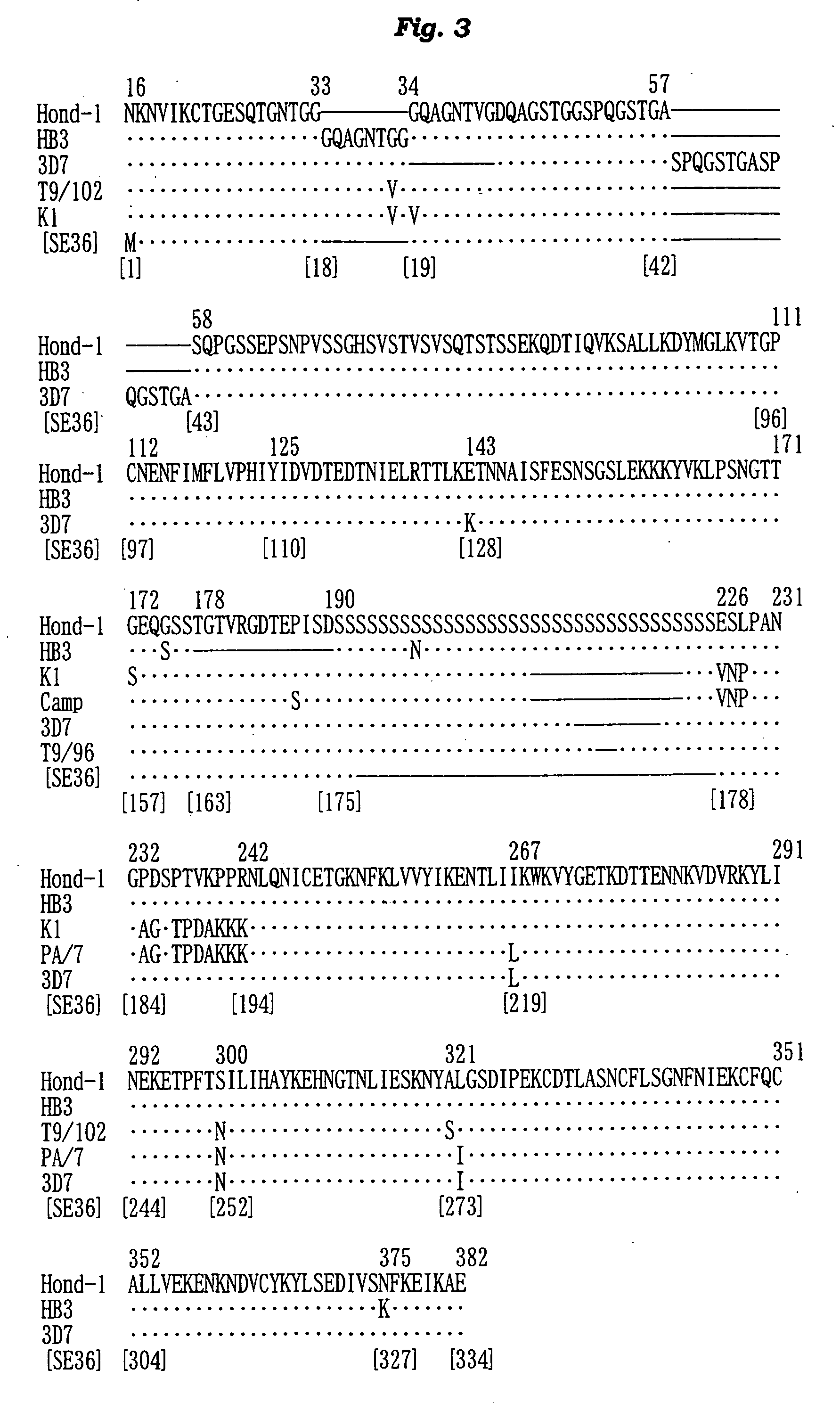
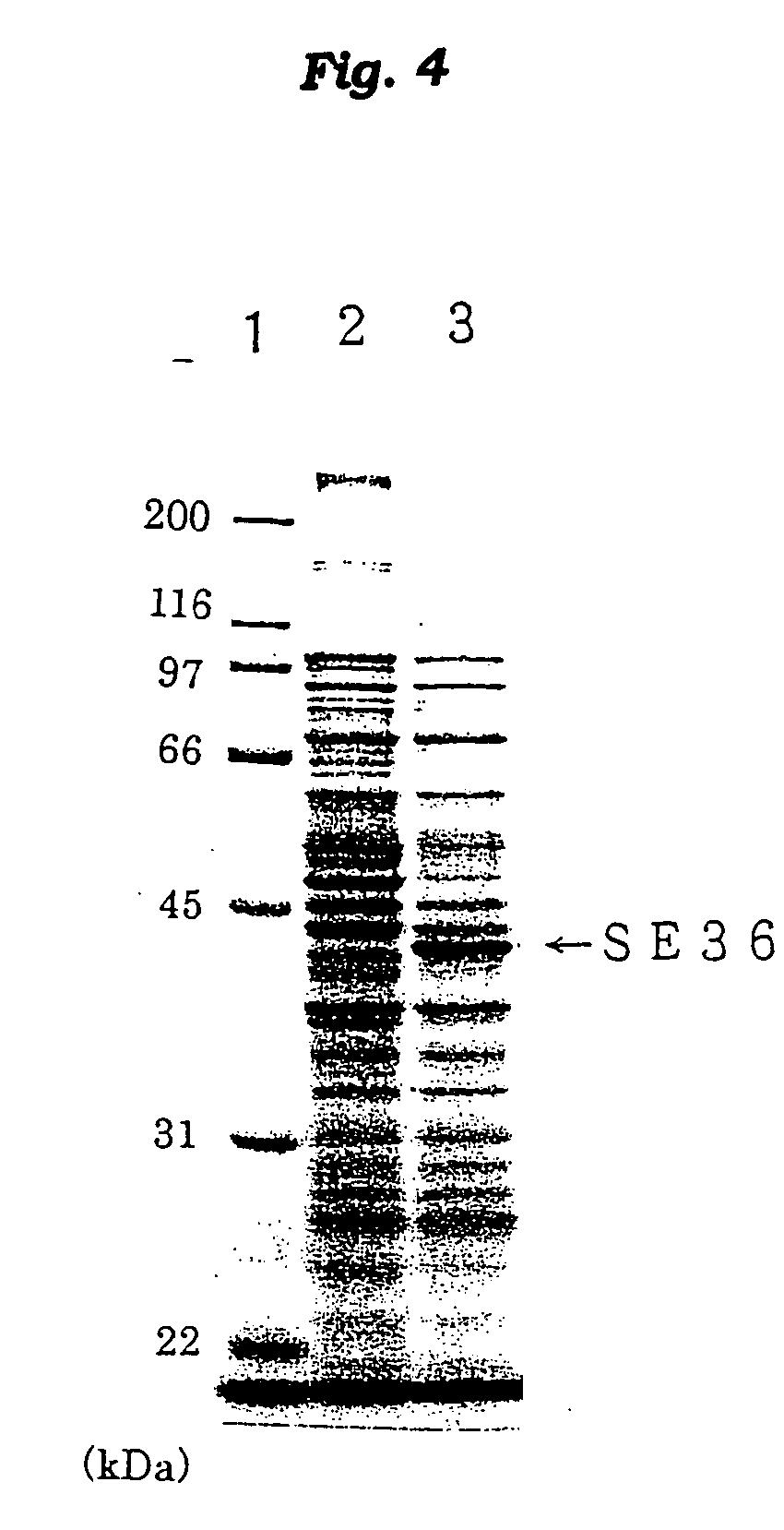
Malaria plasmodium antigen polypeptide se36, method of purifyng the same and vaccine and diagnostic with the use of the thus obtained antigen
The present invention provides a polypeptide SE36 derived from the N-terminal domain (47 kd) of SERA (serine-repeat antigen) produced by malaria parasite, Plasonodium falciparum, at the erythrocyte stage, a process for purifying said polypeptide, and a malaria vaccine and diagnostic agent using as an active component said purified antigen obtained therefrom. SE36 can be produced in Escherichia coli on a large scale by deleting all or part of polymerized serines of the 47 kd serine-repeat region, whereby high purification is permitted. The human IgG3 antibodies specifically binding to SE36 prevents highly effectively growth of the protozoa in the red blood cells to inhibit fever and cerebral malaria, and further prevent the death.
Owner:THE RES FOUND FOR MICROBIAL DISEASES OFOSAKA UNIV +1
Gas-liquid contact apparatus
InactiveUS6503403B2Improve contact efficiencySmall bubbleUsing liquid separation agentMixing methodsDecompositionDissolution
An apparatus and method for enhancing dissolution of gases in liquids by ejecting the gas-liquid mixture through nozzles in a reaction vessel. The nozzles are pressurized, sized and directed to produce micro-fine gas bubbles in the liquid and to initiate rotational flow of the gas-liquid mixture in the reaction vessel. The small bubble size and rotational flow maximizes the time the gas is in contact with the liquid. The apparatus and method are used to increase the dissolution of ozone gas into aqueous solutions to increase the decomposition of aqueous-based organic compounds, precipitation of heavy metals, and destruct and / or deactivate enteric viruses, enteric bacteria, and protozoans. An alternative embodiment mixes the gas with the liquid prior to ejection through the nozzles.
Owner:SANITROL SYST
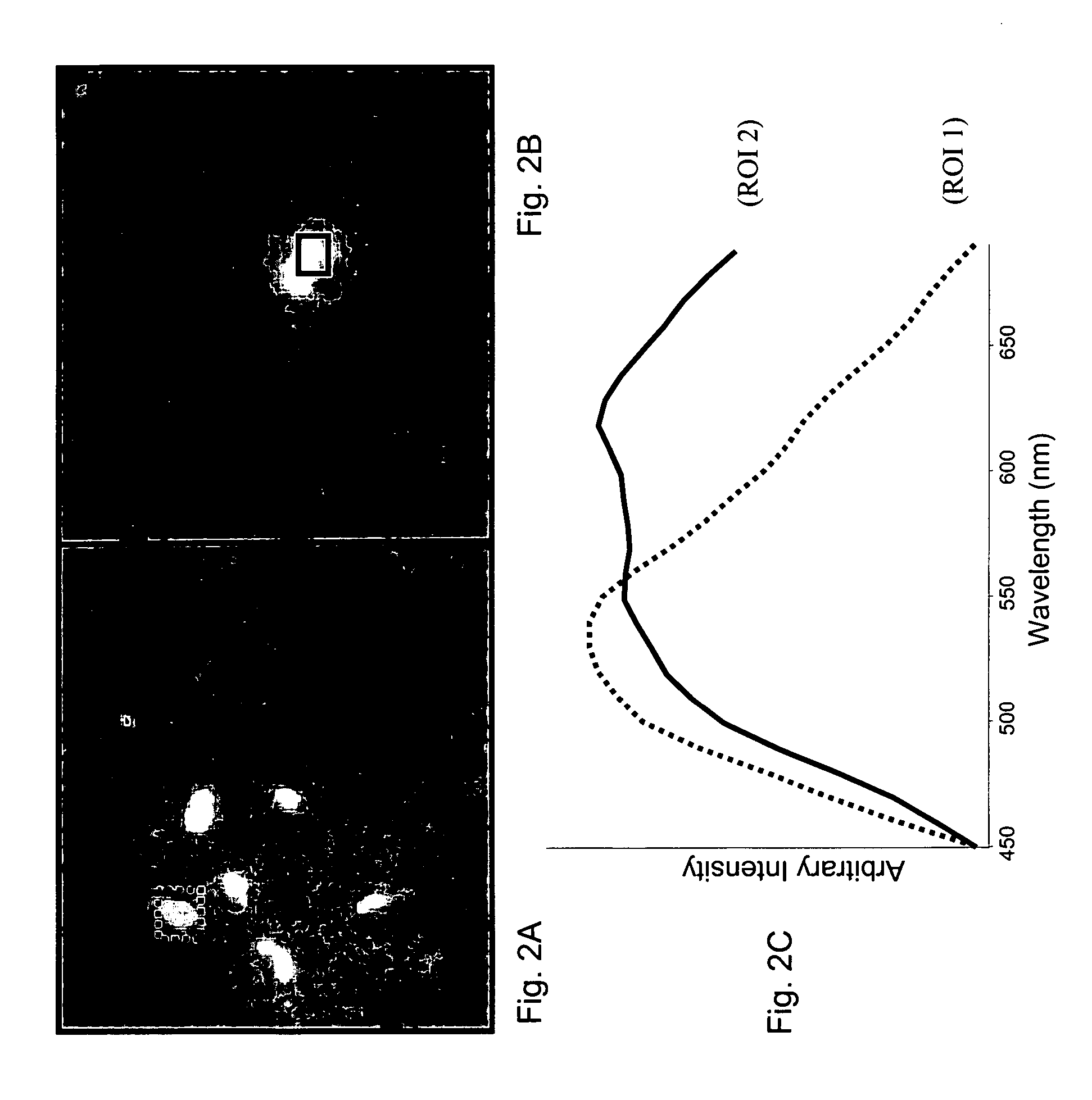
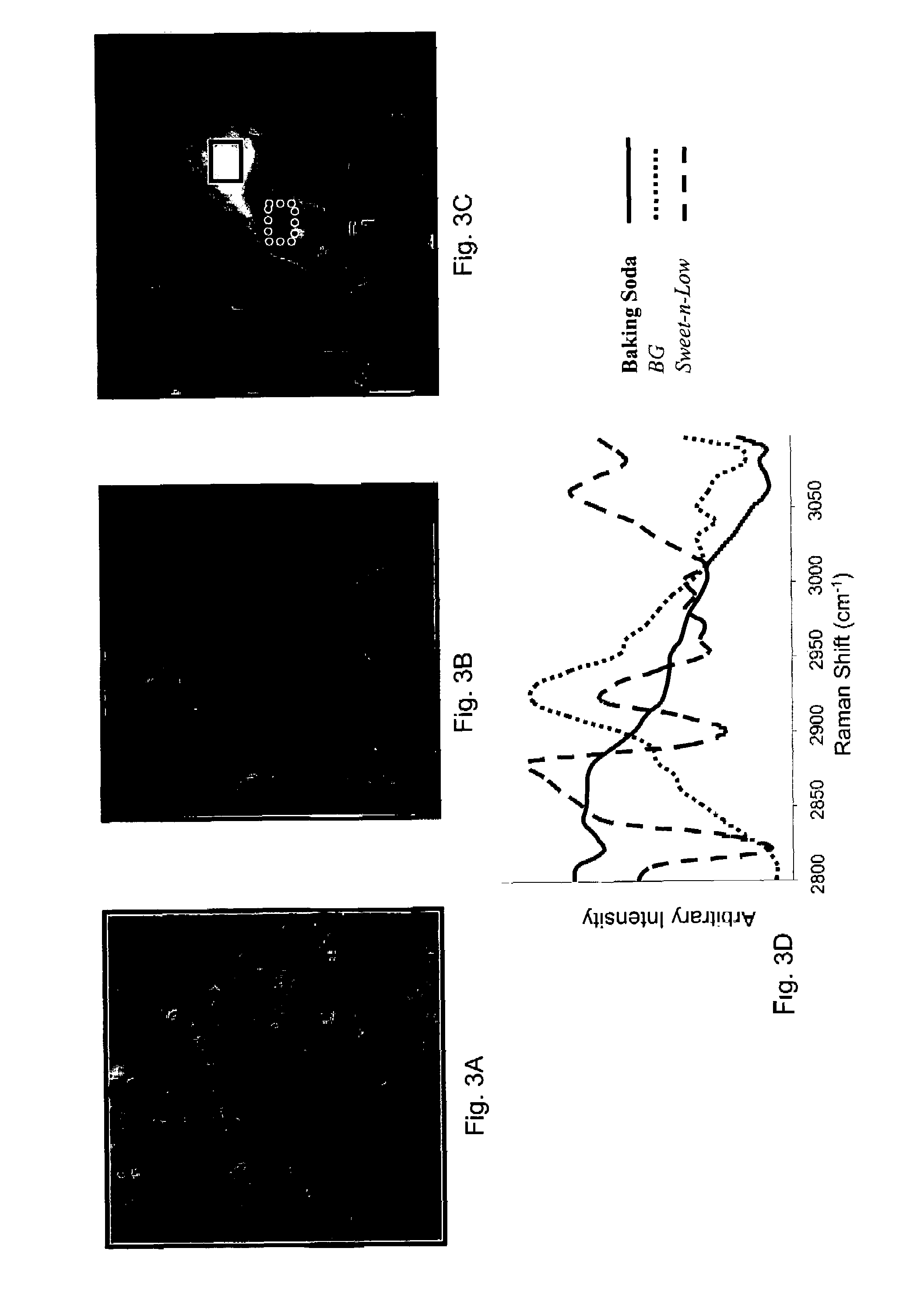
Raman spectral analysis of pathogens
Raman scattering of radiation applied to a water sample is used to assess occurrence of a pathogen in the sample. The method is useful for detecting pathogens that are difficult to detect using other methods, such as protozoa. Examples of organisms that can be detected in water samples using these methods include protozoa of the genus Cryptosporidium and the genus Giardia. The methods described herein have important applications, such as for detection of Cryptosporidium organisms in municipal water systems.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE CORP
66 kDa antigen from Borrelia
InactiveUS6054296AReduce sensitivityHigh selectivityAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsProtozoaAntigen
The present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules, polypeptides encoded by the same, antibodies directed thereto and a method of preparing such polypeptides including: (a) inserting an isolated DNA molecule coding for a polypeptide which is immunoreactive with a 66 kDa polypeptide derived from Borrelia garinii IP90 into an expression vector; (b) transforming a host organism or cell with the vector; (c) culturing the transformed host cell under suitable conditions; and (d) harvesting the polypeptide. The isolated DNA molecule is preferably at least 10 nucleotides in length, and the method may optionally include subjecting the polypeptide to post-translational modification. The host cell can be a bacterium, a yeast, a protozoan, or a cell derived from a multicellular organism such as a fungus, an insect cell, a plant cell, or a mammalian cell.
Owner:SYMBICOM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com








![5h-pyrrolo[3,2-D] pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases 5h-pyrrolo[3,2-D] pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/382d2696-421c-41ef-b7d6-97472bac8513/US07553839-20090630-D00001.png)
![5h-pyrrolo[3,2-D] pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases 5h-pyrrolo[3,2-D] pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/382d2696-421c-41ef-b7d6-97472bac8513/US07553839-20090630-D00002.png)
![5h-pyrrolo[3,2-D] pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases 5h-pyrrolo[3,2-D] pyrimidine inhibitors of nucleoside phosphorylases and nucleosidases](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/382d2696-421c-41ef-b7d6-97472bac8513/US07553839-20090630-C00001.png)