Mono charging system for selectively introducing non-native amino acids into proteins using an in vitro protein synthesis system
A technology of unnatural amino acids and amino acids, which is applied in the field of single-loading system of introducing unnatural amino acids into proteins by using in vitro protein synthesis system, which can solve the problems of high efficiency, poor feasibility, low efficiency, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 1
[0207] Example 1. General method
[0208] Standard methods in molecular biology have been described (Maniatis et al. (1982) Molecular Cloning, A Laboratory Manual (Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual), Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.; Sambrook and Russell (2001) Molecular Cloning Cloning, 3yd ed., Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.; Wu (1993) Recombinant DNA, Vol. 217, Academic Press, San Diego, Calif). The standard method is also published in Bindereif, & Westhof (2005) Handbook of RNA Biochemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany, which describes detailed methods for RNA manipulation and analysis.
[0209] Methods for protein purification, chromatography, electrophoresis, centrifugation, and crystallization have been described (Coligan et al. (2000) Current Protocols in Protein Science, Vol.1, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York ). Methods for cell-free synthesis are described in Spirin & Swartz (2008) Cell-free Pr...
Embodiment 2
[0210] Example 2. In vitro transcription and isolation of tRNA 2', 3'-cyclic phosphoric acid
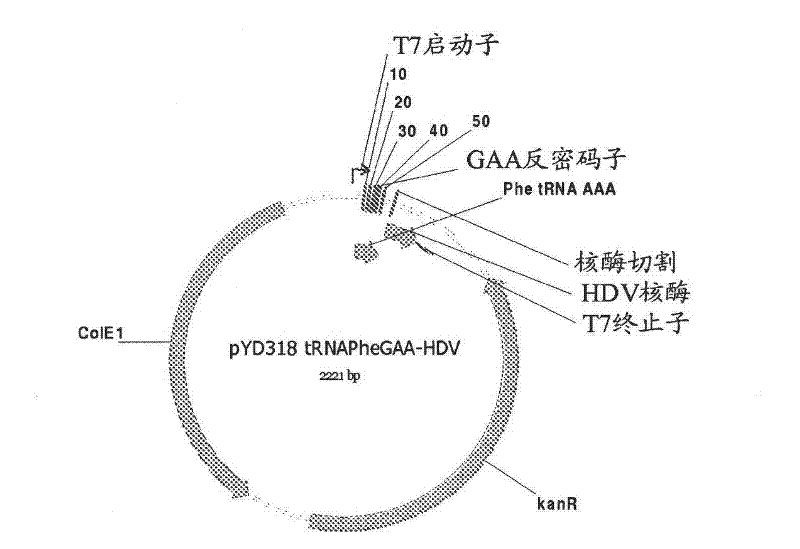
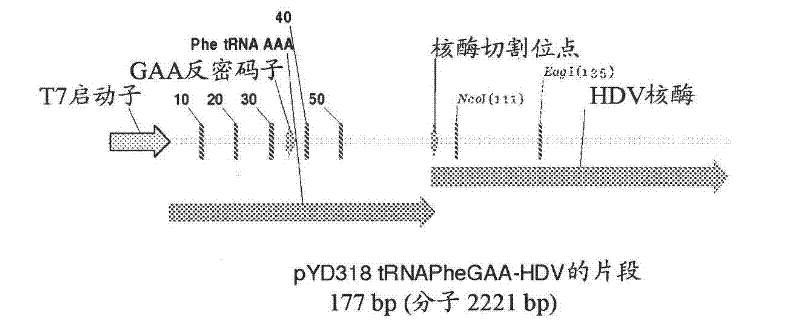
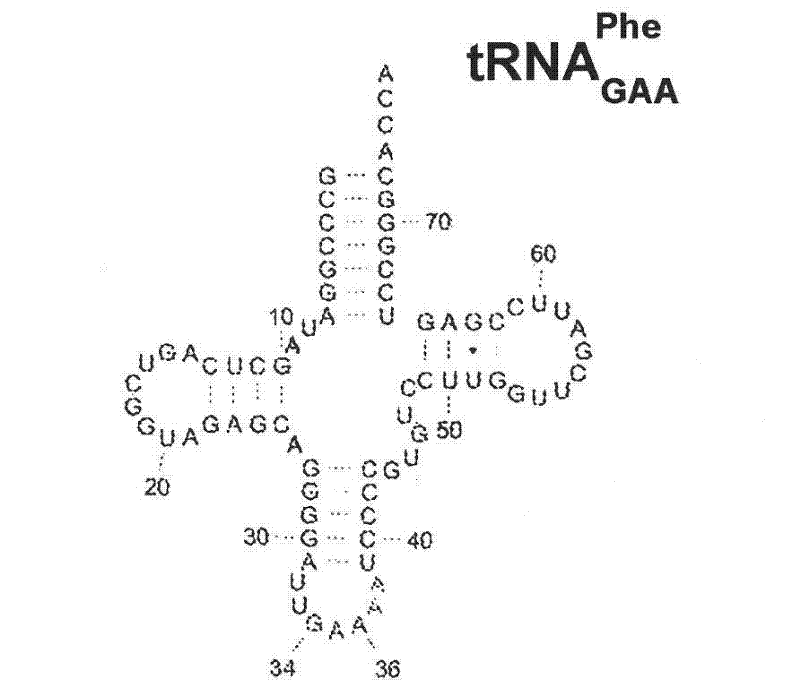
[0211] Isofunctional tRNAs aminoacylated with unnatural amino acids can be generated by in vitro transcription from the designed tRNA-HDV ribozyme template DNA shown in the example in Figure 1, followed by purification by size exclusion chromatography (SEC) to enzymatically remove 2′,3′-cyclic phosphate, and use engineered tRNA synthetase to load tRNA with unnatural amino acid (nnAA), the process as figure 2 shown. To optimize transcription yield, 4 different in vitro transcription protocols were tested image 3 and Figure 4 tRNA transcripts indicated. All 4 different in vitro transcription protocols gave similar tRNA yields. Transcription optimization is usually performed at 37°C in a 50 μL reaction for 2-3 h. The reaction conditions are as follows: (1) 40mM HEPES (pH 7.9), 10mM DTT, 10mM MgCl 2 , 2.5mM spermidine, 4U / ml pyrophosphatase, 0.4U / ml superRNAse-in (Ambion), 20mM N...
Embodiment 3
[0216] Example 3. Dephosphorylation of tRNA 2',3'-cyclic phosphates to release active tRNA
[0217] T4 polynucleotide kinase (PNK), which is required for the removal of 2′,3′-cyclic phosphates from HDV ribozyme-cleaved tRNAs, was produced as follows (cf. figure 2 and 5 ). The PNK gene (DNA 2.0, Menlo Park., CA) with an N-terminal 6-histidine tag was genetically synthesized and cloned into plasmid pYD317. BL21(DE3) cells were transformed with plasmid T4PNK_pYD317. These cells were grown for 18 hours in a Braun 10L fermentor to a final OD of 21 on autoinduction medium (Studier F.W. (2005) Protein Expr. Purif., 41:207-234). Cells were harvested by centrifugation and a 240 g cell pellet was obtained. A 40 g cell pellet was resuspended in 500 ml buffer A (50 mM Tris (pH 7.8), 300 mM KCl, 10 mM imidazole), lysed by homogenization, clarified by centrifugation, and loaded onto a 35 mL Ni-IMAC column. Wash the column with 5 column volumes of buffer A. Buffer A plus 0.5 mM BME, 30...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| composition ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com