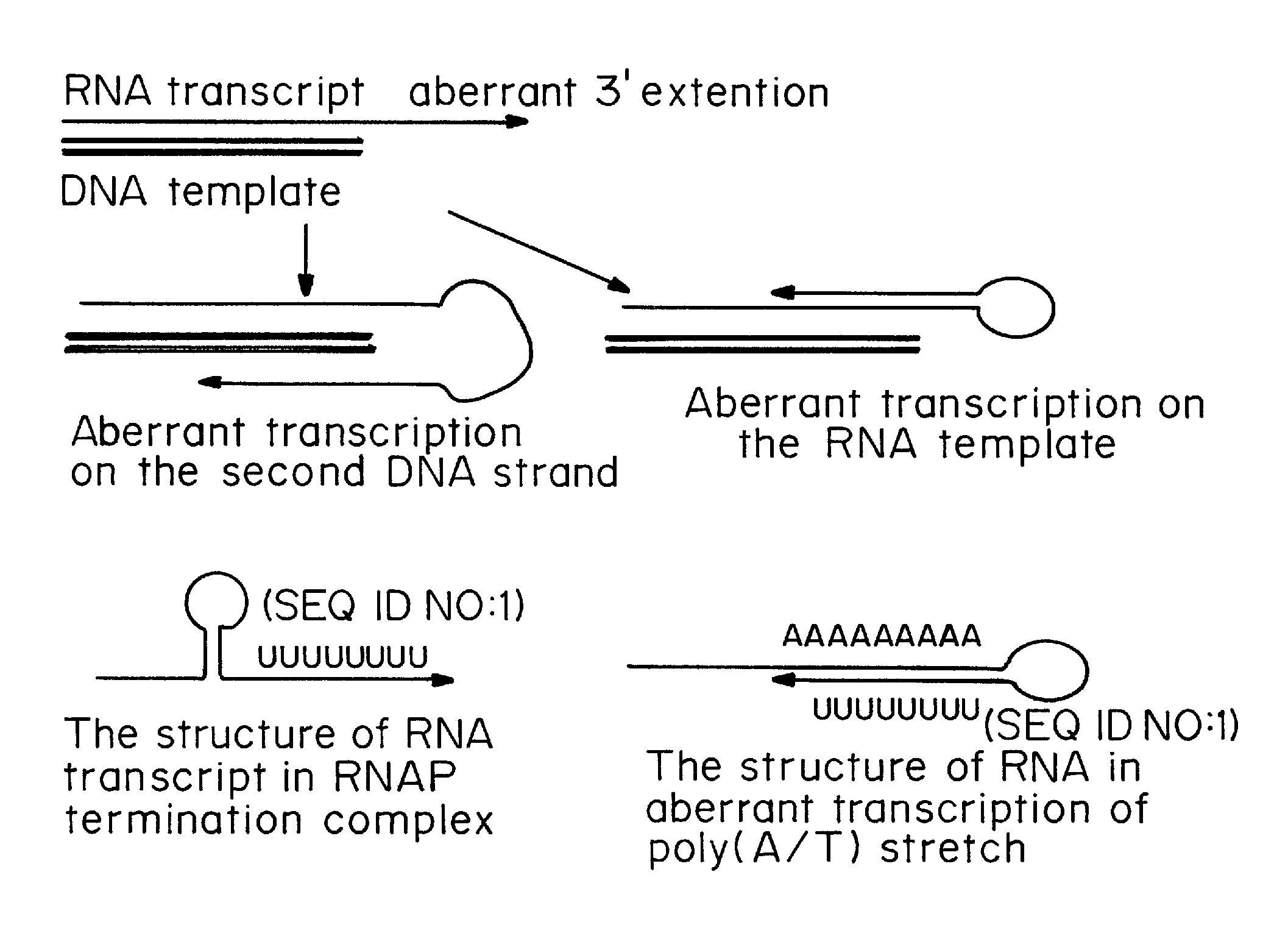
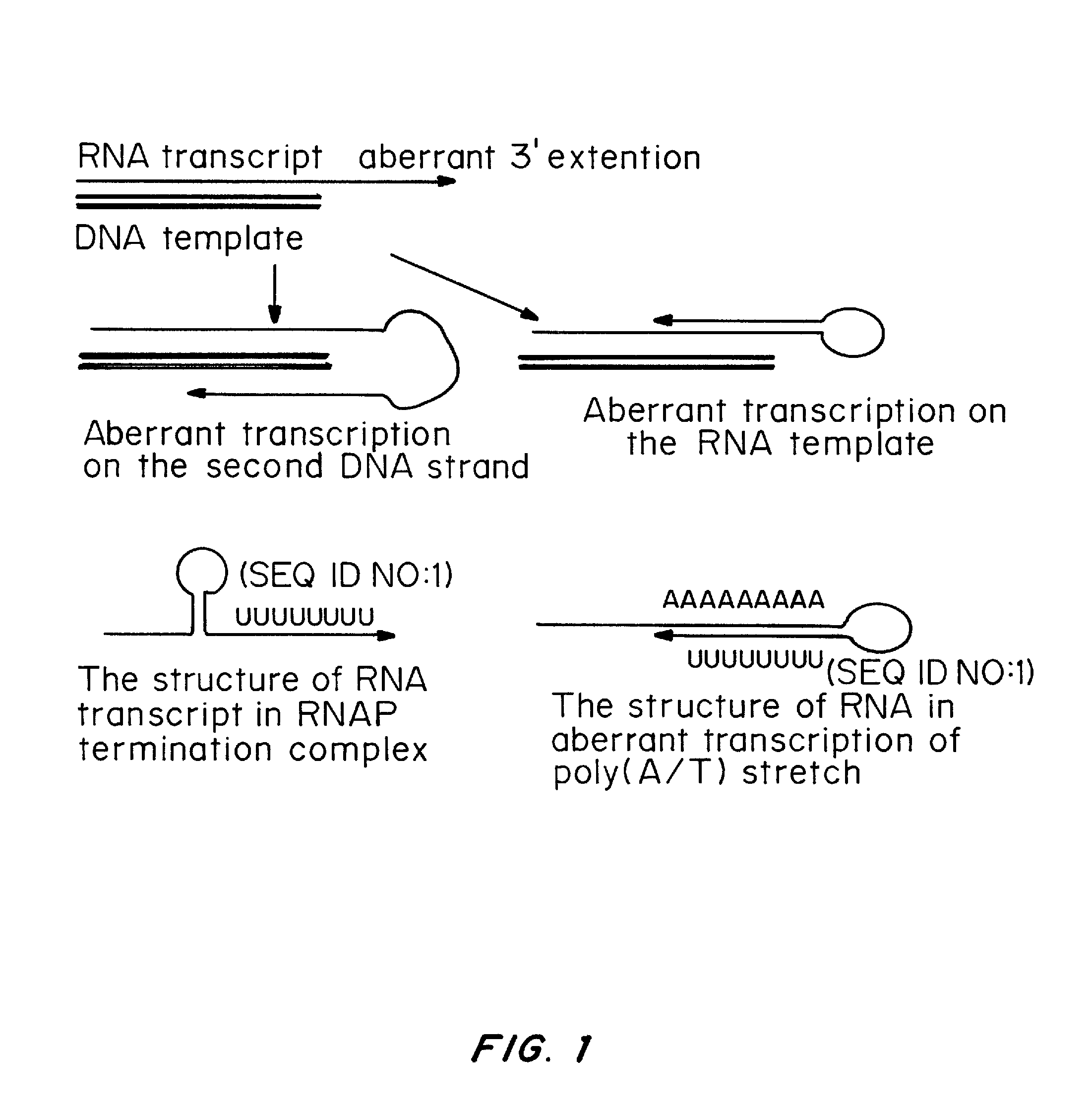
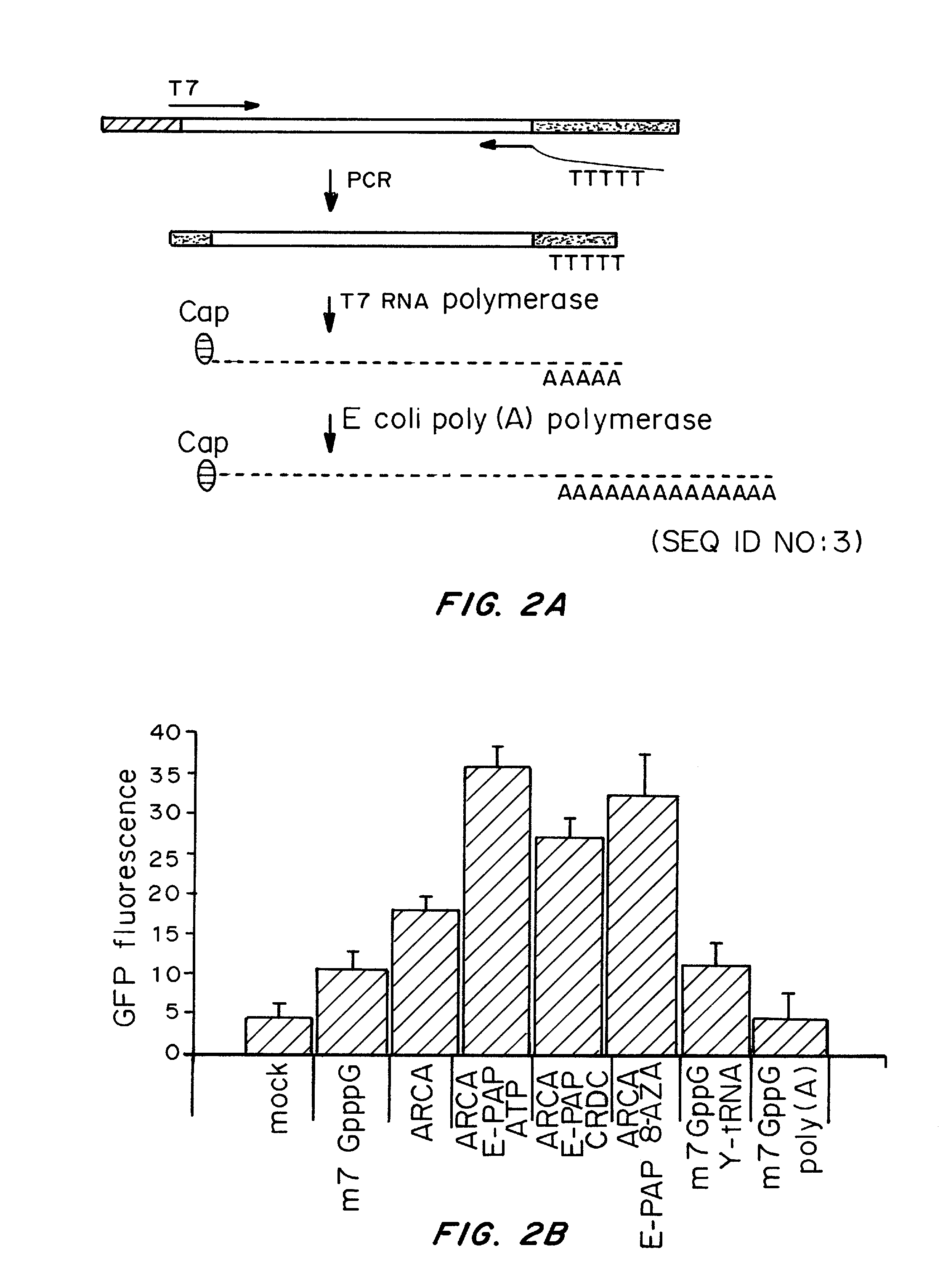
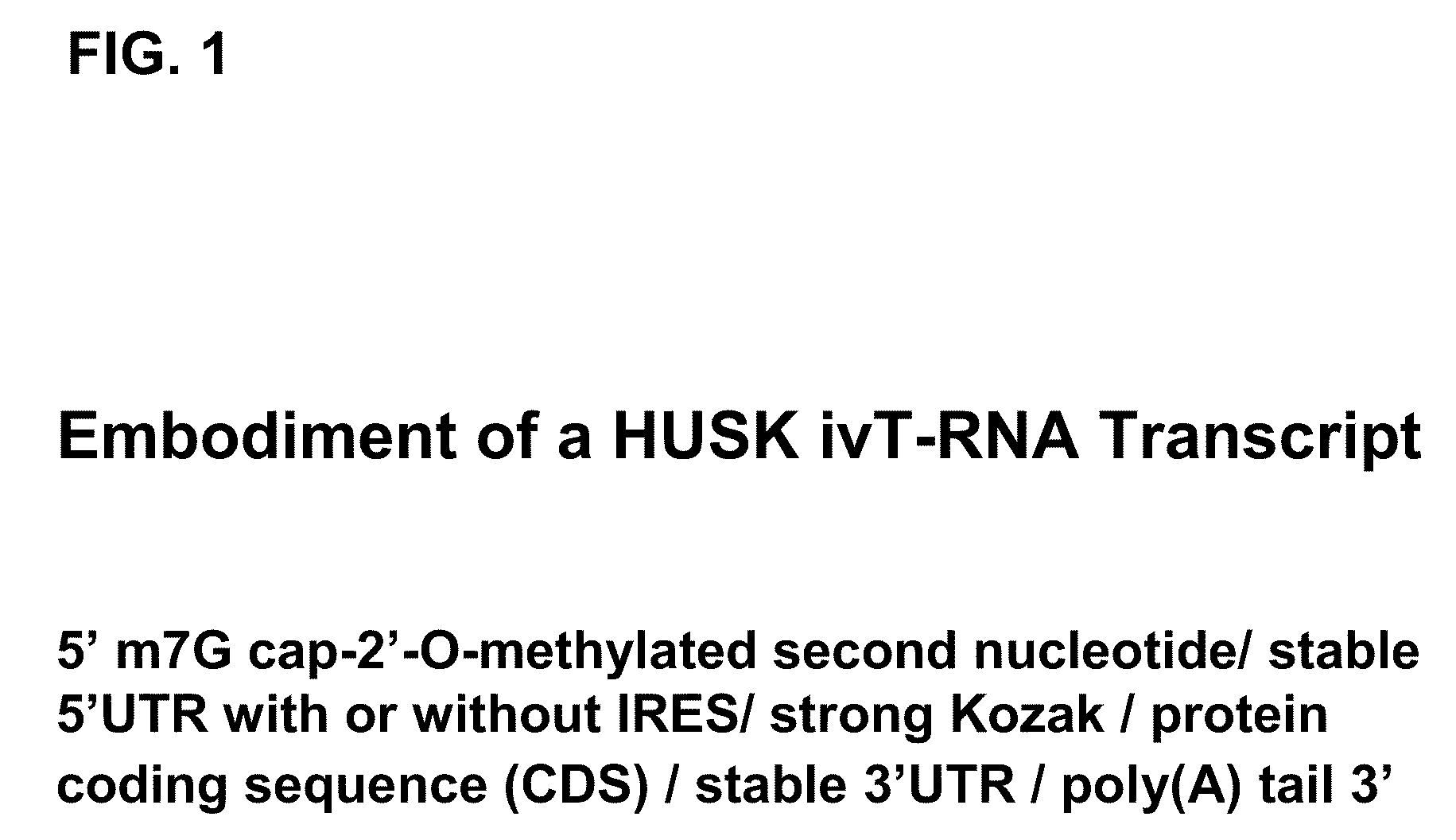
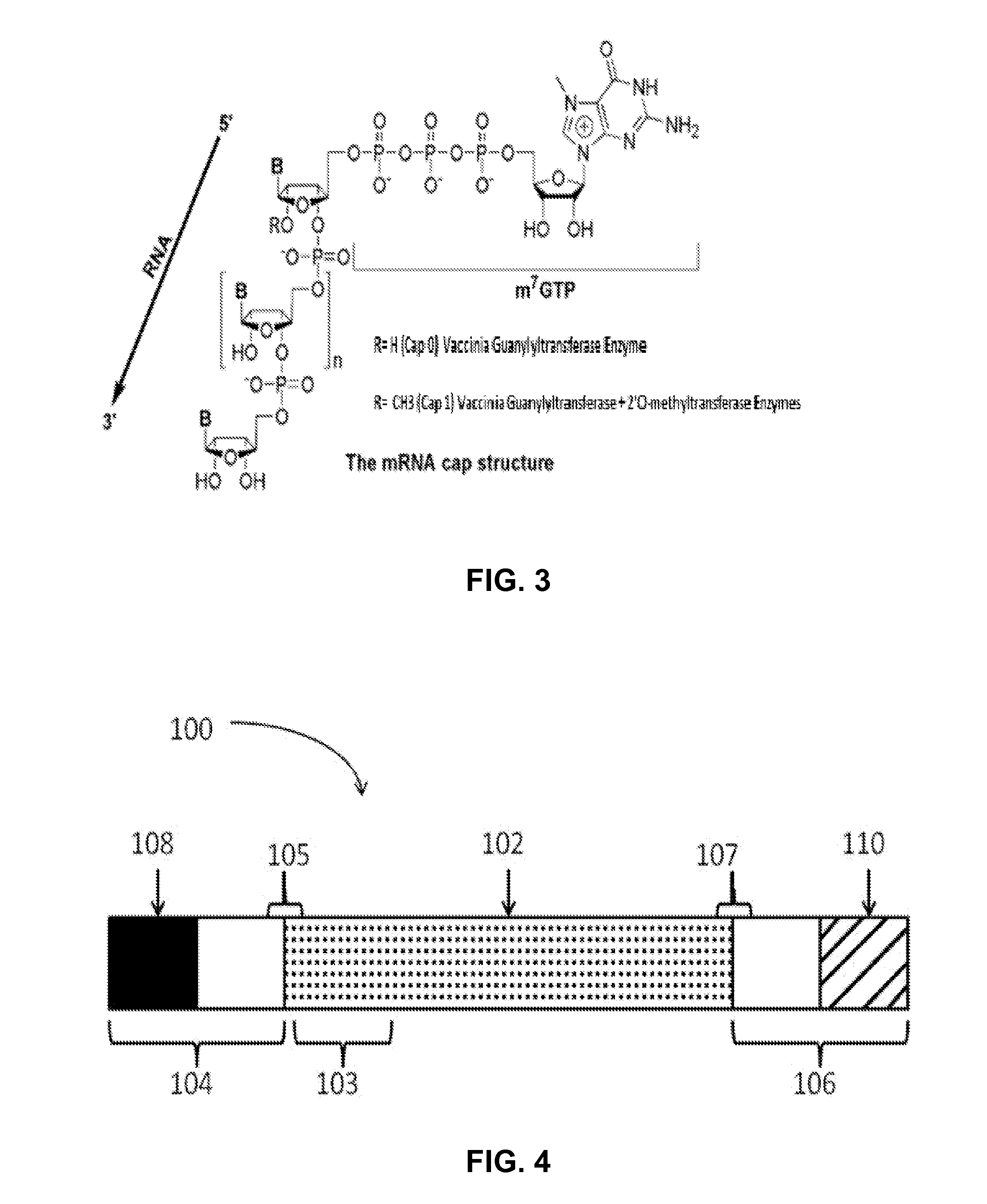
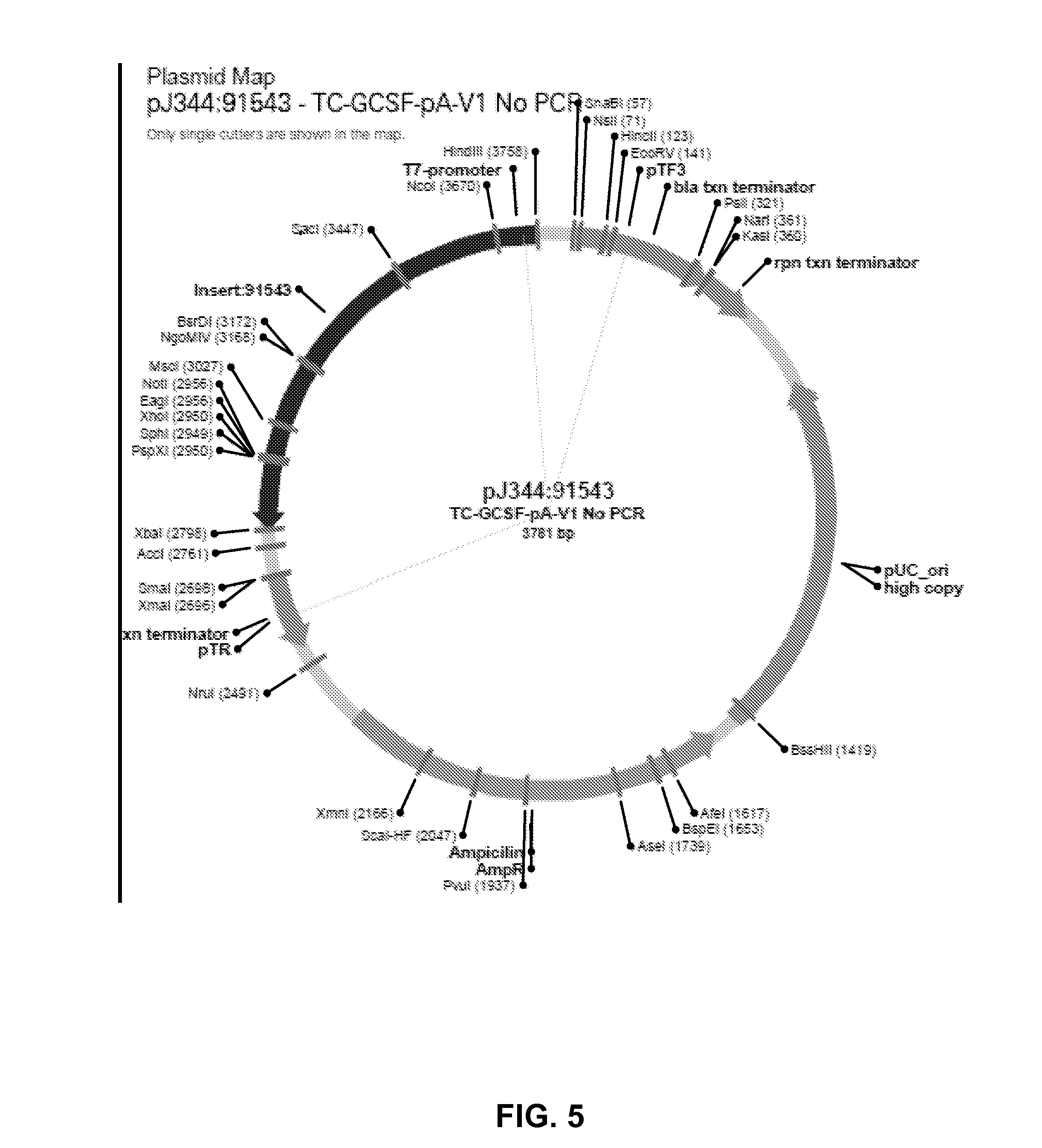
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
374 results about "In vitro transcription" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
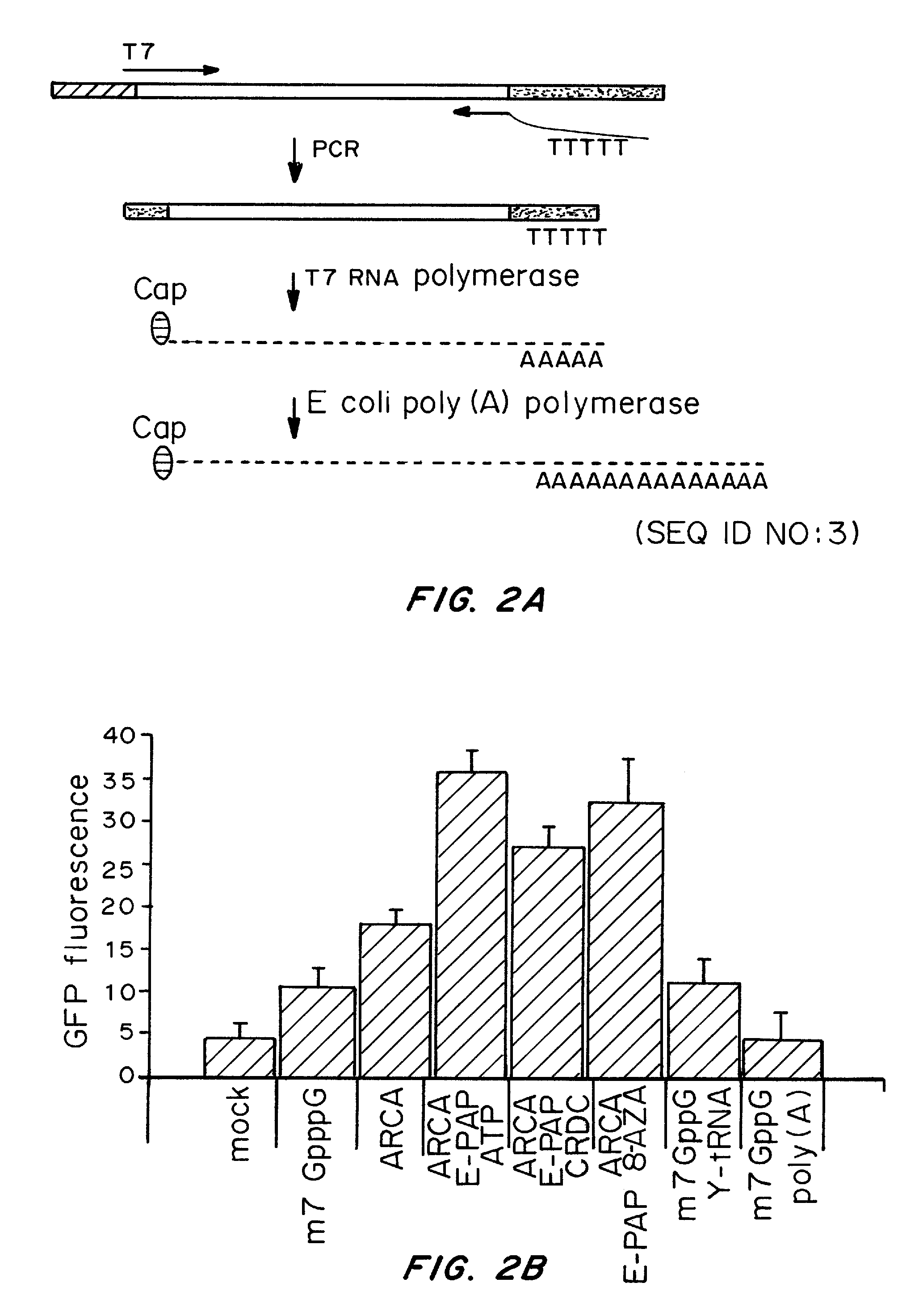
Transient Transfection with RNA
ActiveUS20080260706A1Lymphocyte transfectabilitySimilar efficiencyBiocideGenetic material ingredientsGene deliveryDNA construct
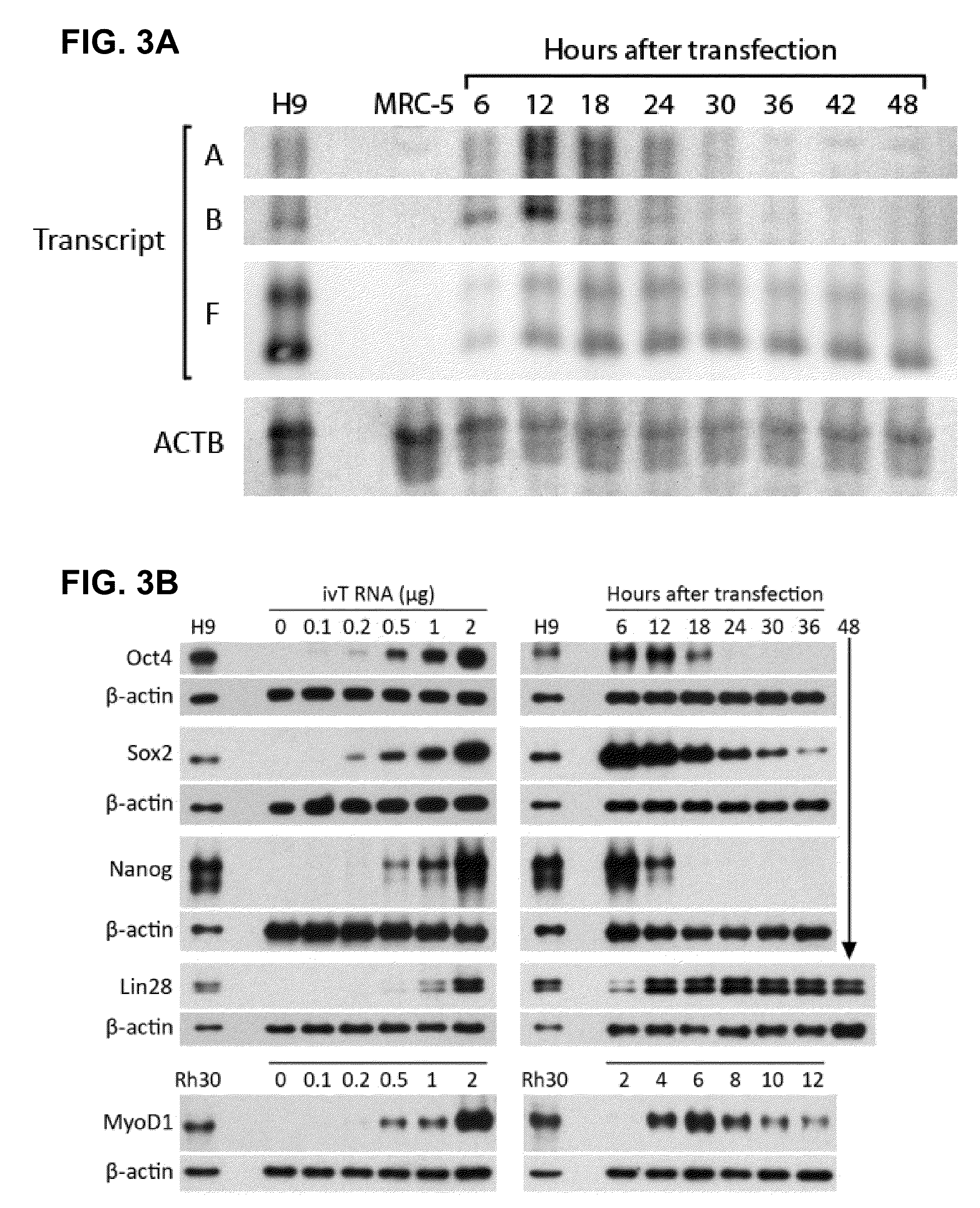
A method of mRNA production for use in transfection is provided, that involves in vitro transcription of PCR generated templates with specially designed primers, followed by polyA addition, to produce a construct containing 3′ and 5′ untranslated sequence (“UTR”), a 5′ cap and / or Internal Ribosome Entry Site (IRES), the gene to be expressed, and a polyA tail, typically 50-2000 bases in length. This RNA can efficiently transfect different kinds of cells. This approach results in increased efficiency (fidelity and productivity) of mRNA synthesis and is less time consuming because it does not require cloning, and also consequently eliminates the unwanted errors and effects related to RNA made on DNA templates obtained with cloning techniques. The results of transfection of RNAs demonstrate that RNA transfection can be very effective in cells that are exceedingly difficult to transfect efficiently with DNA constructs. Further, the levels of gene expression following mRNA transfection are consistent from cell to cell in an experiment and these levels can be controlled over a wide range simply by changing the amount of mRNA that is transfected, and without obvious cytotoxic effects due to the levels of RNA per se. Due to high efficiency the cells can be simultaneously transfected with multiple genetic constructs. The method can be used to deliver genes into cells not- or only poorly transfectable for DNA, in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Innate immune suppression enables repeated delivery of long RNA molecules
InactiveUS20100273220A1Suppressing innate immune responseReduce expressionSugar derivativesArtificial cell constructsENCODETransient transfection
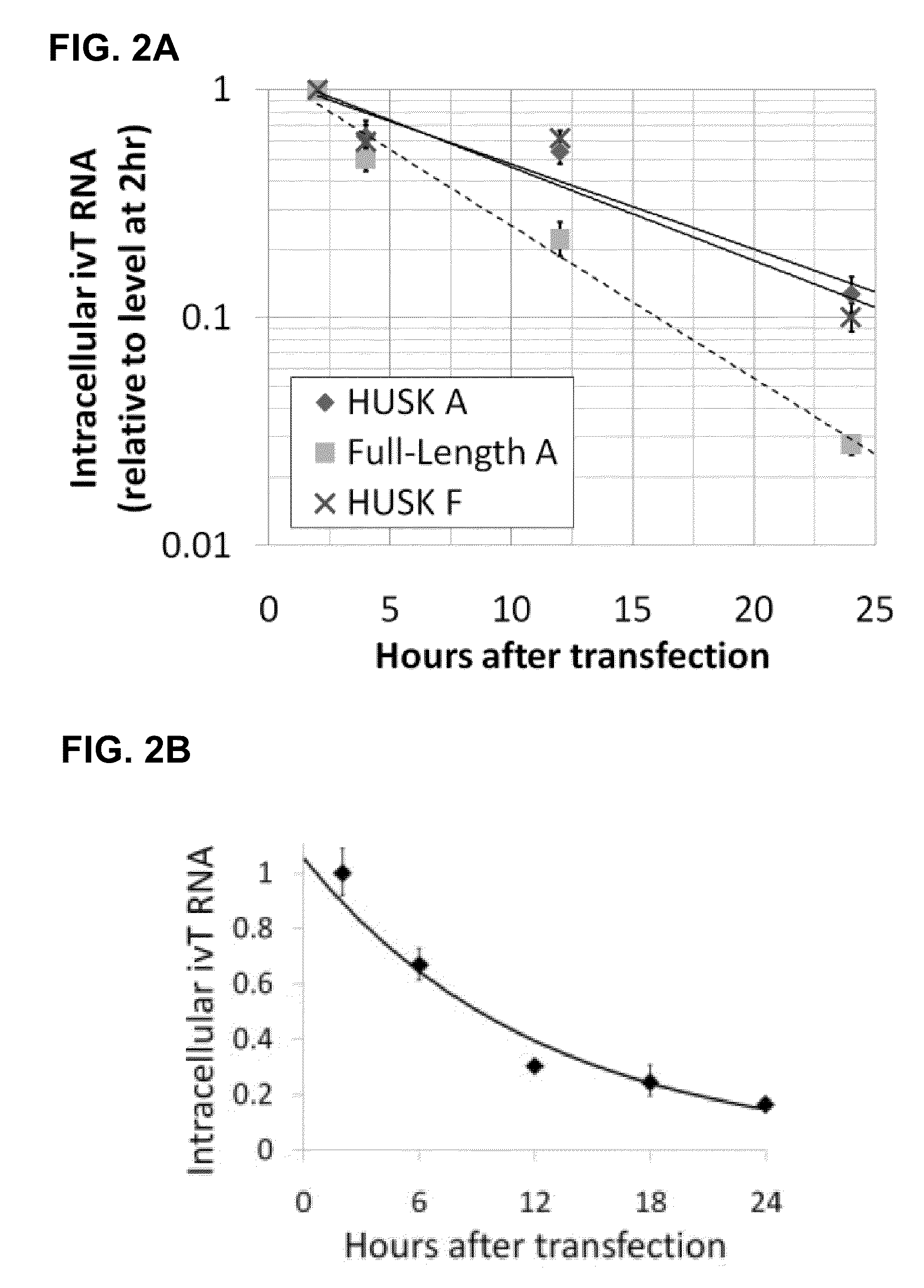
The present invention relates in part to methods for suppressing the innate immune response of a cell to transfection with an exogenous nucleic acid, to methods for increasing expression of a protein encoded by an exogenous nucleic acid by repeated delivery of the exogenous nucleic acid to a cell, and to methods of changing the phenotype of a cell by differentiating, transdifferentiating or dedifferentiating cells by repeatedly delivering one or more nucleic acids that encode defined proteins. A method is provided for extended transient transfection by repeated delivery of an in vitro-transcribed RNA (“ivT-RNA”) to a cell to achieve a high and sustained level of expression of a protein encoded by an ivT-RNA transcripts.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Process for producing peptides by using in vitro transcription/translation system
The present invention relates to a reaction system whereby a peptide produced in an in vitro peptide synthesis system can be efficiently isolated at a high purity from the reaction system. Thus the present invention is a process for producing a peptide or a peptide derivative by using a reaction system of transcribing a DNA into an RNA and then translating the RNA produced or a reaction system of translating an RNA in vitro wherein at least one protein component of the reaction system is labeled with a first substance which adheres to a second substance, and said second substance is used as an adsorbent for capturing said labeled protein components after translating.
Owner:BIOCOMBER
Ribosome complexes as selection particles for in vitro display and evolution of proteins
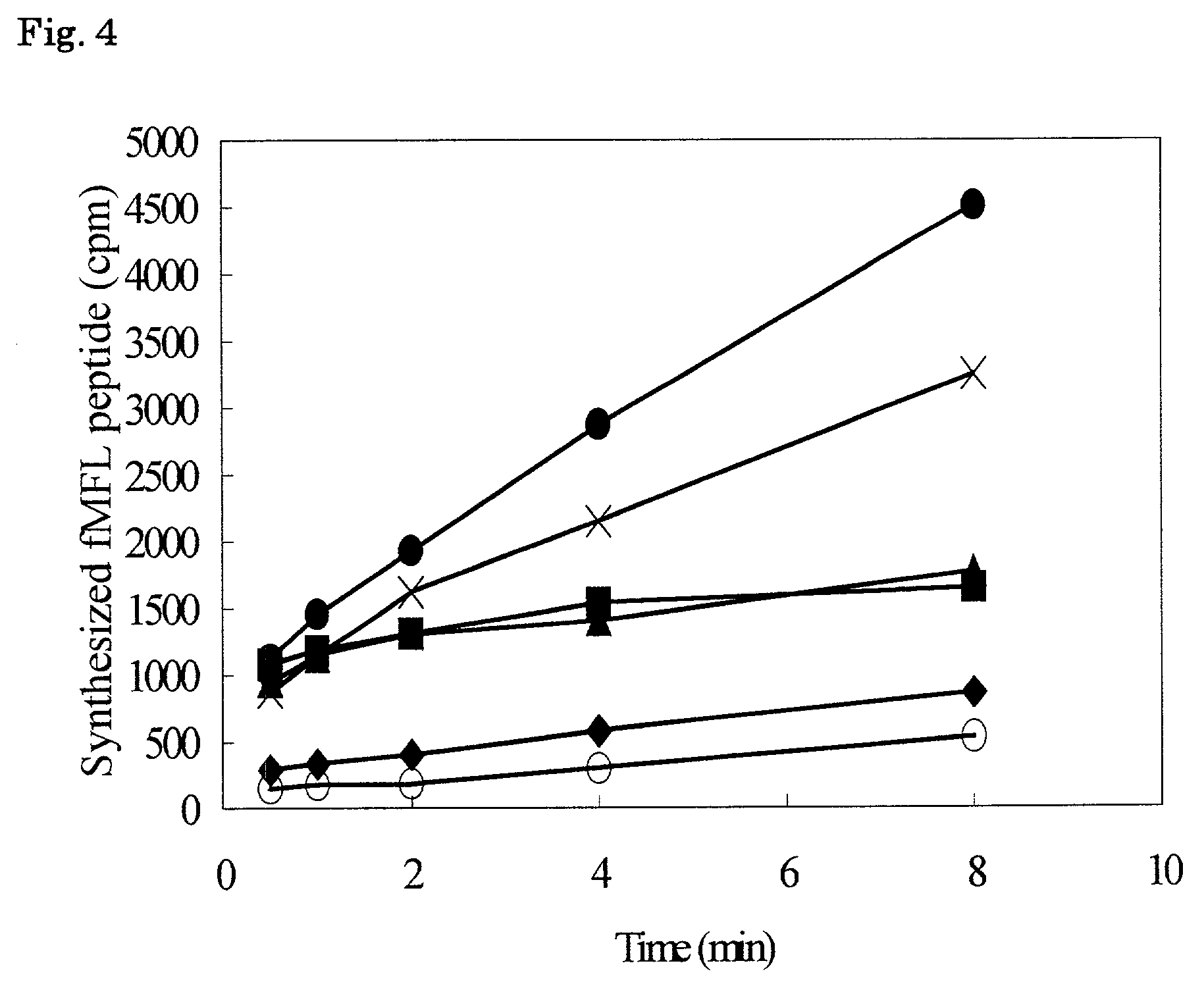
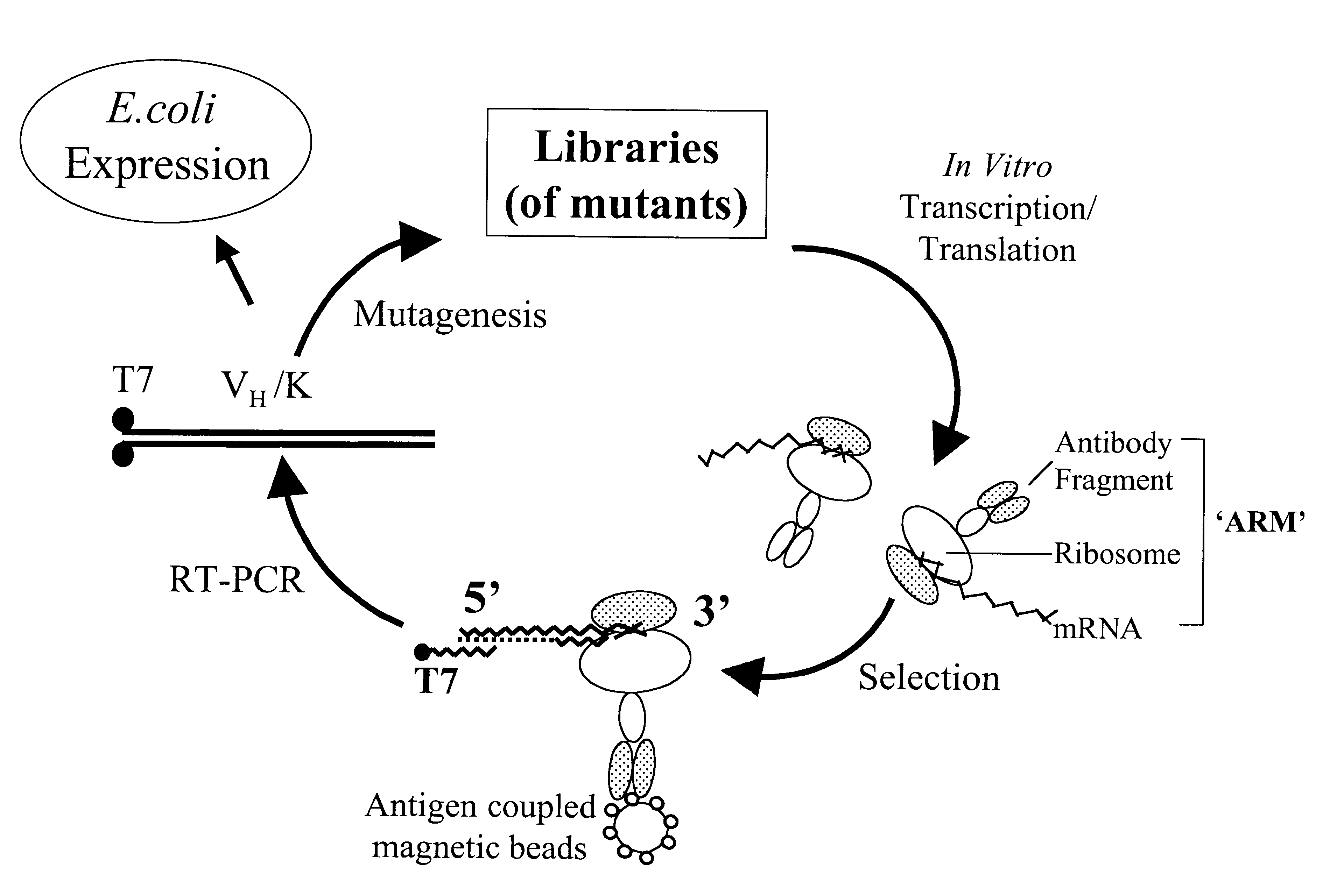
The invention provides a method of displaying nascent proteins or peptides as complexes with eukaryotic ribosomes and the mRNA encoding the protein or peptide following transcription and translation in vitro, of further selecting complexes carrying a particular nascent protein or peptide by means of binding to a ligand, antigen or antibody, and of subsequently recovering the genetic information encoding the protein or peptide from the selected ribosome complex by reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). The RT-PCR recovery step is carried out directly on the intact ribosome complex, without prior dissociation to release the mRNA, thus contributing to maximal efficiency and sensitivity. The steps of display, selection and recovery can be repeated in consecutive cycles. The method is exemplified using single-chain antibody constructs as antibody-ribosome-mRNA complexes (ARMs).
Owner:CRESCENDO BIOLOGICS
Methods and means for enhancing RNA production
ActiveUS20170114378A1Improved and economical meanImproved and economical and methodBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRibonucleosideFiltration membrane
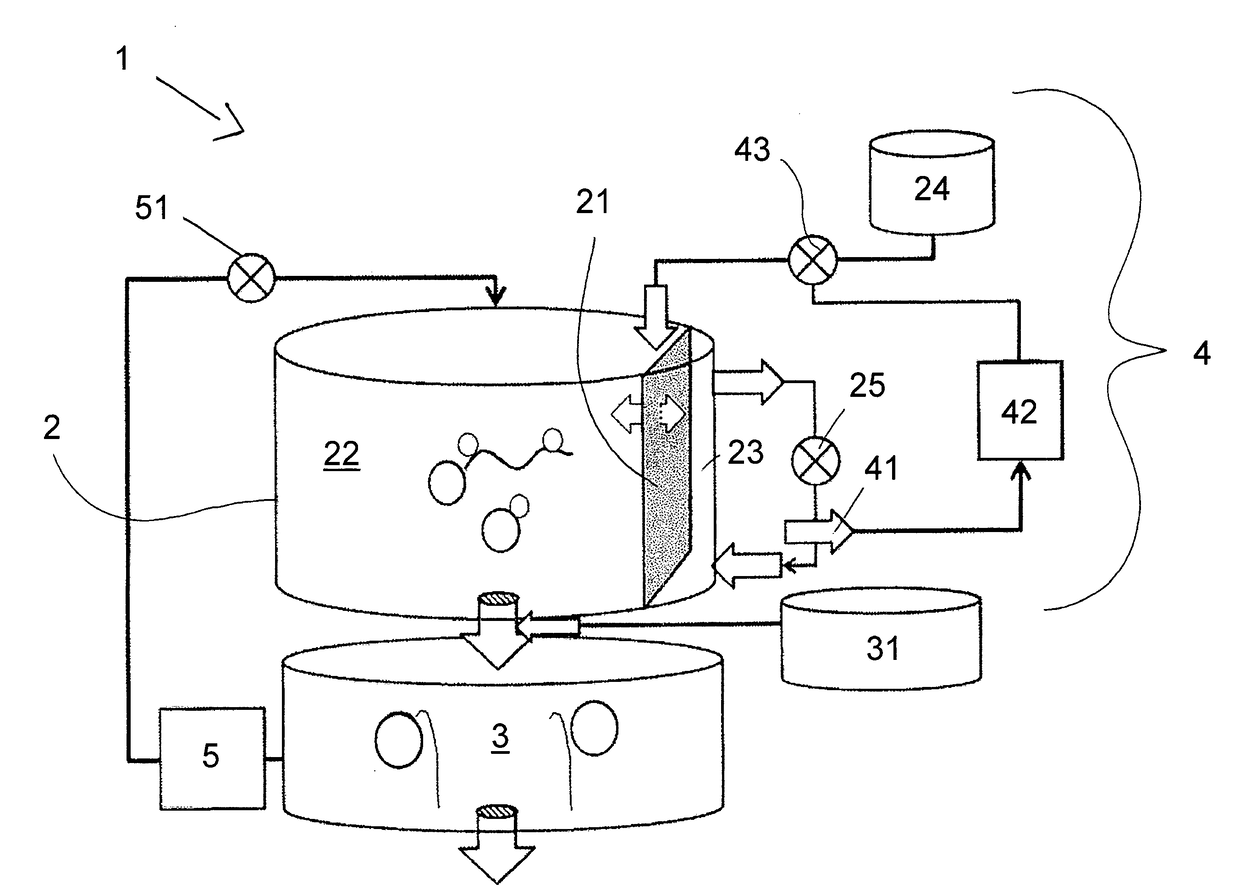
The present invention relates to a method for synthesizing an RNA molecule of a given sequence, comprising the step of determining the fraction (1) for each of the four nucleotides G, A, C and U in said RNA molecule, and the step of synthesizing said RNA molecule by in vitro transcription in a sequence-optimized reaction mix, wherein said sequence-optimized reaction mix comprises the four ribonucleoside triphosphates GTP, ATP, CTP and UTP, wherein the fraction (2) of each of the four ribonucleoside triphosphates in the sequence-optimized reaction mix corresponds to the fraction (1) of the respective nucleotide in said RNA molecule, a buffer, a DNA template, and an RNA polymerase. Further, the present invention relates to a bioreactor (1) for synthesizing RNA molecules of a given sequence, the bioreactor (1) having a reaction module (2) for carrying out in vitro RNA transcription reactions in a sequence-optimized reaction mix, a capture module (3) for temporarily capturing the transcribed RNA molecules, and a control module (4) for controlling the infeed of components of the sequence-optimized reaction mix into the reaction module (2), wherein the reaction module (2) comprises a filtration membrane (21) for separating nucleotides from the reaction mix, and the control of the infeed of components of the sequence-optimized reaction mix by the control module (4) is based on a measured concentration of separated nucleotides.
Owner:CUREVAC REAL ESTATE GMBH
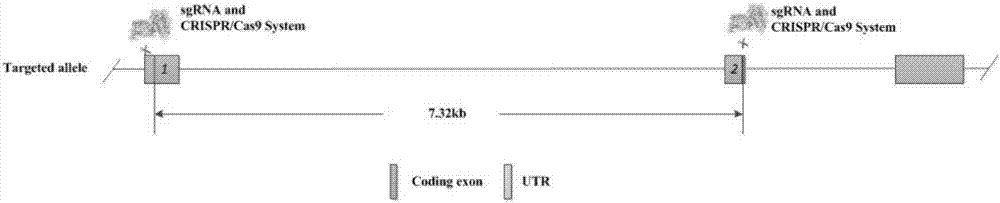
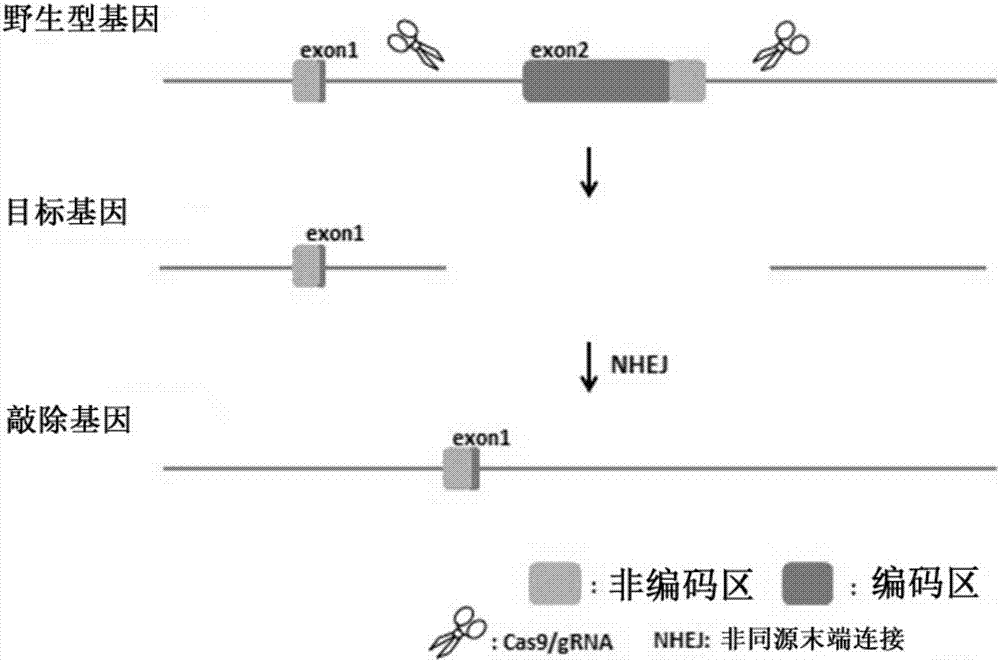
Method for knocking off animal FGF5 gene by using CRISPR-Cas9 system
ActiveCN104531704AThe identification rules are simpleEasy to operateMicroinjection basedVector-based foreign material introductionA-DNAExon
The invention provides a method for knocking off an animal FGF5 gene by using a CRISPR-Cas9 system. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, acquiring a DNA sequence aiming at an sgRNA recognition area of a second FGF5 exon, wherein the base sequence of the DNA sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; secondly, establishing an sgRNA expression structure of the second FGF5 exon, inserting a T7 starter before an sgRNA transcriptional start site, establishing an in-vitro transcription carrier of Cas9 protein, and regulating and controlling by using the T7 starter. Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA are obtained through the in-vitro transcription carrier of Cas9 and sgRNA, and the method can be used for knocking off the animal FGF5 gene.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method of de-differentiating and re-differentiating somatic cells using RNA
ActiveUS20110165133A1Efficient transfectionLess time-consumingBiocideEpidermal cells/skin cellsDiseaseSomatic cell
RNA prepared by in vitro transcription using a polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-generated template can be introduced into a cell to modulate cell activity. This method is useful in de-differentiating somatic cells to pluripotent, multipotent, or unipotent cells; re-differentiating stem cells into differentiated cells; or reprogramming of somatic cells to modulate cell activities such as metabolism. Cells can also be transfected with inhibitory RNAs, such as small interfering RNA (siRNA) or micro RNA (miRNA), or combinations thereof to induce reprogramming of somatic cells. For example, target cells are isolated from a donor, contacted with one or more RNA's causing the cells to be de-differentiated, re-differentiated, or reprogrammed in vitro, and administered to a patient in need thereof. The resulting cells are useful for treating one or more symptoms of a variety of diseases and disorders, for organ regeneration, and for restoration of the immune system.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Method for knocking off animal myostatin gene by using CRISPR-Cas9 system
InactiveCN104531705AThe identification rules are simpleEasy to operateMicroinjection basedVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyTranscription initiation site
The invention provides a method for knocking off an animal myostatin gene by using a CRISPR-Cas9 system. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, acquiring a DNA sequence aiming at an sgRNA recognition area of a second myostatin exon, wherein the base sequence of the DNA sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; secondly, establishing an sgRNA expression structure of the second myostatin exon, inserting a T7 starter before an sgRNA transcriptional start site, establishing an in-vitro transcription carrier of Cas9 protein, and regulating and controlling by using the T7 starter. Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA are obtained through the in-vitro transcription carrier of Cas9 and sgRNA, and the method can be used for knocking off the animal myostatin gene.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Methods and reagents to detect and characterize norwalk and related viruses
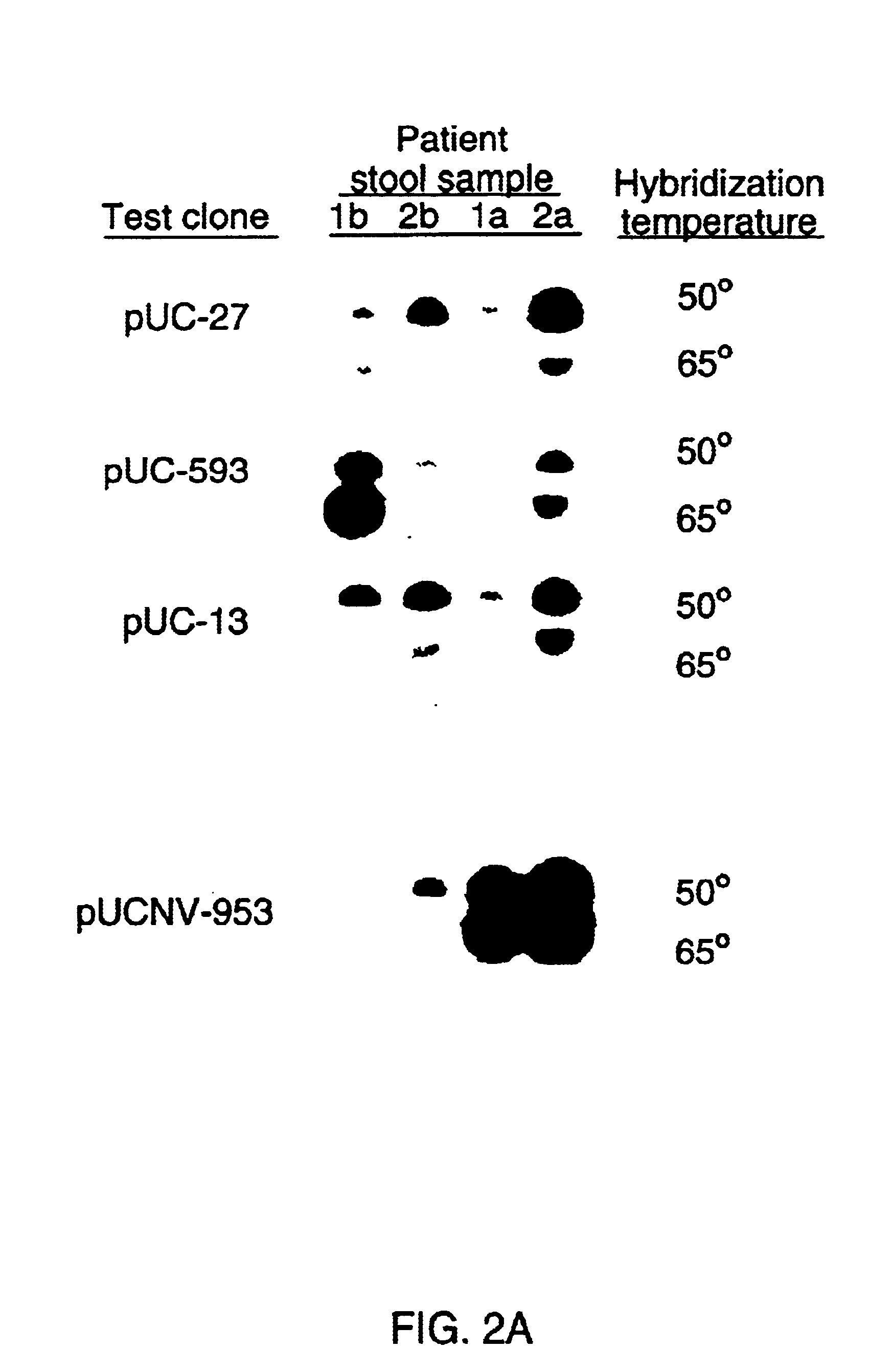
Double-stranded cDNA was synthesized from nucleic acid extracted from Norwalk virus purified from stool specimens of volunteers. One clone was isolated from a cDNA library constructed in a pUC-13 vector after amplification of the cDNA. The specificity of this cDNA (pUCNV-953) was shown by hybridization assays. The cDNA reacted with post (but not pre-) infection stool samples from Norwalk volunteers and with highly purified Norwalk virus, but not with other common enteric viruses such as hepatitis A virus and rotavirus. Finally, the probe detected virus in the same fractions of CsCl gradients in which viral antigen was detected using a specific Norwalk virus radioimmunoassay, and particles were detected by immune electron microscopy. Single-stranded RNA probes derived from the DNA clone after subcloning into an in vitro transcription vector were also used to show that the Norwalk virus contains a ssRNA genome of about 8 kb in size. The original clone was also used to detect additional cDNAs which represent at least 7 kb of nucleic acid of the Norwalk genome. The availability of a Norwalk-specific cDNA and the first partial genome sequence information allow rapid cloning of the entire genome and of establishment of sensitive diagnostic assays. Such assays can be based on detection of Norwalk virus nucleic acid or Norwalk viral antigen using polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies to proteins expressed from the cDNA or to synthetic peptides made based on the knowledge of the genome sequence. Assays using proteins deduced from the Norwlk virus genome and produced in expression systmes can measure antibody responses. Vaccines made by recombinant DNA technology are now feasible.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
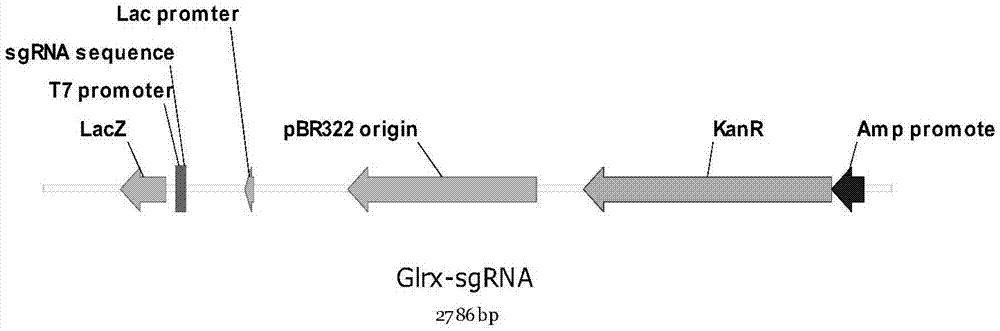
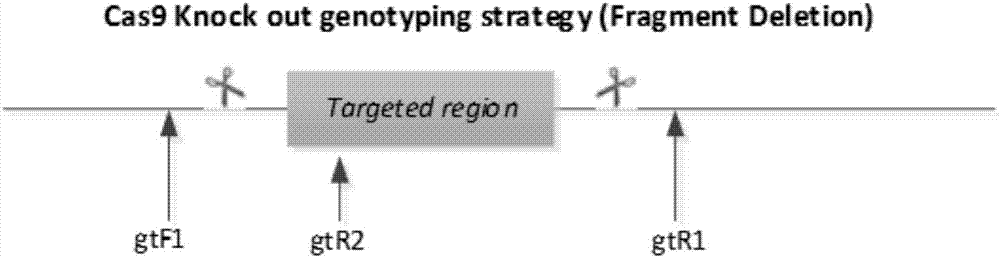
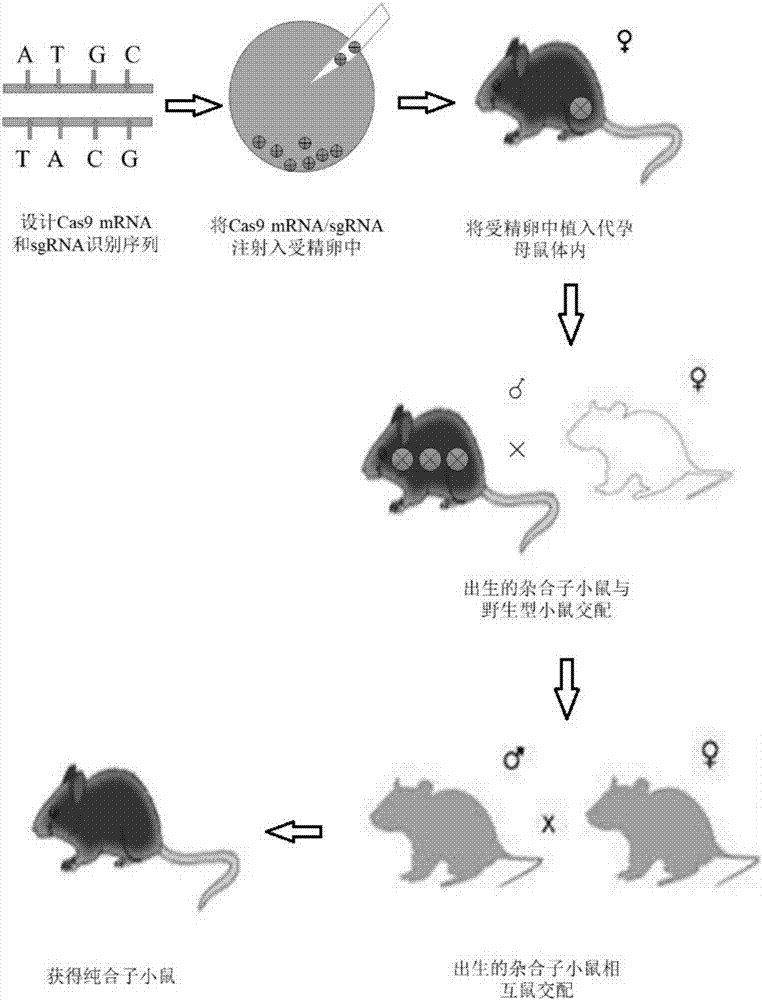
Method for constructing Glrx1 gene knock-out animal model based on CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats)/Cas9 technology
ActiveCN107287245AIncrease positive rateLow miss rateHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAF1 generationBioinformatics
The invention discloses a method for constructing a Glrx1 gene knock-out animal model based on a CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) / Cas9 technology. The method comprises the following steps: 1, selecting and designing gRNA of Glrx1 genes of targeted mice; 2, constructing an sgRNA vector; 3, performing in vitro transcription on sgRNA; 4, injecting one cell stage fertilized eggs of mice; 5, birth and identification of F0-generation mice; and 6, reproducing positive F0-generation mice, and realizing birth and identification of F1-generation mice. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the Glrx1 gene knock-out animal model can be successfully obtained.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Construction method and application of Ifit3-eKO1 gene knockout mouse animal model
The invention relates to a method of constructing an Ifit3-eKO1 gene knockout mouse animal model and belongs to the biotechnical field. The method comprises the following steps: S1, determining specific target sites sgRNA1 and sgRNA2 of a to-be-knocked out gene of an Ifit3-eKO1 mouse, and performing in vitro transcription with Cas9 nuclease to mRNA; and S2, micro-injecting active sgRNA and Cas9RNA into an oosperm of the mouse to obtain the Ifit3-eKO1 gene knockout mouse. The method has the advantages that by using the CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout technology, the Ifit3-eKO1 gene knockout mouse animal model is constructed for the first time, thereby providing a convenient, reliable and economical animal model for researching action of Ifit3 in tumorigenesis and development.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGJI HOSPITAL
Transient transfection with RNA
Owner:YALE UNIV
High purity RNA compositions and methods for preparation thereof
ActiveUS20180363019A1Improved propertyImproved immune silencingAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiochemistryIn vitro transcription
The invention relates to improved RNA compositions for use in therapeutic applications. The RNA compositions are particularly suited for use in human therapeutic application (e.g., in RNA therapeutics). The RNA compositions are made by inproved processes, in particular, improved in vitro-transcription (IVT) processes. The invention also relates to methods for producing and purifying RNA (e.g, therapeutic RNAs), as well as methods for using the RNA compositions and therapeutic applications thereof.
Owner:MODERNATX INC
Construction method for Sqstm1 whole-genome knockout mouse animal model and application
The invention discloses a construction method for a Sqstm1 whole-genome knockout mouse animal model and application. The mouse animal model is a mouse of which the Sqstm1 gene is knocked out. On the basis of a CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) / Cas9 gene knockout technology, the Sqstm1 gene knockout mouse model is constructed. The construction method comprises the following steps: S1: designing sgRNA (Ribonucleic Acid) and Cas9 RNA, carrying out in vitro transcription to obtain mRNA, carrying out microinjection on the sgRNA and the Cas9 RNA with activity into amouse oosperm, to obtain the Sqtm1 gene knockout mouse; S2: identifying the Sqtm1 gene knockout mouse animal model. On the basis of the CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout technology, the Sqstm1 gene knockout mouse animal model is constructed for the first time, and a convenient, reliable and economic animal model is provided for researching a relationship between Sqstm1 and diseases including autophagy, tumors and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGJI HOSPITAL
Method for acquiring Nogo-B knockout mode mouse based on CRISPR/Cas9 technology and application thereof
The invention relates to a method for acquiring a Nogo-B knockout mode mouse based on CRISPR / Cas9 technology and an application thereof, the method for acquiring the Nogo-B knockout mode mouse comprises the following steps of: designing a high-efficiency sgRNA for identifying EGE-ZXH-007 of a specific gene; connecting the sgRNA to a plasmid vector and then carrying out in-vitro transcription to obtain a Ca9 / sgRNA capable of being subject to microinjection; injecting the Ca9 / sgRNA capable of being subject to microinjection into a mouse fertilized egg, and then carrying out genotype detection and identification on the born mouse, and finally obtaining the Nogo-B knock-out mode mouse. According to the invention, the Nogo-B knockout mode mouse is obtained by using the CRISPR / Case9 technology,and compared with the traditional gene knockout technology, the operation is easy and the efficiency is higher, and the homozygous mutation is more easily obtained, thus laying a good foundation for further researching the function of Nogo-B.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Method for establishing Gadd45a knockout rabbit model by adopting knockout technology
InactiveCN107630043APredictive effectReduce the risk of research and developmentStable introduction of DNAAnimal husbandryRabbit modelPlasmid dna
The invention relates to a method for establishing a Gadd45a knockout rabbit model by adopting a knockout technology and belongs to the technical field of biotechnology. The invention aims to establish a rabbit model by knocking out GADD45a gene by utilizing a Grispr / cas9 technology and to provide the method for establishing the Gadd45a knockout rabbit model by adopting the knockout technology andfor researching the influence of the gene on animal liver. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: establishing sgRNA; synthesizing double-stranded DNA; linearizing p UC-57 carrier; linking p UC-57 carrier with double-stranded DNA; converting; performing monoclonal picking and plasmid DNA extraction; identifying plasmid sequence; expressing plasmid with CAS9; and performing digestion linearization for in vitro transcription. Through related detection, the invention successfully acquires the Gadd45a knockout rabbit model; the model is established for simulating theclinic pathological processes of the liver diseases, such as, fatty liver, liver cirrhosis and liver cancer after giving the corresponding alcohol stimulation, is capable of effectively forecasting the clinic application effects of new vaccine, new drugs and new diagnostic reagents, and meanwhile, and is capable of greatly reducing the risk in researching and developing the new drugs; and a basismodel is supplied for the clinical research.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Manufacturing methods for production of RNA transcripts
ActiveUS20160024547A1High purityHigh potencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationOligo dtIn vitro transcription
Owner:MODERNATX INC
Preparation method of zebrafish notch2 gene mutant
ActiveCN108707628AGenetic stabilityFacilitate in-depth researchHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAPUC19Embryo
The invention discloses a preparation method of a zebrafish notch2 gene mutant. The preparation method includes: determining positions of knock-out target spots of the notch2 gene; utilizing pUC19-gRNA scaffold plasmid as a template, and performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification with primers T7-notch2-sfd and tracr rev; subjecting a PCR product to purification and in-vitro transcription to obtain gRNA (guide ribose nucleic acid); introducing the gRNA and Cas9 protein into a cell-stage embryo of zebrafish through micro-injection, and screening to obtain the notch2 gene mutant stable in inheritance. The preparation method has the advantages that by the aid of the CRISPR / Cas9 (clustered regularly interspersed short palindromic repeats, CRISPR / CRISPR-associated genes, cas gene)technology, and by means of selecting a specific section of targeting domain, the notch2 gene in the zebrafish is knocked out, other genes are protected from being 'injured accidentally', the zebrafish without the Notch2 gene is formed, experimental materials are provided for in-depth study on follow-up gene functions, and great significance is achieved on study of Notch signal channels.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Method for producing RNA molecule compositions
ActiveUS20190083602A1Robust processingImprove resolutionSsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsBiologyDNA
The invention relates to a method for producing a ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecule composition comprising n different RNA molecule species, the method comprising a step of RNA in vitro transcription of a mixture of m different deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecule species in a single reaction vessel in parallel, i.e. simultaneously, and a step of obtaining the RNA molecule composition. Also provided is the RNA composition provided by the inventive method and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same as well as a pharmaceutical container. Moreover, the invention provides the RNA composition and the pharmaceutical composition for use as medicament.
Owner:CUREVAC SE
Method for in vitro transcription using an immobilized restriction enzyme
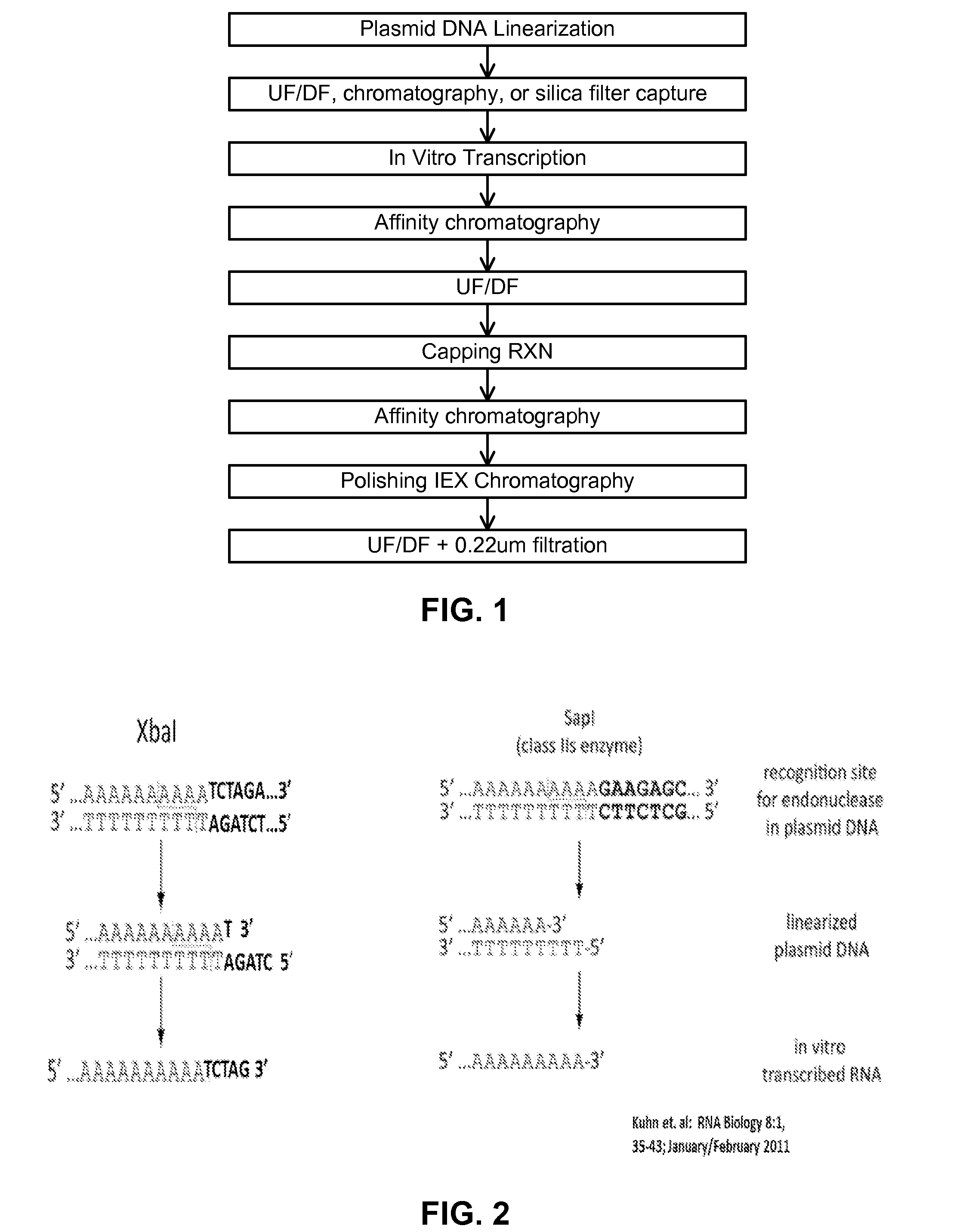
InactiveUS20180208957A1Enhancing and improving linearizationLow costHydrolasesOn/in organic carrierDNA EndonucleaseRestriction enzyme
The present invention relates to a method for in vitro transcription of a linear template DNA which is produced using an immobilized restriction endonuclease. The invention also relates to mutated restriction enzymes which are suitable for immobilization and a solid support to which these restriction enzymes are immobilized. Further, the present invention relates to an enzyme reactor containing said immobilized restriction endonuclease which enzyme reactor can be used for preparing linearized template DNA. Finally, the present invention relates to the use of said enzyme reactor for preparing a linear template DNA for in vitro transcription. In addition, the present invention relates to a kit comprising the immobilized restriction endonuclease.
Owner:CUREVAC SE
RNA analysis by total hydrolysis
The present invention relates to analysis of an RNA molecule. It further relates to the use of this method for the quality control of an RNA molecule produced by in vitro transcription or for the quality control of an RNA molecule produced by chemical synthesis.
Owner:CUREVAC SE
Microfluidic microbead array chip and application thereof in virus analysis
ActiveCN101709261AEasy to makeFast preparationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrosphereMicrostructure
The invention discloses a microfluidic microbead array chip and application thereof in virus analysis, and belongs to the field of biological application of a miniaturized total analysis system. The microfluidic microbead array chip consists of a microbead fixed microstructure array, a microbead transport channel, a reagent transport channel and a microstructure array coverage channel. When high-sensitive virus analysis is performed, virus molecules in a serum sample is prepared into a biotin doped target RNA sequence through PCR and in vitro transcription process, and flows to a testing areaof the chip to react with a functional microbead array; function modified microspheres can specifically identify and capture target sequences; a quantum dot labeled reagent are introduced; surfaces of micro-particles are combined with quantum dots because of specifically capturing; and detection and quantitation are performed by a fluorescence imaging method. The microfluidic microbead array chipprovided by the invention has the advantages of simple process, high detecting sensitivity and quick detection, and provides an effective studying and detecting means for high-sensitive virus analysis.
Owner:香港城市大学深圳研究院
Preparation method of zebrafish notch1b gene mutant
PendingCN108707629AGenetic background is clear and cleanFacilitate in-depth researchHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAPUC19Embryo
The invention discloses a preparation method of a zebrafish notch1b gene mutant. The preparation method includes: determining positions of knock-out target spots of the notch1b gene; utilizing pUC19-gRNA scaffold plasmid as a template, and performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification with primers T7-notch1b-sfd and tracr rev; subjecting a PCR product to purification and in-vitro transcription to obtain gRNA (guide ribose nucleic acid); introducing the gRNA and Cas9mRNA into a cell-stage embryo of zebrafish, and culturing to obtain the notch1b gene mutant stable in inheritance. Thepreparation method has the advantages that by the aid of the CRISPR / Cas9 (clustered regularly interspersed short palindromic repeats, CRISPR / CRISPR-associated genes, cas gene) technology, and by meansof selecting a specific section of targeting domain, the notch1b gene in the zebrafish is knocked out, other genes are protected from being 'injured accidentally', the zebrafish without the Notch1b gene is formed, and great significance is achieved on study of Notch signal channels.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Method for analyzing by-products of RNA in vitro transcription
PendingUS20190049414A1Improve RNA qualityQuality improvementCation exchanger materialsComponent separationQuality controlBiology
Owner:CUREVAC REAL ESTATE GMBH
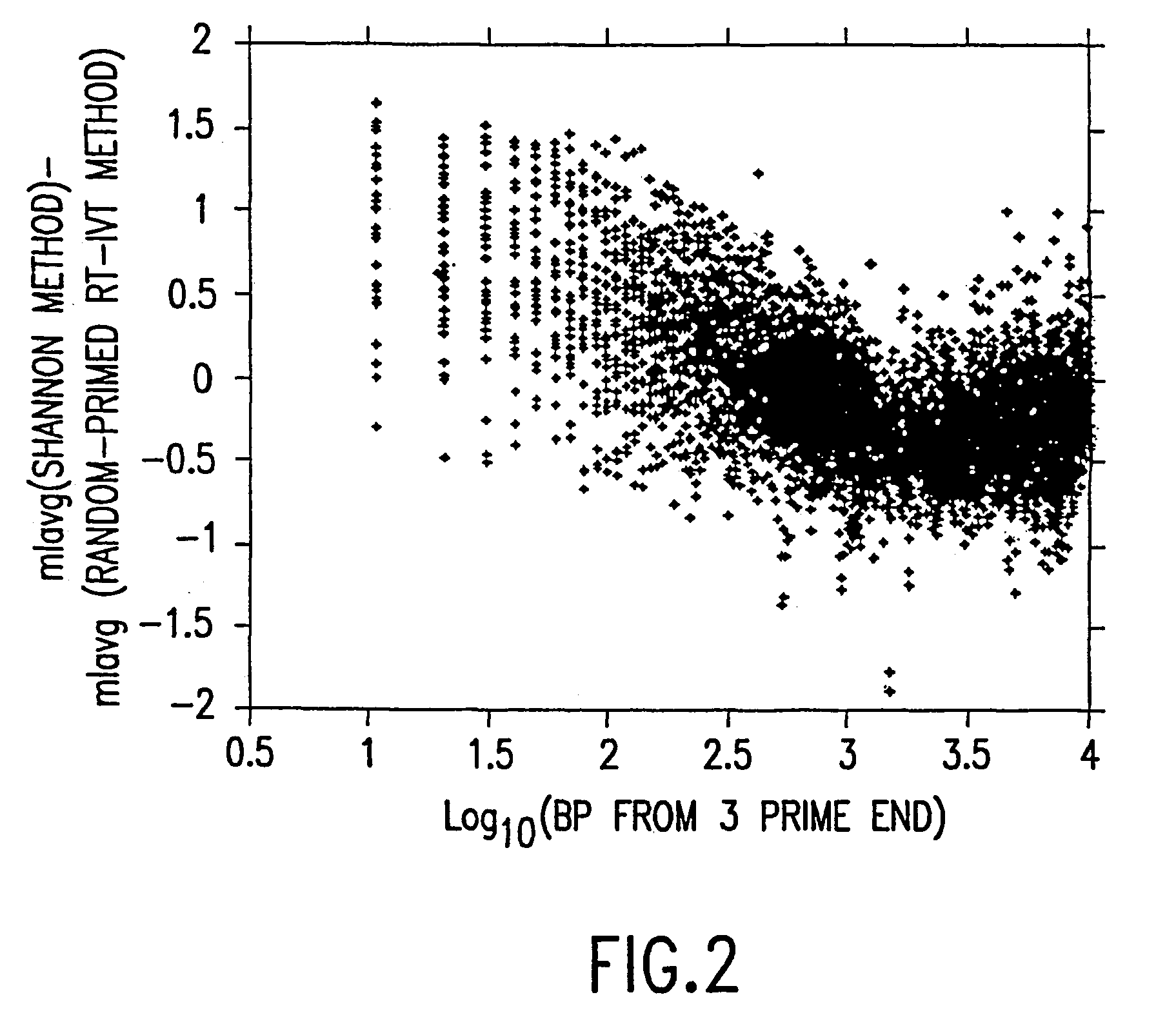
Random-primed reverse transcriptase-in vitro transcription method for rna amplification
InactiveUS20040081978A1Improve representationImprove abilitiesMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationReverse transcriptaseSingle strand
A random-primed reverse transcriptase-in vitro transcription method of linearly amplifying RNA is provided. According to the methods of the invention, source RNA (or other single-stranded nucleic acid), preferably, mRNA, is converted to double-stranded cDNA using two random primers, one of which comprises a RNA polymerase promoter sequence ("promoter-primer"), to yield a double-stranded cDNA that comprises a RNA polymerase promoter that is recognized by a RNA polymerase. Preferably, the primer for first-strand cDNA synthesis is a promoter-primer and the primer for second-strand cDNA synthesis is not a promoter-primer. The double-stranded cDNA is then transcribed into RNA by the RNA polymerase, optimally in the presence of a reverse transcriptase that is rendered incapable of RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity during this transcription step. The subject methods produce linearly amplified RNA with little or no 3' bias in the sequences of the nucleic acid population amplified.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Removal of DNA fragments in mRNA production process
The present invention describes methods of removing DNA from an RNA transcript during the mRNA production process. The method embodies procedures for obtaining an in vitro transcription product, and removing any DNA from the product. The DNA can be removed by adding either free DNase or a resin containing immobilized DNase to the product, and recovering the RNA transcript. Alternatively, the DNA template used in the in vitro transcription reaction is labeled. After transcription, the product is applied to a resin that is configured to bind the label, and the RNA transcript is recovered. To detect whether any residual impurities are left in the RNA transcript product, the product is subjected to nuclease digestion and subsequently to liquid chromato graphy-tandem mass spectrometry analysis to quantitate any residual DNA. The present invention demonstrates efficient and effective methods of isolating an RNA transcript from an in vitro transcription product.
Owner:MODERNATX INC
Random-primed reverse transcriptase-in vitro transcription method for RNA amplification
InactiveUS7229765B2Improve abilitiesImprove representationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationReverse transcriptaseSingle strand
A random-primed reverse transcriptase-in vitro transcription method of linearly amplifying RNA is provided. According to the methods of the invention, source RNA (or other single-stranded nucleic acid), preferably, mRNA, is converted to double-stranded cDNA using two random primers, one of which comprises a RNA polymerase promoter sequence (“promoter-primer”), to yield a double-stranded cDNA that comprises a RNA polymerase promoter that is recognized by a RNA polymerase. Preferably, the primer for first-strand cDNA synthesis is a promoter-primer and the primer for second-strand cDNA synthesis is not a promoter-primer. The double-stranded cDNA is then transcribed into RNA by the RNA polymerase, optimally in the presence of a reverse transcriptase that is rendered incapable of RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity during this transcription step. The subject methods produce linearly amplified RNA with little or no 3′ bias in the sequences of the nucleic acid population amplified.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Method for producing RNA molecule compositions
PendingCN108778308ASsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsRNA - Ribonucleic acidPharmaceutical Substances
The invention relates to a method for producing a ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecule composition comprising n different RNA molecule species, the method comprising a step of RNA in vitro transcription ofa mixture of m different deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecule species in a single reaction vessel in parallel, i.e. simultaneously, and a step of obtaining the RNA molecule composition. Also providedis the RNA composition provided by the inventive method and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same as well as a pharmaceutical container. Moreover, the invention provides the RNA composition and the pharmaceutical composition for use as medicament.
Owner:CUREVAC AG
Method for the in vitro synthesis of short double stranded RNAs
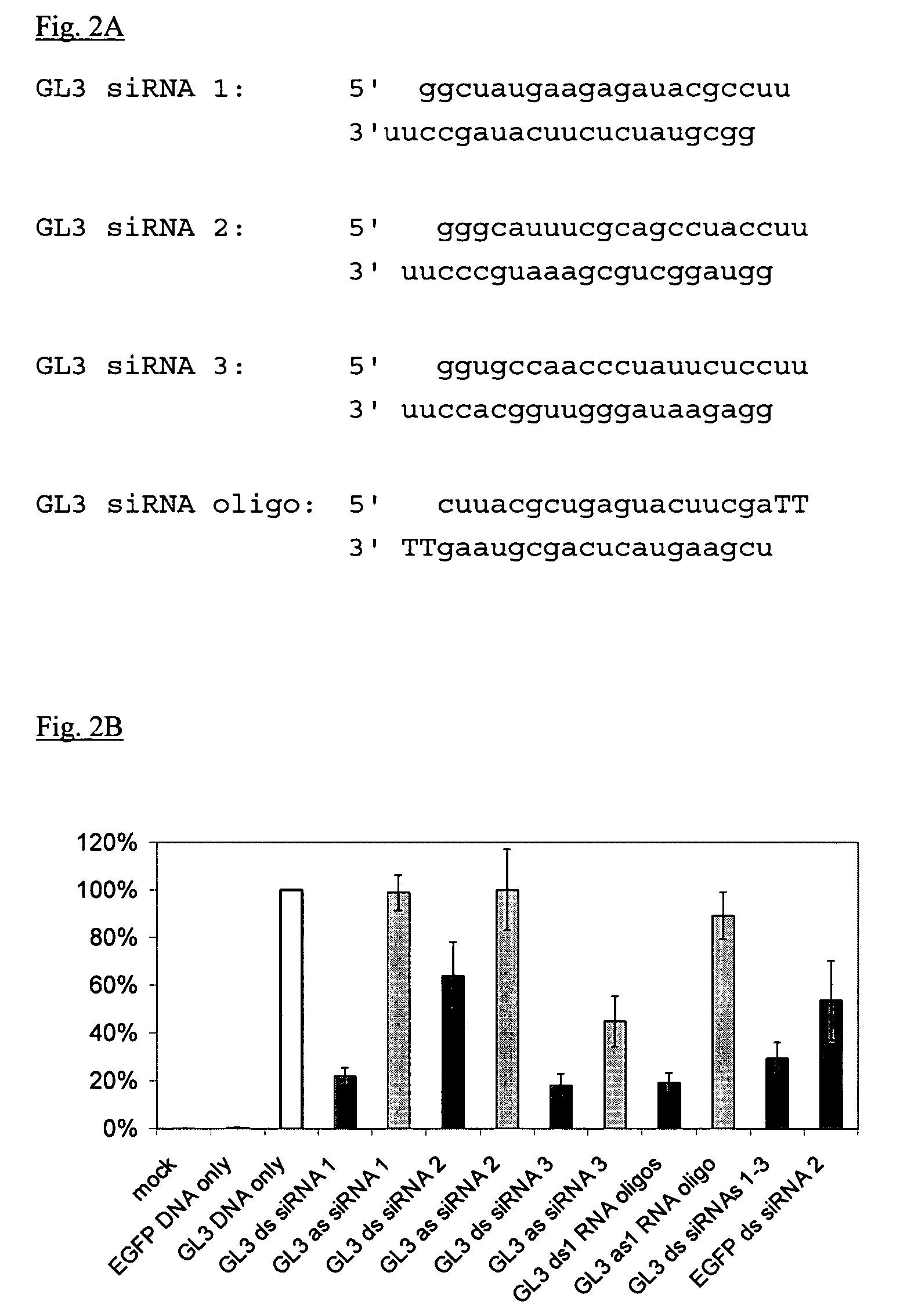
The present invention relates to the field of synthesis of short double-stranded RNAs. An in vitro transcription method using bacteriophage polymerases and target sequence-specific single-stranded DNA oligonucleotides as templates is disclosed. The present invention finds particularly advantageous use in the synthesis of short interfering RNAs (siRNAs) that have been shown to function as key intermediates in triggering sequence-specific RNA degradation during posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants and RNA interference in invertebrates and vertebrate systems.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Therapeutically useful compositions of DNA-RNA hybrid duplex constructs
InactiveUS20040087526A1Inhibiting gene functionLower doseGenetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementGene silencingRna dna hybrids
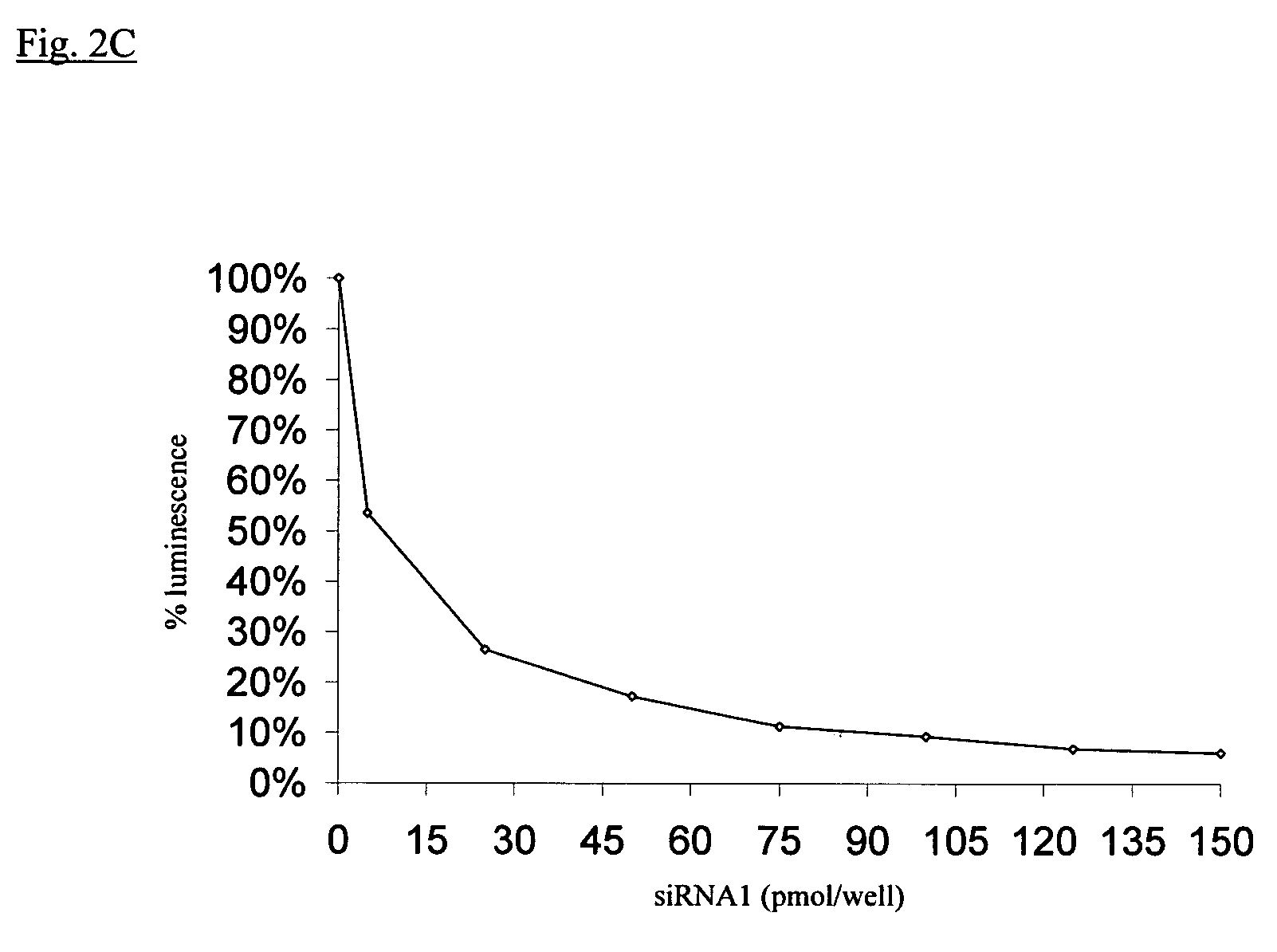
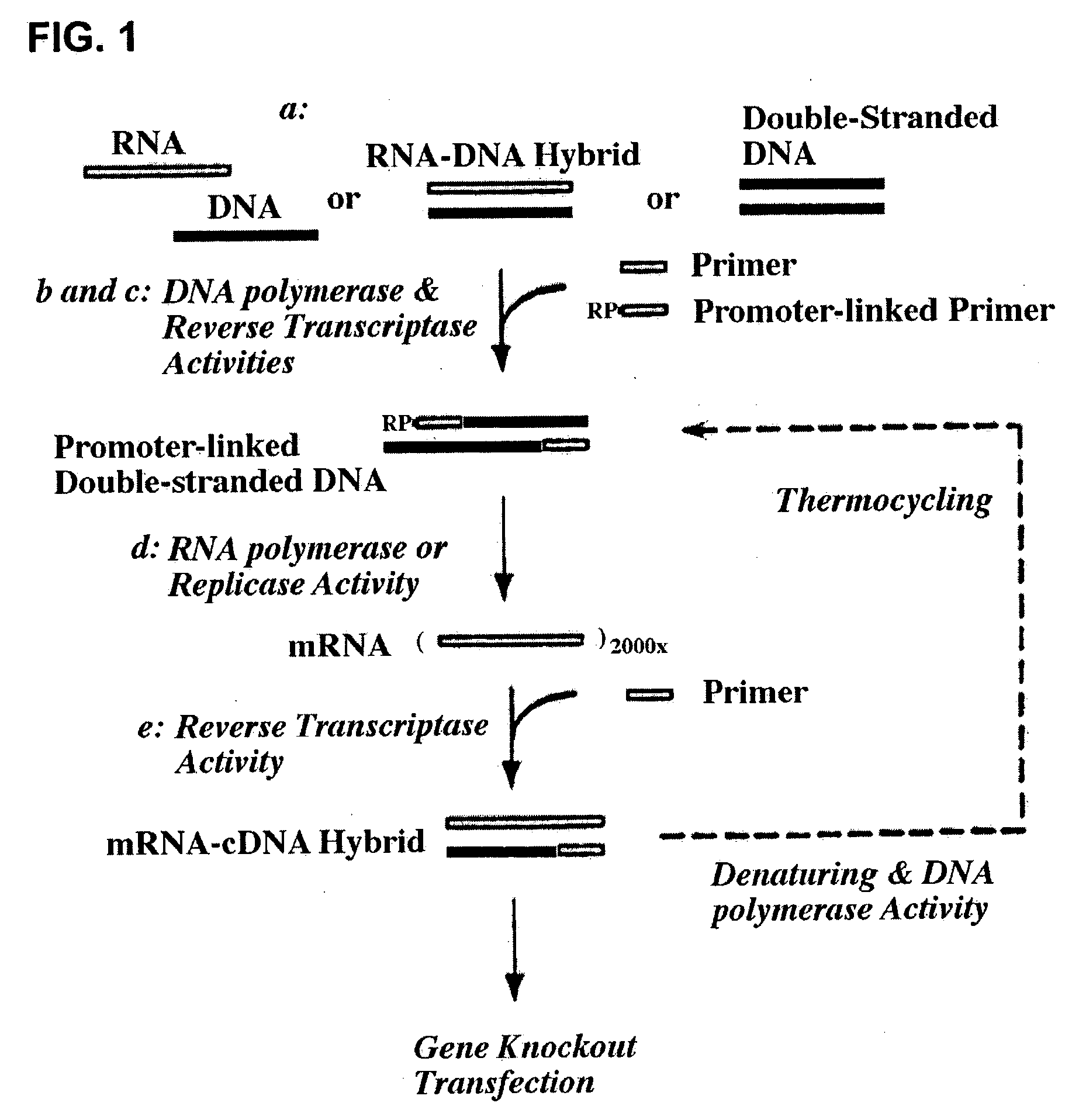
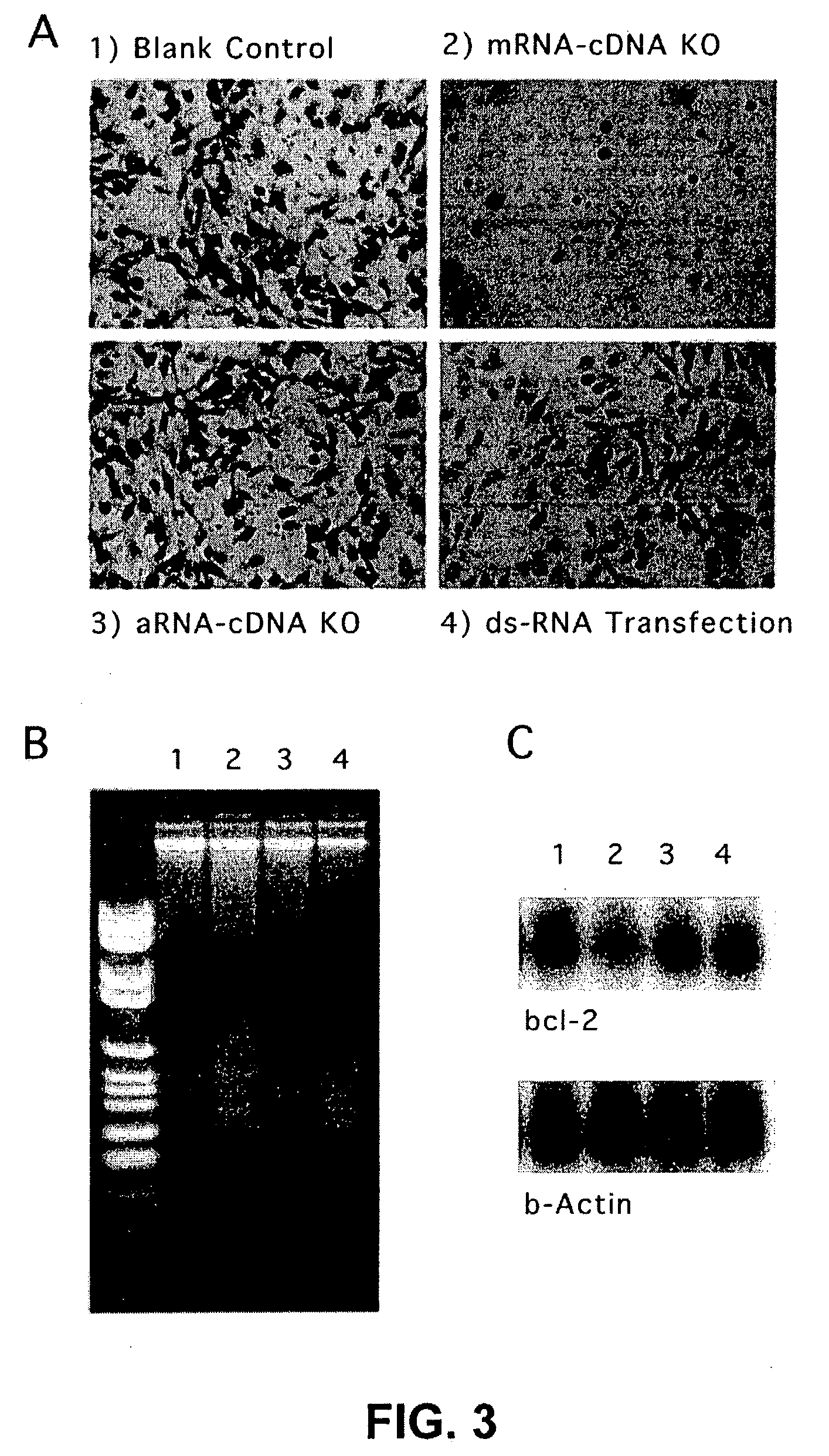
The present invention provides novel compositions and methods for suppressing the expression of a targeted gene using RNA-DNA hybrid constructs. The invention further provides novel methods and compositions for generating or producing RNA-DNA hybrids, whose quantity is high enough to be used for the invention's gene silencing transfection and possibly in therapeutics applications. This improved RNA-polymerase chain reaction method utilizes thermocycling steps of promoter-linked DNA or RNA template synthesis, in vitro transcription and then reverse transcription to bring up the amount of RNA-DNA hybrids up to two thousand folds within one round of the above procedure for specific gene silencing.
Owner:EPICLONE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com