Antibacterial peptide DC and its preparing process and use
A technology of antimicrobial peptides and engineering bacteria, which is applied in the field of antimicrobial peptides, and can solve the problems of high cost and unsuitable industrial production, low content of natural antimicrobial peptides, and low extraction yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
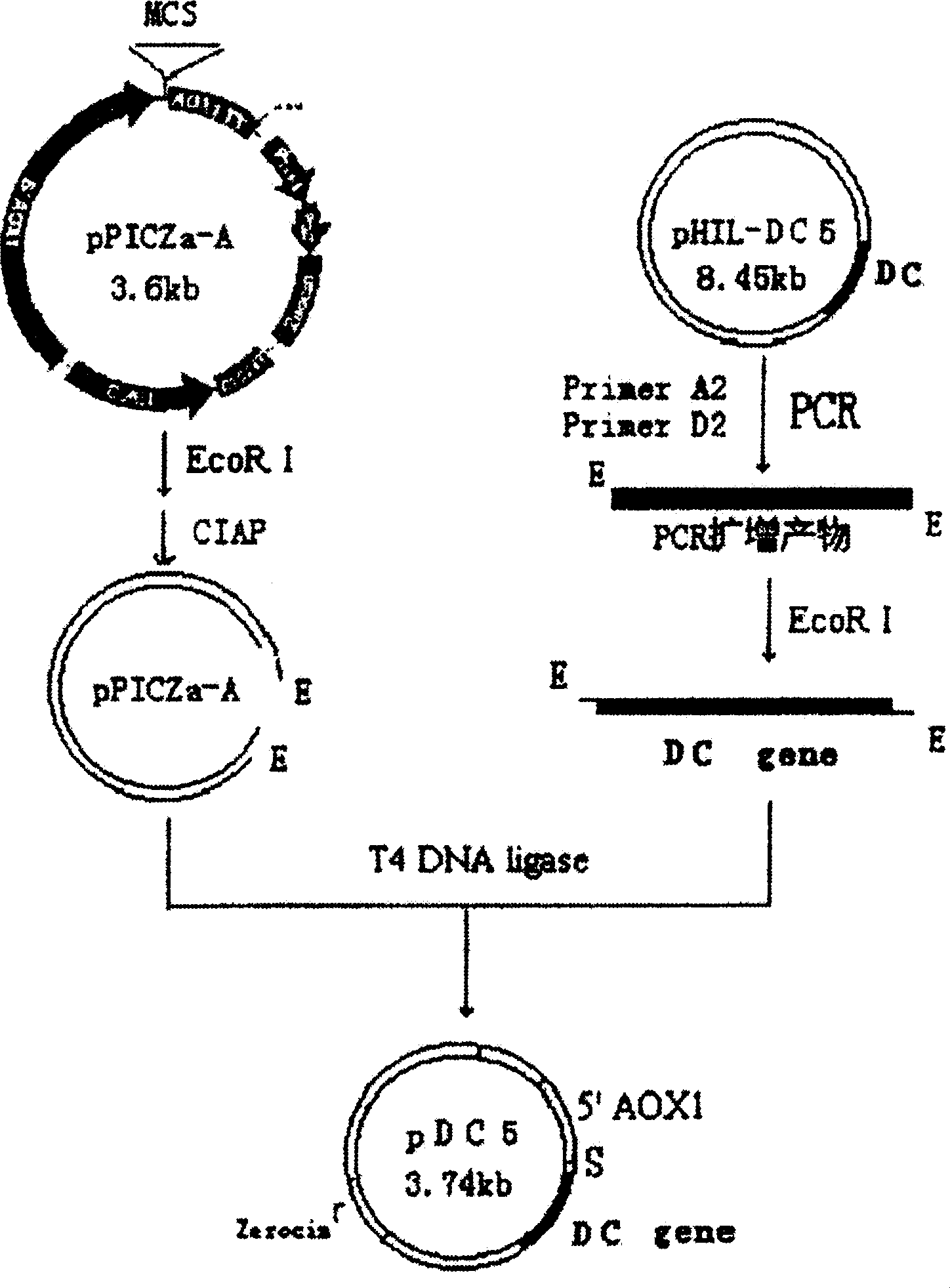
[0099] 1. Design and synthesis of antimicrobial peptide DC gene
[0100] According to the structure of the bactericidal activity of natural antimicrobial peptides, the antimicrobial peptide DC gene was designed and synthesized. The gene is characterized by two α-helices, the 23rd amino acid in the first position constitutes the first hydrophilic helix, and the 27th to 39th amino acids constitute the second hydrophobic helix. Between two α-helices, there is an A-G-P (alanine-glycine-proline) connection, forming a β-sheet. The 39th amino acid residue at the C-terminus is asparagine (N), which is similar to the lysinamide at the end of the natural antimicrobial peptide.
[0101] In the present invention, the designed antimicrobial peptide DC gene is synthesized with a DNA synthesizer for the main chain and auxiliary chain at one time, and annealed to form a 144bp antimicrobial peptide DC gene, in which 120bp of the antimicrobial peptide DC is completely consistent with the design ...
Embodiment 2
[0111] Embodiment 2 antimicrobial peptide DC application effect
[0112] 1. The effect of antimicrobial peptides in the treatment of drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa on upper respiratory tract infection
[0113] The hospital admitted 5 patients with upper respiratory tract infection, complaining of pharyngitis, cough, and no fever. Pseudomonas aeruginosa was isolated from the pharynx and cough sputum, which was Gram-negative.
[0114] Antibiotic resistance testing of isolated Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The bacteria isolated from 3 of the patients were resistant to the following antibiotics. The results are shown in Table 5:
[0115] antibiotics
[0116] Decided to use antimicrobial peptide preparation 2500 units / ml for spray treatment. Use SY-II type nebulizer, temperature 60 ℃, treat antimicrobial peptide liquid as oral spray treatment, about 100ml each time, three times a day. After 5 days of continuous use and supplemented by intravenous injection of cephalo...
Embodiment 3
[0124] The safety evaluation of embodiment 3 antimicrobial peptides
[0125] The bactericidal activity of antibacterial peptide DC fermentation broth purified by ion exchange was 50,000 units / g. Acute and long-term toxicity tests and "three-to-one" tests are carried out respectively to confirm its safety.
[0126] 1. Acute toxicity test
[0127] Experimental animals 50 white mice of insect species were administered orally according to different doses of antimicrobial peptides, and the results of poisoning within one week of investigation are shown in Table 7.
[0128] Dose (g / kg)
[0129] Tests have shown that antimicrobial peptides are not toxic to animals during oral administration, and the lethal dose (LD50) cannot be detected. The maximum tolerated dose is 5g / kg level.
[0130] 2. Antimicrobial peptide long-term toxicity test
[0131] Experimental animals: 60 rats were randomly divided into 4 groups. Antimicrobial peptides were administered orally and observe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com