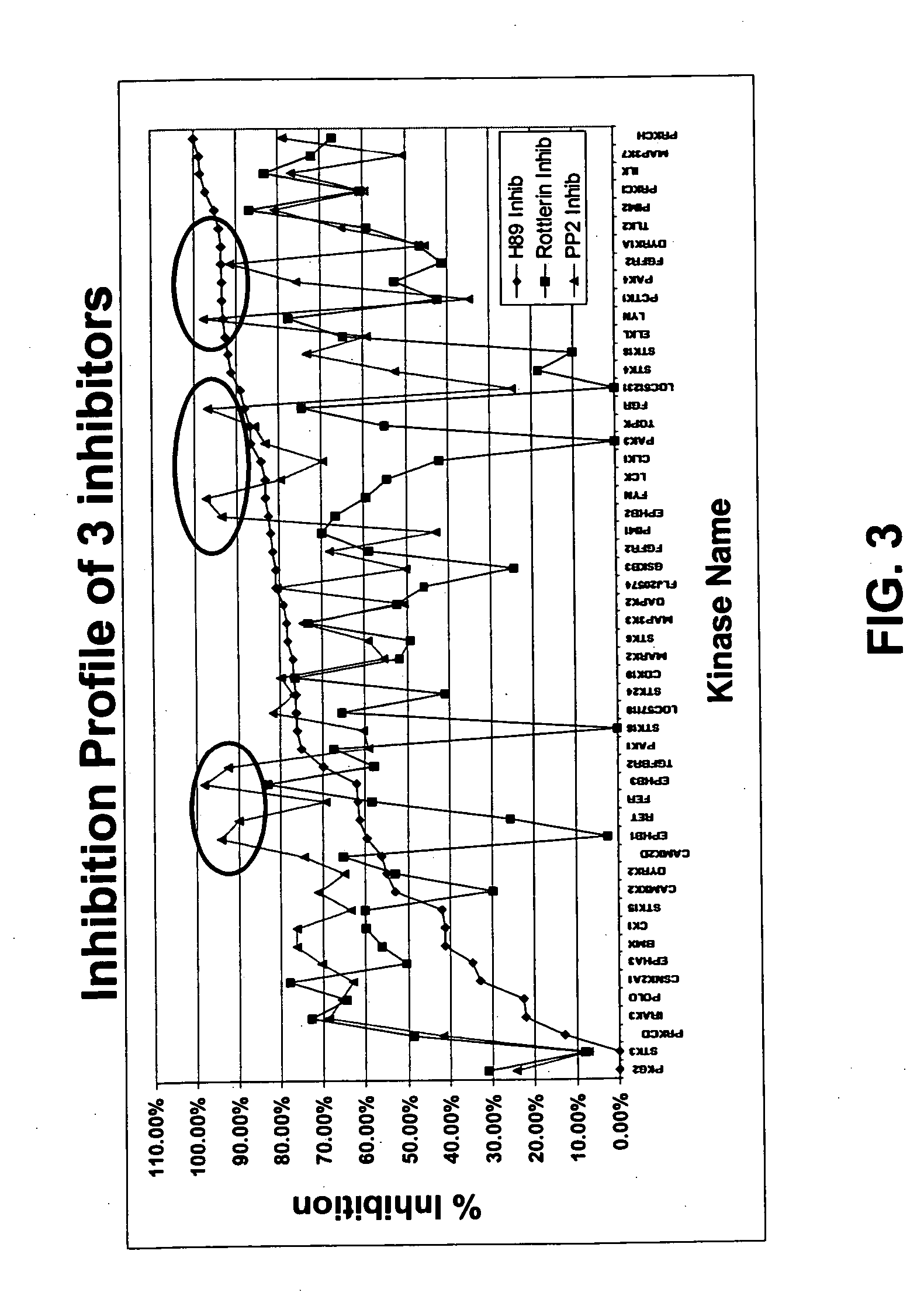
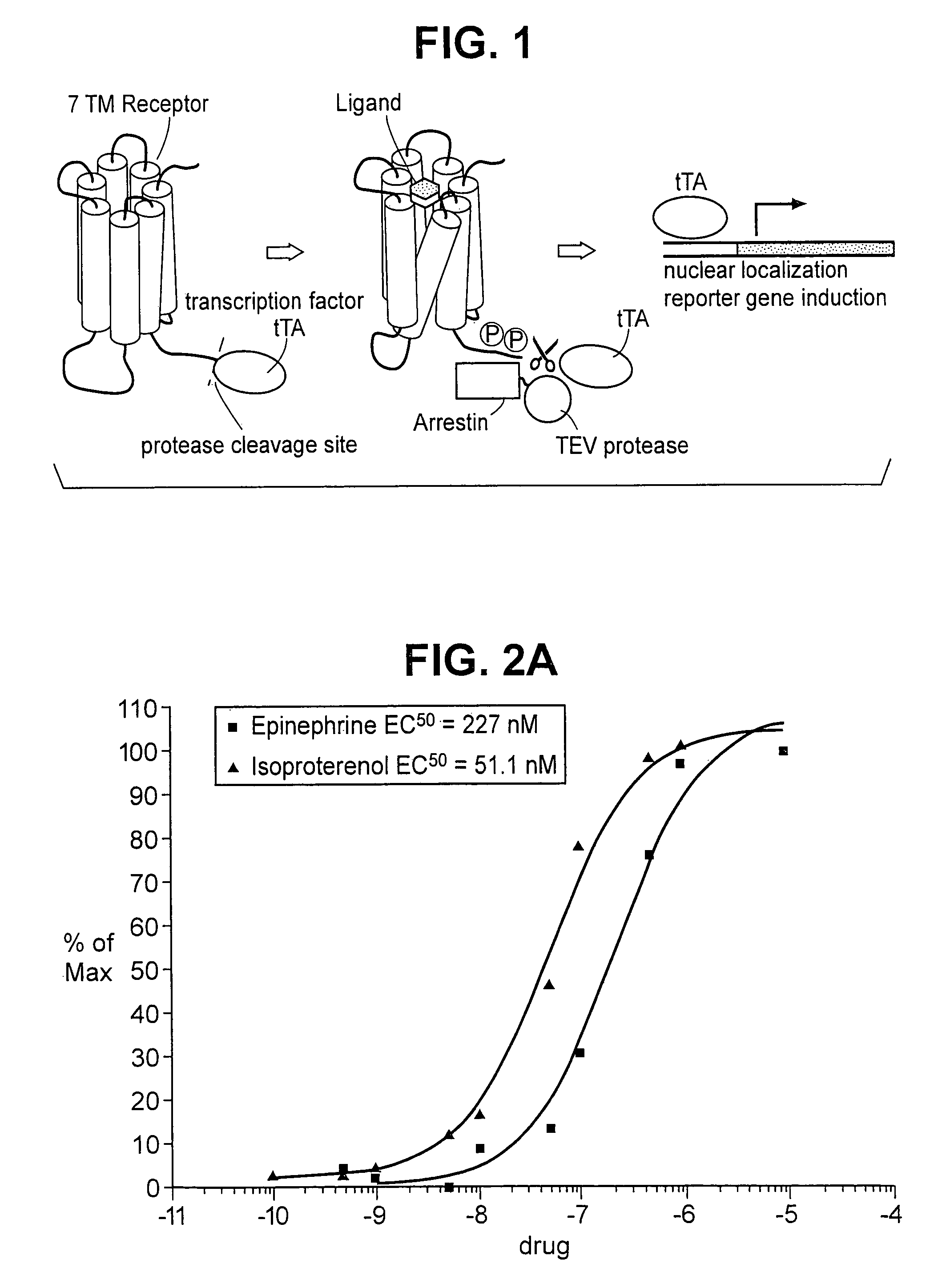
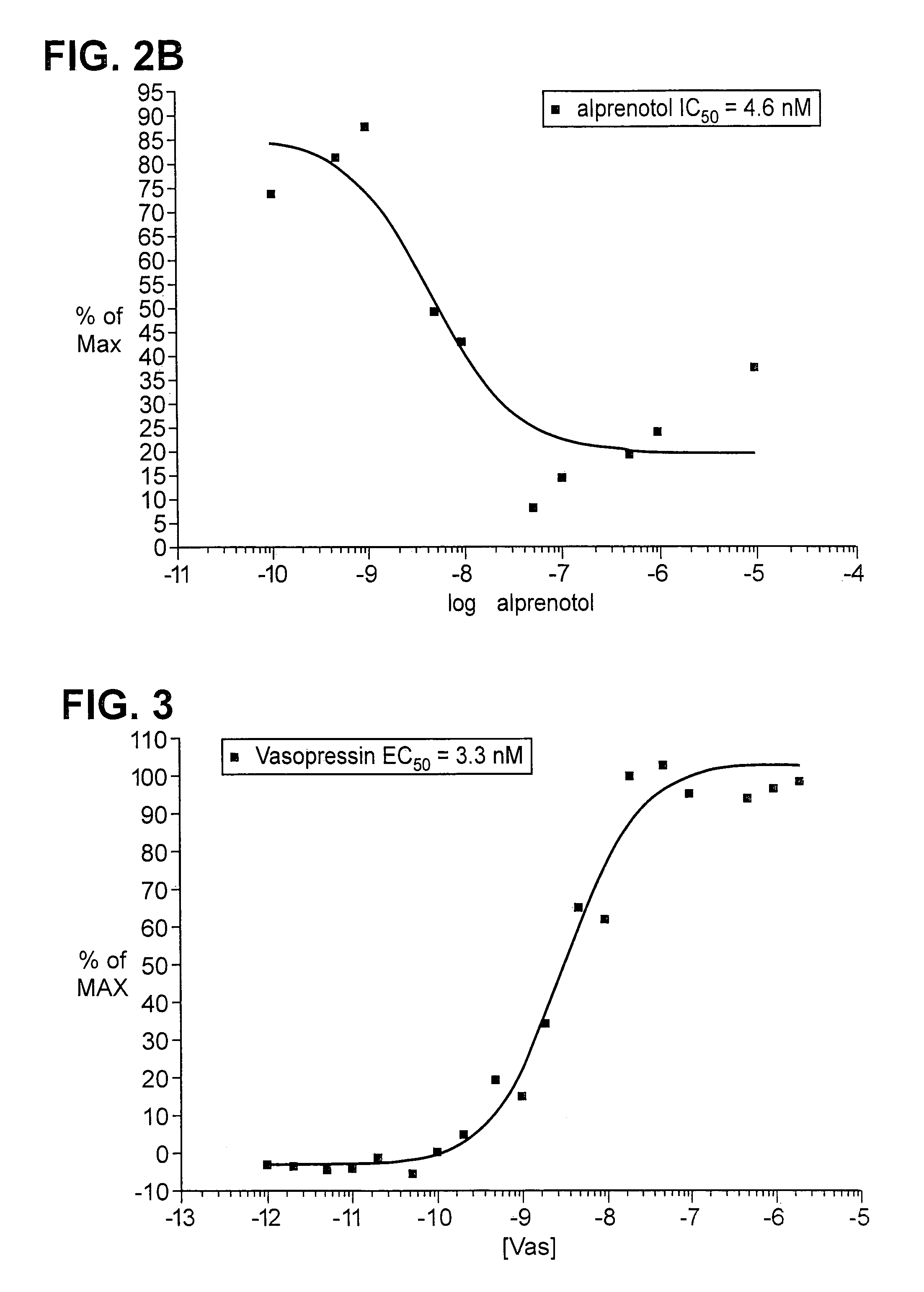
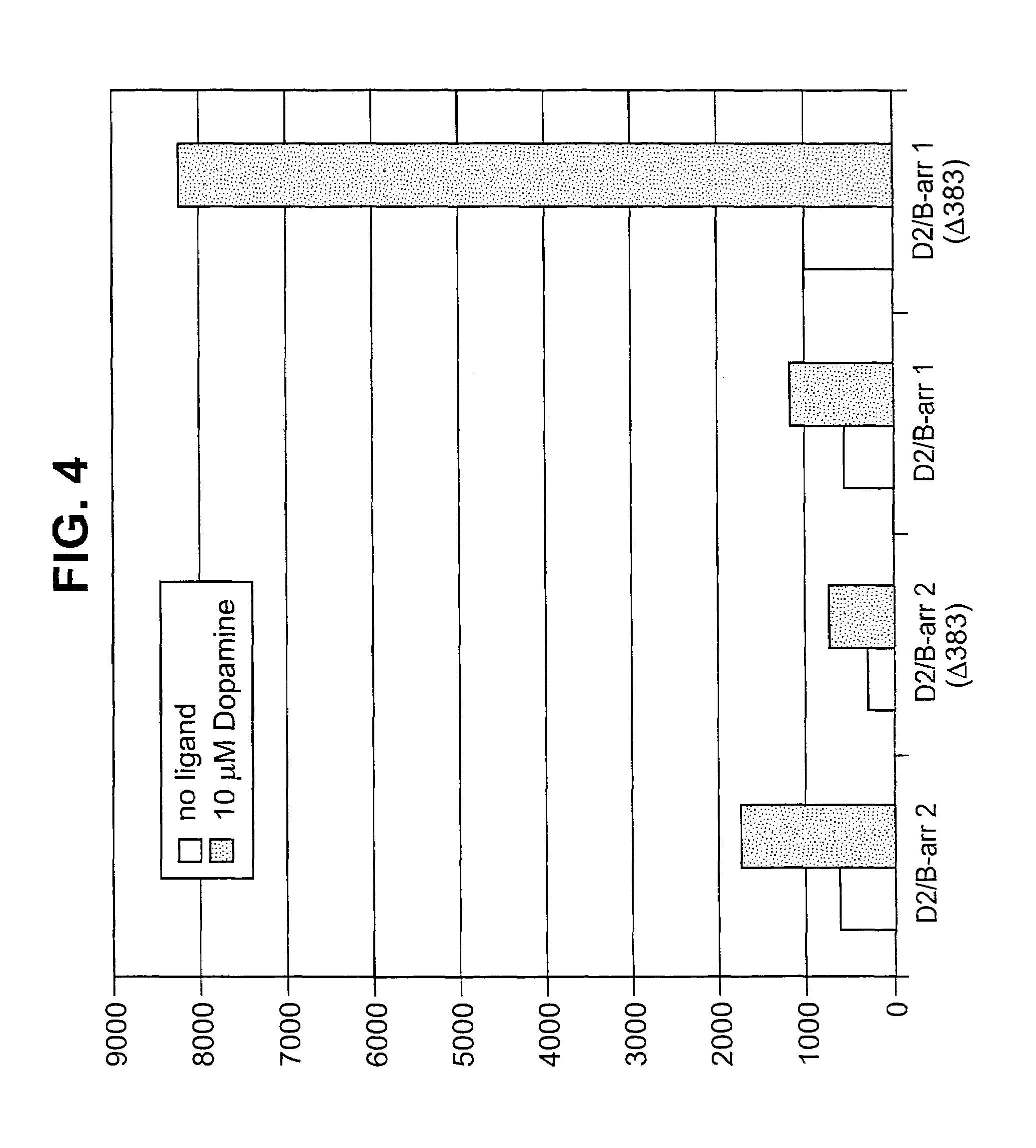
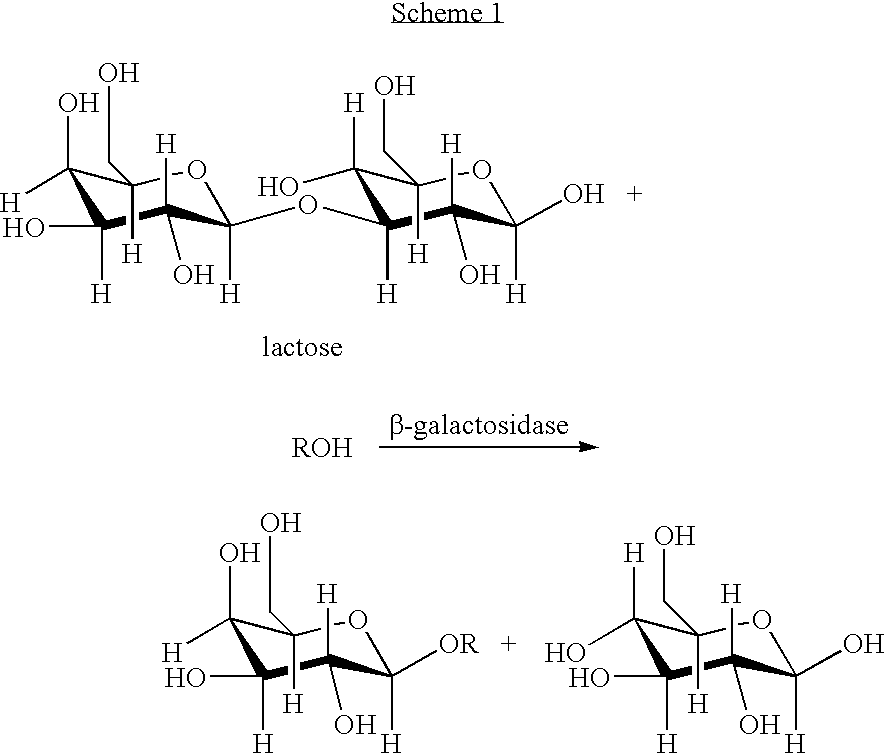
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
234 results about "TARP Protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Immunoassay device with immuno-reference electrode
InactiveUS20060160164A1Reduce distractionsIncrease ionic strengthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImmune profilingImmobilized Antibodies
An electrochemical immunosensor system with reduced interference, comprising: a first immunosensor that generates an electrochemical signal based on the formation of a sandwich between an immobilized antibody, a target analyte and a labeled antibody, wherein a portion of the signal arises from non-specific binding of the labeled antibody in the region of the first immunosensor, and a second immunosensor that acts as an immuno-reference sensor and generates a signal that is the same as or predictably related to the degree of non-specific binding which occurs in the region of the first immunosensor, and has an immunocomplex between an immobilized antibody and an endogenous or exogenous protein that is in the sample and that is not the target analyte.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
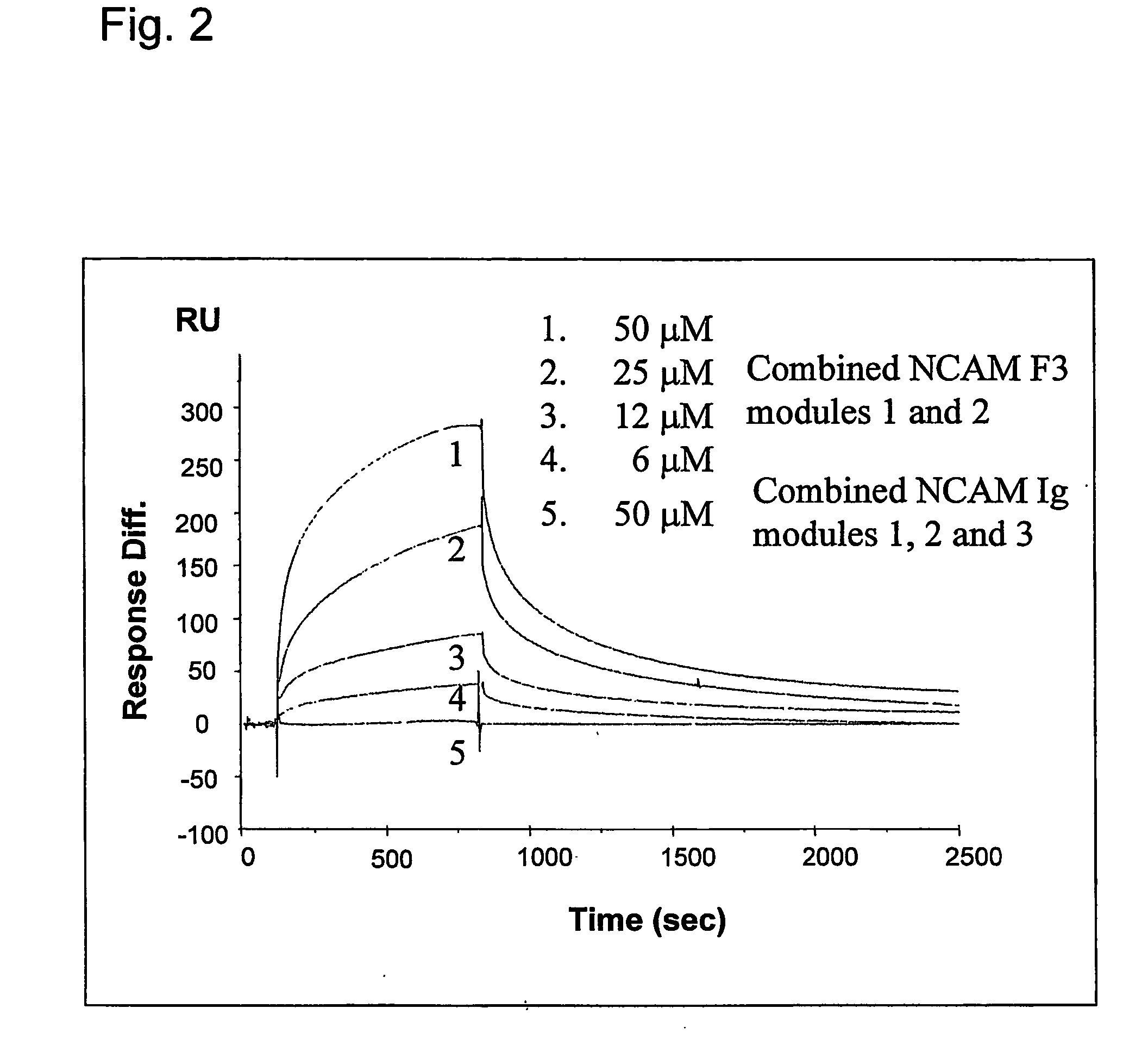
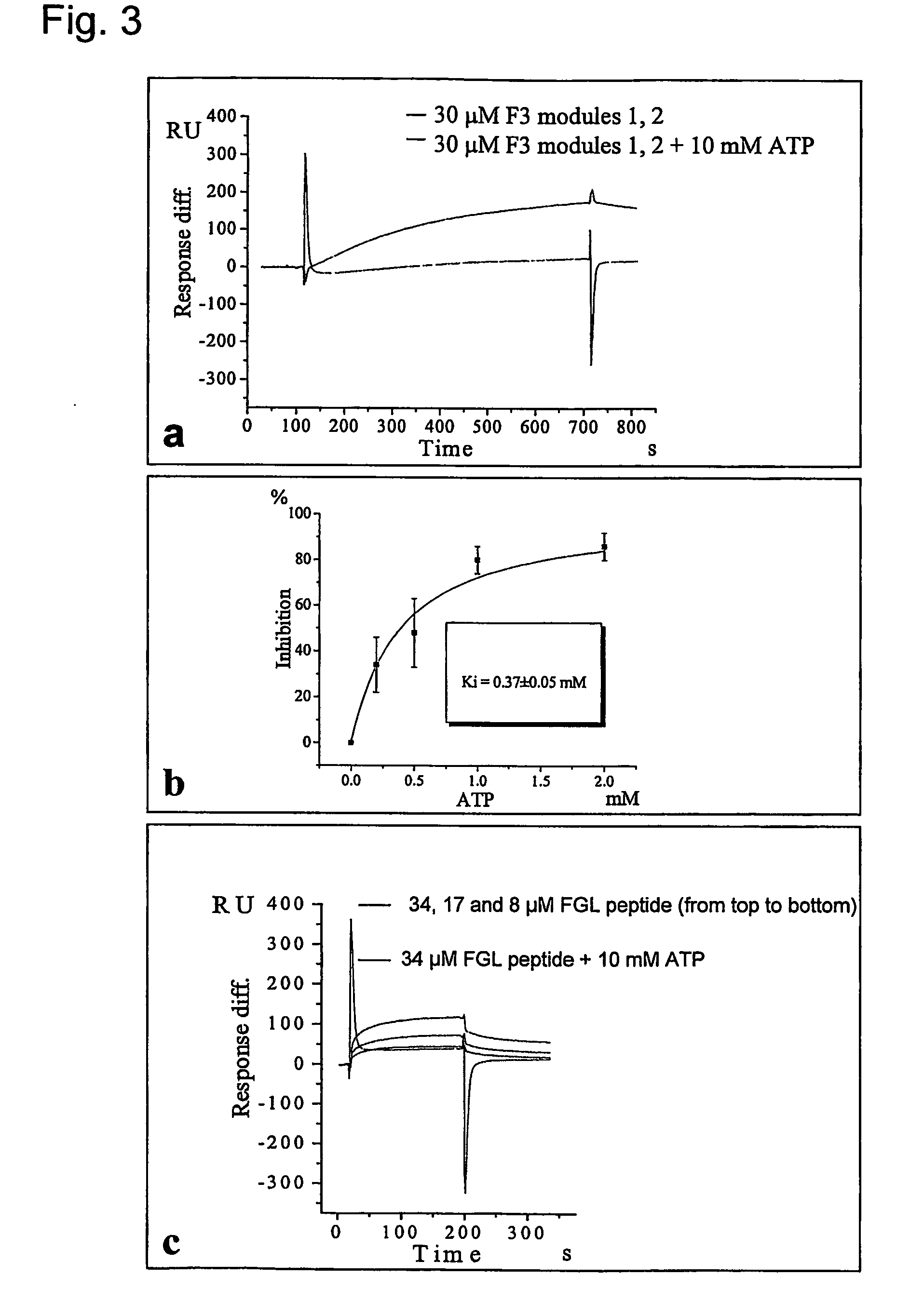
Metod of modulation of interaction between receptor and ligand
The present invention relates to a method for modulating the interaction between at least two proteins, wherein at least one of the two proteins is a functional cell-surface receptor and the other protein is the receptor ligand. The invention features a binding site of said functional cell-surface receptor on the receptor ligand and discloses a series of amino acid sequences, which are part of the structure of said binding site and / or involved in the interaction between the receptor and the ligand. Moreover, the present invention features methods for molecular design and screening of a candidate compound capable of modulating the interaction between the functional cell-surface receptor and receptor ligand through the described binding site, and provides a screening assay for identification of such a compound. The invention further describes an antibody capable of binding to the above binding site and / or to an epitope comprising an amino acid sequence essential for executing the receptor ligand interaction through said binding site. The invention also concerns a variety of uses of the disclosed methods, peptide sequences and antibodies. The invention in preferred embodiments concerns the binding site of the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) on FGFR ligands, compounds capable of modulating the receptor ligand interaction through said binding site, and antibody capable of recognition of said binding site.
Owner:ENKAM PHARMA
Methods for conducting assays for enzyme activity on protein microarrays
The present invention relates to methods of conducting assays for enzymatic activity on microarrays useful for the large-scale study of protein function, screening assays, and high-throughput analysis of enzymatic reactions. The invention relates to methods of using protein chips to assay the presence, amount, activity and / or function of enzymes present in a protein sample on a protein chip. In particular, the methods of the invention relate to conducting enzymatic assays using a microarray wherein a protein and a substance are immobilized on the surface of a solid support and wherein the protein and the substance are in proximity to each other sufficient for the occurrence of an enzymatic reaction between the substance and the protein. The invention also relates to microarrays that have an enzyme and a substrate immobilized on their surface wherein the enzyme and the substrate are in proximity to each other sufficient for the occurrence of an enzymatic reaction between the enzyme and the substrate.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Method for assaying protein—protein interaction
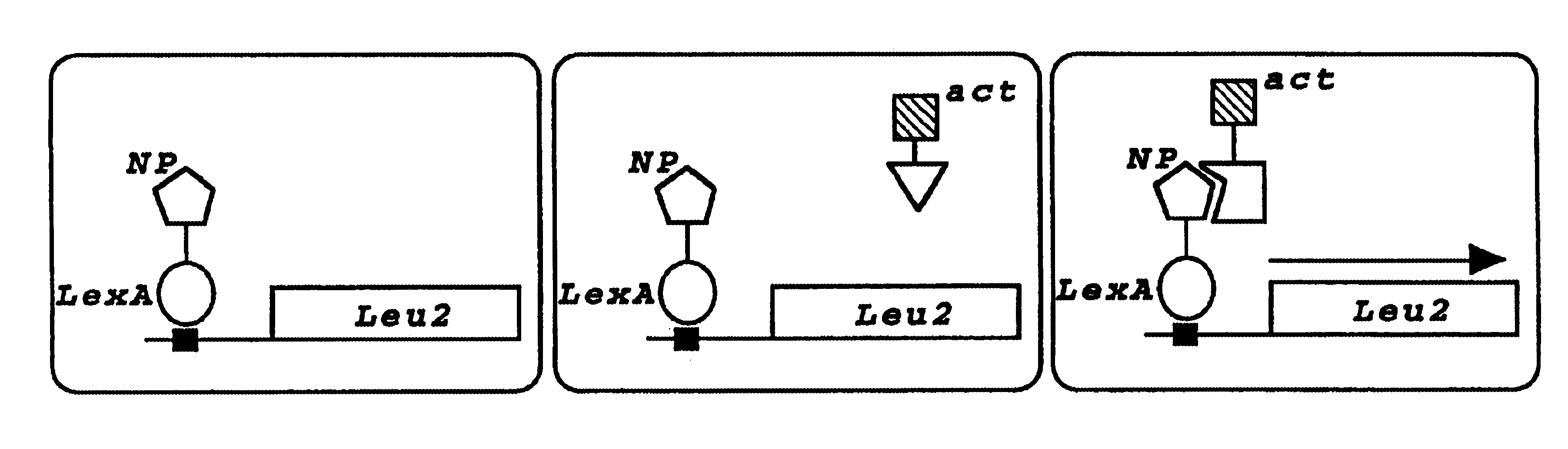
The invention relates to a method for determining if a test compound, or a mix of compounds, modulates the interaction between two proteins of interest. The determination is made possible via the use of two recombinant molecules, one of which contains the first protein a cleavage site for a proteolytic molecules, and an activator of a gene. The second recombinant molecule includes the second protein and the proteolytic molecule. If the test compound binds to the first protein, a reaction is initiated whereby the activator is cleaved, and activates a reporter gene.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP +1
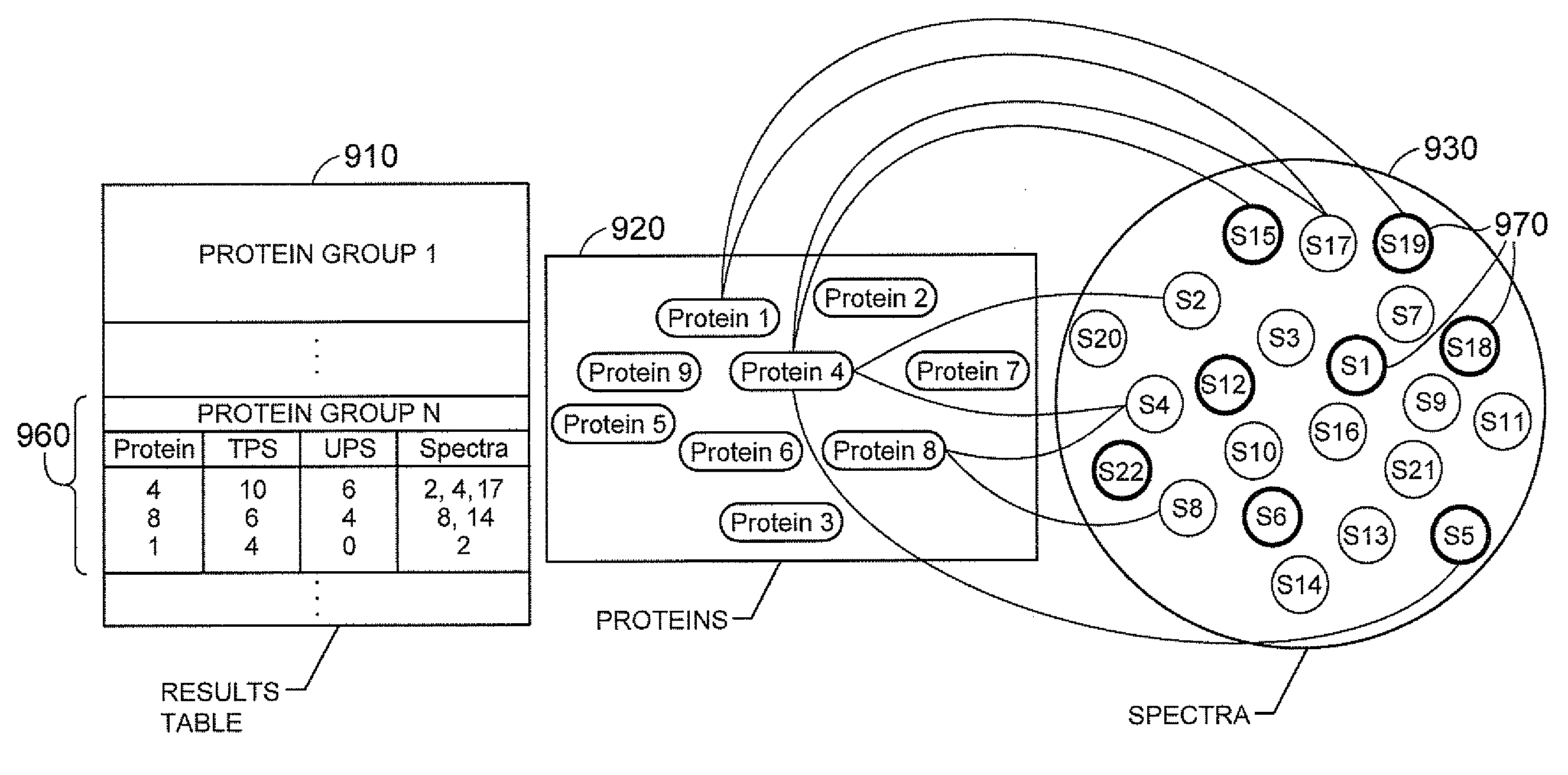
Methods and Systems for Protein and Peptide Evidence Assembly
InactiveUS20090053819A1Reduce manual inspectionTransferrinsAlbumin peptidesProtein insertionMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The present teachings provide methods and systems for the identification of proteins via peptide analysis. Some embodiments analyze proteins identified by analysis techniques such as mass spectrometry and build protein groups out of results. Groups can be formed by collecting like proteins and examining the group so as to identify if it is likely that only one form of a protein is present or, if there is enough evidence to support the presence of alternate forms. Various embodiments provide visual reports that can be interactive. These reports can allow a user to visualize relationships between proteins both intra- and inter-group. Methods are also introduced that can reduce the identification of false positives by taking into account a priori information.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
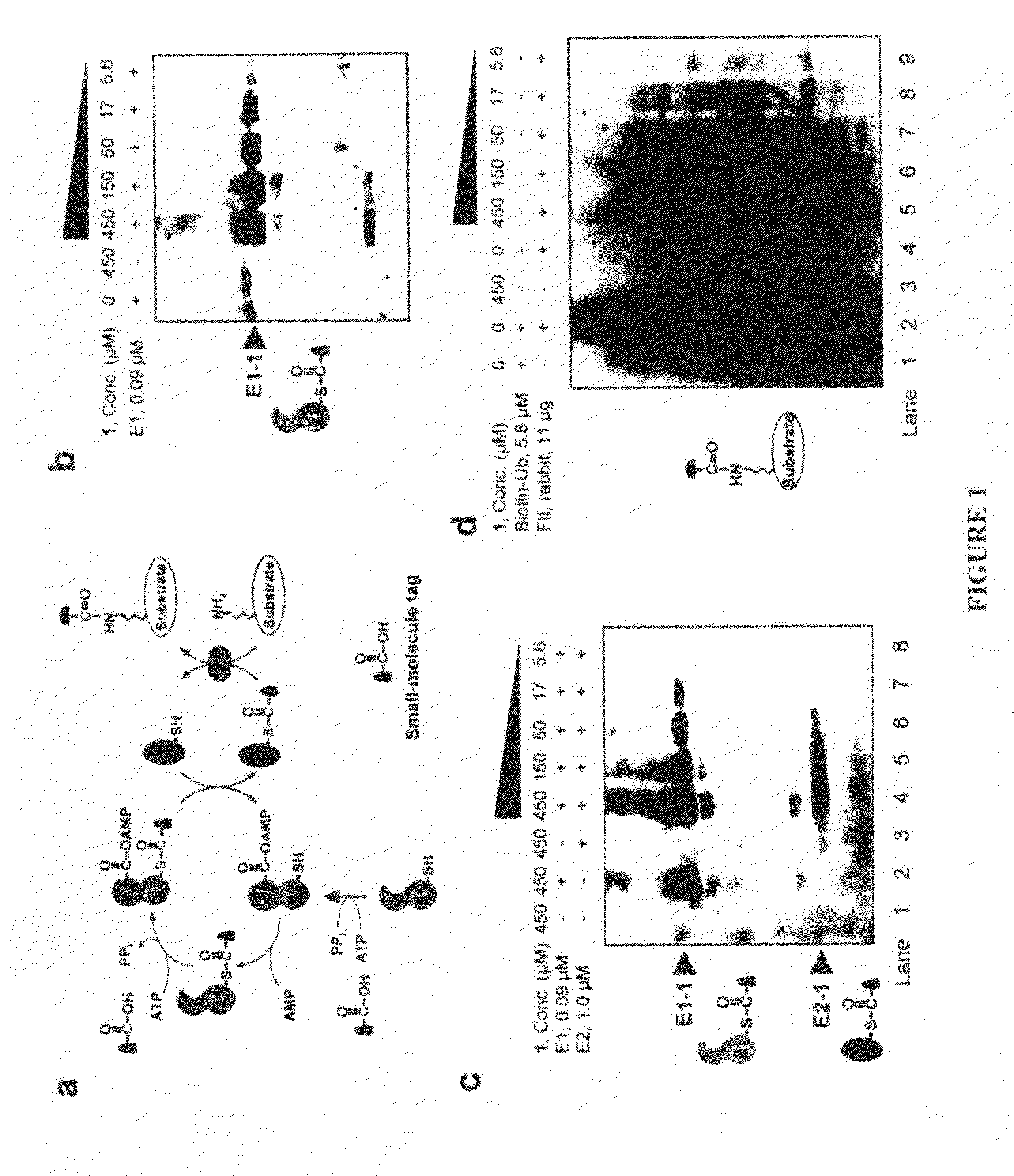
Biochemical method for specific protein labeling
InactiveUS20080305519A1Easy to operatePeptide sourcesTripeptide ingredientsProtein targetProtein insertion
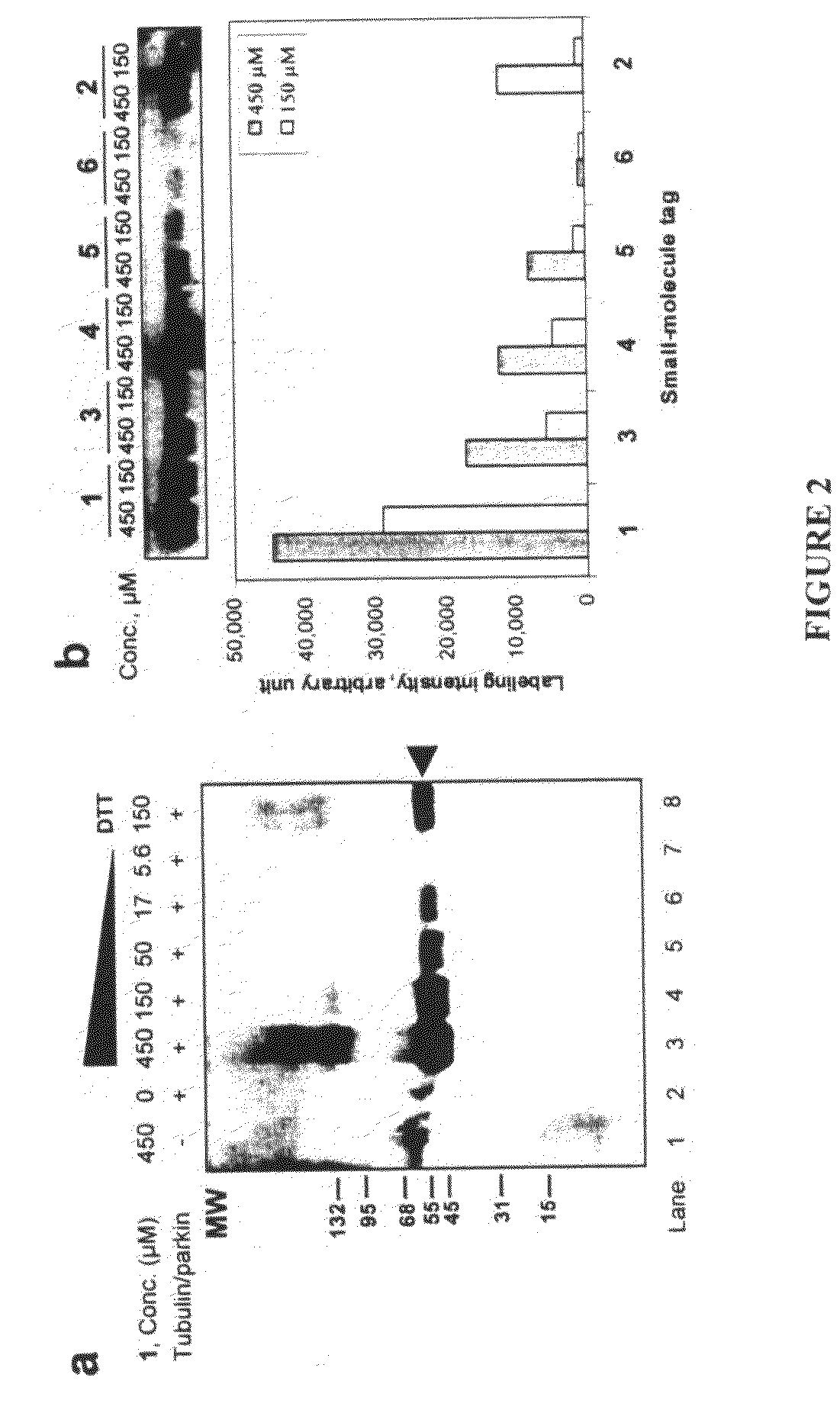
An improved method for protein labeling comprising the steps of providing a synthetic small molecule tag, providing a target protein to be tagged, providing at least two enzymes for catalyzing a conjugation reaction between the tag and the target protein, incubating the tag, the protein and the enzyme, and allowing the tag to conjugate to the target protein. The tag may embody at least one structural feature of an ubiquitin C-terminus, and the structural feature may comprise a recognition sequence that is recognizable by an ubiquitin activating enzyme.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method for expression of proteins on spore surface
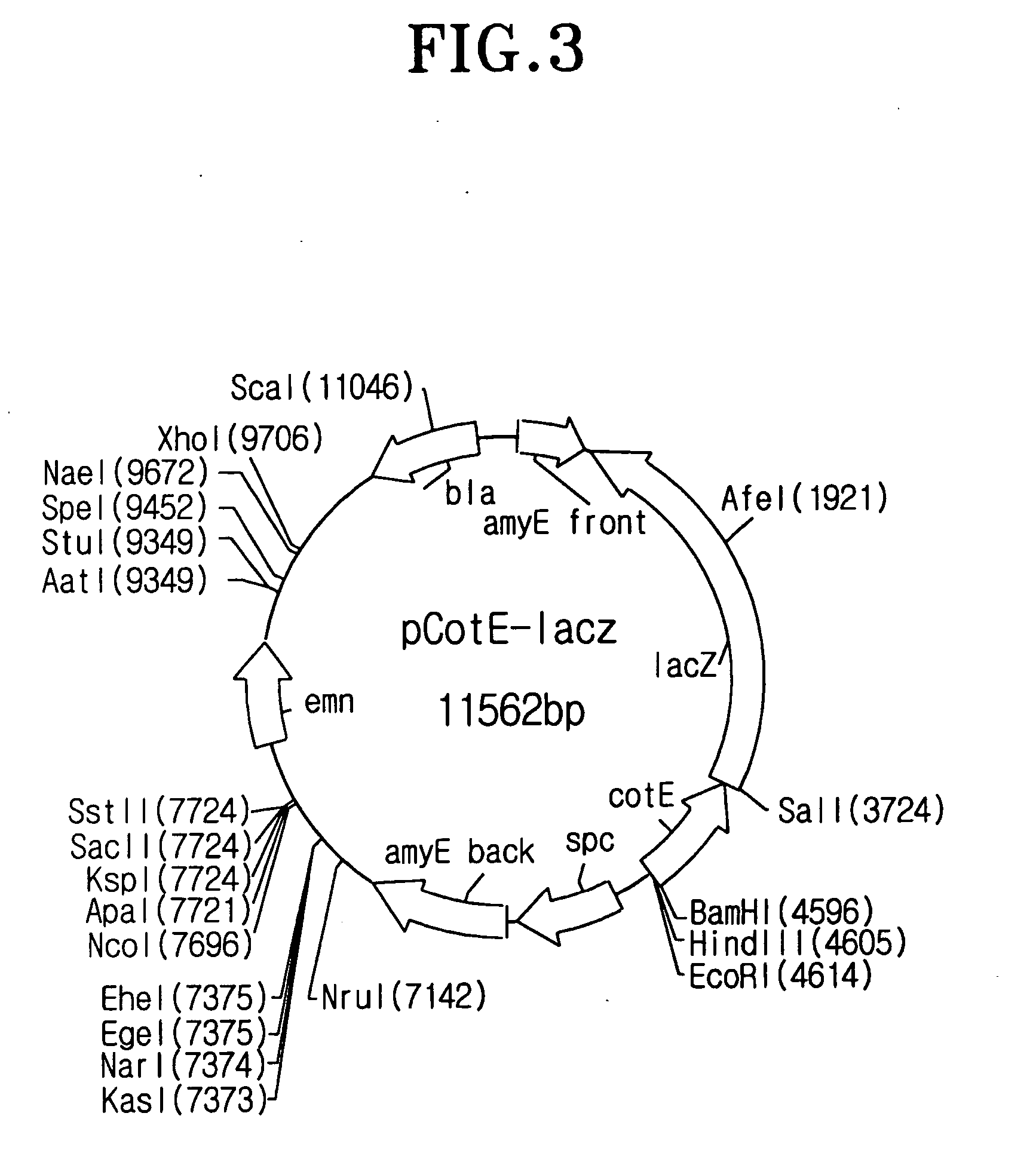
The present invention relates to a method for display of proteinson spore surface and a method for improving protein with rapidity using the same, which comprises the steps of (i) preparing a vector for spore surface display comprising a gene construct containing a gene encoding spore coat protein and a gene encoding a protein of interest, wherein, when expressed, the gene construct expresses a fusion protein between the spore coat protein and the protein of interest, (ii) transforming a host cell with the vector for spore surface display; (iii) displaying the protein of interest on a surface of a spore of the host cell; and (iv) recovering the spore displaying on its surface the protein of interest.
Owner:GENOFOCUS
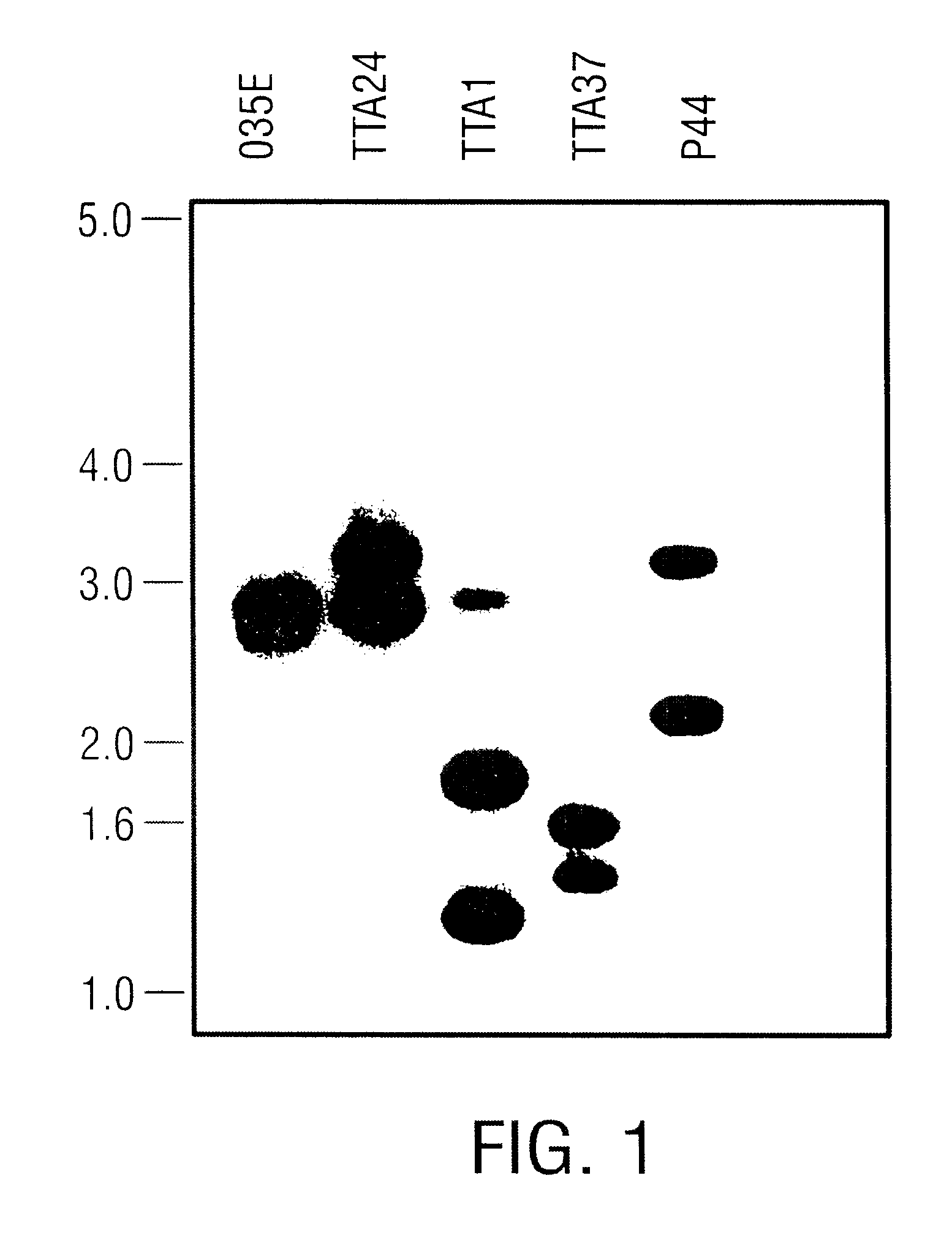
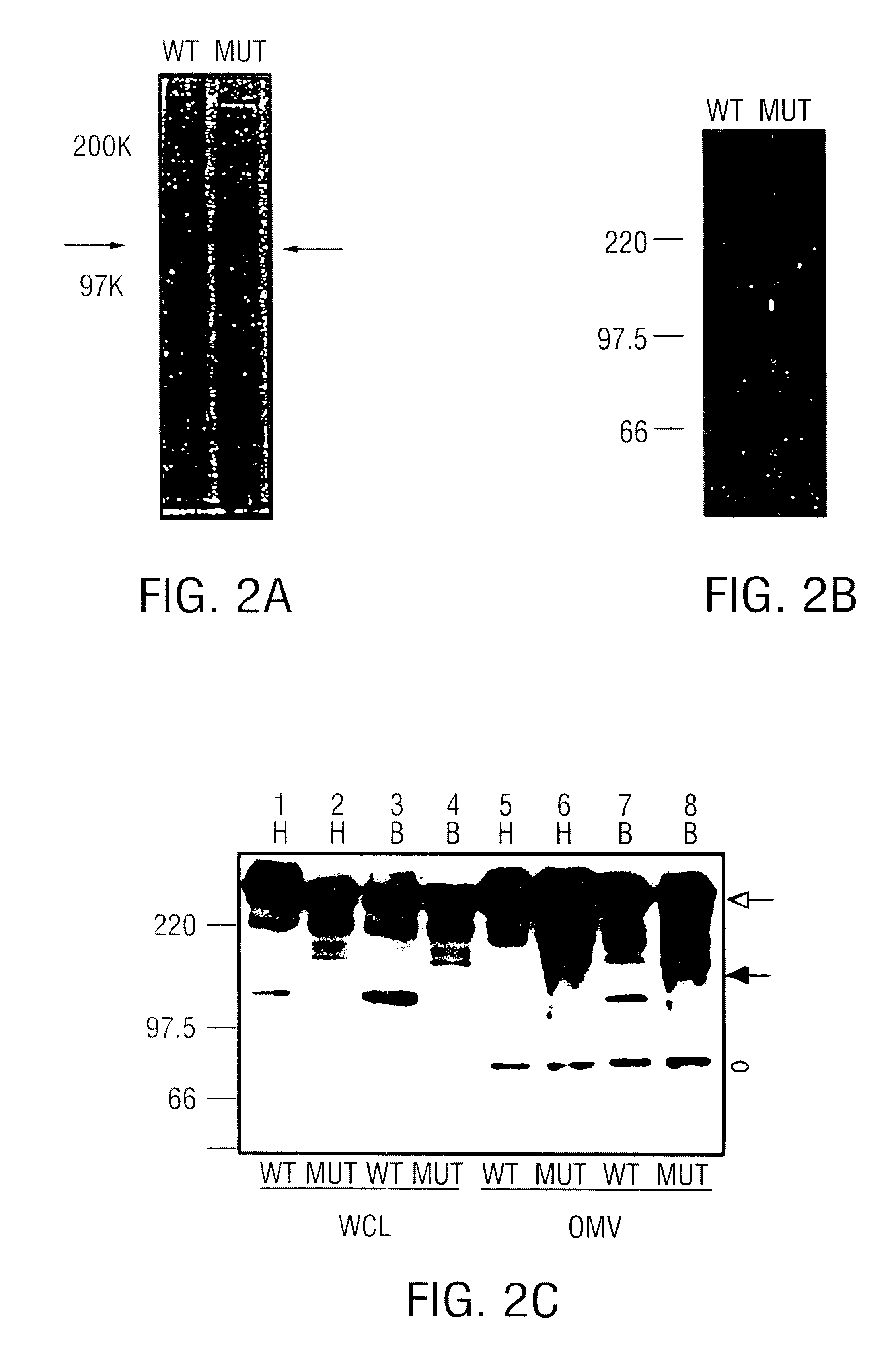
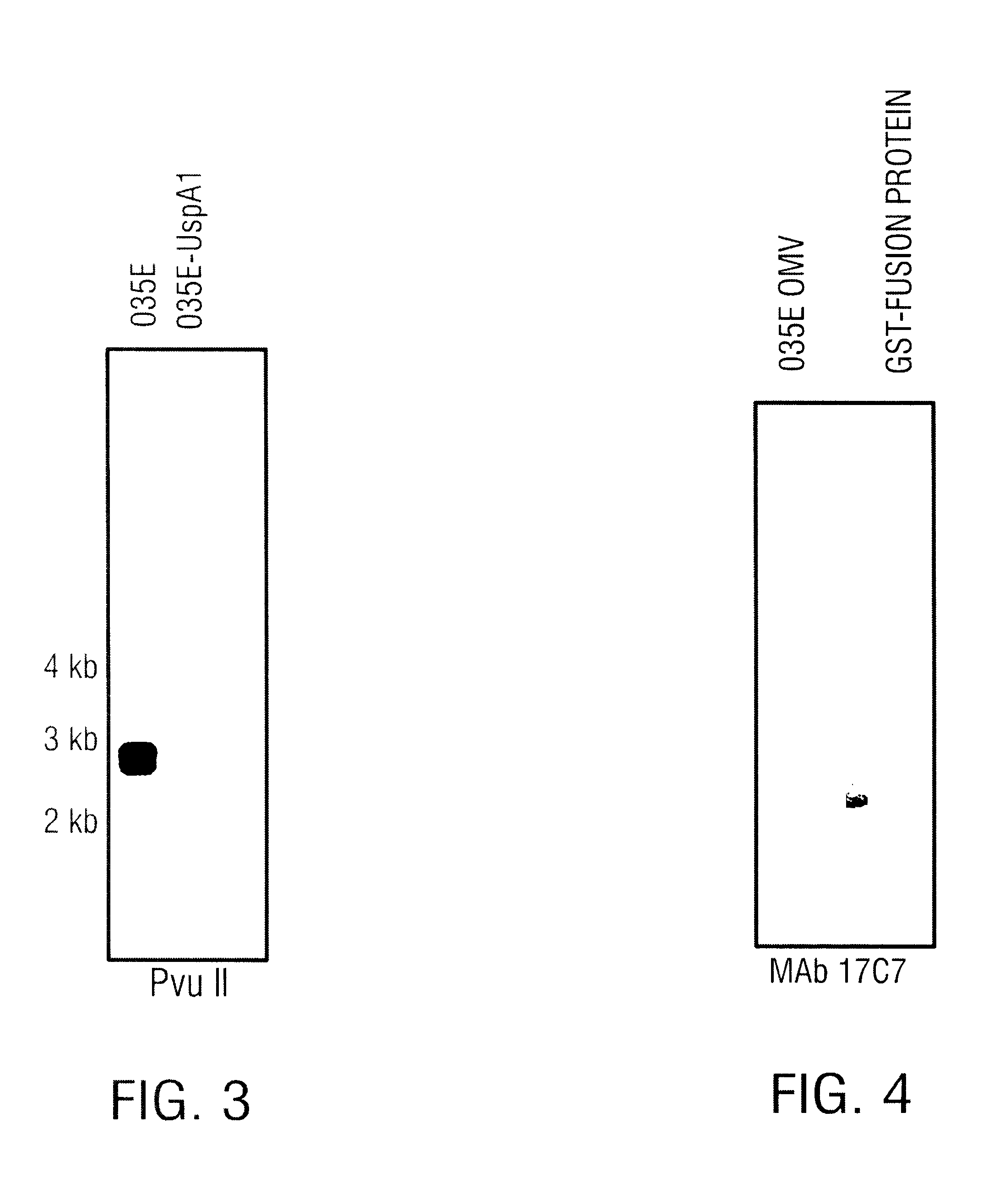
USPA1 and USPA2 antigens of Moraxella catarrhalis
The present invention discloses the existence of two novel proteins UspA1 and UspA2, and their respective genes uspA1 and uspA2. Each protein encompasses a region that is conserved between the two proteins and comprises an epitope that is recognized by the MAb 17C7. One or more than one of these species may aggregate to form the very high molecular weight form (i.e. greater than 200 kDa) of the UspA antigen. Compositions and both diagnostic and therapeutic methods for the treatment and study of M. catarrhalis are disclosed.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Method for producing target substance by fermentation
InactiveUS20030077764A1Improve abilitiesMicroorganism based processesDepsipeptidesMicroorganismGlucose polymers
In a method for producing a target substance by utilizing a microorganism, which comprises culturing the microorganism in a medium to produce and accumulate the target substance in the medium and collecting the target substance from the culture, there is used, as the microorganism, a mutant strain or recombinant strain of a microorganism in which maltose assimilation is controlled by an interaction between IIA.sup.Glc protein of glucose PTS and a protein involved in non-PTS uptake of maltose, and the interaction between the IIA.sup.Glc protein and the protein involved in non-PTS uptake of maltose is reduced or eliminated in the mutant strain or recombinant strain.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Compounds for stimulating p-glycoprotein function and uses thereof
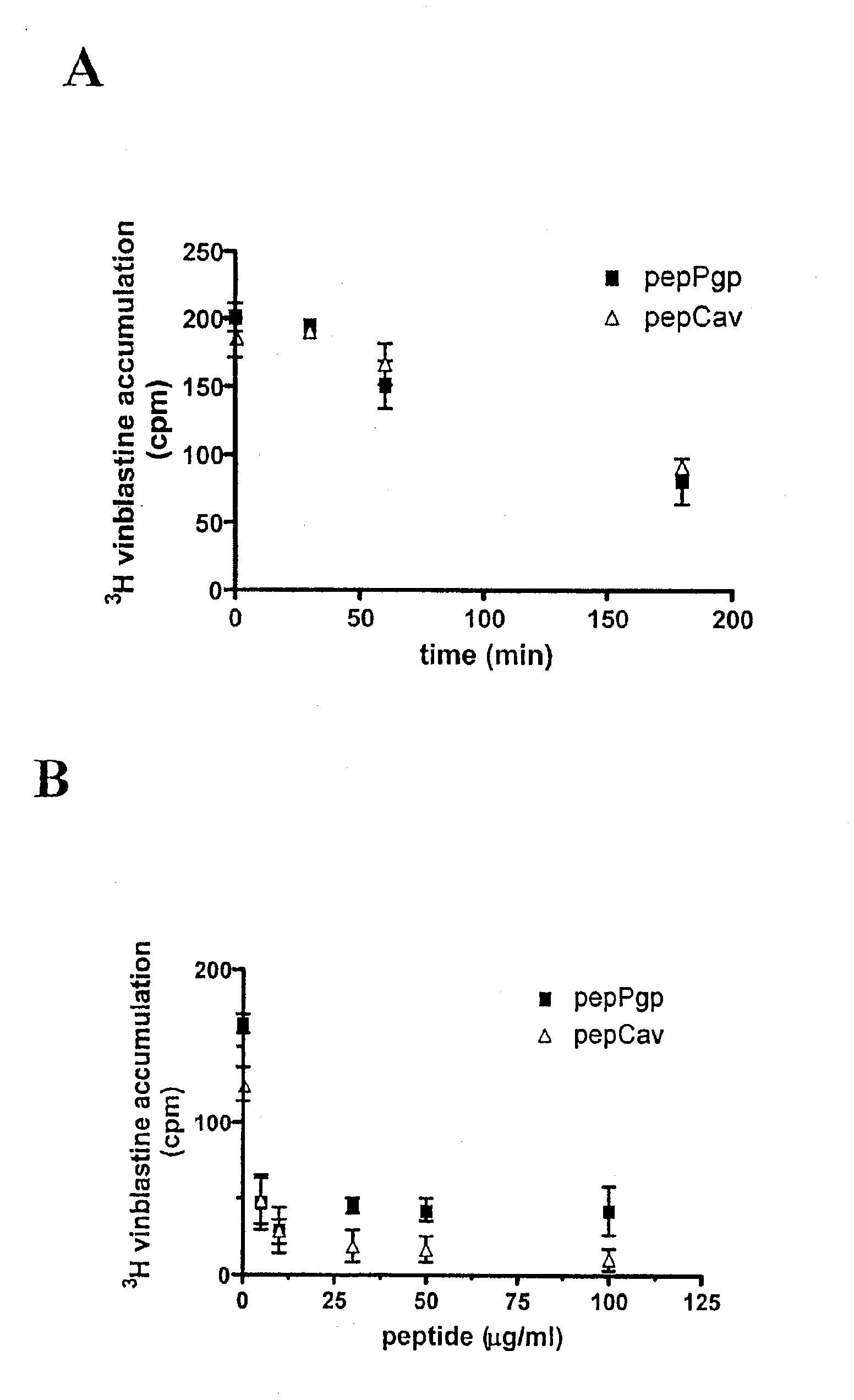
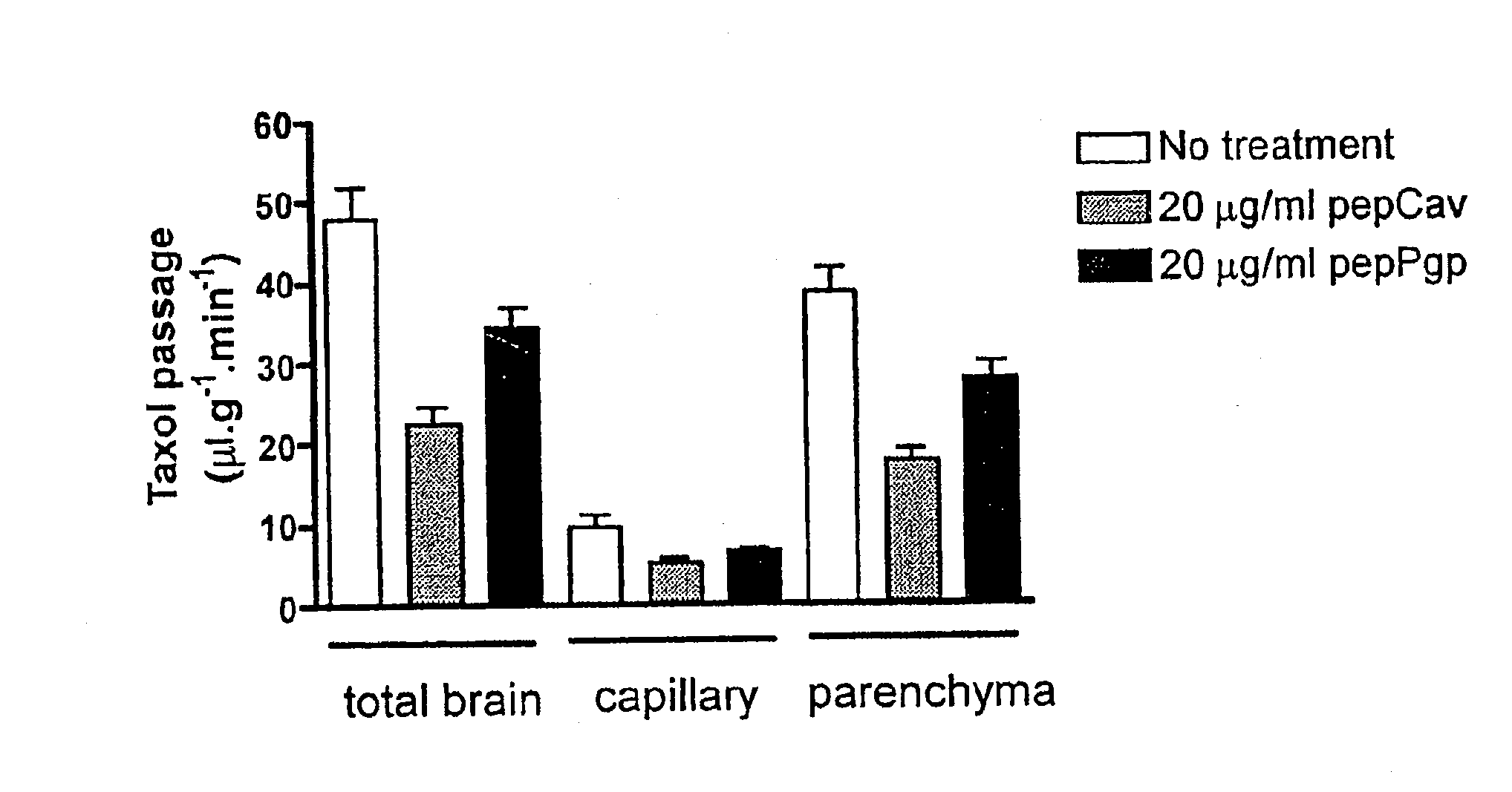
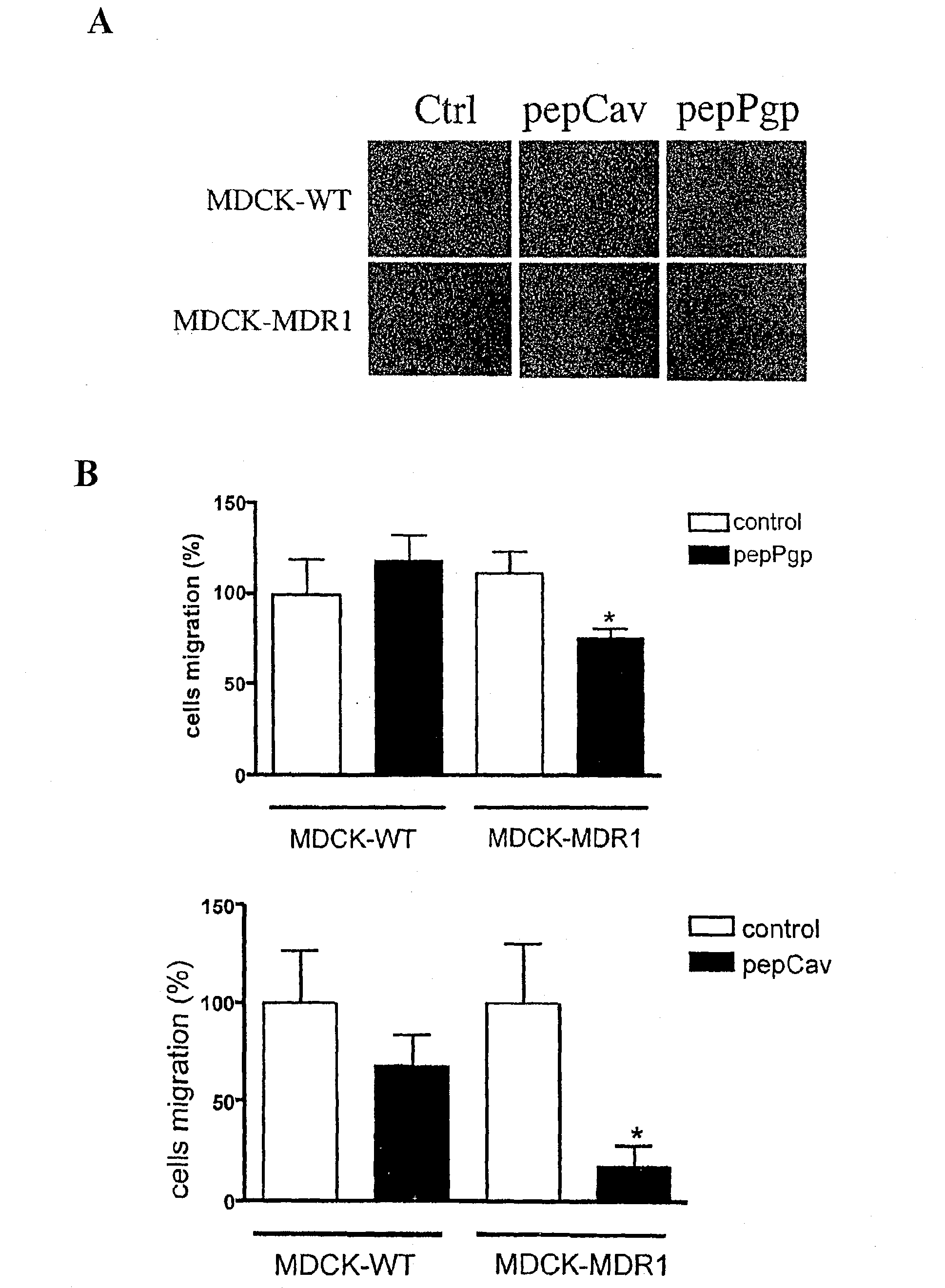
The present invention is directed to polypeptides (e.g., fragments) derived from P-glycoprotein and caveolin-1 which are capable of inhibiting the interaction between these two proteins. Inhibition of this interaction leads to increase of efflux of compounds that are transported by P-gp. The invention further includes methods of treating patients having diseases that benefit from increased P-gp-mediated efflux. Such diseases include neoplasms such as cancer and neurological diseases such as neurodegenerative diseases.
Owner:ANGLACHEM INC
Protein-protein interactions and methods for identifying interacting proteins and the amino acid sequence at the site of interaction
InactiveUS20080009068A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsLibrary screeningBiologyHigh affinity binding
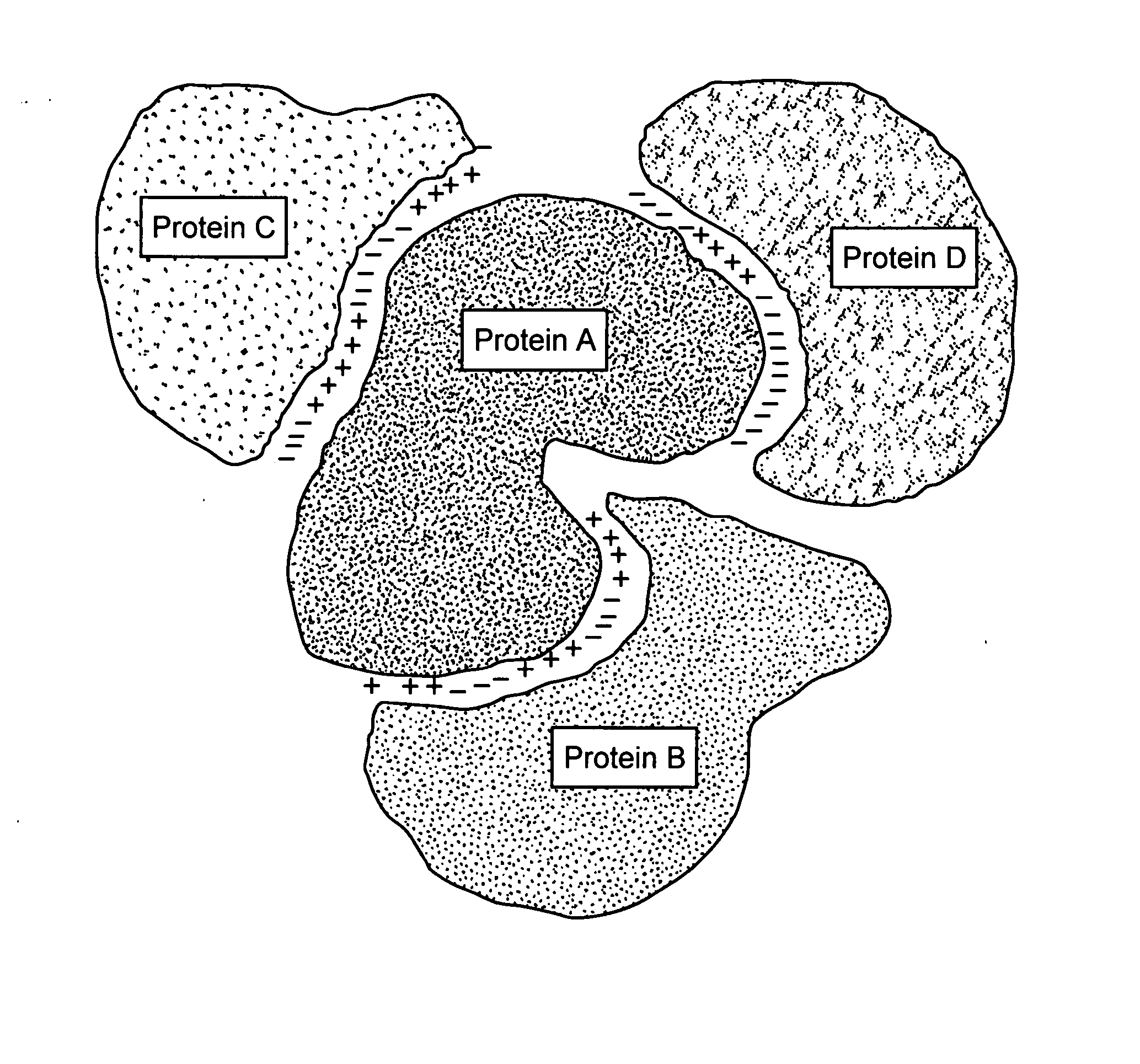
The invention relates to protein-protein interactions and methods for identifying interacting proteins and the amino acid sequence at the site of interaction. Using overlapping hexapeptides that encode for the entire amino acid sequences of the linker domains of human P-glycoprotein gene 1 and 3 (HP-gp1 and HP-gp3), a direct and specific binding between HP-gp1 and 3 linker domains and intracellular proteins was demonstrated. Three different stretches (617EKGIYFKLVTM627, (SEQ ID NO: 1) 658SRSSLIRKRSTRRSVRGSQA677 (SEQ ID NO: 2) and 694PVSFWRIMKLNLT706 (SEQ ID NO: 3) for HP-gp1 and 618LMKKEGVYFKLVNM631 (SEQ ID NO: 4), 648KAATRMAPNGWKSRLFRHSTQKNLKNS674 (SEQ ID NO: 5), and 695PVSFLKVLKLNKT707 (SEQ ID NO: 6) for HP-gp3) in linker domains bound to proteins with apparent molecular masses of ˜80 kDa, 57 kDa and 30 kDa. The binding of the 57 kDa protein was further characterized. Purification and partial N-terminal amino acid sequencing of the 57 kDa protein showed that it encodes the N-terminal amino acids of alpha and beta-tubulins. The method of the present invention was further validated with Annexin. The present invention thus demonstrates a novel concept whereby the interactions between two proteins are mediated by strings of few amino acids with high and repulsive binding energies, enabling the identification of high affinity binding sites between any interacting proteins.
Owner:GEORGES ELIAS
Methods for conducting assays for enzyme activity on protein microarrays
The present invention relates to methods of conducting assays for enzymatic activity on microarrays useful for the large-scale study of protein function, screening assays, and high-throughput analysis of enzymatic reactions. The invention relates to methods of using protein chips to assay the presence, amount, activity and / or function of enzymes present in a protein sample on a protein chip. In particular, the methods of the invention relate to conducting enzymatic assays using a microarray wherein a protein and a substance are immobilized on the surface of a solid support and wherein the protein and the substance are in proximity to each other sufficient for the occurrence of an enzymatic reaction between the substance and the protein. The invention also relates to microarrays that have an enzyme and a substrate immobilized on their surface wherein the enzyme and the substrate are in proximity to each other sufficient for the occurrence of an enzymatic reaction between the enzyme and the substrate.
Owner:PROTOMETRIX
Method for quantum dots namo fluorescence probe combined with biochip to find Chinese medicine target
InactiveCN101034060AExcellent optical propertiesBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceProtein targetFluorescence
This invention supply a method of quanta point nanometer technology combine with biochip technology to search Chinese traditional medicine effective ingredient action target spot, belong to stuff, chemical engineering, pharmacy and biologic cross region. This invention connect quanta point with Chinese traditional medicine effective ingredient, form a 'quanta point - Chinese traditional medicine effective ingredient' fluorescence probe, then put fluorescence probe directly altogether incubate with biochip, after washing, base on fluorescence emit from biochip 's quanta point to ascertain idiosyncratic combine LOCA( namely target spot) between medicament and chip's fixed given protein, then through computer software to analyze protein of these combined LOCA . This invention can easily and rapidly search target protein of Chinese traditional medicine effective ingredient create pharmacodynamic to cell, can supply high duty technology instrument for Chinese traditional medicine study and new drug screening.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
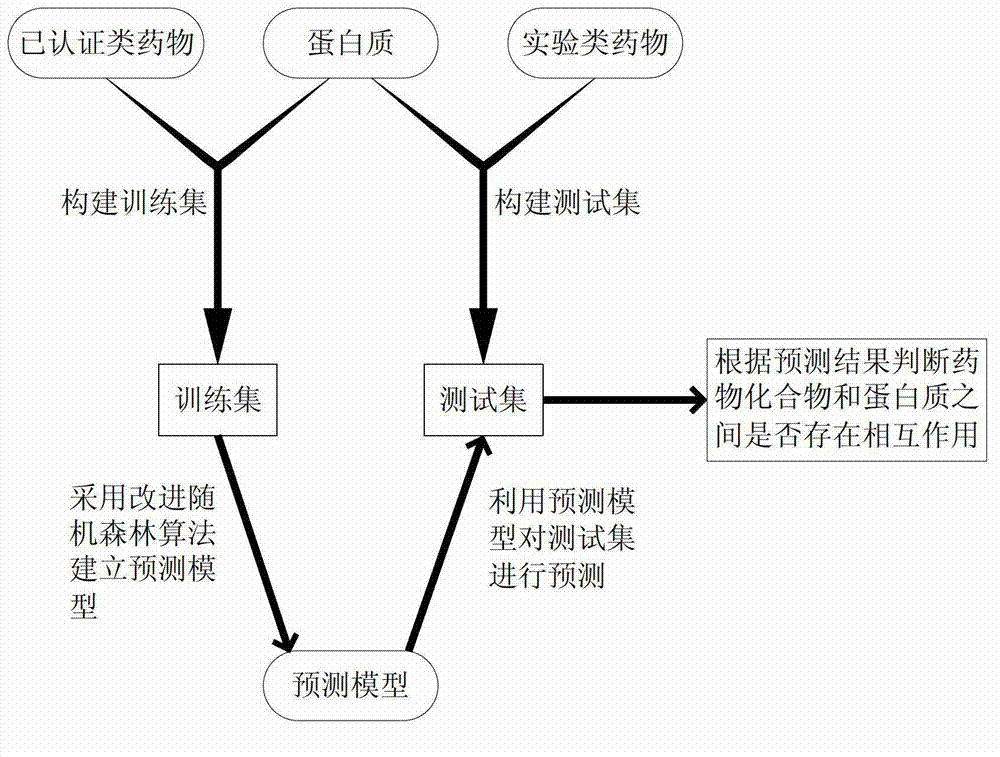
Method of predicting interaction between chemical compounds and proteins based on random forest
ActiveCN103116713AAccurate judgment of reliabilitySpecial data processing applicationsProtein targetPredictive methods
The invention discloses a method of predicting interaction between chemical compounds and proteins based on random forest. The method includes: collecting information of target proteins which tend to interact with drug compounds to establish a target base; collecting the drug compounds for establishment of a training set and information of interaction relation between the drug compounds and the target proteins to establish a compound base; establishing the training set according to the information of the compound base and the target base; training by modified random forest algorithm on the basis of the training set to establish a predicting model; collecting the compounds for prediction and the information of the target proteins obtained in step (A) to establish a test set; predicting the test set on the basis of the predicting model; and (H), judging whether interaction between the compounds to be predicted and the target proteins exists or not according to the prediction result. Accuracy of predicting interaction between the compounds and the proteins by the method can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
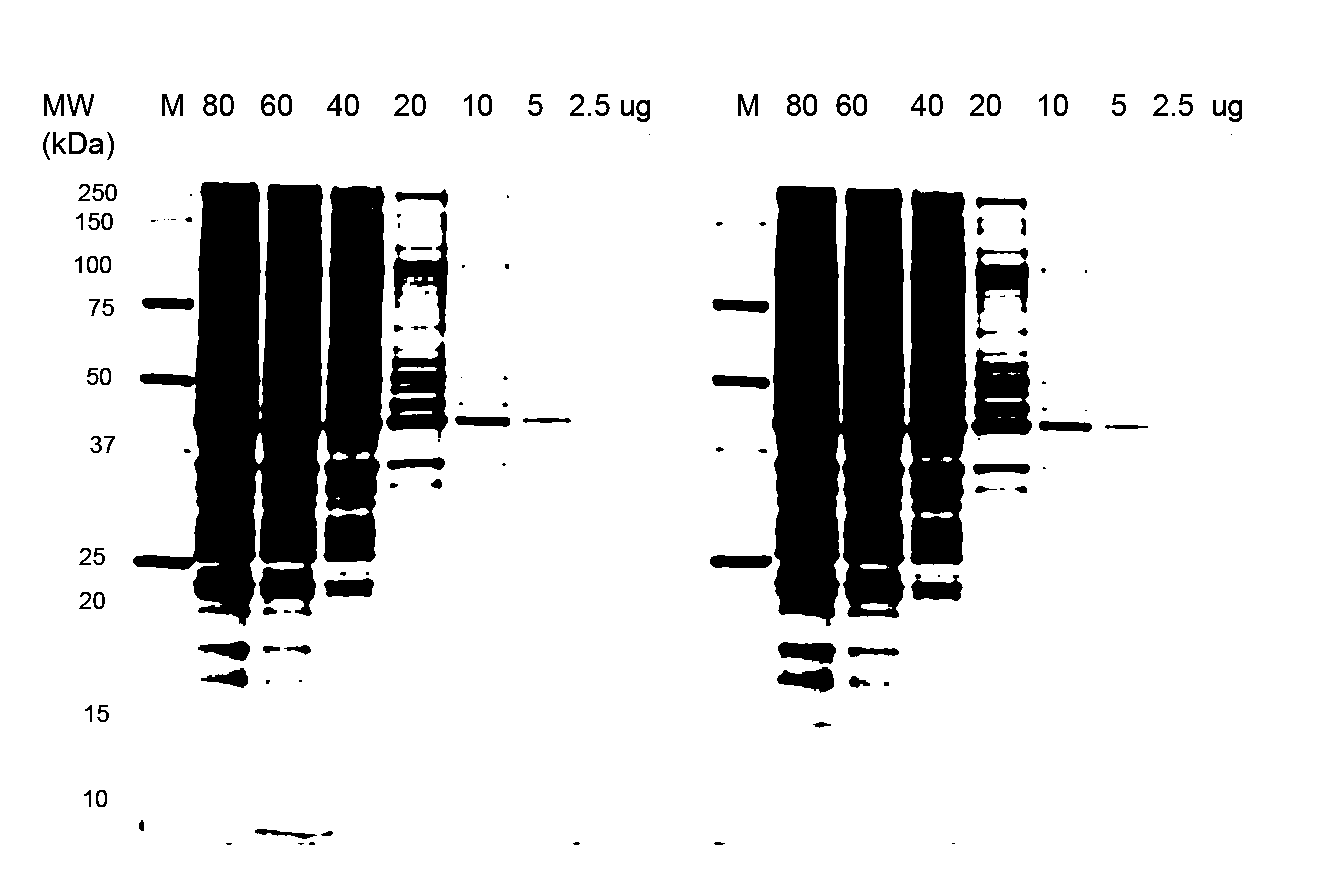
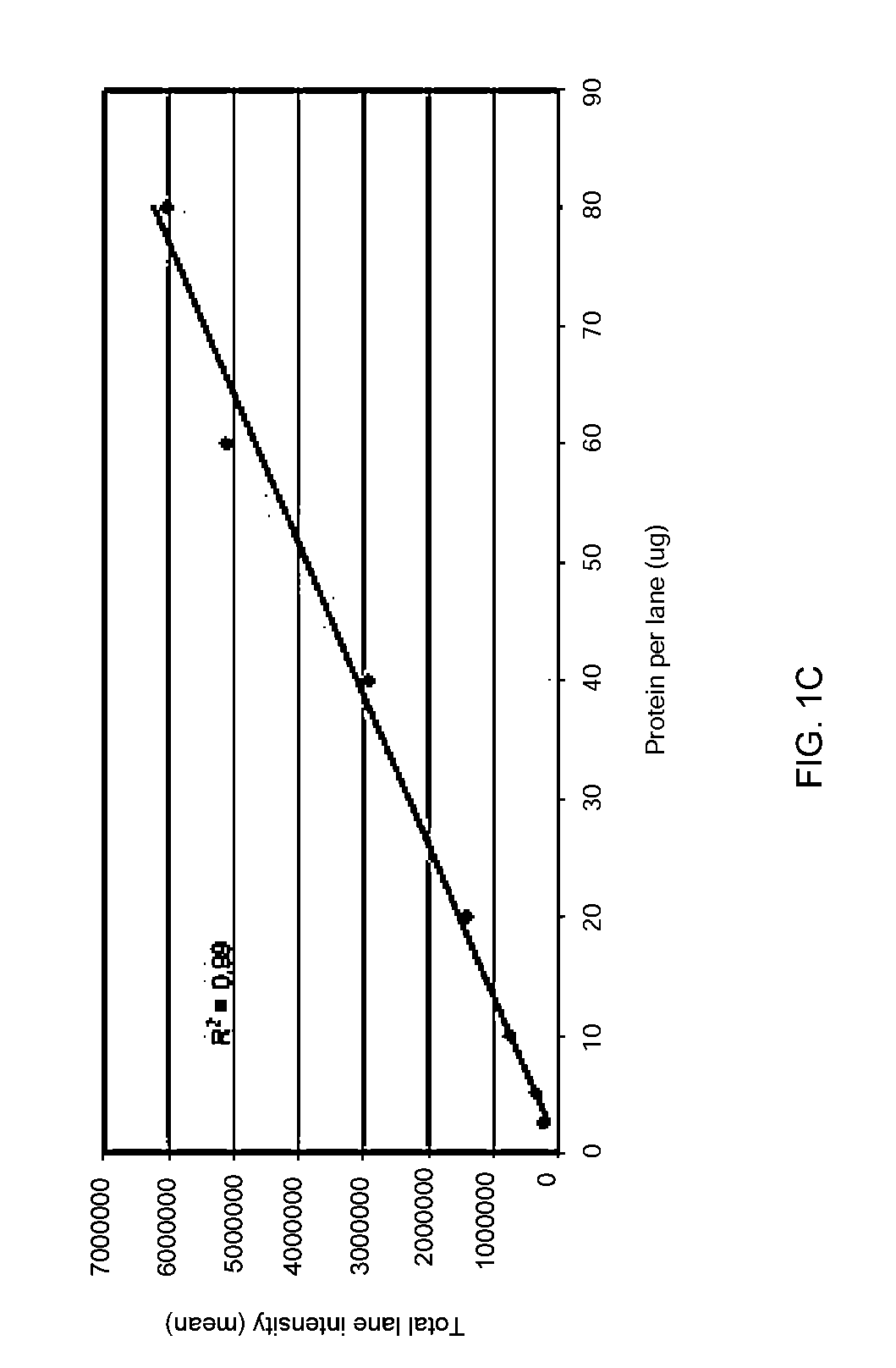
Stain-free protein quantification and normalization
Disclosed herein are methods of protein quantification and normalization using haloalkylated tryptophan fluorescence. Complex protein samples, i.e., samples that each contain 1,000 or more distinct proteins, from diverse sources that do not have common protein profiles are treated with a halo-substituted organic compound (i.e. haloalkane) that reacts with tryptophan residues to form fluorescent products. Irradiation of the samples with ultraviolet light and the detection and quantification of the resultant fluorescent emissions from all proteins in each sample are then used to obtain comparative values for total protein content among the various samples. The values thus obtained are found to be valid indications of comparative total protein content, despite the fact that the tryptophan levels vary widely among the various proteins in any single sample and the samples, due to the diversity of their origins, tend to differ among themselves in the identities and relative amounts of the proteins that they contain. Protein samples are also normalized to correct for differences in sample dilution, sample loading, and protein transfer inconsistencies, by using stain-free detection of total protein in each of the samples, or detection of subsamples within each sample.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Methods for comparing functional sites in proteins
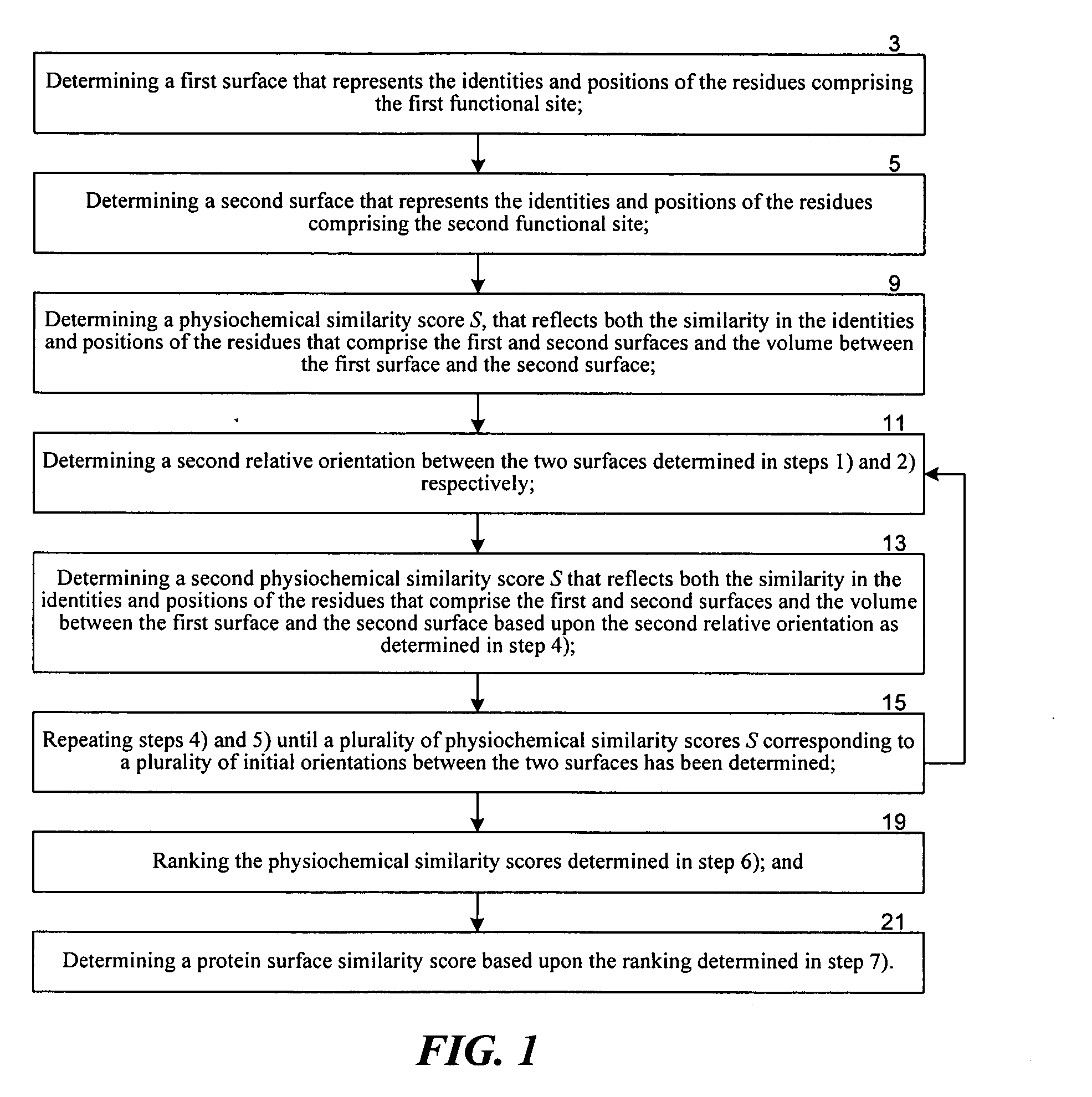
InactiveUS20050192758A1Effective calculationComputationally efficientProteomicsGenomicsTARP ProteinProtein surface
The present invention relates to methods and systems for representing and scoring the similarity of two protein by iteratively rotating and translating one protein surface representation relative to the other protein surface representation in order to maximize (or minimize) a score that represents both the volume between the two surface representations and the similarity in the identities and positions of the residues comprising the two protein surfaces. In another aspect of the invention, such methods and systems are used to compare and annotate a protein comprising a putative functional site of unknown function with a database of reference proteins of known function.
Owner:EIDOGEN SERTANTY INC
Method of modulation of interaction between receptor and ligand
Owner:ENKAM PHARMA
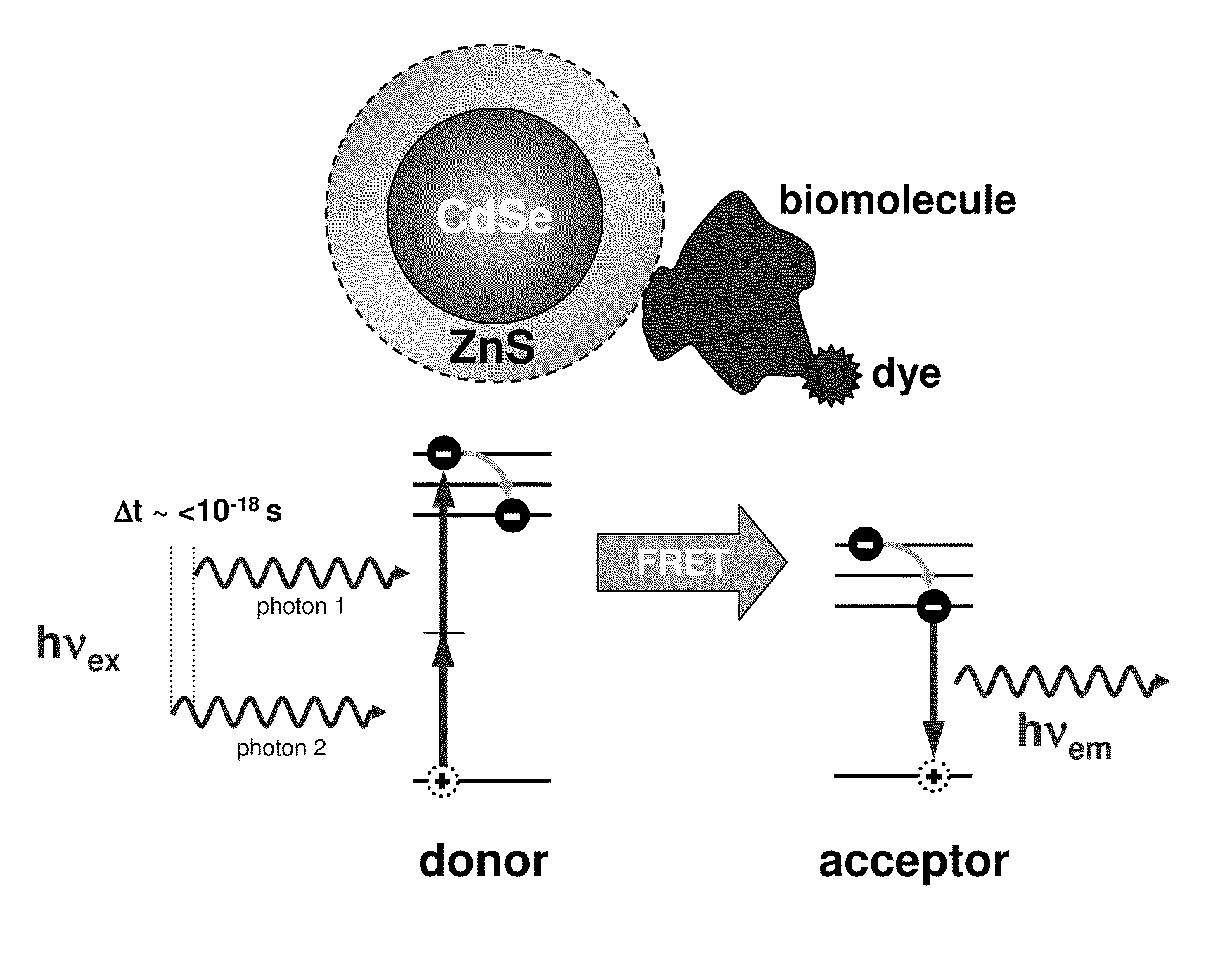
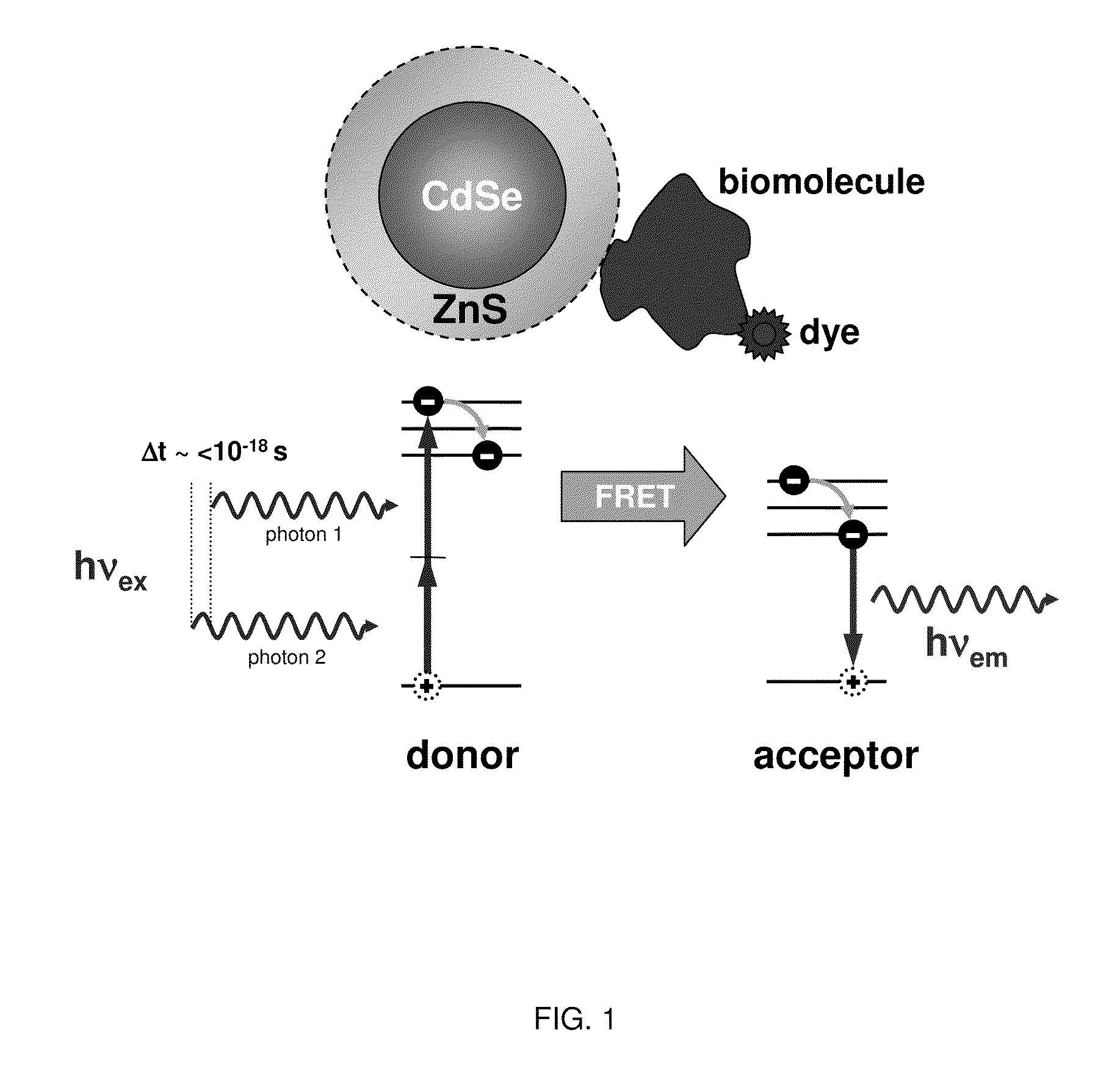
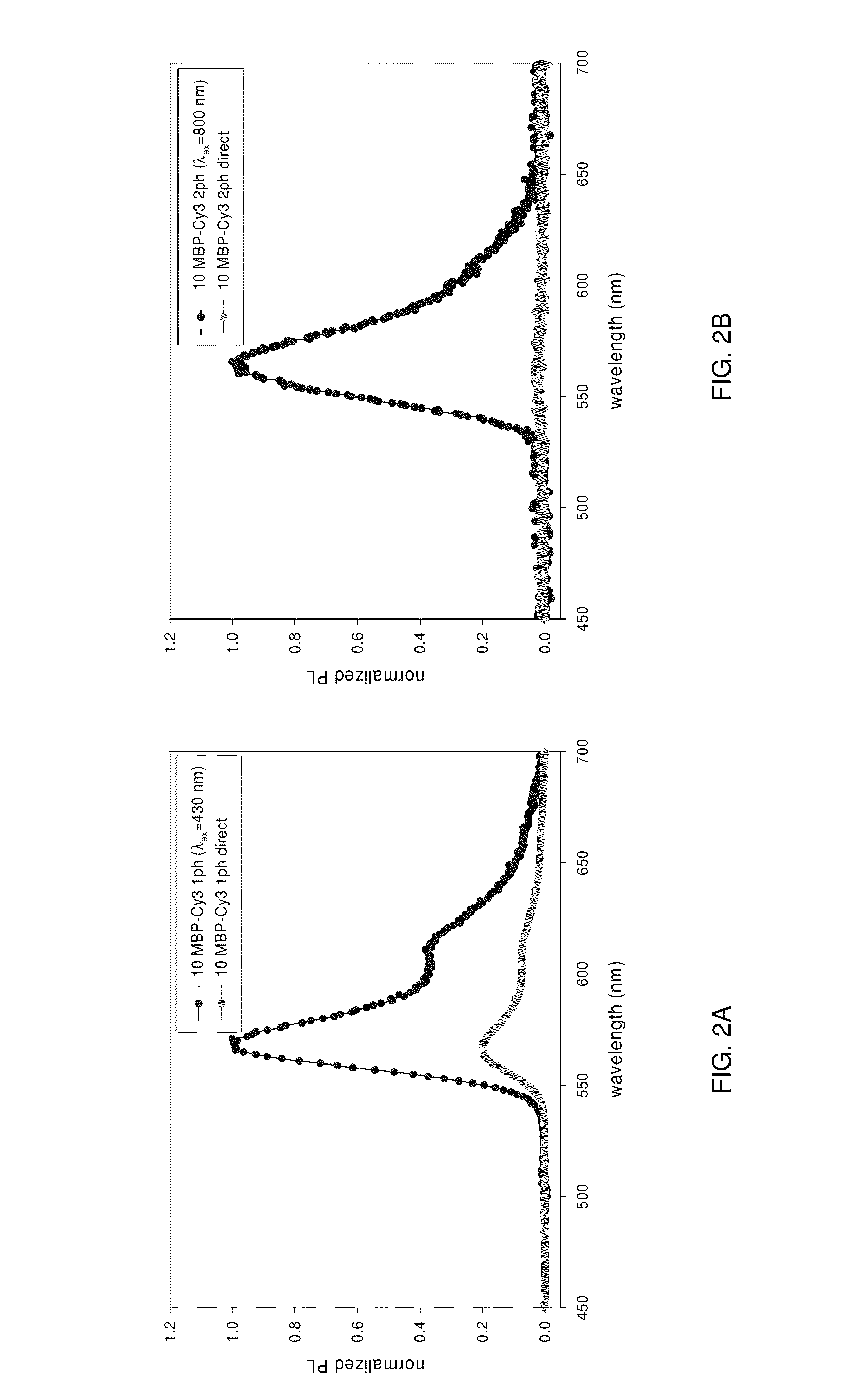
Methods of generating florescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between semiconductor quantum dots and fluorescent dyes/proteins via multi-photon excitation, achieving zero background or direct excitation contributions to the fret signature
InactiveUS20100075361A1Microbiological testing/measurementAnalysis by material excitationSemiconductor quantum dotsBiomolecule
A system and method of sensing physiological conditions in biological applications includes a laser source for optically exciting a plurality of luminescent quantum dots and a plurality of biomolecules in a nanoscale sensing system having a nanocrystal structure, where the plurality of biomolecules is stained with dye. In a multi-photon excitation process, a laser system optically excites, the plurality of luminescent quantum dots and the plurality of biomolecules in the nanoscale sensing system, where fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) occurs between the plurality of quantum dots and the plurality of biomolecules. Stability of self assembly of quantum dot peptide conjugates within the plurality of biomolecules is investigated. Physiological conditions at the cellular level are determined, using a spectrometer to sense fluorosence spectra. The sensing of physiological conditions includes transducing signals into immunoassays, clinical diagnostics and cellular imaging to provide treatment to biological subjects including human patients.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA GOVT REPRESENTED BY THE SECRDETARY OF THE NAVY CHIEF OF NAVAL RES ONR NRL
Methods for assaying protein-protein interactions
The invention relates, in part, to methods for detecting, monitoring, measuring or assessing an interaction between at least two proteins. The invention also relates, in part, to methods for determining if a test compound, or a mix of compounds, modulates an interaction between at least two proteins. In some embodiments, determination is made possible via the use of two recombinant molecules, e.g., one of which contains a first protein cleavage site for a proteolytic molecules, and an activator of a gene. A second recombinant molecule may include a second protein and the proteolytic molecule. Various other formats are provided by the invention. In some embodiments, if the test compound binds to the first protein, a reaction is initiated whereby the activator is cleaved, and activates a reporter gene.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
A protein chip for analyzing interaction between protein and substrate peptide thereof
InactiveCN1732387AImprove responseObesity gene productsLibrary screeningCrystallographyProtein insertion
A protein chip of a S-L-SP form wherein a substrate peptide (SP) is immobilized on a solid substrate (S) by the mediation of a linker protein (L). Such chip is usefully employed in a method for analyzing the interaction between a reactive protein and its substrate peptide involving the steps of: adding to the protein chip a reactive protein showing a specific interaction with the substrate protein immobilized on the protein chip; and detecting the interaction between the reactive protein and the substrate peptide. The use of such protein chip and methodology allows an increase in the reactivity between a peptide with low molecular weight and an enzyme with high molecular weight and between the peptide and a reactive antibody on the protein chip, so that the interaction between the peptide and the protein can be analyzed rapidly and massively.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Cysteine-containing peptides having antioxidant properties
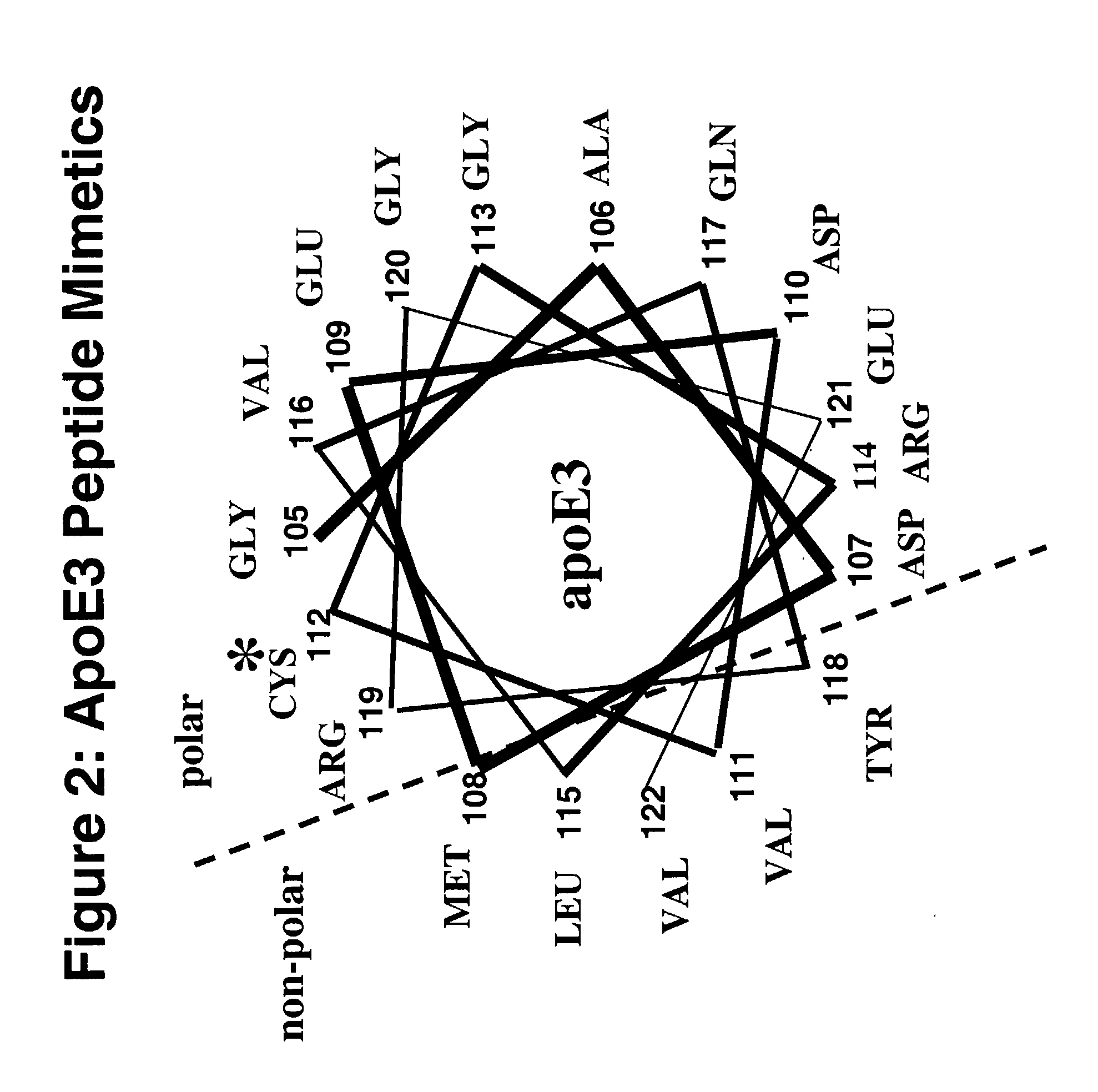
InactiveUS7217785B2Novel antioxidant activityIncrease capacityApolipeptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein DatabasesTARP Protein
The term “homology” or “homologous” means an amino acid similarity measured by the program, BLAST (Altschul et al (1997), “Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs”, Nucleic Acids Res. 25:33 89–3402), and expressed as —(% identity n / n). In measuring homology between a peptide and a protein of greater size, homology is measured only in the corresponding region; that is, the protein is regarded as only having the same general length as the peptide, allowing for gaps and insertions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and system for predicting functions of compound
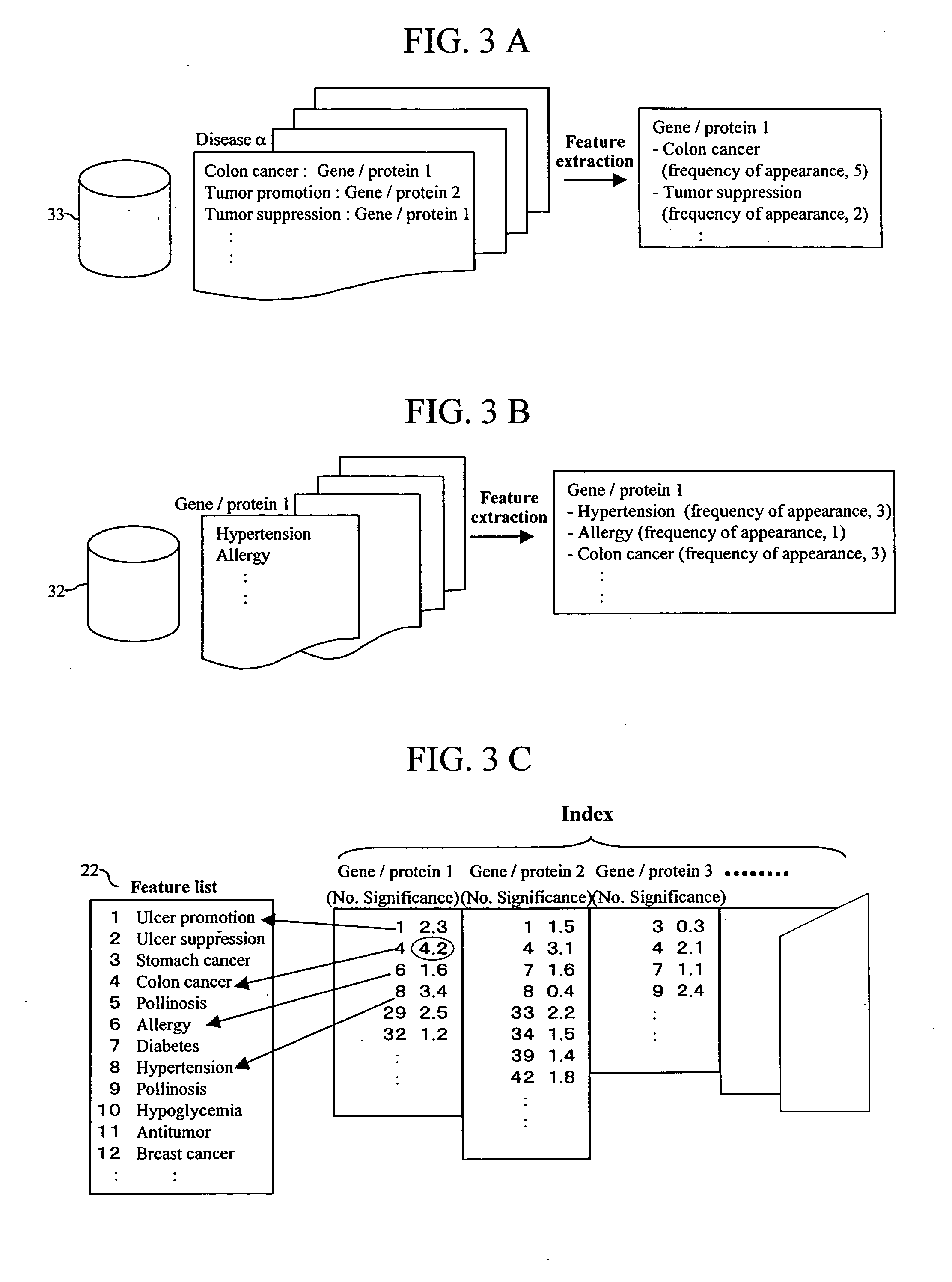
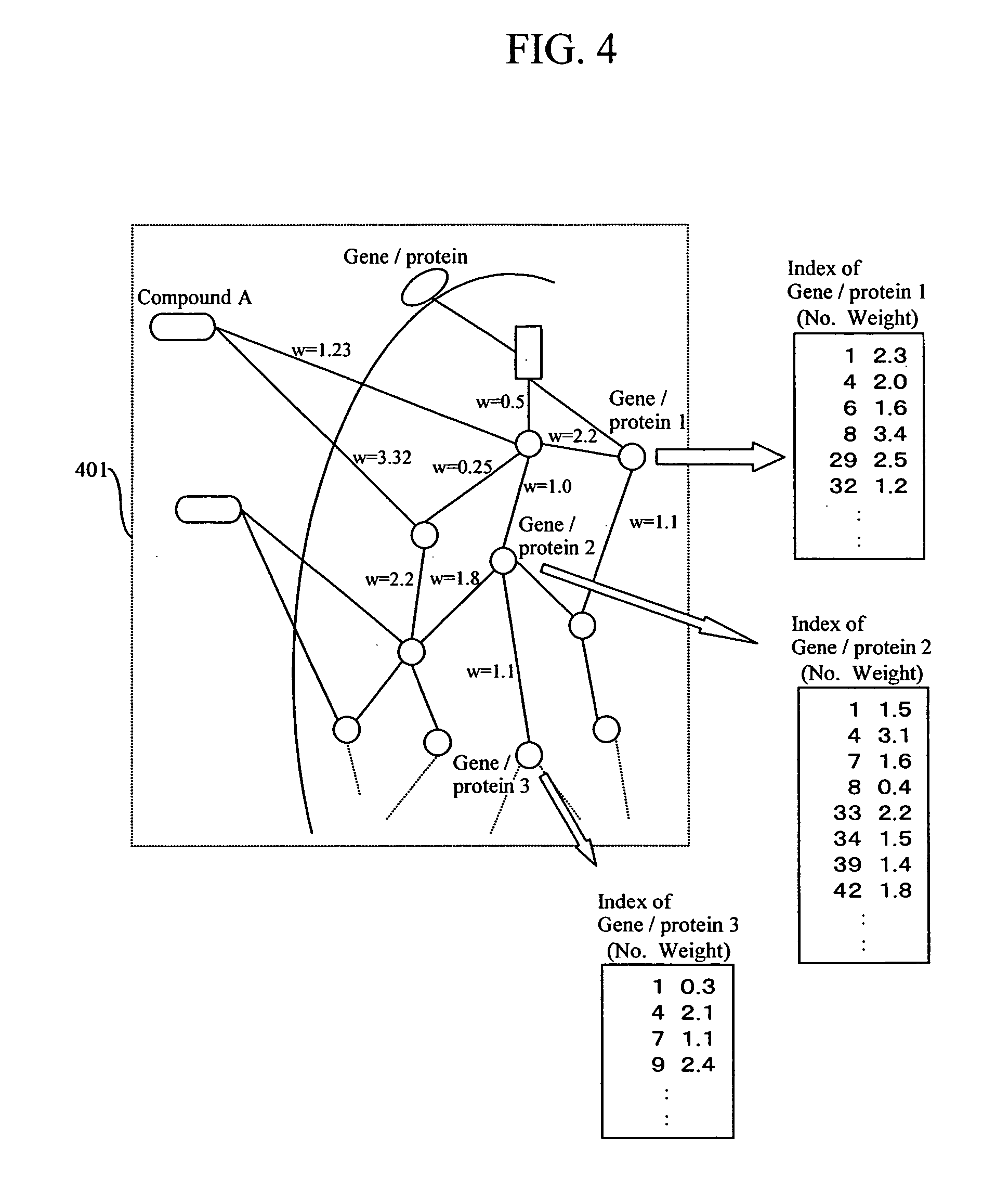
InactiveUS20060106544A1Improve efficiencyShorten the development cycleChemical property predictionMolecular designProtein DatabasesBibliographic database
Feature of a compound is predicted by using information on interactions between substances. A database of interactions between compounds and genes / proteins is constructed on the base of information collected from bibliographic databases, gene / protein databases, and disease databases, and an interaction network is prepared by mapping the collected information to thereby enable prediction of the features of a compound.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Methods and systems for protein and peptide evidence assembly
InactiveUS20060030053A1Reduce manual inspectionTransferrinsAlbumin peptidesPrior informationTARP Protein
The present teachings provide methods and systems for the identification of proteins via peptide analysis. Some embodiments analyze proteins identified by analysis techniques such as mass spectrometry and build protein groups out of results. Groups can be formed by collecting like proteins and examining the group so as to identify if it is likely that only one form of a protein is present or, if there is enough evidence to support the presence of alternate forms. Various embodiments provide visual reports that can be interactive. These reports can allow a user to visualize relationships between proteins both intra- and inter-group. Methods are also introduced that can reduce the identification of false positives by taking into account a priori information.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Identification and use of antiviral compounds that inhibit interaction of host cell proteins and viral proteins required for viral replication
The present invention relates to the identification of host cell proteins that interact with viral proteins required for virus replication, and high throughput assays to identify compounds that interfere with the specific interaction between the viral and host cell protein. Interfering compounds that inhibit viral replication can be used therapeutically to treat viral infection.The invention is based, in part, on the Applicants' discovery of novel interactions between proteins of the influenza virus and a human host cell proteins. One of these host cell proteins, referred to herein as NPI-1, interacts with influenza virus protein NP, and may be an accessory protein required for replication of influenza virus. Another of these host cell proteins, referred to herein as NS1I-1, interacts with influenza virus protein NS1. Compounds that interfere with the binding of the host cell and viral proteins, and inhibit viral replication can be useful for treating viral infection in vivo.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Identification of Compounds Modifying A Cellular Response
The present invention relates to methods for identifying compounds capable of modulating a cellular response. The methods involve attaching living cells to solid supports comprising a library of test compounds. The test compounds are linked to the solid support via cleavable linkers and may thus be released from the solid supports. Solid supports comprising cells, wherein the cellular response of interest has been modulated are selected and the test compound of the solid support can then be identified. The cellular response may for example be changes in complex formation between proteins.
Owner:2CUREX
Method for preparing antibody monolayers which have controlled orientation using peptide hybrid
ActiveUS20100209945A1Easy to fixEasy to usePeptide/protein ingredientsPreparing sample for investigationCrystallographySolid substrate
The present invention relates to a method for preparing an protein monolayer using a peptide hybrid for protein immobilization, more precisely a peptide hybrid for protein immobilization which has improved solubility by introducing a PEG linker and a proper reaction group to the oligopeptide having specific affinity to selected types of proteins and is designed to provide enough space between solid substrates and proteins immobilized, whereby various solid substrates treated by the hybrid catch specific proteins effectively on. The peptide hybrid for protein immobilization of the present invention facilitates the control of orientation of an antibody on various solid surfaces and immobilization of various antibodies of different origins or having different isotypes with different affinity. Therefore, the surface treatment technique using the peptide hybrid of the invention can be effectively used for the production of various immunosensors and immune chips.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
System and method for generating detection of hidden relatedness between proteins via a protein connectivity network
InactiveUS20170098030A1Improve predictive performanceBiostatisticsMachine learningTARP ProteinData value
Systems and methods are for generating a weighted relatedness protein network. The method includes steps of obtaining a protein network; generating training data; generating a weighting function derived from the training data values; and applying the weighting function to a protein network, thereby generating a weighted relatedness protein network. The protein network may be applied for prediction of protein properties by detection of relatedness with annotated sequences.
Owner:OFEK ESHKOLOT RES & DEV
Method of assaying interaction between proteins
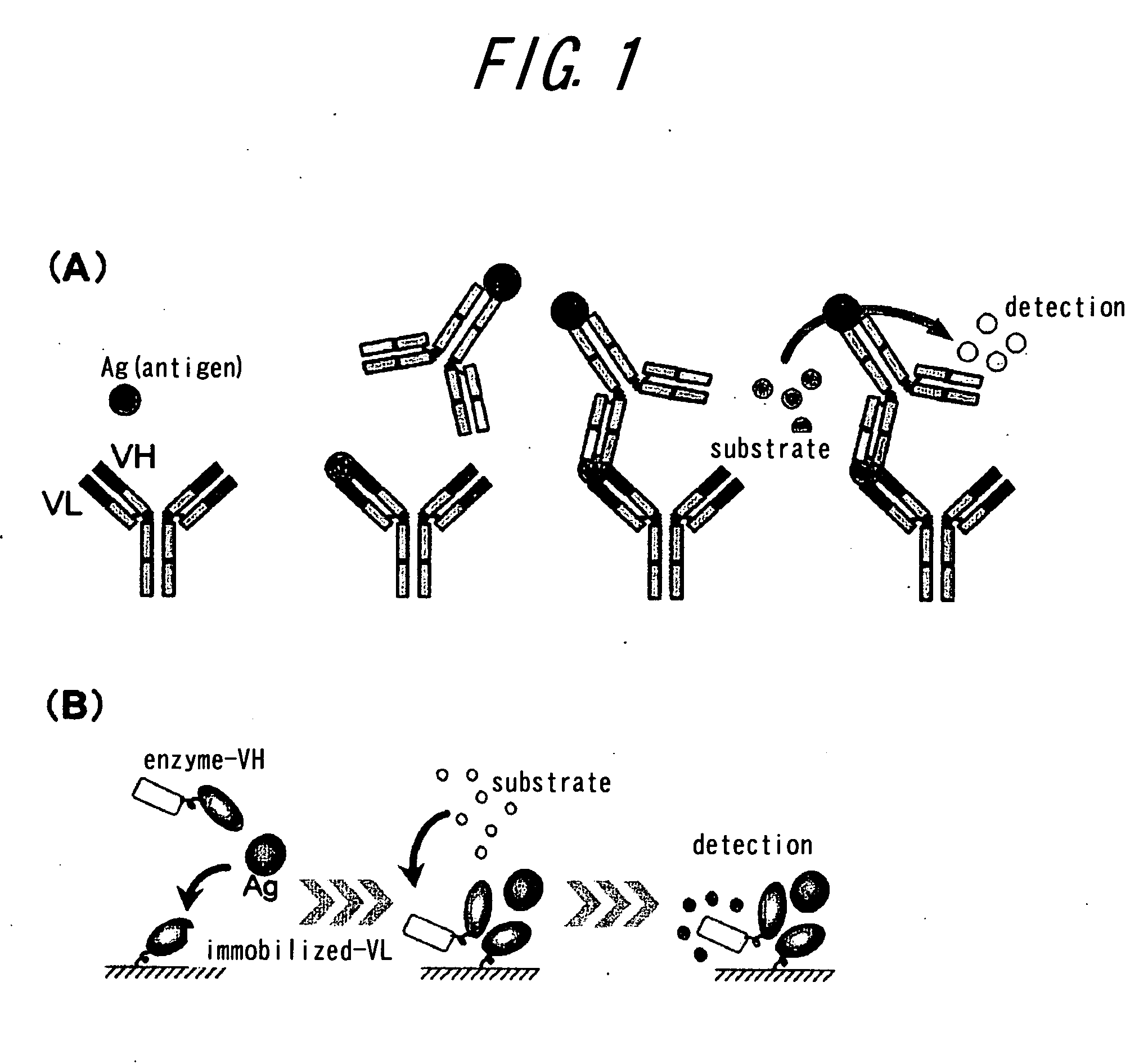
A novel method for determining interaction between VH fragment and VL fragment of the variable region of an antibody is provided by the present invention. The method according to this invention can be widely used for detection of protein interactions. If a phagemid vector containing an amber codon is used for transformation of an amber suppressor strain of E. coli according to the method of the invention to produce phages, both of the VH fragment and the VL fragment will be displayed on the phage particles. In contrast, if the same vector is used to transformation of an amber non-suppressing strain of E. coli to produce phages, for the presence of the amber codon, only the VH fragment will be displayed on the phage particles, while the VL fragment will be secreted into the culture medium by the E. coli. Thus, display switch occurs. The interaction between the VH fragment and the VL fragment can be determined, by immobilizing the VL fragment secreted into the culture medium on a solid phase and quantifying binding between the VH fragment displayed by phages and the VL fragment.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Method for recognizing protein network compound based on semantic density
InactiveCN104992078AReduce time complexityShort timeSpecial data processing applicationsData setGene ontology
The invention discloses a method for recognizing a protein network compound based on a semantic density, which is specifically implemented at the steps that all the protein properties in a network data set are searched in a gene ontology base GO as for a protein-protein interaction network data set without a weight; based on searching results, similarity of connected proteins in the network data set is calculated by a semantic similarity calculation method based on gene ontology; according to obtained similarity results, the given protein-protein interaction network data set is converted into an undirected network data set with a weight, wherein nodes represent the proteins, borders stand for interactions among the proteins, and the similarity among the proteins is the weight of the border; and the protein compound can be recognized from a protein-protein interaction network, wherein recognition accuracy is high and time complexity is low.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Quantitative alkaline-phosphatase precipitation reagent and methods for visualization of protein microarrays
InactiveUS20050124017A1Rapid and economical for visualizationHigh sensitivityMonoazo dyesBiological testingDigital analysisTARP Protein
A system and method are disclosed for the rapid, reproducible and inexpensive visualization, imaging and digital analysis of molecular interactions between ligands and proteins immobilized on an addressable two-dimensional microarray.
Owner:MIRAGENE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com