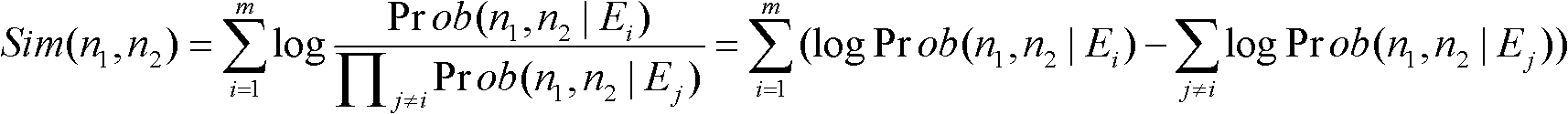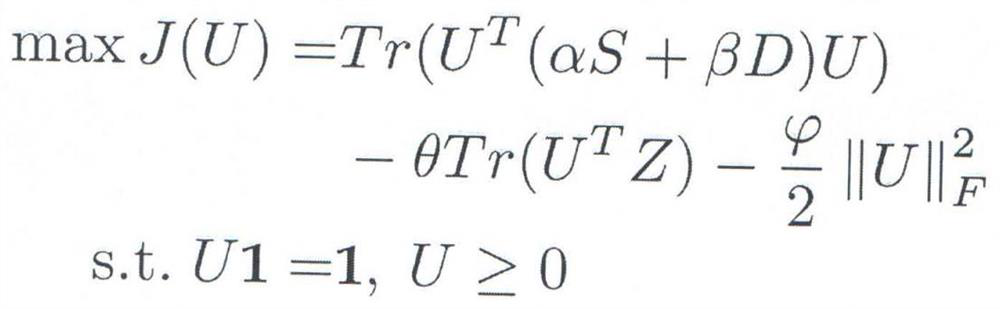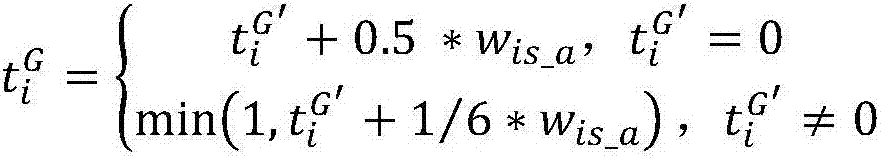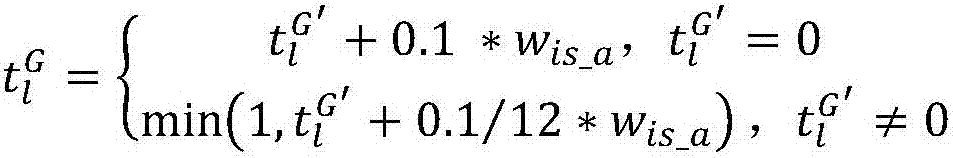Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
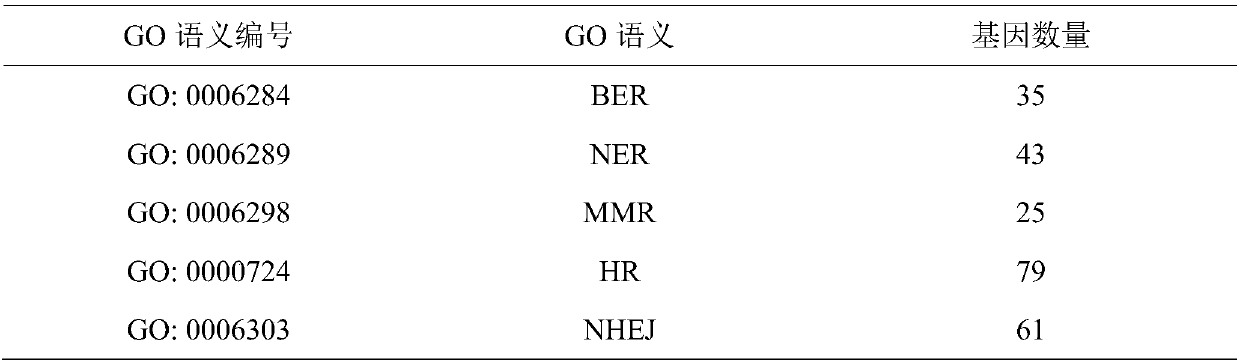
47 results about "Gene ontology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
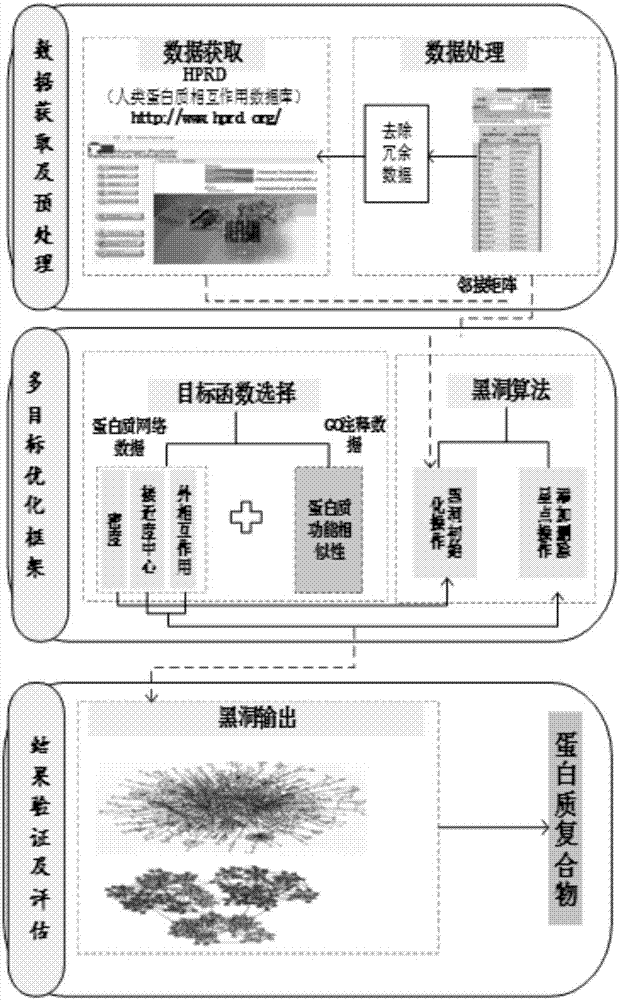
Protein complex recognizing method based on multi-source data fusion and multi-target optimization
InactiveCN108009403AImprove accuracyRecognition speed is fastSpecial data processing applicationsComplex network analysisAlgorithm
The invention discloses a protein complex recognizing method based on multi-source data fusion and multi-target optimization, comprising: preprocessing protein interaction network data to obtain adjacent matrixes; primarily clustering protein complexes to obtain an initial protein complex module; further optimizing the initial protein complex module, fusing topological structural features of the protein interaction network data and functional similar features of GO (gene ontology) annotation data during optimizing, and performing optimizing operation in conjunction with an adaptive multi-target blackhole optimization algorithm to obtain a more precise protein complex module; postprocessing to obtain a final optimal protein complex. The method of the invention has the advantages that protein complex recognition speed and precision are increased, the method is applicable to protein interaction networks and extensible to the analysis of other complex community networks, and the method isvery practical in complex network analysis.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
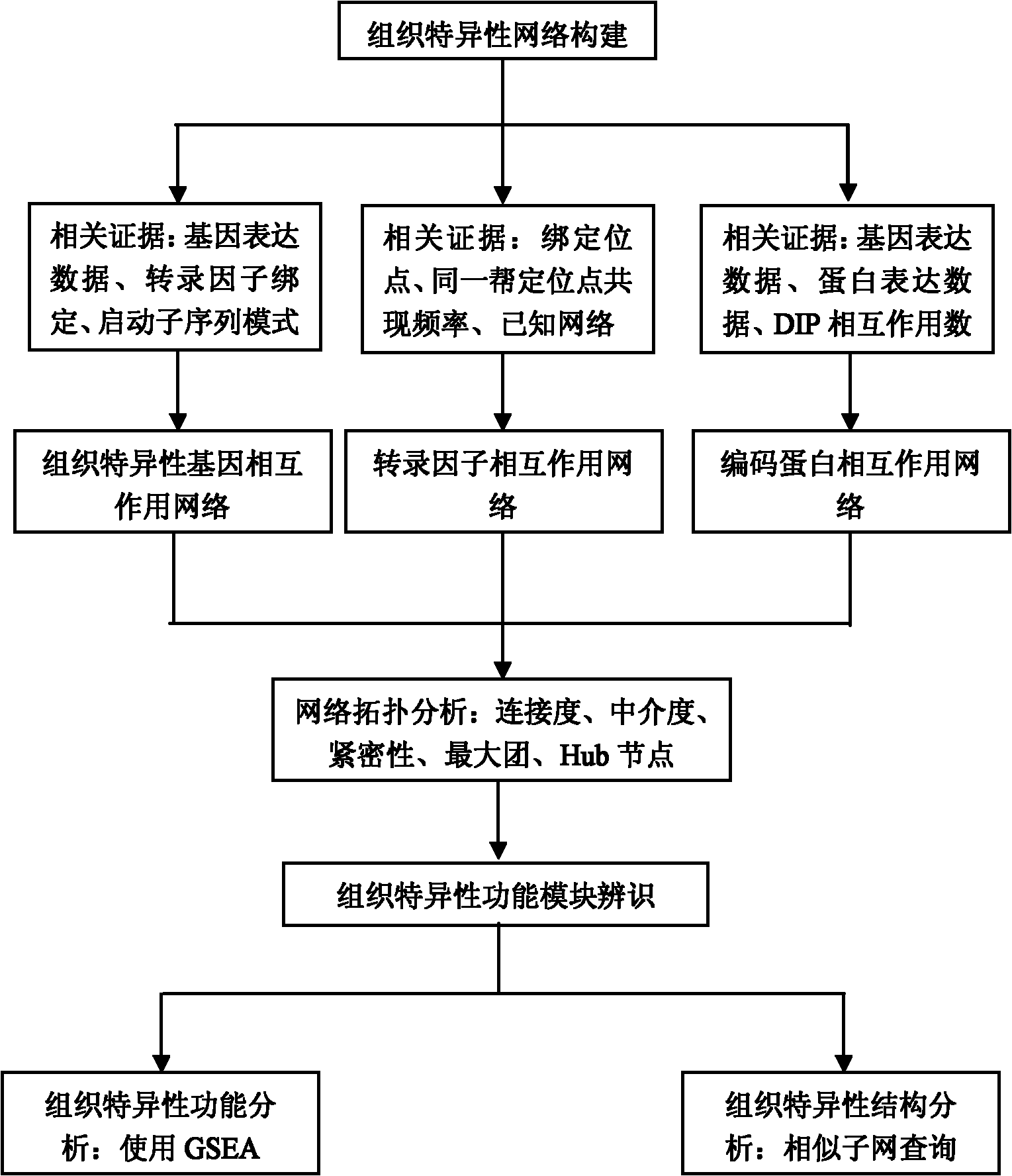
Method for constructing and analyzing tissue-specific interaction topology network
The invention discloses a method for constructing and analyzing a tissue-specific interaction topology network. The method comprises the following steps of: measuring similarity of integrated interaction network nodes; constructing a tissue-specific gene interaction network, a tissue-specific transcription factor interaction network and a tissue-specific encoded protein interaction network by a construction module of the tissue-specific interaction network; counting connection degree of each node in the network, counting betweenness of each node in the network, calculating closeness of each node in the network, calculating max clique in the interaction network and counting a Hub node in the interaction network by a topology analysis module of the interaction network; and acquiring related tissue-specific knowledge from a gene ontology database and a KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) biological field knowledge base by an identification module of the tissue-specific functional module. The invention provides an ideal method for constructing the interaction network from genetic information; and the method is a more ideal analysis tool for researching a tissue-specific intrinsic mechanism.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Protein biological network motif identification method integrating topological attributes and functions
ActiveCN103514381AAccurate identificationEasy to integrateSpecial data processing applicationsGene ontologyLarge scale data
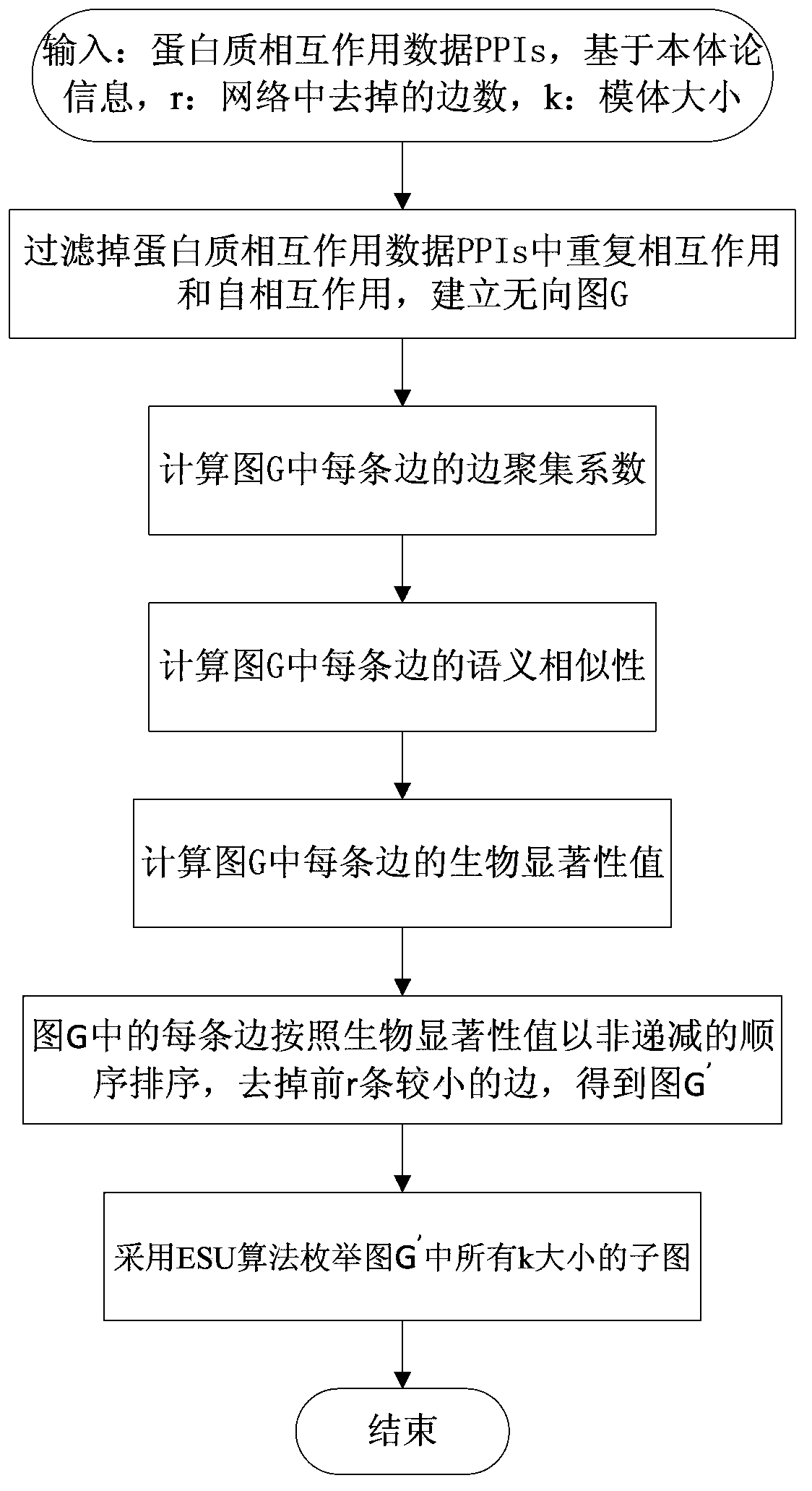
The invention discloses a protein biological network motif identification method integrating topological attributes and functions. The protein biological network motif identification method integrating the topological attributes and functions (Ecc-GOSS) is based on the biology significance of a motif, and comprehensively evaluates the biological significance of protein-protein interaction by integrating edge clustering coefficients and semantic similarity of GO phrases. The protein biological network motif identification method integrating the topological attributes and functions is easy to implement, a great amount of network motifs with biological significance can be identified accurately according to PPI information and gene ontology information, and the protein biological network motif identification method integrating the topological attributes and functions has good robustness on high-percentage false positive prevailing among the large-scale data of the protein-protein interaction.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for recognizing protein network compound based on semantic density
InactiveCN104992078AReduce time complexityShort timeSpecial data processing applicationsData setGene ontology
The invention discloses a method for recognizing a protein network compound based on a semantic density, which is specifically implemented at the steps that all the protein properties in a network data set are searched in a gene ontology base GO as for a protein-protein interaction network data set without a weight; based on searching results, similarity of connected proteins in the network data set is calculated by a semantic similarity calculation method based on gene ontology; according to obtained similarity results, the given protein-protein interaction network data set is converted into an undirected network data set with a weight, wherein nodes represent the proteins, borders stand for interactions among the proteins, and the similarity among the proteins is the weight of the border; and the protein compound can be recognized from a protein-protein interaction network, wherein recognition accuracy is high and time complexity is low.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for analyzing proteins contributing to autoimmune diseases, and method for testing for said diseases
ActiveUS20130273579A1High sensitivityImprove efficiencyDisease diagnosisBiological testingImmunologic disordersDisease
Provided are a detection method for a myriad of proteins involved in an autoimmune disease with high sensitivity and high efficiency, and an analysis method for data resulting from the detection method. In order to construct the detection method and analysis method, there is provided means for comprehensively analyzing the proteins involved in an autoimmune disease by bringing a mammal-derived protein expressed in a cell-free protein synthesis system into contact with a sample derived from a patient with an autoimmune disease to detect autoantibody production, and subjecting the detected data to statistical analysis processing, and further, gene ontology analysis and / or pathway analysis.
Owner:PUBLIC UNIV CORP YOKOHAMA CITY UNIV
Prediction method for protein subcellular site formed based on improved-period pseudo amino acid
InactiveCN102819693AProtein data equalizationLess predictable offsetSpecial data processing applicationsProtein FeatureProtein
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
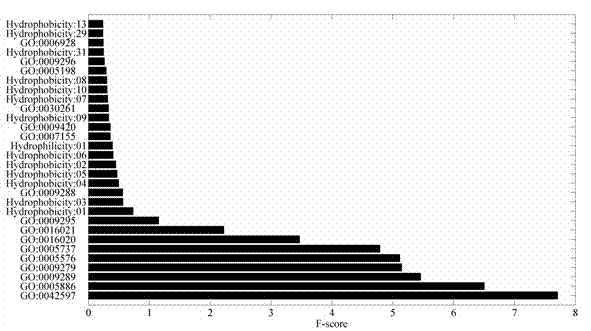
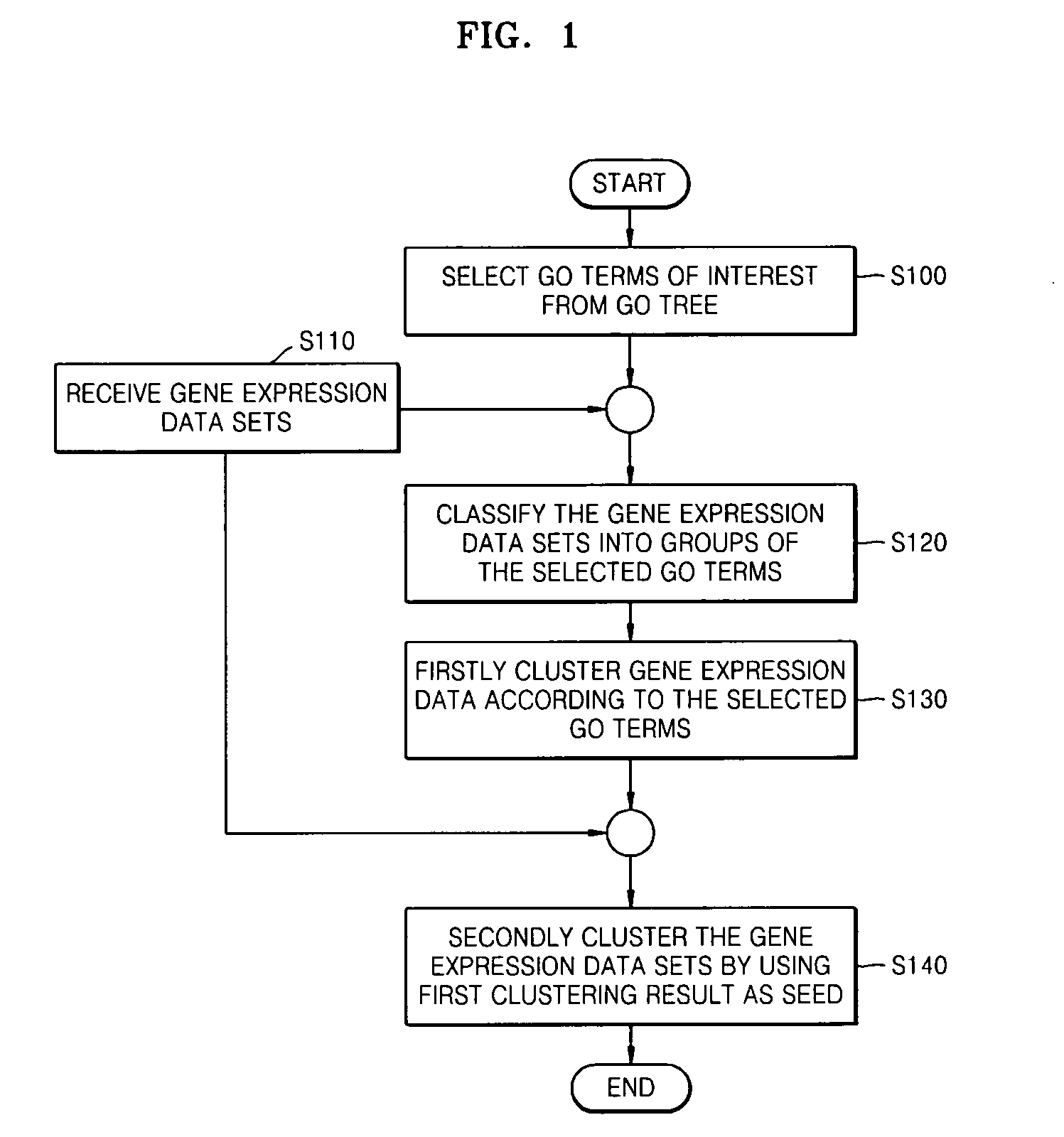
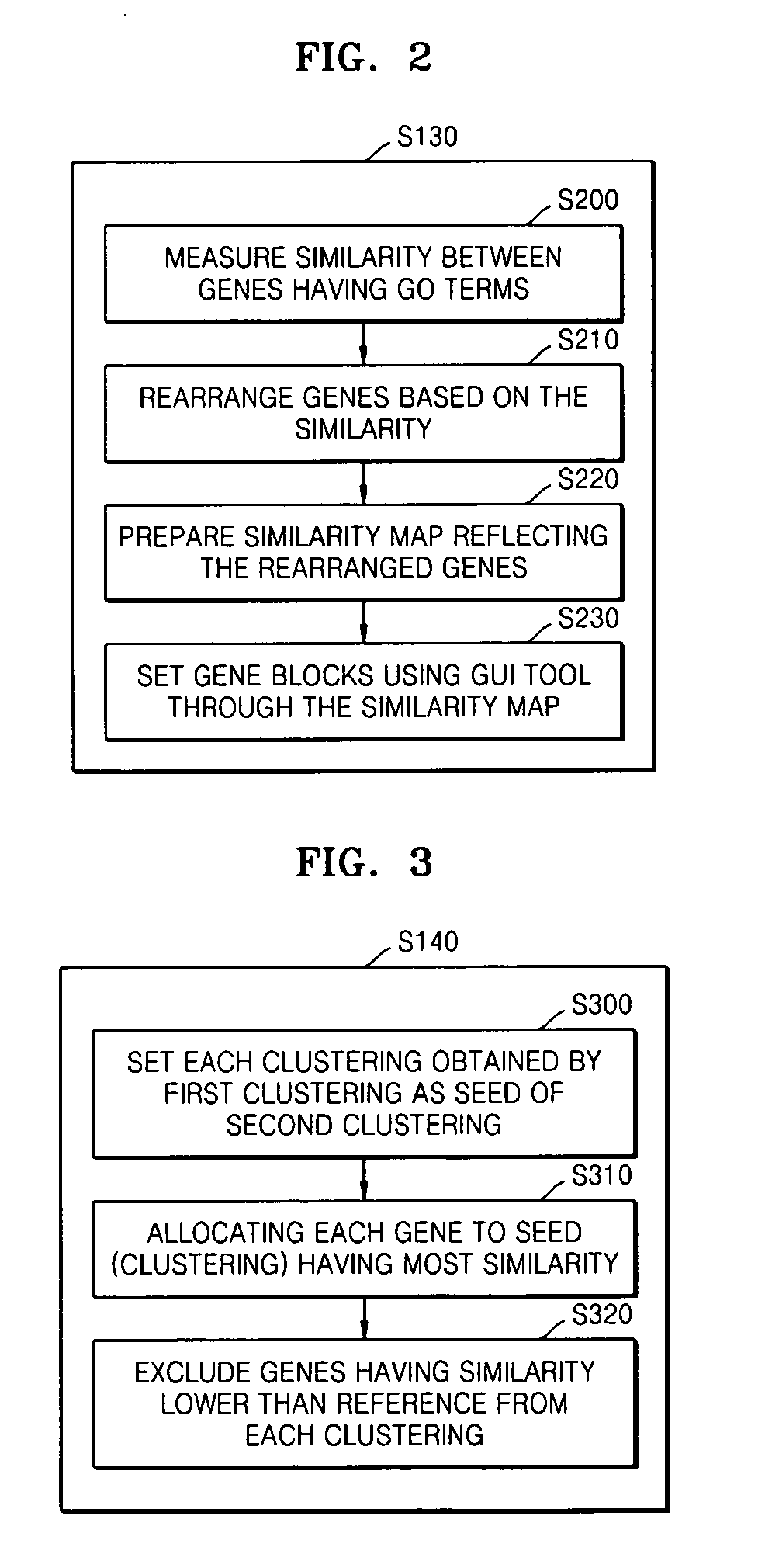
Method and apparatus for clustering gene expression profiles by using gene ontology
InactiveUS20090112480A1Enhancing biological meaningImprove reliabilityBiostatisticsBiological testingData setGene ontology
Provided are a method and apparatus for clustering gene expression profiles by using the Gene Ontology (GO). The method includes: selecting one or more GO terms from a GO tree; receiving gene expression data sets; classifying the gene expression data sets into groups according to the GO terms; firstly clustering gene expression data belonging to each of the groups based on a similarity of the gene expression data; and secondly clustering the gene expression data sets by using the result of the first clustering as a seed.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method for analyzing anti-glandular cystitis action mechanism of pachymaran based on network pharmacology
PendingCN112201365AReduce R&D costsImprove screening efficiencyDrug referencesSystems biologyPharmacometricsNetwork pharmacology
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicine, discloses a method for analyzing an anti-glandular cystitis action mechanism of pachymaran based on network pharmacology, and reports detailed targets and specific pharmacological mechanisms of pachymaran for preventing and treating glandular cystitis for the first time. The method comprises the following main points: obtaining a pachymaran pharmacological target and a glandular cystitis pathogen target through online database analysis of TCMSP, DisGeNET and the like; taking an intersection of the pachymaran and the glandular cystitis target to obtain a drug disease intersection target gene target, and constructing a related protein interaction network to screen a core target; further performing gene ontology GO biological process and KEGGpathway enrichment analysis on the core target by utilizing the R language related packet; and finally, constructing a drug target gene ontology functional pathway disease visualization diagram for deep analysis of a treatment mechanism. The method provided by the invention provides a new idea for explaining a research mechanism of pachymaran for exerting glandular cystitis resistance, and also provides an early-stage research basis for clinical application of pachymaran in glandular cystitis.
Owner:NANNING SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL
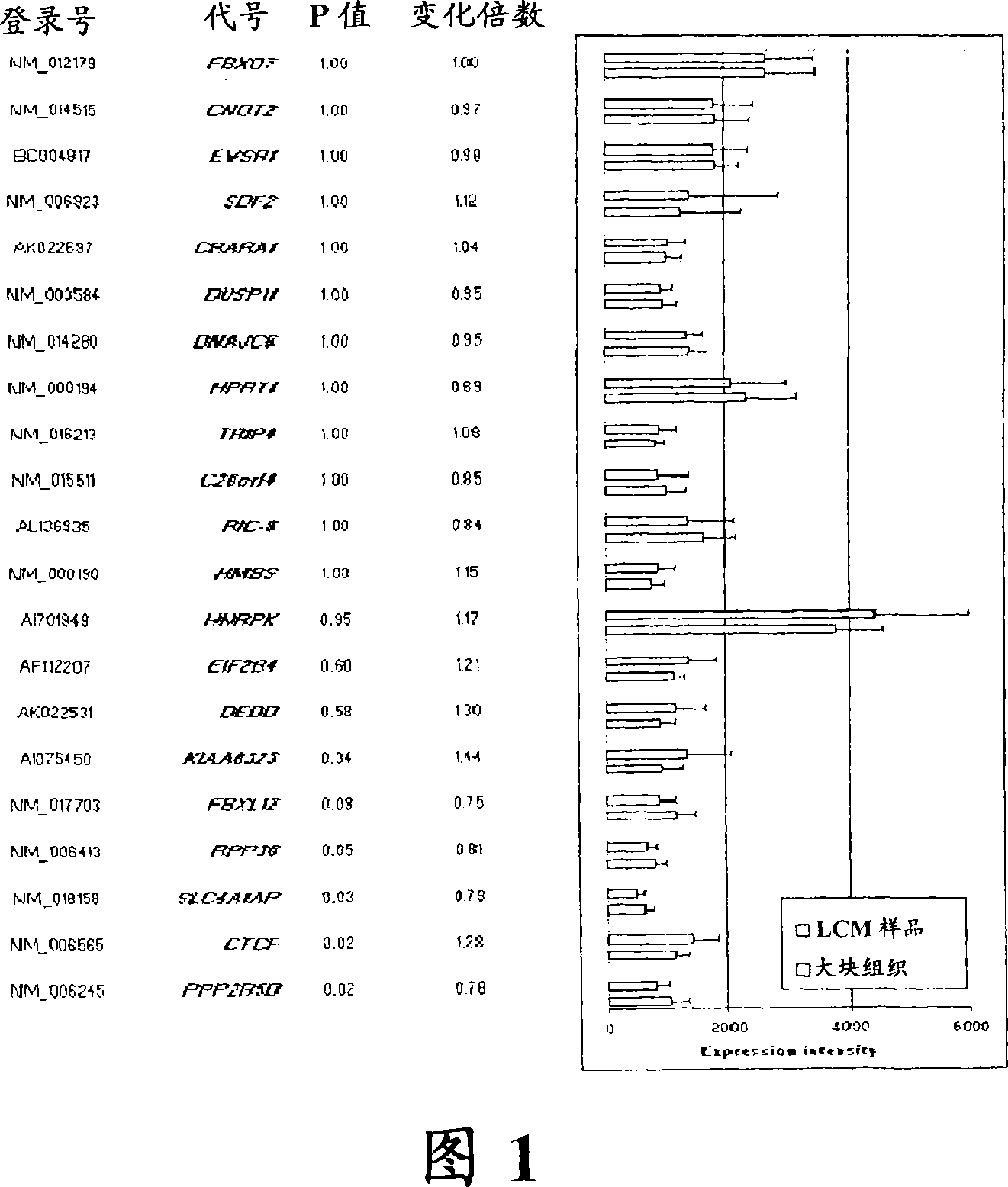
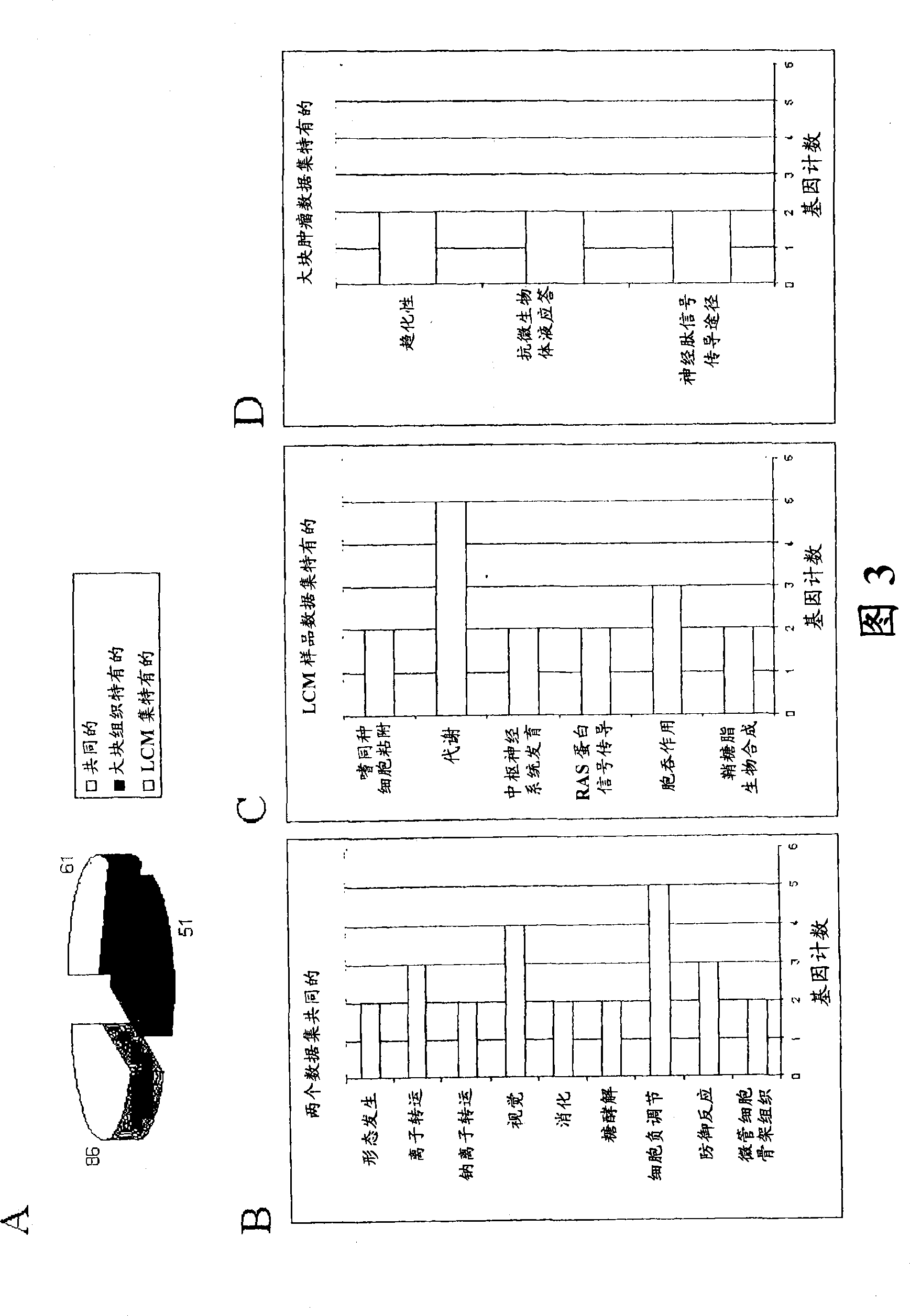
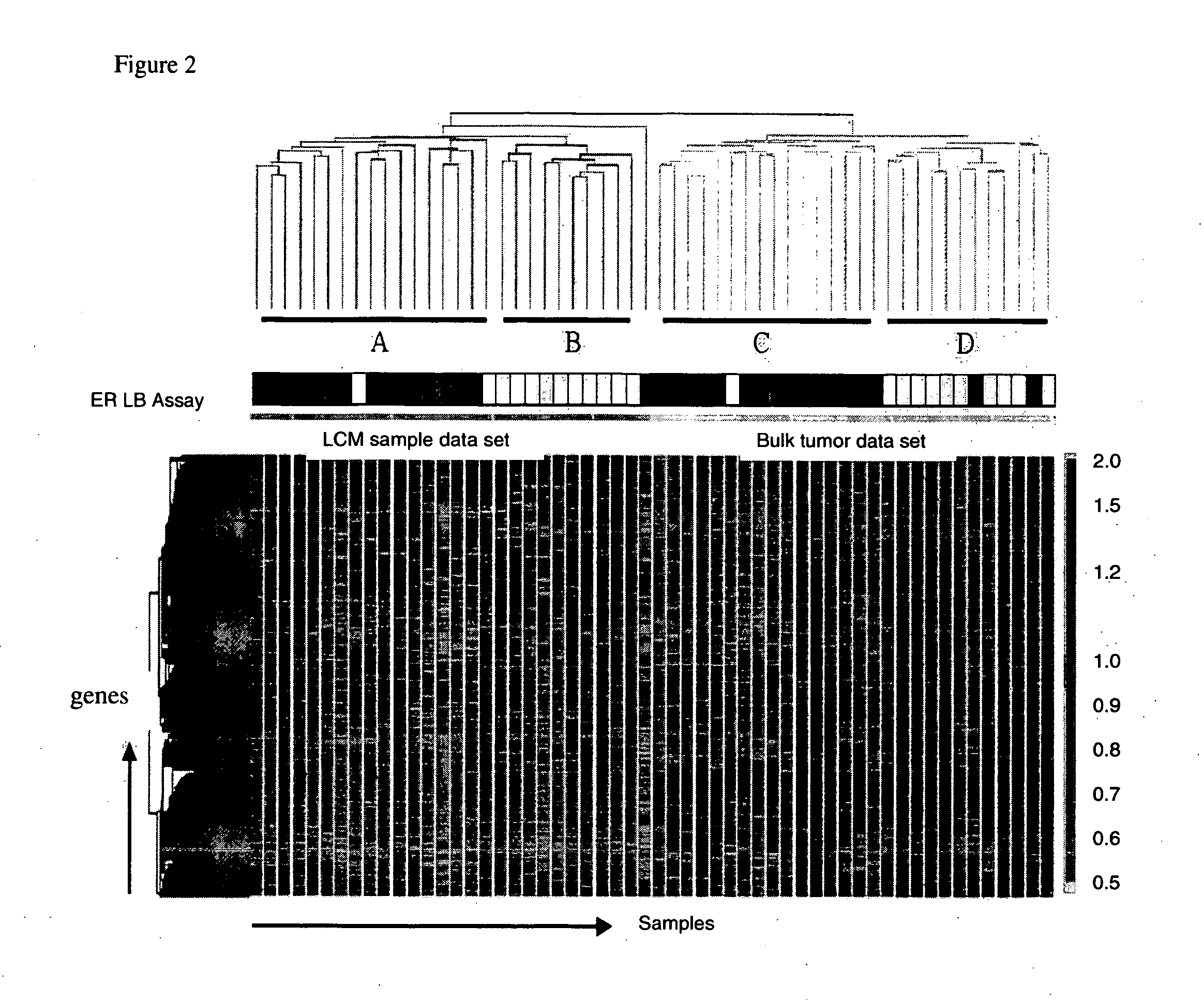
Laser microdissection and microarray analysis of breast tumors reveal estrogen receptor related genes and pathways
InactiveCN101965190APeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementPathway analysisLaser micro dissection
About 70% to 80% of breast cancers express estrogen receptor-a (ERa), and estrogens play important roles in the development and growth of hormone-dependent tumors. Together with lymph node metastasis, tumor size and histological grade, ER status is considered one of the prognostic factors in breast cancer, and an indicator for hormonal treatment. 147 genes and 112 genes with significant P- value and having significant differential expression between ER+ and ER- tumors were identified from the LCM data set and bulk tissue data set, respectively. 61 genes were found to be common in both data sets, while 85 genes were unique to the LCM data set and 51 genes were present only in the bulk tumor data set. Pathway analysis with the 85 genes using Gene Ontology suggested that genes involved in endocytosis, ceramide generation, Ras / ERK / Ark cascade, and JAT- STAT pathway may play roles related to ER. The gene profiling with LCM-captured tumpr cells provides a unique approach to characterize and study epithelial tumor cells and to gain an insight into signaling pathways associated with ER.
Owner:VERIDEX LCC
Network modeling for drug toxicity prediction
InactiveUS20160306948A1Chemical property predictionDrug and medicationsNetwork modelDrug side effect
A computational systems pharmacology framework consisting of statistical modeling and machine learning based on comprehensive integration of systems biology data, including drug target data, protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks, and gene ontology (GO) annotations, and reported drug side effects, can predict drug toxicity or drug adverse reactions (ADRs). Biomolecular network and gene annotation information can significantly improve the predictive accuracy of ADR of drugs under development. The use of PPI networks can increase prediction specificity, and the use of GO annotations can increase prediction sensitivity.
Owner:MEDEOLINX
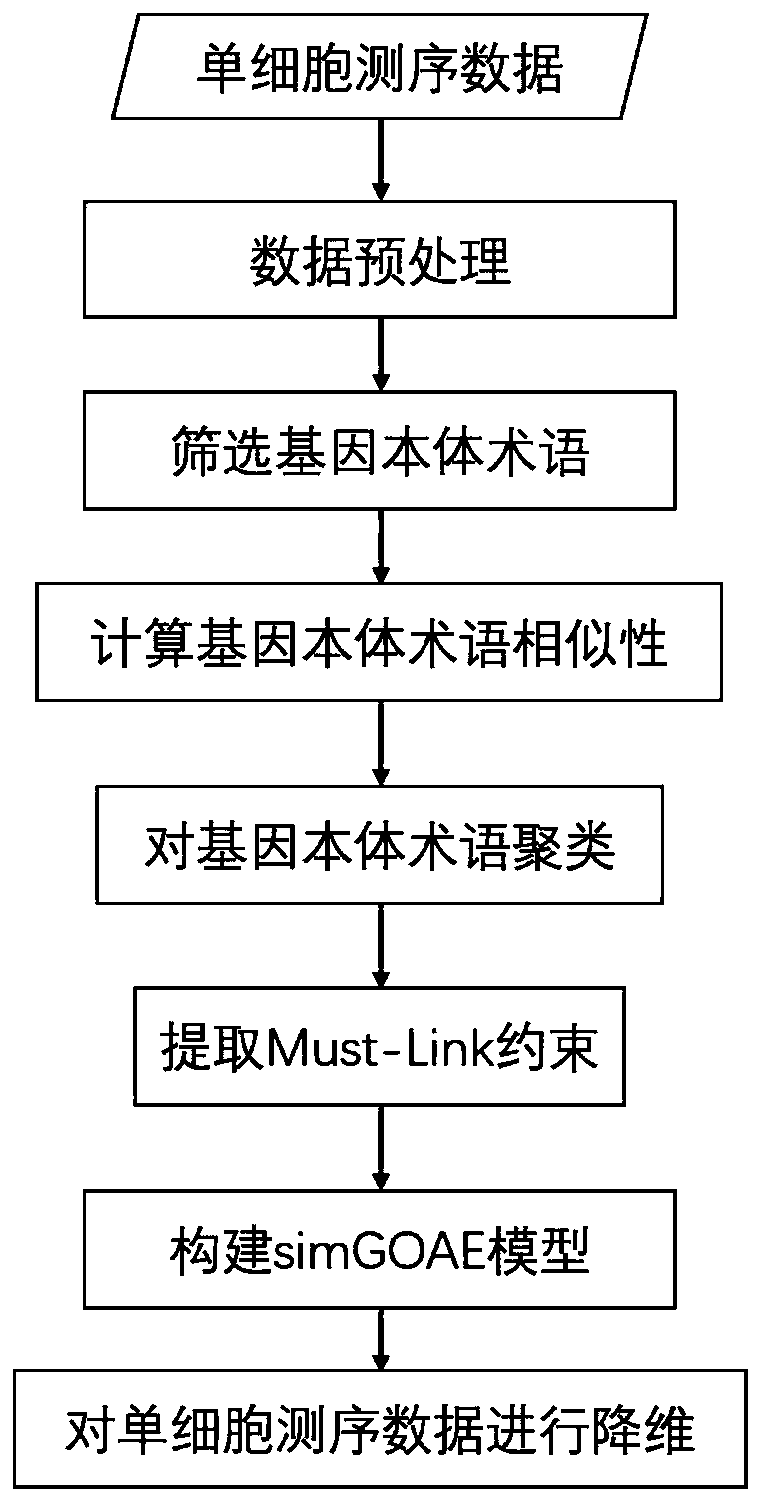
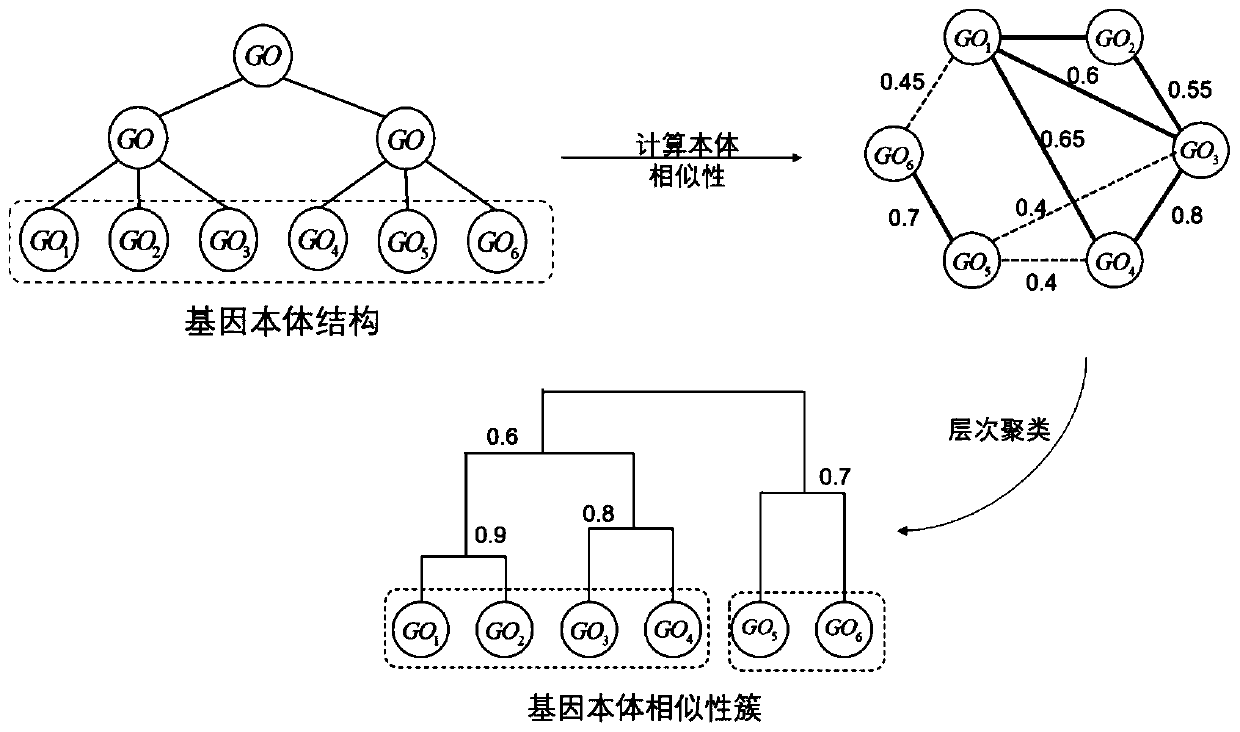
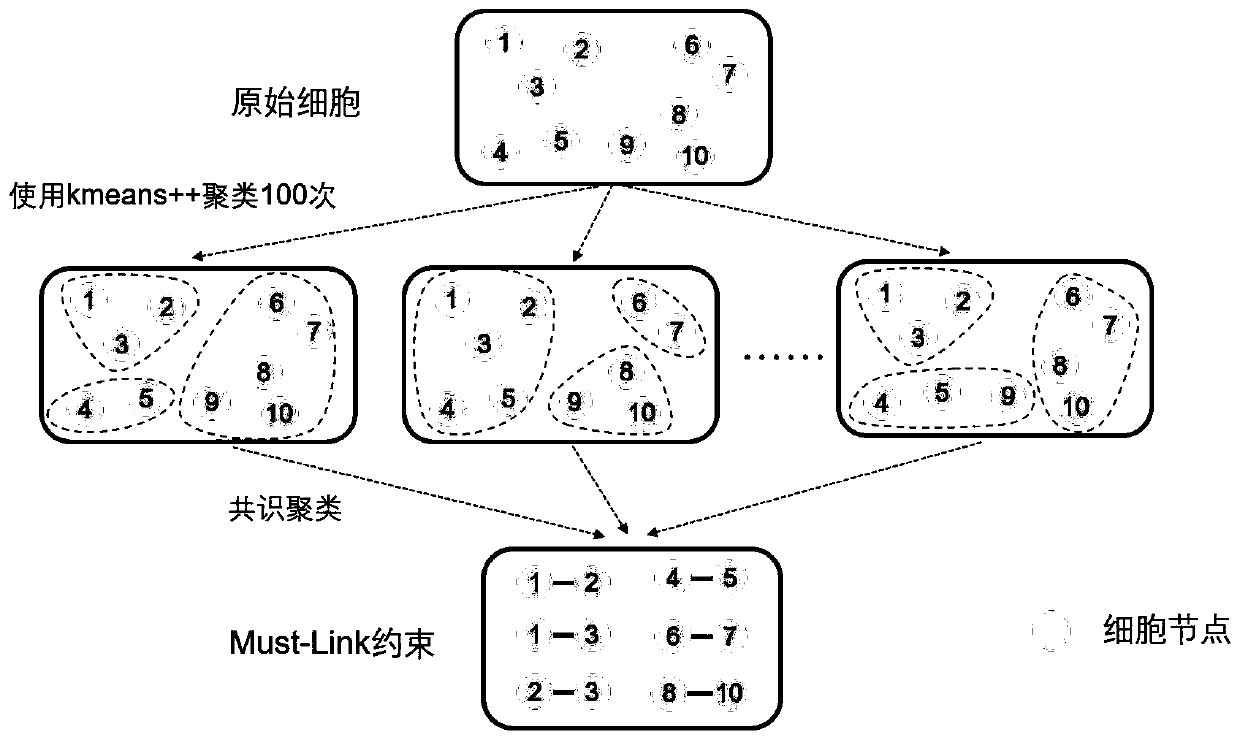
Single-cell sequencing data dimension reduction method fusing gene ontology and neural network
ActiveCN111564183AReduce training parametersAccelerated trainingBiostatisticsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setCell layer
The invention provides a single-cell sequencing data dimension reduction method fusing gene ontology and a neural network. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, extracting gene ontology terms as deep biological information priori knowledge; secondly, extracting Mut-Link constraints among cells as priori knowledge on a cell level; then, combining the two kinds of priori knowledge withan auto-encoder model, and proposing a simGOAE model; and finally, carrying out training dimension reduction on single-cell sequencing data by using the simGOAE model. The simGOAE model provided by the invention not only can adapt to the training of a large sample data set, but also can better mine the biological information of the cells and realize a better single-cell sequencing data dimension reduction effect.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
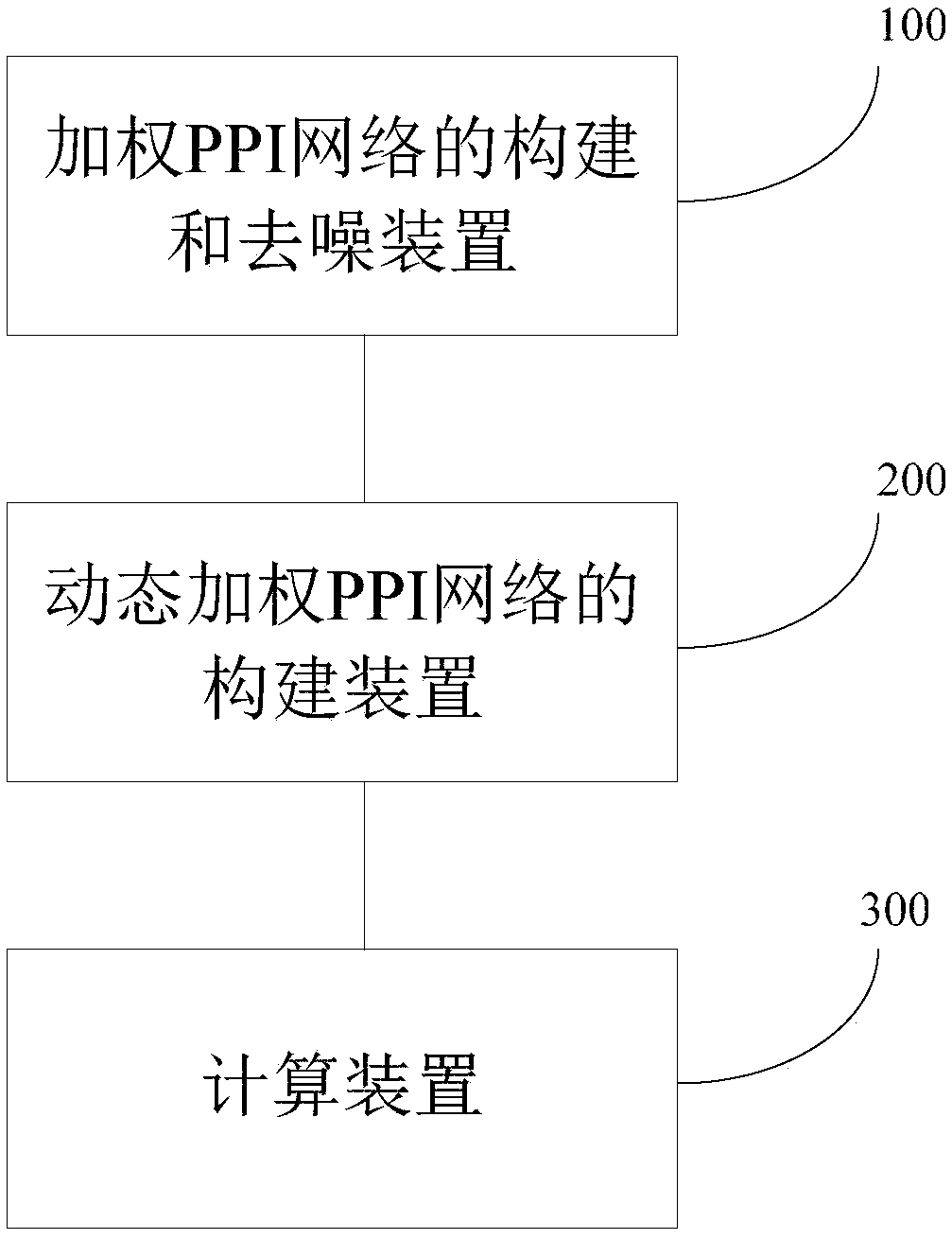
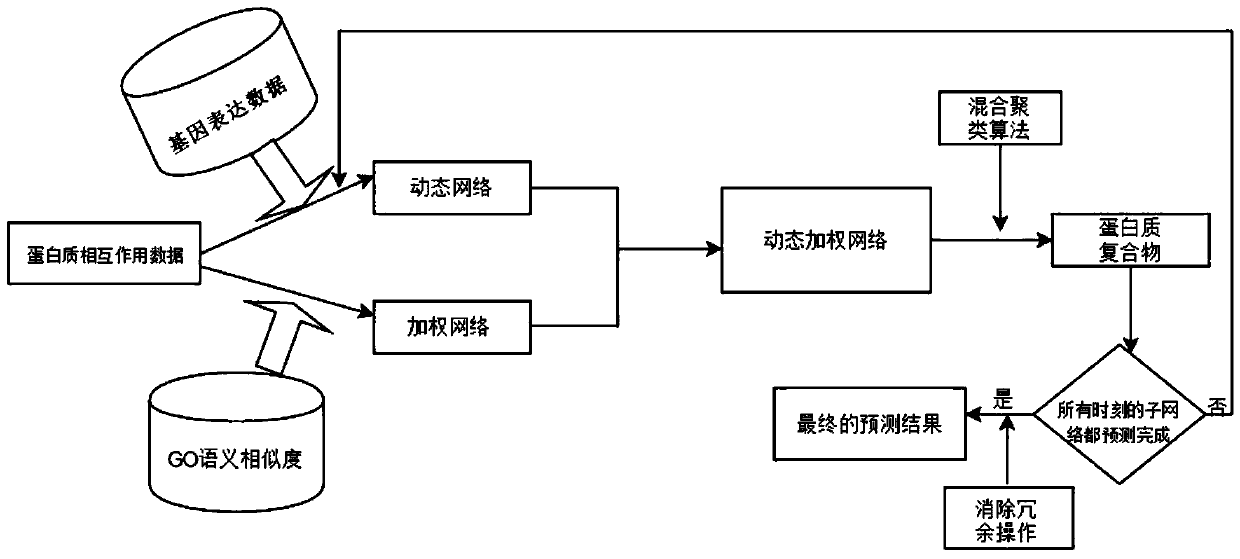
Method for predicting protein compound on the basis of sample data
The invention relates to a method for predicting a protein compound on the basis of sample data. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) on the basis of the sample data, constructing a weighted PPI (Protein-Protein Interaction) network, and carrying out denoising processing on the weighted PPI networok, wherein the denoising processing is that the semantic similarity of gene ontology istaken as the weight of the PPI network for carrying out weighting; (2) on the basis of the weighted PPI network subjected to the denoising processing to construct a dynamic weighted PPI network; and(3) utilizing a hybrid clustering algorithm to predict the protein compound. By use of the method, through the introduction of a GO semantic similarity, the noise of PPI data can be effectively lowered, and in addition, the method has a biological meaning. Meanwhile, real protein activities are reflected, and the dynamic nature of the PPI network is embodied. In addition, the defect of overfittingor underfitting in a traditional clustering algorithm is eliminated, the accuracy of the clustering algorithm is improved, and therefore, the accuracy of a protein compound prediction result is effectively improved.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Calculation method for predicting key proteins by combining multiple data features
ActiveCN109166604ASolve the costResolution cycleProteomicsGenomicsData informationExpression Feature
The invention discloses a calculation method for predicting key proteins by combining multiple data features. According to the method, the features such as aggregation features, co-expression features, functional similarity and positional consistency of key proteins are analyzed; and the edge clustering coefficient of a protein interaction network, the Pearson correlation coefficients of gene expression values, the semantic similarity indexes of gene ontology terms and protein subcellular localization statistical features are effectively integrated. The method of the invention is simple and easy to use; four kinds of data, such as protein interaction relationship data, gene expression spectrum data, gene ontology term information data and protein subcellular localization data information are inputted; and test results indicate that the method of the invention can significantly improve the prediction accuracy and efficiency of the key proteins in the protein interaction network comparedwith an existing method.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Key protein identification method in network based on dynamic weighting interaction
PendingCN109686402AOvercome incompletenessImprove accuracyBiostatisticsProteomicsCorrelation coefficientGene ontology
The invention discloses a key protein identification method use principle in a network based on dynamic weighting interaction. A key protein identification method comprises the steps of calculating aprotein activity time point and a protein activity probability, constructing a dynamic PPI network, then calculating a protein interaction weight according to the protein activity probability, and constructing a dynamic weighted PPI network; based on the established dynamic weighted PPI network, according to the topological characteristic and biological attribute of the protein network, calculating an edge clustering coefficient, a gene body similarity and a Pearson correlation coefficient between the interaction protein pairs; afterwards, obtaining an importance score, and performing arrangement according to the score value from largest to lowest, and outputting k proteins which correspond with the scores as a final result. The method according to the invention improves key protein identification efficiency and expands application range and practicability of the technique in a bioinformation field.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Data processing method for chromatin immunoprecipitation high-throughput sequencing
InactiveCN103853936AImprove work efficiencyReflect the distribution characteristicsSpecial data processing applicationsText fileThroughput
The invention relates to a data processing method for chromatin immunoprecipitation high-throughput sequencing, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. The method comprises the following steps: firstly eliminating low quality sequence data in an initial sequence file, then contrasting the filtered sequence data in a reference genome, counting signal peak amount and density distribution in different areas according to the classification of the reference genome, and determining neighboring genes of each signal peak for gene body function enrichment analysis, and finally generating a gene body function enrichment result text file and a corresponding graphical representation file. The method provides a high-efficiency and high-throughput data analysis process, so that each sequencing process is effectively integrated so as to help scientific research personnel to efficiently complete earlier-stage sequence quality control and sequence filtering of high-throughput data and reflect the advantages and disadvantages of a chromatin immunoprecipitation high-throughput sequencing experiment based on data statistics of contrasted sequence, and the distribution characteristics of the sequence on chromosome can be reflected, thus the work efficiency of sequencing is greatly promoted.
Owner:FENGHE SHANGHAI INFORMATION TECH
Novel protein sequence representation method based on gene ontology information
ActiveCN106845149AImprove prediction success rateReduce dimensionalityProteomicsGenomicsGene ontologyAntibacterial peptide
The invention relates to a novel protein sequence representation method based on gene ontology information, comprising: using BLAST program to search Swiss-Prot database for all similar protein sequences of protein sequence P, inputting all proteins in a training dataset into GO (gene ontology) database, and searching for GO information of each protein; searching the gene ontology database for targeting gene ontology information of P protein; defining the P protein as discrete vectors of M elements according to M labels that a prediction problem has. The protein GO information in a sequence set is fused into novel P protein vector description, and the dimensionality of the GO method is reduced greatly; by applying the method to protein subcellular multi-label positioning prediction and antibacterial peptide functional multi-label prediction, it is possible to significantly increase the prediction success rate of a related predictor; the novel protein sequence representation method based on gene ontology information has a promising application prospect.
Owner:上海司默迪医学信息科技有限公司
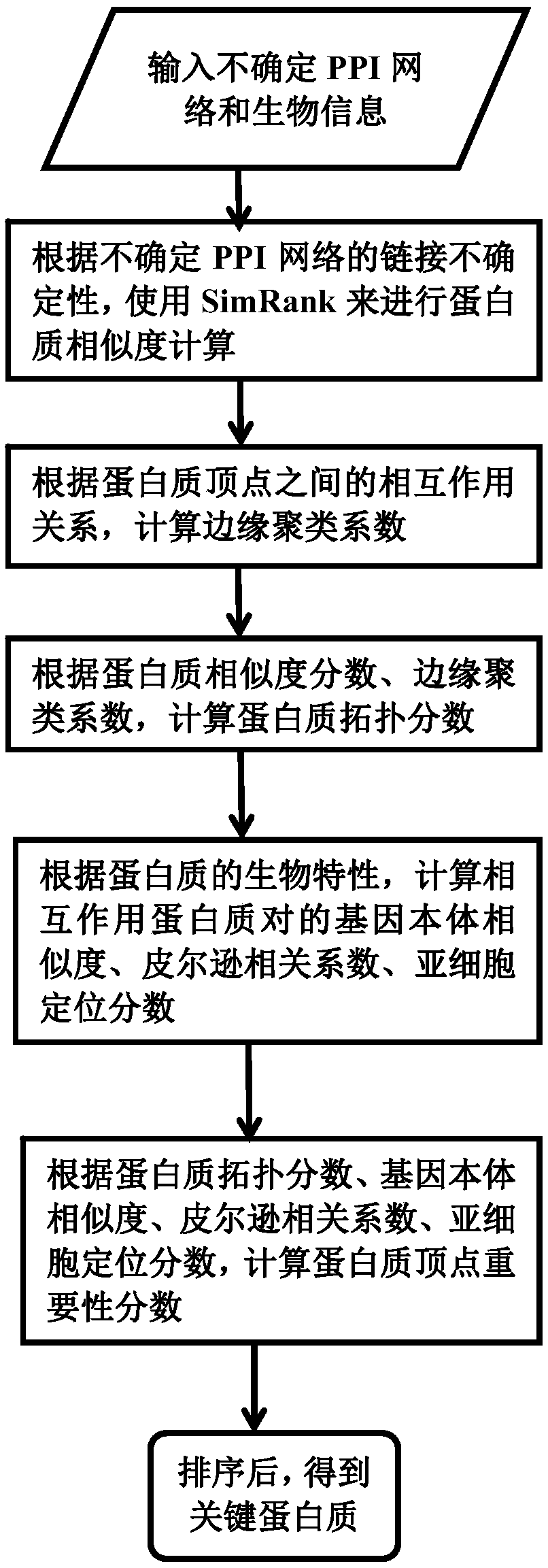
A key protein identification method in an uncertain protein interaction network
PendingCN109686403AImprove accuracyAvoid negative effectsCharacter and pattern recognitionProteomicsProtein recognitionProtein identification
SimRank is used for carrying out protein similarity calculation based on a key protein identification method in an uncertain protein interaction network. A SimRank calculation problem in an uncertainnetwork is converted into SimRank calculation in a deterministic network; and then, considering the topological characteristics of the protein interaction network and the biological characteristics ofthe protein, and calculating an edge clustering coefficient, gene ontology similarity, a Pearson's correlation coefficient and a subcellular localization score to obtain an importance score. And finally, ranking the scores from large to small, and outputting the first k proteins corresponding to the scores as final results. On the basis of an uncertain interaction network, the accuracy of key protein recognition is improved by fusing biological attributes and topological characteristics, meanwhile, the prediction result is more accurate, the prediction efficiency is improved, the applicationrange of the technology in the field of biological information is widened, and the practicability of the technology in the field of biological information is improved.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Method for analyzing iTRAQ (isobaric Tags for Relative and Absolute Quantitation) data
InactiveCN102321733AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingPathway analysisAnalysis data
The invention designs a method for analyzing iTRAQ (isobaric Tags for Relative and Absolute Quantitation) data aiming at the characteristics of iTRAQ protein quantitative data analysis. The method has a main flow which comprises the following steps of: 1, screening differential protein: screening the initial iTRAQ data in groups to acquire a difference result; 2, performing GO (Gene Ontology) analysis: performing query mapping on a GO database to acquire completer gene function information so as to display a directed acyclic graph; 3, performing Pathway analysis which is similar to GO analysis: performing comparative query with a KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) database to construct an interaction pathway between genes; and step 4, performing Gene network analysis: integrating three different interaction relations to obtain a gene interaction network graph.
Owner:SHANGHAI CLUSTER BIOTECH
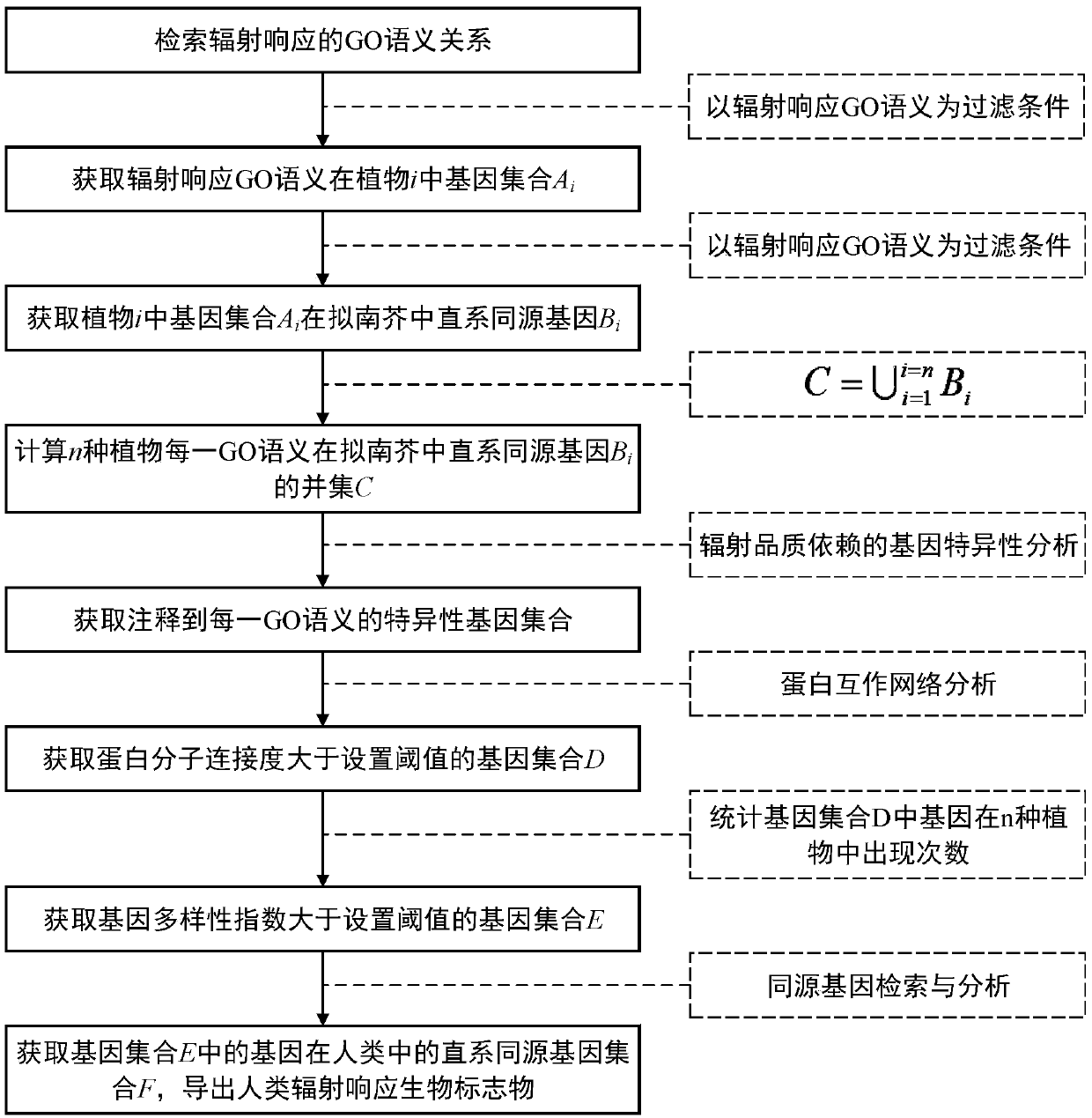
Method for identifying human radiation response biomarkers based on various plant genomes
ActiveCN109584955APromote interdisciplinary researchExtensive referenceBiostatisticsProteomicsOrthologous GeneProtein C
The invention discloses a method for identifying human radiation response biomarkers based on various plant genomes. The method comprises the steps that a gene ontology (GO) semantic relationship of aradiation response is retrieved, and annotated genes in various plants and orthologous genes in arabidopsis are obtained; a union set of the orthologous genes in the arabidopsis and a radiation quality specific gene set for each GO semantics of various plants are calculated; by means of protein interaction network analysis, a gene set with protein connectivity greater than a set threshold value is obtained; the occurrence number of genes in the various plants is counted, and a gene set with the gene diversity greater than the set threshold value is obtained; finally, by means of gene homologyanalysis, the orthologous gene set of the genes in human is obtained, and the human radiation response biomarkers are guided. Accordingly, the problem that new human radiation response biomarkers need to be screened by means of plant genomes. The method has the application prospects in the aspects of radiation dose estimation, radiation damage diagnosis and radiation health risk early warning.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Computation method for annotating semantic similarity by gene
InactiveCN101359349AHelpful for evaluationEasy constructionSpecial data processing applicationsGene ontologyGene Annotation
The invention provides a computation method of gene annotation semantic similarity. The method establishes correlation between the gene and the gene body node through the gene body correlation file provided by the gene body association; then the semantic similarity of the gene body node is firstly computed; the gene annotation semantic similarity is computed finally according to the semantic similarity of the gene body node. The computation method has the advantages of computing the gene annotation semantic similarity automatically and in large quantity.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
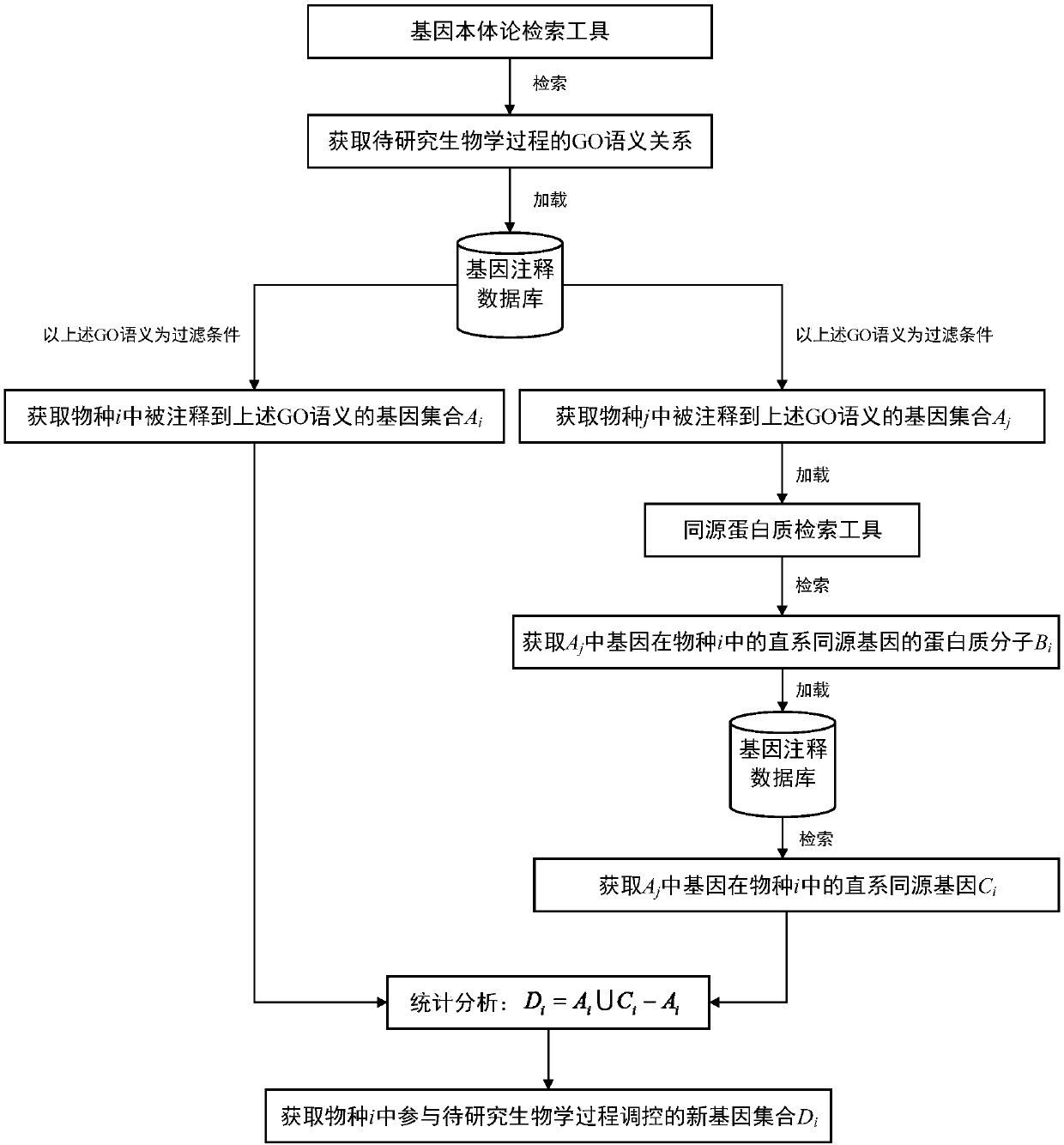
Method for screening regulation new gene participating in biological process
The invention discloses a method for screening a regulation new gene participating in the biological process. A biologic informatics method is used for searching gene ontology for a tool, and the semantic relation in the specific biological process is screened out; in a genome annotation database of different species, gene set information in different species annotated to the semantic is screenedout; homology analysis is performed on the gene set information of the specific species, an orthologous gene in the species to be researched is screened out; comparison and analysis are performed on the gene and the reference gene participating in the biologic process in the species to be researched, and the regulation new gene participating in the biologic process in the specific species is screened out. On the basis that the specific biologic process has the advantage of high conservative property between different species, a method for screening the regulating new gene participating in thebiologic process is built, the supporting effect is supplied for further reconstructing a systematic gene regulation network, and the method is of a great significance in early disease diagnosis, individual treatment and medicine development.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Laser microdissection and microarray analysis of breast tumors reveal estrogen receptor related genes and pathways
InactiveUS20080305959A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPathway analysisEstrogen receptor
About 70% to 80% of breast cancers express estrogen receptor-α (ERα), and estrogens play important roles in the development and growth of hormone-dependent tumors. Together with lymph node metastasis, tumor size and histological grade, ER status is considered one of the prognostic factors in breast cancer, and an indicator for hormonal treatment. 147 genes and 112 genes with significant P-value and having significant differential expression between ER+ and ER− tumors were identified from the LCM data set and bulk tissue data set, respectively. 61 genes were found to be common in both data sets, while 85 genes were unique to the LCM data set and 51 genes were present only in the bulk tumor data set. Pathway analysis with the 85 genes using Gene Ontology suggested that genes involved in endocytosis, ceramide generation, Ras / ERK / Ark cascade, and JAT-STAT pathway may play roles related to ER. The gene profiling with LCM-captured tumor cells provides a unique approach to characterize and study epithelial tumor cells and to gain an insight into signaling pathways associated with ER.
Owner:VERIDEX LCC
Method for identifying cancer driver gene by using consensus prediction result
The invention discloses a method for identifying a cancer driver gene by using a consensus prediction result. The method comprises the following steps: S1, receiving a mutation annotation format (MAF) file as input; S2, processing all the preprocessed input mutation data so as to respectively obtain a candidate driver gene list of each strategy; S3, on the basis of each differential driving gene list, obtaining a common driving gene list by using a rank integration method RobustRankAggreg; S4, evaluating the performance of the result by using Top-N-Precision and Top-N-nDCG, and carrying out KEGG pathway and gene ontology analysis on the common driver gene; S5, obtaining a consensus driving gene list by using an RAA algorithm; S6, employing the SuperExactTest and the Circos for organizing a visualization result. The method has certain superiority in driver gene prediction, although height difference exists between different driver gene identification strategies, not only can the most reliable driver gene be identified through cross analysis of results of each independent strategy, but also potential novel driver genes with undefined features can be found.
Owner:上海基绪康生物科技有限公司
Protein biomarker for sepiella japonica in senescence process
InactiveCN110734485ALow costA large number of screeningComponent separationBiological material analysisPotential biomarkersCarrier protein
The invention provides a protein biomarker for sepiella japonica in the senescence process and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The protein biomarker comprises a mitochondrial ATP / ADP (adenosine triphosphate / adenosine diphosphate) carrier protein SLC25A4S, has relative abundance of 1.82*10<7> before sexual maturation and oviposition, and has relative abundance of 0 during oviposition and articulo mortis after oviposition. A screening method of the protein biomarker comprises the following steps: extracting optic gland protein samples from individuals of sepiella japonicaat different reproductive stages; performing enzymolysis on the protein samples by using trypsin; analyzing the protein samples after enzymolysis by using liquid chromatogram-mass spectrum combination; and performing protein differential expression analysis, gene ontology analysis, signal pathway analysis and protein homologous cluster analysis through LC-MS (liquid chromatogram-mass spectrum) data processing. Through proteomic analysis and screening on the optic gland protein samples of the sepiella japonica at different reproductive stages, potential biomarkers can be obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Mining biological networks to explain and rank hypotheses
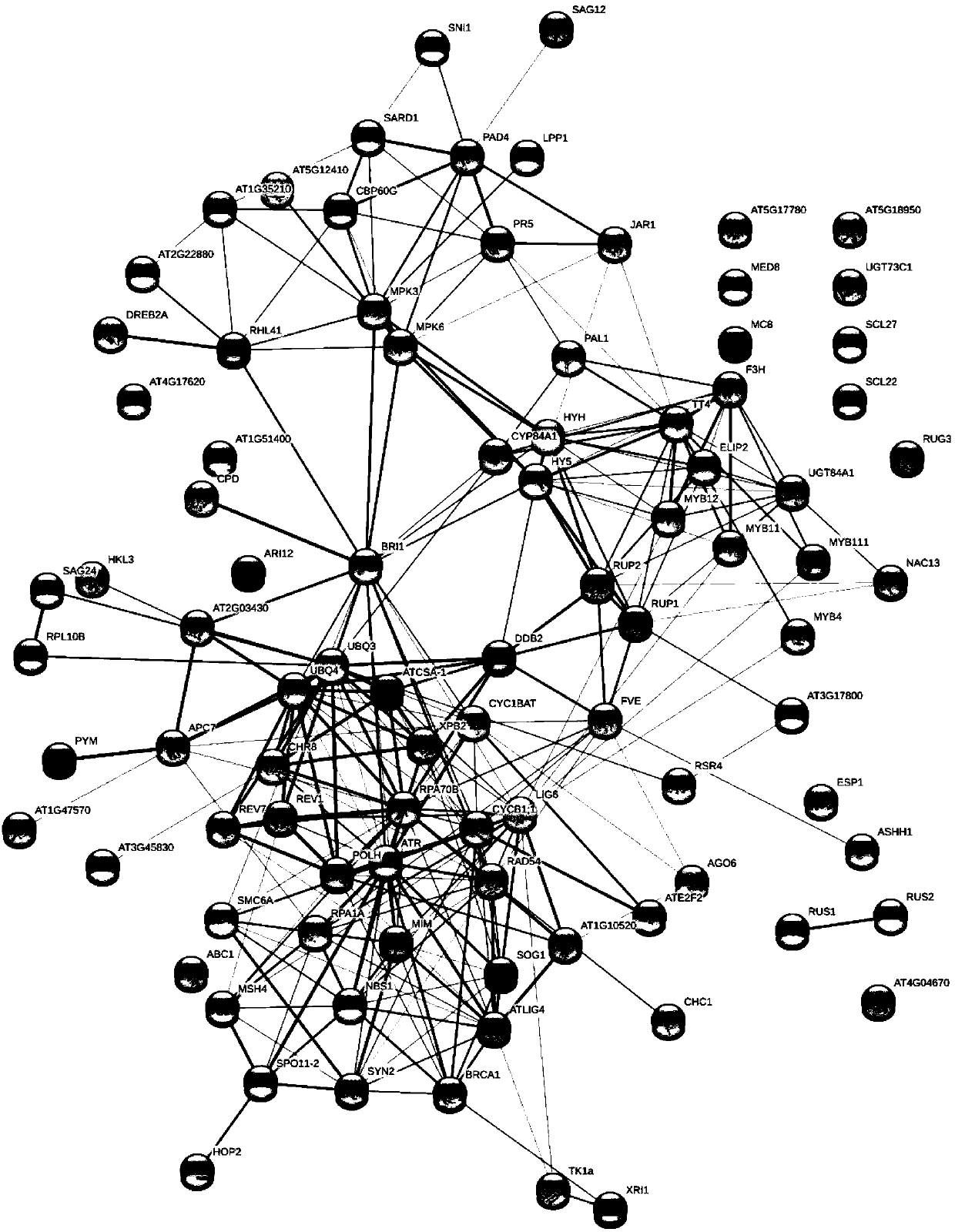
An approach is provided to identify important paths in a biological relationship graph for exploration by researchers. In the approach, a biological meaningfulness analysis is performed on the biological relationship graph that has a number of paths through the graph formed by a number of connected nodes. The biological meaningfulness analysis is based on a process similarity calculation of gene ontologies of the nodes in the paths and a contextual similarity calculation of word occurrences from documents in a corpus where a reference to the respective nodes are found. A biological interestingness analysis is also performed on the biological relationship graph. The paths are screened based on the meaningfulness analysis and the interestingness analysis. The screened data is displayed to the user.
Owner:IBM CORP
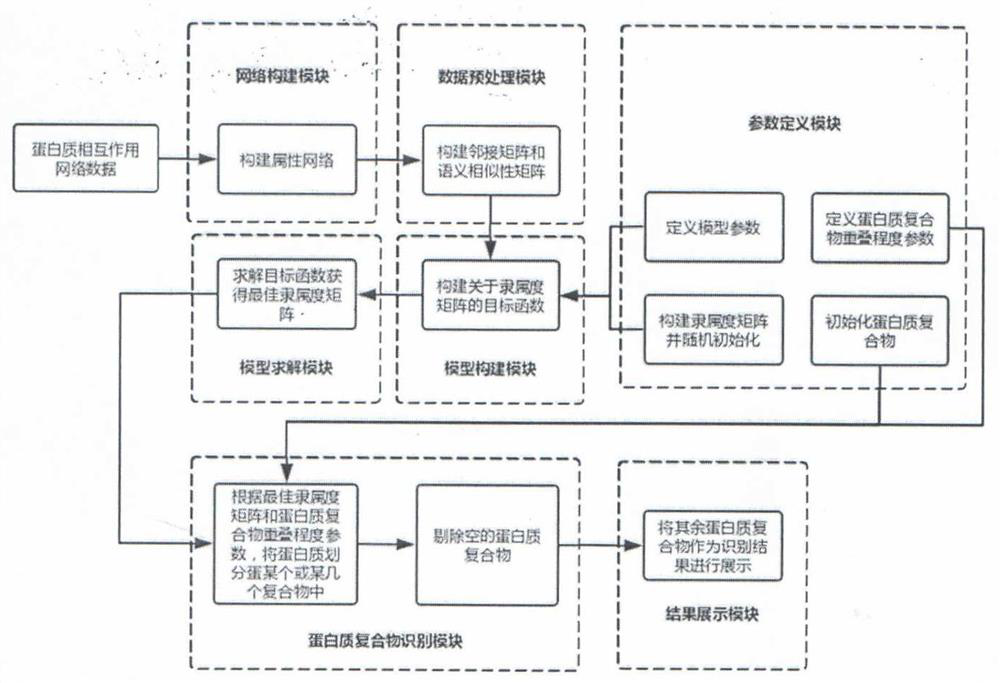
Overlapping protein complex identification method and system based on fuzzy clustering and gene ontology semantic similarity
ActiveCN113470738AMention accuracyImprove accuracyBiostatisticsInstrumentsGene ontologyProtein-protein complex
The invention provides an overlapping protein complex identification method and system based on fuzzy clustering and gene ontology semantic similarity. The system comprises a network construction module, a data preprocessing module, a parameter definition module, a model construction module, a model solving module, a protein complex identification module and a result display module. The protein complex recognition is realized by comprehensively considering the interaction relationship between the proteins in the protein interaction network and the gene ontology semantic similarity between the proteins. The method directly acts on the protein interaction network, can identify the overlapping protein complex in the network, is high in effect accuracy, and can effectively solve the protein complex identification problem in the protein interaction network.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
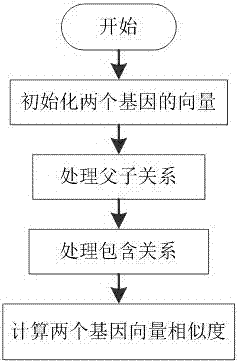
Vector-based intergenic semantic similarity calculation method
The invention discloses a vector-based intergenic semantic similarity calculation method. According to the method, a hierarchical structure of a gene ontology is further considered on the existing basis of calculating gene similarity based on a vector method; and in a vector construction process, not only terms directly annotated by genes but also child nodes and father nodes of the terms in the gene ontology are considered, so that generated vectors can reflect attributes of the genes more comprehensively and more detailedly.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Method for obtaining transcriptome and functional genes of blumea balsamifera
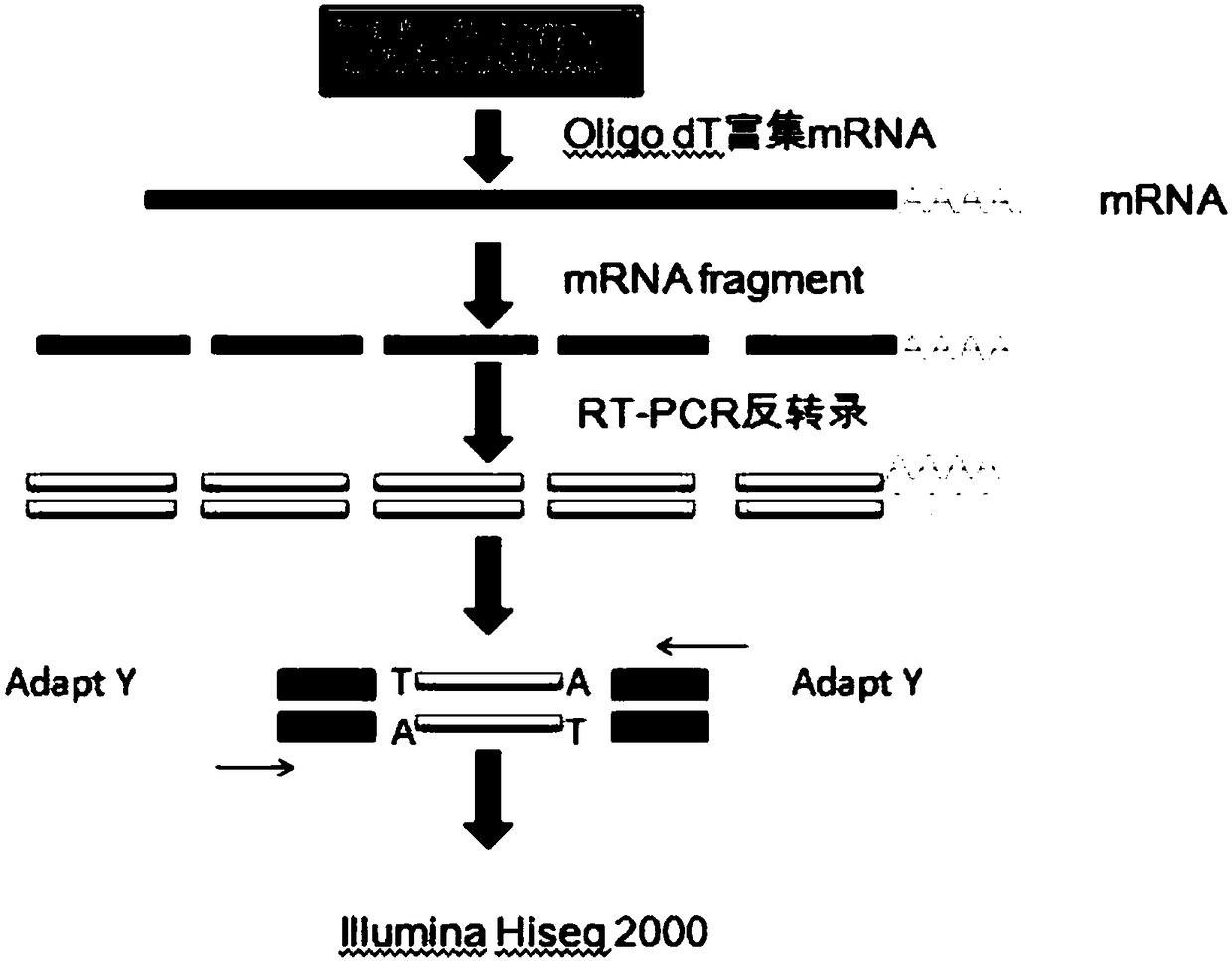
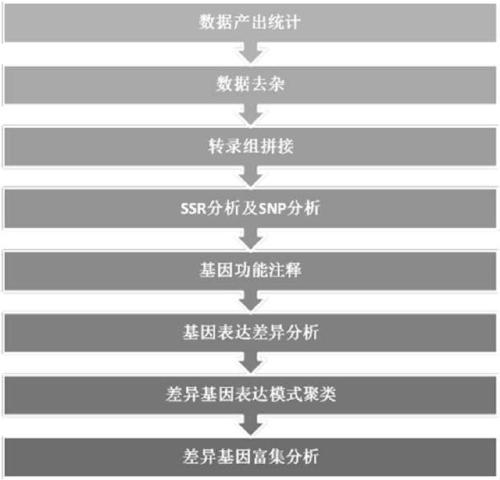
PendingCN109423490AHigh content of active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesPoly-A RNATotal rna
The invention provides a method for obtaining transcriptome and functional genes of blumea balsamifera. The method comprises (a) extracting the total RNA(ribonucleic acid) of blumea balsamifera, separating out mRNA (messenger RNA) with polyA (polyadenylation) at the 3' end, randomly breaking the mRNA, performing inverse transcription to synthesize double-stranded cDNA (complementary DNA); (b) sequencing an obtained sequence; (c) splicing and assembling a sequencing result to obtain Unigene and determining the orientation of the Unigene; (d) performing bioinformatics analysis on an obtained gene transcript to obtain the transcriptome and the function genes of blumea balsamifera. The method for obtaining the transcriptome and the functional genes of blumea balsamifera can help obtain 48197273 pieces of sequence information and 100341 Unigenes, involving 60477 pieces of information including RNA-seq names, sequence length and expression quantity, COG (cluster of ortholog genes) predication, COG functional annotations, KEGG (Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes) annotations, KEGG-pathway and GO (gene ontology) annotations, and 37283 pieces of information protein function annotationsfor performing CDS (coding sequence) prediction on the obtained sequence information.
Owner:TROPICAL CORP STRAIN RESOURCE INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
A json-based gene ontology mapping system and method
ActiveCN112187953BImprove data transfer efficiencyReduce occupancyTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsCellular componentMapping system
The invention discloses a JSON-based gene ontology mapping system and method, including automatic identification and data extraction of gene ontology, a mapping mechanism from gene ontology to JSON, and JSON-based gene ontology data storage. The specific steps are: identify the metadata information in the Gene Ontology, and obtain the three categories of cellular component, molecular function, and biological process in the Gene Ontology metadata, as well as the parent-child relationship (is_a) , part_of and regulation relationship (regulates) three relationship features; establish one-to-one mapping rules between gene ontology metadata features and JSON model, and use semi-supervised learning method to complete metadata extraction; build JSON-based gene ontology storage Model to complete the data migration from Gene Ontology to JSON. The invention establishes a mapping model of gene ontology and JSON, solves the problem that gene ontology data cannot be automatically converted into JSON data, and realizes efficient data interaction and full sharing of gene ontology among heterogeneous Web platforms.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com