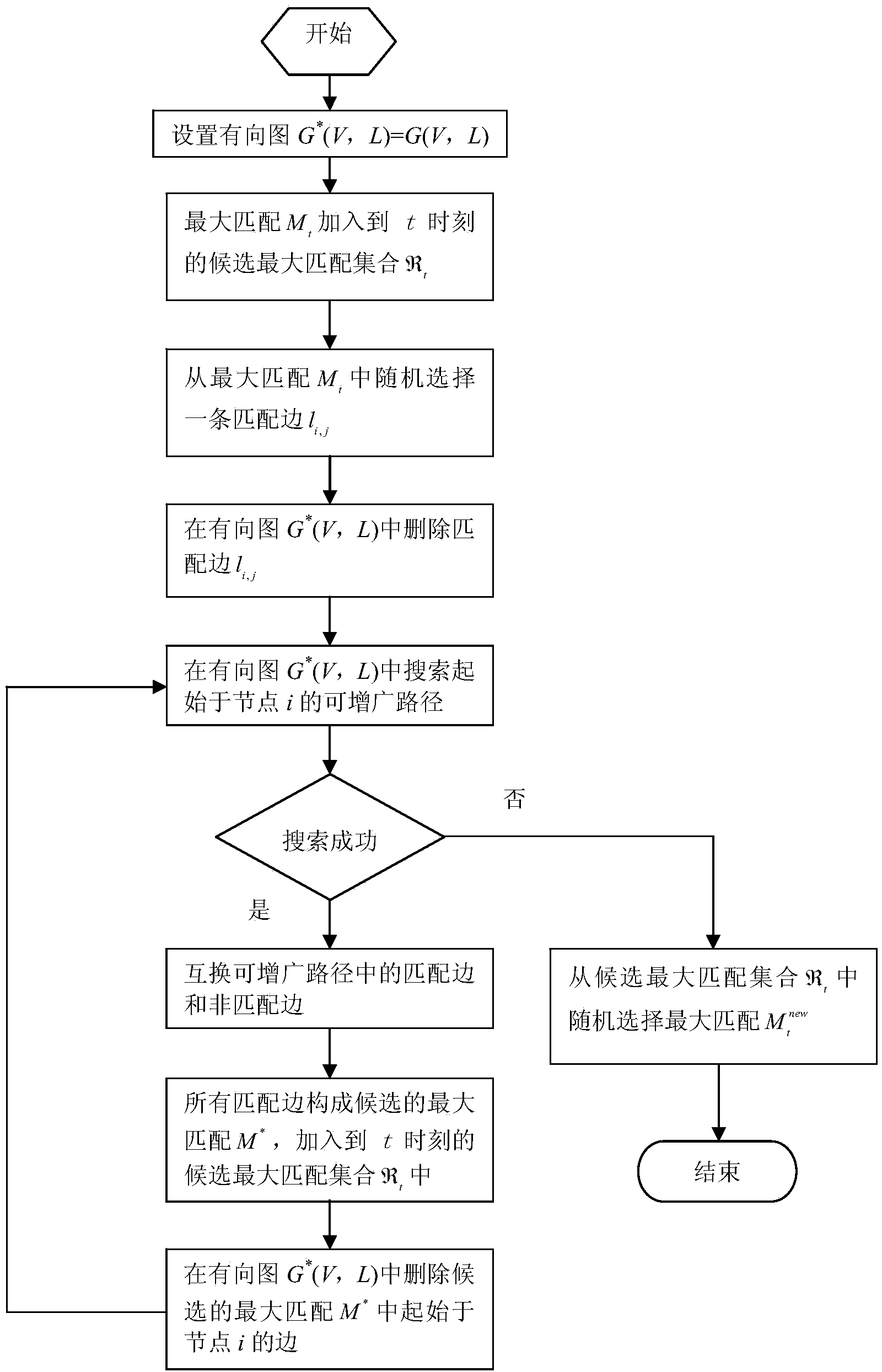
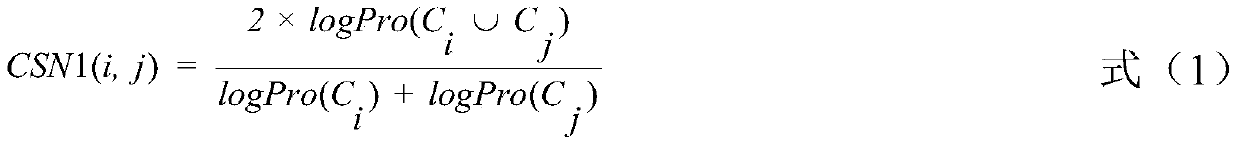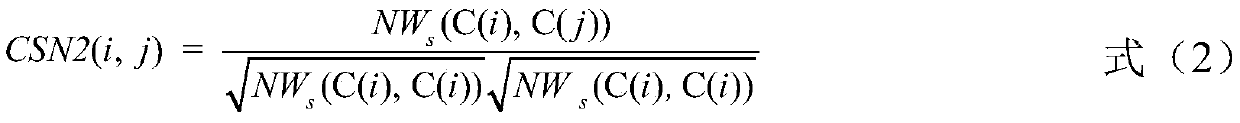Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
60 results about "Functional similarity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Functional Similarity Matrix (FunSimMat) Abstract The Functional Similarity Matrix (FunSimMat) is a comprehensive database providing various precomputed functional similarity values for proteins in UniProtKB and for protein families in Pfam and SMART.
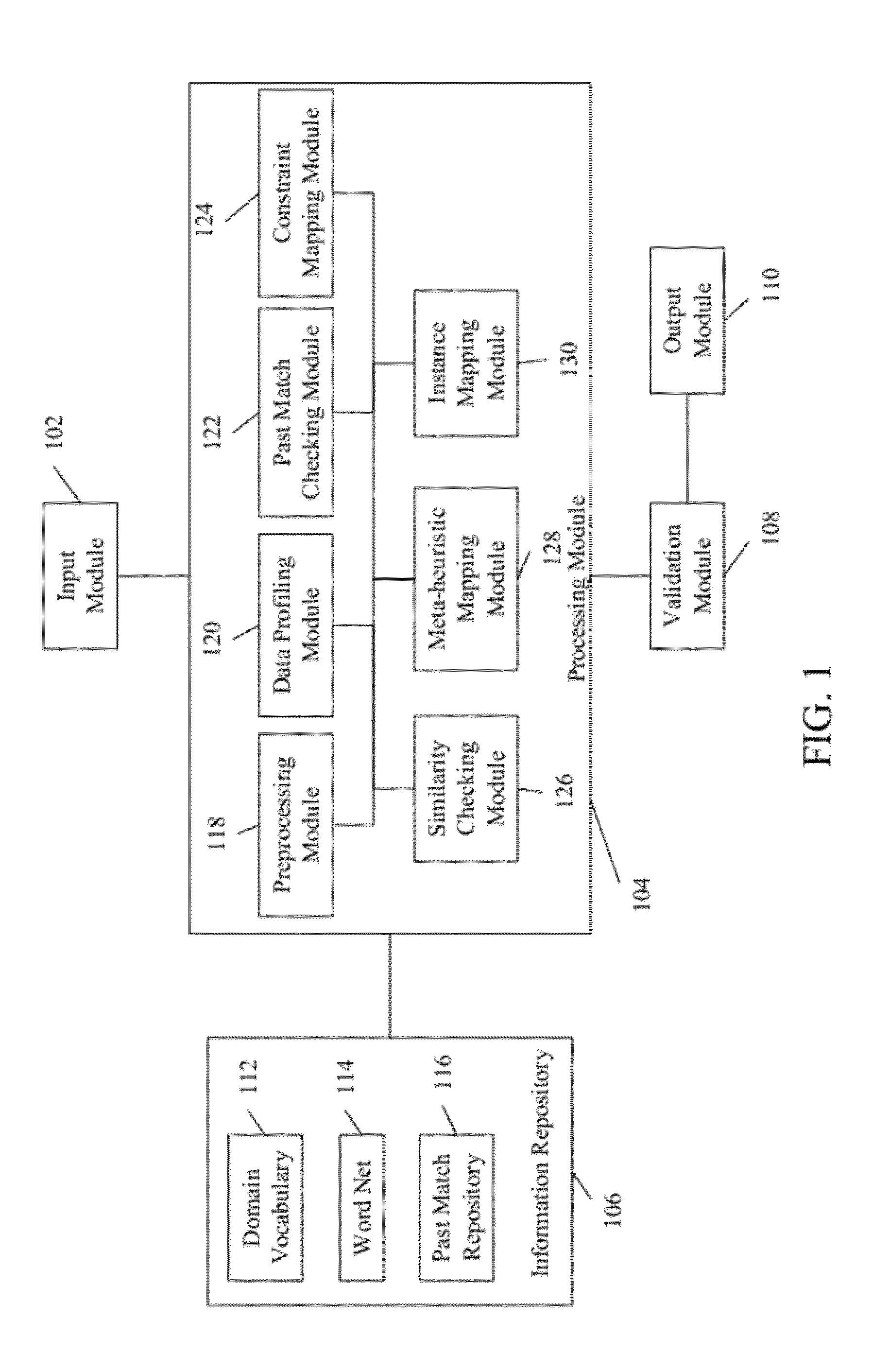
System and method for schema matching
ActiveUS20120078913A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsMinutiaeComputer science
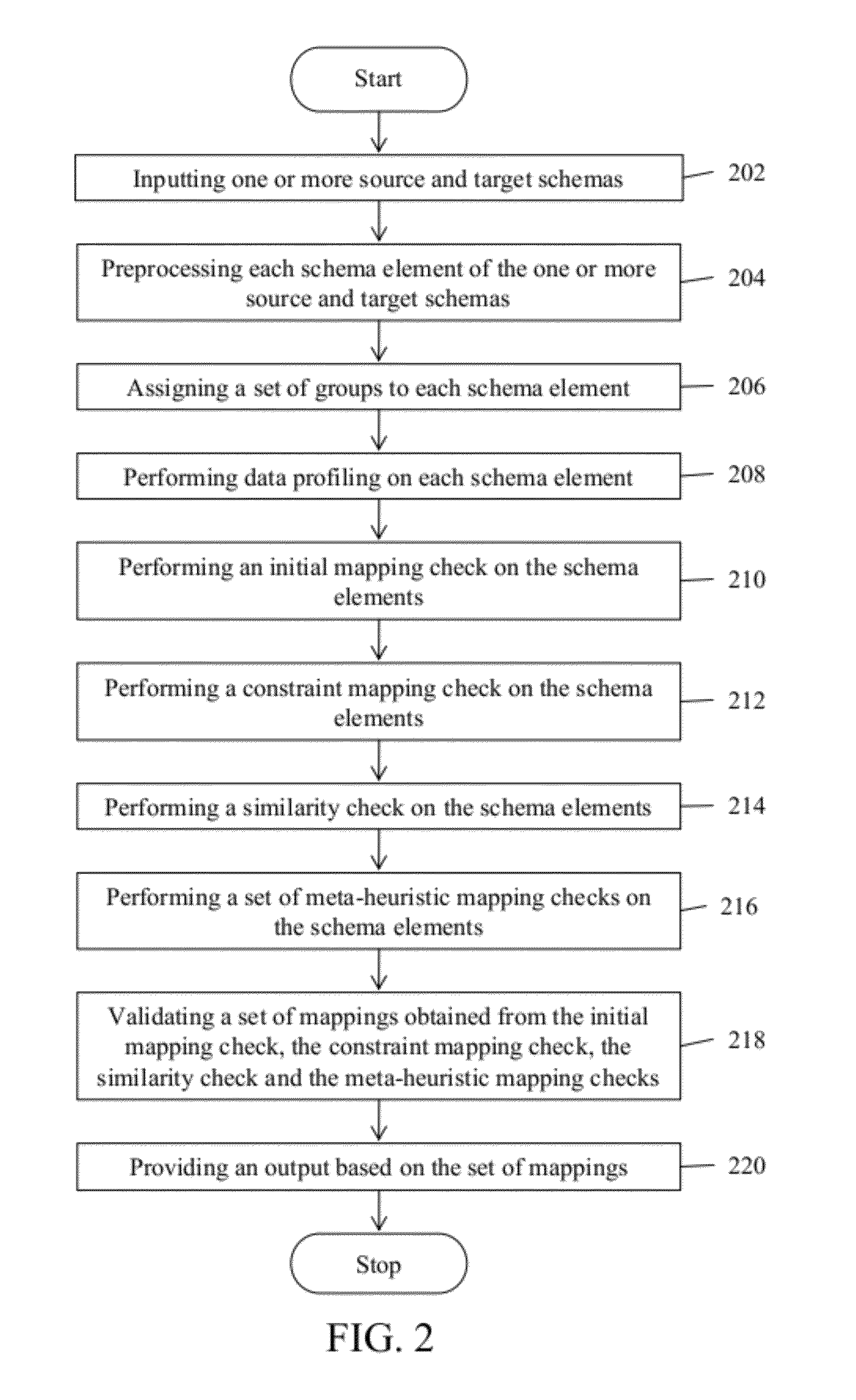
A system and method for matching one or more source schemas with one or more target schemas is provided. The matching between source and target schemas is performed by gathering inputs pertaining to the source and target schemas, wherein the inputs comprises a set of details in a predefined format. Thereafter, the gathered inputs are processed by comparing the source schemas with the target schemas. The processing is performed to identify a set of matches between the source and target schemas based on the linguistic similarity, structural similarity and functional similarity and relationship between the source and target schemas. Subsequently, the identified matches are stored.
Owner:INFOSYS LTD
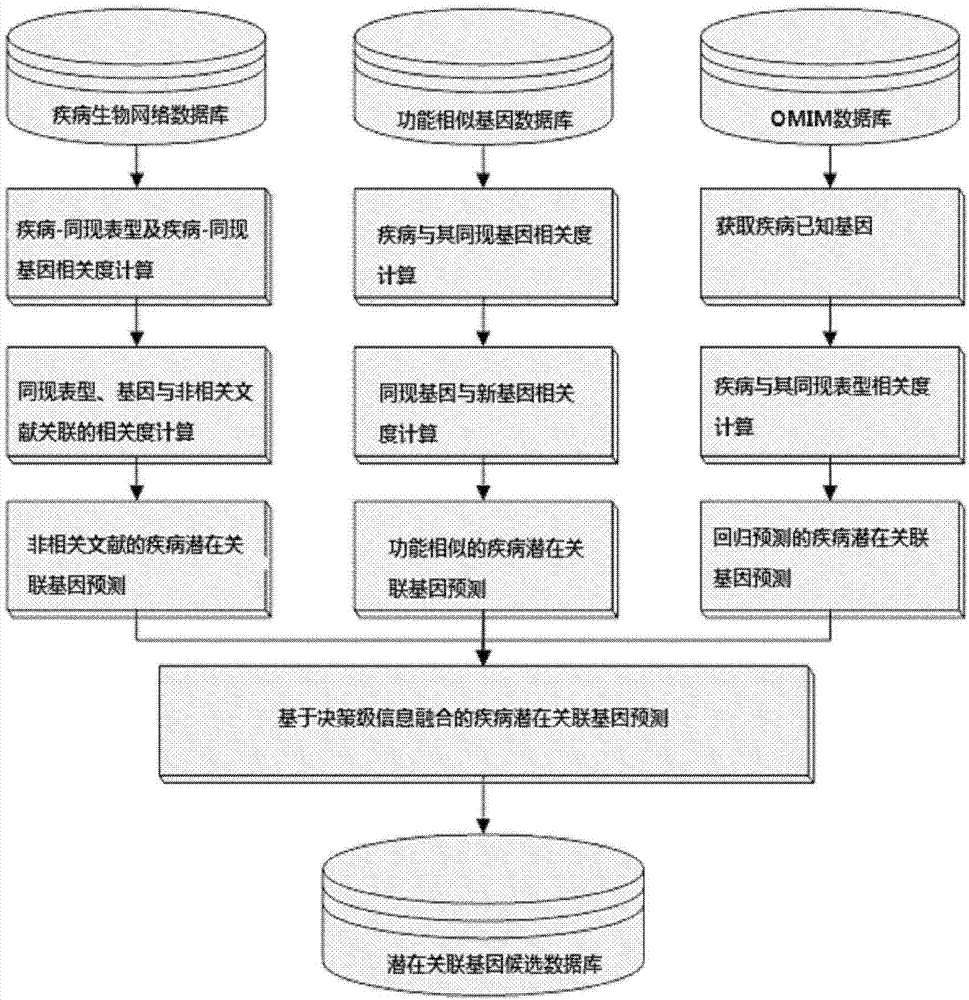
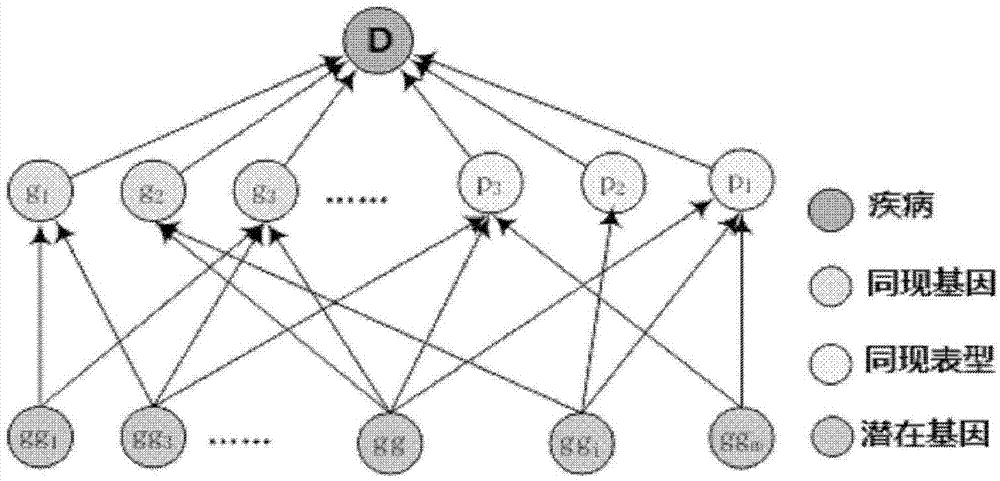
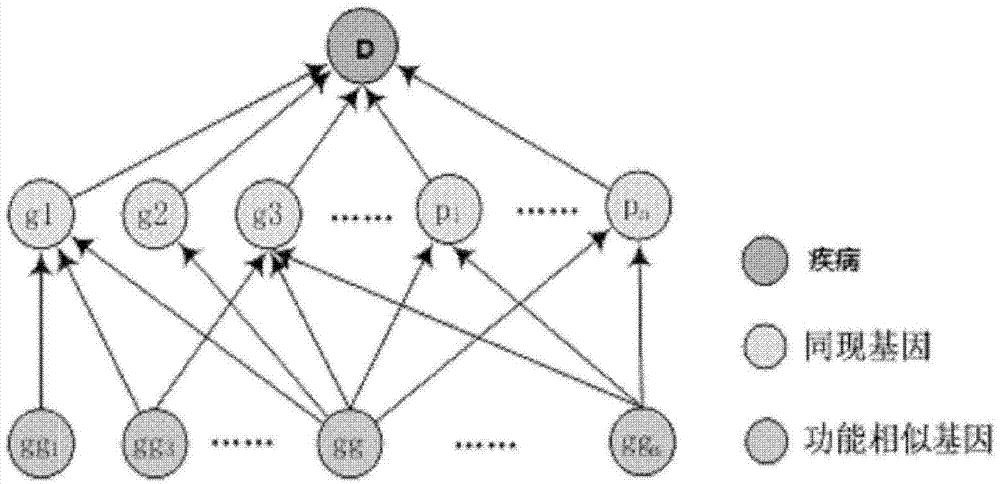
Method for obtaining disease potentially-associated gene based on multi-source information fusion
ActiveCN102855398AOptimal decision resultPromote resultsSpecial data processing applicationsDiseaseGene
The invention discloses a method for obtaining disease potentially-associated genes based on multi-source information fusion. The method comprises the following steps of: predicting disease-associated genes found based on uncorrelated literature knowledge, predicting disease-associated genes based on functional similarity, predicting disease-associated genes based on a regression prediction model, respectively scoring associated genes obtained through prediction of disease-associated genes found based on uncorrelated literature knowledge, prediction of disease-associated genes based on functional similarity and prediction of disease-associated genes based on a regression prediction model, establishing preliminary analysis to the associated genes, and fusing results obtained in all steps to obtain a final judgment result to determine the disease potentially-associated genes.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for identifying key proteins in protein-protein interaction network
ActiveCN105279397AImprove recognition accuracySolve the costSpecial data processing applicationsProtein insertionProtein protein interaction network
The invention discloses a method for identifying key proteins in a protein-protein interaction network. According to the method, an undirected graph G is constructed according to the protein-protein interaction data, and the edge clustering coefficient of the graph is calculated. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention has the advantages of combining the gene expression profile data and the gene function annotation information data on the basis of considering the topological structure characteristics of the protein-protein interaction network, and integrating three groups of data to predict the key proteins, so that the influence caused by the data noise of a single data source on the prediction correctness can be effectively decreased, and the key proteins in the network can be predicted through the key protein characteristics embodied by three types of data, such as the edge clustering coefficient in the protein-protein interaction network, the Pearson's correlation coefficient of the gene expression value and the gene function similarity index. According to the method, the identification correctness of the key proteins in the protein-protein interaction network can be remarkably improved, and abundant key proteins can be predicted once, so that the problem that the biological experiment method is high in cost and time-consuming is solved.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
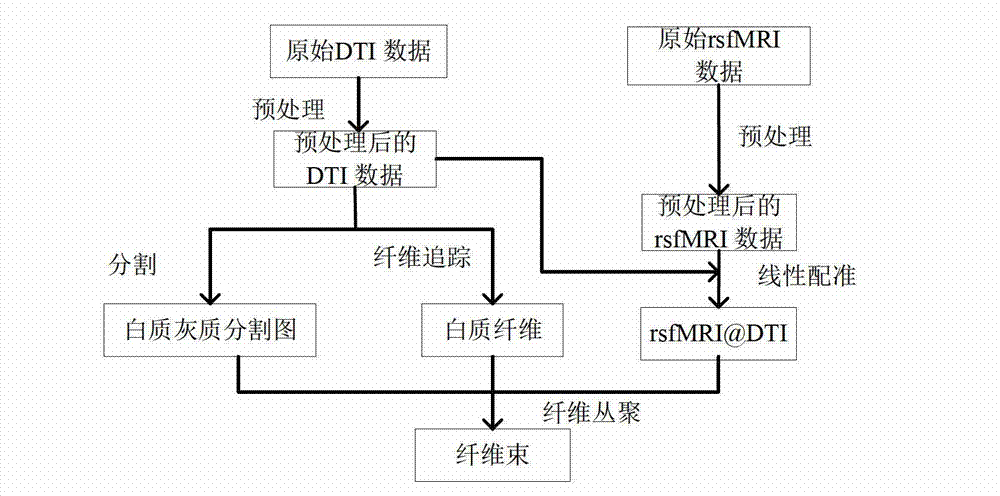
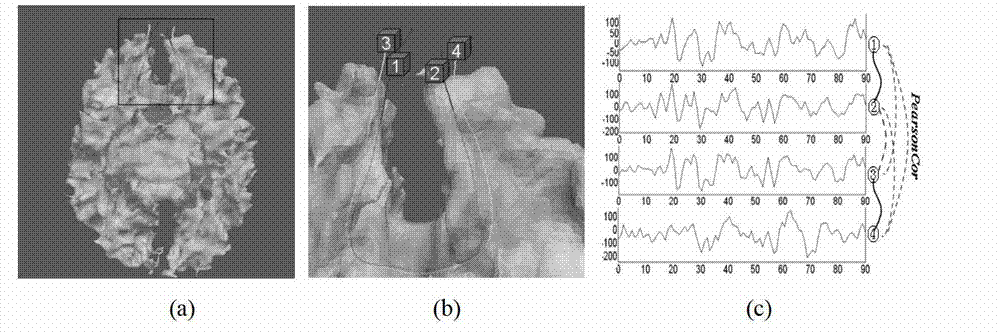
Diffusion tensor imaging white matter fiber clustering method
The invention provides a diffusion tensor imaging white matter fiber clustering method. The method includes the steps of pre-processing original rsf magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data and the original diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) data, registering the pre-processed rsf MRI data into a DTI space, respectively conducting fiber tracking and brain tissue segmentation on the pre-processed DTI data, conducting fiber projection on white matter fiber which can not reach grey matter or exceed a grey matter surface in a white matter fiber obtained by DTI, then calculating functional similarities among the white matter fiber, obtaining a matrix of the similarities and clustering by adopting an affine spread clustering algorithm. Fiber bundle has functional independence, accuracy without need to relay on of a genetic linkage map and require complicated registration.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Construction method for specific cancer differential expression gene regulation and control network
InactiveCN105740651AHigh precisionImprove calculation accuracyHybridisationSpecial data processing applicationsDifferentially expressed genesBioinformatics
The invention discloses a construction method for a specific cancer differential expression gene regulation and control network.The method includes the following steps of firstly, constructing a framework gene interaction network according to function similarity weight numbers between genes; secondly, conducting module division on the framework gene interaction network through a segmenting method; thirdly, screening out differential expression genes through complete genome methylation data; fourthly, classifying the screened-out differential expression genes according to functions; fifthly, using all the differential expression genes mapped to each same function module as a function classification; sixthly, constructing the regulation and control network of all the genes in each function classification function; seventhly, conducting sub-network splicing under guidance of a framework network.The calculation complexity is greatly reduced, and high precision is achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Biomolecular network analysis method based on function module
ActiveCN103778349AHigh functional relevanceEfficient integrationSpecial data processing applicationsRegulation of gene expressionComputer science
The invention belongs to the field of a biotechnology, and provides a comparison method based on a function module and used for biomolecular networks such as a genetic expression regulatory network or protein-protein interaction and the like. The method mainly comprises steps as follows: an adjacency matrix Madj of a biological network is built, a function similarity matrix Msim between network nodes is calculated, a function weight matrix ME of a network side is calculated according to the formula as follows: ME=Madj.*Msim, a network module is mined with a minimum graph entropy algorithm, and finally, function enrichment analysis is performed on the network module, wherein the symbols are defined in the instruction.
Owner:艾吉泰康(嘉兴)生物科技有限公司
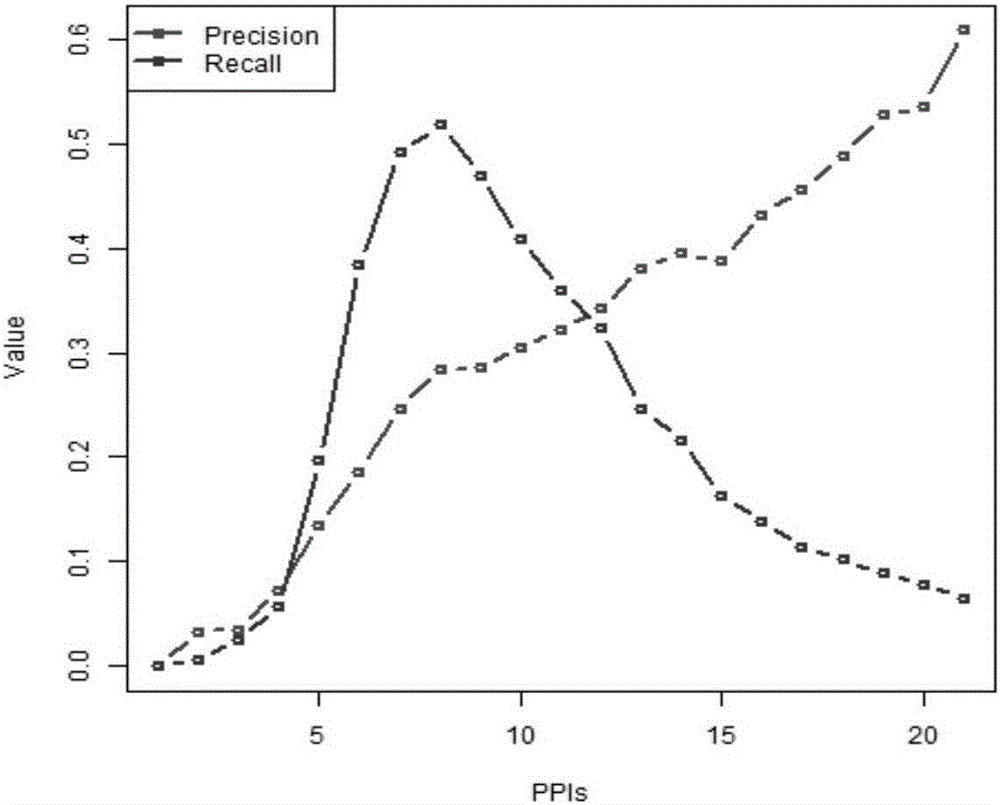
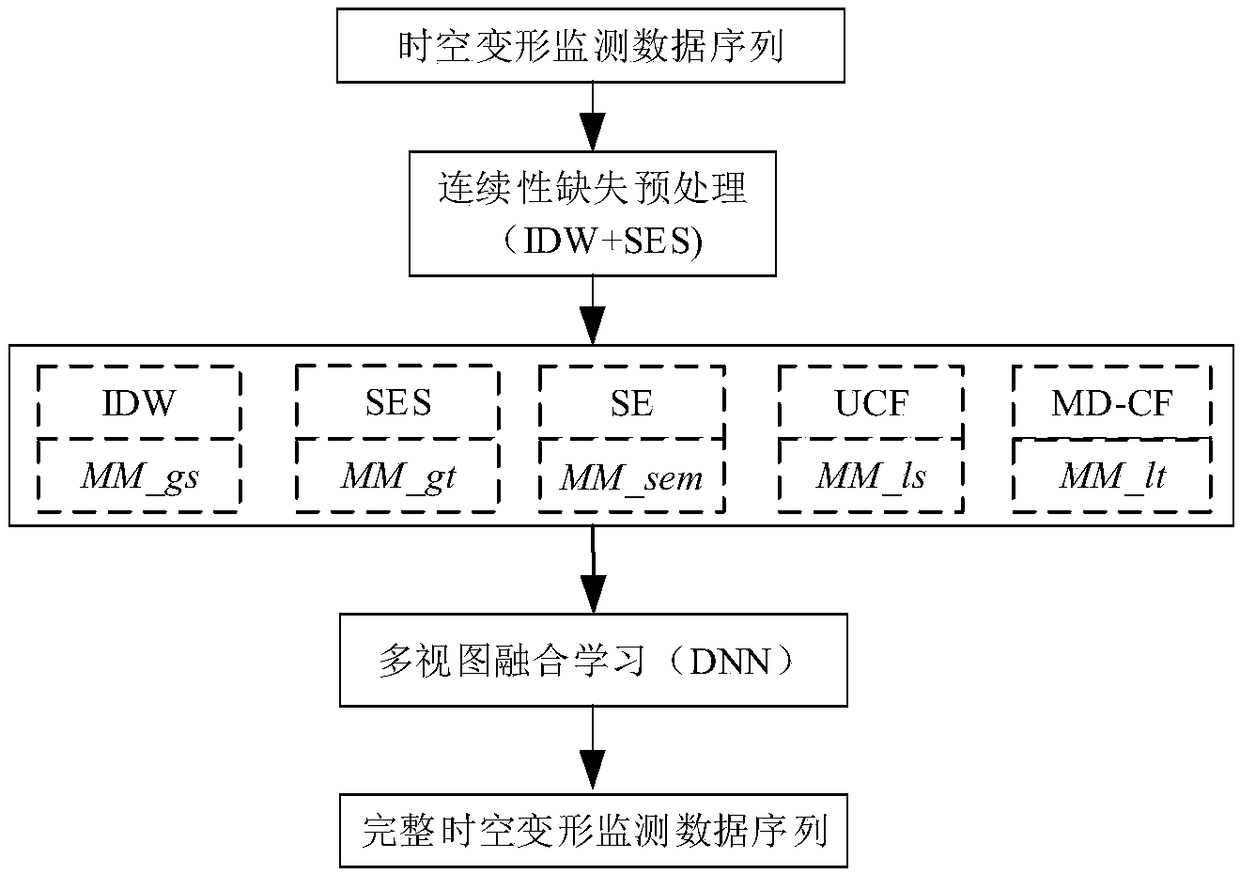
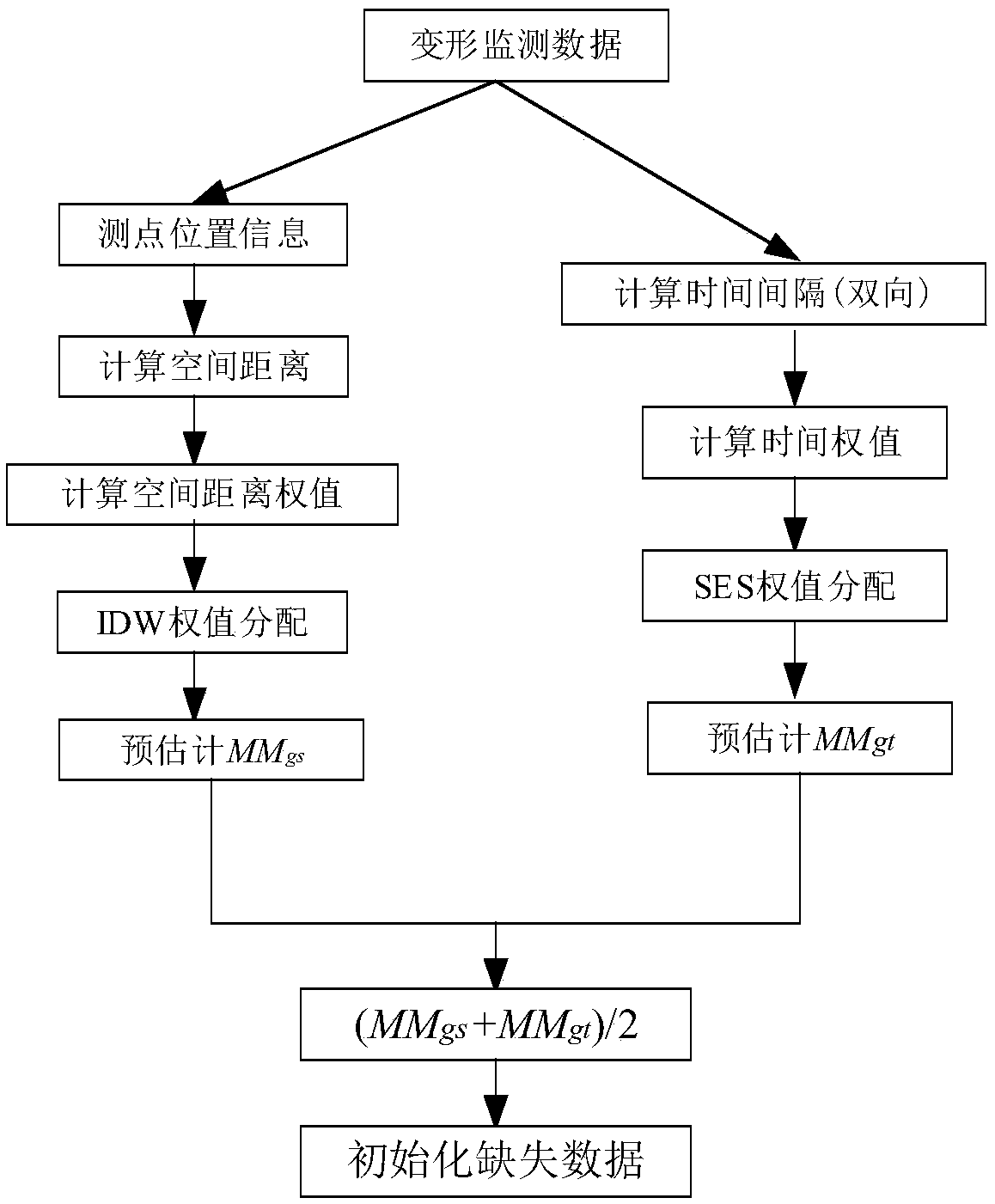
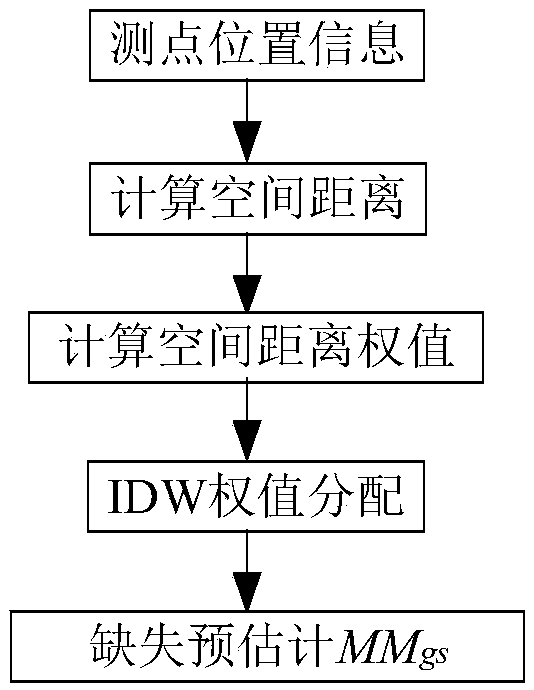
A method for completing continuous missing data of dam deformation monitor
ActiveCN109101638AReduce redundancySolve the sparsity problemData miningNon-redundant fault processingMissing dataAlgorithm
The invention discloses a method for completing continuous missing data of dam deformation monitoring, which solves the problem of completing continuous missing data of dam deformation monitoring. Firstly, the continuity loss of deformation monitoring data is pretreated. Secondly, from the angles of global space, global time, local space, local time and semantics, the spatio-temporal similarity and functional similarity of deformation monitoring points are calculated respectively, and the missing data in deformation monitoring data are interpolated globally and locally in space, time and semantics. Finally, a depth neural network model is constructed to complete the continuous missing data in dam deformation monitoring. The preliminary results of the missing data are used as input, and thenonlinear fusion is realized by using the depth neural network representation ability.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
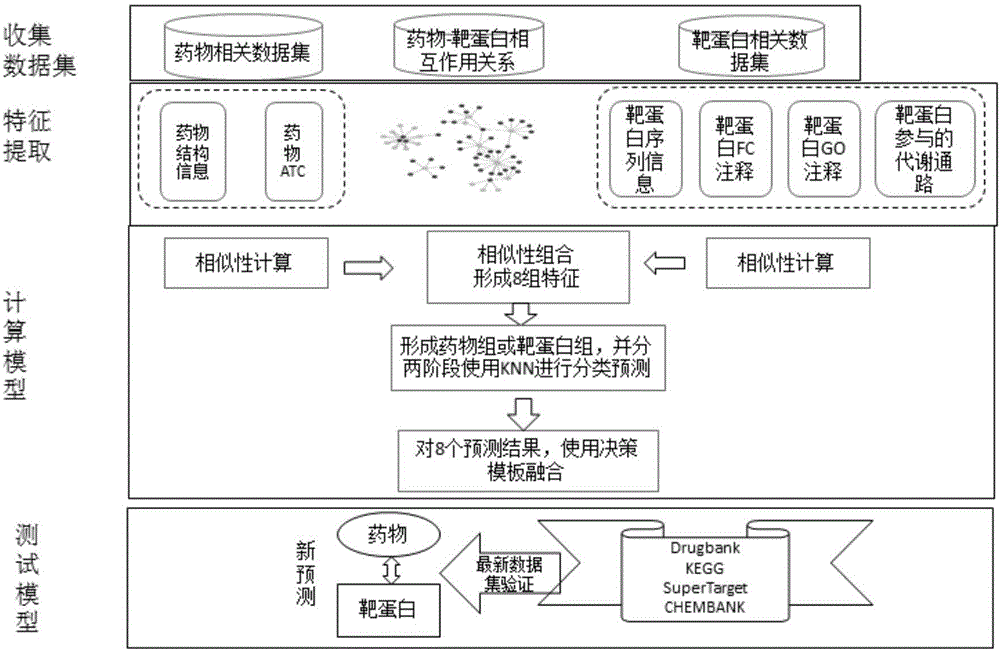
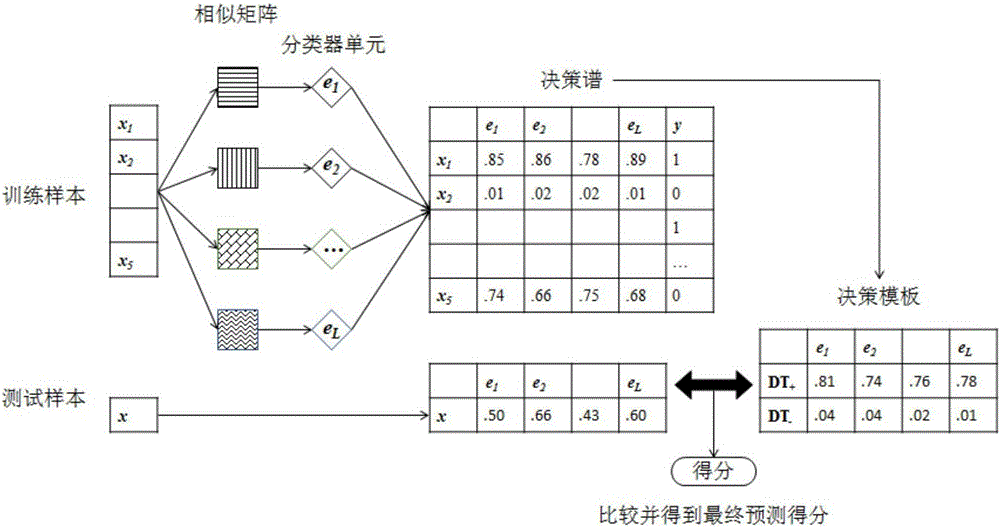
Method and system for predicting drug-target protein interaction relationship based on decision template
ActiveCN106709272ASolve the problem of sparseness (that is, the number of positive samples is small)Improve forecast accuracyBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsProtein targetDecision taking
The invention discloses a method and a system for predicting a drug-target protein interaction relationship based on a decision template. Multiple similarity characteristic combinations are formed in combination with existing drug compound molecular structure similarity, drug ATC annotation similarity, target protein sequence similarity and function similarity through proposing two new target protein similarity measurement policies, namely, GO ontology annotation-based and pathway function mapping-based similarity measurement; and the drug-target protein interaction relationship is predicted by adopting a KNN classification algorithm based on a hypothesis that similar drugs easily interact with similar target proteins. According to the method and the system, a decision template fusion-based policy is proposed; multiple similarity measurement-based classifier prediction results are subjected to decision level fusion; the problem that a known drug-target protein interaction relationship is relatively sparse is effectively solved in combination with concepts of super target proteomes and super drug groups; the prediction precision is improved; and the method and the system can be used for realizing target protein prediction of new drugs or drug prediction of new target proteins.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
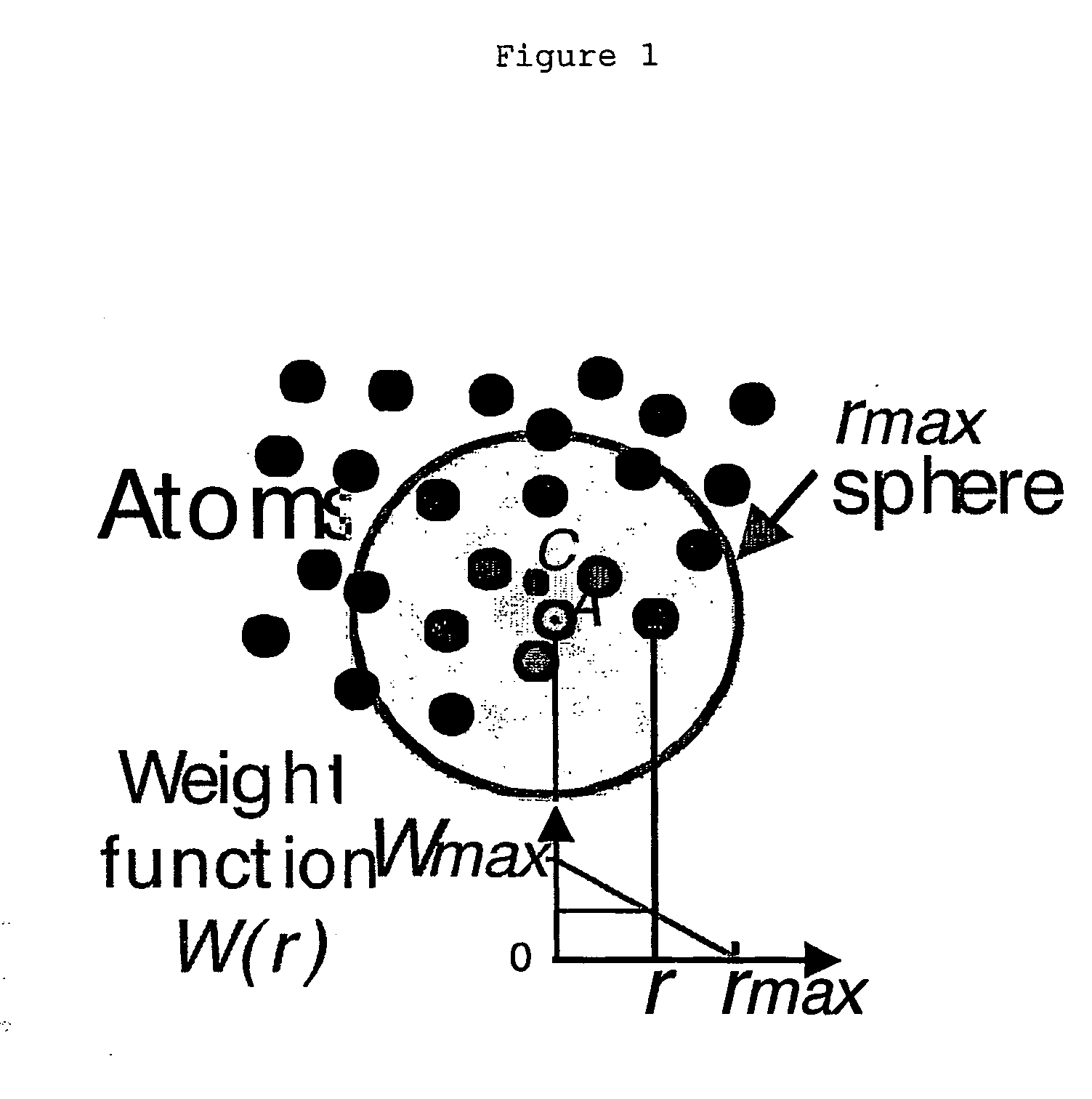
Process for identifying similar 3D substructures onto 3D atomic structures and its applications
InactiveUS20050182570A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingStructural biologyCompound (substance)
The invention pertains to the field of structural biology and relates to a process to compare various three-dimensional (3D) structures and to identify functional similarities among them. The process of comparison of 3D atomic structures of the invention is based on the comparisons of defined chemical groups onto the 3D atomic structures and allows the detection of local similarities even when neither the fold nor sequence for example aminoacid sequences for polypeptides sequences or nucleotide sequences for nucleic acid sequences are conserved. This process requires the attribution of selected physico-chemical parameters to each atom of a 3D atomic structure, then the representation of each 3D atomic structure by a graph of chemical groups.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
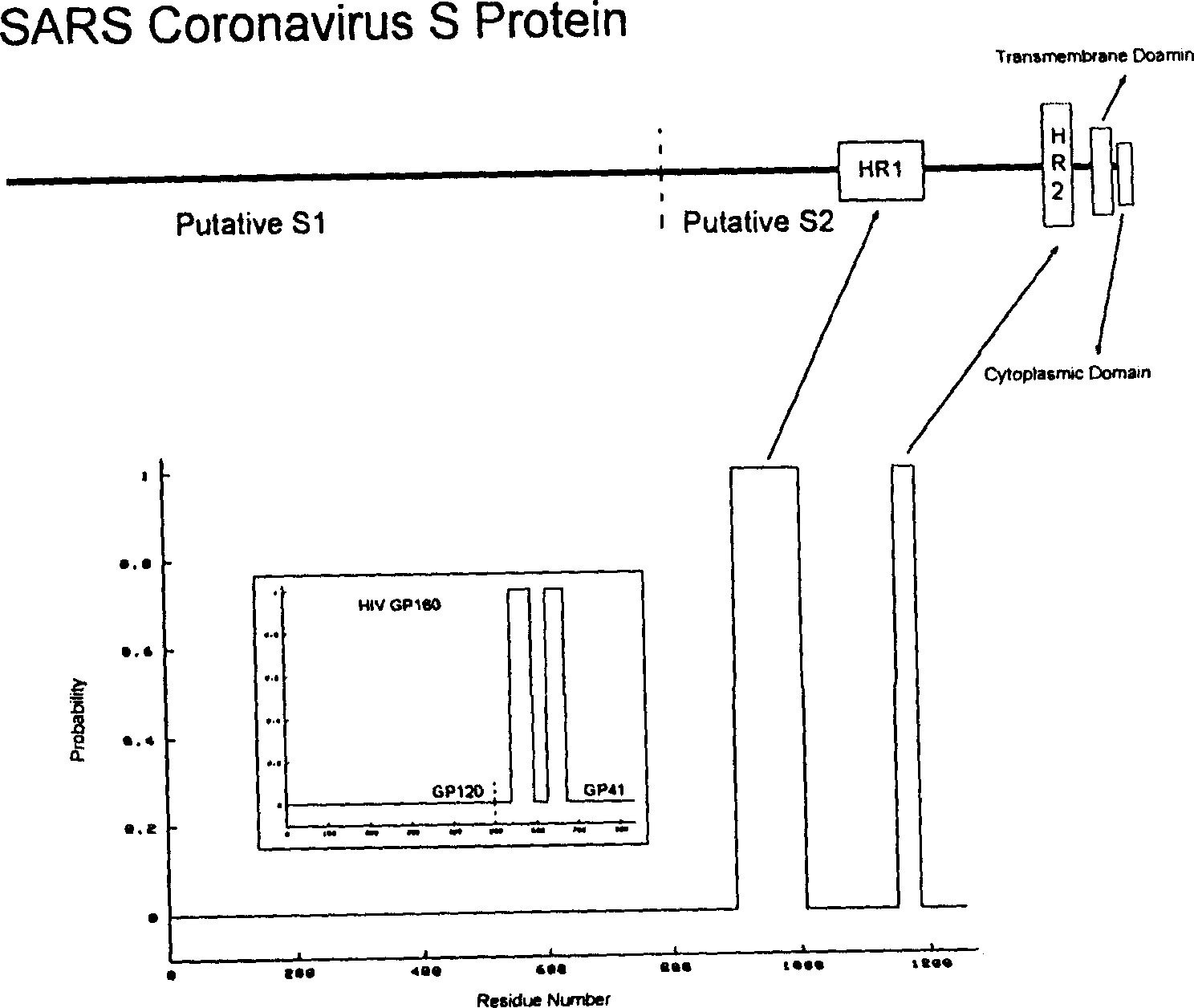
Polypeptide medicine for inhibiting SARS coronavirus, and derivatives and use thereof
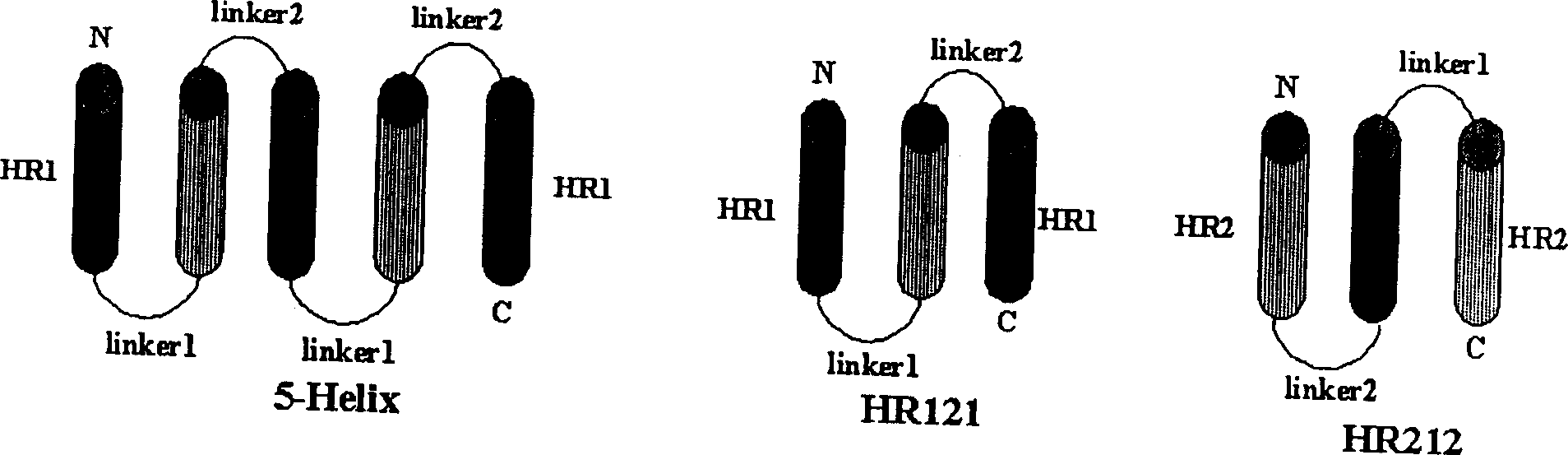
The invention provides a method for blocking SARS coronavirus to infect cell with polypeptide or its derivative. The cistine series of polypeptide comes from two heptad repeat districts HR1 and HR2 of SARS coronavirus spike(S) protein. The invention also provides a method for producing the functional similarity with HR1 and HR2. the invention provides a method for producing HR polypeptide and its derivant with coalescence expression method. All the peptides have rejection capability to SARS.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
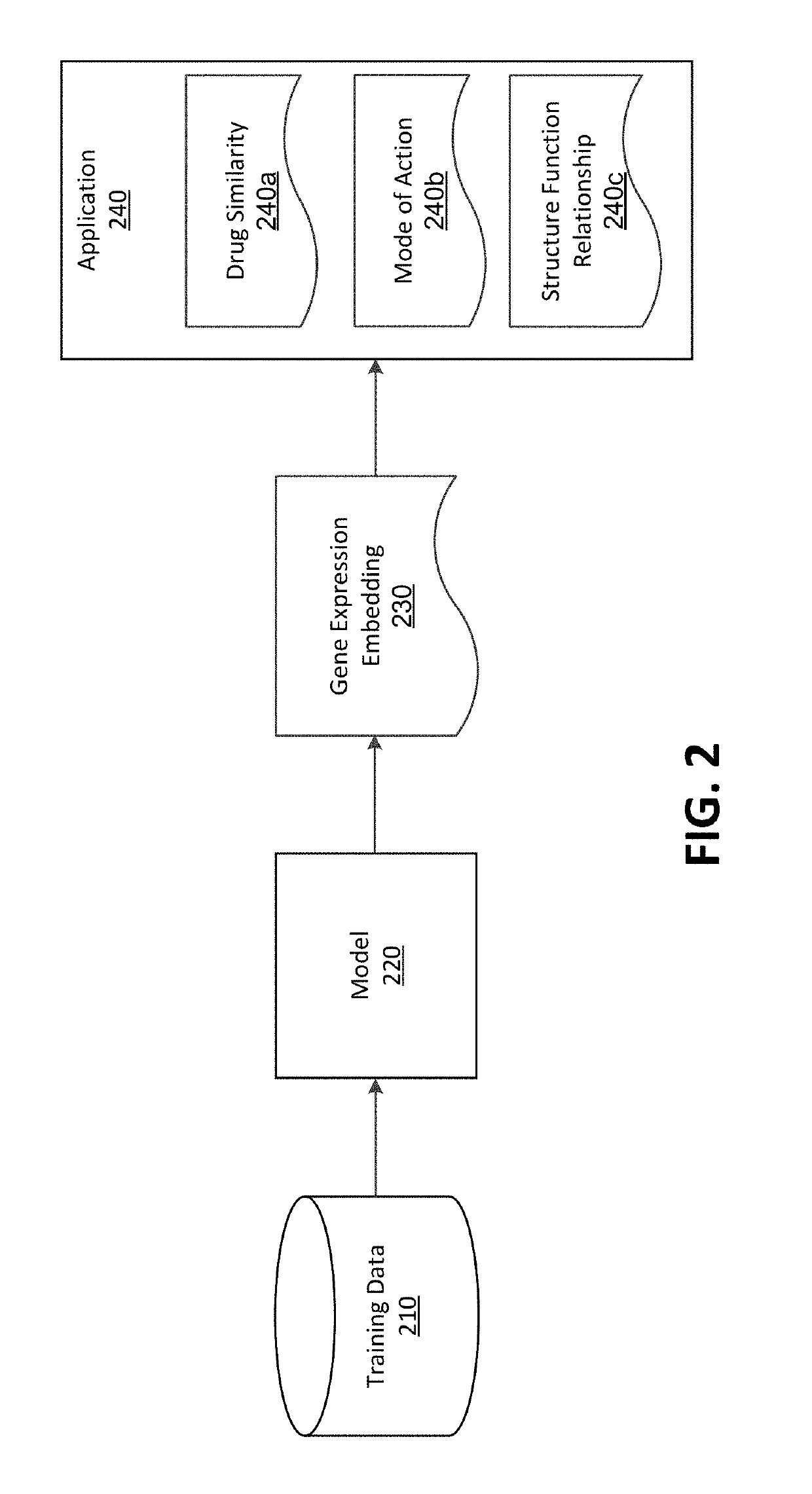
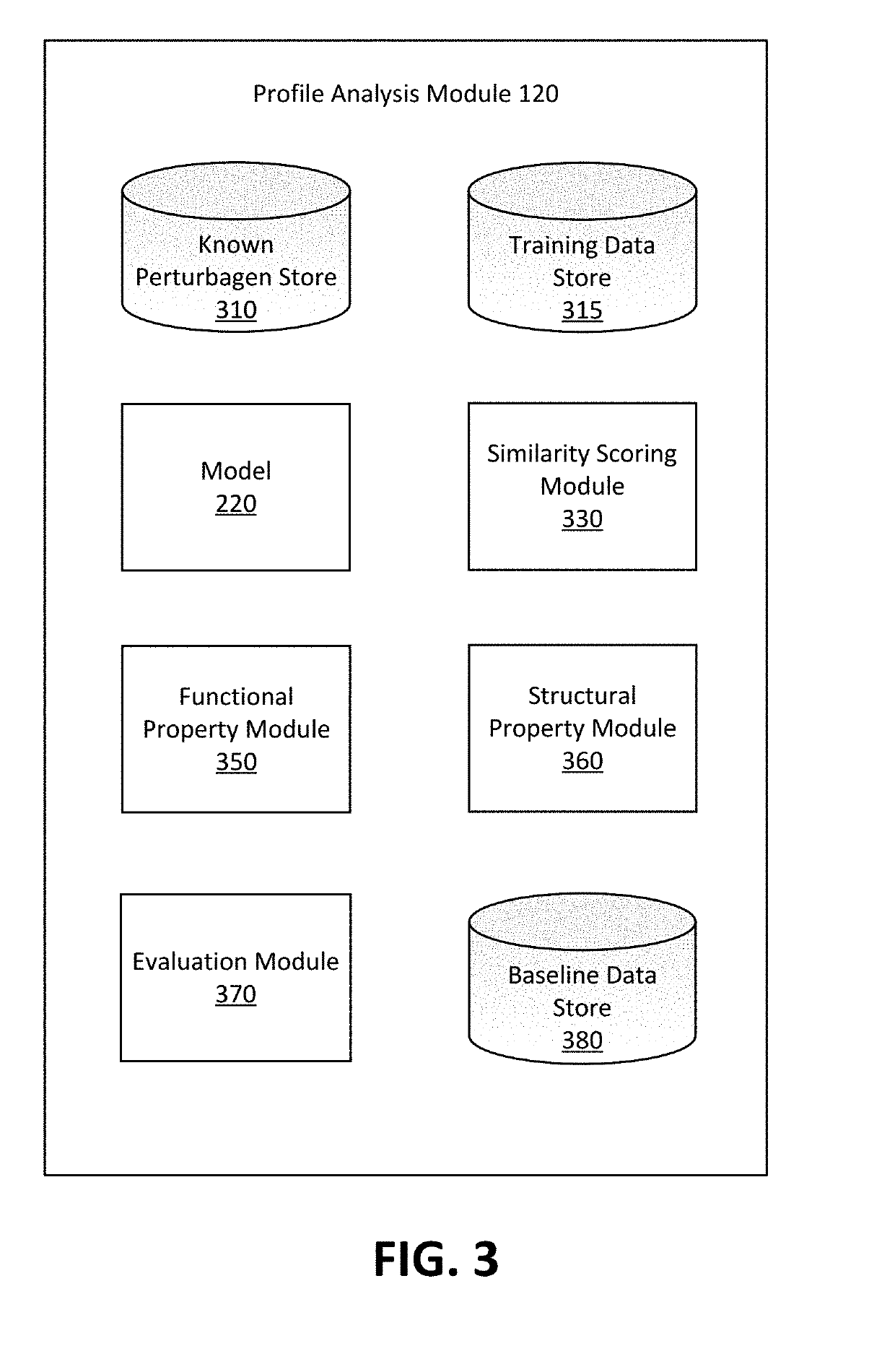
Drug repurposing based on deep embeddings of gene expression profiles
PendingUS20190114390A1Confirming pharmacologic similarityAccurately and effectively pharmacological similarityChemical property predictionMicrobiological testing/measurementPattern recognitionProtein target
A deep learning model measures functional similarities between compounds based on gene expression data for each compound. The model receives an unlabeled expression profile for a query perturbagen including transcription counts of a plurality of genes in a cell affected the query perturbagen. The model extracts an embedding of the expression profile. Using the embedding of the query perturbagen and embeddings of known perturbagens, the model determines a set of similarity scores, each indicating a likelihood that a known perturbagen has a similar effect on gene expression as the query perturbagen. The likelihood, additionally, provides a prediction that the known perturbagen and query perturbagen share pharmacological similarities. The similarity scores are ranked and, from the ranked set, at least one candidate perturbagen is determined to be pharmacologically similar to the query perturbagen. The model may further be applied to determine similarities in structure and biological protein targets between perturbagens.
Owner:BIOAGE LABS INC
System and method for schema matching
ActiveUS8386493B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsMinutiaeComputer science
A system and method for matching one or more source schemas with one or more target schemas is provided. The matching between source and target schemas is performed by gathering inputs pertaining to the source and target schemas, wherein the inputs comprises a set of details in a predefined format. Thereafter, the gathered inputs are processed by comparing the source schemas with the target schemas. The processing is performed to identify a set of matches between the source and target schemas based on the linguistic similarity, structural similarity and functional similarity and relationship between the source and target schemas. Subsequently, the identified matches are stored.
Owner:INFOSYS LTD
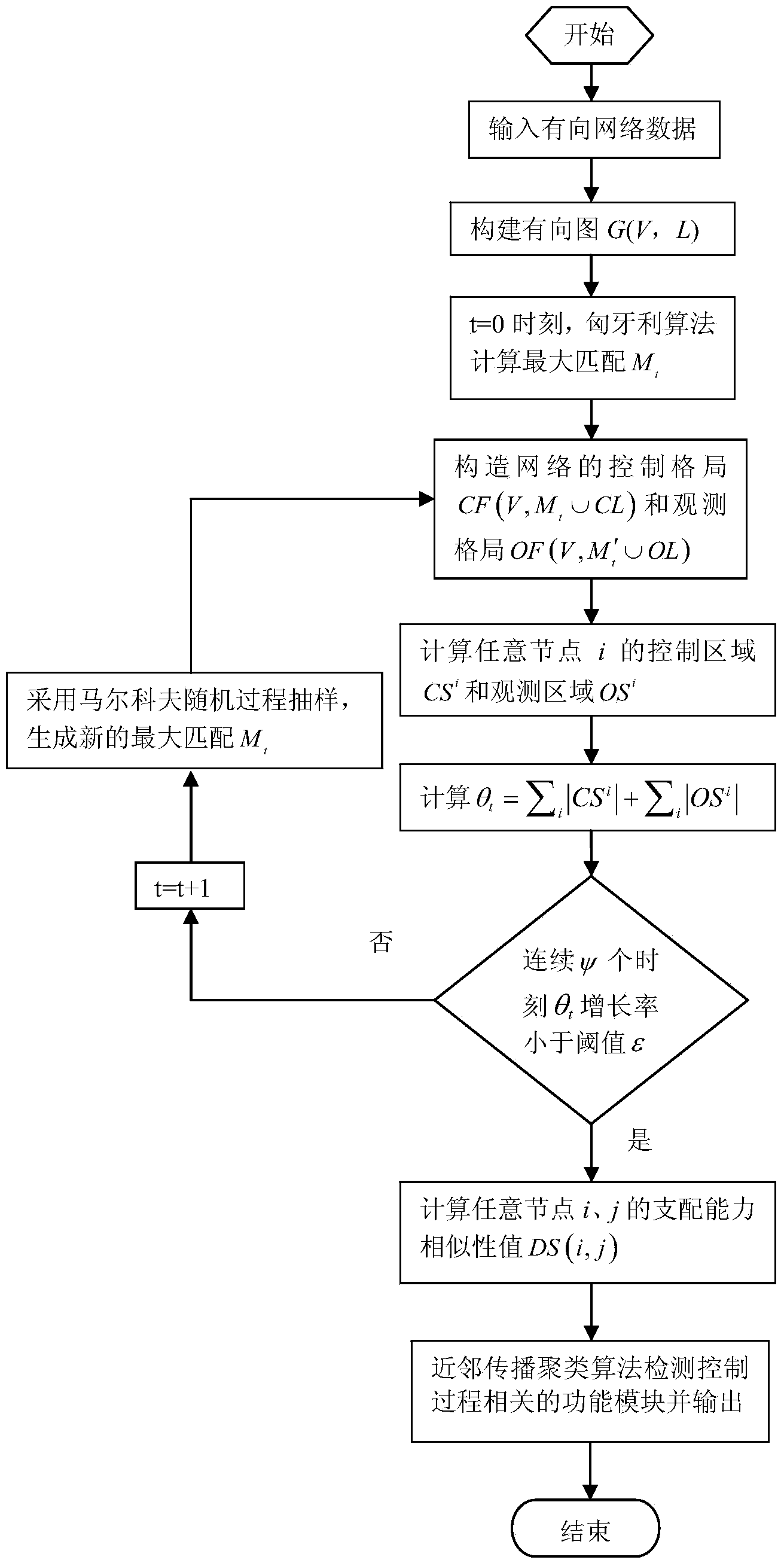
Function module detecting method based on node domination capacity similarity
ActiveCN104021199ASuitable for analysisDoes not affect test resultsBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsNODALAlgorithm
The invention discloses a function module detecting method based on node domination capacity similarity. The function module detecting method mainly solves the problem that in the prior art, sparse function modules cannot be mined in directed network data effectively. According to the technical scheme, the function module detecting method comprises the steps that directed control relationships between nodes are analyzed on the basis of network maximum matching; a node control region and an observation region are used for depicting the capacity magnitude of a density-unrelated node directional domination network; node function similarity is measured from the aspect of the control process of a domination system, a maximum matching enumeration method based on the Markov random sampling process is provided, and domination capacity similarity is calculated; the domination capacity similarity is applied to clustering analysis of a directed network to find out control-relationship-related sparse function modules through detection. The function module detecting method based on the node domination capacity similarity has the advantage that detection results are not affected by weight noise of data and can provide tool support for discovery of knowledge in directed sparse network data.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
System and method for fast and scalable functional file correlation
ActiveUS20160164900A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionComputerized systemComputer science
A method, computer program product, and computer system for obtaining, by a computing device, a file, wherein the file includes a plurality of portions. A first hash of a first portion of the plurality of portions may be generated. The first portion may be combined with a second portion of the plurality of portions. A second hash of the first portion with the second portion of the plurality of portions may be generated, wherein the first hash may be indicative of a first level of functional similarity between a function of the file and a function of a second file, wherein the second hash may be indicative of a second level of functional similarity with the function of the file and the function of the second file.
Owner:REVERSINGLABS INT
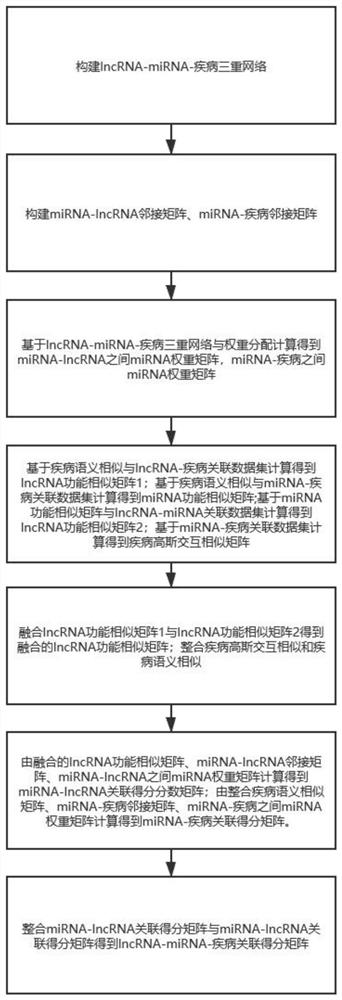
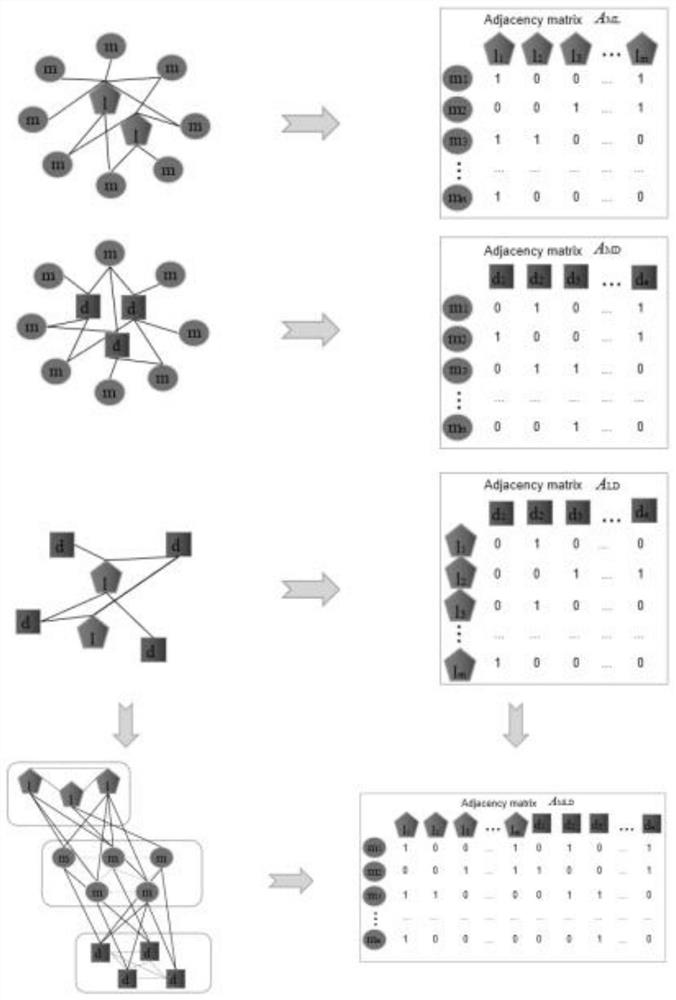
lncRNA-miRNA-disease association method based on fusion similarity
The invention discloses an lncRNA-miRNA-disease association method based on fusion similarity. The method comprises the following steps: constructing an lncRNA-miRNA-disease network; calculating the functional similarity of the fused lncRNA; calculating and integrating disease semantic similarity; obtaining a weight matrix of the miRNAs between the miRNA-lncRNAs and a weight matrix of the miRNAs between the miRNA-diseases according to a weight distribution algorithm; obtaining a miRNA-lncRNA association score matrix according to the fused lncRNA with similar functions, the miRNA-lncRNA adjacency matrix and the weight matrix of miRNA-lncRNA between the miRNA-lncRNAs; integrating the disease semantic similarity, the miRNA-disease adjacency matrix and the weight matrix of miRNAs among miRNA-diseases to obtain a miRNA-disease association score matrix; integrating the two incidence matrixes to obtain an incidence score matrix Smld; and predicting the Smld by using the prediction model. Theunknown incidence relation hidden under the data is revealed through the multi-aspect data relation.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
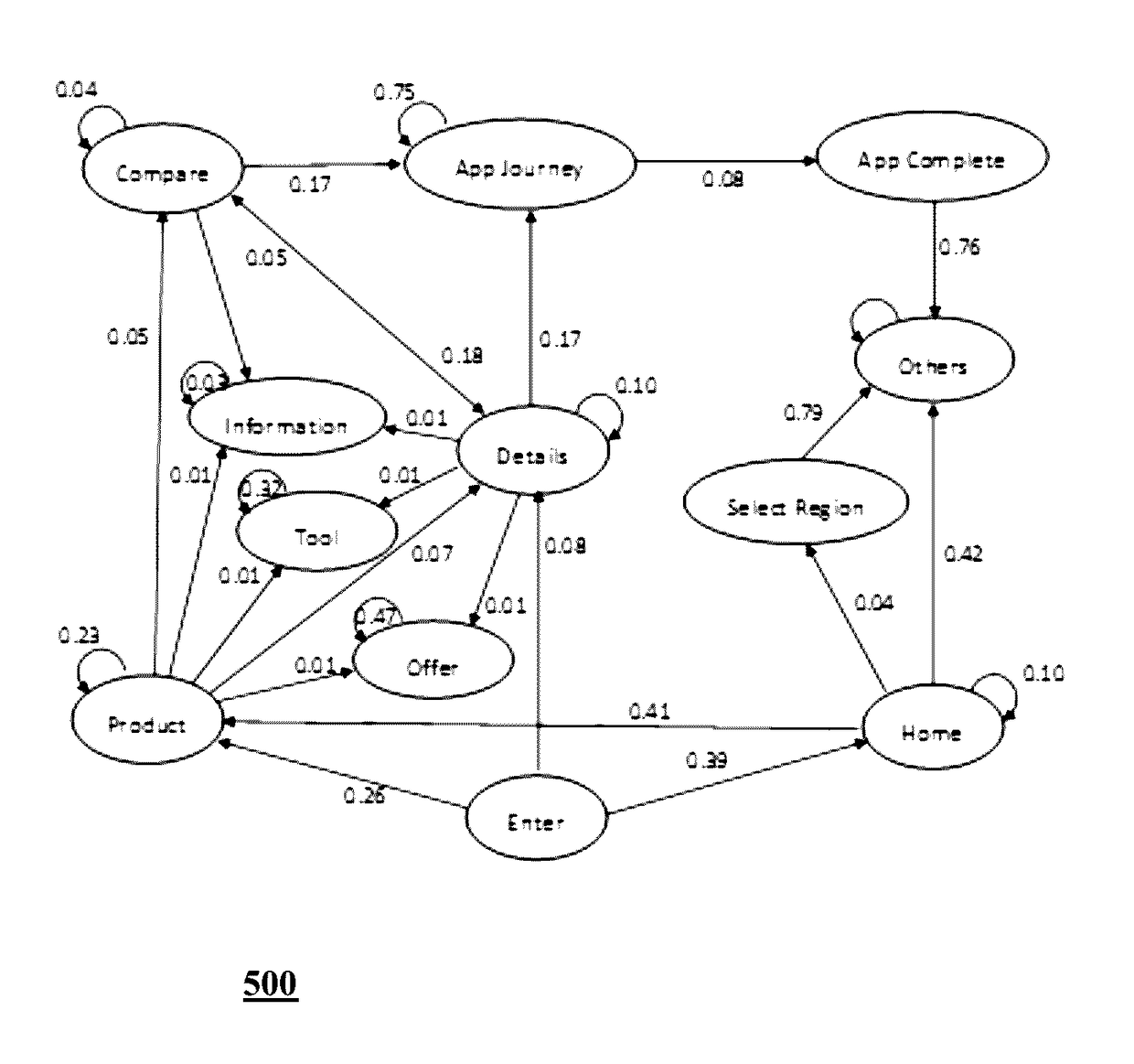
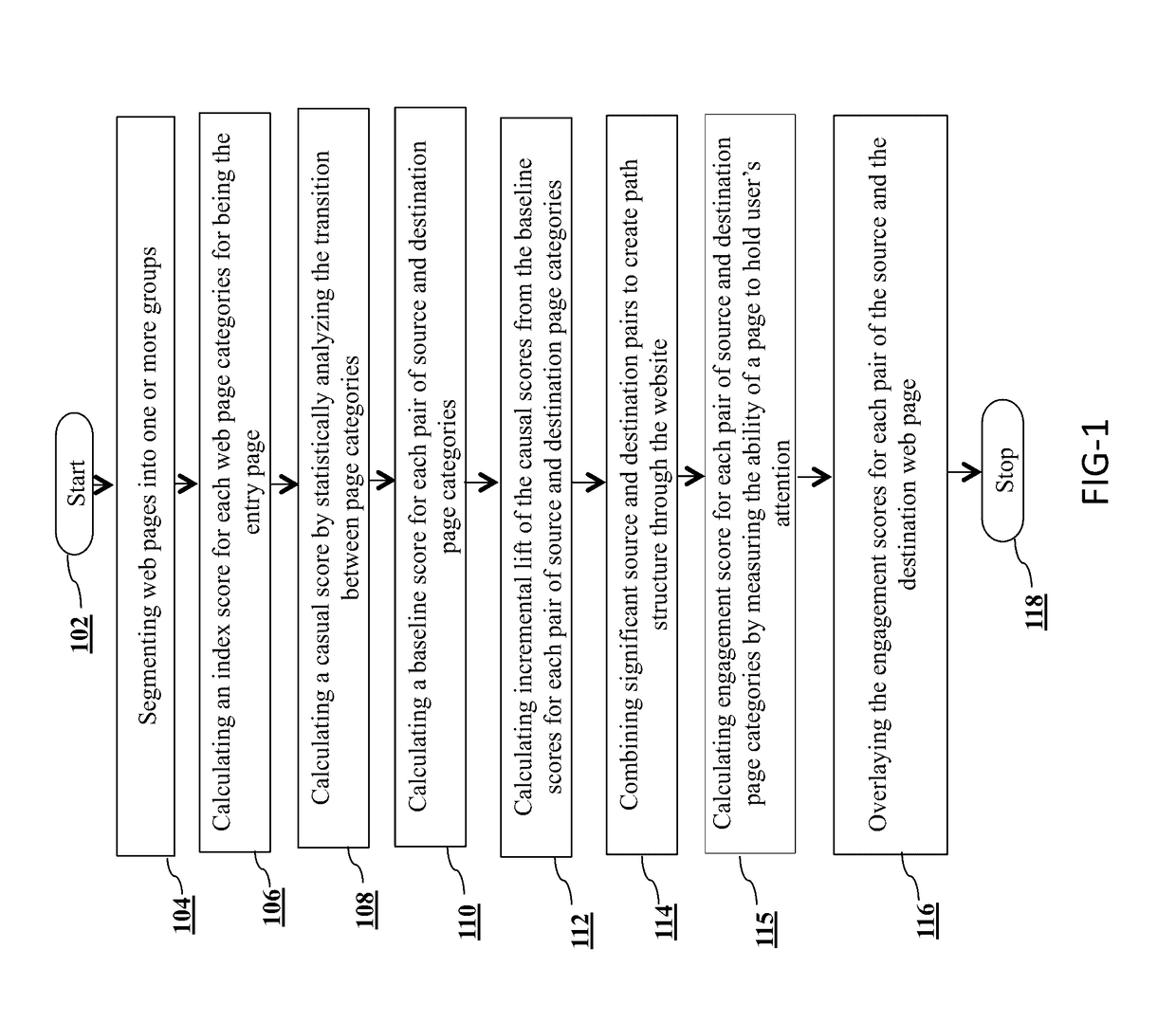
Website navigation path analysis
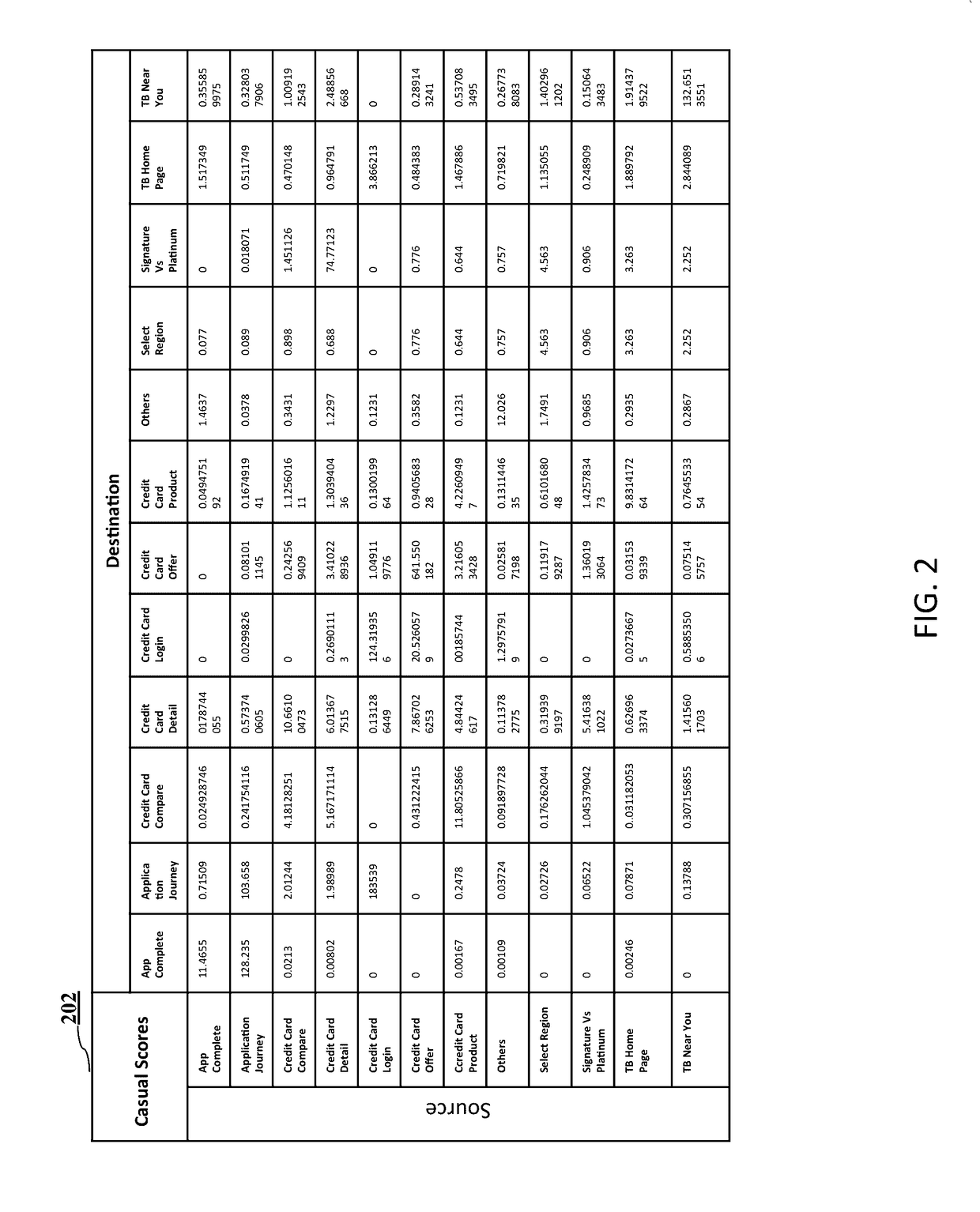
A method and a system for website navigation path analysis are disclosed. The system comprises of a processor; a non-transitory computer-readable storage medium coupled to the processor. The processor executes a plurality of the modules / subsystems stored in the storage medium such as a data categorizing module for categorizing web pages of the website into one or more groups of web pages based on the domain knowledge and functional similarities between the web pages; a score assigning module for calculating an index score, casual score, base line score and engagement score for web page elements and categorized web page pair; a statistical model to be trained with the scores and weight calculated by the score assigning module, and an analyzing module for determining which web pages and transitions correspond to engagement and decision making based on the trained statistical model.
Owner:IQUANTI INC
Protein function prediction method and device
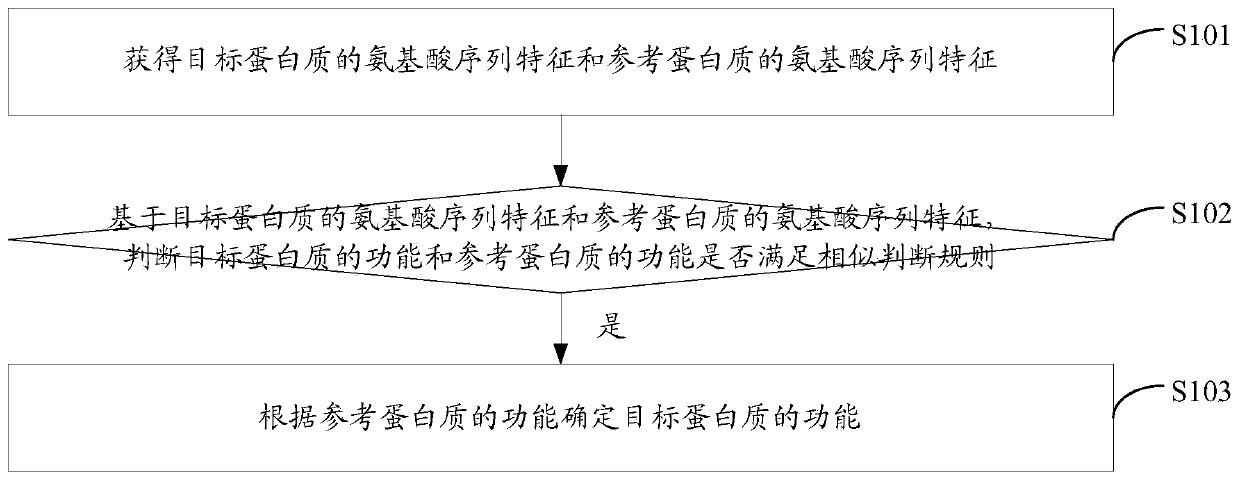
ActiveCN109785901AAchieve forecastAvoid the impact of functional similarity judgmentsBiostatisticsProteomicsProtein function predictionAmbiguity
The embodiment of the invention discloses a protein function prediction method and a protein function prediction device. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining amino acid sequence characteristics of a target protein and amino acid sequence characteristics of a reference protein; based on the amino acid sequence characteristics of the target protein and the amino acid sequence characteristics of the reference protein, judging whether the functions of the target protein and the reference protein meet a similarity judgment rule or not; and if yes, determining the function of the target protein according to the function of the reference protein. The similarity between the function of the target protein and the function of the reference protein is judged from the deep feature level of the amino acid sequence related to the function, so that the influence of the ambiguity of the surface feature of the amino acid sequence on the function similarity judgment can be avoided. Thecoverage rate of protein function prediction is improved.
Owner:NEUSOFT CORP
Calculation method for predicting key proteins by combining multiple data features
ActiveCN109166604ASolve the costResolution cycleProteomicsGenomicsData informationExpression Feature
The invention discloses a calculation method for predicting key proteins by combining multiple data features. According to the method, the features such as aggregation features, co-expression features, functional similarity and positional consistency of key proteins are analyzed; and the edge clustering coefficient of a protein interaction network, the Pearson correlation coefficients of gene expression values, the semantic similarity indexes of gene ontology terms and protein subcellular localization statistical features are effectively integrated. The method of the invention is simple and easy to use; four kinds of data, such as protein interaction relationship data, gene expression spectrum data, gene ontology term information data and protein subcellular localization data information are inputted; and test results indicate that the method of the invention can significantly improve the prediction accuracy and efficiency of the key proteins in the protein interaction network comparedwith an existing method.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
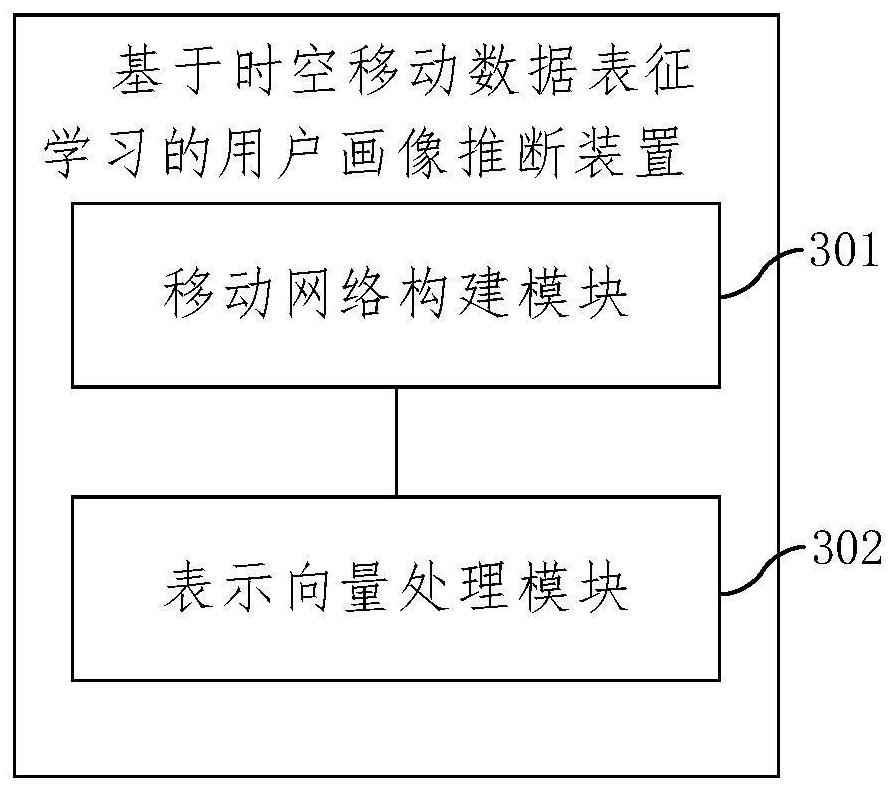
User portrait inference method and device based on spatio-temporal movement data representation learning
ActiveCN111695046AAccurate attribute inferenceEnhance expressive abilityDigital data information retrievalKernel methodsDatasheetEngineering
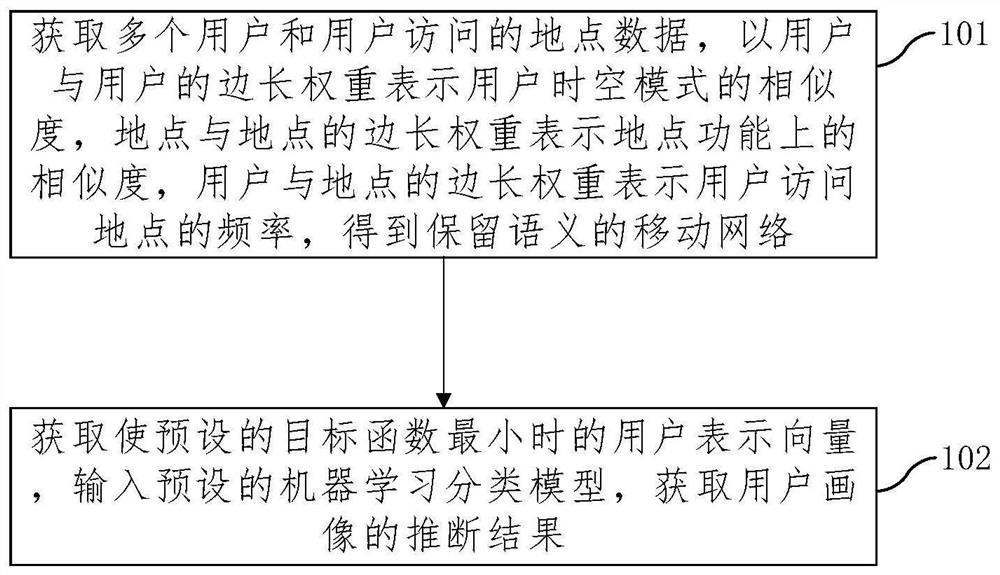
An embodiment of the invention provides a user portrait inference method and device based on spatio-temporal movement data representation learning. The method comprises the following steps: acquiringa plurality of users and place data accessed by the users, representing the similarity of a user space-time mode by side length weights of the users, representing the functional similarity of the places by side length weights of the places, and representing the frequency of the places accessed by the users by side length weights of the users and the places to obtain a mobile network with reservedsemantics; obtaining a user representation vector when the preset target function is minimum, inputting the user representation vector into a preset machine learning classification model, and obtaining an inference result of the user portrait; wherein the target function is constructed according to the three types of side length weights, the user representation vector and the place representationvector. According to the method, a large amount of feature generation and feature screening do not need to be carried out manually, the model training efficiency is high, the labor cost is effectivelysaved, the model performance can be effectively guaranteed, and then accurate user attribute inference based on mobile data is achieved.
Owner:北京清鹏智能科技有限公司
Multidata integration circular RNA and disease correlation prediction method based on double random walk restart
ActiveCN110428899AReduce lossesImprove forecast accuracyBiostatisticsMedical automated diagnosisPattern recognitionUndirected graph
The invention discloses multidata integration circular RNA and a disease correlation prediction method based on double random walk restart. By transforming a circular RNA-disease relationship networkinto an undirected graph, calculating the semantic similarity of circular RNA function annotations, structural similarity and functional similarity, and calculating the disease function and semantic similarity, multiple circular RNA similarity networks and disease similarity networks are integrated into a comprehensive circular RNA similarity network and disease similarity network, a random walk restart algorithm is applied to the integrated circular RNA similarity network and the disease similarity network separately, the cold restart problem is avoided, and a potential circular RNA-disease relationship is predicted. Accordingly, the potential circular RNA-disease relationship can be accurately predicted; simulation experiment results indicate that the precision, recall rate, accuracy, f1-measure and other indexes are better; compared with other relationship prediction methods, the prediction accuracy of the RNA-disease relationship is improved.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Nucleic acid compositions conferring disease resistance
InactiveUS20050019767A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyHeterologous
This invention encompasses the identification and isolation of genes that confer disease control properties in plants, as well as plants comprising such genes. These genes are derived from the following sources: Nicotiana benthamiana, Oryzae sativa (var. Indica IR7), Papaver rhoeas, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Trichoderma harzianum (Rifai 1295-22). The control conferred is against the one or more of the following phytopathogens: Aspergillus flavus, Cercospora zeae-maydis, Fusarium monilforme, Fusarium graminearum, Helminthosporium maydis, Phoma lingam, Phomopsis helianthi, Phytopthera infestans, Pyricularia oryzae, Pythium ultimum, Rhizoctonia solani, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, Ustilago maydis, and Verticillium dahliae. Further, this invention encompasses other homologous and heterologous sequences with a high degree of functional similarity.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
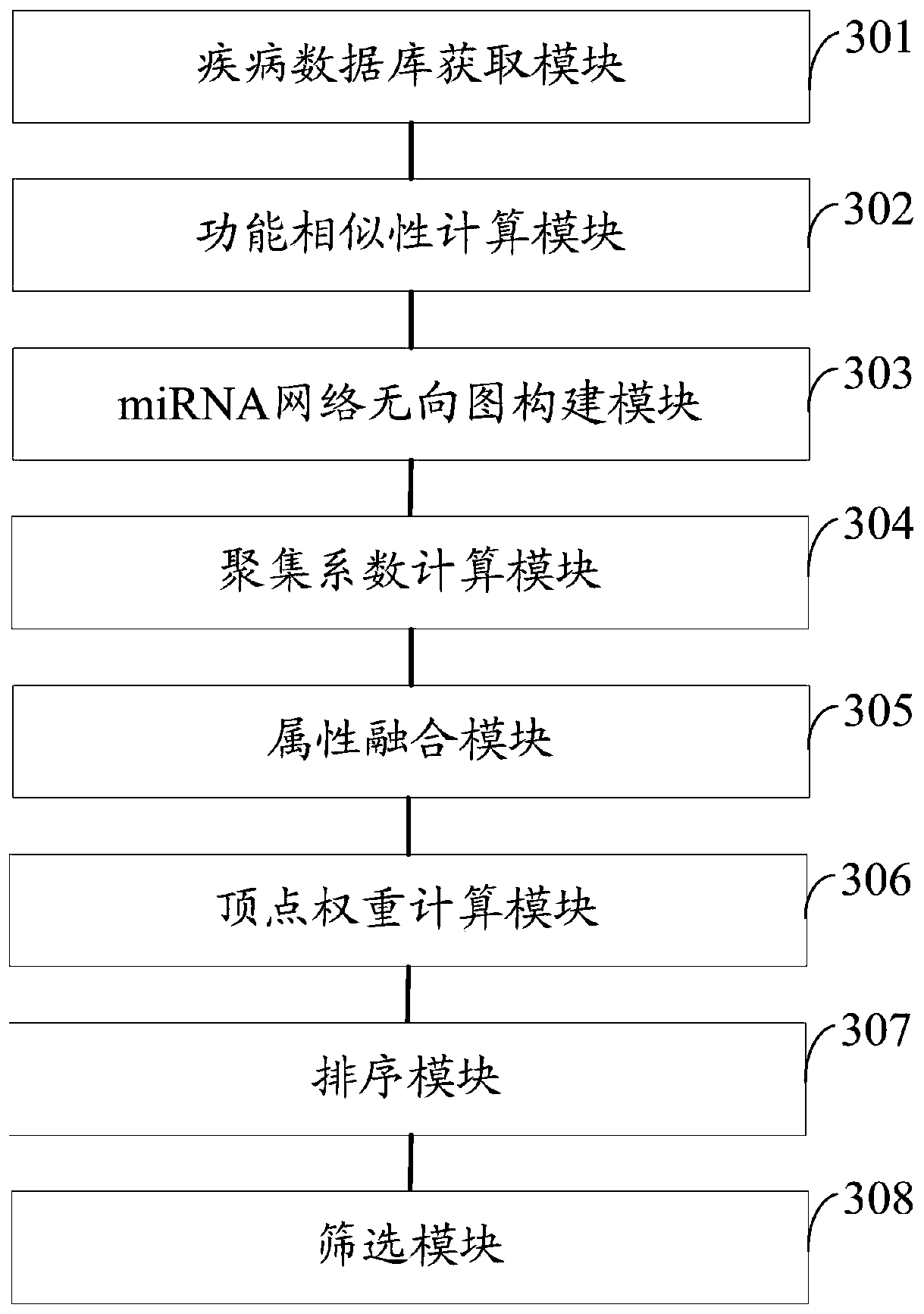
miRNA-disease association identification method and system based on fusion attributes
ActiveCN110853763AImprove accuracyEasy to implementMedical data miningSequence analysisUndirected graphMedical diagnosis
The invention discloses a miRNA-disease association identification method and system based on fusion attributes. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, calculating functional similarity between any two miRNAs in a disease database, constructing an miRNA network undirected graph according to the functional similarity, calculating an aggregation coefficient between any two different miRNAs, and fusing the functional similarity and the aggregation coefficient between the two miRNAs to obtain a combined weight; secondly, calculating the weight of each miRNA vertex according to the combined weight, performing descending sort on each miRNA according to the weight, and screening out potential miRNAs related to diseases according to a descending sort result. The method is simple to implement; on the basis of fusing two attributes of topology attributes and function similarity, the miRNA nodes are weighted and sequenced in a descending order, and then potential correlation between miRNA and diseases is predicted by means of a disease database related to human miRNA and by means of a sequenced result, so the miRNA-disease correlation identification accuracy is improved, and valuable clues can be provided for medical diagnosis.
Owner:HUNAN CITY UNIV
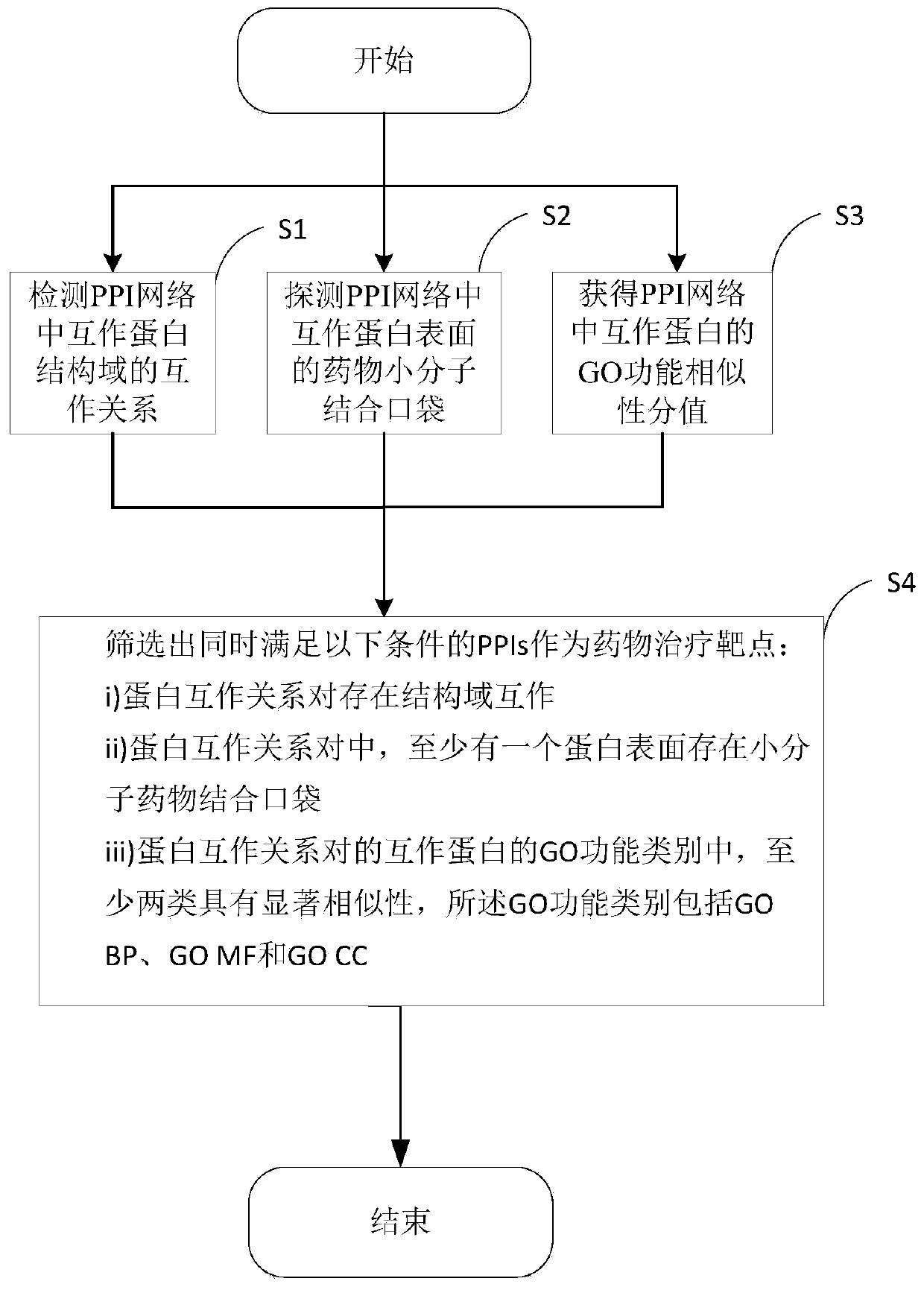
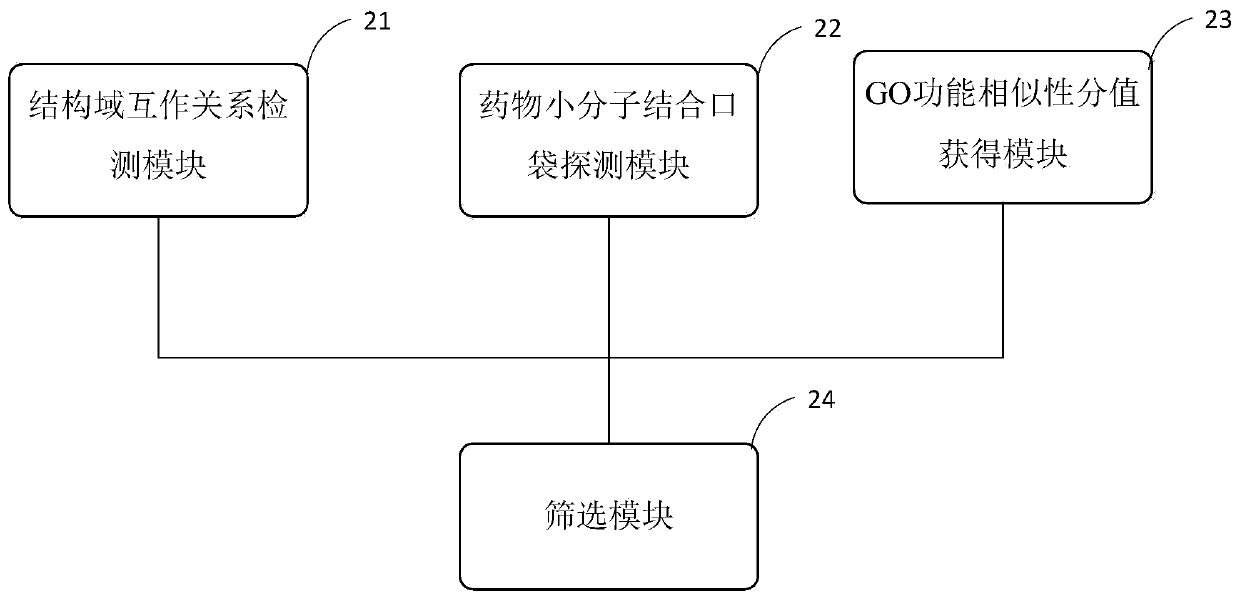
Target PPIs drug property prediction method and device based on protein interaction network
ActiveCN110544506AReliable interactionReduce false positivesProteomicsGenomicsPositive interactionInteractions protein
The invention provides a target PPIs drug property prediction method based on a protein interaction network. The method at least comprises the following steps: S1, detecting the interaction relationship of interaction protein structural domains in the PPI network; S2, detecting a drug small molecule binding pocket on the surface of interaction protein in the PPI network; S3, obtaining a GO function similarity score of the interactive protein in the PPI network; S4, screening out PPIs meeting the following conditions at the same time to serve as drug therapy targets: protein interaction relationship pairs have structural domain interaction; in the protein interaction relationship pair, at least one protein surface has a small molecule drug binding pocket; at least two of the GO function categories of the interaction proteins of the protein interaction relationship pair have significant similarity, and the GO function categories comprise GO BP, GO MF and GO CC. According to the method, three strict mutually independent standards are adopted to comprehensively explore and discover the target PPI, false positive interaction is systematically eliminated, more reliable PPIs are selectedas drug targets, and the calculation result better conforms to objective reality.
Owner:上海源兹生物科技有限公司
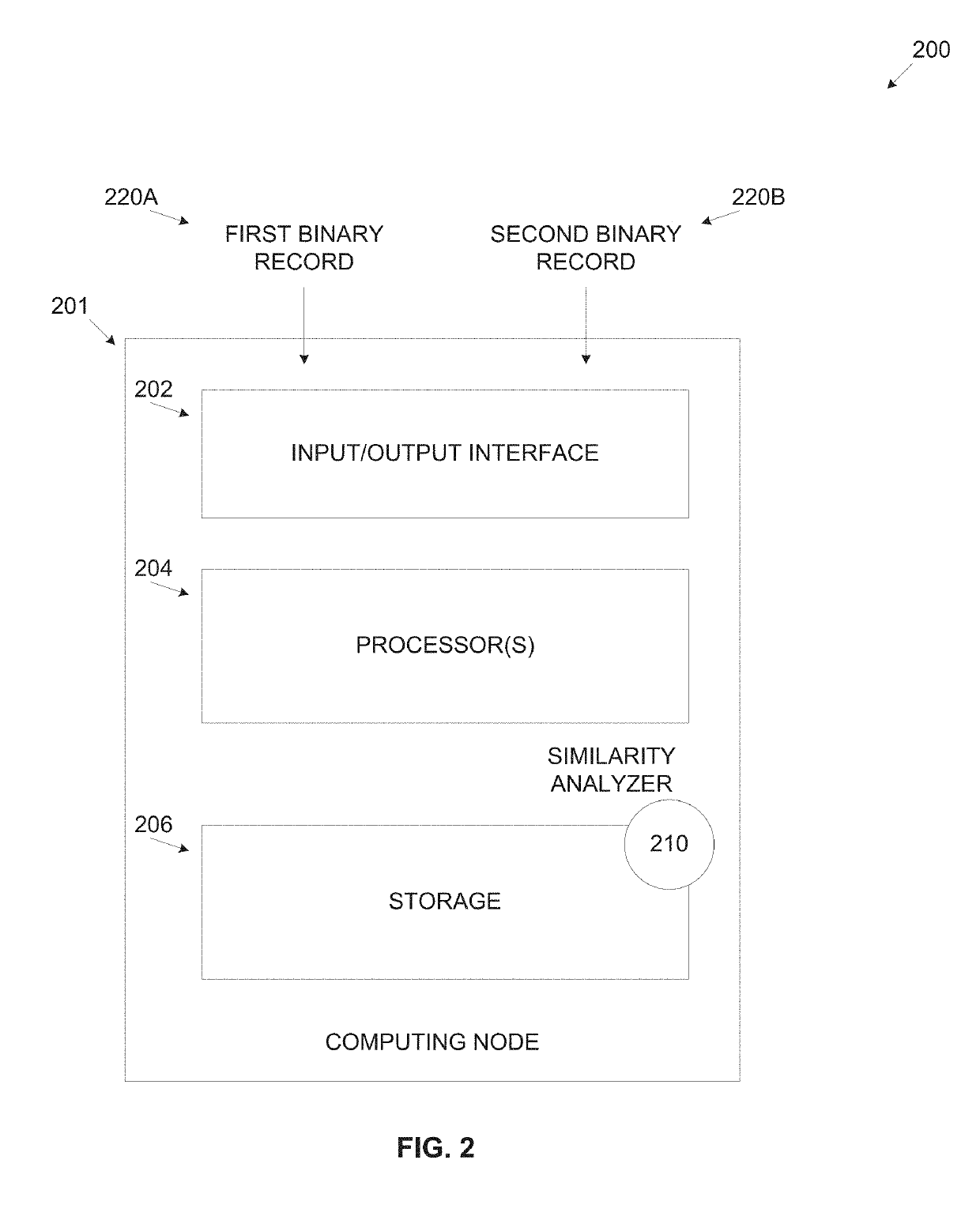
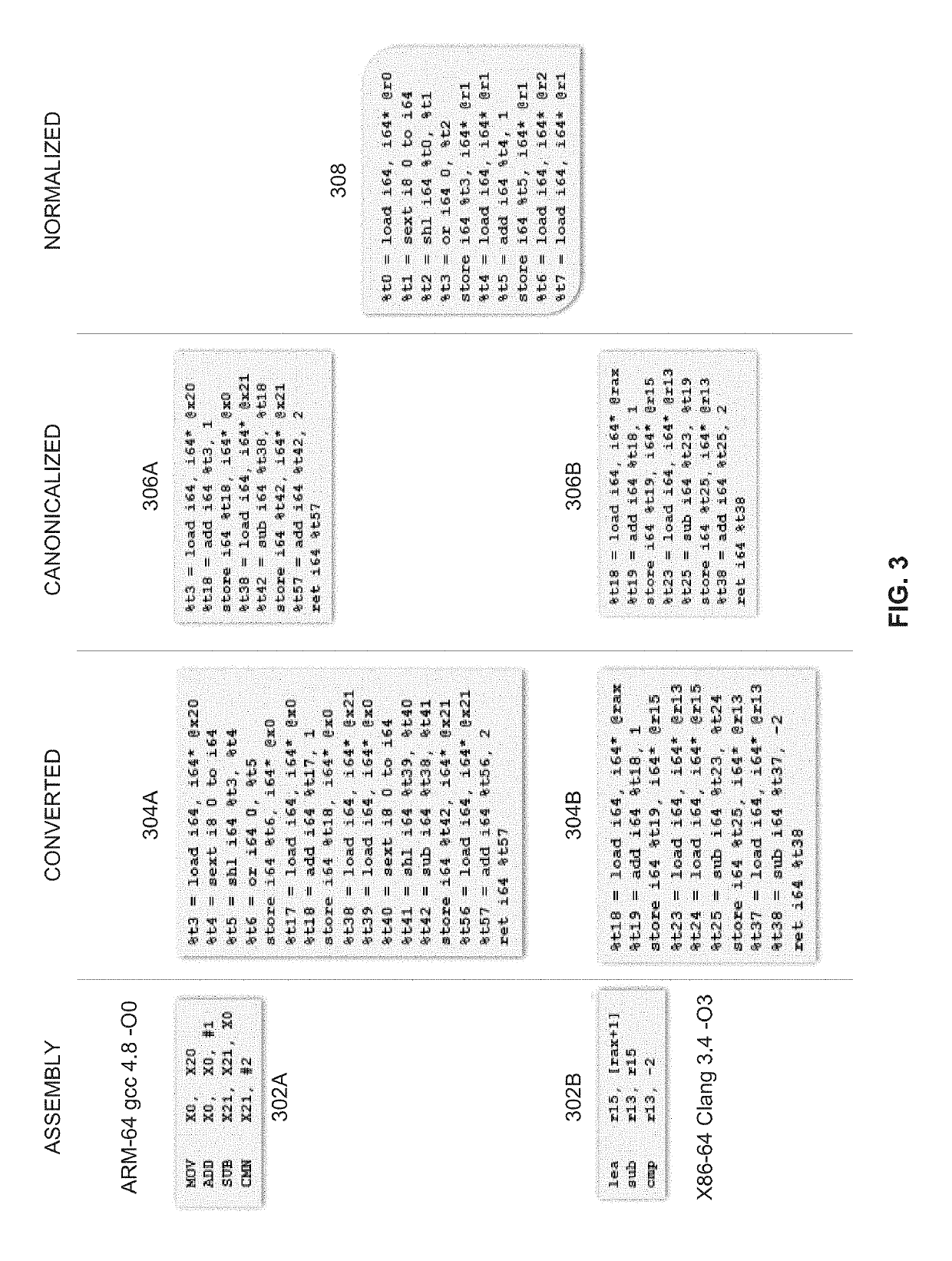
Similarity of binaries
ActiveUS10514909B2The result is accurateImprove accuracyDecompilation/disassemblyReverse engineeringProgram instructionAlgorithm
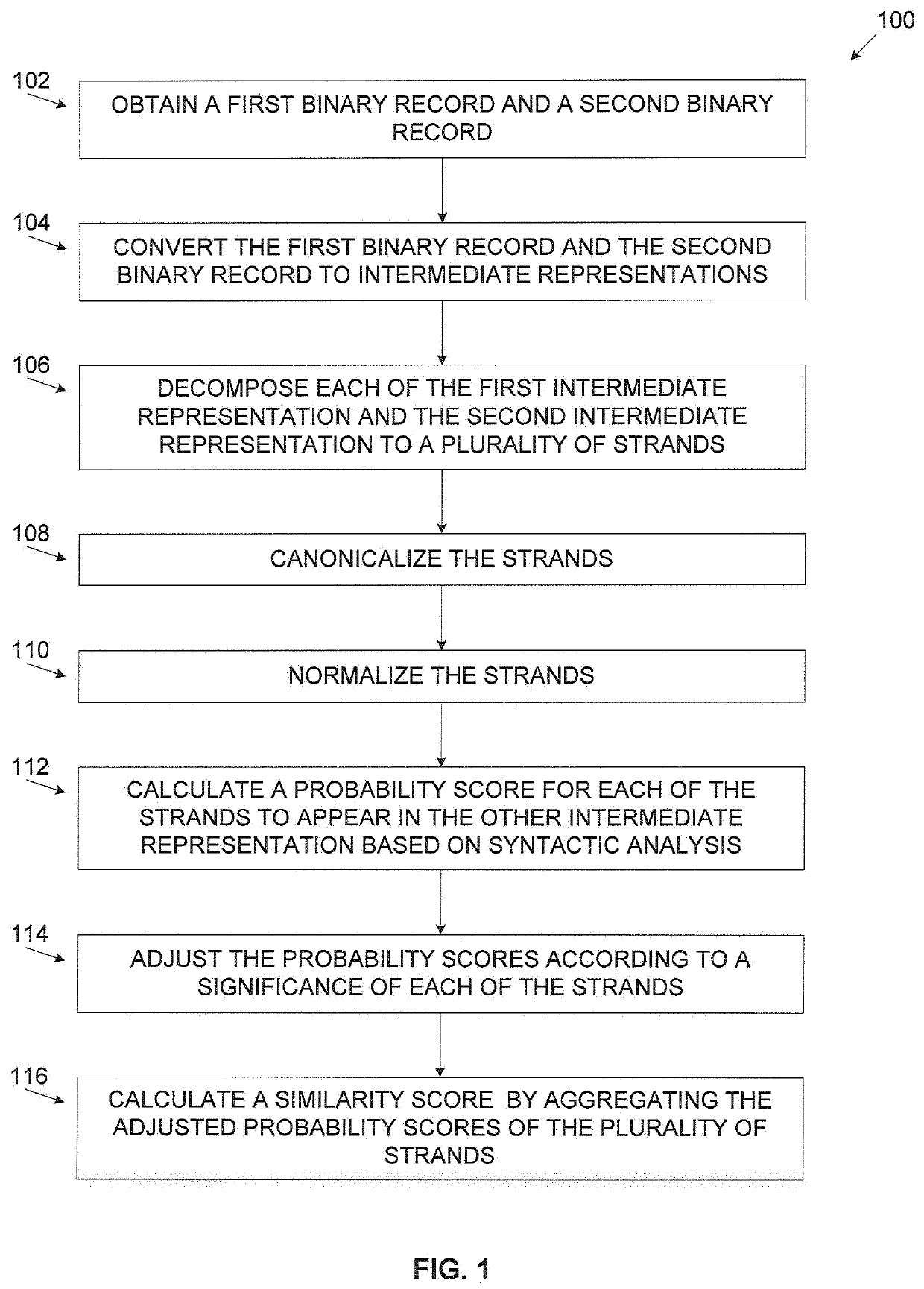
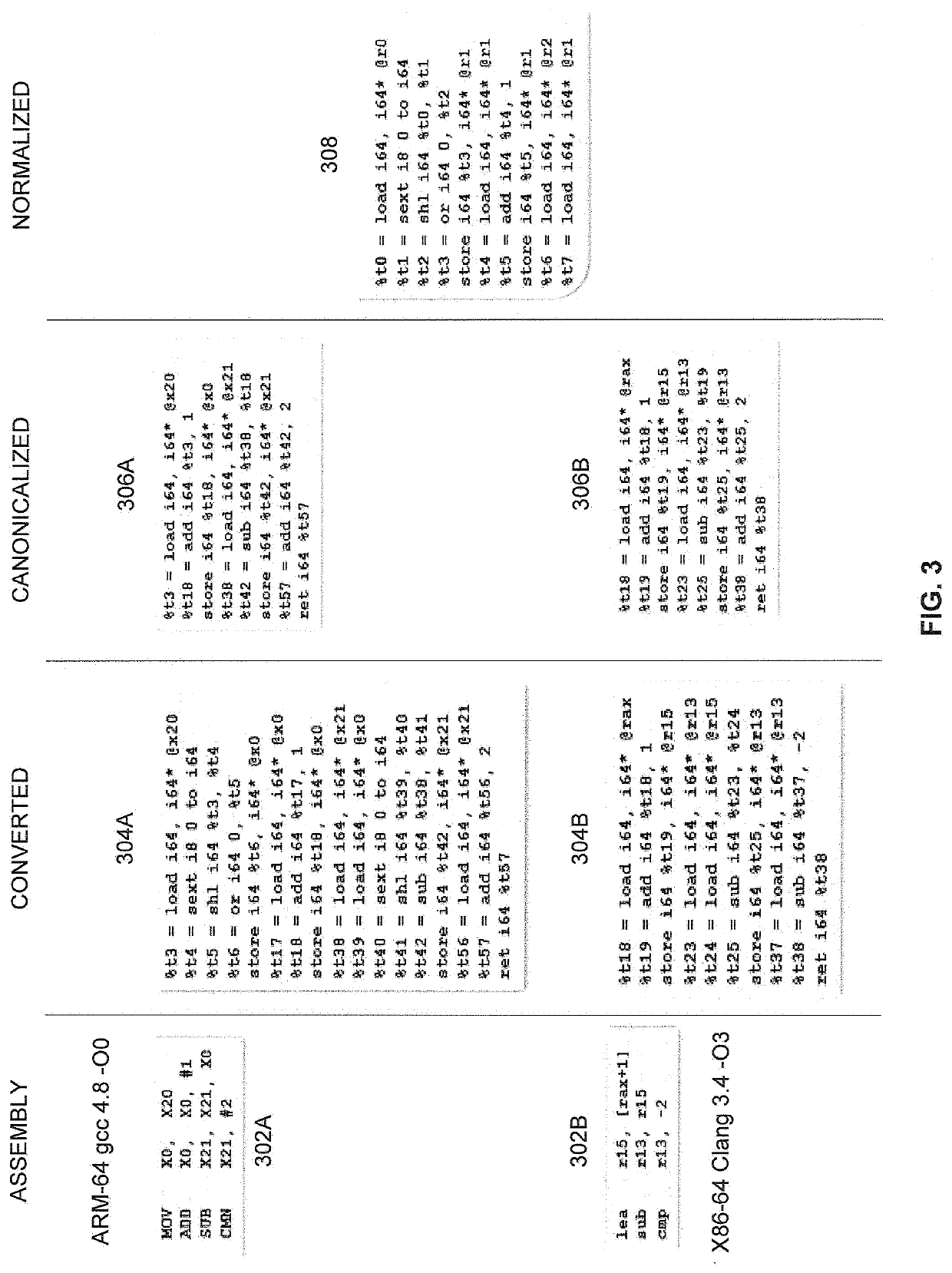
A computer implemented method of estimating a similarity of binary records comprising executable code, comprising converting a first binary record and a second binary record to a first intermediate representation (IR) and a second IR respectively, decomposing each of the first IR and the second IR to a plurality of strands which are partial dependent chains of program instructions, calculating a probability score for each of the plurality of strands of the first IR to have an equivalent counterpart in the second IR by comparing each strand of the first IR to one or more strands of the second IR, adjusting the probability score for each strand according to a significance value calculated for each strand and calculating a similarity score defining a functional similarity between the first IR and the second IR by aggregating the adjusted probability score of the plurality of strands.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
A method for predicting disease-related metabolites by adopting double random walk
PendingCN110610765ATake advantage ofRelationship predictionMedical simulationMedical data miningPattern recognitionAction spectrum
The invention discloses a method for predicting disease-related metabolites by adopting double random walk. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, calculating semantic similarity of a disease by utilizing the semantic information of the disease, and calculating functional similarity of the metabolites according to the relationship between the disease and the metabolites; secondly, according to the known metabolite-disease relationship, calculating Gaussian kernel action spectrum similarity of the disease and the metabolites respectively; thirdly, constructing a final disease similarity network based on the semantic similarity of the disease and the Gaussian kernel action spectrum similarity of the disease, and constructing a final metabolite similarity network based on the function similarity of the metabolites and the Gaussian kernel action spectrum similarity of the metabolites; and finally, constructing a two-part heterogeneous network based on the disease similarity, the metabolite similarity and the known metabolite-disease relationship network, and predicting the disease-related metabolites in the heterogeneous network by utilizing a double random walk method. Tests prove that the method disclosed by the invention can predict the disease-related metabolites, provides a basis for biological experiments and improves diagnosis and treatment level of the disease.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Nucleic acid compositions conferring herbicide resistance
InactiveUS7667100B2Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesPlant cellPlanting seed
The present invention relates to nucleic acid and amino acid sequences that confer herbicide resistance in plants, as well as herbicide resistance in plants, plant seeds, plant tissues and plant cells comprising such sequences. In a preferred embodiment, the sequences of the present invention confer a tolerant phenotype in plants in response to a chronic and / or acute inhibitin dose of auxinic herbicides. The present invention also provides homologous sequences with a high degree of functional similarity.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Similarity of binaries
ActiveUS20200174785A1The result is accurateImprove accuracyDecompilation/disassemblyReverse engineeringProgram instructionAlgorithm
A computer implemented method of estimating a similarity of binary records comprising executable code, comprising converting a first binary record and a second binary record to a first intermediate representation (IR) and a second IR respectively, decomposing each of the first IR and the second IR to a plurality of strands which are partial dependent chains of program instructions, calculating a probability score for each of the plurality of strands of the first IR to have an equivalent counterpart in the second IR by comparing each strand of the first IR to one or more strands of the second IR, adjusting the probability score for each strand according to a significance value calculated for each strand and calculating a similarity score defining a functional similarity between the first IR and the second IR by aggregating the adjusted probability score of the plurality of strands.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
IncRNA and disease association prediction method fusing heterogeneous network and graph neural network
PendingCN114093425AImprove predictive performanceImprove accuracyBiostatisticsNeural architecturesInformaticsNetwork model
The invention relates to the field of data mining in bioinformatics, in particular to an lncRNA and disease association prediction method fusing a heterogeneous network and a graph neural network. The method mainly comprises the following steps: (1) collecting related data; (2) calculating the semantic similarity of the disease, the target similarity of the disease, the sequence similarity of the lncRNA and the functional similarity of the lncRNA; (3) constructing a heterogeneous network net1 by using DDSsem, LLSfun, LDA, LMA and DMA; and constructing a heterogeneous network net2 by using the DDStar, the LLSseq, the LDA, the LMA and the DMS; (4) constructing a neural network model with an attention mechanism, extracting topological structure features in the network by an encoder part through GCN, and fusing the features between nodes, between graphs and between layers by using the attention mechanism; (5) constructing and training a BP neural network; (6) predicting by using the trained BP neural network; and (7) performing an experiment to verify the performance of the prediction model.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Synthetic lethal interaction prediction method based on heterogeneous graph convolutional neural network
The invention relates to the field of data mining in bioinformatics, in particular to a synthetic lethal interaction prediction method based on a heterogeneous graph convolutional neural network. The method mainly comprises the following steps: (1) collecting known synthetic lethal correlation data, gene GO information data and gene PPI data; (2) carrying out gene GO similarity analysis, measuring GO function similarity between genes by utilizing a semantic gene function similarity measurement algorithm, and constructing GO function similarity-based features of the genes; (3) constructing genes based on PPI characteristics, constructing a correlation network between proteins by utilizing protein correlation data, and obtaining the characteristics of each gene based on the protein correlation network in a random walk mode; (4) constructing an adjacent matrix by using synthetic lethal correlation data, and fusing domain features of the gene based on GO function similarity features and PPI features; and (5) constructing a synthetic lethal pair prediction model based on the graph convolutional neural network, predicting potential synthetic lethal interaction, and obtaining a final result.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
An OWL-S-based method for calculating the comprehensive score of Web services
PendingCN109255124AComprehensive considerationSemantic analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionOWL-SWeb service
An OWL-S-based method for calculating the comprehensive score of Web services , includes the following steps: first, calculating the semantic similarity between two concepts A and B in the domain ontology; 2, giving a method for calculating the input similarity degree Simput of the service S1 and the service S2; 3, giving the calculation method of the output similarity Simoutput of the service S1and the service S2; Fourth, calculating the functional similarity FunctionalSim (S1, S2) between the service S1 and the service S2; 5, calculating weights of QoS attributes set by users; 6, verifyingthe consistency of the user judgment according to the paired comparison matrix A constructed in the fifth step and the weight vector W obtained in the fifth step; 7, calculating the weighted result ofthe QoS score and the functional similarity to obtain the comprehensive score result of the service. The invention has more comprehensive consideration angle and better effectiveness.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com