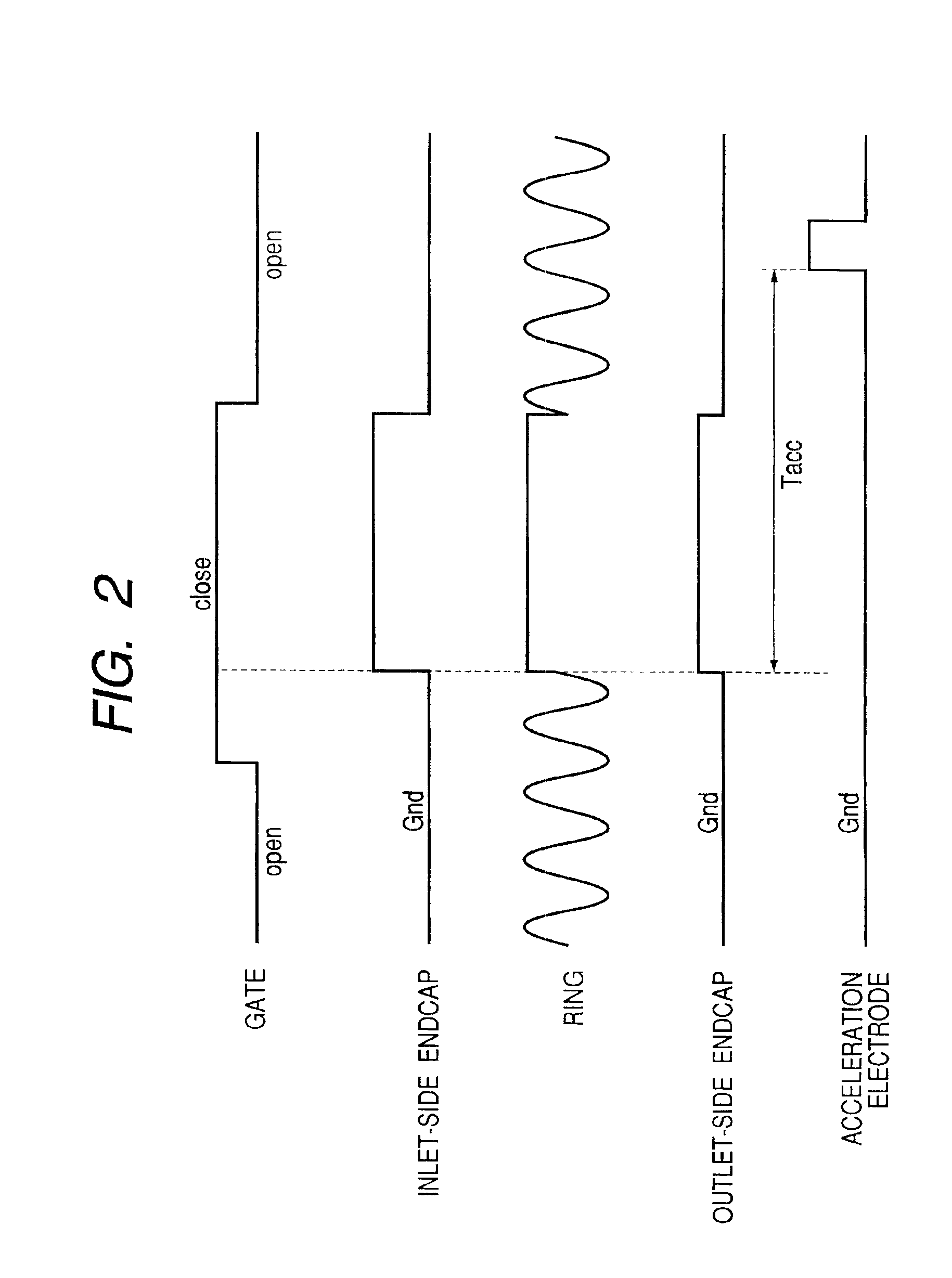
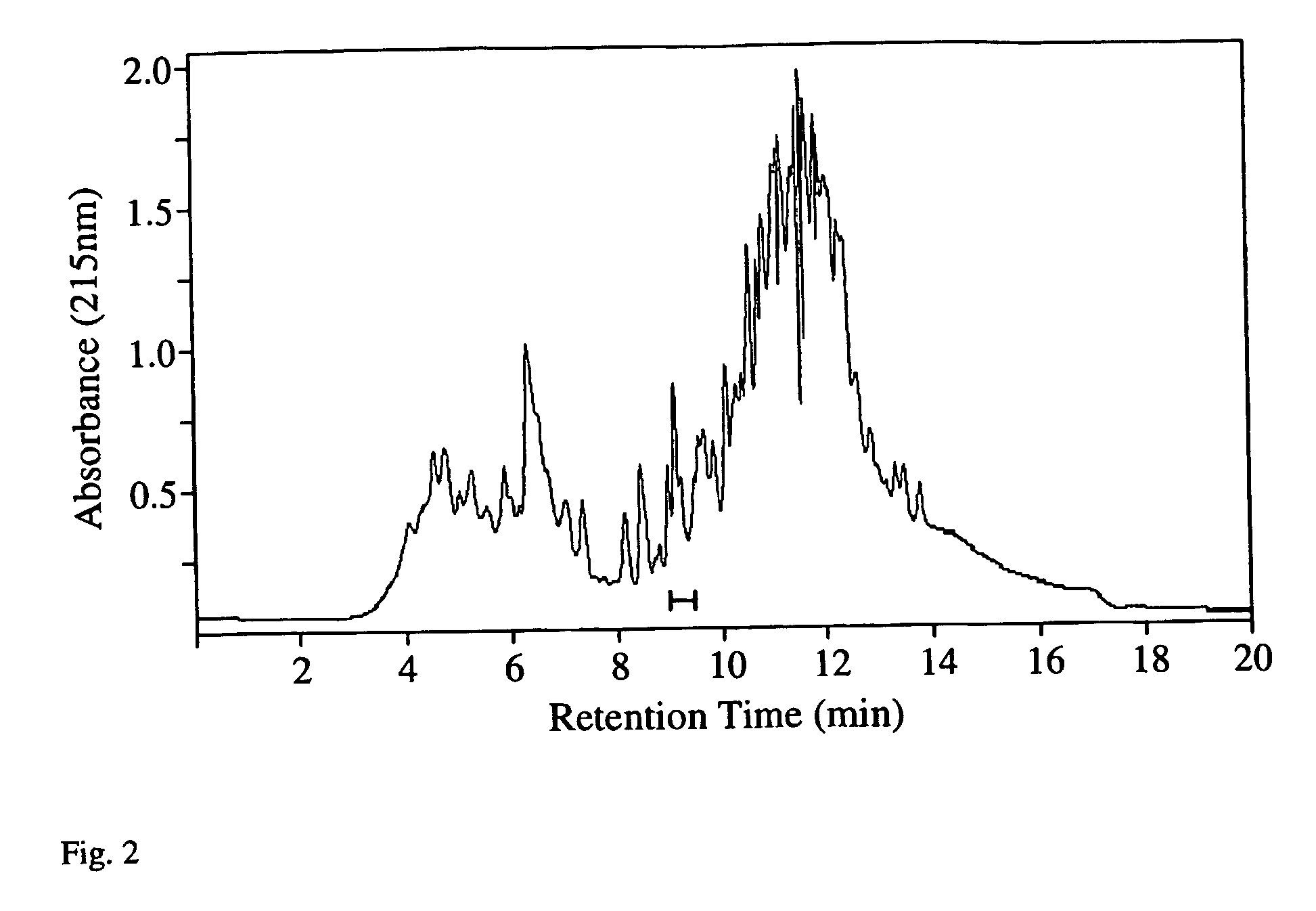
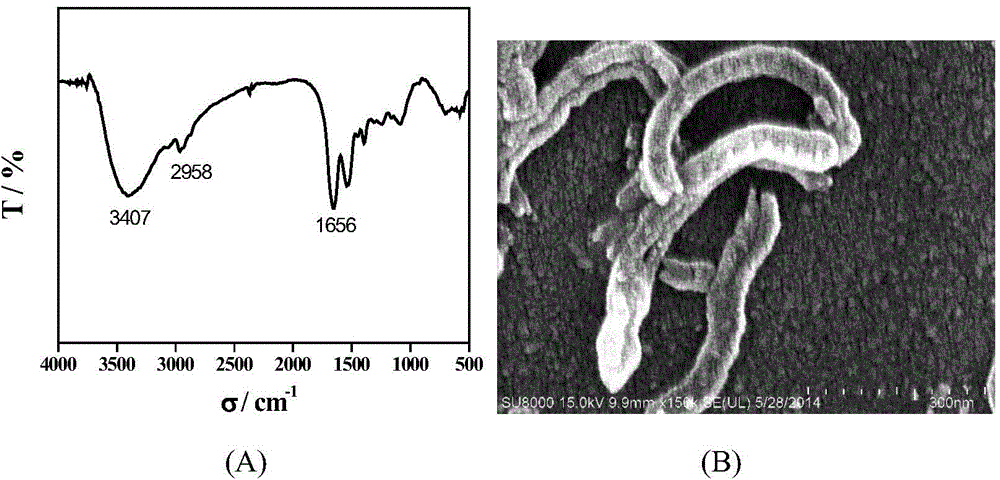
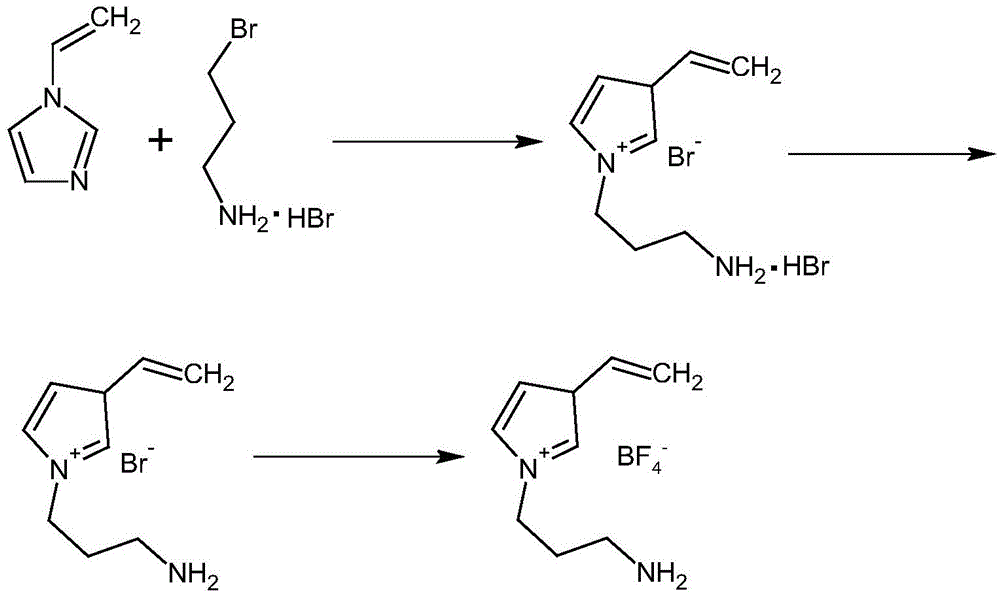
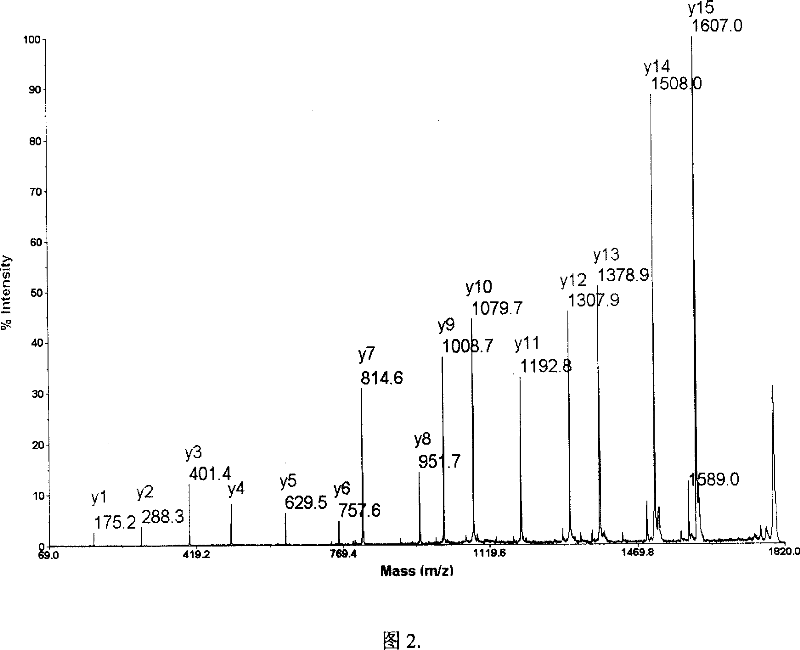
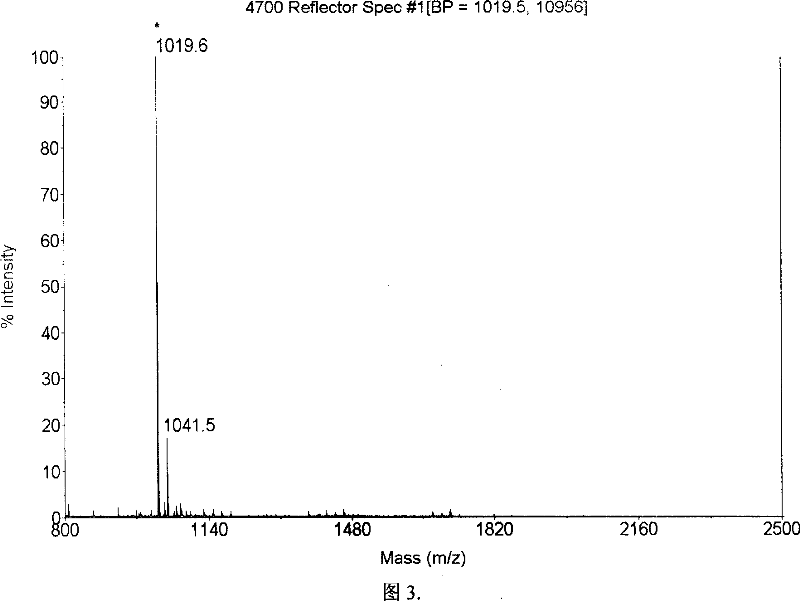
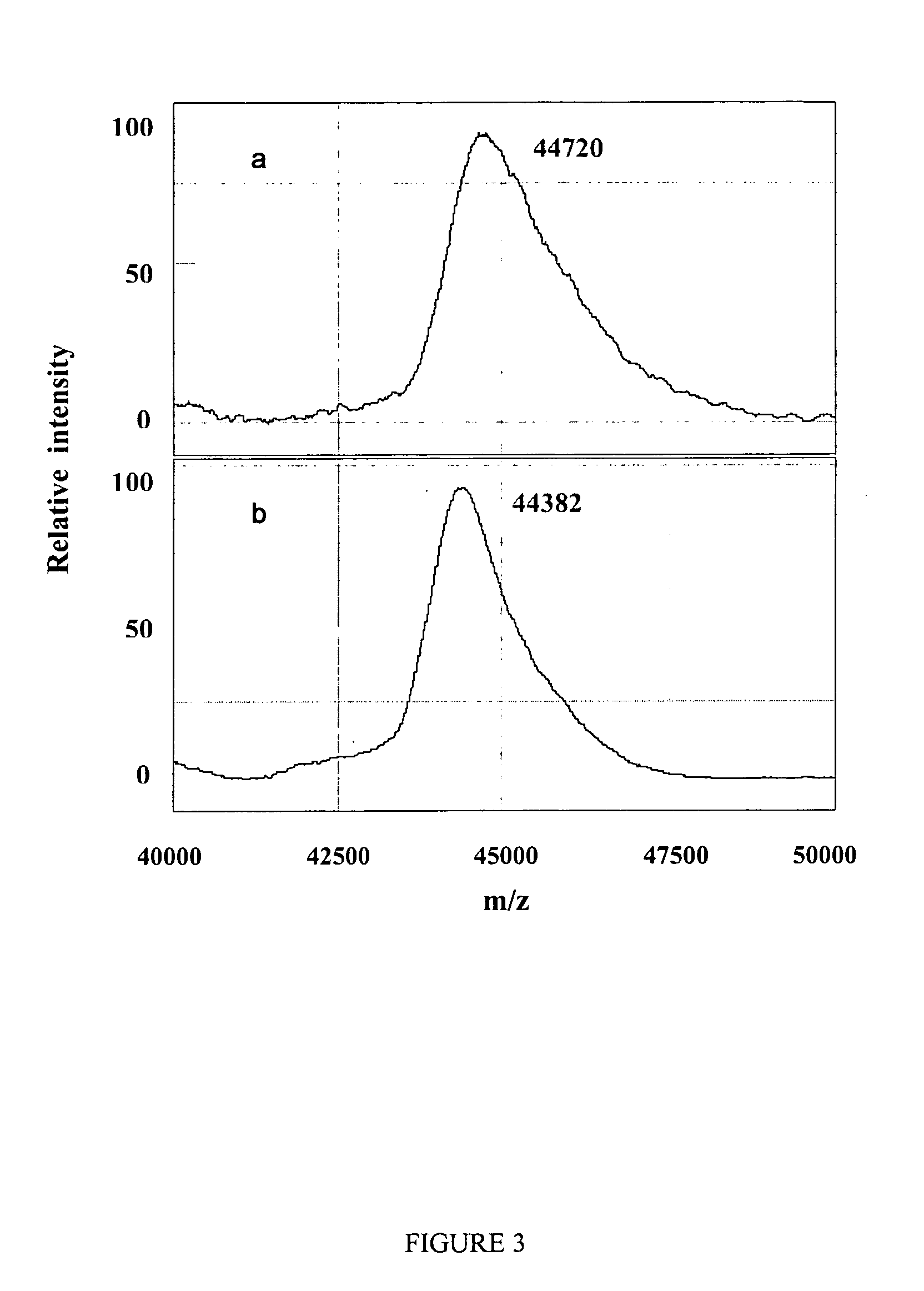
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
181 results about "Protein identification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
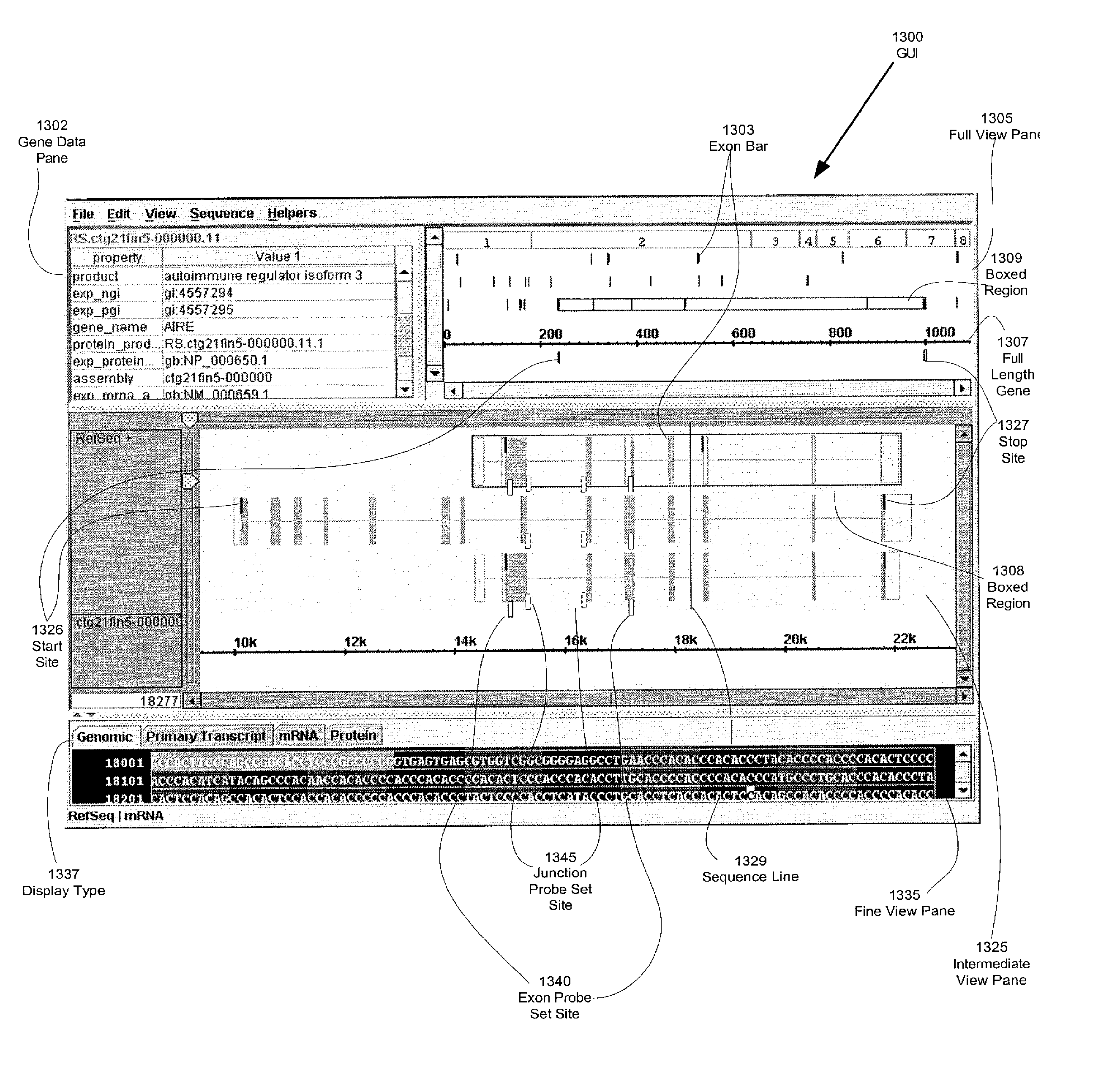
Method, system and computer software for variant information via a web portal
Abstract of Disclosure A genomic web portal is described that receives from a user over the Internet a selection of identifiers of probes for detecting biological molecules. The portal may also receive hybridization intensity values produced from biological probe array experiments. The portal determines alternative splice variants based on factors that may include the hybridization intensity values. The portal correlates alternative splice variants with annotation data and provides for the user a graphical representation of the alternative splice variants and the correlated annotation data. The selection of annotation data to be displayed may be based on a user selection of a genomic, primary-transcript, mRNA, or protein display type. The annotation data may include genomic sequence; presence or relative abundance of alternative splice variants; exon arrangement, content, or sequence; frequency of exon usage in alternative splice variants; RNA, gene, or protein identification, function, structure, or sequence; probe arrangement; and other data.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Method for analysing amino acids, peptides and proteins
The invention provides methods, reagents and kits for amino acid, peptide and protein identification, differential quantitation and for the analysis of post translational modification and cross-linking status, comprising: derivatizing a mixture of amino acids peptides or proteins, to form at least one amino acid peptide or protein containing a fixed-charge ion, other than at the C-terminal or N-terminal end thereof; introducing the mixture of amino acids peptides or proteins containing the fixed charge derivatized amino acid peptide or protein to a mass spectrometer; passing the mixture of amino acids peptides or proteins containing the fixed charge derivatized amino acid peptide or protein through a first mass resolving spectrometer to select precursor protein or peptide ions having a first desired mass-to-charge ratio; subjecting the precursor ions of the first mass to charge ratio to dissociation to form a product ion having a second mass-to-charge ratio that is characteristic of a fragmentation occurring at a site adjacent to the fixed charge; and detecting the product ions having the second mass-to-charge ratio. The product ion having the second mass-to-charge ratio may be either a product ion formed by neutral loss of the fixed charge from the precursor ion, or a product ion formed by charged loss of the fixed charge from the precursor ion.
Owner:LUDWIG INST FOR CANCER RES
Mass spectrometer and measurement system using the mass spectrometer
InactiveUS6900430B2Reducing velocity distributionBroaden mass-to-charge ratio rangeStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersIon trap mass spectrometryMass analyzer
A practical mass spectrometer for proteome analysis is provided. In an ion trap-connected, orthogonal acceleration type time-of-flight mass spectrometer, the mass-to-charge ratio range that may be analyzed by one procedure is increased by providing means for reducing the velocity of ions ejected from an ion trap. The efficiency in protein identification in proteome analysis is thereby improved.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Protein identification from protein product ion spectra
InactiveUS20050221500A1Expand databaseAccurately reflectParticle separator tubesSamplingMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryNatural abundance
Mass spectrometry is used to identify a protein of interest. The protein is first ionized then fragmented into protein product ion. Masses of the observed product ions are compared to product ion masses calculated in silico for database protein sequences to identify product ion matches within a predetermined mass tolerance. An algorithm that weights the product ion to matches based upon one or more factors such as product ion abundance, favored cleavage sites, product ion type, precursor ion charge state and polarity is used to score the possible matches to database proteins in order to identify the protein of interest. The invention represents a “top down” approach and is particularly well-suited for identification of a protein in a complex mixture.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
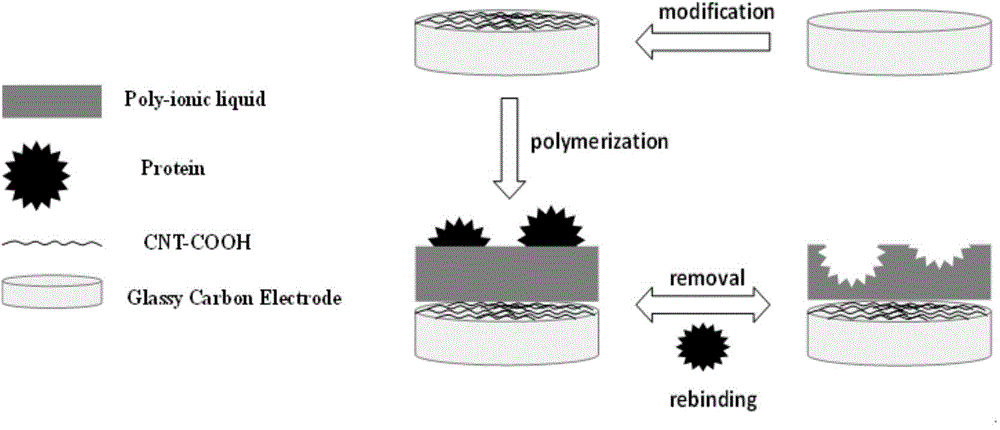
Protein molecular imprinting polyion liquid membrane electrochemical transducer
InactiveCN104142361ALarge specific surface areaGuaranteed stabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiocompatibility TestingIonic liquid
The invention relates to the technical field of electro-analytical chemistry and protein identification transducers, and discloses a synthesizing method of functionalized ionic liquid and a preparation method and application of a molecular imprinting electrochemical transducer composed of the functionalized ionic liquid, carboxylation multiwalled carbon nanotubes and glassy carbon electrodes. The preparation method of the molecular imprinting electrochemical transducer comprises the steps that the polymerizable amino-functionalized ionic liquid is used as a functional monomer, BSA is used as template protein, N, N'-methylene bisacrylamide is used as a cross-linking agent, an oxidation-reduction system composed of ammonium persulfate and TEMED is used as an initiator, after polymerization, a molecularly imprinted polymer film is formed on the surfaces of the glassy carbon electrodes decorating the carboxylation multiwalled carbon nanotubes, and then the template protein is eluted to obtain the molecular imprinting electrochemical transducer which can identify template protein in a specific mode. The molecular imprinting electrochemical transducer has the advantages of being simple in preparation, low in material cost, high in selectivity, good in biocompatibility, and capable of being used for identifying and detecting protein in aqueous solution.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
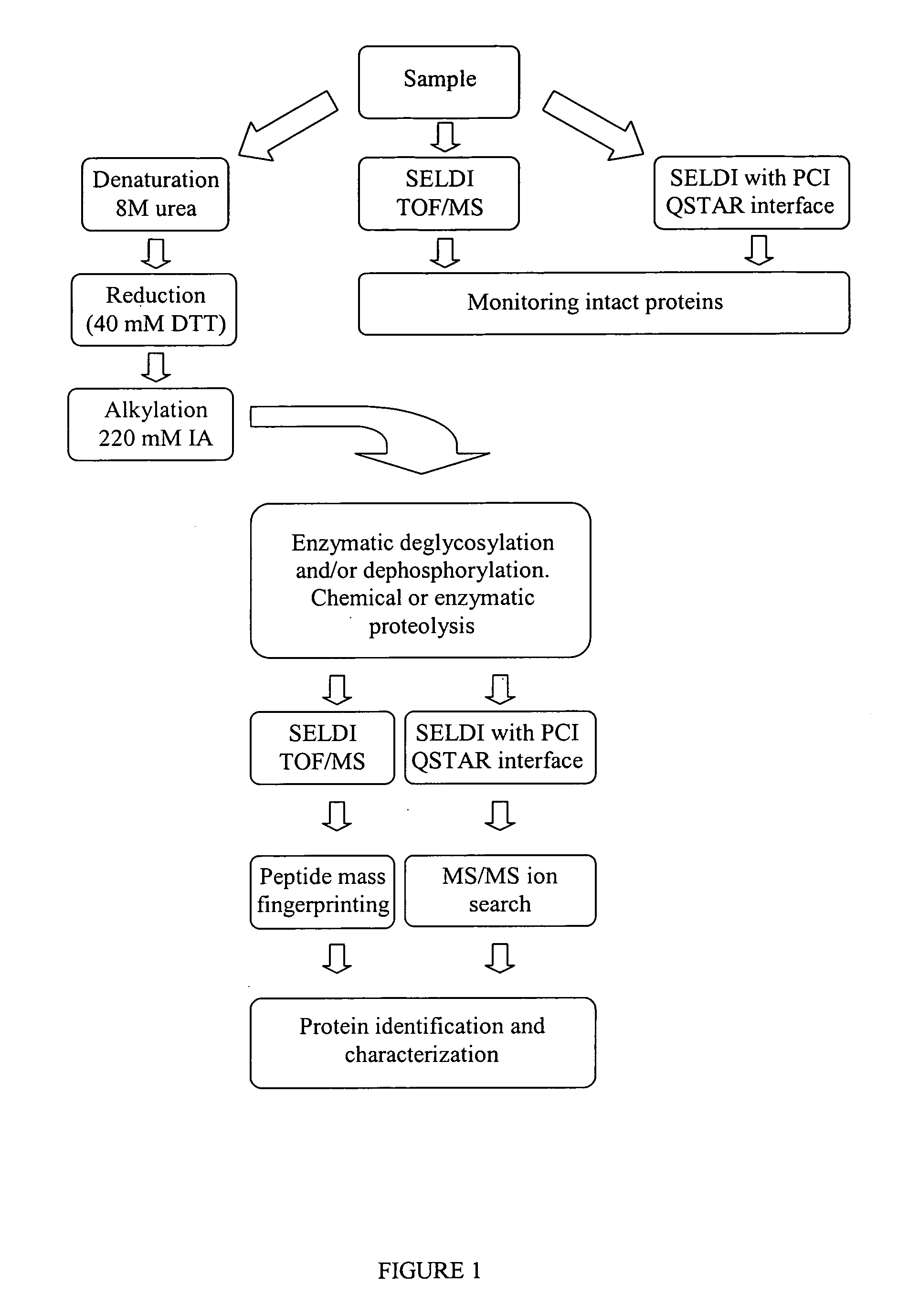
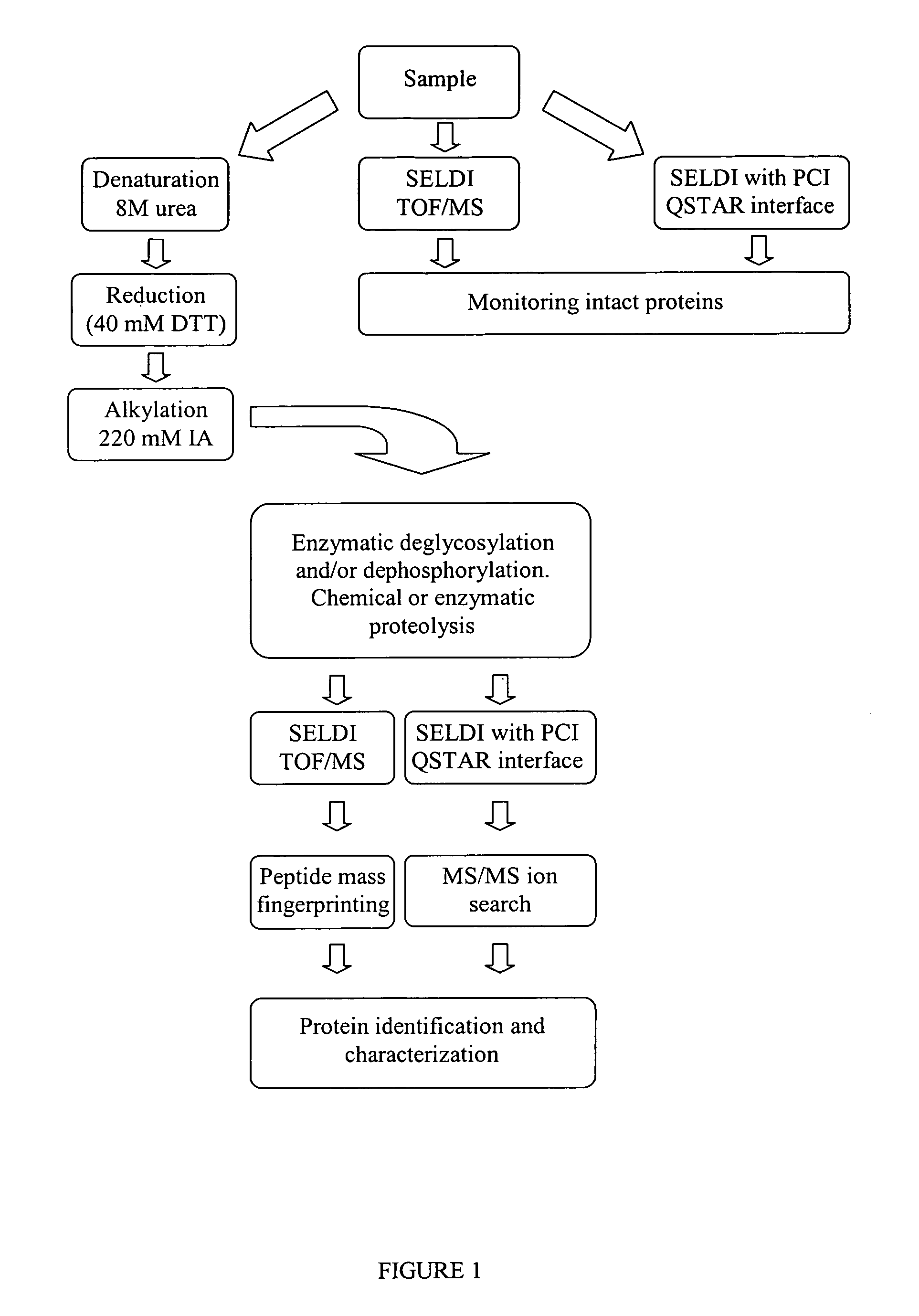
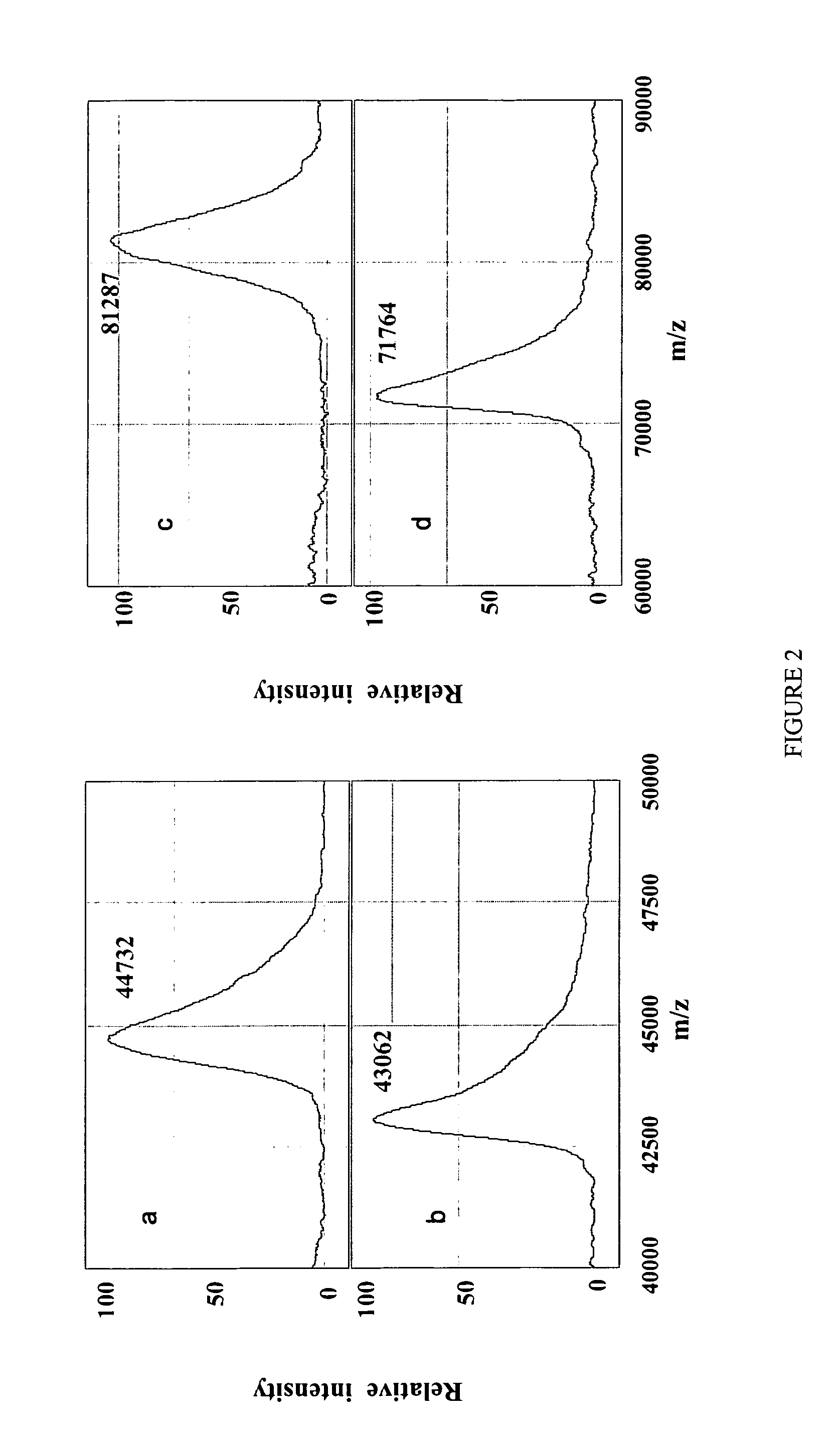
Complete chemical and enzymatic treatment of phosphorylated and glycosylated proteins on protein chip arrays
InactiveUS20060269980A1Quick upgradeSimpler, more sensitive methodologiesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEnzymatic digestionChemical treatment
A simple and quick protocol for chemical treatment, enzymatic or chemical digestion, and subsequent identification of proteins on protein chip arrays is disclosed, together with kits therefor. The chemical treatment comprises denaturation, reduction and alkylation while enzymatic digestion encompasses deglycosylation, dephosphorylation, and digestion by various proteases. Digestion is also accomplished by various chemicals that are known to induce proteolysis. All reactions are carried out sequentially on chip. Subsequent peptide mass fingerprinting or product ion searches allow the identification of specific peptides which can be correlated to proteins. The method of the present invention can be applied to the analysis of biological samples such as urine and plasma to identify biomarkers in diseased states. The methods of the present invention allow complete on chip treatment, which can be used for rapid protein identification and structural characterization of heavily posttranslationally modified proteins.
Owner:GIBBS BERNARD F
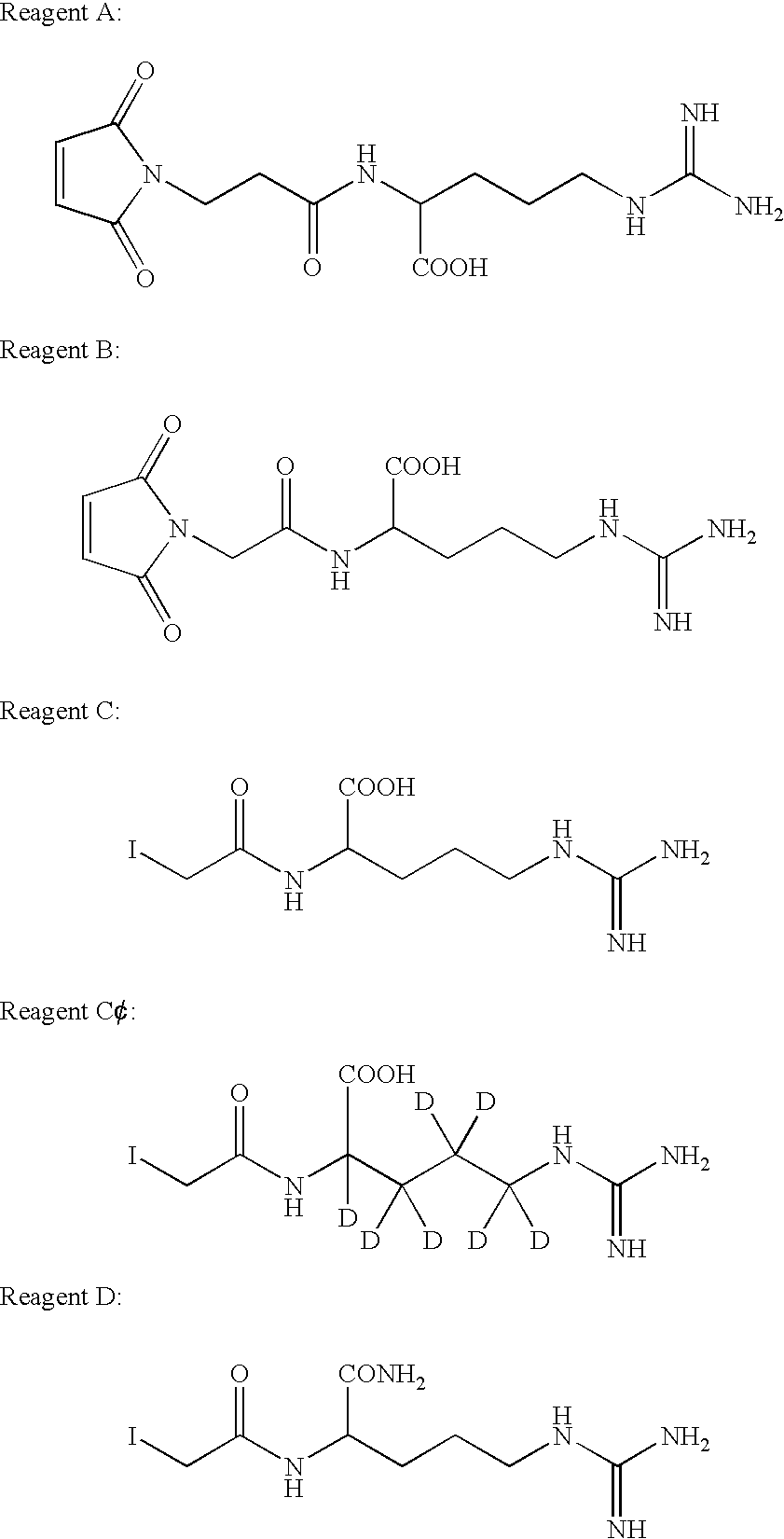
Isotope-coded ionization-enhancing reagents (ICIER) for high-throughput protein identification and quantitation using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry
InactiveUS6905879B2Quantitative precisionReduce disulfide bondSamplingComponent separationLaser desorption ionization mass spectrometryArginine
Arginine-containing cysteine-modifying compounds useful for MALDI-MS analysis of proteins are provided. These compounds termed isotope-coded ionization enhancement reagents (ICIER) can provide ionization enhancement in MALDI-MS, relative quantitation, and additional database searching constraints at the same time without any extra sample manipulation. More specifically, ICIER increase the ionization efficiency of cysteine-containing peptides by attachment of a guanidino functional group. ICIER also increase the overall hydrophilicity of these peptides due to the hydrophilic nature of ICIER and thus increase the percentage of recovery of these peptides during sample handling and processing such as in-gel digestion or liquid chromatography. Finally, a combination of both light and heavy ICIER provides an accurate way to obtain relative quantitation of proteins by MALDI-MS and additional database searching constraints (number of cysteine residues in every single peptide peak) to increase the confidence of protein identification by peptide mass mapping.
Owner:GENETICS INST INC
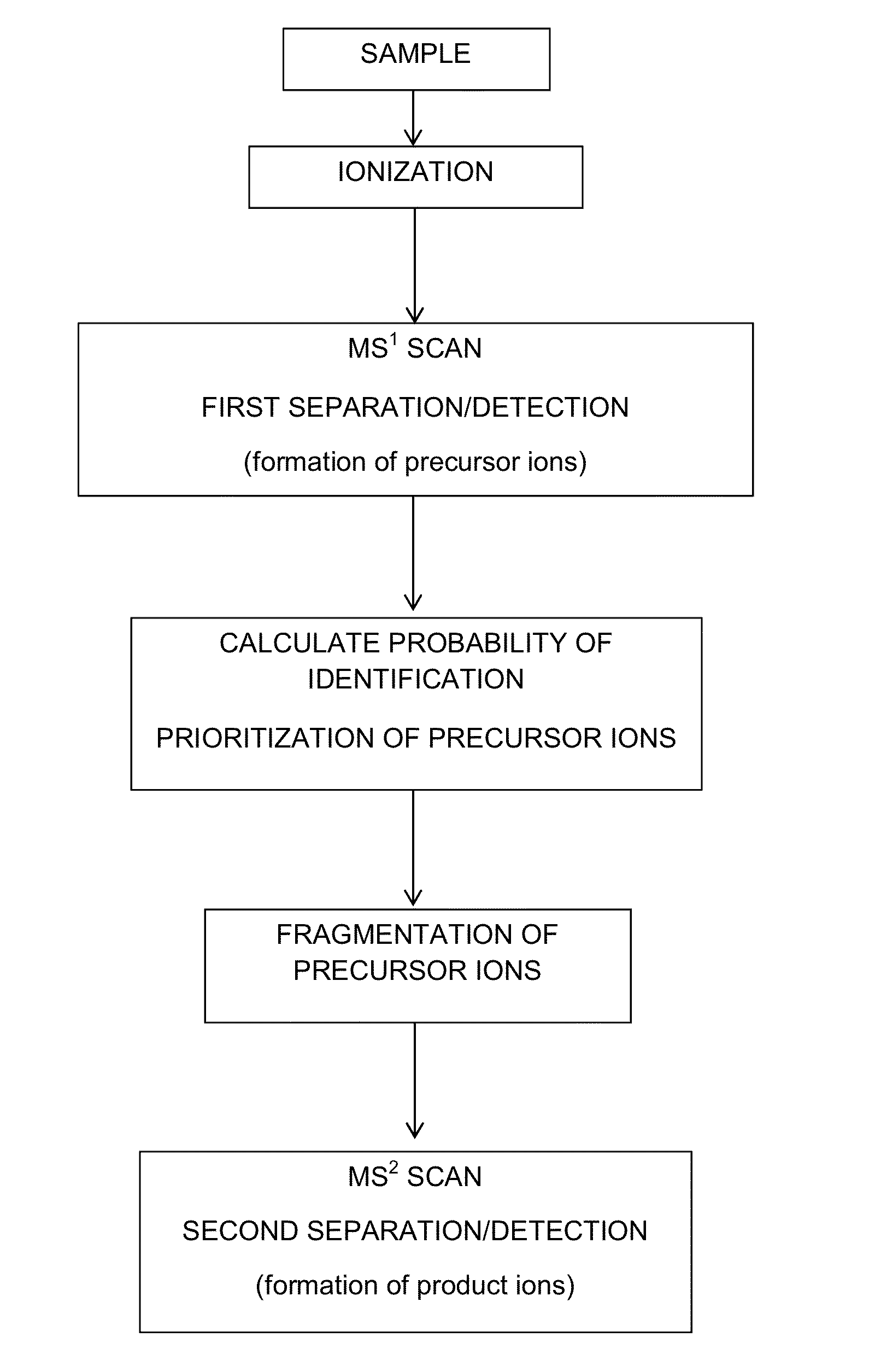
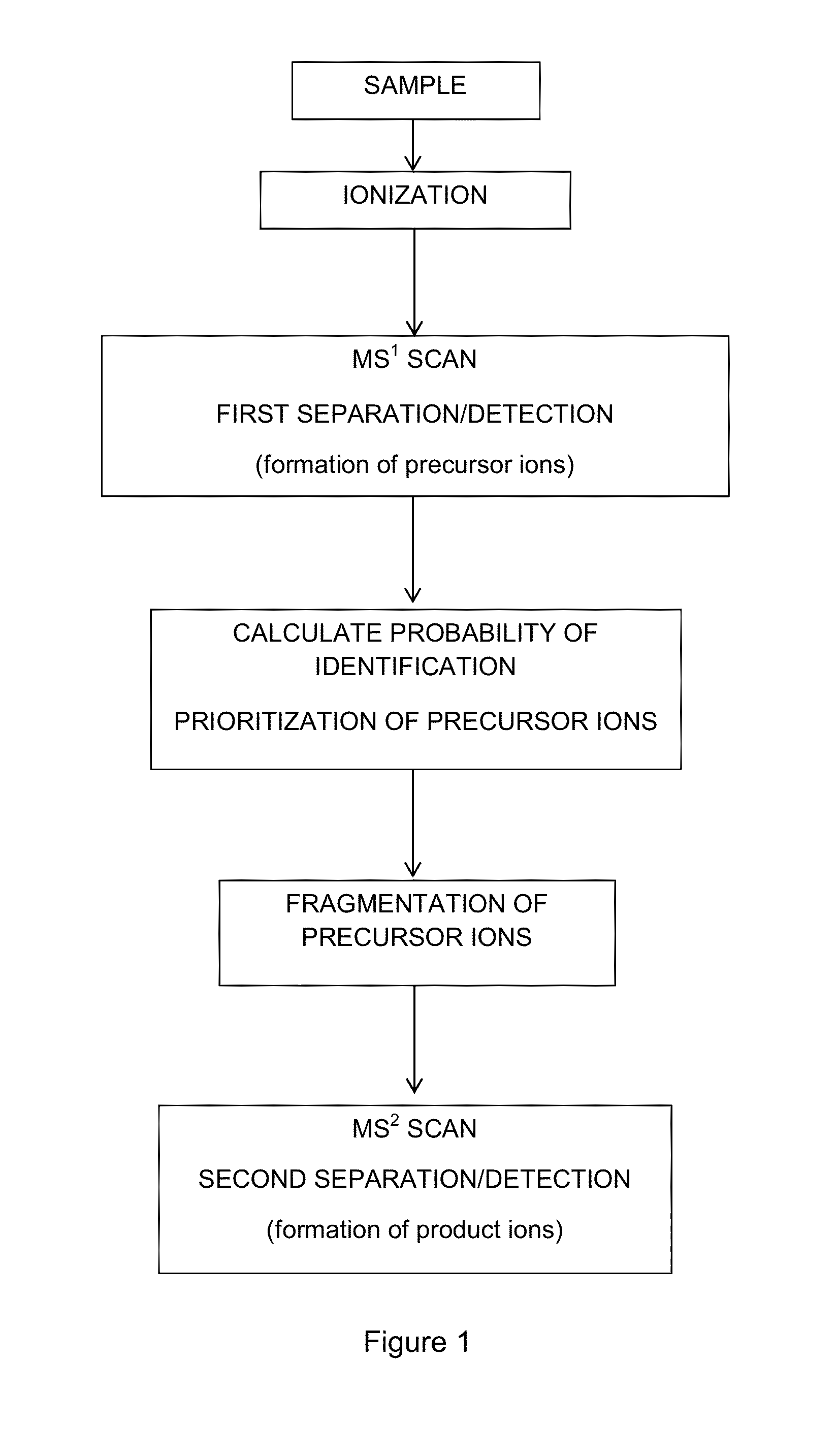
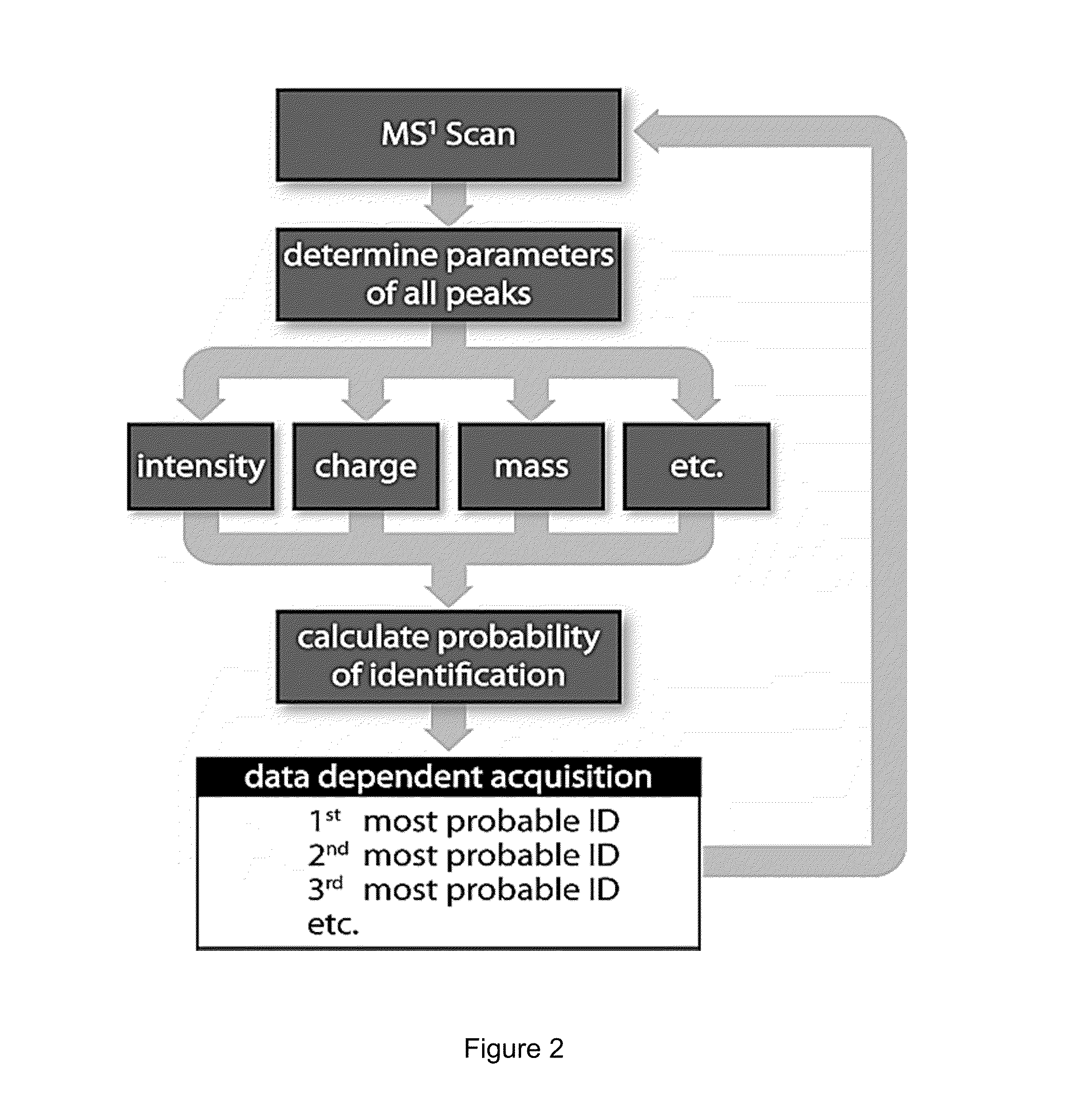
Probability-based mass spectrometry data acquisition method for increased peptide and protein identifications
ActiveUS8530831B1Error minimizationHigher calculated probability of identificationTime-of-flight spectrometersParticle spectrometer methodsMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryData acquisition
An algorithm-based system and method for tandem mass spectrometry data acquisition in which multiple precursor ion attributes, such as mass, intensity, mass-to-charge ratio and charge state, as well as results from previously performed mass spectrometry scans, are used to determine the likelihood of identification for each precursor ion. This information is then used to prioritize subsequent tandem mass spectrometry events, such as which precursor ions are to be fragmented and undergo further mass spectrometry analysis. By interrogating precursor ions in order of probability of successful identification, an increase in identified proteins and peptides is achieved.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for creating multiply charged ions for MALDI mass spectrometry (ESMALDI)
A method of combining ES (ElectroSpray Ionization) and MALDI (Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization) to create enhanced MALDI mass spectrometry to be referred to as ESMALDI (ElectroSpray Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization). ESMALDI technology offers substantial advantages over conventional technology. essentially by combining the high ionization efficiency and multiple charging of ions in ESI with the smaller sample requirements and operational simplicity of MALDI. Biologists should thus be able to achieve higher sensitivity, better protein identification, enhanced quantification potential and enhanced structural information. An additional degree of freedom for ESMALDI MS is flexibility in the choice of solvents that can be used in the ESI component of the process. Substantial differences in ESI behavior can occur with the same analyte or mixture of analytes in different solvents. Such differences often provide clues to the properties of the analyte and its ions which cannot be readily obtained from conventional MALDI experiments.
Owner:FENN JOHN B
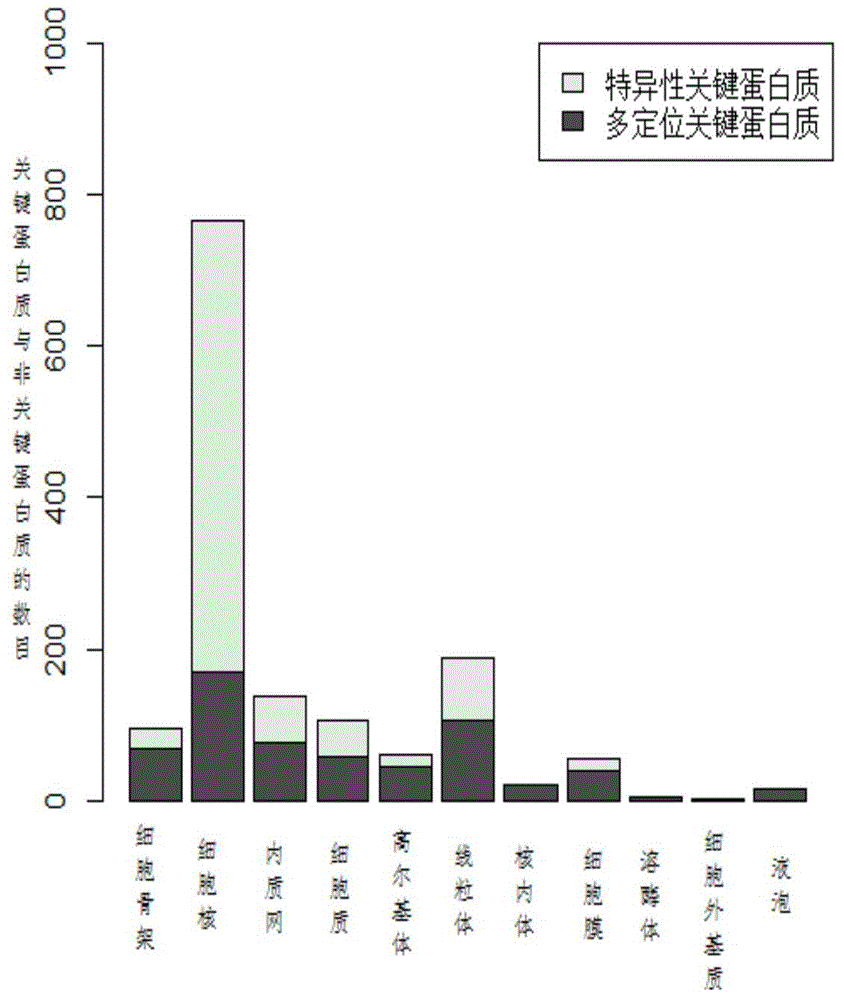
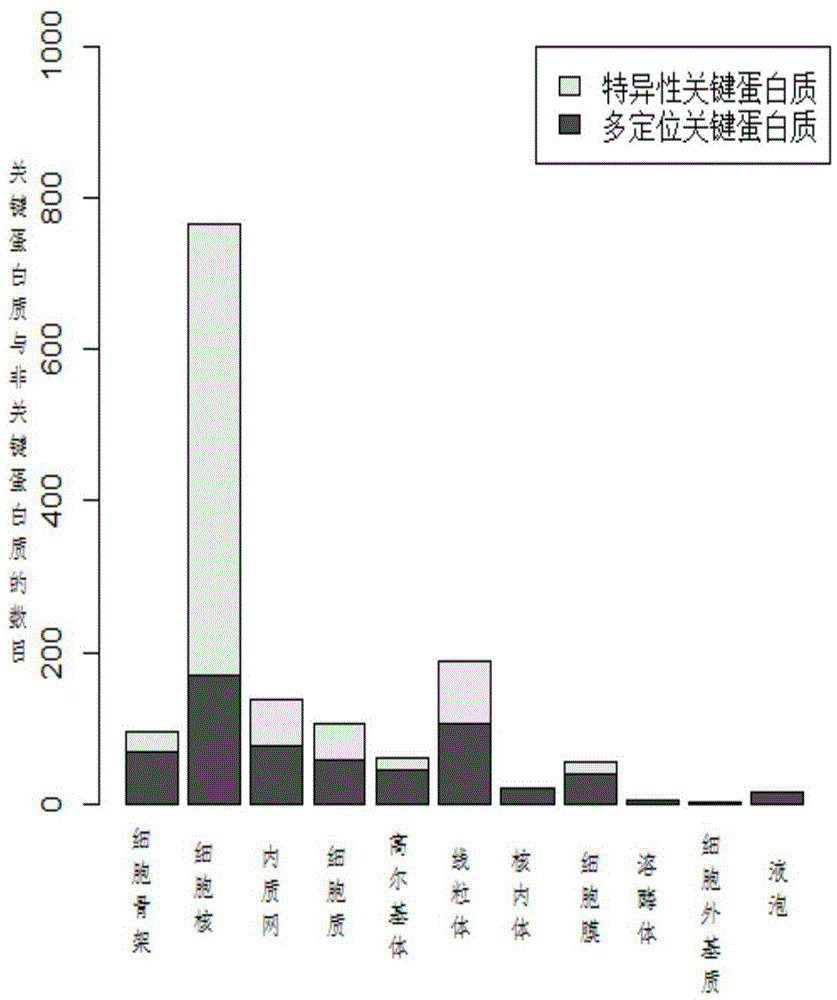
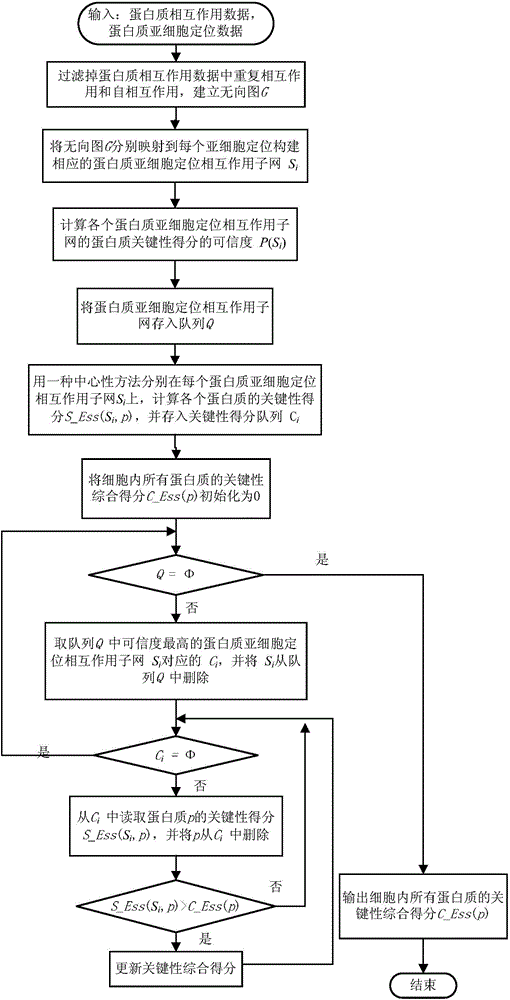
Key protein identification method based on subcellular localization specificity
ActiveCN104156634AImprove accuracyIncreased sensitivitySpecial data processing applicationsProteinProtein identification
The invention discloses a key protein identification method based on subcellular localization specificity. The method includes the first step of establishing subcellular localization protein interaction subnets; the second step of measuring confidence levels of protein key scores of all the subcellular localization interaction subnets of all proteins; the third step of calculating key comprehensive scores of all the proteins; the fourth step of outputting the result, wherein all the proteins in a cell are ranked according to the key comprehensive scores, and the ranking result is output. The key protein identification method based on the subcellular localization specificity is high in accuracy and sensitivity in the identification aspect of key proteins.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
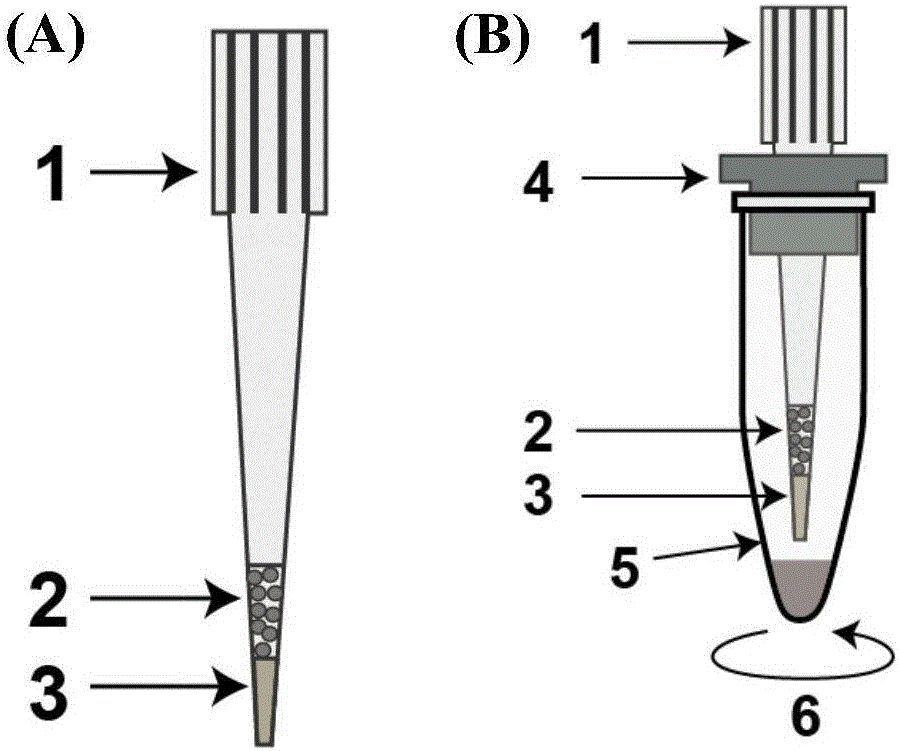
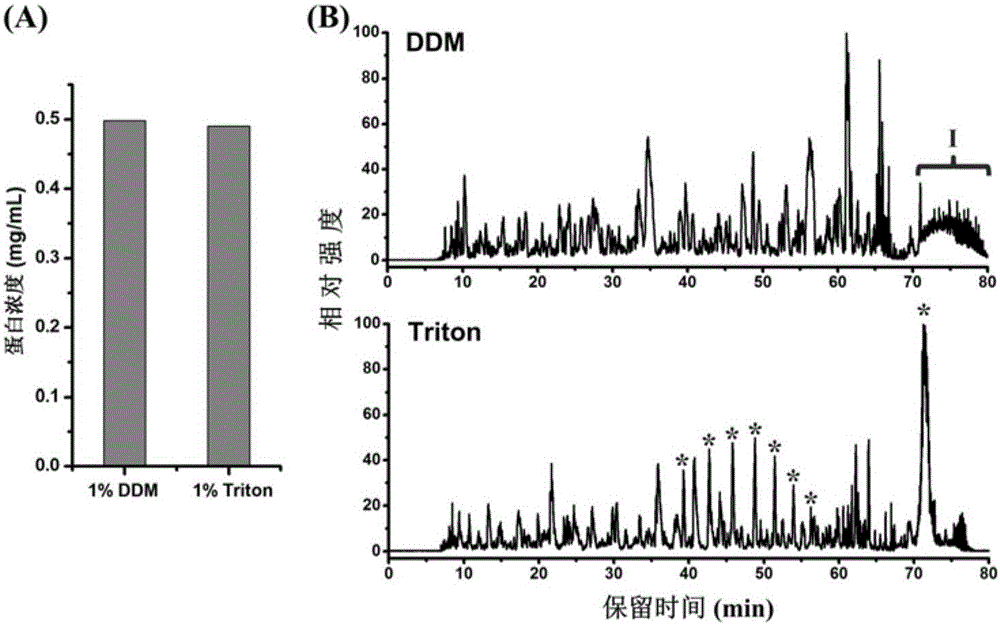
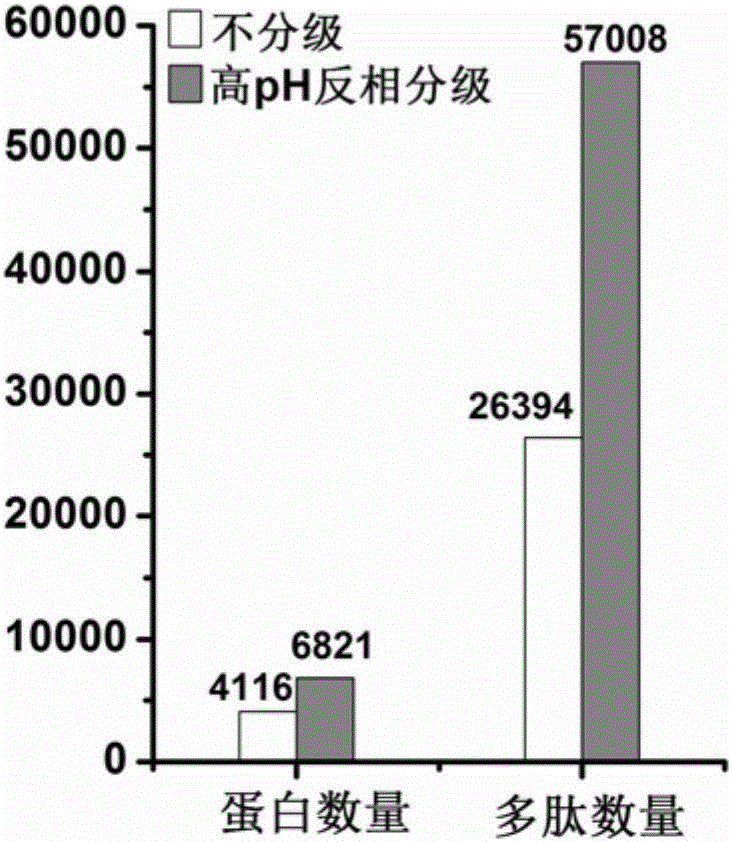
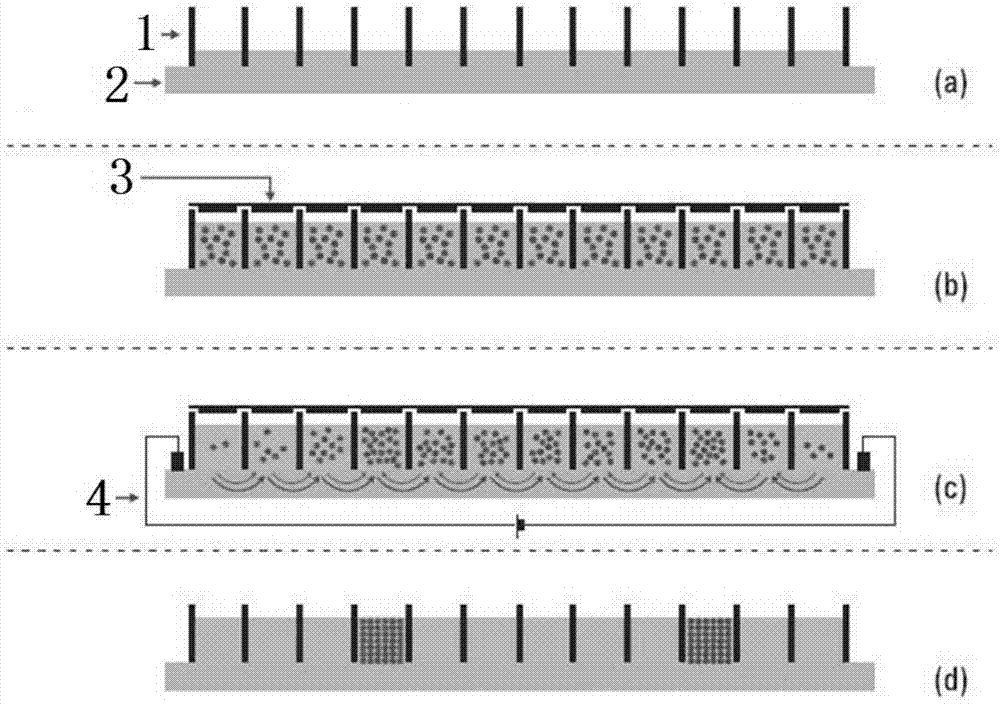
Protein pretreatment and polypeptide high-pH reverse-phase gradation-integrated proteome reactor and application thereof
ActiveCN105866317AAutomate operationEnable mass authenticationComponent separationProtein insertionSolid phase extraction
The present invention relates to a protein pretreatment and polypeptide high-pH reverse-phase gradation-integrated proteome reactor and the application thereof. The proteome reactor comprises a pipette gun head (1), a strong ion-exchange resin filler (2) and a solid-phase extraction membrane (3). The solid-phase extraction membrane (3) is filled in the lower end of the pipette gun head (1) and is positioned above the solid-phase extraction membrane (3). The proteome reactor provided in the invention integrates the operations of protein pre-enrichment, reduction, alkylation, enzymatic hydrolysis, polypeptide desalination, elution and high-pH reverse-phase gradation, thus being applicable to the large-scale protein identification and the quantitative proteomics for a small number of cells or tissue samples. In addition, the proteome reactor technology can realize the automated liquid handling platform-based automatic operation, such as the Agilent bravo platform-based automatic operation. Therefore, the sample processing throughput and the accuracy of the quantitative analysis are improved.
Owner:深圳深维超生物科技有限公司
Identification of discriminant proteins through antibody profiling, methods and apparatus for identifying an individual
InactiveUS20110065594A1Inhibit bindingPeptide librariesLibrary screeningImmune complex depositionStatistical analysis
A method for determining a plurality of proteins for discriminating and positively identifying an individual based from a biological sample. The method may include profiling a biological sample from a plurality of individuals against a protein array including a plurality of proteins. The protein array may include proteins attached to a support in a preselected pattern such that locations of the proteins are known. The biological sample may be contacted with the protein array such that a portion of antibodies in the biological sample reacts with and binds to the proteins forming immune complexes. A statistical analysis method, such as discriminant analysis, may be performed to determine discriminating proteins for distinguishing individuals. Proteins of interest may be used to form a protein array. Such a protein array may be used, for example, to compare a forensic sample from an unknown source with a sample from a known source.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
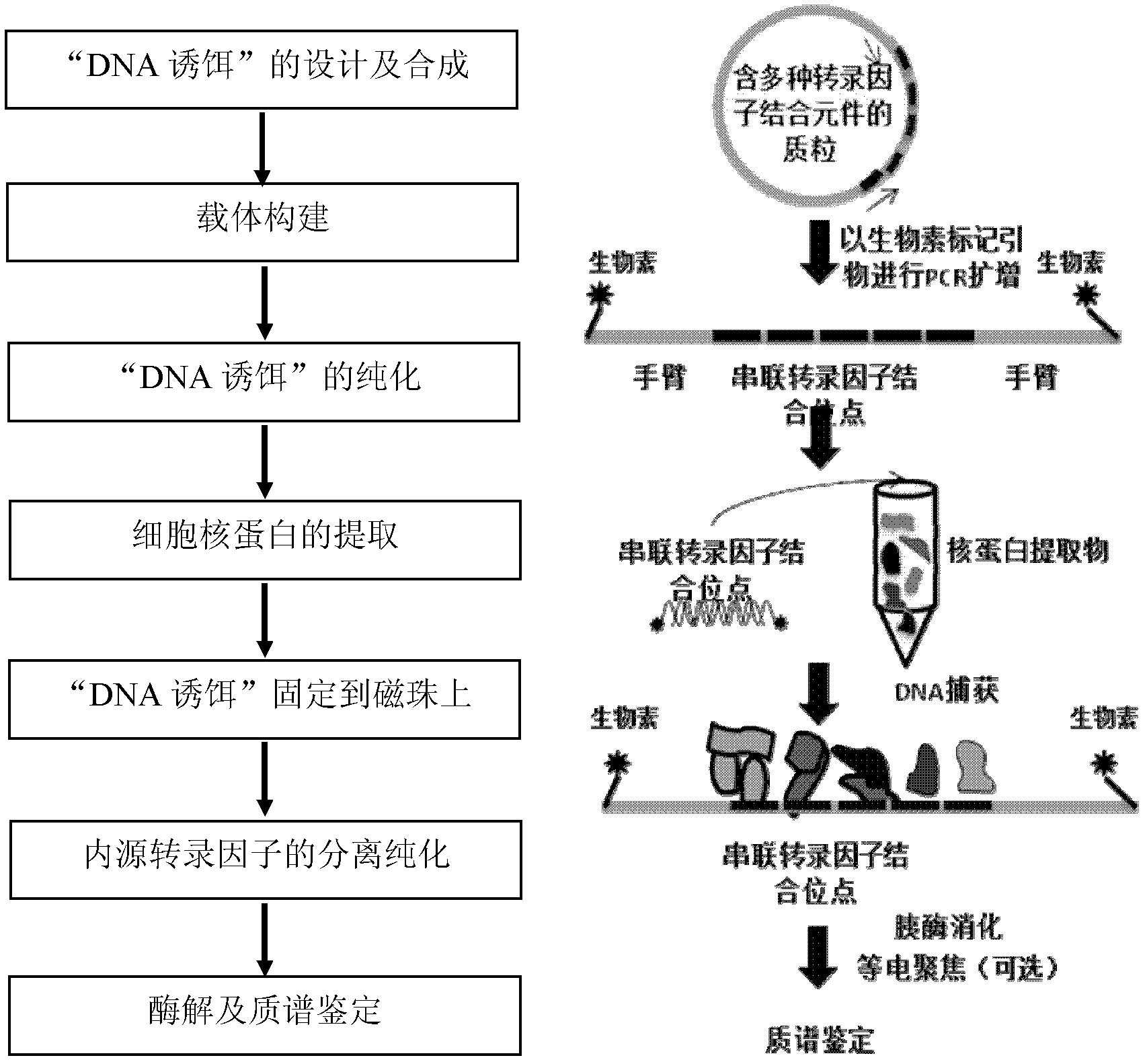
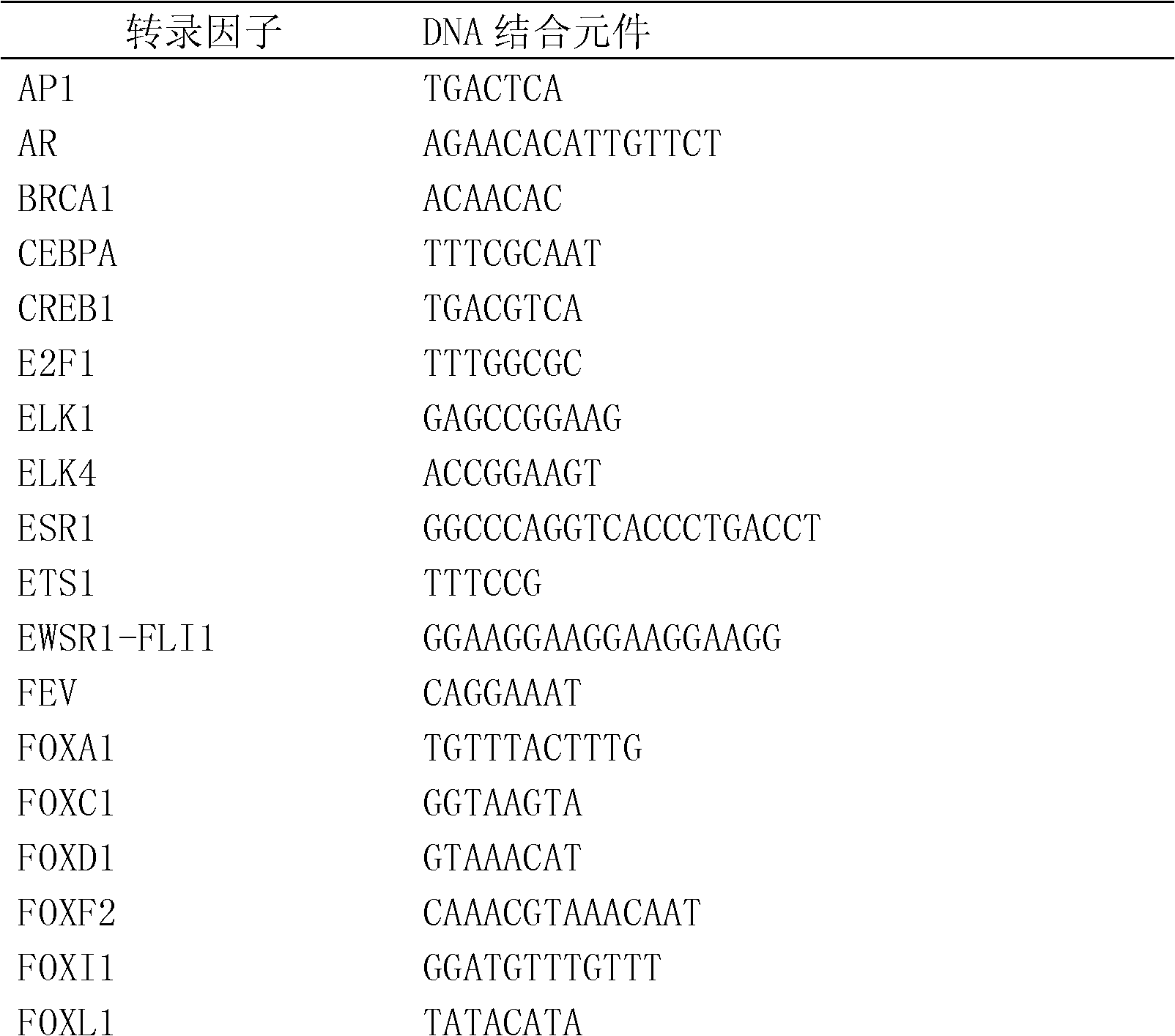
Method for enriching and separating endogenous transcription factors and compounds thereof and concatenated transcription factor response elements special for method
ActiveCN102517282AMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsBiotin-streptavidin complexMagnetic bead
The invention discloses a method for enriching and separating endogenous transcription factors and compounds thereof and concatenated transcription factor response elements special for the method. The method includes of designing multi-copy double-stranded DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) binding elements according to the characteristic that transcription factors are bound with sequence-specific DNA elements, adding double-stranded DNA arms labeled with biotin to two ends of each DNA binding element by the aid of molecular cloning technology to form 'DNA baits', coupling the biotinylated DNA baits which are purified onto magnetic beads enveloped by streptavidin when in separation and purification of the endogenous transcription factors and compounds thereof, incubating the magnetic beads together with the prepared nucleoprotein, and finally separating and purifying the endogenous transcription factors and the compounds thereof from the nucleoprotein. Further, after the endogenous transcription factors and the compounds thereof are separated and purified, protein identification and function analysis of the transcription factors can be performed subsequently.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA +1
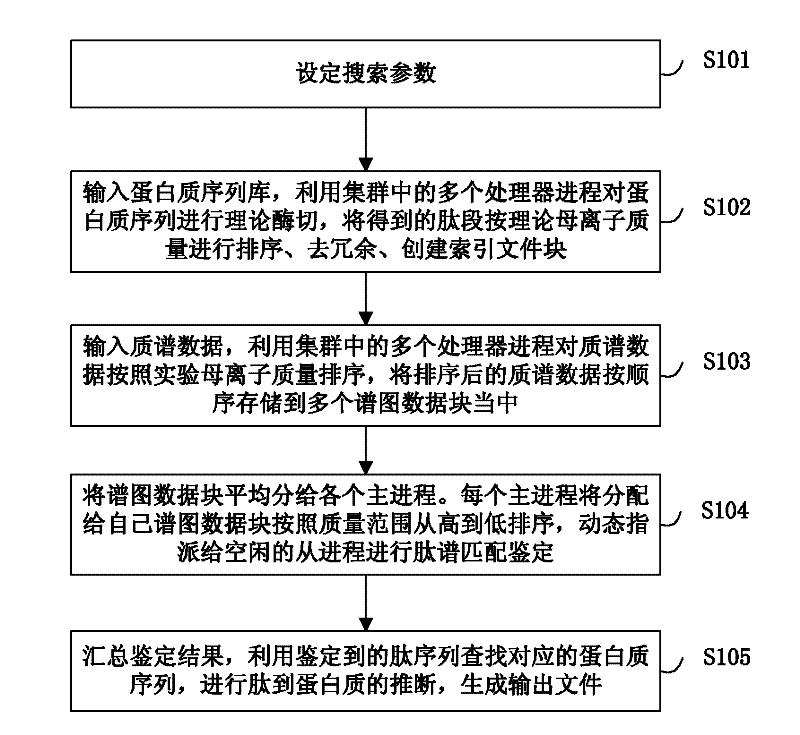
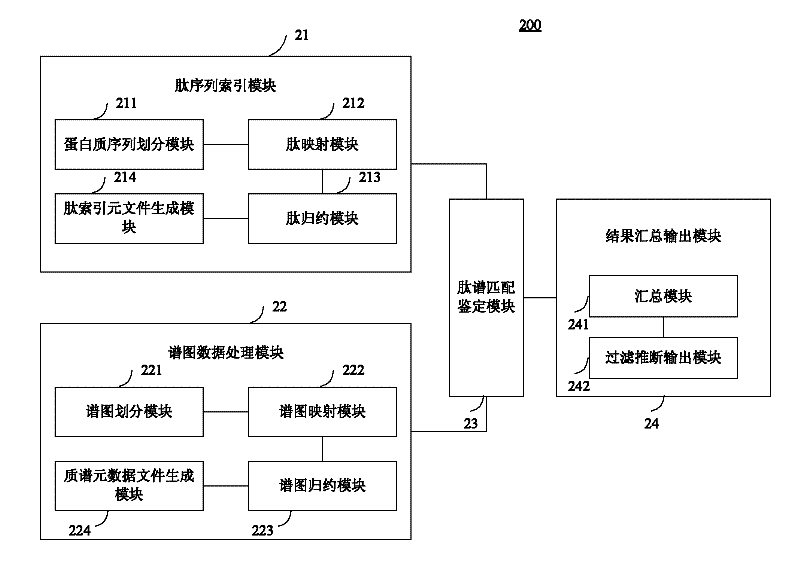
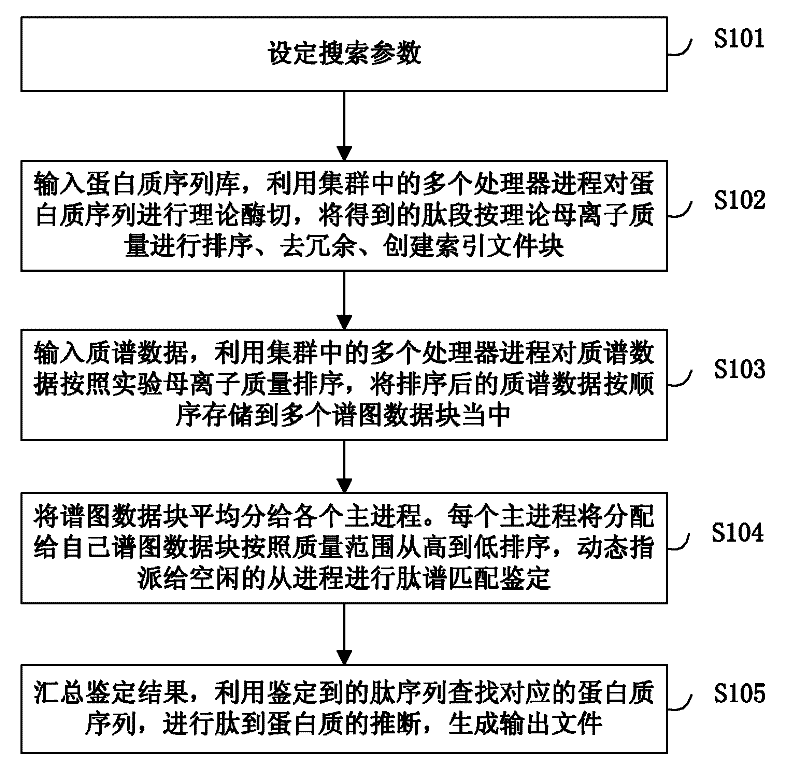
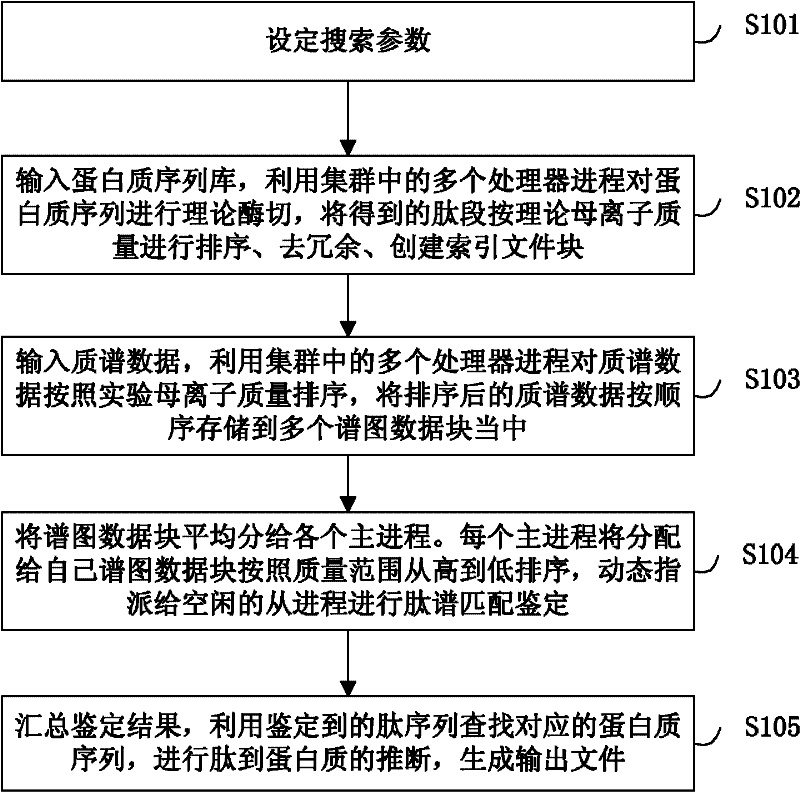
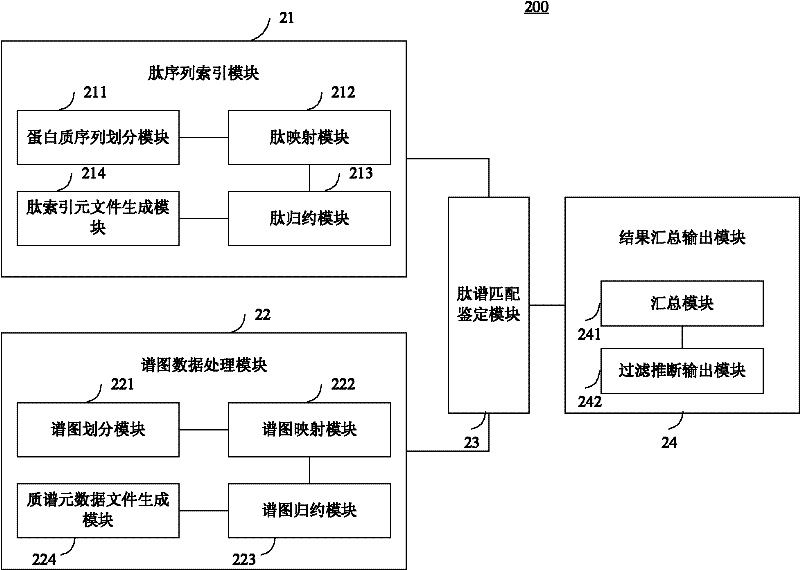
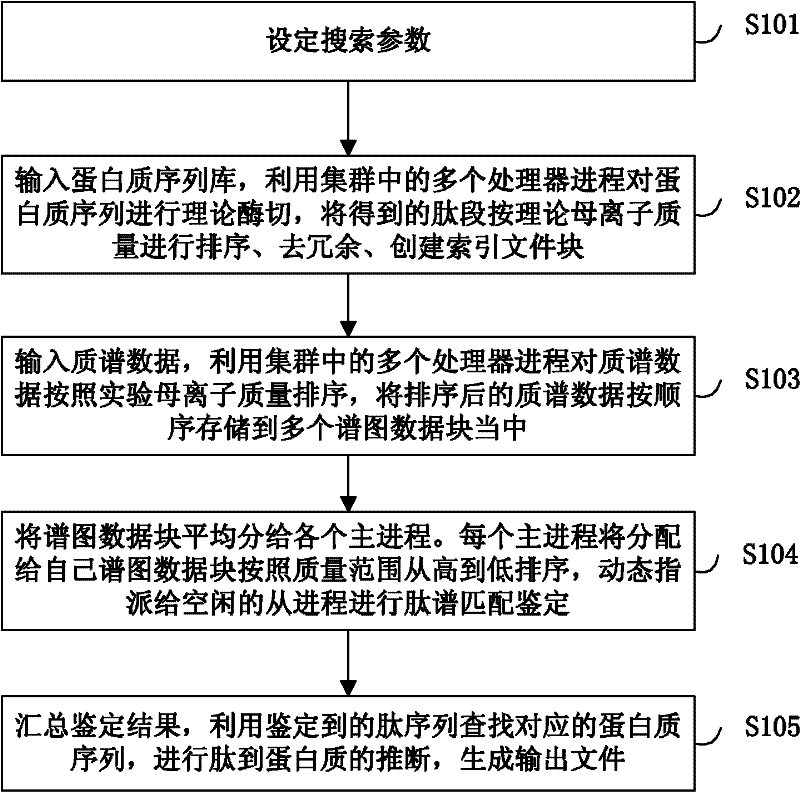
Large-scale distributed parallel acceleration method and system for protein identification
ActiveCN102411679AImprove efficiencySmall amount of calculationSpecial data processing applicationsPeptide sequenceParallel processing
The invention relates to a large-scale distributed parallel acceleration method and system for protein identification. The method comprises the following steps of: by a parallel processing method, theoretically digesting a protein sequence to obtain peptide sequences, and sorting and redundantly processing the peptide sequences so as to create a peptide index file block; by the parallel processing method, sorting mass spectra spectrums, and evenly dividing the sorted mass spectra spectrums into a plurality of spectrum data blocks; and evenly distributing the spectrum data blocks to a plurality of host processes, and each host process sorting the distributed spectrum data blocks and sequentially assigning to idle slave processes for peptide spectrum matching identification; and summarizing identification results by the parallel processing method, inferring the corresponding protein sequences by the peptide sequences obtained by identification, and generating output files. When a processor has hundreds or even thousands of cores, the satisfactory acceleration efficiency can be obtained when the protein identification is carried out.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
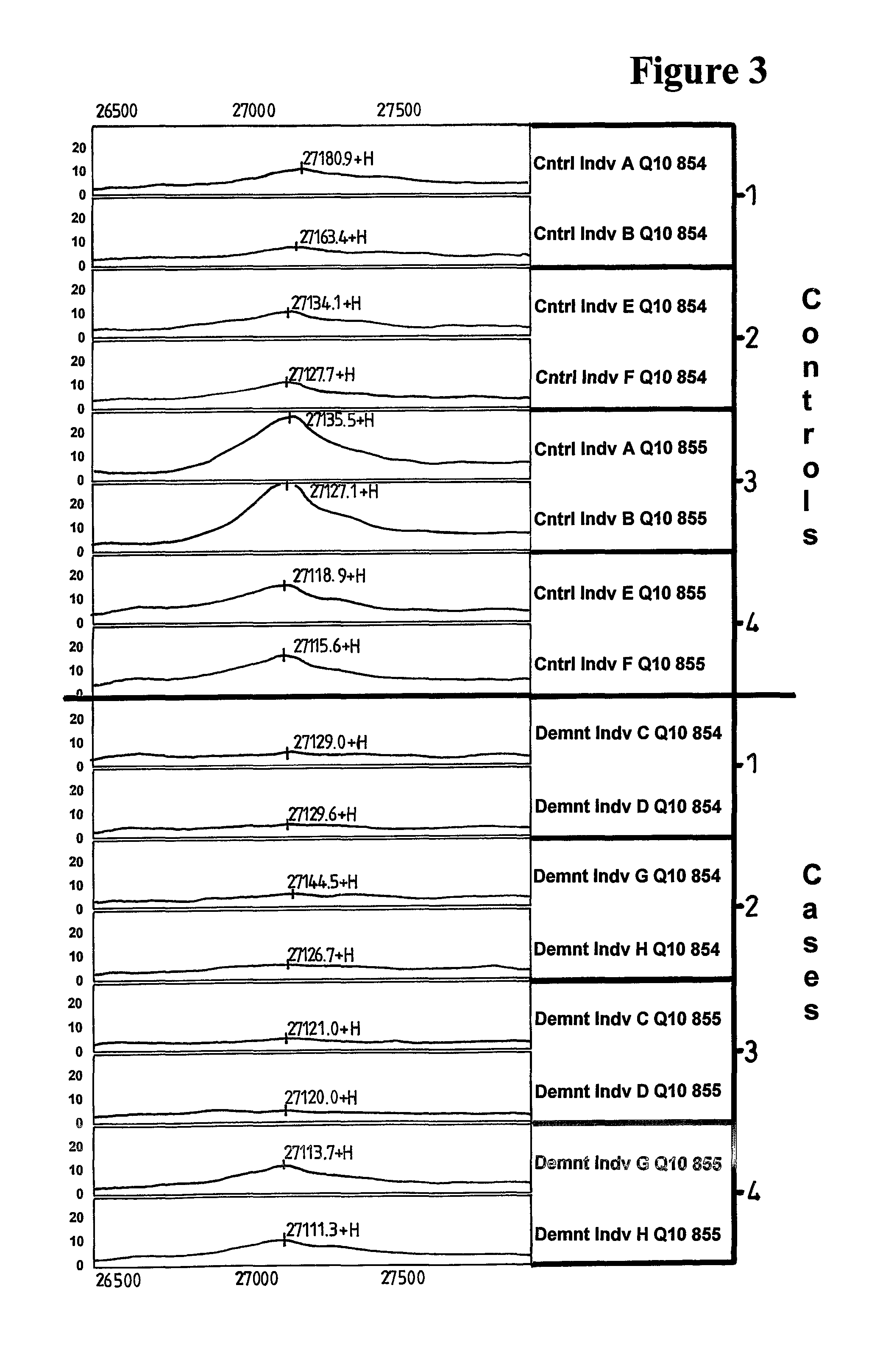
Methods of diagnosing Alzheimer's disease
ActiveUS7897361B2Enhancing likely responseEasy to getNervous disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseasePsychiatry
Methods and compositions relating to Alzheimer's disease are provided. Specifically, proteins that are differentially expressed in the Alzheimer's disease state relative to their expression in the normal state are provided. Proteins associated with Alzheimer's disease are identified and described. Methods of diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease using the differentially expressed proteins are also provided, as are methods for the identification and therapeutic use of compounds for the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:PROTEOME SCI +1
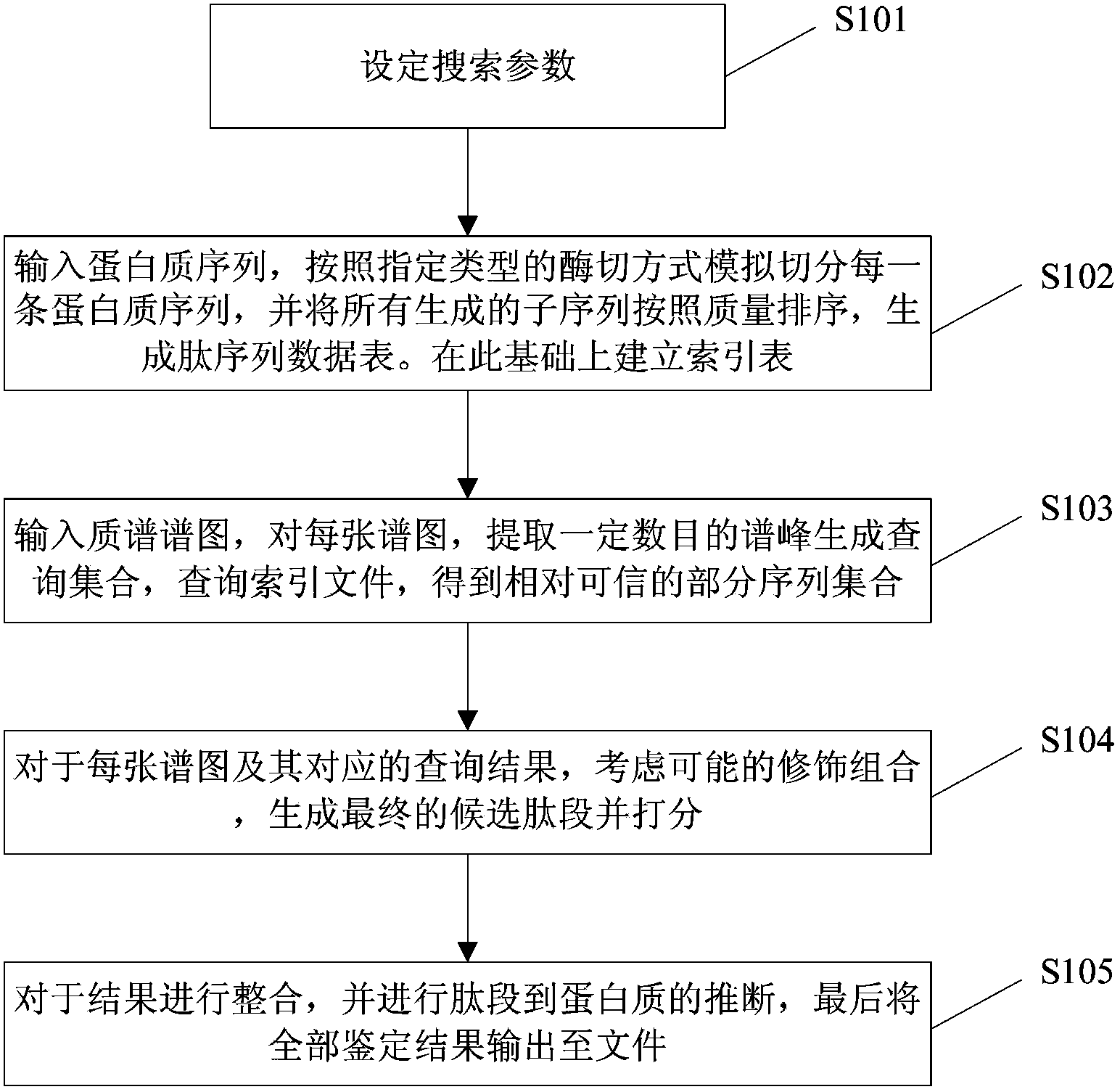
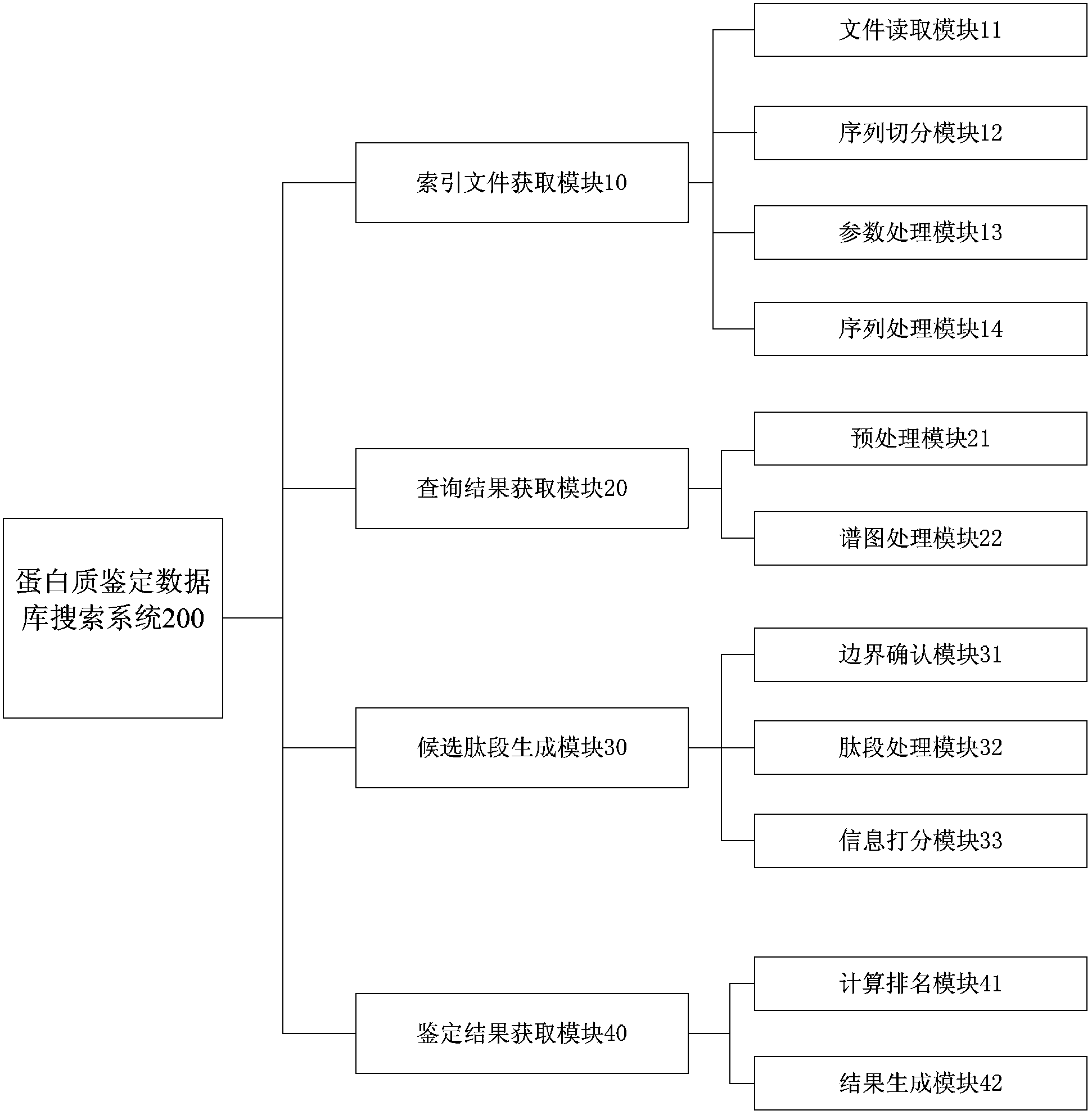
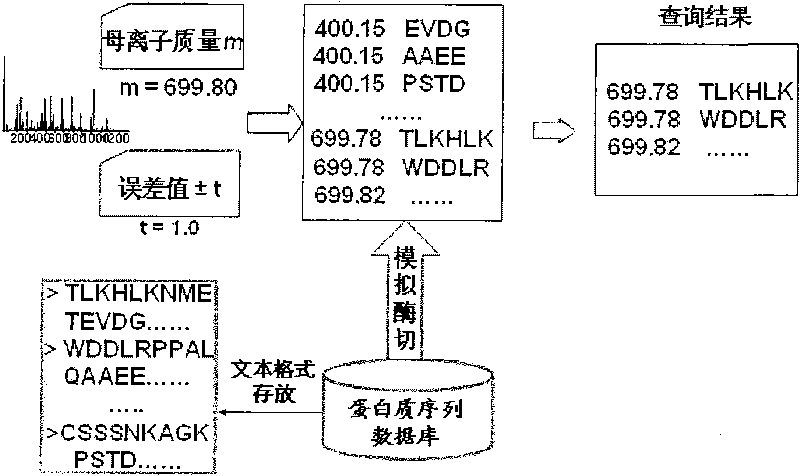
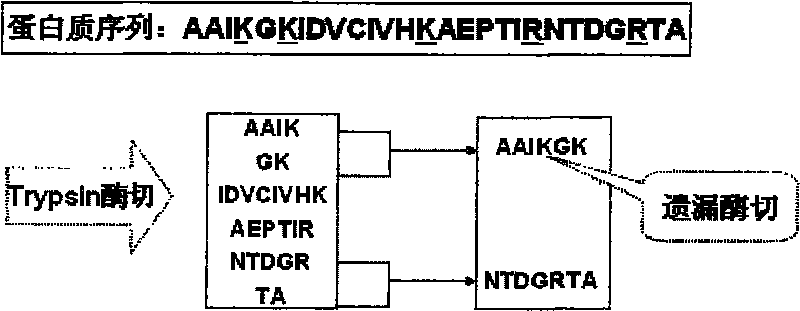
Database searching method and database searching system for open type protein identification
The invention relates to a database searching method and a database searching system for open type protein identification. The database searching method comprises the steps of step 1, inputting protein sequences, simulating and splitting each protein sequence, ranking all generated subsequences according to mass, generating a peptide sequence data list, and establishing an index file according to the peptide sequence data list; step 2, inputting mass spectrums, generating a search set by extracting spectrum peaks from each mass spectrum, searching the index file, and obtaining a sequence set; step 3, generating a candidate peptide fragment according to decoration and combination on each mass spectrum and the sequence set corresponding to each mass spectrum, and marking the candidate peptide fragment; step 4, integrating a marking result, inferring from the peptide fragment to protein, and obtaining an identification result. According to the database searching method disclosed by the invention, the protein identification is carried out in a way that a user is allowed not to assign the types of digestion and decoration or is allowed to assign arbitrary types among the types, and the database searching method is used for solving identification problems of digestion and decoration in the arbitrary types.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and reagent kit for enriching and sequencing peptide fragment containing histidine
InactiveCN101042377AGreat practicabilityIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationProtein insertionAminoacidemia
This invention provides one new method and agent case for collecting and testing group aminoacidemia peptides, which comprises the following steps: protein restores alkyl base and tryptone protein enzyme cut, peptides section N end amidogen decoration and group aminoacidemia peptides color spectrum collection and mass spectrum testing sequence; identifying the protein with peptides sections in mixture objects.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Wild ginseng protein extracting method suitable for dielectrophoresis
InactiveCN101906130AImprove solubilityReduce Denaturing PrecipitationPeptide preparation methodsElectrophoresisCentrifugation
The invention discloses a wild ginseng protein extracting method suitable for dielectrophoresis. The method comprises the following steps of: taking wild ginseng as an experimental material, fully grinding the wild ginseng in liquid nitrogen and transferring the obtained product to a centrifuge tube; adding acetone solution precooled at the temperature of -20 DEG C into the centrifuge tube, washing sample powder for 3 times, collecting sediments by centrifugation and drying the obtained product at room temperature for 20min to obtain the crude extract of the wild ginseng protein; dissolving the crude extract of the wild ginseng protein into lysis buffer, and performing ultrasonic cell disintegration and extracting the supernate by centrifugation to obtain the high-quality solution of the wild ginseng protein. The wild ginseng protein extracting method for the dielectrophoresis is simple and fast, can obtain an electrophoresis pattern having a high repeatability and resolution, is favorable for subsequent protein identification by mass spectrographic analysis and provides a technical support for the proteomic research of the wild ginseng.
Owner:BEIHUA UNIV
Index acceleration method and corresponding system in scale protein identification
InactiveCN101714187AReduce space consumptionEasy to storeSpecial data processing applicationsProtein DatabasesEnzyme digestion
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method to Predict Responsiveness of Breast Cancer to Polyamine-Type Chemotherapy
InactiveUS20110183336A1High expressionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPredictive biomarkerBiology
Methods of-identifying a basal or luminal phenotype of a cell, comprising detecting expression of one or more of a set of predictive biomarker genes or proteins that identify the cell as having a basal or luminal cancer subtype and compositions for treating identified basal or luminal cancers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for measuring ancient cowhair micro-trace based on proteomics
ActiveCN106596970AReduce usageSolve the problem of being helplessPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIn-gel digestionProteomics methods
The invention discloses a method for measuring ancient cowhair micro-trace based on proteomics. A soil sample of the ancient cowhair micro-trace, a soil sample of a surface soil layer and a soil sample of a raw soil layer are extracted and separated, protein is effectively separated by a two-dimensional electrophoretic technique, the electrophoretic results of the three samples are compared, the influence that the soil contains protein and the interference of external factors are excluded, stripes in the electrophoretic results are cut off and subjected to in-gel digestion, mass spectrometric analysis is conducted, and protein identification can be realized by comparing the mass spectrometric analysis result with the amino acid sequence in a protein database. The ancient cowhair micro-trace is measured by a proteomic method, the problem that the common analysis test is helpless during analysis of micro-trace residues is solved, the protein varieties of the samples are obtained accurately through proteomic measurement, and whether the micro-trace sample is the cowhair micro-trace is judged, so that on one hand, the method is high in sensitivity and is simple and convenient to operate, and on the other hand, the use amount of the samples is small.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Protein identification method based on two-end equal-weight label and database search
InactiveCN106596760ATake advantage ofImprove identification efficiencyComponent separationPeptide fragmentIsotopic signature
The invention relates to a protein identification method based on a two-end equal-weight label and database search and belongs to the technical field of biological information. According to the identification method, a protein enzymolysis product obtained by performing isotoplabelling at the two ends of polypeptide is subjected to separation and detection through liquid chromatogram-mass spectrum combination; when identification is conducted by a database search method, identification of polypeptide is realized by establishing a peptide fragment theory spectrogram containing all the fragment ions of the peptide section formed by two labels and matching with the experimental mass spectrogram, so that the protein is obtained through identification, the identification efficiency of polypeptide and the protein is improved, and the method can be used for efficiently identifying the protein sample of the database.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method of selective peptide isolation for the identification and quantitative analysis of proteins in complex mixtures
InactiveUS7244411B2Efficient identificationWidely distributedIn-vivo radioactive preparationsComponent separationProtein insertionArginine
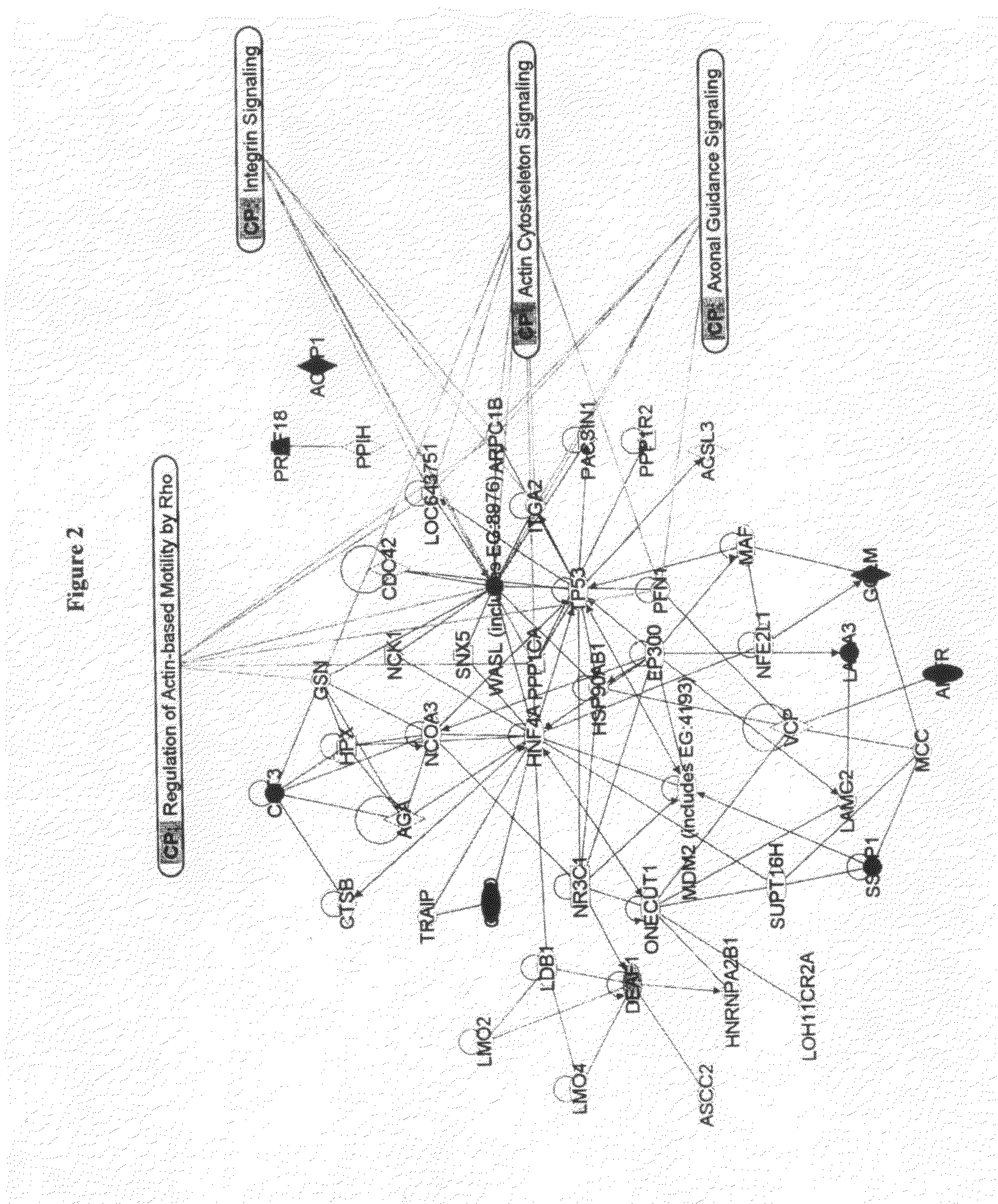
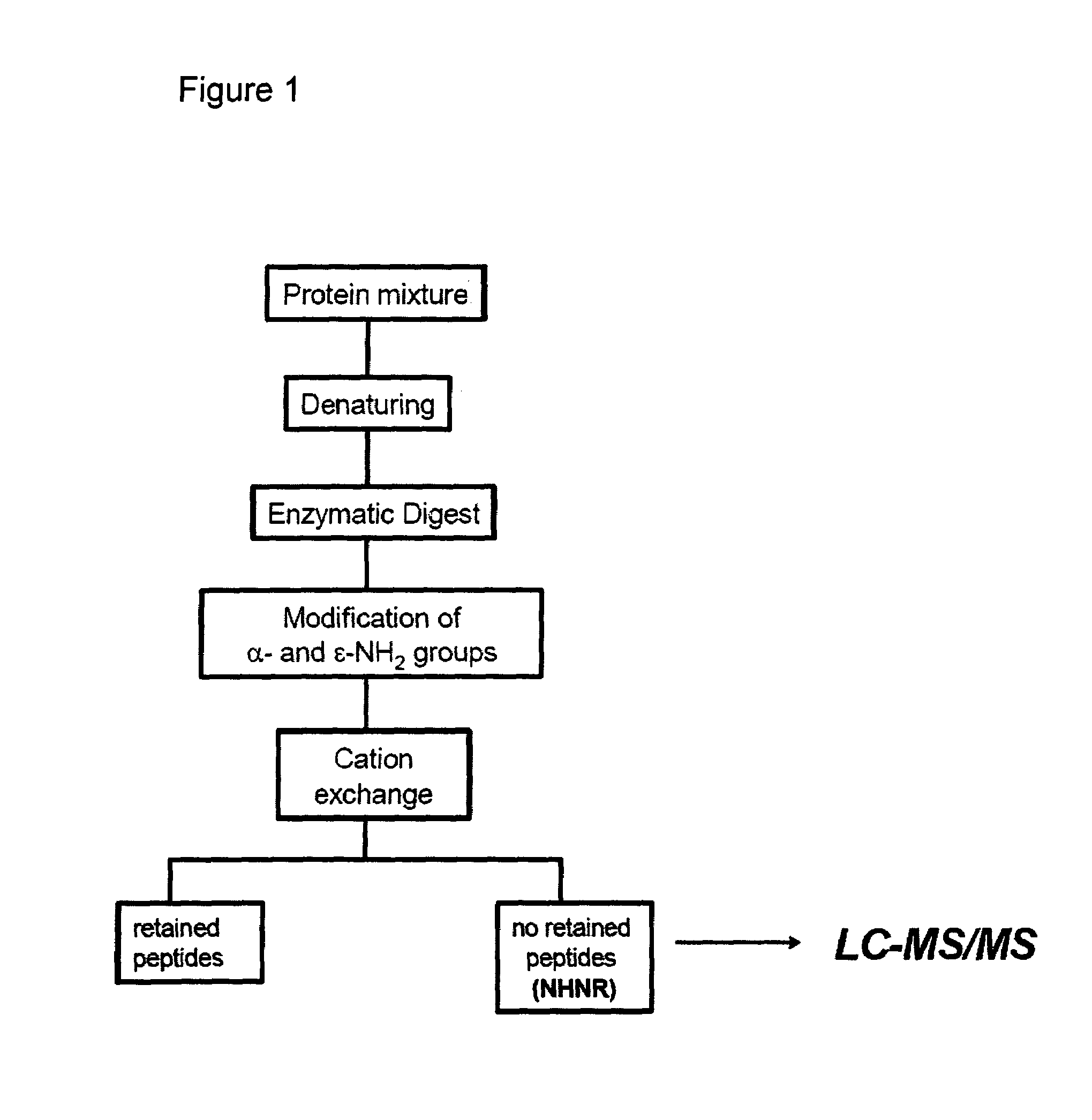
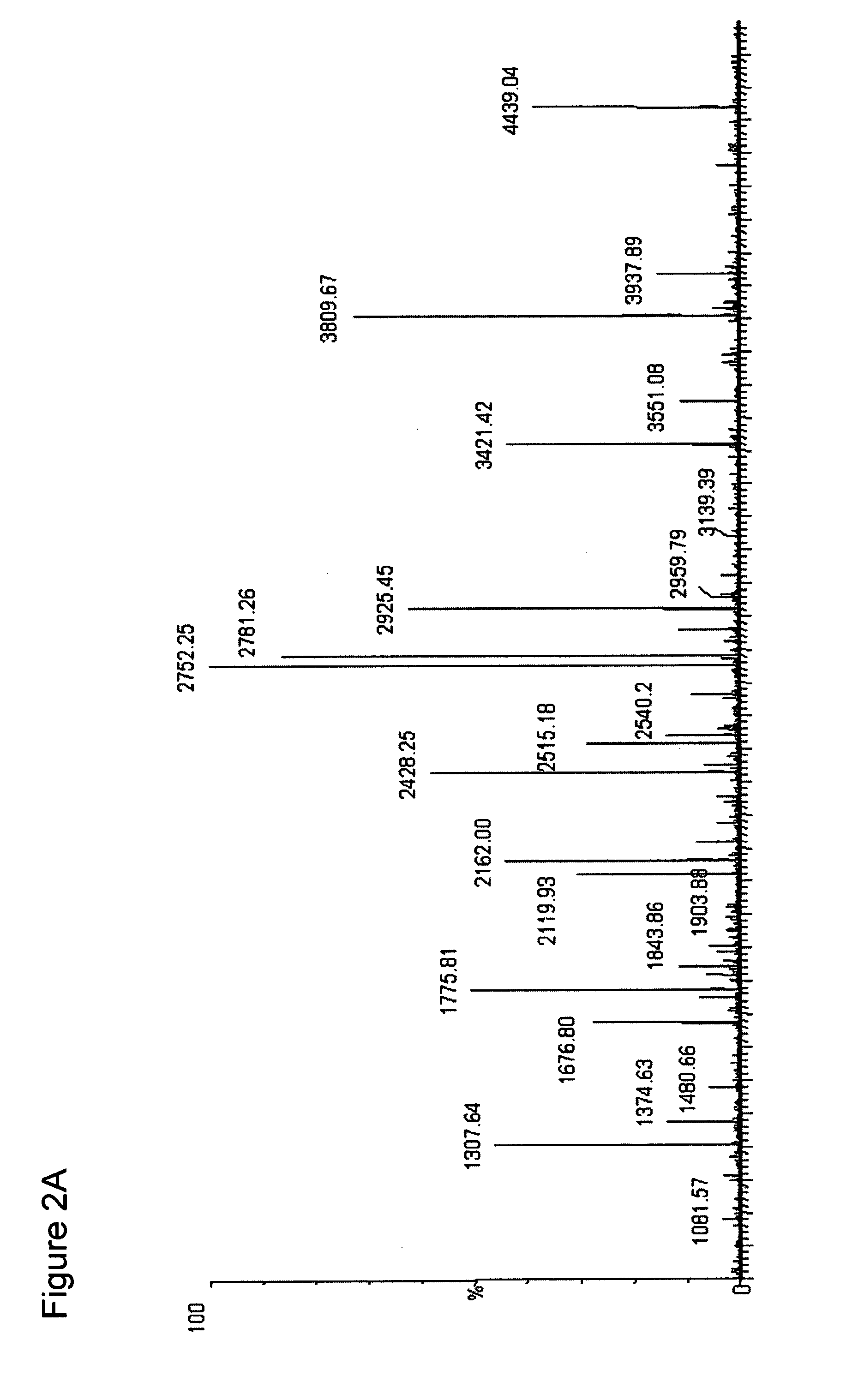
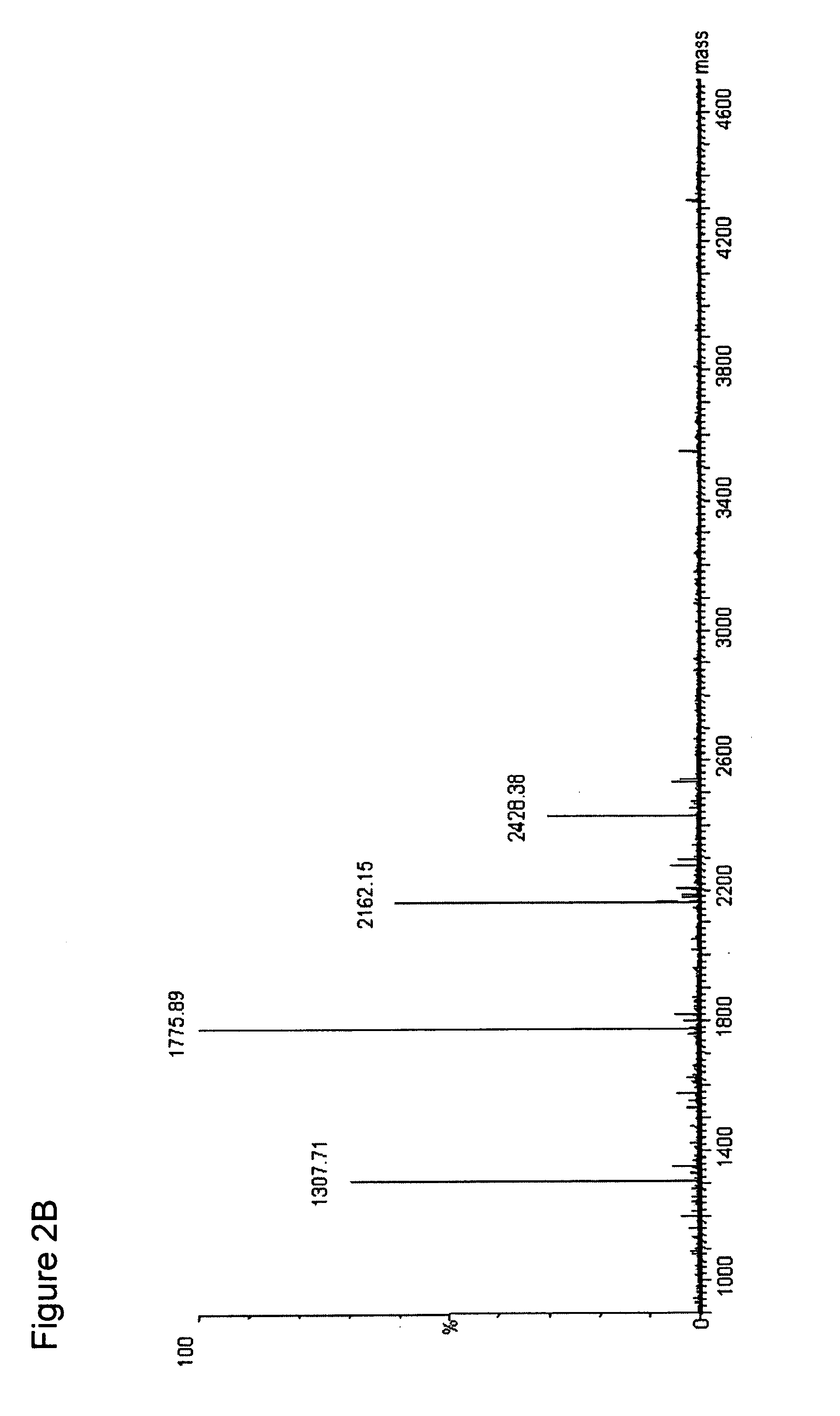
The present invention describes a method of selective peptide isolation for the identification and quantitative analysis of proteins in complex mixture. The method comprises the selective isolation from every protein of those peptides that neither contain arginine nor histidine (NHNR peptides), and the determination of the relative concentrations of one or several proteins in different samples from the ratio between the areas of the estimated theoretical spectra for the NHNR peptides labeled with different isotopes in each sample. The determination of the relative concentration of proteins is valid for any type of isotopic label of the NHNR peptides. The method avoids the separation and purification of the proteins present in a complex mixture, and the analysis of all peptides generated from the enzymatic digest of the samples. The method is applicable to the identification of proteins with vacunal, therapeutic and diagnostic aims.
Owner:CENT DE ING GENETICA & BIOTECNOLOGIA
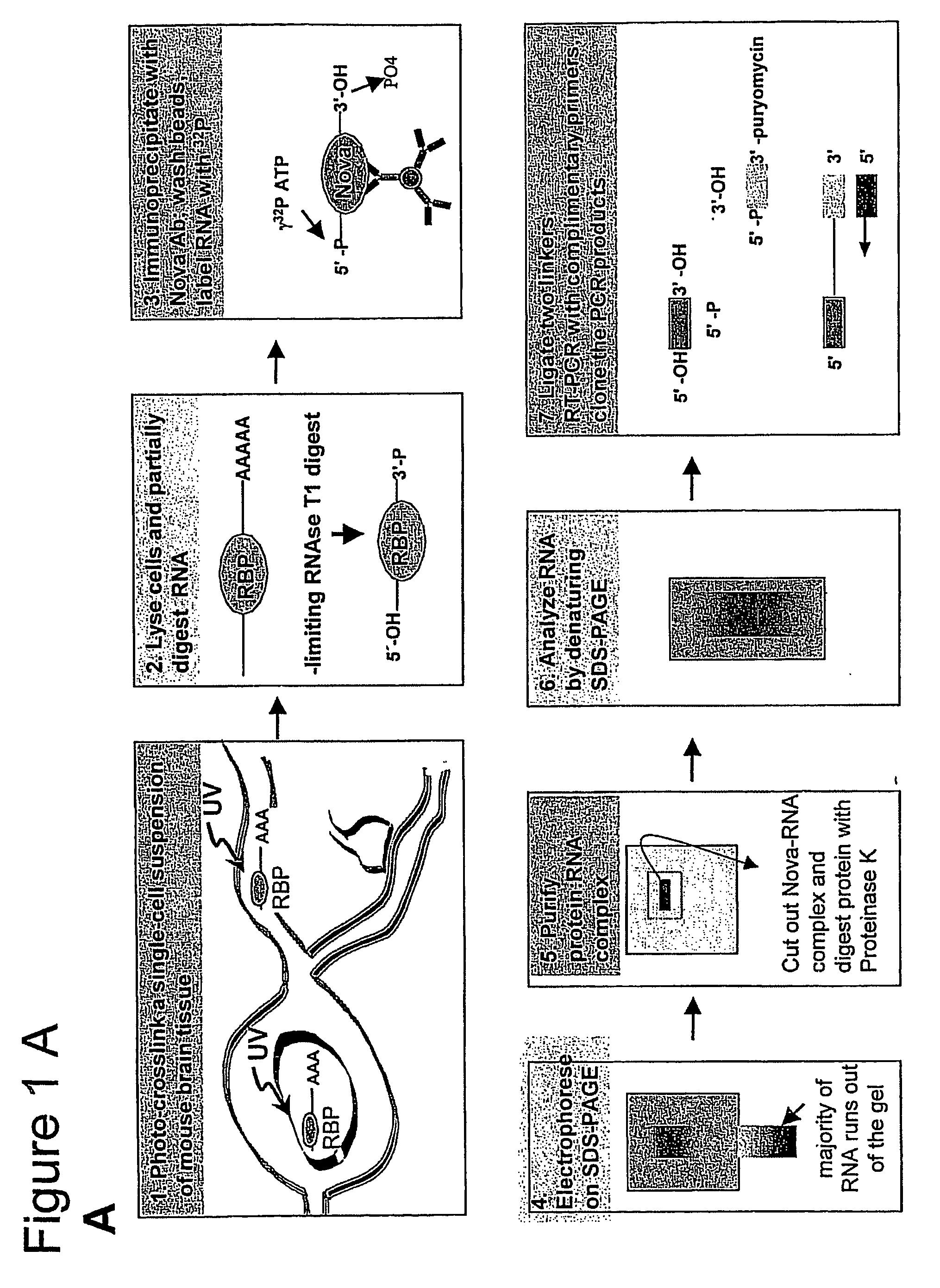
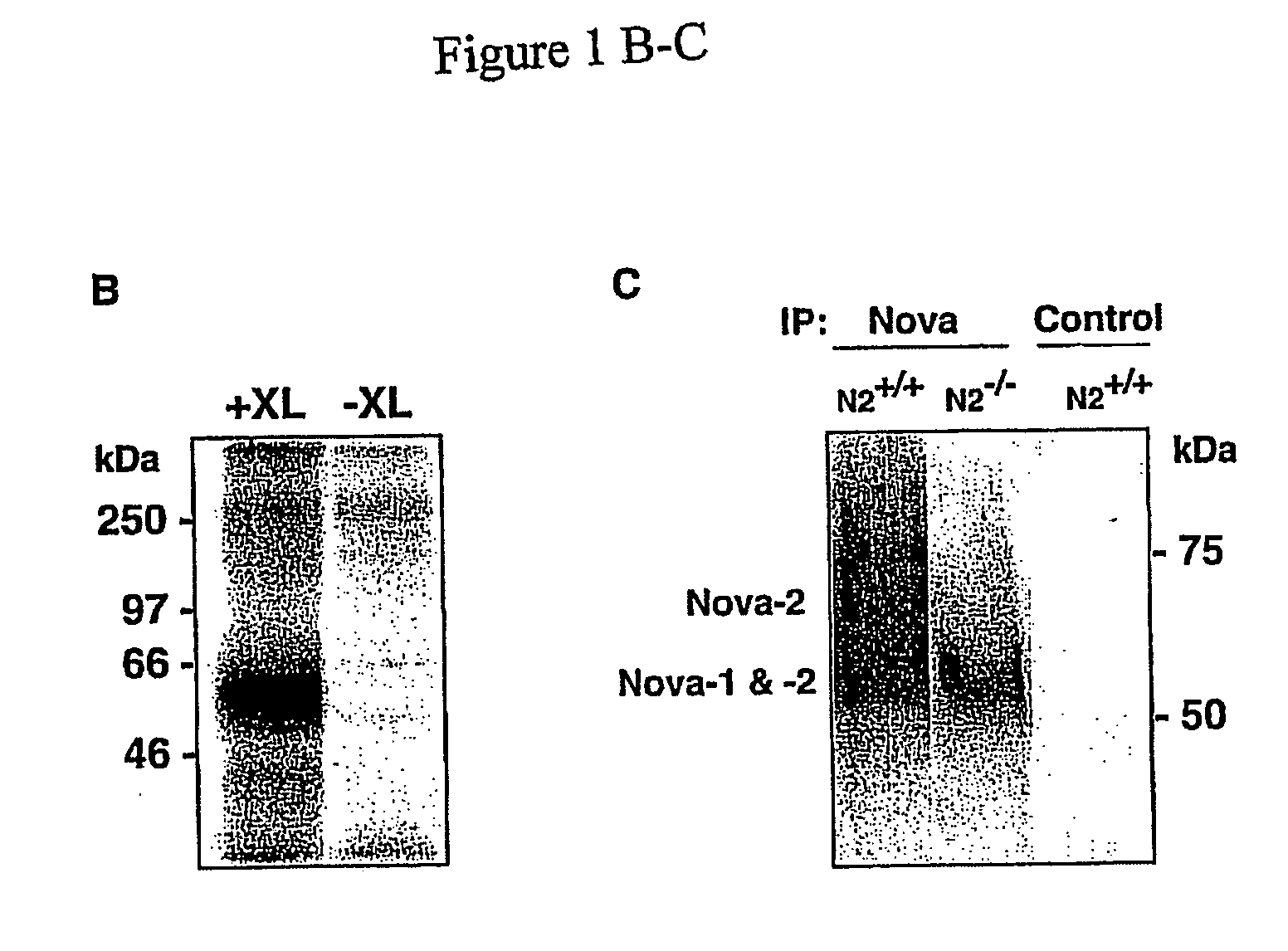
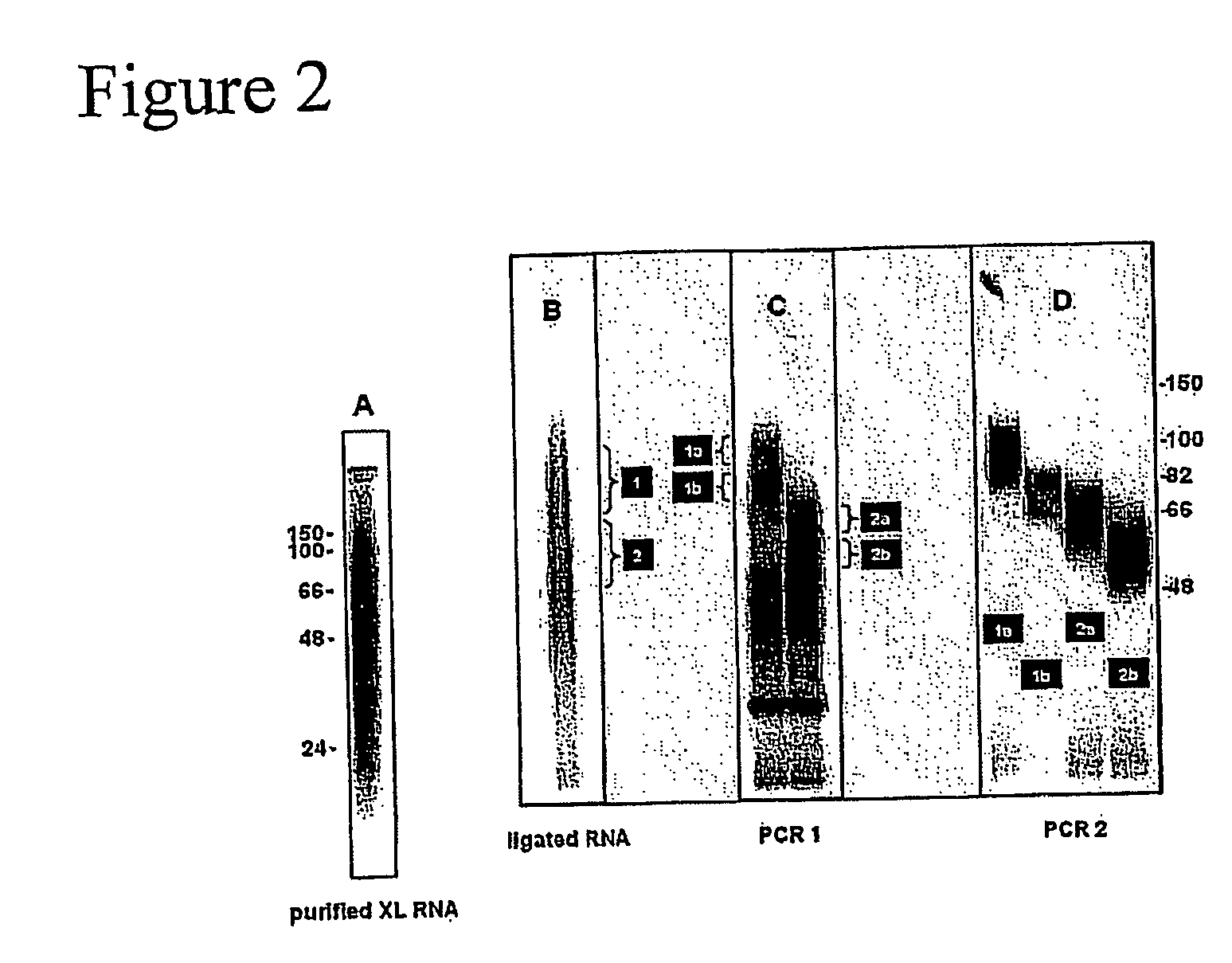
Method of purifying RNA binding protein-RNA complexes
InactiveUS20050227251A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationRNA MotifsGene expression profiling
The present invention provides methods for purifying RNA molecules interacting with an RNA binding protein (RBP), and the use of such methods to analyze a gene expression profile of a cell. The invention also provides sequences of RNA molecules that mediate binding to an RBP, proteins encoded by the sequences, a method of identifying the sequences, and the use of the sequences in a screen to identify bioactive molecules. The invention also provides RNA motifs found among the sequences and compounds that bind the RNA motifs. In addition, the invention provides methods of treating diseases associated with a function of an RNA binding protein.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
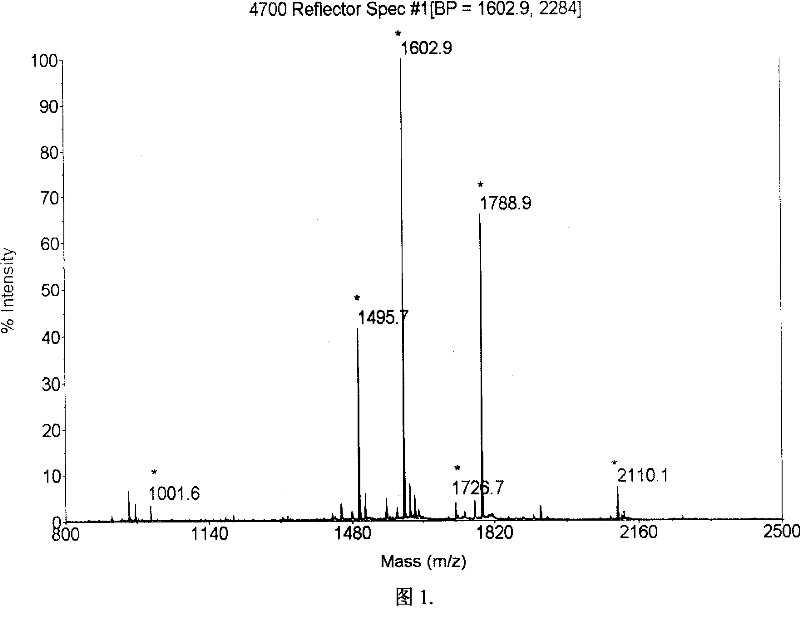
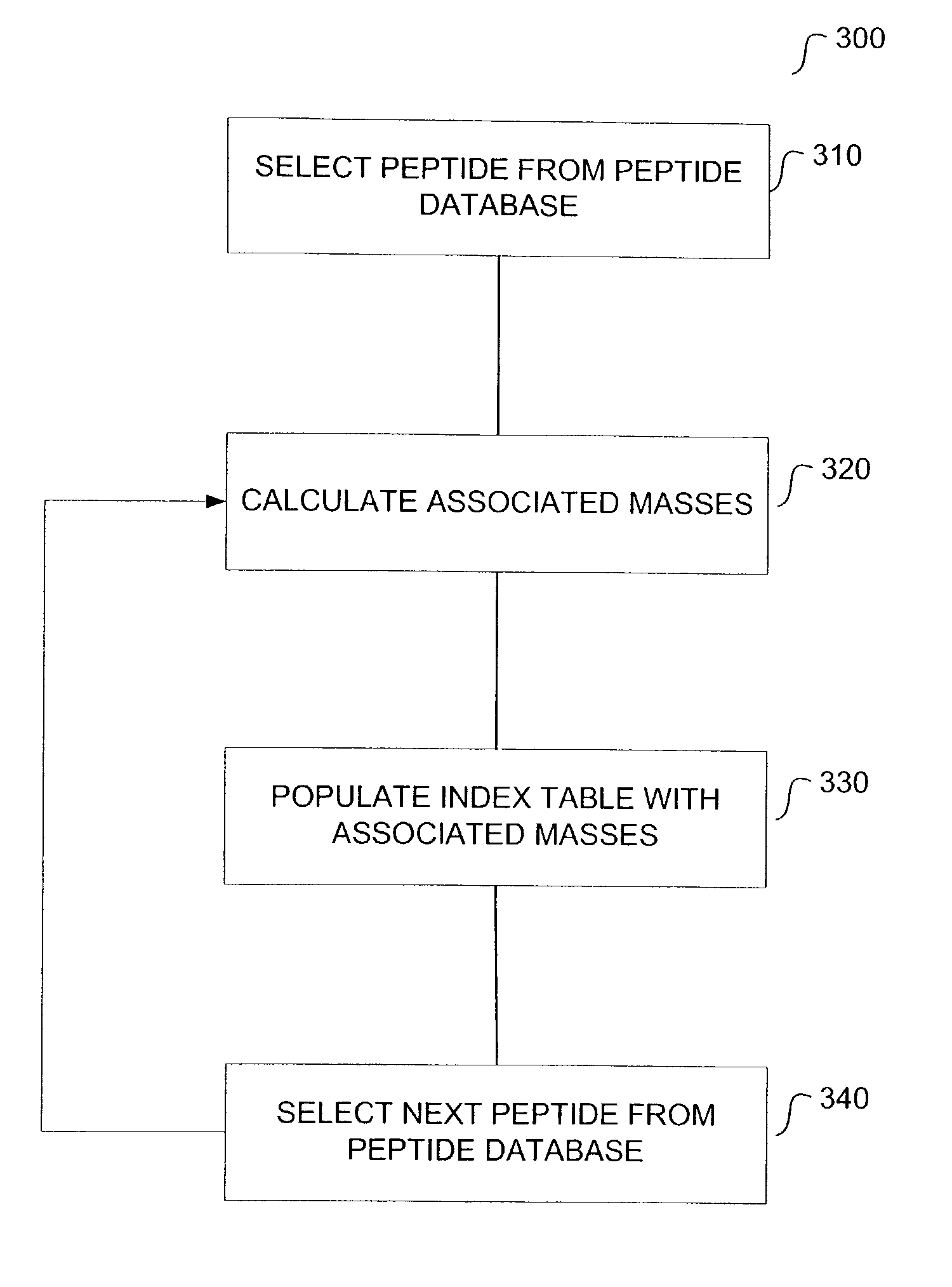
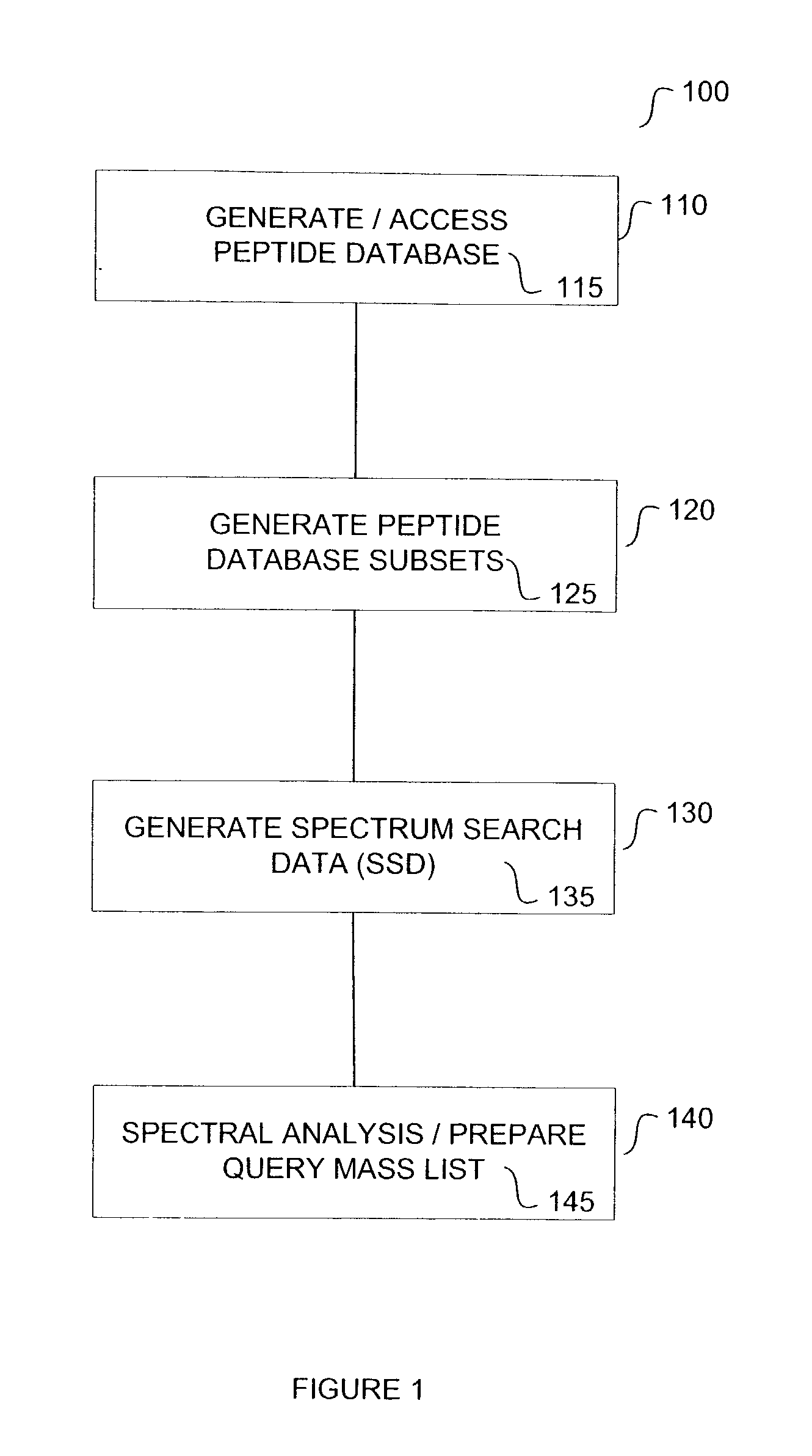
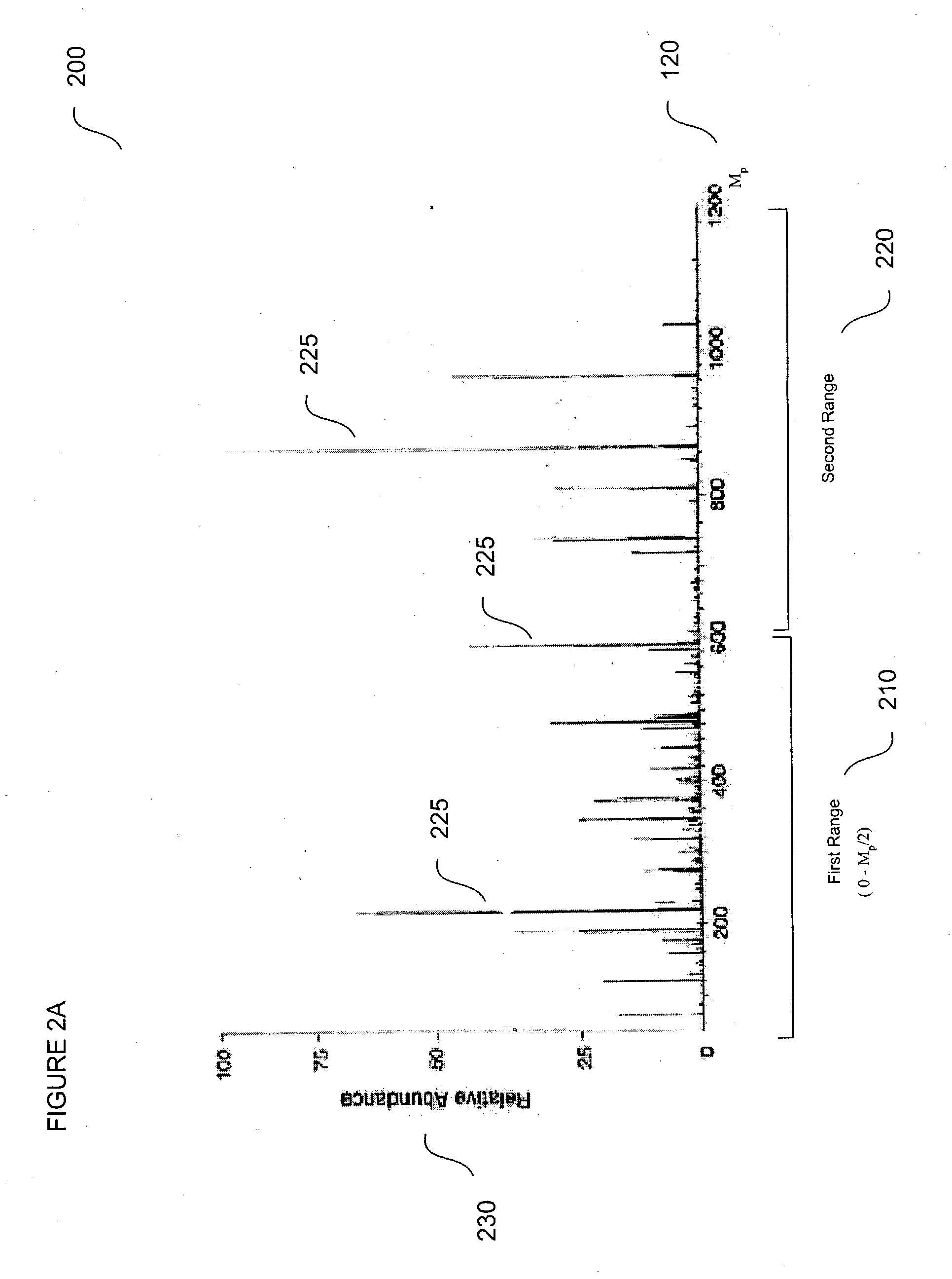
Method for protein identification using mass spectrometry data
InactiveUS20040044481A1Biological testingSpecial data processing applicationsMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryComputer science
The present teachings describe methods for matching a query peptide to a database of known peptides based on a mass analysis approach. The methods described herein facilitate rapid, sensitive, and selective identification of an unknown query peptide and provide the ability to develop applications which perform substantially automated high throughput protein identification. The methods described herein also allow for mass spectrometry data for a query peptide to be categorized and weighted according to its quality. Furthermore, the methods described herein provide robust identification of modified query proteins by either anticipating modifications or adjusting for modified peptide masses.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Polypeptide mixture isoelectric focusing separation method for proteomics analysis
InactiveCN103926301AAvoid lossAvoid degradationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRestriction enzyme digestionIon exchange
The invention discloses a polypeptide mixture isoelectric focusing separation method for proteomics analysis. The method comprises the following steps: performing restriction enzyme digestion on a total protein mixture of a biological sample completely to obtain relatively short peptide fragment mixtures; re-dissolving the peptide fragment mixtures by using a peptide fragment isoelectric focusing buffer solution; performing isoelectric focusing electrophoresis in a loading manner by adopting a loading cup, so as to realize the effective separation of a complex peptide fragment mixture; performing desalination on a taken polypeptide mixture pre-separated from each groove and performing mass spectrometry analysis so as to obtain more polypeptide signals, higher peptide fragment covering rate and higher protein identification number compared with those obtained when a conventional method is adopted. The method is precise, efficient and low in cost, can be used in multidimensional liquid chromatography-mass spectrum identification technology systems of total proteins of the various biological samples, can replace a conventional ion exchange chromatography pre-separation method so as to realize the efficient pre-separation of the peptide fragment mixtures, and avoids the lost of peptide fragments, and therefore, proteome expression profile information with the high covering rate can be established.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method and reagent kit for protein N-terminal peptide specific identification and sequencing
InactiveCN101055266AGreat practicabilityComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationProtein insertionApplication areas
The invention relates to a method and kit of particularity recognition and mass spectrum sequencing of protein N-end peptide section. The method and kit can be used for particularity recognition of protein N-end peptide section, increase determinacy and reliability of identification for protein N-end peptide section, and be adapted for protein identification and N-end analysis in biology, medicine and medicament research and application field.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
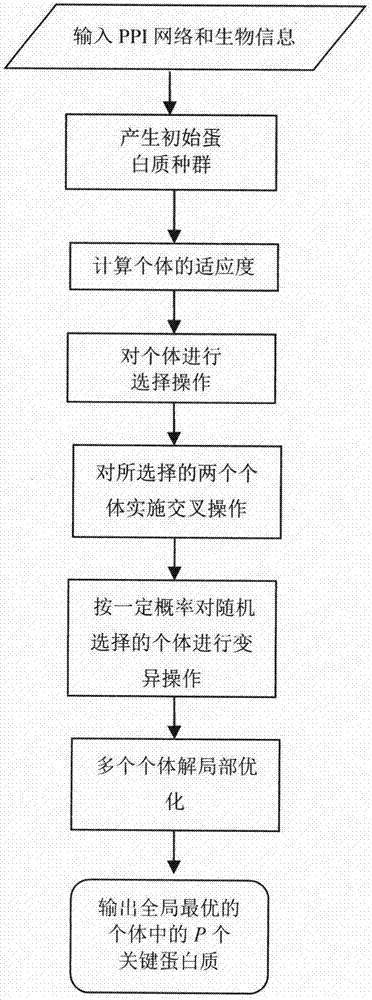
Method for identifying key protein based on genetic algorithm in PPI network
ActiveCN107092812APrediction is accurateImprove reliabilityProteomicsGenomicsAlgorithmMethod selection
The invention relates to an algorithm for identifying a key protein based on a genetic algorithm in a PPI network. The algorithm comprises the steps of generating an initial population in a protein interaction network; calculating the fitness of individuals; performing selection operation by a roulette wheel method; performing crossing operation and mutation operation among the randomly selected individuals; and performing local optimization on multiple individual solutions. According to the algorithm, the defects of existing methods are overcome; indexes are optimized and bio-information is fused, so that the reliability is higher and lots of unnecessary calculations are reduced; and the predicted key protein can be locally optimized, so that the efficiency of key protein identification is improved, and the application range and practicality of the technology in the field of the bio-information are expanded and improved.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Method for chemical and enzymatic treatment of posttranslationally modified proteins bound to a protein chip
InactiveUS7622273B2Quick upgradeSimpler, more sensitive methodologiesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEnzymatic digestionChemical treatment
Owner:GIBBS BERNARD F
Large-scale distributed parallel acceleration method and system for protein identification
ActiveCN102411666AImprove efficiencySmall amount of calculationSpecial data processing applicationsPeptide sequenceParallel processing
The invention relates to a large-scale distributed parallel acceleration method and system for protein identification. The method comprises the following steps of: by a parallel processing method, theoretically digesting a protein sequence to obtain peptide sequences, and sorting and redundantly processing the peptide sequences so as to create a peptide index file block; sorting mass spectra spectrums, and evenly dividing the sorted mass spectra spectrums into a plurality of spectrum data blocks; and evenly distributing the spectrum data blocks to a plurality of host processes, and each host process sorting the distributed spectrum data blocks and sequentially assigning to idle slave processes for peptide spectrum matching identification; and summarizing identification results by the parallel processing method, inferring the corresponding protein sequences by the peptide sequences obtained by identification, and generating output files. When a processor has hundreds or even thousands of cores, the satisfactory acceleration efficiency when the protein identification is carried out can be obtained.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com