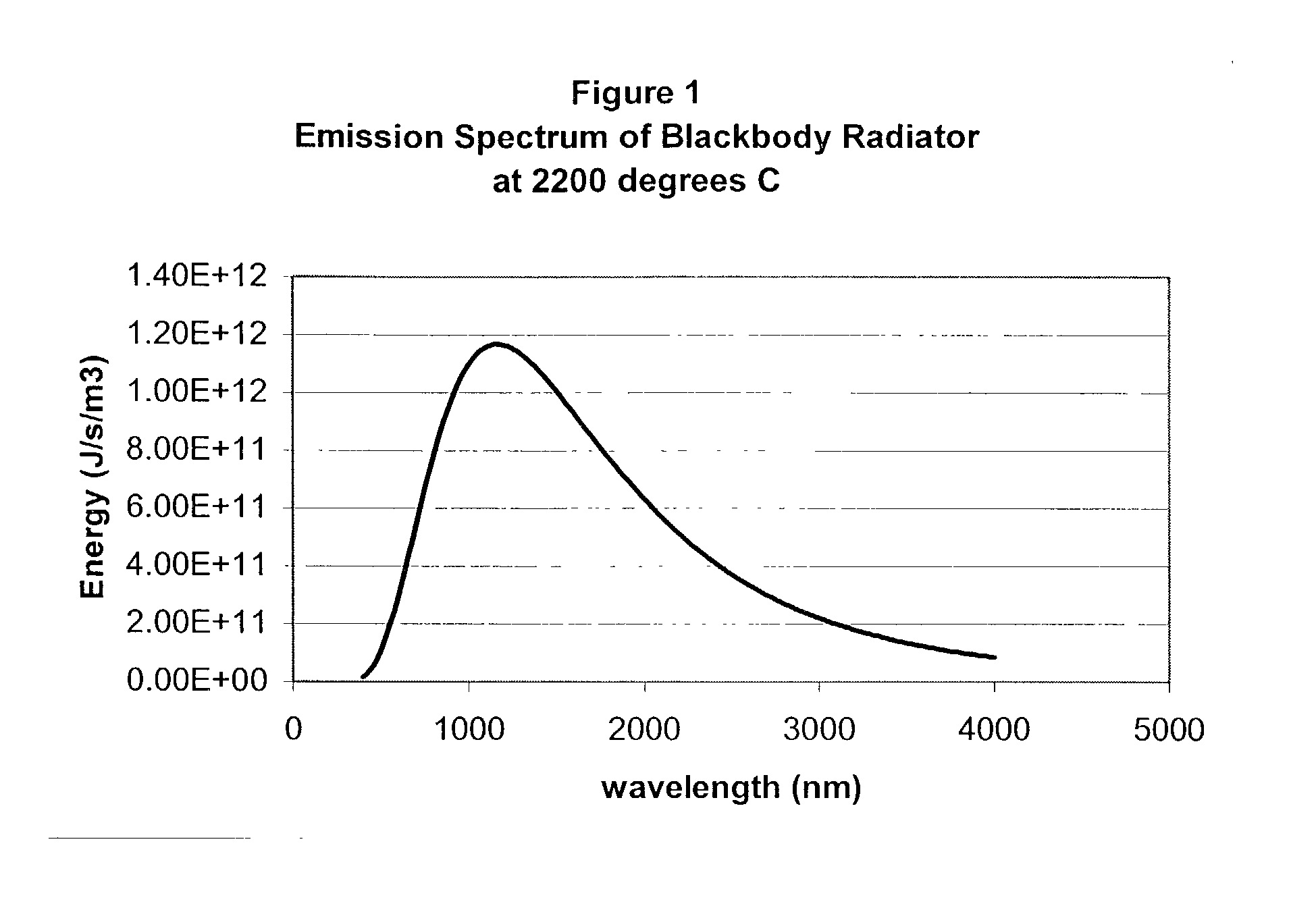
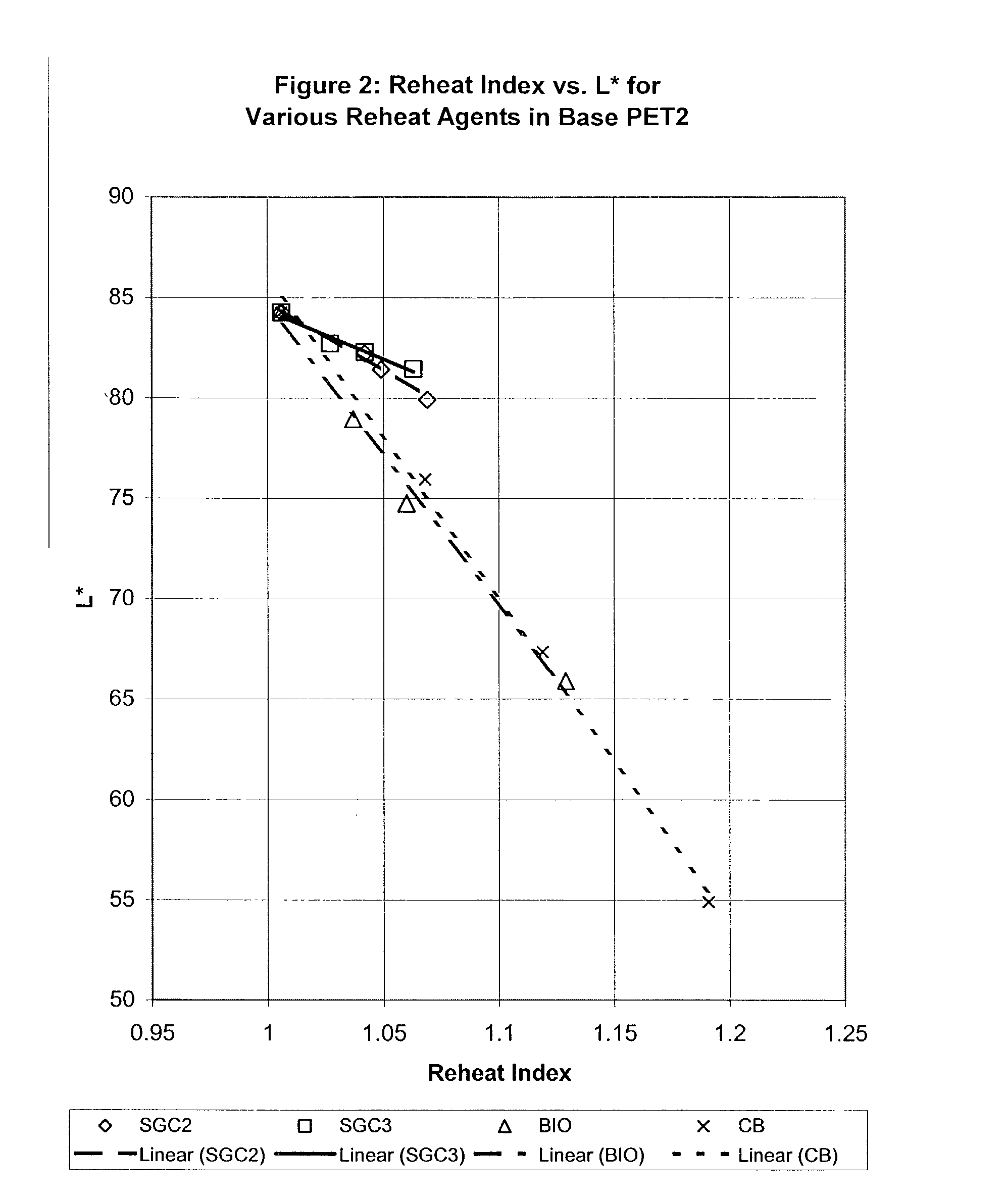
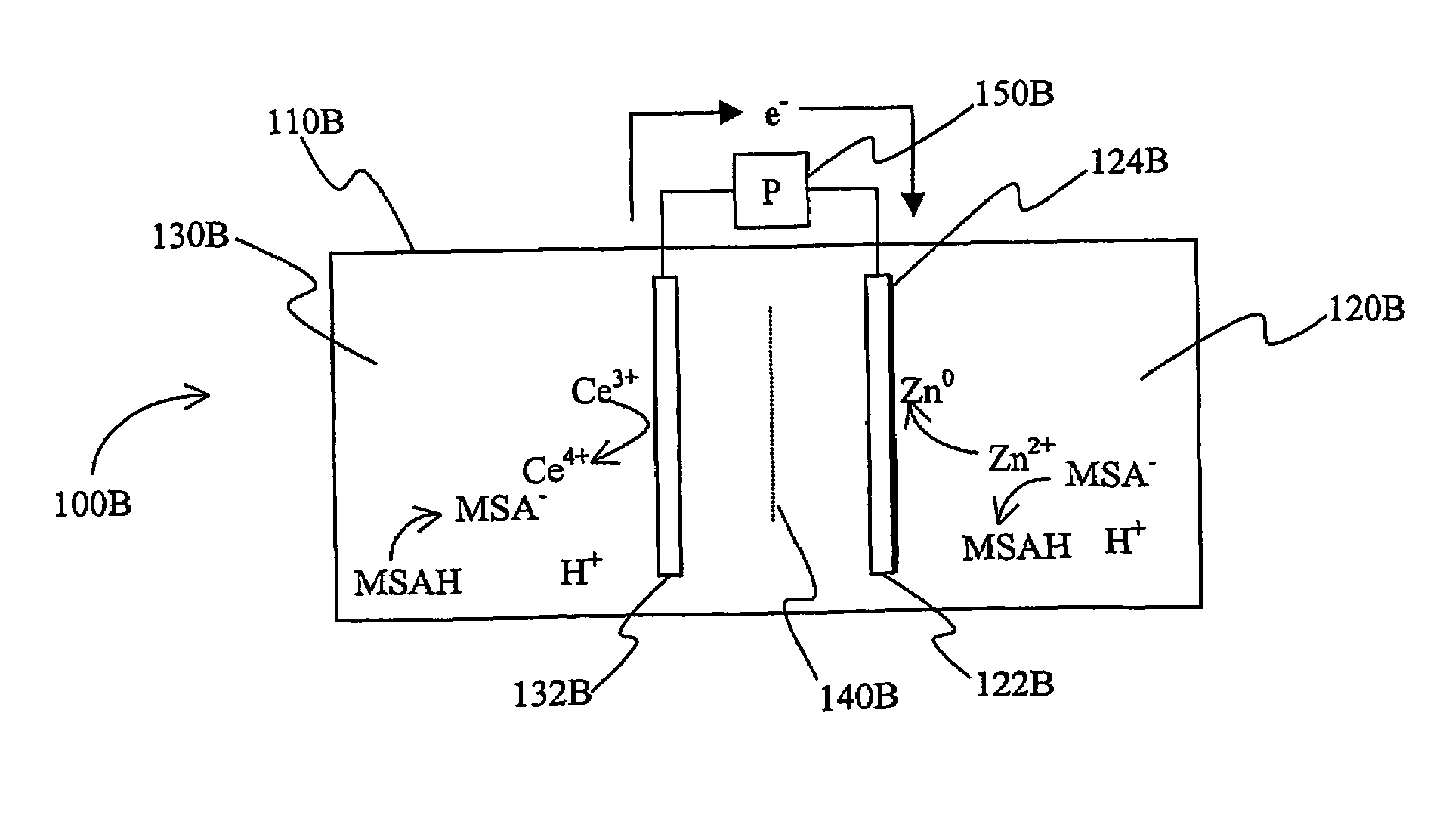
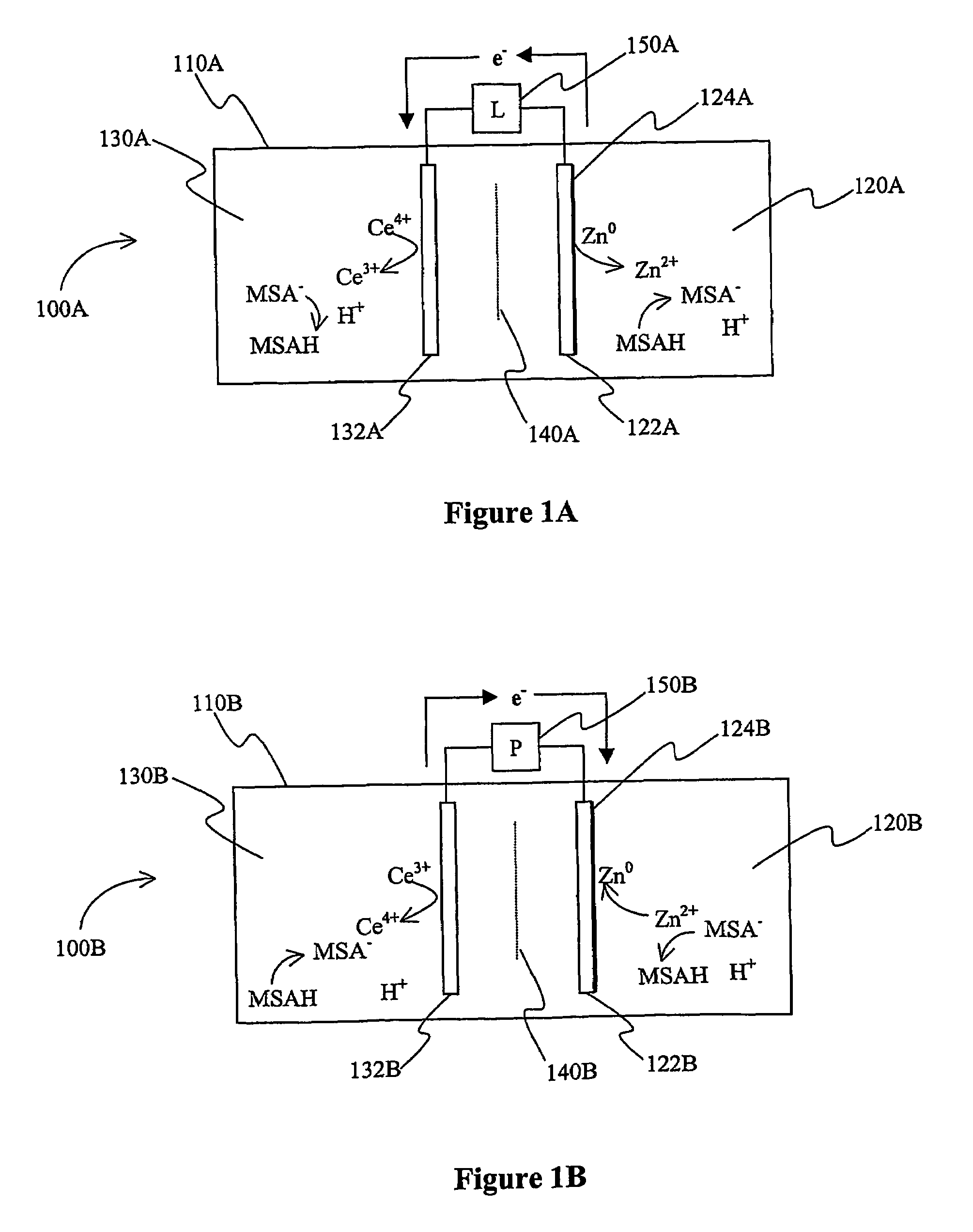
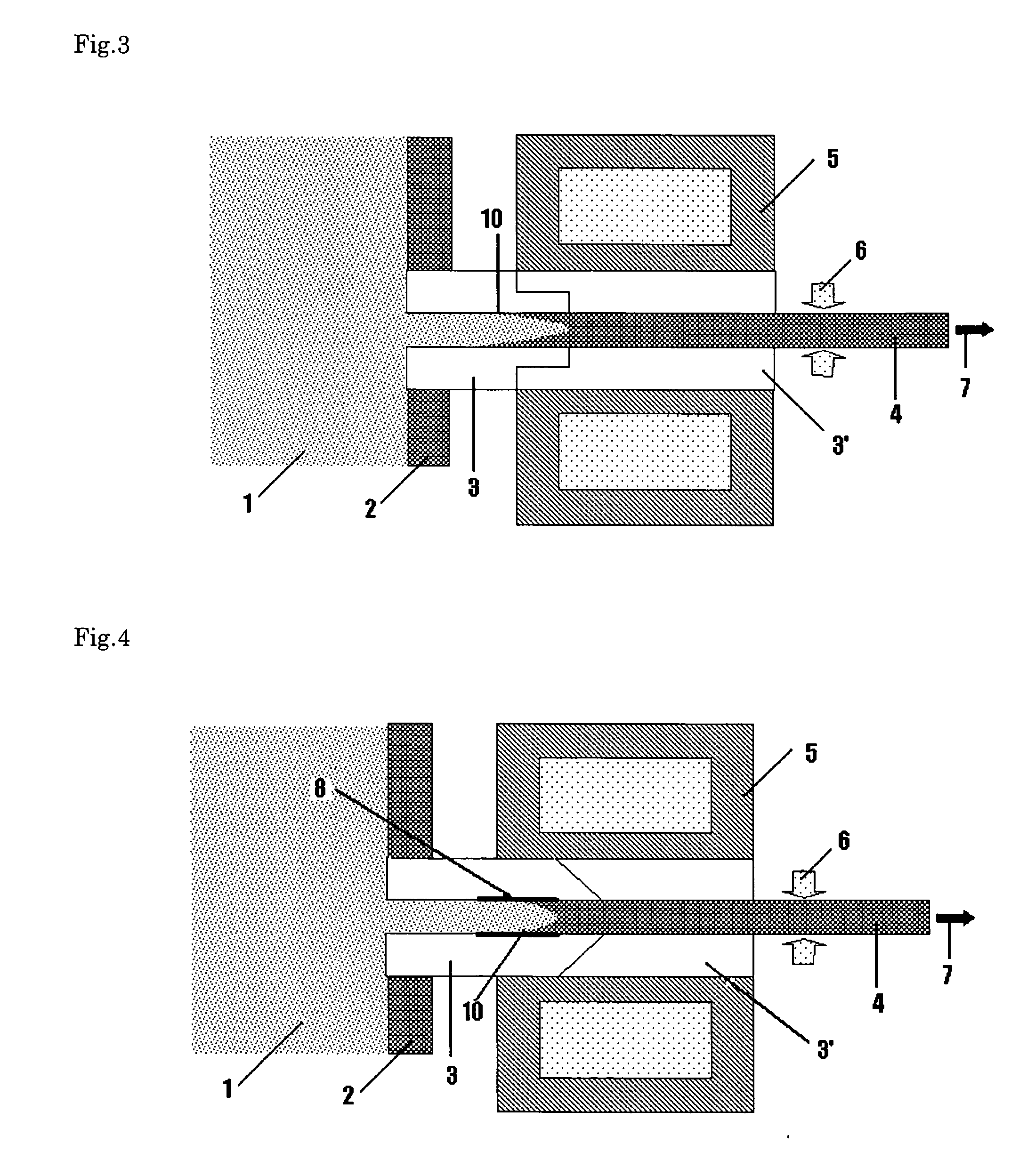
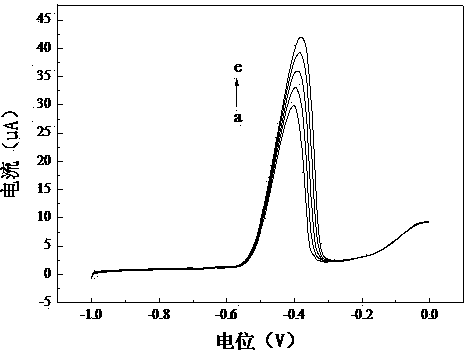
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
396 results about "Glassy carbon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
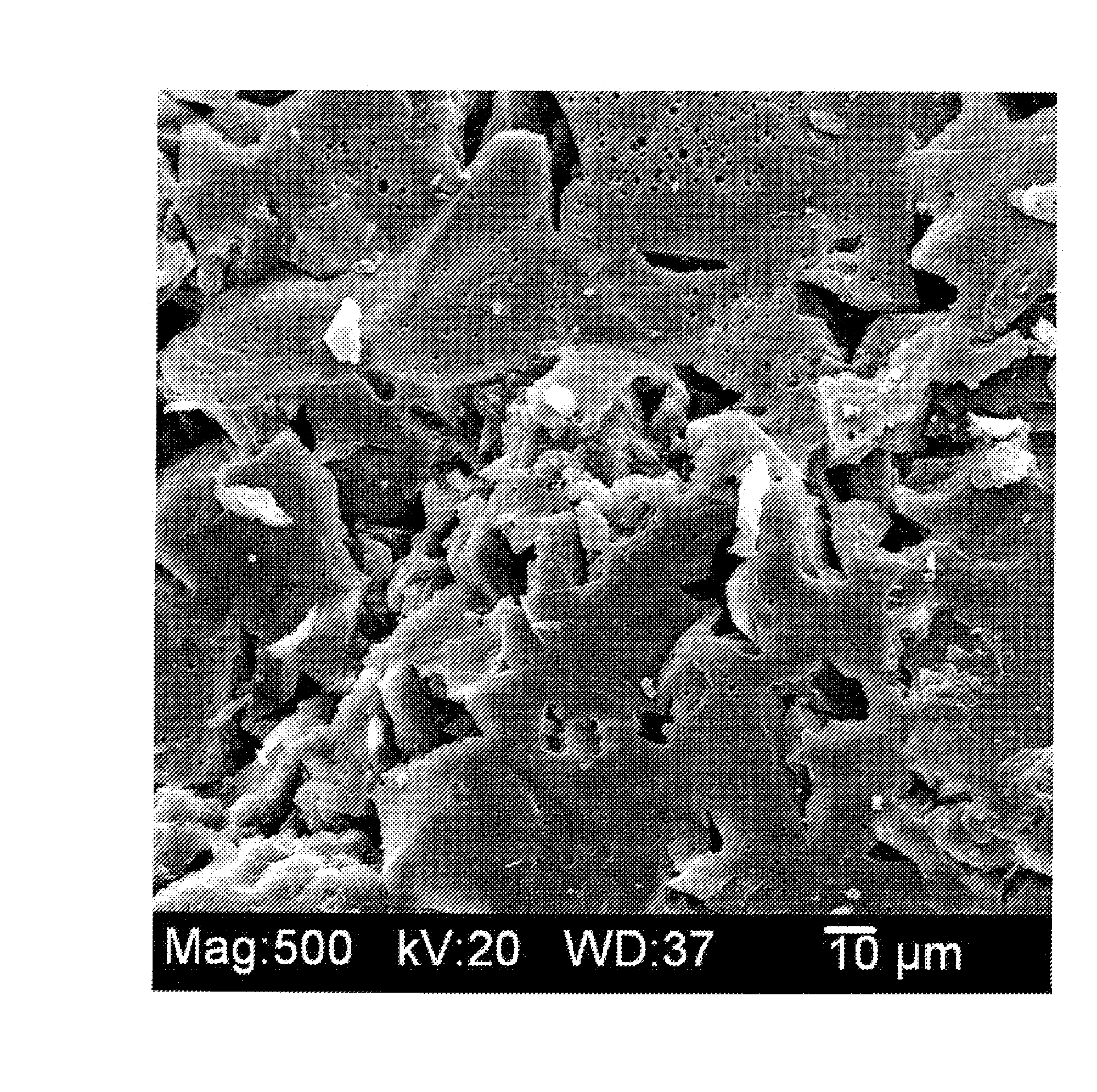
Glass-like carbon, often called glassy carbon or vitreous carbon, is a non-graphitizing, or nongraphitizable, carbon which combines glassy and ceramic properties with those of graphite. The most important properties are high temperature resistance, hardness (7 Mohs), low density, low electrical resistance, low friction, low thermal resistance, extreme resistance to chemical attack and impermeability to gases and liquids. Glassy carbon is widely used as an electrode material in electrochemistry, as well as for high temperature crucibles and as a component of some prosthetic devices, and can be fabricated as different shapes, sizes and sections.
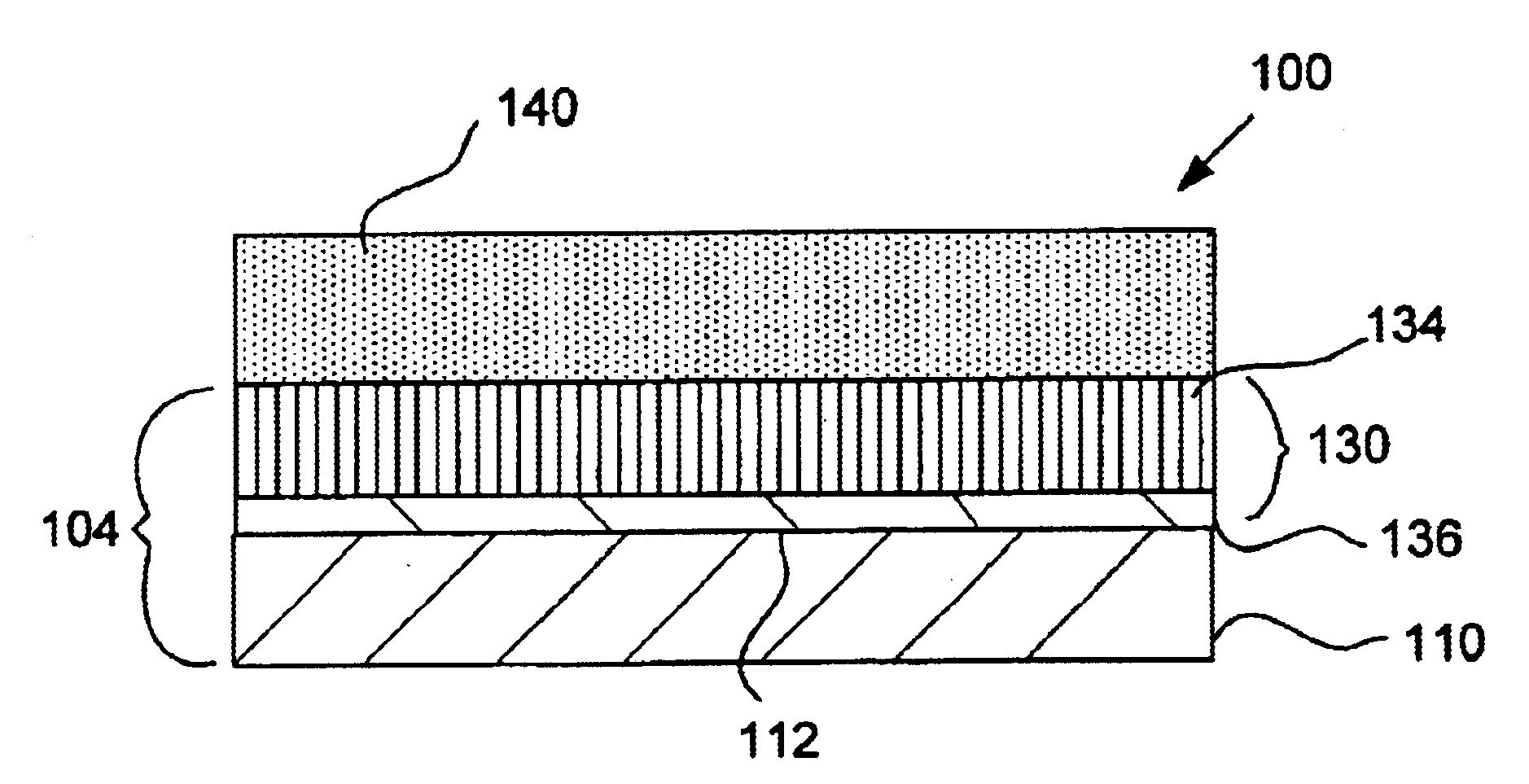
Capacitor and method for producing a capacitor
InactiveUS6842328B2Increase capacitanceAnti-noise capacitorsFixed capacitor electrodesCapacitanceActivated carbon
An electrode for a capacitor includes a substrate comprising at least one of glassy carbon and a metal. According to various embodiments, the substrate may be provided as glassy carbon or any of a variety of metals for use in capacitors. The capacitor also includes an activated carbon material adjacent the substrate. The activated carbon layer includes oxygen-containing functional groups. A material is provided in contact with the activated carbon layer for providing enhanced capacitance for the electrode. Various types of capacitance-enhancing materials may be utilized, including carbon nanotubes and conductive metal oxides.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Glassy carbon thermoplastic compositions
InactiveUS20040101642A1Good reheat rateImproved * b * ratingSynthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingPolyesterStatic friction coefficient
A thermoplastic composition such as a polyester composition including polyethylene terephthalate polymers containing glassy carbon, and the preforms, bottles, sheets, rods, tubes, films and other articles made from these compositions. Also, polyester compositions are provided which have a certain individual or combination of properties, including low coefficient of static friction, low coefficient of static friction and low haze or high L* or low positive b* or a combination thereof, and those having low L* and low positive b* at given reheat rates.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
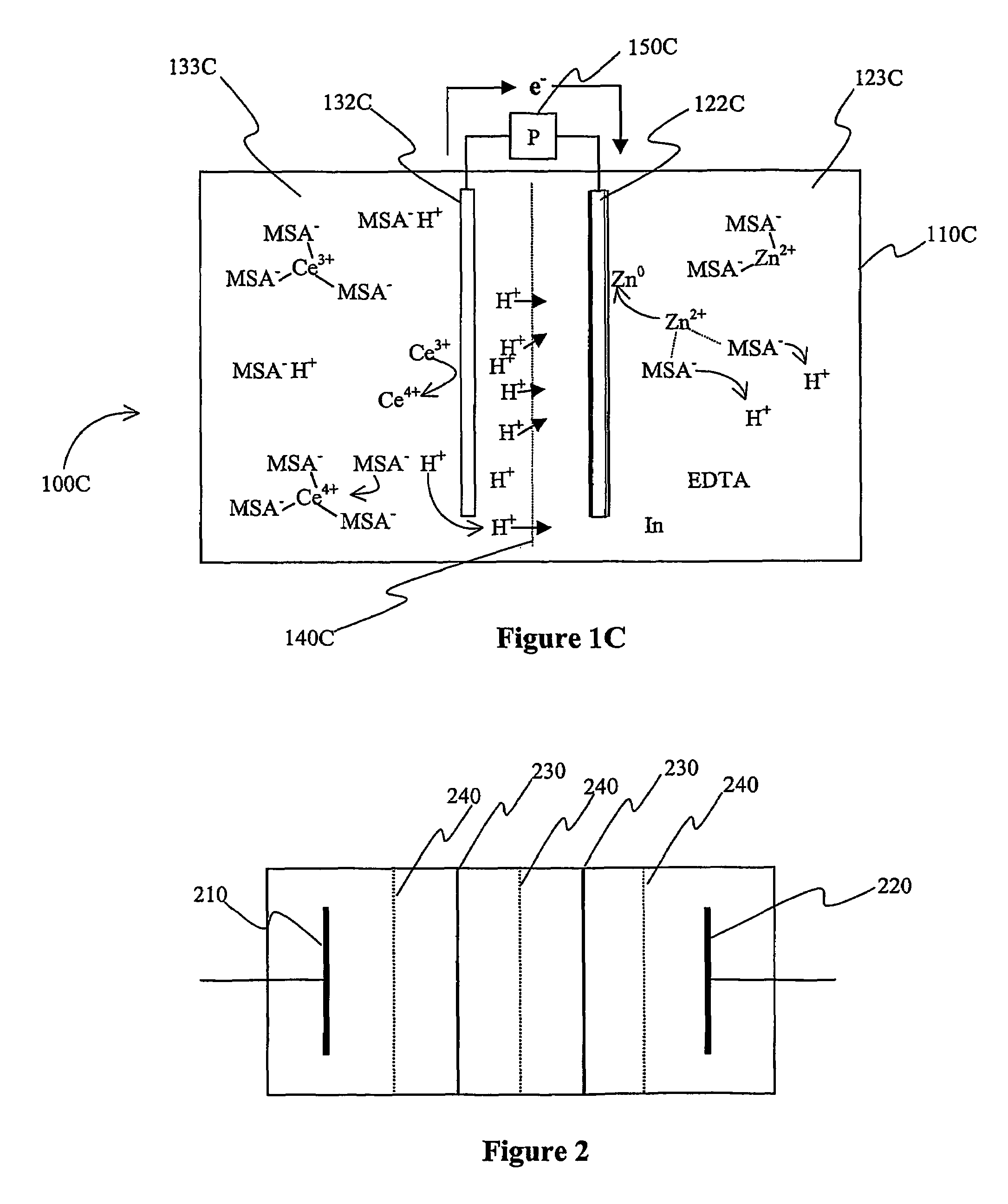
Cerium batteries
InactiveUS7625663B2Reduces hydrogen overpotentialCell electrodesOrganic electrolyte cellsOrganic acidHydrogen
A power cell (100A) has an electrolyte that includes a reodox pair comprising cerium. The electrolyte in preferred cells is an acid electrolyte that comprises a element ion complexed by an organic acid or a chelating agent, and contemplated electrolytes may further include a compound that reduces the hydrogen overpotential. Where the power cell comprises a plurality of cells (100B), preferred configurations may include glassy carbon as bipolar electrolytes.
Owner:ITI SCOTLAND
Semiconductor element
ActiveUS20100252802A1NanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceCarbon nanotube
This invention provides a semiconductor element which uses a plurality of carbon nanotubes as a current path, can reduce contact resistance of its electrode contact part, and has excellent electrical characteristics. This semiconductor element is characterized in that the semiconductor element includes a current path (16) comprised of a plurality of carbon nanotubes (18) and not less than two electrodes (14, 15) connected with the current path, wherein at least one or more of the electrodes is made of a mixture of a metal and a carbon material (17) having SP2 hybridized orbital, such as a multi-walled carbon nanotube, a glassy carbon, and graphite particles.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method of electroplating zinc, nickel, molybdenum and their alloys by using ionic liquid
The invention discloses a novel cleaning plating technology by using an ionic liquid which is a non-aqueous media as an electroplate liquid. Through using the technology, problems of bad environment and unstable qualities of electroplates existing in the condition of electroplating zinc, nickel, molybdenum and their alloys in an aqueous system can be solved. Qualities of coatings generated by using the technology are better than the qualities of coatings generated in the traditional system. The technology comprises the following steps: dissolving zinc salts, nickel salts and molybdate salt into the ionic liquid which is regarded as an electrolyte to prepare the electroplate liquid; electroplating at a current density of 1-30mA / cm2, wherein metallic zinc, nickel, molybdenum and their alloys are taken as soluble anode or graphite, complex carbon, glassy carbon, metal tungsten and titanium base plating platinum are taken as insoluble anode, and components which are needed to be electroplated are taken as cathode. Needed depth of coating can be obtained through controlling the current density and electroplating time.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Induction heating type pure water heating apparatus and pure water heating method
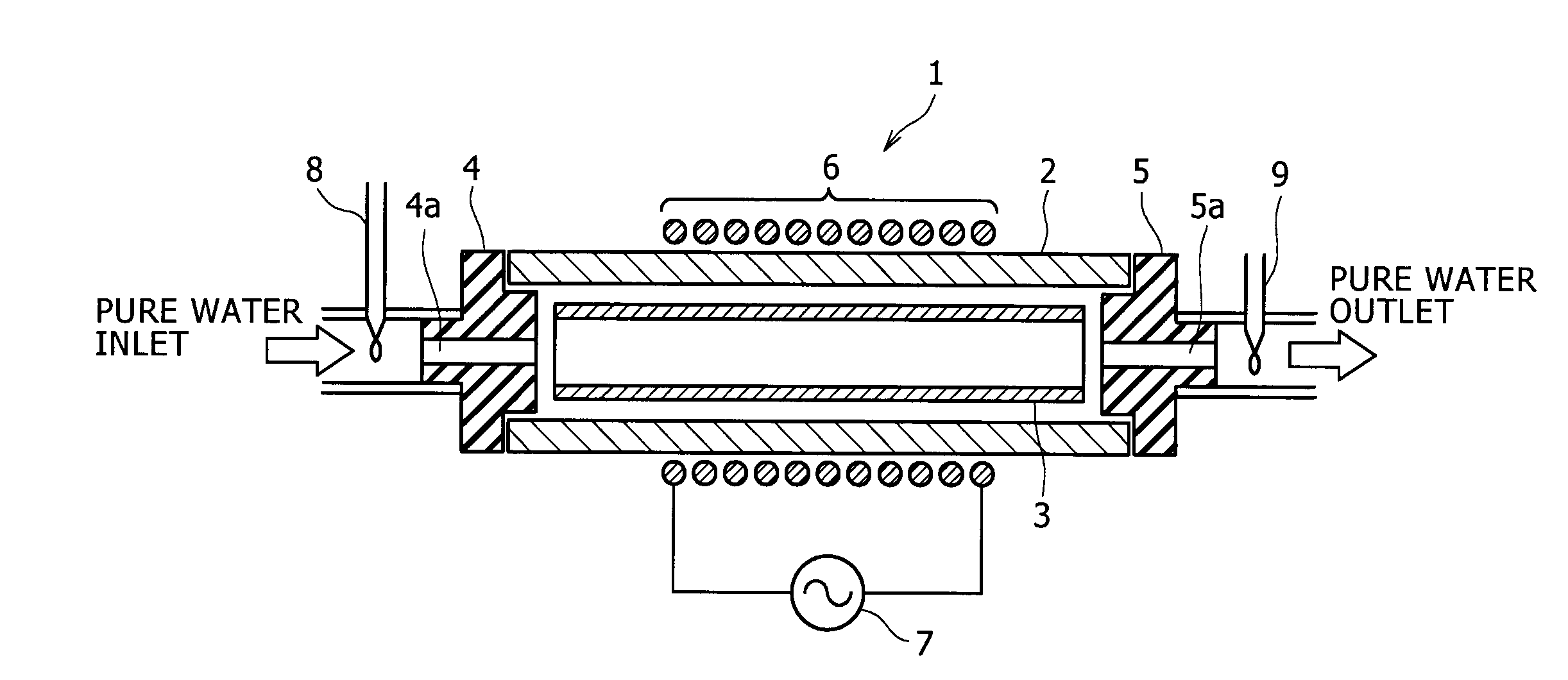
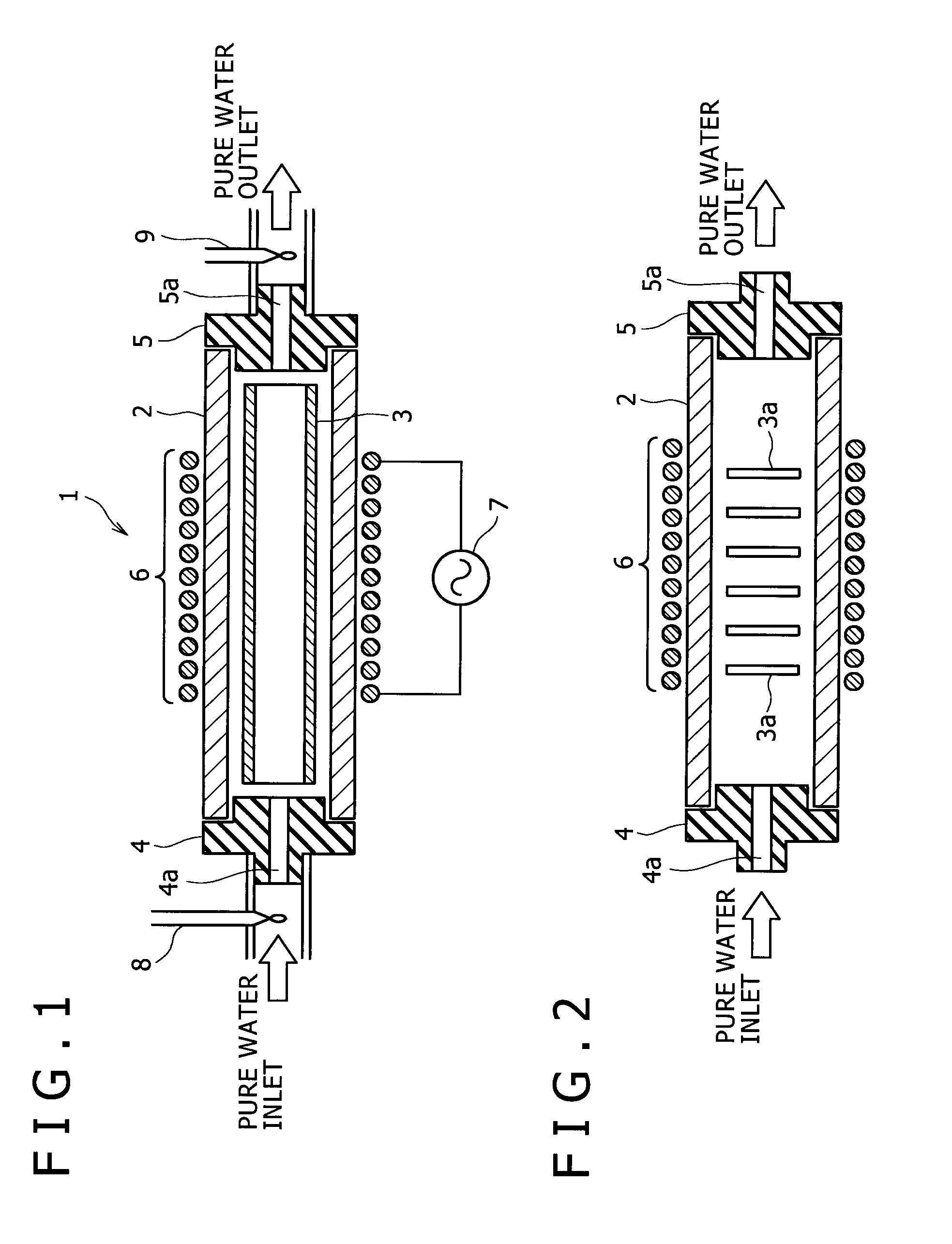
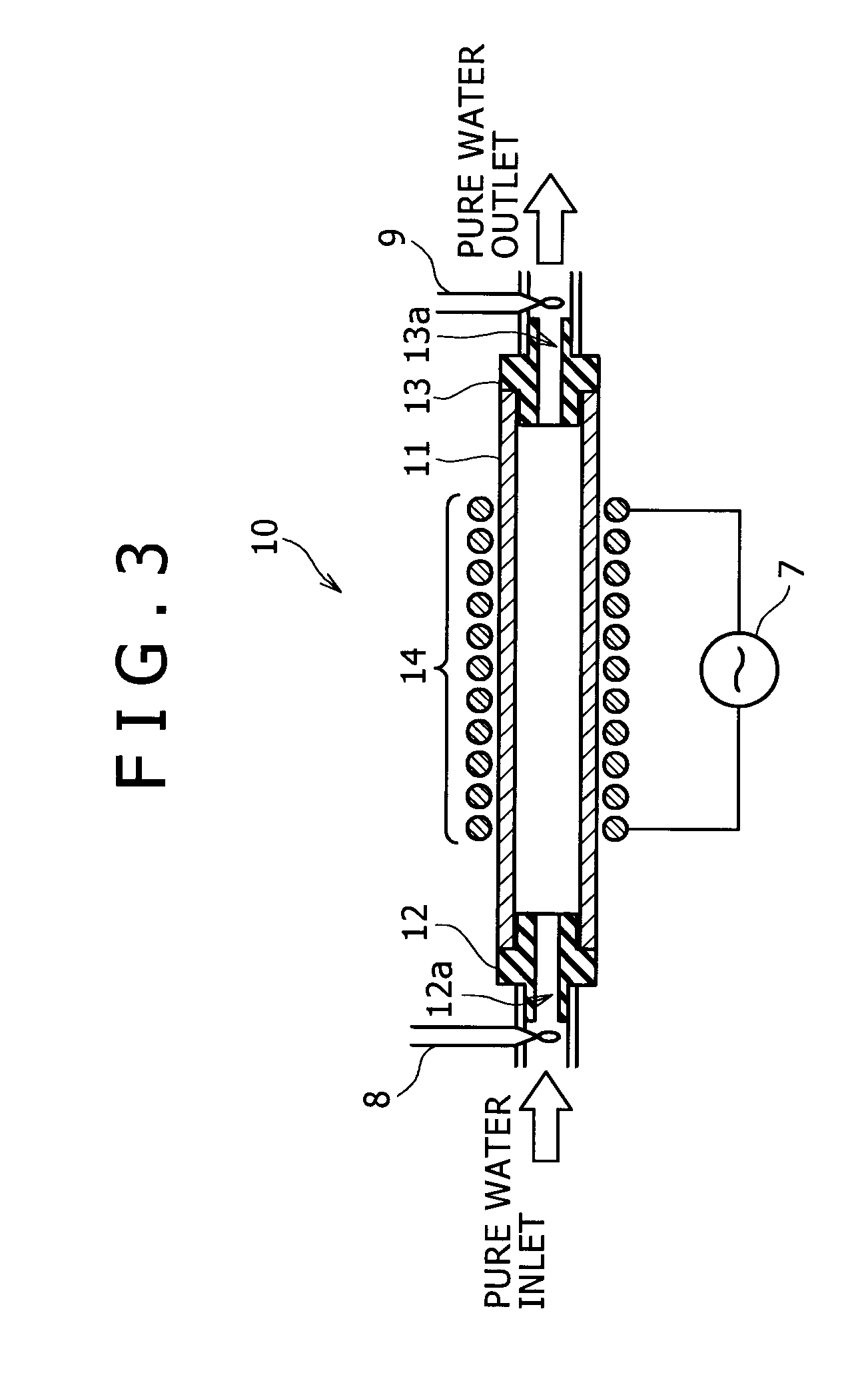
InactiveUS20080011336A1Efficient heatingIncrease surface areaSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWater heatersWater absorption coefficientMagnetic flux
Disclosed is an induction heating type pure water heating apparatus capable of heating pure water with efficiency and without contaminating pure water. The apparatus is characterized by including a susceptor formed of glassy carbon with a water absorption coefficient of 0.5 mass % or less, and capable of contacting with pure water, a container made of a magnetic flux transmissive material, and formed so as to accommodate the susceptor and so as to allow pure water to pass therethrough, and an induction coil disposed in such a state as to surround the container or as to be adjacent to the container.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Detection of biological molecules
InactiveUS20060096870A1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHigh concentrationCorrelation coefficient
An apparatus uses carbon nanotubes for electrochemical analysis of biological molecules of interest such as Uric Acid, illustrating how the voltammetric behaviors of uric acid (UA) and L-ascorbic acid (L-AA) at a well-aligned, carbon nanotube, electrode may be used in a biochemical assay. Compared to glassy carbon, a carbon nanotube electrode reduces troublesome overpotentials. Based on its differential catalytic function toward the oxidation of UA and L-AA, the carbon nanotube electrode can be used for a selective determination of UA in the presence of L-AA. The peak current obtained from DPV was linearly dependent on the UA concentration in the range of 0.2 μM to 80 μM with a correlation coefficient of 0.997. The detection limit (3δ) for UA was found to be 0.1 μM. The device allows for detection of UA in a human urine sample, even in the presence of high concentrations of L-AA, using only simple dilution.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Biphasic nanoporous vitreous carbon material and method of making the same
A biphasic nanoporous vitreous carbon material with a cementitious morphology characterized by presence of non-round porosity, having superior hardness and tribological properties, as useful for high wear-force applications. The biphasic nanoporous vitreous carbon material is produced by firing, under inert atmosphere, of particulate vitrified carbon in a composition containing (i) a precursor resin that is curable and pyrolyzable to form vitreous carbon and, optionally, (ii) addition of one or more of the following: solid lubricant, such as graphite, boron nitride, or molybdenum disulfide; a heat-resistant fiber reinforcement, such as copper, bronze, iron alloy, graphite, alumina, silica, or silicon carbide; or one or more substances to improve electrical conductivity, such as dendritic copper powder, copper “felt” or graphite flake, to produce a superior vitreous carbon that is useful alone or as a continuous phase in reinforced composites, in relation to conventional glassy carbon materials.
Owner:CARBON CERAMICS CO LLC
Continuous casting mold and a continuous casting method of copper alloy
A continuous casting mold for a Cu alloy, using any one member selected from a glassy carbon, a metal-based self-lubricating composite or a graphite with a bulk density exceeding 1.92, at least for the mold member including the solidification starting position of the Cu alloy melt. A continuous casting mold for a Cu alloy, composed of any one member selected from a graphite, a ceramic and a metal member or of a combination of two or more parts of members thereof, in which at least the inner wall in the solidification starting position of the Cu alloy melt is coated with a self-lubricant or a metal-based self-lubricating composite material. A continuous casting method of a Cu alloy, comprised of giving, at the time of continuously casting the Cu alloy by an intermittent pulling out method, a vibration that has a frequency larger than the slab intermittent pulling out frequency by two orders or more and that has a component vertical to the pulling out direction of the slab, or continuously supplying a lubricant or an anti-sticking material between the inner wall of the mold and the slab.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL IND LTD
Electric devices with improved bipolar electrode
An electric device has a plurality of cells in which in an acid electrolyte a lanthanide and zinc form a redox couple that provide a current, and in which at least two of the cells are separated by a bipolar electrode that comprises a glassy carbon or a Magneli phase titanium suboxide.
Owner:ITI SCOTLAND +1
Method for quickly detecting lead and cadmium by adopting scanning anodic stripping voltammetry
InactiveCN103592356AImprove stabilityGuaranteed stabilityMaterial electrochemical variablesRelative standard deviationMercury pollution
The invention discloses a method for quickly detecting lead and cadmium by adopting scanning anodic stripping voltammetry. The method comprises the following steps: a sample to be tested is prepared; lead or cadmium standard liquid is prepared; a three-electrode system consisting of glassy carbon electrodes plated with mercury films, platinum wire counter electrodes and Ag / AgCl reference electrodes is assembled; parameters are set and the scanning anodic stripping voltammetry is adopted to respectively implement parallel determination for current values between working electrodes and reference electrodes of each standard liquid solution until the relative standard deviation of readings is not more than 5%; lead and cadmium heavy metals of the sample are measured through detecting the current values between the working electrodes and the reference electrodes; a working station automatically calculates to obtain detecting results through automatically searching peaks to determine each curve peak area. The detecting method has the advantages of high sensitivity, good accuracy, reduction of mercury pollution, high electrode stability and good reproducibility, and can be applied to the detection of the heavy metals of lead and cadmium with conventional trace and ultratrace.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Protein molecular imprinting polyion liquid membrane electrochemical transducer
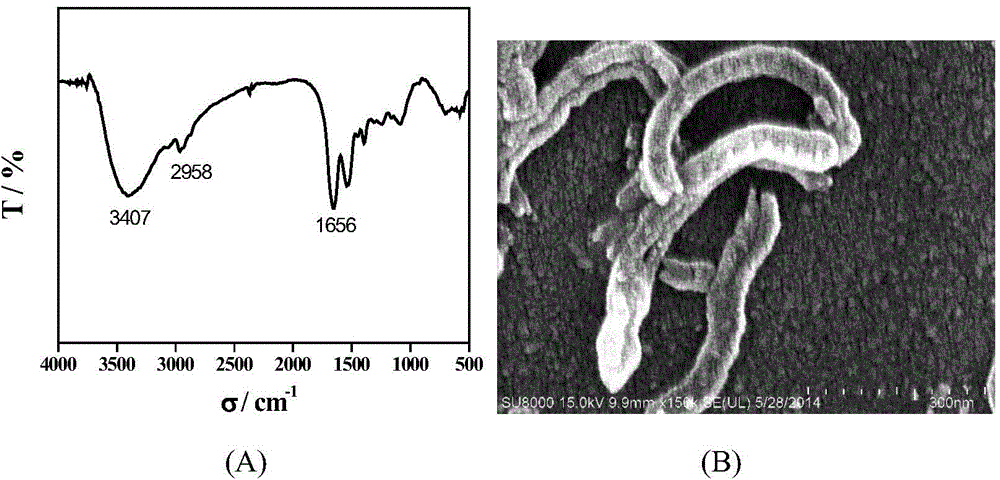
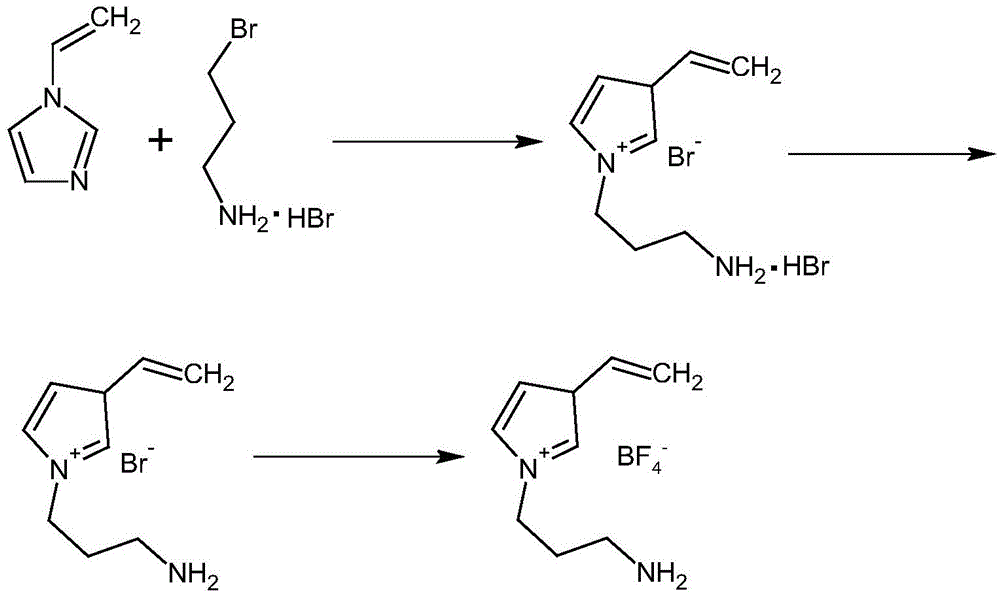
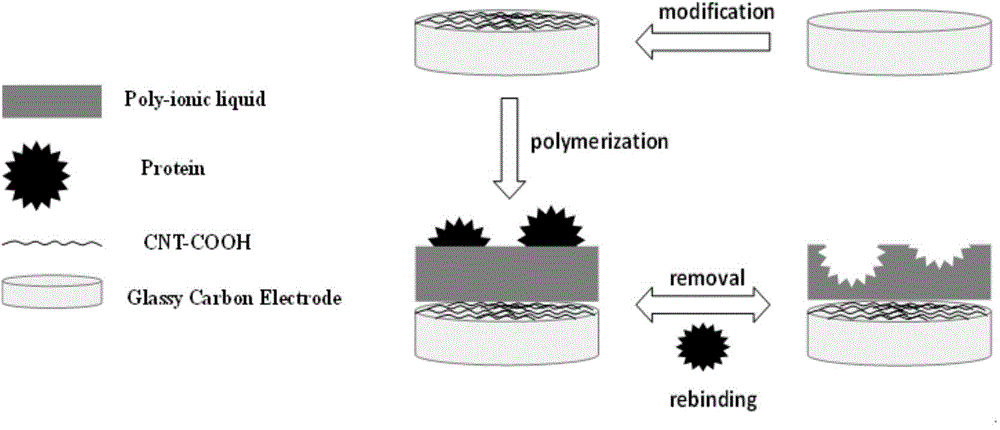
InactiveCN104142361ALarge specific surface areaGuaranteed stabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiocompatibility TestingIonic liquid
The invention relates to the technical field of electro-analytical chemistry and protein identification transducers, and discloses a synthesizing method of functionalized ionic liquid and a preparation method and application of a molecular imprinting electrochemical transducer composed of the functionalized ionic liquid, carboxylation multiwalled carbon nanotubes and glassy carbon electrodes. The preparation method of the molecular imprinting electrochemical transducer comprises the steps that the polymerizable amino-functionalized ionic liquid is used as a functional monomer, BSA is used as template protein, N, N'-methylene bisacrylamide is used as a cross-linking agent, an oxidation-reduction system composed of ammonium persulfate and TEMED is used as an initiator, after polymerization, a molecularly imprinted polymer film is formed on the surfaces of the glassy carbon electrodes decorating the carboxylation multiwalled carbon nanotubes, and then the template protein is eluted to obtain the molecular imprinting electrochemical transducer which can identify template protein in a specific mode. The molecular imprinting electrochemical transducer has the advantages of being simple in preparation, low in material cost, high in selectivity, good in biocompatibility, and capable of being used for identifying and detecting protein in aqueous solution.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
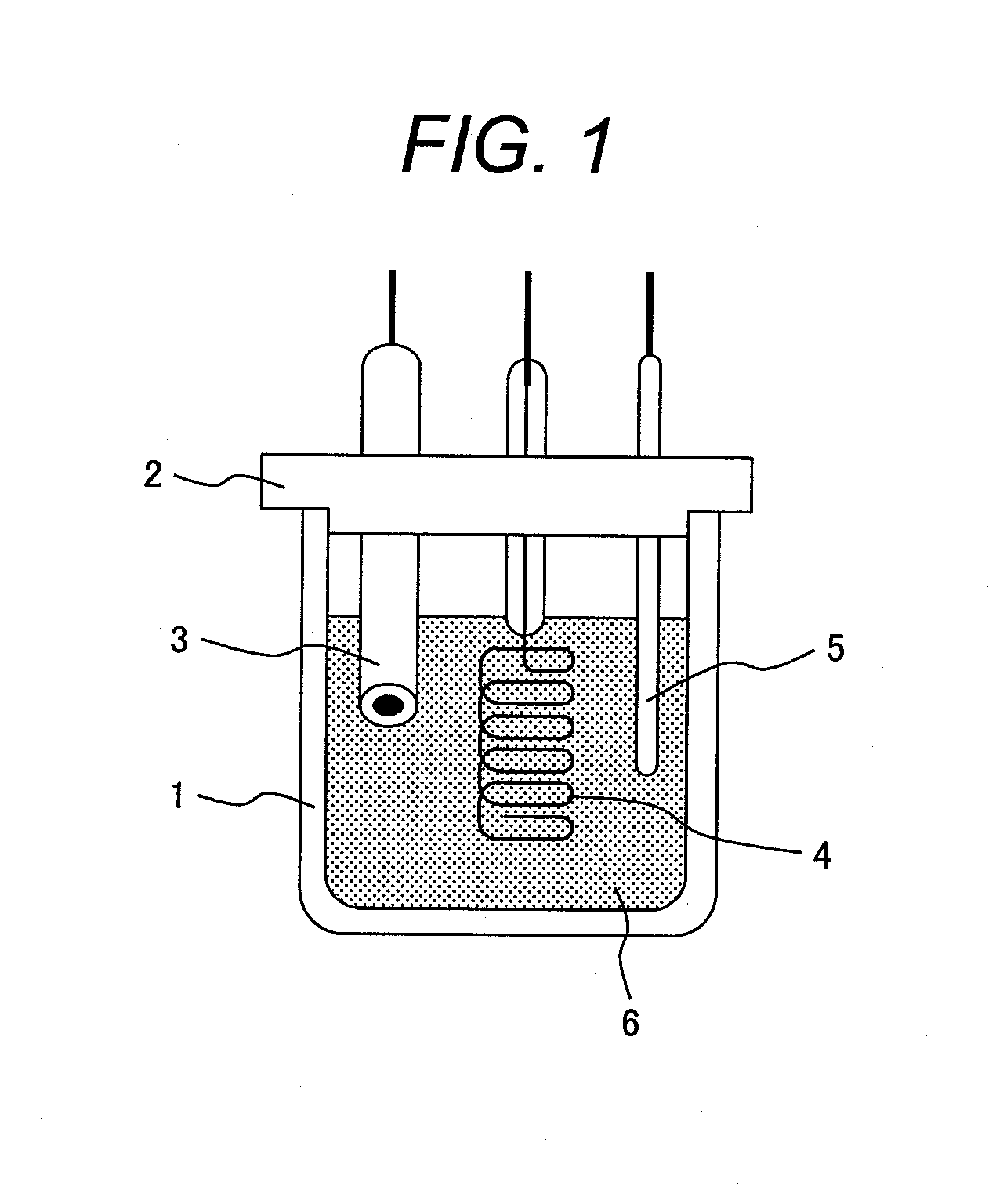
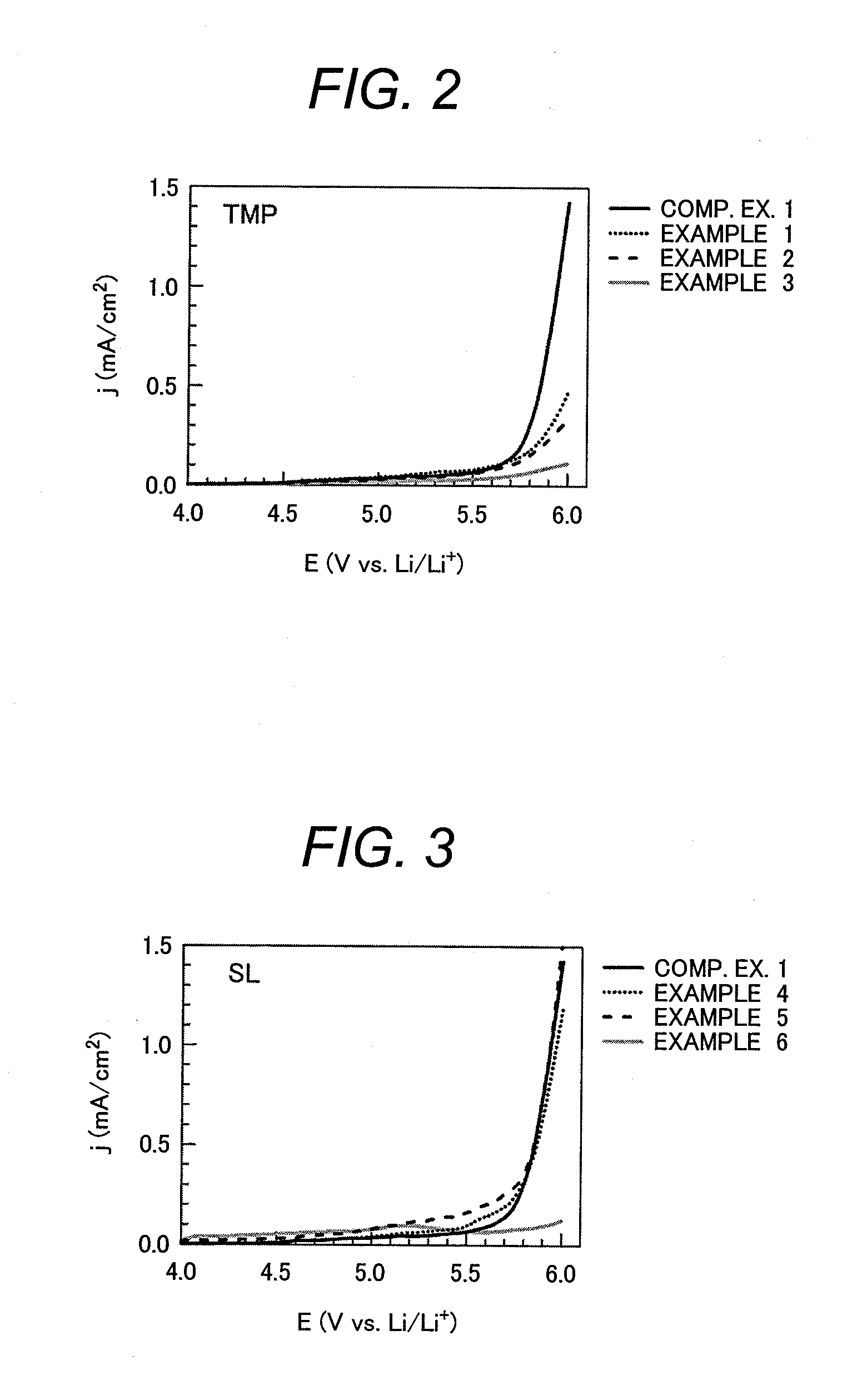
Lithium-ion secondary battery
InactiveUS20120100436A1Solution to short lifeIncrease battery outputCell electrodesOrganic electrolyte cellsSolventCarbonate
Disclosed is a lithium-ion secondary battery which includes a carbonaceous material in an anodic active material mix, and a cyclic carbonate and a chain carbonate both in an electrolytic solution. The solvent contains an additive which is a substance having a LUMO energy determined through molecular orbital calculation of lower than the LUMO energy of ethylene carbonate determined through molecular orbital calculation and having a HOMO energy lower than the HOMO energy of vinylene carbonate determined through molecular orbital calculation, the electrolytic solution contains LiPF6 or LiBF4 as an electrolyte, and the electrolytic solution shows a reduction-reaction current of −0.05 mA / cm2 (provided that a reaction current on the reducing side be negative) or less at a potential lower than 1 V and shows an oxidation-reaction current of 0.5 mA / cm2 (provided that a reaction current on the oxidizing side be positive) or more at a potential higher than 5.7 V in an LSV measurement at a potential sweep rate of 1 mV / s using a glassy-carbon disk electrode as a working electrode, a platinum electrode as a counter electrode, and a lithium electrode as a reference electrode.
Owner:HITACHI VEHICLE ENERGY
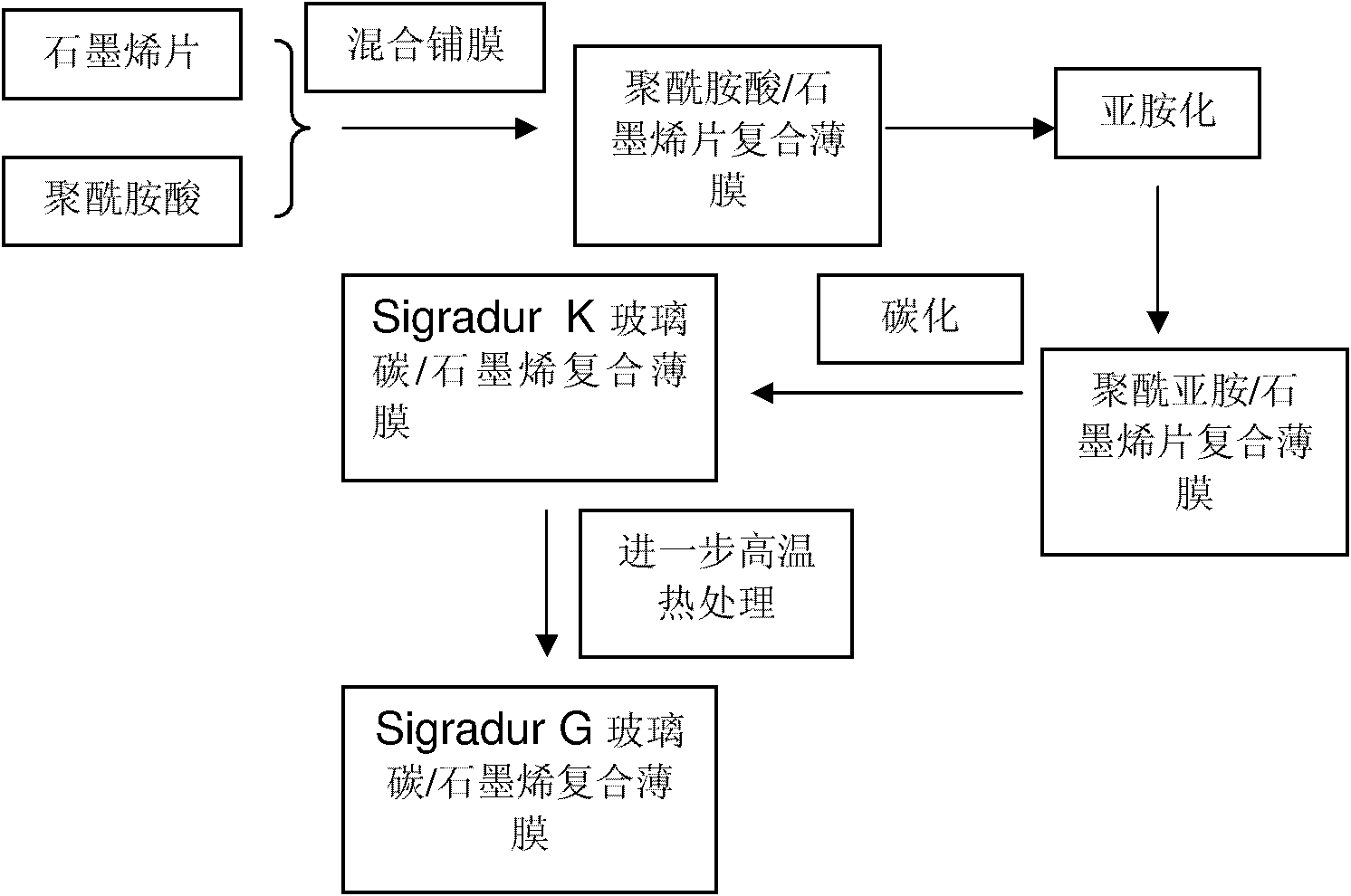
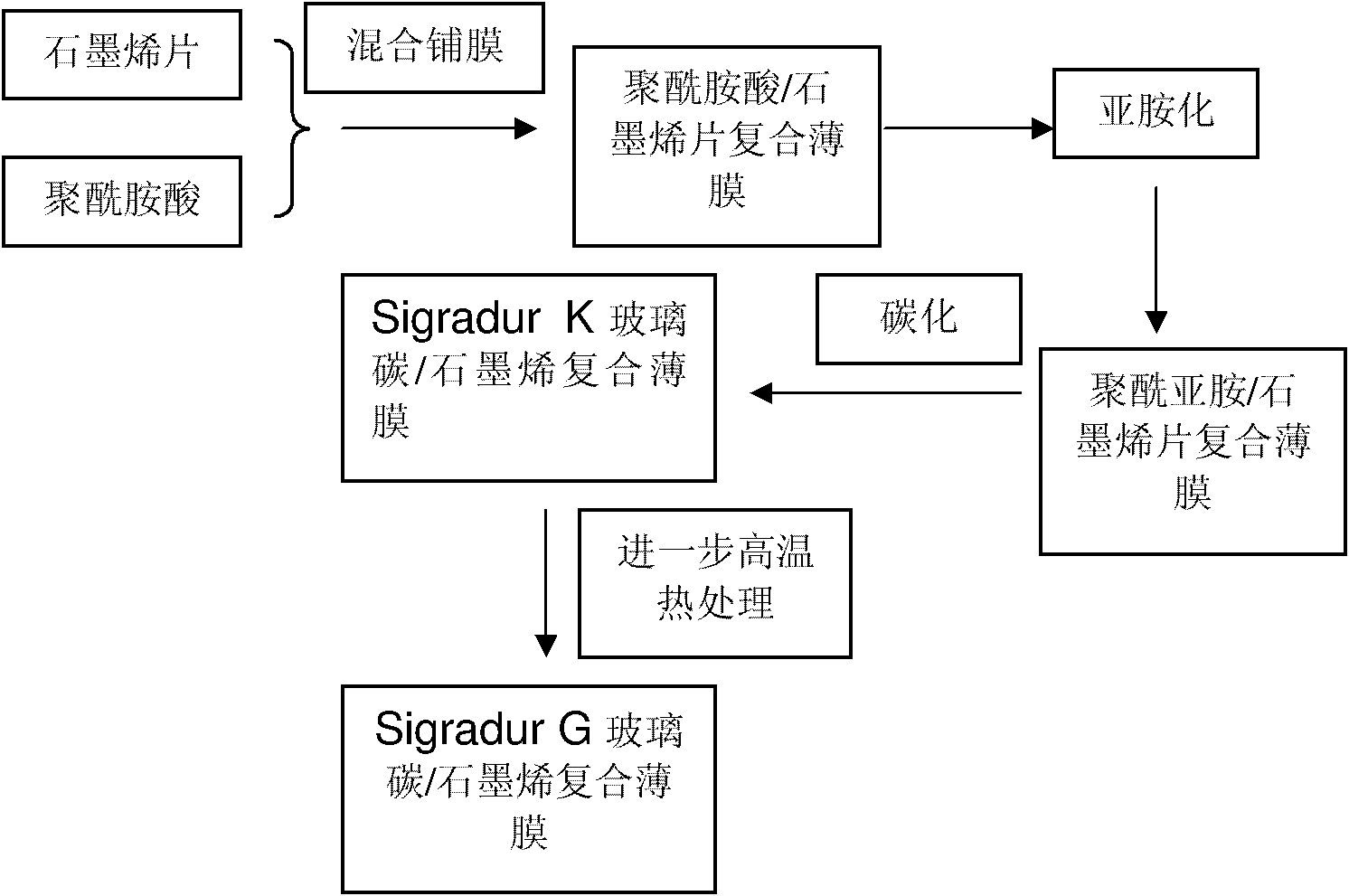
Composite film based on glassy carbon and graphene and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of composite materials and relates to a composite film based on glassy carbon and graphene and a preparation method thereof. A composite film precursor comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 0.1 to 50 percent of graphene sheet and 99.9 to 50 percent of polyimide substrate. The preparation method comprises the following step of: carrying out carbonization on a polyimide precursor film at the temperature of less than 2500 DEG C to obtain the composite film based on the glassy carbon and the graphene. The flexural strength of the prepared composite film can reach more than 600MPa.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Catalysis electrode for preparing formic acid by electrocatalytic reduction of CO2, application and method for preparing formic acid by electrocatalytic reduction on CO2
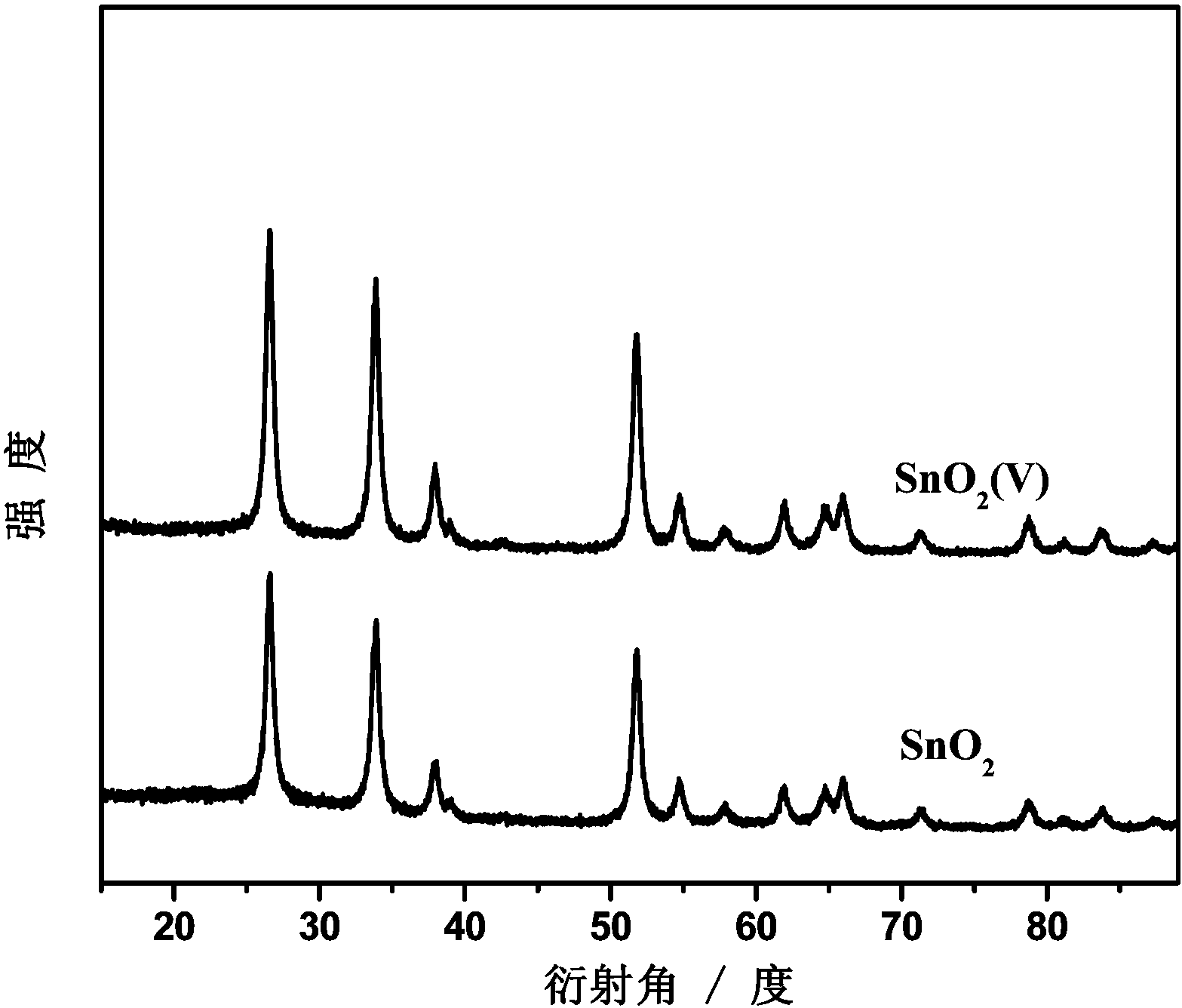
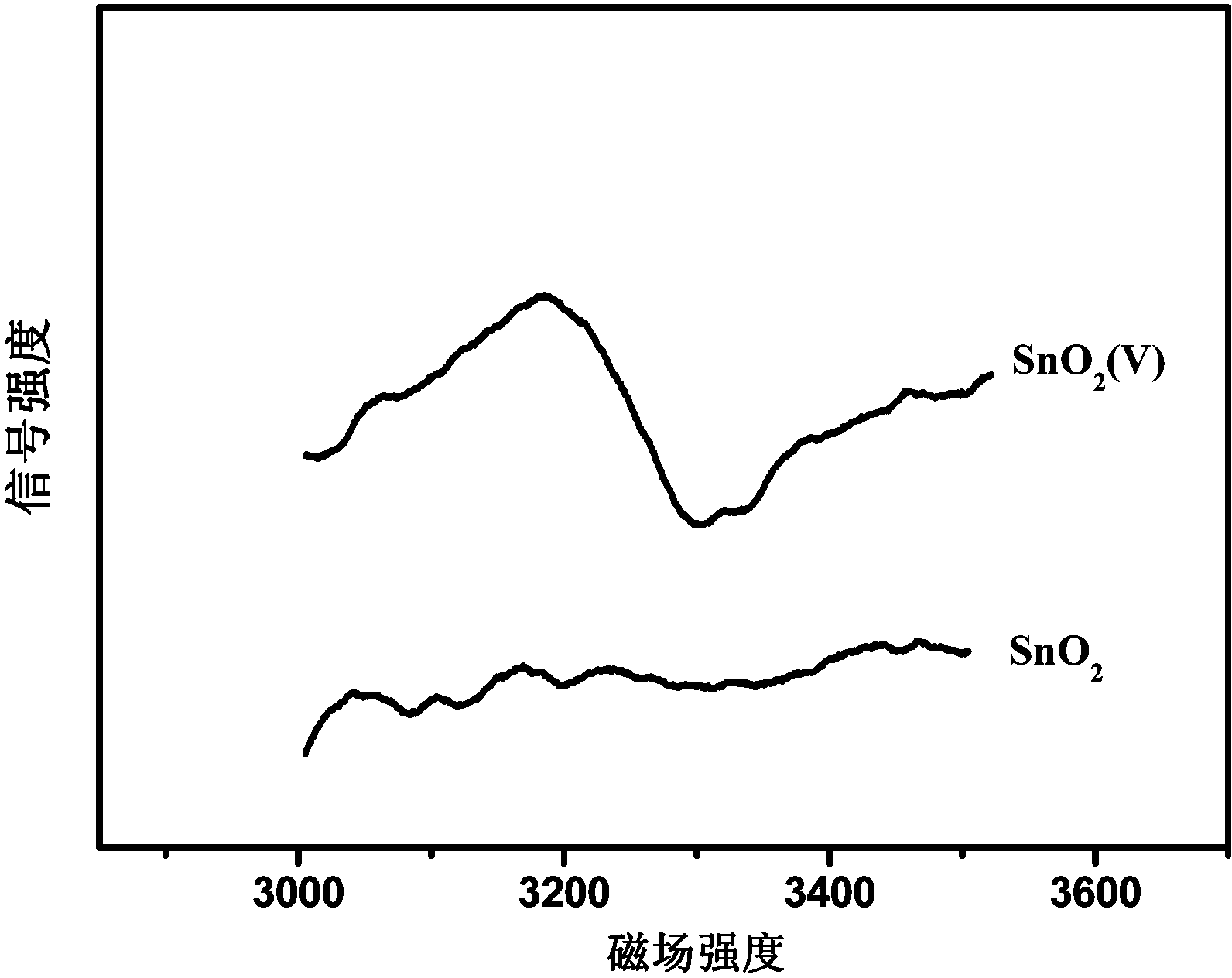
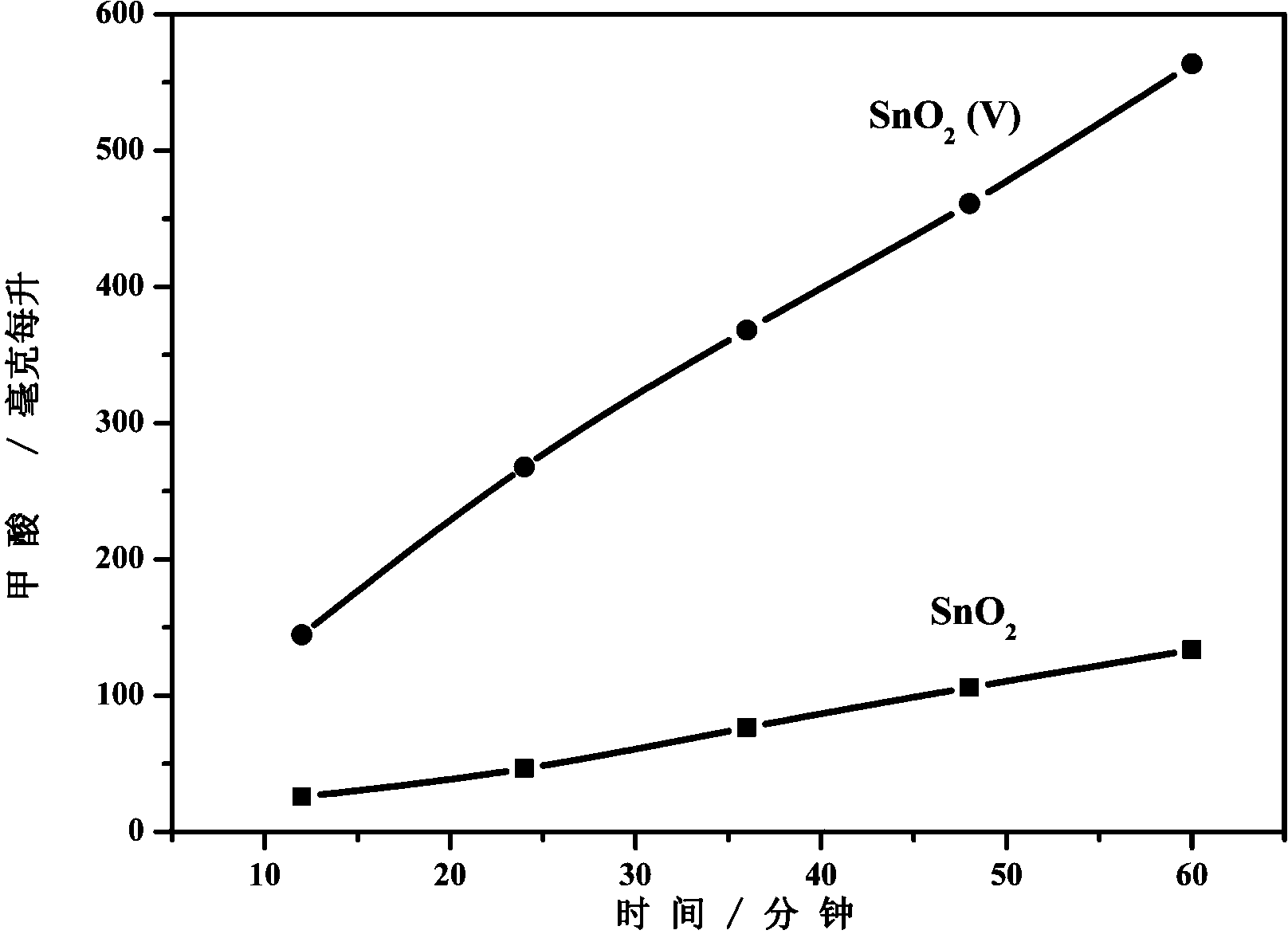
InactiveCN103668311AIncrease speedImprove current efficiencyOrganic chemistryElectrolytic organic productionOxygen vacancyFormic acid
The invention relates to a catalysis electrode for preparing formic acid by electrocatalytic reduction of CO2, application and a method for preparing formic acid by electrocatalytic reduction on CO2. The catalysis electrode for preparing formic acid by electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 comprises a glassy carbon sheet and a coating covering the glassy carbon sheet, wherein the material of the coating is stannic oxide containing oxygen vacancies, and the stannic oxide containing oxygen vacancies is obtained by performing vacuum thermal process on stannic oxide at 200-400 DEG C for 2-4 h. The catalysis electrode for preparing formic acid by electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 is applied to electrocatalytic reduction of CO2, and is capable of improving the rate and the current efficiency of preparing formic acid by electrocatalytic reduction of CO2. At the same electric potential, the rate of preparing formic acid by reducing CO2 by employing the catalysis electrode is increased by nearly 3 times compared with that by employing unprocessed catalysis electrodes, and the current efficiency is improved by nearly one time.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
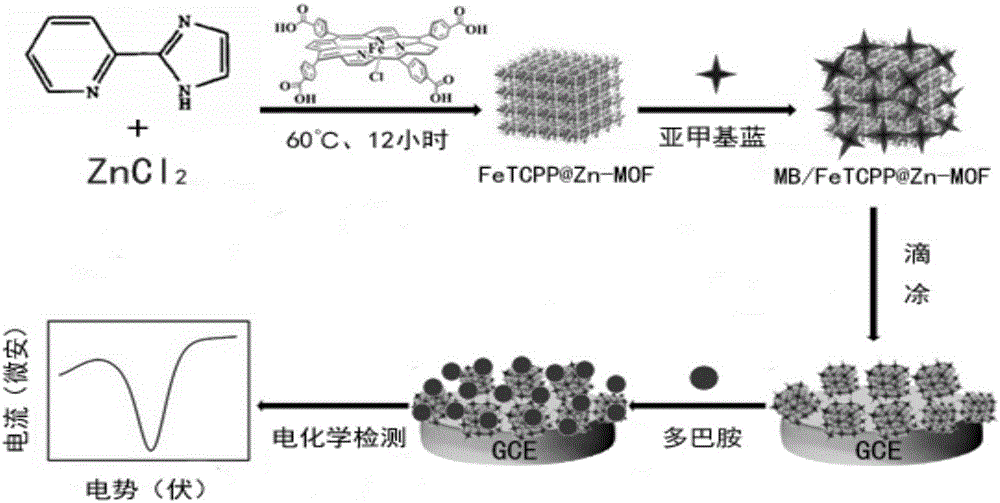
Preparation method and application of electrode of composite material of iron porphyrin chloride/methylene blue @metal-organic framework
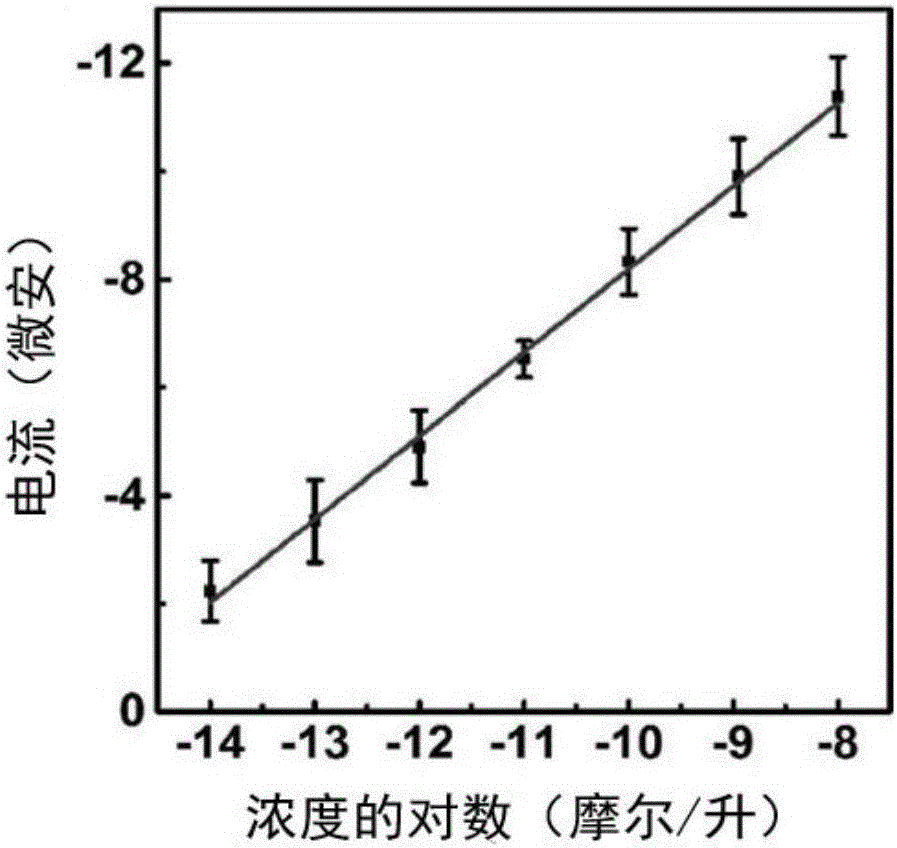
ActiveCN106111196AStrong oxidizingAccurate detectionOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMaterial electrochemical variablesOxidopamineMetal-organic framework
The invention provides a preparation method and application of an electrode of a composite material of an iron porphyrin chloride / methylene blue @metal-organic framework. Iron porphyrin chloride (FeTCPP) is encapsulated to a Zn metal-organic framework (MOF) by a one-pot method, a composite material of the metal-organic framework has negative charges in a solution, and cationic dye methylene blue (MB) with oxidation-reduction activity can be absorbed. The composite material is modified to the surface of a glass carbon electrode, and dopamine can be catalyzed and oxidized so that an electrical signal can be produced, sensitive detection for the dopamine is realized by an electrochemical method, the lowest detection limit can reach 0.48fM, and the detection range is wide. The composite material of the metal-organic framework disclosed by the invention is synthesized for the first time, and besides, the composite material of the metal-organic framework is also applied to the field of electrochemical sensing for the first time, the method is simple, the cost is low, and high electrochemical sensing sensitivity indicates that the composite material of the metal-organic framework functionalized by porphyrin and methylene blue has good application prospects in the field of electrochemical and biological sensing.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Porous structures useful as bipolar plates and methods for preparing same
InactiveUS20060183300A1Reduce porosityExcellent electrochemicalFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFuel cellsCarbon fibers
The invention relates to a porous structure, characterized in that it comprises a porous matrix (15) made of carbon fabric, said porous matrix being bounded on at least one of its faces (17, 21) by an impermeable layer (19, 23) made of an element chosen from carbon fibres, carbon nanotubes and glassy carbon, said impermeable layer being linked to the porous matrix via carbon-carbon bonds. The invention also relates to a process for manufacturing such porous structures. Application to the fields of fuel cells and heat exchangers.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Pyrolytic carbon black composite and method of making the same
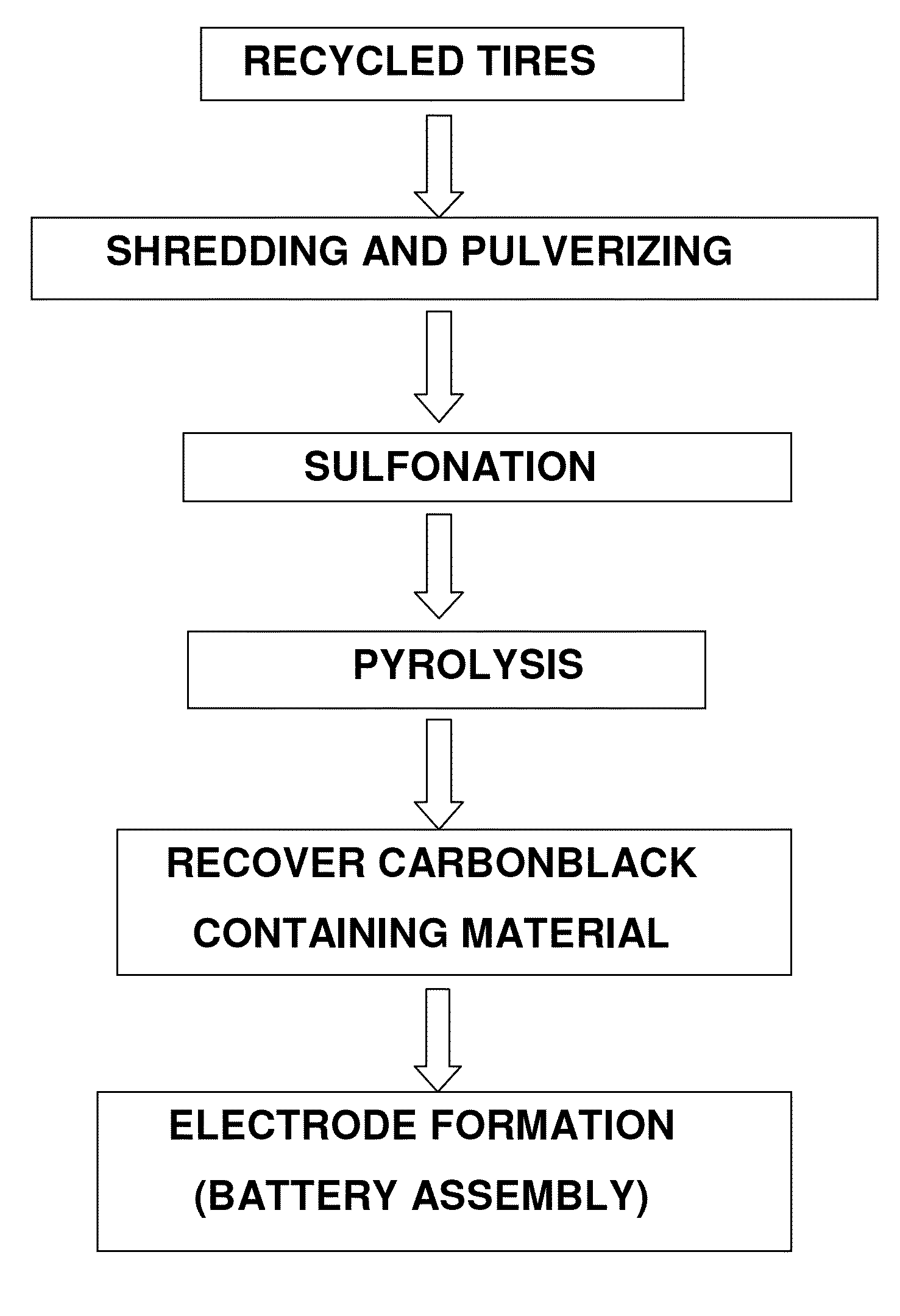
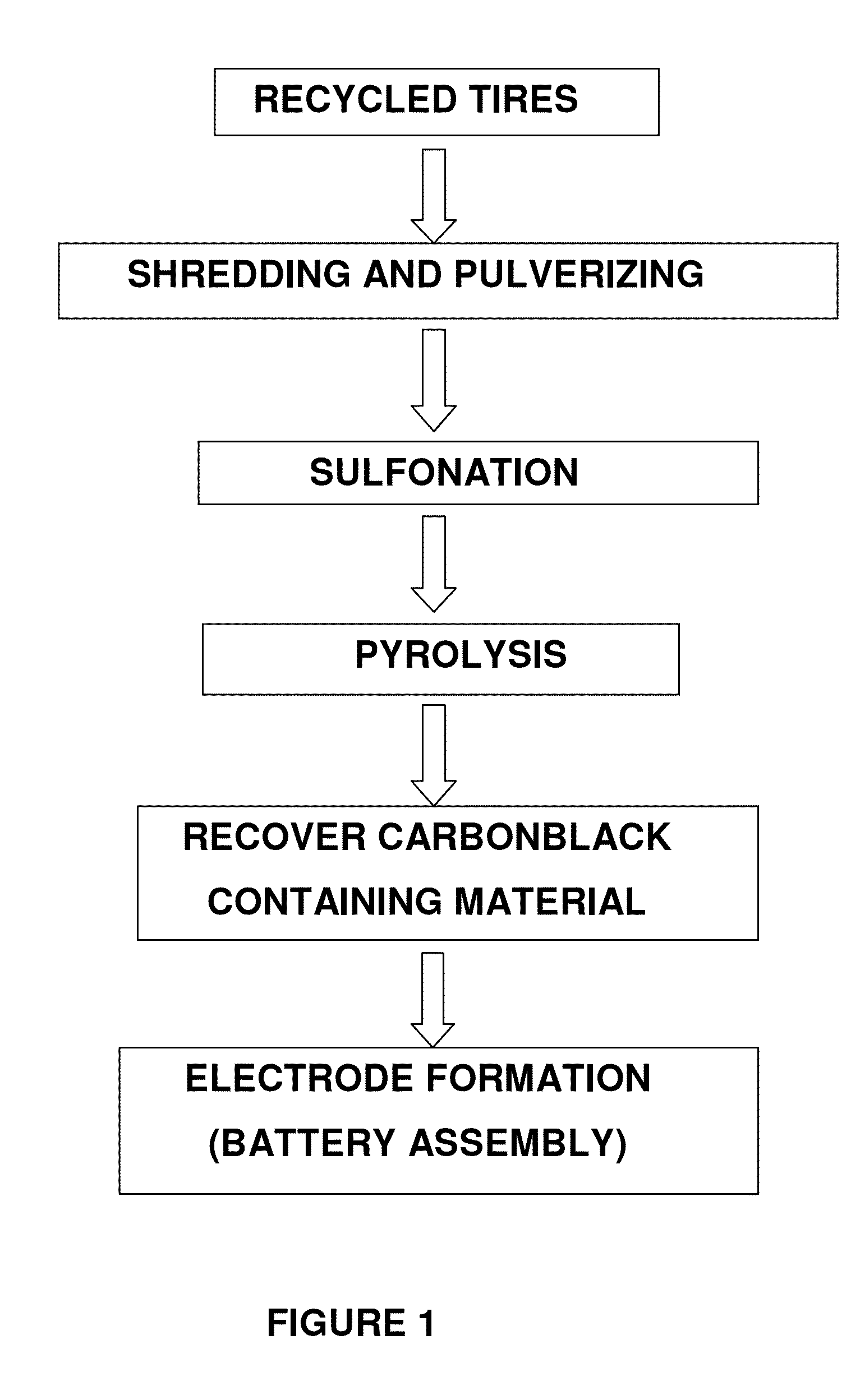
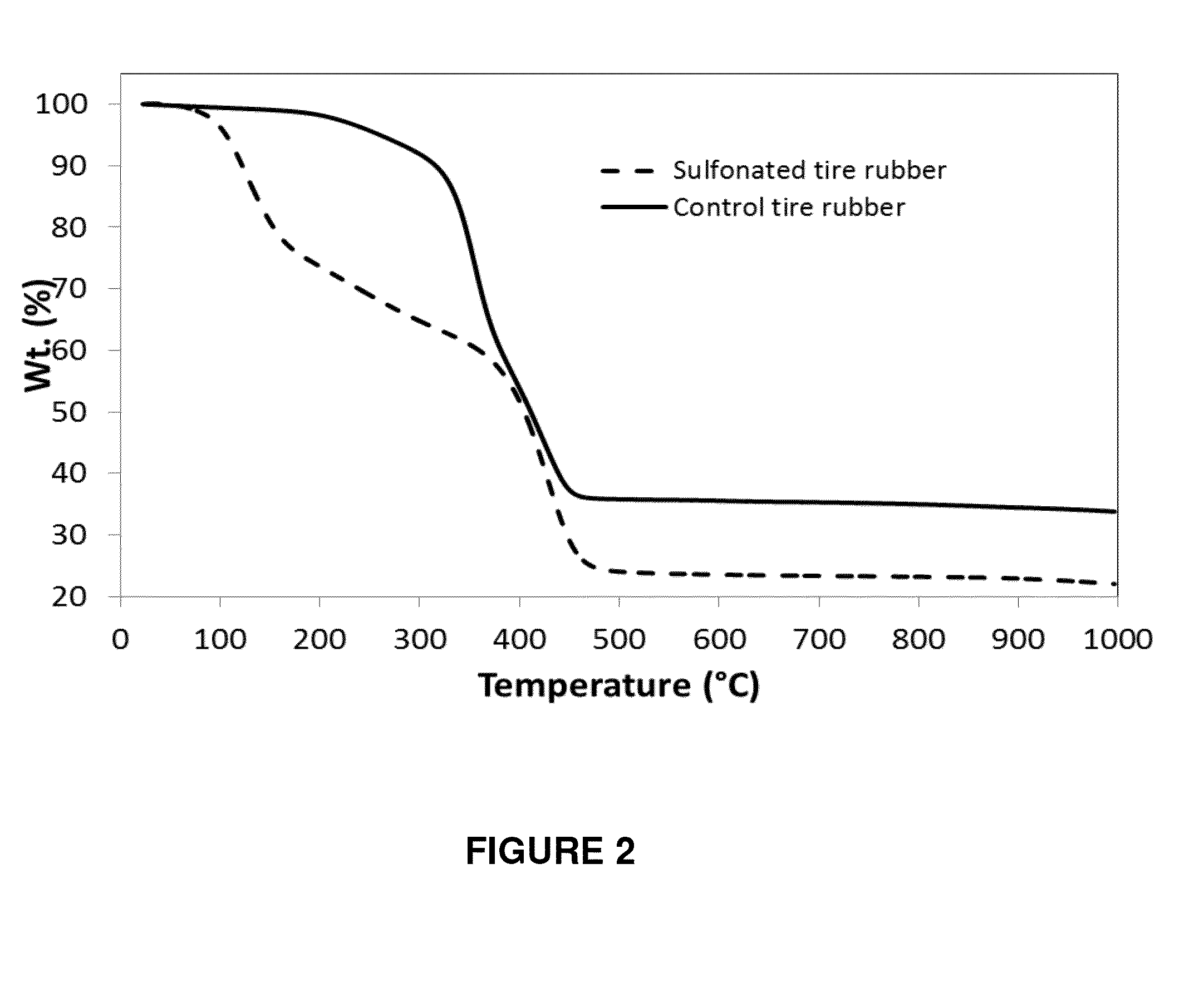
ActiveUS20150021525A1High densityPigmenting treatmentElectrode thermal treatmentSource materialPyrolytic carbon
A method of recovering carbon black includes the step of providing a carbonaceous source material containing carbon black. The carbonaceous source material is contacted with a sulfonation bath to produce a sulfonated material. The sulfonated material is pyrolyzed to produce a carbon black containing product comprising a glassy carbon matrix phase having carbon black dispersed therein. A method of making a battery electrode is also disclosed.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
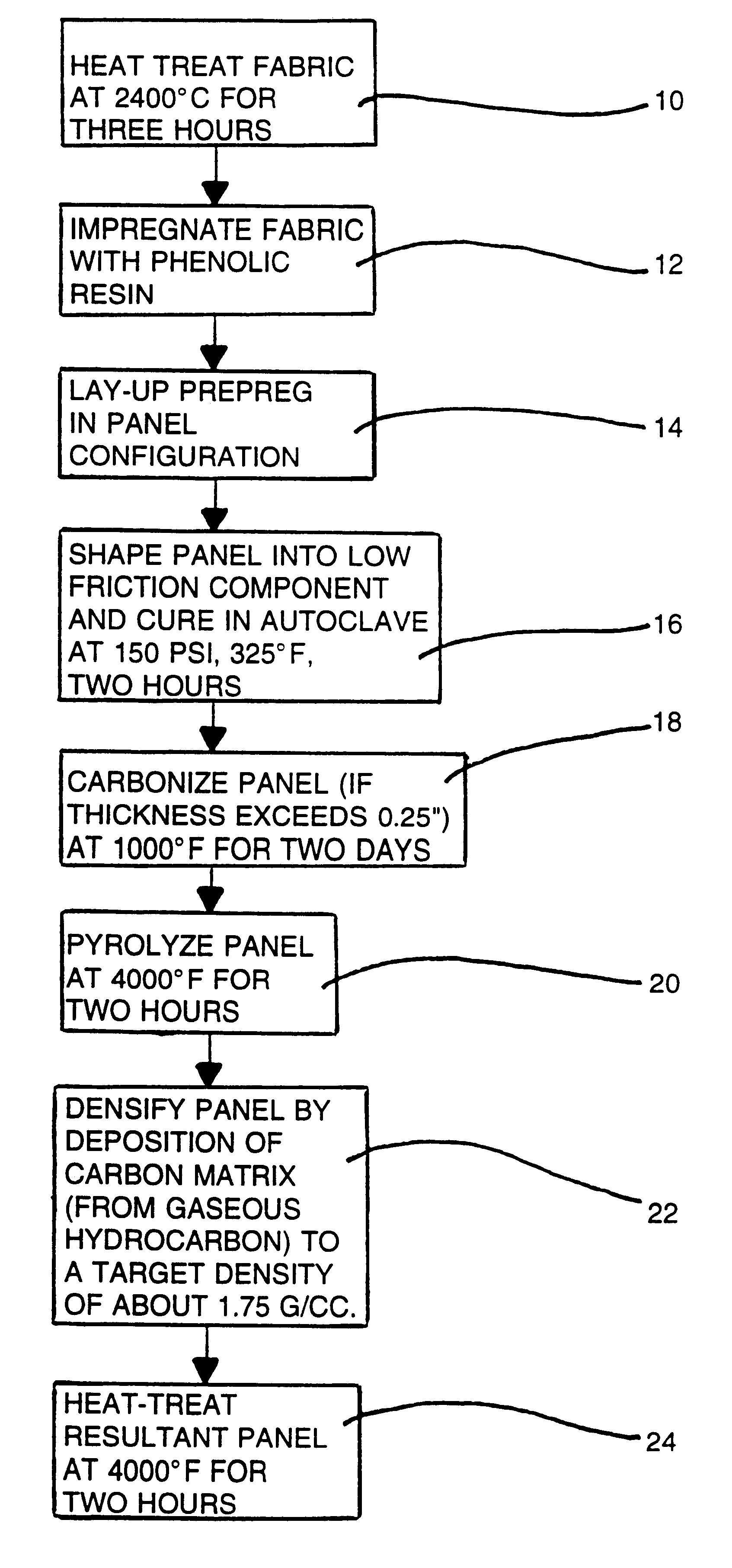
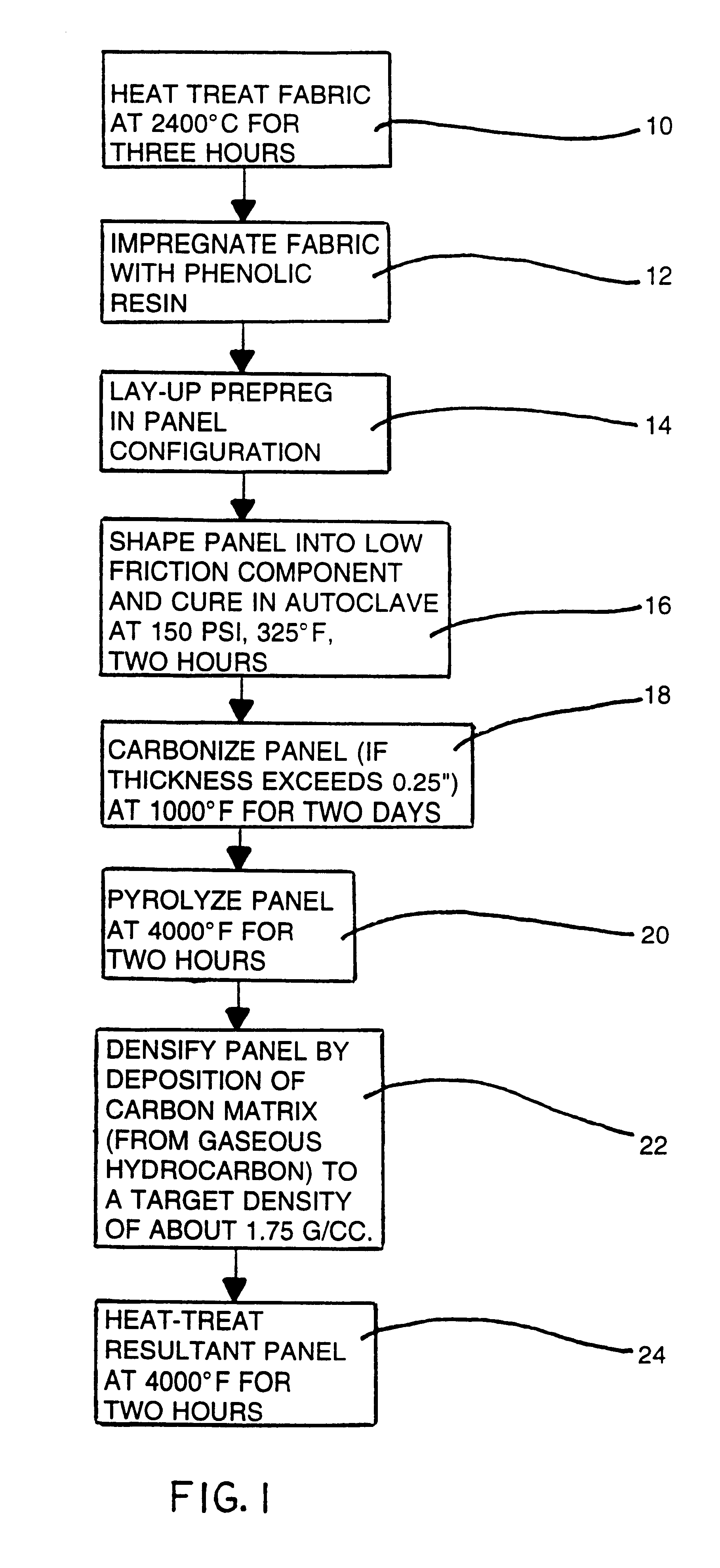
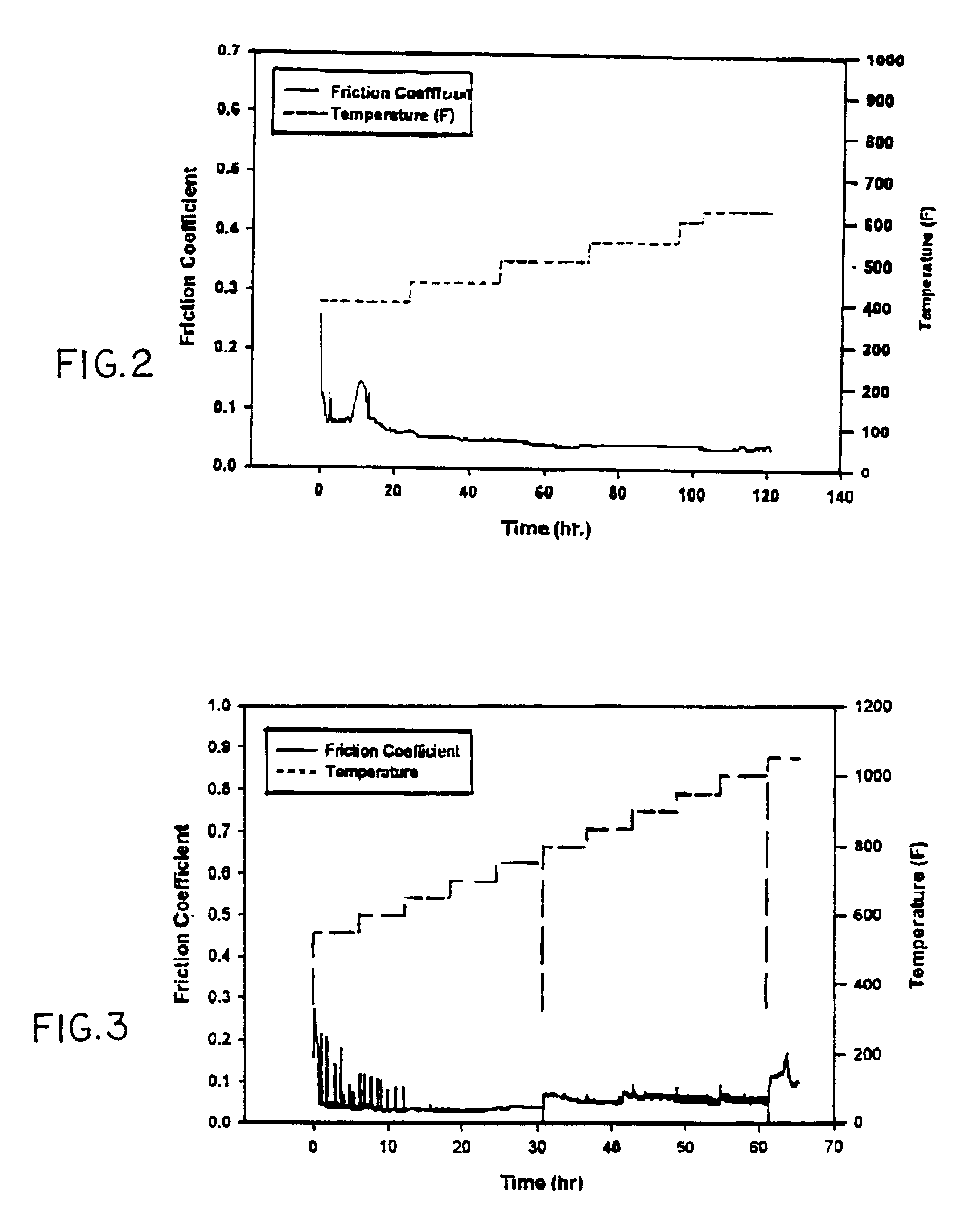
Ultra low friction carbon/carbon composites for extreme temperature applications
InactiveUS6255234B1Excellent high-temperature lubricationImprove wear resistanceSynthetic resin layered productsBearing componentsFiberCarbon composites
A carbon / carbon composite in which a carbon matrix containing a controlled amount of boron or a boron compound is reinforced with carbon fiber exhibits a low coefficient of friction, i.e., on the order of 0.04 to 0.1 at temperatures up to 600° C., which is one of the lowest frictional coefficients for any type of carbonaceous material, including graphite, glassy carbon, diamond, diamond-like carbon and other forms of carbon material. The high degree of slipperiness of the carbon composite renders it particularly adapted for limiting friction and wear at elevated temperatures such as in seals, bearings, shafts, and flexible joints
Owner:SGL CARBON COMPOSITES INC +1
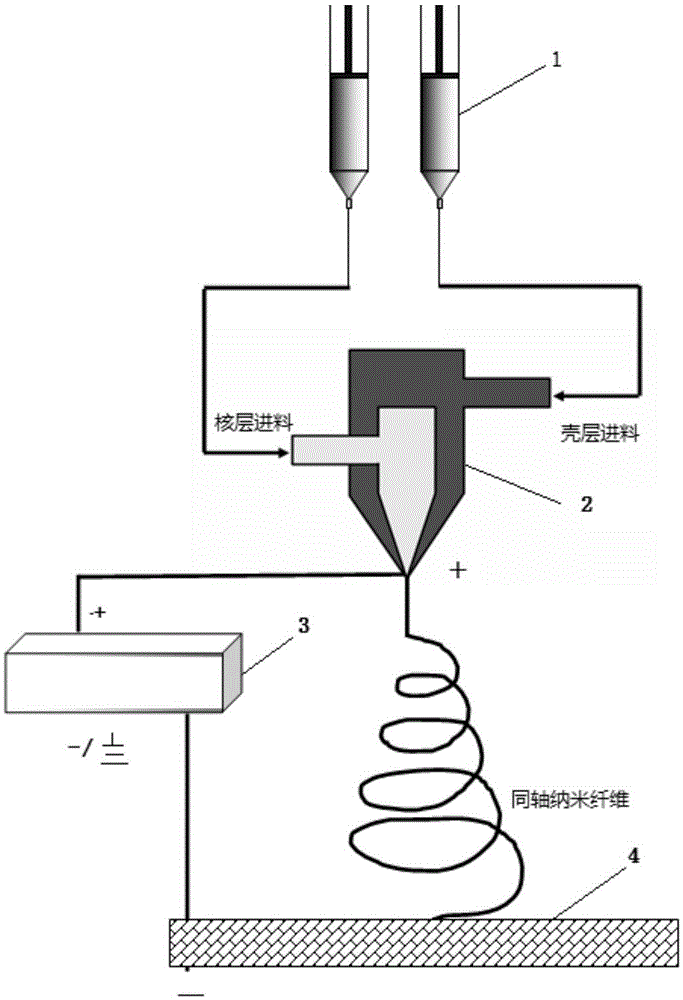
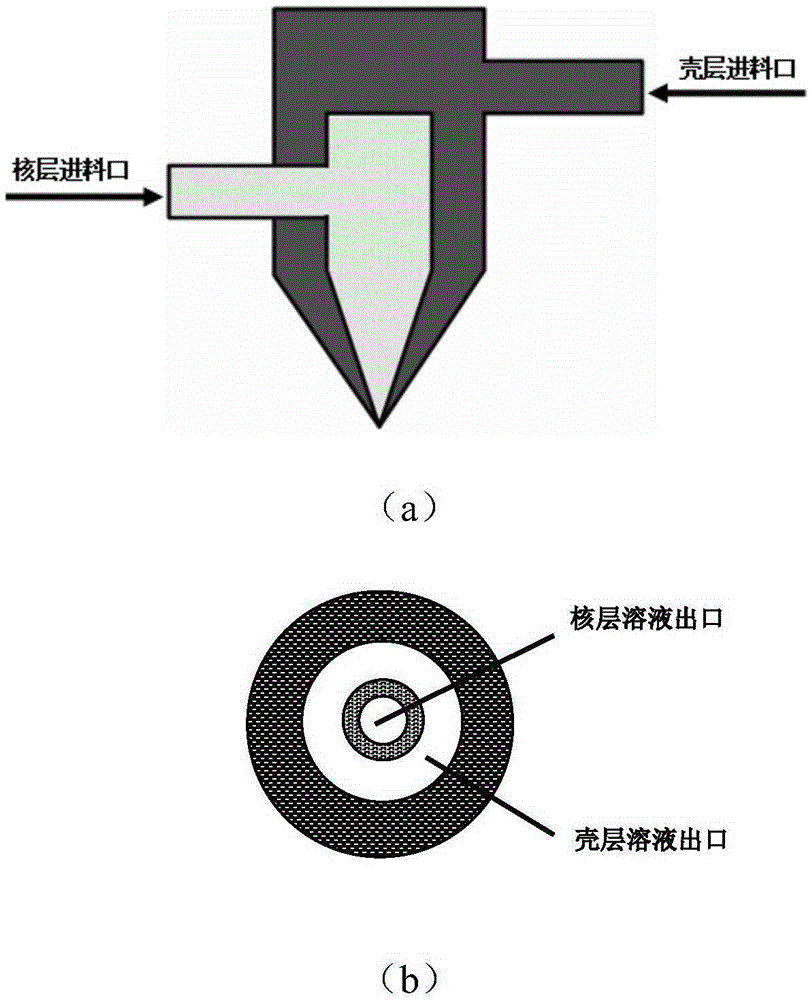
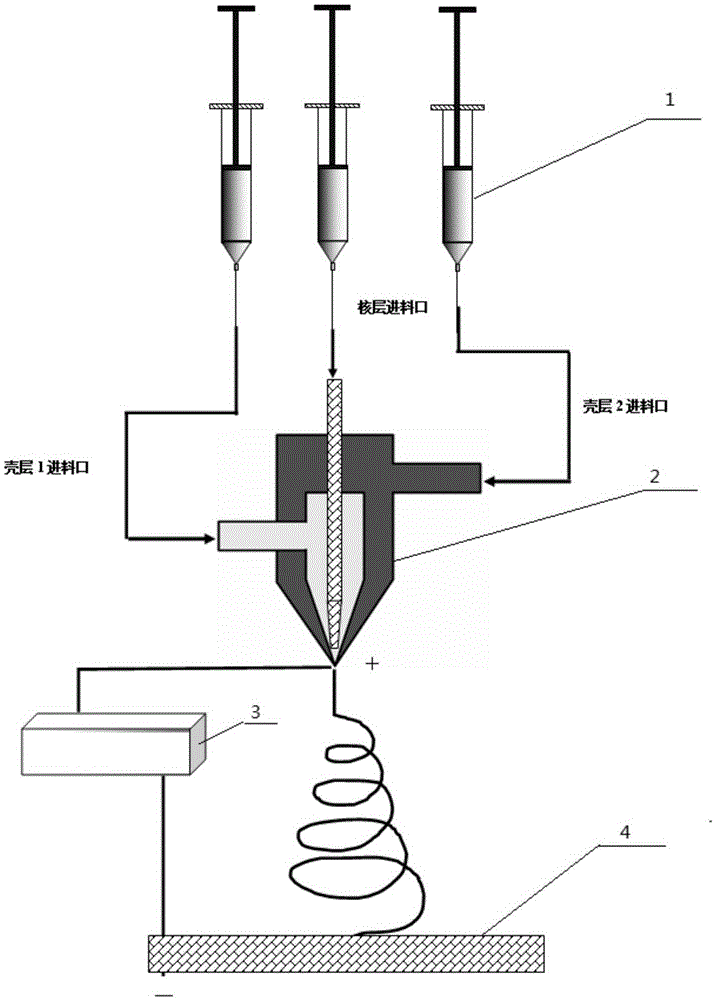
Core-shell type ultra-micro electrode prepared through coaxial electrostatic spinning and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105384138ARealize one-time moldingReserved natureSemi-permeable membranesVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsFiberAnti jamming
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of a core-shell type ultra-micro electrode. The core-shell structure ultra-micro electrode is obtained by preparing ultra-micro electrode fibers of a coaxial structure in a one-step mode through a coaxial electrostatic spinning method and then performing packaging. The coaxial structure comprises a core electrode base layer and one or two surface sensing layers. By the adoption of the one-step forming technology, the complex surface modification process of traditional ultra-micro electrodes (such as glassy carbon electrodes obtained after ablation treatment) is omitted, and the ultra-micro electrode with the diameter ranging from 40 nm to 6 micrometers can be prepared; due to the subsequent treatment temperature ranging from 70 DEG C to 150 DEG C, the structures and functions of organic functional components (such as biological protein and enzymes) in a modification layer of the ultra-micro electrode can be easily maintained, which is of great significance for the pluralistic design of the ultra-micro electrode. The ultra-micro electrode is used for detecting adenosine triphosphate (ATP), dopamine and adrenal hormones and is high in response speed and sensitivity, strong in anti-jamming capability and especially suitable for on-line rapid determination, particularly, real-time non-destructive determination of living cells.
Owner:JIANGXI SCI & TECH NORMAL UNIV
Composite materials
InactiveUS20130330514A1Improve conductivityLittle and no additional weightSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationFiberPolymer resin
A composite material, the composite material comprising at least one prepreg, said prepreg comprising at least one polymeric resin and at least one fibrous reinforcement; and glassy carbon particles dispersed in the polymeric resin.
Owner:HEXCEL COMPOSITES LTD (GB)
Continuous glassy carbon composite materials reinforced with carbon nanotubes and methods of manufacturing same
A method for manufacturing a carbon composite is provided. The method includes providing a carbon-containing resin material having an appropriate concentration of catalyst particles. Thereafter, the resin material may be extruded through an aperture while being exposed to a high temperature range to permit polymerization of the extruded resin material. A subsequent exposure of the extruded resin material to another elevated temperature range causes carbon in the resin material to couple to the catalyst particles to promote carbon nanotube growth and transformation of the resin material to a reinforced composite material. Reinforced composite materials are also provided.
Owner:NANCOMP TECHNOLOGIES INC
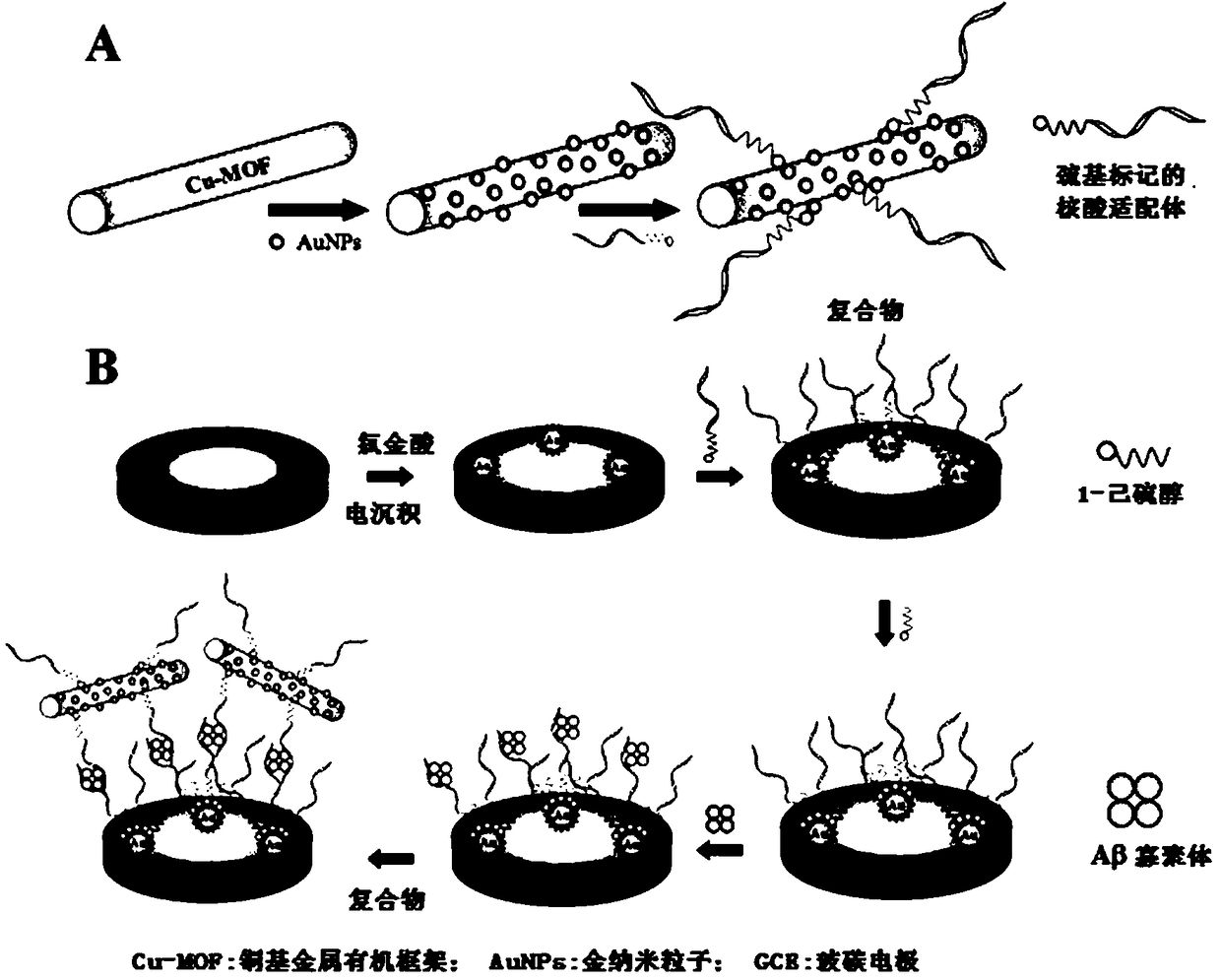
Nucleic acid aptamer electrochemical sensor based on metal organic framework materials as signal probes
ActiveCN108169303AEasy to passSimplify detection stepsMaterial electrochemical variablesAptamerAβ oligomers
The invention relates to a nucleic acid aptamer electrochemical sensor based on metal organic framework materials (MOFs) as signal probes. The senor is used for detection of beta-amyloid (A beta) oligomers and belongs to the technical field of functional nanocomposite materials and biosensor detection. AuNFs-modified glassy carbon electrodes immobilize a first layer of aptamers, the A beta oligomer is further identified and through combination with second layer aptamer-modified gold nanoparticle-loaded Cu-MOFs (AuNPs / Cu-MOFs), the sandwich electrochemical sensor for detection of the A beta oligomer is formed. AuNPs / Cu-MOFs as a redox medium can directly detect a Cu<2+> signal and electrochemically active molecule labeling is avoided so that the detection processes are greatly simplified and the sensitivity of detection is improved.
Owner:SHANGQIU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing high-stability microbial electrochemical sensor
ActiveCN106645348AGuaranteed stabilityStrong acidMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansHigh concentrationStrong acids
The invention discloses a method for preparing a high-stability microbial electrochemical sensor. The microbial electrochemical sensor consists of an organic glass or polytetrafluoroethylene container with a volume of 20 to 1,570mL, a 0.1 to 10cm<2> glassy carbon or graphite working electrode, an Ag / AgCl or saturated calomel reference electrode, a 1cm<2> platinum sheet or platinum wire counter electrode and a weak alkaline solution of dopamine hydrochloride. The prepared microbial electrochemical sensor is used for a monitoring system for rapidly acquiring water body composition information in situ, and a monitoring result of the monitoring system in an extreme environment of a high-concentration organic solvent, a strong acid, high temperature and low temperature is true and effective. The method has the beneficial effects that the defect that a conventional microbial electrochemical system cannot run in the extreme environment of the strong acid, high temperature, low temperature, a high-concentration organic solution and the like is overcome by using the microbial electrochemical sensor, and a novel microbial electrochemical system is stable in running and rapid and accurate in detection.
Owner:天津智慧大数据服务有限公司
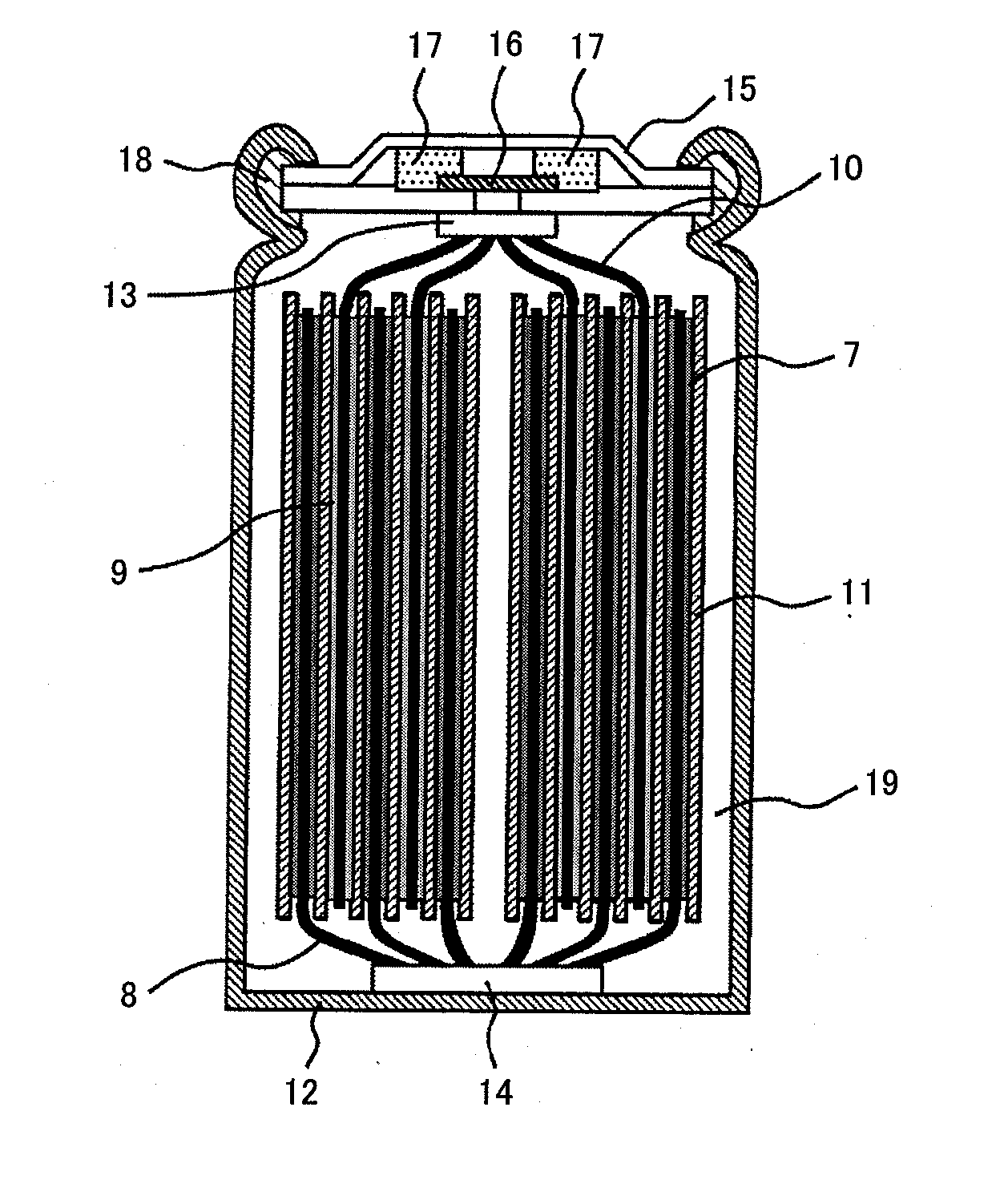
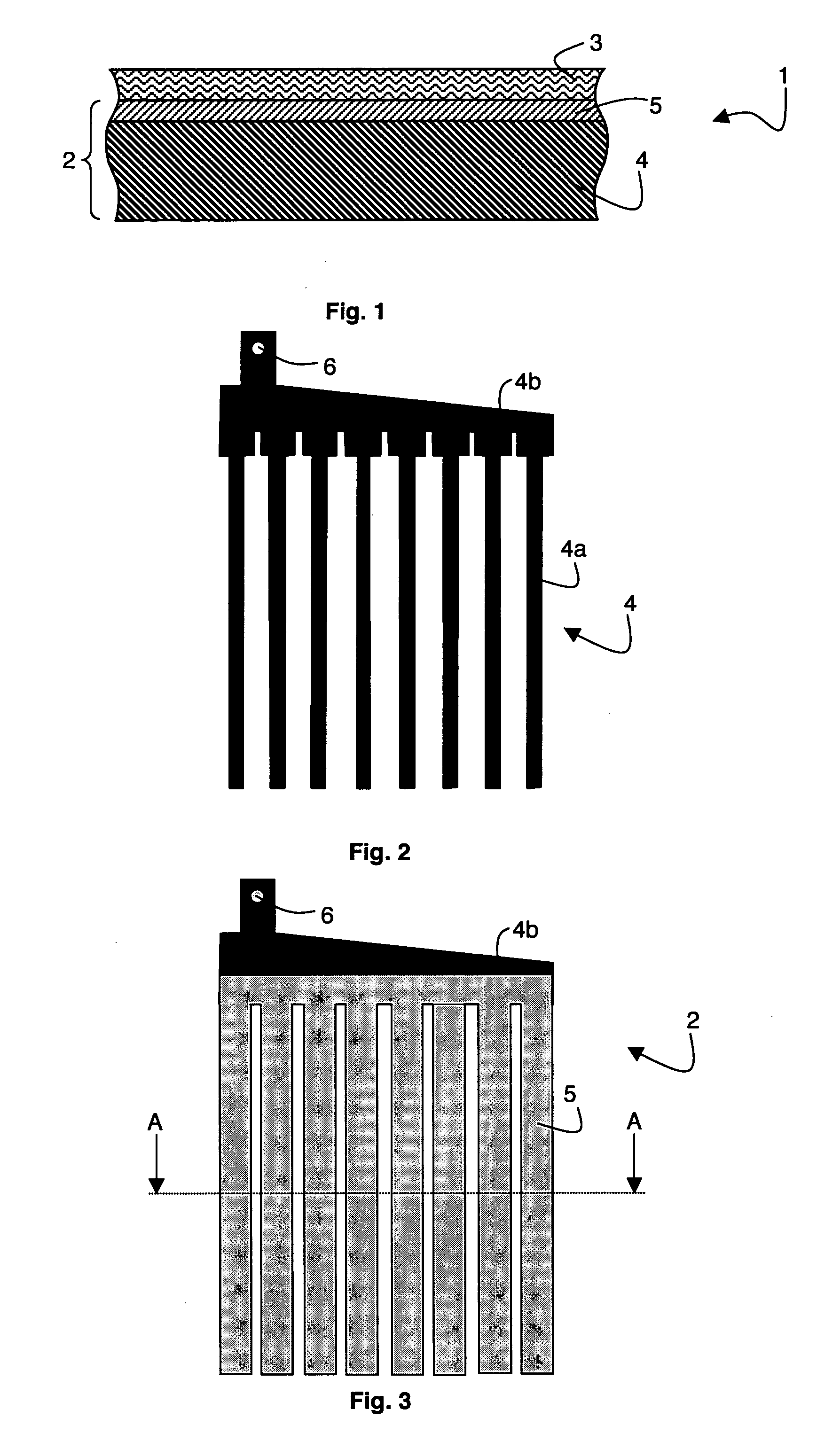
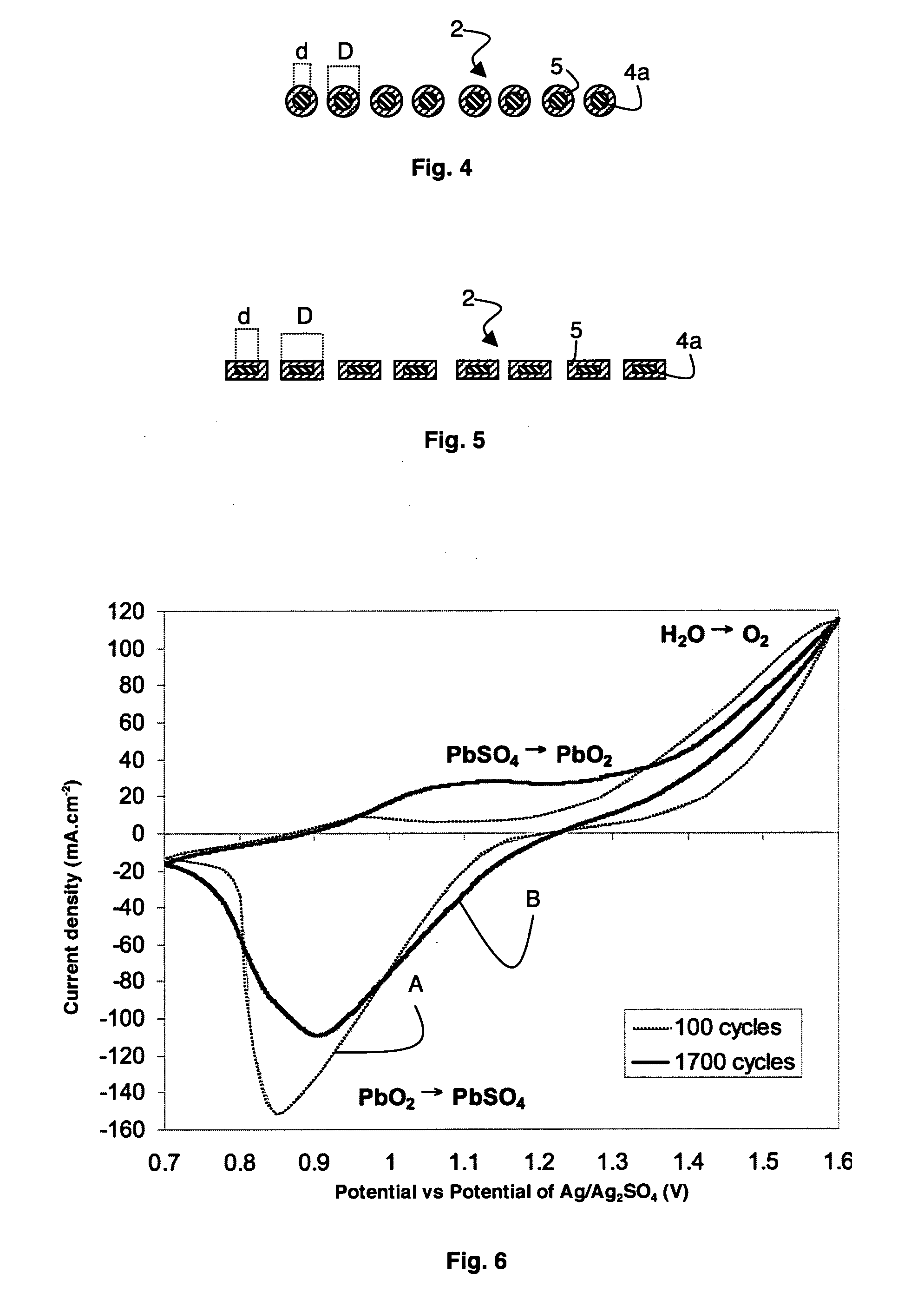
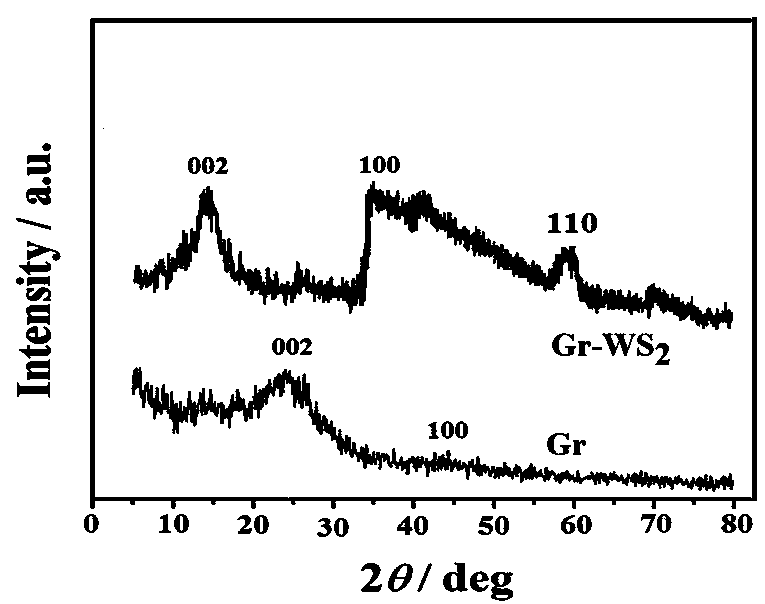
Electrode for lead-acid battery and method for producing such an electrode
InactiveUS20110083966A1Improve mechanical propertiesReliable electrical connectionLead-acid accumulatorsElectrode carriers/collectorsPower flowOptoelectronics
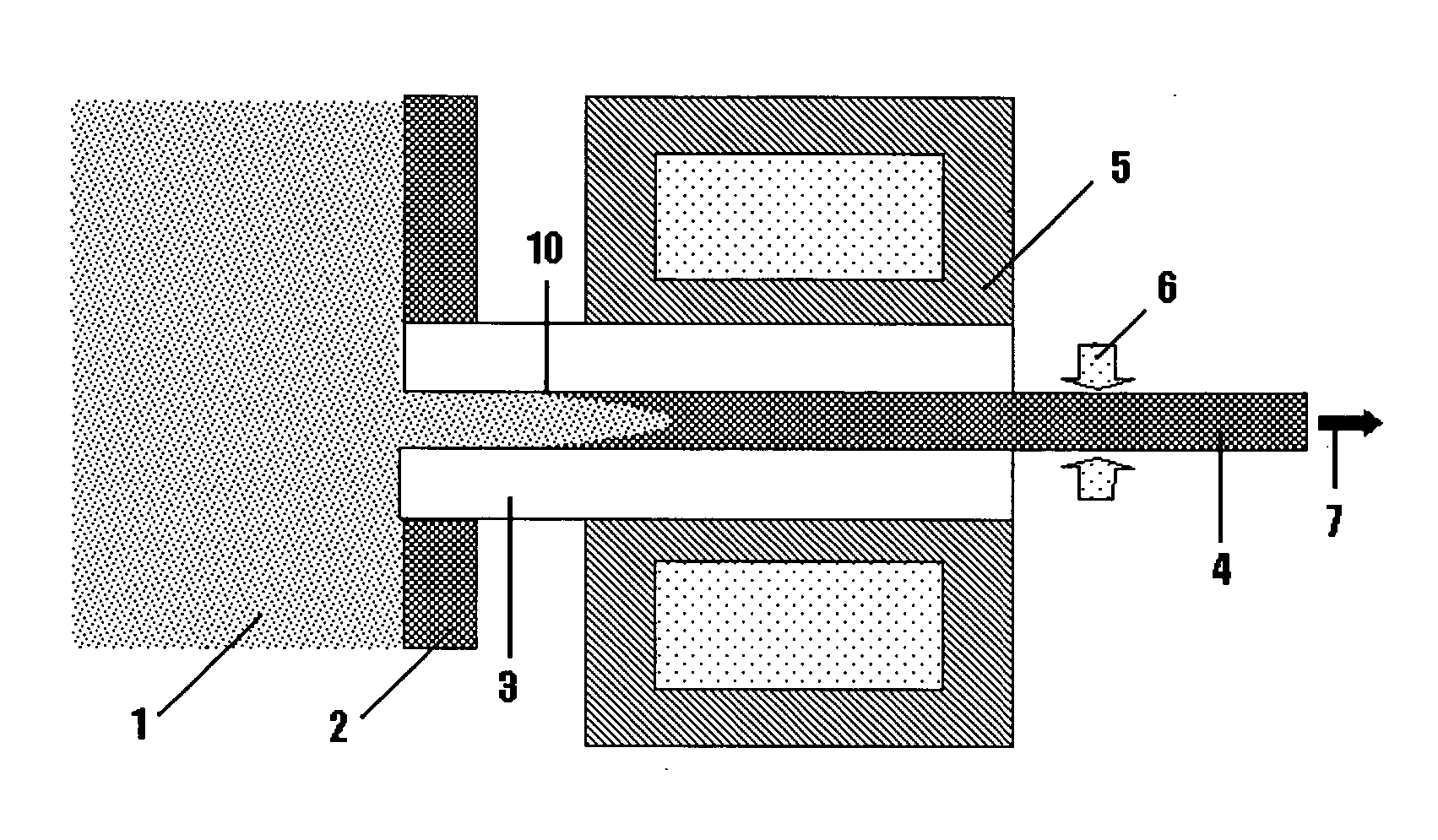
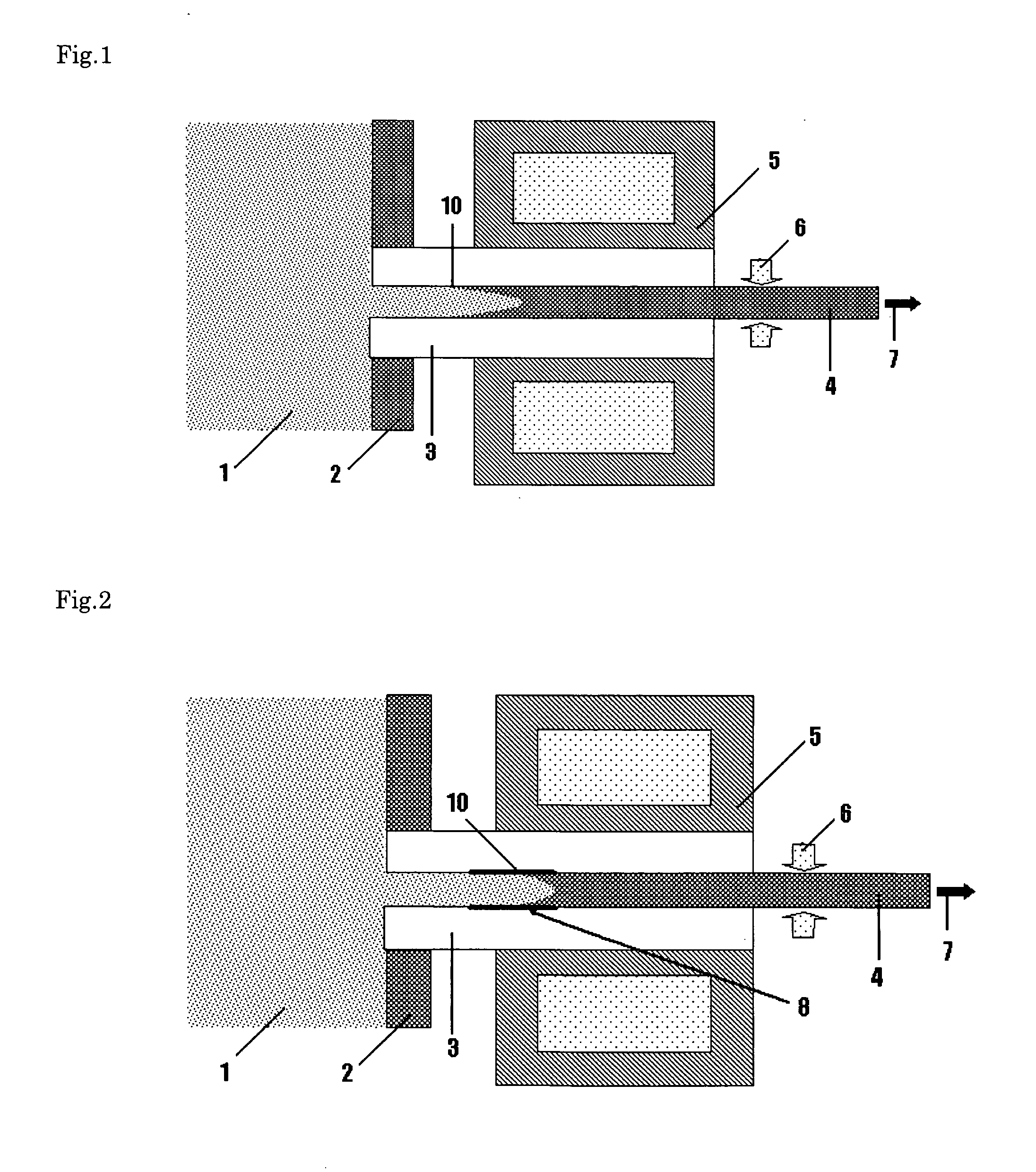
An electrode for lead-battery comprises a current collector covered by an active layer of lead-containing paste. The current is formed by a glassy carbon substrate on which is deposited an intermediate layer. The glassy carbon substrate has preferably a thickness comprised between 1 mm and 3 mm whereas the thickness of the intermediate layer is advantageously comprised between 50 μm and 200 μm. In a particular embodiment, the glassy carbon substrate is in form of a comb.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
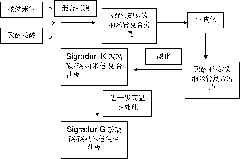
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) electrochemical biosensor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103616418AHigh sensitivityImprove stabilityMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical biosensorA-DNA
The invention relates to a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) electrochemical biosensor and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) adding 1mg / mL Gr-WS2 composite material aqueous dispersion liquid into 1mg / mL chitosan acetic acid solution; carrying out ultrasonic dispersion for 1 hour; and taking 8 microliters of a mixed solution, dripping the solution on a pre-treated glassy carbon substrate and airing; and (2) immersing an electrode into a gold size for 12 hours; washing and airing; reacting the electrode with 1.0*10<-6>mol / L of a DNA probe at 25 DEG C for 10 hours; and washing and sealing by using 1.0*10<-3>mol / L of mercaptoethanol for 2 hours and then reacting with a target DNA at 30 DEG C for 50 minutes to prepare the DNA electrochemical biosensor. According to the DNA electrochemical biosensor provided by the invention, a Gr-WS2 nano composite material and gold nanoparticles are combined so as to be good for simultaneously expressing the advantages of the Gr-WS2 nano composite material and the gold nanoparticles; the DNA electrochemical biosensor has the advantages of good stability, high sensitivity, good selectivity, good repeatability, convenience for carrying, low cost and the like.
Owner:XINYANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing composite thin plate based on glass carbon and carbon nanotube
The invention relates to a method for preparing composite thin plate based on glass carbon and a carbon nanotube, belonging to the technical field of a composite material. The composite thin plate based on the glass carbon and the carbon nanotube is obtained through carbonizing a polyimide Precursor film at the temperature lower than 2500 DEG C. The intensity of the composite thin plate prepared by the invention can reach above 600 MPa.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Process for producing fiber-reinforced silicon carbide composites
InactiveUS20030145934A1Easy to getEasy to produceCeramic shaping apparatusClaywaresCarbonizationUltimate tensile strength
A process produces a fiber-reinforced silicon carbide composite. The resulting composite has a high toughness where bundles of a reinforcing fiber are densely covered with glassy carbon derived from a resin to avoid deterioration of the strength, and it can easily be produced even in complicated shapes. Specifically, a fiber-reinforced silicon carbide composite is produced by preparing a fiber prepreg containing a powdered silicon and a resin and molding the prepreg to yield a green body having a desired shape, or laminating a fiber prepreg containing a resin and a woven fabric prepreg containing a powdered silicon and a resin in alternate order, and molding the laminate to yield a green body having a desired shape; carbonizing the green body at 900° C. to 1350° C. in an inert atmosphere; impregnating the carbonized body with a resin; firing the impregnated body again at 900° C. to 1350° C. in an inert atmosphere; performing the resin impregnation-carbonization procedure one to five times; subjecting the carbonized composite to reaction sintering at a temperature of 1300° C. or more in vacuo or in an inert atmosphere to form open pores, and finally infiltrating molten silicon into the sintered body having open pores at a temperature of about 1300° C. to 1800° C. in vacuo or in an inert atmosphere.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Anti-Reflection Structure Body, Method Of Producing The Same And Method Of Producing Optical Member
An anti-reflection structure body comprises a base member which is made of glassy carbon and at a surface of which is formed an anti-reflection structure including a cluster of minute projections each having a diameter that contracts towards a tip thereof. The minute projections preferably have an average height of from 200 nm to 3000 nm and an average maximum diameter of from 50 nm to 300 nm, and an average pitch of from 50 nm to 300 nm. An anti-reflection structure body which is easily produced, capable of achieving an anti-reflection effect near to non-reflection, and capable of providing the minute structure even to a member having a high melting point such as quartz glass or the like by transfer or the like can be provided.
Owner:TOKYO UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE
Disk, method for making it free of asperities utilizing a step of exposing a surface of the disk to a gas cluster ion beam and disk drive unit for using the disk
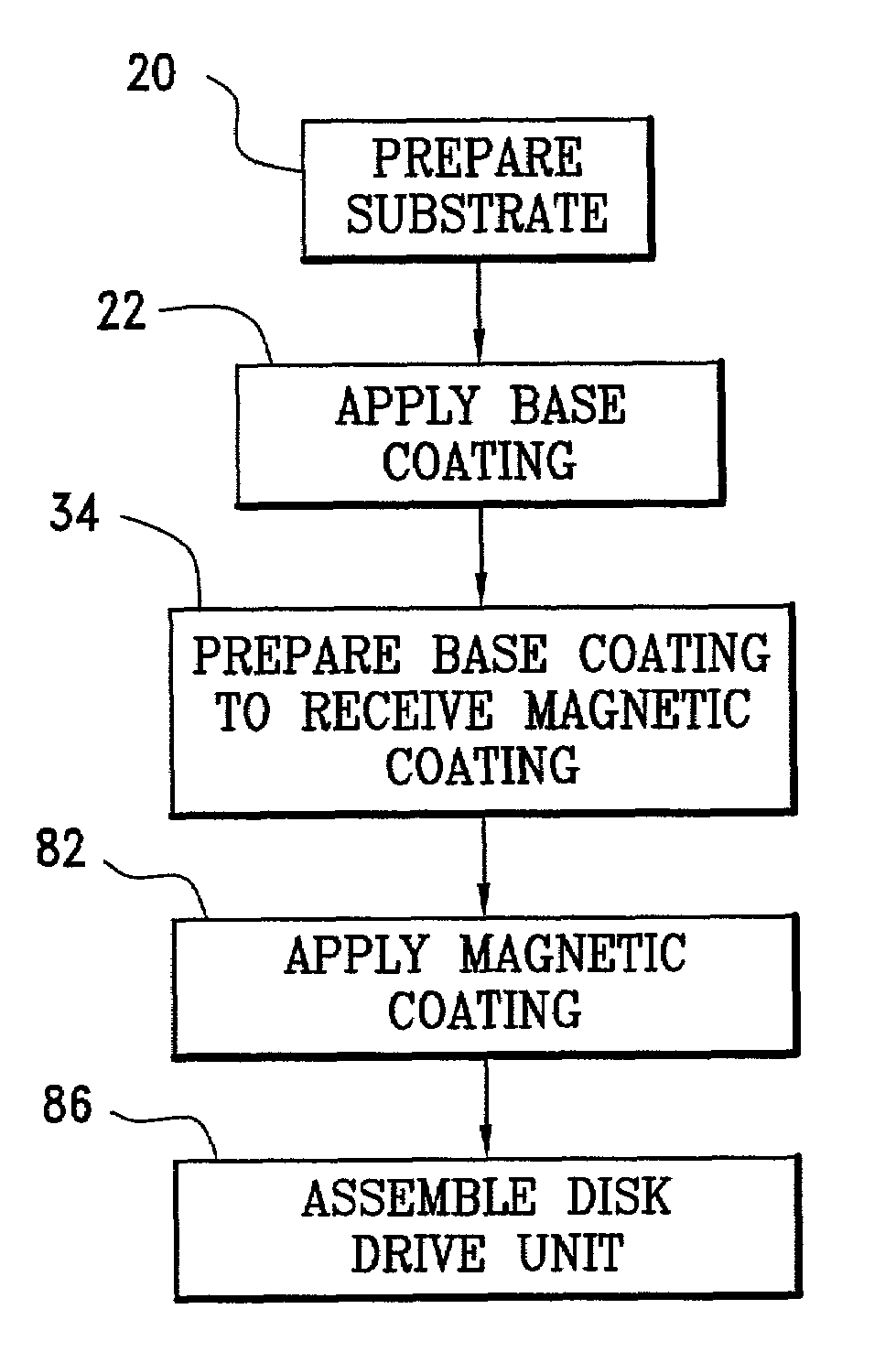
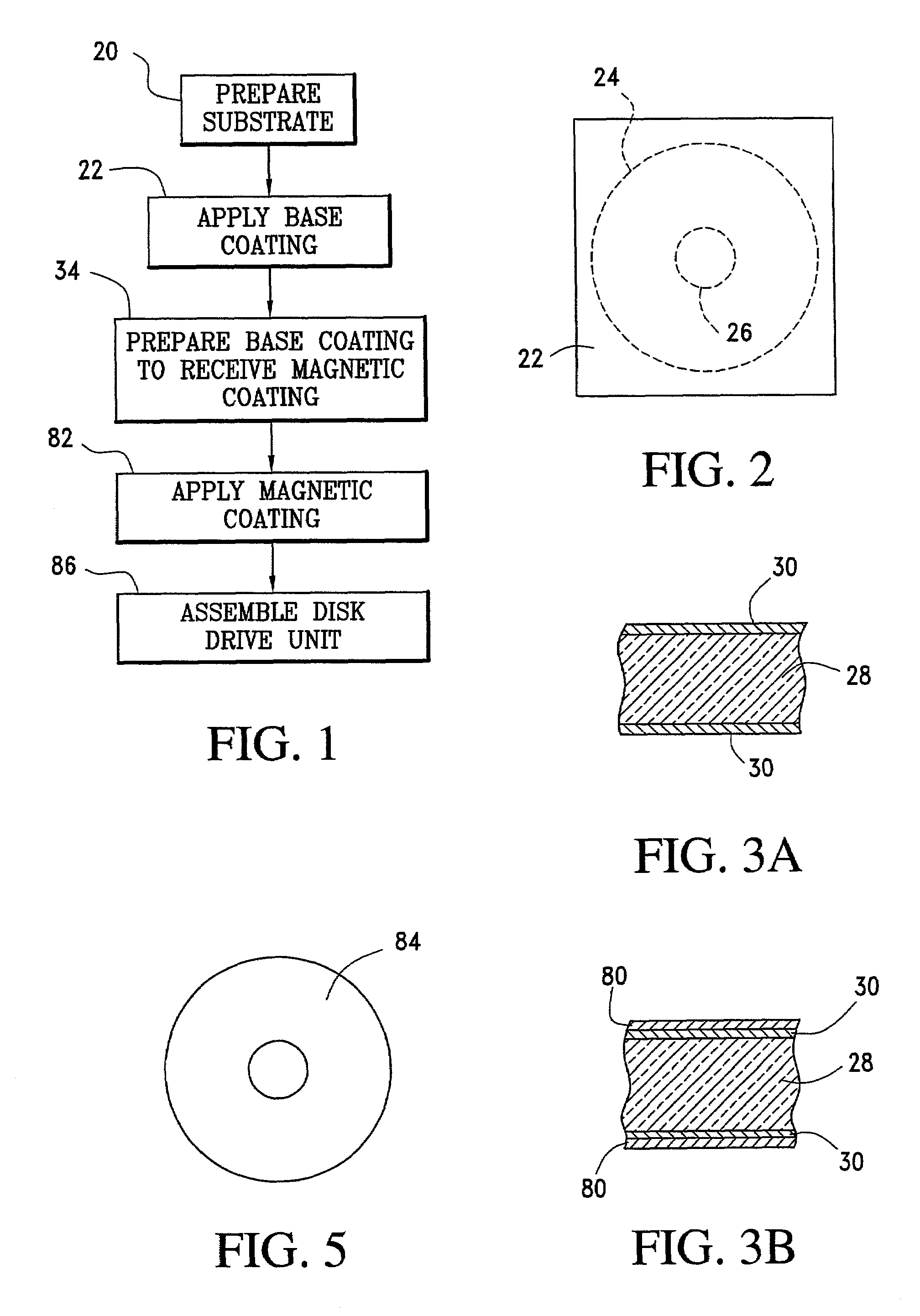
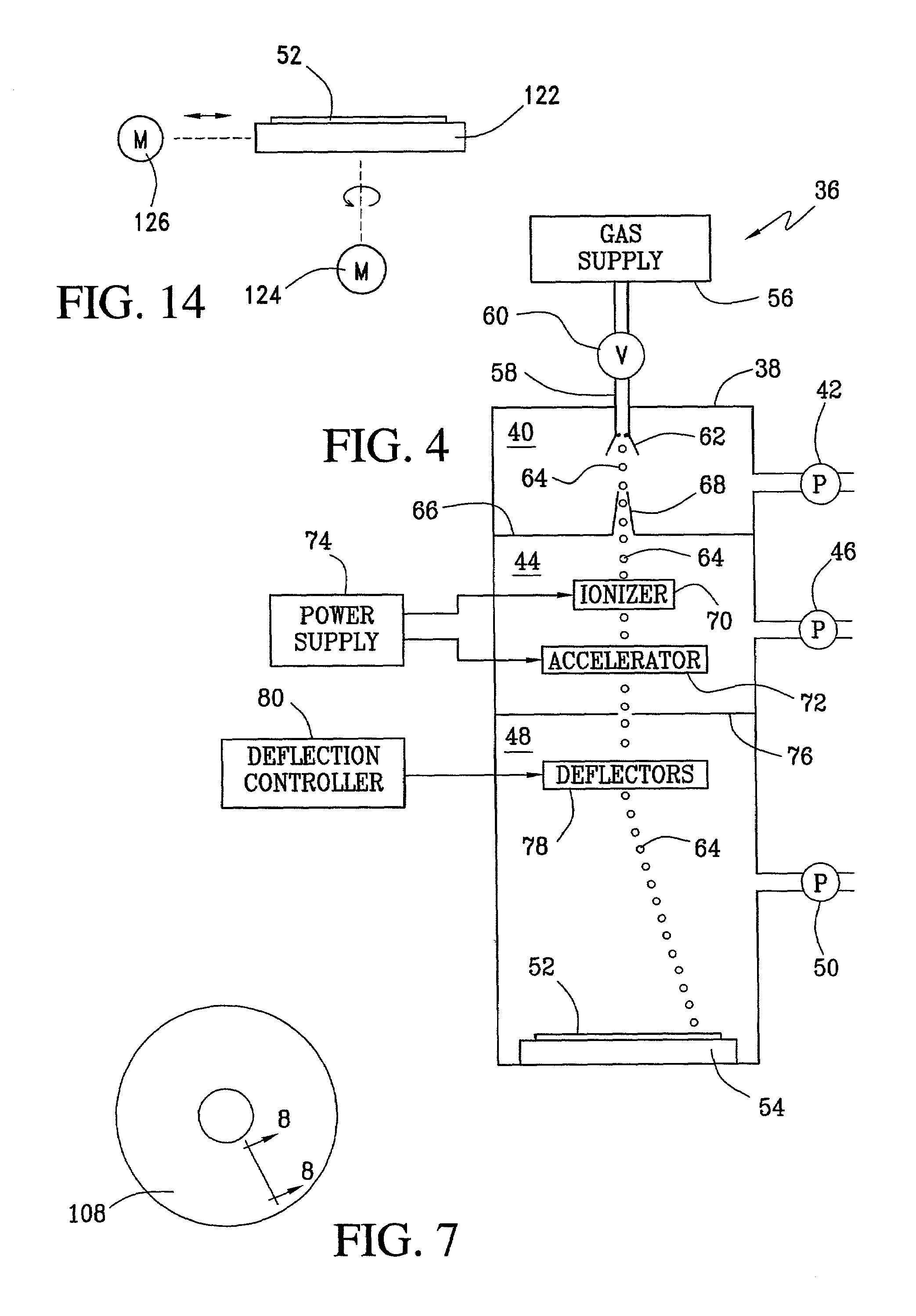
InactiveUS7064927B2Reduce manufacturing costReduce surface roughnessRecord information storageFlat record carrier containersGas cluster ion beamVacuum chamber
A method for making a magnetic disk, without chemical mechanical polishing to remove asperities, includes the steps of placing an annular-shaped element in a vacuum chamber, exposing a surface of the element to a beam of gas clusters while it is in the vacuum chamber, and thereafter applying a magnetic coating. The annular-shaped element may be a substrate, or it may be a substrate with a base coating such as glassy carbon or amorphous carbon. The substrate may be made of glass, preferably high quality fusion glass. The surface of the annular element may be textured by forming a sequence of concentric annular valleys, with plateaus being left between the valleys, before the magnetic coating is applied. A semiconductor wafer may also be smoothed by a beam of gas clusters to prepare the wafer for photolithography.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com