Catalysis electrode for preparing formic acid by electrocatalytic reduction of CO2, application and method for preparing formic acid by electrocatalytic reduction on CO2
A catalytic electrode, carbon dioxide technology, applied in the direction of electrode, electrolysis process, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of copper element, unsatisfactory current efficiency, loss of catalytic activity, etc., to achieve the effect of simple steps, easy production and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] For electrocatalytic reduction of CO 2 Preparation of the catalytic electrode to formic acid:
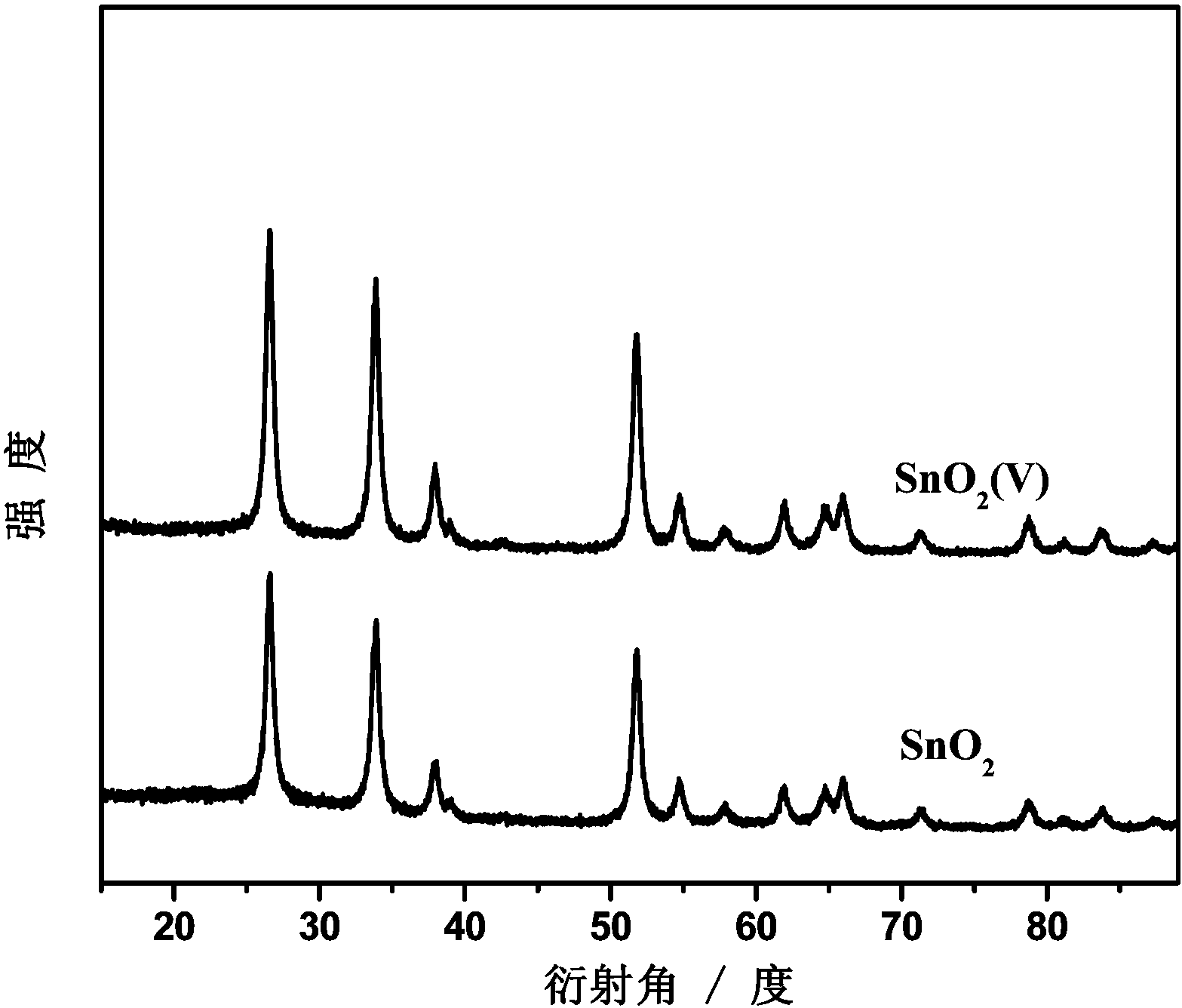
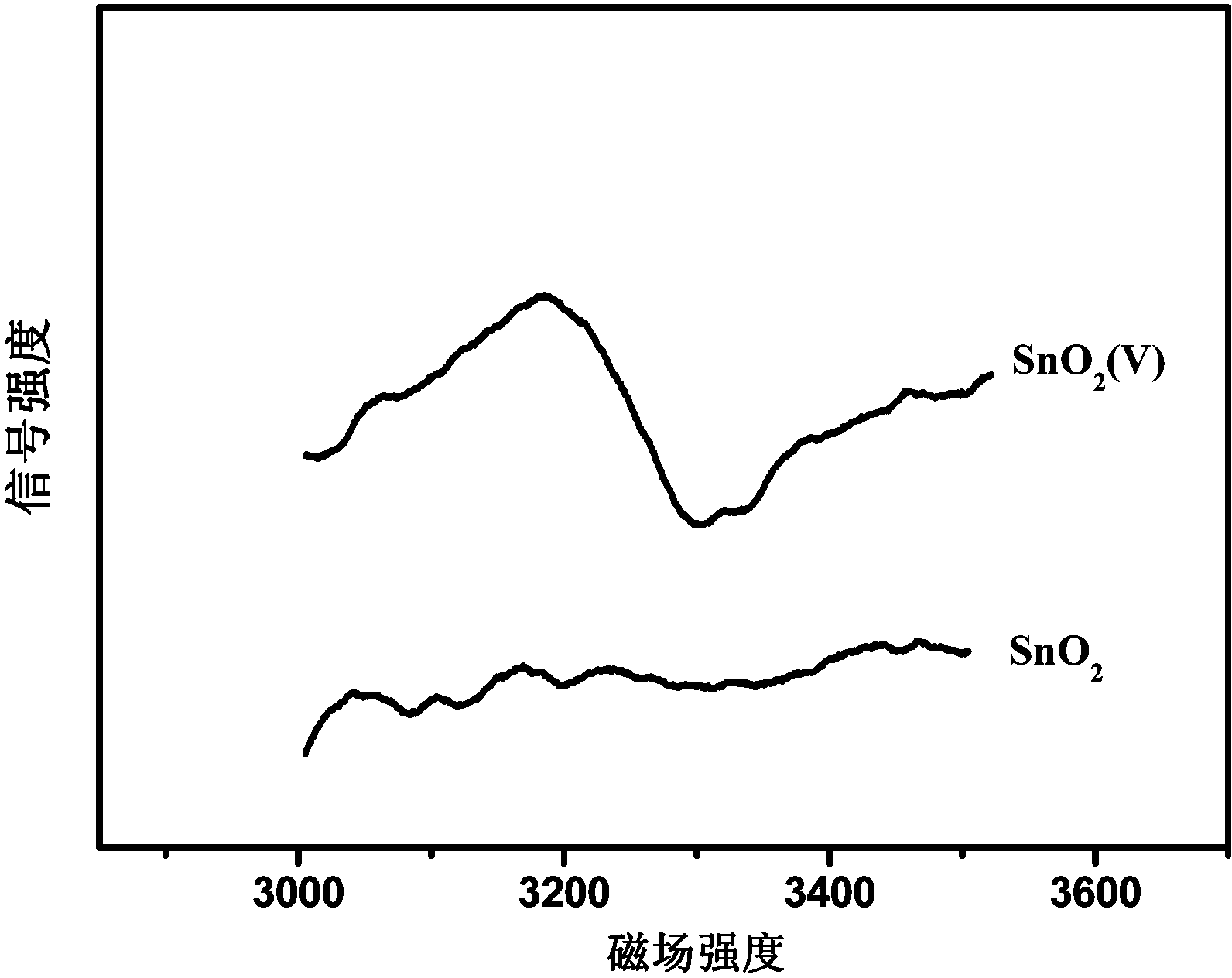
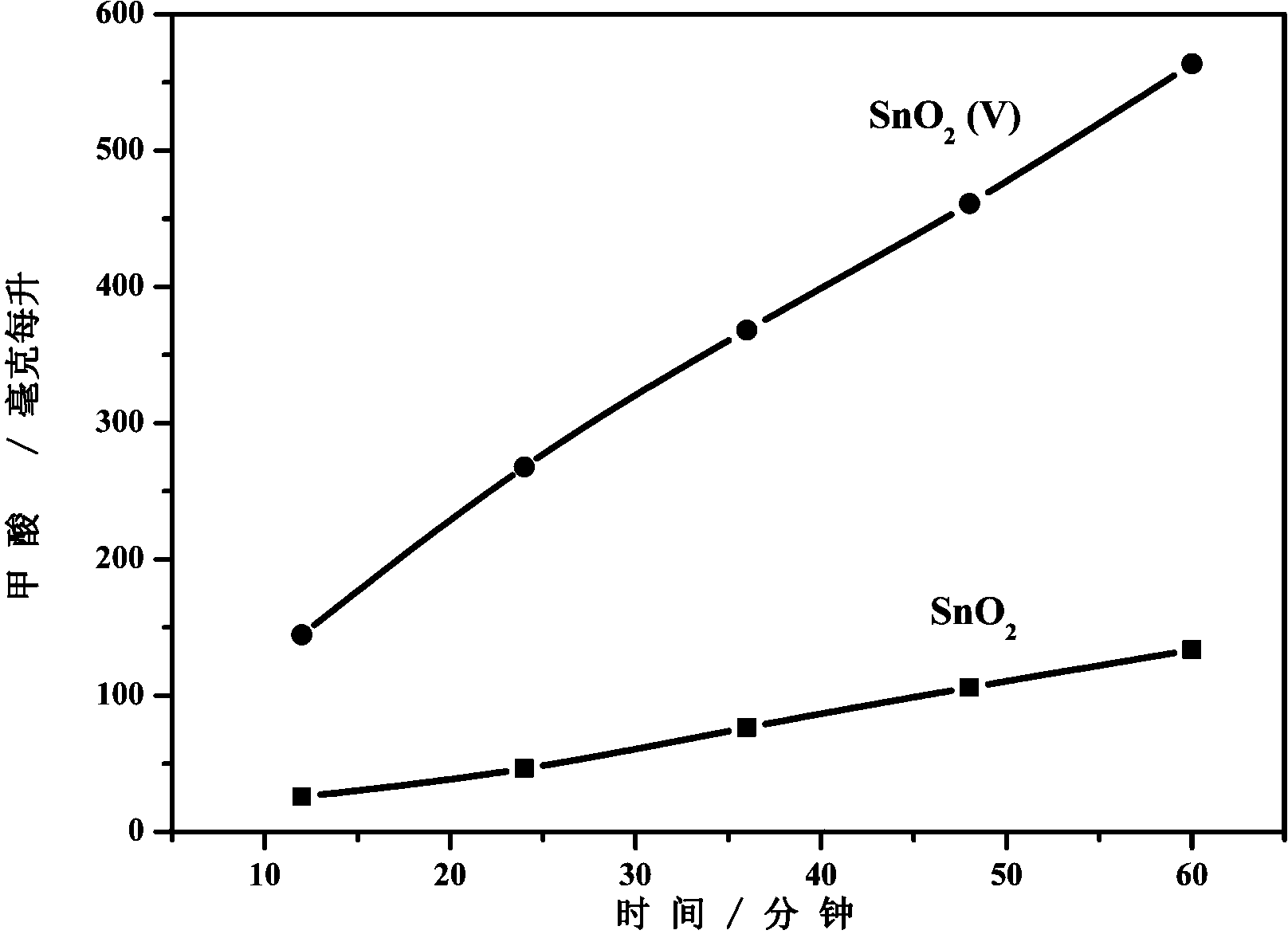
[0027] Step 1: Incorporate commercial SnO 2 Vacuum heat treatment was carried out for 4 hours, the vacuum pressure was 2 Pa, and the treatment temperature was 200 ° C to obtain tin dioxide containing oxygen vacancies (SnO 2 (V)), the XRD diagrams before and after treatment are shown in figure 1 , the electron paramagnetic resonance spectrum see figure 2 ,Depend on figure 2 It can be seen from the results that after the vacuum heat treatment of tin dioxide, the electron paramagnetic resonance signal is stronger, indicating that oxygen vacancy defects are generated on the surface;
[0028] Step 2: The treated tin dioxide containing oxygen vacancies (SnO 2 (V)) was ultrasonically mixed and dispersed with 0.1 wt% Nafion solution to obtain SnO 2 (V) suspension with a mass concentration of 2wt%, and then apply the dispersed suspension to the surface of a glassy carbon shee...
Embodiment 2
[0032] For electrocatalytic reduction of CO 2 Preparation of the catalytic electrode to formic acid:
[0033] Step 1: Incorporate the SnO 2 Vacuum heat treatment was carried out for 3 hours, the vacuum pressure was 8 Pa, and the treatment temperature was 300 °C to obtain tin dioxide (SnO2) containing oxygen vacancies. 2 (V));
[0034] Step 2: SnO (SnO2) containing oxygen vacancies 2 (V)) is ultrasonically mixed and dispersed with 0.3wt% Nafion solution to obtain SnO 2 (V) The mass concentration of the suspension is 5wt%. The dispersed suspension is coated on the surface of the glassy carbon sheet, and it can be used for electrocatalytic reduction of CO after drying. 2 to the catalytic electrode for formic acid.
[0035] A method for catalytically reducing carbon dioxide to formic acid using the catalytic electrode:
[0036]In an electrolytic cell separated by a proton exchange membrane into an anode tank and a cathode tank, the above-mentioned catalytic electrode is used...
Embodiment 3
[0039] For electrocatalytic reduction of CO 2 Preparation of the catalytic electrode to formic acid:
[0040] Step 1: Incorporate the SnO 2 Vacuum heat treatment was carried out for 2 h, the vacuum pressure was 10 Pa, and the treatment temperature was 400 ° C to obtain tin dioxide containing oxygen vacancies (SnO 2 (V));
[0041] Step 2: SnO (SnO2) containing oxygen vacancies 2 (V)) was ultrasonically mixed and dispersed with 0.5 wt% Nafion solution to obtain SnO 2 (V) is a suspension with a mass concentration of 3wt%, and the dispersed suspension is coated on the surface of a glassy carbon sheet, and it can be used for electrocatalytic reduction of CO after drying. 2 to the catalytic electrode for formic acid.
[0042] The method of using the catalytic electrode to catalytically reduce carbon dioxide to formic acid: In an electrolytic cell separated by a proton exchange membrane into an anode tank and a cathode tank, the above-mentioned catalytic electrode is used as the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com