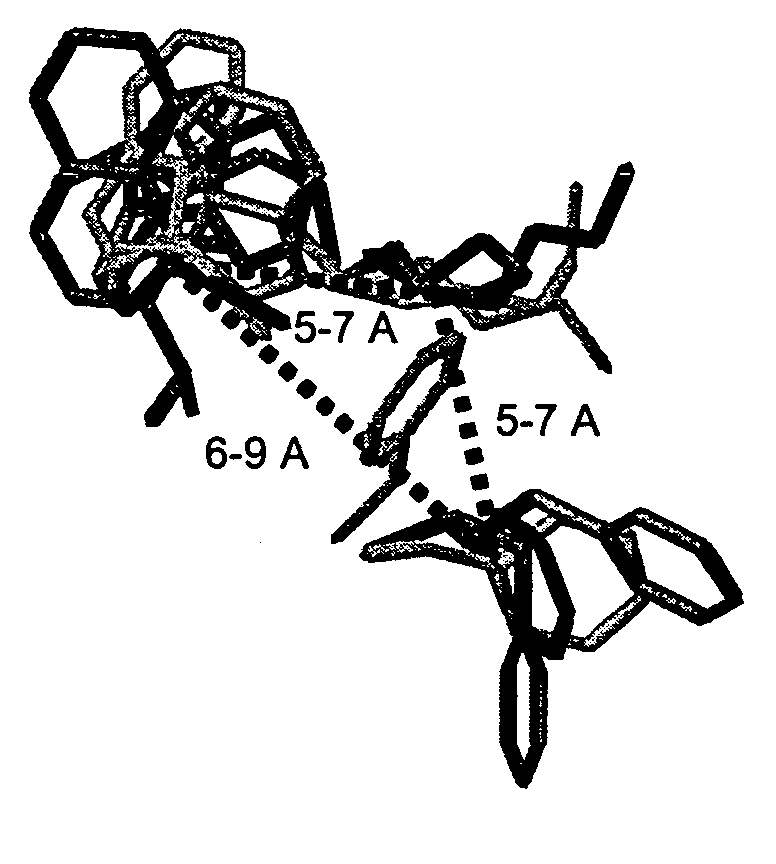
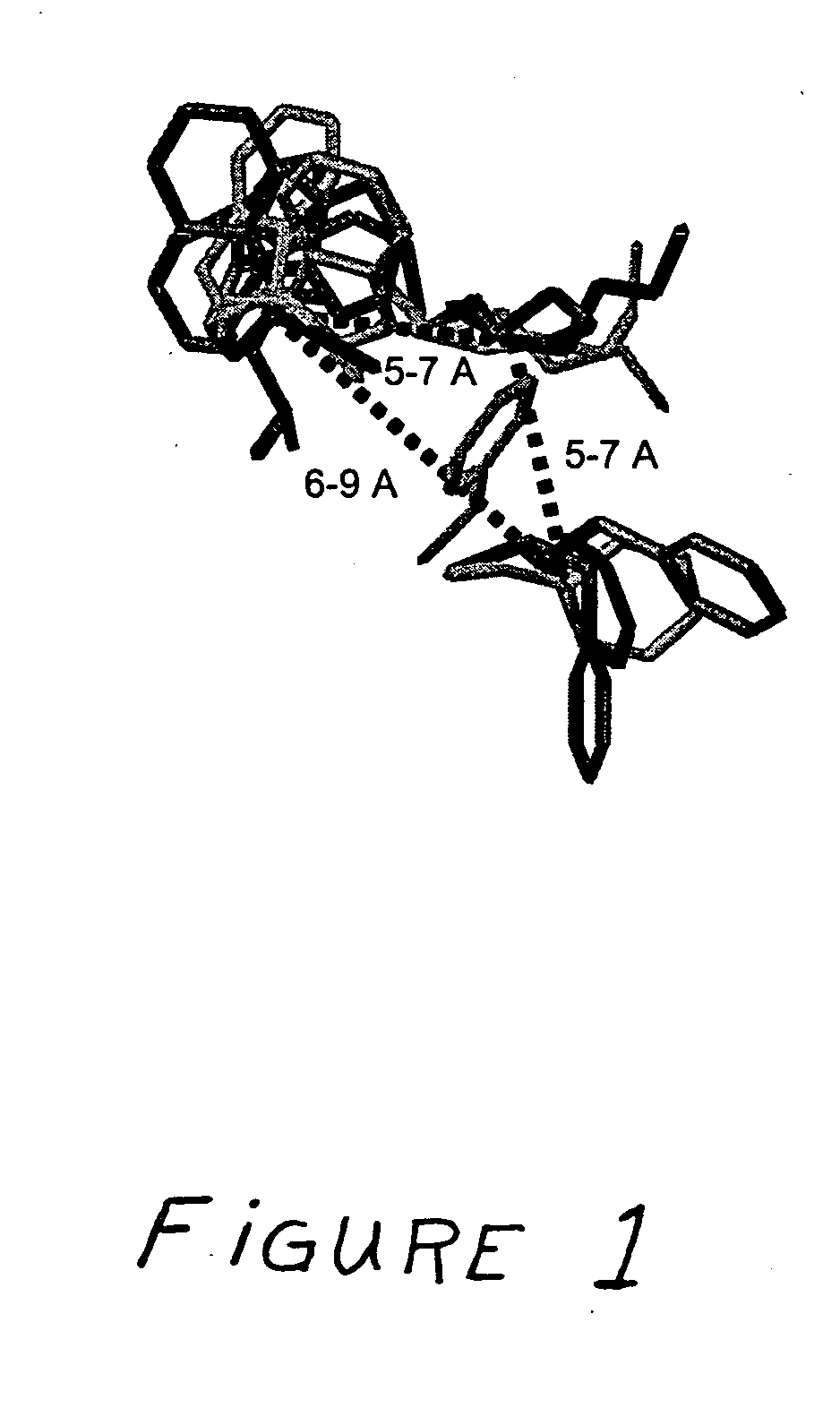
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
333 results about "High affinity binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High-affinity binding results from stronger intermolecular forces between a receptor and its ligand, leading to a a longer residence time at the binding site (higher "on" rate, lower "off" rate). This means that a lower concentration of the ligand is required for full activity, so in that sense they're more "efficient".
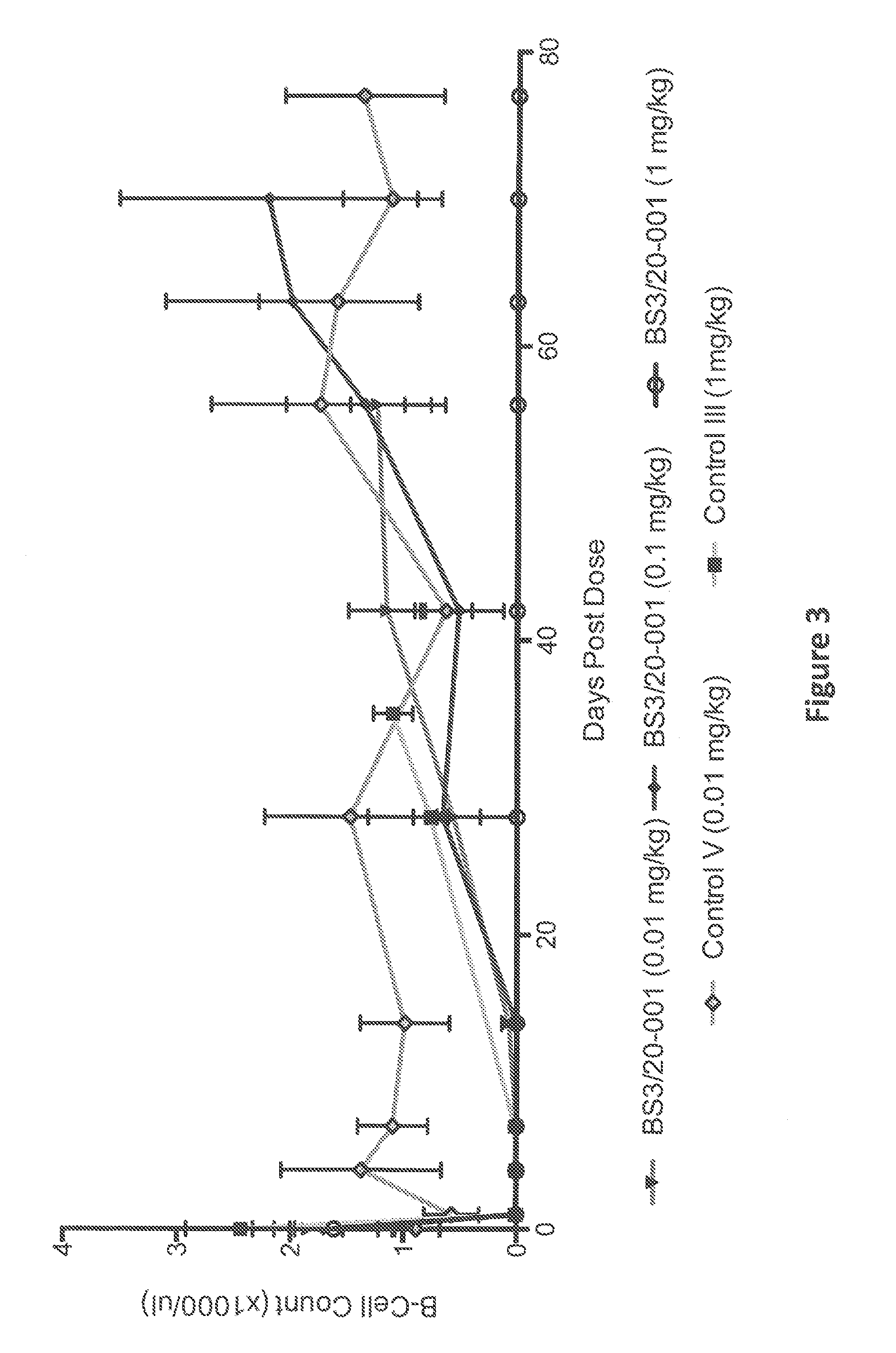
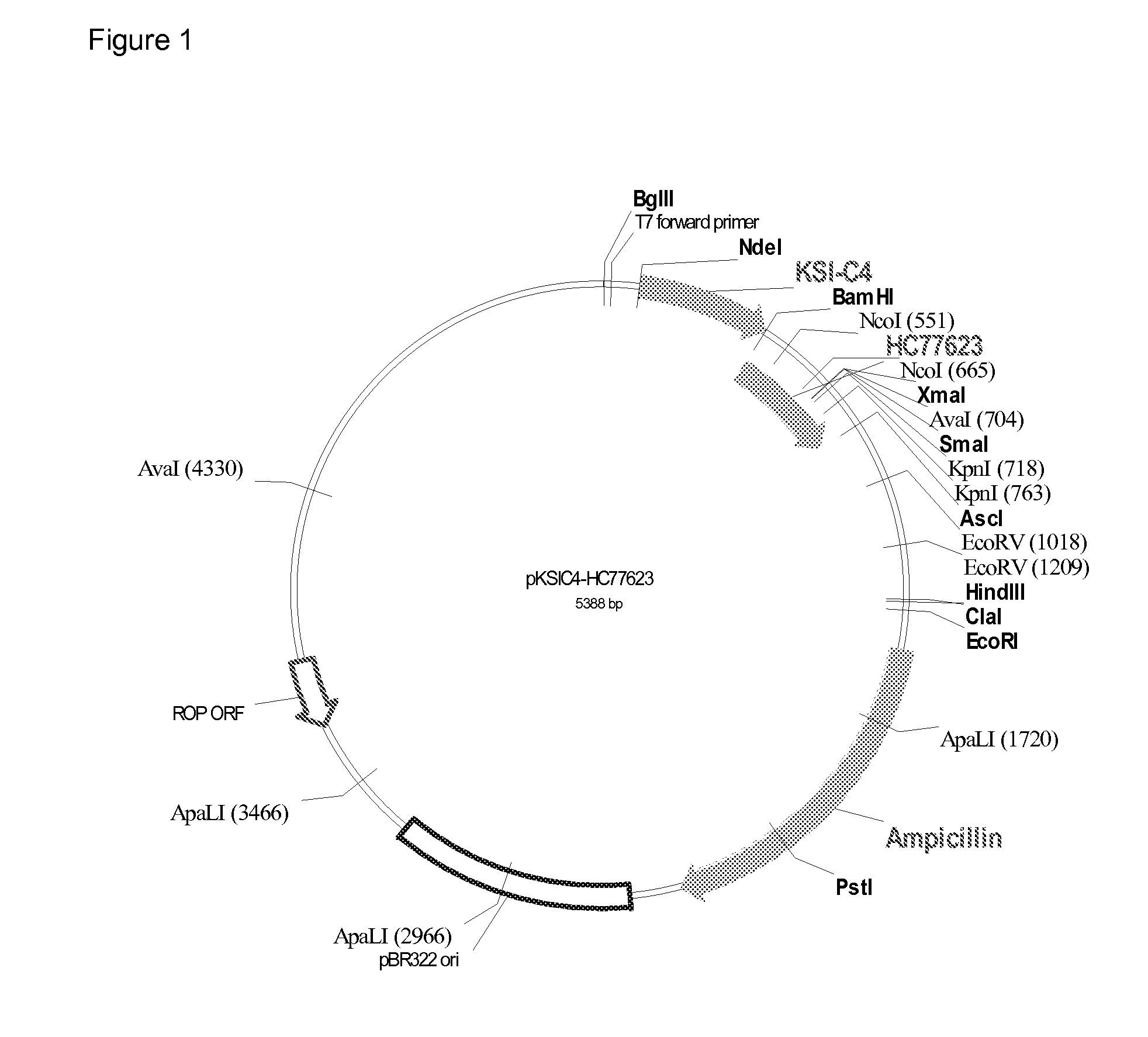
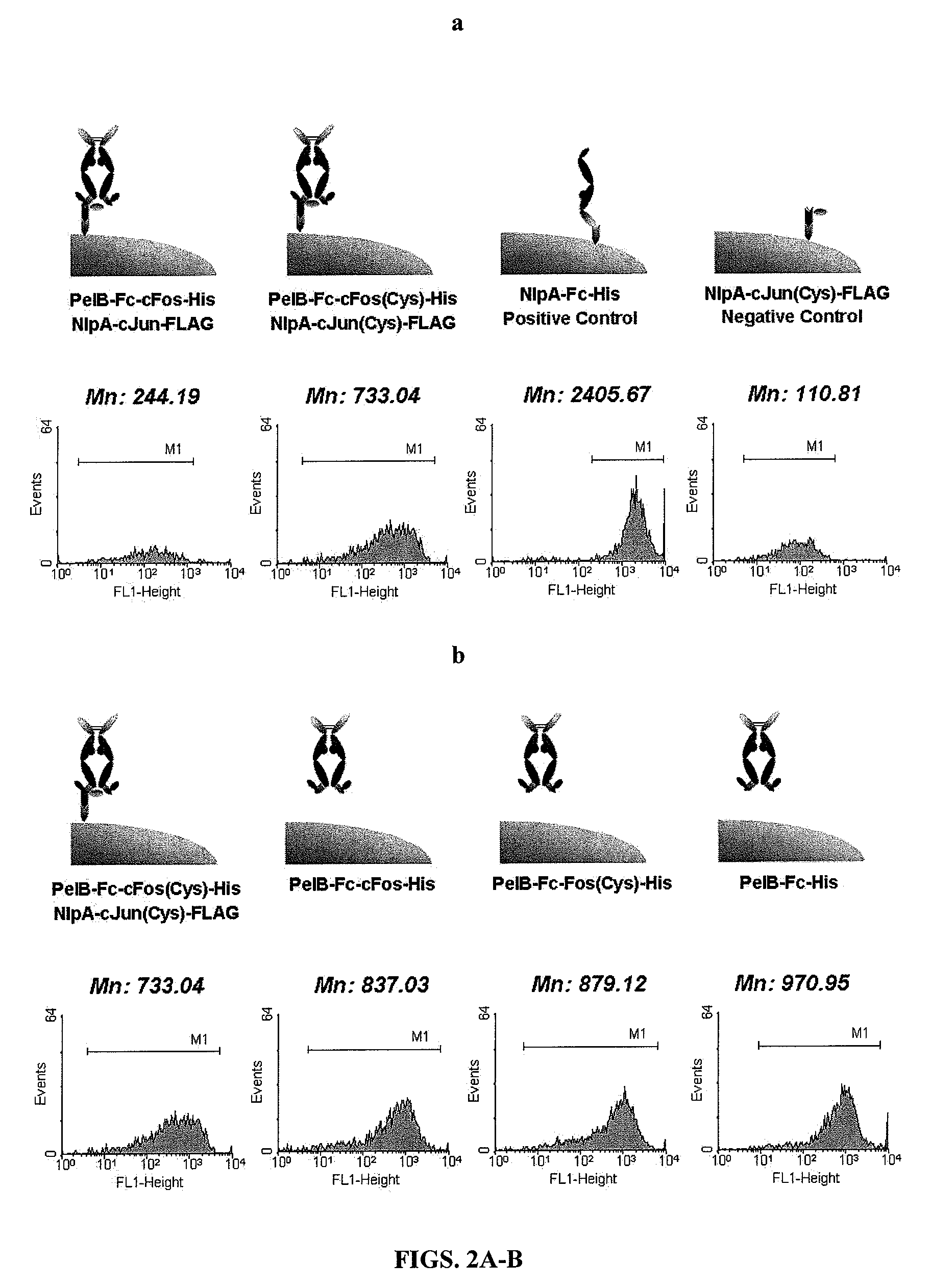
Anti-cd3 antibodies, bispecific antigen-binding molecules that bind cd3 and cd20, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20140088295A1Useful in treatmentFacilitates directed killing (cell lysis) of the targetedImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCD20Disease
The present invention provides antibodies that bind to CD3 and methods of using the same. According to certain embodiments, the antibodies of the invention bind human CD3 with high affinity and induce human T cell proliferation. The invention includes antibodies that bind CD3 and induce T cell-mediated killing of tumor cells. According to certain embodiments, the present invention provides bispecific antigen-binding molecules comprising a first antigen-binding domain that specifically binds human CD3, and a second antigen-binding molecule that specifically binds human CD20. In certain embodiments, the bispecific antigen-binding molecules of the present invention are capable of inhibiting the growth of B-cell tumors expressing CD20. The antibodies and bispecific antigen-binding molecules of the invention are useful for the treatment of diseases and disorders in which an upregulated or induced targeted immune response is desired and / or therapeutically beneficial. For example, the antibodies of the invention are useful for the treatment of various cancers as well as other CD20-related diseases and disorders.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Optimization of antibodies that bind lymphocyte activation gene-3 (lag-3), and uses thereof
ActiveUS20140093511A1Improve physical stabilityGood chemical stabilityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntiviralsLymphocyteLymphocyte activation
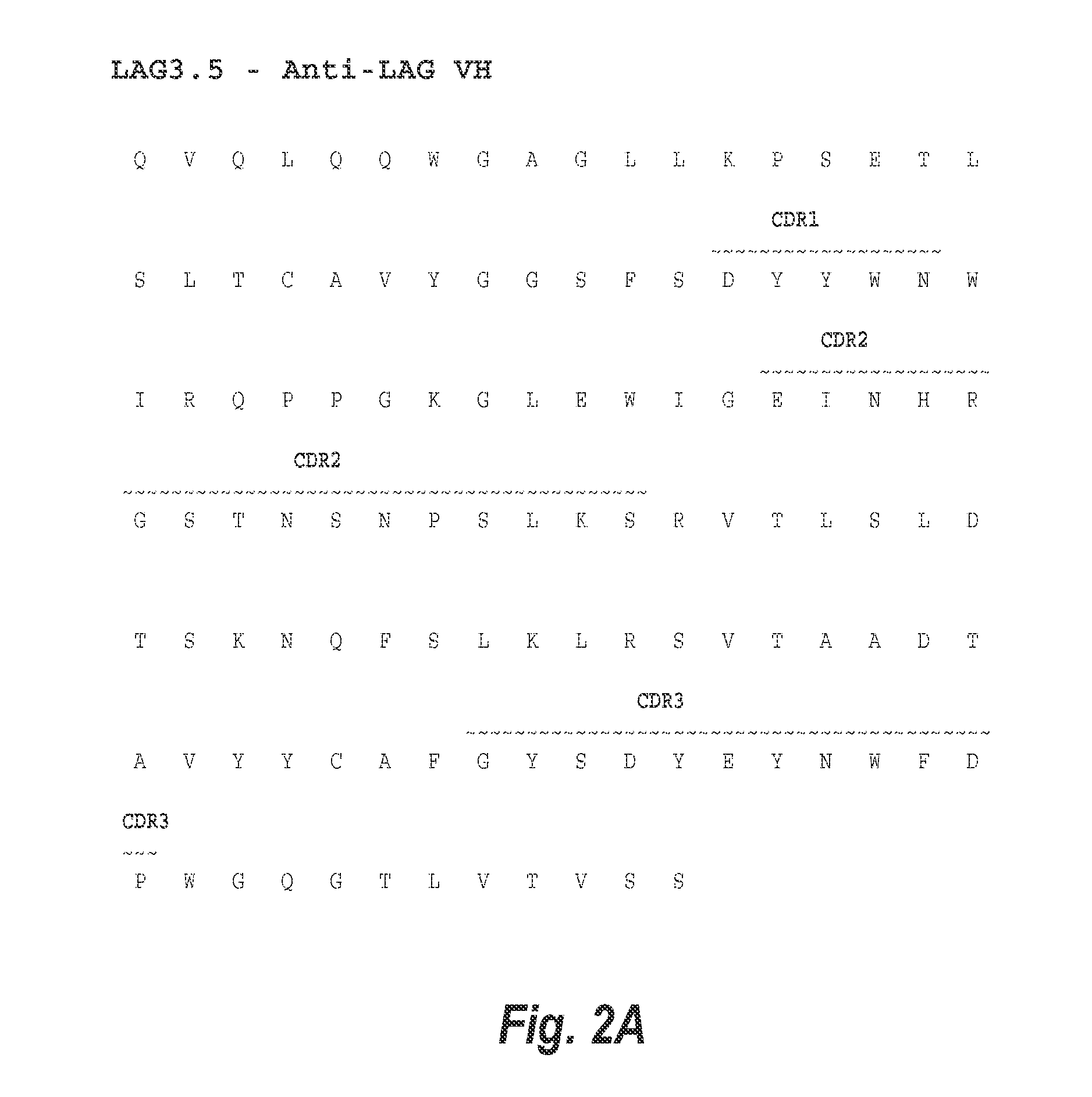
The present invention provides isolated monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind LAG-3, and have optimized functional properties compared to previously described anti-LAG-3 antibodies, such as antibody 25F7 (US 2011 / 0150892 A1). These properties include reduced deamidation sites, while still retaining high affinity binding to human LAG-3, and physical (i.e., thermal and chemical) stability. Nucleic acid molecules encoding the antibodies of the invention, expression vectors, host cells and methods for expressing the antibodies of the invention are also provided, as well as immunoconjugates, bispecific molecules and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies. The present invention also provides methods for detecting LAG-3, as well as methods for treating stimulating immune responses using an anti-LAG-3 antibody of the invention. Combination therapy, in which the antibodies are co-administered with at least one additional immunostimulatory antibody, is also provided.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Multipartite high-affinity nucleic acid probes
InactiveUS6451588B1Accurately determineBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHybridization probeNucleic Acid Probes
The invention provides a collection of probes useful for hybridizing to a target nucleic acid. The probes associate with each other, binding with high affinity to the target nucleic acid, to form three-way junctions and other complexes. At least one of the probes in each collection includes a nucleic acid analog. Methods using the probes in hybridization and as primers are also provided.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Pepetide-based body surface reagents for personal care
Peptides have been identified that bind with high affinity to body surfaces, such as, hair, skin, nails, teeth, gums, corneal tissue, and oral cavity surfaces. Peptide-based body surface reagents formed by coupling a body surface binding peptide to a benefit agent are described. The peptide-based body surface reagents include peptide-based hair conditioners, hair colorants, skin conditioners, skin colorants, nail colorants, and oral care reagents. The peptide-based hair conditioners and hair colorants are comprised of a hair-binding peptide coupled to a hair conditioning agent or a coloring agent, respectively. The peptide-based skin conditioners and skin colorants are comprised of a skin-binding peptide coupled to a skin conditioning agent or a colorant, respectively. The peptide-based nail colorants are comprised of a nail-binding peptide coupled to a coloring agent. The peptide-based oral care reagents are comprised of an oral cavity surface-binding peptide coupled to an oral care benefit agent. In all these compositions, the peptide may be directly coupled to the active agent or the coupling may be via a spacer. Personal care compositions containing these peptide-based body surface reagents are also described.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Antibody compositions and methods
InactiveUS20070065440A1High affinitySmall sizeAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHigh concentrationVariable domain
Provided are concentrated preparations comprising single immunoglobulin variable domain polypeptides that bind target antigen with high affinity and are soluble at high concentration, without aggregation or precipitation, providing, for example, for increased storage stability and the ability to administer higher therapeutic doses.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
Antibodies to Dkk-1
ActiveUS20060127393A1Block and reduce bindingHigh activitySenses disorderNervous disorderConformational epitopeOcular disease
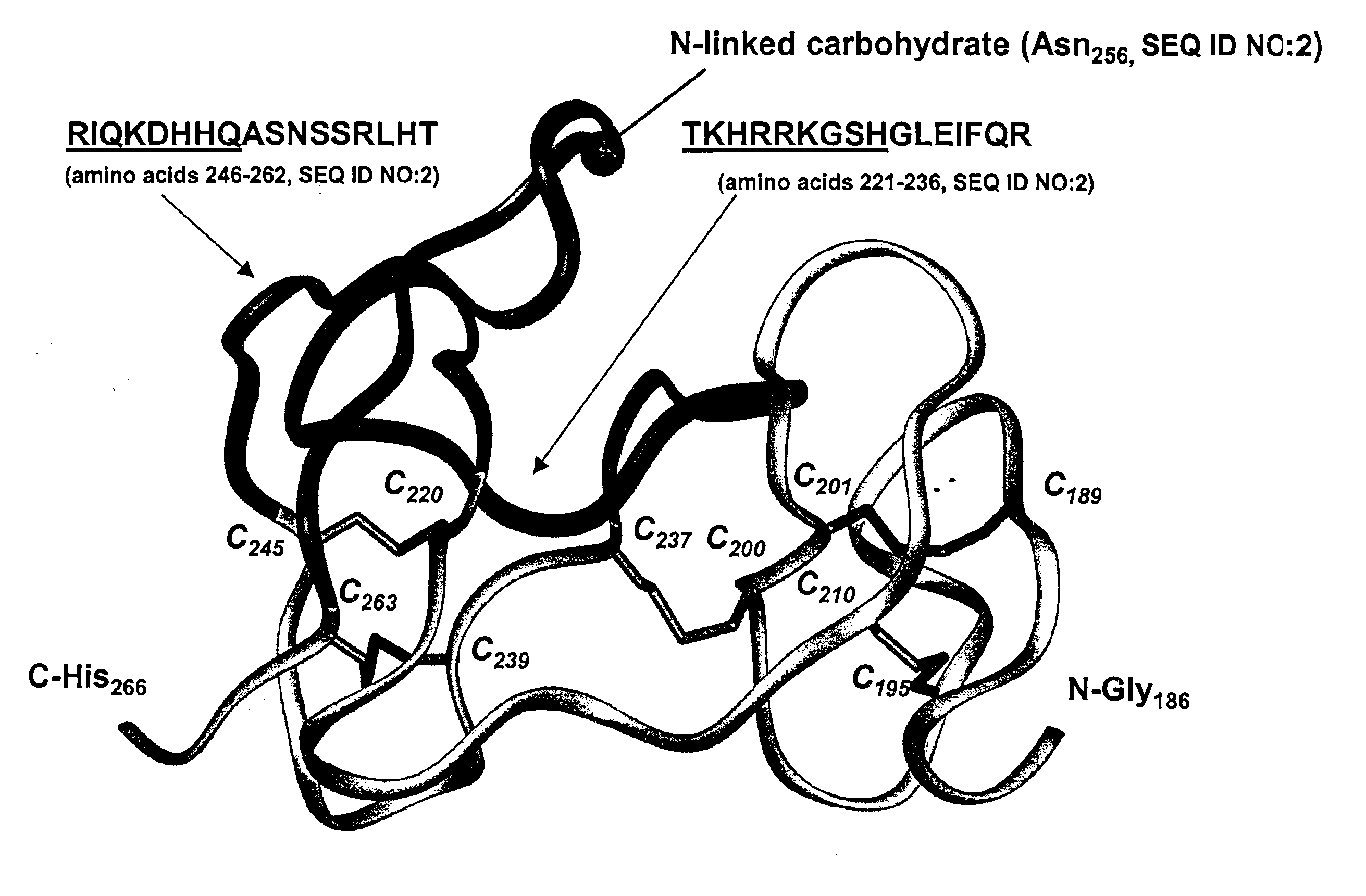
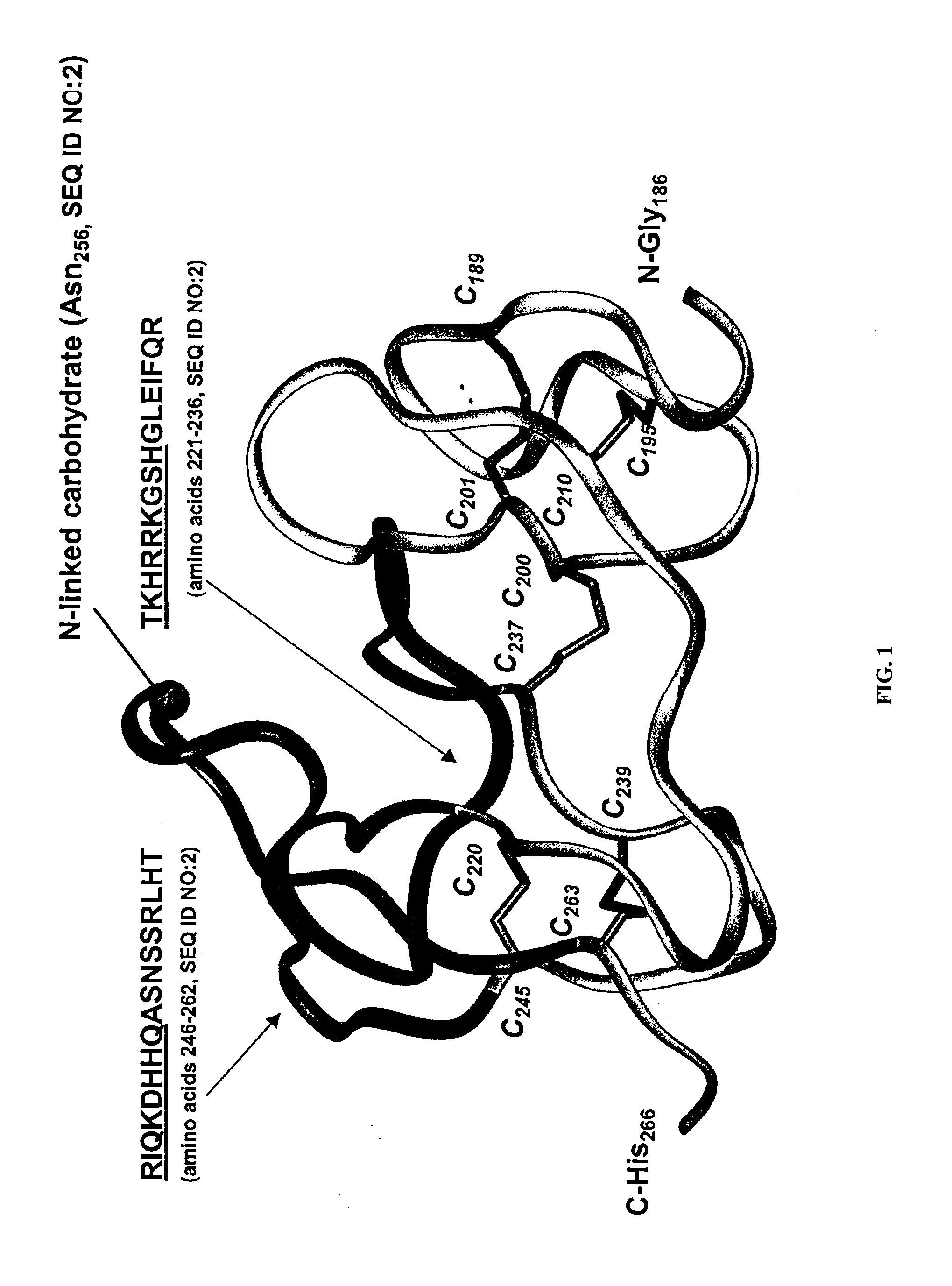
The present invention provides antibodies and immunologically functional fragments thereof that specifically bind Dkk-1 polypeptides. The subject antibodies and fragments bind with high affinity to a conformational epitope located in the carboxy region of the Dkk-1 protein. Methods for preparing such antibodies or fragments thereof as well as physiologically acceptable compositions containing the antibodies or fragments are also provided. Use of the antibodies and fragments to treat various diseases including bone disorders, inflammatory diseases, neurological diseases, ocular diseases, renal diseases, pulmonary diseases and skin diseases are also disclosed.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Functional vitamin D derivatives and a method for determining 25-hydroxy-vitamin D and 1alpha, dihydroxy-vitamin D
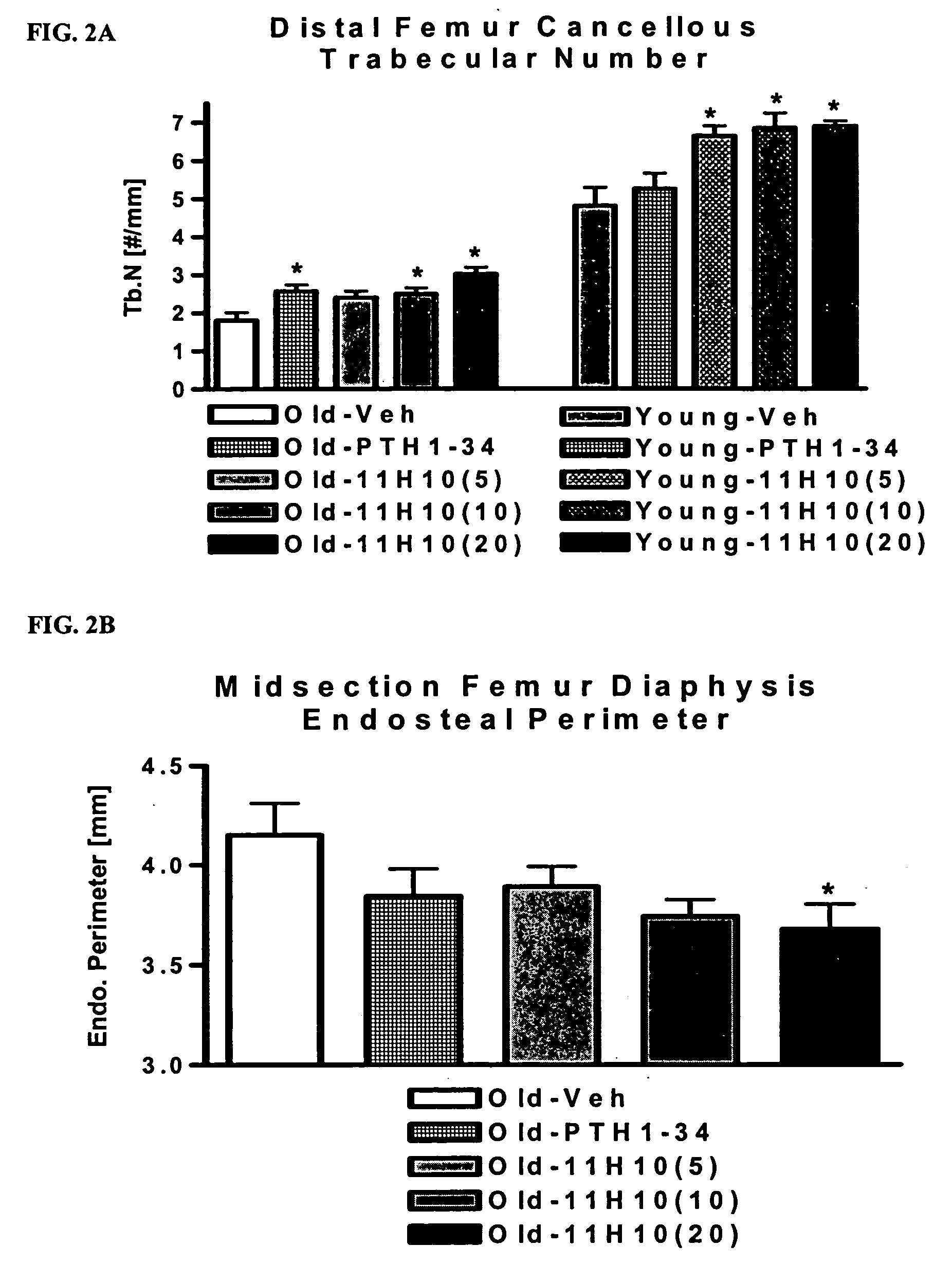
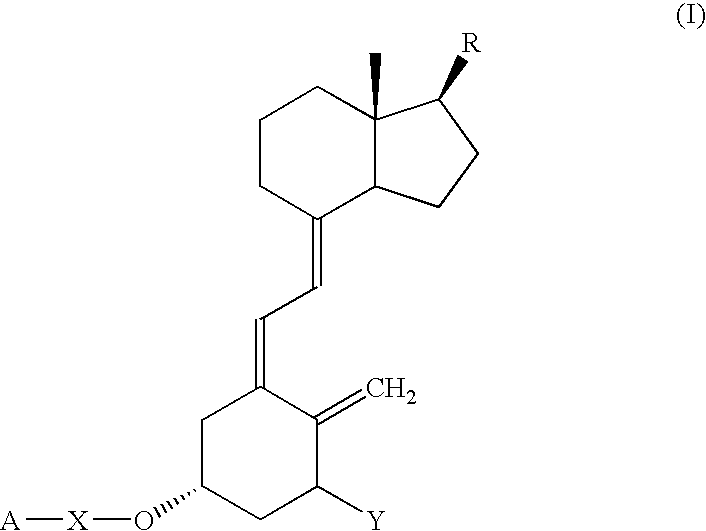
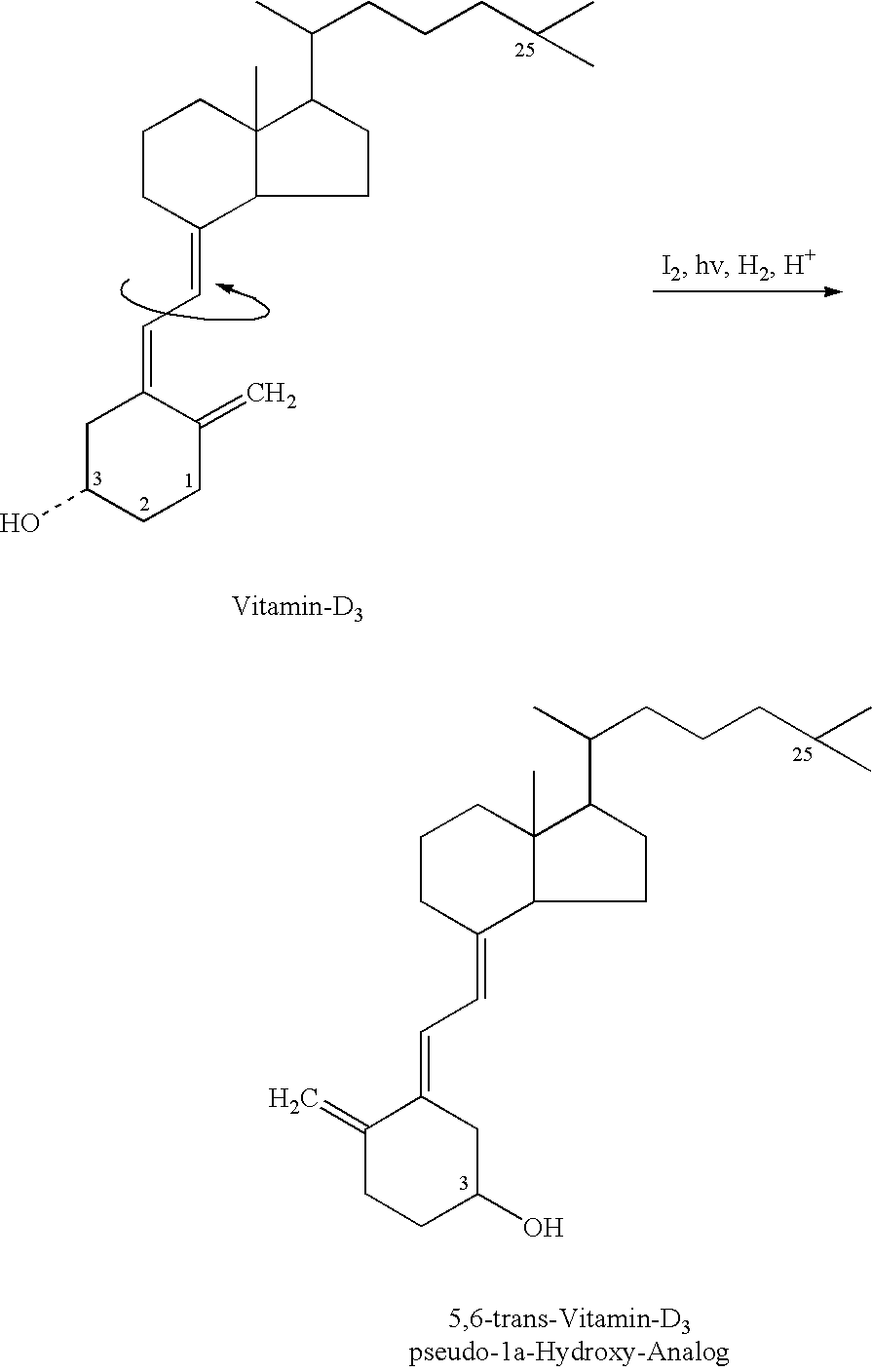
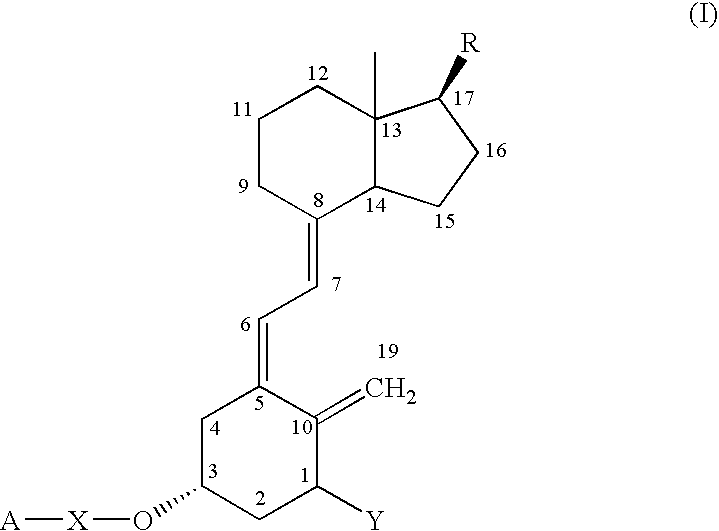
Vitamin D compounds of formula (I) with a label attached to a spacer group in the 3 position are disclosed.In the above formula (I), X is an optionally substituted hydrocarbon group with a length of 0.8-4.2 nm, optionally containing the heteroatoms S, O, N or P; Y is H or OH; A is a label capable of binding with high affinity to a protein; R is an optionally substituted hydrocarbon side chain of a D vitamin or a D vitamin metabolite. Also disclosed is the preparation of formula (I).
Owner:IMMUNDIAGNOSTIK +1
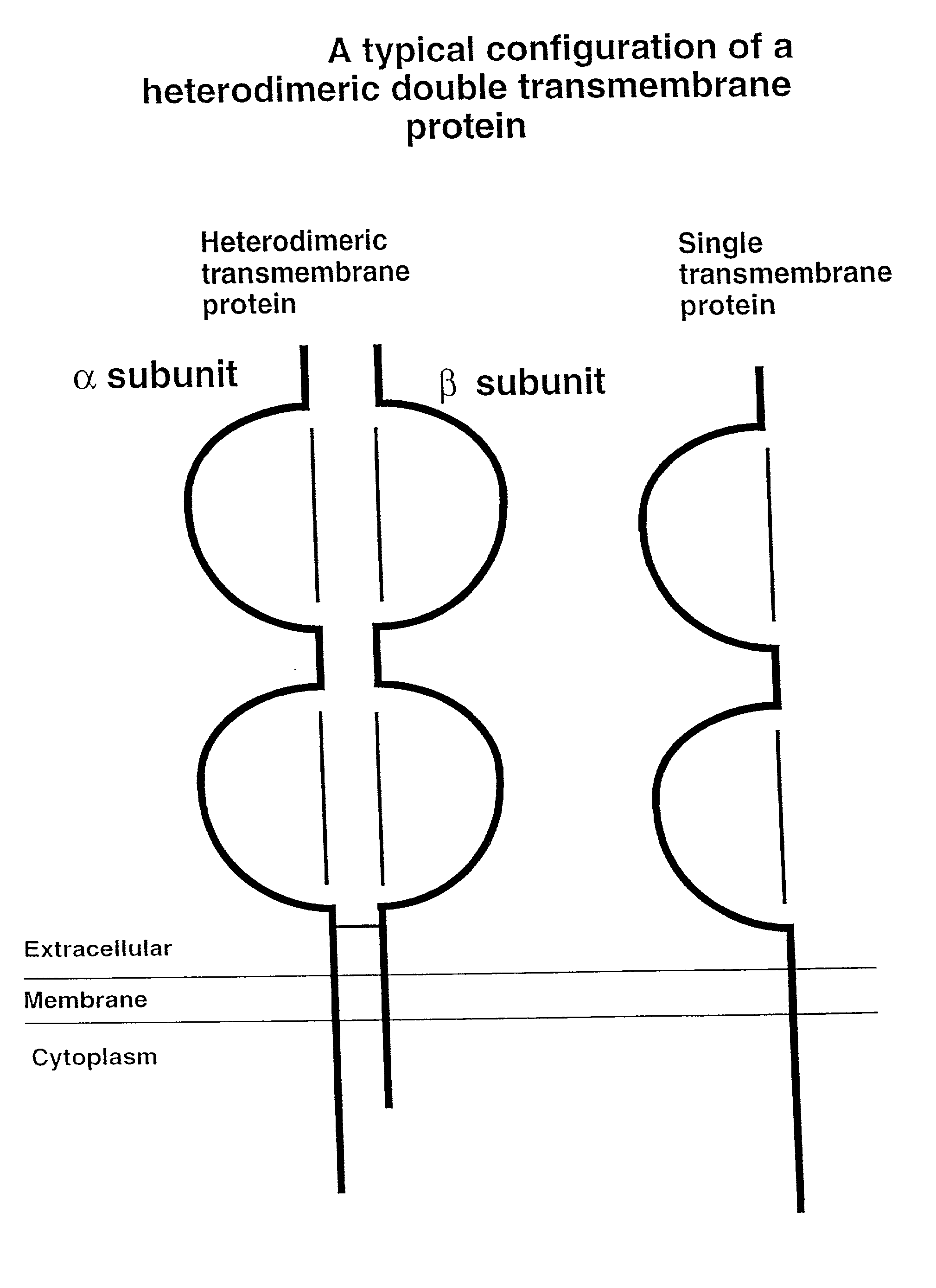
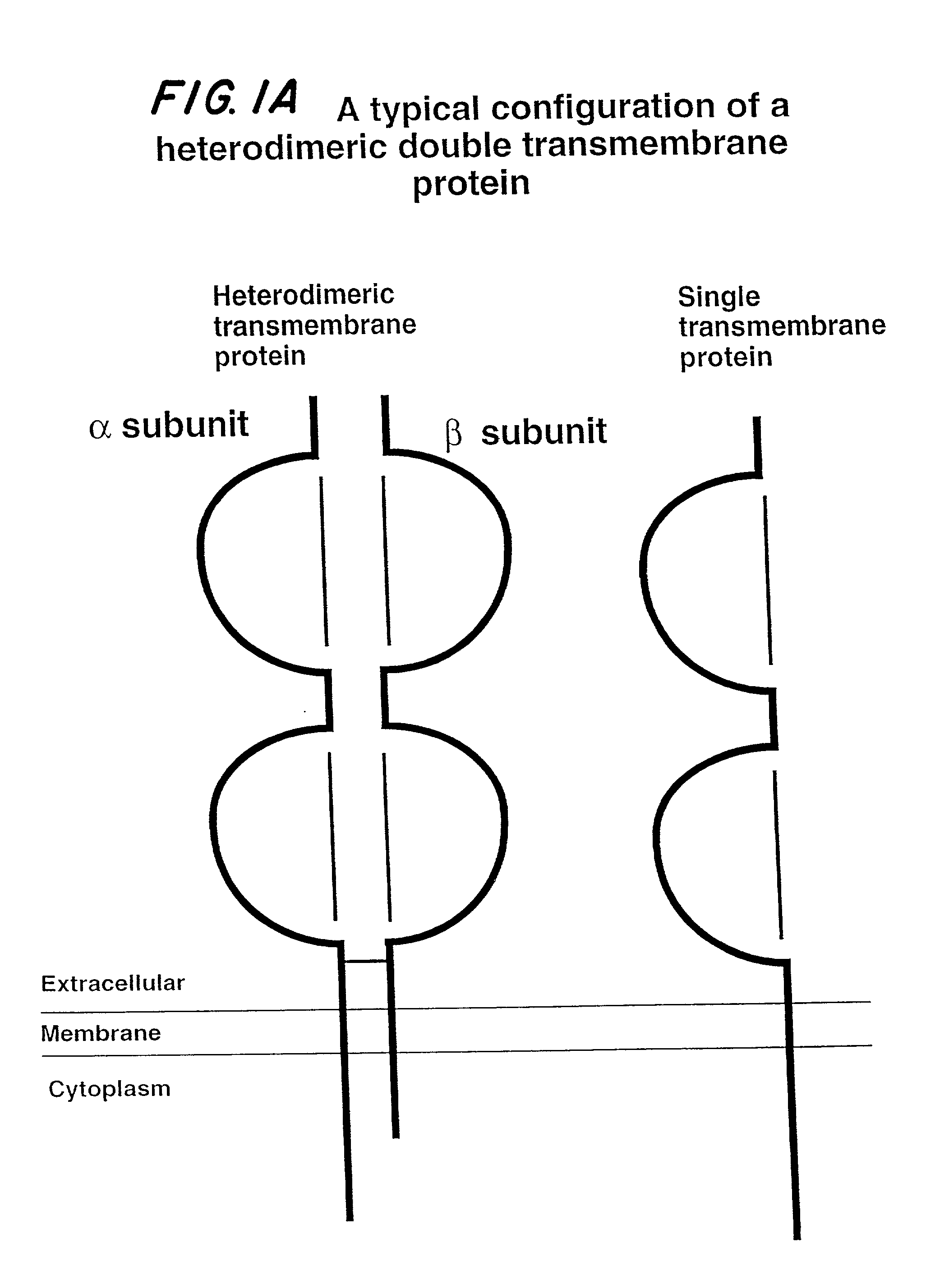
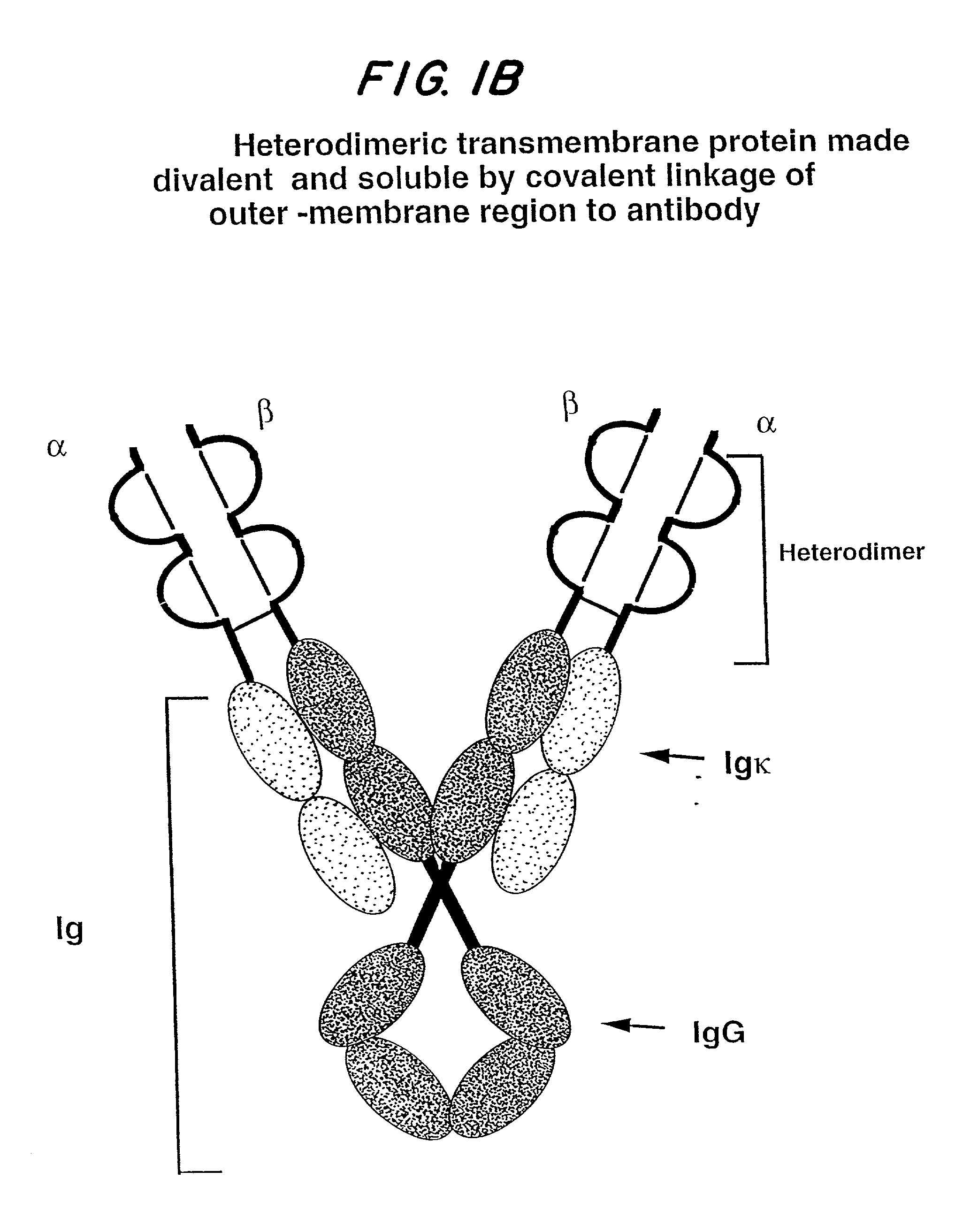
Soluble divalent and multivalent heterodimeric analogs of proteins
InactiveUS20020127231A1Well representedHigh affinityVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsADAMTS ProteinsSpecific immunity
Specificity in immune responses is in part controlled by the selective interaction of T cell receptors with their cognate ligands, peptide / MHC molecules. The discriminating nature of this interaction makes these molecules, in soluble form, good candidates for selectively regulating immune responses. Attempts to exploit soluble analogs of these proteins has been hampered by the intrinsic low avidity of these molecules for their ligands. To increase the avidity of soluble analogs for their cognates to biologically relevant levels, divalent peptide / MHC complexes or T cell receptors (superdimers) were constructed. Using a recombinant DNA strategy, DNA encoding either the MHC class II / peptide or TCR heterodimers was ligated to DNA coding for murine Ig heavy and light chains. These constructs were subsequently expressed in a baculovirus expression system. Enzyme-linked immunosorbant assays (ELISA) specific for the Ig and polymorphic determinants of either the TCR or MHC fraction of the molecule indicated that infected insect cells secreted approximately 1 .mu.g / ml of soluble, conformnationally intact chimeric superdimers. SDS PAGE gel analysis of purified protein showed that expected molecular weight species. The results of flow cytometry demonstrated that the TCR and class II chimeras bound specifically with high avidity to cells bearing their cognate receptors. These superdimers will be useful for studying TCR / MHC interactions, lymphocyte tracking, identifying new antigens, and have possible uses as specific regulators of immune responses.
Owner:SCHNECK JONATHAN +1
Specific and high affinity binding proteins comprising modified sh3 domains of fyn kinase
InactiveUS20100119446A1Maintain good propertiesHigh affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsTransferasesActive componentNucleotide
The present invention relates to a recombinant binding protein comprising at least one derivative of the Src homology 3 domain (SH3) of the FYN kinase, wherein at least one amino acid in or positioned up to two amino acids adjacent to the src loop and / or at least one amino acid in or positioned up to two amino acids adjacent to the RT loop is substituted, deleted or added. Furthermore, the invention is directed to fusion proteins comprising a binding protein according to the invention fused to a pharmaceutically and / or diagnostically active component. In addition, the invention concerns nucleotides coding for these binding and / or fusion proteins as well as corresponding vectors and host cells. Last but not least, the present invention relates to the use of binding and / or fusion proteins of the present invention for preparing a medicament or a diagnostic means as well as to pharmaceutical or diagnostic compositions comprising said binding and / or fusion proteins.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
All field simultaneous radiation therapy
InactiveUS8173983B1Increase dose rateOvercome disadvantagesRadiation pyrometryElectrotherapyProstate cancerEstrogen receptor
This invention describes a system for generating multiple simultaneous tunable electron and photon beams and monochromatic x-rays for all field simultaneous radiation therapy (AFSRT), tumor specific AFSRT and screening for concealed elements worn on to the body or contained in a container. Inverse Compton scattering renders variable energy spent electron and tunable monochromatic x-rays. It's spent electron beam is reused for radiation with electron beam or to generate photon beam. Tumor specific radiation with Auger transformation radiation is facilitated by exposing high affinity tumor bound heavy elements with external monochromatic x-rays. Heavy elements like directly iodinated steroid molecule that has high affinity binding to estrogen receptor in breast cancer and to iodinated testosterone in prostate cancer or with directly implanted nanoparticles into the tumor are exposed with tuned external monochromatic x-rays for tumor specific radiation therapy. Likewise, screening element's atom's k, l, m, n shell specific Auger transformation radiation generated by its exposure to external monochromatic x-rays is used to screen for concealed objects. Multiple beam segments from a beam storage ring or from octagonal beam lines are simultaneously switched on for simultaneous radiation with multiple beams. The beam on time to expose a tumor or an object is only a few seconds. It also facilitates breathing synchronized radiation therapy. The intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and intensity modulated screening for concealed objects (IMSFCO) is rendered by varying beam intensities of multiple simultaneous beams. The isocentric additive high dose rate from simultaneously converging multiple beams, the concomitant hyperthermia and chemotherapy and tumor specific radiation therapy and the AFSRT's very low radiation to the normal tissue all are used to treat a tumor with lower radiation dose and to treat a radioresistant and multiple times recurrent tumors that heave no other alternative treatments.
Owner:SAHADEVAN VELAYUDHAN
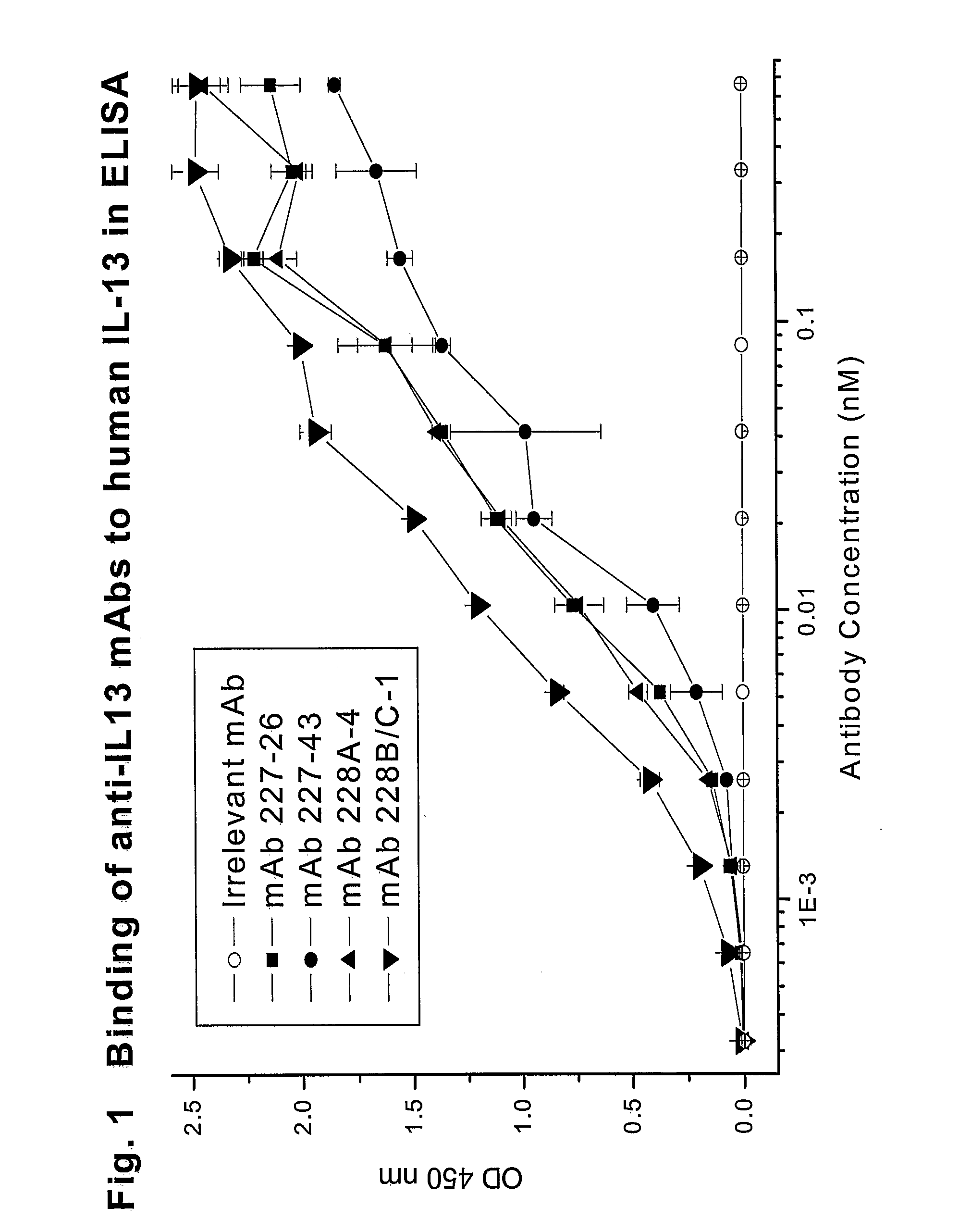
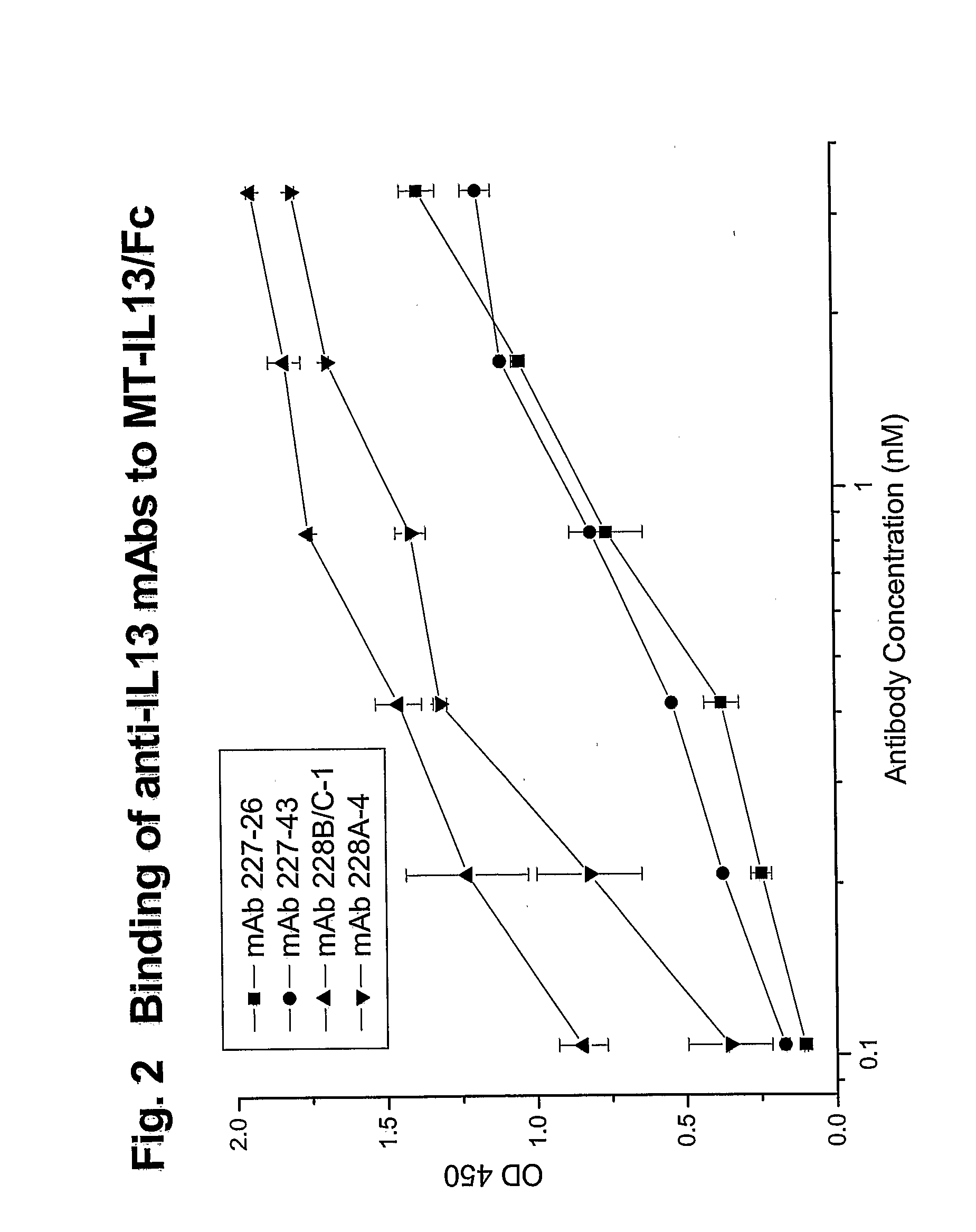
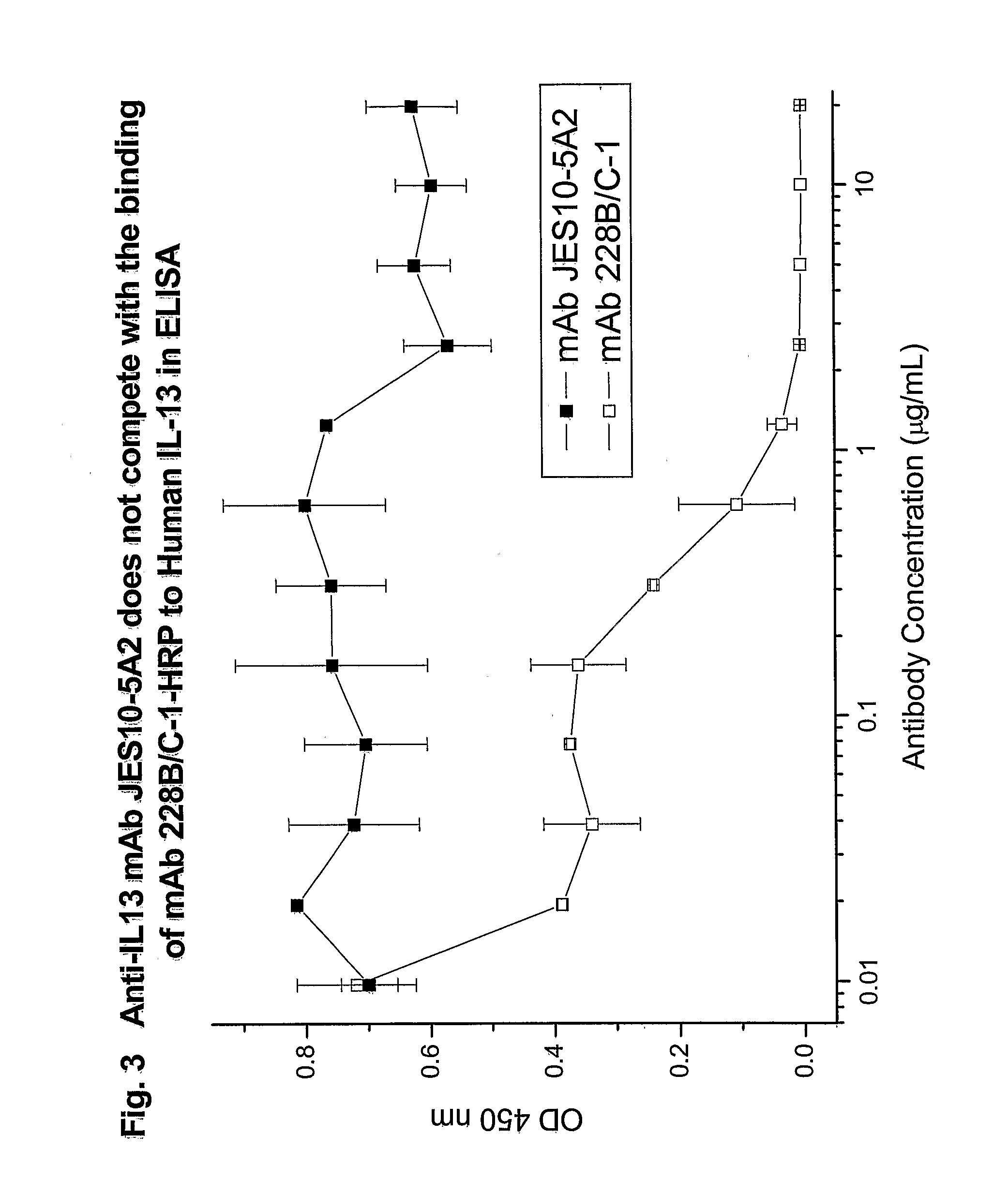
Novel anti-IL13 antibodies and uses thereof
ActiveUS20090214523A1Inhibiting antibody productionRelieve symptomsSenses disorderAntipyreticUveitisNonallergic rhinitis
The present invention relates to anti-IL13 antibodies that bind specifically and with high affinity to both glycosylated and non-glycosylated human IL13, does not bind mouse IL13, and neutralize human IL13 activity at an approximate molar ratio of 1:2 (MAb:IL13). The invention also relates to the use of these antibodies in the treatment of IL13-mediated diseases, such as allergic disease, including asthma, allergic asthma, non-allergic (intrinsic) asthma, allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, allergic conjunctivitis, eczema, urticaria, food allergies, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, ulcerative colitis, RSV infection, uveitis, scleroderma, and osteoporosis.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Peptide-based body surface coloring reagents
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Humanized antibodies against vascular endothelial growth factor
InactiveUS7667004B2High binding affinityInhibit cell proliferationPeptide librariesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiabetic retinopathyAntigen
Methods are provided for designing and selecting antibodies against human antigens with high affinity and specificity in silico and in vitro. In some particular embodiments, methods are provided for designing and selecting humanized or fully human antibodies against vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) with high affinity and specificity. In another aspect of the invention, monoclonal antibodies against VEGF are provided. In particular, humanized or human anti-VEGF monoclonal antibodies are provided with ability to bind to human VEGF with high affinity, inhibit VEGF-induced proliferation of endothelial cells in vitro and inhibit VEGF-induced angiogenesis in vivo. These antibodies and their derivative can be used in a wide variety of applications such as diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of diseases such as cancer, AMD, diabetic retinopathy, and other diseases derived from pathological angiogenesis.
Owner:ABMAXIS
Methods for discovering molecules that bind to proteins
InactiveUS20130053541A1Inhibit functionPeptide/protein ingredientsLibrary screeningProtein targetPeptide ligand
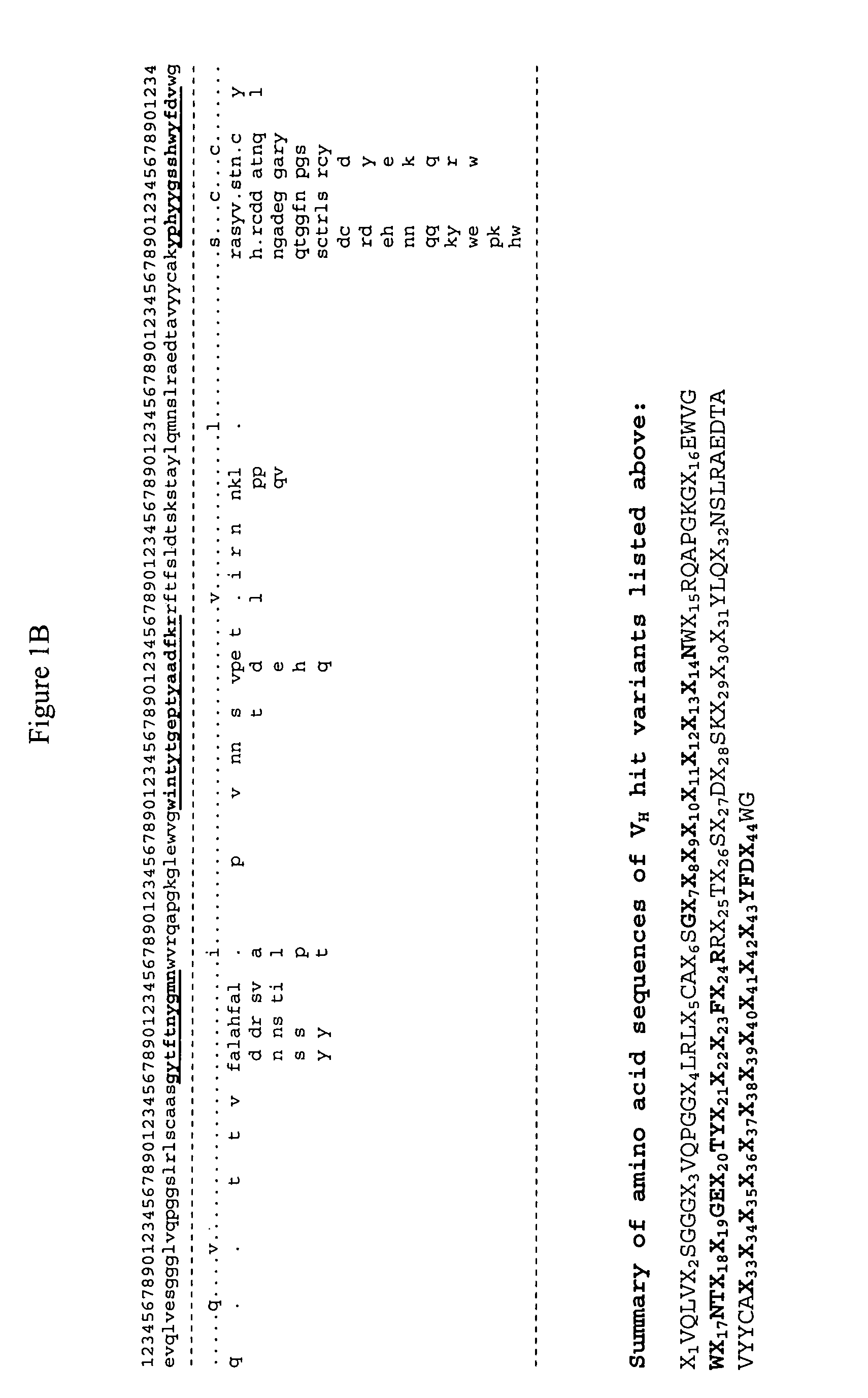
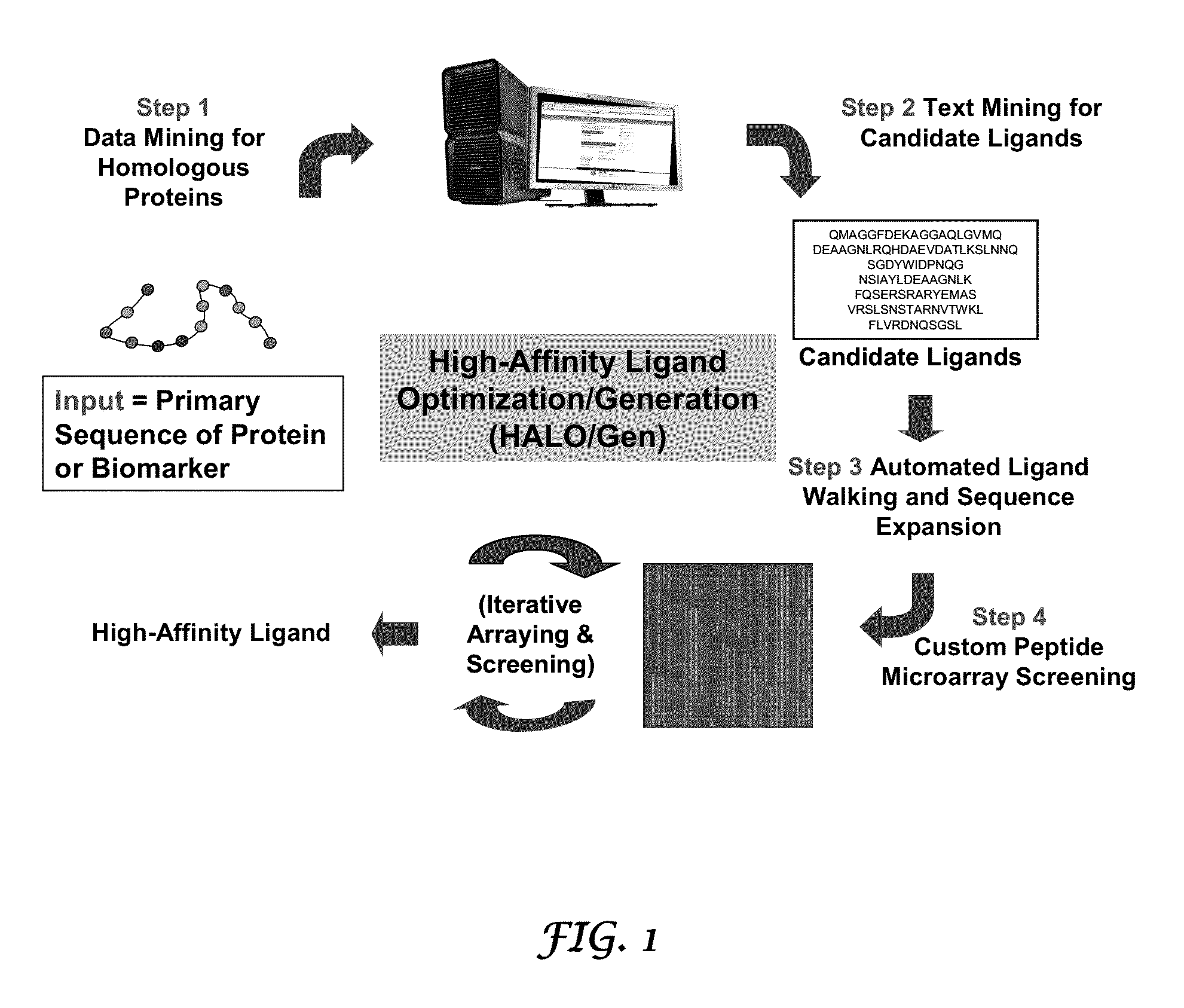
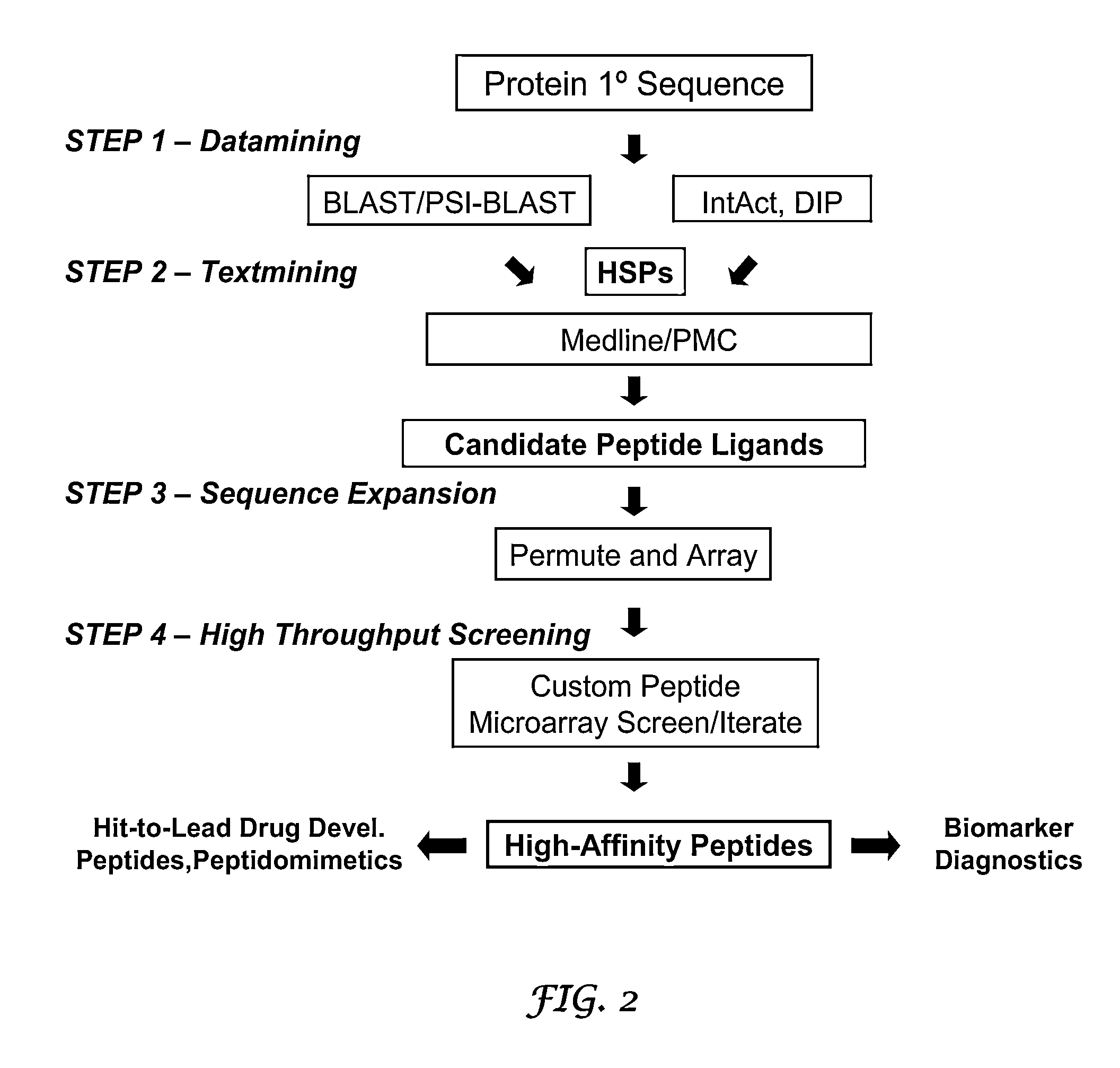
Methods and systems for the discovery of high-affinity peptide ligands and the resulting compositions are described herein. The amino acid sequence of a target protein is used to identify one or more homologous proteins of the target protein. Publications and databases are textmined to retrieve the sequences of peptide ligands that bind to the homologues or the target protein. Complementary proteins, which are proteins that bind to the target or homologous proteins or to DNA, and their target protein- or DNA-binding regions may also be identified. These candidate ligands are predicted to have a high probability of binding to the target protein or the DNA. The library of candidate peptide ligands is modulated by substituting native amino acid residues with suitable amino acids, thus increasing the explored protein space in a knowledge-based manner. Peptides designed in the modulation step are experimentally screened to identify high-affinity binding ligands, and further optimized through iterative application of the modulation and screening steps.
Owner:LYNNTECH
Antibodies against csf-1r
ActiveUS20110243947A1Prevent dimerizationInhibit tumor growthImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsDocetaxel-PNPDocetaxel
The invention provides a human antibody that binds human CSF-1R with high affinity. Antibodies of the present invention have significant advantages over the antibodies known in the art by being multifunctional: inhibiting signaling of CSF-1R, internalizing and inducing CSF-1R degradation and stimulating ADCC in cell including tumors, macrophages and monocytes. They are also shown to be effective in treating leukemia, breast, endometrial and prostate cancer alone or in combination with docetaxel, paclitaxel, Herceptin® or doxorubicin.
Owner:IMCLONE SYSTEMS
Compositions and methods for selective delivery of oligonucleotide molecules to specific neuron types
The invention provides a conjugate comprising (i) a nucleic acid which is complementary to a target nucleic acid sequence and which expression prevents or reduces expression of the target nucleic acid and (ii) a selectivity agent which is capable of binding with high affinity to a neurotransmitter transporter. The conjugates of the present invention are useful for the delivery of the nucleic acid to a cell of interests and thus, for the treatment of diseases which require a down-regulation of the protein encoded by the target nucleic acid as well as for the delivery of imaging agents to the cells for diagnostic purposes.
Owner:PALOMO LTD
Engineered antibody-stress protein fusions
ActiveUS7749501B2Inexpensively fused to a stress proteinHigh affinityAntipyreticAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEscherichia coliMHC class I
Provided are fusion polypeptides comprising an engineered antibody and a stress protein that bind to antigens with high affinity, are highly immunogenic, exhibit MHC class I priming and are able to be produced in non-mammalian cells, such as E. coli.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Peptide-based hair protectants
Peptide-based hair protectants, formed by coupling at least one hair-binding peptide with at least one sunscreen agent, are described. The hair-binding peptide portion of the peptide-based hair protectant binds to hair with high affinity, thus keeping the sunscreen agent attached to the hair for long lasting protection. Hair care compositions comprising the peptide-based hair protectants are also described.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Bispecific binding agents for modulating biological activity
InactiveUS20090181022A1Reduced activityModulating biological activityPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsSurface markerLow affinity
Methods for improving the biological and pharmaceutical properties of bispecific binding agents are described herein where the bispecific binding agent are able to target cells by a high affinity binding domain to a first cell surface marker that does not induce a significant biological effect and a low affinity binding domain that binds specifically to a second cell surface marker, causing a significant and desired biological effect. Compositions of such bispecific binding agents, uses for them, and kits containing them are also provided.
Owner:MERRIMACK PHARMACEUTICALS INC
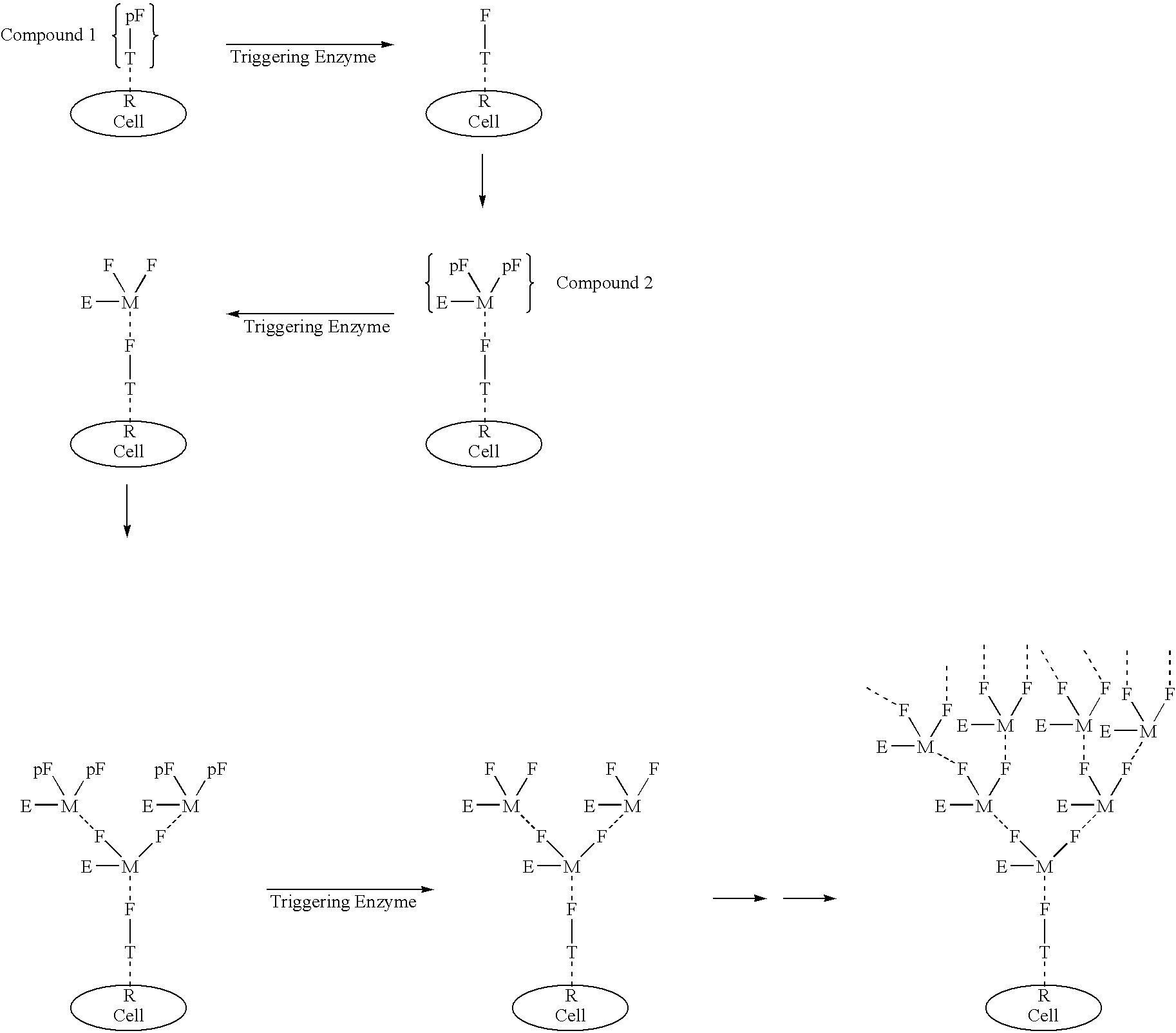
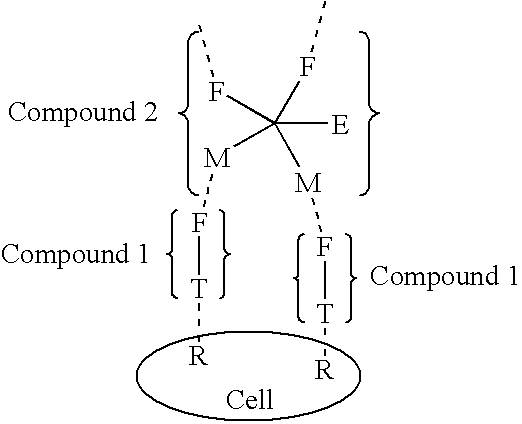
Exponential pattern recognition based cellular targeting compositions, methods and anticancer applications
InactiveUS20070172422A1Saccharide peptide ingredientsProtease inhibitorsCell bindingCellular targeting
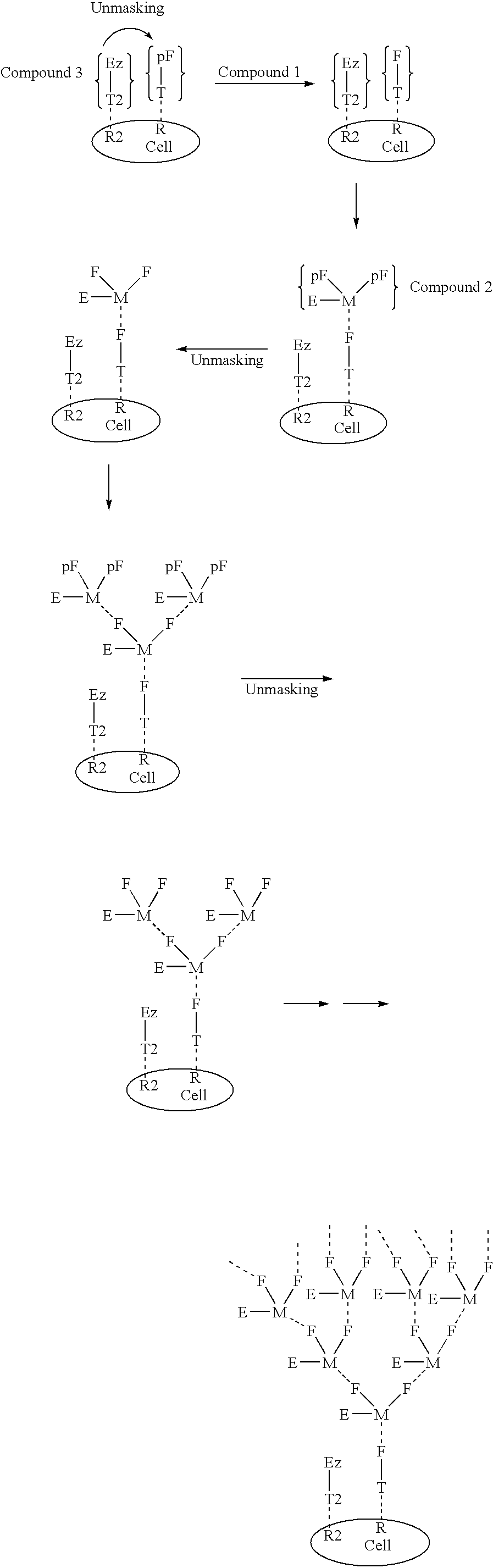
The present invention relates to the compositions, methods, and applications of a new approach to pattern recognition based targeting by which an exponential amplification of effector response can be specifically obtained at a targeted cells. The purpose of this invention is to enable the selective delivery of large quantities of an array of effector molecules to target cells for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. The invention is comprised of two components designated as “Compound 1” and “Compound 2”: Compound 1 is comprised of a cell binding agent and a masked female adaptor. Compound 2 is comprised of a male ligand, an effector agent, and two or more masked female receptors. The male ligand is selected to bind with high affinity to the female adaptor. Compound 1 can bind with high affinity to the target cell and the female receptor can then be unmasked by an enzyme enriched at the tumor cell. The male ligand of Compound 2 can then bind to the unmasked female adaptor bound to the target cell. The masked female adaptor on the bound Compound 2 can then be specifically unmasked. One receptor has in effect become two. Two new molecules of Compound 2 can bind to the unmasked adaptors receptors. After unmasking two receptors in effect become four. The process can continue in an explosive exponential like fashion resulting in enormous amplification of the number of effector molecules specifically deposited at the target cell.
Owner:GLAZIER ARNOLD
Anti-myostatin antibodies
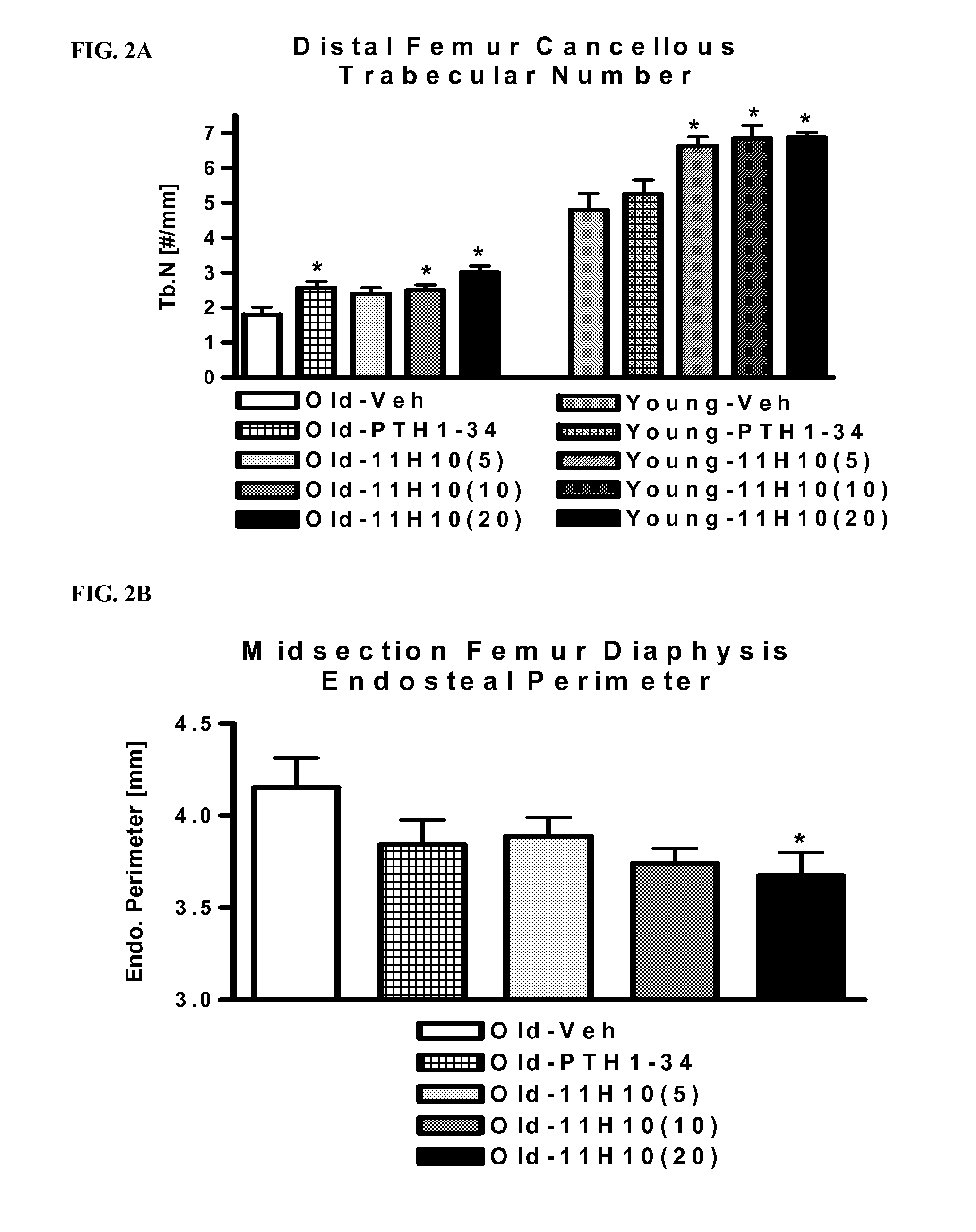
A neutralizing epitope is identified within amino acids 40-64 of the mature form of human myostatin. Antibodies that bind this epitope with high affinity preferentially bind GDF-8 over GDF-11 and may be chimeric, humanized or fully human antibodies, immunoconjugates of the antibodies or antigen-binding fragments thereof. The antibodies of the invention are useful for increasing muscle mass, increasing bone density, or for the treatment of various disorders in mammalian and avian species.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Bispecific nanobodies
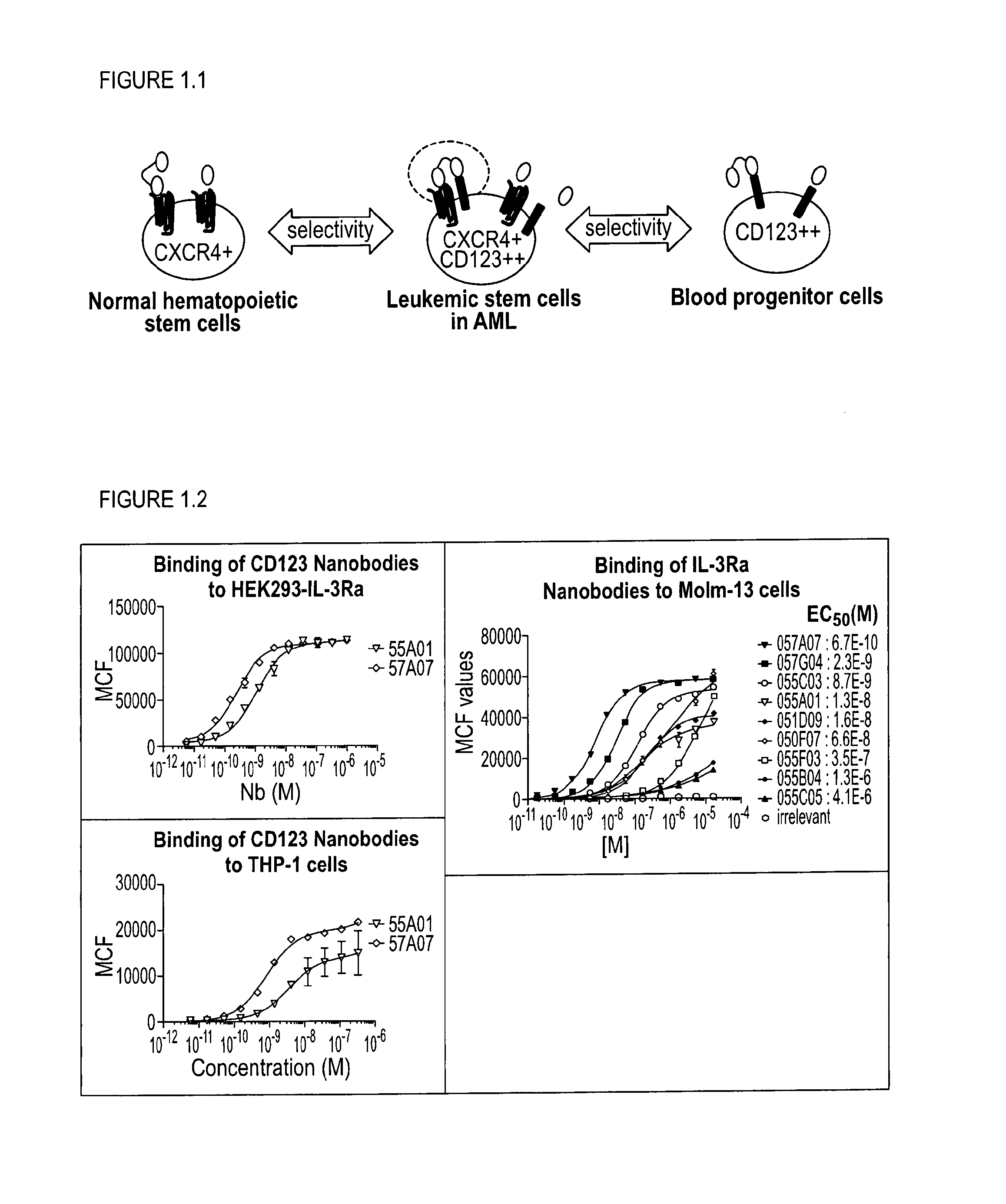
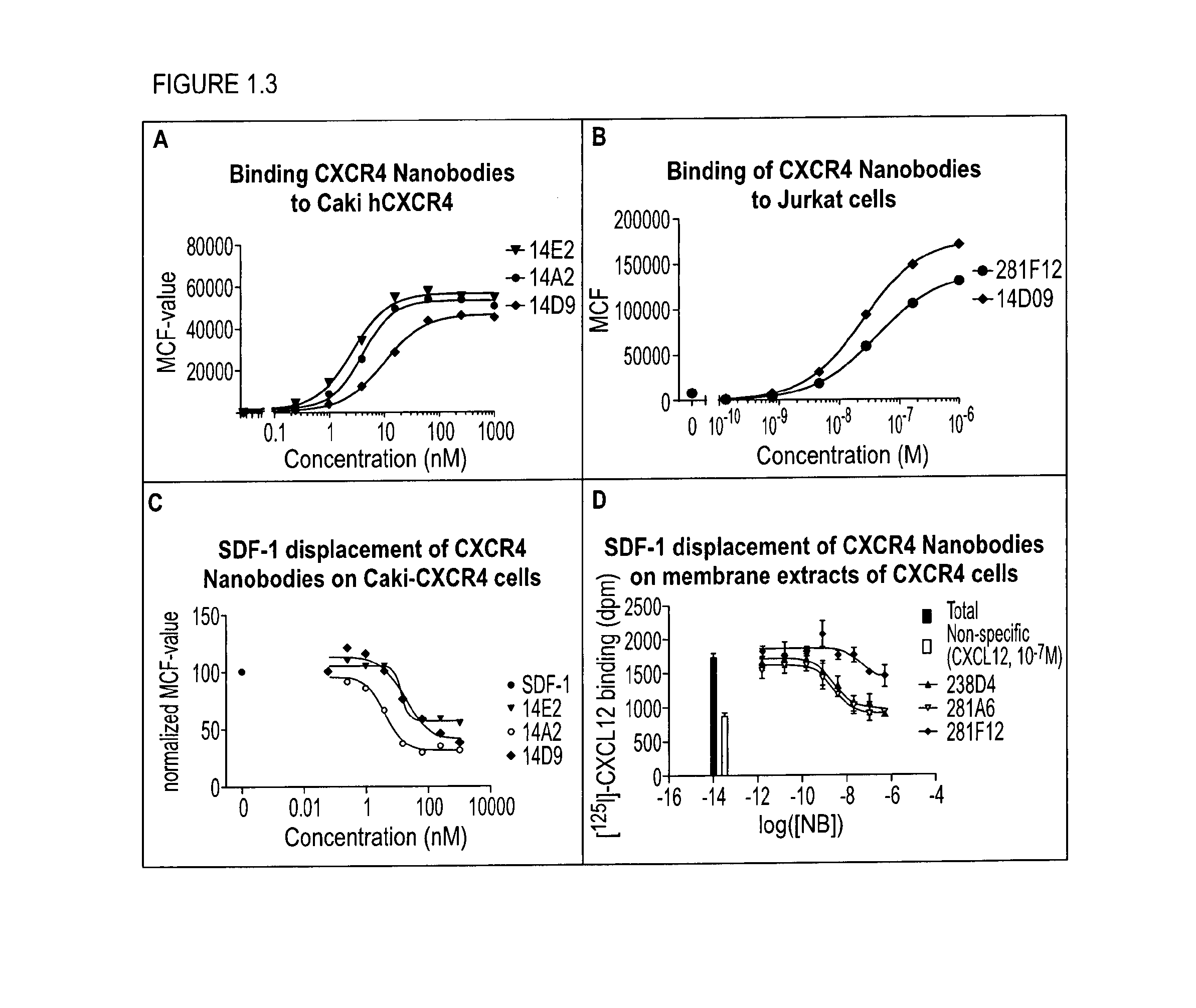
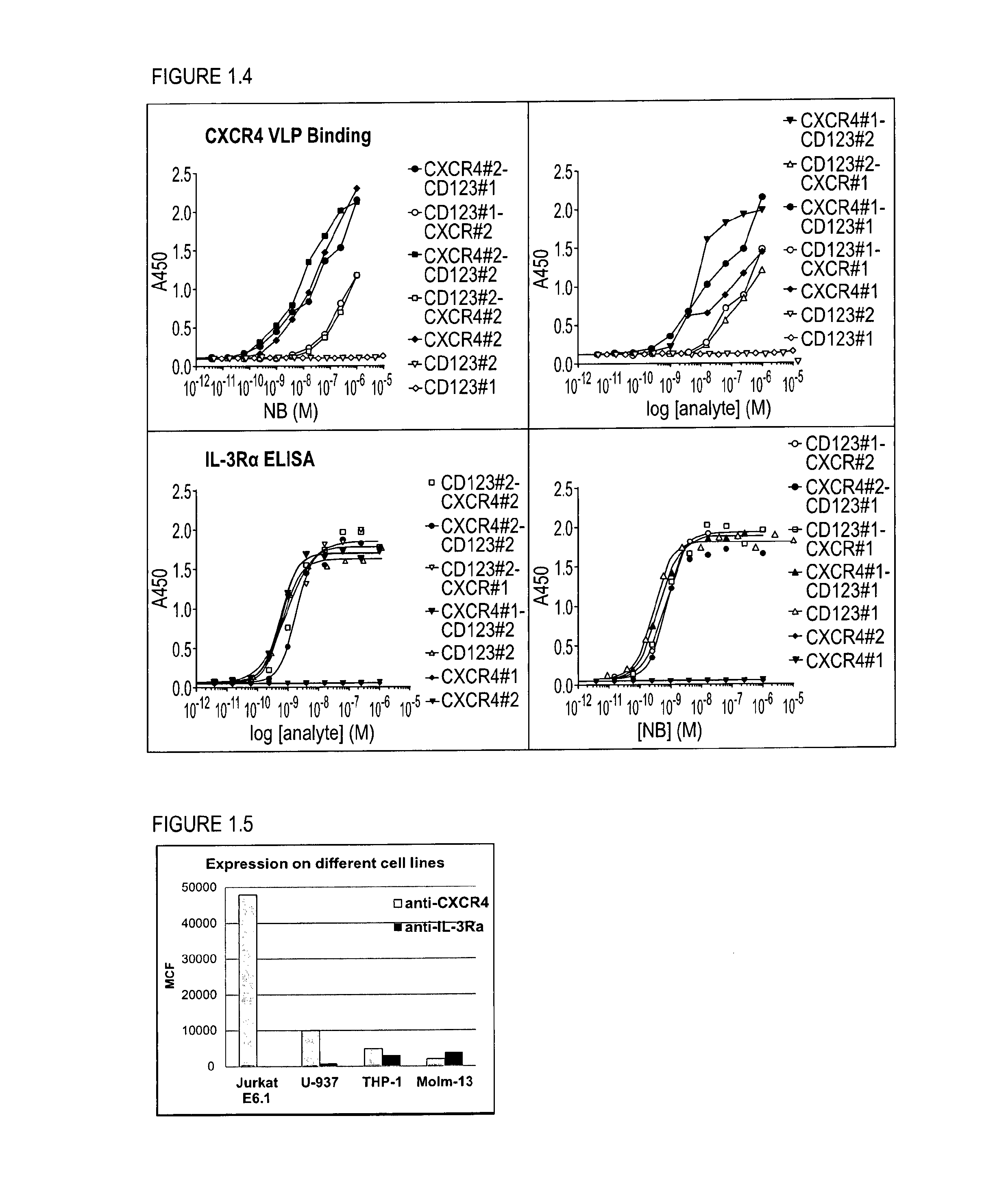
InactiveUS20160251440A1Avoid infectionEasy to neutralizeImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntineoplastic agentsLow affinityCancer cell
The present disclosure relates to bispecific polypeptides comprising a first and a second immunoglobulin single variable domain (ISV), wherein said first ISV binds to a first target on the surface of a cancer cell with a low affinity and, when bound inhibits a function of said first target, and a said second ISV binds to a second target on the surface of said cell with a high affinity and wherein said first target is different from said second target. The present invention further discloses methods for identifying and making the same.
Owner:ABLYNX NV
Treatment methods using dkk-1 antibodies
The present invention provides antibodies and immunologically functional fragments thereof that specifically bind Dkk-1 polypeptides. The subject antibodies and fragments bind with high affinity to a conformational epitope located in the carboxy region of the Dkk-1 protein. Methods for preparing such antibodies or fragments thereof as well as physiologically acceptable compositions containing the antibodies or fragments are also provided. Use of the antibodies and fragments to treat various diseases including bone disorders, inflammatory diseases, neurological diseases, ocular diseases, renal diseases, pulmonary diseases and skin diseases are also disclosed.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Optimization of antibodies that bind lymphocyte activation gene-3 (lag-3), and uses thereof
InactiveUS20150307609A1Improve stabilityHigh binding affinitySugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsLymphocyteLymphocyte activation
The present invention provides isolated monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind LAG-3, and have optimized functional properties compared to previously described anti-LAG-3 antibodies, such as antibody 25F7 (US 2011 / 0150892 A1). These properties include reduced deamidation sites, while still retaining high affinity binding to human LAG-3, and physical (i.e., thermal and chemical) stability. Nucleic acid molecules encoding the antibodies of the invention, expression vectors, host cells and methods for expressing the antibodies of the invention are also provided, as well as immunoconjugates, bispecific molecules and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies. The present invention also provides methods for detecting LAG-3, as well as methods for treating stimulating immune responses using an anti-LAG-3 antibody of the invention. Combination therapy, in which the antibodies are co-administered with at least one additional immunostimulatory antibody, is also provided.
Owner:MEDAREX INC
Single domain antibodies against tnfr1 and methods of use therefor
InactiveUS20080008713A1Reduce riskReduce usageAnimal cellsSugar derivativesHigh concentrationVariable domain
Provided are concentrated preparations comprising single immunoglobulin variable domain polypeptides that bind target antigen with high affinity and are soluble at high concentration, without aggregation or precipitation, providing, for example, for increased storage stability and the ability to administer higher therapeutic doses.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
Bispecific binding agents for modulating biological activity
InactiveUS8124085B2Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsSurface markerLow affinity
Methods for improving the biological and pharmaceutical properties of bispecific binding agents are described herein where the bispecific binding agent are able to target cells by a high affinity binding domain to a first cell surface marker that does not induce a significant biological effect and a low affinity binding domain that binds specifically to a second cell surface marker, causing a significant and desired biological effect. Compositions of such bispecific binding agents, uses for them, and kits containing them are also provided.
Owner:MERRIMACK PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Immunoglobulin fc libraries
ActiveUS20090136936A1Improve binding capabilitySugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFc receptorChemistry
Methods and composition for the screening and isolation of aglycosylated antibody Fc domain polypeptides. For example, in certain aspects methods for identifying aglycosylated Fc domains that bind to Fc receptors or preferentially bind to particular Fc receptors are described. Furthermore, the invention provides aglycosylated Fc domains that bind to Fc receptors with high affinity. Enhanced methods and media for prokaryotic based interaction screening are also provided.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
NMR-solve method for rapid identification of bi-ligand drug candidates
Methods for rapidly identifying drug candidates that bind to an enzyme at both a common ligand site and a specificity ligand site, resulting in high affinity binding. The bi-ligand drug candidates are screened from a focused combinatorial library where the specific points of variation on a core structure are optimized. The optimal points of variation are identified by which atoms of a ligand bound to the common ligand site are identified to be proximal to the specificity ligand site. As a result, the atoms proximal to the specificity ligand site can then be used as a point for variation to generate a focused combinatorial library of high affinity drug candidates that bind to both the common ligand site and the specificity ligand site. Different candidates in the library can then have high affinity for many related enzymes sharing a similar common ligand site.
Owner:TRIAD BIOTECH
2-Substituted imidazo[1,2-A]pyridine derivatives
Disclosed are compounds of the formula: and the pharmaceutically acceptable salts, prodrugs and solvates thereof, wherein X, A, B, C, D and W are defined herein, which compounds bind with high selectivity and high affinity to the benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptors and are therefore useful in the treatment of certain central nervous system (CNS) diseases and as probes for the localization of GABAA receptors in tissue samples.
Owner:NEUROGEN
Receptor(SSTR4)-selective somatostatin analogs
Analogs of SRIF which are selective for SSTR4 in contrast to the other cloned SRIF receptors are useful in determining tissue and cellular expression of the receptor SSTR4 and its biological role in regulating tumor growth. SRIF analog peptides, such as des-AA1,2,4,5,12,13[Ala7]-SRIF; des-AA1,2,4,5,12,13[Aph7]-SRIF, des-AA1,2,4,5,12,13[Aph7]Cbm-SRIF; des-AA1,2,4,5,12,13[Tyr2,Ala7]-Cbm-SRIF, and des-AA1,2,4,5,12,13[Tyr7,CβMe-L-2Nal8]-SRIF, and counterparts incorporating D-Cys3 and / or D-Trp8 and / or Ala11, bind with high affinity to the cloned human receptor SSTR4 and activate the receptor, but they do not bind with significant affinity to human SSTR1, SSTR2, SSTR3 or SSTR5. By incorporating an iodinated tyrosine in position-2 in these SSTR4-selective SRIF analogs, a labeled compound useful in drug-screening methods is provided. Alternatively, for use in therapy, cytotoxins or highly radioactive elements can be N-terminally coupled or complexed thereto.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com











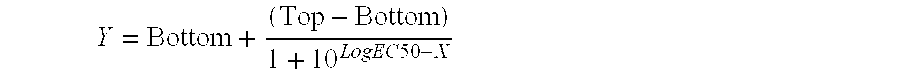







![2-Substituted imidazo[1,2-A]pyridine derivatives 2-Substituted imidazo[1,2-A]pyridine derivatives](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/a616360a-75ae-4ab3-89a9-9271927c371d/US20020032200A1-20020314-C00001.png)
![2-Substituted imidazo[1,2-A]pyridine derivatives 2-Substituted imidazo[1,2-A]pyridine derivatives](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/a616360a-75ae-4ab3-89a9-9271927c371d/US20020032200A1-20020314-C00002.png)
![2-Substituted imidazo[1,2-A]pyridine derivatives 2-Substituted imidazo[1,2-A]pyridine derivatives](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/a616360a-75ae-4ab3-89a9-9271927c371d/US20020032200A1-20020314-C00003.png)