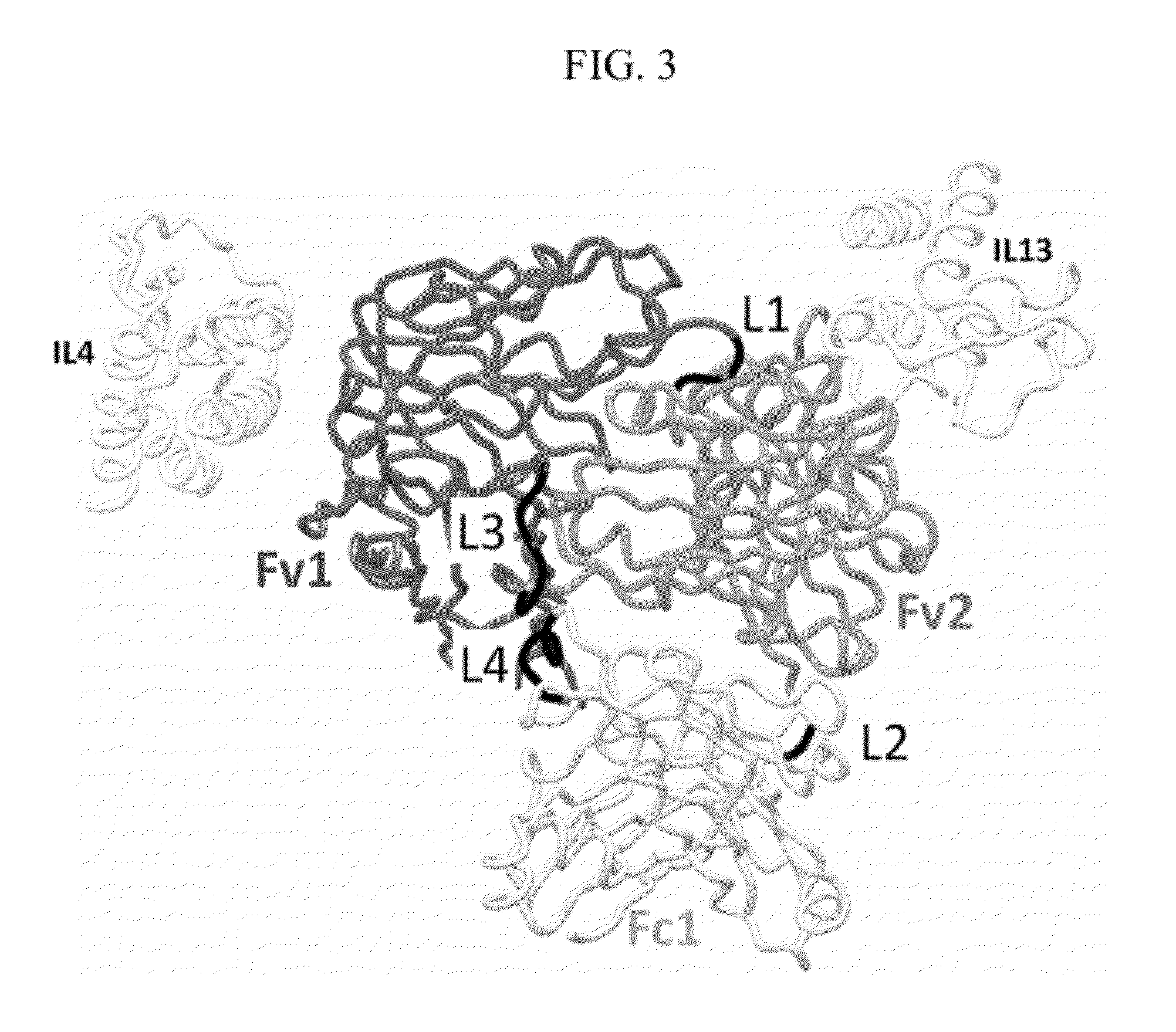
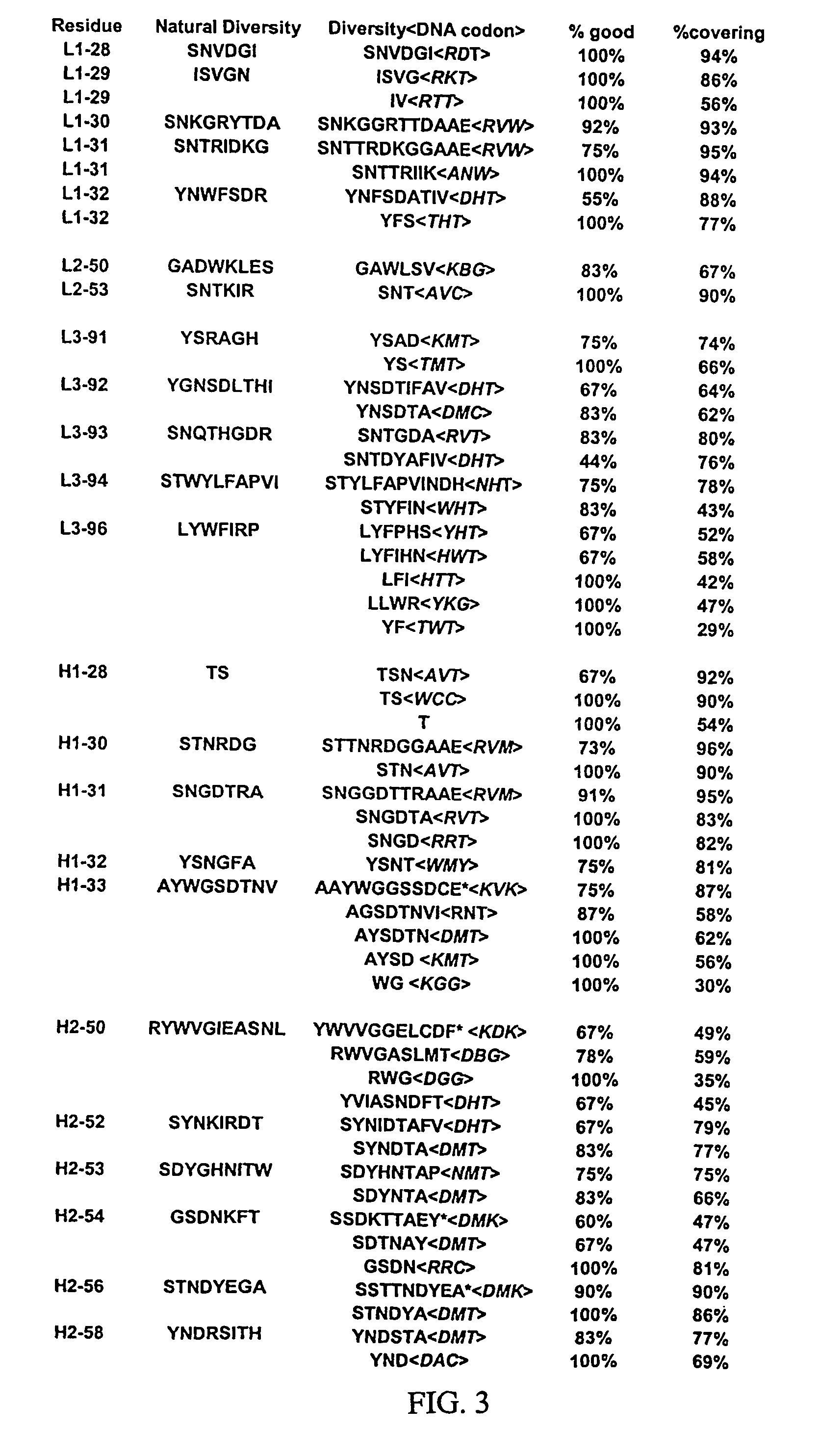
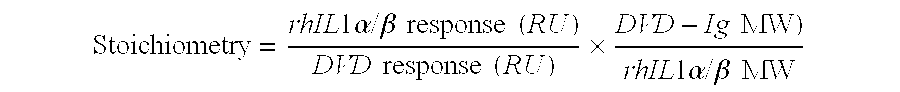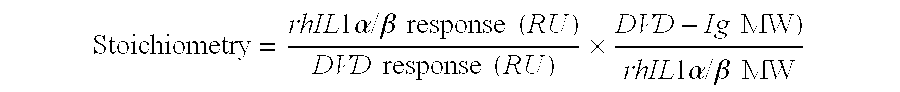Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
297 results about "Variable domain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The domain of a variable is a set of values that the variable can assume (take). Example: Solve the equation x+5(x+2) = 22, given that the domain of the variable is {1,2,3,....}. Solution: From the above table we observe that when x=2, L.H.S=R.H.S.
Binding polypeptides with optimized scaffolds
InactiveUS20070292936A1Improve folding stabilityImprove stabilitySugar derivativesMicroorganismsVariable domainChemistry
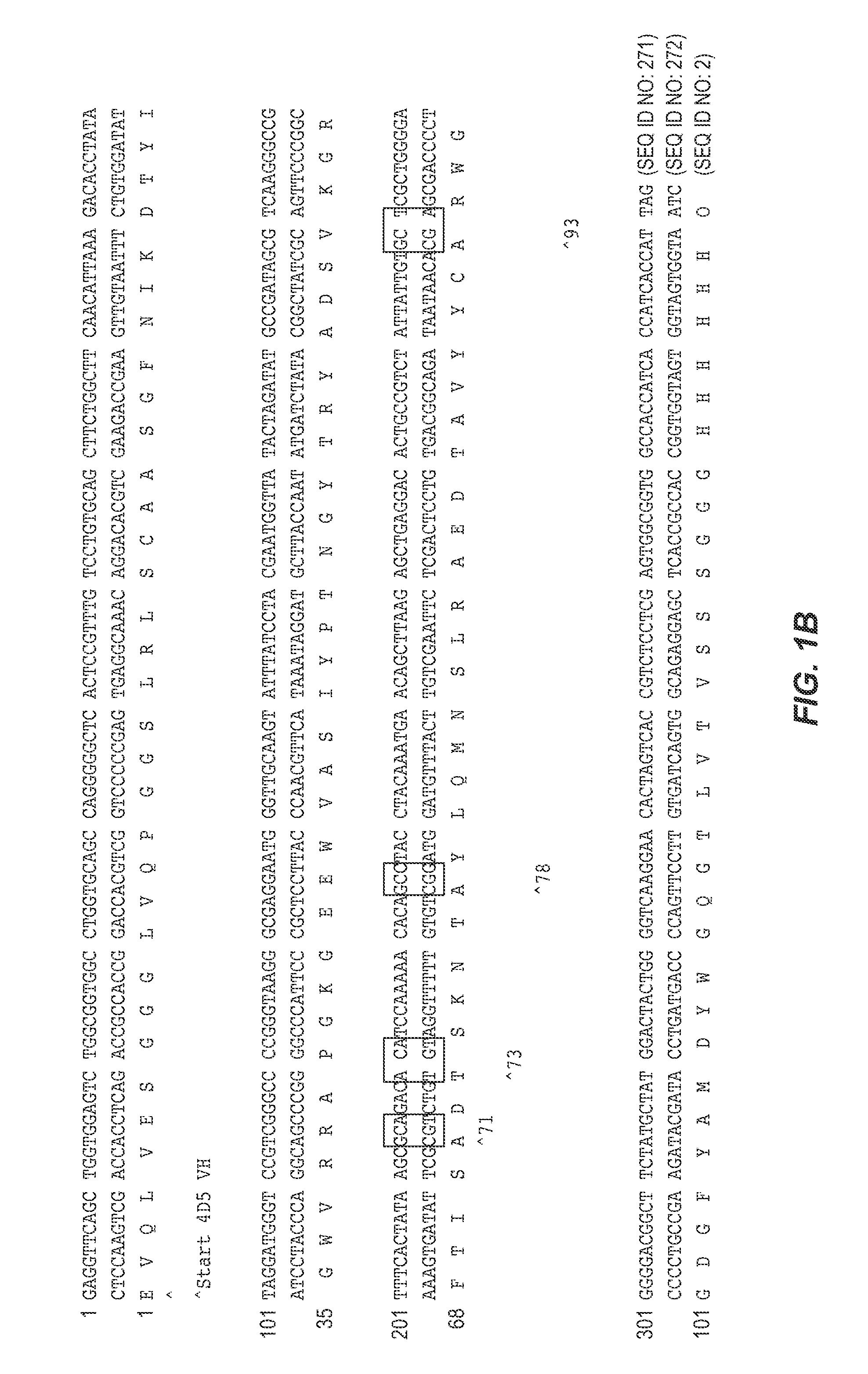
The invention provides variant heavy chain variable domains (VH) with increased folding stability. Libraries comprising a plurality of these polypeptides are also provided. In addition, compositions and methods of generating and using these polypeptides and libraries are provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Variable domain library and uses
ActiveUS20050266000A1Generate efficientlyQuality improvementImmunoglobulins against growth factorsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsComplementarity determining regionAntigen binding
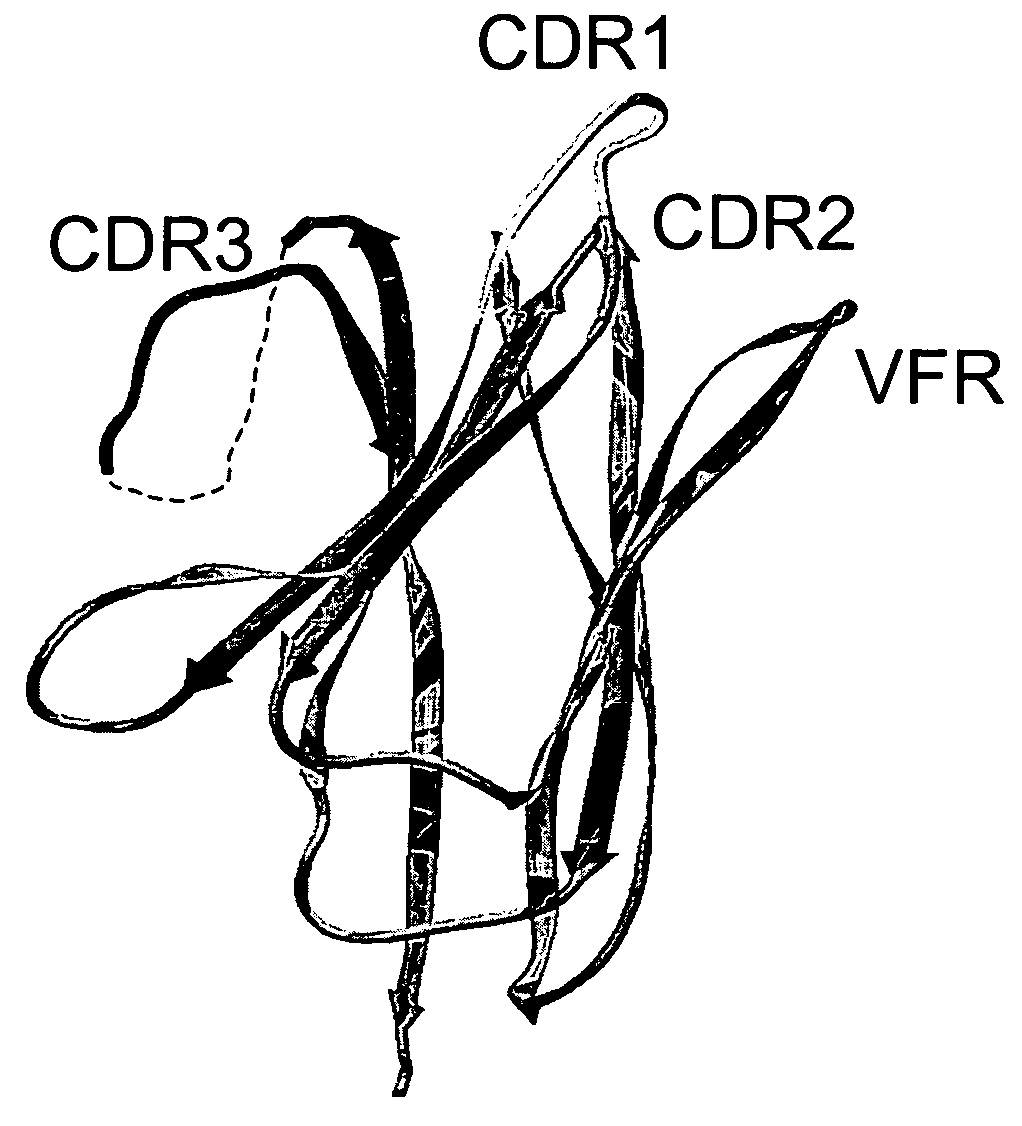
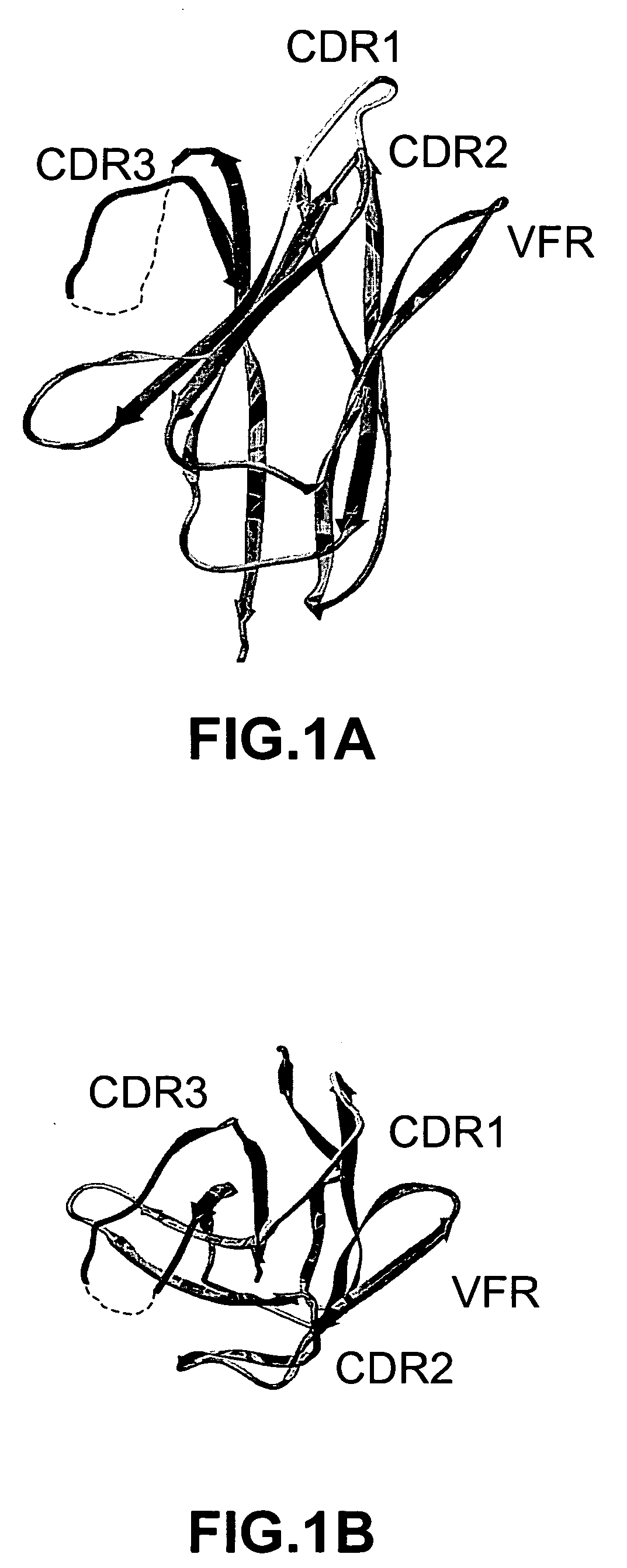
The invention provides polypeptides comprising a variant heavy chain variable framework domain (VFR). In some embodiments, the amino acids defining the VFR form a loop of an antigen binding pocket. In an embodiment, the polypeptide is a variable domain of a monobody and has a variant VFR. The polypeptide may optionally comprise one or more complementary determining regions (CDRs) of antibody variable domains. In an embodiment, the polypeptide is a variable domain of a monobody and has a variant VFR and one or more variant CDRs. Libraries of polypeptides that include a plurality of different antibody variable domains generated by creating diversity in a VFR, and optionally, one or more CDRs are provided and may be used as a source for identifying novel antigen binding polypeptides that can be used therapeutically or as reagents. The invention also provides fusion polypeptides, compositions, and methods for generating and using the polypeptides and libraries.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
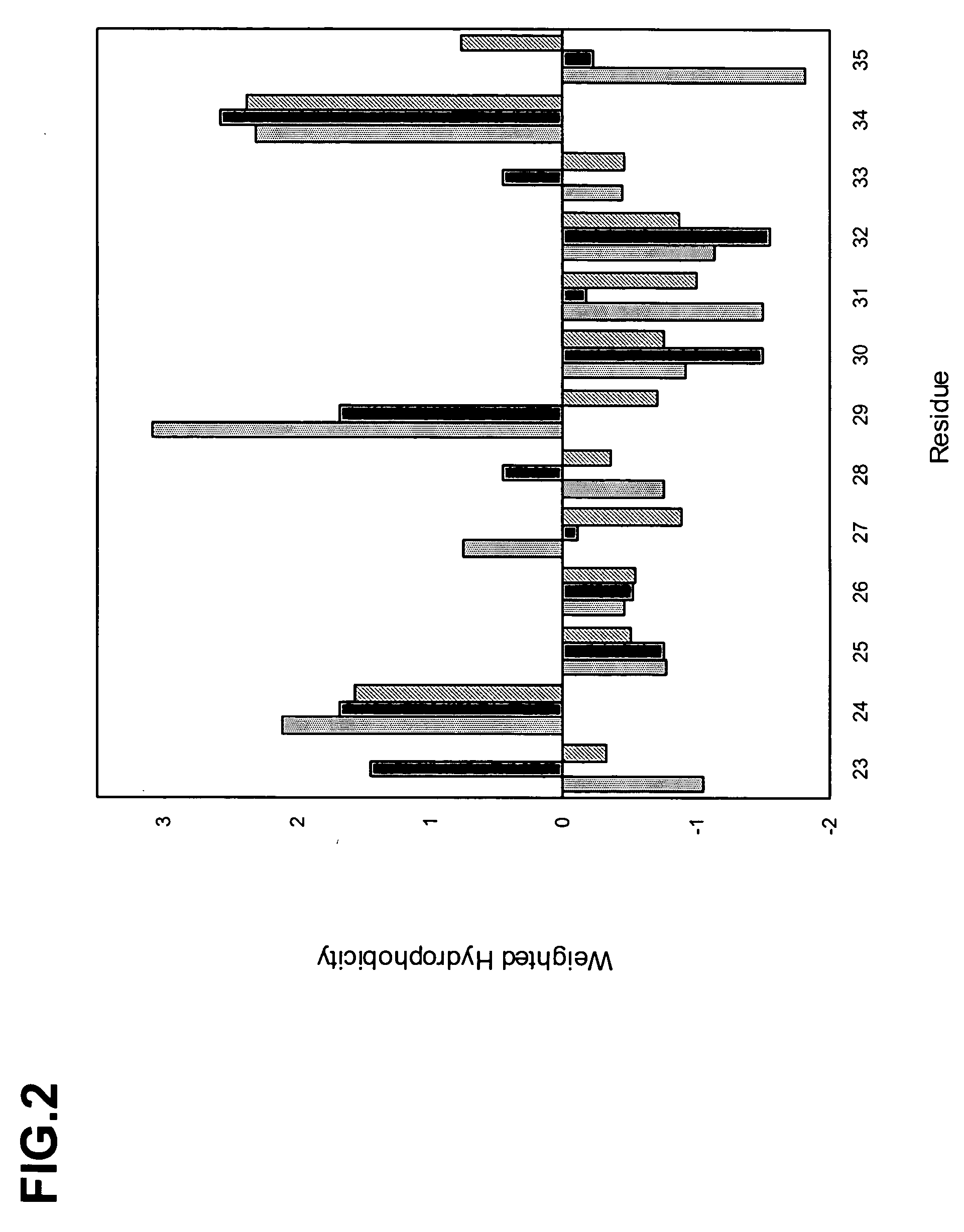
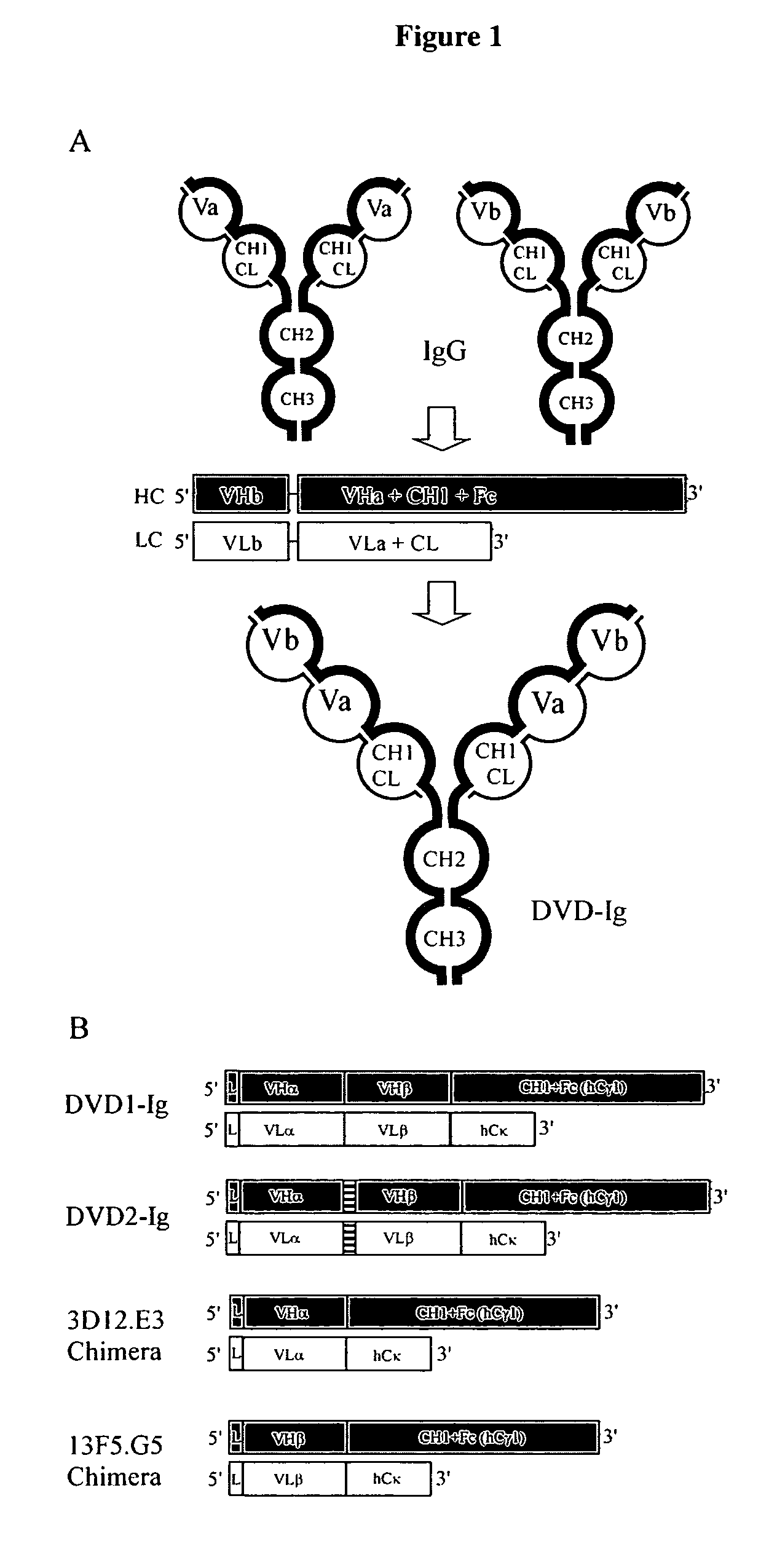
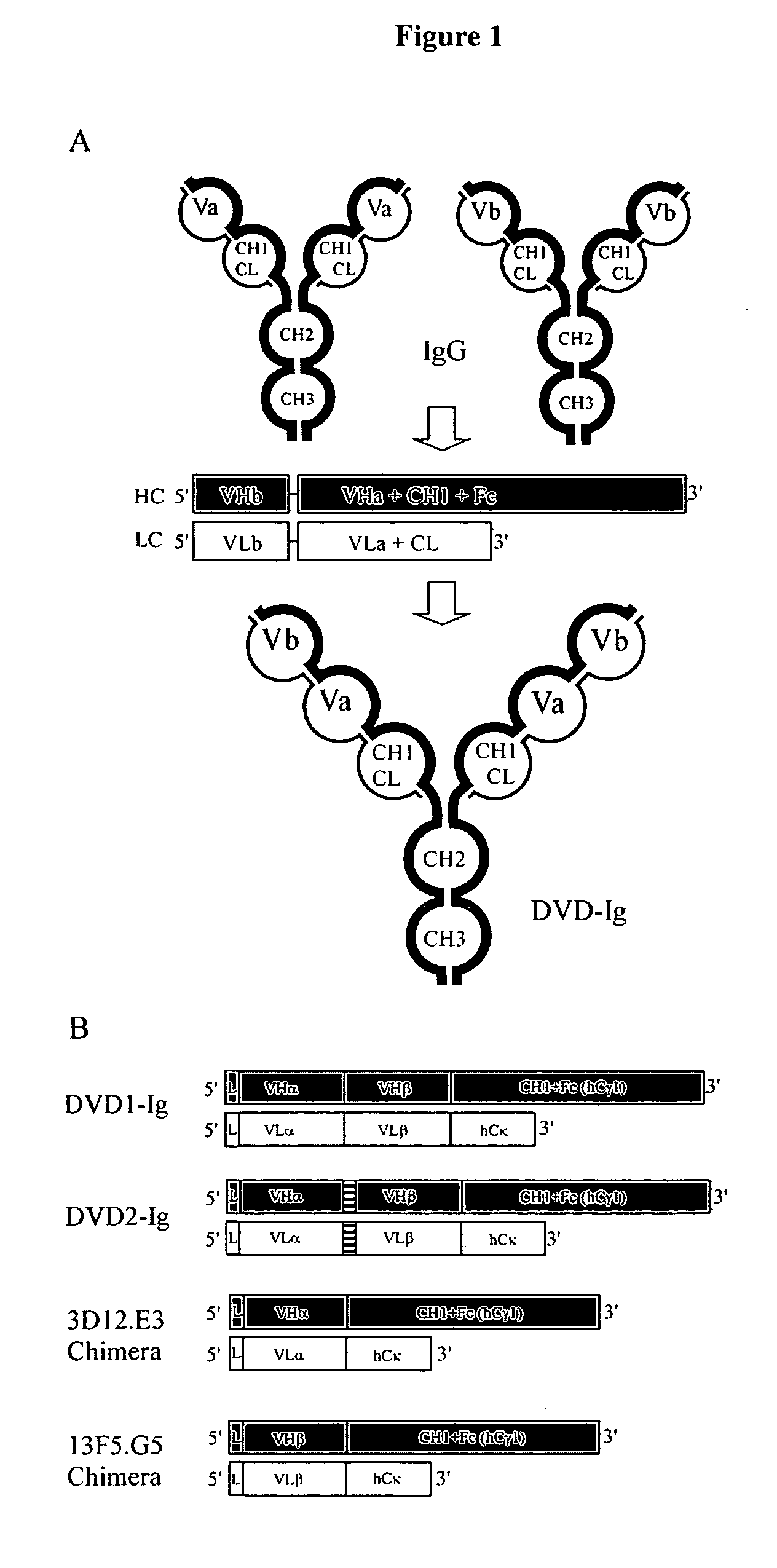
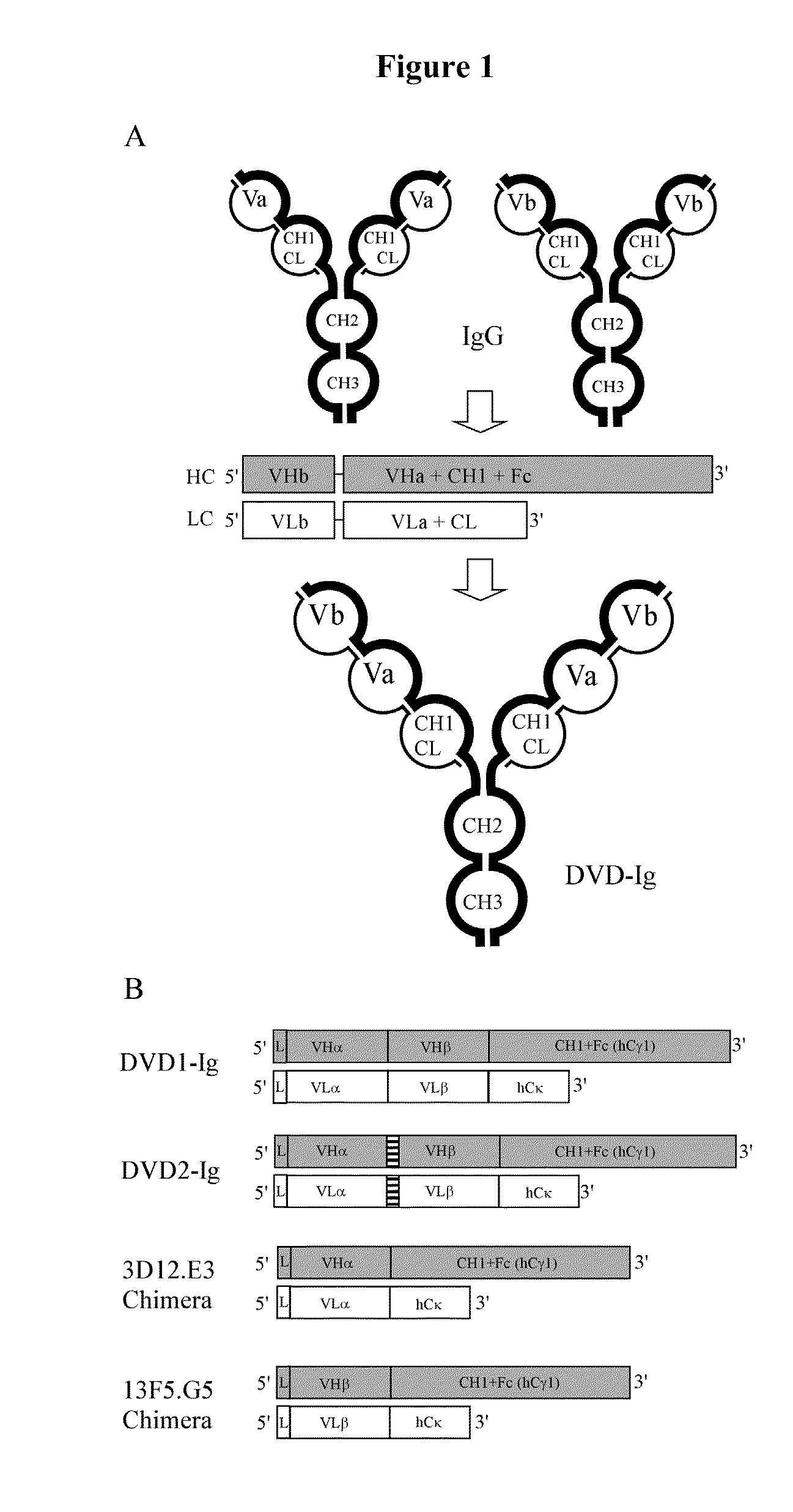
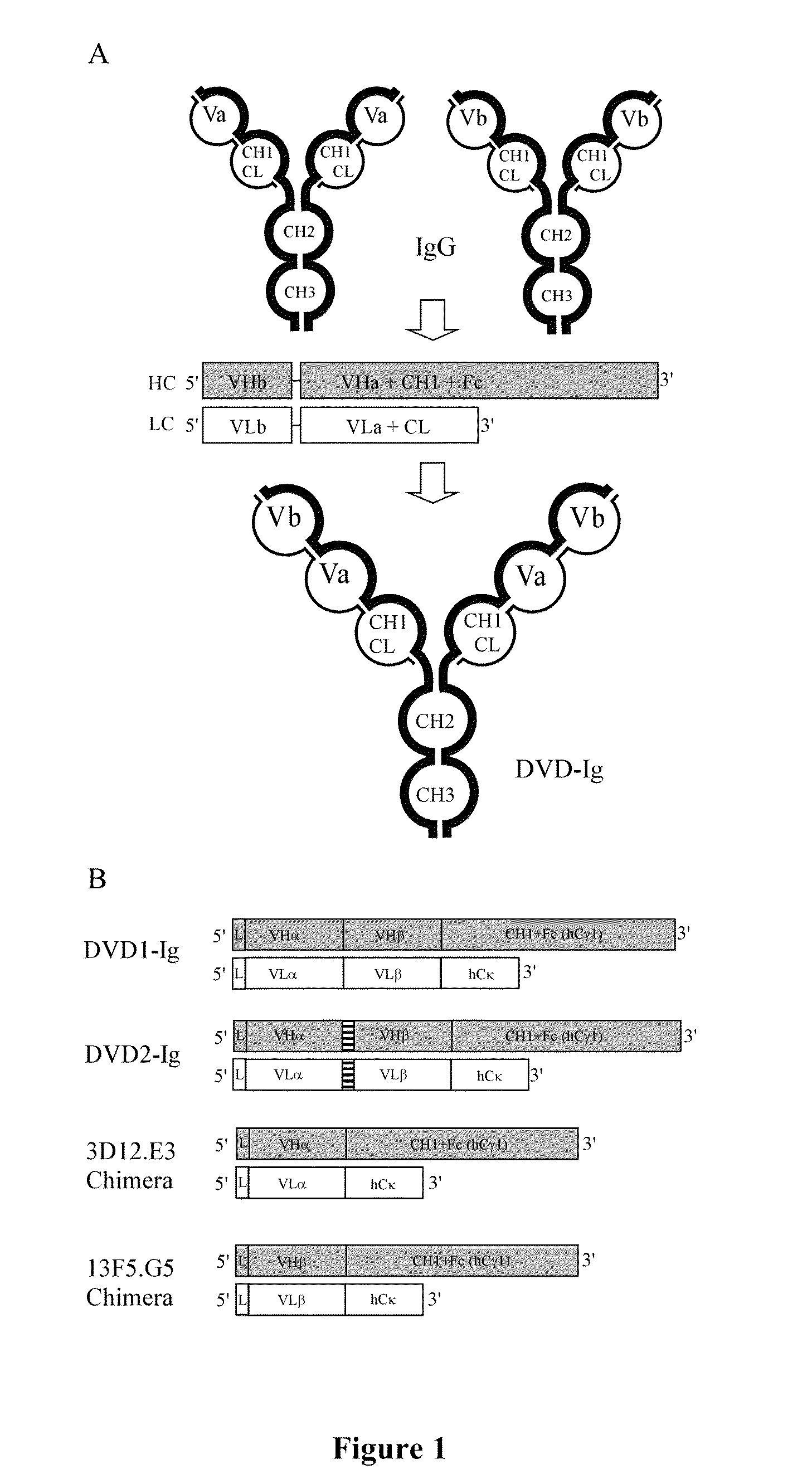
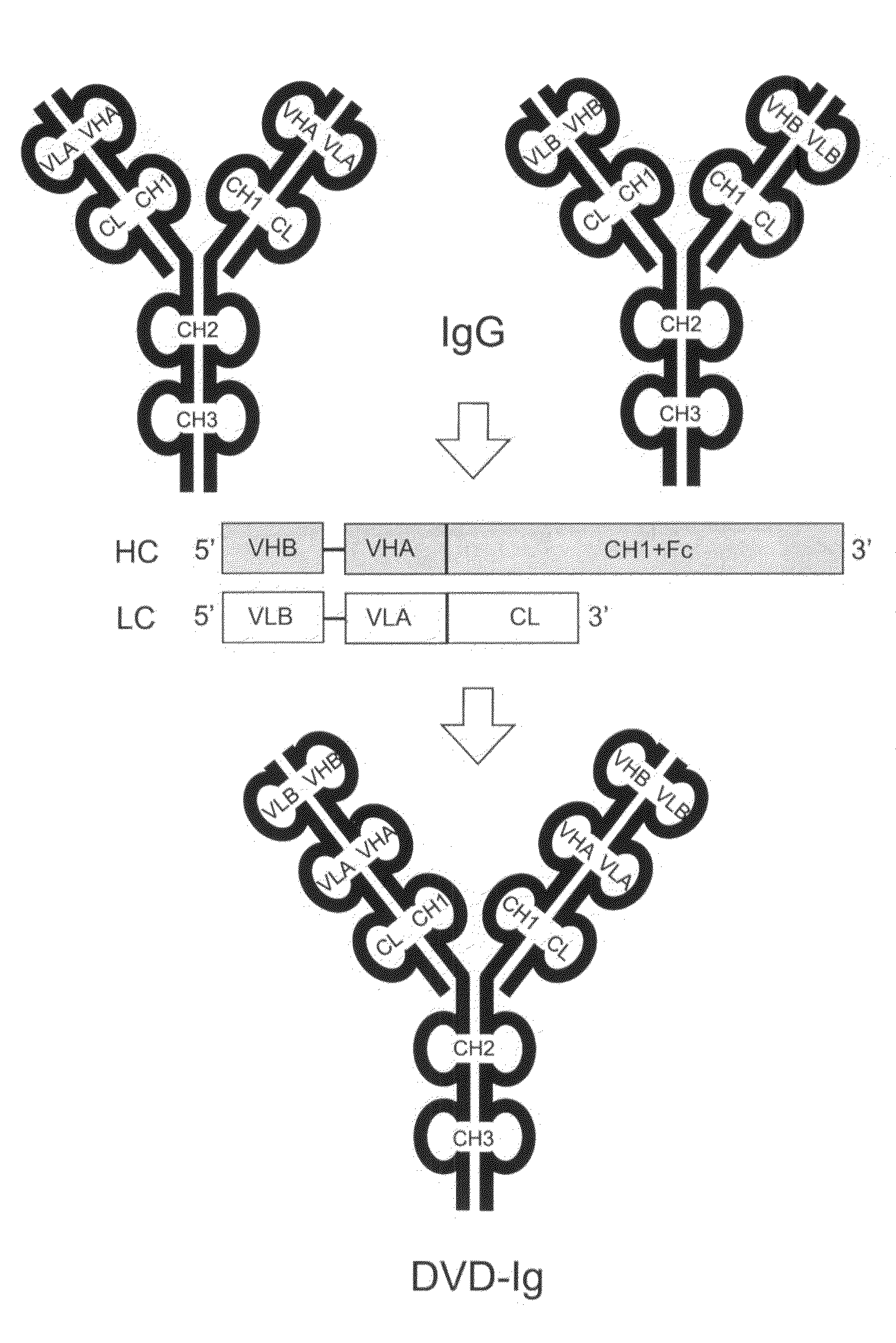
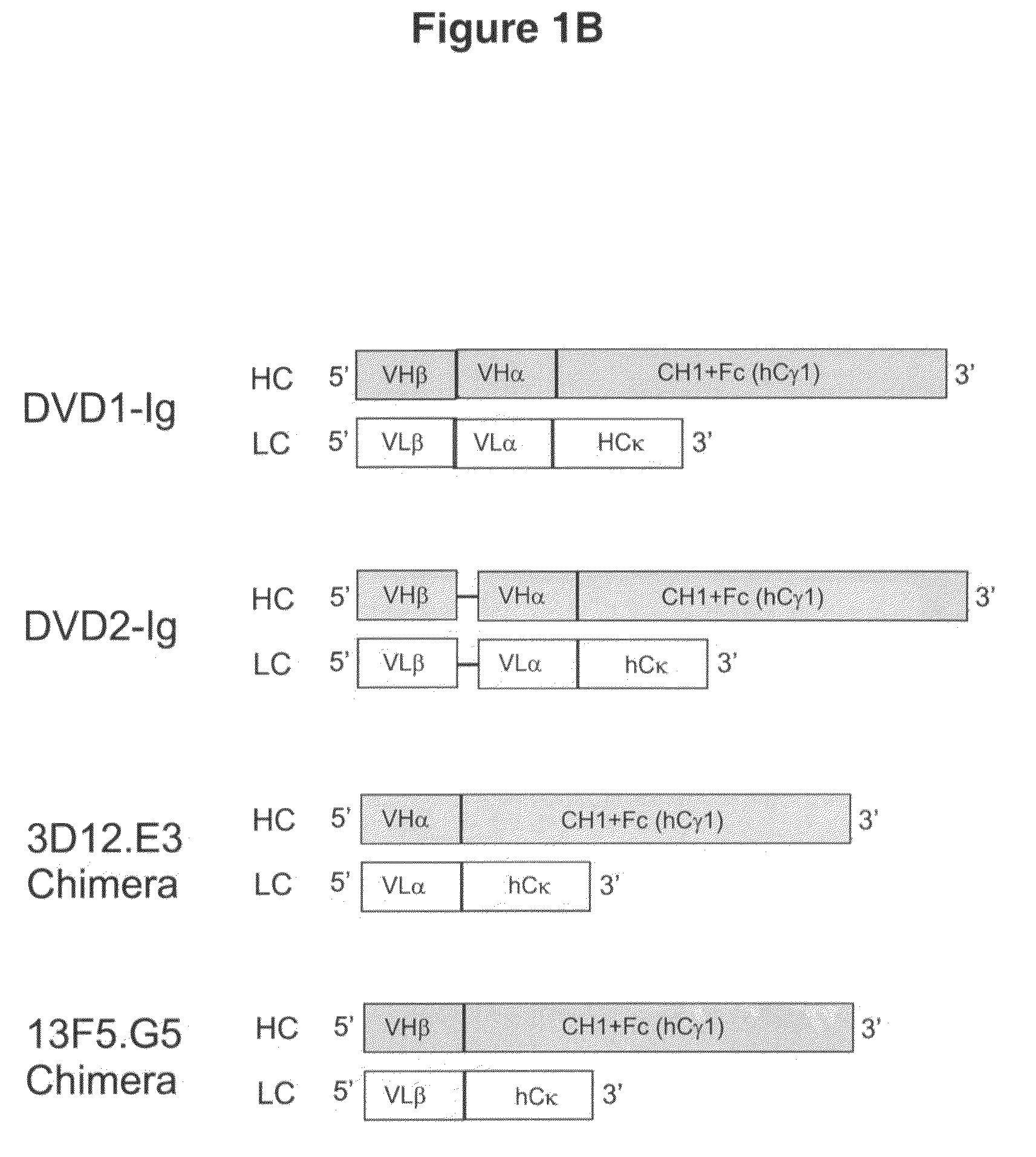
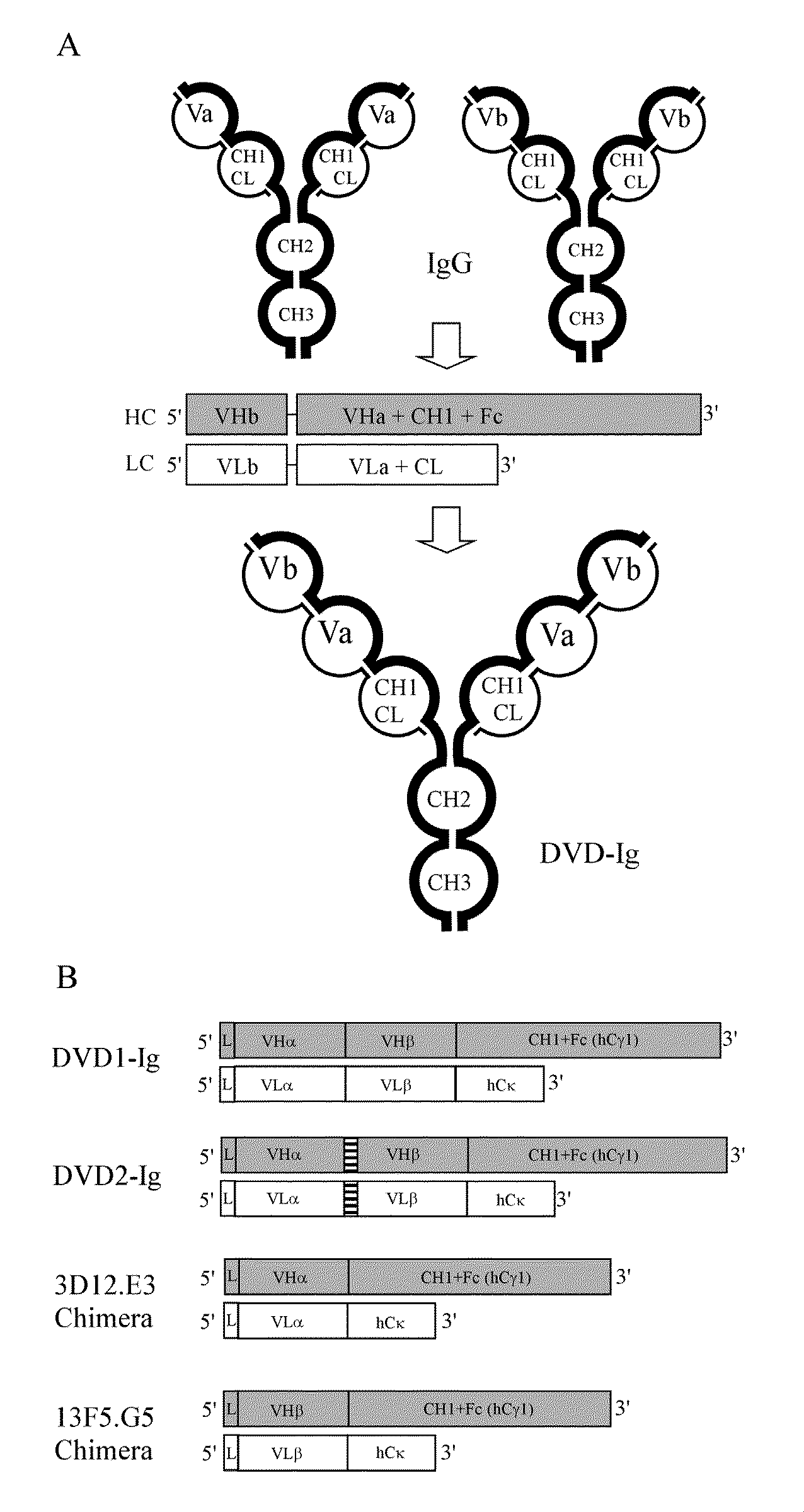
Dual variable domain immunoglobulin and uses thereof
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Dual variable domain immunoglobulin and uses thereof
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Multivalent antibody constructs
InactiveUS7129330B1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsVariable domainPlasmid
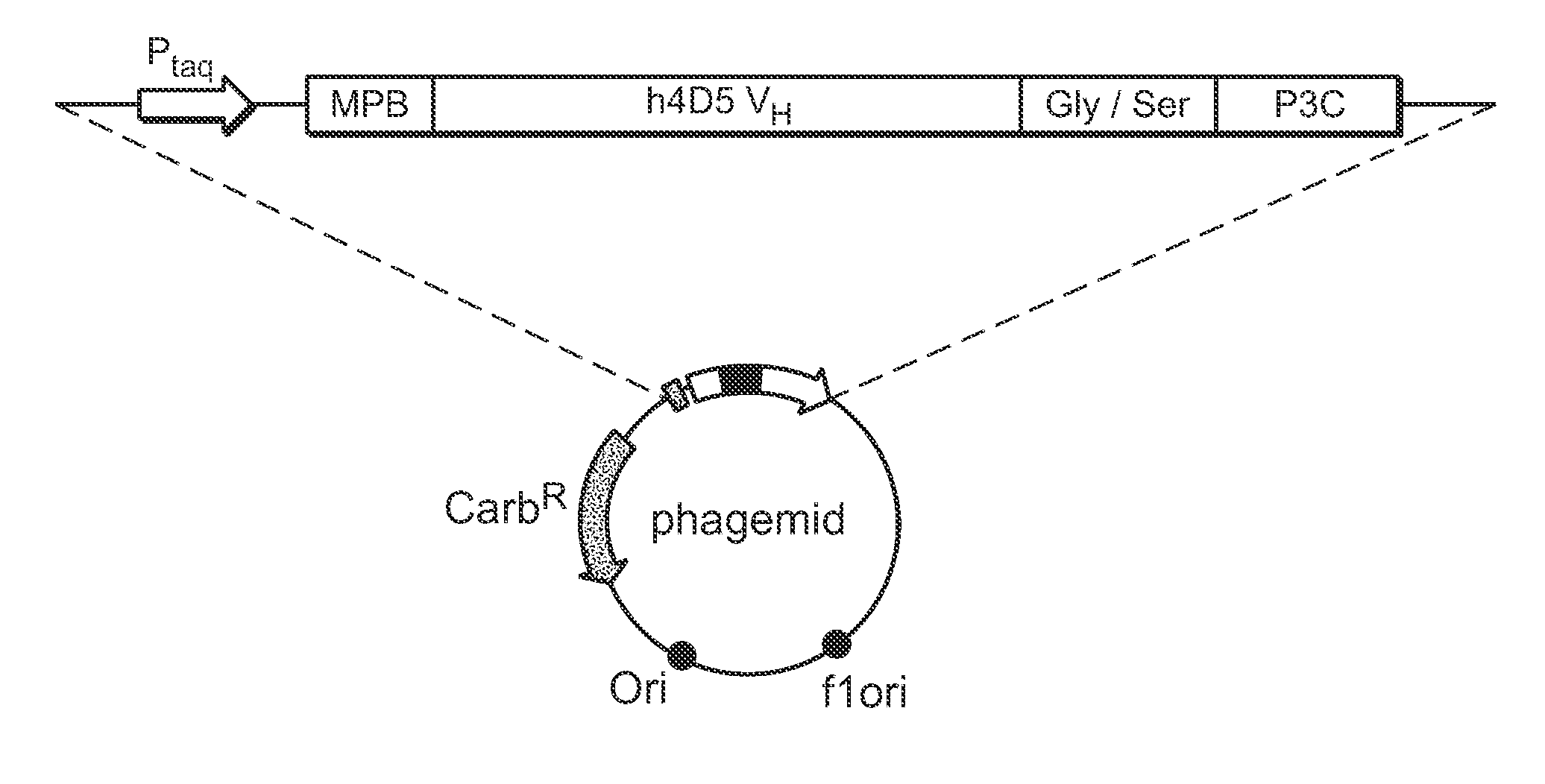
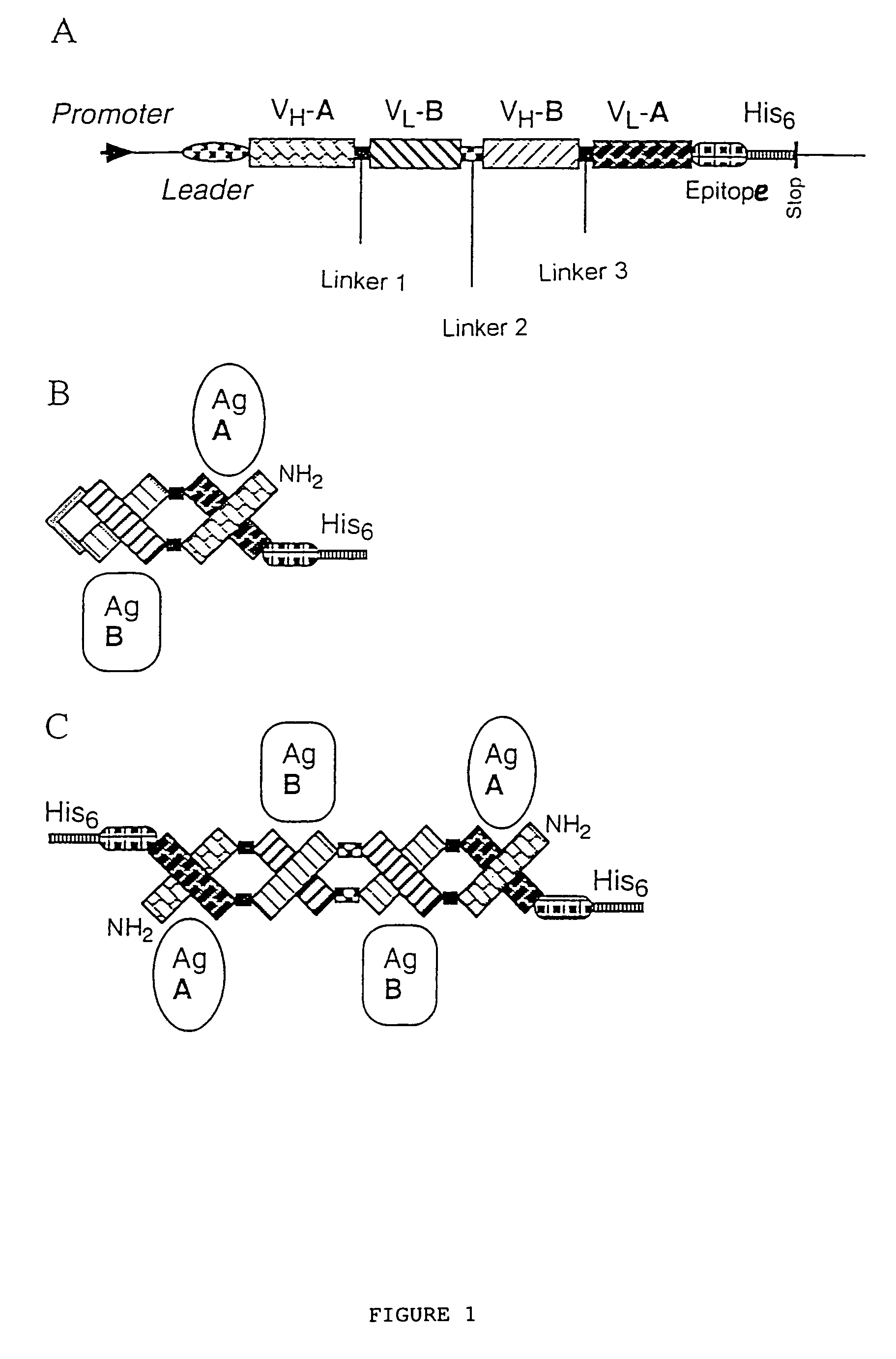
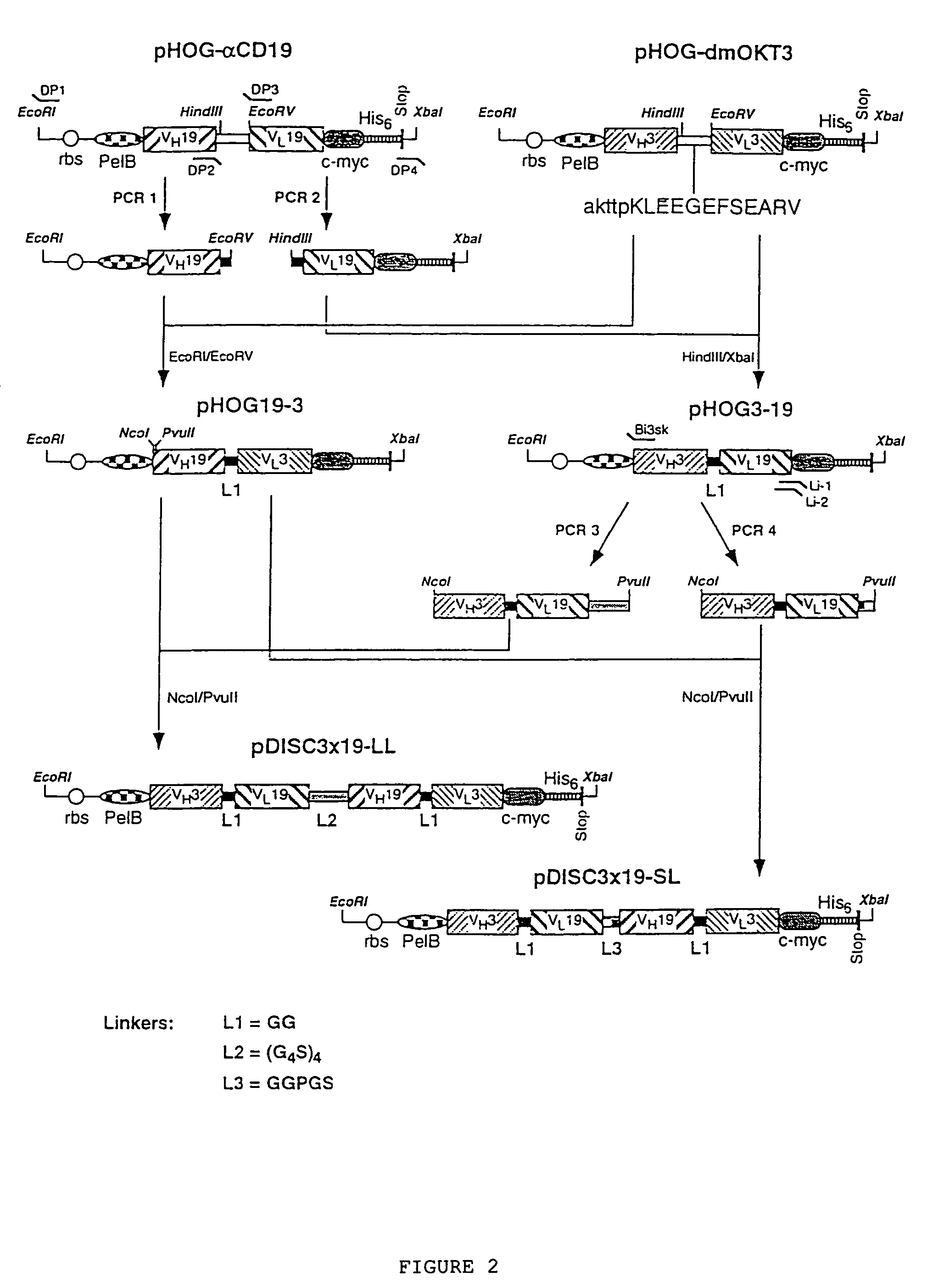
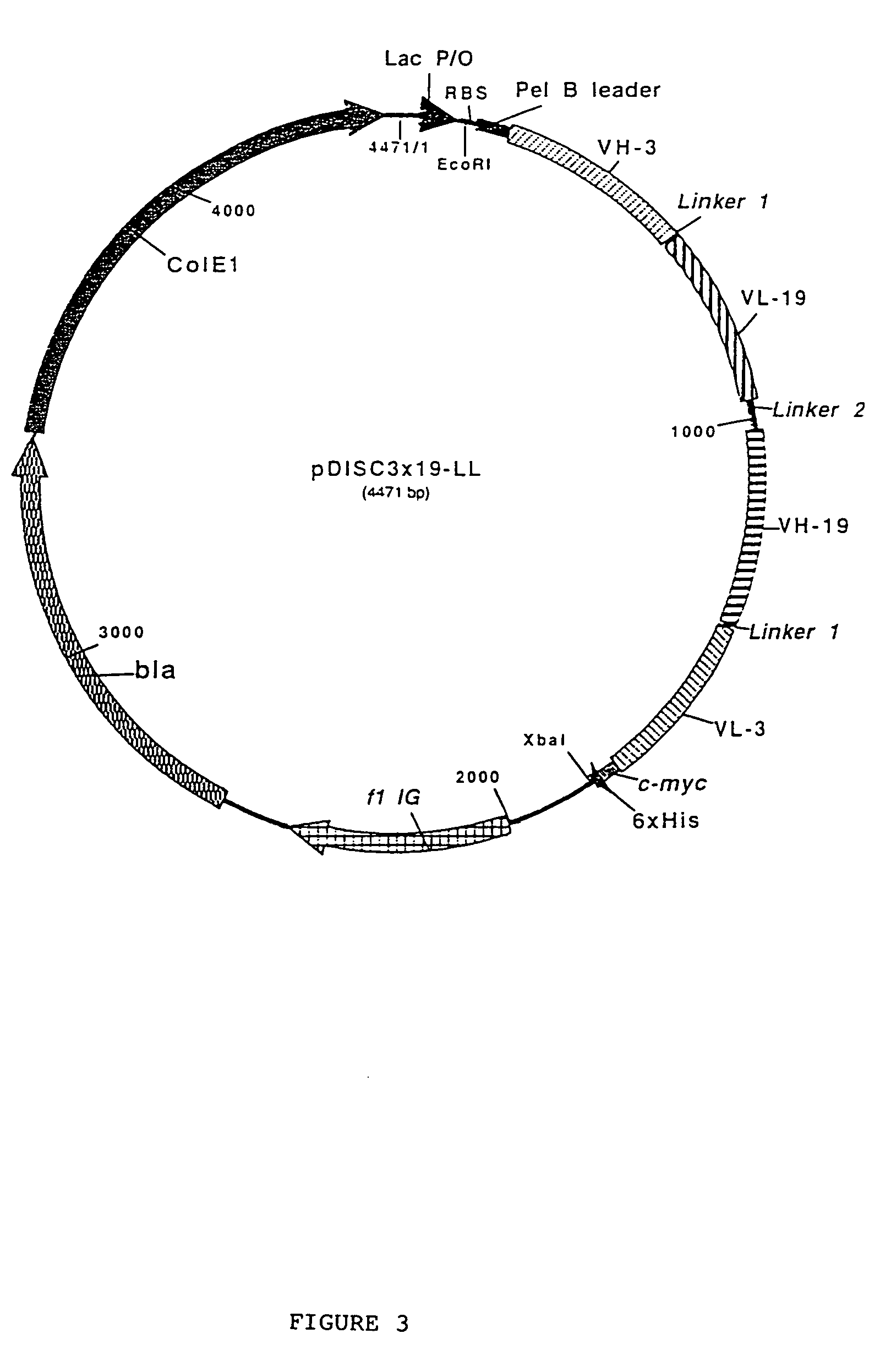
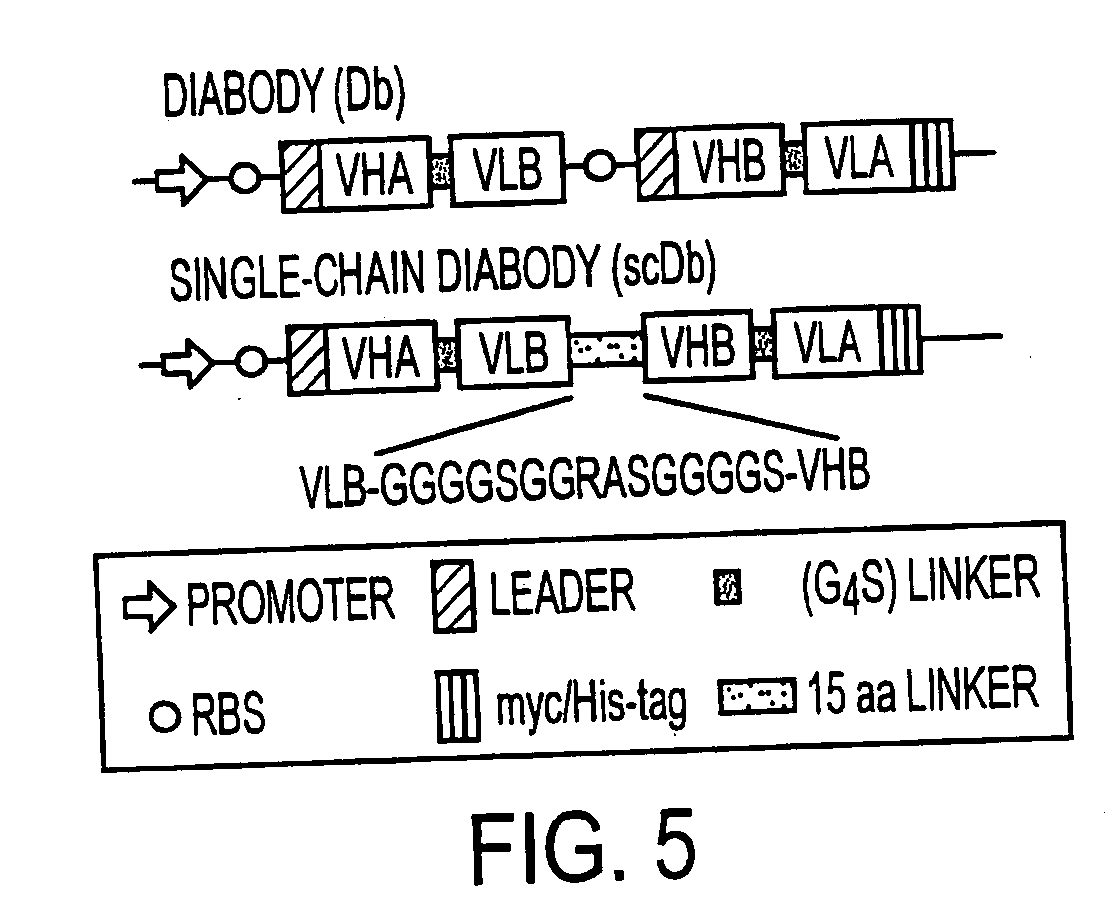
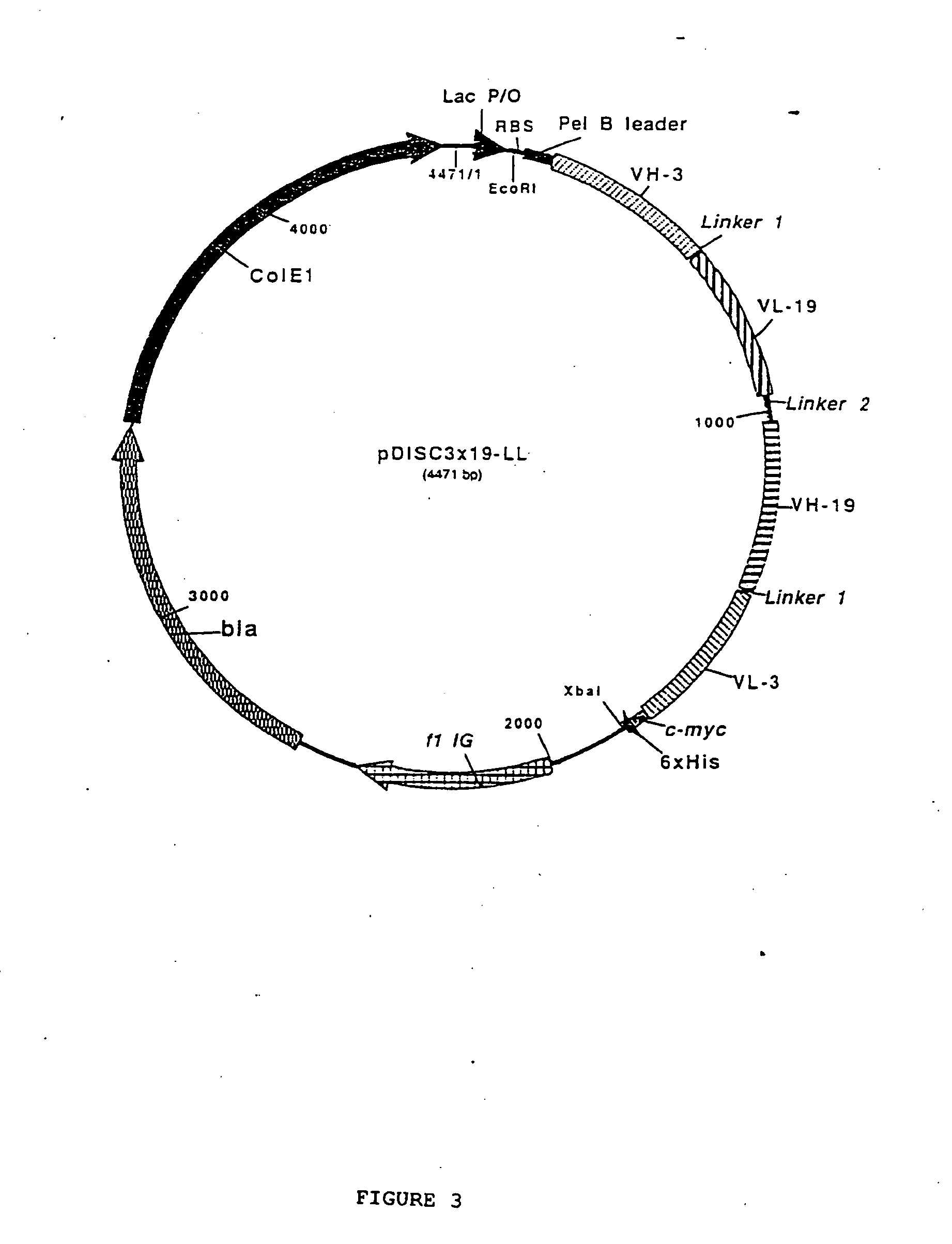
The present invention relates to multivalent Fvantibody construct having at least four variable domains which are linked with each over via the peptide linkers 1, 2 and 3. The invention also concerns expression plasmids which code for such an Fvantibody construct and a method of producing the Fvantibody constructs as well as their use.
Owner:DEUTES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENT STIFTUNG DES OFFENTLICHEN RECHTS
Method for reducing the immunogenicity of antibody variable domains
A unique method is disclosed for identifying and replacing immunoglobulin surface amino acid residues which converts the antigenicity of a first mammalian species to that of a second mammalian species. The method will simultaneously change immunogenicity and strictly preserve ligind binding properties. The judicious replacement of exterior amino acid residues has no effect on the ligind binding properties but greatly alters immunogenicity.
Owner:DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES US SEC THE +1
Bispecific antibodies
ActiveUS7235641B2Improve productivityImprove efficiencyAntipyreticAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBispecific antibodyImmune effector cell
Owner:AMGEN RES (MUNICH) GMBH
Methods For Making Fully Human Bispecific Antibodies Using A Common Light Chain
InactiveUS20130045492A1Reduce in quantitySimple methodAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsEpitopeProtein insertion
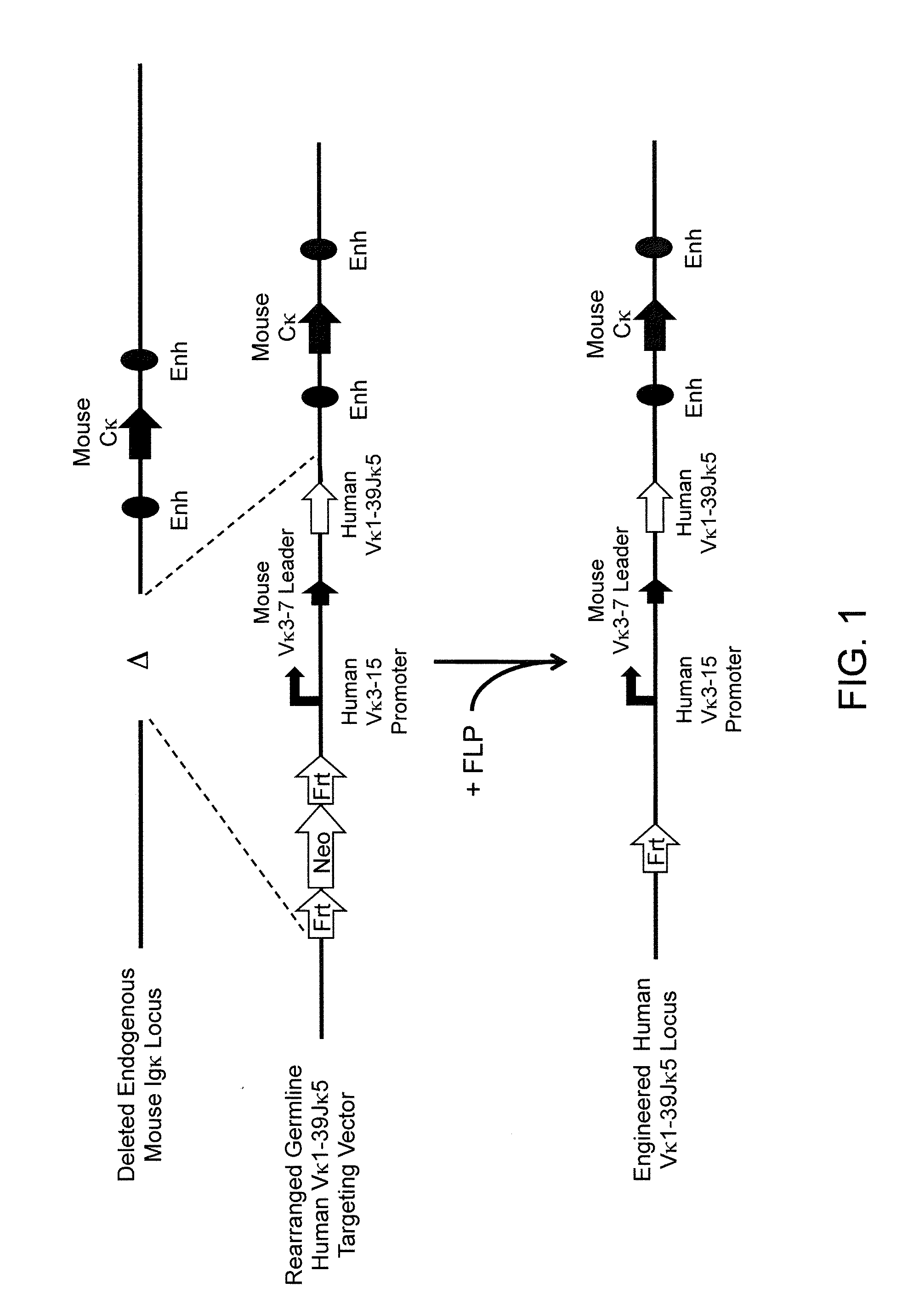
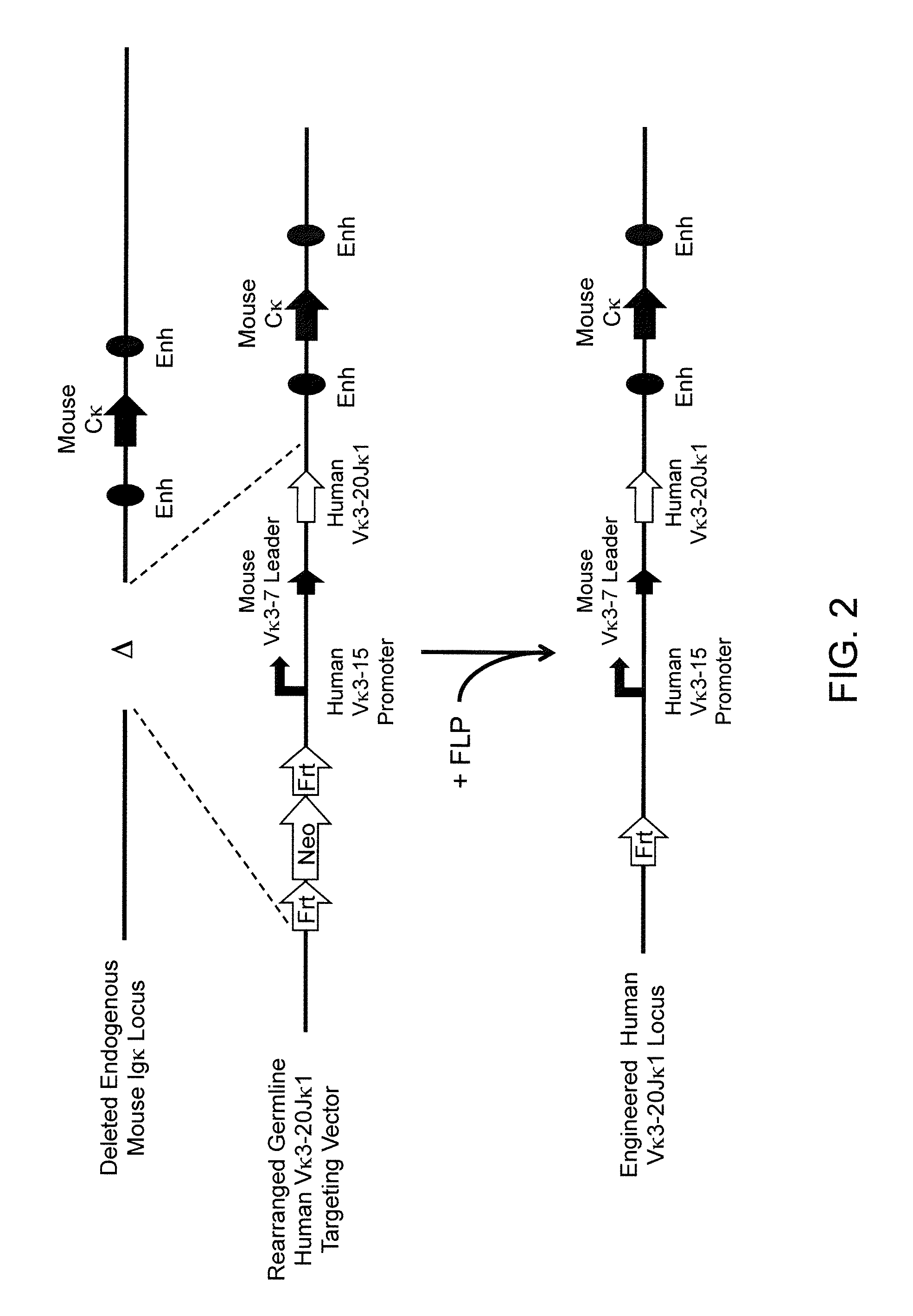
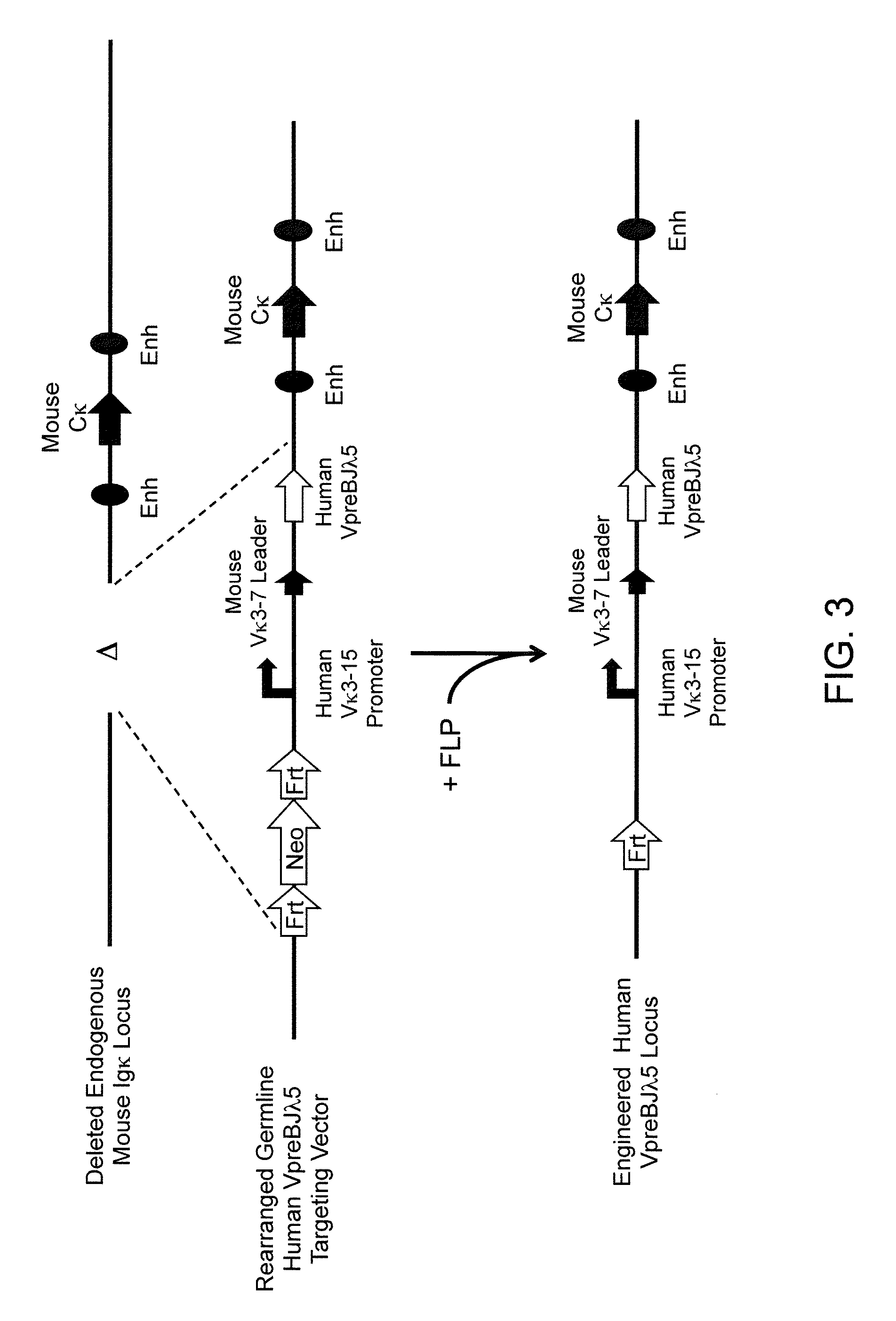
A genetically modified mouse is provided, wherein the mouse expresses an immunoglobulin light chain repertoire characterized by a limited number of light chain variable domains. Mice are provided that express just one or a few immunoglobulin light chain variable domains from a limited repertoire in their germline. Methods for making bispecific antibodies having universal light chains using mice as described herein, including human light chain variable regions, are provided. Methods for making human variable regions suitable for use in multispecific binding proteins, e.g., bispecific antibodies, and host cells are provided. Bispecific antibodies capable of binding first and second antigens are provided, wherein the first and second antigens are separate epitopes of a single protein or separate epitopes on two different proteins are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Single-chain multiple antigen-binding molecule, its preparation and use
InactiveUS20050004352A1Reduce dissociationLess complexOrganic active ingredientsFungiAntigen bindingVariable domain
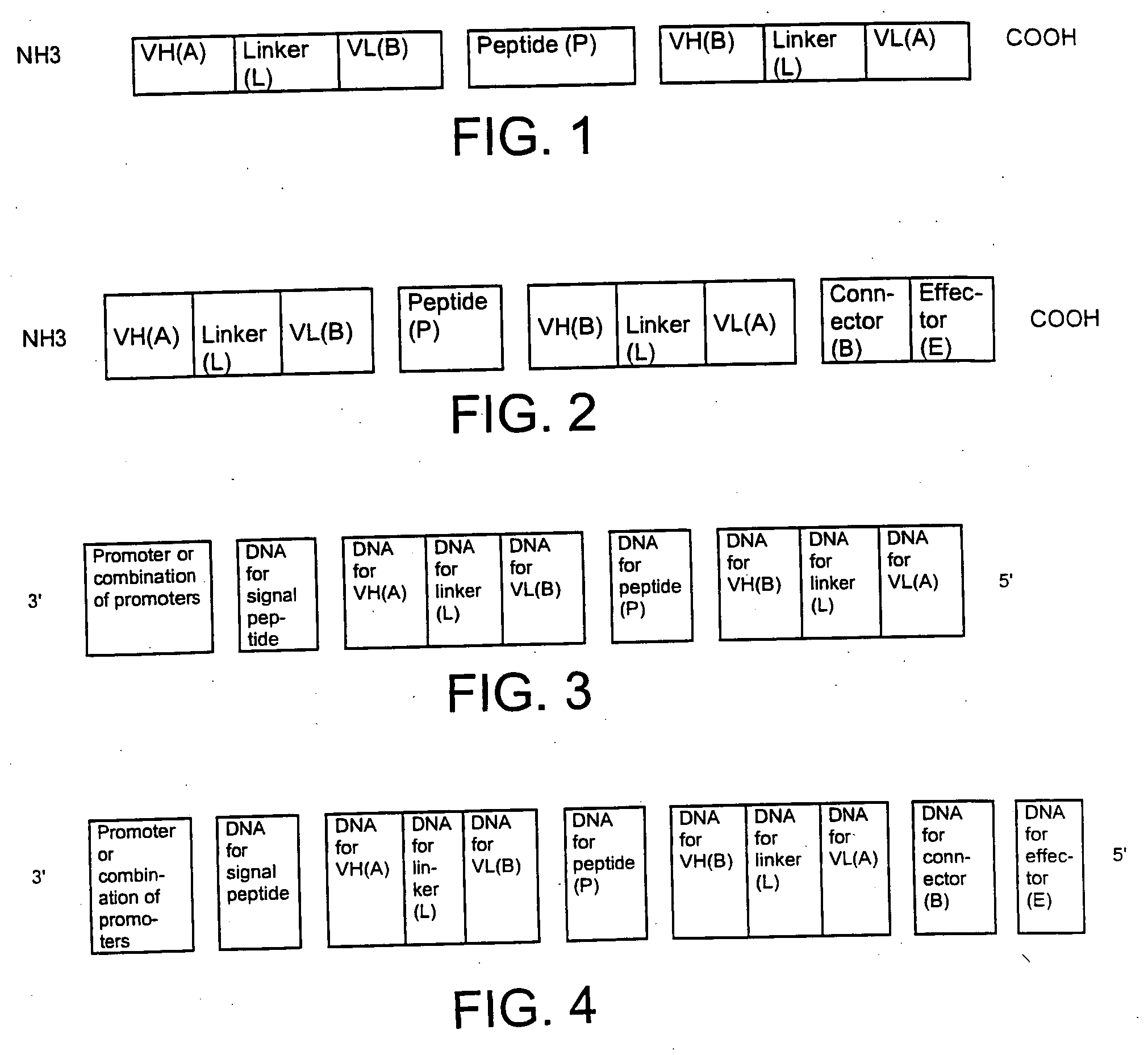
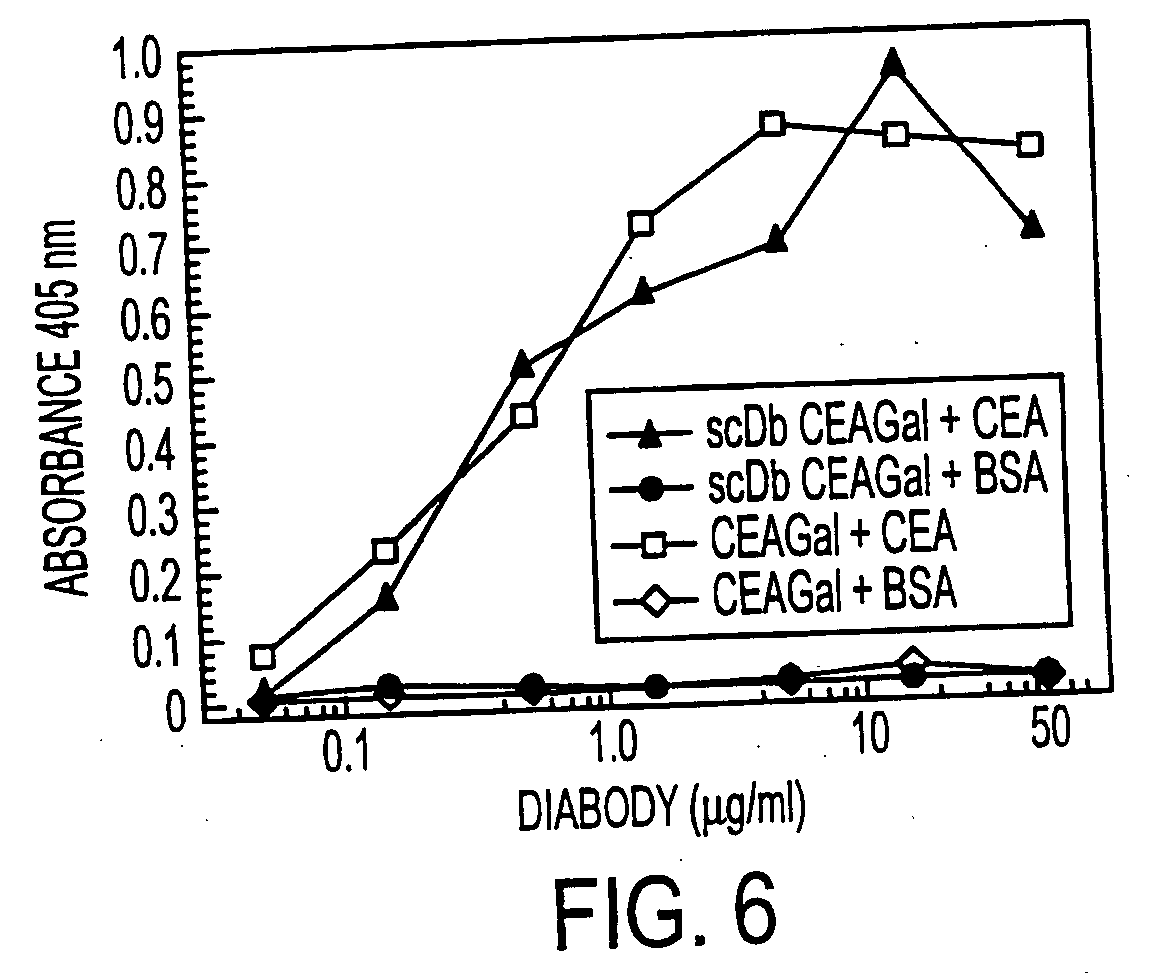
The present invention relates to a single-chain, multiple antigen-binding molecule with diverse variable domains of a heavy and of a light chain of an immunoglobulin, which are connected in the form of a VH-VL construct, which are in turn connected together via a peptide, and to the preparation and use thereof as pharmaceutical or diagnostic aid.
Owner:AFFITECH RESEARCH AS
Dual Variable Region Antibody-Like Binding Proteins Having Cross-Over Binding Region Orientation
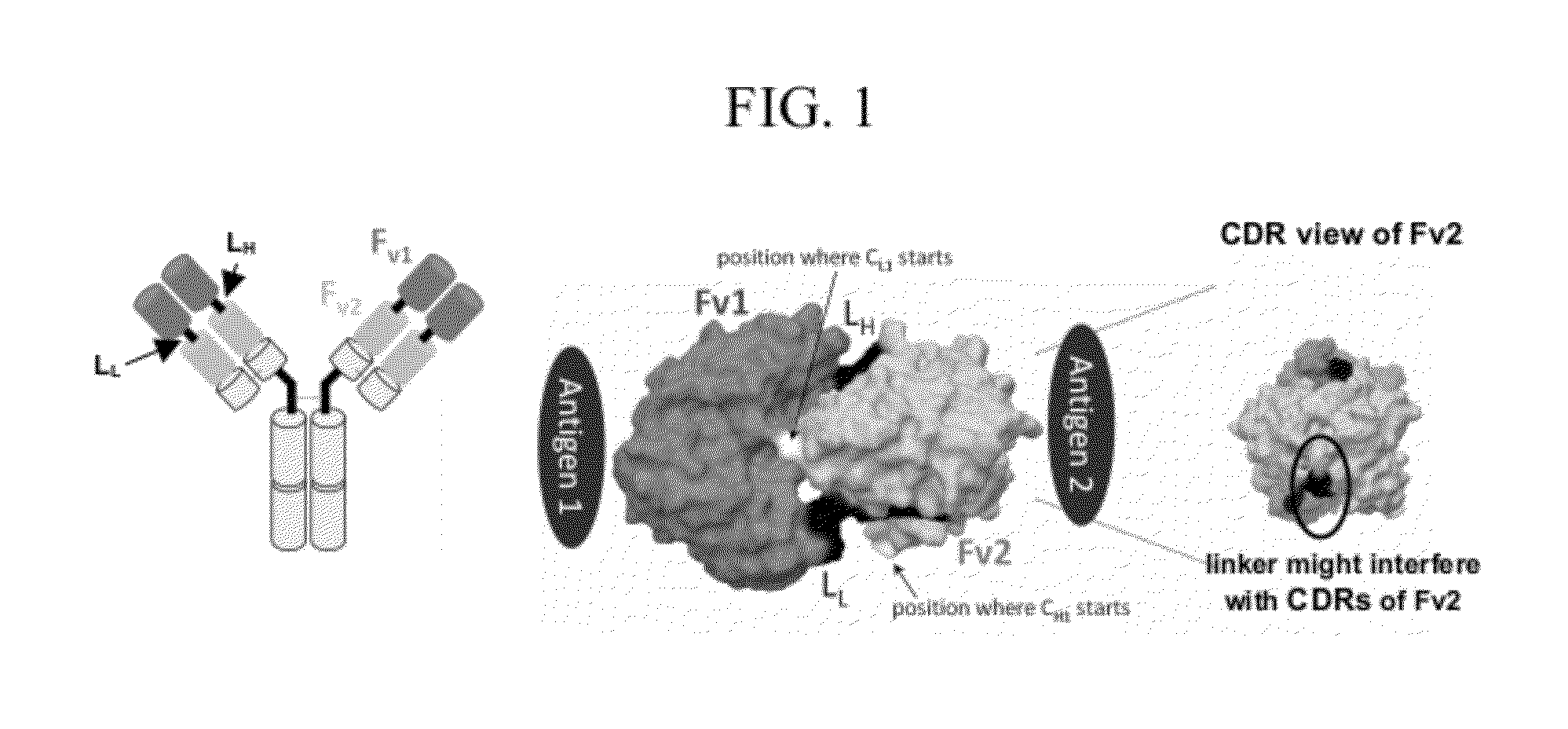
The invention provides antibody-like binding proteins comprising four polypeptide chains that form four antigen binding sites, wherein each pair of polypeptides forming an antibody-like binding protein possesses dual variable domains having a cross-over orientation. The invention also provides methods for making such antigen-like binding proteins.
Owner:SANOFI SA
Synthetic antibody phage libraries
The invention provides comprising variant amino acids in CDRs of antibody variable domains. These polypeptides provide a source of great sequence diversity that can be used as a source for identifying novel antigen binding polypeptides. The invention also provides these polypeptides as fusion polypeptides to heterologous polypeptides such as at least a portion of phage or viral coat proteins, tags, and linkers. Libraries comprising a plurality of these polypeptides are also provided. In addition, methods of and compositions for generating and using these polypeptides and libraries are provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
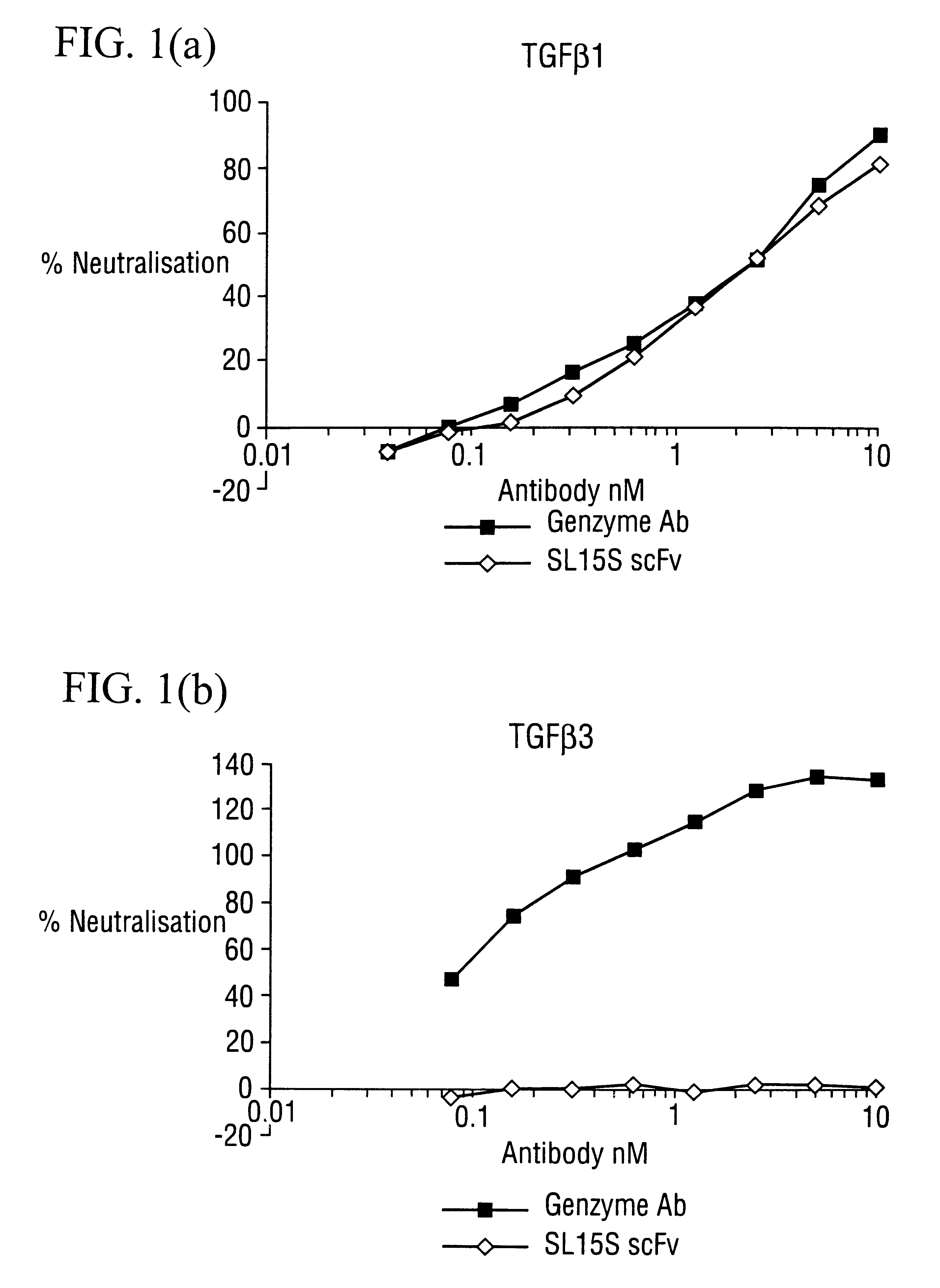
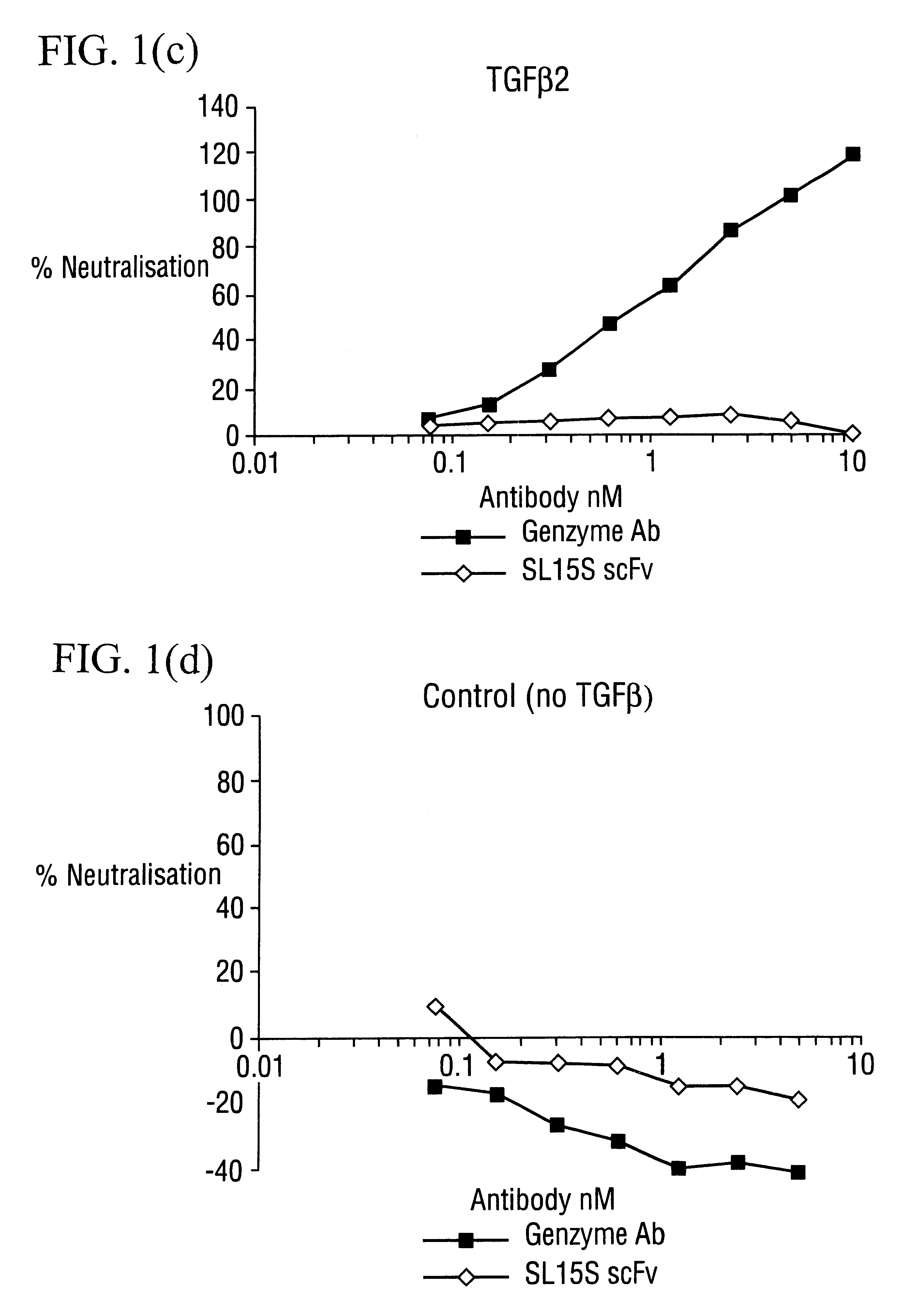
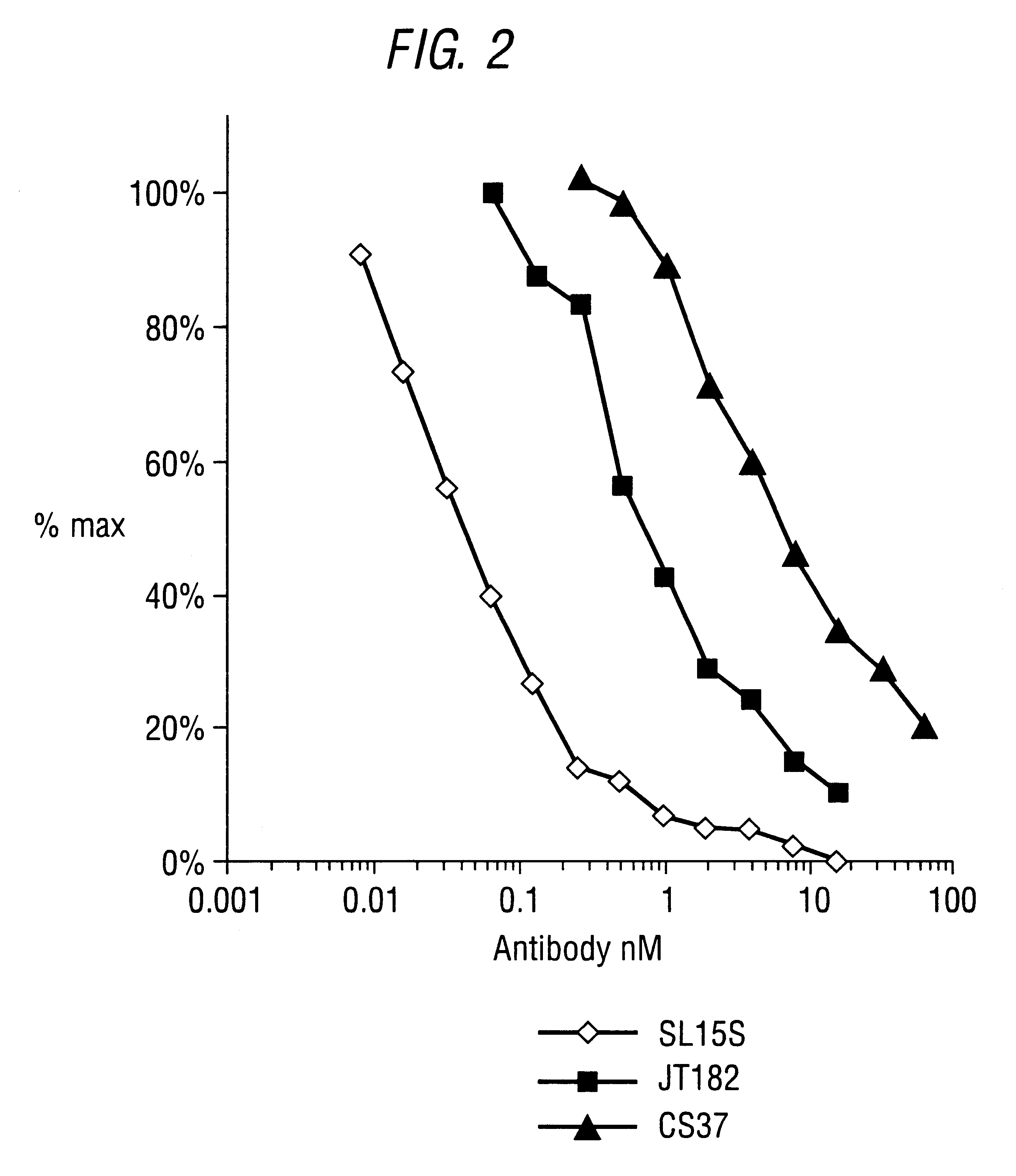
Specific binding members for TGFbeta1
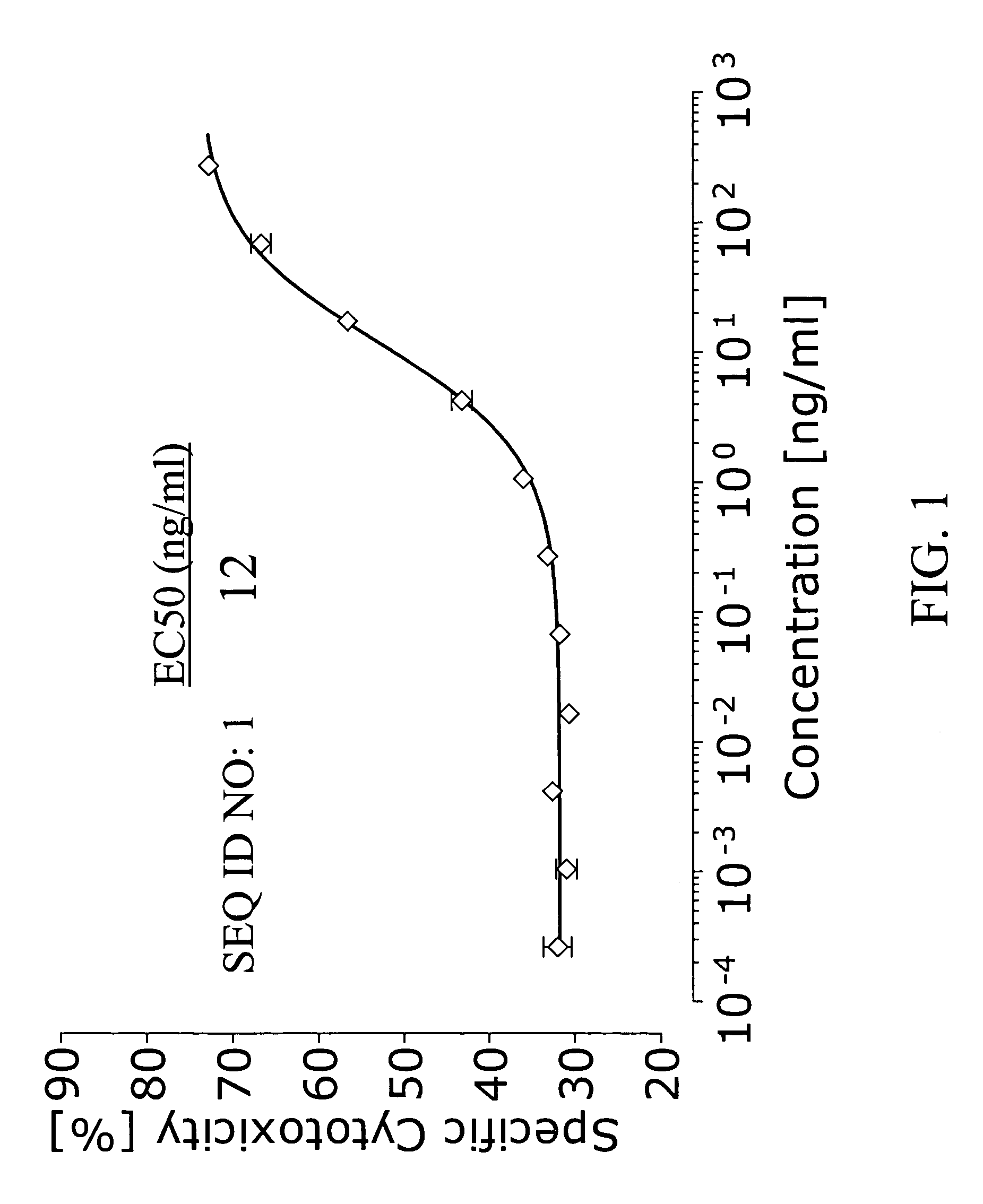
The invention provides specific binding members, for example in the form of antibody variable domains, based on the CDR3 sequences of the antibody VH regions of SL15 (SEQ ID NO:4) and JT182 (SEQ ID NO:10). The antibodies have strong neutralizing activity for TGFbeta1 and are useful in treating conditions associated with excess TGFbeta1 activity, such as fibrosis, immune responses and tumor progression.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LTD
Dual Variable Domain Immunoglobulins and Uses Thereof
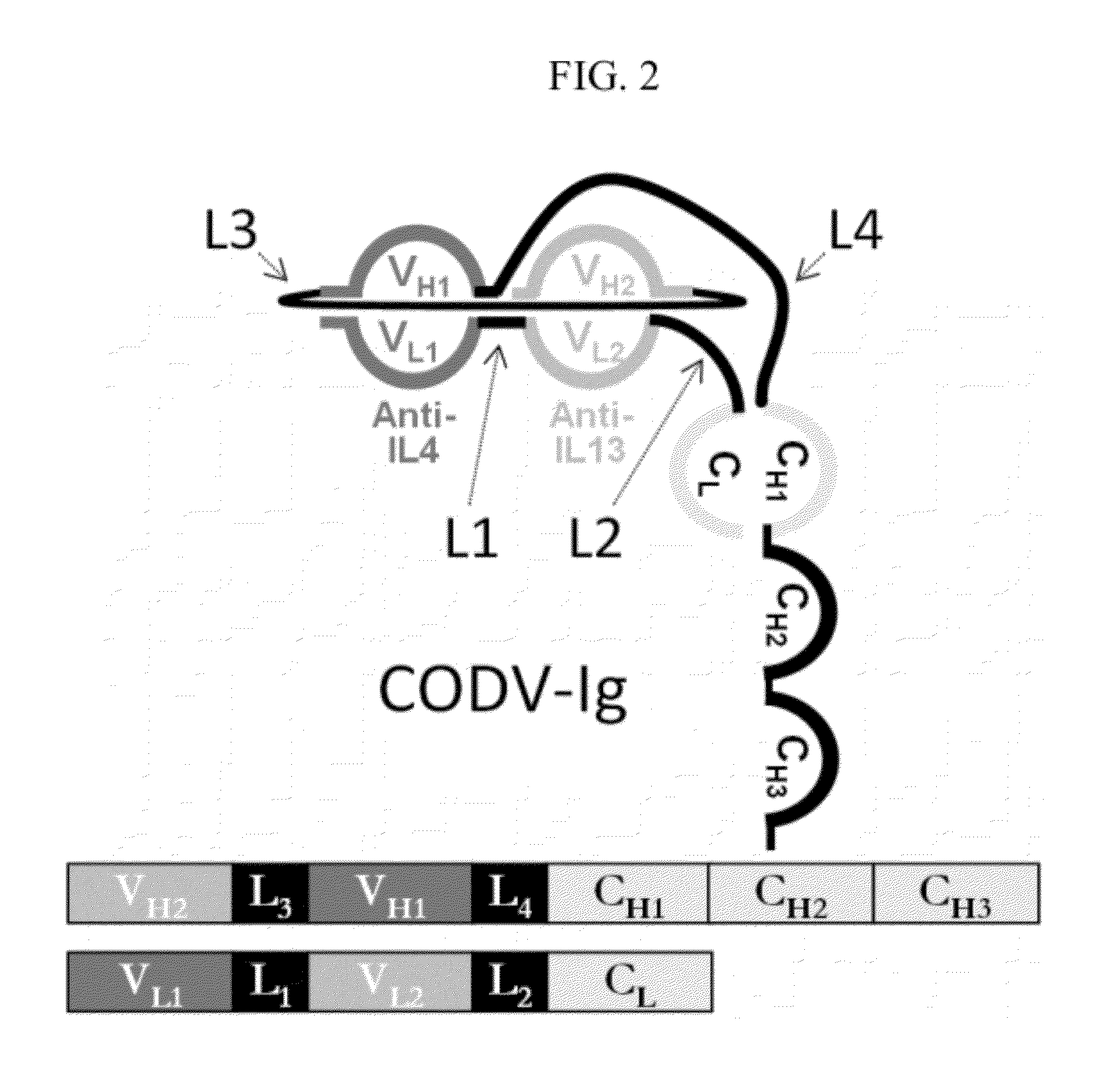
The present invention relates to engineered multivalent and multispecific binding proteins, methods of making, and specifically to their uses in the prevention, diagnosis, and / or treatment of disease.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Bispecific antibodies
ActiveUS20050136050A1Less complexReduce in quantityAntipyreticAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBispecific antibodyImmune effector cell
The present invention discloses bispecific antibodies comprising two antibody variable domains on a single polypeptide chain, wherein a first portion of the bispecific antibody is capable of recruiting the activity of a human immune effector cell by specifically binding to an effector antigen on the human immune effector cell, the first portion consisting of one antibody variable domain, and a second portion of the bispecific antibody specifically binding to a target antigen other than the effector antigen, the target antigen on a target cell other than the human immune effector cell, the second portion comprising one antibody variable domain.
Owner:AMGEN RES (MUNICH) GMBH
Ligand
The invention provides a dual-specific ligand comprising a first immunoglobulin variable domain having a first binding specificity and a complementary or non-complementary immunoglobulin variable domain having a second binding specificity.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
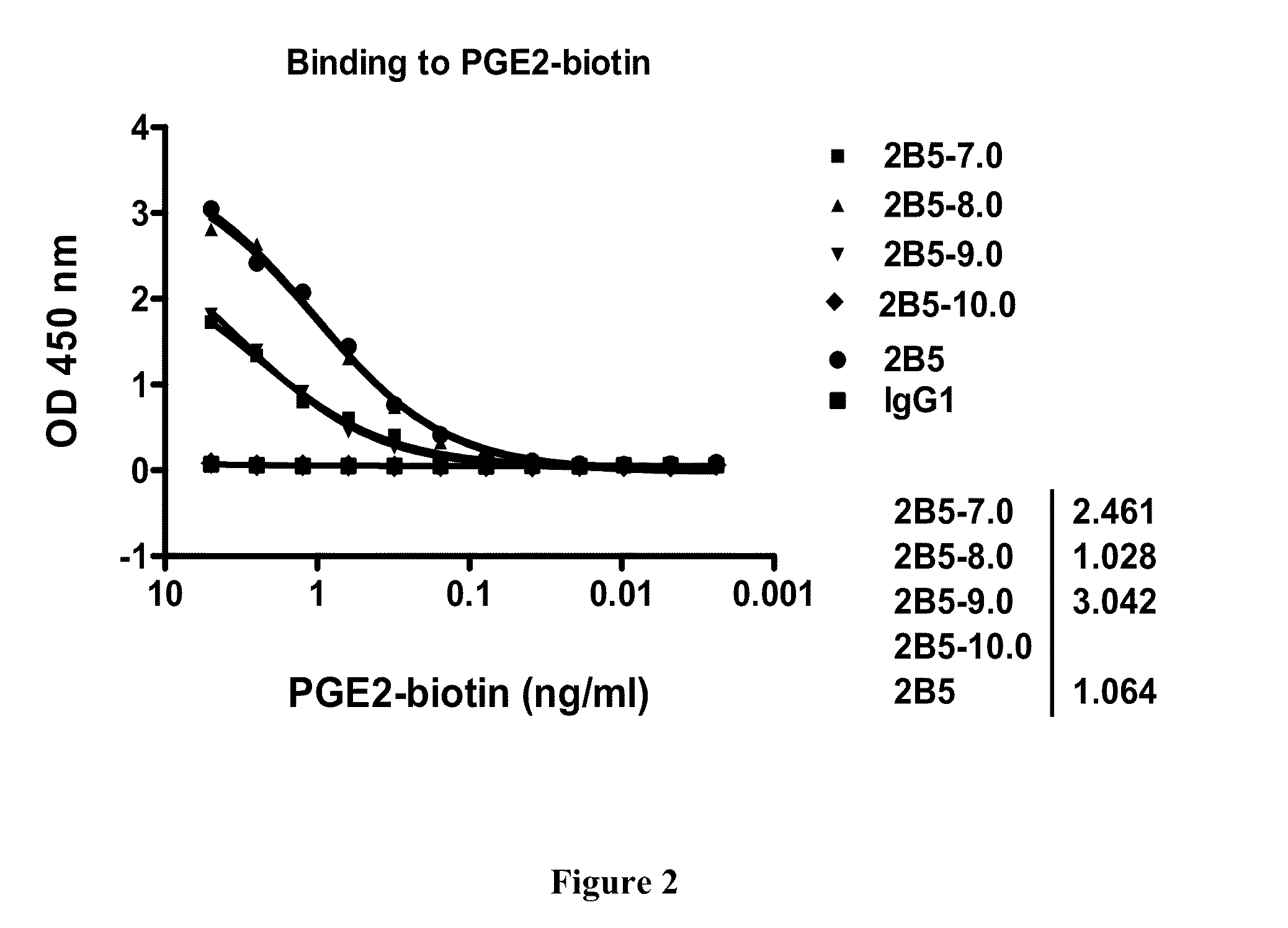
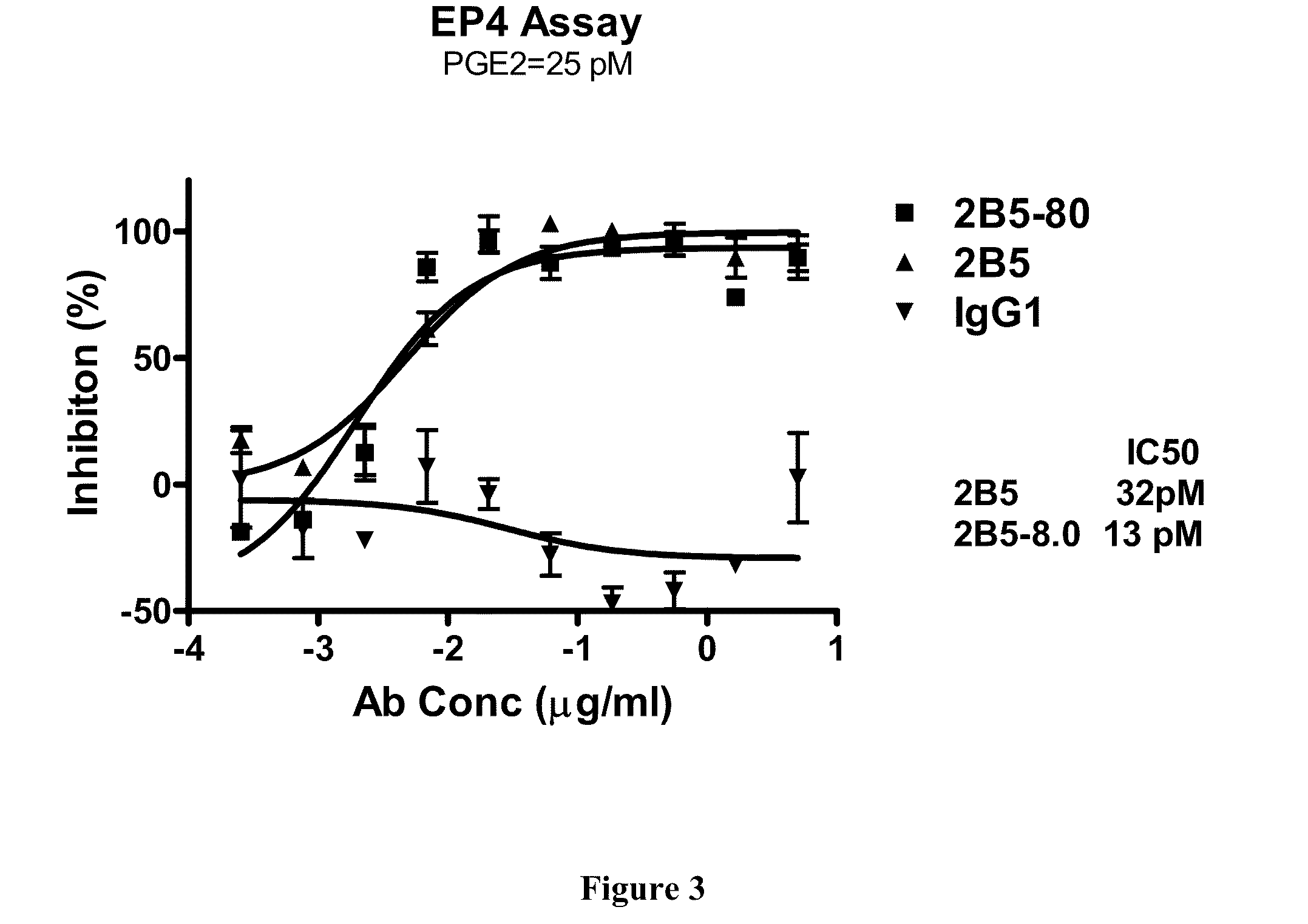
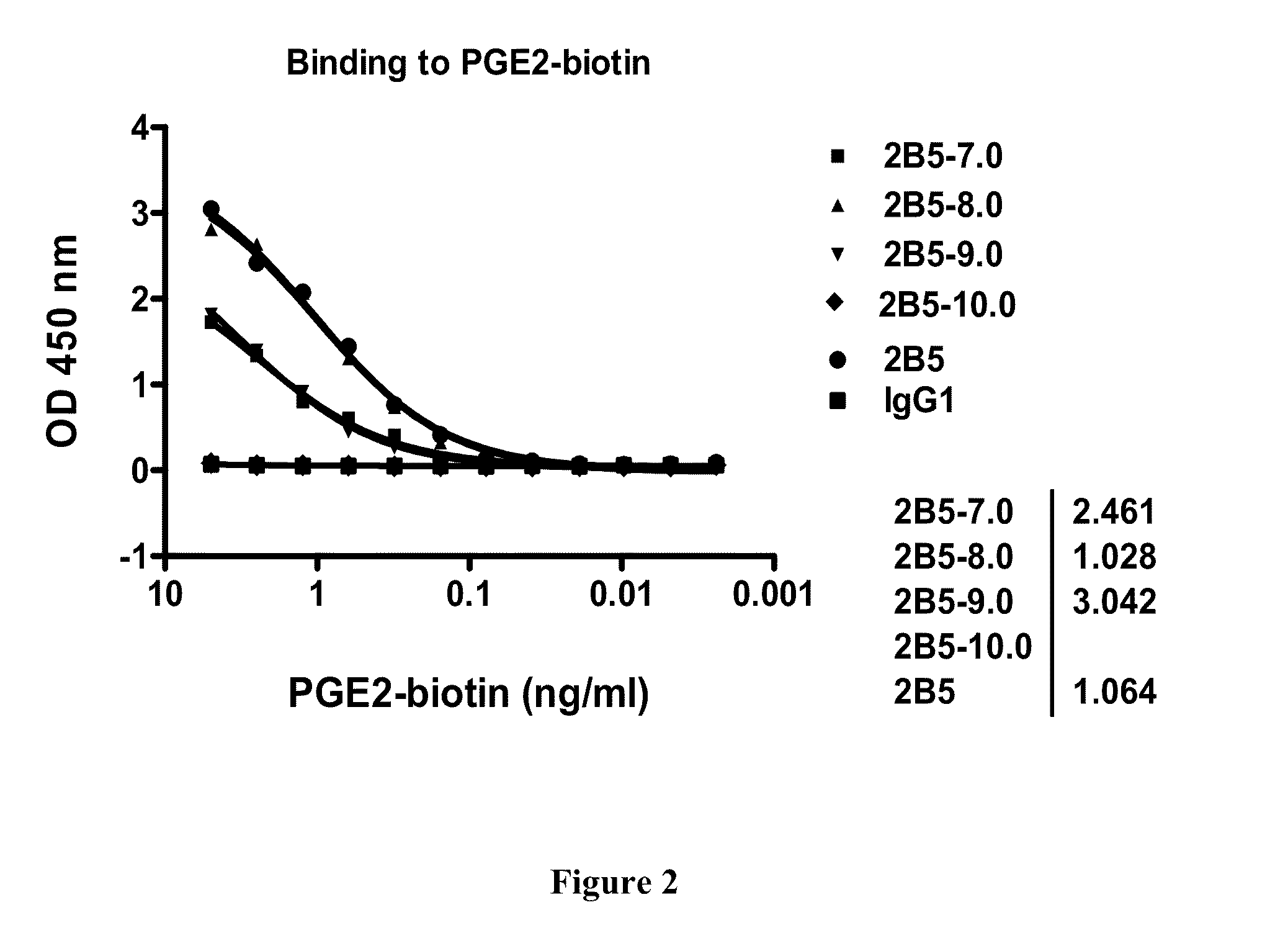
Prostaglandin E2 dual variable domain immunoglobulins and uses thereof
The present invention relates to engineered multivalent and multispecific binding proteins, methods of making, and specifically to their uses in the prevention, diagnosis, and / or treatment of disease.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Antibody compositions and methods
InactiveUS20070065440A1High affinitySmall sizeAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHigh concentrationVariable domain
Provided are concentrated preparations comprising single immunoglobulin variable domain polypeptides that bind target antigen with high affinity and are soluble at high concentration, without aggregation or precipitation, providing, for example, for increased storage stability and the ability to administer higher therapeutic doses.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
Variable domain library and uses
ActiveUS7785903B2Generate efficientlyQuality improvementImmunoglobulins against growth factorsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsComplementarity determining regionAntigen binding
The invention provides polypeptides comprising a variant heavy chain variable framework domain (VFR). In some embodiments, the amino acids defining the VFR form a loop of an antigen binding pocket. In an embodiment, the polypeptide is a variable domain of a monobody and has a variant VFR. The polypeptide may optionally comprise one or more complementary determining regions (CDRs) of antibody variable domains. In an embodiment, the polypeptide is a variable domain of a monobody and has a variant VFR and one or more variant CDRs. Libraries of polypeptides that include a plurality of different antibody variable domains generated by creating diversity in a VFR, and optionally, one or more CDRs are provided and may be used as a source for identifying novel antigen binding polypeptides that can be used therapeutically or as reagents. The invention also provides fusion polypeptides, compositions, and methods for generating and using the polypeptides and libraries.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Method for reducing the immunogenicity of antibody variable domains
InactiveUS20020034765A1Altered immunogenicityLow immunogenicityHybrid immunoglobulinsBiological testingBound propertyVariable domain
A unique method is disclosed for identifying and replacing immunoglobulin surface amino acid residues which converts the antigenicity of a first mammalian species to that of a second mammalian species. The method will simultaneously change immunogenicity and strictly preserve ligind binding properties. The judicious replacement of exterior amino acid residues has no effect on the ligind binding properties but greatly alters immunogenicity.
Owner:DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES US SEC THE +1
Dual variable domain immunoglobulin and uses thereof
Owner:ABBVIE INC
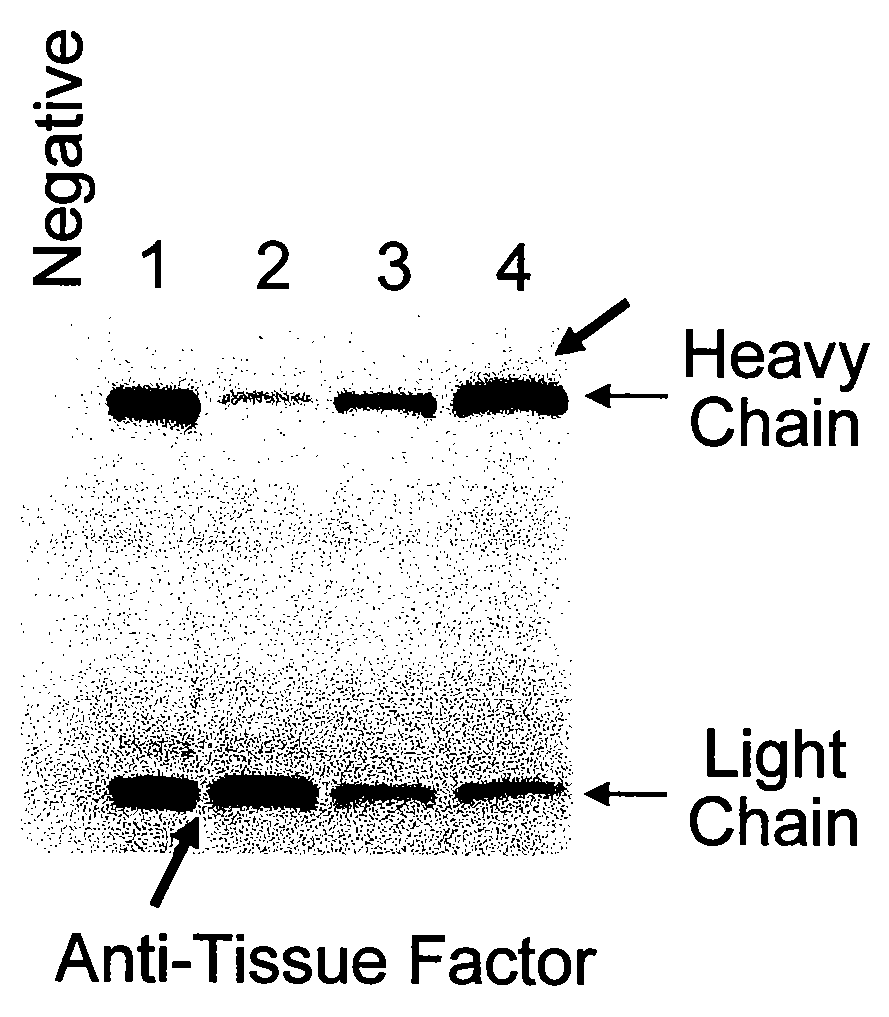
Methods of making antibody heavy and light chains having specificity for a desired antigen
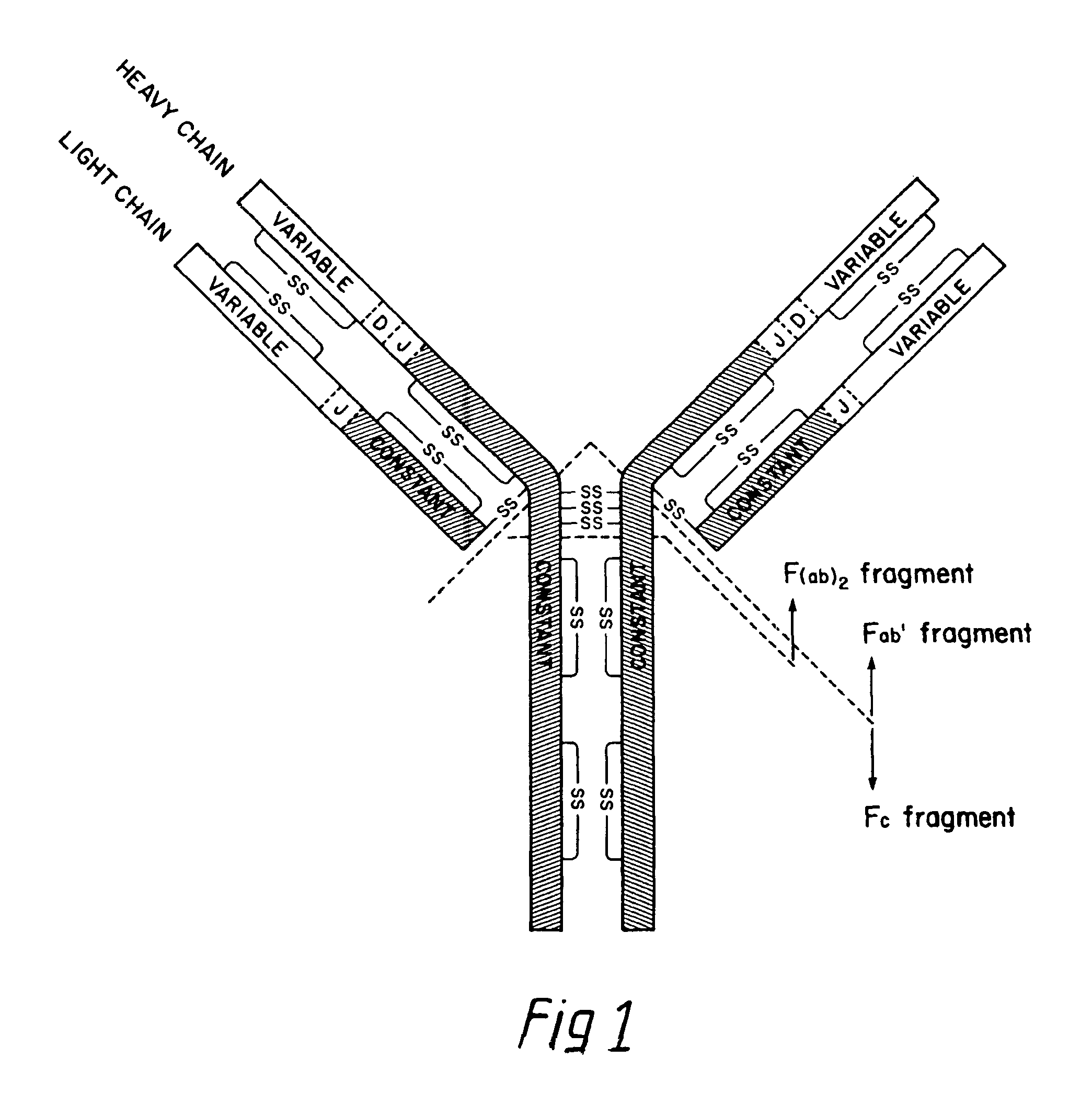
The invention relates to processes for producing an immunoglobulin or an immunologically functional immunoglobulin fragment containing at least the variable domains of the immunoglobulin heavy and light chains. The processes can use one or more vectors which produce both the heavy and light chains or fragments thereof in a single cell. The invention also relates to the vectors used to produce the immunoglobulin or fragment, and to cells transformed with the vectors.
Owner:GENENTECH INC +1
Tri-variable domain binding proteins and uses thereof
The present invention provides engineered multivalent and multispecific binding proteins, as well as methods of making them. Methods for using the multivalent and multispecific binding proteins of the invention in the prevention, diagnosis, and / or treatment of disease are also provided.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Antibodies and methods for making and using them
InactiveUS20080187966A1Speed up the processIncrease productionImmunoglobulins against growth factorsRecombinant DNA-technologyDisulfide bondingAntigen Binding Fragment
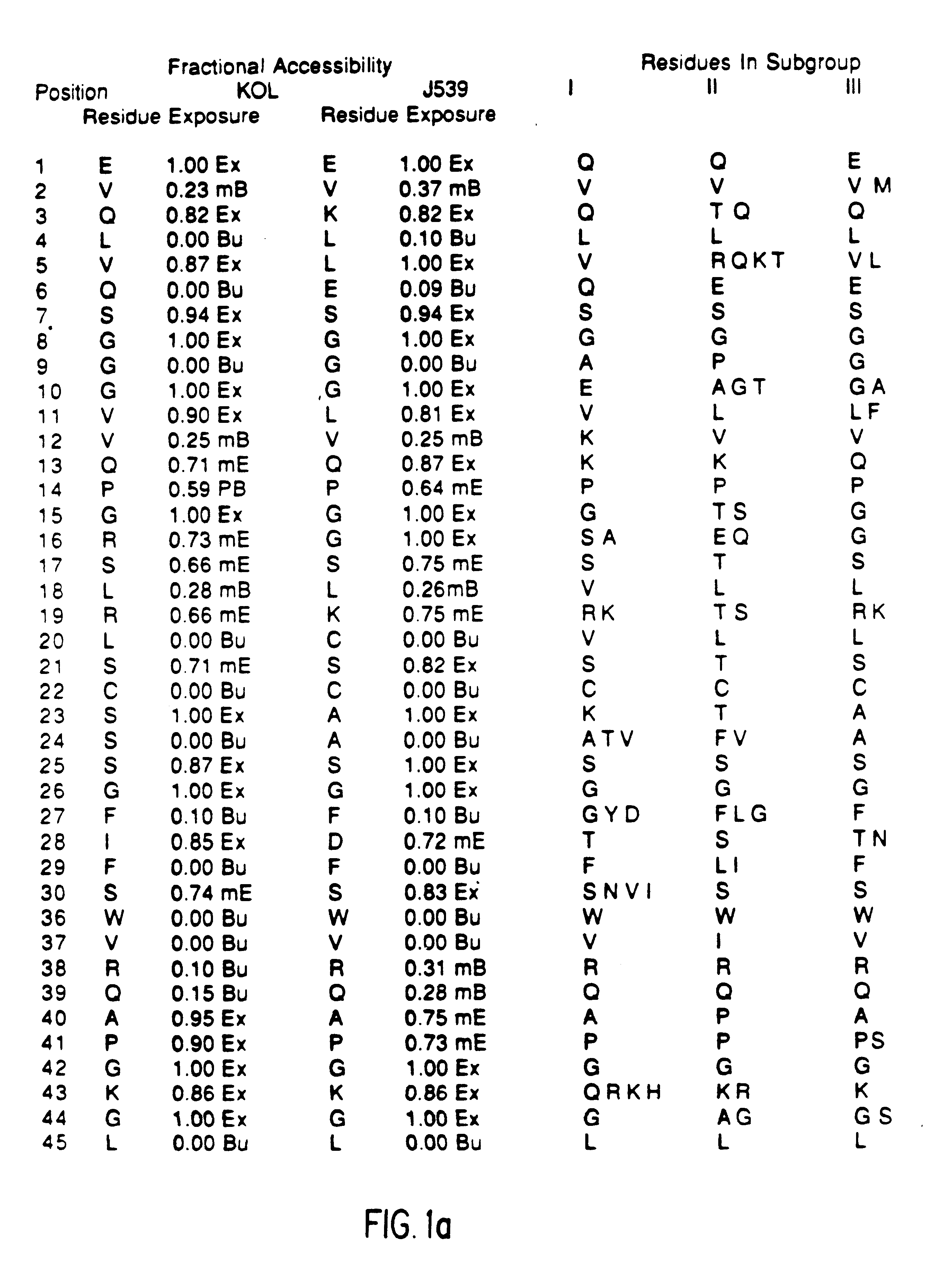
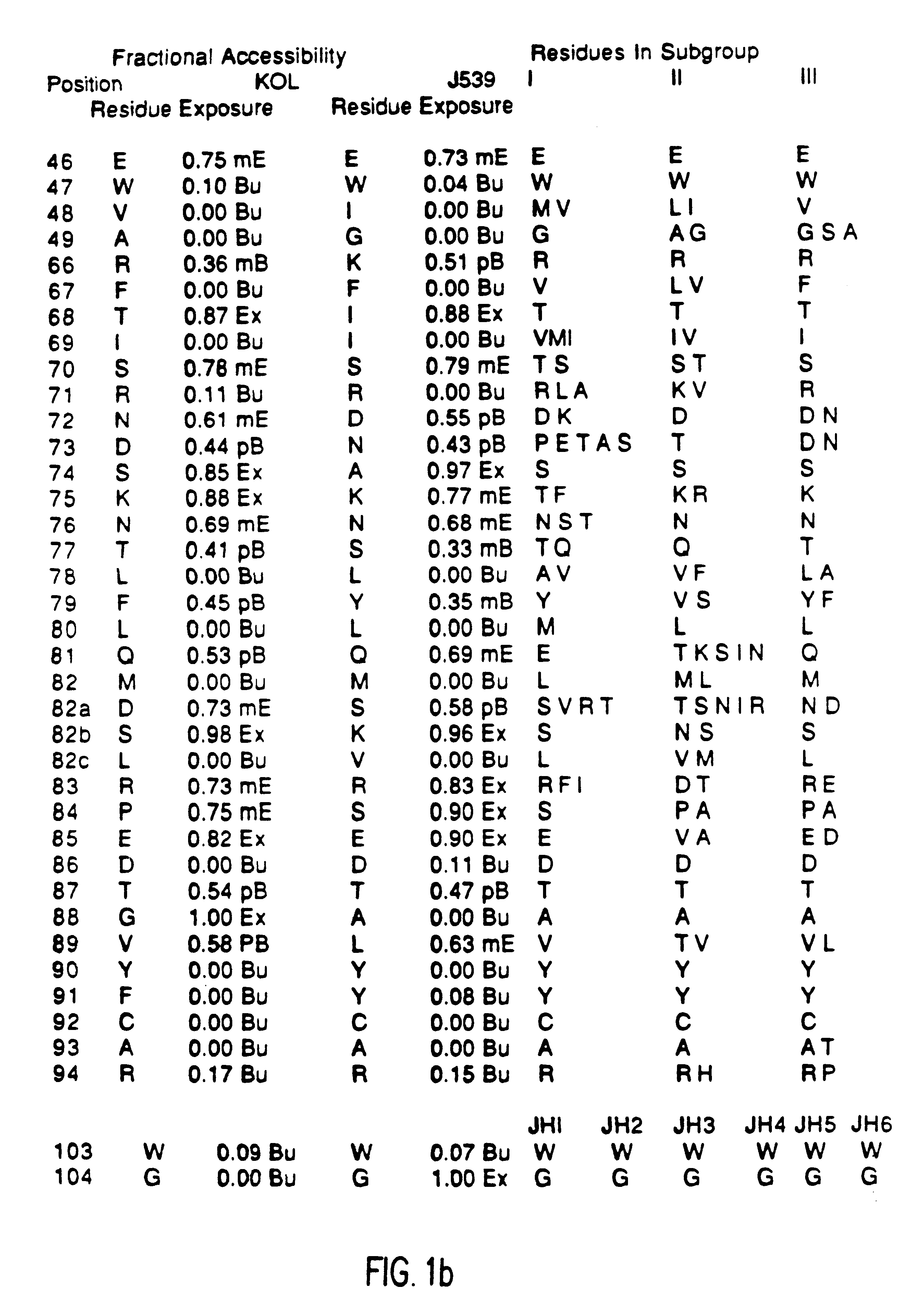
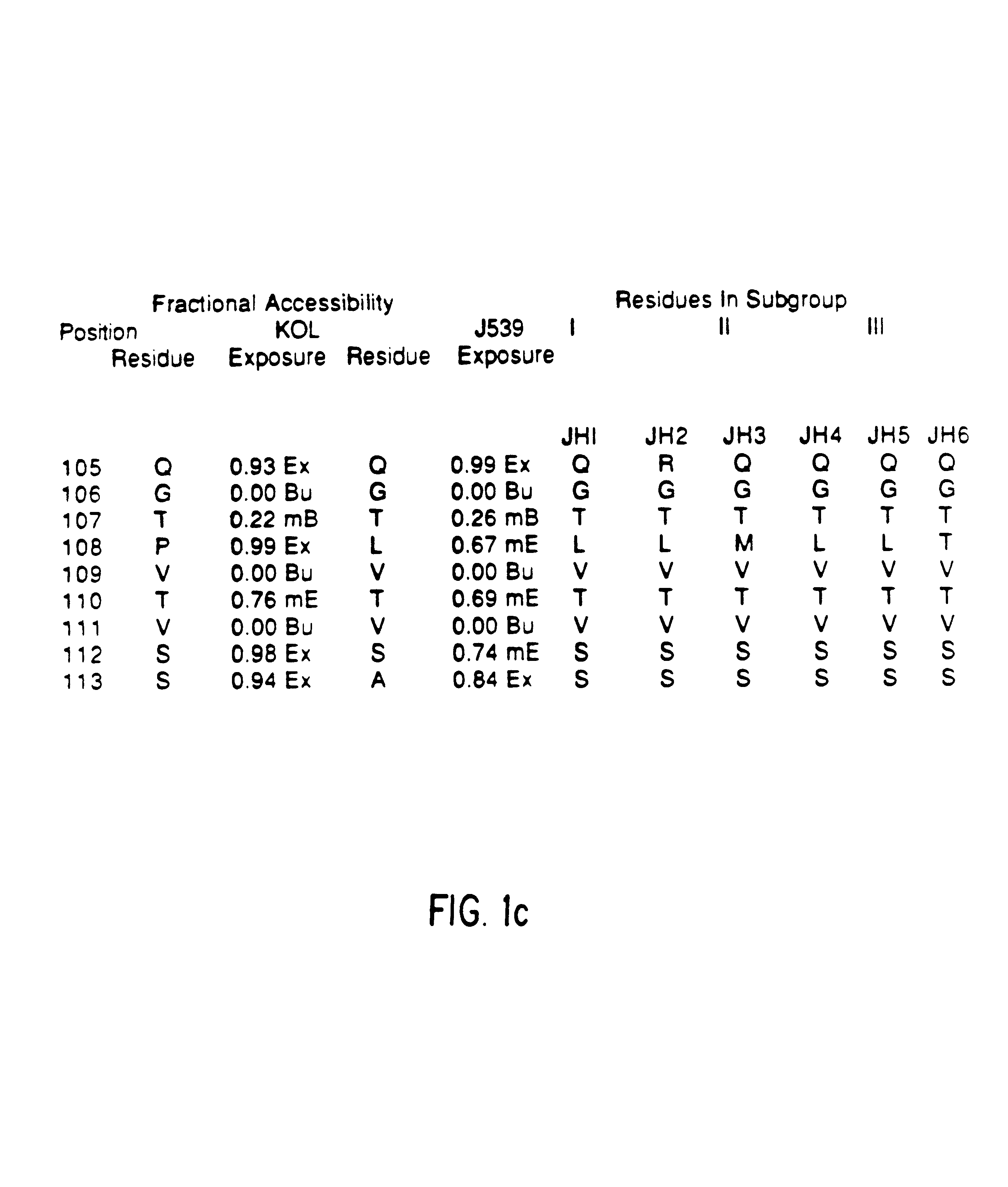
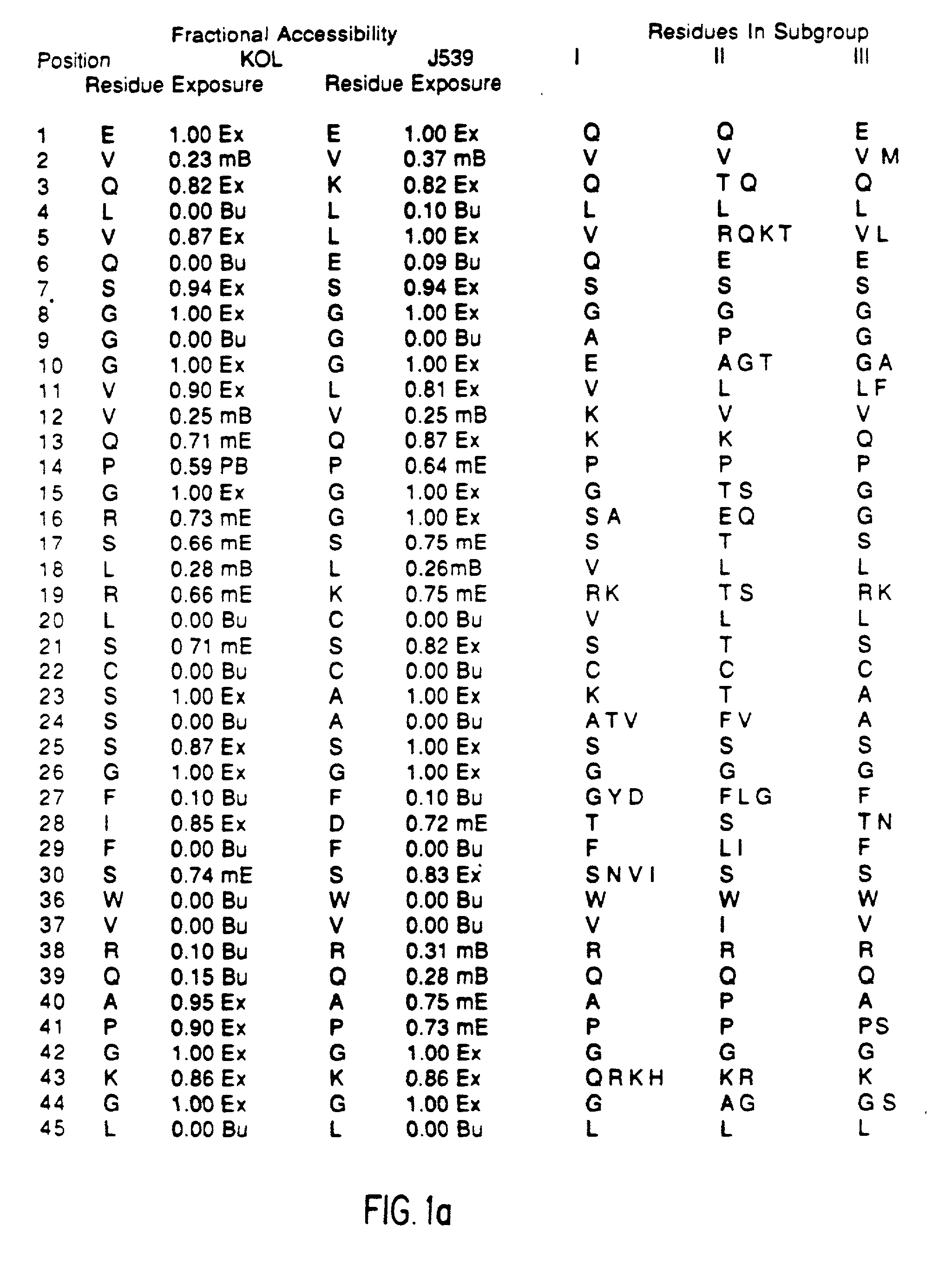
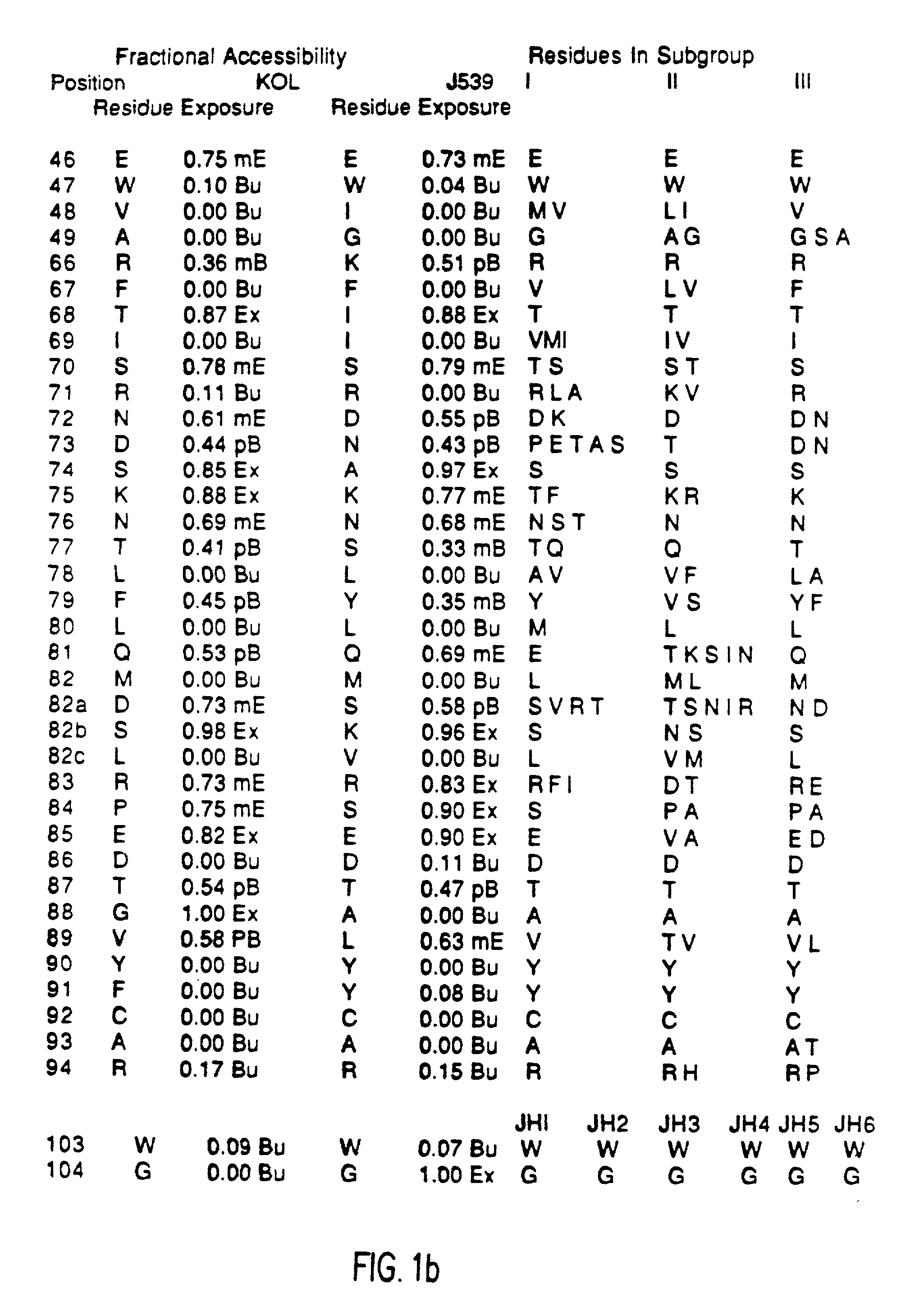
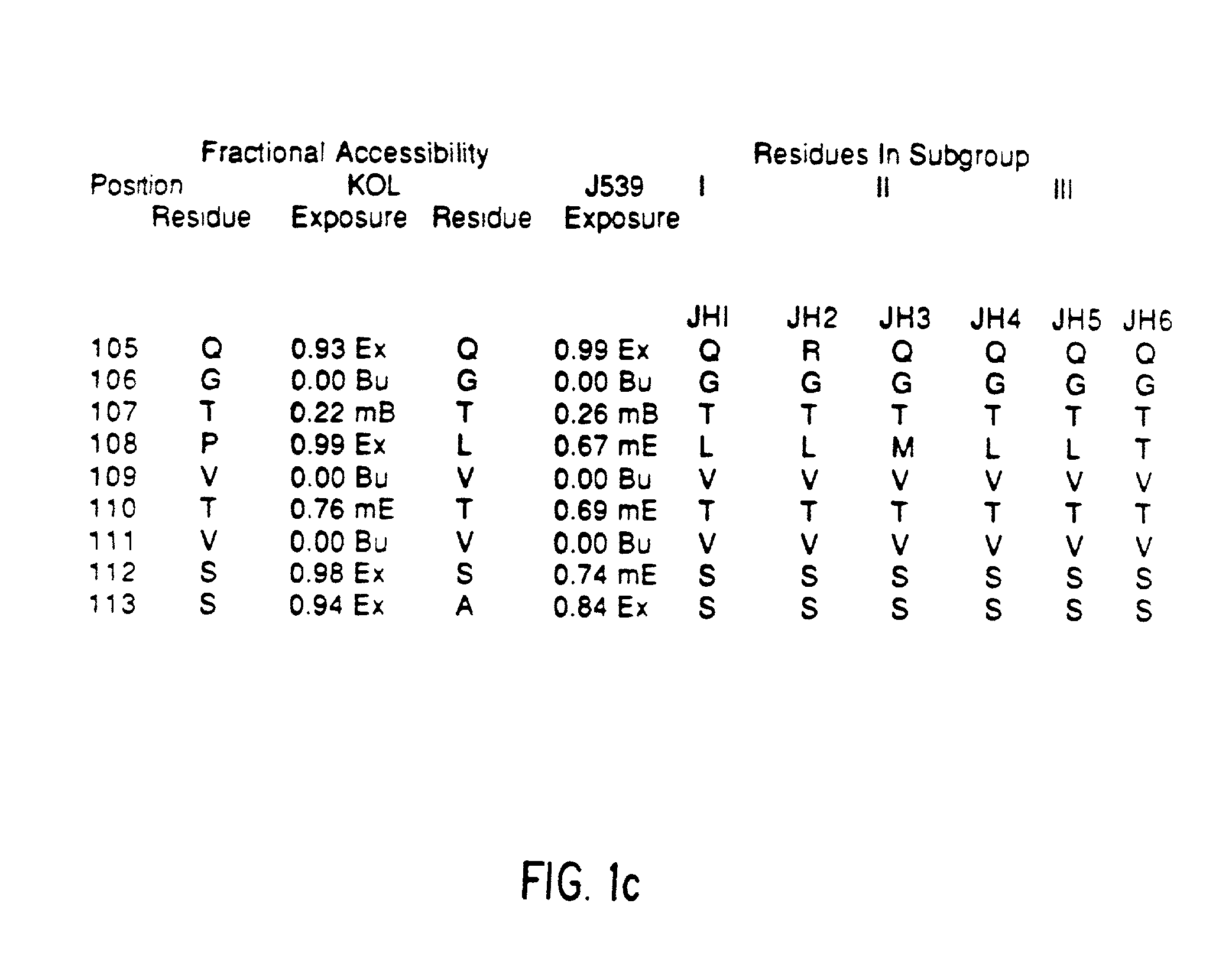
The present invention provides methods for producing humanized antibodies and increasing the yield of antibodies and / or antigen binding fragments when produced in cell culture. In one aspect of the invention, at least one framework region amino acid residue of the variable domain is substituted by a corresponding amino acid from a variable domain consensus sequence subgroup that has the most sequence identity with the HVR1 and / or HVR2 amino acid sequence of the variable domain. In another aspect, an amino acid is placed at a position proximal to a cys residue that participates in an intrachain variable domain disulfide bond that corresponds to an amino acid found at that position in a variable domain consensus sequence subgroup that has the most sequence identity with the HVR1 and / or HVR2 amino acid sequence of the variable domain.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Multivalent antibody contructs
InactiveUS20070031436A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAnimal cellsEukaryotic plasmidsVariable domain
The present invention relates to a multivalent Fv antibody construct having at least four variable domains which are linked with each over via the peptide linkers 1, 2 and 3. The invention also concerns expression plasmids which code for such an Fv antibody construct and a method of producing the Fv antibody constructs as well as their use.
Owner:DEUTES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENT STIFTUNG DES OFFENTLICHEN RECHTS
Cd3 binding polypeptides
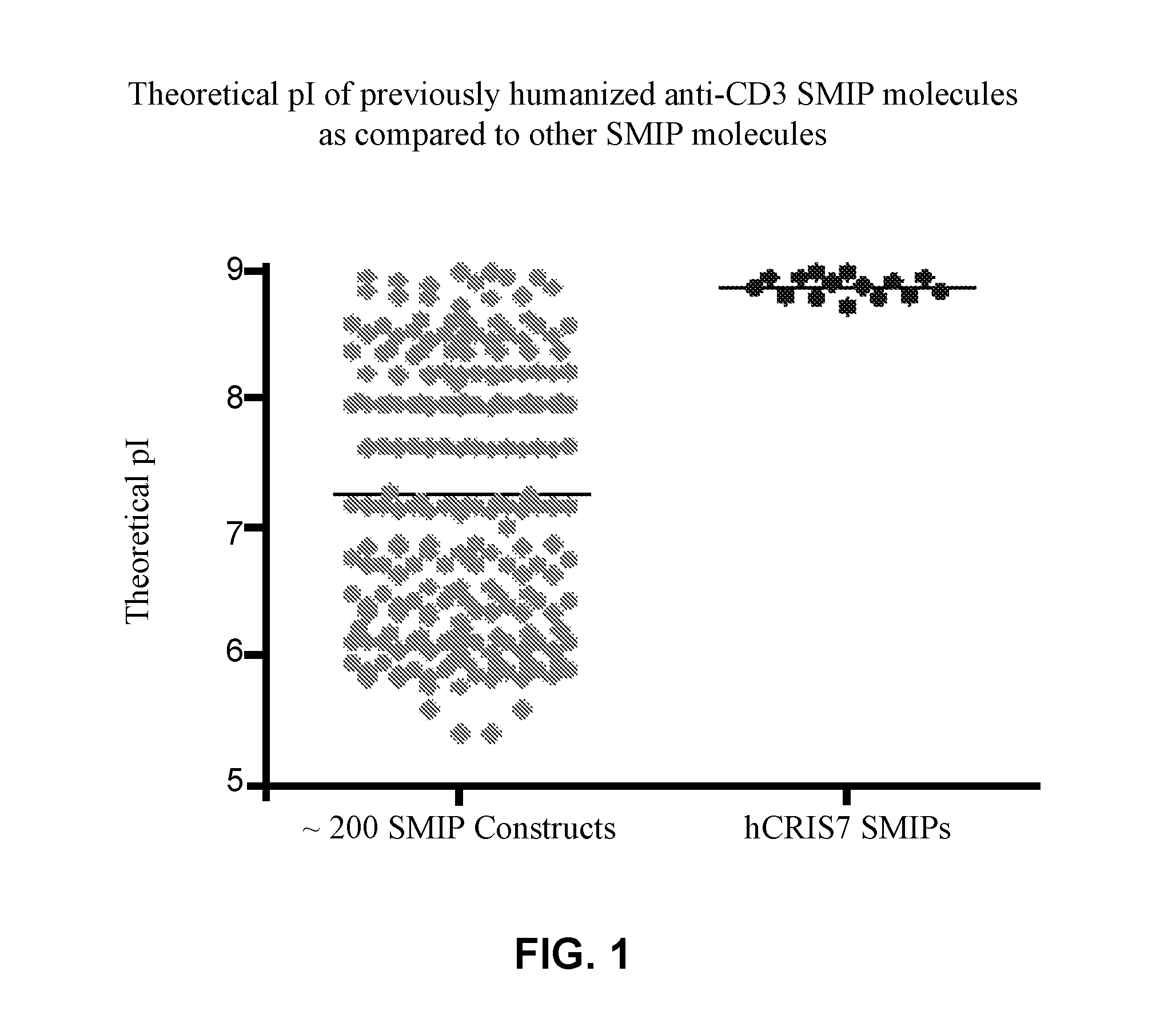
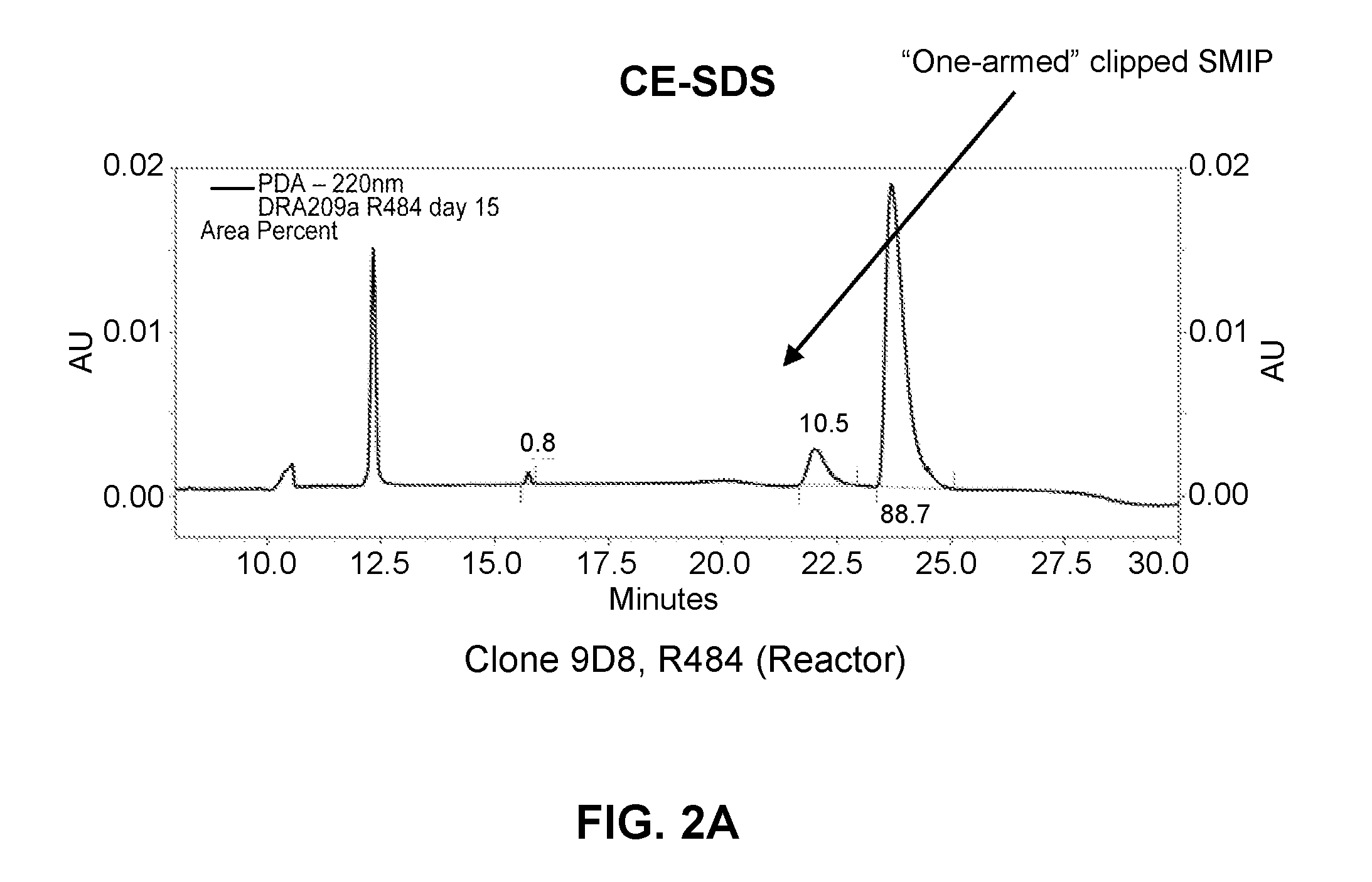
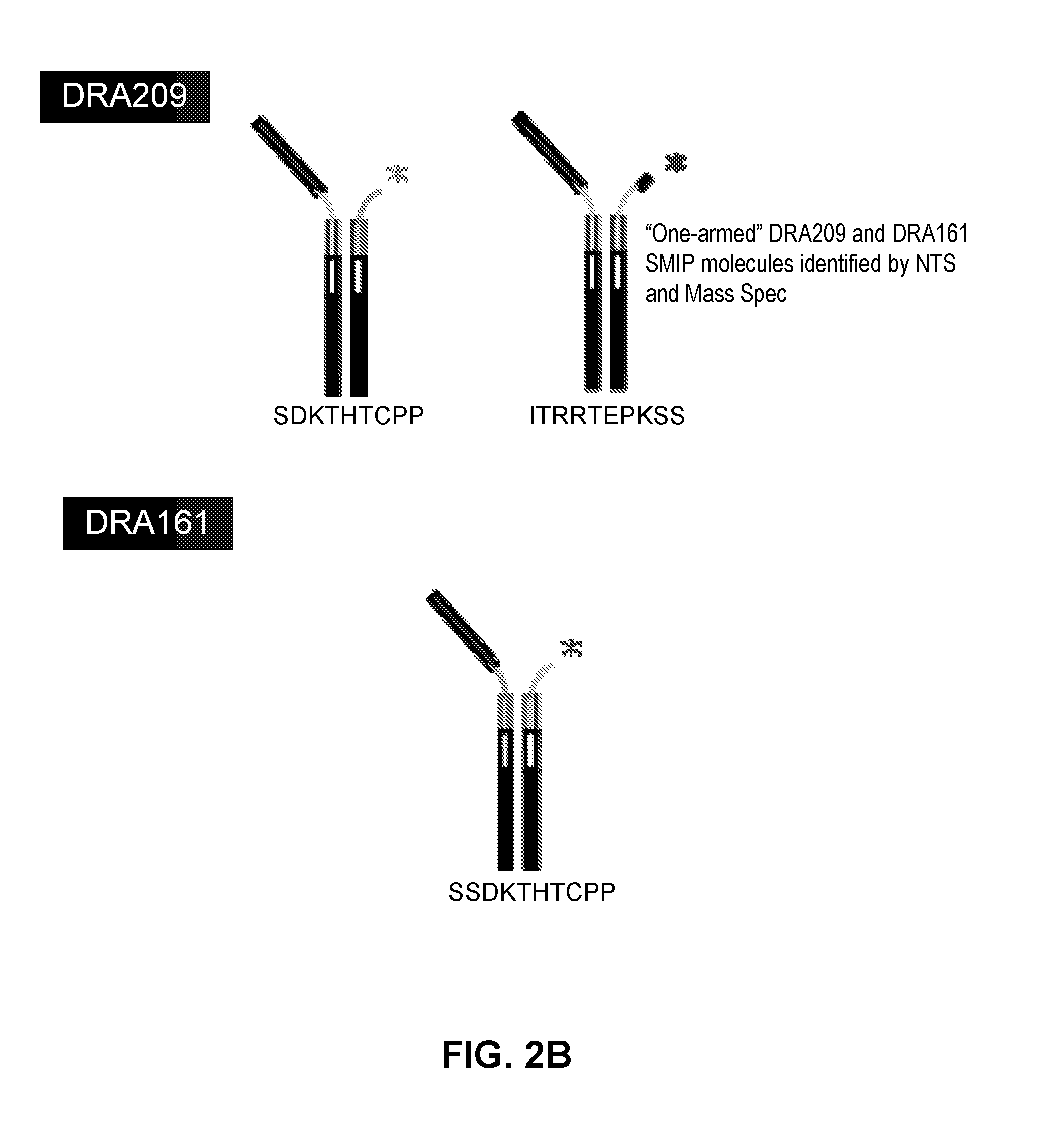
InactiveUS20150232557A1Reduce pointsReduced immunogenicity riskImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsAntibody fragmentsSingle-domain antibody
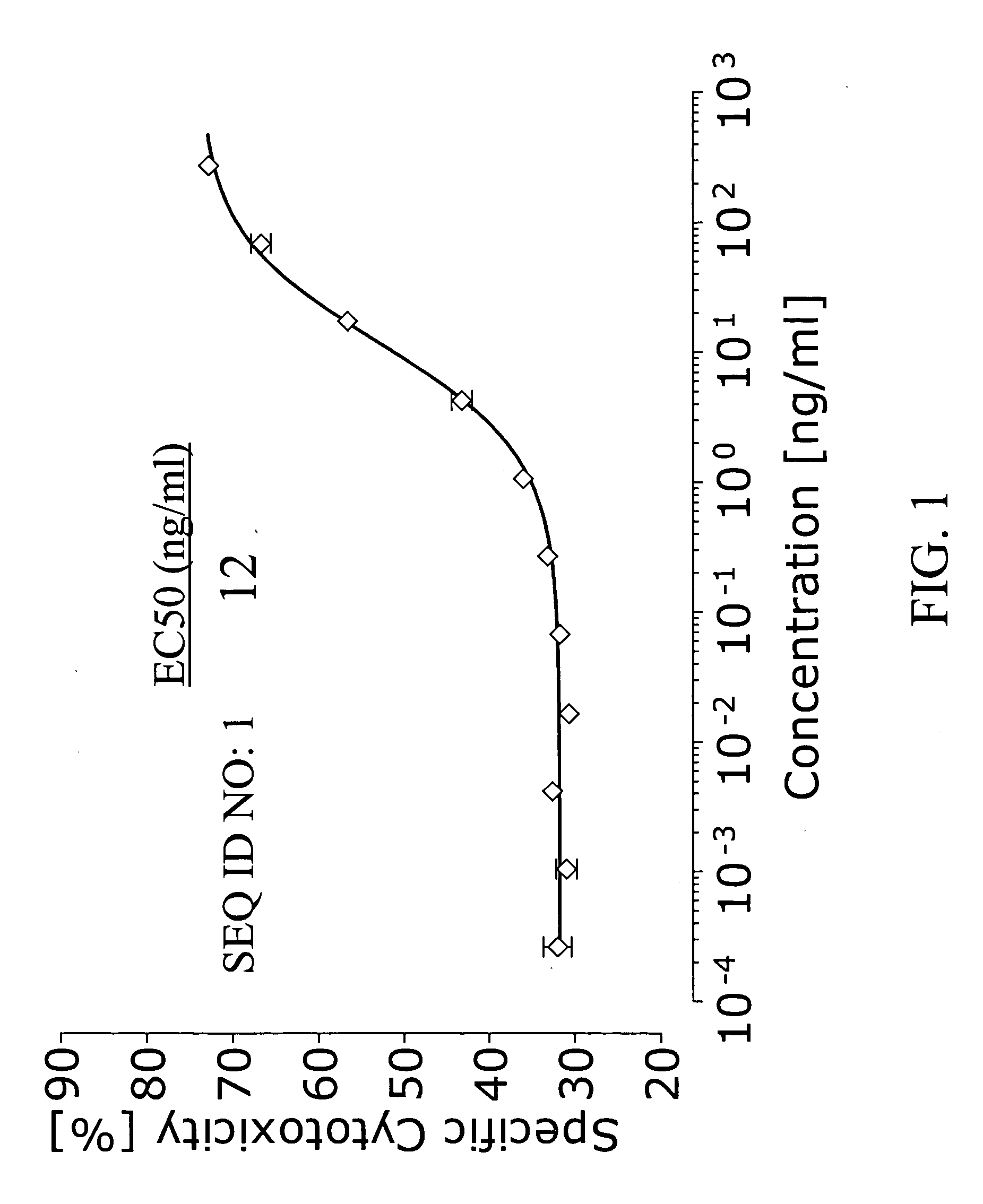
The present invention relates to mono-specific and multi-specific polypeptides that specifically bind or interact with CD3. These polypeptides can be, but are not limited to, antibodies, fragments thereof, scFvs, Fabs, di-scFvs single domain antibodies, diabodies, dual variable domain binding proteins and polypeptides containing an antibody or antibody fragments. In one embodiment, a multi-specific polypeptide binds both a T-cell receptor complex on T-cells and a tumor antigen to induce target-dependent T-cell cytotoxicity, activation and proliferation.
Owner:APTEVO RES & DEV LLC
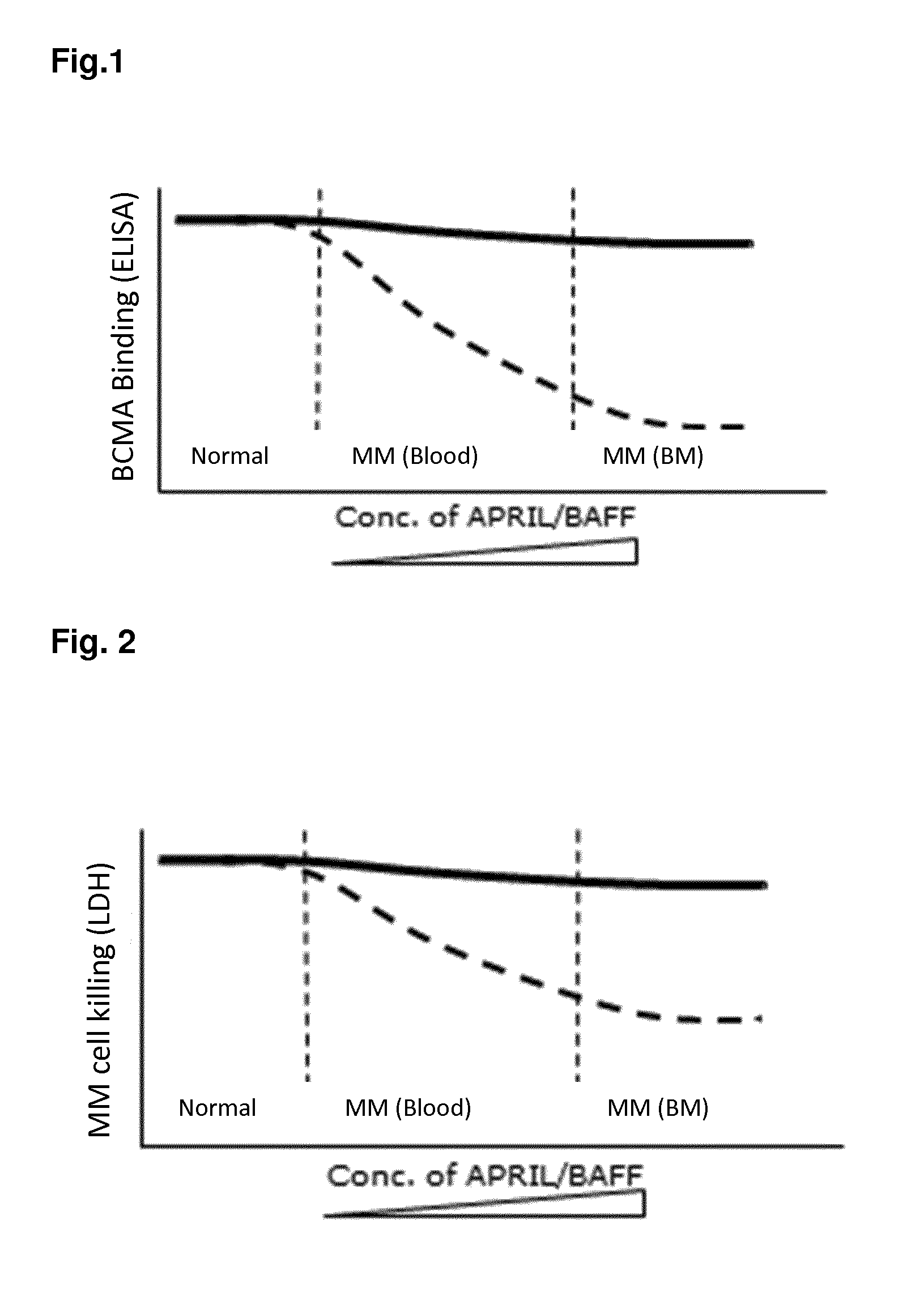
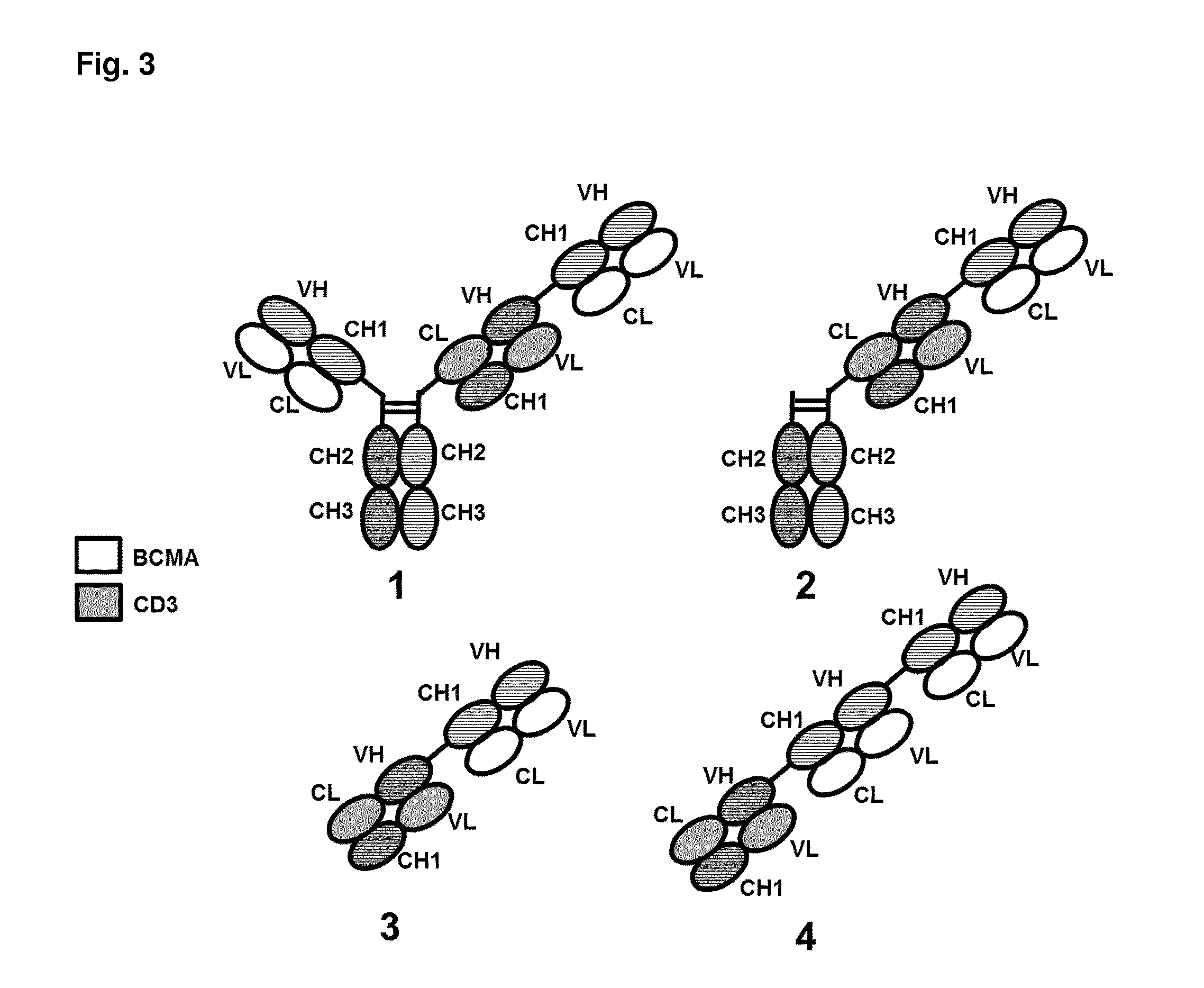
Bispecific antibodies against cd3 and bcma
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
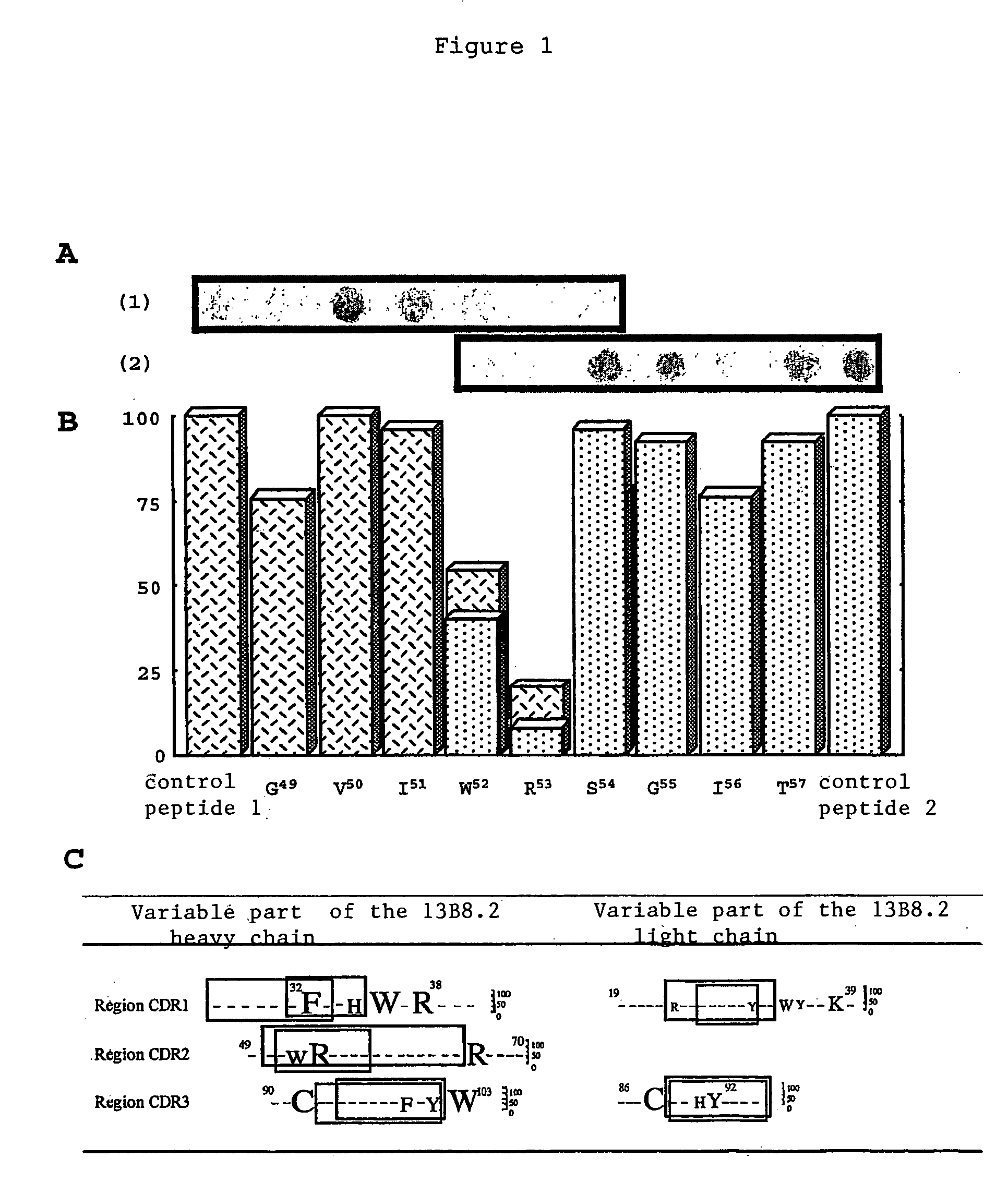
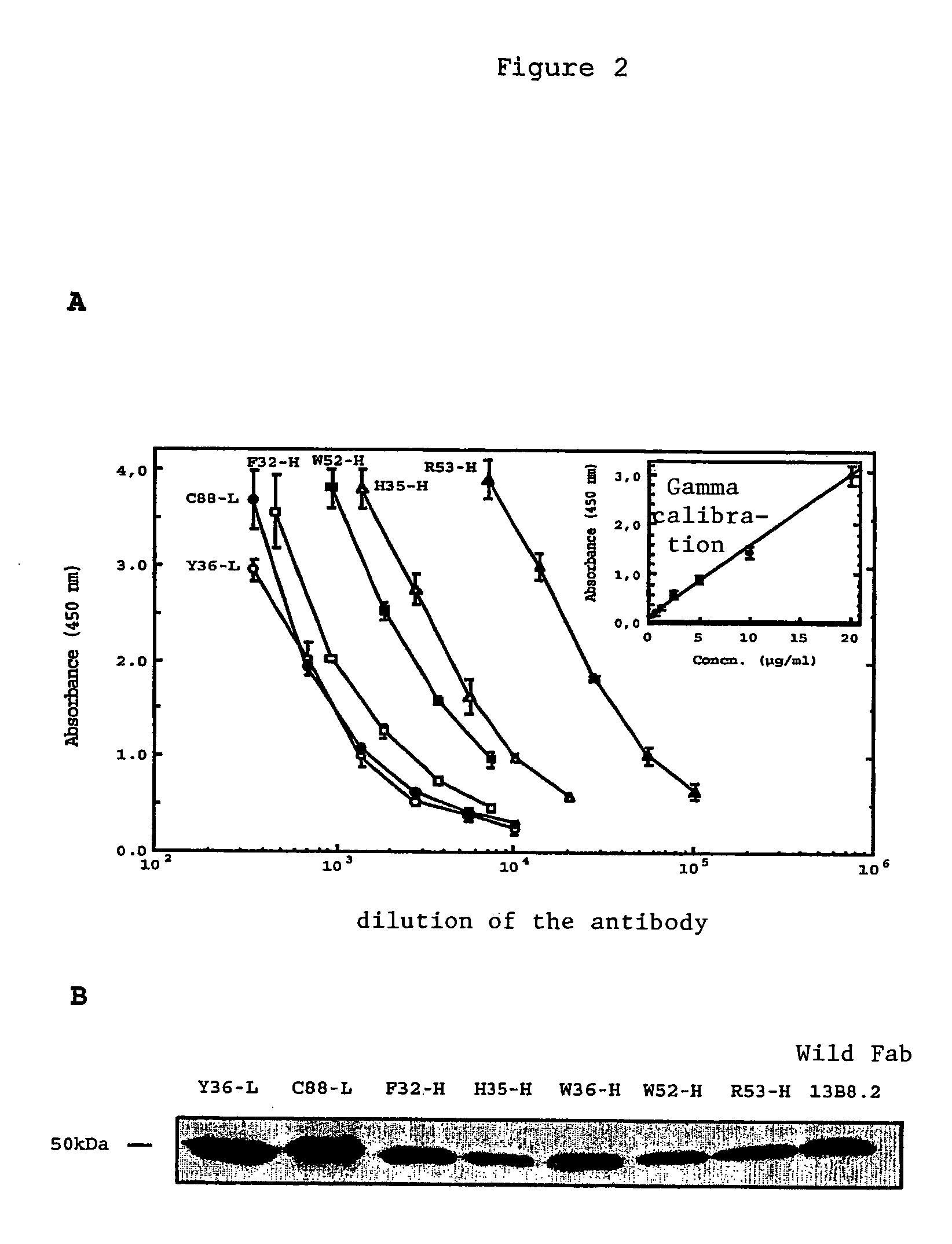
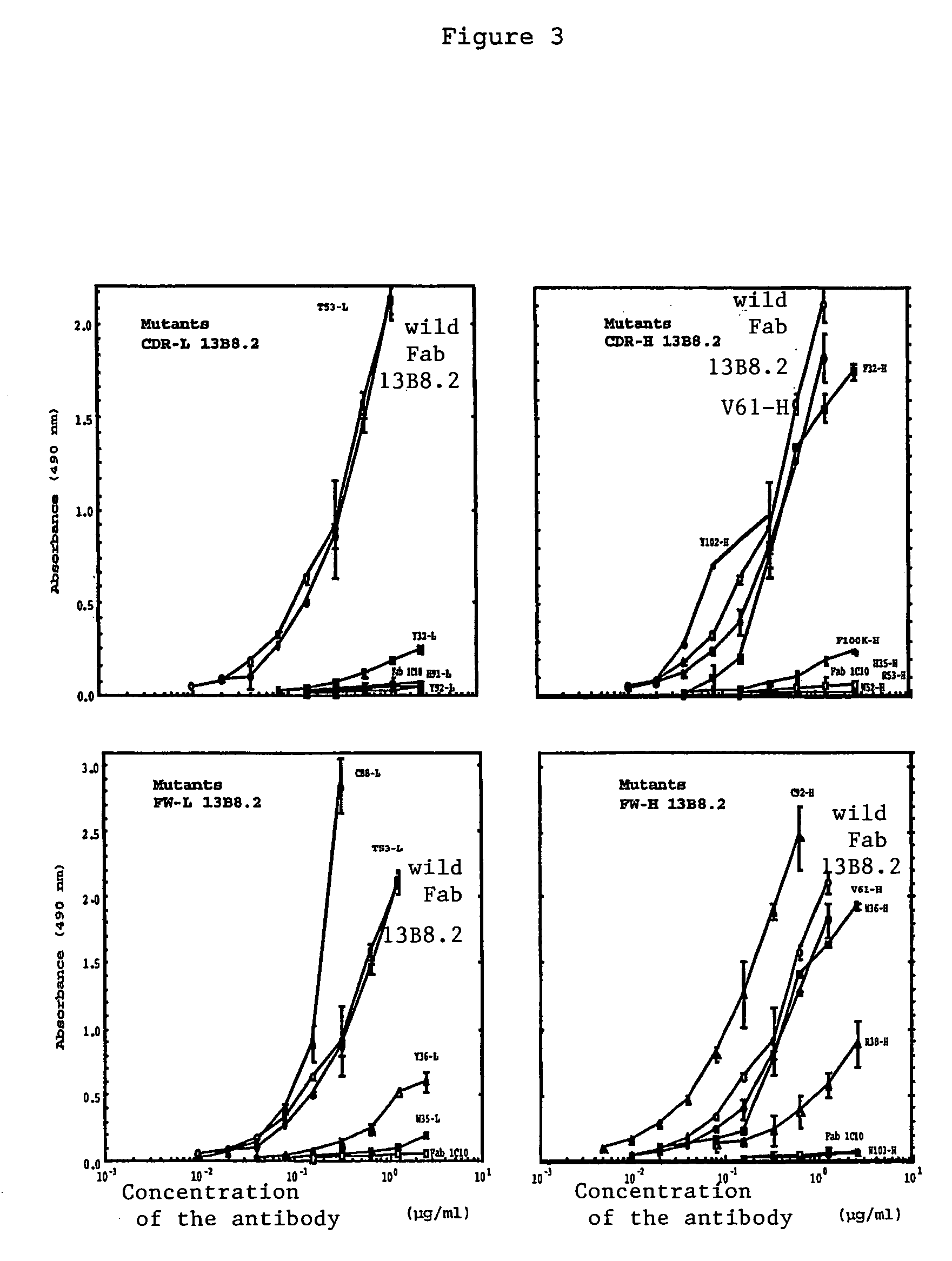
Mutant Fab fragments of the chimeric 13B8.2 anti-CD4 antibody and their applications
A mutant Fab fragment of the 13B8.2 anti-CD4 antibody that binds a CD4 molecule and includes a mutation of at least one residue in a position situated in the VH variable domain of the heavy chain and / or in a position situated in the Vκ variable domain of the light chain.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Isolating Cells Expressing Secreted Proteins
InactiveUS20090137416A1Easy to detectImprove isolationLibrary screeningBiological material analysisSurface displayVariable domain
A method of detecting and isolating cells that produce a secreted protein of interest (POI) that has a T cell receptor variable domain, comprising: a) constructing a cell line transiently or stably expressing a cell surface capture molecule, which binds the POI, by transfecting the cell line with a nucleic acid that encodes such cell surface capture molecule; b) transfecting said cell simultaneously or subsequently with a second nucleic acid that encodes a POI wherein such POI is secreted; c) detecting the surface-displayed POI by contacting the cells with a detection molecule, which binds the POI; and d) isolating cells based on the detection molecule.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
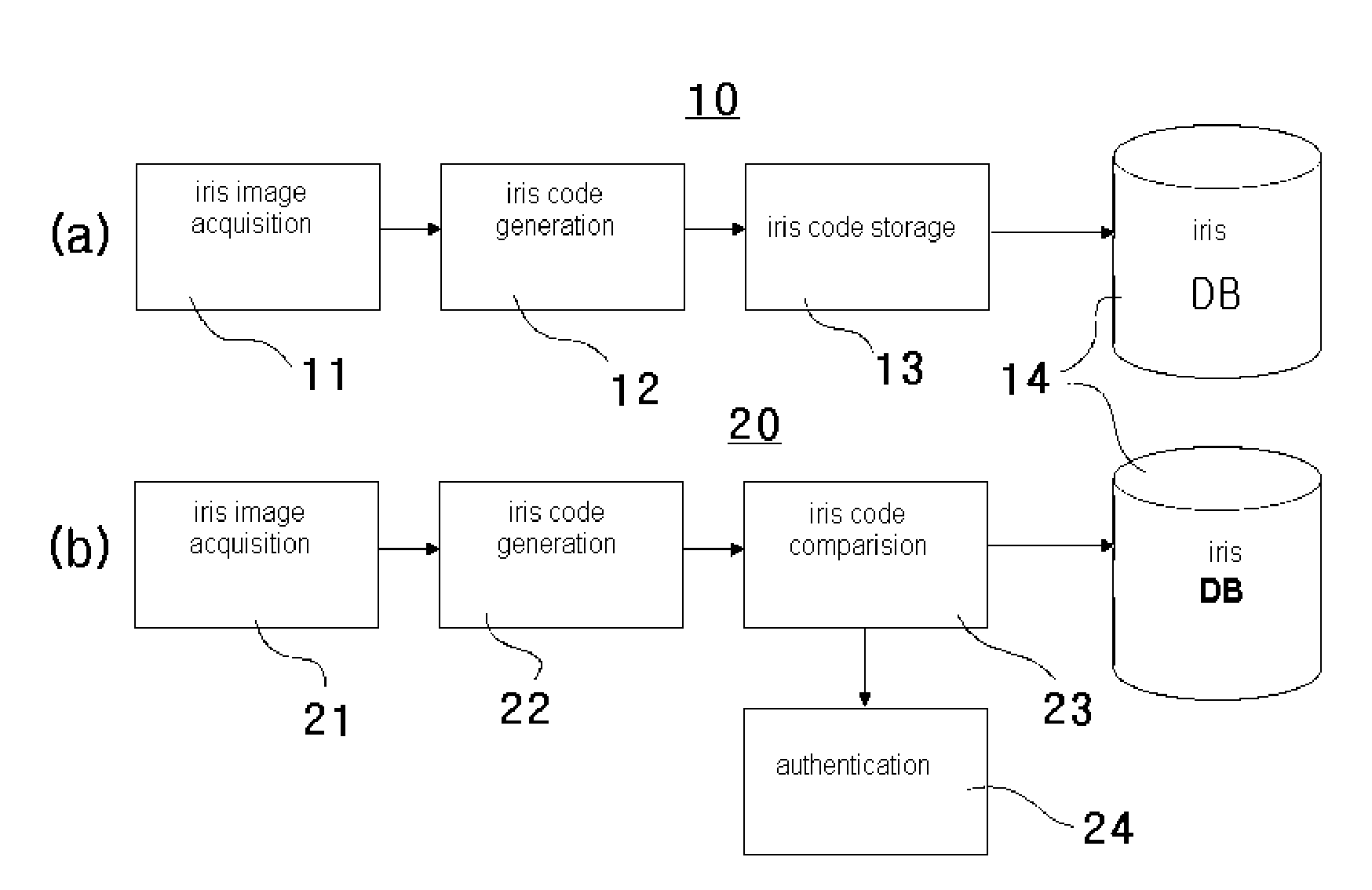
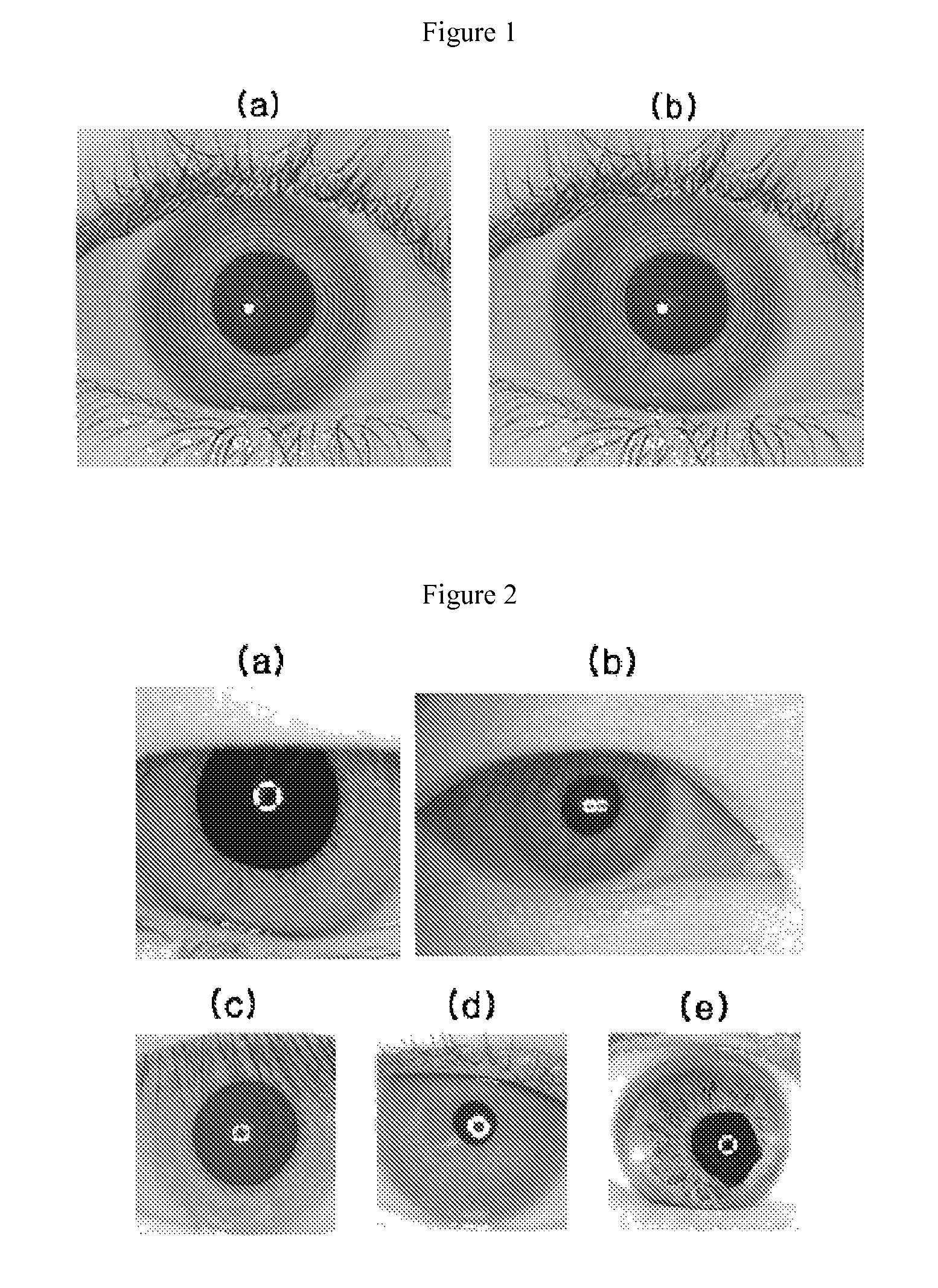
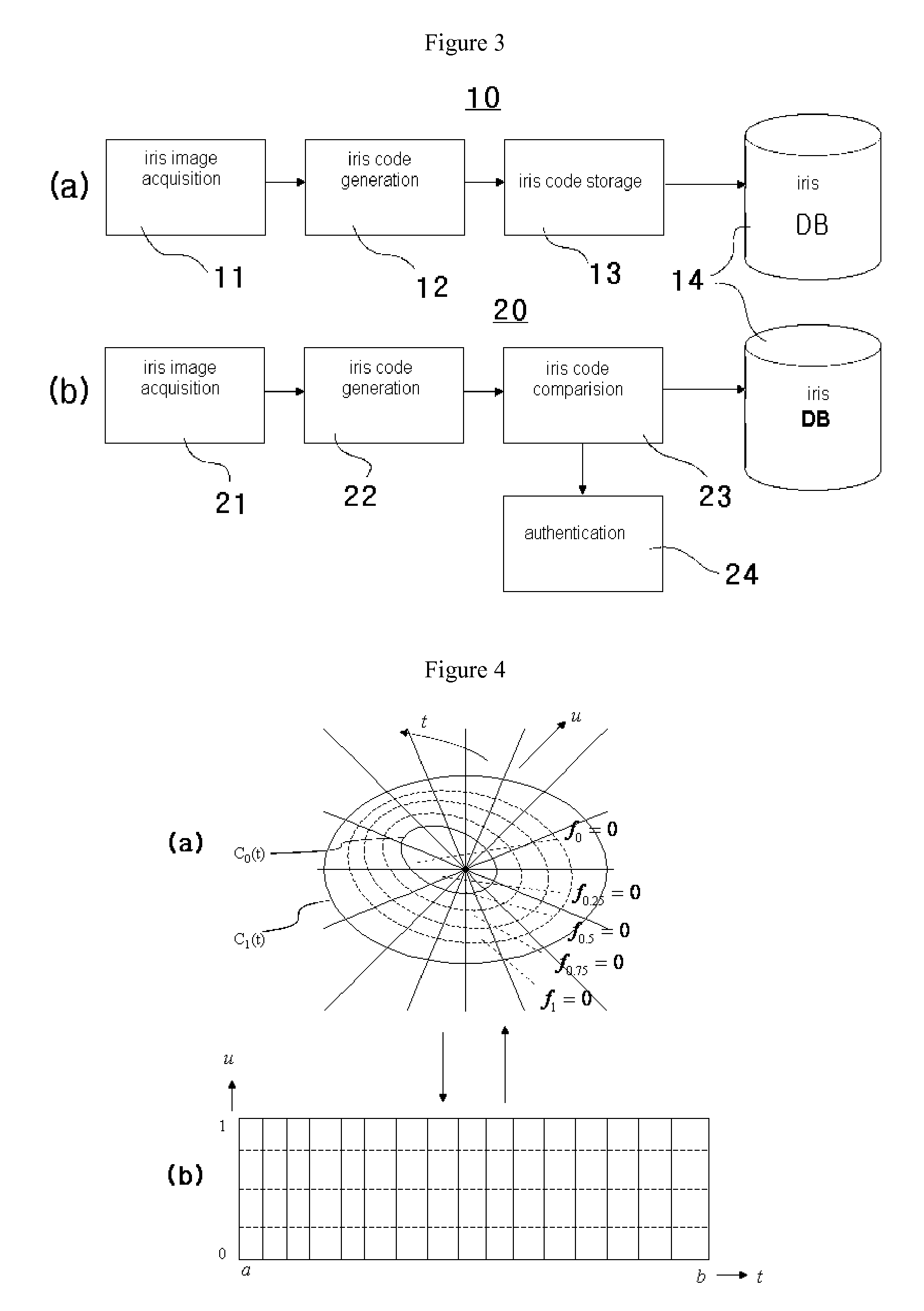
Multi-scale variable domain decomposition method and system for iris identification
InactiveUS8009876B2Quick identificationDrawing from basic elementsAcquiring/recognising eyesVariable domainIris image
An iris identification method and system, which divide an iris image, which is acquired for personal identification, into a plurality of equal / unequal and multiscale regions, generate a corresponding code corresponding to the respective regions, organizing codes into a database, generate a code at the time of authentication in the same manner, and identify a person by comparing this code with the codes stored in the database, thus improving identification speed and rate.
Owner:IRITECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com