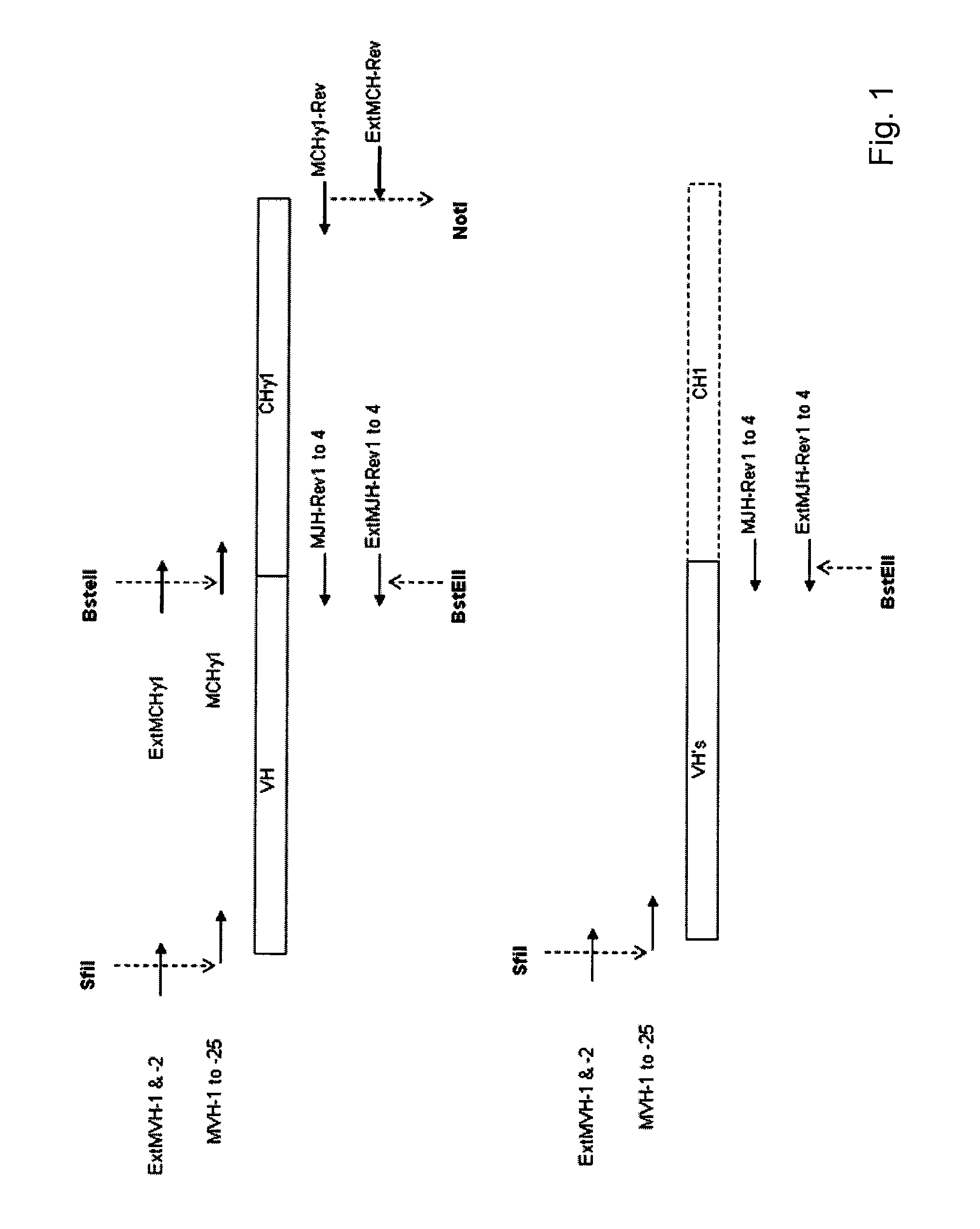
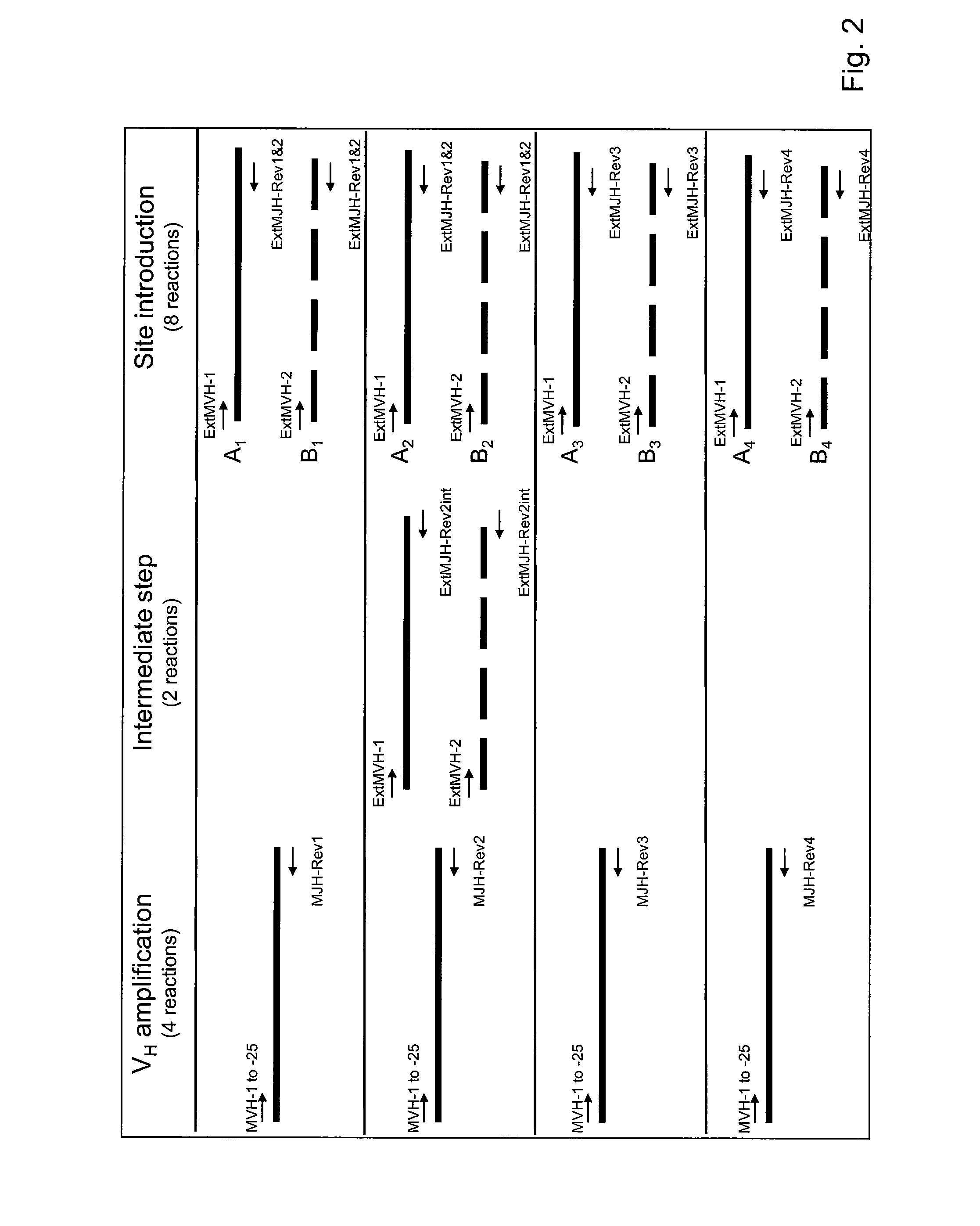
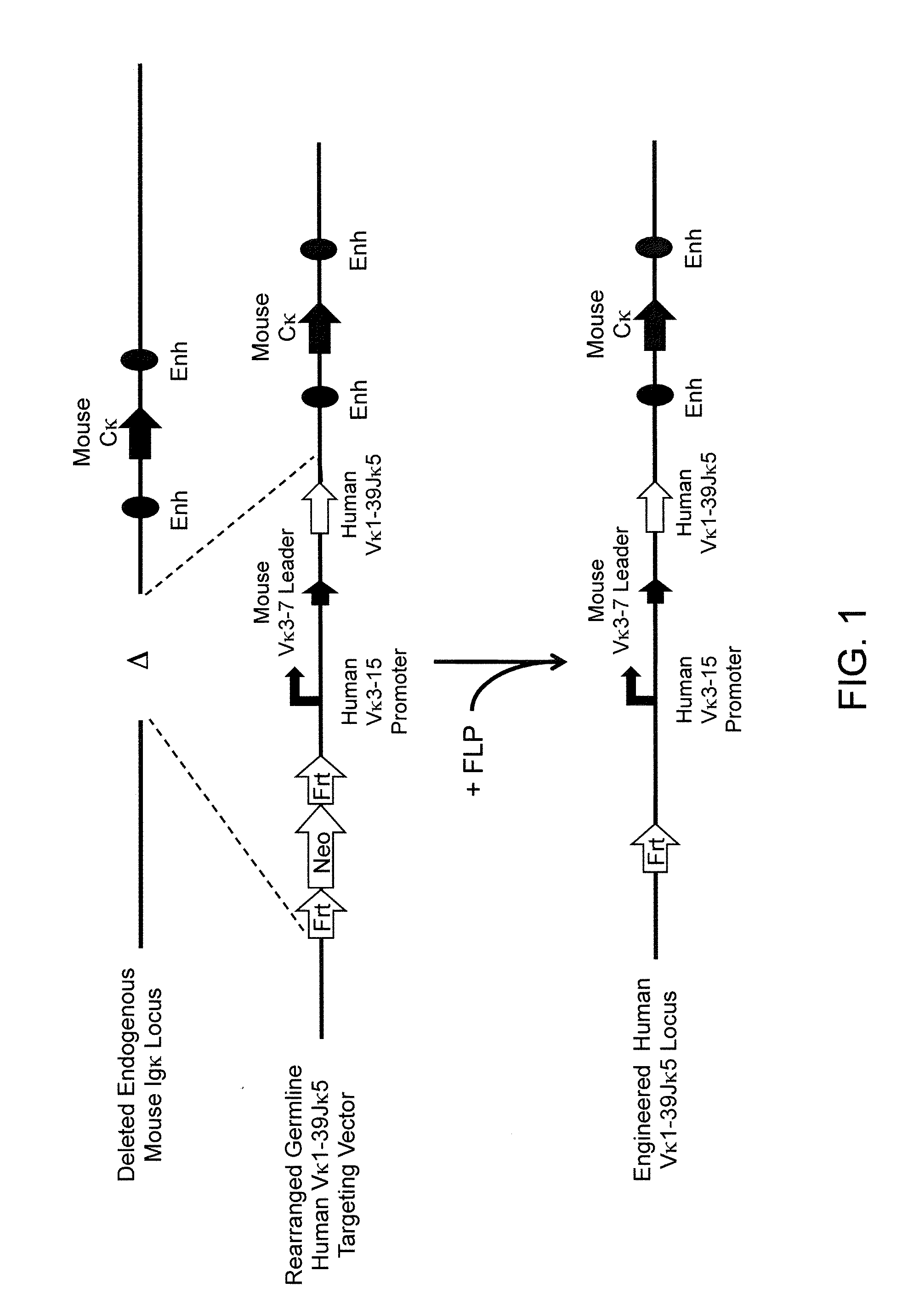
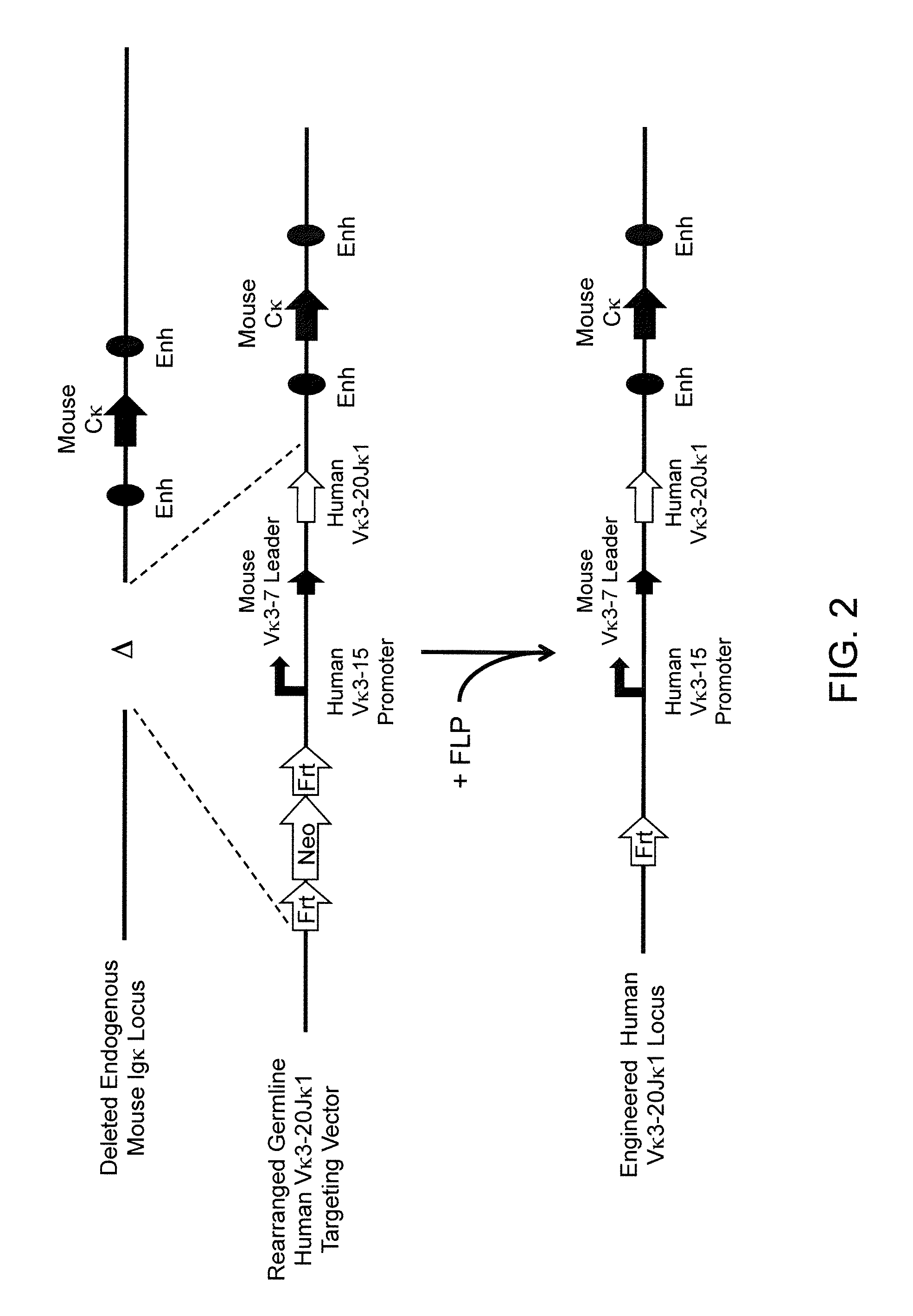
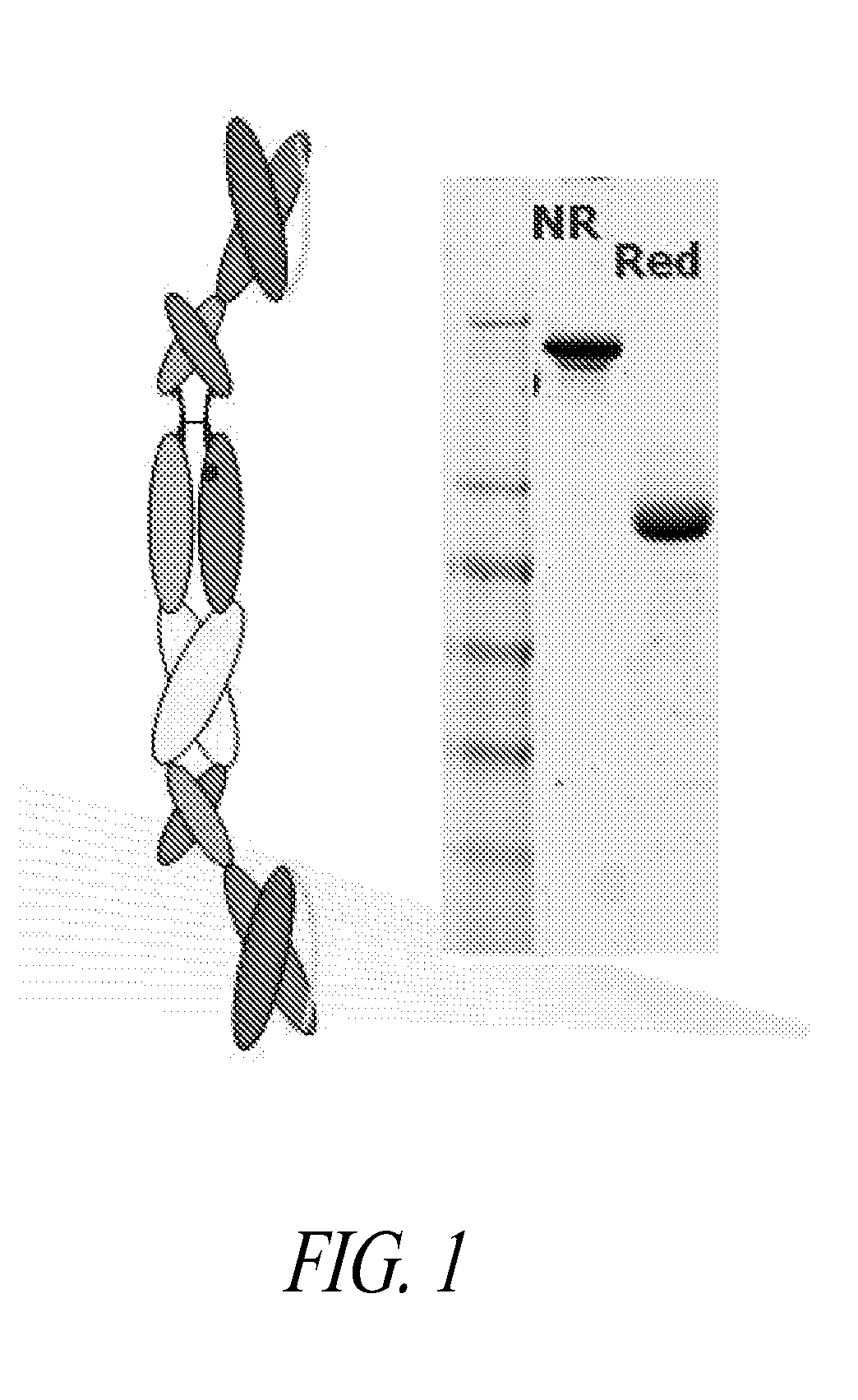
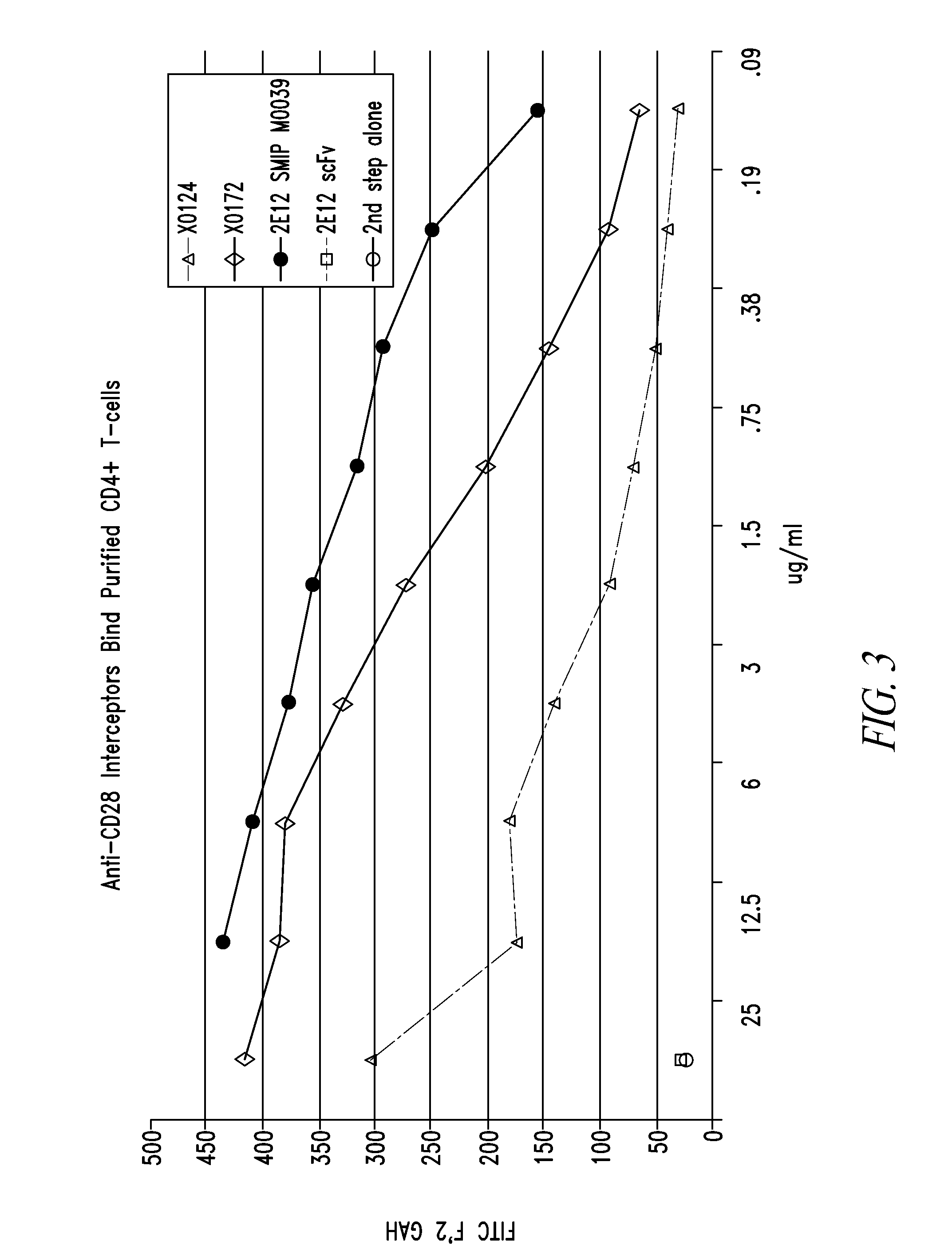
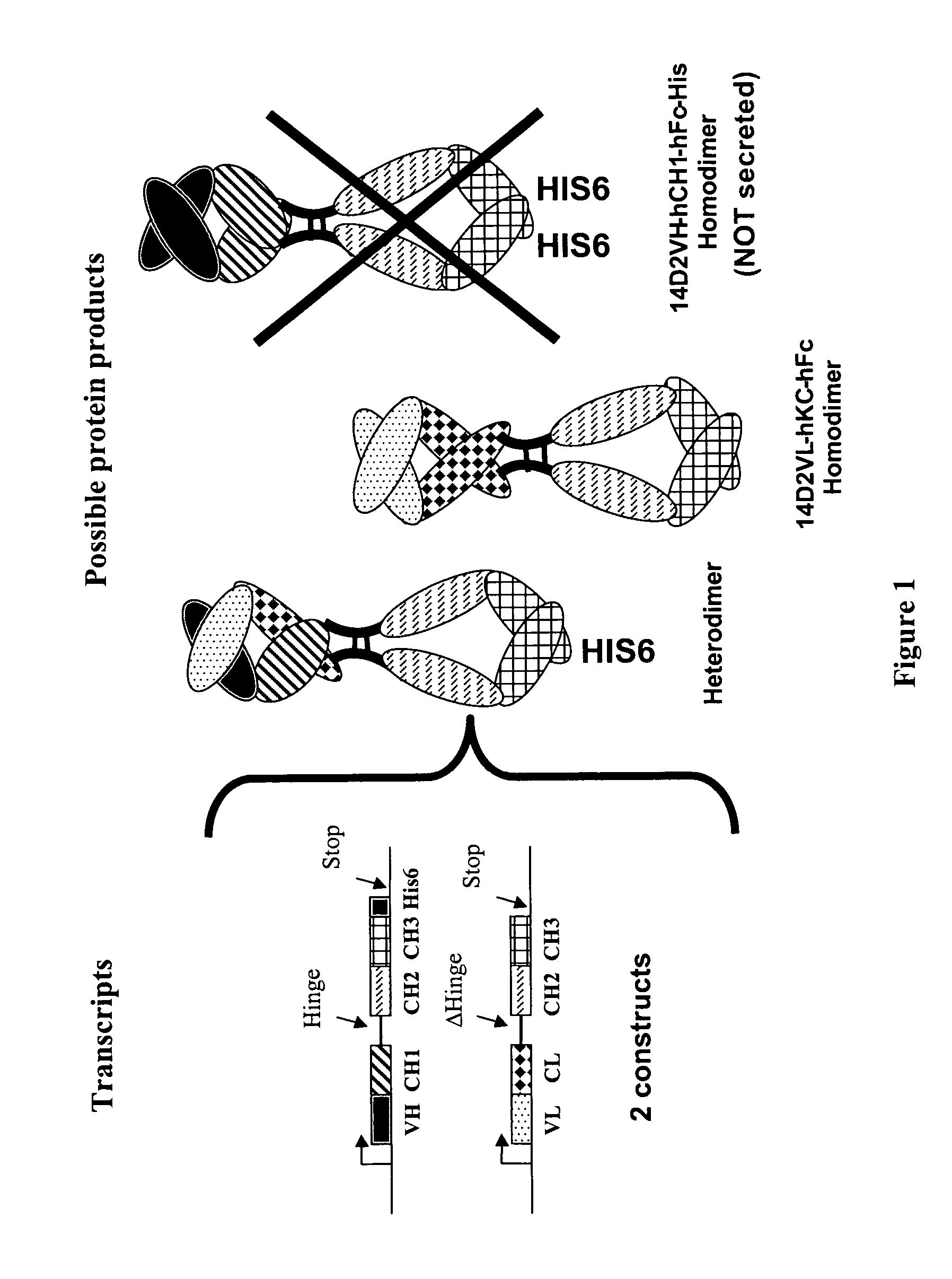
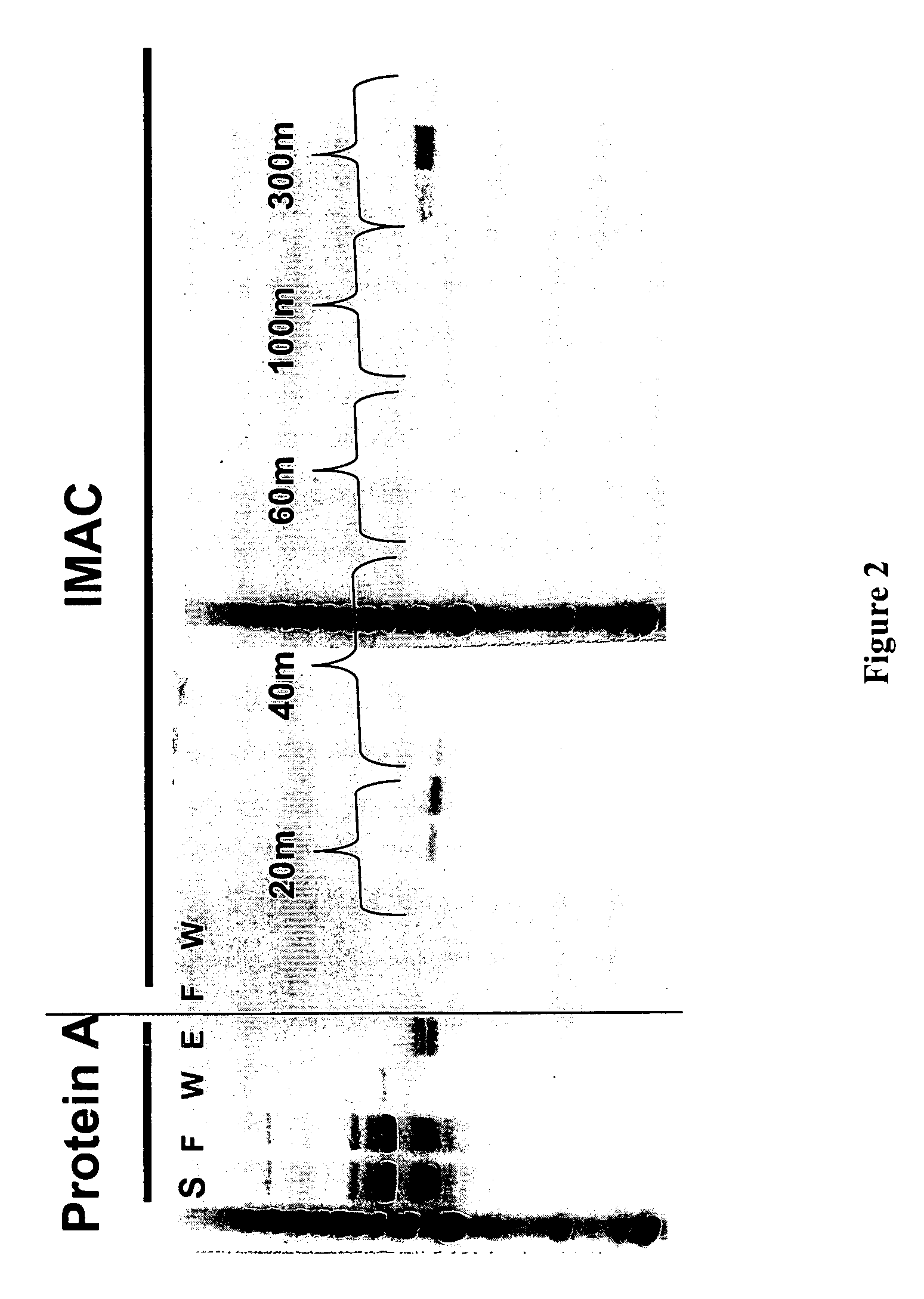
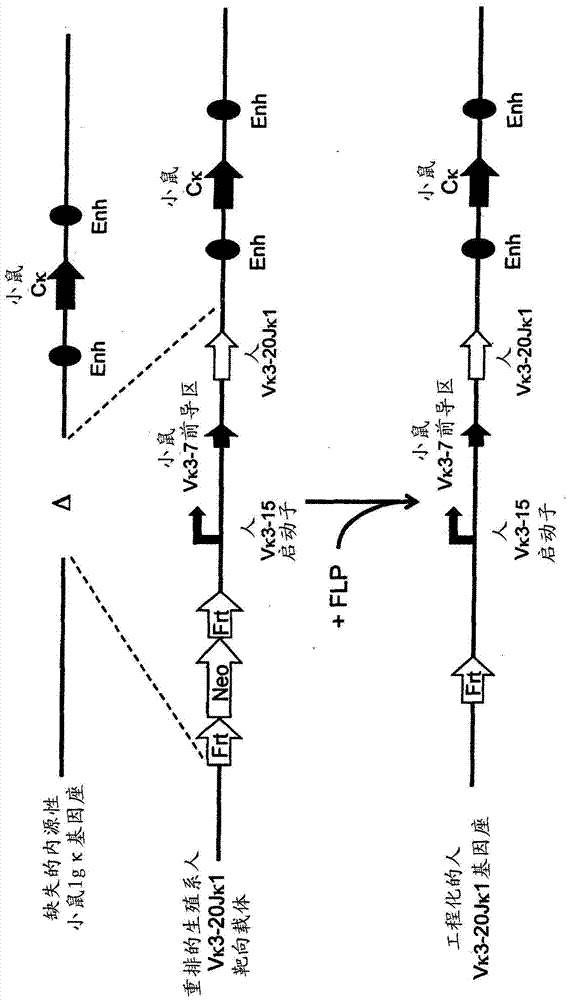
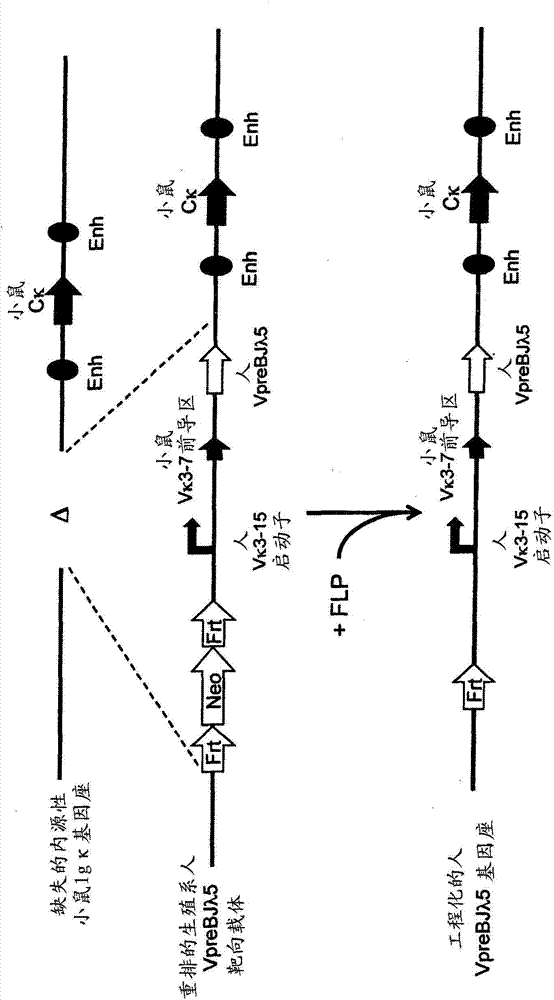
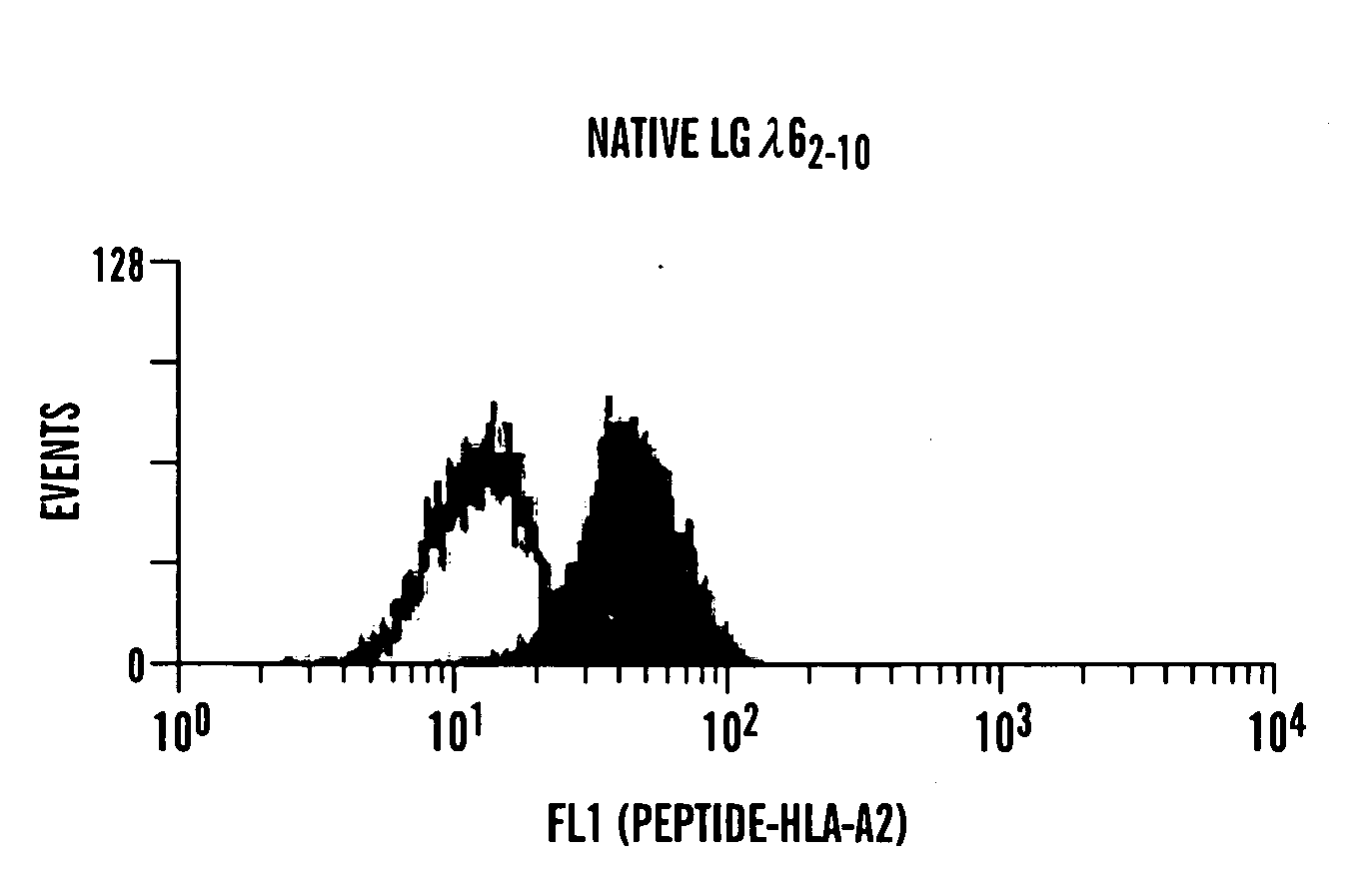
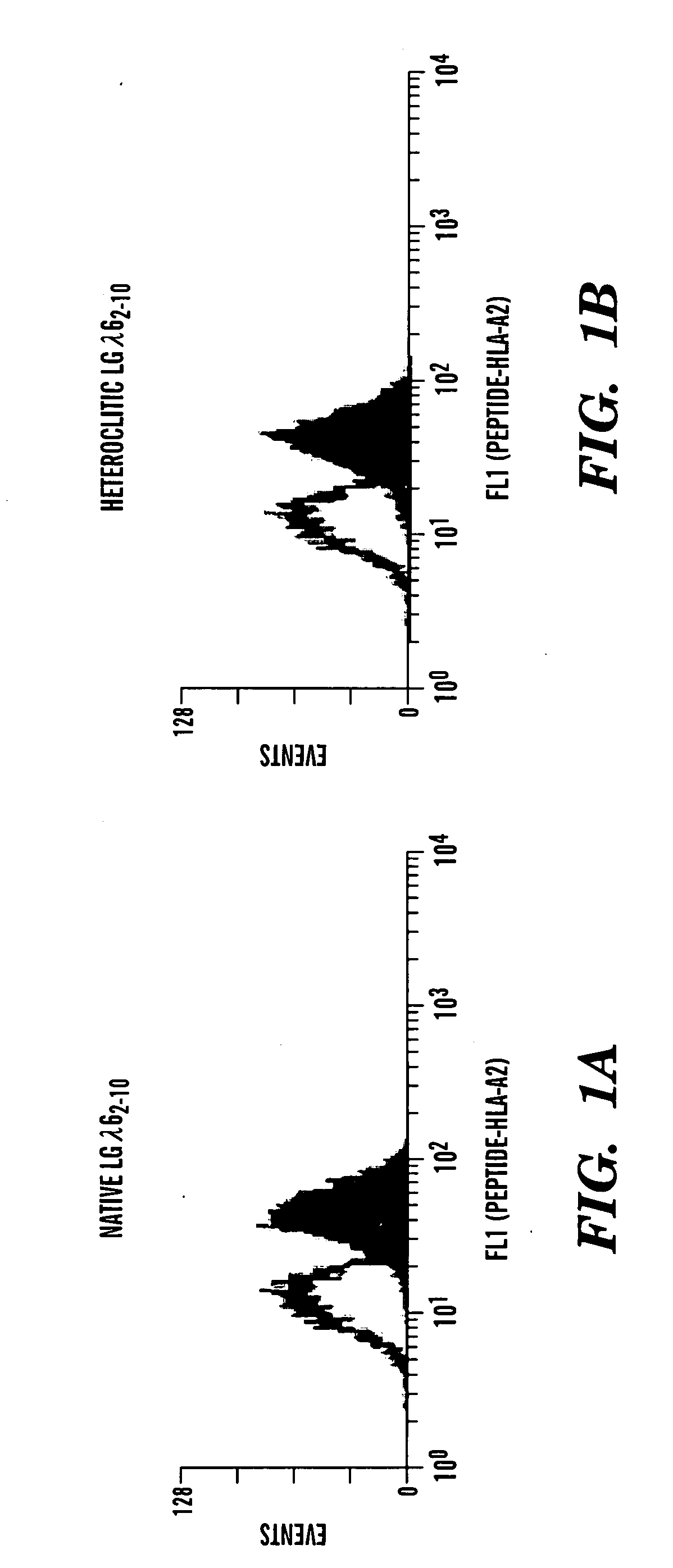
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42 results about "Immunoglobulin light chain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
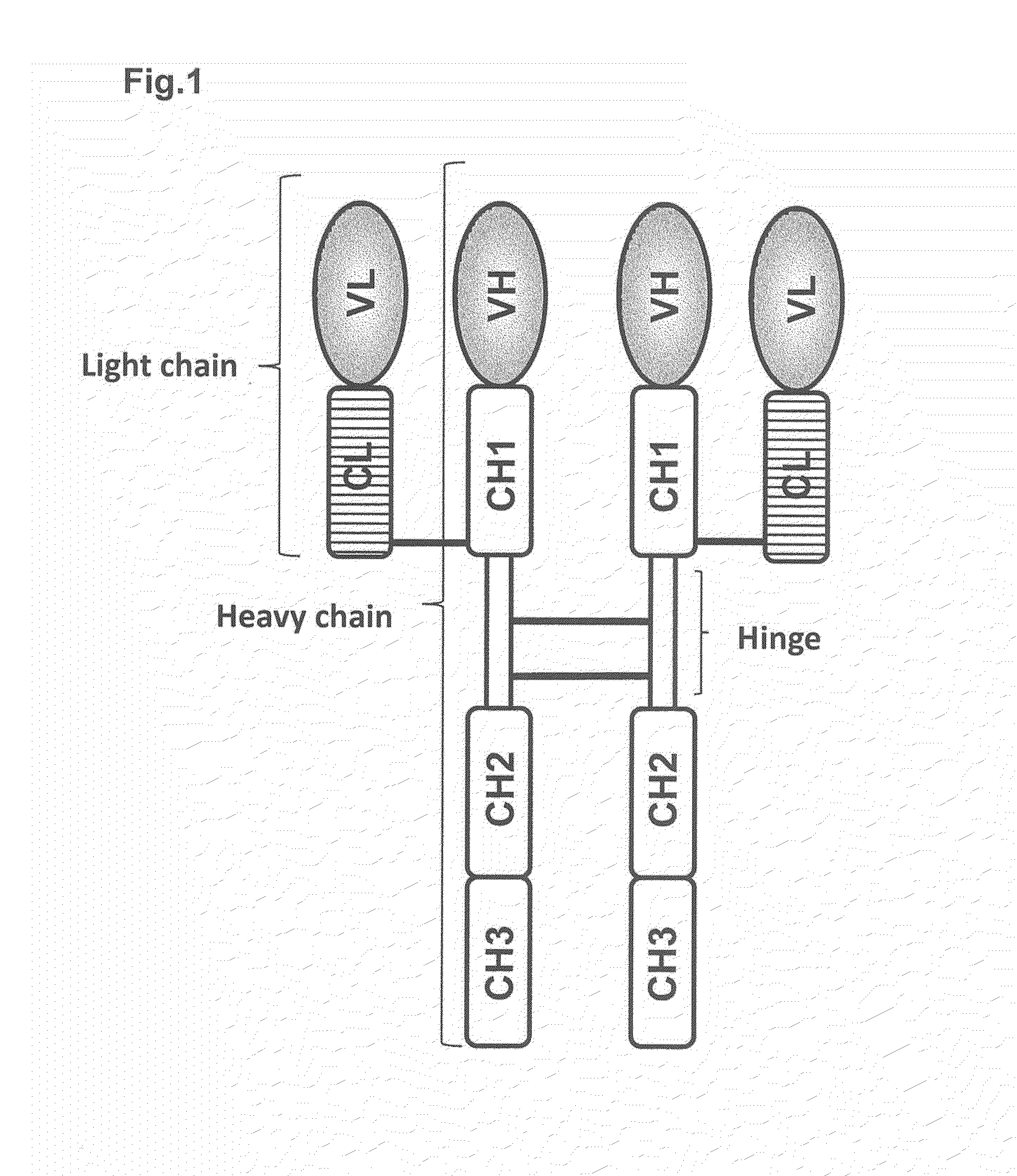
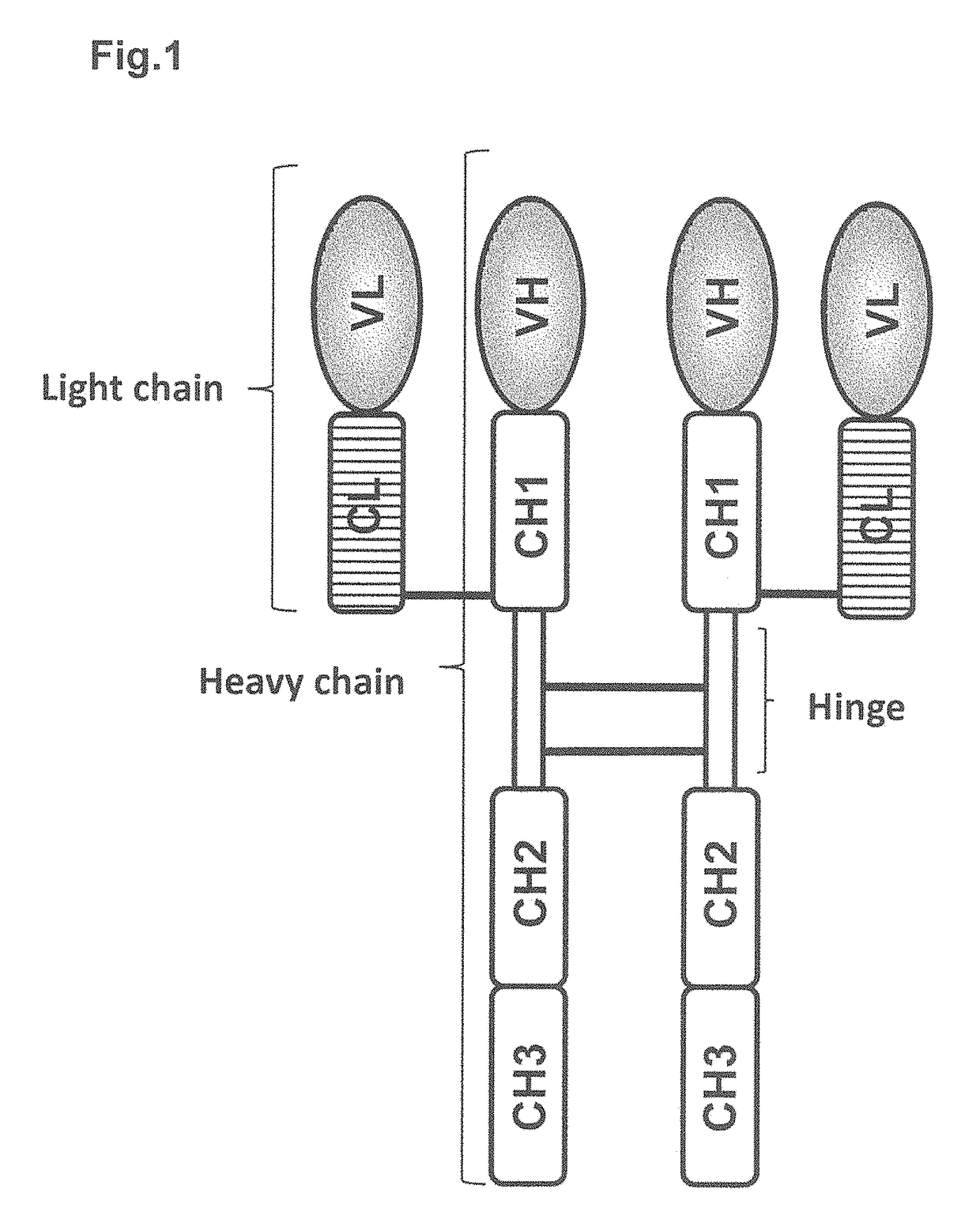
The immunoglobulin light chain is the small polypeptide subunit of an antibody (immunoglobulin). A typical antibody is composed of two immunoglobulin (Ig) heavy chains and two Ig light chains.
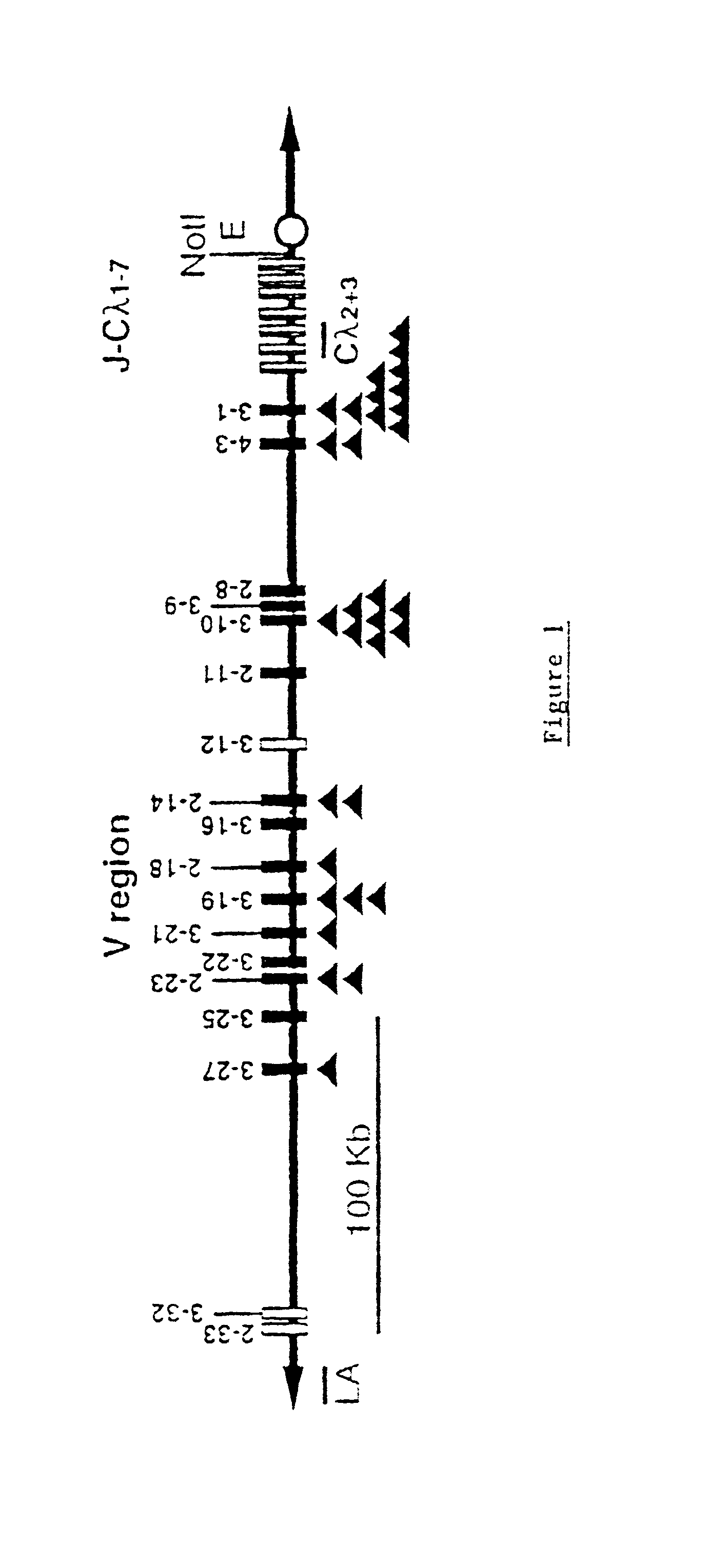
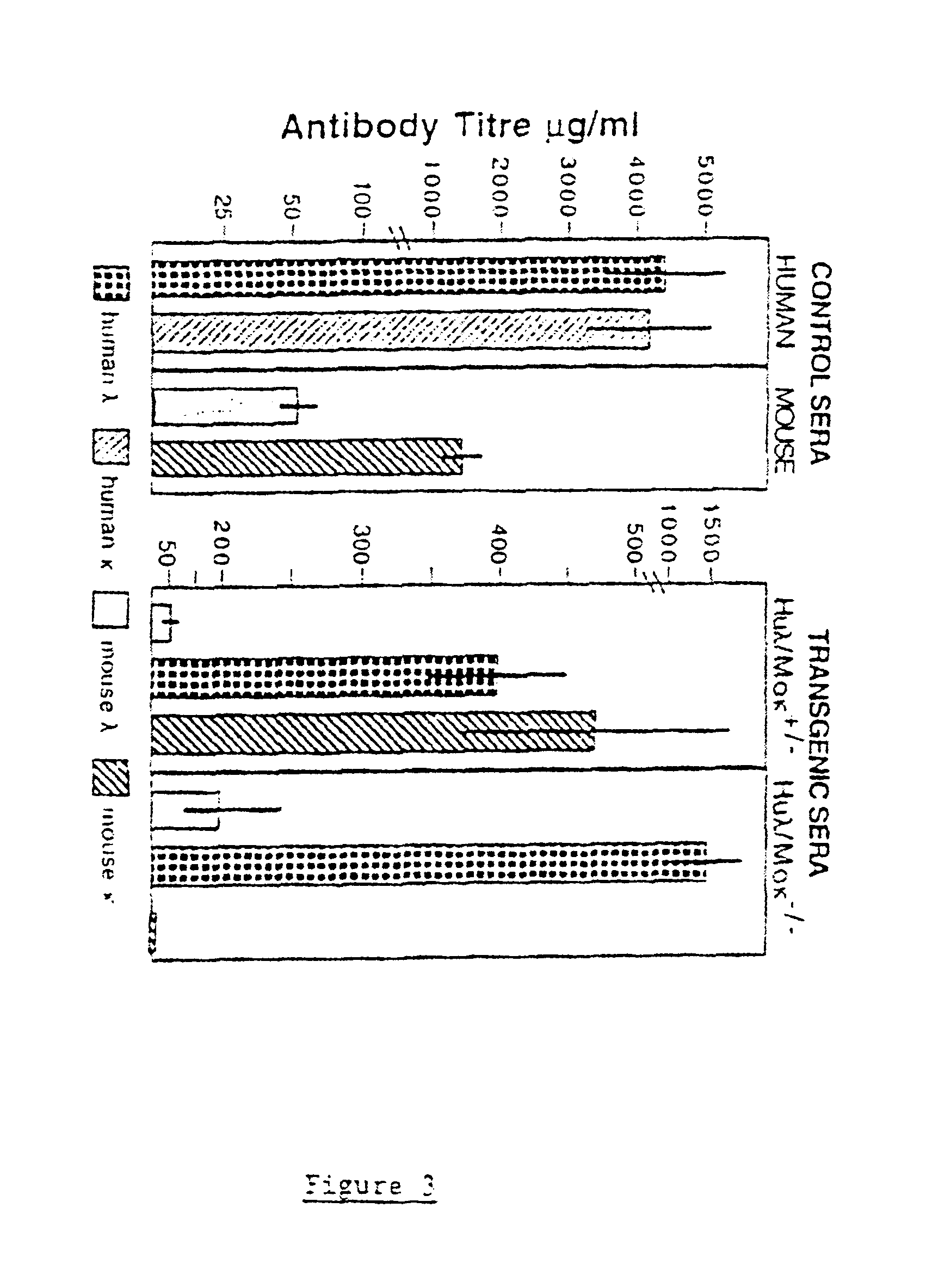
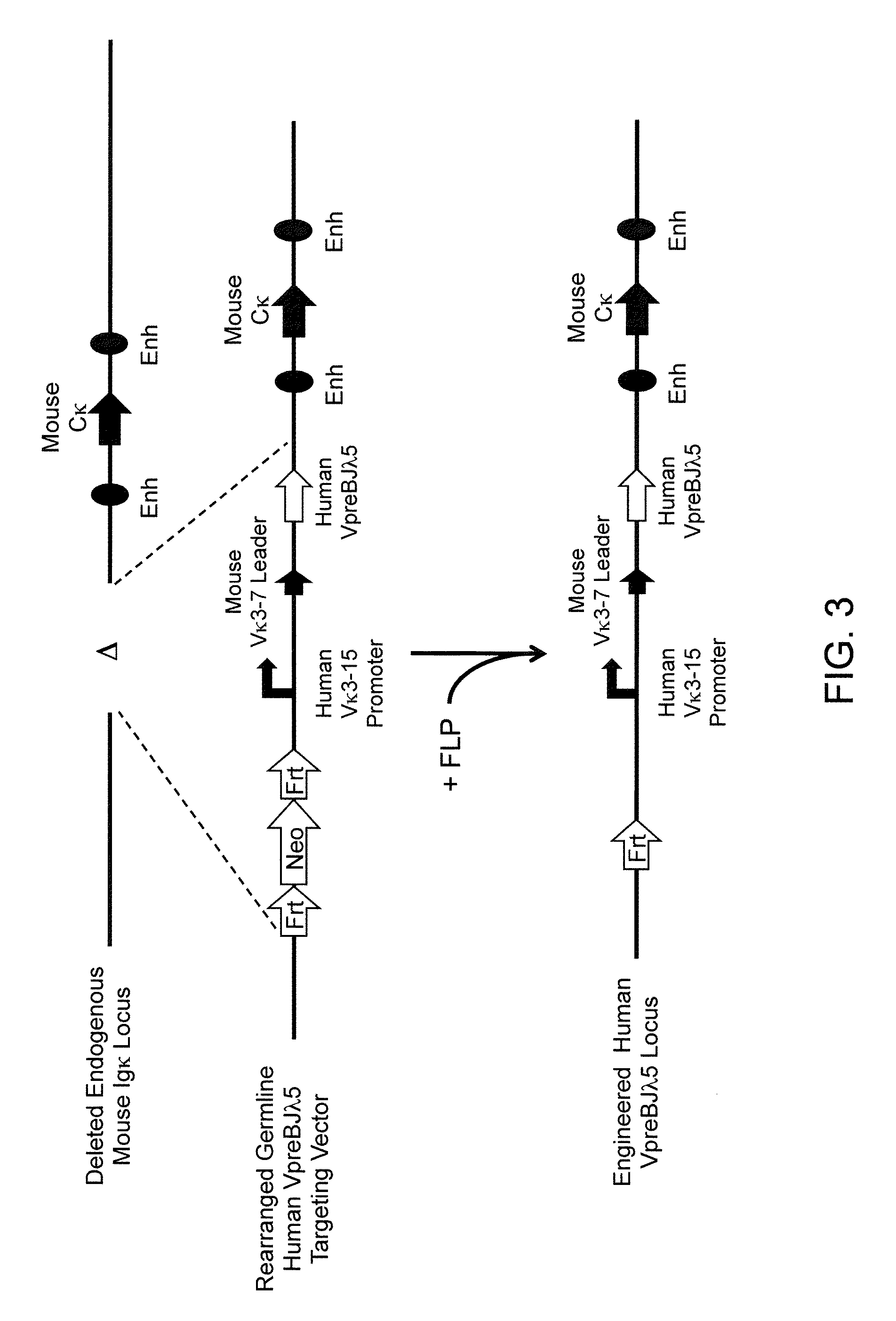
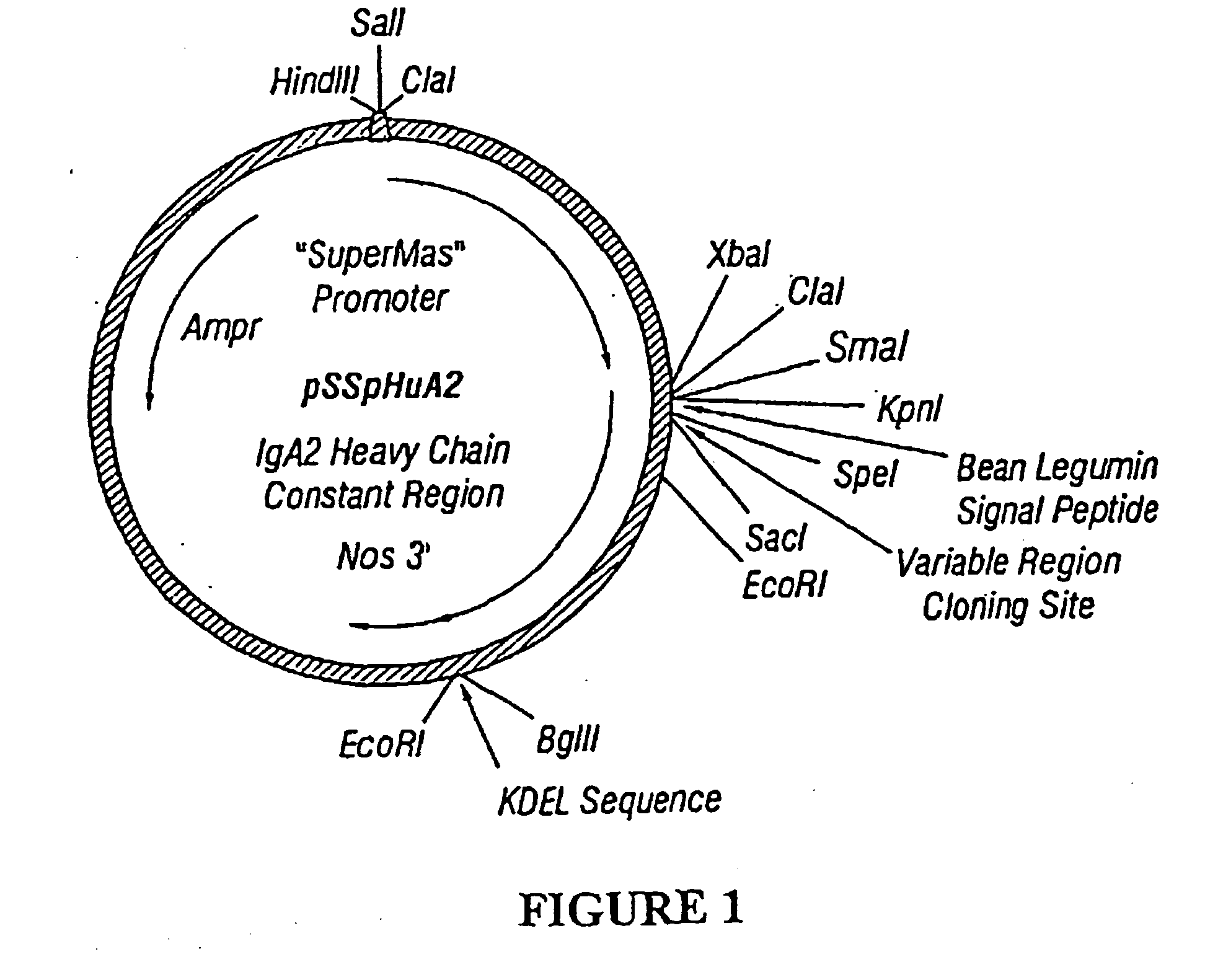
Murine expression of a human IgA lambda locus
InactiveUS6998514B2High expressionTissue cultureImmunoglobulinsImmunoglobulin light chainMonoclonal antibody
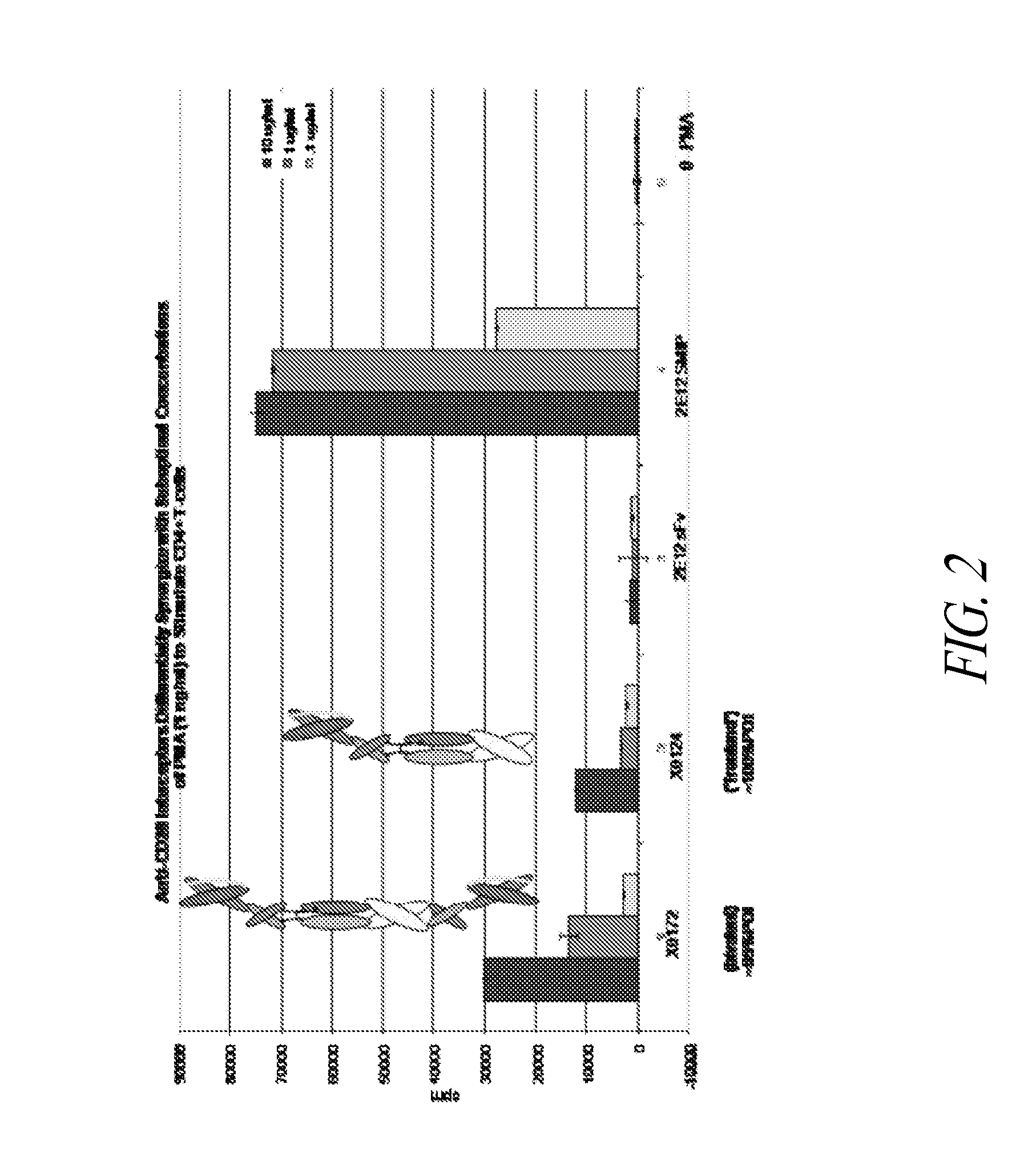
In humans, approximately 60% of expressed immunoglobulin light chains are of the Kappa type and 40% of the Lambda type. In mice, there is almost no expression from the Lambda locus and over 95% of light chains are of Kappa type. The present invention discloses, among other things, transgenic mice carrying most of the human Ig Lambda light chain locus in their genome. The resulting mice express light chains with Kappa / Lambda ratio similar to the human ratio. Breeding of HuIg Lamda mice to Kappa-deficient mice also is described, as well as the generation of human monoclonal antibodies from transgenic mice with human Ig Lambda locus.
Owner:BABRAHAM INST
Antibody producing non-human mammals
ActiveUS20100146647A1Low variabilityLow immunogenicityAnimal cellsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHuman animalDNA rearrangement
Owner:MERUS NV
Methods For Making Fully Human Bispecific Antibodies Using A Common Light Chain
InactiveUS20130045492A1Reduce in quantitySimple methodAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsEpitopeProtein insertion
A genetically modified mouse is provided, wherein the mouse expresses an immunoglobulin light chain repertoire characterized by a limited number of light chain variable domains. Mice are provided that express just one or a few immunoglobulin light chain variable domains from a limited repertoire in their germline. Methods for making bispecific antibodies having universal light chains using mice as described herein, including human light chain variable regions, are provided. Methods for making human variable regions suitable for use in multispecific binding proteins, e.g., bispecific antibodies, and host cells are provided. Bispecific antibodies capable of binding first and second antigens are provided, wherein the first and second antigens are separate epitopes of a single protein or separate epitopes on two different proteins are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Antibody producing non-human mammals
InactiveUS20100069614A1Easy to openEasy maintenanceAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against virusesHuman animalDNA rearrangement
Described are transgenic, non-human animals comprising a nucleic acid encoding an immunoglobulin light chain, whereby the immunoglobulin light chain is human, human-like, or humanized. The nucleic acid is provided with a means that renders it resistant to DNA rearrangements and / or somatic hypermutations. In one embodiment, the nucleic acid comprises an expression cassette for the expression of a desired molecule in cells during a certain stage of development in cells developing into mature B cells. Further provided is methods for producing an immunoglobulin from the transgenic, non-human animal.
Owner:MERUS NV
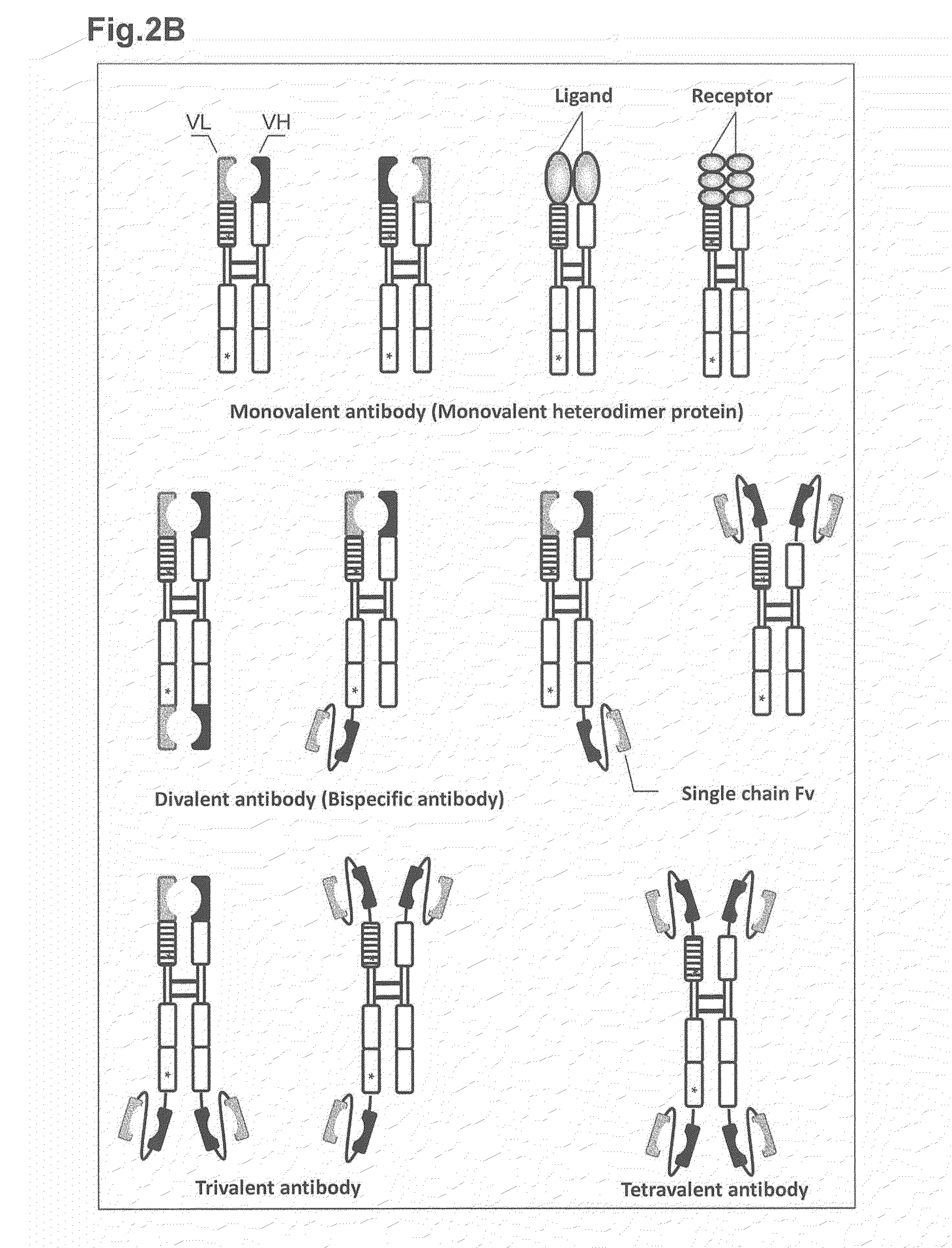
Heterodimer Binding Proteins and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20130129723A1Animal cellsFused cellsImmunoglobulin Joining RegionImmunoglobulin light chain
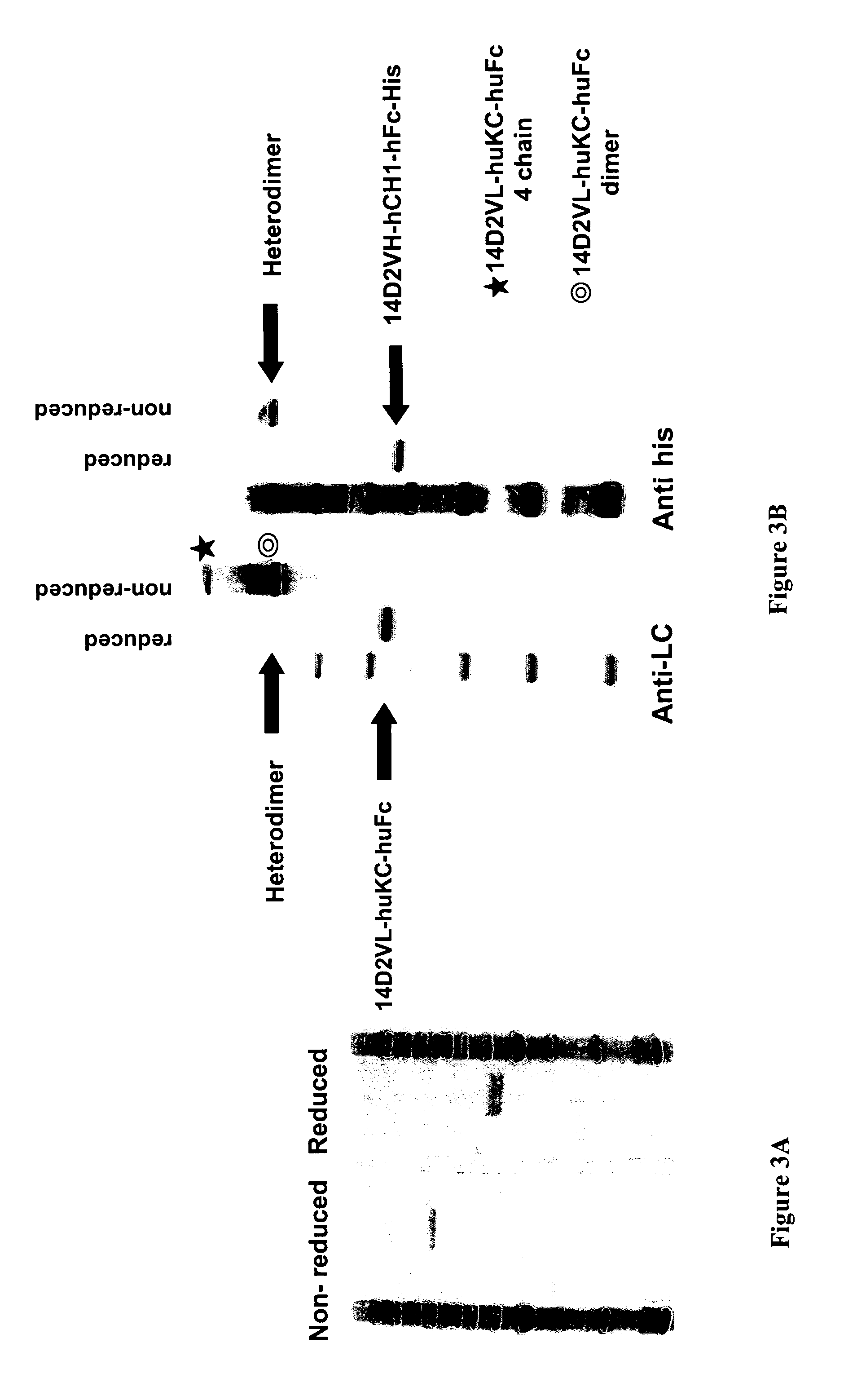
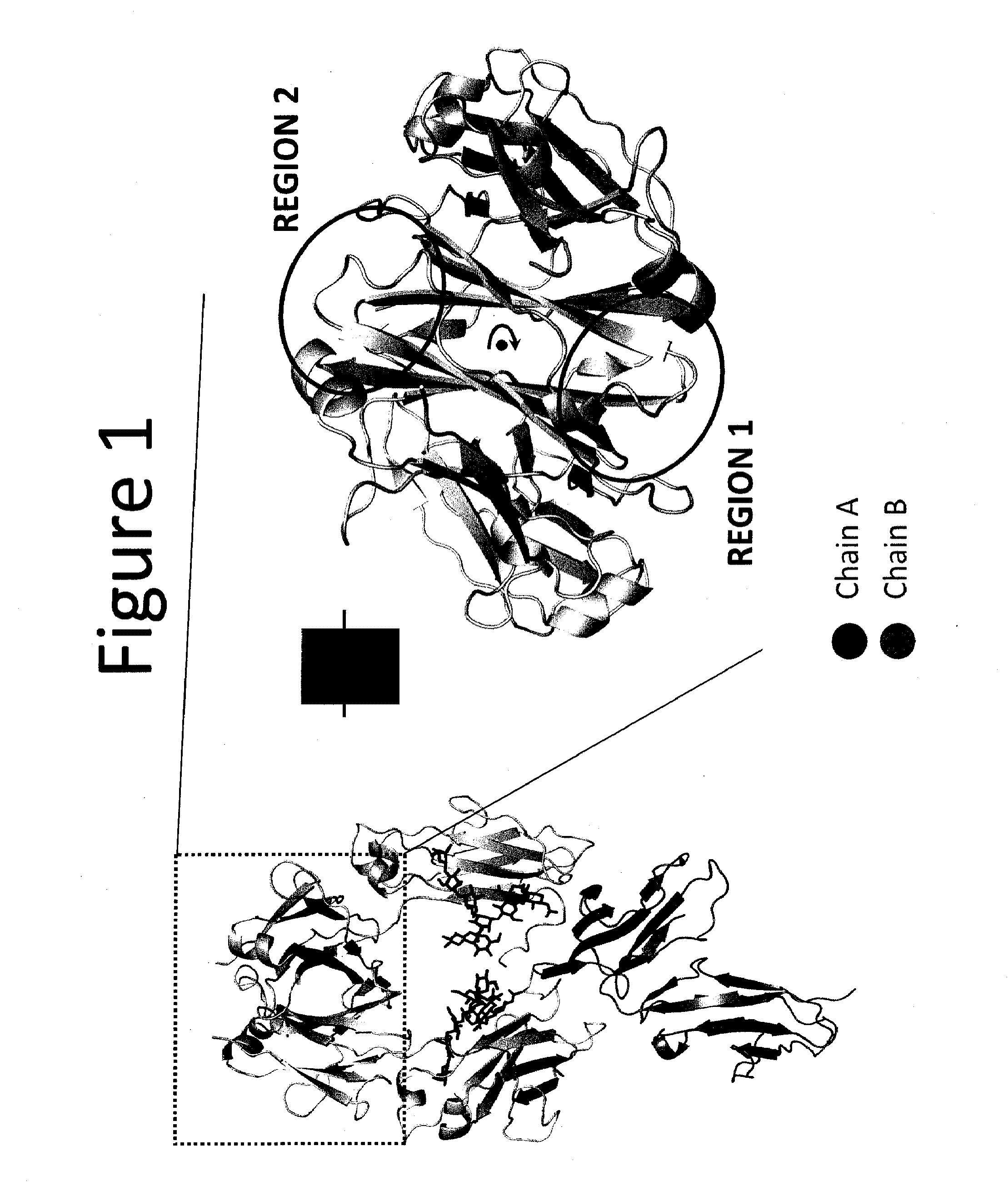
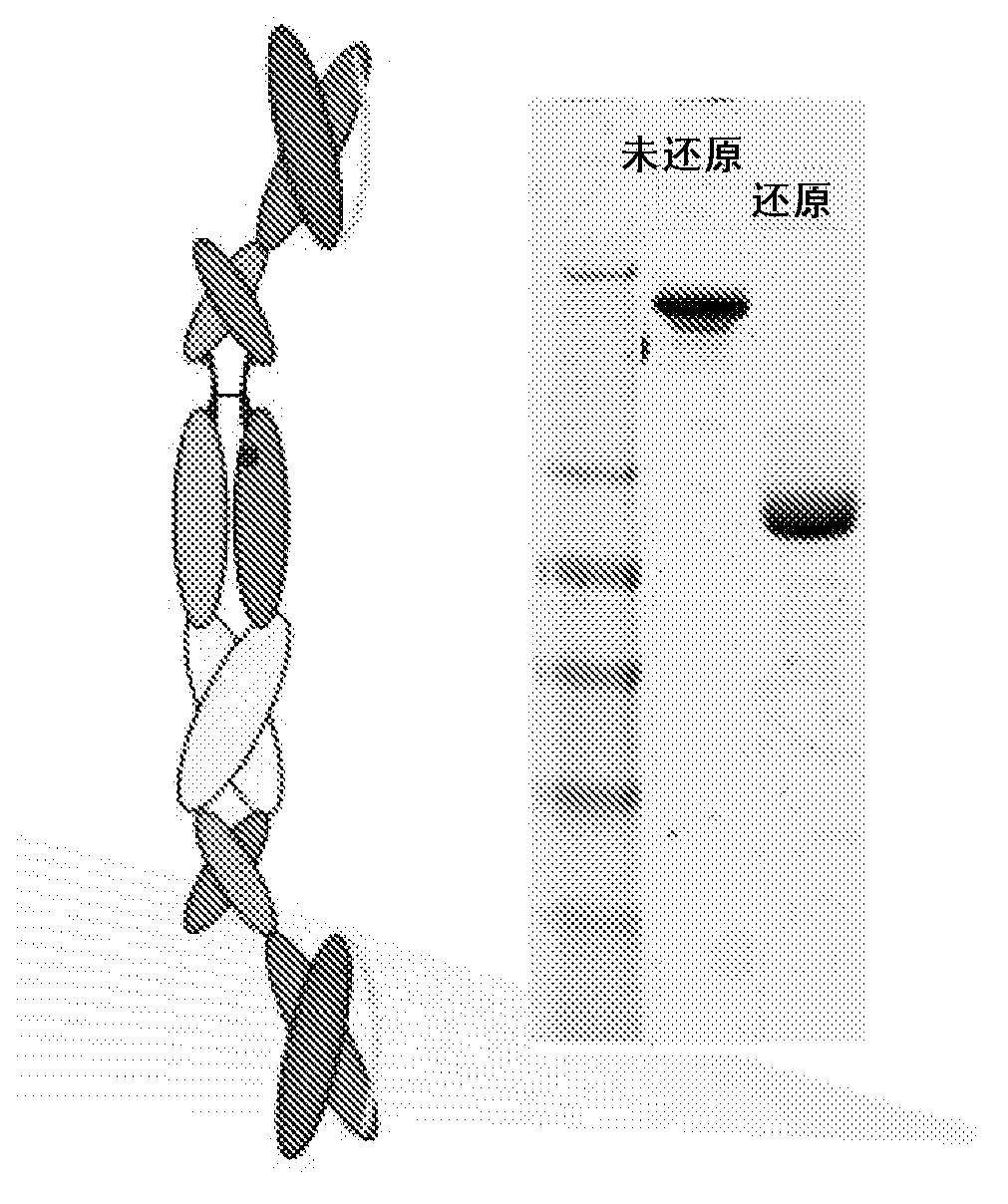
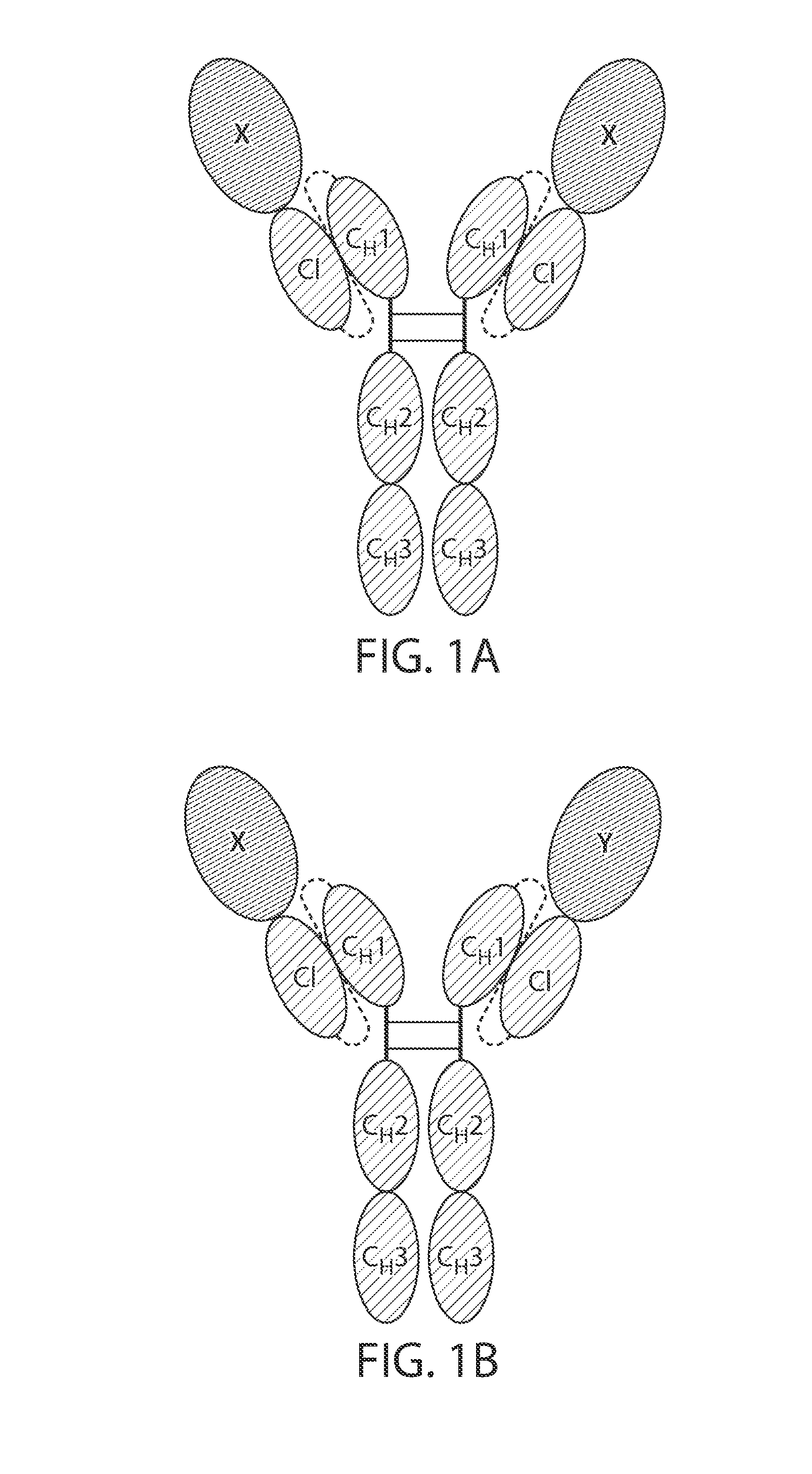
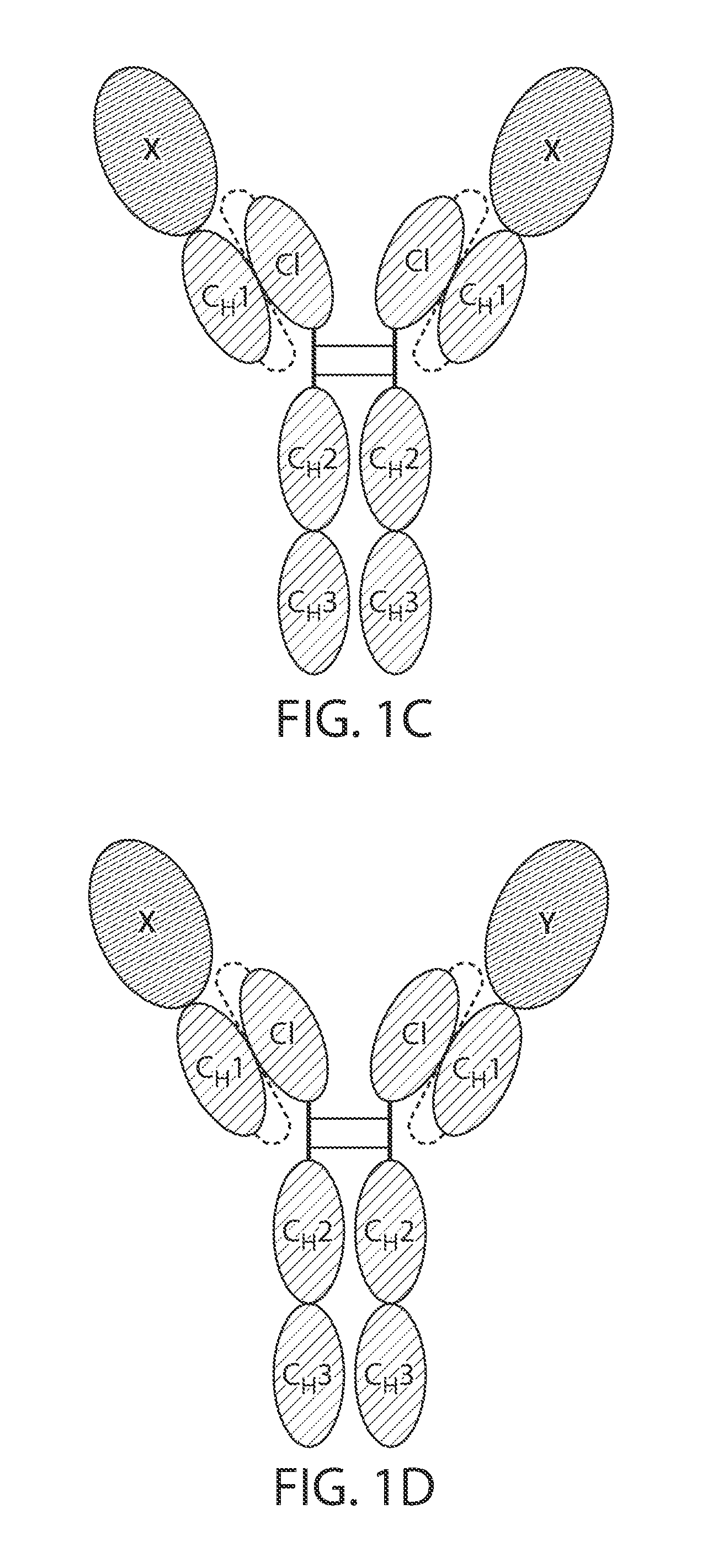
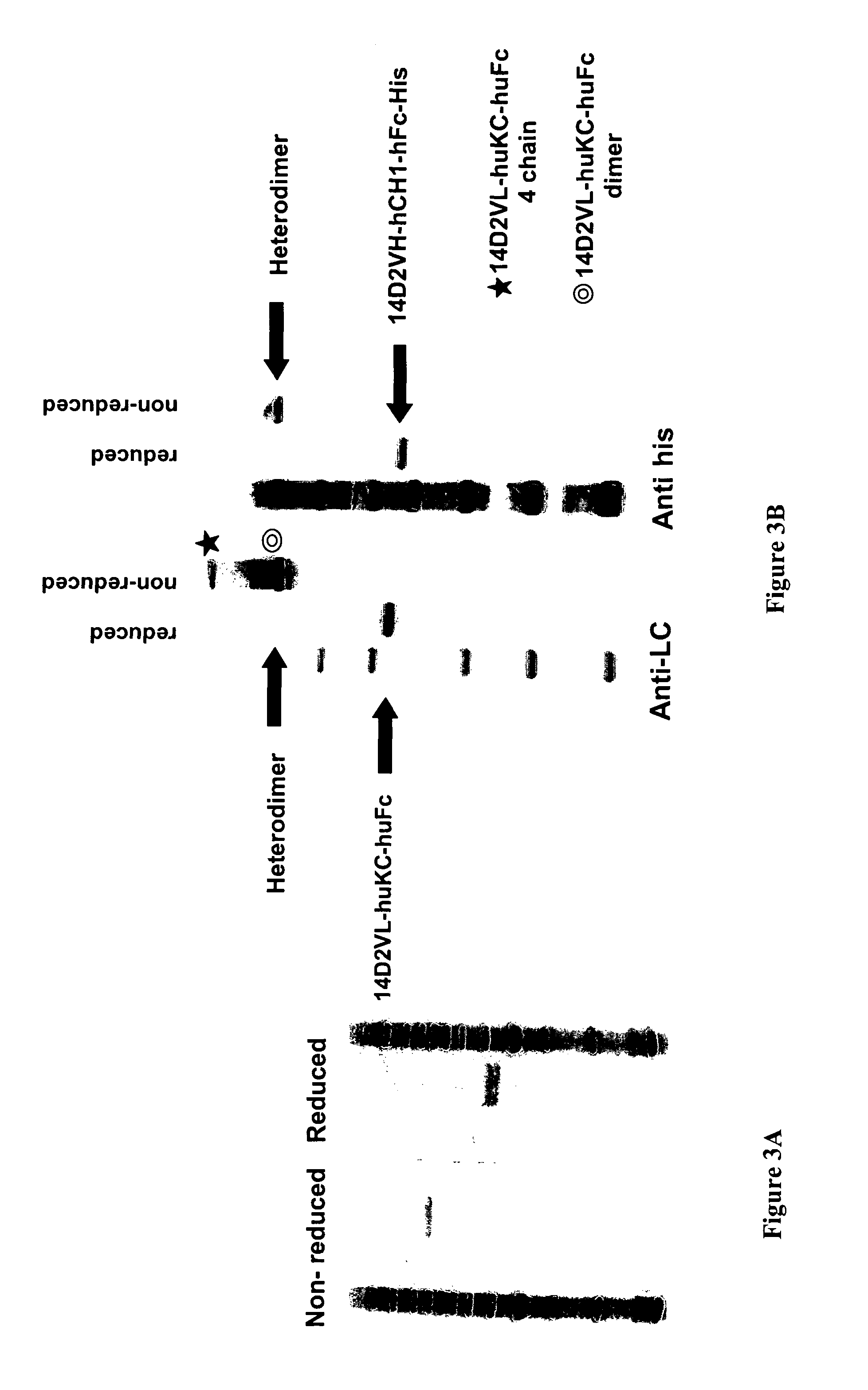
The present disclosure provides polypeptide heterodimers formed between two different single chain fusion polypeptides via natural heterodimerization of an immunoglobulin CH1 region and an immunoglobulin light chain constant region (CL). The polypeptide heterodimer comprises two or more binding domains that specifically bind one or more targets (e.g., a receptor). In addition, both chains of the heterodimer further comprise an Fc region portion. The present disclosure also provides nucleic acids, vectors, host cells and methods for making polypeptide heterodimers as well as methods for using such polypeptide heterodimers, such as in directing T cell activation, inhibiting solid malignancy growth, and treating autoimmune or inflammatory conditions.
Owner:EMERGENT PRODUCTS DEVELOPMENT SEATTLE LLC
Methods for generating monovalent IgG
ActiveUS20070105199A1Nervous disorderAntipyreticImmunoglobulin heavy chainImmunoglobulin light chain
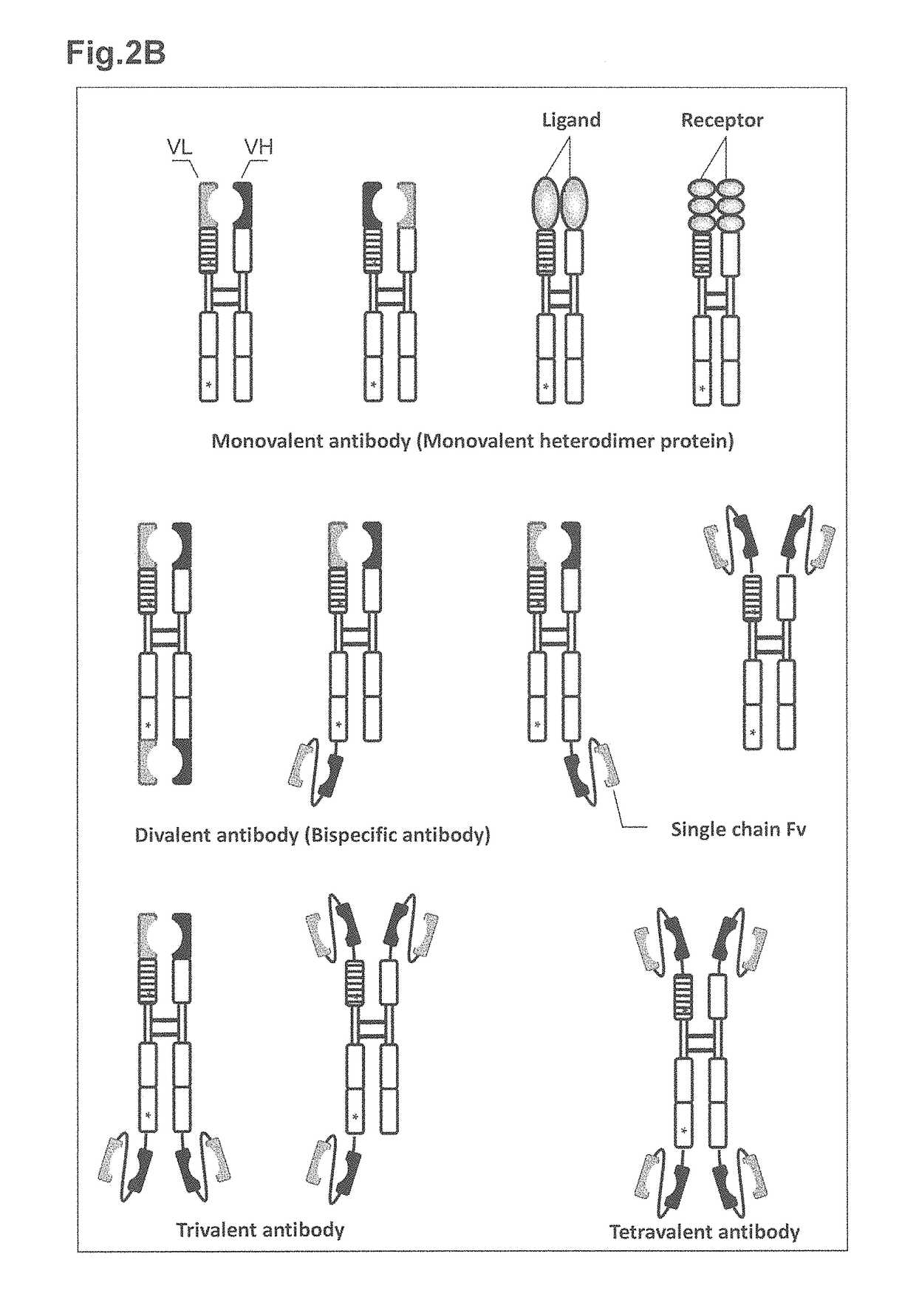
The present invention relates to monovalent antibody, methods of making thereof and therapeutic uses thereof. In particular, the present invention provides a heterodimeric polypeptide comprising an immunoglobulin heavy chain and a fusion protein comprising an immunoglobulin light chain and an Fc molecule.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Heteromultimer Constructs of Immunoglobulin Heavy Chains with Mutations in the Fc Domain
InactiveUS20130336973A1Improve stabilityAnimal cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsImmunoglobulin heavy chainHeterologous
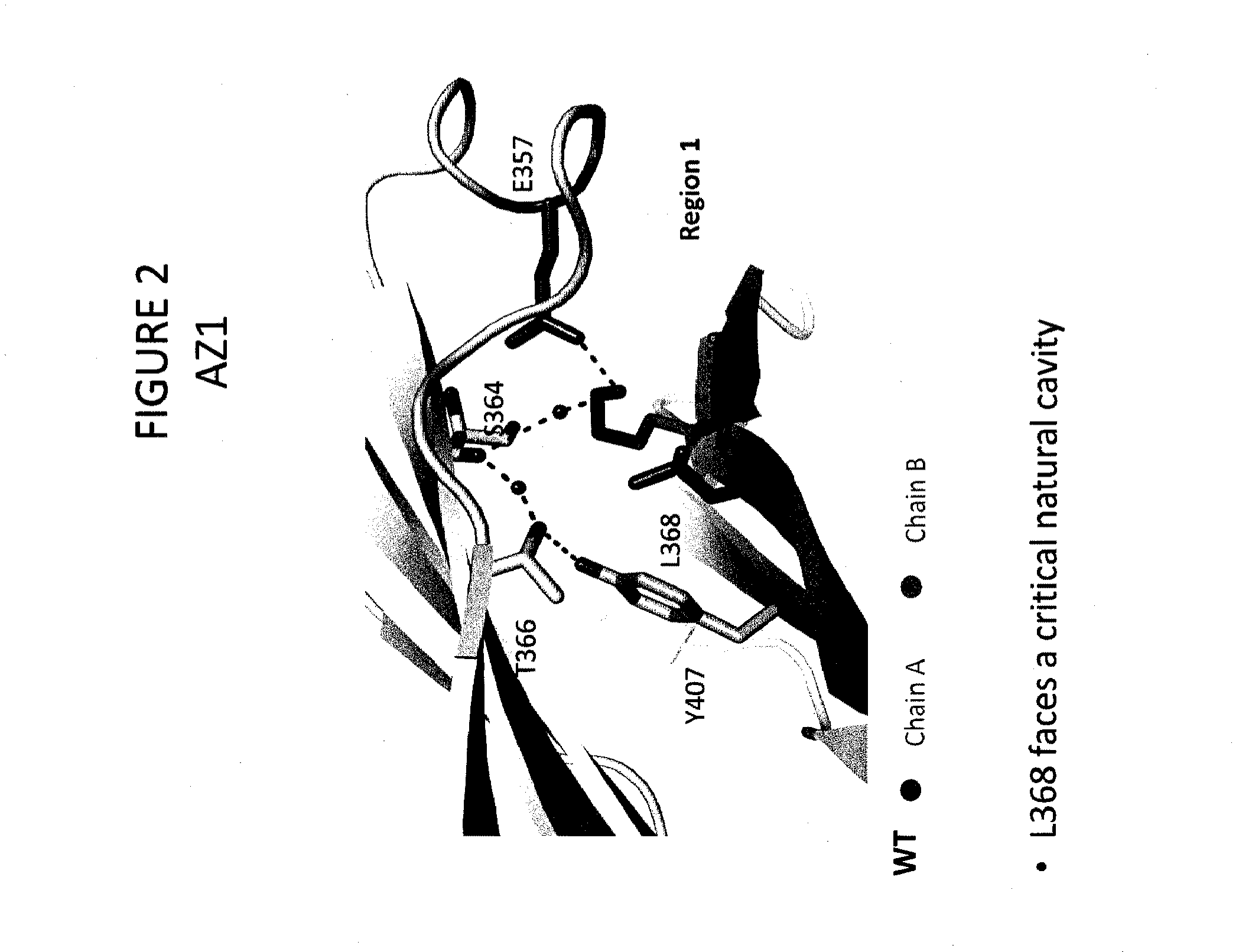
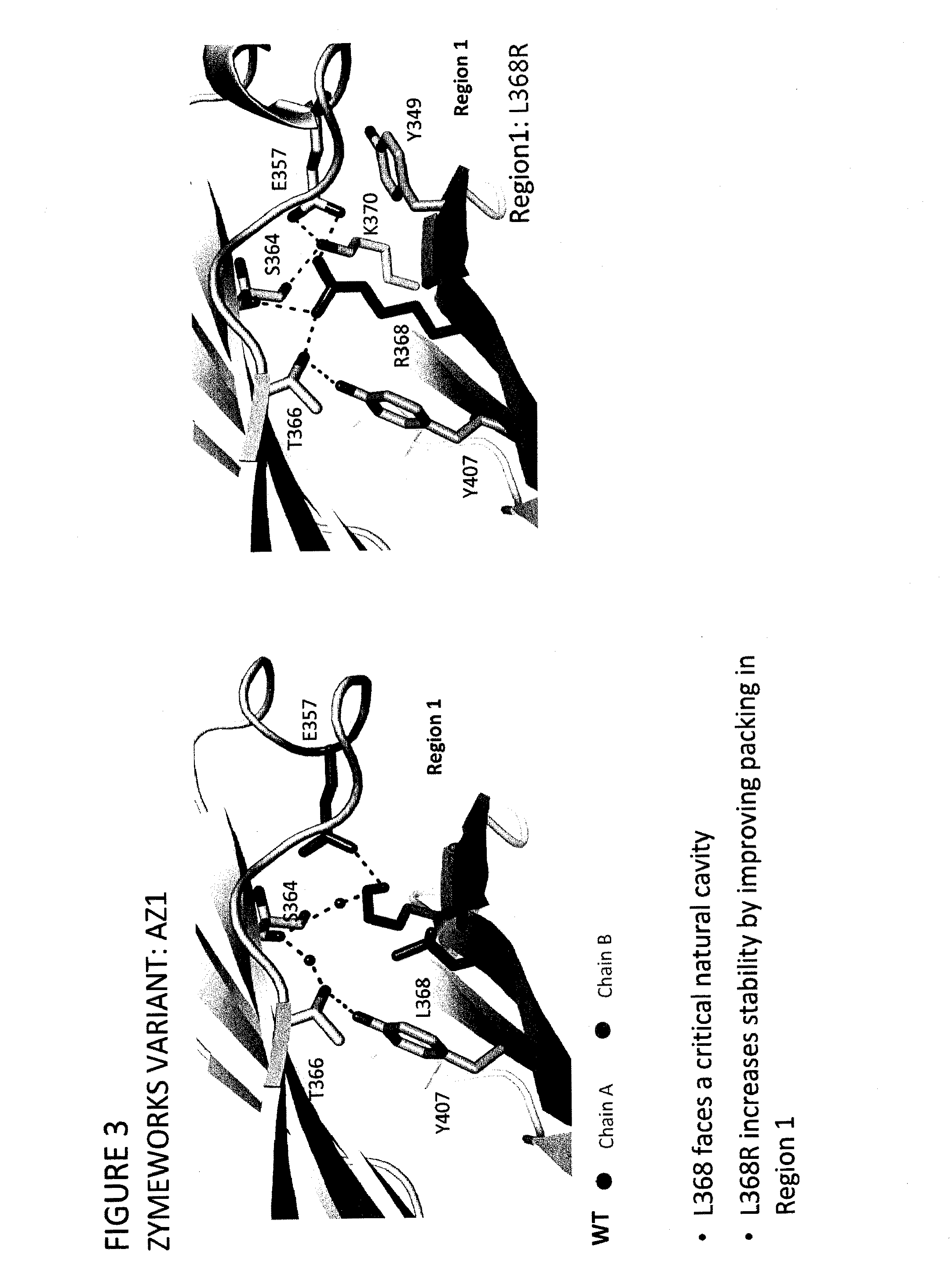
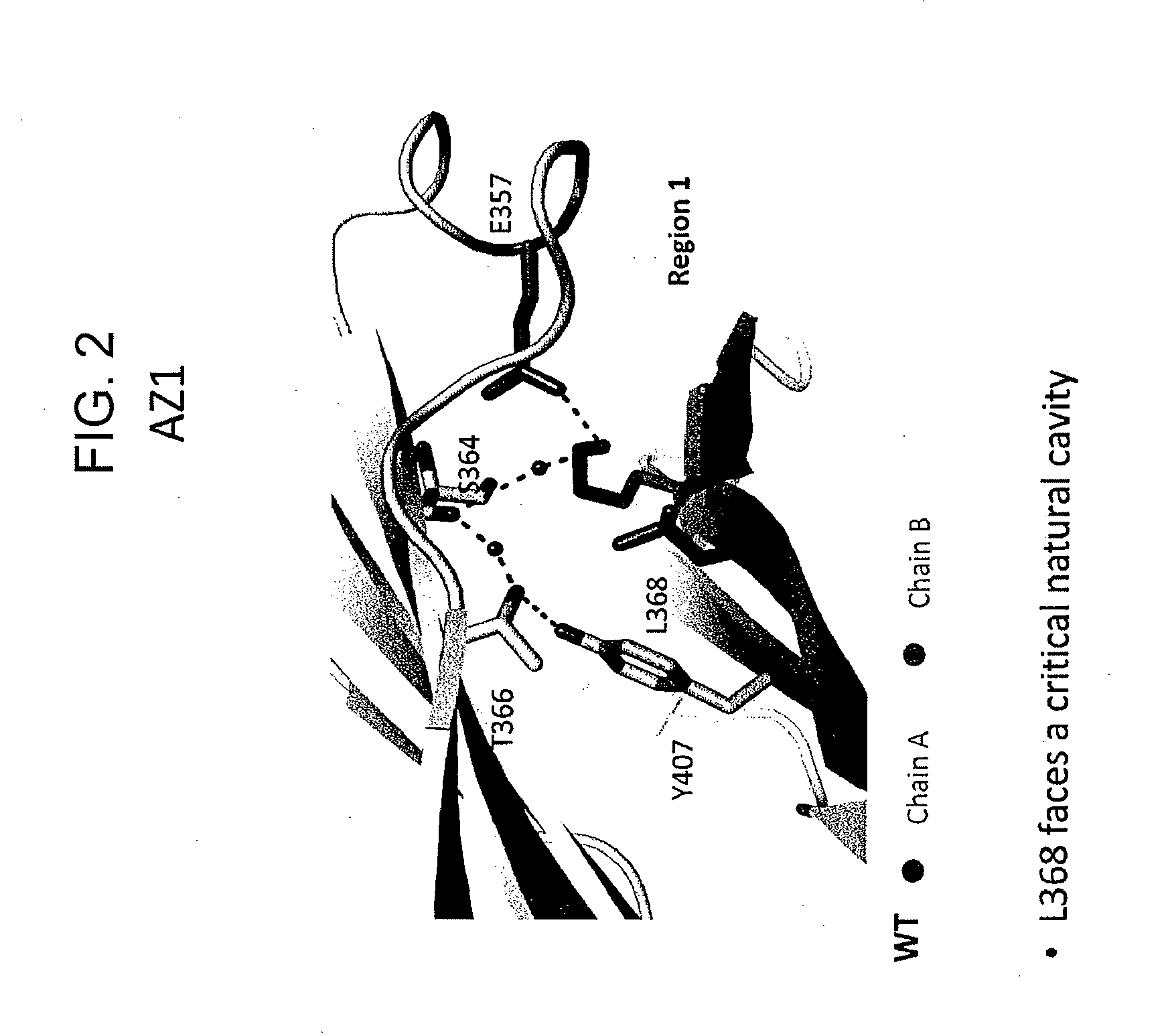
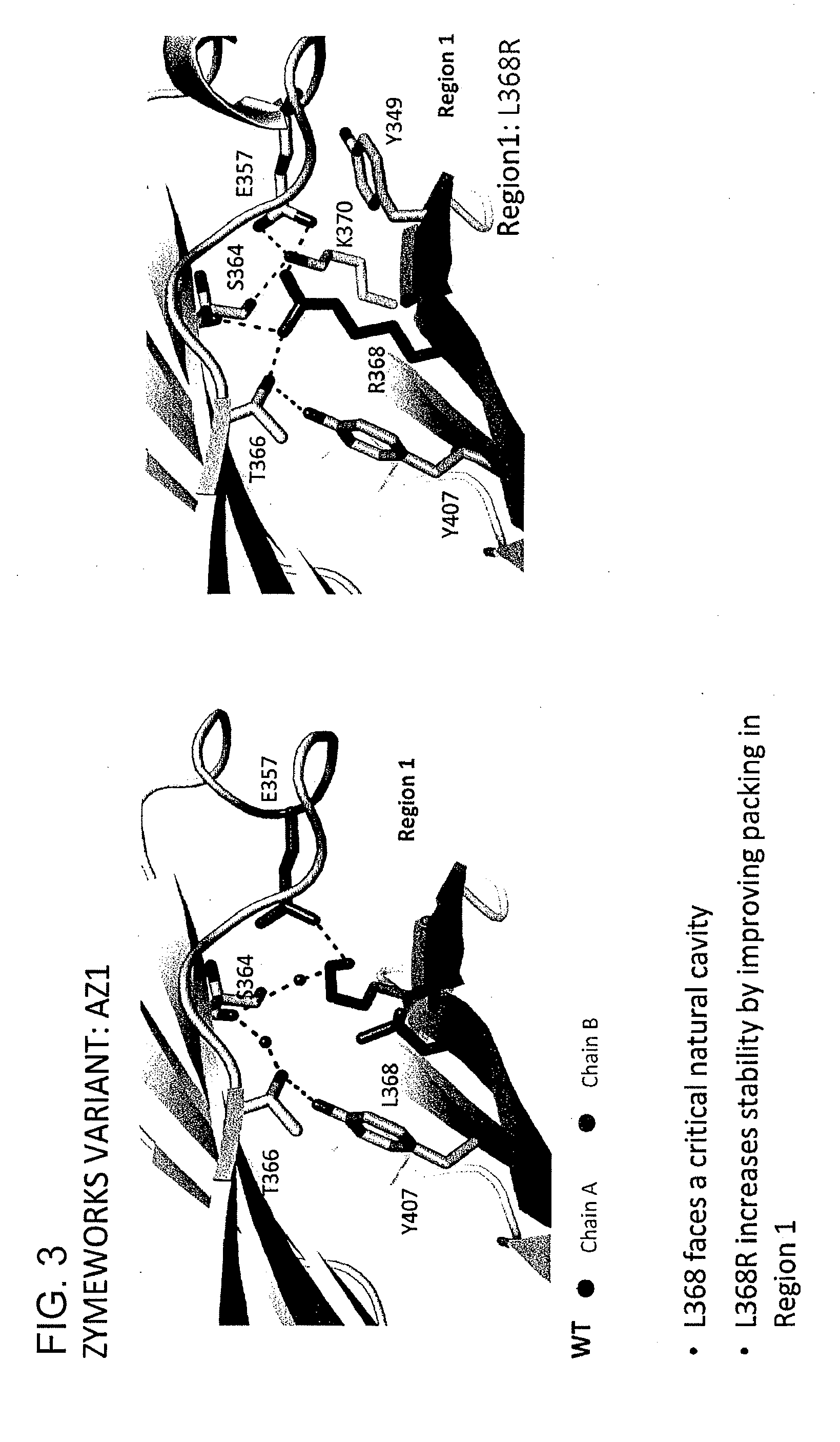
Provided herein are isolated heteromultimers comprising: at least one single domain antigen-binding construct attached to at least one monomer of a heterodimer Fc region; wherein the heterodimer Fc region comprises a variant CH3 domain comprising amino acid mutations that promote the formation of said heterodimer with stability comparable to that of a native Fc homodimer; and wherein said isolated heteromultimer is devoid of immunoglobulin light chains and optionally devoid of immunoglobulin CH1 region. These novel molecules comprise complexes of heterogeneous components designed to alter the natural way antibodies behave and that find use in therapeutics.
Owner:ZYMEWORKS INC
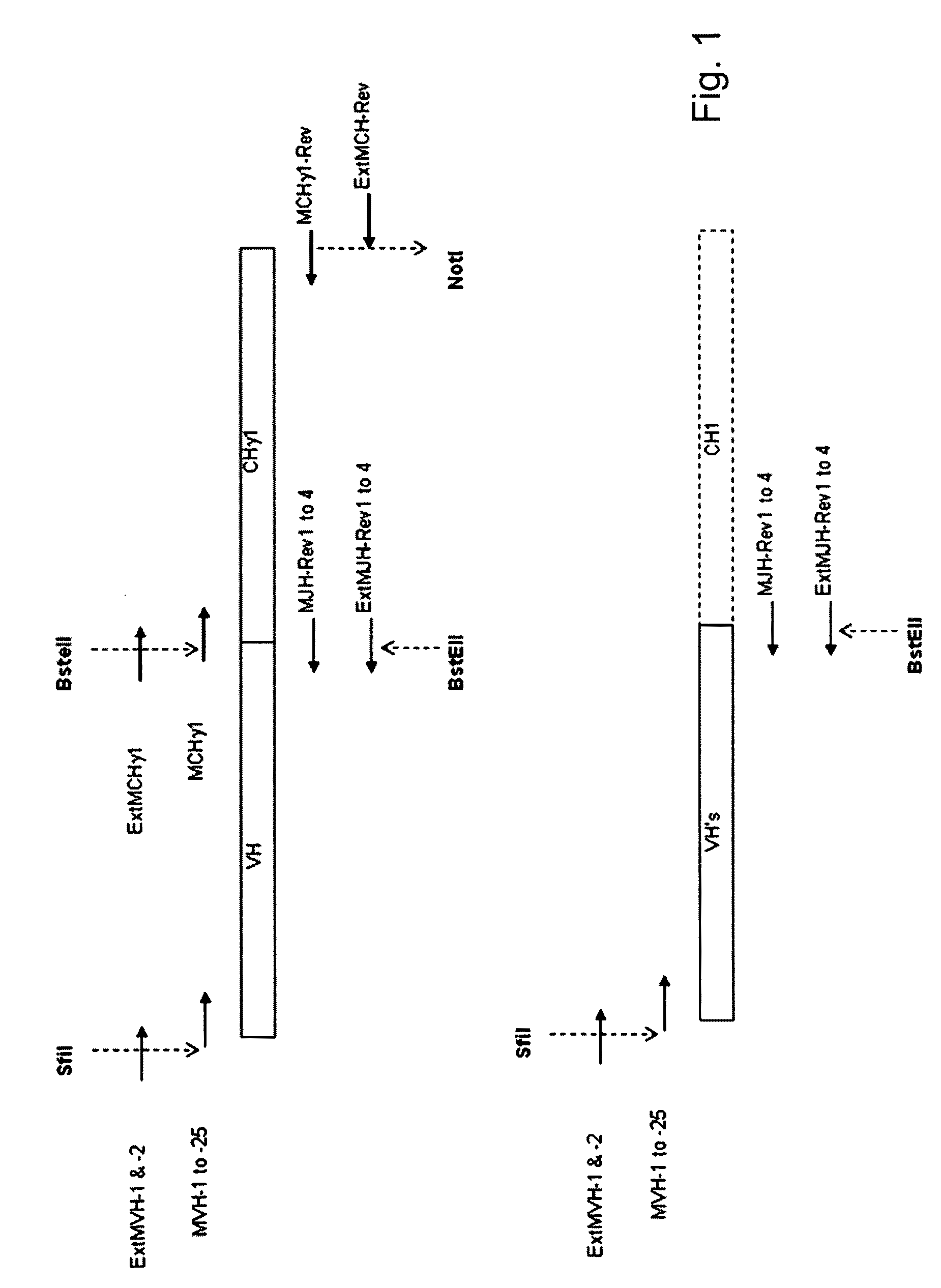
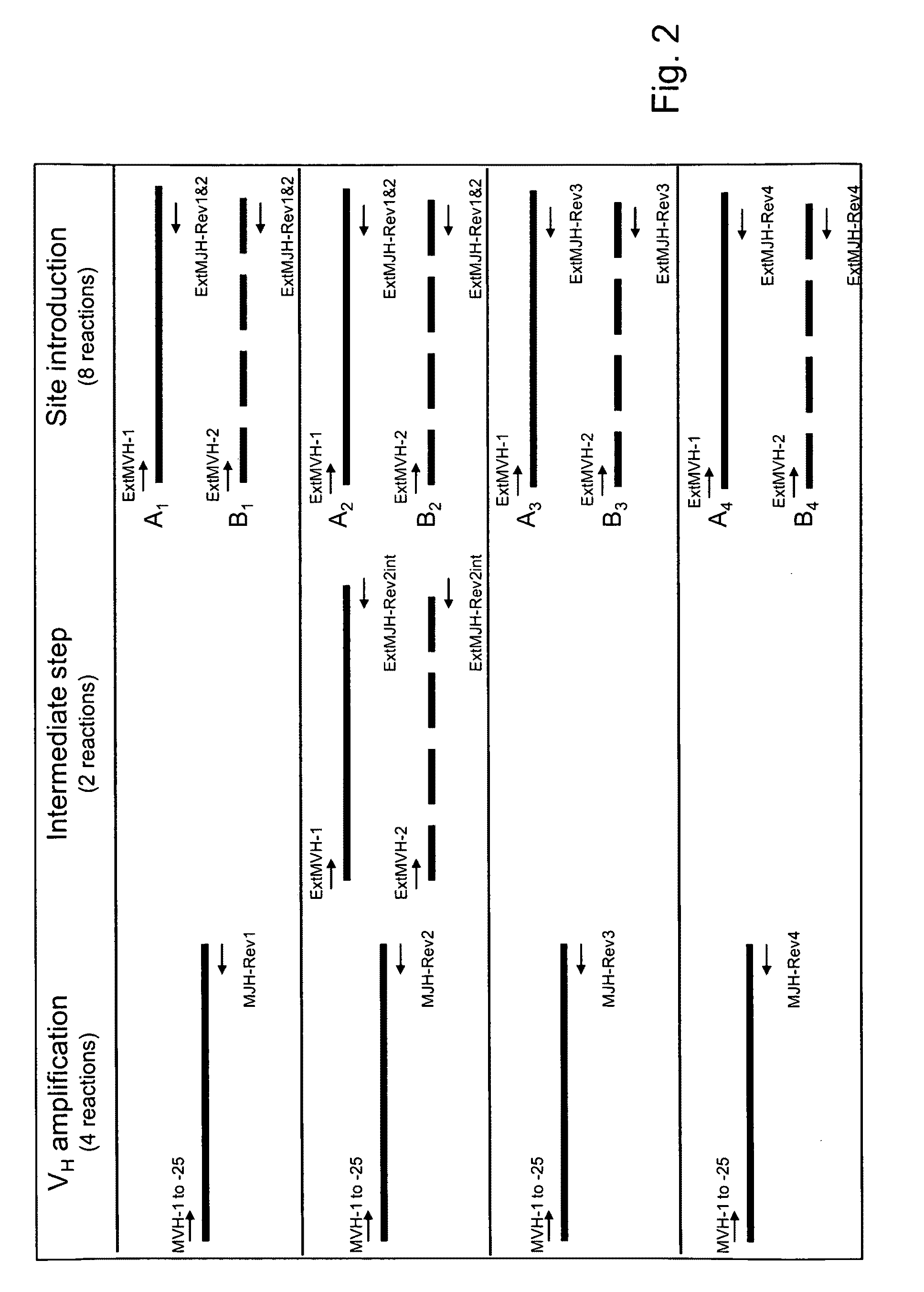
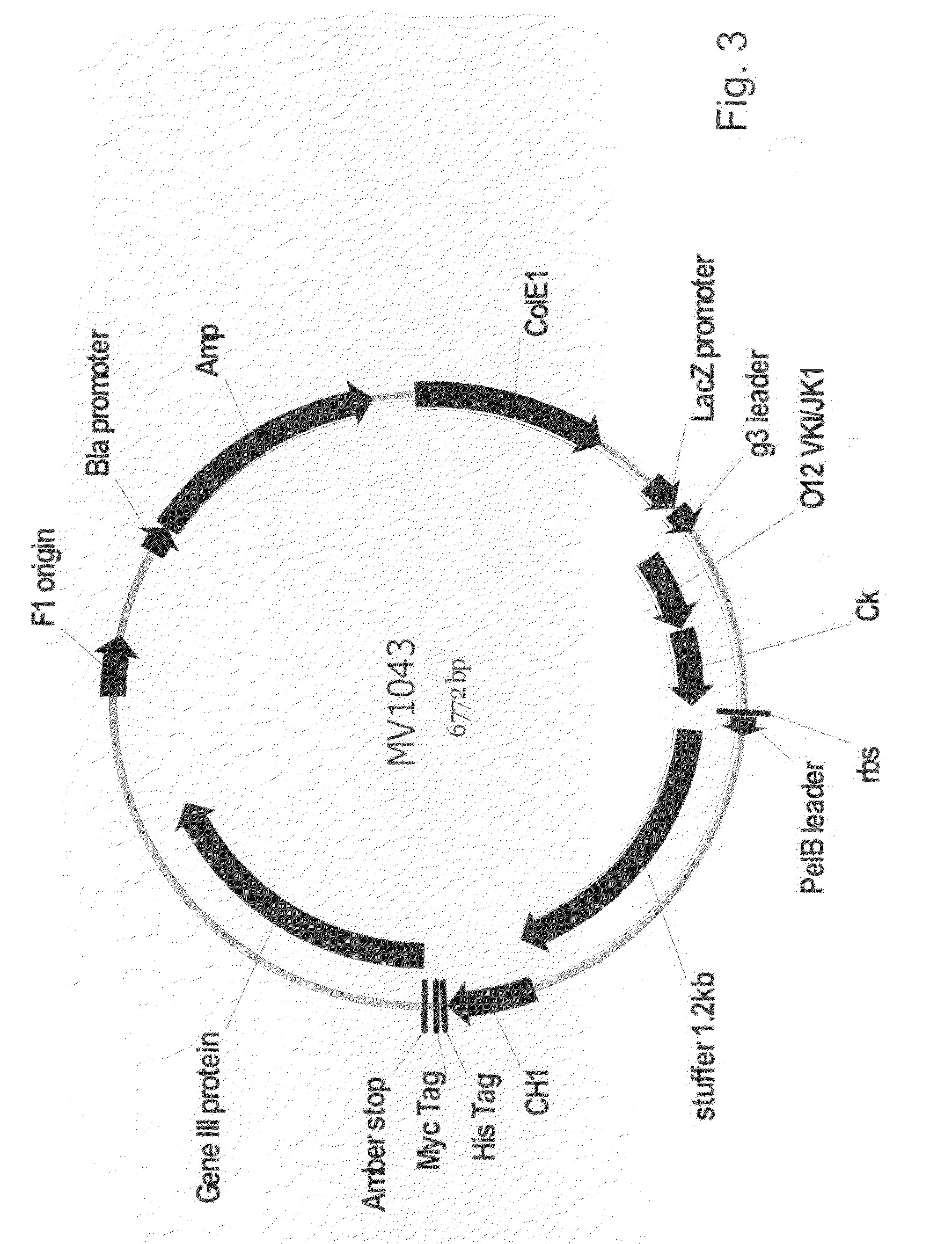
Methods for producing antibody libraries using universal or randomized immunoglobulin light chains
InactiveUS7067284B1Phagemid display technologySugar derivativesMutant preparationImmunoglobulin heavy chainImmunoglobulin light chain
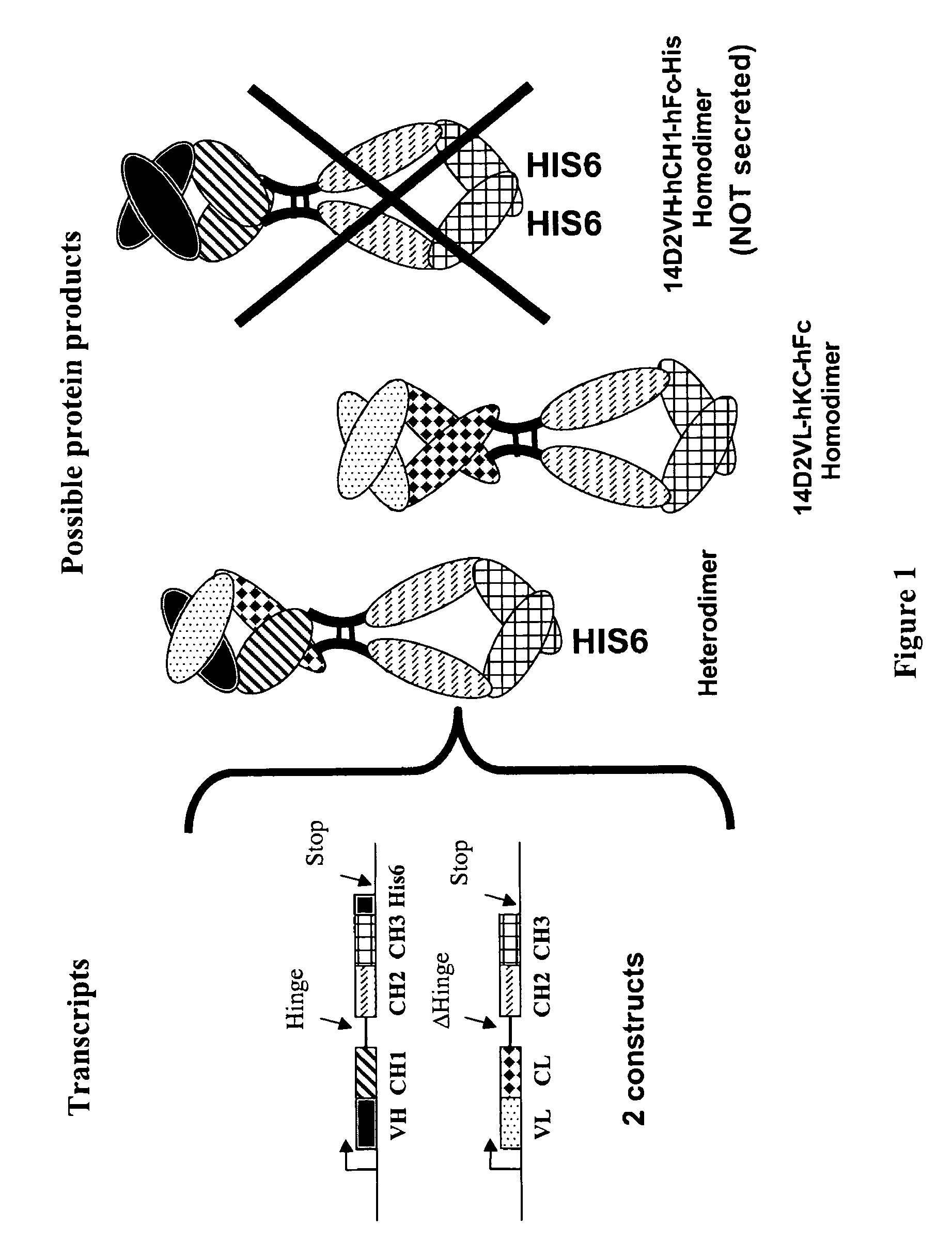
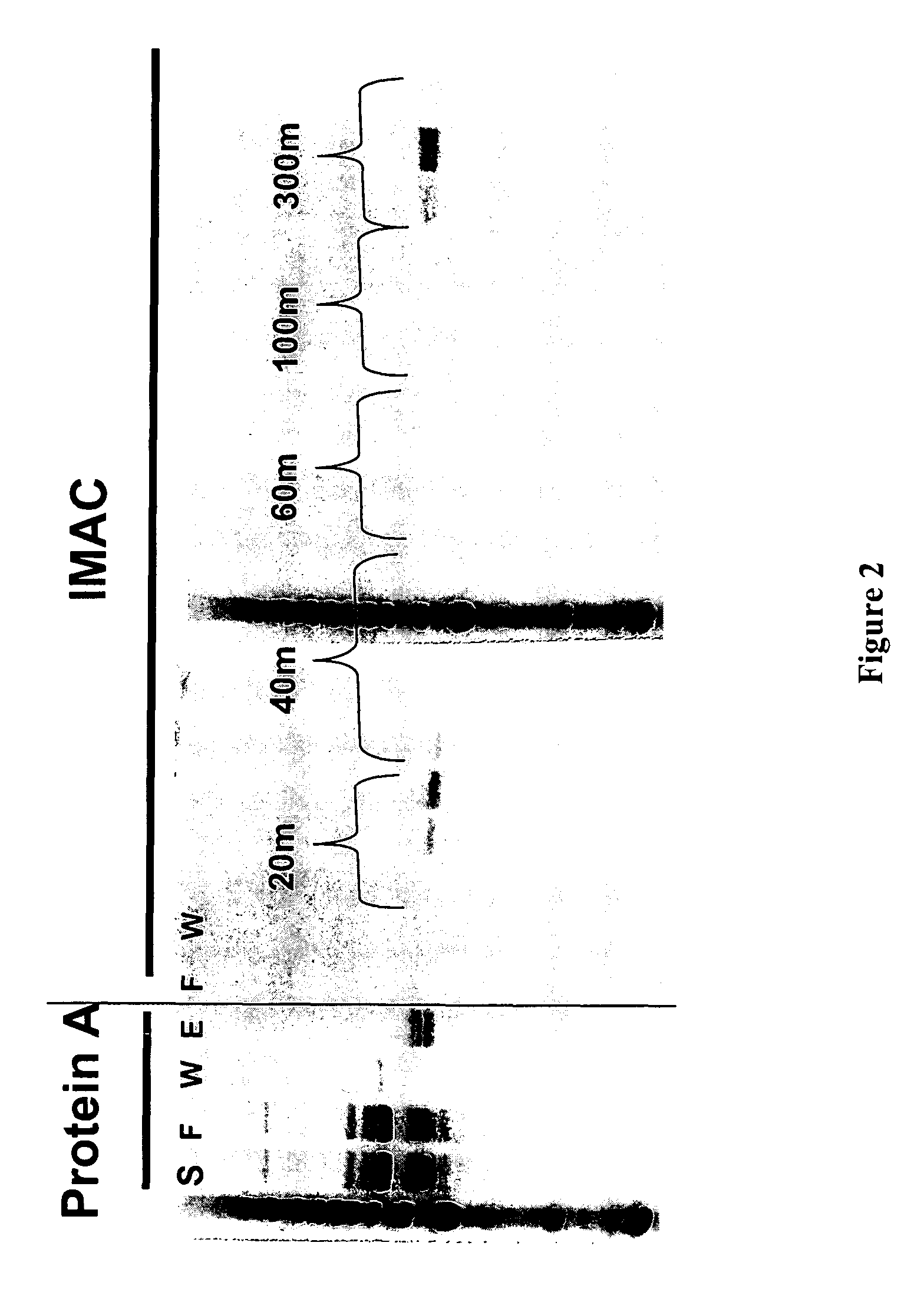
The present invention describes methods for producing antibody libraries, and particularly for increasing antibody library diversity by inducing mutagenesis within the CDR regions of immunoglobulin heavy or light chains that are displayed on the surface of filamentous phage particles comprising the library. The invention also describes oligonucleotides useful for increasing the library diversity, and universal light chains useful in the library production methods.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Heteromultimer constructs of immunoglobulin heavy chains with mutations in the fc domain
InactiveUS20160257763A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsImmunological disordersImmunoglobulin heavy chainImmunoglobulin light chain
Provided herein are isolated heteromultimers comprising: at least one single domain antigen-binding construct attached to at least one monomer of a heterodimer Fc region; wherein the heterodimer Fc region comprises a variant CH3 domain comprising amino acid mutations that promote the formation of said heterodimer with stability comparable to that of a native Fc homodimer; and wherein said isolated heteromultimer is devoid of immunoglobulin light chains and optionally devoid of immunoglobulin CH1 region. These novel molecules comprise complexes of heterogeneous components designed to alter the natural way antibodies behave and that find use in therapeutics.
Owner:ZYMEWORKS INC
Histidine Engineered Light Chain Antibodies and Genetically Modified Non-Human Animals for Generating the Same
InactiveUS20140013456A1Reduce the binding forceNucleic acid vectorImmunoglobulinsNucleotideGenetically modified crops
A genetically modified non-human animal is provided, wherein the non-human animal expresses an antibody repertoire capable of pH dependent binding to antigens upon immunization. A genetically modified non-human animal is provided that expresses human immunoglobulin light chain variable domains derived from a limited repertoire of human immunoglobulin light chain variable gene segments that comprise histidine modifications in their germline sequence. Methods of making non-human animals that express antibodies comprising histidine residues encoded by histidine codons introduced into immunoglobulin light chain nucleotide sequences are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Methods of investigating, diagnosing, and treating amyloidosis
InactiveUS20020019335A1Constant level of amyloid depositsEffective preventionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAA amyloidosisAssay
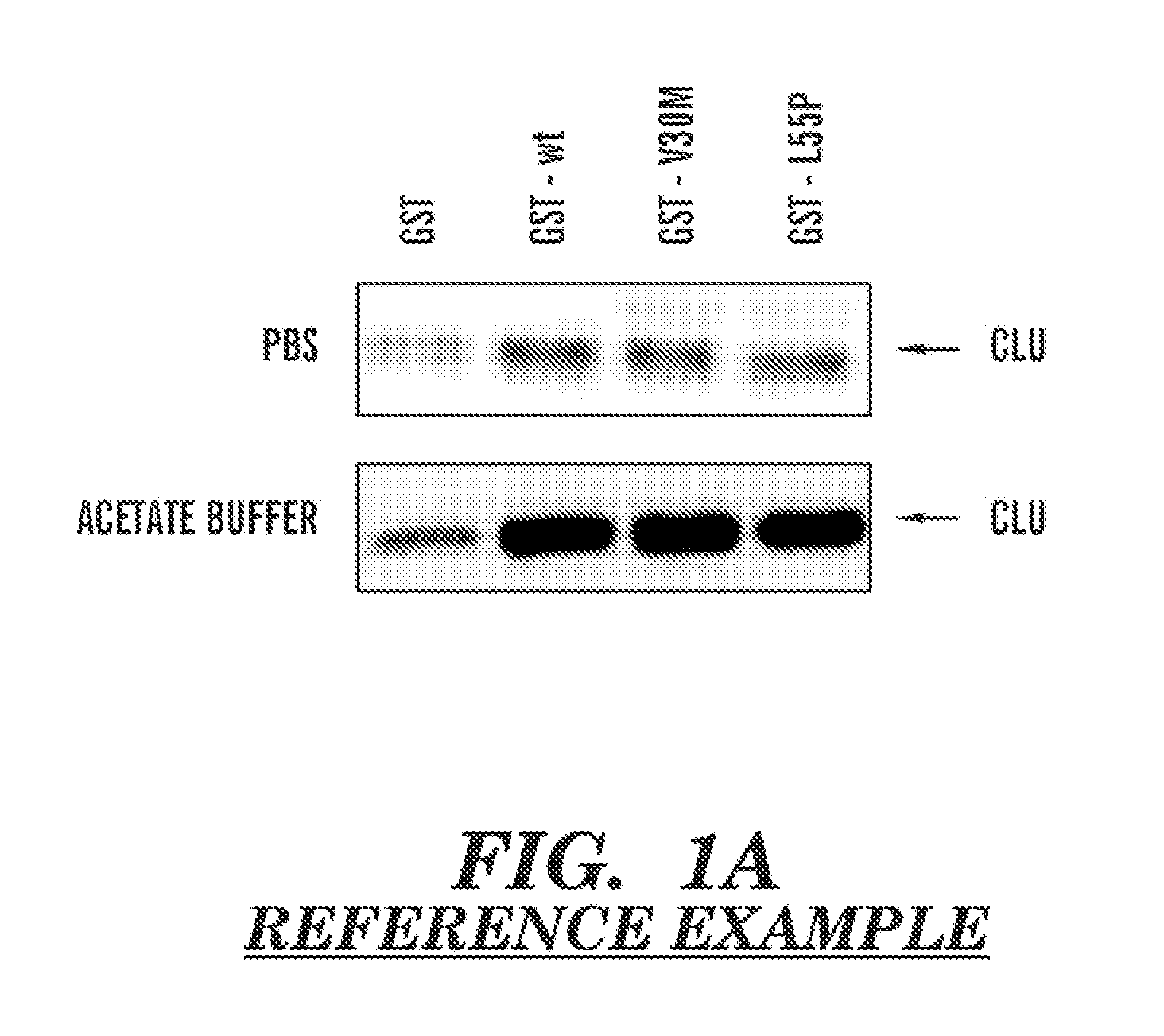
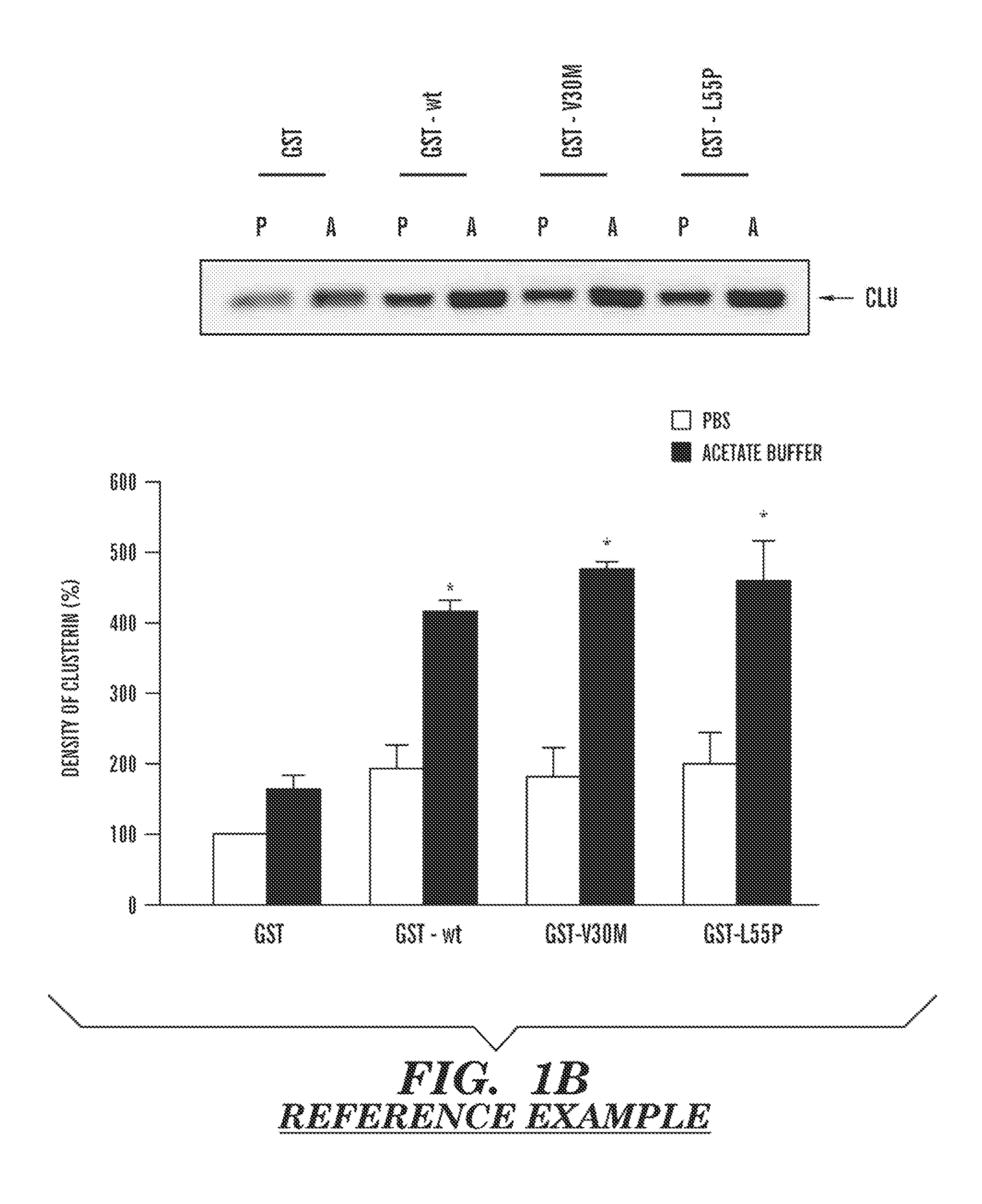
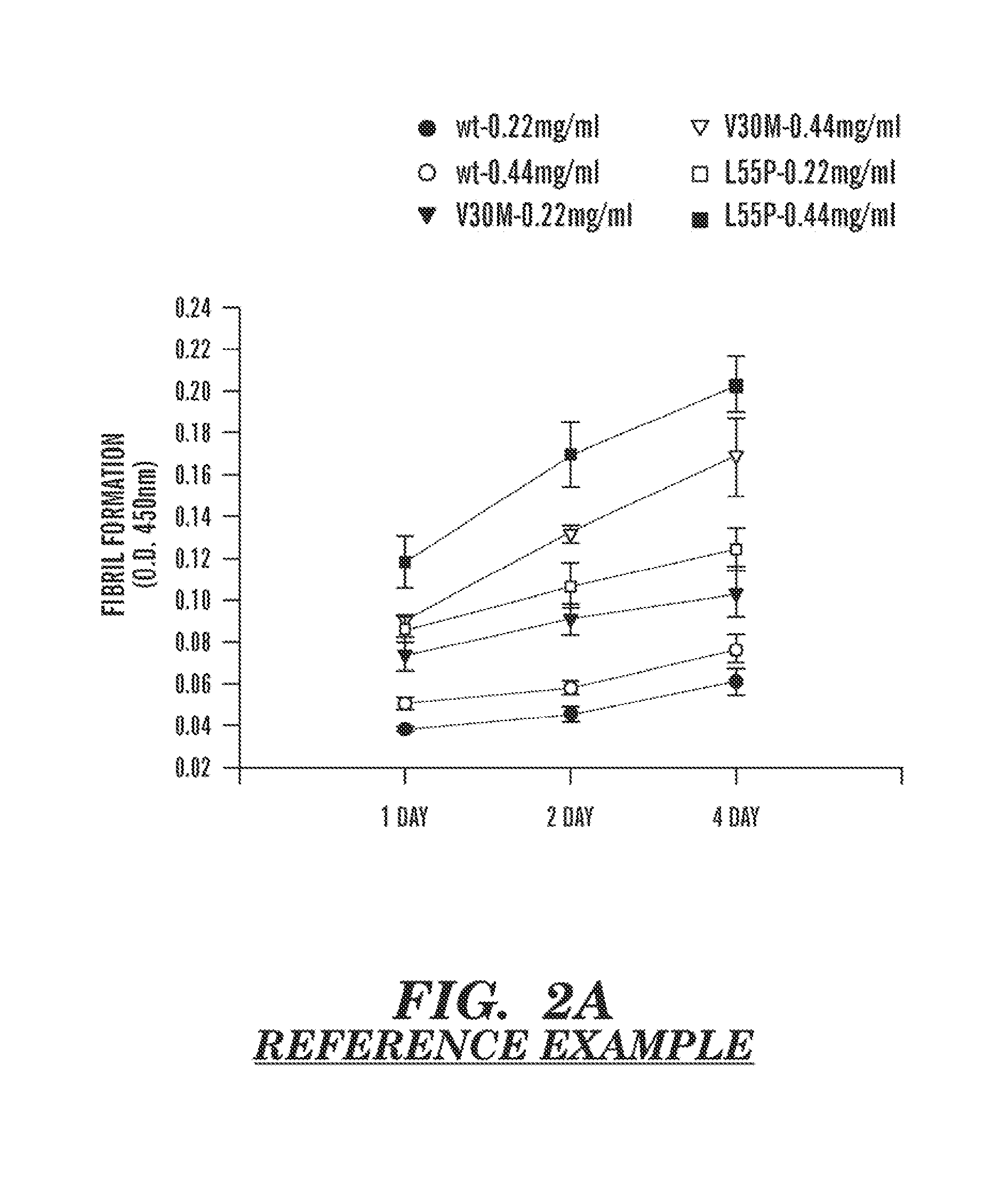
The present invention provides a therapeutic method for removing amyloid fibrils from a patient. The present invention also provides a transgenic animal that develops systemic AA amyloidosis within three weeks for use as a tool to investigate AA amyloidosis and to evaluate agents that may be potentially useful in preventing and treating amyloid-related disorders. Further, the present invention provides diagnostic assays for monitoring immunoglobulin light chain fibrillogenesis in real-time and for identification of the chemical nature of the protein in amyloid deposits which enables the determination of the type of amyloidosis for therapeutic and prognostic purposes.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Chimeric toxin receptor proteins and chimeric toxin receptor proteins for treatment and prevention of anthrax
InactiveUS20070118934A1Reduce manufacturing costReduce the binding forceCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulin heavy chainImmunoglobulin light chain
Chimeric toxin receptor proteins having a toxin receptor associated with an immunoglobulin complex having least a portion of an immunoglobulin heavy chain and at least a portion of an immunoglobulin light chain are described. Such chimeric toxin receptor proteins have improved stability as compared to chimeric toxin receptor proteins lacking the light chain. Anthrax and botulinum chimeric toxin receptor proteins with increased stability are also described.
Owner:PLANET BIOTECH
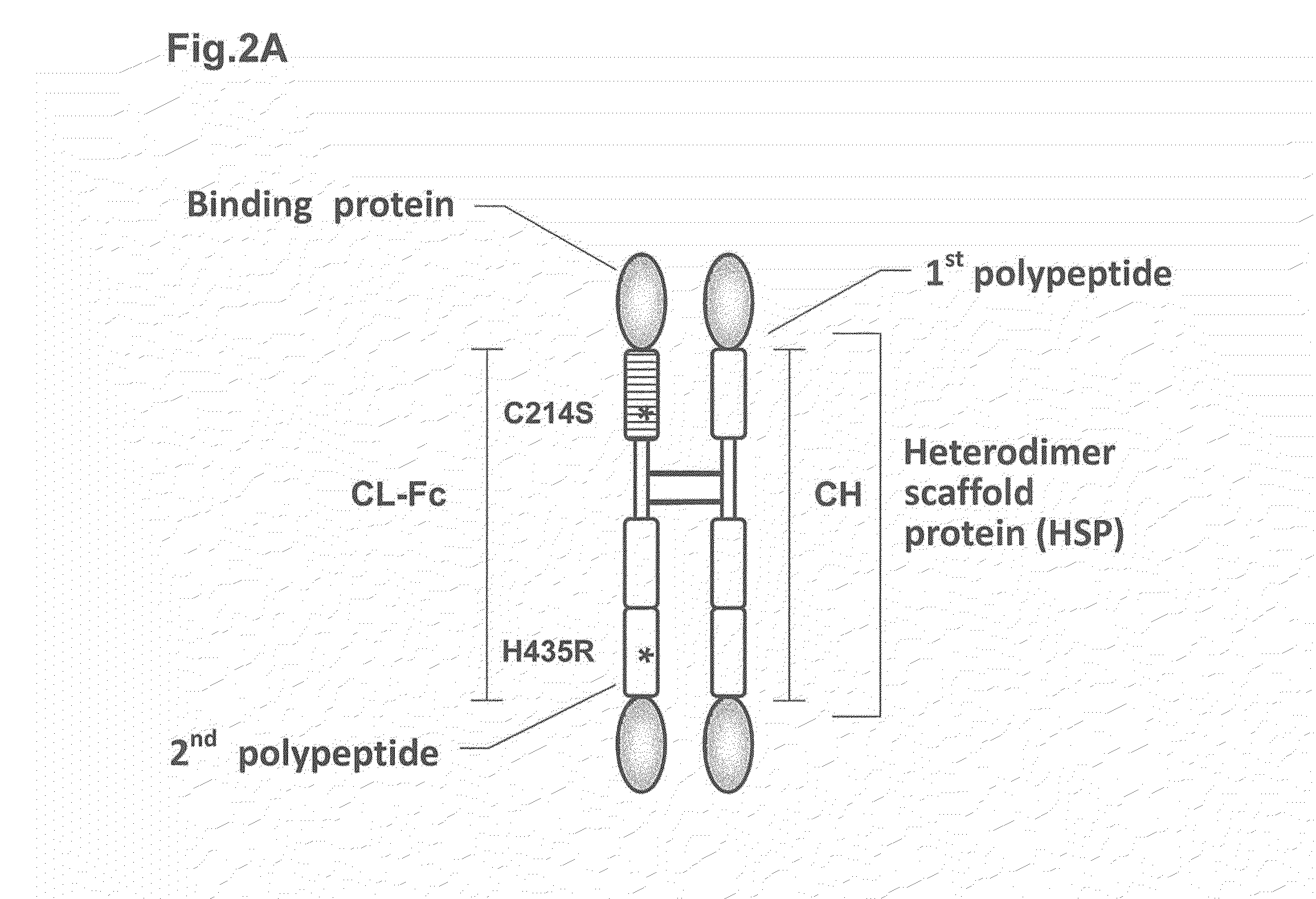
Heterodimer protein composition
ActiveUS20140120581A1Efficient and stable productionAnimal cellsHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulin heavy chainPurification methods
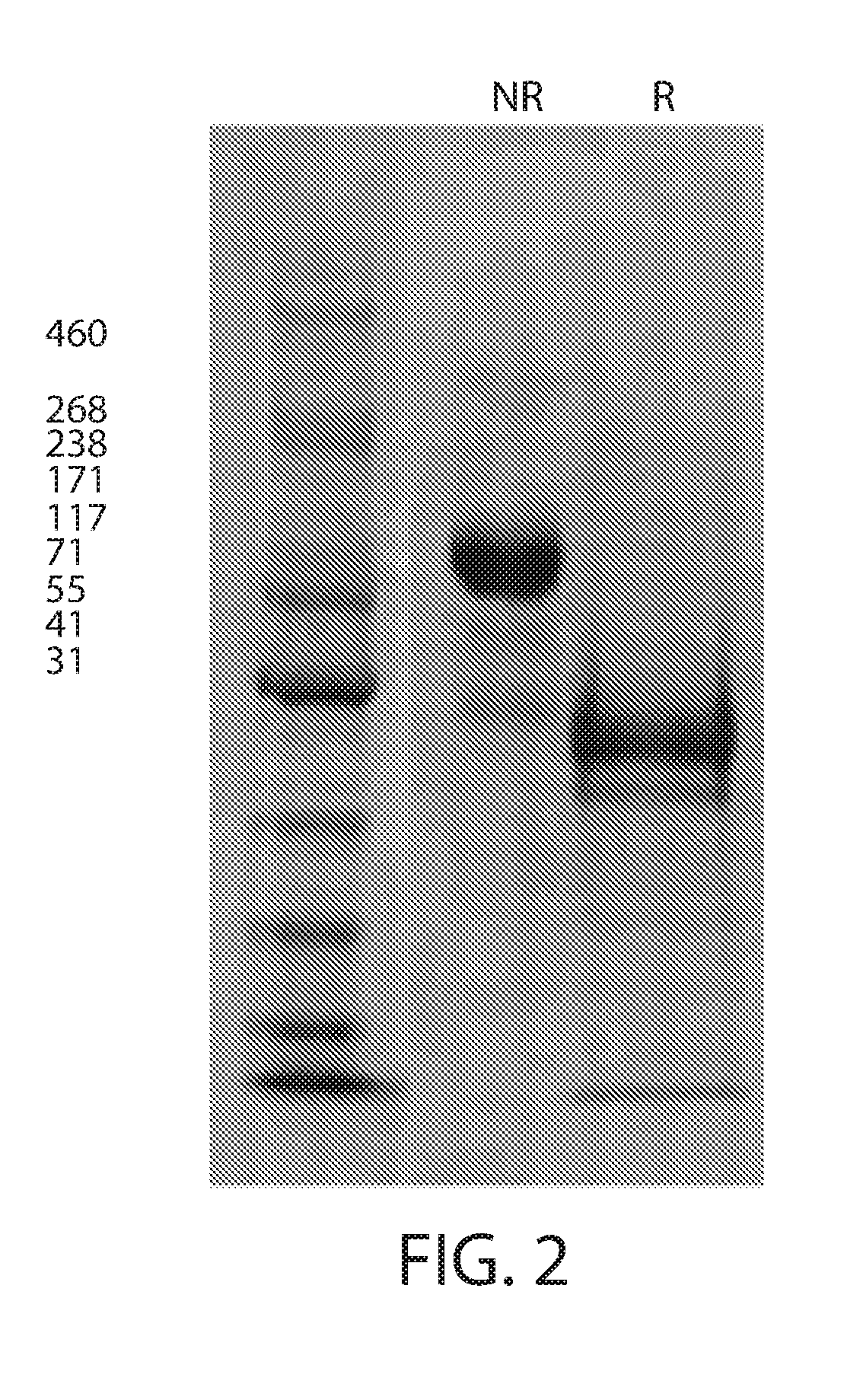
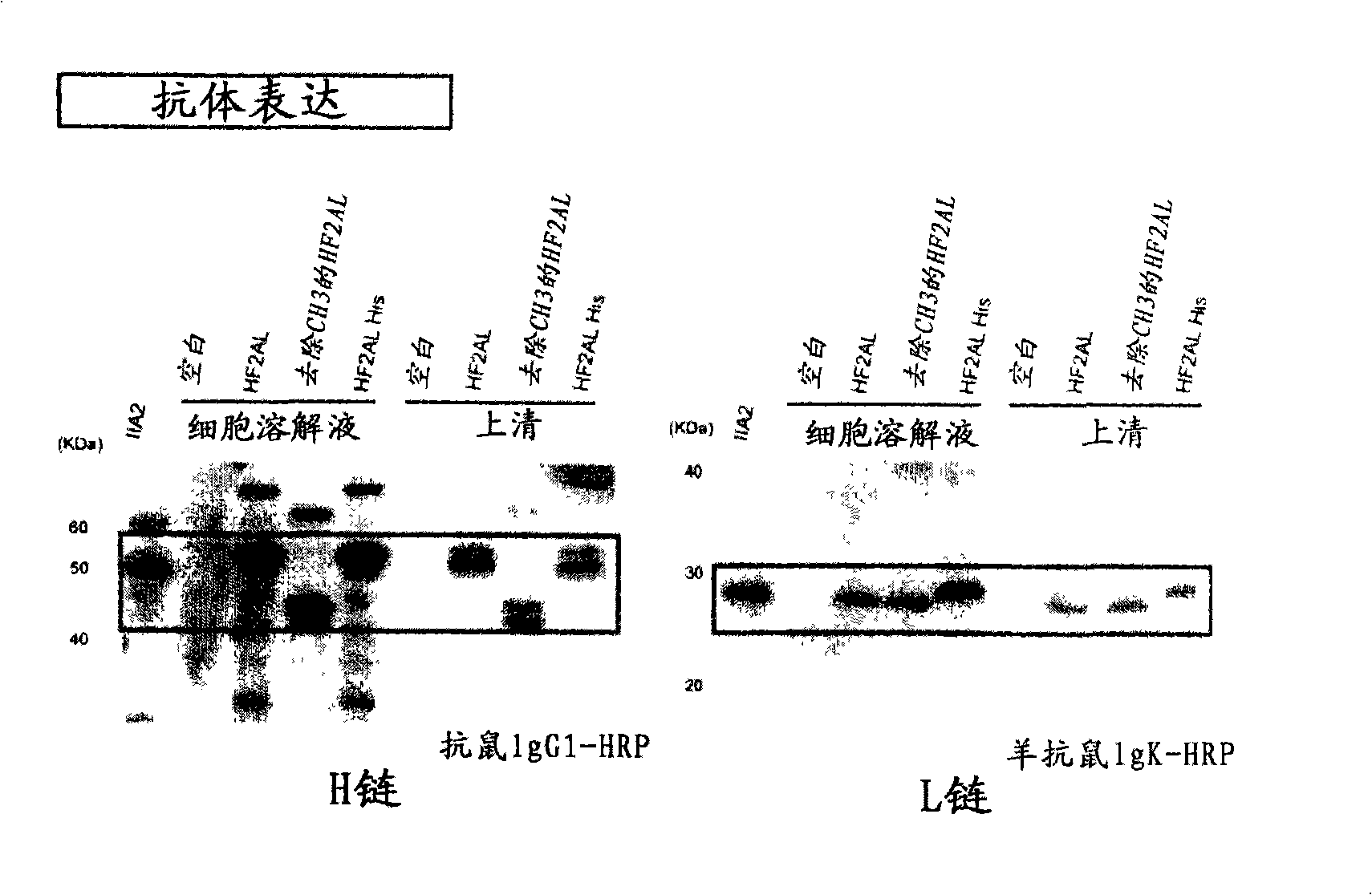
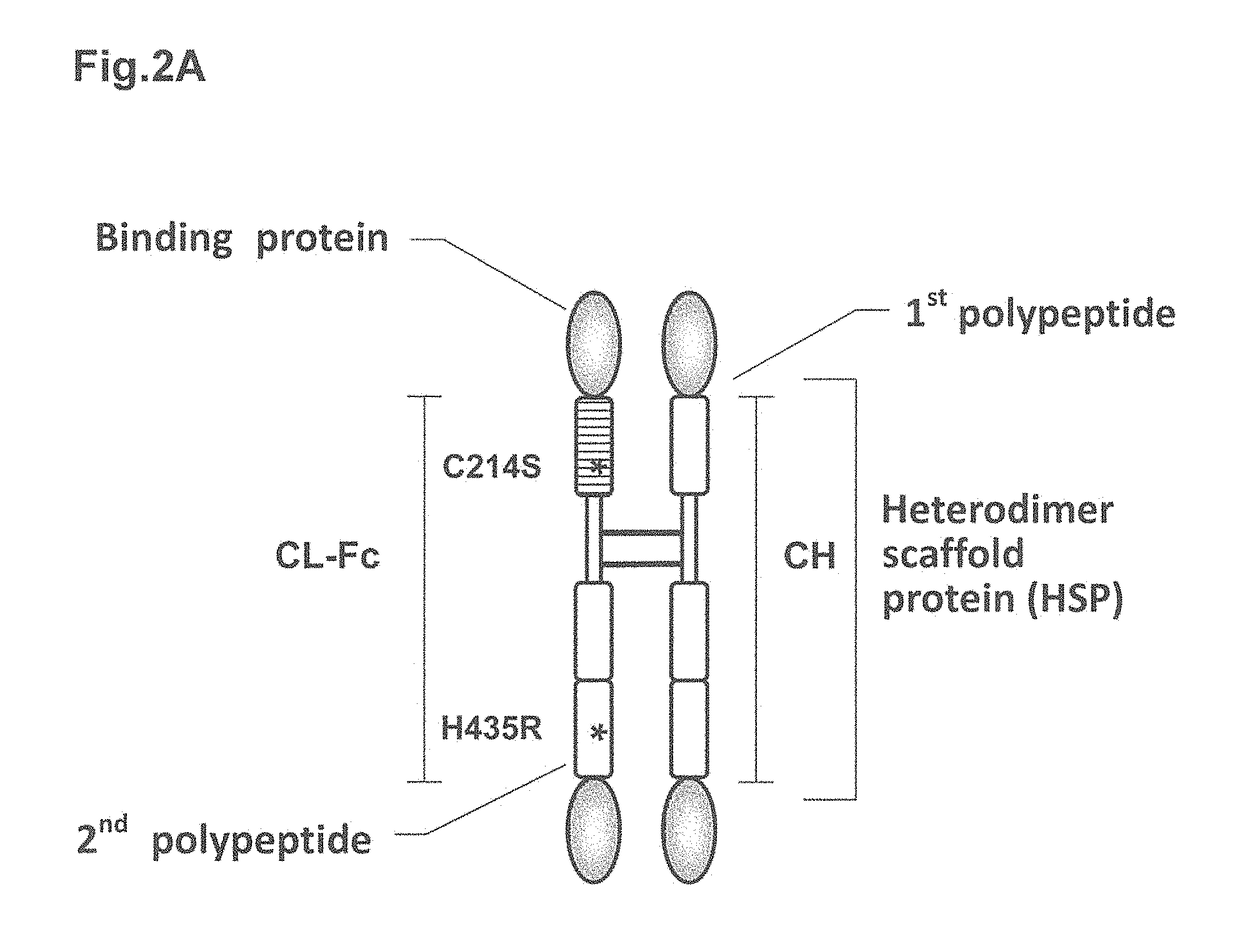
According to the present invention, a heterodimer protein composition that is composed of a first polypeptide comprising an immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region and a second polypeptide comprising CL-Fc prepared by fusion of an immunoglobulin light chain constant region (CL) and Fc region, and also has a deletion or substitution of Cys residues involved in disulfide bonds between CL and CH1, a purification method of the protein composition thereof, a preparation method of the protein composition thereof, a DNA and a vector encoding the protein composition thereof are provided
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
MHC-peptide complex binding ligands
InactiveUS7718777B2Reduce appearance problemsDecreased and stabilization sizeFungiBacteriaImmunoglobulin heavy chainWAS PROTEIN
Disclosed are protein ligands comprising an immunoglobulin heavy chain variable (VH) domain and an immunoglobulin light chain variable (VL) domain, wherein the proteins bind a complex comprising an MHC and a peptide, do not substantially bind the MHC in the absence of the bound peptide, and do not substantially bind the peptide in the absence of the MHC, and the peptide is a peptide fragment of gp100, MUC1, TAX, or hTERT. Also disclosed are methods of using and identifying such ligands.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Heterodimer binding proteins and uses thereof
InactiveCN102958942APeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulin light chainActivation cells
The present disclosure provides polypeptide heterodimers formed between two different single chain fusion polypeptides via natural heterodimerization of an immunoglobulin CH1 region and an immunoglobulin light chain constant region (CL). The polypeptide heterodimer comprises two or more binding domains that specifically bind one or more targets (e.g., a receptor). In addition, both chains of the heterodimer further comprise an Fc region portion. The present disclosure also provides nucleic acids, vectors, host cells and methods for making polypeptide heterodimers as well as methods for using such polypeptide heterodimers, such as in directing T cell activation, inhibiting solid malignancy growth, and treating autoimmune or inflammatory conditions.
Owner:EMERGENT PRODUCTS DEVELOPMENT SEATTLE LLC
Single chain fc fusion proteins
InactiveUS20160175458A1Improve biological activityMaintain good propertiesSenses disorderNervous disorderImmunoglobulin heavy chainHalf-life
The present invention provides novel, single chain Fc fusion proteins having improved properties. The invention provides single chain fusions of soluble proteins fused to the Fc region of an immunoglobulin via a novel linker comprising a constant region of an immunoglobulin light chain linked to a CH1 constant region of an immunoglobulin heavy chain. This novel linker confers favorable properties on the Fc fusion proteins of the invention such as improved bioactivity and increased half-life as compared to non-Fc fusion counterparts or as compared to prior art Fc fusion proteins. The novel Fc fusion protein scaffold as described herein may be designed to include soluble proteins of interest capable of binding or interacting with any target of interest. Preferably, the Fc fusion protein of the invention is a dimer. The dimer preferably forms via a disulfide bond between free cysteine residues in the hinge region of two monomeric Fc fusion proteins of the invention.
Owner:ALKERMES INC
Methods for generating monovalent IgG
ActiveUS8193322B2Nervous disorderAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulin heavy chainImmunoglobulin light chain
The present invention relates to monovalent antibody, methods of making thereof and therapeutic uses thereof. In particular, the present invention provides a heterodimeric polypeptide comprising an immunoglobulin heavy chain and a fusion protein comprising an immunoglobulin light chain and an Fc molecule.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Serum clusterin levels in systemic amyloidosis featuring cardiomyopathy
InactiveUS20130203083A1Reduced cardiac amyloid depositImproved prognosisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiseaseDiagnostic methods
The present invention relates generally to diagnostic methods, systems, assays and kits for identification of subjects with cardiac amyloid deposits, where a low level of clusterin protein in a peripheral fluid sample, e.g., a serum sample from the subject, indicates the subject likely has cardiac amyloid deposits. Other aspects relate to methods of treatment of diseases or disorders characterized by cardiac amyloid deposits and transthyretin (TTR) amyloidosis, and more particularly to methods of treatment of cardiac-related amyloidosis and cardiac amyloid deposits in subjects with familial transthyretin (TTR), senile systemic amyloidosis (SSA), or familial amyloidodic polyneuropathy (FAP), or immunoglobulin light chain (AL) amyloidosis. Other aspects relate to methods and compositions comprising clusterin (CLU) or a clusterin agent (e.g. an agonist of clusterin activity or a biologically active fragment or derivative thereof), and their use in methods to treat a disease or disorder characterized by transthyretin (TTR) amyloidosis, e.g. senile systemic amyloidosis (SSA) or familial amyloidodic polyneuropathy (FAP), and their use in methods to treat amyloidotic cardiomyopathy associated with transthyretin (TTR) amyloidosis.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Histidine Engineered Light Chain Antibodies and Genetically Modified Non-Human Animals for Generating the Same
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Anti-BASIGIN humanized antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN105820250AHigh affinityGuaranteed specificityDigestive systemPharmaceutical delivery mechanismImmunoglobulin Heavy Chain Variable RegionImmunoglobulin light chain
The invention discloses an anti-BASIGIN humanized antibody and application thereof. The antibody contains an immunoglobulin light-chain variable region and an immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable region, wherein the immunoglobulin light-chain variable region contains CDR1 shown as SEQ ID NO:13 in a sequence table, CDR2 shown as SEQ ID NO:14 in the sequence table and CDR3 shown as SEQ ID NO:15 in the sequence table, the immunoglobulin heavychain variable region contains CDR1 shown as SEQ ID NO:16 in the sequence table, CDR2 shown as SEQ ID NO:17 in the sequence table and CDR3 shown as SEQ ID NO:18 in the sequence table. The anti-BASIGIN humanized antibody is applied to the preparation of drugs for treating lung cancers, liver cancers and colorectal cancers and the preparation of drugs for treating malaria.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Development of new-generation gene-therapy immuno-therapy for alzheimer's disease
InactiveCN101491683AConfirmation of validityNervous disorderGenetic material ingredientsImmunoglobulin heavy chainSingle-Chain Antibodies
It is possible to realize gene therapy with immunotherapy for Alzheimer's disease with a sustaining effect compared to antibody investment and a higher antibody capacity compared to a single chain antibody. An integrated anti-[beta]-amyloid antibody or a fragmented carrier is expressed, where the carrier contains a promoter sequence, a coding sequence of an immunoglobulin heavy chain or its fragment of anti-[beta]-amyloid antibody, for coding a self-processing peptide sequence and coding a sequence of an immunoglobulin heavy chain of anti-[beta]-amyloid antibody. Prevention of Alzheimer's disease with the carrier as an active ingredient and therapeutic medication are included.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HISUN PHARMA CO LTD
Single Chain Fc Fusion Proteins
ActiveUS20180289825A1Improve biological activityMaintain good propertiesSenses disorderNervous disorderImmunoglobulin heavy chainHalf-life
The present invention provides novel, single chain Fc fusion proteins having improved properties. The invention provides single chain fusions of soluble proteins fused to the Fc region of an immunoglobulin via a novel linker comprising a constant region of an immunoglobulin light chain linked to a CH1 constant region of an immunoglobulin heavy chain. This novel linker confers favorable properties on the Fc fusion proteins of the invention such as improved bioactivity and increased half-life as compared to non-Fc fusion counterparts or as compared to prior art Fc fusion proteins. The novel Fc fusion protein scaffold as described herein may be designed to include soluble proteins of interest capable of binding or interacting with any target of interest. Preferably, the Fc fusion protein of the invention is a dimer. The dimer preferably forms via a disulfide bond between free cysteine residues in the hinge region of two monomeric Fc fusion proteins of the invention.
Owner:ALKERMES INC
Heterodimer binding proteins and uses thereof
InactiveUS20180273642A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsReceptorImmunoglobulin light chain
The present disclosure provides polypeptide heterodimers formed between two different single chain fusion polypeptides via natural heterodimerization of an immunoglobulin CH1 region and an immunoglobulin light chain constant region (CL). The polypeptide heterodimer comprises two or more binding domains that specifically bind one or more targets (e.g., a receptor). In addition, both chains of the heterodimer further comprise an Fc region portion. The present disclosure also provides nucleic acids, vectors, host cells and methods for making polypeptide heterodimers as well as methods for using such polypeptide heterodimers, such as in directing T cell activation, inhibiting solid malignancy growth, and treating autoimmune or inflammatory conditions.
Owner:APTEVO RES & DEV LLC
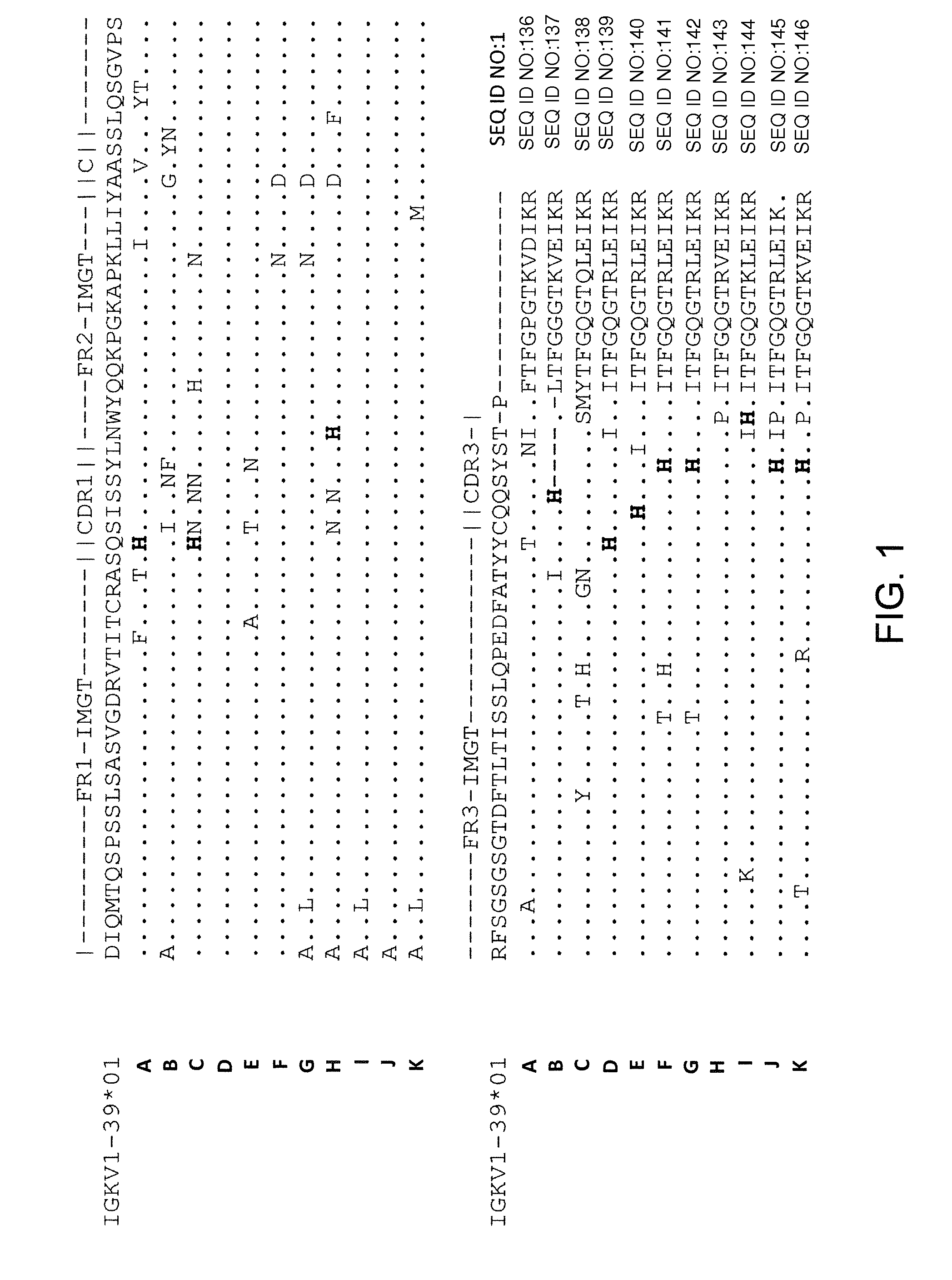
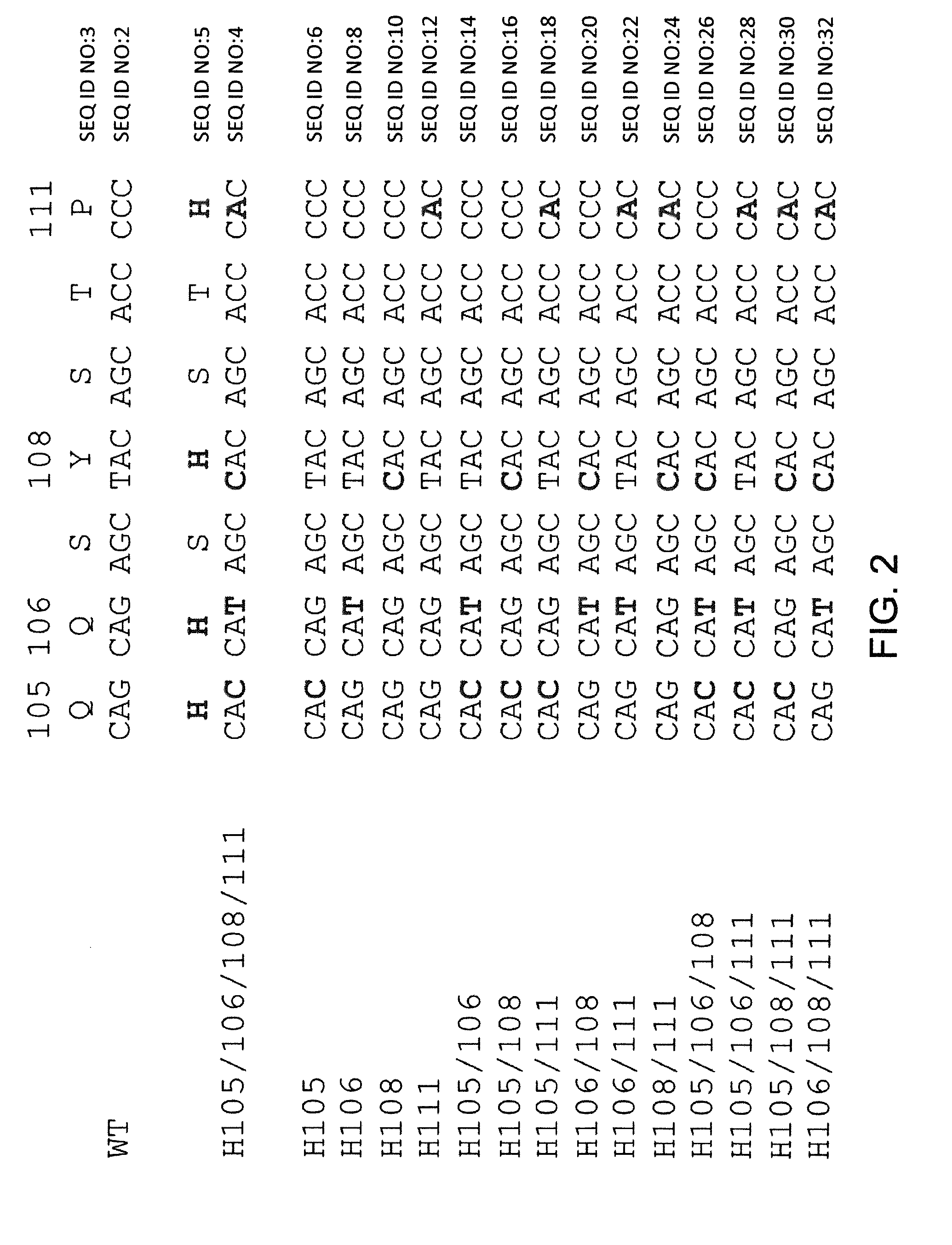
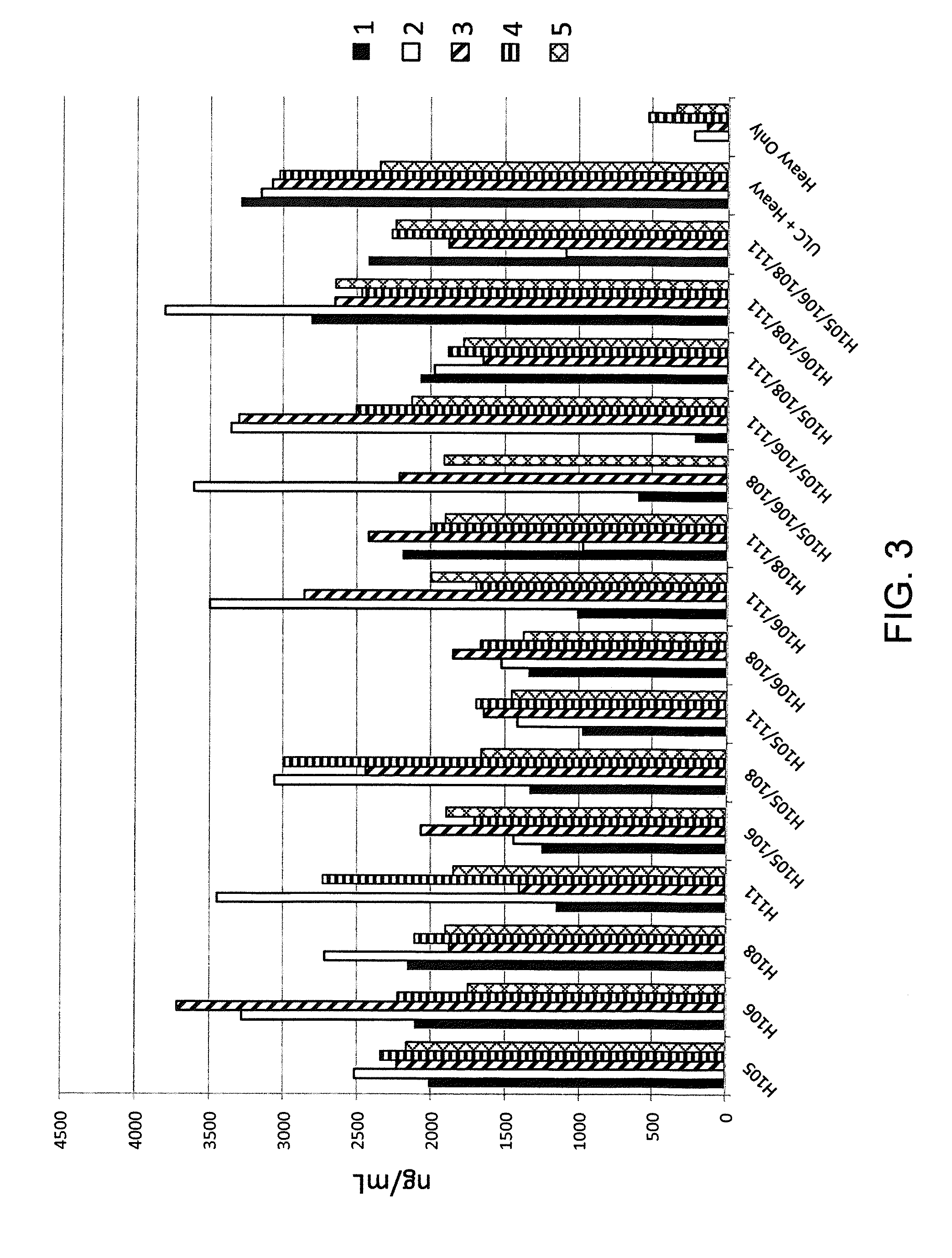
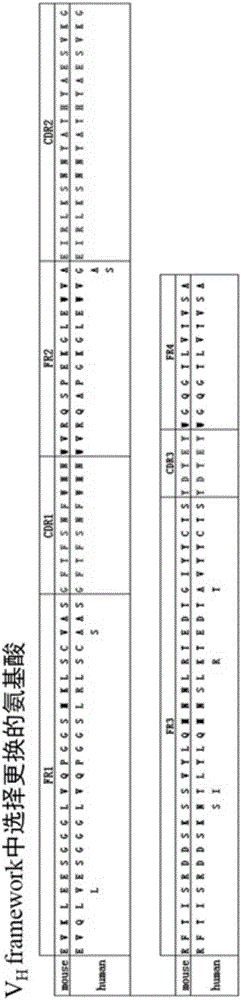
Common light chain mouse
ActiveCN104244709AHigh affinityAffinity matureAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against growth factorsImmunoglobulin light chainBispecific antibody
A genetically modified mouse is provided, wherein the mouse expresses an immunoglobulin light chain repertoire characterized by a limited number of light chain variable domains. Mice are provided that express just one or a few immunoglobulin light chain variable domains from a limited repertoire in their germline. Methods for making light chain variable regions in mice, including human light chain variable regions, are provided. Methods for making human variable regions suitable for use in multispecific binding proteins, e.g., bispecific antibodies, are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
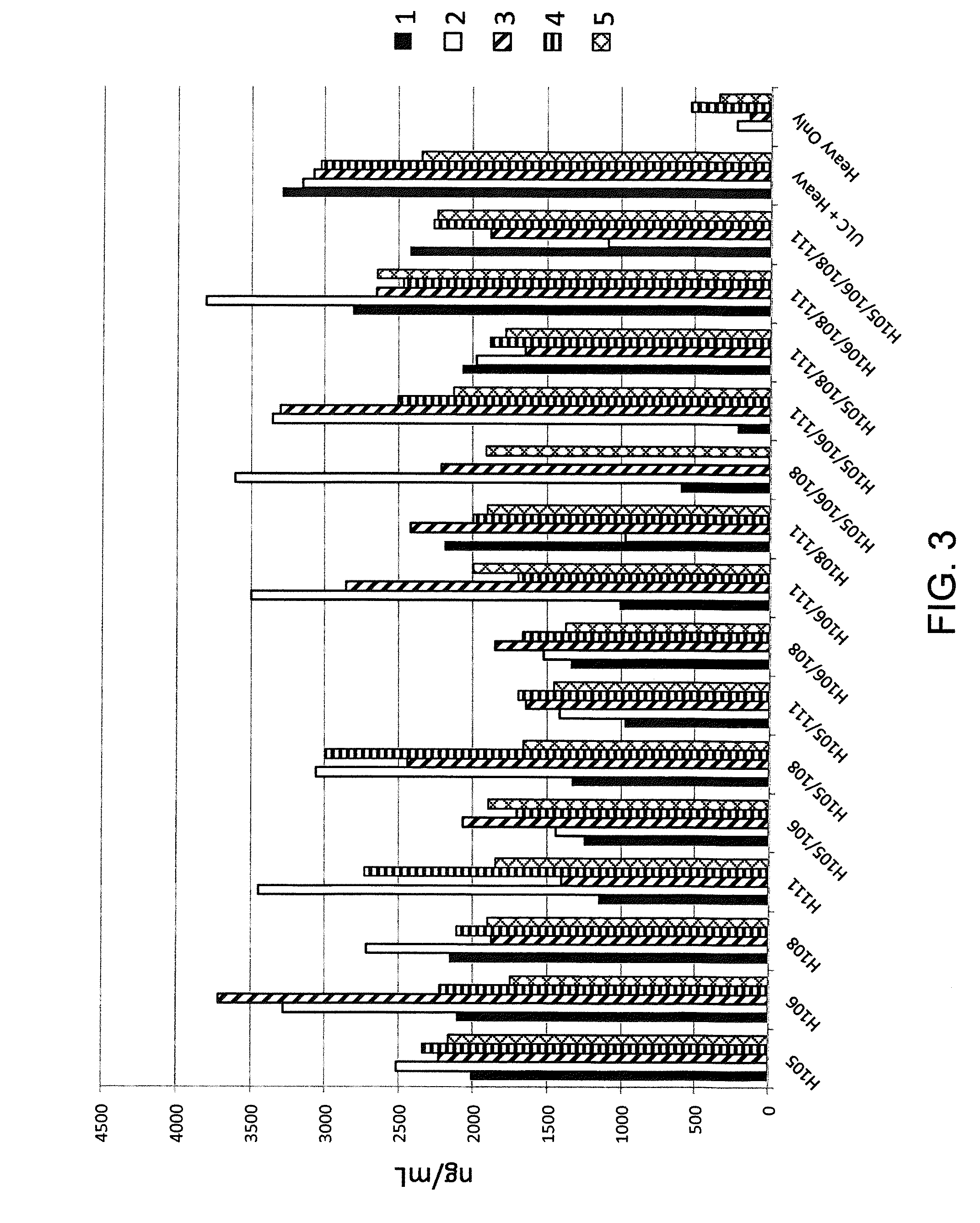
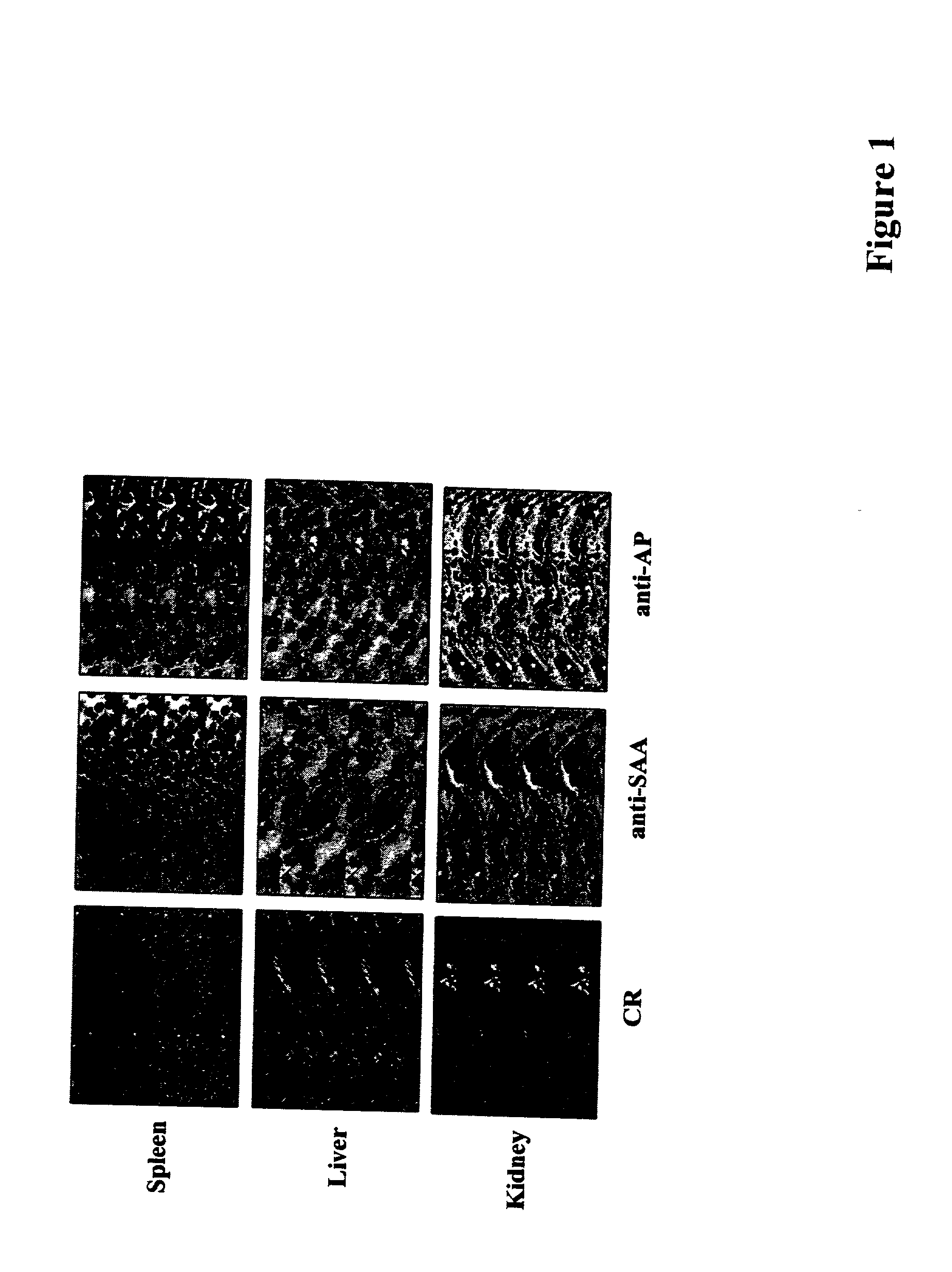
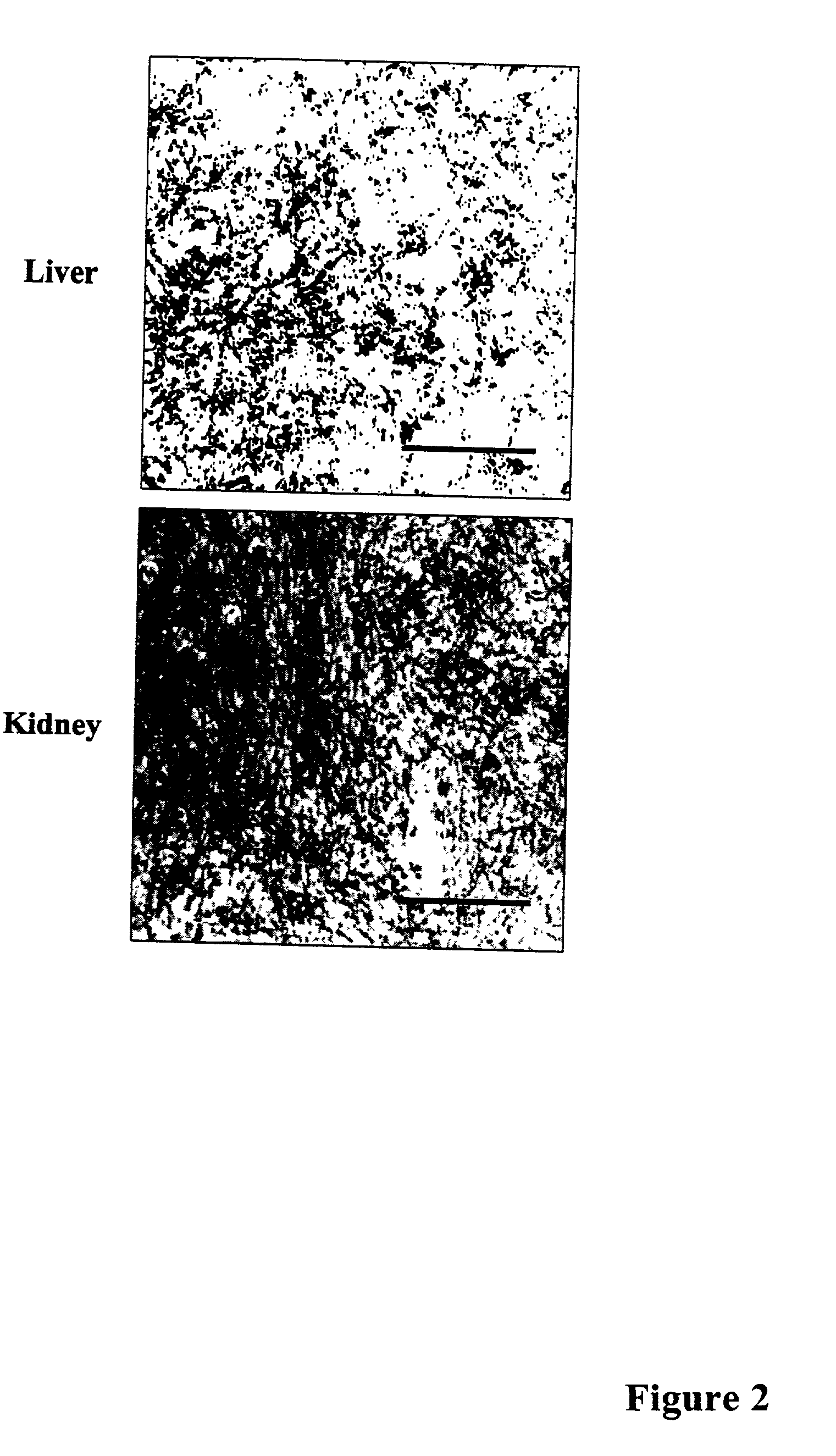
Multiple myeloma and al amyloid immunotherapy targeting immunoglobulin light chains and uses thereof
The present invention relates generally to the prevention and treatment of disease states, and more particularly to the treatment and prevention of plasma cell disorders and plasma cell dyscrasias and other malignancies, amyloidosis and amyloid-associated diseases. In particular, the present invention relates to methods and compositions comprising immunogenic peptides for the treatment and prevention of diseases and malignancies, for example plasma cell disorders, plasma cell dyscrasias and amyloidosis or amyloid-associated diseases. The present invention also provides methods for an assay to screen for therapeutic vaccines for plasma cell disorders, plasma cell dyscrasias and amyloidosis or amyloid-associated diseases.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Binding domains
InactiveUS20130045895A1Increase the number ofPeptide librariesSugar derivativesImmunoglobulin light chainBinding domain
The invention relates to amino acid residues within an immunoglobulin light chain amino acid sequence (VL) which stabilize the monomeric state of the immunoglobulin single variable domain. In particular, but not exclusively, the invention describes a number of mutations that stabilize the monomeric state of DPK9 framework Vκ domain antibodies.
Owner:DE WILDT RUDOLF MARIA +4
Methods for making fully human bispecific antibodies using a common light chain
ActiveCN104582476AVector-based foreign material introductionImmunoglobulins against enzymesEpitopeImmunoglobulin light chain
A genetically modified mouse is provided, wherein the mouse expresses an immunoglobulin light chain repertoire characterized by a limited number of light chain variable domains. Mice are provided that express just one or a few immunoglobulin light chain variable domains from a limited repertoire in their germline. Methods for making bispecific antibodies having universal light chains using mice as described herein, including human light chain variable regions, are provided. Methods for making human variable regions suitable for use in multispecific binding proteins, e.g., bispecific antibodies, and host cells are provided. Bispecific antibodies capable of binding first and second antigens are provided, wherein the first and second antigens are separate epitopes of a single protein or separate epitopes on two different proteins are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Application of tunicamycin in preparing tumour cell reversing drug
InactiveCN101530420AReduce drug useThe effect is accurateOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsAntigenTumor therapy
The invention relates to the technical field of medication. The tumour is always cured by operation, irradiation and chemical medication, and the induction differentiation therapy of malignant tumour becomes the research hotpot and frontier field of cancer biology and tumor therapeutics at present. The invention aims at providing a now application of tunicamycin which is the application in preparing a tumour cell reversing drug. The concentration of low-dosage tunicamycin adopted by the invention is 0.1-0.5mug / ml. After a myeloma cell line is treated, myeloma cell strain is differentiated in state, which is shown as cells are transited into mature plasma cell state; cell differentiation antigen CD49e is raised; and excreted immune globulin light chains are also increased. The invention has the advantages of low drug dosage of the tunicamycin, exact effect, less influence on normal cell and benefit for improving the living state of tumour patients.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
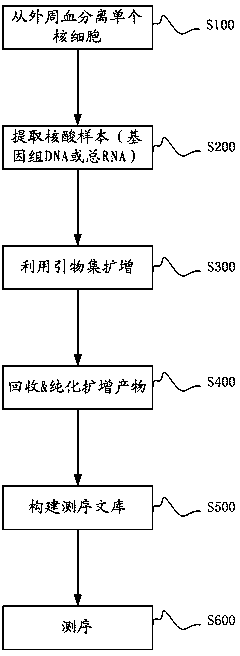
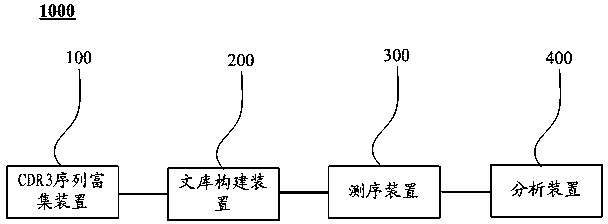
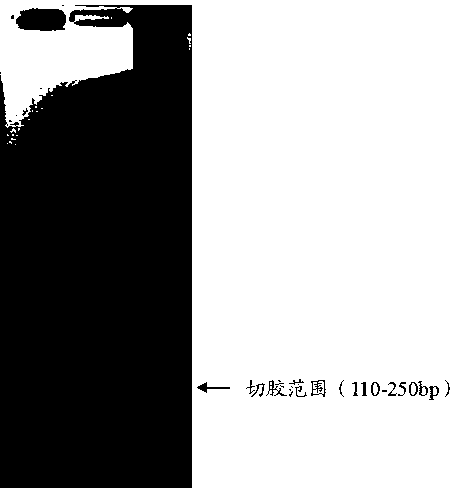
Primer set used for amplifying immunoglobulin light-chain CDR3 sequences, and its uses
ActiveCN103215255BEfficient enrichmentMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationForward primerImmunoglobulin light chain
The invention relates to a primer set used for amplifying immunoglobulin light-chain CDR3 sequences, a kit and methods thereof, a method for enriching the immunoglobulin light-chain CDR3 sequences, a method for constructing a sequencing library of the immunoglobulin light-chain CDR3 sequences, a method for determining the sequence information of the immunoglobulin light-chain CDR3 sequences, a method for determining individual immunization states, and a system for determining the individual immunization states. The primer set comprises: a forward primer group, wherein the forward primer group is composed of at least one V region primer, and each of the at least V region primer includes a sequence complementary with at least one V gene fragment; and a backward primer group, wherein the backward primer group is composed of at least one J region primer, and each of the at least J region primer includes a sequence complementary with at least one J gene fragment. The primer set can effectively enrich the immunoglobulin light-chain CDR3 sequences, so the primer set provides a convenient tool for deep-going researches on CDR3.
Owner:BGI SHENZHEN CO LTD +1
Heterodimer protein composition
ActiveUS9714291B2Efficient and stable productionHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsImmunoglobulin heavy chainProtein composition
According to the present invention, a heterodimer protein composition that is composed of a first polypeptide comprising an immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region and a second polypeptide comprising CL-Fc prepared by fusion of an immunoglobulin light chain constant region (CL) and Fc region, and also has a deletion or substitution of Cys residues involved in disulfide bonds between CL and CH1, a purification method of the protein composition thereof, a preparation method of the protein composition thereof, a DNA and a vector encoding the protein composition thereof are provided.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com