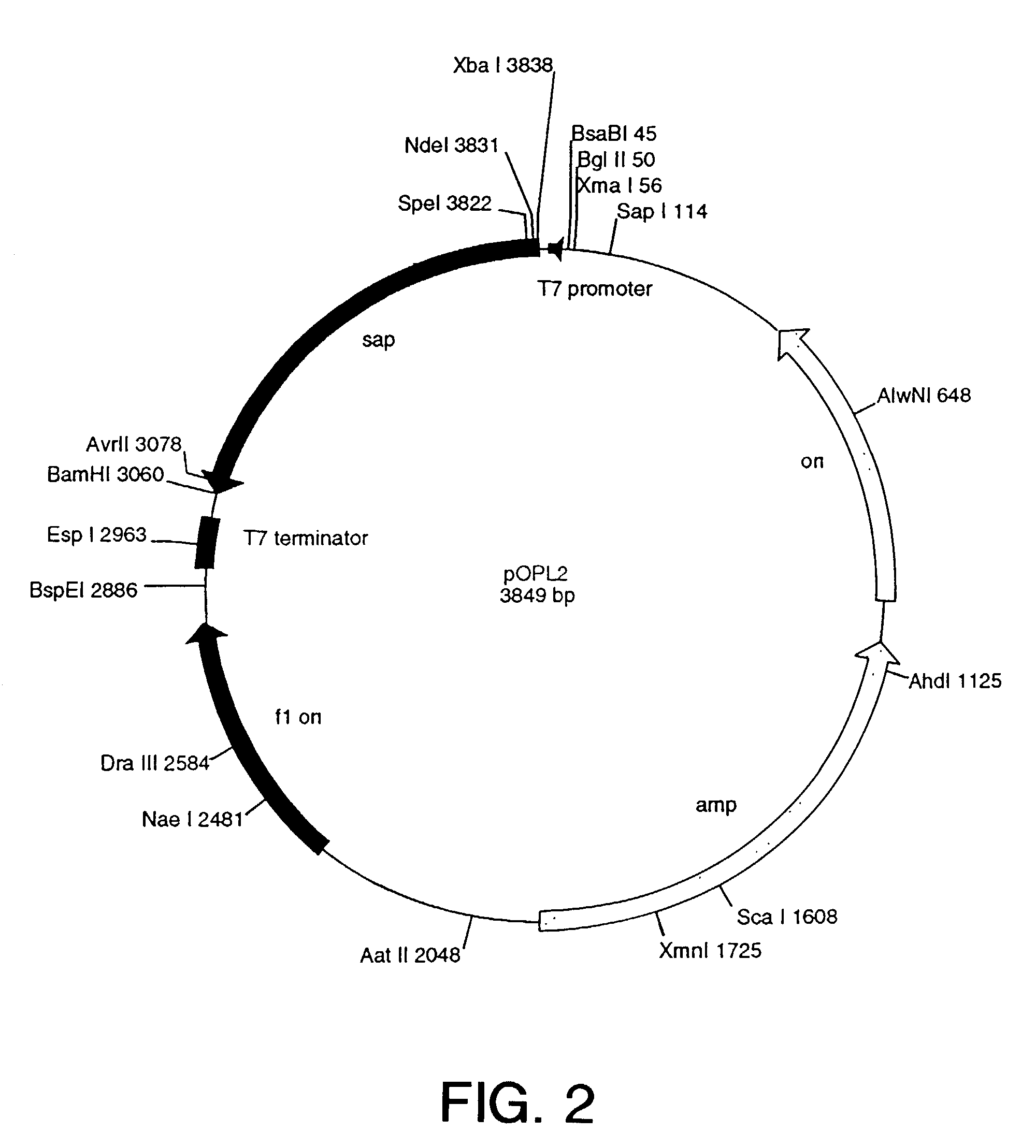
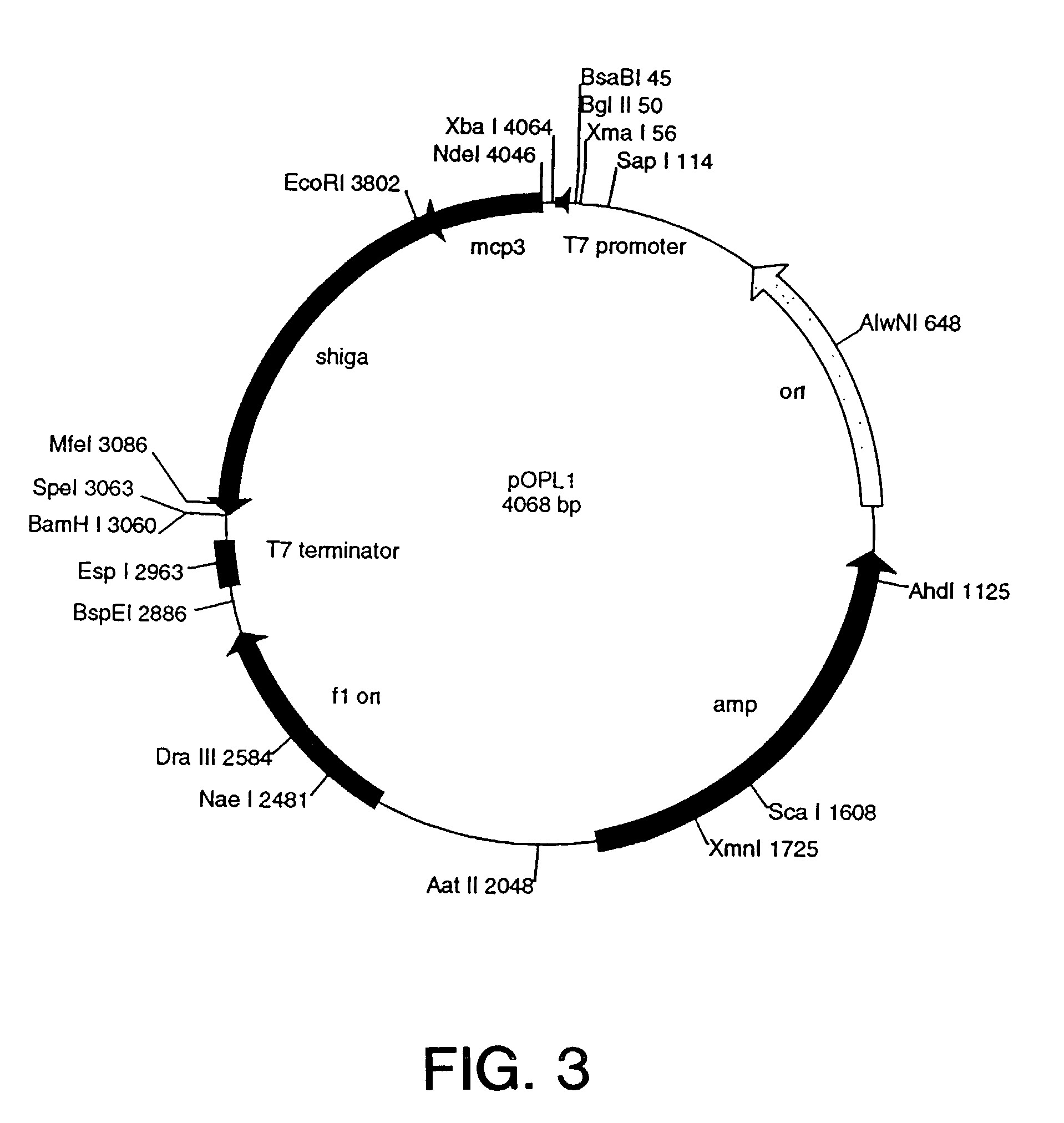
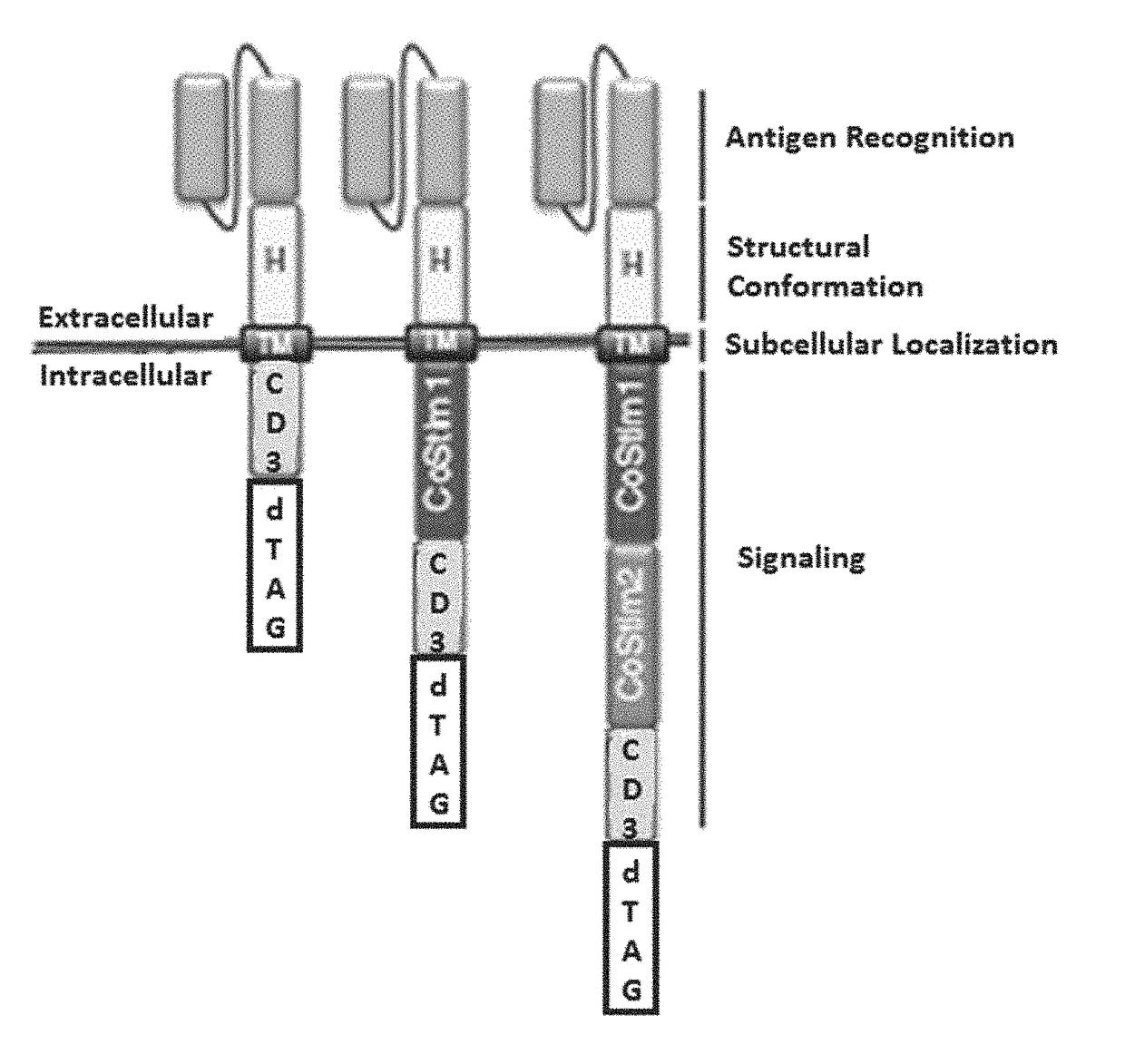
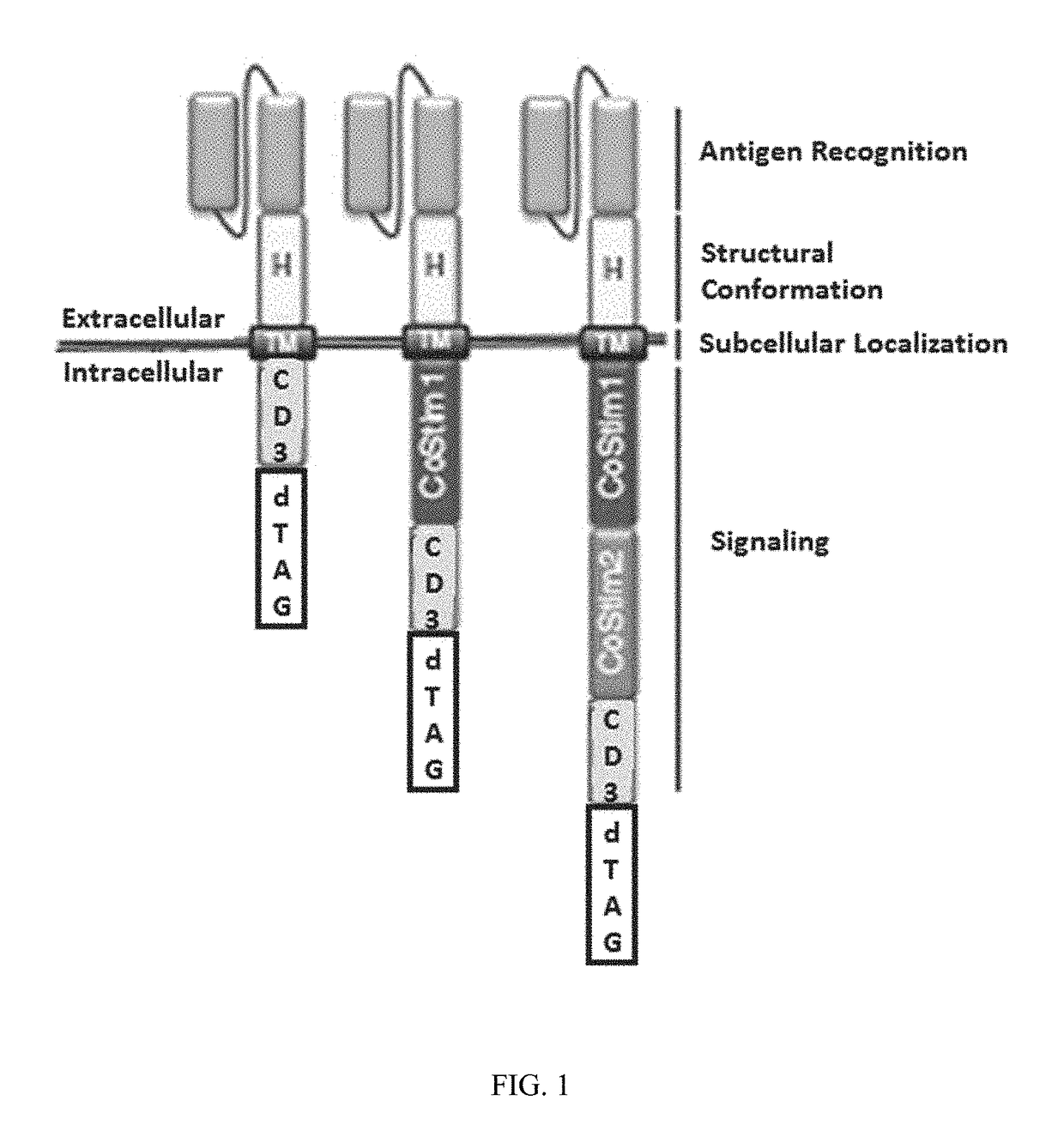
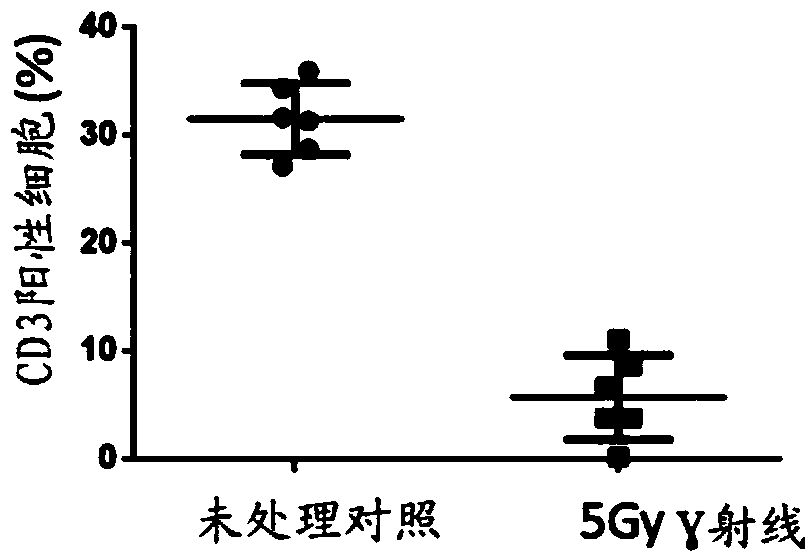
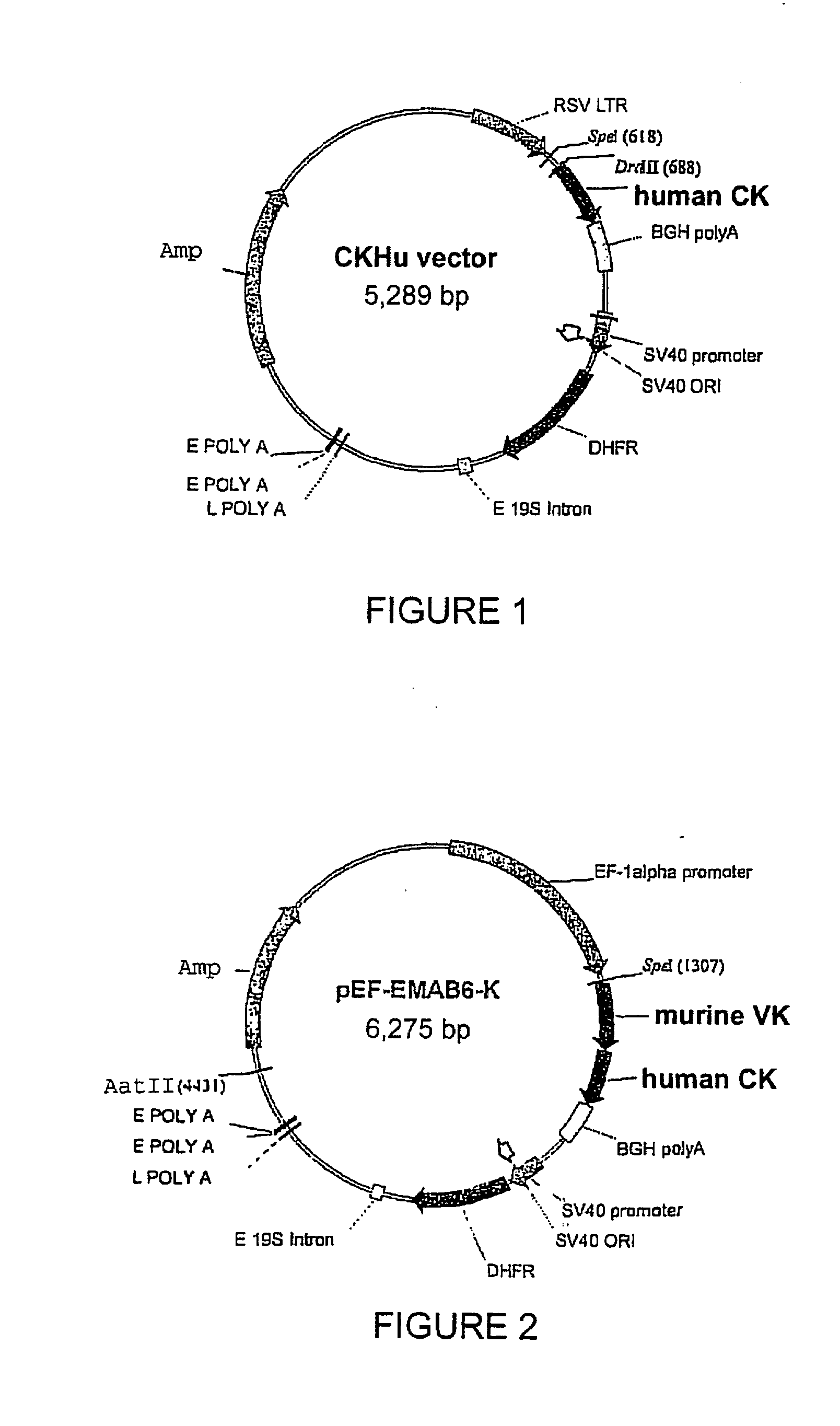
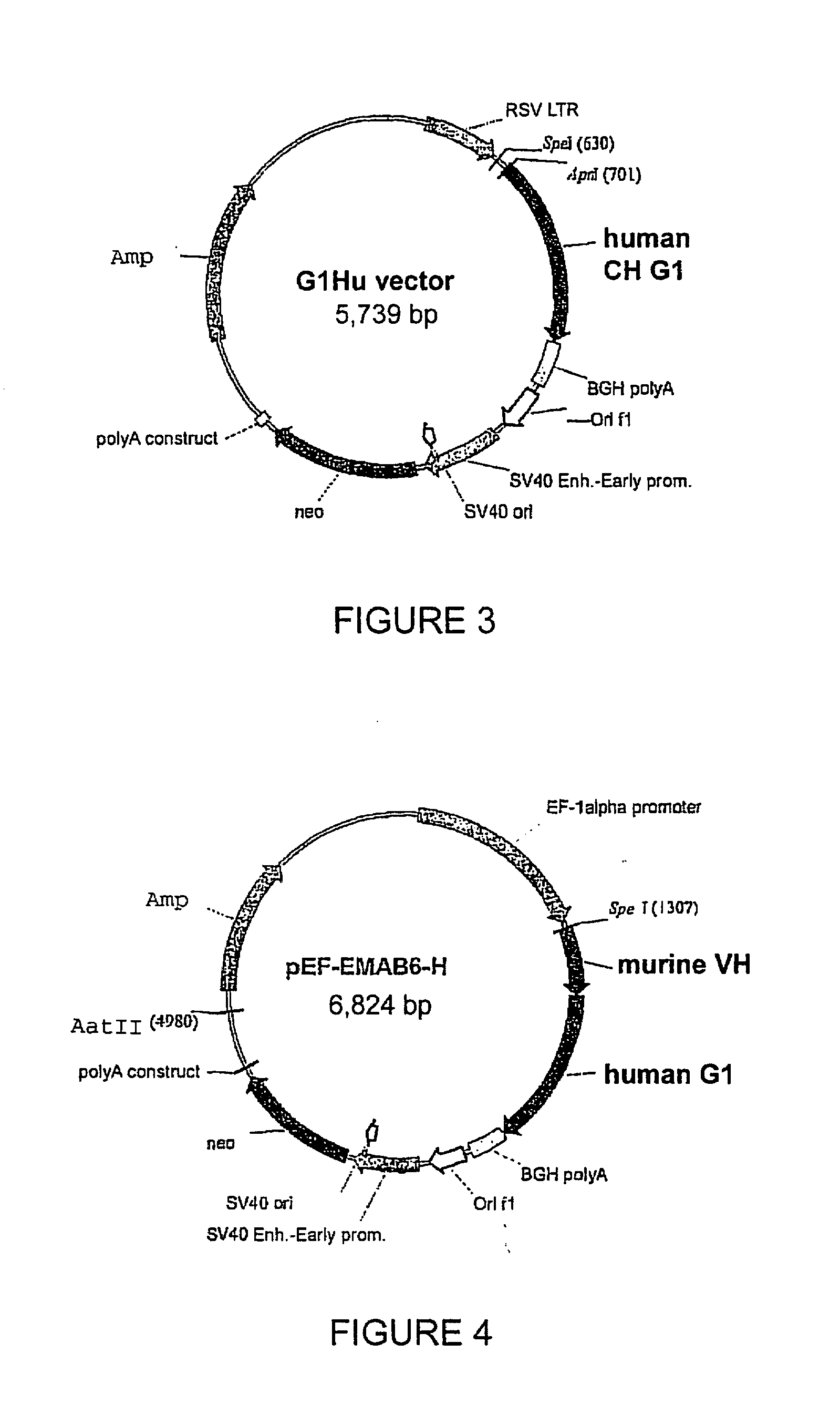
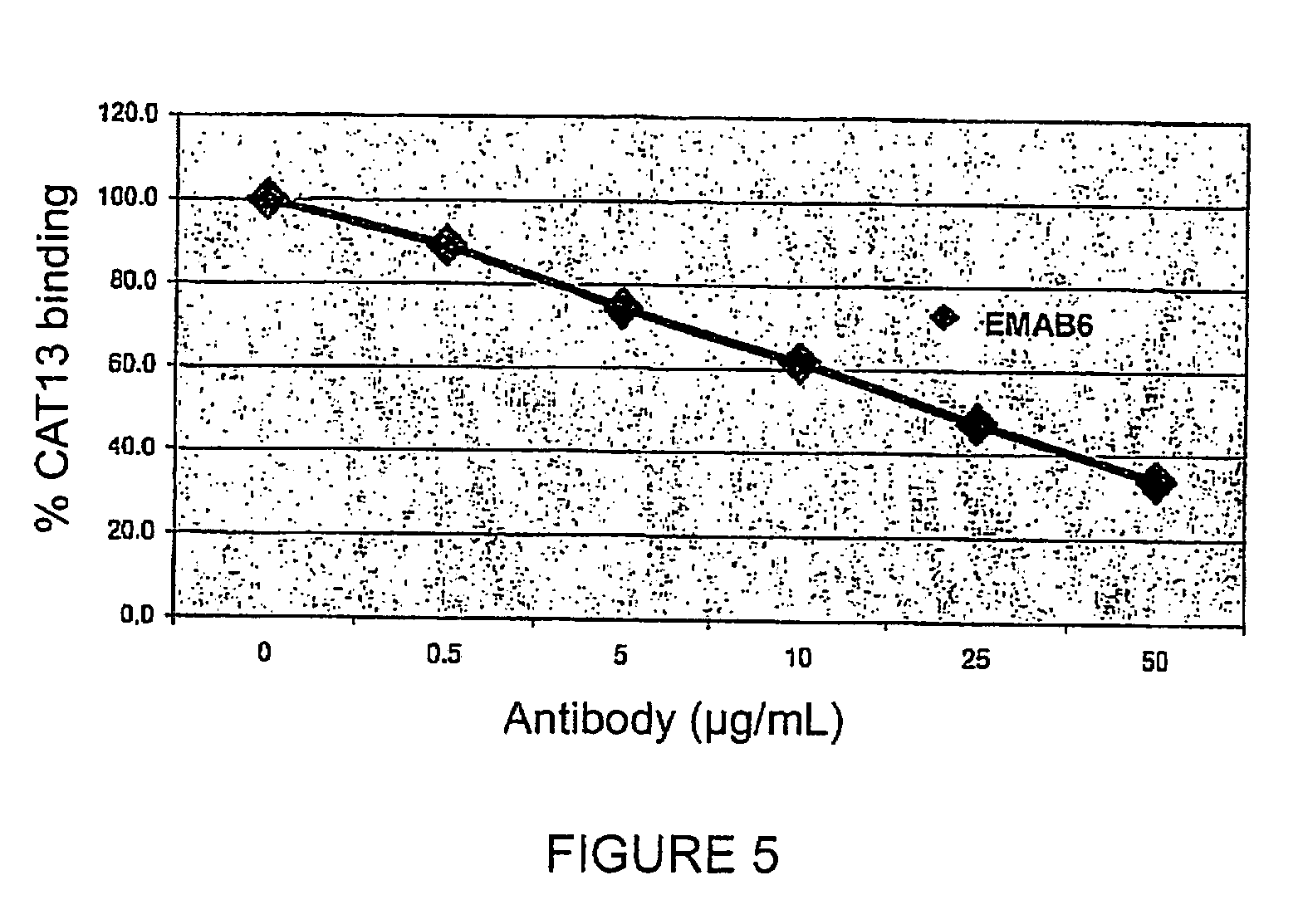
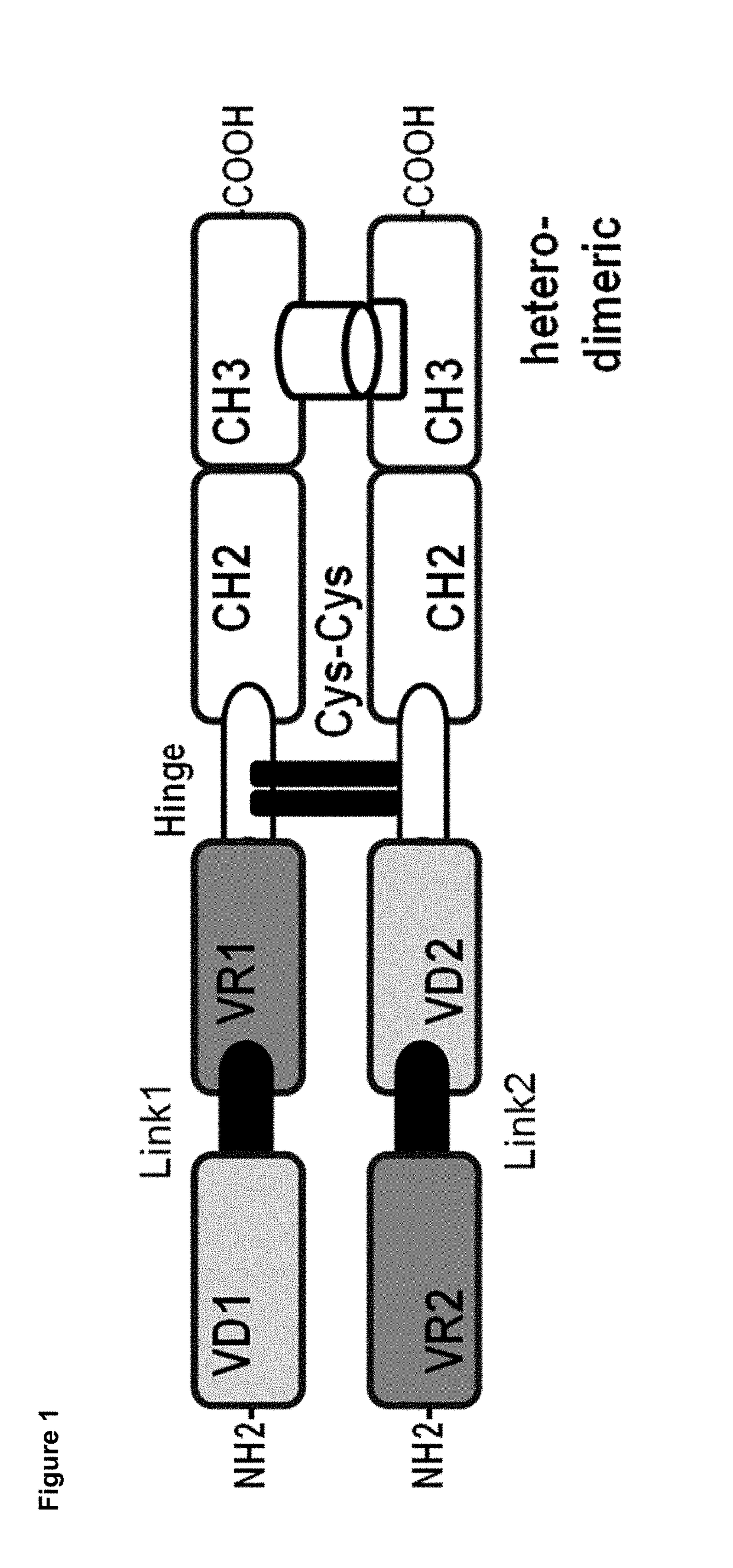
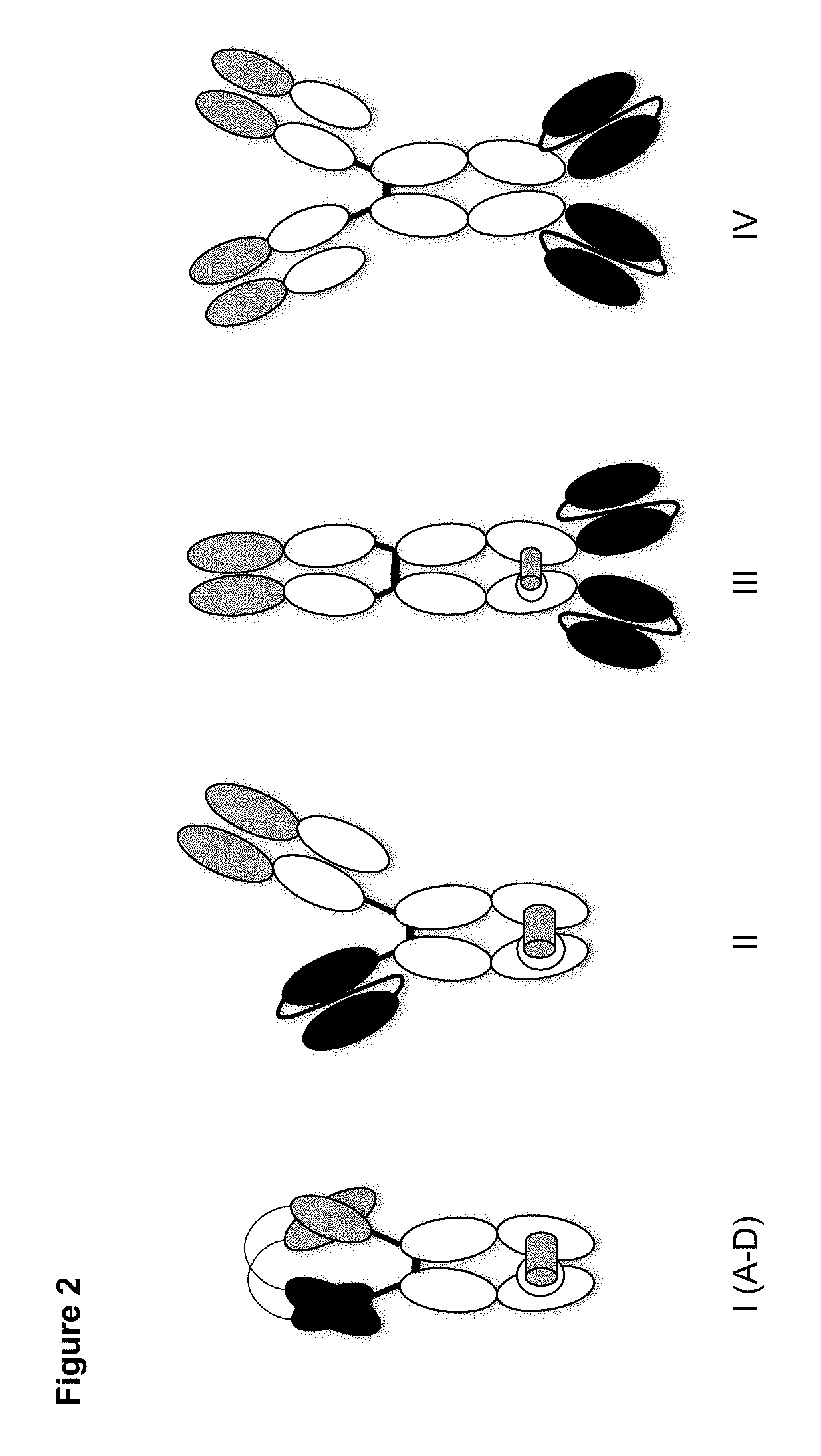
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
237 results about "Immune effector cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Effector cell. A cell that carries out the final response or function of a particular process. The main effector cells of the immune system, for example, are activated lymphocytes and phagocytes—the cells involved in destroying pathogens and removing them from the body.
Bispecific antibodies
ActiveUS7235641B2Improve productivityImprove efficiencyAntipyreticAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBispecific antibodyImmune effector cell
Owner:AMGEN RES (MUNICH) GMBH
Bispecific antibodies
ActiveUS20050136050A1Less complexReduce in quantityAntipyreticAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBispecific antibodyImmune effector cell
The present invention discloses bispecific antibodies comprising two antibody variable domains on a single polypeptide chain, wherein a first portion of the bispecific antibody is capable of recruiting the activity of a human immune effector cell by specifically binding to an effector antigen on the human immune effector cell, the first portion consisting of one antibody variable domain, and a second portion of the bispecific antibody specifically binding to a target antigen other than the effector antigen, the target antigen on a target cell other than the human immune effector cell, the second portion comprising one antibody variable domain.
Owner:AMGEN RES (MUNICH) GMBH
Bispecific igg antibodies as t cell engagers
ActiveUS20140120096A1Induce killingInduce target-specific activationImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsSpecific iggImmune effector cell
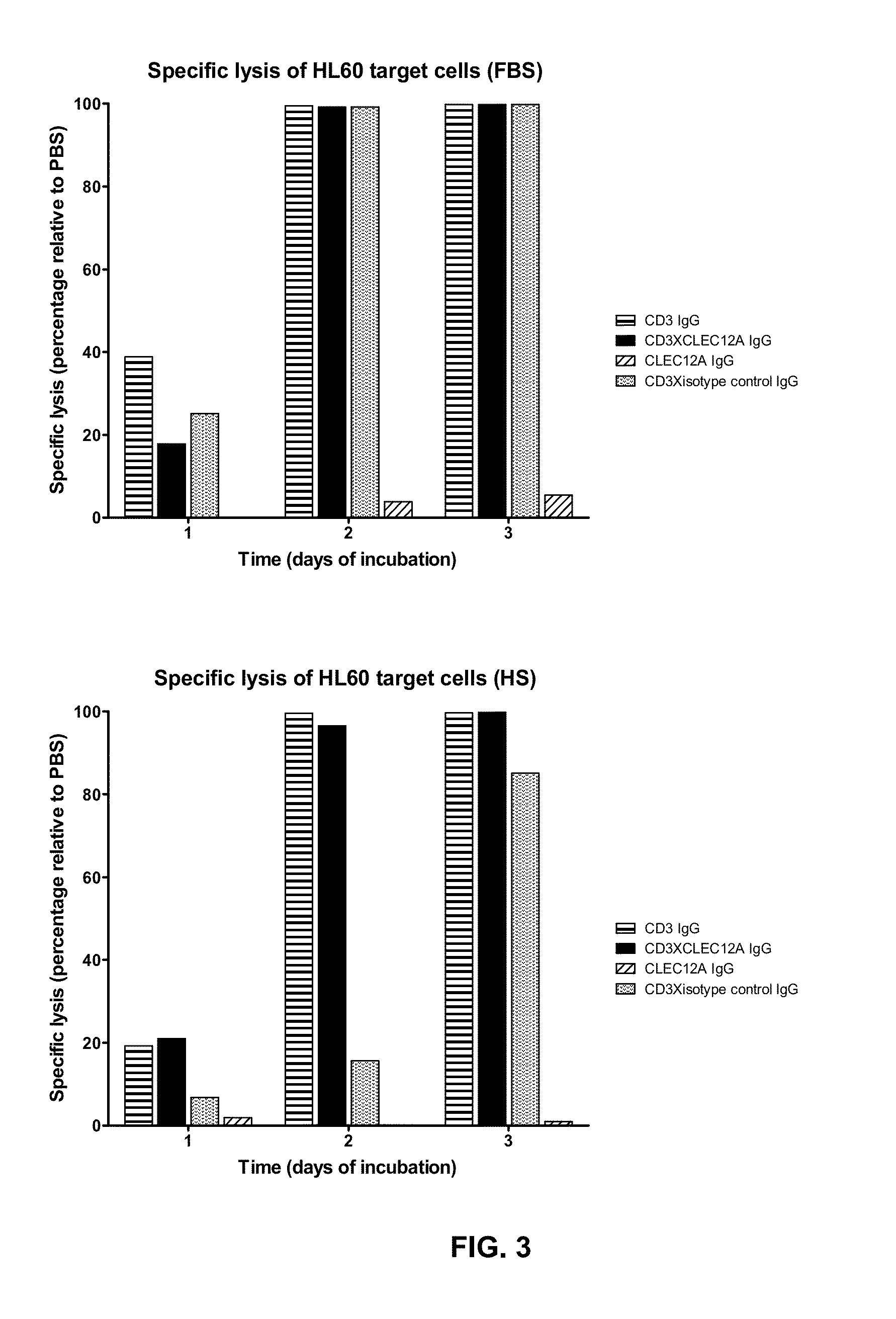
Bispecific IgG antibodies which bind to CLEC12A and an antigen on an immune effector cell are provided.
Owner:MERUS NV
Combinations of low, immune enhancing, doses of mtor inhibitors and cars
InactiveUS20170274014A1Increase the number ofImprove performanceSsRNA viruses negative-sensePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmune effector cellPharmacology
The invention relates, in part, to a method of treating a subject comprising administering to the subject a low, immune enhancing of a mTOR inhibitor and an immune effector cell engineered to express a CAR.
Owner:BROGDON JENNIFER +4
Production of fc-fusion polypeptides in eukaryotic algae
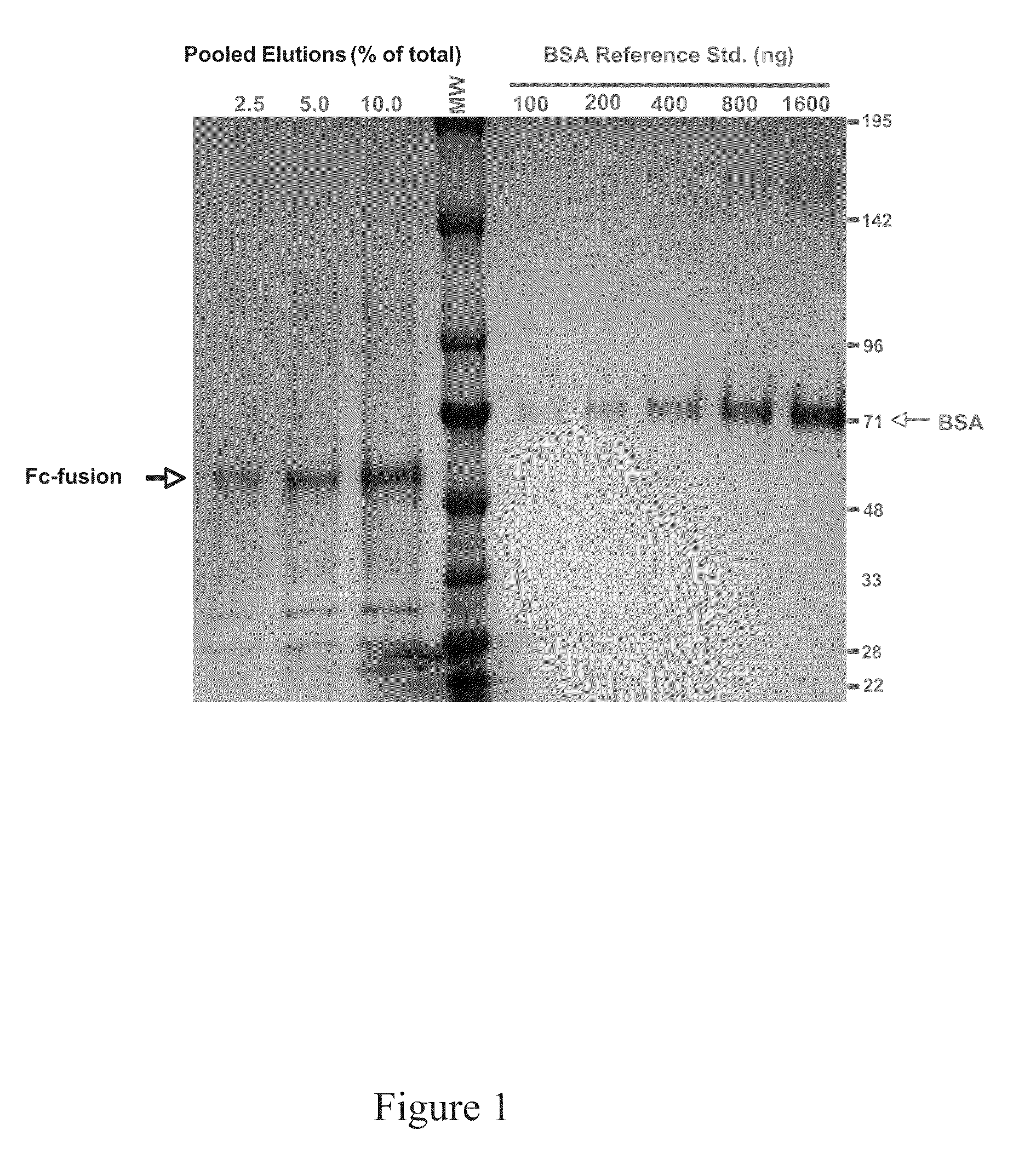
InactiveUS20110151515A1Increase serum stabilityEfficient separation and purificationUnicellular algaeVaccinesHeterologousProtein regulation
Methods and compositions are disclosed to engineer plastids comprising heterologous genes encoding immuno-activating domains fused to an extracellular domain (ECD) of a receptor or surface glycoprotein, a growth factor or an enzyme and produced within a subcellular organelle, such as a chloroplast. The immuno-activating domains may include those regions of a protein capable of modulating the interaction between immune effector cells via proteins containing stereoselective binding domains and specific ligands, such as the Fc regions of antibodies. The present disclosure also demonstrates the utility of plants, including green algae, for the production of complex multi-domain fusion proteins as soluble bioactive therapeutic agents.
Owner:SAPPHIRE ENERGY
Compositions and methods to enhance the immune system
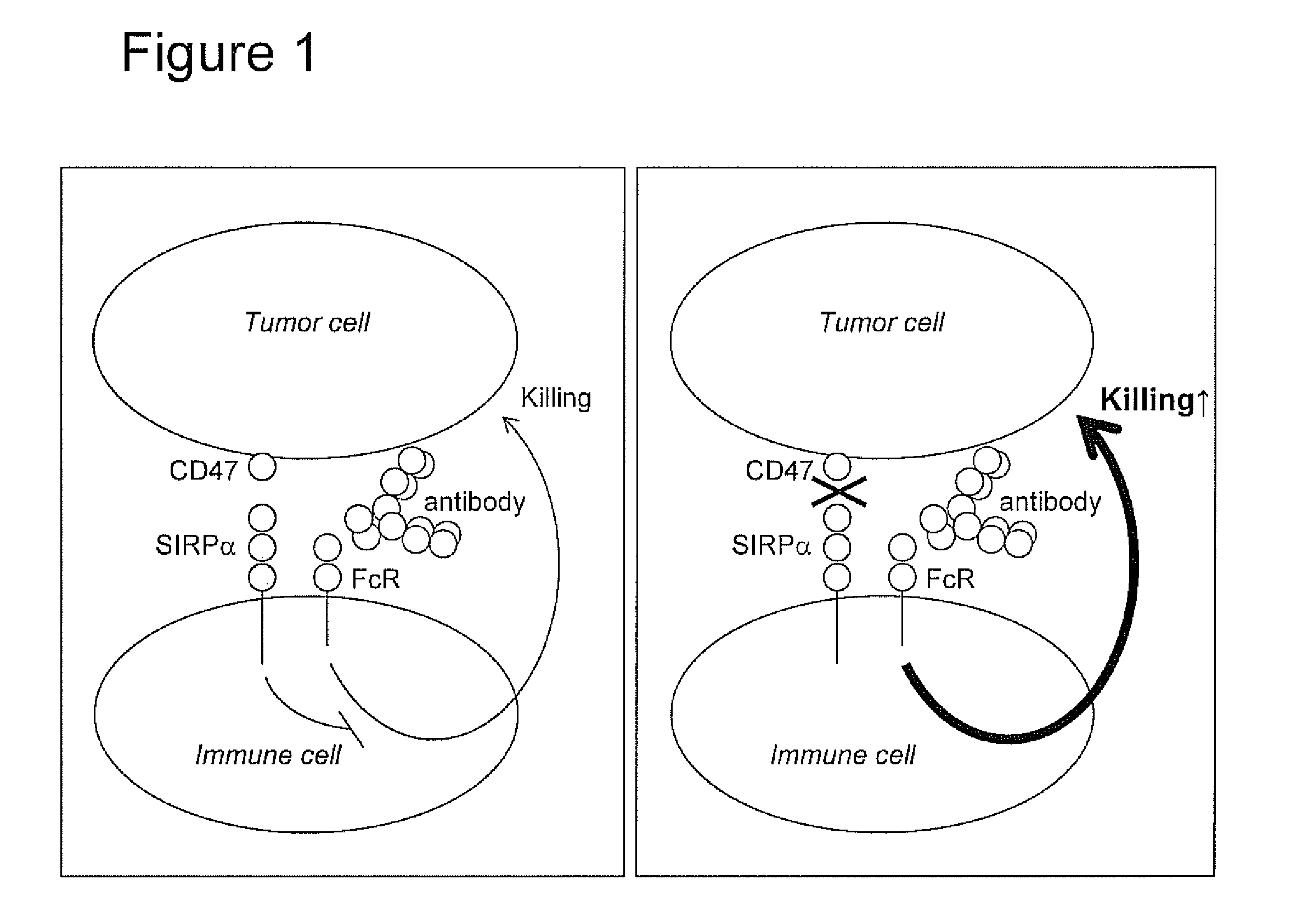
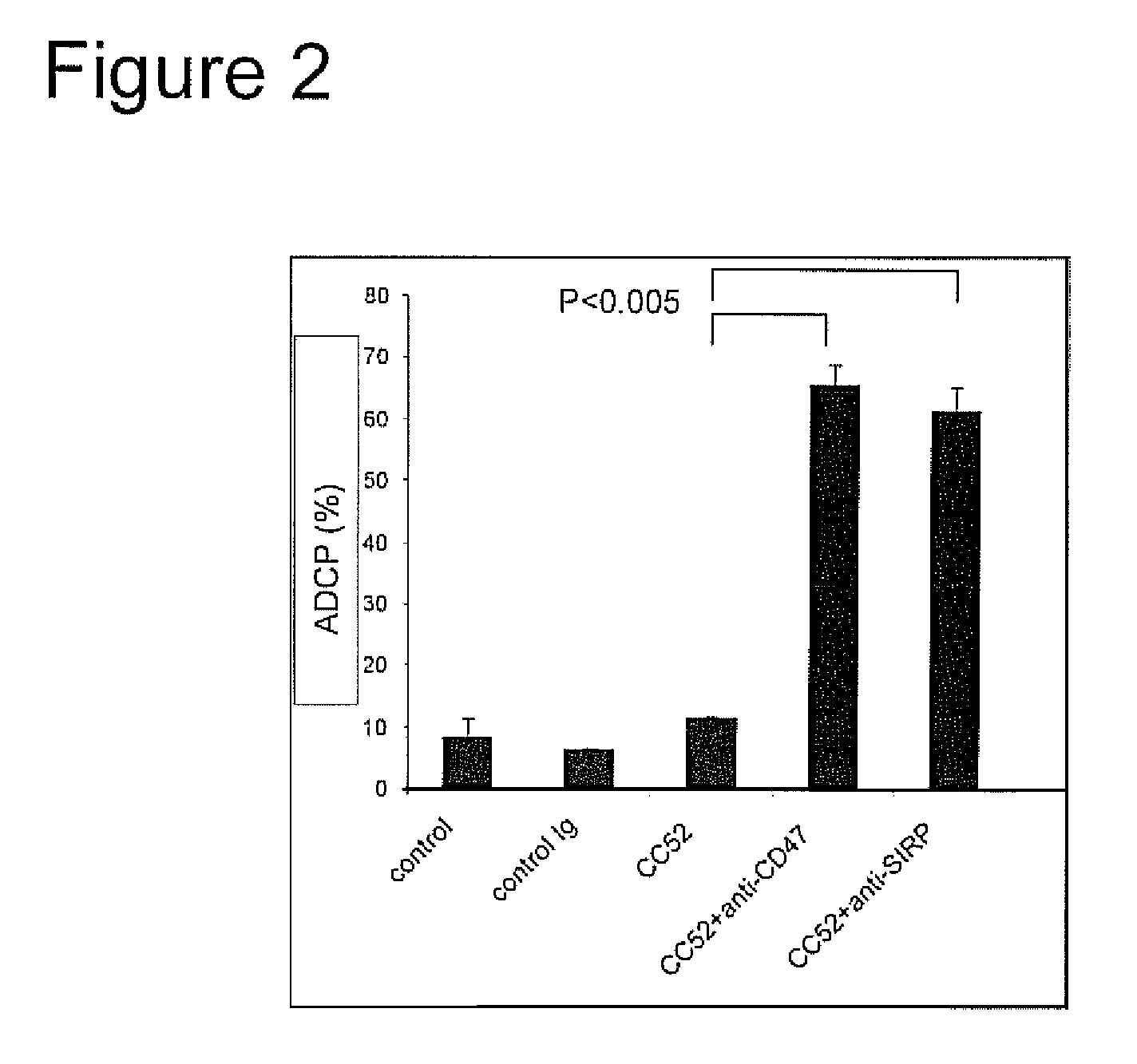
InactiveUS8728476B2Enhance in vivo efficacyImprove immunityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic antibodyCancer cell
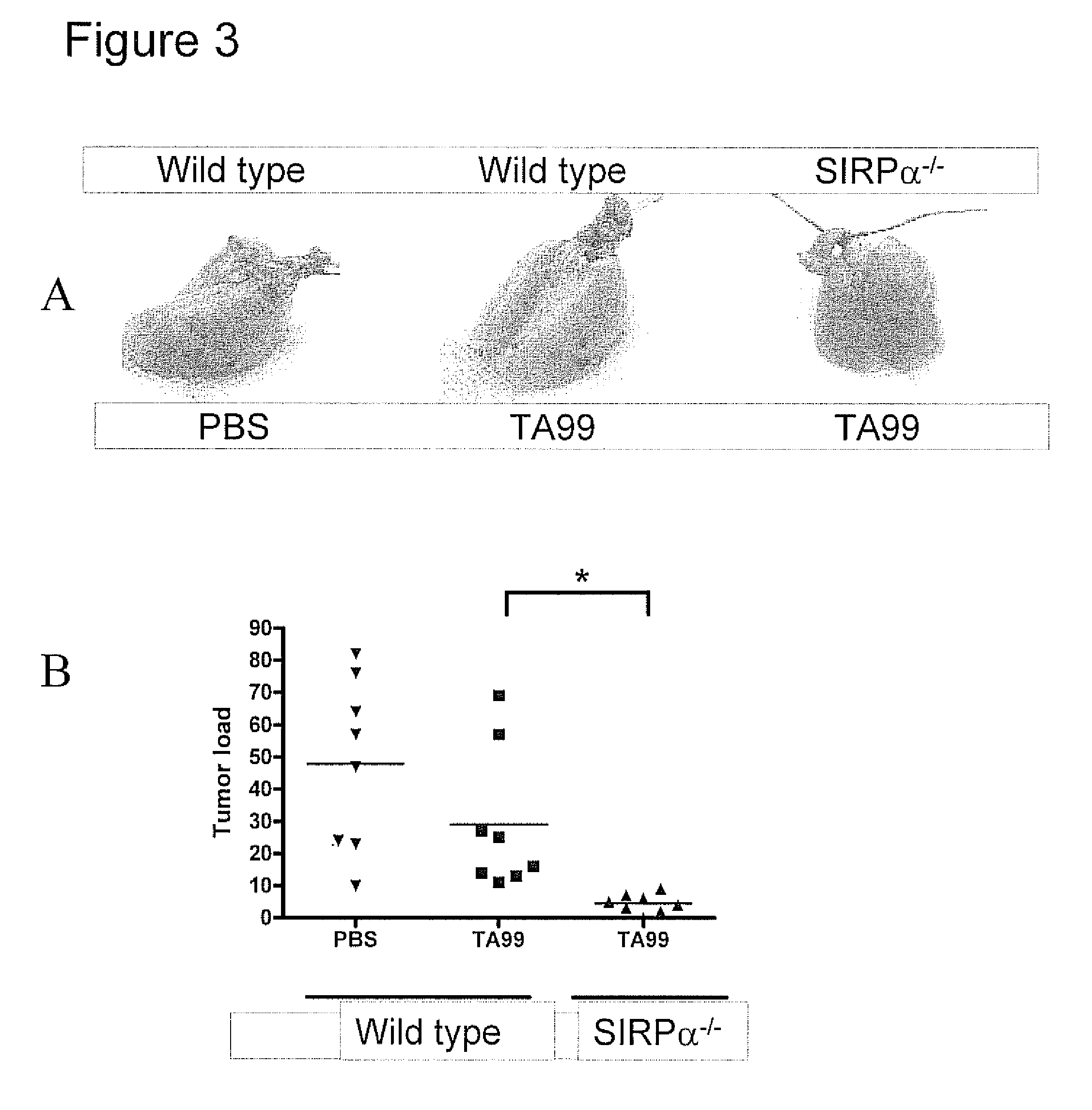
The invention relates to the field of molecular medicine. In particular, it relates to compositions and methods to enhance the clearance of aberrant cells, e.g. cancer cells or virus-infected cells, by the host's immune system. Provided is a composition comprising (i) a therapeutic compound that can trigger a host's immune effector cells against an aberrant cell, such as a therapeutic antibody, and (ii) at least one agent capable of reducing or preventing inhibitory signal transduction initiated via SIRPalpha.
Owner:STICHTING SANQUIN BLOEDVOORZIENING
Genes differentially expressed in cancer cells to design cancer vaccines
Owner:GENZYME CORP
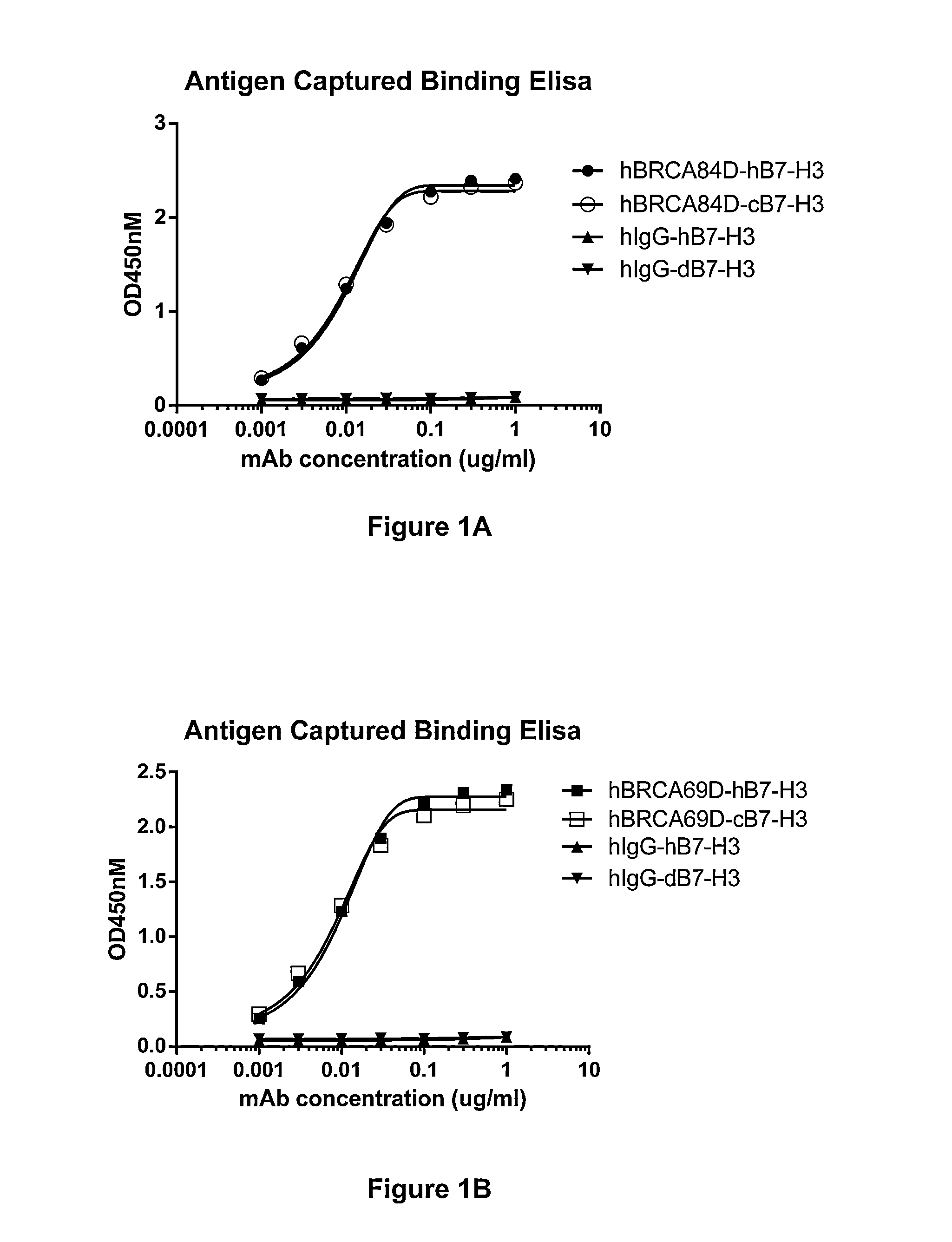
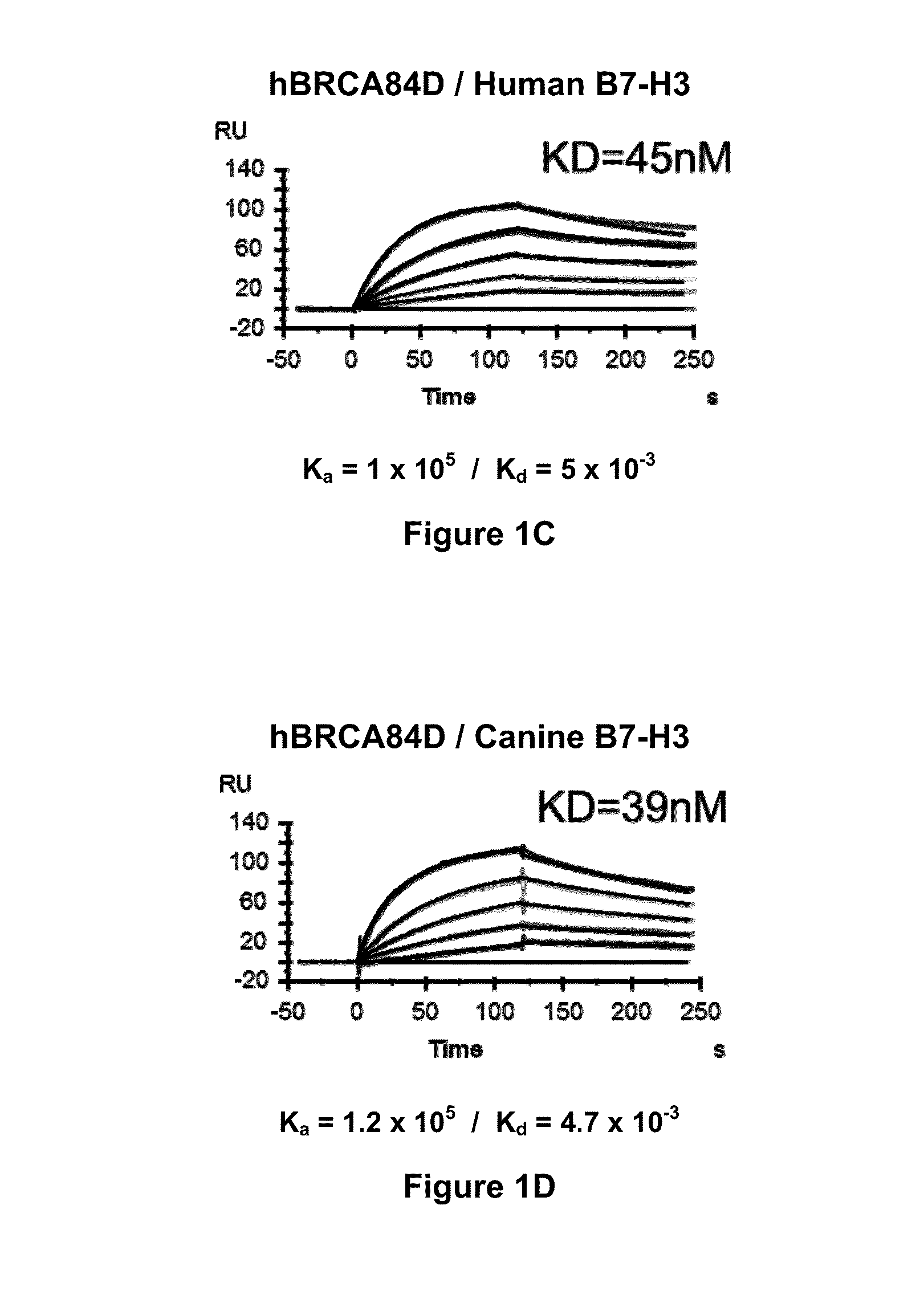
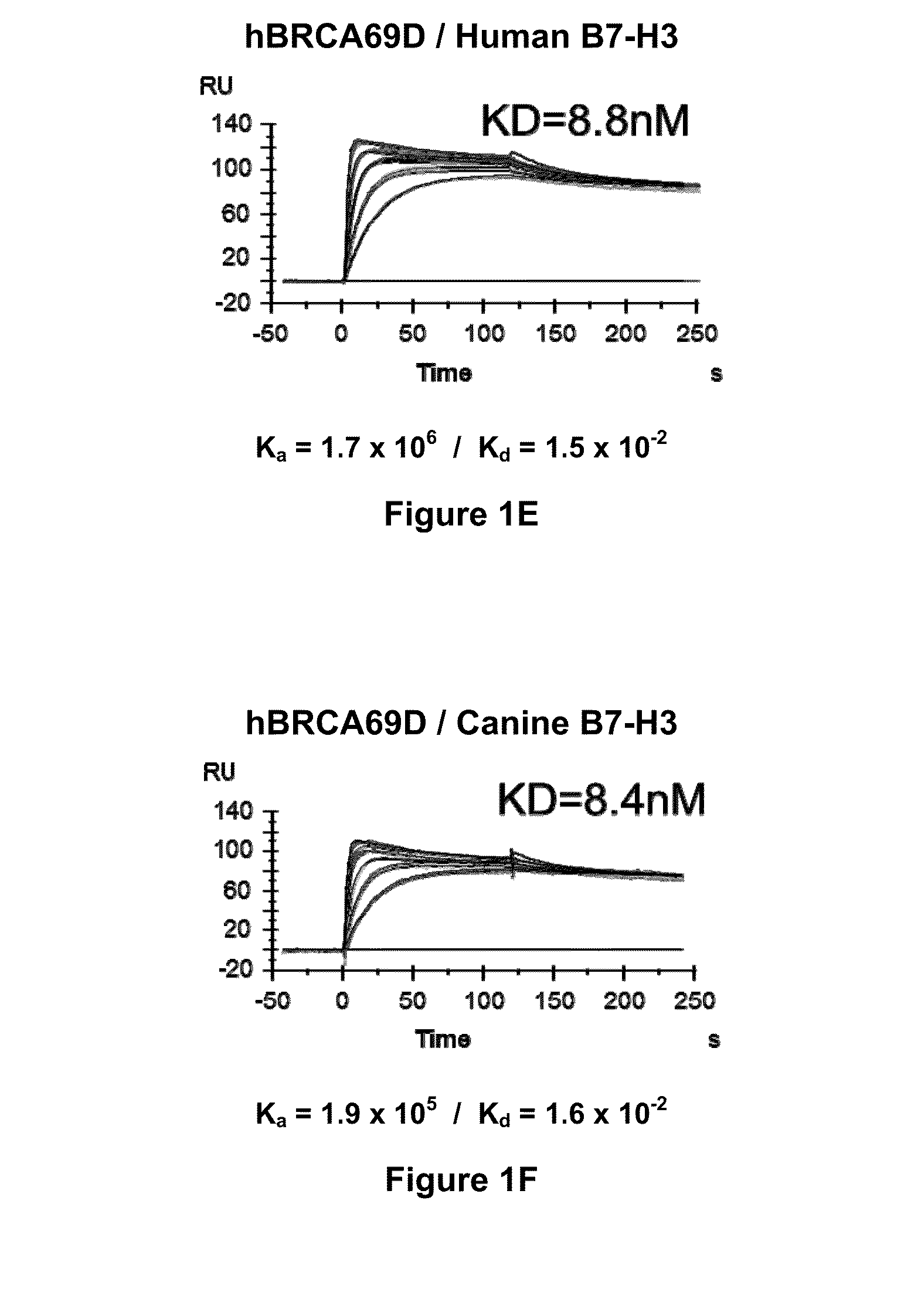
Bispecific Molecules That Are Immunoreactive with Immune Effector Cells of a Companion Animal That Express an Activating Receptor and Cells That Express B7-H3 and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20140255407A1Facilitate killingIncreased activationImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody medical ingredientsImmune effector cellCancer therapy
The present invention relates to bispecific molecules that are immunoreactive to an activating receptor of a companion animal immune effector cell and to B7-H3, and to the use of such bispecific molecules in the treatment of cancer in companion animals.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
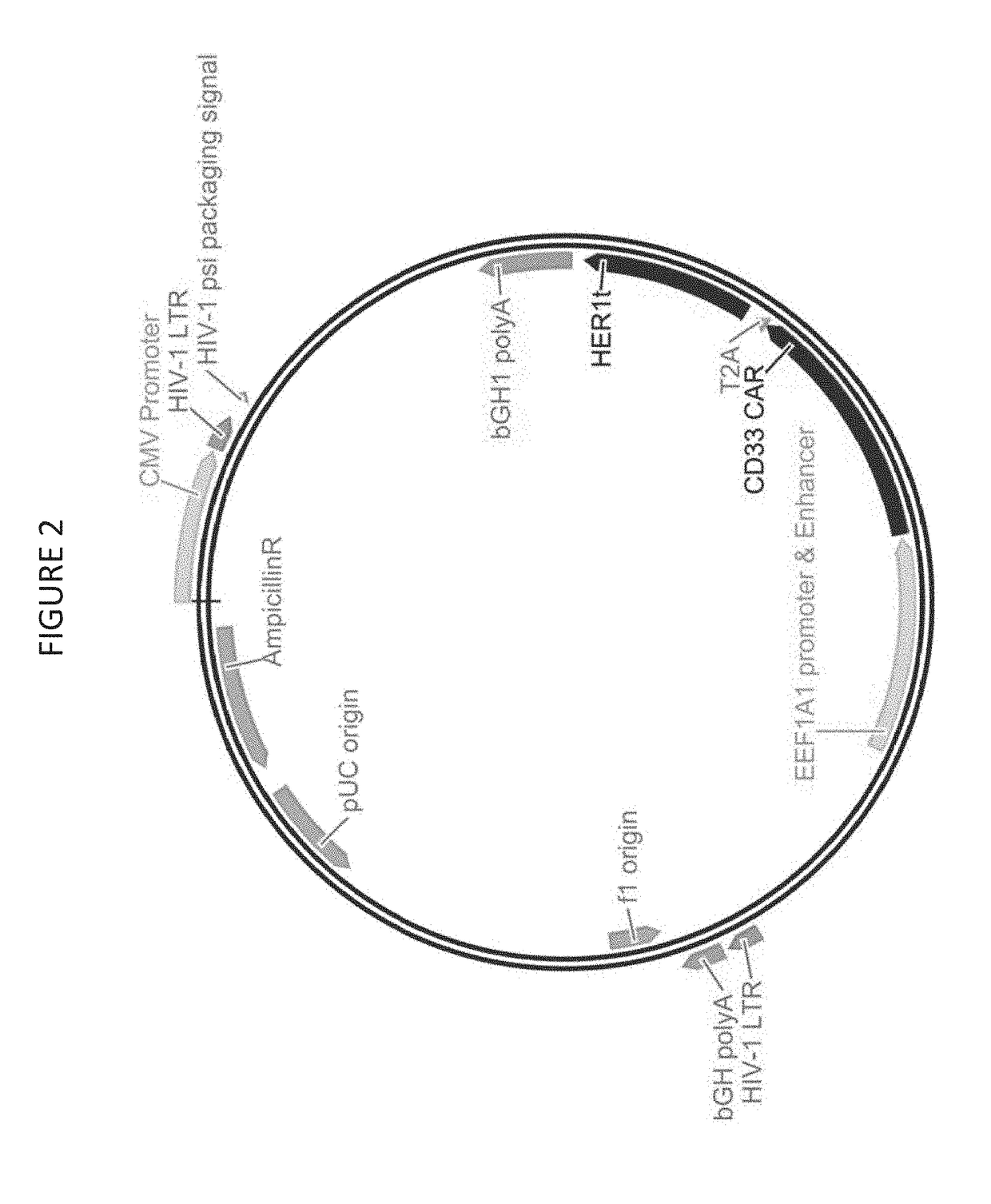
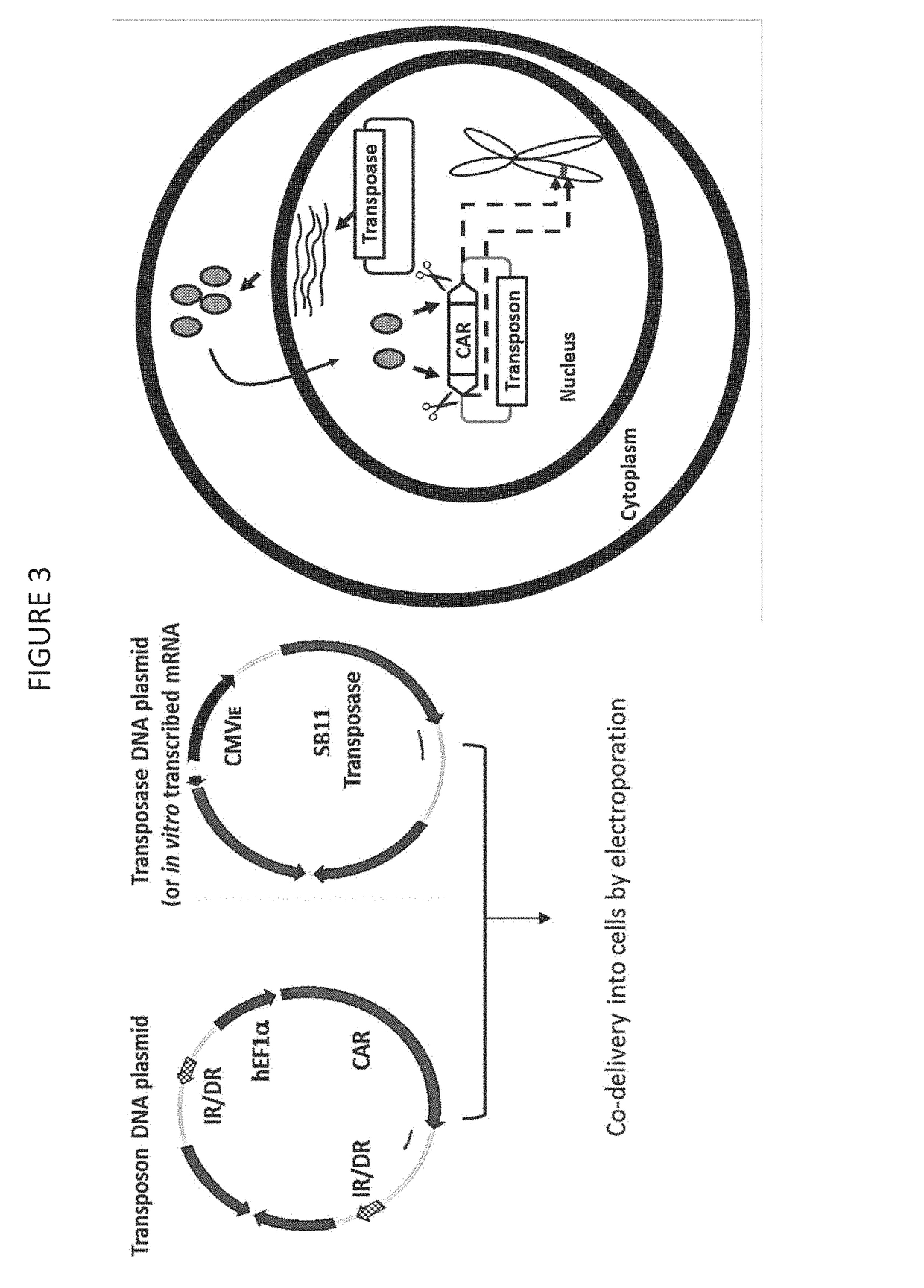
Cd33 specific chimeric antigen receptors
PendingUS20180002397A1Easy SurvivalEfficiently and specifically eliminatePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyMyeloid leukemiaCD33
Provided herein are chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) for cancer therapy, and more particularly, CARs containing a scFv from a CD33 monoclonal antibody. Provided are immune effector cells containing such CARs, and methods of treating proliferative disorders such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML), and relapsed or refractory AML.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
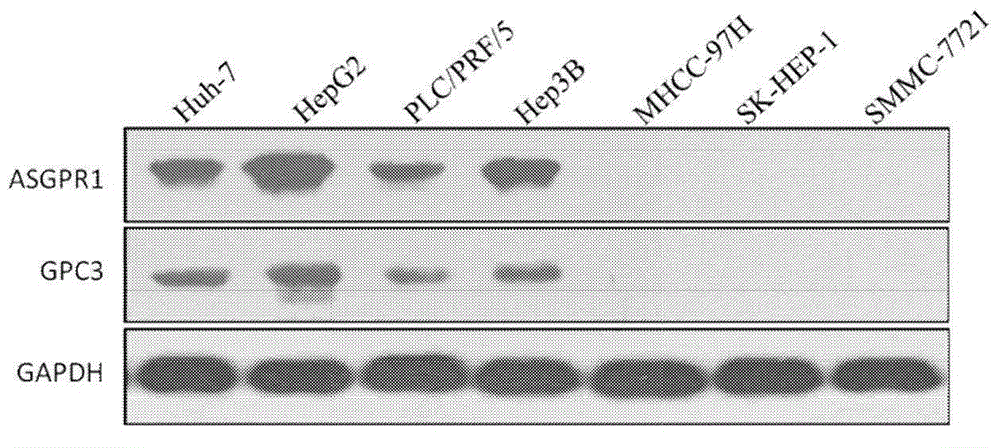
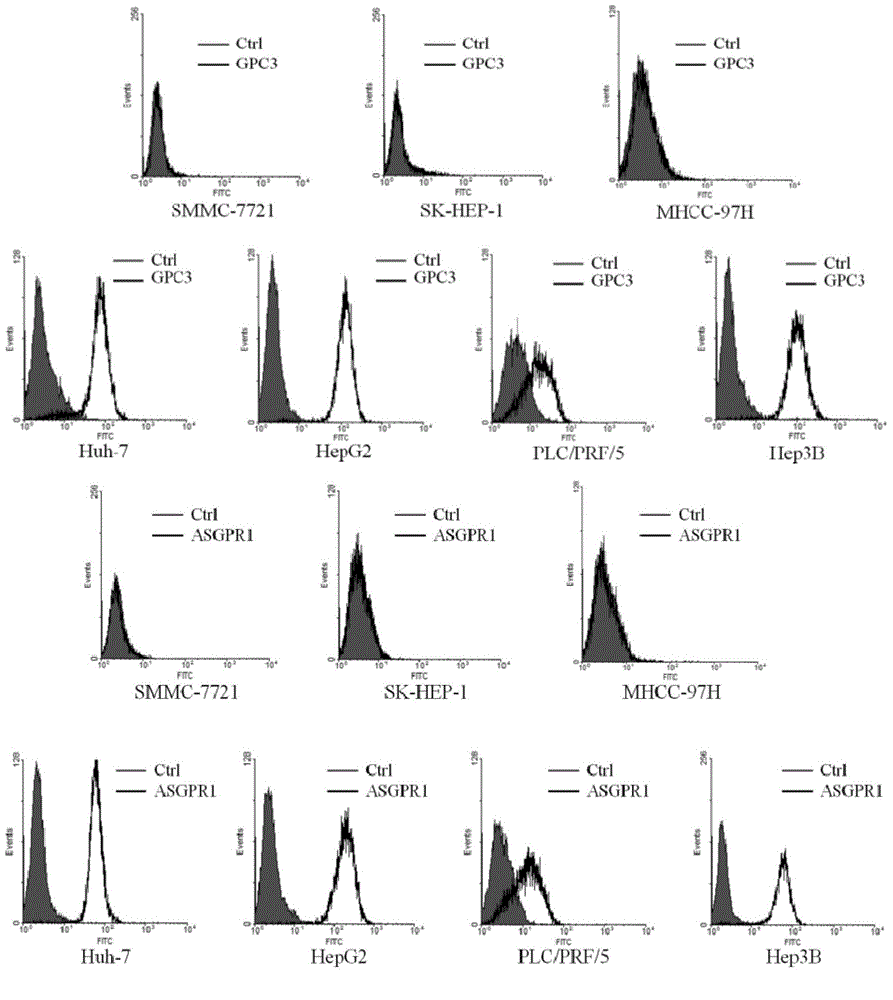
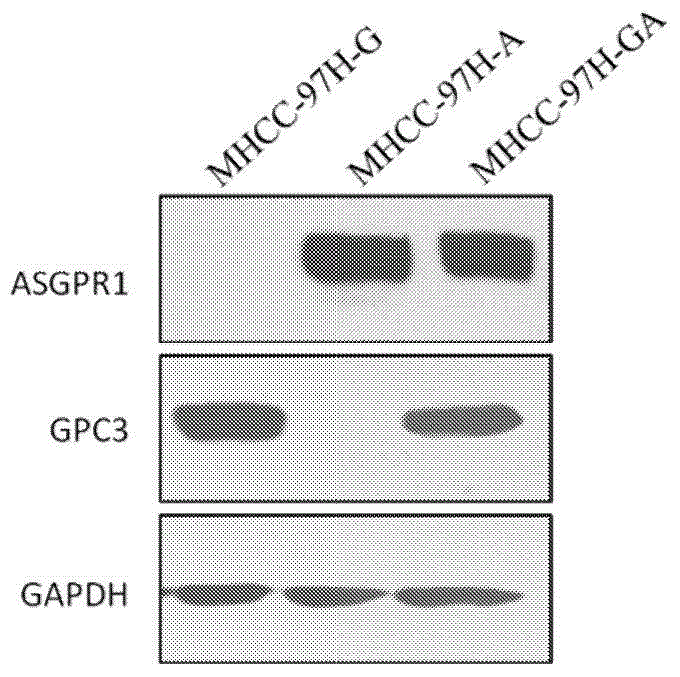
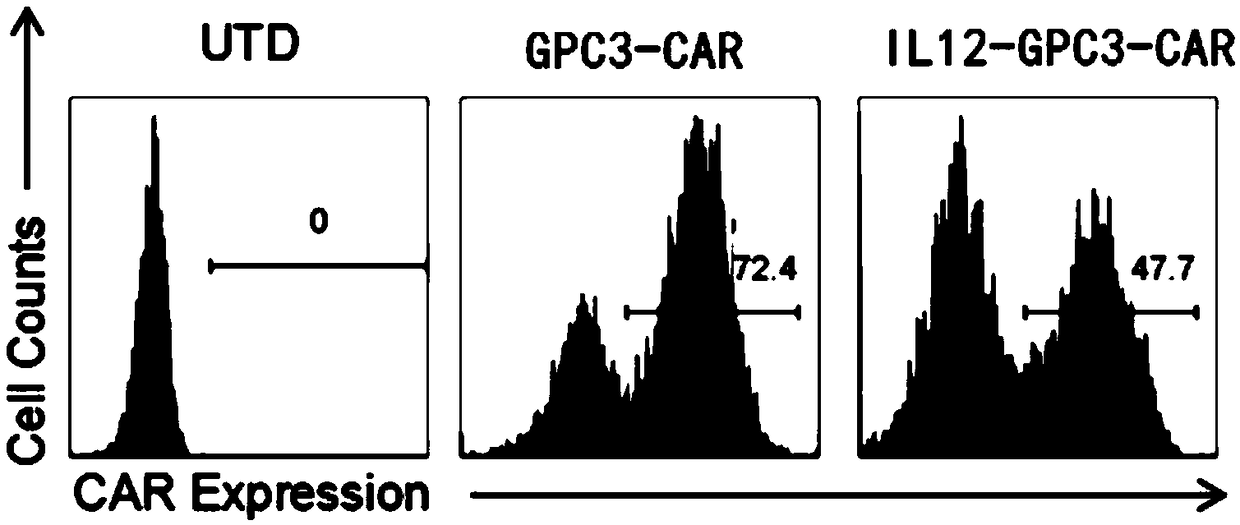
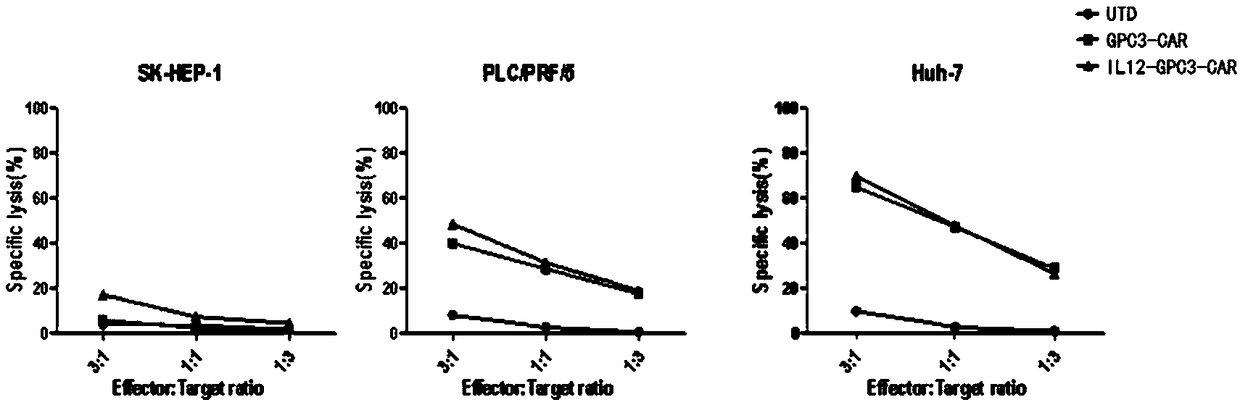
Dual-targeting genetically modified immunologic effector cell aiming at GPC3 (Glypican-3) and ASGPR1 (asialoglycoprotein receptor 1) and applications of dual-targeting genetically modified immunologic effector cell
ActiveCN105713881APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyImmune effector cellEffector cell
The invention relates to a dual-targeting genetically modified immunologic effector cell aiming at GPC3 (glypican-3) and ASGPR1 (asialoglycoprotein receptor 1) and applications of the dual-targeting genetically modified immunologic effector cell. The invention discloses the gene-modified immunologic effector cell capable of simultaneously identifying GPC3 and ASGPR1 for the first time, and the gene-modified immunologic effector cell can be used for the treatment of the GPC3 and ASGPR1 double-positive tumor, such as liver cancer.
Owner:CARSGEN THERAPEUTICS
Methods and compositions for treating secondary tissue damage and other inflammatory conditions and disorders
InactiveUS7157418B1Enhance and aid in survivalPrevent proliferationAntibacterial agentsBiocidePhagocyteDendritic cell
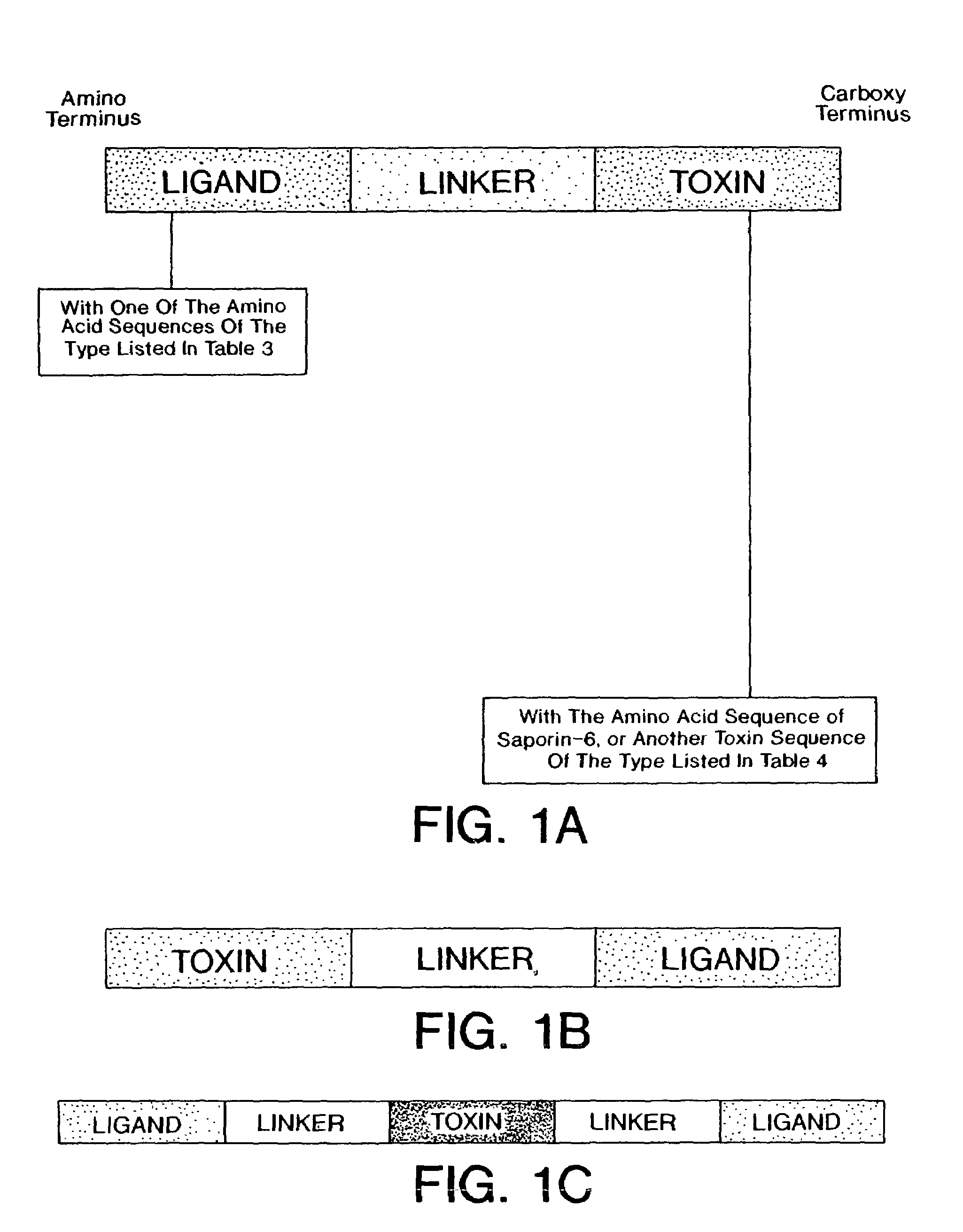
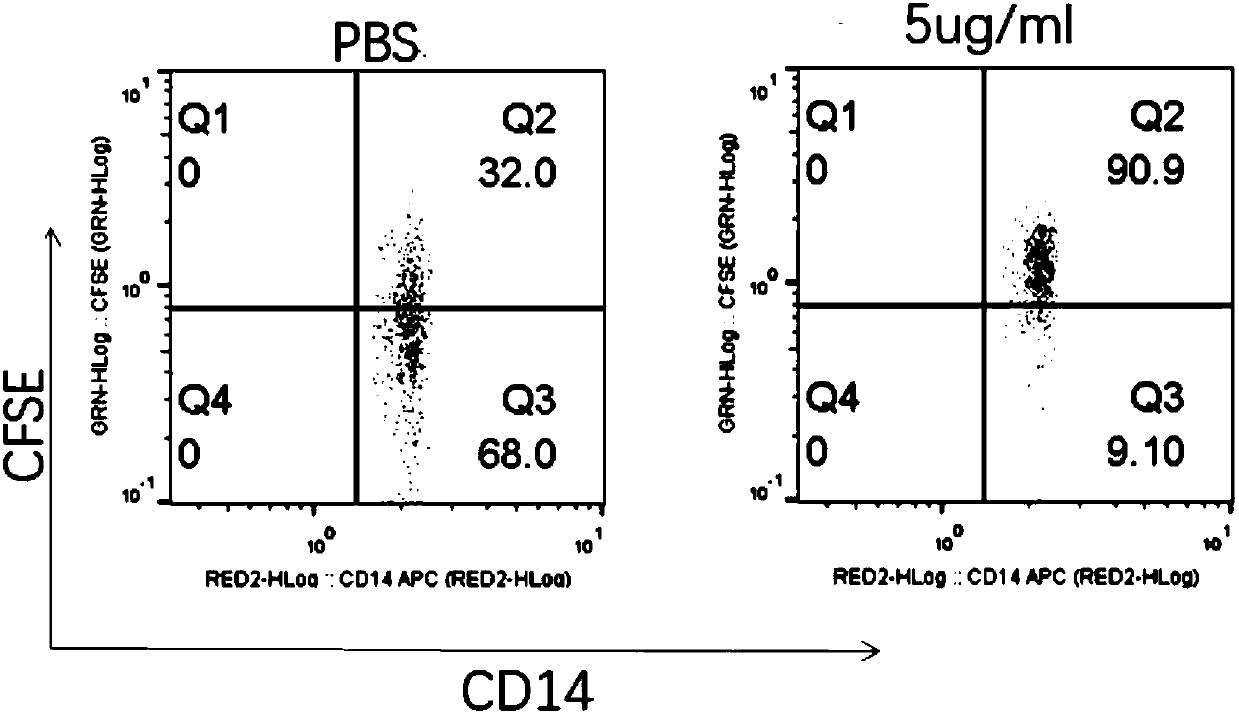
Conjugates containing as a ligand a chemokine receptor targeting agents, such as chemokines, and a targeted agent, such as a toxin are provided. These conjugates are used to treat inflammatory responses associated with activation, proliferation and migration of immune effector cells, including leukocyte cell types, neutrophiles, macrophages, and eosinophils. The conjugates provided herein are used to lessen or inhibit these processes to prevent or at least lessen the resulting secondary effects. In particular, the conjugates are used to target toxins to receptors on secondary tissue damage-promoting cells. The ligand moiety can be selected to deliver the cell toxin to such secondary tissue damage-promoting cells as mononuclear phagocytes, leukocytes, natural killer cells, dendritic cells, and T and B lymphocytes, thereby suppressing the proliferation, migration, or physiological activity of such cells. Among preferred conjugates are fusion proteins having a chemokine, or a biologically active fragment thereof, as the ligand moiety linked to a cell toxin via a peptide linker of from 2 to about 60 amino acid residues.
Owner:OSPREY PHARMA USA INC
Targeted protein degradation to attenuate adoptive t-cell therapy associated adverse inflammatory responses
ActiveUS20180169109A1Rapid cell deathOrganic active ingredientsFusion with degradation motifTumor lysis syndromeTumor Syndrome
This invention is in the area of compositions and methods for regulating chimeric antigen receptor immune effector cell, for example T-cell (CAR-T), therapy to modulate associated adverse inflammatory responses, for example, cytokine release syndrome and tumor lysis syndrome, using targeted protein degradation.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Cytotoxic conjugates comprising a chemokine receptor targeting agent
InactiveUS7166702B1Enhance and aid in survivalPrevent proliferationPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifChemokinesPhagocyteDendritic cell
Owner:OSPREY PHARMA USA INC
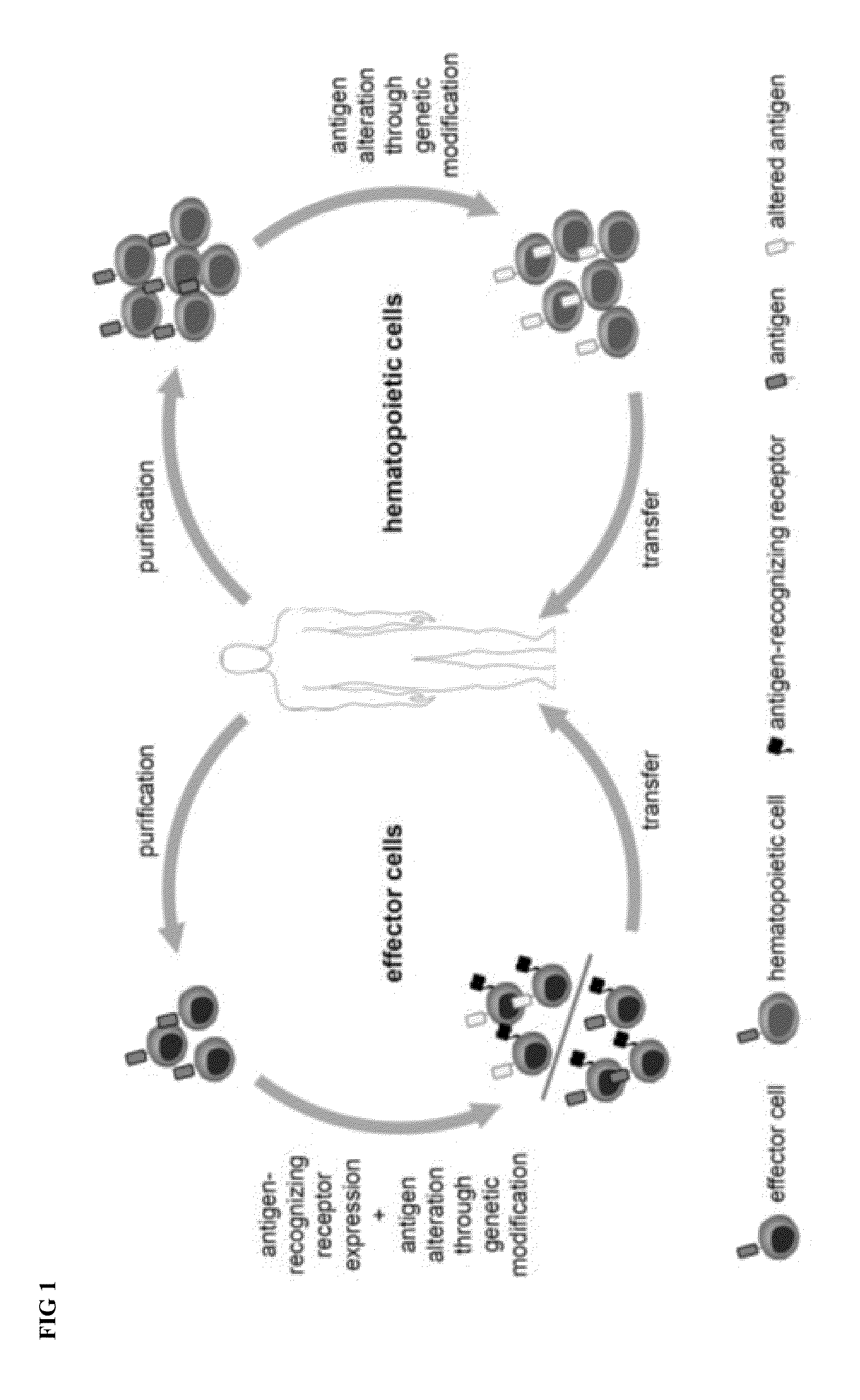
Combination immunotherapy of antigen-recognizing receptors and hematopoietic cells for the treatment of diseases
The invention provides a system that comprises pharmaceutical agents for use in immunotherapy for reducing the side-effects of an antigen-recognizing receptor against antigen-expressing non-target cells in an individual. The system includes an antigen-recognizing receptor that specifically recognizes an antigen on target cells and at least on one hematopoietic cell type in the individual. The antigen-recognizing receptor is exemplified by chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) be expressed on the surface of an immune effector cells. The system also includes hematopoietic cells resistant to recognition of the same antigen by the antigen-recognizing receptor.
Owner:MILTENYI BIOTEC B V & CO KG
Chimeric antigen receptor immune cell provided with safety switch as well as preparation method and application of chimeric antigen receptor immune cell
InactiveCN106755023AImprove effectivenessImprove securityGenetic material ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthAntigen receptors
The invention relates to a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) immune cell provided with a safety switch as well as a preparation method and an application of the CAR immune cell. The CAR immune cell carrying the safety mechanism (the safety switch) comprises a CAR coding nucleotide sequence, wherein the structure of the nucleotide sequence comprises a receptor structural domain for recognizing tumor-specific antigen or tumor-associated antigen, a transmembrane-stimulation structural domain, a CD3[zeta] stimulating signal transduction region and a suicide gene region. The CAR immune cell can be obtained as different immunological effect cells are amplified and a CAR sequence carrying a suicide mechanism is transduced; corresponding antigens of tumor cells are recognized by virtue of CAR; and the CAR immune cell can generate a specific killing effect on the tumor cells. The CAR immune cell, when used, is infused in a gradient mode and dynamic change in related cell factor levels is monitored; in case of need, a suicide gene can be started by virtue of drugs to scavenge the immunological effect cells, so that optimal balance between safety and a curative effect is achieved; therefore, the safety of the technology applied to the treatment of tumors in the clinical field is guaranteed to the greatest extent.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL CHINA ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI +1
Genetically modified mesenchymal stem cells expressing an immune response-stimulating cytokine to attract and/or activate immune cells
The invention relates to a genetically modified mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) and medical use thereof in the treatment of tumours, said MSC comprising one or more exogenous nucleic acid molecule(s), wherein said exogenous nucleic acid molecule(s) comprise a region encoding one or more immune response-stimulating or immune response-modulating cytokine(s) operably linked to a promoter or promoter / enhancer combination. The invention encompasses the use of said cells in modulating the tumour microenvironment in order to attract immune effector cells and facilitate their activation and / or adoption of a memory phenotype. One aspect of the invention relates to the use of said cells in anti-tumour treatment comprising the combined administration of said mesenchymal stem cells with anti-tumour immunotherapies, such as checkpoint inhibitors, immune cells, for example T cells, such as T cells with artificial T cell receptors, for example a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR-Ts) or exogenous T-Cell Receptor (TCR) transduced cells, NK cells or macrophages / monocytes, or a cancer vaccine.
Owner:APCETH GMBH & CO KG
Tumor antigenic polypeptide and application thereof as tumor vaccine
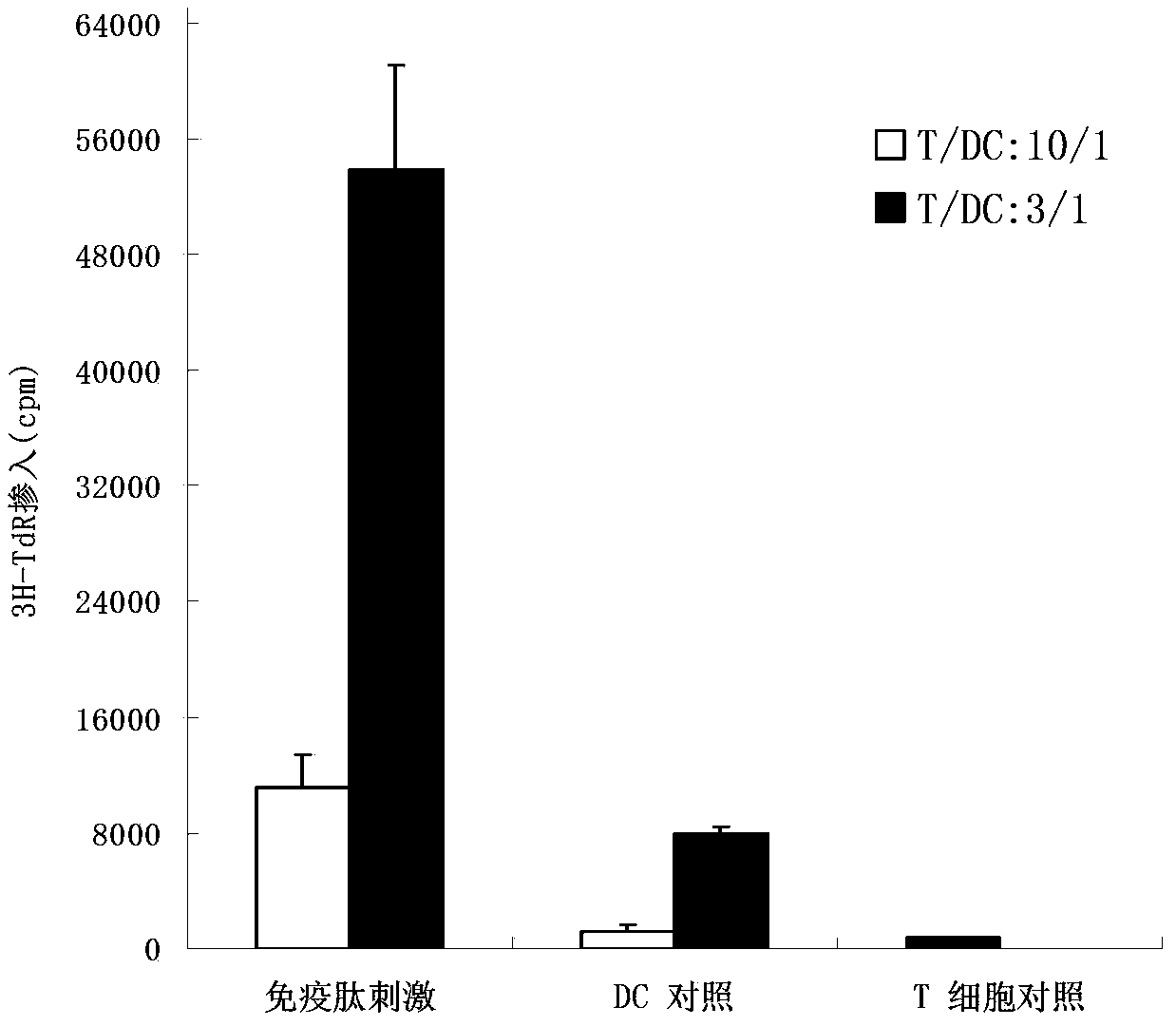
The invention provides a human mucin-1 tumor antigenic polypeptide with an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 or variants thereof, wherein the polypeptide can be combined with an HLA (Human Leukocyte Antigen) I and can be recognized by a cell CD8<+>T. The invention further provides nucleic acids coding the polypeptide. The invention further provides an antigen presenting cell capable of presenting the polypeptide on the surface of the cell and an immune effector cell capable of recognizing the polypeptide or antigen presenting cell. The invention further provides application of the polypeptide or variants thereof, the nucleic acids, the antigen presenting cell or the immune effector cell in the preparation of vaccines or pharmaceutical compositions for treating or preventing cancer. Tumor vaccines provided by the invention have a good treatment effect on relatively large crowds and are particularly applicable to the Asian, e.g. Chinese.
Owner:BEIJING ZHIFEI LVZHU BIOPHARM +1
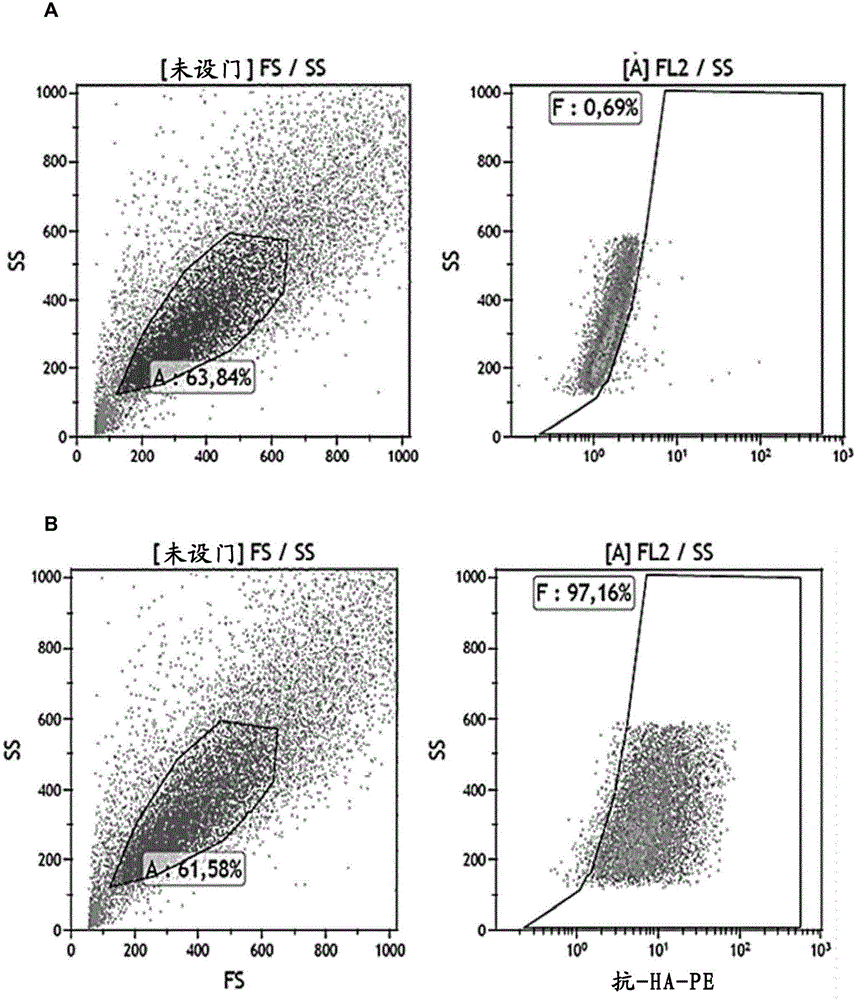
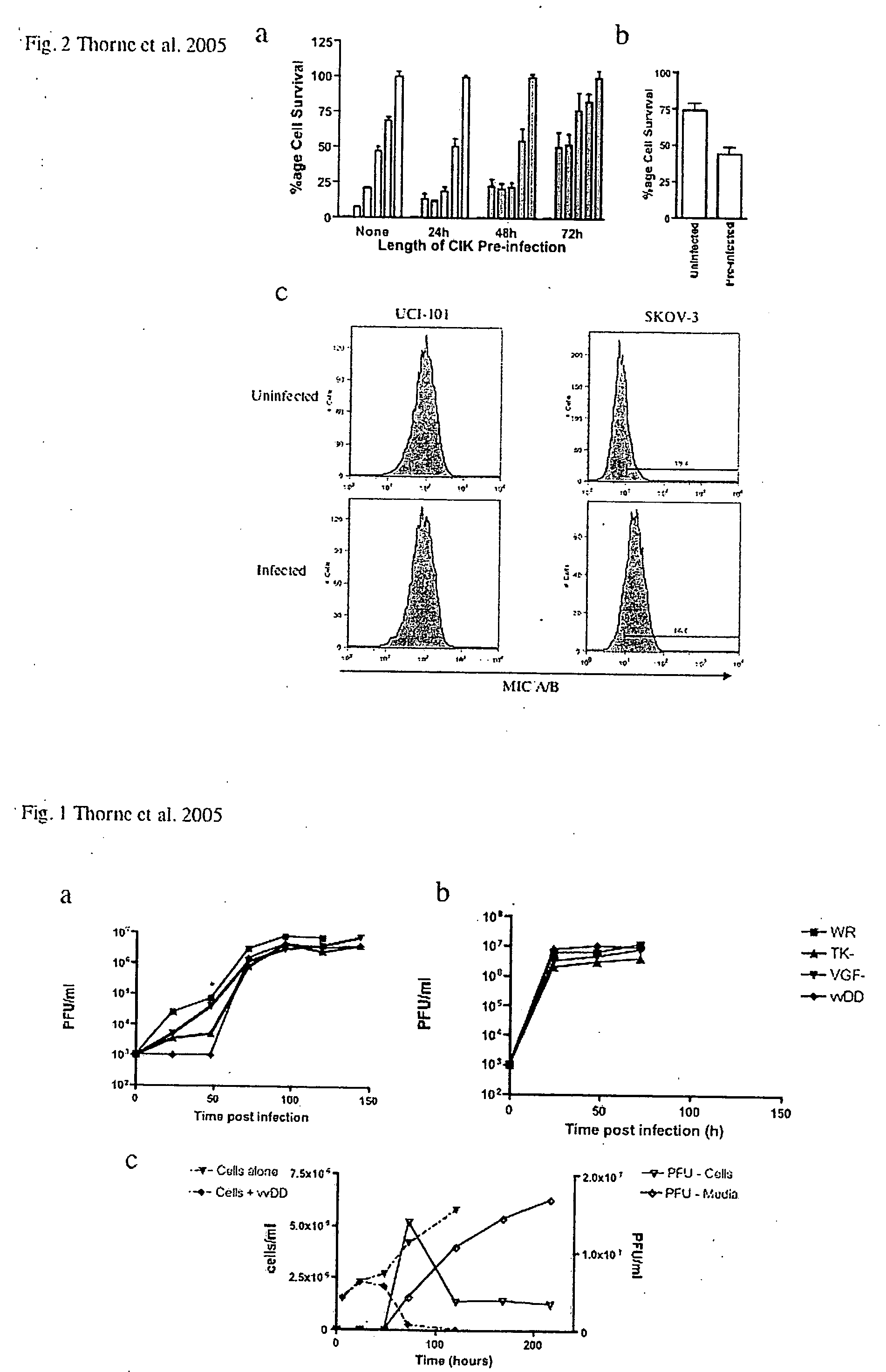
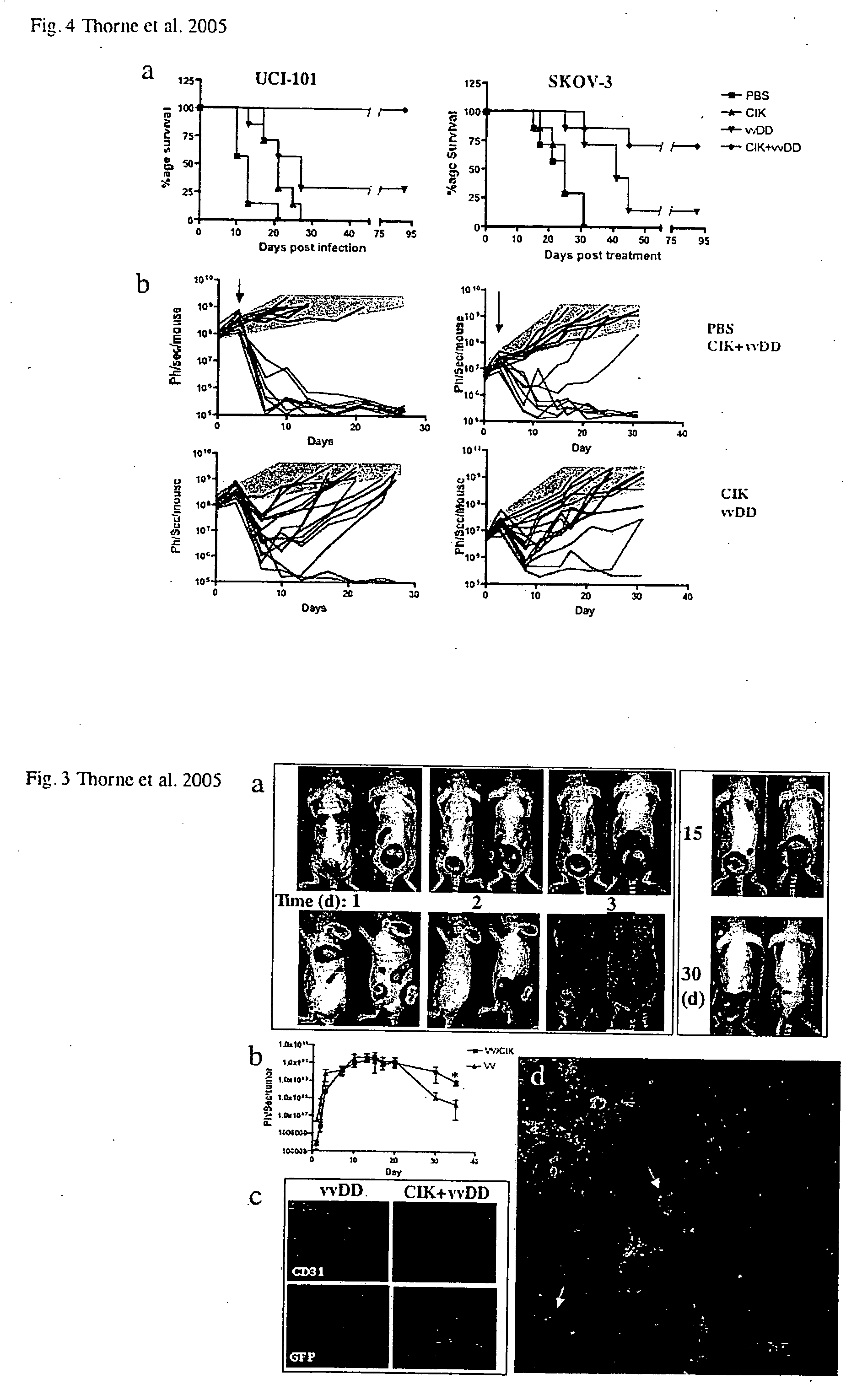
Immune effector cells pre-infected with oncolytic virus
InactiveUS20070077231A1Improved biodistributionMinimal viral infectionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthImmune effector cell
Compositions and methods are provided for the treatment of cancer. An immune effector cell population is pre-infected with an oncolytic virus. The combined therapeutic is safe and highly effective, producing an enhanced anti-tumor effect compared to either therapy alone. The methods of the invention thus provide for a synergistic effect based on the combined biotherapeutics.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
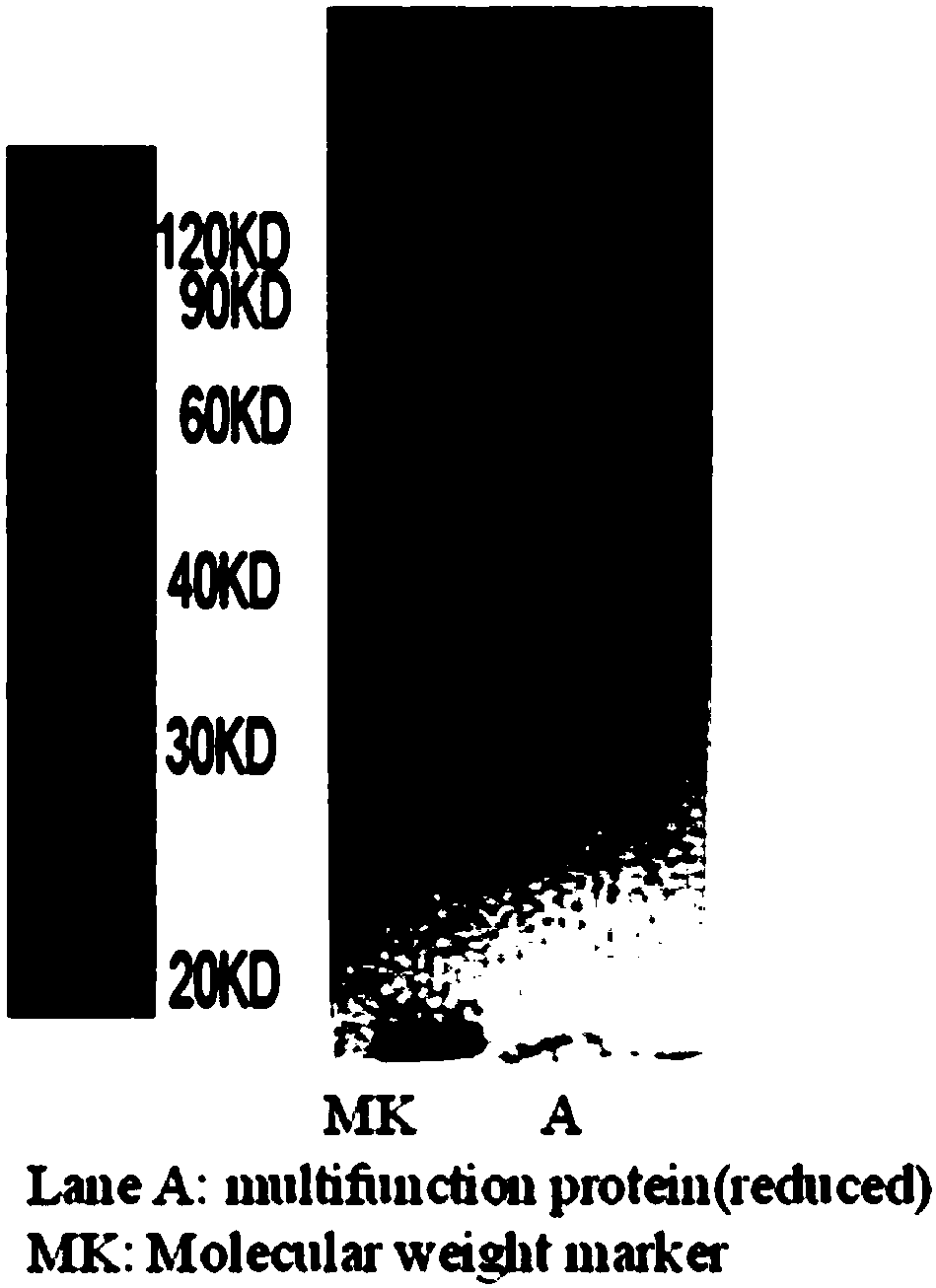
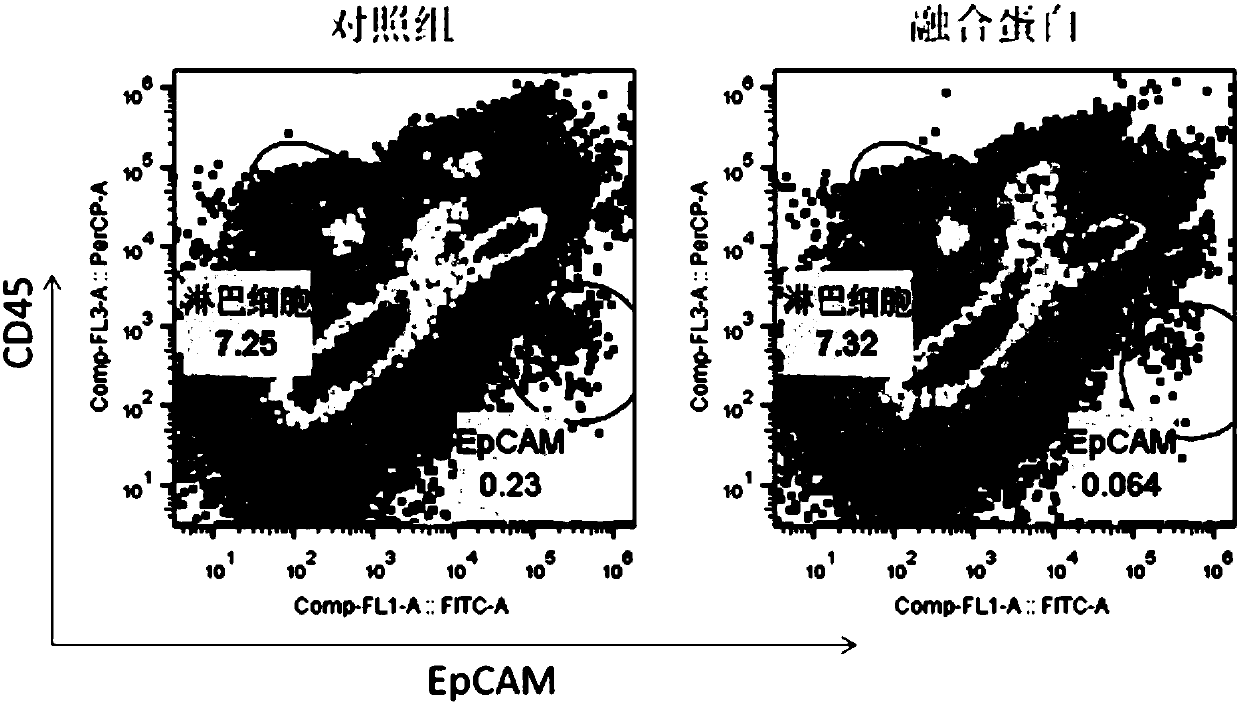
Multifunctional fusion protein and application thereof
InactiveCN107857819AMeet the needs of tumor immunotherapyInfection controlPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsFc(alpha) receptorAbnormal tissue growth
The invention relates to multifunctional fusion protein and an application thereof. The multifunctional fusion protein comprises: a. a functional area for identifying positive tumor cells CD47: an extracellular part of SIRP alpha, b. a functional area for identifying positive tumor cells PD-L1: an extracellular part of PD-1 and c. a functional area for being bonded to immune cells: a high-affinityhuman IgG1Fc part. The fusion protein disclosed by the invention can meet the needs of patients on immunotherapy of tumors; the recombinant fusion protein can identify positive tumor cells (CD47 andPD-L1) and can also be bonded to immune effector cells with Fc receptors; and due to clinical application of the fusion protein, the functions of inhibiting tumor growth and controlling viral infection can be enhanced, so that the fusion protein has very good clinical prospects and extensive range of application.
Owner:JIANGSU CTL BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Nucleic acid molecules encoding cytotoxic conjugates that contain a chemokine receptor targeting agent
InactiveUS7192736B2Enhance and aid in survivalPrevent proliferationBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsCell biologyWhite blood cell
Nucleic acid moleucles that encode conjugates containing as a ligand a chemokine receptor targeting agent, such as a chemokine, and a targeted agent, such as a toxin are provided. These conjugates are used to treat inflammatory responses associated with activation, proliferation and migration of immune effector cells, including leukocyte cell types, neutrophils, macrophages, and eosinophils.
Owner:SAMSUNG ENGINEERING CO LTD +1
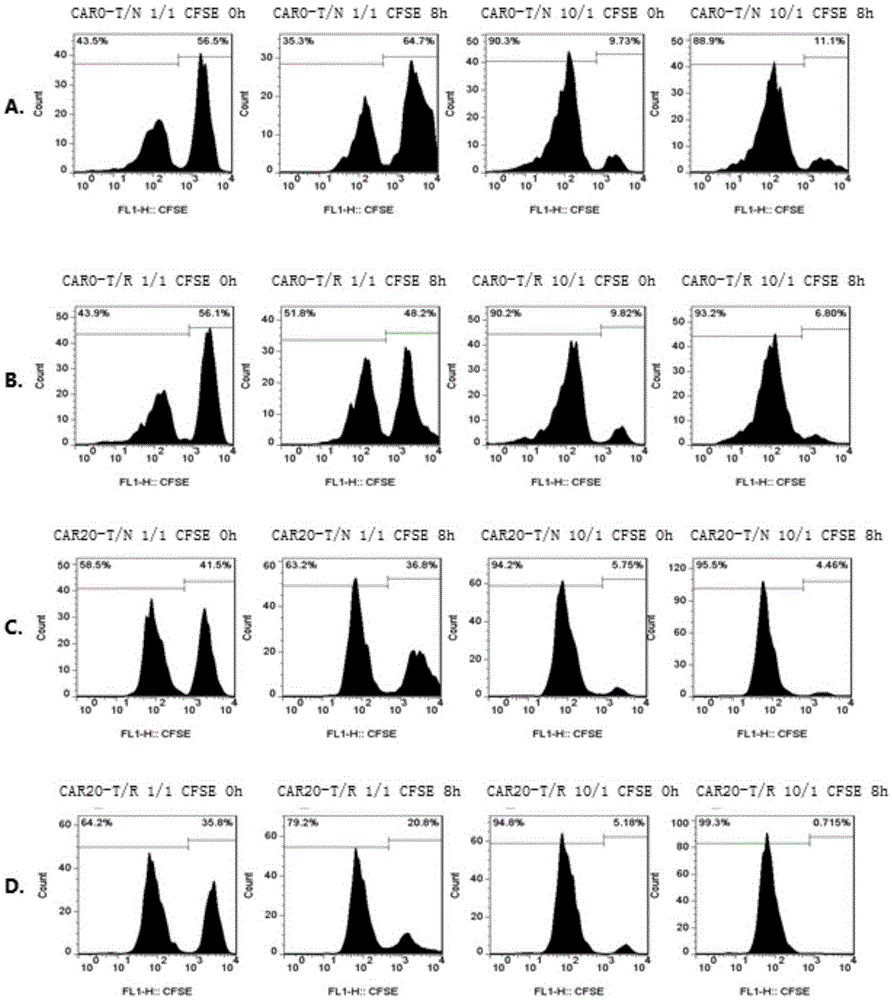
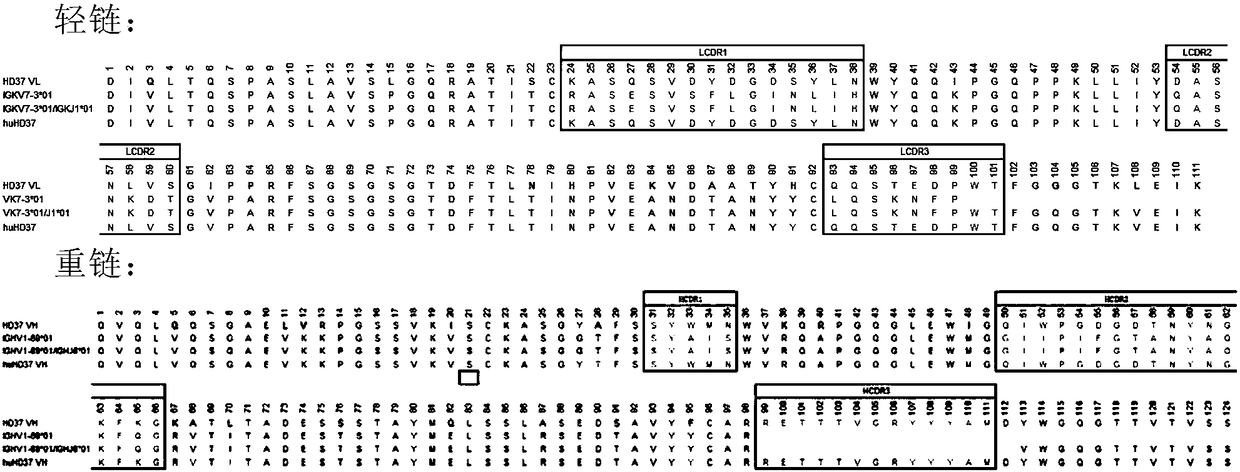
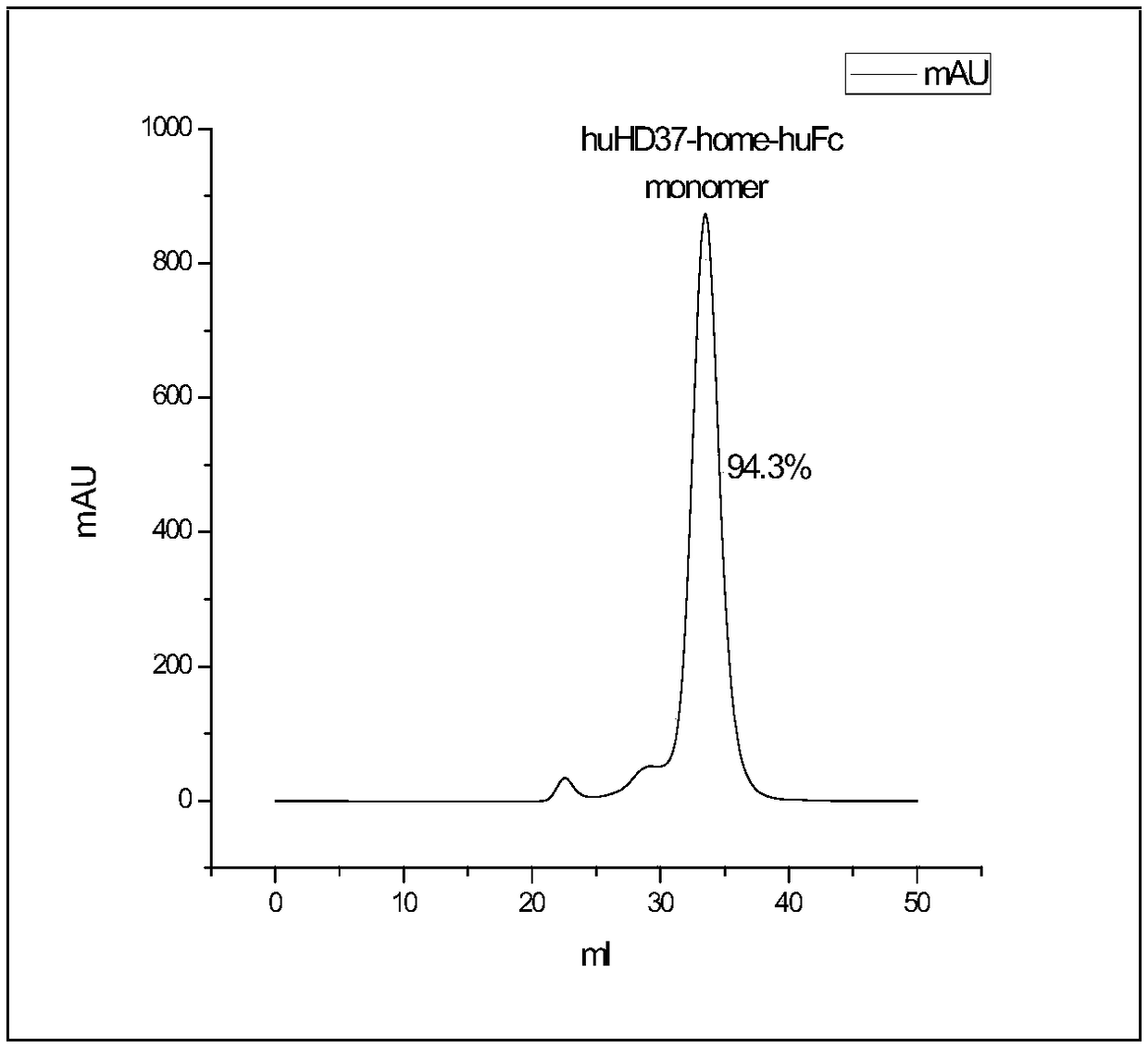
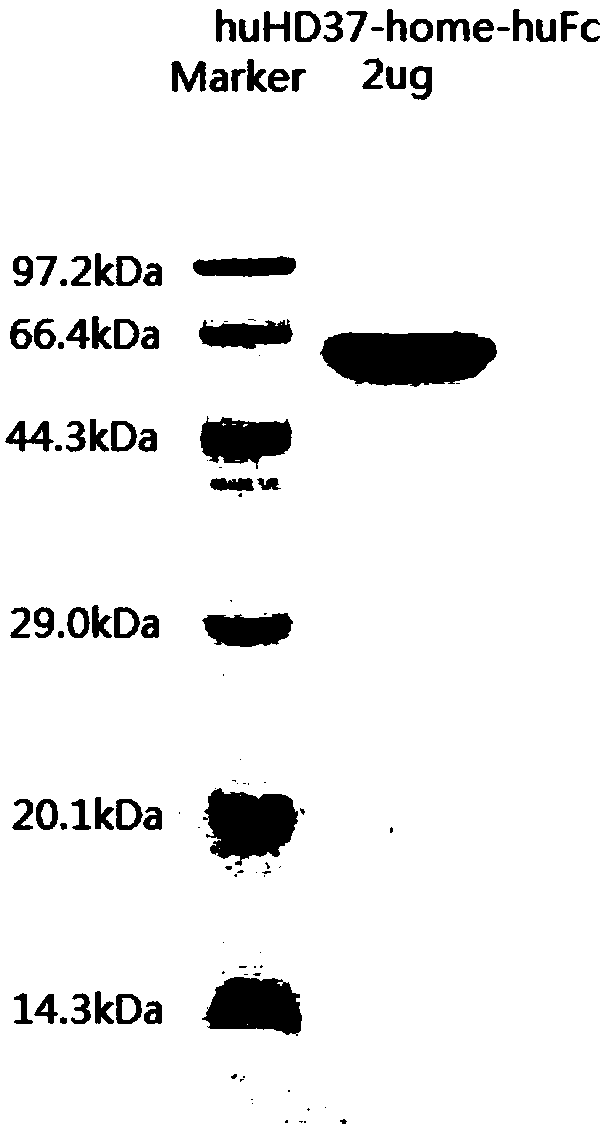
Humanized antibody against CD19 and immune effector cells targeting to CD19
The invention relates to an anti-CD19 humanized antibody prepared from a murine monoclonal antibody, a chimeric antigen receptor containing the humanized antibody, and immune cells expressing the humanized antibody. The humanized antibody of the invention does not produce an anti-antibody reaction (AAR) and a human anti-mouse antibody reaction (HAMA), has better affinity than a murine antibody, and presents excellent activity and safety, so a novel means is provided for treating tumors expressing CD19.
Owner:CARSGEN THERAPEUTICS
Chimeric protein, immune effector cell expressing chimeric protein and application thereof
PendingCN109880803APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyPathogenic microorganismImmune effector cell
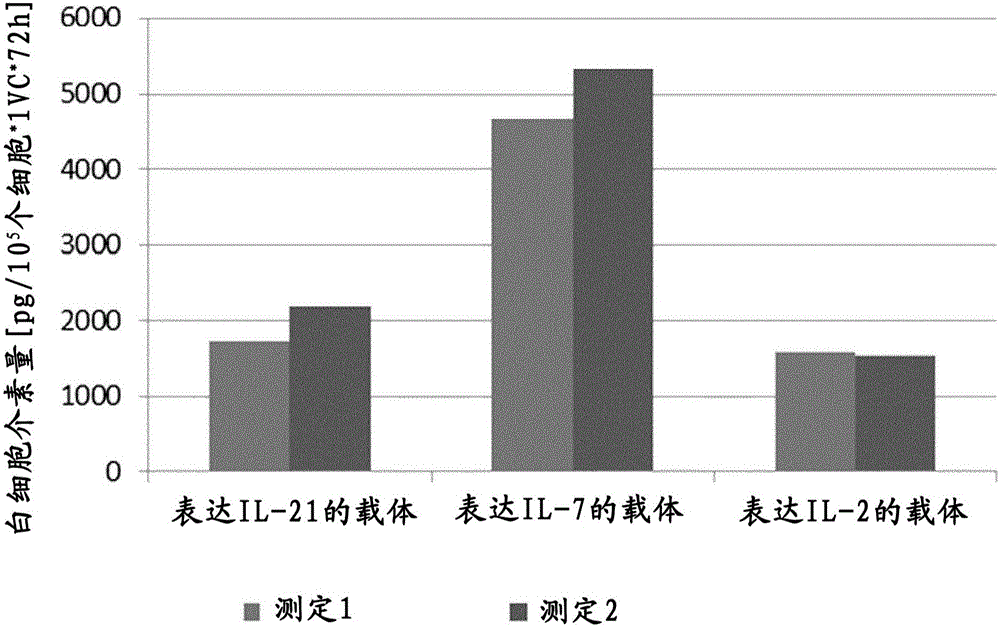
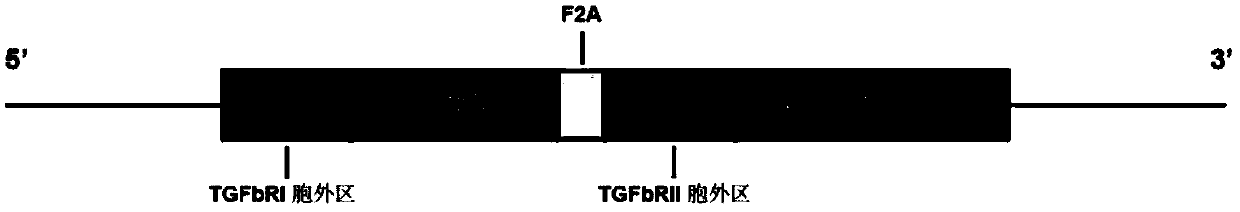
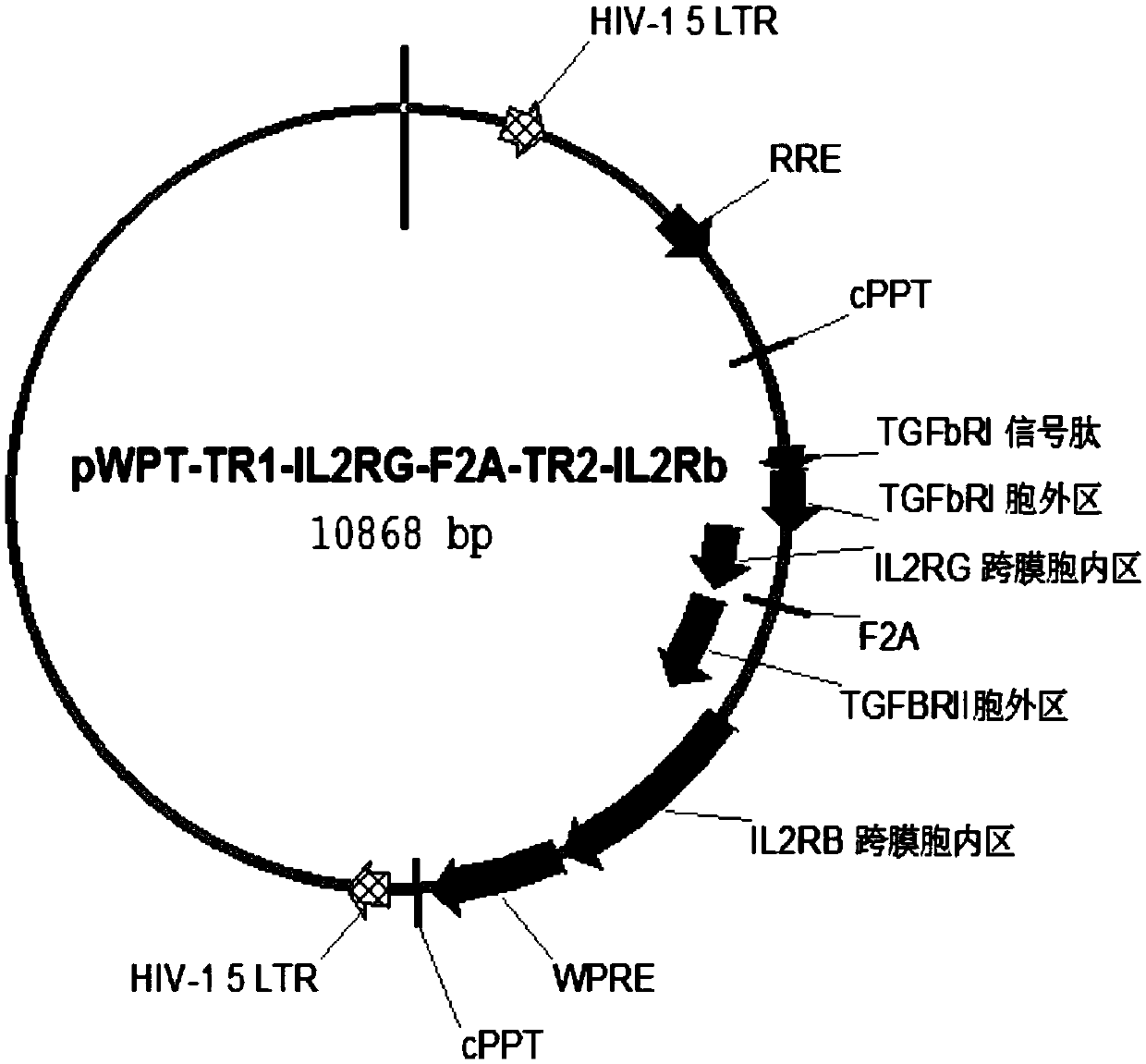
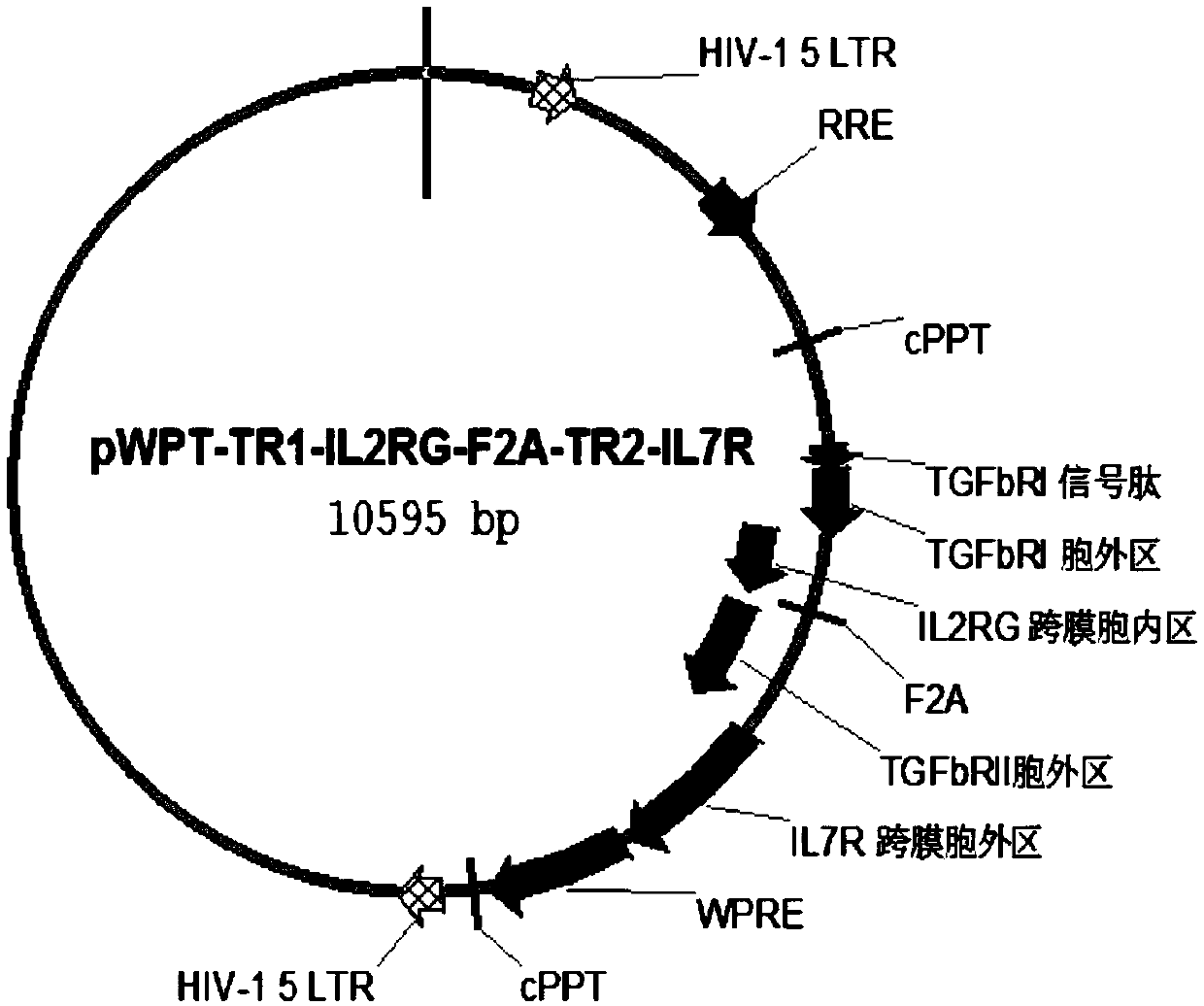
The present invention relates to an immune effector cell expressing a chimeric protein and an application thereof, in particular to the immune effector cell of the chimeric protein expressing an extracellular domain containing a TGF-beta receptor and an intracellular signal domain of IL-2 family protein, a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same, and the application of the immunological effector cell or a pharmaceutical composition as described above for preparing a drug for preventing or treating a tumor or pathogenic microorganism infection. The immune effector cell expressing the chimeric protein is capable of transforming the stimulation of TGF-beta into a positive signal of IL-2, IL-7 or IL-21, inhibiting TGF-beta-induced Treg differentiation, and promoting the proliferation and survival of immune cells; also reduces the effect of TGF-beta on cell killing ability, and shows a better anti-tumor ability.
Owner:CRAGE MEDICAL CO LTD
Joint use of immunologic effector cells and radiation in tumor treatment
PendingCN109908176AImprove anti-cancer effectAvoid damageEnergy modified materialsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsLocal radiotherapyCAR T-cell therapy
The invention relates to a tumor treatment method and particularly provides joint use of immunologic effector cells and radiation in tumor treatment, and a method of treating an individual with tumorsby joint use of immunologic effector cells and local radiation. The method provides no lymphocyte removal for the individual; the immunologic effector cells comprise a receptor to recognize tumor antigens to tumors. Tests prove that the method provided herein has significant antitumor effect for solid tumors; at the premise of pretreatment without removing lymphocytes, the joint treatment of CAR-T cell therapy and local radiotherapy with no lymphocyte removal helps attain better treatment effect than CAR-T treatment with lymphocyte removal; antitumor treatment effect is improved greatly.
Owner:CRAGE MEDICAL CO LTD
Preparation of high efficiency immune active cell and method of using for anti tumour
InactiveCN1869206AMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsChemical treatmentAbnormal tissue growth
This invention relates to producing of high efficiency immune cell group and method of its using to tumor preventing, it belongs to biotechnology field. Dendritic cell is induced by oligonucleotide and cytokine, cell is induced and wounded by the cytokine, then dendritic cell and wounded cell are mixed with certain ratio to get new kind cell group that cultured by immune effect cell group dendritic that induced by oligonucleotide and the wounded cell. Compared to cell group cultured by wounded cell and dendritic cell, the proliferation activity is stronger. The cell poisonous activity is higher than the wounded cell. The oligonucleotide can be artificially synthesized. Immune cell group that anti cancer activity is higher than the wounded cell can also be induced to patient that operation opportunity is gone and tumor antigen is hard to get. It can be used to self-body tumor curing, chemical treatment and assistant curing to radiotherapy.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
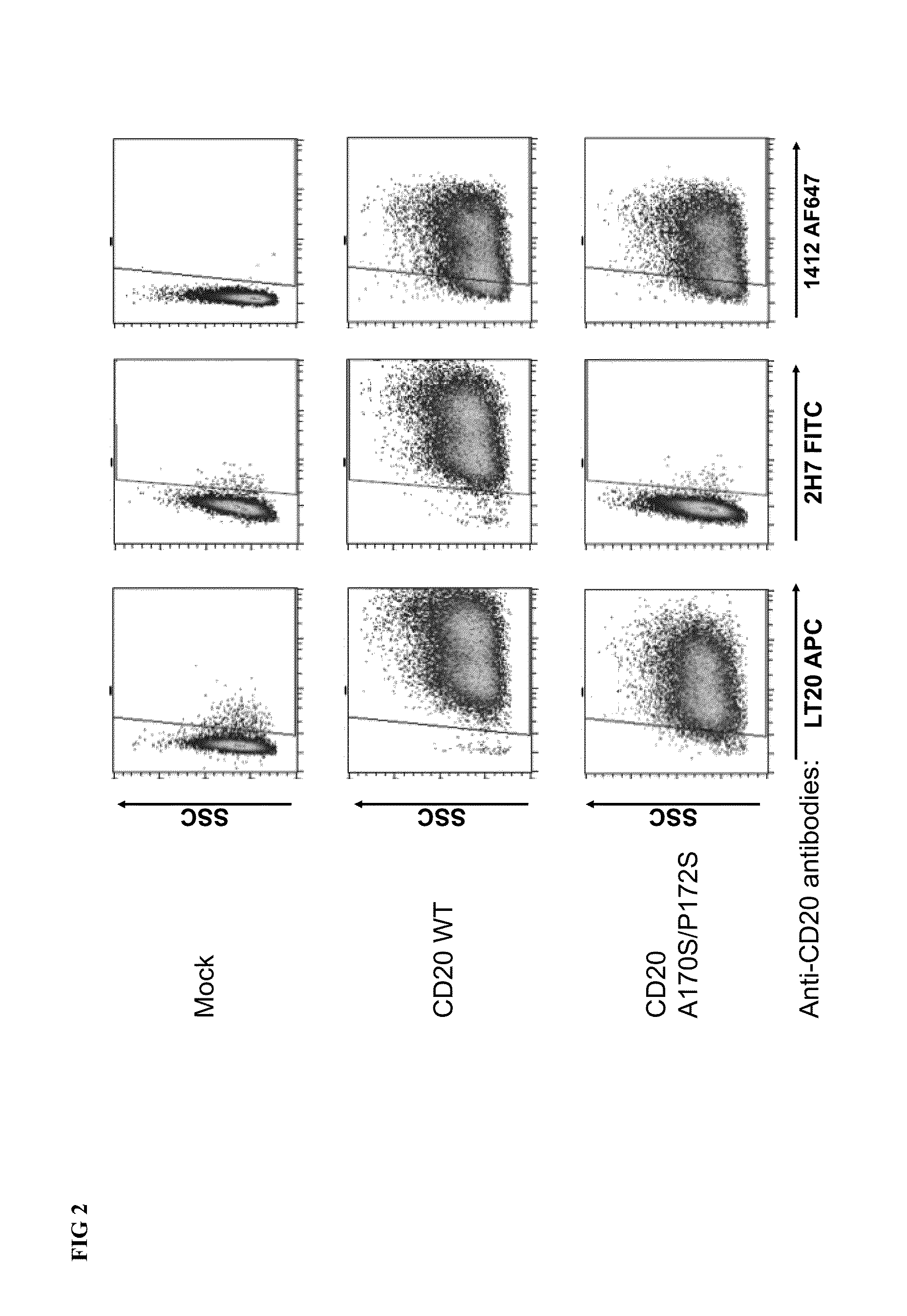
Cytotoxic Antibody Directed Against Type B Lymphoid Hematopoietic Proliferations
ActiveUS20090053233A1Reduced dosLow immunogenicityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsImmunological disordersCD20Cytotoxic antibody
The present invention relates to a monoclonal antibody directed against the CD20 antigen, wherein the variable region of each of the light chains thereof is encoded by a sequence which shares at least 70% identity with murine nucleic acid sequence SEQ ID No. 5, the variable region of each of the heavy chains thereof is encoded by a sequence which shares at least 70% identity with murine nucleic acid sequence SEQ ID No. 7, and the constant regions of light and heavy chains thereof are constant regions from a non-murine species, as well as for activation of FcγRIIIA receptors in immune effector cells, and for the manufacture of a drug especially for the treatment of leukaemia or lymphoma.
Owner:LABE FR DU FRACTIONNEMENT & DES BIOTECH SA
Dual specificity polypeptide molecule
PendingUS20190016801A1Hybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against virusesEpitopeMajor histocompatibility
The present invention relates to a bispecific polypeptide molecule comprising a first polypeptide chain and a second polypeptide chain providing a binding region derived from a T cell receptor (TCR) being specific for a major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-associated peptide epitope, and a binding region derived from an antibody capable of recruiting human immune effector cells by specifically binding to a surface antigen of said cells, as well as methods of making the bispecific polypeptide molecule, and uses thereof.
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
Immunologic effector cell targeting CPC3 and application thereof
PendingCN109468279AGenetically modified cellsMammal material medical ingredientsAntigenImmune effector cell
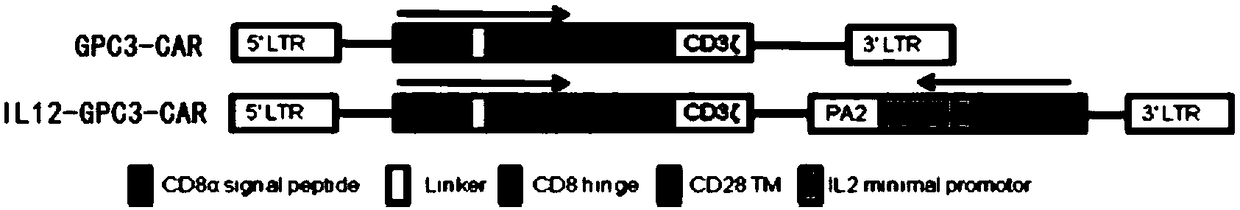
The invention relates to an immunologic effector cell which expresses a chimeric antigen receptor targeting GPC3 and exogenous IL12. The invention also provides a medicinal composition containing theimmunologic effector and a method for treating tumor, particularly GPC3 positive tumor through the immunologic effector cell or the medicinal composition. The immunologic effector cell is effective toentity tumor cell in vitro, and is outstanding in effect of extinguishing the entity tumor cell in vivo.
Owner:CRAGE MEDICAL CO LTD
Combination of TOLL-like receptor stimulating agent and immune effector cell
PendingCN108853144APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifOrganic active ingredientsToll-like receptorImmune effector cell
The invention provides use of a combination of a TOLL-like receptor stimulating agent and an immune effector cell in preparation of antitumor drugs or anti-pathogen drugs or anti-immunosuppression drugs. The TOLL-like receptor stimulating agent can be used for reinforcing the effect of the immune effector cell. The invention further provides a composition of the TOLL-like receptor stimulating agent and the immune effector cell.
Owner:CRAGE MEDICAL CO LTD
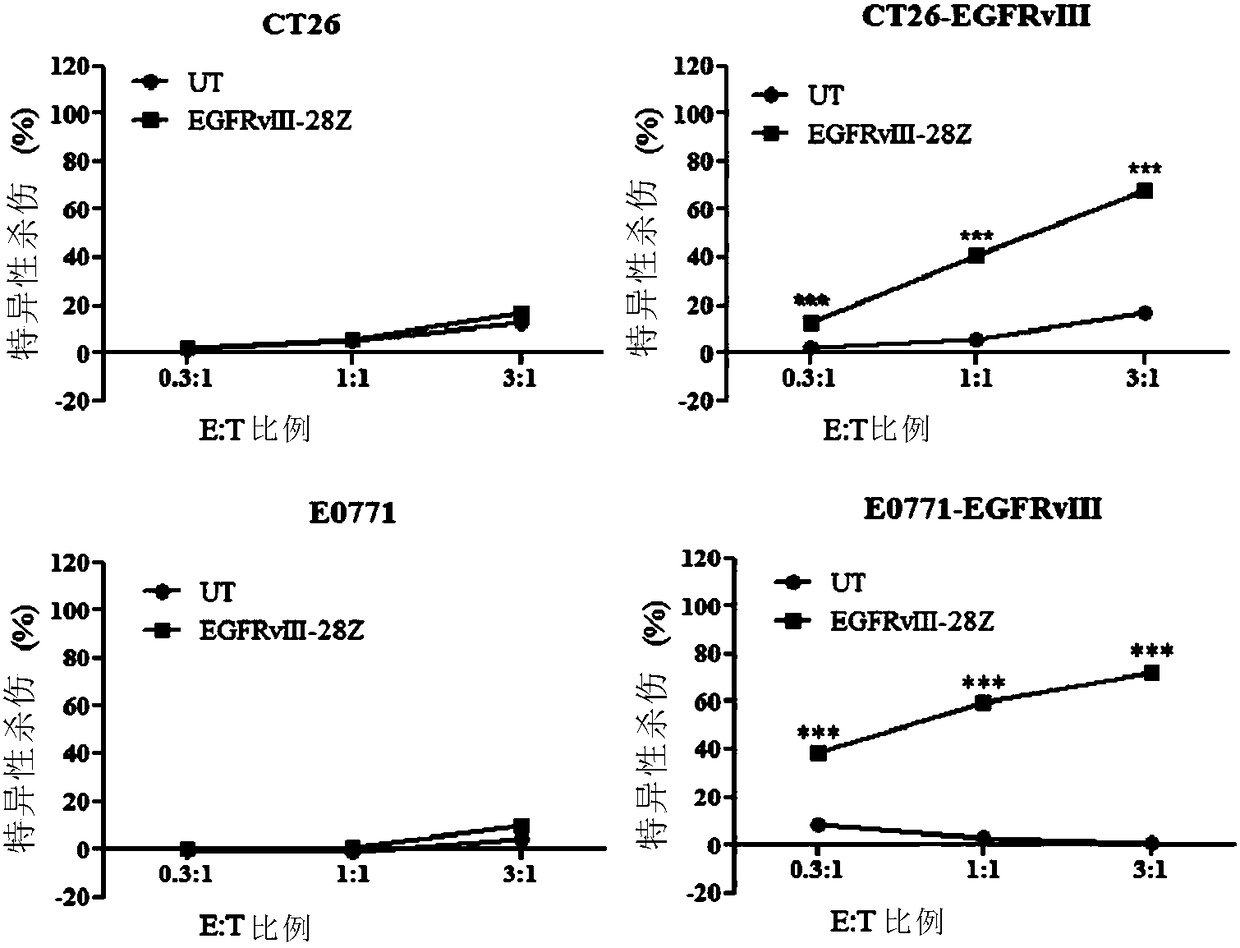
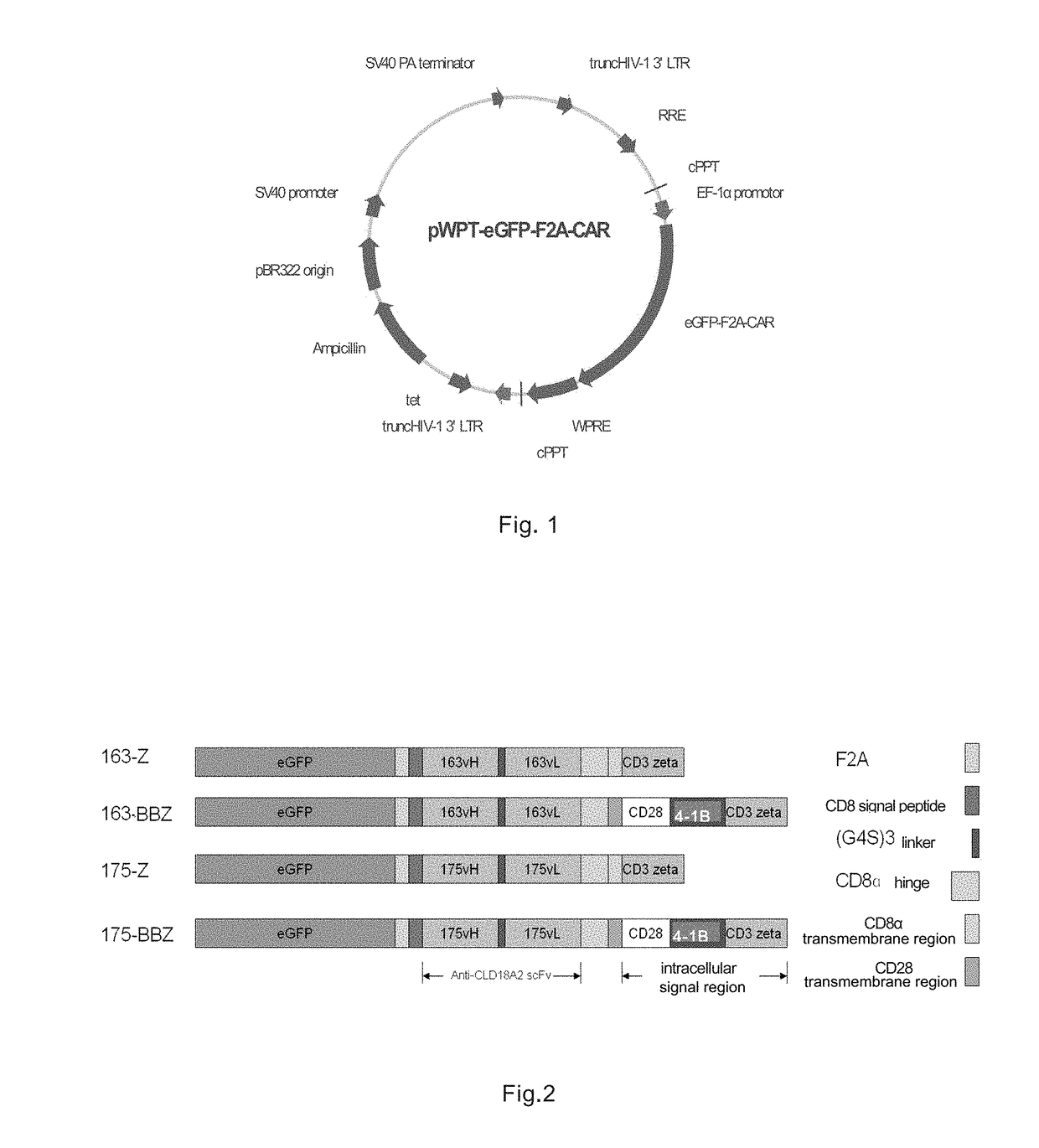
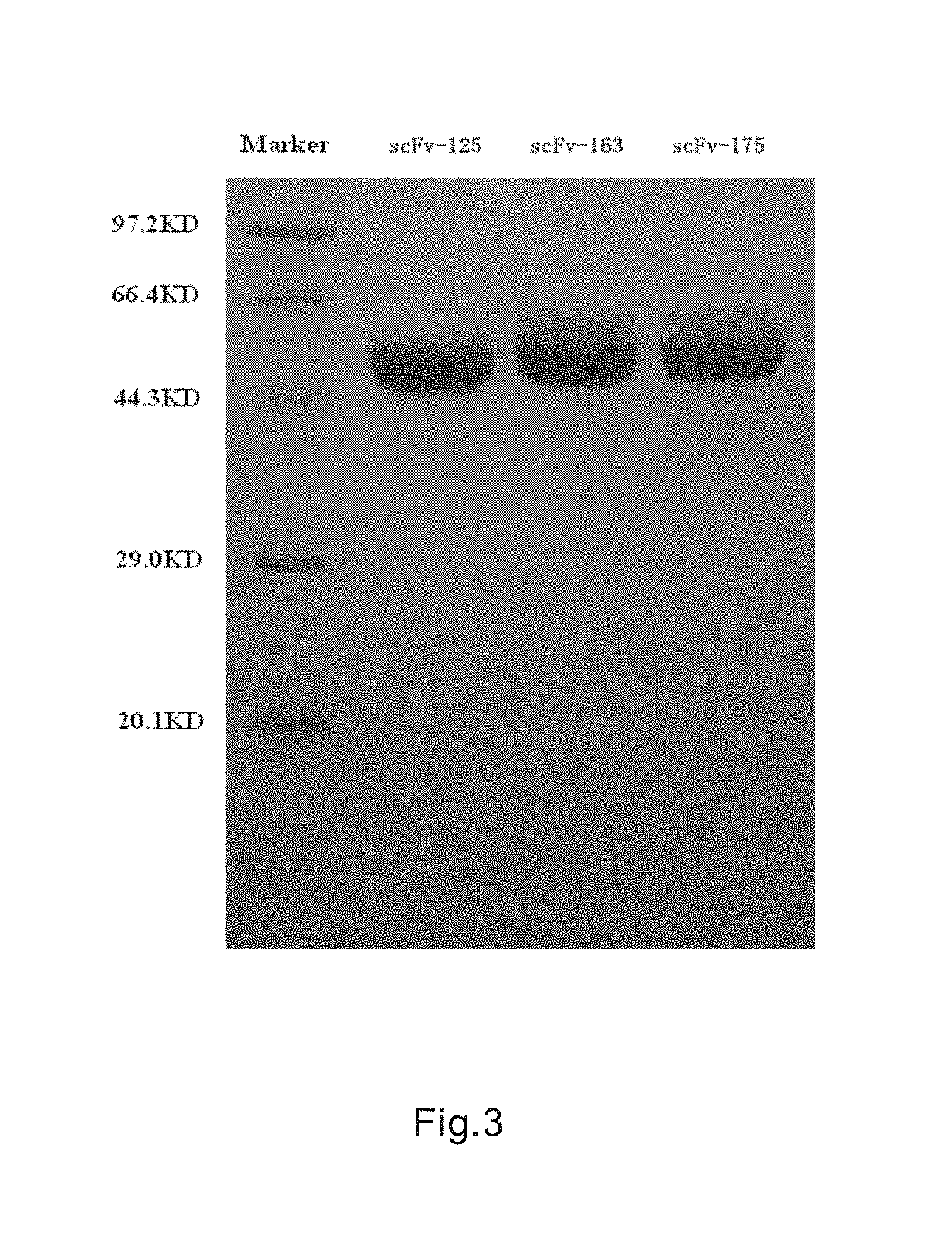
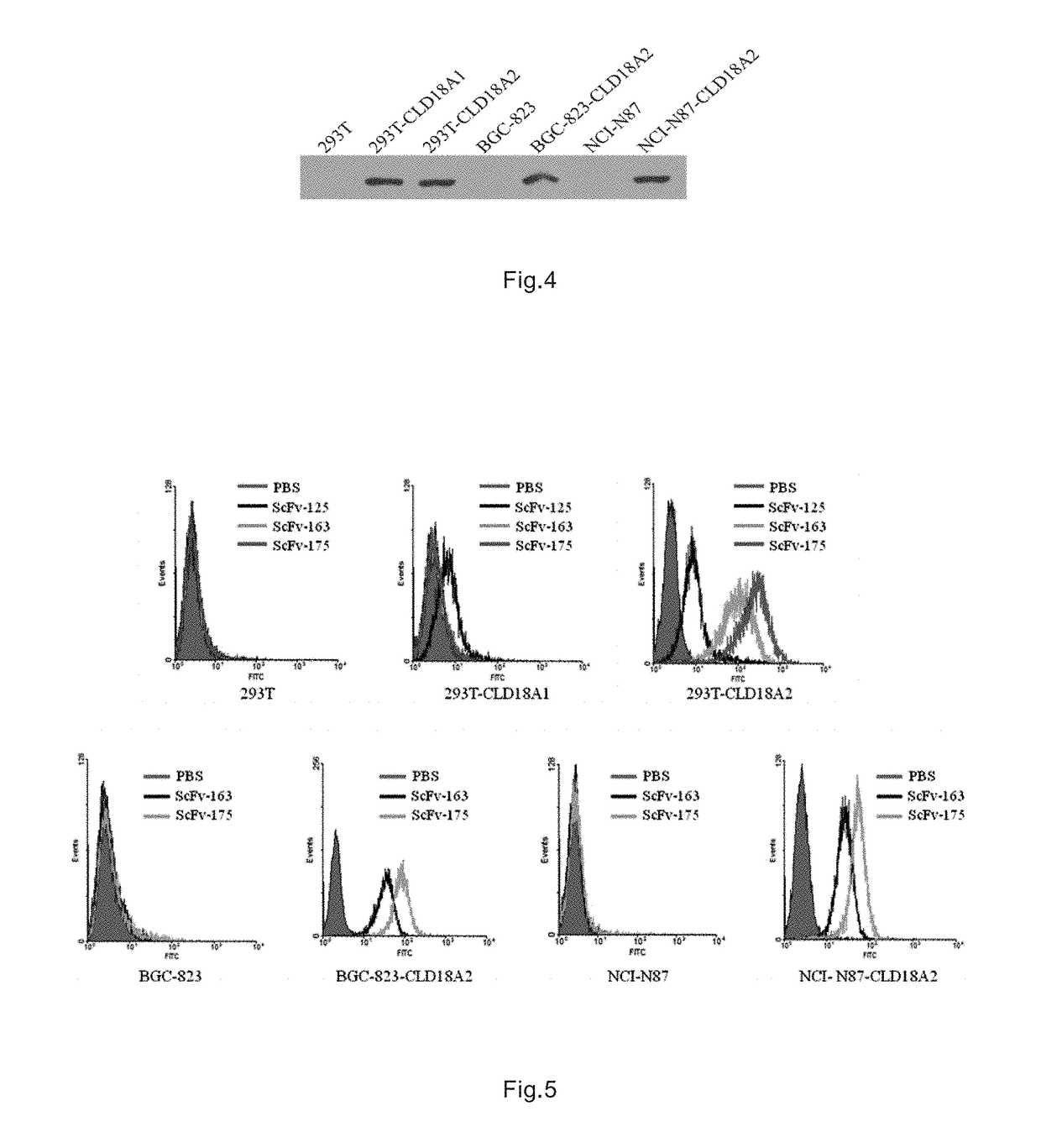
Immunologic effector cell of targeted cld18a2, and preparation method and use thereof
Disclosed are a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) targeting CLD18A2, and preparation method and use thereof. The extracellular binding region of the CAR comprises a protein specifically recognizing CLD18A2. The immune effector cell modified by the CAR can be used to treat tumors such as pancreatic cancer and stomach cancer.
Owner:CRAGE MEDICAL CO LTD
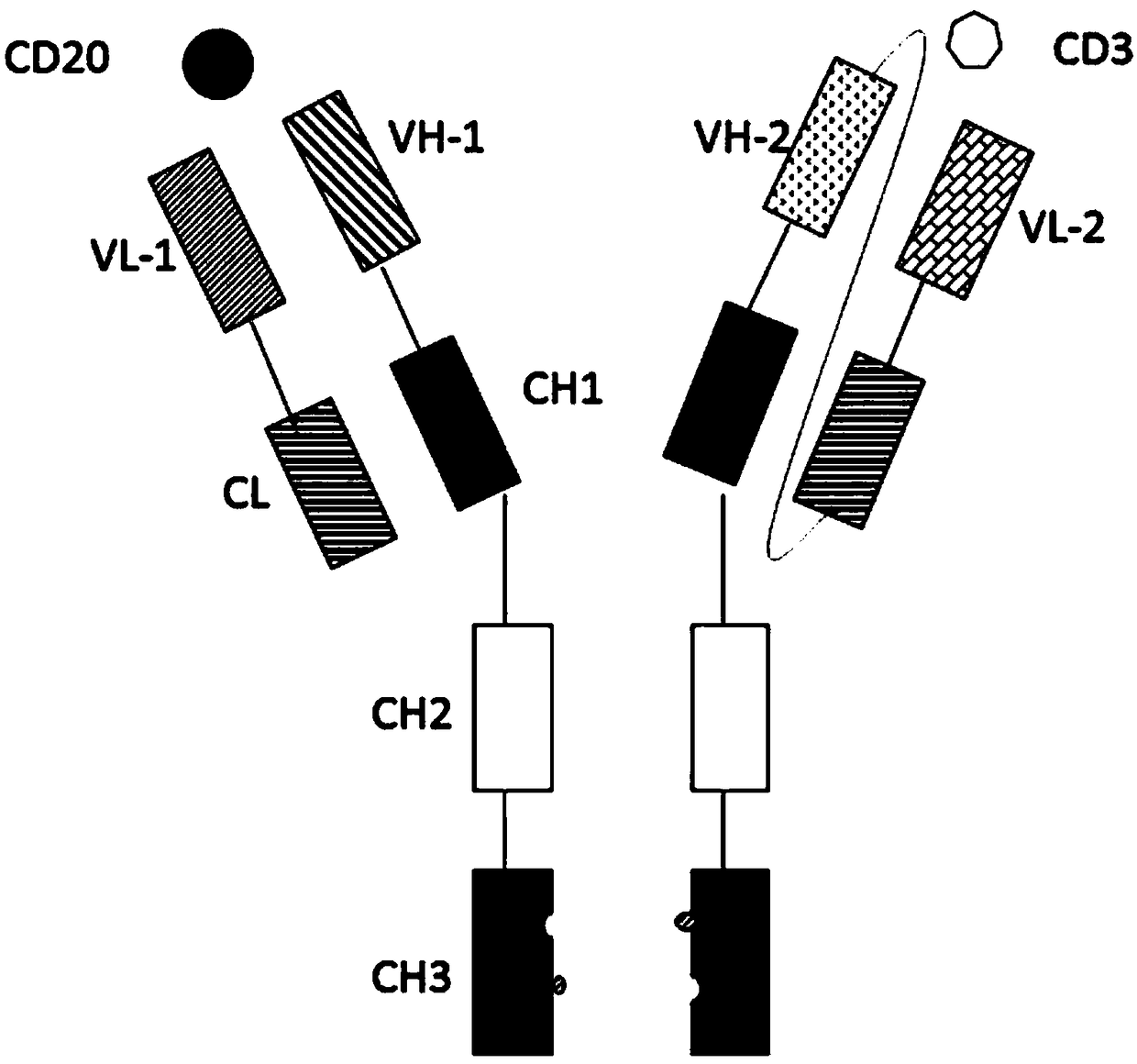
Bispecific antibody for CD20 and CD3
ActiveCN108059680AImprove stabilityOvercome stabilityHybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody ingredientsAntigenCD20
The invention relates to the technical field of biological pharmacy and particularly discloses a bispecific antibody for CD20 and CD3. The bispecific antibody comprises univalent unit, a single-chainunit and a linker, wherein the univalent unit is a light chain-heavy chain pair with a specific binding capability for an antigen CD20 on the surface of a tumor cell; the single-chain unit can be usedfor specifically binding a CD3 antigen on the surface of an immune cell; the end N of a heavy chain and the end C of a light chain of the single-chain unit are connected by the linker to form a Fab-Fc form; the univalent unit is connected with the single-chain unit through a disulfide bond of a hinge region and a pestle mortar structure of a CH3 structural domain. According to the bispecific antibody, CD20 and CD3 can be specifically bound and the immune effector cell can be targeted to the tumor cell, so that the killing effect of the immune effector cell on the tumor cell is improved; the bispecific antibody can be used for treating CD20 antigen positive B-cell neoplasms, comprising non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia and the like, and has a broad application prospect inthe field of immunotherapy of tumors.
Owner:BEIJING DONGFANG BIOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com