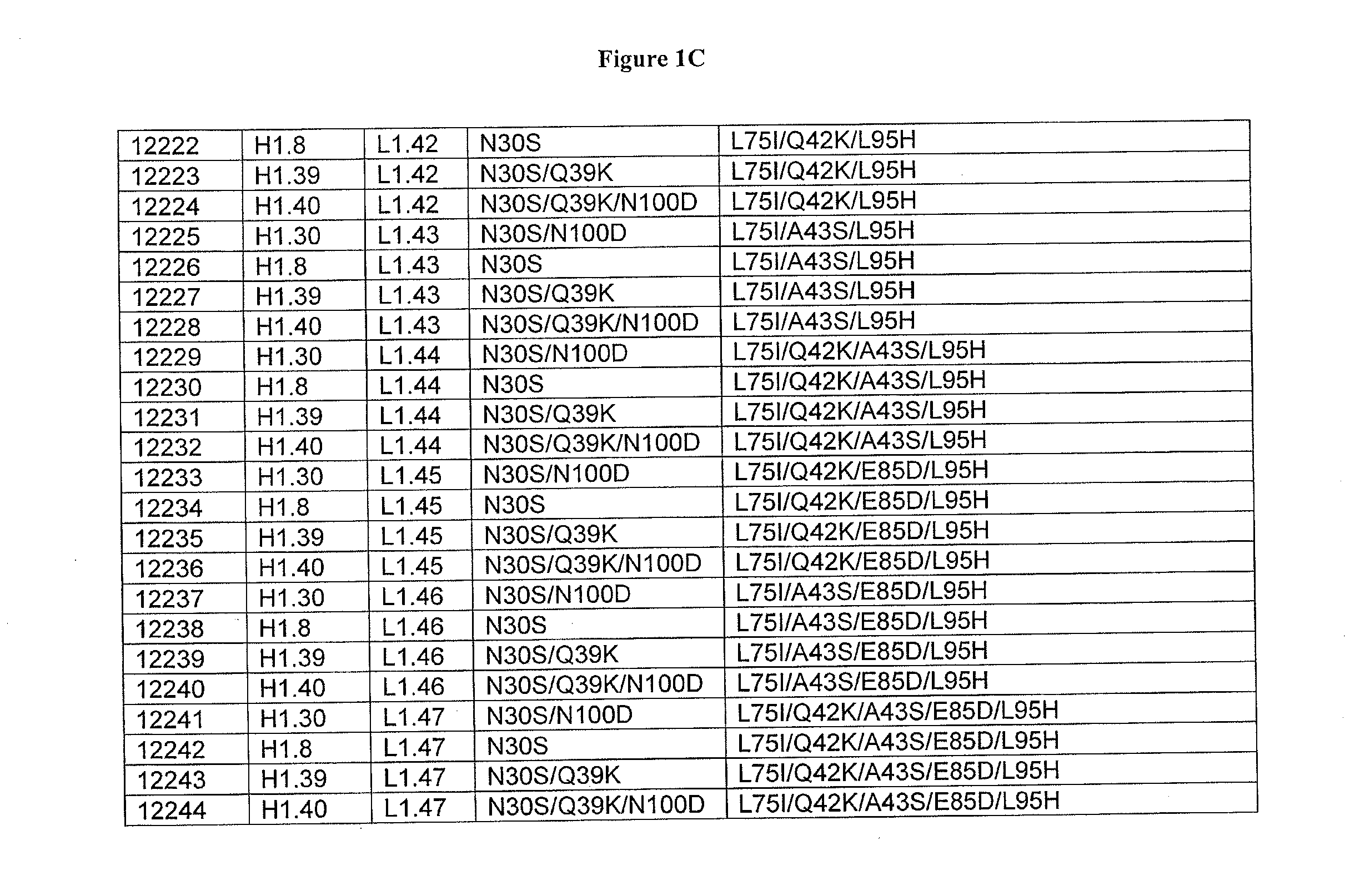
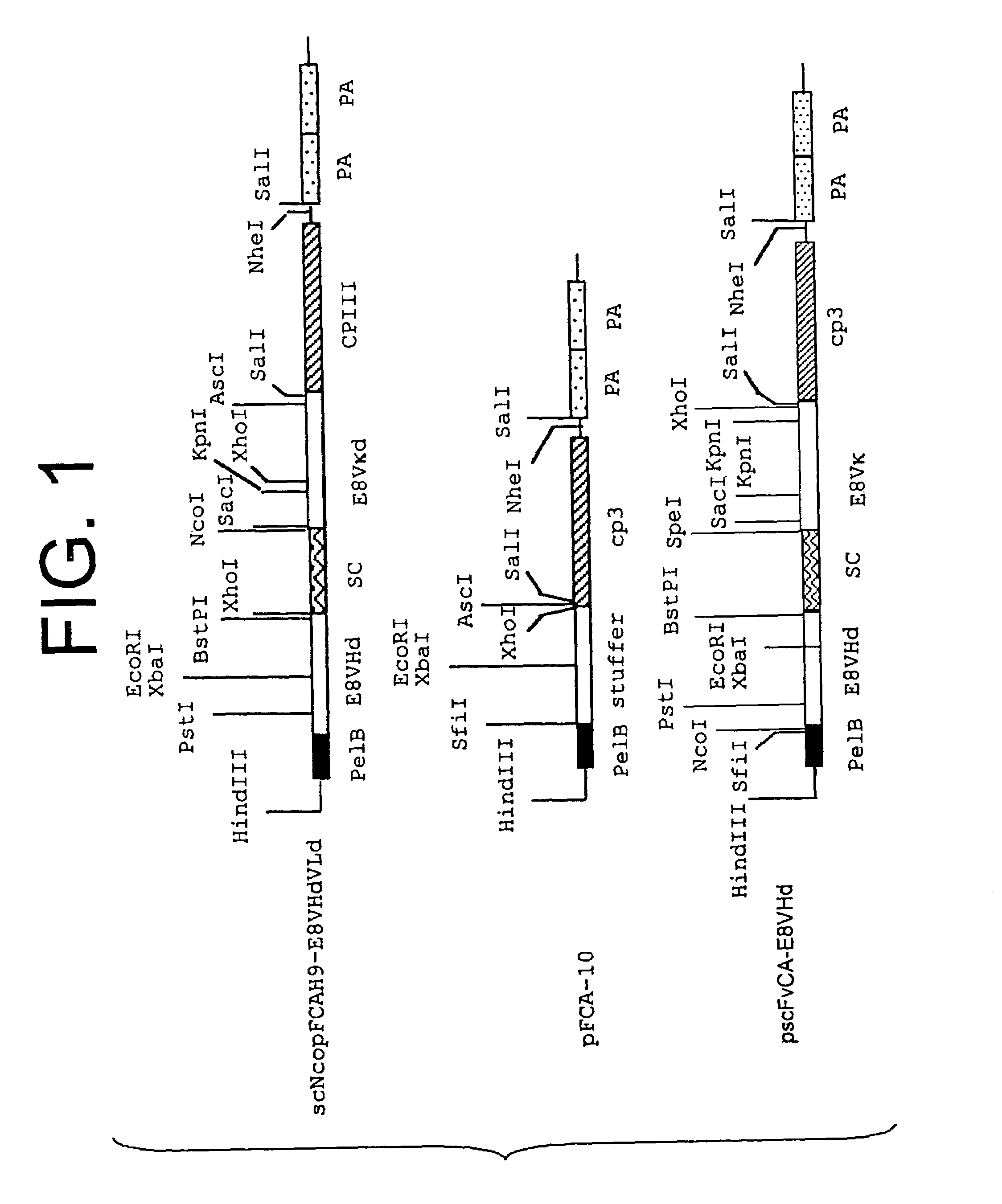
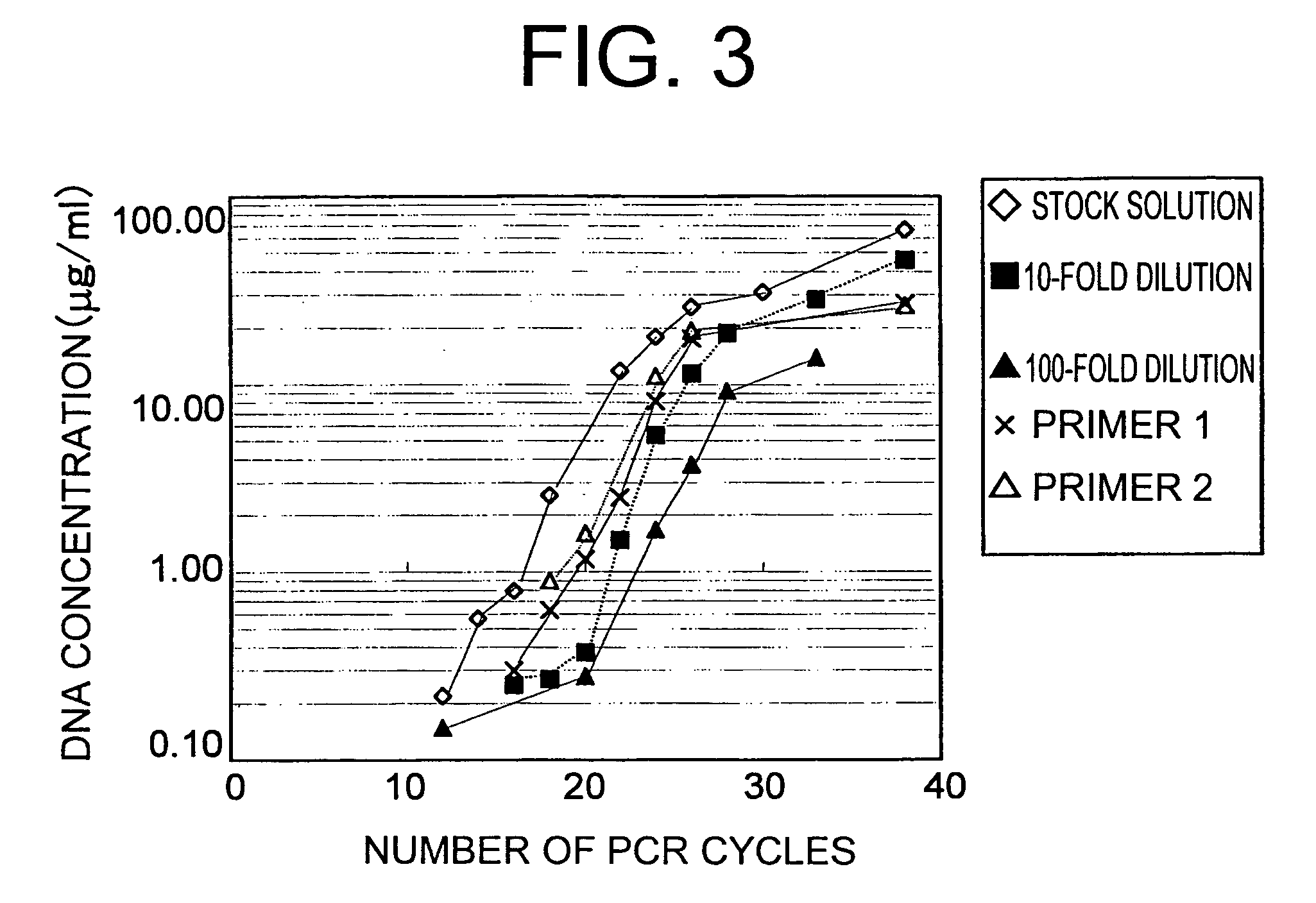
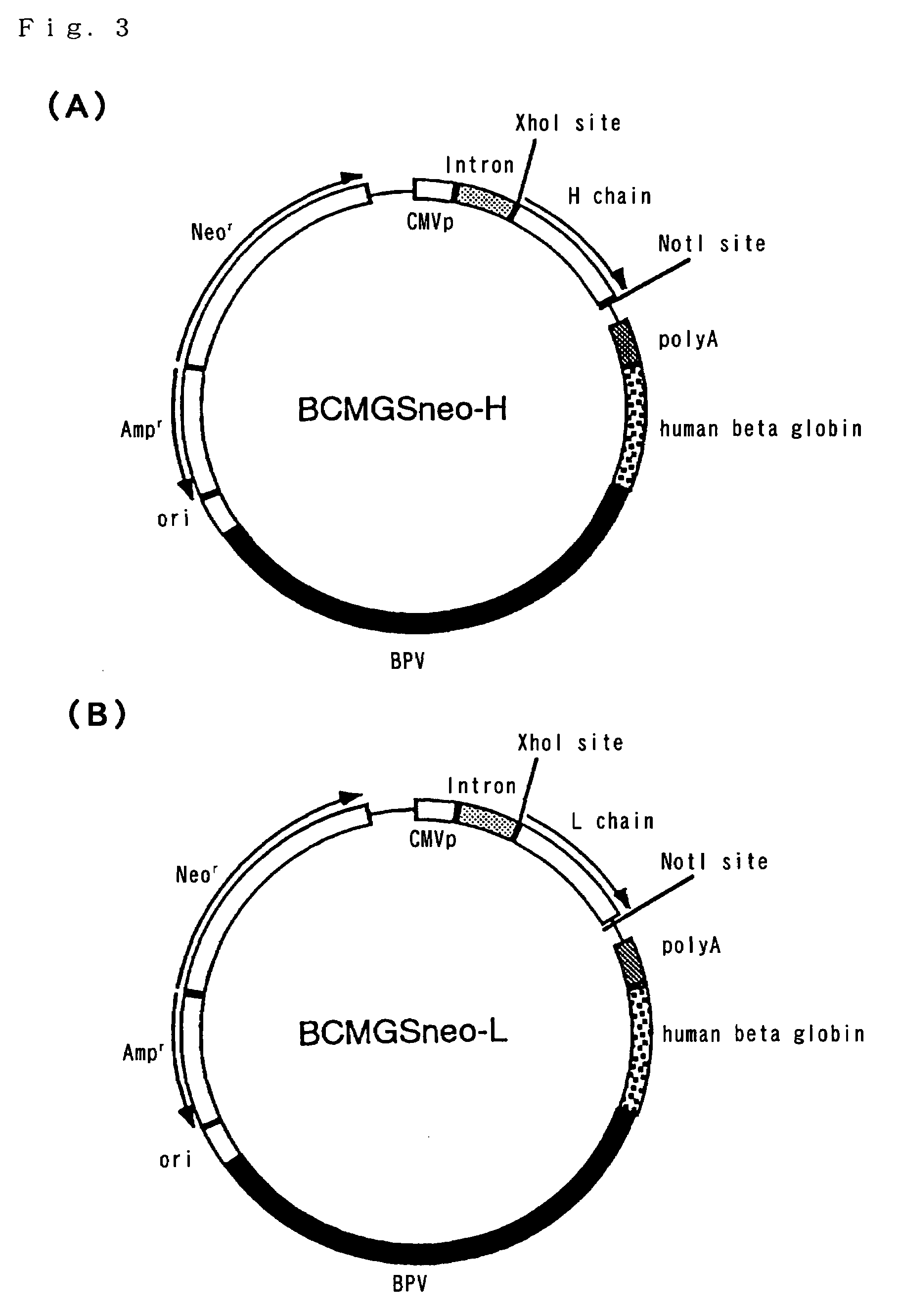
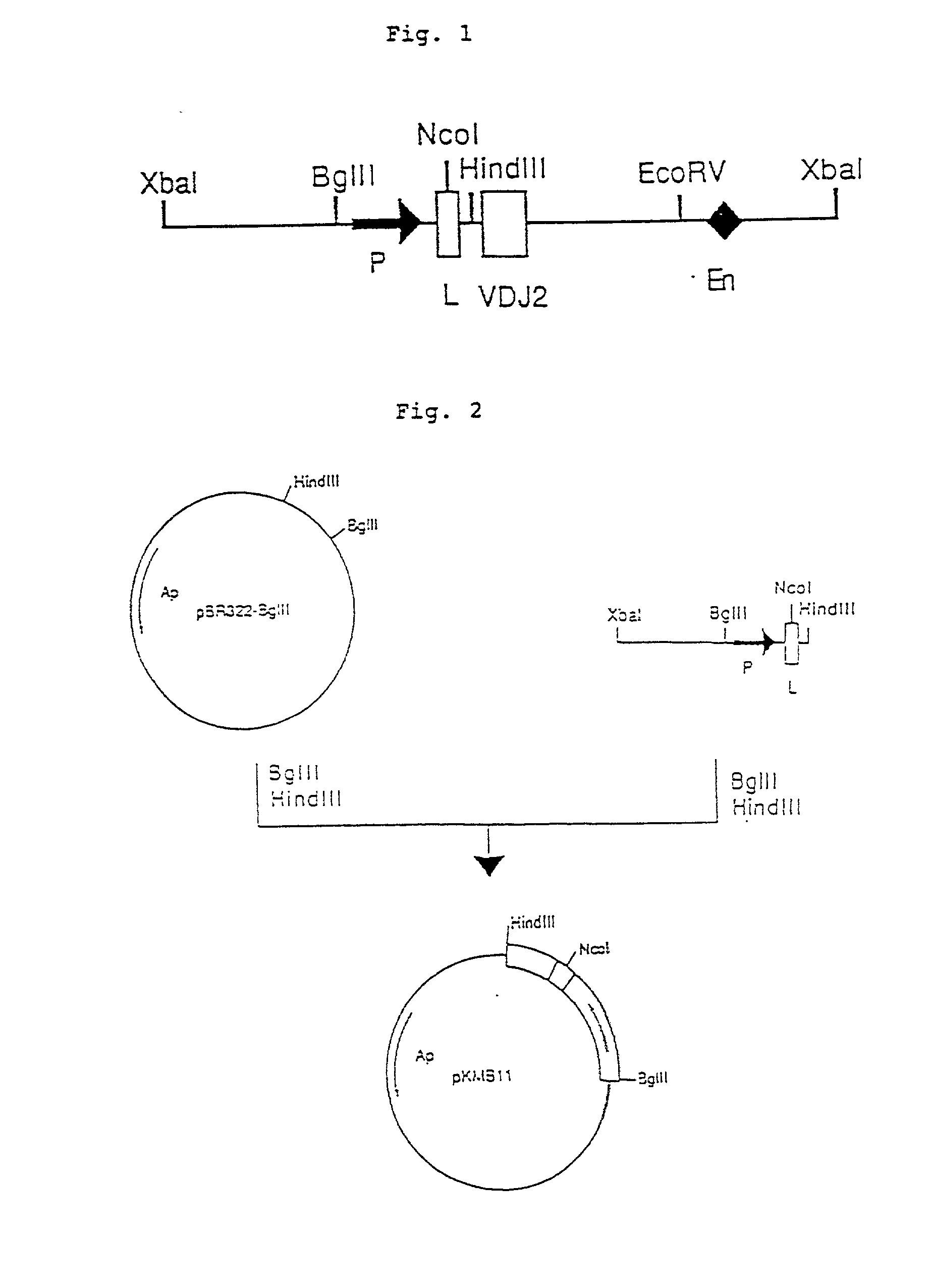
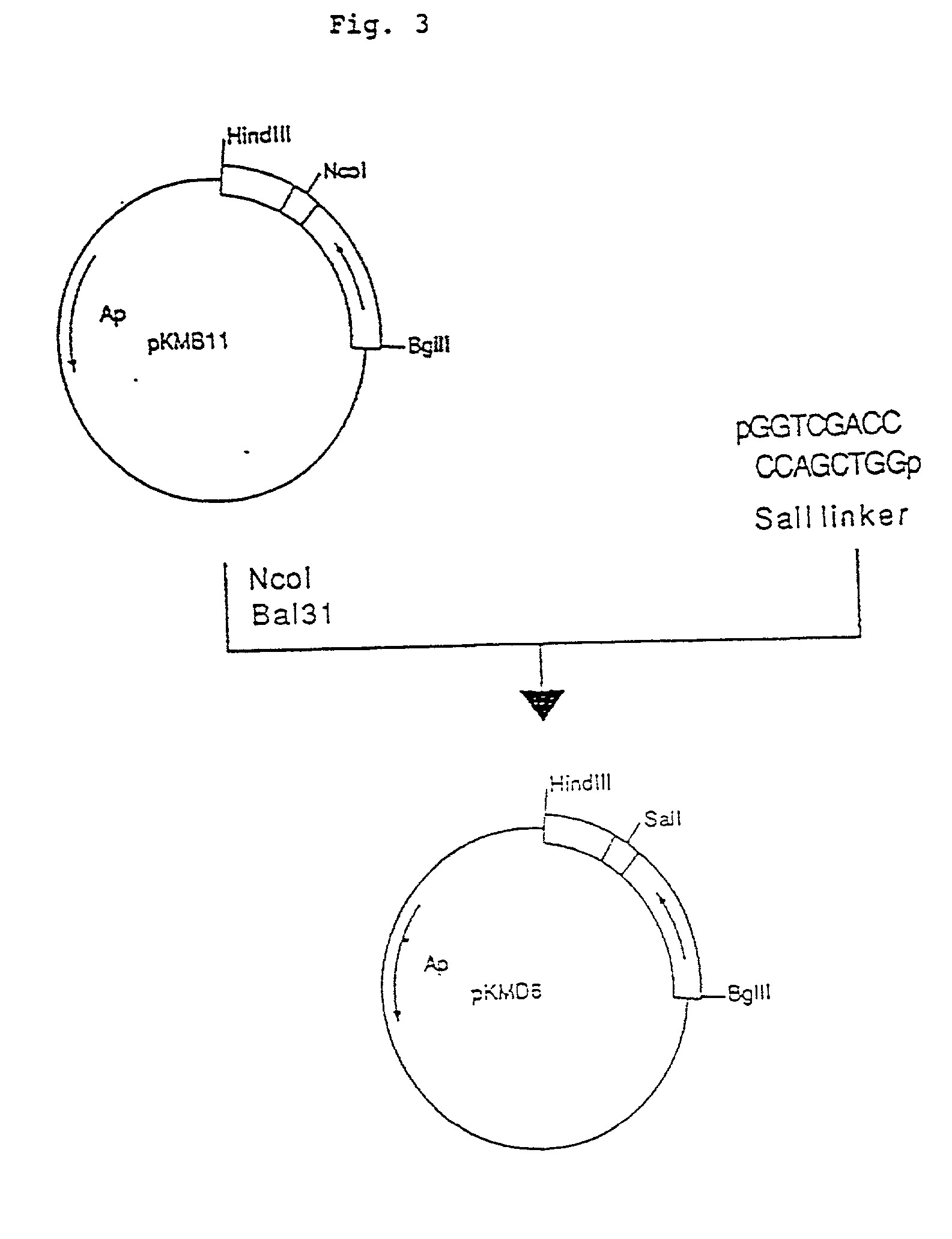
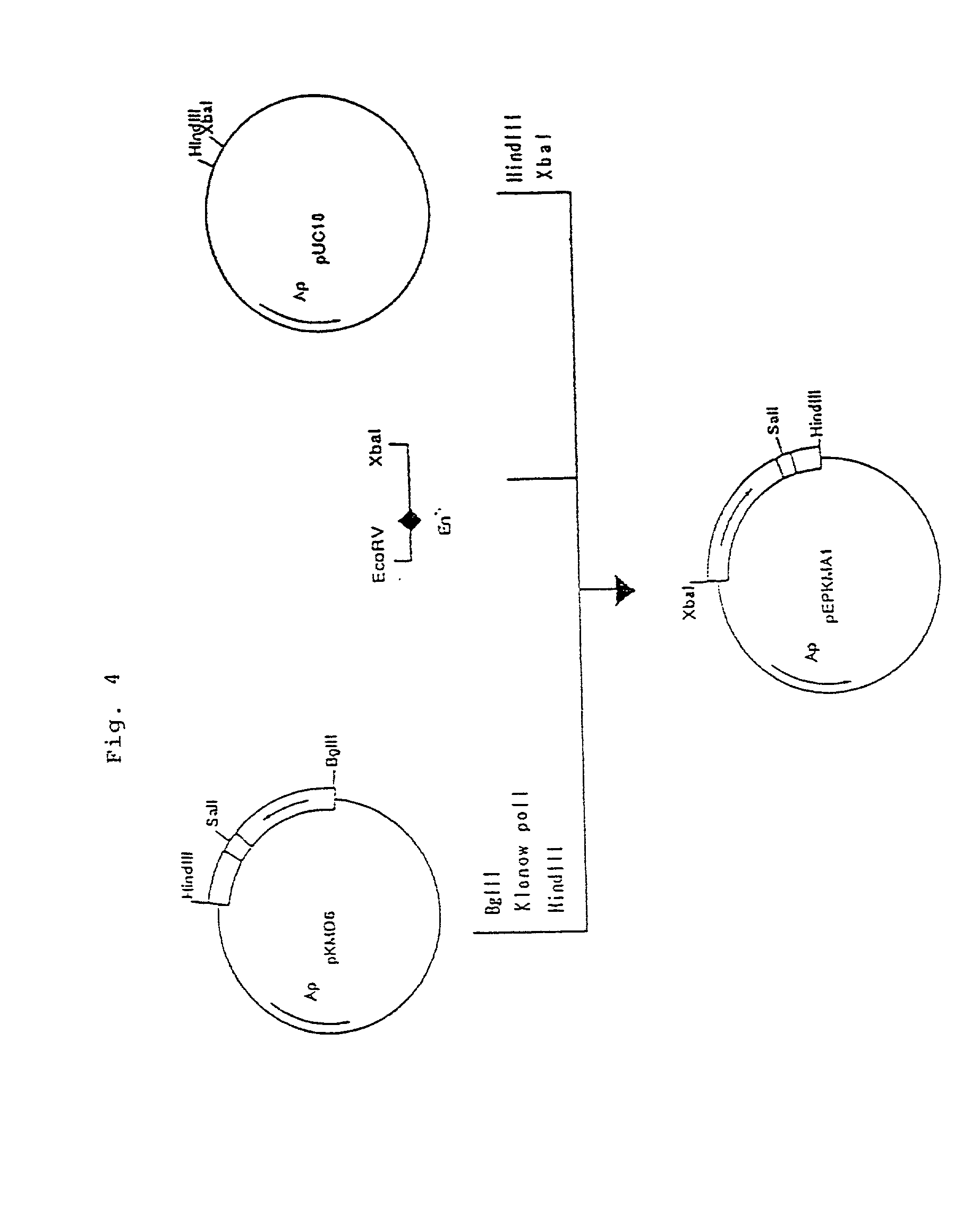
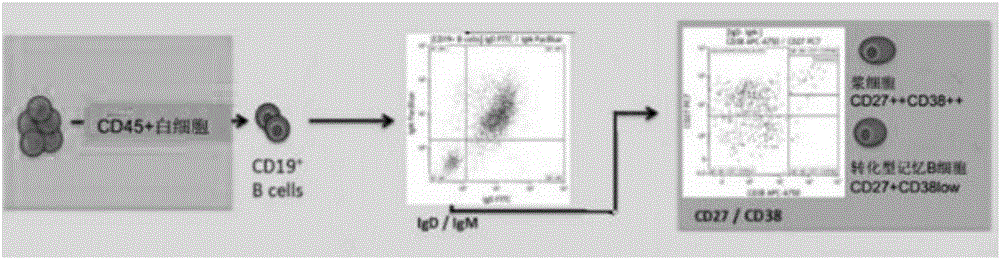
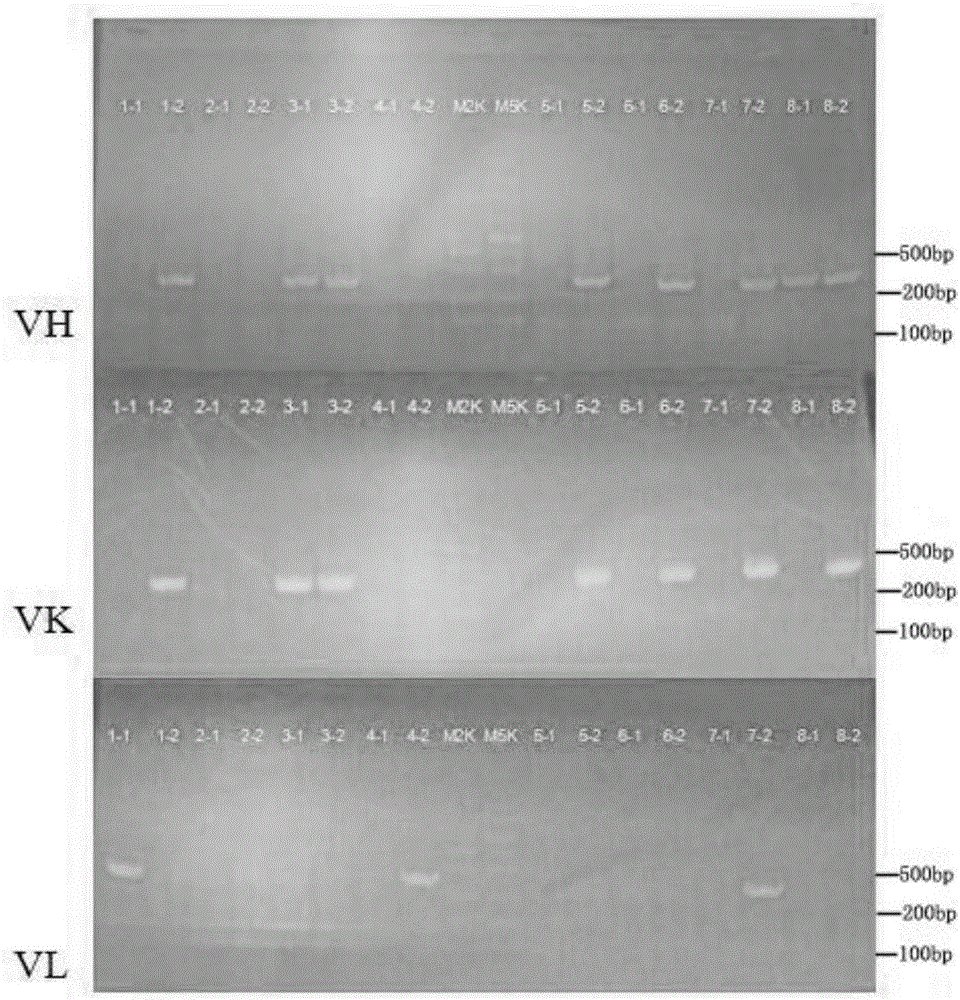
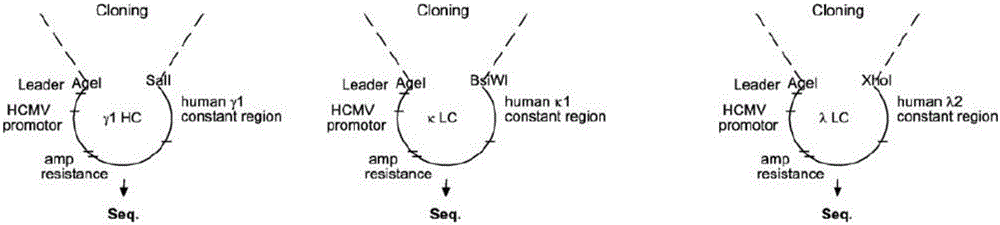
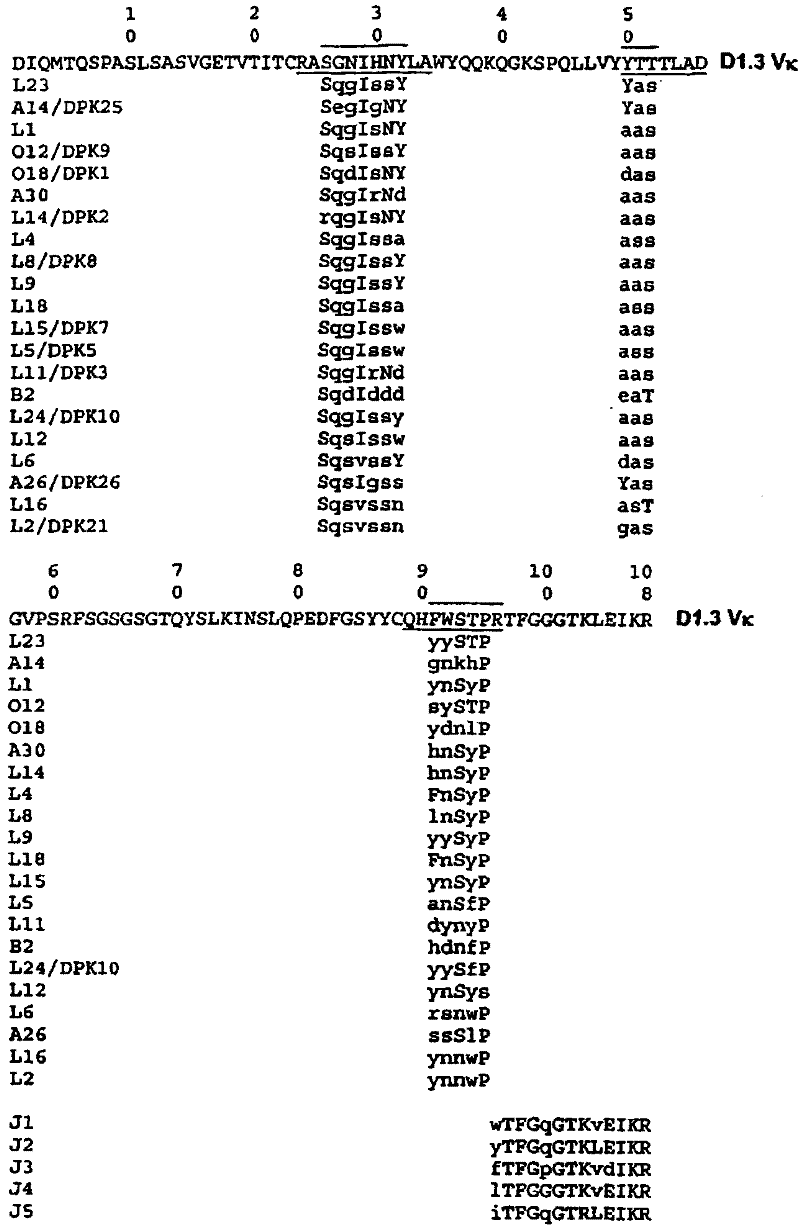
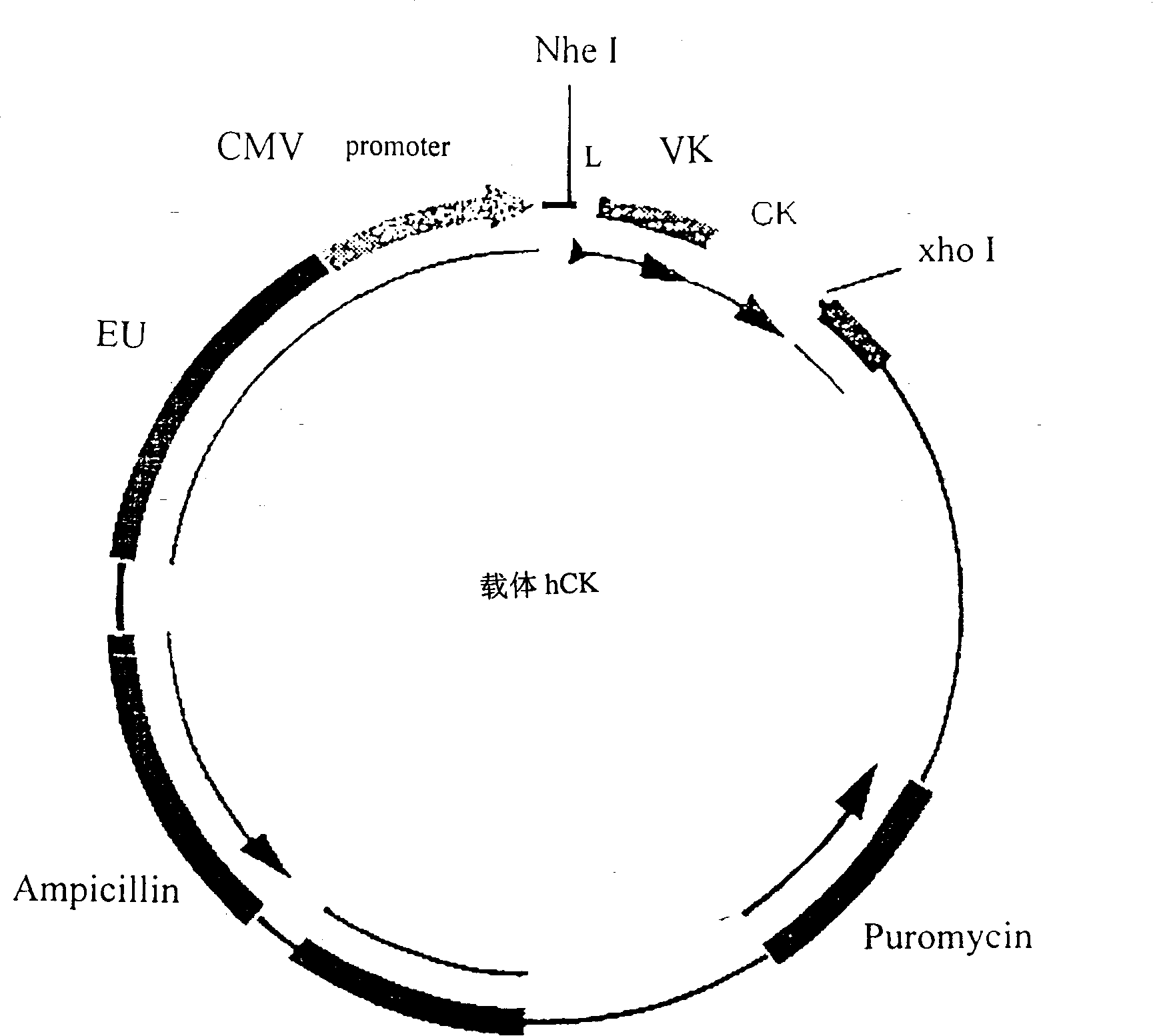
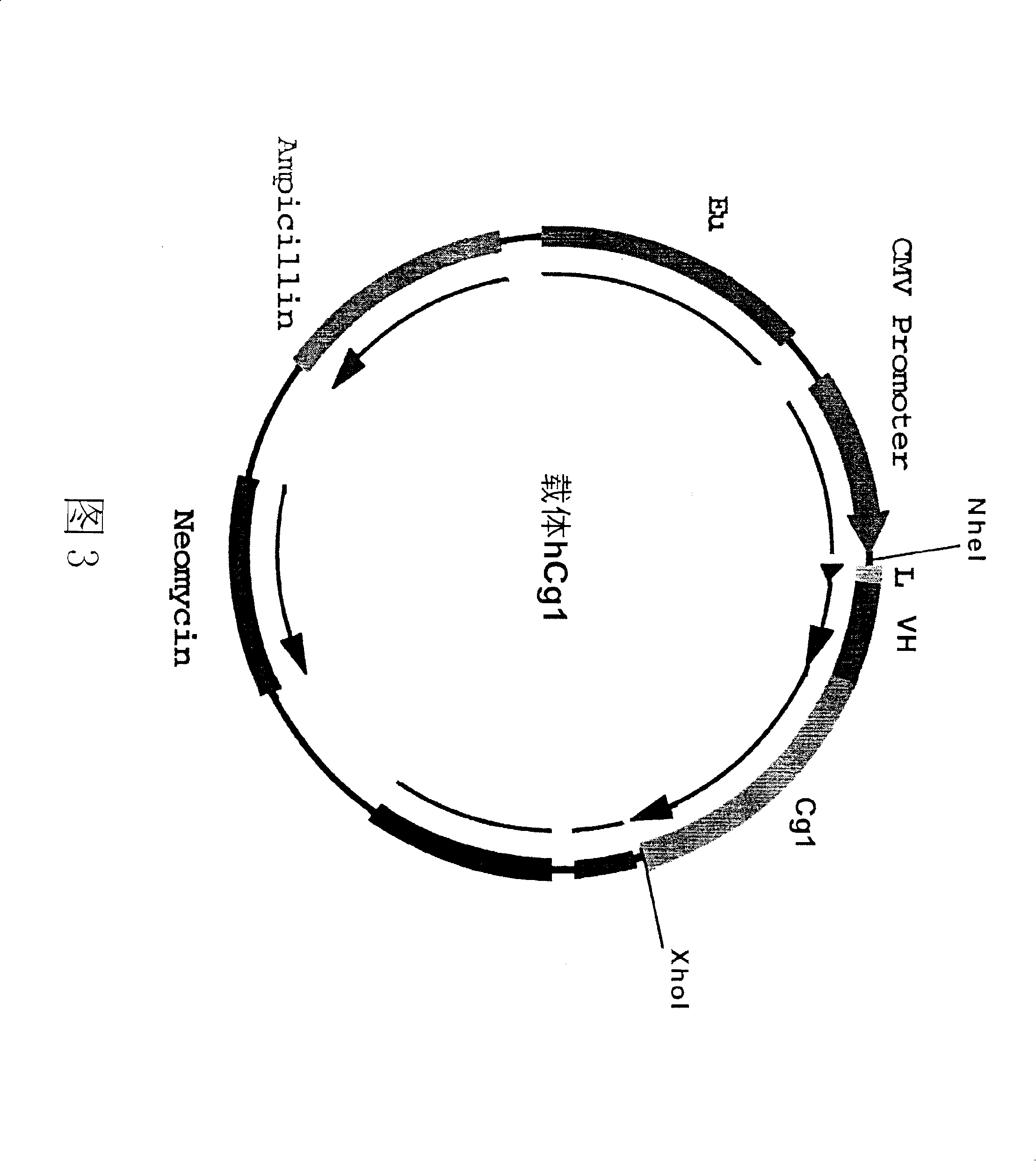
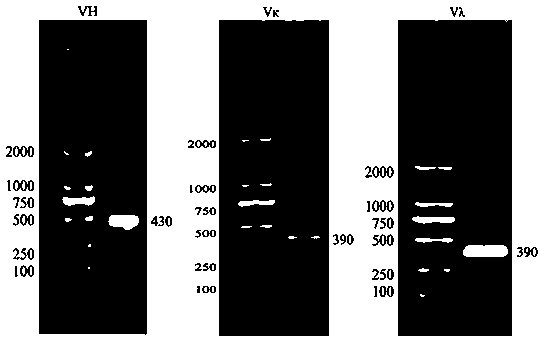
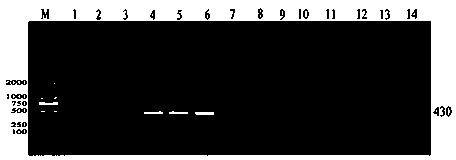
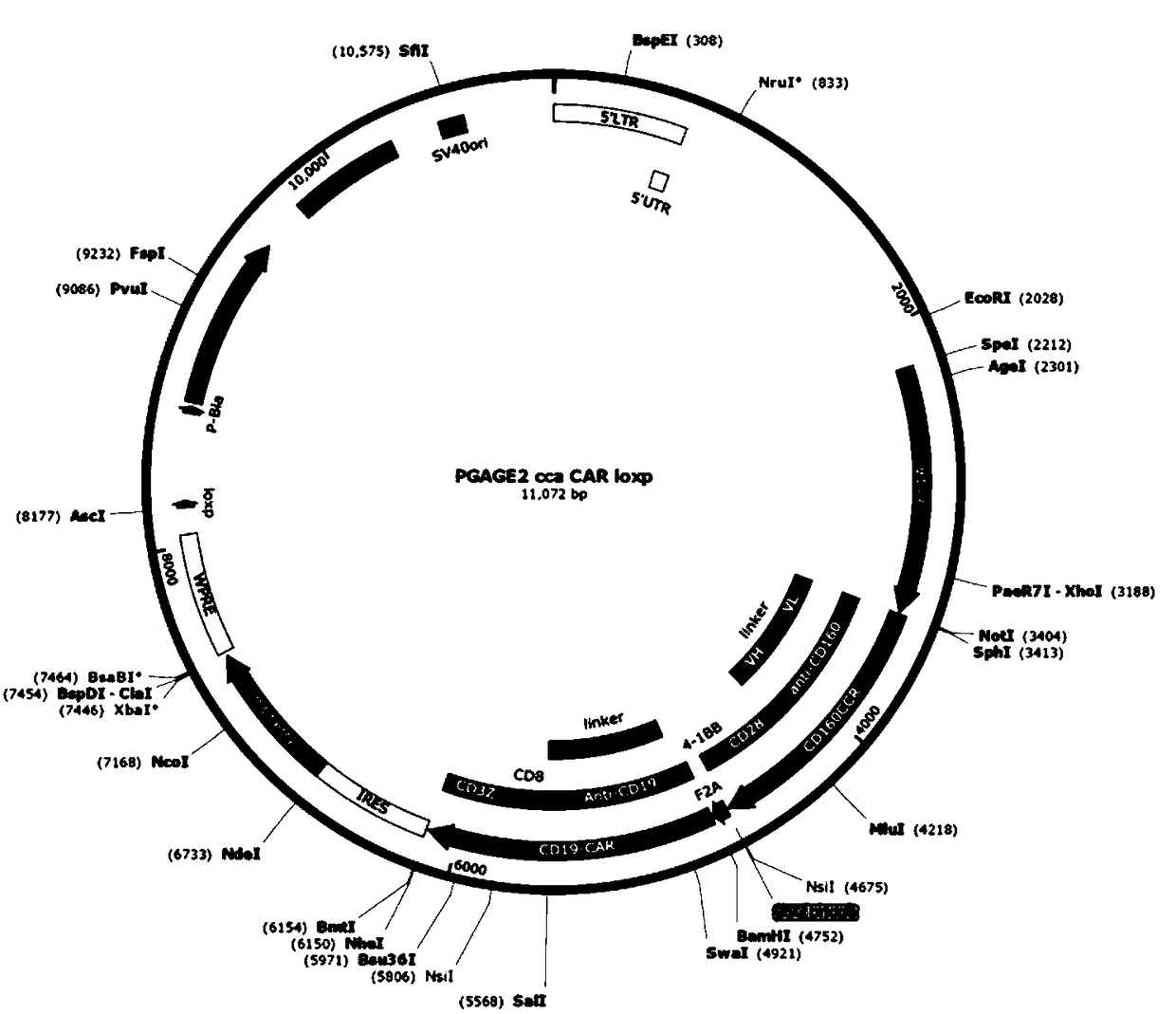
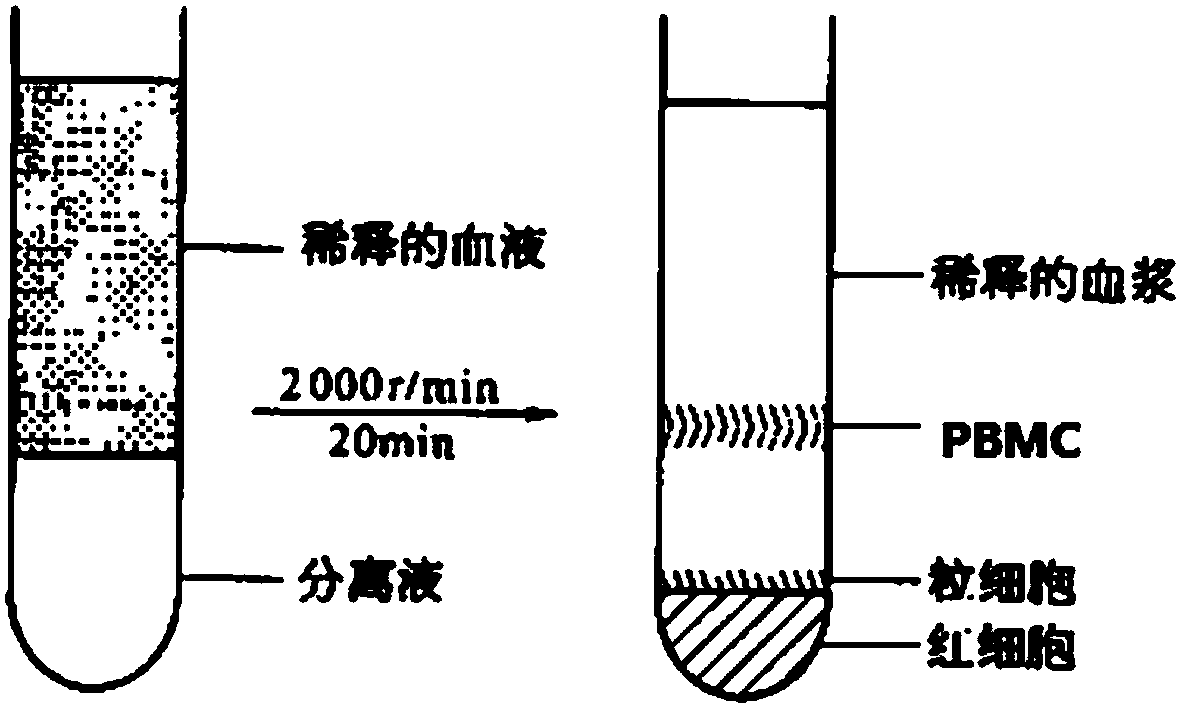
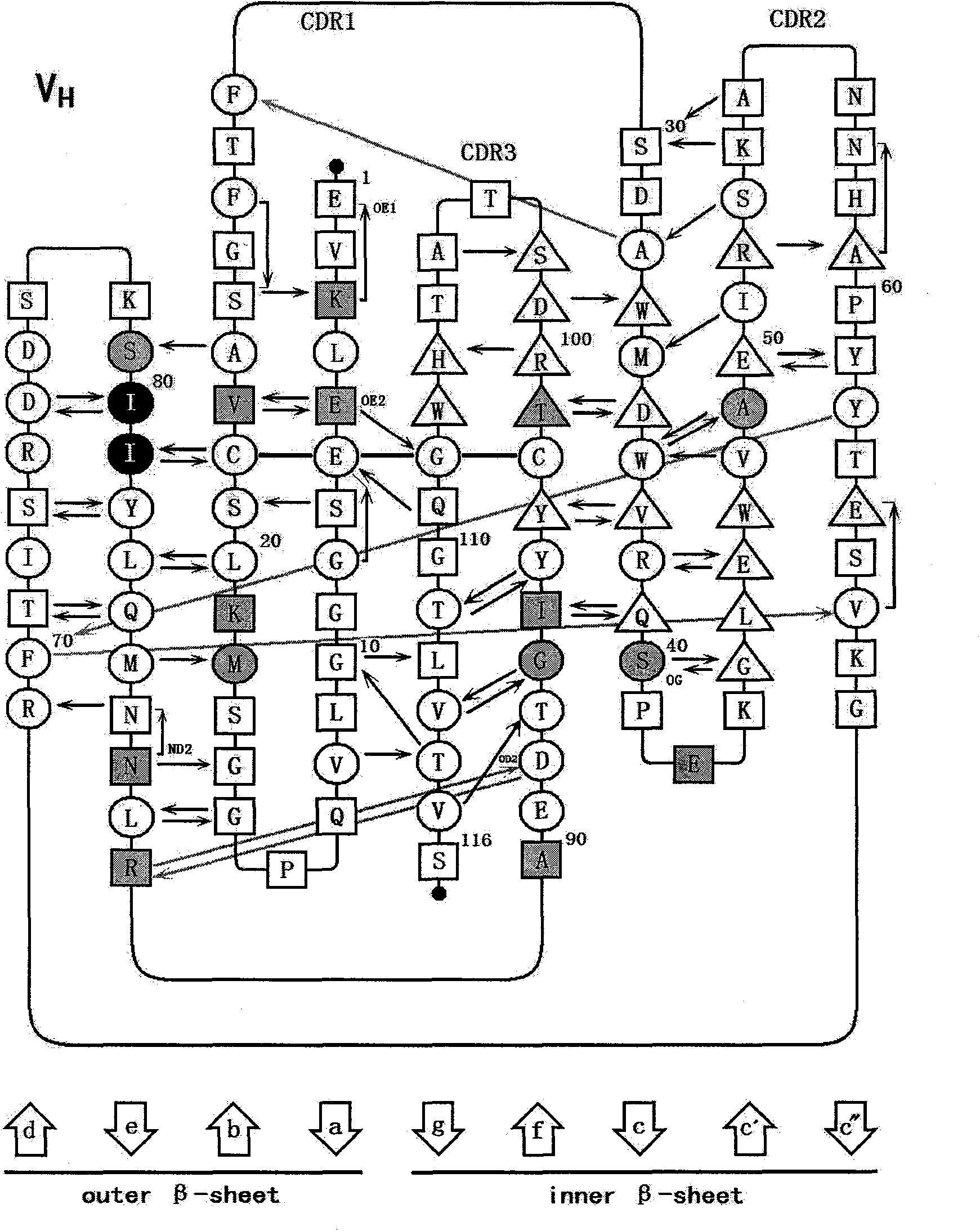
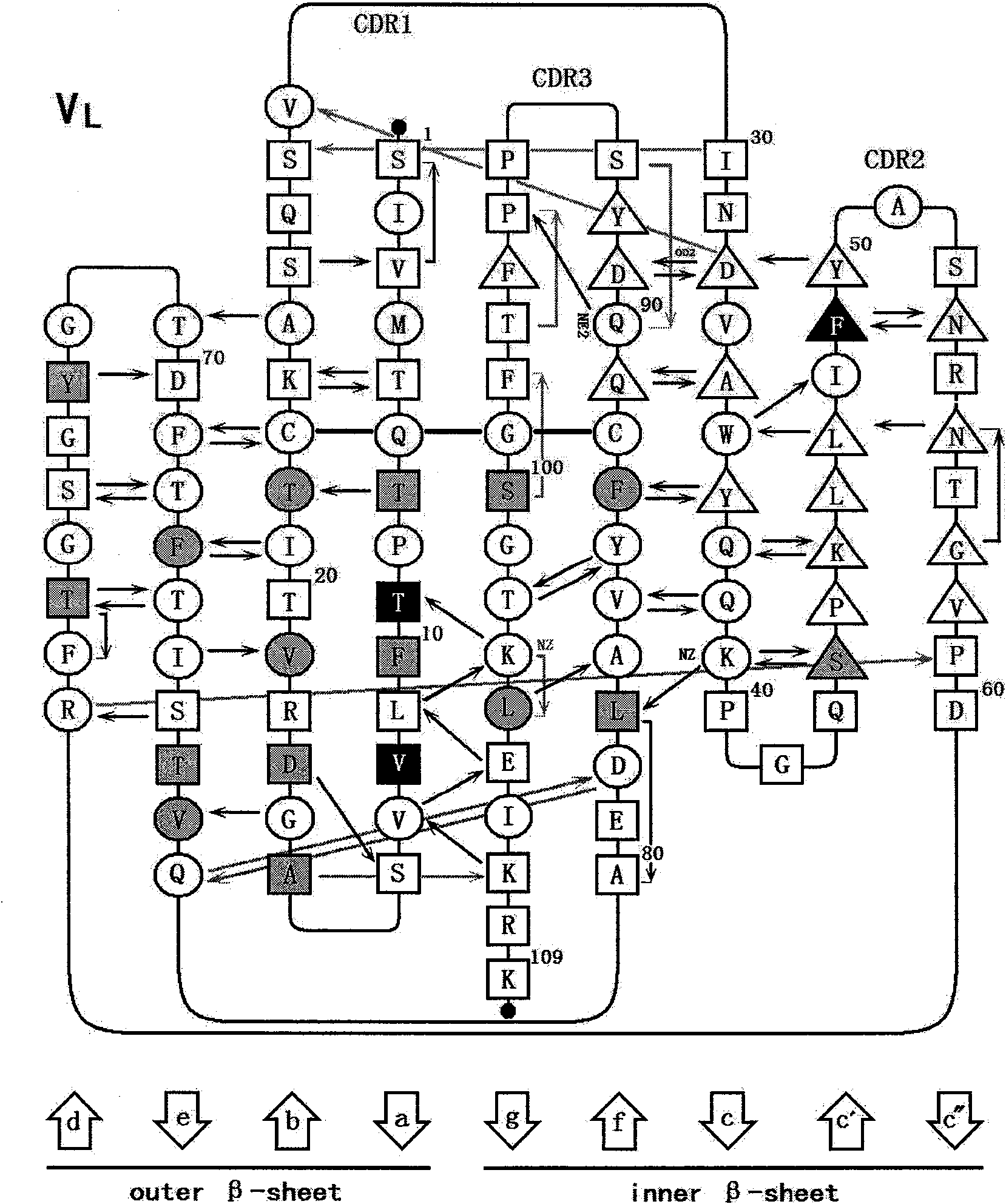
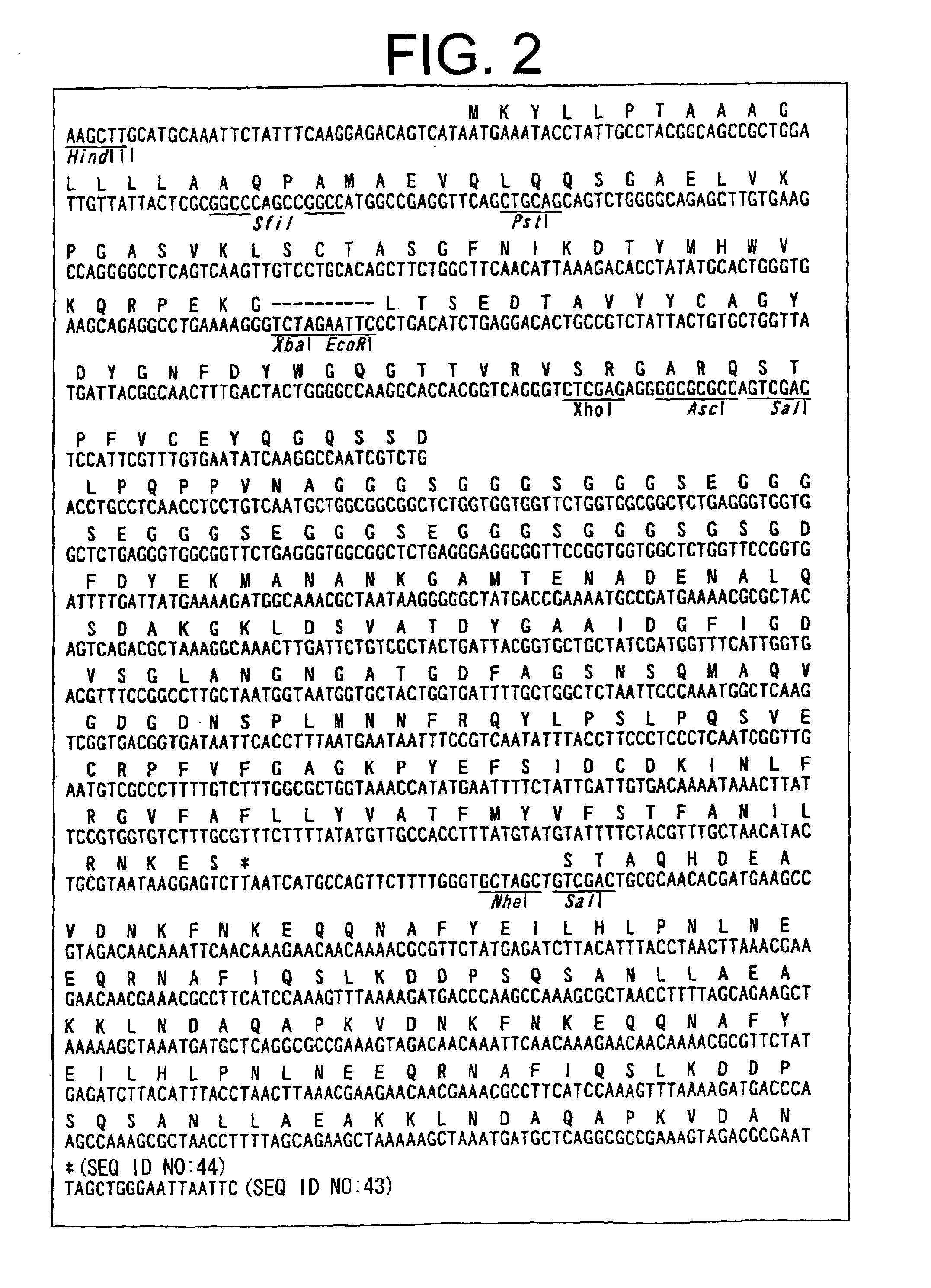Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
143 results about "Antibody variable region" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
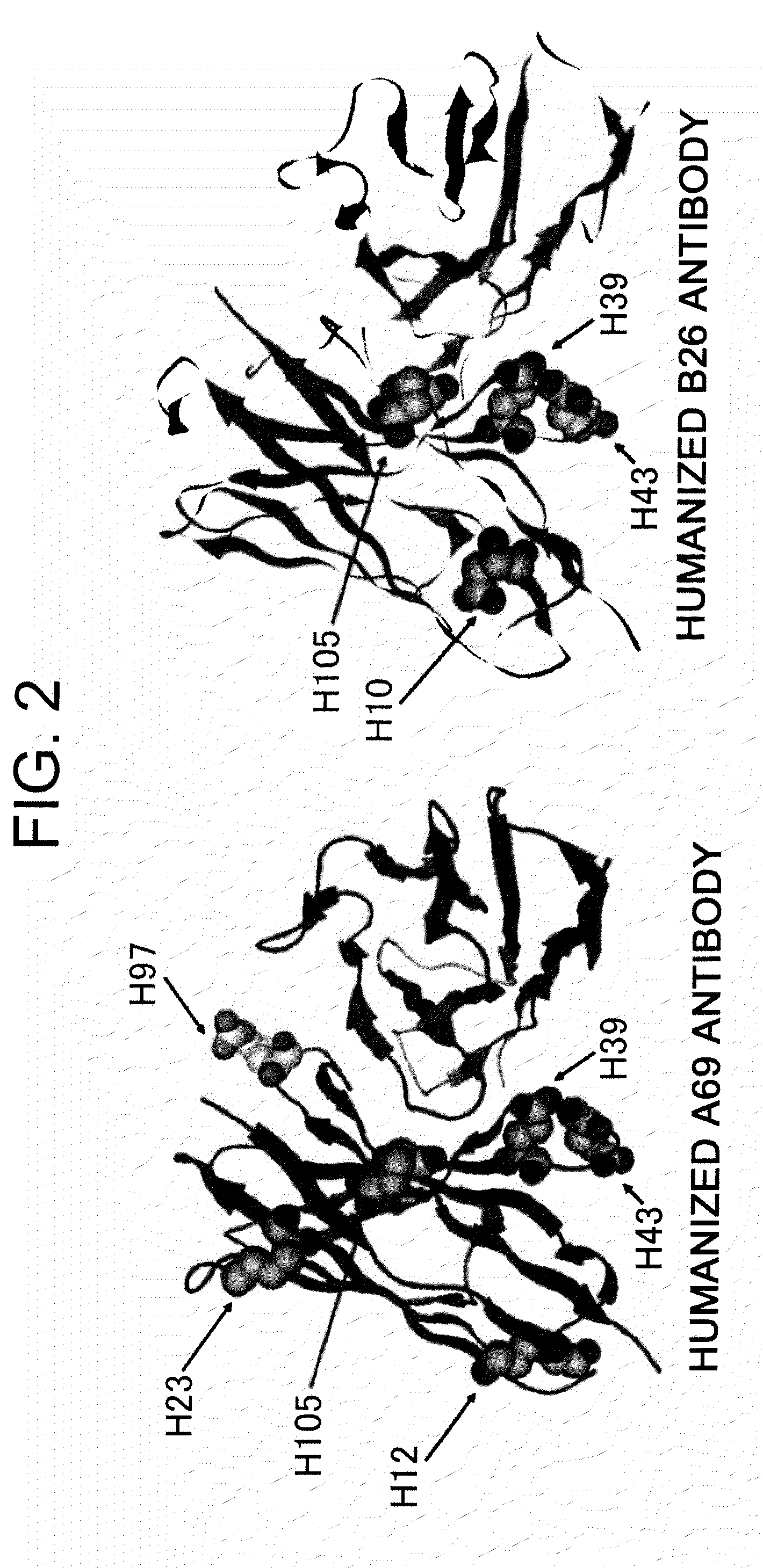
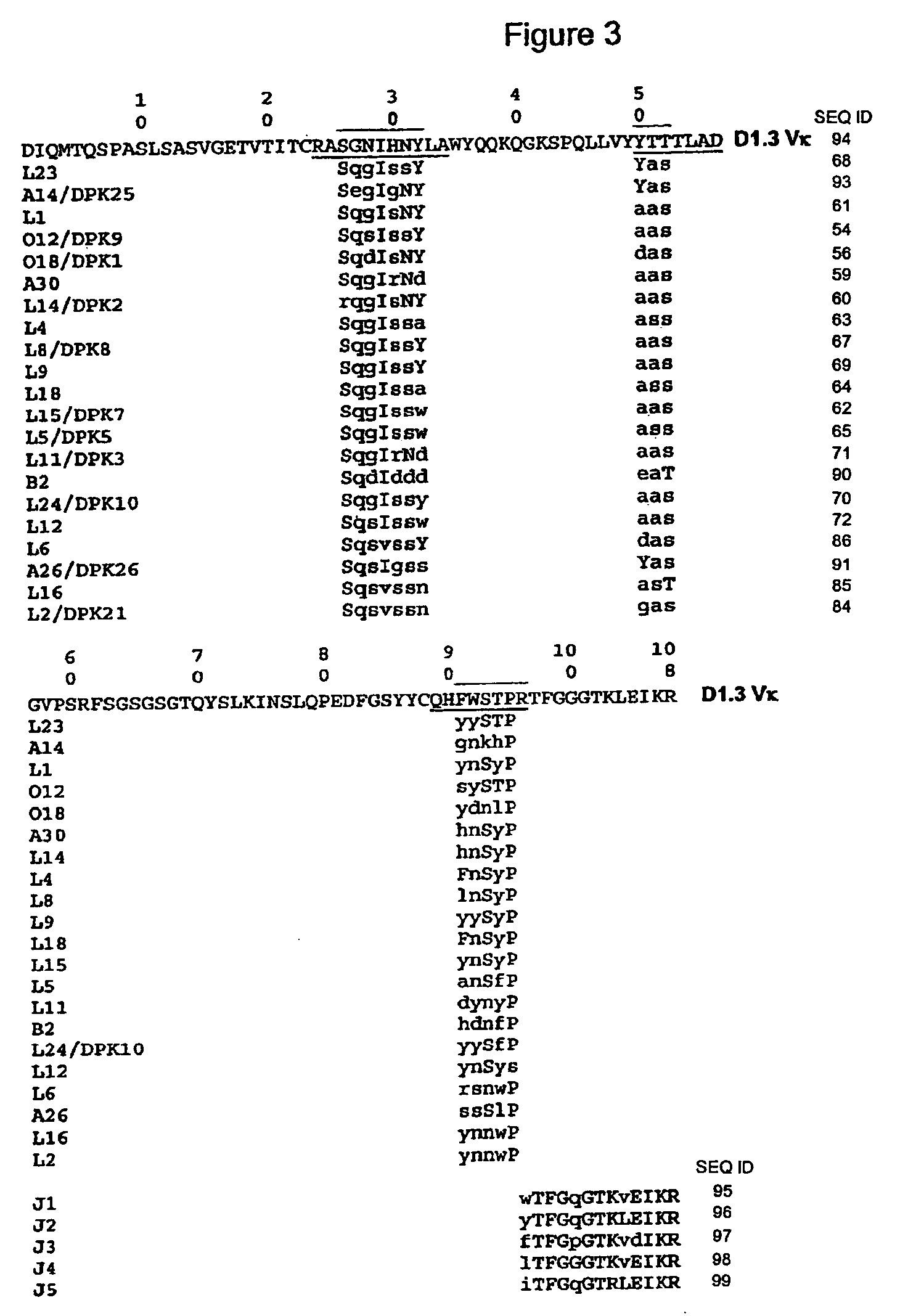
Super humanized antibodies
InactiveUS6881557B2Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsAnalogue computers for chemical processesHuman sequenceHumanized antibody
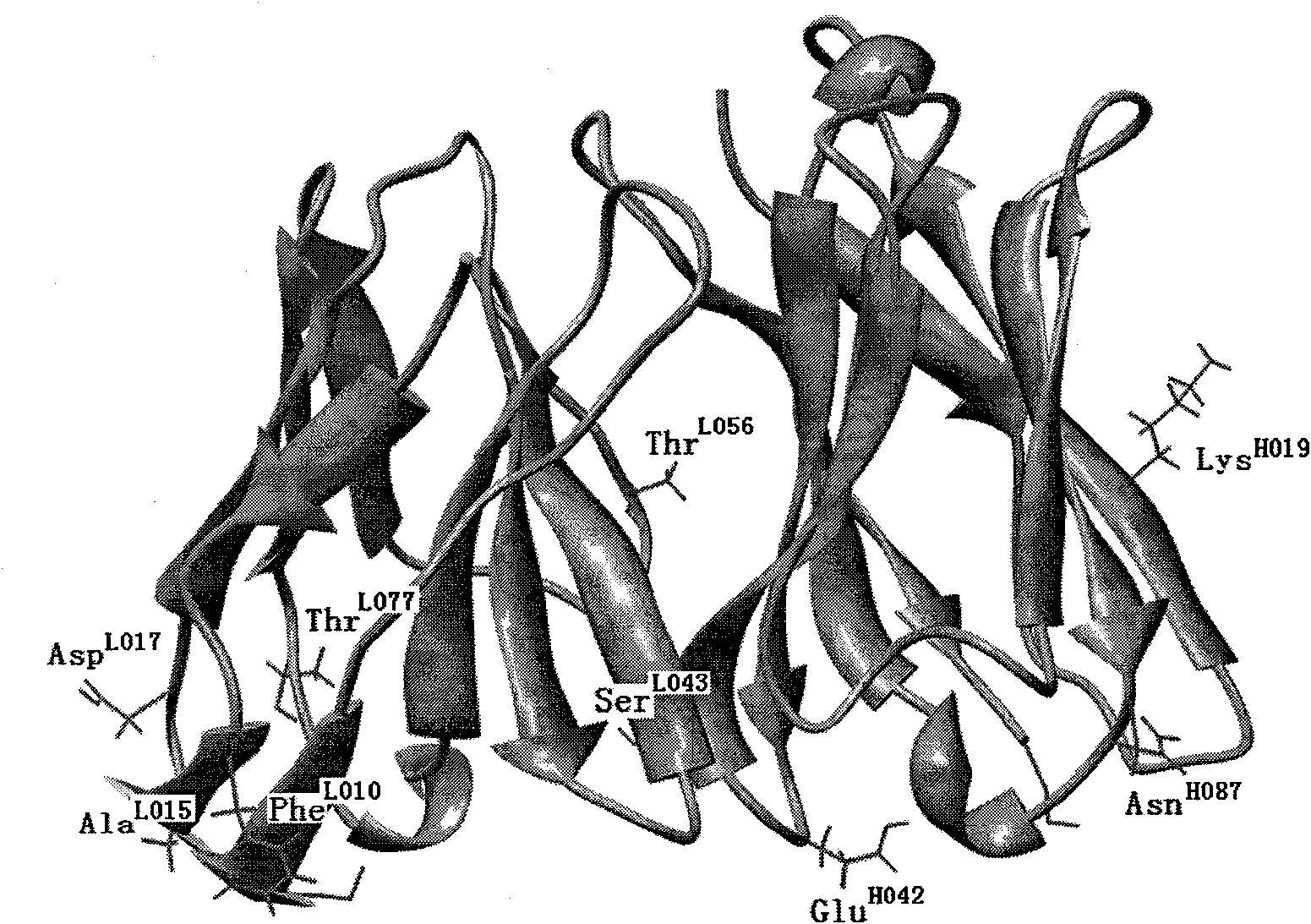
Disclosed herein are methods for humanizing antibodies based on selecting variable region framework sequences from human antibody genes by comparing canonical CDR structure types for CDR sequences of the variable region of a non-human antibody to canonical CDR structure types for corresponding CDRs from a library of human antibody sequences, preferably germline antibody gene segments. Human antibody variable regions having similar canonical CDR structure types to the non-human CDRs form a subset of member human antibody sequences from which to select human framework sequences. The subset members may be further ranked by amino acid similarity between the human and the non-human CDR sequences. Top ranking human sequences are selected to provide the framework sequences for constructing a chimeric antibody that functionally replaces human CDR sequences with the non-human CDR counterparts using the selected subset member human frameworks, thereby providing a humanized antibody of high affinity and low immunogenicity without need for comparing framework sequences between the non-human and human antibodies. Chimeric antibodies made according to the method are also disclosed.
Owner:ARROWSMITH TECH
Methods of modifying antibodies for purification of bispecific antibodies
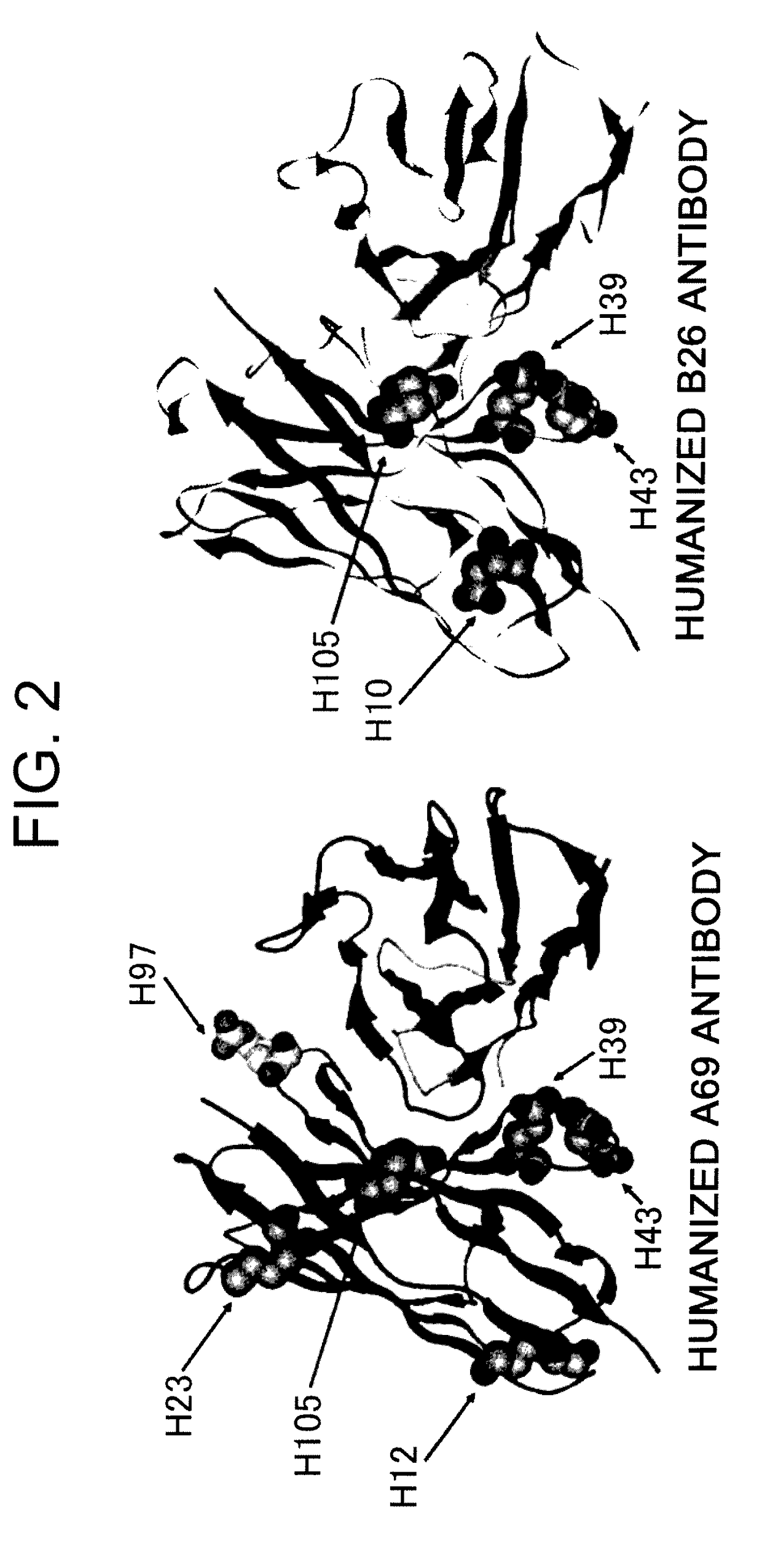
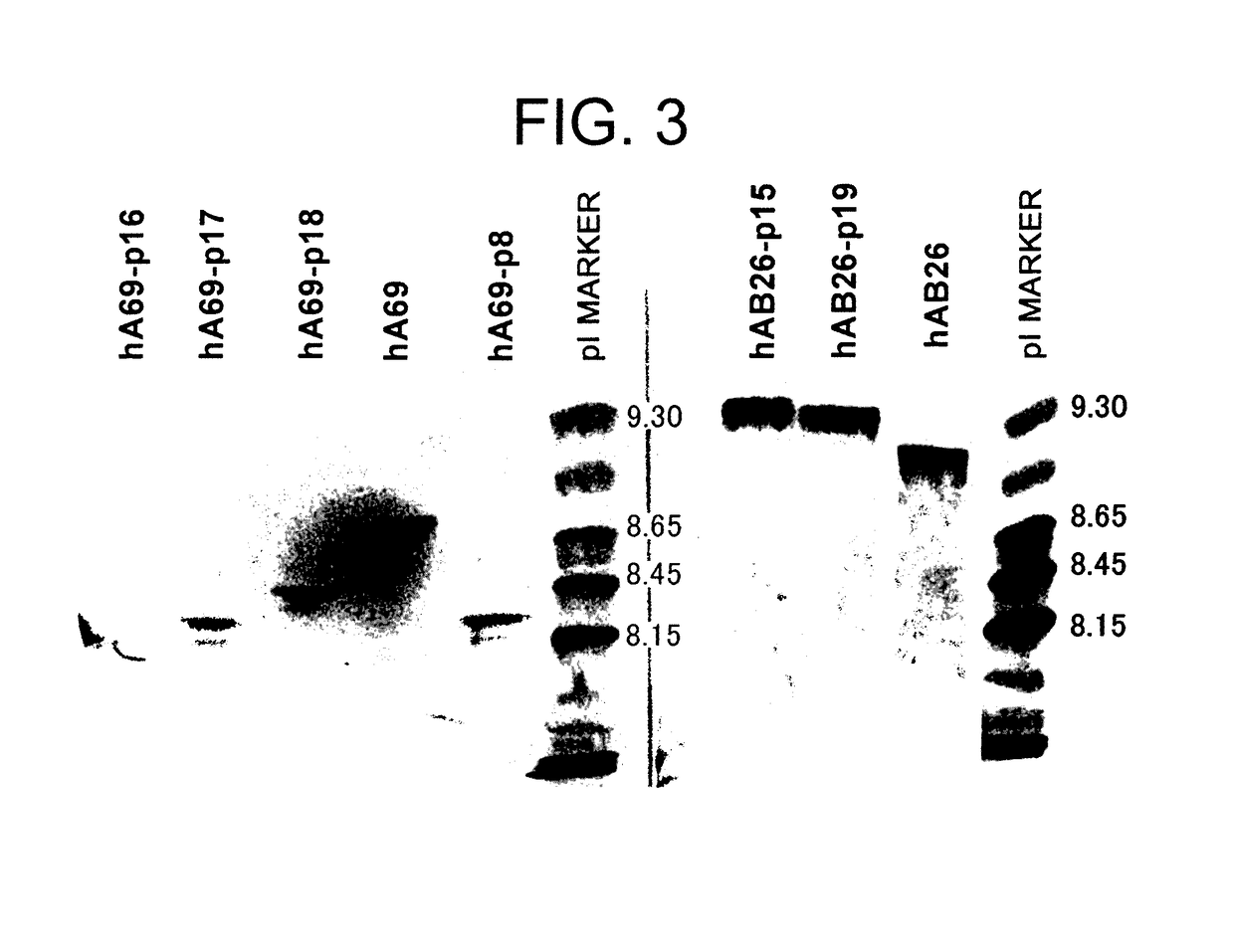
ActiveUS20090263392A1Efficient purificationFunction increaseSugar derivativesAntibody ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesBinding site
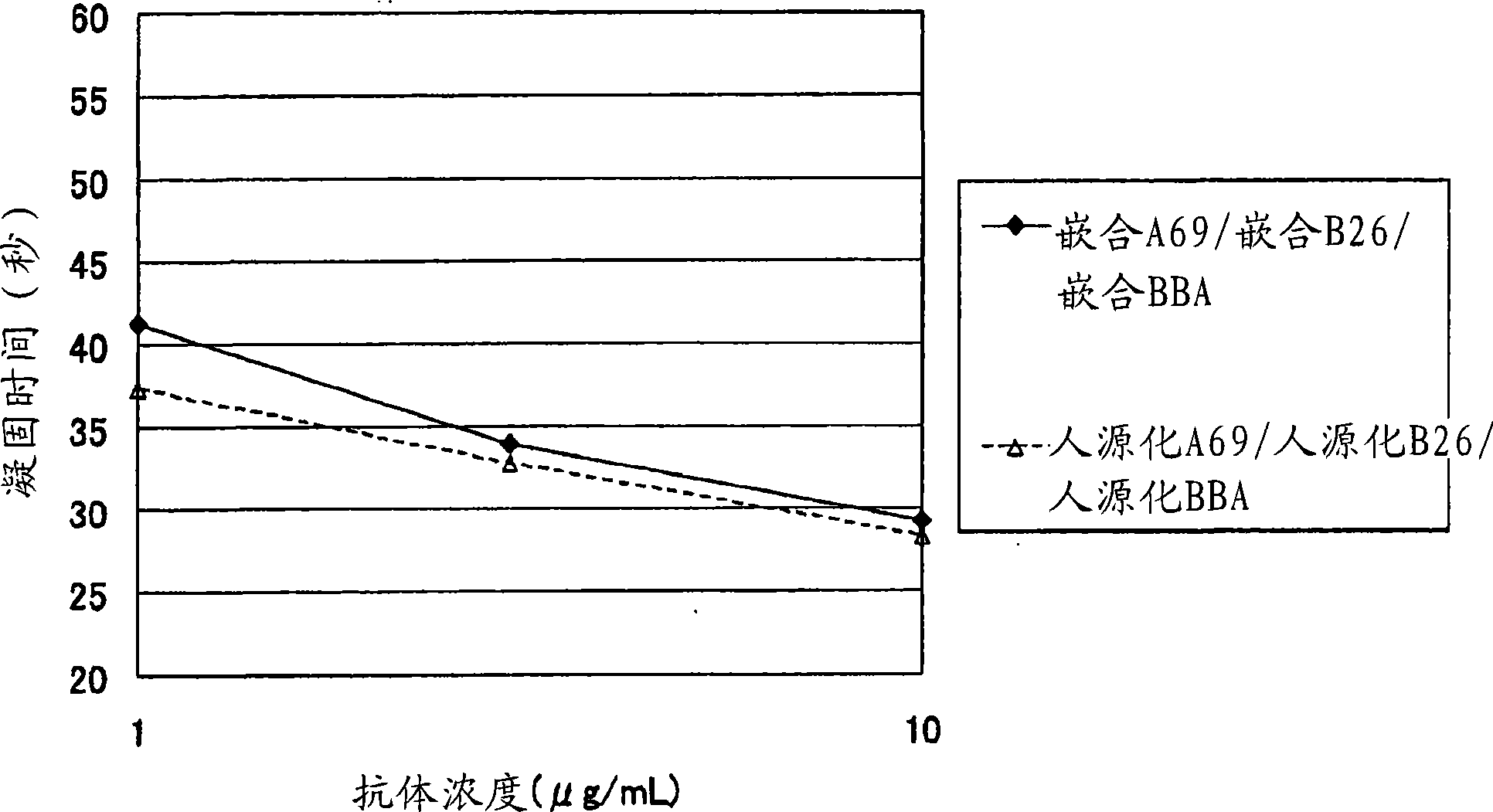
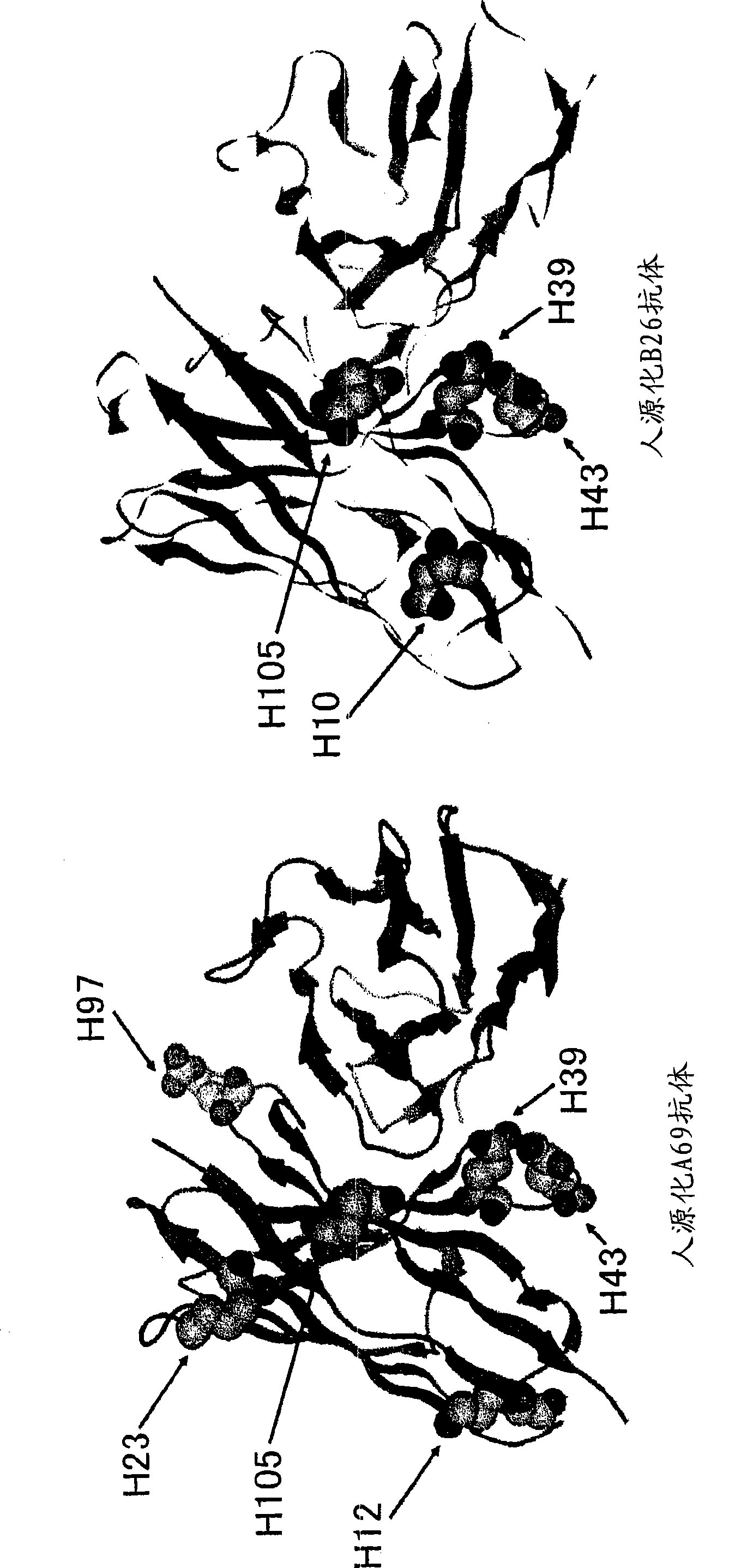
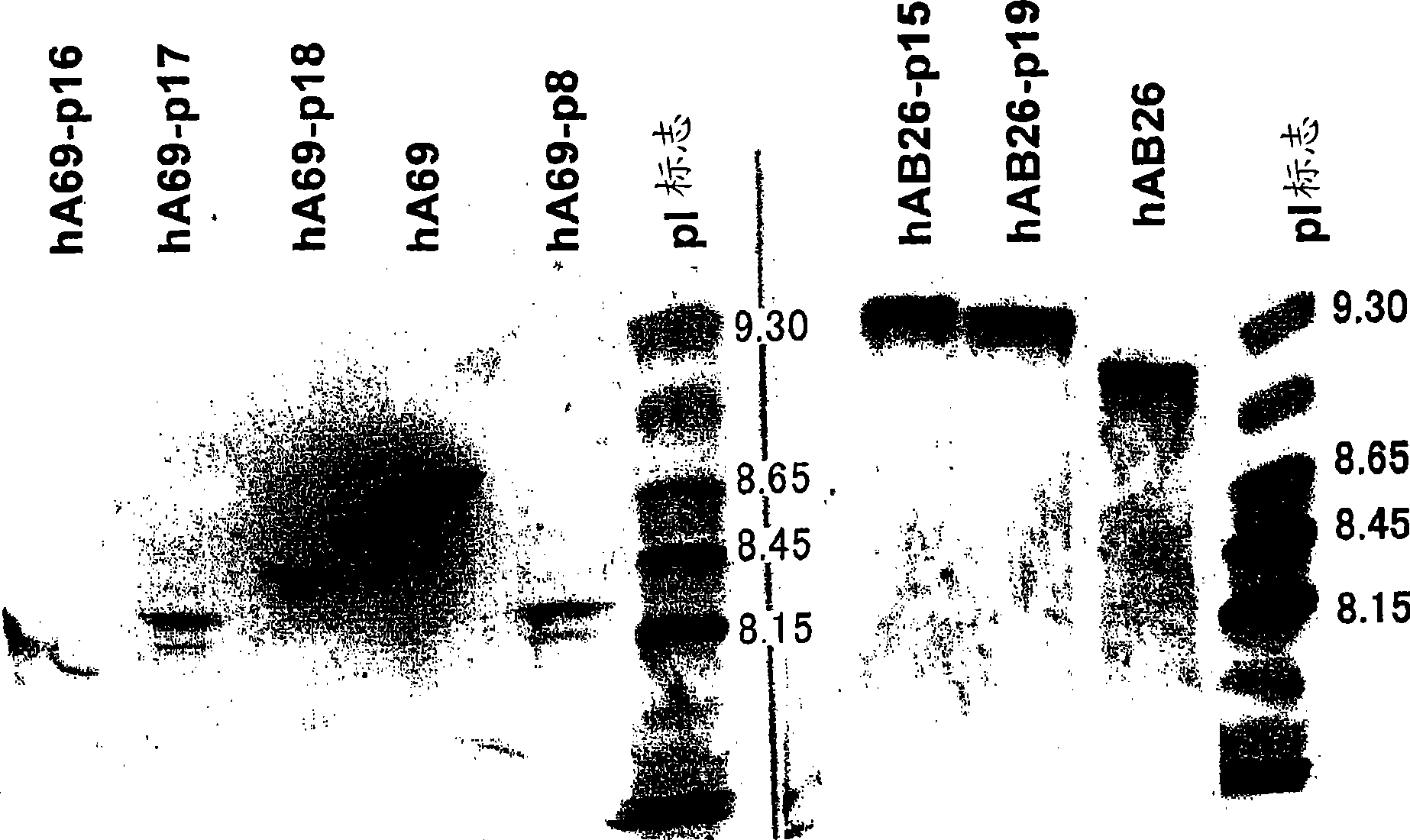
The present inventors devised methods for efficiently purifying bispecific antibodies using a chromatography column based on the difference in isoelectric points between the H chains of two types of antibodies, wherein the difference is introduced by modifying the amino acids present on the surface of the antibody variable regions of two types of antibodies that constitute a bispecific antibody. Furthermore, the inventors devised methods for efficiently purifying bispecific antibodies using a chromatography column by linking respective antigen binding sites (heavy chain variable regions) to the antibody constant regions having different isoelectric points, and then coexpressing these antibodies.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Bispecific antibodies
ActiveUS7235641B2Improve productivityImprove efficiencyAntipyreticAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBispecific antibodyImmune effector cell
Owner:AMGEN RES (MUNICH) GMBH
Optimized antibody variable regions
Owner:XENCOR INC
Methods of constructing camel antibody libraries
InactiveUS7371849B2Deleterious effect can be avoidedAvoid developmentPeptide librariesSugar derivativesSolubilityAntigen
The present invention provides camel antibody libraries that maintain in vivo diversity of camelid antibody variable region genes. The in vivo diversity of antibody variable region genes can be accomplished by, for example, mixing genes derived from a plurality of animals or modifying gene amplification conditions. Conventional methods yield only VHHs with limited repertoire diversity. However, the present invention provides libraries comprising genes encoding functional VHHs with sufficient repertoire size. According to the present invention, libraries that enable to freely obtain VHHs against arbitrary antigens are provided. VHHs have excellent solubility and stability, and show a reactivity that usually cannot be expected from tetrameric IgGs.
Owner:INST FOR ANTIBODIES
Methods of optimizing antibody variable region binding affinity
InactiveUS6849425B1Immunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsHybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody variable regionAvidity
The invention provides a method of conferring donor CDR binding affinity onto an antibody acceptor variable region framework. The invention also provides a method of simultaneously grafting and optimizing the binding affinity of a variable region binding fragment. A method of optimizing the binding affinity of an antibody variable region is also provided.
Owner:IXSYS
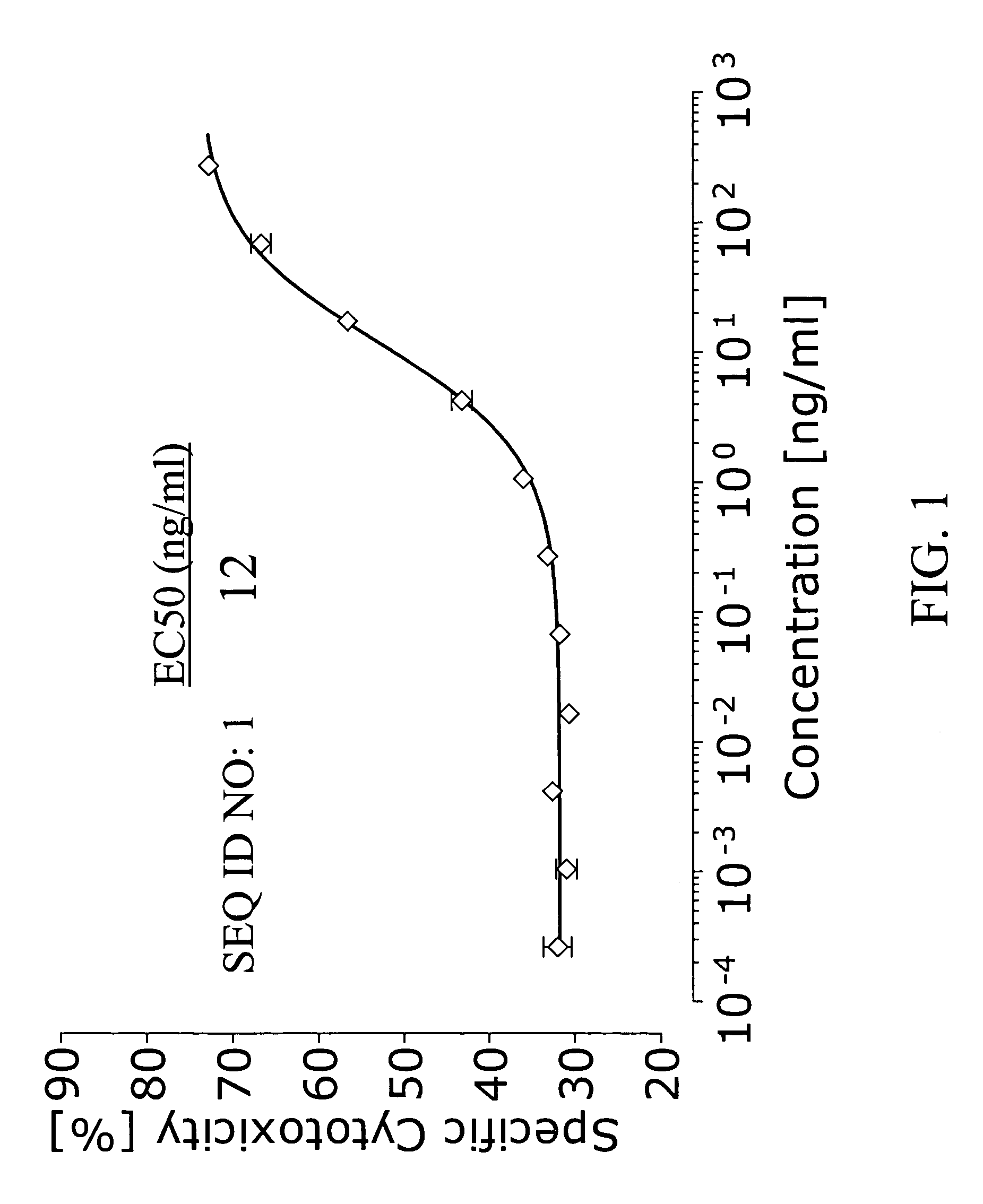
Aflatoxin nano antibody gene pool, construction method and application of aflatoxin nano antibody gene pool as well as aflatoxin B1 nano antibody 2014AFB-G15
ActiveCN103866401AEasy to buildResistant to organic reagentsImmunoglobulins against fungi/algae/lichensBiological testingGene poolAntibody variable region
The invention relates to an aflatoxin nano antibody gene pool, a construction method and application of the aflatoxin nano antibody gene pool as well as an aflatoxin B1 nano antibody 2014AFB-G15. The aflatoxin nano antibody gene pool is prepared by extracting RNA (ribonucleic acid) in alpaca blood after immunization of an aflatoxin B1 antigen, performing specific amplification on a variable region gene of an alpaca heavy chain antibody by adopting an RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) method to obtain an aflatoxin nano antibody VHH gene, and then performing transformation after connecting with a pCANTAB5E (his) vector. The aflatoxin B1 nano antibody 2014AFB-G15 obtained by screening, disclosed by the invention, has the characteristics of organic reagent resistance, high temperature resistance and the like, and is good in stability; the IC50 (half maximal inhibitory concentration) of the aflatoxin B1 nano antibody 2014AFB-G15 to the aflatoxin B1 is 0.66ng / mL, and the cross reactivity of the aflatoxin B1 nano antibody 2014AFB-G15 to the aflatoxins B2, G1,G2 and M1 is 22.6%, 0.95%, 32.1% and 26% respectively.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
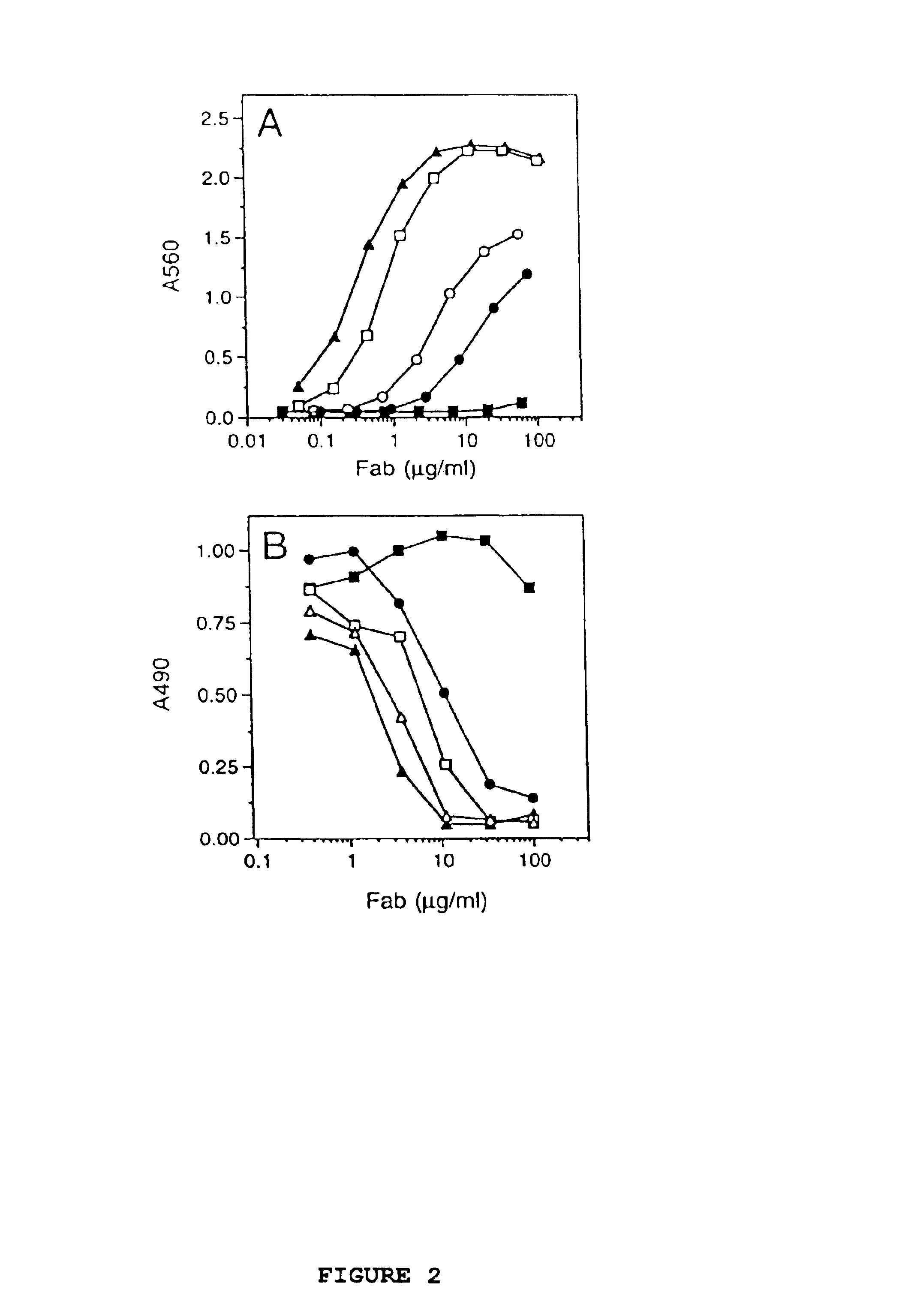
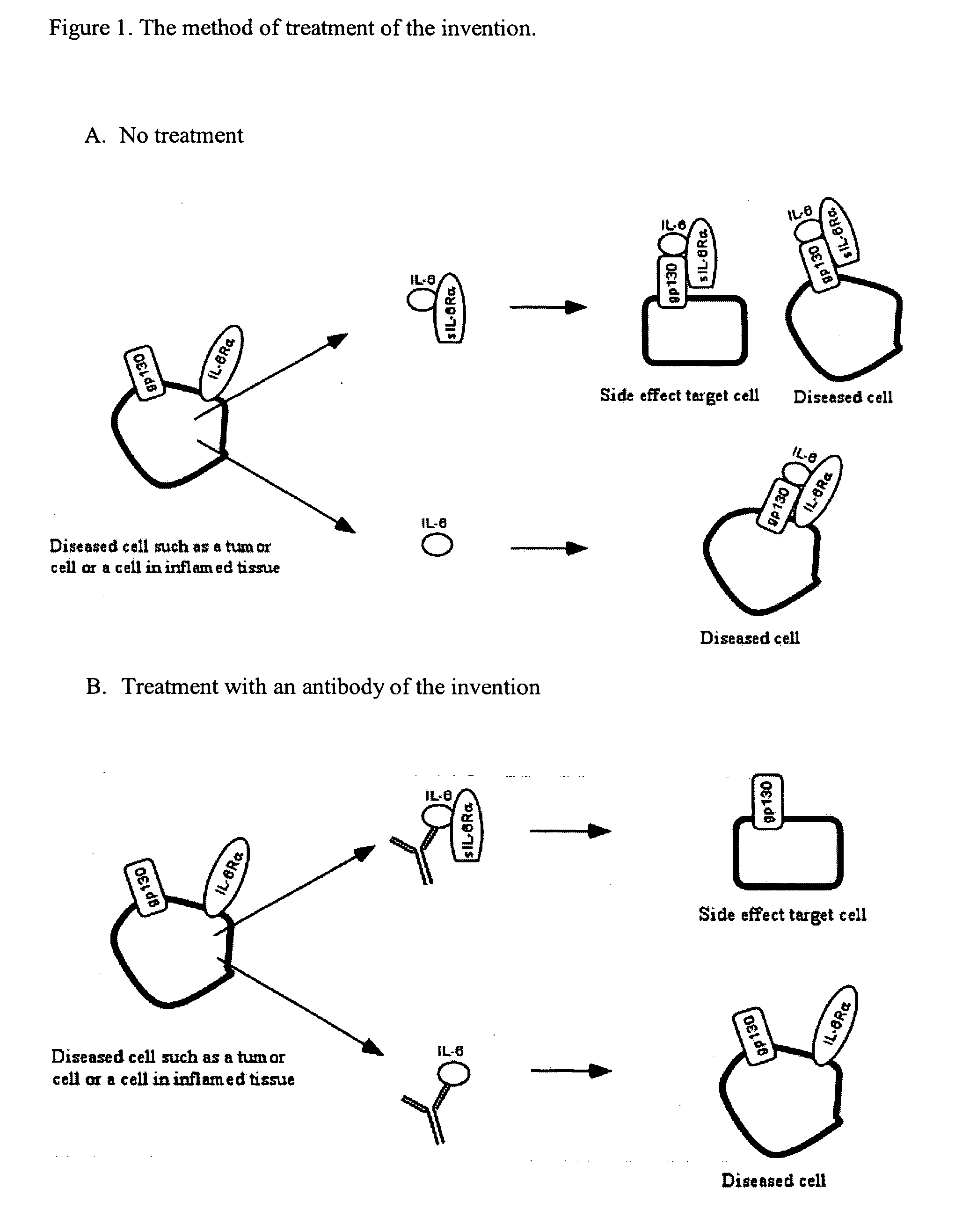
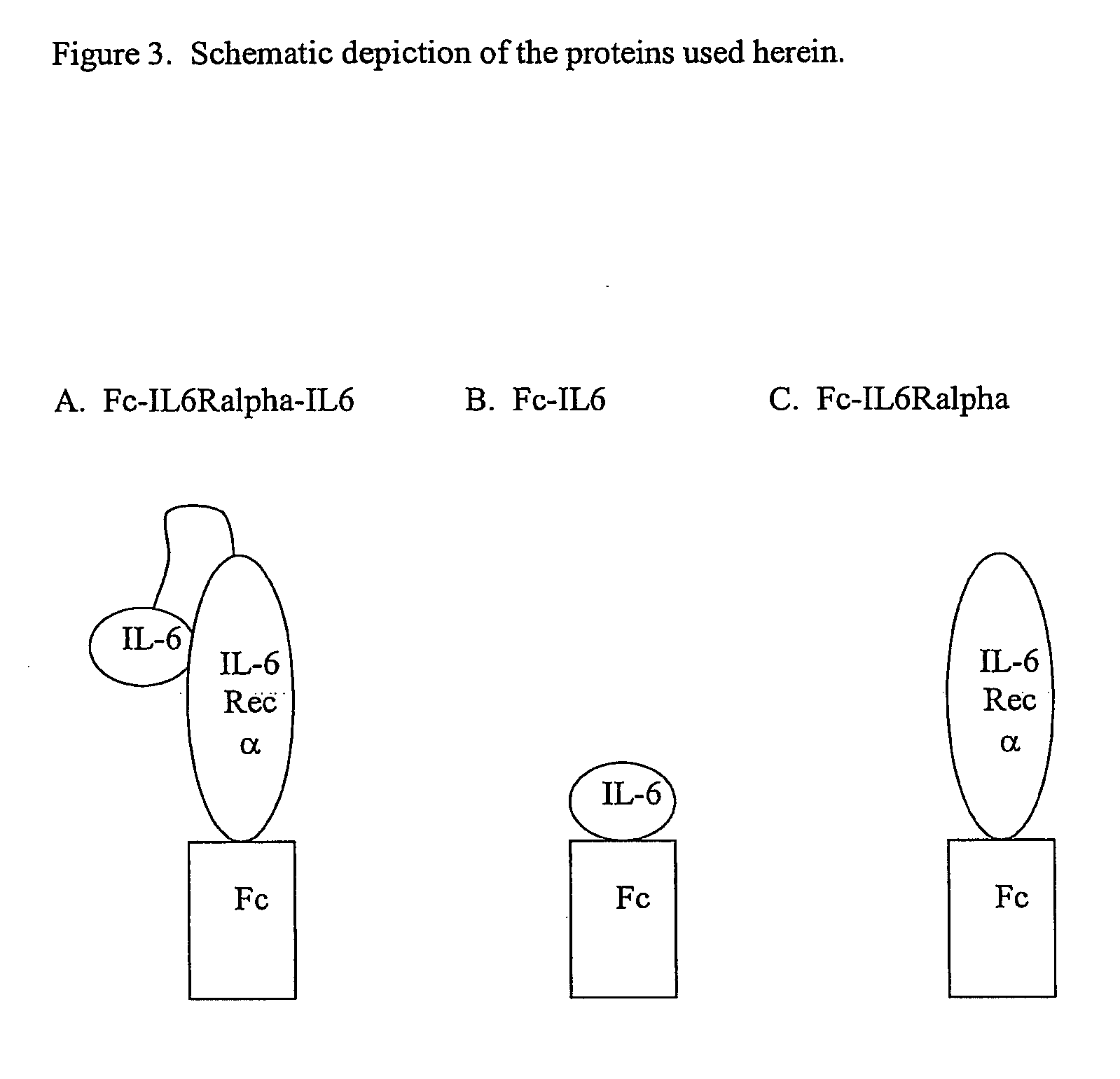
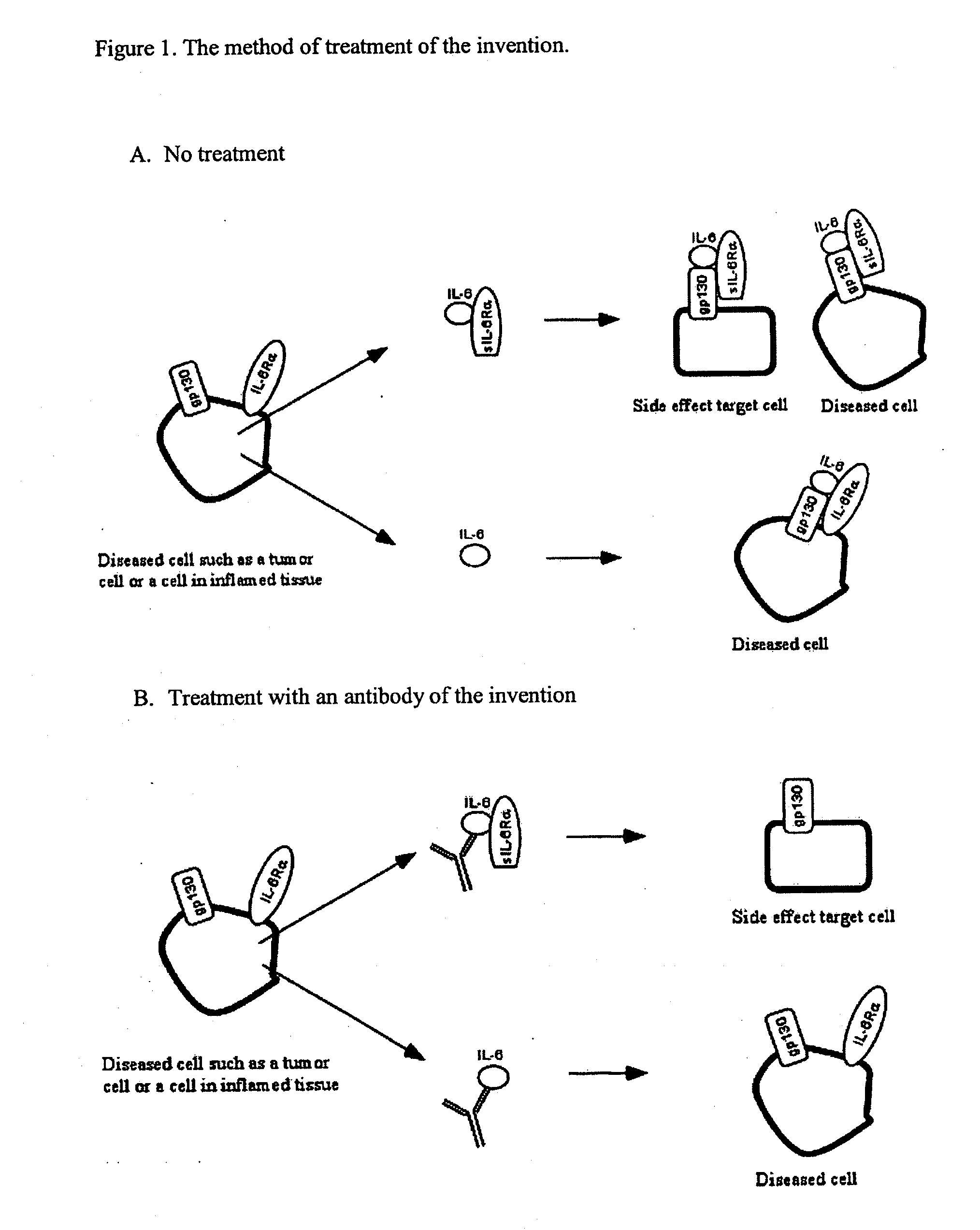
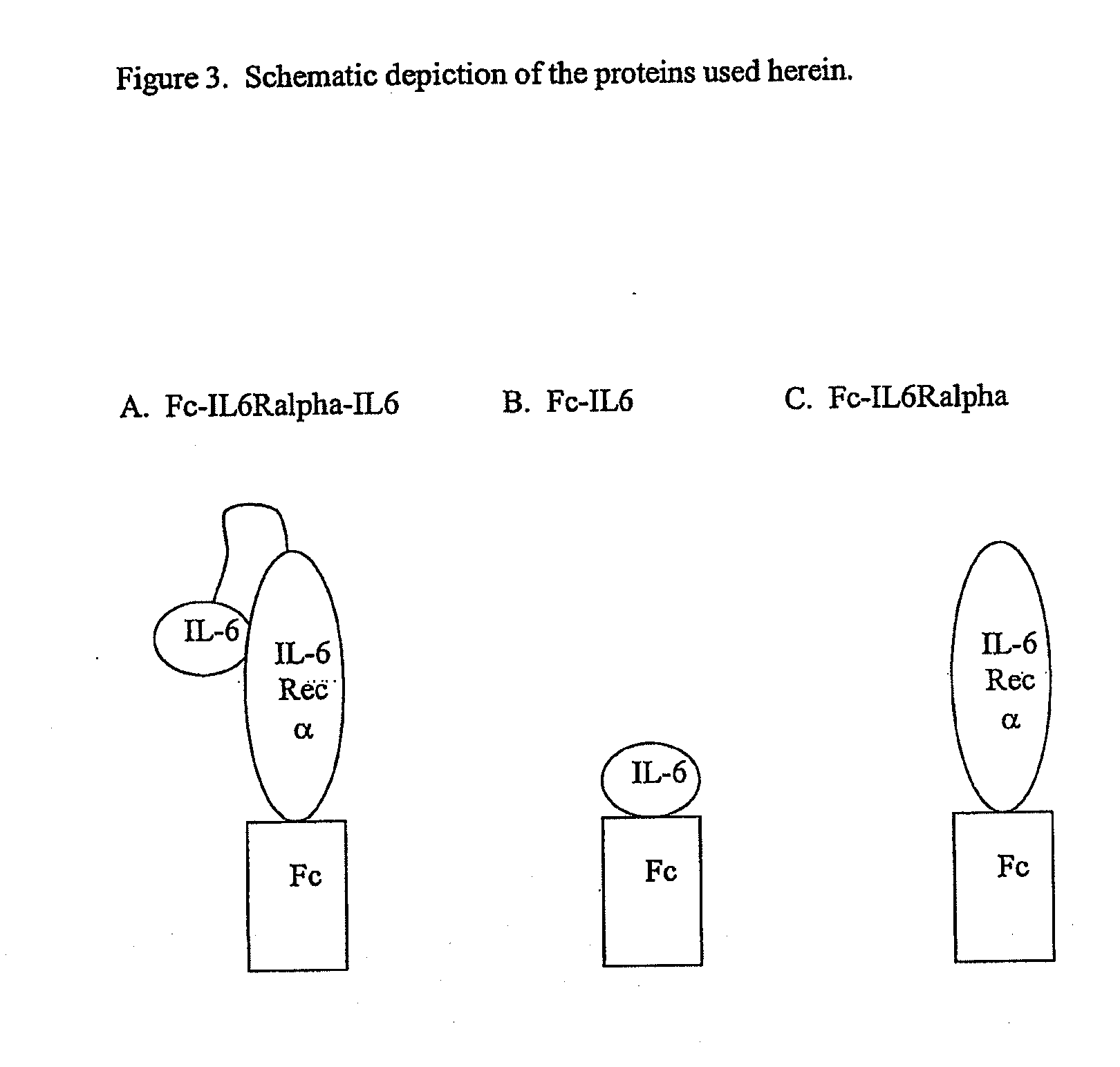
Interleukin-6 antagonists
InactiveUS20070178098A1Avoid interactionPromote formationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsInterleukin 6Antagonist
The present invention provides an isolated IL-6 antagonist including an antibody variable region that prevents IL-6 from binding to gp130. The present invention also provides compositions and methods for treating IL-6 related diseases based on the IL-6 antagonists of the invention.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
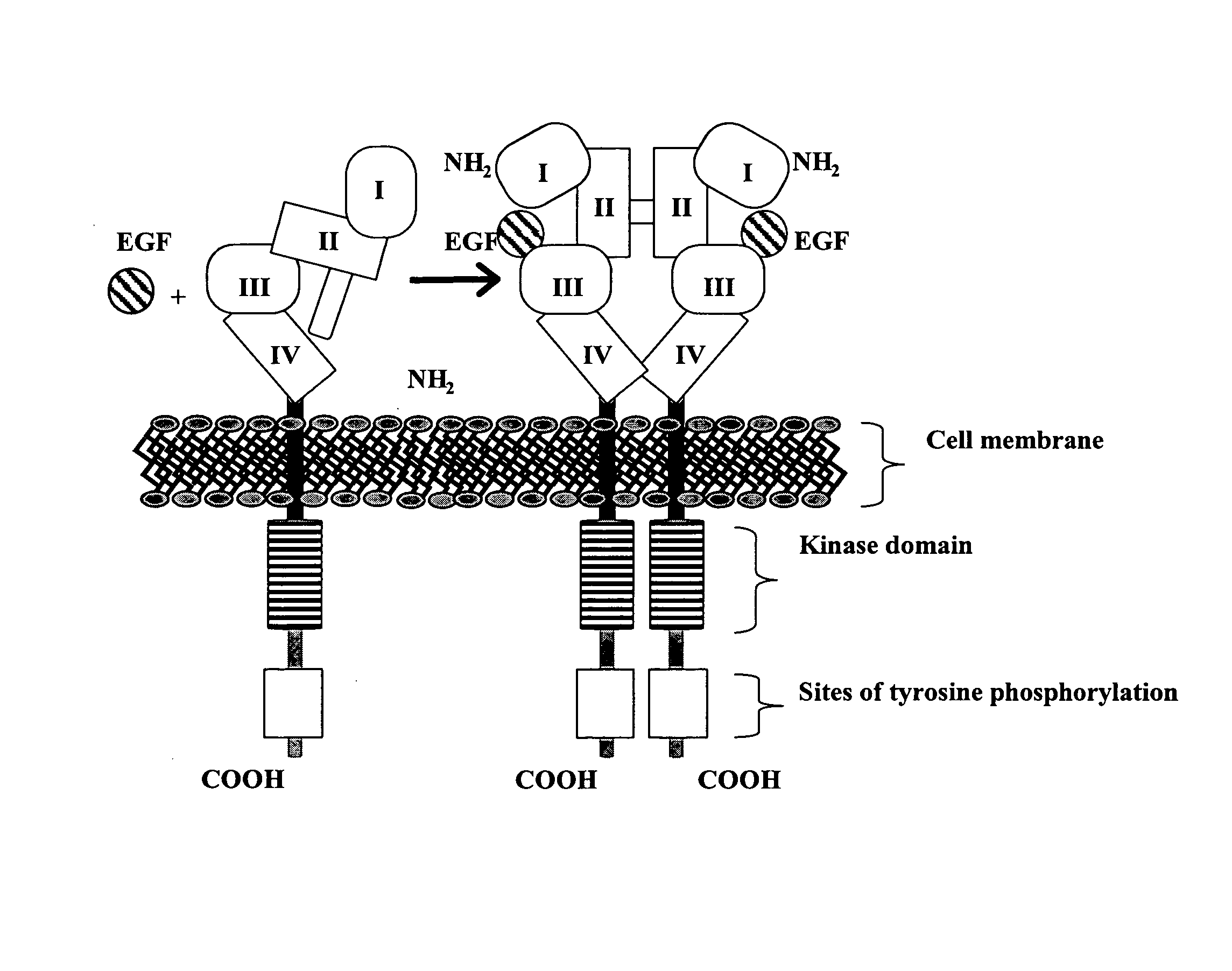
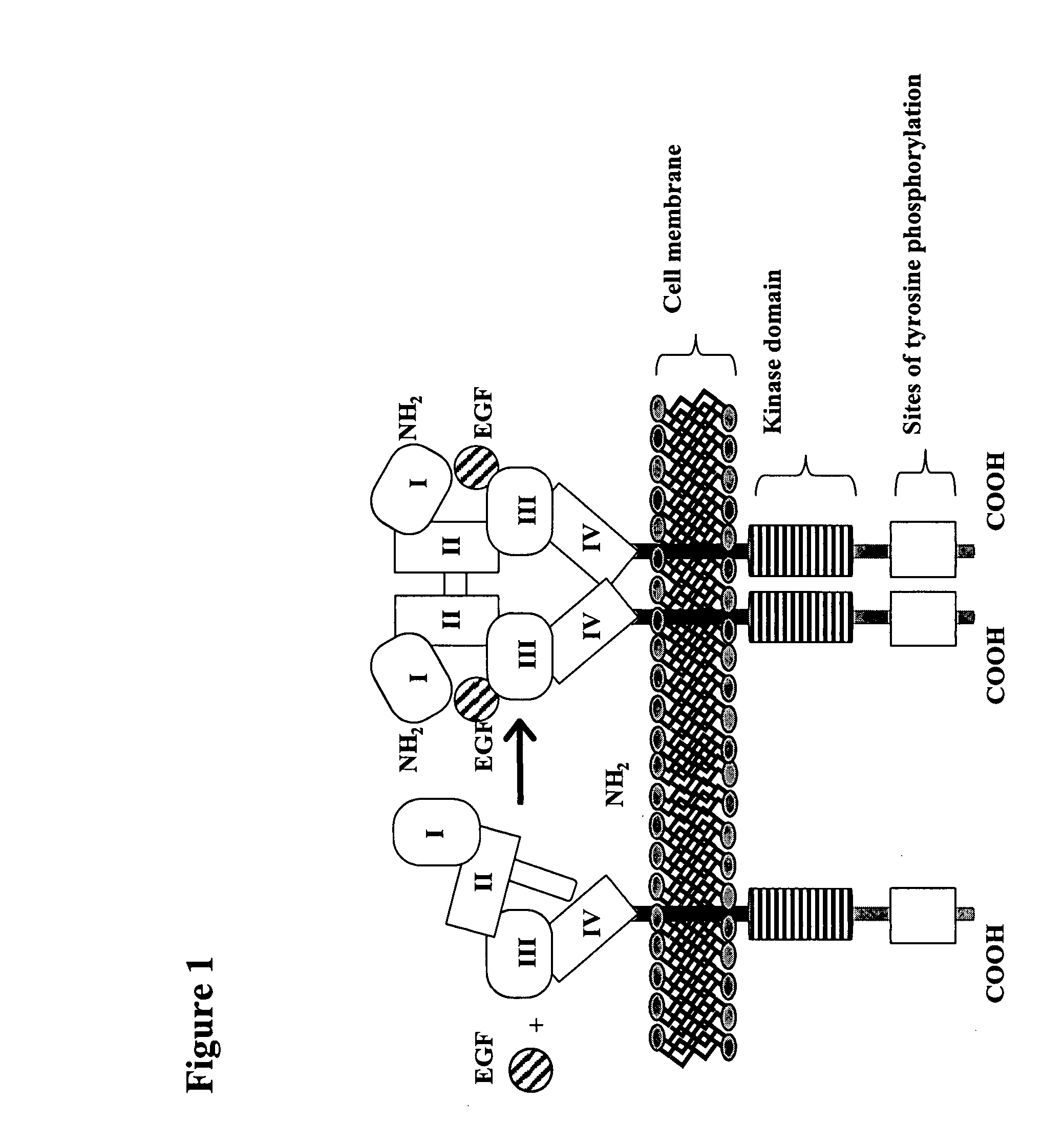
Treatment of tumors expressing mutant EGF receptors
InactiveUS20070274991A1Shrink tumorSlowing and preventing in size of tumorAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsEpitopeWilms' tumor
The invention discloses methods of treatment of tumors that express oncogenic forms of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), such as EGFRvIII. The methods include testing of cancer patients for expression of EGFRvIII in their tumors, followed by treatment with a protein that contains antibody variable regions that recognize specific epitopes on the surface of the EGFR.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
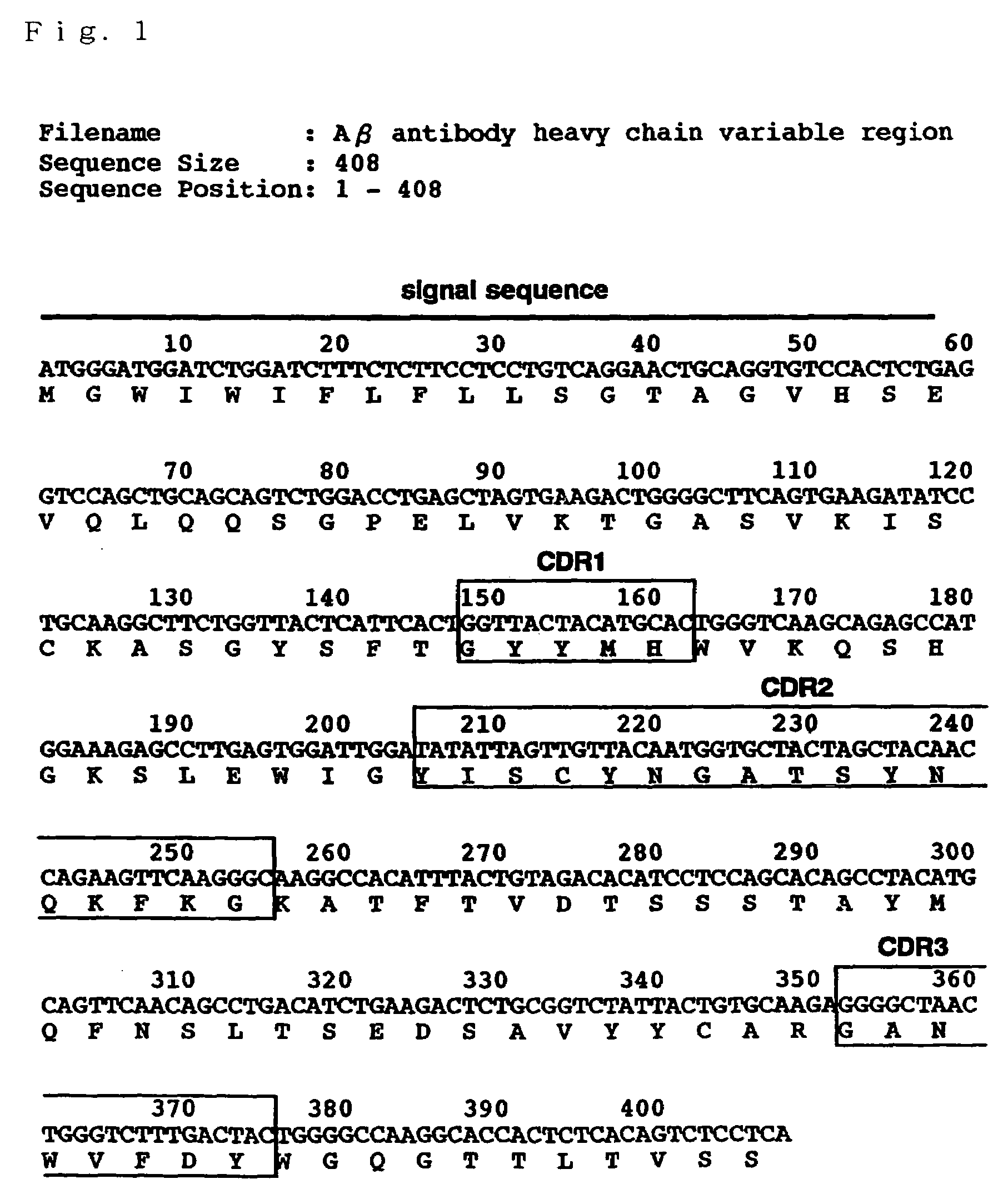
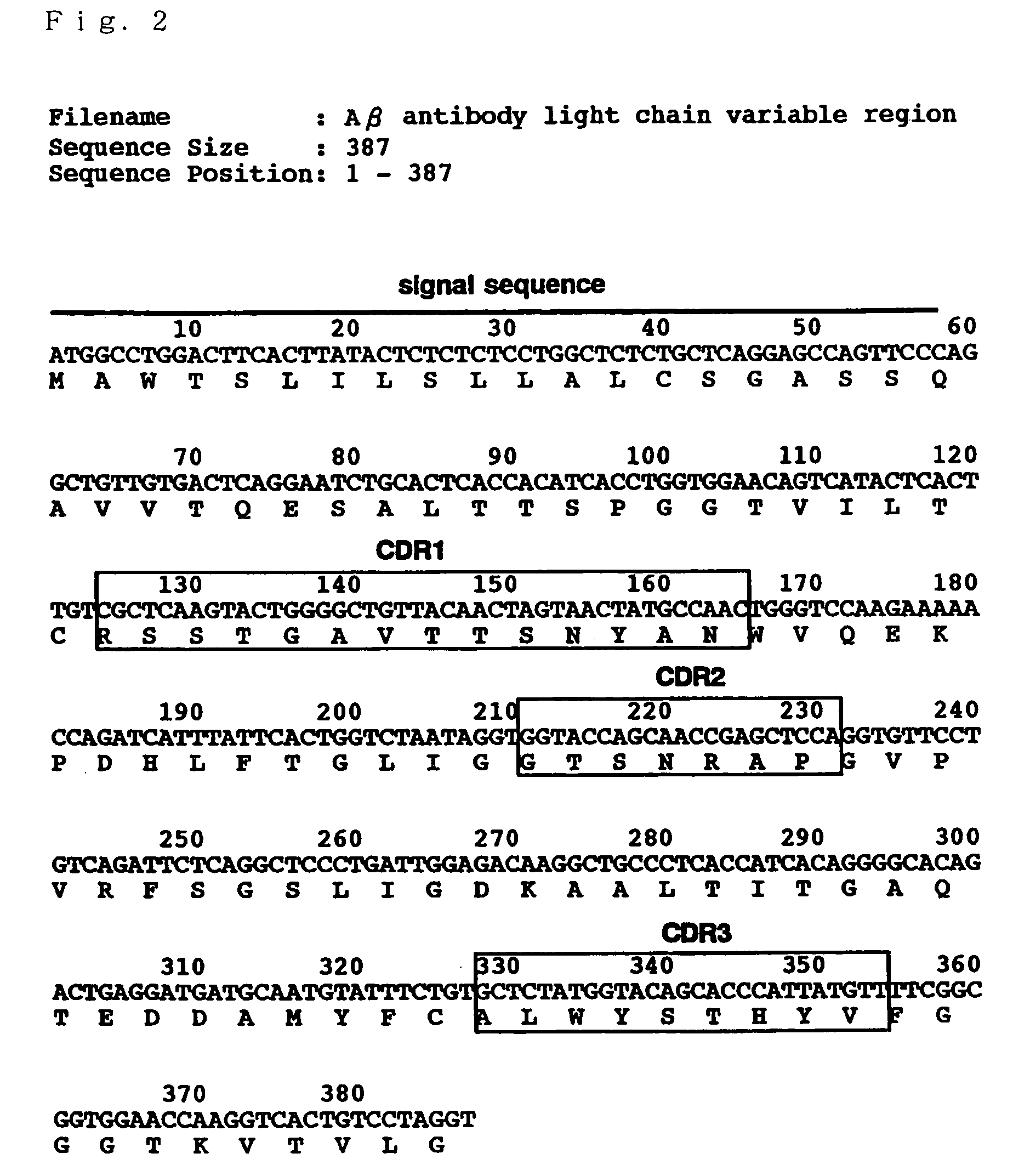
Antibody recognizing GM1 ganglioside-bound amyloid beta-protein and DNA encoding the antibody
InactiveUS7339035B2Effective diagnosisEffective treatmentImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsAmyloid betaGm1 ganglioside
It is intended to provide an antibody efficacious in diagnosing, preventing or treating Alzheimer's disease, DNA encoding the antibody, a method of screening a drug and drugs. The amino acid sequence and the gene sequence of the variable region of an antibody, which specifically recognizes a GM1 ganglioside-bound amyloid β-protein occurring in the early stage of β-amyloid fibril formation, are determined. Based on the data of the amino acid sequence and the gene sequence thus obtained, an antibody is designed.
Owner:MEDICAL & BIOLOGICAL LAB CO LTD +2
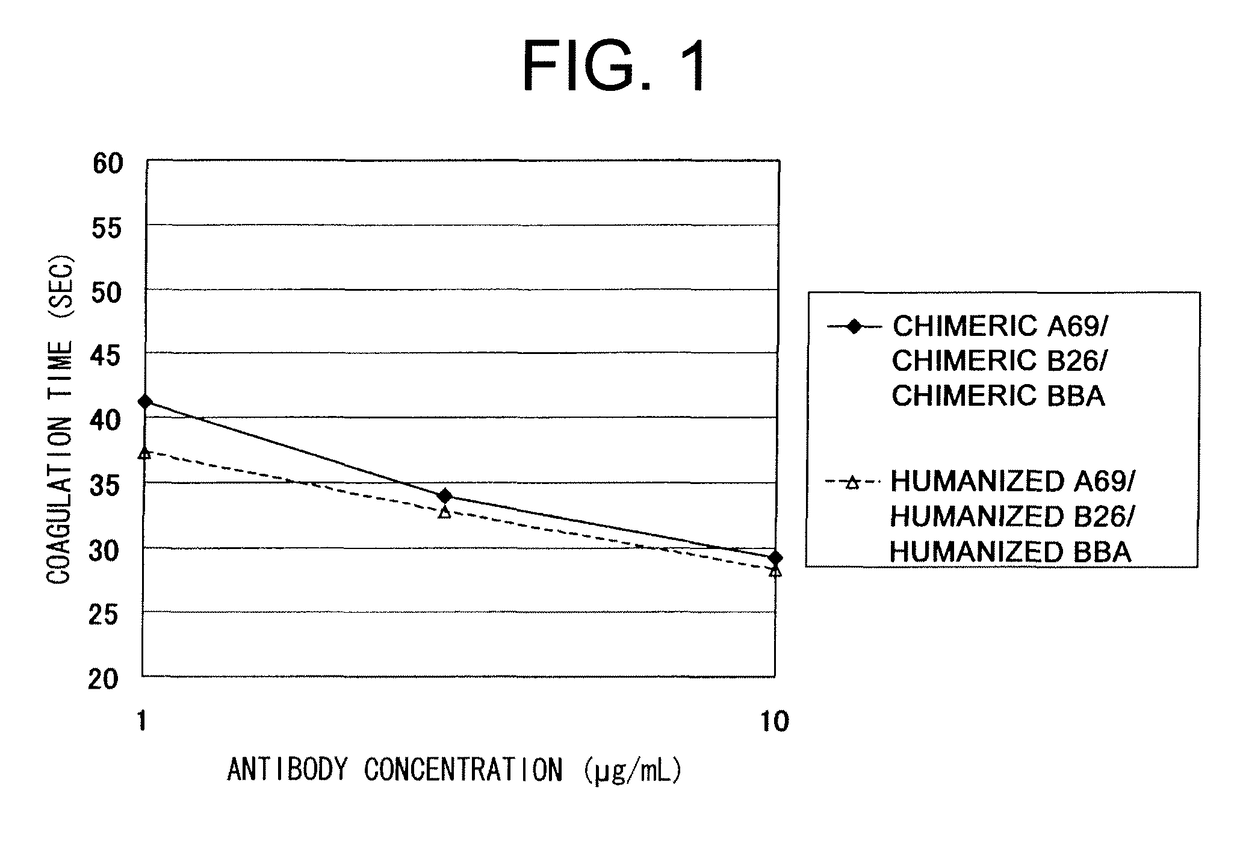
Process for producing humanized chimera antibody
InactiveUS20020026036A1Easy to produceEasy constructionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsRestriction enzyme digestionSynthetic DNA
A process for the production of humanized chimera antibody, wherein the chimera antibody is produced easily without changing any of the amino acids of its mouse antibody variable region, which comprises the steps of: (1) constructing a cassette vector by inserting a cDNA coding for a heavy chain constant region of human antibody into an expression vector for animal cell use and establishing a cloning site in the upstream region of the heavy chain constant region of said cassette vector for inserting a cDNA which encodes a heavy chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody; (2) digesting a cDNA coding for the heavy chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody with restriction enzymes; (3) inserting said cDNA coding for the heavy chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody into the cassette vector, using a synthetic DNA which comprises a base sequence corresponding to the 5'-end side of said heavy chain constant region of human antibody and a base sequence corresponding to the 3'-end side of said heavy chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody and is possessed of the restriction enzyme recognition sites on both of its ends, thereby constructing a humanized chimera antibody heavy chain expression vector in which said cDNA coding for the heavy chain constant region of human antibody and said cDNA coding for the heavy chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody are linked together through said synthetic DNA; (4) constructing a cassette vector by inserting a cDNA coding for a light chain constant region of human antibody into an expression vector for animal cell use and establishing a cloning site in the upstream region of the light chain constant region of said cassette vector for inserting a cDNA which encodes a light chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody; (5) digesting a cDNA coding for the light chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody with restriction enzymes; (6) inserting said cDNA coding for a light chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody into the cassette vector using a synthetic DNA which comprises a base sequence corresponding to the 5'-end side of said light chain constant region of human antibody and a base sequence corresponding to the 3'-end side of said light chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody and is possessed of the restriction enzyme recognition sites on both of its ends, thereby constructing a humanized chimera antibody light chain expression vector in which said cDNA coding for the light chain constant region of human antibody and said cDNA coding for the light chain variable region of nonhuman animal antibody are linked together through said synthetic DNA; (7) introducing these expression vectors into host cells to obtain a transformant; and (8) culturing said transformant in an appropriate culture medium, thereby allowing the transformant to produce and accumulate a humanized chimera antibody, and collecting said humanized chimera antibody from the resulting culture broth.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
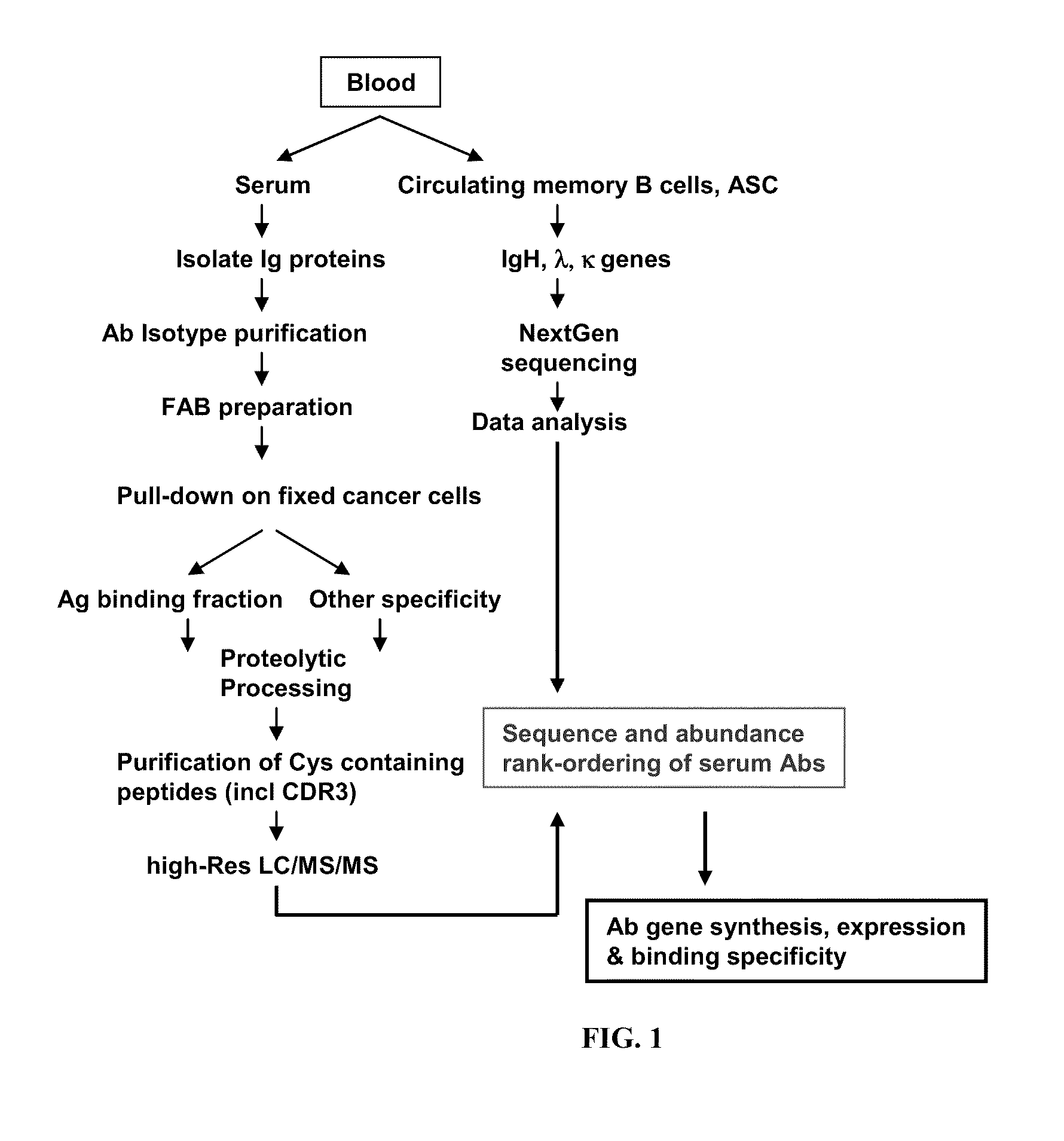
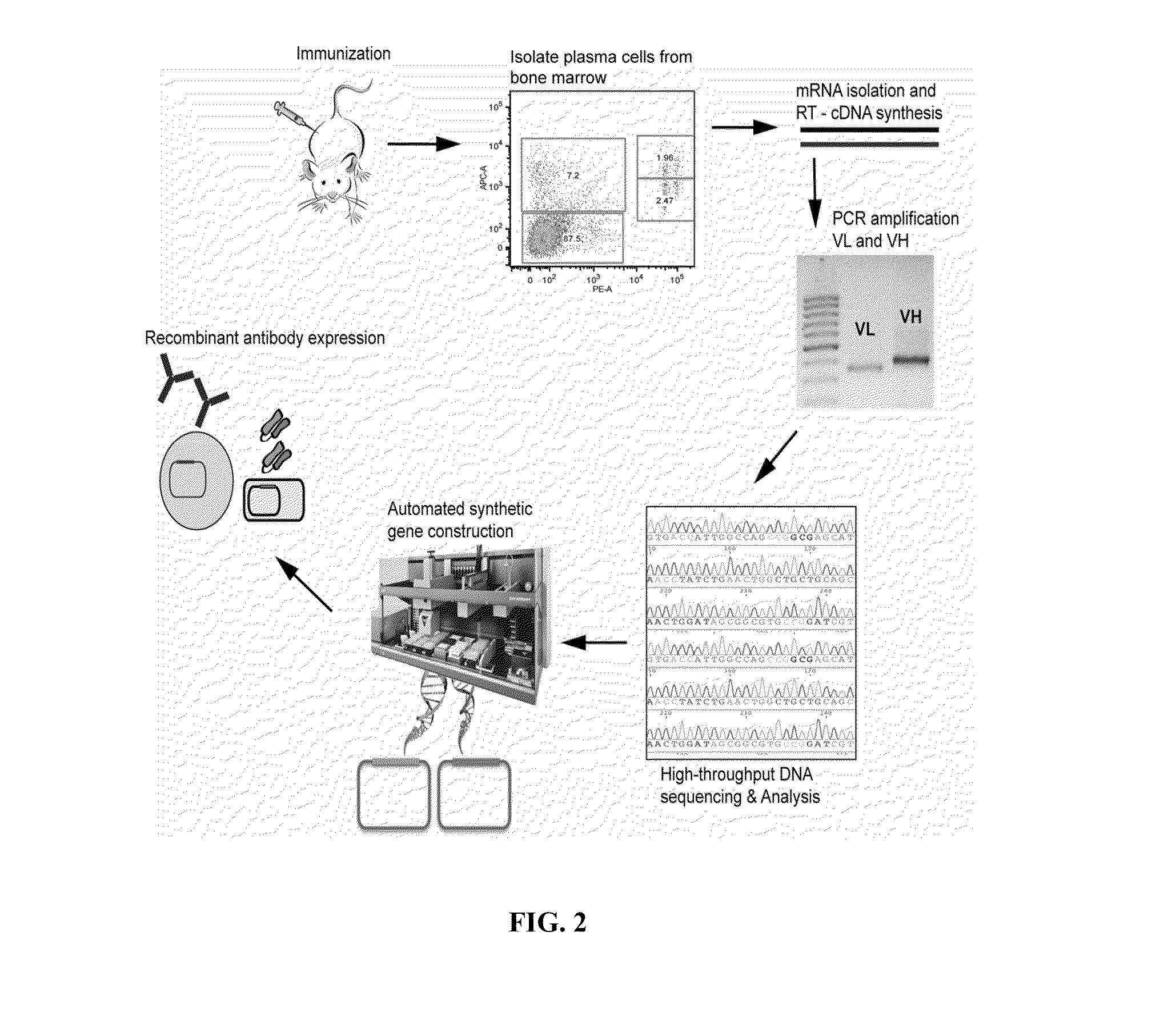
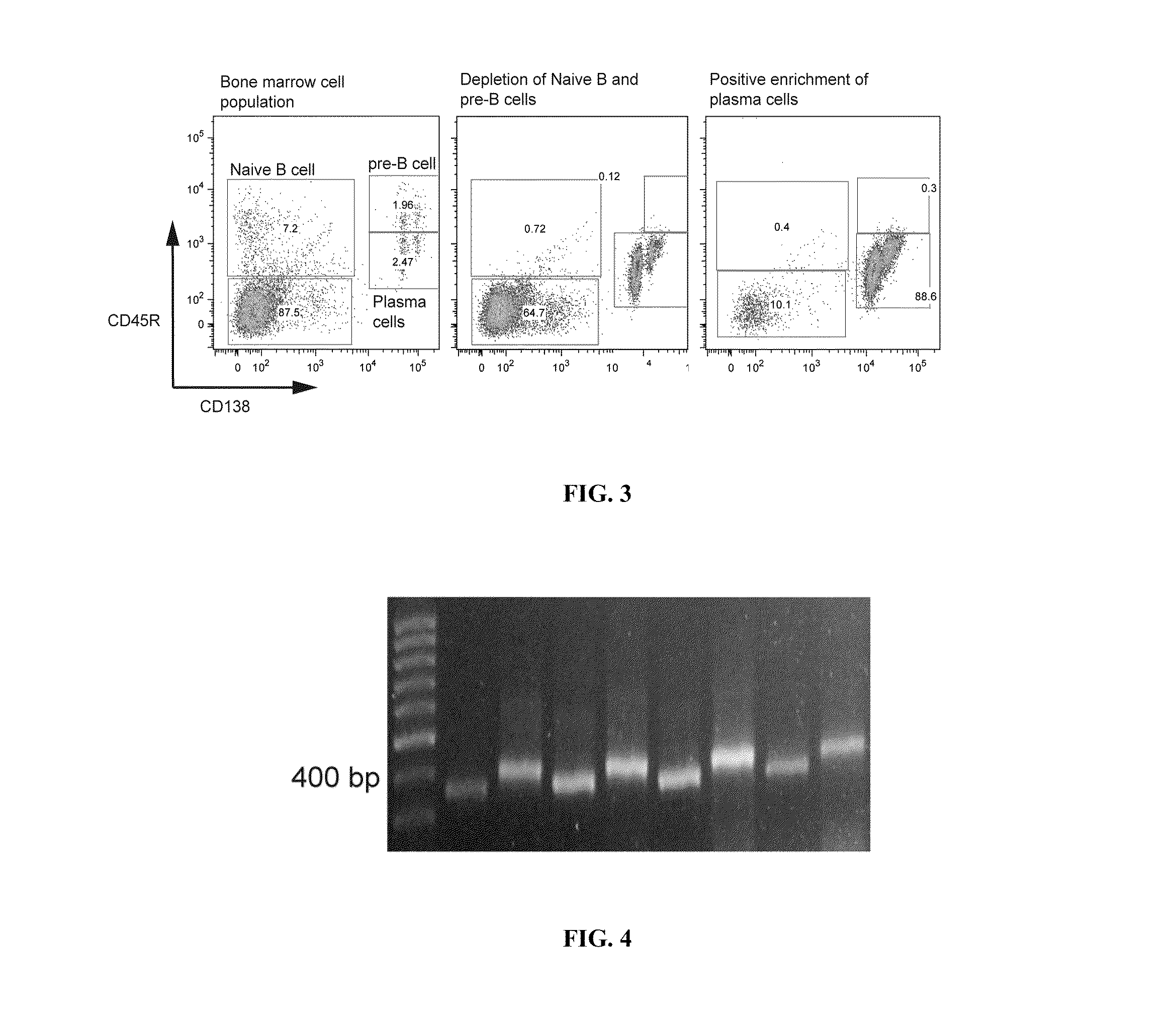
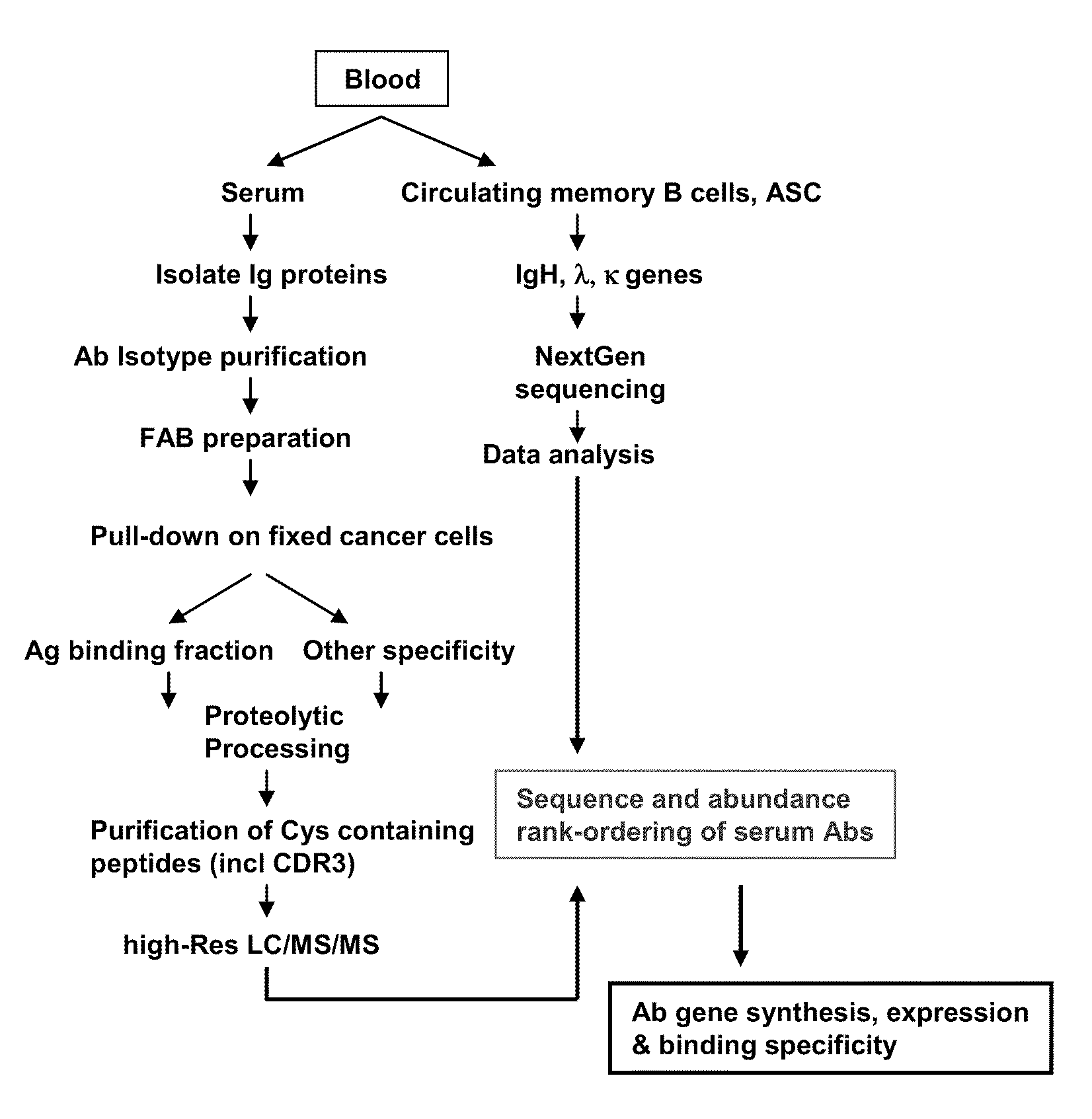
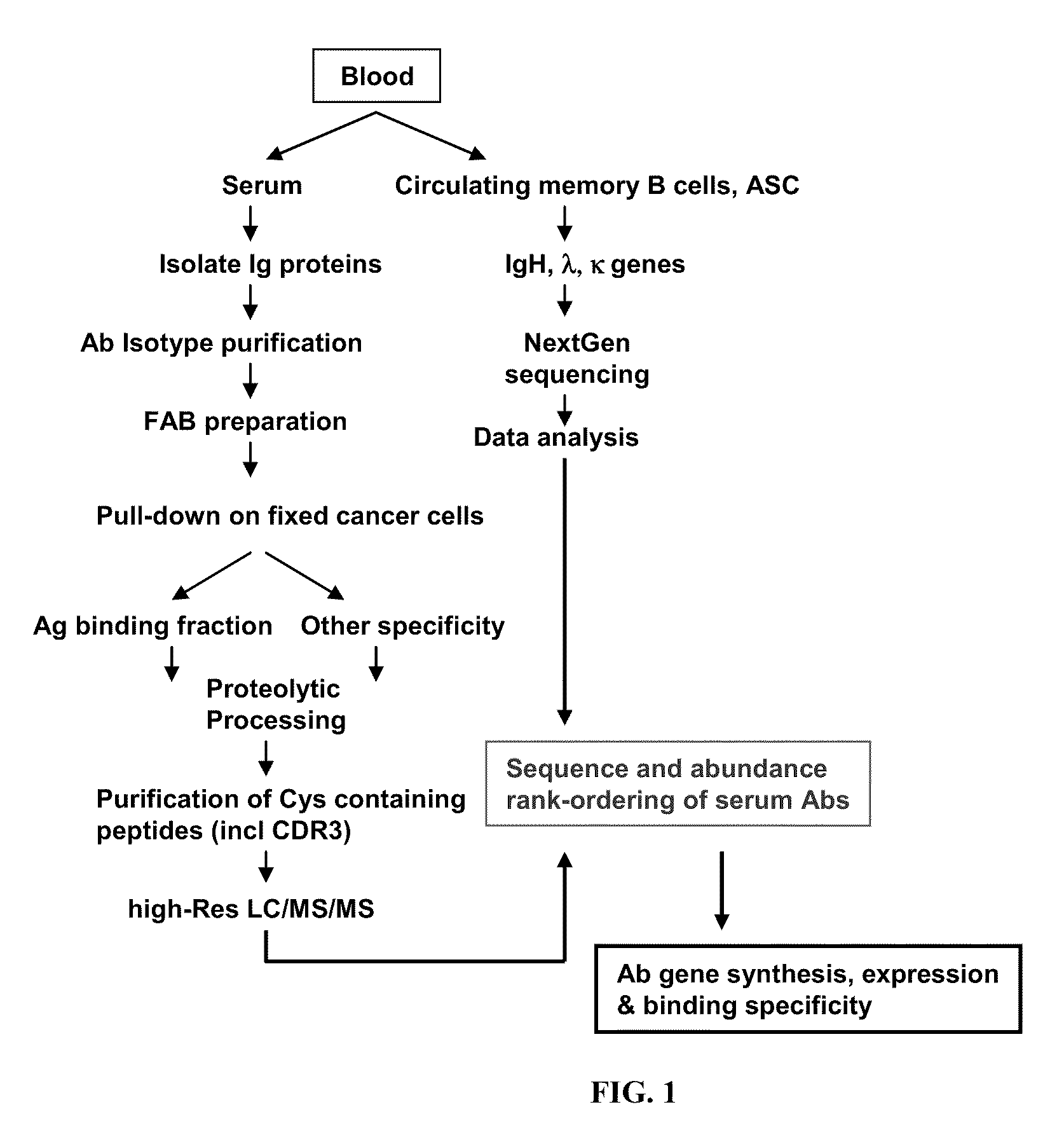
Rapid Isolation of Monoclonal Antibodies from Animals
ActiveUS20110312505A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningSerum igeAntigen Binding Fragment
Methods and compositions for identification of candidate antigen-specific variable regions as well as generation of antibodies or antigen-binding fragments that could have desired antigen specificity are provided. For example, in certain aspects methods for determining amino acid sequences of serum antibody CDR and abundancy level are described. In some aspects, methods for determining nucleic acid sequences of antibody variable region sequences and frequency are provided. Furthermore, the invention provides methods for identification and generation of antibody or antigen-binding fragments that comprise highly-represented CDR.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Super humanized antibodies
InactiveUS20050261480A1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHuman sequenceHumanized antibody
Disclosed herein are methods for humanizing antibodies based on selecting variable region framework sequences from human antibody genes by comparing canonical CDR structure types for CDR sequences of the variable region of a non-human antibody to canonical CDR structure types for corresponding CDRs from a library of human antibody sequences, preferably germline antibody gene segments. Human antibody variable regions having similar canonical CDR structure types to the non-human CDRs form a subset of member human antibody sequences from which to select human framework sequences. The subset members may be further ranked by amino acid similarity between the human and the non-human CDR sequences. Top ranking human sequences are selected to provide the framework sequences for constructing a chimeric antibody that functionally replaces human CDR sequences with the non-human CDR counterparts using the selected subset member human frameworks, thereby providing a humanized antibody of high affinity and low immunogenicity without need for comparing framework sequences between the non-human and human antibodies. Chimeric antibodies made according to the method are also disclosed.
Owner:ARROWSMITH TECH
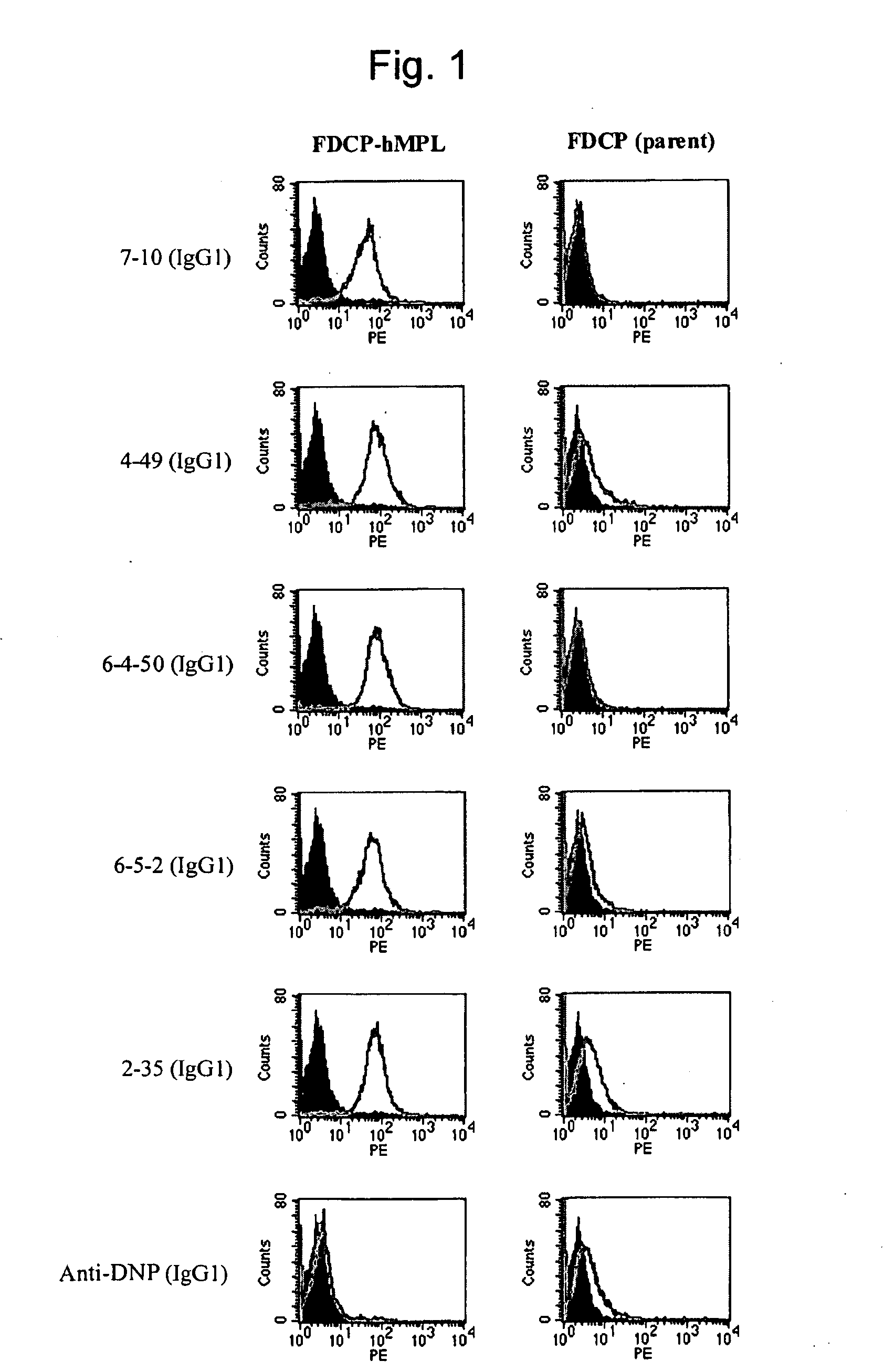
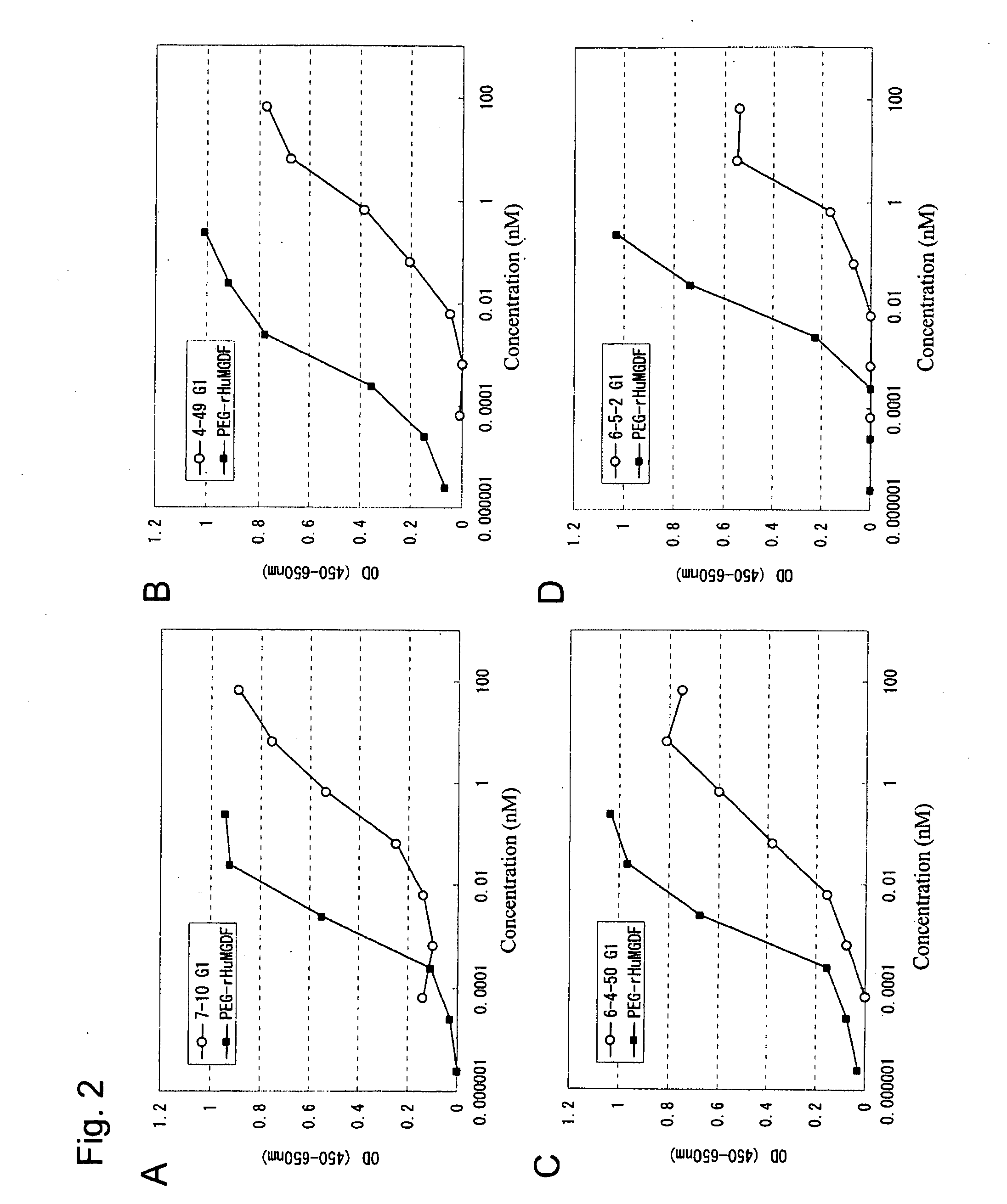
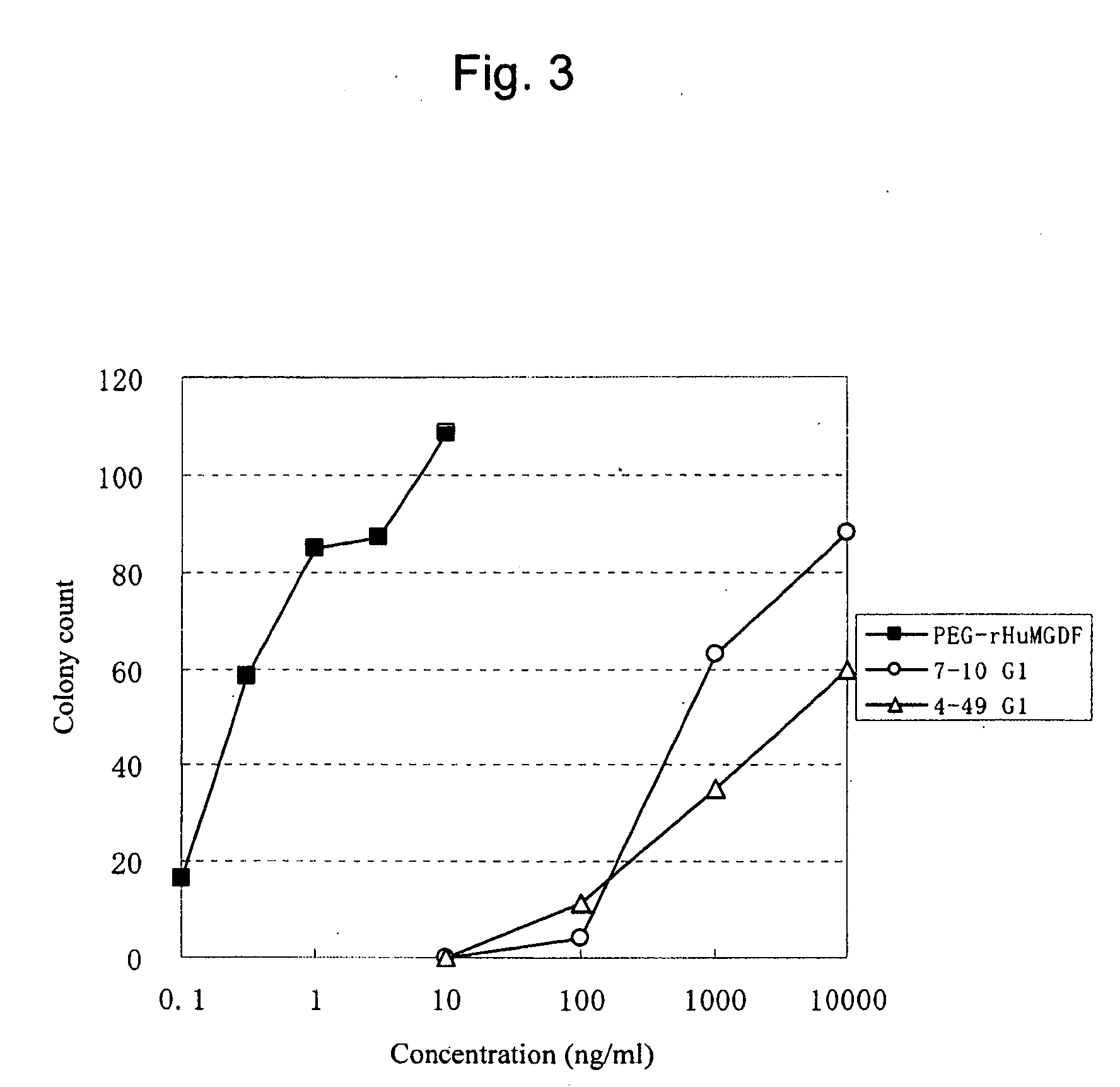
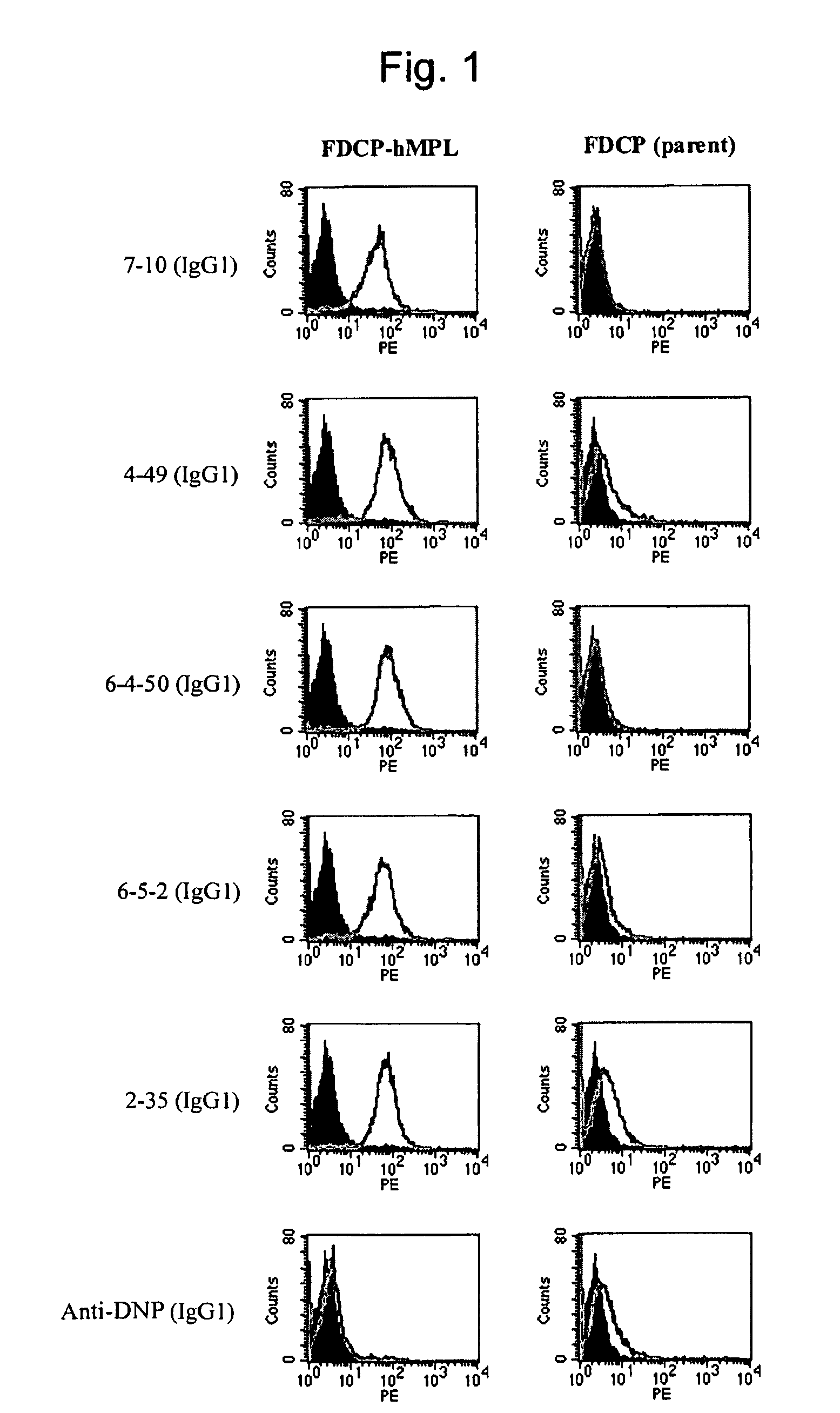
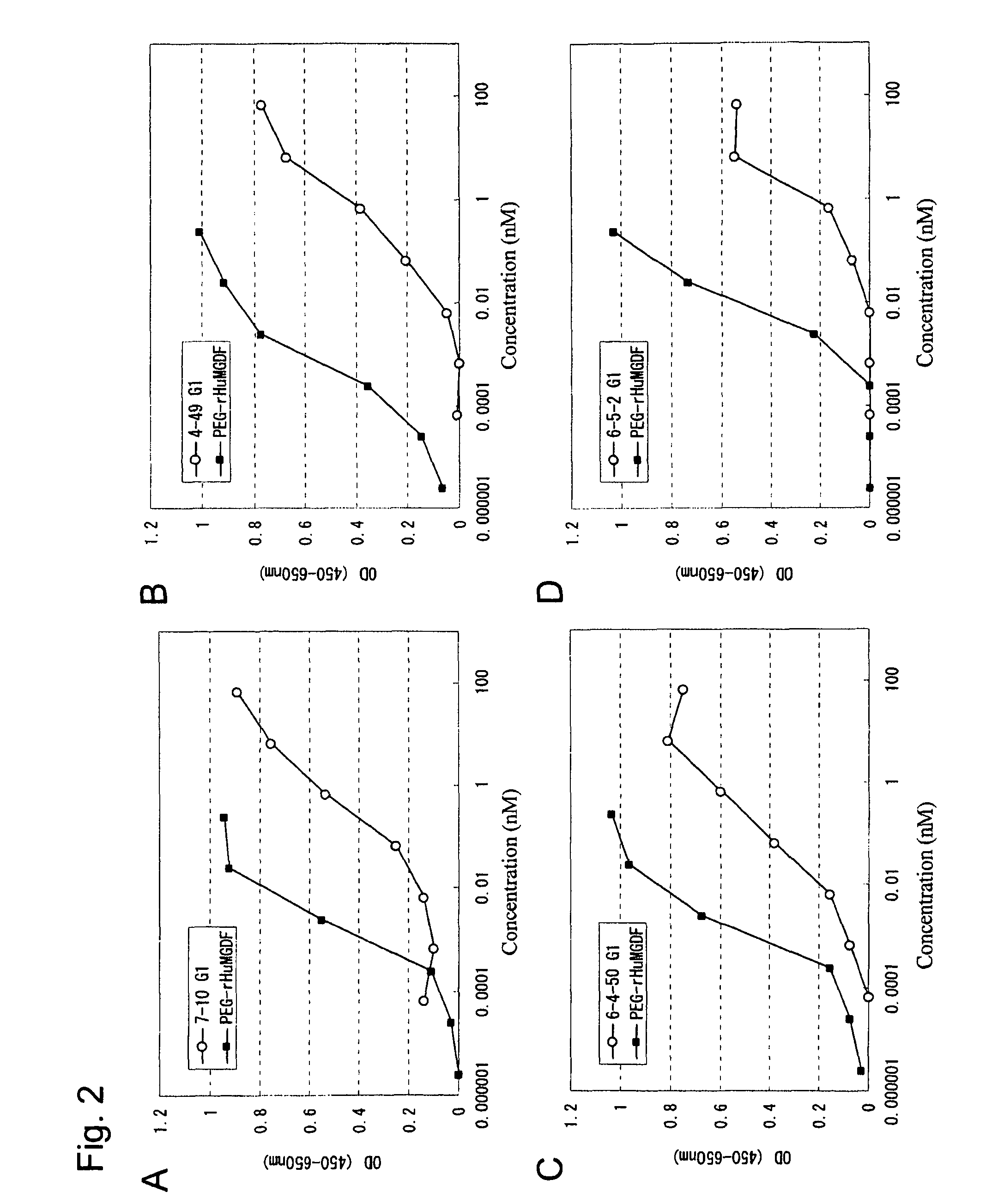
Agonist antibody to human thrombopoietin receptor
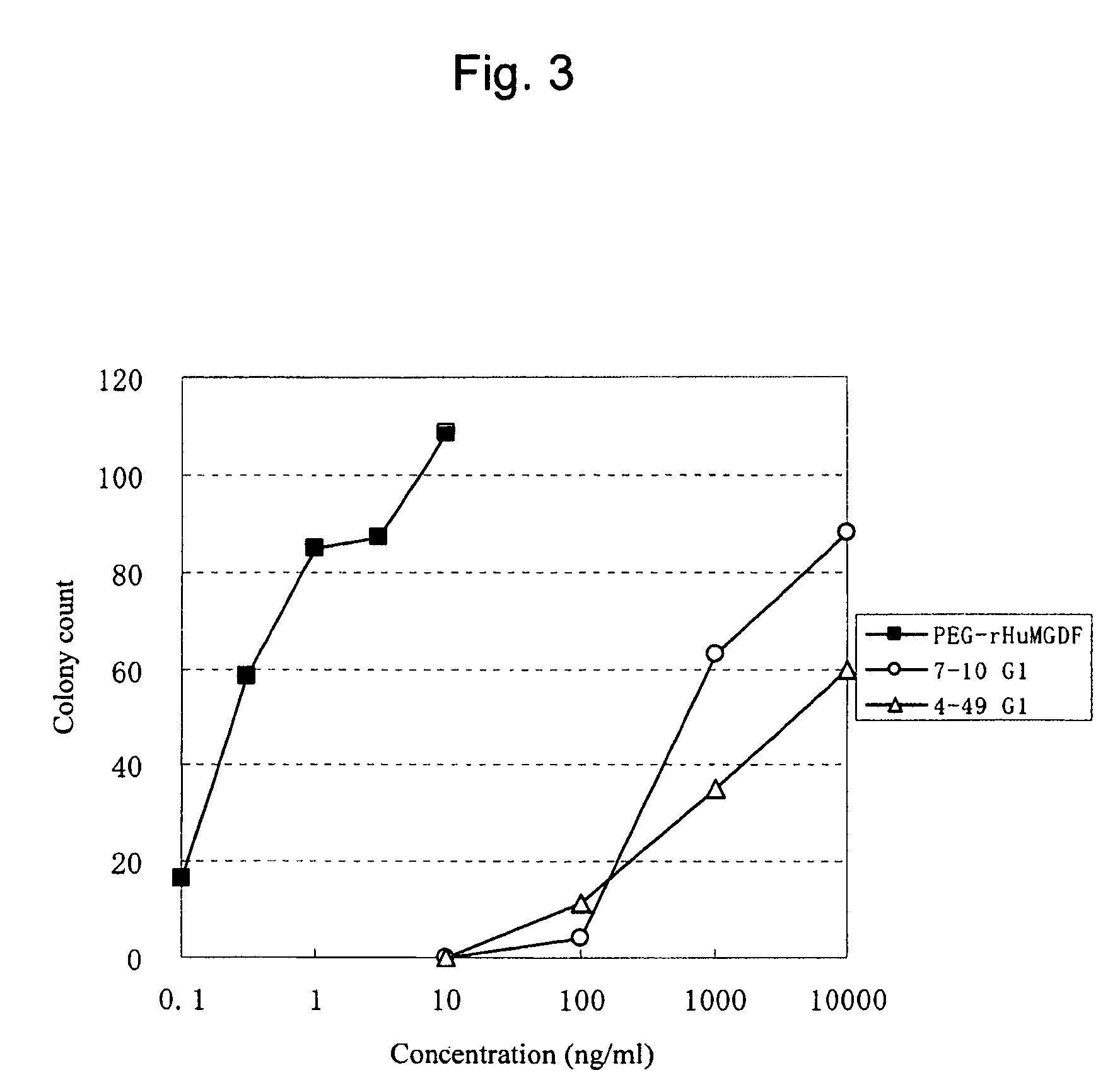
InactiveUS20100004429A1High activityLow antigenicityThrombopoietinHybrid immunoglobulinsHuman plateletUmbilical cord
This invention provides an agonist antibody to a human thrombopoietin receptor (alias: human c-Mpl). More particularly, this invention provides an agonist antibody to a human thrombopoietin receptor, wherein the agonist antibody comprises: antibody constant regions comprising (1) amino acid sequences in a heavy chain constant region and a light chain constant region of a human antibody, (2) an amino acid sequence of a heavy chain constant region with a domain substituted between human antibody subclasses, and an amino acid sequence of a light chain constant region of a human antibody, or (3) amino acid sequences comprising a deletion(s), substitution(s), addition(s), or insertion(s) of one or several amino acid residues in the amino acid sequences of (1) or (2) above; and antibody variable regions capable of binding to and activating a human thrombopoietin receptor; and wherein the agonist antibody has the properties: (a) that the antibody induces colony formation at a concentration of 10,000 ng / ml or lower as determined by the CFU-MK colony formation assay using human umbilical-cord-blood-derived CD34+ cells; and (b) that the antibody has a maximal activity at least 50% higher than that of PEG-rHuMGDF and an 50% effective concentration (EC50) of 100 nM or less in the cell proliferation assay using UT7 / TPO cell. Also provided is a pharmaceutical composition for treating thrombocytopenia comprising said antibody.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
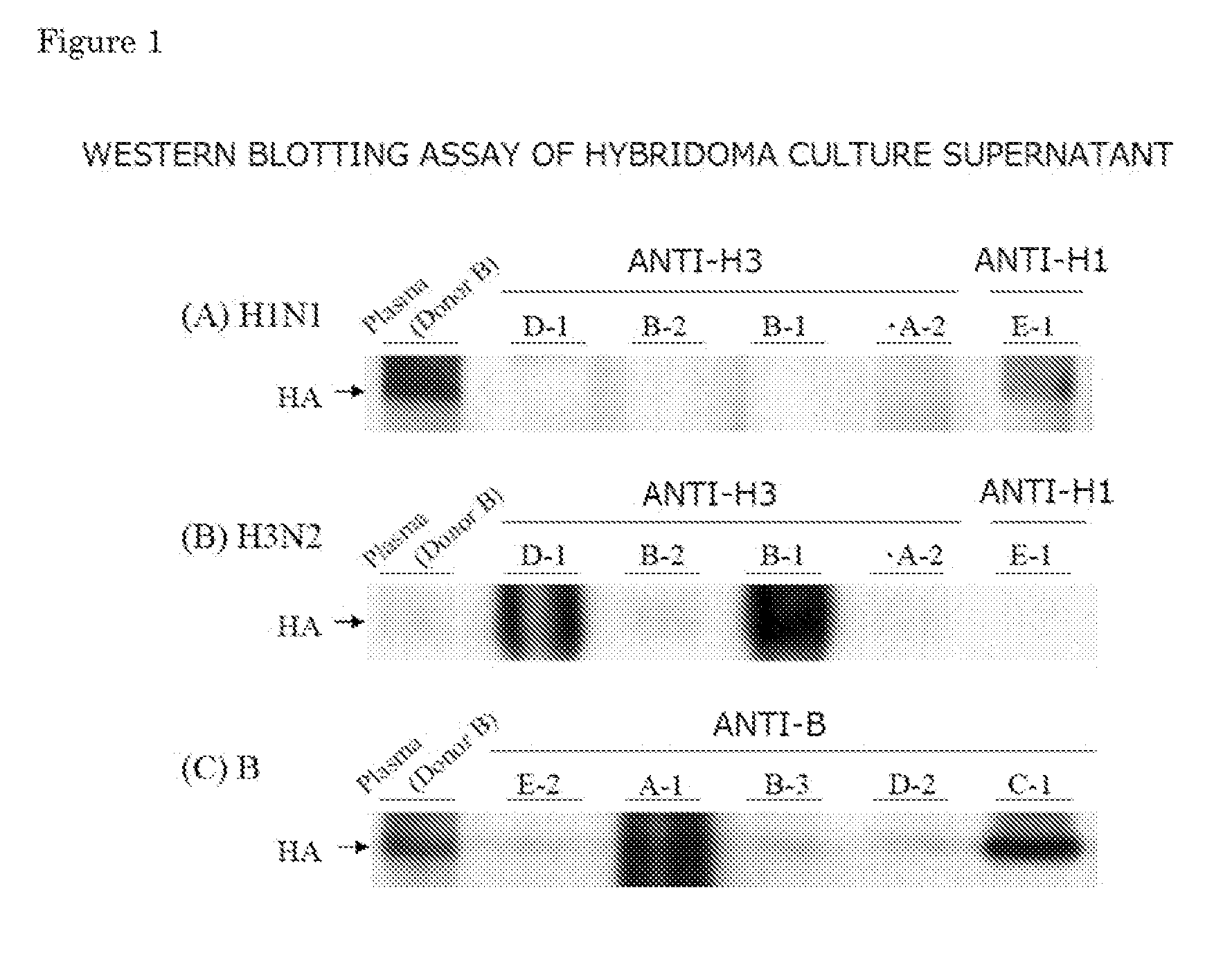
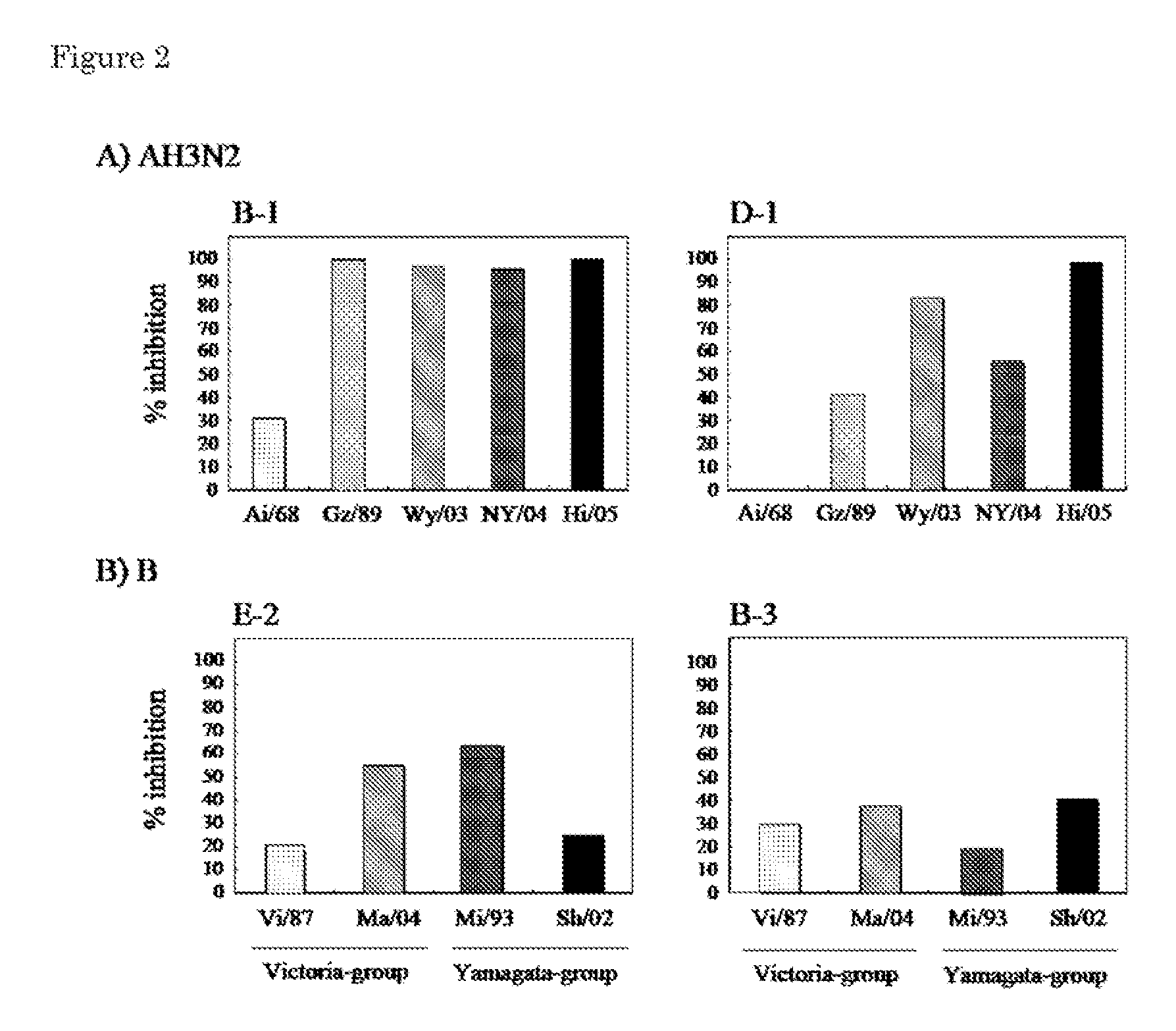
Human Anti-Human Influenza Virus Antibody
InactiveUS20110319600A1Effect survival rateEffect weight lossSugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against virusesHemagglutininHuman Influenza A Virus
Provided is a human antibody having a neutralization activity against a human influenza virus. More specifically, provided is a human antibody which recognizes a highly conserved region in a human influenza A virus subtype H3N2 or a human influenza B virus and has a neutralization activity against the virus. The human antibody is a human anti-human influenza virus antibody, which has a neutralization activity against a human influenza A virus subtype H3N2 and binds to a hemagglutinin HA1 region of the human influenza A virus subtype H3N2, or which has a neutralization activity against a human influenza B virus, and includes, as a base sequence of a DNA encoding a variable region of the antibody, a sequence set forth in any one of SEQ ID NOS: 5 to 12.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV +1
Pramyxovirusl vectors encoding antibody and utilization thereof
InactiveUS20050191617A1Good effectImprove efficiencySsRNA viruses negative-senseNervous disorderSingle-Chain AntibodiesAntibody fragments
The present invention provides paramyxoviral vectors expressing polypeptides that comprise antibody variable regions. A vector of this invention, encoding antibody variable regions of the H and L chains, succeeded in simultaneously expressing these antibody chains to form a Fab, and further succeeded in expressing a single chain antibody at a high level. The vectors of this invention are suitable as vectors for gene therapy, to be administered in vivo or ex vivo to living bodies. In particular, vectors expressing antibody fragments against neurite outgrowth inhibitors are useful in gene therapies for nerve lesions. Further, vectors of this invention that express antibodies which inhibit immune activation signal transduction enable the long-term expression of genes from the vectors.
Owner:DNAVEC RES
Methods of modifying antibodies for purification of bispecific antibodies
ActiveUS9670269B2Efficient purificationFunction increaseImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsImmunological disordersBinding siteBispecific antibody
The present inventors devised methods for efficiently purifying bispecific antibodies using a chromatography column based on the difference in isoelectric points between the H chains of two types of antibodies, wherein the difference is introduced by modifying the amino acids present on the surface of the antibody variable regions of two types of antibodies that constitute a bispecific antibody. Furthermore, the inventors devised methods for efficiently purifying bispecific antibodies using a chromatography column by linking respective antigen binding sites (heavy chain variable regions) to the antibody constant regions having different isoelectric points, and then coexpressing these antibodies.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Interleukin-6 antagonists
InactiveUS20110038877A1Avoid interactionPromote formationSugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseInterleukin 6
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Agonist antibody to human thrombopoietin receptor
This invention provides an agonist antibody to a human thrombopoietin receptor (alias: human c-Mpl). More particularly, this invention provides an agonist antibody to a human thrombopoietin receptor, wherein the agonist antibody comprises: antibody constant regions comprising (1) amino acid sequences in a heavy chain constant region and a light chain constant region of a human antibody, (2) an amino acid sequence of a heavy chain constant region with a domain substituted between human antibody subclasses, and an amino acid sequence of a light chain constant region of a human antibody, or (3) amino acid sequences comprising a deletion(s), substitution(s), addition(s), or insertion(s) of one or several amino acid residues in the amino acid sequences of (1) or (2) above; and antibody variable regions capable of binding to and activating a human thrombopoietin receptor; and wherein the agonist antibody has the properties: (a) that the antibody induces colony formation at a concentration of 10,000 ng / ml or lower as determined by the CFU-MK colony formation assay using human umbilical-cord-blood-derived CD34+ cells; and (b) that the antibody has a maximal activity at least 50% higher than that of PEG-rHuMGDF and an 50% effective concentration (EC50) of 100 nM or less in the cell proliferation assay using UT7 / TPO cell. Also provided is a pharmaceutical composition for treating thrombocytopenia comprising said antibody.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Preparation method and application for monoclonal antibody against HPV16 L1 protein
ActiveCN108586607AImprove developmentStable antibody secretion abilityBiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against virusesHeavy chainA-DNA
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application for a monoclonal antibody against an HPV16 L1 protein. The invention also discloses the monoclonal antibody against the HPV16 L1 protein, and a DNA sequence and an amino acid sequence of the monoclonal antibody in a heavy chain variable region and a light chain variable region. The invention designs the preparation method for the monoclonal antibody against the HPV16 L1 protein. The monoclonal antibody against the HPV16 L1 protein is applied to immunological detection, antigen or antibody detection kits. The monoclonal antibody against the HPV16 L1 protein can specifically recognize a main epidemic subtype namely HPV16, has good reactivity with HPV16 pseudovirus and the HPV16 L1 protein, and is free of cross reactions with subtypes of L1 proteins. A good foundation is laid for further modification of the antibody variable region sequence of the monoclonal antibody to prepare genetically engineered antibodies with differentcombination forms and for clinical detection research on different subtypes of HPV pathogens.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV +1
Proteomic identification of antibodies
ActiveUS20130178370A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningAntigen Binding FragmentAntigen binding
Methods and compositions for identification of candidate antigen-specific variable regions as well as generation of antibodies or antigen-binding fragments that could have desired antigen specificity are provided. For example, in certain aspects, methods for determining amino acid sequences of serum antibody CDR3 and abundancy levels are described. In some aspects, methods for determining nucleic acid sequences of antibody variable region sequences and the frequency thereof in biological samples are provided. Furthermore, the invention provides methods for identification and generation of antibodies or antigen-binding fragments that comprise highly-represented CDR domains.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method for rapidly preparing Zika-virus specific full human monoclonal antibodies and application
InactiveCN106478815AEasy to operateImprove screening efficiencyImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsZika virusPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The invention belongs to the field of medical biology, and particularly relates to a method for rapidly preparing Zika-virus specific full human monoclonal antibodies and an application. The method for rapidly preparing the Zika-virus specific full human monoclonal antibodies includes the steps of peripheral blood mononuclear cell separating, plasma cell separating, antibody-variable-region-gene PCR amplification, antibody cloning, cotransfection and identifying and the like. The method for rapidly preparing the Zika-virus specific full human monoclonal antibodies is simple and fast and convenient, antigens do not need to be marked, functional antibodies of conformation structural domains which exists in vivo and is difficult to emulate in vitro can be separated, the obtained specific antibodies have important guiding significance on researching of Zika vaccine, and some antibodies can have clinic-treatment application prospects.
Owner:GUANGZHOU EIGHTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Super-humanized antibody
The invention discloses a method for humanizing an antibody. In the invention, through comparing a standard CDR (Complementarity-Determining Region) structure type of a CDR sequence in a variable region of an inhuman antibody with a standard CDR structure type of a corresponding CDR in a human antibody sequence library, a frame sequence of the variable region is selected from human antibody genes, preferably the gene segments of an embryonic system antibody. The variable region of the human antibody which has the standard CDR structure type similar to an inhuman CDR forms a subgroup of a member antibody sequence and a human frame sequence can be selected from the subgroup. The subgroup members can be further rated through the amino acid similarity between the human and inhuman CDR sequences. The ahead human sequence in the rating is selected to provide the frame sequence and construct a chimeric antibody by utilizing the selected the subgroup member human frame. The chimeric antibody replaces the human CDR sequence by the counterpart functionality of the inhuman CDR, therefore, the humanized antibody which has high affinity and low immunogenicity is provided without comparing the frame sequences between the inhuman antibody and the human antibody. The invention also discloses the chimeric antibody prepared according to the method of the invention.
Owner:杰斐逊 富特
Preparation and application of humanized anti-spasmotoxin monoclone antibody
InactiveCN101220096ADoes not induce allergic reactionsProtection attackImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsAnimal virusHypersensitive response
The invention provides a human McAb to tetanus toxin, which is a human antibody comprising a variable region of the antibody. The antibody consists of or not consists of a constant region of the antibody and has the ability of neutralizing the tetanus toxin, with the variable region gene and protein sequence indicated as the sequence table 1. The antibody is characterized in that the antibody can not induce obvious allergic reaction, has higher titer and longer effect without any animal virus pollution, and can be produced in an unlimited quantity. The antibody also provides the relating biological functions, the testing methods, the manufacturing method and the application.
Owner:龚小迪
Canine single-chain antibody, and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN104017080AImprove immunityHave diversityPeptide librariesImmunoglobulins against blood group antigensSingle-Chain AntibodiesElisa method
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and particularly discloses a canine single-chain antibody, and a construction method and application thereof. By designing the canine antibody variable region degenerate primers, the canine heavy chain variable region VH and light chain variable region VL genes are successfully amplified. On such basis, a bacteriophage display technique is utilized to successfully construct the canine single-chain antibody scFv library. The scFv single-chain antibody library has diversity and enough storage capacity. A Dot-ELISA method is utilized to screen 3 single chain antibodies capable of being combined with the canine DEA 1.1 blood group antigen from the scFv single-chain antibody library by using the canine DEA 1.1 blood group antigen, wherein Clone 16 has stronger combination characteristic. A pET-32a-Clone16 recombinant protein is constructed according to the Clone 16 gene to perform prokaryotic expression, and the purified antibody has combination activity. The canine single-chain antibody lays solid foundation for preparing canine DEA 1.1 blood grouping reagents.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Rapid isolation of monoclonal antibodies from animals
ActiveUS9090674B2Serum immunoglobulinsMicrobiological testing/measurementSerum igeAntigen Binding Fragment
Methods and compositions for identification of candidate antigen-specific variable regions as well as generation of antibodies or antigen-binding fragments that could have desired antigen specificity are provided. For example, in certain aspects methods for determining amino acid sequences of serum antibody CDR and abundancy level are described. In some aspects, methods for determining nucleic acid sequences of antibody variable region sequences and frequency are provided. Furthermore, the invention provides methods for identification and generation of antibody or antigen-binding fragments that comprise highly-represented CDR.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Bi-target CAR-T cell as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108220247AIncreased specificity of killingLow specificityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMammal material medical ingredientsInflammatory factorsSide effect
The invention discloses a bi-target CAR-T cell. The bi-target CAR-T cell is characterized in that two target antigens which are in co-expression in tumor cells and are not in co-expression in normal cells are utilized, an antibody variable region of one target antigen is fused with a killing signal in a T cell, and an antibody variable region of the other target antigen is fused with a co-stimulating signal in the T cell, and two different expression cassettes are formed, so that the bi-target CAR-T cell is constructed; the constructed bi-target CAR-T cell can just identify tumor cells which can express the two target antigens at the same time and cannot identify the normal cells which just express one target antigen. The invention also discloses a preparation method and application of thebi-target CAR-T cell. According to the bi-target CAR-T cell disclosed by the invention, not only killing specificity is increased, but also killing of the normal cells is reduced, and side effects brought by an inflammatory factor storm are reduced.
Owner:浙江史迪姆生物科技有限公司
Humanized single anti-Hu-ScFv18 light and heavy chain variable region gene and coding polypeptide thereof and application thereof
ActiveCN101550416AGenetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementHeavy chainSingle-Chain Antibodies
The present invention relates to a humanized single anti-Hu-ScFv18 light and heavy chain variable region gene for resisting HAb18G / CD147 and A coding polypeptide thereof and application thereof. The invention uses a set of designed primers to humanizedly reconstruct the anti-HAb18G / CD147 single light and heavy chain variable region gene excreted from HAb18 hybridoma, and the humanized single anti-Hu-ScFv18 heavy chain and light chain variable region gene may encode a correct antibody variable region. Based on the cloned anti-HAb18G / CD 147 humanized single anti-Hu-ScFv18 light and heavy chain variable region gene, it is capable of constructing and expressing various small molecule genetic engineering antibodies such as single-chain antibody, jogged antibody, Fab antibody and the like against the HAb18G / CD 147 molecule by a genetic engineering method, so as to be used for diagnosis and treatment of hepatocarcinoma.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Binding protein molecule
InactiveUS20090130776A1Take advantage ofImprove accuracyMaterial nanotechnologyImmunoglobulins against animals/humansNin one binding proteinBinding site
A binding protein molecule, characterized in that it has a first domain having a binding site to an inhibitor of non-specific adsorption in which the domain comprises a part of the variable region of an antibody as the binding site and a second domain having a binding site to a target substance in which the domain comprises a part of the variable region of an antibody as the binding site, wherein the first and second domains are bound via a linker.
Owner:CANON KK
Antibody modification method for purifying bispecific antibody
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com