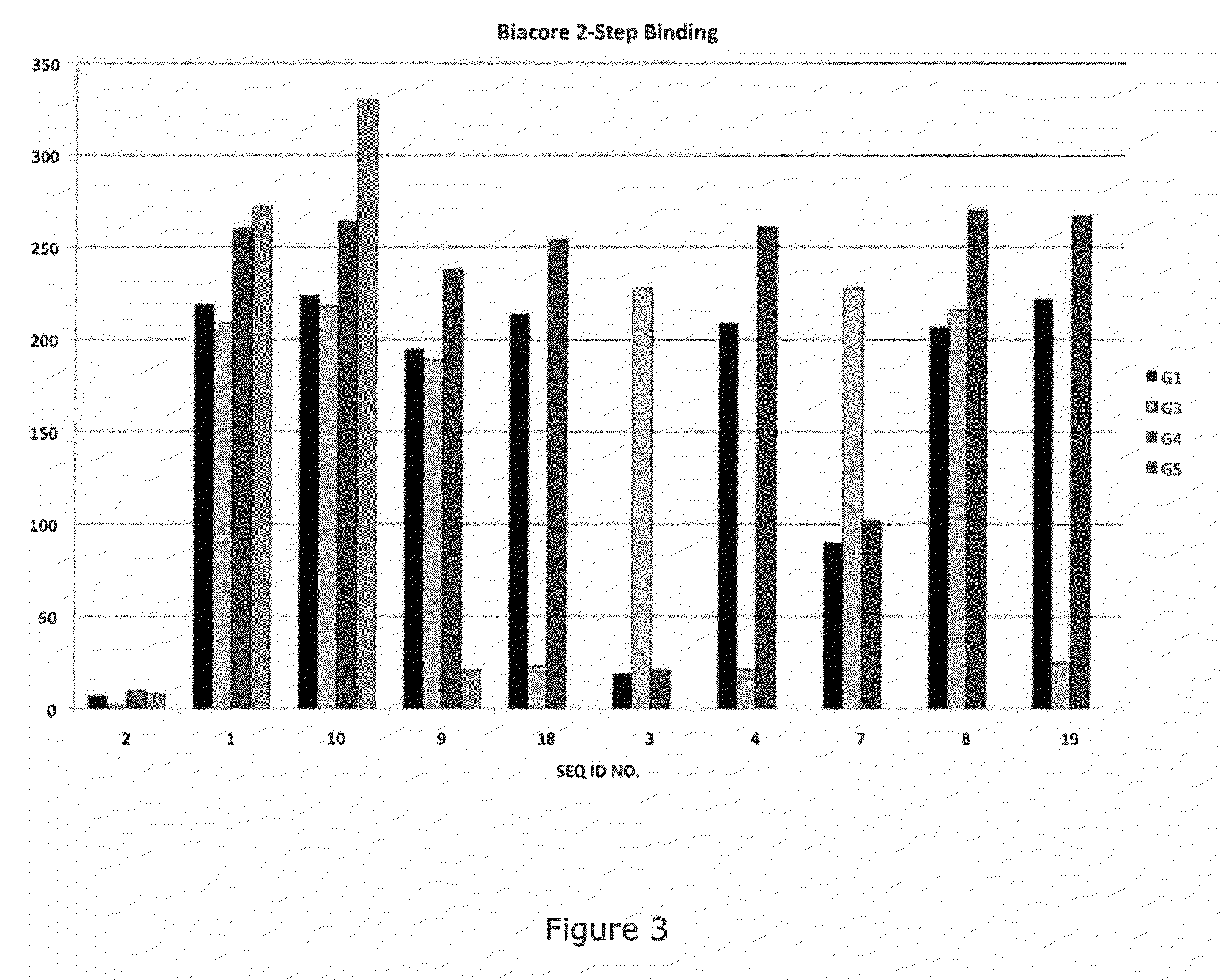
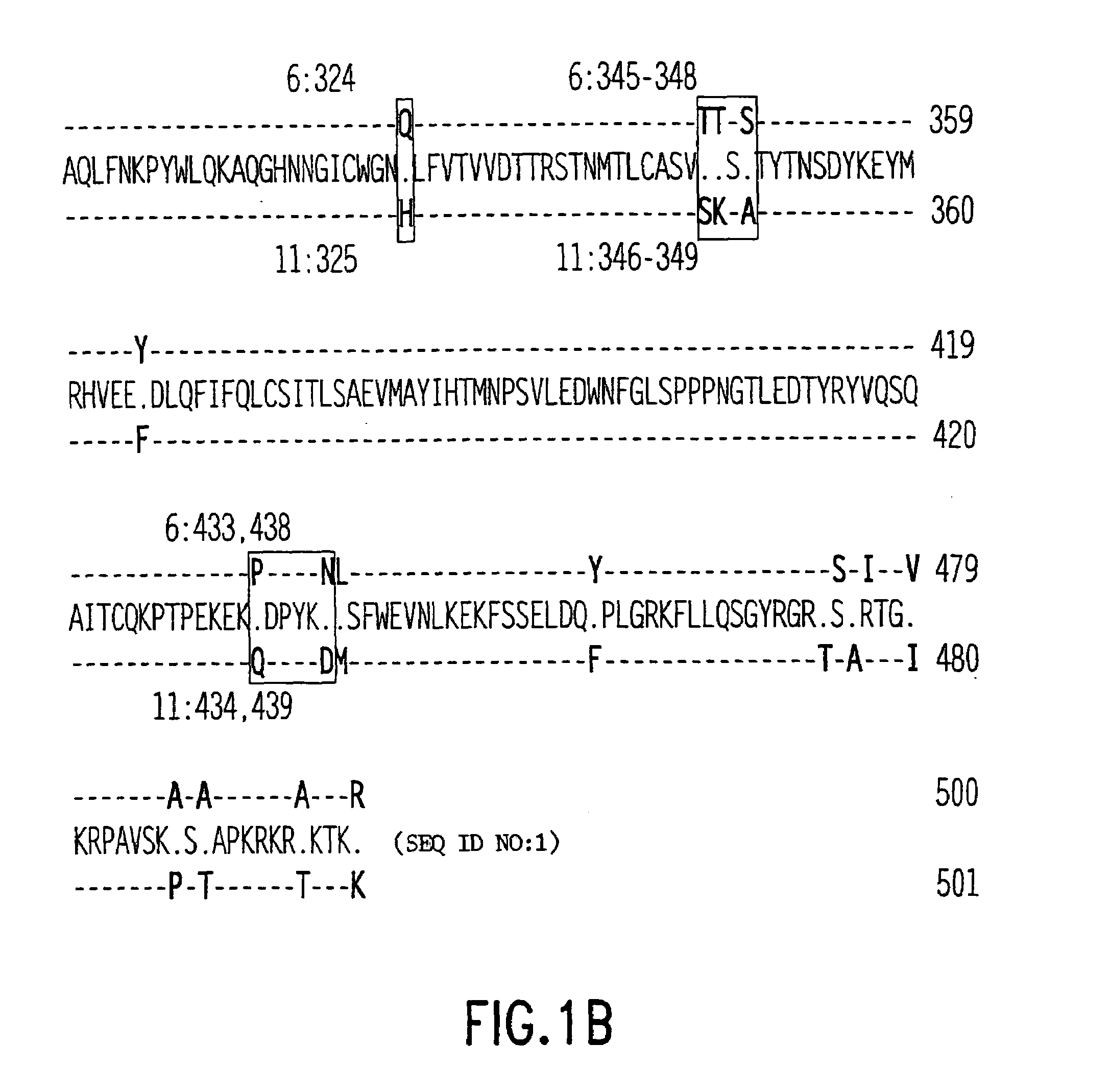
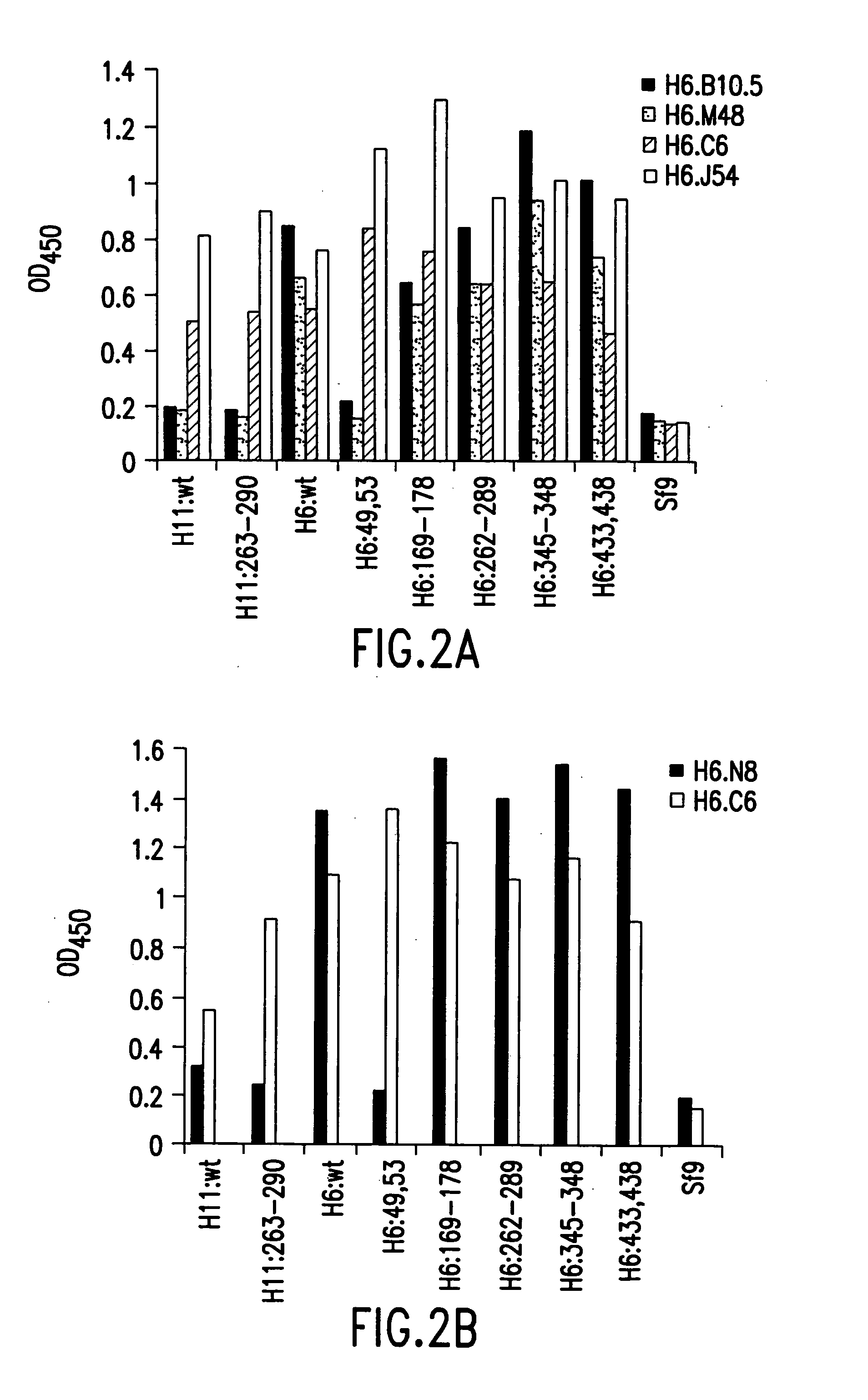
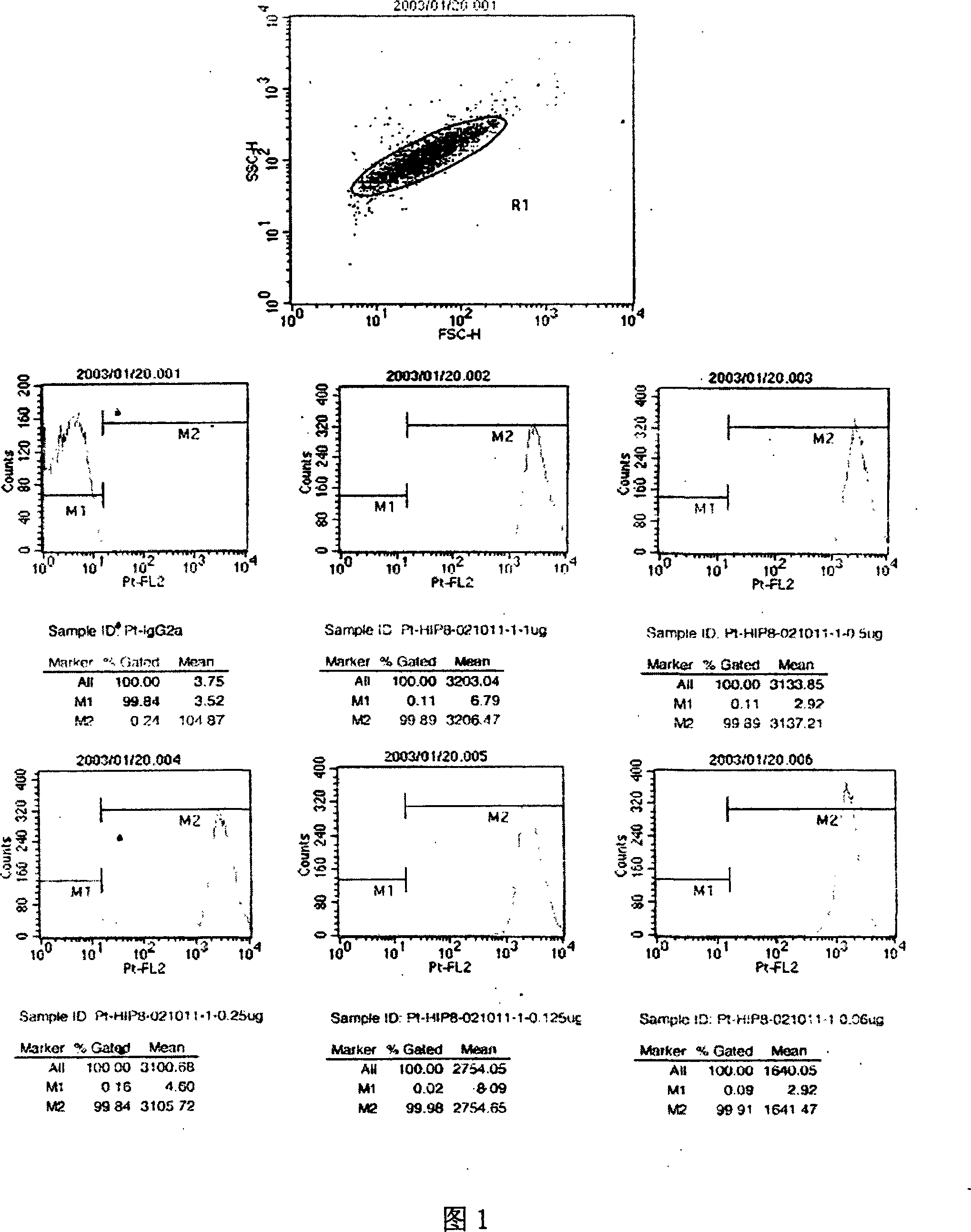
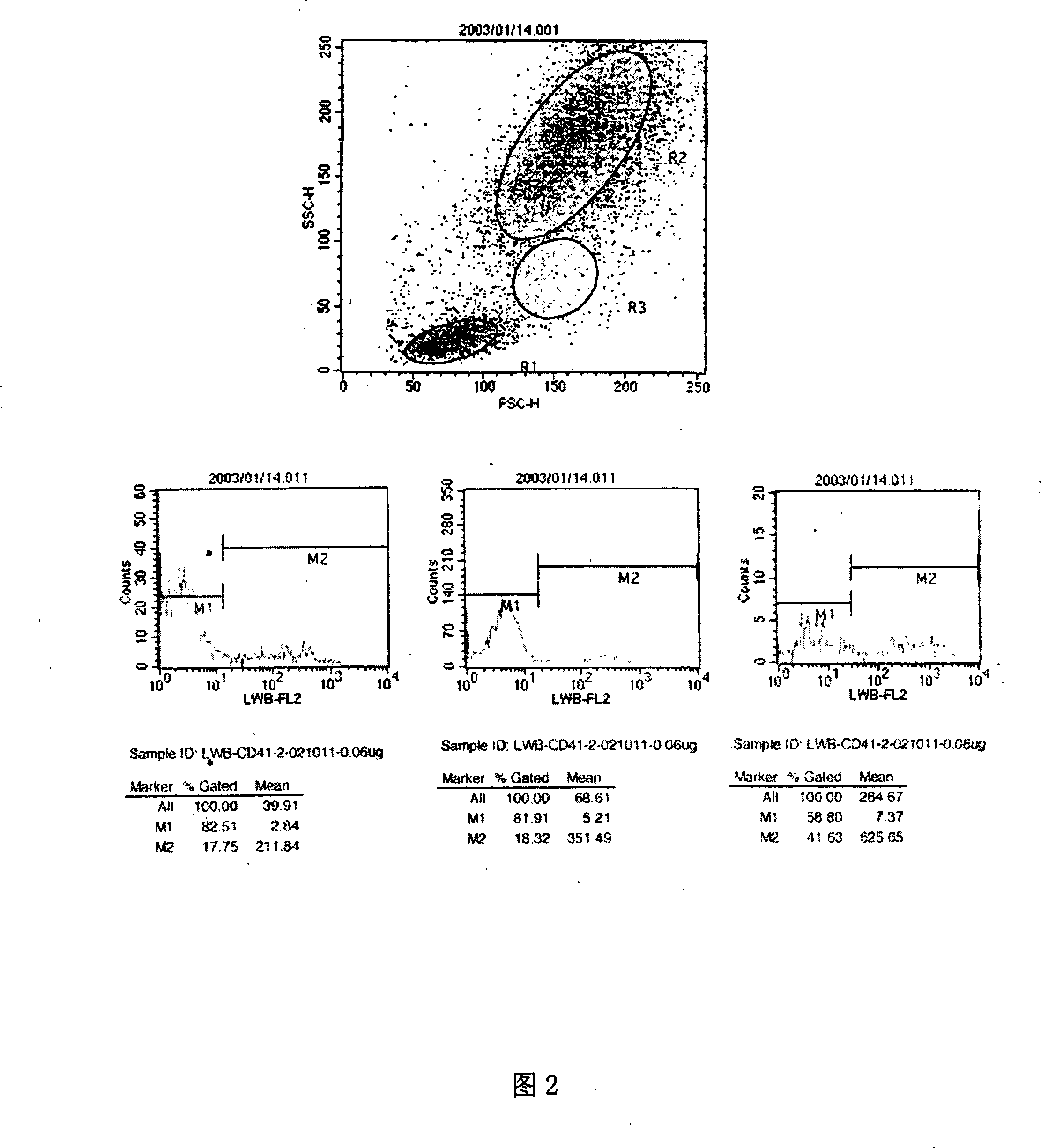
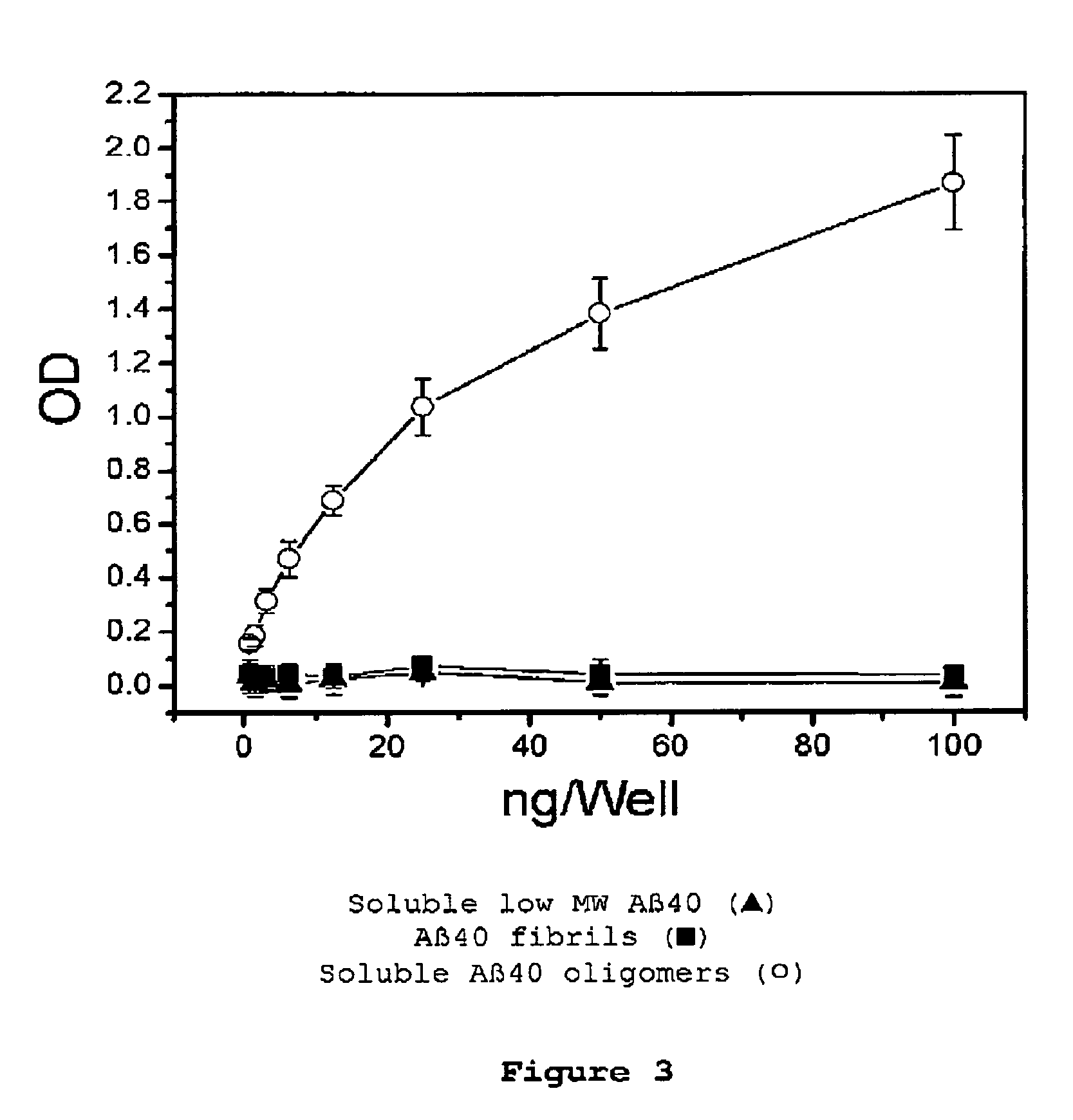
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
109 results about "Conformational epitope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
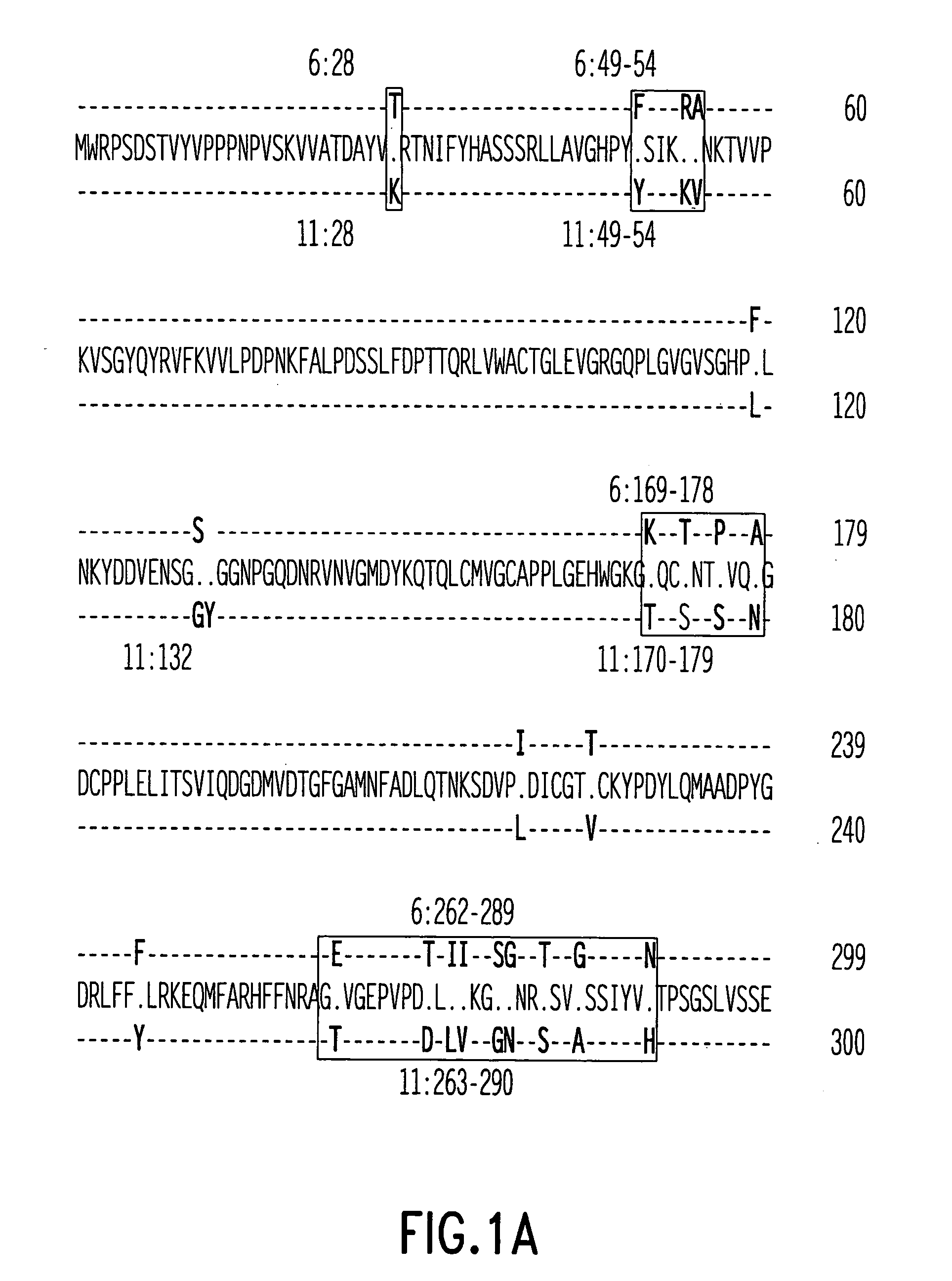
A conformational epitope is a sequence of sub-units (usually amino acids) composing an antigen that come in direct contact with a receptor of the immune system. An antigen is any substance that the immune system can recognize as foreign. Antigens are usually proteins that are too large to bind as a whole to any receptor so only specific segments, that form the antigen, bind with a specific receptor. Such segments are called epitopes. Likewise, it is only paratope of the receptor that comes in contact with the epitope.
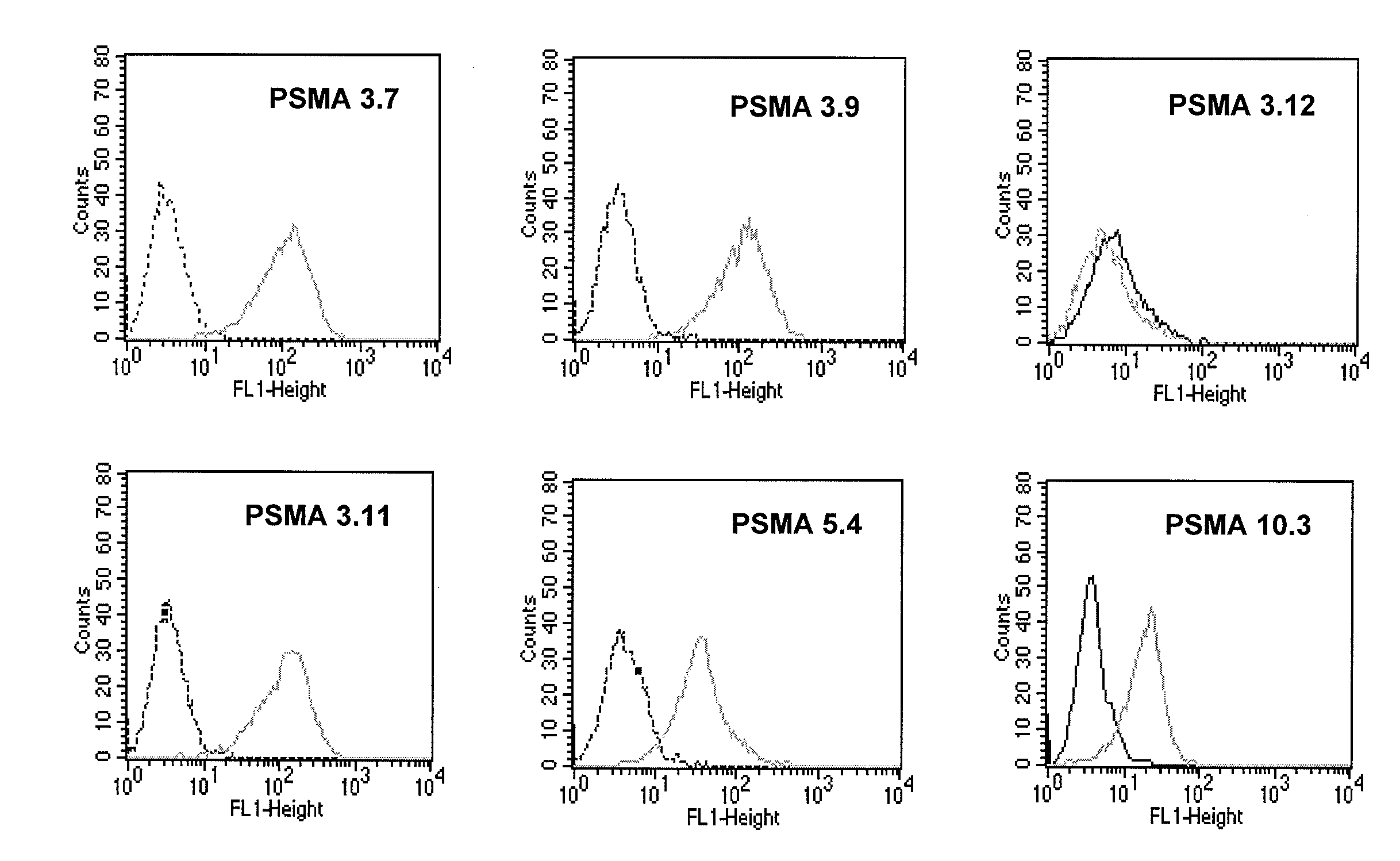
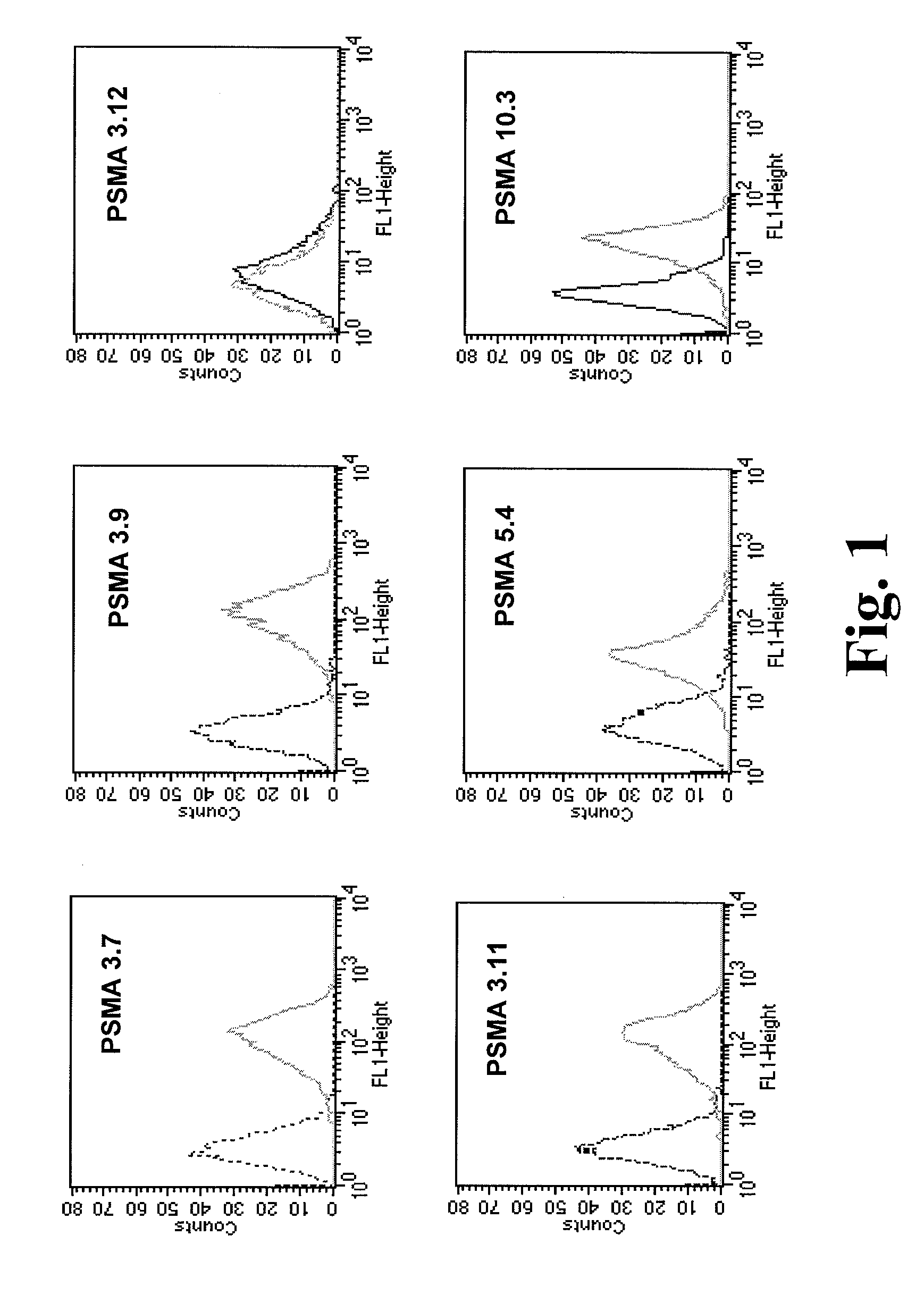
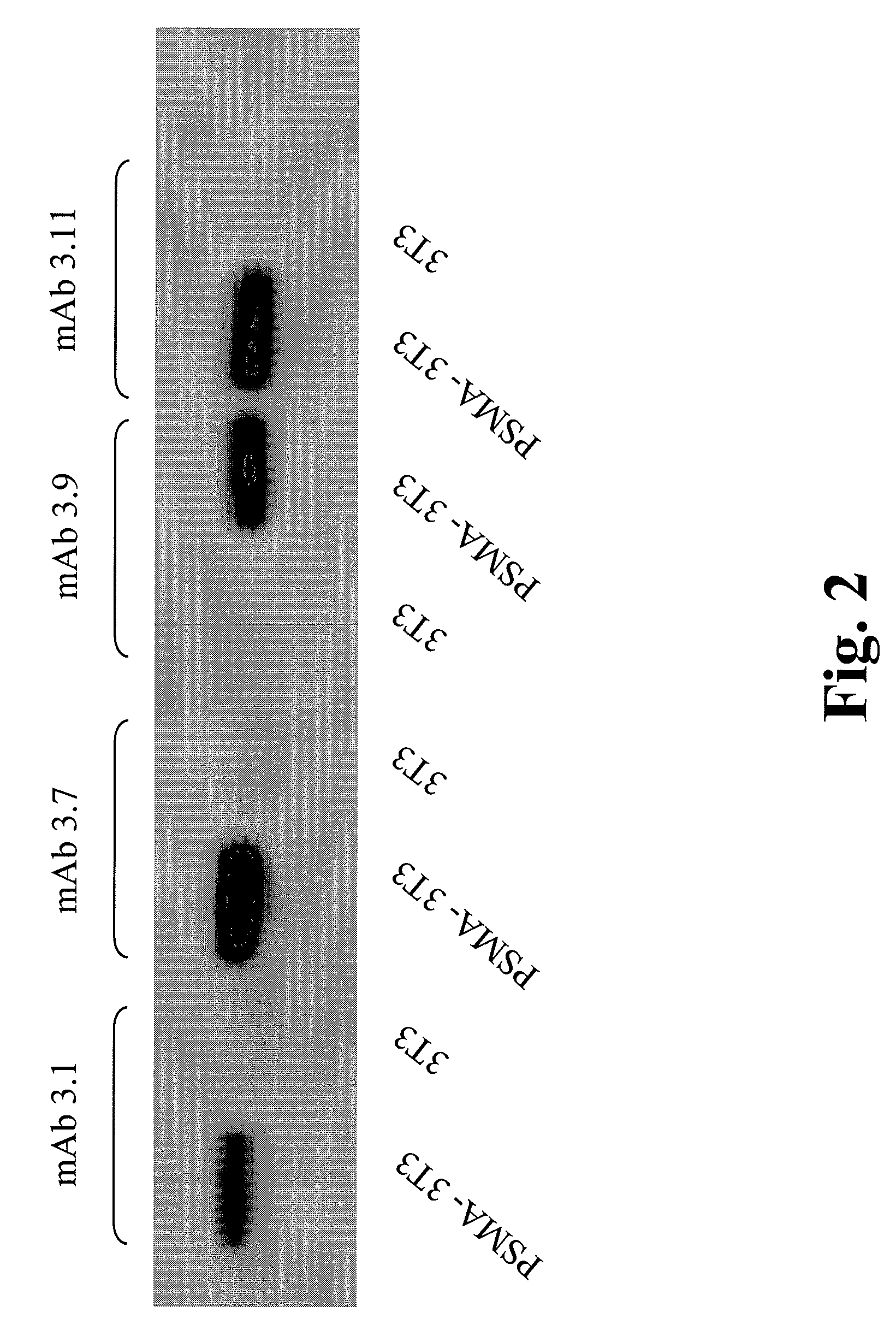
Compositions of PSMA antibodies
InactiveUS20080286284A1Effectiveness of treatmentOrganic active ingredientsFungiAntigen Binding FragmentCancers diagnosis
The invention includes antibodies or antigen-binding fragments thereof which bind specifically to conformational epitopes on the extracellular domain of PSMA, compositions containing one or a combination of such antibodies or antigen-binding fragments thereof, hybridoma cell lines that produce the antibodies, and methods of using the antibodies or antigen-binding fragments thereof for cancer diagnosis and treatment. The invention also includes oligomeric forms of PSMA proteins, compositions comprising the multimers, and antibodies that selectively bind to the multimers.
Owner:AMGEN FREMONT INC +1
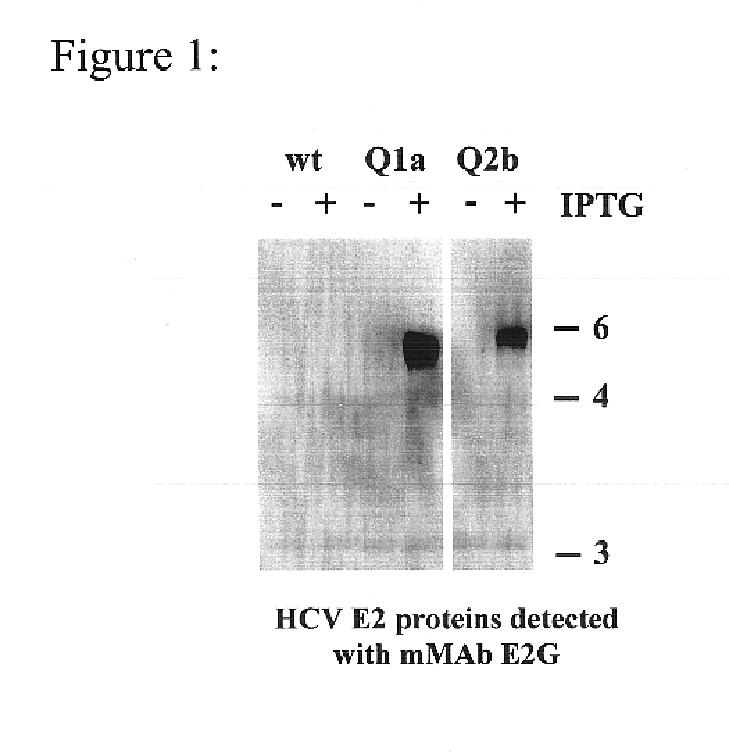
Prevention and treatment of HCV infection employing antibodies that inhibit the interaction of HCV virions with their receptor
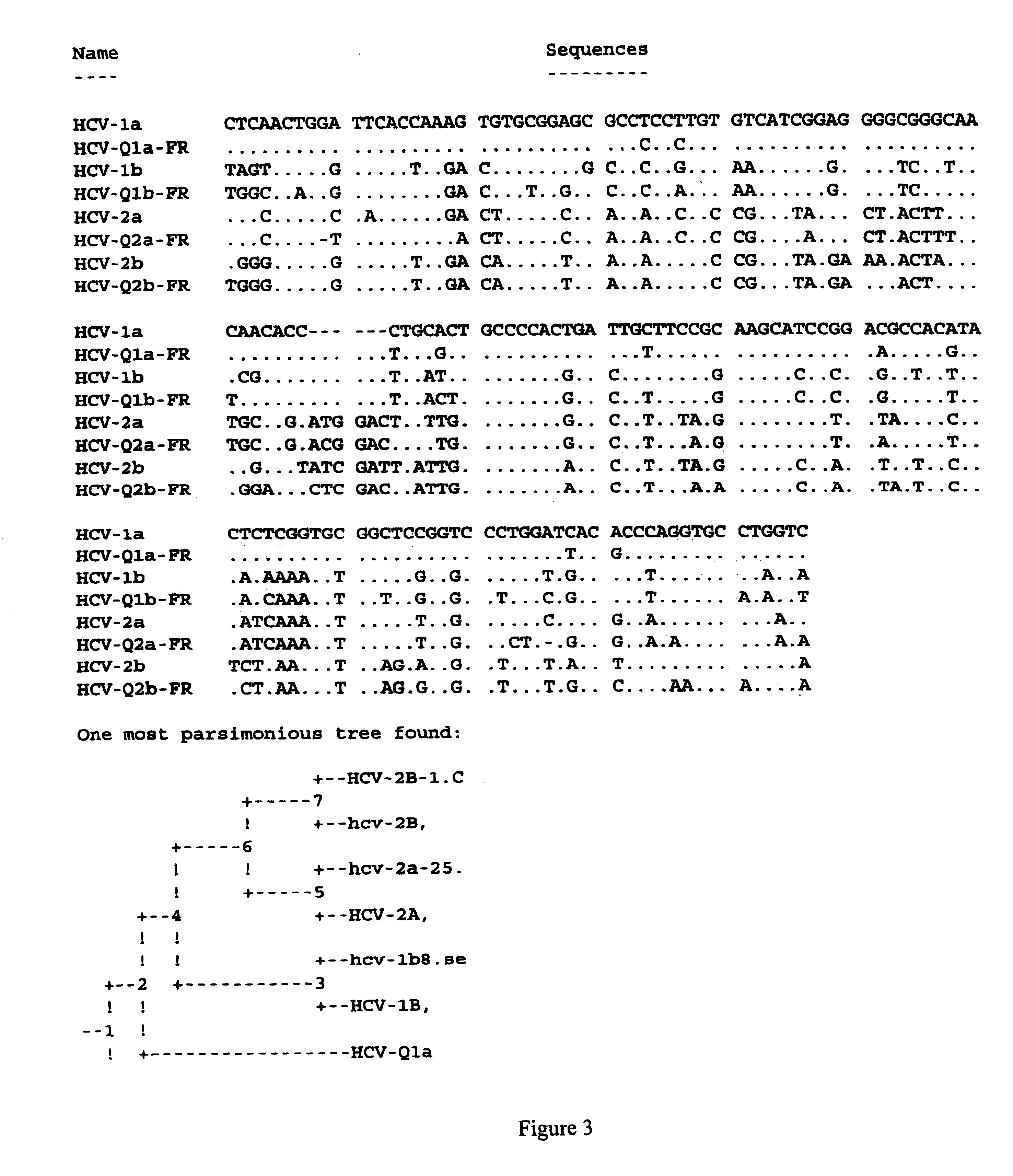
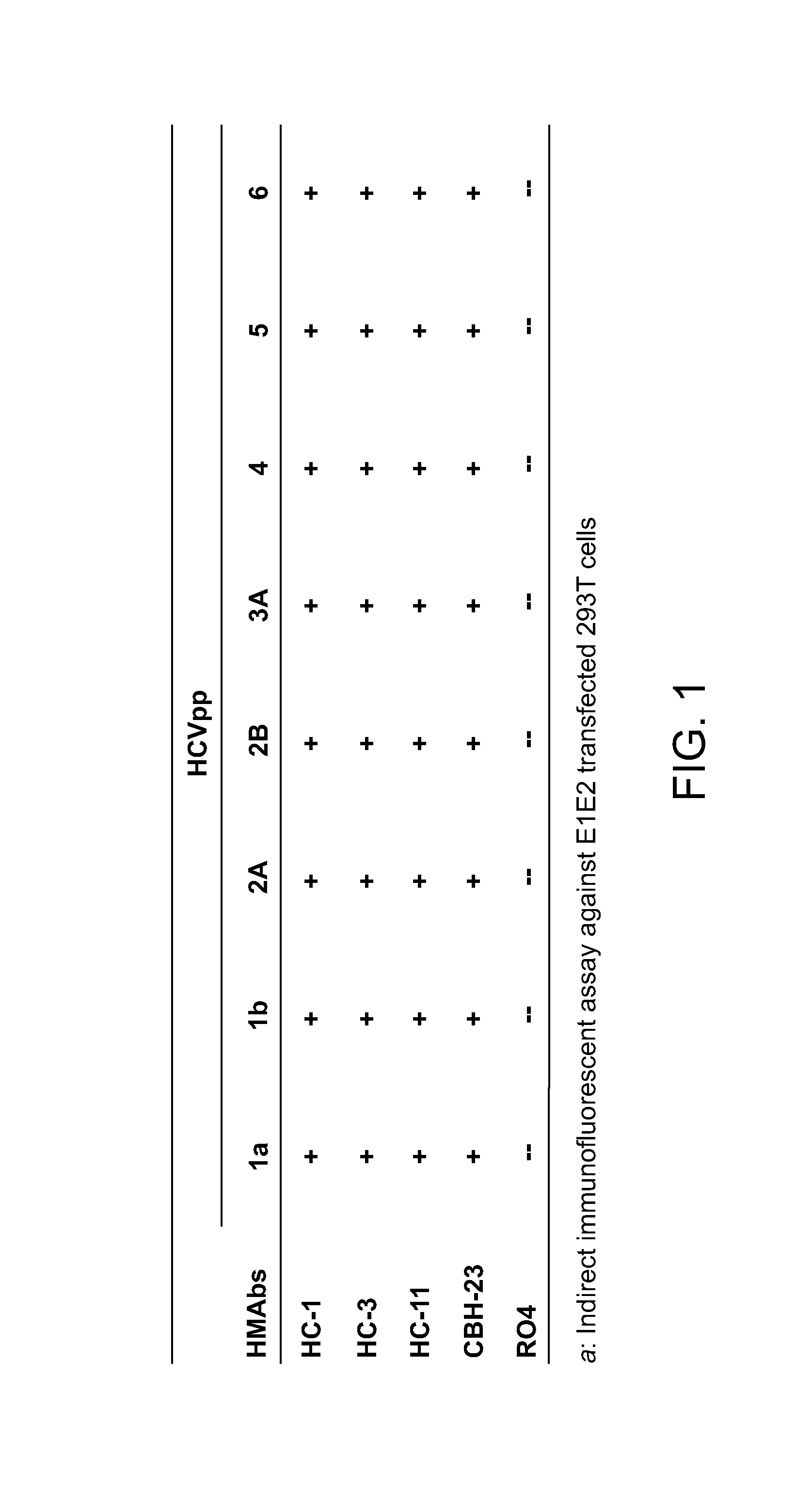
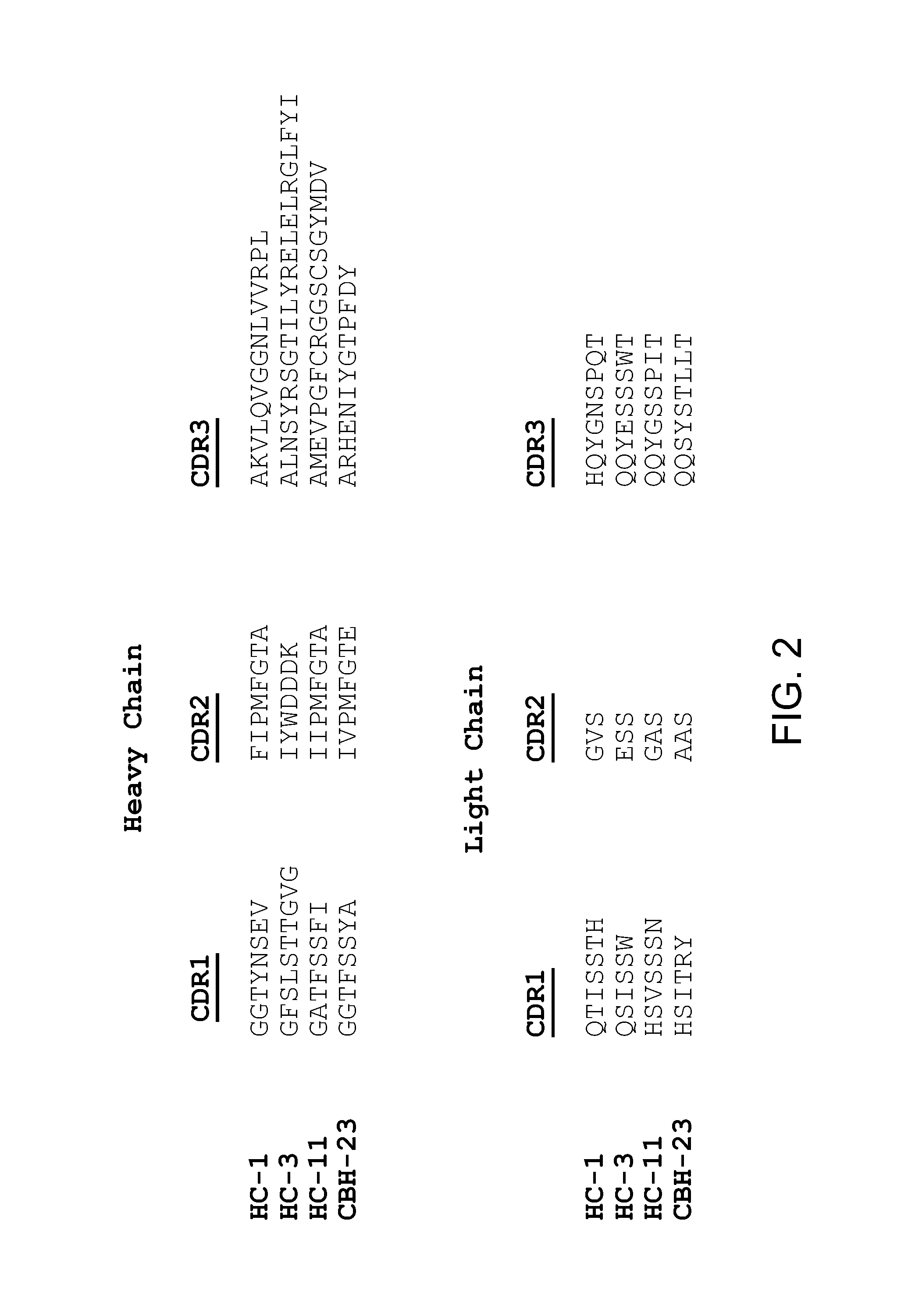
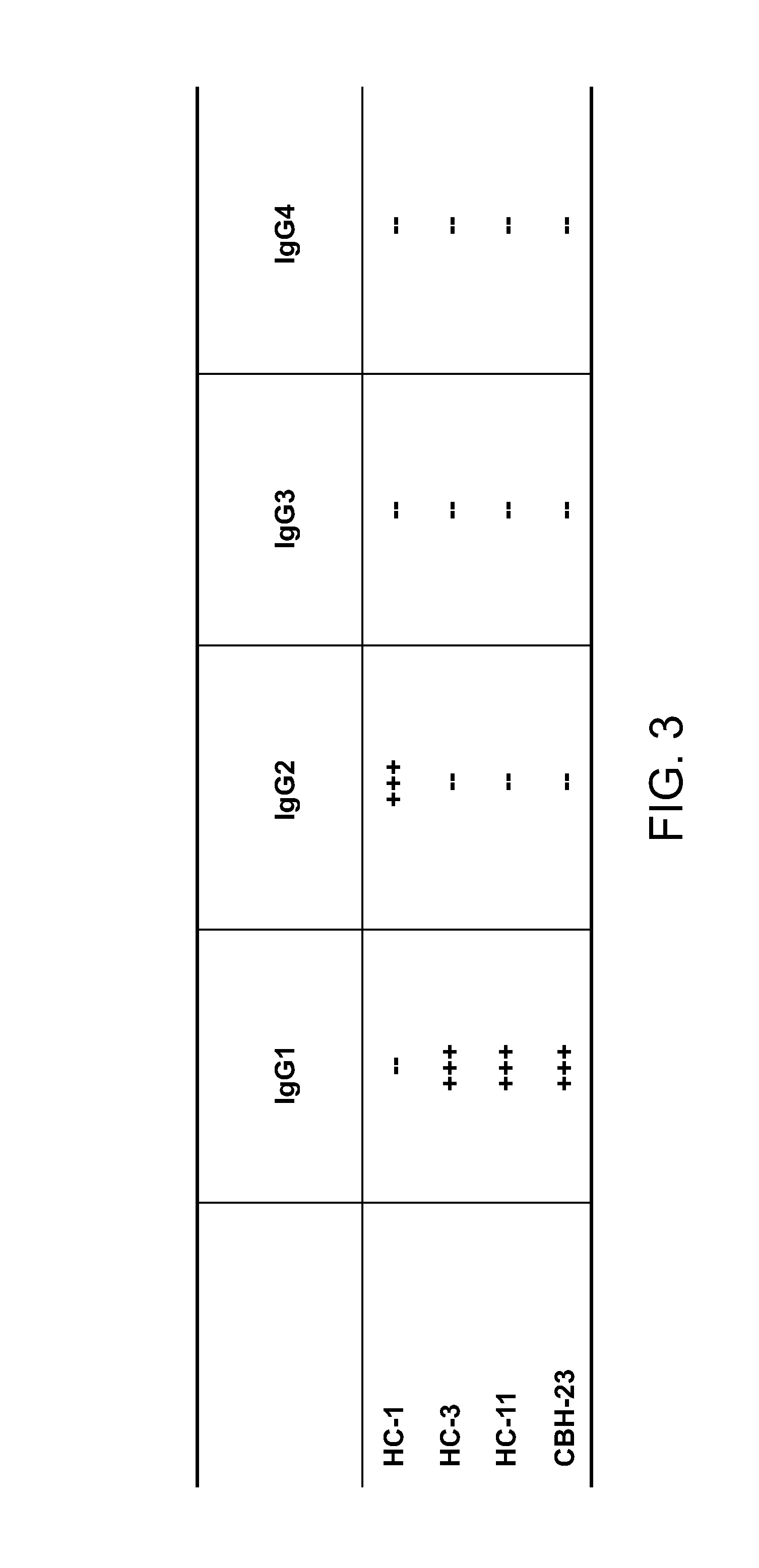
Human monoclonal antibodies binding to epitopes common to type 1 and 2 HCV are provided, as well as conformationally conserved HCV E2 2a and 2b proteins. Compositions comprising the antibodies find use in diagnosis and therapy. The antibodies recognize conformational epitopes that are conserved across multiple genotypes of HCV. Thus the antibodies have the potential to be useful in the prevention and treatment of the majority of HCV infections. A subset of the antibodies (CBH-2, CBH-5, CBH-7, CBH-8C, CBH-8E, and CBH-11) have the ability to prevent the binding of HCV E2 proteins of multiple genotypes to human CD81, a possible co-receptor for HCV infection. A subset of the antibodies (CBH-2 and CBH-5) have been shown to inhibit the binding of HCV virions (as opposed to purified E2 protein) to human CD81. A further subset of the antibodies (CBH-4D, CBH4B, CBH-8C, and CBH-9) have been shown to prevent HCV envelope mediated fusion using an HCV psuedotype system.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Measurement of bioactive hepcidins
ActiveUS20060019339A1Enhancing innate immunityAntibacterial agentsBiocideMicroorganismVertebrate Animals
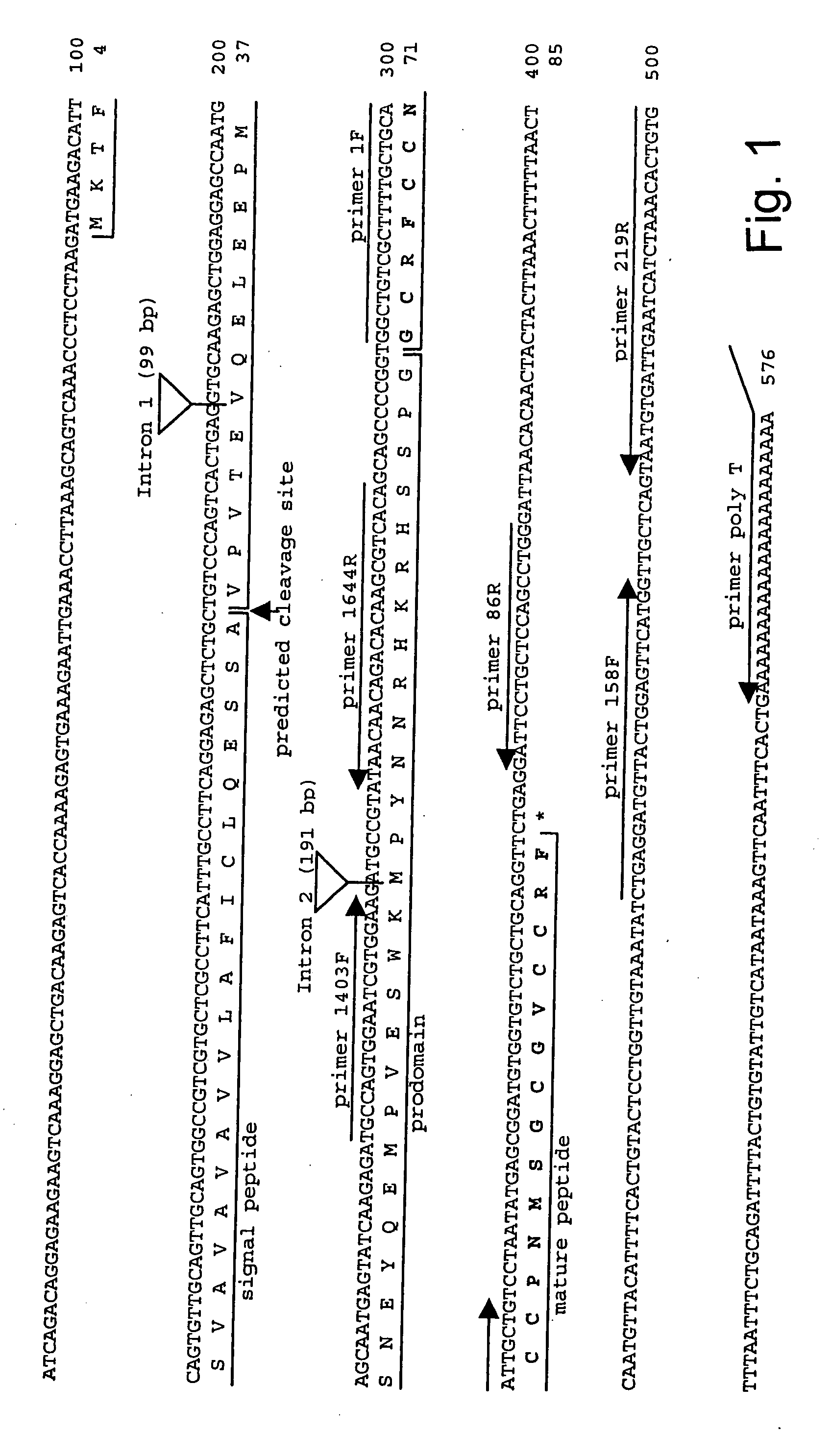
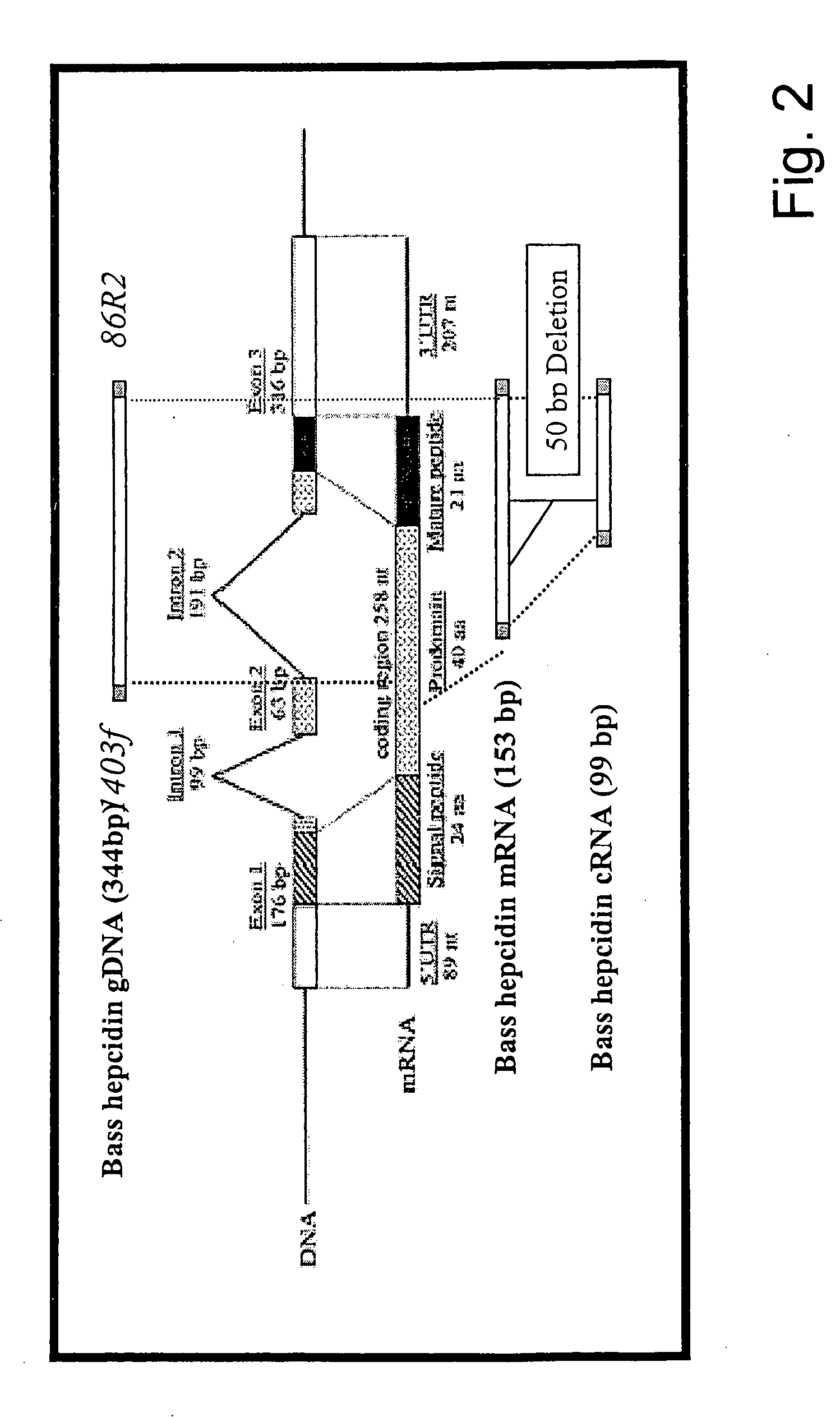
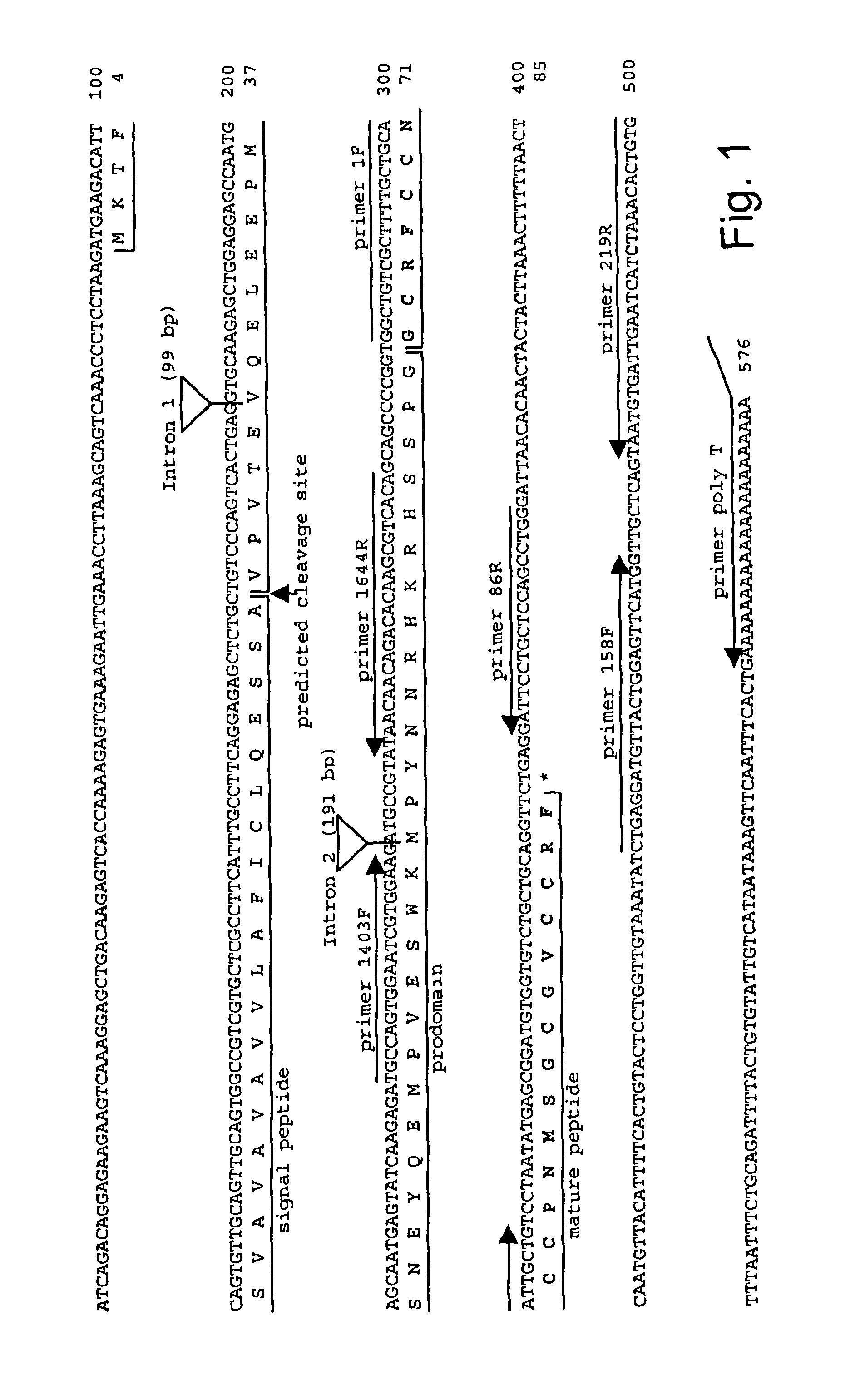
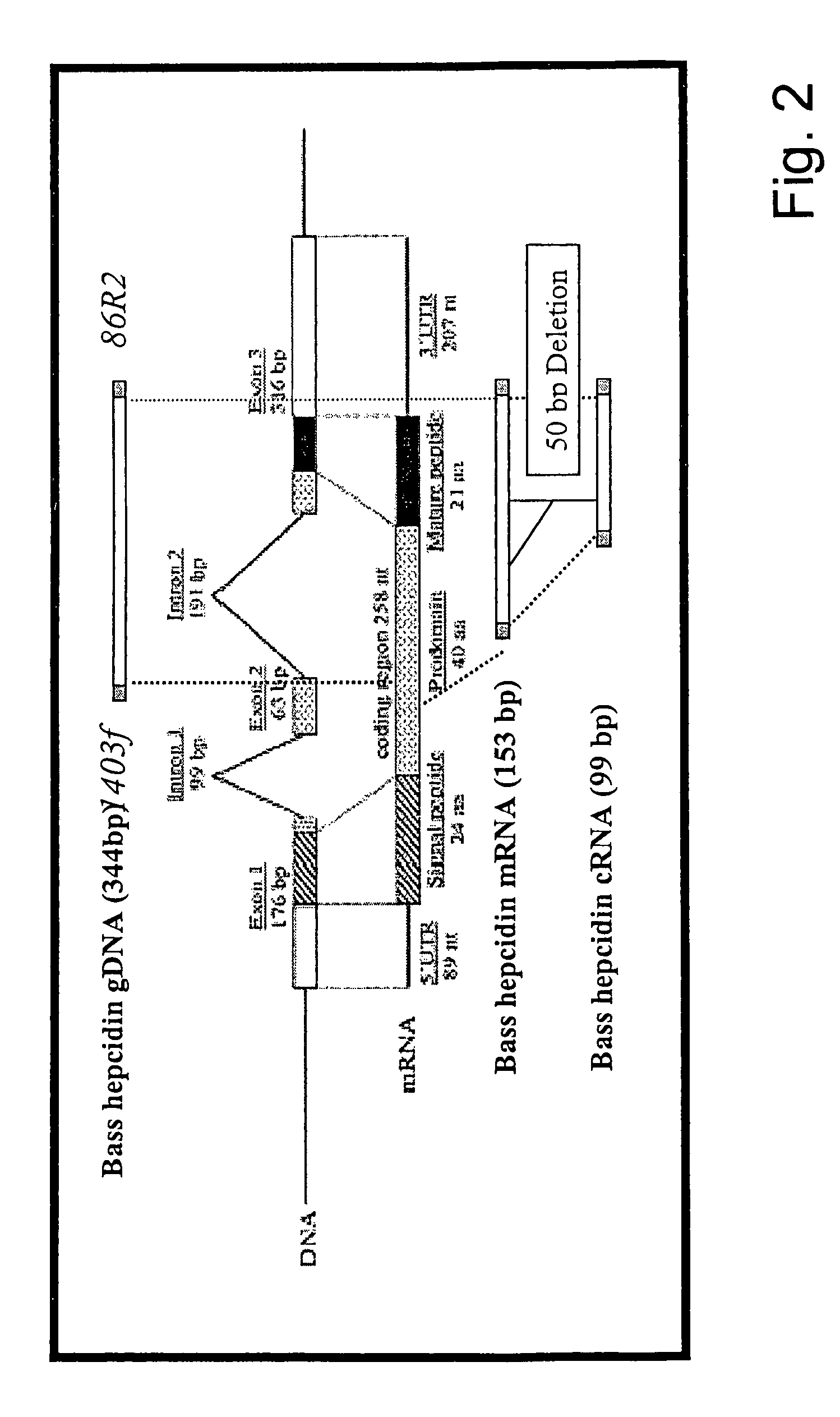
The present invention concerns a method for the oxidative refolding of a hepcidin polypeptide to a form that is mature, bioactive and folded as in the native configuration and molecular mass; a method for measuring the level of native, bioactive hepcidin in a vertebrate animal; a method for measuring the level of hepcidin gene expression in a vertebrate animal; and a method for regulating the production of native, bioactive hepcidin in a vertebrate animal in vivo. The present invention also concerns an antibody or fragment thereof that specifically binds to a continuous, discontinuous, and / or conformational epitope of a mature and bioactive hepcidin folded as in the native configuration; and a pharmaceutical composition that includes the antibody or a hepcidin polypeptide and that provides antimicrobial, agonistic, or antagonistic activities in vivo in a vertebrate animal.
Owner:INTRINSIC LIFESCIENCES LLC
Antibodies to Dkk-1
ActiveUS20060127393A1Block and reduce bindingHigh activitySenses disorderNervous disorderConformational epitopeOcular disease
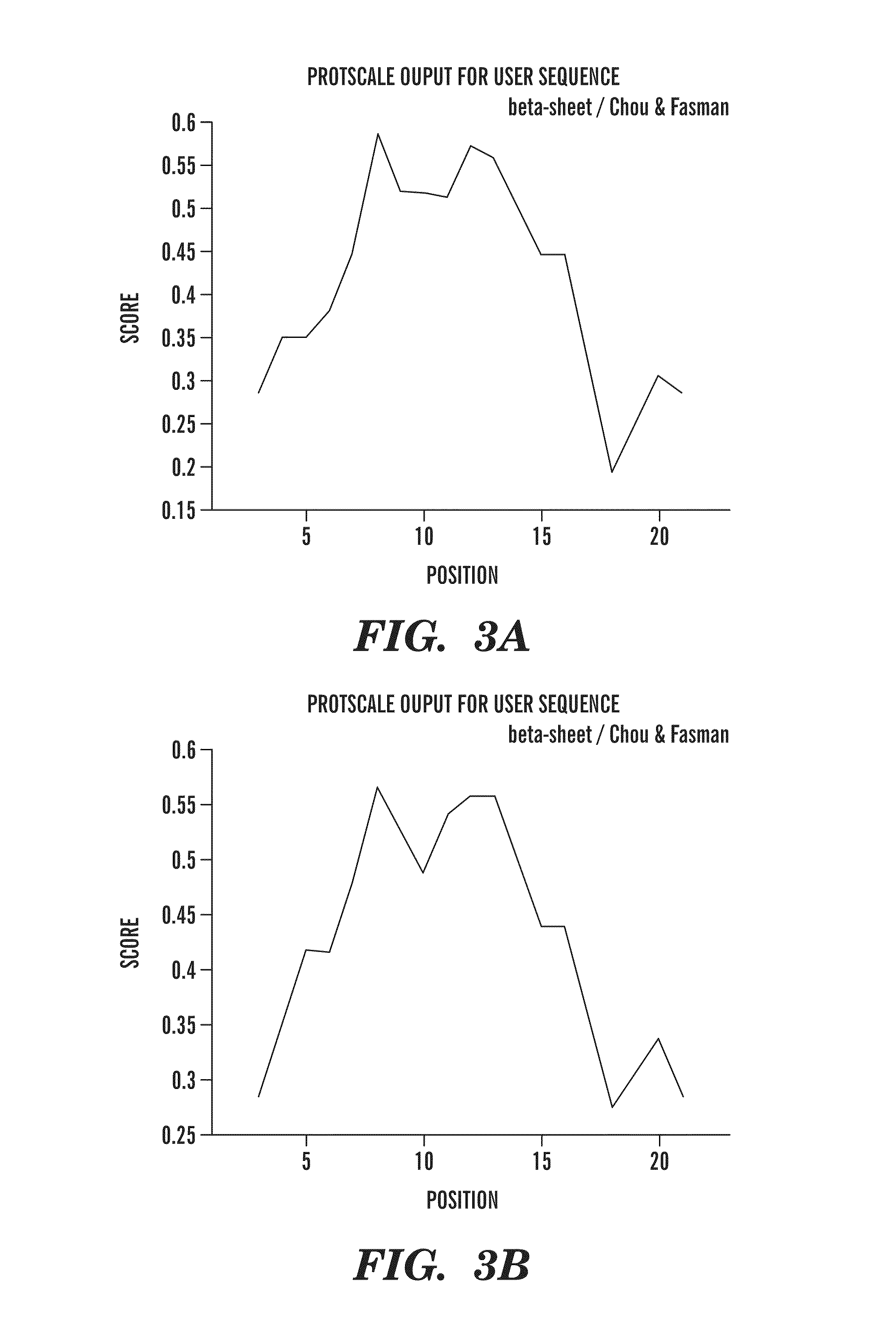
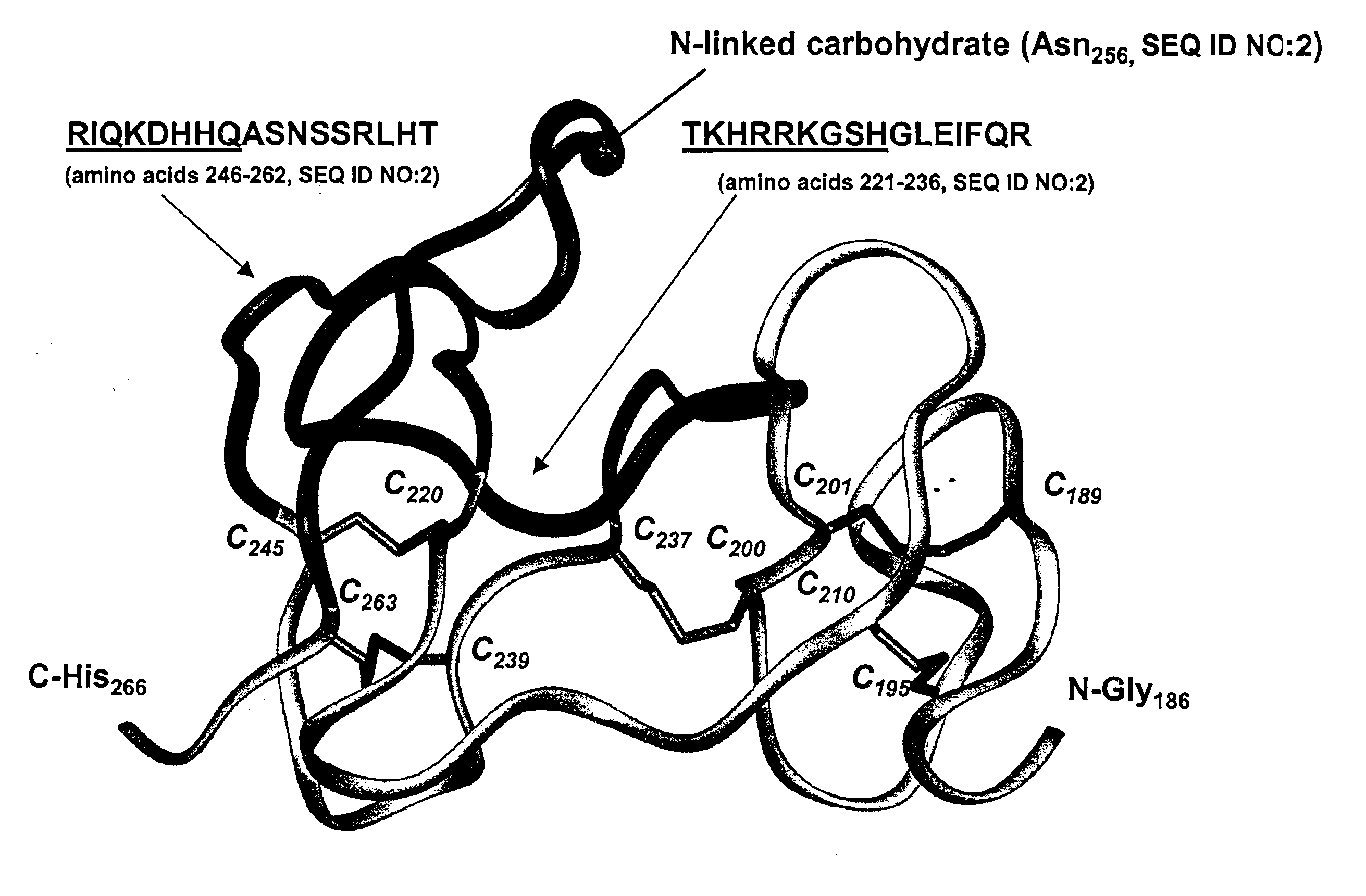
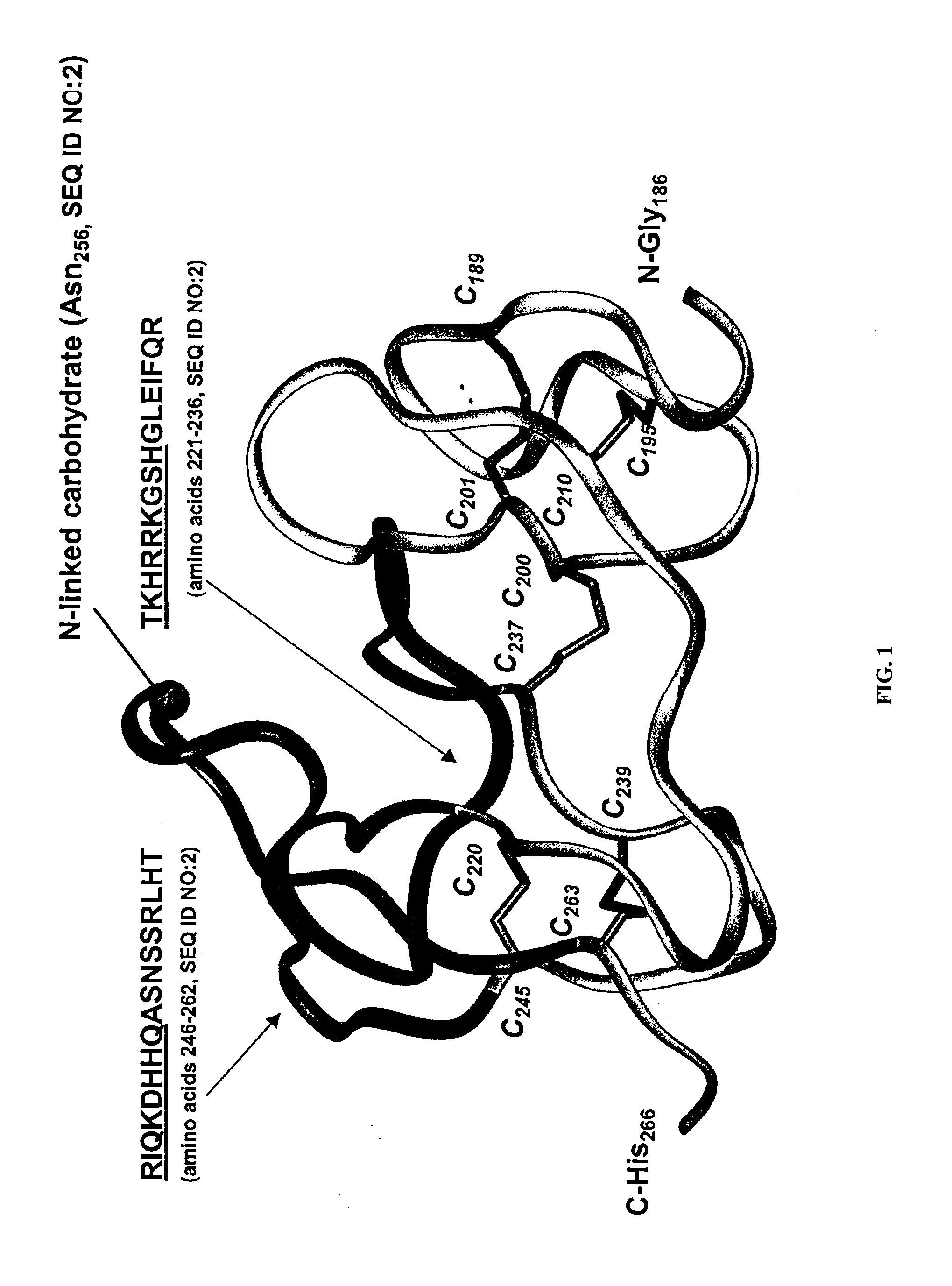
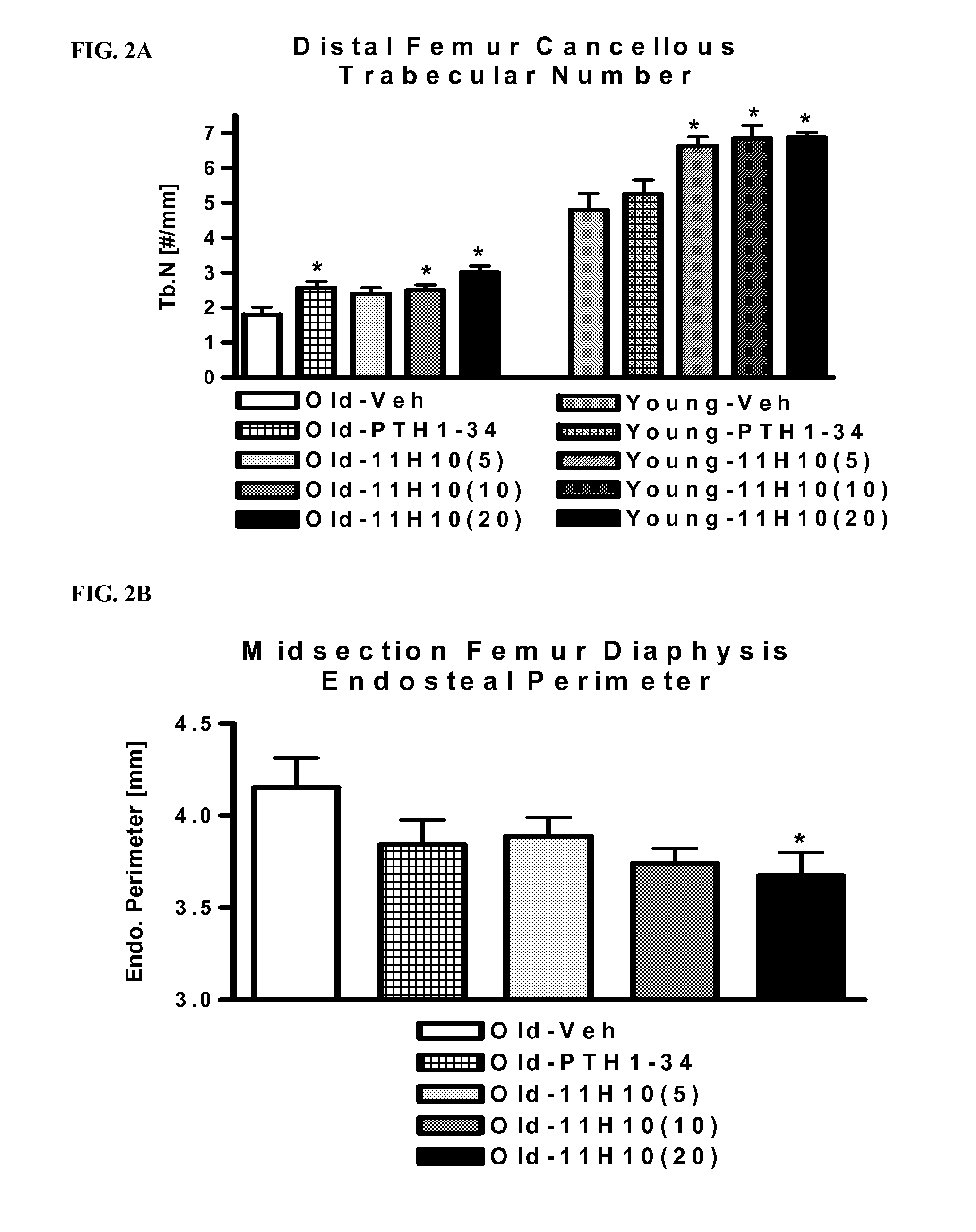
The present invention provides antibodies and immunologically functional fragments thereof that specifically bind Dkk-1 polypeptides. The subject antibodies and fragments bind with high affinity to a conformational epitope located in the carboxy region of the Dkk-1 protein. Methods for preparing such antibodies or fragments thereof as well as physiologically acceptable compositions containing the antibodies or fragments are also provided. Use of the antibodies and fragments to treat various diseases including bone disorders, inflammatory diseases, neurological diseases, ocular diseases, renal diseases, pulmonary diseases and skin diseases are also disclosed.
Owner:AMGEN INC
PSMA antibodies and protein multimers
The invention includes antibodies or antigen-binding fragments thereof which bind specifically to conformational epitopes on the extracellular domain of PSMA, compositions containing one or a combination of such antibodies or antigen-binding fragments thereof, hybridoma cell lines that produce the antibodies, and methods of using the antibodies or antigen-binding fragments thereof for cancer diagnosis and treatment. The invention also includes oligomeric forms of PSMA proteins, compositions comprising the multimers, and antibodies that selectively bind to the multimers.
Owner:PSMA DEV COMPANY
Immunogens and corresponding antibodies specific for high molecular weight aggregation intermediates common to amyloids formed from proteins of differing sequence
ActiveUS20060280733A1Low toxicityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsHigh molecular massAmyloid disease
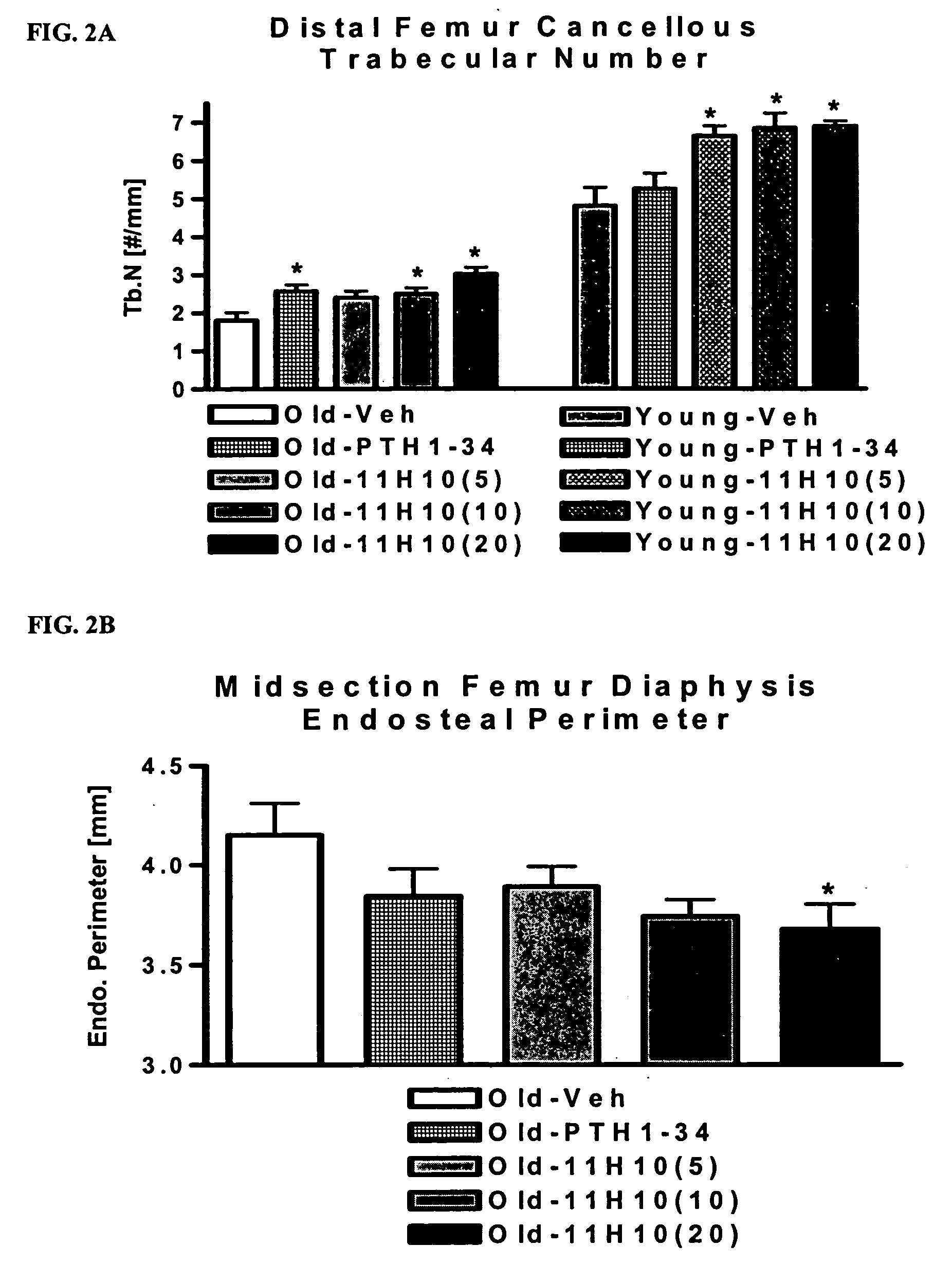
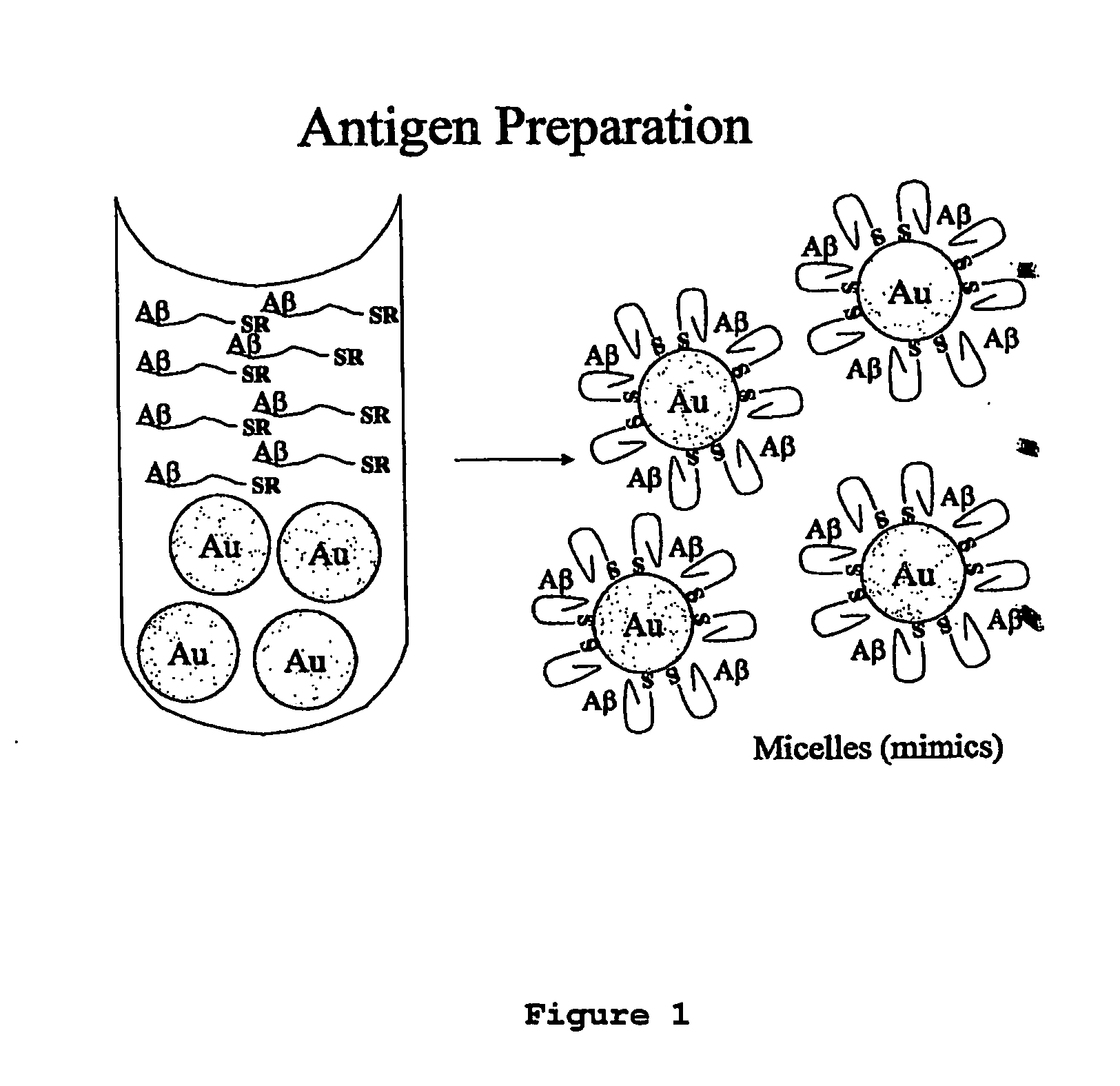
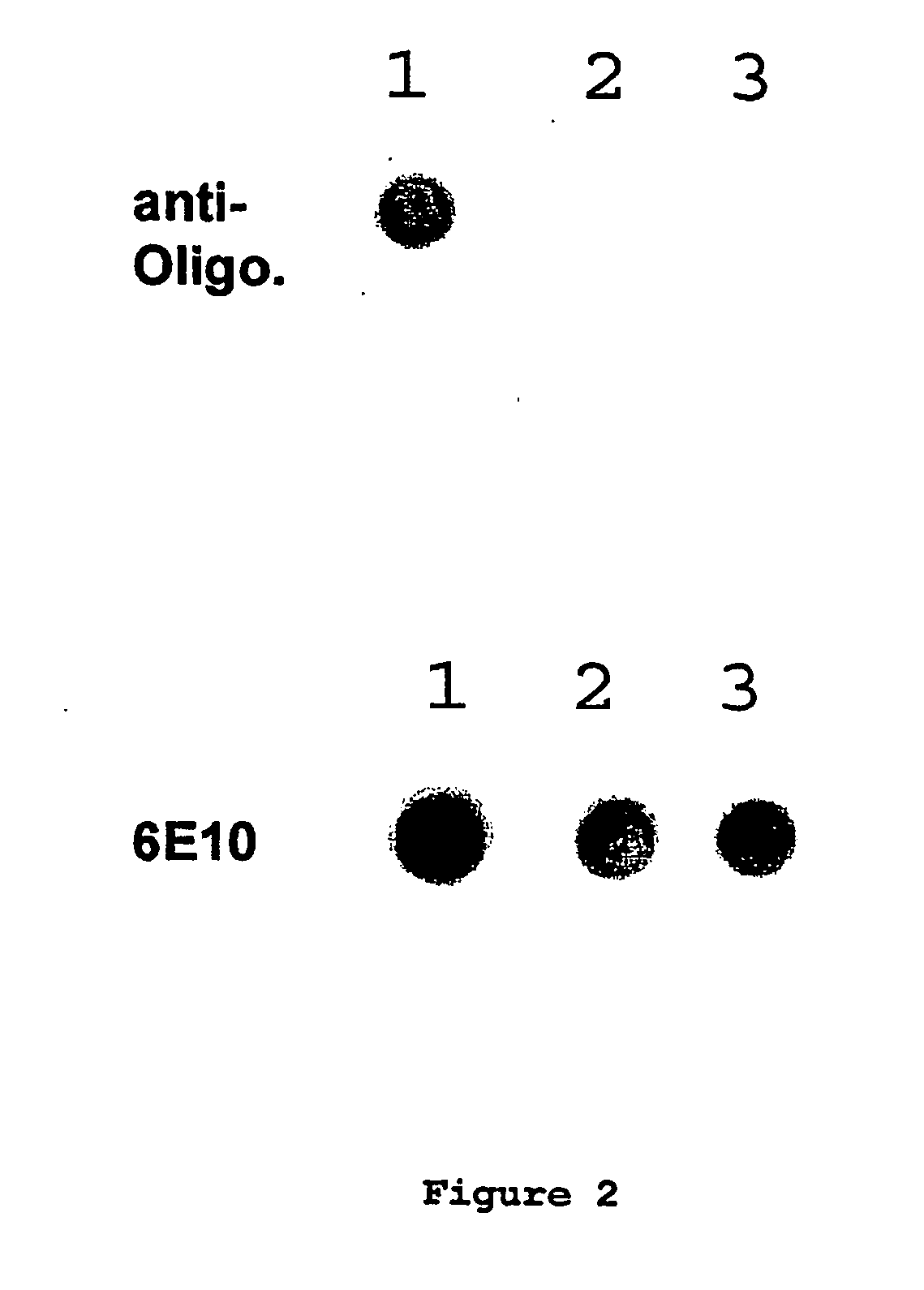
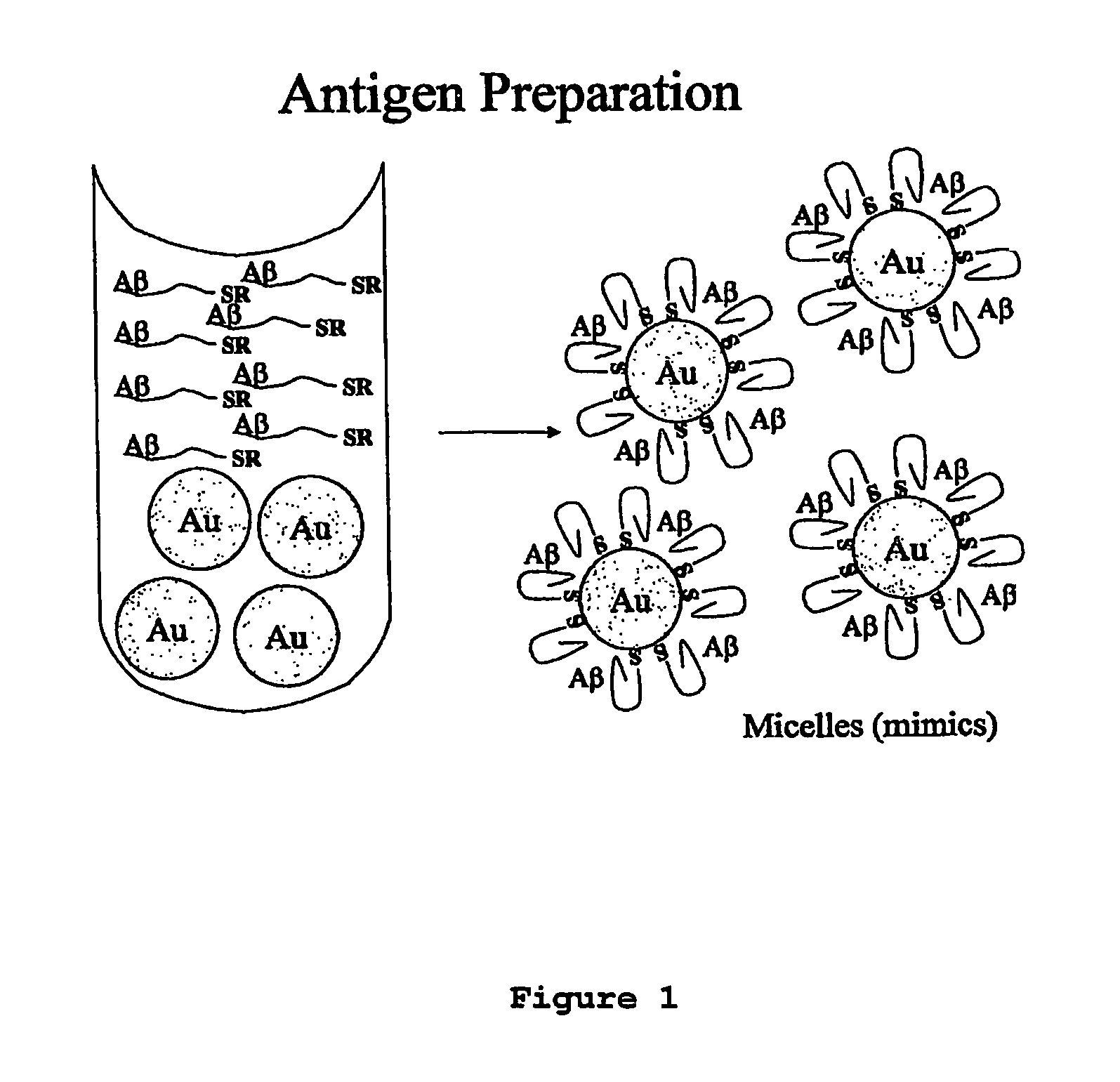
Compositions of matter that comprise one or more conformational epitopes found on amyloid peptide aggregates, antibodies to such epitopes and methods for making and using the compositions, eptitopes and / or antibodies. The invention includes synthetic or isolated compositions that contain or consist of certain conformational epitopes that are found on peptide aggregates (e.g., toxic peptide aggregates) present in human or veterinary patients who suffer from, or who are likely to develop, amyloid diseases (e.g., Alzheimer's Disease). The invention includes methods for the detection, treatment and prevention of diseases in humans or animals, using such compositions. The invention further includes antibodies which bind to the conformational epitopes as well as methods for making such antibodies and methods for the detection, treatment and prevention of diseases and / or identification of potential therapies (e.g., drug screening) using such antibodies.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
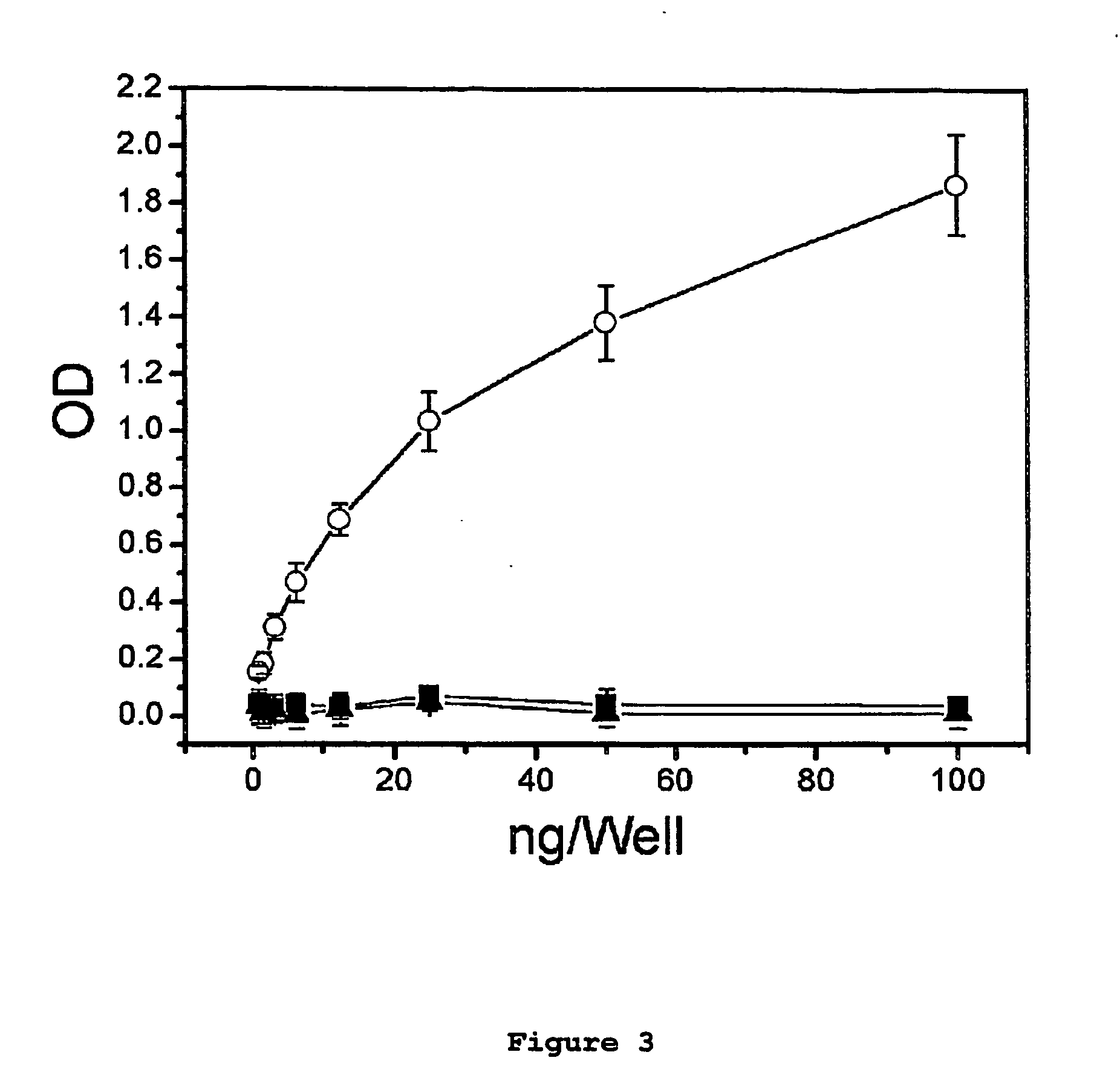
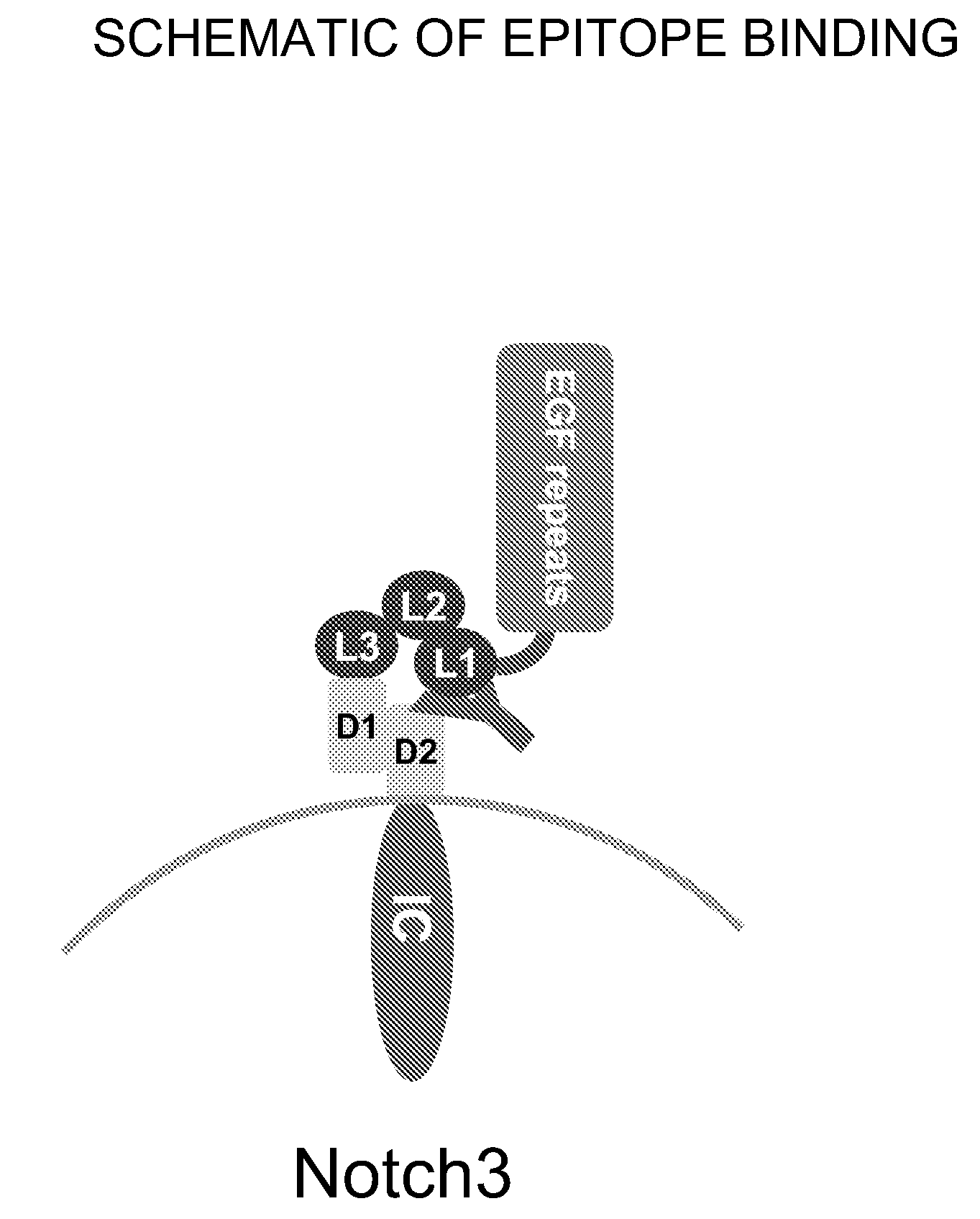
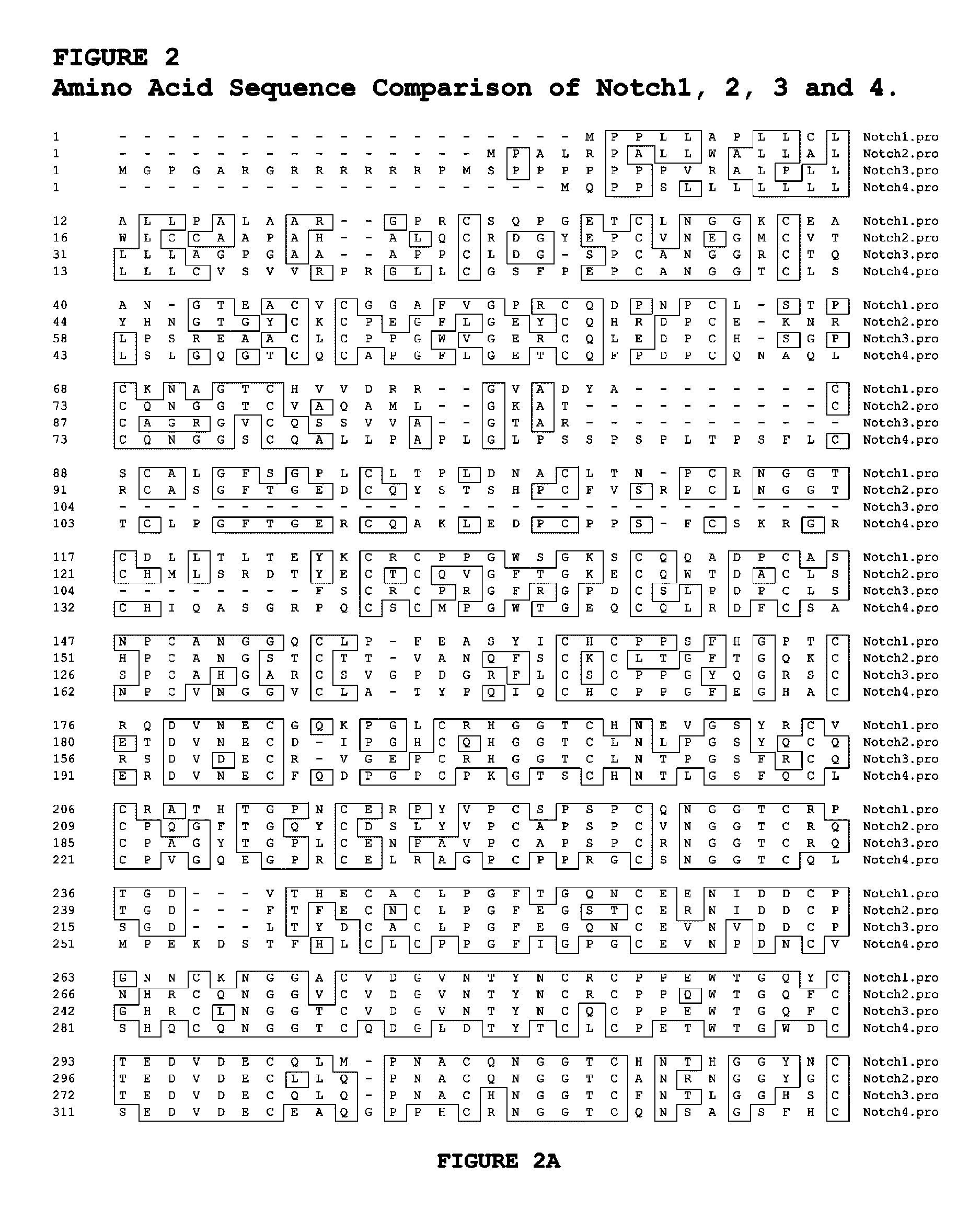
Antagonist Anti-notch3 antibodies and their use in the prevention and treatment of notch3-related diseases
InactiveUS20080226621A1Organic active ingredientsAntipyreticBiological activationConformational epitope
The present invention relates to antagonist antibodies that specifically bind to Notch 3 and inhibit its activation. The present invention includes antibodies binding to a conformational epitope comprising the first Lin12 domain and the second dimerization domain. The present invention also includes uses of these antibodies to treat or prevent Notch 3 related diseases or disorders.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Monoclonal antibodies specific for high molecular weight aggregation intermediates common to amyloids formed from proteins of differing sequence
InactiveUS20070110750A1Low toxicityPreventing and limiting formationSenses disorderNervous disorderAmyloid diseaseDisease cause
Methods for the production of monoclonal antibodies specific to conformational epitope(s) of a prefibrilar aggregate(s) which contribute to amyloid fibril formation in human or animal subjects who suffer from amyloid diseases (e.g. Alzheimer's Disease) and the hybridomas and monoclonal antibodies produced therefrom. Also, the use of such monoclonal antibodies in the immunization of human or animal subjects against Alzheimer's Disease or other amyloid diseases and / or for the diagnosis or detection of Alzheimer's Disease or other amyloid diseases. The monoclonal antibodies may be administered concomitantly or in combination with anti-inflammatory agents, such as gold or gold containing compounds, to decrease neural inflammation associated with amyloid diseases (e.g. Alzheimer's Disease).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Antibodies That Bind Myostatin, Compositions And Methods
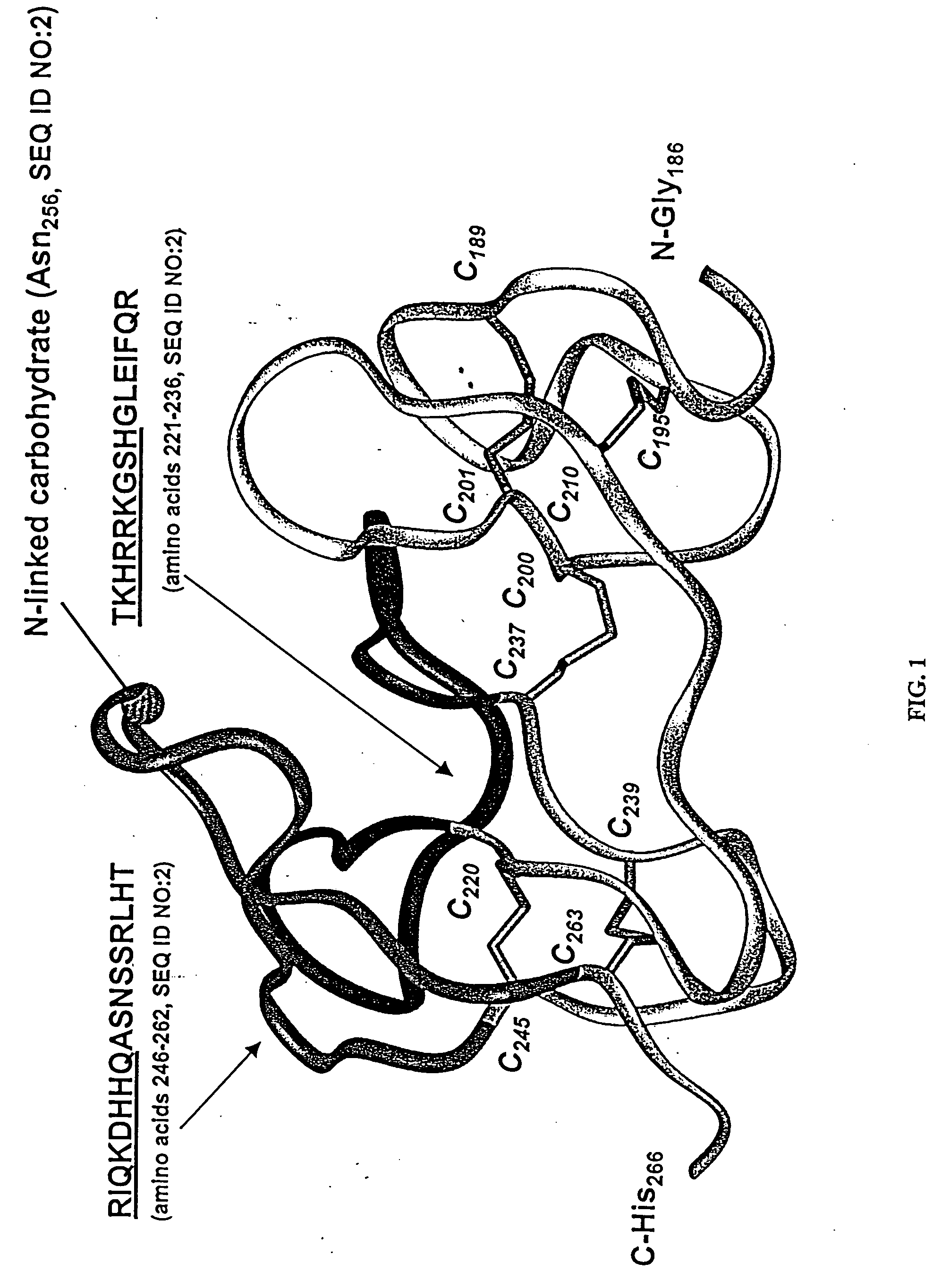
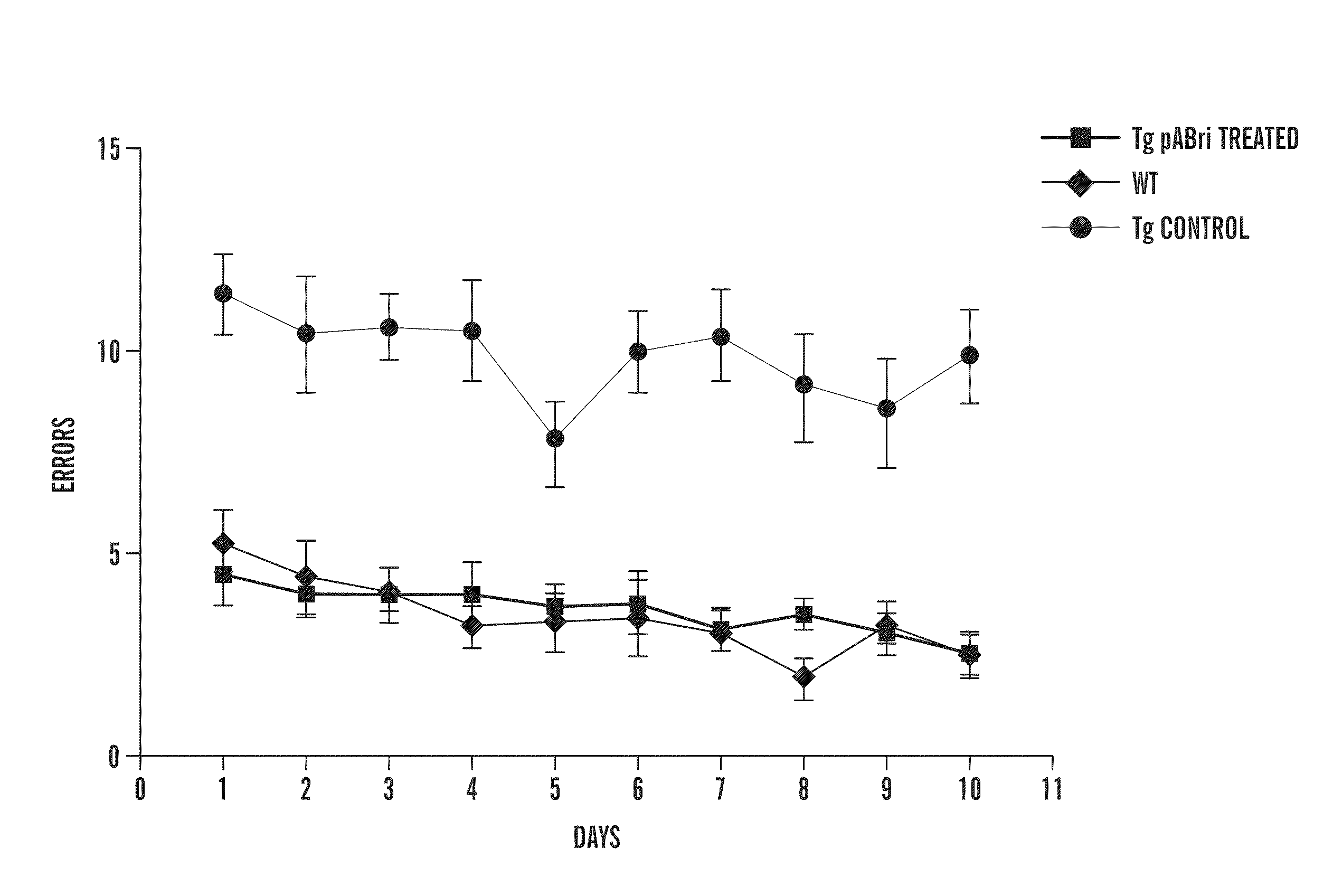
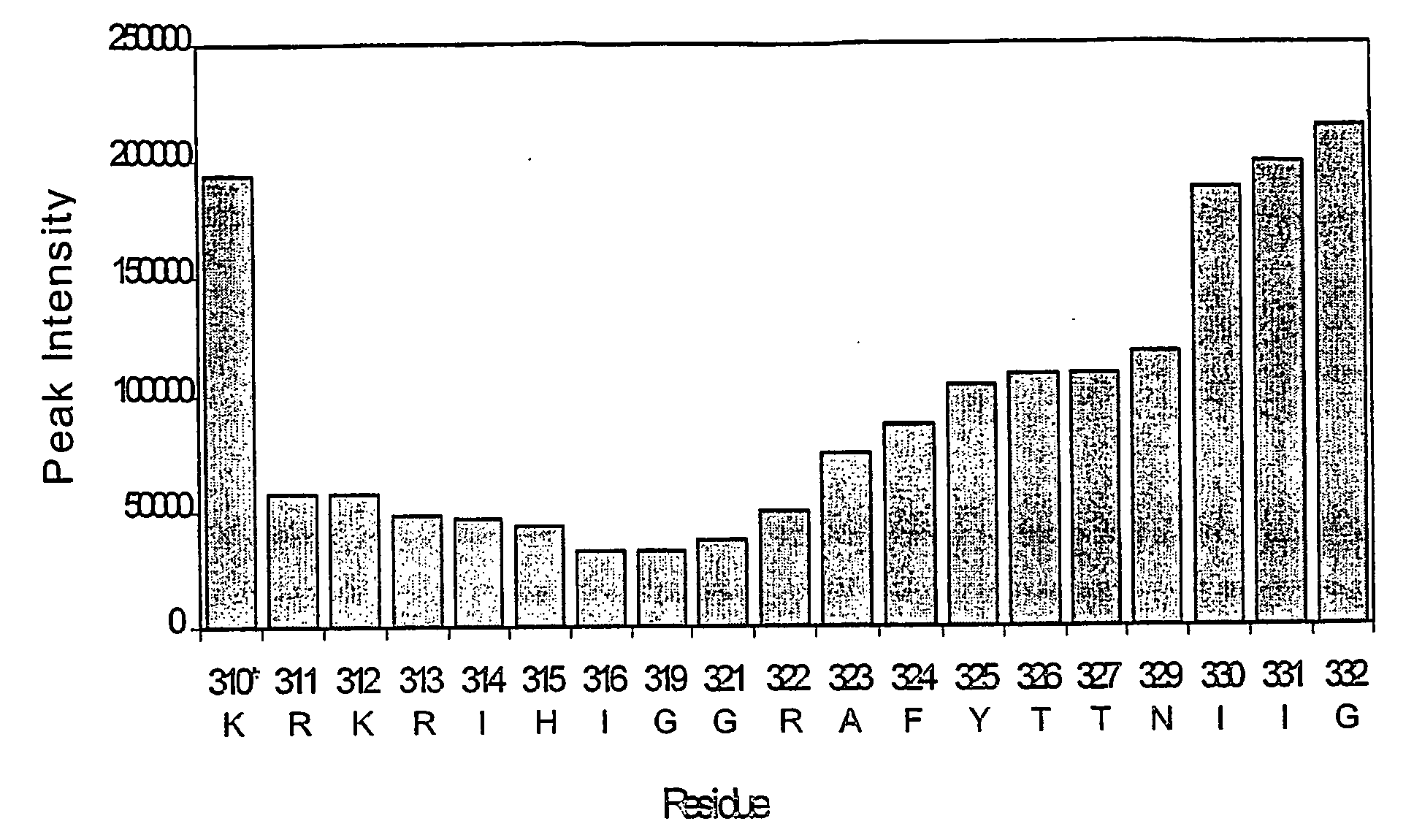
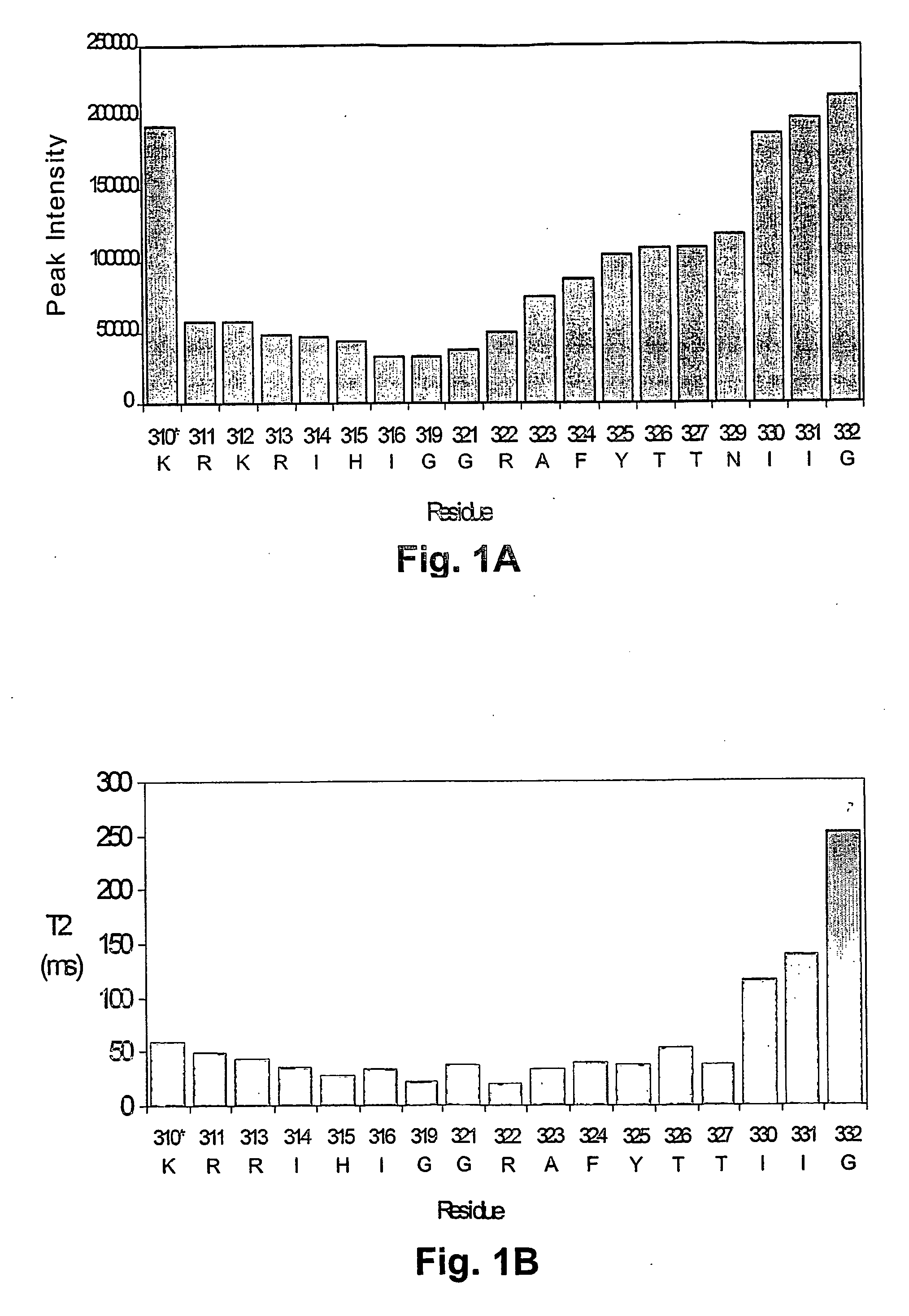
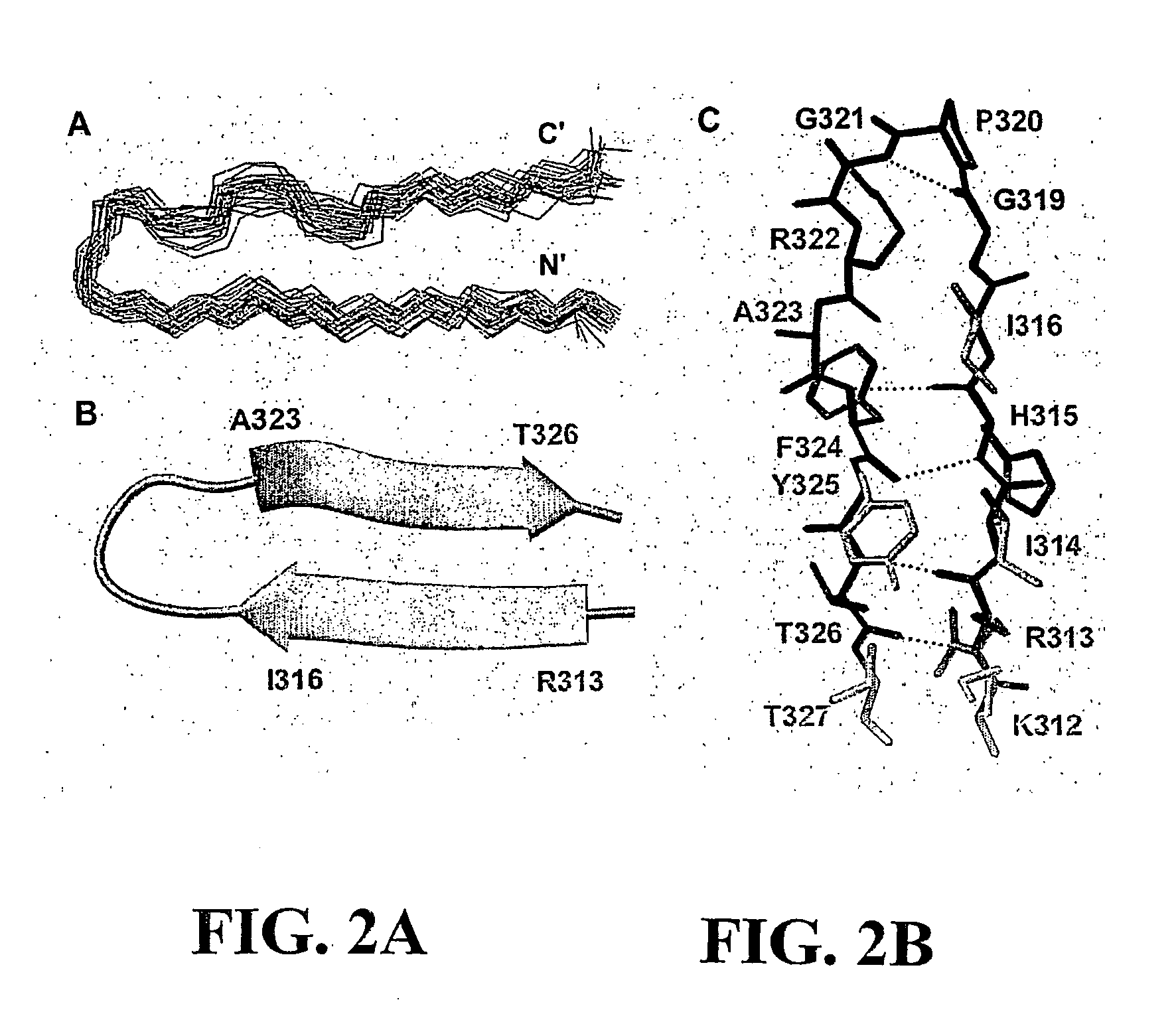
There are disclosed selective myostatin antagonists (including antibodies), nucleic acids encoding them, and methods of making and using them. Neutralizing antibodies recognizing the conformational epitope near position 21 to 31 and position 50 to 60.
Owner:AMGEN INC
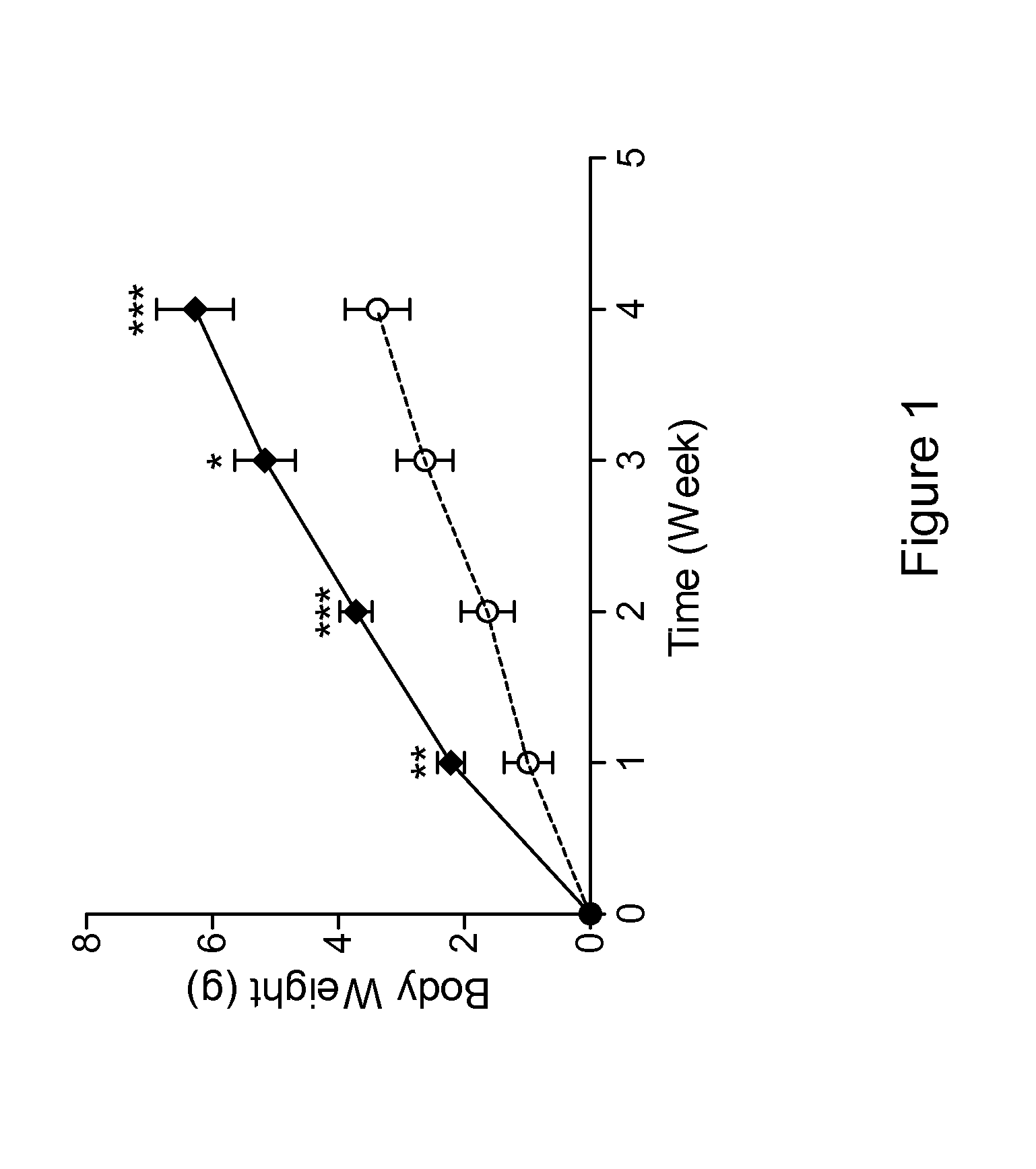
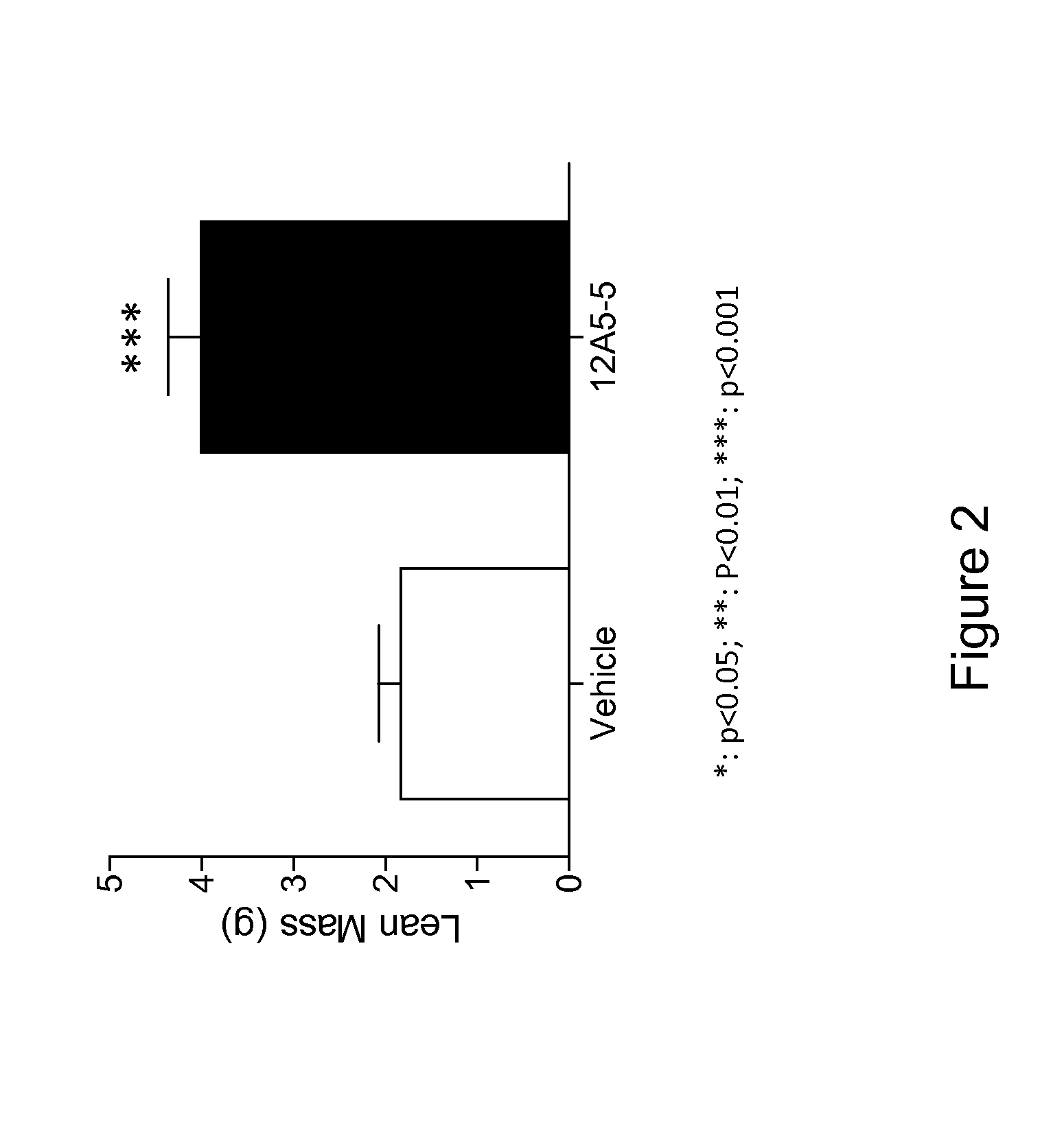
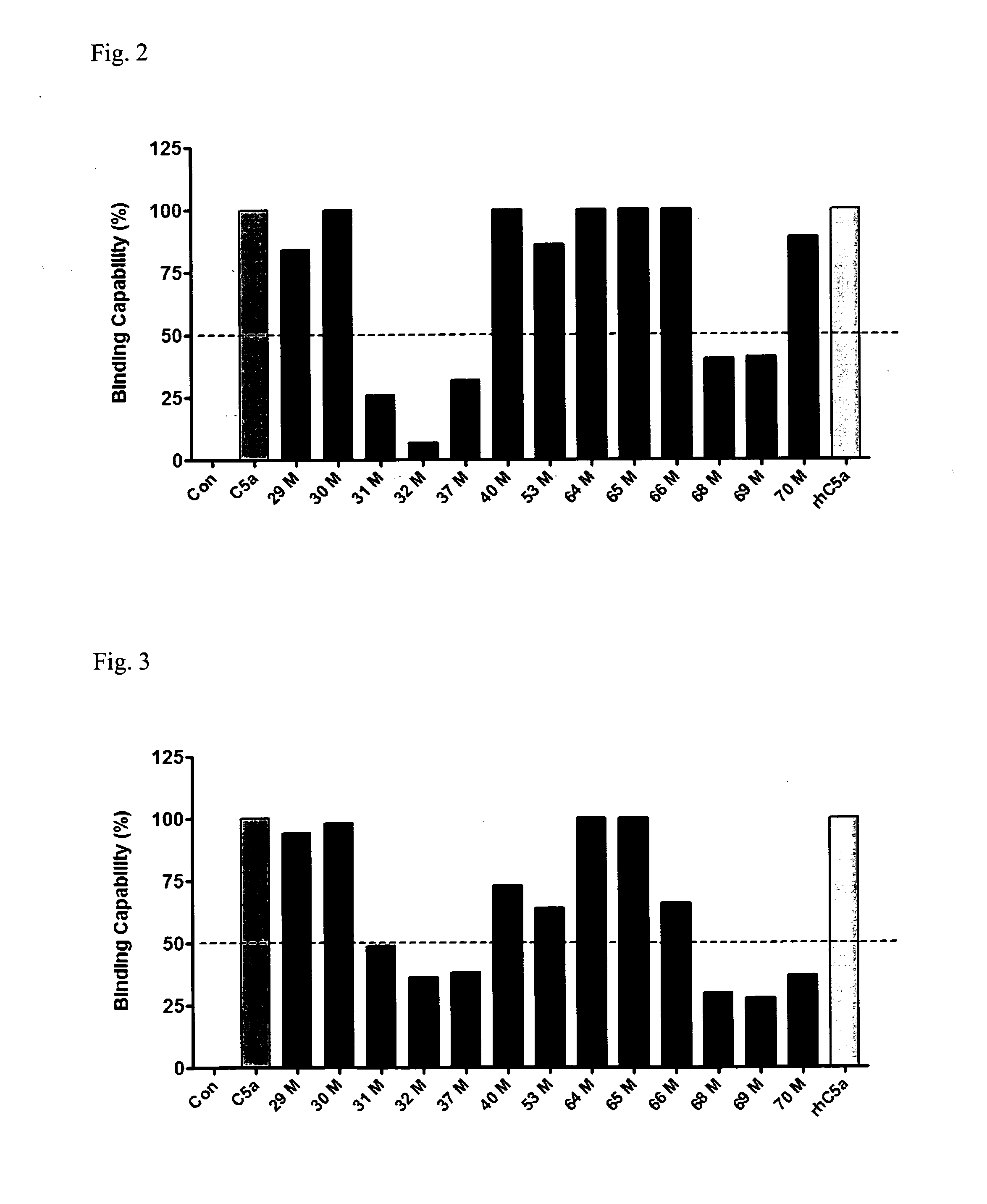
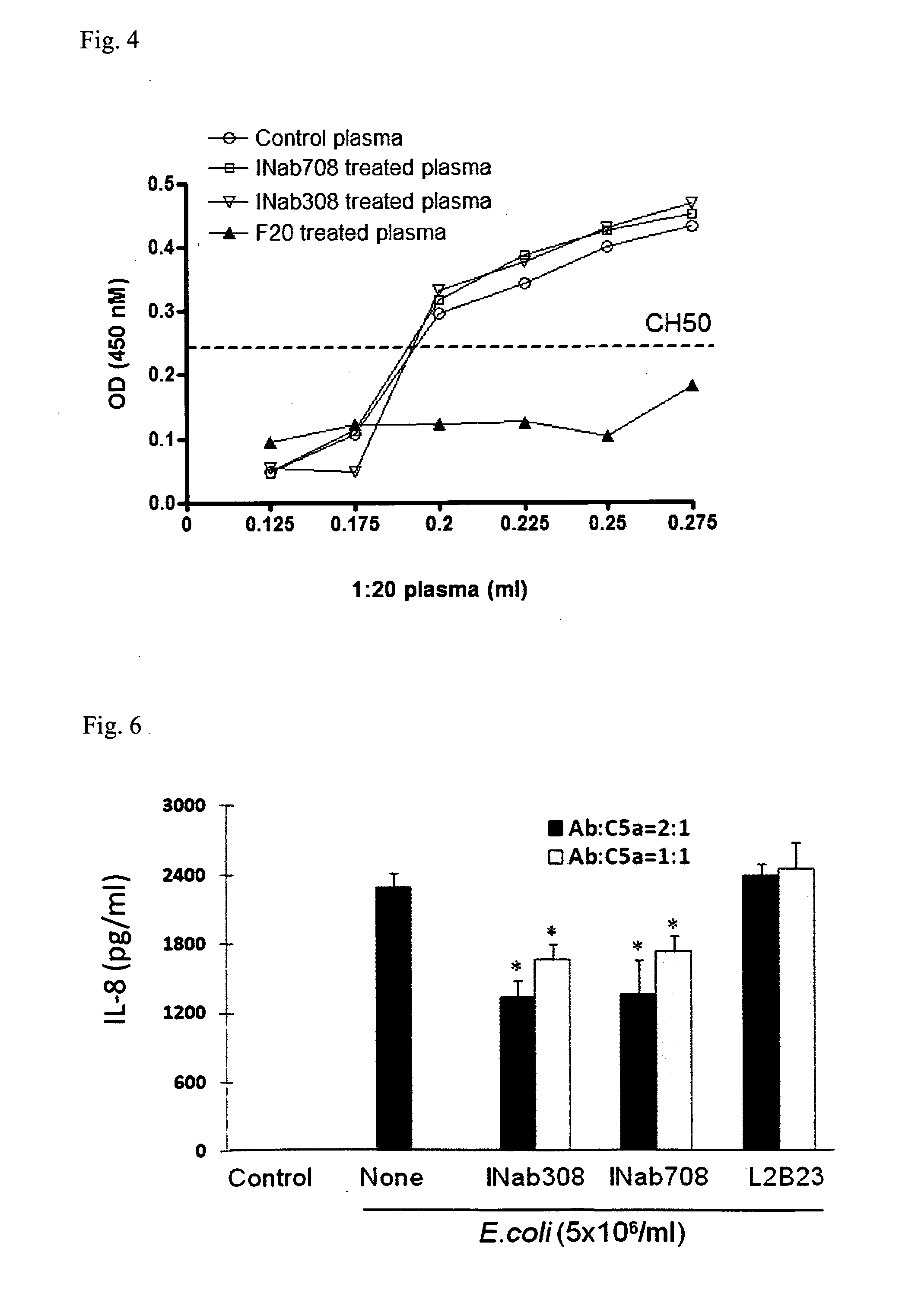
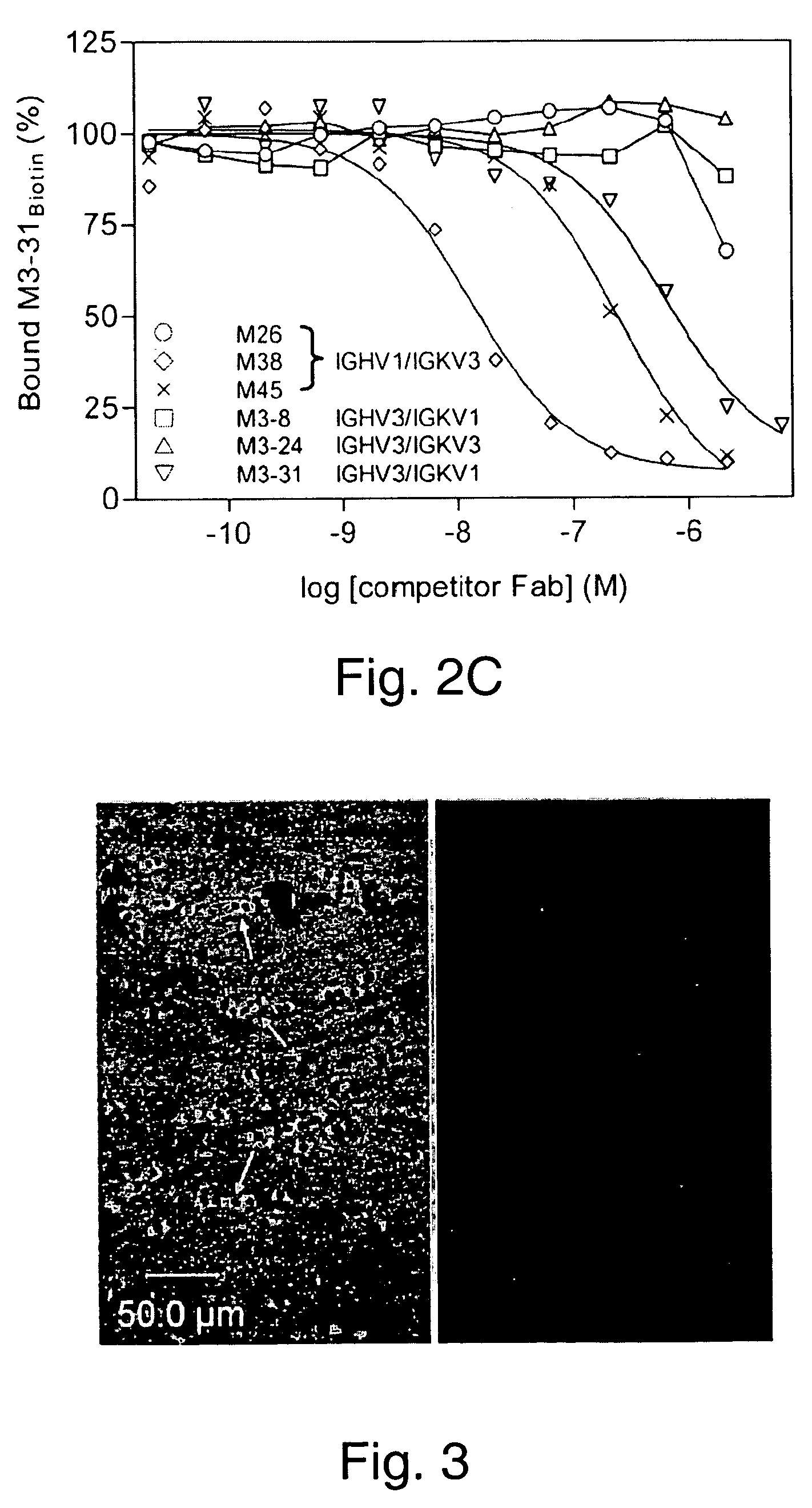
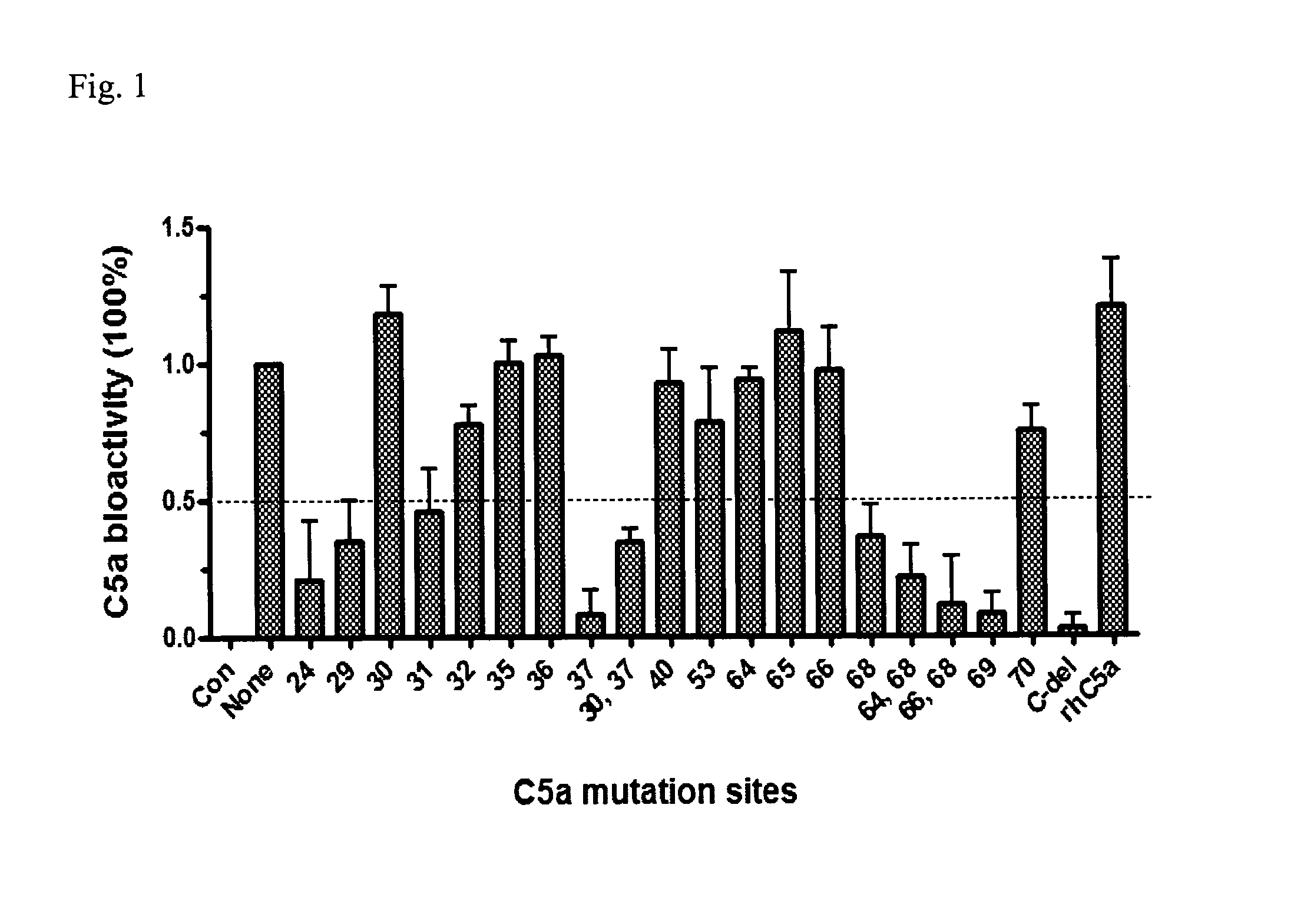
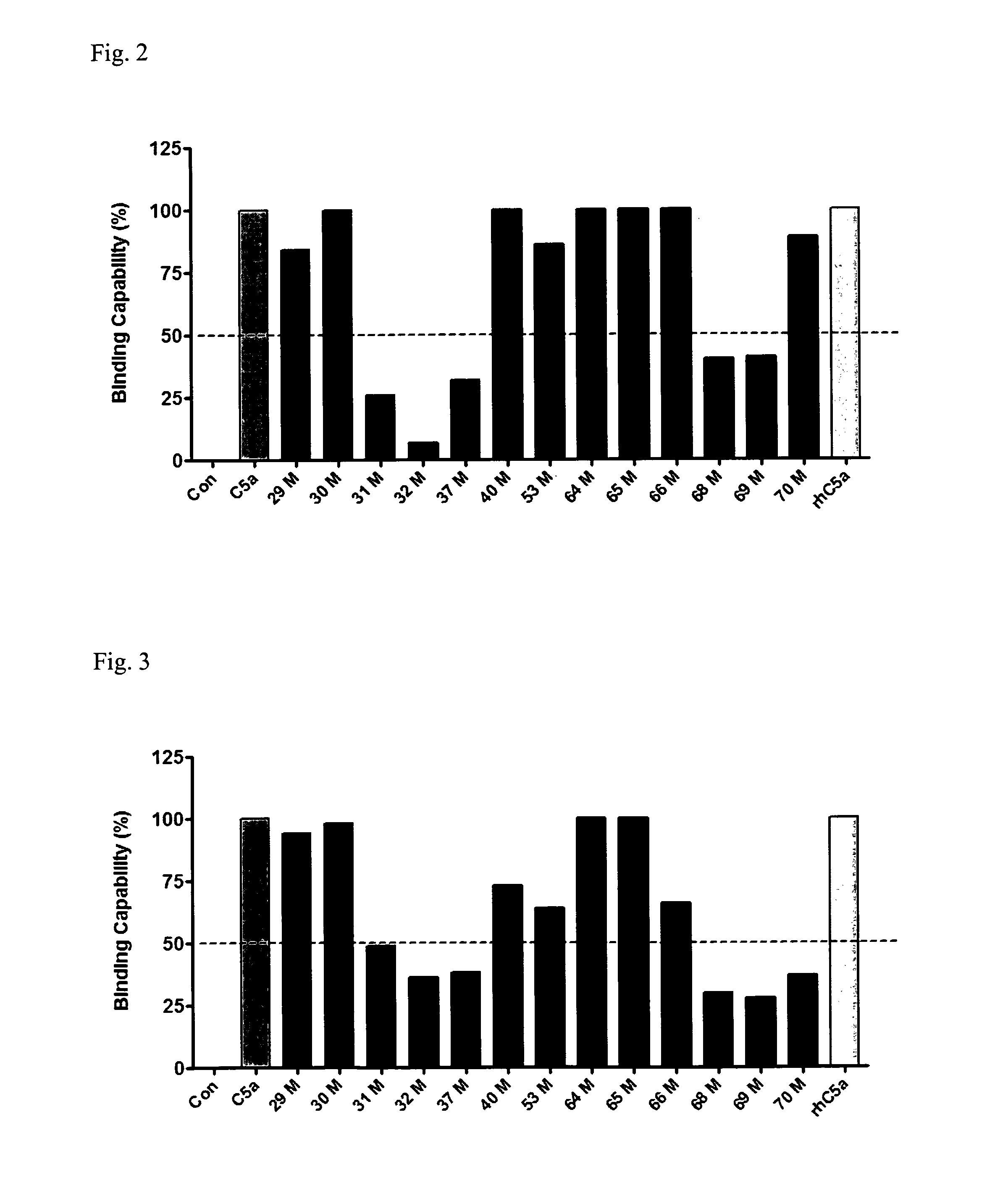
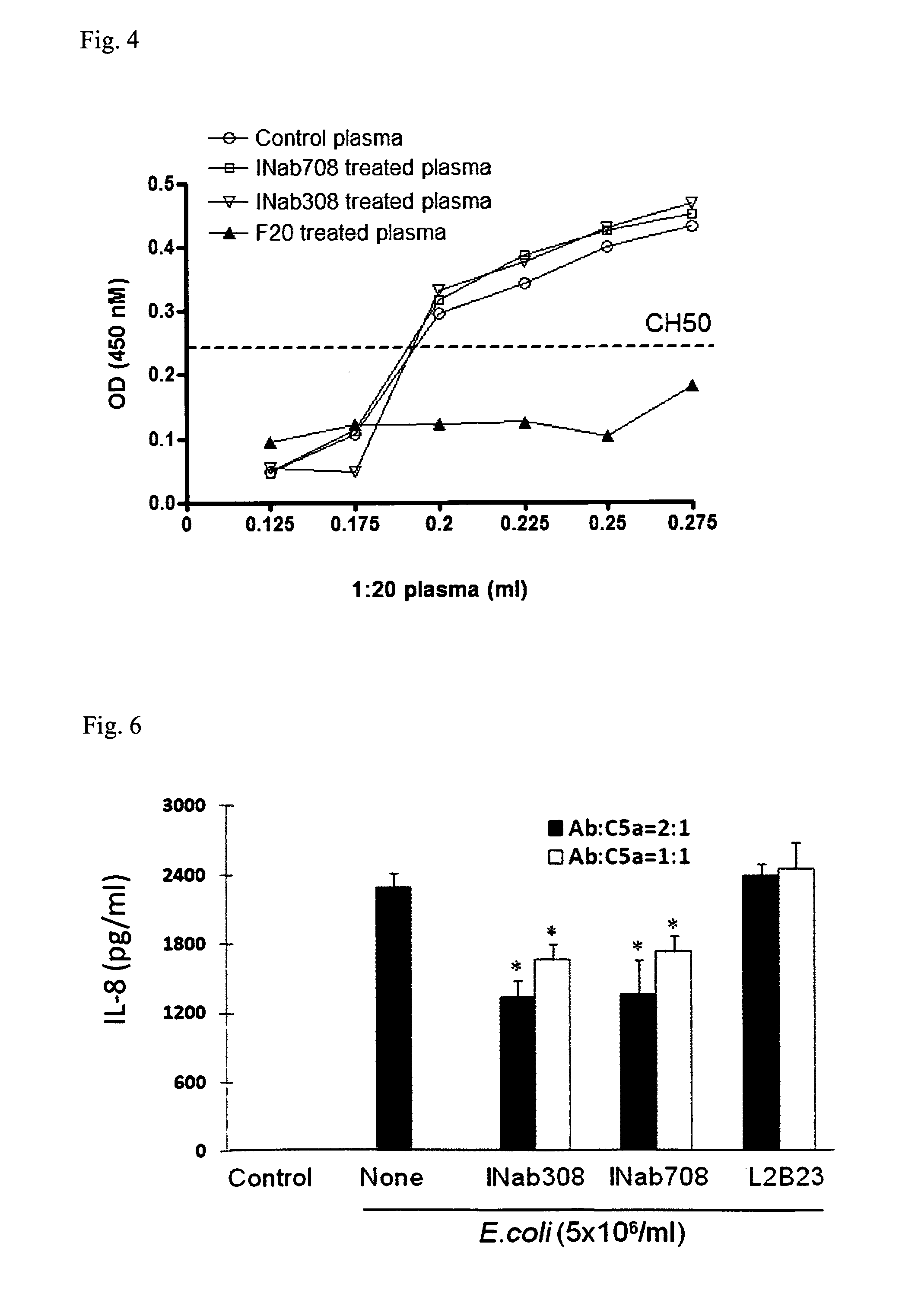
Anti-C5A Binding Moieties with High Blocking Activity
ActiveUS20120231008A1Easy to prepareProlong half-life in vivoAntipyreticGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
The present invention relates to binding moieties that specifically bind to a conformational epitope of C5a, in particular human C5a. Preferred binding moieties are anti-C5a antibodies that bind to this conformational epitope. The binding moieties described herein are useful as active agents in pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment and prevention of various acute and chronic diseases, in particular acute inflammatory diseases, such as the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), and different degrees of sepsis including sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock.
Owner:INFLARX
Immunotherapy targeting of the shared abnormal conformational state of amyloidogenic peptides/proteins
ActiveUS20100284909A1Effective immunotherapeuticPoor efficacyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseAmyloid disease
The present invention is directed to pharmaceutical agents and compositions useful for the treatment and prevention of amyloid disease in a subject. The invention further relates to isolated antibodies that recognize a common conformational epitope of amyloidogenic proteins or peptides that are useful for the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of amyloid disease.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Treatment methods using dkk-1 antibodies
The present invention provides antibodies and immunologically functional fragments thereof that specifically bind Dkk-1 polypeptides. The subject antibodies and fragments bind with high affinity to a conformational epitope located in the carboxy region of the Dkk-1 protein. Methods for preparing such antibodies or fragments thereof as well as physiologically acceptable compositions containing the antibodies or fragments are also provided. Use of the antibodies and fragments to treat various diseases including bone disorders, inflammatory diseases, neurological diseases, ocular diseases, renal diseases, pulmonary diseases and skin diseases are also disclosed.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Antagonist anti-Notch3 antibodies and their use in the prevention and treatment of Notch3-related diseases
The present invention relates to antagonist antibodies that specifically bind to Notch 3 and inhibit its activation. The present invention includes antibodies binding to a conformational epitope comprising the first Lin12 domain and the second dimerization domain. The present invention also includes uses of these antibodies to treat or prevent Notch 3 related diseases or disorders.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Method for diagnosis and prognosis of multiple sclerosis
This invention provides methods utilizing detection / quantification of autoantibodies to specific epitopes of myelin components (e.g. to conformational epitope of myelin / oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG)) for the definitive diagnosis, and / or staging or typing, and / or prognosis of multiple sclerosis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Anti-C5a binding antibodies with high block activity
ActiveUS8802096B2Easy to prepareProlong half-life in vivoAntipyreticGenetic material ingredientsActive agentAcute inflammatory disease
Owner:INFLARX
Monoclonal antibodies specific to hemagglutinin from influenza virus H5-subtype and uses thereof
ActiveUS8444986B2SsRNA viruses negative-senseMicrobiological testing/measurementHemagglutininAvian influenza virus
Monoclonal antibodies and related binding proteins that are specific for conformational epitopes of avian influenza virus K5 subtype hemagglutinin glycoprotein are provided. The antibodies can be used for the detection and treatment of H5 subtype AIV in specimens.
Owner:TEMASEK LIFE SCIENCES LABORATORY +1
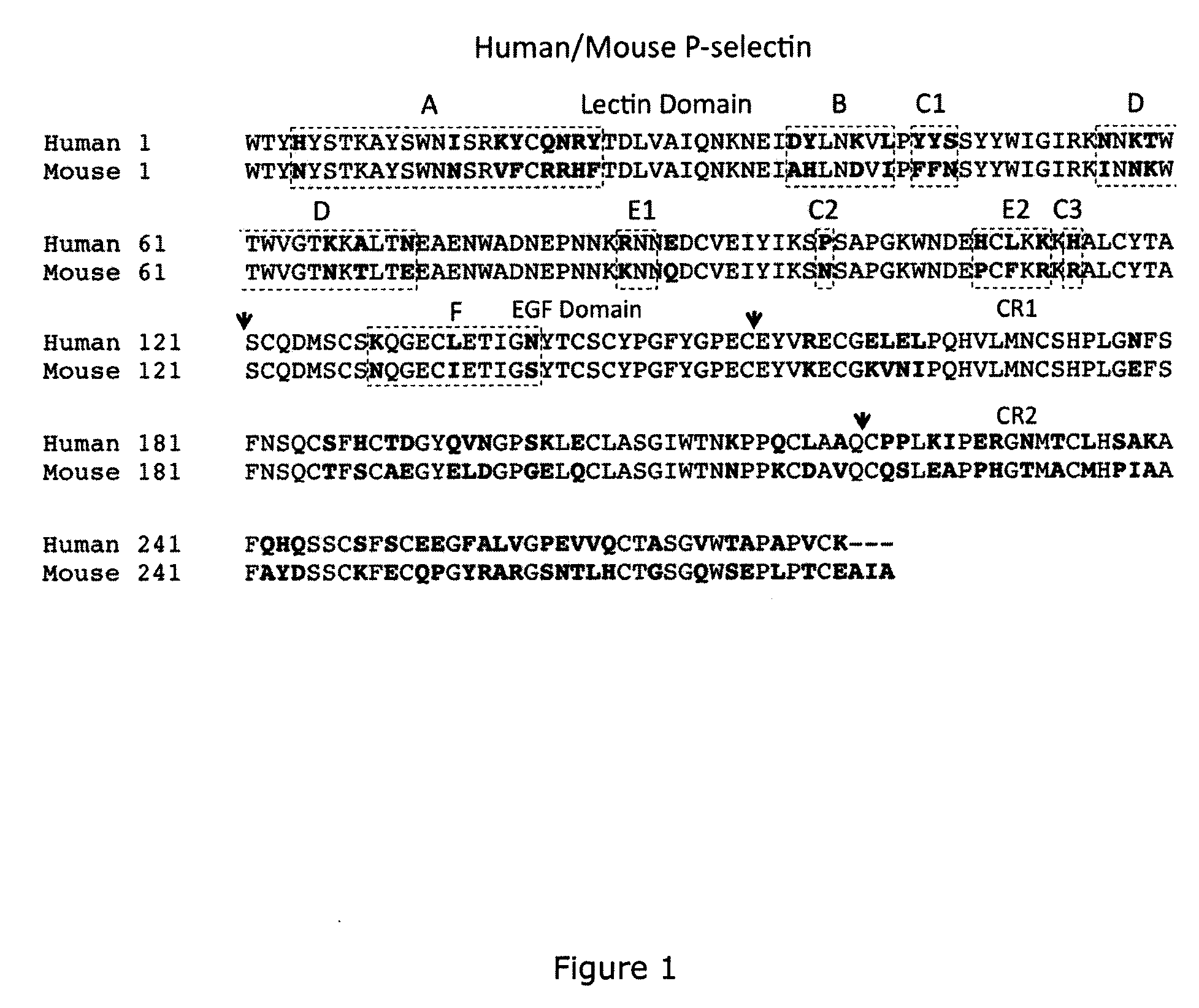
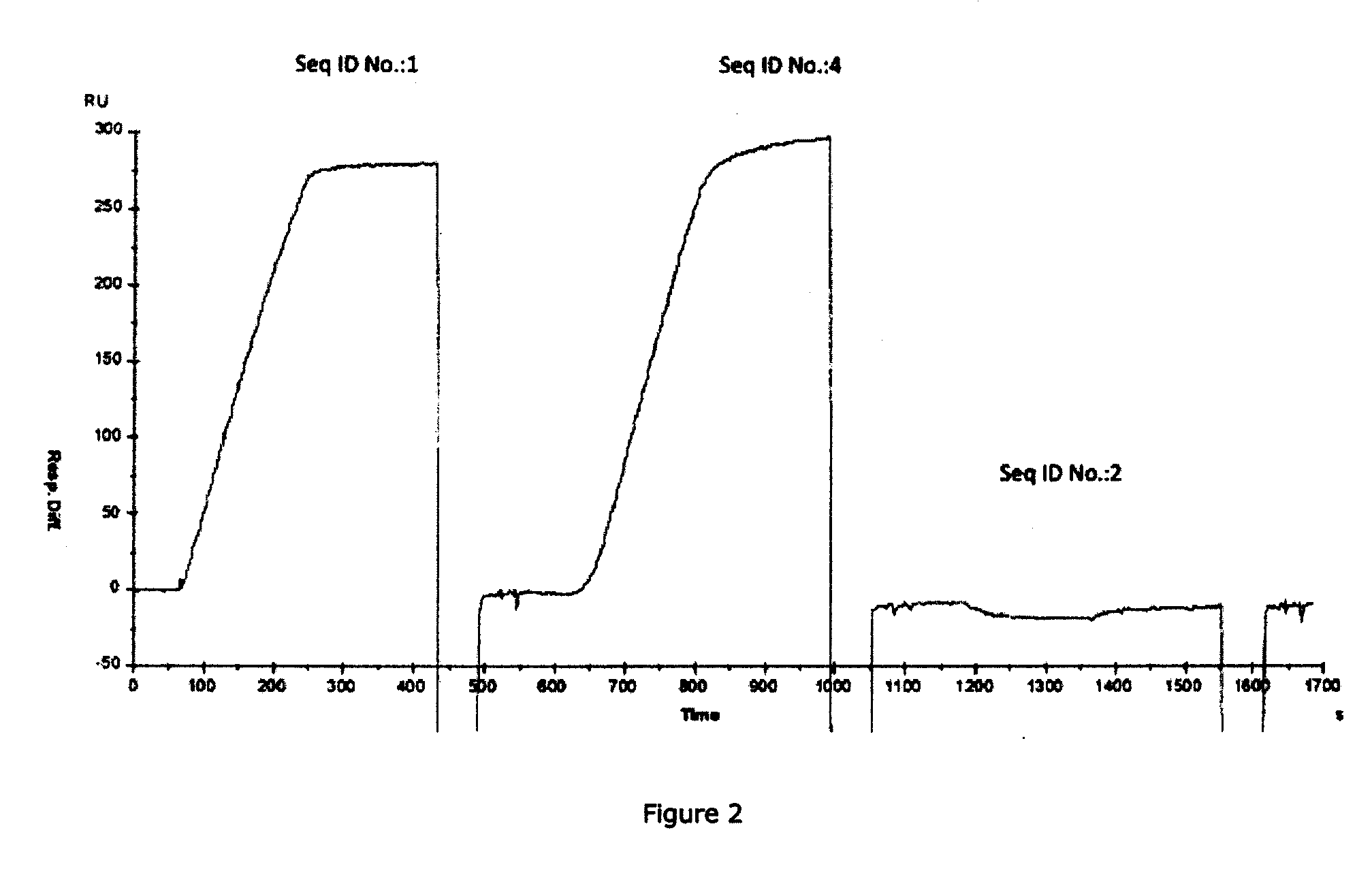
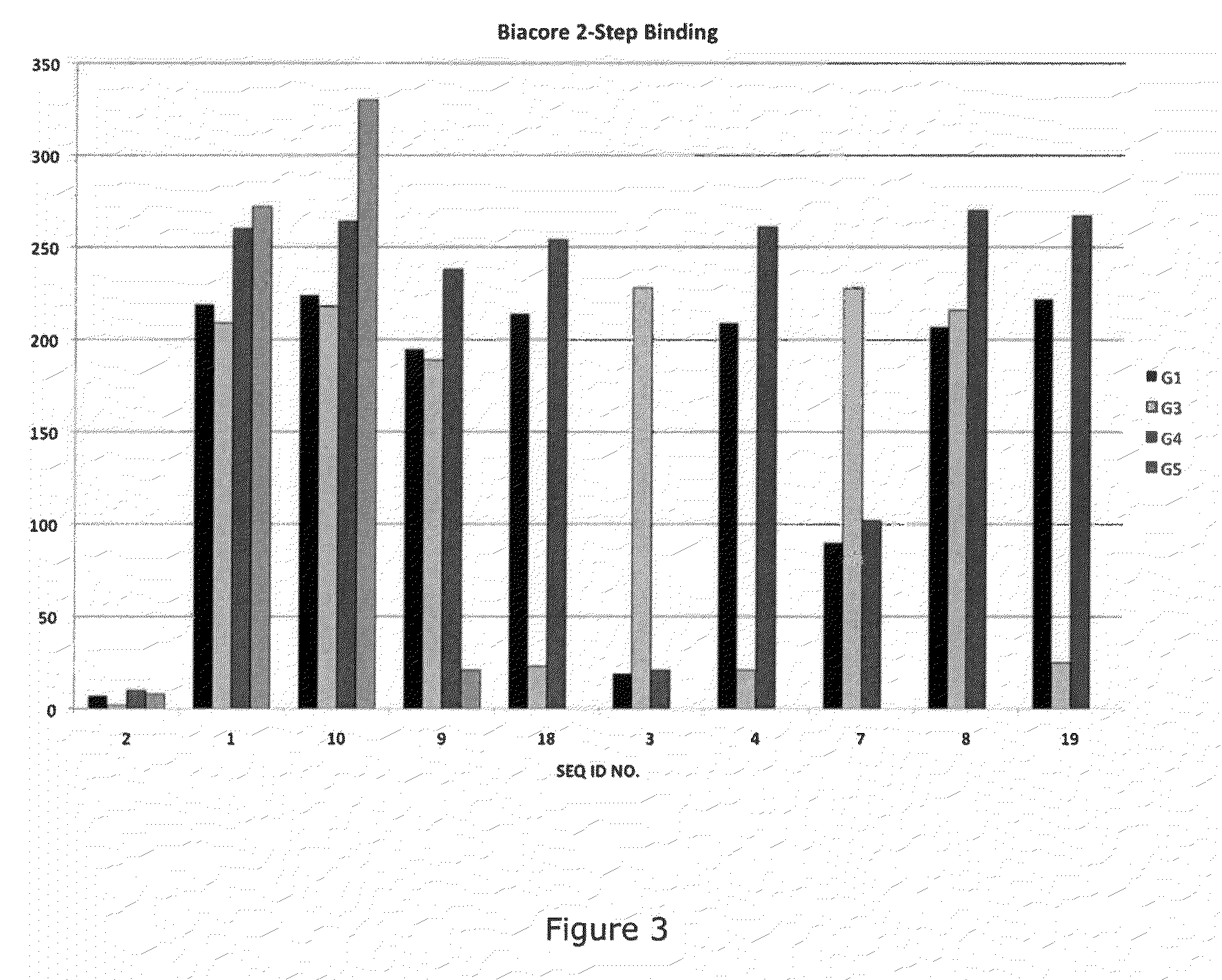
Anti-p-selectin antibodies and methods of their use and identification
ActiveUS20110293617A1Reduce vasoocclusionImprove the level ofAnimal cellsFungiP-selectinBinding domain
Antibodies are disclosed which bind specifically to P-selectin and which block the binding of PSGL-1 to P-selectin. These anti-P-selectin antibodies may also cause dissociation of preformed P-selectin / PSGL-1 complexes. The disclosure identifies a heretofore unrecognized, near N-terminal, antibody binding domain (a conformational epitope) of P-selectin to which the function-blocking antibodies (which may be chimeric, human or humanized antibodies for example) bind. Antibodies are disclosed which bind to the conformational epitope of P-selectin and which have a dual function in blocking binding of PSGL-1 to P-selectin, and in causing dissociation of preformed P-selectin / PSGL-1 complexes. Such single and dual function anti-P-selectin antibodies and binding fragments thereof may be used in the treatment of a variety of inflammatory and thrombotic disorders and conditions. Screening methods for identifying such antibodies are also disclosed.
Owner:SELEXYS PHARMA CORP +1
Mesothelin antibodies and methods for eliciting potent antitumor activity
ActiveCN104955845AAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiological material analysisSingle-domain antibodyTumor cells
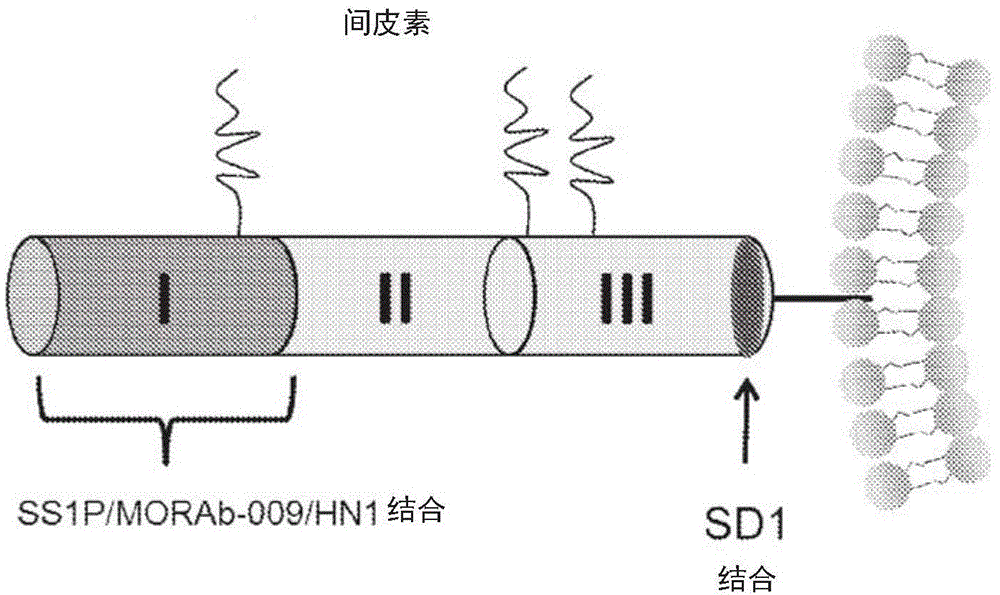
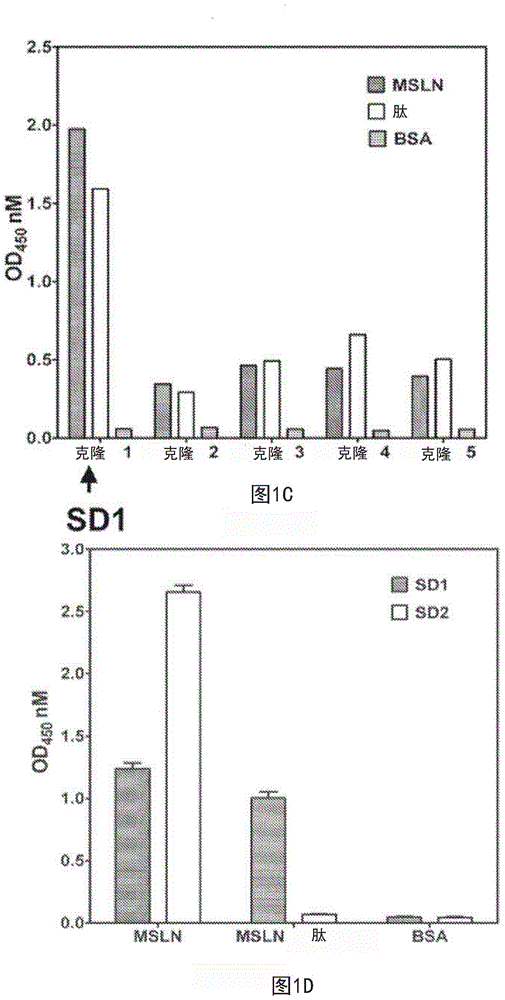
Described herein is the use of phage display antibody engineering technology and synthetic peptide screening to identify SDl and SD2, human single-domain antibodies to mesothelin. SDl recognizes a conformational epitope at the C-terminal end (residues 539-588) of human mesothelin close to the cell surface. SD2 binds full-length mesothelin. To investigate SDl as a potential therapeutic agent, a recombinant human Fc (SDl-hFc) fusion protein was generated. The SDl-hFc protein exhibits strong complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), in addition to antibody- dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), against mesothelin-expressing tumor cells. Furthermore, the SDl-hFc protein causes significant tumor growth inhibition of tumor xenografts in nude mice. SDl and SD2 are the first human single-domain antibodies targeting mesothelin-expressing tumors.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Methods of treating inflammatory or thrombotic conditions with anti-P-selectin antibodies
Antibodies are disclosed which bind specifically to P-selectin and which block the binding of PSGL-1 to P-selectin. These anti-P-selectin antibodies may also cause dissociation of preformed P-selectin / PSGL-1 complexes. The disclosure identifies a heretofore unrecognized, near N-terminal, antibody binding domain (a conformational epitope) of P-selectin to which the function-blocking antibodies (which may be chimeric, human or humanized antibodies for example) bind. Antibodies are disclosed which bind to the conformational epitope of P-selectin and which have a dual function in blocking binding of PSGL-1 to P-selectin, and in causing dissociation of preformed P-selectin / PSGL-1 complexes. Such single and dual function anti-P-selectin antibodies and binding fragments thereof may be used in the treatment of a variety of inflammatory and thrombotic disorders and conditions. Screening methods for identifying such antibodies are also disclosed.
Owner:SELEXYS PHARMA CORP +1
Hybridoma cell strain for stable secretion of anti-PEDV monoclonal antibody and secreted antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN106380515ABiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against virusesMicroorganismBiological property
The invention discloses a hybridoma cell strain for stable secretion of anti-PEDV monoclonal antibody and the secreted antibody and application thereof. The hybridoma cell strain capable of stably secreting the anti-PEDV monoclonal antibody is named as 1B9, and the microbial preservation number is CGMCC No.12695. Researches prove that recognition epitope of the monoclonal antibody secreted by the hybridoma cell strain is conformational epitope. It shows through virus neutralization tests that the monoclonal antibody can effectively neutralize the strain of PEDV G2 subtype but has no neutralization activity to a strain of PEDV G1 subtype. In view of biological characteristics of the monoclonal antibody, the monoclonal antibody can be used for identification of the strains of PEDV G1 and G2 subtypes, and on this basis, a series of diagnostic methods are established. In addition, the monoclonal antibody also can be used for treating diseases caused by porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. The invention provides a novel technological means for diagnosis and treatment of PEDV G1 subtype.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Methods for measuring levels of bioactive human hepcidin
Owner:INTRINSIC LIFESCIENCES LLC
Compositions and Methods for Inhibiting Drusen Formation and for Diagnosing or Treating Drusen-Related Disorders
InactiveUS20110020237A1Facilitating break-down and degradation and clearanceInhibition formationHeavy metal active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseDrusen
Compositions of matter and methods for inhibiting drusen or drusen-like deposits and / or for treating diseases related to drusen or drusen-like deposits in human or animal subjects by administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of i) a conformational epitope of an aggregate that contributes to the formation or biosynthesis of drusen or drusen-like deposits and / or ii) an antibody that binds to a conformational epitope of an aggregate that contributes to the formation or biosynthesis of drusen or the drusen-like deposit.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Synthetic virus-like particles with heterologous epitopes
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Mouse anti-human CD14 monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell line, monoclonal antibody, immunohistochemical reagent kit and uses thereof
InactiveCN101200708AShorten primary antibody incubation timeShorten the timeImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsAntigenCD61
The present invention discloses a mouse anti-human CD41 monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell system, a monoclonal antibody and an immunohistochemical kit and an application thereof. A traditional hybridoma preparation technology is used to obtain hybridoma cell strain which excretes anti-human CD41 molecular monoclonal antibody stably. The excreted antibody can identify the conformational epitopes of the combination of human CD41 antigen and CD61 antigen and can inhibit the aggregation effect caused by ADP, collagen, HIP2, etc. The monoclonal antibody is marked biotin directly and combined with alkali phosphatase-strep avidin working fluid, substrate solution and fast red to form the immunohistochemical kit which uses SAP method to detect megakaryocyte. The kit and the detection method provided by the present invention can shorten the detection time and avoid repeated washing, so the status of cell chipping can not occur, the detection efficiency is improved greatly and the present invention is fit for common technicians to operate.
Owner:UNION STEMCELL & GENE ENG
Hepatitis c antibodies and uses thereof
InactiveUS20120039846A1Reduce loadReduce in quantityPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemConformational epitopeHCV Antibody
The present invention provides identification and characterization of conformational epitopes of the envelope protein E2 of the Hepatitis C virus (HCV). The present invention provides a panel of human monoclonal antibodies that recognize conformational epitopes of E2. The antibodies are derived from patients infected with HCV. The present invention provides methods for utilizing HCV antibodies as therapeutic, diagnostic, and / or prophylactic agents. The present invention provides mimotopes with conformational epitopes intact and methods of using mimotopes. The present invention provides methods of stratifying patients based on their response to HCV. The present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions for prevention and treatment of HCV comprising one or more HCV antibodies.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Immunotherapy targeting of the shared abnormal conformational state of amyloidogenic peptides/proteins
ActiveUS8409584B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPeptide/protein ingredientsAmyloid betaConformational epitope
The present invention is directed to pharmaceutical agents and compositions useful for the treatment and prevention of amyloid disease in a subject. The invention further relates to isolated antibodies that recognize a common conformational epitope of amyloidogenic proteins or peptides that are useful for the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of amyloid disease.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
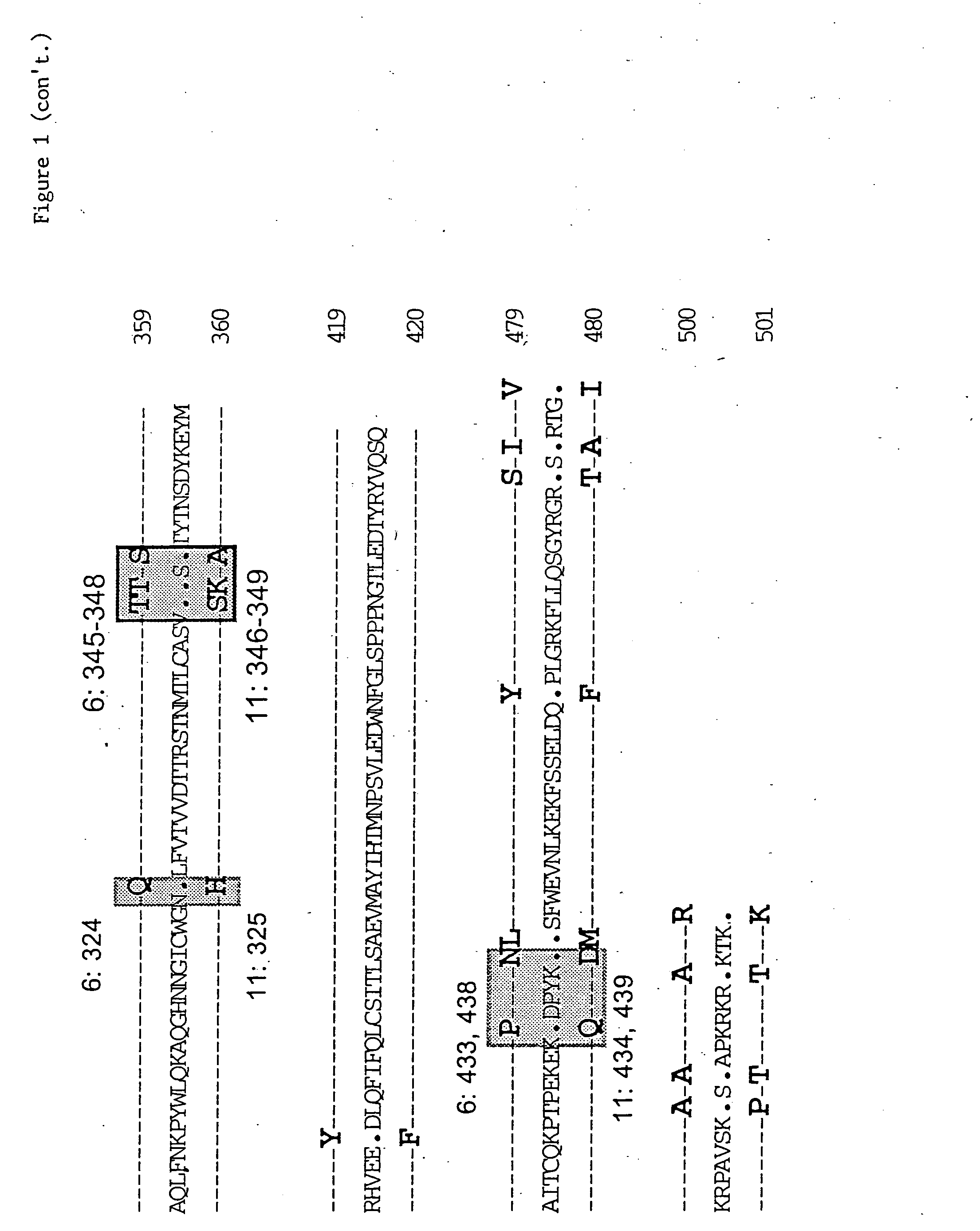
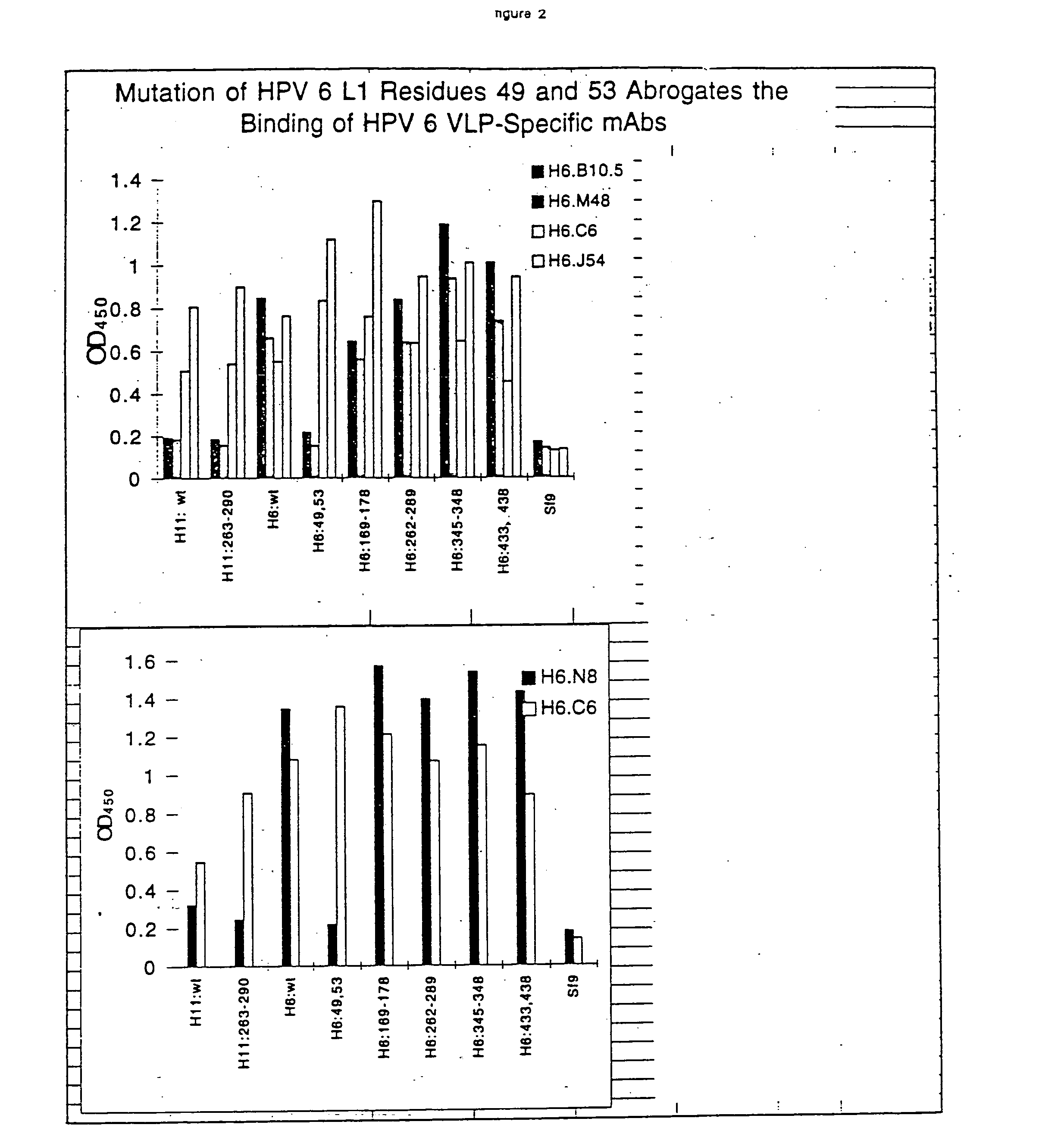
Synthetic virus-like particles with heterologous epitopes
The invention is a series of synthetic virus-like particles comprising a heterologous conformational epitope useful in the characterization of human papillomavirus infection, and useful to vaccinate individual for protection against HPV 6 and HPV 11 infections, and assays employing the synthetic virus-like particles.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Anti-p-selectin antibodies and methods of their use and identification
InactiveUS20110212096A1Reduce vasoocciusionImprove the level ofAntipyreticMicroorganismsDiseaseP-selectin
Antibodies are disclosed which bind specifically to P-selectin and which block the binding of PSGL-1 to P-selectin. These anti-P-selectin antibodies may also cause dissociation of preformed P-selectin / PSGL-1 complexes. The disclosure identifies a heretofore unrecognized, near N-terminal, antibody binding domain (a conformational epitope) of P-selectin to which the function-blocking antibodies (which may be chimeric, human or humanized antibodies for example) bind. Antibodies are disclosed which bind to the conformational epitope of P-selectin and which have a dual function in blocking binding of PSGL-1 to P-selectin, and in causing dissociation of preformed P-selectin / PSGL-1 complexes. Such single and dual function anti-P-selectin antibodies and binding fragments thereof may be used in the treatment of a variety of inflammatory and thrombotic disorders and conditions. Screening methods for identifying such antibodies are also disclosed.
Owner:SELEXYS PHARMA CORP +1
Constrained Hiv V3 Loop Peptides as Novel Immunogens and Receptor Antagonists
InactiveUS20080206264A1Potent and broad activitySuppress infectivityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCyclic peptideDisease
The present invention provides constrained peptides and other organic molecules, that mimic the three dimensional characteristics of the HIV-1 V3 loop peptide when bound by a highly potent human neutralizing monoclonal antibody specific for a V3 conformational epitope, which structure is determined by NMR. Methods for screening for, and designing such molecules are disclosed. These molecules are useful as immunogens for inducing broadly-neutralizing antibodies against HIV-1 as well as antagonists for inhibiting the binding of HIV-1 to the relevant co-receptors, and may therefore be used in method of preventing or treating HIV-1 infection and disease.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
Immunogens and corresponding antibodies specific for high molecular weight aggregation intermediates common to amyloids formed from proteins of differing sequence
Compositions of matter that comprise one or more conformational epitopes found on amyloid peptide aggregates, antibodies to such epitopes and methods for making and using the compositions, eptitopes and / or antibodies. The invention includes synthetic or isolated compositions that contain or consist of certain conformational epitopes that are found on peptide aggregates (e.g., toxic peptide aggregates) present in human or veterinary patients who suffer from, or who are likely to develop, amyloid diseases (e.g., Alzheimer's Disease). The invention includes methods for the detection, treatment and prevention of diseases in humans or animals, using such compositions. The invention further includes antibodies which bind to the conformational epitopes as well as methods for making such antibodies and methods for the detection, treatment and prevention of diseases and / or identification of potential therapies (e.g., drug screening) using such antibodies.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com