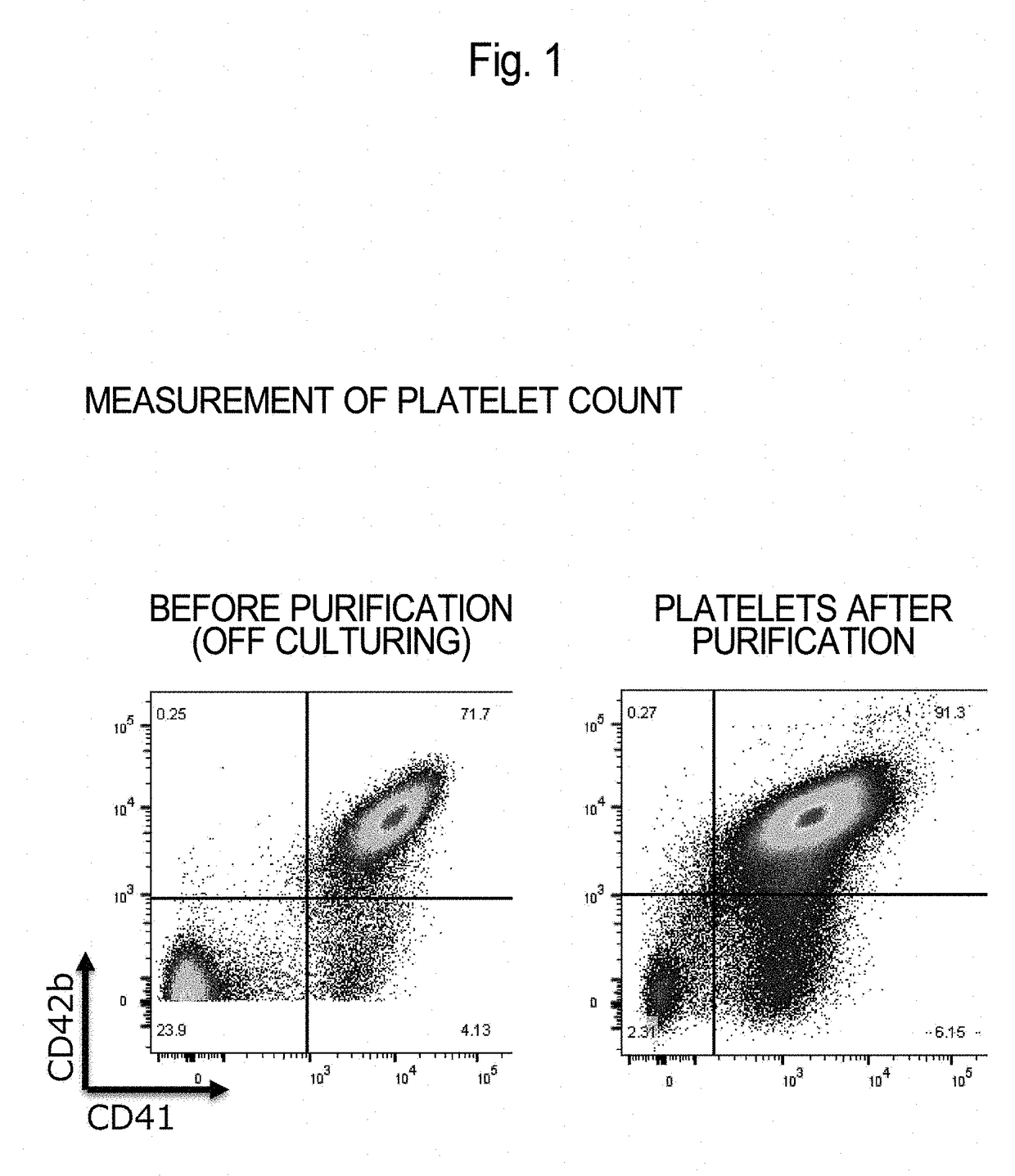
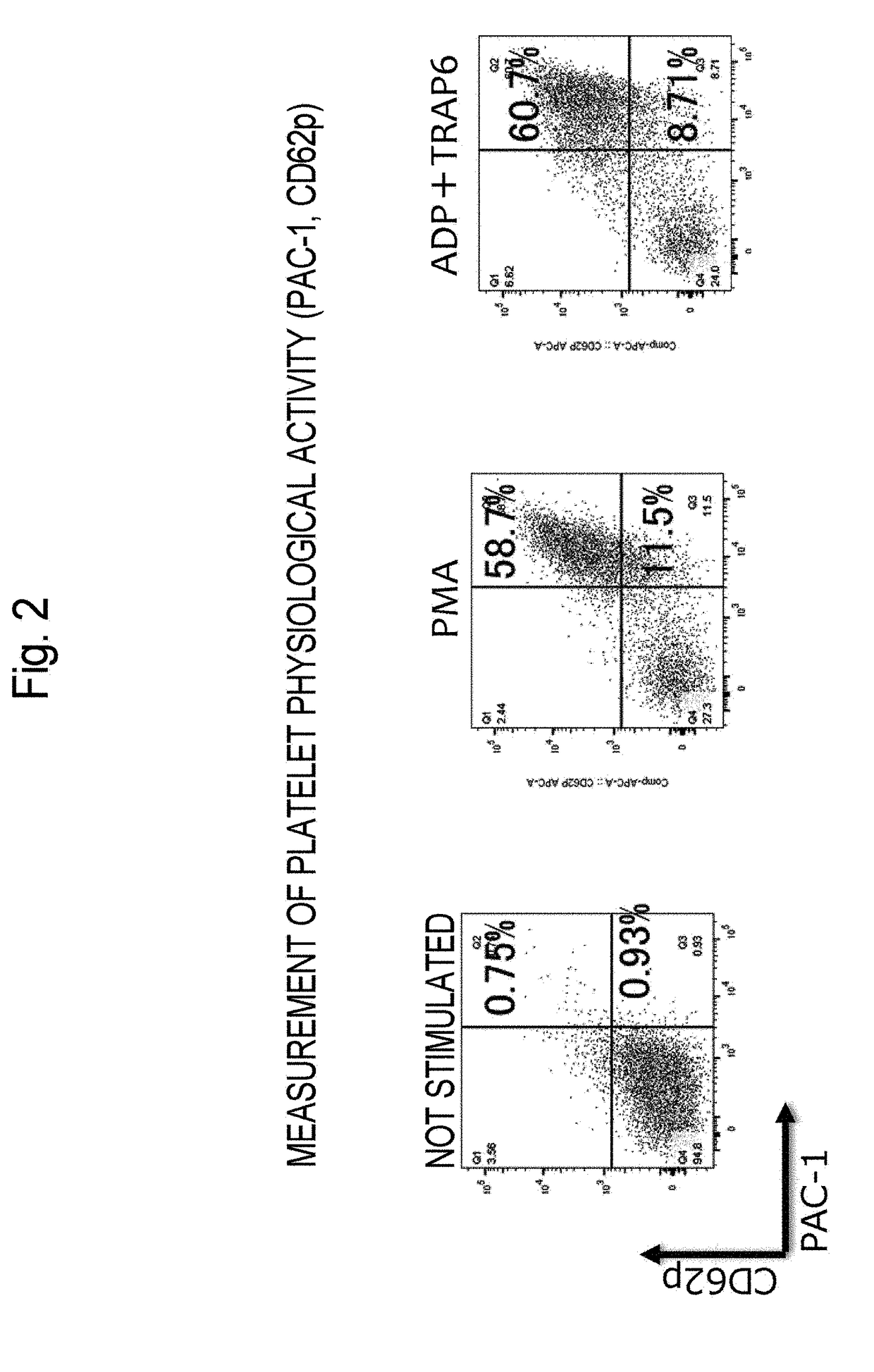
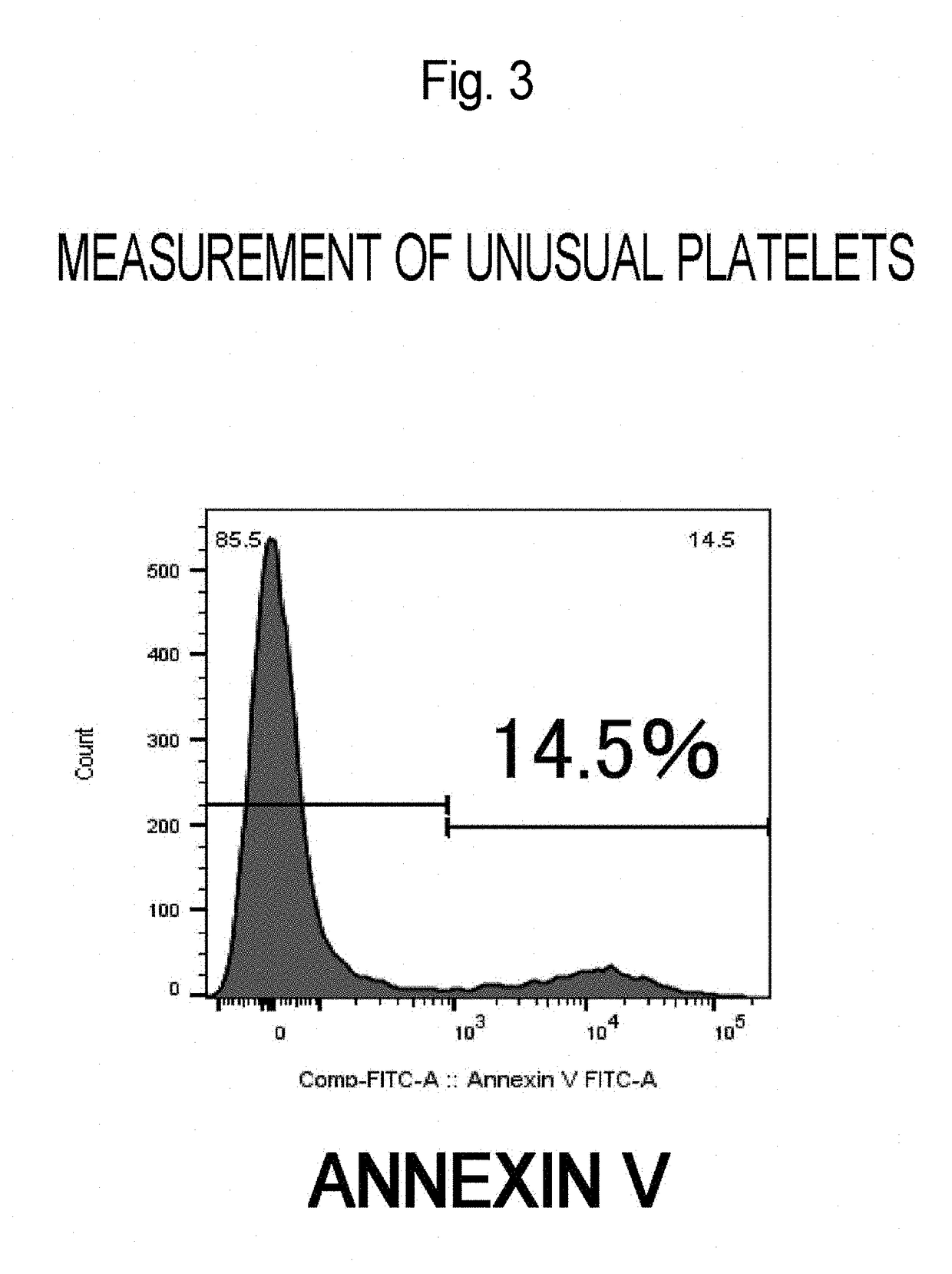
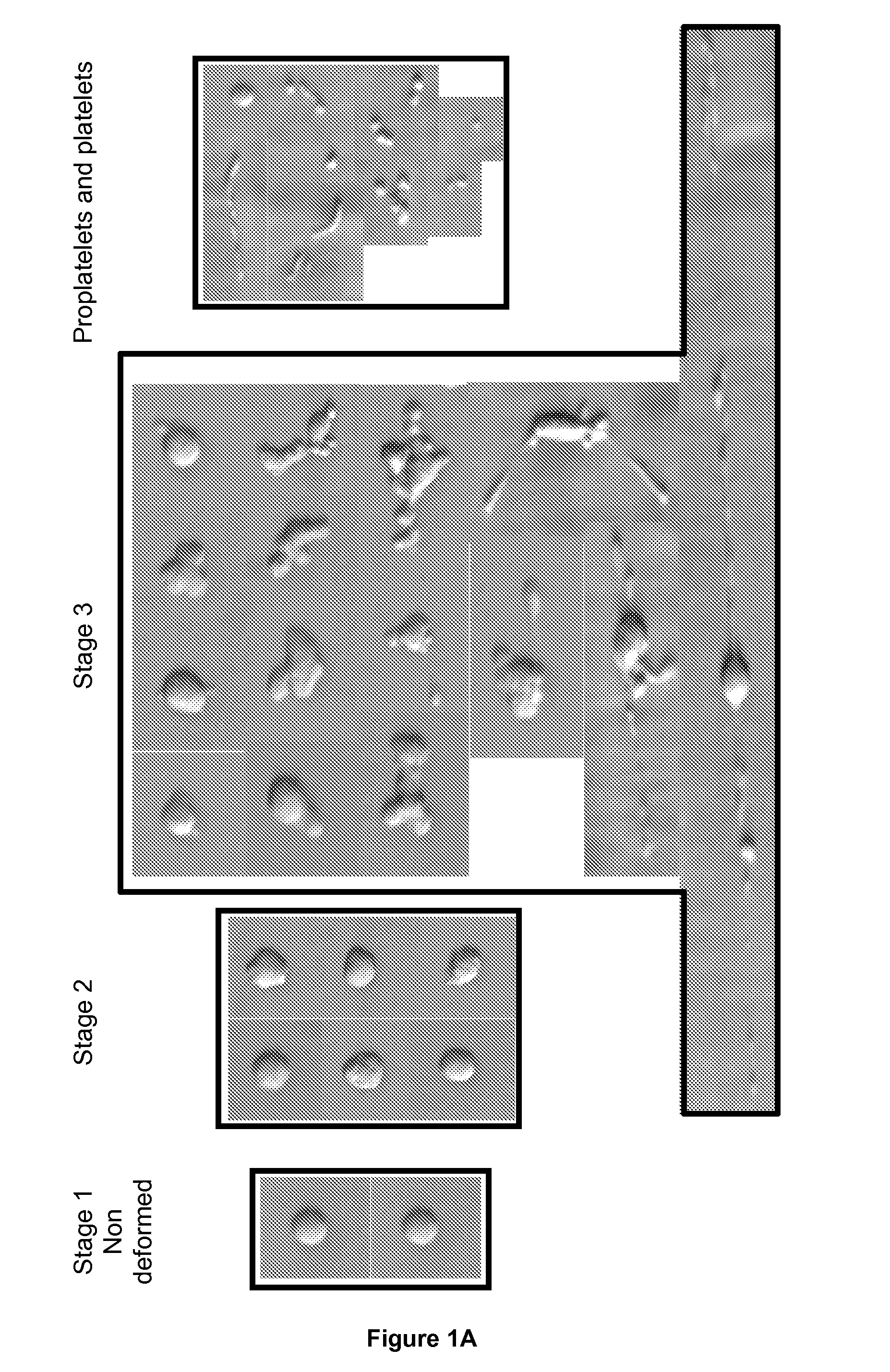
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
125 results about "Megakaryocyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A megakaryocyte (mega- + karyo- + -cyte, "large-nucleus cell") is a large bone marrow cell with a lobated nucleus responsible for the production of blood thrombocytes (platelets), which are necessary for normal blood clotting. Megakaryocytes usually account for 1 out of 10,000 bone marrow cells in normal people, but can increase in number nearly 10-fold during the course of certain diseases. Owing to variations in combining forms and spelling, synonyms include megalokaryocyte and megacaryocyte.
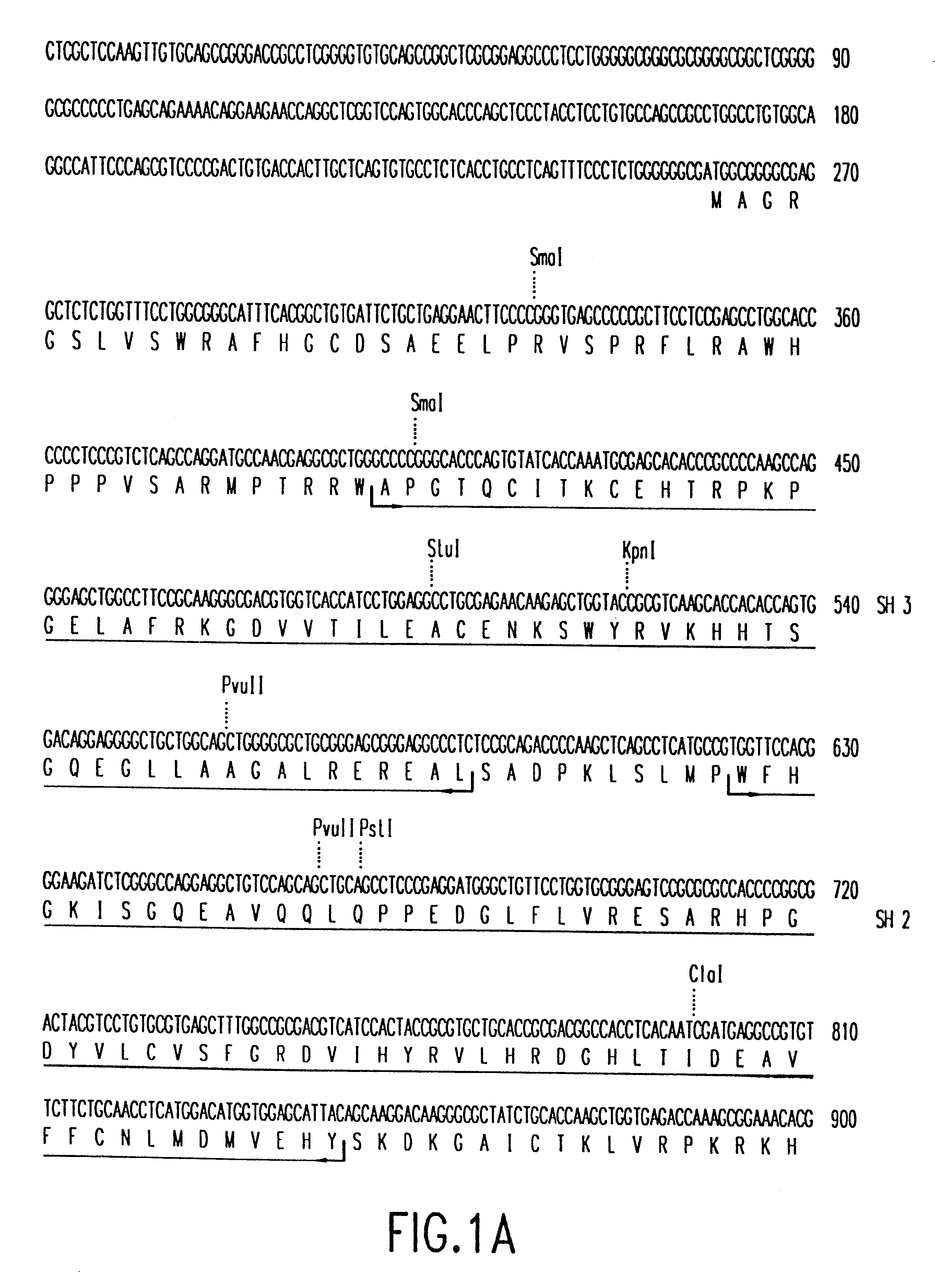
Megakaryocytic protein tyrosine kinases
InactiveUS6326469B1Reduced megakaryocyte growthReduce differentiationVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseProtein-Tyrosine Kinases
The present invention relates to novel cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases isolated from megakaryocytes (megakaryocyte kinases or MKKs) which are involved in cellular signal transduction pathways and to the use of these novel proteins in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. The present invention further relates to specific megakaryocyte kinases, designated MKK1, MKK2 and MKK3, and their use as diagnostic and therapeutic agents.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV +1
Methods and compositions for the differentiation of stem cells
ActiveUS20100216181A1Overcome limitationsPromote cell differentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementCulture processProgenitorInduced pluripotent stem cell
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the production of hematopoietic progenitor cells or endothelial progenitor cells from human pluripotent stem cells using a defined cell culture medium without the need to utilize feeder cells or serum. In some embodiments, differentiation is accomplished using hypoxic atmospheric conditions. The defined medium of the present invention may contain growth factors and a matrix component. The hematopoietic progenitor cells may be further differentiated into cell lineages including red blood cells, macrophages, granulocytes, and megakaryocytes. The endothelial progenitor cells may be further differentiated into endothelial cells. Also disclosed are screening assays for identification of candidate substances that affect differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into progenitor cells.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Megakaryocyte and Platelet Production from Stem Cells
ActiveUS20120238020A1Improve platelet releaseFacilitated releaseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMegakaryocyteEx vivo
Methods for obtaining purified populations of megakaryocytes and platelets by ex vivo culture of stem cells are provided herein.
Owner:NEW YORK BLOOD CENT
Megakaryocyte stimulating factors
InactiveUS7030223B2Peptide/protein ingredientsMicroorganism based processesMegakaryocyteMEGAKARYOCYTE-STIMULATING FACTOR
Novel polypeptides of human megakaryocyte stimulating factors (MSFs). Pharmaceutical compositions containing same, and methods for their preparation and use are provided.
Owner:GENETICS INST INC
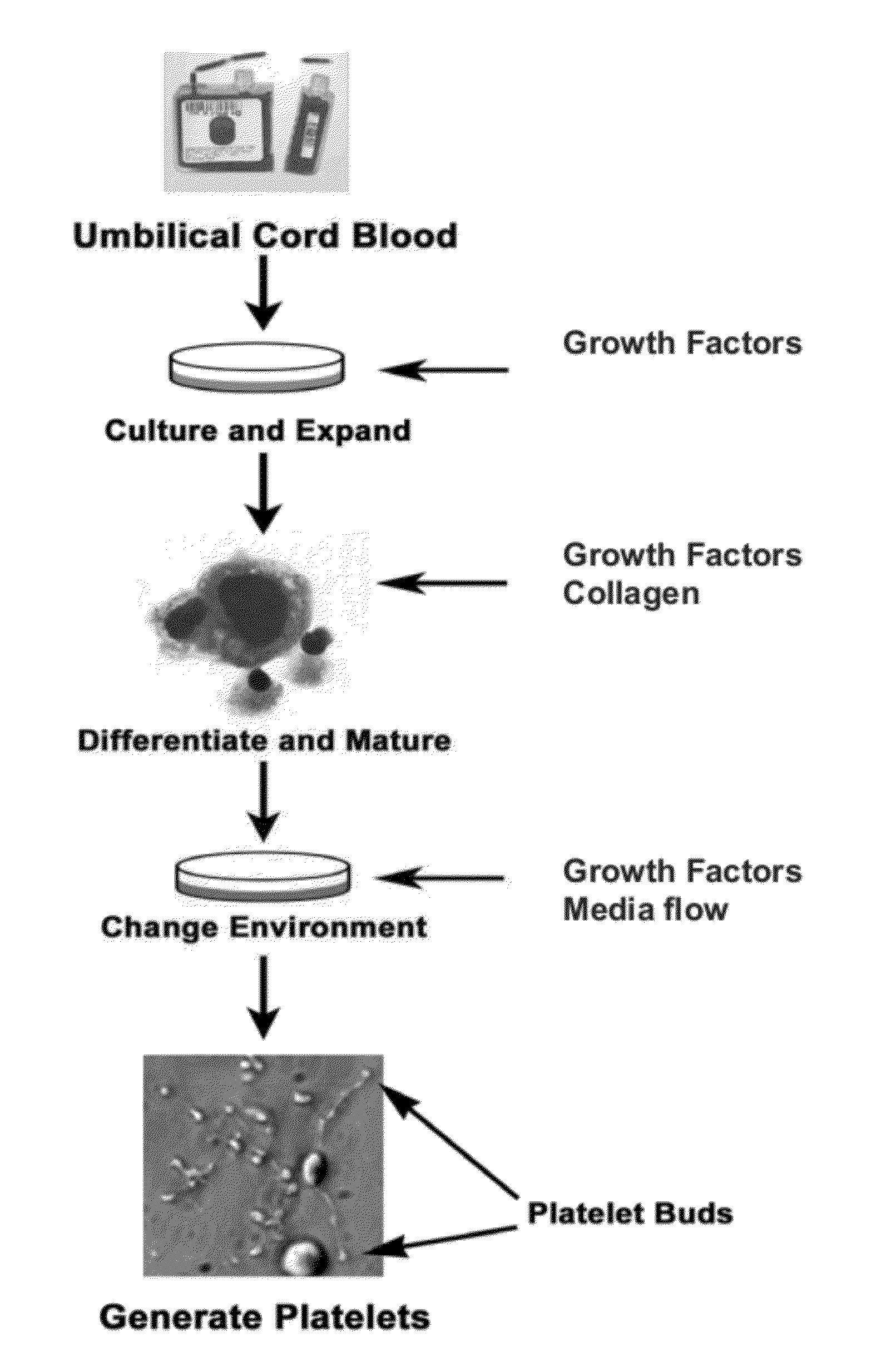
Platelets from stem cells
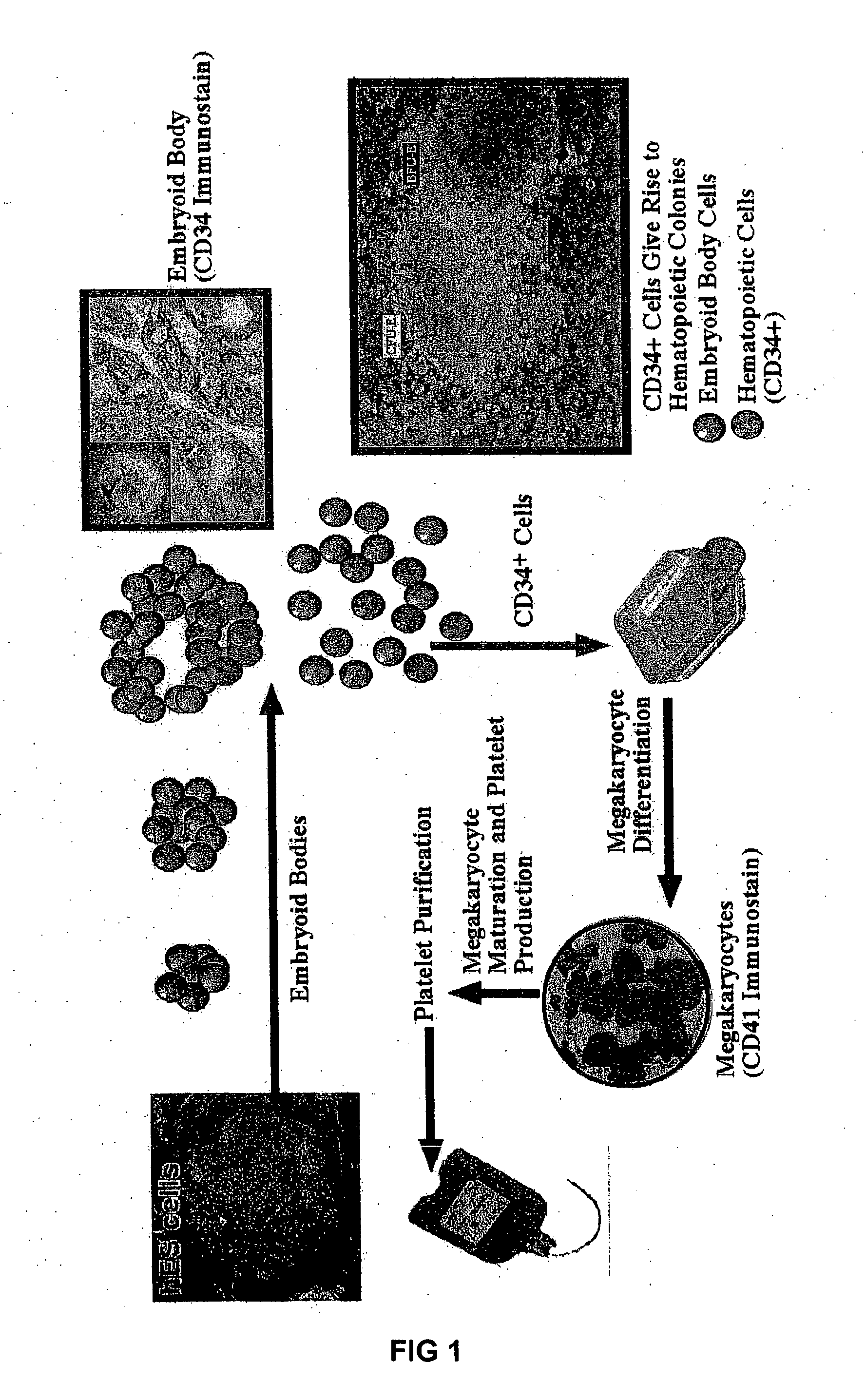
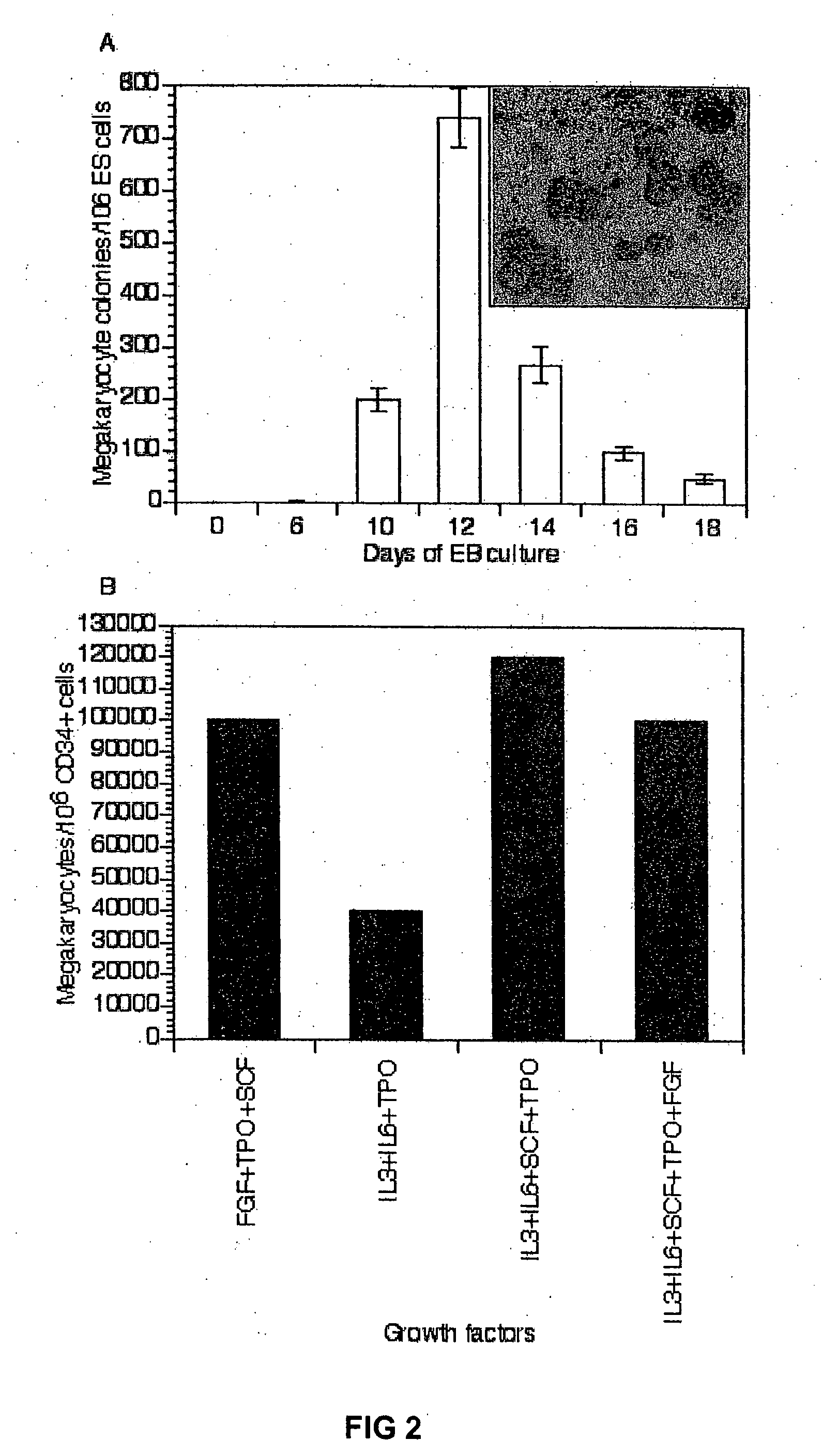
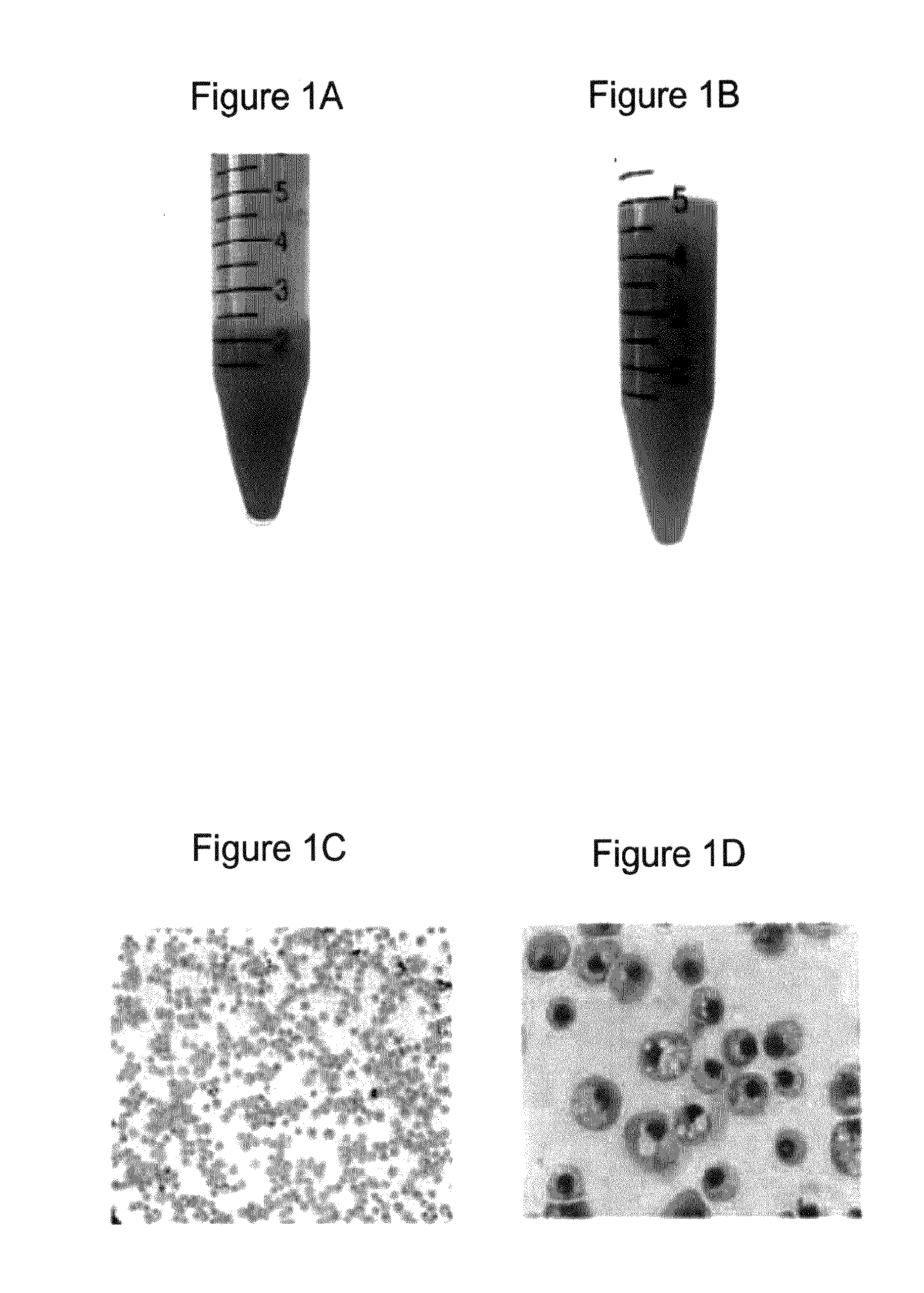
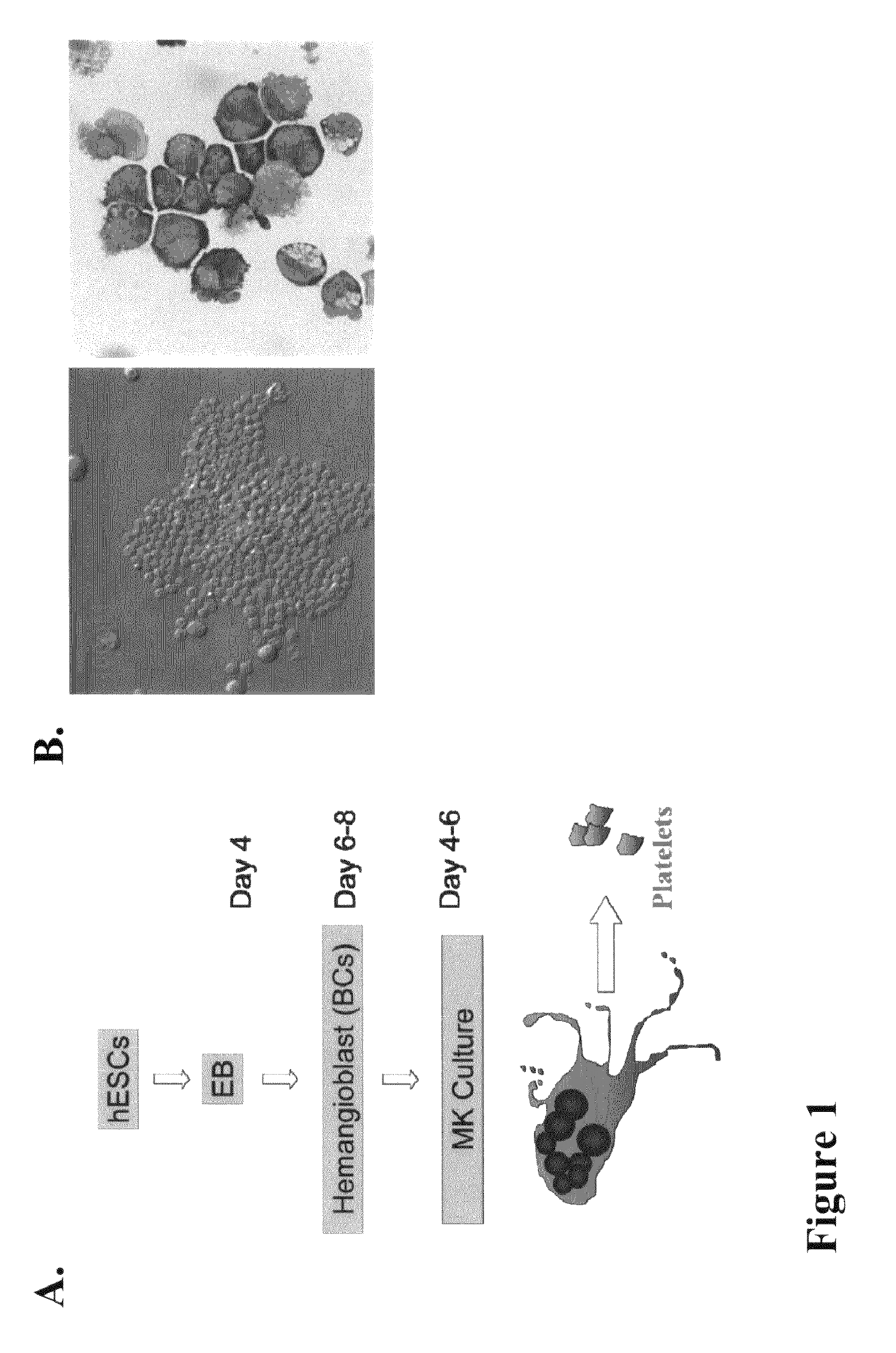
Human embryonic stem cells are induced to differentiate first into the hematopoietic lineage and then into megakaryocytes, the cells which generate platelets. The proper in vitro culture of megakaryocytes results in the production and shed of platelets. This makes possible, for the first time, the in vitro production of a human blood factor needed by many patients.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Methods and compositions for modulating interleukin-21 receptor activity
InactiveUS7198789B2Enhance immune cell activityReduce Fc receptor bindingBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsInfectious DisorderNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
Methods and compositions for modulating interleukin-21 (IL-21) / IL-21 receptor (MU-1) activity using agonists or antagonists of IL-21 or IL-21 receptor (“IL-21R” or “MU-1”), are disclosed. IL-21 / IL-21R antagonists can be used to induce immune suppression in vivo, e.g., for treating or preventing immune cell-associated pathologies (e.g., pathologies associated with aberrant activity of one or more of mature T cells (mature CD8+, mature CD4+ T cells), mature NK cells, B cells, macrophages and megakaryocytes, including transplant rejection and autoimmune disorders). IL-21 / IL-21R agonists can be used by themselves or in combination with an antigen, e.g., as an adjuvant (e.g., a vaccine adjuvant), to up-regulate an immune response in vivo, e.g., for example, for use in treating cancer and infectious disorders.
Owner:GENETICS INST INC
Production methods for megakaryocytes and platelets
InactiveUS20160002599A1Suitably producedMammal material medical ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsApoptosisPlatelet
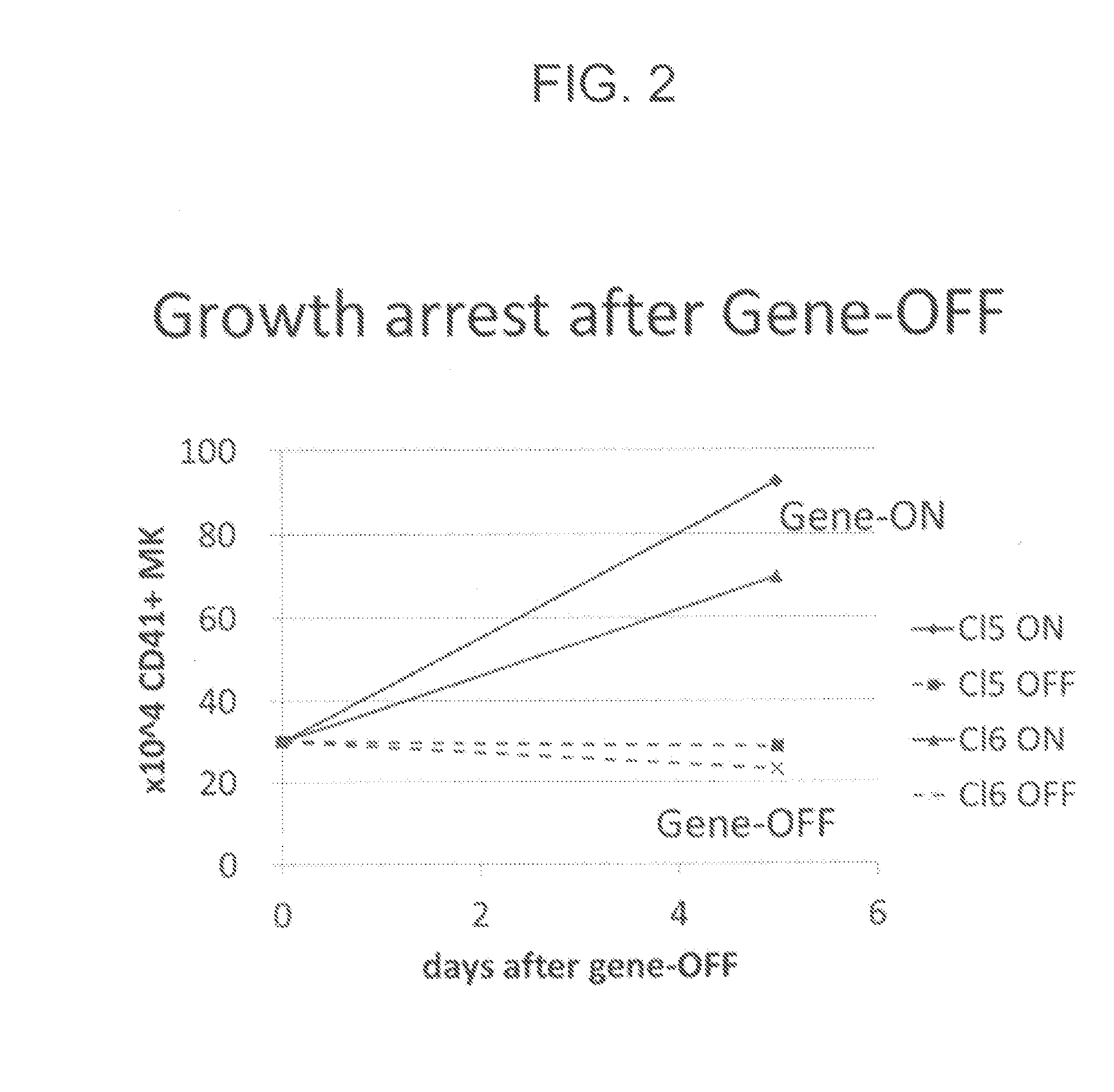
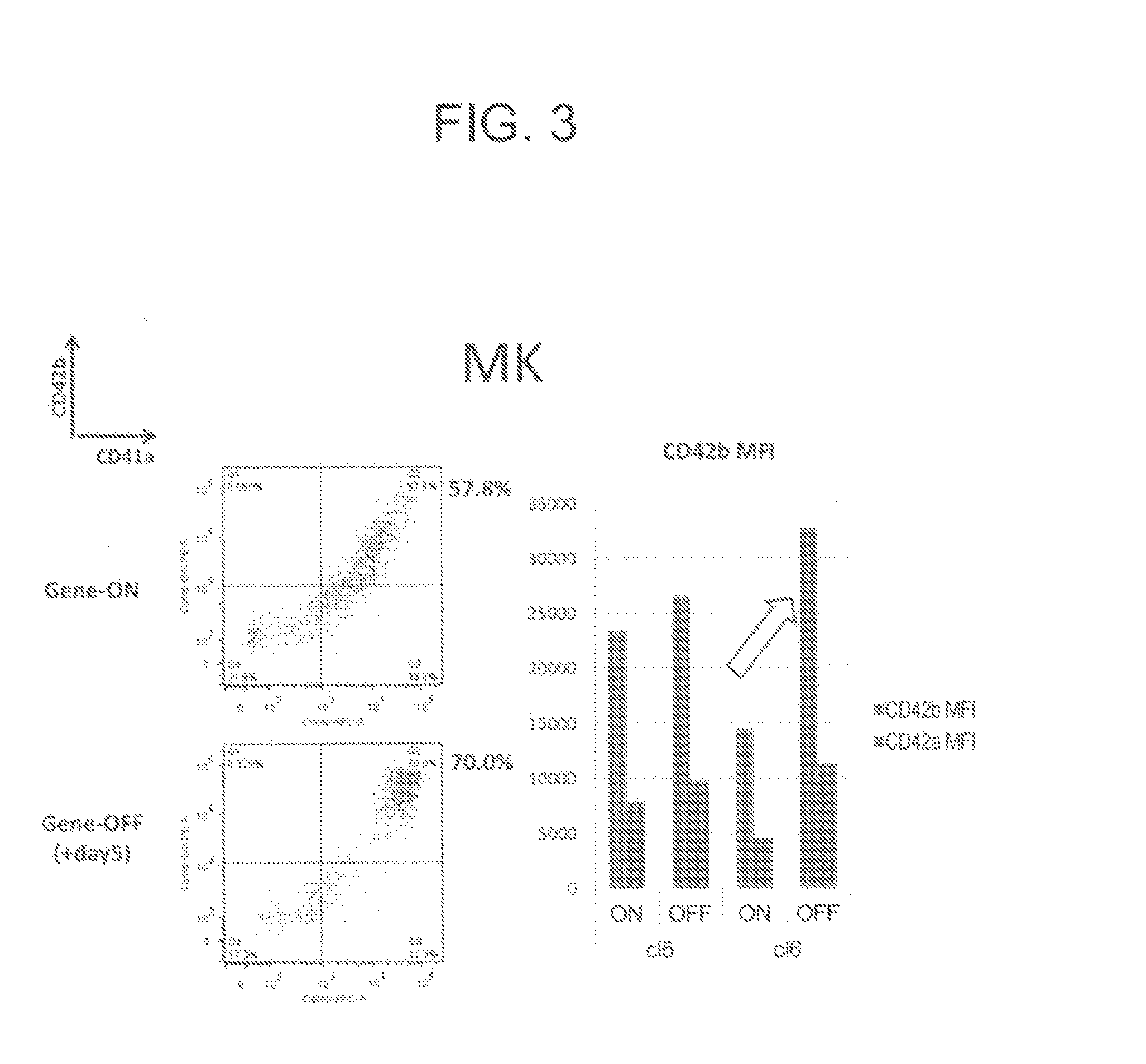
An object of the present invention is to provide a method of efficiently producing a maturated megakaryocytic cell line from hematopoietic progenitor cells. The present invention provides a method for producing megakaryocytes from hematopoietic progenitor cells, comprising(i) forcibly expressing an apoptosis suppression gene and an oncogene in hematopoietic progenitor cells and culturing the cells, and(ii) arresting forced expression of the apoptosis suppression gene and the oncogene and culturing the hematopoietic progenitor cells.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Megakaryocyte and Platelet Production from Stem Cells
ActiveUS20160002586A1Sufficient flow rateIncrease in platelet productionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMegakaryocyteEx vivo
Methods for obtaining purified populations of megakaryocytes and platelets by ex vivo culture of stem cells are provided herein.
Owner:NEW YORK BLOOD CENT
Method of prodcing megacaryocyle using umbilical blood CD 344+cell in vitro induction method
InactiveCN1556197AIncrease multipleImprove production efficiencyTissue cultureHuman plateletWhite blood cell
A process for generating megacaryocyte by in vitro induction to umbilical blood cell CD34+ includes in vitro amplifying the CD34+ in the culture medium containing fetal calf serum, human SCF, human TPO and / or ligand flt-3 and inducing the generation of megacaryocytes in the non-serum culture medium containing human TPO, human interleukin 3(IL-3) and / or human GM-CSF. Its advantage is high inducing efficiency.
Owner:上海伯瑞生物技术发展有限公司 +1
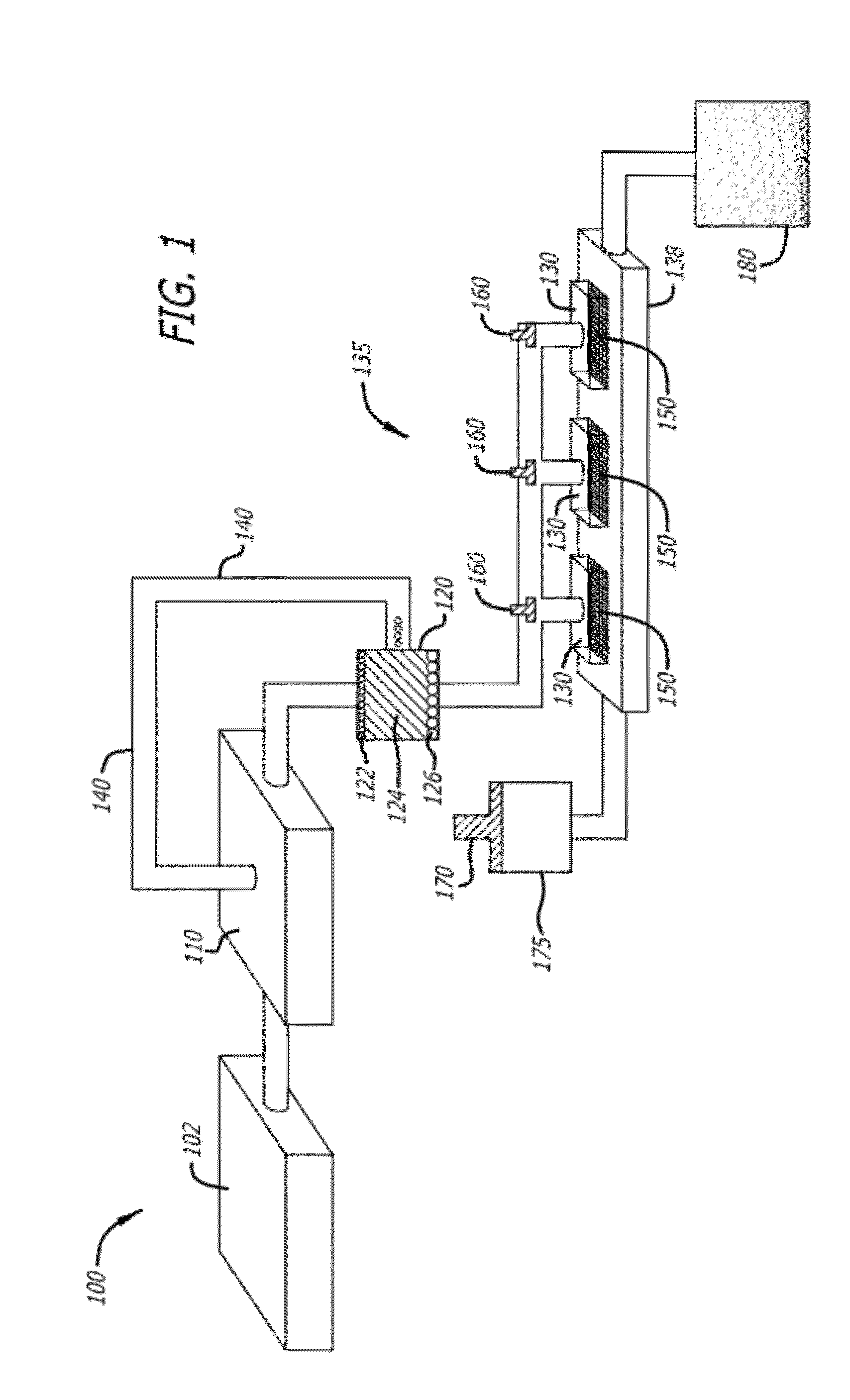
Bioreactor for Isolation of Rare Cells and Methods of Use
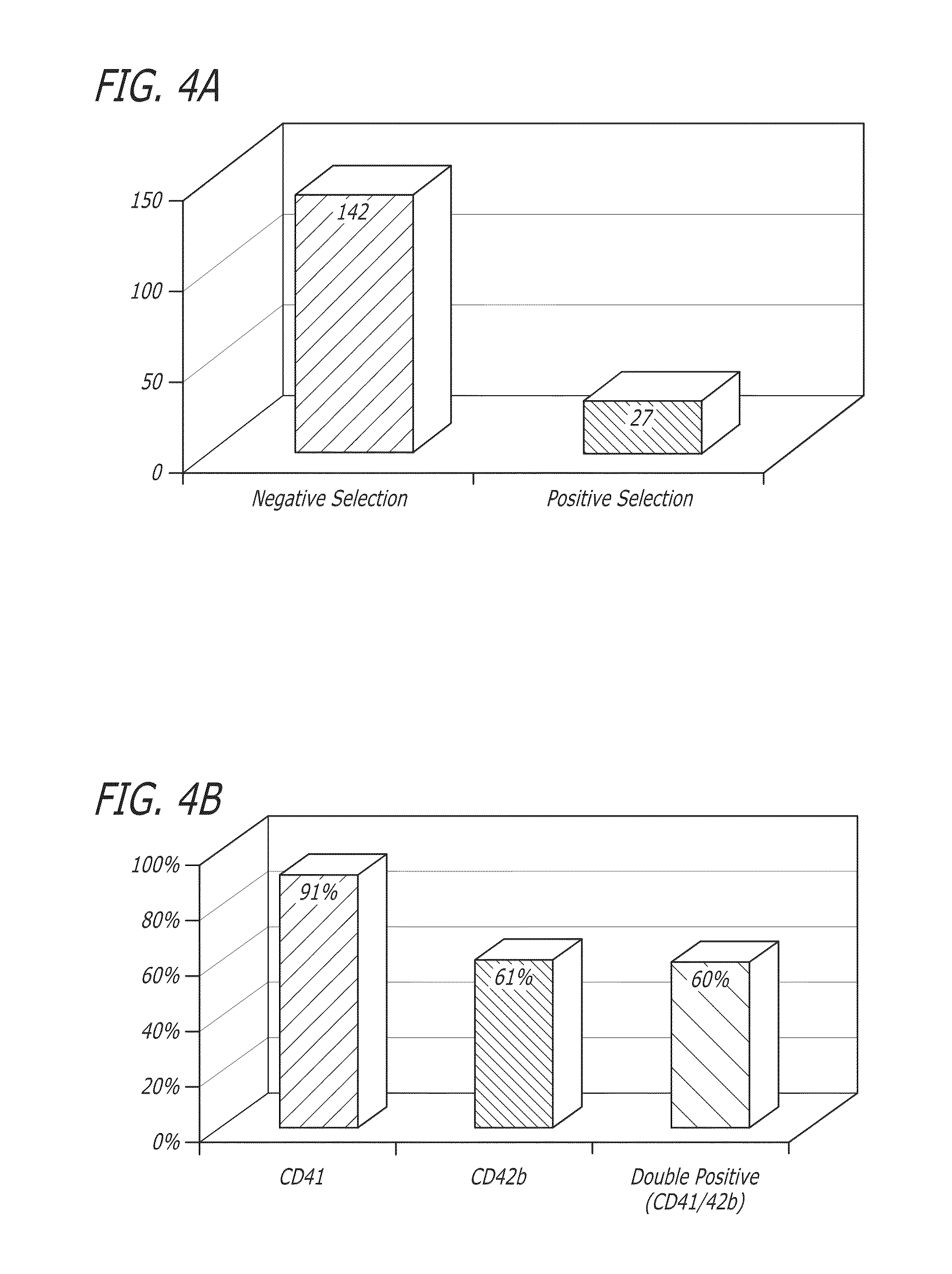
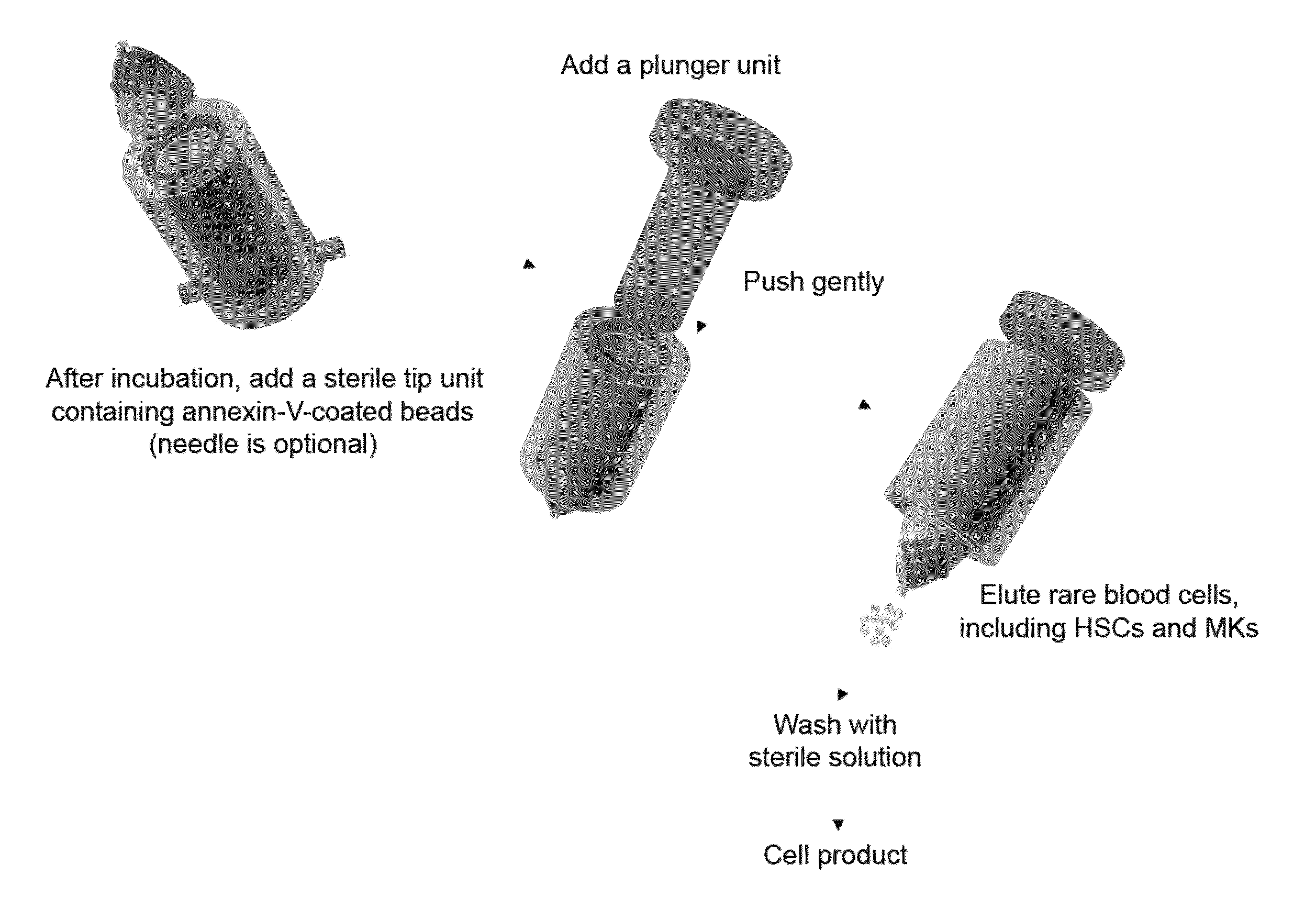
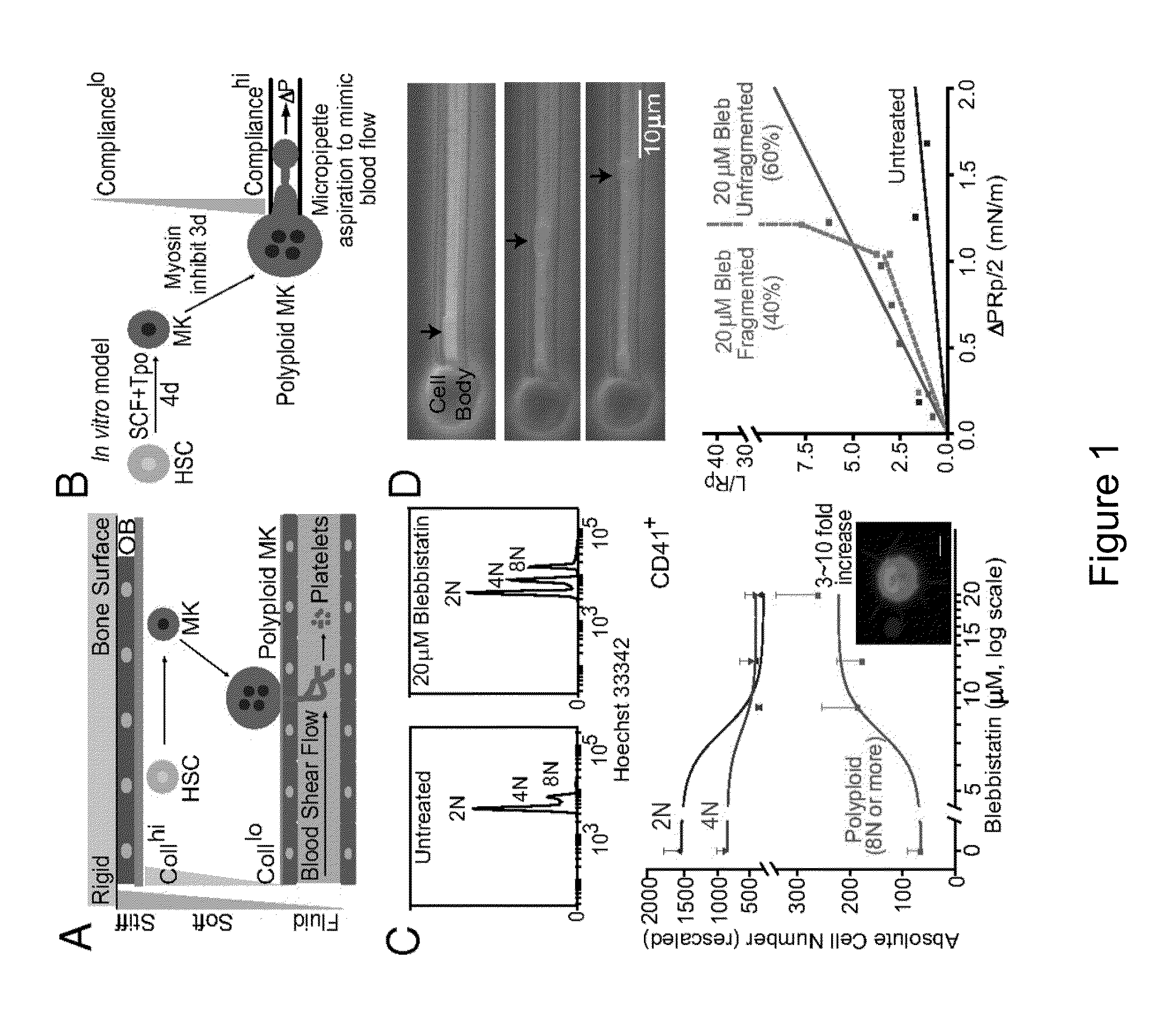
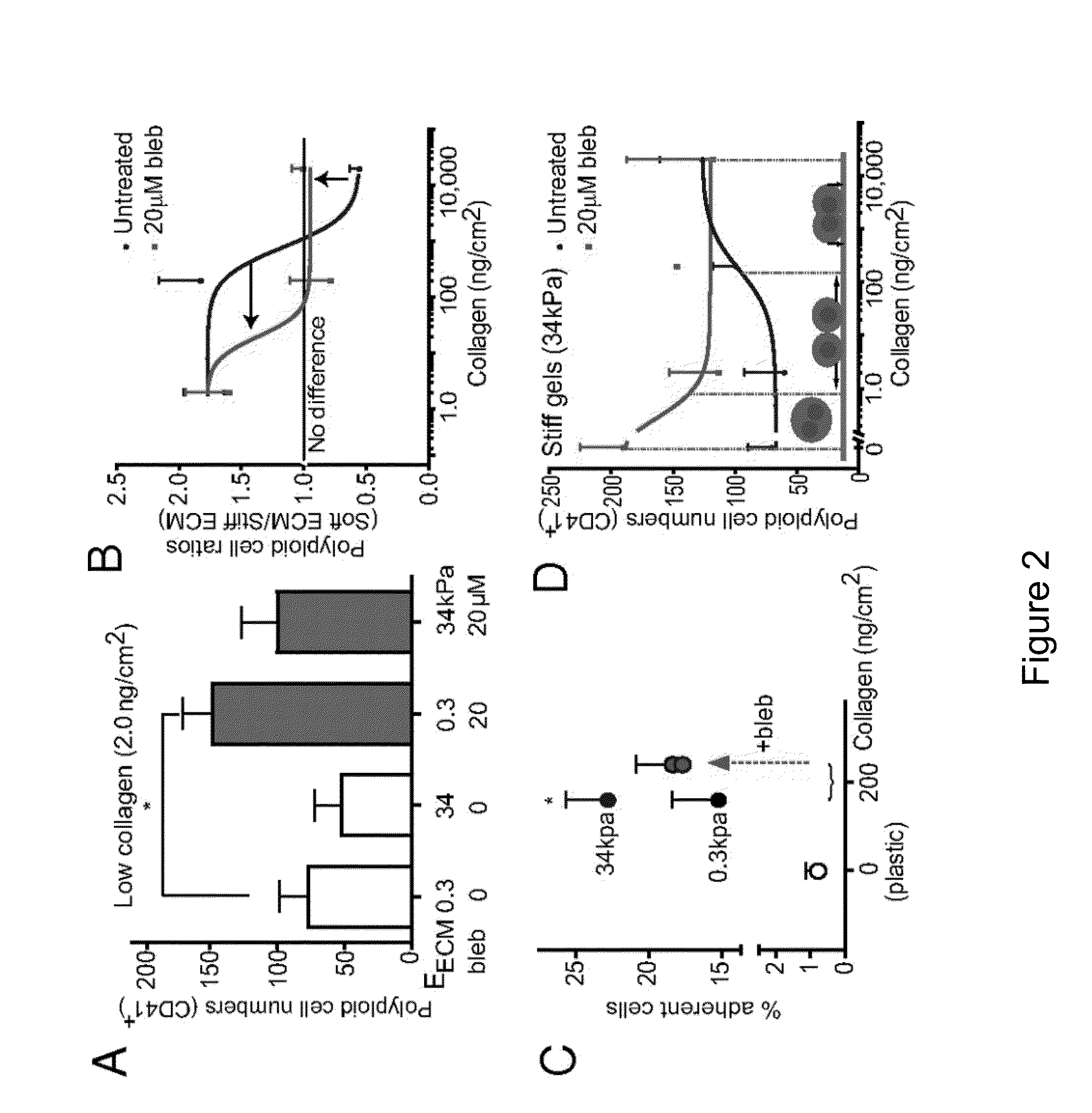
The present invention relates to a bioreactor apparatus, and methods of use, for the isolation of rare blood cells, including hematopoietic stem cells and megakaryocytes. The apparatus includes a soft substrate and an anti-contractility agent, thereby providing a soft microenvironment to cultured cells. The apparatus of the invention is permissive for the survival of non-dividing cells while dividing cells are eliminated. This unique property allows for the simple isolation of rare blood cells without the use of costly equipment and antibodies.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Methods for producing enucleated erythroid cells derived from pluripotent stem cells
InactiveUS20110086424A1Nervous system cellsMammal material medical ingredientsInduced pluripotent stem cellPlatelet
Methods for generating enucleated erythroid cells using pluripotent stem cells are provided. The methods permit the production of large numbers of cells. The cells obtained by the methods disclosed may be used for a variety of research, clinical, and therapeutic applications. Methods for generating megakaryocyte and platelets are also provided.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Large scale generation of functional megakaryocytes and platelets from human embryonic stem cells under stromal-free conditions
ActiveUS20120315338A1Transfusion is neededReduce or eliminate an immunity mediated host reactionCulture processMammal material medical ingredientsSerum igeBiology
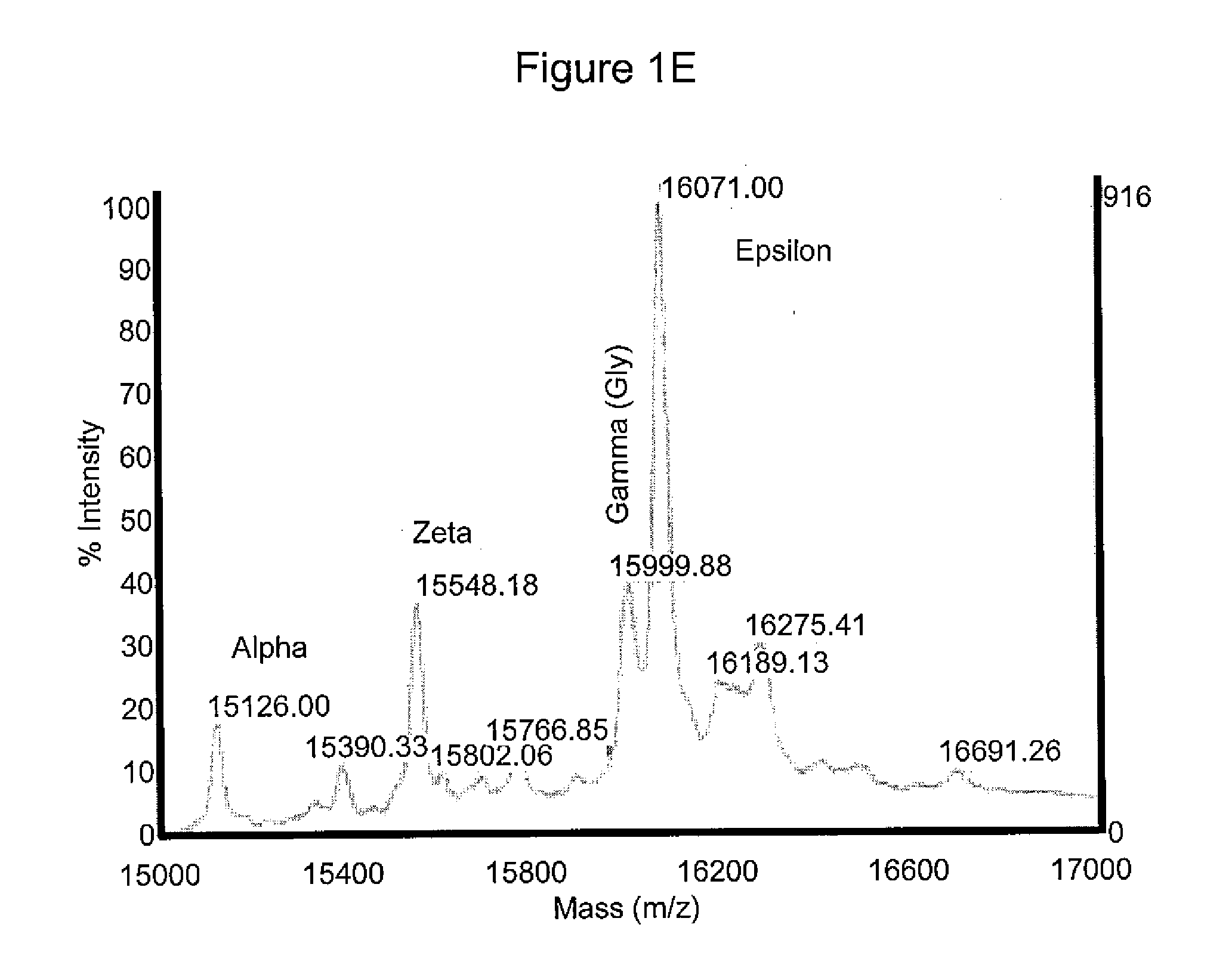
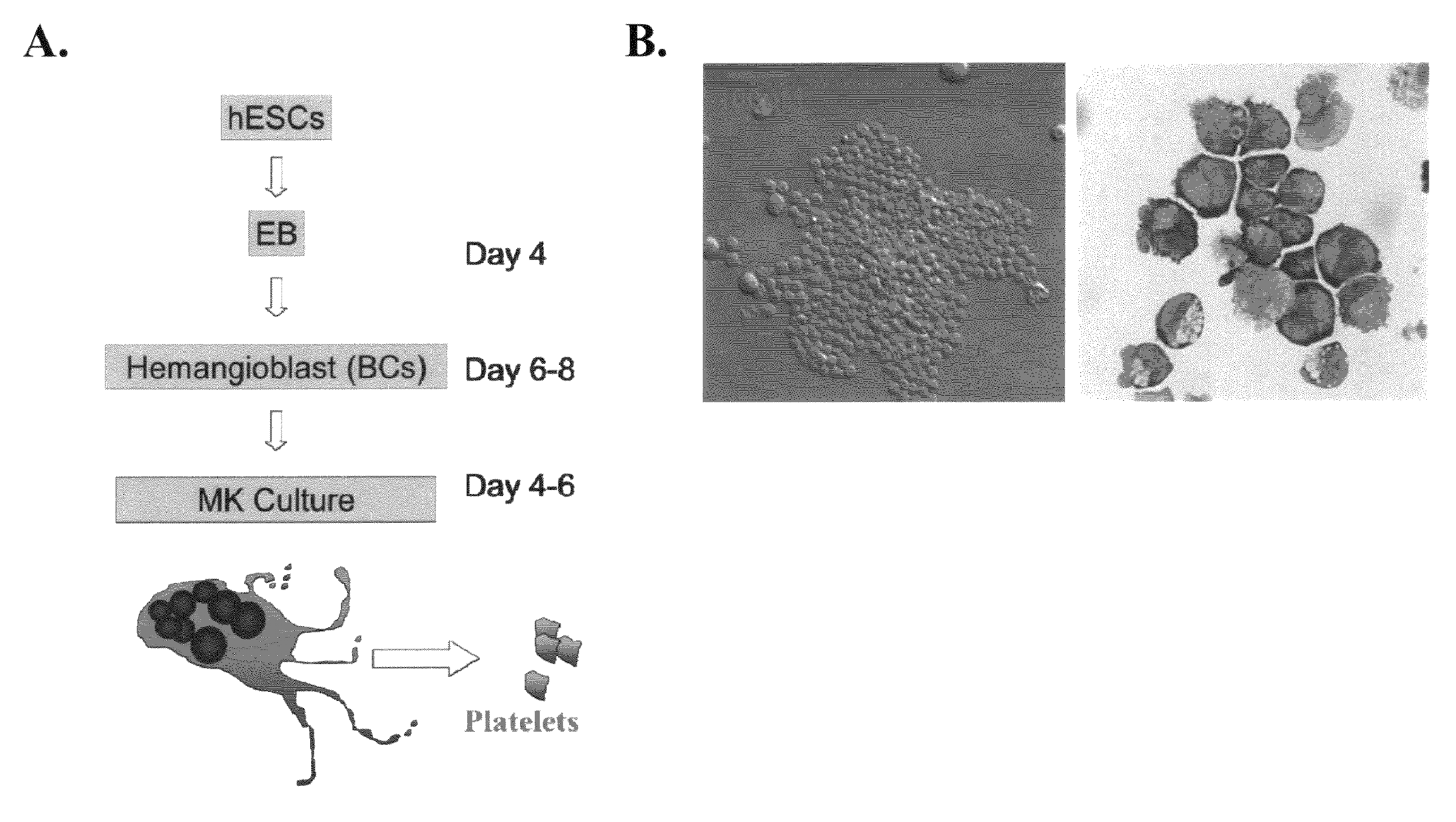
The present invention provides a method of generating megakaryocytes and platelets. In various embodiments, method involves the use of human embryonic stem cell derived hemangioblasts for differentiation into megakaryocytes and platelets under serum and stromal-free condition. In this system, hESCs are directed towards megakaryocytes through embryoid body formation and hemangioblast differentiation. Further provided is a method of treating a subject in need of platelet transfusion.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
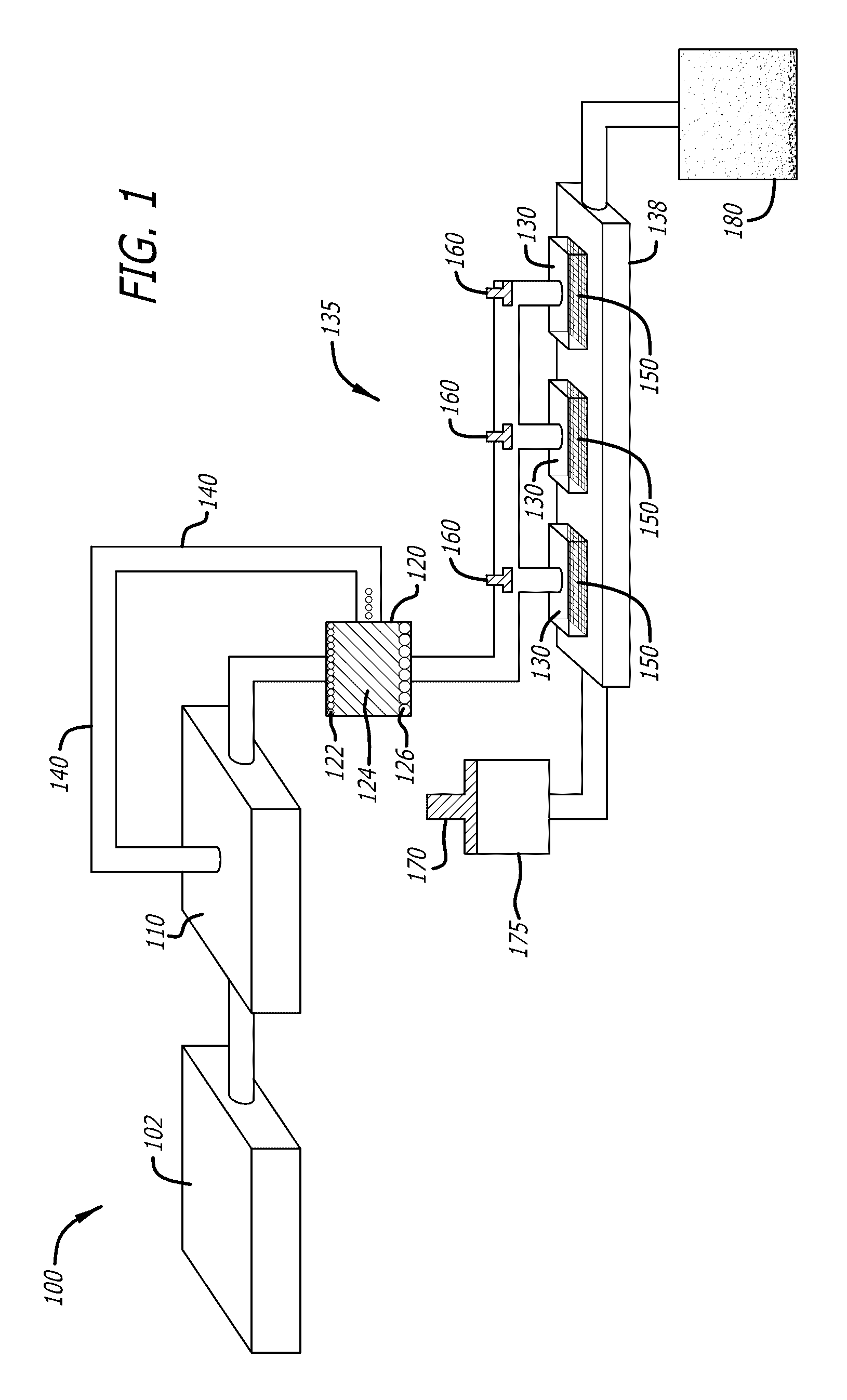
Method for Producing Platelets
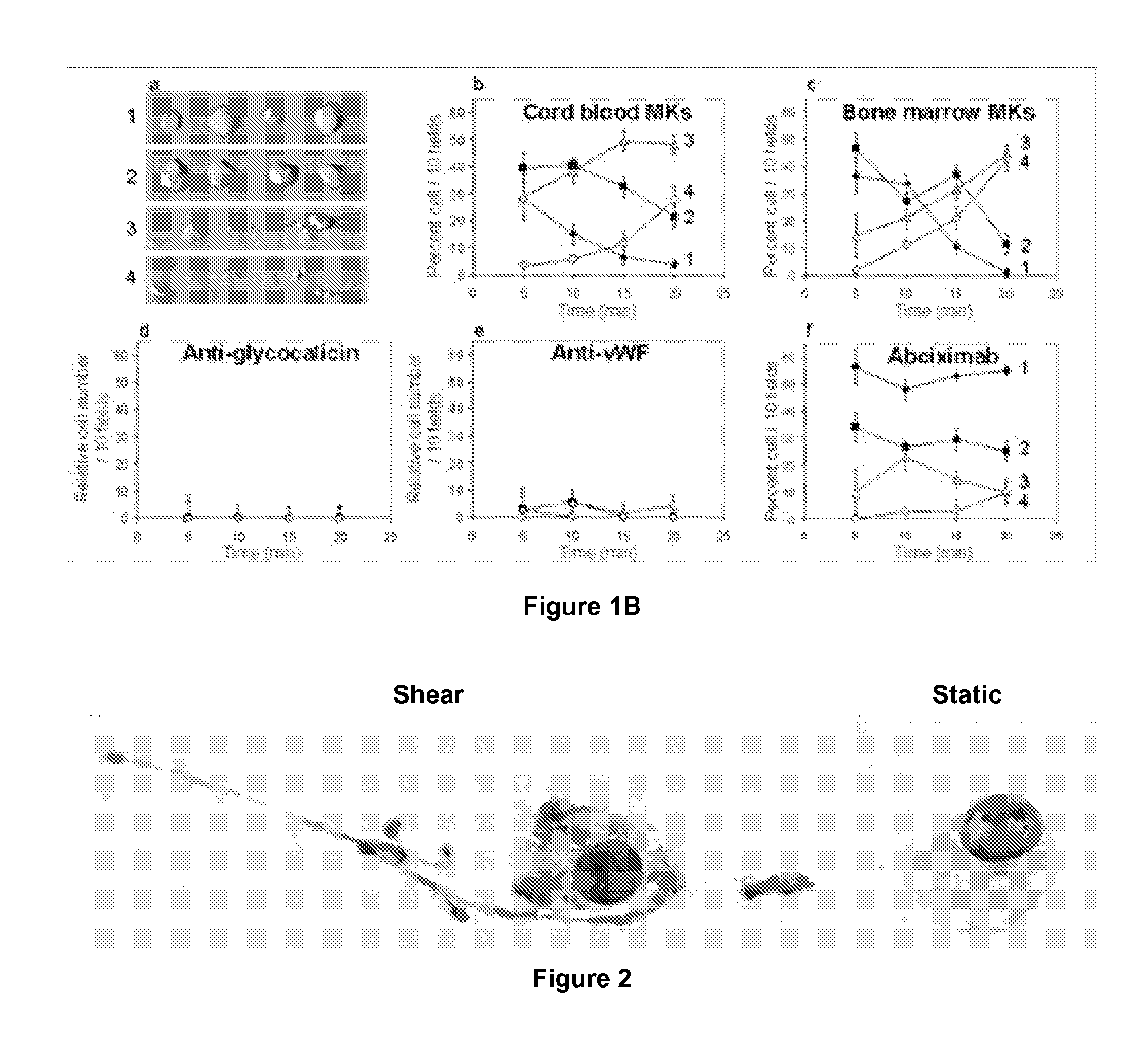
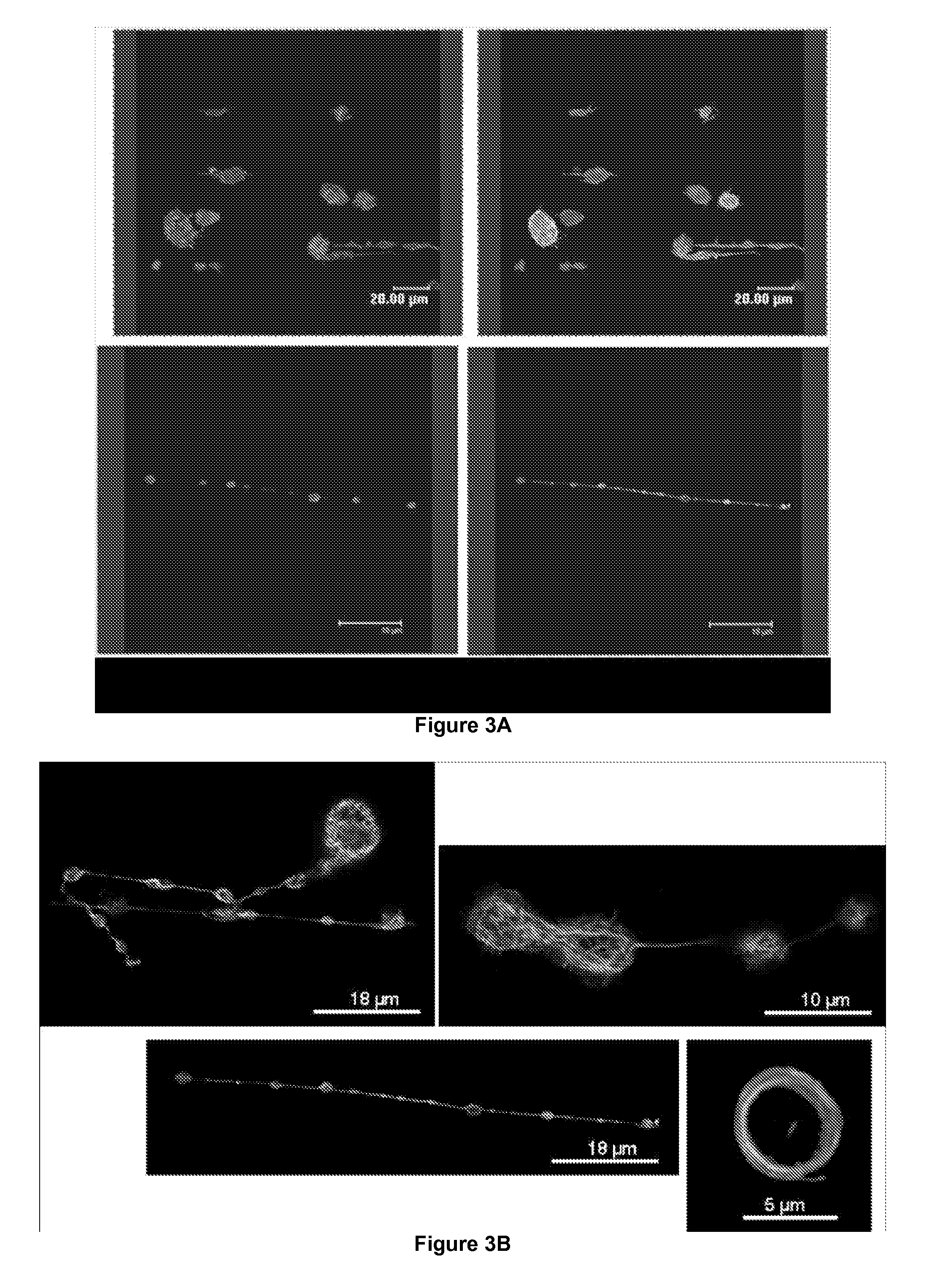
ActiveUS20120014933A1Easy to produceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiocideFactor VIII vWFShear rate
The present invention relates to a method for producing platelets from mature megakaryocytes. More particularly, the invention relates to an ex vivo method for producing platelets, from mature megakaryocytes, said method comprising a step of subjecting a suspension of mature megakaryocytes to a flow having a minimal shear rate of 600 s−1 on a solid phase coated with Von Willebrand factor.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +3
Megakaryocyte and platelet production from stem cells
ActiveUS9574178B2Facilitated releaseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMegakaryocyteEx vivo
Methods for obtaining purified populations of megakaryocytes and platelets by ex vivo culture of stem cells are provided herein.
Owner:NEW YORK BLOOD CENT
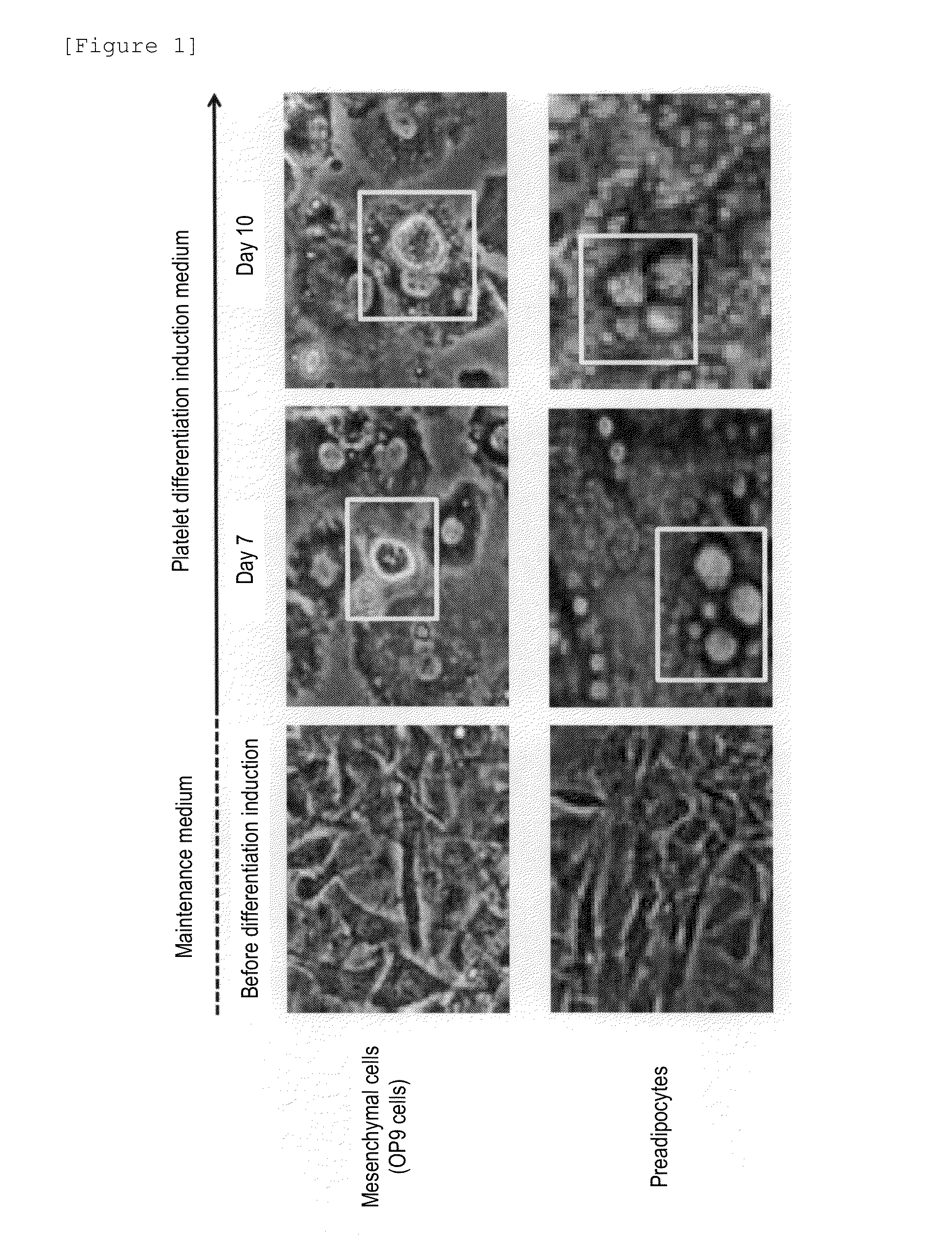
Method for producing megakaryocytes, platelets and/or thrombopoietin using mesenchymal cells
ActiveUS20160177265A1Improve efficiencyLow costCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsMethyl xanthineMegakaryocyte
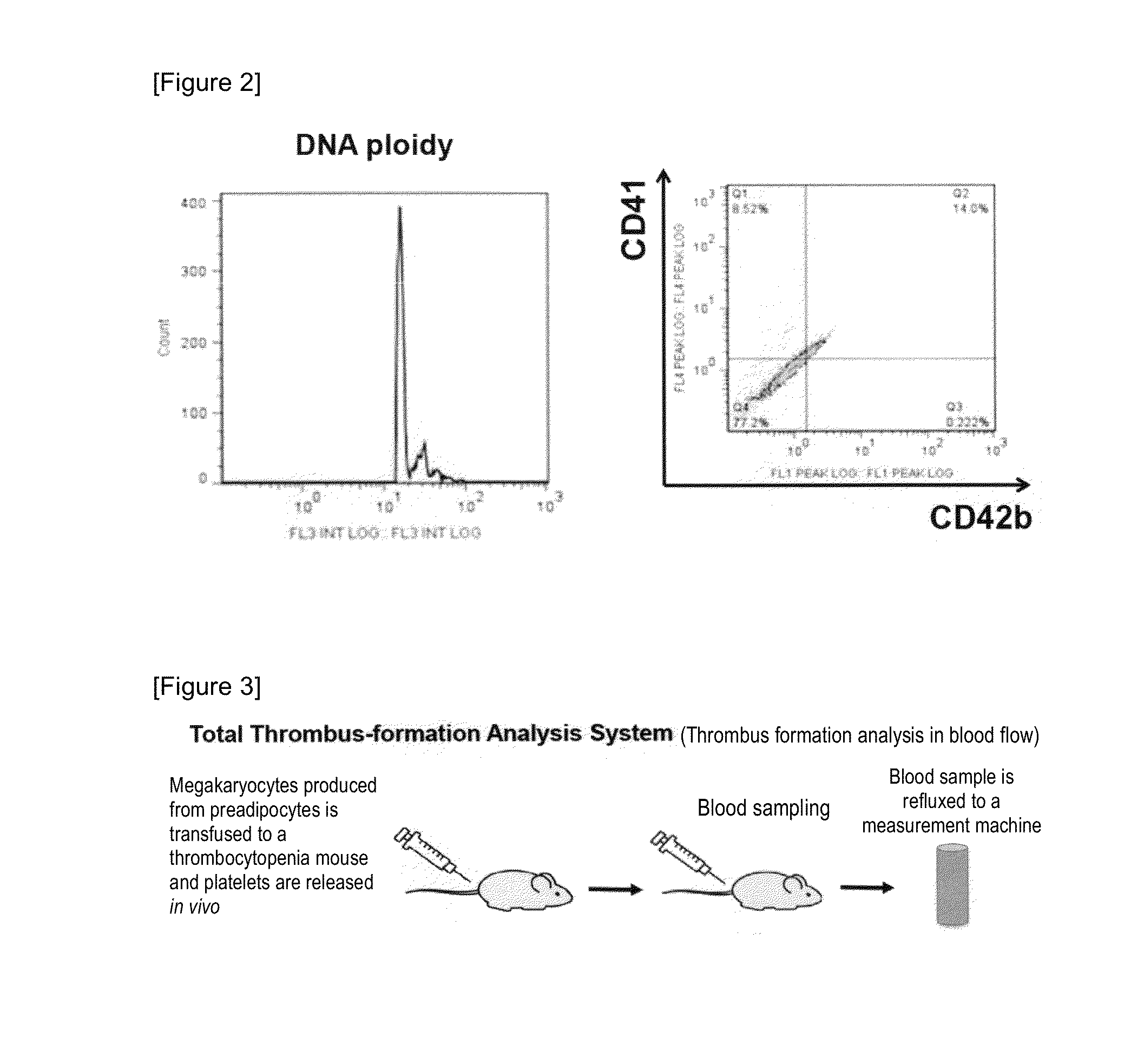
Provided is a megakaryocyte and / or platelet production method, enabling to produce a megakaryocyte and / or platelet from mesenchymal cells such as preadipocytes in a relatively short period of time, simply, in a large amount and at lower cost or more efficiently in vitro and a method for producing TPO simply and in a larger amount. A first invention is a method for producing a megakaryocyte and / or platelet, comprising culturing a mesenchymal cell in a mesenchymal cell culturing basic medium containing an iron ion and an iron transporter and collecting megakaryocytes and / or platelets from a culture. A second invention is a method for producing thrombopoietin, comprising culturing a mesenchymal cell or mesenchymal cell-derived megakaryocyte in a mesenchymal cell culturing basic medium containing an iron ion and an iron transporter and collecting thrombopoietin from a culture. A third invention is a method for producing thrombopoietin, comprising culturing a preadipocyte in a preadipocyte culturing basic medium containing dexamethasone, 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine and insulin and collecting thrombopoietin from a culture.
Owner:ADIPOSEEDS INC
Methods and compositions for the differentiation of stem cells
ActiveUS8557580B2Microbiological testing/measurementCulture processProgenitorInduced pluripotent stem cell
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the production of hematopoietic progenitor cells or endothelial progenitor cells from human pluripotent stem cells using a defined cell culture medium without the need to utilize feeder cells or serum. In some embodiments, differentiation is accomplished using hypoxic atmospheric conditions. The defined medium of the present invention may contain growth factors and a matrix component. The hematopoietic progenitor cells may be further differentiated into cell lineages including red blood cells, macrophages, granulocytes, and megakaryocytes. The endothelial progenitor cells may be further differentiated into endothelial cells. Also disclosed are screening assays for identification of candidate substances that affect differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into progenitor cells.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Production of red blood cells and platelets from stem cells
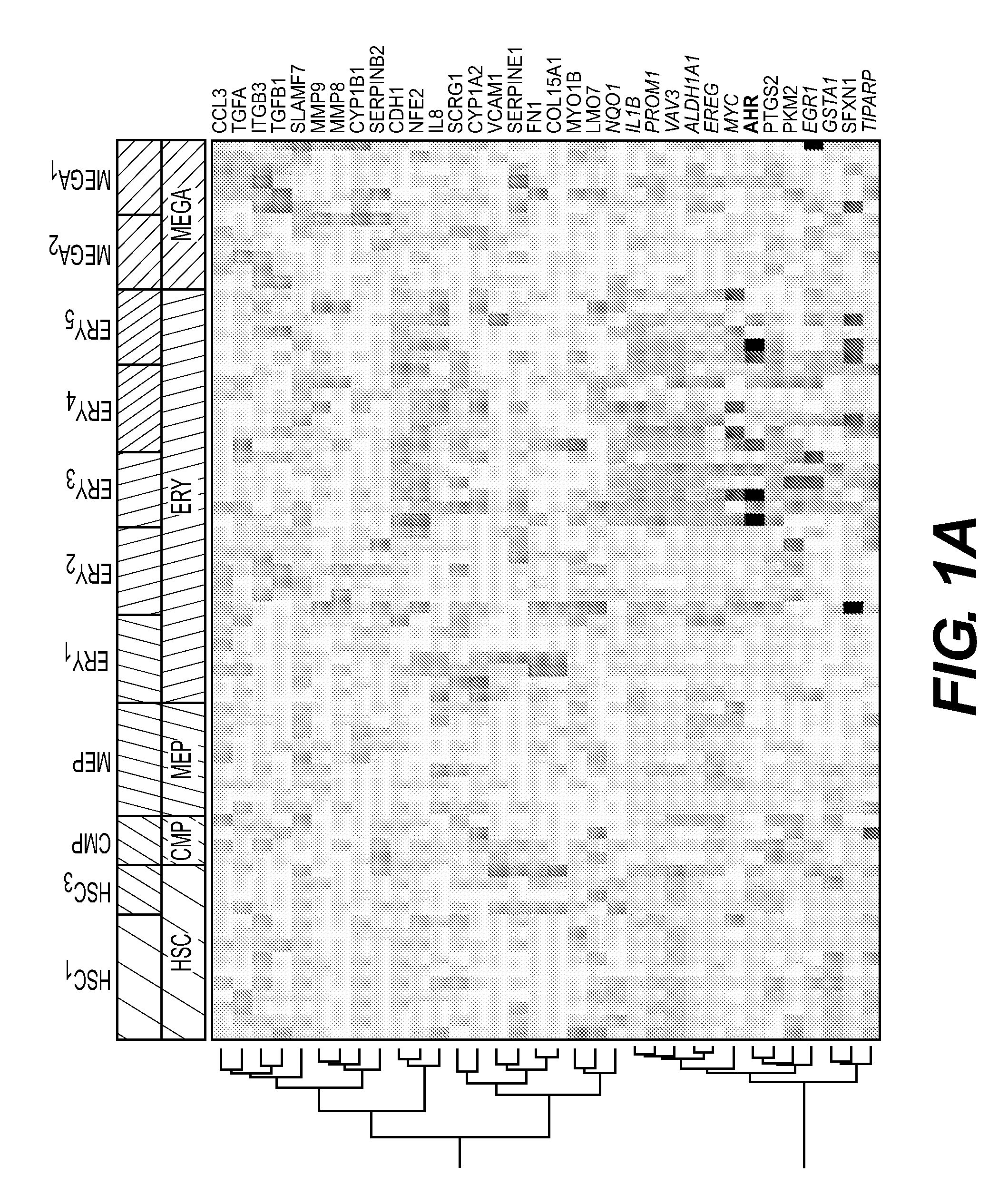
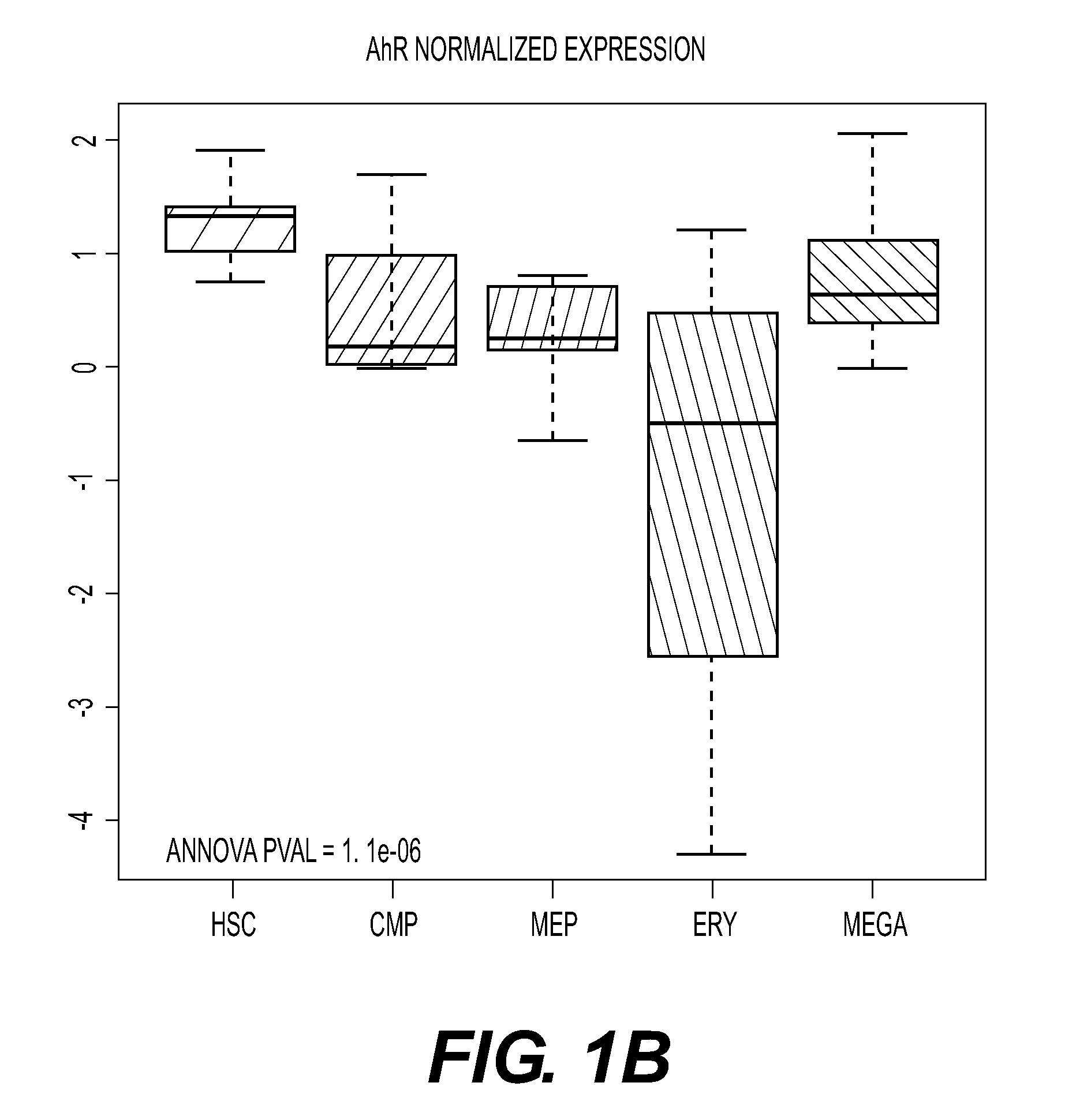
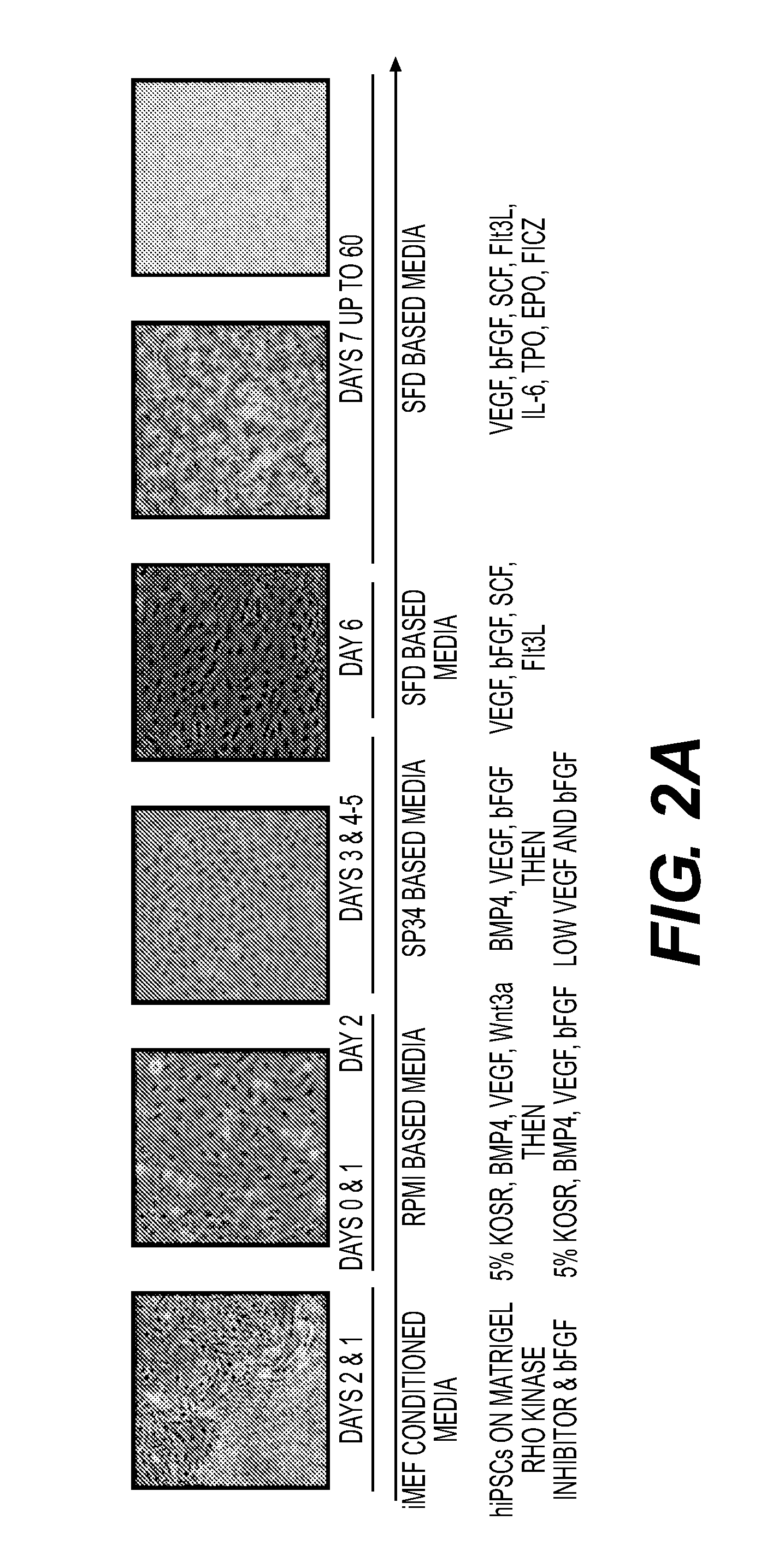
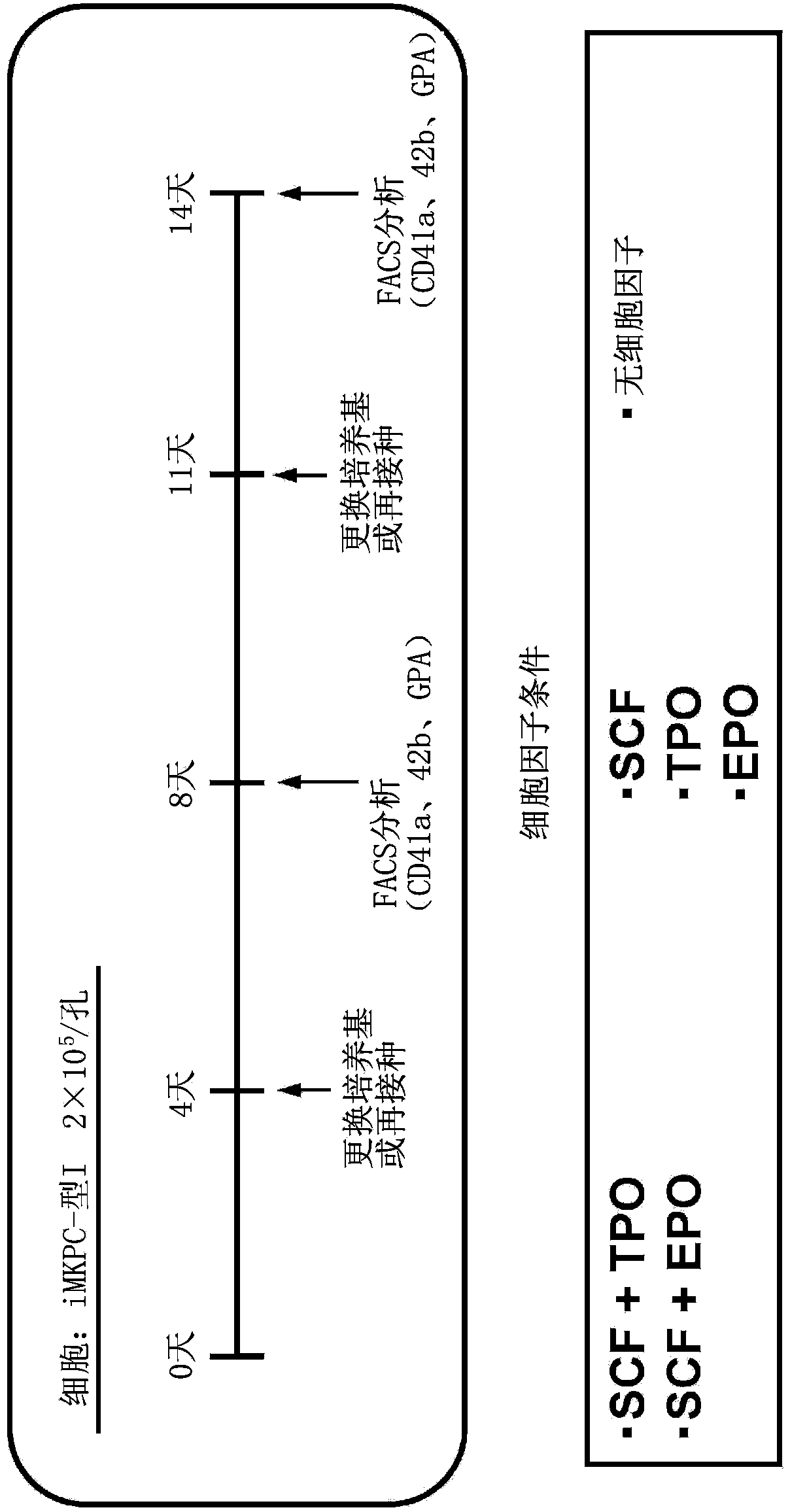
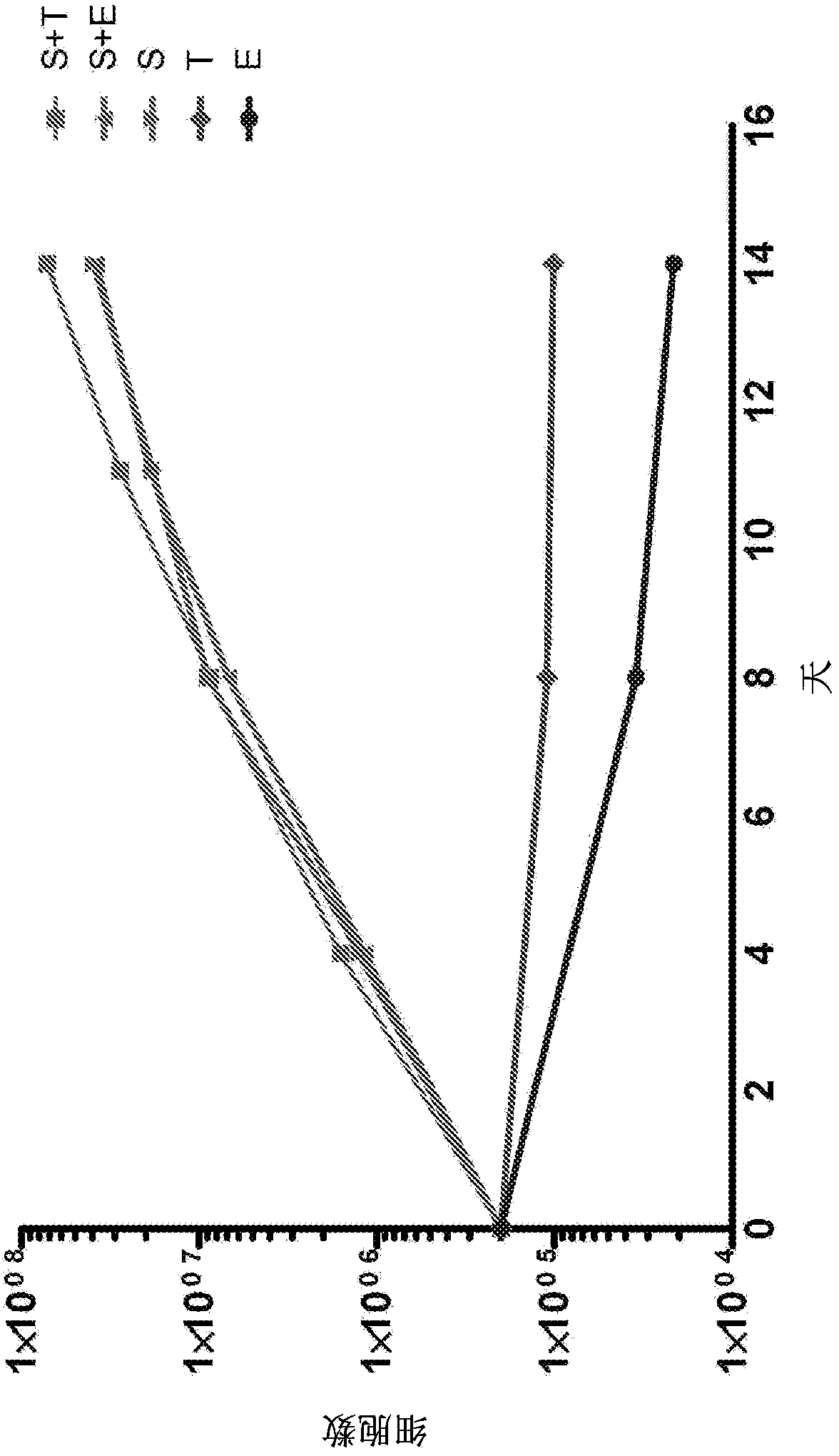
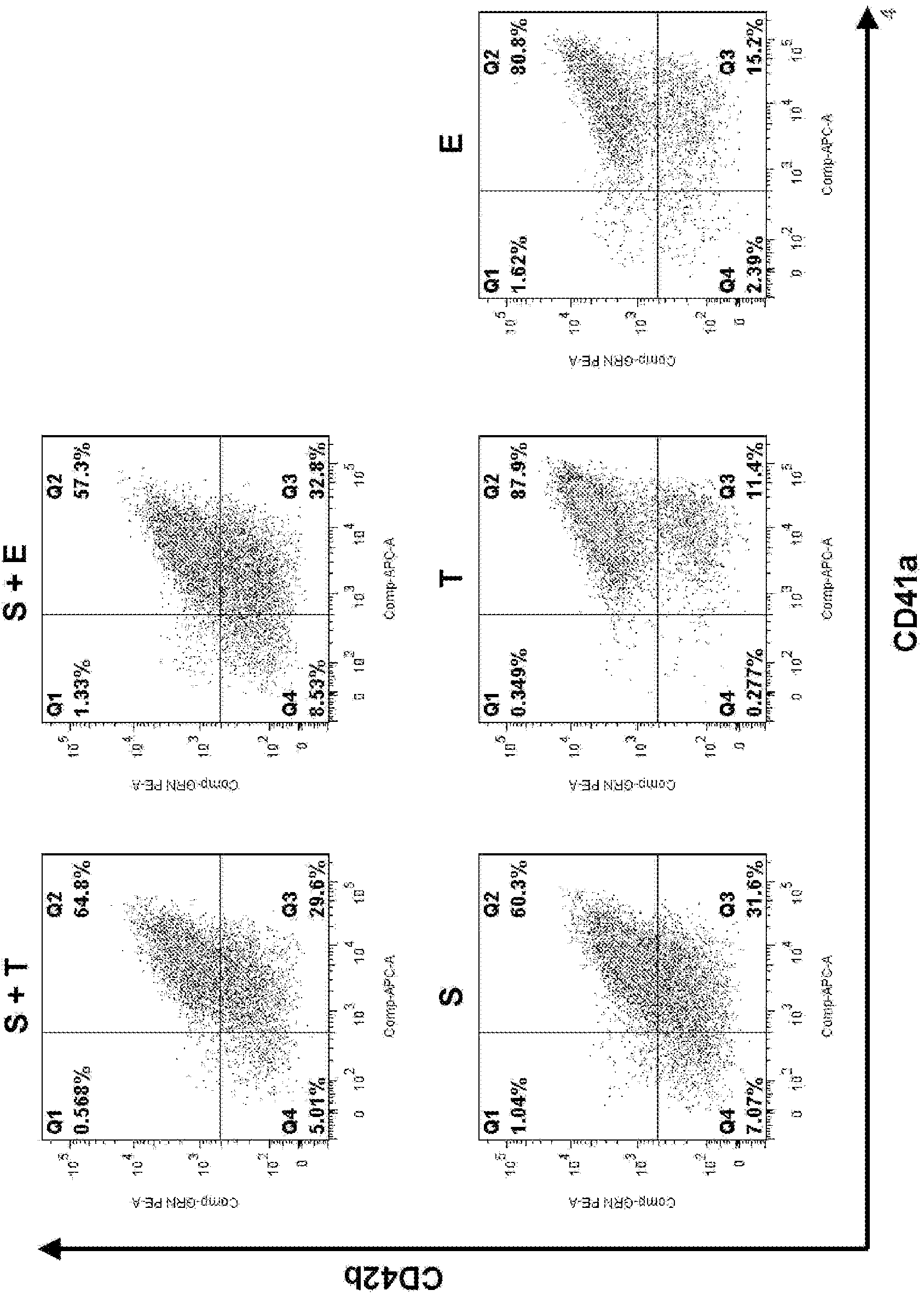
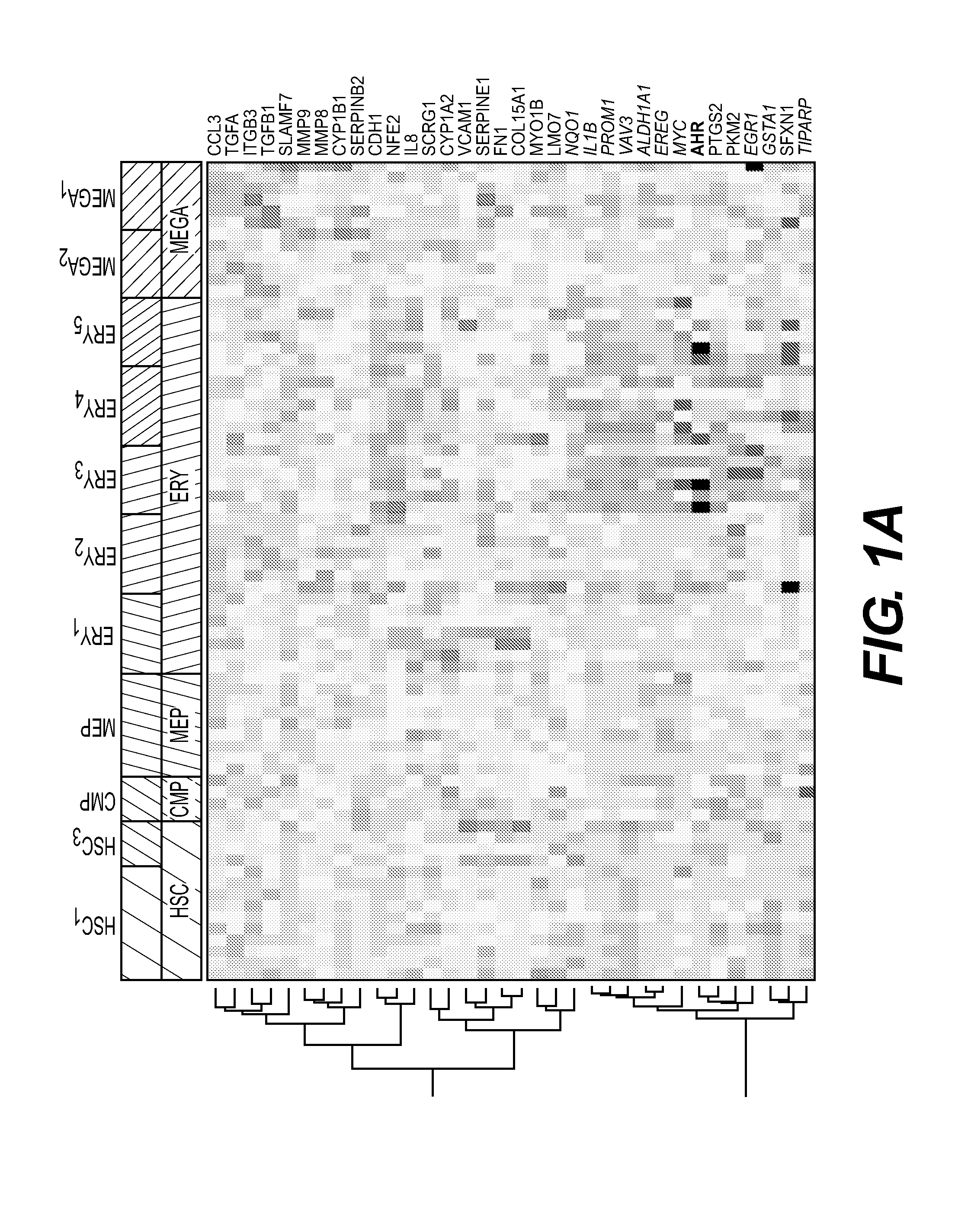
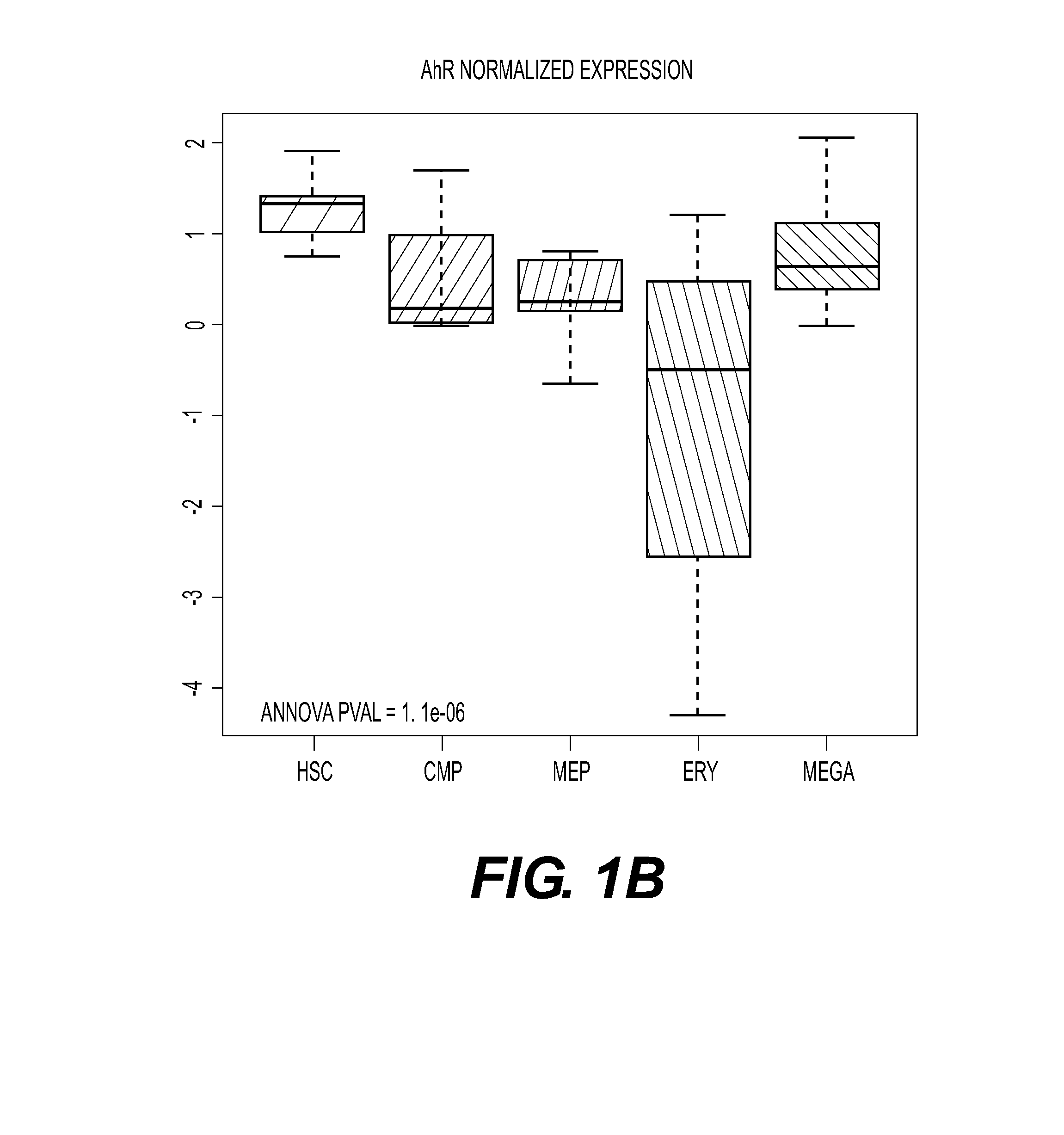
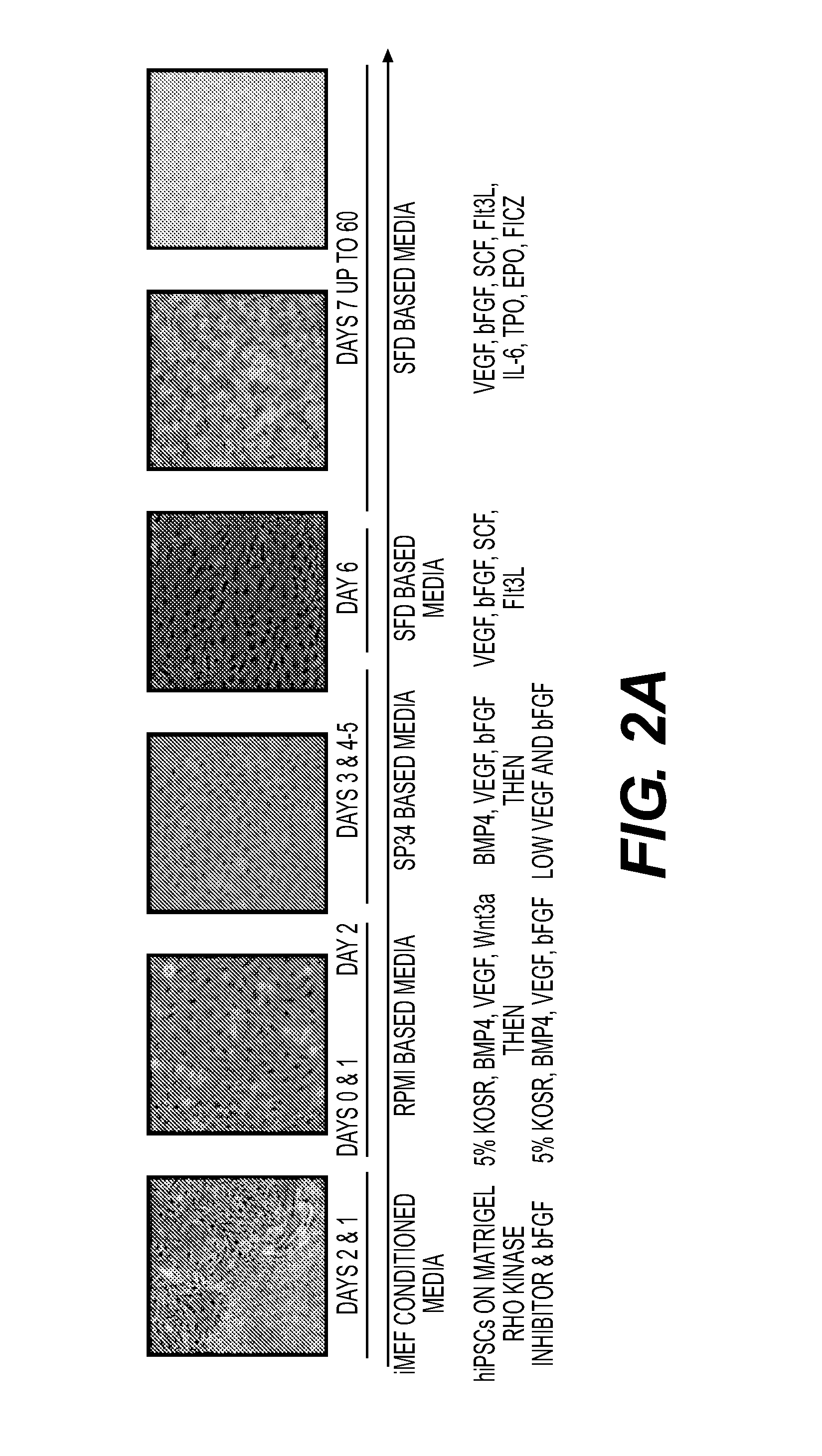
This disclosure provides methods of making a megakaryocyte-erythroid progenitor cell (MEP), comprising differentiating a stem cell into a MEP in culture in the presence of an aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) agonist. In some embodiments the stem cell is a pluripotent stem cell. In some embodiments the MEP co-expresses CD41 and CD235. In some embodiments the number of MEPs produced in the culture increases exponentially. Methods of making a red blood cell (RBC) by culturing a MEP in the presence of an AhR agonist are also provided. Methods of making a megakaryocyte and / or a platelet, comprising culturing a MEP in the presence of an AhR modulator are also provided. In some embodiments the AhR modulator is an AhR antagonist. This disclosure also provides compositions comprising at least 1 million MEPs per ml and compositions in which at least 50% of the cells are MEPs.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV +1
Polynucleated megakaryocytic cell and method for manufacturing platelets
ActiveCN103814126APromote multi-coreHigh degree of multi-coreMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsMultinucleateSuppressor
An object of the present invention is to provide a method of promoting polynucleation of megakaryocytic cells to form polynucleated megakaryocytic cells with higher polynucleation, and to further provide a method for efficiently producing platelets from polynucleated megakaryocytic cells. The present invention provides a method for producing polynucleated megakaryocytic cells, wherein the method includes a step for inducing forced expression of an apoptosis suppressor gene in megakaryocytic cells prior to polynucleation and culturing of these cells.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Production of red blood cells and platelets from stem cells
This disclosure provides methods of making a megakaryocyte-erythroid progenitor cell (MEP), comprising differentiating a stem cell into a MEP in culture in the presence of an aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) agonist. In some embodiments the stem cell is a pluripotent stem cell. In some embodiments the MEP co-expresses CD41 and CD235. In some embodiments the number of MEPs produced in the culture increases exponentially. Methods of making a red blood cell (RBC) by culturing a MEP in the presence of an AhR agonist are also provided. Methods of making a megakaryocyte and / or a platelet, comprising culturing a MEP in the presence of an AhR modulator are also provided. In some embodiments the AhR modulator is an AhR antagonist. This disclosure also provides compositions comprising at least 1 million MEPs per ml and compositions in which at least 50% of the cells are MEPs.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV +1
Mouse anti-human CD14 monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell line, monoclonal antibody, immunohistochemical reagent kit and uses thereof
InactiveCN101200708AShorten primary antibody incubation timeShorten the timeImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsAntigenCD61
The present invention discloses a mouse anti-human CD41 monoclonal antibody hybridoma cell system, a monoclonal antibody and an immunohistochemical kit and an application thereof. A traditional hybridoma preparation technology is used to obtain hybridoma cell strain which excretes anti-human CD41 molecular monoclonal antibody stably. The excreted antibody can identify the conformational epitopes of the combination of human CD41 antigen and CD61 antigen and can inhibit the aggregation effect caused by ADP, collagen, HIP2, etc. The monoclonal antibody is marked biotin directly and combined with alkali phosphatase-strep avidin working fluid, substrate solution and fast red to form the immunohistochemical kit which uses SAP method to detect megakaryocyte. The kit and the detection method provided by the present invention can shorten the detection time and avoid repeated washing, so the status of cell chipping can not occur, the detection efficiency is improved greatly and the present invention is fit for common technicians to operate.
Owner:UNION STEMCELL & GENE ENG
Platelets from stem cells
Human embryonic stem cells are induced to differentiate first into the hematopoietic lineage and then into megakaryocytes, the cells which generate platelets. The proper in vitroculture of megakaryocytes results in the production and shed of platelets. This makes possible, for the first time, the in vitro production of a human blood factor needed by many patients.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Process method for bone marrow smear digitization
InactiveCN108896363AReduce turnaround timeImprove consistencyPreparing sample for investigationSkeletal/connective tissue cellsRelevant informationTurnover time
The invention discloses a process method for bone marrow smear digitization. The process method comprises the following steps: acquiring related information of bone marrow smears, generating global images, and performing digital labeling after obtaining the to-be-digitized area as well as karyocyte collecting quantity and megakaryocyte classifying quantity; feeding the bone marrow smears into scanning equipment for performing shooting scanning: a to-be-digitized area generated by low-power lens scanning, and labeling and recognizing object observers therein; generating a spliced image in the scanning area; switching to megakaryocyte in the megakaryocyte classifying quantity generated by high-power lens scanning, and labeling and recognizing the megakaryocyte; generating the scanned megakaryocyte image; switching to karyocyte in the karyocyte collecting quantity in the to-be-digitized area generated by oil lens scanning, labeling and recognizing the karyocyte; generating the scanned karyocyte image; and generating digitalized smears of physical bone marrow smears. The artificial microscopy process is simplified; the consistency and standardization of the bone marrow examination report results are improved; and remote consultation is conveniently carried out, and the turn-round time of the physical smears is reduced.
Owner:HANGZHOU ZHIWEI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Method for Producing Purified Platelets
ActiveUS20180282697A1Reduce riskHigh recovery rateCell dissociation methodsCulture processPlateletCentrifugal force
The present invention provides a method for producing purified platelets from a culture of megakaryocytes, comprising a first centrifugal separation step of centrifugally separating the culture at a centrifugal force of 150×g to 550×g, and a second centrifugal separation step of centrifugally separating, at a centrifugal force of 600×g to 4000×g, a liquid component recovered in the first centrifugal separation step.
Owner:MEGAKARYON CORP
Method for producing platelets from megakaryocytes
The present invention relates to a method for producing platelets from mature megakaryocytes. More particularly, the invention relates to an ex vivo method for producing platelets, from mature megakaryocytes, said method comprising a step of subjecting a suspension of mature megakaryocytes to a flow having a minimal shear rate of 600 s−1 on a solid phase coated with Von Willebrand factor.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +3
Methods for producing enucleated erythroid cells derived from pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20170121681A1Mammal material medical ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsInduced pluripotent stem cellErythroid cell
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
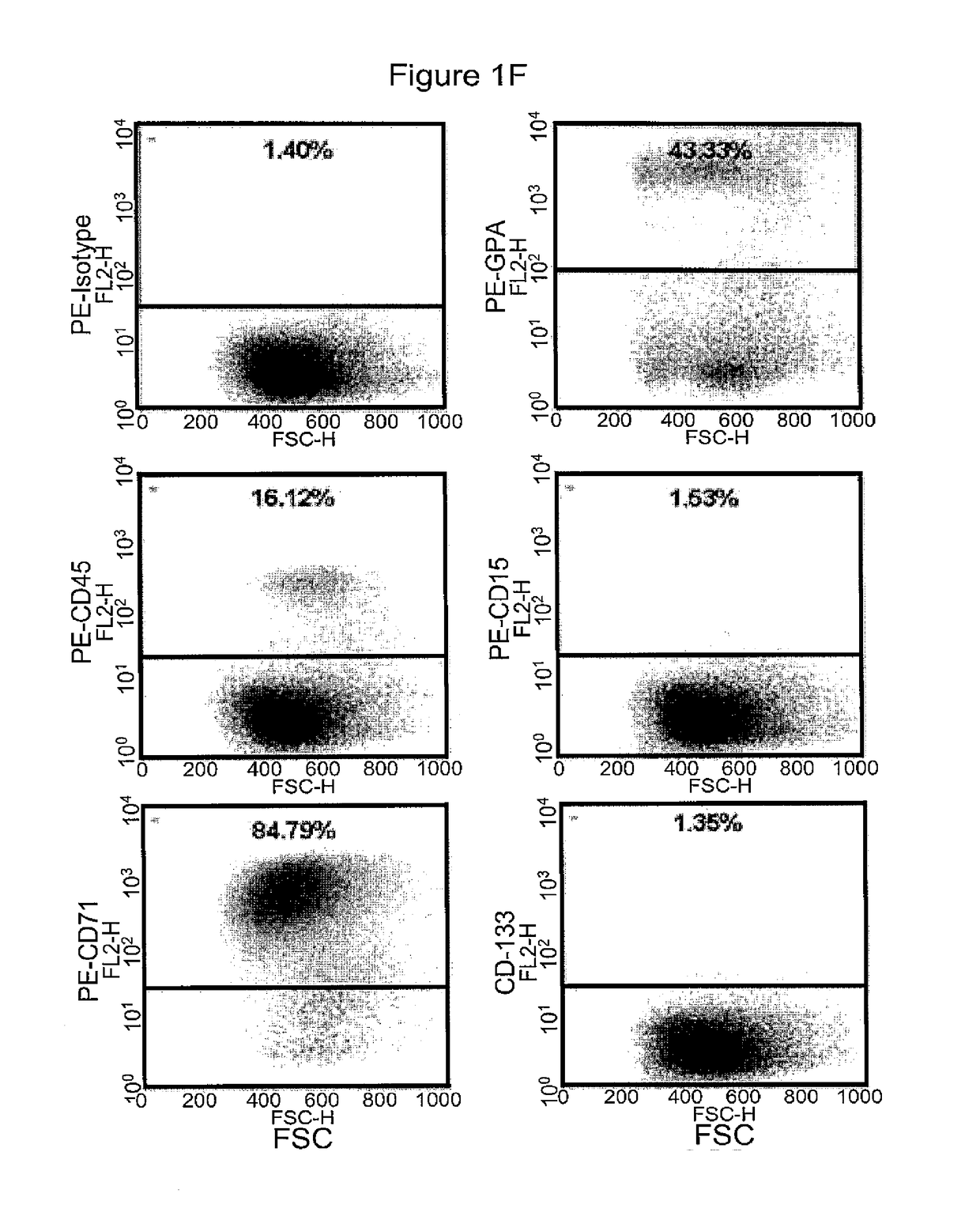
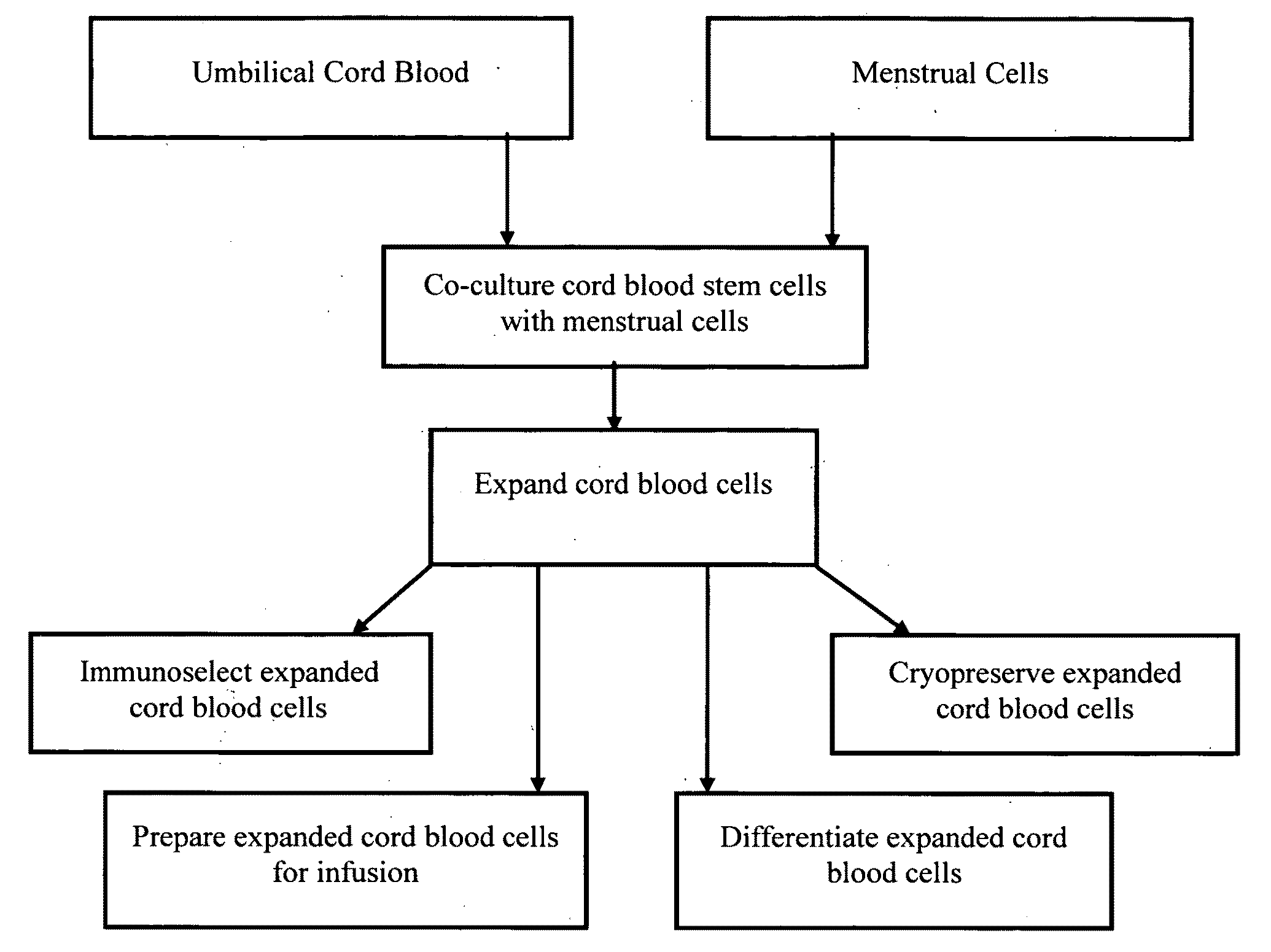
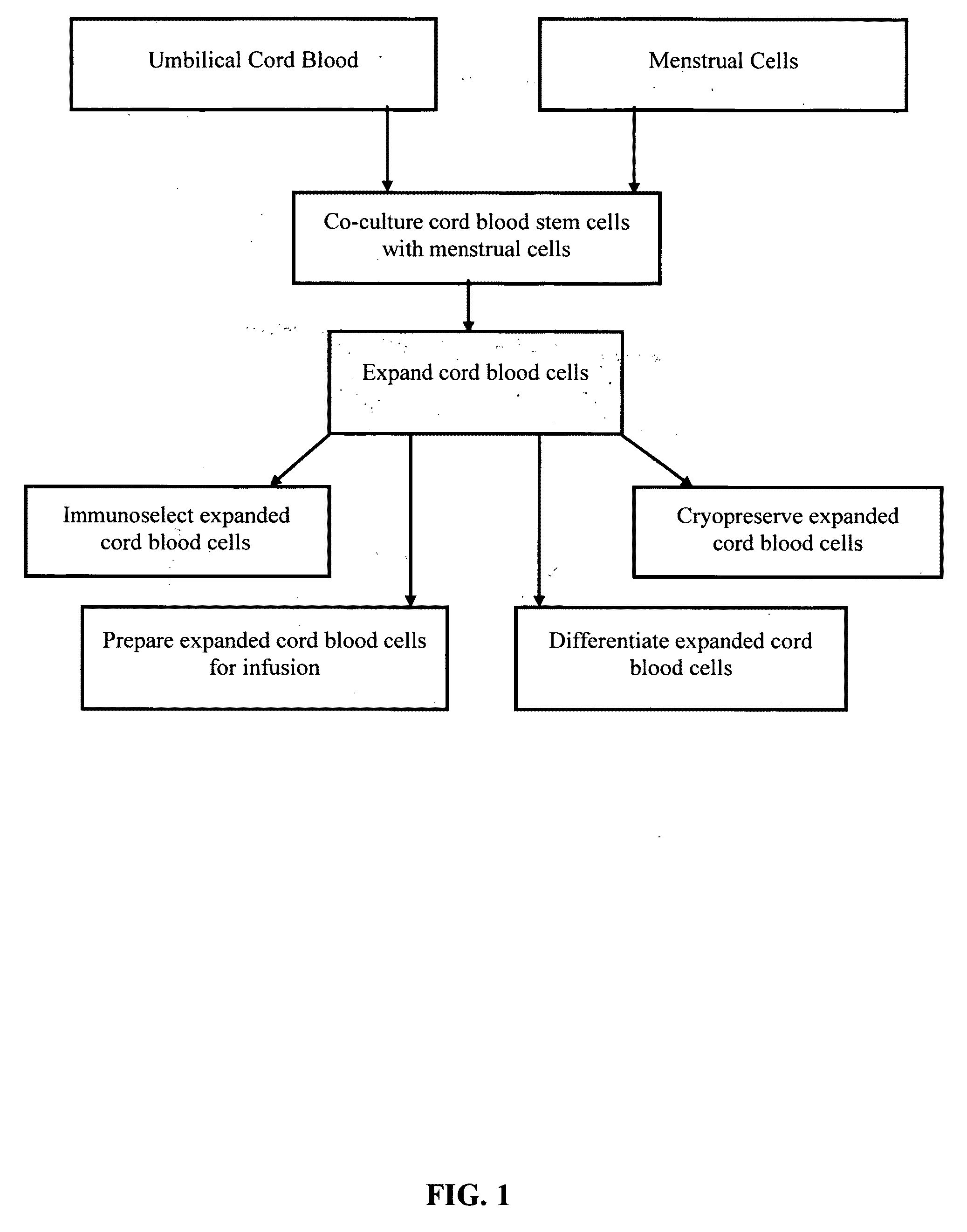
Methods for co-culturing cord blood derived cells with menstrual stem cells
InactiveUS20090191628A1Increased proliferationArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPopulation doublingCord blood stem cell
Methods are provided for obtaining expanded human cord blood cells expressing CD34. The methods involve seeding a sufficient amount of cord blood cells with a sufficient amount of menstrual cells under co-culture conditions suitable to promote expansion of the cord blood cells, and co-culturing the cord blood cells with the menstrual cells under culture conditions that support at least two or more population doublings of the cord blood cells. Methods are also provided for growing expanded human cord blood cells to give rise to any one of colony forming units, colony forming unit granulocyte macrophages (CFU-GM), burst forming unit erythroids (BFU-E), and colony forming unit granulocyte erythrocyte macrophage megakaryocyte (CFU-GEMM) blood lineage precursor cells. The expanded cells may express CD34, SSEA-4, and HLA-II. Compositions of the expanded cells are also provided.
Owner:CRYO CELL INTERNATIONAL INC
Method for preparation of platelet from iPS cell
ActiveUS8546141B2The process is stable and efficientAvoid it happening againMammal material medical ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsHematopoietic progenitor cell differentiationHematopoietic progenitor
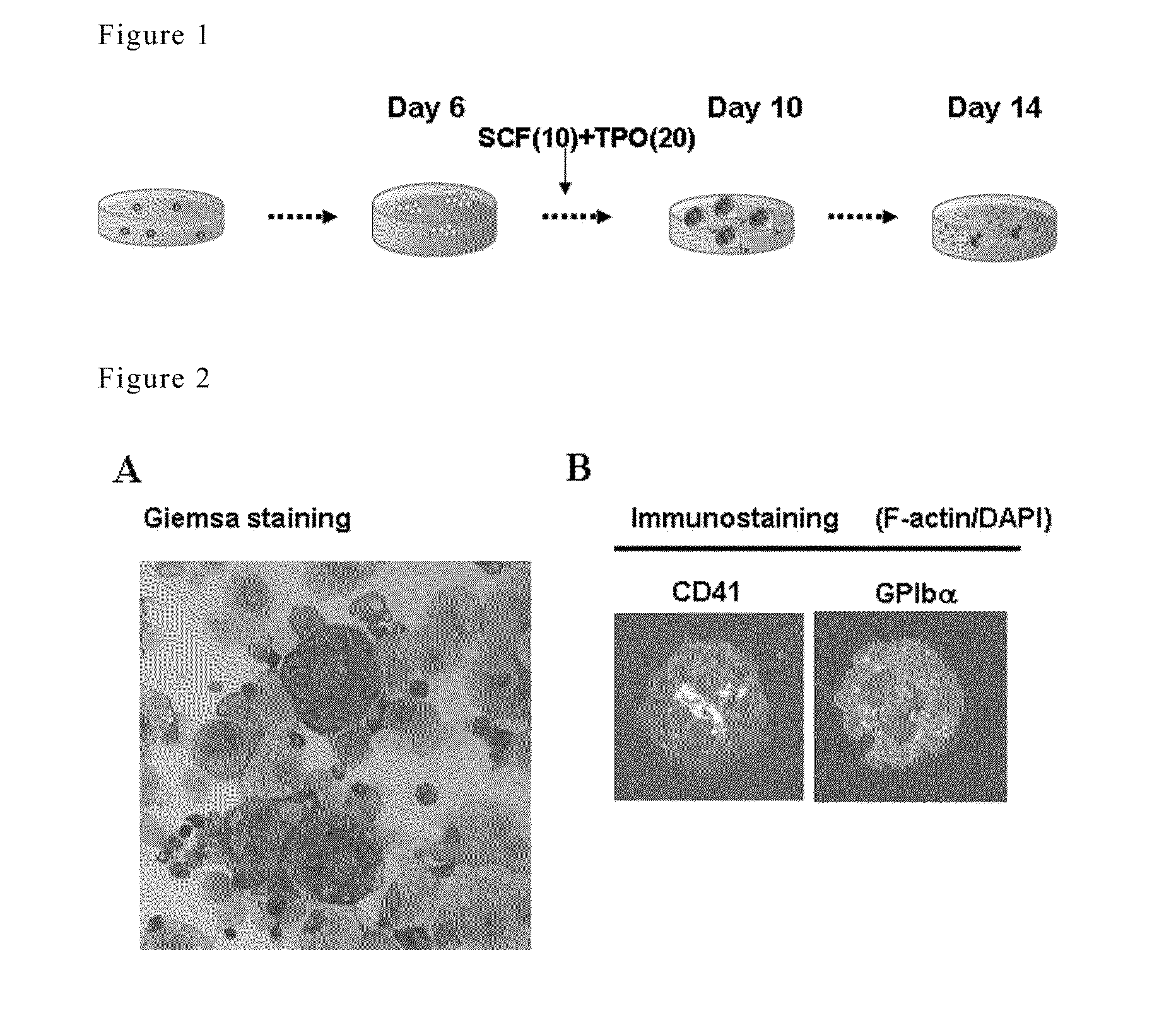
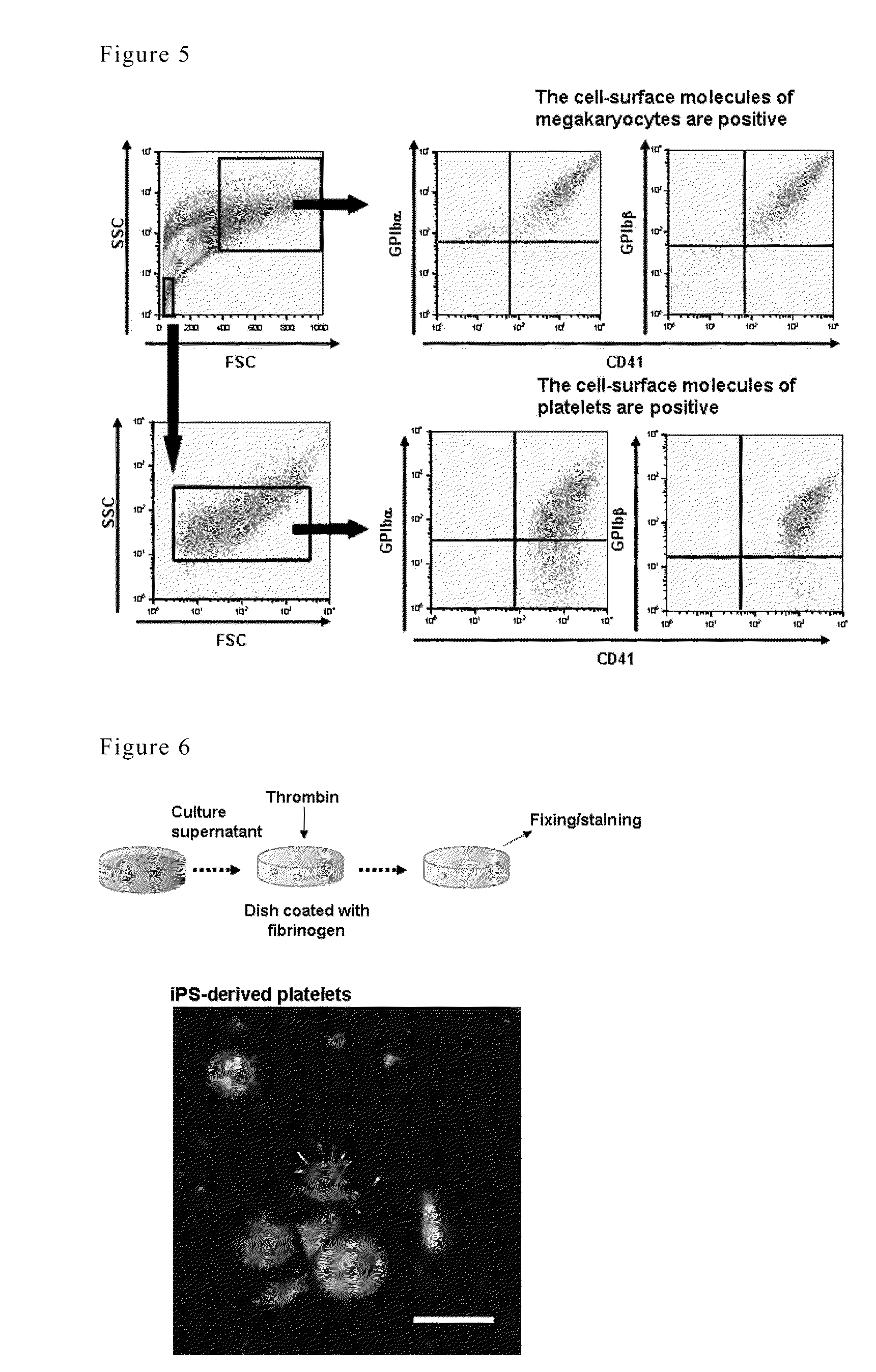
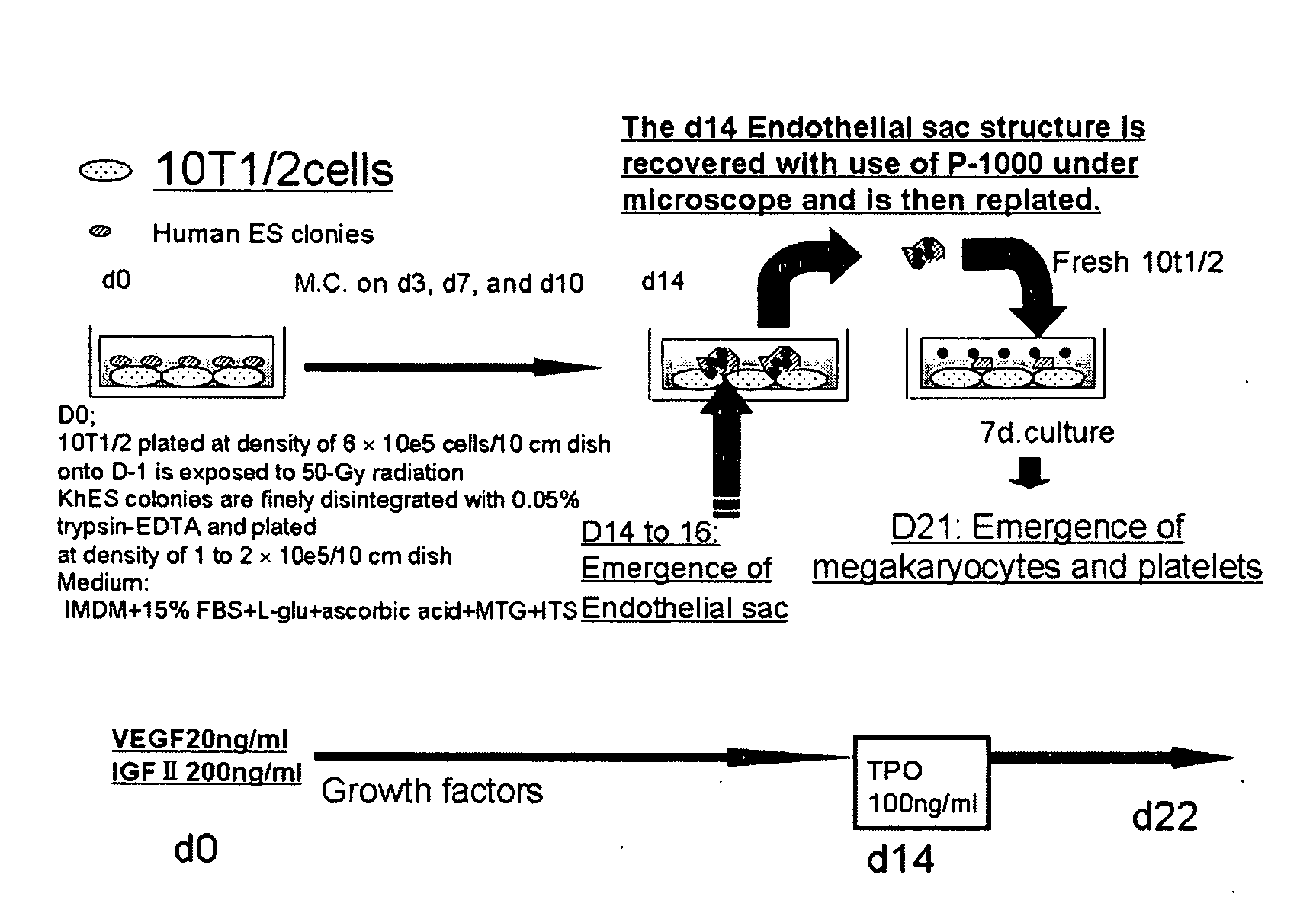
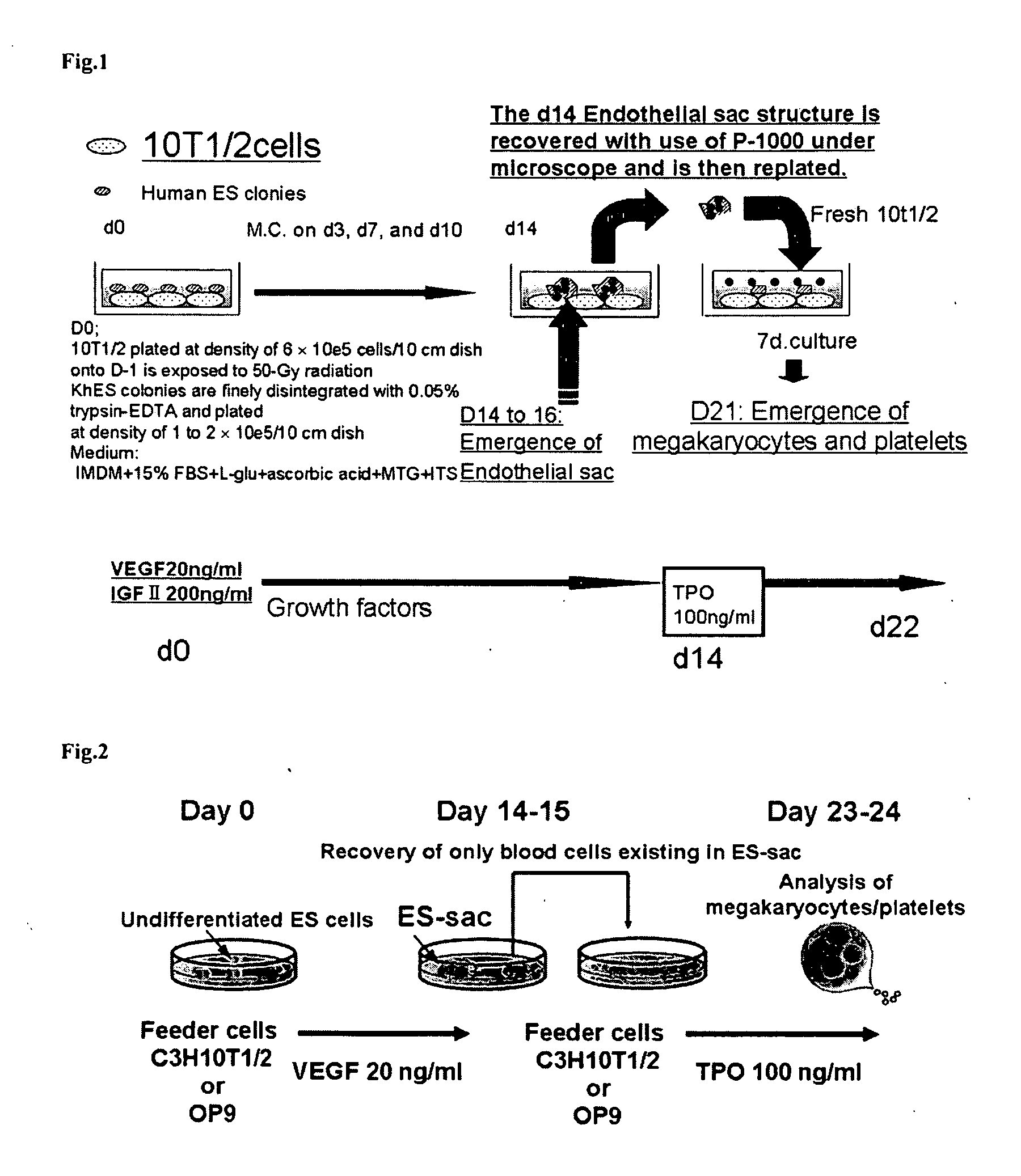
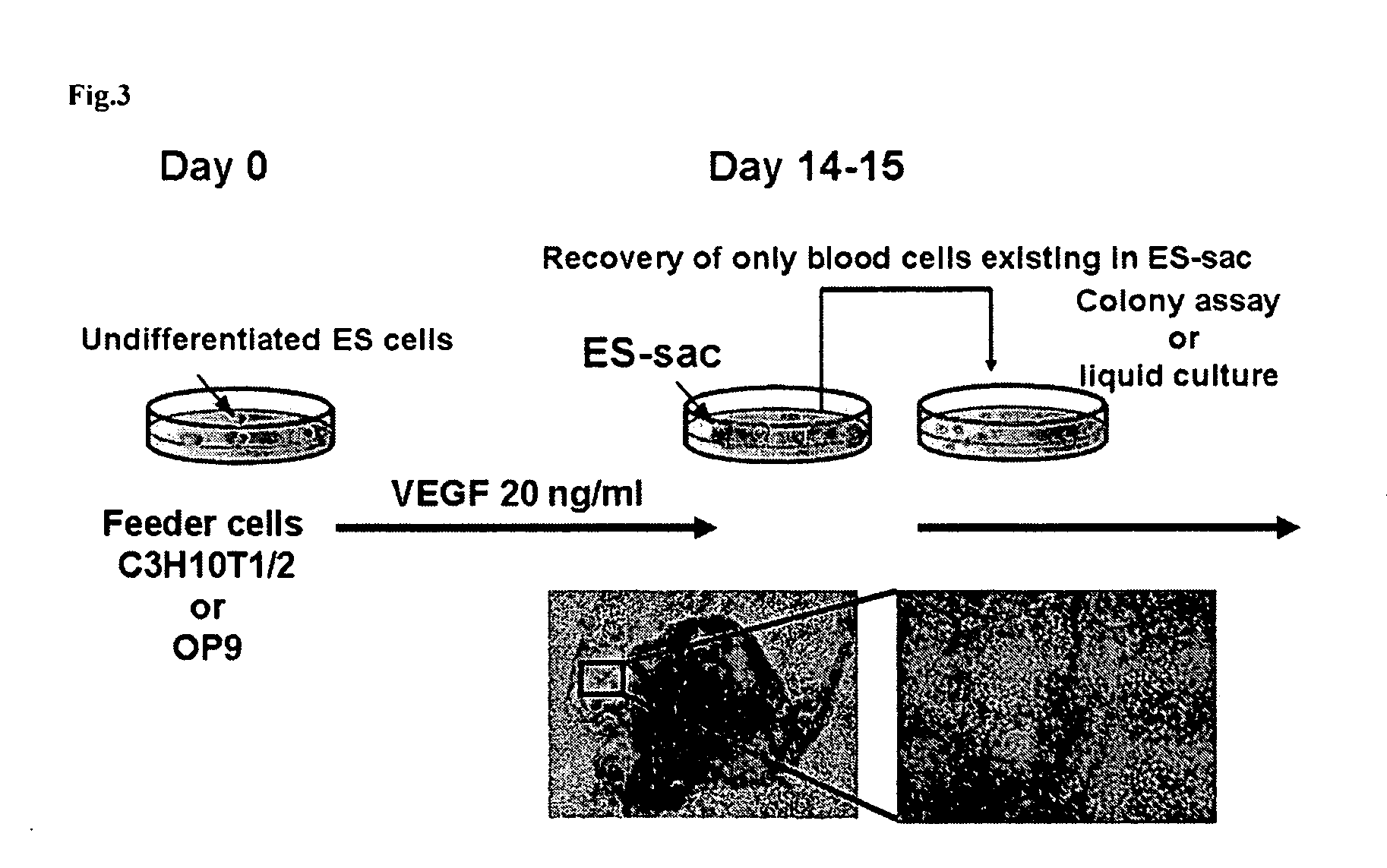
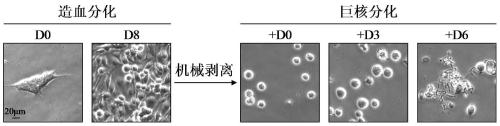
A method for efficiently preparing blood cells, such as mature megakaryocytes and platelets, from iPS cells is achieved in an in vitro culture system. A sac-like structure encloses hematopoietic progenitor cells, which is obtained by inoculating iPS cells onto feeder cells and then culturing the iPS cells under conditions suitable for inducing the differentiation of hematopoietic progenitor cells. Moreover, a method for producing various types of blood cells, comprises culturing hematopoietic progenitor cells enclosed in the sac-like structure under conditions suitable for inducing the differentiation of blood cells. Furthermore, a method for producing various types of blood cells, particularly megakaryocytes and platelets, is achieved without involving the sac-like structure.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Regulation of Integrin Surface Expression
InactiveUS20100048677A1Preventing and treating atherosclerosisPreventing and treating thrombosisOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesMedicineIntegrin
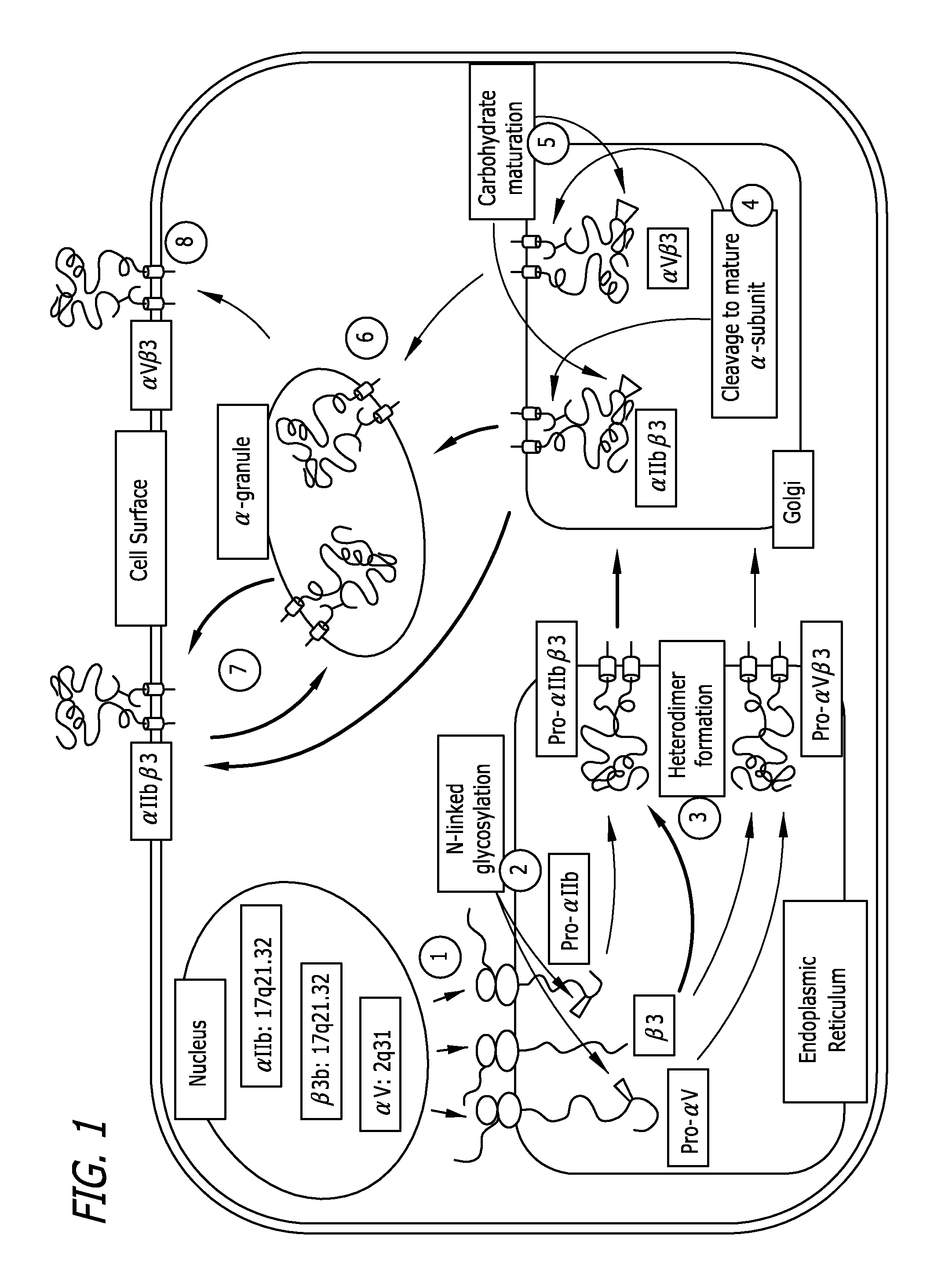
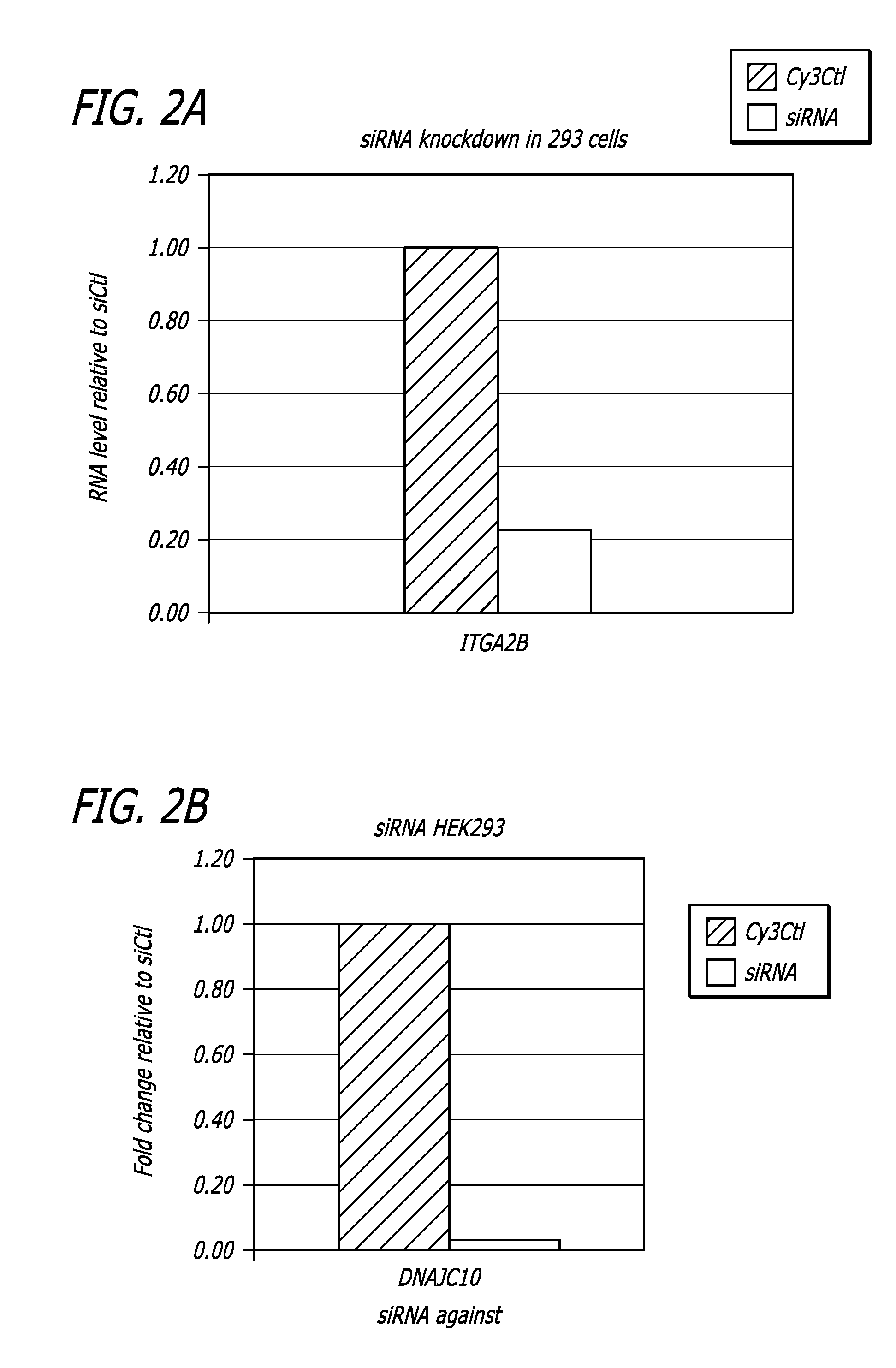
Disclosed are methods and compositions for preventing and treating conditions associated with platelet aggregation, comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a composition that modifies the interaction of DNAJC10 with αIIbβ3 in a megakaryocyte, thereby altering the expression of αIIbβ3 on the surface of the megakaryocyte.
Owner:NEW YORK BLOOD CENT
Structure enclosing hematopoietic progenitor cells from ES cells and method for preparing blood cells using the same
ActiveUS20100197016A1Efficient inductionEfficiently obtainedArtificial cell constructsMammal material medical ingredientsHematopoietic progenitor cell differentiationHematopoietic progenitor
An object of the present invention is to provide a sac-like structure enclosing hematopoietic progenitor cells and a method for preparing the sac-like structure as well as a method for efficiently preparing blood cells such as mature megakaryocytes and platelets from the sac-like structure. The present invention provides a sac-like structure enclosing hematopoietic progenitor cells, the sac-like structure being obtained by plating ES cells onto feeder cells and culturing the ES cells under suitable conditions for inducing hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation. Moreover, the present invention provides a method for producing various blood cells, the method comprising further culturing hematopoietic progenitor cells enclosed in the sac-like structure under suitable conditions for inducing blood cell differentiation.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
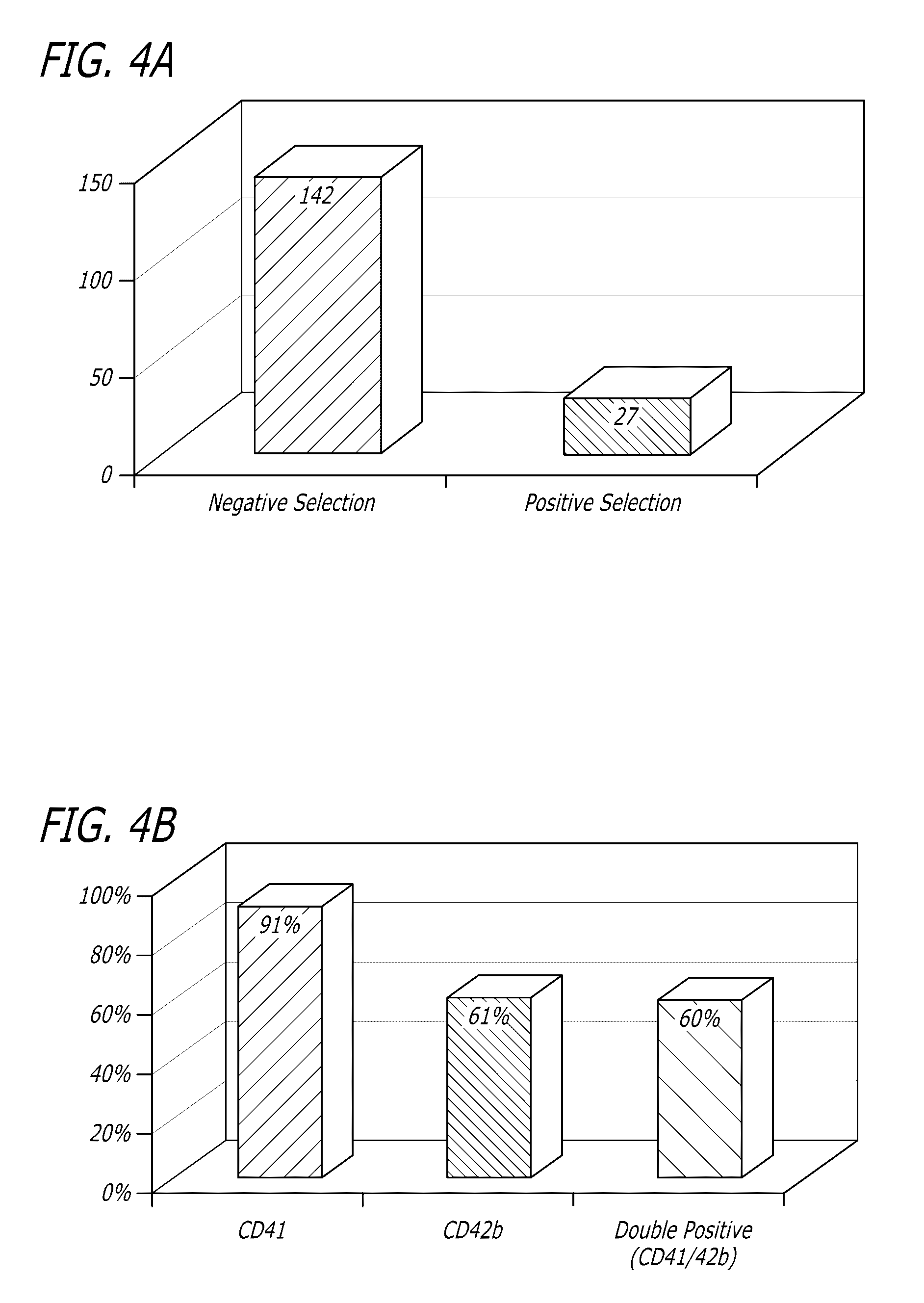
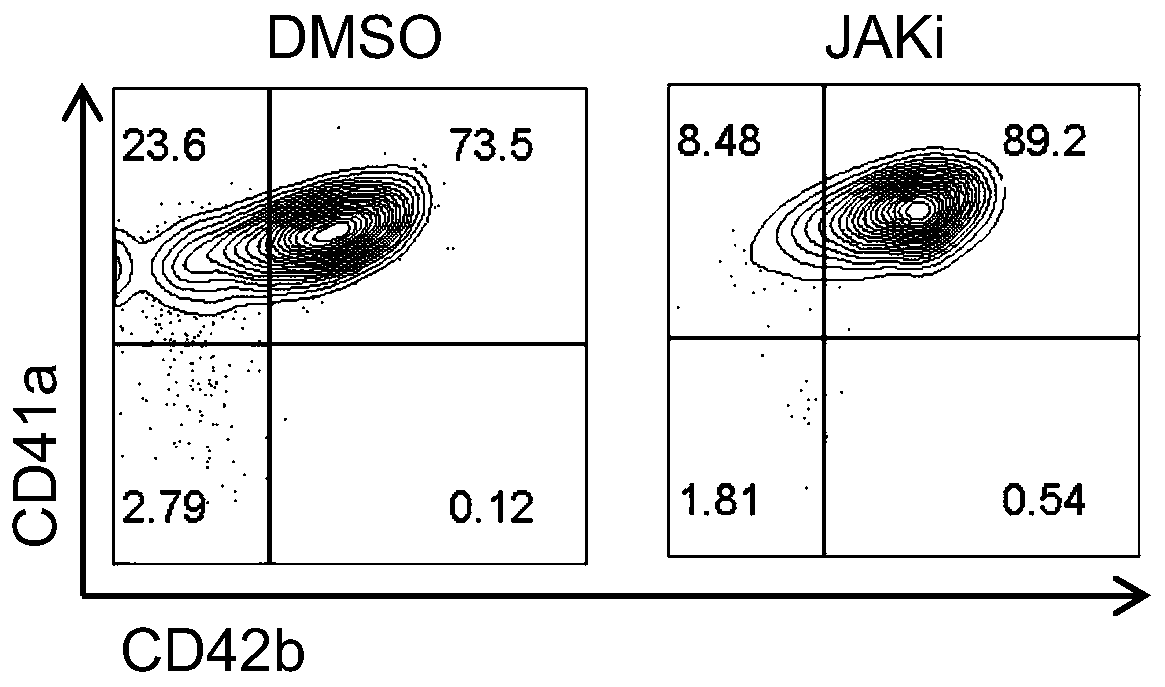
Application of JAK (Janus kinase) in preparation of products for promoting induction of multipotent stem cells to generate megakaryocytes and platelets
InactiveCN110373386AHigh yieldEasy to operateDigestive systemMammal material medical ingredientsOperabilityJanus kinase
The invention discloses application of JAK (Janus kinase) in the preparation of products for promoting induction of multipotent stem cells to generate megakaryocytes and platelets. A megakaryocytic differentiation system established herein has higher operability and repeatability and can provide efficient rapid in-vitro generation of active platelets. Rapid efficient in-vitro generation of platelets is achieved under serum-free stromal cell-free culture conditions; specific functional micromolecules are added in the megakaryocytic differentiation stage through small-scale molecular screening,and the ratio of active platelets (CD41a<+>CD42b<+>) is further increased. Statistical results show that the generation of 27-36 CD41a<+>CD42b<+> active platelets can be induced through single human polypotent stem cells, and the results are evidently higher than the results of the prior art. The rapid simple serum-free stromal-free culture strategy lays the basis for the large-scale production offunctional platelets for clinical therapy.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com