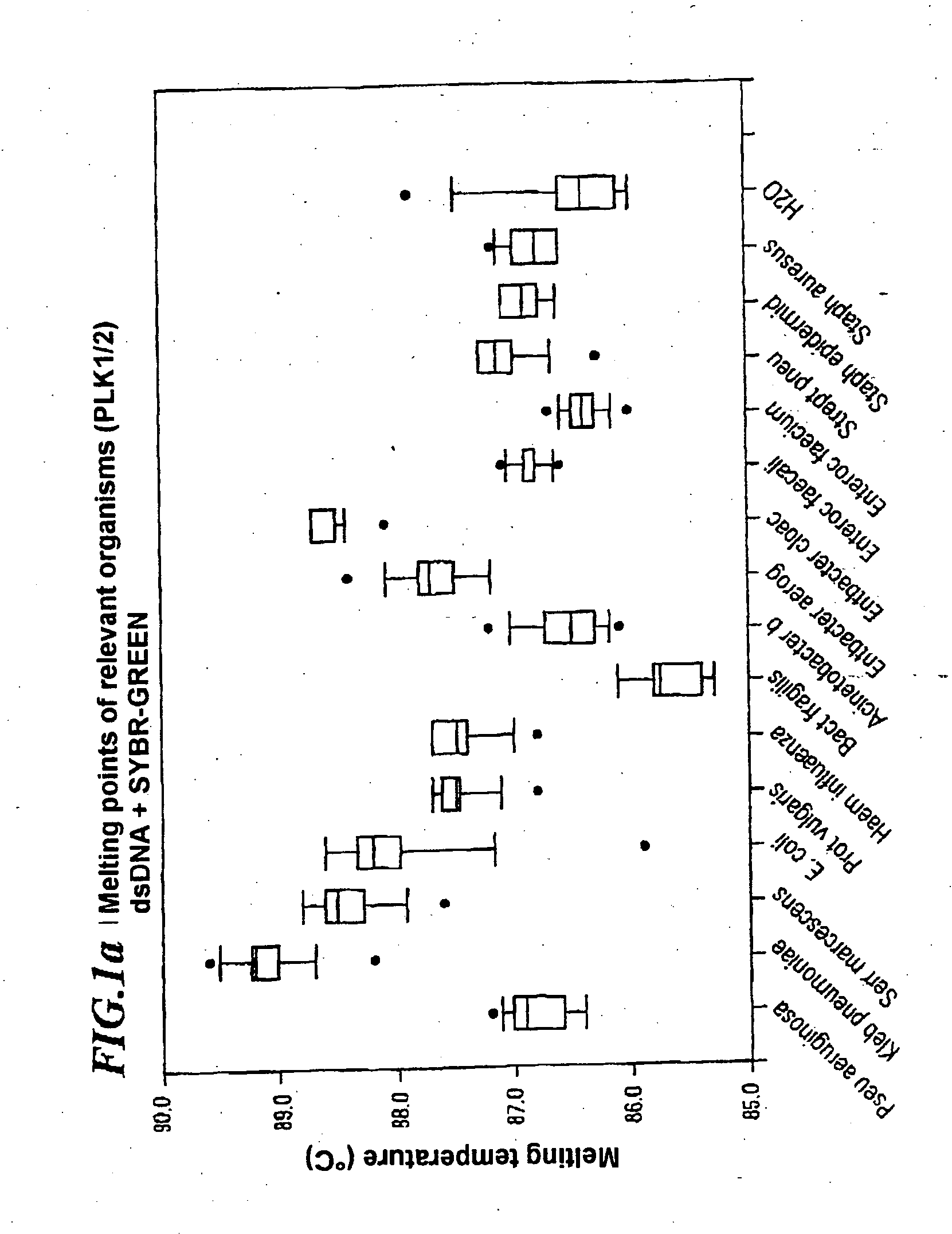
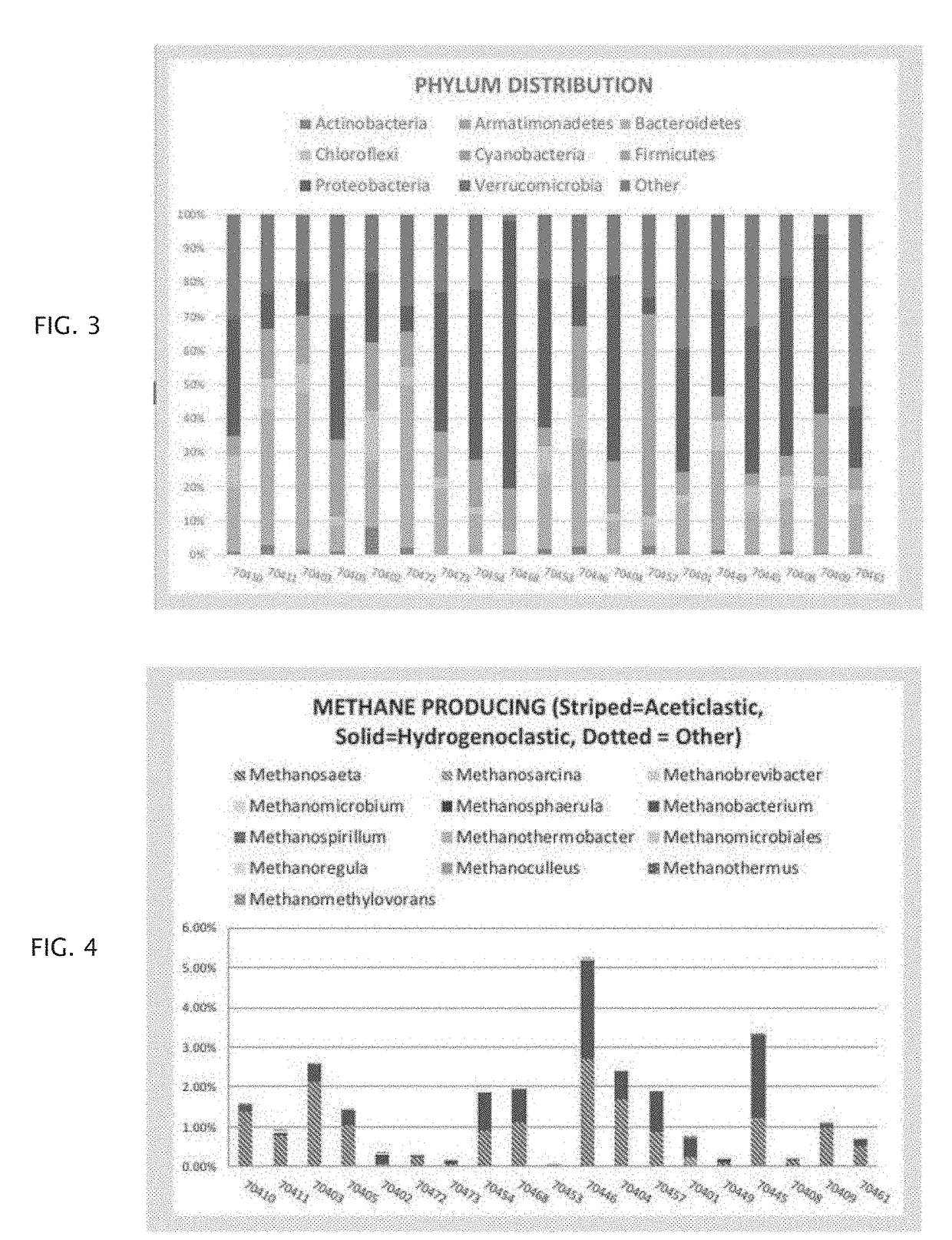
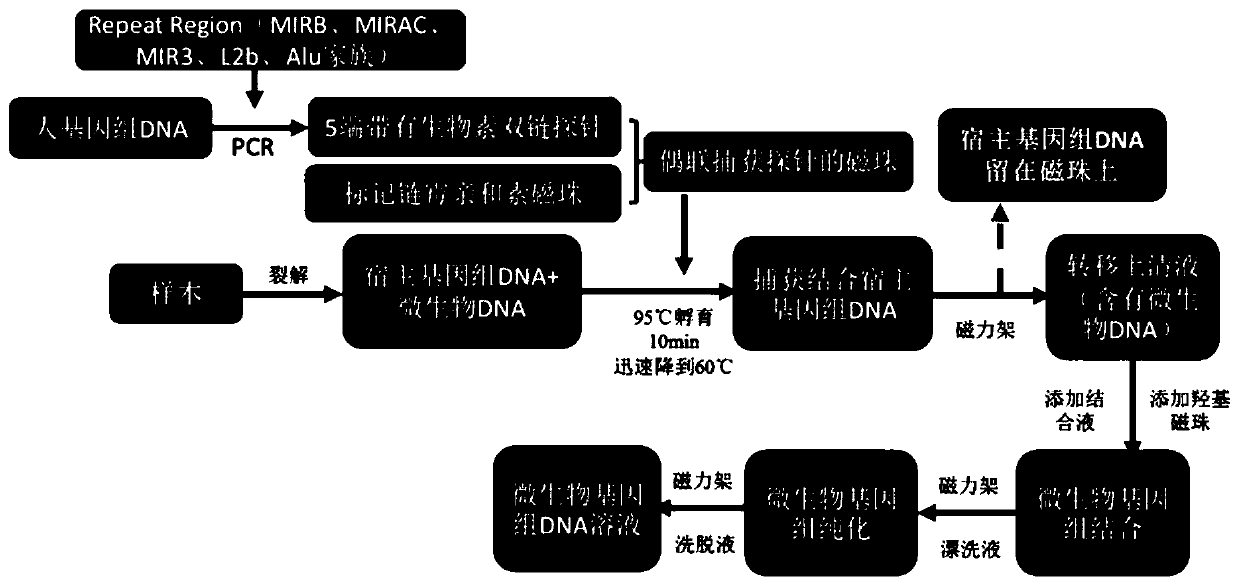
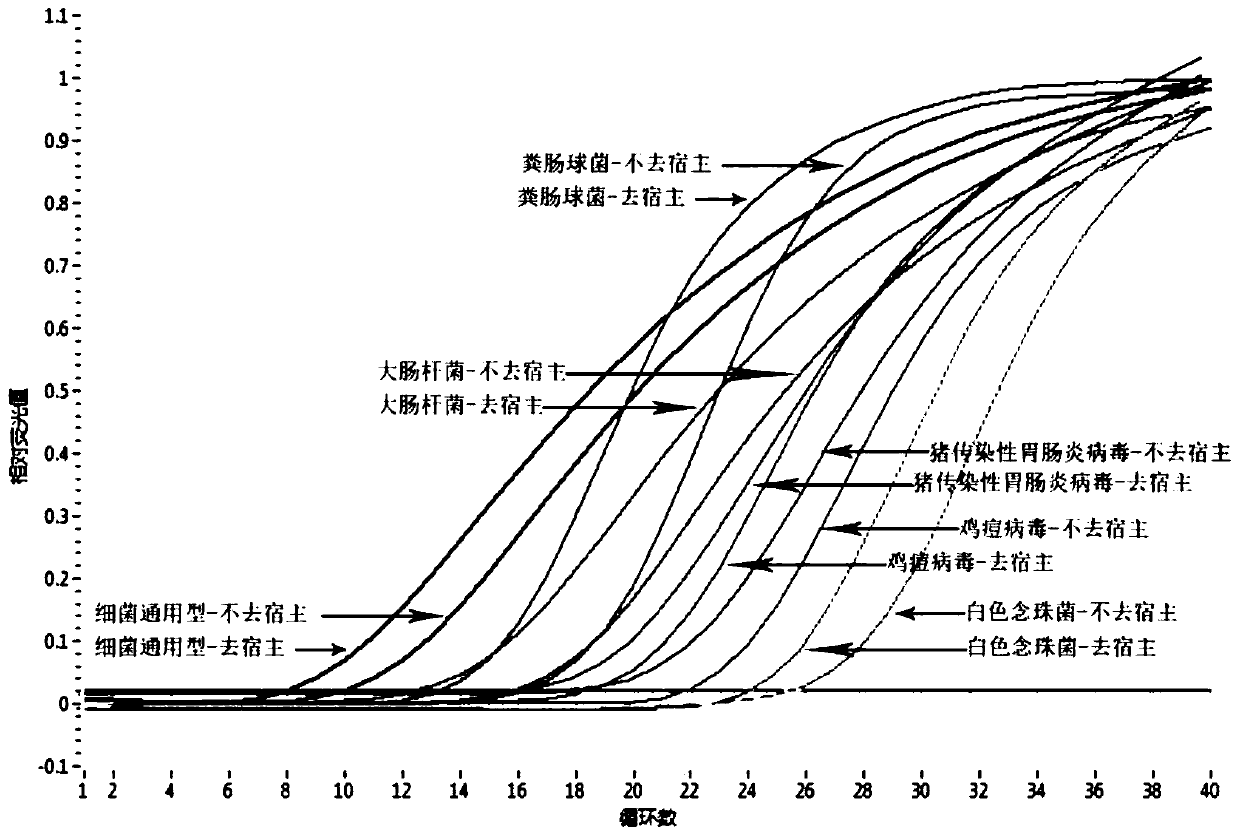
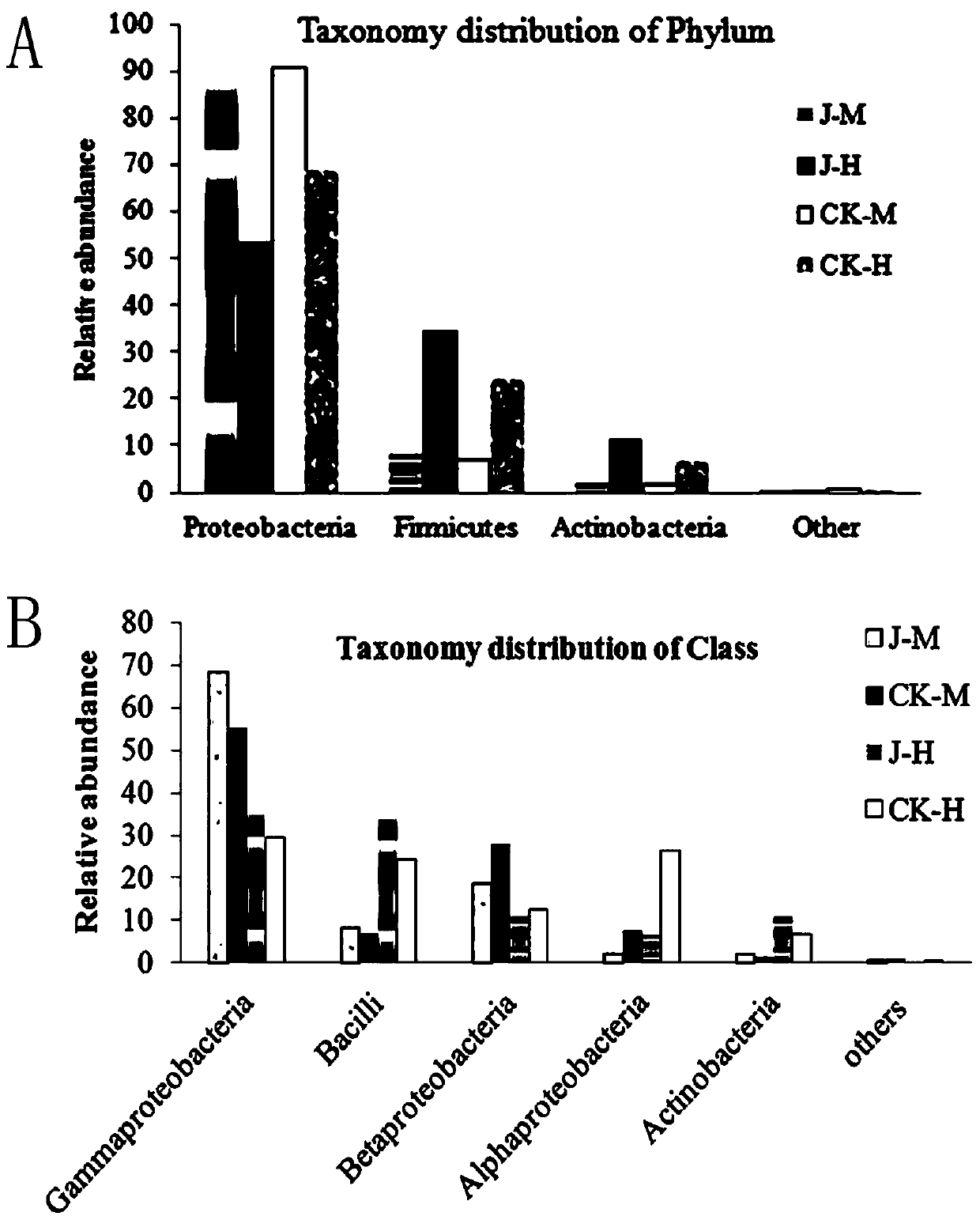
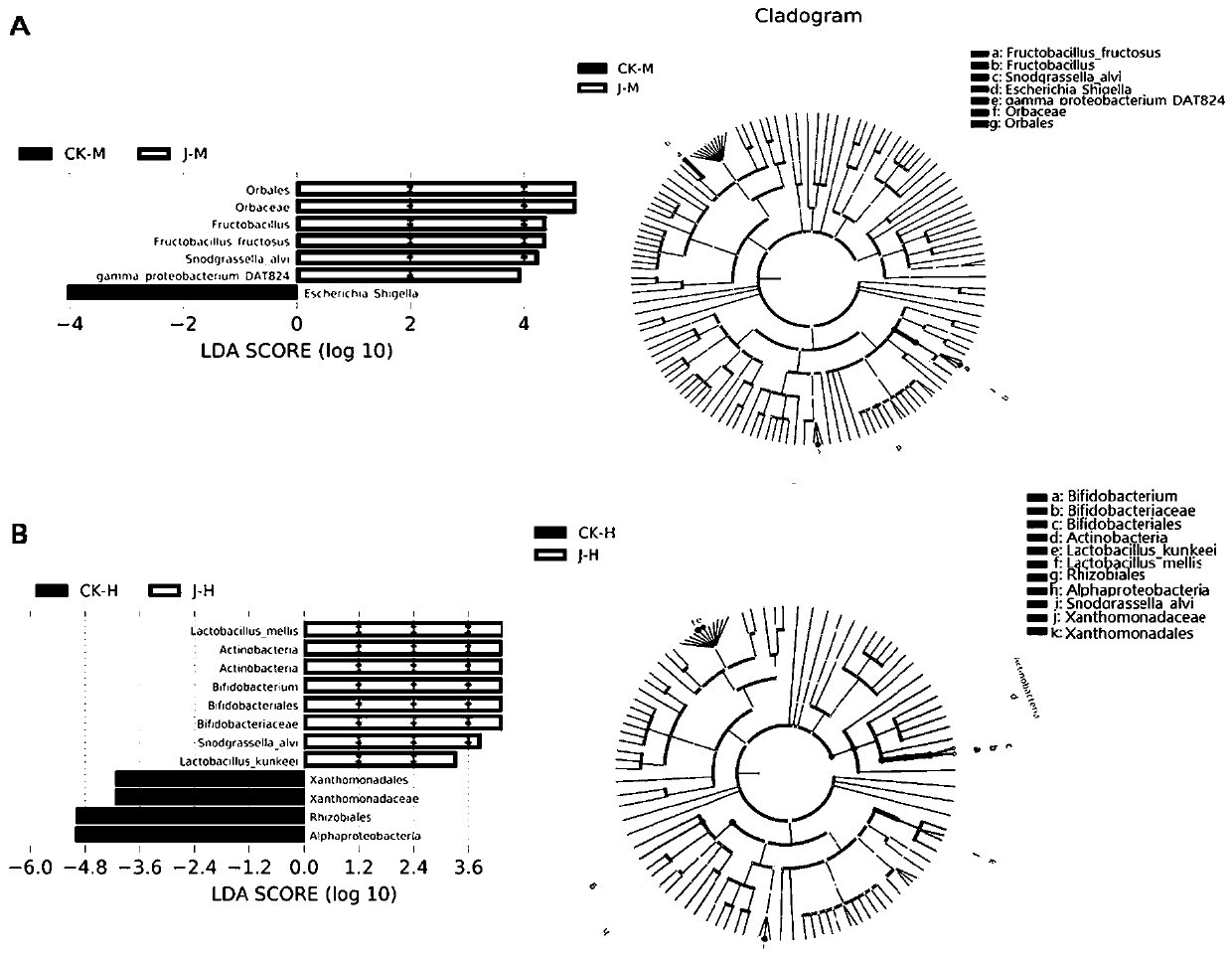
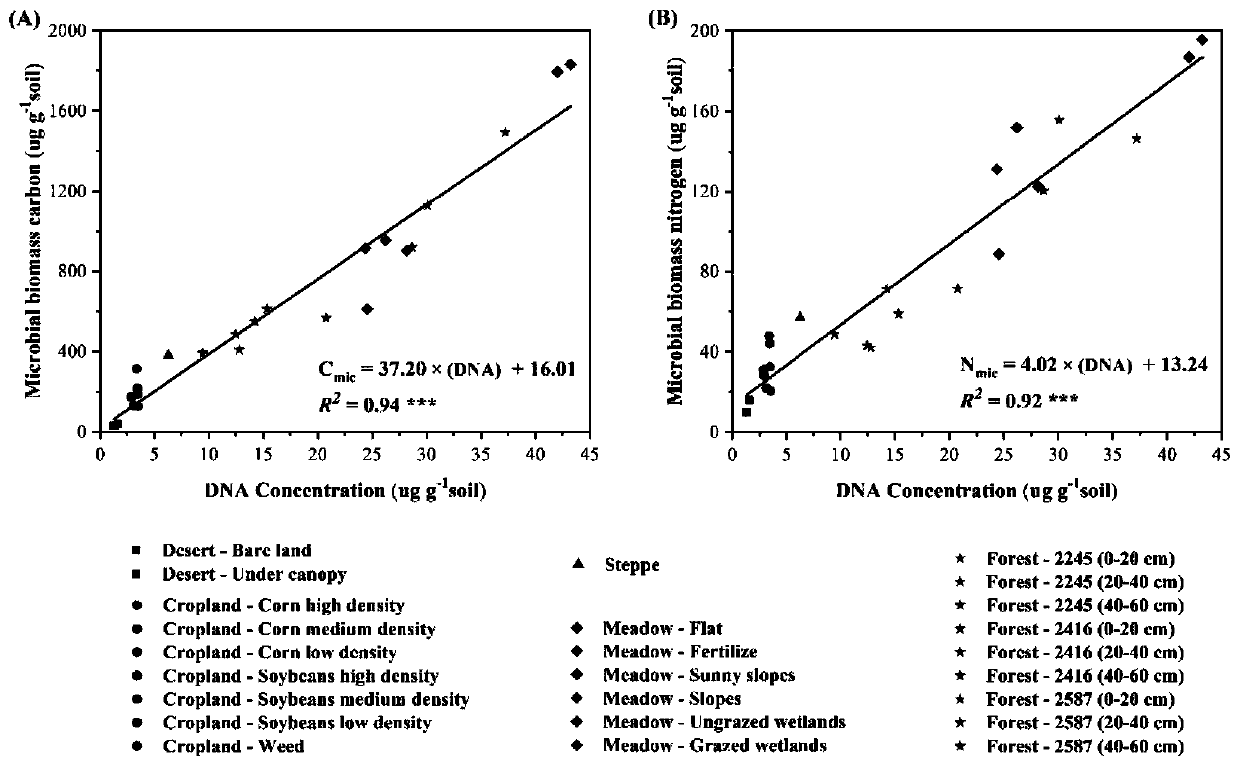
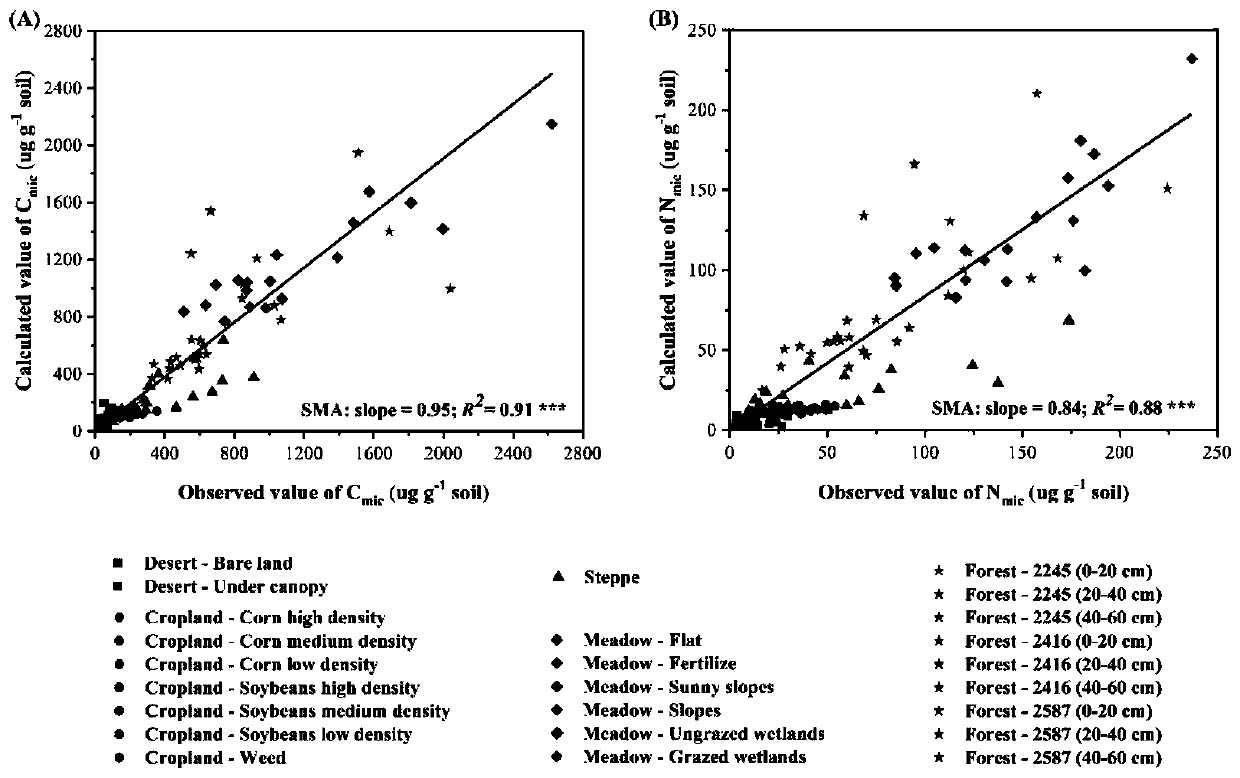
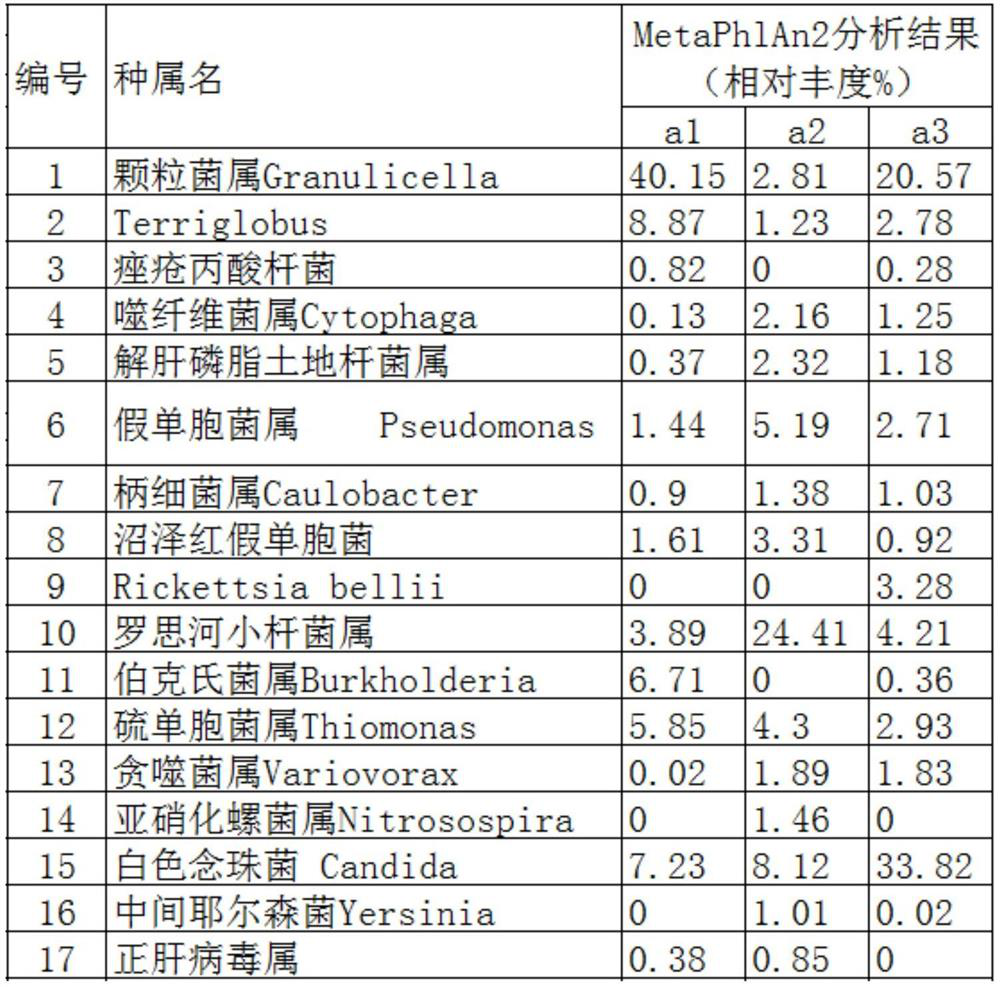
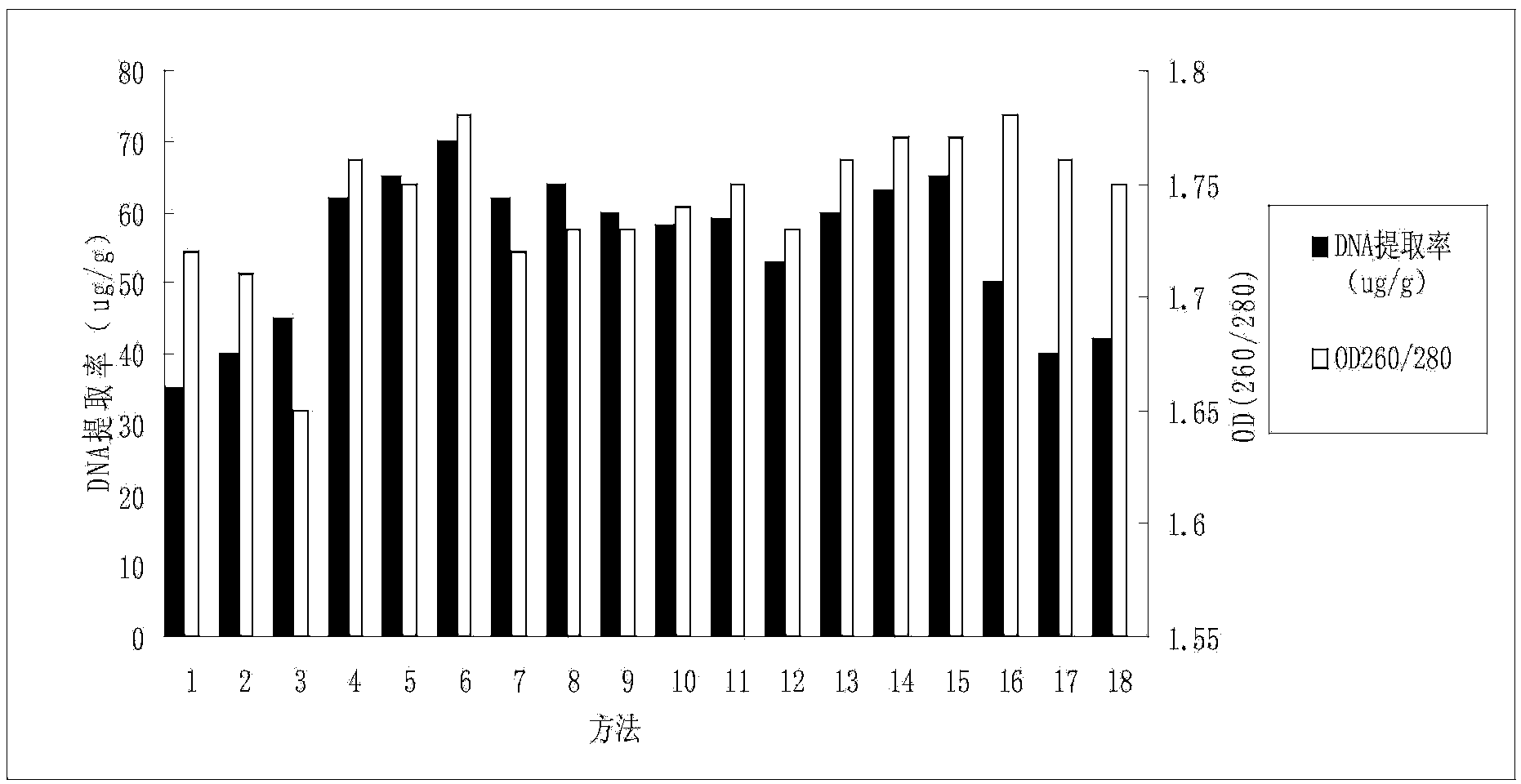
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
73 results about "Microbial DNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
DNA that originates from a microbe.
Method for quickly detecting microbial dna/rna, kit therefor and the use of said method
InactiveUS20050079490A1Early detectionAccurate identificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismMicrobe DNA
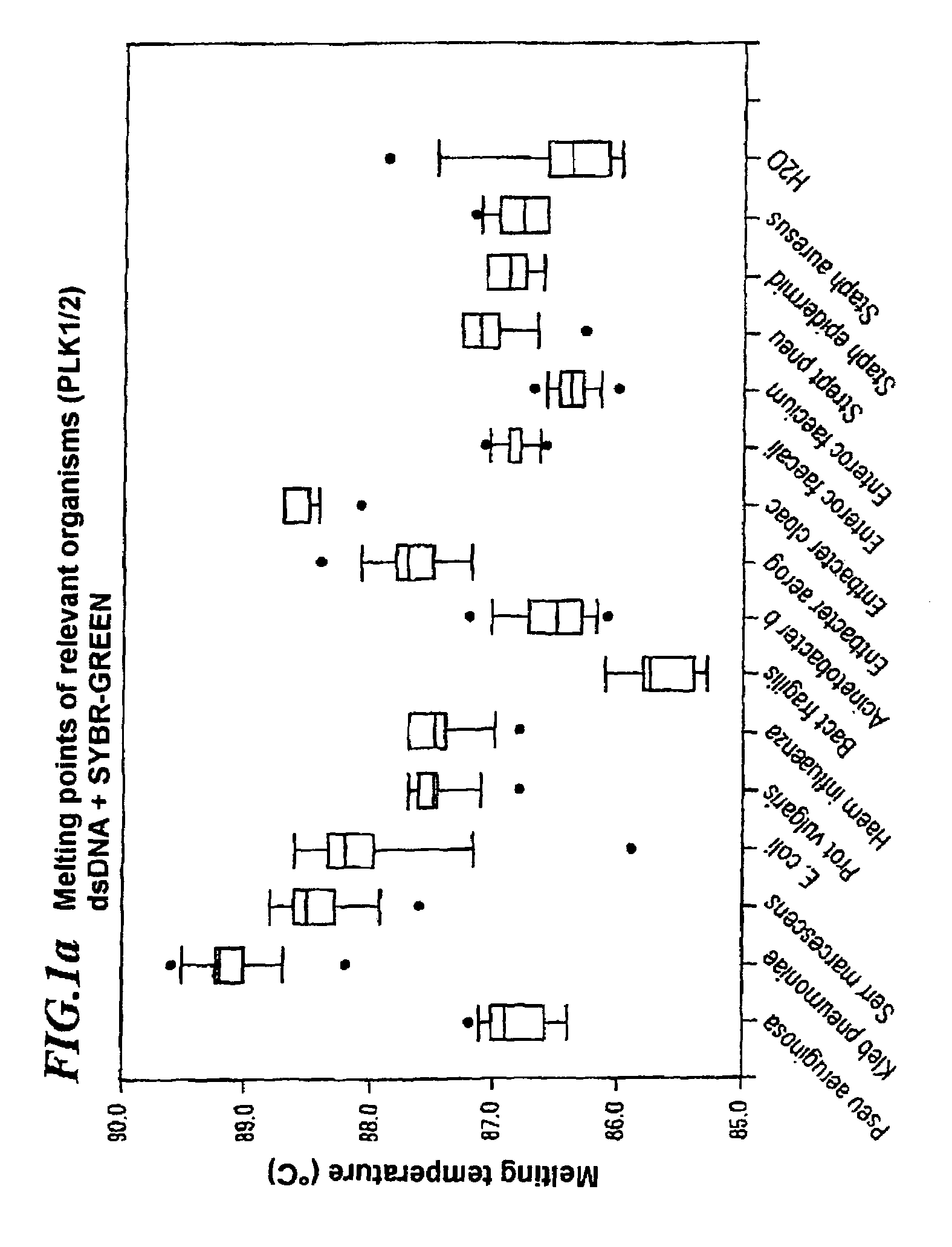
A method for identifying microbial DNA / RNA comprising providing a sample containing microbial DNA / RNA; enriching DNA / RNA in the sample by a PCR method wherein the DNA / RNA that is identified comprise copies which are amplified by the PCR method; preliminarily classifying at least one microorganism by identifying the microbial DNA / RNA by a melting curve; adding at least one labeled oligonucleotide whereby temperature-dependent hybridization takes place and identifying the DNA / RNA on the basis of a physical property of the resultant DNA / RNA oligonucleotide complex, such as the temperature-dependence of the hybridization.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Kit and method for extracting microbial DNA
ActiveCN101935647AImprove bindingReduce adsorptionDNA preparationSodium acetateAluminum ammonium sulfate
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology and discloses a kit and a method for extracting microbial DNA. The kit comprises lysis solution, inhibitor removal solution and binding solution, wherein the lysis solution comprises 50 to 200mM of Tris-HCl, 50 to 150mM of EDTA, 0.5 to 3M of NaCl, 0.5 to 2 percent of CTAB, 0.5 to 2 percent of PVP and 0.5 to 2 percent of SDS; the inhibitor removal solution comprises 100 to 300mM potassium acetate, sodium acetate or ammonium acetate and 50 to 200mM aluminum sulfate, ammonium sulfate or aluminum ammonium sulfate; and the binding solution comprises 3 to 6M guanidine hydrochloride, 10 to 50mM Tris-HCl and 5 to 50 percent isopropanol. The kit and the method for extracting the microbial DNA have the advantages of high purity, high universality, high extraction speed, direct use for a downstream experiment, and application to extracting DNA from a microbe-containing sample.
Owner:中生方政生物技术股份有限公司
Method for indentifying microbial DNA or RNA
InactiveUS7169555B2Early detectionAccurate identificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismPcr method
The invention relates to a method for quickly detecting bacterial DNA. The sample containing bacterial DNA is provided and treated according to a PCR method. The DNA copies which are multiplied by means of PCR are detected.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Method of detecting microorganisms
InactiveUS7303870B2Broad specificityAccurately determineSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisMedical diagnosis
The present invention relates generally to a method for detecting, enumerating and / or identifying microorganisms in a sample. More particularly, the present invention provides a method for determining total microbial content in a sample by detecting the presence of nucleotide sequences associated with all or part of 16S rDNA or its corresponding 16S rRNA or its homologue, functional equivalent or derivative. The nucleotide sequences of the present invention may be used as an indicator of any microorganism and, hence, represents a universal target sequence which is indicative of total microbial content in a sample. The universal target sequence may also be varied to render same genus or species specific or the universal target used to trap microbial DNA or RNA which may be subsequently analyzed by sequence analysis or genetic probe technology. The universal target sequence is useful inter alia to design as universal primers and probes to amplify any microbial-derived genomic sequence, as a means to detect and enumerate total microorganisms and to identify microorganisms in a sample at the genus or species level. Such uses enable improved methods of enviroprotection, bioremediation, medical diagnosis and industrial microbiology. The present invention further relates to the universal target sequence in isolated form and / or primers or probes capable of hybridizing to same and kits for the detection of total microbial content in a sample.
Owner:THE UNIV OF SYDNEY +1
Method for extracting prawn intestinal microbial DNA
The invention relates to a method for extracting prawn intestinal microbial DNA, and belongs to the fields of microbiology and molecular ecology. The method comprises the following steps of: grinding by using liquid nitrogen; breaking cell walls by using mechanical force; cracking cells by adopting lysozyme and SDS lysate; obtaining DNA deposit through separation and precipitation; and finally dissolving the DNA deposit with TE to obtain the DNA with good quality. The product DNA fragment obtained by the method is greater than 20Kb; and can be subjected to gene magnification and sequencing. The method has good generality and is used for extracting the intestinal microbial DNA of various crustacean aquatic animals. High-quality template DNA can be obtained through extraction at one time without repeated experiment; and the obtained DNA can be applied to the research of molecular ecology, system evolution and the like.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for extracting soil microbial DNA
InactiveCN1978453ALow humusReduce organic acid contentSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationDNA SolutionsMicroorganism
This invention relates to an extracting method of soil microorganism DNA. The stated method includes steps as following: cell disruption of soil microorganism, obtaining crude DNA solution, obtaining soil microorganism DNA; the stated method of this invention is using PVPP, protease K etc for valid combination. After organic solvent such as PEG20000, isopropyl alcohol and so on are precipitated, use spectrophotometer to determine value of OD260 / OD230, OD260 / OD280 close to standard value. It can be directly used for molecule operation, possessing great application perspective.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
New method for isolating microbial DNA
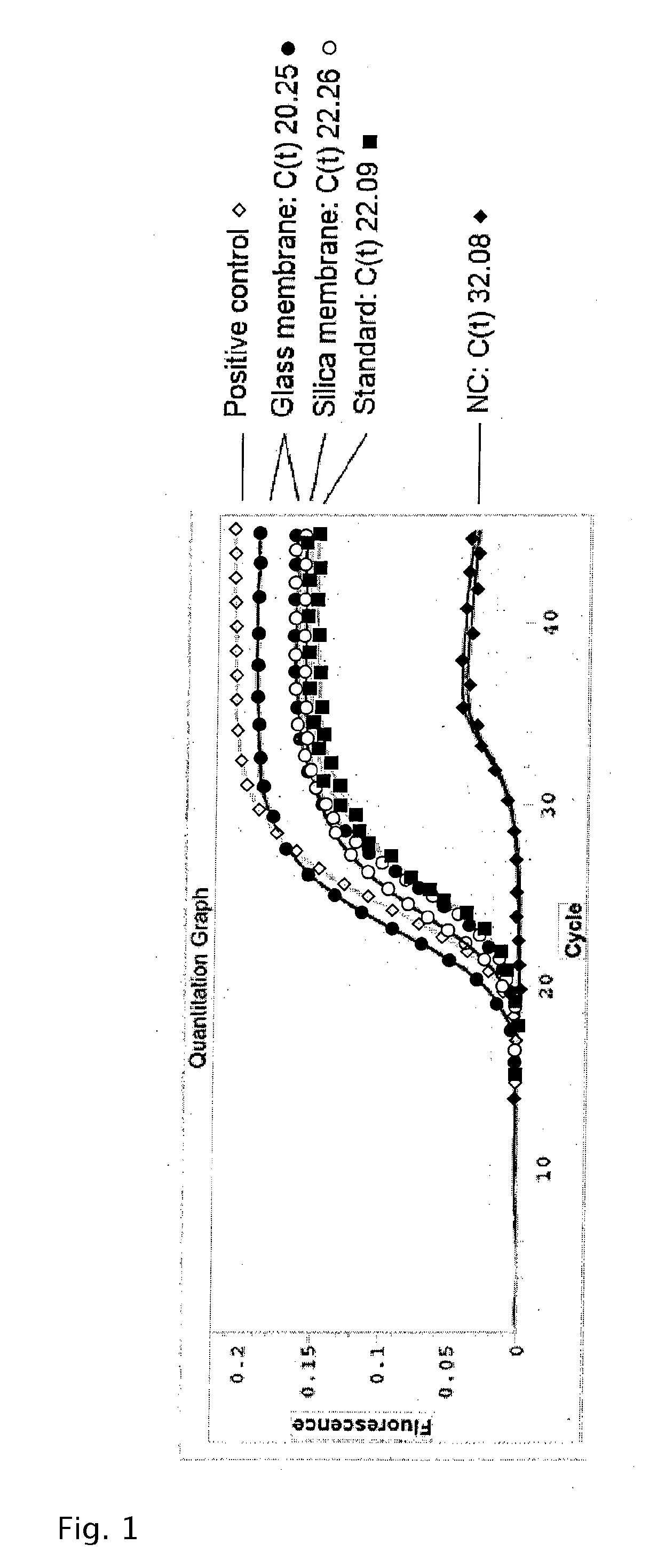
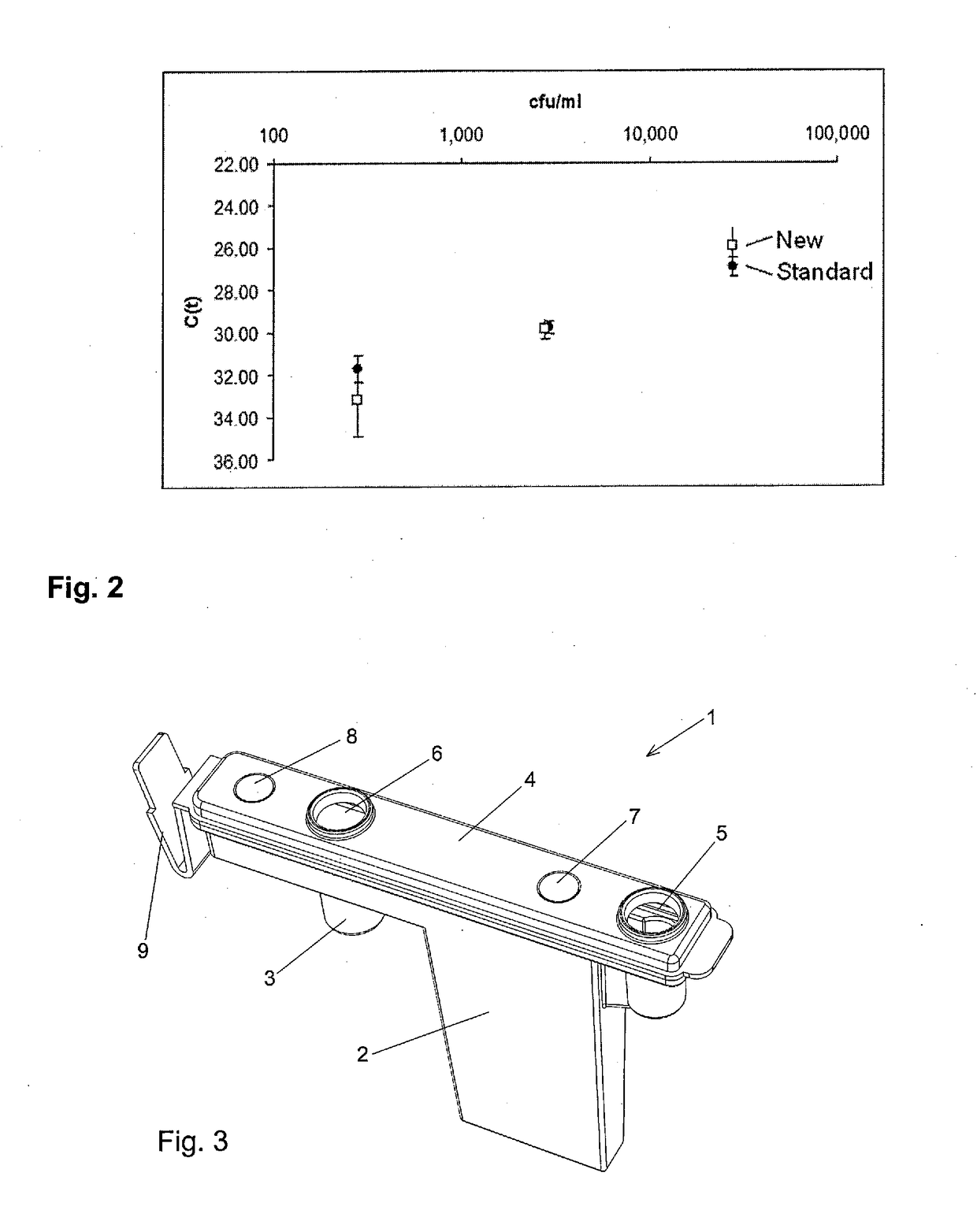
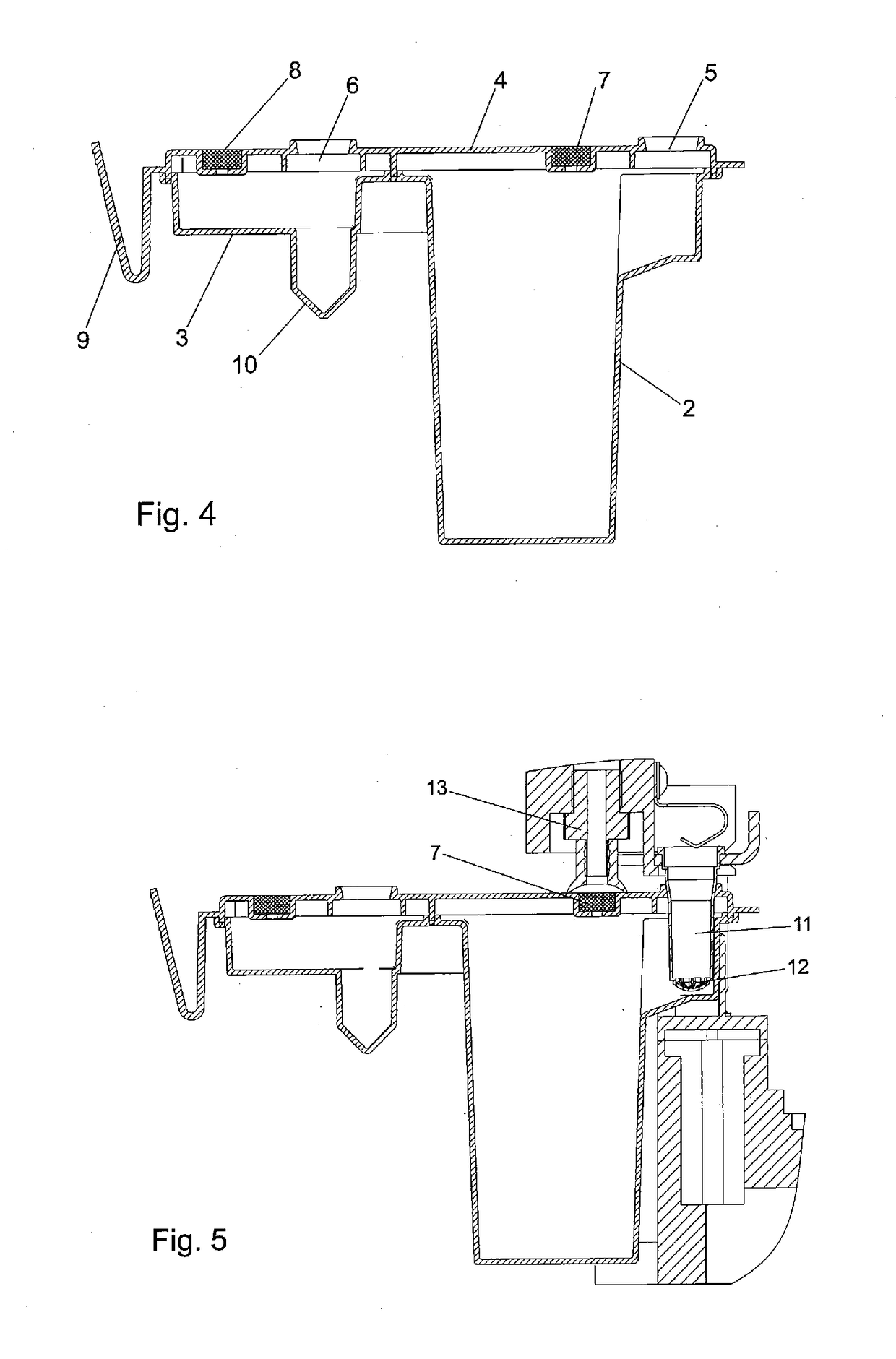
The present invention relates to a new method for enriching and / or isolating nucleic acids from microbial cells which comprises filtering a liquid sample through a nucleic acid-binding matrix which has a pore size small enough to retain microbial cells, lysing the microbial cells on the matrix to release the nucleic acids from the microbial cells, binding the nucleic acids to the matrix and subsequently eluting the DNA. The invention also relates to a method for enriching and / or isolating nucleic acids from microbial cells which are present in a liquid sample that comprises microbial cells and higher eukaryotic cells and / or tissues. The invention also provides a cartridge for carrying out the methods of the invention. Finally, the invention relates to kits for carrying out the methods of the invention.
Owner:MOLZYM
Kit and method for extracting microbial genome DNA by magnetic bead method
InactiveCN110283816AAvoid interferenceProtection from cleavageMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMicroorganism preservationLithium chloride
The invention relates to a kit and method for extracting a microbial genome DNA by a magnetic bead method. The kit comprises a microbial preservation buffer solution, a bacteriolytic agent solution I, proteinase K, silica gel magnetic beads, isopropanol and an ethanol water solution, and further comprises a bacteriolytic agent II, a lysis adsorption solution and a reinforced scrubbing solution. The bacteriolytic agent II comprises MES, EDTA, Triton X-100, lysozyme and a lysozyme enhancer. The lysis adsorption solution comprises Tris-HCl, sodium chloride, EDTA, TrionX-100 and a nucleic acid separation and absorption promoter; and the reinforced scrubbing solution comprises Tris-HCl, lithium chloride and ethanol. By adopting the kit provided by the invention, cell walls of gram-positive bacteria and various fungi can be completely destroyed to form protoplasts, DNA of the protoplast cells can be rapidly released under the action of the lysis adsorption solution, the DNA is efficiently adsorbed on the silica gel magnetic beads, and after the DNA is washed by the scrubbing solution and eluted by an elution solution, microbial DNA with high concentration and purity can be obtained.
Owner:WUXI NO 2 PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Method for detecting microbial community structure of pu'er tea
InactiveCN103361413AComprehensive and systematic analysisHigh continuous stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFreeze thawingCommunity structure
The invention discloses a method for detecting the microbial community structure of pu'er tea. The method is implemented through collecting microbial bacteria of tea leaves of the pu'er tea by using a glass bead oscillating method; then, extracting a total microbial DNA by using the combination of a liquid nitrogen freezing-thawing and enzymatic method and a CTAB (cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide) method; carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on the extracted genomic DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) by respectively using universal primers of bacterial 16S rRNA and fungal 18S rRNA variable regions; separating a PCR product by using DGGE (denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis) and dyeing the obtained product so as to obtain a band map, and carrying out relative quantitative analysis on bands by using Quantity One software; carrying out cut gel extraction on the DNA of the bands, carrying out the PCR amplification on extracted nucleic acids, connecting a product with a T carrier, and selecting positive clones to carry out community PCR with a GC-clamp; carrying out comparison again by using DGGE electrophoresis, and selecting a PCR product corresponding to a target band to carry out sequencing identification. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for detecting the changes of the microbial community structure and relative quantity of the pu'er tea in the process of fermentation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Identification of pathogens
InactiveCN101501219AImprove treatmentReduce recovery careMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationMicrobe DNAMicroorganism
Disclosed is a method for identification of microbial pathogens in a body fluid sample comprising the following steps: a) providing a body fluid sample; b) lysing the microbial pathogens and performing a nucleic acid amplification reaction on the microbial DNA encoding 16S or 18S rRNA wherein or whereafter the amplified nucleic acids are labelled; c) contacting the labelled amplified nucleic acids of step b) with a microarray comprising on defined areas on the microarray's surface immobilised probes for microbial DNA encoding 16S or 18S rRNA from microbial pathogens; d) detecting the binding of one or more species of the labelled amplified nucleic acids to a probe by detecting a labelled amplified nucleic acid being specifically bound to the microarray; and e) identifying a microbial pathogen in the body fluid sample by correlating the detected binding of the labelled amplified nucleic acids with the defined areas of the immobilised probes for microbial DNA encoding 16S or 18S rRNA from microbial pathogens.
Owner:奥地利研究中心有限公司
Method for detecting prokaryotic microorganisms in crop rhizosphere based on high-throughput sequencing
The invention relates to a method for detecting prokaryotic microorganisms in rhizosphere soil of different crops based on 16S rDNA high-throughput sequencing. The method comprises the following stepsof 1, collecting shaking-off soil (as a system control) of different genotype crops outside root zones or at root systems and the rhizosphere soil; 2, extracting total microbial DNA from each samplesoil; 3, using a double-label primer method for PCR amplification of V5-V7 hypervariable region fragments of 16S rDNA in the total DNA to construct a library; 4, for a qualified library, simultaneously conducting synthesis and sequencing of a double-end 300 nucleotide pattern by using an Illumina Miseq platform; 5, splicing after pure paired READS is obtained, and generating 40,000 effective TAGsfrom each sample for clustering into operable classification units; 6, according to the system control, accurately determining the composition, structure, diversity and relative abundance saliency analysis of prokaryotic microbial communities in the rhizosphere soil of each sample, and comparing similarities and differences between different crops.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Efficient and economical soil microbial DNA extraction method
ActiveCN109337900AImprove extraction qualitySimplify the collection processDNA preparationWater bathsMicrobe DNA
The invention discloses an efficient and economical soil microbial DNA extraction method. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, obtaining a microbial suspension; weighing 1 g of soil, adding 2 ml of suspension Buffer C1, 1 g of glass beads having the particle diameter of 0.09-0.12 mm, 500 muL of humic acid adsorbent Buffer C2 and 10 muL of proteinase K (10 mg / mL), mixing and shaking; step 2, obtaining microbial DNA; step 3, obtaining crude DNA; placing the material obtained in the last step in a water bath of 60 DEG C while stirring, then centrifuging at a high speed of 4 DEG C, and collecting the first supernatant; and step 4, obtaining purified DNA. The method is based on the requirements of soil-contaminated microbial detection, can extract DNA containing no inhibiting factor from complex environmental samples such as soil and feces, and is high in extraction speed and accurate in analysis result.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Method of using microbial DNA sequencing in recovering renewable resources from wastewater and other waste streams
ActiveUS20180354830A1Reliable and renewable streamAvoid serious impactWater treatment parameter controlBacteriaWaste streamMicrobiome
A method is described for recovering resources from a microbe supporting environment such as a water treatment system, comprising the steps of using microbial DNA sequencing to analyze the microbiome of the microbe supporting environment and identifying adjustments to the microbial content of the microbiome that will be useful in extracting resources from the microbe supporting environment such as a water treatment system, wherein the resources extracted can include, for example, methane released by microbes, nitrogen, phosphorus, or other contaminants generated by microbes, and / or clean water obtained by removing contaminants in a water treatment system.
Owner:MICROBE DETECTIVES LLC
Extraction method for microbial DNA in milk
The invention discloses an extraction method for microbial DNA in milk. The method comprises the following steps: adding 0.8 mL of a milk sample into 0.3 to 0.5 mL of an ES solution (EDTA with a pH value of 7.5 and concentration of 0.5 mol / L and SDS with concentration of 2%), carrying out uniform mixing and centrifugation and discarding supernatant; adding 0.8 to 1.2 mL of a PBS buffer solution, carrying out oscillation and shaking up, then carrying out centrifugation and discarding supernatant; adding 20 to 30 [mu]L of Staphylococcus lysozyme with a mass concentration of 0.02 mg / mL; adding 150 to 200 [mu]L of an aqueous Chelex-100 solution with a mass concentration of 10%, carrying out violent oscillation for 5 to 10 s and then carrying out heating in boiling water with a temperature of 100 DEG C for 8 to 12 min; and carrying out centrifugation and taking supernatant for a PCR reaction. The method provided by the invention employs a Chelex-100 process and can economically, rapidly, efficiently and directly extract bacterial DNA from the milk sample; and the bacterial DNA can be used for PCR detection of main pathogenic bacteria causing mastitis in cow.
Owner:CHINTEM TECH CONSULTING BEIJING CO LTD
Microbial nucleic acid extraction method with host genome DNA removal function and kit
PendingCN111057747AIncrease concentrationLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMicrobial GenomesMicroorganism
The invention discloses a microbial nucleic acid extraction method with a host genome DNA removal function and a kit. The invention provides a complete set of primer pairs, including one or more primer pairs. Each primer pair correspondingly amplifies one highly repetitive sequence in host genome DNA, wherein the highly repetitive sequence is selected from at least one gene in the following gene family: the gene family includes an MIR family gene and / or an ALu family gene. The microbial DNA extraction method with the host genome DNA removal function has the advantage that the microbial genomeDNA enrichment effect is stronger. According to the method, the host genome DNA is removed after the nucleic acid is released through lysis, then the microbial genome DNA is enriched for purificationand recovery, and meanwhile, viral nucleic acid in host cells can be enriched without changing the metagenome flora structure.
Owner:MGI TECH CO LTD
Method for efficiently extracting underground water microbial DNA for PCR amplification
The invention discloses a method for efficiently extracting underground water microbial DNA for PCR amplification. The method comprises the following steps: 1, collecting underground water microbes, collecting microbes by using an aseptic millipore filter, and eluting with a buffer solution containing cetyltrimethylammonium bromide to prepare a microbial cytochylema; 2, disrupting underground water microbial cells, adding lysozyme and protease K to the microbial cytochylema, carrying out warm water bathing, and centrifuging to obtain a cell lysis supernatant; 3, purifying the obtained lysate, and carrying out centrifuging purification of the obtained cell lysis supernatant a plurality of times to obtain a crude DNA solution; and 4, purifying microbial genome DNA, carrying out centrifuging purification of the crude DNA solution, and extracting with ethanol having a volume concentration of 70% to obtain purified microbial genome DNA. The method has the advantages of efficient extraction of the high-quality underground microbial genome DNA, simple operation and high extraction purity.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for researching toxicity effect of jujube nectar on bees based on intestinal flora
ActiveCN111197096AHigh selectivityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the technical field of biotechnology and agriculture, and provides a method for researching the toxic effect of jujube flower nectar on bees based on intestinal flora for thecurrent situation that the toxic effect of jujube nectar on bees cannot be explained in the existing research. Based on changes of microbial intestinal flora of bees and functional analysis of differential bacteria by the jujube nectar, the occurrence mechanism of the jujube nectar to the jujube blossom diseases of bees is excavated, and a basis is provided for prevention and treatment of the jujube blossom diseases of bees. Microbial DNA in intestinal feces of bees is collected, the regulation of jujube nectar on intestinal flora of bees is researched by using a Hiseq2500 PE250 sequencing platform and based on a bacterium 16s rDNA V3-V4 variable region, and the up-regulated or down-regulated bacterium genus in a jujube flower disease group is determined. The mechanism that the jujube nectar inhibits biodegradation and detoxification pathways of exogenous substances by changing intestinal flora, up-regulates biosynthesis of alkaloid amino acids and generates toxic effects on bees is clarified, and the method is applied to target selection in prevention and treatment of jujube blossom diseases through bees.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
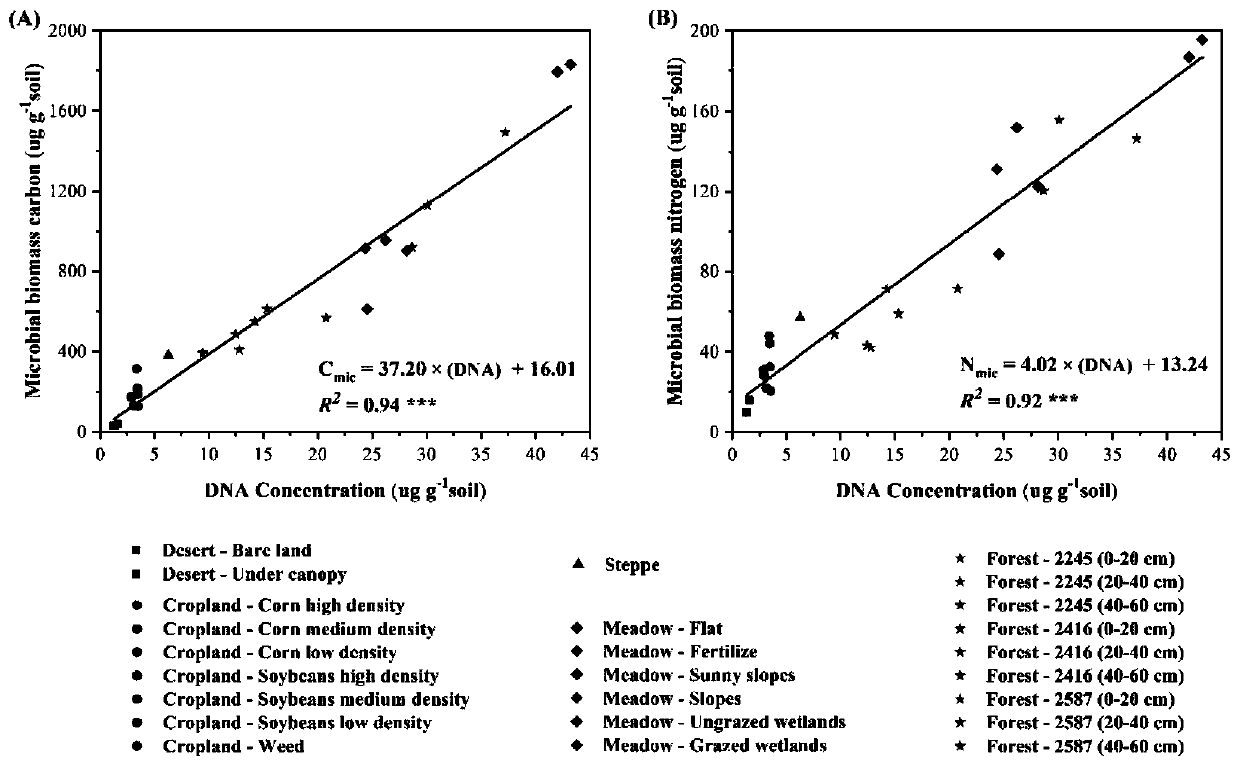
Method for measuring soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen content
InactiveCN109916840APrecise estimation of biomass carbon and nitrogen contentAccurately estimate carbon and nitrogen contentProteomicsColor/spectral properties measurementsMicroorganismBiomass carbon
The invention relates to a method for measuring soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen content, comprising the steps of: extracting the soil microbial DNA in a soil sample to be measured; measuring the concentration of the extracted DNA by using a micro spectrophotometer and converting the concentration into a unit mass soil microbial DNA content; and separately multiplying the soil microbialDNA content by a microbial biomass carbon content conversion coefficient and a microbial biomass nitrogen content conversion coefficient, to calculate the soil microbial biomass carbon content and thesoil microbial biomass nitrogen content. The method of the invention can accurately estimate the soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen content just by extracting the microbial DNA from a small number of soil samples, omits a chloroform fumigation step, is accurate and reliable in conversion coefficient, improves the measurement efficiency of soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen content, and is relatively easy and safe to operate, and high in safety.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Kit and method for extracting microbial DNA
ActiveCN101935647BHigh purityImprove versatilityDNA preparationSodium acetateAluminum ammonium sulfate
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology and discloses a kit and a method for extracting microbial DNA. The kit comprises lysis solution, inhibitor removal solution and binding solution, wherein the lysis solution comprises 50 to 200mM of Tris-HCl, 50 to 150mM of EDTA, 0.5 to 3M of NaCl, 0.5 to 2 percent of CTAB, 0.5 to 2 percent of PVP and 0.5 to 2 percent of SDS; the inhibitor removal solution comprises 100 to 300mM potassium acetate, sodium acetate or ammonium acetate and 50 to 200mM aluminum sulfate, ammonium sulfate or aluminum ammonium sulfate; and the binding solution comprises 3 to 6M guanidine hydrochloride, 10 to 50mM Tris-HCl and 5 to 50 percent isopropanol. The kit and the method for extracting the microbial DNA have the advantages of high purity, high universality, high extraction speed, direct use for a downstream experiment, and application to extracting DNA from a microbe-containing sample.
Owner:中生方政生物技术股份有限公司
Method for extracting microbial DNA in water body
The invention relates to a method for extracting microbial DNA in a water body. The method comprises: collecting microorganisms by using a sterile microporous filtration membrane; breaking the microbial cells by using physical and chemical methods; removing humic acid and other impurities by using potassium acetate, guanidine isothiocyanate, sodium citrate and other reagents; carrying out centrifugal purification on the cell lysate a plurality of times; and extracting with ethanol and potassium acetate to obtain the purified microbial genomic DNA. According to the present invention, the extracted microbial DNA has advantages of good integrity, high purity and high yield, and has the OD260 / OD280 ratio of 1.8-2.0; after the extracted microbial DNA is subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis and staining is performed, the DNA band is clear and single, and the phenomena such as tailing and impurity band do not exist; and the extraction method has advantages of high microbial DNA yield, simple operation, low cost, no requirement of purification during the extraction process, extraction step reducing and extraction cost reducing, and is suitable for the diversity analysis of various water microorganisms.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Index analysis method based on microbial diversity in selenium-rich soil
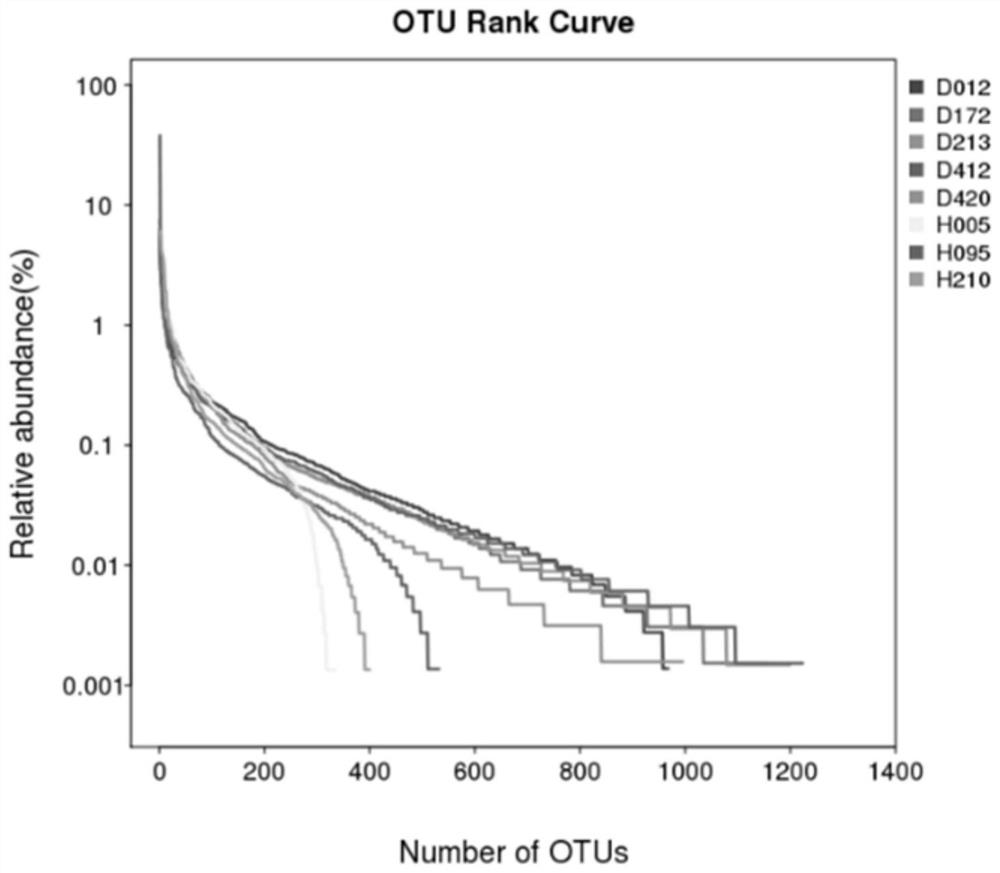
PendingCN112176047AAccurate estimation of relative abundanceComprehensive and accurate analysis resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyOriginal data
The invention discloses an index analysis method based on microbial diversity in selenium-rich soil. The method comprises the following steps of A, weighing a selenium-rich soil sample, and carrying out microbial DNA extraction; B, performing quality detection on extracted metagenome DNA, completing purity and integrity detection of the genome DNAthrough a NanoDrop microspectrophotometer and horizontal agarose gel electrophoresis respectively, and obtaining the DNA mass concentration through Qubit detection; C, performing high-throughput sequencing by adopting a next-generation sequencing technology, and performing library construction on an extracted metagenome sample; and D, performing data analysis: in original data obtained by sequencing, performing quality control on offline data by using FastQC, filtering the data according to a quality inspection report result, accurately estimating the relative abundance of species through rapid comparison, obtaining microbial community composition information, drawing a visual evolutionary tree based on a classification grade by using GraPhlAn, and constructing a species community structure chart.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for extracting total microbial DNA from strong-flavor yeasts
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology and in particular relates to a method for extracting total microbial DNA from strong-flavor yeasts. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, adding quartz sand into the strong-flavor yeasts for grinding, adding a CTAB solution and mercaptoethanol for water bath treatment, adding proteinase K, and centrifuging; adding Tris-balanced phenol and chloroform isopentyl alcohol into supernatant liquid, and centrifuging; adding chloroform isopentyl alcohol into supernatant liquid, and centrifuging; adding isopropanol into supernatant liquid, freezing, and centrifuging; pouring away upper-layer liquid, washing lower-layer settlings by using ethanol, centrifuging, adding a TE buffer solution into the lower-layer settlings, and storing. The method can be well applied to extraction of total microbial DNA from the strong-flavor yeasts, and the extraction operation is convenient, quick and accurate.
Owner:LUZHOU PINCHUANG TECH CO LTD
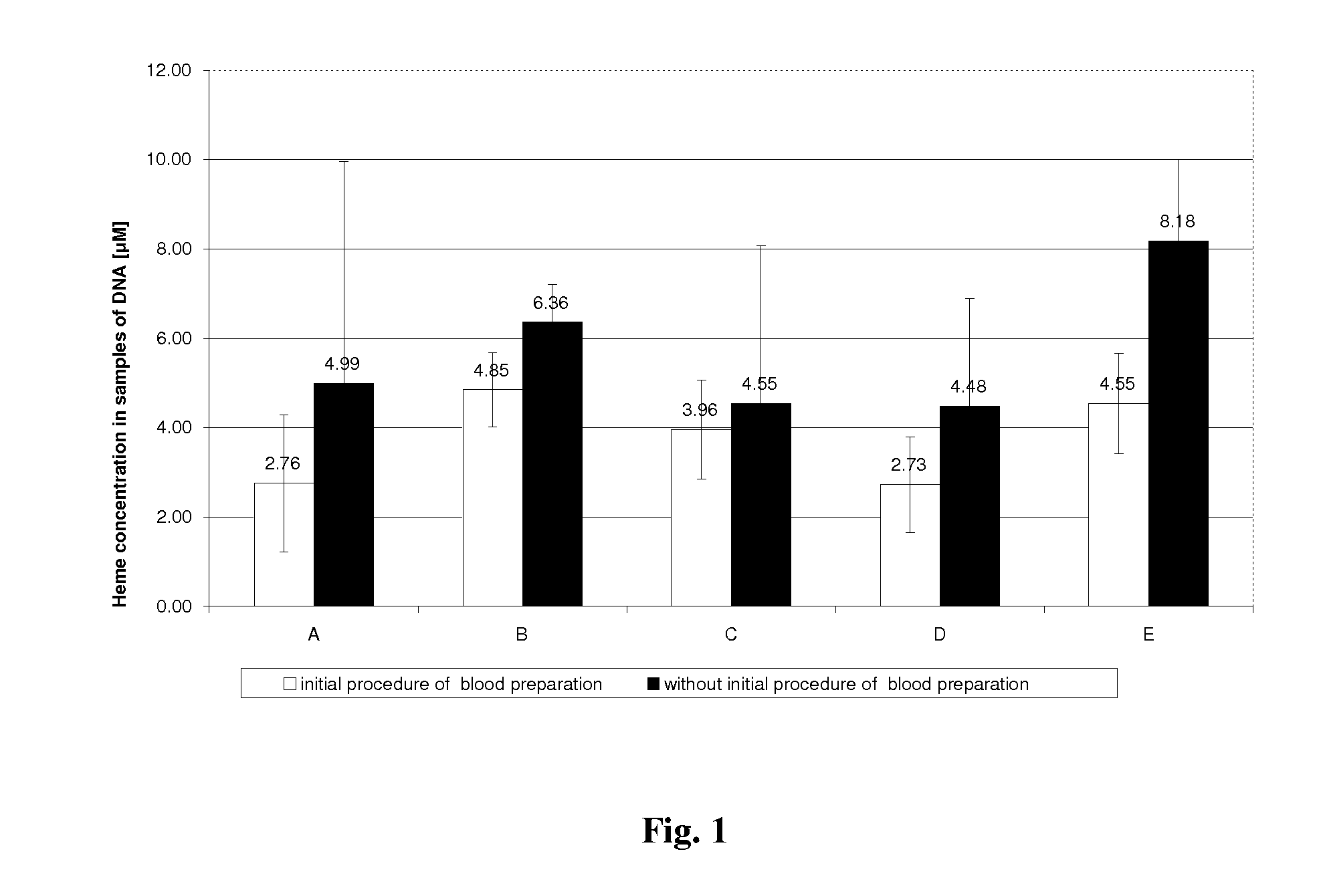
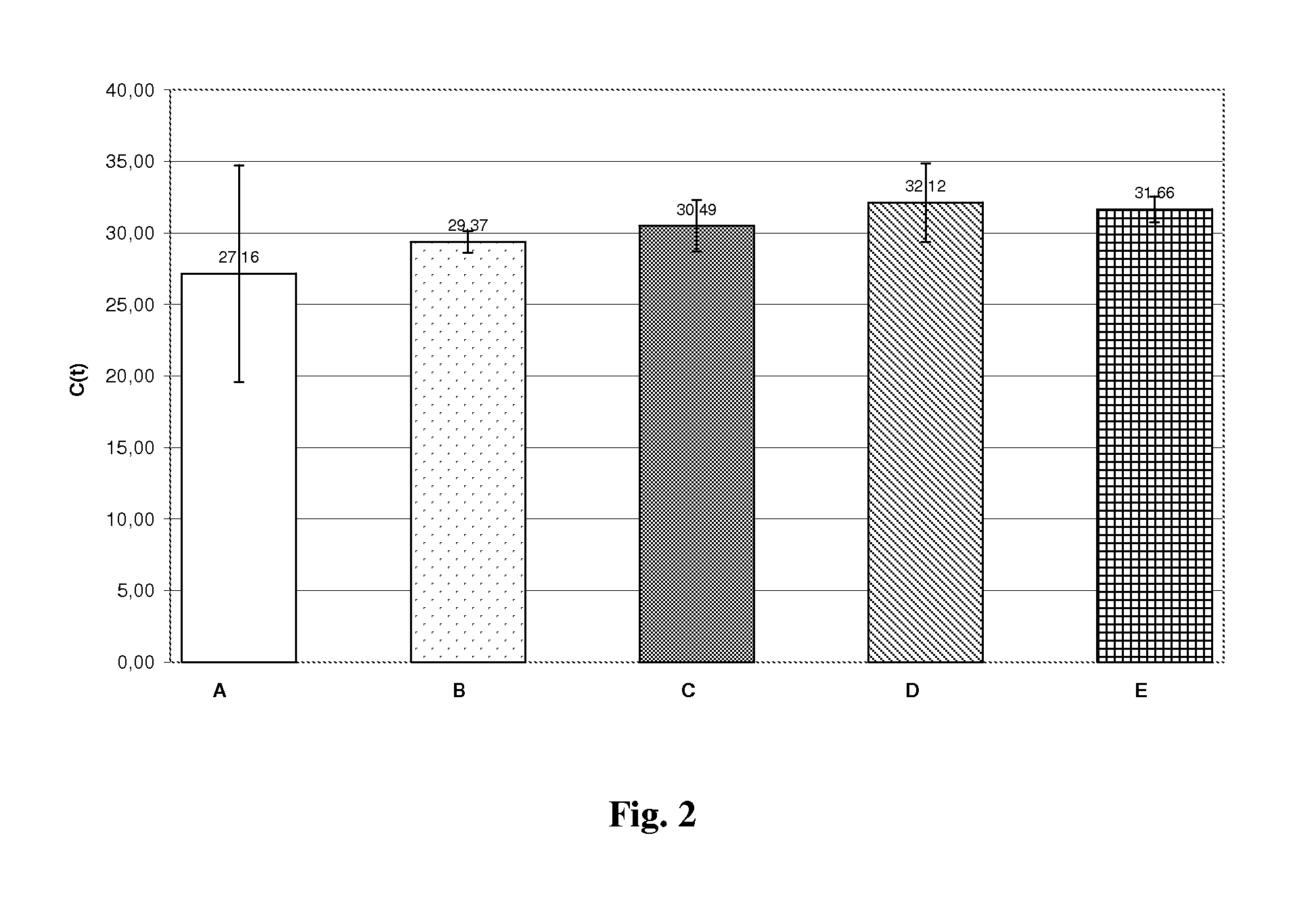
Method for efficient isolation of microbial DNA from blood
A method allows the simultaneous isolation of bacterial and fungal DNA from blood. The method uses the enzymatic, mechanical and thermal lysis.
Owner:JAGIELLONIAN UNIVERSITY
Method for separating inner-layer and outer-layer substances of wetland plant root surface iron film
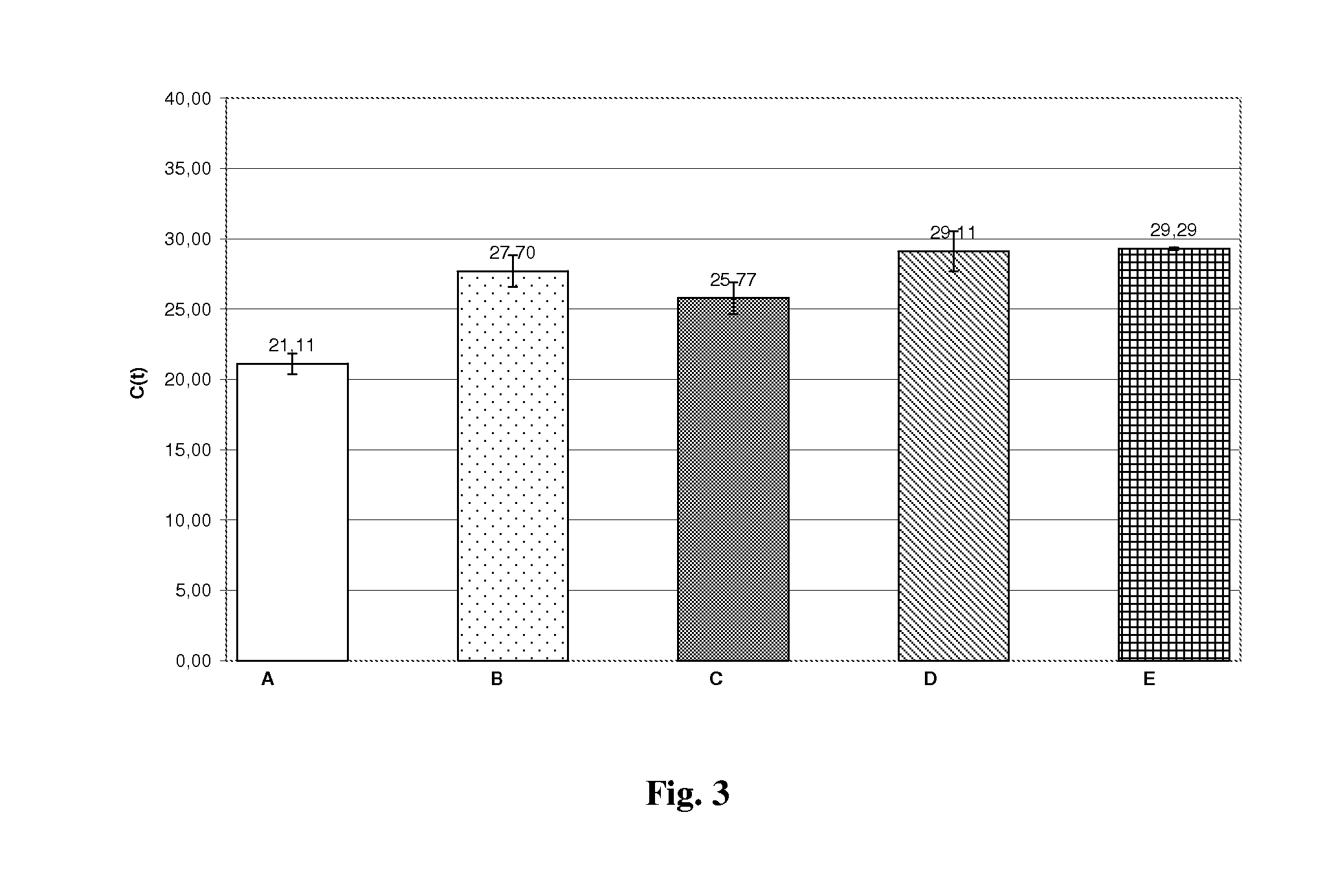
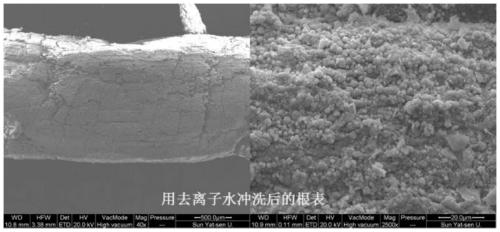
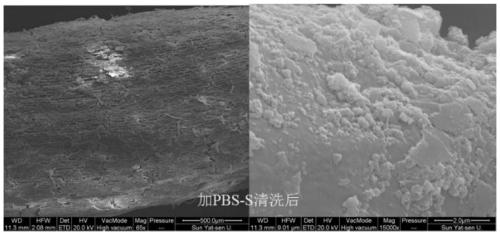
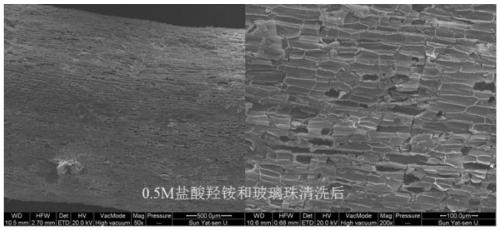
The invention discloses a method for separating inner-layer and outer-layer substances of a wetland plant root surface iron film. The method comprises the following steps: S1, taking roots, shaking off soil, and washing the roots with sterile water; S2, cutting the roots into root segments and placing in a centrifuge tube, adding a PBS-S phosphate buffer solution, carrying out vortexes, then taking the roots out of the centrifuge tube, centrifuging the solution and then carrying out microbial DNA extraction of an outer layer of the root surface iron film, wherein solid substances in a suspension in the centrifuge tube are substances of the outer layer of the root surface iron film; and S3, putting the roots after the vortexes into another new centrifuge tube, adding 0.5 Mhydroxylamine-0. 5M hydrogen chloride solution and sterile glass beads into the centrifuge tube, and manually shaking the centrifuge tube up and down for 5 minutes till that the surfaces of the roots become white so asto obtain a solid substance in a suspension in the centrifuge tube, wherein the solid substance is a root surface iron film inner-layer substance. In the invention, a circulation process of inner andouter layers of substances and a change condition of microorganisms can be analyzed so that the influence of an oxygen concentration gradient on rhizosphere iron-sulfur circulation can be better revealed.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Kit and method for extracting microbial DNA
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular biology, in particular to a kit and a method for extracting microbial DNA. The kit for extracting the microbial DNA comprises a lysate and anequilibrium liquid. The lysate comprises 5-chloro-2-methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, 2-methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, RNaseA, polyvinylpyrrolidone, 2-(N-morpholino) ethanesulfonic acid, bromophenol red andxylene cyanol FF. The equilibrium liquid comprises 3-(2-aminoethylamino) propyl trimethoxysilane, tartrazine and trihydroxymethyl aminomethane. The invention provides the kit and the method for extracting microbial DNA, wherein the method can complete the operation at room temperature, the extraction is quick, the DNA extracted by the method does not contain the interference of RNA and has high flux; and the lysate and the equilibrium liquid in the kit can effectively inhibit the growth of microorganisms, and have great advantages for processing and transporting samples containing infectious sources.
Owner:成都罗宁生物科技有限公司
Method of identifying putative antibiotic resistance genes
InactiveUS7125662B2Effectively combat the resistance capacity of these putative antibiotic resistance genesHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobe DNAAntibiotic Agents
The present invention relates to methods of identifying putative antibiotic resistance genes. According to one embodiment, this is carried out by first isolating a microbial DNA molecule or cDNA which encodes a putative antibiotic resistance protein or polypeptide and then determining whether the microbial DNA molecule or cDNA confers resistance against an antibiotic agent. According to another embodiment, this is carried out by first determining whether a microbial DNA molecule or cDNA confers resistance against an antibiotic agent when the microbial DNA molecule is expressed in its native cell following transformation of the cell and then isolating the microbial DNA molecule or cDNA which confers resistance against the antibiotic agent.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Microbial marker for bovine endometritis and application thereof
InactiveCN112080561AIncrease abundanceReduce abundanceMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySpirochaetae
The invention discloses a microbial marker for bovine endometritis. The microbial marker comprises the following microorganisms with remarkably increased abundance: Bacteriodetes, Elusimicrobia, Verrucomicrobia, Spirochaetae and Lentisphaerae. The microbial marker also comprises the following microorganisms with remarkably increased abundance: Akkermansia, biogas bacillus, CF231 and Oscillosporia.The microbial marker also comprises the following microorganisms with remarkably decreased abundance: Ureaplasma urealyticum, Butyrivibrio, Doria, Sphingomonas sp, Rothia and Streptococcus. The invention discloses an application of the microbial marker for bovine endometritis in preparation of a tool for early screening or prediction of bovine endometritis. The applicant performs 16S rRNA gene sequencing on microbial DNA of a uterine mucus sample, compares structural differences of uterine florae between healthy and sick dairy cows, and finds differences in microbial community composition ofthe uterine florae between the healthy and sick dairy cows. The result provides a theoretical basis for better prevention and treatment of clinical endometritis.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for extracting total microbial DNA from milk
PendingUS20210292809A1Simple and rapid and efficient methodImprove integrityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
In a method for extracting microbial DNA from milk, the extracted DNA can be directly used for PCR amplification. The method includes the following steps: treating milk with TE solution, fully disrupting microbial cells by bead milling, immobilizing proteins in the middle layer between the aqueous and organic phases with high-vacuum silicone grease so as to prevent impurities in the middle layer from entering the aqueous phase, etc. The extracted DNA has a high degree of intactness, high concentration and purity.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
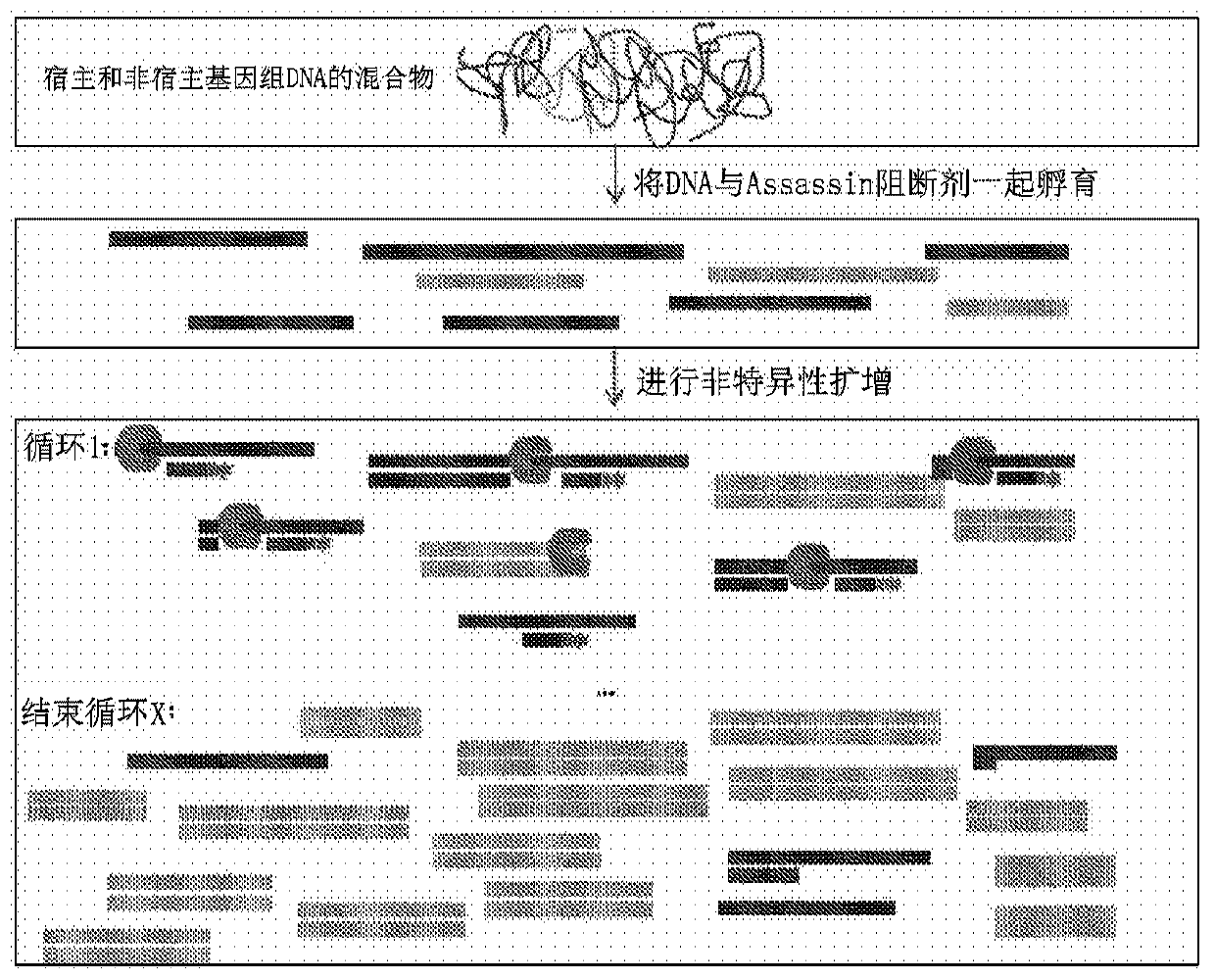
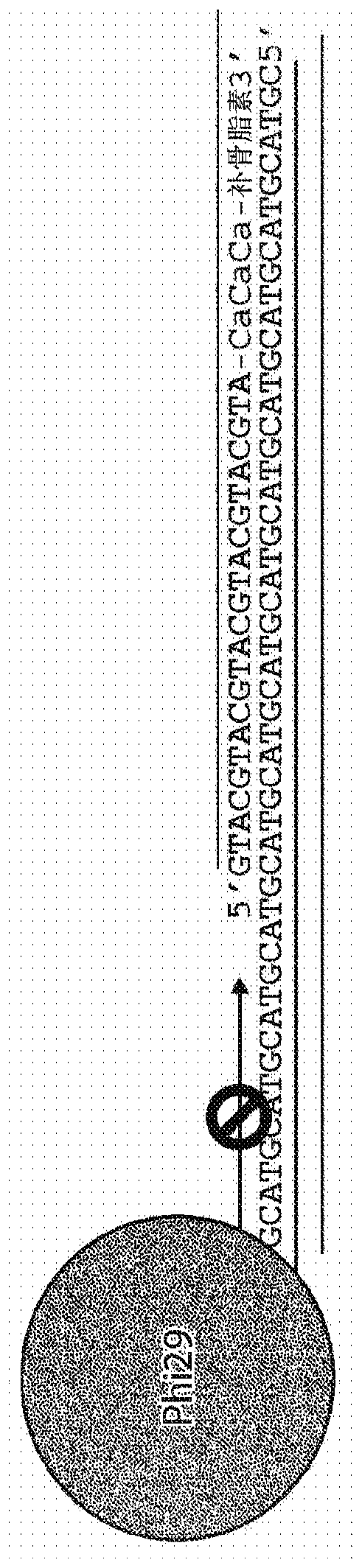
Selective enrichment of population of DNA in mixed DNA sample through targeted suppression of DNA amplification
PendingCN111566118ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismMicrobiology
The present disclosure provides method and products for the selective enrichment of one population of DNA in a mixed sample comprising multiple populations of DNA. In some embodiments, the mixed sample comprises one or more populations of microbial DNA and the mammalian host DNA, particularly including pathogenic microbial DNA mixed with mammalian host DNA in a clinical sample from an infected individual.
Owner:零日诊断有限公司
Methods, systems, and compositions for detection of microbial DNA by PCR
InactiveUS20120295806A1Sensitive and accurate and inexpensiveSensitive and accurate and inexpensive and easy to performSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesMicroorganismNatural abundance
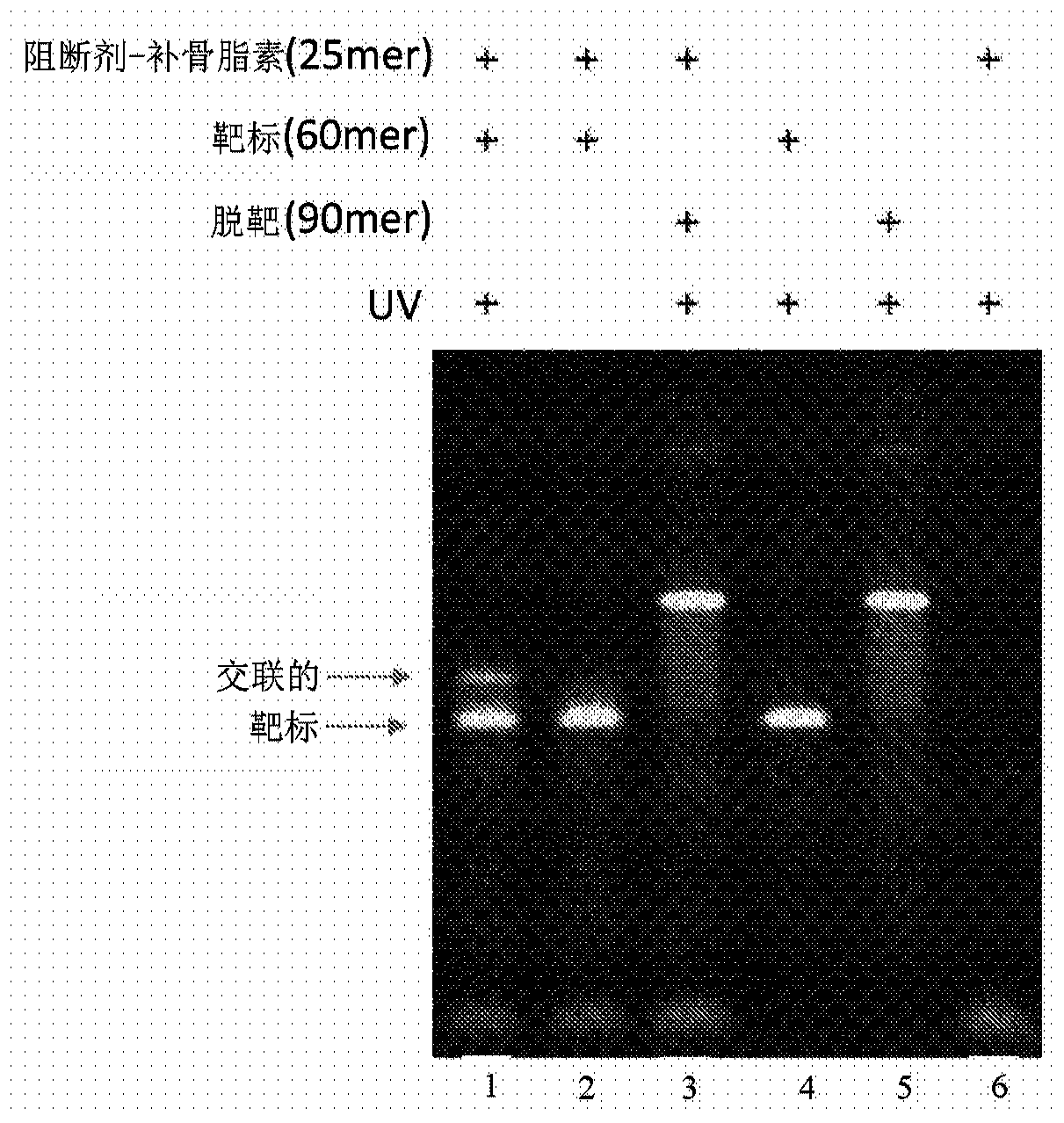
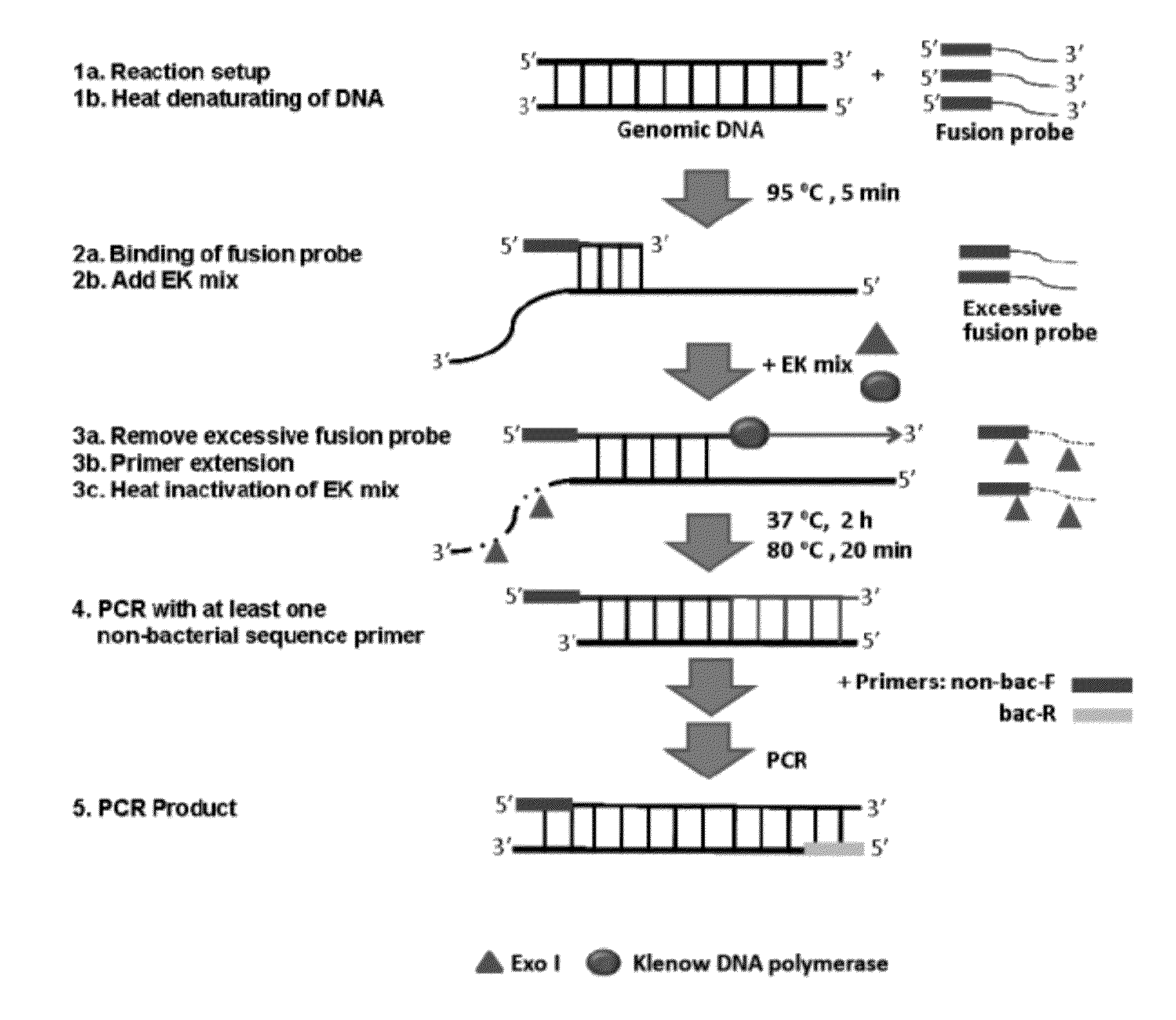
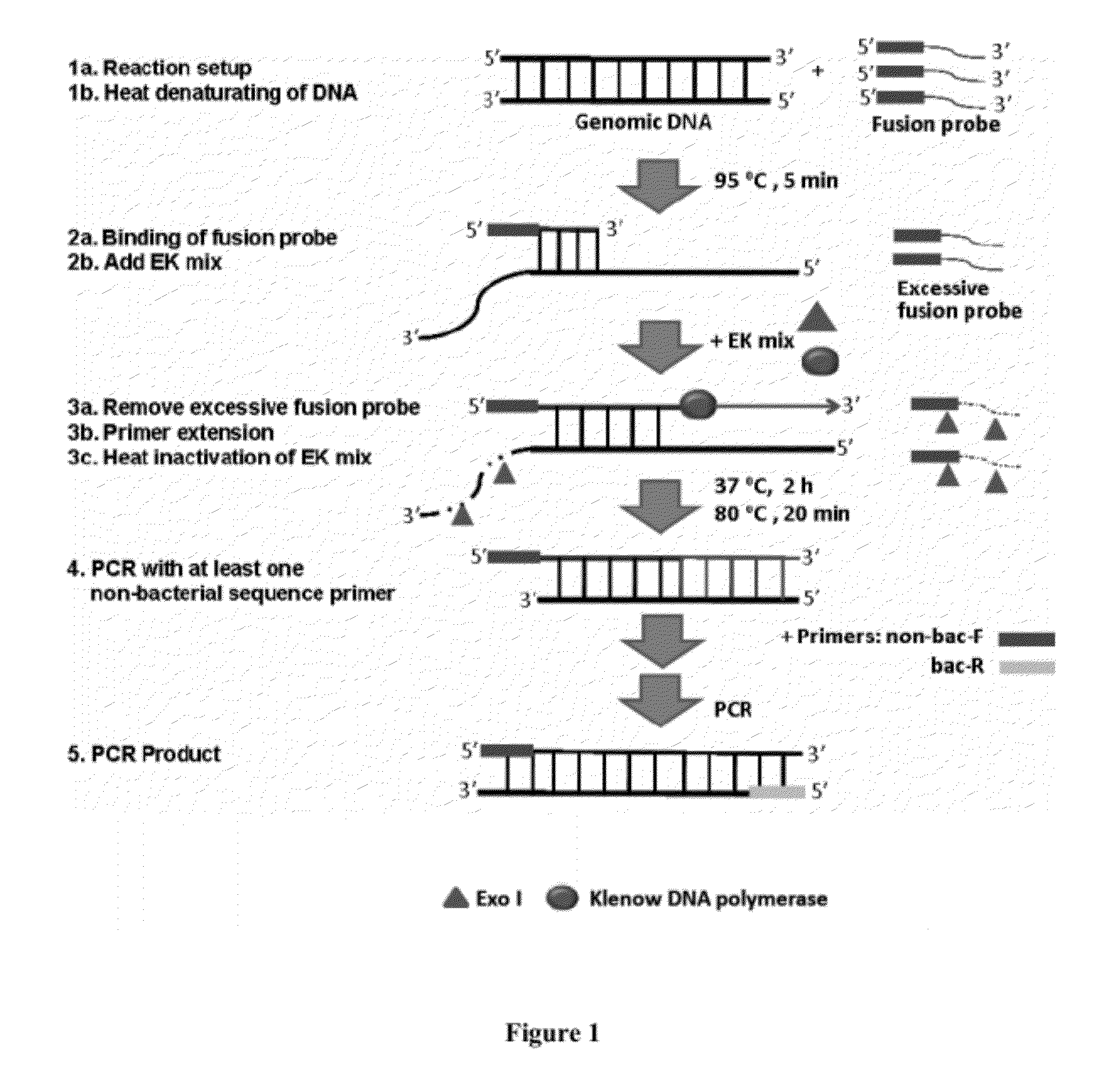
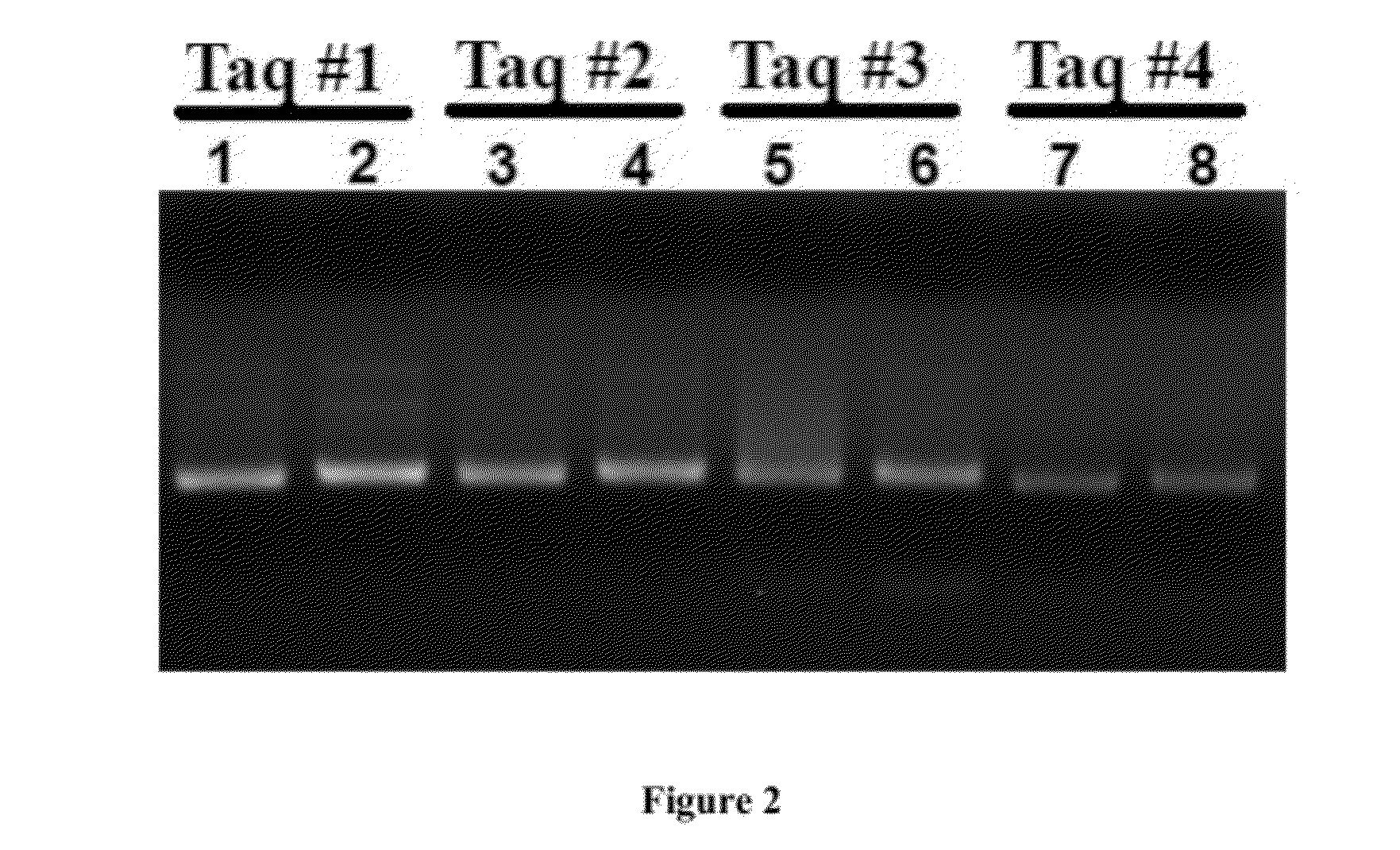
This invention provides methods, systems, and compositions for detecting low abundance microbial DNA in a sample by broad-range PCR. Methods of the present invention are based on a novel strategy that tags the 5′-end of the target DNA templates with a non-bacterial tagging sequence so as to set the templates apart from the endogenous contaminants present in the PCR reagents. There is also provided fusion probes for tagging the templates and primer sets to amplify the tagged templates. Systems and kits for facilitating and automating methods of the present invention are also provided.
Owner:DYNOCUBE INVESTMENTS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com