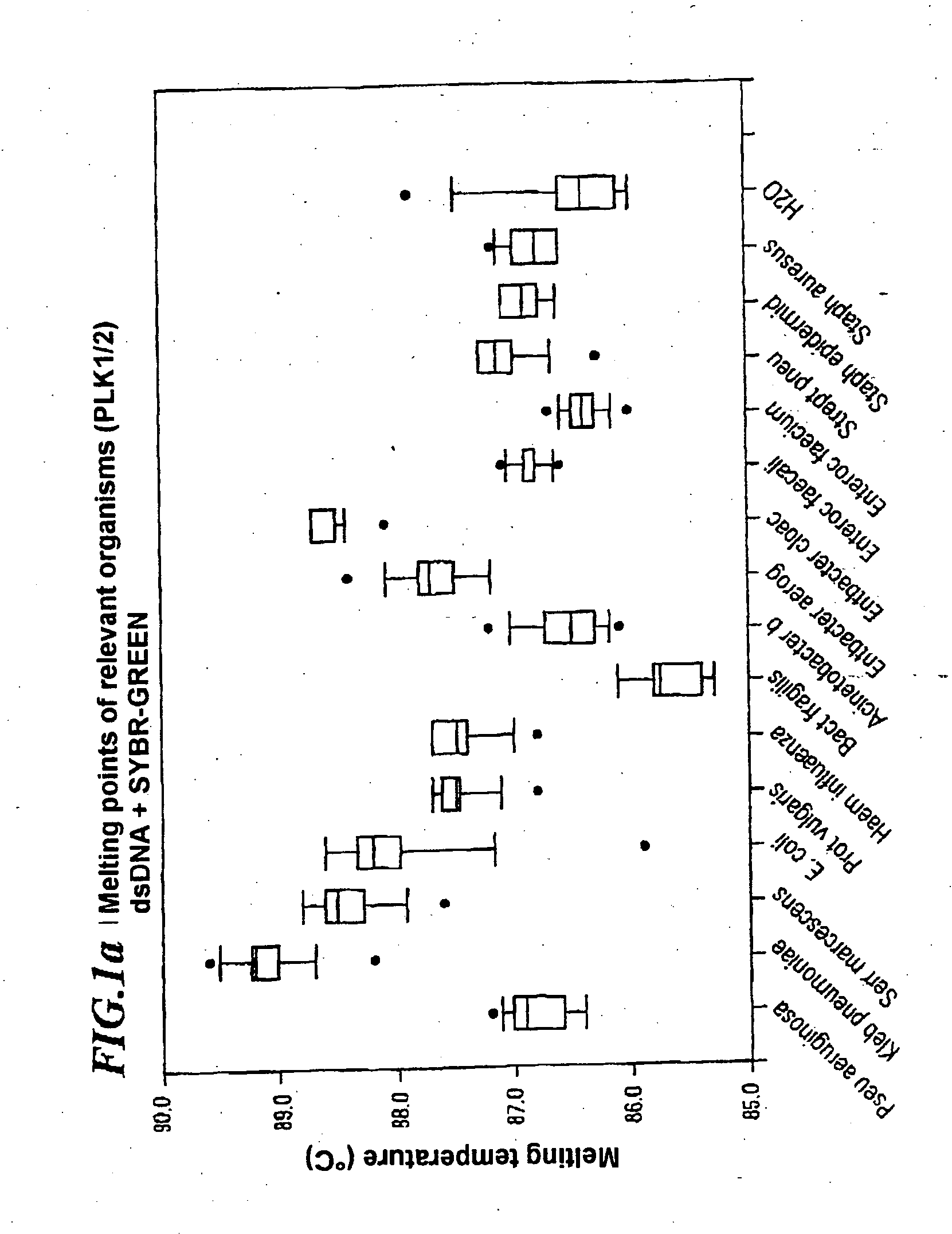
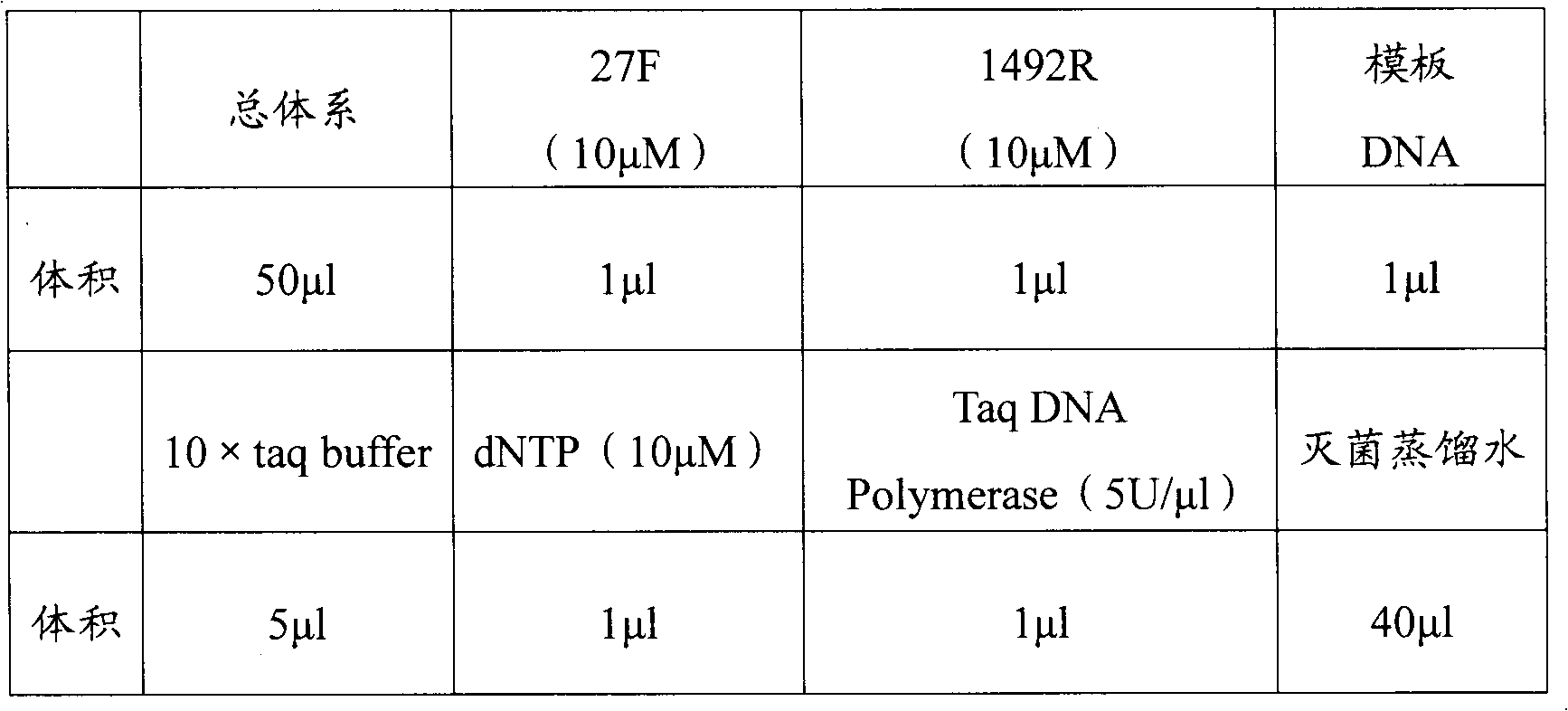
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
75 results about "Microbe DNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The genomes or DNA of microbes contain defined DNA patterns called genome signatures. Such signatures may be used to establish relationships and to search for DNA from viruses or other organisms in the microbes' genomes. Foreign DNA in bacteria has often been associated with disease-causing abilities.
Method for quickly detecting microbial dna/rna, kit therefor and the use of said method
InactiveUS20050079490A1Early detectionAccurate identificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismMicrobe DNA
A method for identifying microbial DNA / RNA comprising providing a sample containing microbial DNA / RNA; enriching DNA / RNA in the sample by a PCR method wherein the DNA / RNA that is identified comprise copies which are amplified by the PCR method; preliminarily classifying at least one microorganism by identifying the microbial DNA / RNA by a melting curve; adding at least one labeled oligonucleotide whereby temperature-dependent hybridization takes place and identifying the DNA / RNA on the basis of a physical property of the resultant DNA / RNA oligonucleotide complex, such as the temperature-dependence of the hybridization.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Kit and method for extracting microbial DNA
ActiveCN101935647AImprove bindingReduce adsorptionDNA preparationSodium acetateAluminum ammonium sulfate
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology and discloses a kit and a method for extracting microbial DNA. The kit comprises lysis solution, inhibitor removal solution and binding solution, wherein the lysis solution comprises 50 to 200mM of Tris-HCl, 50 to 150mM of EDTA, 0.5 to 3M of NaCl, 0.5 to 2 percent of CTAB, 0.5 to 2 percent of PVP and 0.5 to 2 percent of SDS; the inhibitor removal solution comprises 100 to 300mM potassium acetate, sodium acetate or ammonium acetate and 50 to 200mM aluminum sulfate, ammonium sulfate or aluminum ammonium sulfate; and the binding solution comprises 3 to 6M guanidine hydrochloride, 10 to 50mM Tris-HCl and 5 to 50 percent isopropanol. The kit and the method for extracting the microbial DNA have the advantages of high purity, high universality, high extraction speed, direct use for a downstream experiment, and application to extracting DNA from a microbe-containing sample.
Owner:中生方政生物技术股份有限公司
Pathogenic microorganism DNA detecting chip and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101113476ASensitive hybridization detectionAccurate readingMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesESCHERICHIA COLI ANTIGENNucleic Acid Probes
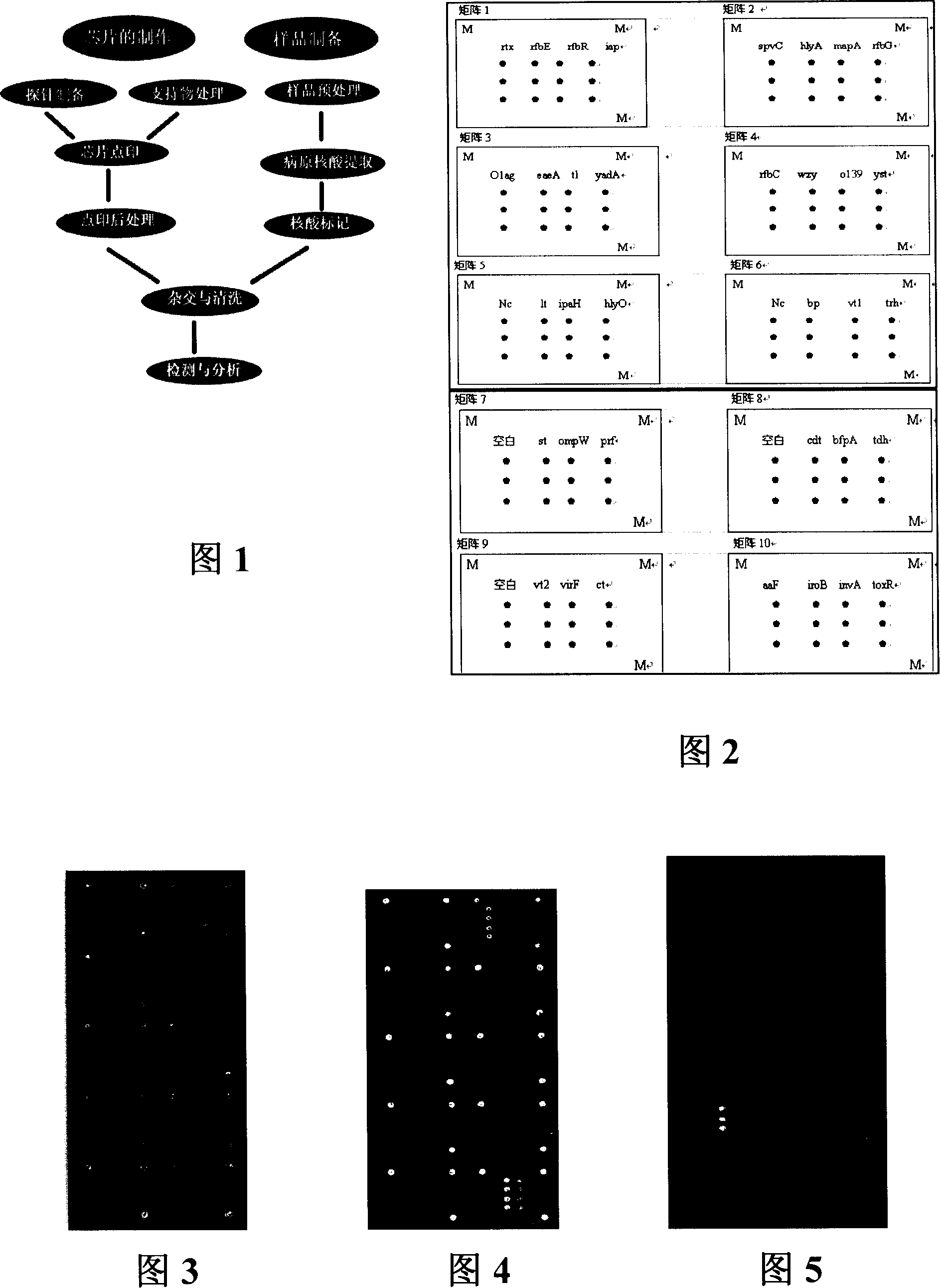
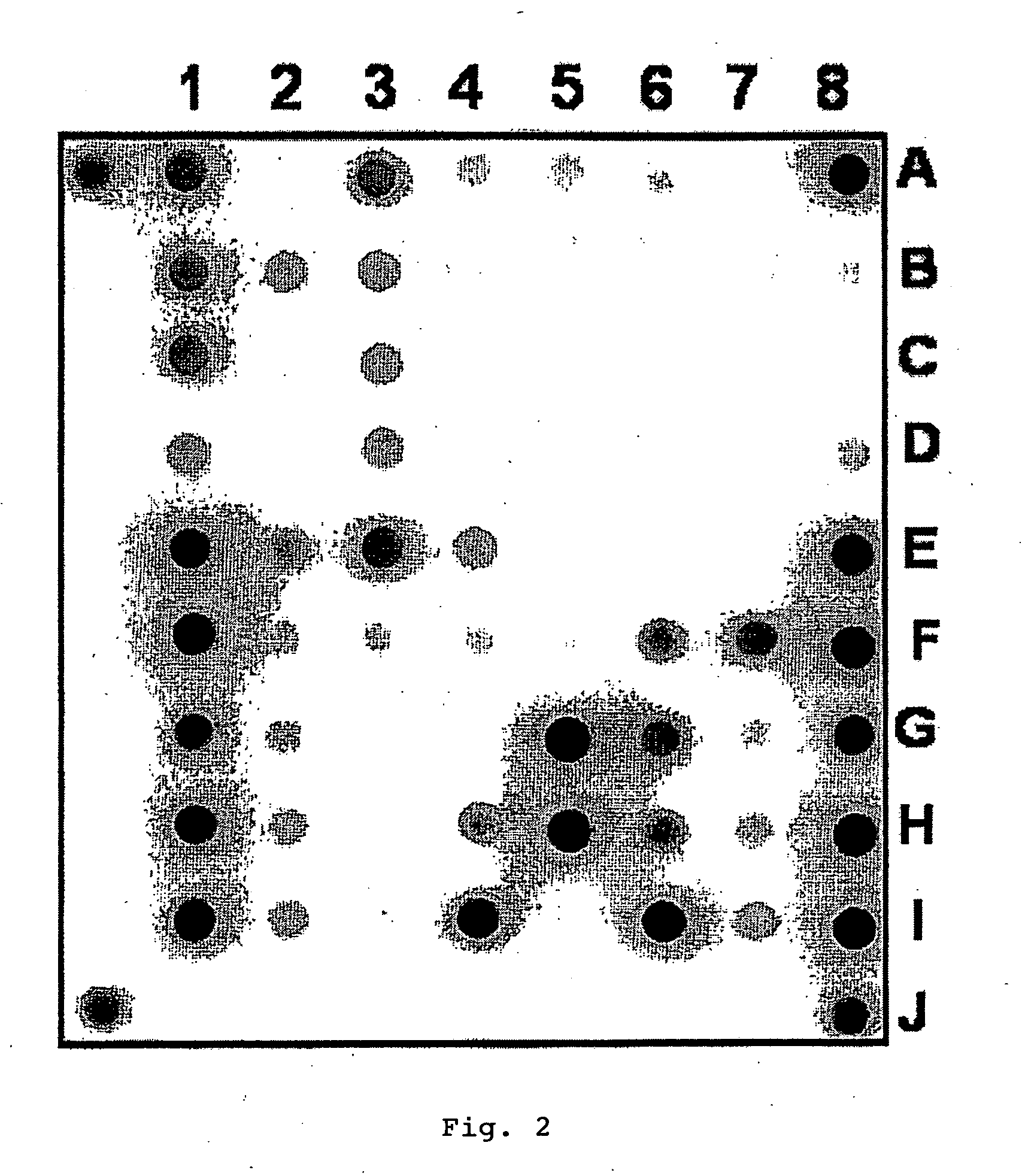
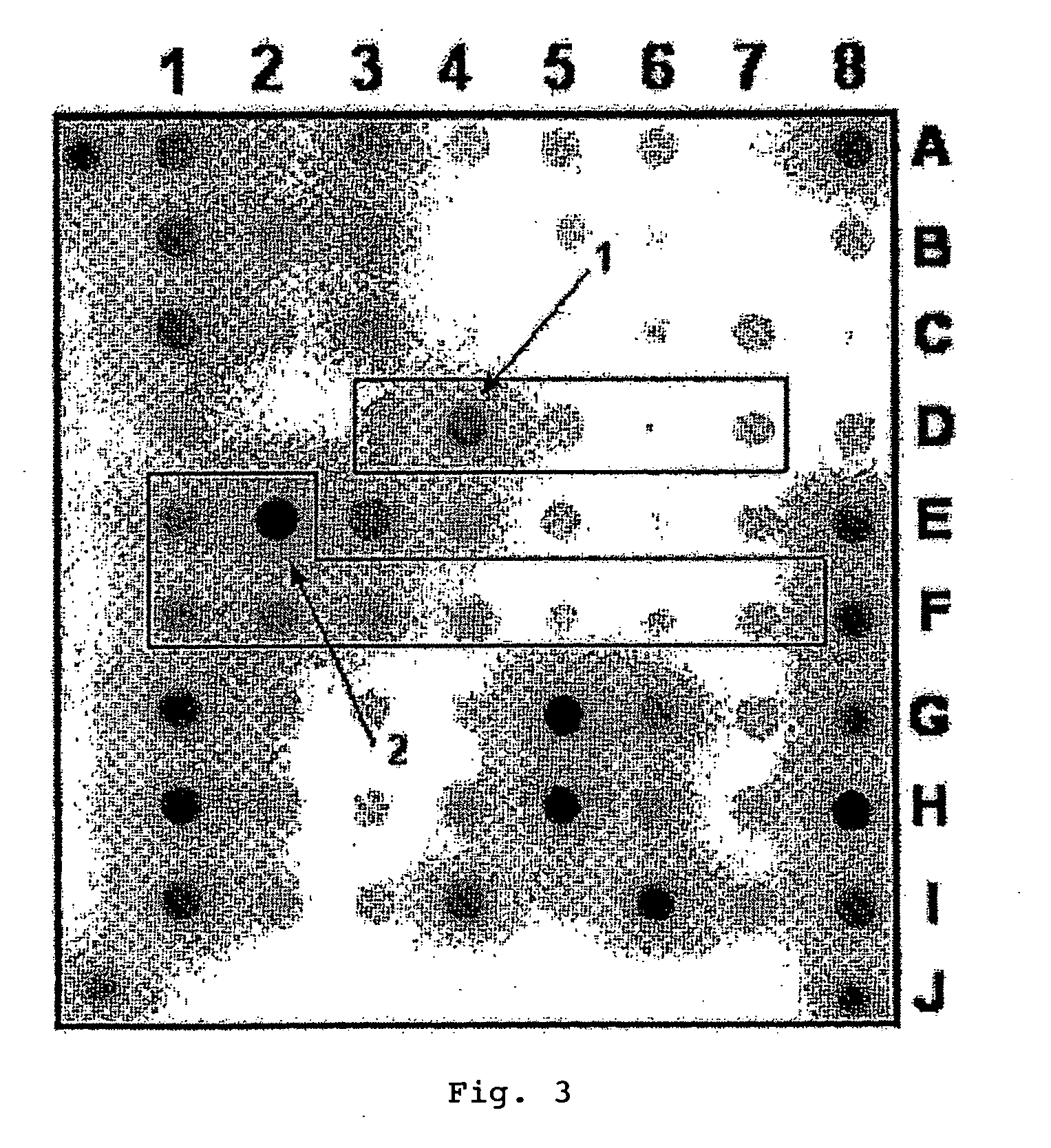
The invention relates to a pathogenic microorganism DNA detection chip and the chip comprises a carrier and a nucleic acid probe on the carrier. The nucleic acid probe is provided with a target detection probe used for detecting target gene of pathogenic microorganism. The pathogenic microorganism comprises but not limits to vibrio cholerae, pathogenic escherichia coli, campylobacter jejuni, Yersinia enterocolitica, parahemolytic vibrio, salmonella, and shigella and Listeria monocytogenes. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the pathogenic microorganism DNA detection chip and provides applications of the pathogenic microorganism DNA detection chip in detection of pathogenic microorganism. Also a pathogenic microorganism DNA detection chip kit is provided.
Owner:ICDC CHINA CDC
Method for simultaneous detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex and identification of mutations in mycobacterial DNA resulting in the resistance of microorganisms to rifampicin and isoniazid on biological microarrays, set of primers, biochip, and set of oligonucleotide probes used in the method
InactiveUS20100261163A1Low costShort timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIsoniazidNucleotide
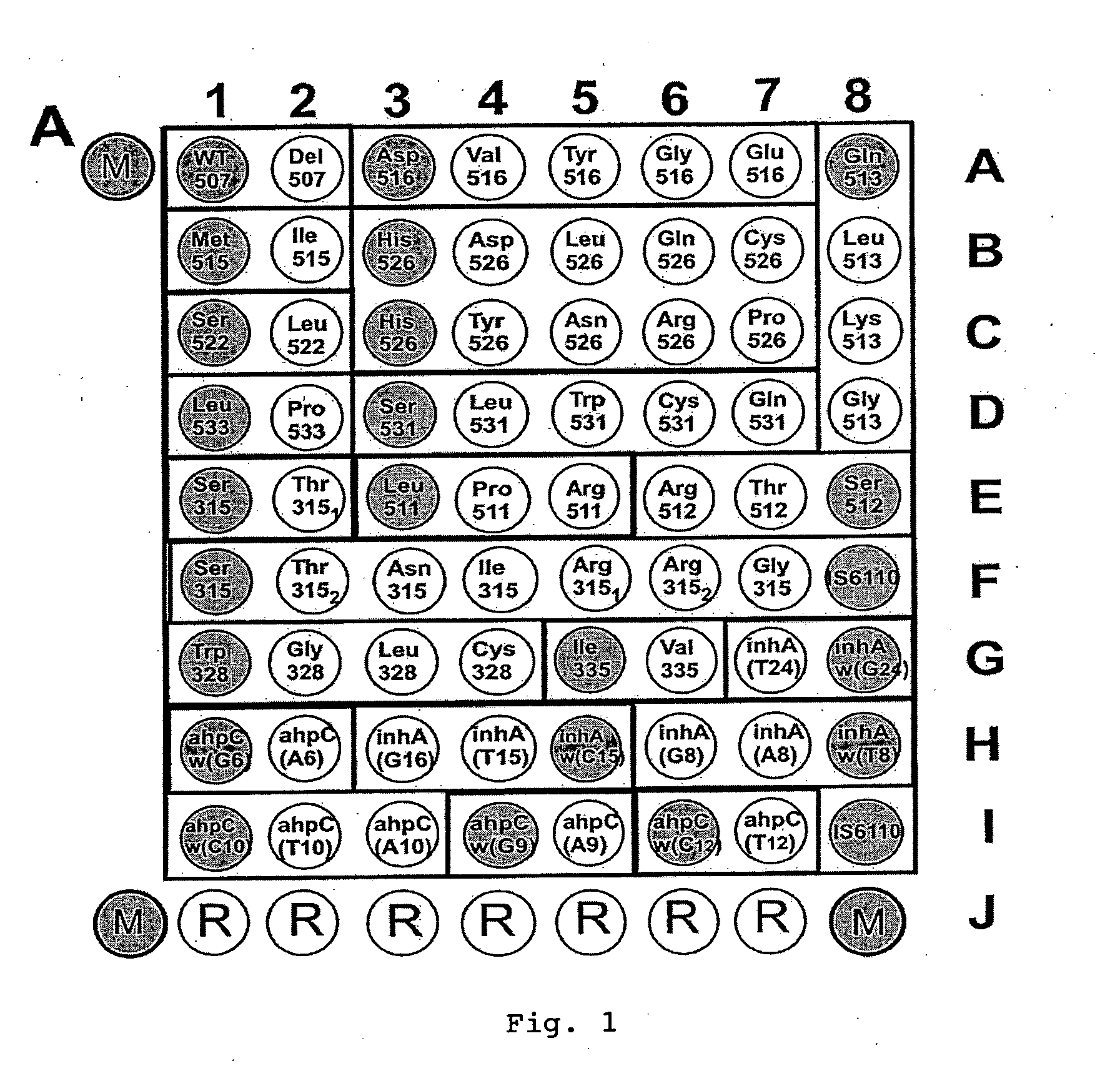
The present invention relates to molecular biology, microbiology, and medicine and provides the method for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex with simultaneous evaluation of sensitivity of the strains to rifampicin and isoniazid in clinical sample on differentiating biochip. The method is based on two-stage multiplex PCR to obtain fluorescent DNA fragments followed by hybridization of these fragments on microarray containing the set of specific discriminating oligonucleotides. The determination of the resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to rifampicin and isoniazid is carried out by evaluation of point nucleotide substitutions in DNA of microorganism. The present invention allows conduct analysis directly in clinical sample, to evaluate a number of mutations simultaneously, to decrease the cost price of analysis, and to reduce the time of its conducting. The present invention also relates to set of primers, biochip, and set of oligonucleotide probes used in realization of the method.
Owner:UCHREZHDENIE ROSSIISKOI AKADI NAUK INST MOLEKULYARNOI BLOLOGII IM V A ENGELGARDTA RAN IMB RAN
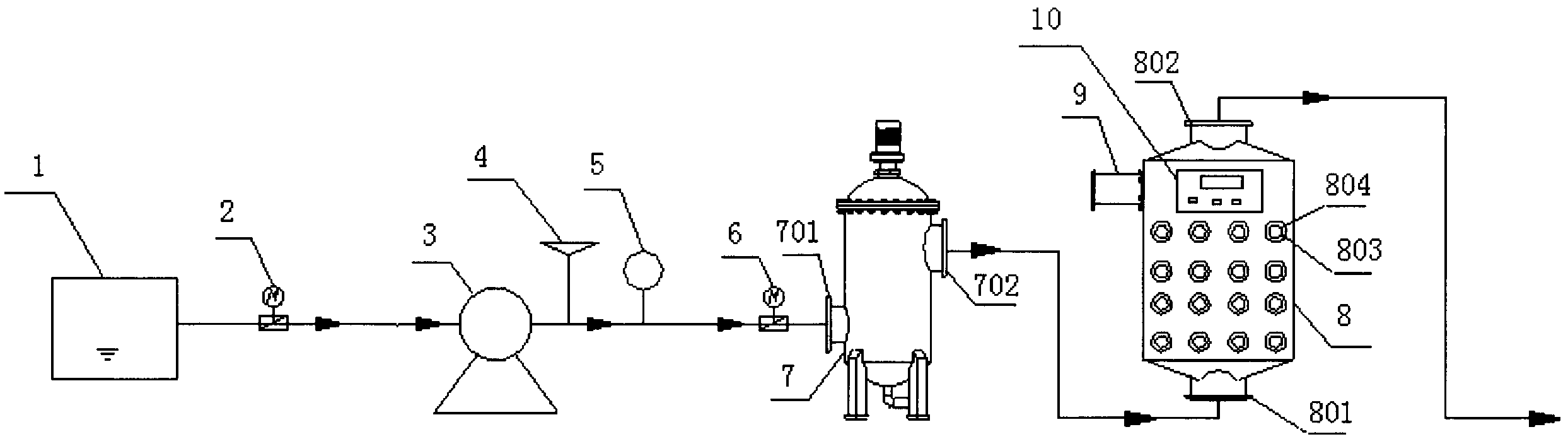
Method and apparatus for processing ship ballast water through filtration, ultraviolet and ultrasound
InactiveCN102367192AEfficient killingImprove reliabilityWater treatment parameter controlWater/sewage treatment by irradiationAutomatic controlFiltration
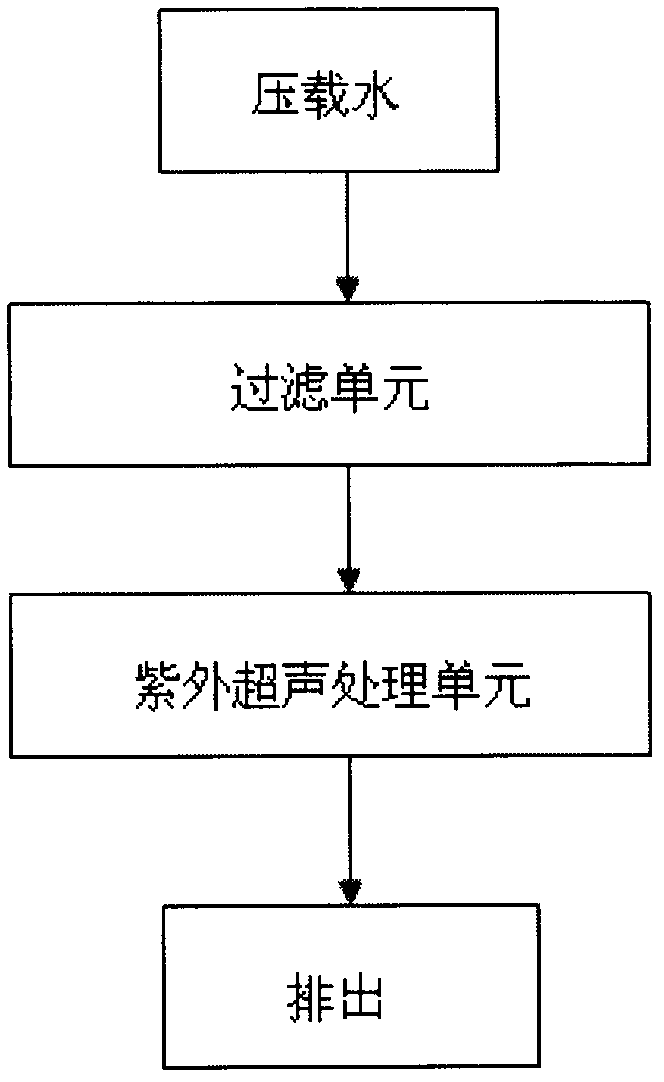
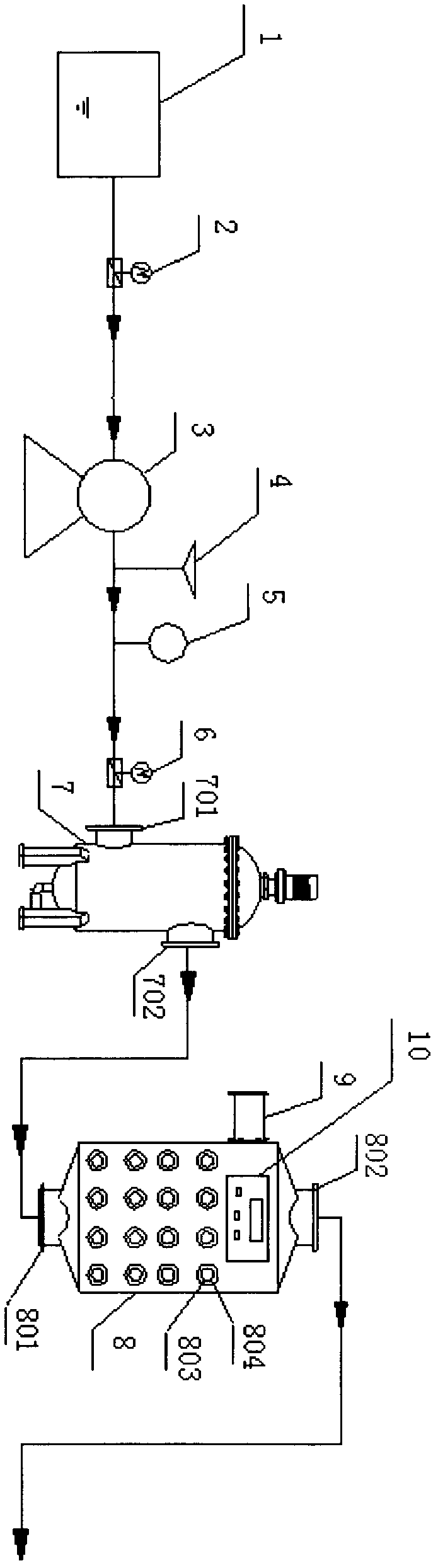
The invention which belongs to the field of ship ballast water processing equipment especially relates to a method and an apparatus for processing ship ballast water through filtration, ultraviolet and ultrasound. The apparatus of the invention comprises a water pump, a pressure transducer, a flowmeter, a filter, a comprehensive processing unit of ultraviolet and ultrasound, a control system, an electromagnetic valve and a pipeline. Water enters the filter through the water pump, then enters the comprehensive processing unit of ultraviolet and ultrasound to be subjected to biological inactivation, and is finally discharged. The synergetic disinfection of the ultraviolet-ultrasound unit allows the disinfection effect to be good, ultrasonic waves destroy protective layers of microbes, the ultraviolet radiation destroys DNA and RNA of the microbes, and the ultrasonic waves have certain cleaning effects on ultraviolet lamps. The apparatus of the invention, which can effectively kill the microbes in the ship ballast water, has the advantages of low energy consumption, high reliability, simple operation and maintenance, realization of one-key operation through an automatic control unit, and flexible selection of an installation platform according to practical cases.
Owner:NANTONG ELITE MARINE EQUIP & ENG INC JIANGSU
Simple extraction method for DNAs of microbes in river environment sample
The invention relates to a simple extraction for the DNAs of microbes in a river environment sample. The method disclosed by the invention comprises: dividing the river environment sample into a water sample and a bottom sediment sample; and extracting the DNAs of the microbes in the water sample and bottom sediment sample respectively. The method can also be used for extracting any environment sample alone. In the invention, by combining a liquid nitrogen repeated freezing and thawing process, a sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) process, a lysozyme process and the like, the microbial cells in theenvironment sample can be fully lysed to fully release DNA; and analysis on bacterial diversity by polymerase chain reaction-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (PCR-DGGE) technique indicates theextraction method can effectively reflect the integrity and diversity of microbes in the river environment sample.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for determining microorganism varieties and pathogenic microorganism pollution conditions in air
InactiveCN105087797AMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesPathogenic microorganismMicrobe DNA
The invention discloses a method for determining microorganism varieties and pathogenic microorganism pollution conditions in air. The method for determining microorganism varieties in air comprises the following steps: 1) acquiring microorganisms in air to be detected by using a sampling filter membrane to obtain microorganisms in the air to be detected on the sampling filter membrane; 2) extracting DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acids) in the air to be detected on the sampling filter membrane to obtain unpurified microorganism DNAs; purifying the unpurified microorganism DNAs with magnetic beads to obtain microorganism DNAs in the air; and 3) sequencing the microorganism DNAs in the air, and determining the microorganism varieties in the air to be detected according to the sequences of the microorganism DNAs in the air. The experiment proves that the method for determining microorganism varieties in air can be used for determining the microorganism varieties in the air, and the method for determining pathogenic microorganism pollution conditions in air can be used for determining the existence of pathogenic microorganism pollution in the air.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method of detecting microorganisms
InactiveUS7303870B2Broad specificityAccurately determineSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisMedical diagnosis
The present invention relates generally to a method for detecting, enumerating and / or identifying microorganisms in a sample. More particularly, the present invention provides a method for determining total microbial content in a sample by detecting the presence of nucleotide sequences associated with all or part of 16S rDNA or its corresponding 16S rRNA or its homologue, functional equivalent or derivative. The nucleotide sequences of the present invention may be used as an indicator of any microorganism and, hence, represents a universal target sequence which is indicative of total microbial content in a sample. The universal target sequence may also be varied to render same genus or species specific or the universal target used to trap microbial DNA or RNA which may be subsequently analyzed by sequence analysis or genetic probe technology. The universal target sequence is useful inter alia to design as universal primers and probes to amplify any microbial-derived genomic sequence, as a means to detect and enumerate total microorganisms and to identify microorganisms in a sample at the genus or species level. Such uses enable improved methods of enviroprotection, bioremediation, medical diagnosis and industrial microbiology. The present invention further relates to the universal target sequence in isolated form and / or primers or probes capable of hybridizing to same and kits for the detection of total microbial content in a sample.
Owner:THE UNIV OF SYDNEY +1
Microbial genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) indirect extraction method for evaluating diversity of animal intestinal microflora
The invention relates to a microbial genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) indirect extraction method for evaluating diversity of animal intestinal microflora. Before cell lysis, the method performs pretreatment on a sample and separates microbial cells from the excrement sample to avoid the problems that pollutants are difficult to remove and the DNA recovery rate is low in a purification step. According to the invention, phenol and chloroform are not used in the extraction process, thus harm to the physical health of experimenters is reduced. The OD260 / OD230 and OD260 / OD280 of the extracted intestinal microorganism DNA are approximate to standard values, and the intestinal microorganism DNA can be directly applied to molecular operation to evaluate the diversity of animal intestinal microflora.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Extraction method of total DNA of metagenome of fish enteric microorganisms and kit
ActiveCN106754888AAvoid pollutionImprove integrityDNA preparationIntestinal microorganismsTriton x100
The invention provides an extraction method of total DNA of metagenome of fish enteric microorganisms and a kit. The extraction method comprises the following steps: (1) fish sample sampling and fixing treatment of microorganisms on the surface of the fish; (2) acquisition of enteric microorganisms and collection of thalli; (3) embedding and cracking of cells; (4) extraction of DNA; and (5) DNA preservation. The kit comprises the following main components: a solution A which is a mixed solution of Tris and EDTA; a solution B which is a mixed solution of Tris, EDTA, NaCL, PVP, guanidinium isothiocyanate, Triton-X100, PMSF, and beta-mercaptoethanol; a solution C which is a mixed solution of Tris, EDTA, NaCl and DTT; a solution D which is a mixed solution of proteinaseK, a lysozyme, Tris, NaCl and SDS; a solution E which is a mixed solution of Tris saturated phenol and chloroform; F which is isopropanol; and G which is an ethanol aqueous solution. The DNA fragment obtained by the invention is high in purity, and the content of DNA of a host and the microorganisms on the surface of the fish is small.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Method for extracting prawn intestinal microbial DNA
The invention relates to a method for extracting prawn intestinal microbial DNA, and belongs to the fields of microbiology and molecular ecology. The method comprises the following steps of: grinding by using liquid nitrogen; breaking cell walls by using mechanical force; cracking cells by adopting lysozyme and SDS lysate; obtaining DNA deposit through separation and precipitation; and finally dissolving the DNA deposit with TE to obtain the DNA with good quality. The product DNA fragment obtained by the method is greater than 20Kb; and can be subjected to gene magnification and sequencing. The method has good generality and is used for extracting the intestinal microbial DNA of various crustacean aquatic animals. High-quality template DNA can be obtained through extraction at one time without repeated experiment; and the obtained DNA can be applied to the research of molecular ecology, system evolution and the like.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and material for simultaneously detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis compound and identifying its medicament resistance
InactiveCN101210265AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisIsoniazidFluorescence
The present invention relates to molecular biology, microbiology and medicine, and provides a method for detecting nodule offshoot bacilli complex body in clinic samples and evaluating the sensitivity of strain to rifampicin as well as isoniazid in distinguish biochip. The method obtains fluorescence DNA segments based on two-step multiple PCR, then to hybridize said segments on a micro-array containing differential distinguished oligonucleotide group. To determine the resistance of concretion offshoot bacilli to rifampicin and isoniazid by means of evaluating point nucleotide replacement in microbiology DNA. The present invention allows analyze directly clinic sample to evaluate mass mutation at one time, so as to reduce analysis cost and implement time. The present invention also relates to primer group, biochip and oligonucleotide probe group for implementing said method.
Owner:RUSN ACAD V A ENGERHARDT MOLECULAR BIOLOGY INST
Method for separation and purification of large-fragment DNA from soil
InactiveCN103103180AEasy to operateOperation steps are adjustableDNA preparationMicrobe DNABiological studies
The invention belongs to the fields of soil microorganisms, biochemistry and molecular biology and relates to a method for separation and purification of a large-fragment DNA from soil. The method is used for indirect separation and purification of a large-fragment DNA having molecular weight more than 30kb from various types of soil, wherein the large-fragment DNA is used for construction of a metagenomic library, or is used for separation of soil microbial gene clusters. The method solves the problem that separation of microbial cells from soil and preparation of large-fragment soil DNA having high purity and satisfying various biological study demands are realized difficultly by the existing indirect method, and is an efficient method for extraction of soil microorganism DNA having a large fragment and high purity.
Owner:XINJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for extracting soil microbial DNA
InactiveCN1978453ALow humusReduce organic acid contentSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationDNA SolutionsMicroorganism
This invention relates to an extracting method of soil microorganism DNA. The stated method includes steps as following: cell disruption of soil microorganism, obtaining crude DNA solution, obtaining soil microorganism DNA; the stated method of this invention is using PVPP, protease K etc for valid combination. After organic solvent such as PEG20000, isopropyl alcohol and so on are precipitated, use spectrophotometer to determine value of OD260 / OD230, OD260 / OD280 close to standard value. It can be directly used for molecule operation, possessing great application perspective.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Soil DNA extracting method for evaluating diversity of microbial community of plant root system
InactiveCN101709298AEasy to operateLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationPlant rootsDna recovery
The invention discloses a soil DNA extracting method for evaluating diversity of a microbial community of a plant root system. In the method, pretreatment is carried out on a sample before cell splitting, extracellular DNA and humic substances are removed, and the problems of difficult removal of the humic substances and low DNA recovery rate existing in a purification step are solved. In the extraction process of the method, phenol or chloroform is not used so as to reduce harm on the health of experimenters, obtain complete DNA and molecular fragments greater than 10kb and achieve high yield. OD260 / OD230 and OD260 / OD280 of the extracted soil microorganism DNA are close to standard values and can be directly applied to molecular operation so as to evaluate the diversity of the microbial community of the plant root system.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
DNA extracting method for evaluating community diversity of the intestinal microorganisms of animals
InactiveCN101712953AEasy to operateLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMicrobe DNAPHENOL LIQUID
The invention discloses a DNA extracting method for evaluating the community diversity of the intestinal microorganisms of animals. Before cell disruption, a sample is pretreated, and DNA and pollutants outside the cells are removed, thereby avoiding the problems of difficult removal of the pollutants and low recovery rate of the DNA in a purification step. In the extracting process of the invention, phenol and chloroform are not used, and damage to the health of experiment personnel is reduced; and the obtained DNA is integral and has high yield, and the molecular fragment is larger than 10kb. The OD260 / OD230 and OD260 / OD280 of the DNA of the extracted intestinal microorganisms are close to standard values and can be directly applied to molecule operation to evaluate the community diversity of the intestinal microorganisms of animals.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Kit and method for extracting microbial genome DNA by magnetic bead method
InactiveCN110283816AAvoid interferenceProtection from cleavageMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMicroorganism preservationLithium chloride
The invention relates to a kit and method for extracting a microbial genome DNA by a magnetic bead method. The kit comprises a microbial preservation buffer solution, a bacteriolytic agent solution I, proteinase K, silica gel magnetic beads, isopropanol and an ethanol water solution, and further comprises a bacteriolytic agent II, a lysis adsorption solution and a reinforced scrubbing solution. The bacteriolytic agent II comprises MES, EDTA, Triton X-100, lysozyme and a lysozyme enhancer. The lysis adsorption solution comprises Tris-HCl, sodium chloride, EDTA, TrionX-100 and a nucleic acid separation and absorption promoter; and the reinforced scrubbing solution comprises Tris-HCl, lithium chloride and ethanol. By adopting the kit provided by the invention, cell walls of gram-positive bacteria and various fungi can be completely destroyed to form protoplasts, DNA of the protoplast cells can be rapidly released under the action of the lysis adsorption solution, the DNA is efficiently adsorbed on the silica gel magnetic beads, and after the DNA is washed by the scrubbing solution and eluted by an elution solution, microbial DNA with high concentration and purity can be obtained.
Owner:WUXI NO 2 PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Identification of pathogens
InactiveCN101501219AImprove treatmentReduce recovery careMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationMicrobe DNAMicroorganism
Disclosed is a method for identification of microbial pathogens in a body fluid sample comprising the following steps: a) providing a body fluid sample; b) lysing the microbial pathogens and performing a nucleic acid amplification reaction on the microbial DNA encoding 16S or 18S rRNA wherein or whereafter the amplified nucleic acids are labelled; c) contacting the labelled amplified nucleic acids of step b) with a microarray comprising on defined areas on the microarray's surface immobilised probes for microbial DNA encoding 16S or 18S rRNA from microbial pathogens; d) detecting the binding of one or more species of the labelled amplified nucleic acids to a probe by detecting a labelled amplified nucleic acid being specifically bound to the microarray; and e) identifying a microbial pathogen in the body fluid sample by correlating the detected binding of the labelled amplified nucleic acids with the defined areas of the immobilised probes for microbial DNA encoding 16S or 18S rRNA from microbial pathogens.
Owner:奥地利研究中心有限公司
Method for extracting endophytic fungi genomes of wild roses
The invention discloses a method for extracting endophytic fungi genomes of wild roses. The method comprises the following steps: disinfecting the surfaces of wild roses and then performing liquid nitrogen treatment, and extracting endophytic fungi genomes by adopting combination of a CTAB mixed solution and a soil microorganism DNA brutal extracting kit. The method is designed aiming at the specificity of wild rose samples, and the adverse influences of quinones substances, phenol substances, polyphenol oxidase contained in wile rose plants, incomplete dilapidated walls, and the like on the extraction efficiency of genomes DNA can be avoided. The method can be applied to extraction of endophytic fungi genomes of all the wild roses, and has the characteristics of being wide in application range and high in extraction rate. The method can achieve a good extraction effect after being applied to extraction of endophytic fungi genomes in Dali purple flowers of wild roses and the endophytic fungi genomes of seven-sister wild roses, and the extracted genomes DNA can be used for various molecules experiments.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
PCR pollution prevention method and applications thereof
InactiveCN106337045ADoes not affect amplificationEasy to handleMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMicrobe DNAEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a PCR pollution prevention method. The method comprises the following steps: 1, adding a certain amount of Benzonase nuclease into a routine PCR system free of primers and templates to make the Benzonase nuclease play a role in enzyme digestion at a proper temperature in order to completely digest DNA polluted by exogenous microbes or aerosols existing in the PCR system; 2, keeping the Benzonase nuclease treated PCR system at a high temperature to inactivate the Benzonase nuclease in a reaction solution; and 3, adding corresponding primers and templates, and carrying out subsequent PCR amplification. The invention also discloses applications of the method in common qualitative PCR, fluorescent quantitative PCR and high-flux sequencing molecule database creation. The method effectively solves the exogenous microbe DNA or PCR product aerosol pollution problem appearing in the PCR amplification process, and has wide application prospect in high-flux sequencing.
Owner:TINYGENE BIOTECH SHANGHAI CO LTD
Efficient and economical soil microbial DNA extraction method
ActiveCN109337900AImprove extraction qualitySimplify the collection processDNA preparationWater bathsMicrobe DNA
The invention discloses an efficient and economical soil microbial DNA extraction method. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, obtaining a microbial suspension; weighing 1 g of soil, adding 2 ml of suspension Buffer C1, 1 g of glass beads having the particle diameter of 0.09-0.12 mm, 500 muL of humic acid adsorbent Buffer C2 and 10 muL of proteinase K (10 mg / mL), mixing and shaking; step 2, obtaining microbial DNA; step 3, obtaining crude DNA; placing the material obtained in the last step in a water bath of 60 DEG C while stirring, then centrifuging at a high speed of 4 DEG C, and collecting the first supernatant; and step 4, obtaining purified DNA. The method is based on the requirements of soil-contaminated microbial detection, can extract DNA containing no inhibiting factor from complex environmental samples such as soil and feces, and is high in extraction speed and accurate in analysis result.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Advanced oxidation method
InactiveCN102557185AImprove securityEfficient removalWater/sewage treatment by irradiationUsing liquid separation agentMicrobe DNAHydroxyl radical
The invention belongs to the field of oxidation method, and especially provides an advanced oxidation method. The method comprises the steps that: (1) with a towing type reversed gas transmission wheel, air or oxygen is injected into water, such that stable dissolved oxygen is produced; (2) with ultraviolet rays generated by an ultraviolet lamp, the stable dissolved oxygen is converted into dissolved ozone that can not be released into air; (3) the dissolved ozone that cannot be released into air is subject to an effect of ultraviolet rays generated by the ultraviolet lamp, such that hydroxyl free radicals in water are produced; (4) the ozone free radicals in water and the hydroxyl free radicals in water act together, such that advanced oxidized purified water is obtained; (5) the advanced oxidized purified water is used for washing air, such that a purpose of air purification wetting is realized. According to the invention, dissolved ozone is directly produced by using dissolved oxygen in water, such that a safety property is good. Also, the ozone and hydroxyl free radical advanced oxidation method is combined with a capacity of the ultraviolet for directly damaging microbe DNA, such that a method for effectively killing microbes in water is further formed.
Owner:ZHENGJIANG MALIPURE ENVIRONMENTAL SCI & TECH +1
Method of using microbial DNA sequencing in recovering renewable resources from wastewater and other waste streams
ActiveUS20180354830A1Reliable and renewable streamAvoid serious impactWater treatment parameter controlBacteriaWaste streamMicrobiome
A method is described for recovering resources from a microbe supporting environment such as a water treatment system, comprising the steps of using microbial DNA sequencing to analyze the microbiome of the microbe supporting environment and identifying adjustments to the microbial content of the microbiome that will be useful in extracting resources from the microbe supporting environment such as a water treatment system, wherein the resources extracted can include, for example, methane released by microbes, nitrogen, phosphorus, or other contaminants generated by microbes, and / or clean water obtained by removing contaminants in a water treatment system.
Owner:MICROBE DETECTIVES LLC
Simple, efficient and cheap method for purifying forest soil sample DNA
The invention provides a method for purifying microorganism DNA in forest soil, which comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining the rough DNA of a microorganism by a conventional method; (2) dissolving the rough DNA by extracted buffer solution; after the rough DNA is subjected to water bath and isovolumetric chloroform-isoamyl alcohol solution extraction, adding isopropanol which is 0.6 time of the volume of supernatant into the supernatant to precipitate DNA sediments; washing by 70 percent of pre-cooled alcohol and dissolving in the TE buffer solution; and (3) further purifying the initially purified DNA by a silica gel column. The method can remove most of impurities in a rough product of the extracted soil microorganism DNA and obtain the DNA with high purity and can be directly used for the conventional polymerase chain reaction (PCR) which is quite sensitive for an inhabiting matter. The invention has simple operation, low cost, less time consumption and wide application range and can be used for purifying the soil DNA in various types after other prior soil direct extraction methods.
Owner:JISHOU UNIVERSITY
Extraction method of microbe DNA for high-throughput sequencing in sample
InactiveCN105176970AHigh yieldReduce the degree of degradationMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationMicrobe DNAMicroorganism
The invention provides an extraction method of a microbe DNA for high-throughput sequencing in a sample and belongs to the field of a genome DNA extraction technology. According to the invention, DNA of a microbe in a sample is extracted by a SDS method; an inhibitor is removed after precipitation by the use of a sodium chloride solution and a aluminum ammonium sulfate solution, and then a supernatant is taken; and separation and purification are carried out by a silica gel film-column to obtain soil microbe genome DNA for high-throughput sequencing. The aluminum ammonium sulfate solution is prepared from 50-200 mM of Al2(SO4)3 and 50-200 mM of (NH4)2SO4 according to volume ratio of 1:1. The sample's microbe genome DNA extracted by the above method has high purity, good universality and fast extraction speed, can be directly used in a downstream high-throughput sequencing experiment and has a good application prospect.
Owner:BIOMARKER TECH
Broad-spectrum detection method of carcinogenic pathogenic microorganisms
PendingCN106498093AEfficient detectionReduce use costMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobe DNAPathogenic microorganism
The invention relates to the field of detection and identification of pathogenic microorganism preparation, especially to a kit for detecting DNA / RNA of carcinogenic pathogenic microorganisms in biological samples. The kit contains a synthesized polynucleotide reagent. The polynucleotide contains primer sequences SEQ ID NO.1-SEQ ID NO.70 of forward and reverse primers of a specific gene sequence of DNA / RNA carcinogenic pathogenic microorganisms, base expanded probe sequences SEQ ID NO. 75-SEQ ID NO.109, DNA / RNA quality control primer sequences SEQ ID NO.71-SEQ ID NO. 74, and probe sequences SEQ ID NO.110 and SEQ ID NO.111.
Owner:北京万泉麟科技有限公司
Extraction method for microbial DNA in milk
The invention discloses an extraction method for microbial DNA in milk. The method comprises the following steps: adding 0.8 mL of a milk sample into 0.3 to 0.5 mL of an ES solution (EDTA with a pH value of 7.5 and concentration of 0.5 mol / L and SDS with concentration of 2%), carrying out uniform mixing and centrifugation and discarding supernatant; adding 0.8 to 1.2 mL of a PBS buffer solution, carrying out oscillation and shaking up, then carrying out centrifugation and discarding supernatant; adding 20 to 30 [mu]L of Staphylococcus lysozyme with a mass concentration of 0.02 mg / mL; adding 150 to 200 [mu]L of an aqueous Chelex-100 solution with a mass concentration of 10%, carrying out violent oscillation for 5 to 10 s and then carrying out heating in boiling water with a temperature of 100 DEG C for 8 to 12 min; and carrying out centrifugation and taking supernatant for a PCR reaction. The method provided by the invention employs a Chelex-100 process and can economically, rapidly, efficiently and directly extract bacterial DNA from the milk sample; and the bacterial DNA can be used for PCR detection of main pathogenic bacteria causing mastitis in cow.
Owner:CHINTEM TECH CONSULTING BEIJING CO LTD
Detection method for phytopathogen content in soil
ActiveCN104694658AShorten detection timeStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMicrobe DNA
The invention discloses a detection method for phytopathogen content in soil. The detection method for the phytopathogen content in the soil includes that S1) using a soil microorganism DNA extracting method to extract the microorganism DNA of the soil to be detected to obtain the microorganism DNA of the soil to be detected; S2) using the microorganism DNA of the soil to be detected as a template, using reagent set for identifying the phytopathogen to perform fluorescent quantitative PCR, and confirming the content of the phytopathogen in the soil to be detected through the fluorescence intensity of the PCR product. The soil microorganism DNA extracting method includes that S21) adding extracting buffer solution to the soil to obtain cell suspension; S22) adding SDS to the cell suspension to obtain cell lysis solution, performing cell lysis to obtain lysate, wherein the mass percent concentration of the SDS in the cell lysis solution is 4%; removing impurities from the lysate to obtain the microorganism DNA of the soil to be detected.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for rapidly separating anaerobic denitrifying bacteria and particular primer thereby
InactiveCN101519643AEasy to getPromote degradationBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesMicrobe DNA
The invention relates to a method for rapidly separating bacteria and a particular primer thereby, in particular to a method for rapidly separating anaerobic denitrifying bacteria and a particular primer thereby, solving the problems that the prior anaerobic denitrifying bacteria have long separation period and great workload and are difficult to obtain bacterial strains and pure bacterial strains with the destination functions. The method comprises the following steps: 1, extracting microorganism DNA from a sample for PCR augmentation and separation culture and prescreening the anaerobic denitrifying bacteria; 2, preparing particular culture media to be purified until a colony grows up; 3, carrying out the enrichment culture of the colony for the PCR augmentation and re-screening the anaerobic denitrifying bacteria; 4, repeating the separation culture, the purification culture and the enrichment culture, identifying and carrying out the PCR augmentation for removing repetitive bacterial strains and then, repeating the separation culture and the purification culture to obtain the pure bacterial strains. An upstream primer is SEQ ID of NO.1, and a downstream primer is SEQ ID NO.2.The invention shortens the separation period by 40 percent to 50 percent, has little workload and is easy to obtain destination bacterial strains and pure bacterial strains.
Owner:HARBIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting rumen microorganisms of Holstein cows
InactiveCN104789675AQuick checkComprehensive detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobe DNAInformation analysis
The invention provides a method for detecting rumen microorganisms of Holstein cows and belongs to methods for detecting rumen microorganisms of animals. According to the method, rumen fluid of the Holstein cows is extracted, DNA of microorganisms in the rumen fluid is extracted and types and relative quantity of microorganisms of the Holstein cows are determined through sequencing; the method comprises the following steps: (1), genome DNA extraction, (2) PCR amplification, (3) fluorescent quantitation, (4) high-throughput sequencing platform library construction, (5) high-throughput sequencing platform sequencing, (6) biological information analysis and (7) sequencing results. According to the method, the types and relative quantity of rumen microorganisms of the Holstein cows can be rapidly, comprehensively and efficiently detected, so that people can conveniently analyze types and quantity of rumen microorganisms of Holstein cows and study absorption digestion mechanisms for absorbing nourishment of rumen microorganisms. The method has the advantages as follows: detection time is shortened, the detection results are accurate and comprehensive, and types and relative quantity of all microorganisms in the Holstein cows can be accurately detected.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com