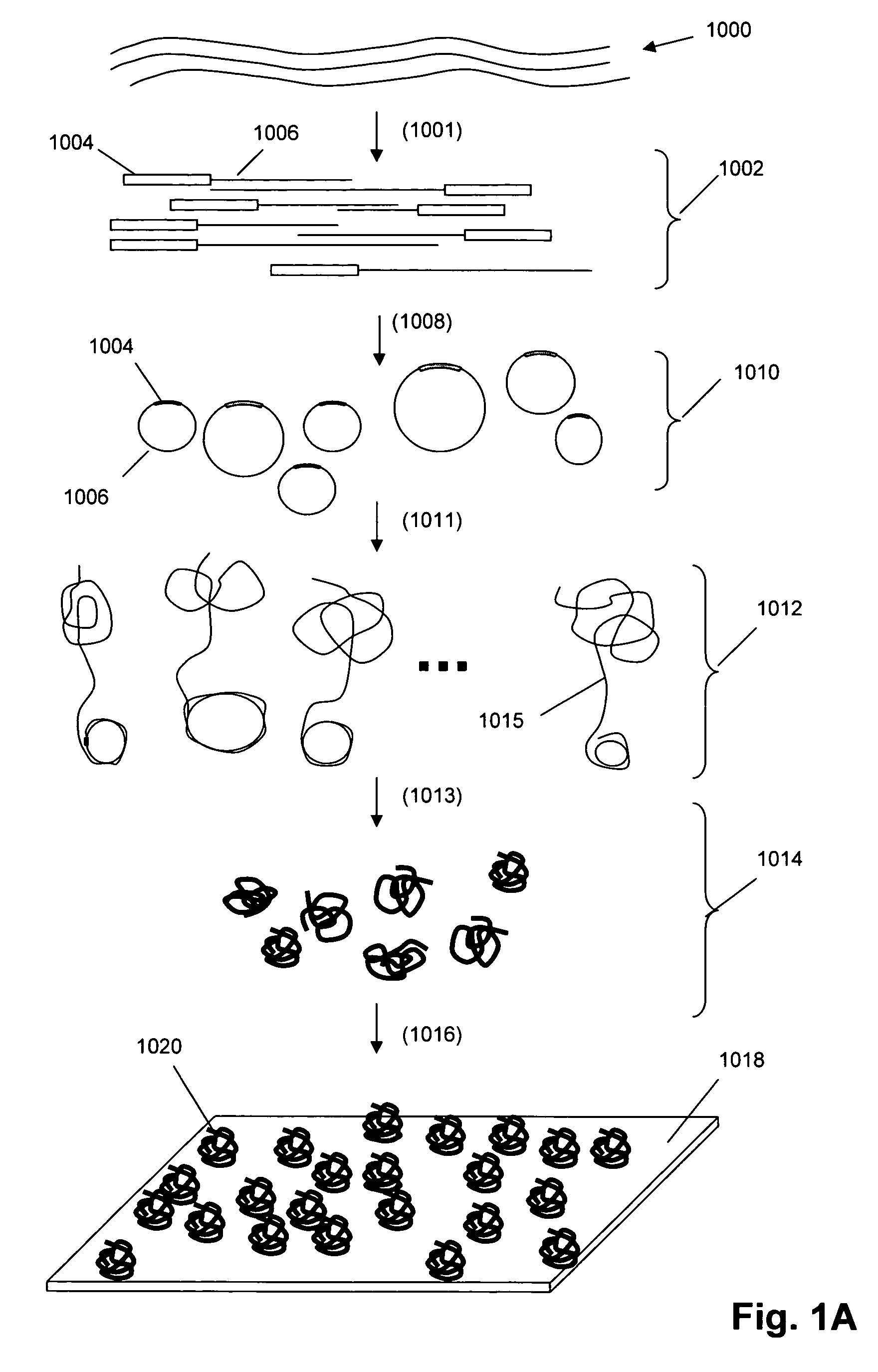
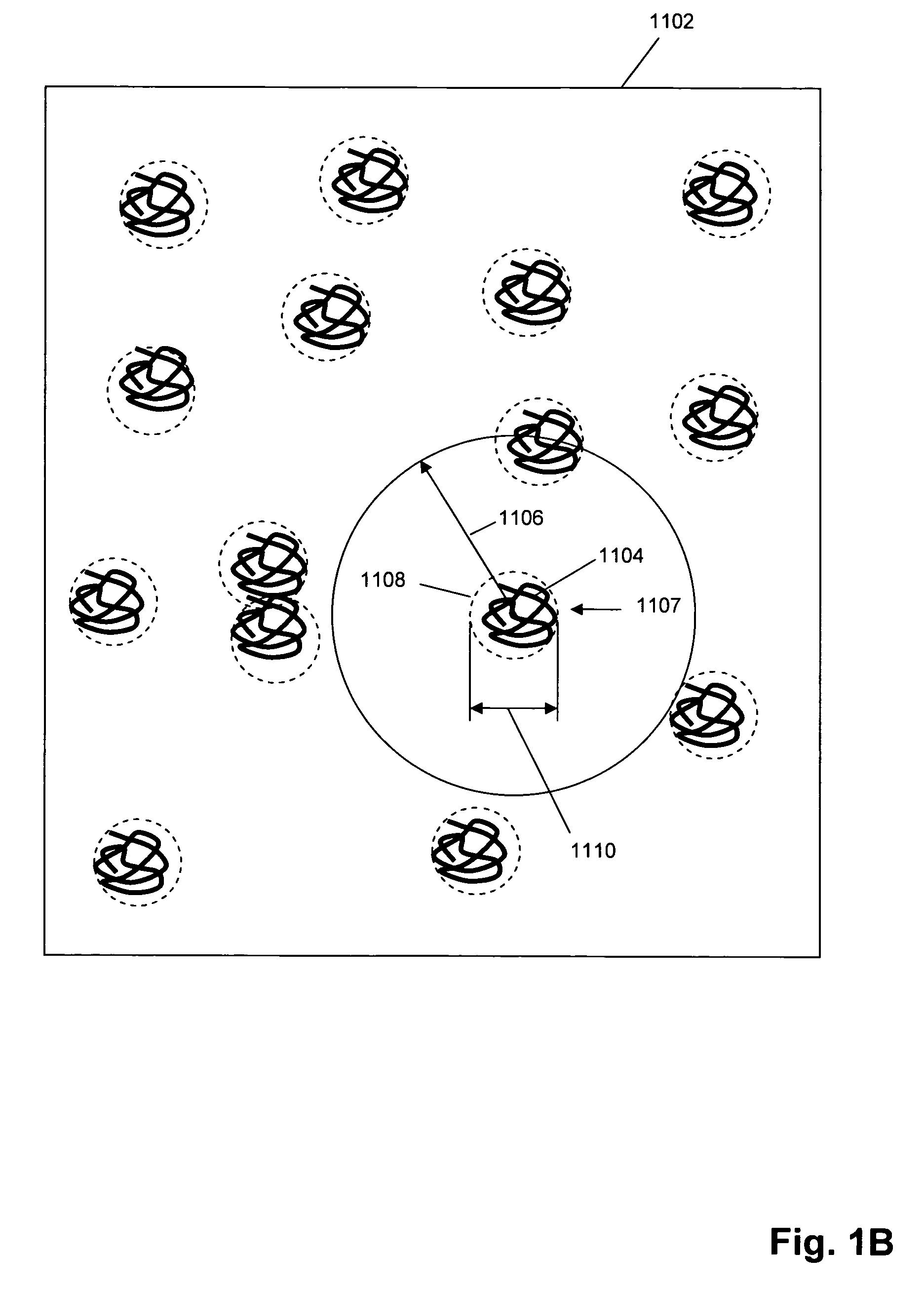
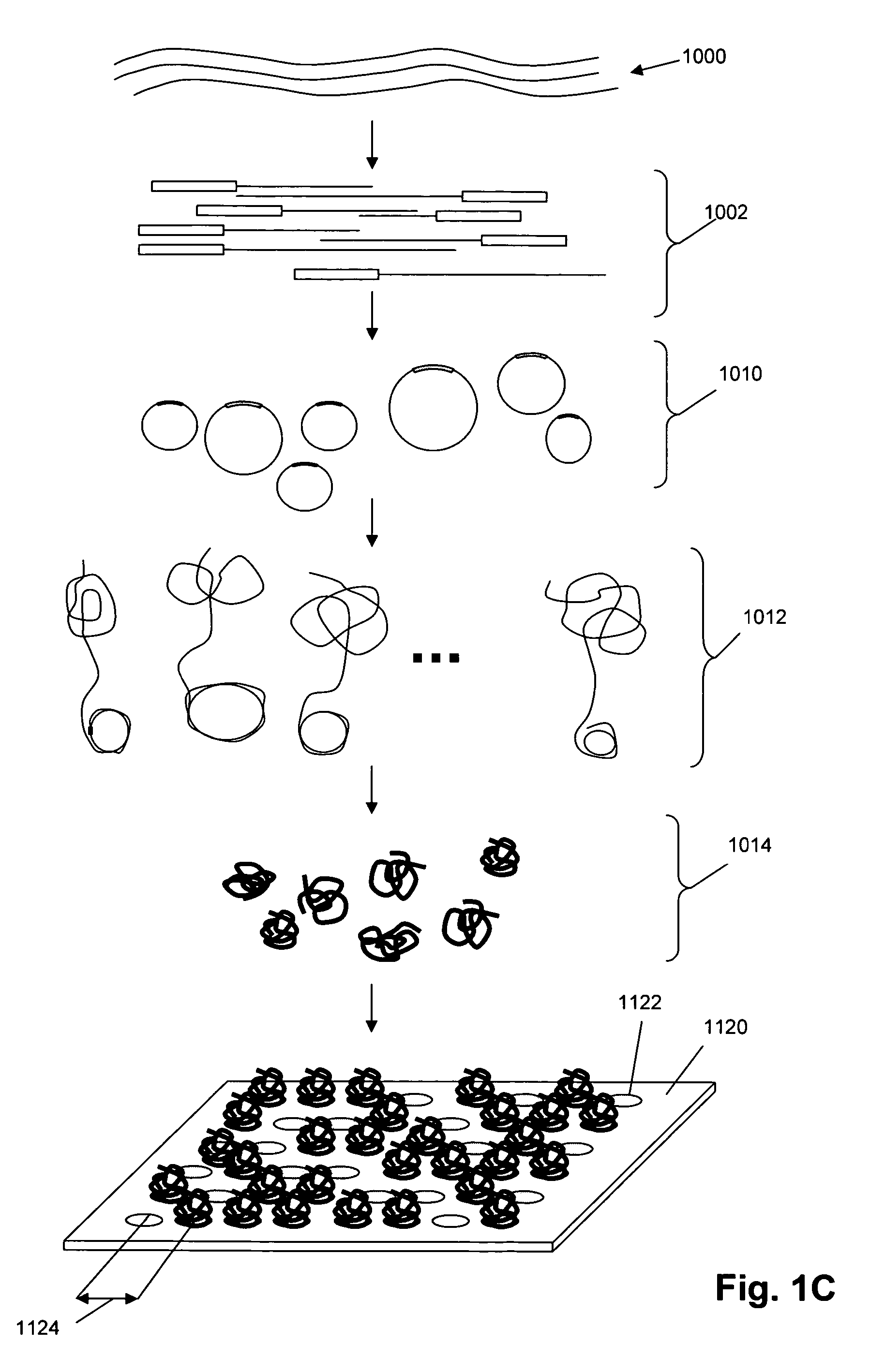
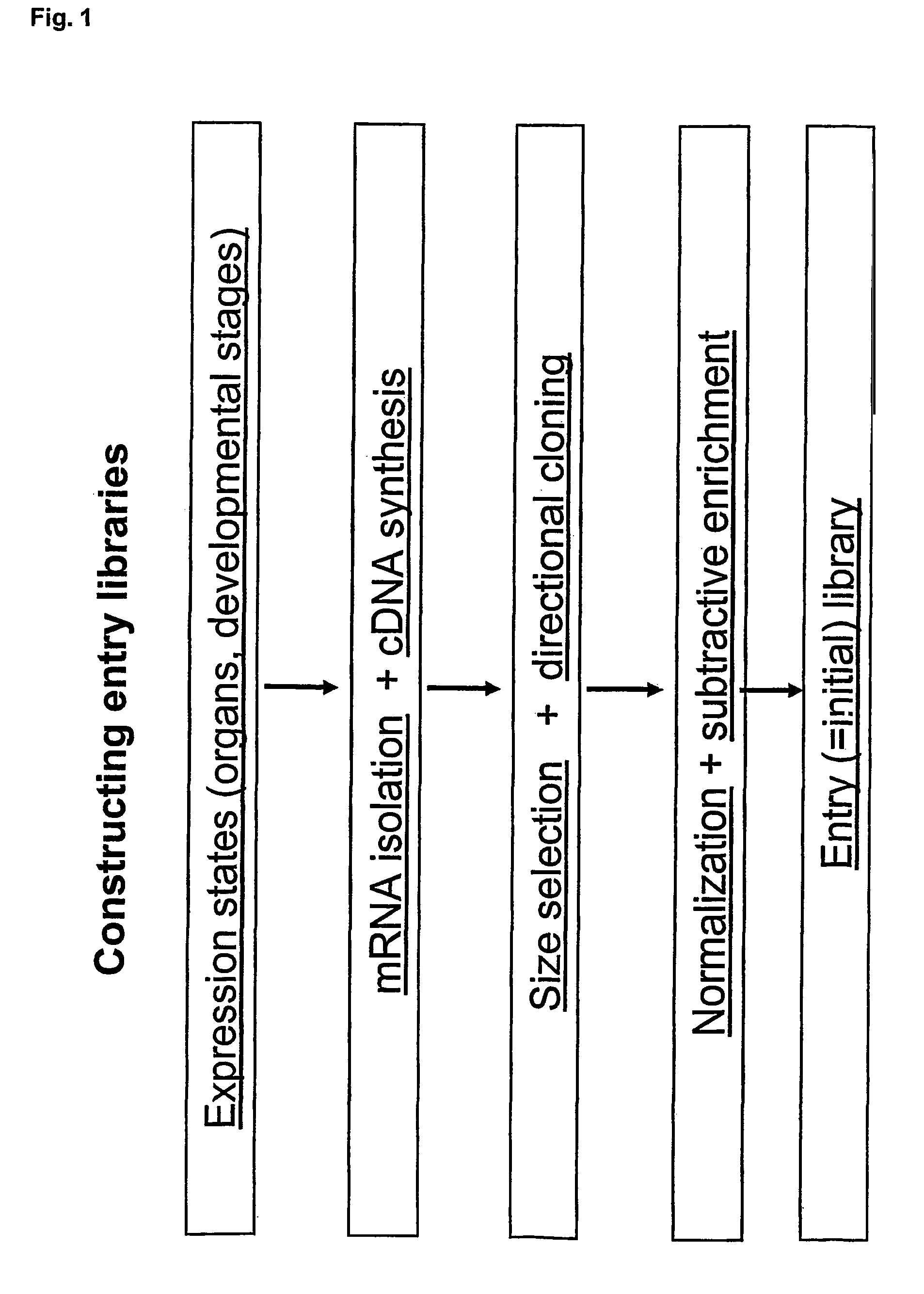
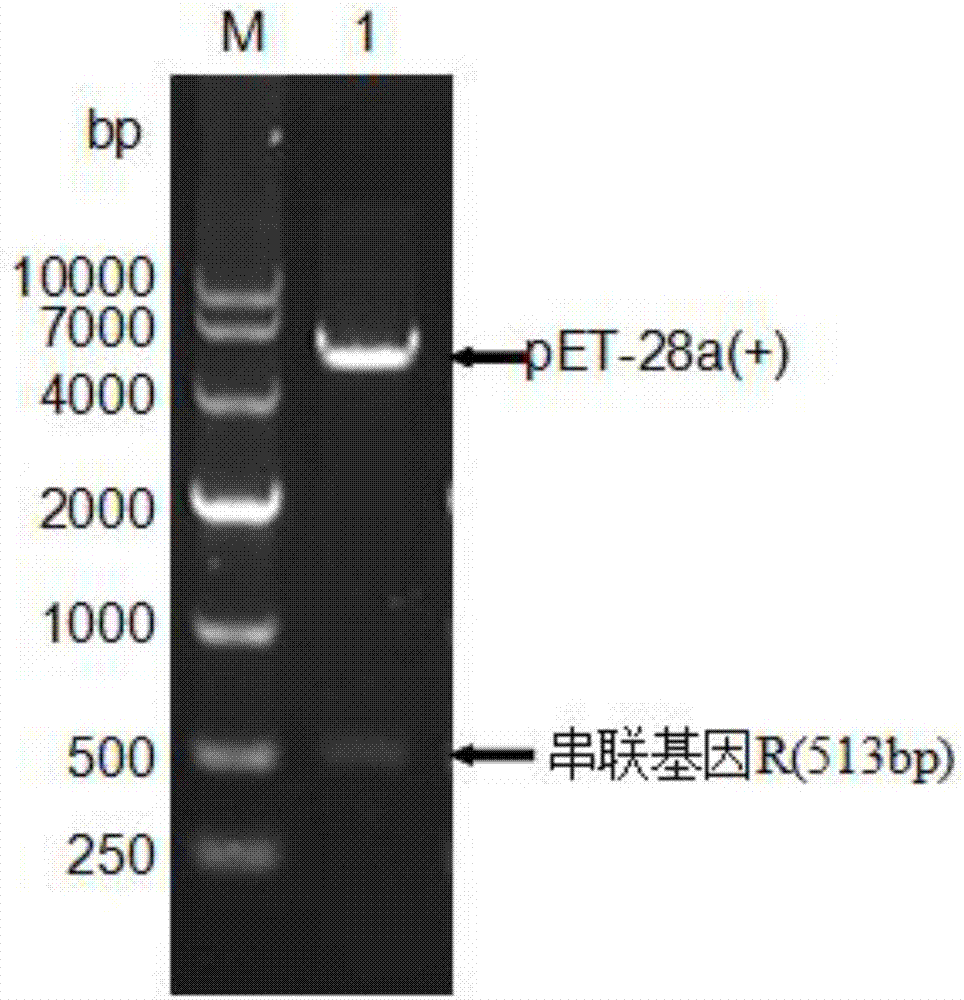
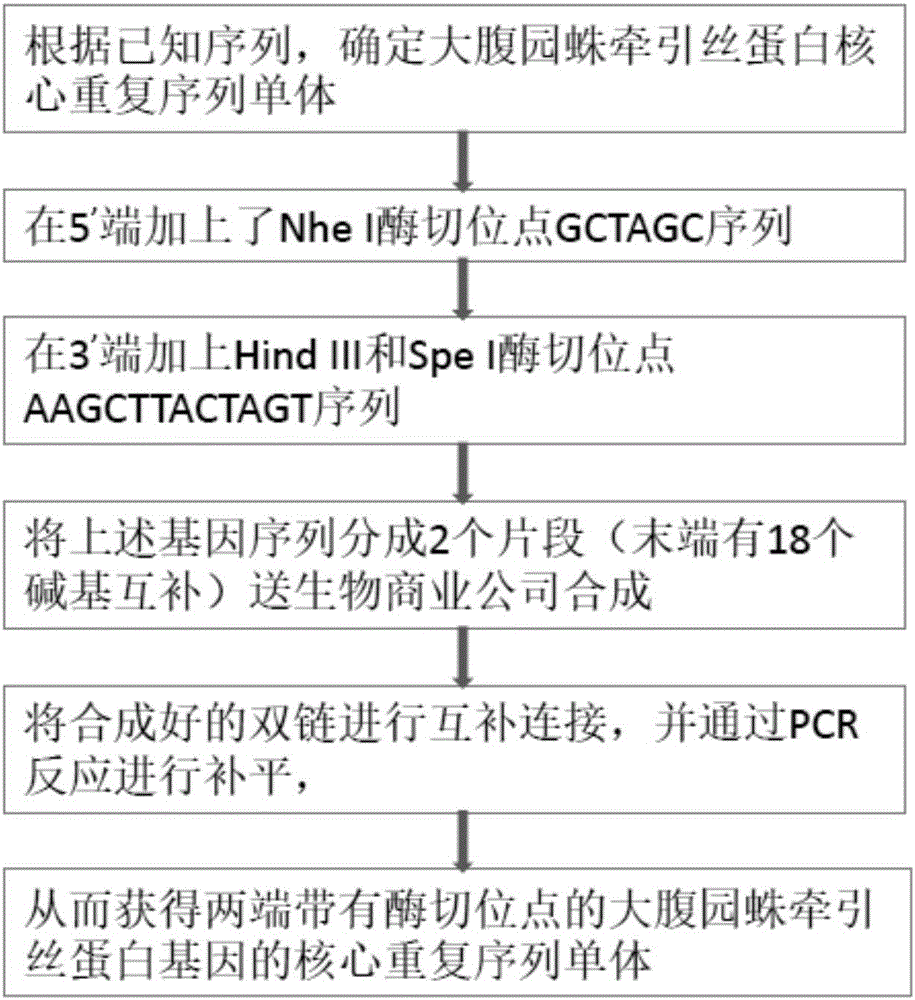
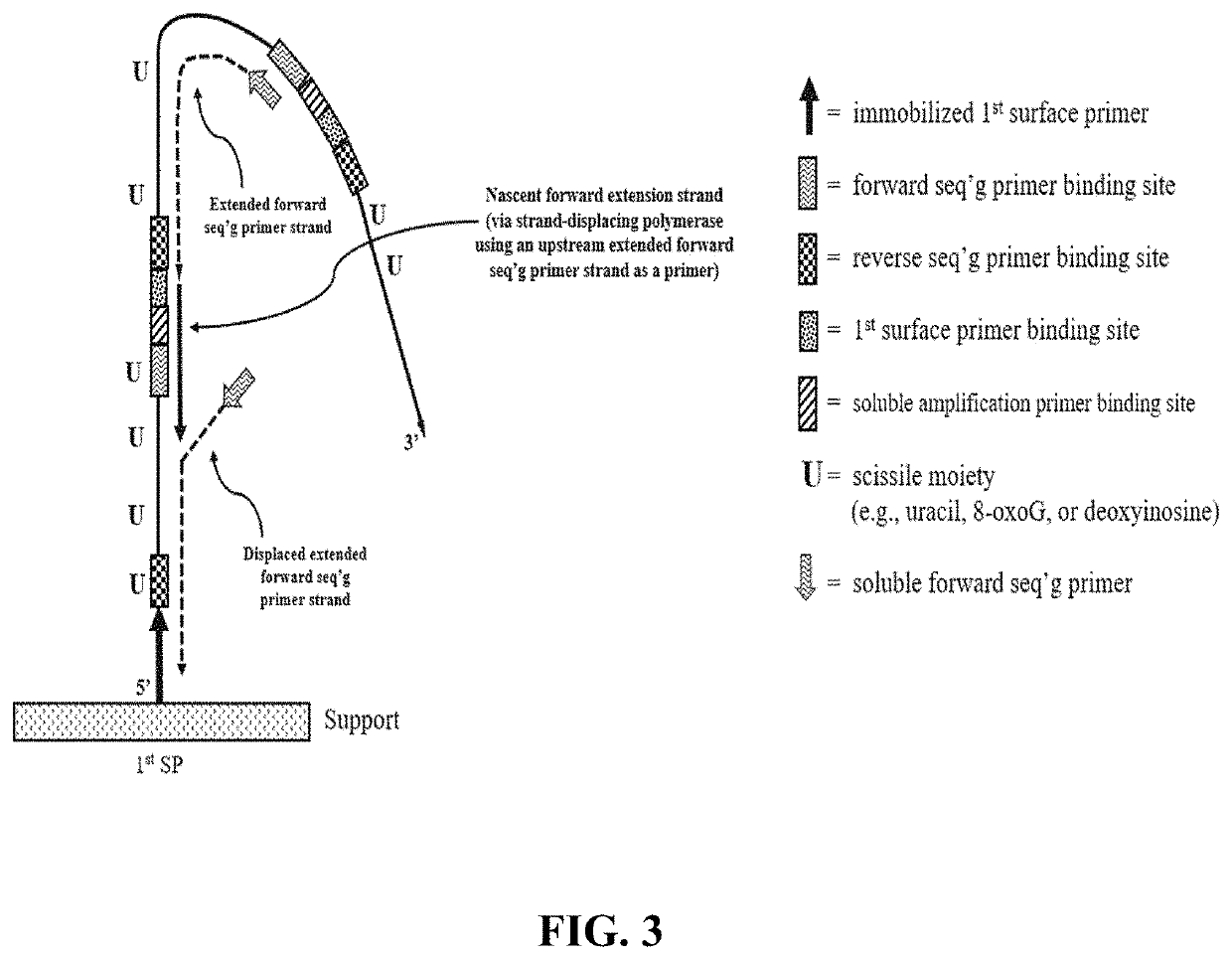
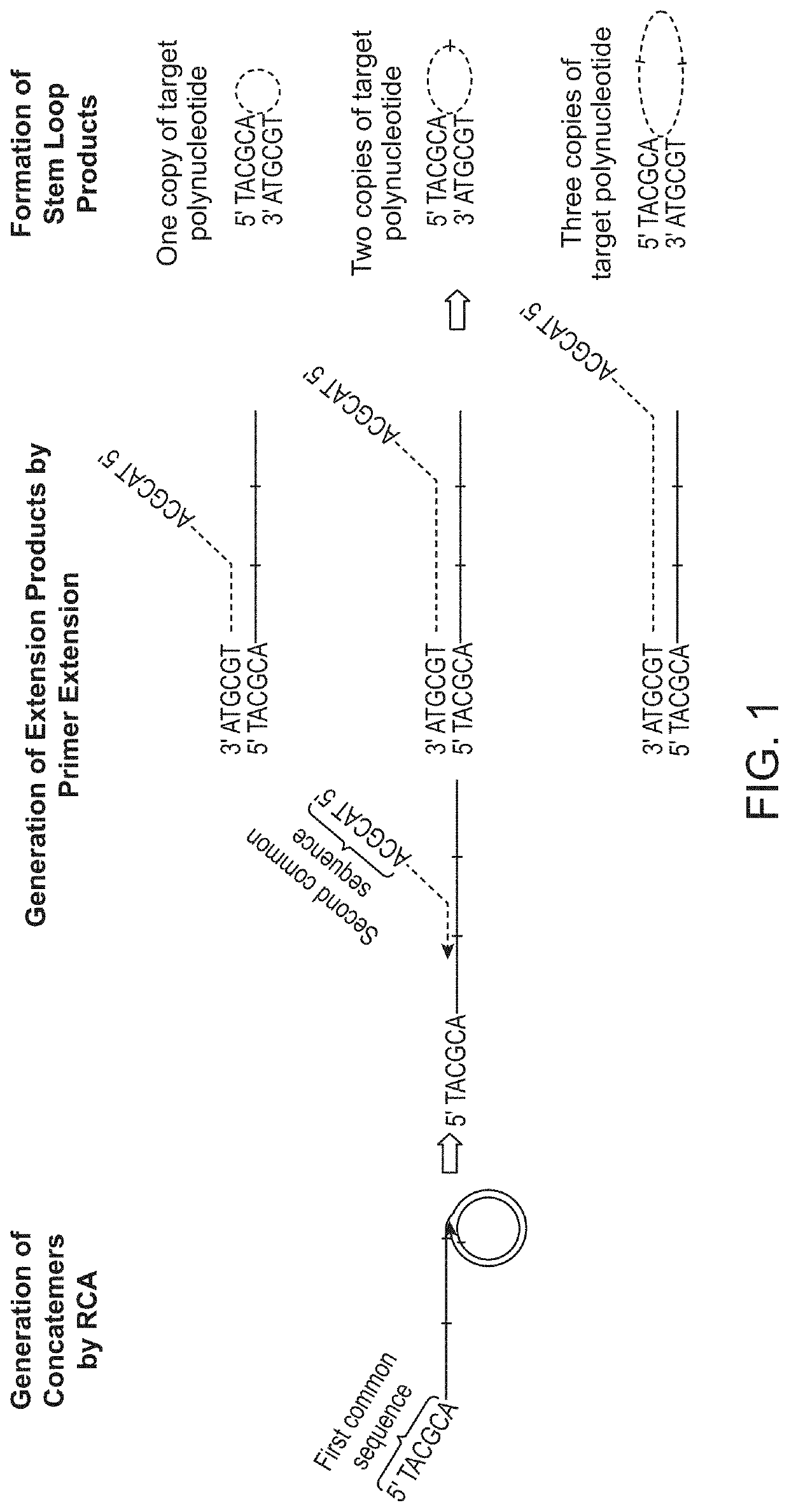
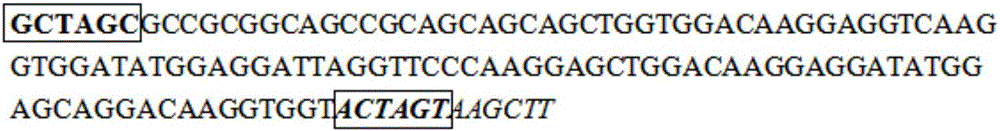Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
83 results about "Concatemer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
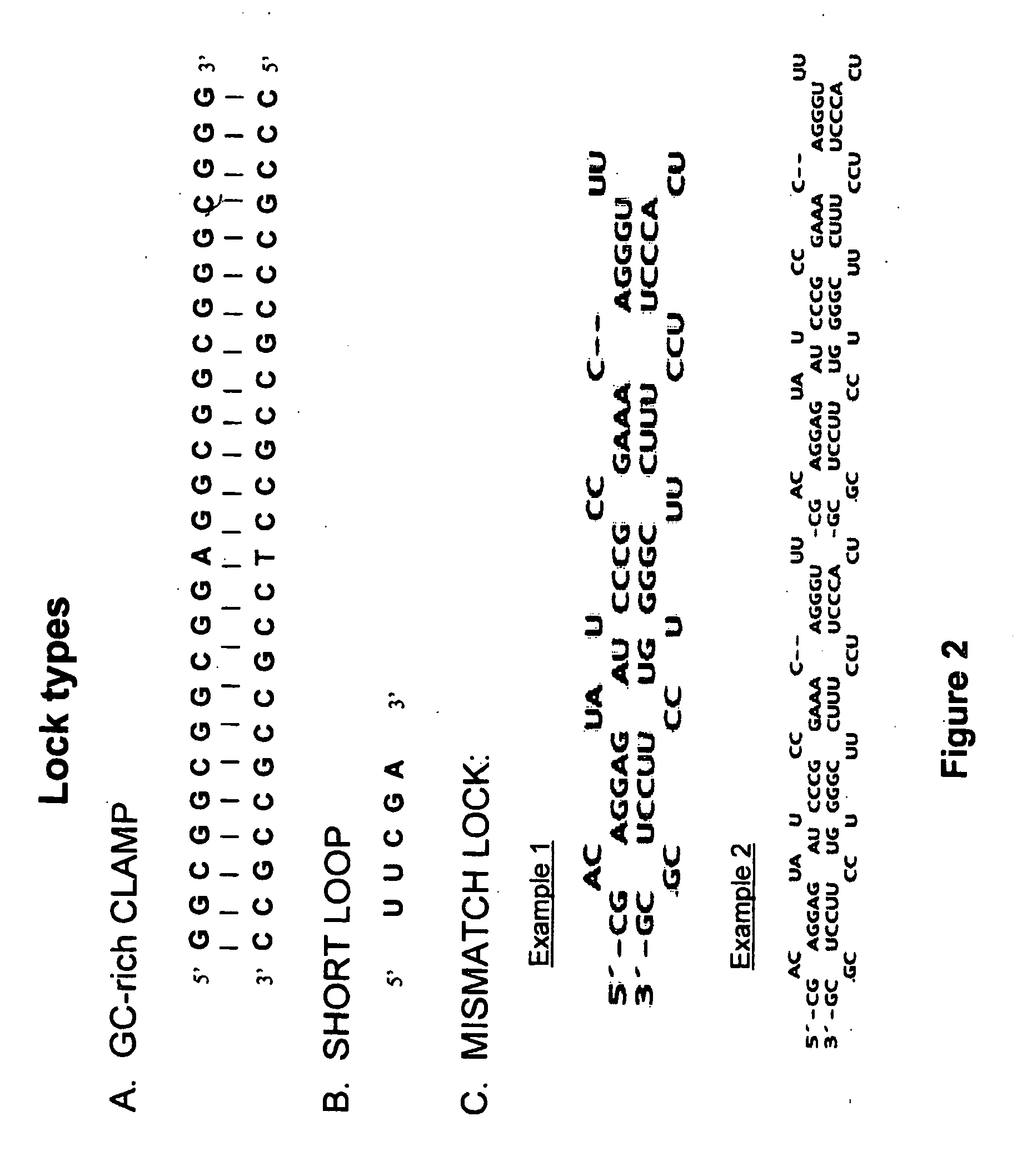
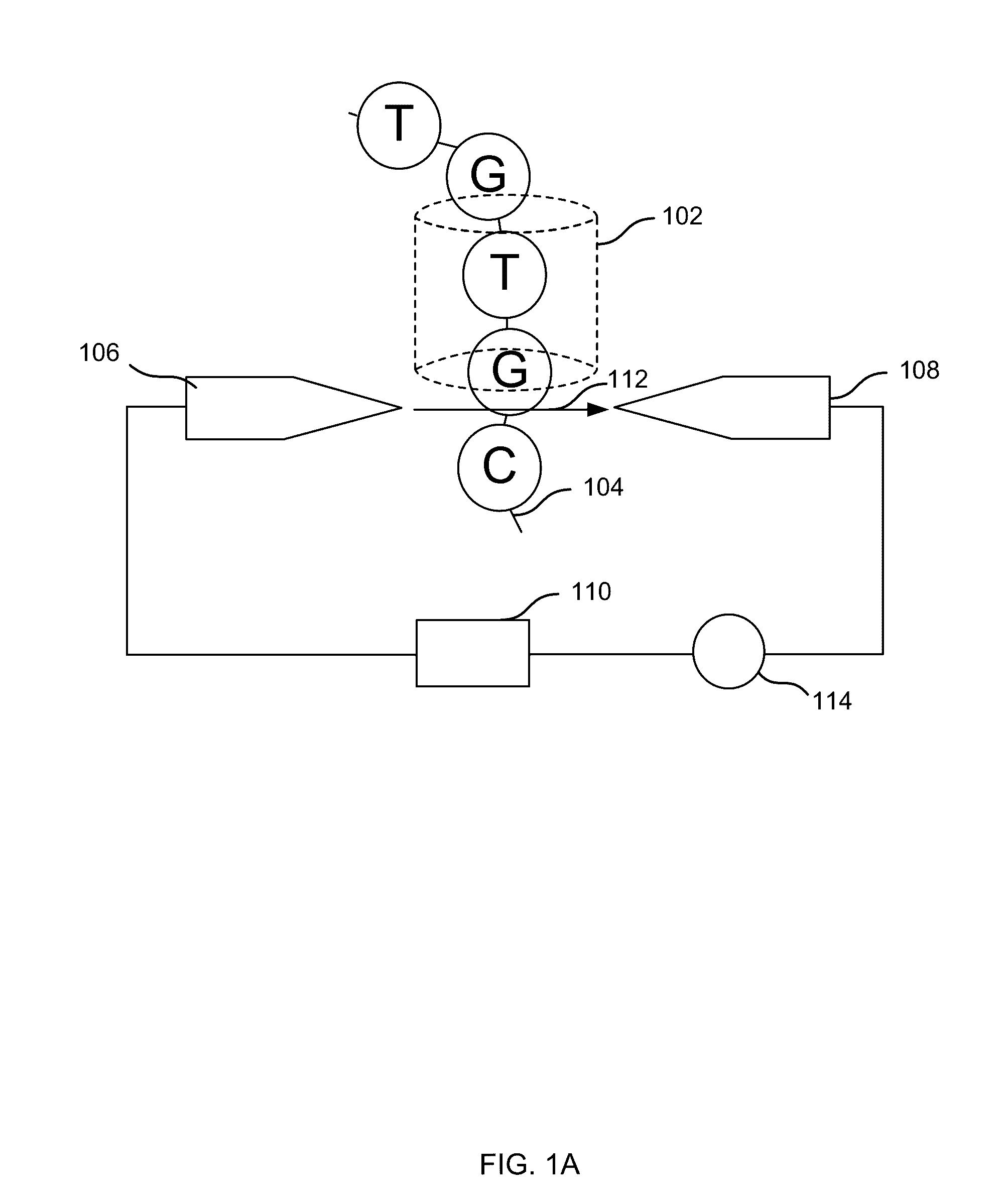
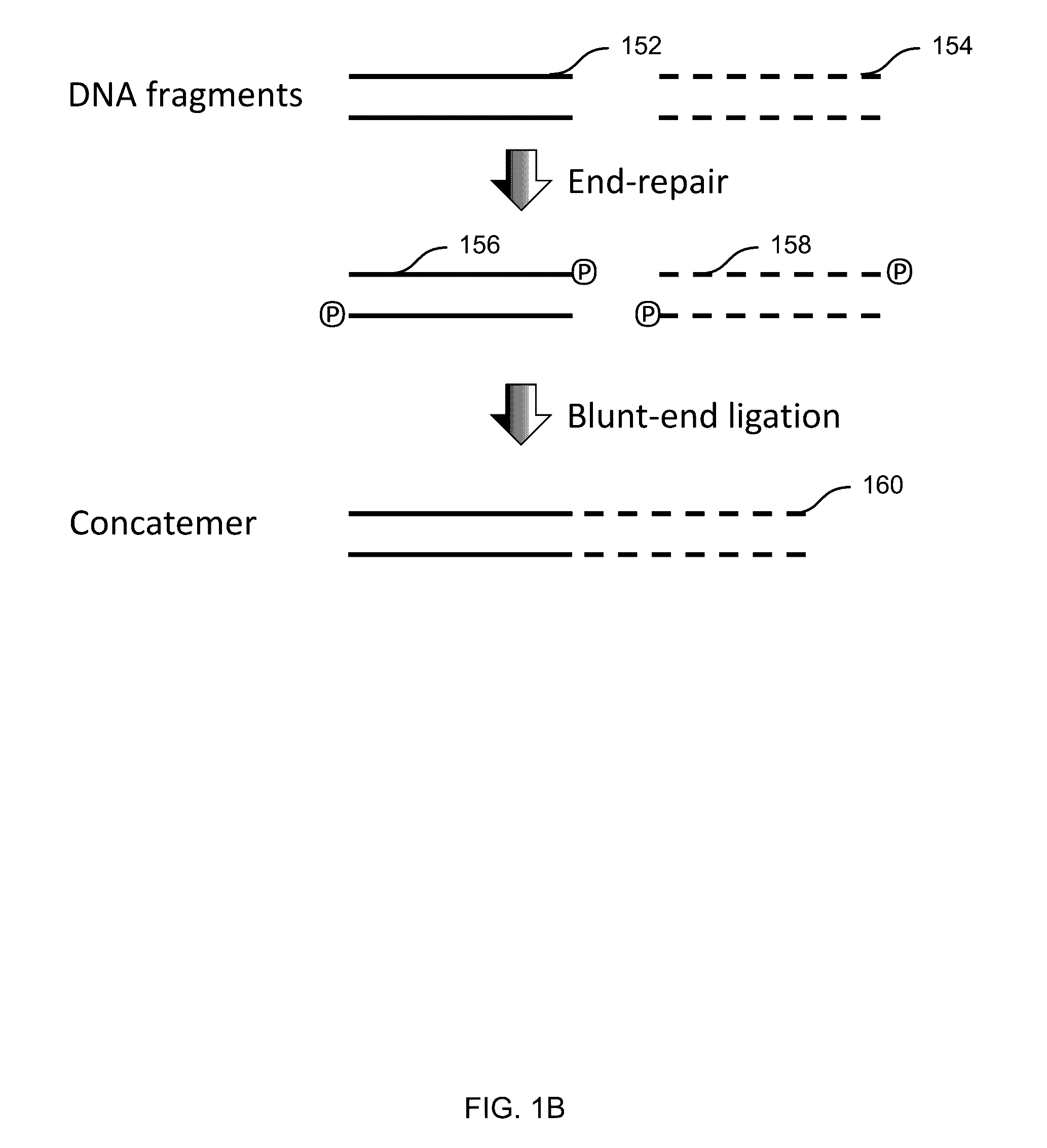
A concatemer is a long continuous DNA molecule that contains multiple copies of the same DNA sequence linked in series. These polymeric molecules are usually copies of an entire genome linked end to end and separated by cos sites (a protein binding nucleotide sequence that occurs once in each copy of the genome). Concatemers are frequently the result of rolling circle replication, and may be seen in the late stage of bacterial infection by phages. As an example, if the genes in the phage DNA are arranged ABC, then in a concatemer the genes would be ABCABCABCABC and so on. They are further broken by ribozymes.
Single molecule arrays for genetic and chemical analysis
ActiveUS20070099208A1Efficient high resolution analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanotechImage resolutionRandom array
Random arrays of single molecules are provided for carrying out large scale analyses, particularly of biomolecules, such as genomic DNA, cDNAs, proteins, and the like. In one aspect, arrays of the invention comprise concatemers of DNA fragments that are randomly disposed on a regular array of discrete spaced apart regions, such that substantially all such regions contain no more than a single concatemer. Preferably, such regions have areas substantially less than 1 μm2 and have nearest neighbor distances that permit optical resolution of on the order of 109 single molecules per cm2. Many analytical chemistries can be applied to random arrays of the invention, including sequencing by hybridization chemistries, sequencing by synthesis chemistries, SNP detection chemistries, and the like, to greatly expand the scale and potential applications of such techniques.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
Concatemers of differentially expressed multiple genes
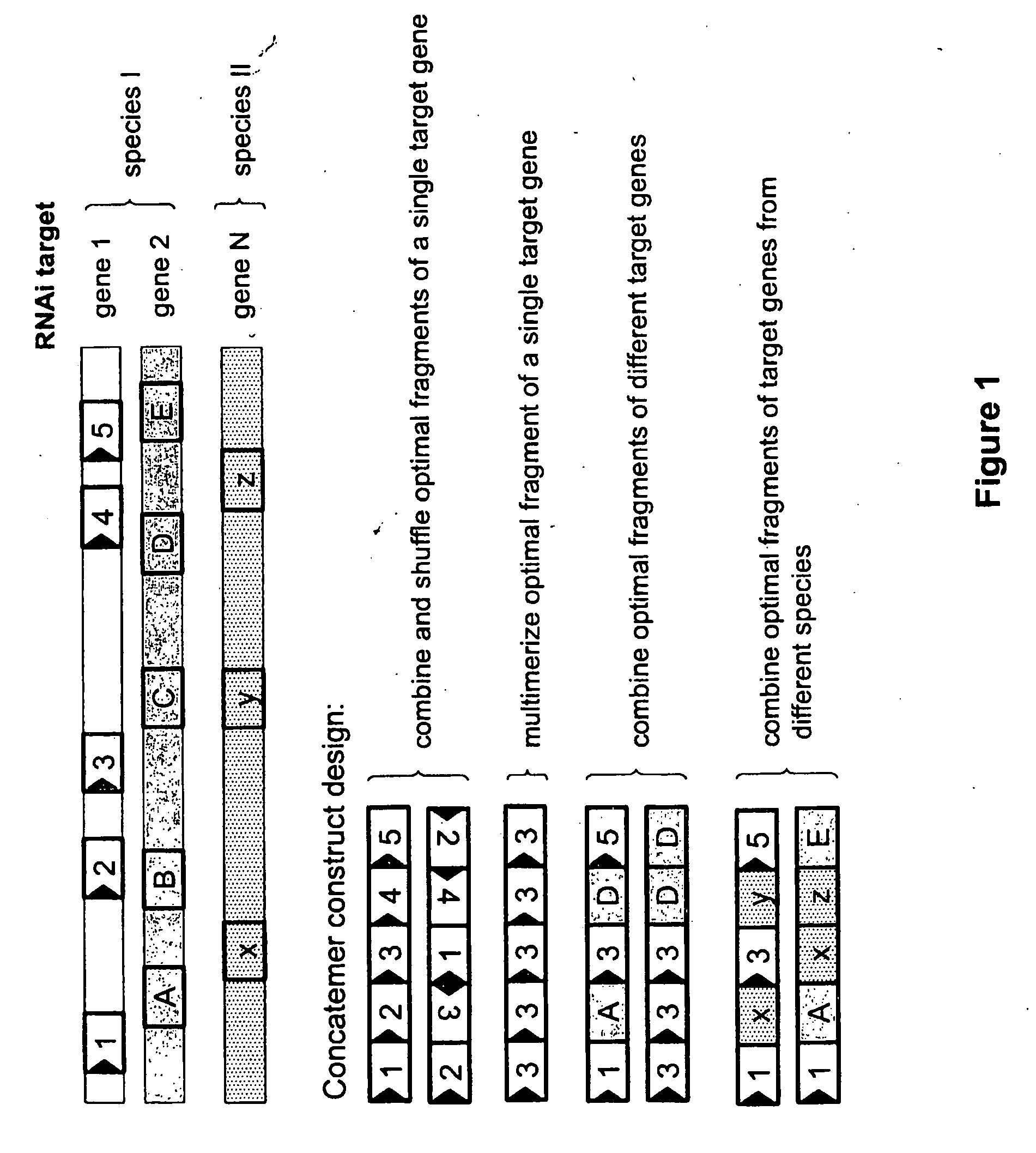
In the present invention are disclosed concatemers of concatenated expression cassettes and vectors that enable the synthesis of such concatemers. The concatemer comprises in the 5′→3′ direction a cassette of nucleotide sequence of the general formula [rs2-SP-PR-X-TR-SP-rs1]n wherein rs1 and rs2 together denote a functional restriction site, SP individually denotes a spacer of at least two nucleotide bases, PR denotes a promoter, capable of functioning in a cell, X denotes an expressible nucleotide sequence, TR denotes a terminator, and SP individually denotes a spacer of at least two nucleotide bases, and n> / =2, and wherein at least a first cassette is different from a second cassette. The main purpose of these concatemers is the controllable and co-ordinated expression of large numbers of heterologous genes in a single host. Furthermore, the invention relates to a concatemer of cassettes of nucleotide sequences and a method for preparing the concatemers. In a further aspect, the invention relates to transgenic host cells comprising at least one concatemer according to the invention, as well as to a method for preparing the transgenic host cells. Finally, the invention relates to a vector comprising a cassette of nucleotides, a method for preparing said vector, a nucleotide library comprising at least two primary vectors each comprising a cassette of nucleotides, a method for preparing the library.
Owner:EVOLVA SA
Method for preparing polynucleotides for analysis
Owner:LINGVITAE AS
cDNA amplification for expression profiling
ActiveUS20040180372A1Consistent outputQuick buildMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationRNA analysisOligonucleotide
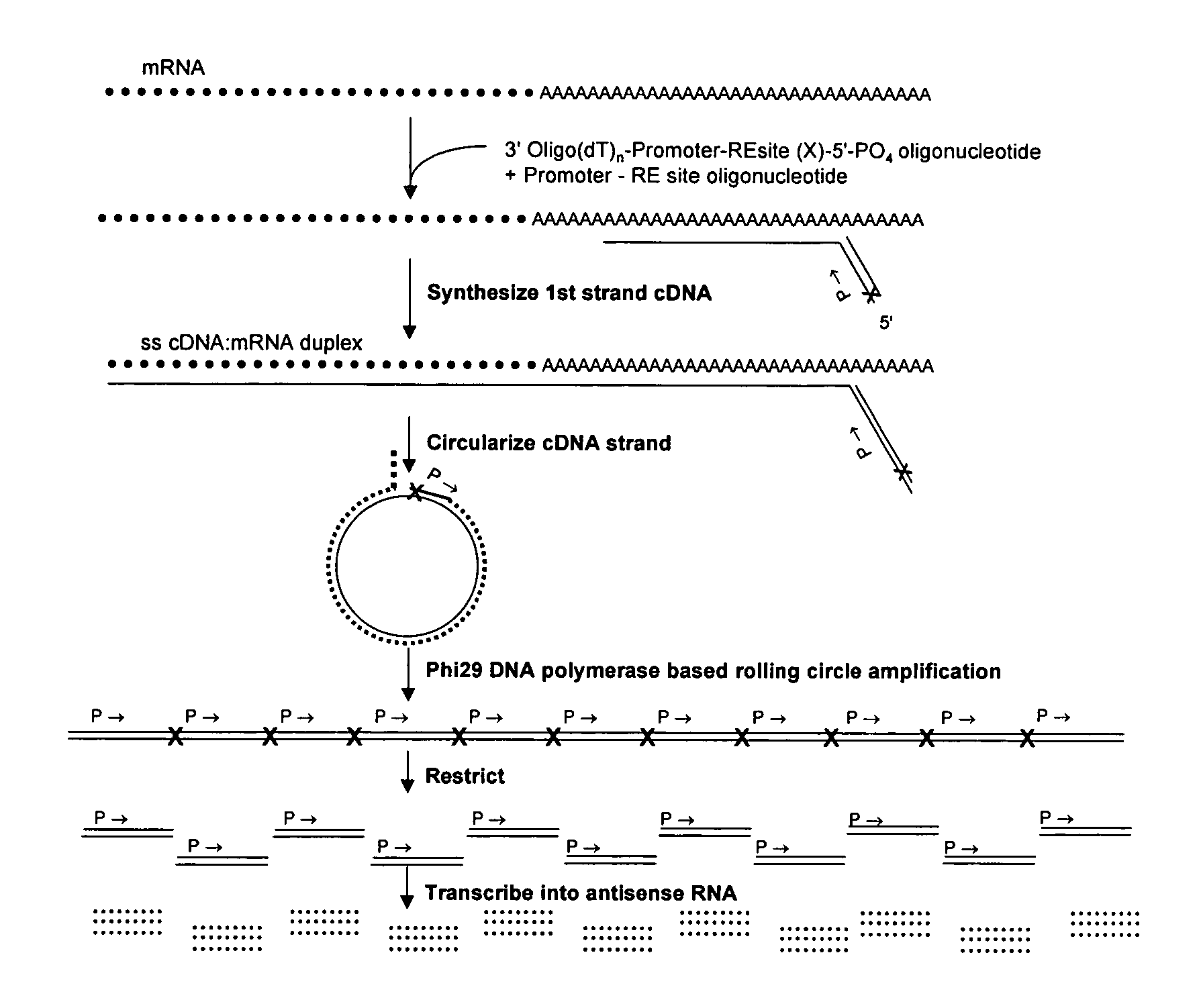
This invention presents a new cDNA amplification method. RNA is first converted to cDNA. The synthesis of cDNA can include a promoter tagged oligonucleotide, and then this cDNA is ligated to form circles (or possibly concatemers). This is then amplified using a Phi29 DNA polymerase based rolling circle and strand displacement amplification. The invention allows for RNA promoter sequences to be attached to the cDNA to facilitate additional amplification through the generation of RNA from the amplified cDNA. The resulting product can then be used to make materials for gene expression studies or other RNA analysis procedures.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Sequencing library, preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN104695027ASmall initial amountShort fragmentNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle strandDna amplification
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
Rna constructs
InactiveUS20090126038A1Effective in gene silencingEffective absorptionOrganic active ingredientsFungiGeneticsPest control
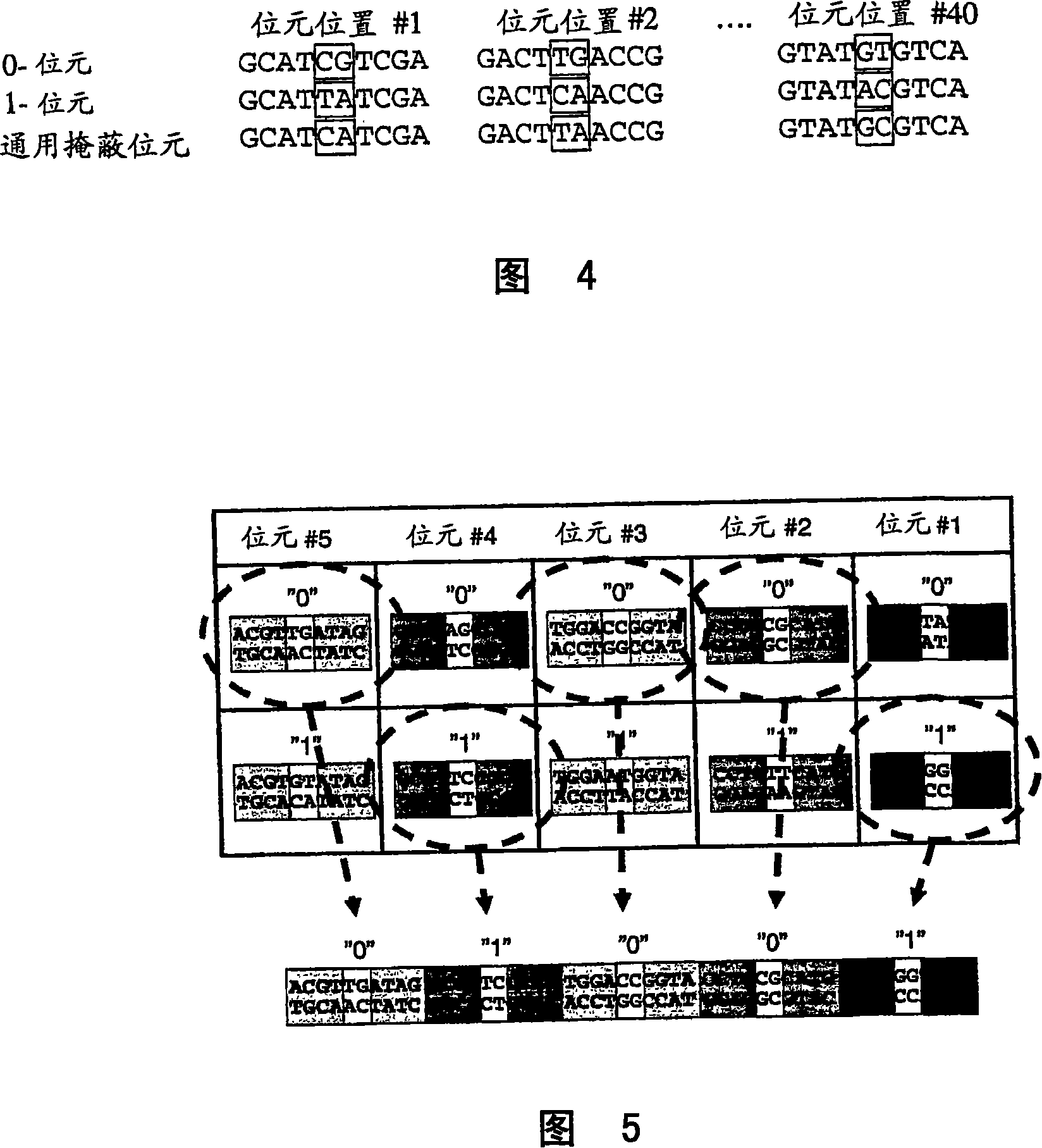
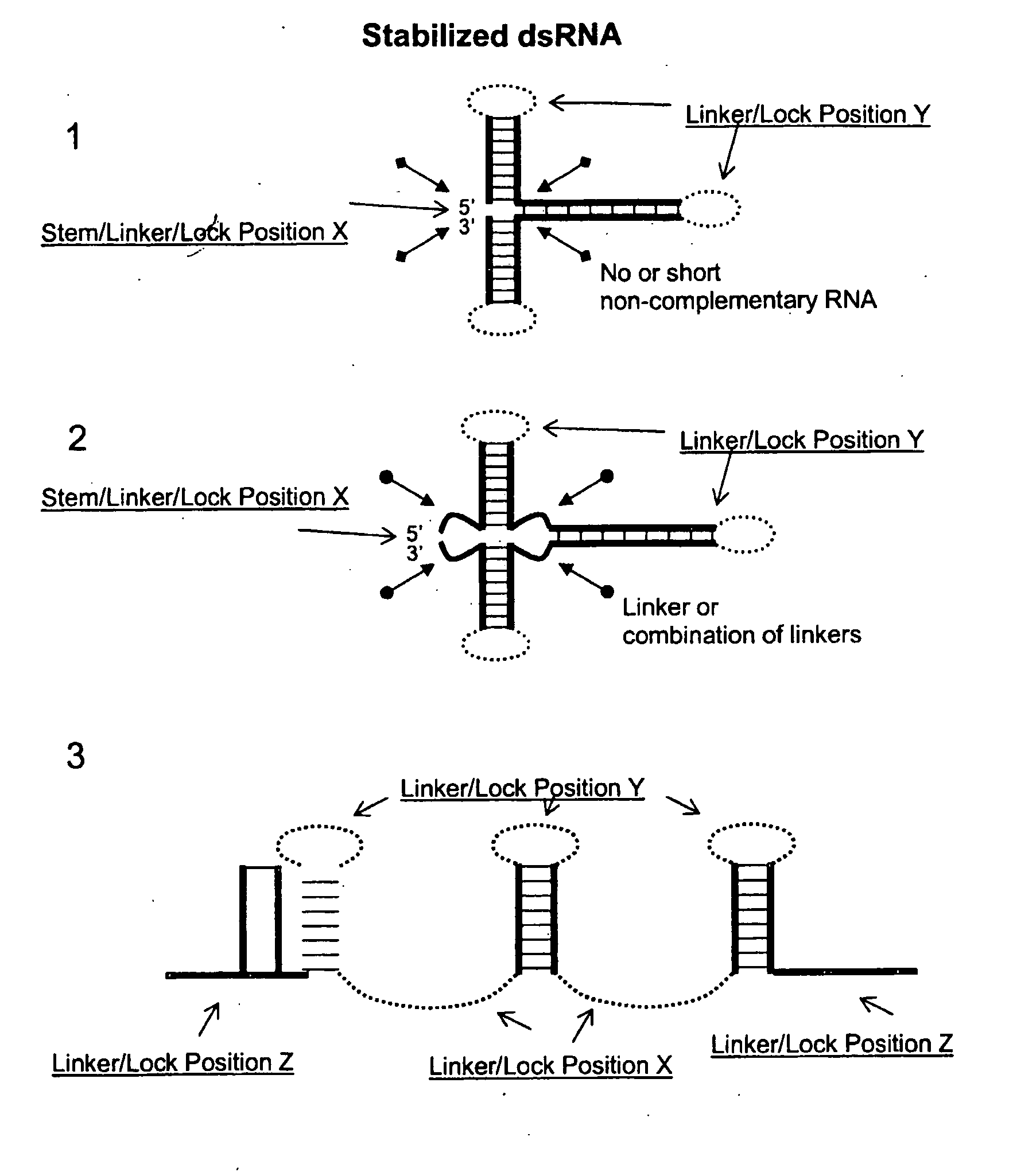
The present invention concerns concatemer and / or stabilized RNA constructs capable of forming dsRNA, optionally comprising a sequence capable of protecting the dsRNA against RNA processing in a host cell. The invention also relates to methods of producing these constructs and to methods for using these constructs. The constructs according to the present invention are particularly useful in plant pest control.
Owner:DEVGEN NV
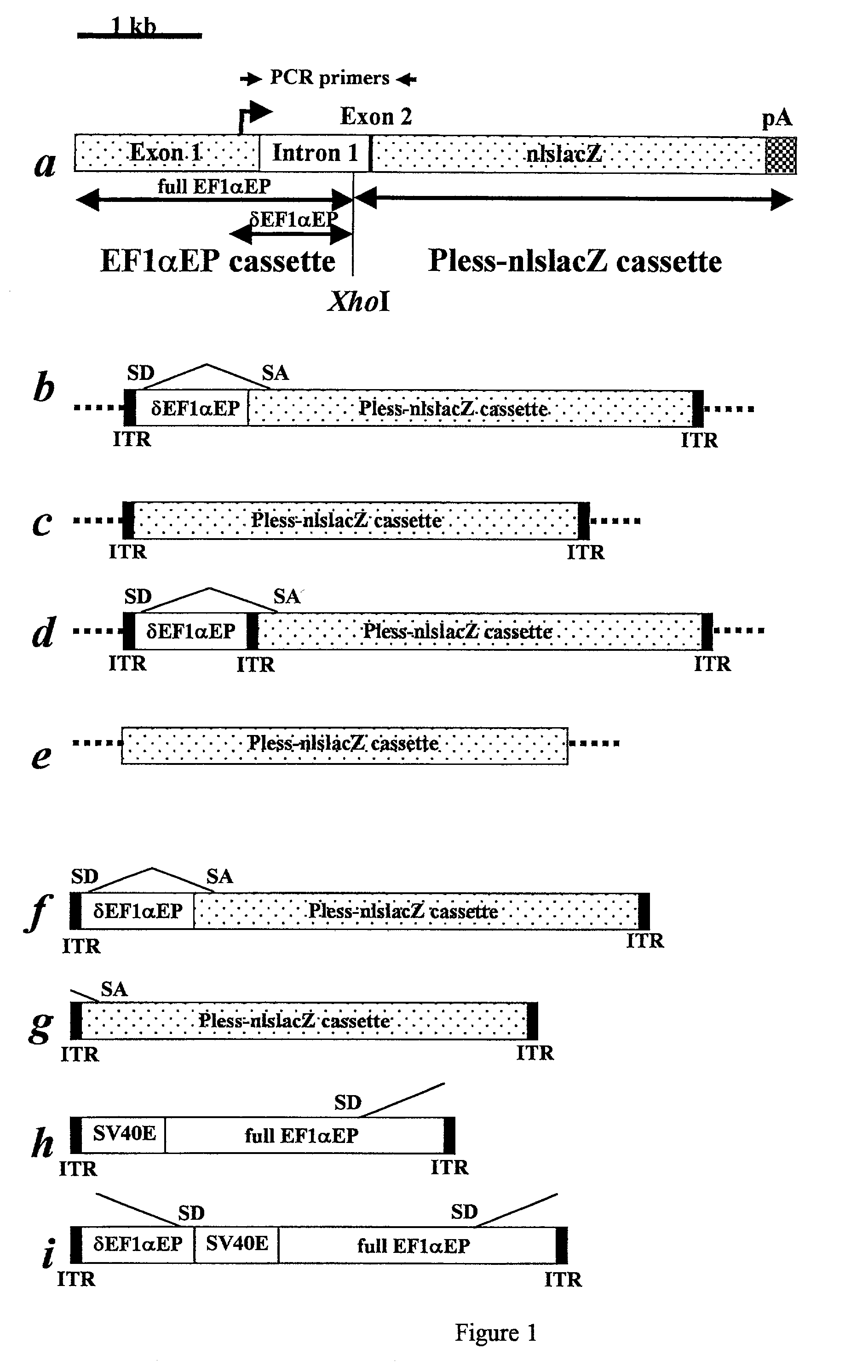
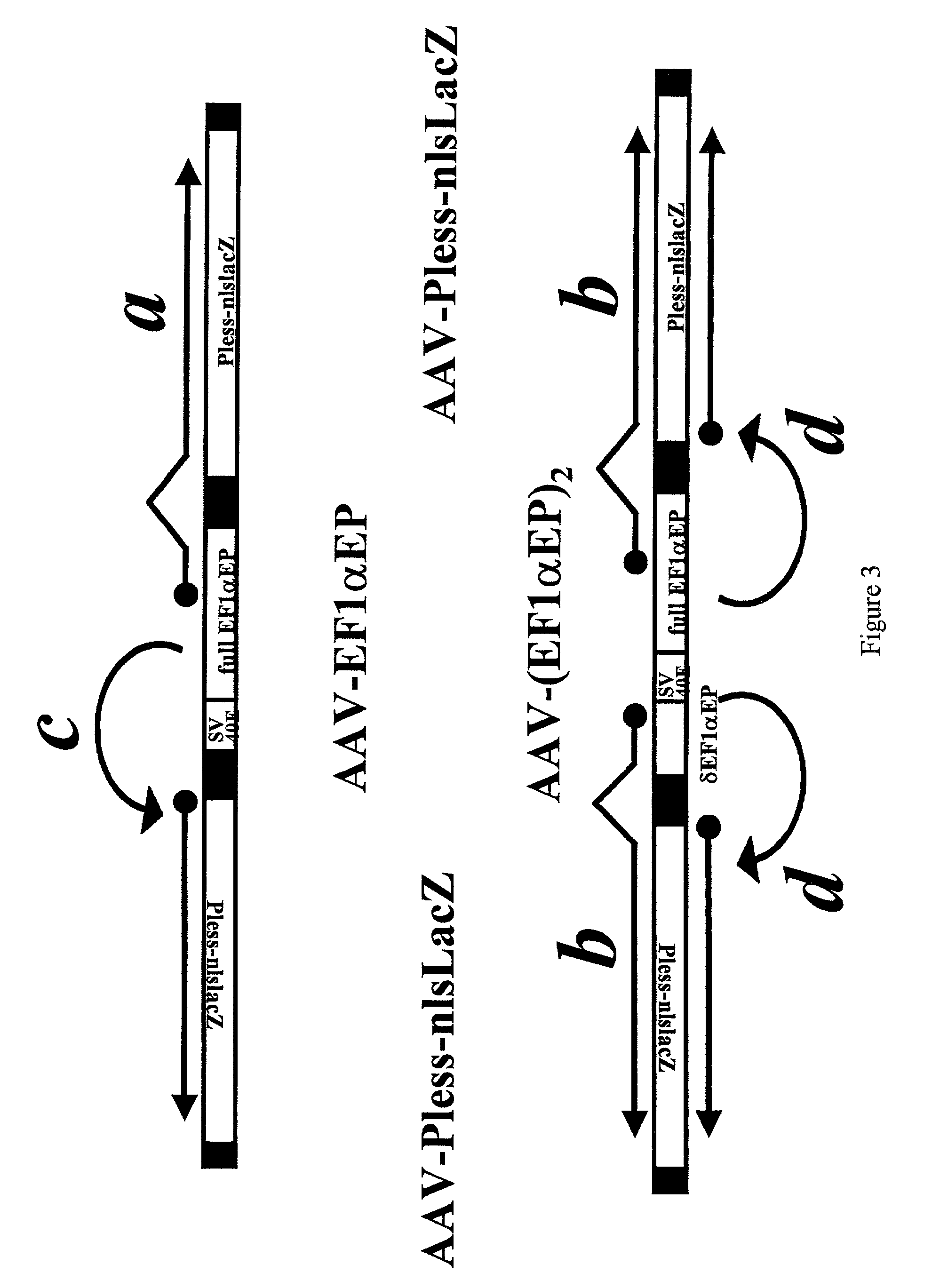
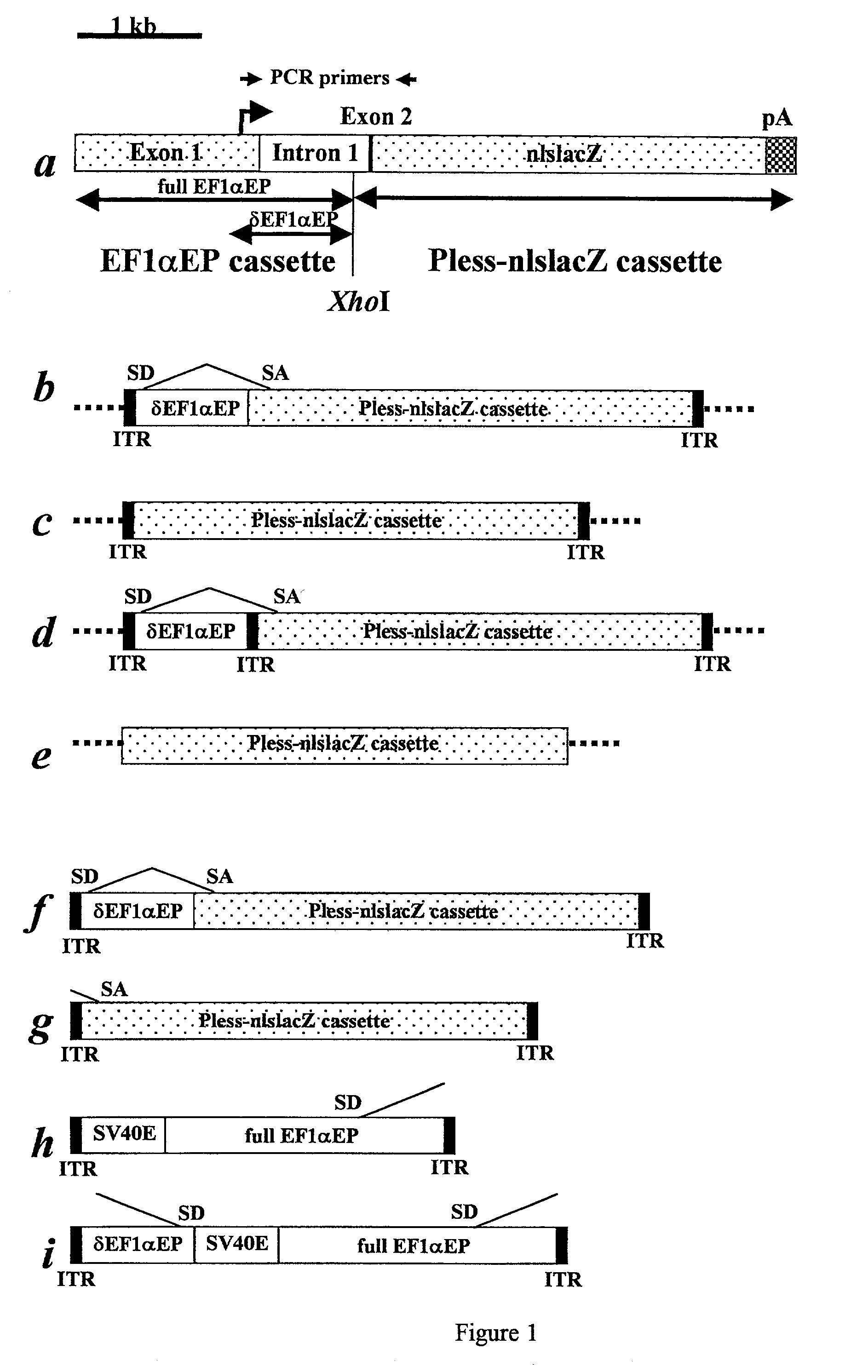
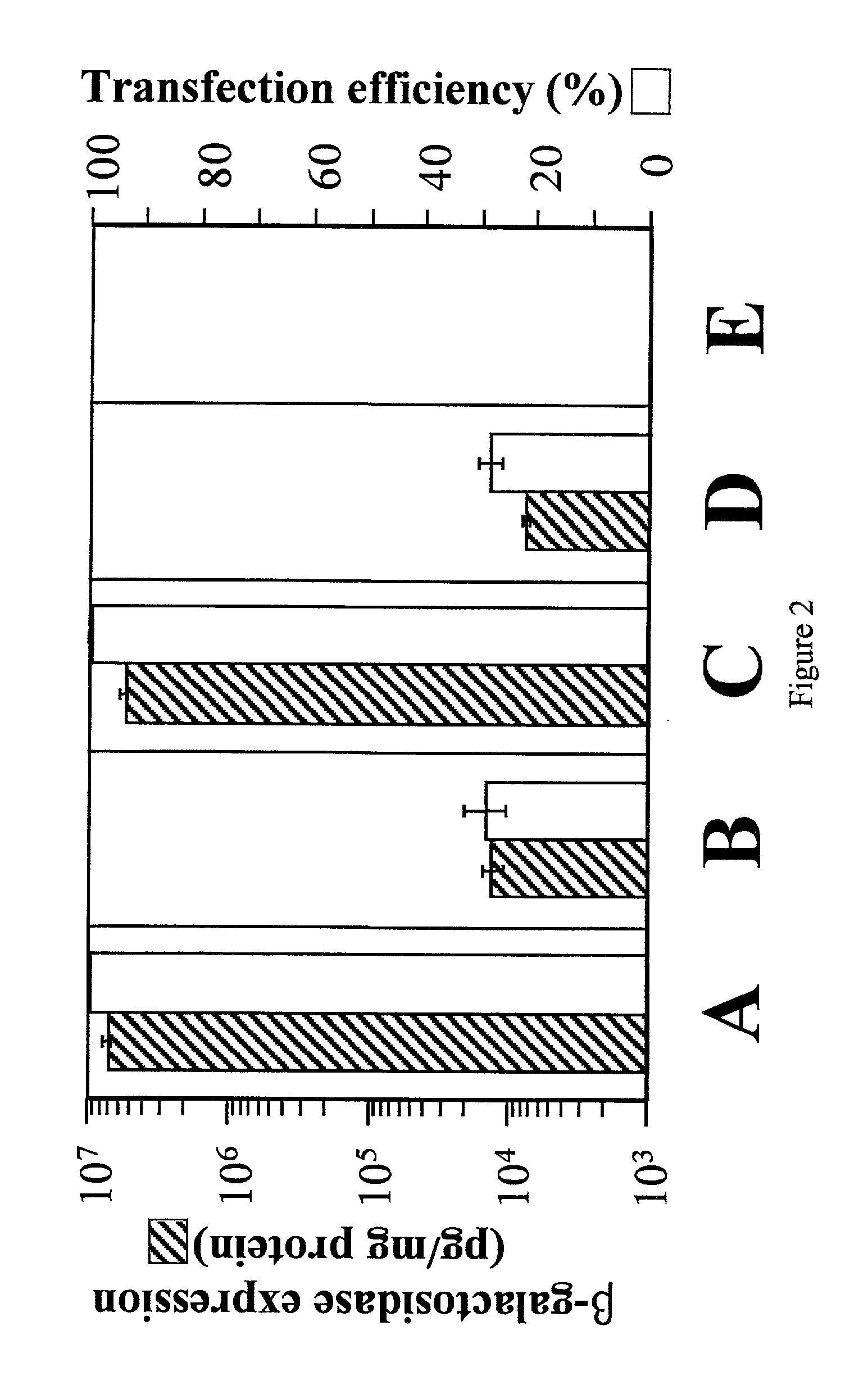
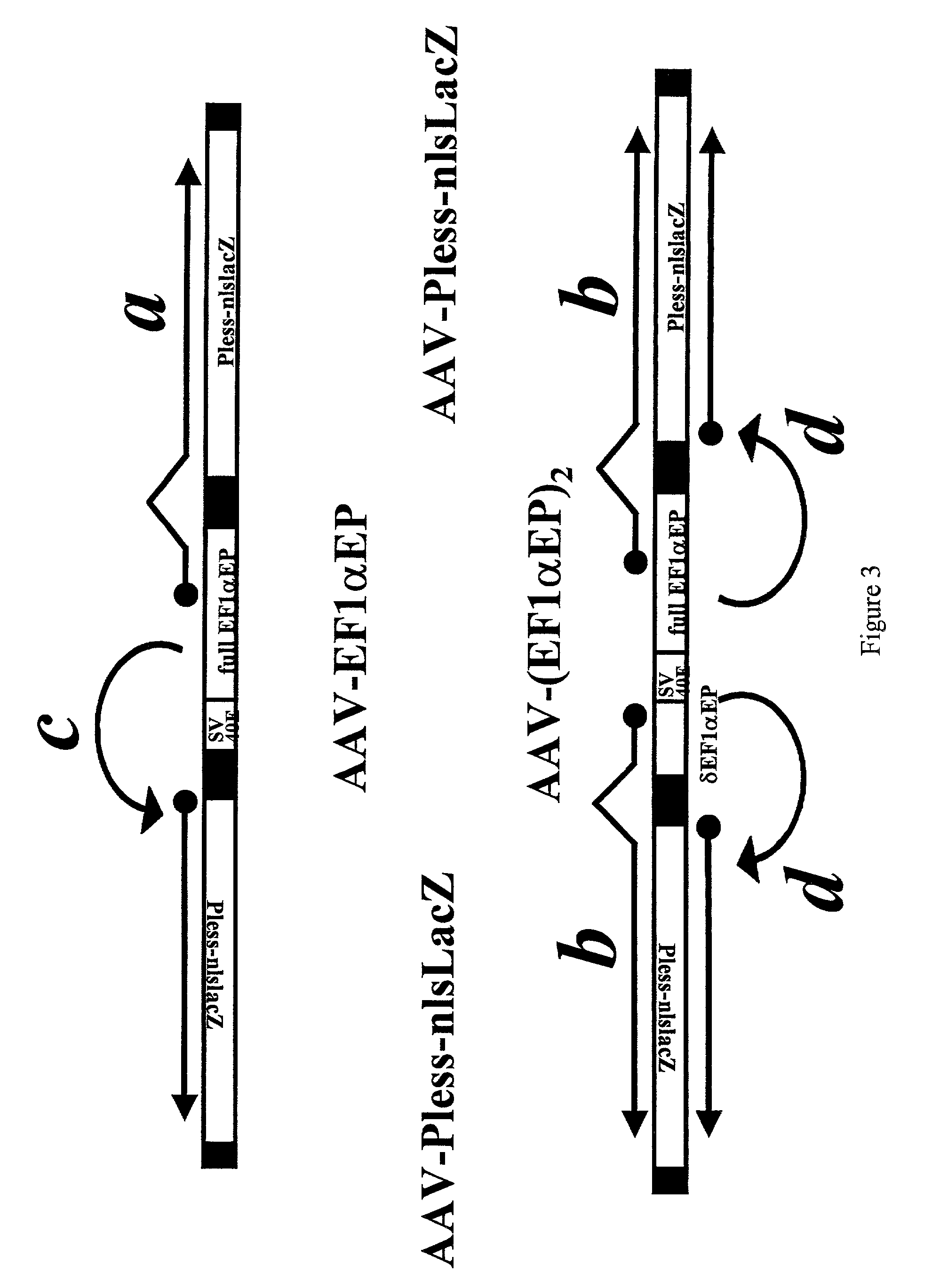
Adeno-associated viral vector-based methods and compositions for introducing an expression cassette into a cell
Methods and compositions are provided for introducing an expression cassette into a cell. In the subject methods, a population of at least two distinct adeno-associated viral particles is provided, where each distinct type of viral particle in the population comprises a different portion of the expression cassette to be introduced into the cell. The target cell is contacted with population of adeno-associated viral vectors under conditions sufficient to produce a hetero-concatemer in the cell, where the hetero-concatemer includes a functional expression cassette having an intron that includes an ITR sequence. Also provided by the subject invention are vector preparations for practicing the subject methods as well as kits for use in producing the vectors employed in the subject methods. The subject methods find use in a variety of different gene transfer applications, including both in vivo and in vitro gene transfer applications, and are particularly suited for use in the transfer of long genes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
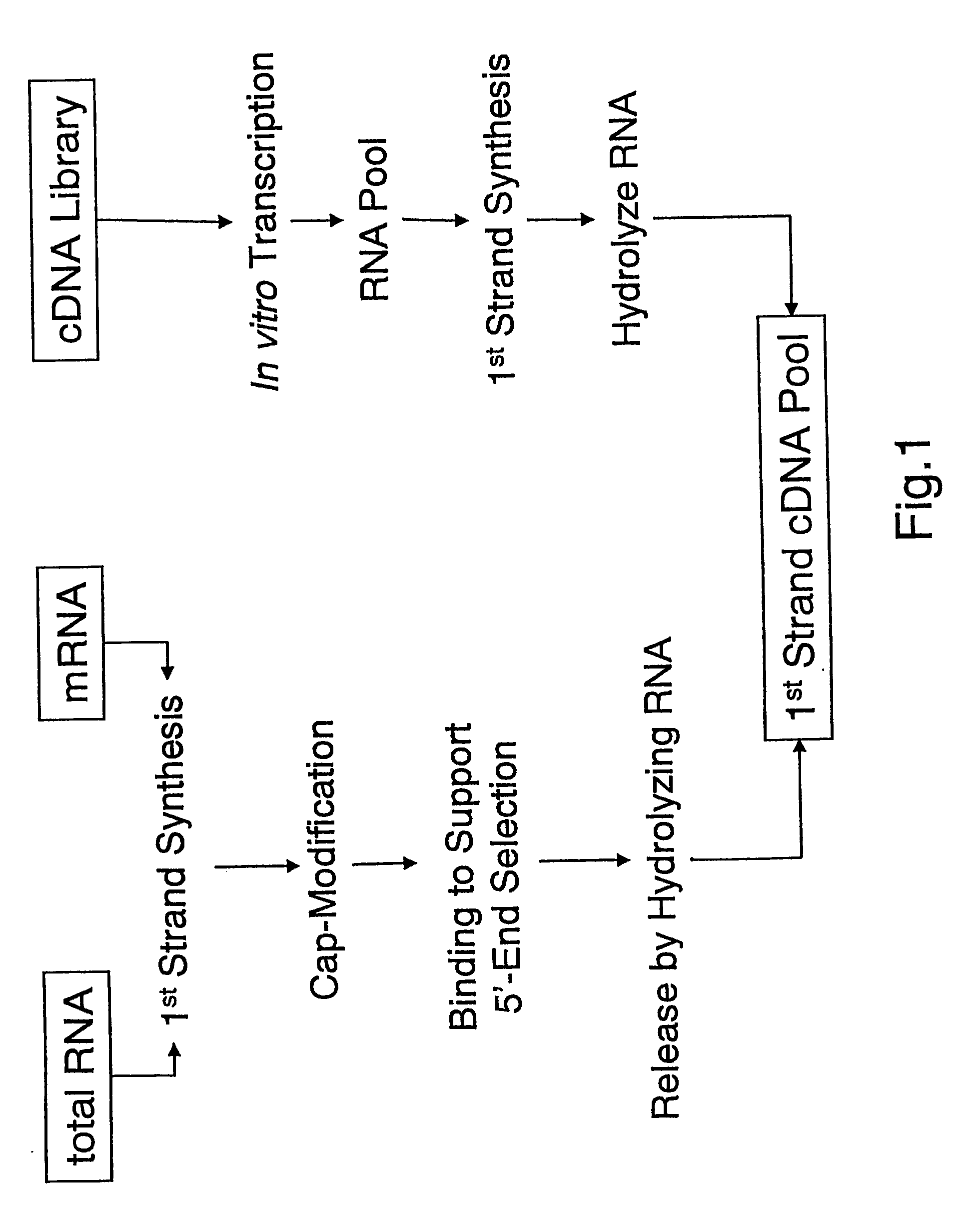
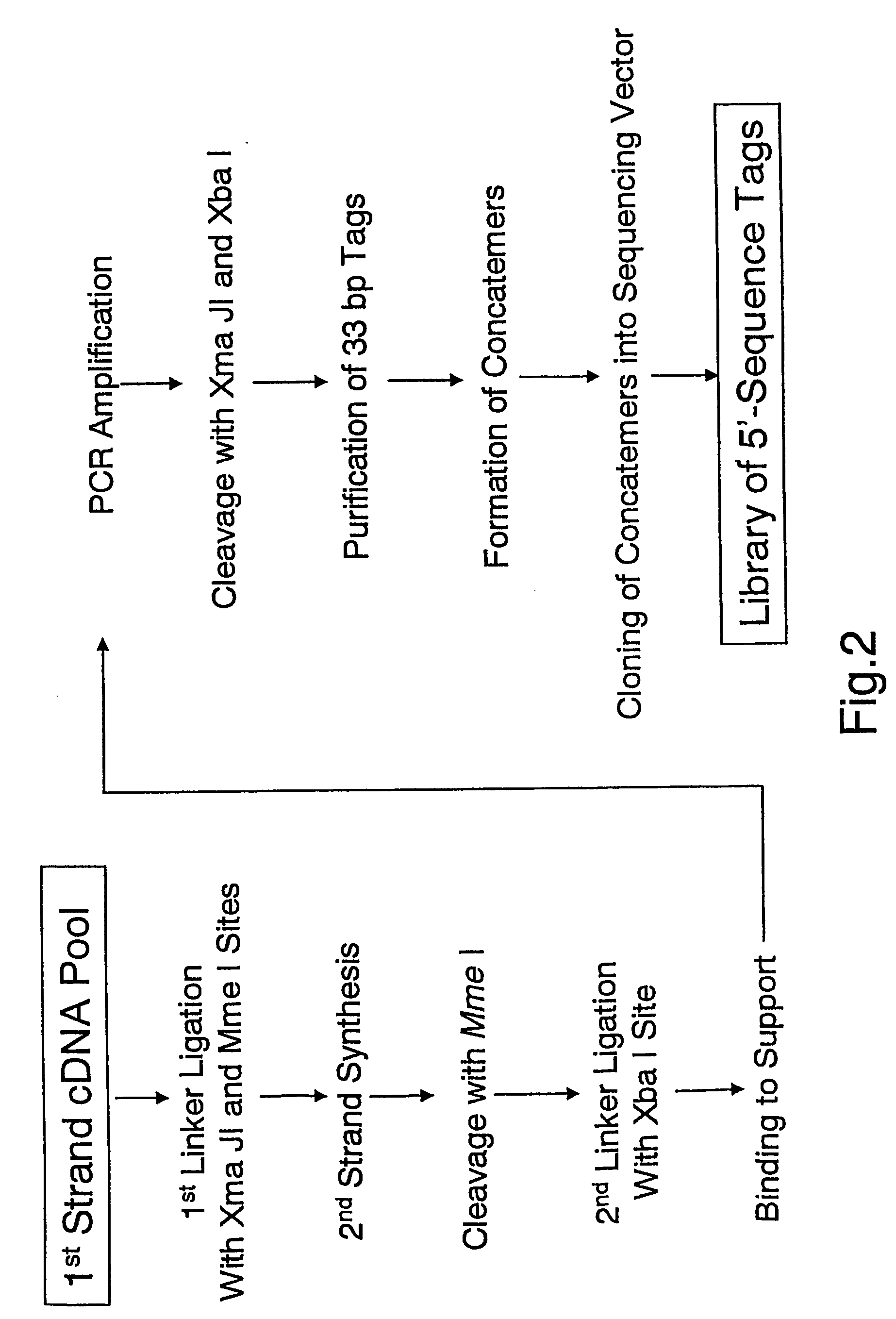
Method of utilizing the 5'end of transcribed nucleic acid regions for cloning and analysis
InactiveUS20050250100A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationIndividual analysisBiological materials
A method is disclosed for obtaining the 5′ends of transcribed regions from a plurality of nucleic acid fragments obtained from biological materials or synthetic pools. DNA fragments encoding the 5′ends are enriched for their individual analysis or for the analysis of concatemers thereof. The sequence information derived from 5′ ends can be used for characterization and cloning of the transcriptome.
Owner:RIKEN +1
Single-molecule sequencing of plasma DNA
ActiveUS20170044606A1Improve efficiencyEfficient readingMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisDNA fragmentationNucleic acid sequencing
Embodiments may include a method of determining a nucleic acid sequence. The method may include receiving a plurality of DNA fragments. The method may also include concatemerizing a first set of the DNA fragments to obtain a concatemer. The method may include performing single-molecule sequencing of the concatemer to obtain a first sequence of the concatemer. In some embodiments, single-molecule sequencing may be performed using a nanopore, and the method may include passing the concatemer through a nanopore. A first electrical signal may then be detected as the concatemer passes through the nanopore. The first electrical signal may correspond to a first sequence of the concatemer. In addition, the method may include analyzing the first electrical signal to determine the first sequence. Subsequences of the first sequence may be aligned to identify sequences corresponding to each of the first set of the DNA fragments.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Multi-pass sequencing
ActiveCN107002130AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansData setConcatemer
Improved single molecule sequencing methods, compositions, and devices, are provided. In a first aspect, the present invention provides a multi-pass method of sequencing a target sequence using nanopore sequencing, the method comprising: i) providing a non-naturally occurring concatemer nucleic acid molecule comprising a plurality of copies of the target sequence; ii) nanopore sequencing at least three copies of the target sequence in the concatemer, thereby obtaining a multi-pass sequence dataset, wherein the multi-pass sequence dataset comprises target sequence datasets for the at least three copies of the target sequence; and iii) using the multi-pass sequence dataset to determine the target sequence.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST +1
Preparation method of highly sensitive photoelectrochemical sensor for detecting microRNA
ActiveCN110412097AIncrease surface areaEnhance photoelectric signalMaterial electrochemical variablesBismuth sulfideBismuth vanadate
The invention discloses a highly sensitive paper-based photoelectrochemical sensor for detecting microRNA. A paper chip is prepared by means of a wax printing technology, gold nano-particles are grownin situ in a hydrophilic working area to achieve functionalization of the paper chip, a cuprous oxide / bismuth sulfide / bismuth vanadate tertiary sensitizer is modified subsequently, and microRNA is captured through a fixed hairpin DNA chain; by means of identification of specificity and digestion effect of duplex-specific nuclease, signal amplification on microRNA is achieved, and then by means ofa multibranched hybrid chain, platinum nanoparticles are embedded into a main part of the chain, branch parts form a chlorhematin / G-tetrad structure, and a DNA concatemer with catalase bological characteristics is formed; signal amplification is further achieved, thus preparation of the photoelectrochemical sensor is completed, and highly sensitive and accurate detection on microRNA is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Adeno-associated viral vector-based methods and compositions for introducing an expression cassette into a cell
Methods and compositions are provided for introducing an expression cassette into a cell. In the subject methods, a population of at least two distinct adeno-associated viral particles is provided, where each distinct type of viral particle in the population comprises a different portion of the expression cassette to be introduced into the cell. The target cell is contacted with population of adeno-associated viral vectors under conditions sufficient to produce a hetero-concatemer in the cell, where the hetero-concatemer includes a functional expression cassette having an intron that includes an ITR sequence. Also provided by the subject invention are vector preparations for practicing the subject methods as well as kits for use in producing the vectors employed in the subject methods. The subject methods find use in a variety of different gene transfer applications, including both in vivo and in vitro gene transfer applications, and are particularly suited for use in the transfer of long genes.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
DNA sequence for constituting T carrier and the T carrier constituting process
InactiveCN1344795ASimple and fast operationEasy to operateVector-based foreign material introductionDNA preparationDNA fragmentationEndoenzyme
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
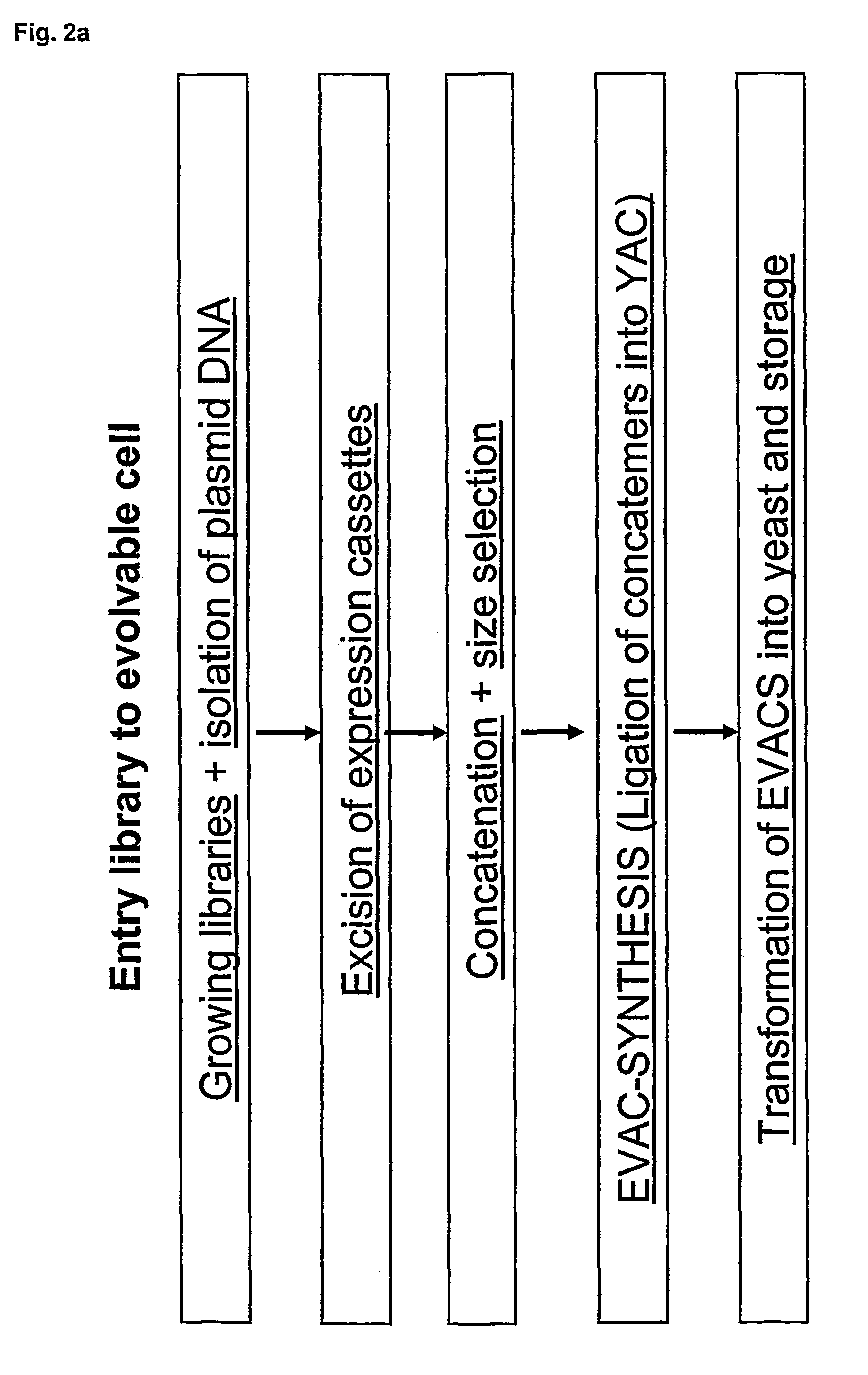
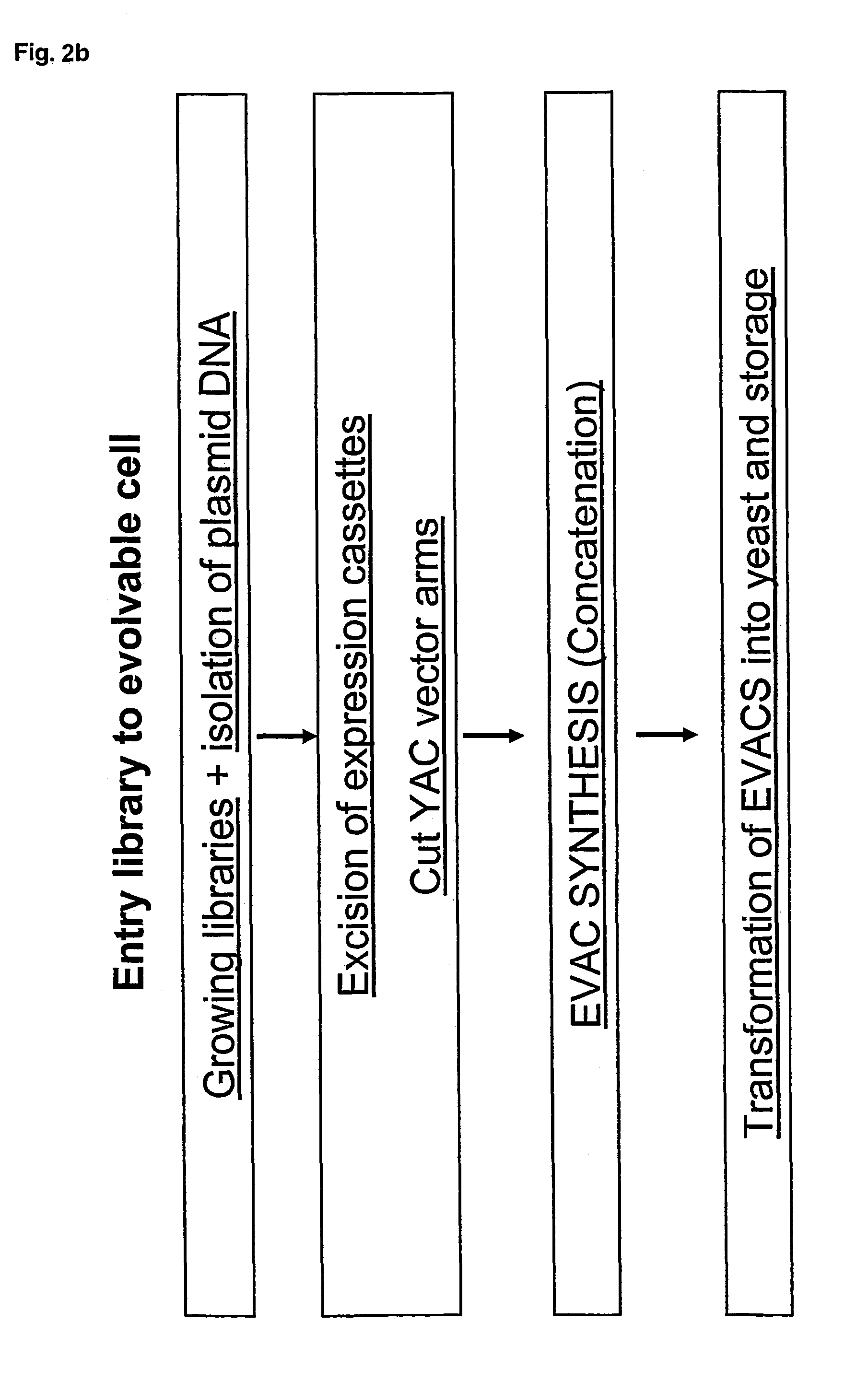
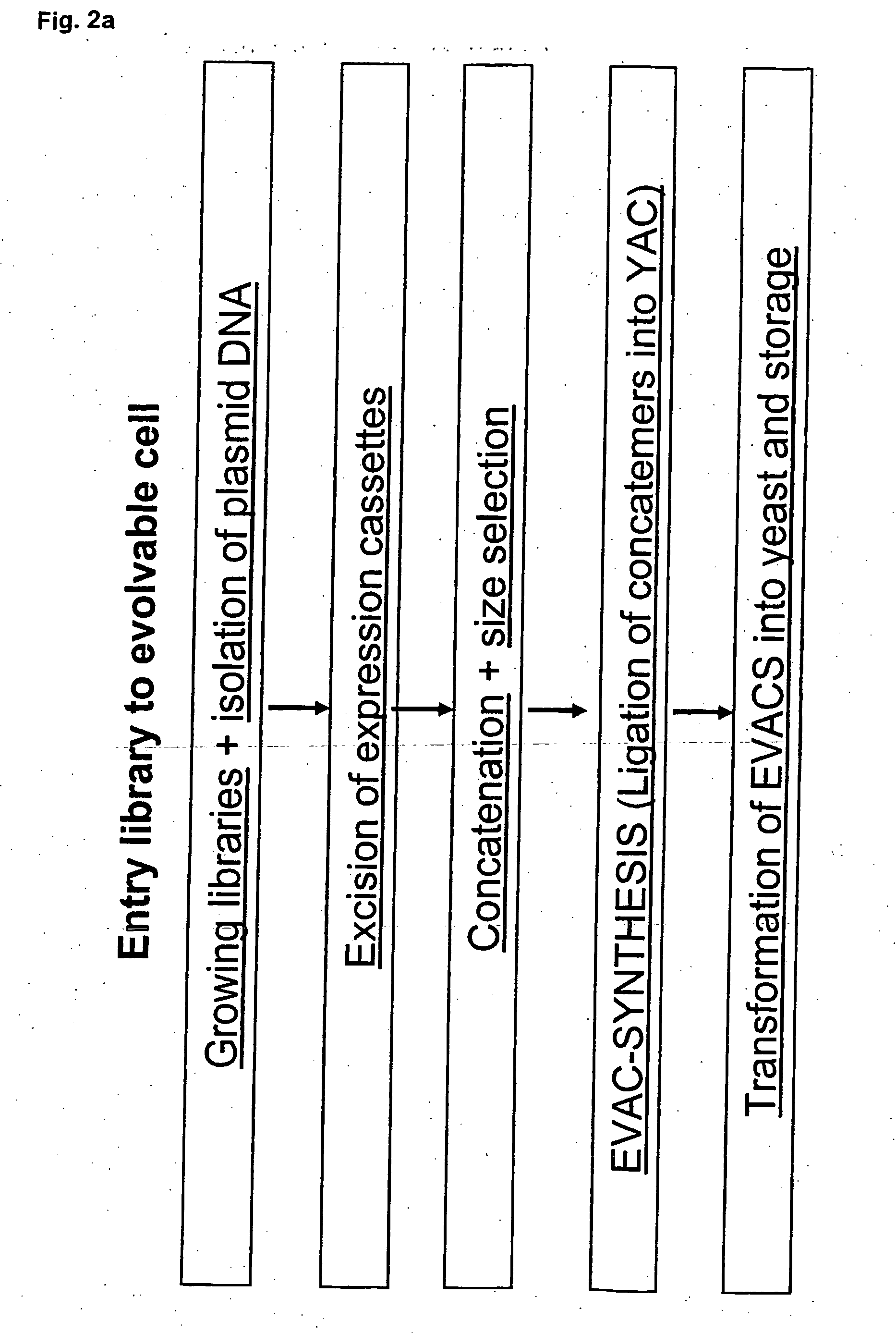
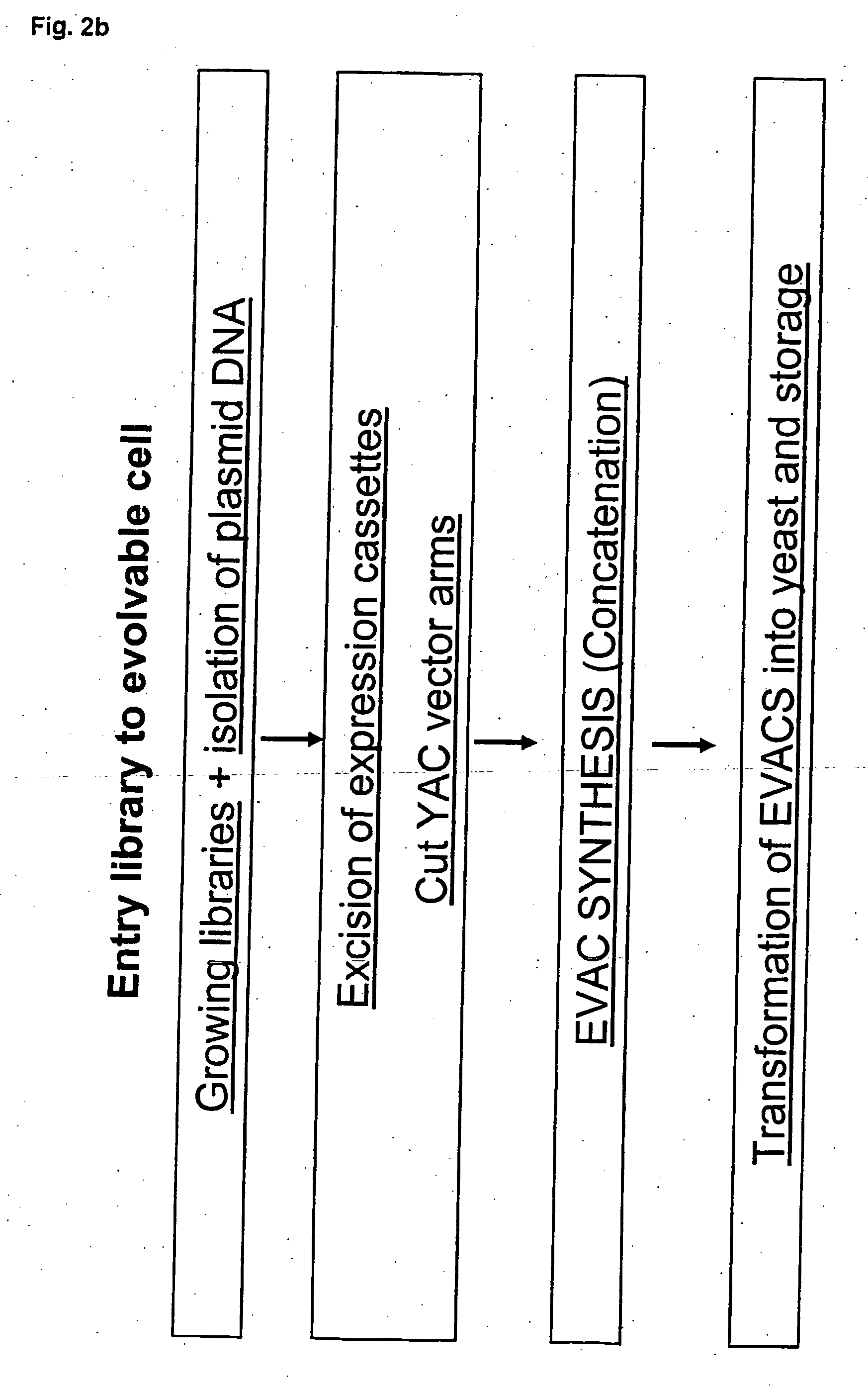
Method for evolving a cell having desired phenotype and evolved cells
The present invention relates to evolution of a cell or a composition of cells having a desired property or functionally. The principle behind the evolution of cells according to the invention is to produce a great diversity of genes in each cell subjected to evolution and a great diversity of genes among the cells in a composition according to the invention and to exchange the genes between the cells from time to time. In preferred embodiments the genes are arranged in expression cassettes in concatemers in the cells, as well as in artificial chromosomes. Said methods comprising the steps of a) obtaining a composition of cells, at least one cell of said composition comprising a1) at least two expressible nucleotide sequences, at least one of said sequences being incorporated into an artificial chromosome in the cell and / or a2) at least two expression cassettes of the following formula: [rs2-SP-PR-X-TR-SP-rs11 wherein rs1 and rs2 together denotes a restriction site, SP individually denotes a spacer, PR denotes a promoter, capable of functionning in the first cell, X denotes an expressible nucleotide sequence, TR denotes a terminator, and / or a3) at least two expressible nucleotide sequences, said sequences being heterologous to the cell, determining at least one screening functionality. The genes are preferably co-ordinately controllable for increasing diversity. The desired property of functionality is preferably a compound, or a series of compounds synergistically acting to each other.
Owner:EVOLVA SA
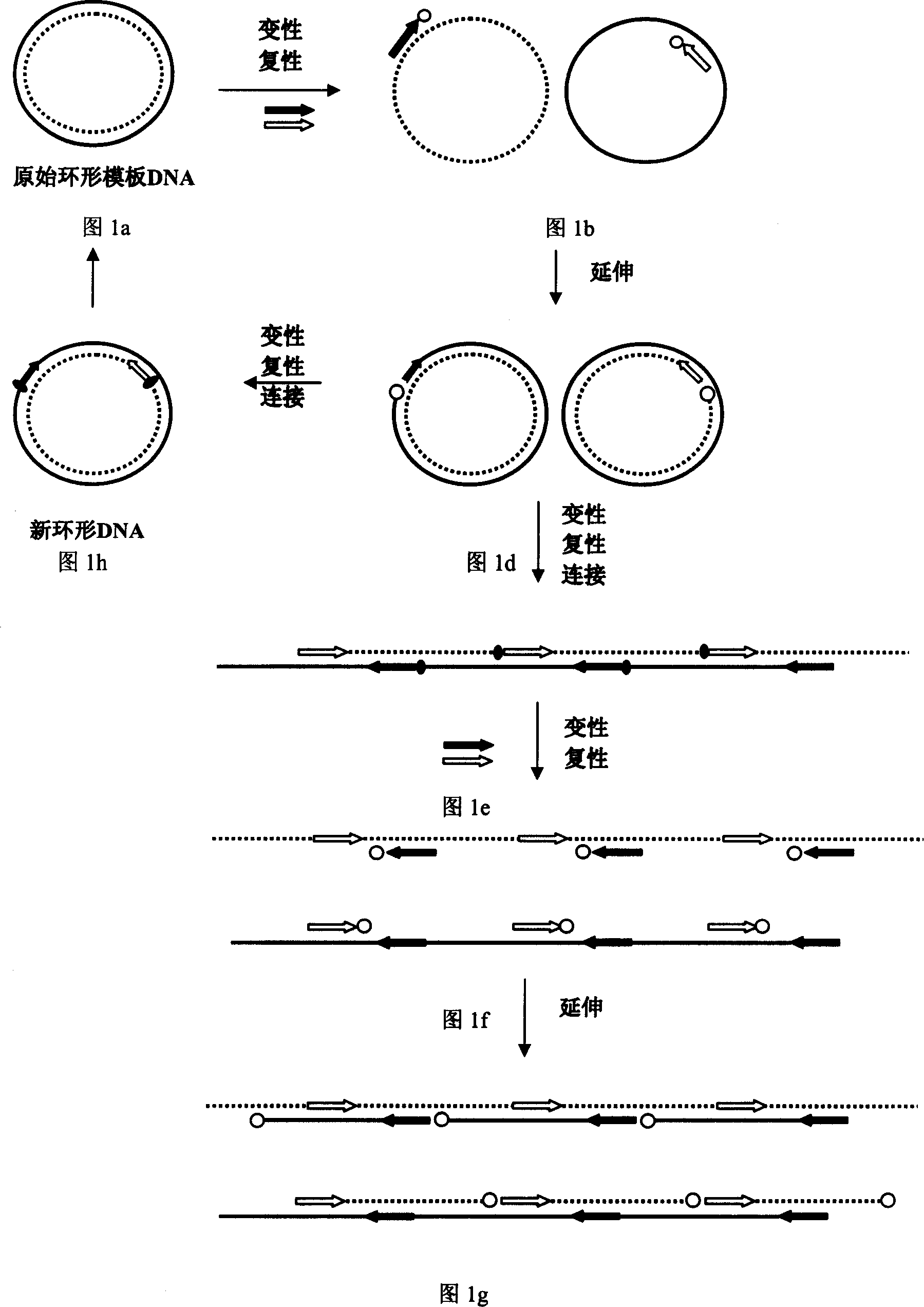
Method for externally amplifying specific ring type or concatemer nucleic acid
The externally amplifying process of specific ring form or concatemer nucleic acid includes the pre-denaturation of ring type or concatemer nucleic acid containing target sequence as the template, one pair of 5'-phosphorylated oligonucleotide primers, four kinds of triphosphodeoxyribonucleotides and thermonucleic acid synthetase in proper buffing system at 90-99 deg.c for 1-30; and subsequent 1-40 thermal circulation treatment. The said thermal circulation includes three steps of: denaturation via maintaining at 90-99 deg.c for 1 sec to 5 min; renaturation and connection at 30-85 deg.c for 10 sec to 15 min; and extension at 65-85 deg.c for 1-30 min. The present invention can produce and amplify ring form or serial DNA externally and optionally.
Owner:包振民 +1
Methods and compositions for enrichment of amplification products
In some aspects, the present disclosure provides methods for enriching amplicons, or amplification products, comprising a concatemer of at least two or more copies of a target polynucleotide. In some embodiments, a method comprises sequencing the amplicons comprising at least two or more copies of a target polynucleotide. In some embodiments, the target polynucleotides comprise sequences resulting from chromosome rearrangement, including but not limited to point mutations, single nucleotide polymorphisms, insertions, deletions, and translocations including fusion genes. In some aspects, the present disclosure provides compositions and reaction mixtures useful in the described methods.
Owner:ACCURAGEN HLDG LTD
Methods and compositions for enrichment of amplification products
ActiveUS20180298434A1Reduce errorsRaise the ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationNucleotidePolynucleotide
In some aspects, the present disclosure provides methods for enriching amplicons, or amplification products, comprising a concatemer of at least two or more copies of a target polynucleotide. In some embodiments, a method comprises sequencing the amplicons comprising at least two or more copies of a target polynucleotide. In some embodiments, the target polynucleotides comprise sequences resulting from chromosome rearrangement, including but not limited to point mutations, single nucleotide polymorphisms, insertions, deletions, and translocations including fusion genes. In some aspects, the present disclosure provides compositions and reaction mixtures useful in the described methods.
Owner:ACCURAGEN HLDG LTD
Recombinant multi-epitope antigen of bovine coronavirus and application thereof
ActiveCN107033250AAvoid infectionImprove prokaryotic expression efficiencySsRNA viruses positive-senseBacteriaMolecular ImmunologyAgricultural science
The invention discloses a recombinant multi-epitope antigen of bovine coronavirus, also discloses application of the recombinant multi-epitope antigen of the bovine coronavirus in bovine coronavirus prevention ad diagnosis and belongs to the field of molecular immunology. An amino acid sequence of the recombinant multi-epitope antigen of the bovine coronavirus is a concatemer of a bovine coronavirus BCoV S protein epitope. The recombinant multi-epitope antigen, capable of causing a neutralizing antibody, of the bovine coronavirus serves as an immunogen or a vaccine, the neutralizing antibody oriented to the bovine coronavirus BCoV can be produced after the animal body is immunized, and the BCoV can be neutralized in vitro to prevent the animal body from virus infection. In addition, the recombinant multi-epitope antigen of the bovine coronavirus can also serve as a reagent for detecting a bovine coronavirus BCoV antibody or a polypeptide antibody.
Owner:DAIRY CATTLE RES CENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +2
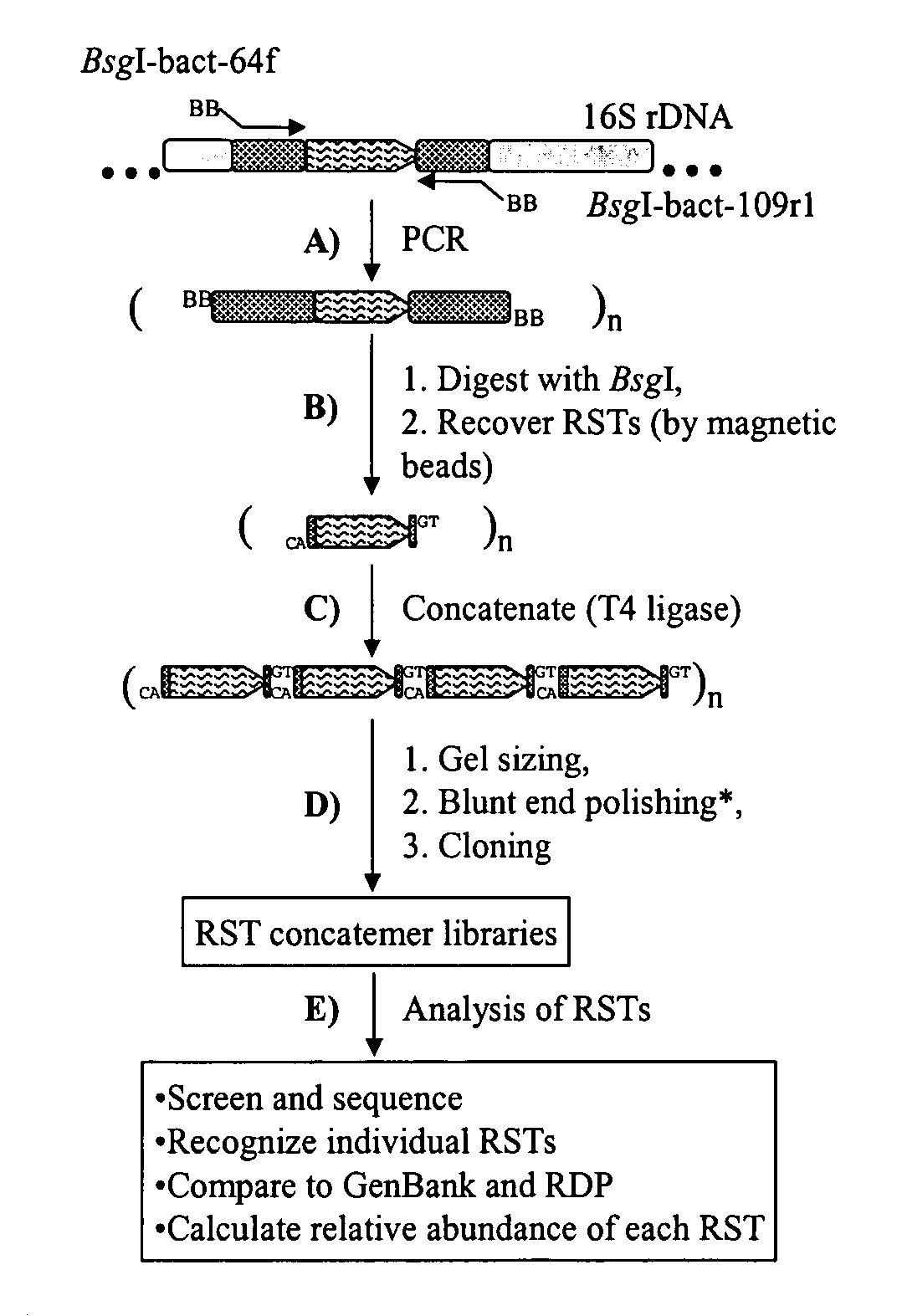
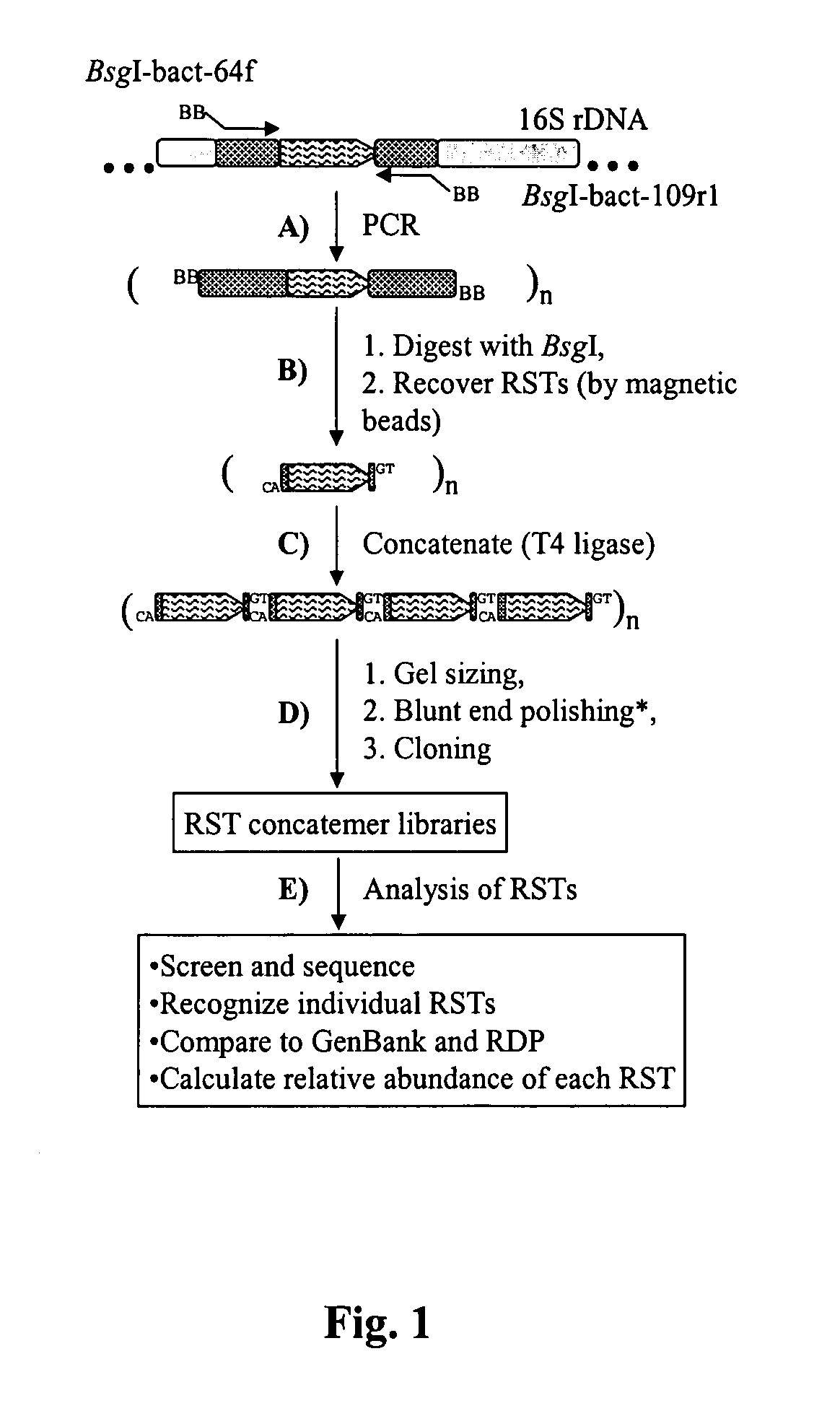
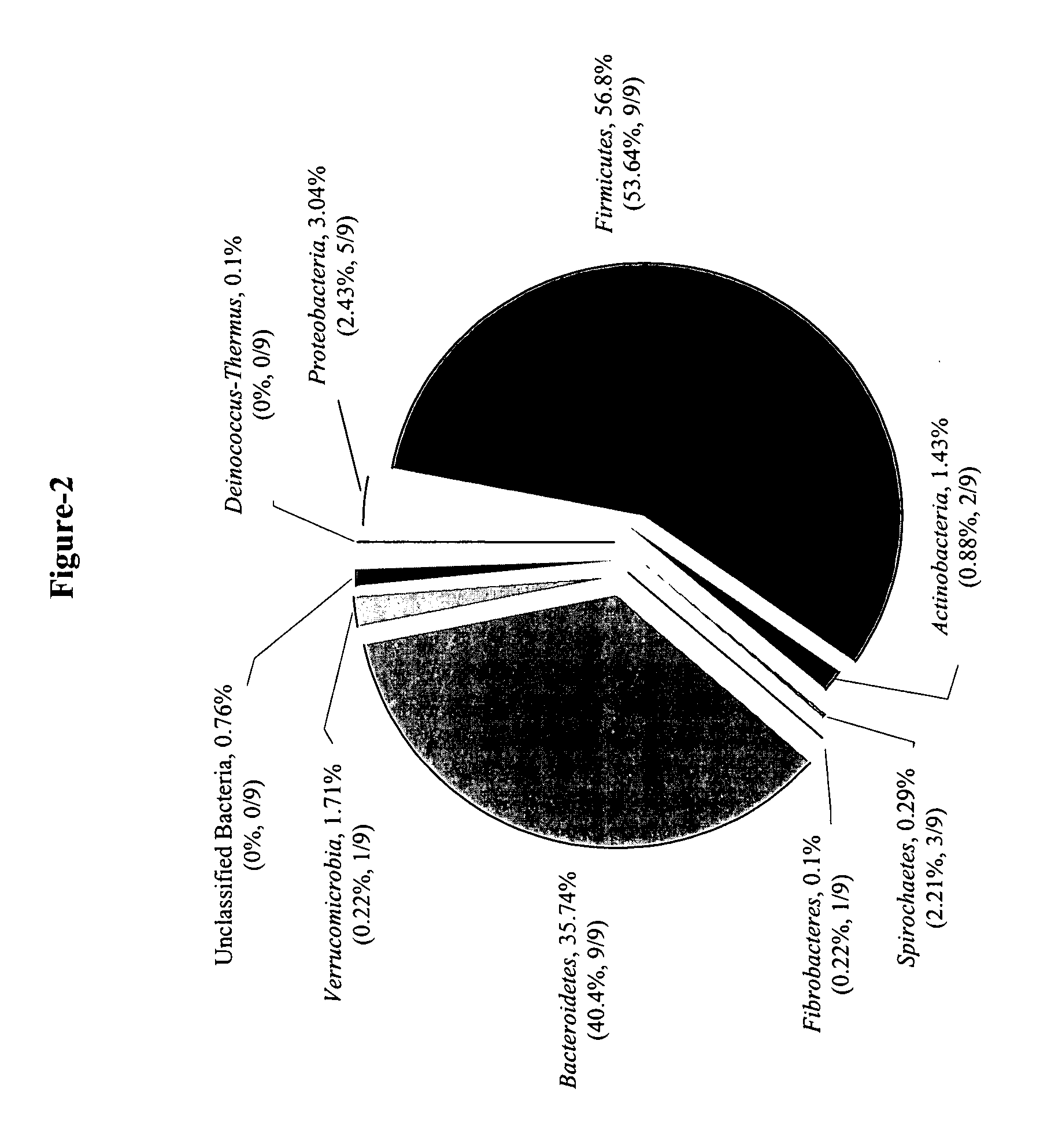
Serial analysis of ribosomal and other microbial sequence tags
InactiveUS20070003924A1Improved and robustIncrease variabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSequence analysisMicroorganism
A simple and robust method for genetic analysis of complex microbial communities involves the steps of PCR amplification of V1 region of rrs genes in the community DNA sample using two universal primers, followed by cleavage by BsgI and removal of dual-biotinylated primers using streptavidin-coated magnetic beads to purify RSTs, and concatemerization of the RSTs and size selection of resultant concatemers by agarose gel electrophoresis. The isolated concatamers are then cloned and sequenced and subjected to sequence analyses to enable identification of the members of the microbial community.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
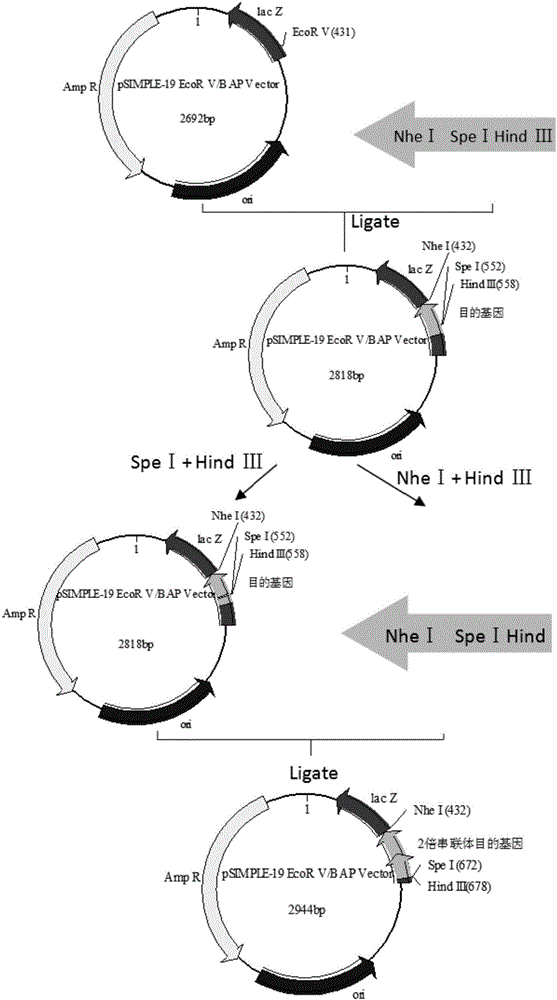
Artificially constructed araneus ventricosus dragline silk protein gene and construction method thereof
InactiveCN106754946ASimple and efficient processLow costFermentationAnimals/human peptidesEscherichia coliRestriction Enzyme Cut Site
The invention discloses an artificially constructed araneus ventricosus dragline silk protein gene and a construction method thereof. The sequence of the araneus ventricosus dragline silk protein gene is shown as SEQIDNO.6. According to part of cDNA sequence of araneus ventricosus dragline silk protein, first, most-representative core repeat 108BP is selected, and artificially synthesized, both ends of the core repeat sequence are additionally added restriction enzyme cutting sites, then the core repeat sequence is connected with a pSIMPLE-19EcoRV / BAP vector, and transformed into Escherichia coli to obtain monomer recombinant plasmid, by an isocaudarner recursive directional ligation method, gene monomers are polymerized into a 16-time concatemer, 1836bp araneus pseudoventricosus dragline silk protein gene can be successfully obtained, the 1836bp araneus pseudoventricosus dragline silk protein gene can be successfully expressed for production of the araneus ventricosus dragline silk protein, and the whole process is simple and efficient, saves the cost, improves the work efficiency, and has good application prospects.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
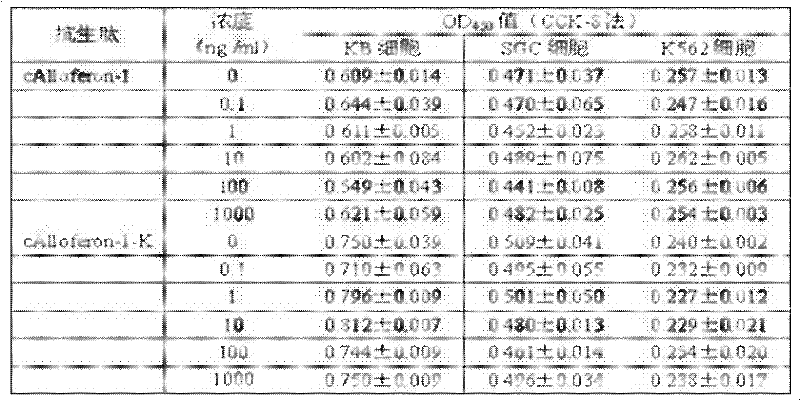
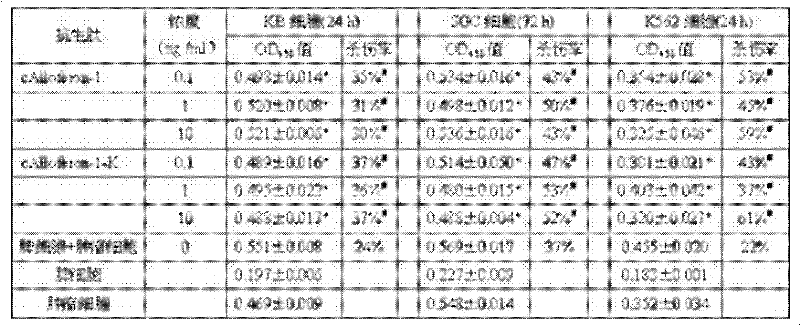
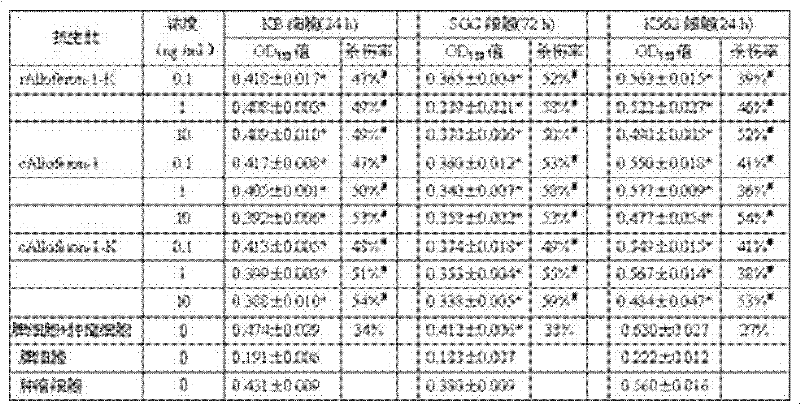
Preparation method of serial antibacterial peptide Alloferon-1 and application of rAlloferon-1-K
InactiveCN102242127AGrowth inhibitionPrevent proliferationPeptide/protein ingredientsFermentationSingle strand dnaAntibacterial peptide
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of an antibacterial peptide. The invention aims to provide a preparation method of an antibacterial peptide Alloferon-1, which has simple steps and high expression efficiency and keeps the in-vitro anti-tumor activity of the antibacterial peptide, and provide application of rAlloferon-1-K. The technical scheme is as follows: the preparation method of the serial antibacterial peptide Alloferon-1 comprises the following steps of: (1) designing a pair of terminal single-stranded DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acids); (2) generating a concatemer in a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) system; (3) carrying out electrophoretic screening on a 14 Alloferon-1 concatemer; (4) constructing a prokaryotic recombinant expression system E.coliBL21DE3pET42a-14Alloferon-1-K; (5) expressing and purifying recombinant protein 14rAlloferon-1-K; and (6) performing trypsin digestion on the 14rAlloferon-1-K, and purifying to obtain the rAlloferon-1-K.
Owner:严杰
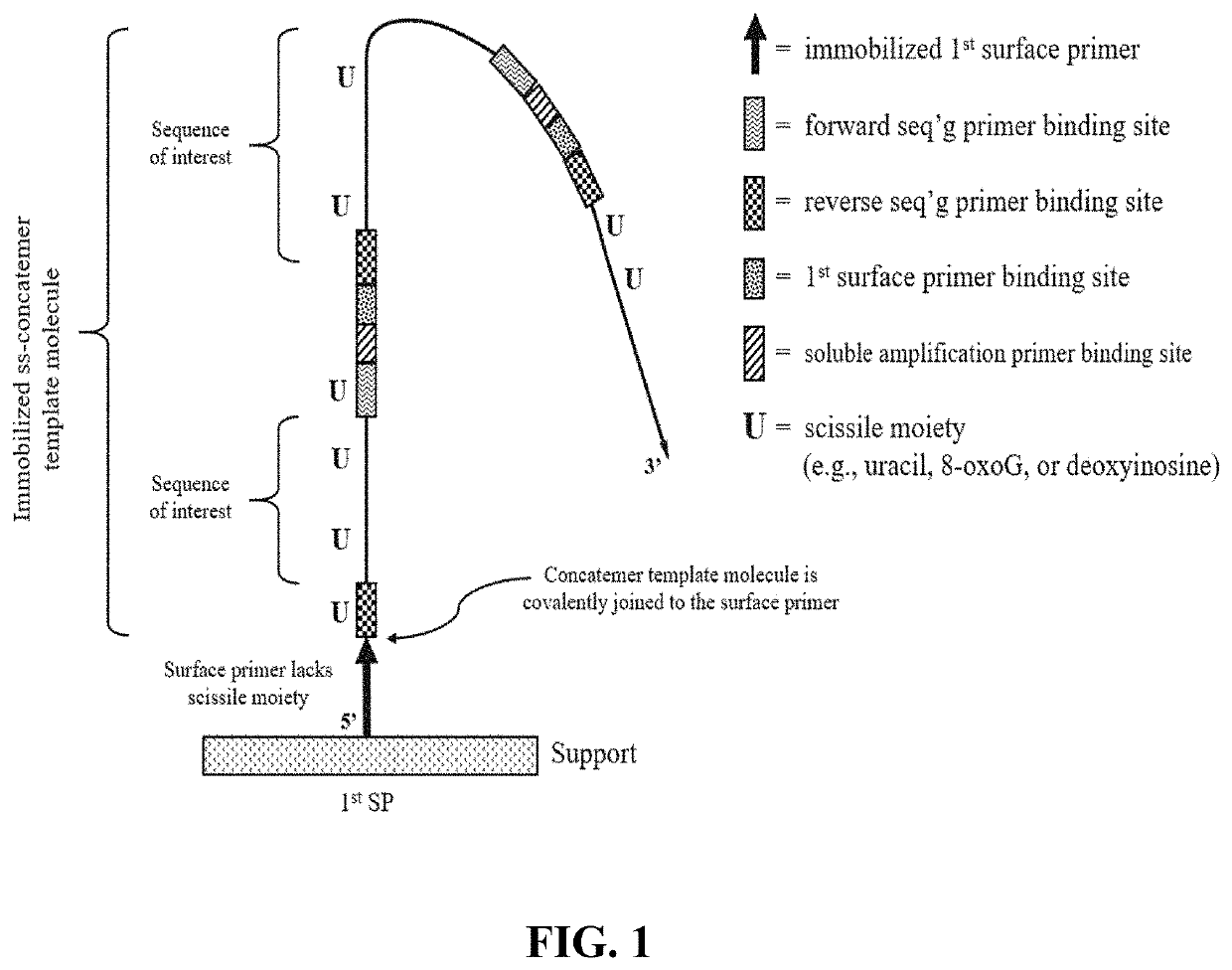
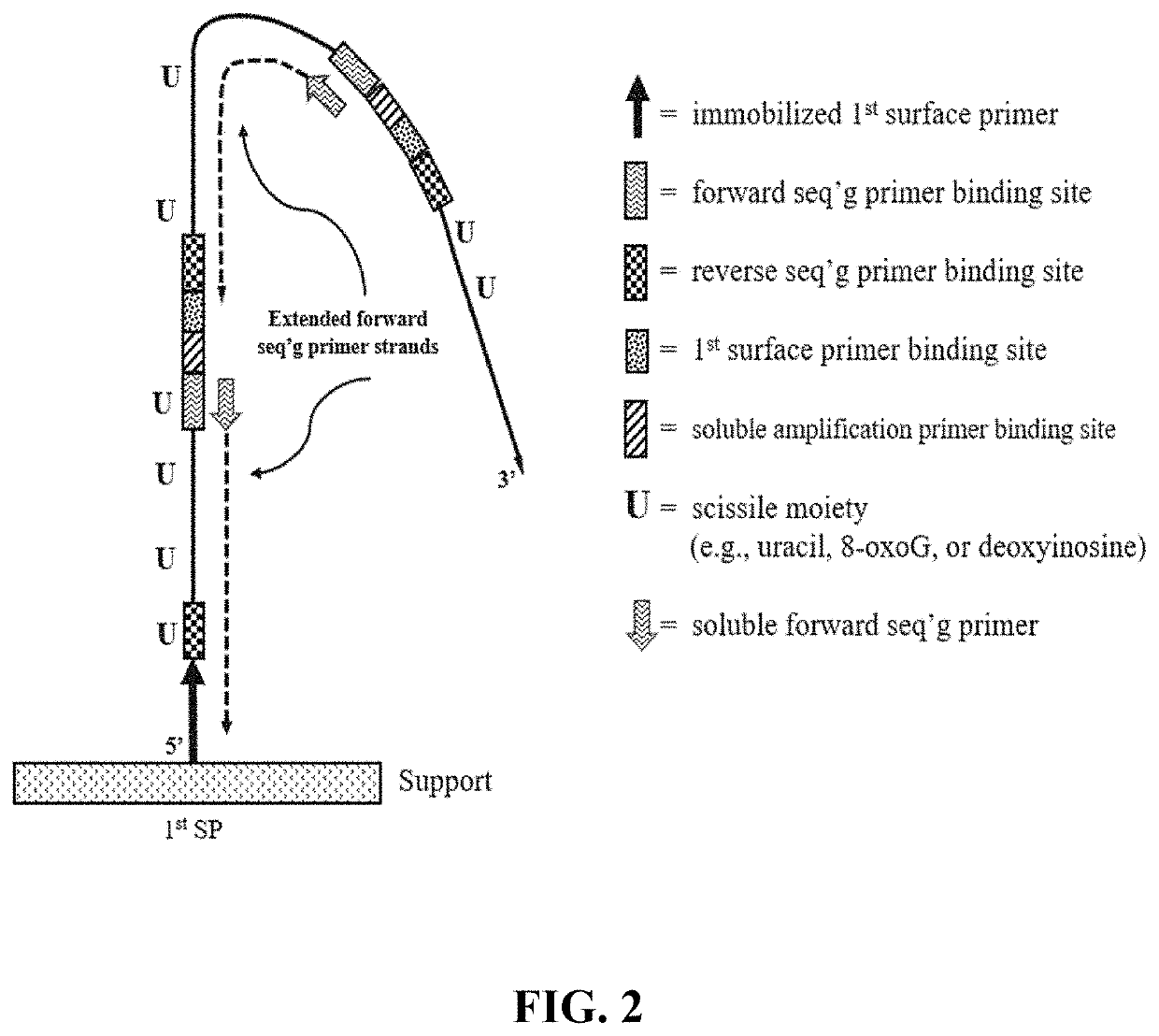
Compositions and methods for pairwise sequencing
ActiveUS11220707B1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansNucleotideGenetics
The present disclosure provides compositions and methods that employ the compositions for conducting pairwise sequencing and for generating concatemer template molecules for pairwise sequencing. The concatemers can be generated using a rolling circle amplification reaction which is conducted either on-support, or conducted in-solution and then distributed onto a support. The rolling circle amplification reaction generates concatemers containing tandem copies of a sequence of interest and at least one universal adaptor sequence. An increase in the number of tandem copies in a given concatemer increases the number of sites along the concatemer for hybridizing to multiple sequencing primers which serve as multiple initiation sites for polymerase-catalyzed sequencing reactions. When the sequencing reaction employs detectably labeled nucleotides and / or detectably labeled multivalent molecules (e.g., having nucleotide units), the signals emitted by the nucleotides or nucleotide units that participate in the parallel sequencing reactions along the concatemer yields an increased signal intensity for each concatemer.
Owner:ELEMENT BIOSCI INC
Methods and compositions for enrichment of amplification products
ActiveUS10752942B2Reduce errorsRaise the ratioSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePolynucleotide
In some aspects, the present disclosure provides methods for enriching amplicons, or amplification products, comprising a concatemer of at least two or more copies of a target polynucleotide. In some embodiments, a method comprises sequencing the amplicons comprising at least two or more copies of a target polynucleotide. In some embodiments, the target polynucleotides comprise sequences resulting from chromosome rearrangement, including but not limited to point mutations, single nucleotide polymorphisms, insertions, deletions, and translocations including fusion genes. In some aspects, the present disclosure provides compositions and reaction mixtures useful in the described methods.
Owner:ACCURAGEN HLDG LTD
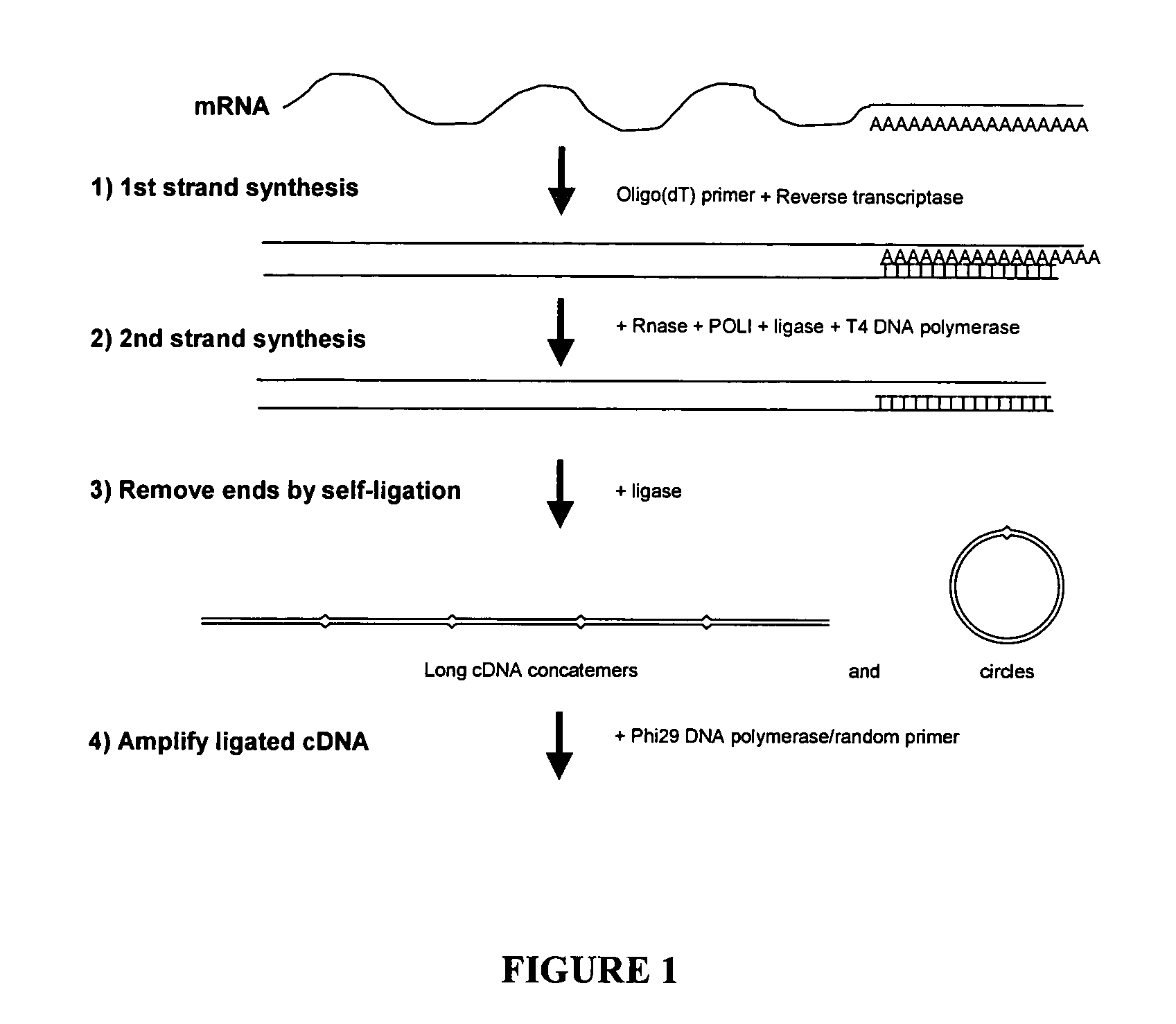
Amplification of self-ligated, circularized cDNA for expression profiling
ActiveUS7309571B2Reduce concentrationMinimize concatenationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationRNA analysisOligonucleotide
This invention presents a new cDNA amplification method. RNA is first converted to cDNA. The synthesis of cDNA can include a promoter tagged oligonucleotide, and then this cDNA is ligated to form circles (or possibly concatemers). This is then amplified using a Phi29 DNA polymerase based rolling circle and strand displacement amplification. The invention allows for RNA promoter sequences to be attached to the cDNA to facilitate additional amplification through the generation of RNA from the amplified cDNA. The resulting product can then be used to make materials for gene expression studies or other RNA analysis procedures.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Method for transducing buffalo embryo with PEP-1 peptide concatemer mediated green fluorescent protein
ActiveCN106480091ARapid transductionImprove targetingAnimals/human peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionEmbryoGenetic engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of targeting transport of cell penetrating peptides, in particular to a method for transducing a buffalo embryo with PEP-1 peptide concatemer mediated green fluorescent protein. The method comprises steps as follows: design and optimization of PEP-1-PEP-1-EGFP, construction of a prokaryotic expression vector pCZN1-PEP-1-PEP-1-EGFP, prokaryotic expression of the protein, protein transfection and the like. By means of genetic engineering, the PEP-1 concatemer mediated expression vector plasmid pCZN1-PEP-1-PEP-1-EGFP is constructed, the optimal condition for transducing buffalo embryo cells with the PEP-1 peptide concatemer mediated green fluorescent protein is explored, the green fluorescent protein can be transduced into the buffalo embryo accurately and efficiently, a research foundation is laid for study of target transduction of nutrient substances and target effects of drugs, and the mediation effect of PEP-1 concatemers can be exerted efficiently.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION BUFFALO INST
Methods of Determining Multiple Interactions Between Nucleic Acids in a Cell
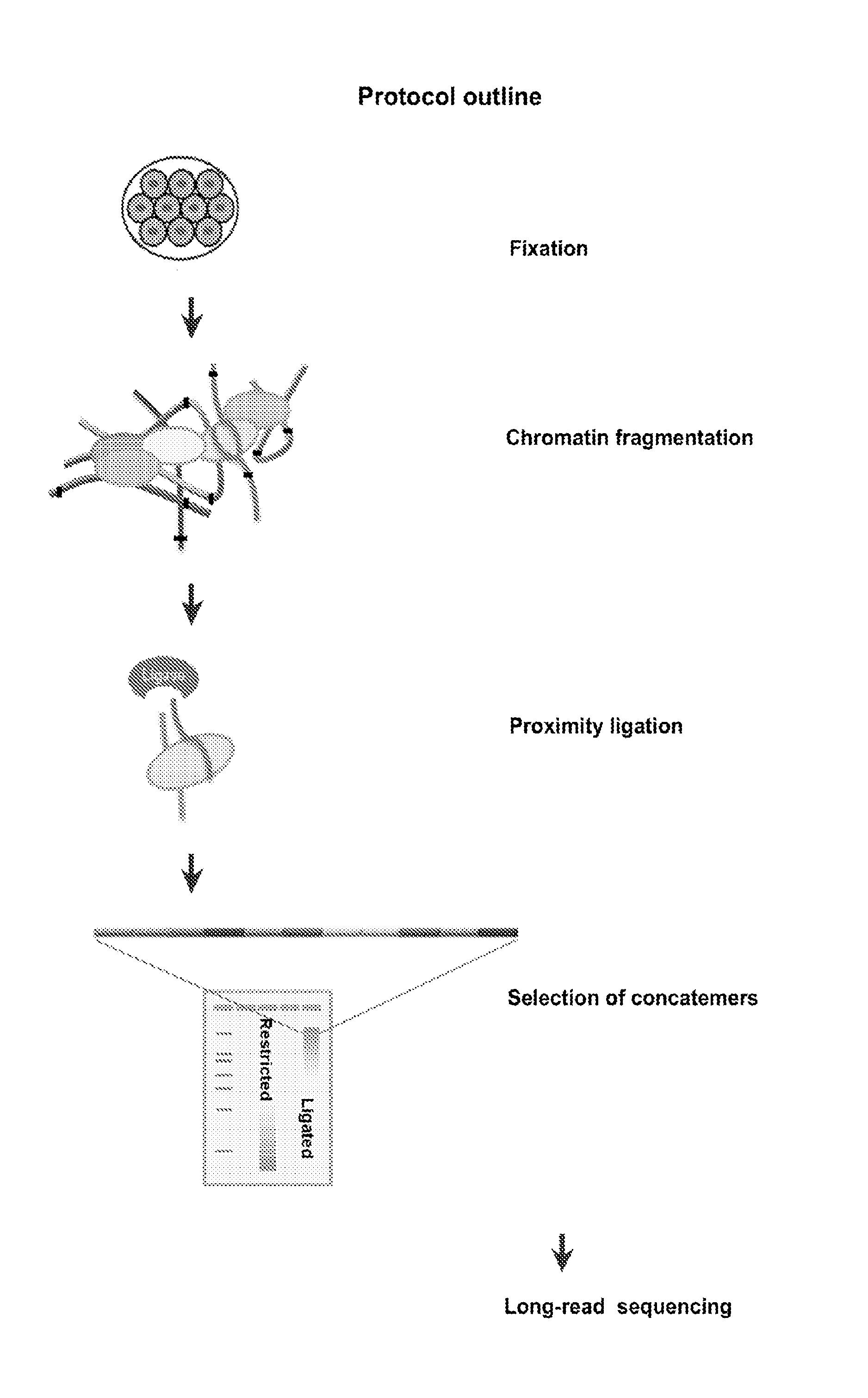
Disclosed are methods for detecting spatial proximity relationships between nucleic acid sequences in a cell. The methods include: providing a sample of one or more cells comprising nucleic acids; fragmenting the nucleic acids present in the cells, wherein the fragmented nucleic acids have ends capable of joining to other fragmented nucleic acids; joining ends of fragmented nucleic acids to other ends fragmented nucleic acid to create at least one nucleic acid concatemer having at least one junction between the joined fragmented nucleic acids, and wherein the at least one nucleic acid concatemer encodes the information about the proximity of the DNA sequences in the cell; and determining the sequence at least one junction of the at least one nucleic acid concatemer, thereby detecting spatial proximity relationships between nucleic acid sequences in a cell.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +1
Cell-free protein expression using double-stranded concatameric DNA
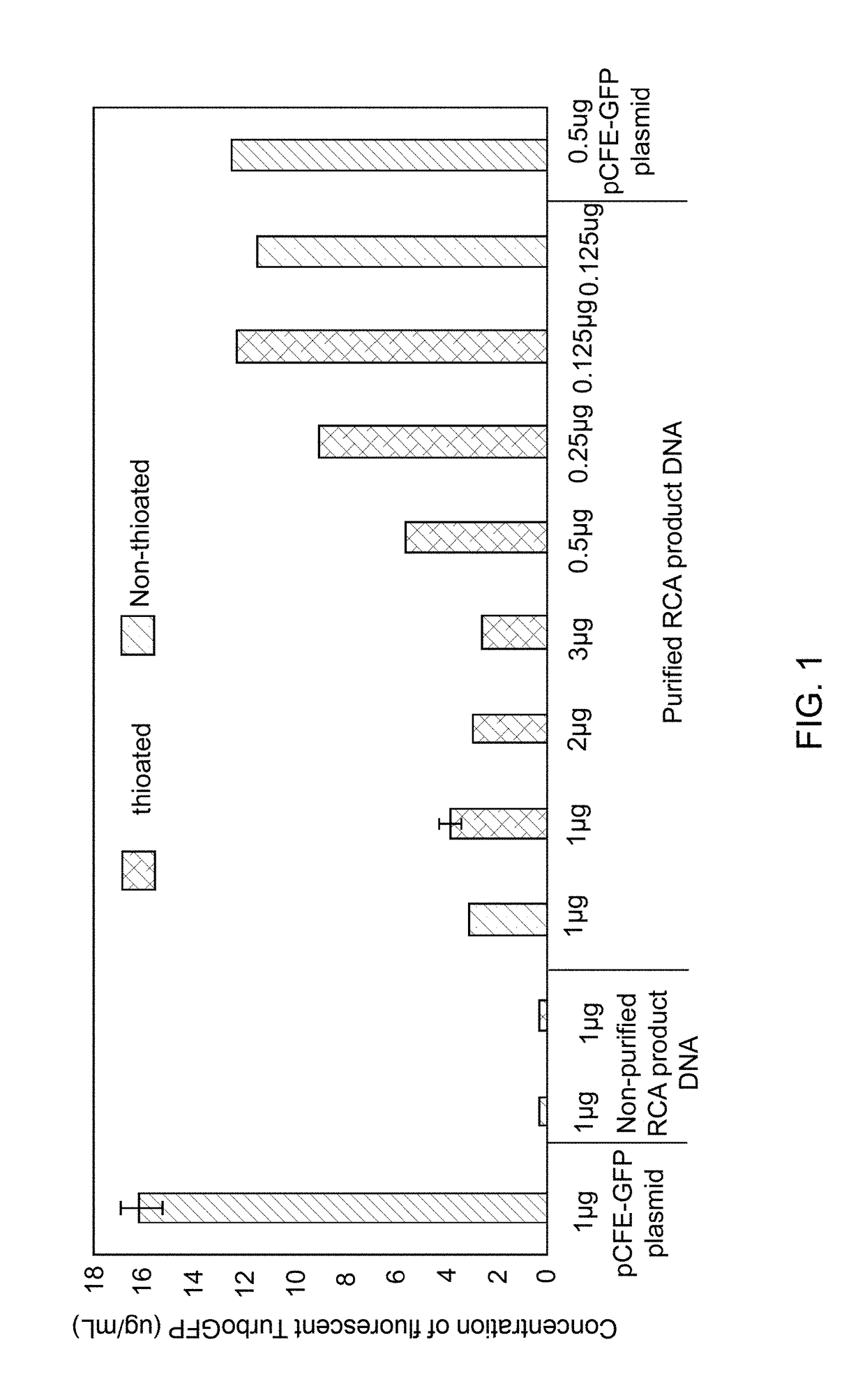
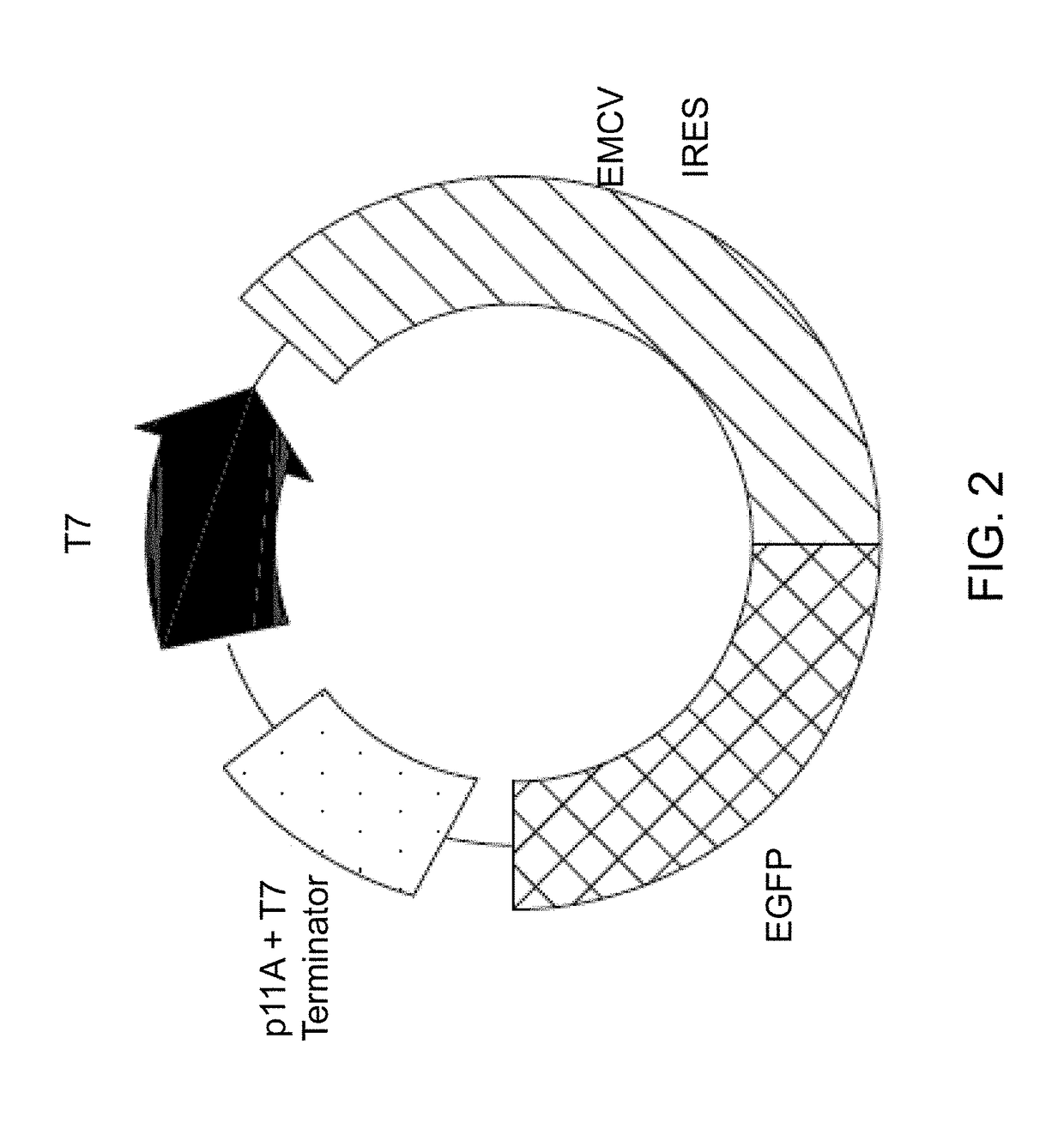
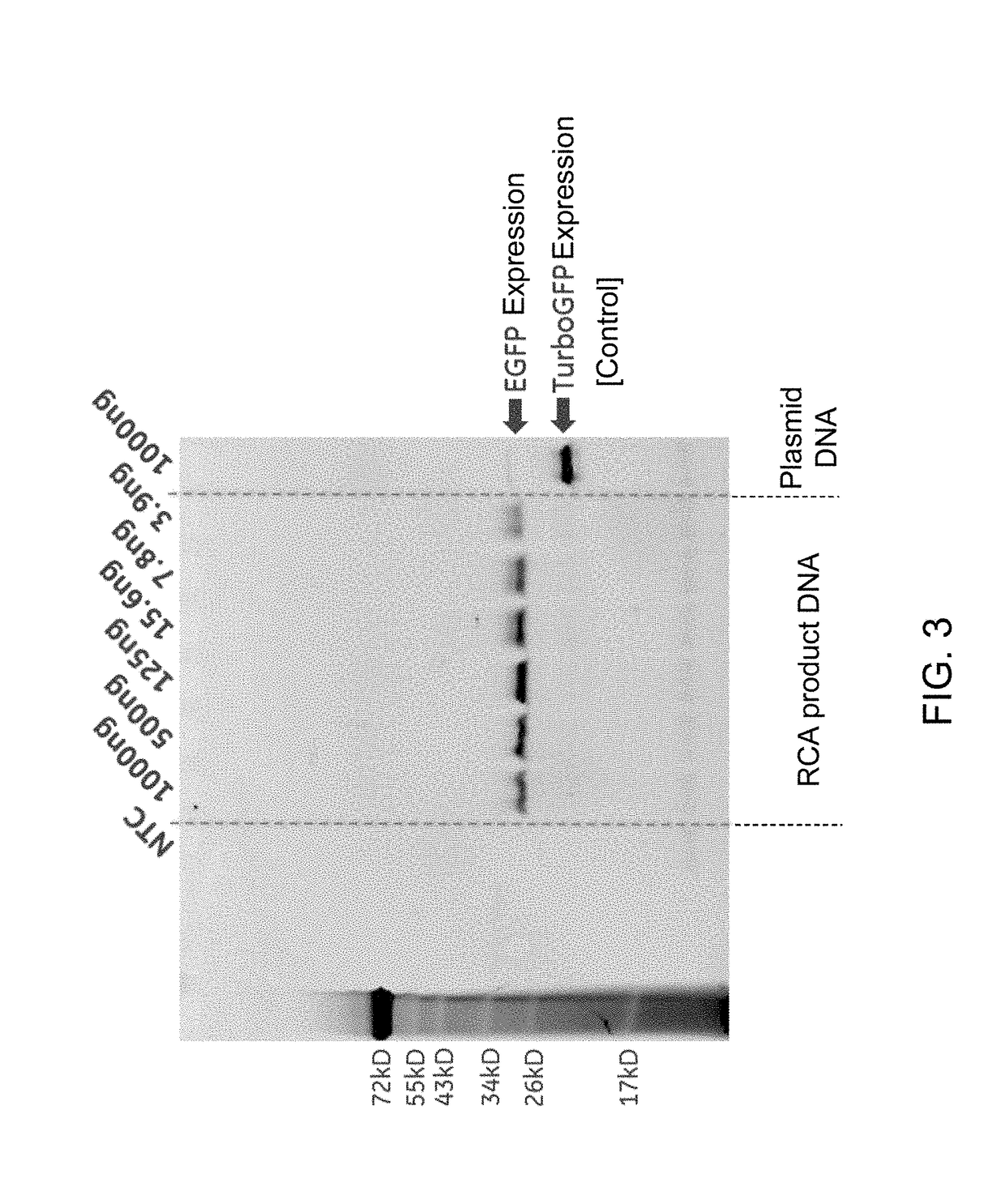
Methods for in vitro transcription and translation using a double-stranded concatemeric DNA in a eukaryotic cell-free expression system are provided. The method includes the steps of (a) contacting a double-stranded concatemeric DNA with a eukaryotic cell-free expression system, and (b) expressing a protein in vitro from the double-stranded concatemeric DNA in the eukaryotic cell-free expression system. The double-stranded concatemeric DNA includes a plurality of tandem repeat sequences. The plurality of tandem repeat sequences includes an expression sequence including a promoter, a cap-independent translation element (CITE), and an open reading frame. A final concentration of the double-stranded concatemeric DNA in the eukaryotic cell-free expression system is in a range from about 0.1 ng / μL to about 35 ng / μL. A RCA product DNA may be used as the double stranded concatemer DNA for the methods.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS OPERATIONS UK LTD
Nucleic acid sample preparation methods
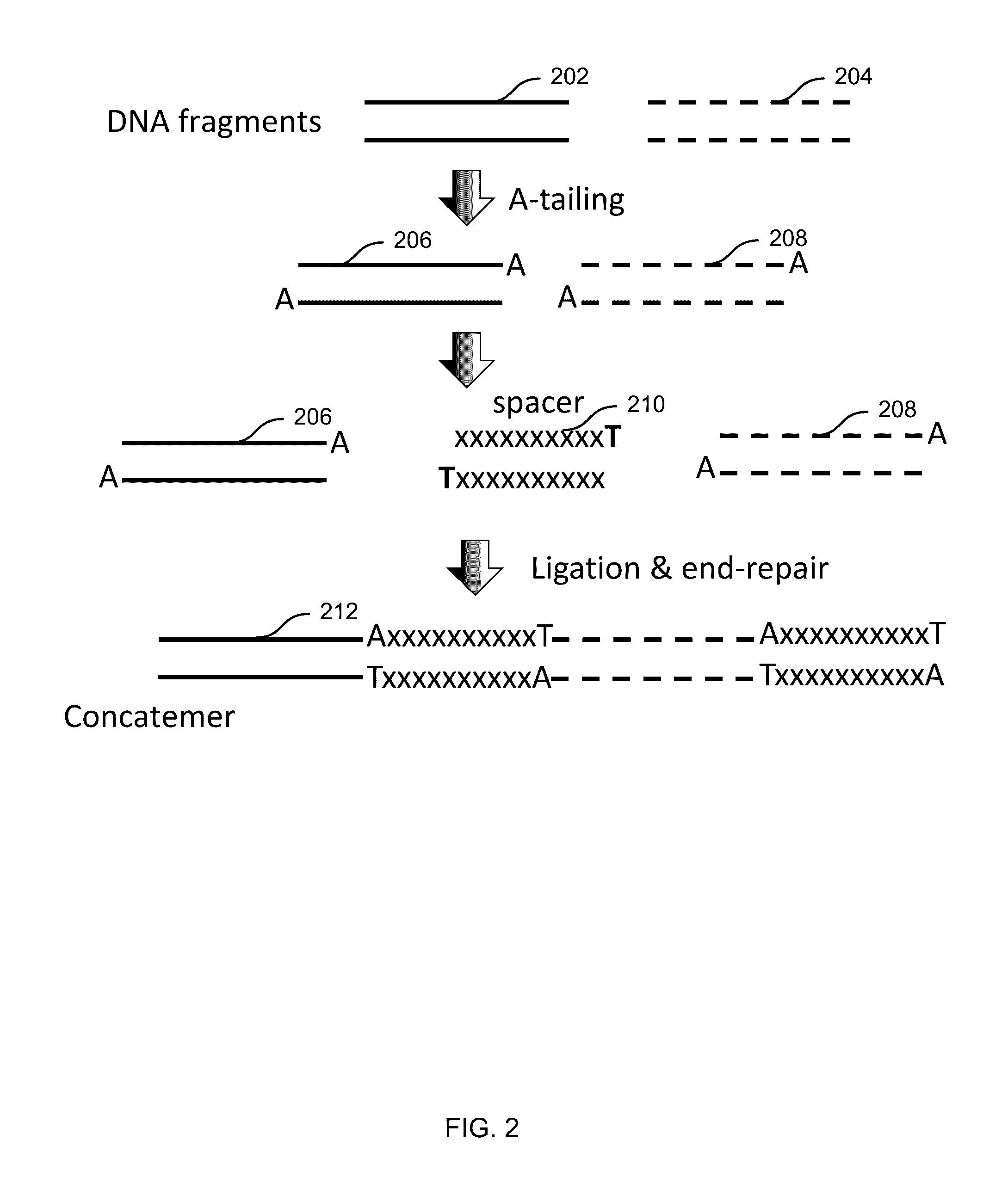
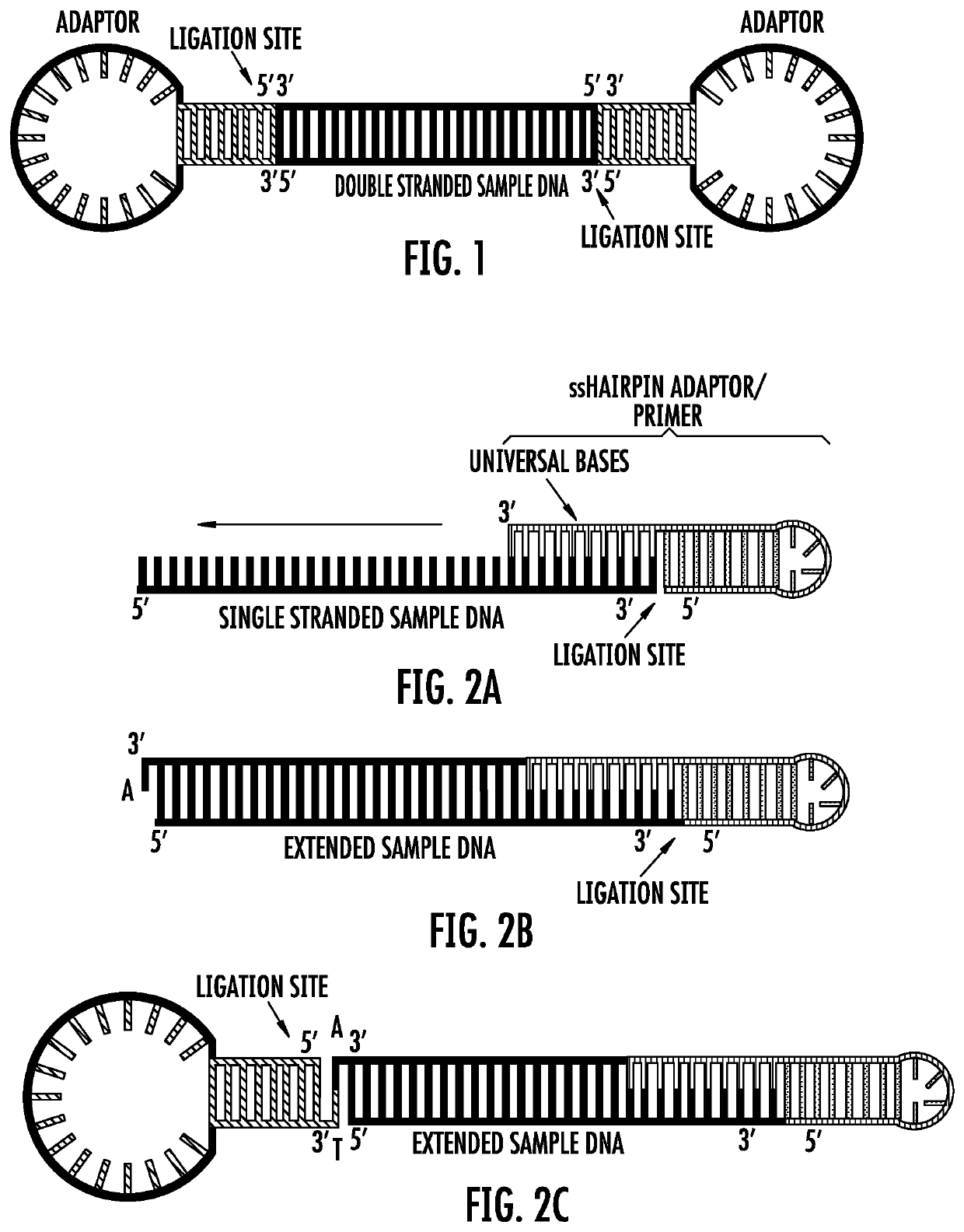
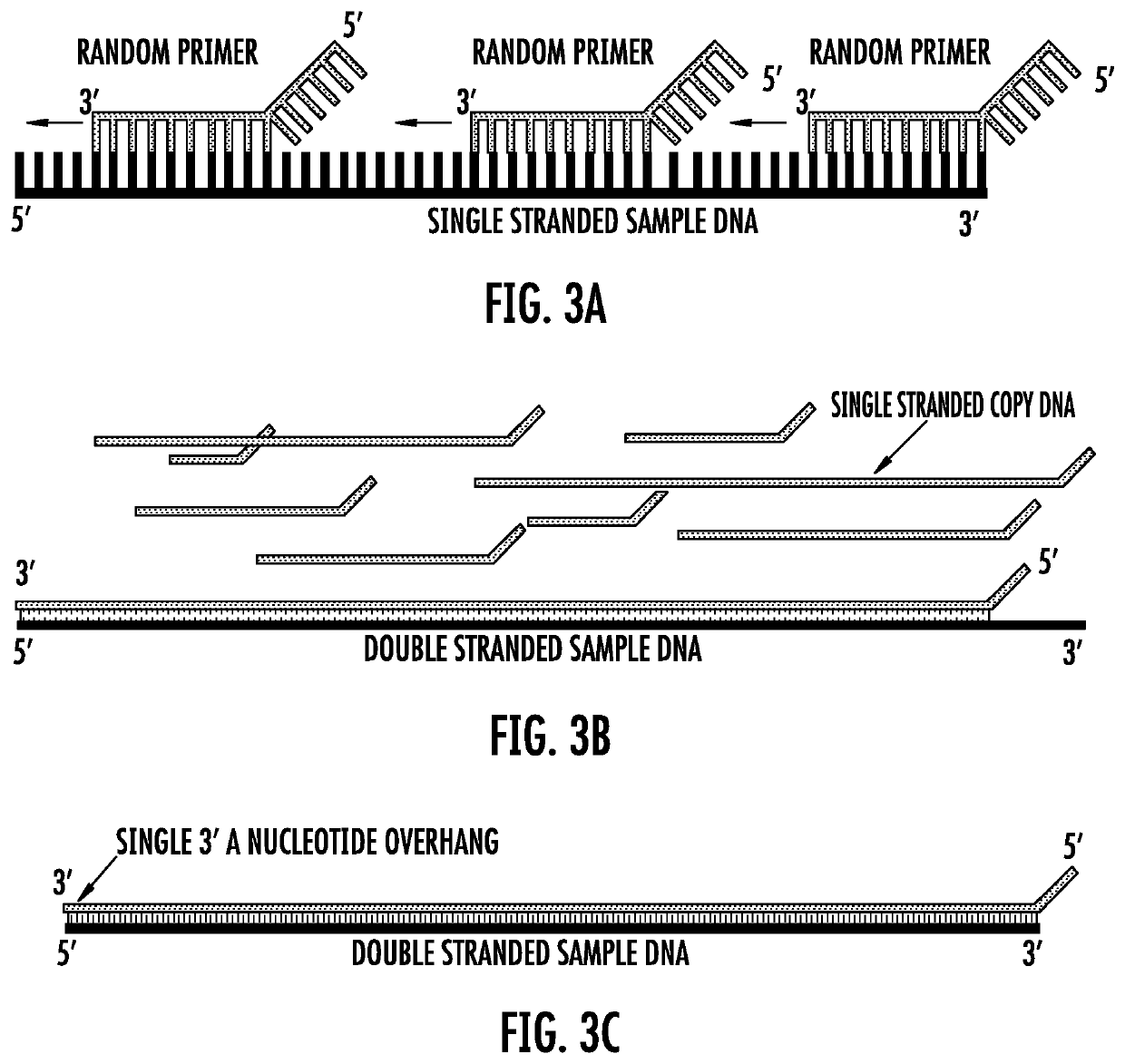
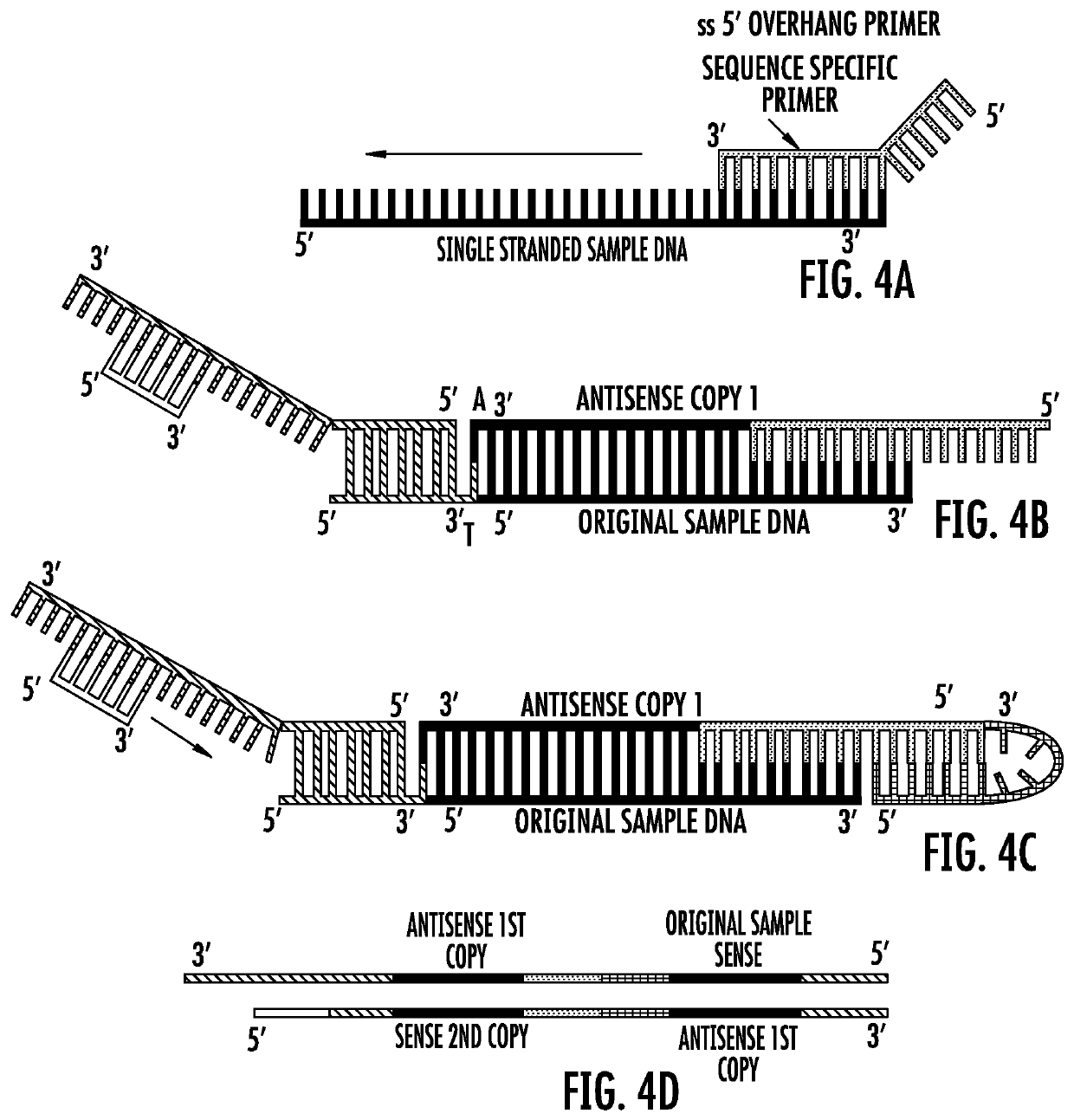
Provided are methods of nucleic acid sample preparation for analysis, including analysis using nanopore sequencing applications. In particular provided are methods that allow for the creation of circular and linear DNA samples that contain asymmetric ends to ligate different and desired adaptors to the end of the sample, methods to create single nucleic acid molecules that automatically form concatemers for higher sequencing throughput; methods to create multiple copies (temperature dependent, multi-primed, open-fold replication) of one original nucleic acid sample, or to create single nucleic acid molecules containing multiple copies of more than one original nucleic acid sample (concatemerized samples) for improved accuracy and throughput are described; and methods for improved modified base calling.
Owner:ROCHE SEQUENCING SOLUTIONS INC
Method for preparing active small peptide by establishing oligopeptide concatemer yeast expression plasmid
InactiveCN103194483AReduce development costsVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationYeastSmall peptide
The invention discloses a method for preparing an active small peptide by establishing an oligopeptide concatemer yeast expression plasmid, belongs to the technical field of biologic engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: amplifying by using an SOE-PCR (Splicing by Overlap Extension-Polymerase Chain Reaction) method so as to obtain a full-length gene of the oligopeptide; directionally and serially connecting the genes of a plurality of oligopeptides; establishing the obtained serial connected genes into an expression carrier of saccharomycete so as to convert the saccharomycete; and performing inducible expression on and the serial connected polypeptide and cutting into the target oligopeptide. The method has the characteristics that the various small molecule oligopeptides are effectively expressed by using saccharomycete, and the oligopeptides have important application values; and in addition, by utilizing the efficient expression of the serially connected oligopeptide plasmid, a product is very low in development cost.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Detection module and method
InactiveCN108823288AComprehensive detection effectVarious methodsMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle strandDigestion
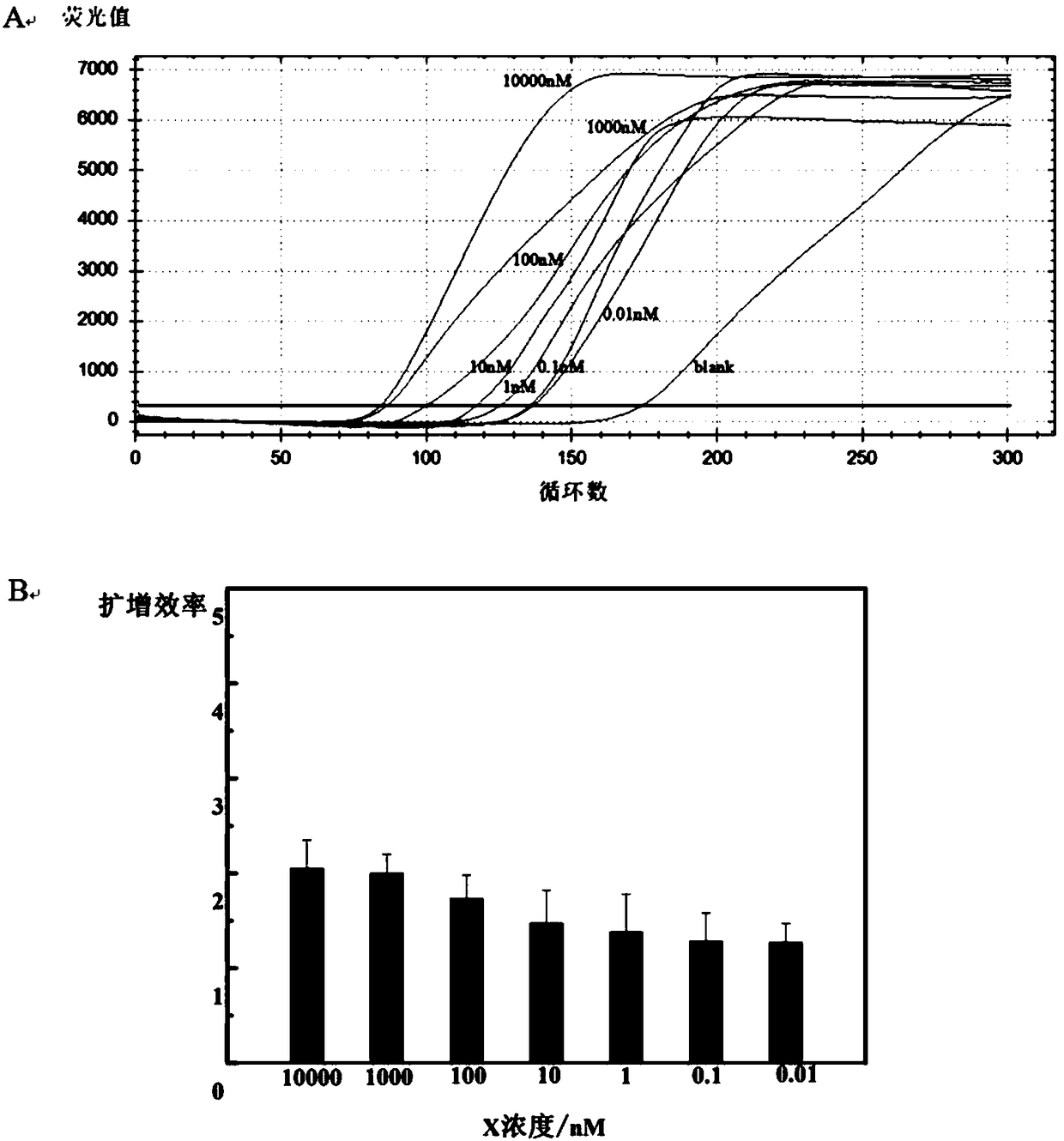
The invention provides a detection module and method. The detection module and method are established on the basis of an EXPAR (exponential amplification reaction) tandem digestion type HCR (hybridization chain reaction). When a to-be-detected object contains a target substance, a large quantity of digestion single strands are formed by amplification with the established module and method for an EXPAR, detection signals of the target substance are amplified, then the formed digestion single strands are used for digesting a modified digestion type HCR product, and the detection signals of the target substance are converted. In one specific embodiment, supermolecular double-strand concatemers are modified and upgraded by modifying hairpin structures used in the HCR, so that not only can DNAdouble strands be self-assembled by nucleic acid hairpins, but also the nucleic acid hairpins can be digested efficiently by nucleic acid single strands. Dual induction of signals is realized. In another embodiment, when the designed and modified digestion type hairpin sequences and digestion sequences are applied to practical detection, detection sensitivity is high, and 1nM X substrate can be detected at lowest.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com