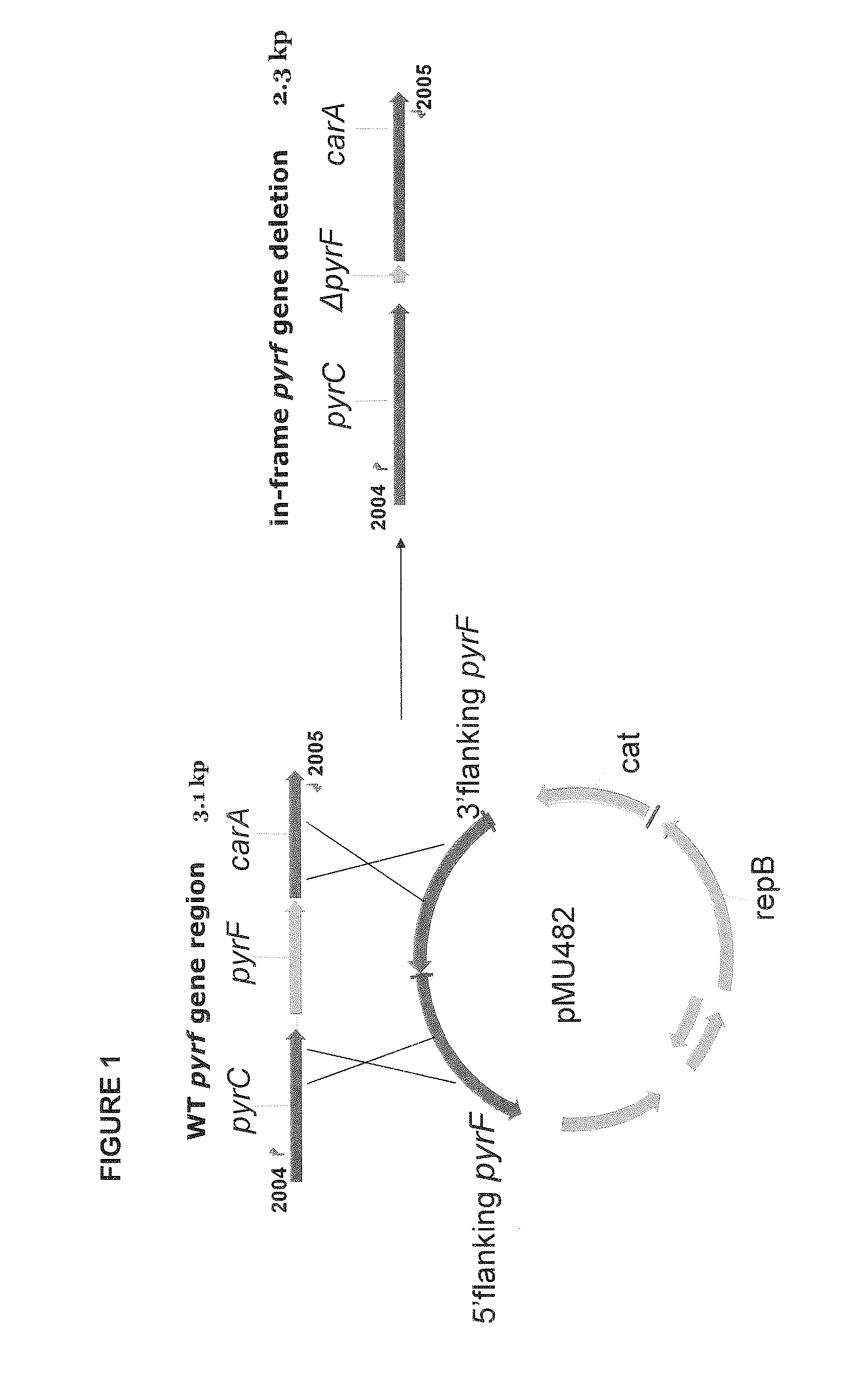
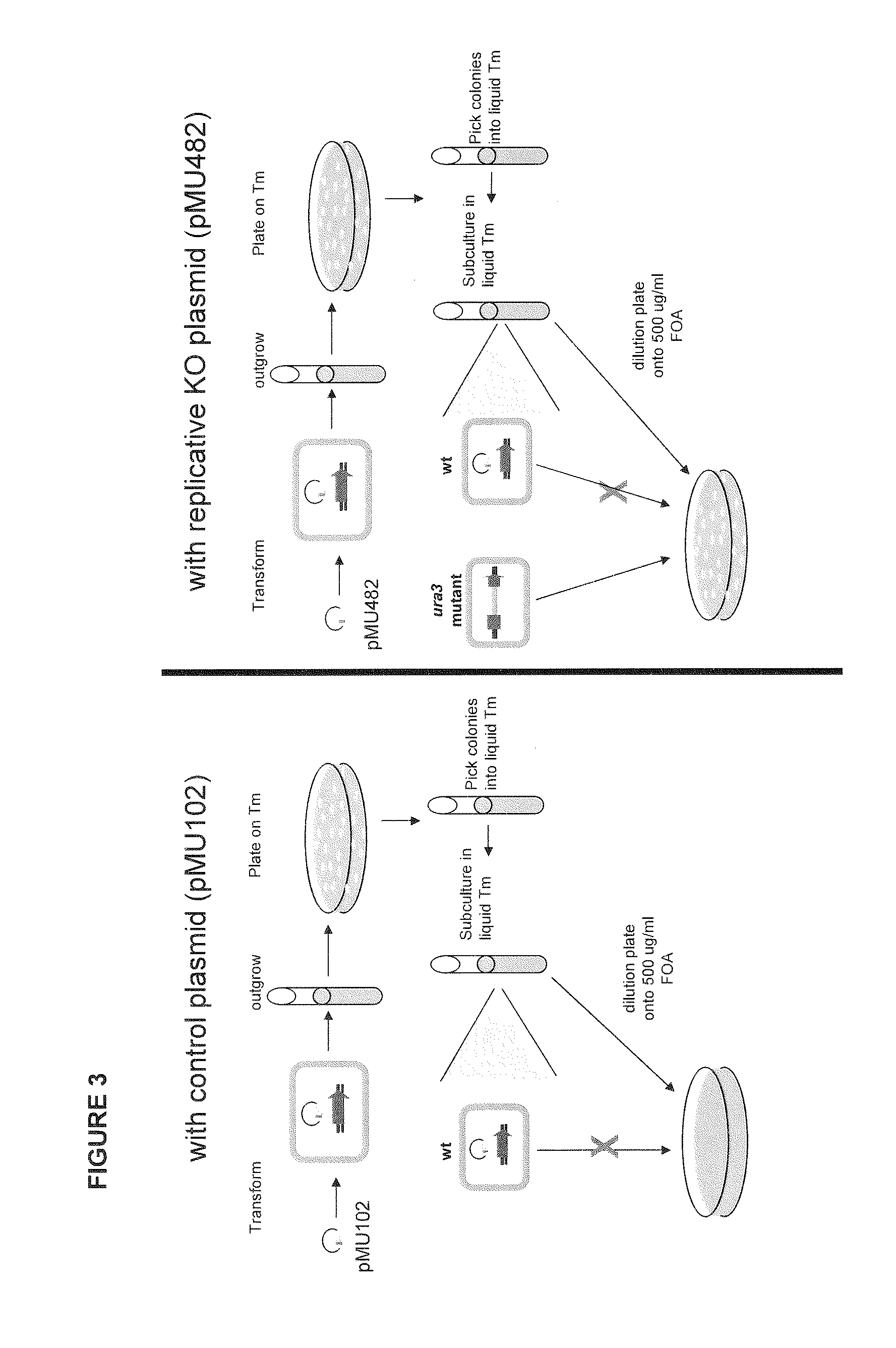
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46 results about "Negative selection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In natural selection, negative selection or purifying selection is the selective removal of alleles that are deleterious. This can result in stabilizing selection through the purging of deleterious genetic polymorphisms that arise through random mutations.
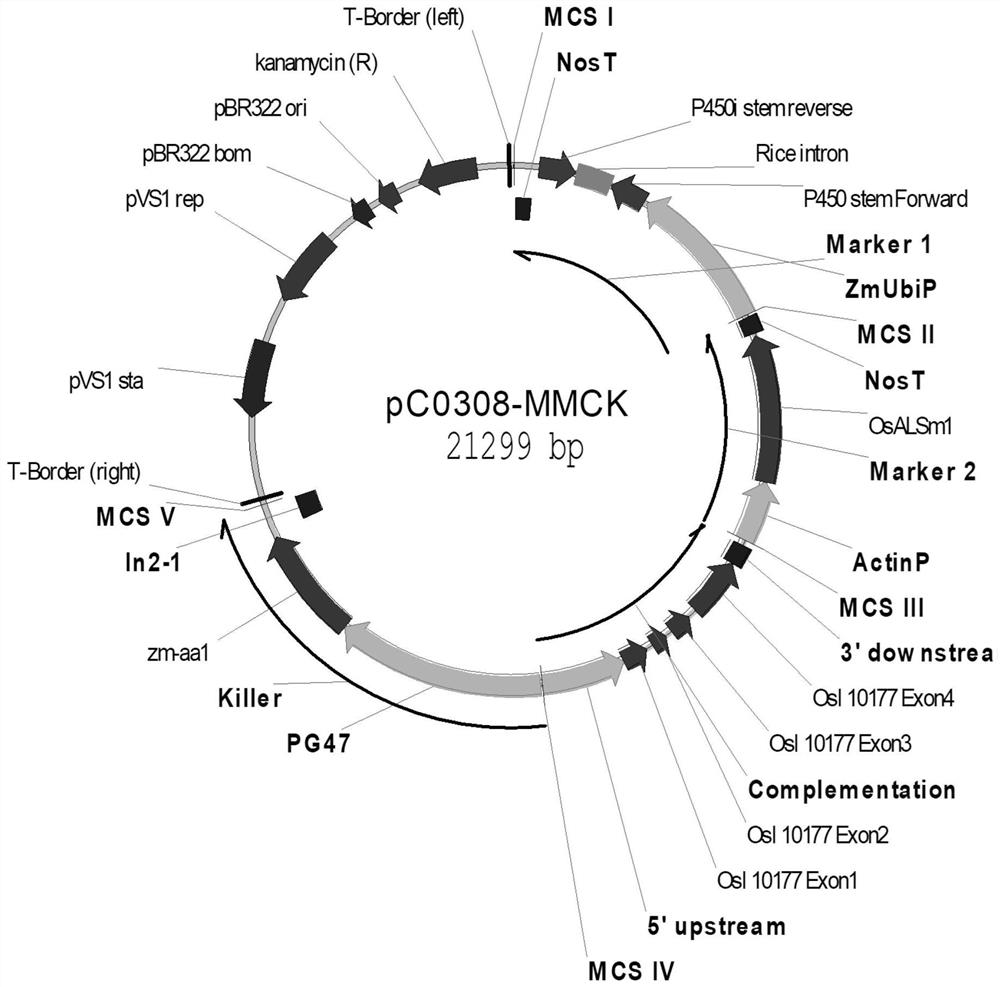
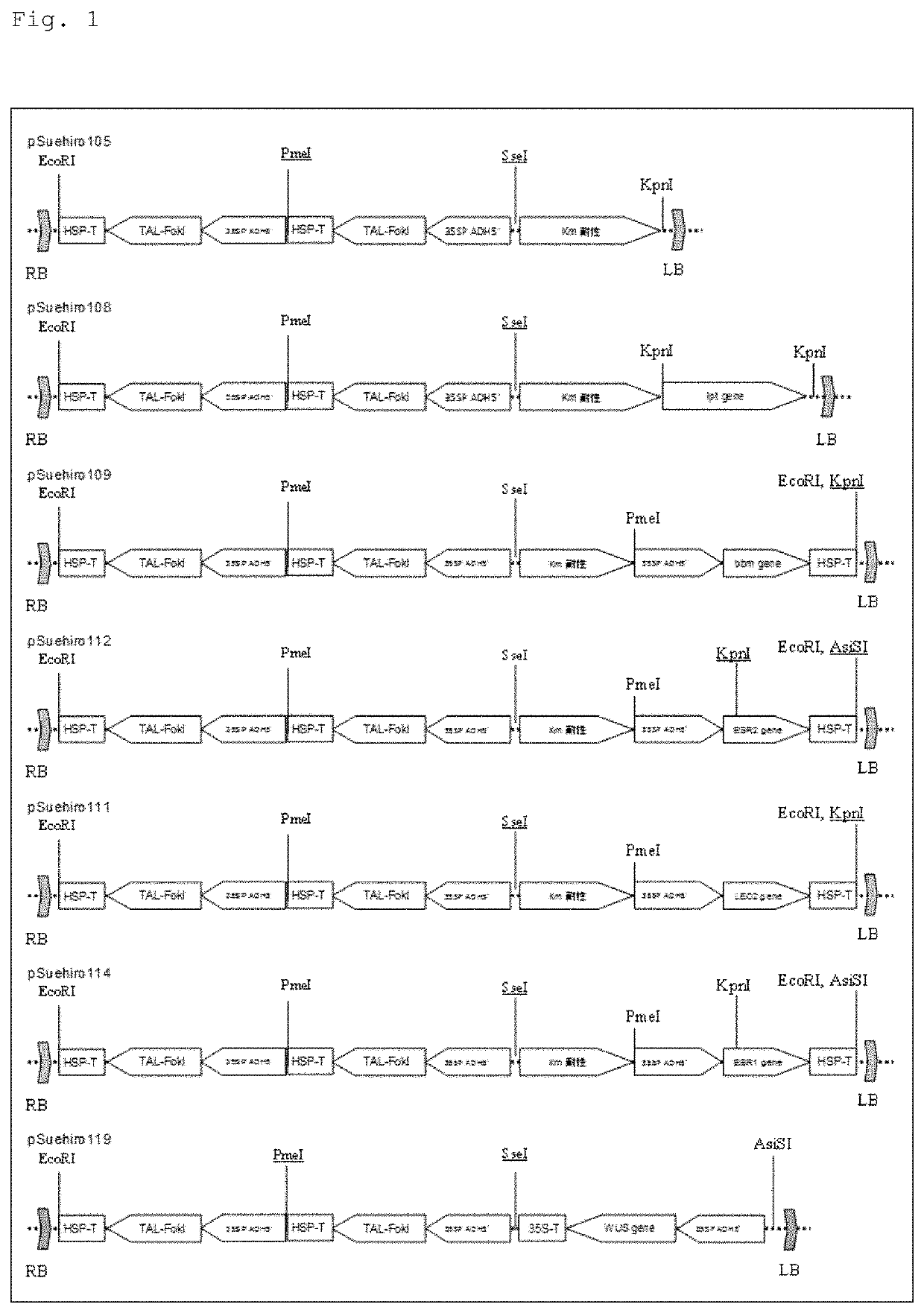
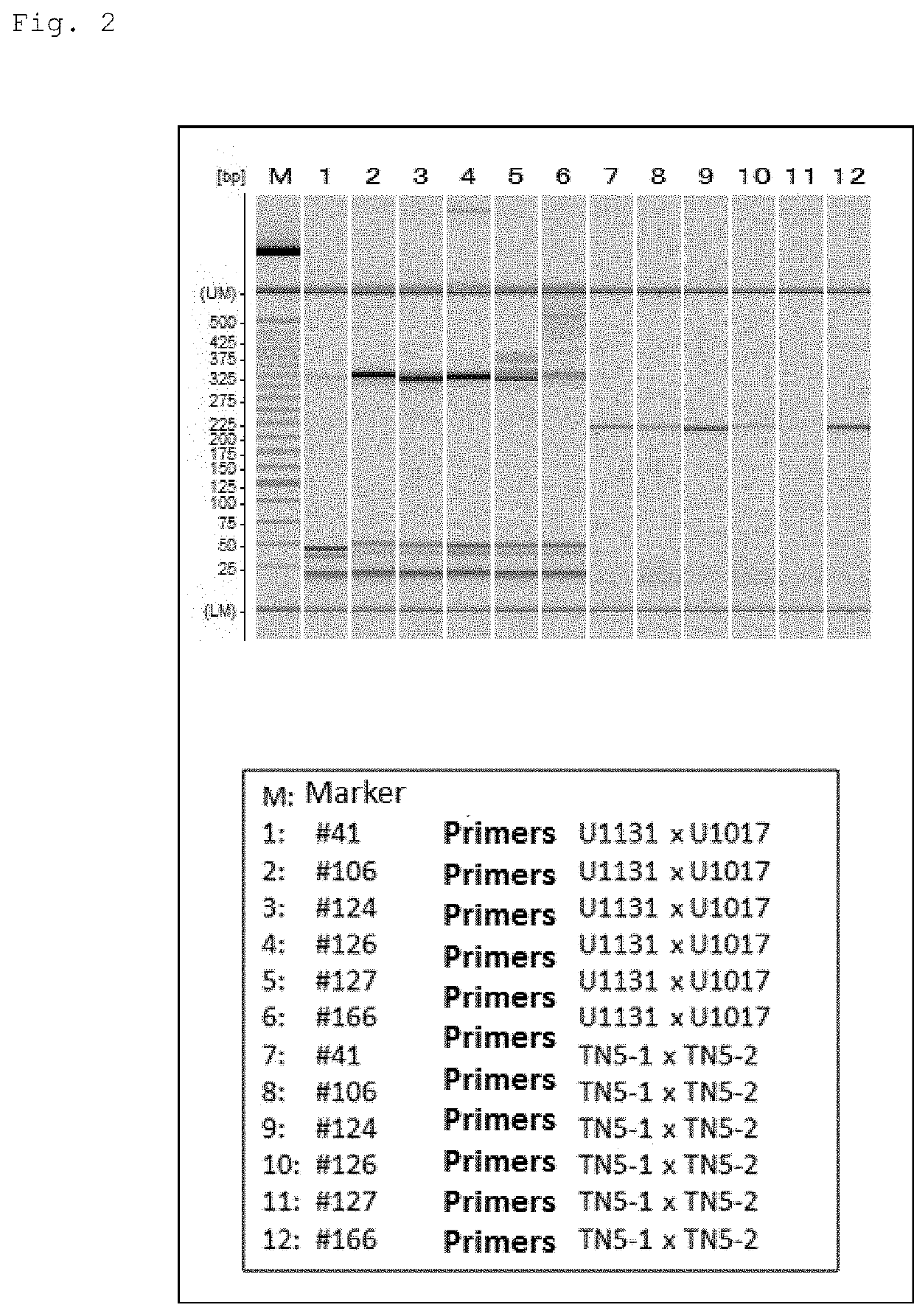
Overexpression porcine co-stimulatory 4-1BB vector and application thereof
InactiveCN105087620AHigh copy numberLower activation thresholdVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryInteinEmbryo
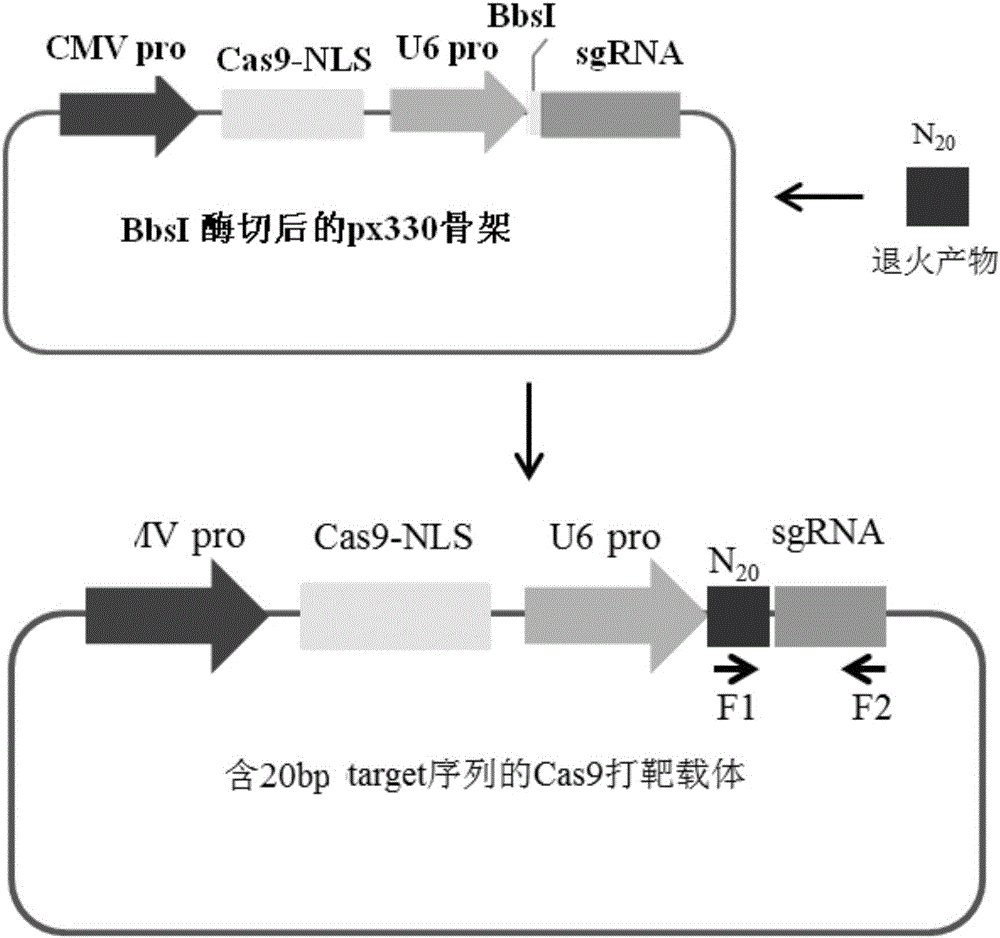
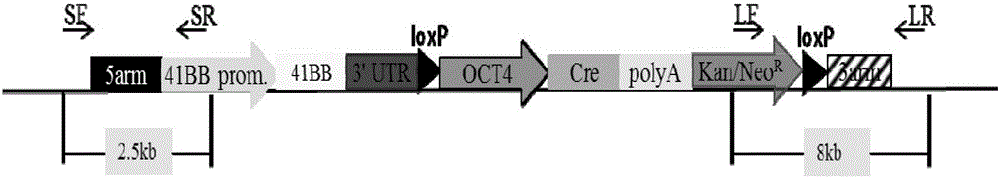
The invention provides an overexpression porcine co-stimulatory 4-1BB vector and application thereof. PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification is performed on a left homologous arm and a right homologous arm of an intron 1 of a rosa26 gene, a 4-1BB regulatory sequence and an OCT4 specific promoter; the left homologous arm, a 4-1BB expression cassette, LoxP locus-contained Cre and Neo expression cassettes, the right homologous arm and negative selection DTA diphtheria toxin are connected in sequence to obtain a 4-1BB homologous recombinant vector p4BOCNDR; the vector and a CRISPR / Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats / CRISPR-associated) targeting vector of sgRNA (small guide ribonucleic acid) containing the intron 1 of the specific targeting porcine rosa26 gene are transferred together into a porcine fetus fibroblast; by taking a positive cell as a donor cell and an oocyte as a recipient cell, a cloned embryo is obtained through a somatic cell nuclear transfer technique; the cloned embryo is transplanted into a porcine uterus for fetation to obtain a transgenic pig integrating a 4-1BB gene at the fixed point of a first intron of the rosa26 gene and automatically deleting a marker gene.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
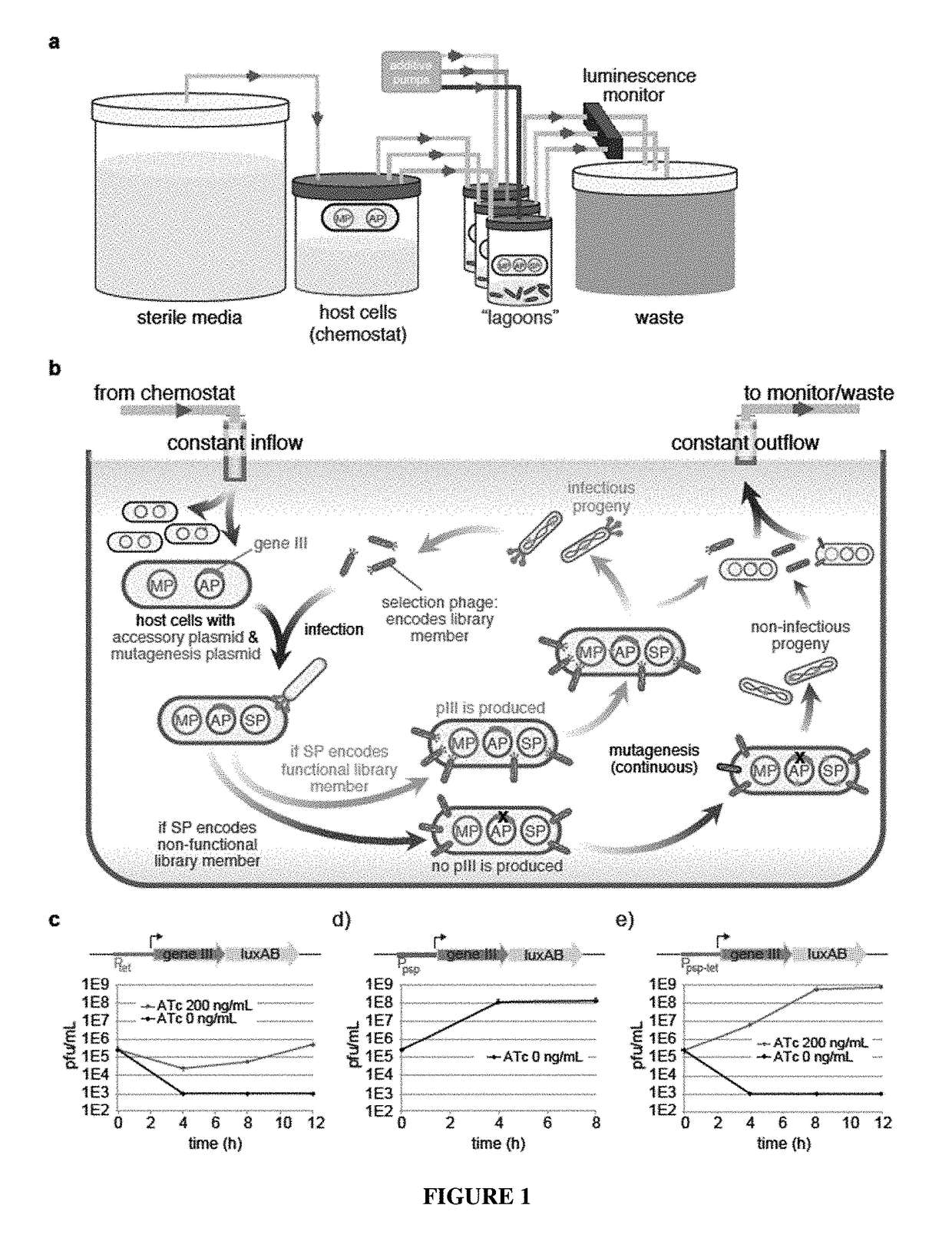
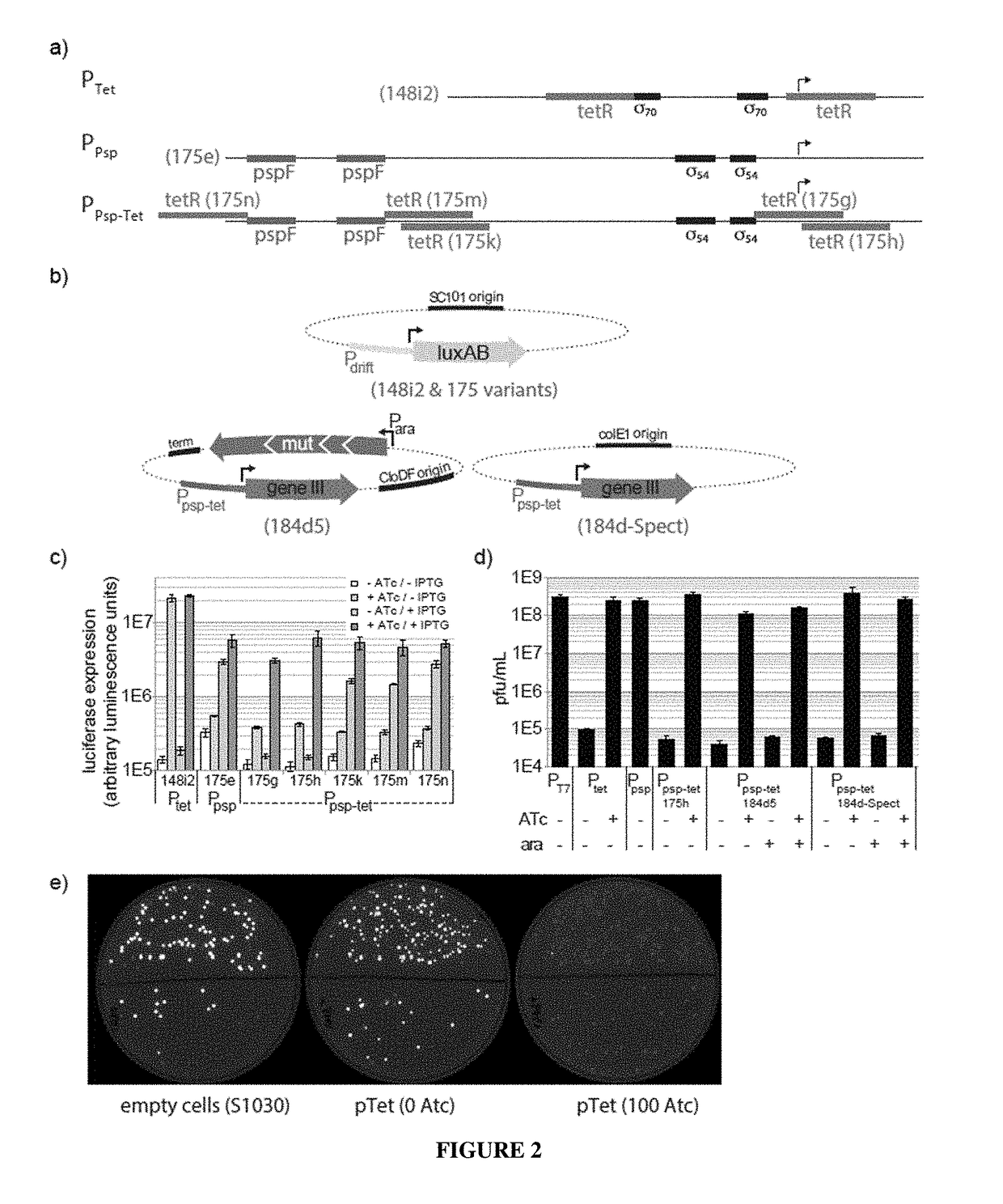
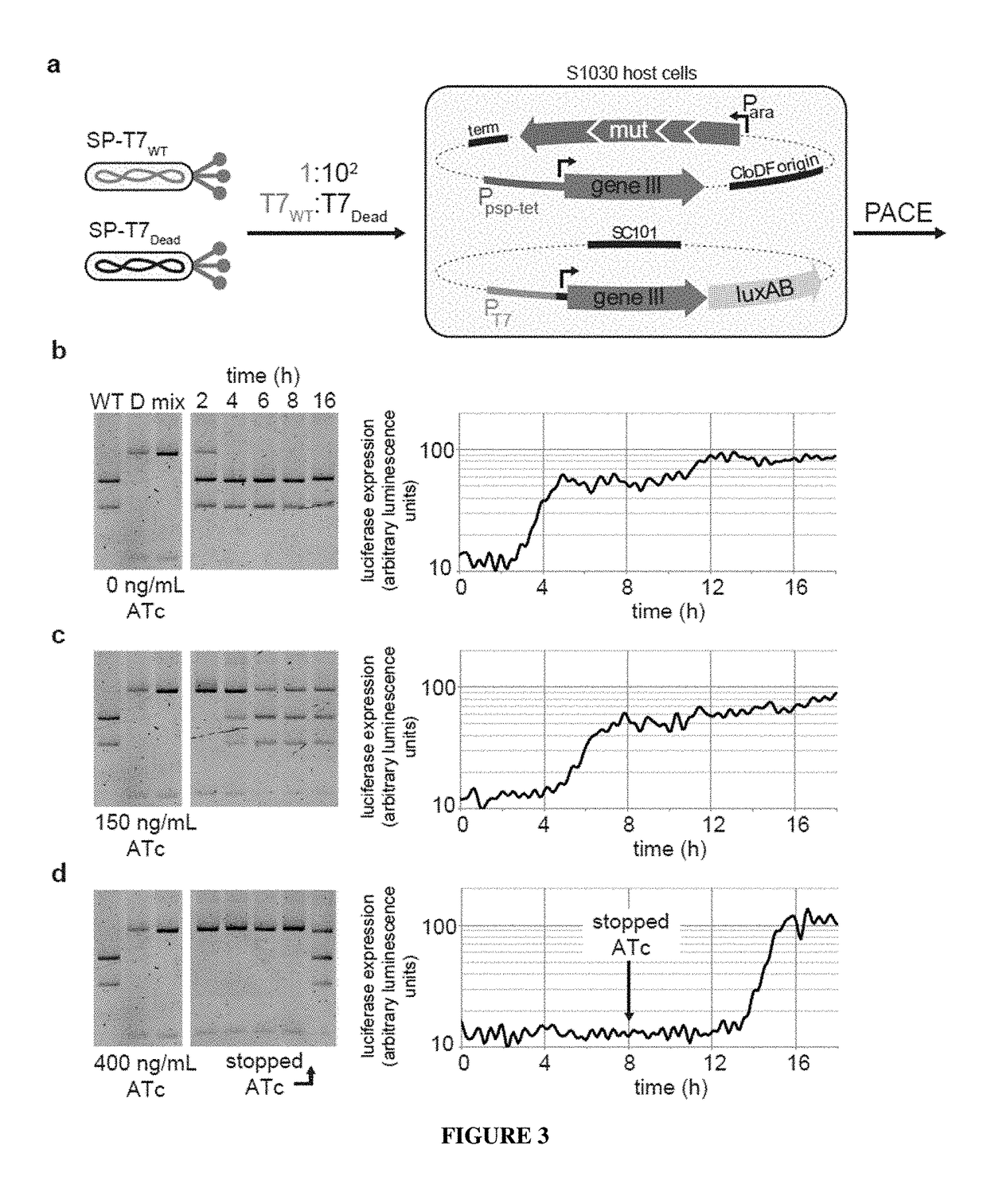
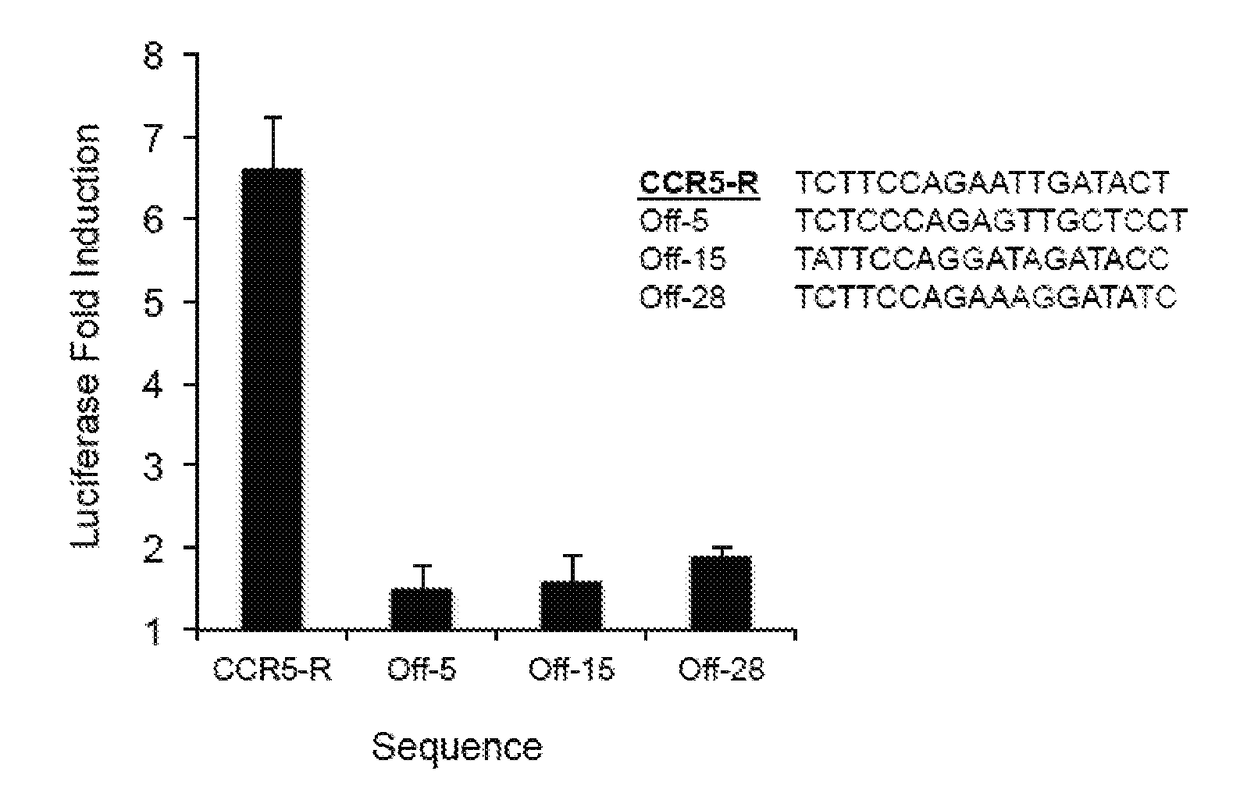
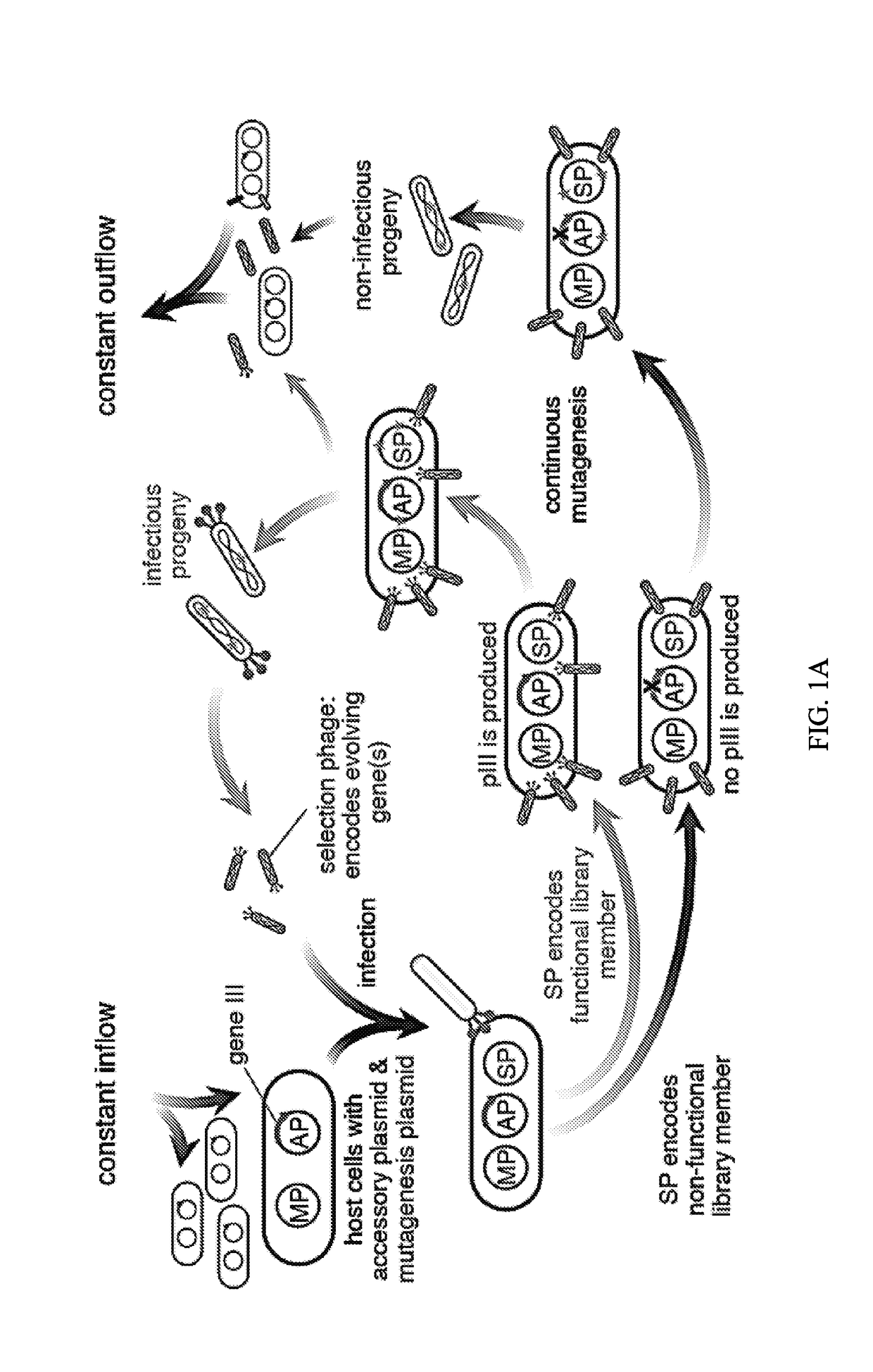
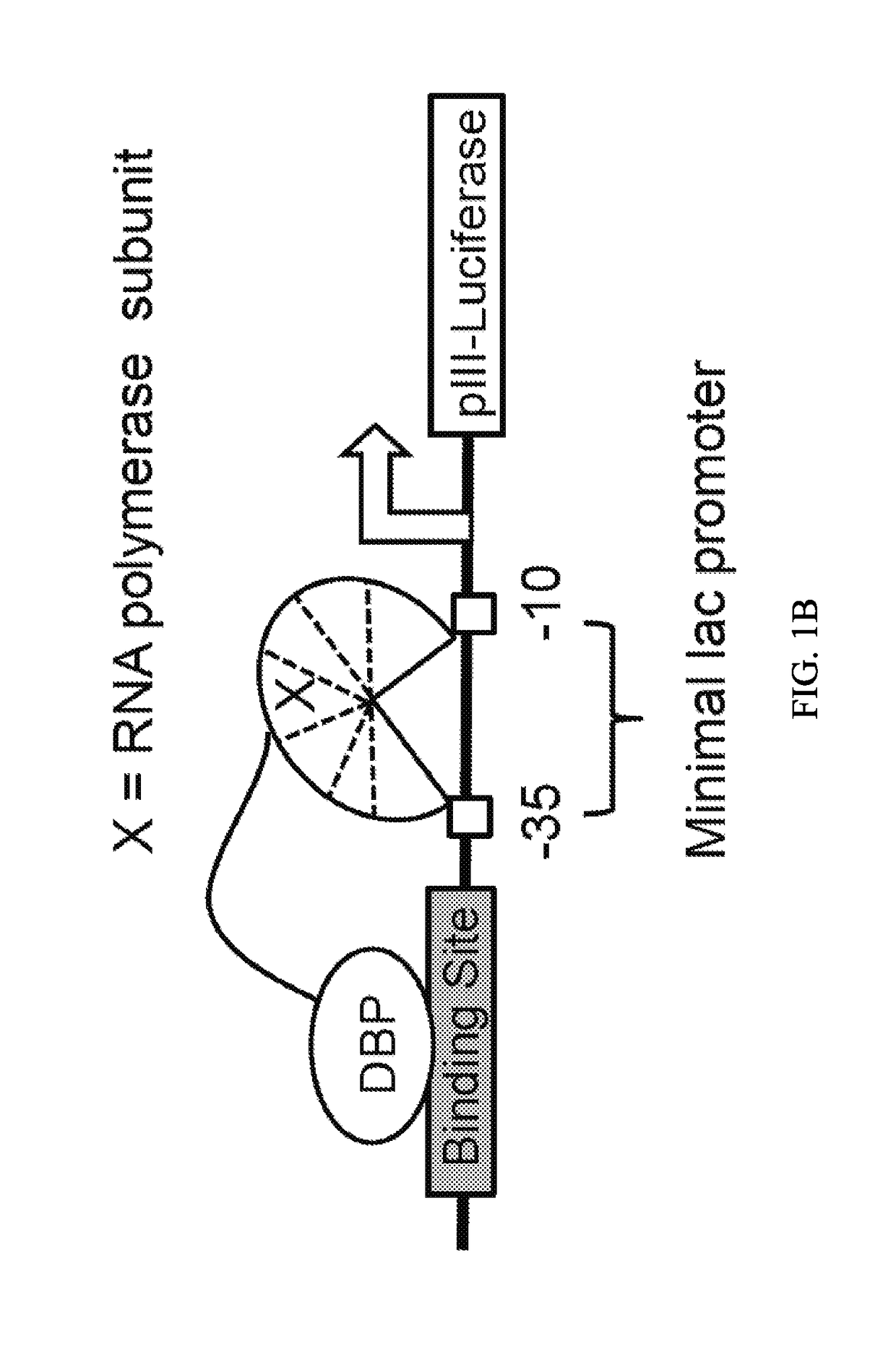
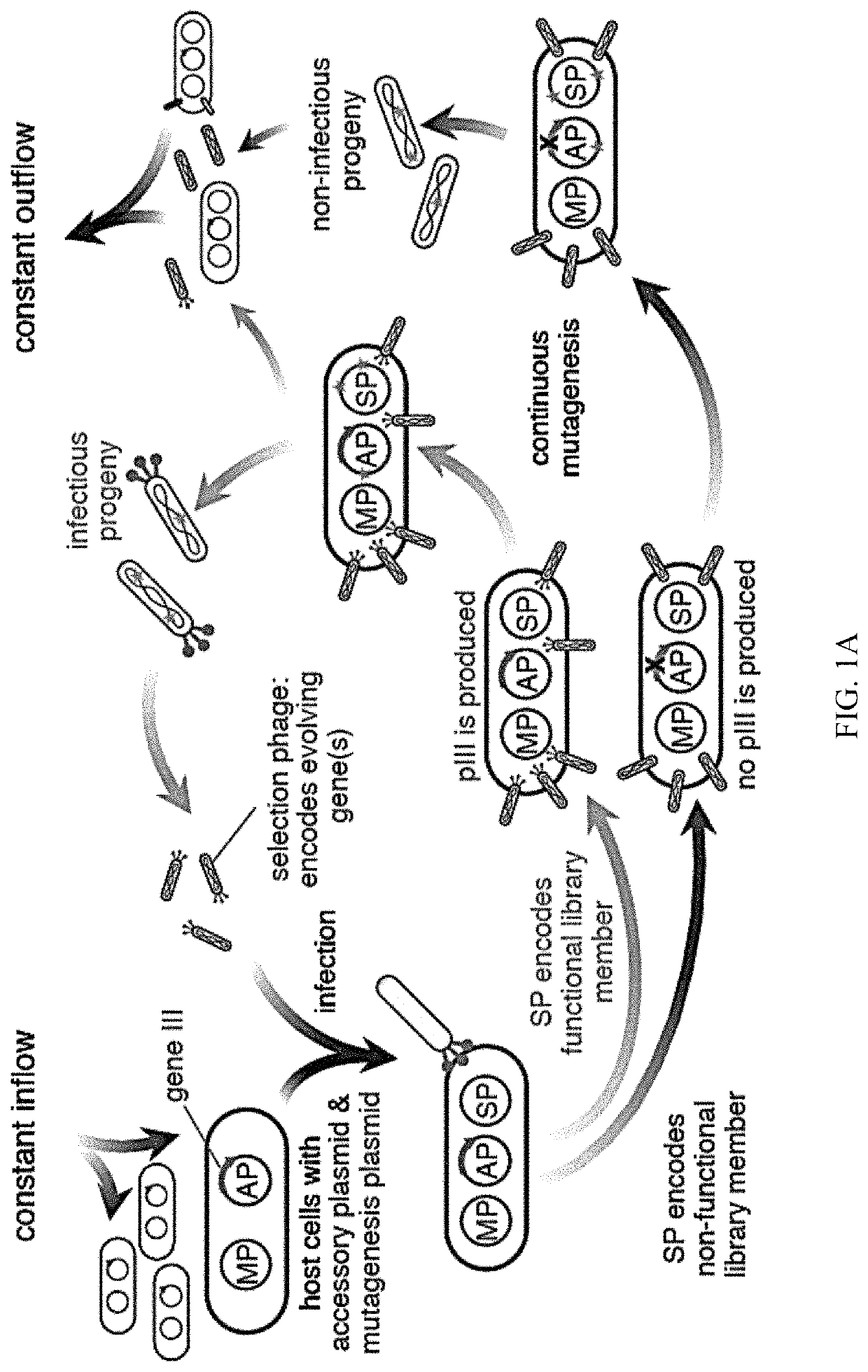
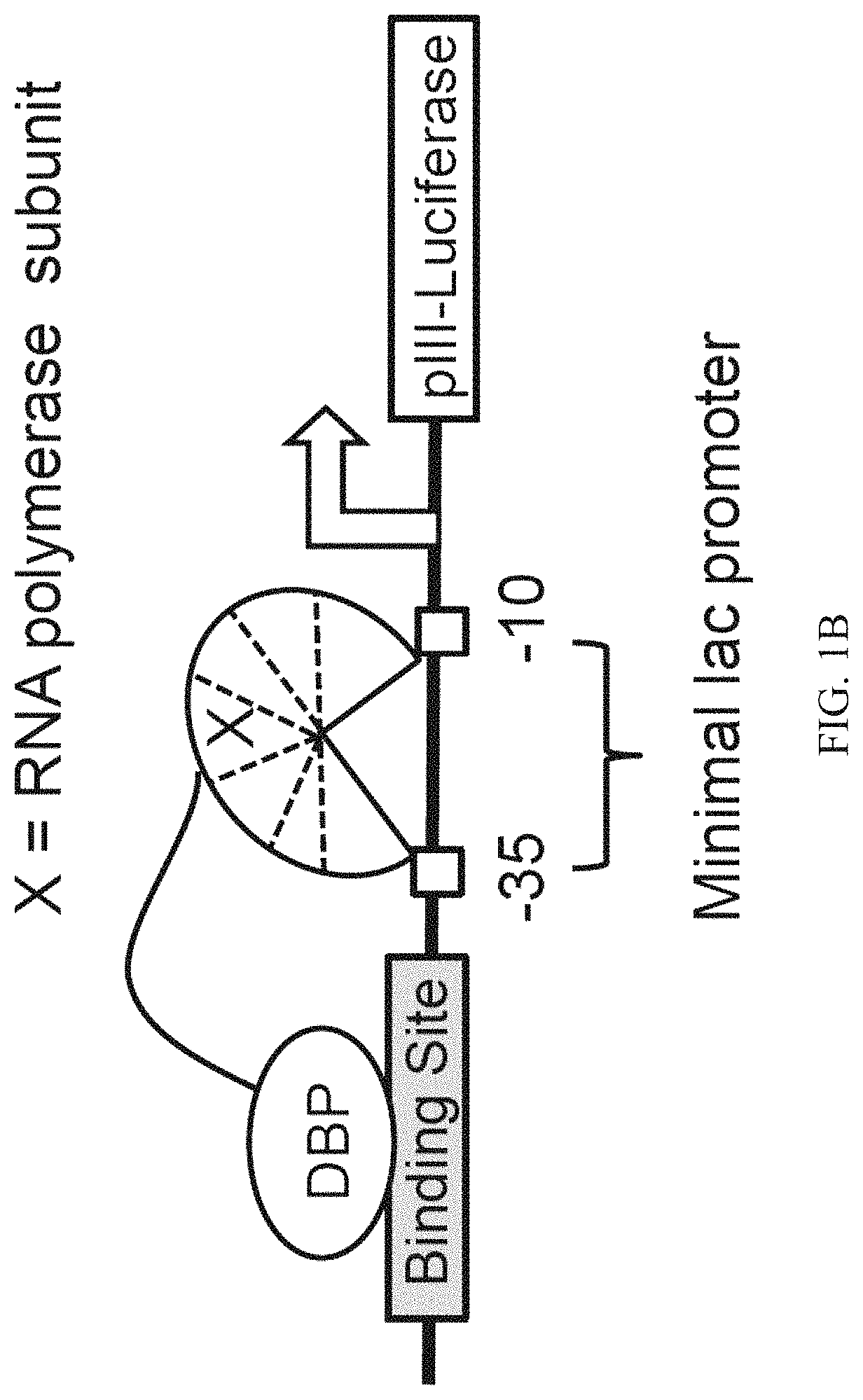
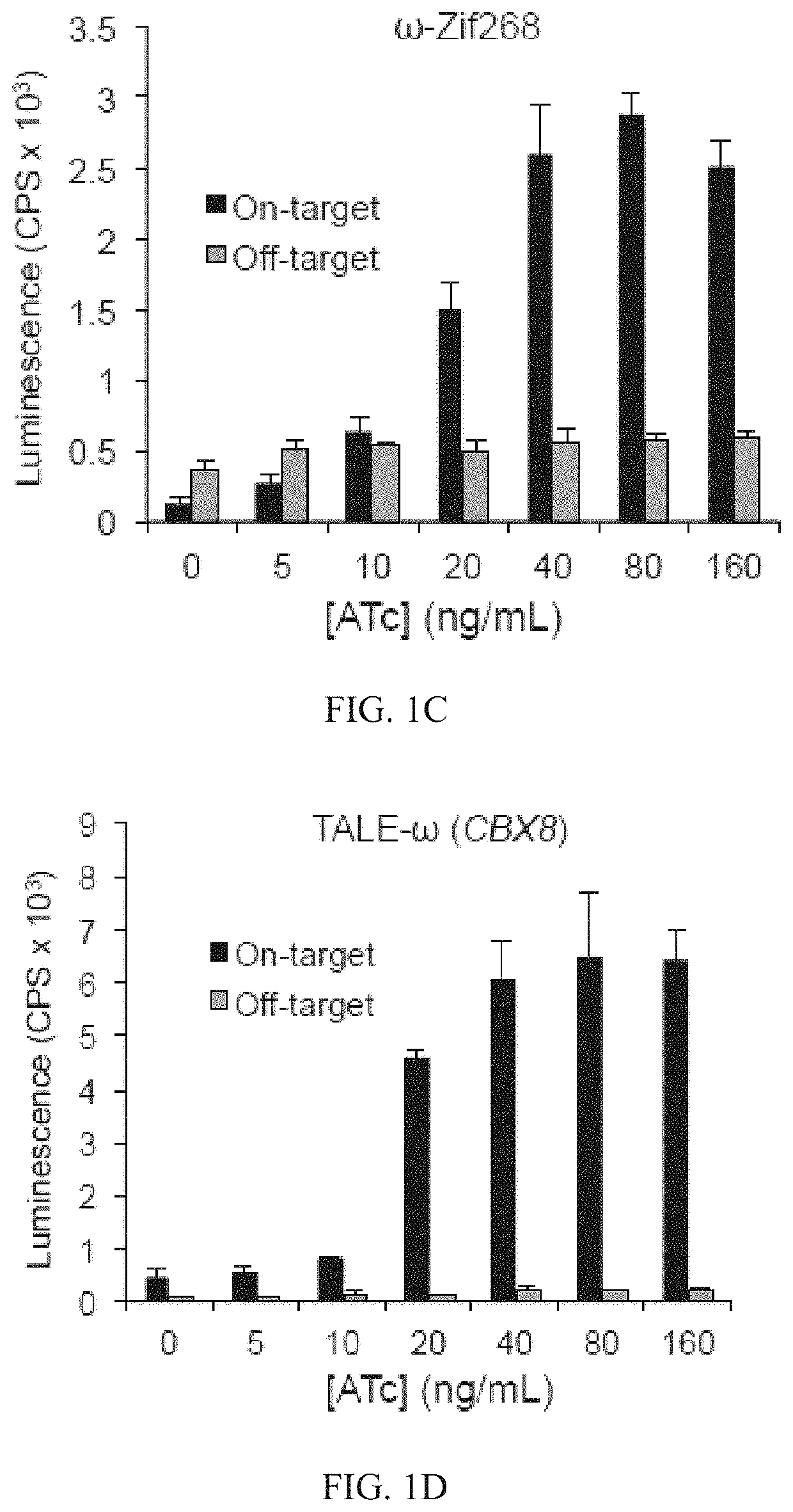
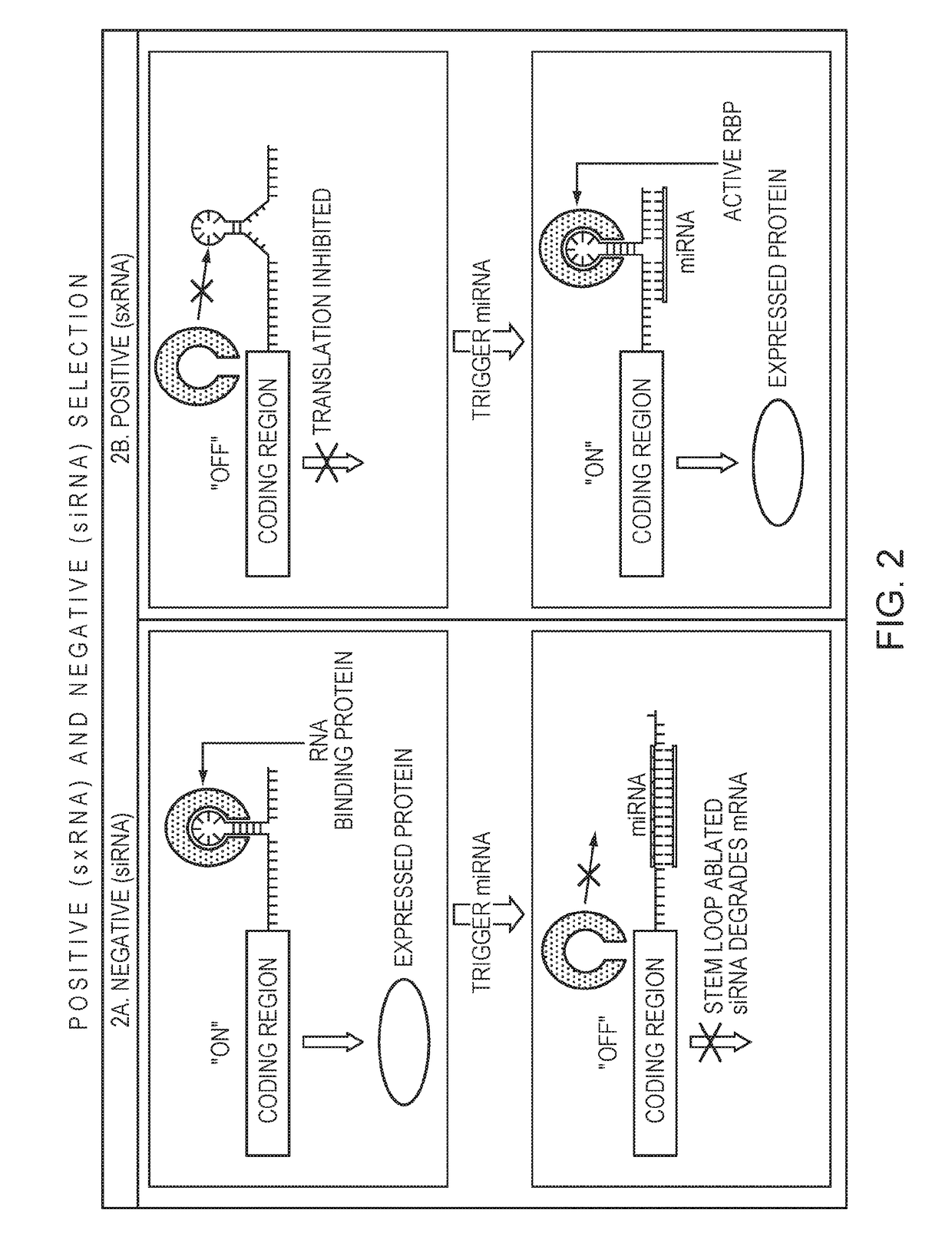
Negative selection and stringency modulation in continuous evolution systems
ActiveUS10179911B2High selectivityStrong specificityFusion with DNA-binding domainAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPositive selectionBiology
Strategies, systems, methods, reagents, and kits for phage-assisted continuous evolution are provided herein. These include strategies, systems, methods, reagents, and kits allowing for stringency modulation to evolve weakly active or inactive biomolecule variants, negative selection of undesired properties, and / or positive selection of desired properties.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Evolution of talens
ActiveUS20200277587A1Strong specificityHydrolasesGenetic therapy composition manufactureNucleotideEpigenetic Profile
Engineered transcriptional activator-like effectors (TALEs) are versatile tools for genome manipulation with applications in research and clinical contexts. One current drawback of TALEs is that the 5′ nucleotide of the target is specific for thymine (T). TALE domains with alternative 5′ nucleotide specificities could expand the scope of DNA target sequences that can be bound by TALEs. Another drawback of TALEs is their tendency to bind and cleave off-target sequence, which hampers their clinical application and renders applications requiring high-fidelity binding unfeasible. This disclosure provides methods and strategies for the continuous evolution of proteins comprising DNA-binding domains, e.g., TALE domains. In some aspects, this disclosure provides methods and strategies for evolving such proteins under positive selection for a desired DNA-binding activity and / or under negative selection against one or more undesired (e.g., off-target) DNA-binding activities. Some aspects of this disclosure provide engineered TALE domains and TALEs comprising such engineered domains, e.g., TALE nucleases (TALENs), TALE transcriptional activators, TALE transcriptional repressors, and TALE epigenetic modification enzymes, with altered 5′ nucleotide specificities of target sequences. Engineered TALEs that target ATM with greater specificity are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Evolution of talens
ActiveUS20180237758A1Strong specificityHydrolasesGenetic therapy composition manufactureDNA-binding domainOff targets
Engineered transcriptional activator-like effectors (TALEs) are versatile tools for genome manipulation with applications in research and clinical contexts. One current drawback of TALEs is that the 5′ nucleotide of the target is specific for thymine (T). TALE domains with alternative 5′ nucleotide specificities could expand the scope of DNA target sequences that can be bound by TALEs. This disclosure provides methods and strategies for the continuous evolution of proteins comprising DNA-binding domains, e.g., TALE domains. In some aspects, this disclosure provides methods and strategies for evolving such proteins under positive selection for a desired DNA-binding activity and / or under negative selection against one or more undesired (e.g., off-target) DNA-binding activities. Some aspects of this disclosure provide engineered TALE domains and TALEs comprising such engineered domains, e.g., TALE nucleases (TALENs), TALE transcriptional activators, TALE transcriptional repressors, and TALE epigenetic modification enzymes, with altered 5′ nucleotide specificities of target sequences. Engineered TALEs that target ATM with greater specificity are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Evolution of TALENs
ActiveUS10612011B2Strong specificityHydrolasesGenetic therapy composition manufactureNucleotideEpigenetic Profile
Engineered transcriptional activator-like effectors (TALEs) are versatile tools for genome manipulation with applications in research and clinical contexts. One current drawback of TALEs is that the 5′ nucleotide of the target is specific for thymine (T). TALE domains with alternative 5′ nucleotide specificities could expand the scope of DNA target sequences that can be bound by TALEs. This disclosure provides methods and strategies for the continuous evolution of proteins comprising DNA-binding domains, e.g., TALE domains. In some aspects, this disclosure provides methods and strategies for evolving such proteins under positive selection for a desired DNA-binding activity and / or under negative selection against one or more undesired (e.g., off-target) DNA-binding activities. Some aspects of this disclosure provide engineered TALE domains and TALEs comprising such engineered domains, e.g., TALE nucleases (TALENs), TALE transcriptional activators, TALE transcriptional repressors, and TALE epigenetic modification enzymes, with altered 5′ nucleotide specificities of target sequences. Engineered TALEs that target ATM with greater specificity are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Positive and negative selectable markers for use in thermophilic organisms
InactiveUS20130052646A1BacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementThermophilic organismGenetic marker
The present invention relates to the field of molecular biology and genetic tool development in thermophilic bacteria. In particular, it relates to the use of positive and / or negative selection markers that can be used to efficiently select modified strains of interest. By providing such capabilities, the disclosed invention facilitates the recycling of genetic markers in thermophilic bacterial host cells. The present invention also allows the creation of unmarked strains. The genetic tools disclosed in the present invention are prerequisites for making targeted higher order mutations in a single thermophilic strain background.
Owner:MASCOMA CORPORATION
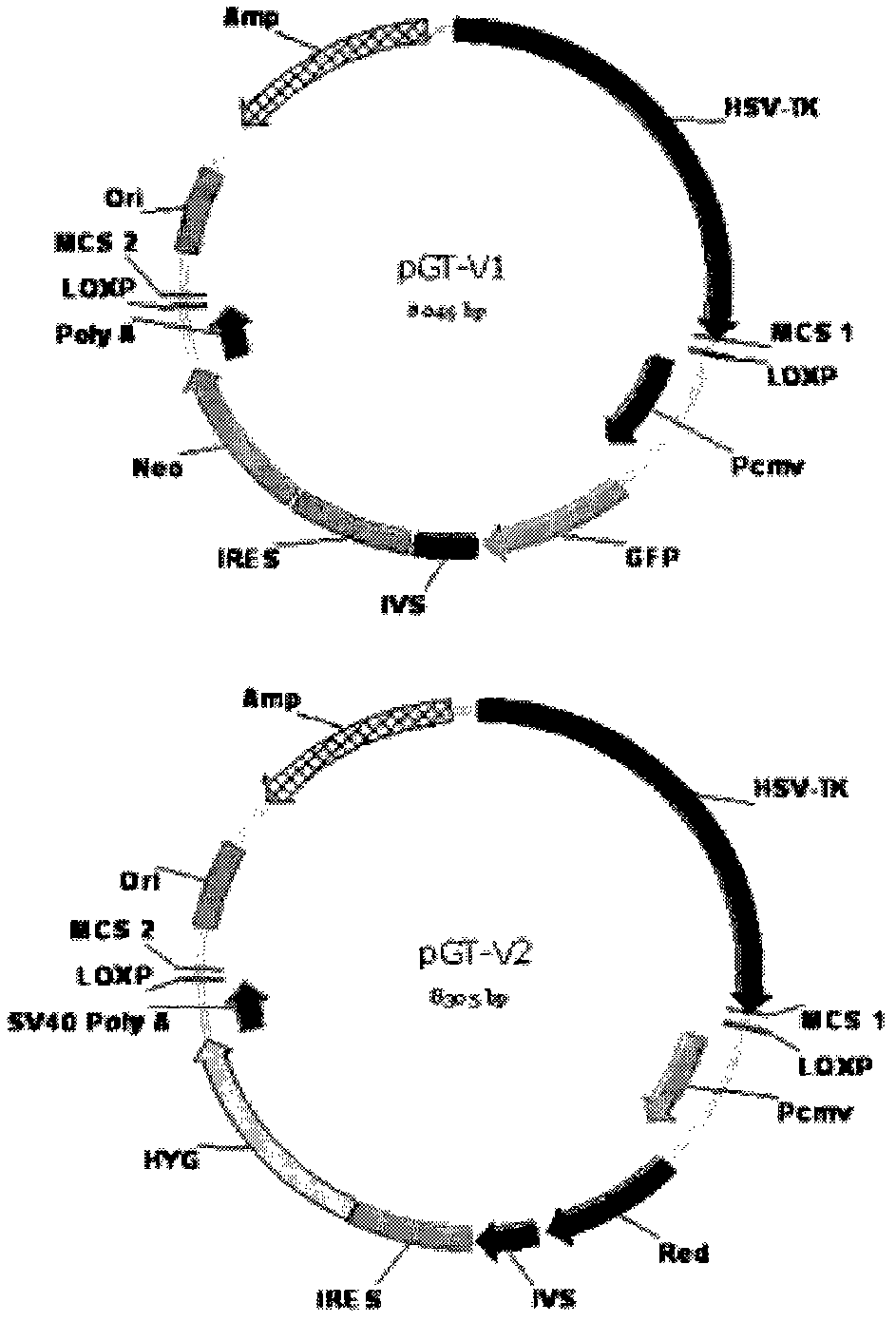
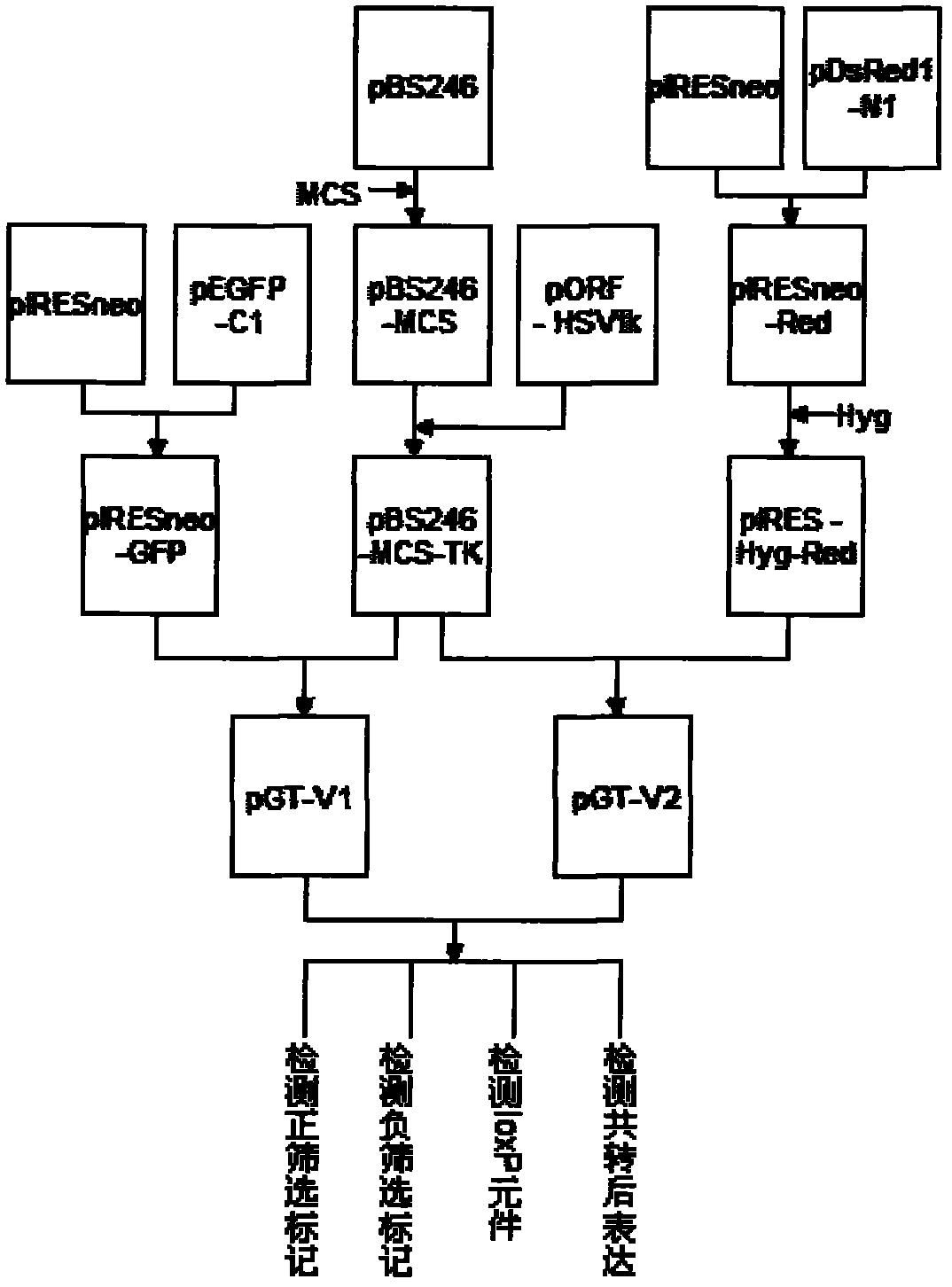
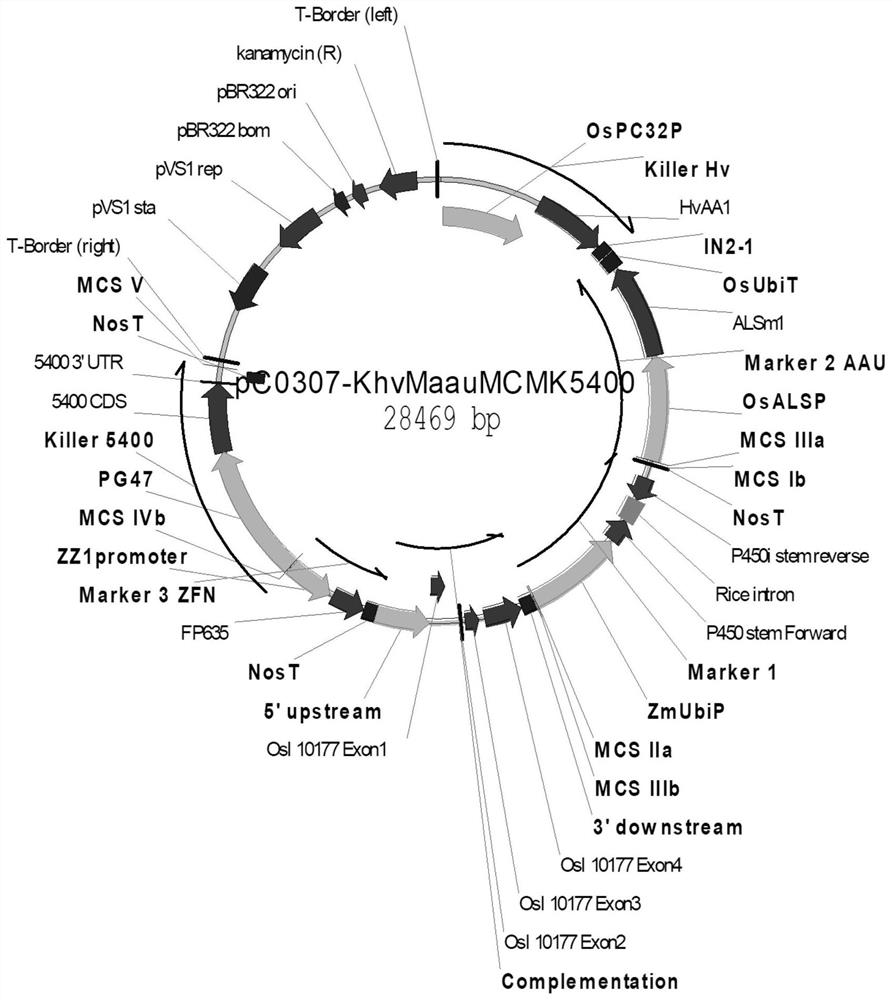
Allele double knockout targeting vector system and construction method thereof
InactiveCN102094036AHigh target shooting efficiencyShorten experiment timeVector-based foreign material introductionFluorescenceTransgene
The invention relates to an allele double knockout targeting vector system and a construction method thereof. The system of the invention consists of two complementary vectors, namely pGT-V1 and pGT-V2, wherein each vector contains two in phase LoxP elements which contain a positive selection marker gene Neo / GFP and Hyg / RFP respectively; and the outside of each vector contains a negative selection marker gene TK. Meanwhile, two 8-basic group multiple cloning sites are designed and arranged between the two LoxP elements and the negative selection marker for the insertion of the homology arm. By adopting the constructed targeting vector system of the invention, two complementary targeting vectors are cotransfected into the recipient cell; through the selection of drug and fluorescent double-selection marker, the genetic modification or knockout of the two alleles of the target gene can be realized once; and the interaction of the transfected Cre enzyme and the LoxP elements can be utilized to remove the selection marker gene integrated with the genome, the time of obtaining the homozygous knockout target cell can be shortened, the safety of the transgenic animal can be increased and a valuable technology platform is provided to develop the animal transgenic researches.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
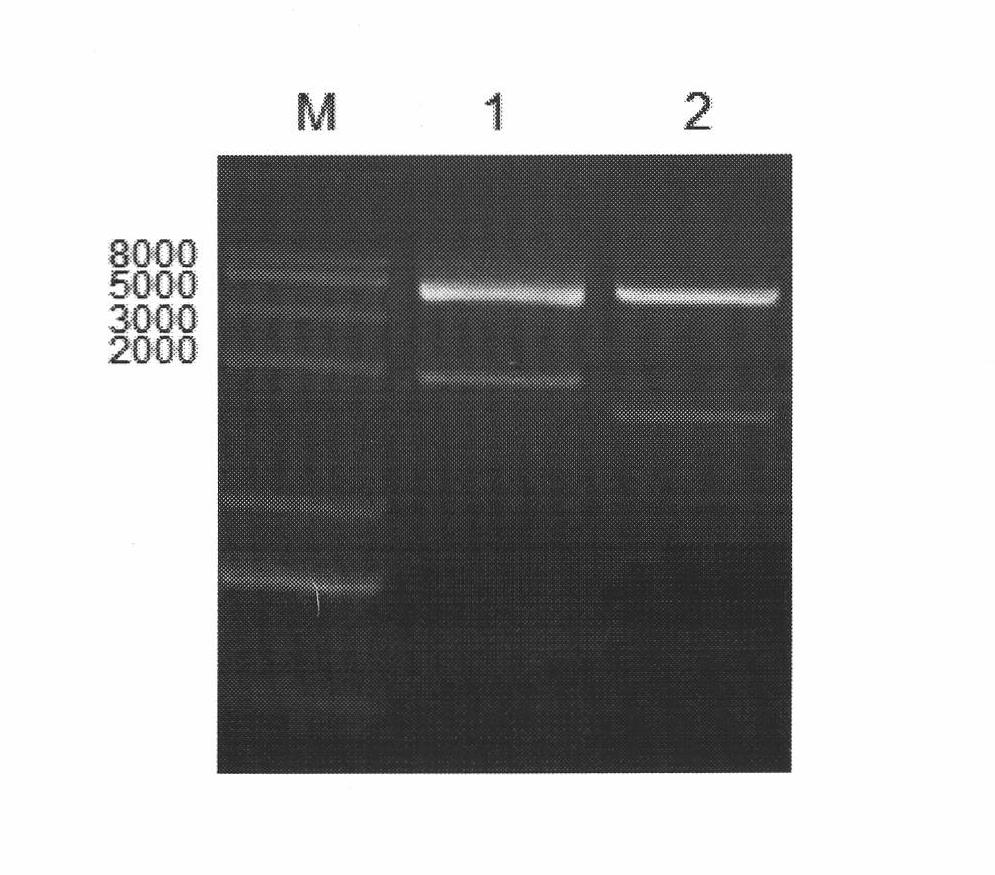
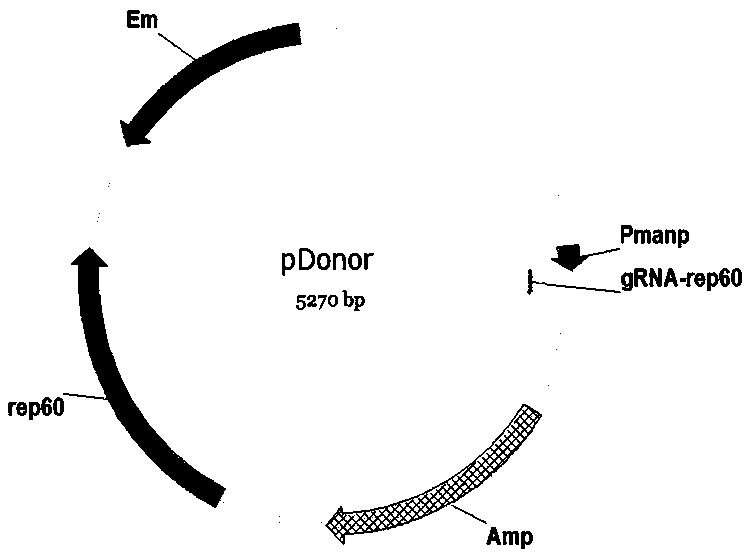
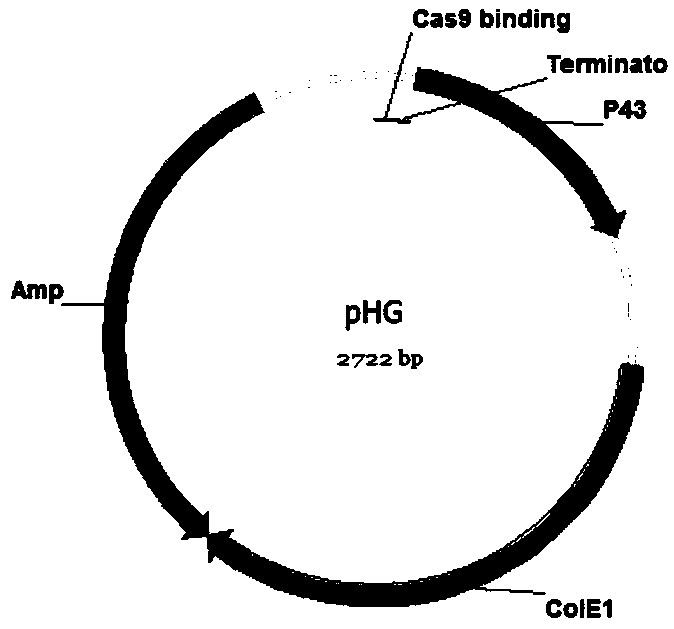
Bacillussubtilis CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing system
ActiveCN110628798AImprove efficiencyHigh precisionHydrolasesNucleic acid vectorMulti siteGenome editing
The invention discloses a bacillussubtilis CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing system. A building method of the system comprises the following steps of (1) building a plasmid pBSCas9; (2) building a plasmid pDonor; (3) building an auxiliary plasmid pHG in a multi-site gRNA expression process; and (4) forming the bacillussubtilis CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing system by the pBSCas9, the pDonor and the pHG. Thebacillussubtilis CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing system solves the problems in the existing bacillussubtilis conventional genome editing technology; no negative selection marker is introduced; and a CRISPR-Cas9 and CRISPR-Cas9n genome non-trace editing system with high efficiency and high precision is built. The single-site and multi-site different-type gene editing operation can be realized; and meanwhile, the iterative editing cycle of an editing flow process can be realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Genetic intelligent seed breeding and production system for crossbreeding and production of crops and application thereof
PendingCN113621642ARealize comprehensive utilizationAchieve commercial productionVector-based foreign material introductionPlant protectionBiotechnologyPositive selection
The invention provides a genetic intelligent seed breeding and production system for crossbreeding and production of crops and application thereof. The system contains a GAT system vector, and the vector comprises five functional element expression cassettes: a plant male fertility restoration gene element expression cassette used for restoring male fertility of recessive genic male sterility mutants, a plant pollen abortion gene element expression cassette used for removing pollen containing GAT and keeping a heterozygotic state or a hemizygotic state of a GAT maintainer line, a chemical herbicide positive selection expression cassette used for gene transformation and GAT maintainer line impurity removal and purification, a chemical herbicide negative selection expression cassette used for removing herbicide-sensitive GAT maintainer line pollen and seed escape and removing impurities and purifying a GAT sterile line, and a seed screening element expression cassette used for mechanically sorting seeds. The system can be used for crossbreeding and hybrid seed production of plant recessive genic male sterility materials, so that new varieties of plants with high quality, high yield, wide applicability and high resistance and seeds of the plants are obtained.
Owner:HAINAN BOLIAN RICE GENE TECH CO LTD
Path coverage test data generation method based on a negative selection genetic algorithm
ActiveCN109918307AIncrease coverageReduce generationGenetic modelsSoftware testing/debuggingTest efficiencyDynamical optimization
The invention discloses a path coverage test data generation method based on a negative selection genetic algorithm which aims to ensure that generated test data has a relatively high coverage rate and contain least redundant data, thereby improving the quality of the test data and the efficiency of software testing. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, generating an initial population of a negative selection genetic algorithm in a supervised manner according to a negative selection generation strategy. Then, according to a negative selection detection strategy, dynamically optimizing population data of a negative selection genetic algorithm, and evolving to generate test data covering the target path. The test data generated by the conventional method only guarantees the coverage of a target path. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that the number of generated test data cannot be guaranteed to be minimum, a large number of redundant test data arecontained, the problems can be effectively solved, generation of redundant test data is reduced, premature convergence of an algorithm can be avoided, and the software test efficiency can be improvedto a great extent.
Owner:MUDANJIANG NORMAL UNIV
Construction and use of catalogued nucleic acid libraries that contain advantageously adjusted representations of defined components
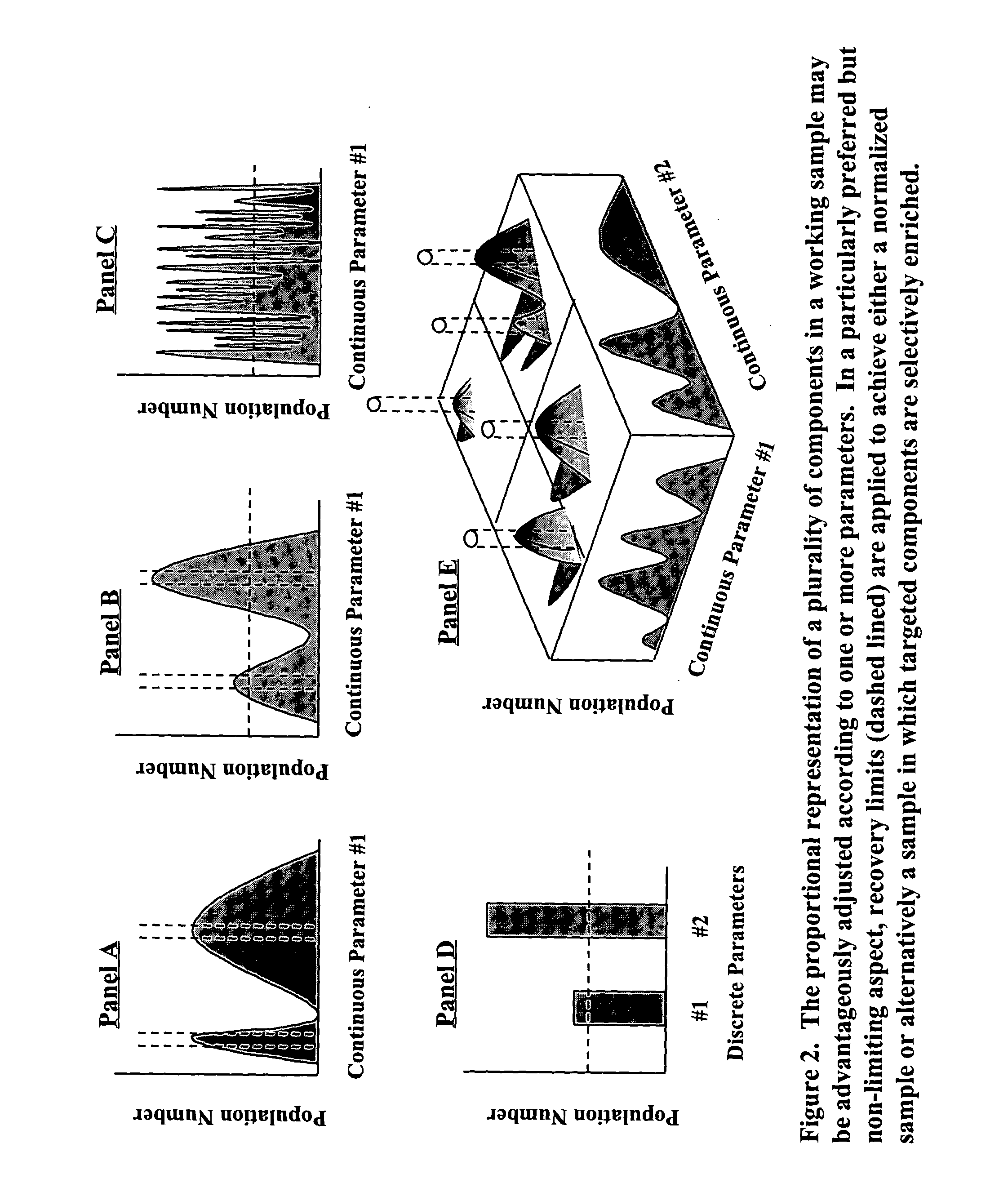
InactiveUS20060088821A1Reduce redundancyIncreases proportional representationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAscendencyAgriculture
A process for constructing a catalogued nucleic acid library in which the proportional representation of the constituents is adjusted to advantage through the use of disclosed technologies for positive and negative selection. The resultant benefit is that significantly fewer library constituents will need to be screened in order to identify a potentially desired constituent. Moreover, library constituents that previously would have been essentially “lost” are now recoverable. Preferred embodiments of this invention include the cataloguing, normalization, and enrichment of library constituents. By way of example, but not limitation, this technology is serviceable for constructing a library that contains an adequate representation of desirable constituents that (1) are initially found in low-copy numbers within a sample source or (2) originate from an organism that is problematic to culture. Applicable uses of this invention include any library-screening endeavor previously hindered by logistical impediments. By expanding previous logistical frontiers this invention allows for a novel generation of previously unattainable molecules—particularly molecules that are “unclonable” from conventional, unadjusted libraries—to now be detected, cloned, manipulated, expressed, studied, and used. By disclosing the construction and screening of high yielding nucleic acid libraries from mixed and uncultivated organisms, the instant technology eclipses former boundaries in the area of biological discovery and enables the full breadth of biological diversity to be accessed in the search for previously undiscovered genes and gene products. The benefits of the present invention are seen to extend to areas of diagnosis, medicine, agriculture, manufacturing, and academia.
Owner:DIVERSA
Separation of living untouched neurons
The present invention provides the use of the cell surface antigen CD51 as a negative selection marker for neuronal cells and a method for enrichment, isolation and / or detection of neuronal cells comprising the steps a) contacting a sample containing neuronal cells with an antigen-binding fragment specific for the CD51 antigen coupled to a solid phase, thereby labeling the CD51 positive cells of said sample and b) isolating the non-labeled cells of said sample.
Owner:MILTENYI BIOTEC B V & CO KG
Compositions and methods for negative selection of non-desired nucleic acid sequences
ActiveUS9957549B2Reduce the ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationTotal rnaNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides methods, compositions and kits for the generation of next generation sequencing (NGS) libraries in which non-desired nucleic acid sequences have been depleted or substantially reduced. The methods, compositions and kits provided herein are useful, for example, for the production of libraries from total RNA with reduced ribosomal RNA and for the reduction of common mRNA species in expression profiling from mixed samples where the mRNAs of interest are present at low levels. The methods of the invention can be employed for the elimination of non-desired nucleic acid sequences in a sequence-specific manner, and consequently, for the enrichment of nucleic acid sequences of interest in a nucleic acid library.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
Construction and use of catalogued nucleic acid libraries that contain advantageously adjusted representations of defined components
InactiveUS8476011B1Reduce redundancyIncreases proportional representationSugar derivativesOrganic chemistry methodsBiological bodyGene product
A process for constructing a catalogued nucleic acid library in which the proportional representation of the constituents is adjusted to advantage through the use of disclosed technologies for positive and negative selection. The resultant benefit is that significantly fewer library constituents will need to be screened in order to identify a potentially desired constituent. Moreover, library constituents that previously would have been essentially “lost” are now recoverable. Preferred embodiments of this invention include the cataloguing, normalization, and enrichment of library constituents. By way of example, but not limitation, this technology is serviceable for constructing a library that contains an adequate representation of desirable constituents that (1) are initially found in low-copy numbers within a sample source or (2) originate from an organism that is problematic to culture. Applicable uses of this invention include any library-screening endeavor previously hindered by logistical impediments.By expanding previous logistical frontiers this invention allows for a novel generation of previously unattainable molecules—particularly molecules that are “unclonable” from conventional, unadjusted libraries—to now be detected, cloned, manipulated, expressed, studied, and used. By disclosing the construction and screening of high yielding nucleic acid libraries from mixed and uncultivated organisms, the instant technology eclipses former boundaries in the area of biological discovery and enables the full breadth of biological diversity to be accessed in the search for previously undiscovered genes and gene products. The benefits of the present invention are seen to extend to areas of diagnosis, medicine, agriculture, manufacturing, and academia.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Negative selection marker for escherichia coli gene knock-in
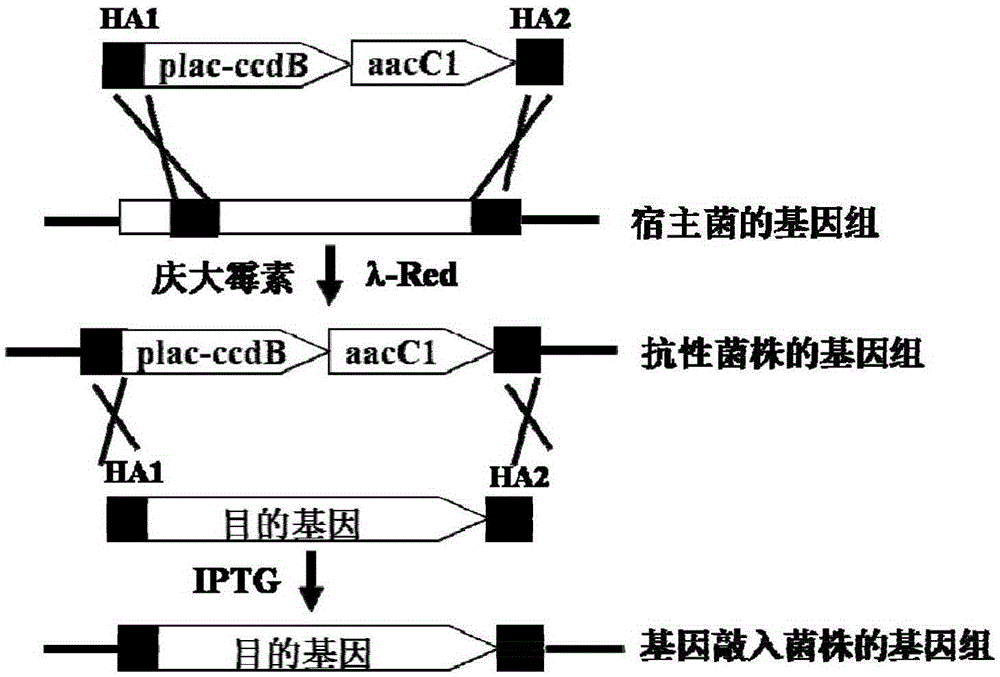
InactiveCN105238820AConvenient researchStable introduction of DNAMicroorganism based processesThiogalactosidesDNA fragmentation
The invention relates to a negative selection marker for escherichia coli gene knock-in, namely, the virulent gene ccdB driven by a plac promoter, and plac-ccdB and the gentamicin resistance gene aacC1 form a gene cassette for gene knock-in. In the first step, DNA fragments containing homologous arms plac-ccdB and aacC1 are obtained through amplification, and electro-transformed into escherichia coli for expression of recombinase. Under gentamicin screening, recombinase catalyzes homologous recombination and the DNA fragments are integrated into escherichia coli genome. In the second step, same homologous arms are utilized for amplification of foreign DNA fragments, ccdB is expressed in the bacterial strains obtained in the first step during the electrotransformation for expression of recombinase under the screening of isopropyl-beta-d-isopropylthiogalactoside, the toxicity serves as the feature of the negative selection marker, recombinase catalyzes homologous recombination among homologous arms, and foreign DNA fragments replace a plac-ccdB-aacC1 gene cassette to realize gene knock-in.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
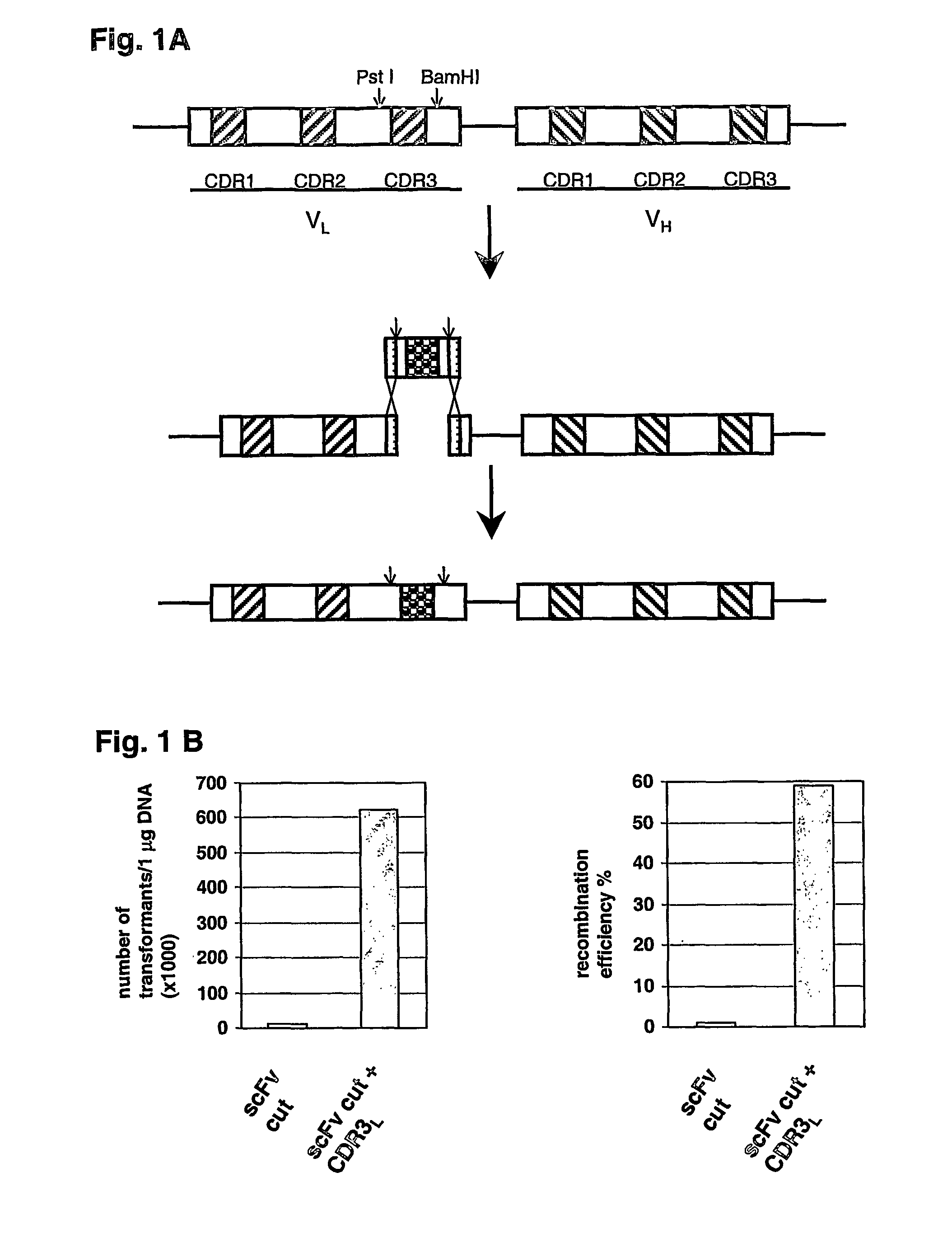
Molecular Display Method
InactiveUS20130244883A1Rapid and efficientLibrary screeningLibrary member identificationComputational biologyAffinity Reagent
There is provided herein a method for identifying and / or recovering at least one genetically encoded affinity reagent specific for a target molecule by screening using molecular display in conjunction with the sequencing of positive and negative selection pools from the screen.
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO
Synthetic auxotrophs with ligand dependent essential genes for biosafety
ActiveUS20180155711A1Generation is different and superiorSimple methodBacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionPeptideMutation
Synthetic auxotrophs with one or more ligand-dependent essential gene functions and methods of production that can be used for biosafety. The ligand-dependent function of an essential gene product can be produced by a series of mutations in the ORF of an essential gene; N, C, or insertional fusions of ligand-binding domains with essential genes or an engineered ligand-dependent intein splicing to alter essential gene function. A positive and / or negative selection can be used to identify auxotrophs from created mutant libraries. The positive selection is performed by growing a mutant library in conditions where growth or viability depends on the function of mutagenized essential genes. The negative selection eliminates constitutively growing cells that do not require a ligand for growth by growing the library in the absence of complementing ligand and in conditions where growing cells are eliminated. Desirable phenotypes are collected after the selections.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
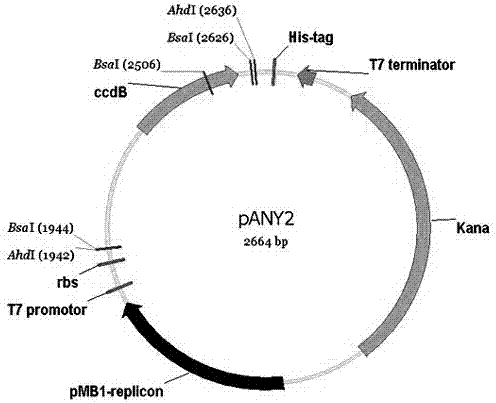
Plasmid vector and construction method thereof
ActiveCN107287230AAchieving directional TA cloningAvoid end to endVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliPlasmid Vector
The invention relates to specifically relates to a plasmid vector capable of realizing directional TA cloning, background sticky end-free cloning and expression, and a construction method thereof, belonging to the field of gene engineering. The plasmid vector is a closed circular double-stranded DNA and contains two multiple cloning sites, wherein a ccdB expression cassette exist between the two multiple cloning sites, and the ccdB expression cassette can realize constitutive expression of toxic protein ccdB, which is used as a negative selection marker, in most Escherichia coli strains. The multiple cloning sites are designed on the basis of the plasmid vector; and the plasmid vector is applicable to directional TA cloning and improved background sticky end-free cloning. Moreover, the plasmid vector is directly applicable to expression and purification of proteins. Each function of the plasmid vector is verified. The plasmid vector provided by the invention is expected to play an important role in the field of gene engineering due to its convenience and high efficiency.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Inferring selection in white blood cell matched cell-free DNA variants and/or in RNA variants
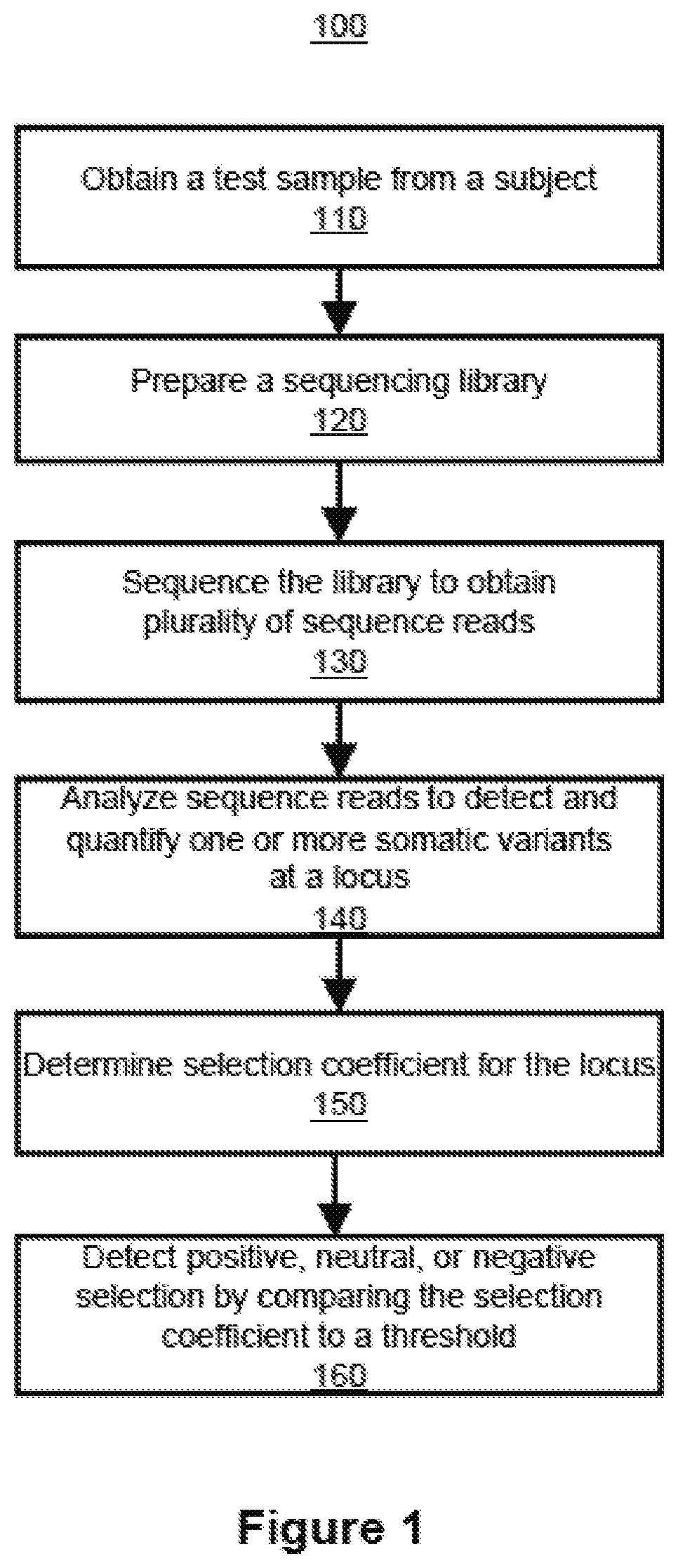
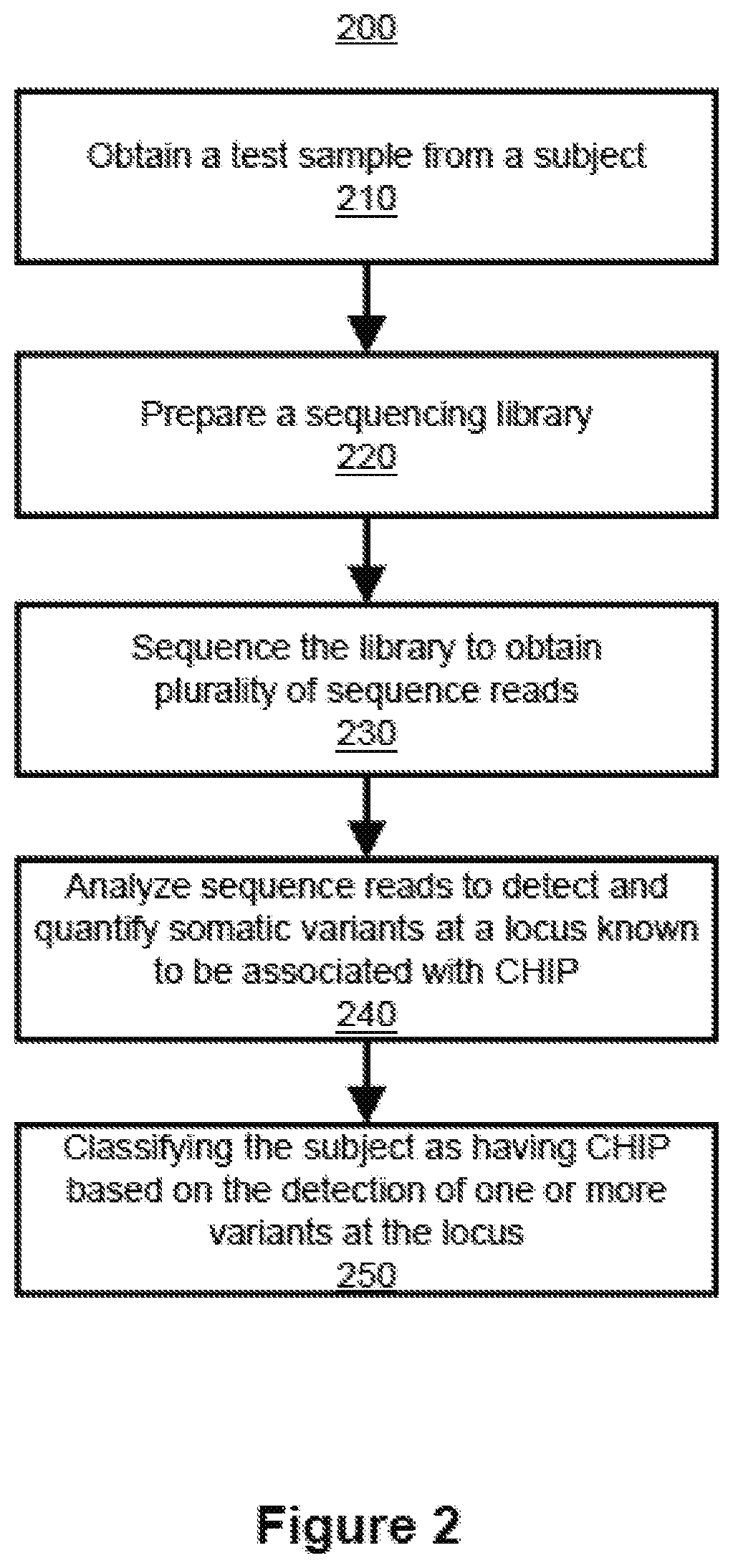
Methods and systems for detecting positive, neutral, or negative selection at a locus include obtaining a test sample of cell-free nucleic acids from a subject, preparing a sequencing library of the cell-free nucleic acids, sequencing the library to obtain a plurality of sequence reads, analyzing the sequence reads to detect and quantify one or more somatic mutations at the locus, determining a selection coefficient for the locus, and comparing the selection coefficient with a threshold value to detect positive, neutral, or negative selection at the locus.
Owner:GRAIL LLC
Mapping new sites for antibiotic action in the ribosome
InactiveUS20090042186A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismSmall subunit
The present invention provides a method of mapping and identifying new sites for antibiotic action in the ribosome of a microorganism. The method comprises: (a) providing a random mutant library of the rRNA genes of the microorganism prepared by randomly mutating the rRNA genes of the microorganism; (b) enriching the library in clones with deleterious rRNA mutants by negative selection; (c) screening for clones with deleterious rRNA mutations; (d) mapping the deleterious rRNA mutations in the clones obtained from step (c) to identify sites in the rRNA which are important functional sites in the ribosome; and (e) selecting functional sites identified in the rRNA in step (d) which are not targeted by a known antibiotic as new sites for antibiotic action for the microorganism. The rRNA gene can be the 16S rRNA of the small subunit or the 23S rRNA or the 5S rRNA of the large subunit of the ribosome of the microorganism.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Gene editing system based on CRISPR-Cas9 technology and application of gene editing system
The invention provides a gene editing system based on a CRISPR-Cas9 technology and application of the gene editing system. Based on an endogenous U6 promoter dependent-form vector system, a negative selection marker is added into a Cas9 expression box of an expression vector, an anti-drug selection marker on a rescue vector containing a homologous arm is transferred onto the expression vector, thus the base size of the rescue vector is decreased, and the capacity of the rescue vector is increased; and an exogenous gene segment lengthening out to 6.3 kb can be input in human plasmodium in a mediated mode, obtained recombinant plasmodium does not contain the anti-drug selection marker and Cas9 protein expression plasmid residue, continuous gene editing can be conducted through the same drugselection marker, and the gene editing system is stable in performance, efficient, concise, and powerful in function, and has wide application prospects and huge market value.
Owner:BLUE ELEGANT BIOTECH CO LTD
Genetic manipulation method for manually controlling spontaneous mutation rate of bacillus subtilis and application thereof
ActiveCN108865963AHigh mutation rateIncrease the relative mutation rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGeneticsBacterial strain
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to a genetic manipulation method for manually controlling a spontaneous mutation rate of bacillus subtilis and application thereof. The genetic manipulation method comprises the following steps: regulating and controlling an operon MutSL which is responsible for a mismatch repair system of the bacillus subtilis by axylose induced promoter and repressor protein, and establishing recombinant plasmids in corresponding inducible expression; integrating the recombinant plasmids to a bacterial strain genome by utilizing Spizizen double exchange, and carrying out positive-negative selection, thus obtaining objective engineering strains; regulating different expression levels of the operon MutSL of the mismatch repair system through different xylose addition concentration, thus realizing manual control on the spontaneous mutation rate of the bacillus subtilis.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Novel effective conversion method of helianthus and oil plant seed based on positive selection
The invention describes a highly improved, reproducible and a consistent method of transformation and regeneration that results in obtaining 12-15% transgenic plants. The present invention relates to a method of selecting genetically transformed Sunflower explants based on their ability to utilize Xylose as a sole carbohydrate source. Further disclosed is the nucleic acid sequence of the Xylose Isomerase gene, vector construction for incorporation of the selection marker gene and the process of Agrobacterium Mediated Transformation of target host plant with the vector comprising the gene encoding the enzyme Xylose isomerase under the functional combination of the heterologous regulatory sequences. Also disclosed is the method of selecting the putative transformants post transformation with the said vector that possess a metabolic advantage of utilizing Xylose as a sole carbon source.; Increased efficiency of regeneration, better growth and survival has been observed on subjection to the described method of positive selection. The subject invention alleviates the disadvantages of negative selection methods such as the undesired elimination of the transformed cells and the potential environmental harm caused due to the dispersal of the antibiotic and the herbicide resistant genes.
Owner:阿维沙基因有限公司
Genome-edited plant production method
ActiveUS20200385747A1Maintaining identityReduce contentHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyGenome editing
It was found that it is possible to construct a genome-edited plant in which no exogenous gene is incorporated in a genome by performing negative selection using morphological defects and the like as indices in a regenerated plant originated from a plant cell in which a gene that induces regeneration of the plant and a gene of the genome editing enzyme are introduced.
Owner:RIKEN
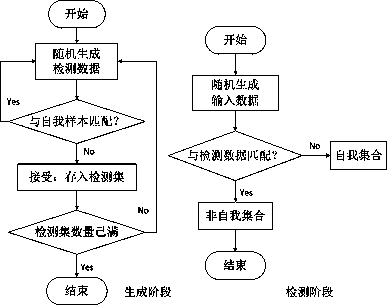
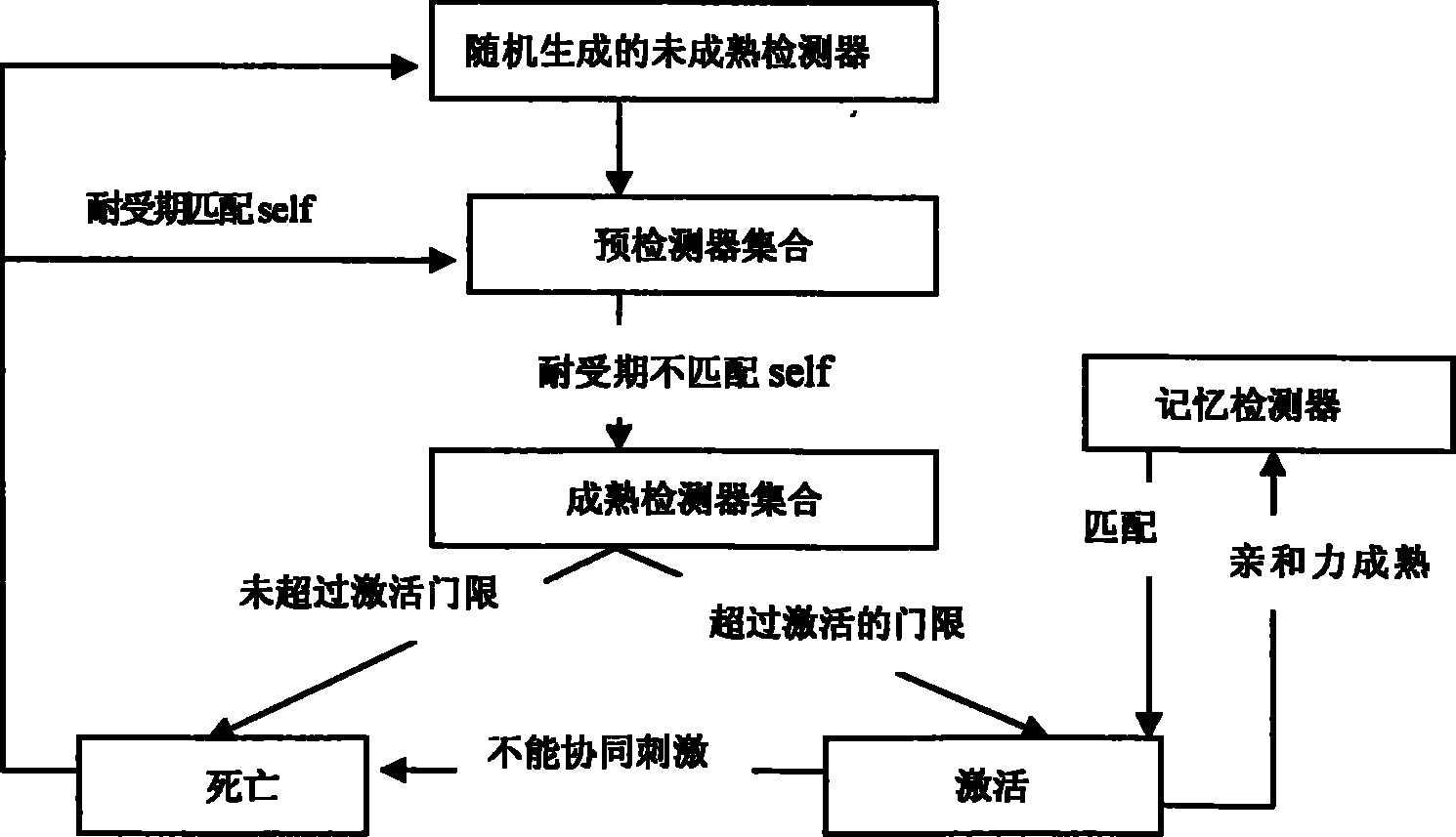
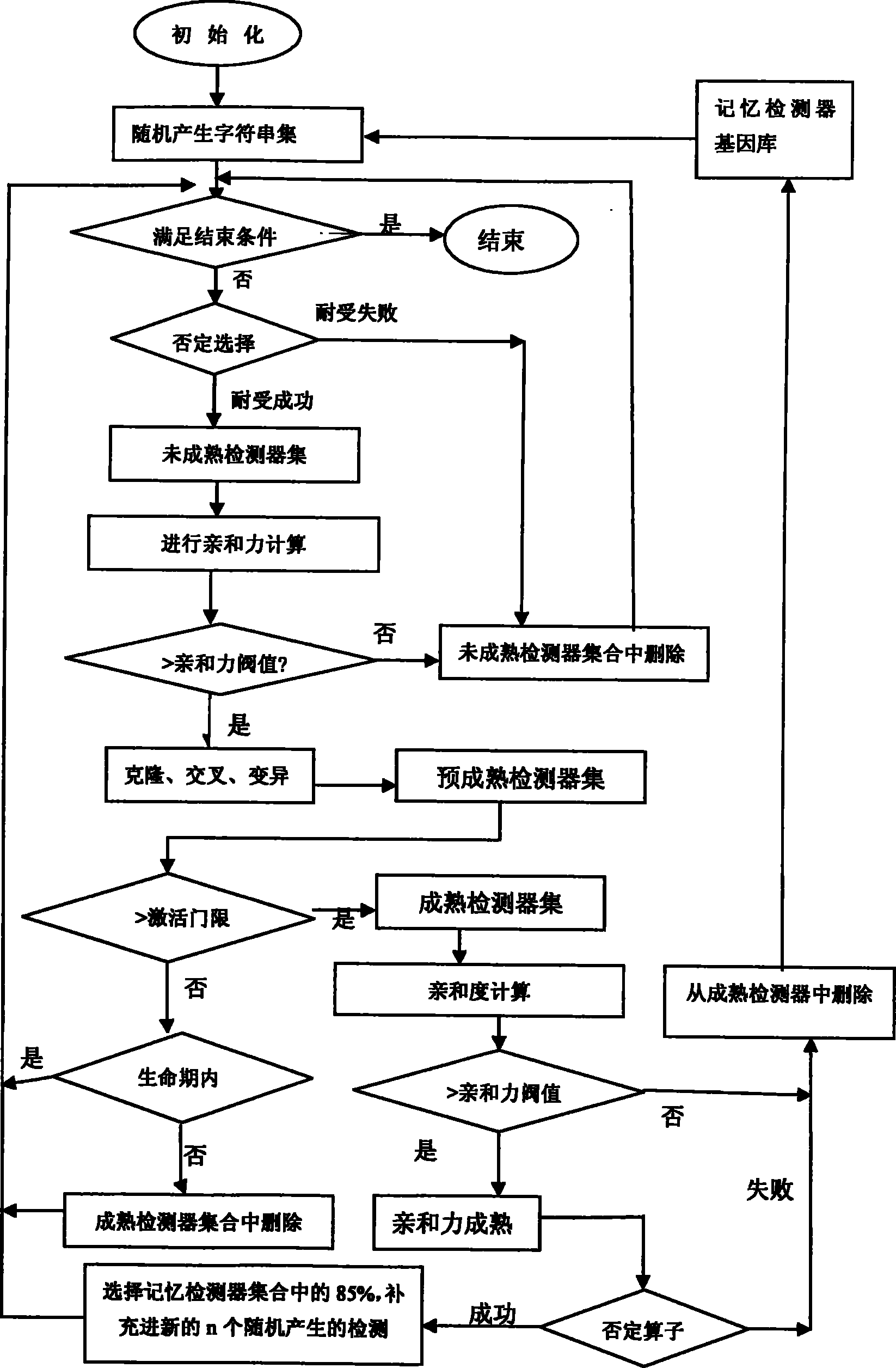
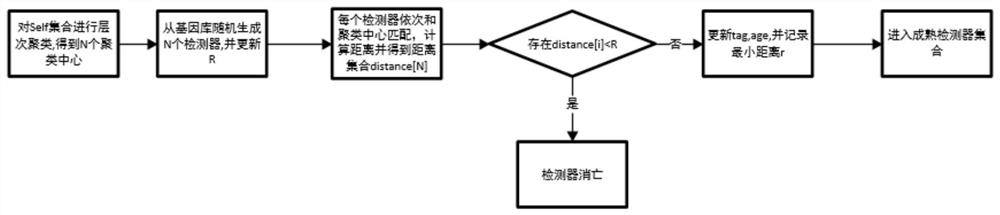
Method for detecting dynamic gridding instruction based on artificial immunity
InactiveCN101299691BDetection speedQuality improvementGenetic modelsData switching networksClonal selectionClonal selection algorithm
A method for detecting dynamic gridding instruction based on artificial immunity, is a method for detecting instruction facing to gridding which takes use the artificial immunity technique for reference. According to the dynamic and real time requirement of the instruction detection under gridding surroundings, the method takes the prior clonal selection algorithm as main body, combines negative selection, clonal selection, affinity maturation and memory detector gene bank method, so at to dynamic handle the instruction detection under gridding surroundings. The method includes a dynamic detector evolvement process and a gridding instruction detection process which are based on artificial immunity, which is characterized in by using the artificial immunity technique for reference, and combining the negative selection, clonal selection, affinity maturation and memory detector gene bank method; firstly obtaining an evolvement matured detector; and then dynamically handling the instruction detection problem in the gridding surroundings under the coordination of the artificial immunity mechanism, to complete the entire process of dynamic gridding instruction detection.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Unknown threat detection method based on artificial immune thought
PendingCN114065933AFix overlap detection issuesAvoid falling intoCharacter and pattern recognitionArtificial lifeVaccinationInternet traffic
The invention discloses an unknown threat detection method based on an artificial immune thought, which is used for effectively detecting known and unknown threats. A pre-classification module introduces a convolutional neural network to solve the problems of pre-collection of a self set and pre-classification of network traffic in detection; a negative selection module introduces a gene bank to solve the random generation problem of an initial detector and the specific immunity problem for unknown threats, and introduces hierarchical clustering to improve the training efficiency of the detector; a cloning variation module is used for solving the overlapping detection problem of a high-affinity detector by introducing a detector optimization algorithm based on a genetic algorithm; meanwhile, an LRU-based memory detector fading mechanism is introduced, so that the storage space is effectively released, and the detection efficiency is improved; and an mRNA vaccination module introduces an mRNA vaccine algorithm based on feature importance sorting, decomposes the detected unknown threats according to gene importance and injects the unknown threats into a gene bank, and generates a corresponding detector to realize specific immunization of the unknown threats and variants thereof.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Methods and compositions for use of non-coding RNA in cell culturing and selection
ActiveUS20170298350A1Promotes amountPromotes cell survival of cellNucleic acid vectorScreening processPositive selectionNegative selection
Described herein are methods and compositions for producing a gene of interest (GOD, which, in certain embodiments, can reduce the metabolic burden on cells and reduce decoupling of GOI production from marker production, as compared to prior art methods. The methods relate to positive selection and negative selection approaches to establishing high GOI-producing cell lines, e.g., CHO lines. In certain embodiments, the methods comprise transfecting a cell with (a) an oligonucleotide comprising a GOI and a non-coding RNA, and (b) an oligonucleotide encoding a selection protein; wherein the non-coding RNA promotes or inhibits production of the selection protein. The cell producing the can be identified and / or selected as a result of or by detecting the absence or the presence of the selection protein.
Owner:HOCUSLOCUS +1
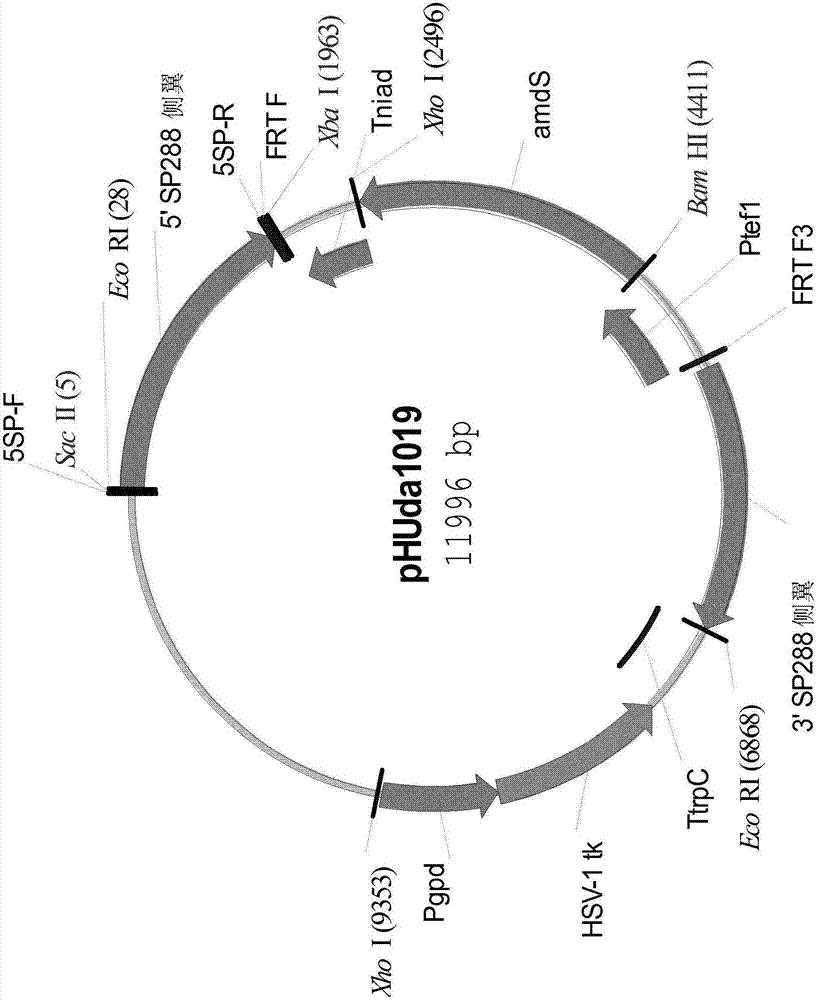
Simultaneous site-specific integrations of multiple gene-copies in filamentous fungi
The invention relates to a method for the simultaneous integration of two or more copies of a polynucleotide of interest into the chromosome of a fungal host cell comprising at least two pairs of recognition sequences of a site-specific recombinase, each pair flanking a resident negative selection marker; transformation of the cell with a construct carrying a gene of interest also flanked by the recognition sequences to ensure double-crossover events after transient expression of the recombinase, followed by selection for excision of all negative selection markers from the cell.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Method for the construction of randomized gene sequence libraries in cells
An in vivo method for the construction of randomized gene libraries and / or domain replacement in gene libraries by homologous recombination using a Kluyveromyces lactis killer toxin, in particular the (γ-subunit of the K. lactis killer toxin, as negative selection marker is described. The use of the (γ-subunit of K. lactis as negative selectable marker increases the percentage of randomized clones.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Molecular Display System
There is provided herein a method for identifying and / or recovering at least one genetically encoded affinity reagent specific for a target molecule by screening using molecular display in conjunction with the sequencing of positive and negative selection pools from the screen.
Owner:THE GOVERNING COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORONTO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com