Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Spontaneous mutation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spontaneous mutations can be generated by different processes. Replication errors and spontaneous lesions generate most of the base-substitution and frameshift mutations. Replication errors may also cause some deletions that occur in the absence of mutagenic treatment.
Production of Cellulose in Halophilic Photosynthetic Prokaryotes (Cyanobacteria)
InactiveUS20080085536A1Limit potential for unplanned growthCharacteristic changeBacteriaUnicellular algaePhylum CyanobacteriaSaline water
The present invention includes compositions and methods for making and using halophilic cyanobacterium comprising a spontaneous mutation causing constitutive cellulose biosynthesis, whereby the cyanobacterium is capable of producing cellulose in brine. The compositions and methods of the present invention may be used as a new global crop for the manufacture of cellulose, CO2 fixation, for the production of alternative sources of conventional cellulose as well as a biofuel and precursors thereof.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
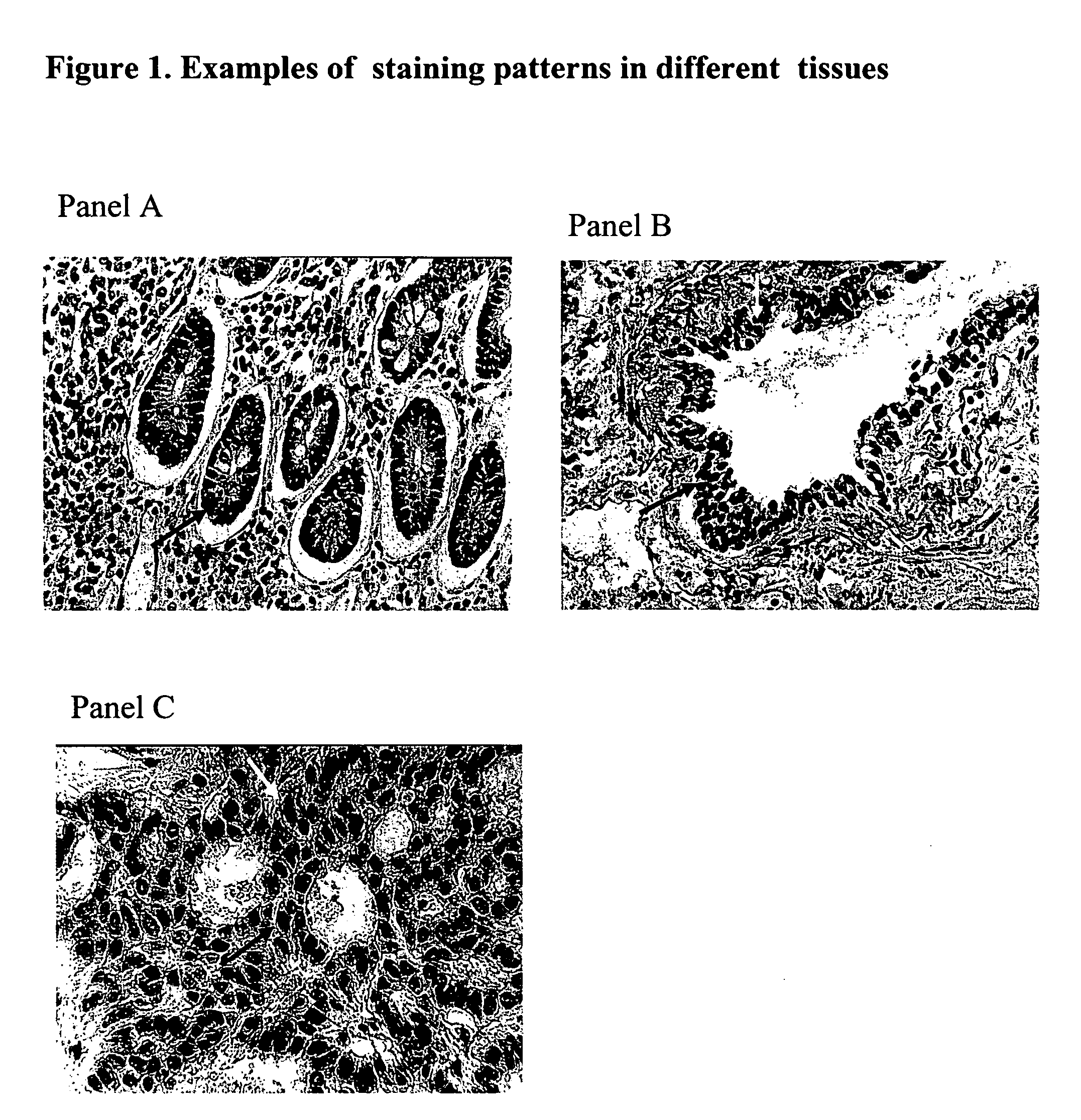
Measurement of mutation load using the p53 gene in human cells from paraffin embedded tissues
InactiveUS20070020648A1Assessing cancer riskAssessing prognosisMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCarcinogenMutated protein
A method for determining mutation load in a somatic cell is determined by mutation analysis of the p53 gene. The p53 gene has been found to be a useful indicator of predisposition to spontaneous mutations or prior carcinogen exposure. Cells that contain mutated p53 tend to accumulate the mutant protein. Thus, DNA from a cell identified by p53 accumulation is amplified and the amplification product further analyzed for mutations in the p53 gene.
Owner:SOMMER STEVEN S +2
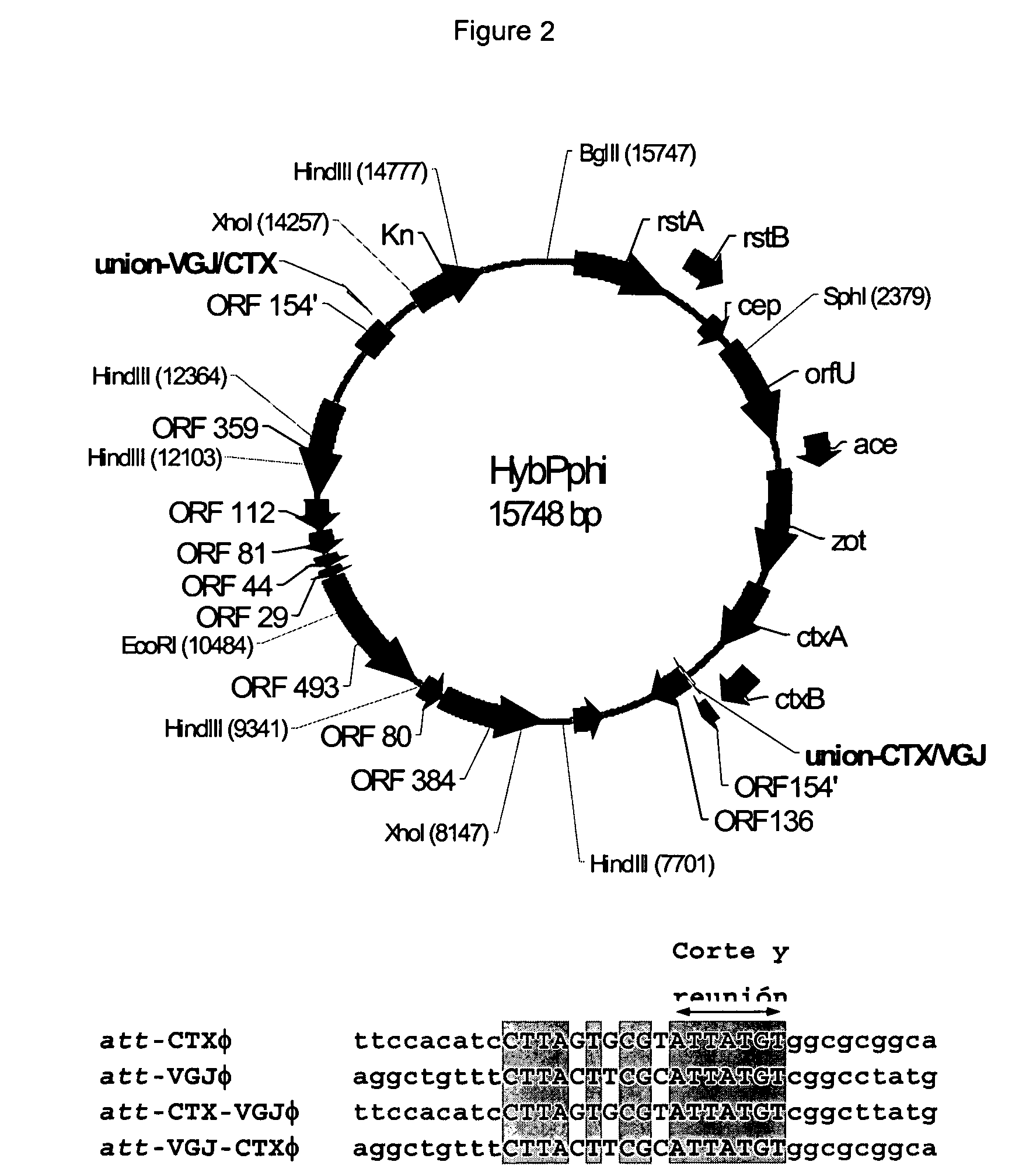
Attenuated strains of vibrio cholerae with improved biological safety features in freeze dried form for oral vaccination
ActiveUS20070071775A1Simple compositionEasy to manipulateInternal-combustion engine testingBacteriaSpontaneous mutationToxin
The present invention discloses new live attenuated strains for oral immunization against cholera that are provided in freeze dried formulations for long term storage and administration to humans. These strains combine the two most important properties of live attenuated cholera vaccine candidates. One such property is being well tolerated by people ingesting them. This was achieved by virtue of mutations already described in the art. The second property is having enhanced environmental safety due to the absence of VGJΦ DNA in their genomes and also due to null mutations in the mshA gene or other spontaneous mutations conducive to the lack of MSHA type IV fimbria on the bacterial surface. This was done envisioning that VGJΦ is a filamentous phage able to recombine with CTXΦ and disseminate the cholera toxin genes. This VGJΦ phage as well as the VGJΦ-CTXΦ recombinants uses the MSHA fibers as receptor. Being devoid of MSHA fimbria the vaccine candidates are protected from acquiring CTXΦ from the recombinant hybrid VGJΦ-CTXΦ. Being devoid of VGJΦ, the vaccine candidates are impaired in the dissemination of CTXΦ, via VGJΦ.
Owner:CENT NACIONAL DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CINC)
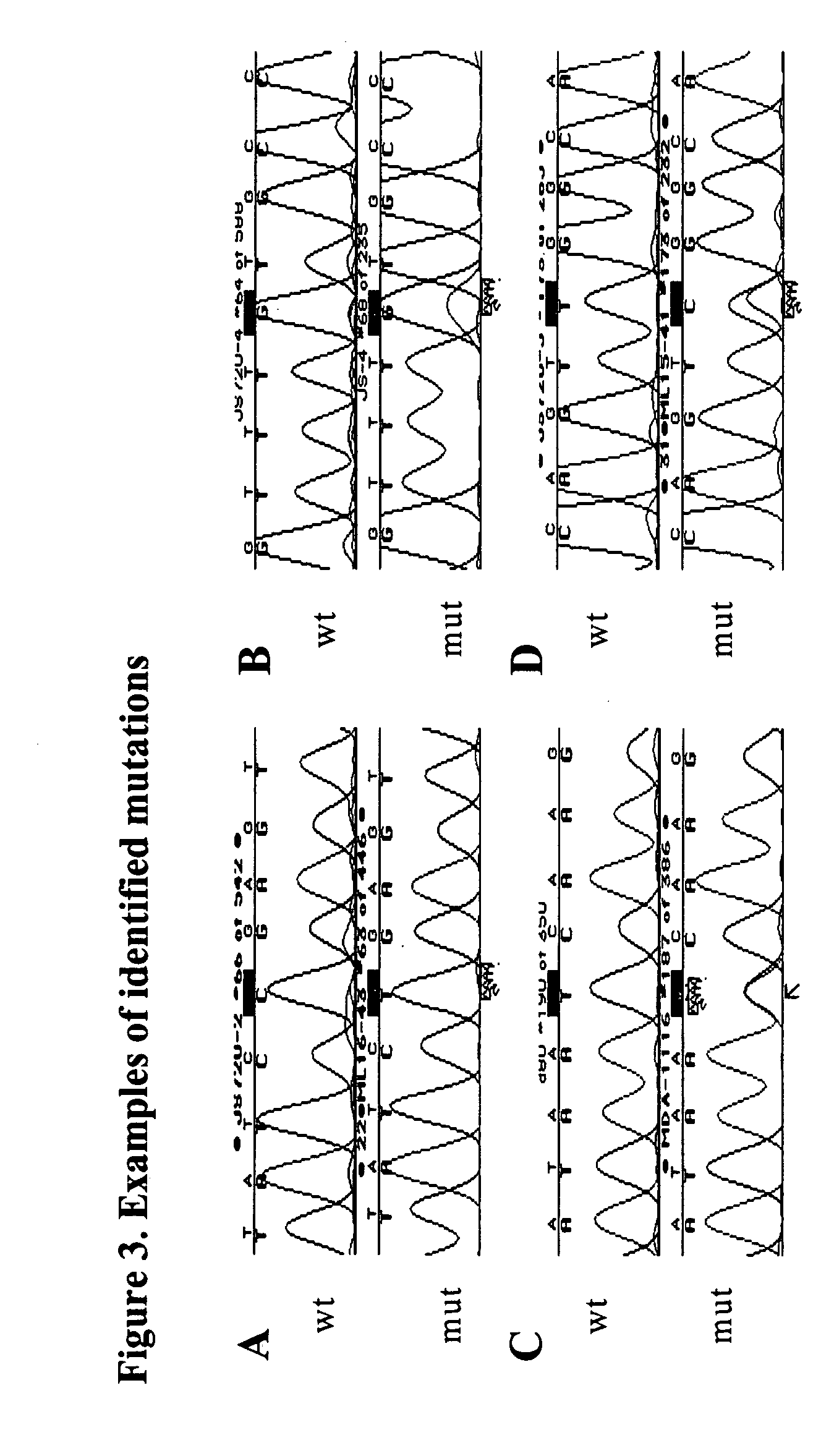
Method for separating and detecting spontaneous mutation gene based on agarose gel denaturation and renaturation and biotin affinity adsorption
InactiveCN102094091AScan accuratelyAccurate and Fast ScanningMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotin-streptavidin complexHeteroduplex
The invention relates to a method for separating and detecting a spontaneous mutation gene based on agarose gel denaturation and renaturation and biotin affinity adsorption, which belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to a method for separating and detecting a mutation gene. The method comprises the following steps of: marking wild deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) fragments by using biotin, mixing the biotin-marked wild DNA fragments and DNA fragments to be detected, and performing denaturation and renaturation, wherein at the moment, DNA fragments which contain mutation sites cannot form heteroduplex DNA molecules because the biotin-marked wild DNA fragments with the same migration rate as the DNA fragments are not hybridized with the DNA fragments, DNA fragments which do notcontain the mutation sites are hybridized with the corresponding biotin-marked wild DNA fragments to form the heteroduplex DNA molecules, and the heteroduplex DNA molecules carry biotin marks; and adsorbing and recovering the molecules which carry the biotin marks by using streptavidin magnetic beads to separate the DNA fragments which contain the mutation sites. Compared with the conventional method, the method is simpler and more convenient and sensitive, can be used for accurately identifying and detecting the mutation sites, and has high reliability.
Owner:POMOLOGY RES INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Genetic engineering strain utilize sucrose to produce succinic acid from and method for production of succinic acid by fermenting the same
ActiveCN103937733AImprove fermentation effectIncrease useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliLactate dehydrogenase
Belonging to the technical field of bioengineering, the invention relates to a genetic engineering strain producing succinic acid and a method for production of succinic acid by fermenting the strain, particularly a recombinant strain efficiently utilizing cane sugar and molasses to grow and produce succinic acid. The genetic engineering strain producing succinic acid is classified and named as Escherichia coli BA501, and has a preservation registration number of CCTCC NO:M2014014. The construction process of the strain mainly includes: taking Escherichia coli AFP111 that lacks lactate dehydrogenase gene and pyruvate formate lyase activity and has the chromosome ptsG gene undergoing spontaneous mutation as the starting strain, expressing exogenous sucrose permease, sucrose hydrolase and fructokinase genes, and then carrying out continuous domestication cultivation to obtain the strain efficiently utilizing cane sugar and molasses to grow and produce succinic acid. Thus, the synthesis efficiency of succinic acid is greatly improved. The fermentation method adopts a two-stage fermentation way, in the aerobic stage the biomass is improved oxygen, and in the anaerobic stage, fermentation and acid production are achieved.
Owner:态创生物科技(广州)有限公司
Yeast mutant and yeast extract
A natural yeast extract which is rich in glutamic acid and therefore has an impact at first taste. Further, provided is a yeast extract which is also rich in 5′-guanylic acid or 5′-inosinic acid and therefore has strong umami. Further, provided is a yeast mutant capable of accumulating a large amount of glutamic acid, glutamine and ribonucleic acid for obtaining such a yeast extract. A yeast mutant to which resistance to organic acids and analogues thereof has been imparted by inducing spontaneous mutation, accumulates a significant amount, i.e., 10% by weight or more of the total of free glutamic acid and glutamine in the cell, and further accumulates 5% by weight or more of a ribonucleic acid. The yeast extract produced by using this strain contains 20% by weight or more of L-glutamic acid, and further contains 3% by weight or more of 5′-IG.
Owner:KOHJIN CO LTD
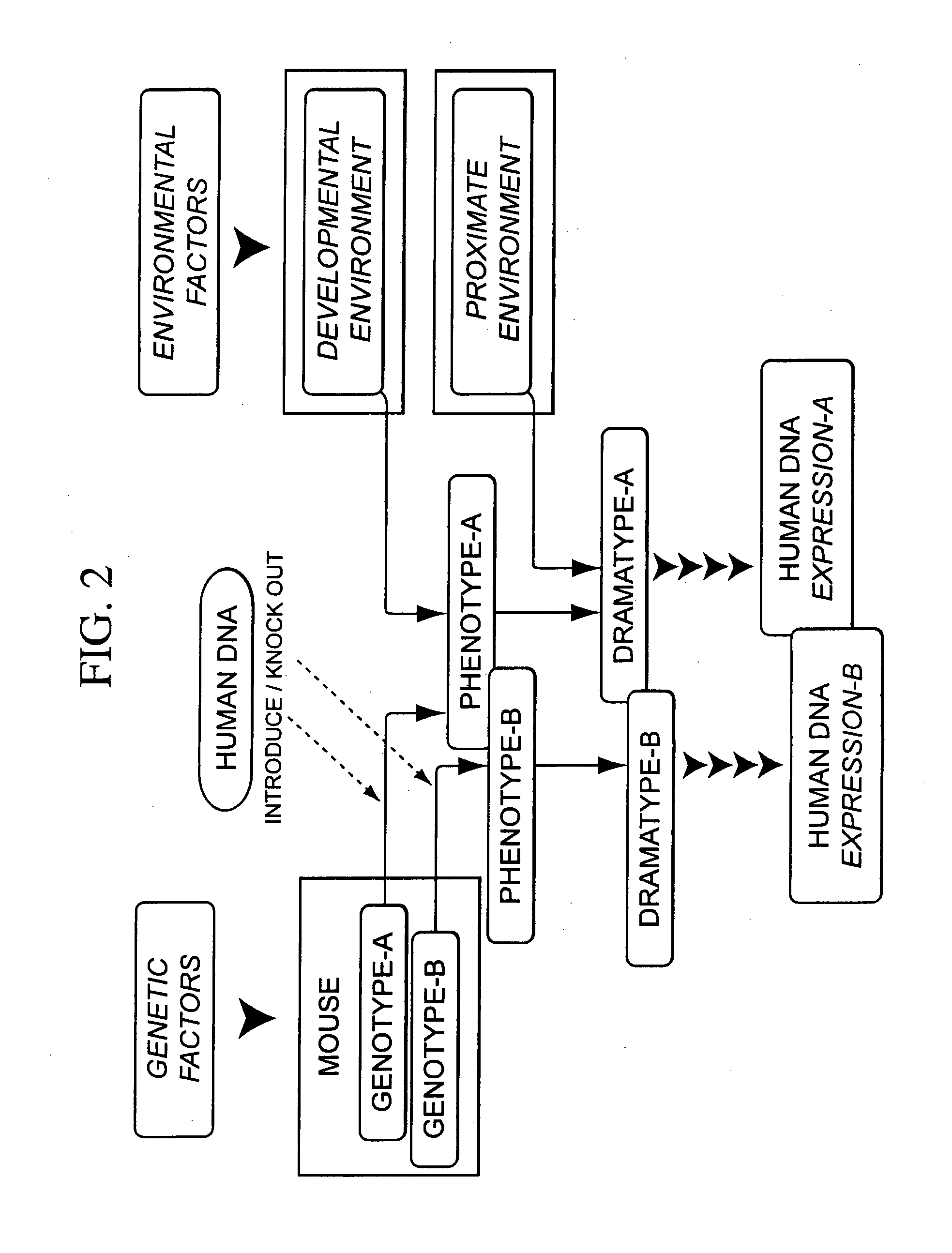
Integrated in vivo animal experimentation systems
The invention concerns methods for the development of mutant animals, including genetically engineered animals and those carrying spontaneous mutations, as human disease models. In particular, the invention provides an integrated technology, including rigorous specifications and quality control, for the development of animal models that can serve as a living assay system, useful in biomedical research and in the development of human therapeutics.
Owner:CENT FOR THE ADVANCEMENT OF HEALTH & BIOSCI
Shrub rose plant named `Radcon`
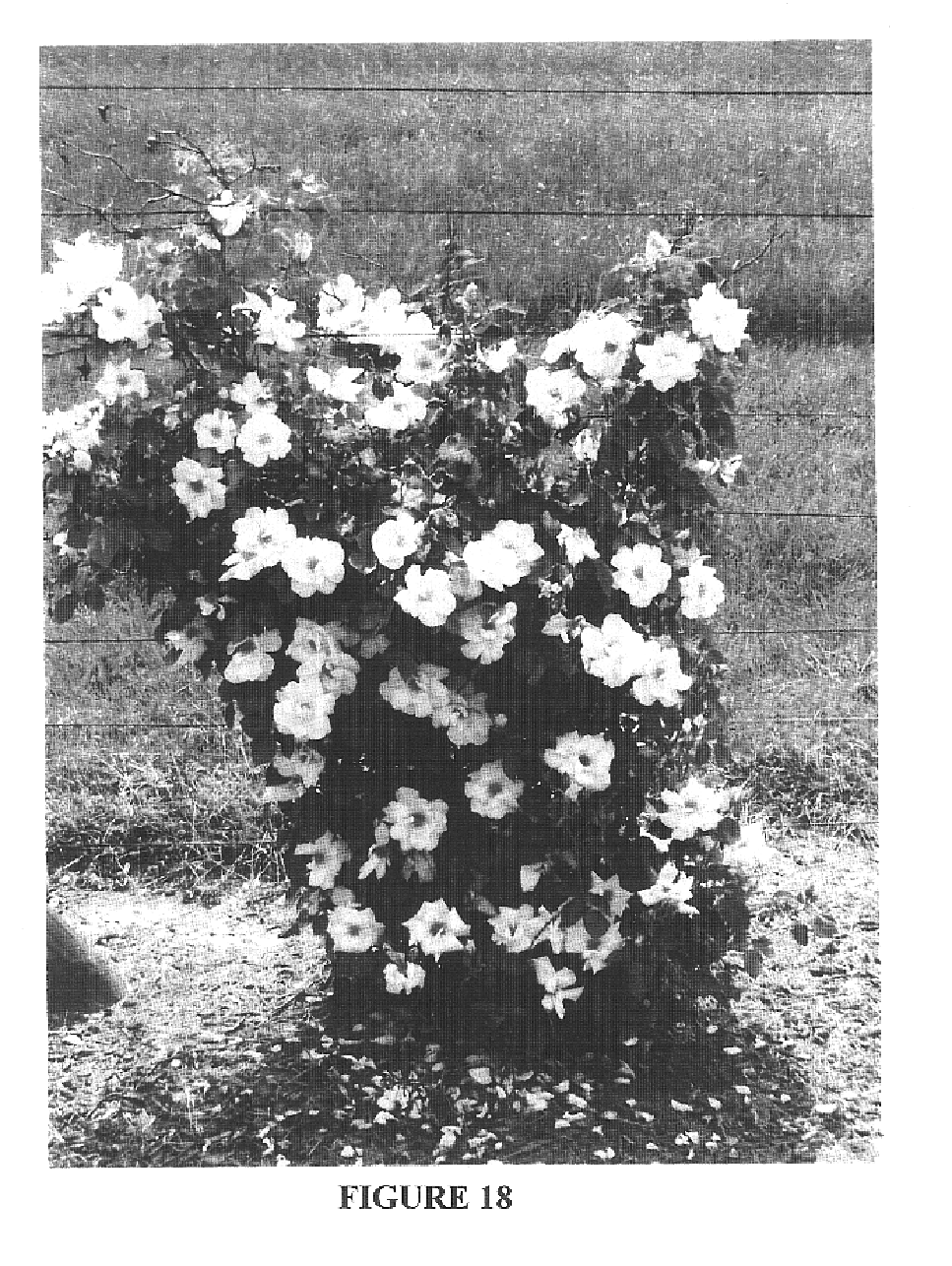
A new and distinct variety of landscape shrub rose plant is provided which forms in abundance on a substantially continuous basis attractive single blossoms that are pink in coloration. The new variety is a spontaneous mutation of unknown causation of the `Radrazz` variety (U.S. Plant Pat. No. 11,836) that forms vivid red single blossoms. The vegetation is vigorous and the growth habit is compact and mounding. Attractive ornamental satiny green foliage is formed. Excellent disease resistance to blackspot is exhibited. The new variety is particularly well suited for growing as distinctive ornamentation in the landscape.
Owner:CONARD PYLE
Engineering strain capable of producing succinic acid at low pH value and method for producing succinic acid by fermentation
InactiveCN104232553APromote progressBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliButanedioic acid
The invention discloses a genetic engineering strain capable of producing succinic acid at a low pH value. The classification name of the genetic engineering strain is Escherichia coli BA601, and the collection number is CCTCCNO: M2014210. The invention further discloses a method for producing succinic acid by using the strain. According to the strain disclosed by the invention, an Escherichia coli AFP111 which is lack of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) genes and has activity of pyruvate formate lyase (PFL) genes and ptsG spontaneous mutation of a phosphotransferase system is taken as a starting strain for over-expression of acid-resistant genes gadBC. The method of enabling the Escherichia coli AFP111 which can not grow under low-pH (pH 5.6) conditions originally and can not produce acid by fermentation to efficiently utilize glucose to produce succinic acid through a biological and microbial acclimation means is not disclosed before, and the application can greatly promote the progress and development of the succinic acid industry.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Climbing shrub rose plant named `Radsunsar`
Owner:CONARD PYLE
Method for constructing succinic-acid-producing Escherichia coli and application of Escherichia coli
InactiveCN106676052AImprove secretion capacityPromote growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSpontaneous mutationBacterial growth
The invention relates to a method for constructing succinic-acid-producing Escherichia coli and the application of Escherichia coli. The method comprises the following steps: taking Escherichia coli which lacks of activities of lactate dehydrogenase genes and pyruvate formate-lyase genes and in which a ptsG chromosome of a phosphotransferase system is subjected to spontaneous mutation as an original strain, and constructing recombinant Escherichia coli containing corynebacterium glutamicum NCg12130. According to the recombinant Escherichia coli constructed by the method disclosed by the invention, the secretion ability of succinic acid is obviously improved, and the bacterial growth, sugar consumption and succinic acid production capacity in the whole process are obviously enhanced. The method disclosed by the invention provides a novel excellent transport protein for enhancing the capacity of transporting the succinic acid by the Escherichia coli and further provides a new way for enhancing the succinic acid secretion performance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Cordyceps militaris rejuvenation breeding process
InactiveCN109526537AGuaranteed purityStable traitsCultivating equipmentsMushroom cultivationBiotechnologySpore germination
The invention discloses a cordyceps militaris rejuvenation breeding process. The concrete steps are as follows: carrying out activation culture of a degraded cordyceps militaris strain; inoculating the activated cordyceps militaris strain in a shake flask culture medium for culturing, and the inoculating the strain on a wheat or rice culture medium for culturing; selecting fruiting bodies, cuttingoff tips, hanging the tips on the cup of the cultivation culture medium for culturing until spores on the surface of the culture medium are germinated thoroughly, removing the fruiting body tips, andcontinuing to culture the tips for 30-40 d; and picking and drying the mature cordyceps militaris, detecting cordycepin, the main active ingredient of the cordyceps militaris, and using the cordycepsmilitaris as an original cultivation species until the traits are stable. The cordyceps militaris rejuvenation breeding process does not need to use a spore collector, is simplified in operation andsaves breeding cost. Furthermore, since the process is monospore purification rejuvenation, the purity of the strain can be guaranteed. The excellent strains with stable traits are orientedly screenedas the original cultivation species, and are suitable for the rejuvenation of strains degraded by spontaneous mutation and inappropriate environmental factors.
Owner:LIAONING FUYUDA AGRI SCI & TECH
Multiplex-PCR detection method for single sperm
InactiveCN105420395APreventing the Risk of Interrupted BirthImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant Germ CellsMicro cell
The invention discloses a multiplex-PCR detection method for a single sperm. The method comprises the steps that A, sperms are pretreated; B, micromanipulation is performed to pick up a single sperm; C, the sperm is subjected to multiplex-PCR detection. The multiplex-PCR detection method for a single sperm breaks through the limitation, only targeting female eggs and embryos, of past genetic disease gene detection on micro-cells and makes it possible for analysis of whether a male germ cell is a chimera. Through the method, very rare spontaneous mutation which only exists in a single sperm and cannot be detected in a somatic cell or sperm groups can be detected, auxiliary diagnosis analysis of de novo mutation can be performed on a paternal age effect series genetic disease caused by de novo mutation of a paternal germ cell, and on this basis, the risk of birth of a child patient with the genetic disease can be prevented and interdicted in combination with the preimplantation genetic diagnosis technology.
Owner:REPRODUCTIVE & GENETIC HOSPITAL OF CITIC XIANGYA CO LTD
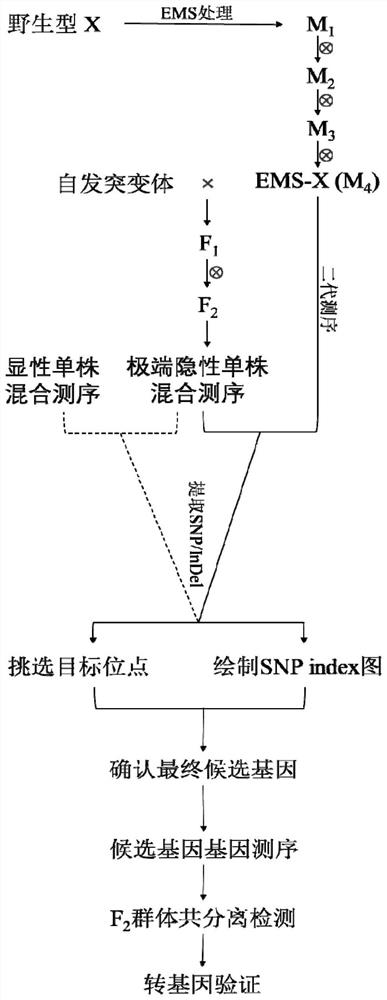
Rapid mapping and cloning method for plant spontaneous mutation genes bridged by neutral mutant
ActiveCN112154910AEnriched nucleotide polymorphismRapid positioningMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsBiotechnologyEthylmethane Sulfonate
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and particularly relates to rapid mapping and cloning method for plant spontaneous mutation genes bridged by a neutral mutant. The invention aims to overcome the defects in the prior art, and the neutral mutant produced by mutagenesis of an ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS) mutagenic agent composition is utilized to rapidly mapthe spontaneous mutation genes. Under the same genetic background, the neutral mutant (namely, no macroscopic phenotypic variation) produced by mutagenesis of the EMS mutagenic agent composition is hybridized with a spontaneous mutant to obtain F1, and selfing is continued to obtain an F2 generation. By performing screening and hybrid sequencing of extremely recessive phenotypic single plants in an F2 population, combining with EMS mutated neutral mutant sequencing data, and utilizing a bioinformatics method, the mutation genes are rapidly mapped. Compared with known methods, the rapid mappingand cloning method has the outstanding advantages of high screening efficiency, short consumed time, low cost and the like. The rapid mapping and cloning method can be used for rapid cloning of the spontaneous mutation genes.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Methods for developing animal models
InactiveUS20080289059A1Vector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryAssayQuality control
The invention concerns methods for the development of mutant animals, including genetically engineered animals and those carrying spontaneous mutations, as human disease models. In particular, the invention provides an integrated technology, including rigorous specifications and quality control, for the development of animal models that can serve as a living assay system, useful in biomedical research and in the development of human therapeutics.
Owner:NOMURA TATSUJI
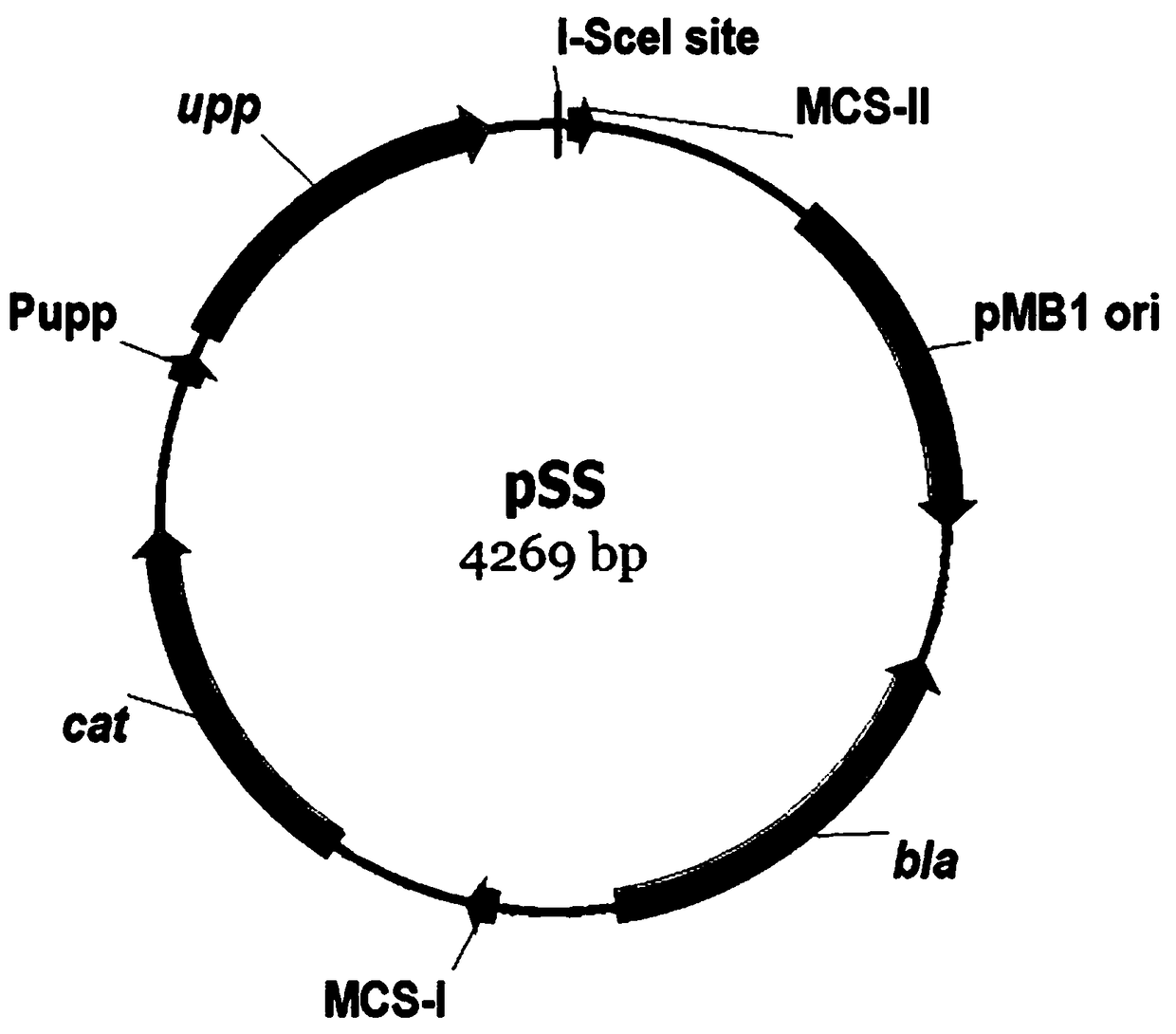
Plasmid for improving spontaneous mutation frequency of bacillus subtilis
PendingCN113801888AIncreased spontaneous mutation rateImprove trait stabilityBacteriaStable introduction of DNAGenes mutationMutation frequency
The invention discloses a plasmid for improving spontaneous mutation frequency of bacillus subtilis. The plasmid is selected from any one of a PUS20D9M, a PUS20XP1 and a PUS20XP2; wherein the plasmid pUS20D9M has a sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, the plasmid pUS20XP1 has a sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2, and the plasmid pUS20XP2 has a sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 3. Bacillus subtilis is an important microorganism. Many breeding works need to improve gene mutation frequency of bacillus subtilis. However, an ideal method for controlling spontaneous mutation frequency of bacillus subtilis does not exist at present. According to the invention, by virtue of a CRISPRi technology and a method for overexpressing error-prone DNA polymerase, the spontaneous mutation frequency of a host is improved (as high as 5128 times). The whole operation can be realized through transformation and elimination of plasmids, and gene knockout of a host is not needed.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A genetically engineered strain using sucrose to produce succinic acid and its fermentation method for producing succinic acid
ActiveCN103937733BImprove fermentation effectIncrease useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliLactate dehydrogenase
Belonging to the technical field of bioengineering, the invention relates to a genetic engineering strain producing succinic acid and a method for production of succinic acid by fermenting the strain, particularly a recombinant strain efficiently utilizing cane sugar and molasses to grow and produce succinic acid. The genetic engineering strain producing succinic acid is classified and named as Escherichia coli BA501, and has a preservation registration number of CCTCC NO:M2014014. The construction process of the strain mainly includes: taking Escherichia coli AFP111 that lacks lactate dehydrogenase gene and pyruvate formate lyase activity and has the chromosome ptsG gene undergoing spontaneous mutation as the starting strain, expressing exogenous sucrose permease, sucrose hydrolase and fructokinase genes, and then carrying out continuous domestication cultivation to obtain the strain efficiently utilizing cane sugar and molasses to grow and produce succinic acid. Thus, the synthesis efficiency of succinic acid is greatly improved. The fermentation method adopts a two-stage fermentation way, in the aerobic stage the biomass is improved oxygen, and in the anaerobic stage, fermentation and acid production are achieved.
Owner:态创生物科技(广州)有限公司
Hybrid tea rose plant named 'meitravia'
A new and distinct Hybrid Tea rose plant is provided which forms attractive blossoms that are hot pink in coloration. The new variety is a spontaneous mutation of unknown causation of the ‘Meilavio’ variety (U.S. Plant Pat. No. 10,845) that forms vivid red blossoms. The blossoms are fully double, long lasting, and very quartered in the sense the petals of the fully opened blossoms tend to be arranged in a plurality of zones when viewed from above. The vegetation is strong and vigorous and the growth habit is erect. Many large thorns are exhibited. The foliage is very decorative, dark green, and semi-glossy and contrasts nicely with the hot pink blossom coloration. Good resistance to Black Spot and Powdery Mildew is displayed. The new variety is well suited for providing attractive ornamentation in the garden.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Climbing shrub rose plant named 'radsunsar'
A new and distinct variety of climbing rose plant is provided which forms in abundance on a substantially continuous basis attractive clusters of semi-double informal clear yellow blossoms having approximately ten petals on average. The new variety is a spontaneous mutation of unknown causation of the ‘Radsun’ variety (U.S. Plant Pat. No. 13,063). The climbing growth habit can be readily distinguished from the free-standing growth habit of the ‘Radsun’ variety. Vigorous vegetation is formed. The foliage is dense medium green with a satin finish. Excellent resistance to Black Spot is displayed. Attractive dense ornamentation in the form of foliage and blossoms is made possible when the new variety is grown on a support.
Owner:CONARD PYLE
Genetic manipulation method for manually controlling spontaneous mutation rate of bacillus subtilis and application thereof
ActiveCN108865963AHigh mutation rateIncrease the relative mutation rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGeneticsBacterial strain
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to a genetic manipulation method for manually controlling a spontaneous mutation rate of bacillus subtilis and application thereof. The genetic manipulation method comprises the following steps: regulating and controlling an operon MutSL which is responsible for a mismatch repair system of the bacillus subtilis by axylose induced promoter and repressor protein, and establishing recombinant plasmids in corresponding inducible expression; integrating the recombinant plasmids to a bacterial strain genome by utilizing Spizizen double exchange, and carrying out positive-negative selection, thus obtaining objective engineering strains; regulating different expression levels of the operon MutSL of the mismatch repair system through different xylose addition concentration, thus realizing manual control on the spontaneous mutation rate of the bacillus subtilis.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Stress, signaling and transcriptional regulatory genes involved in regulating act production in Streptomyces
The application belongs to the technical field of microbial fermentation engineering, and specifically relates to genes related to the production of polyketide actin (ACT) in streptomyces. This application specifically relates to the application of stress, signal and transcription regulation genes in the regulation of Streptomyces ACT production. There are 14 stress, signal and transcription regulation genes in total; mutations of such genes have regulatory effects on the ACT production of Streptomyces. The inventor carried out mutagenesis on Streptomyces coelicolor M145, and screened the strains with changed actin rhodopsin production. The position of the transposon on the genome was located by enzyme digestion, self-ligation and sequencing of the screened positive clones, and the principle of multiple screening to locate the same gene was used to exclude the spontaneously mutated gene, and finally determine the factor affecting the production of actinhodine. Gene.
Owner:HENAN BUSINESS SCI RES INST
Vibrio cholerae with improved biological safety features in freeze dried form
ActiveUS7592171B2Easy to storeEasy to prepareInternal-combustion engine testingBacteriaFiberBacteroides
The present invention discloses new live attenuated strains for oral immunization against cholera that are provided in freeze dried formulations for long term storage and administration to humans. These strains combine the two most important properties of live attenuated cholera vaccine candidates. One such property is being well tolerated by people ingesting them. This was achieved by virtue of mutations already described in the art. The second property is having enhanced environmental safety due to the absence of VGJΦ DNA in their genomes and also due to null mutations in the mshA gene or other spontaneous mutations conducive to the lack of MSHA type IV fimbria on the bacterial surface. This was done envisioning that VGJΦ is a filamentous phage able to recombine with CTXΦ and disseminate the cholera toxin genes. This VGJΦ phage as well as the VGJΦ-CTXΦ recombinants uses the MSHA fibers as receptor. Being devoid of MSHA fimbria the vaccine candidates are protected from acquiring CTXΦ from the recombinant hybrid VGJΦ-CTXΦ. Being devoid of VGJΦ, the vaccine candidates are impaired in the dissemination of CTXΦ, via VGJΦ.
Owner:CENT NACIONAL DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CINC)
A transporter-encoding gene involved in the regulation of act production in Streptomyces
The application belongs to the technical field of microbial fermentation engineering, and specifically relates to genes related to the production of polyketide actin (ACT) in streptomyces. This application specifically relates to the application of the transporter gene in the regulation of Streptomyces ACT production, and there are 6 genes encoding the transporter; including: SCO2254 , SCO2534 , SCO3765 , SCO6160 , SCO2519 , SCO3185 ; After the mutation of this type of gene, it has a regulation effect on the production of Streptomyces ACT. The inventor carried out mutagenesis on Streptomyces coelicolor M145, and screened the strains with changed actin rhodopsin production. The position of the transposon on the genome was located by enzyme digestion, self-ligation and sequencing of the screened positive clones, and the principle of multiple screening to locate the same gene was used to exclude the spontaneously mutated gene, and finally determine the factor affecting the production of actinhodine. Gene.
Owner:HENAN BUSINESS SCI RES INST
A method for rapid mapping and cloning of plant spontaneously mutated genes bridged by neutral mutants
ActiveCN112154910BEnriched nucleotide polymorphismRapid positioningMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsPlant genetic engineeringGenetic engineering
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
A strain of anti-phage aspartase variant production bacteria and its selection method and application
ActiveCN112391326BSolving the conundrum of susceptibility to phage infectionGood genetic stabilityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses an anti-bacteriophage aspartase variant production bacterium, a breeding method and an application thereof. The present invention carries out continuous spontaneous mutation breeding on the aspartase variant producing bacteria pL181 which is easily polluted by phages, and then utilizes the low-energy ion implantation mutagenesis method to efficiently breed a strain of aspartase with phage resistance Acidase variant producing bacteria Escherichia coli CGMCC NO.18005. The strain not only has the resistance to bacteriophage (CGMCC NO.17999), but also has 31% higher enzyme activity than the original strain pL181. While improving the enzyme-producing ability of the producing bacteria, the present invention fundamentally solves the difficult problem that β-alanine is easily infected by phages in the production, and improves the economic benefits of β-alanine production enterprises.
Owner:QINHUANGDAO HUAHENG BIOENG CO LTD +1
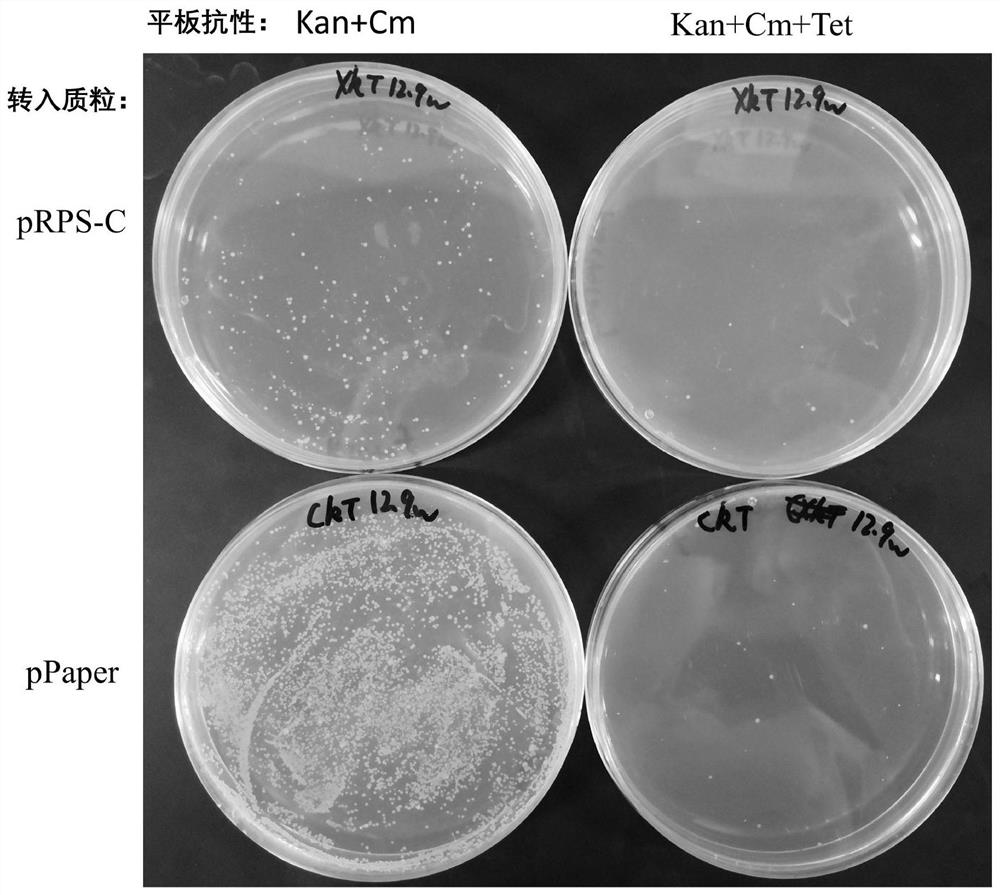
Gene editing tool, preparation method thereof and multi-round gene editing method
ActiveCN111850050AImprove editing speedReduce spontaneous mutationStable introduction of DNAMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGene engineering
The invention discloses a gene editing tool, a preparation method thereof and a multi-round gene editing method, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The problem that an existing multi-round gene editing method wastes time and labor is solved. The invention provides a gene editing tool, which comprises the following three sgRNA expression parent plasmids: pRock series mother plasmids, pPaper series mother plasmids and pScissors series mother plasmids, wherein each mother plasmid can express sgRNA used for editing a target gene and can also express sgRNA targeting one of theother two mother plasmids. In the process of implementing gene editing, when the gene editing plasmids constructed by the three mother plasmids are recycled, the gene editing plasmids which are firstly used in host cells or the selection markers are eliminated by the gene editing plasmids which are later used. According to the method, the editing period is shortened, the multi-round gene editing speed is increased, and the possibility of spontaneous mutation of the genome can be reduced due to fewer culture times.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
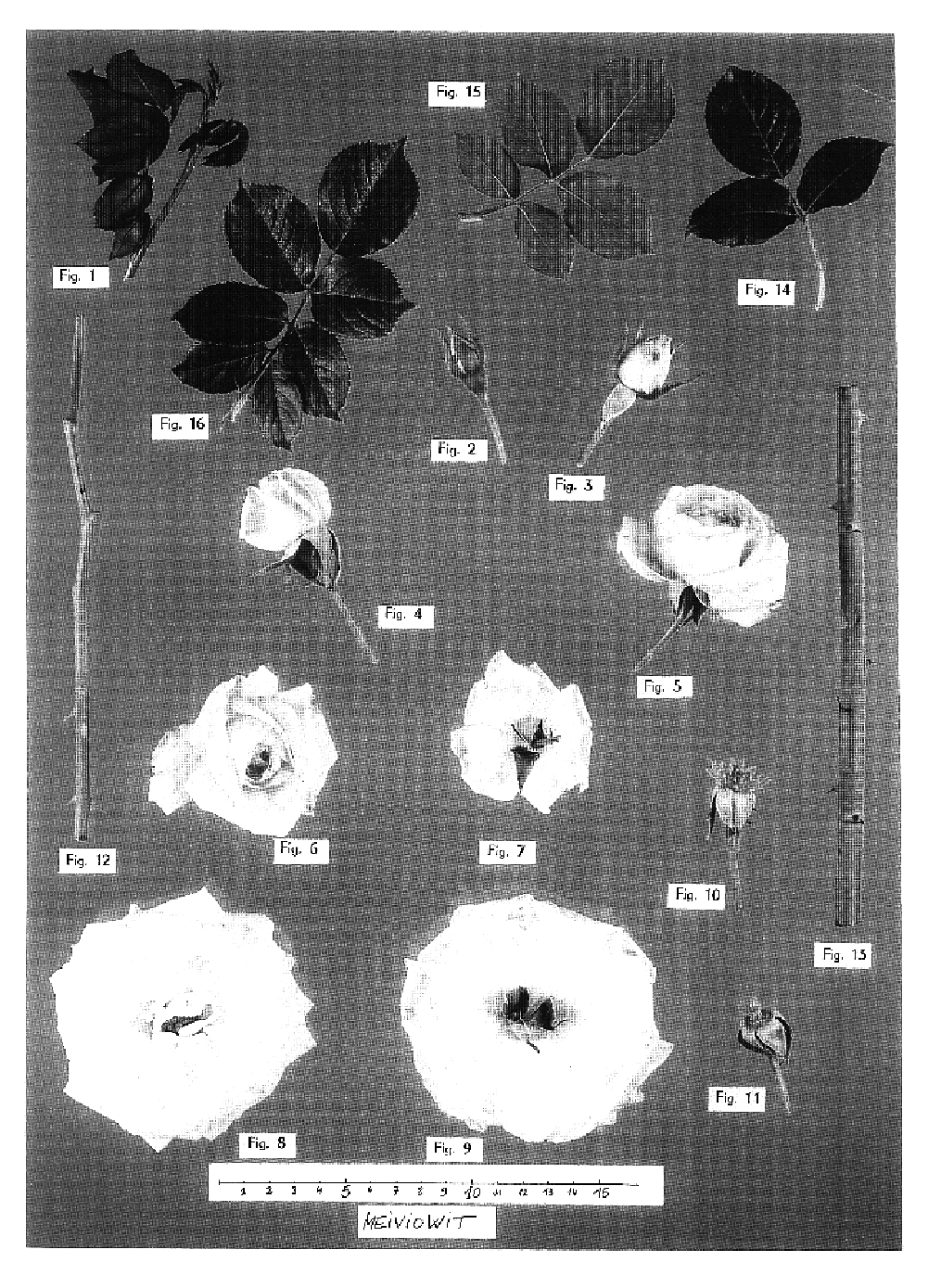
Climbing shrub rose plant named 'meiviowit'
A new and distinct variety of climbing shrub rose plant is provided. The new plant is a spontaneous mutation of unknown causation of the ‘Meiviolin’ variety (U.S. Plant Pat. No. 6,892). Attractive near white long-lasting very double blossoms having an ancient rose configuration are formed on a substantially continuous basis. Vigorous medium green semi-glossy foliage is formed that contrasts well with the near white blossom coloration. Good resistance to Black Spot and good tolerance to frost are displayed. The new variety is particularly well suited for providing attractive ornamentation in the landscape. It can be grown to advantage on a trellis, lamppost or gazebo.
Owner:CONARD PYLE
Shrub rose plant named `Meigadraz`
Owner:CONARD PYLE
Method for reducing spontaneous mutation background of wild type human-rat hybridoma AL cells
ActiveCN103529202BLow mutational backgroundReduced background of mutationsPreparing sample for investigationFluorescenceFluorescent protein
The invention discloses a method for reducing a spontaneous mutation background of wild type human-rat hybridoma AL cells. The method comprises the following steps: collecting wild type cells; combining with a fluorescent antibody; preparing a sampling suspension solution; sorting the cells; and preserving. The method is simple to operate; the whole process from the collection of the cells and the combination with specific fluorescent proteins to sorting only needs 4-5 hours; continuously-cultured un-mutant (CD59<+>) cells and mutant (CD59<->) cells can be obtained at the same time so that the efficiency of detecting CD59 gene mutation can be improved greatly. With the adoption of the method, the spontaneous mutation rate of the AL cells can be reduced and about 30 mutant cells exist in 105 survival cells and are reduced by two times as much as the spontaneous mutation after Panning, so that the experiment sensitivity of a mutation detection system is improved effectively.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Climbing shrub rose plant named `Meiviowit`
Owner:CONARD PYLE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com