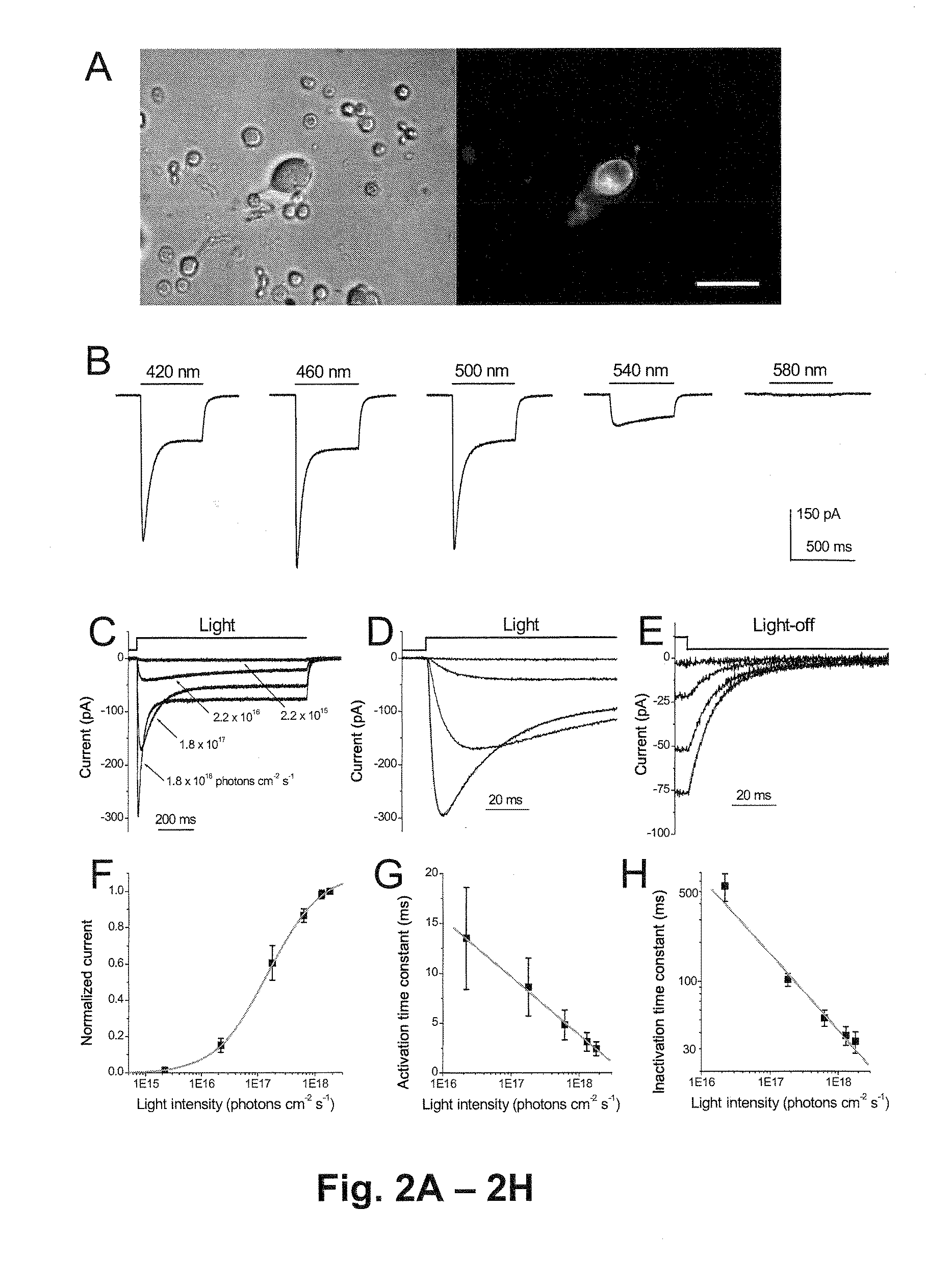
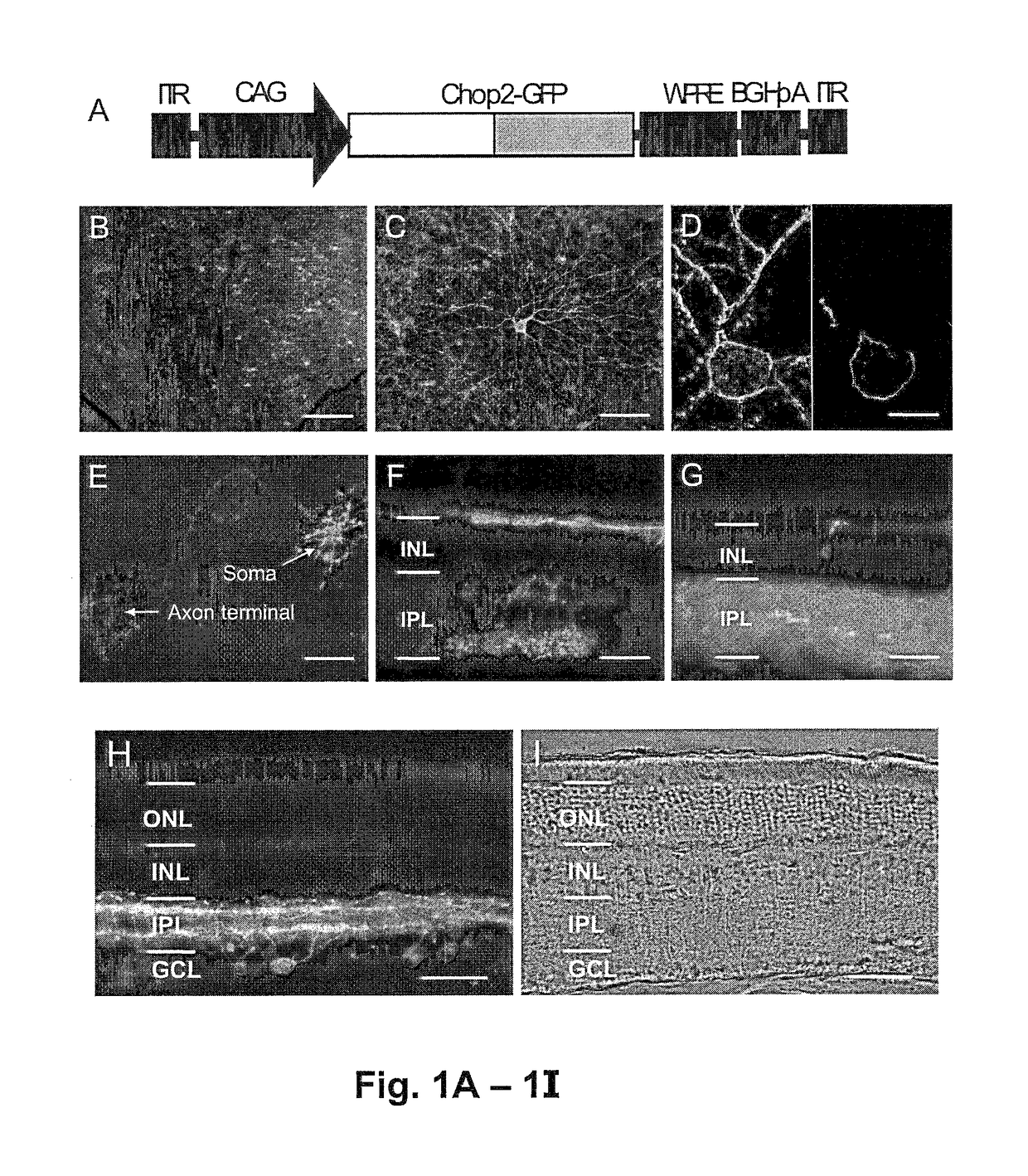
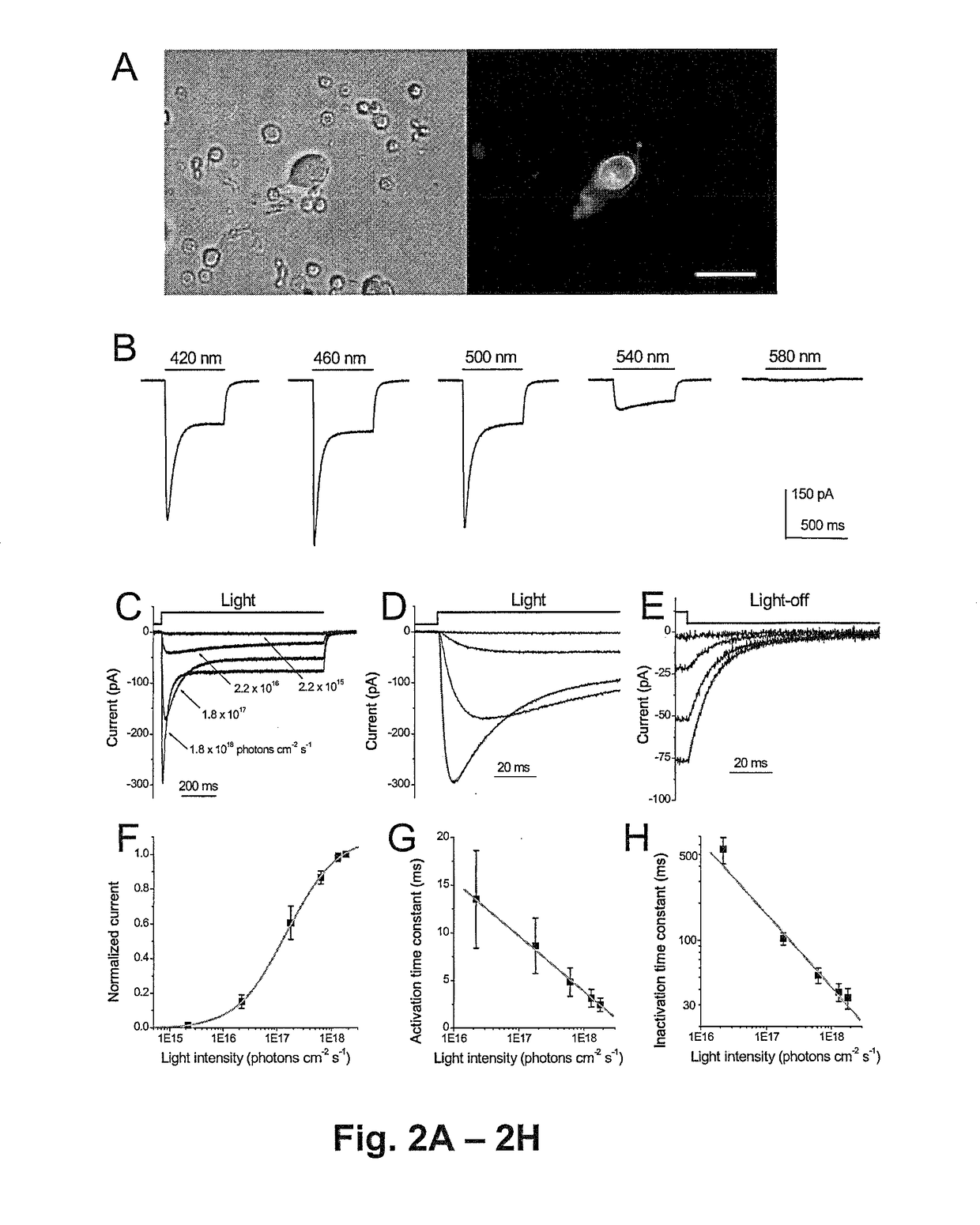
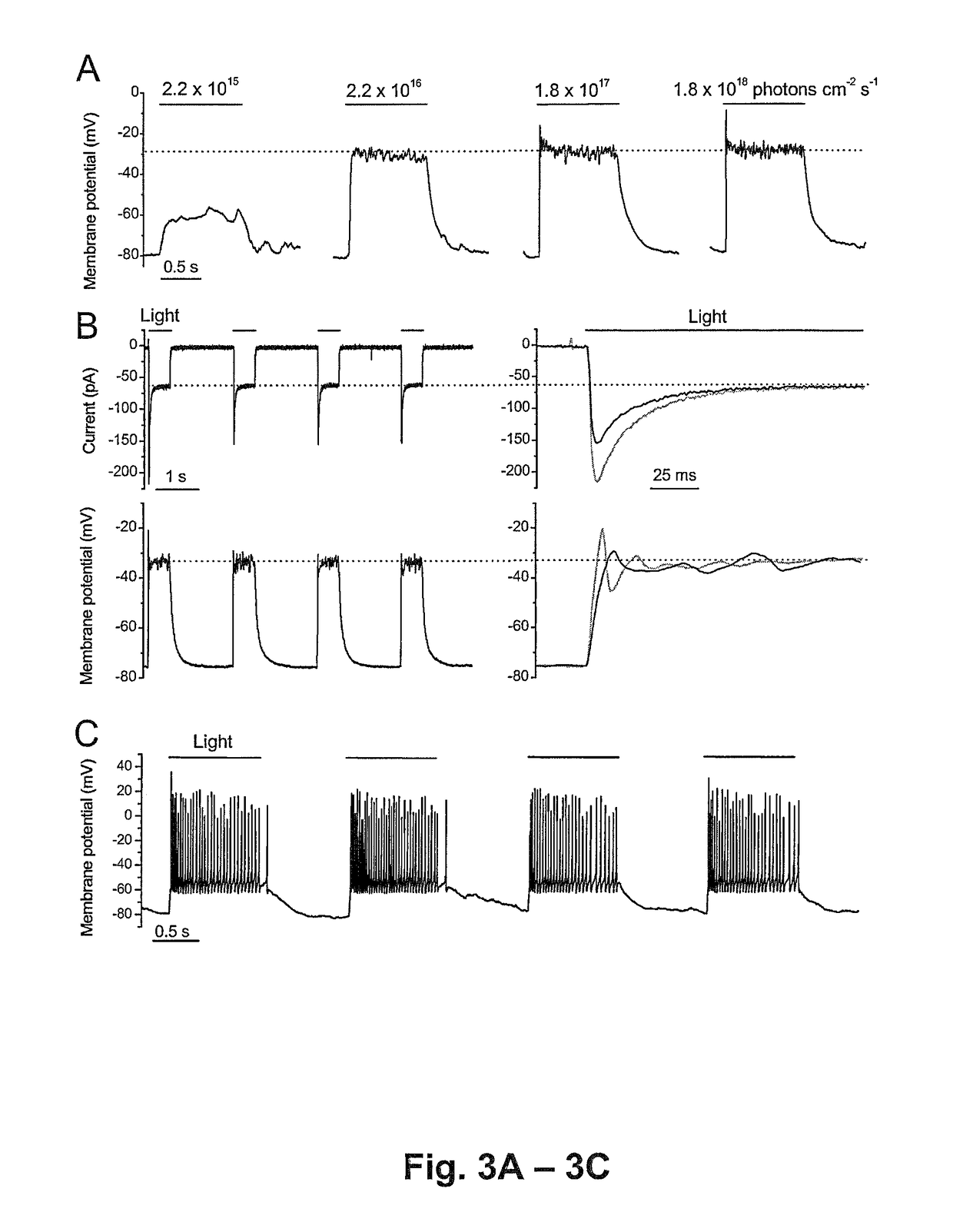
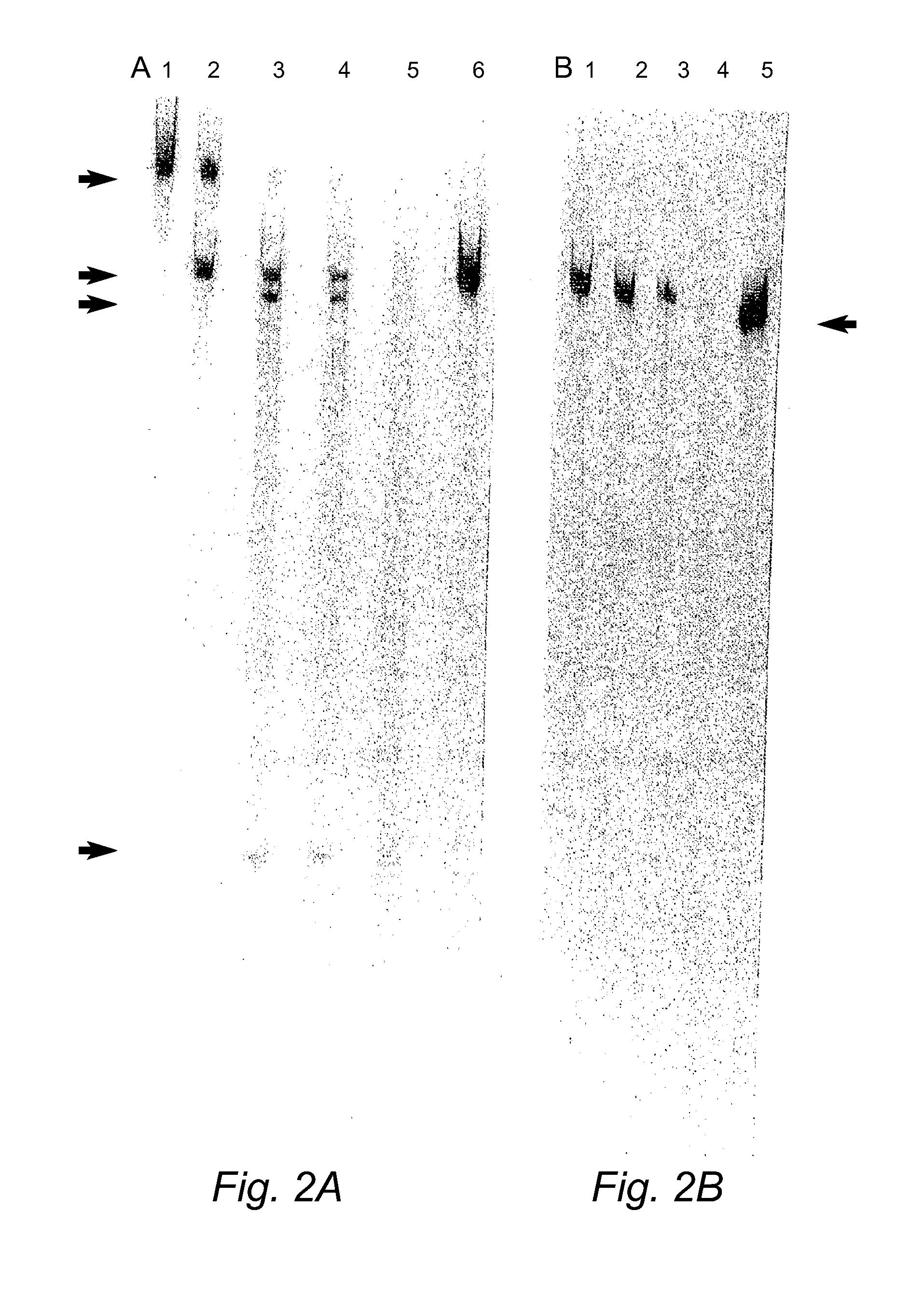
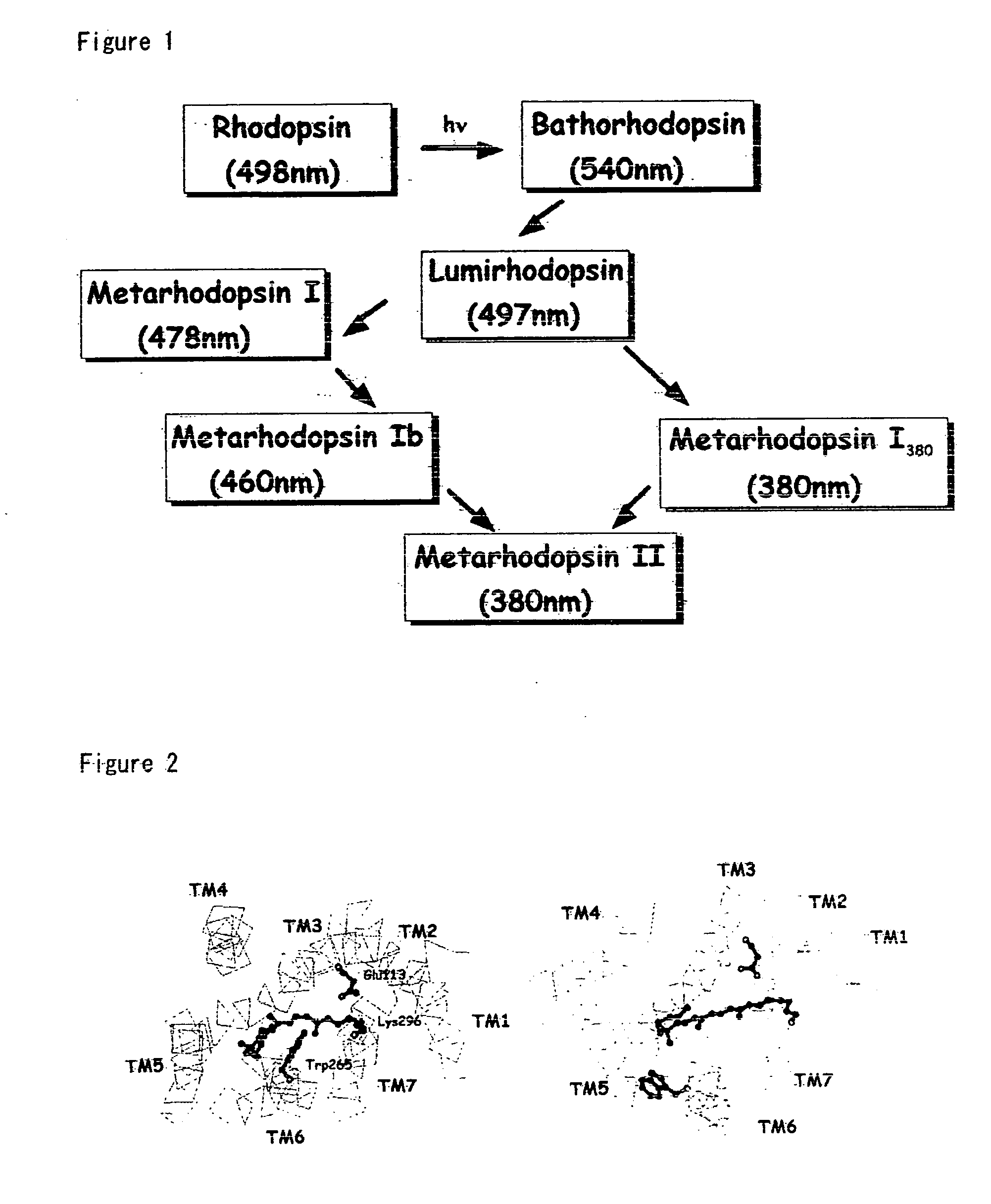
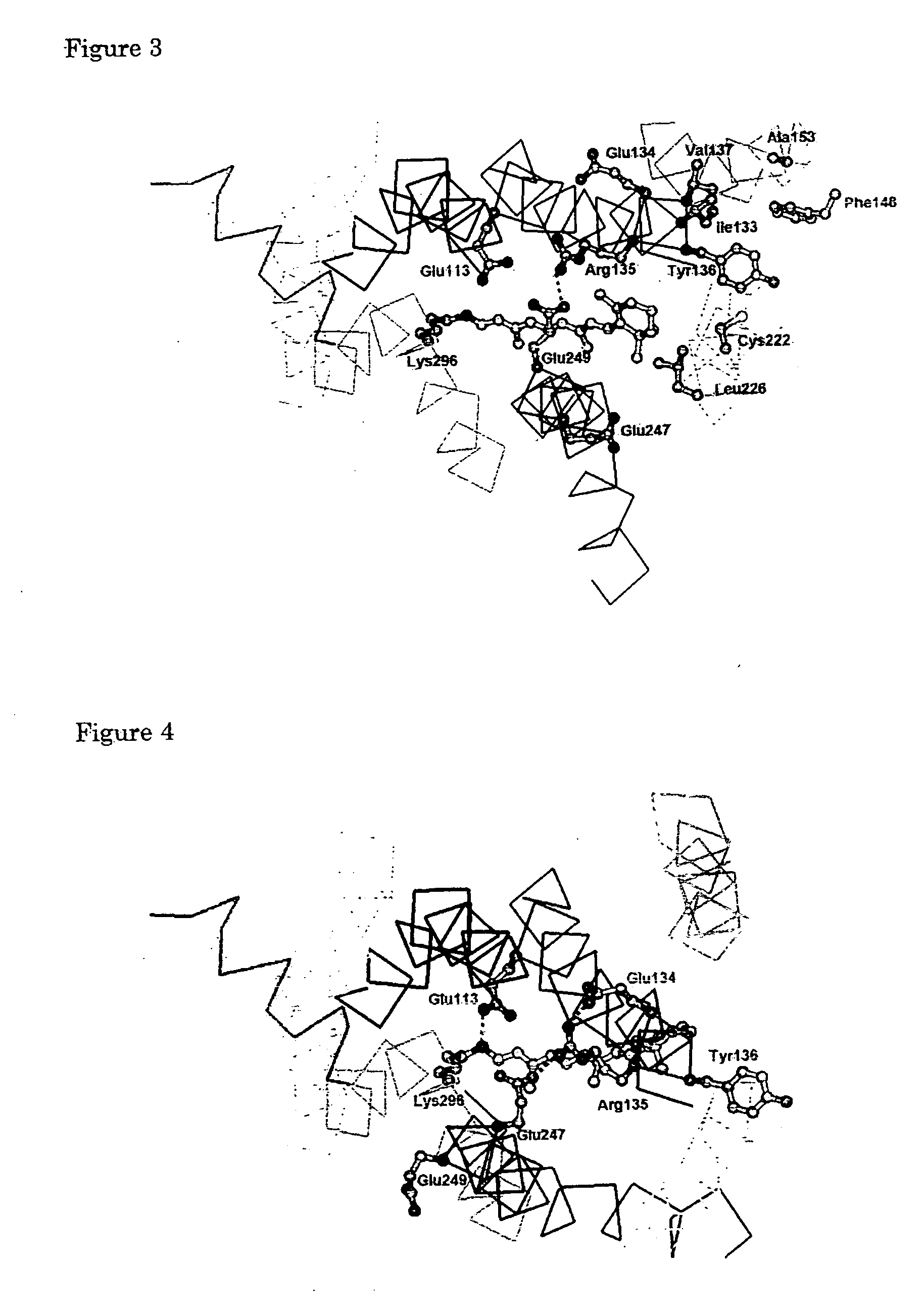
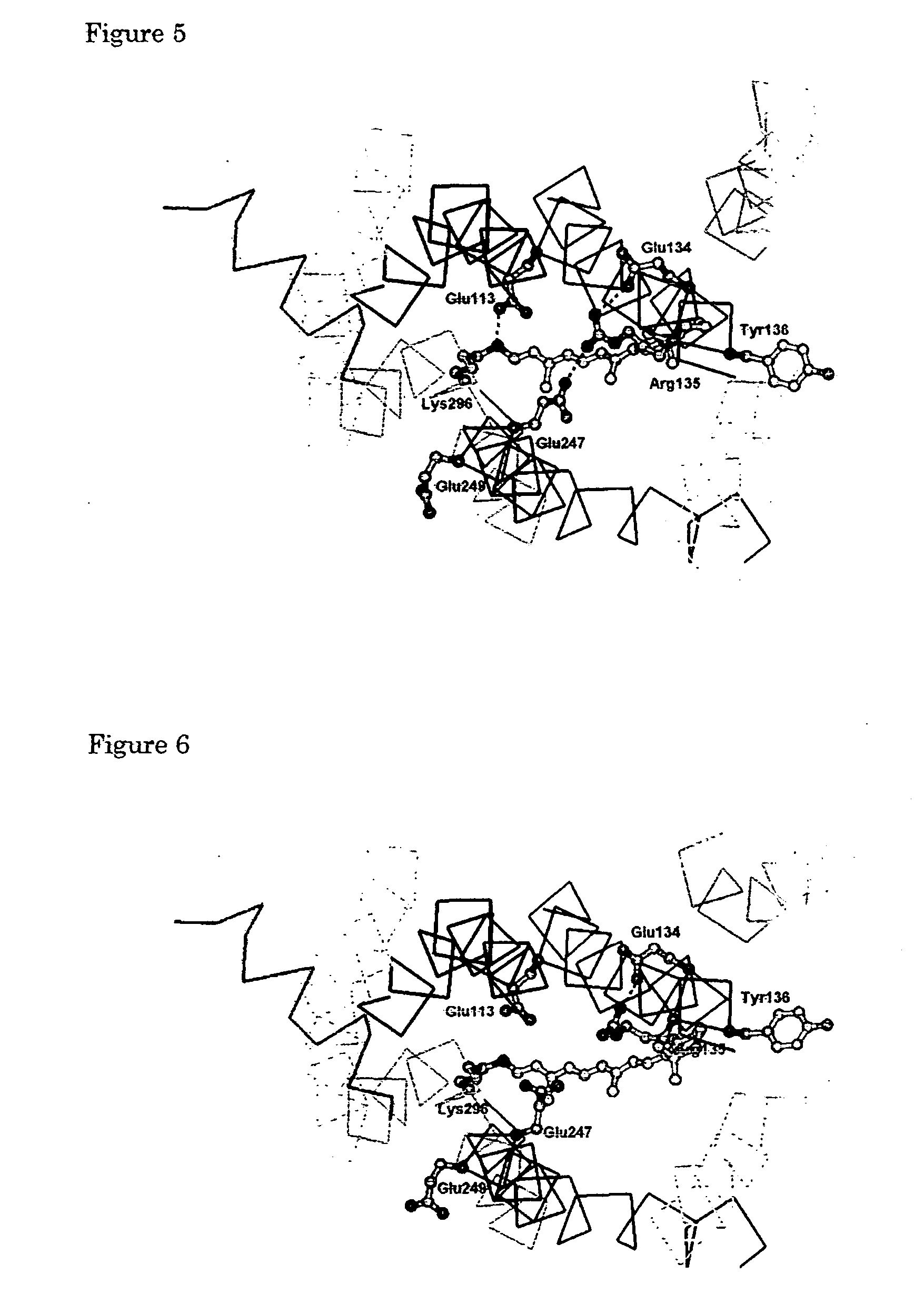
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
51 results about "Rhodopsin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
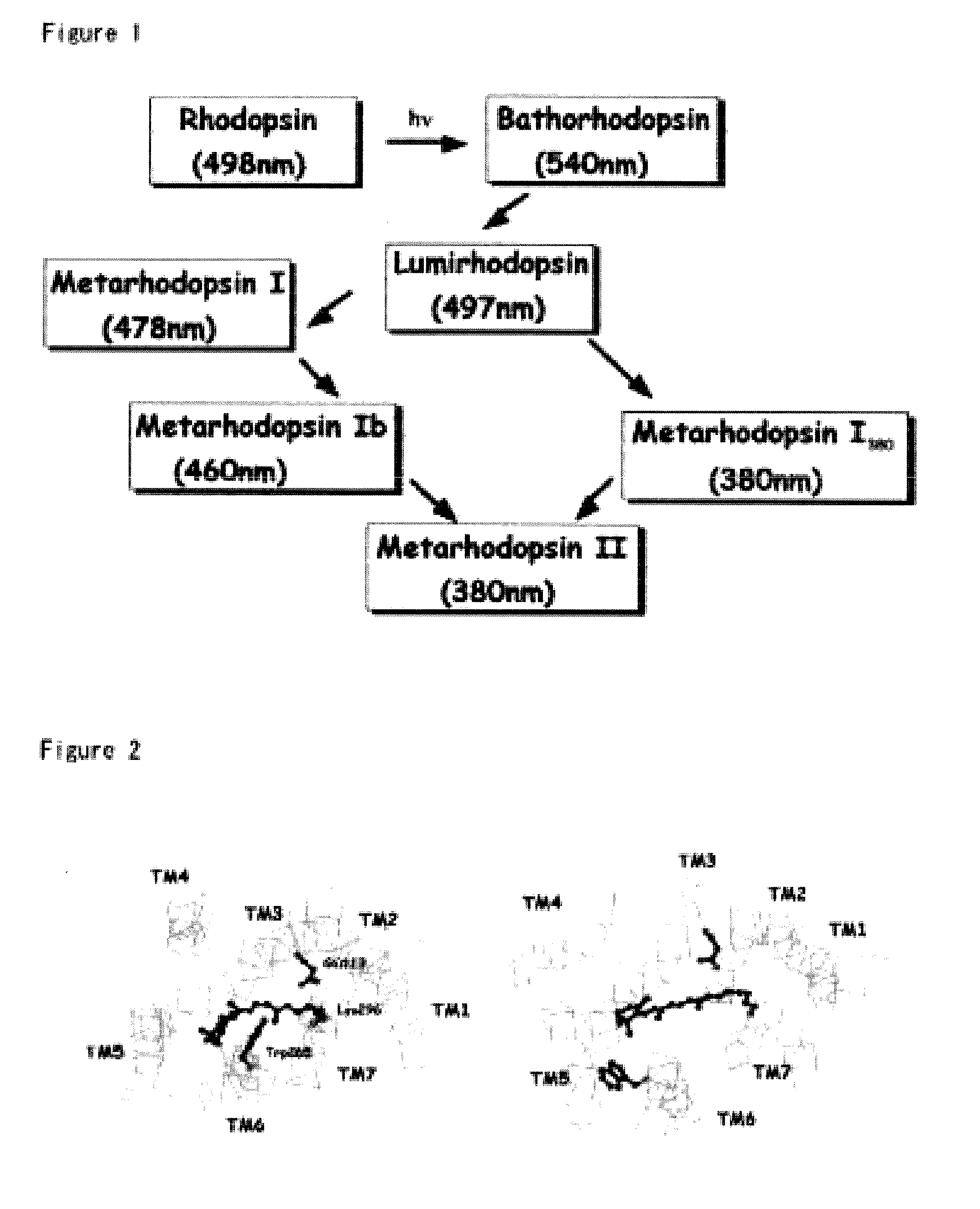
Rhodopsin (also known as visual purple) is a light-sensitive receptor protein involved in visual phototransduction. It is named after ancient Greek ῥόδον (rhódon) for rose, due to its pinkish color, and ὄψις (ópsis) for sight. Rhodopsin is a biological pigment found in the rods of the retina and is a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It belongs to opsins. Rhodopsin is extremely sensitive to light, and thus enables vision in low-light conditions. When rhodopsin is exposed to light, it immediately photobleaches. In humans, it is regenerated fully in about 30 minutes, after which rods are more sensitive.
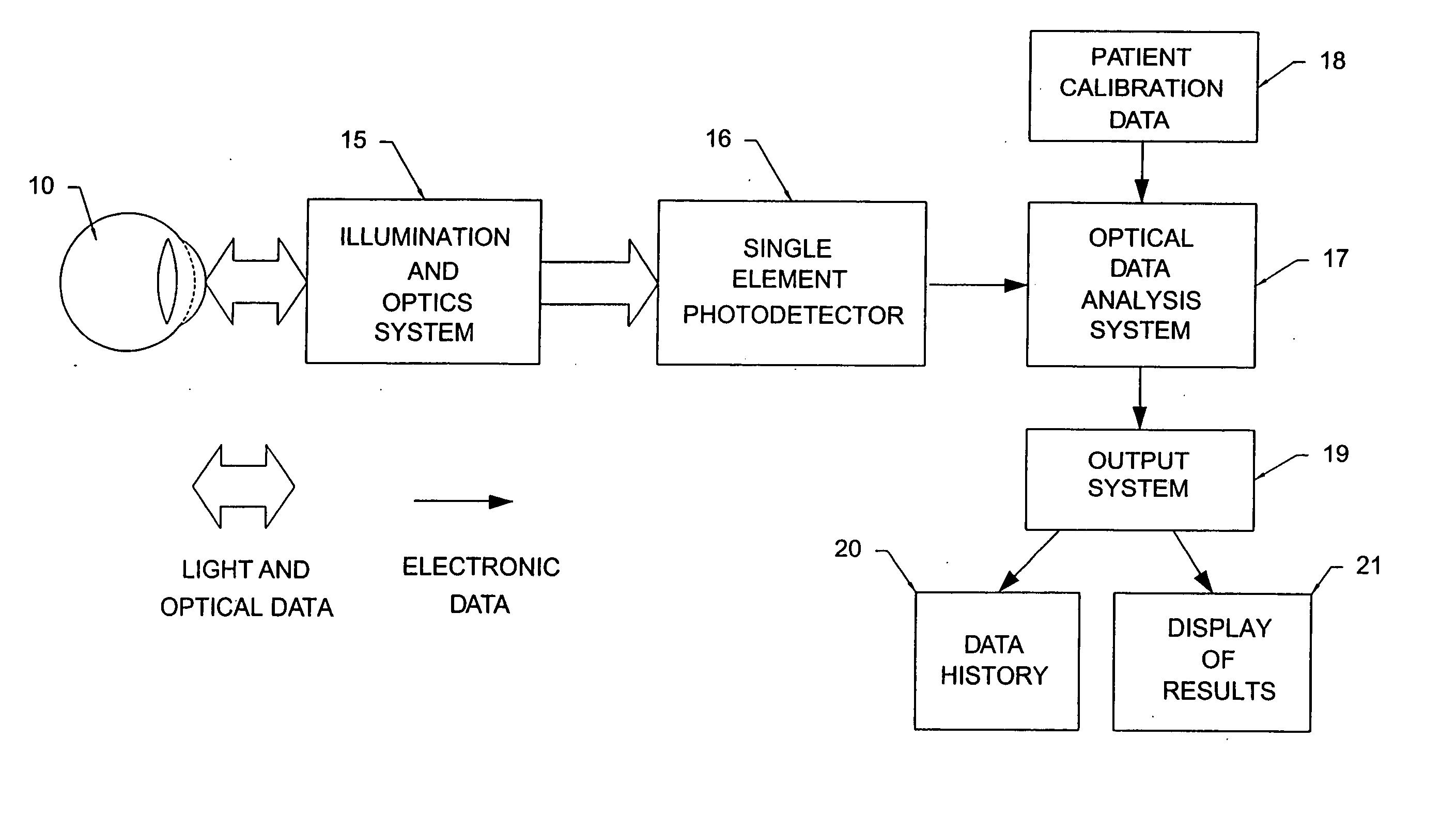
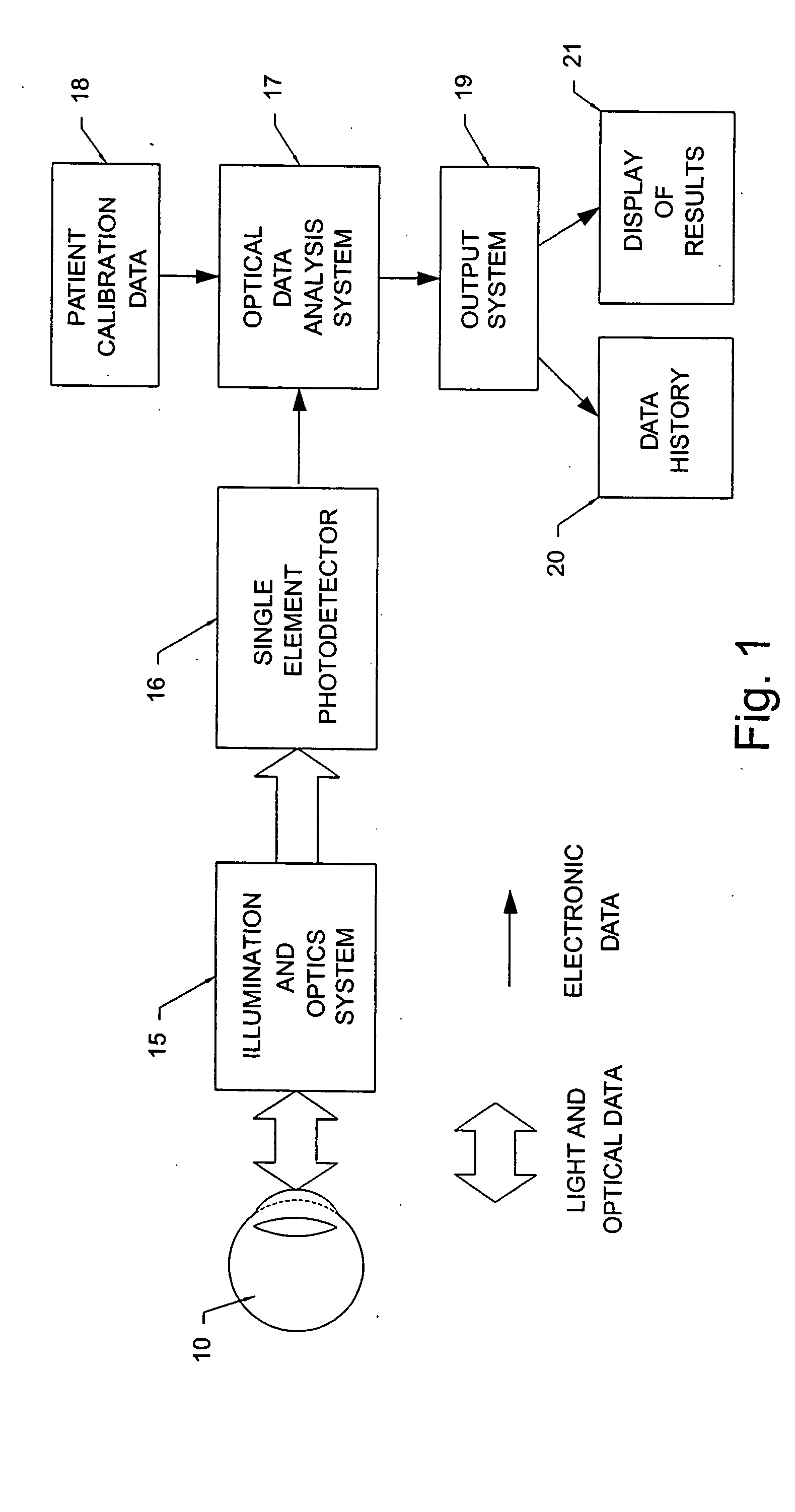
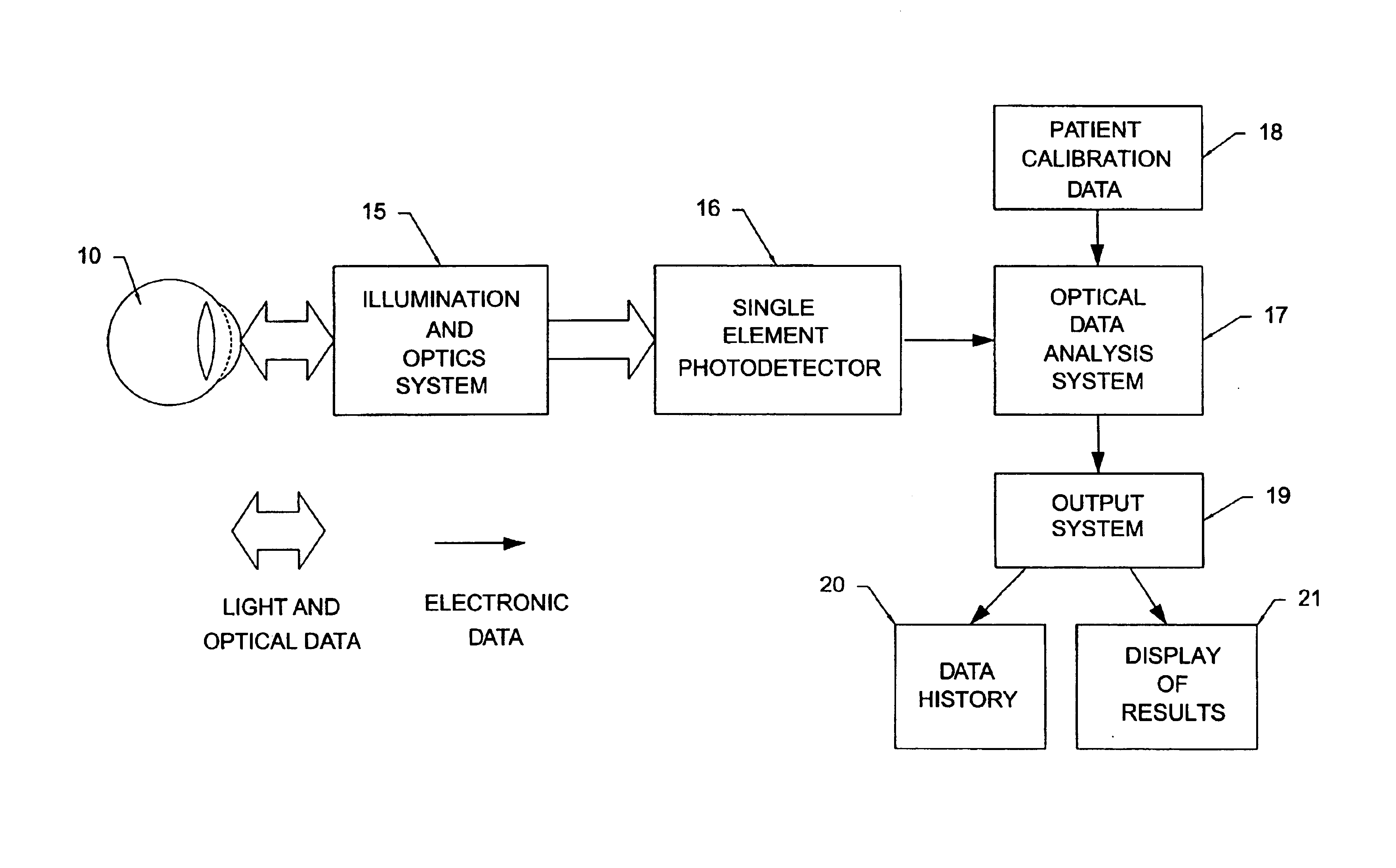
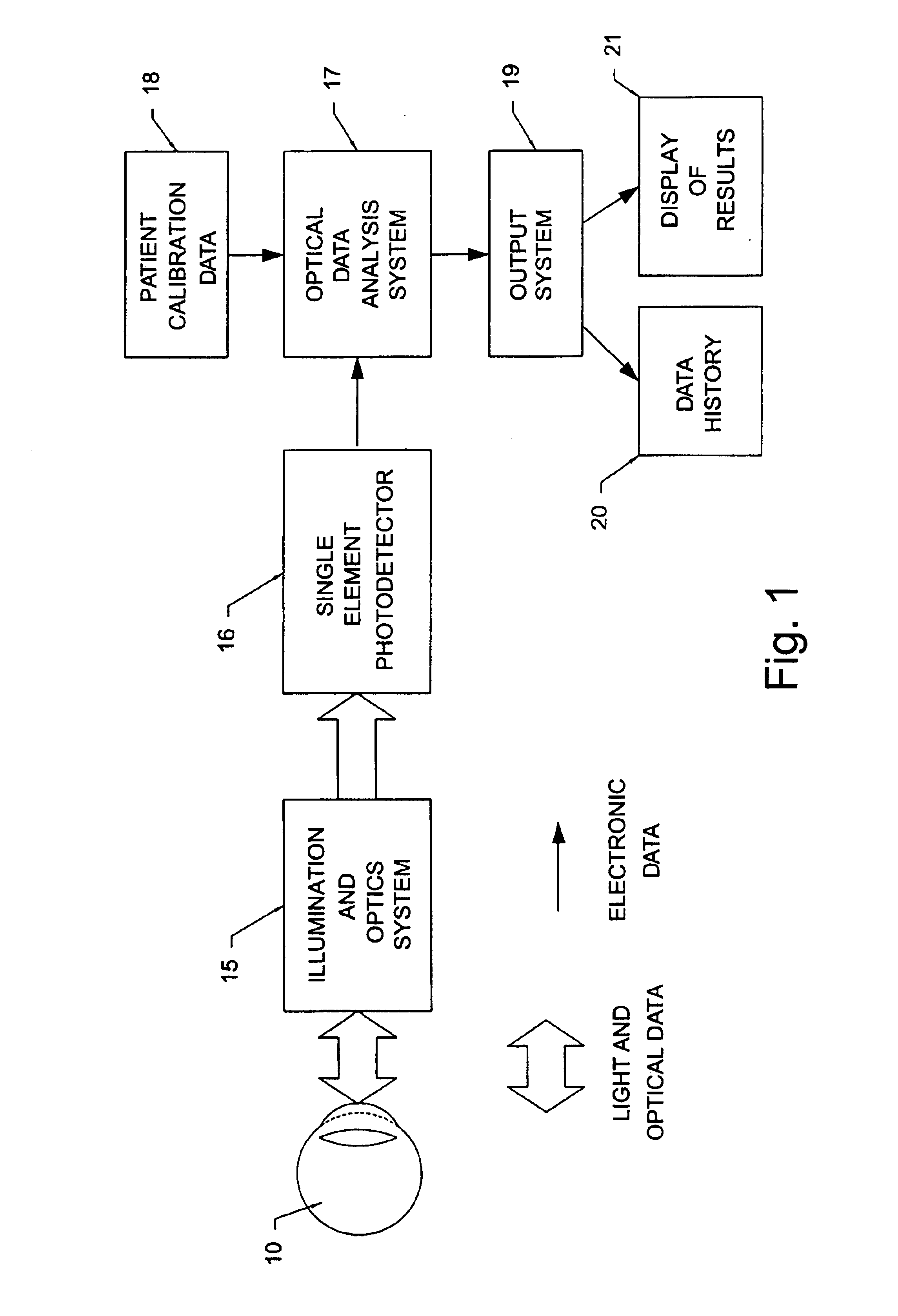
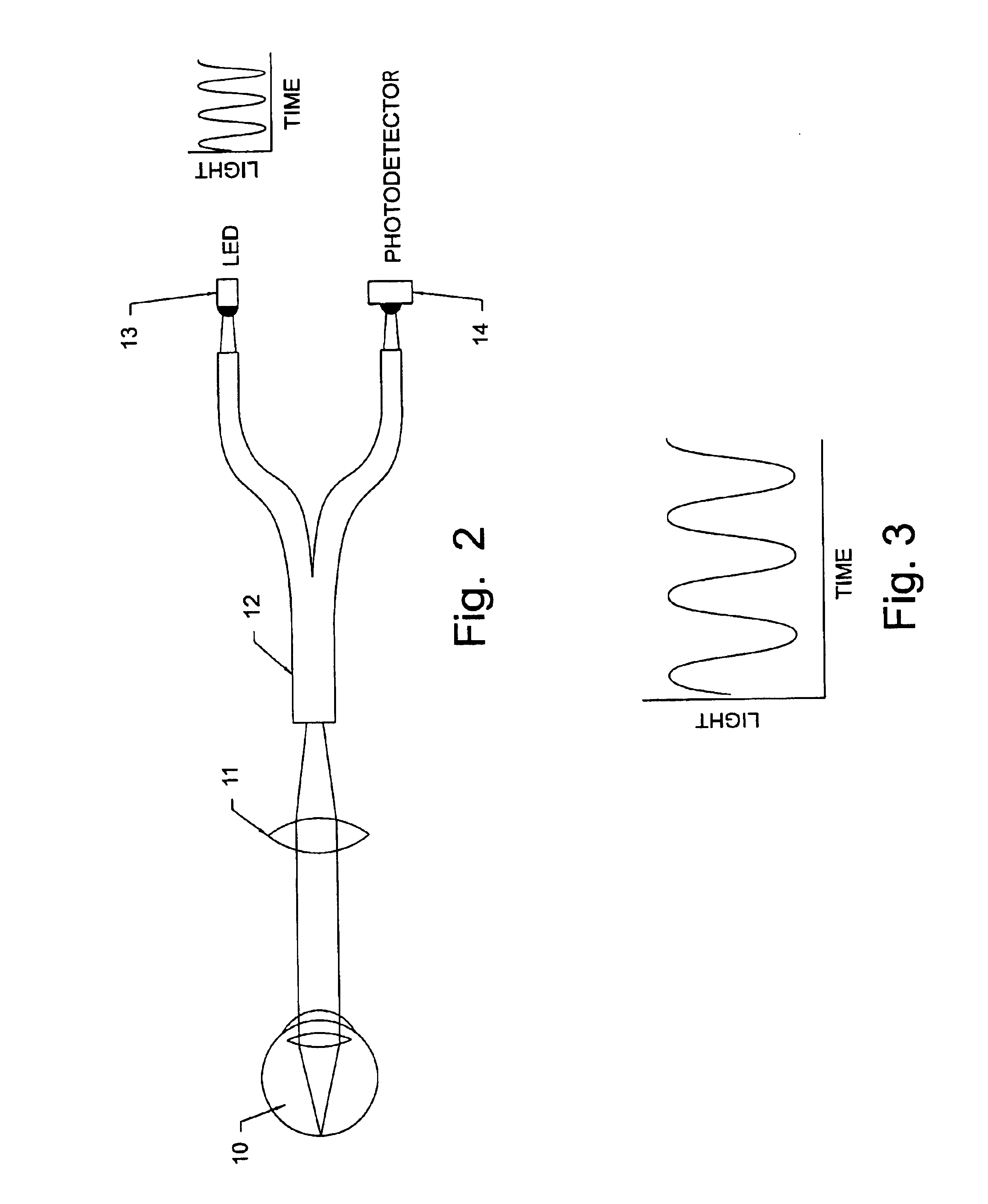
Non-invasive measurement of blood analytes using photodynamics
InactiveUS20050101847A1Rapidly-repeatable non-invasiveNon-invasive determination of glucoseDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAnalyteHarmonic
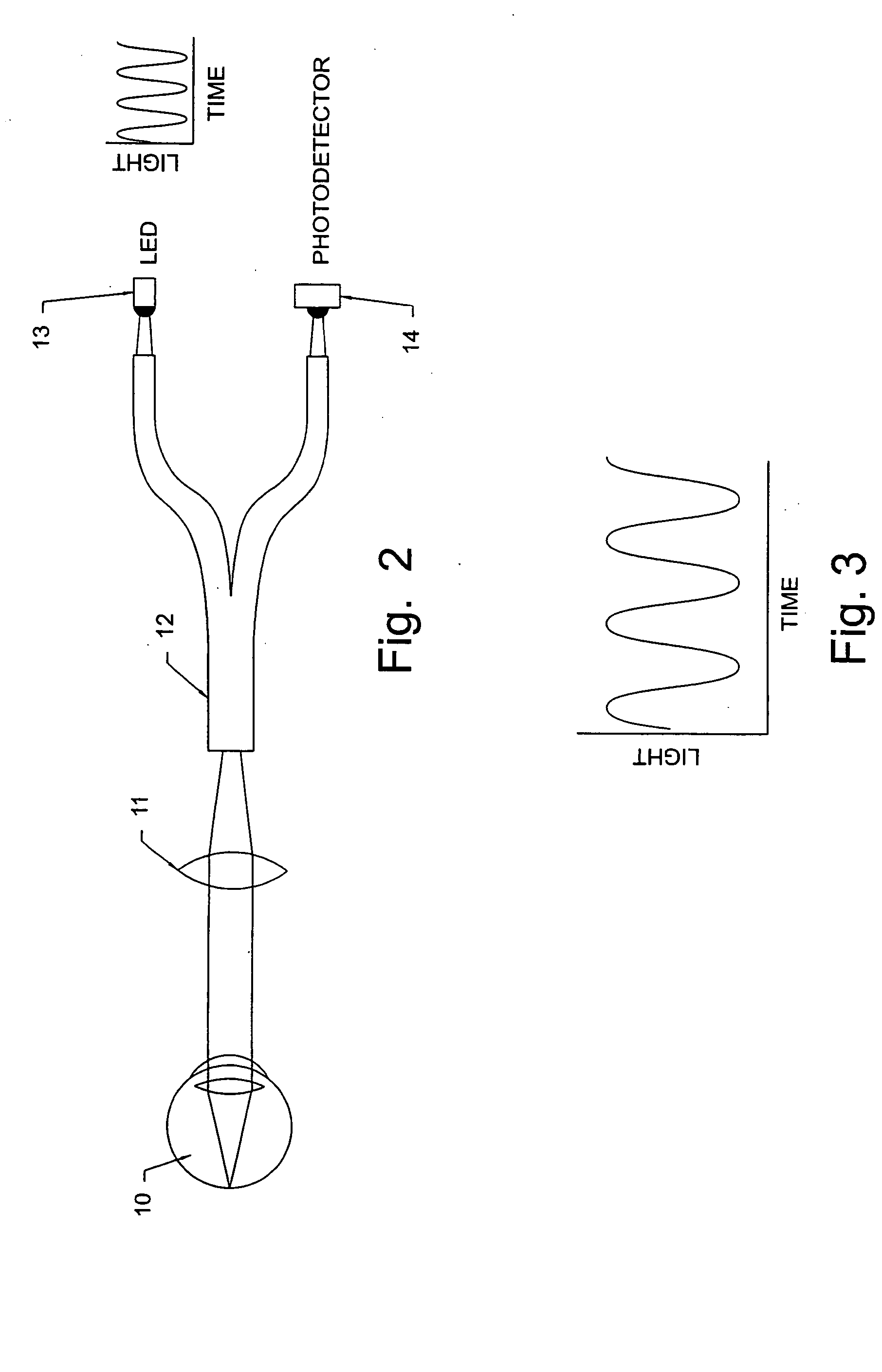
The determination of blood glucose in an individual is carried out by projecting illuminating light into an eye of the individual to illuminate the retina with the light having wavelengths that are absorbed by rhodopsin and with the intensity of the light varying in a prescribed temporal manner. The light reflected from the retina is detected to provide a signal corresponding to the intensity of the detected light, and the detected light signal is analyzed to determine the changes in form from that of the illuminating light. For a biased sinusoidal illumination, these changes can be expressed in terms of harmonic content of the detected light. The changes in form of the detected light are related to the ability of rhodopsin to absorb light and regenerate, which in turn is related to the concentration of blood glucose, allowing a determination of the relative concentration of blood glucose. Other photoreactive analytes can similarly be determined by projecting time varying illuminating light into the eye, detecting the light reflected from the retina, and analyzing the detected light signal to determine changes in form of the signal due to changes in absorptivity of a photoreactive analyte.
Owner:ROUTT WILSON +1
Non-invasive measurement of blood analytes using photodynamics
InactiveUS6889069B2Rapidly-repeatableAccurately determineDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAnalyteHarmonic
The determination of blood glucose in an individual is carried out by projecting illuminating light into an eye of the individual to illuminate the retina with the light having wavelengths that are absorbed by rhodopsin and with the intensity of the light varying in a prescribed temporal manner. The light reflected from the retina is detected to provide a signal corresponding to the intensity of the detected light, and the detected light signal is analyzed to determine the changes in form from that of the illuminating light. For a biased sinusoidal illumination, these changes can be expressed in terms of harmonic content of the detected light. The changes in form of the detected light are related to the ability of rhodopsin to absorb light and regenerate, which in turn is related to the concentration of blood glucose, allowing a determination of the relative concentration of blood glucose. Other photoreactive analytes can similarly be determined by projecting time varying illuminating light into the eye, detecting the light reflected from the retina, and analyzing the detected light signal to determine changes in form of the signal due to changes in absorptivity of a photoreactive analyte.
Owner:FOVIOPTICS INC
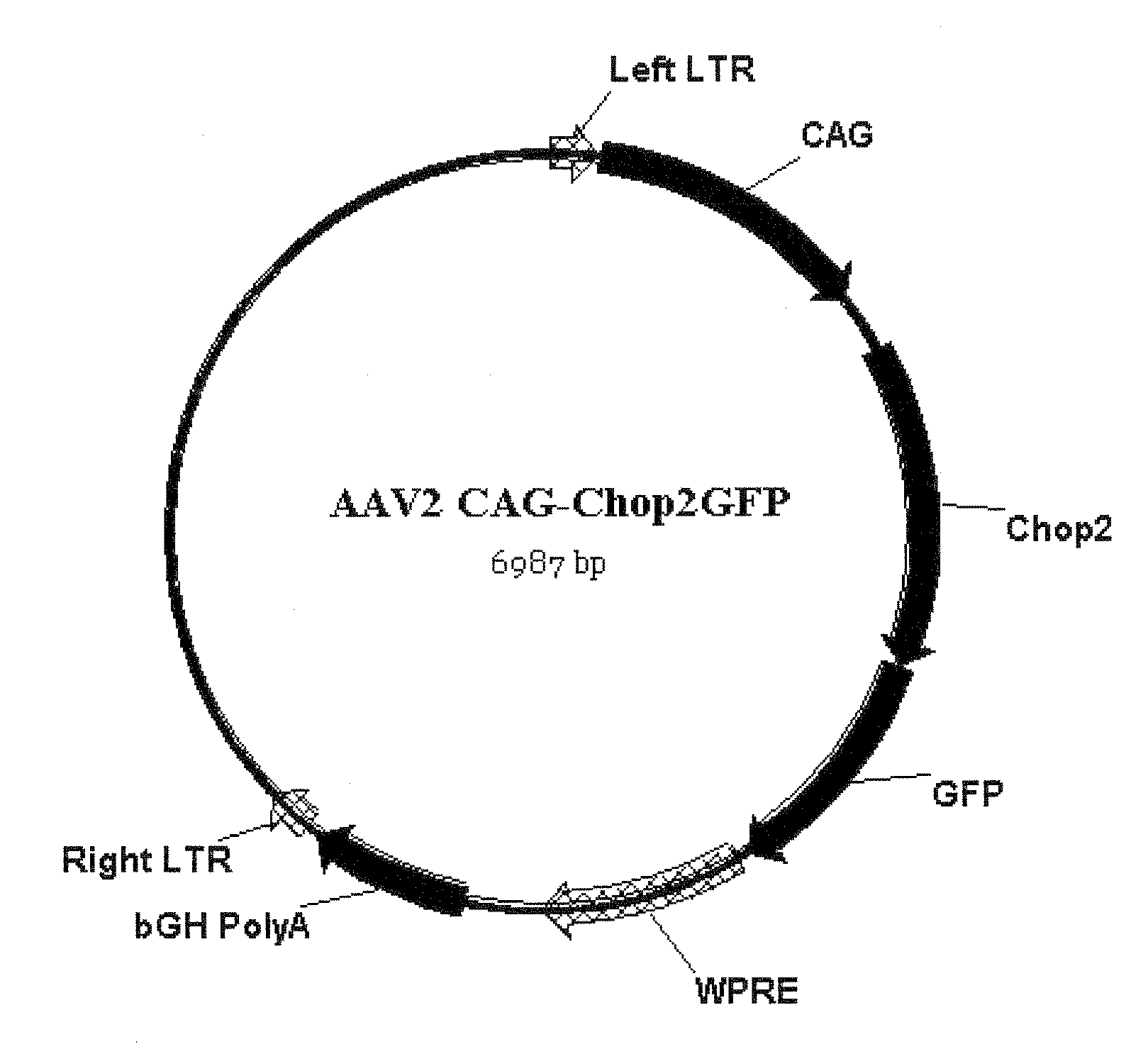
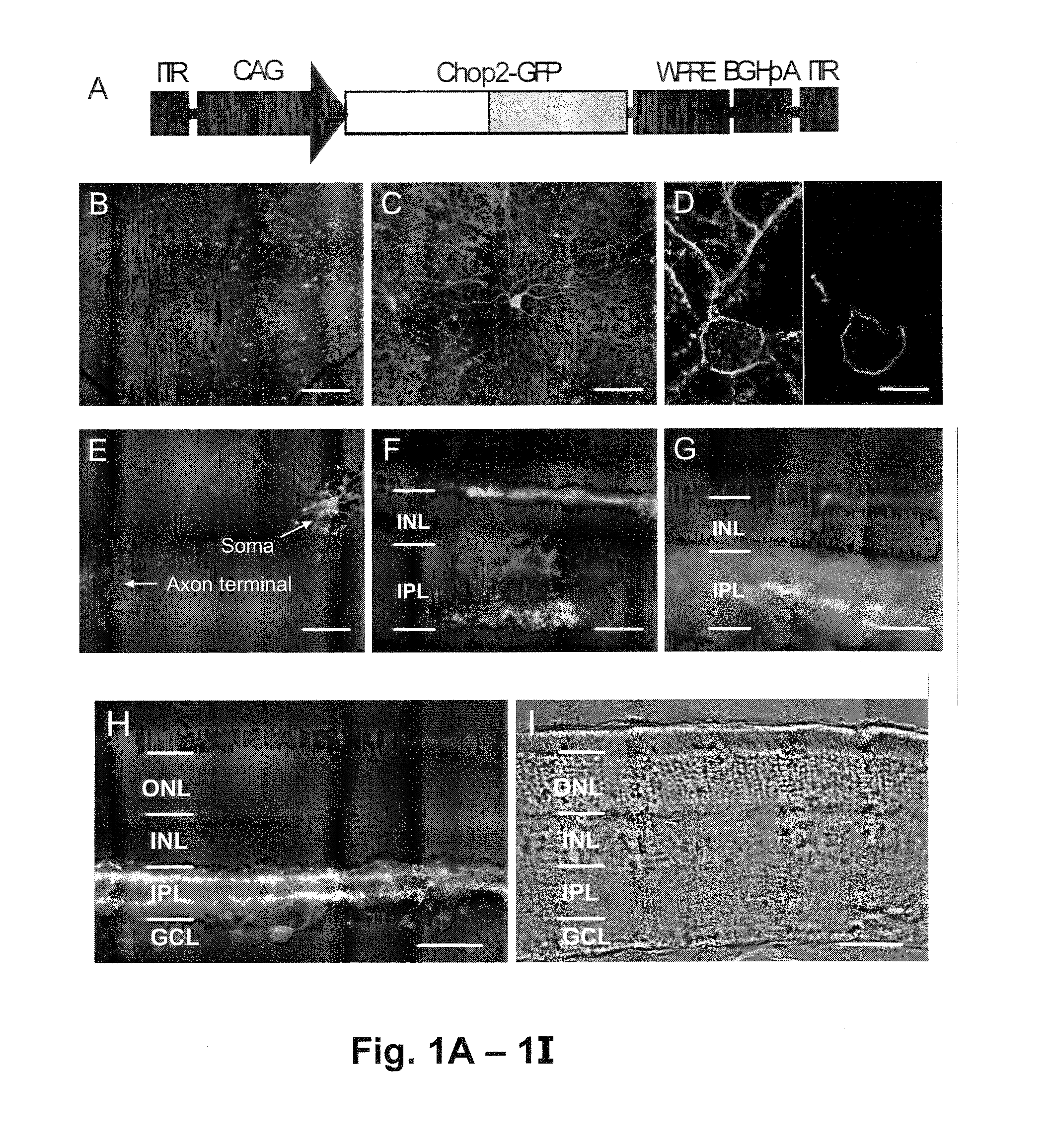
Restoration of visual responses by in vivo delivery of rhodopsin nucleic acids
ActiveUS20100015095A1Restoring light sensitivityLoss can be compensatedOrganic active ingredientsBiocideOpen reading frameIn vivo
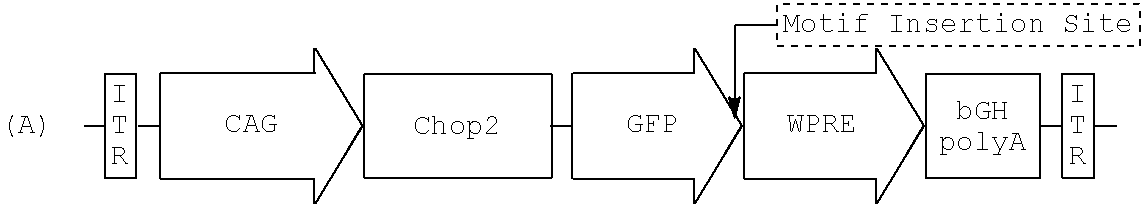
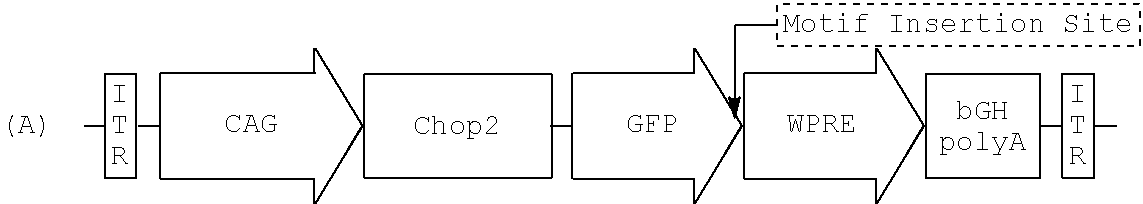
Nucleic acid vectors encoding light-gated cation-selective membrane channels, in particular channelrhodopsin-2 (Chop2), converted inner retinal neurons to photosensitive cells in photoreceptor-degenerated retina in an animal model. Such treatment restored visual perception and various aspects of vision. A method of restoring light sensitivity to a retina of a subject suffering from vision loss due to photoreceptor degeneration, as in retinitis pigmentosa or macular degeneration, is provided. The method comprises delivering to the subject by intravitreal or subretinal injection, the above nucleic acid vector which comprises an open reading frame encoding a rhodopsin, to which is operatively linked a promoter and transcriptional regulatory sequences, so that the nucleic acid is expressed in inner retinal neurons. These cells, normally light-insensitive, are converted to a light-sensitive state and transmit visual information to the brain, compensating for the loss, and leading to restoration of various visual capabilities.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV +1
Light-receiving channel rhodopsin having improved expression efficiency
Disclosed is a Volvox carteri-derived light-receiving channel rhodopsin with an improved expression efficiency on a cell membrane. Specifically disclosed is a modified Volvox carteri-derived light-receiving channel rhodopsin protein. The protein is modified to contain an N-terminal region of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii-derived channel rhodopsin-1 at the N-terminal of the Volvox carteri-derived light-receiving channel rhodopsin protein, wherein the N-terminal region is involved in cell membrane-localized expression and contains no transmembrane domain of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii-derived channel rhodopsin-1.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Restoration of visual responses by in vivo delivery of rhodopsin nucleic acids
ActiveUS8470790B2Restore sensitivityLoss can be compensatedBiocideSenses disorderOpen reading frameIn vivo
Nucleic acid vectors encoding light-gated cation-selective membrane channels, in particular channelrhodopsin-2 (Chop2), converted inner retinal neurons to photosensitive cells in photoreceptor-degenerated retina in an animal model. Such treatment restored visual perception and various aspects of vision. A method of restoring light sensitivity to a retina of a subject suffering from vision loss due to photoreceptor degeneration, as in retinitis pigmentosa or macular degeneration, is provided. The method comprises delivering to the subject by intravitreal or subretinal injection, the above nucleic acid vector which comprises an open reading frame encoding a rhodopsin, to which is operatively linked a promoter and transcriptional regulatory sequences, so that the nucleic acid is expressed in inner retinal neurons. These cells, normally light-insensitive, are converted to a light-sensitive state and transmit visual information to the brain, compensating for the loss, and leading to restoration of various visual capabilities.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV +1
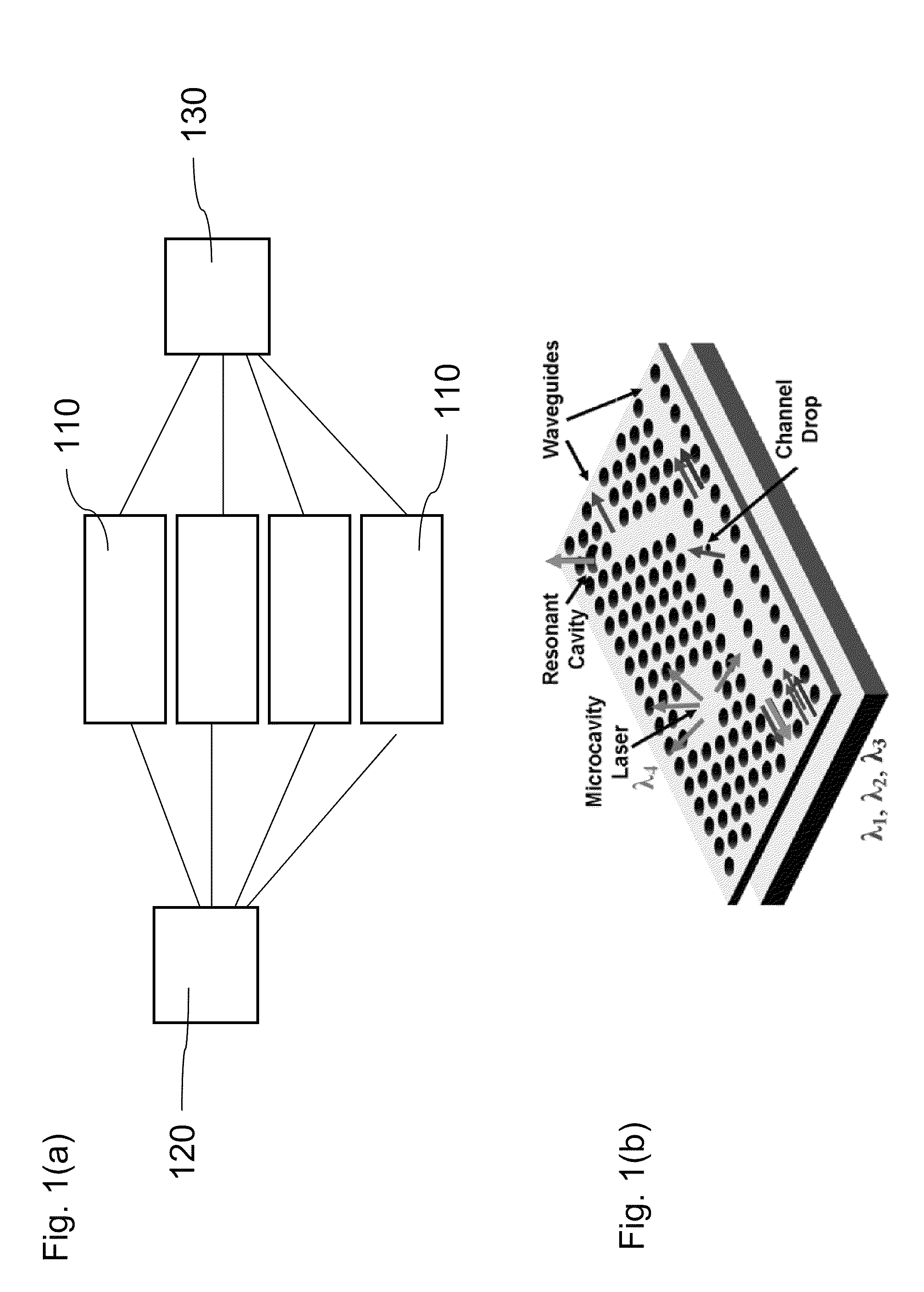
Methods, materials and devices for light manipulation with oriented molecular assemblies in micronscale photonic circuit elements with High-Q or slow light
An optical device that comprises an input waveguide, an output waveguide, a high-Q resonant or photonic structure that generate slow light connected to the input waveguide and the output waveguide, and an interface, surface or mode volume modified with at least one material formed from a single molecule, an ordered aggregate of molecules or nanostructures. The optical device may include more than one input waveguide, output waveguide, high-Q resonant or photonic structure and interface, surface or mode volume. The high-Q resonant or photonic structure may comprise at least one selected from the group of: microspherical cavities, microtoroidal cavities, microring-cavities, photonic crystal defect cavities, fabry-perot cavities, photonic crystal waveguides. The ordered aggregate of molecules or nanostructures comprises at least one selected from the group of: organic or biological monolayers, biological complexes, cell membranes, bacterial membranes, virus assemblies, nanowire or nanotube assemblies, quantum-dot assemblies, one or more assemblies containing one or more rhodopsins, green fluorescence proteins, diarylethers, lipid bilayers, chloroplasts or components, mitochondria or components, cellular or bacterial organelles or components, bacterial S-layers, photochromic molecules. Further, the molecular aggregate may exhibit a photoinduced response.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
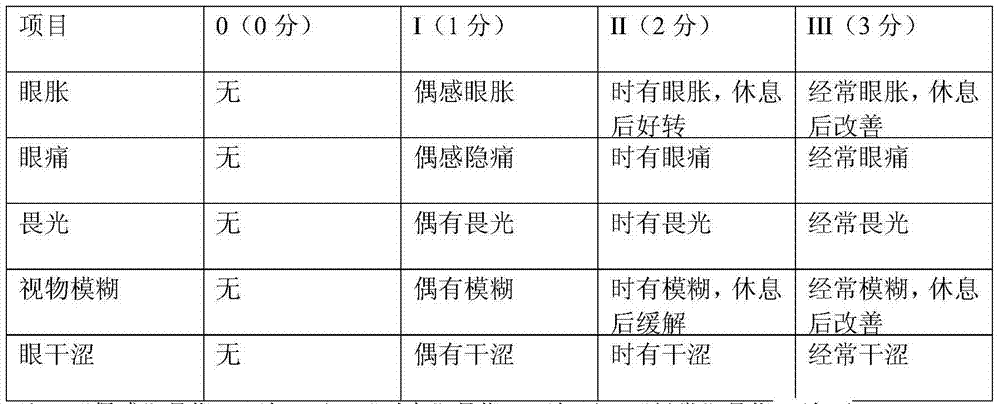
Health food for relieving visual fatigue and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104489677APromote generationEasy to synthesizeSenses disorderHydroxy compound active ingredientsLingonberry extractVitamin C
The invention discloses a health food for relieving visual fatigue and a preparation method thereof. The health food comprises the following components in parts by weight: 12-20 parts of lutein, 20-60 parts of cowberry extractives, 3-10 parts of vitamins C and 3-14 parts of zinc gluconate. The health food disclosed by the invention can exert the function of relieving the visual fatigue from the multiple aspects of supplementing eye nutrients, promoting the generation of rhodopsin, promoting the synthesis of opsin, scavenging a free radical, improving microcirculation, and the like through raw material combination.
Owner:北京世纪合辉医药科技股份有限公司
Biomarkers
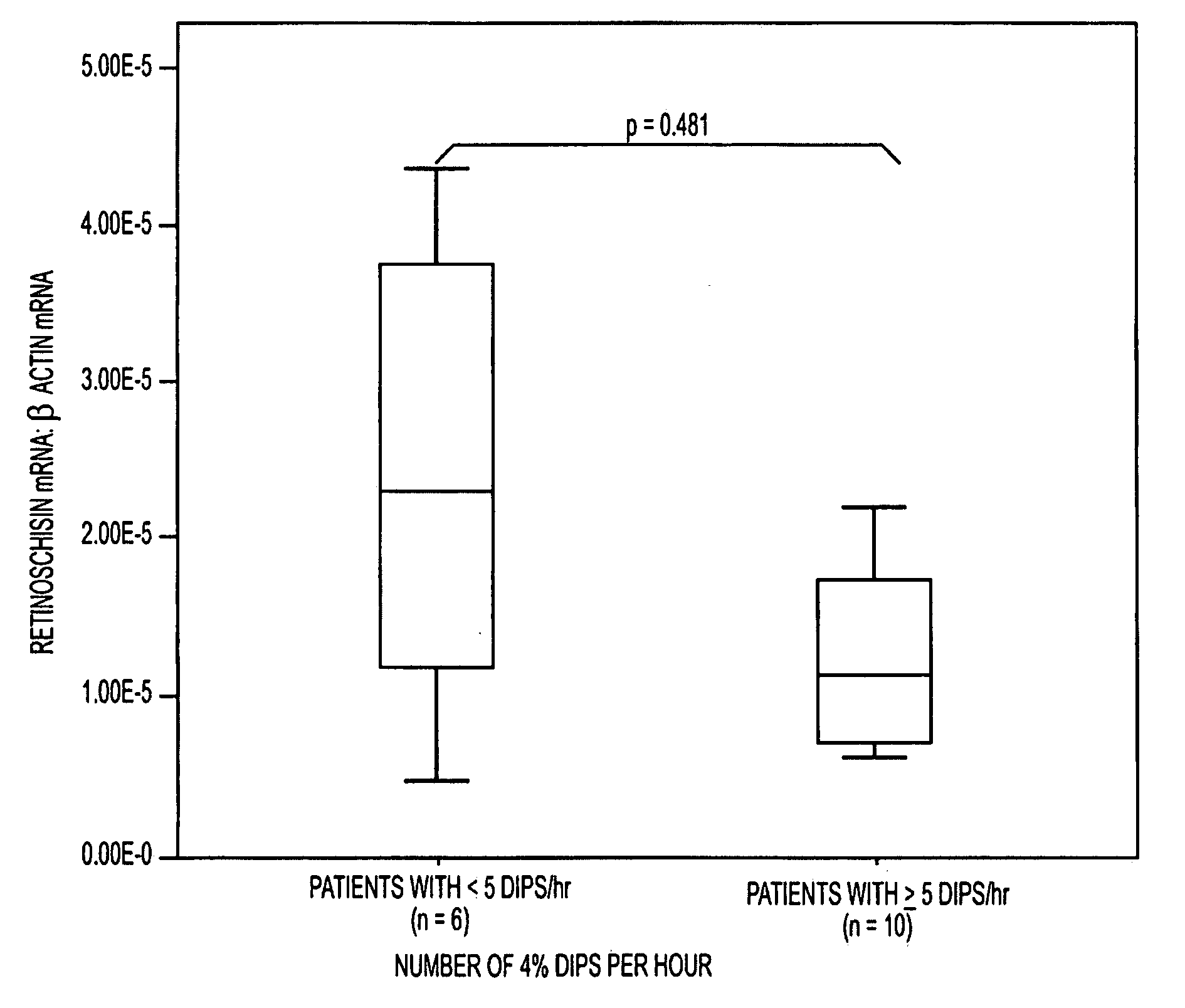
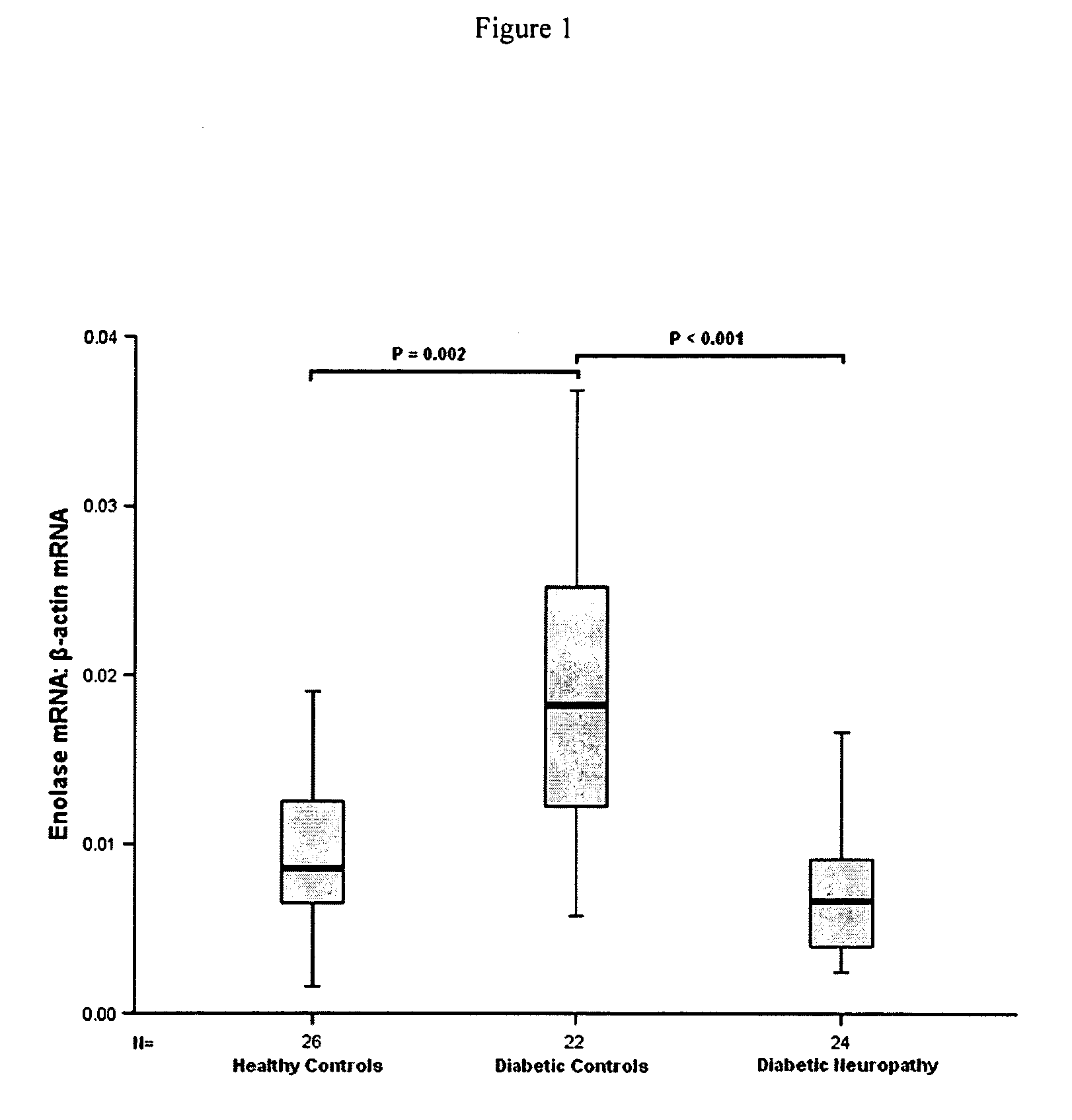
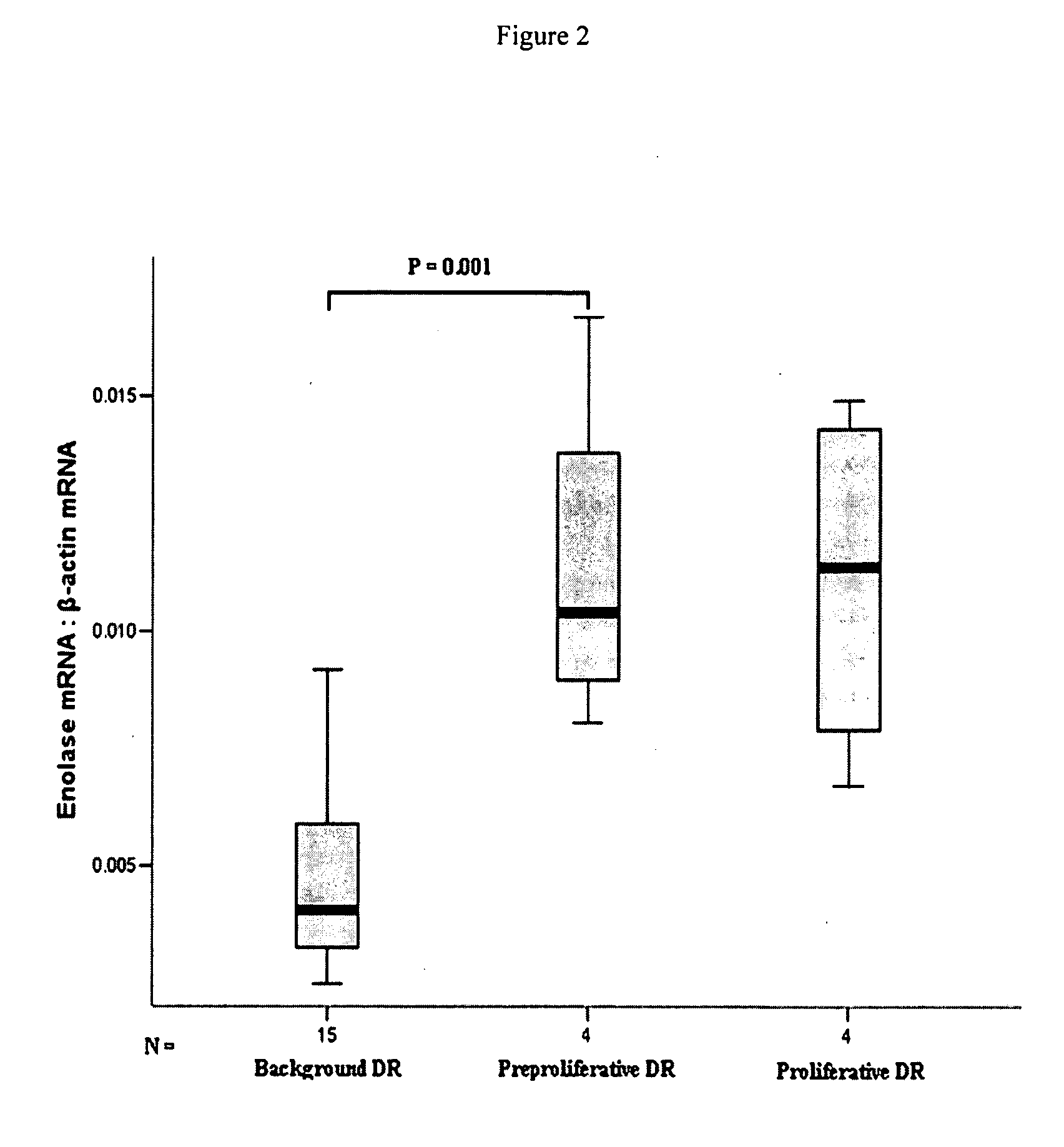
InactiveUS20100047779A1Rapid and early detectionQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementBiomarker (petroleum)RETINOSCHISIN
The present invention provides circulating biomarkers for conditions associated with metabolic syndrome, including diabetes mellitus, hypertension and congestive heart failure. The biomarkers include plasma DNA, neuron-specific enolase, 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, rhodopsin, retinoschisin, RPE65 and cardiac troponin T. Methods and kits for detecting these biomarkers in the prediction, monitoring and diagnosing of disease are provided, particularly for determining mRNA levels thereof in a subject's blood.
Owner:KING'S COLLEGE LONDON
AAV-Mediated Subcellular Targeting of Heterologous Rhodopsins in Retinal Ganglion Cells
ActiveUS20130259833A1Enhanced spatial controlStrong specificityBiocideSenses disorderHeterologousDisease
Microbial type rhodopsins, such as the light-gated cation-selective membrane channel, channelrhodopsin-2 (Chop2 / ChR2) or the ion pump halorhodopsin (HaloR) are expressed in retinal ganglion cells upon transduction using recombinant AAV vectors. Selective targeting of these transgenes for expression in discrete subcellular regions or sites is achieved by including a sorting motif in the vector that can target either the central area or surround (off-center) area of these cells. Nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding such rhodopsins and sorting motifs and their use in methods of differential expression of the transgene are disclosed. These compositions and methods provide significant improvements for restoring visual perception and various aspects of vision, particular in patients with retinal disease.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
AAV-mediated subcellular targeting of heterologous rhodopsins in retinal ganglion cells
Microbial type rhodopsins, such as the light-gated cation-selective membrane channel, channel-rhodopsin-2 (Chop2 / ChR2) or the ion pump halorhodopsin (HaloR) are expressed in retinal ganglion cells upon transduction using recombinant AAV vectors. Selective targeting of these transgenes for expression in discrete subcellular regions or sites is achieved by including a sorting motif in the vector that can target either the central area or surround (off-center) area of these cells. Nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences encoding such rhodopsins and sorting motifs and their use in methods of differential expression of the transgene are disclosed. These compositions and methods provide significant improvements for restoring visual perception and various aspects of vision, particular in patients with retinal disease.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
Method and apparatus for enhancing biological photon receptors using plasmon resonance
InactiveUS20050239048A1Improve eyesightBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNanoparticleResonance
A method for enhancing the light detection capabilities of a chromophore. In one embodiment the method includes the steps of providing a plasmon resonant nanoparticle and placing the nanoparticle in close juxtaposition to the chromophore. In one embodiment the chromophore includes 11-cis-retinal and the nanoparticle is a metal such as gold. In one embodiment the chromophore is chlorophyll. In another aspect the invention relates to an enhanced rhodopsin having a chromophore and a plasmon resonant nanoparticle in close juxtaposition with the chromophore. Yet another aspect of the invention is a method of enhancing vision in an eye including providing a plasmon resonant nanoparticle and placing the nanoparticle in close juxtaposition to a retinal molecule in the eye.
Owner:SOLARIS NANOSCI
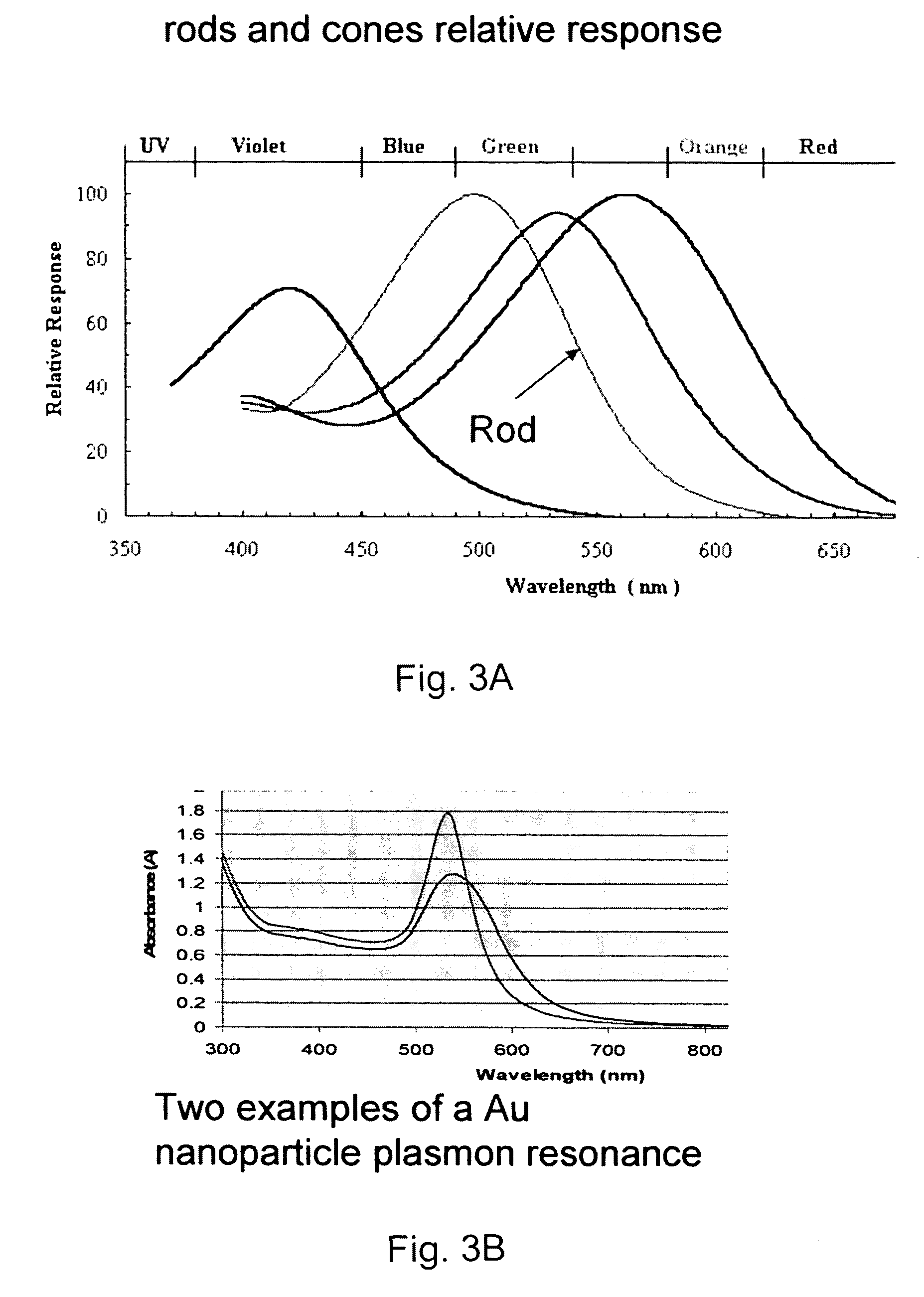
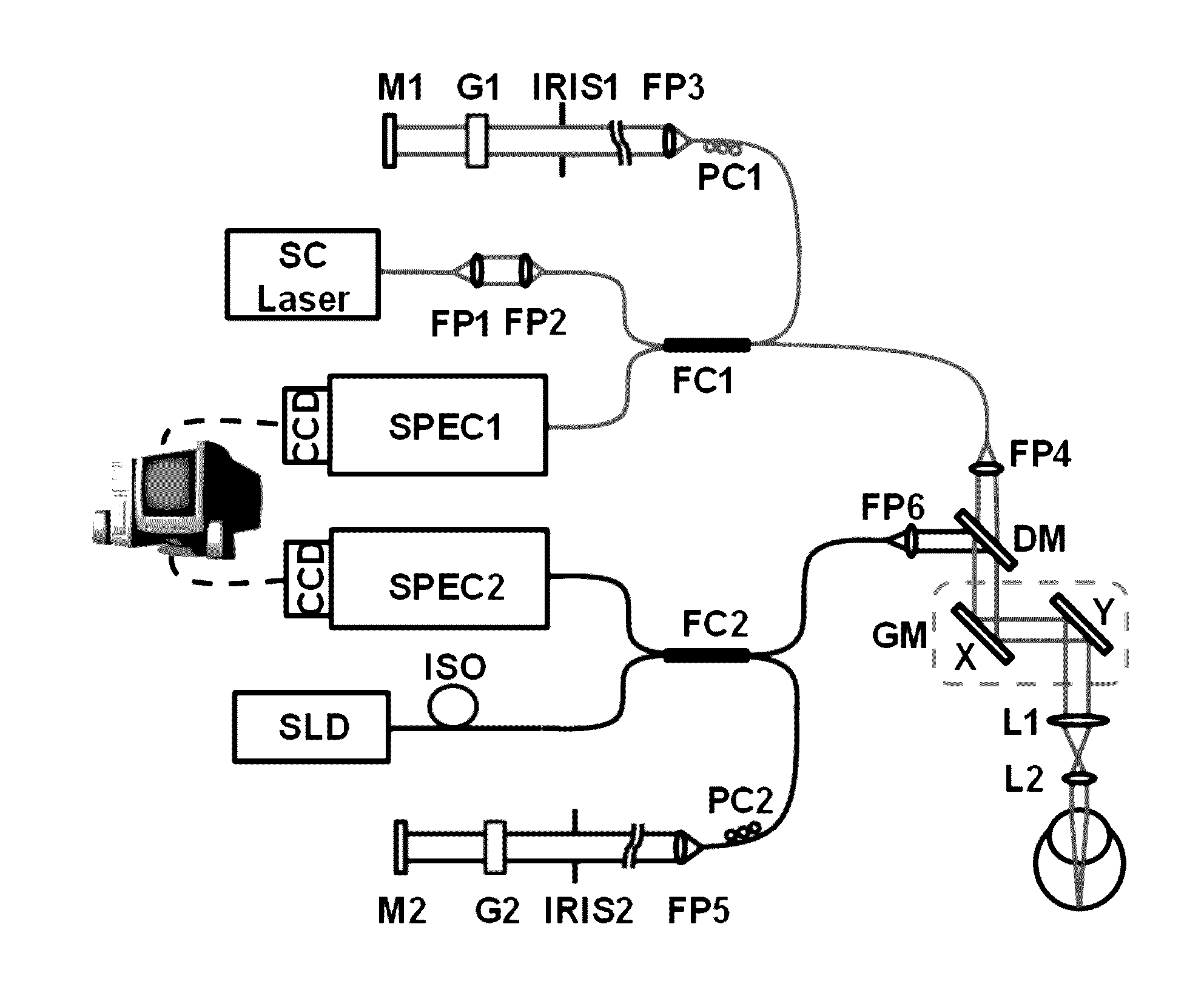
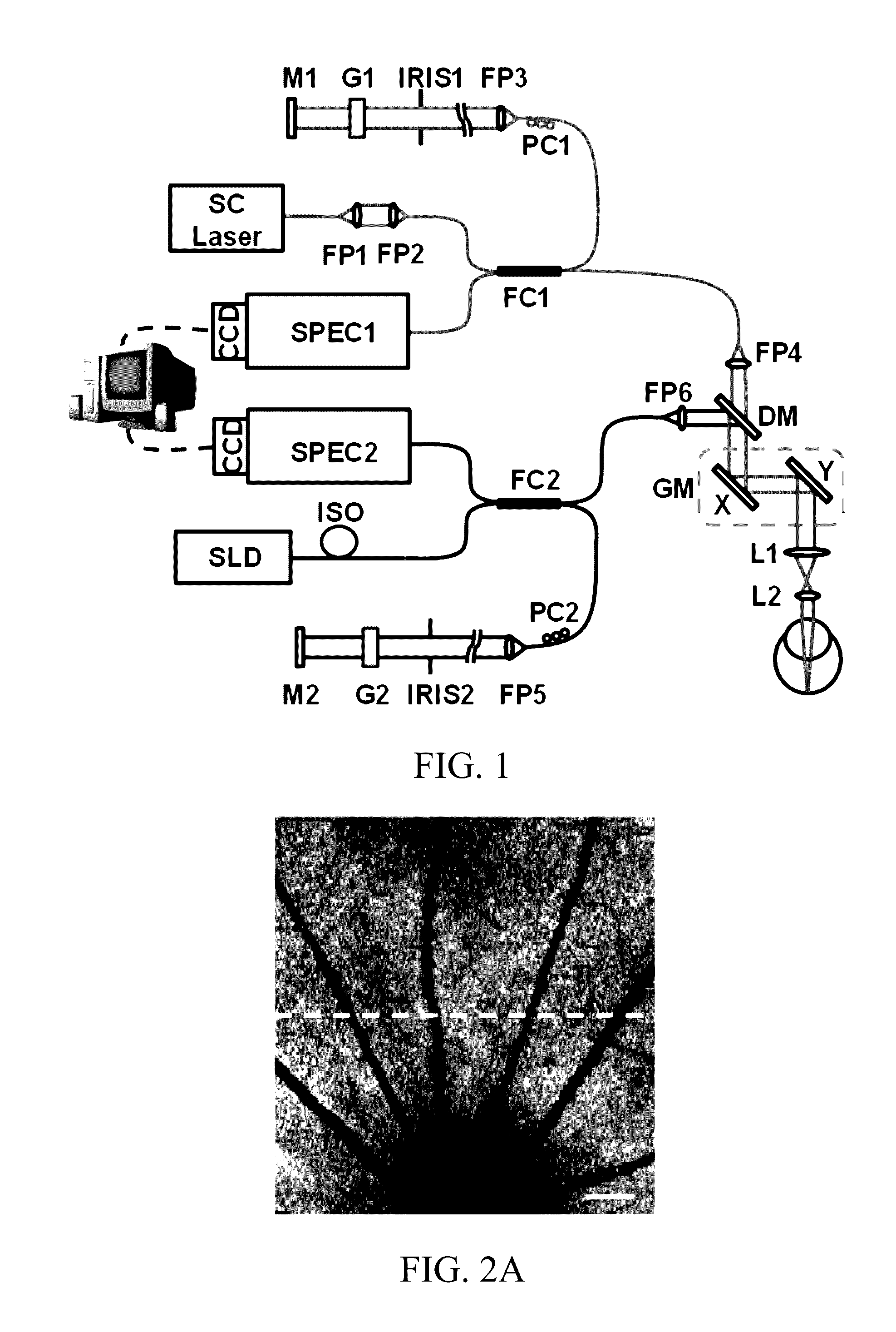
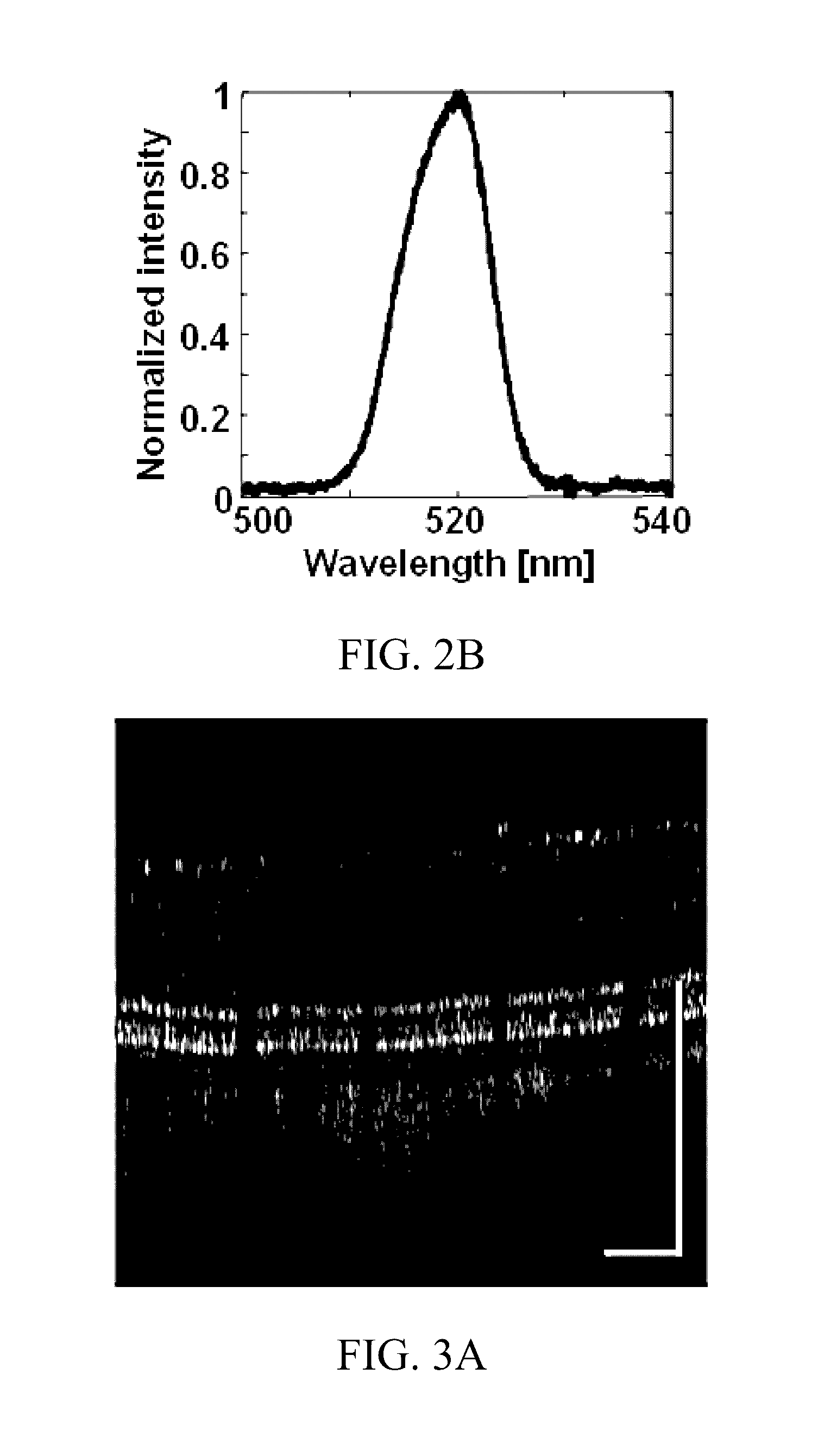
Functional imaging of photoreceptors in the retina by rhodopsin mapping
The subject invention provides novel apparatuses and methods for assessing the structure and function of photoreceptors in retina. In a specific embodiment, the assessment is accomplished by imaging rhodopsin, pigmented protein responsible for initiating vision acquisition of the eye, in living subjects. Advantageously, the technologies provided herein can be used for clinical evaluation of retinal photoreceptors for diagnosis, disease staging and follow-up, and outcome measurement for clinical trials of retinal degenerative disorders, including, for example, hereditary retinal degeneration and age-related macular degeneration.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
Blended blueberry juice and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105192800AAvoid destructionKeep active ingredientsFood ingredient functionsFood preparationPectinaseFruit juice
The invention discloses a blended blueberry juice and a preparation method of the blended blueberry juice. The blended blueberry juice is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30 to 40 parts of highbush blueberries, 20 to 25 parts of juicy peaches, 1 to 6 parts of pectin, 12 to 15 parts of black currant, 6 to 8 parts of granulated sugar, 1 to 3 parts of pectinase, 1 to 4 parts of cellulase, 2 to 4 parts of hemicellulase, 1 to 3 parts of protease, 12 to 15 parts of lonicera edulis, 22 to 24 parts of grape seeds, 1 to 4 parts of propolis and 3 to 5 parts of vitamin E. According to the blended blueberry juice disclosed by the invention, a large amount of anthocyanin active ingredients in blueberries are reserved, and the blended blueberry juice contains rich nutritional ingredients and has the functions of activating retinas, promoting the regeneration of rhodopsin in retina cells, preventing myopia, increasing the eyesight and removing eye fatigue.
Owner:ANHUI HUI KING FOOD
Two-step enzymolysis identification method based on protein reversible fixation
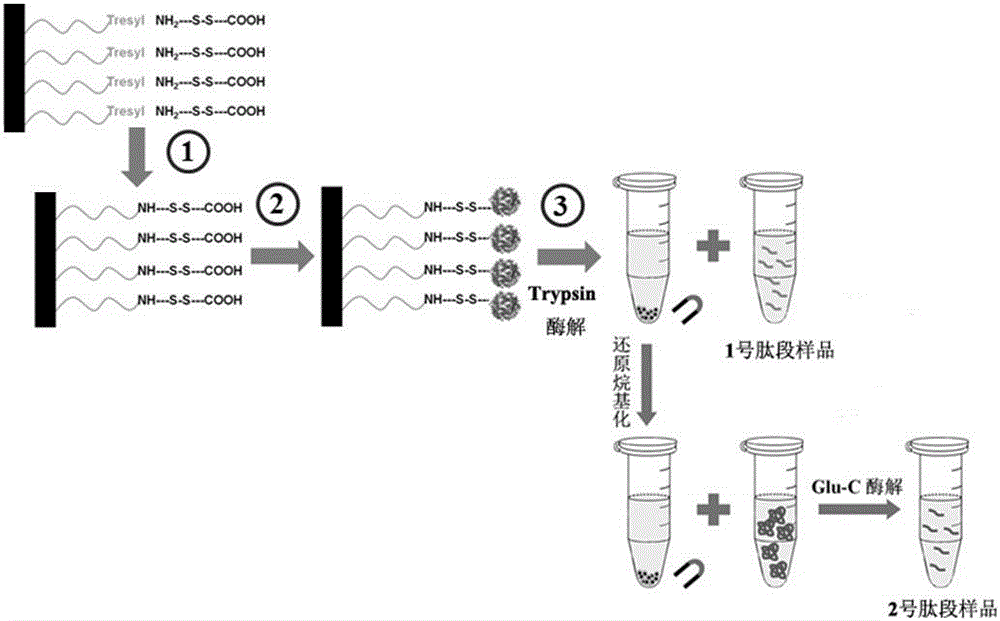
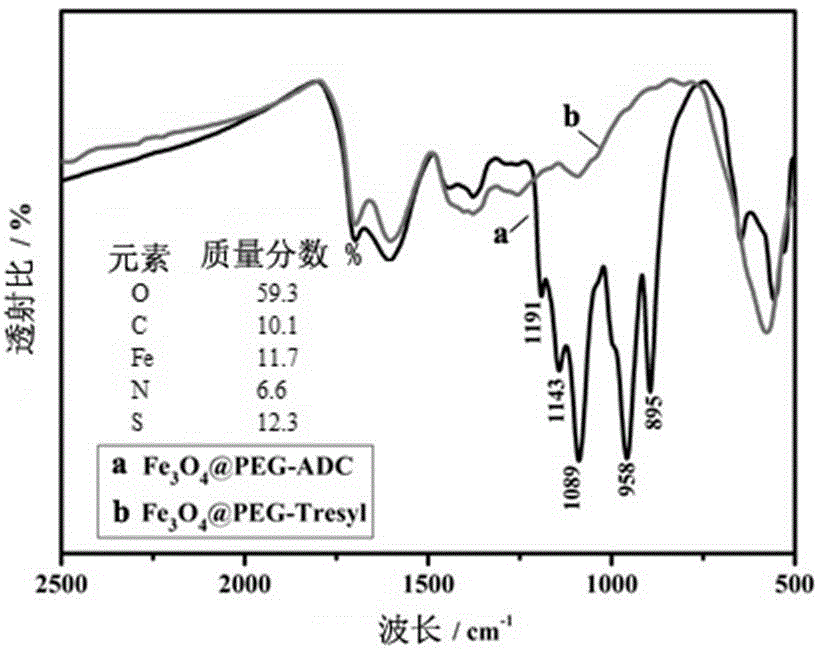
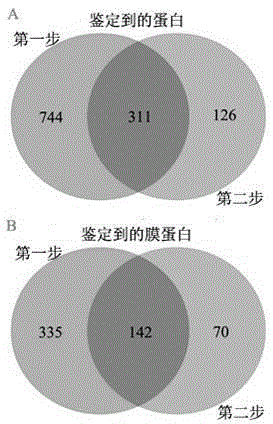
InactiveCN105400855ASolve the real problemImprove stabilityBiological testingFermentationDigestionDisulfide bond
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological analysis and detection and particularly provides a two-step enzymolysis identification method based on protein reversible fixation. The method includes the steps that firstly, a formyl group, an epoxy group, trifluoro ethyl sulfonic acid ester base and other active groups are modified on the surface of a Fe<3>O<4>@PEG magnetic nano material, then a group containing a disulfide bond is bonded to the outer layer of the magnetic nano material, and the magnetic nano material Fe<3>O<4>@PEG@ADC is obtained; then a two-step enzymolysis strategy is adopted; firstly trypsin is adopted to conduct first-step digestion, so that hydrophilic carboxyl is exposed out of hydrophobic membrane protein; then reductive alkylation is conducted, and the disulfide bond between the a peptide fragment not subjected to digestion and a material is destroyed; residual peptide fragments eluted out of the surface of the material are continuously subjected to enzymolysis of Glu-C. It is proved by experiments that the two-step enzymolysis strategy has a good enzymolysis effect on special membrane protein, such as rhodopsin bacteria, and a quite good result is further achieved in membrane proteomics research of complex samples. The two-step enzymolysis identification method is practical, efficient, good in repeatability and high in stability and has wide application prospect in scaled identification of membrane protein.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Genetic suppression and replacement
InactiveUS8551970B2Avoid symptomsGood flexibilityBiocideSugar derivativesAntisense nucleic acidMutant allele
Methods and agents for suppressing expression of a mutant allele of a gene and providing a replacement nucleic acid are provided. The methods of the invention provide suppression effectors such as, for example, antisense nucleic acids, ribozymes, or RNAi, that bind to the gene or its RNA. The invention further provides for the introduction of a replacement nucleic acid with modified sequences such that the replacement nucleic acid is protected from suppression by the suppression effector. The replacement nucleic acid is modified at degenerate wobble positions in the target region of the suppression effector and thereby is not suppressed by the suppression effector. In addition, by altering wobble positions, the replacement nucleic acid can still encode a wild type gene product. The invention has the advantage that the same suppression strategy could be used to suppress, in principle, many mutations in a gene. Also disclosed is a transgenic mouse that expresses human rhodopsin (modified replacement gene) and a transgenic mouse that expresses a suppression effector targeting rhodopsin. Also disclosed in intraocular administration of siRNA.
Owner:SPARK THERAPEUTICS IRELAND LTD
G protein-coupled receptor structural model and a method of designing ligand binding to g protein-coupled receptor by using the structural model
InactiveUS20070010948A1Receptors for hormonesBiological testingModeling softwareG protein-coupled receptor
The present invention provides a method for constructing a structural model of a complex that a G protein-coupled protein receptor forms with a ligand capable of binding the G protein-coupled receptor and a three-dimensional structural model of an activated intermediate in the structural model of the complex. The present invention also provides a method for identifying, screening for, searching for, evaluating, or designing a ligand capable of binding a GPCR by using the three-dimensional model. In one specific method by the present invention, a three-dimensional structural model of a photoactivated intermediate of rhodopsin is constructed by using a molecule modeling software and by using the three-dimensional structural coordinate of the crystal structure of rhodopsin in such a manner that amino acid residues highly conserved among GPCRs are taken into consideration. The three-dimensional stractural model of the photoactivated intermediate of rhodopsin is subsequently used to construct structural models of activated intermediates of other GPCRs. The present invention further provides a method for identifying, screening for, searching for, evaluating, or designing a ligand that binds a GPCR to act as an agonist or an antagonist. This method employs the three-dimensional structural model constructed by the above-described method.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Methods for the diagnosis and therapy of retinitis pigmentosa
InactiveUS20130071373A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementRetinitis pigmentosaRhodopsin
The present invention relates to a method of identifying a subject having or at risk of having or developing a retinitis pigmentosa, comprising detecting in a sample obtained from said subject, the presence of at least one mutation in the rhodopsin (RHO) gene selected from the group consisting of c.263T>C, c.620T>A and c. 1031A>C wherein the presence of said mutation indicates an increased risk of having or being at risk of having or developing the retinitis pigmentosa.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
Biomarkers
The present invention provides circulating biomarkers for conditions associated with metabolic syndrome, including diabetes mellitus, hypertension and congestive heart failure. The biomarkers include plasma DNA, neuron-specific enolase, 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, rhodopsin, retinoschisin, RPE65 and cardiac troponin T. Methods and kits for detecting these biomarkers in the prediction, monitoring and diagnosing of disease are provided, particularly for determining mRNA levels thereof in a subject's blood.
Owner:GUYS & ST THOMAS NHS FOUND TRUST +1
Probes for myctophid fish and a method for developing the same
The DNA probes produced by molecular cloning and the characterization of specific gene region sequences is provided, these can be used as genetic markers for the genes such as Cytochrome b (cyt b); Mitochondrial control region (D-Loop); Inter Transcribed Spacers (ITS2) and Rhodopsin (ROD), 12S rRNA and 16S rRNA in mesopelagic lantern fishes which are found in the mesopelagic zones of the oceans where the photic regime is of dim light and associate themselves with the oxygen minimum layer, it also includes the recombinant DNA techniques for the preparation of specific gene probes and sequences of species specific primers of lantern fishes, novel gene probes and novel oligonucleotides for amplification of myctophid genes are disclosed.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Halophile photosensitive protein-titanium dioxide nanotube composite and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102332532AQuick responseVisible light response ability is strongMaterial nanotechnologySolid-state devicesProtein solutionElectron hole
The invention provides a halophile photosensitive protein-titanium dioxide nanotube composite and a preparation method thereof. Photosensitive protein is halophilic archaea rhodopsin protein, and the colibacillus is modified to express the rhodopsin protein in a large quantity. After bacteria are broken ultrasonically, Beta-mercaptoethanol and acyl sarcosine are used for extracting membrane protein, and the membrane protein is then processed by TritonX-100. The preparation method for the composite includes the following steps: titanium dioxide nano material is put into protein solution, vacuumized for a period of time and then dehydrated under low temperature, and thereby the halophile photosensitive protein-titanium dioxide nanotube composite is prepared. The process flow related to the invention is simple, used reagents are cheap, and the composite has good visible light-responding ability, can effectively reduce the recombination probability of photoinduced electron-hole pairs and increase the photoelectric response of a TiO2 nanotube array, and has a broad application prospect in the field of photoelectric devices.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Blueberry anthocyanin oral liquid capable of improving eyesight and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106539086AHigh biological potencyMellow flavor and aromaFood ingredient functionsZINC LACTATEFruit juice
The invention discloses a blueberry anthocyanin oral liquid capable of improving the eyesight and a preparation method thereof. The blueberry anthocyanin oral liquid is prepared from the following raw materials and auxiliary materials: a blueberry anthocyanin concentrated solution, blueberry original juice, ascorbic acid, zinc lactate and xylitol. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: adding deionized water which accounts for 1 / 5 of the overall volume of raw materials and auxiliary materials, fully dissolving the raw materials and auxiliary materials at a temperature of 35 DEG C, setting the volume to the container scale, fully stirring to dissolve the raw materials and auxiliary materials, performing filtration, blending and encapsulation, sealing, sterilization, lamp inspection and packaging, and inspecting the obtained product after the obtained product passes inspection, thereby obtaining a finished product. The blueberry anthocyanin oral liquid capable of improving eyesight disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the blueberry anthocyanin can accelerate regeneration of eye rhodopsin and clarify eye diseases, and has an efficacy of preventing eye diseases, and the added nutrients have the effect of further enhancing and improving the eyesight and also have a protective effect on the anthocyanin stability.
Owner:GUIYANG UNIV
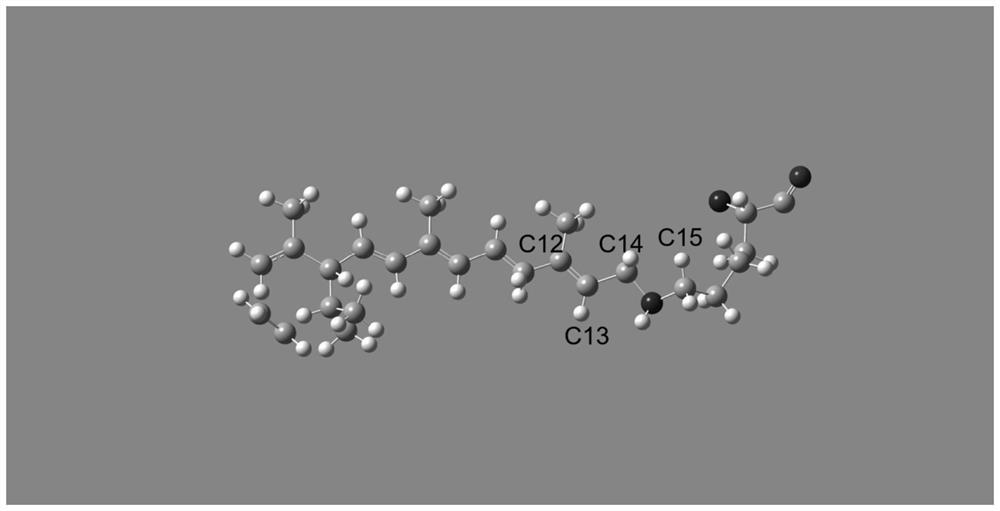
Visual violet light cycle simulation method based on molecular dynamics
PendingCN114530192AImprove the shortcomings of insufficient kinetic samplingImprove the shortcomings of insufficient samplingDesign optimisation/simulationSystems biologyCell membraneMolecular dynamics
The invention relates to a molecular dynamics visual purple protein light cycle simulation research method, which is used for carrying out simulation research by using a monopolymer, and belongs to the field of neuroscience and the field of molecular dynamics. The method comprises the following specific steps: (1) twisting a chromophore C12-C13 = C14-C15 dihedral angle by using Gaussian software, and adjusting the angle; (2) embedding a monomer protein in a CHARMM-GUI software embedding cell membrane environment, and carrying out independent force field setting on chromophore small molecules; (3) carrying out equilibrium state molecular dynamics simulation by using NAMD software; (4) analyzing a molecular dynamics track, and carrying out corresponding analysis through a cpptraj module of AMBER and a tcl file of VMD. And (5) calculating the free energy by using a stretching molecular dynamics and umbrella-shaped sampling mode. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the structural change of the rhodopsin in the light circulation process is researched by utilizing molecular dynamics, so that the simulation of light circulation is further realized, and the method plays an important role in clinical application, brain function research and engineering material design of the rhodopsin in the field of neuroscience.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Sea-buckthorn black fruit mountain ash berry eye-protection milk tablets and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN109619189AAvoid damagePromote regenerationMilk preparationCardiovascular sclerosisCoronary heart disease
The invention discloses sea-buckthorn black fruit mountain ash berry eye-protection milk tablets and a preparing method thereof. The sea-buckthorn black fruit mountain ash berry eye-protection milk tablets comprise dry powder of a sea-buckthorn extract, dry powder of a black fruit mountain ash berry extract, defatted milk, citric acid and xylitol, and the eye-protection milk tablets are prepared through a series of steps. The prepared sea-buckthorn black fruit mountain ash berry eye-protection milk tablets are convenient to carry and eat and have a strong eye protection function, the harm of blue light to the eyes can be effectively avoided, regeneration of rhodopsin in retina cells can be promoted, severe myopia and retinal detachment can be prevented, and the vision can be enhanced and protected; meanwhile, cell and organ damage of free radicals in the human body can be resisted, and cardiovascular sclerosis, coronary heart diseases, phymatosis and other symptoms triggered by the body are effectively prevented.
Owner:JIAMUSI UNIVERSITY
Cake roll containing spinach, yam and blueberry mixed fruits and vegetables and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109769898ATo promote metabolismRelieve fatigueDough treatmentModified nutritive productsRhodopsinEye Fatigue
The invention relates to a cake roll containing spinach, yam and blueberry mixed fruits and vegetables, which comprises the following components in parts by weight: 50-80 parts of low-gluten flour, 40-80 parts of yam paste, 25-50 parts of spinach juice, 50-80 parts of fresh eggs, 25-45 parts of treated water, 20-80 parts of white granulated sugar, 9-12 parts of vegetable oil, 8-12 parts of dried blueberry, 1-5 parts of low-fat milk, 0.3-1.2 parts of edible salt and 0.8-1 part of a sour agent. The cake roll takes the yam paste, the spinach juice and the dried blueberry as main characteristic components; the spinach contains rich plant coarse fibers, vitamins and minerals, and has the functions of promoting bowel circulation and defecation and promoting metabolism of a human body; the yam isrich in starch saccharifying enzyme, has the functions of strengthening spleen and benefiting stomach and promoting digestion, and the choline contained in the yam is the material basis of neurotransmitter substances for learning and memorizing; the anthocyanin rich in blueberry can relieve eye fatigue, improve vision, and accelerate synthesis and regeneration of retina and rhodopsin.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Concentrated blueberry juice and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105192799AKeep active ingredientsPromote regenerationFood ingredientsFood preparationPectinaseFruit juice
The invention discloses a concentrated blueberry juice and a preparation method thereof. The concentrated blueberry juice is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 50 to 55 parts of blueberries, 4 to 8 parts of pectinase, 7 to 12 parts of grape skin, 17 to 20 parts of tremella fuciformis, 4 to 6 parts of shell powder, 15 to 17 parts of cranberries, 5 to 7 parts of black rice, 1 to 3 parts of tartaric acid, 3 to 7 parts of coenzyme, 11 to 13 parts of atap seeds, 1 to 3 parts of edible salt, 11 to 13 parts of edible alcohol and 1 to 3 parts of sodium citrate. The concentrated blueberry juice disclosed by the invention has a good taste, reserves a large amount of anthocyanin active ingredients in the blueberries and has the functions of activating retinas, promoting the regeneration of rhodopsin in retina cells, preventing myopia, increasing the eyesight and removing eye fatigue.
Owner:ANHUI HUI KING FOOD
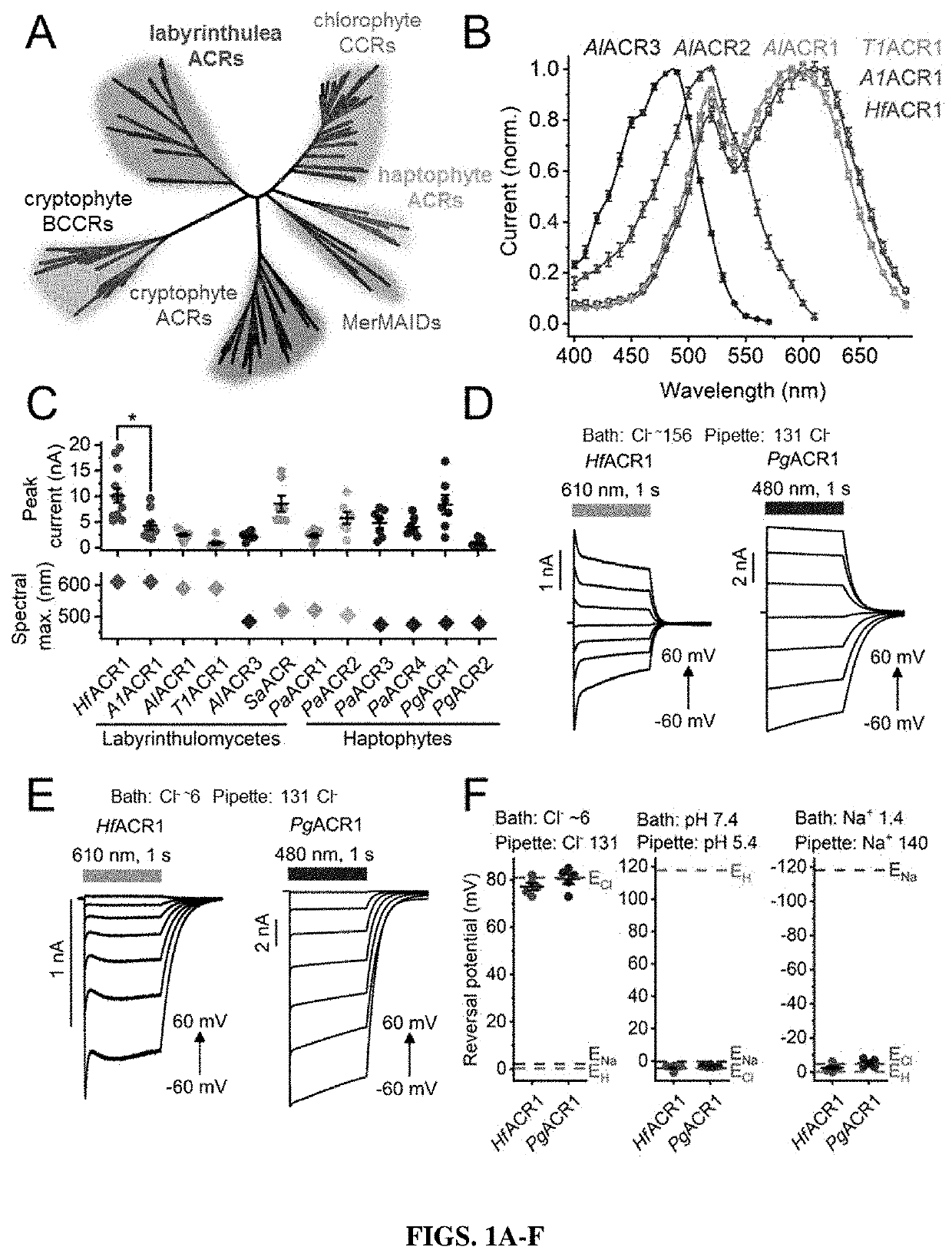
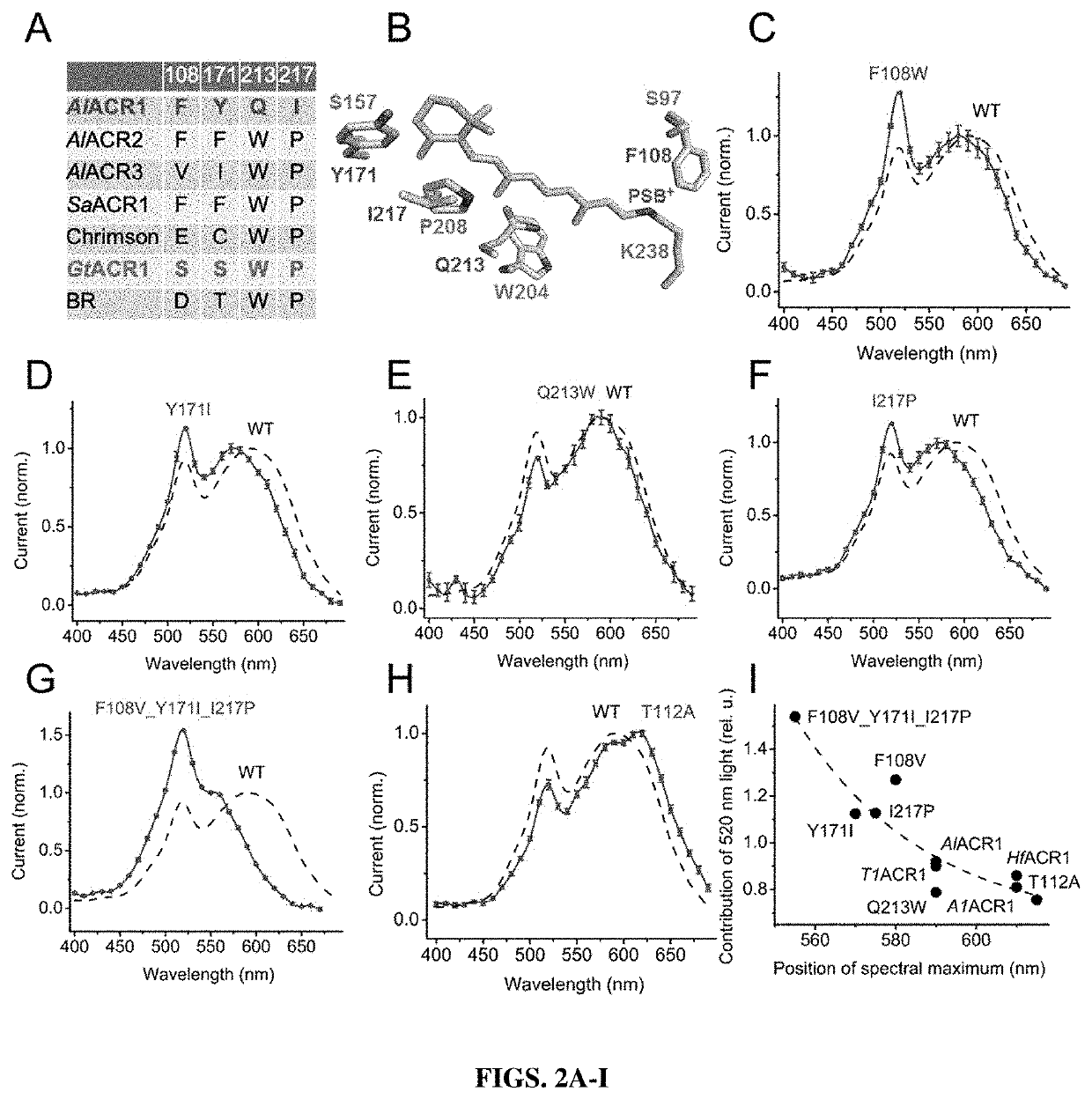
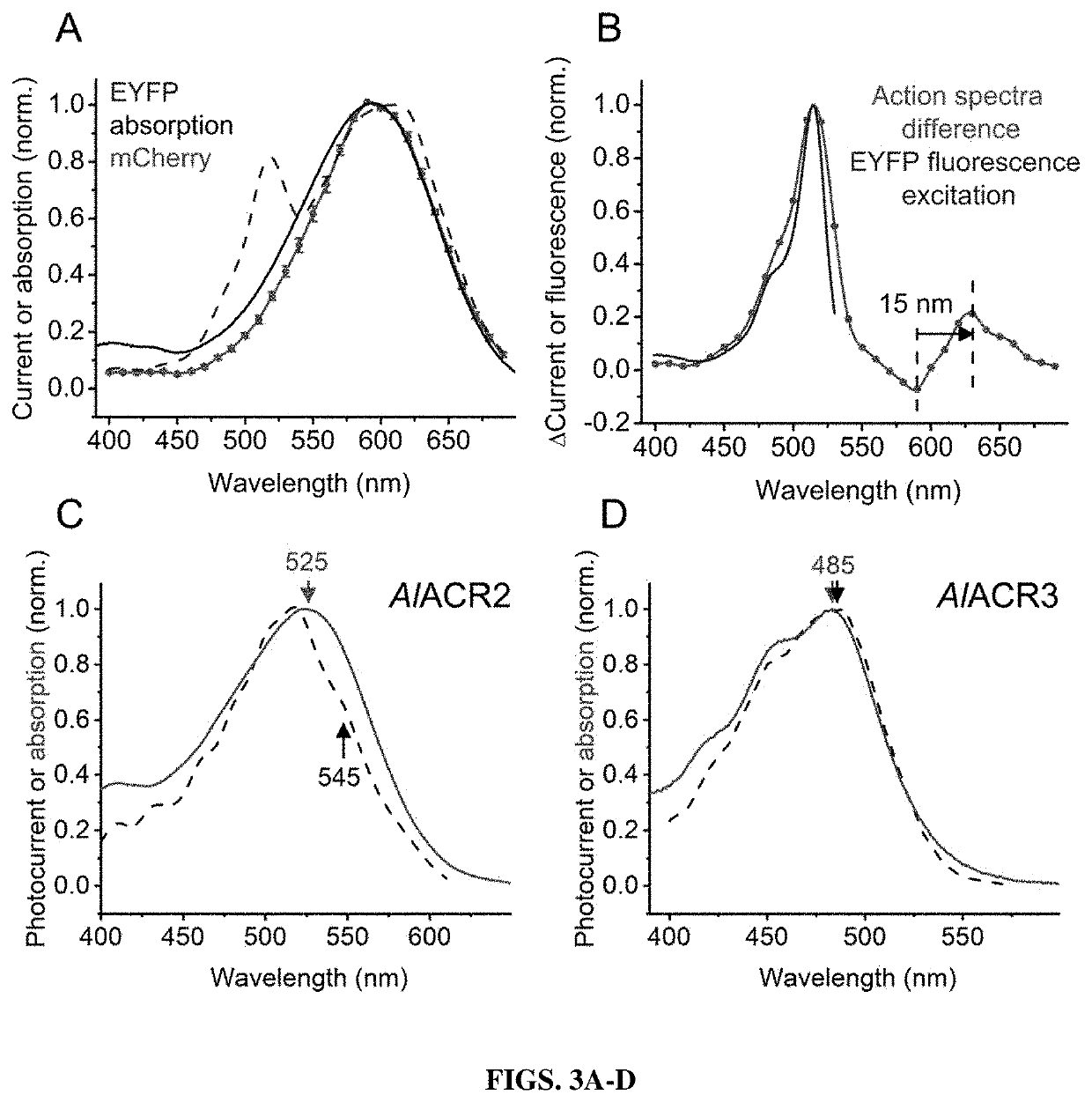
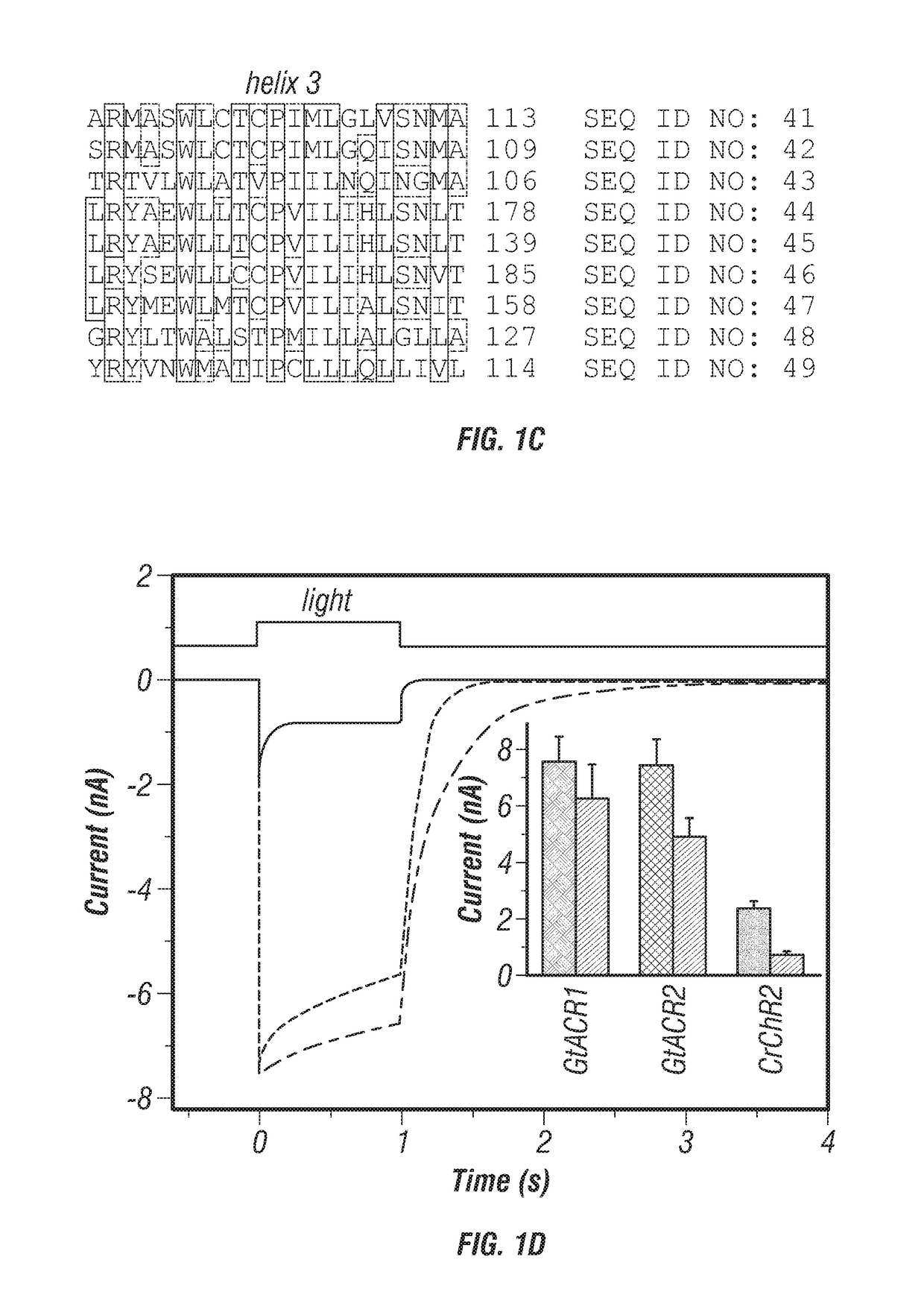
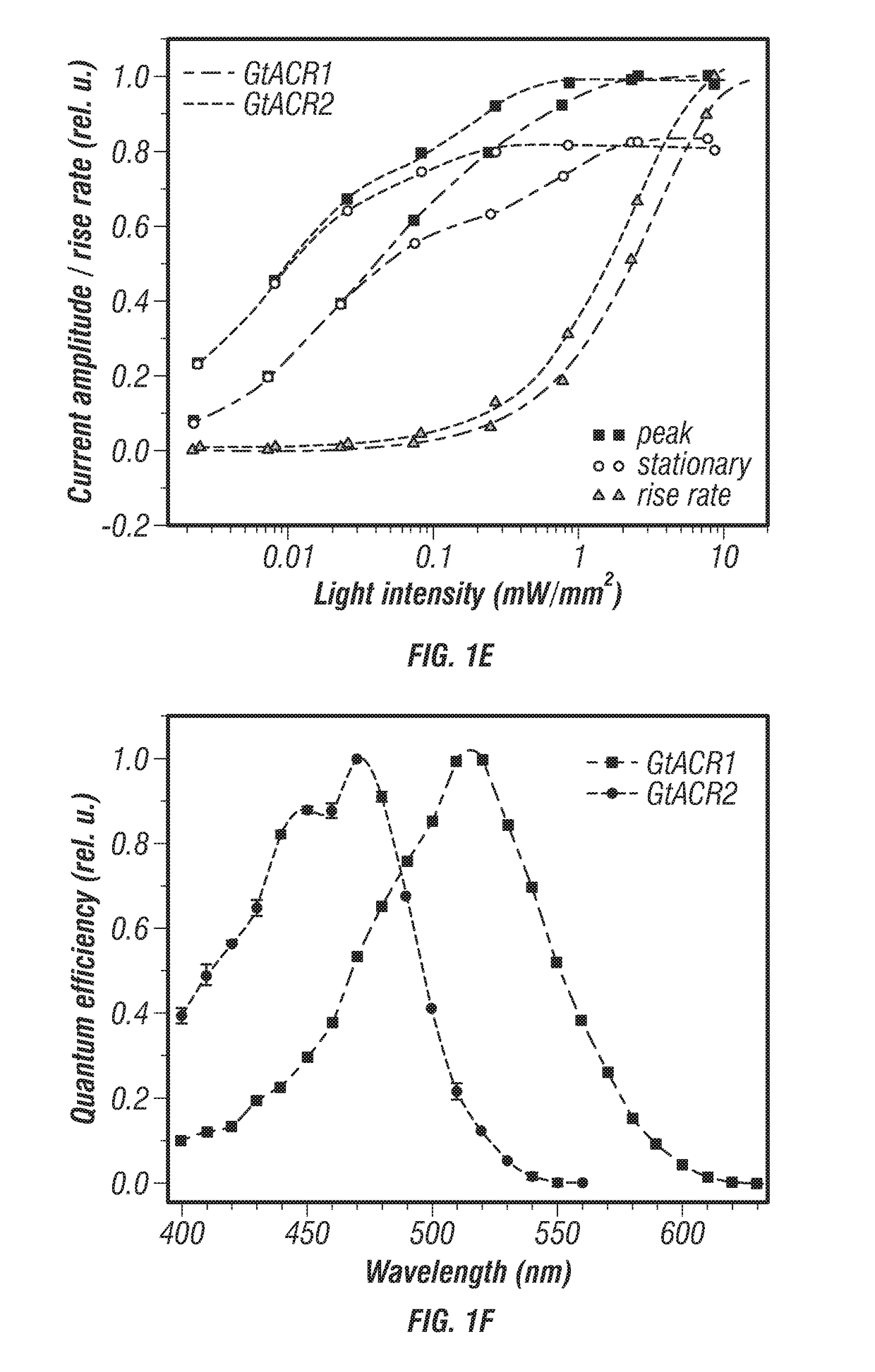
Compositions and methods for use of red-shifted anion channel rhodopsins
PendingUS20220056100A1Maximal spectral sensitivityCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsActive cellRhodopsin
Methods and compositions used to identify and characterize novel rhodopsin domains, which are anion-conducting channelrhodopsins. The rhodopsin domain of these anion-conducting channelrhodopsins have been cloned, optimized and expressed in mammalian systems and thus may be used in, among others, optogenetic applications and as therapeutic agents for electrically active cell mediated disorders.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Structural Model Of G Protein-Coupled Receptor And Method For Designing Ligand Capable Of Binding To G Protein-Coupled Receptor Using The Structural Model
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Compositions and methods for use of anion channel rhodopsins
ActiveUS20180118793A1Hyperpolarize membraneFast dynamicsSenses disorderSugar derivativesActive cellAlgae
Methods and compositions used to identify and characterize a new class of rhodopsins derived from algae, which are highly sensitive and efficient anion-conducting channelrhodopsins. The rhodopsin domain of these anion-conducting channelrhodopsins have been cloned and expressed in mammalian systems and thus may be used in, among others, optogenetic applications and as therapeutic agents for electrically active cell mediated disorders.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
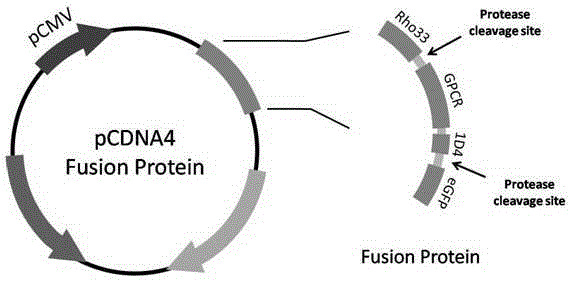
Fusion gene building method for effectively screening GPCR (G Protein-Coupled Receptor) expression
InactiveCN105154470AHigh expressionGuaranteed functionVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationProtein targetWestern blot
The invention relates to the field of molecular imaging and cytobiology, and discloses a fusion gene building method for screening GPCR (G Protein-Coupled Receptor) expression. According to the method, 33 residues at the starting end of human Rhodopsin and corresponding protein endonuclease sites are inserted into the front section of a GPCR; His (5 residues) or ID4 (9 residues) epitopes, corresponding endonuclease sites and eGFP (Enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein) are inserted into the tail end of the GPCR; and Rho33-protease-GPCR-1D4-protease-eGFP is built, wherein the Rho33 can effectively guide GPCR insertion into a membrane, can increase the functional molecule proportion and can improve the protein yield; the 1D4 epitope is used for Western Blot detection and protein purification; the eGFP is a main index for screen authentication; and the endonuclease sites can be used for cutting parts beyond target proteins and maintaining the protein function. The method has the advantages that the function protein proportion can be effectively improved; the protein yield is improved; the influence of fusion protein can be completely eliminated through protein digestion in a later period; and high efficiency, convenience and high speed are realized.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Genetic suppression and replacement
InactiveUS20110190371A1Improve pathologyLower Level RequirementsTissue cultureDrug compositionsAntisense nucleic acidWild type
Methods and agents for suppressing expression of a mutant allele of a gene and providing a replacement nucleic acid are provided. The methods of the invention provide suppression effectors such as, for example, antisense nucleic acids, ribozymes, or RNAi, that bind to the gene or its RNA. The invention further provides for the introduction of a replacement nucleic acid with modified sequences such that the replacement nucleic acid is protected from suppression by the suppression effector. The replacement nucleic acid is modified at degenerate wobble positions in the target region of the suppression effector and thereby is not suppressed by the suppression effector. In addition, by altering wobble positions, the replacement nucleic acid can still encode a wild type gene product. The invention has the advantage that the same suppression strategy could be used to suppress, in principle, many mutations in a gene. Also disclosed is a transgenic mouse that expresses human rhodopsin (modified replacement gene) and a transgenic mouse that expresses a suppression effector targeting rhodopsin. Also disclosed in intraocular administration of siRNA.
Owner:SPARK THERAPEUTICS IRELAND LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com