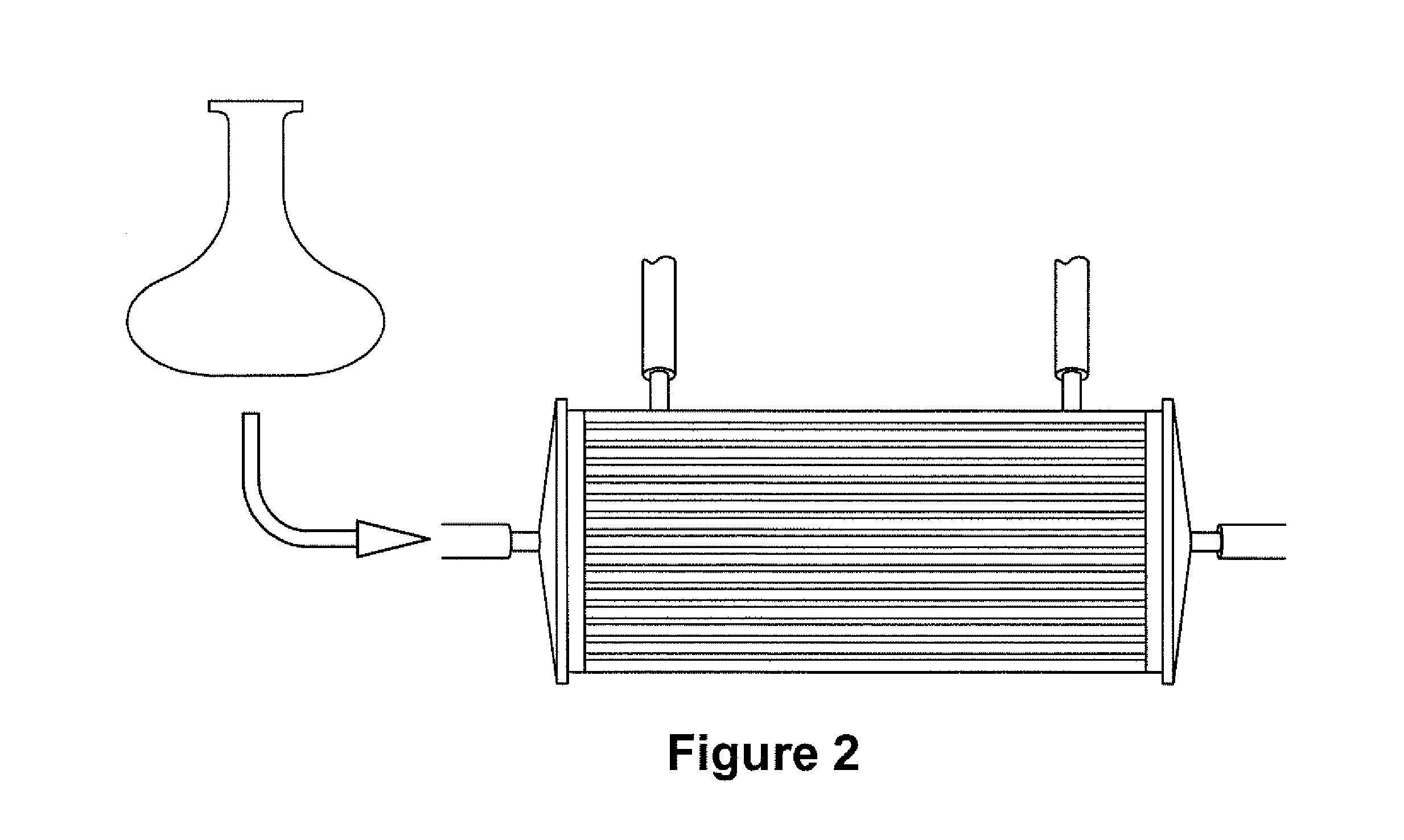
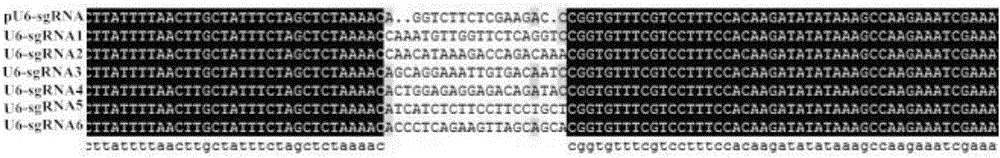
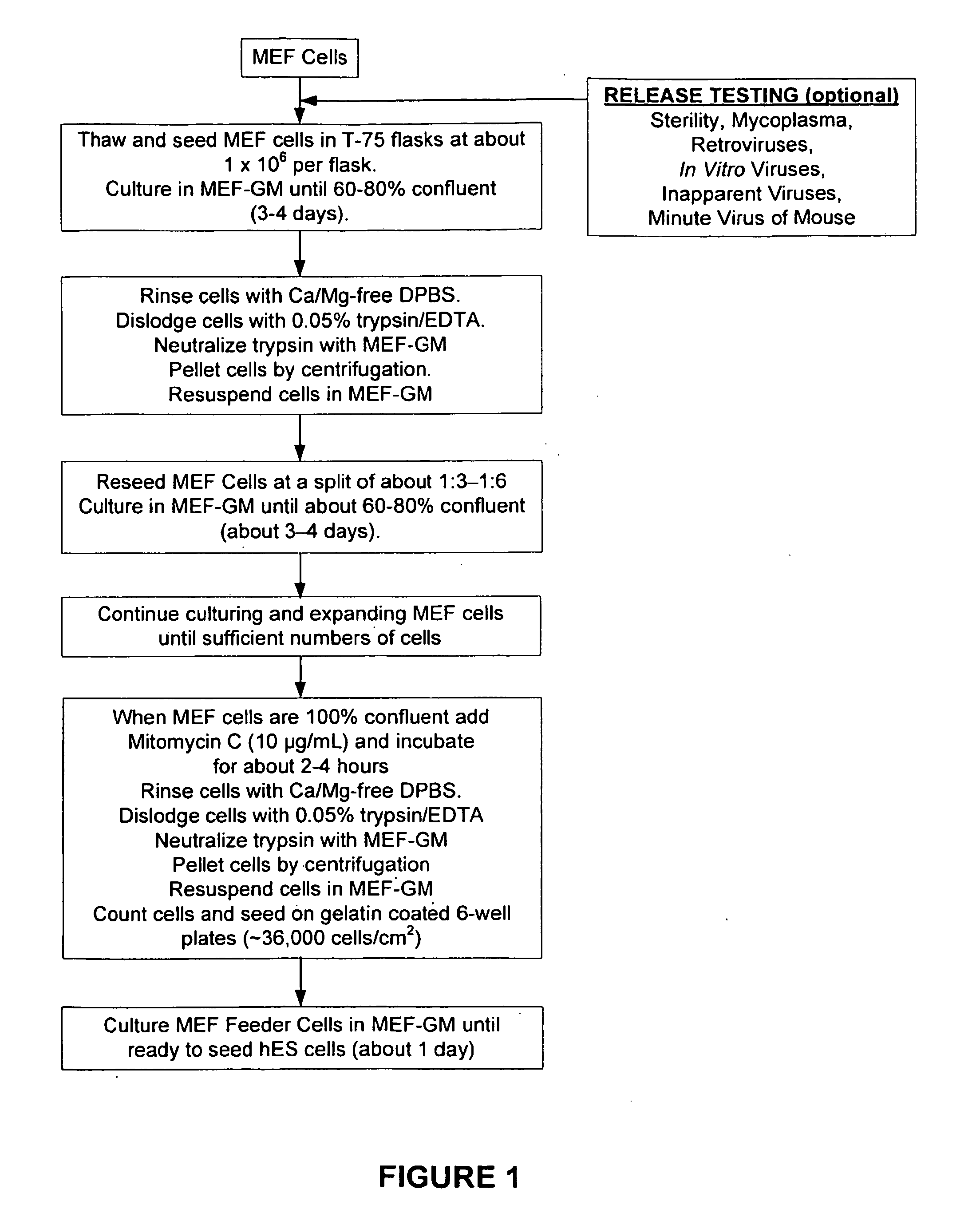
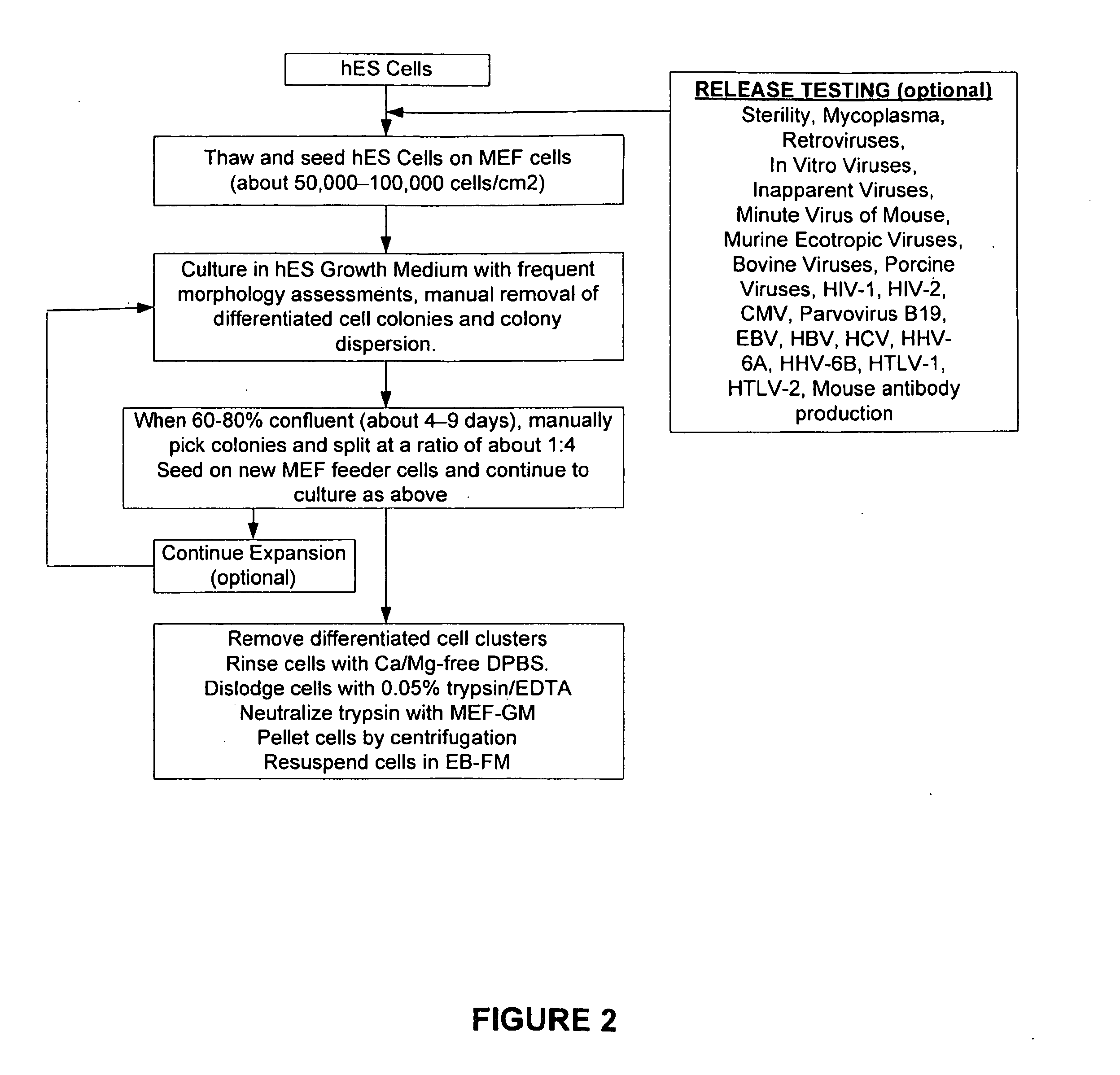
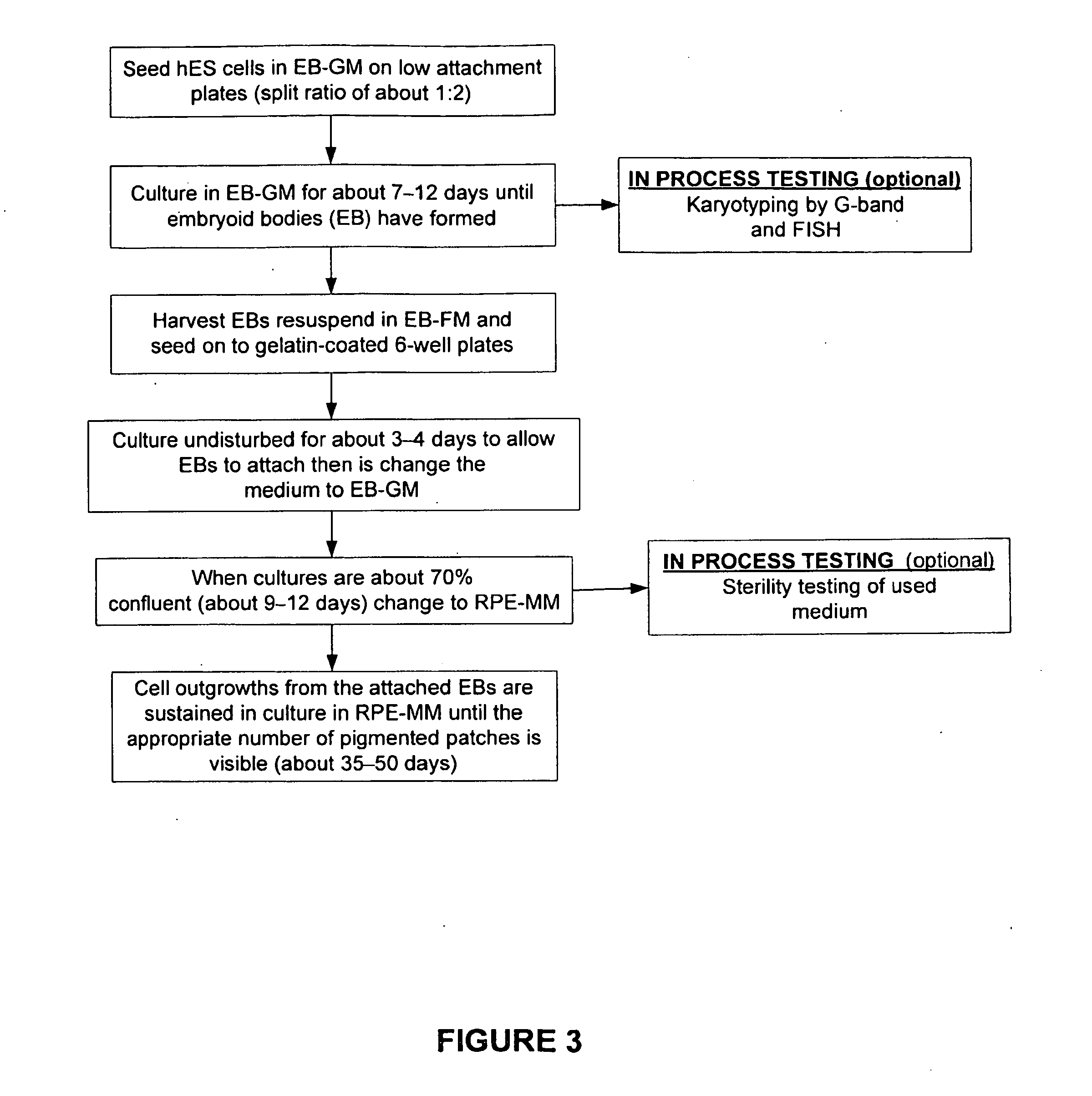
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
413 results about "Plant Germ Cells" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In many animals, the germ cells originate in the primitive streak and migrate via the gut of an embryo to the developing gonads. There, they undergo meiosis, followed by cellular differentiation into mature gametes, either eggs or sperm. Unlike animals, plants do not have germ cells designated in early development.
Pluripotential embryonic stem cells and methods of making same
The present invention provides a non-mouse, including human, pluripotential embryonic stem cell which can:(a) be maintained on feeder layers for at least 20 passages; and(b) give rise to embryoid bodies and multiple differentiated cell phenotypes in monolayer culture.The invention further provides a method of making a pluripotential embryonic stem cell comprising culturing germ cells and germ cell progenitors in a composition comprising a growth enhancing amount of basic fibroblast growth factor, leukemia inhibitory factor, membrane associated steel factor, and soluble steel factor to primordial germ cells under cell growth conditions, thereby making a pluripotential embryonic stem cell.Also provided are compositions useful to produce the pluripotent embryonic stem cells and methods of screening associated with the method of making the embryonic stem cell.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
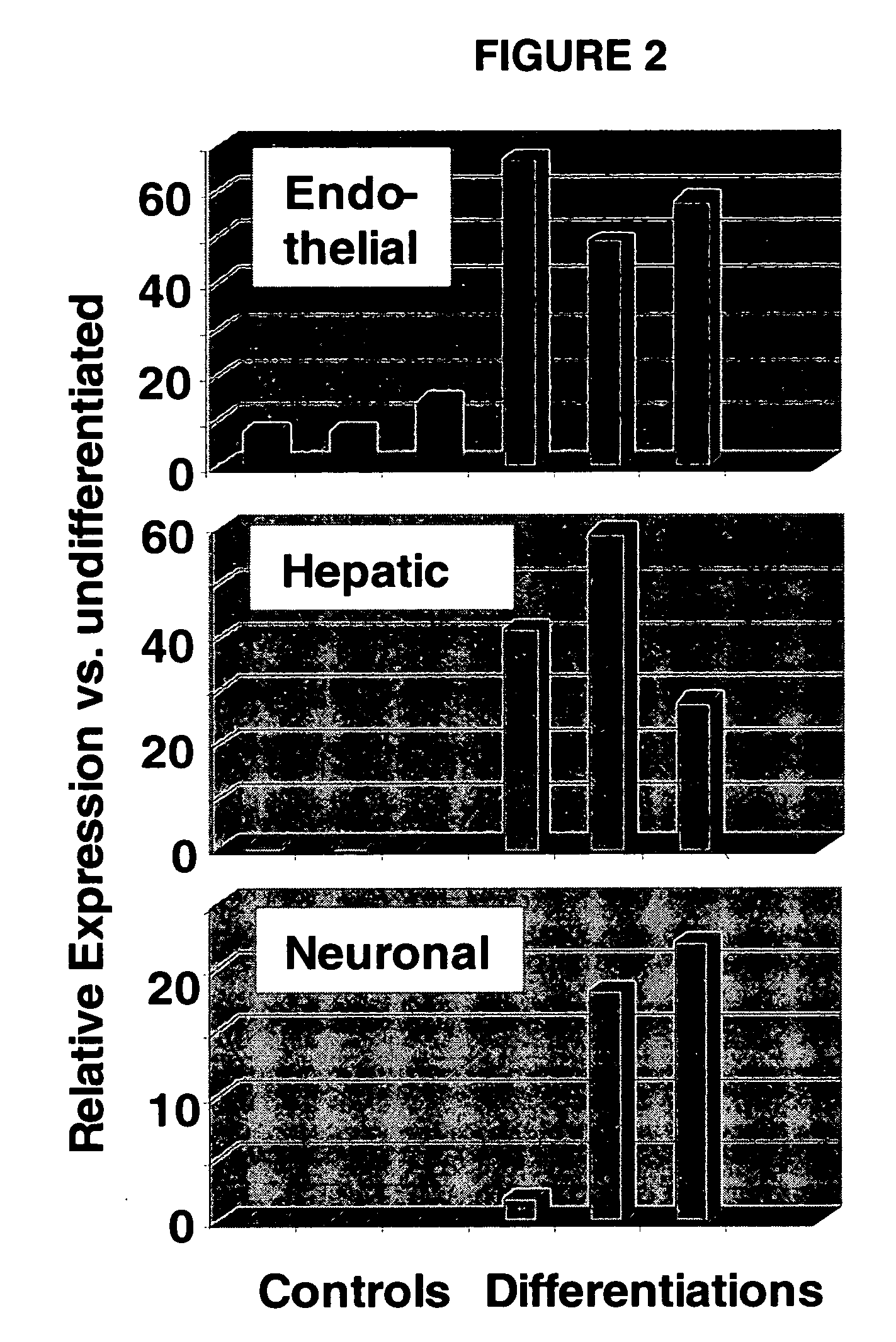
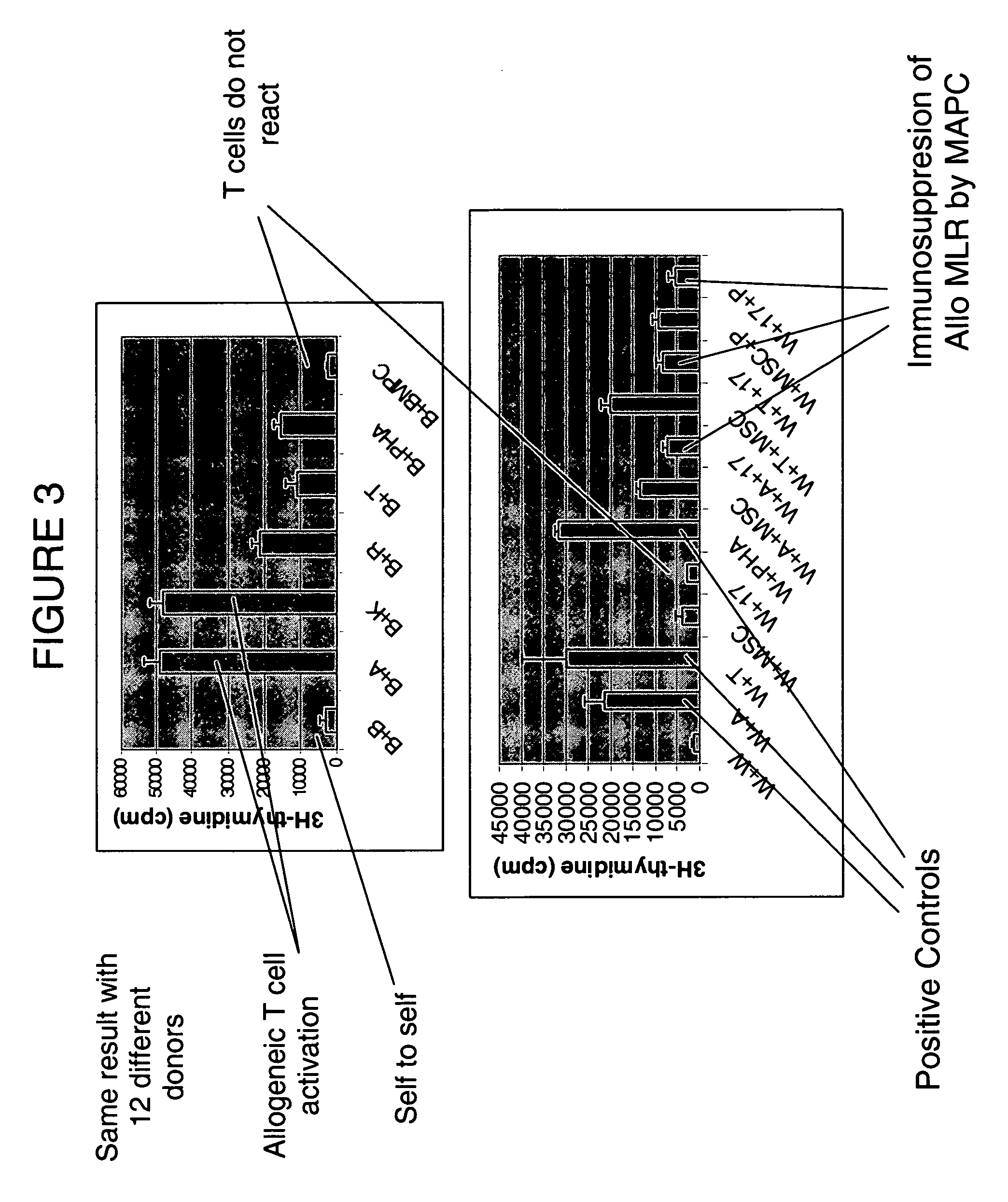
Immunomodulatory properties of multipotent adult progenitor cells and uses thereof
Isolated cells are described that are not embryonic stem cells, not embryonic germ cells, and not germ cells. The cells can differentiate into at least one cell type of each of at least two of the endodermal, ectodermal, and mesodermal lineages. The cells do not provoke a harmful immune response. The cells can modulate immune responses. As an example, the cells can suppress an immune response in a host engendered by allogeneic cells, tissues, and organs. Methods are described for using the cells, by themselves or adjunctively, to treat subjects. For instance, the cells can be used adjunctively for immunosuppression in transplant therapy. Methods for obtaining the cells and compositions for using them also are described.
Owner:ABT HOLDING COMPANY +1
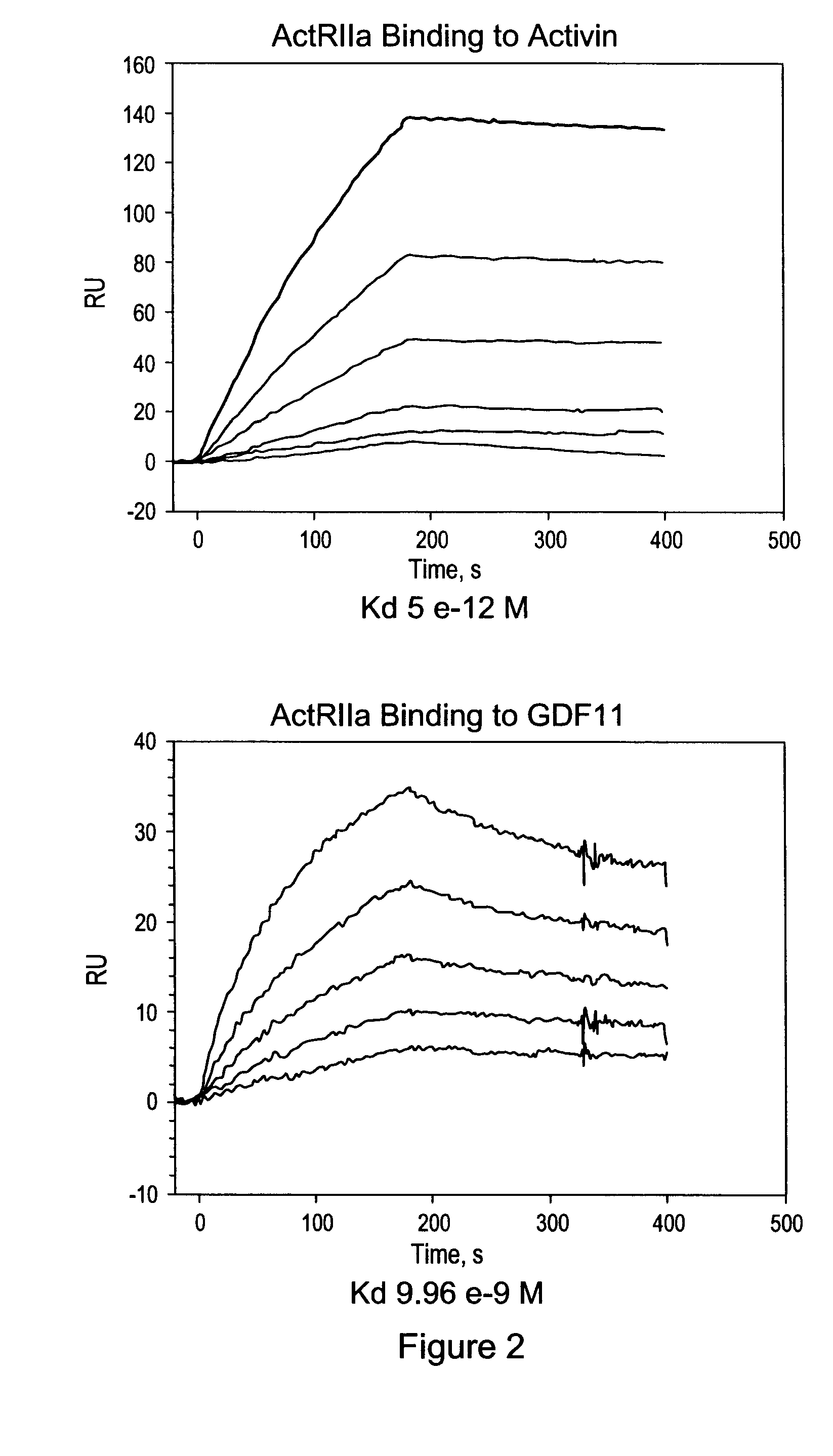
Activin-actriia antagonists and uses for decreasing or inhibiting FSH secretion
ActiveUS20090118188A1Inhibit growthAvoid survivalHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsAndrologyPlant Germ Cells
In certain aspects, the present invention provides compositions and methods for decreasing FSH levels in a patient. The patient may, for example, be diagnosed with an FSH-related disorder or desire to delay or inhibit germ cell maturation.
Owner:ACCELERON PHARMA INC
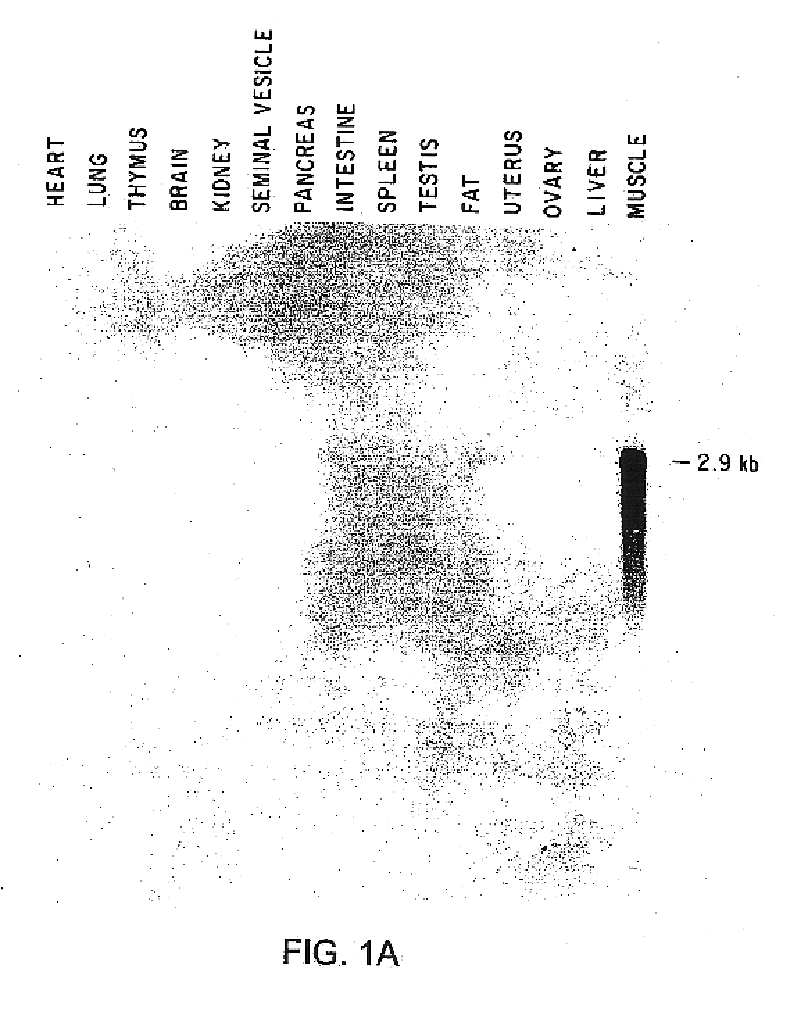
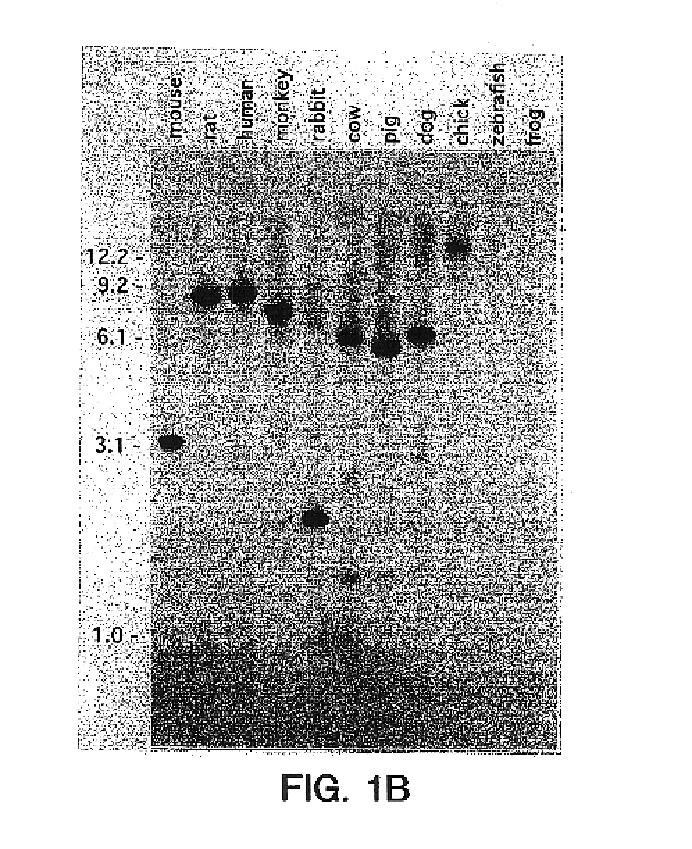
Growth differentiation factor-8
InactiveUS6858208B2Improved muscle contentPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHuman animalMuscle tissue
A transgenic non-human animal of the species selected from the group consisting of avian, bovine, ovine and porcine having a transgene which results in disrupting the production of and / or activity of growth differentiation factor-8 (GDF-8) chromosomally integrated into the germ cells of the animal is disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for making such animals, and methods of treating animals with antibodies or antisense directed to GDF-8. The animals so treated are characterized by increased muscle tissue.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Prolonged culturing of avian primordial germ cells (PGCs) using specific growth factors, use thereof to produce chimeric avians
InactiveUS6156569AEliminate needArtificially induced pluripotent cellsCell culture active agentsFowlPlant Germ Cells
A culture system for maintaining avian PGCs for long periods in tissue culture is provided. This culture system uses LIF, bFGF, IGF and SCF. The resultant PGCs are useful for the production of transgenic and chimeric avians, in particular, chickens or turkeys.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF
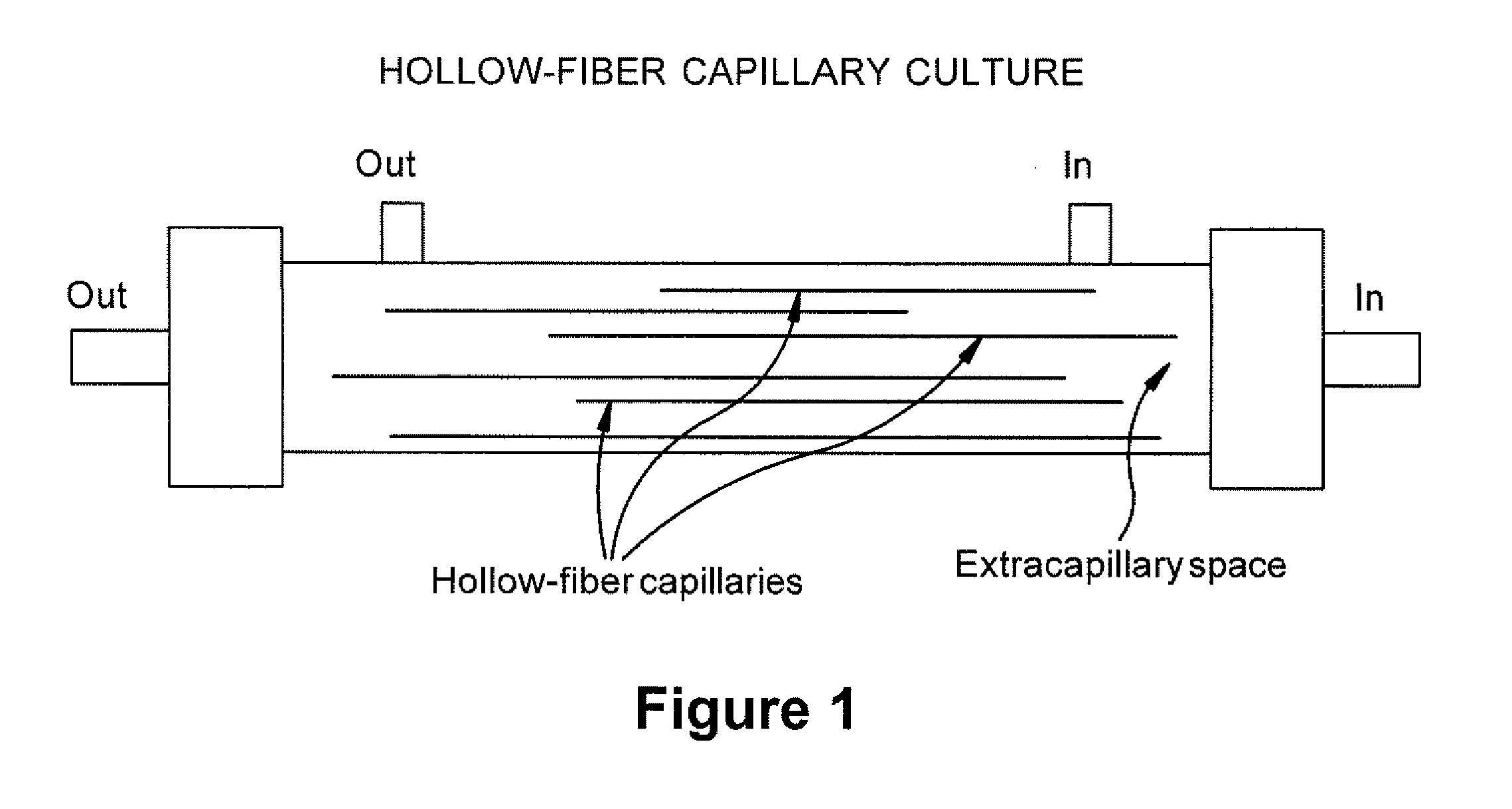
Expansion of Stem Cells in Hollow Fiber Bioreactors
InactiveUS20120308531A1Enhanced cell attachmentEasy to harvestBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsTelomerasePlant Germ Cells
The invention is directed to producing large numbers of cells using hollow fiber bioreactor technology. The cells are non-embryonic stem, non-germ cells that can be characterized by one or more of the following: extended replication in culture and markers of extended replication, such as telomerase, markers of pluripotentiality, and broad differentiation potential, without being transformed.
Owner:REGENESYS
Immunomodulatory Properties of Multipotent Adult Progenitor Cells and Uses Thereof
Isolated cells are described that are not embryonic stem cells, not embryonic germ cells, and not germ cells. The cells can differentiate into at least one cell type of each of at least two of the endodermal, ectodermal, and mesodermal lineages. The cells do not provoke a harmful immune response. The cells can modulate immune responses. As an example, the cells can suppress an immune response in a host engendered by allogeneic cells, tissues, and organs. Methods are described for using the cells, by themselves or adjunctively, to treat subjects. For instance, the cells can be used adjunctively for immunosuppression in transplant therapy. Methods for obtaining the cells and compositions for using them also are described.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV +1
Depletion of endogenous primordial germ cells in avian species
InactiveUS20060095980A1Decrease in primordial germ cell numberIncrease in primordial germ cell numberVertebrate antigen ingredientsFermentationAntigenHigh concentration
Methods for modulating primordial germ cell (PGC) numbers and / or development in avians are provided. In one embodiment, the presently disclosed subject matter provides a method for modulating primordial germ cells numbers in an avian embryo comprising immunizing a female bird with an antigen associated with primordial germ cells, whereby an egg produced by the female bird comprises a sufficiently high concentration of antibodies specific for the antigen to modulate numbers of endogenous PGCs in an avian embryo present within in the egg. Also provided are methods for producing chimeric avians, methods for increasing the proportion of male birds in a plurality of eggs, methods of producing avian gametes, and methods for enhancing germ line transmission of nucleic acids in birds.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Phasor Method to Fluorescence Lifetime Microscopy to Discriminate Metabolic State of Cells in Living Tissue
ActiveUS20120276578A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPlant Germ CellsPorphyrin
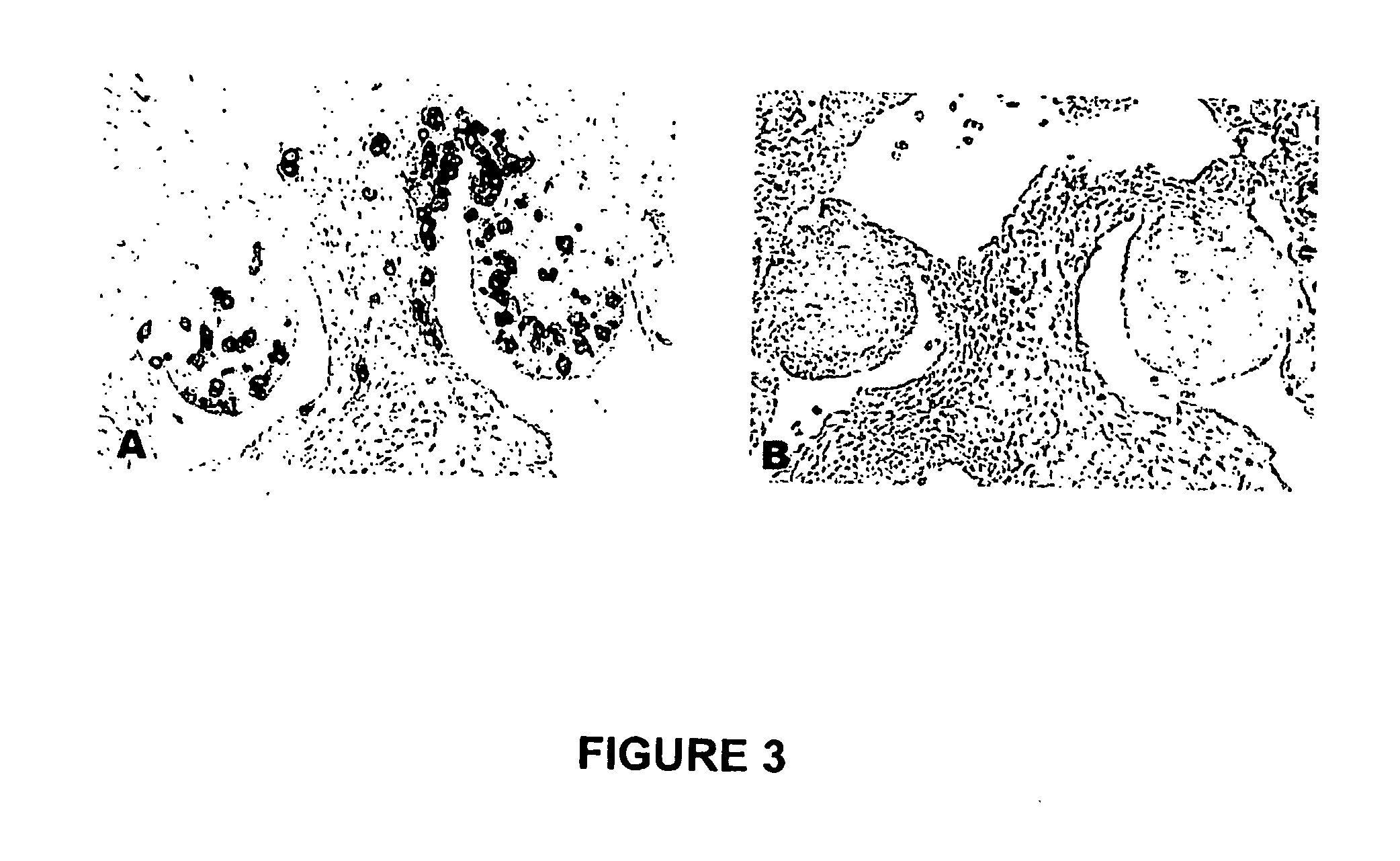
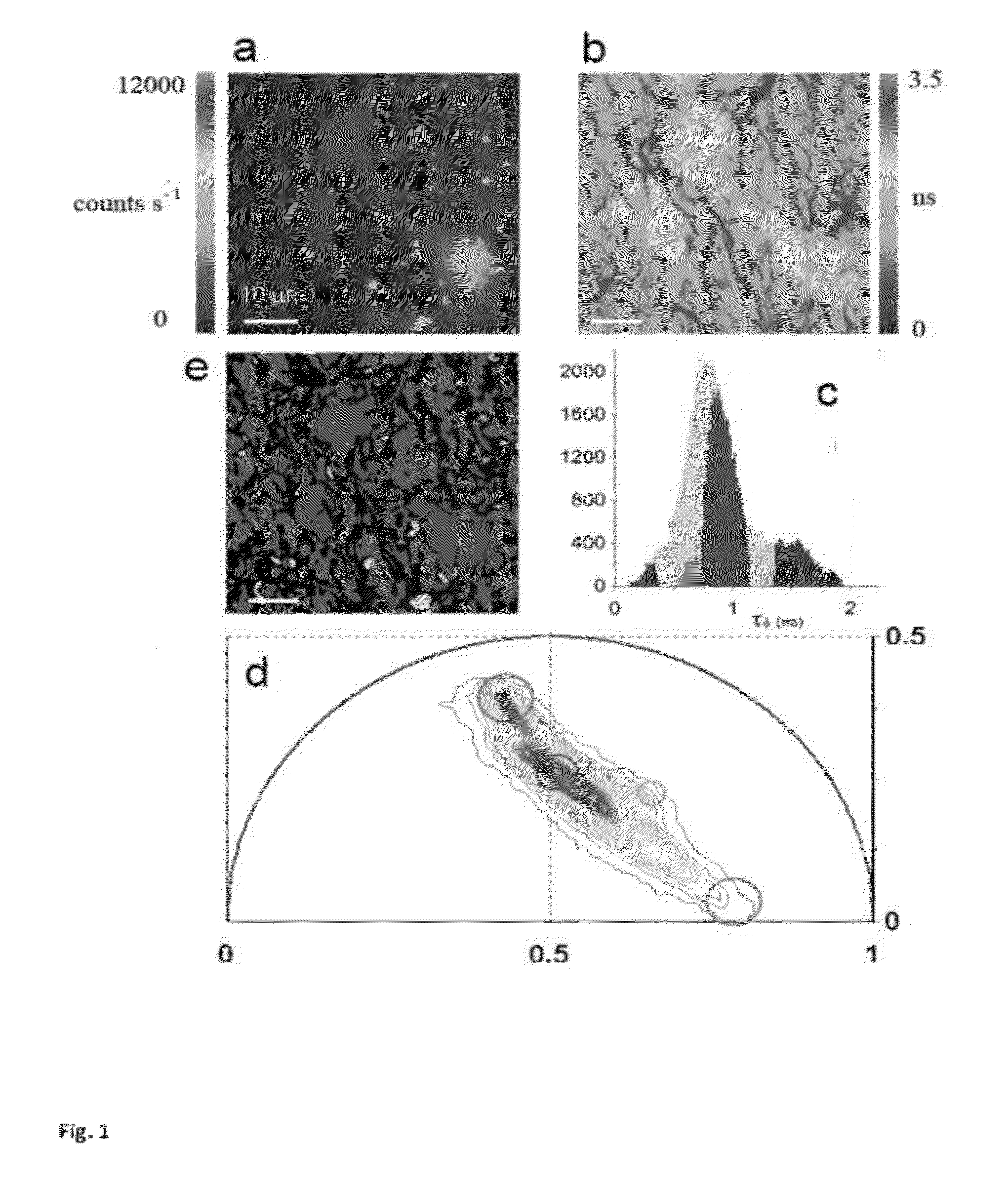
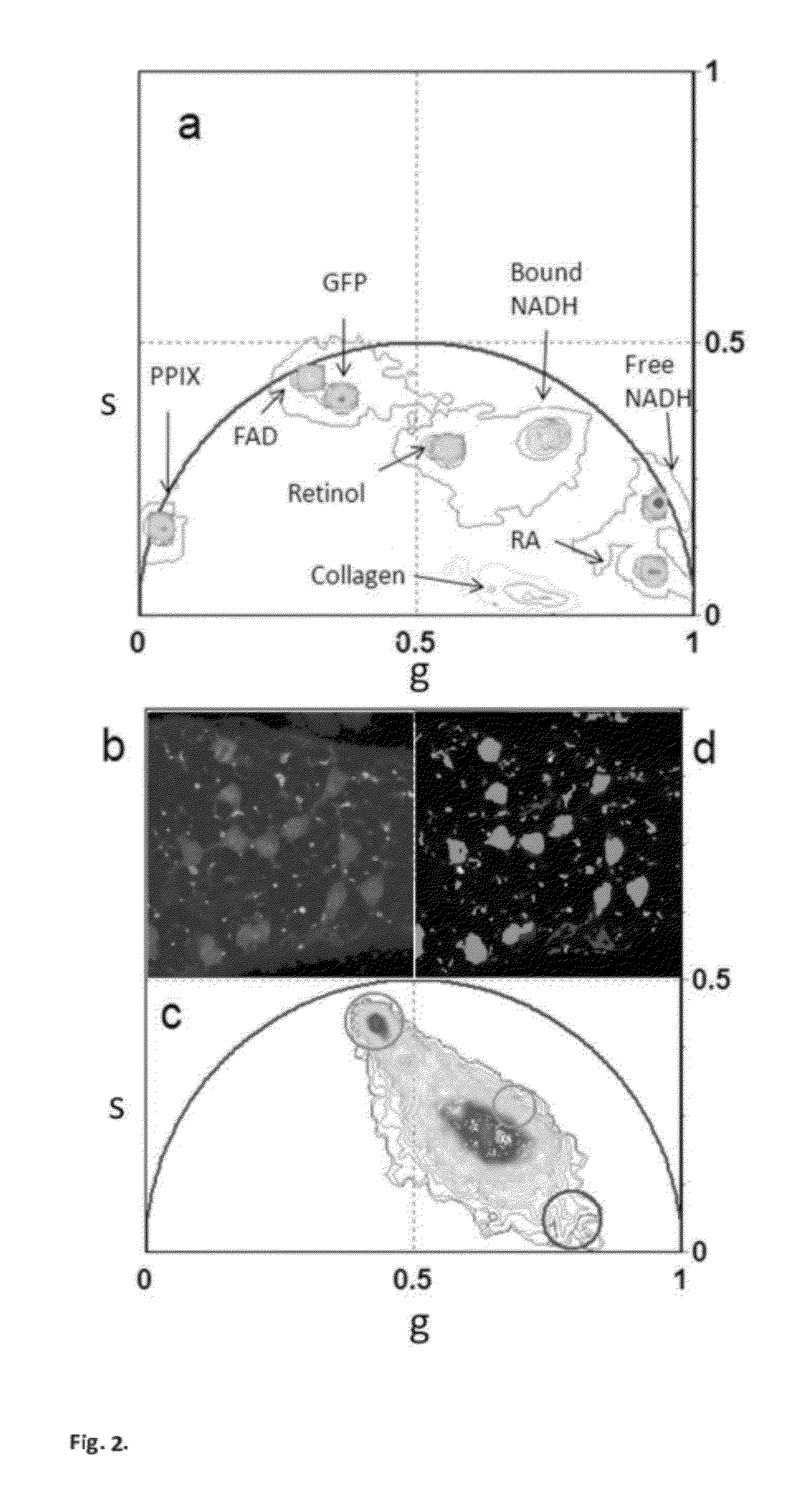
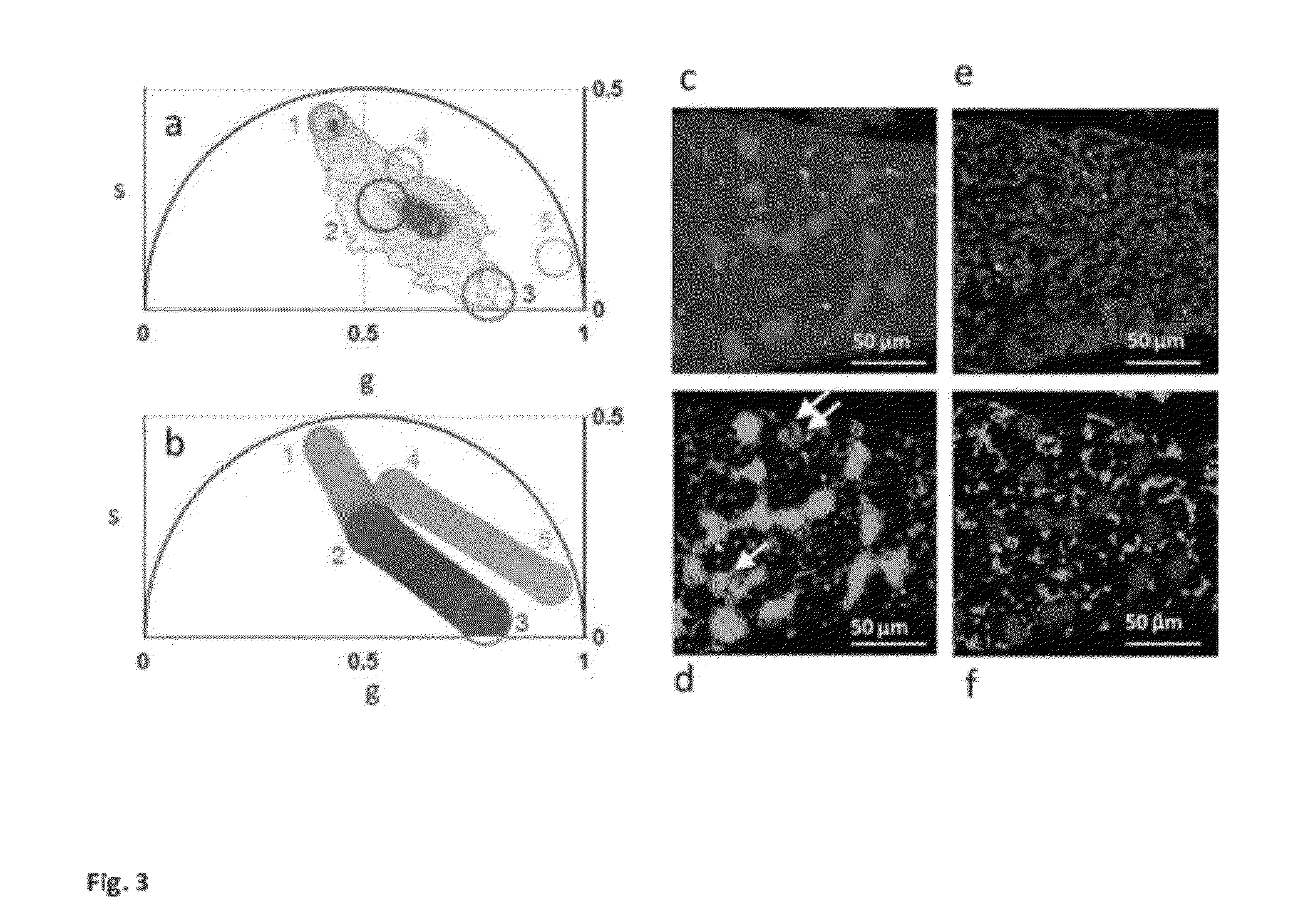
“A label-free imaging method to monitor stem cell metabolism discriminates different states of stem cell as they differentiate in a living tissues. We use intrinsic fluorescence biomarkers and the phasor approach to Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy (FLIM). We identify and map intrinsic fluorophores such as collagen, retinol, retinoic acid, flavins, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) and porphyrin. We measure the phasor values of germ cells in C. Elegans germ line. Their metabolic fingerprint cluster according to their differentiation state, reflecting changes in FAD concentration and NADH binding during the differentiation pathway. The phasor approach to lifetime imaging provides a label-free, fit-free and sensitive method to identify different metabolic state of cells during differentiation, to sense small changes in the redox state of cells and may identify symmetric and asymmetric divisions and predict cell fate.”
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Growth Differentiation Factor-8
InactiveUS20080213426A1Improved muscle and bone contentPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyHuman animal
A transgenic non-human animal of the species selected from the group consisting of avian, bovine, ovine and porcine having a transgene which results in disrupting the production of and / or activity of growth differentiation factor-8 (GDF-8) chromosomally integrated into the germ cells of the animal is provided. Also provided are methods for making such animals, and methods of treating animals, including humans, with antibodies or antisense directed to GDF-8. The animals so treated are characterized by increased muscle tissue and bone content.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Industrialized artificial seedling cultivation method for rockfishes
InactiveCN101375673AIncrease seedling yieldNeat specificationClimate change adaptationWater aerationPlant Germ CellsWater quality
The invention relates to a method of industrial and artificial breeding of Epinephelus, which is applicable to the breeding of Epinephelus malabaricus and E.coioides. The method comprises the following steps: (1) treating a nursery pond and water; (2) preparing before breeding; (3) putting larval fishes of Epinephelus or germ cells; (4) controlling the quality of the breeding water body; and (5) feeding baits. The method is applied to conduct the industrial and artificial breeding, so that the water quality of the breeding is stable, the output for the unit water body breeding is high, the bred sizes of advanced fries are uniform, no antibacterial drugs are used, no special breeding is conducted to unicellular alga, no bottom-attaching happens in the process of breeding, and the operation is simple.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Mimic ecological propagation method for breeding parent fish of American hilsa herring
InactiveCN101669452AMeet the changing rhythm of ecological factorsMeeting nutritional needsClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaBroodstockPlant Germ Cells
The invention discloses a mimic ecological propagation method for breeding parent fish of American hilsa herring, comprising the following steps: establishing a mimic ecological breeding system suitable for natural growth and maturity of the sexual gland of hilsa herring by adopting a circulation water breeding technique and an automation control technique of water environmental factor; regulatingthe mimic natural seasonal rhythmicity for the major physical factors, water chemical factors, and the like of the breeding environment, including factors such as salinity, water temperature, water flow and period of lighting daily variation while fortification; injecting hormone to the parent fish before the spawning season to promote maturity of the sexual gland, and causing the hilsa herring to spawn naturally through enhance water flow stimulation; arranging a spawn collecting box at a circulation water outlet to collect the germ cells and then placing the germ cells in a semi-floating germ cell separation incubator for incubation. The invention can remarkably improve the spawning efficiency of the parent fish of hilsa herring and the incubation rate of the germ cell, and provide thetechnical support for the industrialization of artificial propagation technique for breeding hilsa herring.
Owner:刘青华
Animal sex control method based on Rbmy gene editing and application
ActiveCN105861554AIncrease productivityNucleic acid vectorFermentationControl animalPlant Germ Cells
The invention discloses an animal sex control method based on Rbmy gene editing and application. The method controls animal sex by using CRISPR / Cas9 system to specifically cut Rbmy gene on Y chromosome. Rbmy gene encodes a germ cell specific nucleoprotein, this protein is an important factor related to spermatogenesis, and by cutting Rbmy gene, it is possible to deactivate Rbmy gene, thus Y sperm or fertilized ovum with Y sperm is deactivated and cannot develop into a normal embryo, birth ratio of female animals is finally increased and sex control is achieved. Therefore, sex ratio of animal offspring can be controlled through the method so that the ratio of female animals with better economic value is increased and production efficiency and economic effect are greatly improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for cultivating hybridized and backcrossed marine product fries
ActiveCN102301969AGrowth advantageDominant individual sizeClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaUnfertilized EggsPlant Germ Cells
The invention relates to a method for cultivating hybridized and backcrossed marine product fries. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: selecting excellent individuals that only a female area grows in a hybridized first filial generation family or group of Argopecten purpuratus and Argopecten irradians, and synchronously maturing the selected excellent individuals with excellent individuals of the Argopecten irradians; inducing the hybridized first filial generation individuals to spawn by using a conventional shade drying and temperature stimulation method so as to obtain unfertilized eggs; simultaneously, stimulating the Argopecten irradians to spawn and discharge seminal fluid, and filtering through 500-mesh bolting cloth to obtain the seminal fluid of the Argopecten irradians; and fertilizing the hybridized first filial generation eggs with the seminal fluid of the Argopecten irradians, cultivating according to a conventional method after hatching germ cells, and thus obtaining the hybridized and backcrossed marine product fries which are above 1.5 cm in shell height and used for commercial cultivation. The hybridized and backcrossed marine product fries cultivated by using the method provided by the invention simultaneously have the characteristics of the Argopecten irradians and the Argopecten purpuratus; compared with the Argopecten purpuratus, the hybridized and backcrossed marine product fries have obvious advantages on growth, individual size and temperature tolerance, therefore, the hybridized and backcrossed marine product fries can be cultivated in sea areas in the north, such as Qingdao, Dalian and the like; and, compared with the Argopecten irradians, the yield at the same year is increased by more than 50%.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Methods of producing human rpe cells and pharmaceutical preparations of human rpe cells
The present invention provides improved methods for producing retinal pigmented epithelial (RPE) cells from human embryonic stem cells, human induced pluripotent stem (iPS), human adult stem cells, human hematopoietic stem cells, human fetal stem cells, human mesenchymal stem cells, human postpartum stem cells, human multipotent stem cells, or human embryonic germ cells. The RPE cells derived from embryonic stem cells are molecularly distinct from adult and fetal-derived RPE cells, and are also distinct from embryonic stem cells. The RPE cells described herein are useful for treating retinal degenerative conditions including retinal detachment and macular degeneration.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Polymeric broad spectrum antimicrobial coatings
A sustained and controlled release form of iodine is achieved by a complex of polyvinyl alcohol starch and iodine, characterized by the PVA based coating being insoluble in boiling water. The polyvinyl alcohol is in the form of a coating reacted with varying types of non-mineral acid containing catalysts / curing or insolubilizing agents deposited on cellulose sponge or other substrates and subsequently complexed with iodine. These cost effective sponges or wipers are topically applied as a solid state antimicrobial device, which releases controlled amounts of iodine on contact sufficient to kill germ cells, and leaves minimal residue.
Owner:ROSENBLATT SOLOMON
Method for remarkably improving fish genome editing efficiency
ActiveCN104195177AImprove cutting efficiencyHigh homologous recombination efficiencyMicroinjection basedGenome editingPlant Germ Cells
The invention discloses a method for remarkably improving fish genome editing efficiency. The method for remarkably improving fish genome editing efficiency comprises the following steps: designing a genome editing tool for specifically identifying and cutting a specified site sequence of the fish genome, designing a homologous donor corresponding to the specified site sequence and containing a knock-in exogenous gene fragment, introducing the genome editing tool, the homologous donor and mRNA for specifically and stably expressing fluorescent protein in primordial germ cells into fish animal embryos by using a codominant microinjection method, and selecting the embryos by detecting fluorescent protein expressed by the fluorescent protein mRNA and obtaining stable inheritable characters. The efficiency of the method for knocking the exogenous gene fragment into the specified site of the fish genome so as to obtain a first filial generation of fish with the knock-in exogenous gene fragment is remarkably higher than that of the prior art.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Methods and compositions for producing germ cells from bone marrow derived germline stem cells
InactiveUS20060010509A1Restore gonadal functionReplenish and expand germ cell reserveMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsProgenitorPlant Germ Cells
The present invention relates to the use of bone marrow derived germline stem cells and their progenitors, methods of isolation thereof, and methods of use thereof.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase-S (GAPDHS), a glycolytic anzyme expressed only in male germ cells, is a target for male contraception
Methods for identifying modulators of a male germ cell-specific glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDHS) are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for screening potential modulators for an ability to modulate biological functions of a GAPDHS polypeptide.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES +1
Non-Embryonic Totipotent Blastomere-Like Stem Cells And Methods Therefor
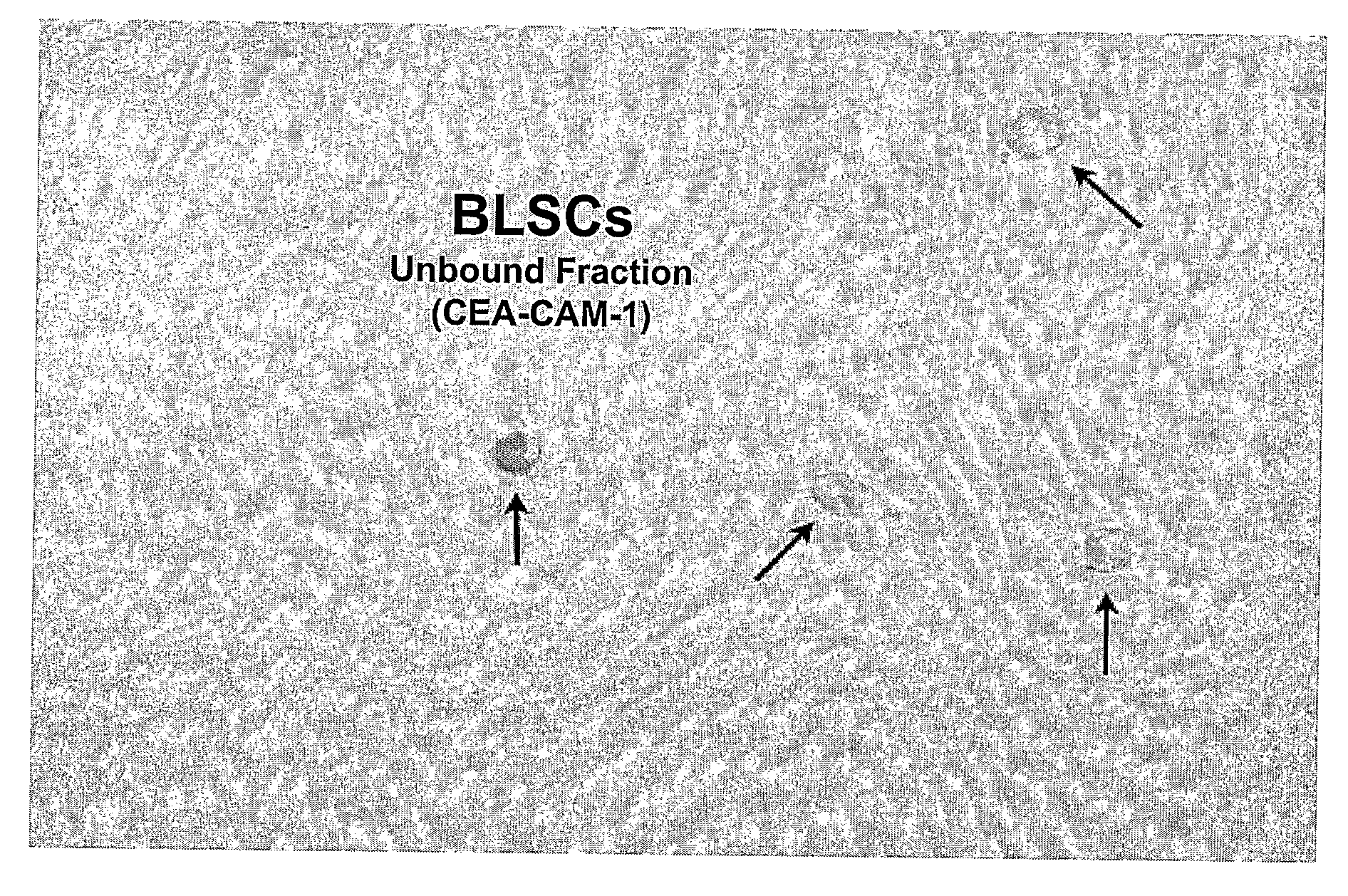
Non-embryonic blastomere-like totipotent stem cells are disclosed. Most preferably, such cells are obtained from various tissues of postnatal mammals (e.g., using tissue biopsied from the mammal), are smaller than 1 μm, have normal karyotype, and do not spontaneously differentiate in serum-free medium without differentiation inhibitors. These non-embryonic blastomere-like totipotent stem cells typically express CD66e, CEA-CAM-1 and telomerase, but do not typically express CD10, SSEA-1, SSEA-3, and SSEA-4. Such blastomere-like totipotent cells can be differentiated into ectodermal, mesodermal, or endodermal tissues, including placental tissues and germ cells. Moreover, when implanted into a mammal, such cells will not be teratogenic.
Owner:MORAGA BIOTECH CORP
Isolation, characterization and differentiation of in vitro adult human germ line stem cells
A method of in vitro maturation of adult human germ line cells in an artificial biological environment, which entails:a) isolating human spermatogonial stem cells (SSCs), and optionally purifying the same; andb) co-culturing the isolated and optionally purified SSCs with a suitably adjusted Sertoli cell environment to obtain haploid germ cells.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Dynamic Lab on a Chip Based Point-Of-Care Device For Analysis of Pluripotent Stem Cells, Tumor Cells, Drug Metabolites, Immunological Response, Glucose Monitoring, Hospital Based Infectious Diseases, and Drone Delivery Point-of-Care Systems
The invention provides for a novel dynamically configurable point-of-care device for clinical diagnostics and research for analysis of activity associated with pluripotent stem cells, tumor cells, drug metabolites, immunological response, glucose monitoring, cardiovascular diseases, liver cell therapy, cell-cell signaling, epidemic outbreaks, hospital based infectious diseases, pathogens, germ cells, pharmacological compounds, oxidation reduction, microscopy, tomography, flow cytometry, clinical lab testing, and for providing immunoassays, ELISA, electrophoresis, PCR, chromatography, and other laboratory functions. The device comprises a biochemical processing module further comprising a processor and at least one controller, receiving microfluidic elements, sensors, software scripts, an electrically operated interface, flow ports, a user interface, memory, and a communications link, configurable based on analysis of patient data. The invention further provides for multiple-criteria decision analysis for hospital administrators, a wearable device, mobile medical device, molecular electronics configuration, touchscreen recognition, data analytics application, and a drone delivery based point-of-care system.
Owner:PATEL NILESH
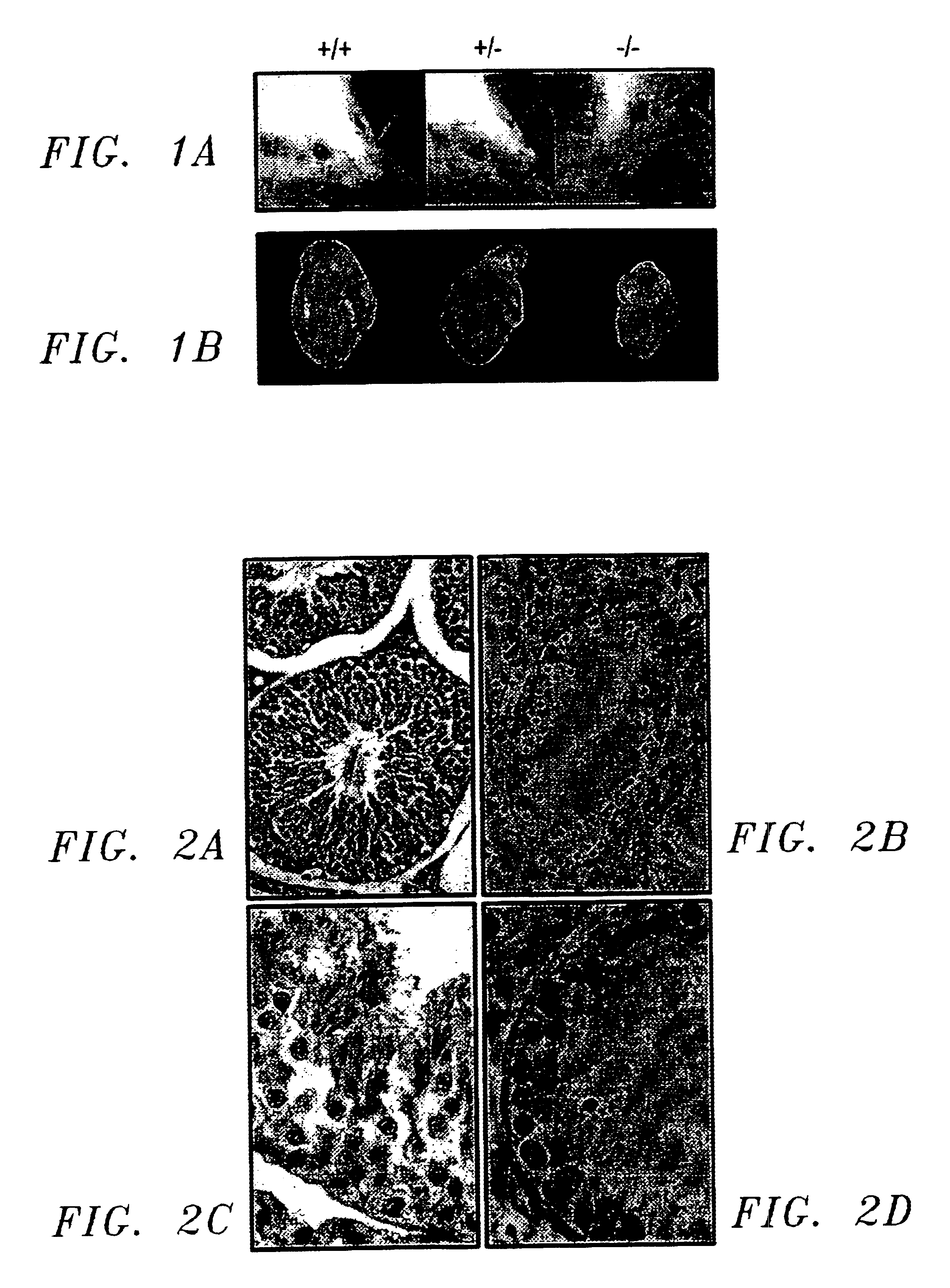
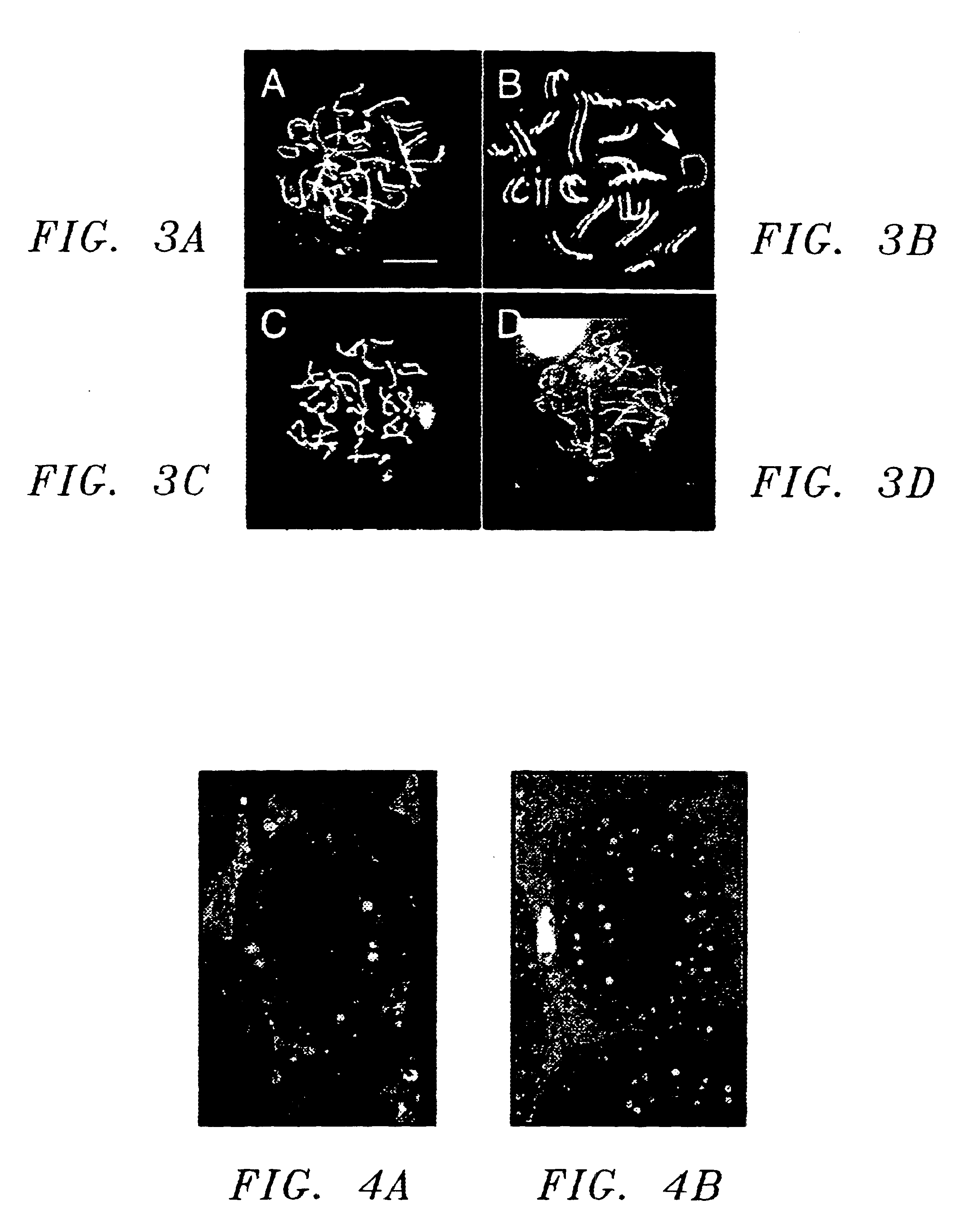
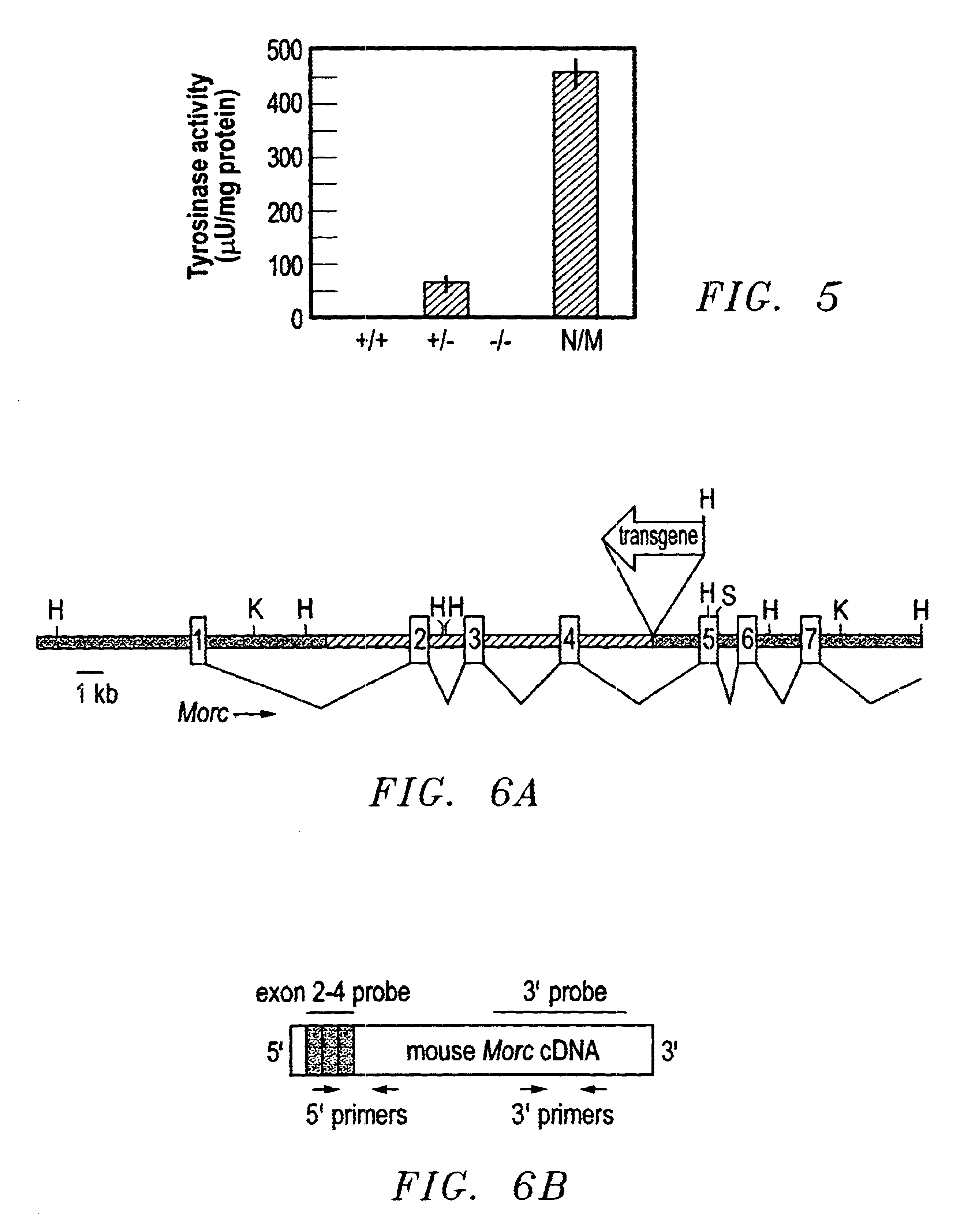
MORC gene compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS6632934B1Easy to storeInhibit microbial growthSugar derivativesAnimals/human peptidesPlant Germ CellsNucleotide
Disclosed are compositions and methods comprising a novel mammalian gene, designated MORC, that is expressed in male germ cells. Also disclosed are polynucleotide compositions comprising a MORC gene from human and murine sources, and polypeptides encoded by these nucleic acid sequences. Methods for preparing MORC polypeptides, transformed host cells, and antibodies reactive with MORC polypeptides are also provided. In certain embodiments, the invention describes methods for diagnosing and treating infertility or testicular cancer, as well as methods for identifying MORC-related polynucleotide and polypeptide compositions.< / PTEXT>
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Egg collector for artificially propagating loach
InactiveCN101278662AImprove hatchabilityGuaranteed quantityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWeatherfishBroodstock
The invention discloses a fish nest used for breeding loach artificially, which comprises a pot with an opening at the top and palm barks. The pot has a double-layer structure, a separation net with 10 to 15mm of meshes is fixedly arranged between an upper layer and a lower layer, and the middle part of the upper surface of the separation net is provided with an inducing fish nest. The palm barks are laid on the inducing fish nest. The lower layer of the pot is provided with an egg-collecting bed with mesh holes which are less than or equal to 120 meshes, and the area of the egg-collecting bed is larger than 90 percent of the area of the pot bottom. At least a net piece at one lateral side of the lower layer of the pot is connected with a pot body in demountable form. The fish nest of the invention can effectively prevent parent fishes from swallowing germ cells, and the egg grain at the bottom of the pot can also be collected, which further improves the hatch rate of the germ cells, improves the breeding quantity of unit parent fish, thus being convenient for using and having good application prospect.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Hmgi proteins in cancer and obesity
InactiveUS20030051260A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein regulationEmbryonic Stage
The present invention pertains to a method for treating obesity in a mammal which comprises reducing the biological activity of HMGI genes in the mammal. In another embodiment, the invention pertains to a method for treating a tumor in a patient by reducing the biological activity of normal HMGI genes which comprises administering to the patient a therapeutically effective amount of an inhibitor compound active against normal HMGI-C or HMGI(Y) genes. In another embodiment, the invention pertains to a method of producing a transgenic non-human mammal, the germ cells and somatic cells of which contain an inactivated HMGI gene sequence introduced into the mammal at an embryonic stage. In another embodiment, the invention pertains to a method for screening candidate compounds capable of inhibiting the biological activity of normal HMGI proteins. In another embodiment, the invention pertains to a method for screening candidate compounds capable of inhibiting the biological activity of normal HMGI genes. In another embodiment, the invention pertains to a method for detecting normal HMGI proteins as a diagnostic marker for a tumor using a probe. that recognizes normal HMGI proteins, which comprises the steps of (a) contacting normal HMGI proteins from a sample from a patient with a probe which binds to HMGI proteins; and (b) analyzing for normal HMGI proteins by detecting levels of the probe bound to the normal HMGI proteins, wherein the presence of normal HMGI proteins in the sample is positive for a tumor. In another embodiment, the invention pertains to a method for detecting antibodies to normal HMGI proteins using a probe that recognizes antibodies to HMGI normal proteins, which comprises the steps of (a) treating a sample from a patient with a probe which binds to antibodies to normal HMGI proteins; and (b) analyzing for antibodies to HMGI proteins by detecting levels of the probe bound to the antibodies to HMGI proteins, wherein the presence of antibodies to normal HMGI proteins in the sample is positive for a tumor. In another embodiment, the invention pertains to HMGI genes and proteins for use as a starting point to isolate downstream target genes regulated by the HMGI genes and proteins.
Owner:MEDICINE & DENTISTRY OF NEW YORK UNIV OF
Compositions and methods for enhancing bioenergetic status in female germ cells
ActiveUS20130059384A1Quality improvementImprove mitochondrial functionSugar derivativesHydroxy compound active ingredientsIsolated mitochondriaPhysiology
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Method for cultivating glyptosternum maculatum fries and fingerlings through artificial feed
The invention relates to a method for cultivating glyptosternum maculatum fries and fingerlings through artificial feed. In an indoor cement pool, clean water resources from rivers are utilized, micro water flow is controlled through manpower, manual mixed feed is provided for feeding, and fries hatched from germ cells are cultivated to fingerlings 3cm in length. The rate of survival of the glyptosternum maculatum fries which live for 2-3 days to be fingerlings which are 3cm long is more than 80%.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Methods for in vitro fertilization
InactiveUS6838235B2Improve developmentSpeed up the processNew breed animal cellsCulture processPlant Germ CellsReproductive tract
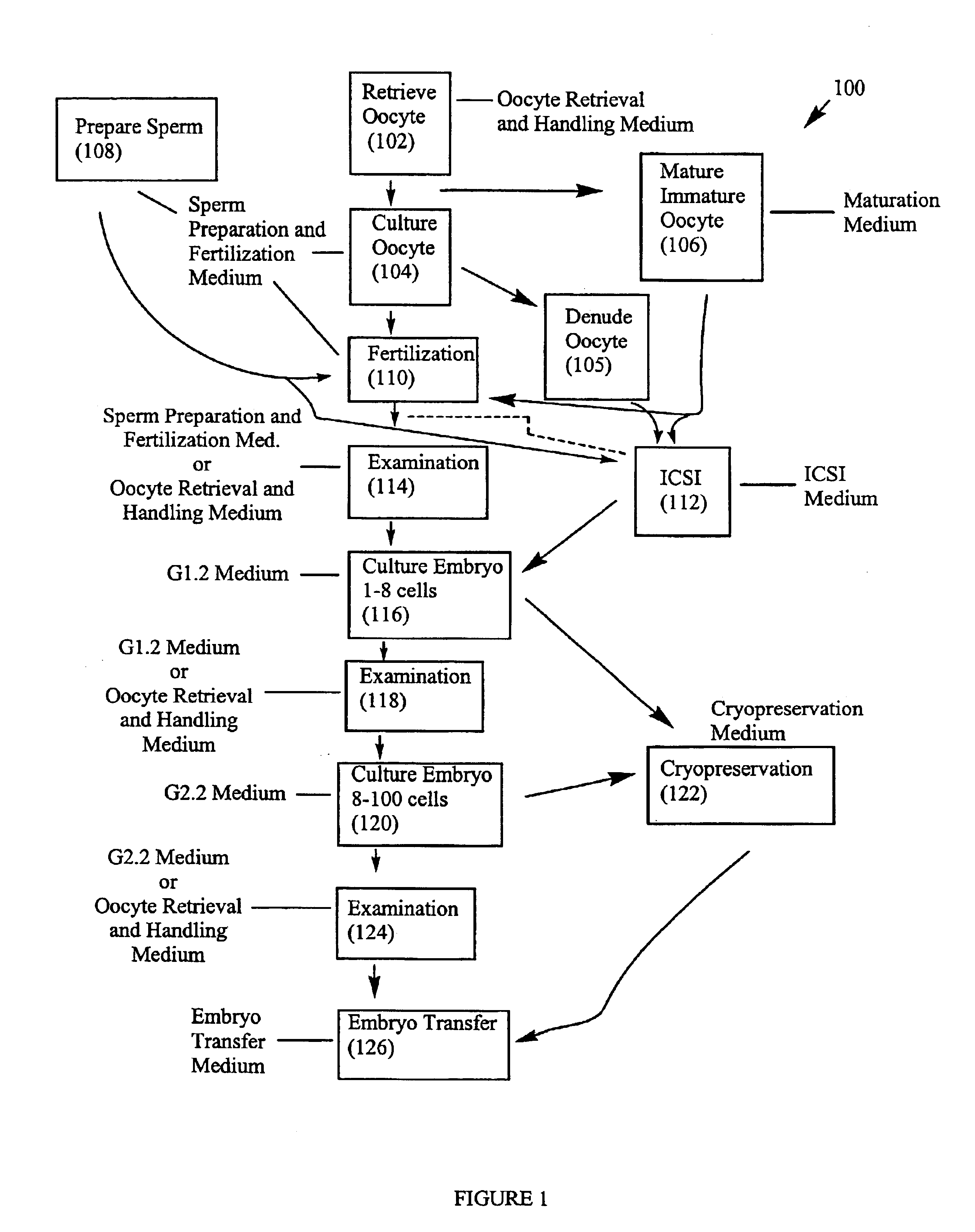
Instead of immersing human reproductive cells in a single culture medium throughout the various procedures used in IVF, a process is provided by which the reproductive cells may be moved through a sequence of distinct culture media as the various IVF procedures are carried out. In one implementation, the culture media specifically formulated to provide a physical environment similar to that found within the female reproductive tract and conducive to growth and development of human reproductive cells during the various stages of the IVF process. In this regard, specifically formulated culture media can be applied to support the reproductive cells in one or more of the following procedures: oocyte retrieval and handling; oocyte maturation; ordinary fertilization; oocyte, zygote and embryo examination and biopsy; embryonic development to the eight-cell stage; embryonic development to the blastocyst stage; embryo transfer; and cryopreservation.
Owner:VITROLIFE AB
Method for incubating largemouth basses ahead of time
ActiveCN103749361AExtended growing seasonClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaSebastesBroodstock
The invention discloses a method for incubating largemouth basses ahead of time. By using the method, the largemouth basses are bred in a greenhouse, sexual maturity is achieved ahead of time, and the largemouth basses are bred artificially. The method comprises the following steps of selecting largemouth basses with the weight of 0.5-0.8 kilogram in the middle ten days of the October and breeding the largemouth basses in the greenhouse in cold days; controlling the temperature of water from the middle ten days of the October, controlling the temperature of the water in the January to be in a range of 11-13 DEG C, then gradually raising the temperature of the water, and raising the temperature of the water to be in a range of 20-22 DEG C in middle ten days of the March; anatomically observing the condition of sexual maturity of parent basses; injecting oxytocin to the parent basses at the beginning of the April, and enabling the parent basses to lay eggs in a plastic-covered tunnel with palm sheets; and placing the palm sheets with germ cells in an indoor incubation pond and incubating the germ cells. By using the method, 1281 fries with the total length of 3.5 millimeters are obtained. At the present stage, largemouth basses cannot be artificially incubated in the northern China, and particularly, the largemouth basses cannot be incubated in the April of the northern China. The largemouth basses fries can be obtained ahead of time for 40 days. The growing period of the fries in the current year is prolonged for 40 days.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com