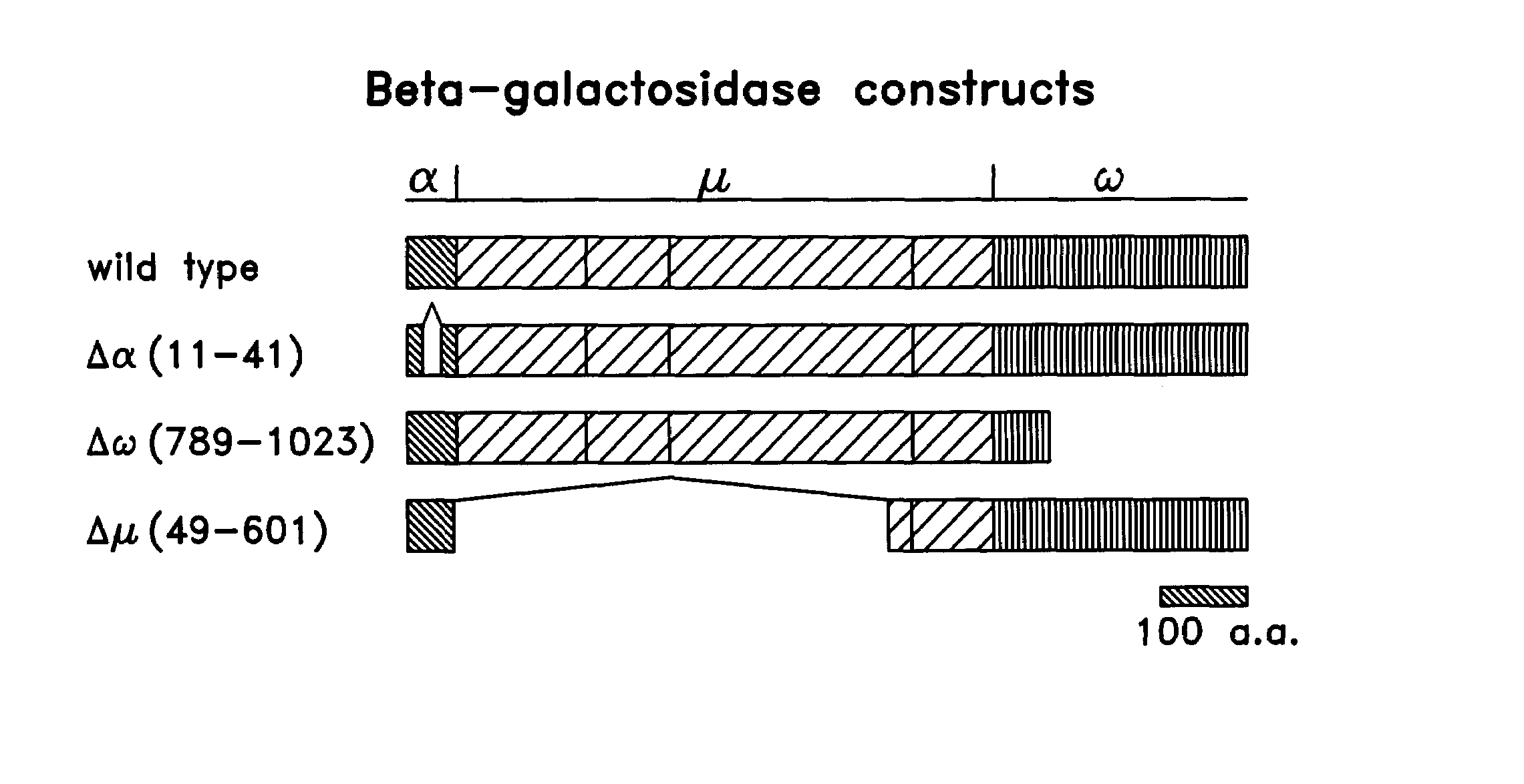
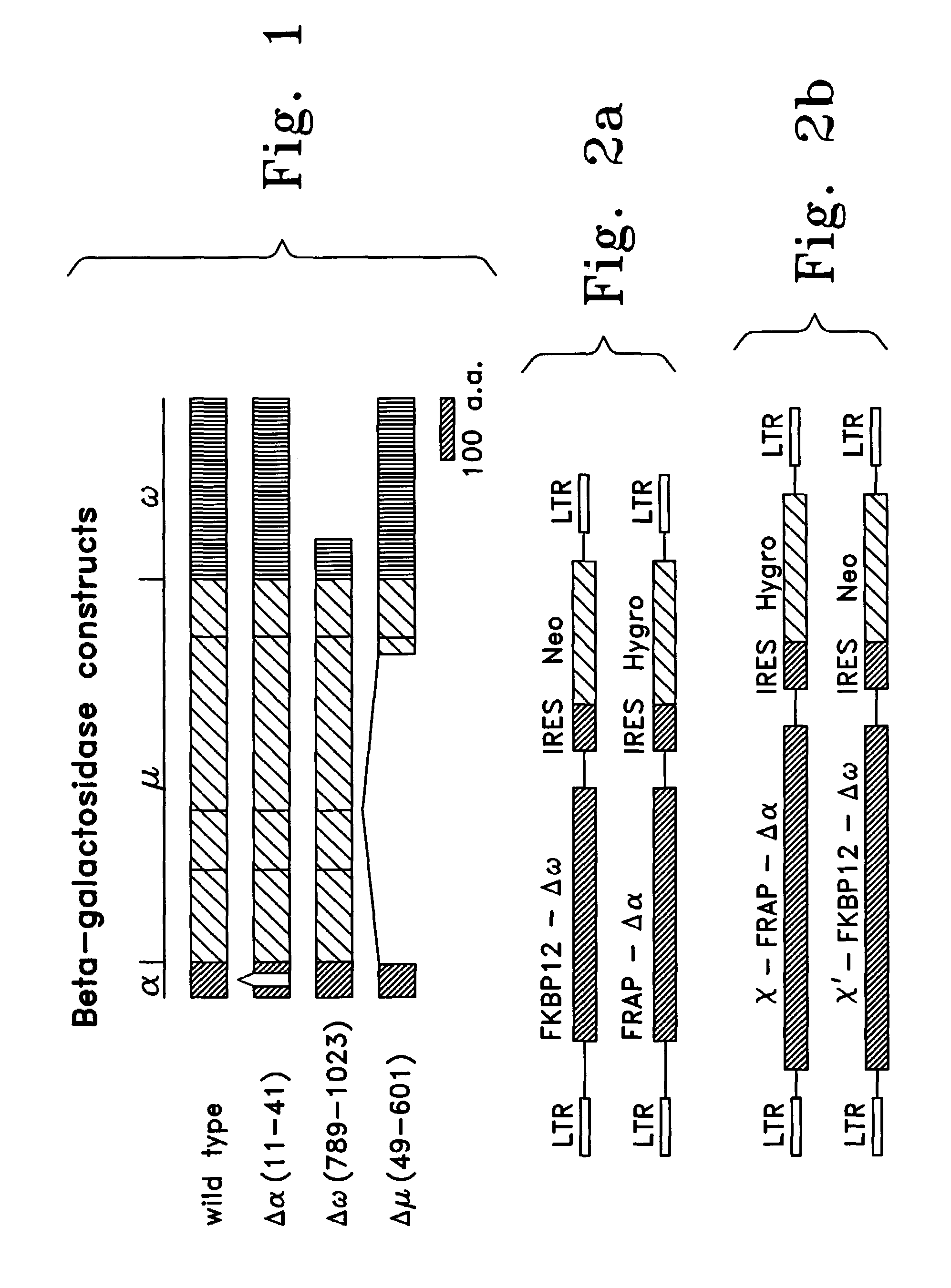
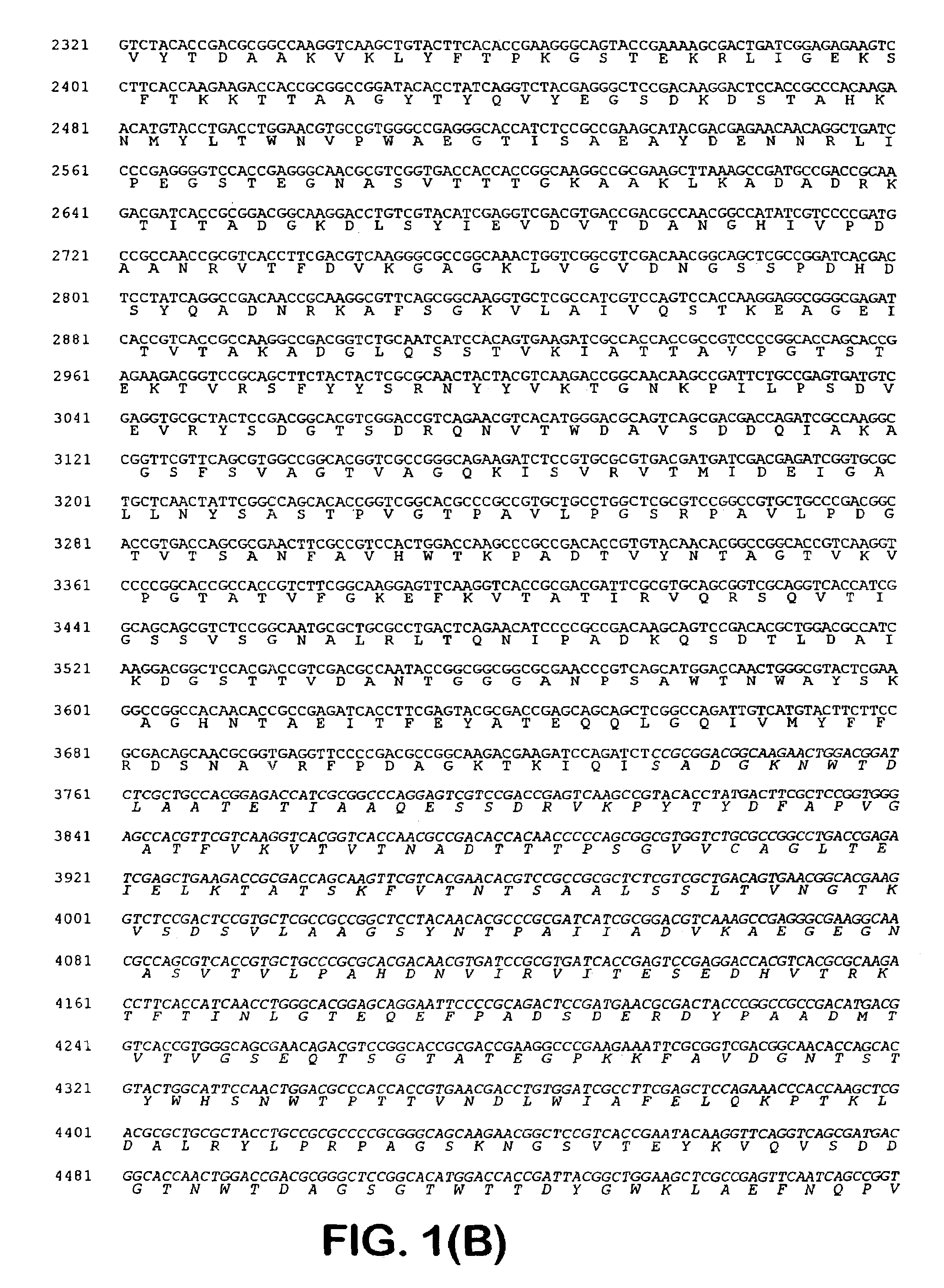Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48 results about "Beta-galactosidase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Β-galactosidase, also called lactase, beta-gal or β-gal, is a glycoside hydrolase enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of β-galactosides into monosaccharides through the breaking of a glycosidic bond. β-galactosides include carbohydrates containing galactose where the glycosidic bond lies above the galactose molecule. Substrates of different β-galactosidases include ganglioside GM1, lactosylceramides, lactose, and various glycoproteins.
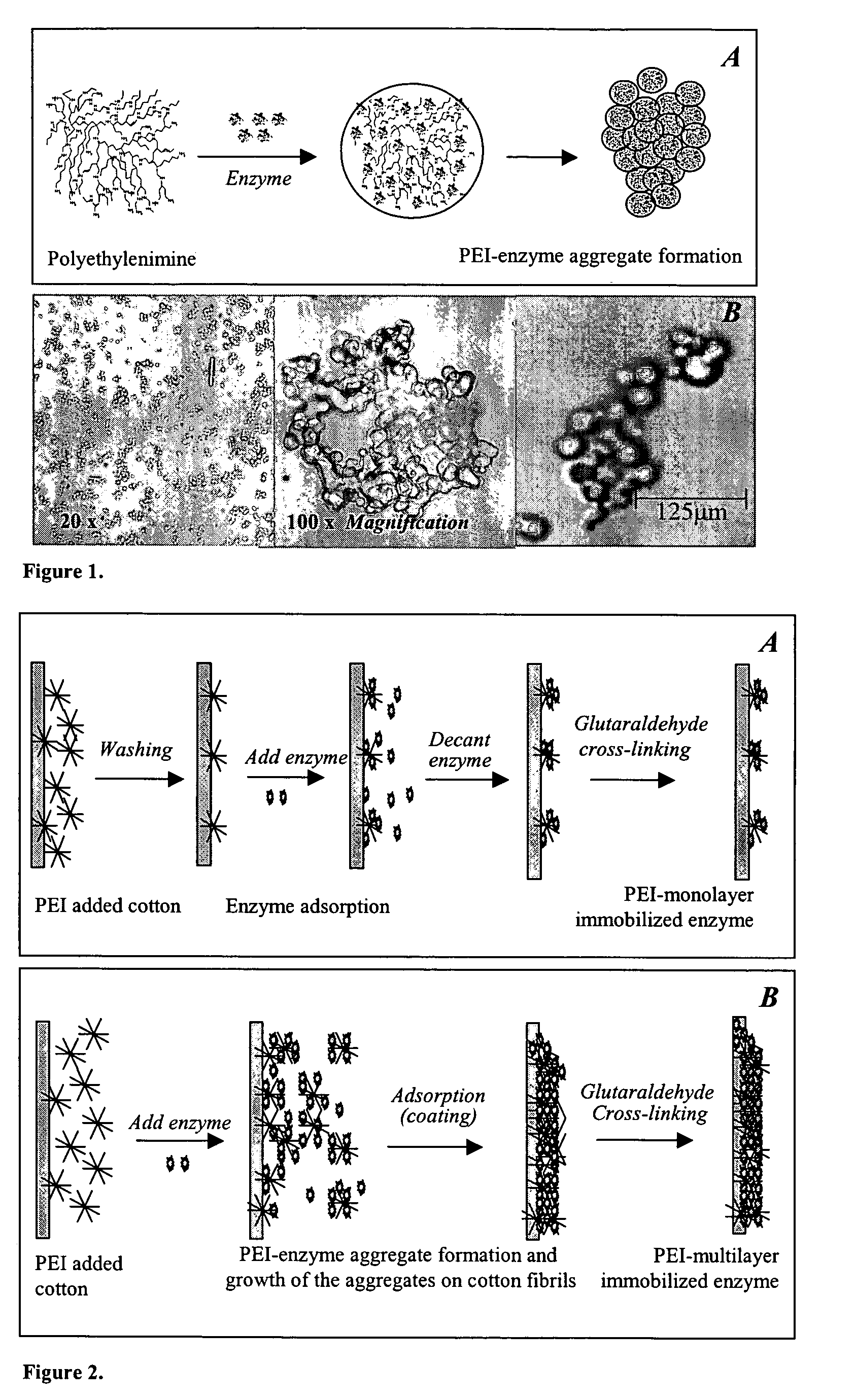
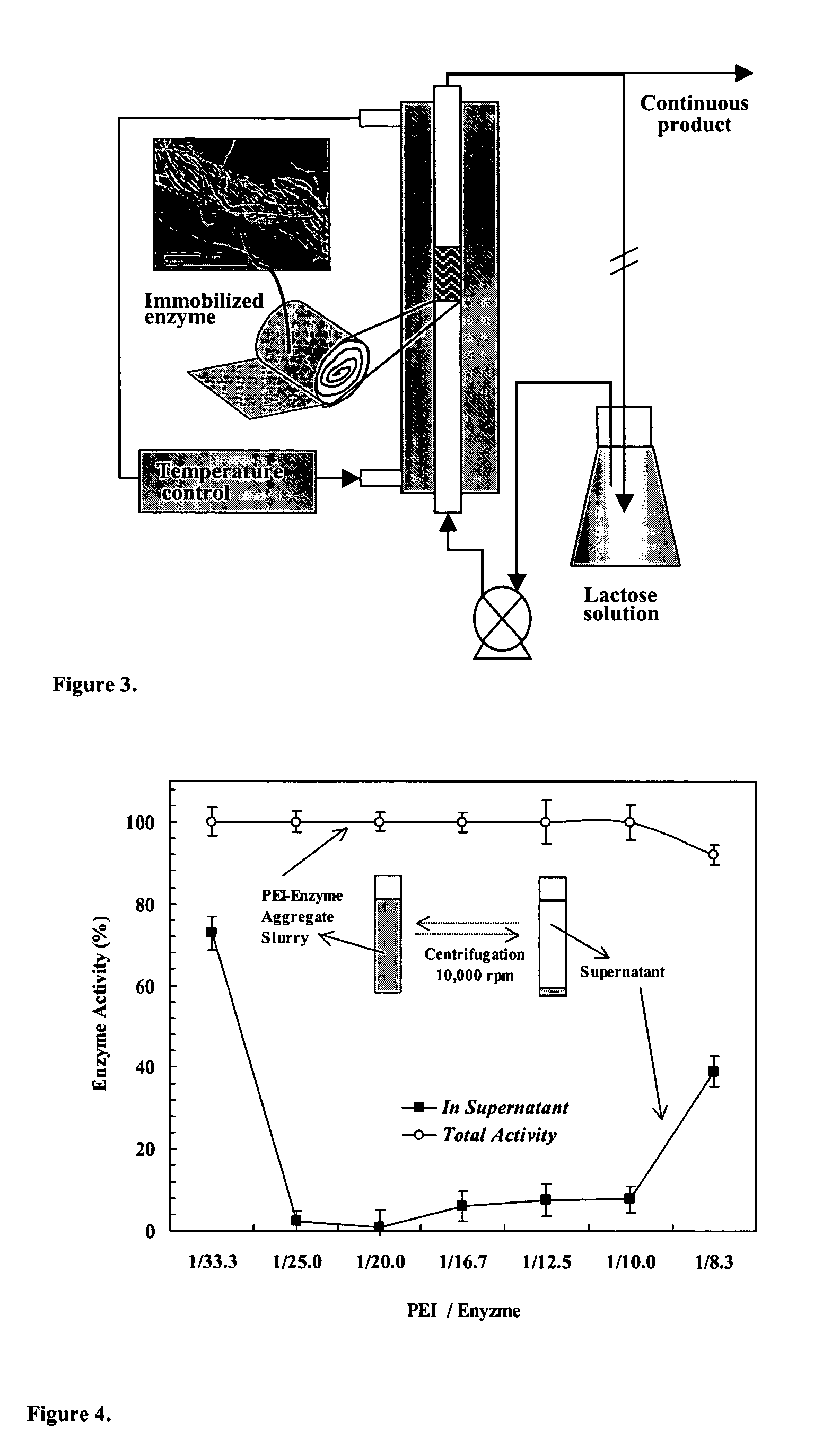
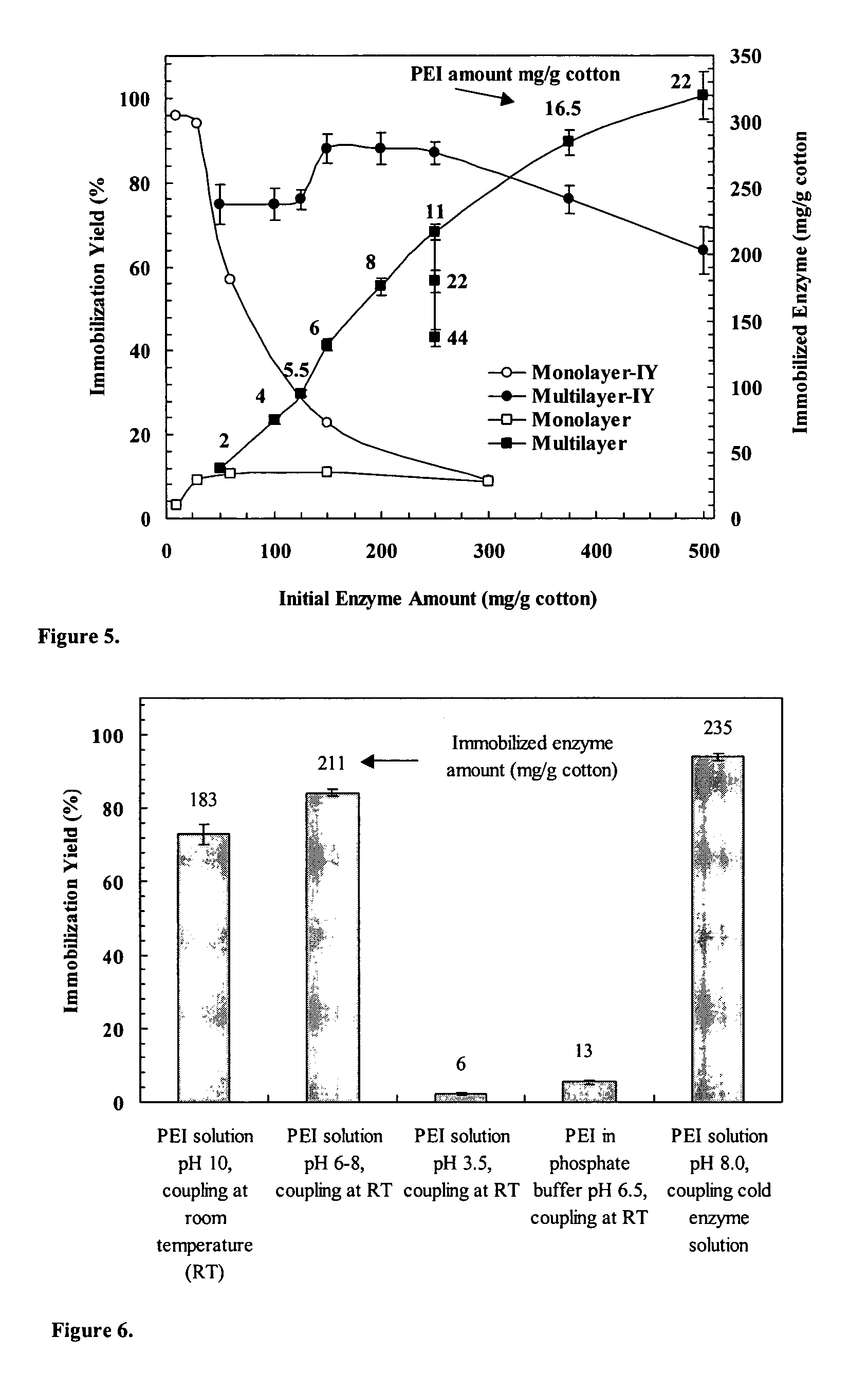
Immobilization of enzyme on a fibrous matrix
ActiveUS7166451B1The process is simple and clearHigh enzyme loadingOn/in organic carrierFermentationFiberCross-link
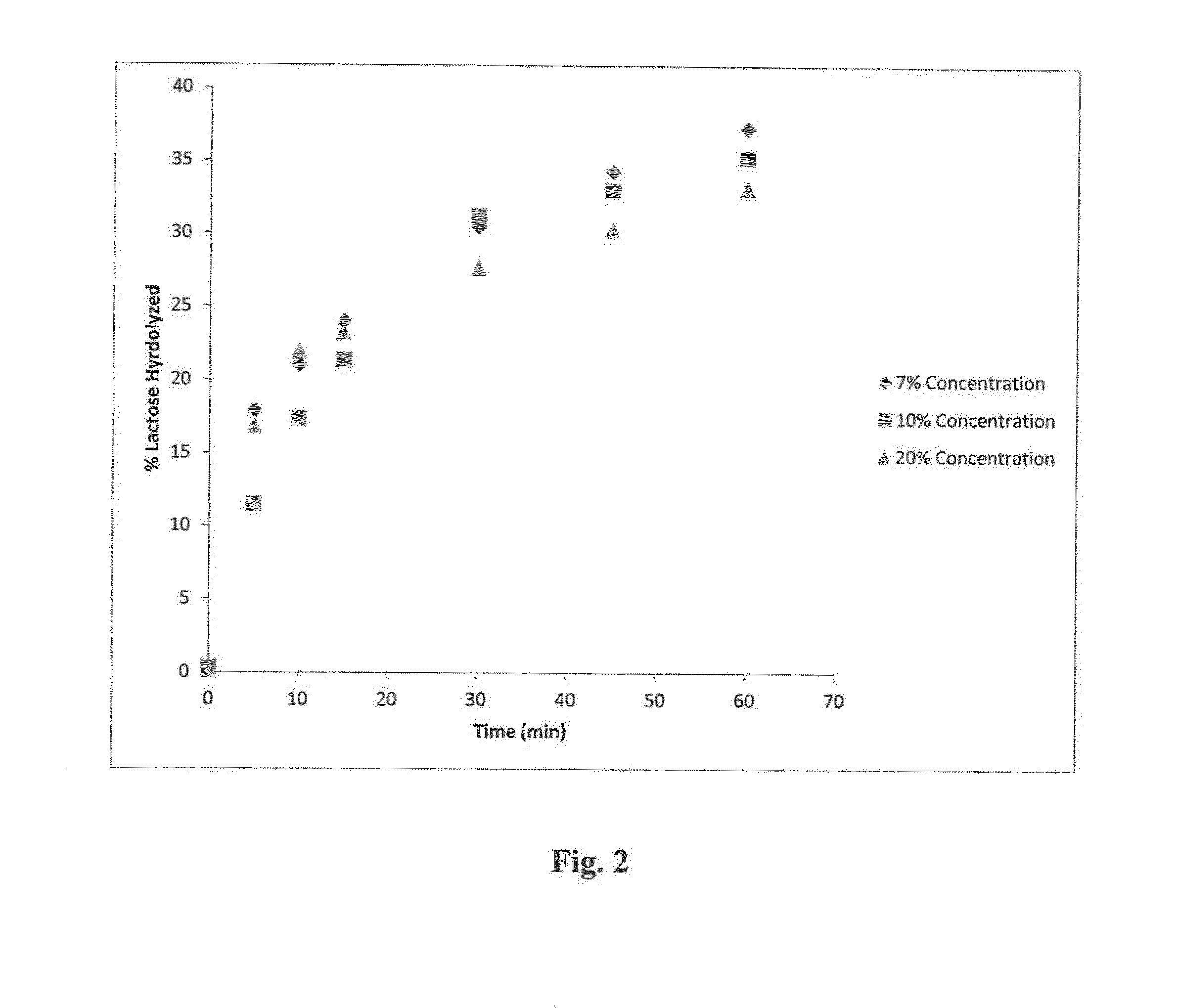
A multilayer enzyme immobilization process is provided comprising adsorbing a polyethyleneimine (PEI) solution in a fibrous matrix, and adding an enzyme to the fibrous matrix, which comprises a plurality of fibrils. The process further comprises forming at least two layers of PEI-enzyme aggregates on the fibrils, and cross-linking the multilayer PEI-enzyme aggregates. The process can further comprise washing the fibrils containing the cross-linked PEI-enzyme aggregates with distilled water and acetic acid buffer subsequent to cross-linking. However, the PEI-containing matrix is not washed prior to the addition of enzyme. The enzyme can be β-galactosidase and the fibrous matrix can be cotton cloth. The multilayer immobilized enzyme can be employed in a biocatalyst reactor for production of galacto-oligosaccharides from lactose and the hydrolysis of lactose to glucose and galactose.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
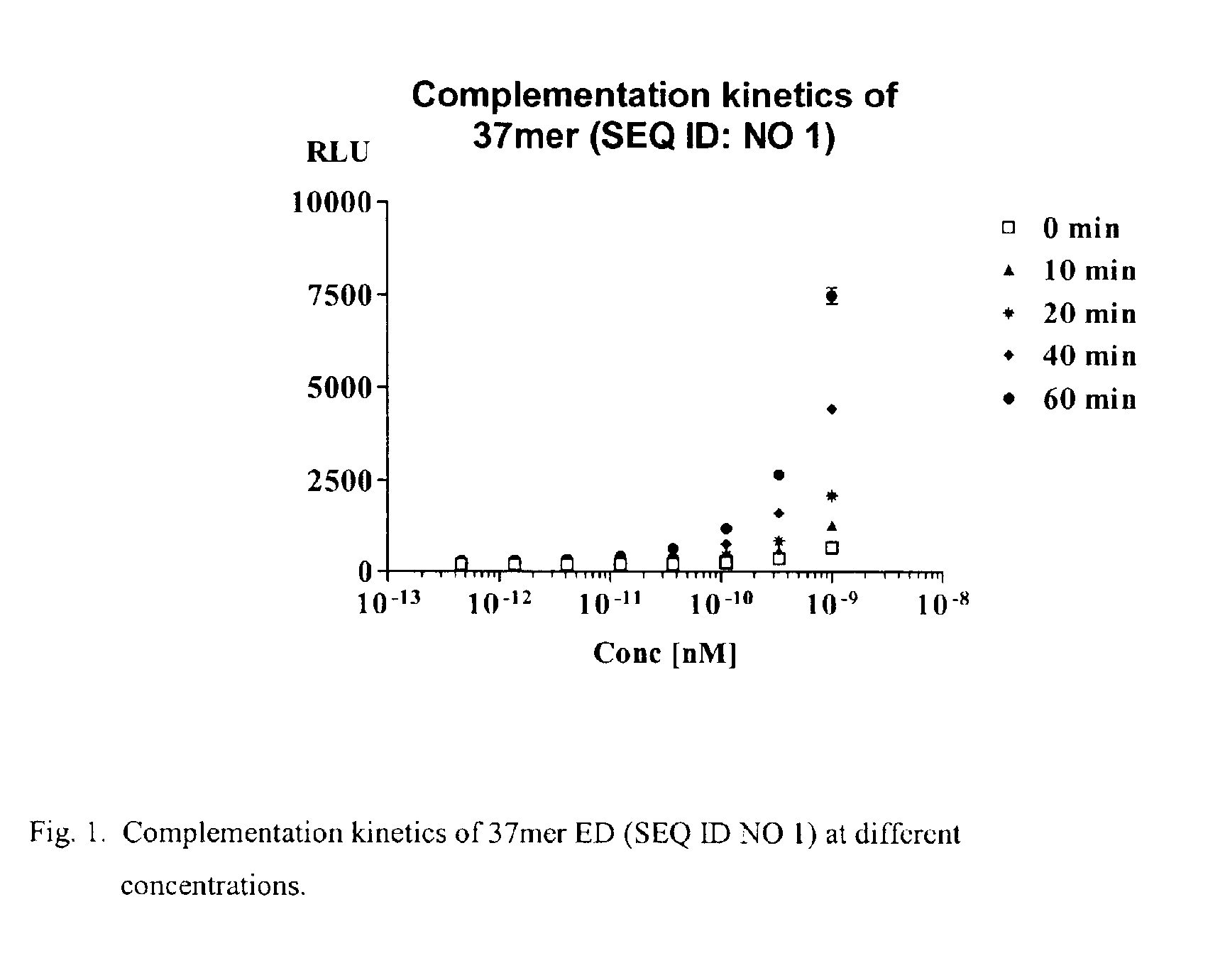
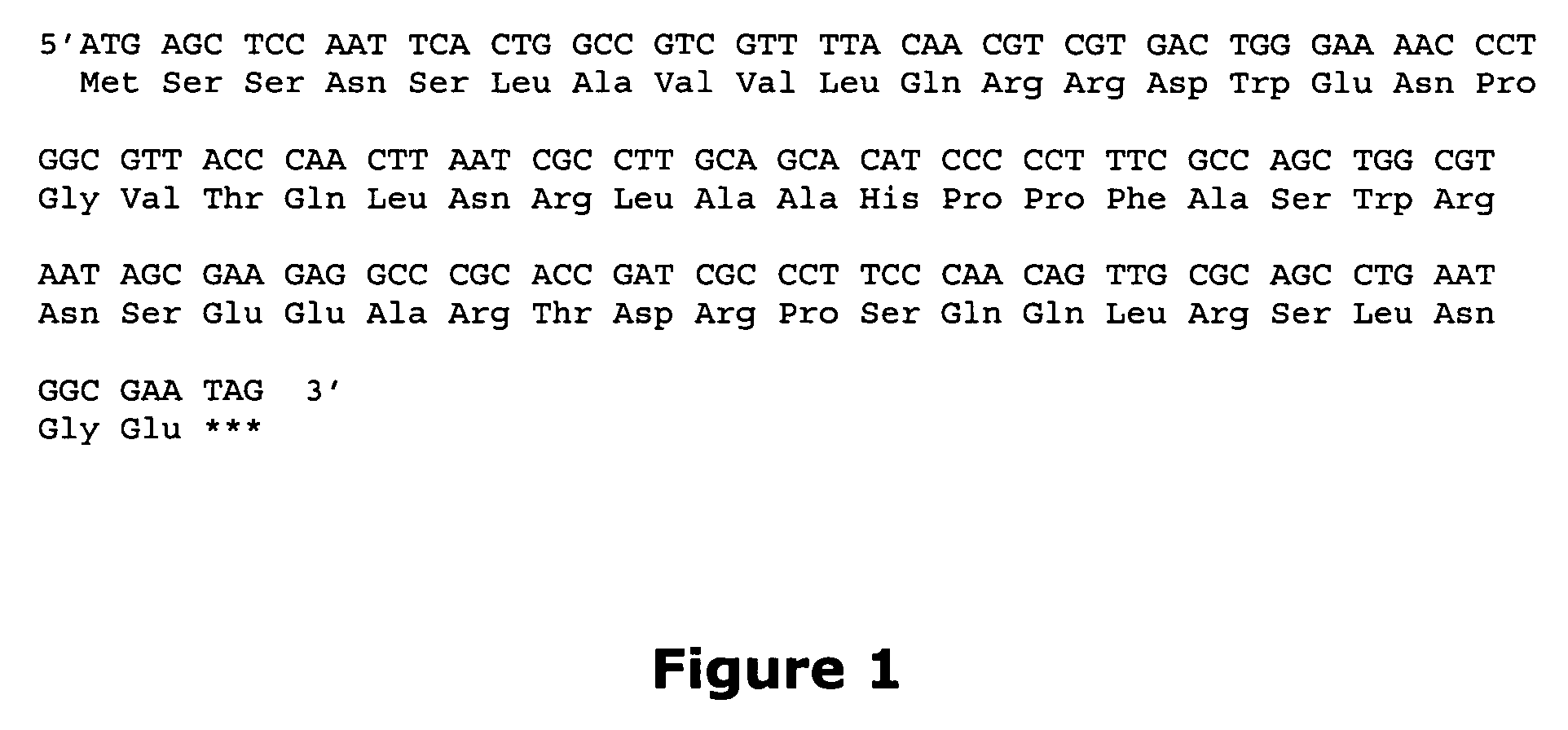
Short enzyme donor fragment
InactiveUS7135325B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFunctional activityOrganic compound
Short enzyme donor fragments of β-galactosidase are provided of not more than 40 amino acids, where the short fragments are used as a label and may be substituted with a wide variety of organic compounds, particularly polypeptides having independent functional activity. The enzyme donor finds use in competitive and non-competitive assays, monitoring intracellular events, or other processes where a sensitive non-interfering label is desired.
Owner:DISCOVERYX CORP
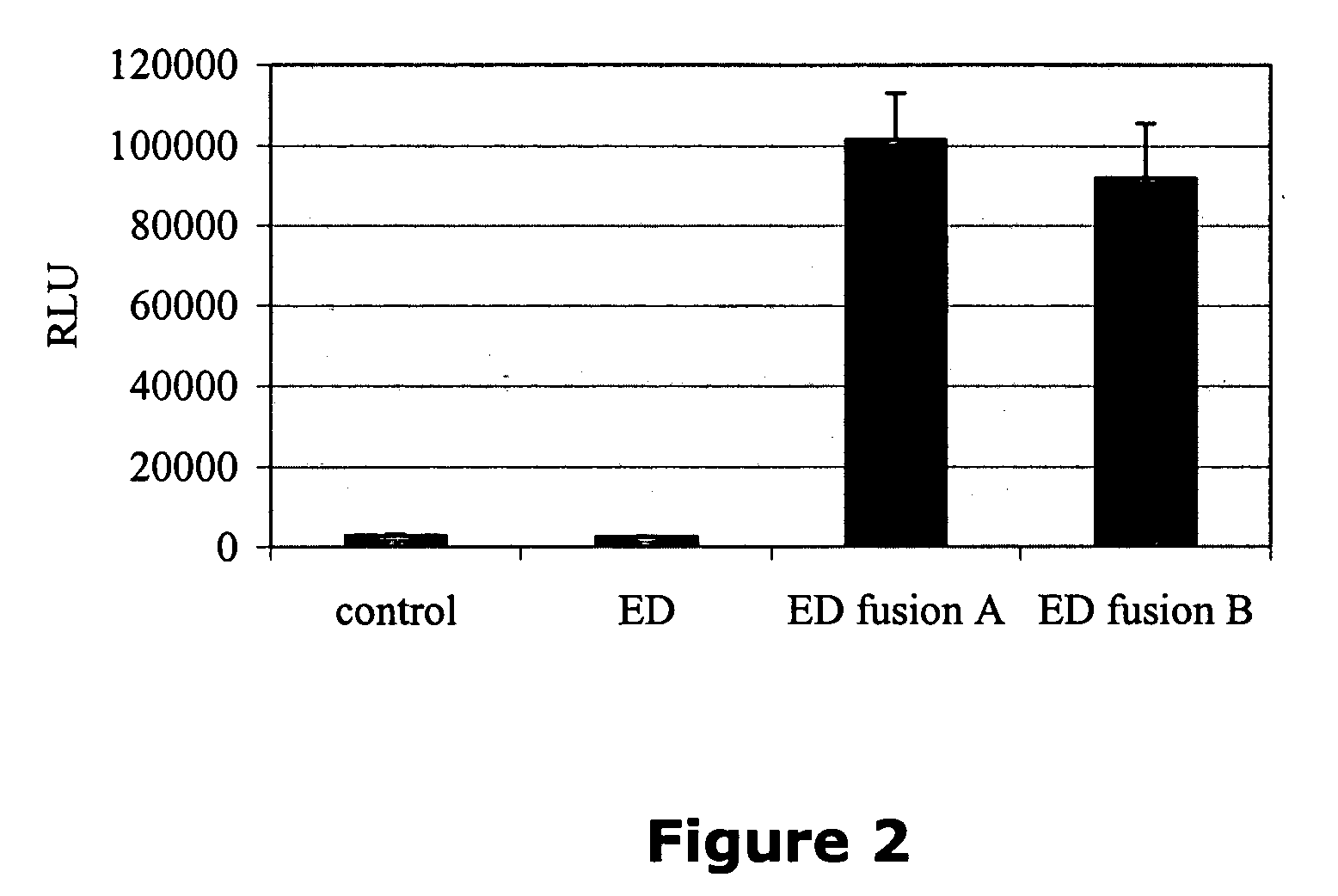
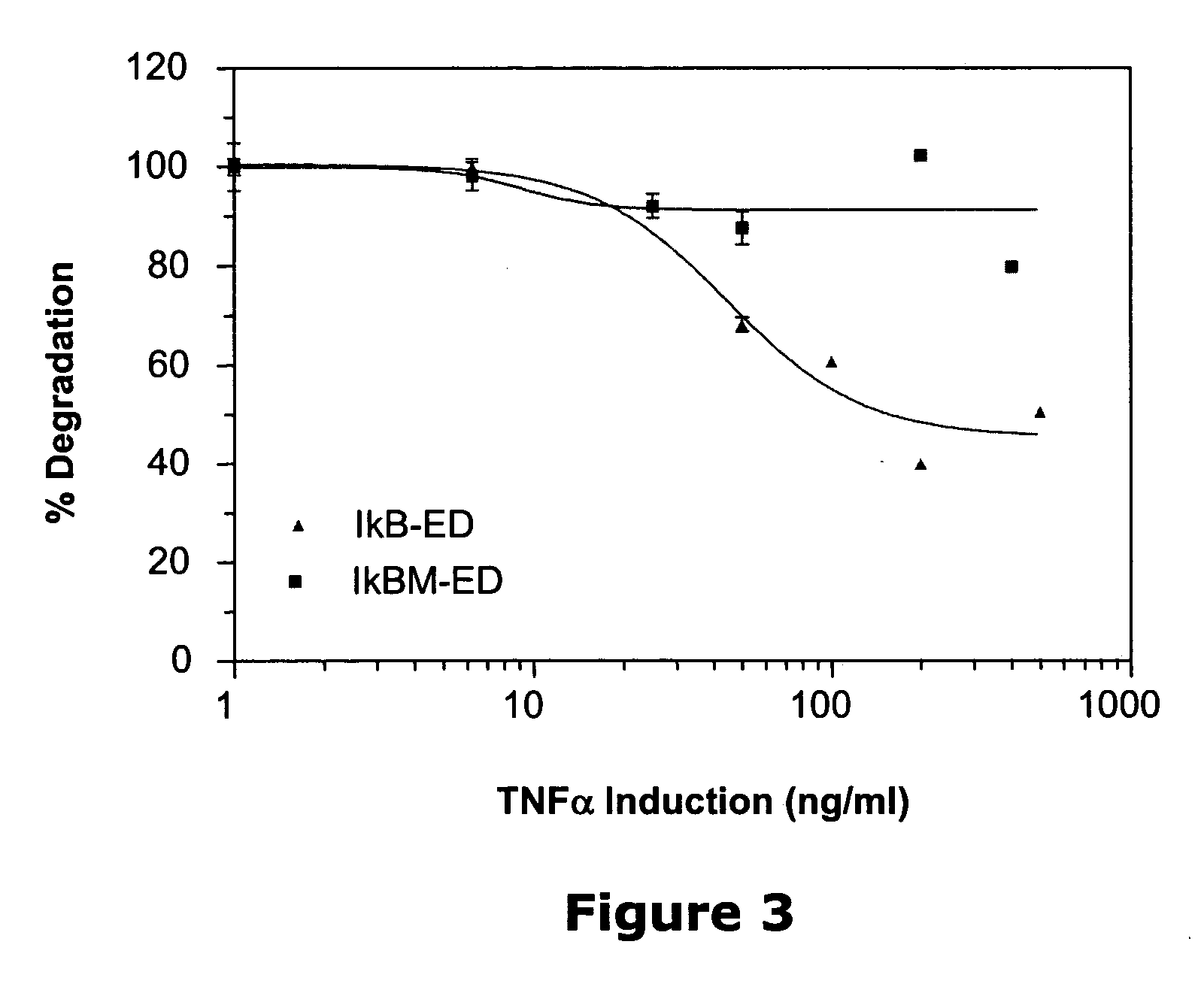
Monitoring intracellular proteins
InactiveUS20040137480A1Compound screeningApoptosis detectionProtein insertionBeta-galactosidase activity
Methods and compositions are provided for analyzing intracellular events employing fusion proteins comprising the small beta-galactosidase fragment fused to a protein of interest or fragment thereof. By expressing the fusion protein in a cellular host, one can determine the effect of various agents on the activity of the fusion protein, adding the large beta-galactosidase fragment to the fusion protein, either intracellularly or in a lysate and determining the activity of the formed beta-galactosidase using a substrate that forms a detectable product. In this manner, degradation, complex formation, RNAi inhibition or other situation that affects beta-galactosidase activity can be determined.
Owner:DISCOVERX INC
Method for remodelling cell wall polysaccharide structures in plants
InactiveUS20030159178A1Reduce the ratioImprove gel propertiesSurgical adhesivesDead animal preservationReticulum cellNucleotide
Methods for providing transgenic plants and parts hereof that, relative to the wild type state, is modified in a complex cell wall polysaccharide structure including pectins and hemicelluloses, the modification being in the overall glycosidic linkage pattern or the monosaccharide profile, comprising transforming a plant cell with a nucleotide sequence that causes an altered production of a complex cell wall polysaccharide-modifying enzyme such as endo-rhamnogalacturonan hydrolase, an endo-rhamnogalacturonan lyase, an endo-galactanase, an endo-arabinanase, an arabinofuranosidase, a galactosidase such as a beta-galactosidase, a xylosidase and an exo-galacturosidase. The modification can occur in vivo or post harvest, in which latter case the modifying enzyme is separated in the growing plant from its substrate, e.g. by targeting the enzyme to the Golgi, the endoplasmic reticulum or a vacuole, or is in a form that is inactive in the plant. After harvest the enzyme is brought into contact with its substrate or it is activated to provide the desired post harvest modification of the cell wall polysaccharide. The transgenic plant materials have improved functionalities and are useful in food and feed manufacturing and as pharmaceutically or medically active substances.
Owner:POALIS
Enzyme isolated from a Bifidobacterium
InactiveUS7081355B2High transgalactosylatingImprove scalabilityFungiBacteriaBifidobacteriumDairy industry
The present invention concerns a new β-galactosidase with transgalactosylating activity isolated from Bifidobacterium bifidum and a truncated enzyme where the C-terminal end of the β-galactosidase protein has been deleted, resulting in an enzyme with a higher transgalactosylating activity than hydrolase activity. When lactose is used as a substrate, galacto-oligosaccharides are products of the transgalactosylase activity. Galacto-oligosaccharides enhance growth of health-promoting Bifidobacterium that may be used in a number of applications in the dairy industry.
Owner:ARLA FOODS AMBA
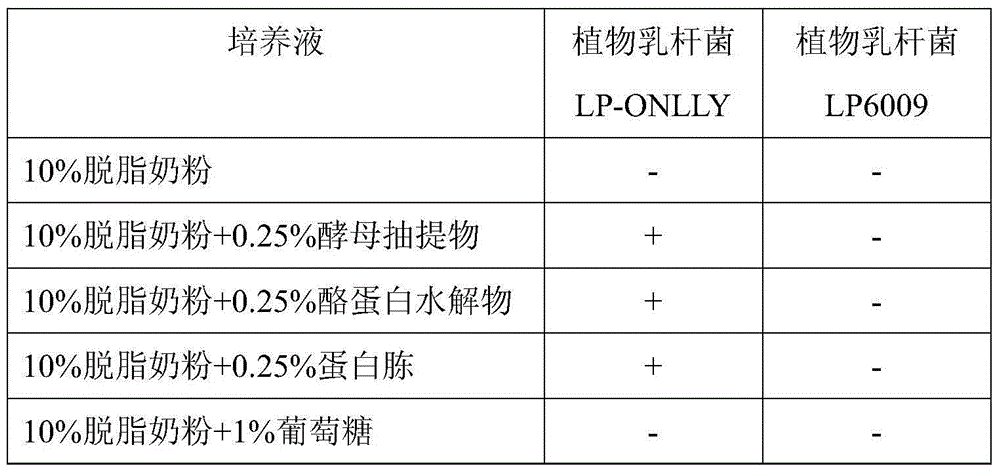
Lactobacillus plantarum (LP-ONLLY) and application thereof in active fermented milk
ActiveCN104531587AFunction healthyHigh aminopeptidase activityMilk preparationBacteriaMicroorganismAlglucerase
The invention discloses a lactobacillus plantarum (LP-ONLLY) and the application thereof in active fermented milk. The LP-ONLLY is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on December 6, 2004, and the preservation register number is CGMCC NO.1258. The LP-ONLLY has the high aminopeptidase activity, high beta-galactosidase activity and high glucosidase activity, and frozen and dried living bacterium powder is used as an independent leavening agent which can be applied for preparation of the active fermented milk. The active fermented milk contains the high probiotics live bacteria, the live bacteria have the high stability and can supplement probiotics, and the health function of the LP-ONLLY is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAODA ONLLY CO LTD +1
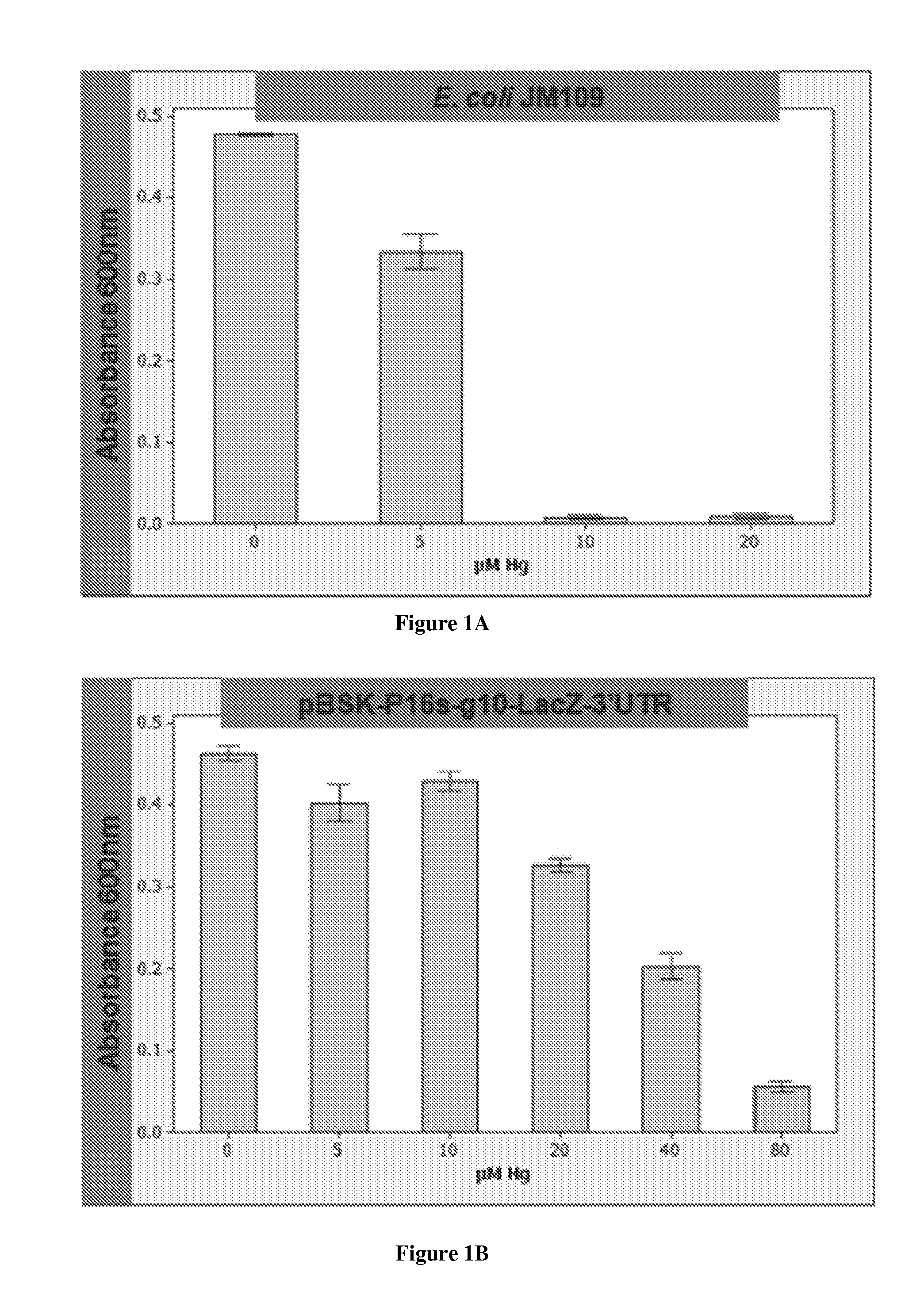
Heavy metal remediation system
InactiveUS20110220570A1Easy to moveReduce capacityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHeavy metal chelationBacteriophage
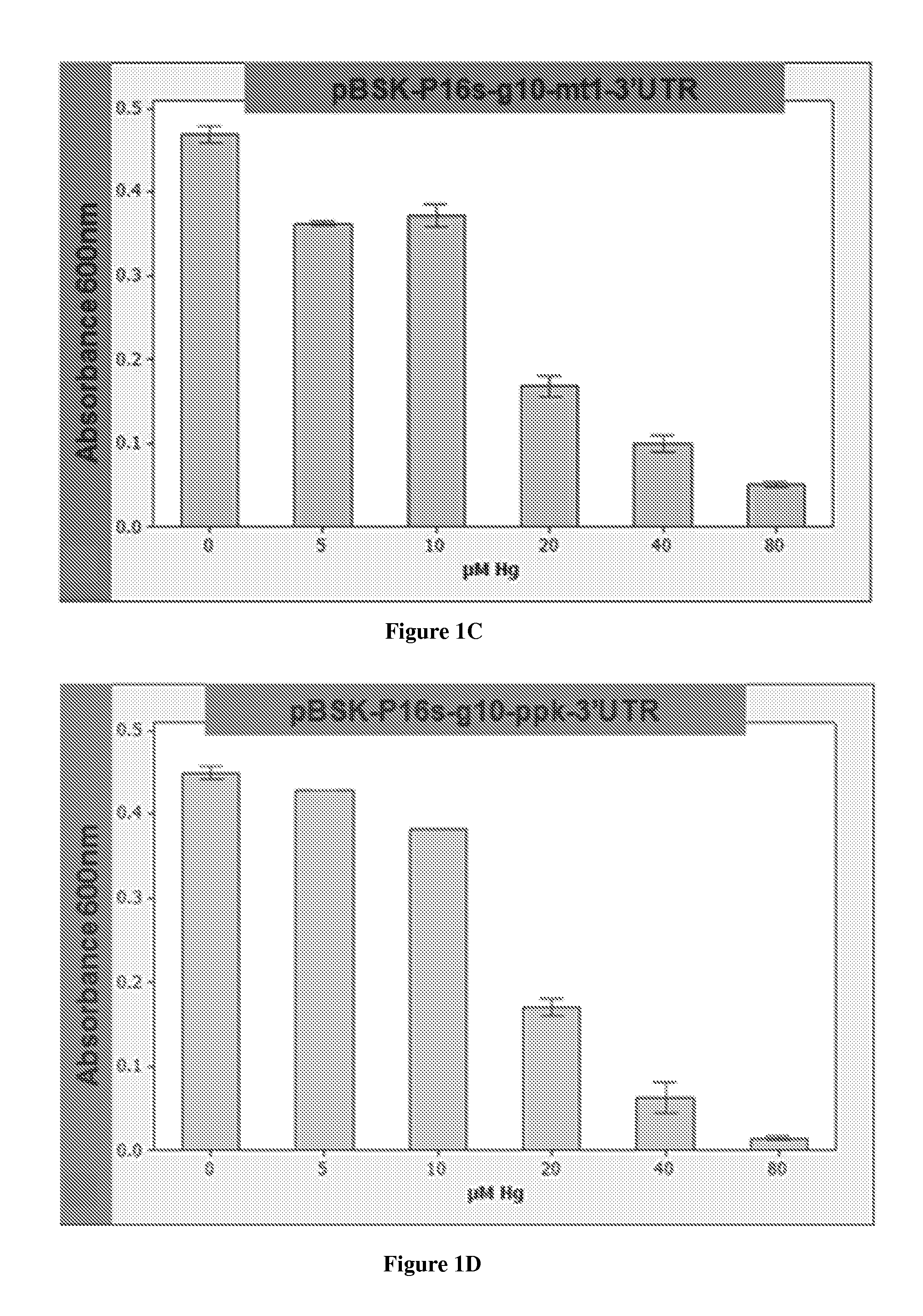
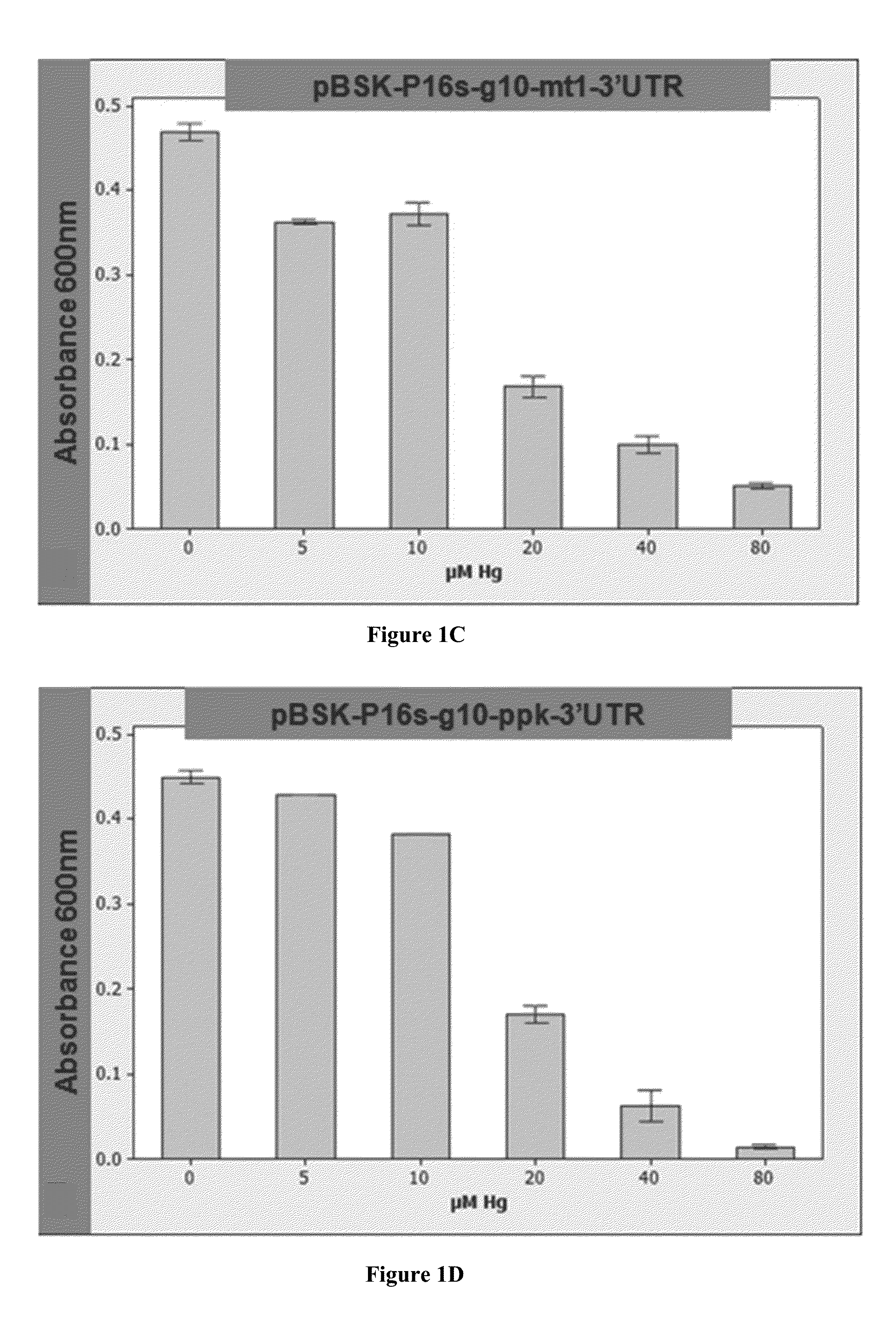
The invention provides a system of heavy metal sequestration by bacteria. The bacteria expresses the ppk, mt, and / or β-galactosidase (lacZ) genes and can tolerate at least 25 μM mercury, 1,000 μM zinc, 250 μM cadmium, and 3,000 μM Pb. The system allows for facile determination of the presence of heavy metal contaminants in a liquid and the facile collection of the bacteria that has sequestered large amounts of heavy metal. Further provided is a system of gene expression in bacteria that comprises phage and plastid gene expression elements and delivers a particularly high level of protein expression and heavy metal resistance.
Owner:INTER AMERICAN UNIV OF PUERTO RICO
Synthesis and applications of beta-galactosidase sensor with aggregation induced emission enhancement performance
ActiveCN106243170AOvercoming easy bleachingOvercoming detectionSugar derivativesFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh concentrationQuantum yield
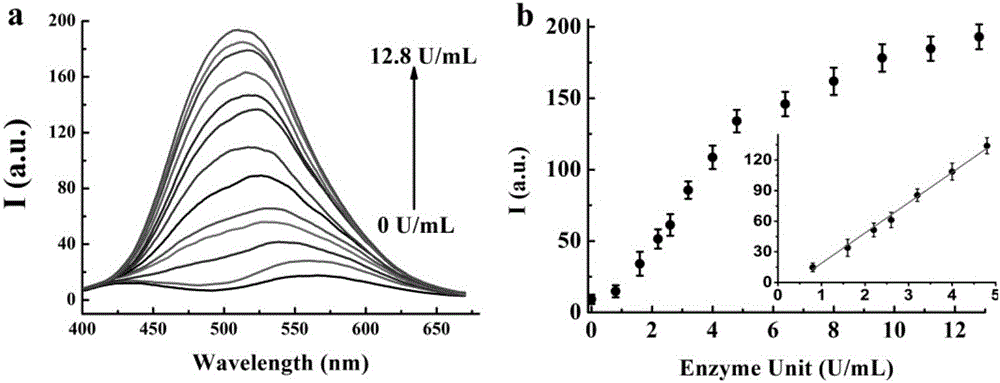
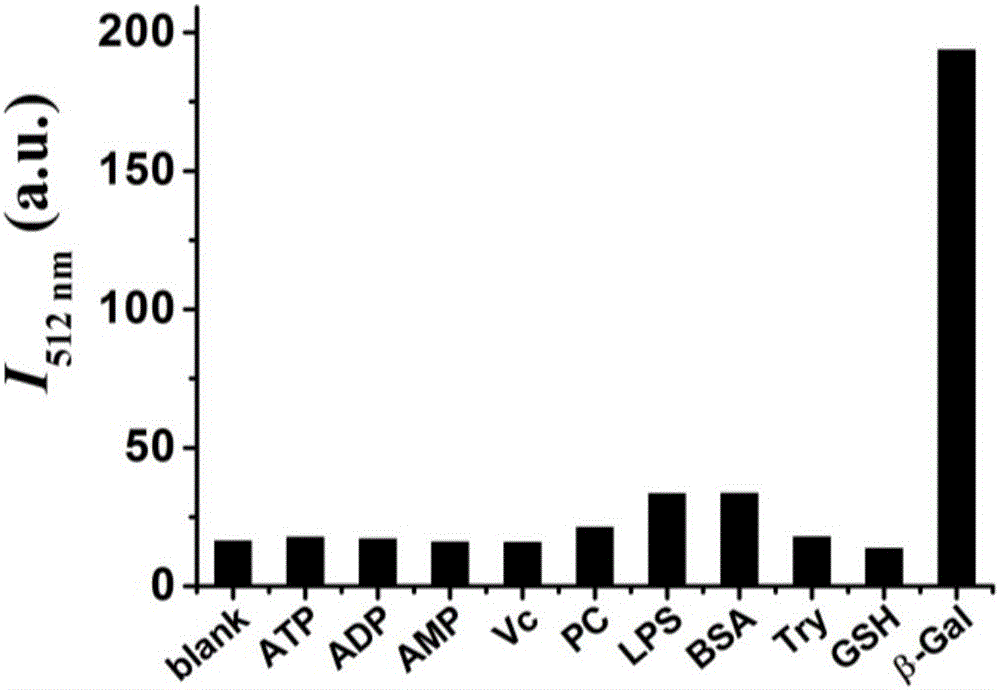
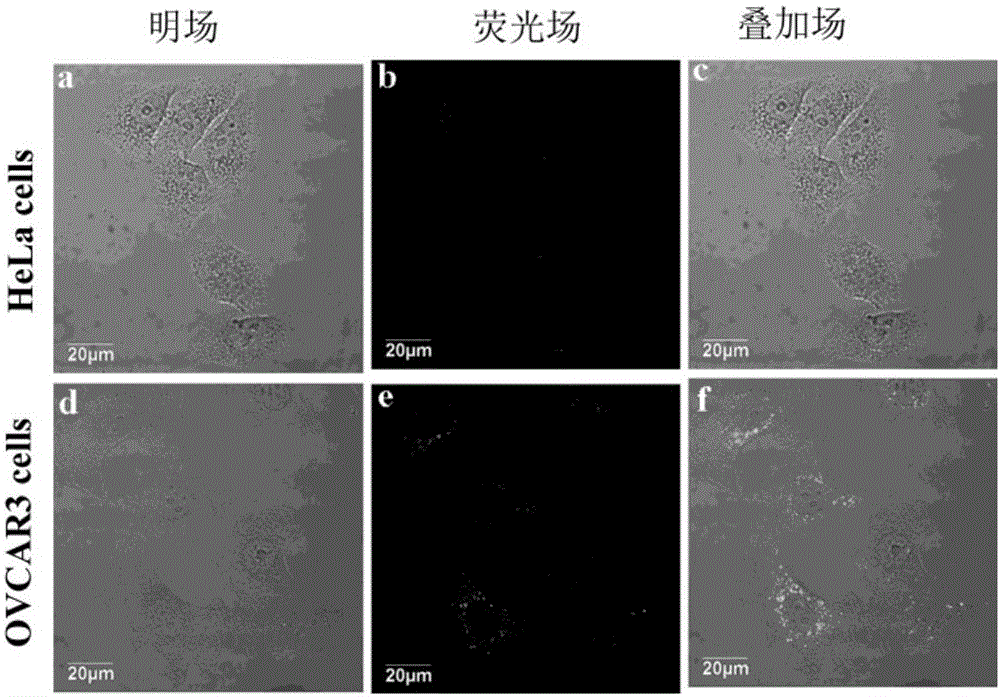
The invention relates to a beta-galactosidase sensor with aggregation induced emission enhancement performance, and a synthesis method and applications of the beta-galactosidase sensor. According to the synthesis method, a diphenyl ketone derivative is taken as a starting material to synthesize a target compound 1. Detection study of the target compound 1 on beta-galactosidase is carried out, and it is found that the target compound 1 possesses high sensitivity and selectivity in beta-galactosidase detection. Compared with the prior art, the synthesis raw materials are easily available, target compound fluorescence quantum yield is high, and photobleaching resistance is excellent, a defect of conventional fluorescent dyes that detection at a high concentration is difficult to realize is avoided, the target compound 1 is successively applied to fluorescence imaging of beta-galactosidase in OVCAR3, and application prospect of the target compound 1 in detection of content of beta-galactosidase in cells is promising.
Owner:GANNAN NORMAL UNIV
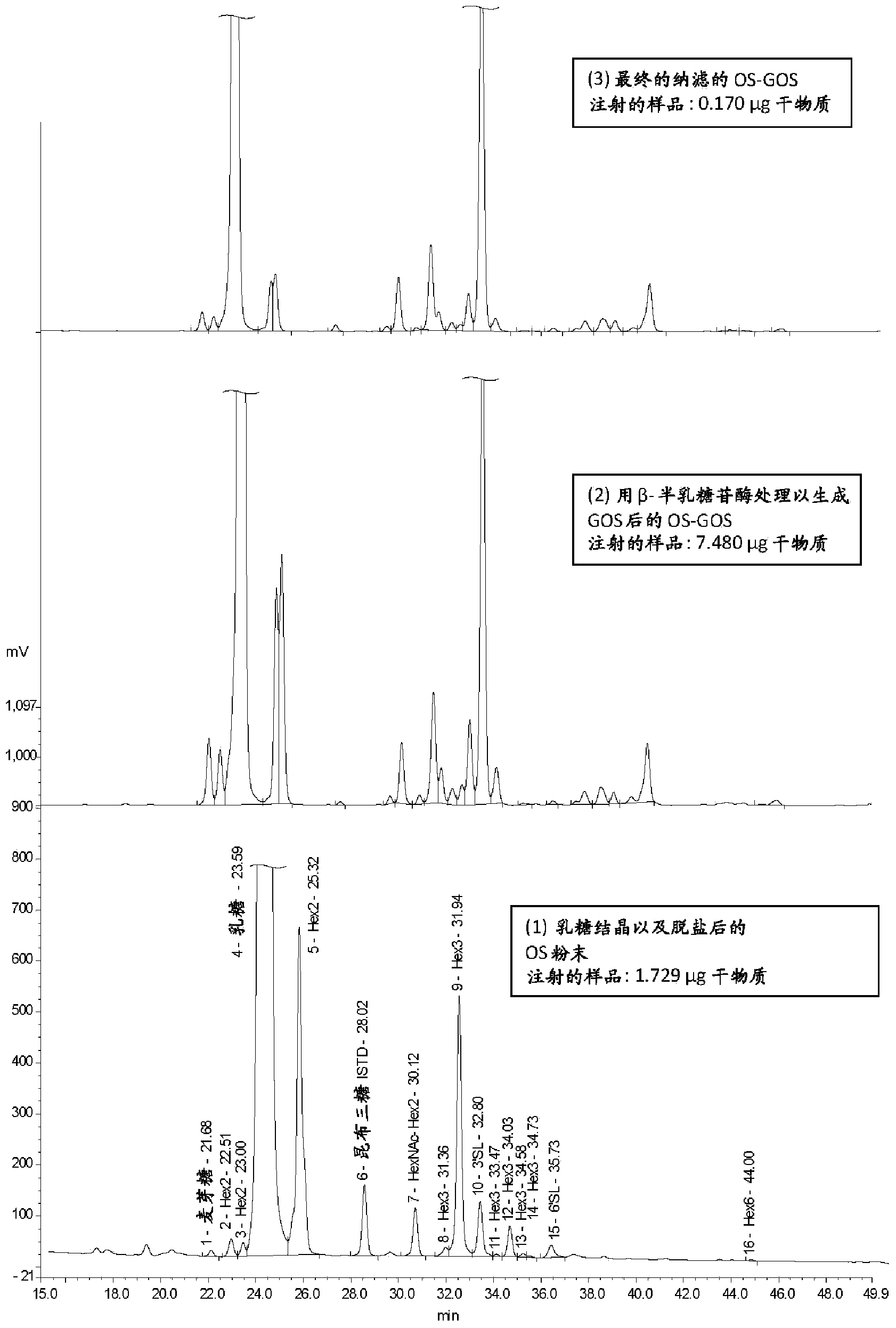
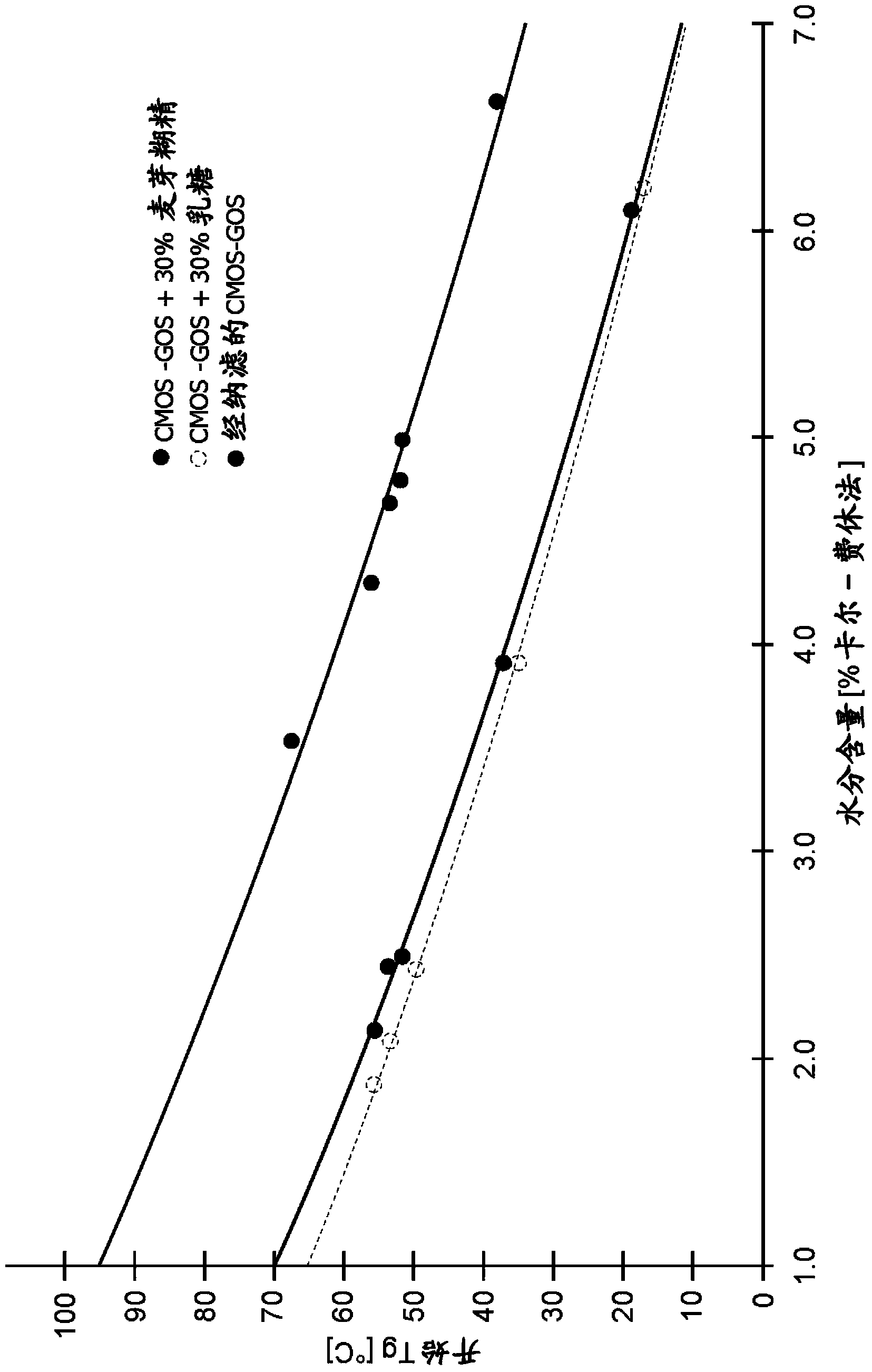
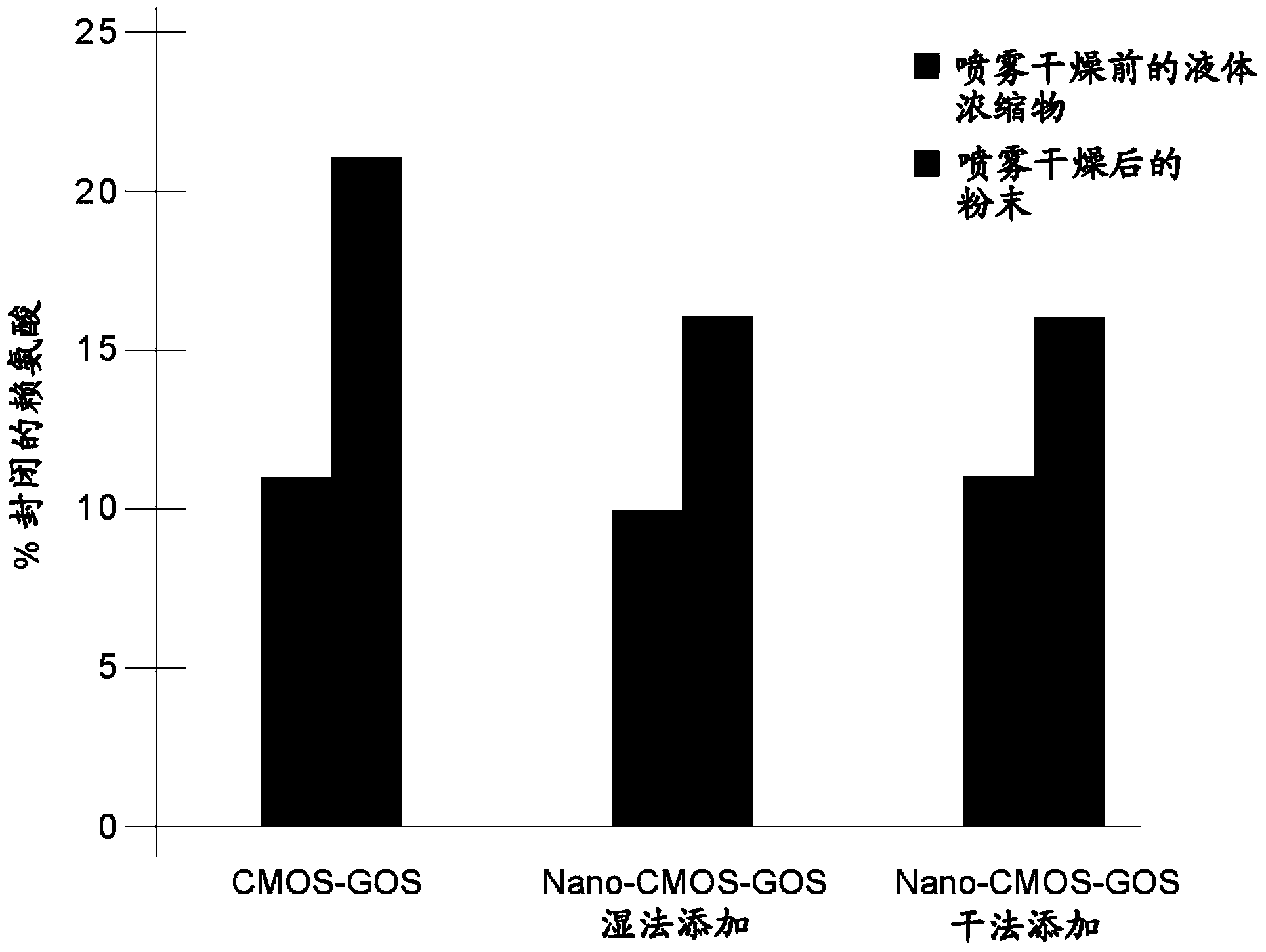
Milk oligosaccharide-galactooligosaccharide composition for infant formula containing the soluble oligosaccharide fraction present in milk, and having a low level of monosaccharides, and a process to produce the composition
InactiveCN103547173AAvoid smallEasy to produceOrganic active ingredientsOther dairy technologySpray driedLactose
The invention discloses an oligosaccharide mixture derived from cow's milk that can be easily spray dried comprising (a) a soluble oligosaccharide population which is the same as that of soluble oligosaccharides found in cow's milk and (b) ²-galactooligosaccharides formed by the action of ²-galacotsidase on lactose and the milk oligosaccharides. The mixture having a total monosaccharide content of less than 5% w / v and a lactose:oligosaccharide ratio of less than 20. A process for obtaining such a mixture, which includes a nanofiltration step, is disclosed. Nutritional compositions, especially infant formula, comprising said oligosaccharide mixture are also disclosed.
Owner:NESTEC SA
Wild-Type Receptor Assays
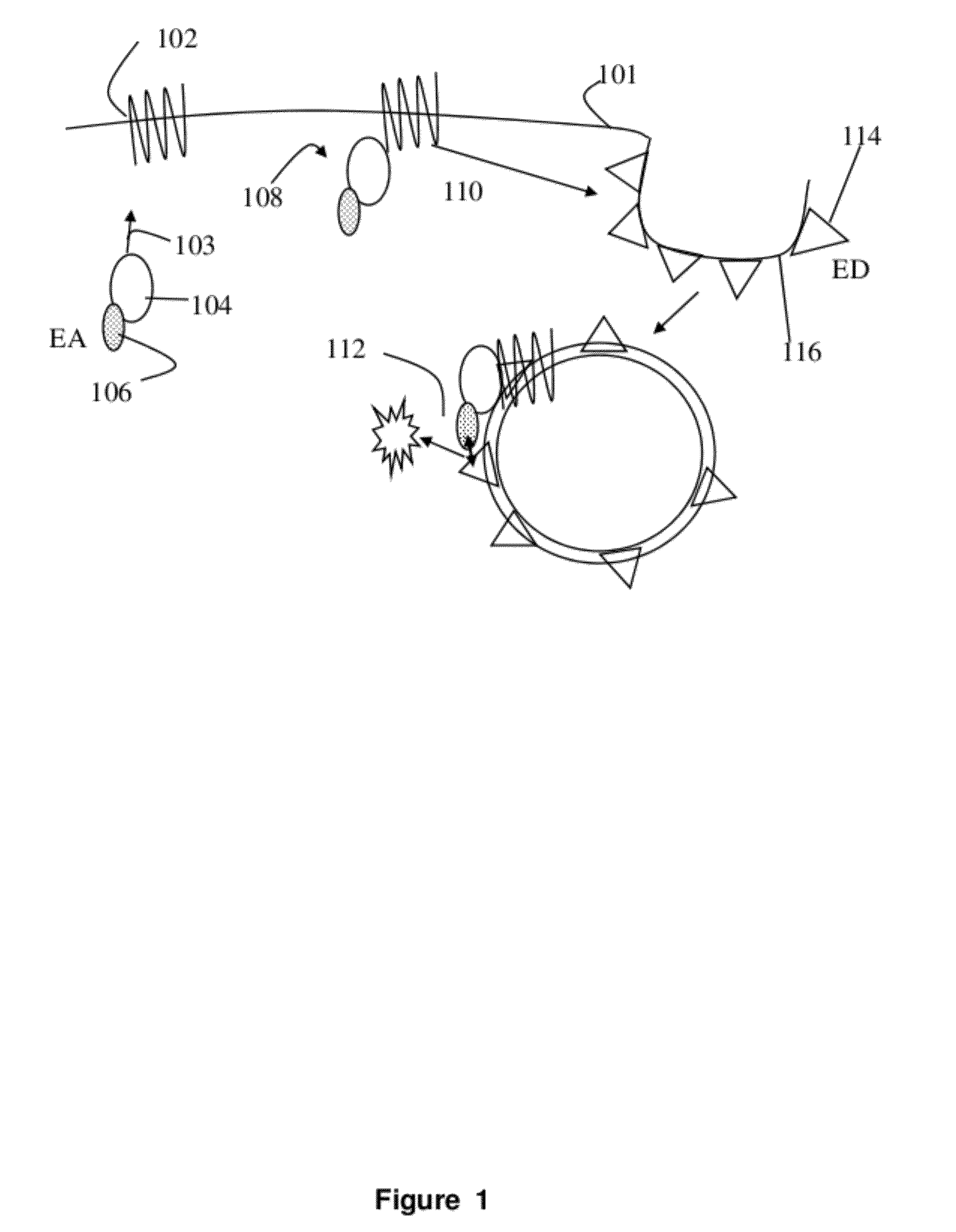
A method for determining ligand activation of receptors using cells expressing genetic constructs of a fusion protein of at least a binding domain of an auxiliary protein and a fragment of β-galactosidase, a fusion protein of an endosome-associated protein and a complementary fragment of β-galactosidase, and a wild-type receptor. The receptors are characterized by binding to the auxiliary protein-binding domain upon activation by an agonist and then endocytosing associated with an endosome to which the endosome-associated protein binds. Cells are incubated with a candidate ligand followed by lysis with a lysing medium comprising a substrate for the β-galactosidase. The enzyme product is then detected as a measure of the activation of the receptor.
Owner:DISCOVERYX CORP
GPCR Arrestin Assays
InactiveUS20100120063A1Improve bindingEnhance arrestin bindingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisSmall fragmentLarge fragment
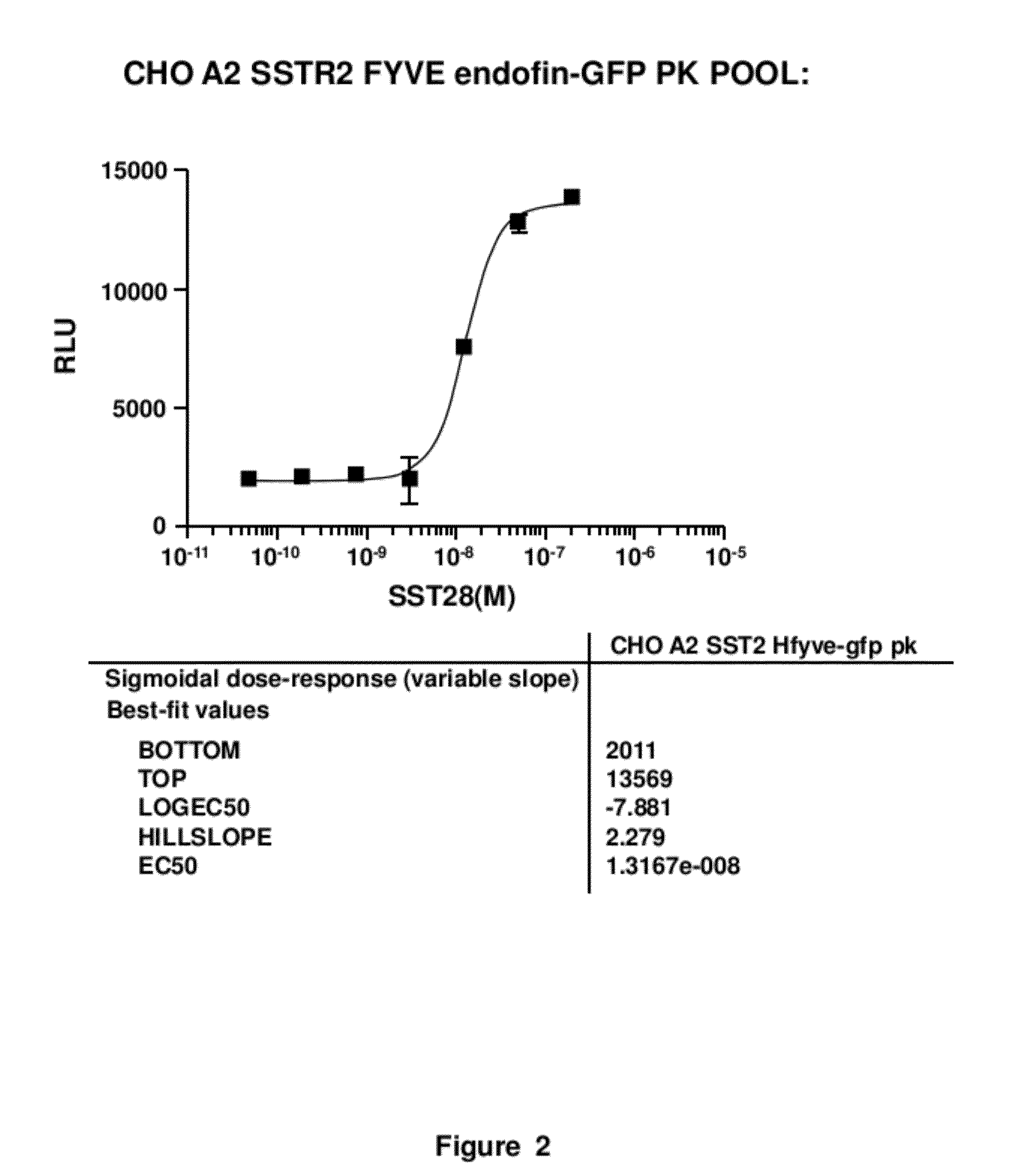
Sensitive assays for candidate compounds affecting GPCR activity are provided using a cell containing fusion proteins comprising a first fusion protein comprising (a) a target GPCR fused to a small fragment of β-galactosidase through a linker comprising a phosphorylation site or (b) a GPCR or a protein of interest, where the GPCR and protein of interest form a complex and one of them is fused to the small fragment of β-galactosidase; and a second fusion protein comprising arrestin fused to a large fragment of β-galactosidase. In (a), the affinity of the small and large fragments is optimized based on the background to signal ratio and the absolute signal observed. The assay is performed using a β-galactosidase substrate that provides a detectable optical signal.
Owner:DISCOVERYX CORP
Detection of molecular interactions by reporter subunit complementation
InactiveUS7223537B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with DNA-binding domainMutantAntagonist
Methods and compositions for detecting molecular interactions, particularly protein-protein interactions, are provided. The invention allows detection of such interactions in living cells or in vitro. Detection of molecular interactions in living cells is not limited to the nuclear compartment, but can be accomplished in the cytoplasm, cell surface, organelles, or between these entities. In one embodiment, the method utilizes novel compositions comprising fusion proteins between the molecules of interest and two or more inactive, weakly-complementing β-galactosidase mutants. Association between the molecules of interest brings the complementing β-galactosidase mutants into proximity so that complementation occurs and active β-galactosidase is produced. The active β-galactosidase may be detected by methods well-known in the art. Among the uses of the invention are the study of protein-protein interactions, functional genomics, agonist and antagonist screening and drug discovery.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for detecting quorum sensing quenching bacterial strain
ActiveCN103215342AImprove accuracyImprove targetingMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBeta-galactosidase activityN-Acyl homoserine lactone
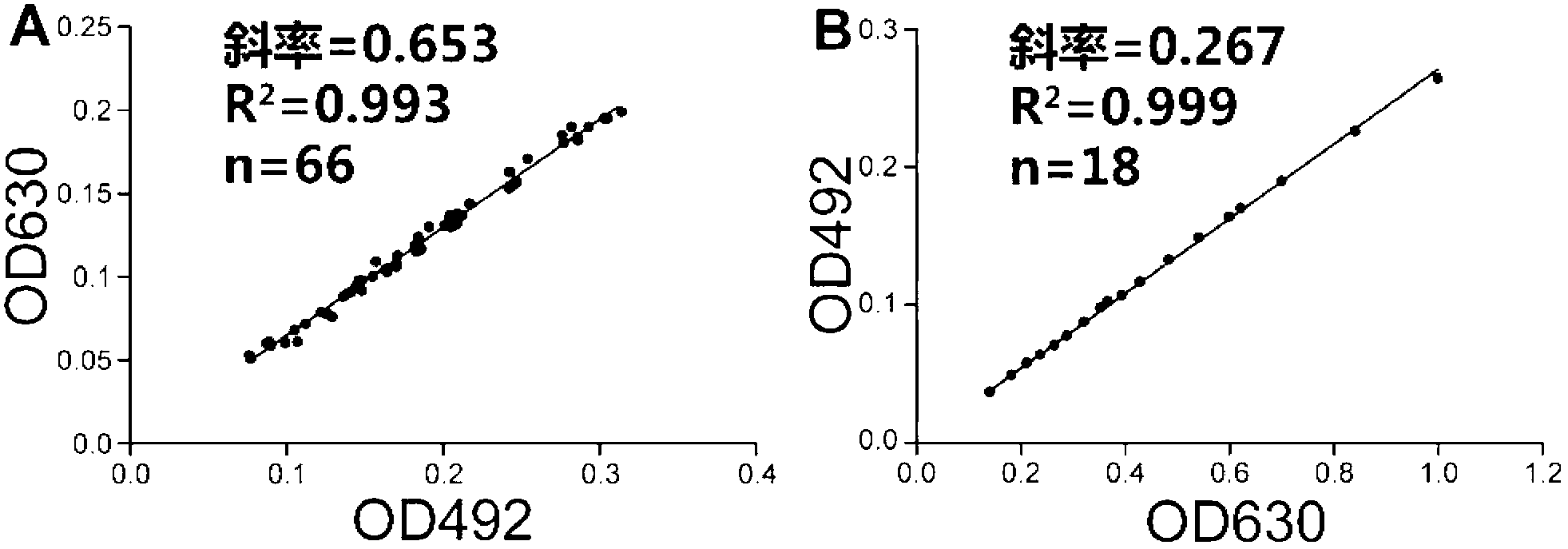
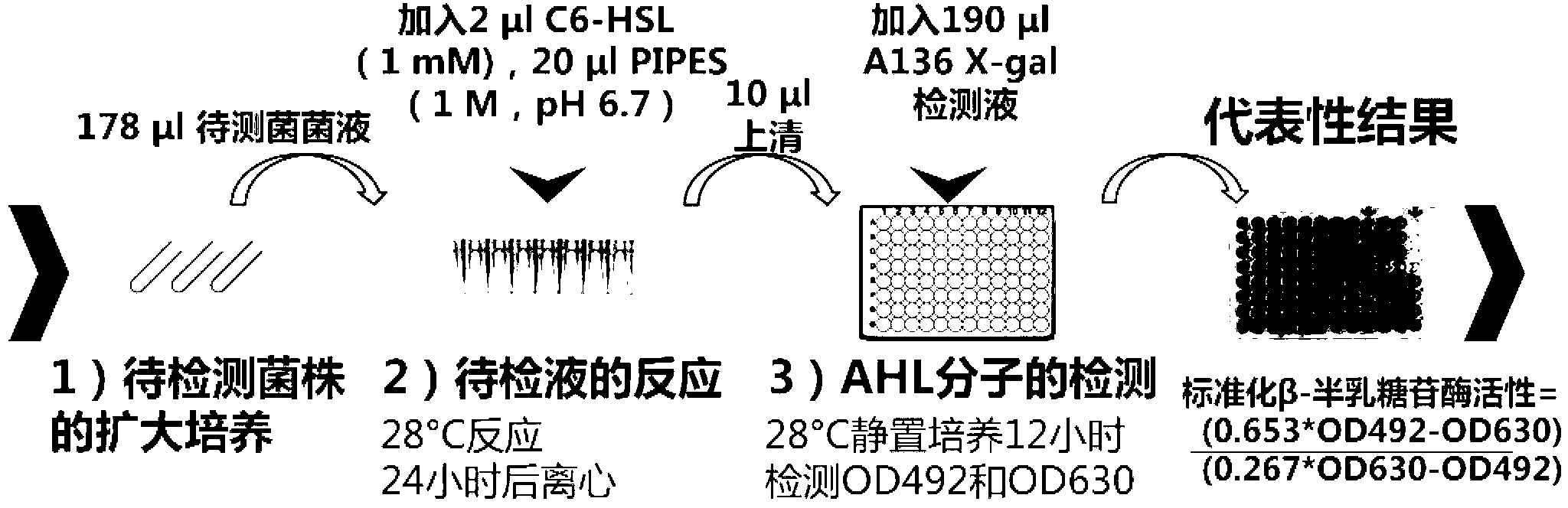
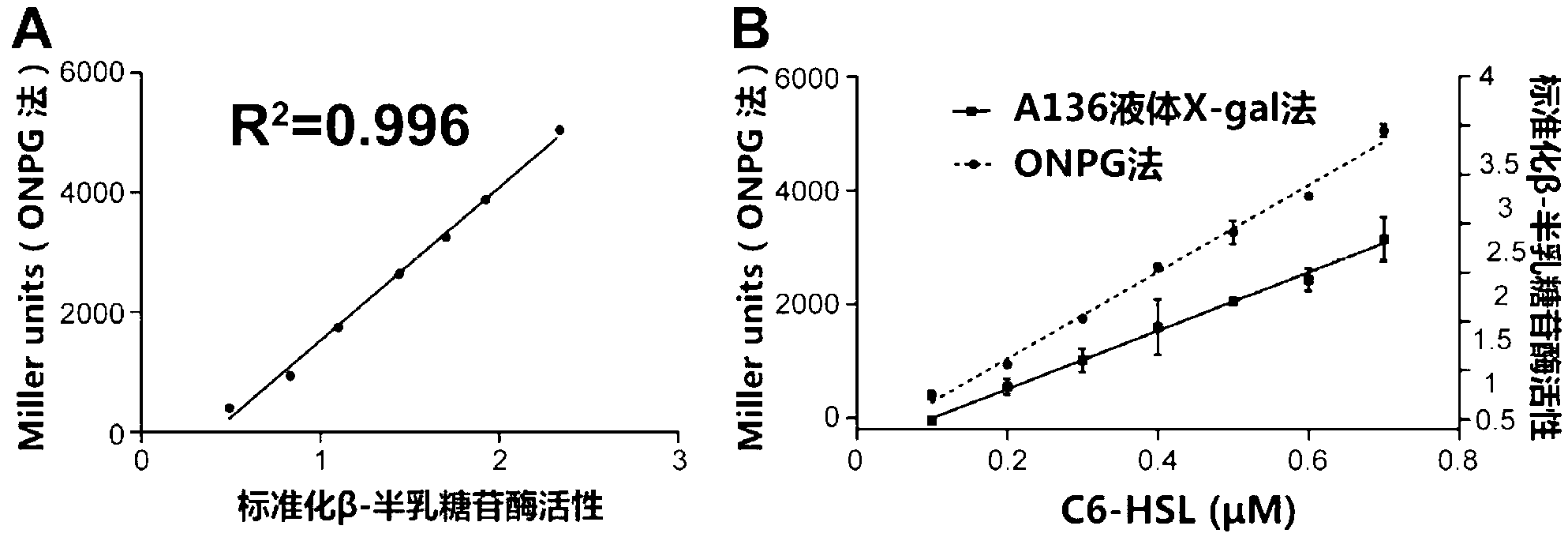
The invention relates to a method for detecting a quorum sensing quenching bacterial strain. The method comprises the steps of: adding a bacterial strain to be detected in a PIPES (1,4-piperazinediethanesulfonic acid) buffer solution with a pH value of 6.7 to prepare a solution to be detected, wherein AHL (N-acyl Homoserine Lactone) is dissolved in the PIPES buffer solution, then enabling supernatant of the solution to be detected to react with a bacterial solution of A.tumefaciens A136 added with X-gal; after the reaction is ended, detecting OD492 and OD630 (Optical Density) values of a reaction solution, and calculating a standardized beta-galactosidase activity value through a formula of (0.653*OD492-OD630) / (0.267*OD630-OD492), and carrying out different significance analysis through comparing the standardized beta-galactosidase activity value, and finally, determining whether the bacterial strain to be detected is a quorum sensing quenching bacterial strain. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of being simple and rapid, being high in sensitivity, achieving high throughput detection, eliminating most of false positive bacterial strains, and being capable of effectively determining whether the bacterial strain to be detected is the quorum sensing quenching bacterial strain, thereby remarkably improving the accuracy and the pertinence of screening the quorum sensing quenching bacterial strain and saving the time and labor cost.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Genetically engineered virus of Chinese ballworm
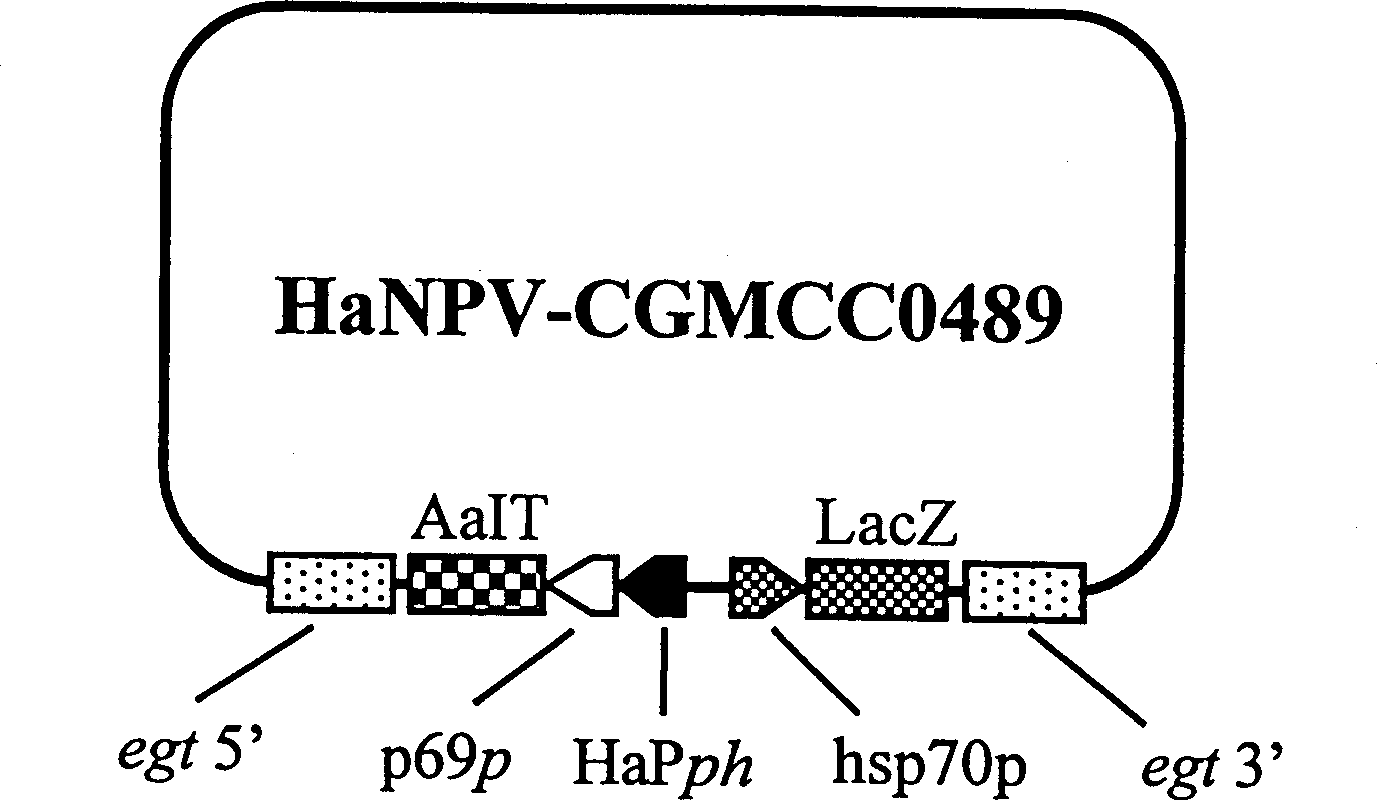
InactiveCN1109105CFast insecticideGood field application effectBiocideViruses/bacteriophagesWild typeEngineered genetic
A genetically engineered virus of Chinese ballworm is obtained by double recombination of wild virus. Its genome is deficient is egt gene. At the position deficient in egt gene, the insect-specific neurotoxic AaIT gene controlled by the promoters of Chinese ballworm virus' alkaline DNA binding protein gene (p6.9) and polyhedrin protein gene (ph) and the beta-galactosidase (LacZ) gene controlled by the promoter of heat shock protein gene (hsp70) are inserted. Its advantages are higher insecticiding speed and better application effect.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Genes coding for tomato beta-galactosidase polypeptides
A novel beta -galactosidase gene family and DNA sequences derived from the cloning of cDNAs encoding products of these genes are provided, as exemplified by a beta -galactosidase II protein which is encoded by a cDNA clone, pZBG2-1-4. A method for modifying cell wall metabolism which involves modifying the activity of at least one beta -galactosidase, and thus modifying the quality of the fruit is also provided. Also provided by the present invention is a DNA construct including some or all of a beta -galactosidase DNA sequence under control of a transcriptional initiation region operative in plants, so that the construct can generate RNA and, optionally, beta -galactosidase polypeptide in plant cells. The present invention also relates to recombinant vectors, which include the isolated nucleic acid molecules of the present invention, and to host cells containing the recombinant vectors, as well as to methods of making such vectors and host cells and for using them for production of beta -galactosidase polypeptides or peptides by recombinant techniques. The present invention also provides plant cells containing DNA constructs of the present invention; plants derived therefrom having modified beta -galactosidase gene expression; and seeds produced from such plants.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
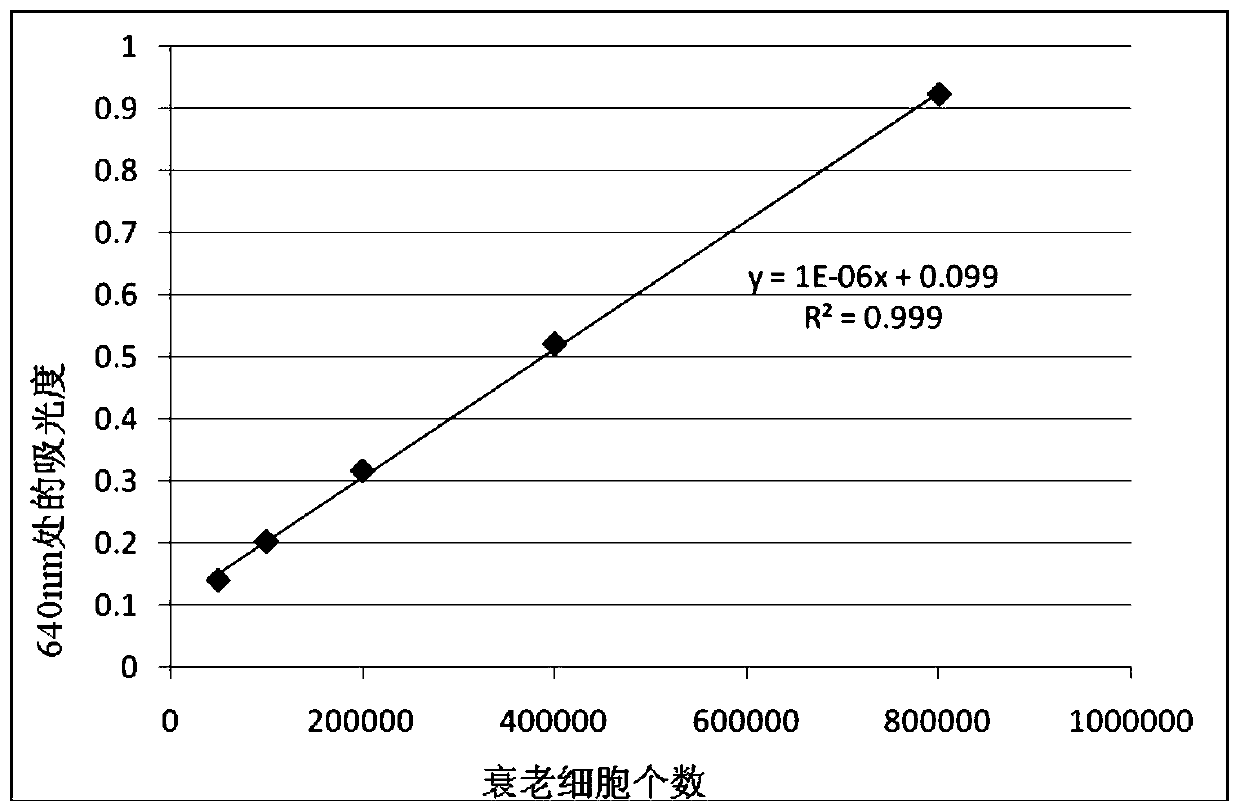
Rapid quantitative senescence cell detection method based on senescence-associated beta-galactosidase
ActiveCN109797192AReduce exposureReduce stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementSenescence-associated beta-galactosidasePhosphate
The invention discloses a rapid quantitative senescence cell detection method based on senescence-associated beta-galactosidase. Culture solution is discarded from in-vitro cultured adherent cells, the adherent cells are cleaned by PBS (phosphate buffer solution), staining solution is added, the adherent cells are placed into a 37 DEG C carbon-dioxide-free incubator, all the staining solution is transferred into a centrifugal tube after staining and then discarded after centrifugation, a blue product is cleaned by the PBS, DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide) is added to dissolve the blue product, the blue product is centrifuged, supernatant is taken, the absorbance of the solution at a 640nm position is measured, a standard curve between the number of senescence cells and the absorbance is built bythe same method, and the number of the senescence cells of a test sample can be known according to the standard curve after the absorbance is measured. The method has the advantages of high reproducibility and reliability, strong objectivity, fewer influence factors, high speed and the like, and animal and human senescence cells can be rapidly quantified.
Owner:ANHUI GUJING DISTILLERY +1
Galactosidase and polynucleotide encoding galactosidase
InactiveCN103937767AHigh catalytic activityImprove utilization efficiencyFermentationGlycosylasesIntestinal structureNucleotide
The invention discloses beta-galactosidase (beta-D-galactosidase, EC3.2.1.23) cloned from metagenome of a thermal spring at the temperature of 65 DEG C in Eryuan in Dali as well as nucleotide encoding the galactosidase. The galactosidase has relatively high catalytic activity at the temperature of 37-55 DEG C, can serve as a lactose degradation and disaccharides synthesis catalyst and has polysaccharide and galactose residues stored in hydrolyzed organisms. In addition, the galactosidase has a glucoside transforming effect, and some functional oligosaccharides, such as galactooligosaccharide can be generated. The oligosaccharides are hardly digested by small intestines and are water-soluble dietary fibers which are low in molecular weight and not viscous. The oligosaccharides serve as multiplication factors of bifidobacterium species in intestines and only can be utilized by the bifidobacterium species, the multiplied bifidobacterium species are competitively antagonistic to growth of putrefying bacteria, the generated toxins and enzymes are reduced, and an effect of regulating intestinal tract is achieved.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
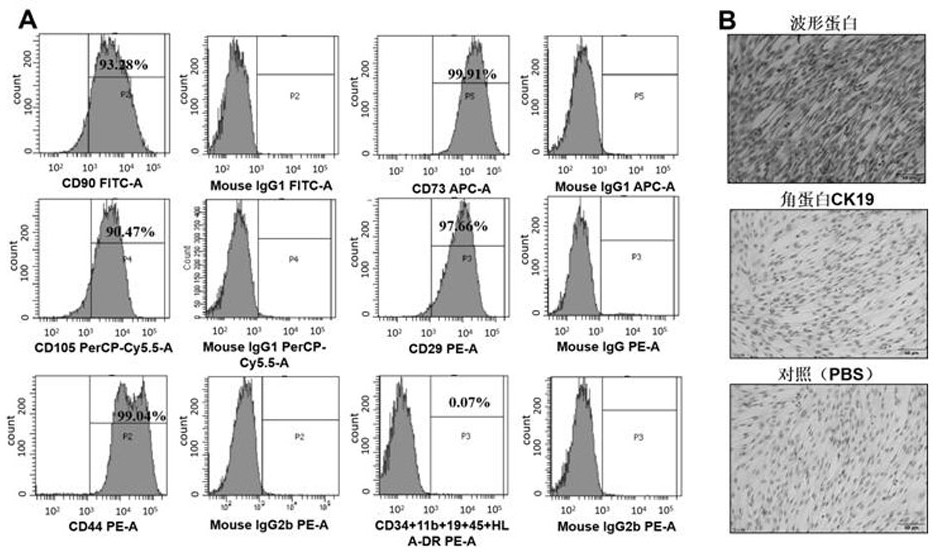
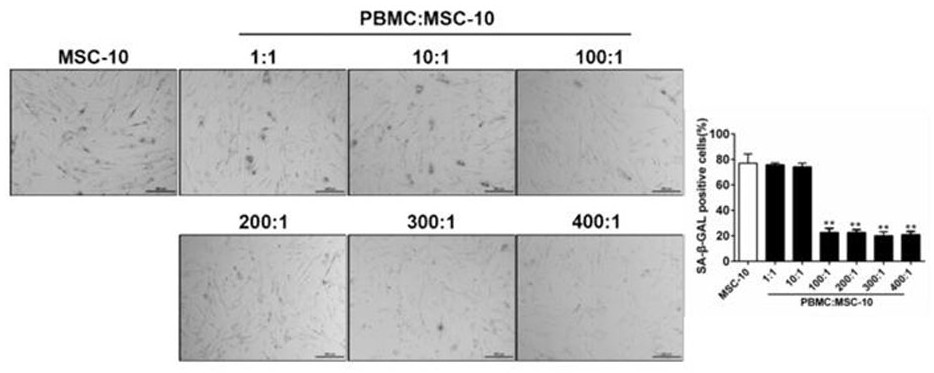
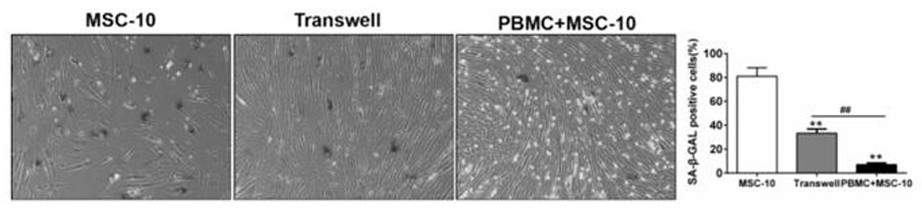
Method for resisting human mesenchymal stem cell aging and enhancing stem characteristics of human mesenchymal stem cells
ActiveCN111979187AReverse the signs of agingDelayed signs of agingDigestive systemUnknown materialsCellular AgingProliferative capacity
The invention discloses a method for resisting human mesenchymal stem cell aging and enhancing stem characteristics of human mesenchymal stem cells. According to the method, immune cells in human peripheral blood and aged human mesenchymal stem cells are cultured in a cell-to-cell contact mode, the aging characteristics of the aged human mesenchymal stem cells can be remarkably reversed, the expression of cell aging markers such as beta galactosidase, P21 and P16 proteins is reduced, and meanwhile, the cell cycle of the aged human mesenchymal stem cells can be obviously adjusted, specifically,the number of cells in the G1 stage is reduced, and the number of cells in the S stage is increased. More importantly, the method can remarkably enhance the stem characteristics of the aged human mesenchymal stem cells, such as self-renewal capacity, multiplication capacity and multi-directional differentiation potential, and the cells obtained by the culture mode are used for treating disease models and are safe and effective. The method can be directly applied to long-term in-vitro amplification of the human mesenchymal stem cells, the problem of cell aging in the amplification process is solved, the cell activity is recovered, and the clinical application effect is improved.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZUNYI UNIV
Prebiotic Composition and its Methods of Production
ActiveUS20180303857A1Efficient deliveryWell mixedCompounds screening/testingCompound screeningCell culture mediaBacterial strain
The present invention relates to a prebiotic composition comprising a galacto oligosaccharide (GOS) produced from Lactobacillus plantarum, wherein the GOS acts as a selective growth medium for a chosen Lactobacillus plantarum probiotic bacterial strain, and wherein the GOS is substantially the same as the form produced by reverse β-galactosidase reaction in the chosen probiotic bacterial strain. The present invention also relates to methods of producing GOS and related composition incorporating the GOS.
Owner:OPTIBIOTIX
Immunoassay detection method for neonicotinyl insecticides
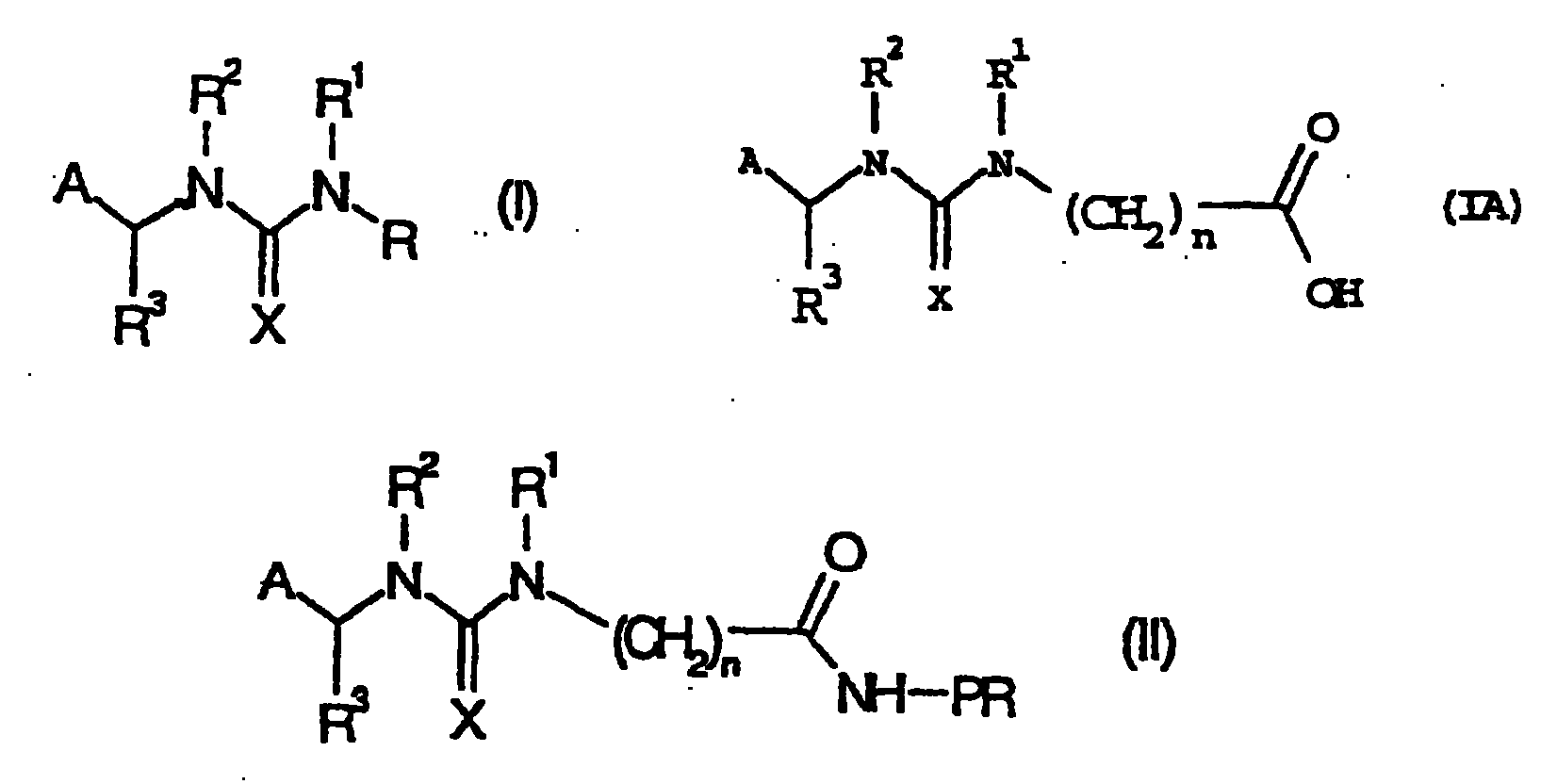
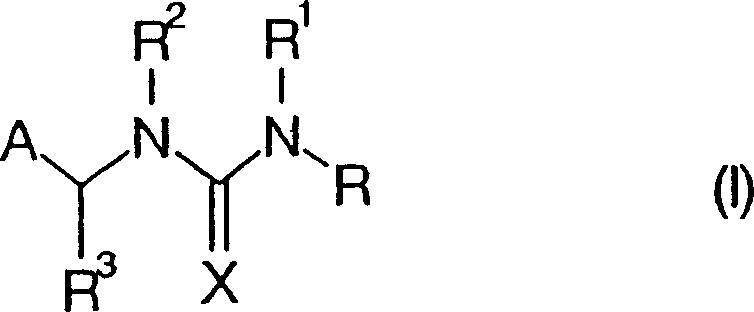
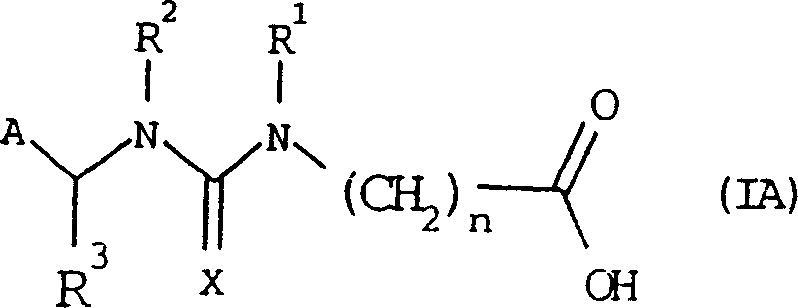
The present invention provides immunogens for generating anti-neonicotinoid antibodies as well as antibodies, methods, reagents, and kits for determining the presence of one or more neonicotinoid insecticides in a sample by immunoassay. The present invention has particular application to determination of the concentration of neonicotinoid insecticides applied to a plant propagation materials such as seed, said antibody is selective for a compound of formula (I) wherein A is 2-chloropyrid-5-yl or 2-chlorothiazol-5-yl; R and R<3> independently are hydrogen or C1-C4alkyl; R<1> and R<2> independently are hydrogen or C1-C4alkyl or R<1> and R<2> are taken together with the nitrogen atoms to which they are attached to form an imidazoline or an oxadiazine ring; and X is N-NO2 or N-CN. Also claimed is a compound of formula (IA) and protein conjugate of formula (II) in which PR is a protein residue of a carrier molecule selected from the group consisting of a purified protein derivative (PPD, Tuberculin) from Diptheria virus, bovine serum albumin, cationized bovine serum albumin, human serum albumin, ovalbumin and keyhole limpet hemocyanin; or an enzyme residue selected from the group consisting of alkaline phosphatase, horseradish peroxidase, and beta -galactosidase.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Transformant for screening of inhibitors for human immunodeficiency virus
InactiveUS7033596B1Conducive to screeningSimple methodFungiBacteriaMicroorganismImmunodeficiency virus
A microorganism cotransformed with a gene expressing HIV nucleocapsid protein and a plasmid vector containing HIV ψ gene and β-galactosidase reporter gene, and a method for screening HIV inhibitors employing the transformant. The invented method comprising the steps of culturing the transformant, treating it with putative compounds or compositions of HIV inhibitors, and measuring the degree of change in β-galactosidase expression in the culture, can be practically applied in screening HIV packaging inhibitors by which the interaction between HIV nucleocapsid and HIV ψ sequence is blocked.
Owner:YOU JI CHANG
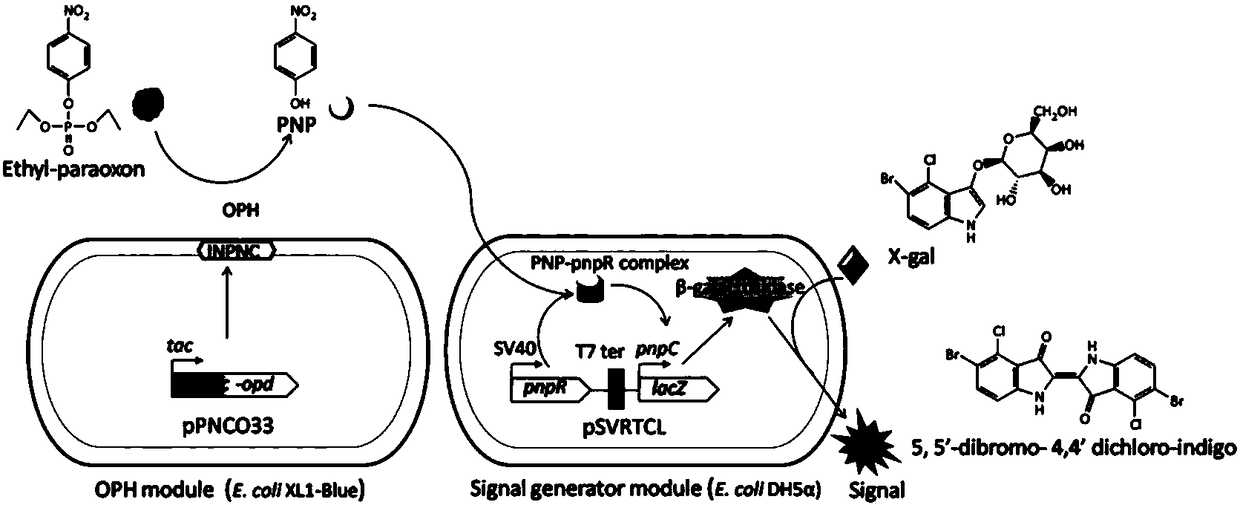
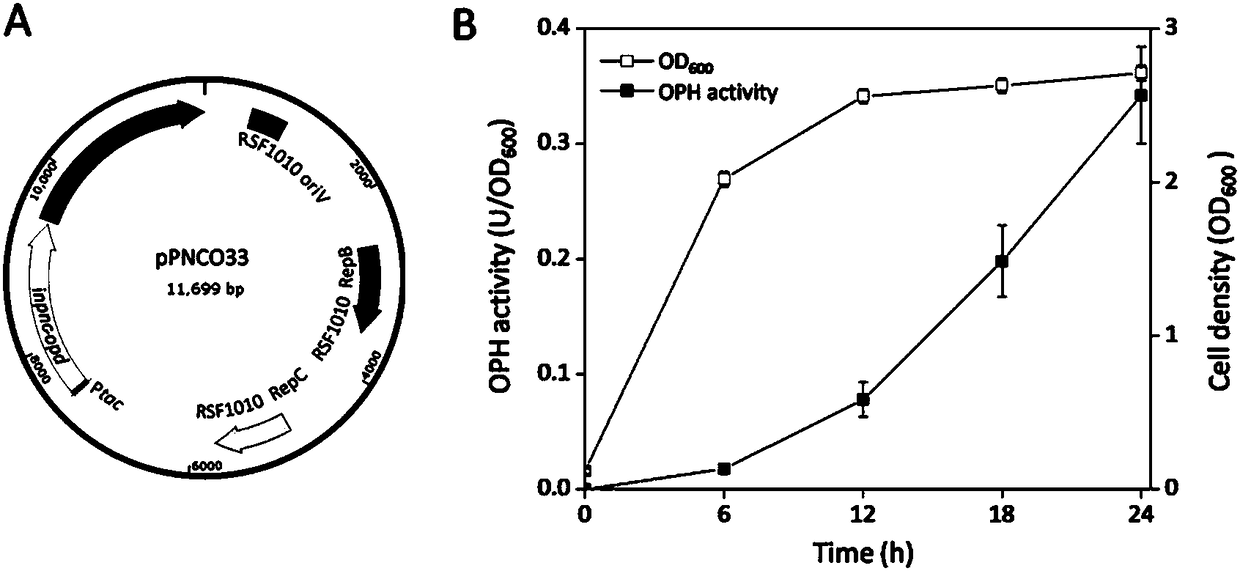
Method for detecting organophosphorus pesticide by flora-based sensing system
ActiveCN108486024ALow detection limitIncreased sensitivityBacteriaHydrolasesGenetic engineeringBiology
The invention provides a method for detecting an organophosphorus pesticide (OP) by a flora-based sensing system. The sensing system comprises an OPH signal sensing module and a genetic engineering flora containing a signal generating module. One of the modules is used to hydrolyze OPs into p-nitrophenol (PNP), and the other one converts a PNP signal into beta-galactosidase generation for colorimetric detection. Through optimization, the sensing system can detect ethyl paraoxon at a concentration of 1*10<-9>M within 3.5 hours of induction at 28 DEG C, and is about 200 times more sensitive thana single-cell whole-cell sensor. In addition, the sensing system can detect various types of OPs commonly used in agriculture. Besides, the sensing system can be prepared into filter paper for detection of organophosphorus pesticides, showing the prospect of portable on-site detection. The invention provides a sensitive, fast and portable biological sensing platform for pollutant detection, and also shows a practical novel environmental application of an engineering microbial ecosystem.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
A kind of Lactobacillus plantarum cz401 strain producing exopolysaccharide and β-galactosidase and its application
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
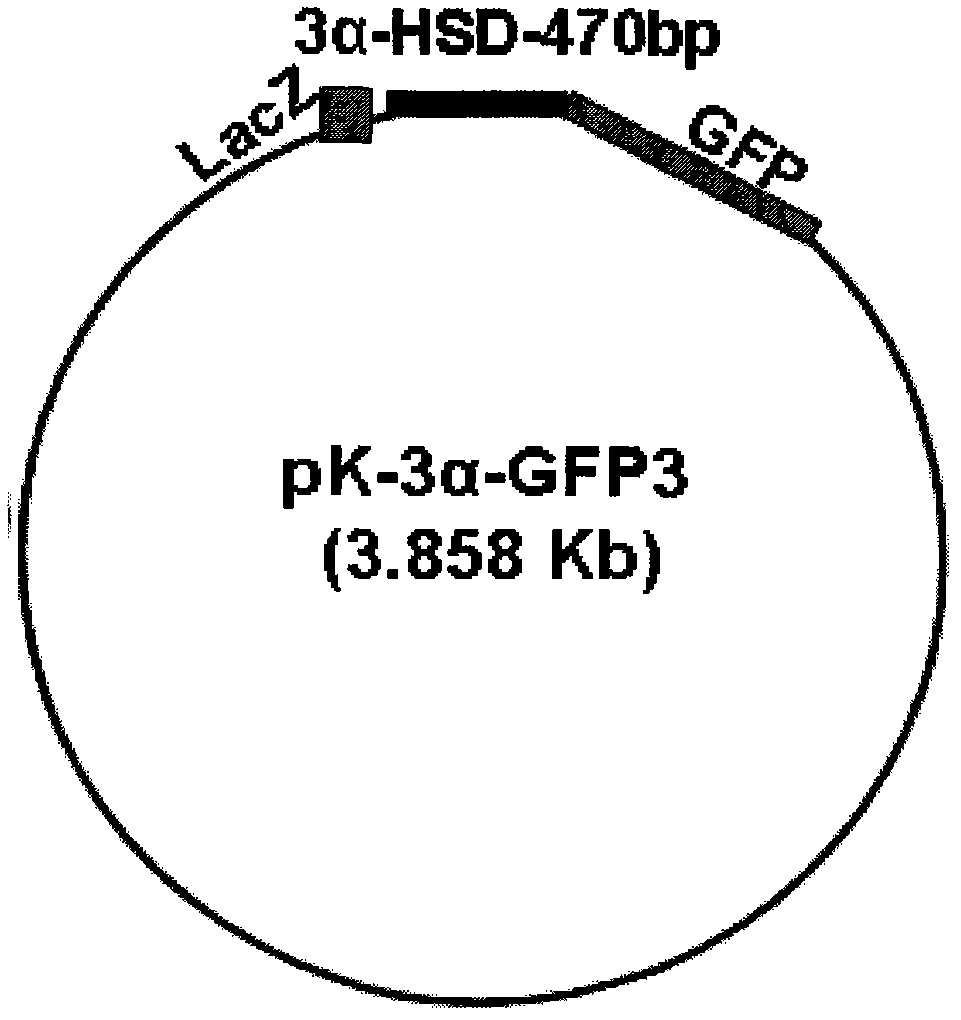
Anabolic steroids and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon high-efficiency bioluminescence sensor and construction method thereof
InactiveCN102128938AWide detection linear rangeSimple technical operationBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceAnabolic steroidFluorescence
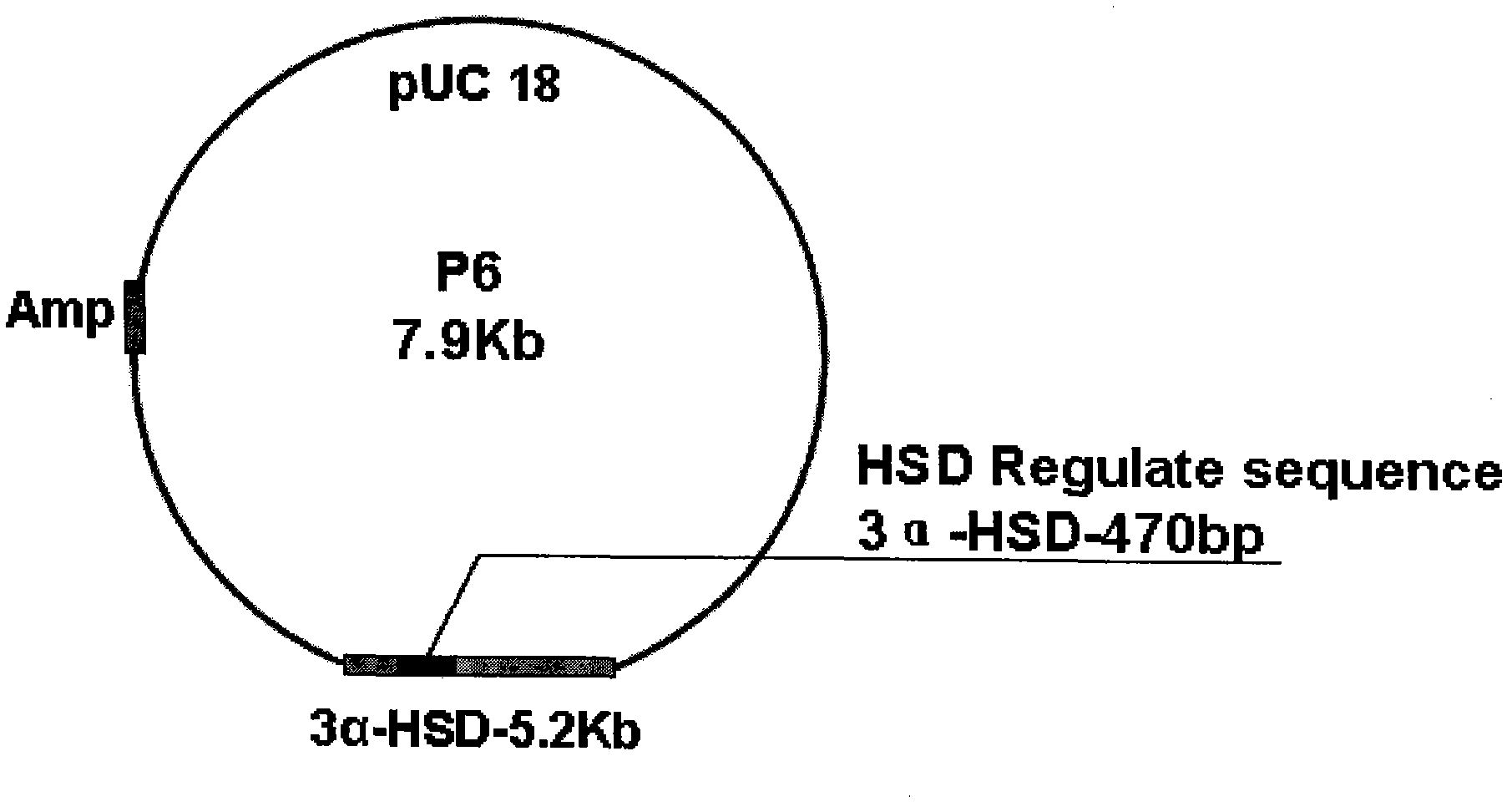
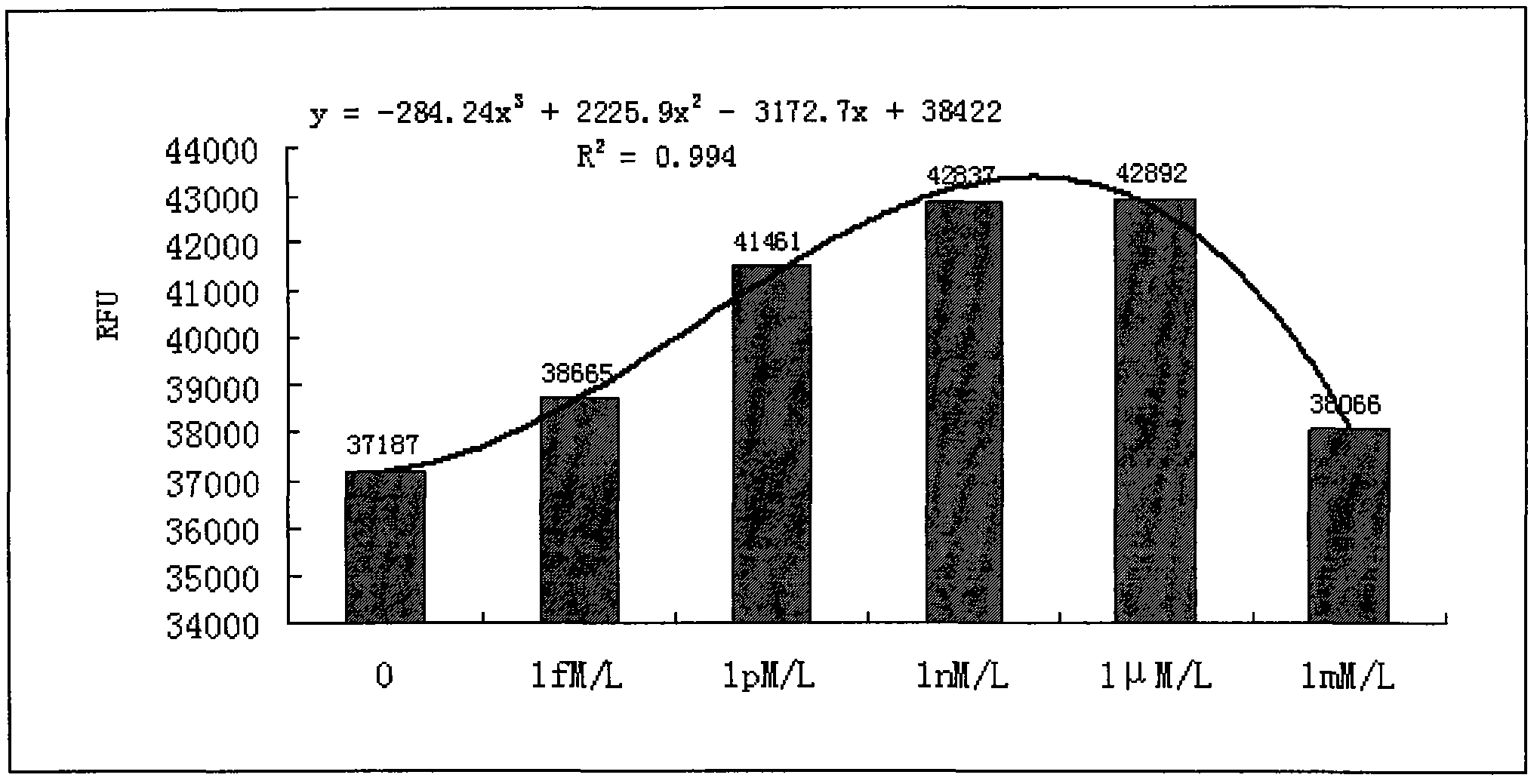
The invention relates to an anabolic steroids and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon high-efficiency bioluminescence sensor, belonging to the technical field of molecular biology; the bioluminescence sensor is characterized in that plasmids pK-3[alpha]-GFP3 and p6 are respectively transformed into colibacillus and respectively prepared into cell-free system testing agent; 3[alpha]-HSD promoters suchas regulatory sequence 486 base pair and GFP reporter gene 722 base pair are inserted at the down stream of the cis-[belta]-galactosidase (LacZ) promoter gene of recombinant plasmid pK-3[alpha]-GFP3 in sequence; the regulatory sequence of 3[alpha]-HSD on p6 plasmid can be induced to express protein with regulatory function; the protein can promote the promoter on the plasmids pK-3[alpha]-GFP3 so as to express the GFP protein; at the moment, the expression quantity of the GFP is controlled by the quantity of induction substrate strictly. The bioluminescence sensor and the construction method thereof have the following benefits: aiming at the shortcomings of strict instrument requirement, long detection cycle, high cost, low sensitivity and single test piece in the existing testing system, the bioluminescence sensor and the construction method thereof have wide test linearity width, simple technical operation and low instrument requirement, and are applicable to popularize and apply to detect anabolic steroids and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollutant in the environment and food.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Sodium (ion) diagnosis/measuring reagent kit and sodium (ion) concentration determination method
InactiveCN101464355AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsEnzymatic ColorimetryAbsorbance
The invention relates to a kit for diagnosing / measuring sodium (ions) by utilizing the technologies of the enzymic colorimetry and the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. The invention further relates to a method, a principle and the composition and the components of a reagent for measuring the concentration of sodium (ions), and belongs to the technical field of medical / food / environmental inspection and measurement. The main components of the kit include a buffer solution, coenzyme, lactose, beta-galactosidase, glucose-6-phosphatase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and a stabilizer. Through mixing a sample and the reagent by a certain volume ratio, a series of enzymatic reactions occur, then the reactant is placed under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer, and the degree / velocity of the increase in absorbance at 340 nm of the dominant wavelength is detected, thereby measuring the concentration of sodium (ions).
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Methods For Processing Acid Whey
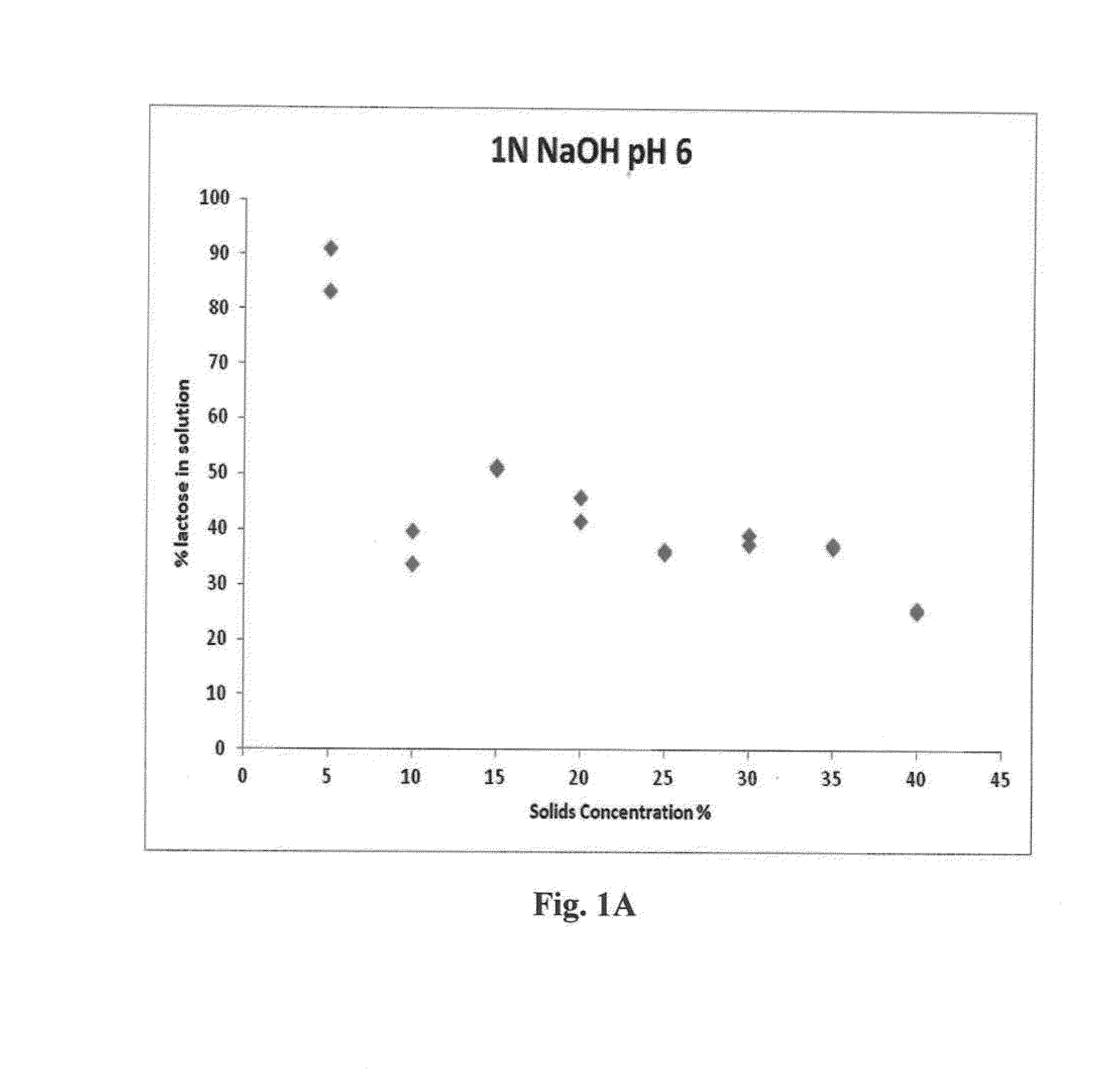
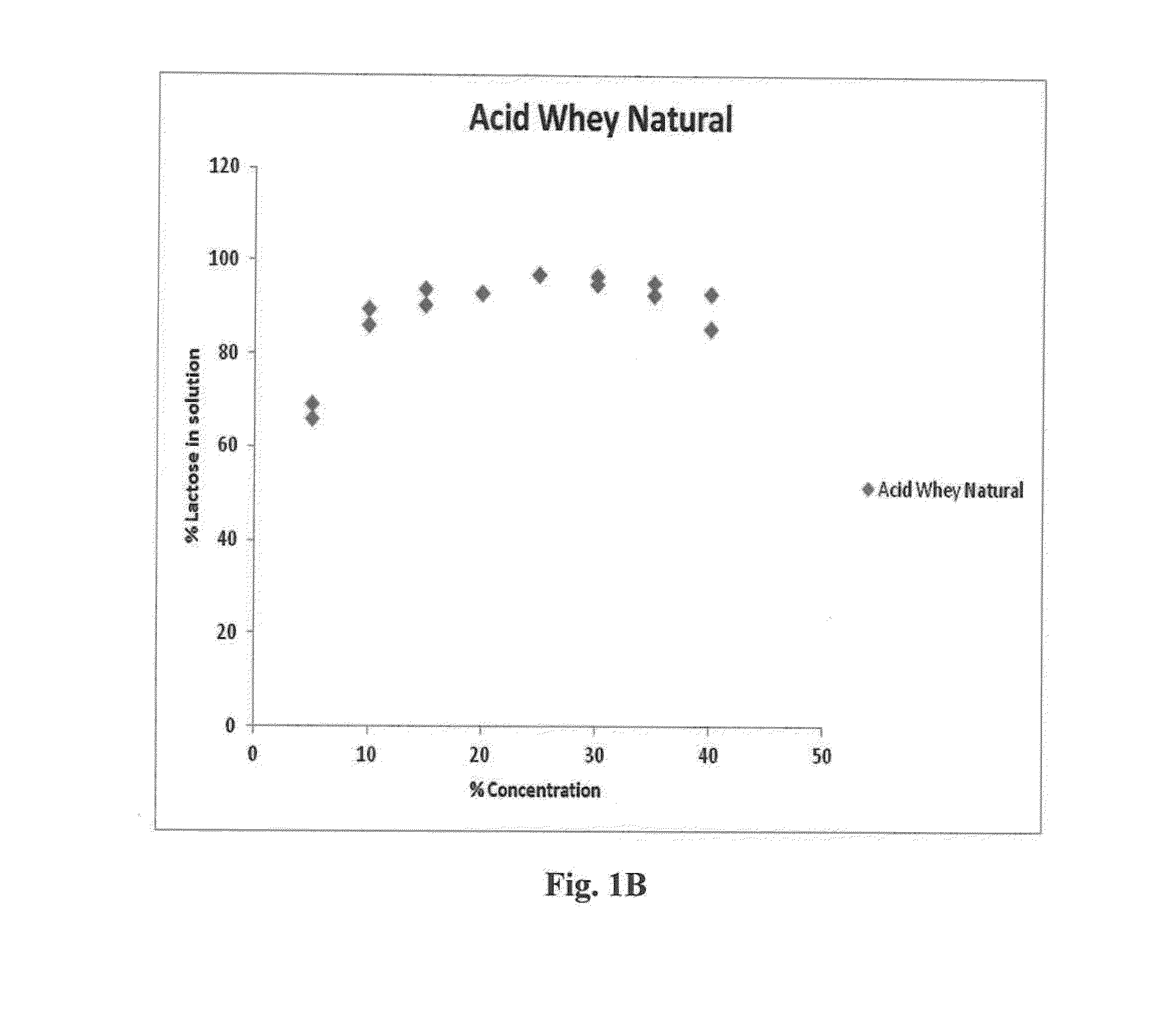
Methods for processing acid whey, involving treating acid whey solution with α-galactosidase and / or β-galactosidase, at a pH of about 3.2 to about 5.2 for about 20 minutes to about 16 hours at about 20° C. to about 60° C. to produce an acid whey solution containing at least about 40% less lactose than the original acid whey solution, filtrating the tempered acid whey solution to form a retentate containing proteins and a permeate containing lactose and residual proteins, recovering lactose from the permeate, optionally drying the retentate to form acid whey powder, and optionally texturizing the acid whey powder.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Activator protein of human acid maltase and uses thereof
InactiveUS20010027250A1High activityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderLactaseGlycogen storage disease type Ia
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for treating glycogen storage disease, such as GSD II. A human activator enzyme, termed ASA, of acid a a-glycosidase, (GAA) or acid maltase, a lysosomal enzyme, is specifically defined and characterized. The AGA has been found to increase the activity of human acid .alpha. glycosidase activity to at least 10-fold, relative to the activity of GAA in the absence of the activator protein. The invention thus also provides for a method of increasing the activity of GAA, particularly through the action of AGA. The AGA has an approximate molecular weight of 25-30 kD, and is found to be heat stable. In addition, the AGA is found to have an extended shelf life without significant loss of ability to activate GAA. The invention further reports other enzymes such as .beta.-Fucosidase, .beta.-Lactase, and .beta.-Galactosidase, that provide enhancement of enzymatic activity nine-fold, six-fold, and five-fold, for breakdown of their respective substrate protein. These enzymes are non-lysosomal enzymes. These are anticipated to be useful in treatment of disease related to reduced enzymatic activity levels in an animal.
Owner:MARTINIUK FR T
Heavy metal remediation system
The invention provides a system of heavy metal sequestration by bacteria. The bacteria expresses the ppk, mt, and / or β-galactosidase (lacZ) genes and can tolerate at least 25 μM mercury, 1,000 μM zinc, 250 μM cadmium, and 3,000 μM Pb. The system allows for facile determination of the presence of heavy metal contaminants in a liquid and the facile collection of the bacteria that has sequestered large amounts of heavy metal. Further provided is a system of gene expression in bacteria that comprises phage and plastid gene expression elements and delivers a particularly high level of protein expression and heavy metal resistance.
Owner:INTER AMERICAN UNIV OF PUERTO RICO
Wild-type receptor assays
ActiveUS8211655B2Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesLysisWild type
A method for determining ligand activation of receptors using cells expressing genetic constructs of a fusion protein of at least a binding domain of an auxiliary protein and a fragment of β-galactosidase, a fusion protein of an endosome-associated protein and a complementary fragment of β-galactosidase, and a wild-type receptor. The receptors are characterized by binding to the auxiliary protein-binding domain upon activation by an agonist and then endocytosing associated with an endosome to which the endosome-associated protein binds. Cells are incubated with a candidate ligand followed by lysis with a lysing medium comprising a substrate for the β-galactosidase. The enzyme product is then detected as a measure of the activation of the receptor.
Owner:DISCOVERYX CORP
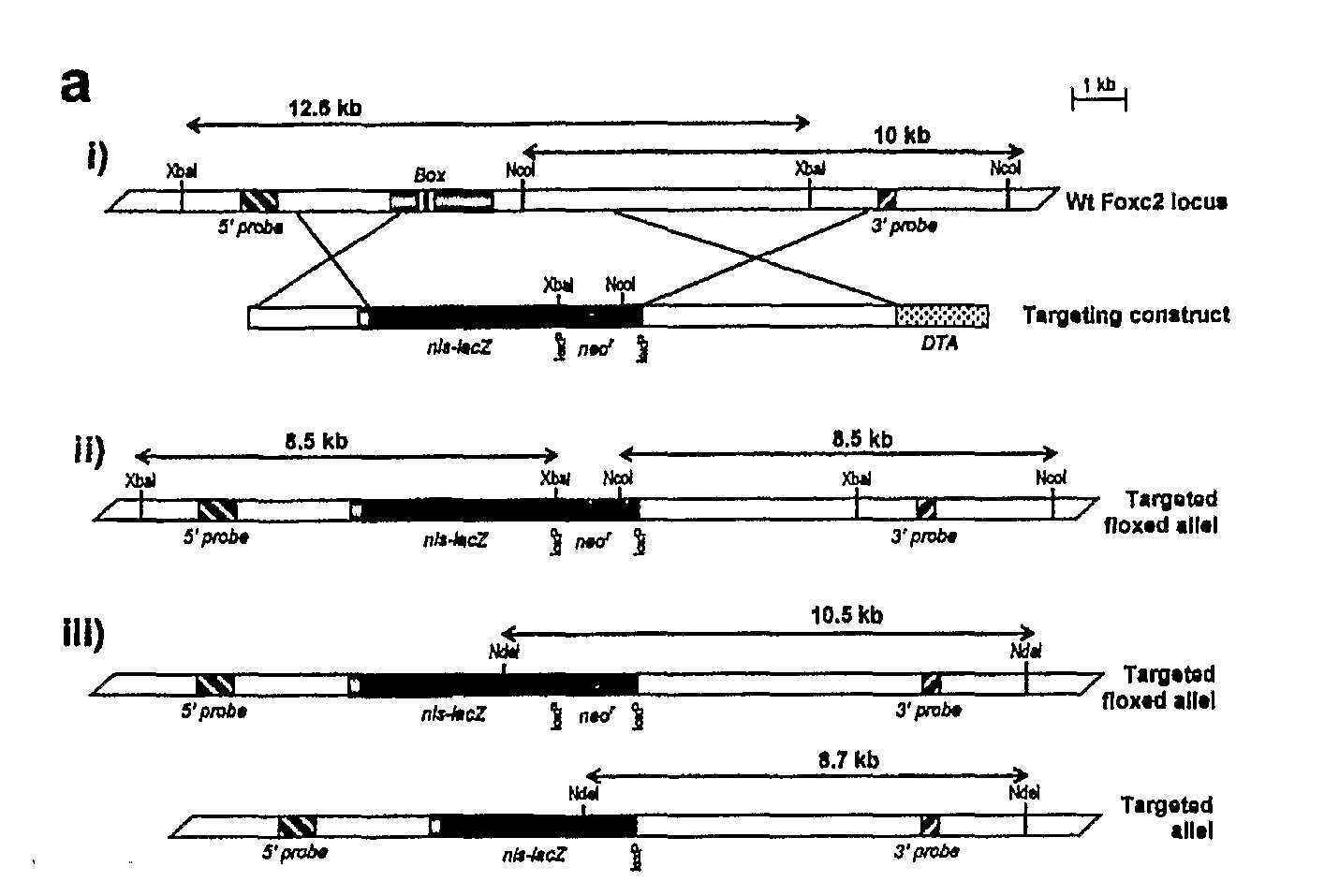
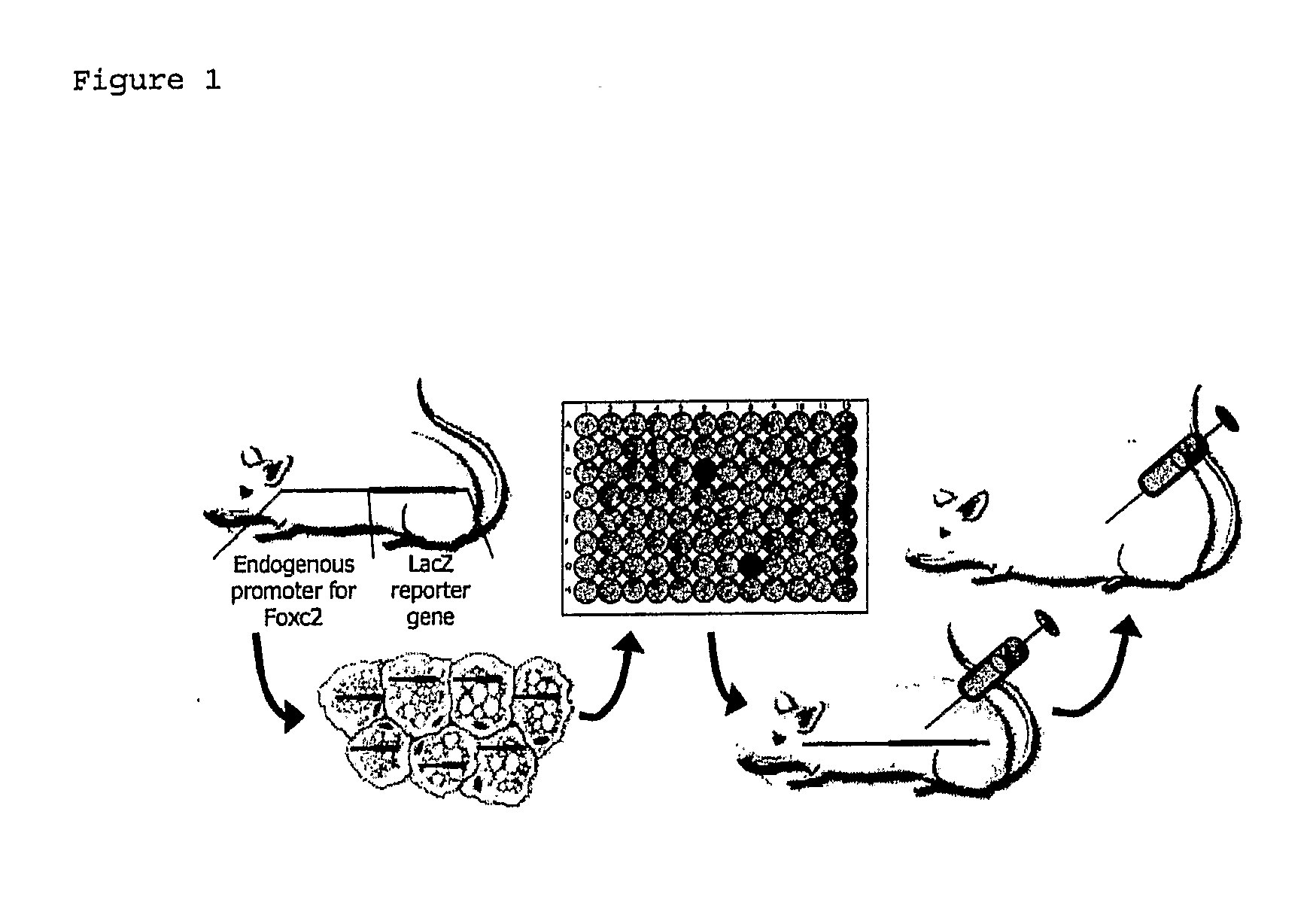
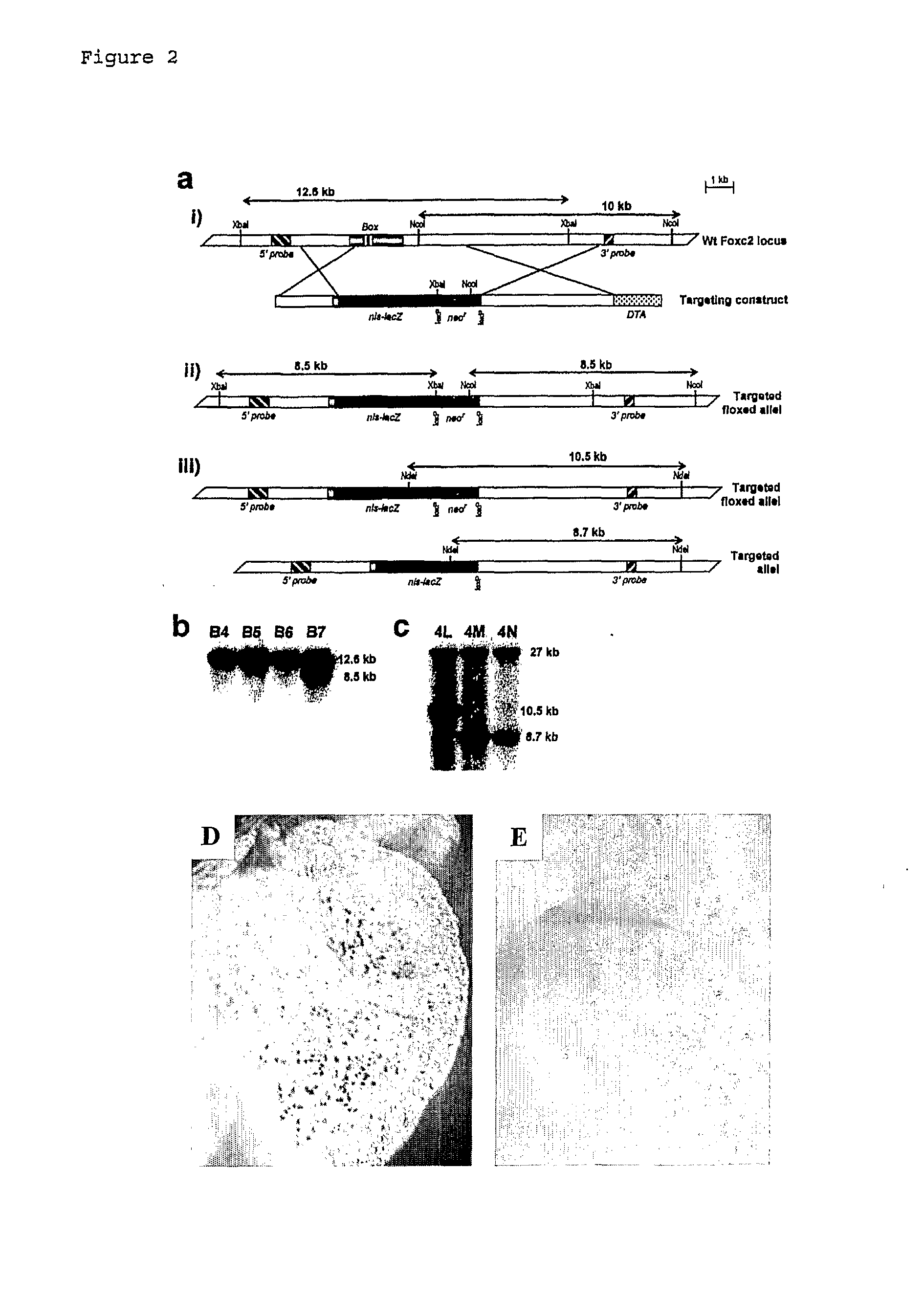
Method For Monitoring the Effect of Compounds on Foxc2 Expression
InactiveUS20080181877A1High expressionHigh activityBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsDiabetes mellitusDisease
The present invention relates to a method for monitoring / detecting compounds capable to regulate the transcription and / or expression of the forkhead transcription factor Foxc2, which compounds may be useful for the treatment of obesity related diseases and diabetes. The screening for the compounds has been performed in recombinant mouse cells containing the Foxc2 gene and the β-galactosidase gene in a suitable targeting vector
Owner:LEANGENE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com