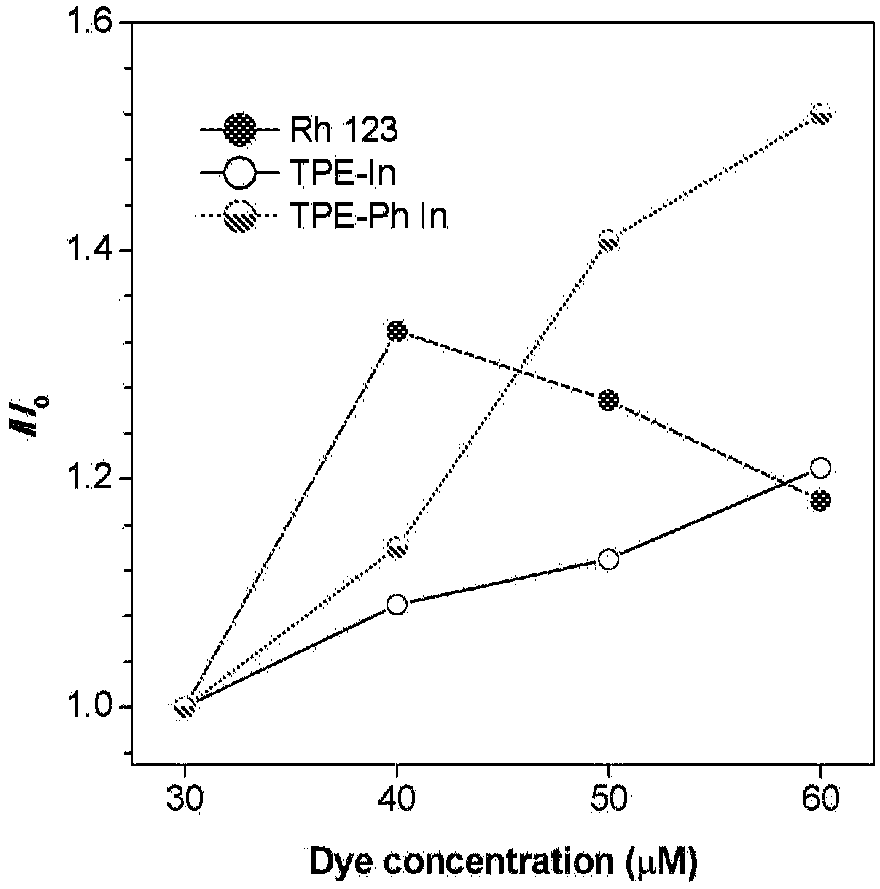
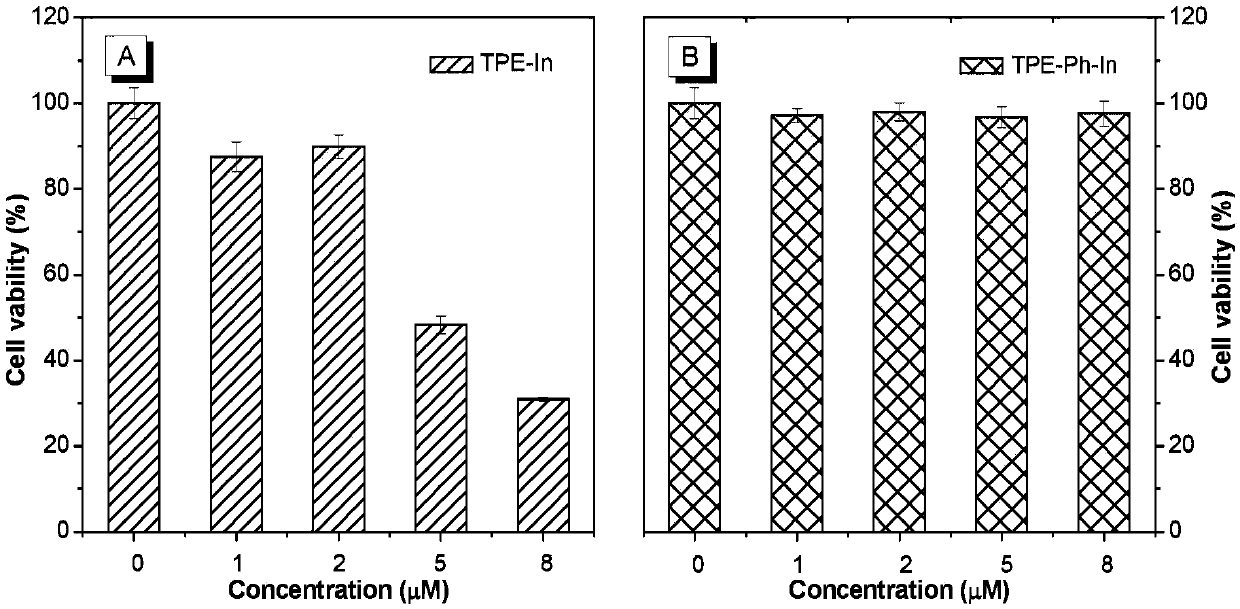
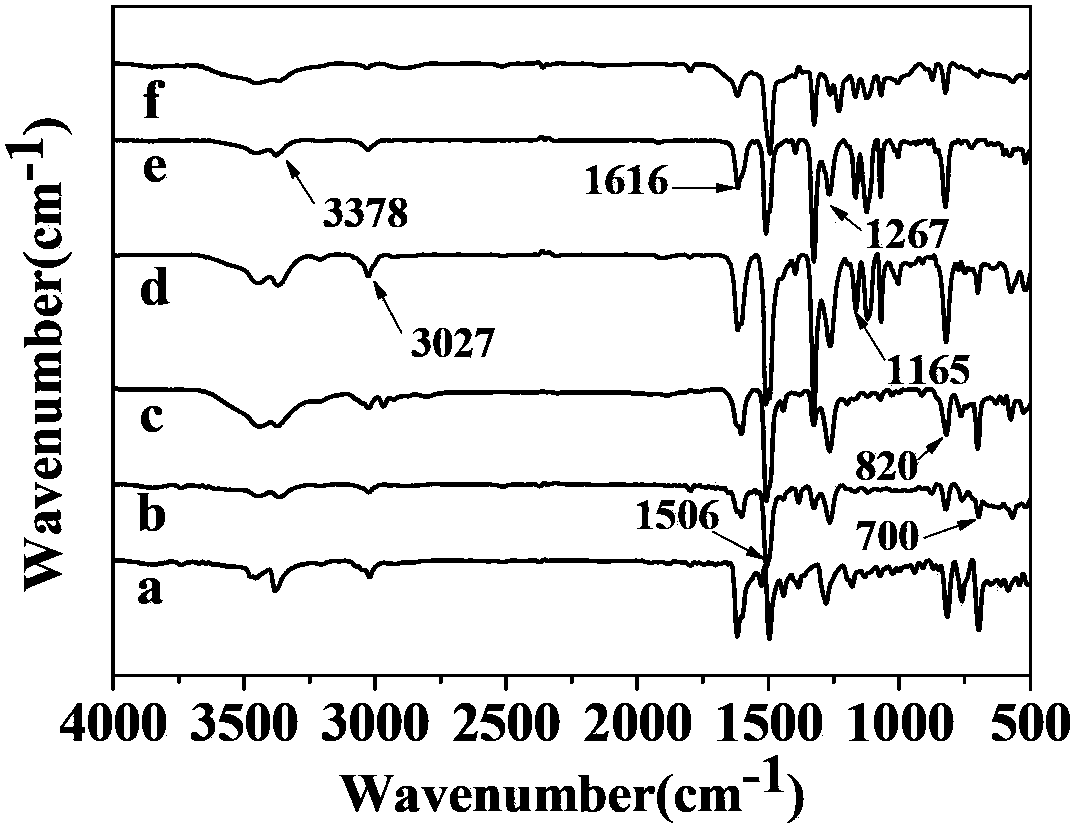
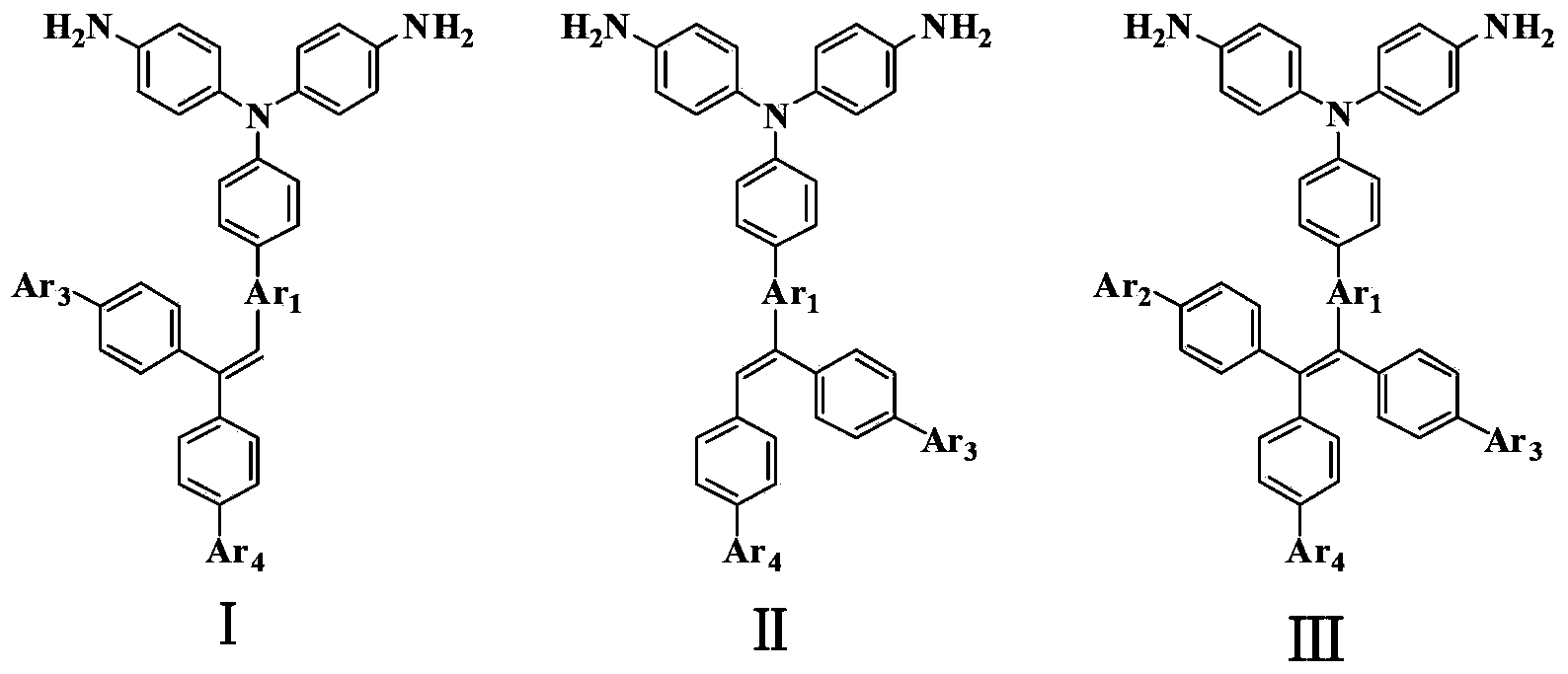
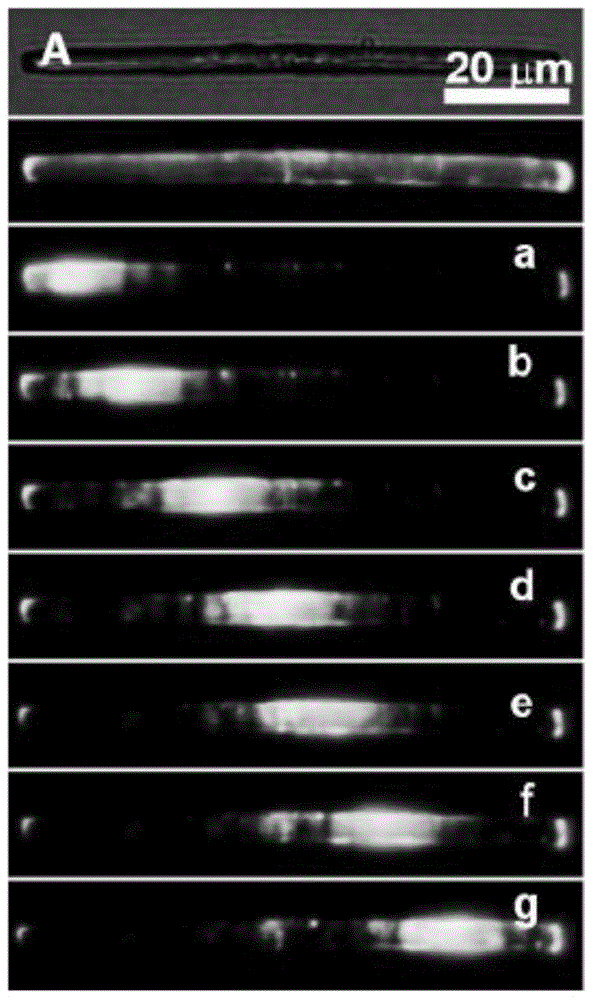
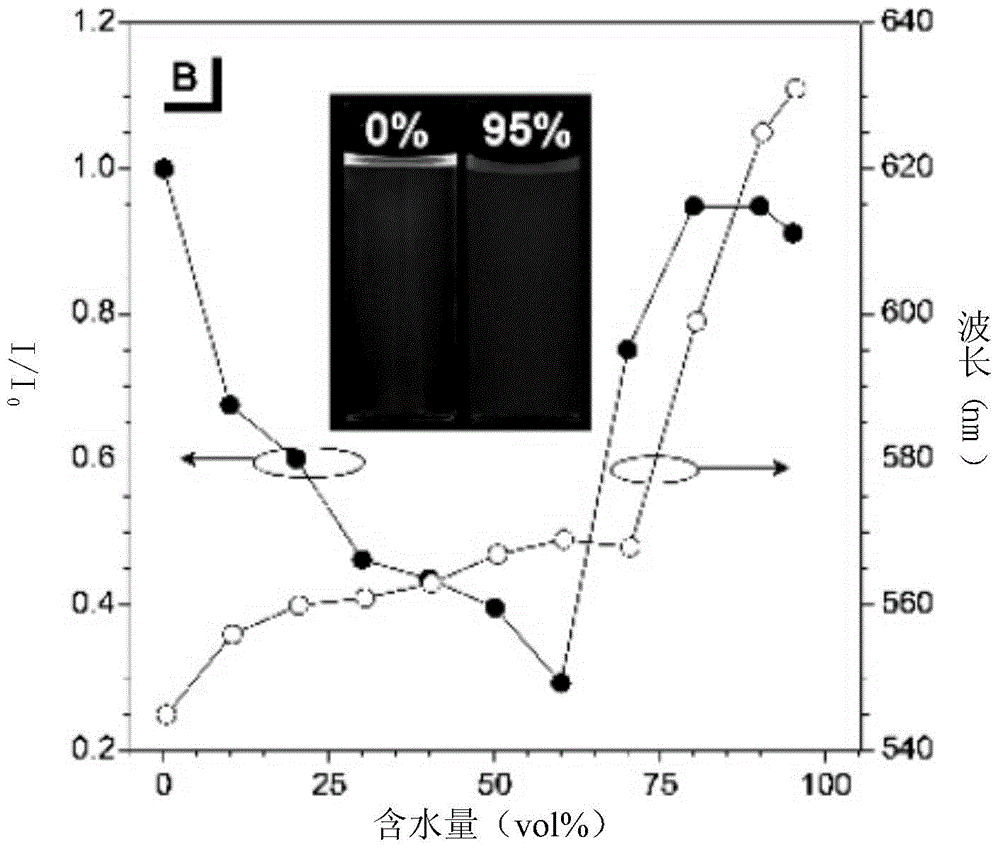
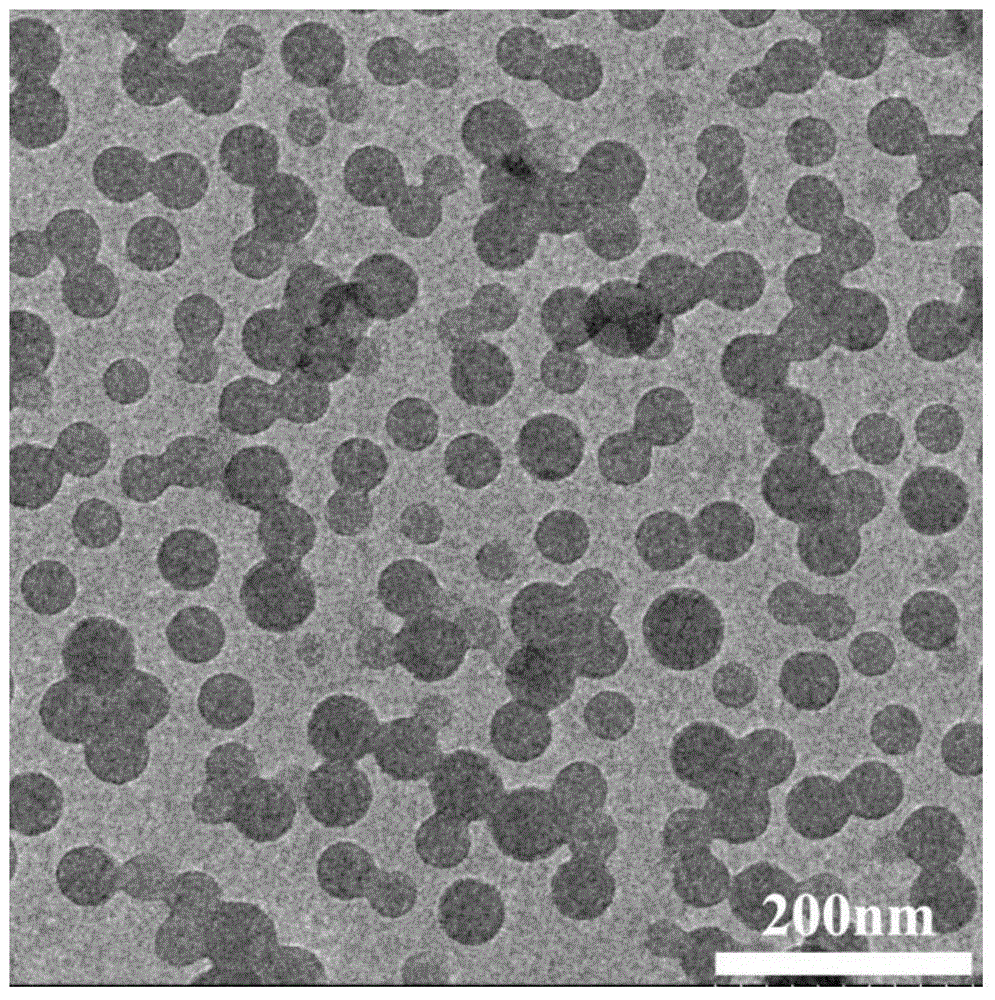
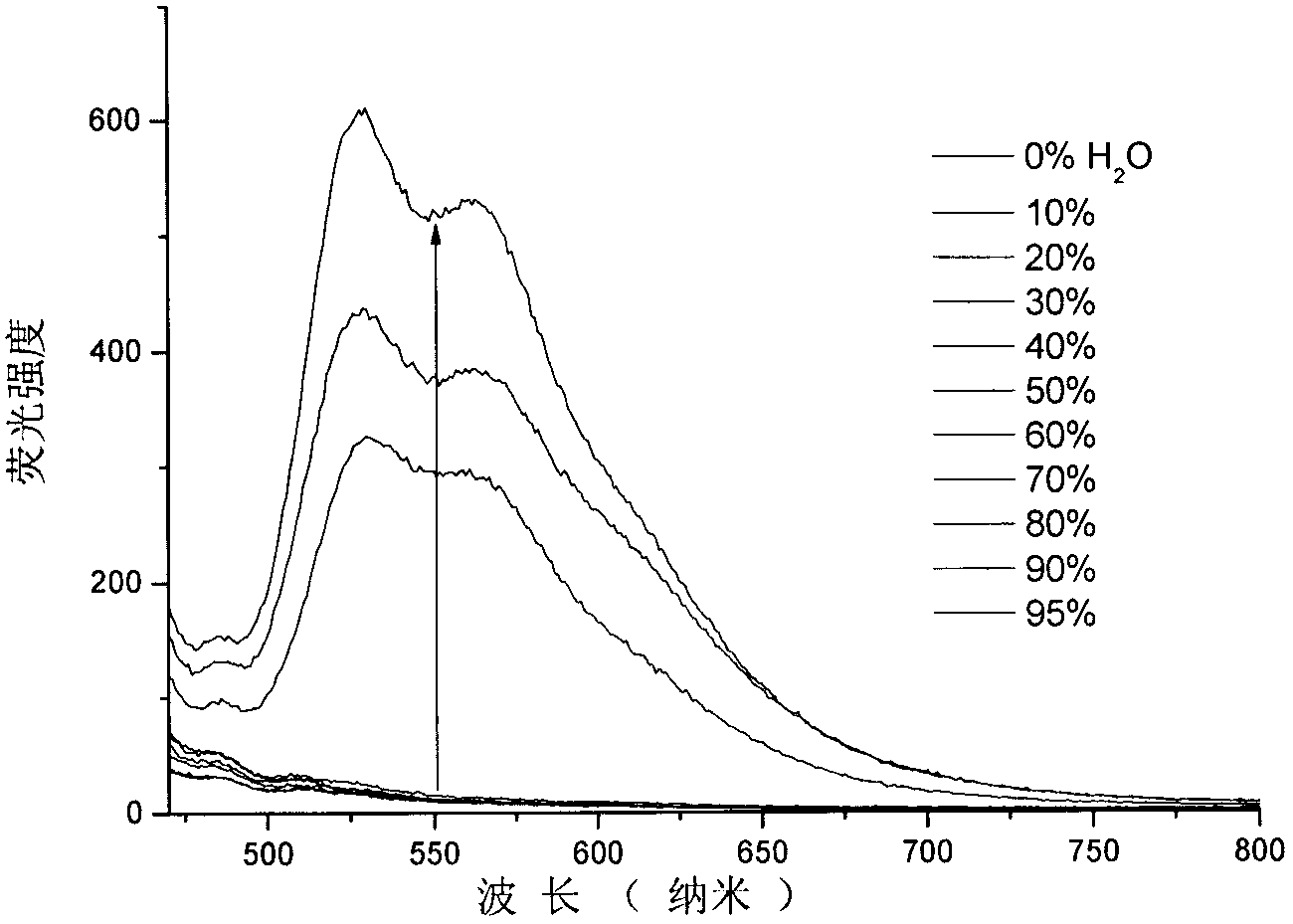
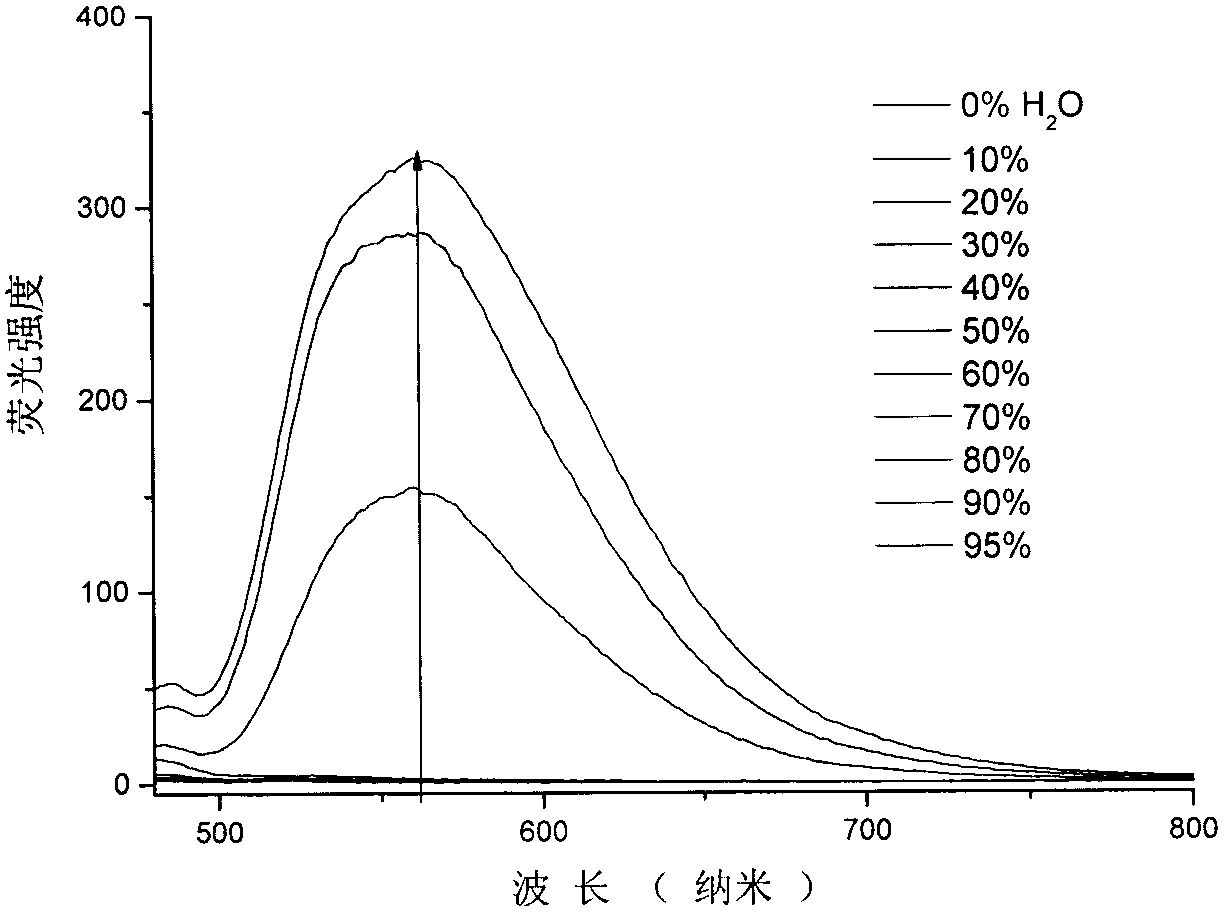
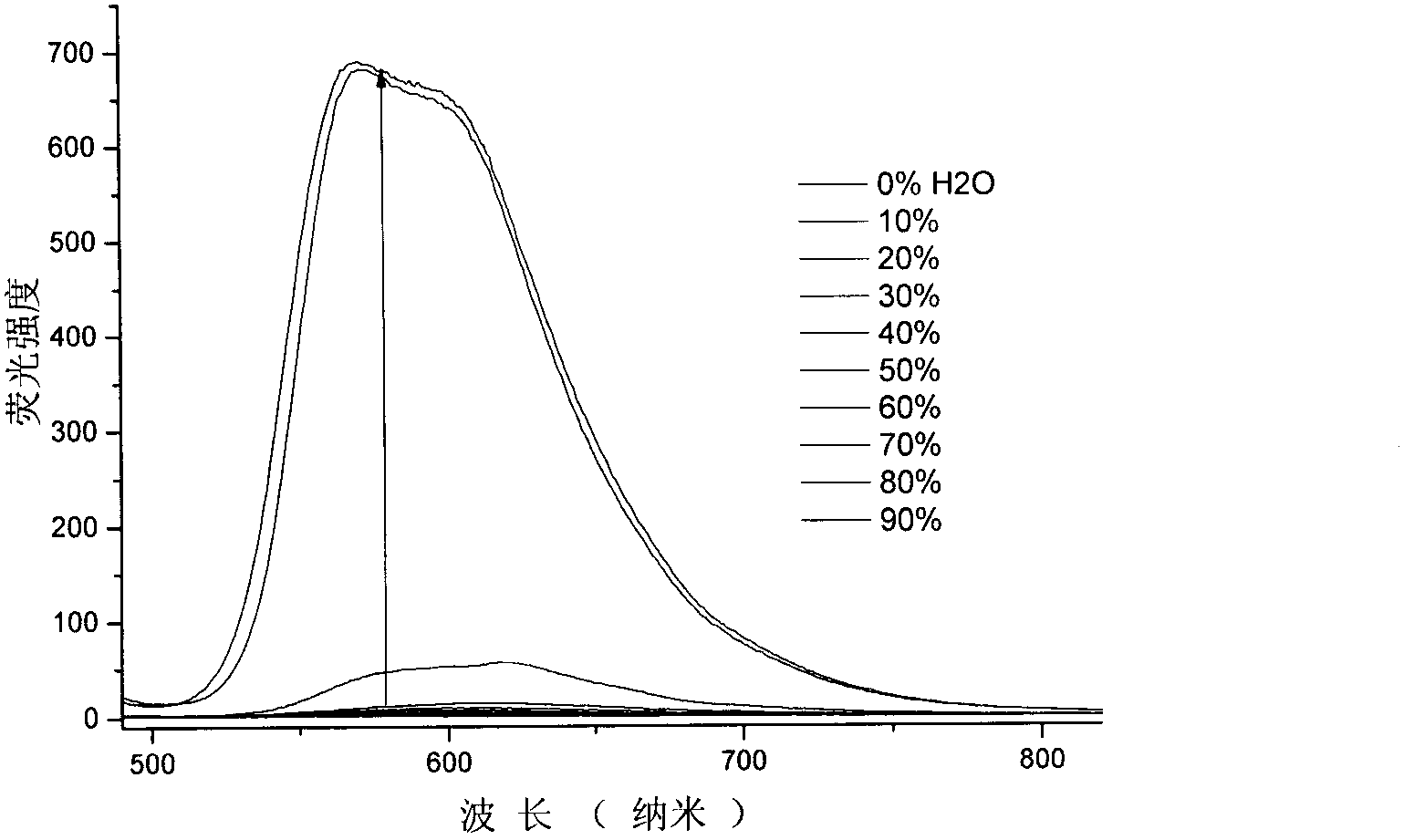
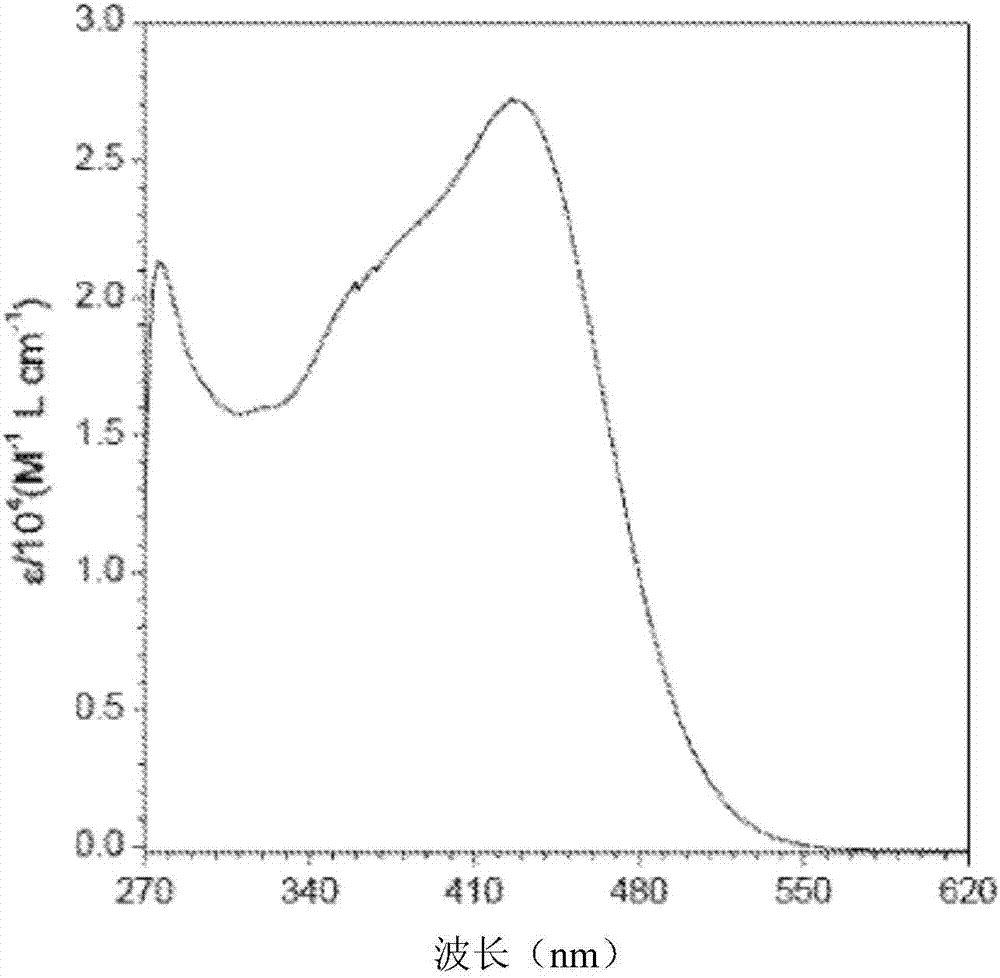
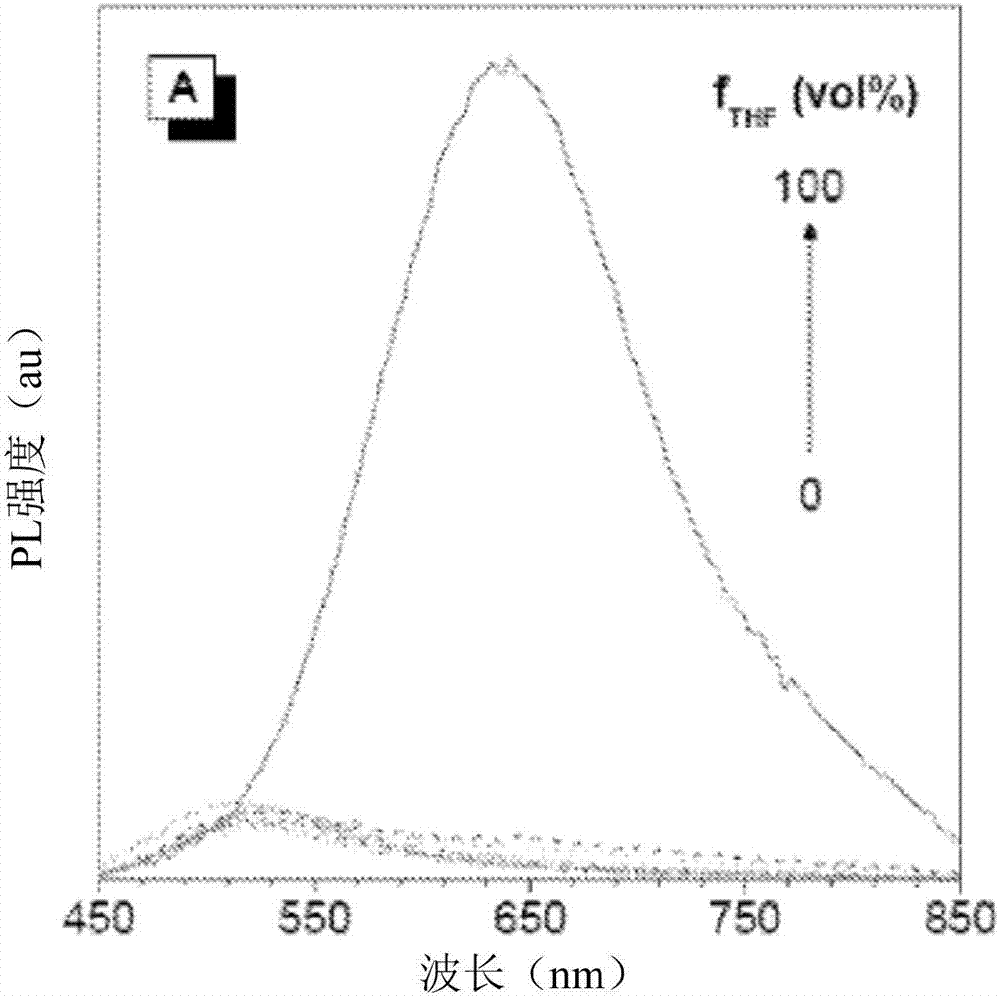
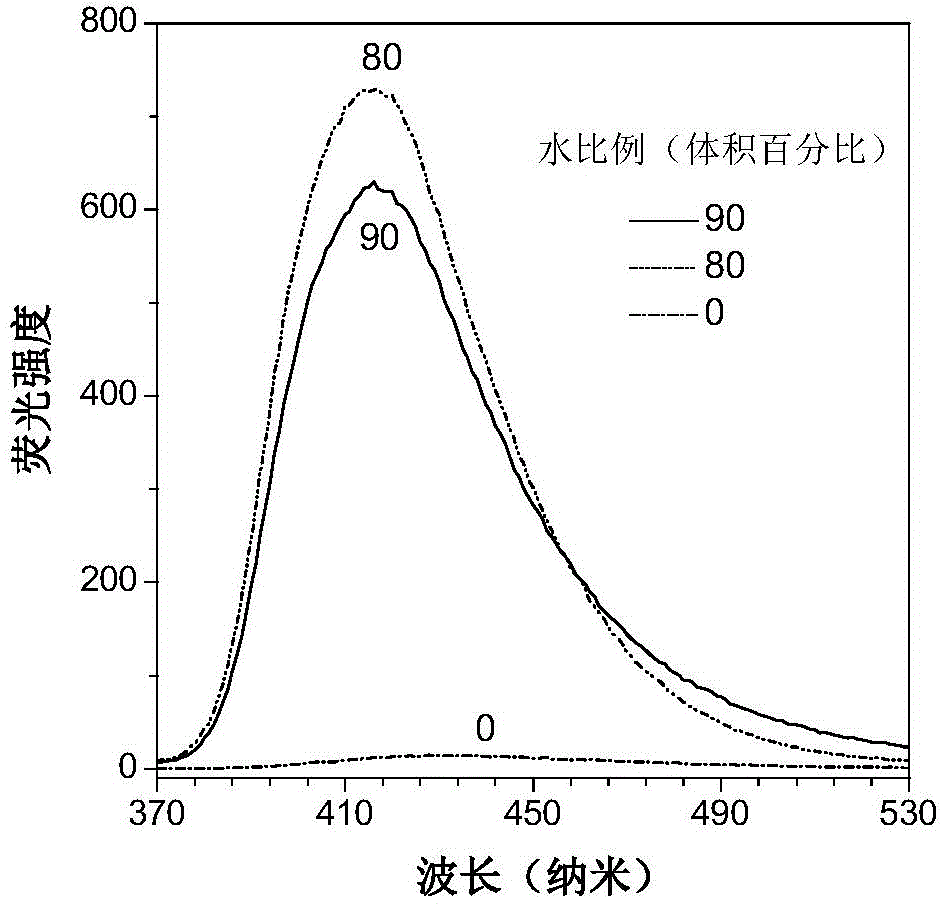
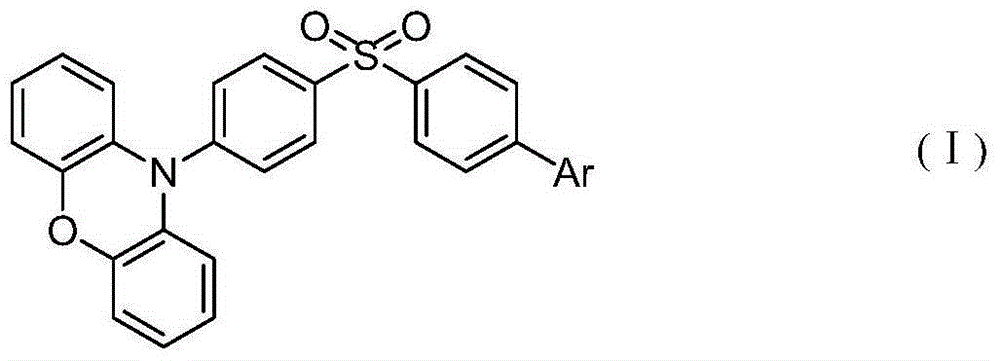
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
329 results about "Aggregation-induced emission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
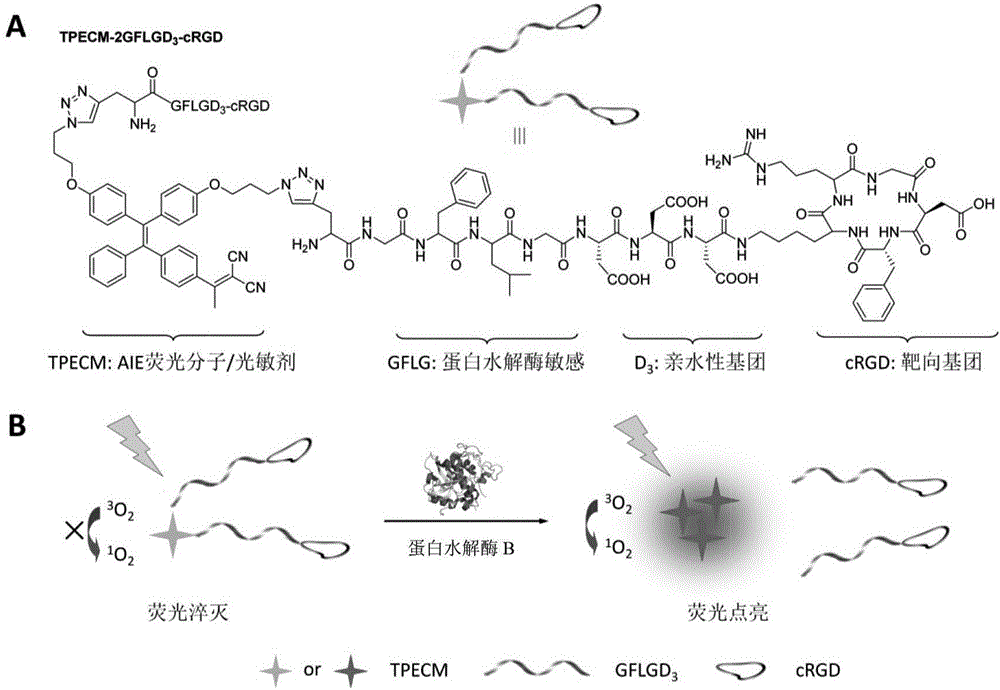
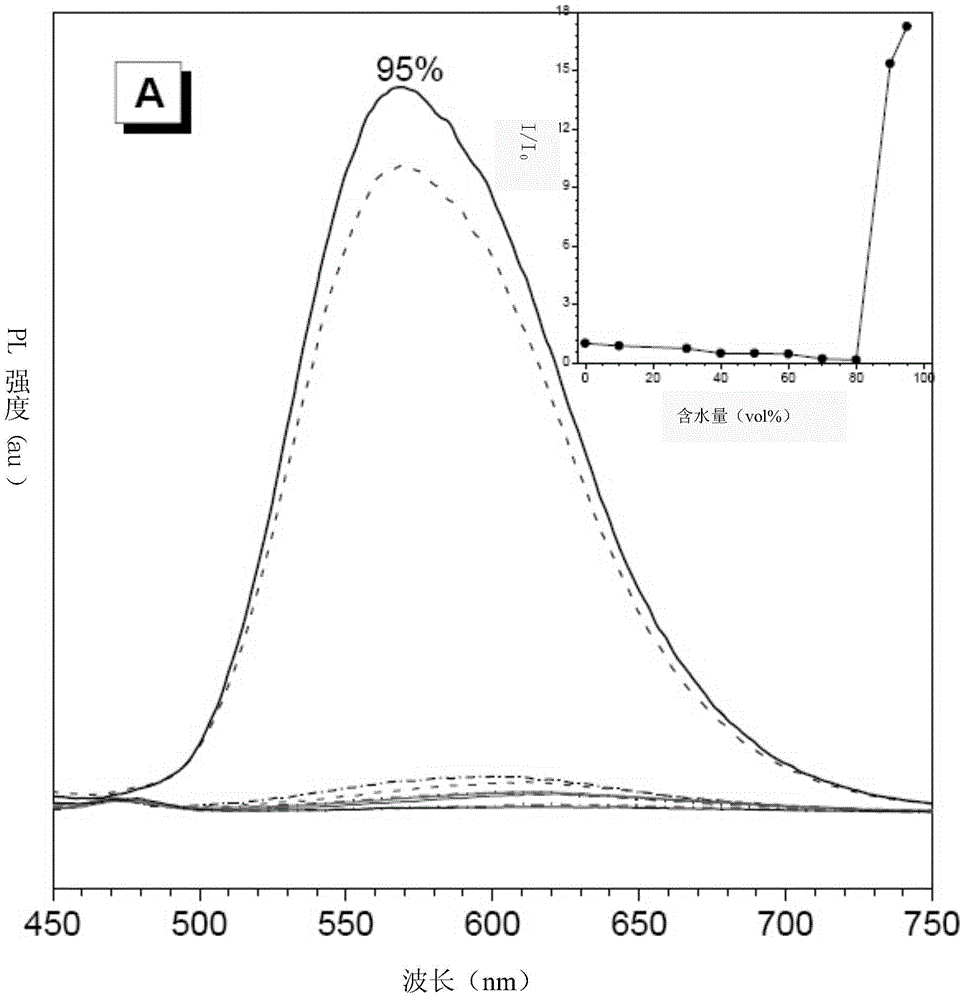
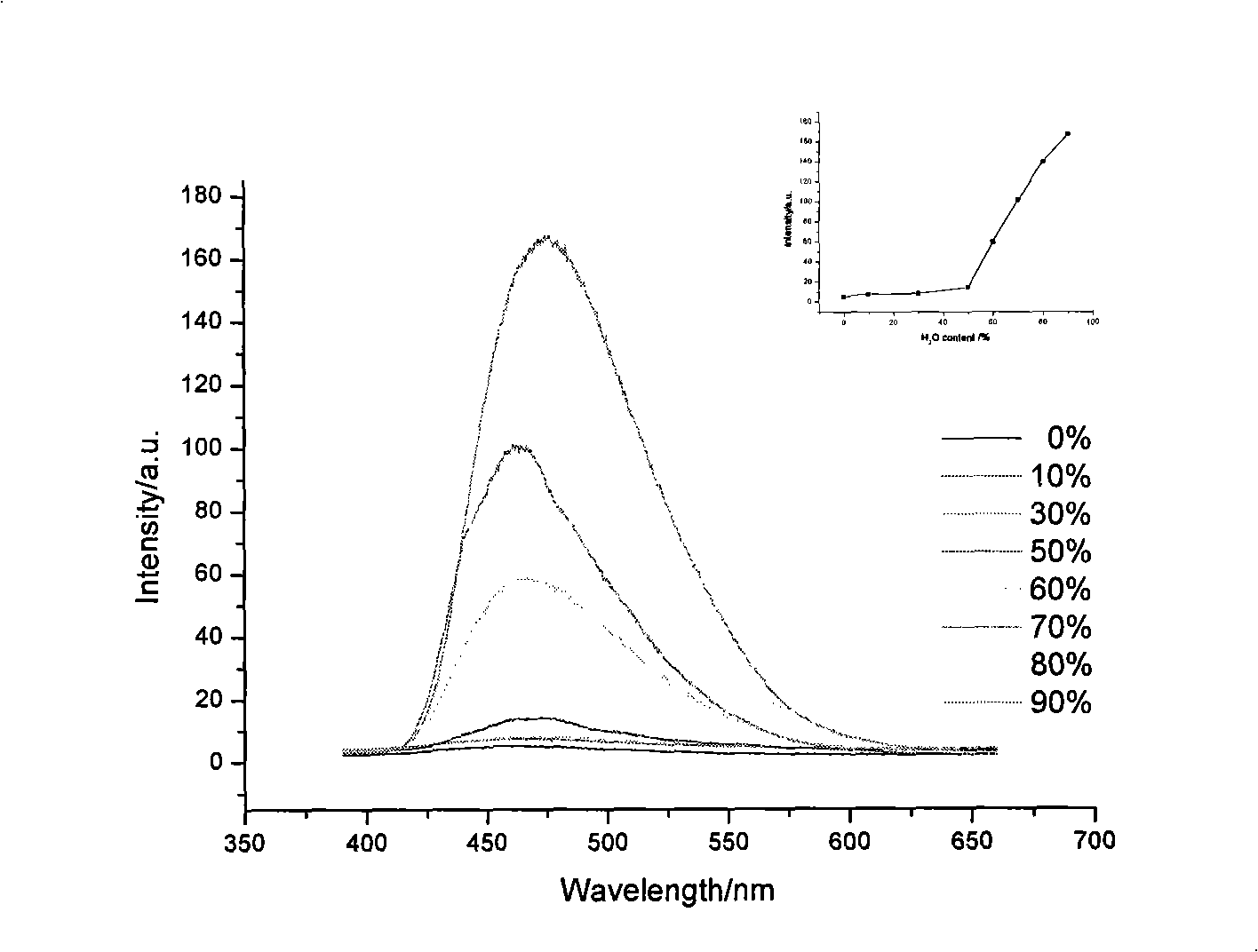
Aggregation-induced emission (AIE) is an abnormal phenomenon that is observed with certain organic luminophores (fluorescent dyes). Most organic compounds have planar structures and higher photoemission efficiencies in solution than in the solid state. Otherwise said, these fluorophores or fluorescent dyes are much more emissive in solution compared to just the solid form, in that the intensity of their emission is greater in solution. However, some organic luminophores have freely-rotating groups (rotational degrees of freedom), when these molecules are excited instead of releasing that energy as light they relax back down through these rotations. When these luminophores aggregate or crystallize, which restricts those rotations, they can become very fluorescent or emissive, and the photoluminescence efficiency (i.e. quantum yield) increases.
Novel piezoluminescence material with thermal activation delayed fluorescence and aggregation-induced emission properties and synthetic method and application of novel piezoluminescence material
ActiveCN103483332AHigh luminous intensityHigh activityOrganic chemistryLuminescent compositionsOrganic electroluminescenceAggregation-induced emission
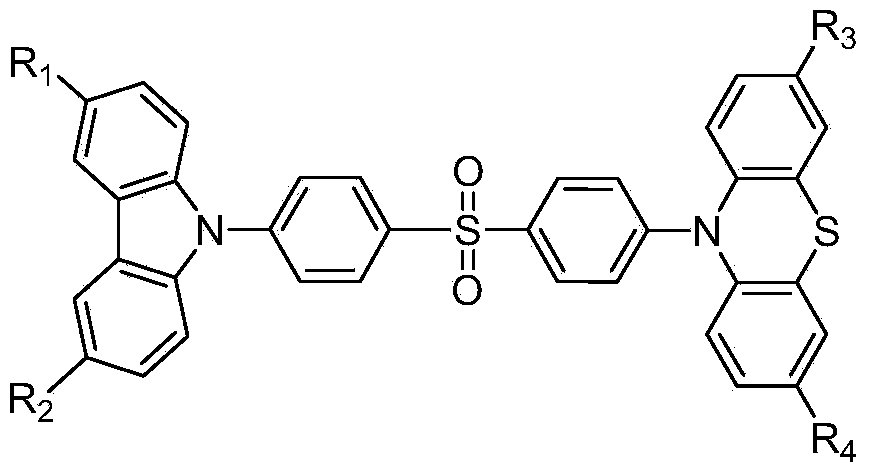
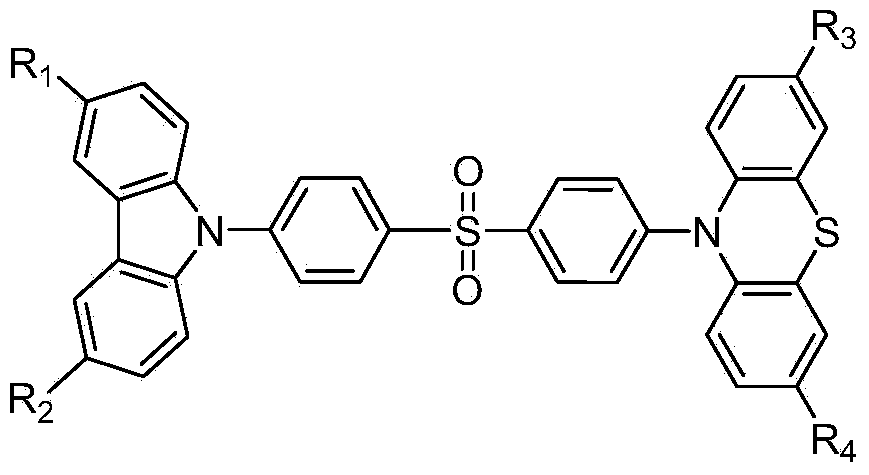
The invention discloses a novel piezoluminescence material with thermal activation delayed fluorescence and aggregation-induced emission properties and a synthetic method and the application of the novel piezoluminescence material. The core structure of the novel piezoluminescence material is carbazole phenothiazine substituted diphenyl sulfone, and the novel piezoluminescence material has a piezoluminescence property, the thermal activation delayed fluorescence property and the aggregation-induced emission property. The synthetic method of the novel piezoluminescence material is simple in process, purification is easy, and the obtained novel piezoluminescence material is high in piezoluminescence intensity and suitable for preparing non-doping luminescent layer materials in pressure sensors or anti-counterfeiting trademark or organic electroluminescent material devices.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Biocompatible nanoparticles with aggregation induced emission characteristics as fluorescent bioprobes and methods of using the same for in vitro and in vivo imaging
ActiveCN103842472APowder deliveryMicrobiological testing/measurementAggregation-induced emissionBiocompatible nanoparticles
The development of fluorescent bioprobes comprising organic fluorescent compounds that exhibit aggregation induced emission (AIE) properties, methods of producing the same, and their practical applications for in vitro and in vivo bioimaging.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Polymers and oligomers with aggregation-induced emission characteristics for imaging and image-guided therapy
A fluorophore or conjugated polymer with aggregation-induced emission characteristics useful for drug tracking and delivery, identification and labeling of biological subjects, such as cells or parts of a cell, as well as for imaging, and image-guided photodynamic therapy are described herein.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE +1
Fluorescent water-soluable conjugated polyene compounds that exhibit aggregation induced emission and methods of making and using same
ActiveUS20100009362A1Styryl dyesMethine/polymethine dyesAggregation-induced emissionWater dispersible
The presently described subject matter is directed to water-soluble conjugated polyene compounds that exhibit aggregation induced emission, as well as to water dispersible, fluorescent, polymeric microparticles and / or nanoparticles comprising the water-soluble conjugated polyene compounds. Also provided are methods of making and using the compounds and particles. The described conjugated polyene compounds are useful as bioprobes for the detection biomacromolecules, as well as in the manufacture of sensors.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Amphiphilic illuminant with aggregation induced emission characteristics and applications thereof
ActiveCN104974745ANecrosis can be observedThe effect of phototherapy can be observedOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryBiopolymerBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to an amphiphilic illuminant with aggregation induced emission characteristics and applications thereof. The illuminant is prepared by connecting a hydrophilia unit on a classical hydrophobicity unit of the classical aggregation induced emission characteristics (AIE), and can be applied to a fluorescent light chemical sensor and is used for preparing fluorescent light coloring agent which is used for coloring living cells and animal imaging fluorescent light. The amphiphilic coloring agent is specifically suitable for the fluorescent light mark on biopolymer, and can be used as a biocompatibility probe for AIE activation so that the amphiphilic coloring agent can be applied to clinic cancer imaging, diagnose and treatment.
Owner:HKUST SHENZHEN RES INST +1
Aggregation-induced emission fluorescent molecule as well as preparation method and fluorescent dye composition, and application of aggregation-induced emission fluorescent molecule and fluorescent dye composition in mitochondria dyeing
InactiveCN103788940ALow toxicityGood luminous stabilityOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementAggregation-induced emissionCytotoxicity
The invention provides an aggregation-induced emission fluorescent molecule as well as a preparation method of the aggregation-induced emission fluorescent molecule. Furthermore, the invention provides a fluorescent dye composition containing the aggregation-induced emission fluorescent molecule. In addition, the invention provides application of the aggregation-induced emission fluorescent molecule and the fluorescent dye composition in mitochondria dyeing. The aggregation-induced emission fluorescent molecule (fluorescent probe) disclosed by the invention is low in cytotoxicity and luminescence stability, and the fluorescent molecule can effectively dye mitochondria and can simultaneously indicate membrane potential of the mitochondria; the fluorescent molecule can be used for marking and tracking mitochondria in cell for a long time, and can be used for detecting membrane potential of the mitochondria.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Luminescent material having aggregation-induced emission, method of making and application thereof
ActiveCN104877665AHas aggregation-induced luminescent propertiesImprove the possibility of applicationOrganic compound preparationFluorescence/phosphorescenceAggregation-induced emissionElectrical polarity
The invention discloses a luminescent material having aggregation-induced emission, a method of making and an application thereof. The luminescent material herein has properties of aggregation-induced emission / aggregation-enhanced emission with the maximum absorption wavelength red shift to a visible area so that this type of luminescent material has potential applications in the field of biology. The luminescent material allows the formation of transfer of electric charges in a molecule and exhibits strong polar dependent emission in different solvents. The luminescent material does not emit due to strong dipoalr interaction in a molecule, but emits in a weak-polar environment with a cell. The luminescent material can serve as intracellular lipid droplet and intramicroalgae lipid droplet, and has the advantages of high selectivity, high emission stability and high biological compatibility.
Owner:HKUST SHENZHEN RES INST +1
Aggregation-induced emission molecule as well as preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN103194215AControl Conjugate LengthEfficient luminous efficiencyAmino preparation from aminesSolid-state devicesStructural formulaLight-emitting diode
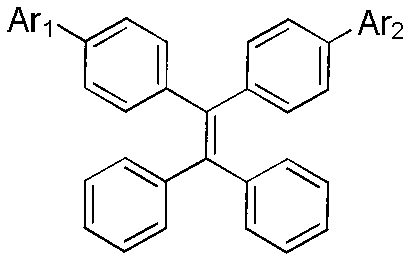
The invention discloses an aggregation-induced emission molecule as well as a preparation method and use thereof. The aggregation-induced emission molecule has a structural formula (shown in the description), wherein when Ar1 and Ar2 are same groups, Ar2 is a group shown in the description; and when Ar2 is hydrogen, Ar1 is a group shown in the description. The preparation method comprises the steps of: starting from a group shown in the description, wherein X=br, and Y=H or X=H, and Y=Br and tetraphenyl ethylene boric acid ester, obtaining derivatives of fluorene containing toluene and triphenylamine units by utilizing an acid-induced intramolecular dehydration reaction, linking tetraphenyl ethylene to a ninth site of the fluorine in a conjugated manner by utilizing a Suzuki reaction, and finally obtaining a target compound. According to the compound disclosed by the invention, the heat stability and the aggregation-induced emission property are good, the solid fluorescence quanta of the compound are high in yield and are emitted by blue lights, and the compound can be applied to a luminescent layer material of a blue-light inorganic light emitting diode; and the reaction conditions of the preparation method are mild, and the yield is high.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Organic white light material with thermal activation delay and aggregation-induced emission performance and synthetic method and application thereof
ActiveCN105481794AHigh glass transition temperatureThe synthesis method is simpleOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesVitrificationAggregation-induced emission
The invention provides an organic white light material with the terminal activation delay and aggregation-induced emission performance and a synthetic method and application thereof. The general molecular formula of the white light material is Ar-Ar1-Ar2, wherein Ar is a phenothiazine electron-donating substituent group, Ar1 is a strong electron-withdrawing group, and Ar2 is an aromatic fused ring or heterocyclic aromatic substituent group except phenothiazine. The synthetic method of the material is simple, the thermal performance, luminous efficiency and white light color purity of an end product can be adjusted through connection of different aromatic fused ring or heterocyclic aromatic groups, the white light material has the thermal activation delay and aggregation-induced emission properties, the glass transition temperature is high, and the emission performance is excellent. The obtained white light material is a light emitting layer applied to preparing a non-doped OLED device, the illumination brightness is high, the stability is good, and the practicability requirement can be met.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
AIE bioprobes emitting red or yellow fluorescence
InactiveCN108055852AMethine/polymethine dyesOrganic chemistryAggregation-induced emissionSubject matter
The present subject matter relates to red emitting mitochondria-targeted aggregation induced emission (AIE) probes as an indicator for membrane potential and mouse sperm activity. The present subjectmatter relates to AIE-active fluorescent probes for reactive oxygen species (ROS) detection and related biological applications, such as inflammation imaging and glucose assay, as well as the preparation and application of red fluorescent AIEgens.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel diamine compound, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104341311AThe synthesis process is simpleEasy to purifyAmino preparation from aminesOrganic compound preparationSynthesis methodsNitrobenzene
The invention discloses a novel diamine compound, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method of the novel functional diamine compound comprises the following steps: a large conjugate structure comprising benzophenone carbonyl group is obtained; the ketone carbonyl group is subjected to a Wittig or Wittig-Horner reaction, such that a large conjugate system with a triphenylethylene / tetraphenylethylene structure and comprising a halogen atom is obtained; the halogen atom is further subjected to a Suzuki reaction or a plurality steps of reactions, such that a monoamine compound comprising a triphenylethylene / tetraphenylethylene large conjugate system is obtained; the monoamine compound is subjected to a reaction with halogenated nitrobenzene, such that a dinitro monomer comprising triphenylamine and the triphenylethylene / tetraphenylethylene large conjugate system is obtained; and the dinitro monomer is reduced into the novel diamine compound, such that the novel functional diamine compound comprising triphenylamine and a triphenylethylene / tetraphenylethylene structure is obtained. The synthesis method provided by the invention is simple. Purification is easy. The method is suitable for industrial productions. The synthesized diamine compound has a significant aggregation-induced emission property, and can be used for synthesizing high-performance and functional polymers such as polyamide, polyimide, polyamideimide, polyesterimide, and the like.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
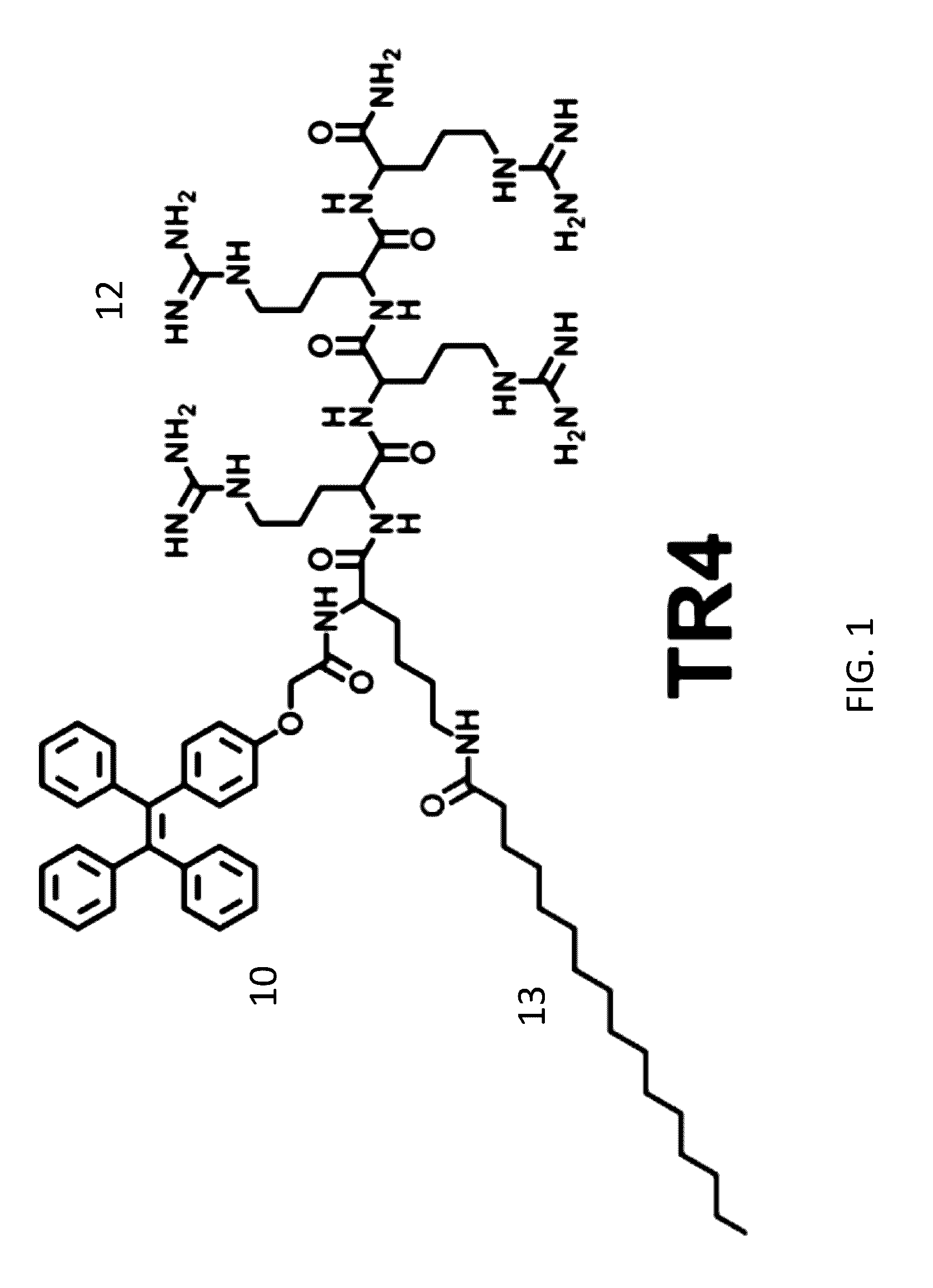
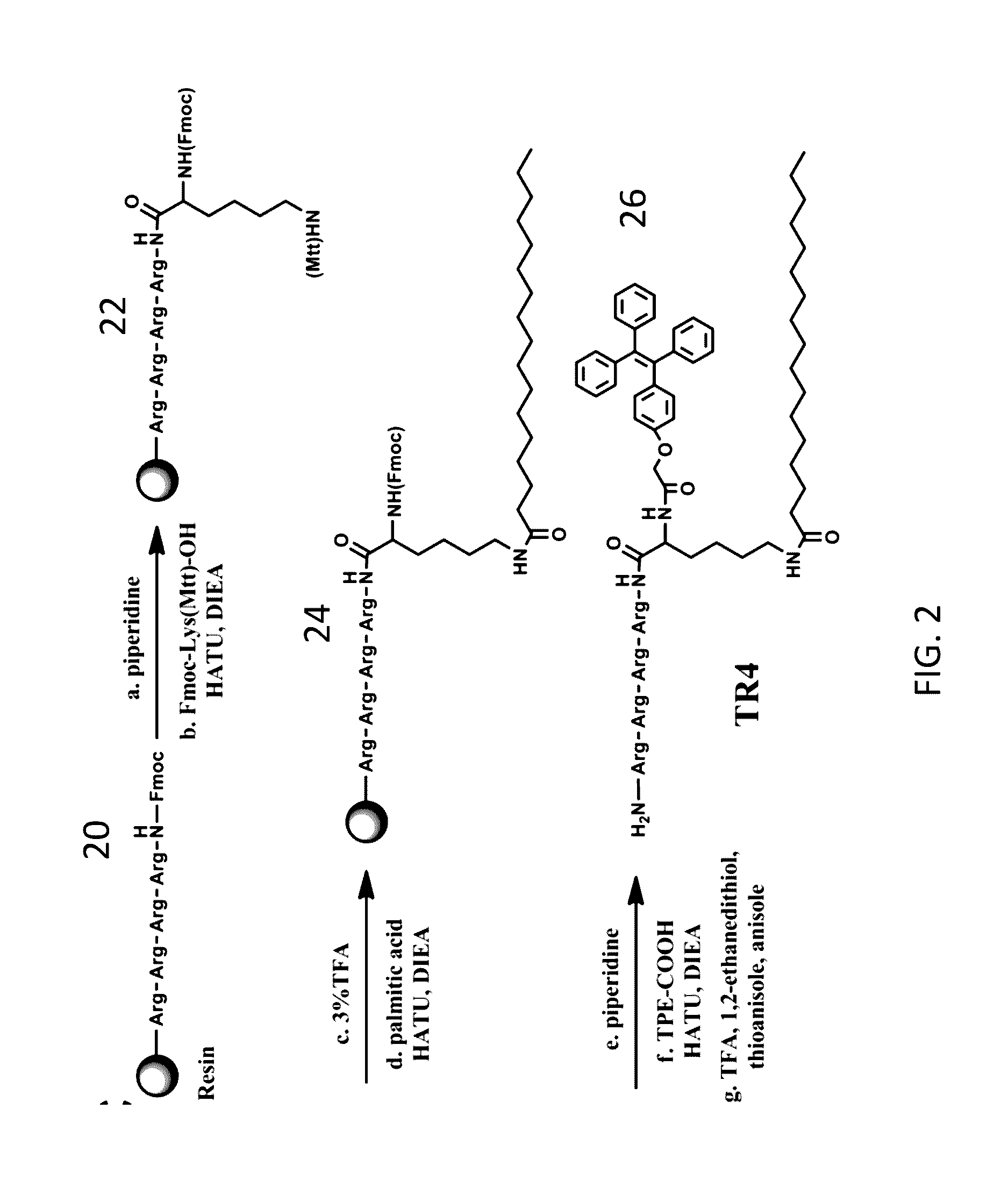
Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogen Having An Peptide Sequence And Its Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20160349245A1Low costSynthetic is simpleBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceAggregation-induced emissionCell membrane
A fluorescence molecular probe having a hydrophilic polypeptide backbone conjugated with a hydrophobic alkyl chain and a function group with aggregation induced emission is disclosed. The hydrophilic peptide sequence renders DNA binding capacity and the hydrophobic alkyl chain provides capacity for embedding within cell membrane. The aggregation induced emission renders real time tracking for live cell function studies. The synthesis of the probe is simple and easy for purification.
Owner:ZHANG CHUNQIU +1
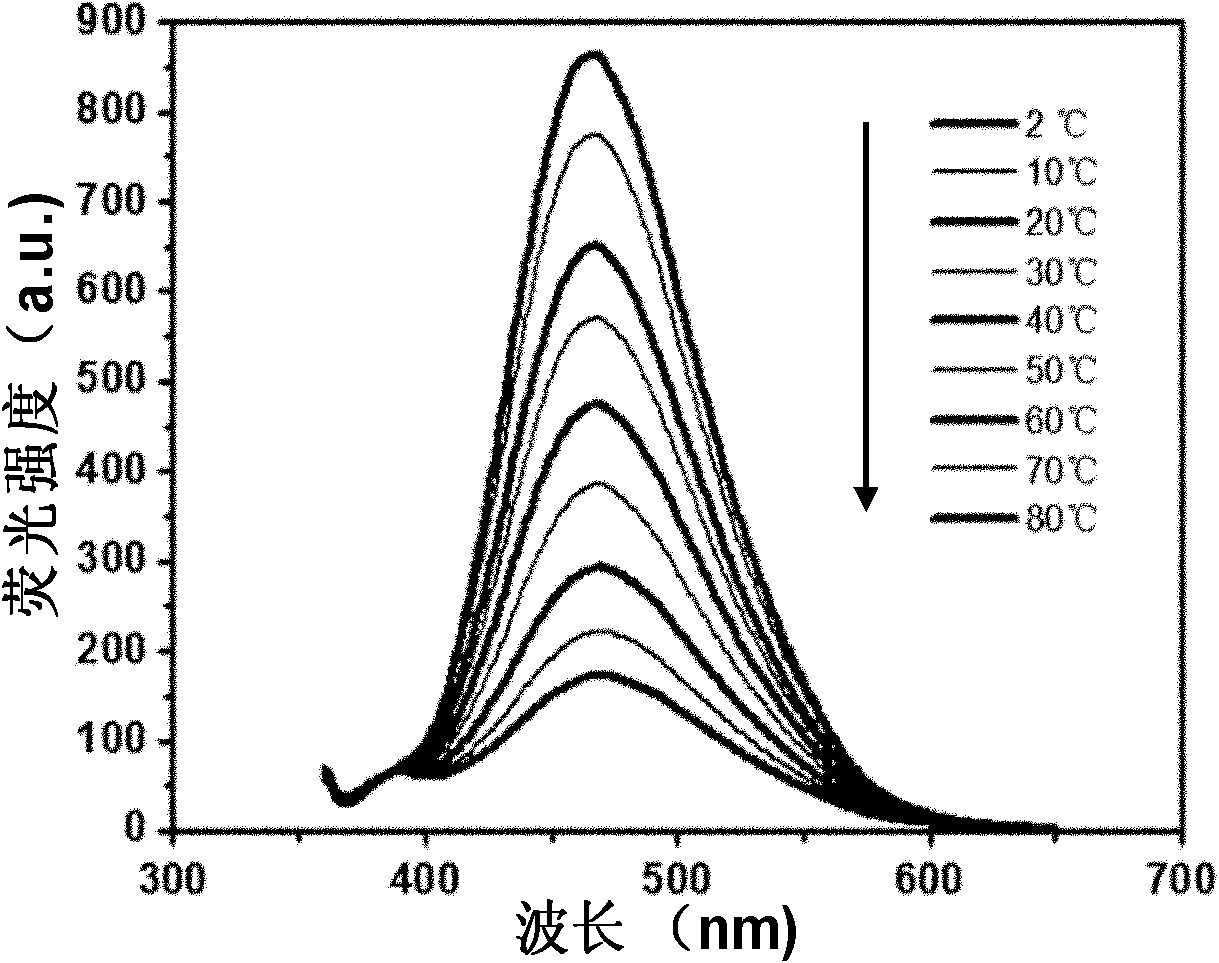
Method for preparing nano fluorescence thermometer
InactiveCN102115570AImprove stabilityWith reversible changeThermometers using physical/chemical changesLuminescent compositionsAggregation-induced emissionMulti response
The invention belongs to the field of high polymer materials, and relates to a method for preparing a nano fluorescence thermometer based on thermosensitive controllable nano microspheres with fluorescence property. The method comprises the following steps of: synthesizing core / shell-structured polymer nano microspheres with thermosensitive characteristic; and compounding fluorescent molecules with aggregation-induced emission (AIE) property into the shell layers of the microspheres to realize sudden fluorescence enhancement of the fluorescent molecules so as to obtain the thermosensitive controllable nano hydrogel microspheres with the fluorescence property, wherein the fluorescence intensity of the microspheres is linearly reversibly reduced or enhanced with the rise and reduction of the ambient temperature, and the microspheres have high stability in a range of 2 to 95DEG C. The thermosensitive hydrogel material has high application value and good prospect in the aspects such as nano fluorescence thermometers, nano-biomaterials, multi-response sensors and the like.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Side-chain liquid crystal polymer with aggregation-induced emission property and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107011469AEasy to synthesizeEasy to purifyLiquid crystal compositionsBenzaldehydeSide chain
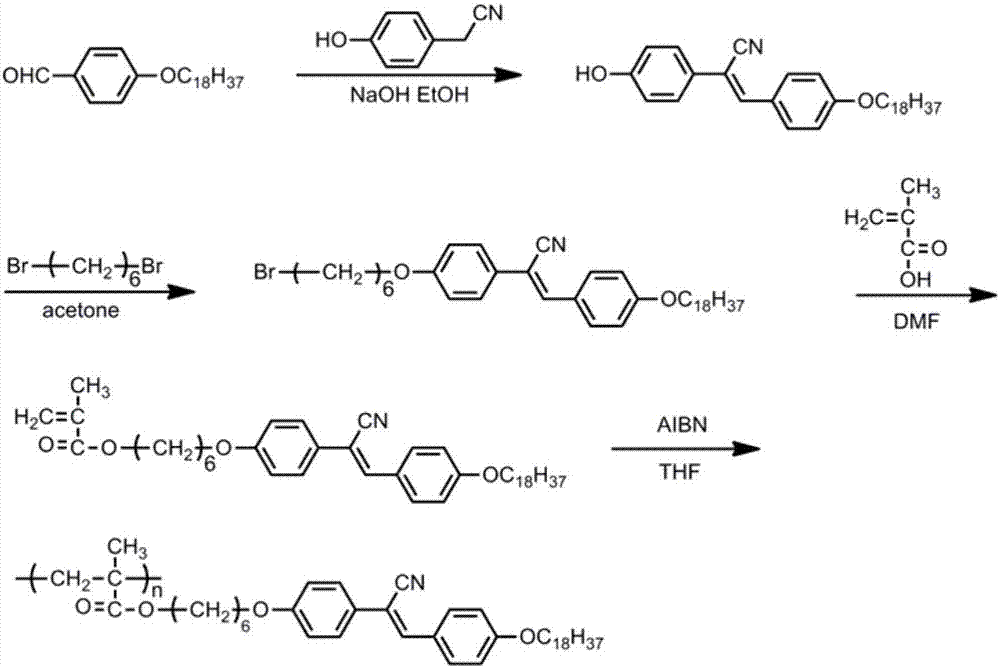
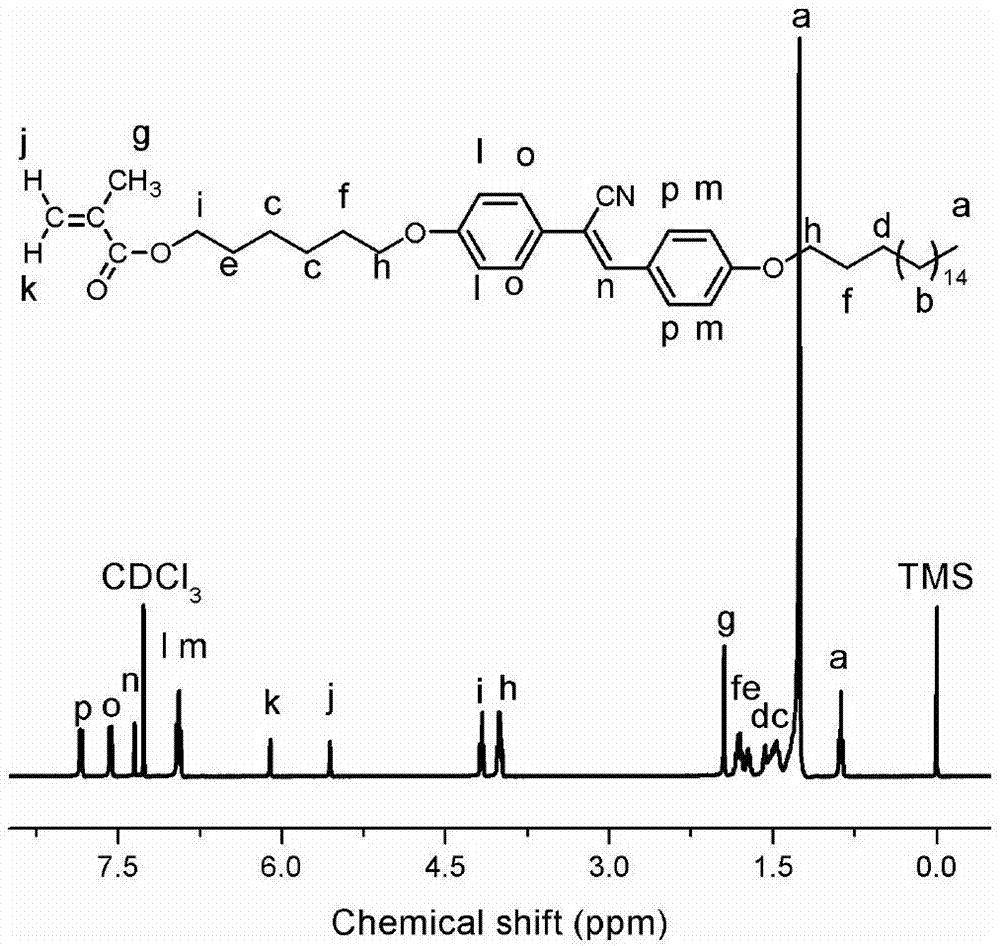
The invention discloses a side-chain liquid crystal polymer with aggregation-induced emission property and a preparation method thereof. A substituted cyano-distyrene compound is generated by using a substituent-containing para benzaldehyde derivative and hydroxybenzyl cyanide through Knoevenagel reaction, so that, on one hand, the substituted cyano-distyrene compound can react with polymerizable double bond-containing acids such as saturated dihalide, methacrylic acid or acrylic acid in sequence to generate a polymerizable monomer and a side-chain liquid crystal polymer with a flexible spacer is obtained through free radical polymerization; and on the other hand, the substituted cyano-distyrene compound can directly react with polymerizable double bond-containing acyl chloride such as methacryloyl chloride or acryloyl chloride to generate the polymerizable monomer and a side-chain liquid crystal polymer free of the flexible spacer is obtained through free radical polymerization. A fluorescent chromogenic group and a liquid crystal unit are combined into one; the method is simple in synthesis and easy to purify, and the obtained polymer has an obvious aggregation-induced emission effect, has excellent liquid crystal property and has a good application prospect.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
A method for monitoring the aggregation process of β-amyloid protein using aggregation-induced luminescence
InactiveCN102279270AHigh selectivityIncreased hydrophobicity of the environmentBiological testingAggregation-induced emissionCell Aggregations
The invention discloses a method for monitoring beta amyloid protein aggregation process by aggregation-induced emission, belonging to the technical field of biomedical research and clinical detection. With the method, the high affinity between sulfydryl on cysteine and maleimide is utilized to specially combine the beta amyloid protein on an aggregation-induced emission probe. The beta amyloid protein aggregation process is monitored on the basis of aggregation-induced emission enhancement phenomenon. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity, high selectivity, good stability, low manufacture cost and the like and is easy to control. The A beta42 and A beta40 contents can be monitored in a micromole, even a nano-mole level, the detection speed of the method is improved by 15 times if being compared with that of the detection method which utilizes probes, such as ANS (8-aniline-1-naphthalene sulfonic acid) and the like. The beta amyloid protein aggregation process can be qualitatively and quantitatively monitored, the method has a good application prospect if being applied to the pathologic diagnosis of latent patients suffering from senile dementia.
Owner:SHANGQIU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
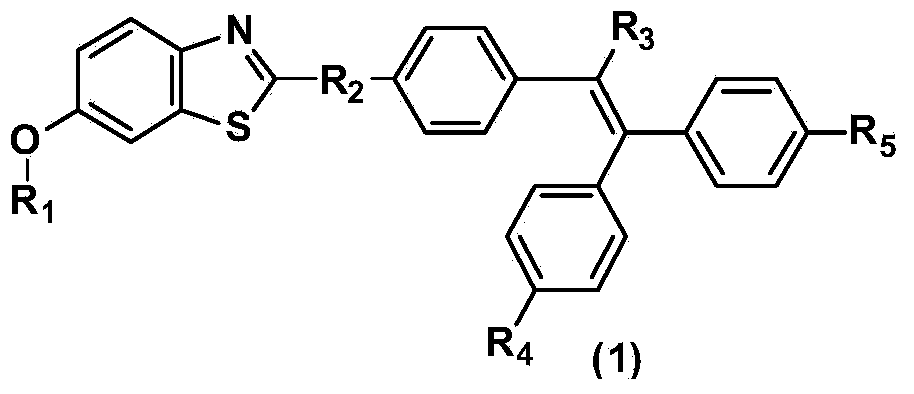
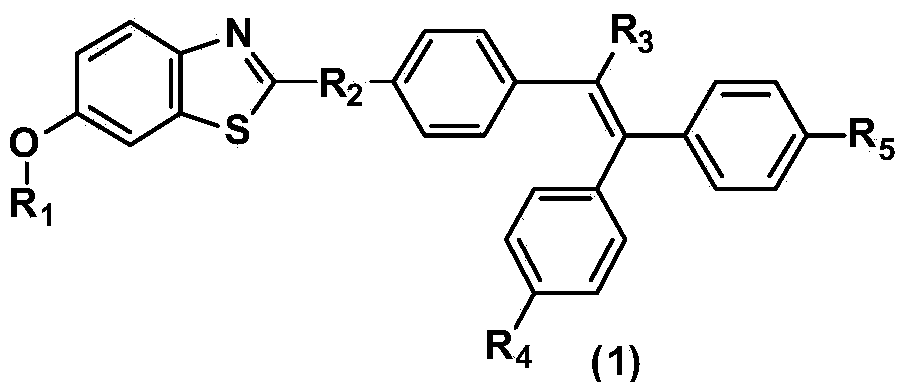
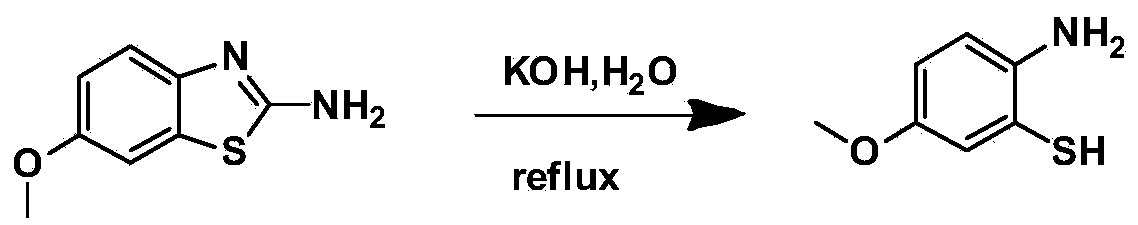
Benzothiazole derivative containing triphenylethylene or tetraphenylethylene structure and having aggregation-induced emission property and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103804318AWeak luminous intensityLow costOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesLuminous intensityPhotochemistry
The invention discloses a benzothiazole derivative containing a triphenylethylene or tetraphenylethylene structure and having aggregation-induced emission property and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: with 2-amino-6-methoxybenzothiazole as a start raw material, performing a ring-opening reaction under an alkaline condition to generate 2-amino-5-methoxythiophenol; performing a ring-closing reaction with an aromatic aldehyde compound containing a triphenylethylene or tetraphenylethylene structure to obtain a methoxy-containing benzothiazole derivative, or performing demethylation to obtain a hydroxyl-containing benzothiazole derivative, wherein the compound also can be modified through a group substitution reaction to generate a benzothiazole derivative containing other functional groups. The benzothiazole derivative disclosed by the invention has relatively low luminous intensity in a solution, emits strong fluorescence in an aggregation state or solid state, and belongs to good aggregation-induced emission materials; the synthesis is relatively simple, and the cost of the raw materials is low, so that large-scale commercial production is easy to realize; the benzothiazole derivative plays an important role in the fields of electroluminescent devices, fluorescent probes, fluorescent switches, organism imaging and the like.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Luminescent material having aggregation-induced emission, method of making and application thereof
ActiveCN104877666AHas aggregation-induced luminescent propertiesImprove the possibility of applicationOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesAggregation-induced emissionLength wave
The invention discloses a luminescent material having aggregation-induced emission, a method of making and an application thereof. The luminescent material herein has properties of aggregation-induced emission (AIE) / aggregation-enhanced emission (AEE) with the maximum absorption wavelength red shift to a visible area so that this type of luminescent material has the potential applications in the field of biology and photoelectricity. The luminescent material herein also has excellent optical waveguide property with an optical loss lower to 0.100dB / [mu]m, and is applicable to produce optical waveguide materials and also applicable to organic light emitting diodes. The luminescent material herein also has the characteristic of mechanochromism and reversible mechanochromism, thus having potential application in the aspect of smart materials.
Owner:HKUST SHENZHEN RES INST +1
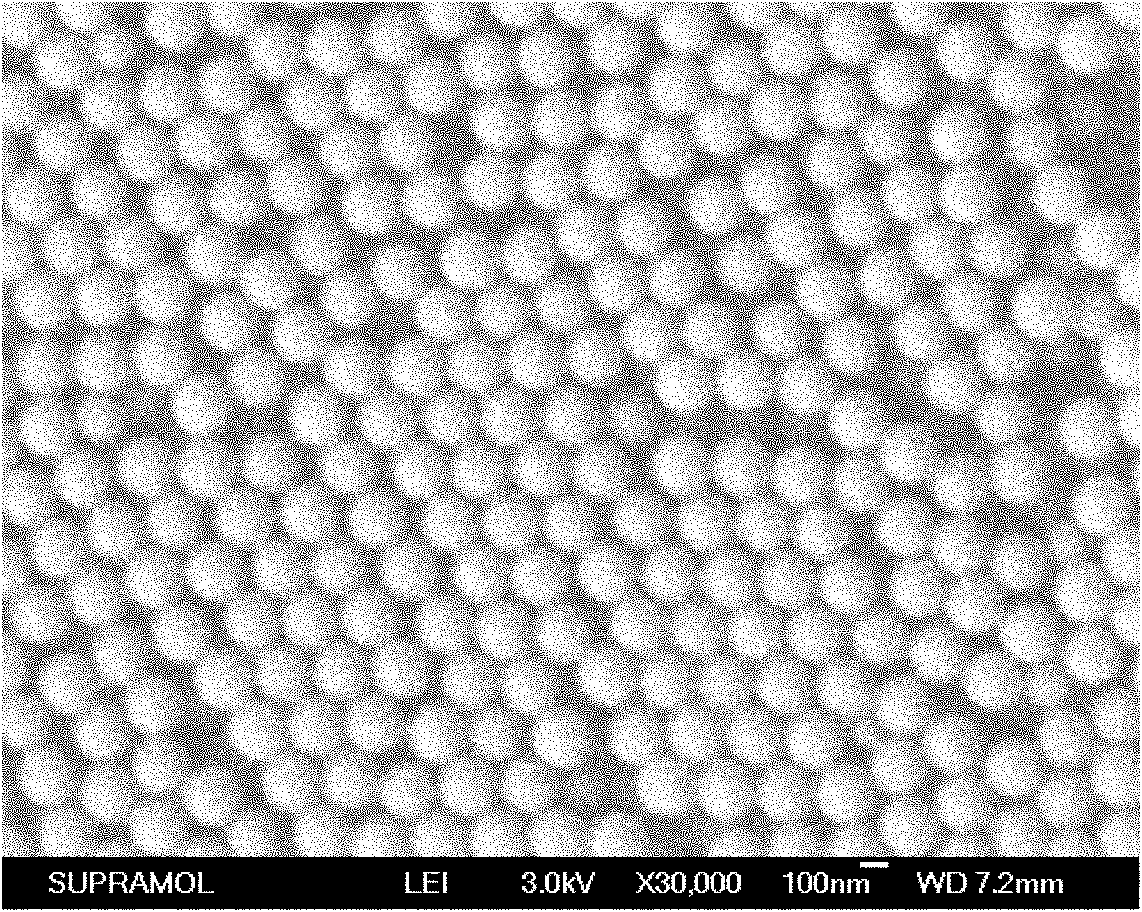
Method for preparing aggregation-induced emission type polymer fluorescent nanoparticle through mini-emulsion polymerization initiated by oil-soluble initiator
InactiveCN104628923ASimple processEasy to scale up productionLuminescent compositionsIce waterOil phase
The invention discloses a method for preparing an aggregation-induced emission type polymer fluorescent nanoparticle through mini-emulsion polymerization initiated by an oil-soluble initiator. The method comprises the steps of dissolving an aggregation-induced emission type fluorescent monomer, a co-stabilizer and an oil-soluble initiator into a monomeric compound to obtain an oil-phase solution; dissolving a water-soluble emulsifying agent into water to obtain a water solution of the emulsifying agent; and adding the oil-phase solution into the water solution of the emulsifying agent, stirring and pre-emulsifying to obtain a rough emulsion, carrying out ultrasonic dispersion on the rough emulsion in a 0-DEG C ice water bath to prepare a monomeric mini-emulsion, then, introducing nitrogen, removing oxygen, and reacting at the temperature of 40-90 DEG C for 0.5 hour to 2 days under the protection of nitrogen gas to prepare an emulsion of the aggregation-induced emission type polymer fluorescent nanoparticle. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the nanoparticle size, size distribution and fluorescent brightness are conveniently regulated, the stability of a system is good, the preparation process is simple, the process flow is short, and no organic solvents are consumed in preparation and after-treatment processes.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Quinoline nitrile derivative with aggregation-induced emission performance
ActiveCN102702096AStrong fluorescenceSignificant aggregation-induced luminescence characteristicsOrganic chemistryLuminescent compositionsQuinolineOrganism
The invention relates to a quinoline nitrile derivative. A method comprises the following steps of: reacting 2-methylquinoline serving as an initial raw material with the corresponding alkyl halide to obtain quaternary ammonium salt, performing Michael addition-elimination reaction on the quaternary ammonium salt and malononitrile, and performing Knoevenagel condensation reaction on the obtained compound and the corresponding aromatic aldehyde to obtain a target product. The aggregate or solid substance of the derivative has strong fluorescence and large wavelength, is a good aggregation-induced emission material, and has considerable application prospects in the fields of electroluminescent devices, fluorescent probes, intelligent materials, organism imaging and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Aie luminogens for bacteria imaging, killing, photodynamic therapy and antibiotics screening, and their methods of manufacturing
ActiveCN107001927ASimplify the imaging processEasy to filterGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsOrganic active ingredientsPhotodynamic therapyCritical micelle concentration
The invention relates to synthesis of fluorescent molecules with aggregation-induced emission (AIE) characteristics and application as fluorescent probes for cellular imaging, killing, and antibiotic screening, wherein the cells are bacteria or mammalian cells. The fluorescent molecules generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) upon light irradiation. The invention also relates to a probe comprising fluorescent molecules exhibiting AIE phenomenon, wherein the probe is used for bacterial and biological study. The invention further relates to a method of imaging and quantifying bacterial, a method of killing cells, a method of high throughput antibiotics screening and determining bacteria resistance, a method of photodynamic therapy, and a method of determining critical micelle concentration.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel function diamine monomer containing carbazole and large conjugated structure and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102766085AHas the effect of aggregation-induced luminescenceThe synthesis process is simpleOrganic chemistryPolyesterImide
The invention discloses a novel function diamine monomer containing carbazole and a large conjugated structure and a preparation method and application thereof. The novel function diamine monomer is started from a basic monomer element and obtained through a series of chemical reaction of helogenation reaction, Wittig-Horner reaction, UIImann reaction, Suzuki reaction and the like. A synthetic method of the novel function diamine monomer is simple in process, easy to purify and suitable for industrial production. The monomer has a large non-planar large conjugated structure, has the effect of aggregation-induced emission, and can be used for synthetizing high-performance functionalized polymers of polyamide, polyimide, polyamide-imide, polyester-imide and the like.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Preparation method and application of star polymer
The invention relates to a novel preparation method and application of a cationic amphiphilic tetra-armed star polymer. In particular, the star polymer can be obtained through synthetic means such as atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) and click chemistry. A core of the star polymer is tetraphenylethylene with the characteristic of aggregation-induced emission. A polymer linear arm is a cationic amphiphilic random copolymer with excellent antibacterial effects. A covalently labeled T1 type magnetic resonance (MR) contrast agent is an organic gadolinium chelate. By using the cationic amphiphilic tetra-armed star polymer, fluorescence / MR double quantitative detection of Gram positive and negative bacteria with negative charges on the surfaces in the environment of pure water is achieved, and meanwhile good antibacterial effects are gained.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
High-polymer vesicle containing AIE (aggregation-induced emission) molecules as well as preparation method and application of high-polymer vesicle
InactiveCN105524441AOvercoming the disadvantages of aggregation-induced fluorescence quenchingAvoid identificationOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryCopolymerClinical imaging
The invention belongs to the field of high-polymer materials and discloses a high-polymer vesicle containing AIE (aggregation-induced emission) molecules as well as a preparation method and an application of the high-polymer vesicle. The high-polymer vesicle is mainly formed through self-assembly of the AIE molecules and amphiphilic block copolymers; the outer layer and the inner layer of a high-polymer vesicle film are hydrophillic layers, each hydrophillic layer is formed by hydrophilic chain sections in the amphiphilic block copolymers, and a film intermediate layer between the outer layer and the inner layer is formed by hydrophobic chain sections in the amphiphilic block copolymers and the AIE molecules. The high-polymer vesicle has high fluorescence intensity and can meet different fluorescent staining demands. The preparation method is simple and feasible, the production efficiency is high, and the repeatability is good. The high-polymer vesicle can be used for related fields of optical bioimaging, biological detection and clinical imaging, high-polymer vesicle research and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Tetrapherylpyrazine low-molecular-weight derivate, tetrapherylpyrazine polymer and aggregation-induced emission material
ActiveCN104447582AWith AIE performanceEasy to synthesizeGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsLuminescent compositionsAggregation-induced emissionHalogen
The invention discloses a tetrapherylpyrazine low-molecular-weight derivate, a tetrapherylpyrazine polymer and an aggregation-induced emission material. The tetrapherylpyrazine low-molecular-weight derivate is of a structure as shown in a formula (1), wherein R1, R2, R3 and R4 are independently selected from hydrogen, alkoxy, substituted or unsubstituted phenyl, halogen or acetenyl; the substituent of phenyl is aromatic group. The tetrapherylpyrazine derivate is basically prepared by two methods, namely, (1) the method for preparing by the cyclization reaction of a benzoin derivative, and (2) preparing by the cyclization reaction of dibenzoyl derivate and 2-diphenyl diaminoethane; the synthesized diyne derivate can be derived by clicking polymerizing through an AIE (Aggregation Induced Emission) polymer. In light of the simple and convenient synthesis, tetrapherylpyrazine can be used as a novel AIE mother nucleus following after hexaphenyl silole and tetraphenyl ethylene and is wide in applicable scope. The formula is described in the specification.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Asymmetrical thermal-activation-delayed aggregation-induced emission material based on diphenyl sulfone phenoxazine, as well as synthesis method and application of material
ActiveCN105038764AHas aggregation-induced luminescent propertiesHigh thermal decomposition temperatureOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesSynthesis methodsNon doped
The invention discloses an asymmetrical thermal-activation-delayed aggregation-induced emission material based on a diphenyl sulfone phenoxazine, as well as a synthesis method and application of the material. A core structure of the material comprises a diphenyl sulfone unit and a phenoxazine group, and further comprises an electronic structure unit made from aryl heterocyclic groups except a phenoxazine substituent. The synthesis method and the purification process of the material are simple, the thermal performance, luminous performance and the like of an end product can be adjusted according to the connection of different groups, the obtained emission material has thermal-activation-delayed fluorescent and aggregation-induced emission performance at the same time, is good in heat stability, higher in glass transition temperature and excellent in luminous performance. A non-doped OLED device manufactured by using the emission material as the luminous layer is high in luminous brightness and good in stability, so that the luminous efficiency and the service life of the OLED device can meet the practical requirements.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Boron-containing luminescent material and its preparation method and use
ActiveCN102899027AGood optical performanceRaw materials are easy to getSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAggregation-induced emissionOptical property
The invention relates to the technical field of organic chemistry and discloses a boron-containing luminescent material and its preparation method and use. The boron-containing luminescent material solves the problem that the existing luminescent materials in a solid state do not emit fluorescent light. The boron-containing luminescent material has good optical properties and aggregation-induced emission effects and can emit fluorescent light in a solid state. The preparation method has simple processes, adopts easily available raw materials and has a high yield.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing aggregation-induced emission type polymer fluorescent nanoparticle through mini-emulsion polymerization initiated by water-soluble initiator
The invention discloses a method for preparing an aggregation-induced emission type polymer fluorescent nanoparticle through mini-emulsion polymerization initiated by a water-soluble initiator. The method comprises the steps of dissolving an aggregation-induced emission type fluorescent monomer and a co-stabilizer into a monomeric compound to obtain an oil-phase solution; dissolving a water-soluble emulsifying agent into water to obtain a water solution of the emulsifying agent; and adding the oil-phase solution into the water solution of the emulsifying agent, stirring and pre-emulsifying to obtain a rough emulsion, carrying out ultrasonic dispersion on the rough emulsion in a 0-DEG C ice water bath to prepare a monomeric mini-emulsion, adding a water-soluble initiator, then, introducing nitrogen, removing oxygen, and reacting at the temperature of 40-90 DEG C for 0.5 hour to 2 days under the protection of nitrogen gas to prepare an emulsion of the aggregation-induced emission type polymer fluorescent nanoparticle. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the nanoparticle size, size distribution and fluorescent brightness are conveniently regulated, the stability of a system is good, the preparation process is simple, the process flow is short, and no organic solvents are consumed in preparation and after-treatment processes.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Compound containing tetraphenyl ethylene unit, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN103396285AReduce the degree of conjugationIncrease brightnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum yieldAniline
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Synthesis of novel organic luminescent material containing carbazolyl toluylene derivant structure and application thereof
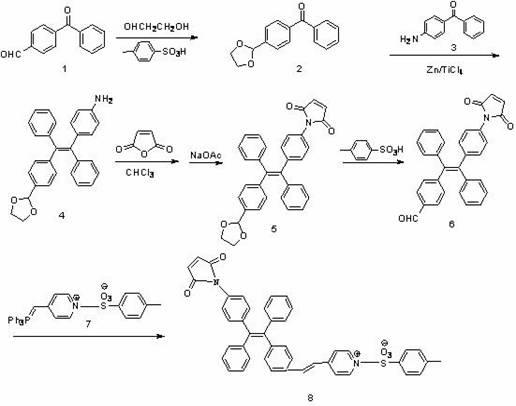
ActiveCN101343539AImprove thermal stabilityHigh glass transition temperatureOrganic chemistryElectrical apparatusVitrificationAggregation-induced emission
The invention relates to novel luminous material containing a carbazyl stilbene derivative structure, which belongs to the technical field of the organic luminous materials. When the synthesis is performed, two carbazyl diphenyl ketones (2) are connected by an aromatic compound containing two ylide groups; or the carbazyl diphenyl ketones are changed into an intermediate body (3) or an intermediate body (4) firstly, and then the carbazyl stilbene is coupled by a crossed coupling method. The art of the synthetic method provided by the invention is simple, the purification is easy, the synthesized organic luminous material containing the carbazyl stilbene derivative structure has a high thermal stability, a high glass-transition temperature and a strong illumination intensity, the material is suitable for preparing the material of photogenic layers in organic electroluminescent material devices, the luminous material with aggregation-induced emission effect can be serviced as stimuli-response functional material to be applied to chemical / biochemical sensors.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Novel chiral aggregation-induced emission material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107383094AExcellent optical propertiesGood optical performanceOrganic chemistry methodsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsQuantum yieldPhosphate
The invention discloses a novel chiral aggregation-induced emission material and a preparation method and application thereof. The structural formula of the chiral aggregation-induced emission material is as shown in formula (II). The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly designing and synthesizing a type of novel tetraphenyl ethylene phosphate, wherein the structural formula of the novel tetraphenyl ethylene phosphate is as shown in formula (I), and enabling the tetraphenyl ethylene phosphate to react with (R)-[1,1'-binaphthyl]-2,2'-biformaldehyde so as to generate the novel aggregation-induced emission material with the chiral structure. The chiral aggregation-induced emission material has the good optical property. In a mixed system of tetrahydrofuran and water, an ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum and a fluorescence emission spectrum of the chiral aggregation-induced emission material are changed along with the change of optical rotation. The material can be stimulated by 451 nm of blue light in the solid state, and emits 520 nm of green light. The solid-state fluorescence quantum yield is 29%. The chiral aggregation-induced emission material can be used as the chiral material applied to the fields, such as a photoelectric device and a biosensor, and has the larger application prospect.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com