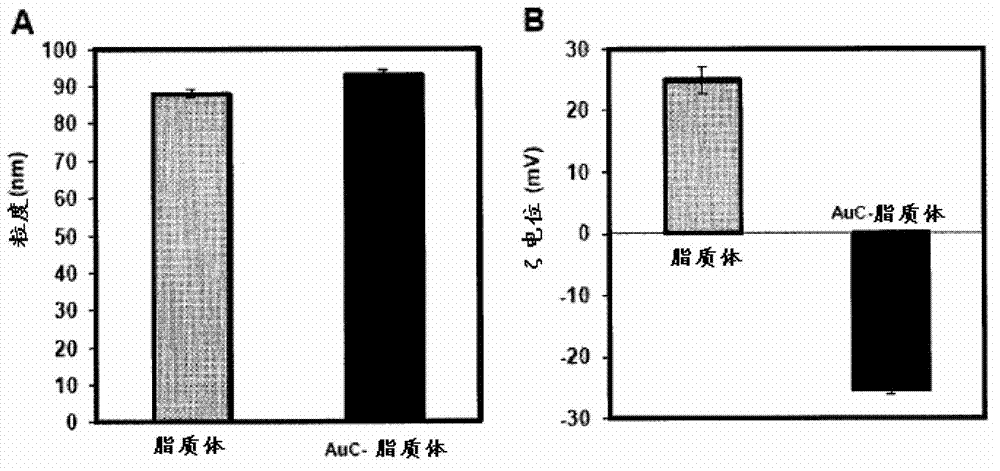
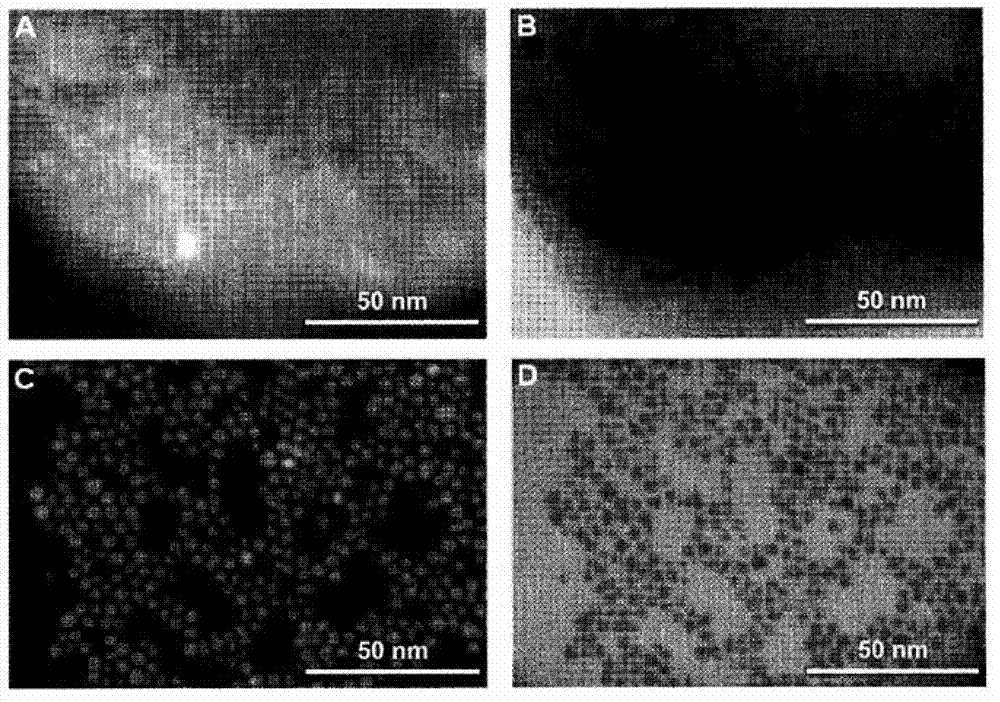
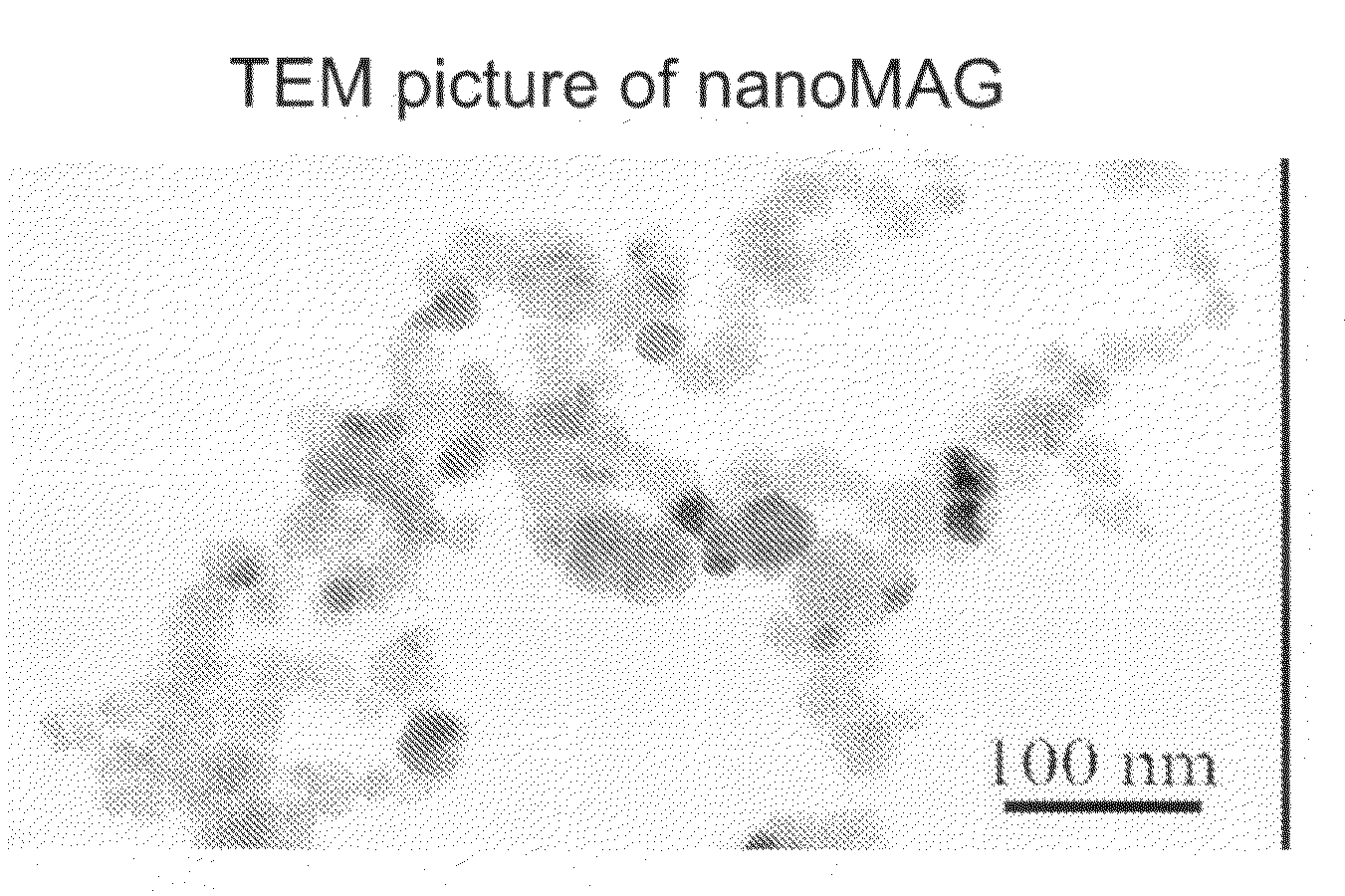
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Biocompatible nanoparticles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Biocompatible nanoparticle compositions and methods
ActiveUS20080255537A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryTherapeutic effectBiocompatible nanoparticles
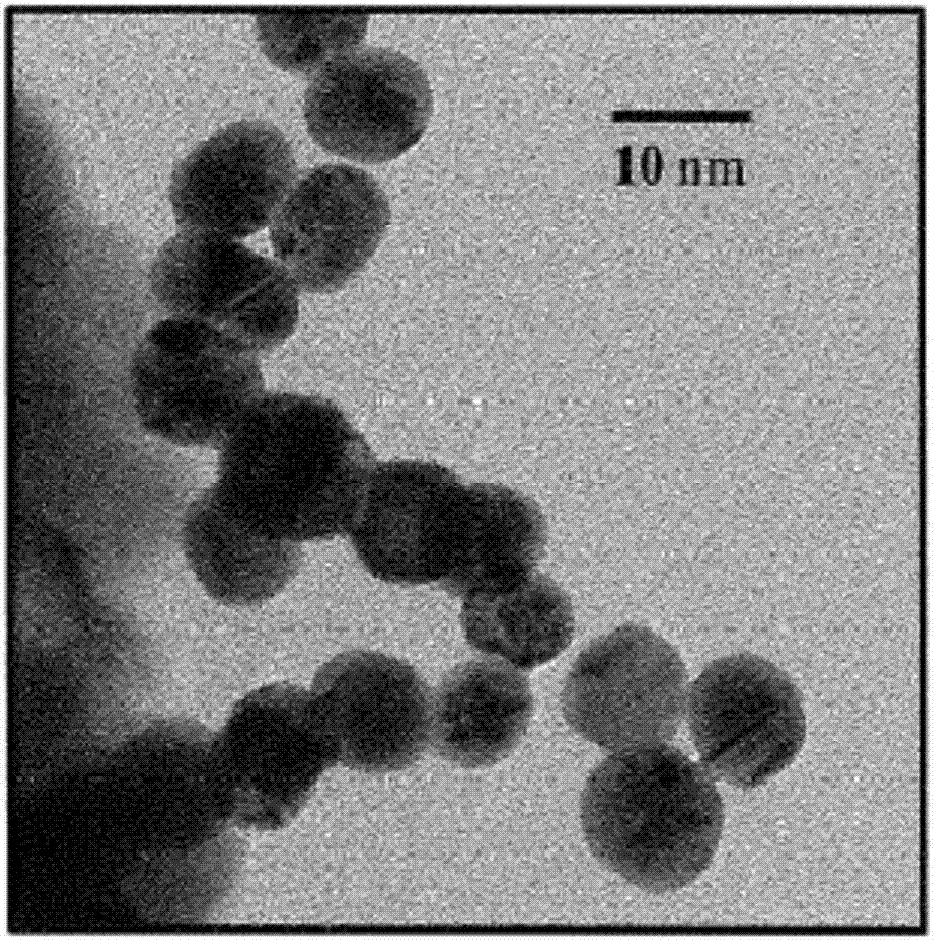
Various compositions, methods, and devices are provided that use fluorescent nanoparticles, which can function as markers, indicators, and light sources. The fluorescent nanoparticles can be formed from a fluorophore core surrounded by a biocompatible shell, such as a silica shell. In one embodiment, the fluorescent nanoparticles can be delivered to tissue to mark the tissue, enable identification and location of the tissue, and / or illuminate an area surrounding the tissue. In another embodiment, the fluorescent nanoparticles can be used on a device or implant to locate the device or implant in the body, indicate an orientation of the device or implant, and / or illuminate an area surrounding the device or implant. The fluorescent nanoparticles can also be used to provide a therapeutic effect.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Biocompatible nanoparticles with aggregation induced emission characteristics as fluorescent bioprobes and methods of using the same for in vitro and in vivo imaging
ActiveCN103842472APowder deliveryMicrobiological testing/measurementAggregation-induced emissionBiocompatible nanoparticles
The development of fluorescent bioprobes comprising organic fluorescent compounds that exhibit aggregation induced emission (AIE) properties, methods of producing the same, and their practical applications for in vitro and in vivo bioimaging.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Drug-eluting catheter and method of manufacturing the same
Owner:ANGES MG INC +2
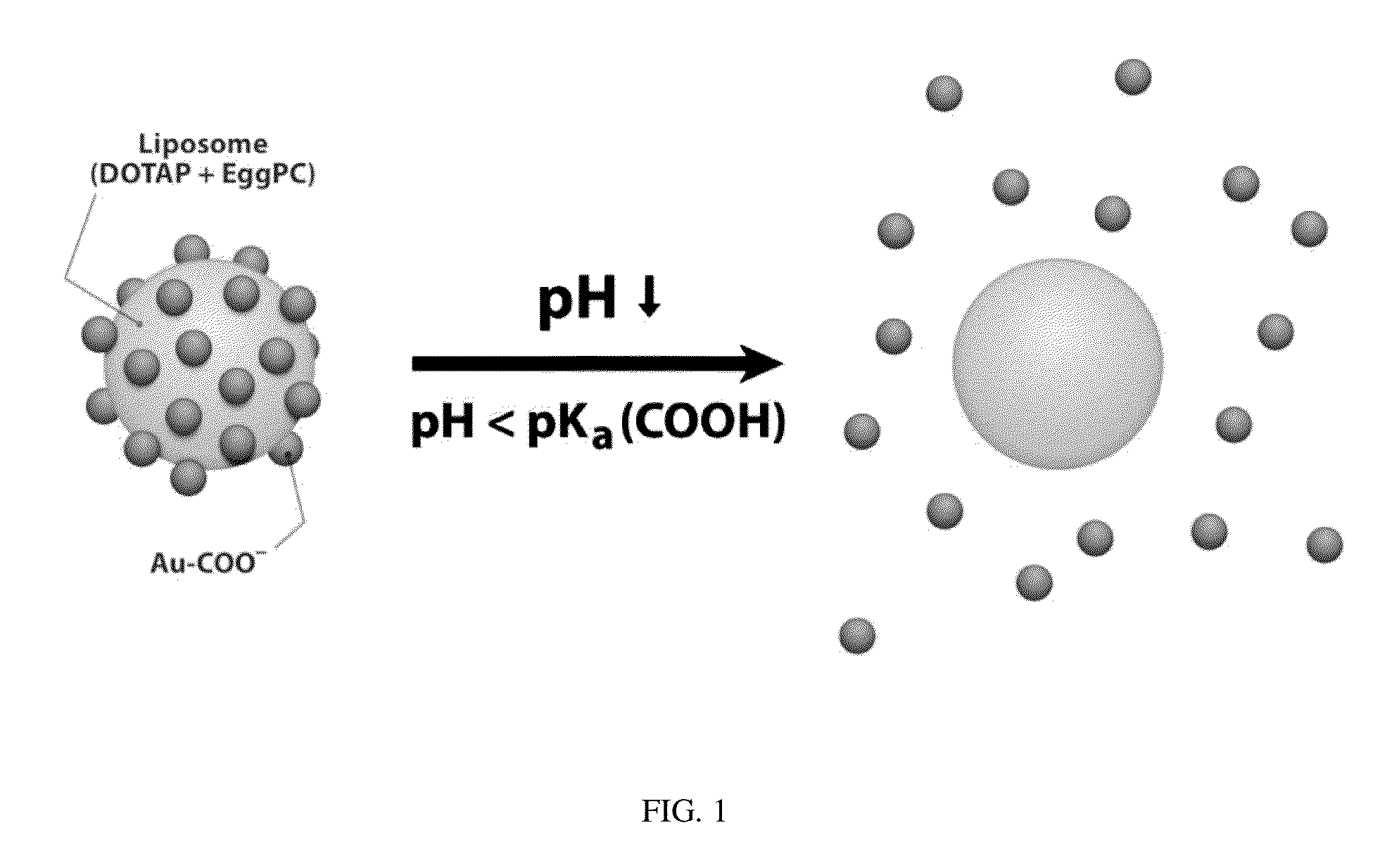
Triggered Cargo Release from Nanoparticle Stabilized Liposomes
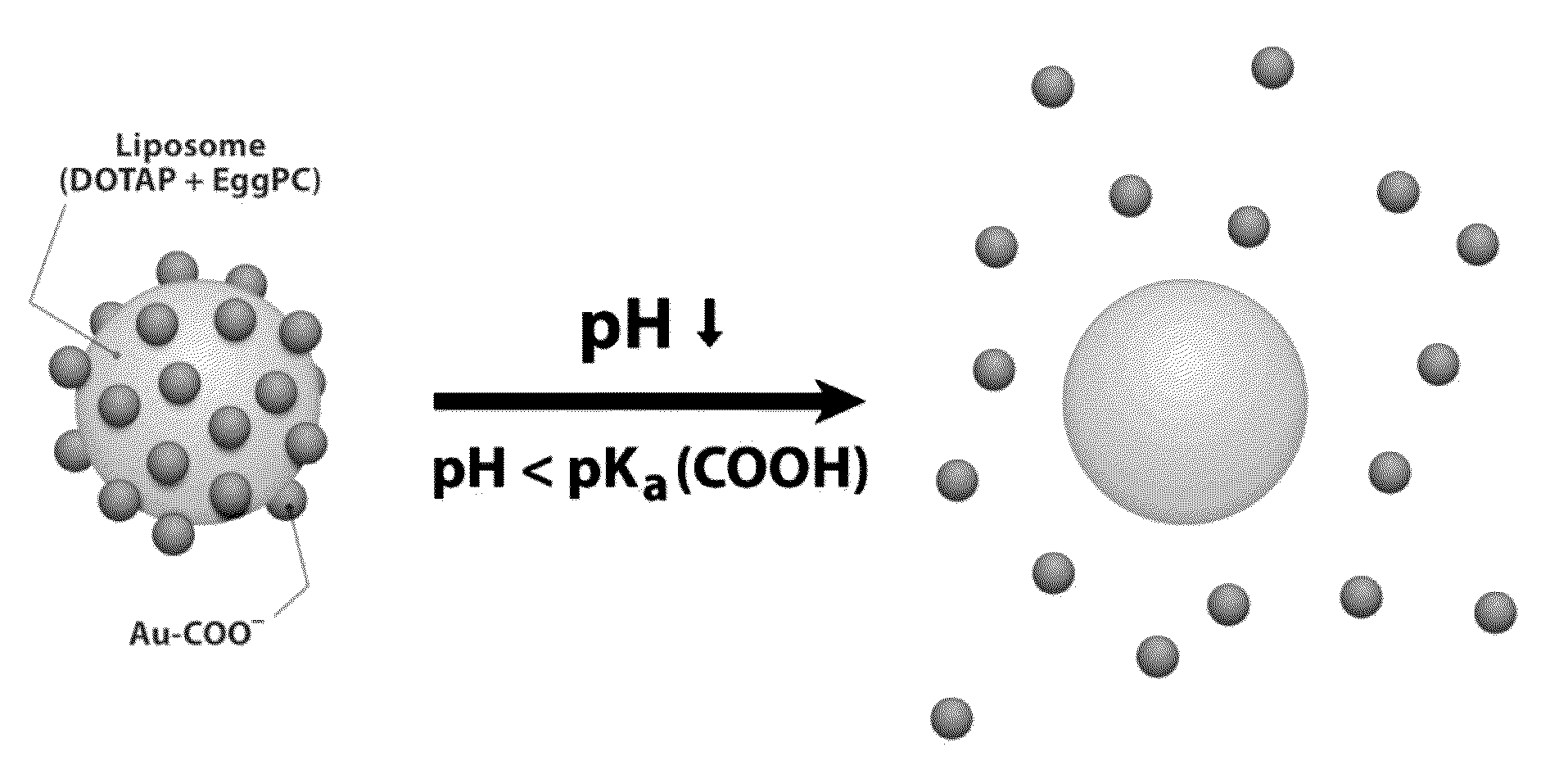
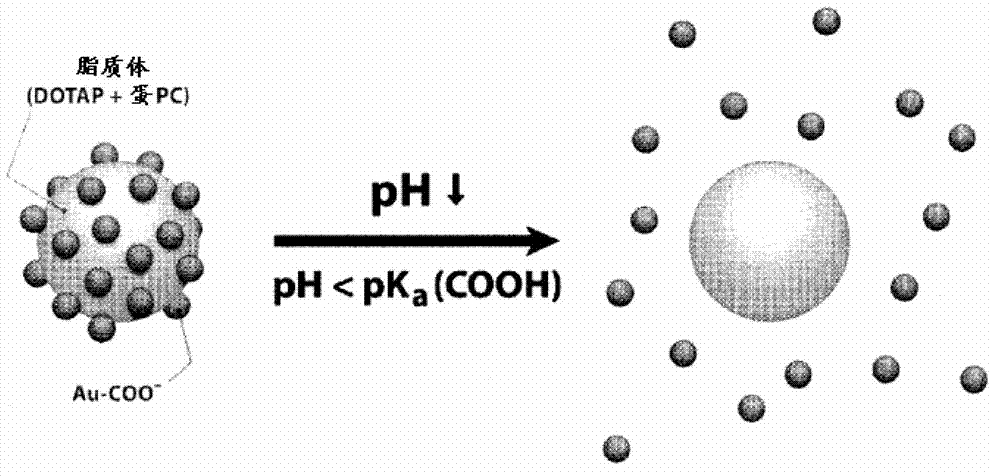
Control of the fusion activity of liposomes by adsorbing biocompatible nanoparticles to the outer surface of phospholipid liposomes is disclosed. The biocompatible nanoparticles effectively prevent liposomes from fusing with one another. Release of cargo from the liposome is accomplished via trigger mechanisms that include pH triggers, pore forming toxing triggers and photosensitive triggers. Dermal drug delivery to treat a variety of skin diseases such as acne vulgaris and staph infections is contemplated.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Cell culture system
The invention relates to a cell culture system comprising a three-dimensional biocompatible skeleton structure and biocompatible nanoparticles, to a method for cultivating cells, to the preparation ofcells, cell products and tissue and to the targeted production of cells or cell products and tissue using a cell culture system of this type.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method for production of biocompatible nanoparticles containing dental adhesive
InactiveUS20100166680A1High purityImproved diametral tensile strengthCosmetic preparationsBiocideZeta potentialApatite
A method of synthesizing hydroxyapatite nanorods, having high purity, high crystallinity and high aspect ratio is disclosed here. In one embodiment, high crystalline hydroxyapatite nanorods with relatively stoichiometric structure are prepared via hydrothermal method at 200° C. and under moderate acidic conditions. The synthesized hydroxyapatite nanorods have a diameter of 30-95 nm, a length of 850-1400 nm with an average aspect ratio of 24, degree of crystallinity of 73% and stoichiometry ratio of 1.69. Further it discloses the use of HAp in dental adhesive. The dental adhesive comprising synthesized HAp shows improved diametral tensile strength and high microshear bond strength. Energy dispersive X-ray mapping confirmed the uniform distribution of nanorods in the adhesive matrix. The synthesized hydroxyapatite nanorods have high colloidal stability in the dental adhesive solution. The nanorods are well dispersed and protected from aggregation by their high surface charges confirmed by zeta potential measurement.
Owner:SADAT SHOJAI MEHDI +2
Chelated nanoceria for the treatment of oxidative stress
A process for making cerium-containing nanoparticles with biocompatible stabilizers is described, wherein an aqueous reaction mixture comprising cerous ion, citric acid, a stabilizer (chelator) selected from the group consisting of nitrilotriacetic acid, ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid and diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid, and an oxidant, is provided, followed by a heating step to effectively form the nanoparticles. These biocompatible nanoparticles can be used to treat oxidative stress related diseases and events, such as ischemic stroke.
Owner:CERION
Medical device for placement into a lumen and manufacturing method thereof
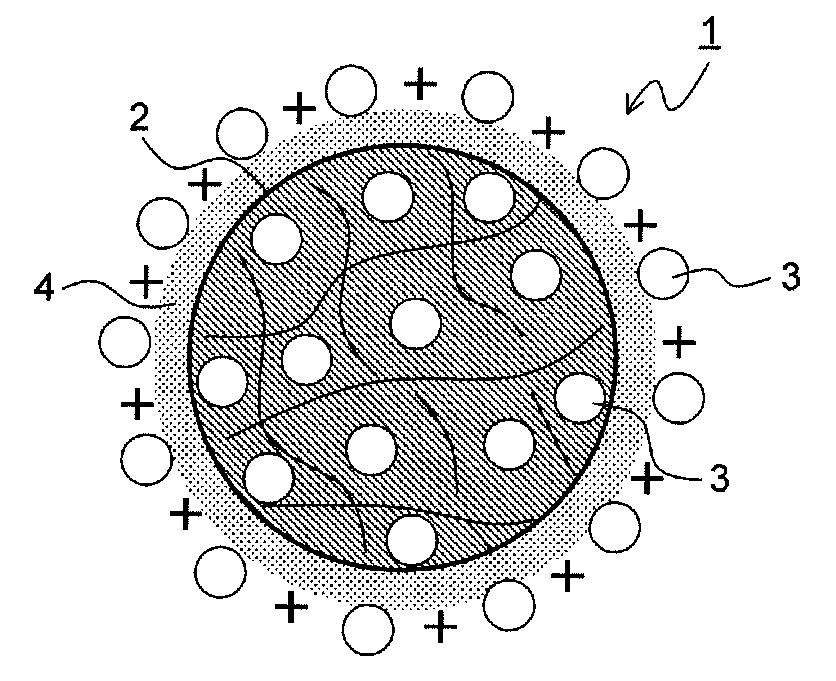
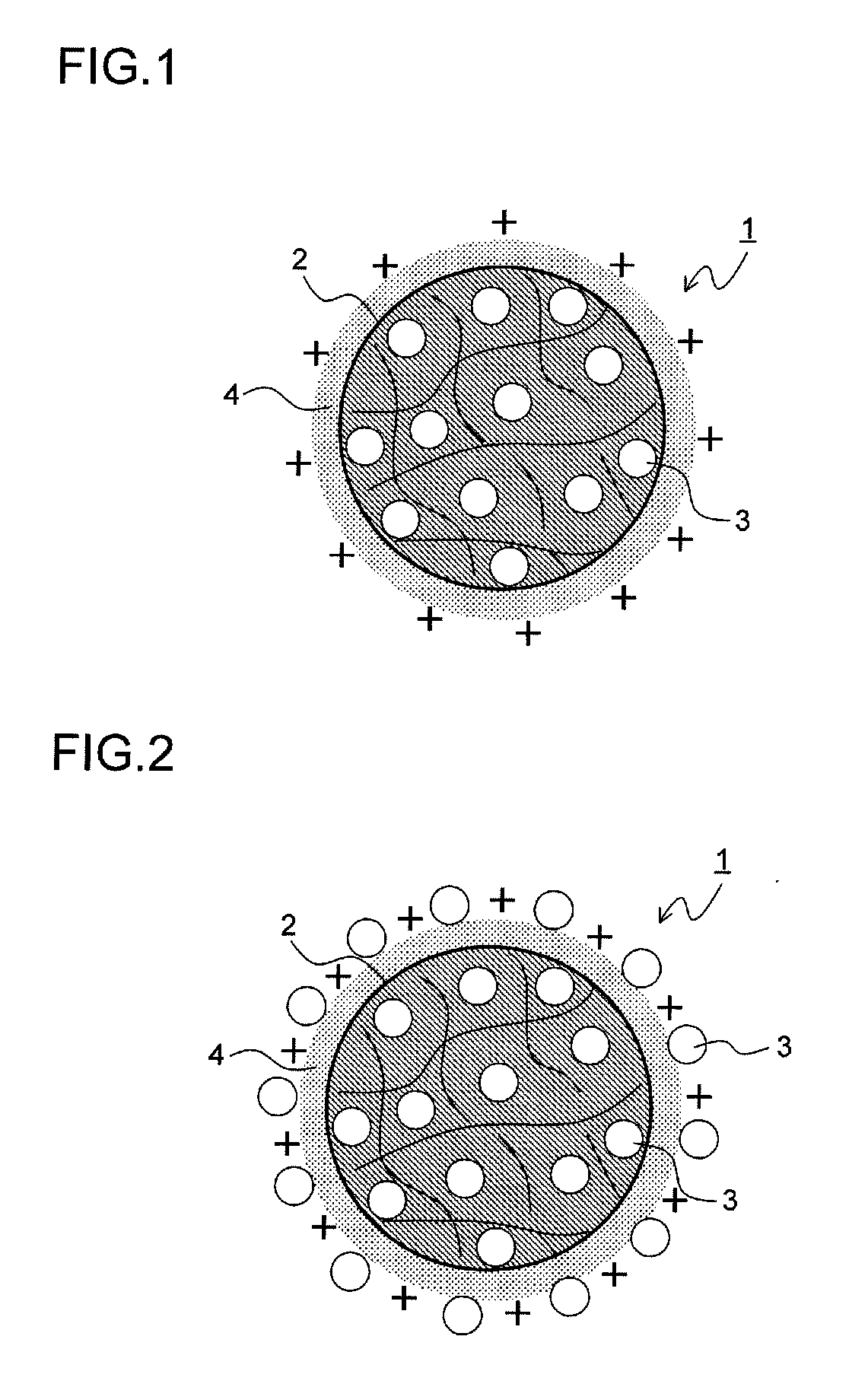
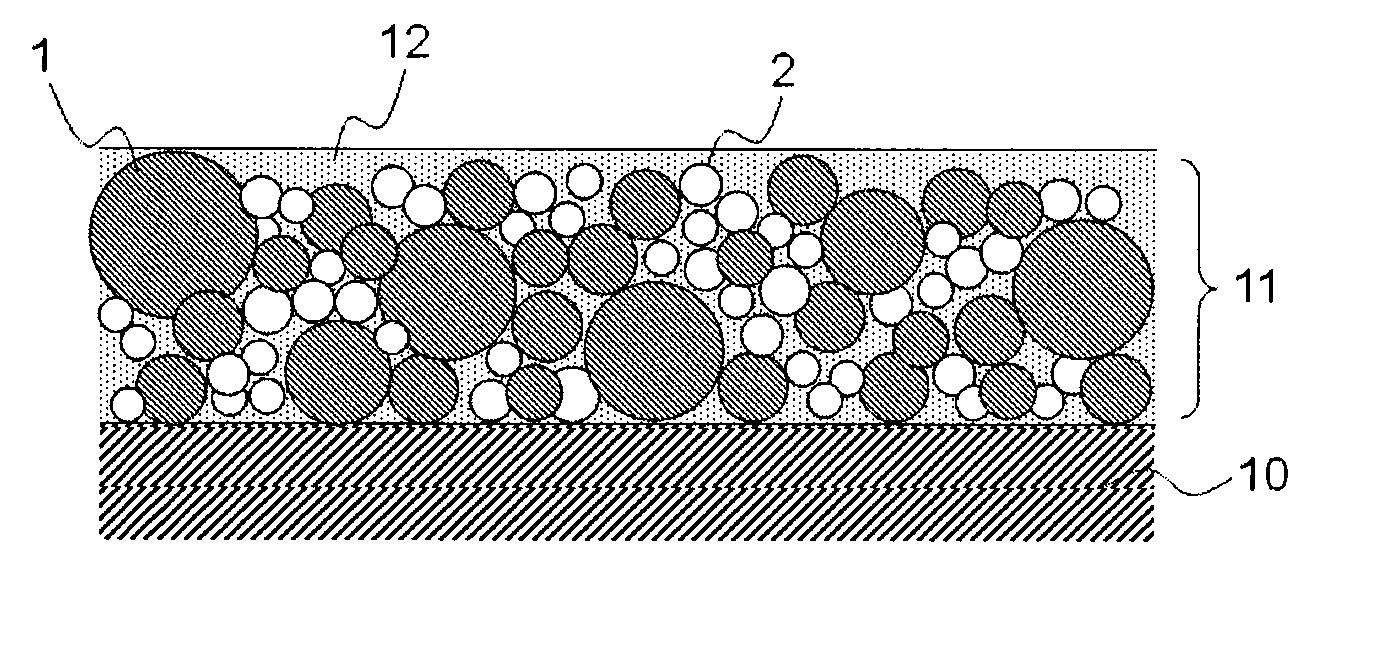
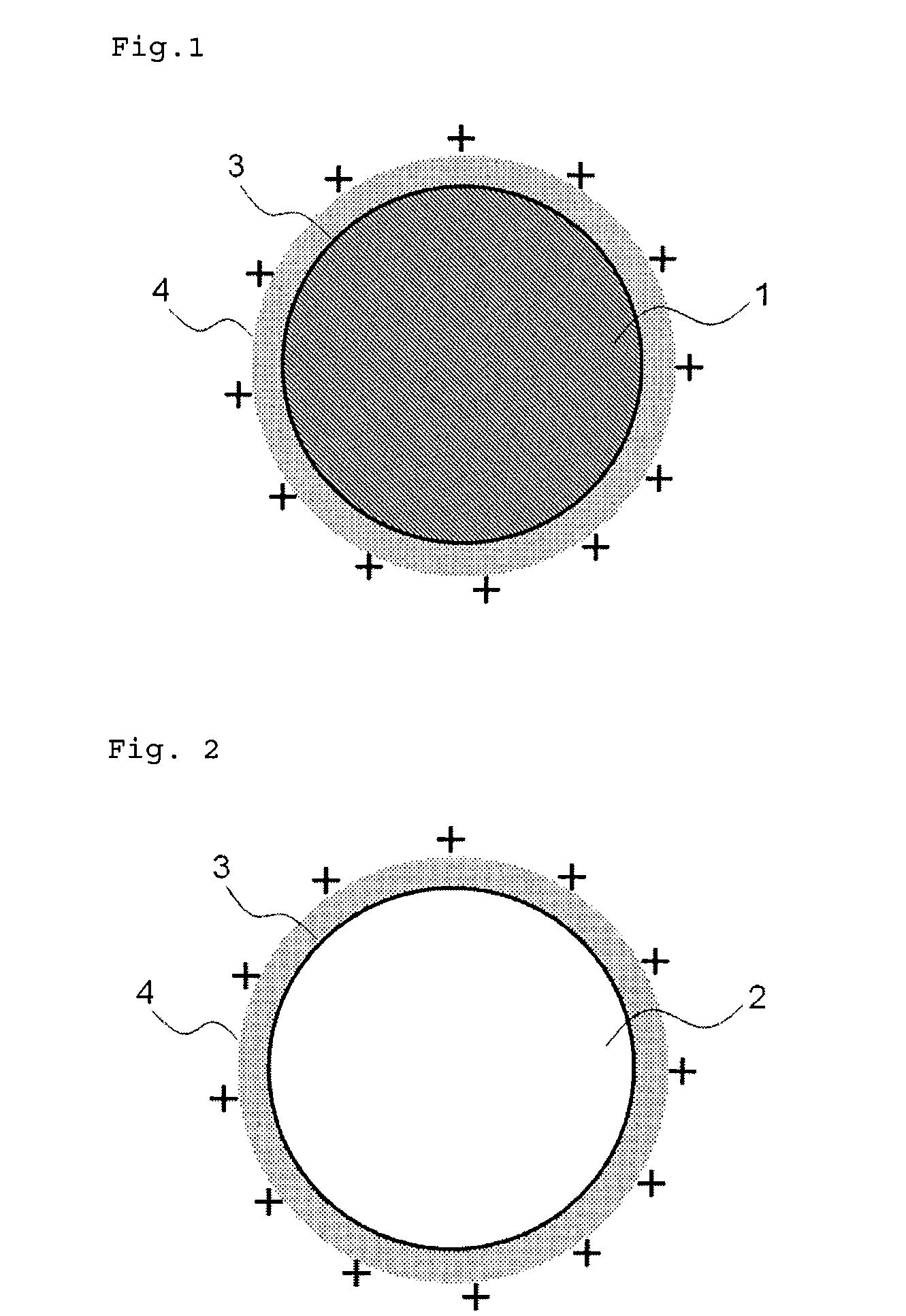
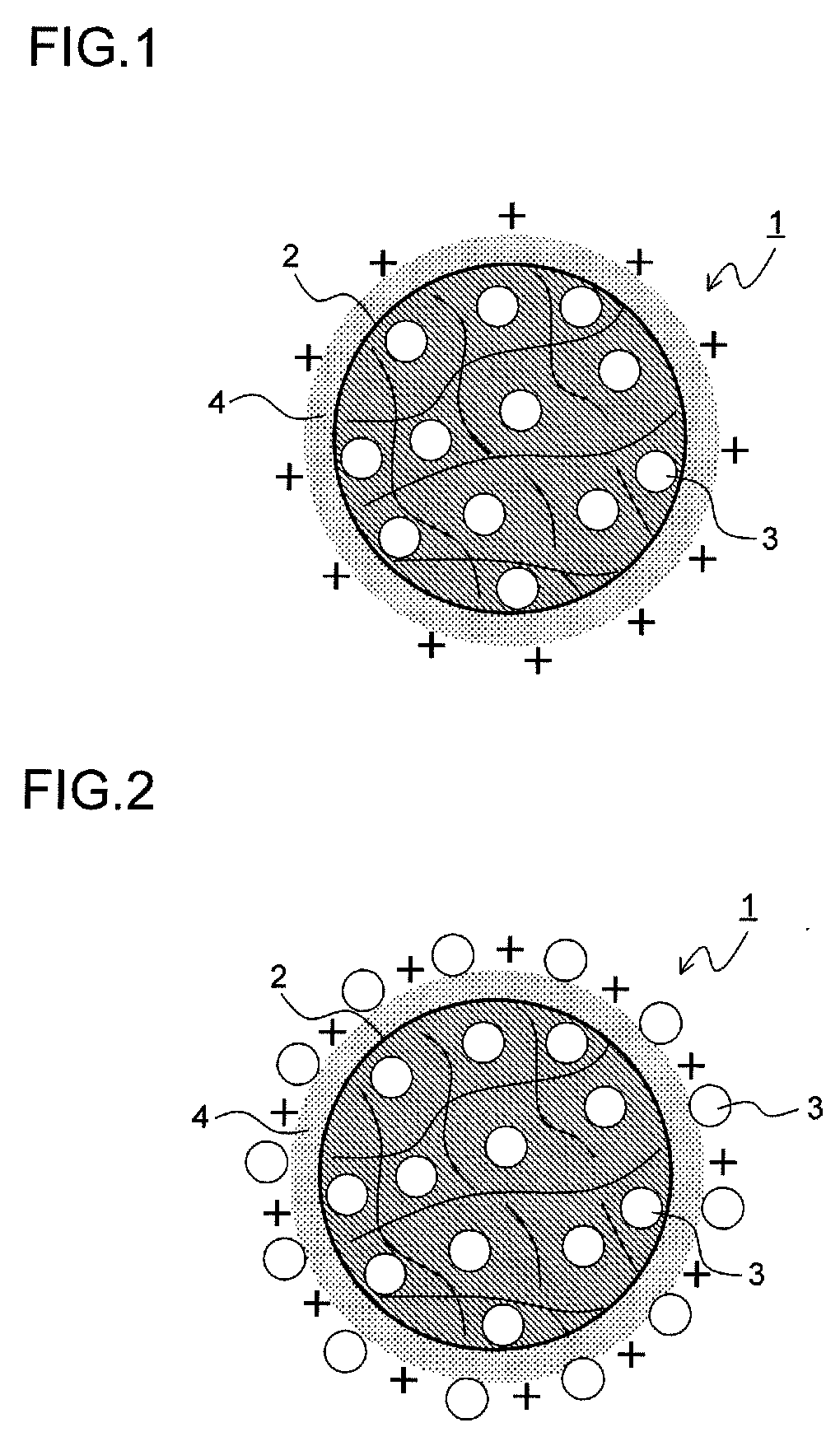
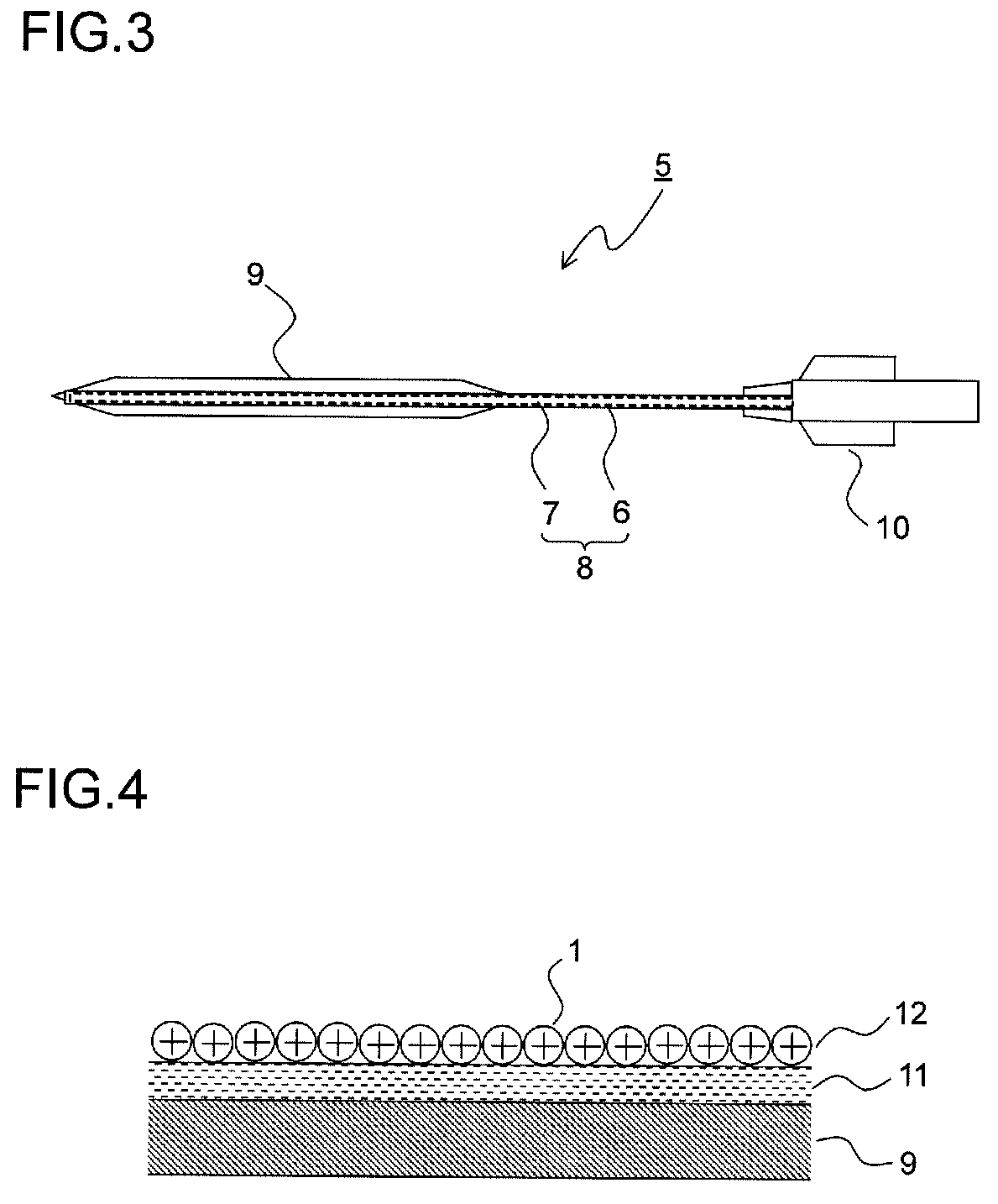
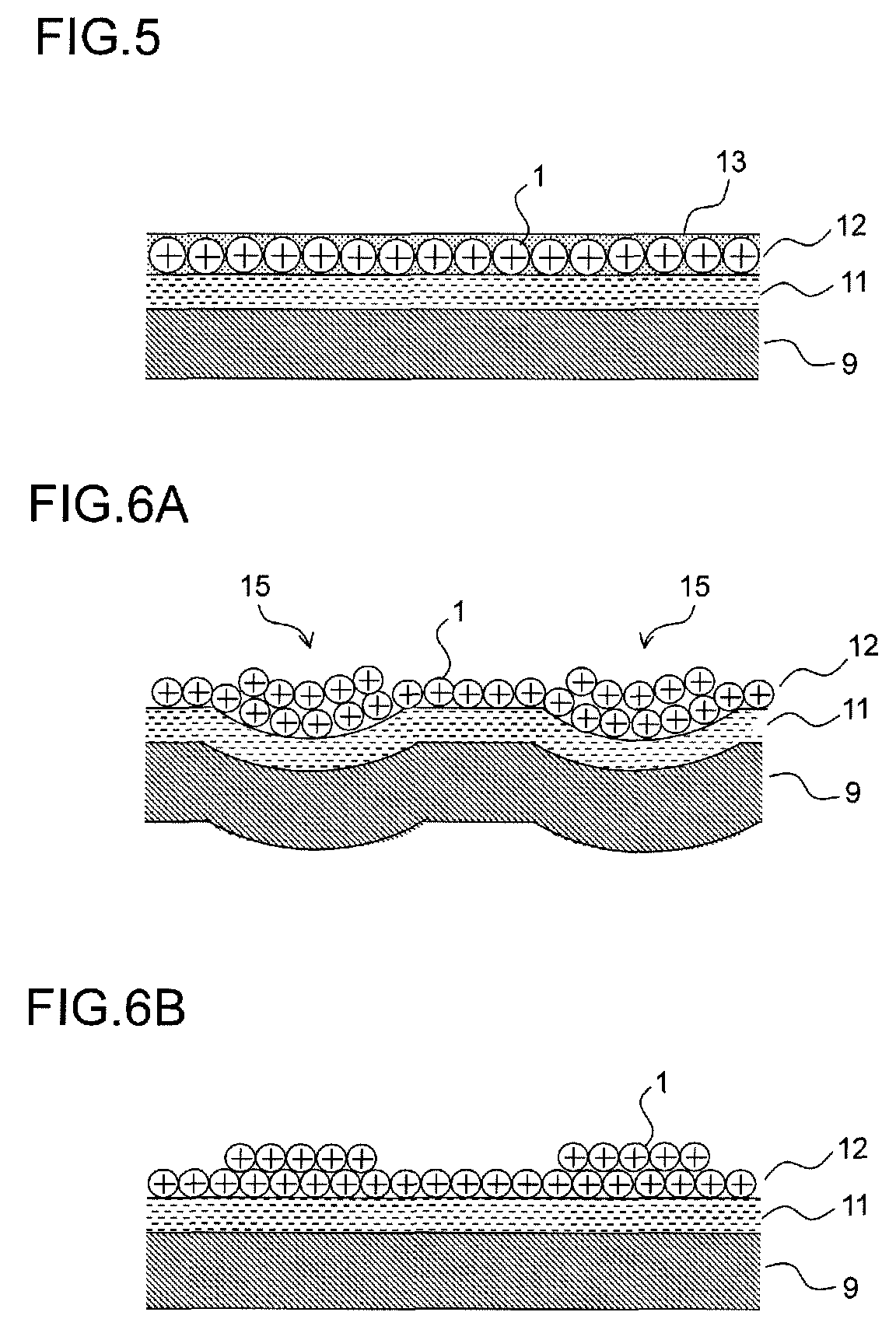
Provided is a medical device for placement into a lumen and a simple and inexpensive manufacturing method thereof, said medical device being a stent or a catheter and the surface thereof being uniformly and sufficiently coated with a drug. Drug particles having positive-charge modified surfaces and biocompatible nanoparticles are mixed and stuck to the medical device. After the DES is placed inside a living organism, the drug particles are eluted together with the biocompatible nanoparticles and efficiently taken into cells.
Owner:OTSUKA MEDICAL DEVICES
Medical device for placement into a lumen and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20120213838A1Low adhesivenessEfficient preparationOrganic active ingredientsVolume/mass flow measurementBiological bodyDissolution
The present invention provides a medical device for placement into a lumen such as a stent and a catheter whose surface is uniformly and sufficiently coated with a drug, and a process thereof with easy way and with low cost. The medical device is coated with mixed particles of drug particles whose surface is modified with positive-charge and biocompatible nanoparticles. In the invention, a drug can be taken into a cell through the dissolution of the drug particle together with the biocompatible nanoparticle after a DES is placed in a biological body.
Owner:OTSUKA MEDICAL DEVICES
Triggered cargo release from nanoparticle stabilized liposomes
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Magnetic Nanoparticles Compositions and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20100040555A1Preserve integrityEnsure and improve biocompatibilityBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsMagnetite NanoparticlesBiocompatible nanoparticles
The present invention relates to the use of a biocompatible nanoparticle or nanoparticle aggregate, in combination with an external non-oscillating magnetic field, wherein said nanoparticle comprises: a) a core comprising magnetic material; b) a biocompatible shell surrounding the core, and, optionally; c) a labelling agent wherein the outer diameter of the shell is less than about 100 nm, to prepare a composition, wherein the composition is deprived of any cell targeting means. The present invention further relates to the compositions thus obtained and to their uses in the field of human health, for the treatment of cancer, or in diagnostic (imaging for example), for the monitoring of tumor evolution.
Owner:NANOBIOTIX SA
Nanoparticulate Materials and Methods for Targeting Iron Acquisition and Metabolism for Treating Bacterial Infections
InactiveUS20200016086A1Prevent bacterial growthReadily internalizedHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideBiotechnologyCell membrane
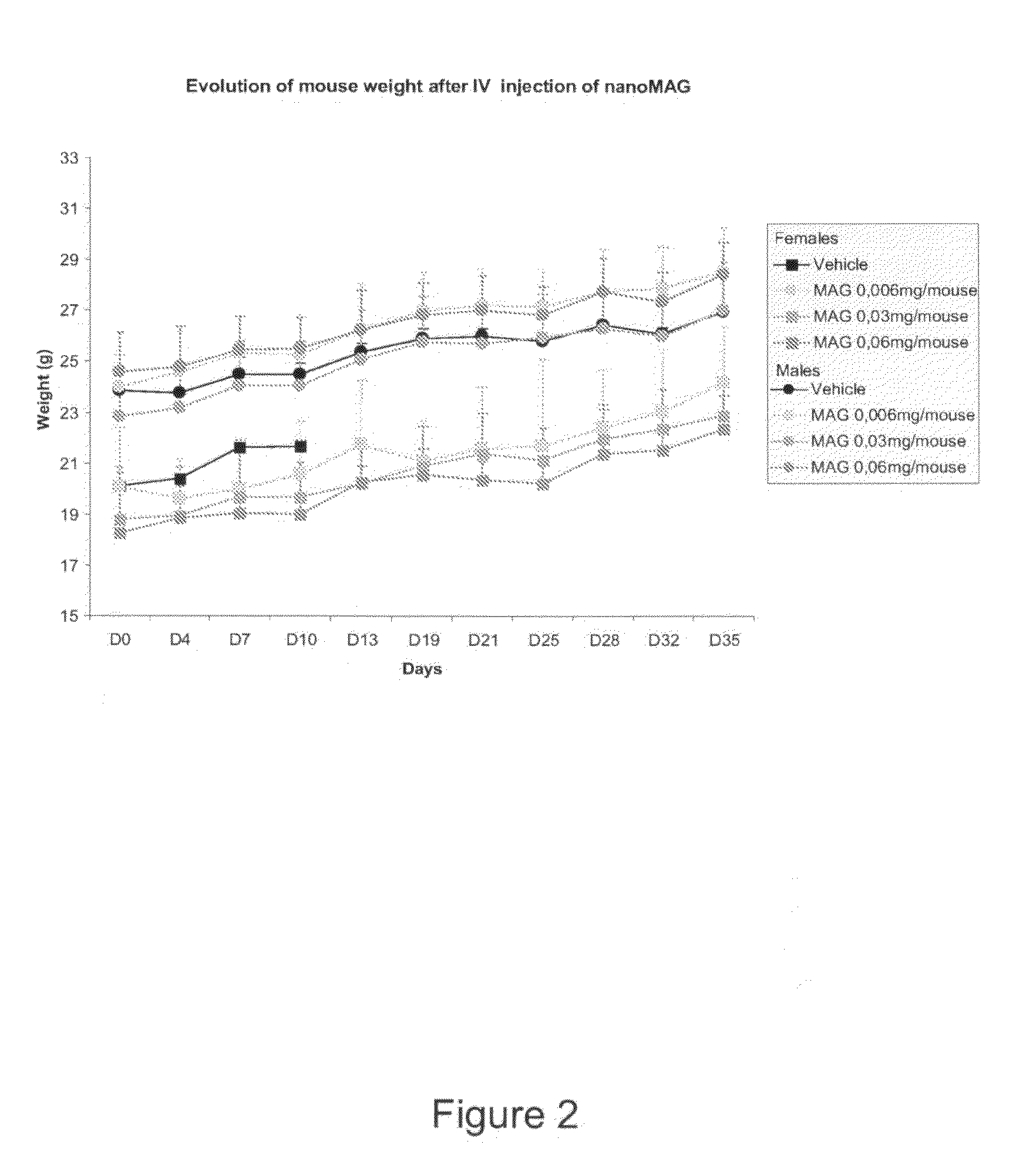
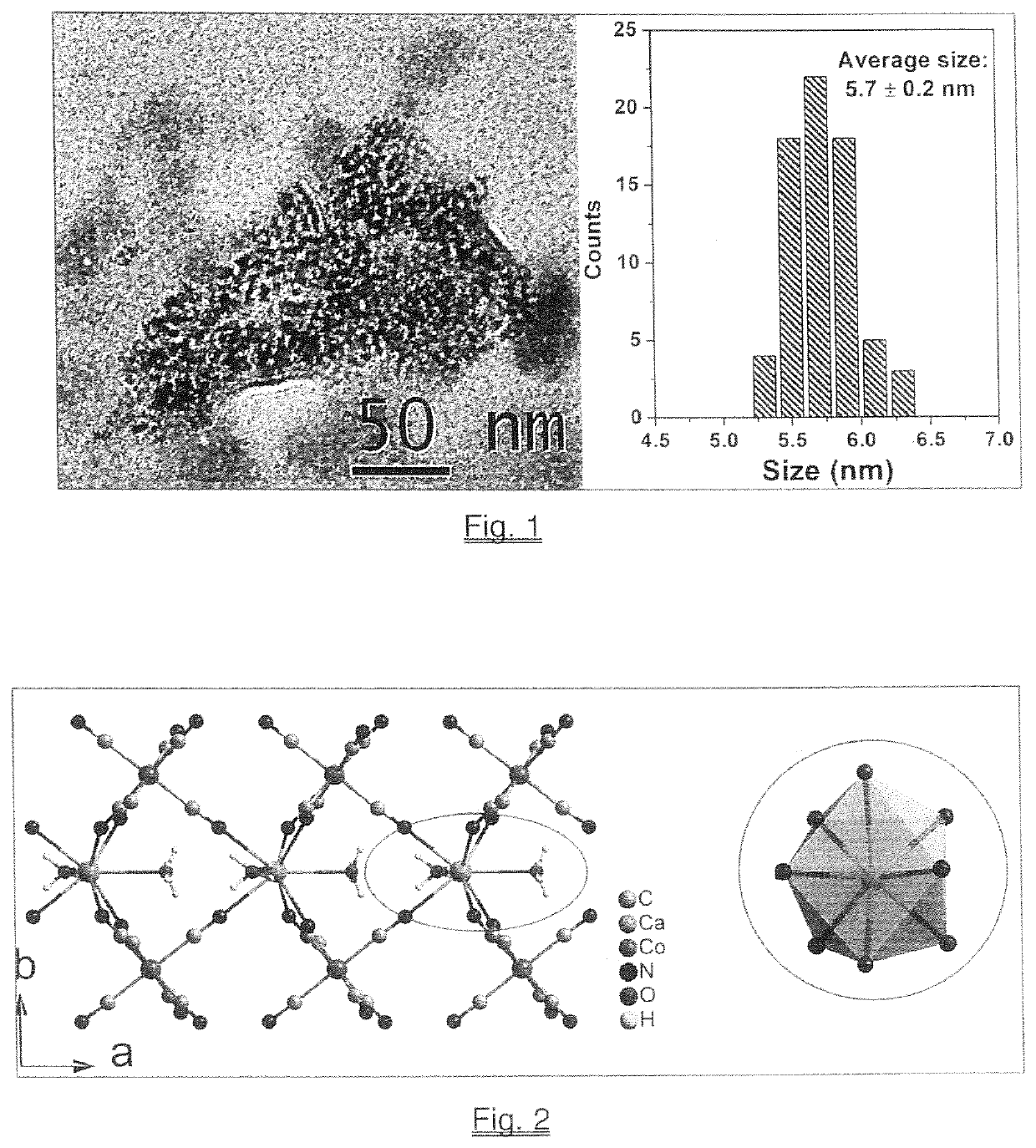
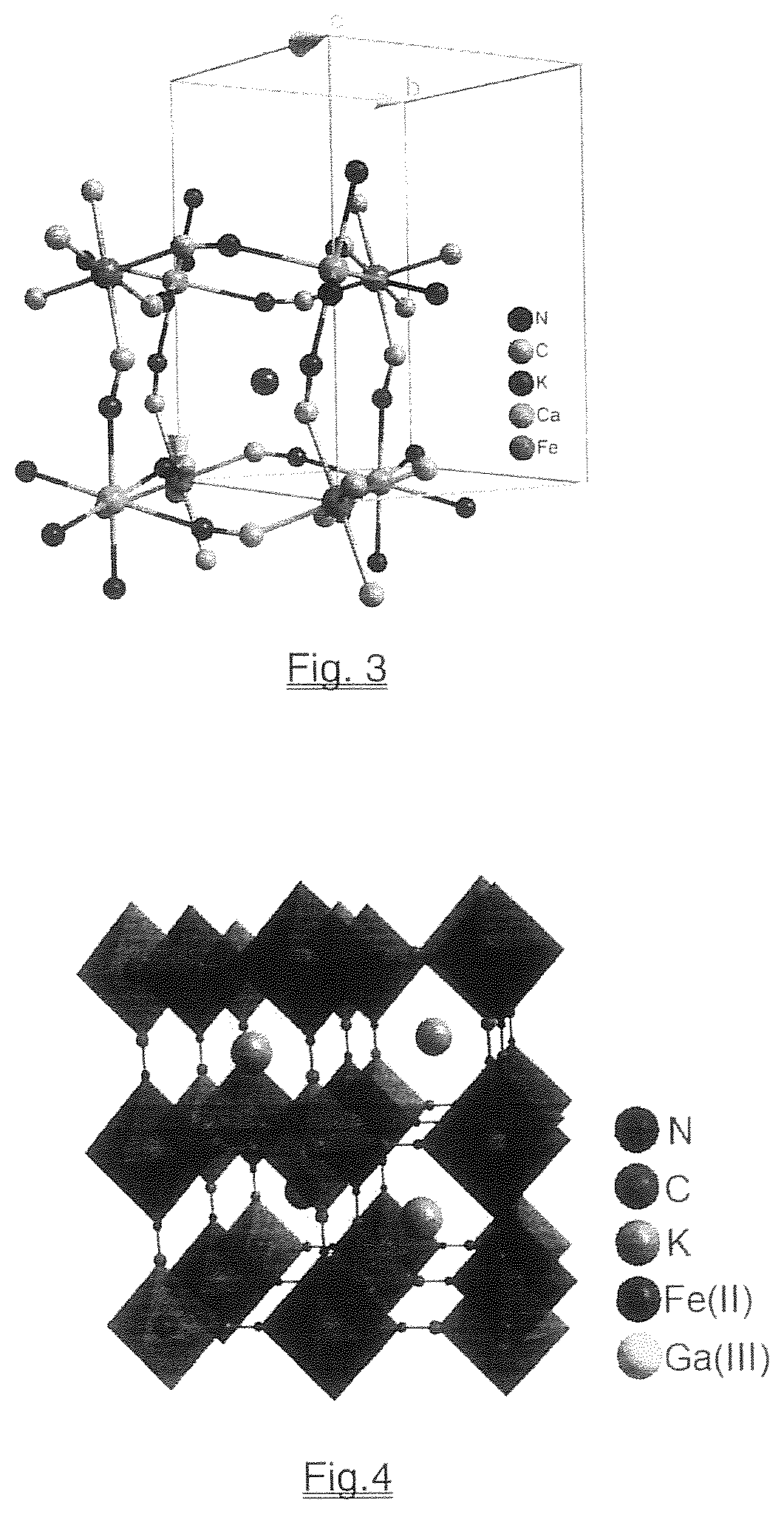
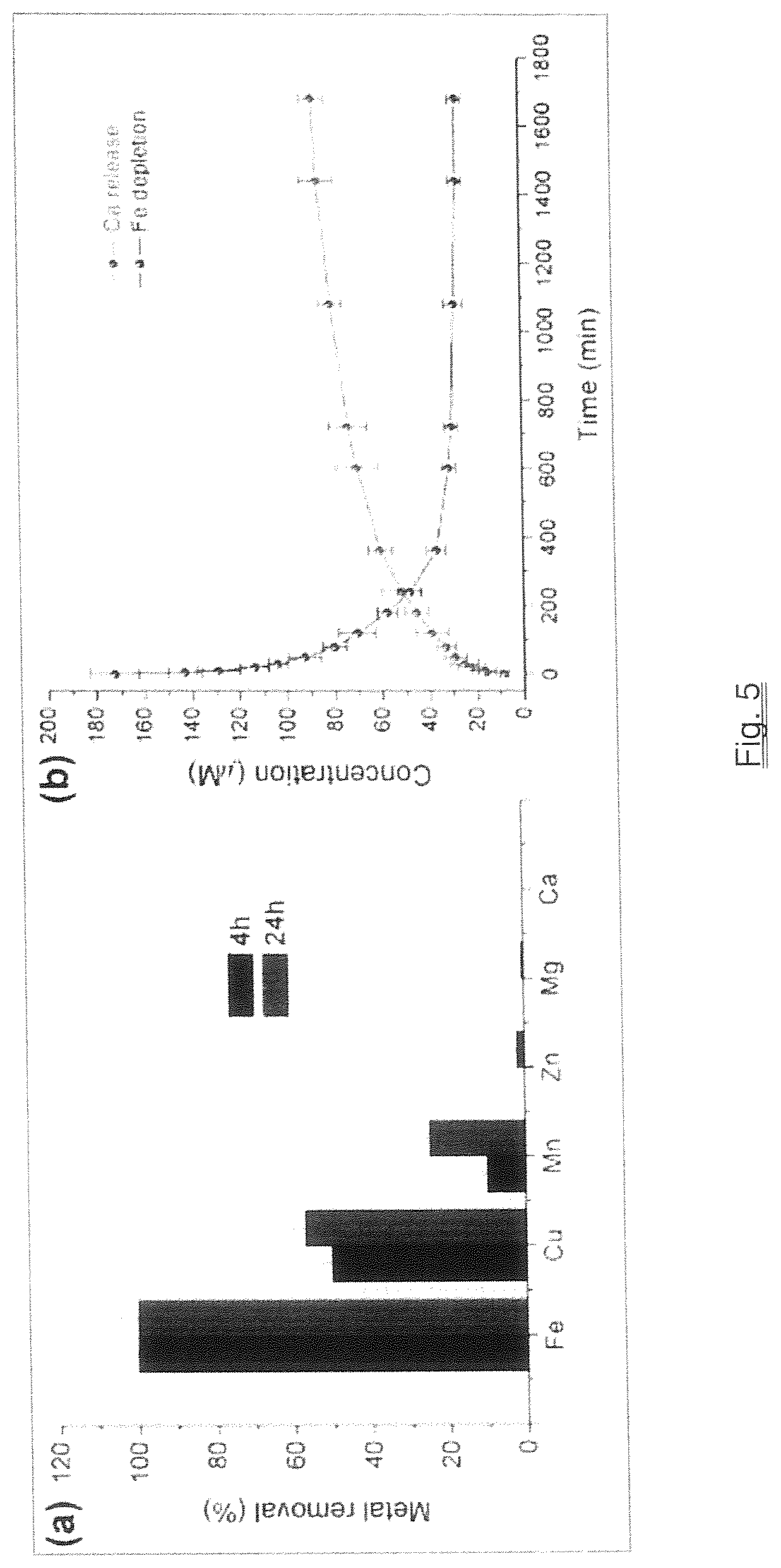
Novel biocompatible nanoparticles preferably based on a calcium or gallium analogue of Prussian blue, or independently an analogue of magnesium, or aluminum were designed and synthesized to take advantage of their ability to penetrate the bacterial cell membrane of the invading pathogen in an animal such as a human in both Gram-positive bacteria (e.g. Staphylococcus aureus) and Gram-negative bacteria (e.g. Pseudomonas aeruginosa), and undergo selective ion exchange with intracellular iron to disrupt iron metabolism in such pathogenic bacteria for antibacterial applications.
Owner:KENT STATE UNIV
Pharmaceutical composition, preparation and uses thereof
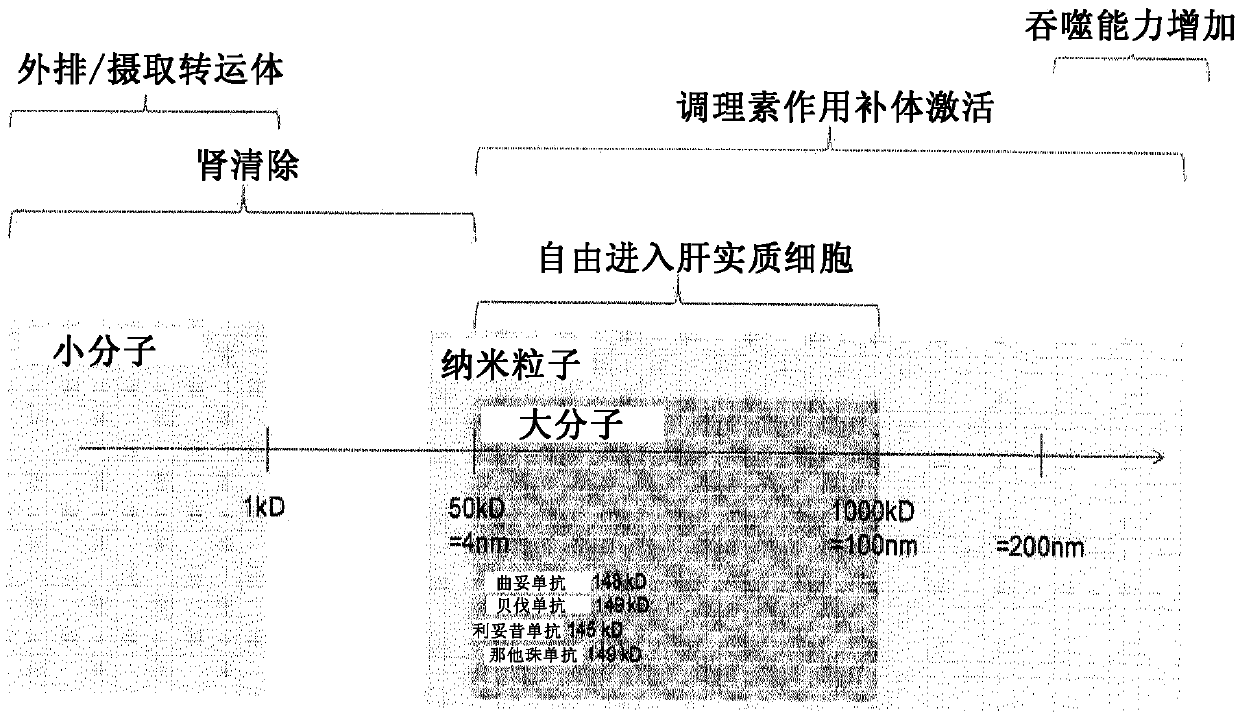
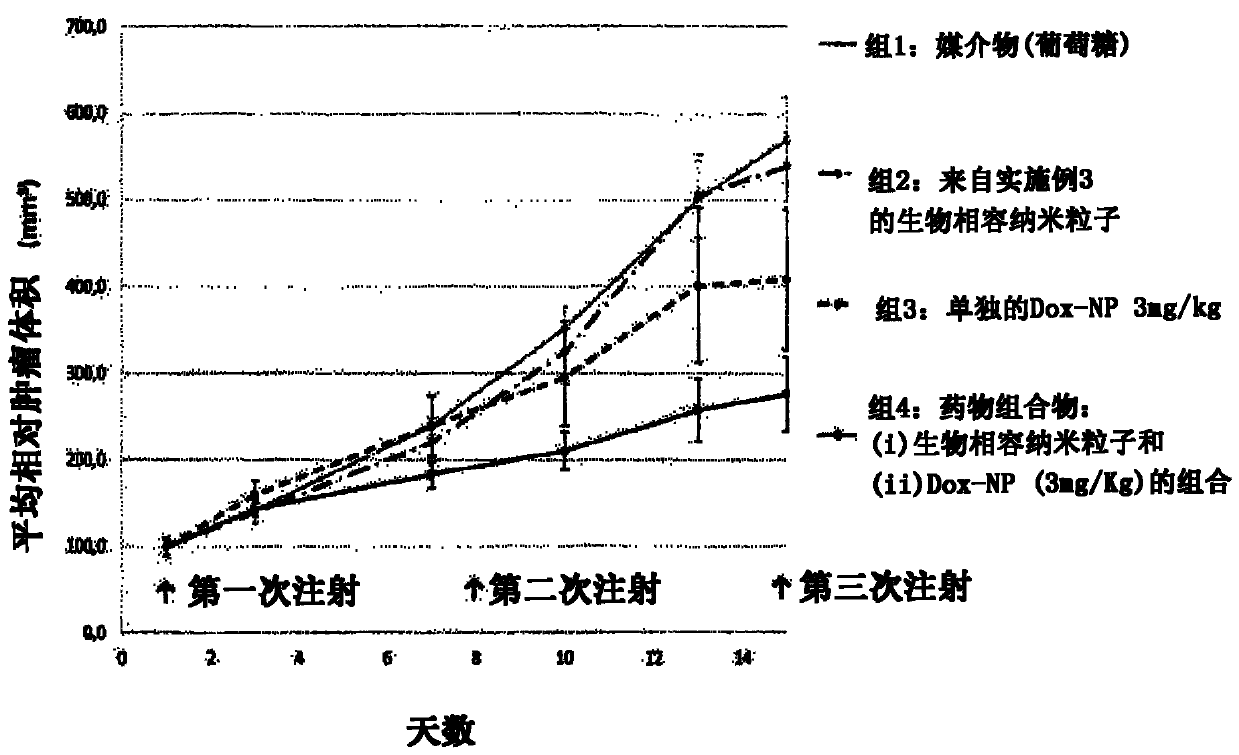
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the combination of (i) a biocompatible nanoparticle and of (ii) a pharmaceutical compound of interest, to be administered to a subject in need of such a compound of interest, wherein the nanoparticle potentiates the compound of interest efficiency. The longest dimension of the biocompatible nanoparticle is typically between about 4 and about 500 nm, and its absolute surface charge value is of at least 10 m V (|10 m V|). The invention also relates to such a composition for use for administering the compound of interest in a subject in need thereof, wherein the nanoparticle and the compound of interest are to be administered in said subject between more than 5 minutes and about 72 hours one from each other.
Owner:キュラダイムソシエテパールアクシオンサンプリフィエ
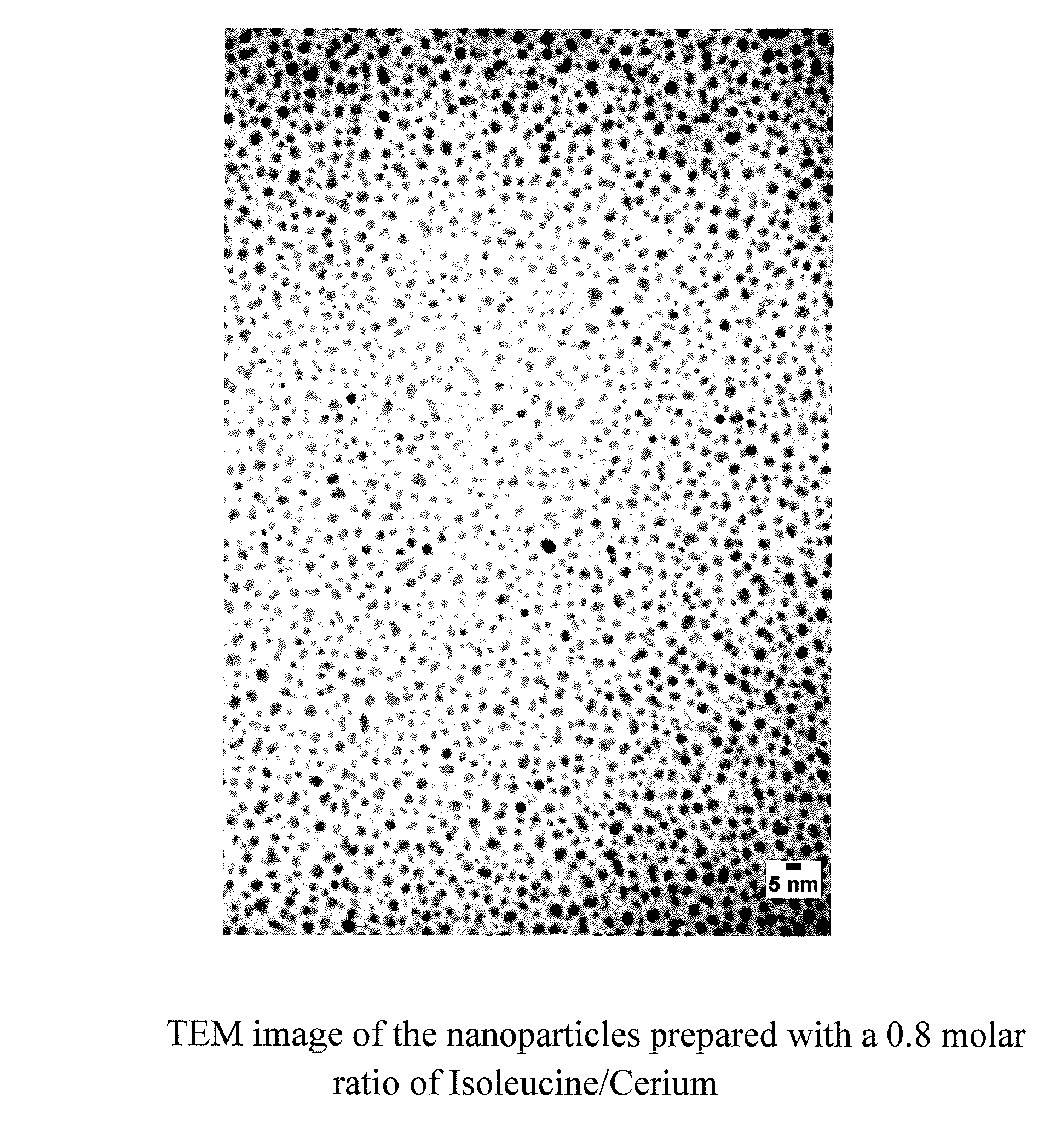
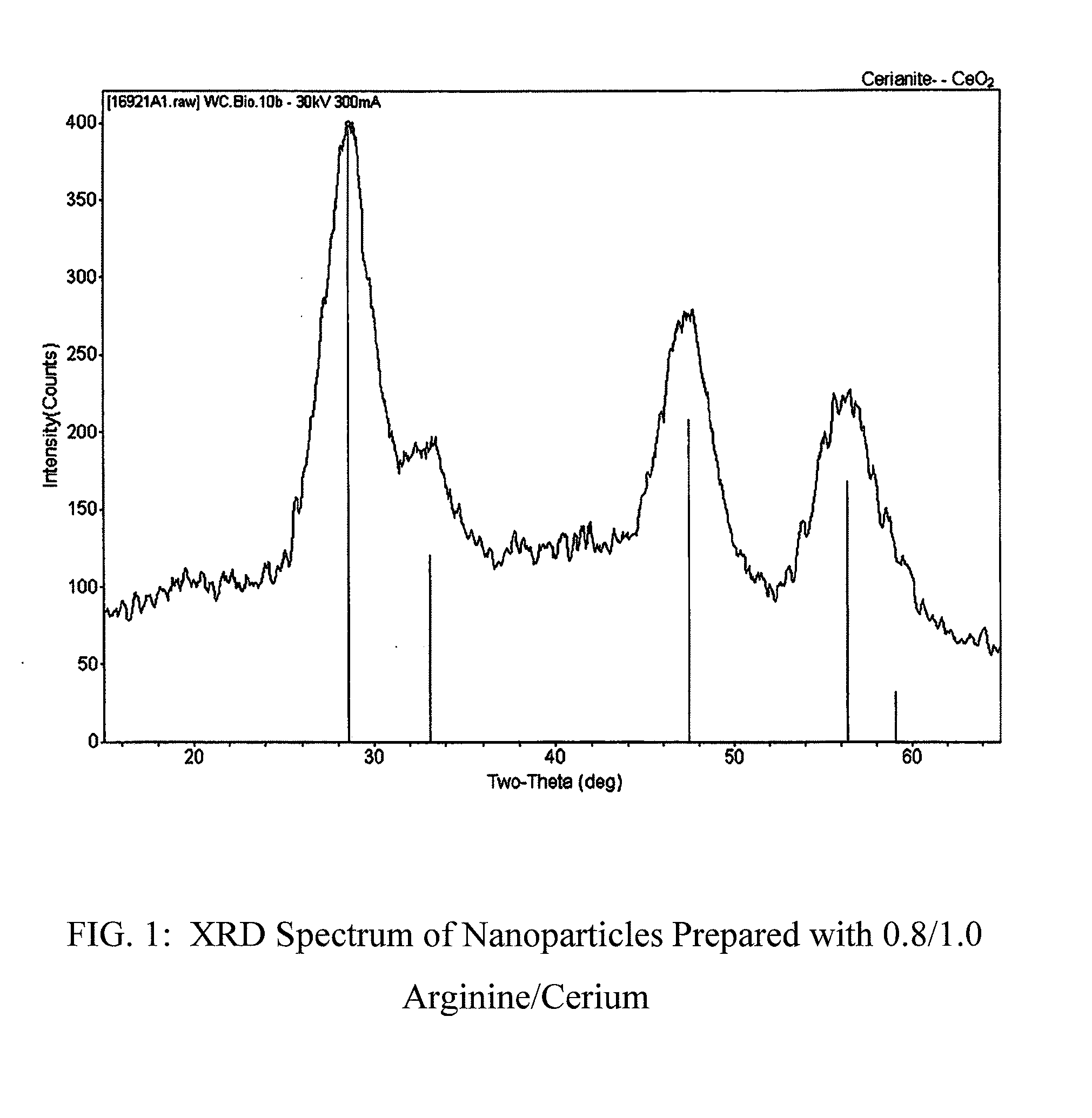
Nanoparticles of cerium and amino acids
A process for making nanoparticles of biocompatible materials is described, wherein an aqueous reaction mixture comprising cerous ion, an α-amino acid, an oxidant and water is provided along with temperature conditions to effectively form nanoparticles. These biocompatible nanoparticles may be further conjugated to biologically active agents, such as plasmid DNA, siRNA or proteins, such that a cell transfection agent is formed.
Owner:CERION
Mitochondrion-targeting BODIPY compound and preparation method and application of liposome-coated nanoparticles of BODIPY compound
ActiveCN111848658AUniform particle sizeLow dark toxicityPhotodynamic therapyAzo dyesLiposomeNanoparti cles
The invention relates to a mitochondria-targeting BODIPY compound and a preparation method and application of liposome-coated nanoparticles of the BODIPY compound. The BODIPY compound contains a cationic group which is easily combined with a mitochondrial membrane with negative electricity in cells, so that the BODIPY compound is targeted to mitochondrial organelles of the cells. The BODIPY compound is wrapped by liposome, and liposome nanoparticles with uniform particle size are prepared in an aqueous solution. The nanoparticles have high stability and good biocompatibility in an aqueous solution. After the nanoparticles are taken by tumor cells, the liposome structure is destroyed, and the released BODIPY compound is targeted to cell mitochondria. Besides, under the 665nm illumination condition, active oxygen generated by the BODIPY compound causes oxidative damage to active molecules in mitochondria, so that tumor cells are killed. The liposome nanoparticles can be applied to tumorphotodynamic therapy as a drug for delivering various photosensitizers.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Nanoparticles of a metal and a biguanide
A process for making nanoparticles of biocompatible materials is described, wherein an aqueous reaction mixture comprising a metal ion, a biguanide, an oxidant, and water; optionally further comprising an alpha-amino acid or a nucleobase; is provided along with temperature conditions to directly form within the reaction mixture, a stable dispersion of metal-containing nanoparticles. Biocompatible nanoparticles comprised of cerium and a biguanide, and optionally containing an alpha-amino acid or a nucleobase, are also described. The use of metal oxide nanoparticles comprising a biguanide as a nanoparticle core / corona in the preparation of nanoscale ionic (liquid) material compositions is disclosed.
Owner:CERION
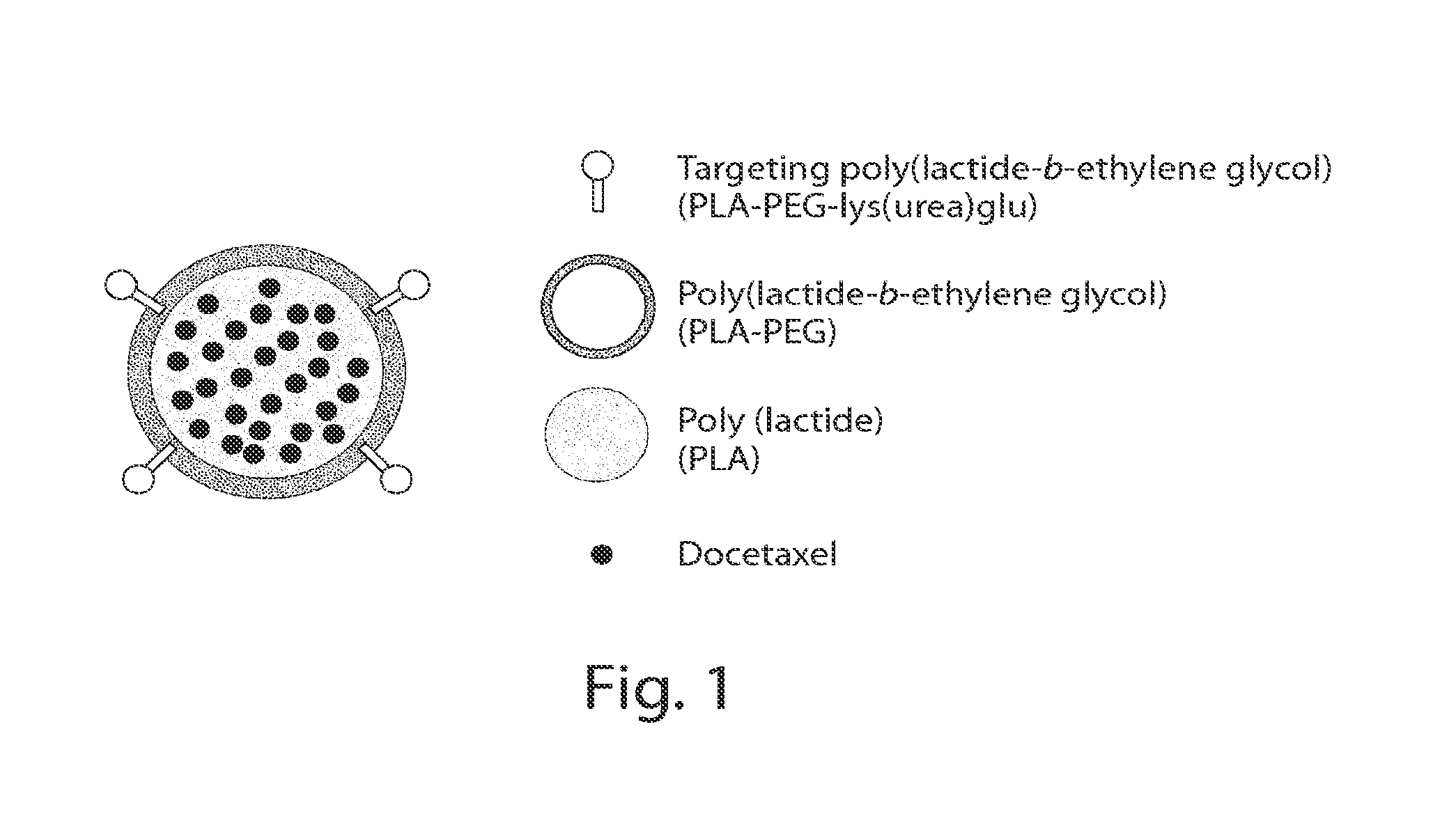
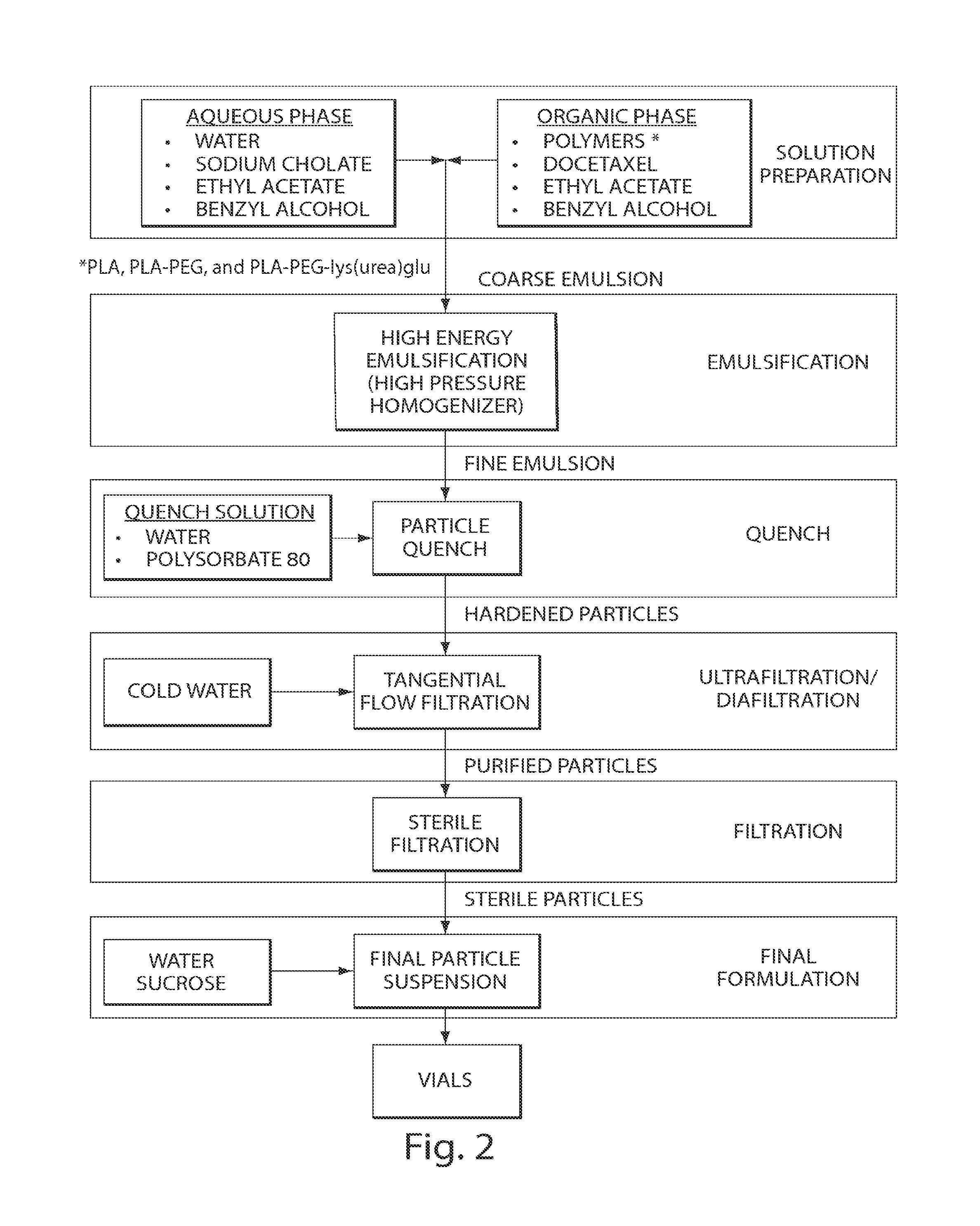
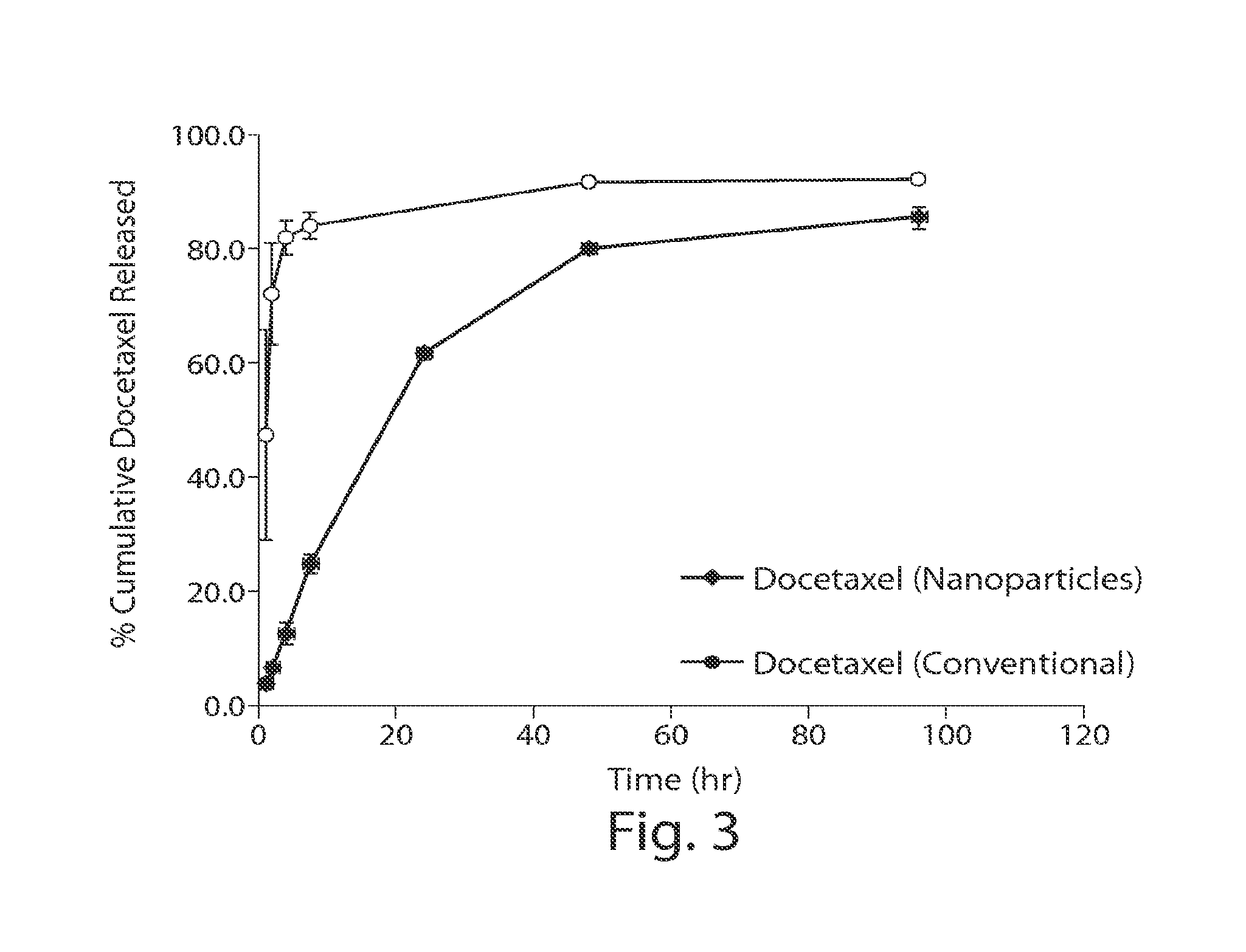
Long circulating nanoparticles for sustained release of therapeutic agents
ActiveUS9198874B2Lower the volumeMinimizing effectsPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsPolyesterMedicine
The present disclosure is directed in part to a biocompatible nanoparticle composition comprising a plurality of non-colloidal long circulating nanoparticles, each comprising a α-hydroxy polyester-co-polyether and a therapeutic agent, wherein such disclosed compositions provide a therapeutic effect for at least 12 hours.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Material for medical use comprising nanoparticles with superparamagnetic properties and its utilization in surgery
This invention relates to a material for medical use that comprises biocompatible nanoparticles having superparamagnetic properties, where the superparamagnetic properties of said nanoparticles are used to localize their action on a determined space or tissue. In particular, said nanoparticles having superparamagnetic properties are composed of magnetite. The material according to the invention has various applications, both in surgical and in therapeutic treatments.
Owner:NANOPHTHALMICS
Targeting intracellular copper ions for inhibiting angiogenesis using nanoparticles of ternary inorganic metal sulfide m1m2s4 (m1, independently, is mg, ca, mn, fe, or zn; m2=mo or w) compounds to treat metastatic cancer
InactiveCN107197623AHeavy metal active ingredientsMagnesium/calcium/strontium/barium sulfides/polysulfidesDiseaseIon exchange
This invention describes a new type of covalent-network ternary inorganic metal sulfide compounds M1M2S4 (M1, independently, is, Mg, Ca, Mn, Fe, or Zn; M2=Mo or W) and a process for preparing the biocompatible nanoparticles of such compounds. The nanoparticles are surface-modified with a capping agent and / or a biocompatible polymer and have the size from a few nanometers to several thousand nanometers. These nanoparticles are nontoxic and can be internalized by cells to deplete copper ions via a highly selective ion-exchange reaction between the intracellular copper ions and the divalent ion bound in the nanoparticles for the application of inhibiting angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases.
Owner:KENT STATE UNIV
Method for production of biocompatible nanoparticles containing dental adhesive
Owner:SADAT SHOJAI MEHDI +2
Chelated nanoceria for the treatment of oxidative stress
A process for making cerium-containing nanoparticles with biocompatible stabilizers is described, wherein an aqueous reaction mixture comprising cerous ion, citric acid, a stabilizer (chelator) selected from the group consisting of nitrilotriacetic acid, ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid and diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid, and an oxidant, is provided, followed by a heating step to effectively form the nanoparticles. These biocompatible nanoparticles can be used to treat oxidative stress related diseases and events, such as ischemic stroke.
Owner:CERLON ENTERPRISES LLC
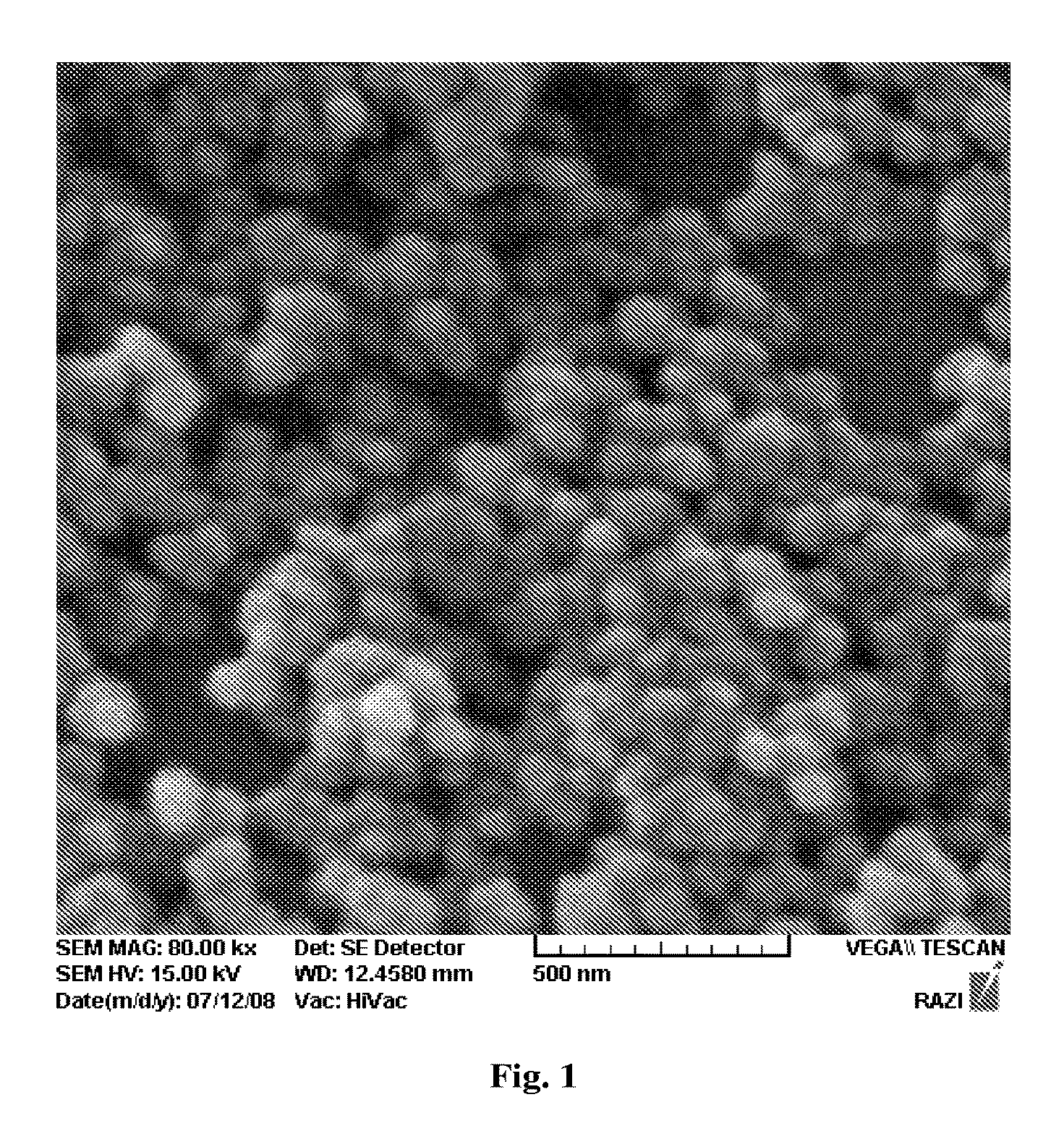
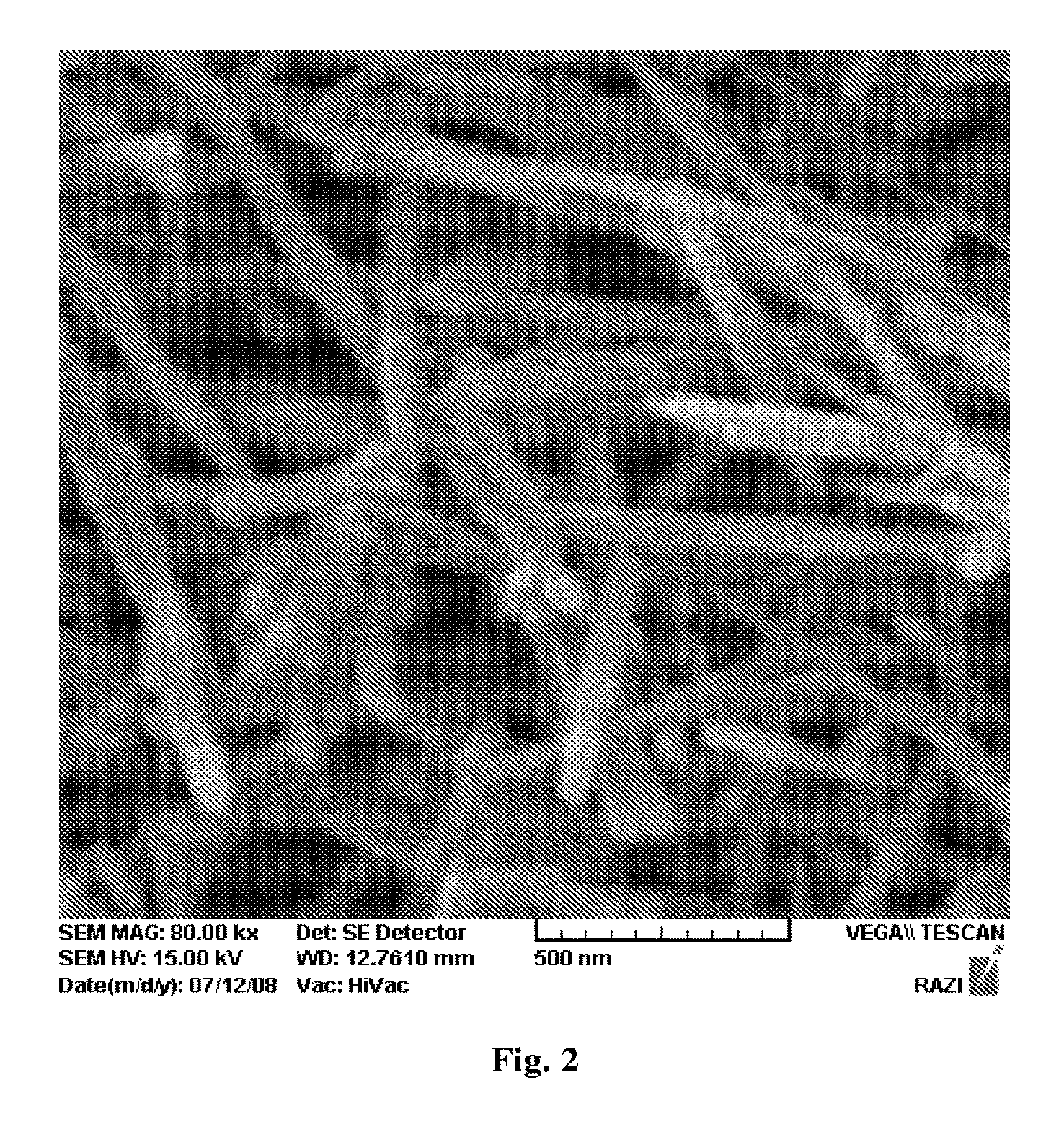
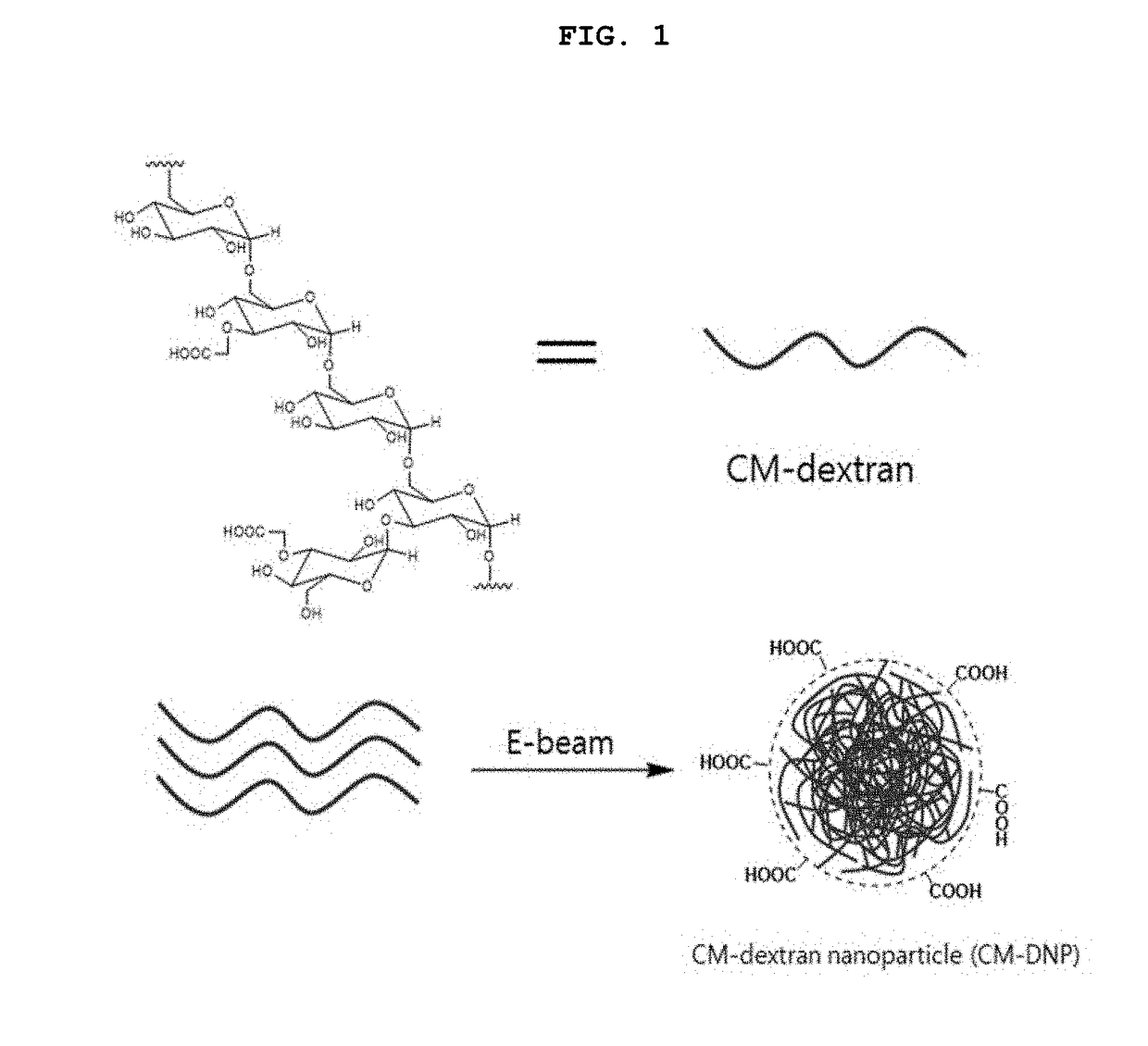
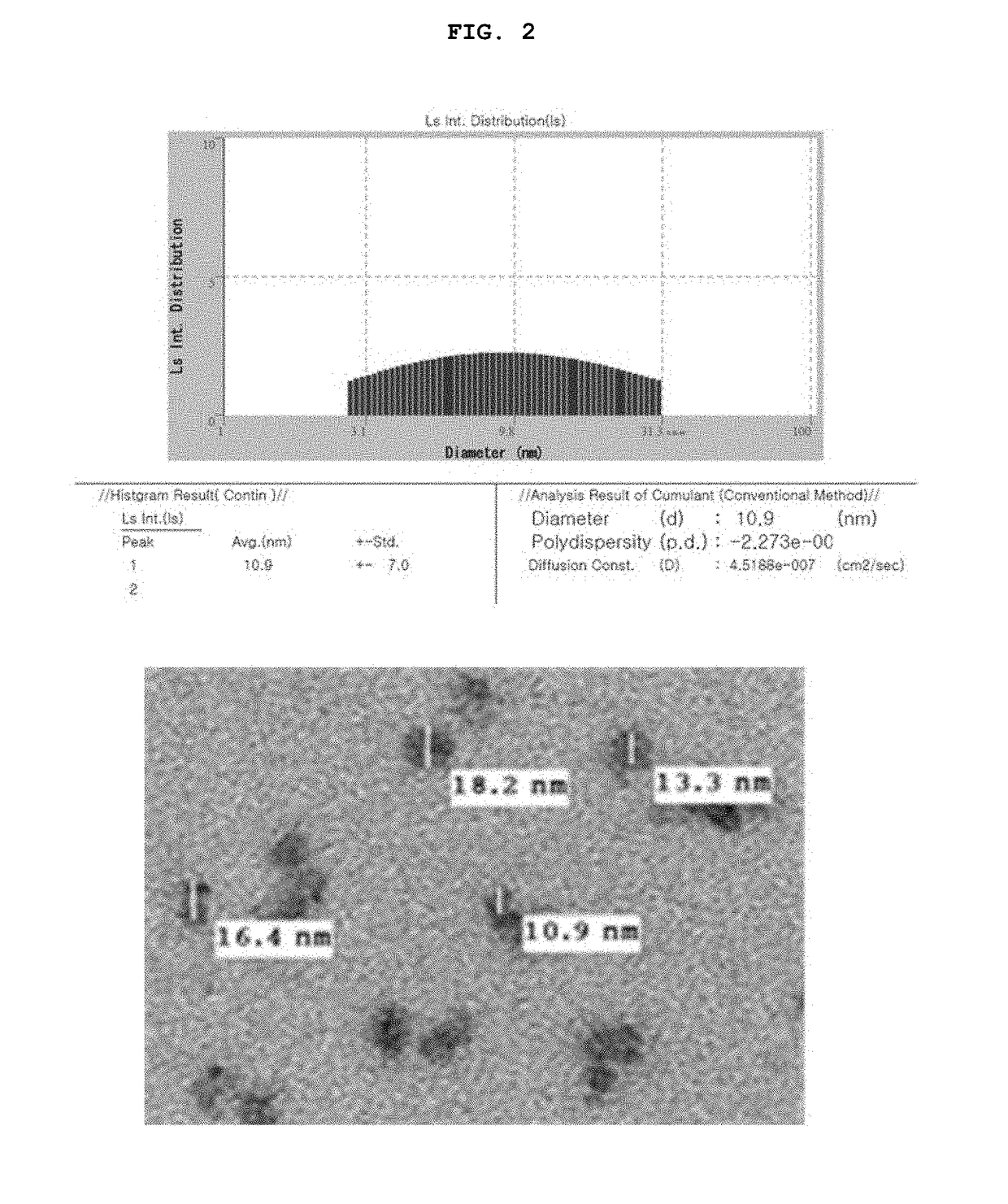
Biocompatible nanoparticle and use thereof
ActiveUS20180327554A1Increase production capacityNervous disorderAntipyreticDiagnostic agentMedicine
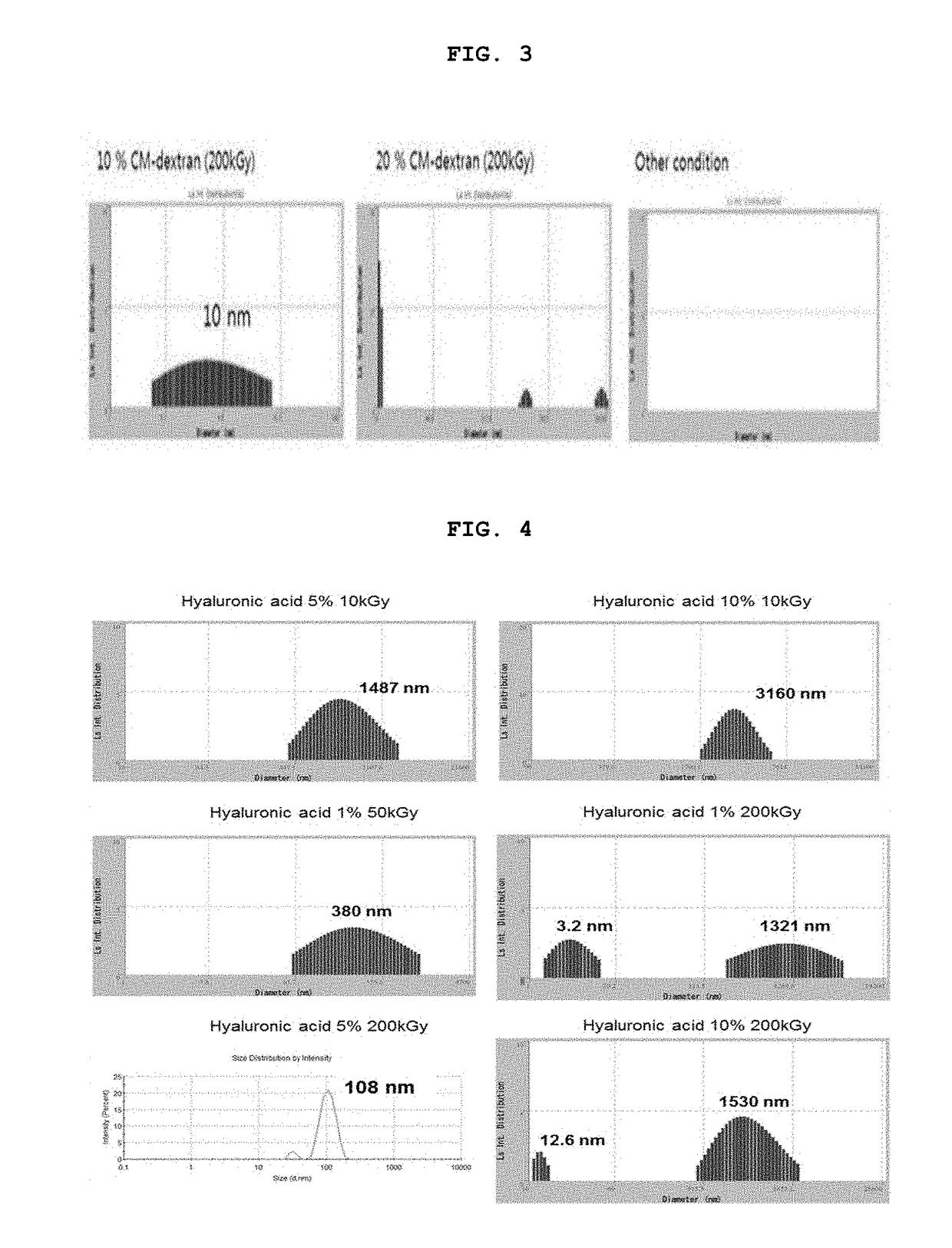
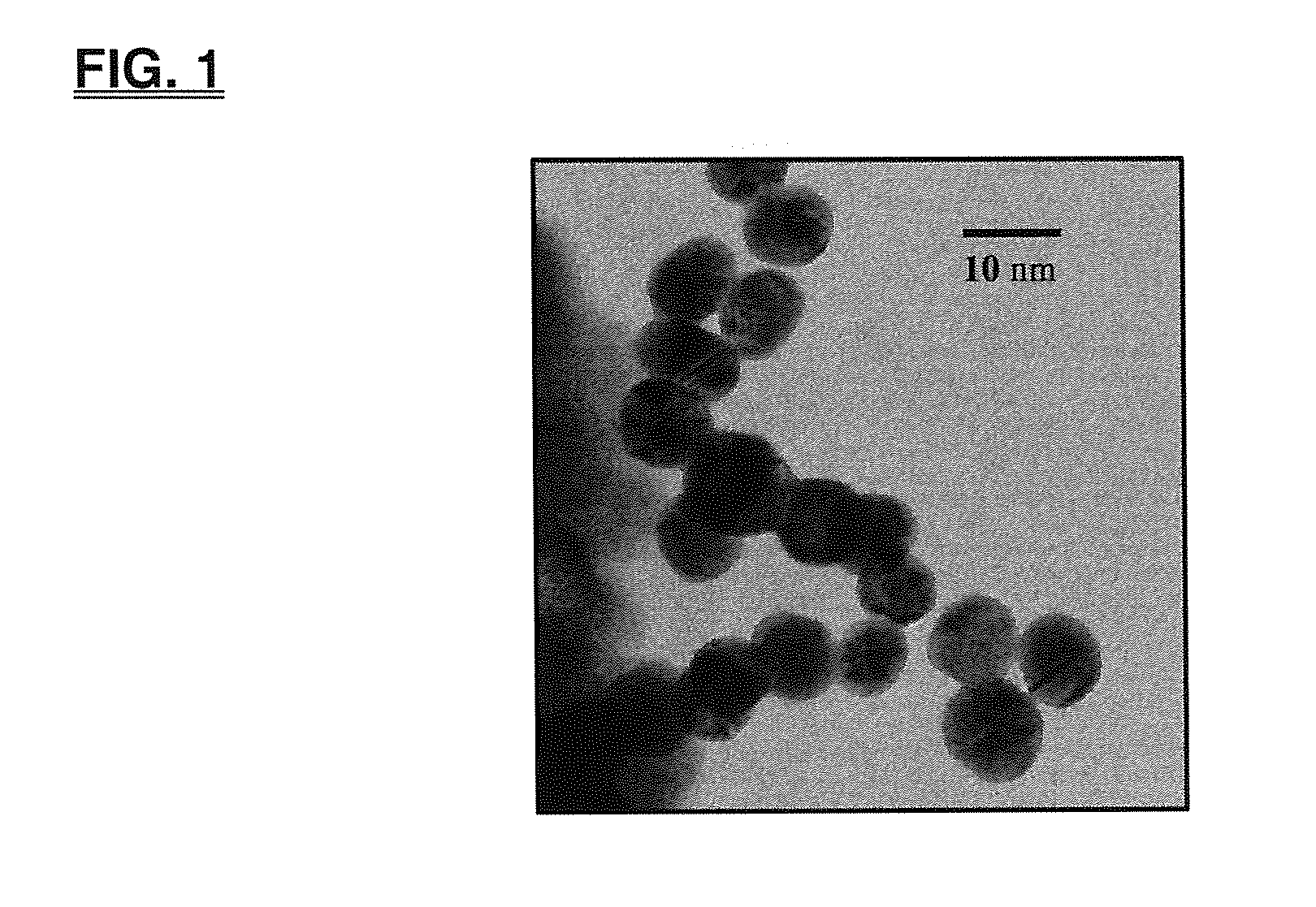
The present invention relates to a biocompatible nanoparticle and a use thereof and, more specifically, to a biocompatible nanoparticle formed by irradiation an electron beam to an aqueous solution comprising at least one substance selected from the group consisting of a polysaccharide, a derivative thereof and a polyethylene glycol, thereby inducing inter-molecular cross-linking or intra-molecular cross-linking, and to a use of the biocompatible nanoparticle in a drug carrier, a contrast agent, a diagnostic agent or an intestinal adhesion prevention agent or for disease prevention and treatment.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Malic acid stabilized nanoceria particles
ActiveUS20160331697A1Powder deliveryInorganic active ingredientsProphylactic treatmentBiocompatible nanoparticles
A process for making nanoparticles of biocompatible materials is described, wherein an aqueous reaction mixture comprising cerous ion, malic acid, an oxidant, and water, is provided along with temperature conditions to directly form within the reaction mixture, a stable dispersion of nanoceria particles. Biocompatible nanoparticles comprised of ceria and malic acid are described. A reduction in cell death in a murine model of ischemic stroke utilizing intact brain slices is demonstrated by a prophylactic treatment of ceria nanoparticles prepared with malic acid.
Owner:CERION
Targeting Intracellular Copper Ions for Inhibiting Angiogenesis Using Nanoparticles of Ternary Inorganic Metal Sulfide M1M2S4 (M1, independently, is Mg, Ca, Mn, Fe, or Zn; M2 = Mo or W) Compounds to Treat Metastatic Cancer
InactiveUS20160220500A1Reduce decreasePromote migrationHeavy metal active ingredientsMagnesium/calcium/strontium/barium sulfides/polysulfidesDiseaseIon exchange
This invention describes a new type of covalent-network ternary inorganic metal sulfide compounds M1M2S4 (M1, independently, is, Mg, Ca, Mn, Fe, or Zn; M2=Mo or W) and a process for preparing the biocompatible nanoparticles of such compounds. The nanoparticles are surface-modified with a capping agent and / or a biocompatible polymer and have the size from a few nanometers to several thousand nanometers. These nanoparticles are nontoxic and can be internalized by cells to deplete copper ions via a highly selective ion-exchange reaction between the intracellular copper ions and the divalent ion bound in the nanoparticles for the application of inhibiting angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases.
Owner:KENT STATE UNIV
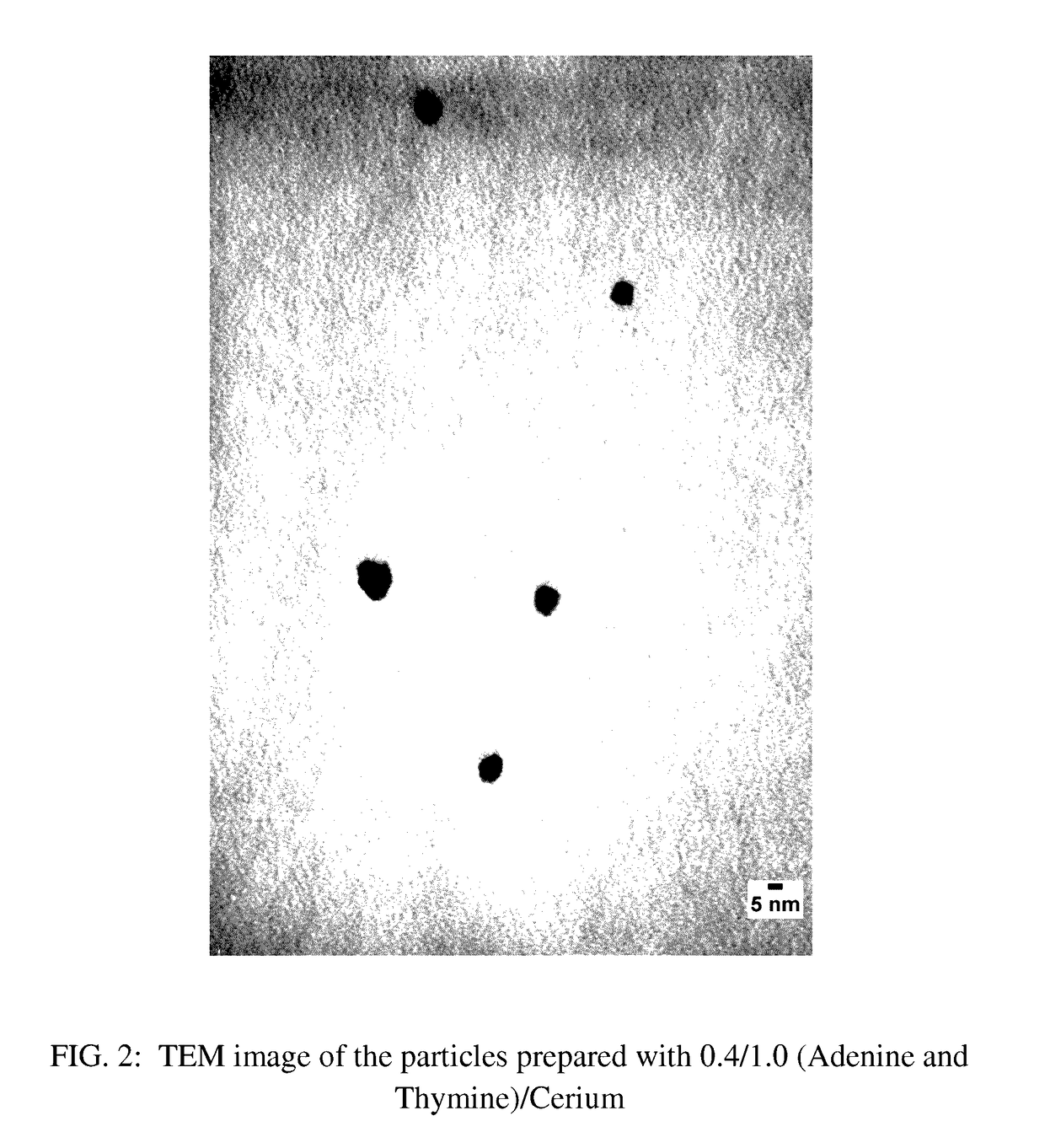
Nanoparticles of a metal and a nucleobase
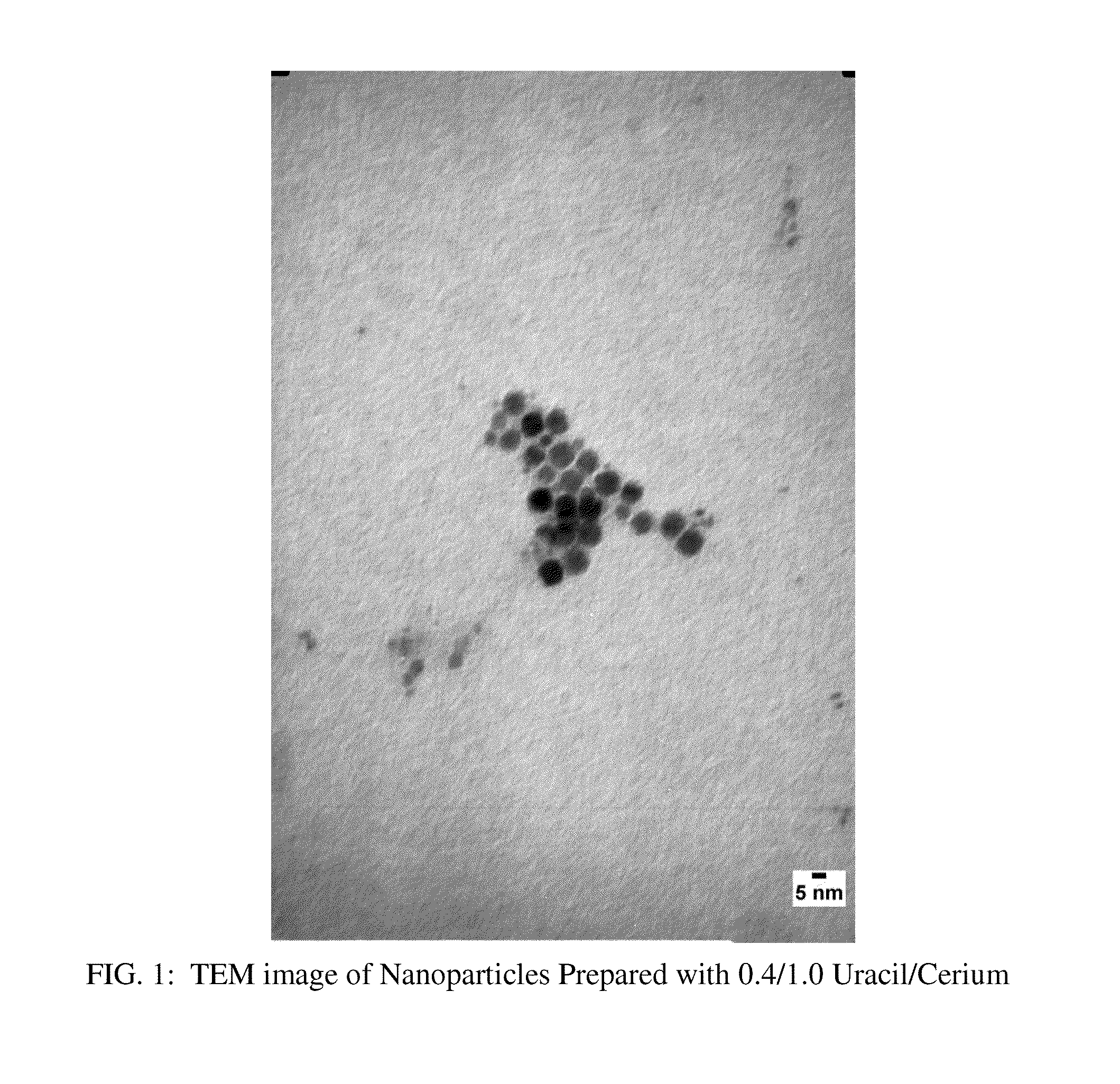
A process for making nanoparticles of biocompatible materials is described, wherein an aqueous reaction mixture comprising a metal ion, a nucleobase, an oxidant, and water, is provided along with temperature conditions to directly form within the reaction mixture, a stable dispersion of nanoparticles. Biocompatible nanoparticles comprised of cerium or iron as the metal ion, and a purine and / or a pyrimidine as the nucleobase, are described.
Owner:CERION
Malic acid stabilized nanoceria particles
ActiveUS10143661B2Powder deliveryInorganic active ingredientsProphylactic treatmentBiocompatible nanoparticles
A process for making nanoparticles of biocompatible materials is described, wherein an aqueous reaction mixture comprising cerous ion, malic acid, an oxidant, and water, is provided along with temperature conditions to directly form within the reaction mixture, a stable dispersion of nanoceria particles. Biocompatible nanoparticles comprised of ceria and malic acid are described. A reduction in cell death in a murine model of ischemic stroke utilizing intact brain slices is demonstrated by a prophylactic treatment of ceria nanoparticles prepared with malic acid.
Owner:CERION
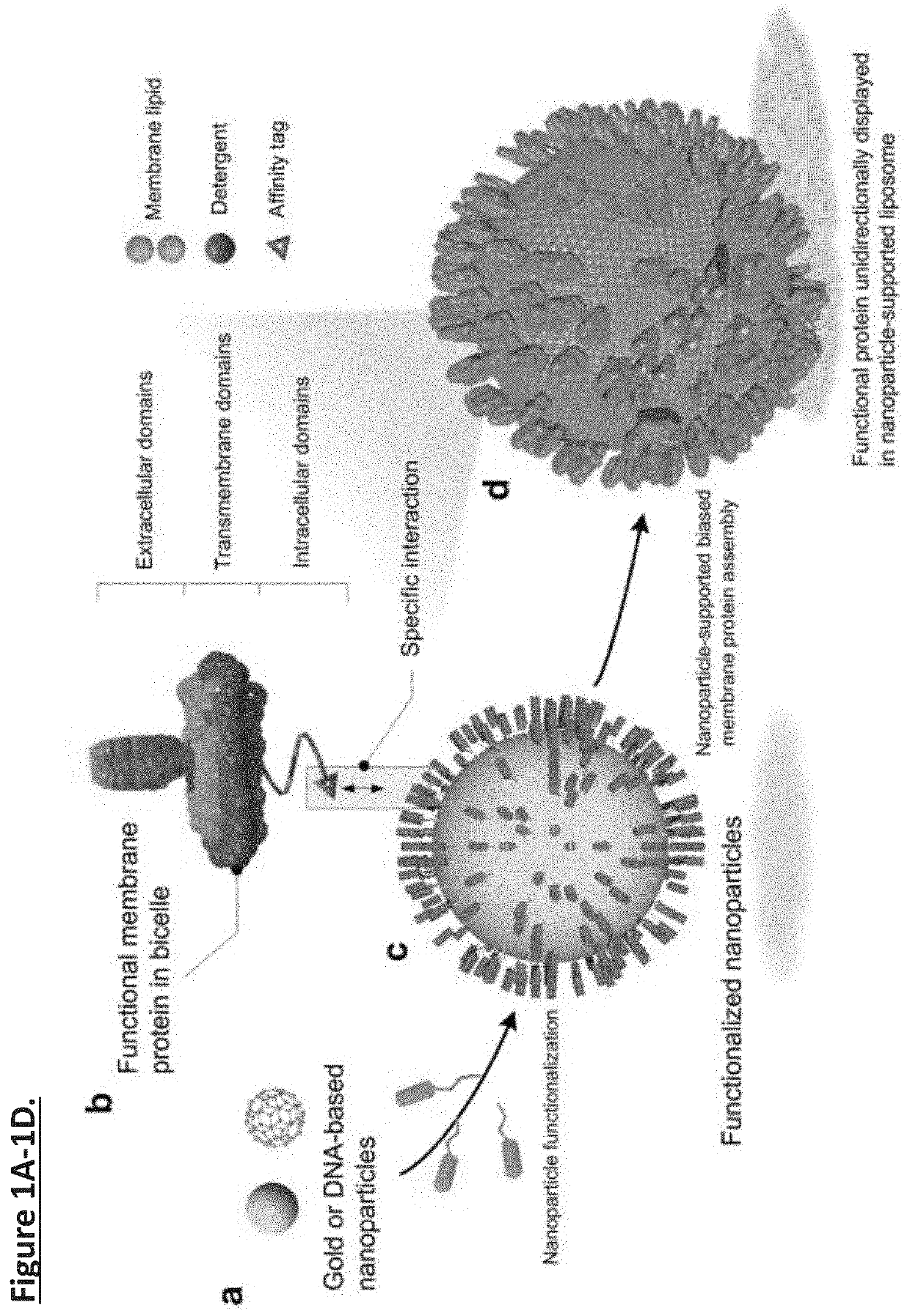
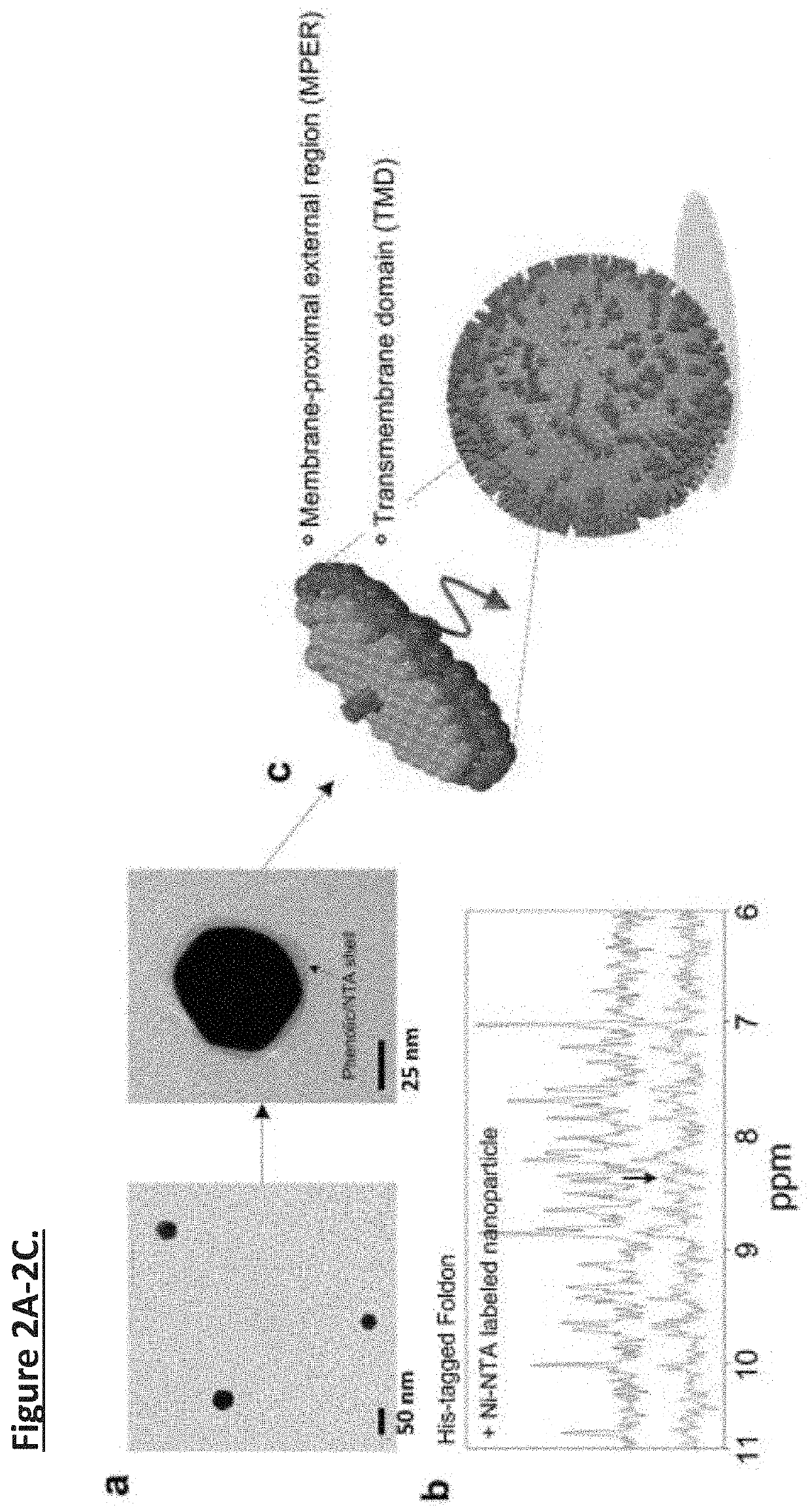
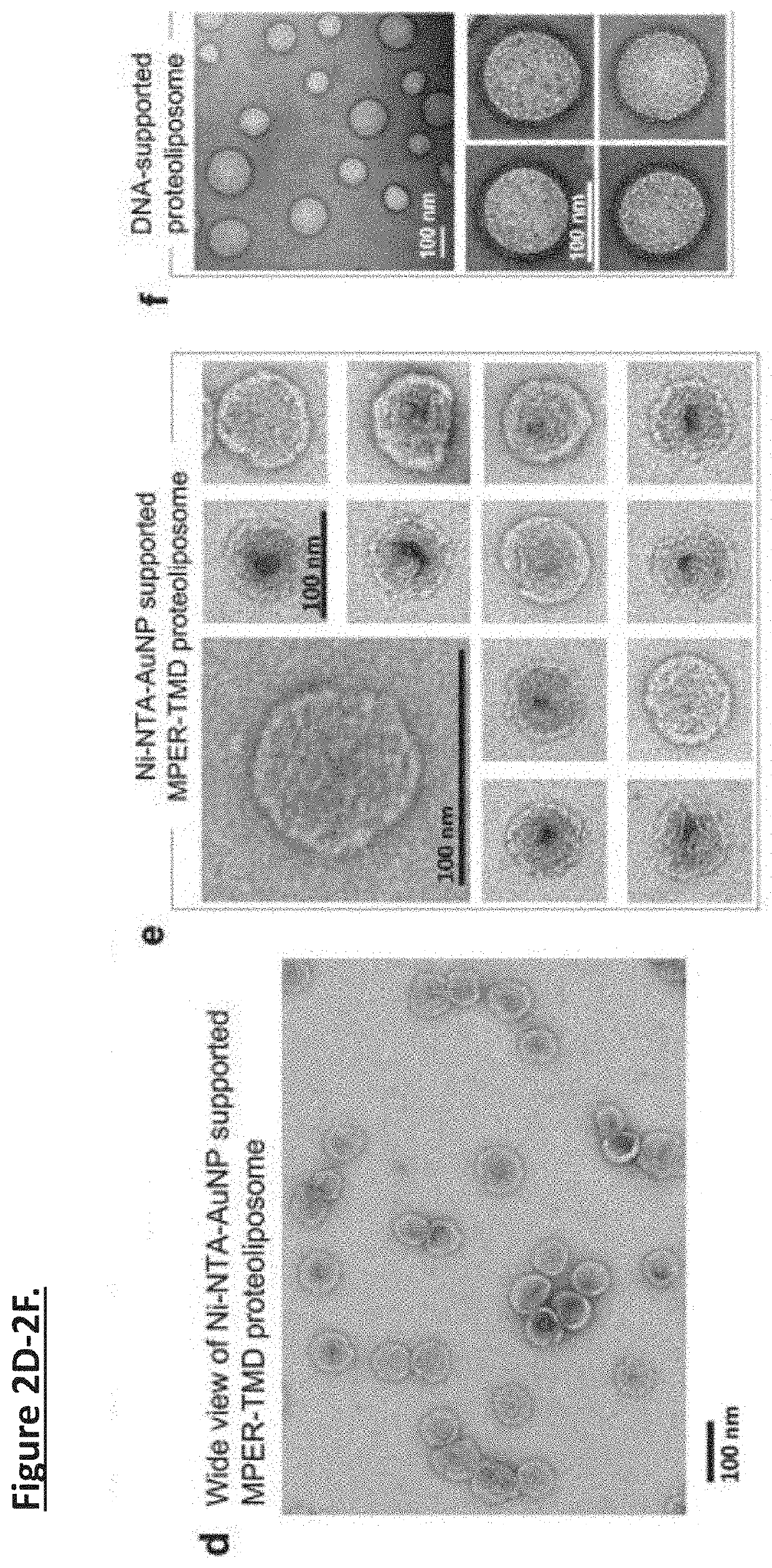
Unidirectional presentation of membrane proteins in nanoparticle-supported liposomes
Presentation of membrane proteins to host immune systems has been a challenging problem due to complexity arising from the poor in vivo stability of the membrane-mimetic media often used for solubilizing the membrane proteins. The Inventors report the use of functionalized, biocompatible nanoparticles as substrates to guide the formation of proteoliposomes that can present many copies of membrane proteins in a unidirectional manner. The approach was demonstrated to present the membrane-proximal region of the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein. These nanoparticle-supported liposomes are broadly applicable as membrane antigen vehicles for inducing host immune responses. In some instances, the technology supports generation of antibodies that do not generate an immunogenic response in comparison to conventional protein presentation (i.e., liposome).
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Compositions and methods for keloidless healing
InactiveUS20190374556A1Cut woundReduce scarsPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsWound healingKeloid
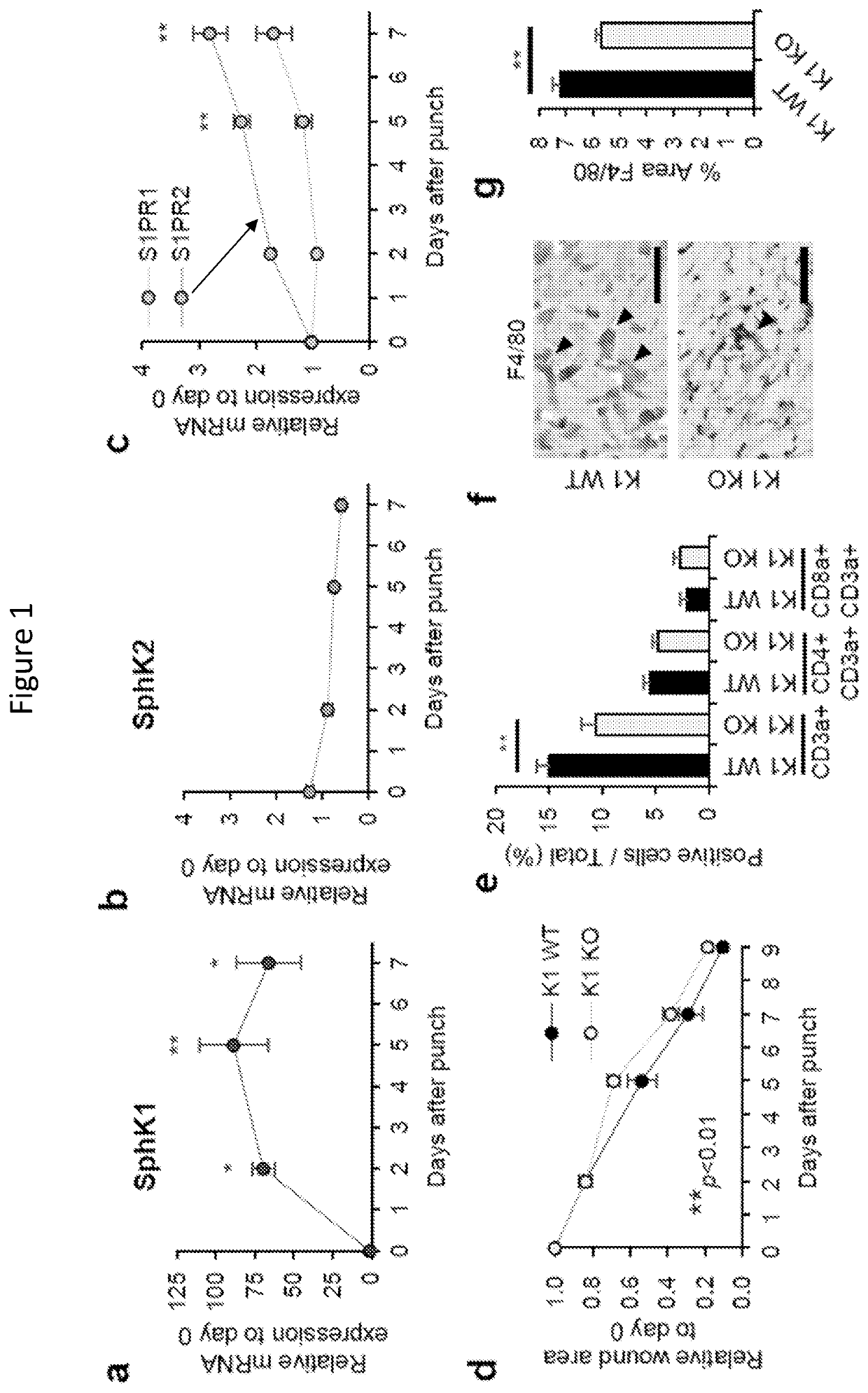
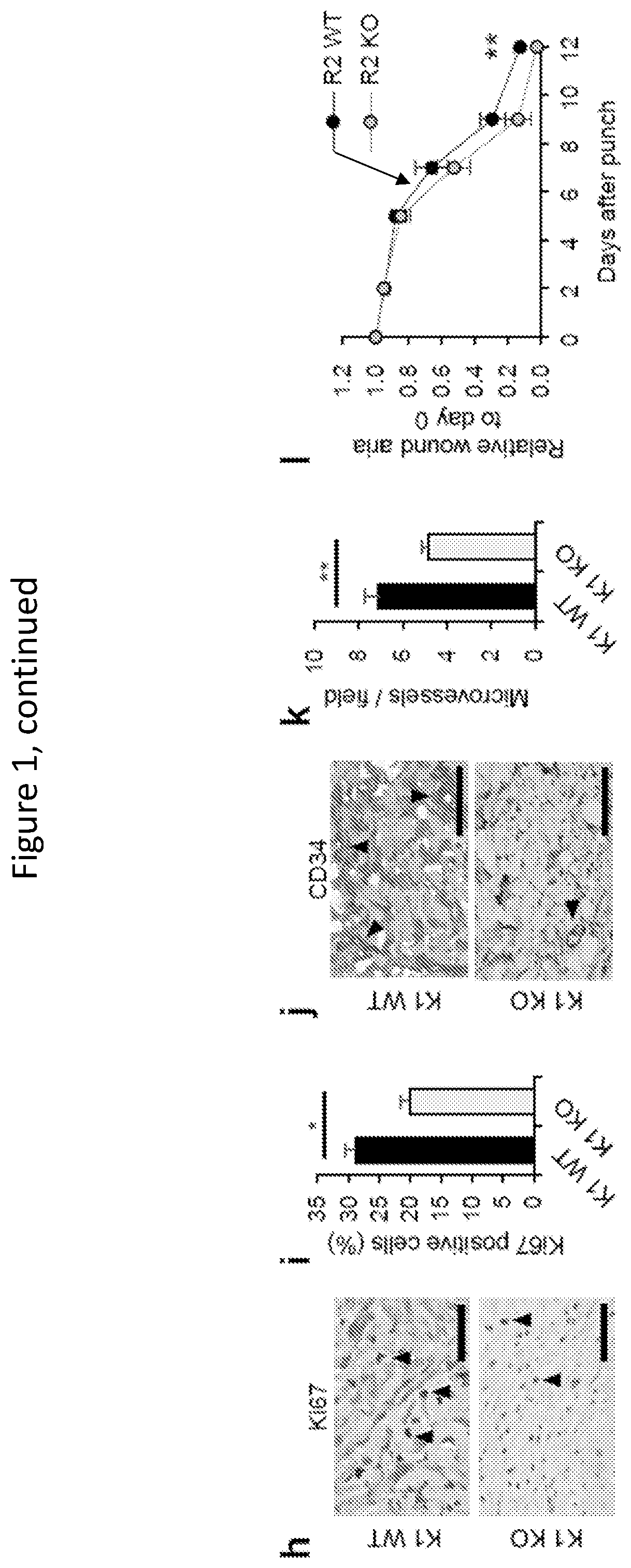
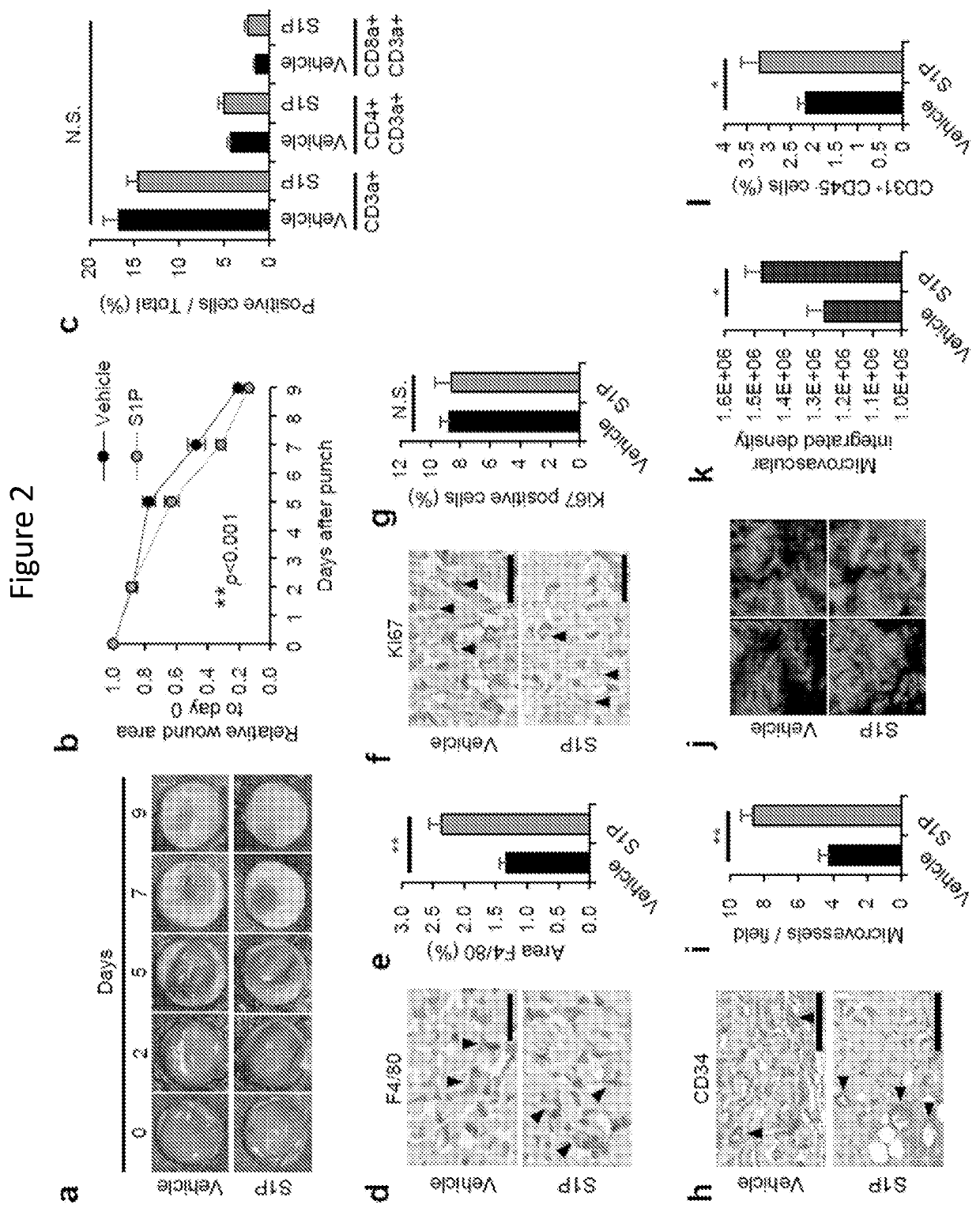
Provided are compositions, methods and devices for reducing scarring during healing of a tissue wound. The compositions and methods involve use of sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), and / or an expression vector that encodes sphingosine kinasel (SphK1). The compositions can be combined with other agents and implements, such as biocompatible nanoparticles, and medical devices involved with promoting wound healing. The approaches can reduce formation or prevent the occurrence of keloids.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
Nanoparticles of a metal and a nucleobase
A process for making nanoparticles of biocompatible materials is described, wherein an aqueous reaction mixture comprising a metal ion, a nucleobase, an oxidant, and water, is provided along with temperature conditions to directly form within the reaction mixture, a stable dispersion of nanoparticles. Biocompatible nanoparticles comprised of cerium or iron as the metal ion, and a purine and / or a pyrimidine as the nucleobase, are described.
Owner:CERLON ENTERPRISES LLC
Drug-eluting catheter and method of manufacturing the same
Owner:ANGES MG INC +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com