Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
616 results about "Inducible promoters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Inducible promoters are a very powerful tool in genetic engineering because the expression of genes operably linked to them can be turned on or off at certain stages of development of an organism or in a particular tissue. This section presents a general view of patents directed to promoters whose activity is...
Methods and compositions for amplifying DNA clone copy number
A method for retrofitting DNA in a single-copy or high-copy vector, such as a fosmid or BAC, whereby an artificial transposon is used to introduce a conditional multi-copy origin of replication (“ori”) into the DNA in said vector. Following random in vitro or in vivo transposition of the ori-containing transposon into DNA in the single-copy or low-copy vector, the resulting insertion clones are introduced into a special host strain that contains a gene which encodes a polypeptide required for replication from the multi-copy ori. However, since the gene for this polypeptide is expressed from a tightly-regulated inducible promoter, the polypeptide is not expressed in the absence of inducer. On addition of inducer to the culture medium, the host cell synthesizes the polypeptide, which in turn activates replication from the multi-copy ori, thereby increasing the amount of clone DNA synthesized by the cell.
Owner:EPICENT TECH CORP
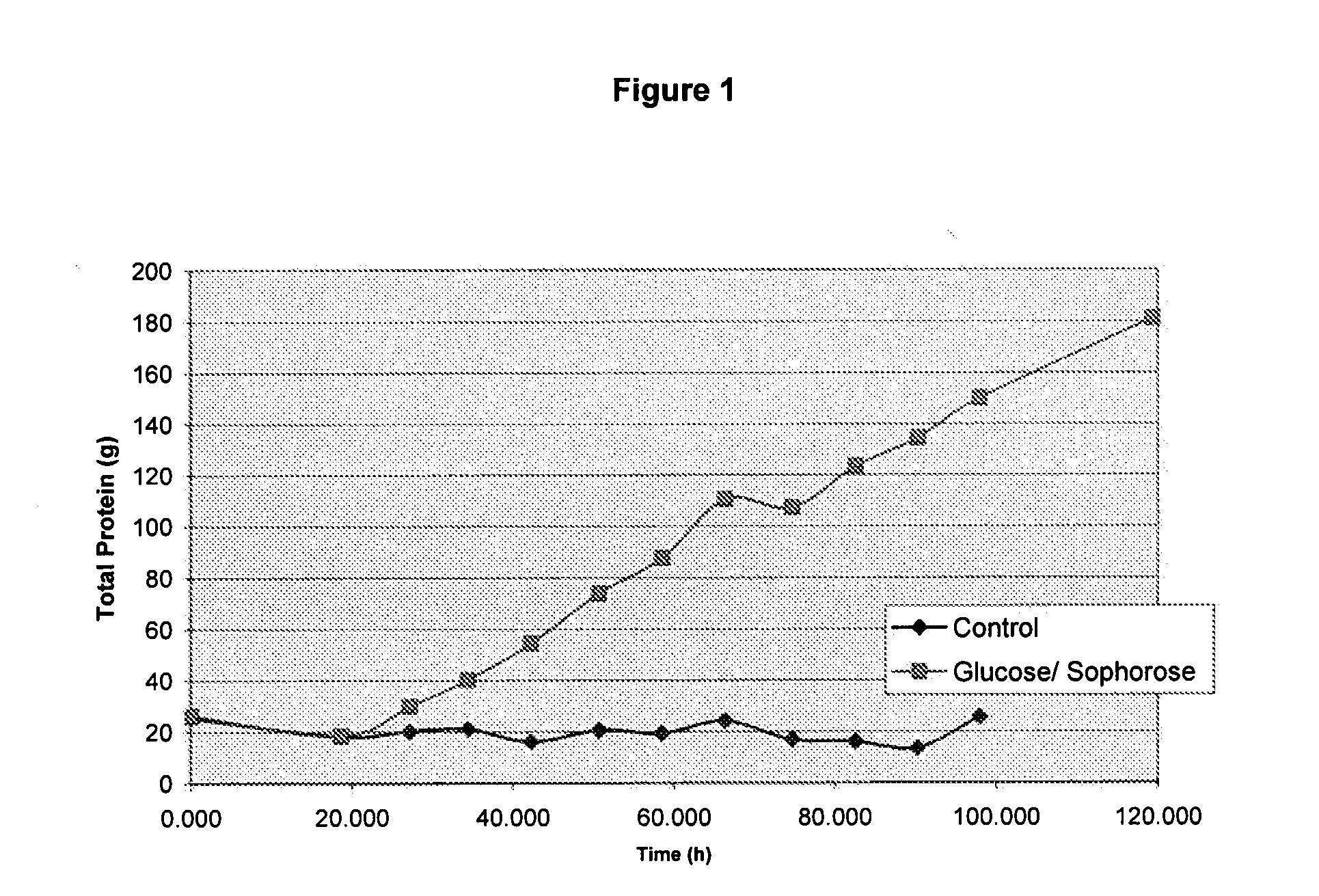
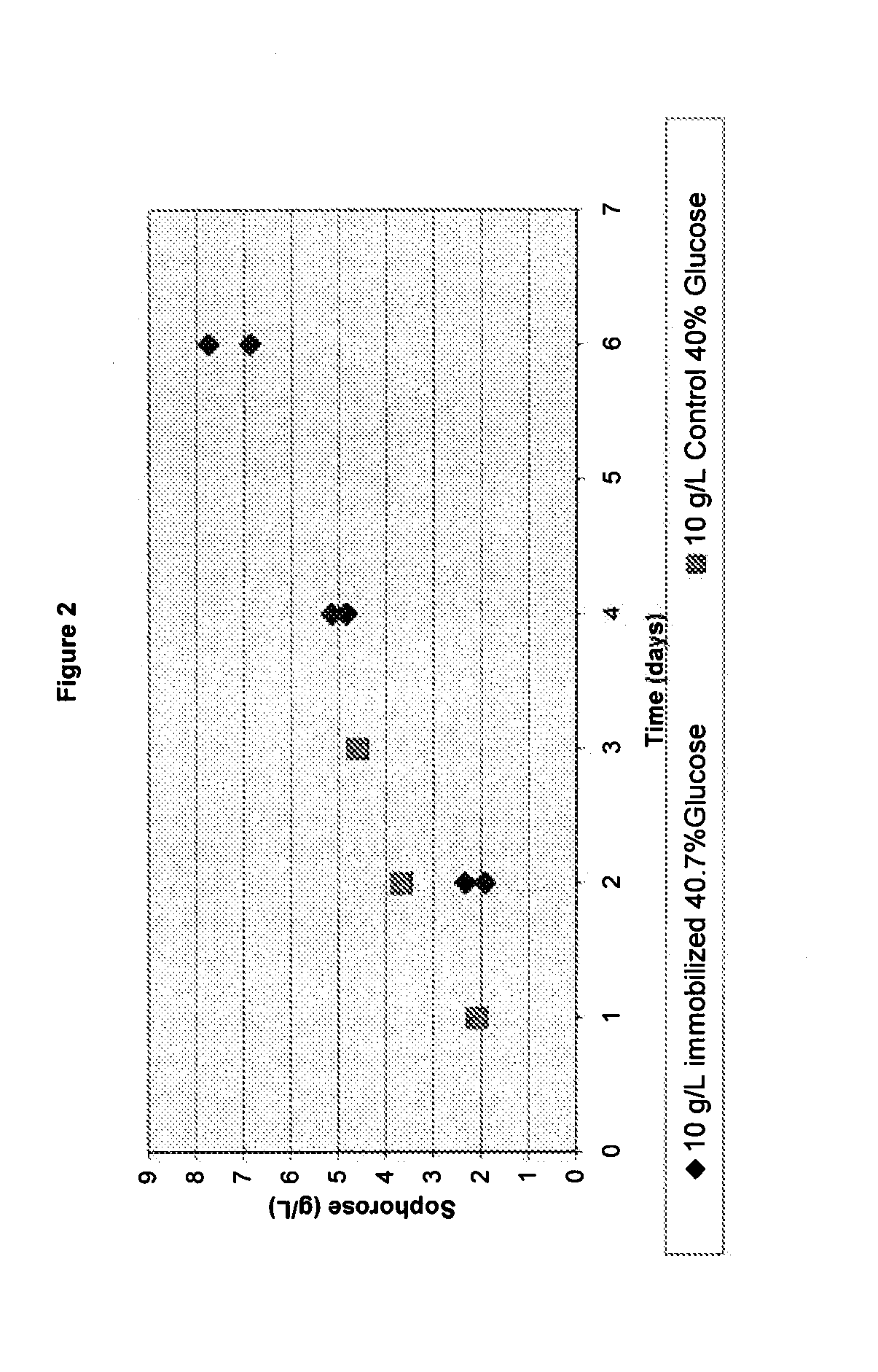
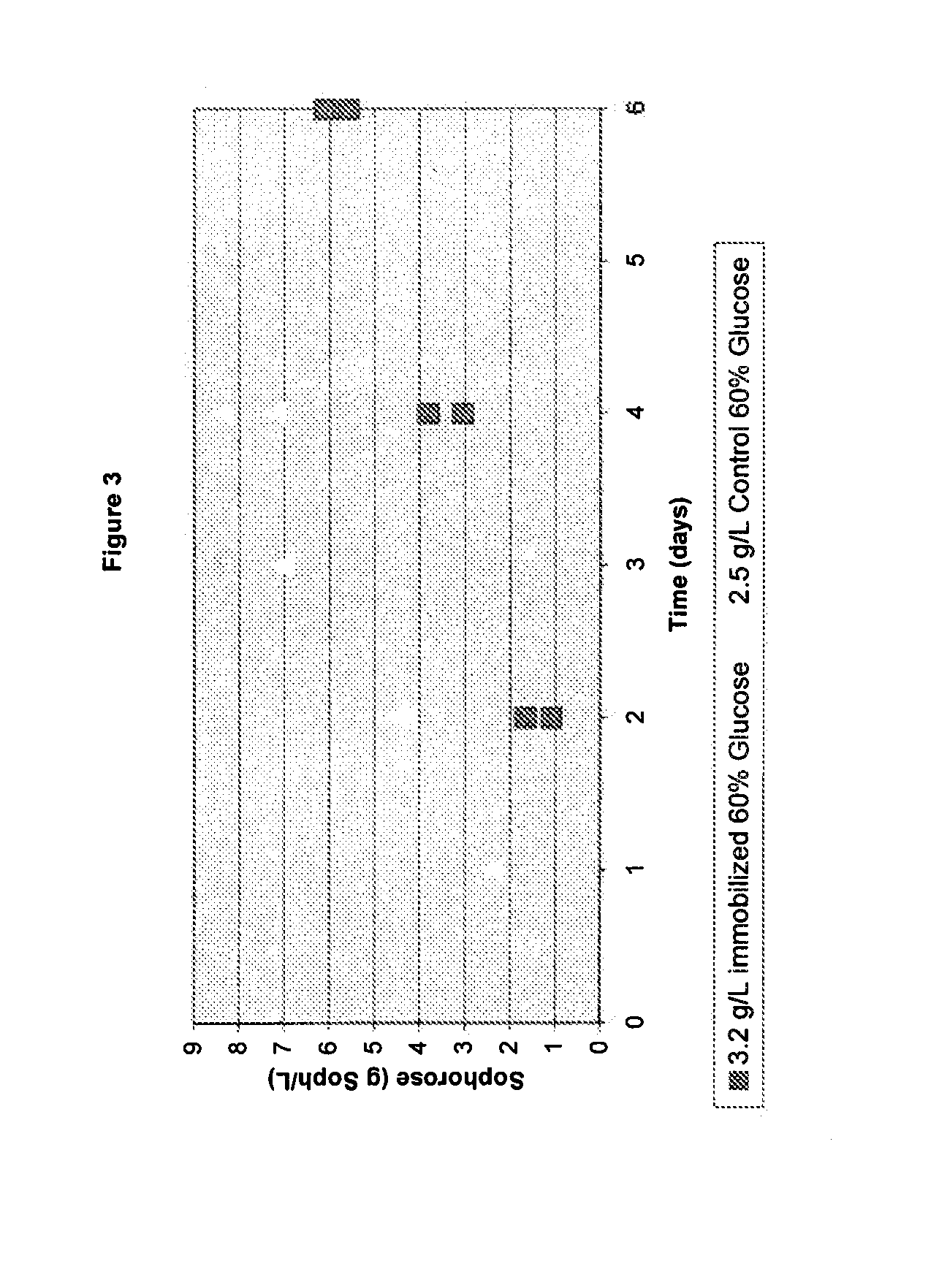
Induction of gene expression using a high concentration sugar mixture
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
Use of human neural stem cells secreting GDNF for treatment of parkinson's and other neurodegenerative diseases
A method of treating brain disorders involving loss of cells that respond to GDNF is disclosed. In one embodiment, the invention comprises the steps of (a) transducing human neural stem cells with glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), wherein the GDNF gene is under control of an inducible promoter system, and (b) transplanting the transduced cells into the brain of a patient.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
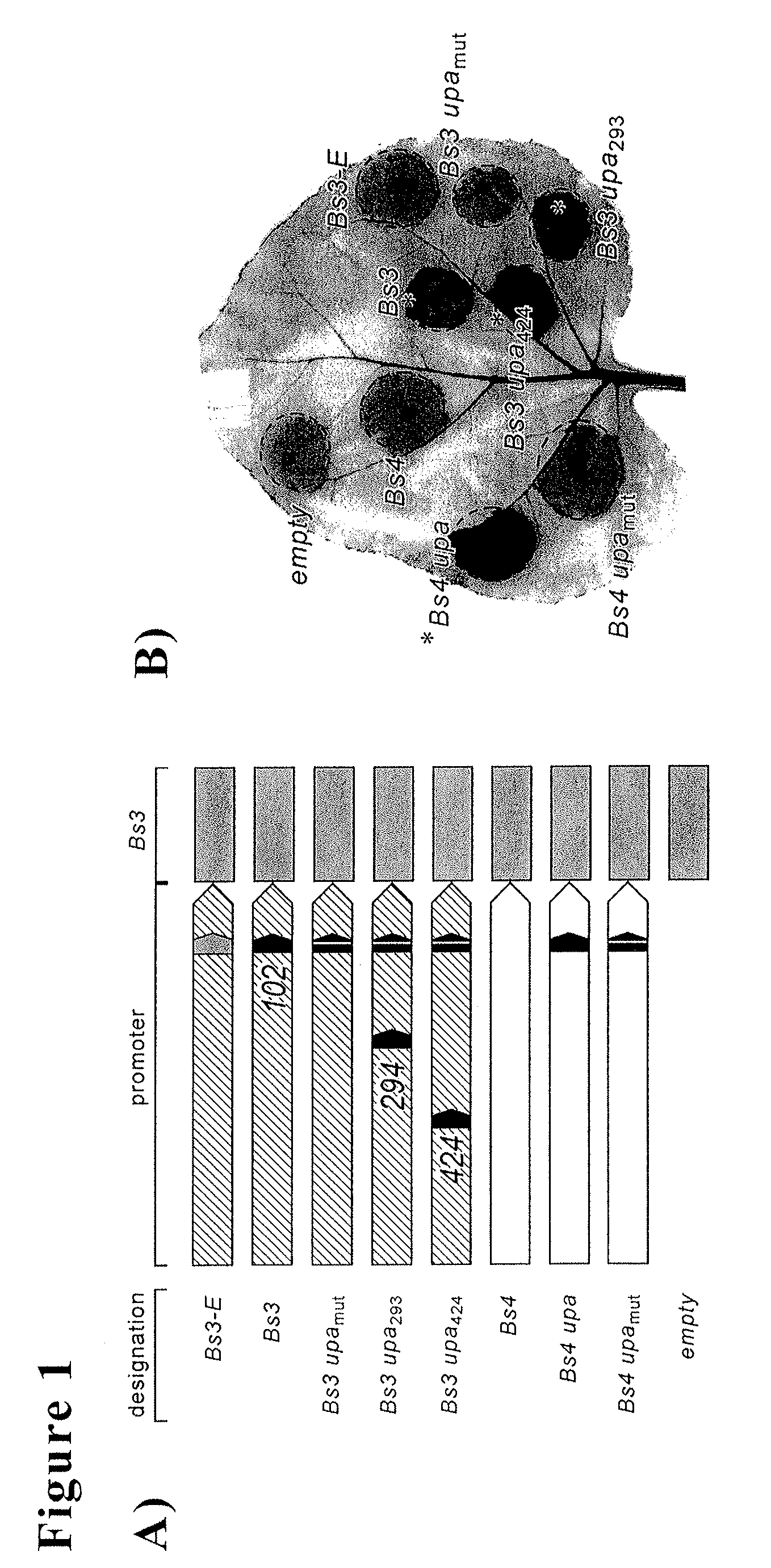
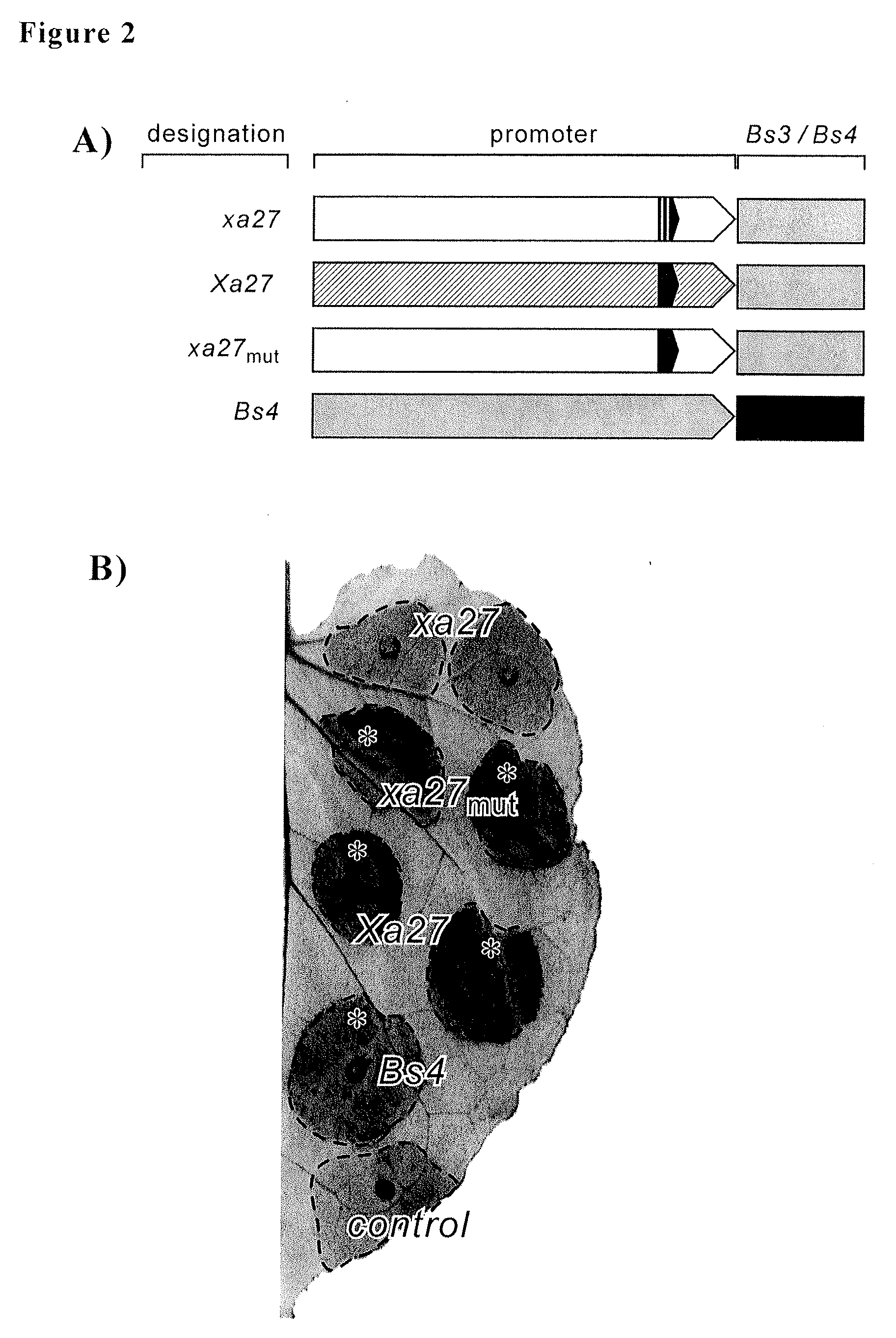
Pathogen-inducible promoters and their use in enhancing the disease resistance of plants
Methods for producing pathogen-inducible promoters for the expression of genes in plants are provided. The pathogen-inducible promoters are inducible by one, two, three, or more plant pathogens. Methods for producing R genes that are inducible in a plant by more than one plant pathogen are further provided. Additionally, provided are R genes and other nucleic acid molecules comprising the pathogen-inducible promoters and that are made by such methods as well as plants, plant parts, plant cells, seeds, and non-human host cells comprising the R genes and other nucleic acid molecules
Owner:TWO BLADES FOUND
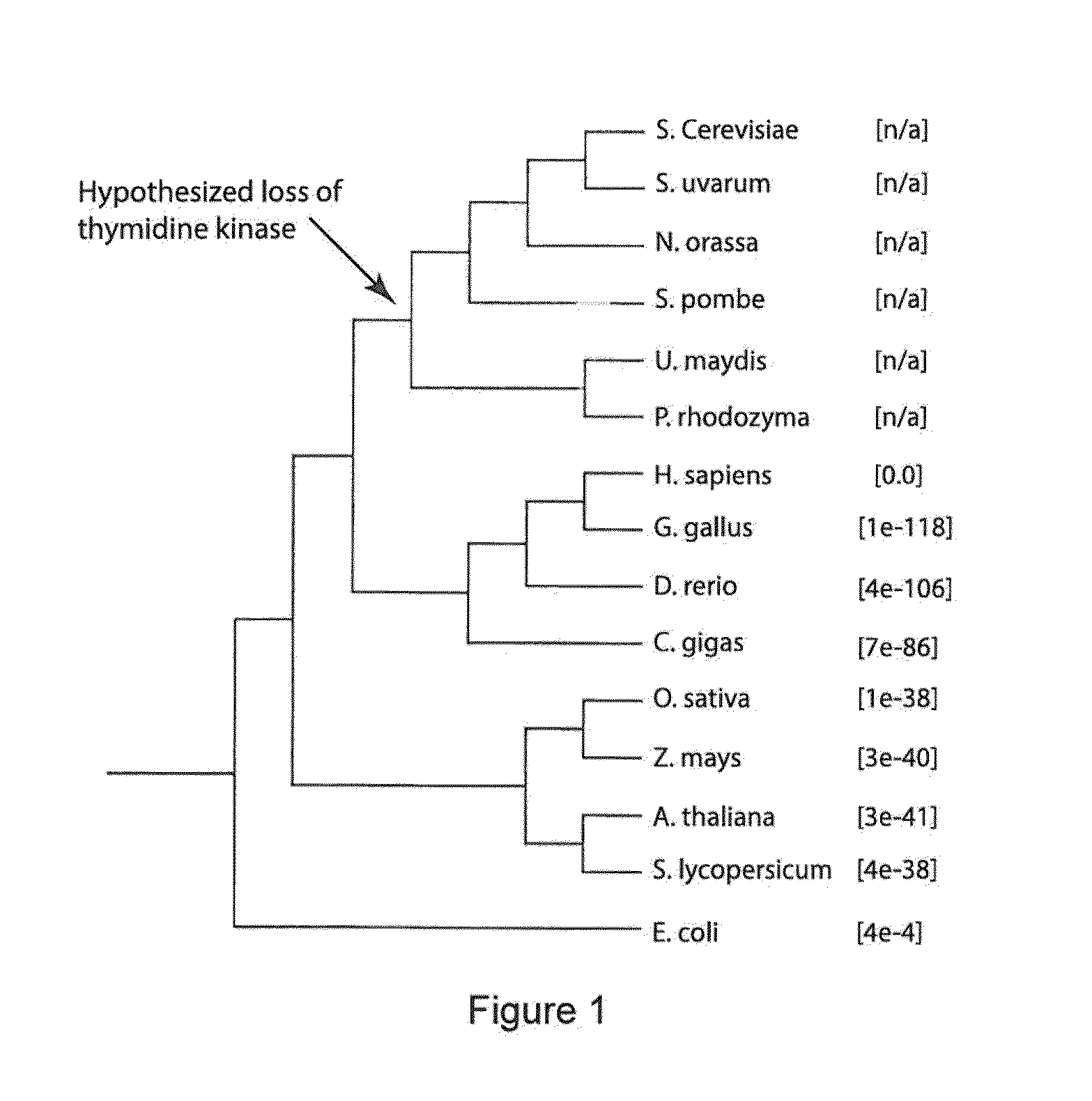
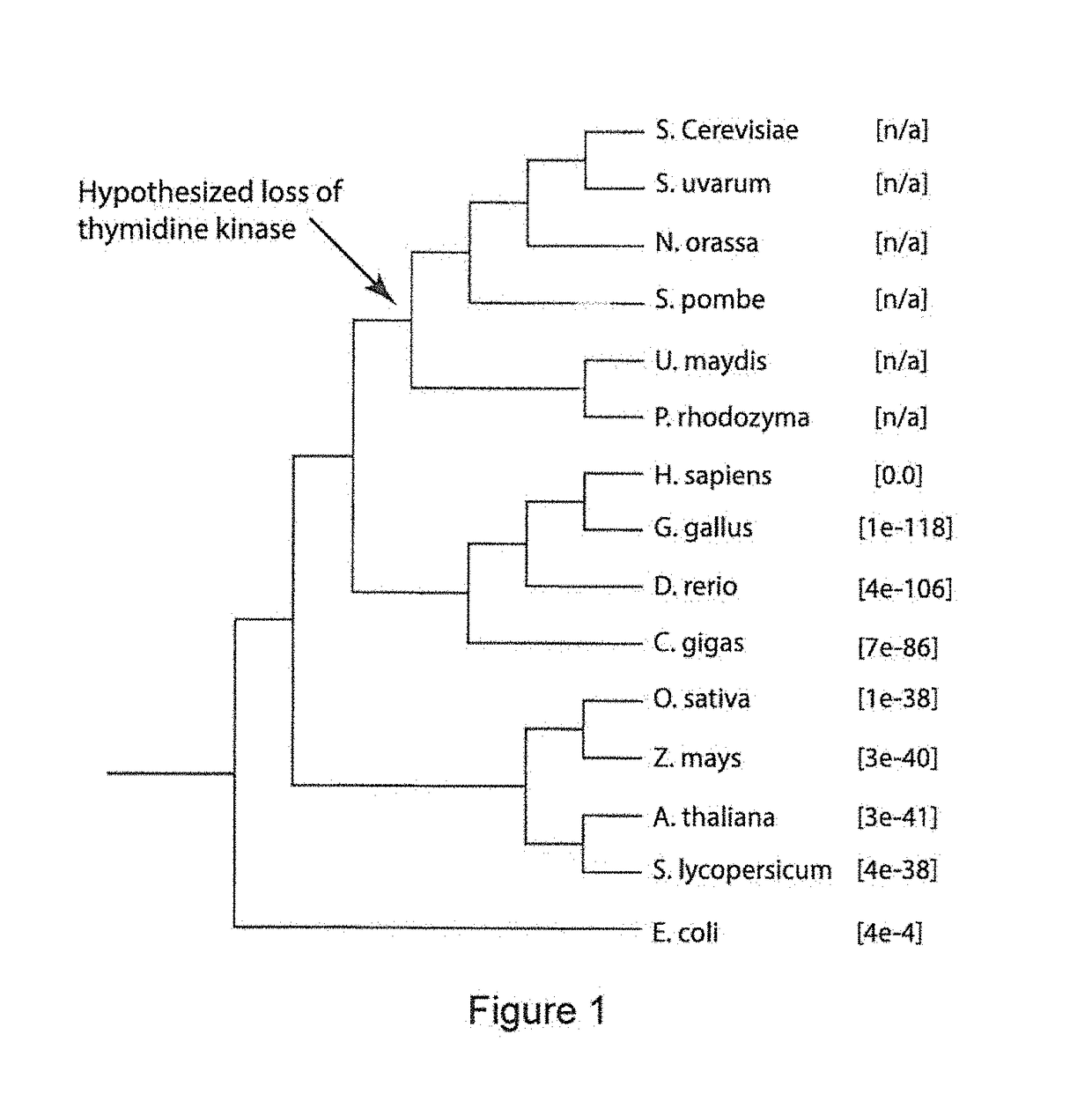
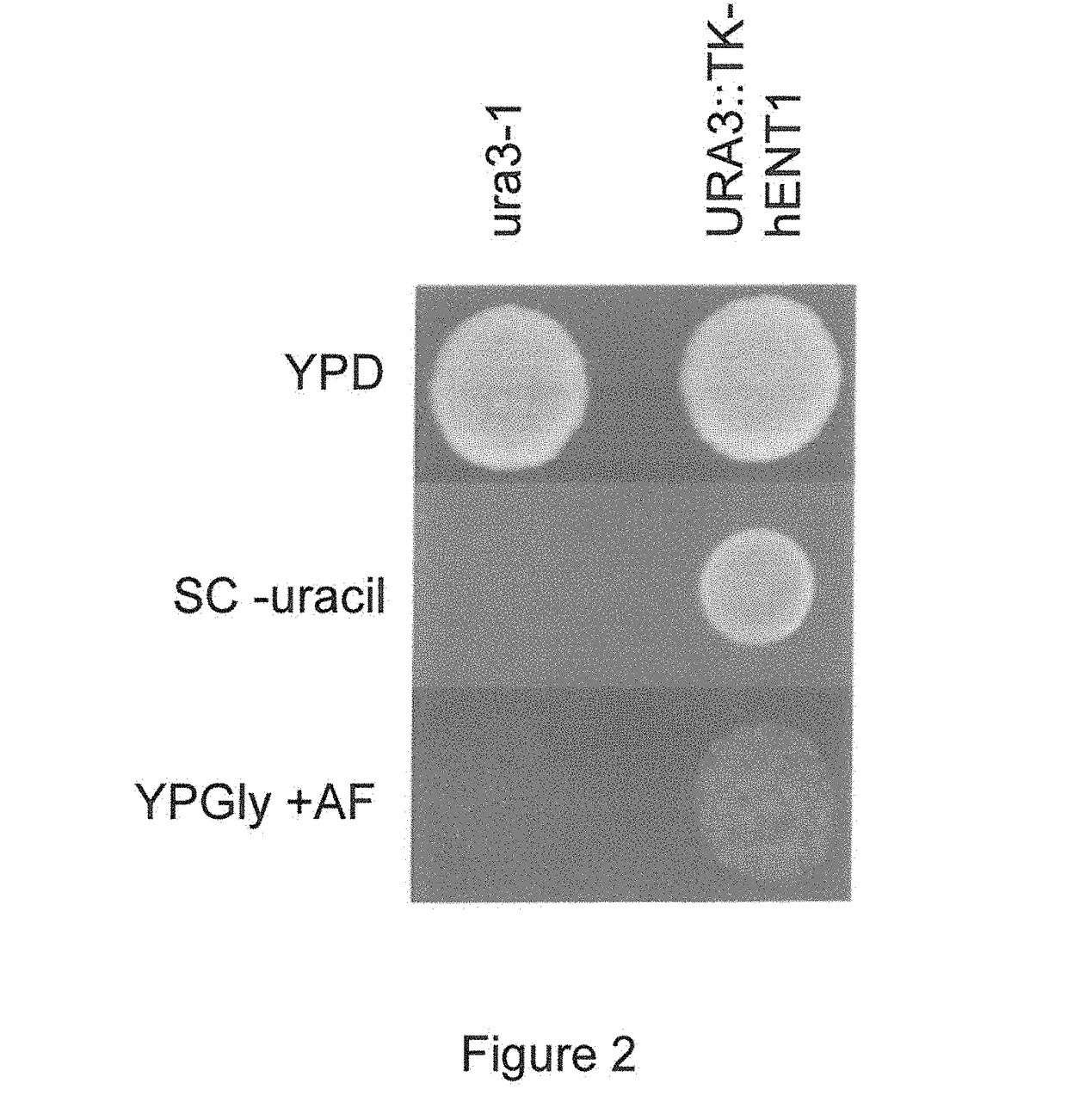
Constructs and methods for genome editing and genetic engineering of fungi and protists
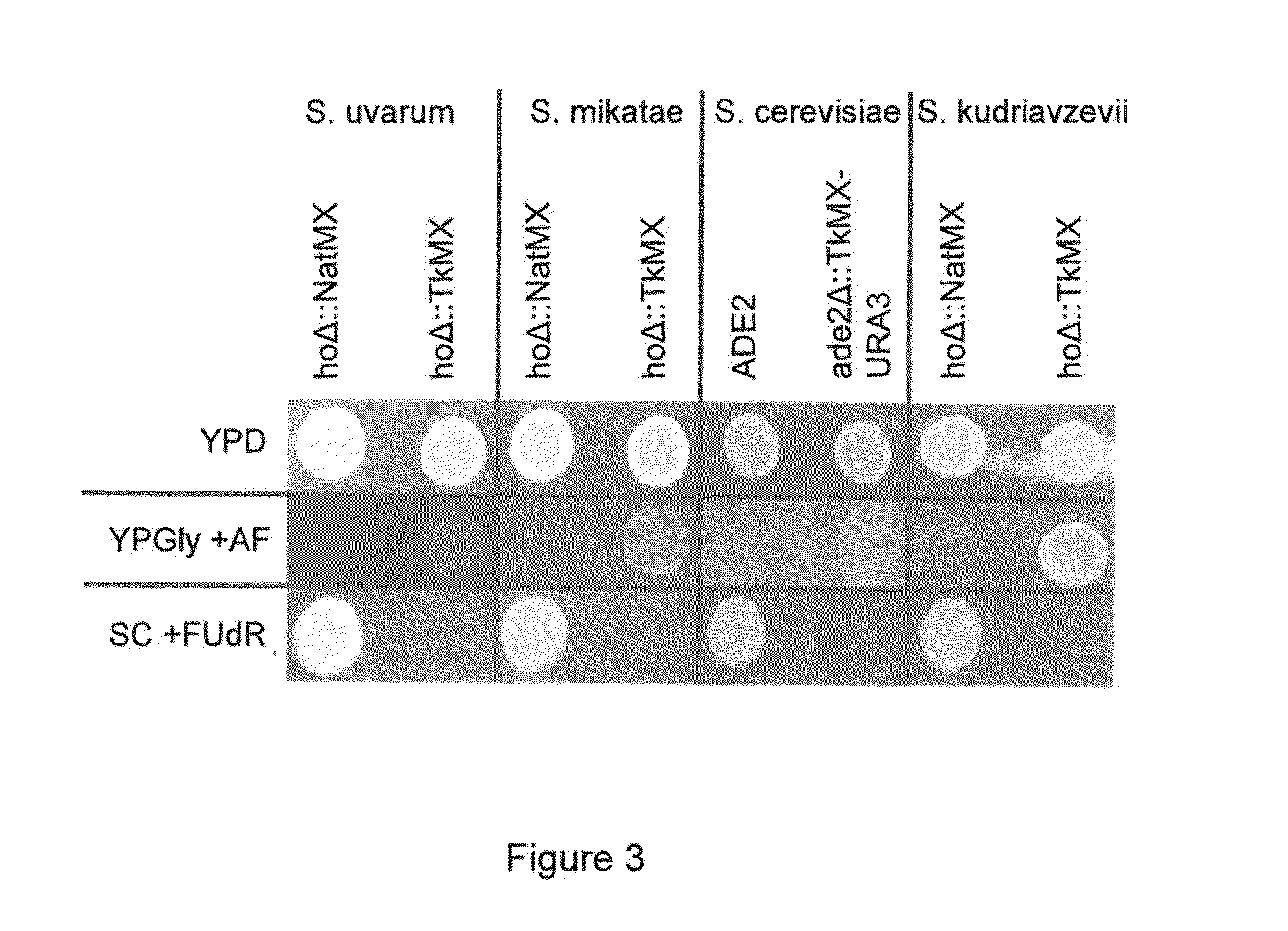
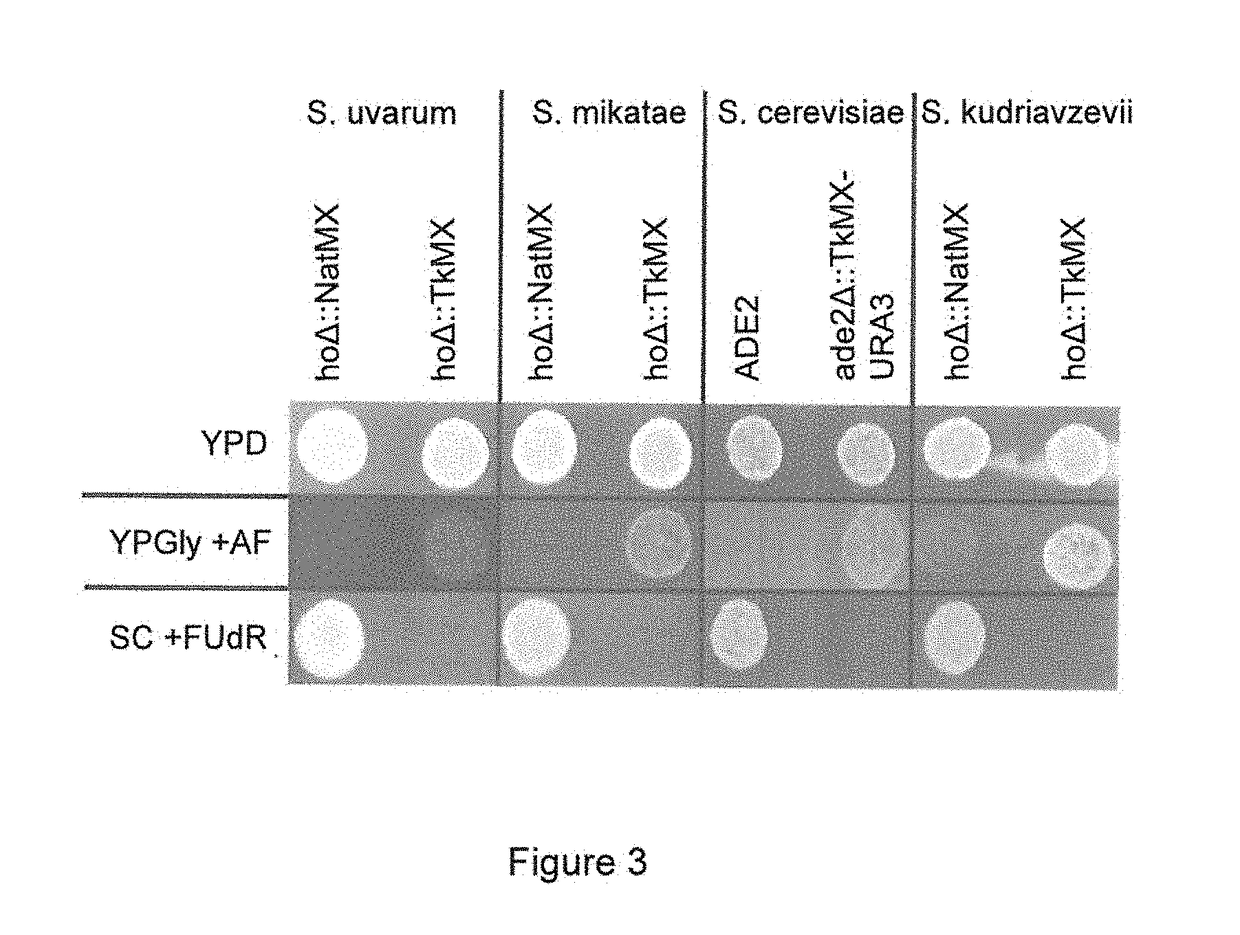
Provided herein are constructs for genome editing or genetic engineering in fungi or protists, methods of using the constructs and media for use in selecting cells. The construct include a polynucleotide encoding a thymidine kinase operably connected to a promoter, suitably a constitutive promoter; a polynucleotide encoding an endonuclease operably connected to an inducible promoter; and a recognition site for the endonuclease. The constructs may also include selectable markers for use in selecting recombinations.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Novel fusion protein preparation method and application of novel fusion protein for increasing protein synthesis
ActiveCN108690139APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifHydrolasesIncreased Protein SynthesisProtein C
The invention provides a novel fusion protein preparation method and an application of the novel fusion protein for increasing protein synthesis. The provided fusion protein can greatly increase the in-vitro translation efficiency. In addition, a composition-type or induction-type promoter (such as pK1PGK1) is inserted before eIF4G, and the synthesis capability of the in-vitro protein is obviouslyenhanced.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
Culturing method of auxilliary bud less tobacco after topping
The present invention discloses a tobacco cultivation method. Said method is characterized by that it adopts a molecular biological technique to identify key gene capable of promoting axillary bud germination and growth after the tip is pruned, then uses nocuity inducible promoter to drive antisense RNA and make it promptly express after the tip is pruned so as to inhibit the expression of said key gene capable of promoting axillary bud germination and growth and make the axillary bud can not be germinated or grown.
Owner:贾朝钧
Root-specific, stimulant inducible promoter and its use
ActiveUS7196247B2Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesAntisense OrientationStimulant
This invention relates to an isolated isoflavone synthase 1 (IFS1) promoter nucleic acid fragment. The invention also relates to the construction of chimeric genes comprising all or a portion of the IFS1 promoter directing the expression of transgenes, in sense or antisense orientation.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC +1
Disease-inducible promoters
Disease-inducible promoter sequences have been identified that may be used to produce transgenic plants that are both more resistant to disease than control plants, and are wild-type or nearly wild type in appearance. Any of these disease-inducible promoters may be incorporated into expression vectors that each comprise a defense response protein operably linked to the promoter. The expression vectors can be introduced into plants and the defense response protein then ectopically expressed. Transgenic plants transformed with many of these expression vectors have been shown to be more resistant to disease, in some cases, to more than one type of pathogen, and yet are similar to wild type plants in their morphology and development.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Constructs and methods for genome editing and genetic engineering of fungi and protists
ActiveUS9879270B2Microbiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionGenome editingOrganism
Provided herein are constructs for genome editing or genetic engineering in fungi or protists, methods of using the constructs and media for use in selecting cells. The construct include a polynucleotide encoding a thymidine kinase operably connected to a promoter, suitably a constitutive promoter; a polynucleotide encoding an endonuclease operably connected to an inducible promoter; and a recognition site for the endonuclease. The constructs may also include selectable markers for use in selecting recombinations.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Induction of Gene Expression Using a High Concentration Sugar Mixture
Described herein is a composition useful for inducing expression of genes whose expression is under control of an inducible promoter sequence and methods for the compositions preparation and use.
Owner:ENGLAND GEORGE R +2
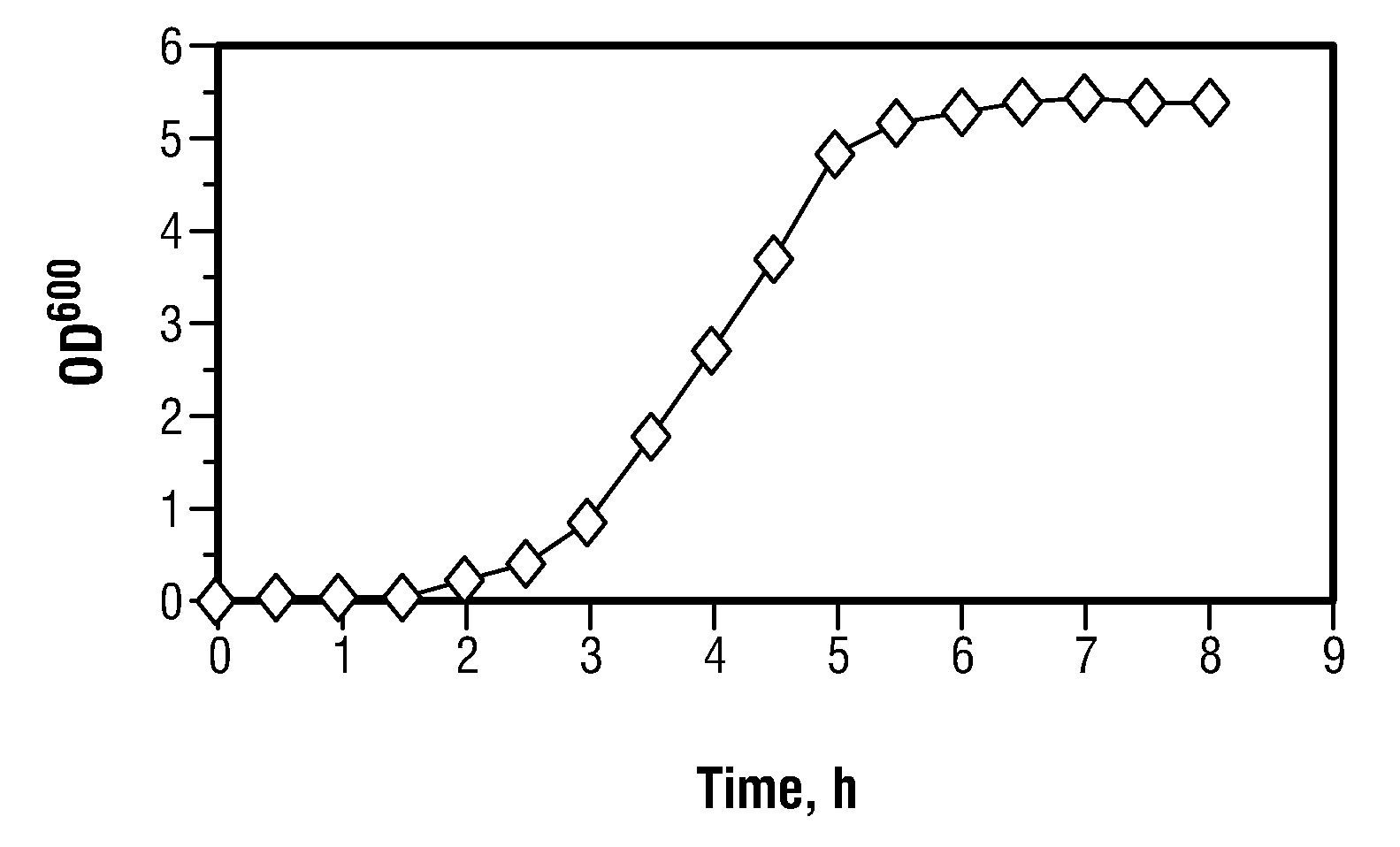
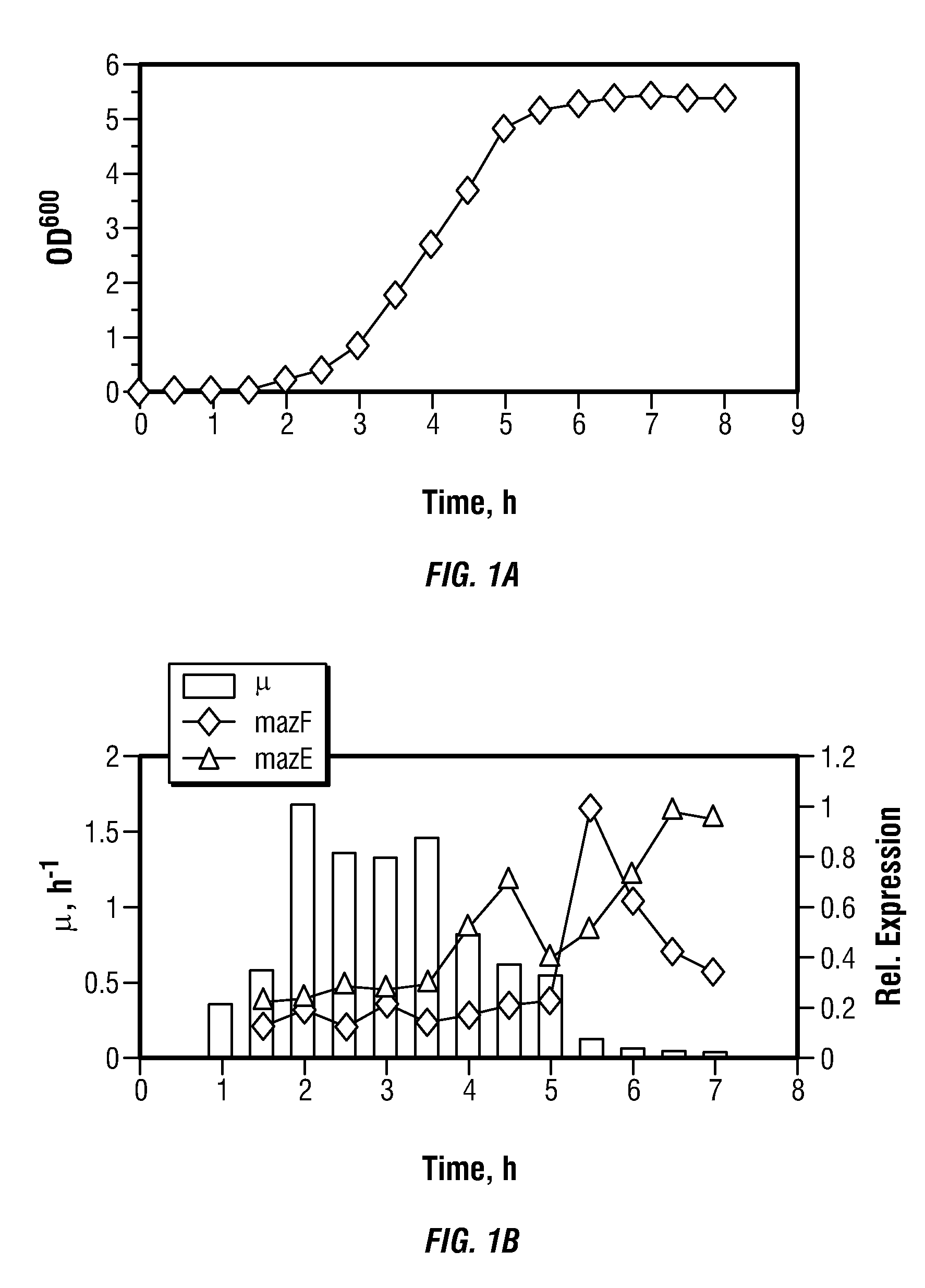
Toxin/antitoxin systems and methods for regulating cellular growth, metabolic engineering and production of recombinant proteins
The present invention provides compositions and method for regulating cellular growth and metabolism, intra- and extracellular enzymatic activities, and synthesis of endogenous and / or heterologous proteins, comprising the steps of cloning genes encoding an mRNA interferase (toxin) and its cognate antitoxin; expressing these proteins in a host cell from two separate constitutive or inducible promoters on one or more plasmid vectors or on a chromosome; and regulating the cellular growth and metabolism by controlling the ratio of toxin and antitoxin present in the host cell. Optionally, the method provides further steps of modifying an endogenous or heterologous gene of interest to substitute all mRNA recognition sequences with sequences that are not cleavable by the mRNA interferase being expressed without any change in the amino acid sequence of the protein encoded by the gene; and co-expressing the gene of interest in the same host cell.
Owner:MAZEF BIOSCI
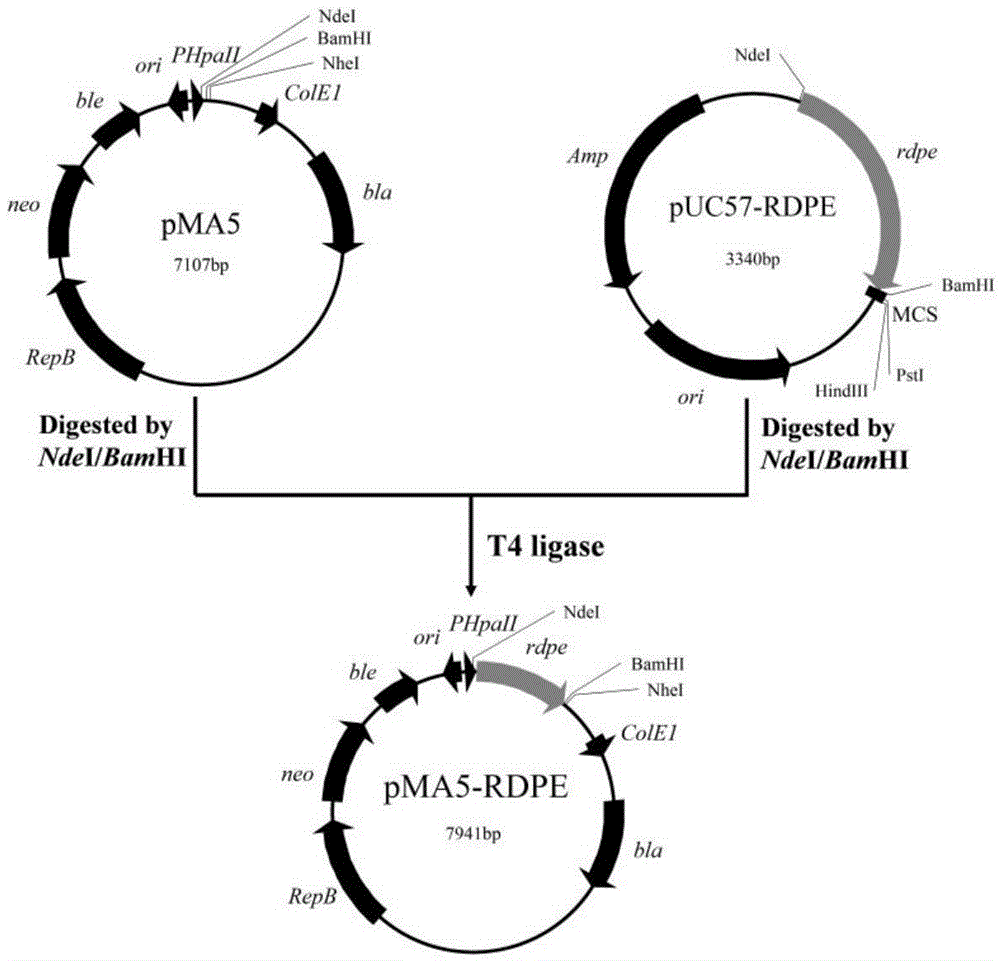
Genetic engineering strain capable of effectively secreting D-psicose 3-epimerase and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN105602879ASimple purification processLow production costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPsicoseRumen
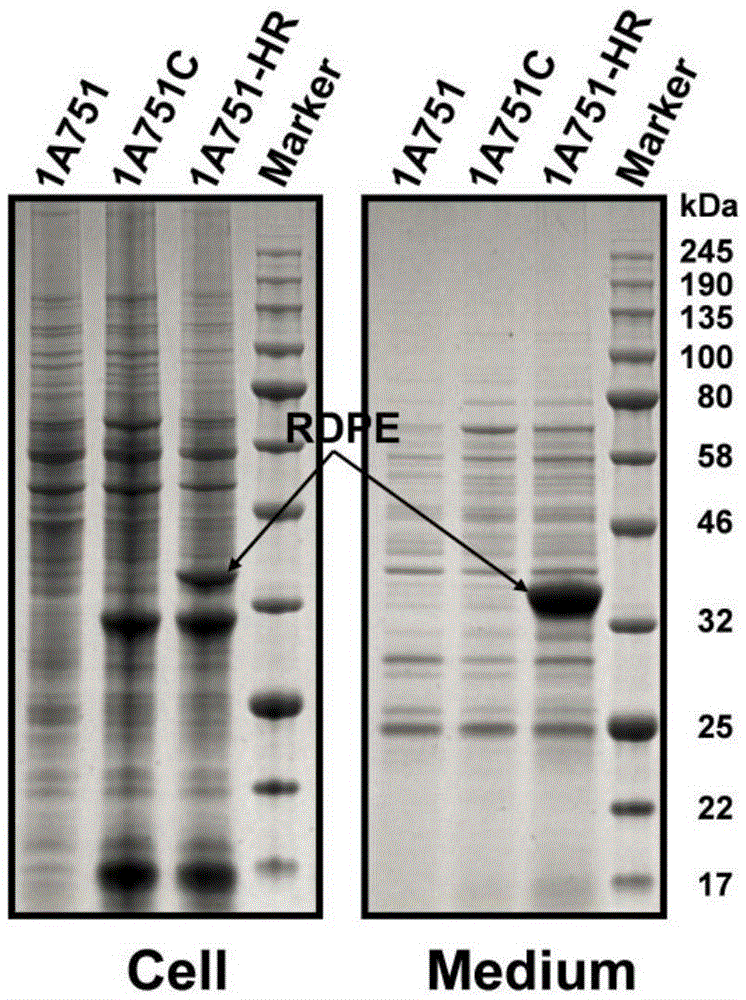
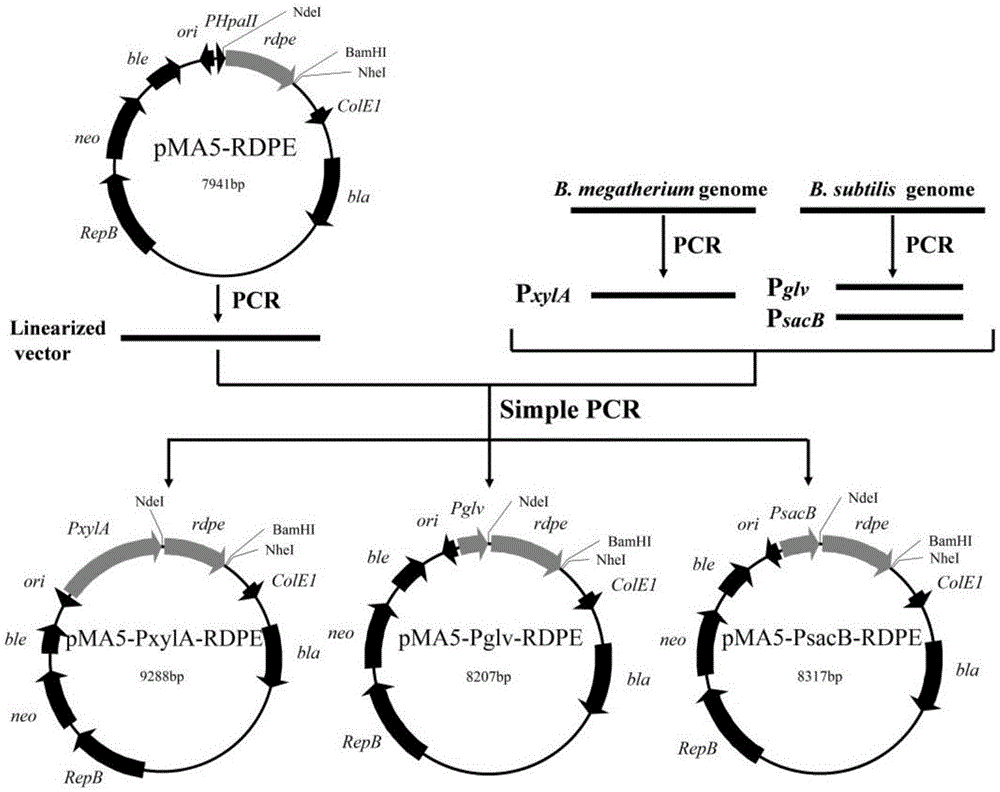
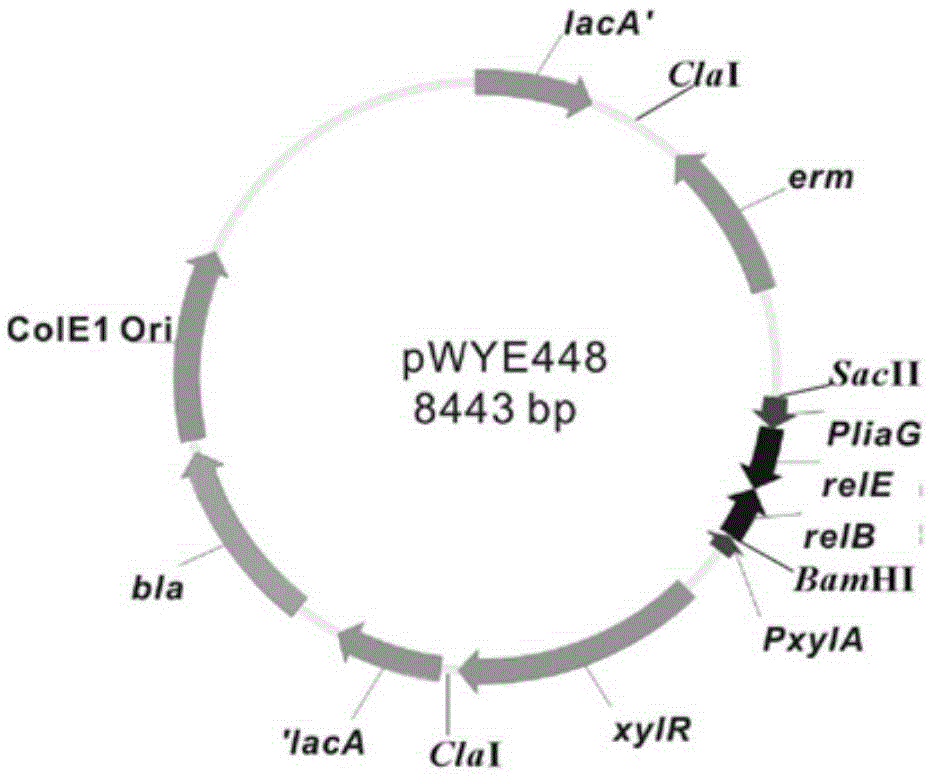
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and particularly relates to a genetic engineering strain capable of effectively secreting D-psicose 3-epimerase and a construction method thereof. A D-psicose 3-epimerase gene rdpe from rumen bacterium Ruminococcus sp. 5_1_39B_FAA is obtained firstly, recombinant plasmid pMA5-RDPE construction and bacillus subtilis conversion are conducted, and then constitutive and secretive expression of RDPE in bacillus subtilis is achieved. By comparing three glucose-induced promoters, the optimal inducible promoter P[xylA] is obtained, and the RDPE secretion level is increased remarkably. By knocking out the xylose utilization gene xylAB (xylA and xylB), the xylose metabolism pathway of bacillus subtilis is blocked, the secretion amount of RDPE is further increased, and the optimal induced concentration of the inducer xylose is reduced to 0.5% from 4.0%. Finally, the engineered strain 1A751SD-XR is evaluated in a 7.5 L fermentation tank, and the RDPE secretion level can be as high as 95 U / mL and 2.6 g / L.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
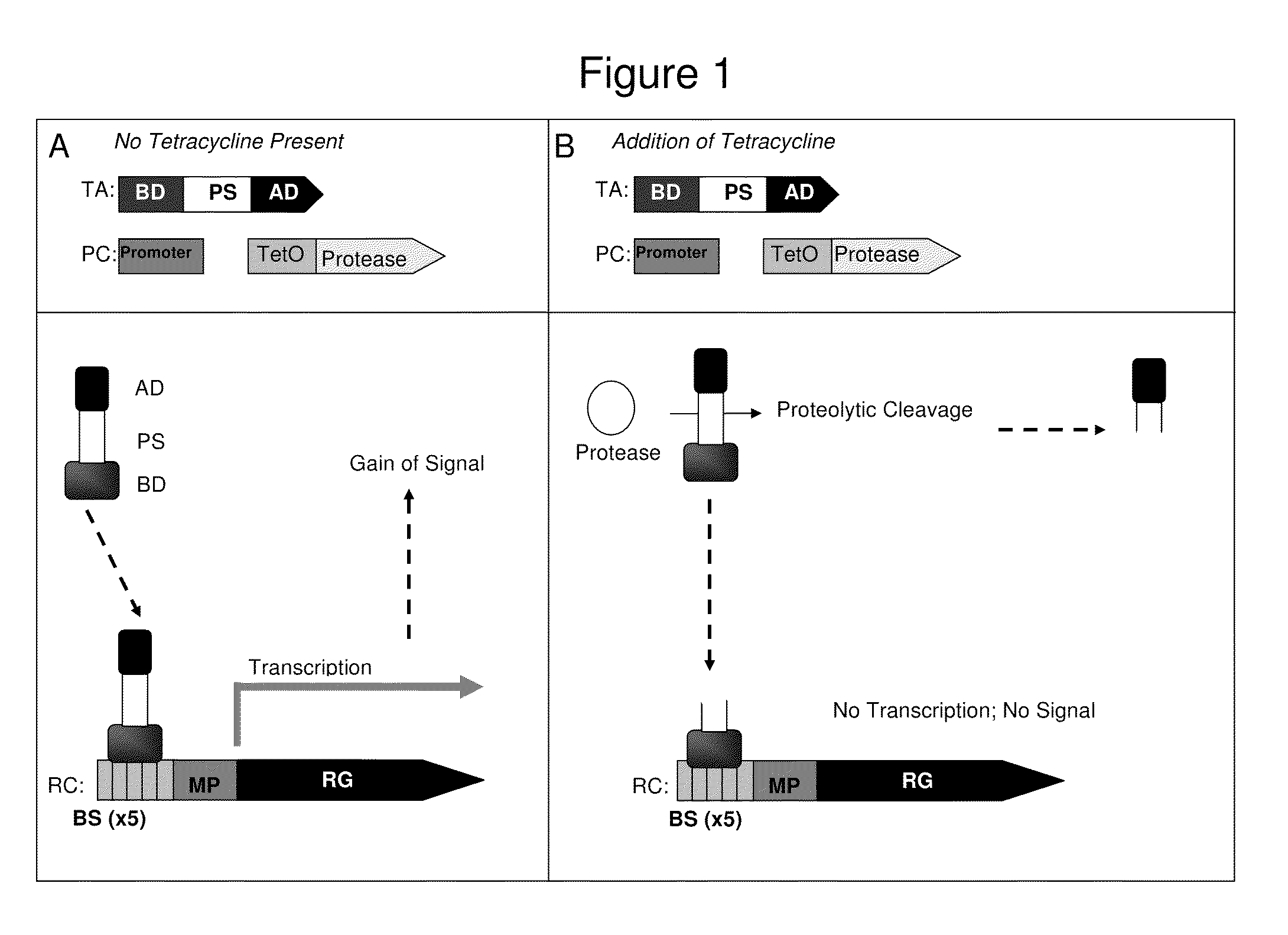
Method for identification of protease activity inhibitors and assaying the presence of protease activity
A system for the identification of proteases and protease inhibitors is provided. The system has at least two components. The first component is a reporter construct with at least one binding site, a transcriptional promoter, an inducible promoter region, and at least one reporter gene, all functionally connected for expression of the reporter gene(s) in functional coordination with a transcriptional activation agent. The second component is a transcriptional activation agent comprising a nucleic acid binding domain, at least one protease substrate domain, and at least one transcriptional activation domain for an inducible promoter. The system allows detection and evaluation of agents affecting protease activity directed to the protease substrate domain. The system also allows for the detection of the presence of proteases in environmental samples.
Owner:SYNAPTIC RES
Process for production of recombinant proteins as a soluble form
ActiveUS20080076156A1Reduce necessityEfficiently obtainedSugar derivativesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsProtein targetNucleotide
A target protein is prepared as soluble protein using a recombinant protein expression system. An expression vector is used that includes (1) an expression-inducible promoter sequence; (2) a first coding sequence including a polynucleotide coding for a polypeptide that is represented by the formula (Z)n; and (3) a second coding sequence that includes a polynucleotide that codes for a target protein. A method of producing the target protein is also used that includes expressing protein using this expression vector.
Owner:JNC CORP
Method for selective expression of therapeutic genes by hyperthermia
A method for controlling in vivo heat-inducible gene expression for provision of therapeutic polypeptide. The method includes the steps of: (a) providing a construct comprising a polynucleotide encoding a therapeutic polypeptide, wherein the polynucleotide is operatively linked to a heat-inducible promoter; (b) administering the construct to a warm-blooded vertebrate at a site at or near the tumor; and (c) applying heat to the site at or near the tumor to express the therapeutic polypeptide, whereby anti-tumor activity is observed.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
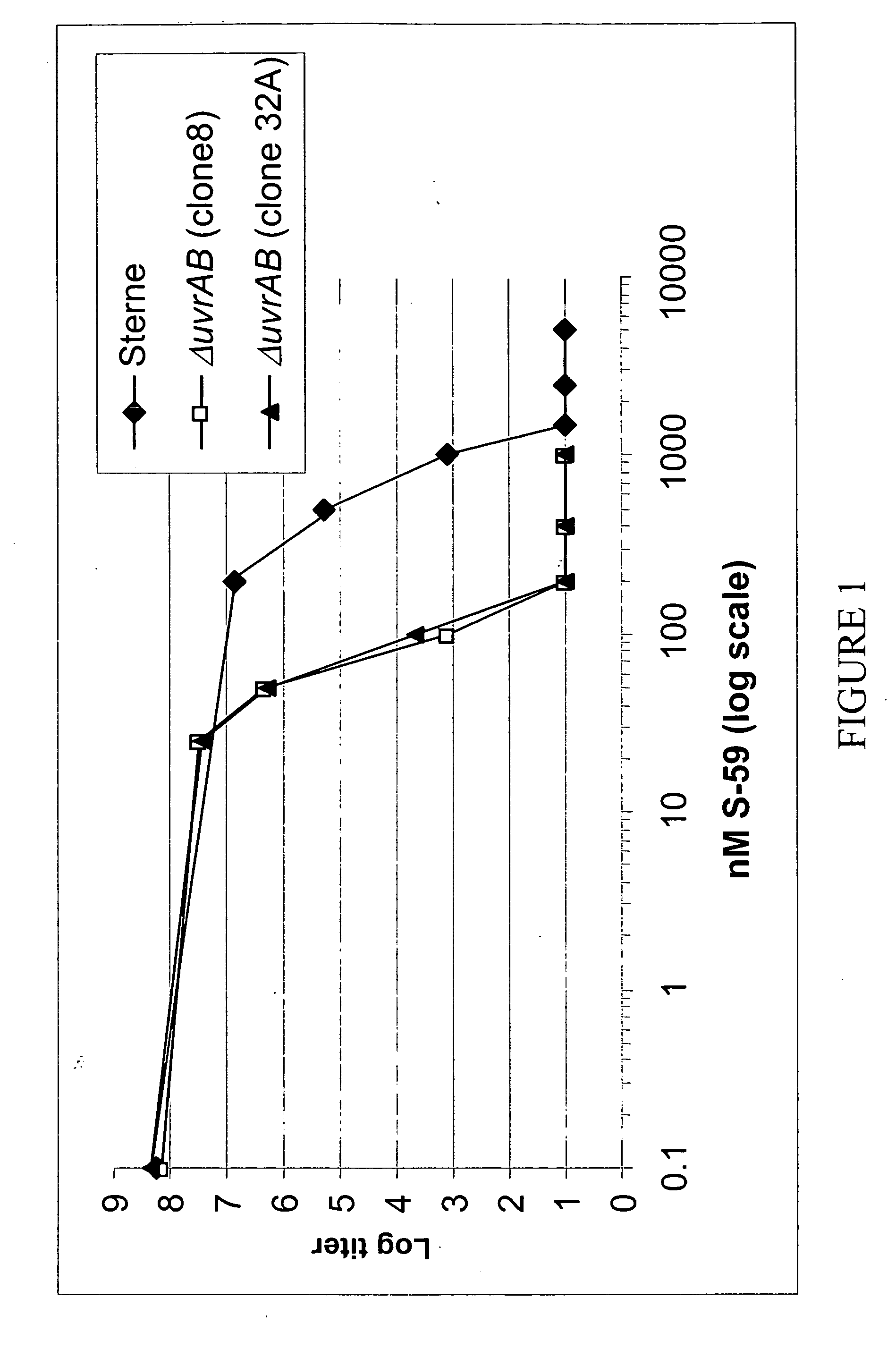
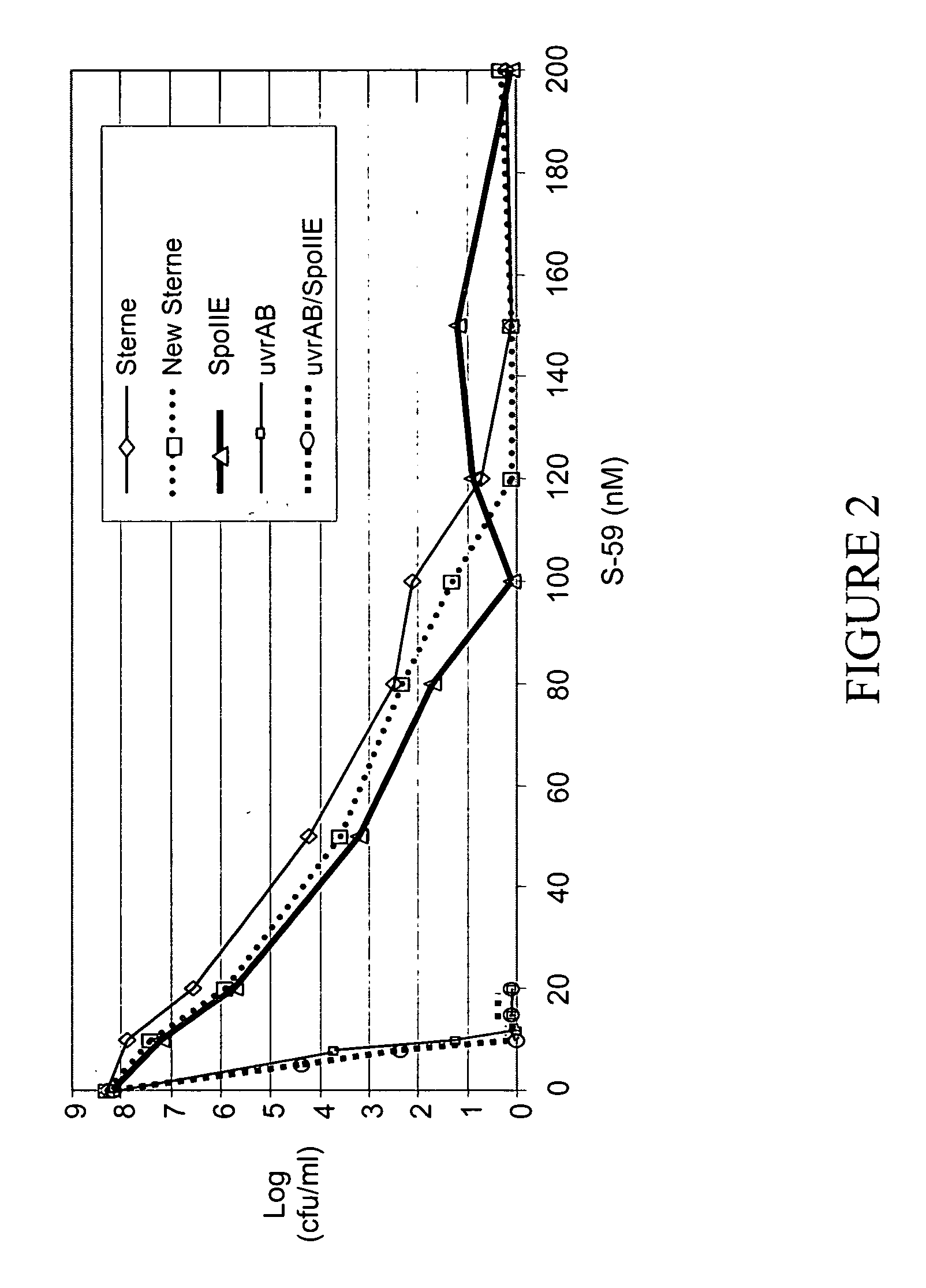
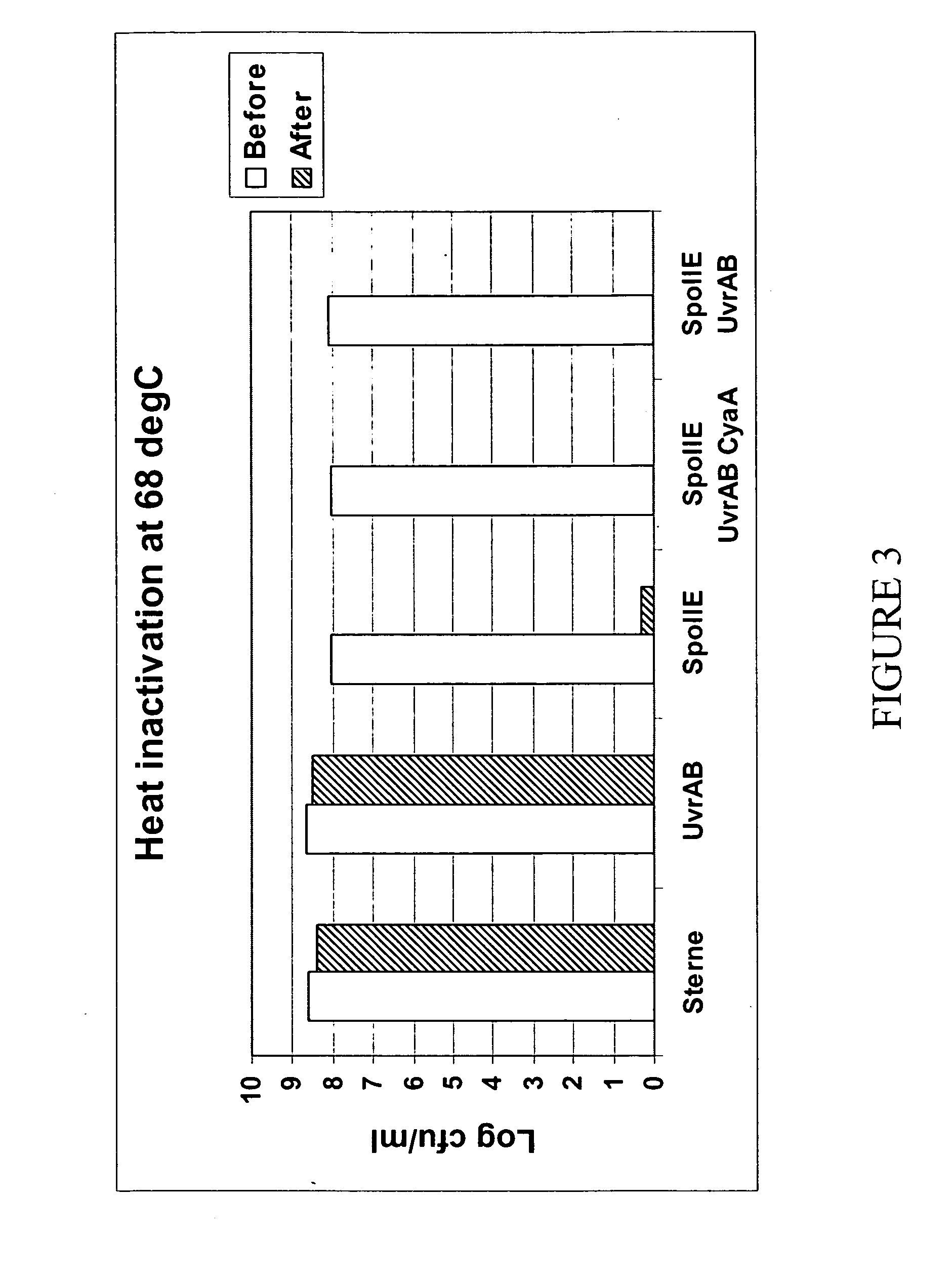
Modified Bacillus anthracis, vaccine compositions and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20070031457A1Low toxicityReduce maintenanceBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaAntigenProtective antigen
A variety of modified Bacillus anthracis bacteria useful in vaccines are provided. For instance, asporogenic strains of Bacillus anthracis are provided. In addition, Bacillus anthracis strains attenuated in their ability to repair their nucleic acid, such as in their nucleic acid excision repair ability or recombination repair ability, are provided. Strains expressing an antigen, such as protective antigen, under the control of a heterologous promoter and / or an inducible promoter are also provided. Bacillus anthracis bacteria comprising mutations in toxin genes are further provided. Vaccine compositions comprising the bacteria, methods of making the modified strains, and methods of using the vaccines are also provided.
Owner:ANZA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Bacterial traceless genetic manipulation vector and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN106676119AAvoid toxicityImprove function and effectBacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionAntibiotic YToxin protein
The invention provides a bacterial traceless genetic manipulation vector. The vector contains a toxin inverse-screening element controlled by an antitoxin switch and an antibiotics resistance gene. The invention also provides a construction method of the vector and a method for application of the vector in bacterial traceless gene knock-out, knock-in, replacement, point mutation and insertion and deletion of large DNA fragments (larger than 194kb). By the utilization of a constitutive promoter for continuous expression of toxin protein and by the utilization of an inducible promoter for inducible expression of antitoxin protein, the toxin inverse-screening element (TCCRAS) controlled by the antitoxin switch is established, and the problem that specificity of existing genetic manipulation systems of gram-positive bacterium is not high, the systems are instable and screening is difficult is solved.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Drought inducible promoters and uses thereof
The present invention is directed to drought responsive promoter sequences, polynucleotide constructs comprising the drought responsive promoters and methods of identifying the drought responsive promoters or fragments thereof. The invention further relates to the use of the present drought responsive promoters to modulate transcript levels.
Owner:CERES INC
Corn drought inducible gene promoters and activity analysis thereof
InactiveCN102154289ASolving the food crisisSolve problems such as ecological deteriorationVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses corn drought inducible gene promoters and activity analysis thereof, which belong to the technical field of bioengineering. The invention provides the sequences of the obtained corn drought inducible promoters and provides a drought inducible plant expression vectors for corn transfer, and a transgenic plant transferred by the plant expression vector and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primers suitable for amplifying a DNA fragment having a sequence SEQ ID No.1. The prompters can be used for promote the high-efficiency expression of an anti-drought gene, are used in drought-resistance transgenic plants and have an active significance for solving food crisis, ecological deterioration and the like in drought areas.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Methods of affecting plant growth with microRNA
ActiveUS20090094711A1Promote plant growthIncrease biomassTobacco preparationDough treatmentGrowth plantNucleotide
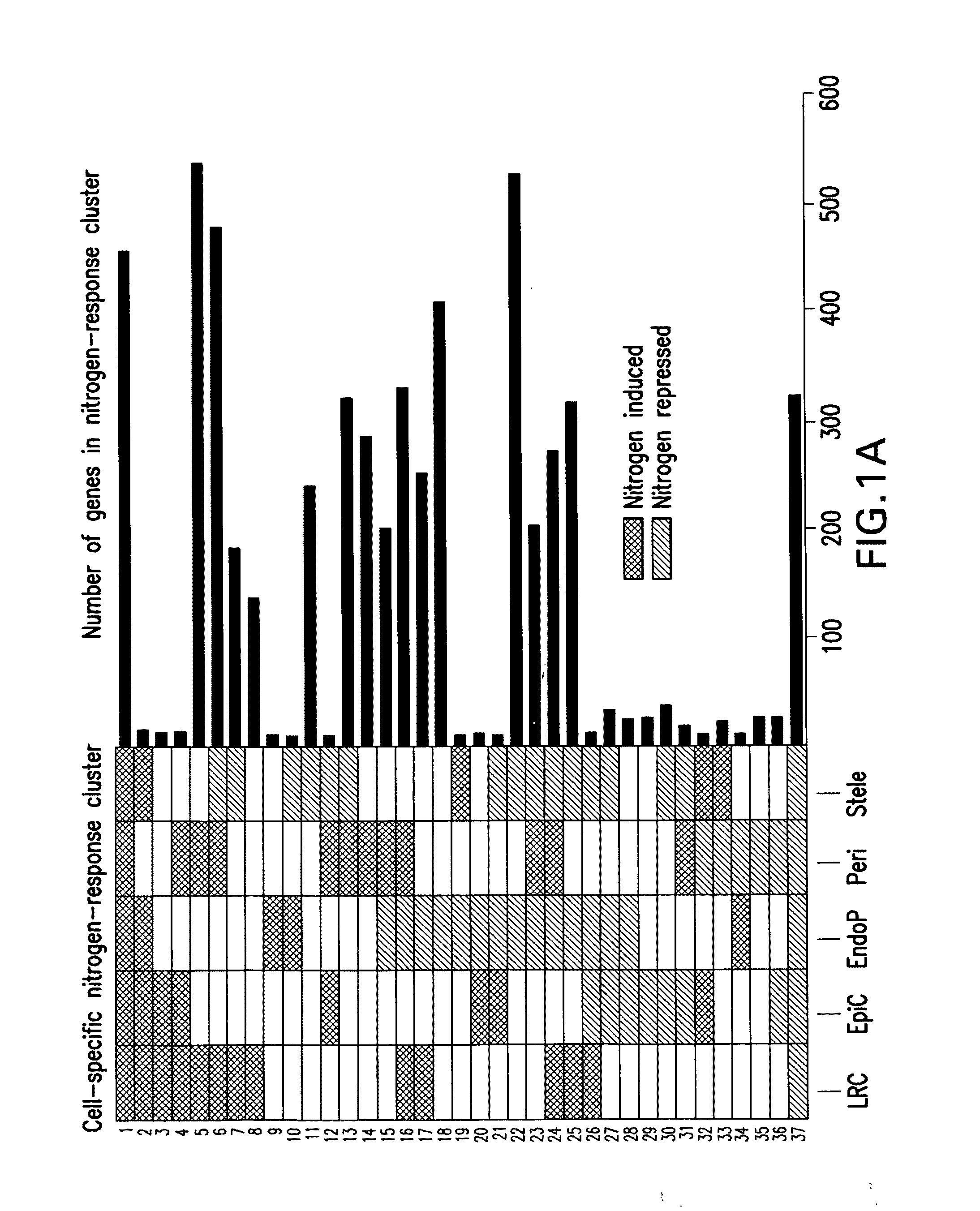
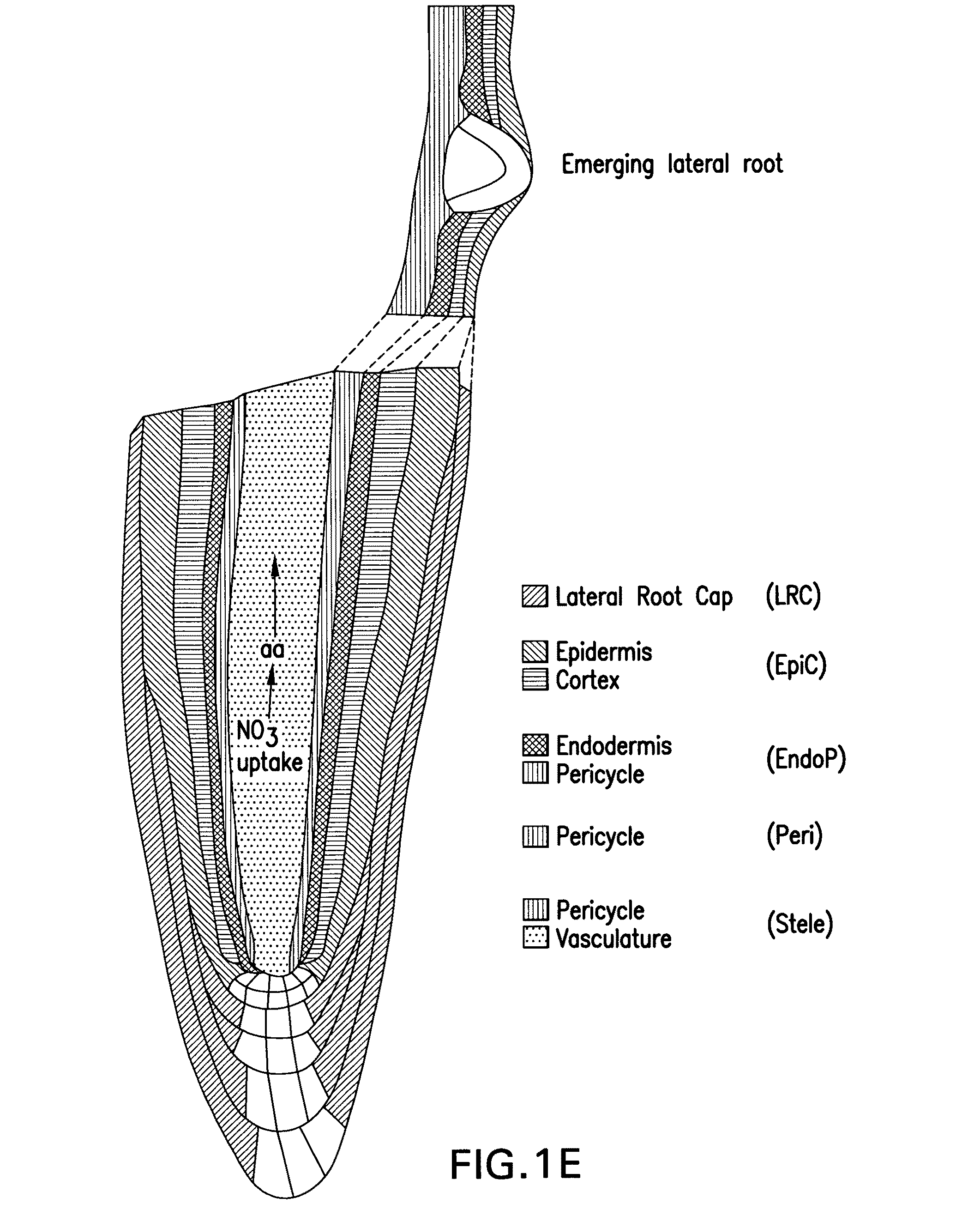
Provided herein are compositions and methods for producing transgenic plants. In specific embodiments, transgenic plants comprise a construct comprising a polynucleotide encoding microRNA167 (miR167), or precursor thereof, operably linked to a plant pericycle-specific promote, wherein the miR167 is ectopically overexpressed in the transgenic plants, and wherein the promoter is optionally a constitutive or inducible promoter. In some embodiments, the transgenic plant has an improved agronomic or nutritional characteristic when cultivated in nitrogen-rich conditions as compared to a wild type plant cultivated in the same conditions. Also provided herein are commercial products (e.g., pulp, paper, paper products, or lumber) derived from the transgenic plants (e.g., transgenic trees) produced using the methods provided herein.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Salmonella vectored vaccines against Chlamydia and methods of use
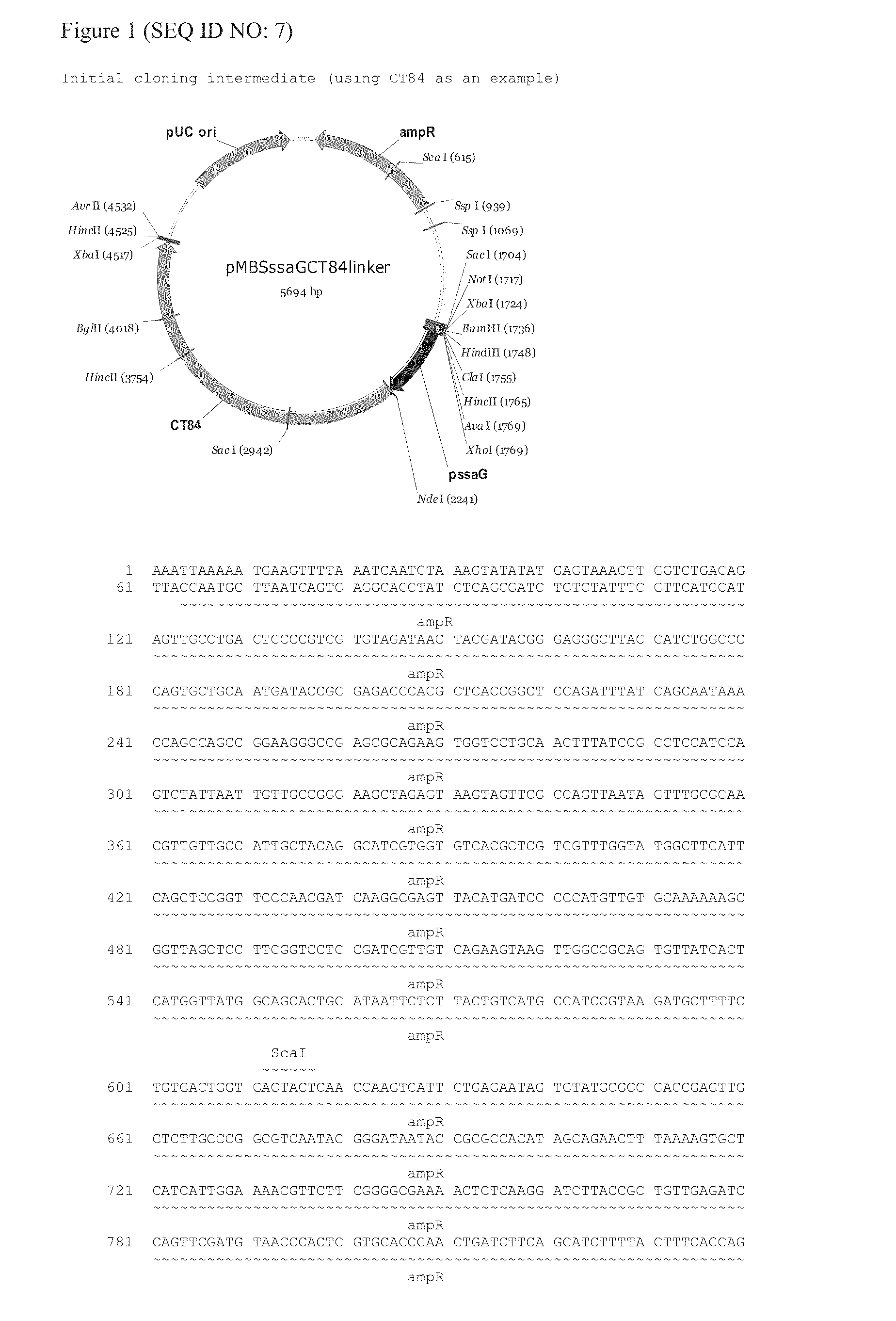
The invention provides an attenuated Salmonella vaccine vector comprising one or more heterologous polynucleotides that encode immunogenic Chlamydial peptides. In one embodiment, the attenuated Salmonella vaccine vector comprises aroC and ssaV attenuating mutations. The heterologous polynucleotides encoding the immunogenic Chlamydial peptides can be under the control of an inducible promoter such as a Salmonella ssaG promoter. In one embodiment of the invention, the immunogenic Chlamydial peptide is a PmpG peptide, for instance, a CT110, CT84 or CT40 peptide.
Owner:PROKARIUM
Gateway cloning entry vector, construction method and use thereof
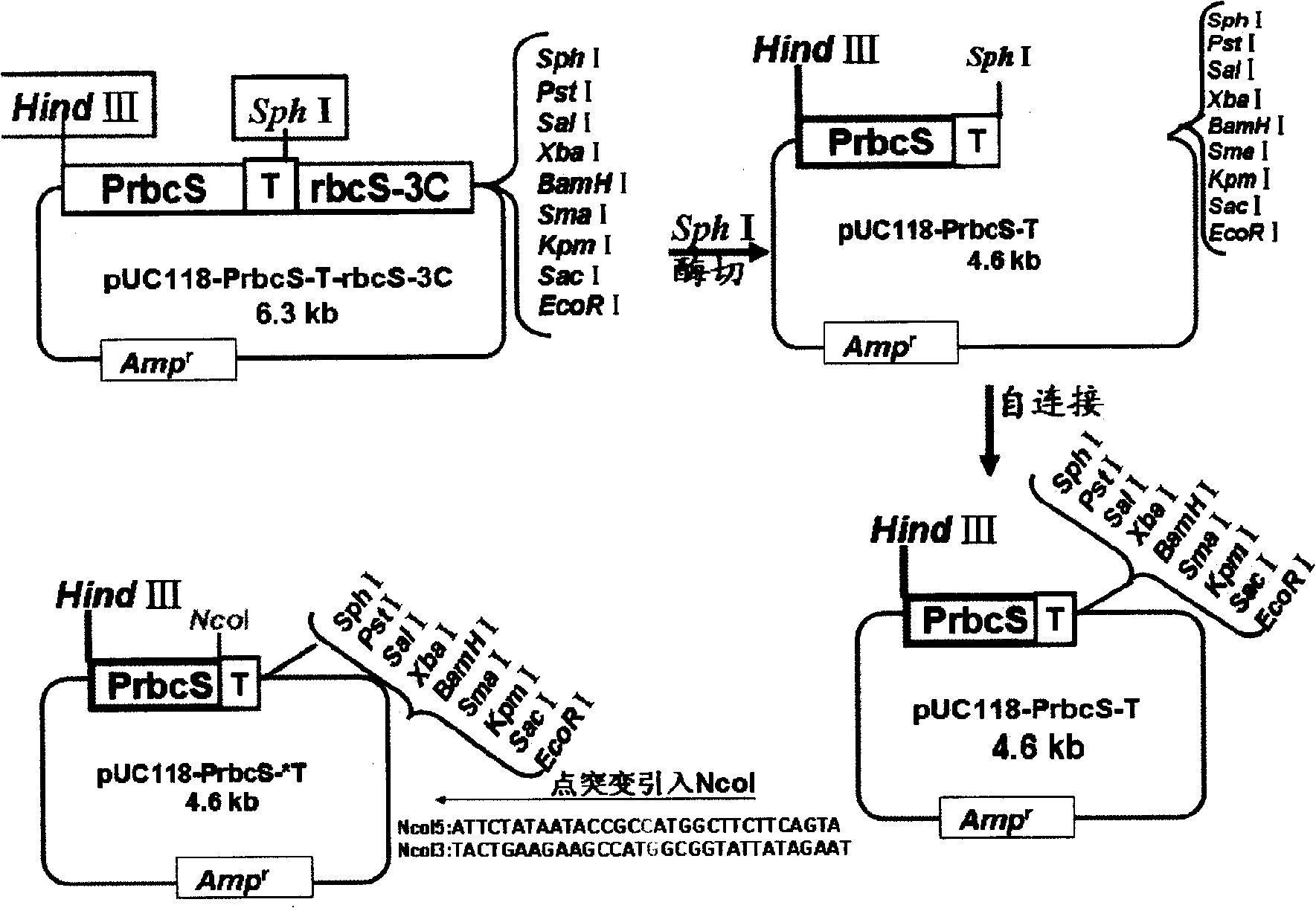
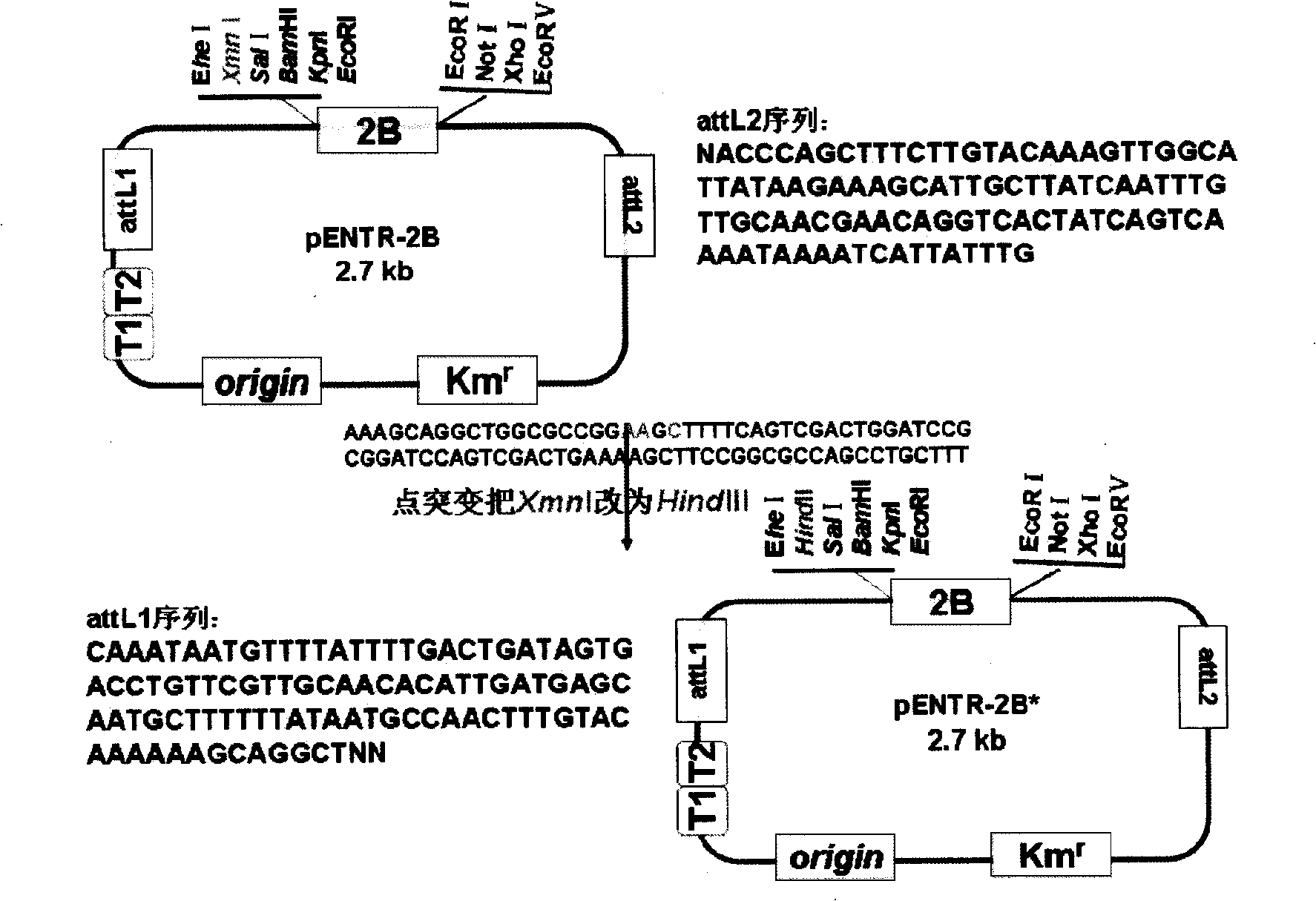
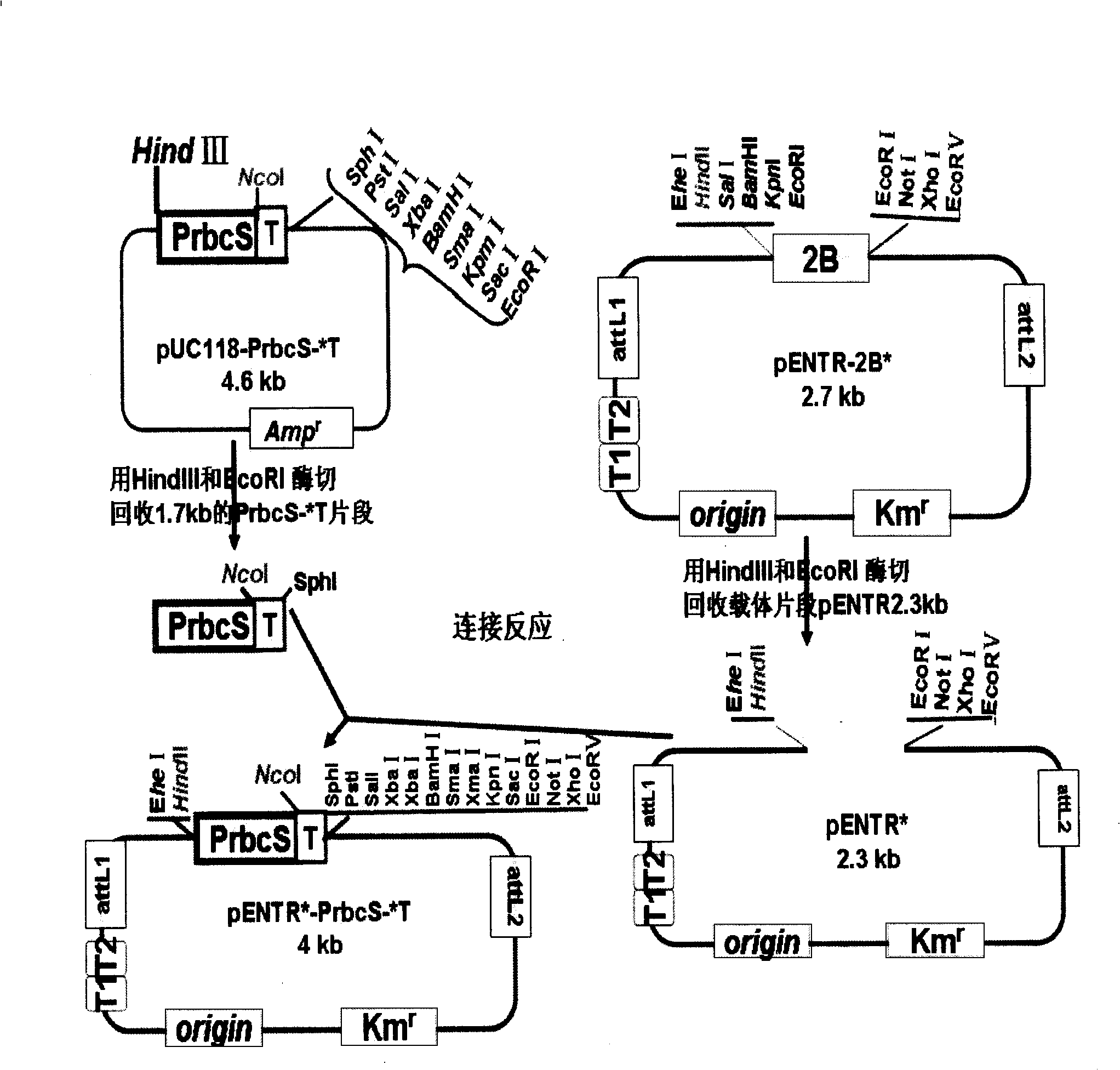
The invention discloses a gateway cloning technology entry plasmid vector. The vector contains a photoinducible promoter (Prbcs) of a small subunit gene of 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase (Rubisco) and a green fluorescent protein (GFP) reporter gene. The invention also discloses a construction method and application of the vector. Through the vector, the gateway cloning technology can be utilized to quickly construct a photoinducible plant expression vector of a target gene to realize the high level expression of the target gene in plant leaves, the expression of the target gene is adjusted by light intensity, and expressed target protein can be positioned into chloroplast or cytoplasm.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
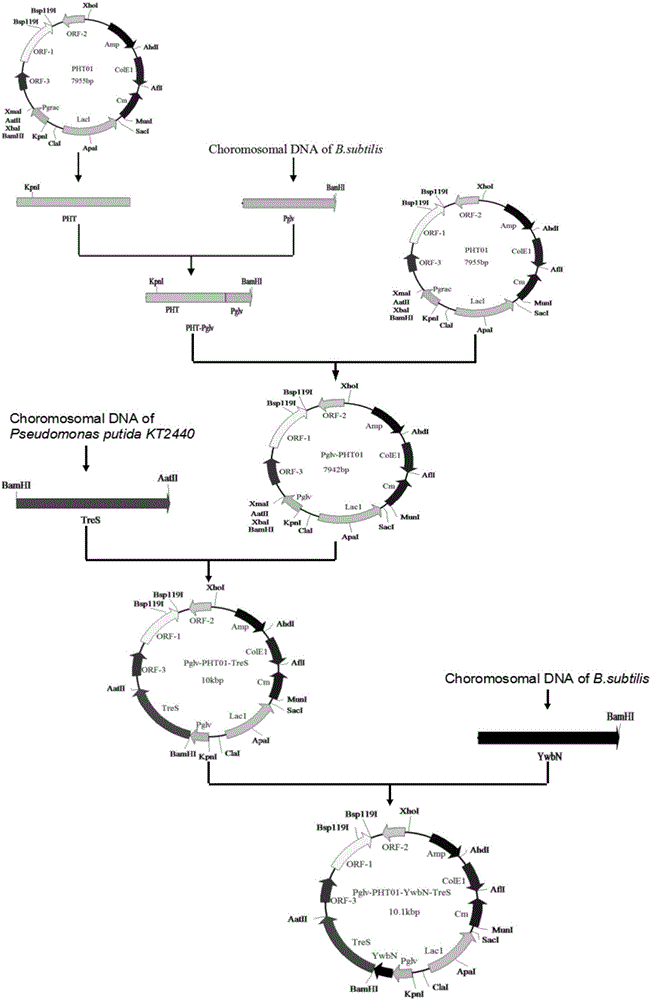
Maltose inducible trehalose synthase synthesis engineering bacterium, method for preparing same and application
The invention relates to a maltose inducible trehalose synthase synthesis engineering bacterium, a method for preparing the same and application. The maltose inducible trehalose synthase synthesis engineering bacterium is characterized in that maltose inducible promoters are inserted in the fronts of BamHI cleavage sites of PHT01 plasmids of recombinant plasmid vectors instead of Pgrac promoters on the PHT01 plasmids, expression genes of Tat type signal peptides are inserted in the fronts of the BamHI cleavage sites, and expression genes of trehalose synthase are inserted in the rears of the BamHI cleavage sites. The maltose inducible trehalose synthase synthesis engineering bacterium, the method and the application have the advantage that expression effects realized after the maltose inducible promoters and the trehalose synthase are fused with one another are obviously superior to other inducible expression effects.
Owner:山东开盾生物科技有限公司
Methods and compositions for heat activated gene therapy using cytolethal distending toxin
The invention provides compositions and methods for gene therapy using cytolethal distending toxins (CDTs). In a preferred embodiment, a gene therapy vector according to the invention includes a gene encoding a B subunit of a CDT and an antisense oligonucleotide that inhibits a DNA repair mechanism. An inducible promoter is operably linked to the gene and oligonucleotide. Preferably, the promoter is strictly inducible by heat shock.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
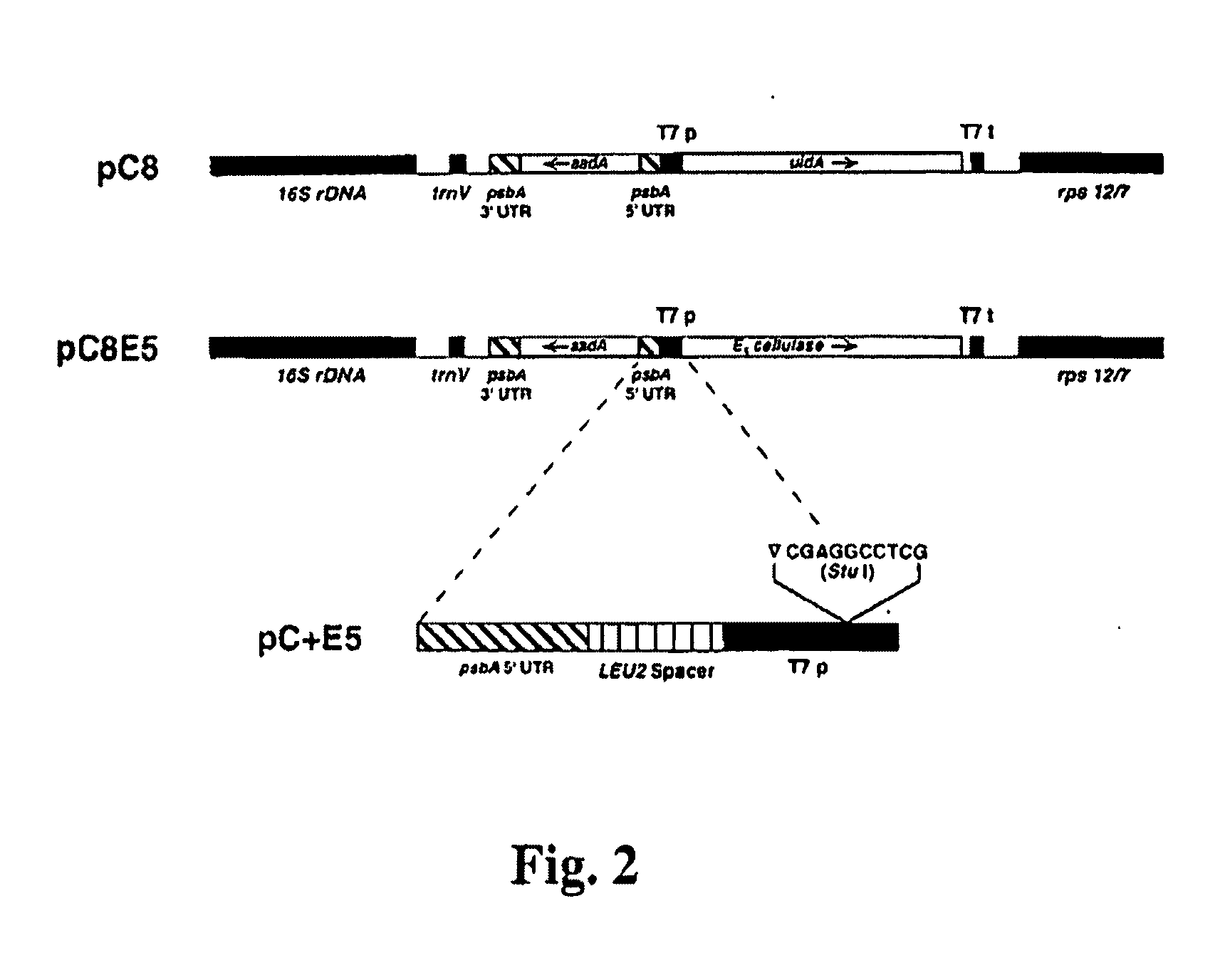
Transgenic plants expressing a cellulase
InactiveUS20080022425A1Improve scalabilityHigh yield of biomassBryophytesSugar derivativesBiotechnologyCellulose breakdown
The instant disclosure describes the application of genetic engineering techniques to produce cellulase in plants. Cellulase coding sequences operably linked to promoters active in plants may be transformed into the nuclear genome and / or the plastid genome of a plant. As cellulases may be toxic to plants, chemically-inducible or wound-inducible promoters may be employed. Additionally, the expressed cellulases may be targeted to vacuoles or other cellular organelles.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Genes Implicated In Resistance To Soybean Cyst Nematode Infection And Methods Of Their Use
ActiveUS20120260368A1Increased nematode resistanceInhibit expressionClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyPlant roots
Genes whose expressions are up-regulated or down-regulated in plant roots in response to nematode infection are disclosed. These genes may play an important role in plant defense against SCN infection. Several nematode-inducible promoters have also been identified in plants which ma be used in nematode inducible gene expression construct. Expression of these SCN responsive genes may be manipulated to obtain SCN resistant lines.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Inducible promoter for pathogenic bacteria of rice
InactiveCN103074342AAngiosperms/flowering plantsDNA/RNA fragmentationSalicylic acidPlant genetic engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of plant gene engineering and provides an inducible promoter for pathogenic bacteria of rice. The promoter can be activated by rice bacterial leaf blight bacterium xanthomonas PXO99 and PXO61, a rice baeterial leaf streak bacterium RS105 and a corn banded sclerotial blight bacterium YWK-196, and can also be activated by abscisic acid, gibberellic acid, salicylic acid and sodium chloride. Truncation of the promoter verifies that two sections from -513bp to -411bp and from -411bp to -309bp are critical areas induced by the pathogenic bacteria. Various plant expression vectors can be constructed with the adoption of the promoter, and the promoter can be used for improving plant quality and other beneficial production traits through a plant gene engineering technology.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Transgenic plants expressing a cellulase
InactiveUS20080078005A1High yieldImprove scalabilityTransferasesBiofuelsBiotechnologyGenetic engineering
The instant disclosure describes the application of genetic engineering techniques to produce cellulase in plants. Cellulase coding sequences operably linked to promoters active in plants may be transformed into the nuclear genome and / or the plastid genome of a plant. As cellulases may be toxic to plants, chemically-inducible or wound-inducible promoters may be employed. Additionally, the expressed cellulases may be targeted to vacuoles or other cellular organelles.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com