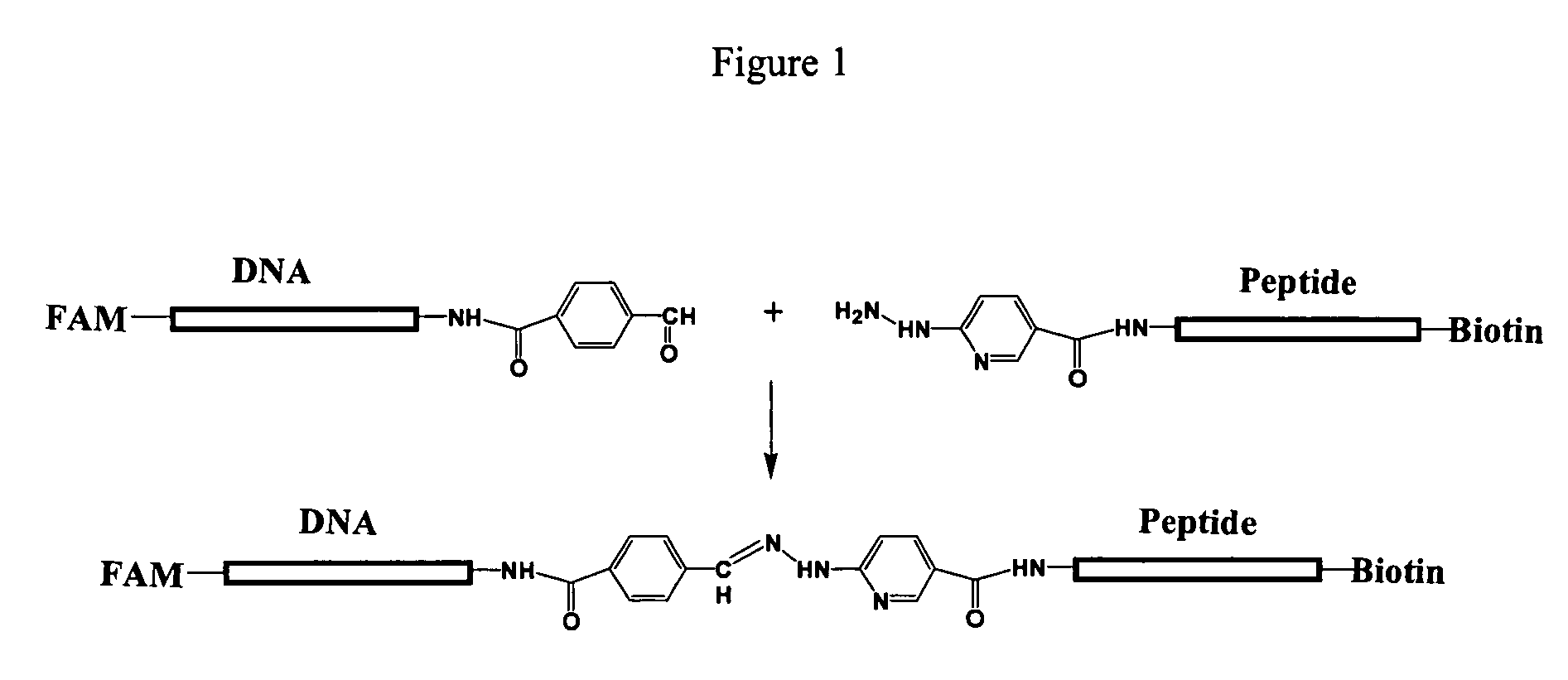
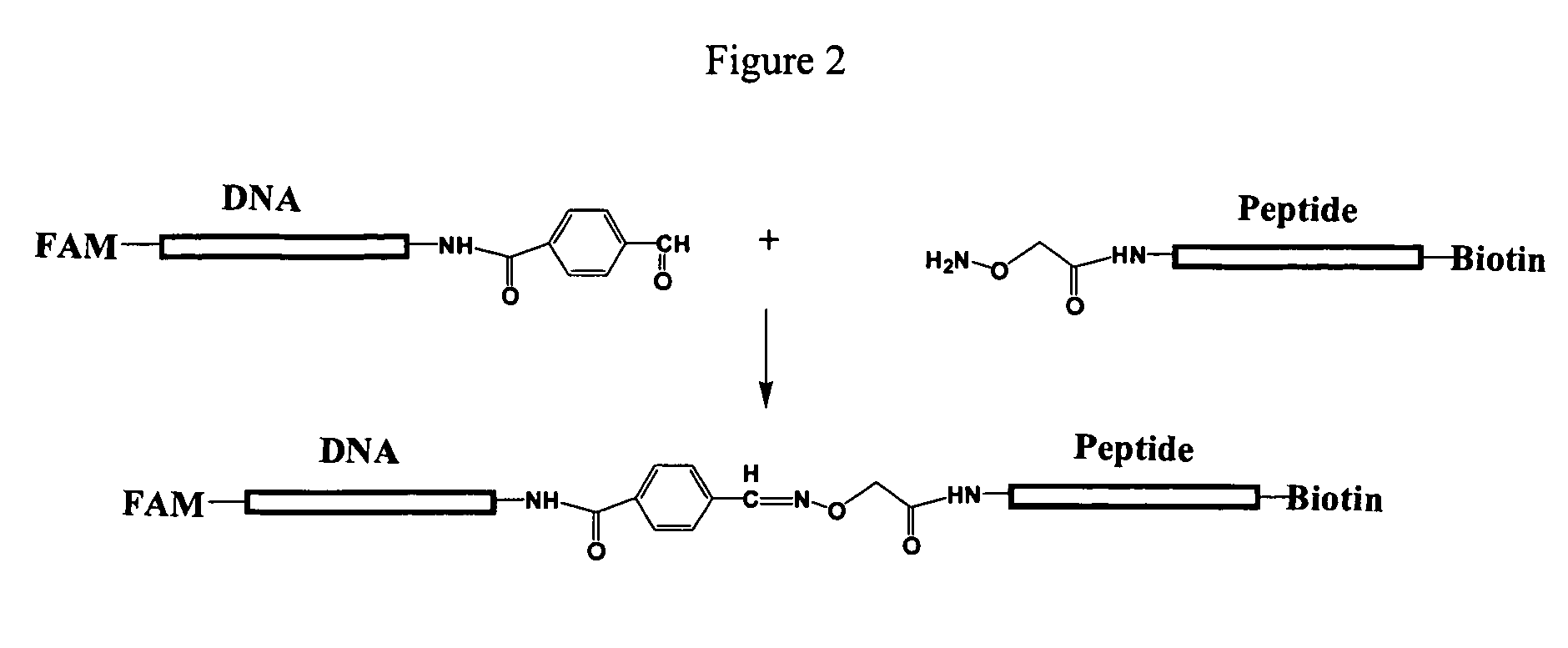
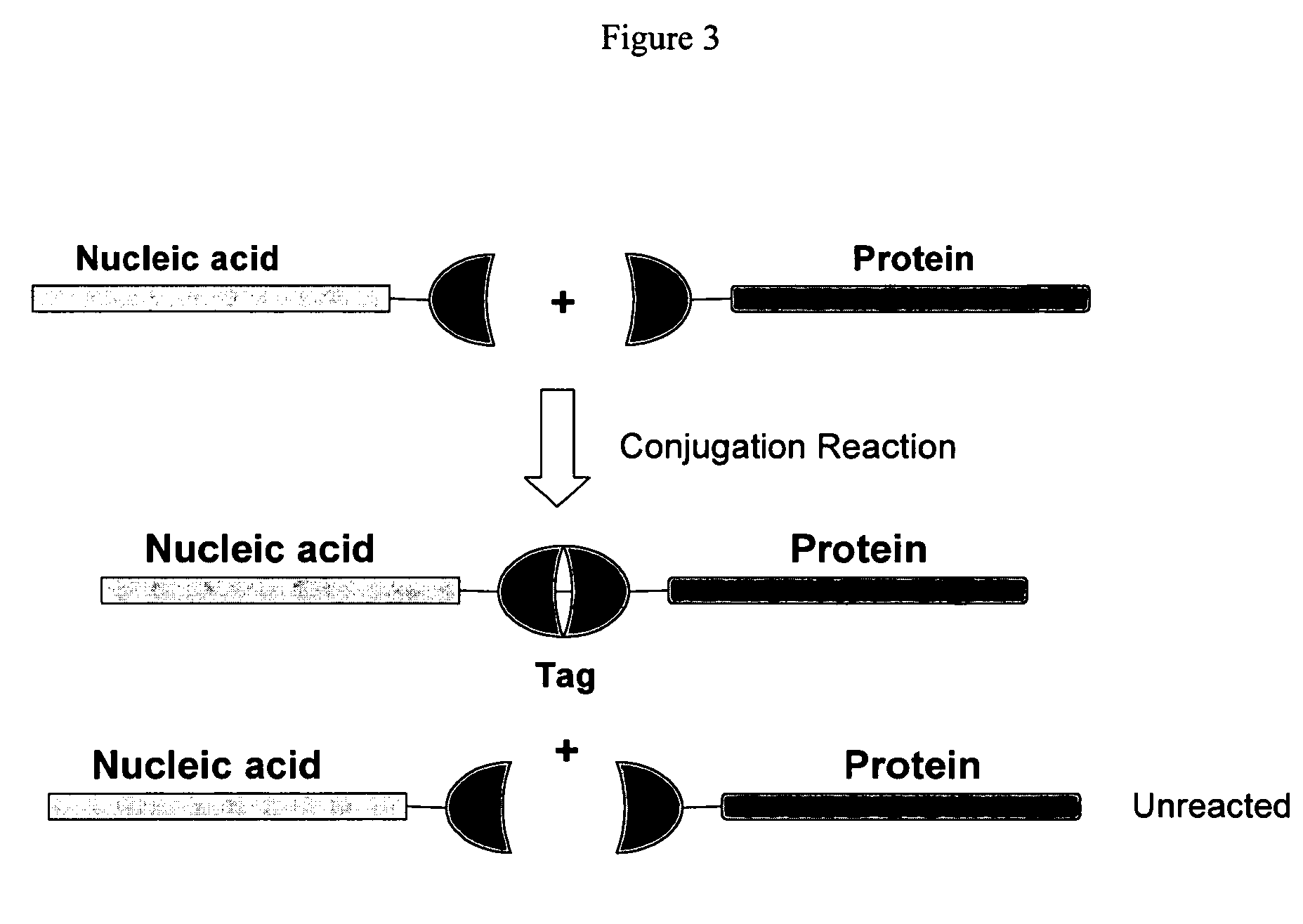
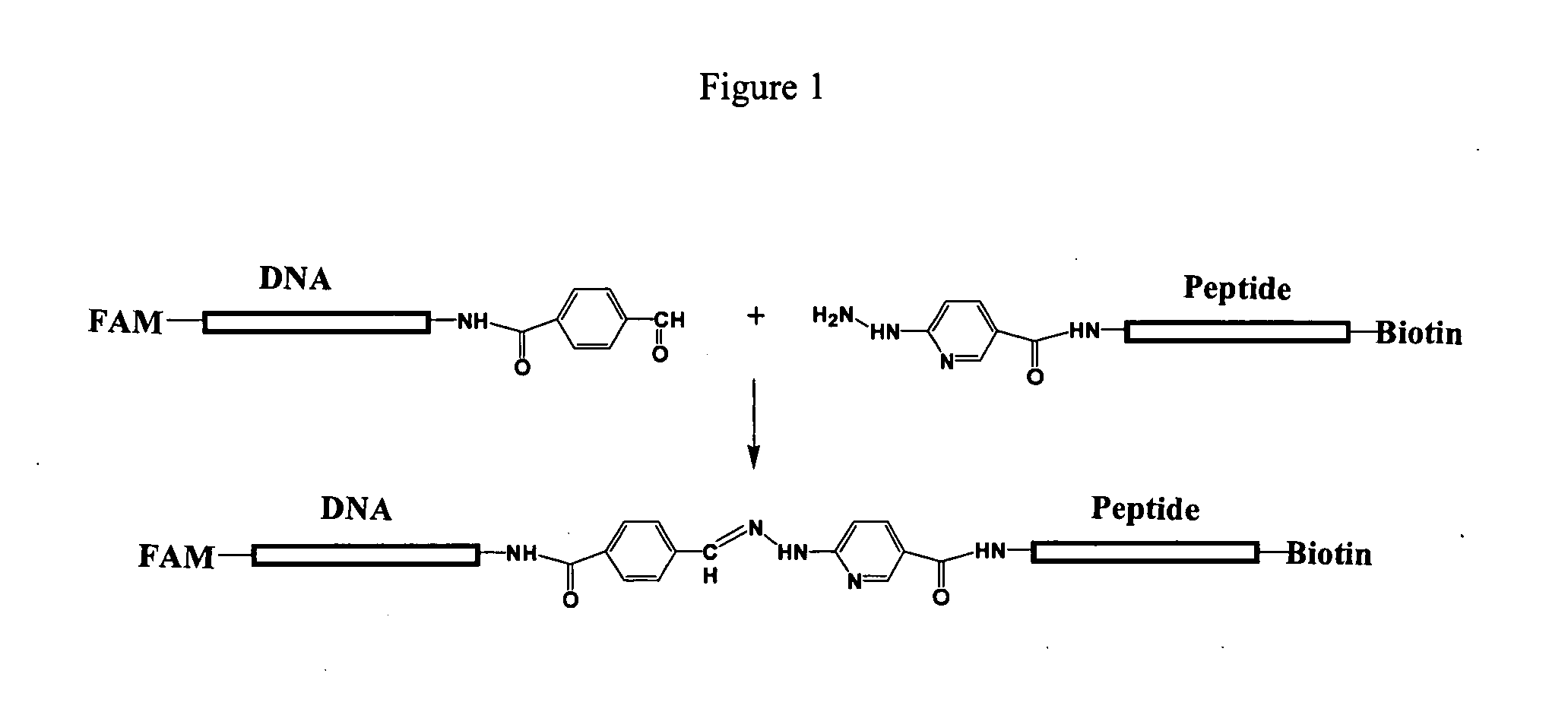
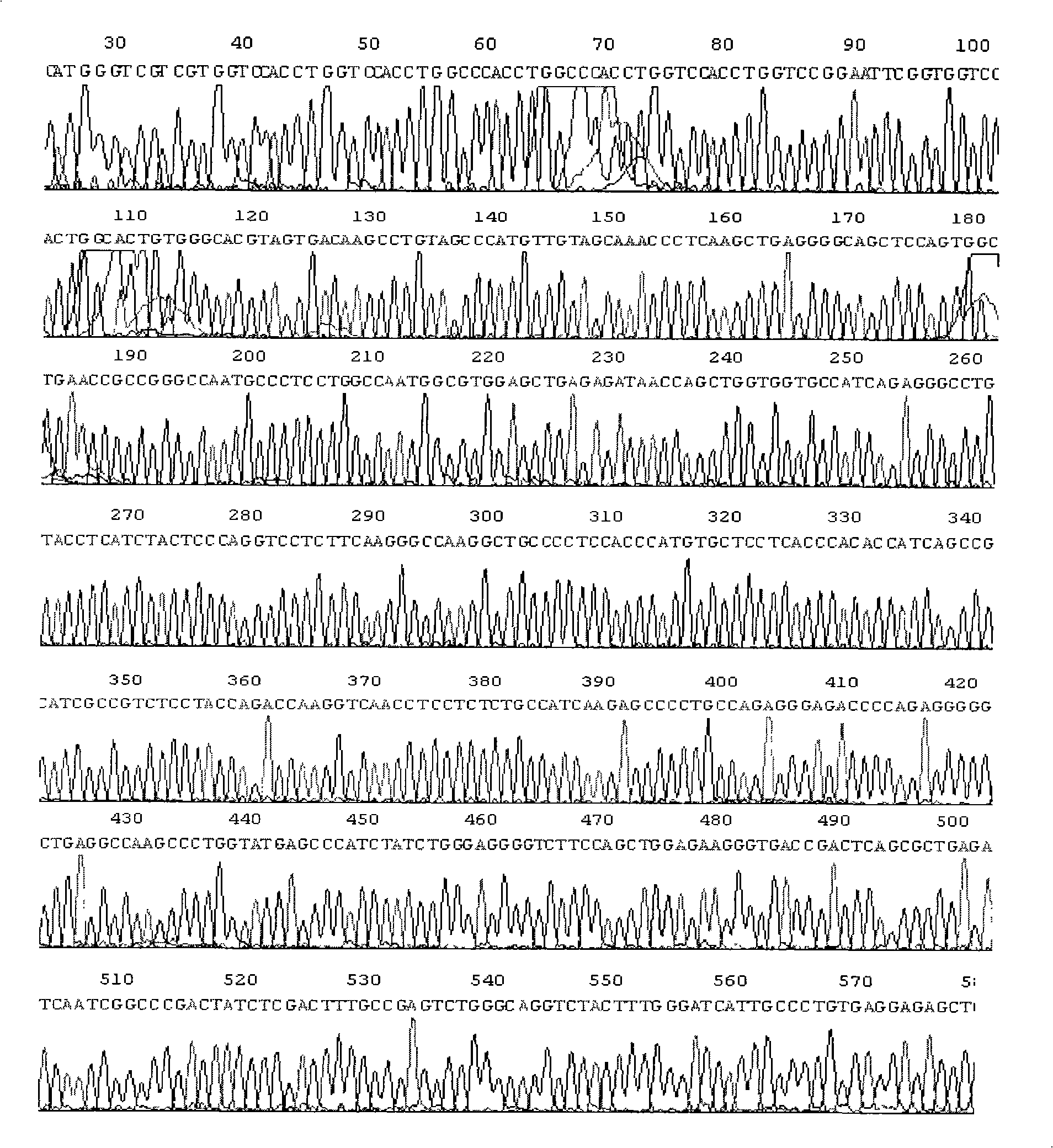
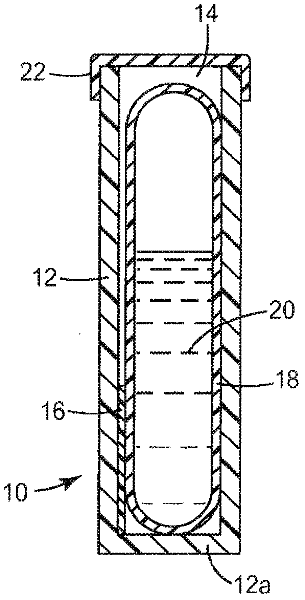
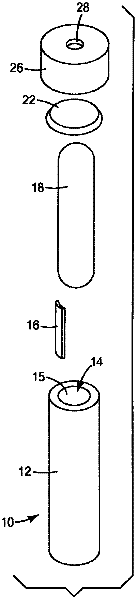
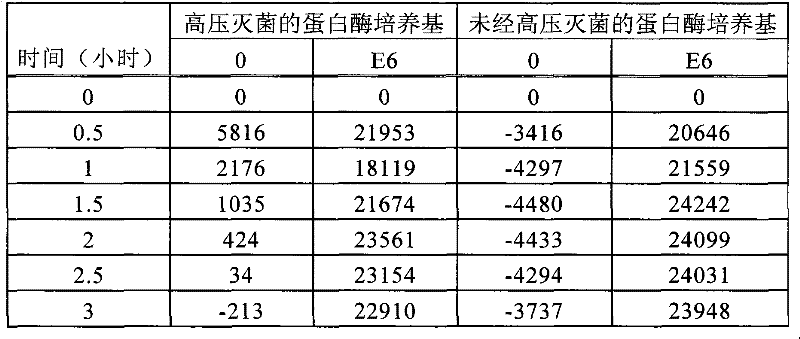
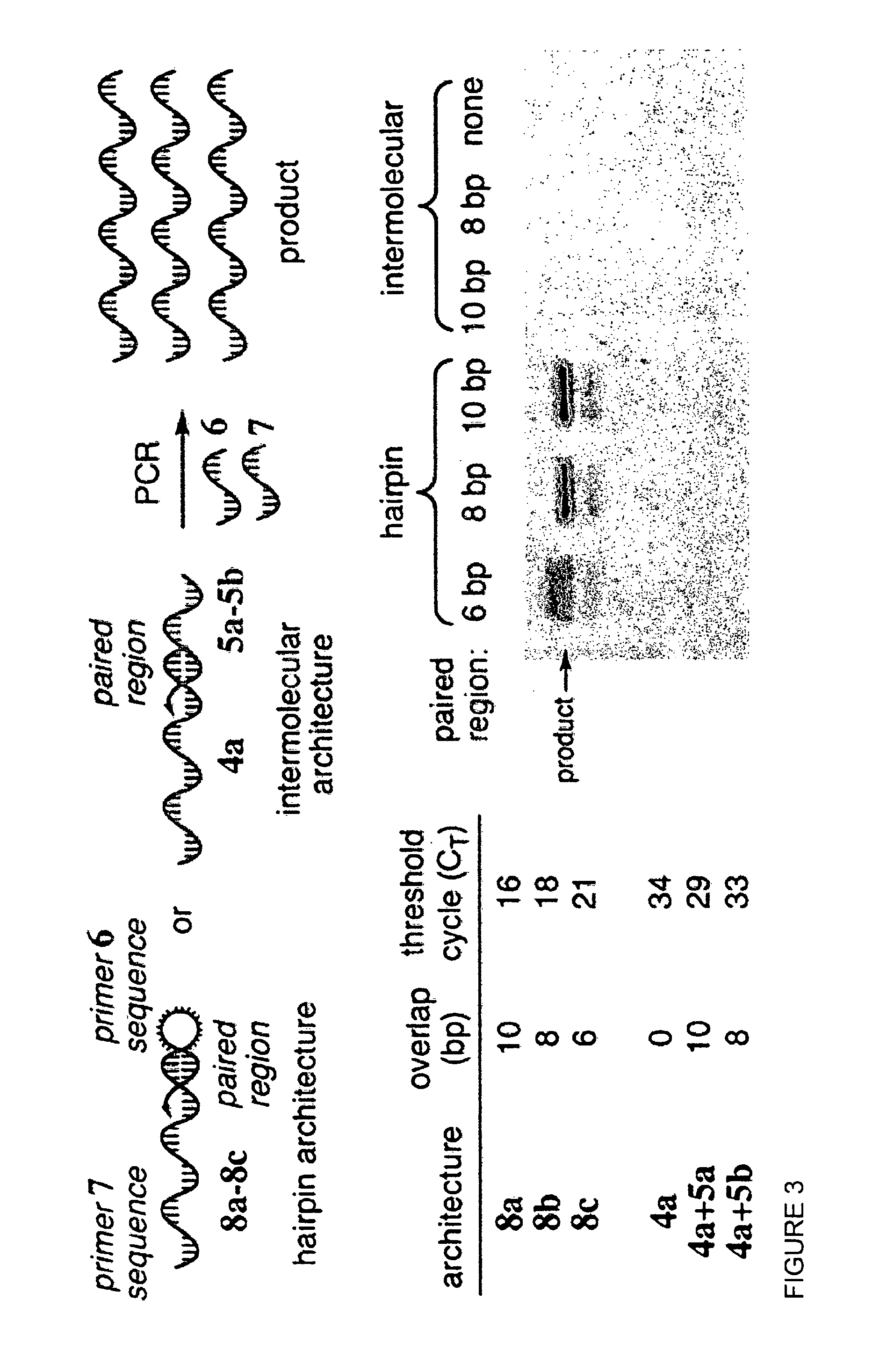
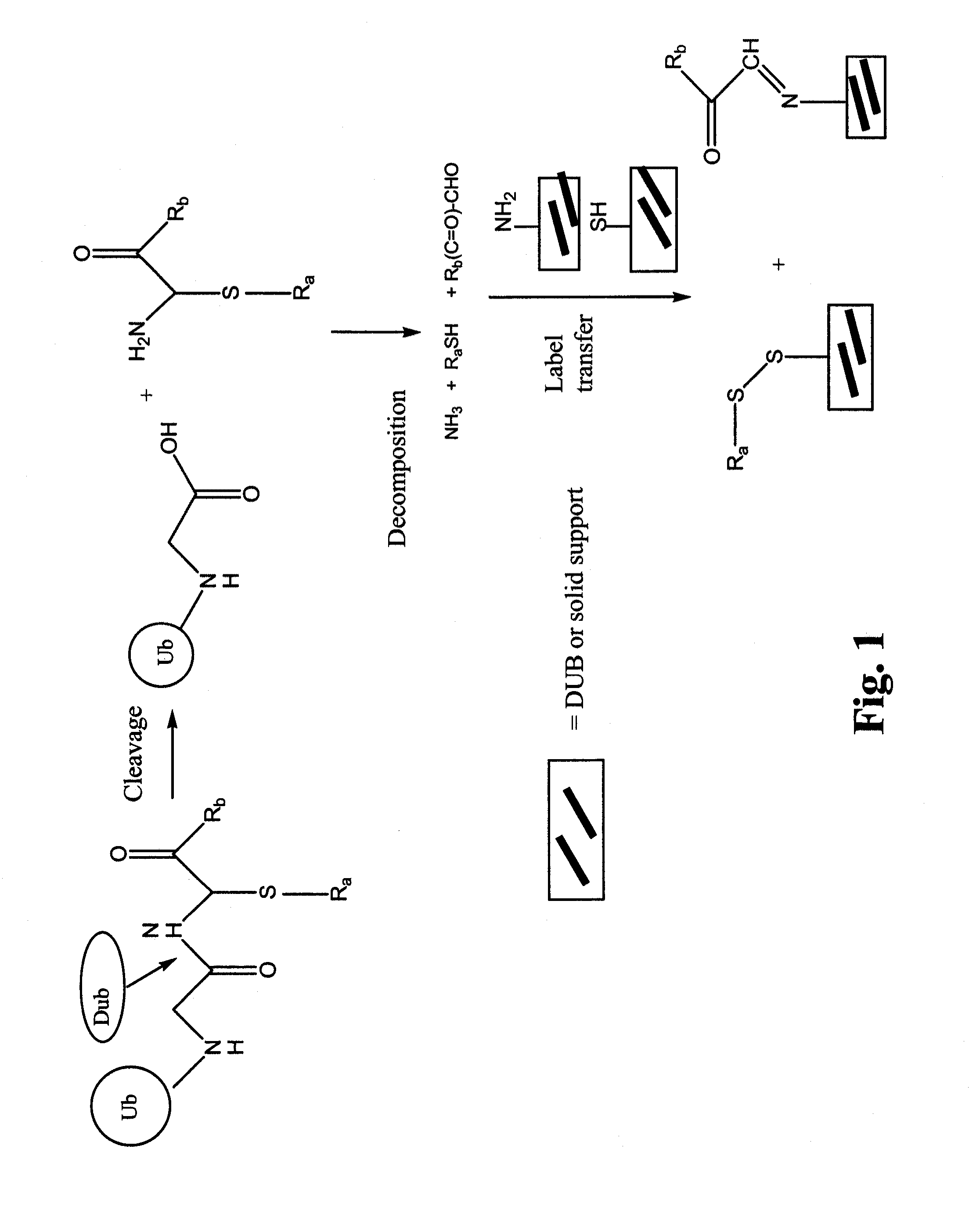
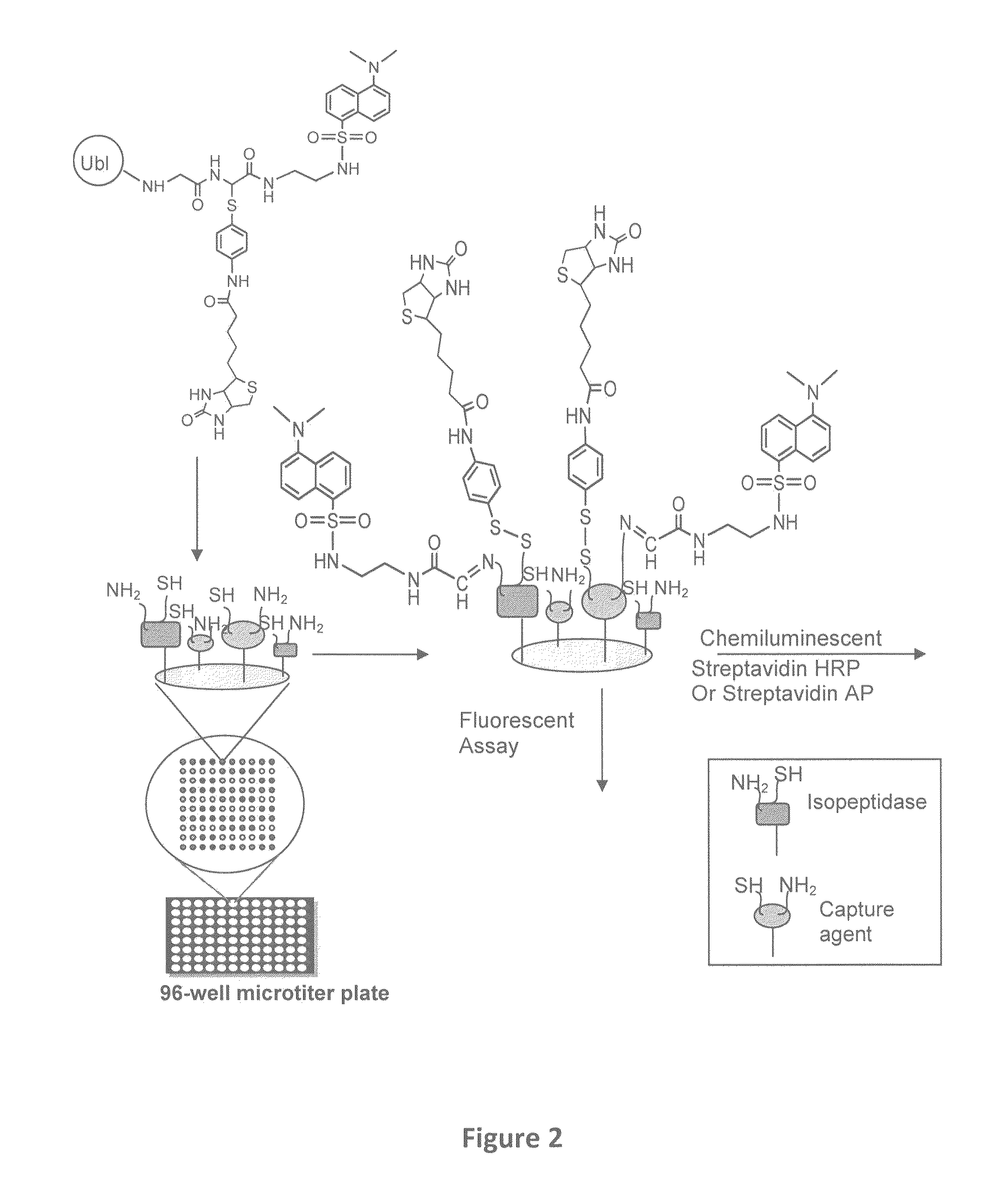
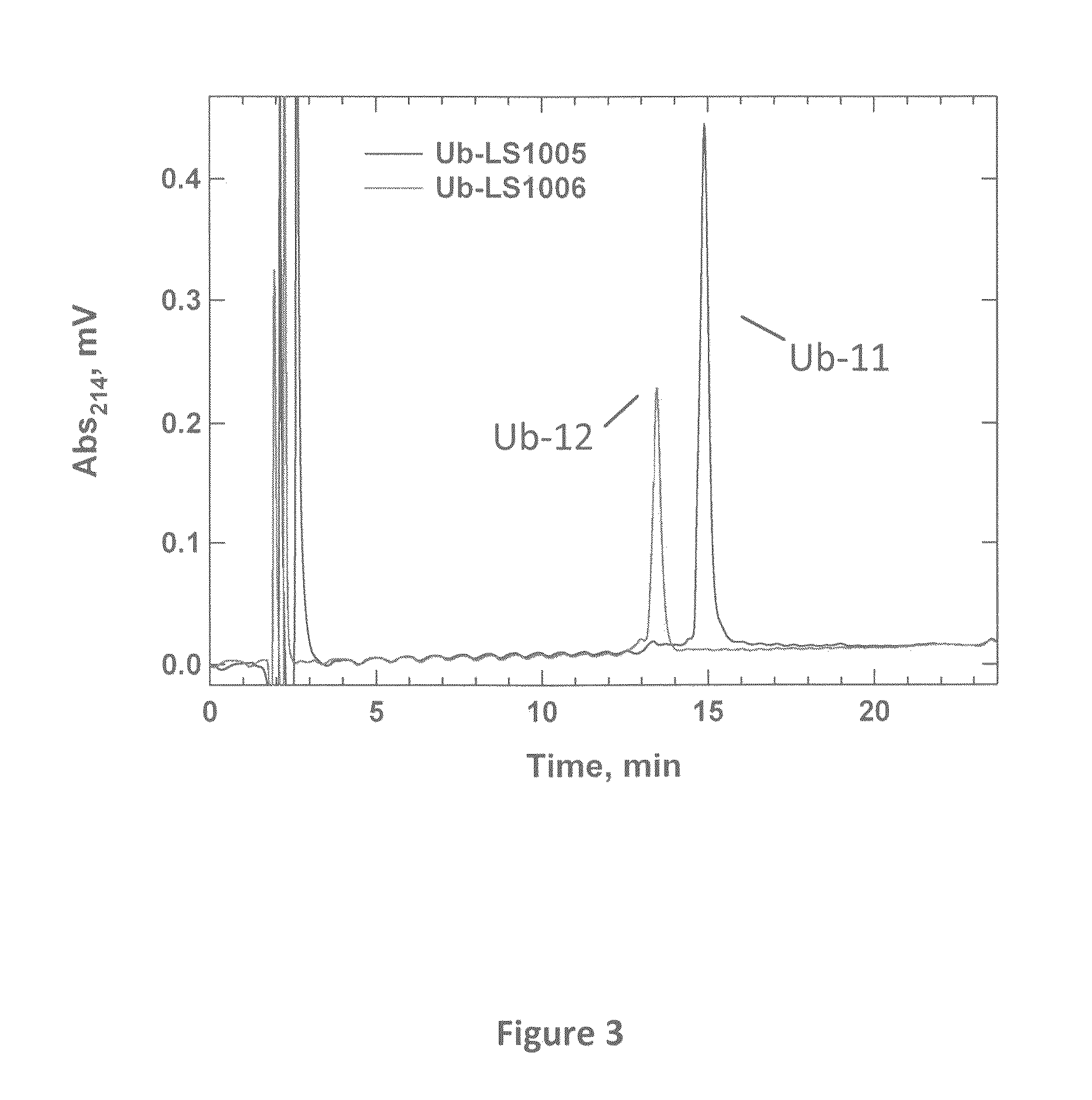
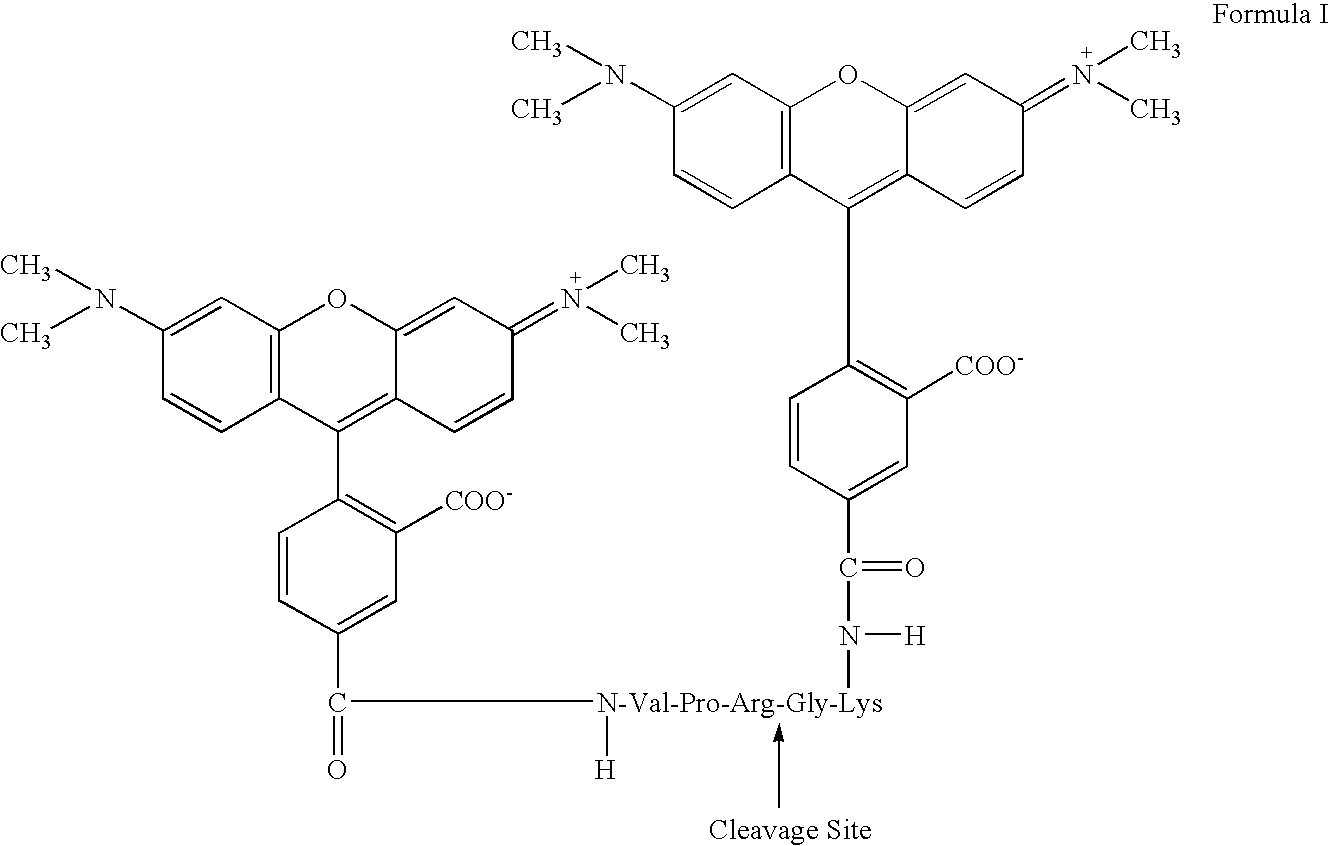
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
55 results about "Protease substrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
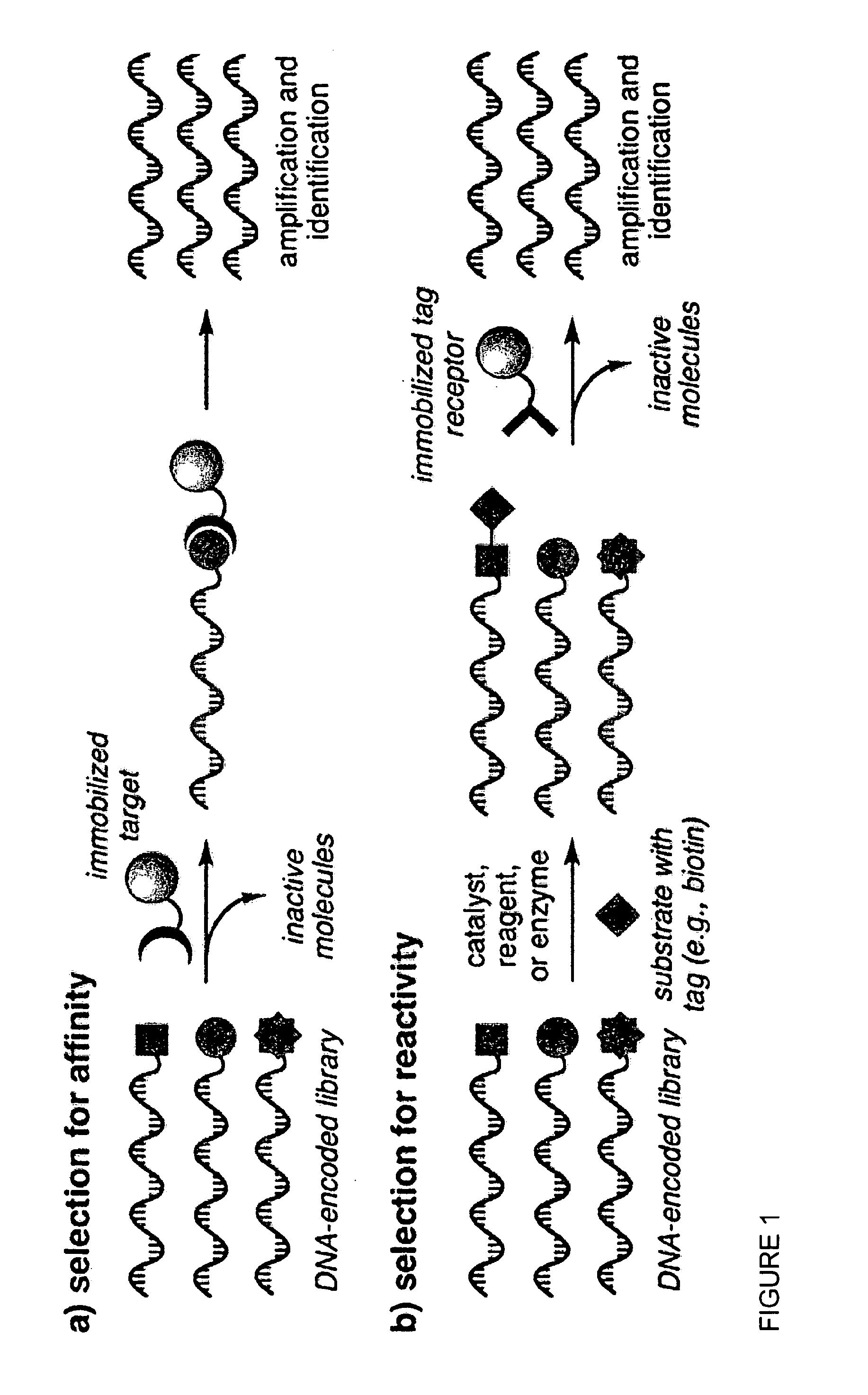
Protease Substrate/Inhibitor. Proteases are the enzymes that are responsible for proteolysis that is cleave of proteins by hydrolysis of peptide bonds that links amino acids which are in peptide chain.
Compositions and methods for detecting protease activity
ActiveUS7229769B2Microbiological testing/measurementFungi medical ingredientsProteinase activityProtein anabolism
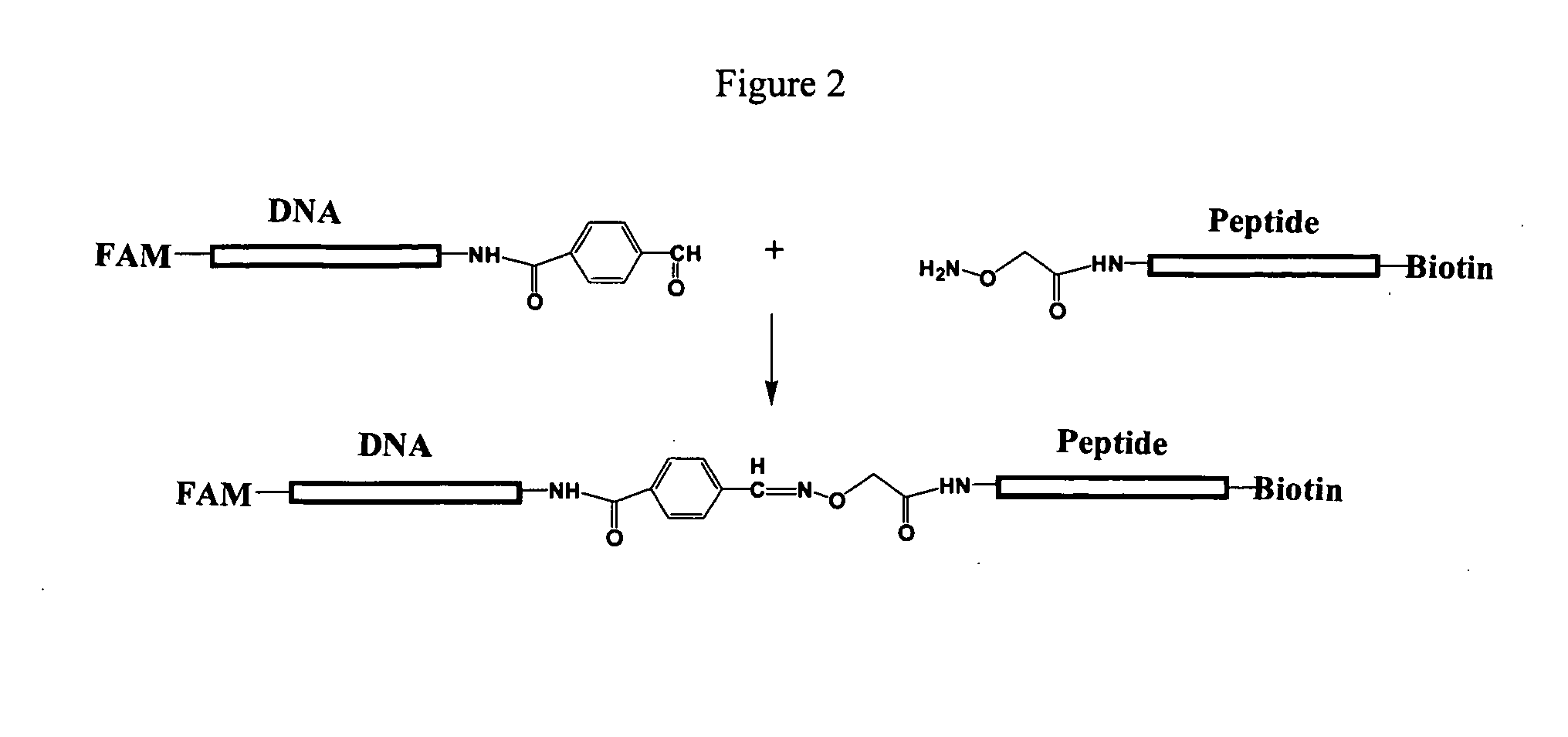
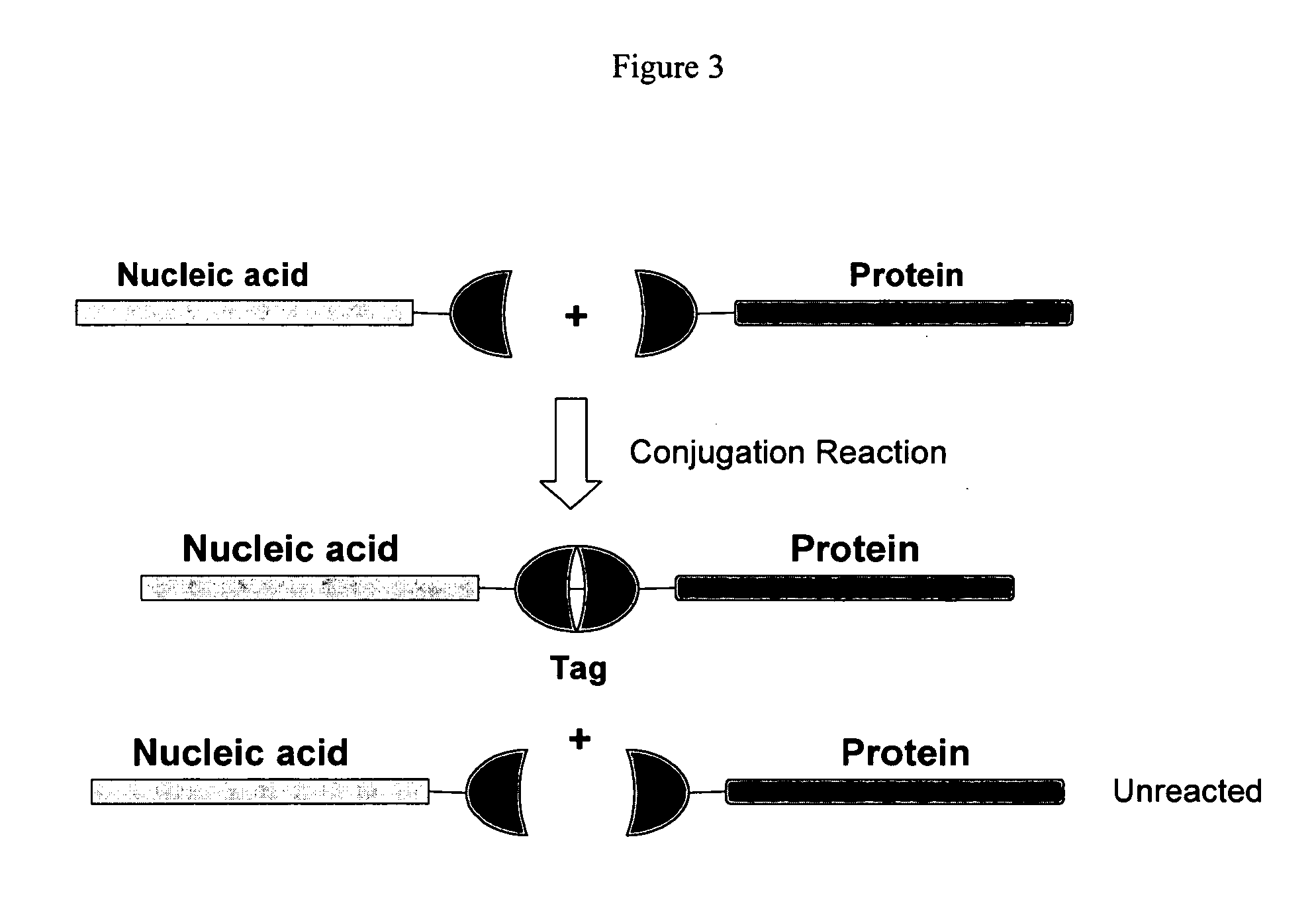
The invention provides a method of determining activity of a protease. The method can include the steps of (a) providing a protease substrate including a protein moiety attached to a nucleic acid moiety and a ligand moiety; (b) contacting the protease substrate with a protease under conditions wherein the protease catalyzes cleavage of the protein moiety, thereby producing a proteolytic product wherein the nucleic acid moiety is separated from at least a portion of the protein moiety and the ligand moiety; (c) contacting the proteolytic product with a receptor under conditions wherein the ligand moiety binds to the receptor to form a complex; (d) separating the complex from the nucleic acid moiety, thereby forming a separation product including the nucleic acid moiety; (e) contacting the separation product with a probe nucleic acid under conditions wherein the nucleic acid moiety hybridizes to a complementary sequence of the probe; and (f) detecting hybridization of the separation product to the probe, thereby determining activity of the protease.
Owner:MURPHY JOHN T
Compositions and methods for detecting protease activity
The invention provides a method of determining activity of a protease. The method can include the steps of (a) providing a protease substrate including a protein moiety attached to a nucleic acid moiety and a ligand moiety; (b) contacting the protease substrate with a protease under conditions wherein the protease catalyzes cleavage of the protein moiety, thereby producing a proteolytic product wherein the nucleic acid moiety is separated from at least a portion of the protein moiety and the ligand moiety; (c) contacting the proteolytic product with a receptor under conditions wherein the ligand moiety binds to the receptor to form a complex; (d) separating the complex from the nucleic acid moiety, thereby forming a separation product including the nucleic acid moiety; (e) contacting the separation product with a probe nucleic acid under conditions wherein the nucleic acid moiety hybridizes to a complementary sequence of the probe; and (f) detecting hybridization of the separation product to the probe, thereby determining activity of the protease.
Owner:MURPHY JOHN T
High density reagent array preparation methods
InactiveUS20050074898A1High densityHigh and consistent recoveryMaterial nanotechnologyAnalysis using chemical indicatorsHigh densityProteinase activity
This invention provides reagent array chips having, e.g., reagents spotted at a high density onto self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) for consistent and high recovery. The invention teaches, e.g., methods to make and use reagent array chips to screen for protease substrates. Identified substrates can, e.g., then be used to screen for modulators of the protease activity and to establish quantitative assays for the protease.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Protease detection assay
ActiveUS7803572B2Efficient electron transferEasy to detectGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsMicrobiological testing/measurementProteinase activityChemistry
The invention provides methods and compounds for detecting protease activity in a sample solution comprising contacting the sample solution with a protease substrate labelled with an electrochemically active marker, providing conditions under which any protease which may be present in the sample may degrade the protease substrate and electrochemically determining information relating to the electrochemically active marker.
Owner:ATLAS GENETICS
Gynaecologic multi-item dry chemical united detection test paper strip and its measuring method
InactiveCN101320040AReflect cleanlinessComprehensive detectionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological testingWhite blood cellPaper tape
The invention relates to a test paper tape which can be used in the gynecological multiprogramming dry-chemistry joint detection. The test paper tape provided by the utility model comprises a dry-chemistry multiprogramming detection test paper tape which consists of a plastic substrate tape and various solidified regent blocks, and sample diluent. The dry regent blocks include combinations formed by increasing or decreasing at least three or more regent blocks of a Ph test regent block, a lactic acid regent block, a hydrogen peroxide concentration regent block, a leukocyte esterase concentration regent block, a neuraminidase activity regent block, an amine test regent block, a proline aminopeptidase substrate reagent block, an oxidase substrate reagent block, a N-acetylamine hexosidase substrate reagent block, a trichomonas specific protease substrate hydrolysis reagent block. the gynecological multiprogramming dry-chemistry joint detection test paper test provided by the utility model can detect Ph, lactic acid, hydrogen peroxide, leukocyte esterase, neuraminidase, amine test, proline aminopeptidase, oxidase, N-acetylamine hexosidase and trichomonas specific protease which are contained in leucorrhea sample at the same time, and can accurately reflect the microorganism environment of a women reproductive tract, the cleanness of leucorrhea secretion and the conditions of Candida albicans, trichomonas, gonococcus and the pathogens of bacterial vaginosis, thereby making the gynecological trichomonas detection more comprehensive; besides, the test paper tape provided by the utility model can be used easily and conveniently, and results can be obtained quickly. If the test paper tape is used together with a gynecological dry-chemistry analyzer, the operation can become easier and the result can be obtained more quickly.
Owner:杭州健宝医疗器械有限公司
Method for identification of protease activity inhibitors and assaying the presence of protease activity
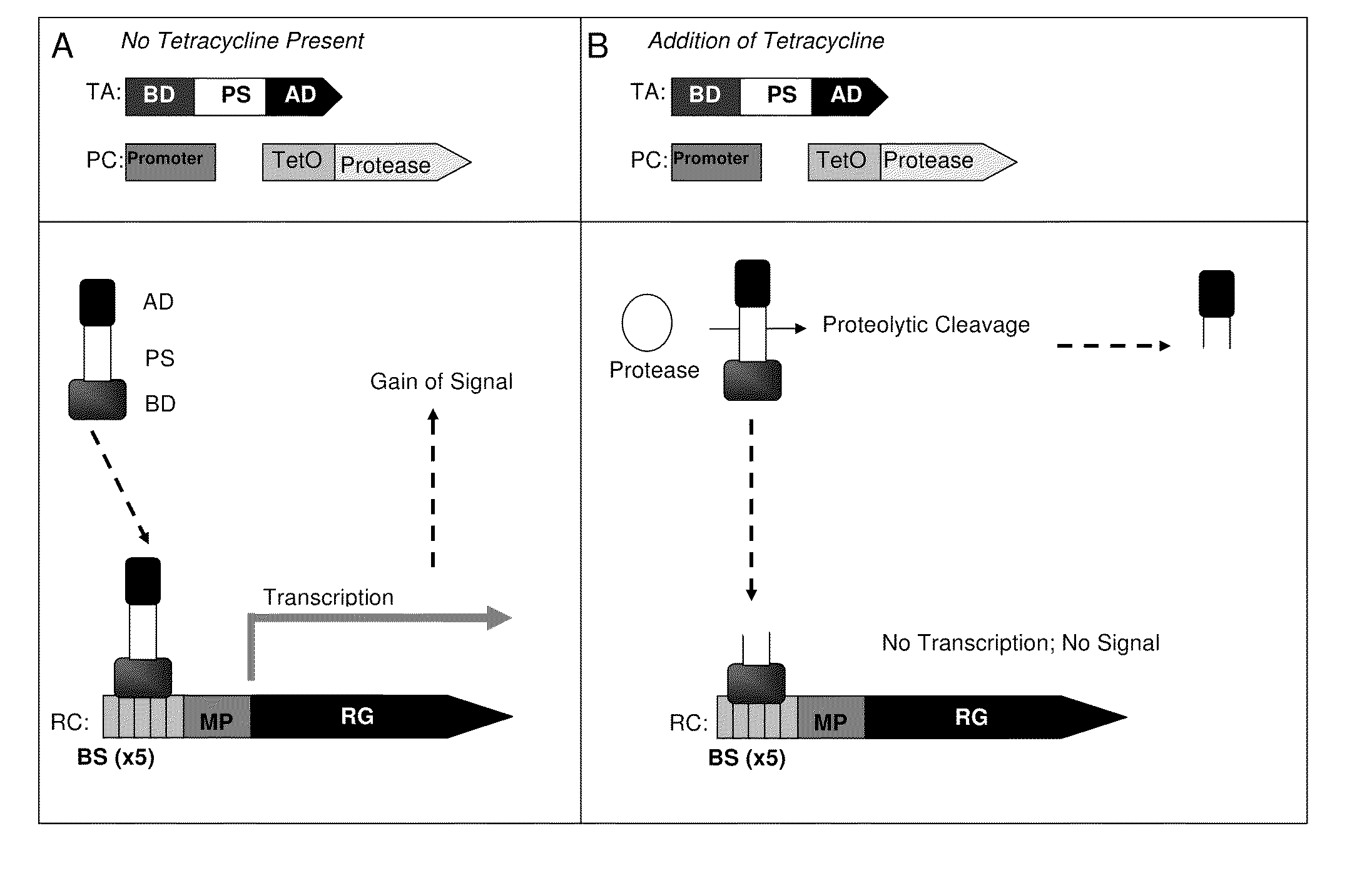
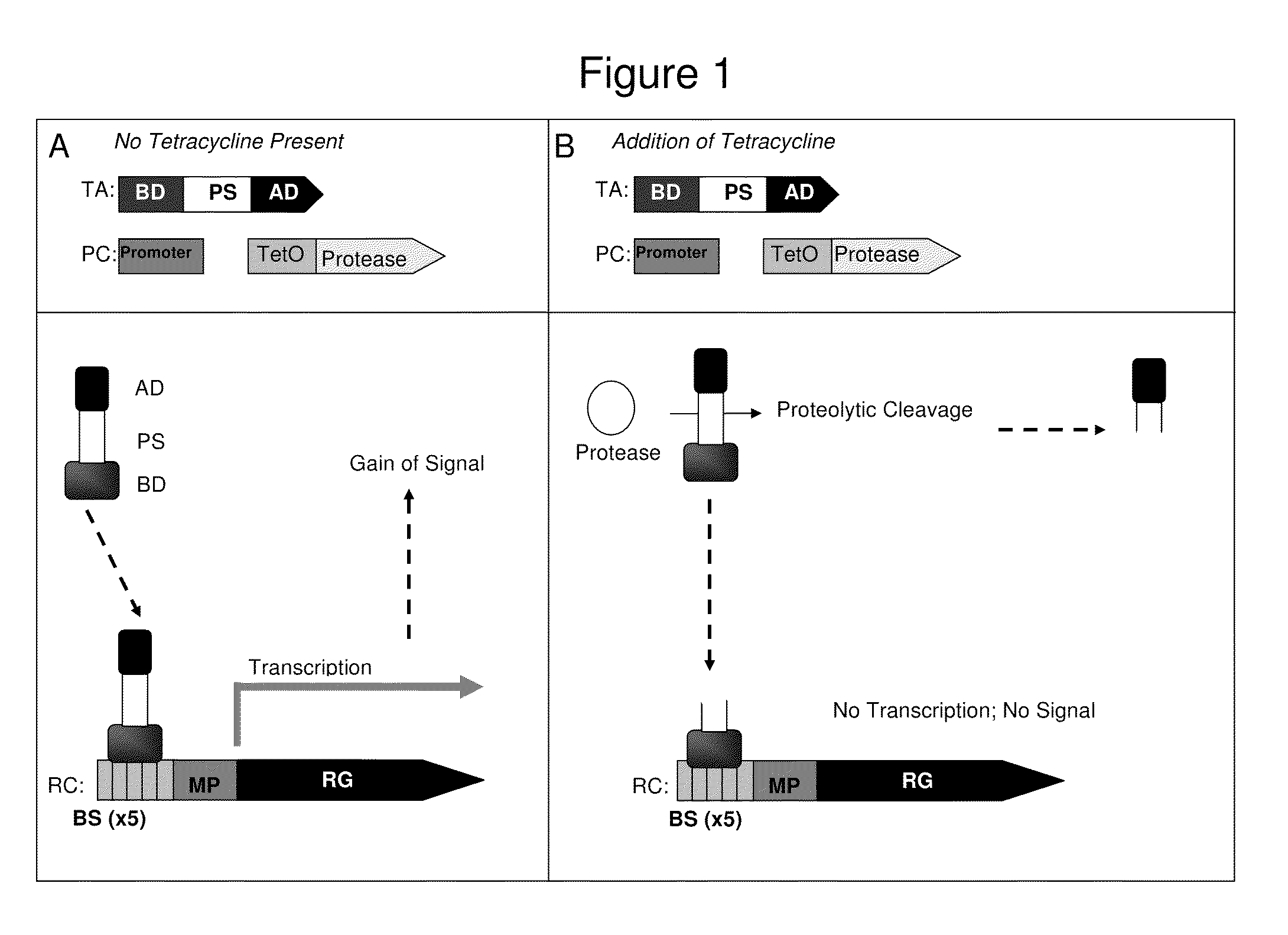
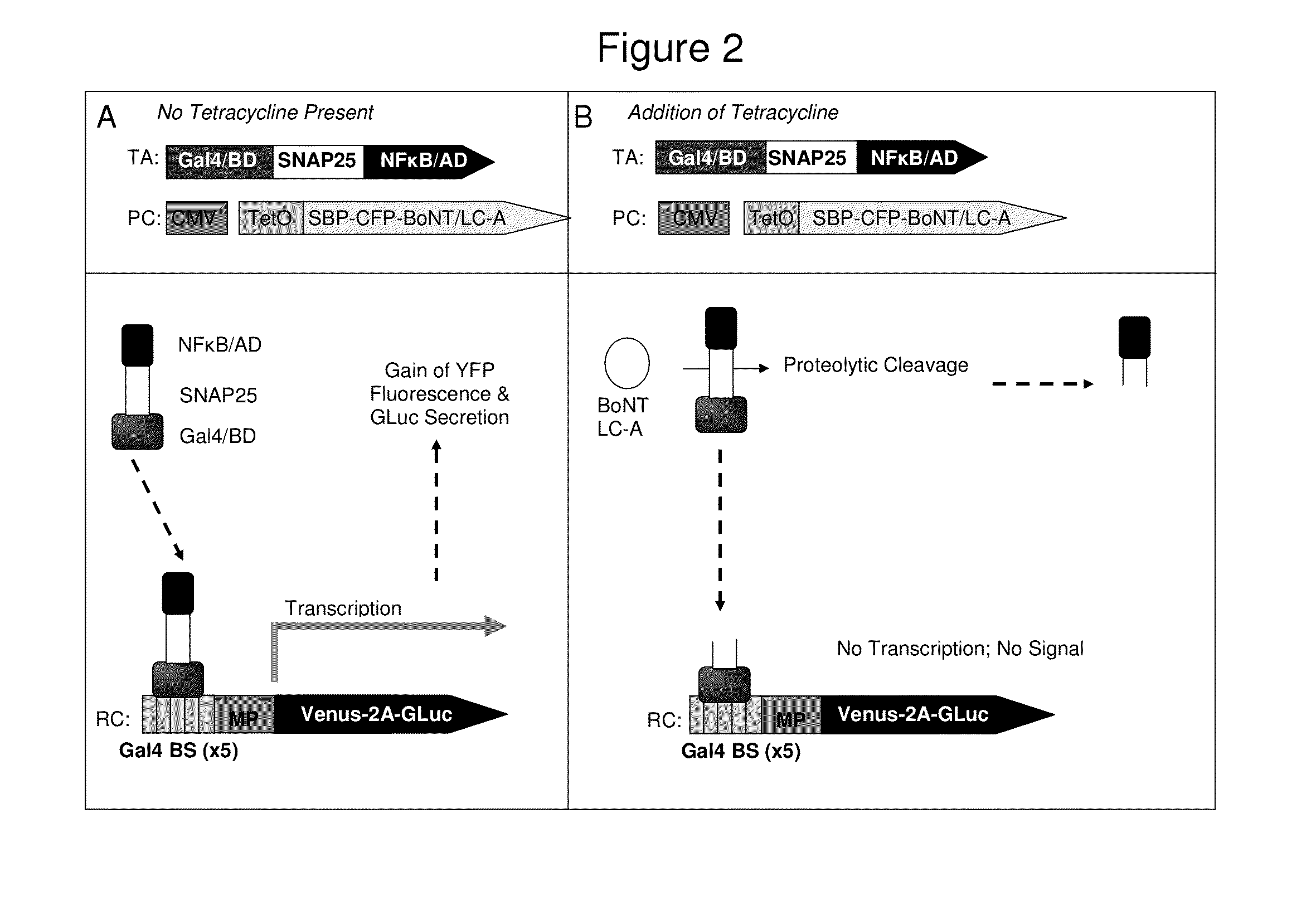
A system for the identification of proteases and protease inhibitors is provided. The system has at least two components. The first component is a reporter construct with at least one binding site, a transcriptional promoter, an inducible promoter region, and at least one reporter gene, all functionally connected for expression of the reporter gene(s) in functional coordination with a transcriptional activation agent. The second component is a transcriptional activation agent comprising a nucleic acid binding domain, at least one protease substrate domain, and at least one transcriptional activation domain for an inducible promoter. The system allows detection and evaluation of agents affecting protease activity directed to the protease substrate domain. The system also allows for the detection of the presence of proteases in environmental samples.
Owner:SYNAPTIC RES
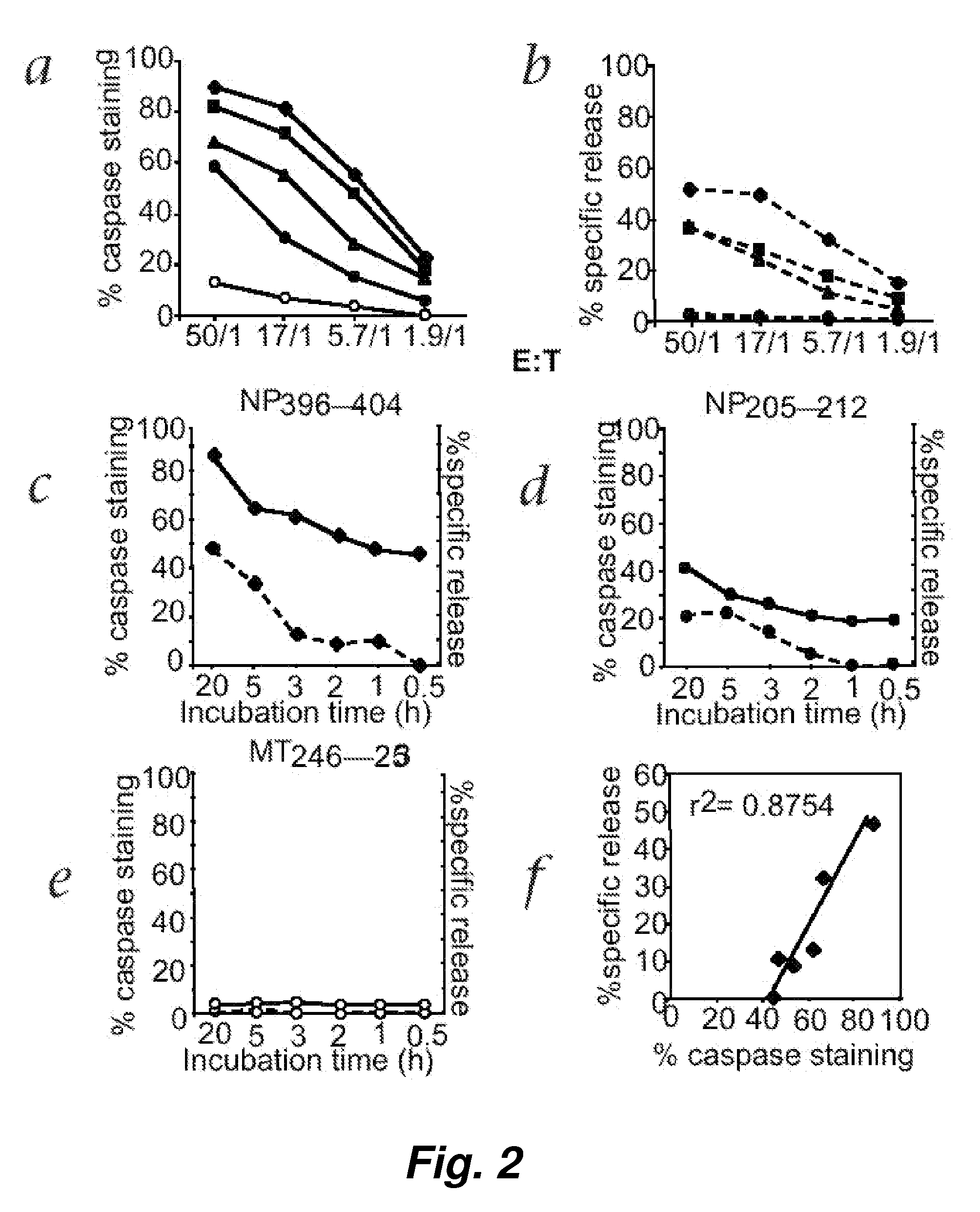
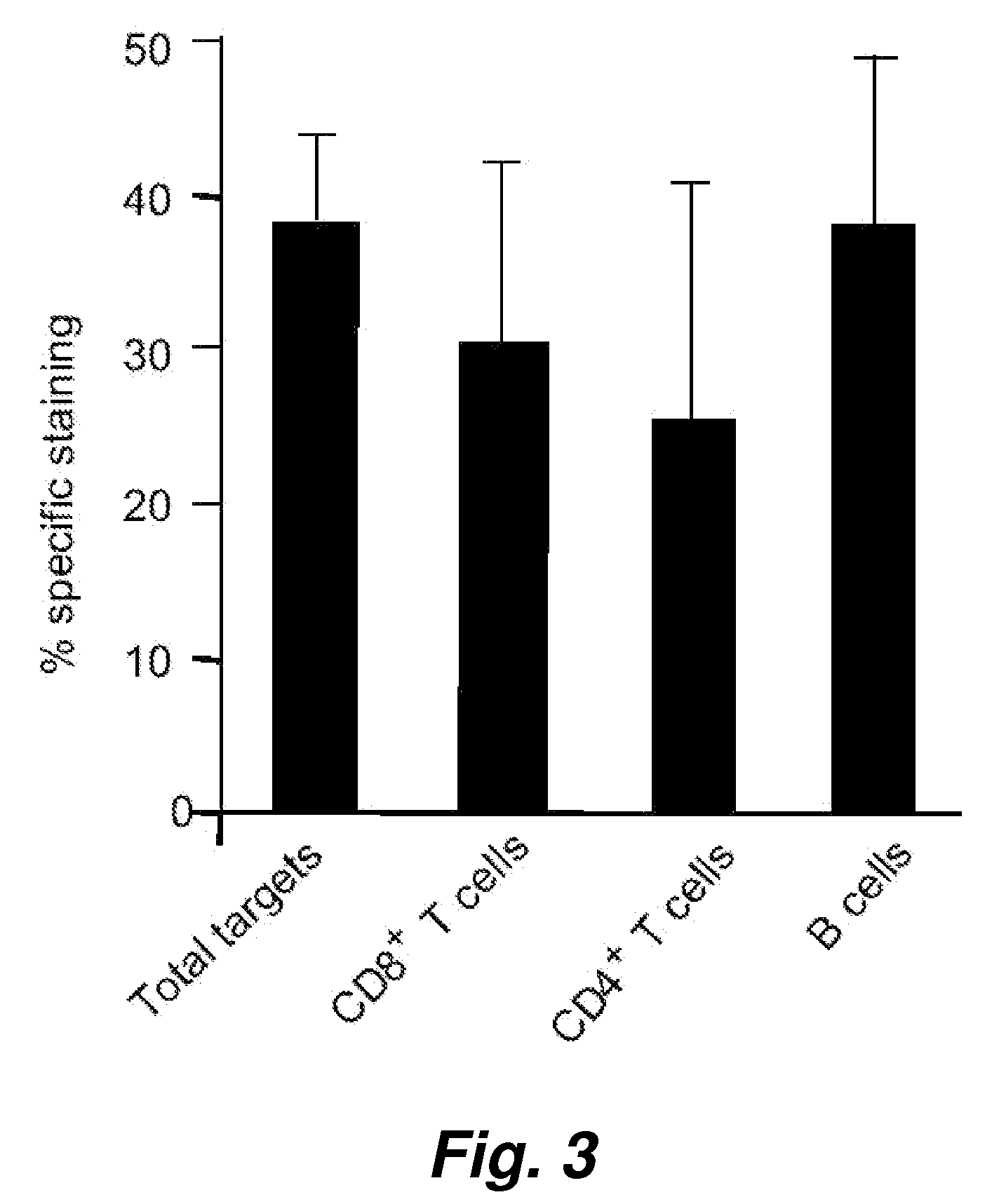
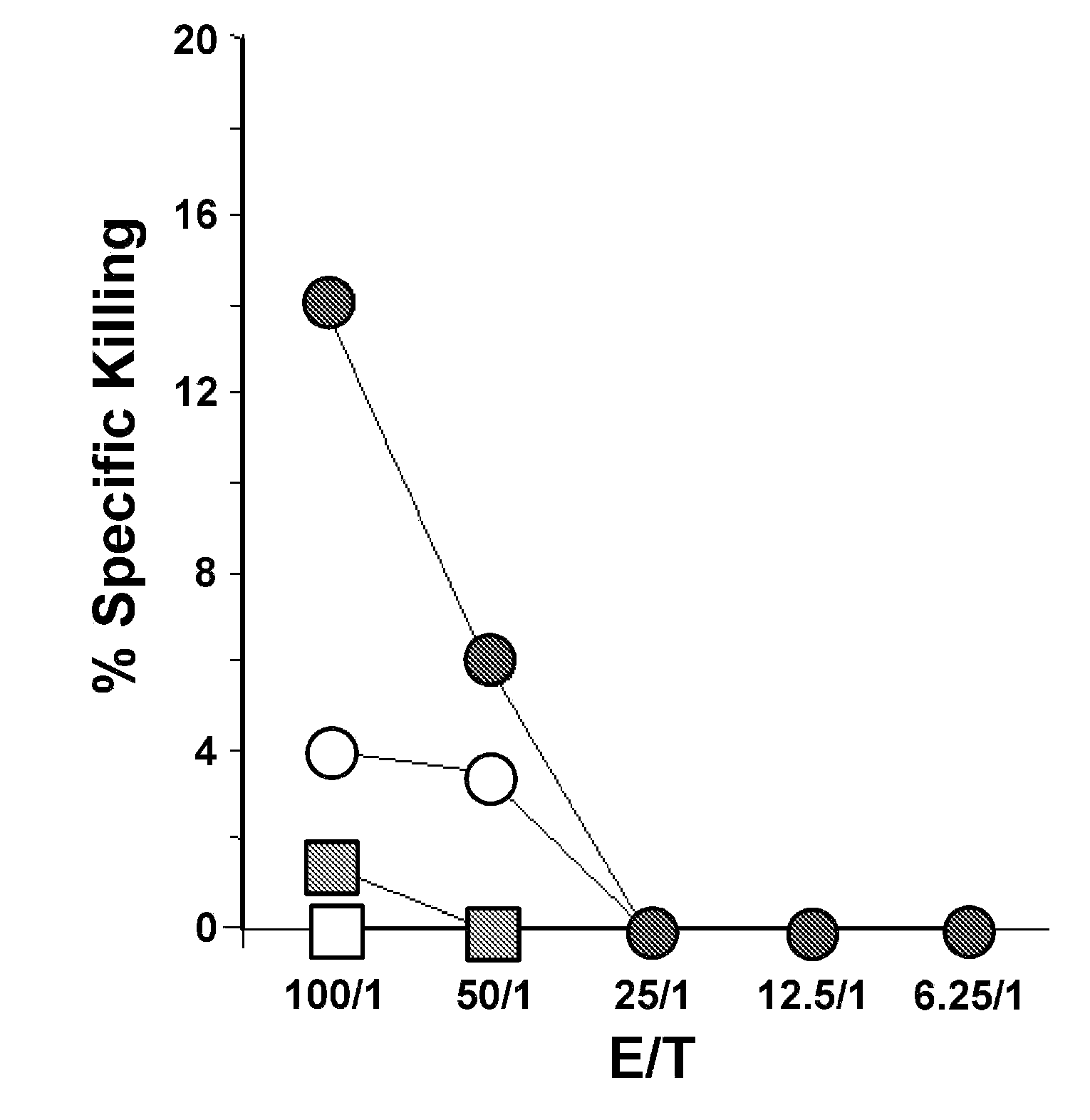
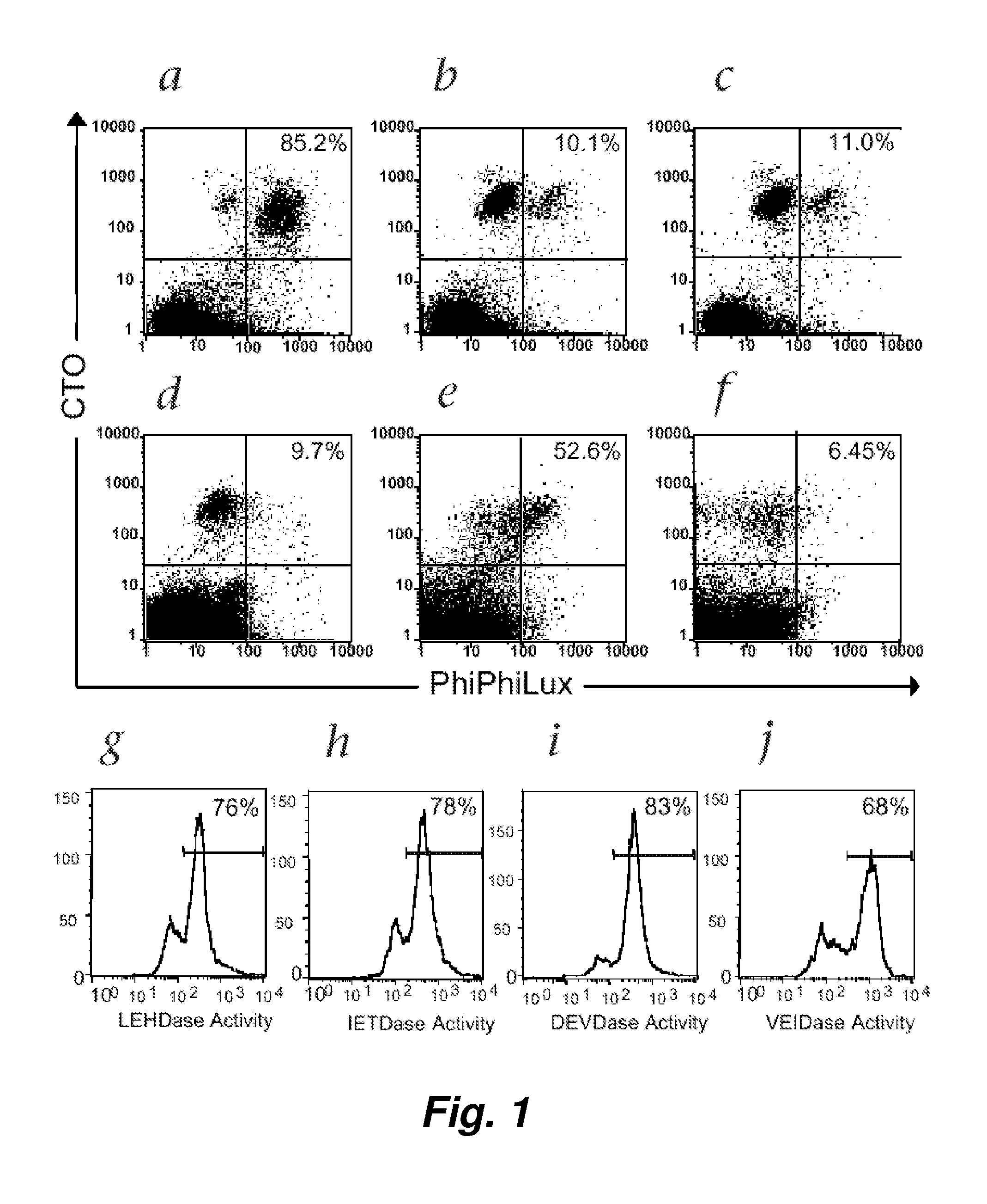
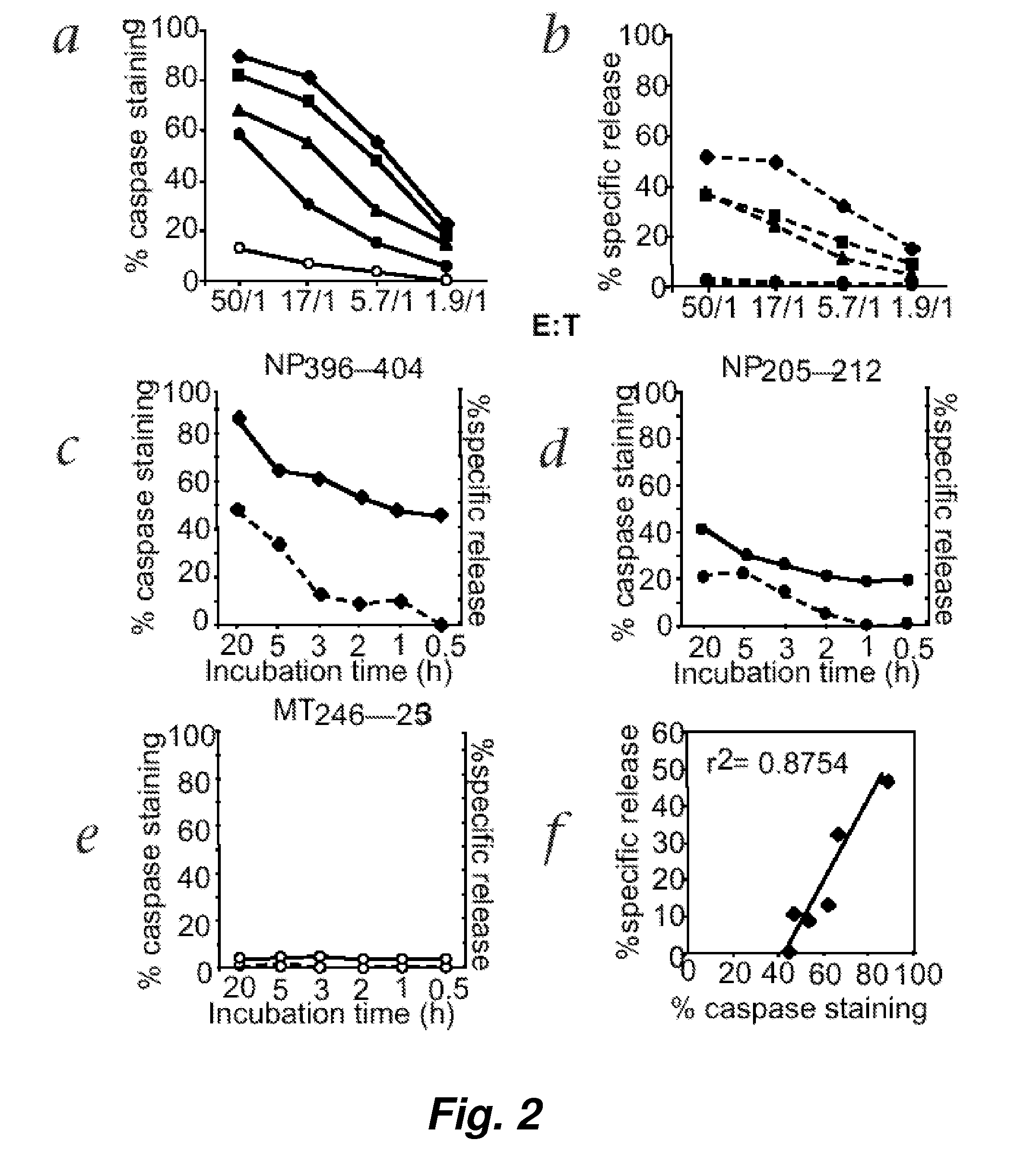
Visualization and quantitation of cellular cytotoxicity using cell-permeable fluorogenic protease substrates and caspase activity indicator markers
ActiveUS20070184493A1Microbiological testing/measurementTetrapeptide ingredientsFluorescenceApoptosis pathways
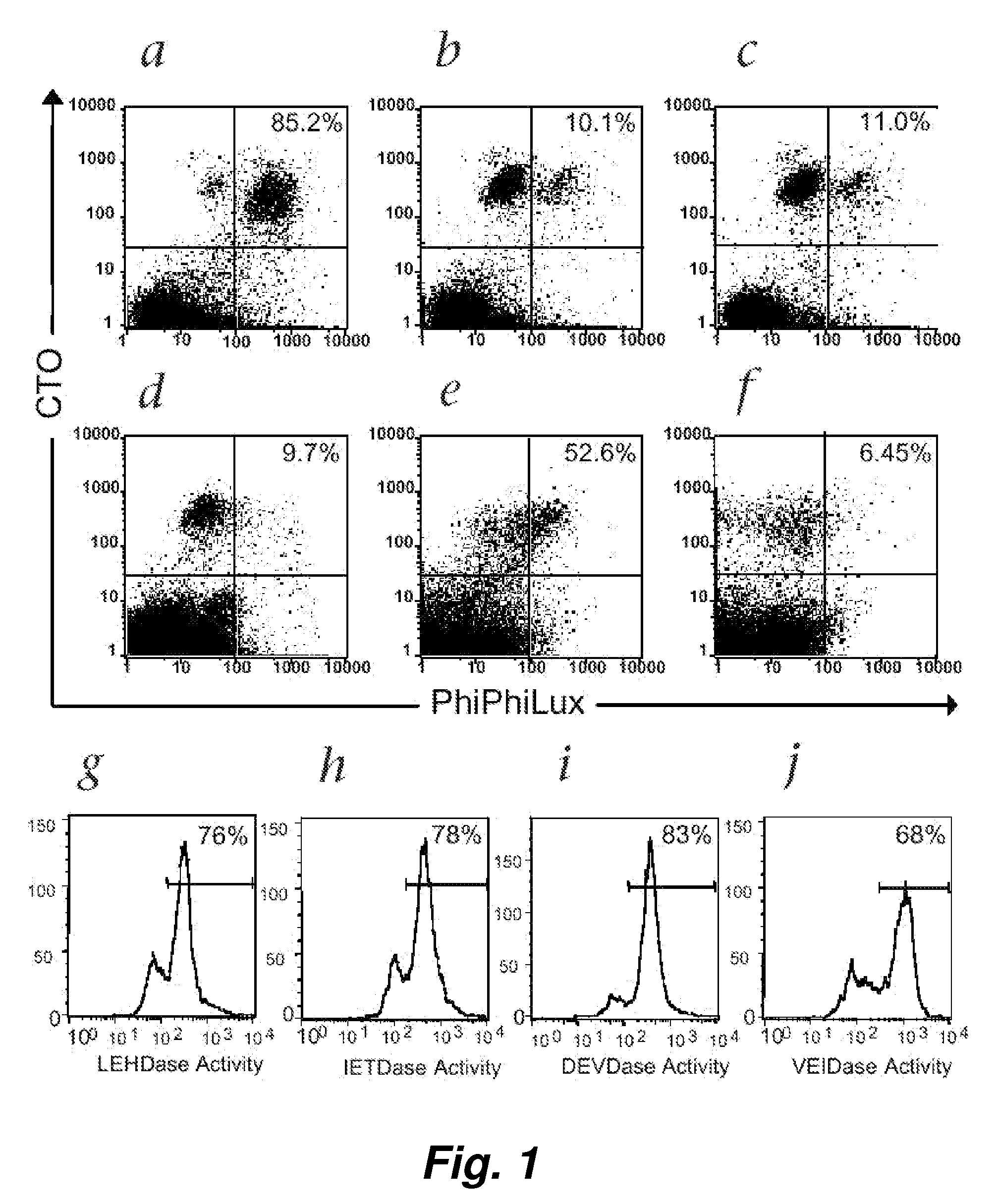
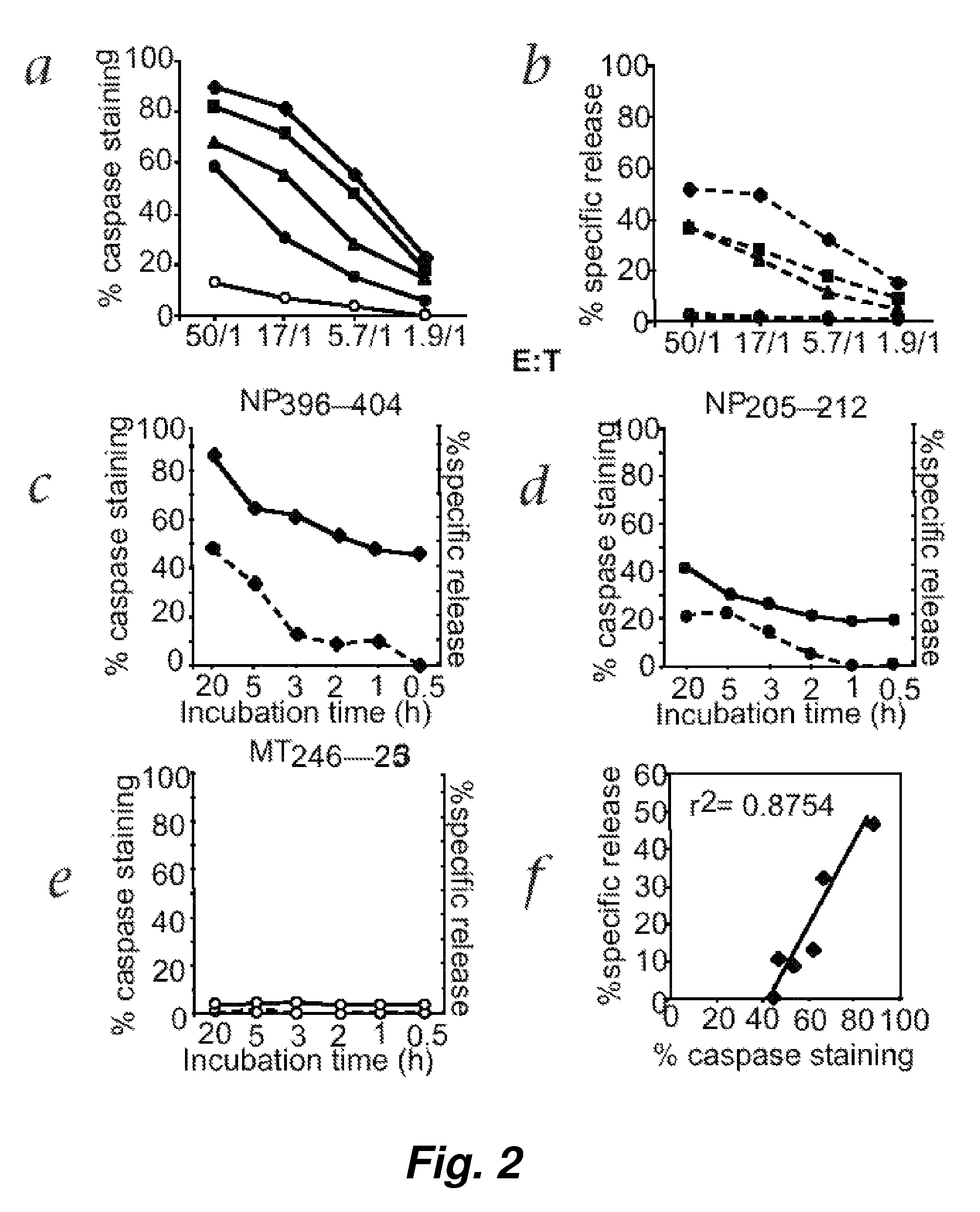
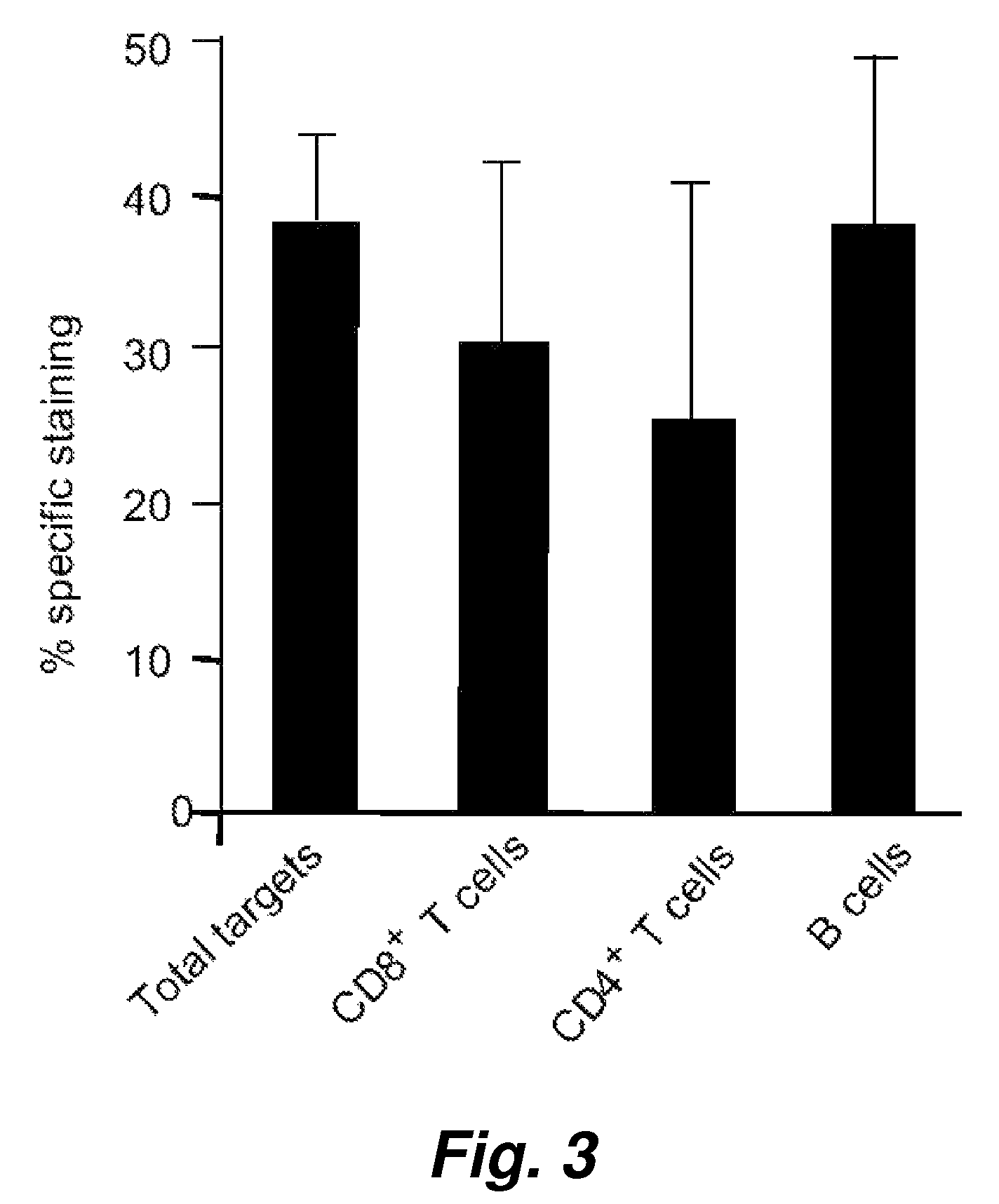
This invention provides a non-radioactive assay to monitor and quantify the target-cell killing activities mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). This assay is predicated on the discovery that apoptosis pathway activation and, in particular, granzyme B activity, provides a measure of cytotoxic effector cell activity. In one embodiment, measurement of CTL-induced granzyme B activation in target cells is achieved through detection of the specific cleavage of fluorogenic granzyme B substrates. This assay reliably detects antigen-specific CTL killing of target cells, and provides a more sensitive, more informative and safer alternative to the standard 51Cr-release assay most often used to quantify CTL responses. The assay can be used to study CTL-mediated killing of primary host target cells of different cell lineages, and enables the study of antigen-specific cellular immune responses in real time at the single-cell level. As such, the assay can provide a valuable tool for studies of infectious disease pathogenesis and development of new vaccines and immunotherapies.
Owner:ONCOIMMUNIN
Papaya-like protease inhibitor screening kit and application thereof
ActiveCN113930481AStrong specificityQuick filterMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceEDANSBoronic acid
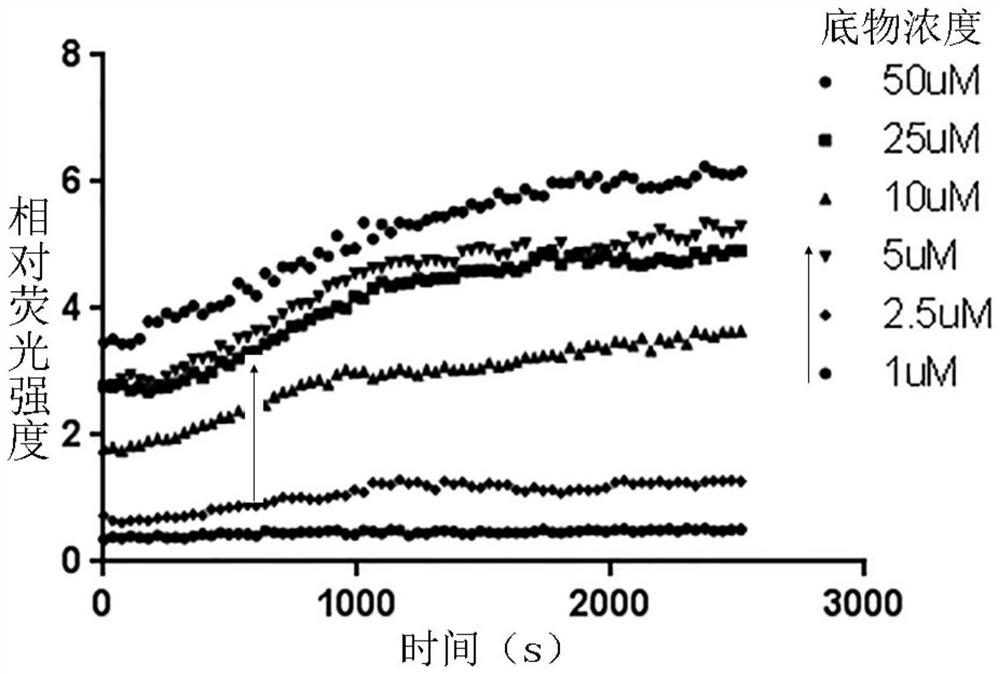
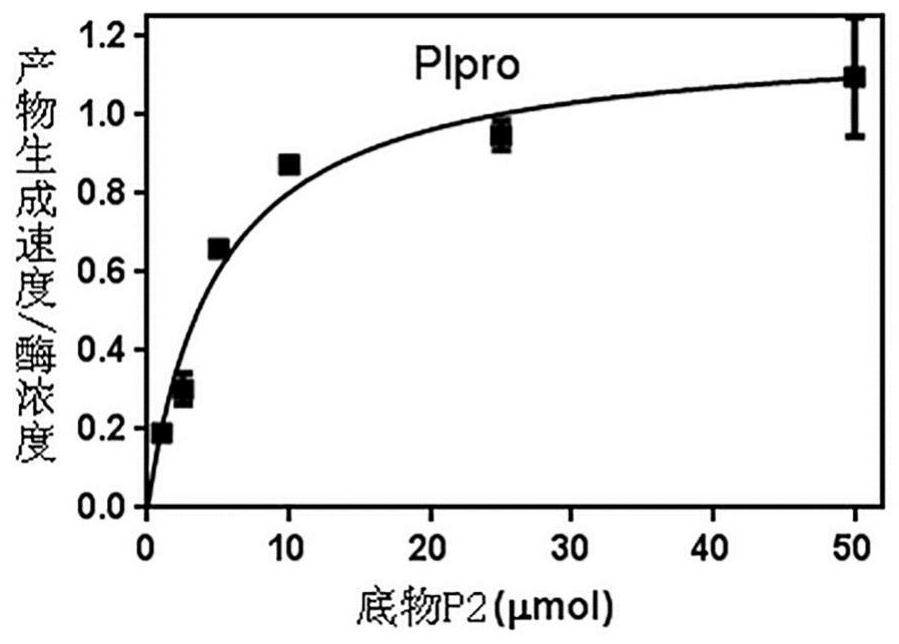
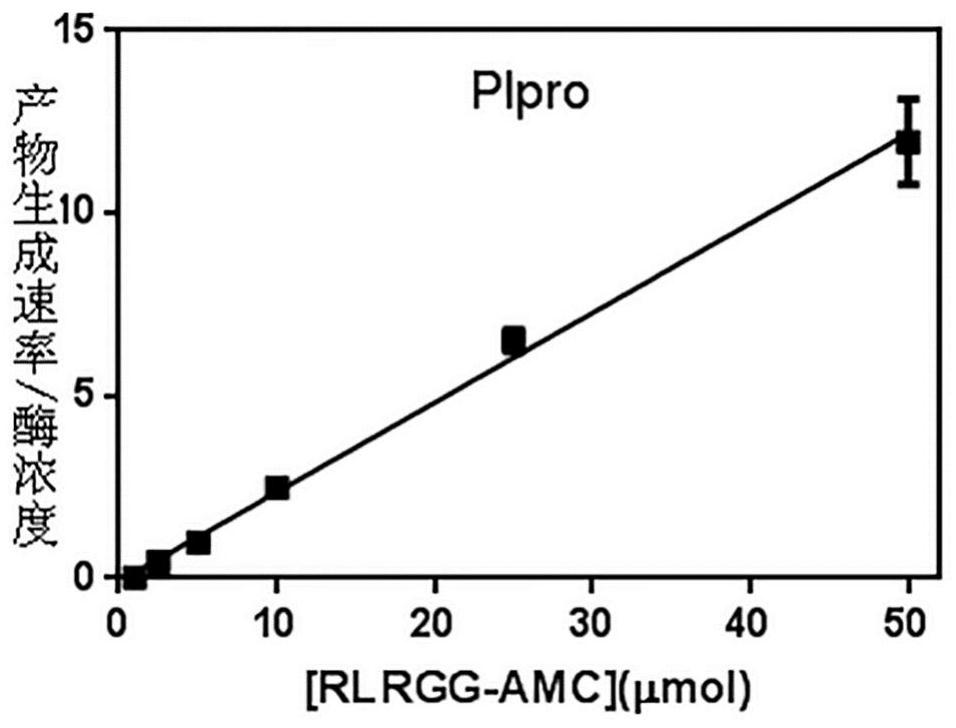
The invention relates to an SARS-Cov-2 papaya-like protease inhibitor screening kit and a screening method thereof. The invention provides a screening method of an inhibitor capable of being used for SARS-Cov-2 papaya-like protease. The kit comprises the following components: SARS-Cov-2 papaya-like protease, a substrate peptide Dabcyl-FTLKGGAPTKVT-E(Edans), and a boric acid and borax buffer solution. According to the substrate peptide, fluorophore quenching is relieved under the action of the SARS-Cov-2 papaya-like protease, activity detection of the SARS-Cov-2 papaya-like protease is achieved through the difference of fluorescence properties before and after the reaction, and the method can be used for rapid screening of high-flux inhibitors which are simple, convenient and good in specificity.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Urinary trypsin inhibitor assay containing a chelating agent
InactiveUS7001737B2Avoid interferenceAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementChemistryUrine sample
Disclosed is an assay for determining the presence and concentration of trypsin inhibitor in urine samples. The assay reagents, which may be used either in the liquid or dry states, include trypsin, a trypsin substrate and a polycarboxylic chelating agent. The inclusion of the chelating agent in the assay has been found to reduce variation in the assay results.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Selective exosite inhibition of papp-a activity against igfbp-4
ActiveUS20100310646A1Improve transcription efficiencyInhibit bindingAntibacterial agentsFungiDifferential inhibitionProteinase activity
The present invention relates in one embodiment to PAPP-A exosite(s) interactors such as antibodies which bind to a region comprising LNR3 of PAPP-A and efficiently inhibit proteolysis of IGFBP-4, but not -5. The region comprising LNR3 represents a substrate binding exosite, which can be targeted for selective proteolytic inhibition. Accordingly, the present invention relates in one embodiment to differential inhibition of natural protease substrates by exosite targeting.
Owner:AARHUS UNIV
Visualization and quantitation of cellular cytotoxicity using cell-permeable fluorogenic protease substrates and caspase activity indicator markers
ActiveUS7927871B2Microbiological testing/measurementTetrapeptide ingredientsFluorescenceCytotoxicity
This invention provides a non-radioactive assay to monitor and quantify the target-cell killing activities mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). This assay is predicated on the discovery that apoptosis pathway activation and, in particular, granzyme B activity, provides a measure of cytotoxic effector cell activity. In one embodiment, measurement of CTL-induced granzyme B activation in target cells is achieved through detection of the specific cleavage of fluorogenic granzyme B substrates. This assay reliably detects antigen-specific CTL killing of target cells, and provides a more sensitive, more informative and safer alternative to the standard 51Cr-release assay most often used to quantify CTL responses. The assay can be used to study CTL-mediated killing of primary host target cells of different cell lineages, and enables the study of antigen-specific cellular immune responses in real time at the single-cell level. As such, the assay can provide a valuable tool for studies of infectious disease pathogenesis and development of new vaccines and immunotherapies.
Owner:ONCOIMMUNIN
Matrix metalloproteinase targeted recombined human tumor necrosis factor and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101302255AHybrid peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionTumor targetHuman tumor
The invention relates to matrix metallic protease-directed recombination human tumor necrosis factor fused protein and a method for making the same. The amino acid sequence of the fused protein consists of three parts, i.e. a collagen sequence, a (a sort or a class of) human matrix metallic protease substrate sequence and a human tumor necrosis factor-alpha sequence (as shown in graph 1) which are arranged in turn from an N-end. When tumor necrosis factor-alpha is formed into a trimerical active form, the collagen sequence is formed into right hand triple helix, and plays a role in closing the recipient binding site of tumor necrosis factor-alpha along with the human matrix metallic protease substrate sequence. The specific cutting of the fused protein can be completed by matrix metallic protease excreted by a tumor tissue inside the tumor tissue so as to expose the recipient binding site of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and to represent cytotoxic activity; however, the fused protein does not represent cytotoxic activity in most normal tissues. The fused protein has tumor-targeting characteristics and the action of killing tumor cells, thereby having enormous application prospect in curing tumor.
Owner:GUANGDONG MEDICAL UNIV
Sterility indicating biological compositions, articles and methods
The present invention discloses a sterility indicating composition comprising a plurality of sterilization process resistant spores which contain an active protease during germination and initial outgrowth of the spores; and a germination medium comprising at least one labeled protease substrate and at least one nutrient for germination of the spores; wherein the medium is essentially free of a) any active protease other than the active protease contained by the plurality of spores and b) any protease substrate other than the at least one labeled protease substrate, other than any protease substrate originating from the plurality of spores, and other than any protease substrate which does not compete with the labeled protease substrate for the active protease; and wherein the at least one labeled protease substrate comprises a peptide which can be cleaved by the active protease and which is labeled with one or more dye groups, at least one of which undergoes a detectable change when the peptide is cleaved by the active protease, and wherein the labeled protease substrate is stable at least at a temperature for incubating the spores, a sterilization process indicator comprising the composition, and a method of determining the effectiveness of a sterilization process using the composition and indicator are disclosed.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
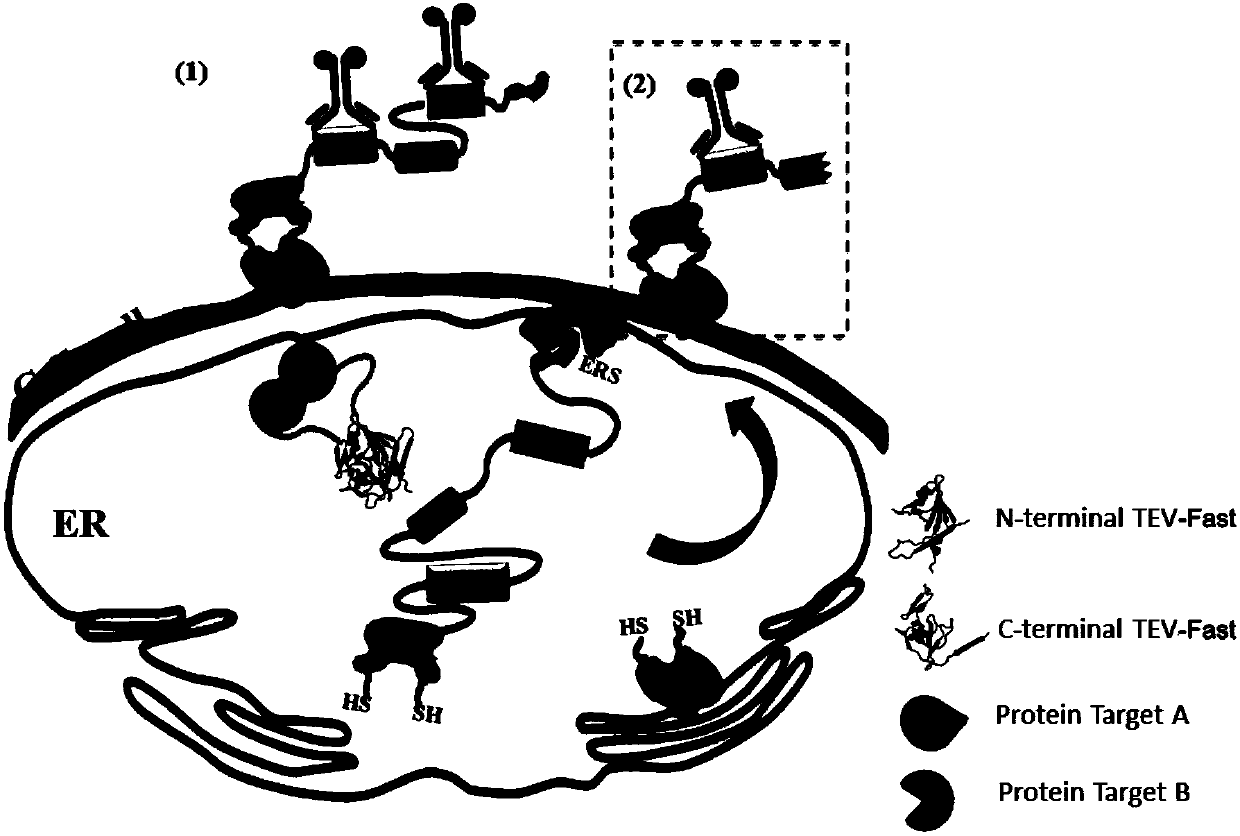
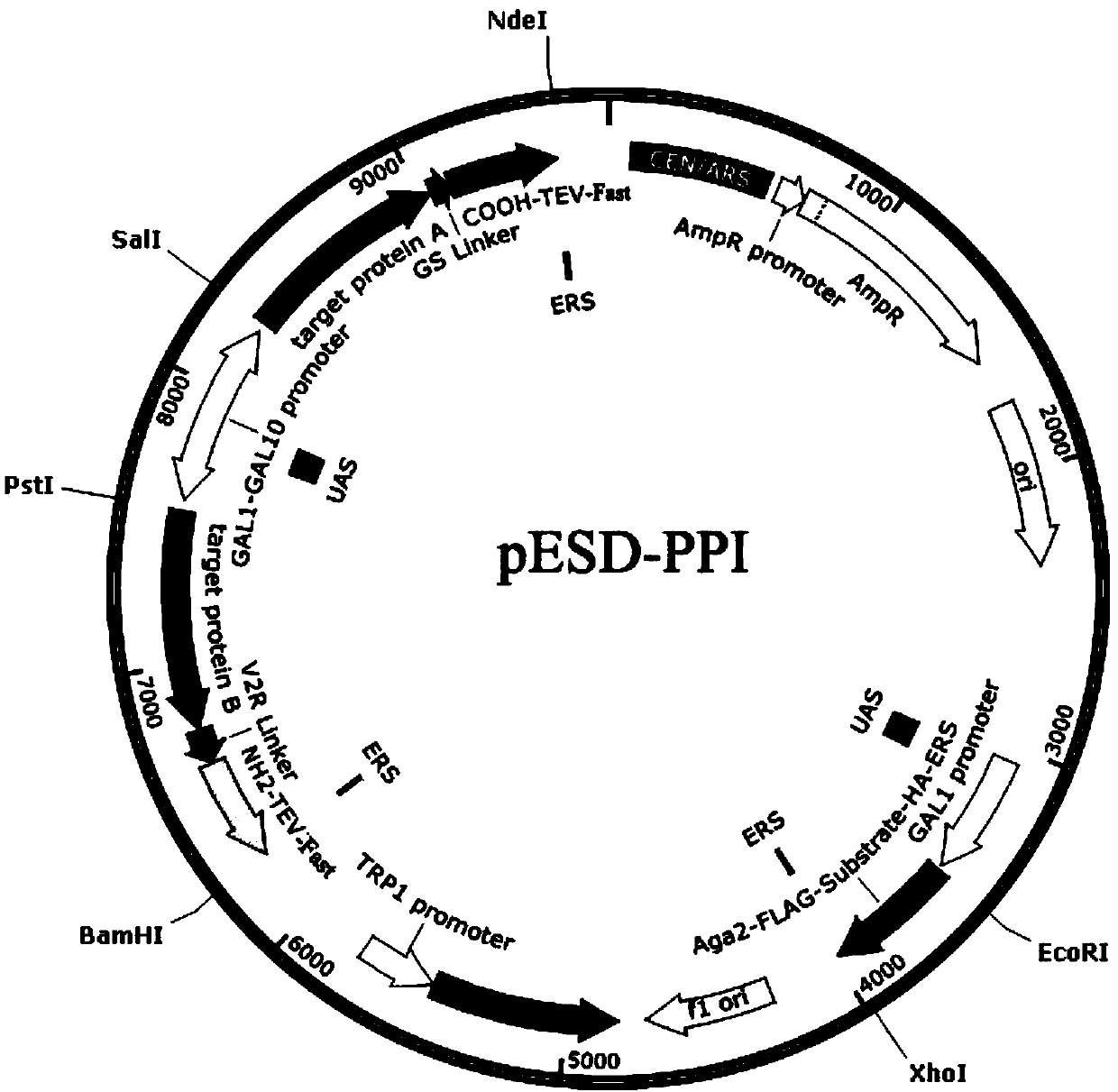
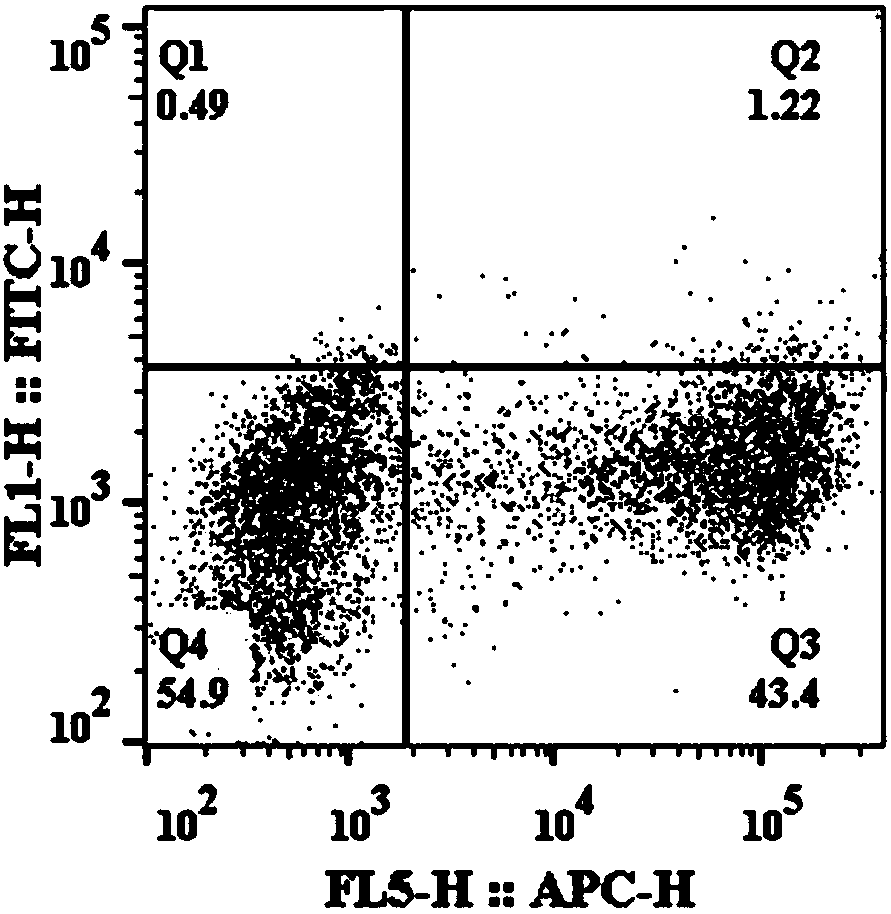
Construction method of split-TEV-Fast system and application of split-TEV-Fast system in detecting protein interaction
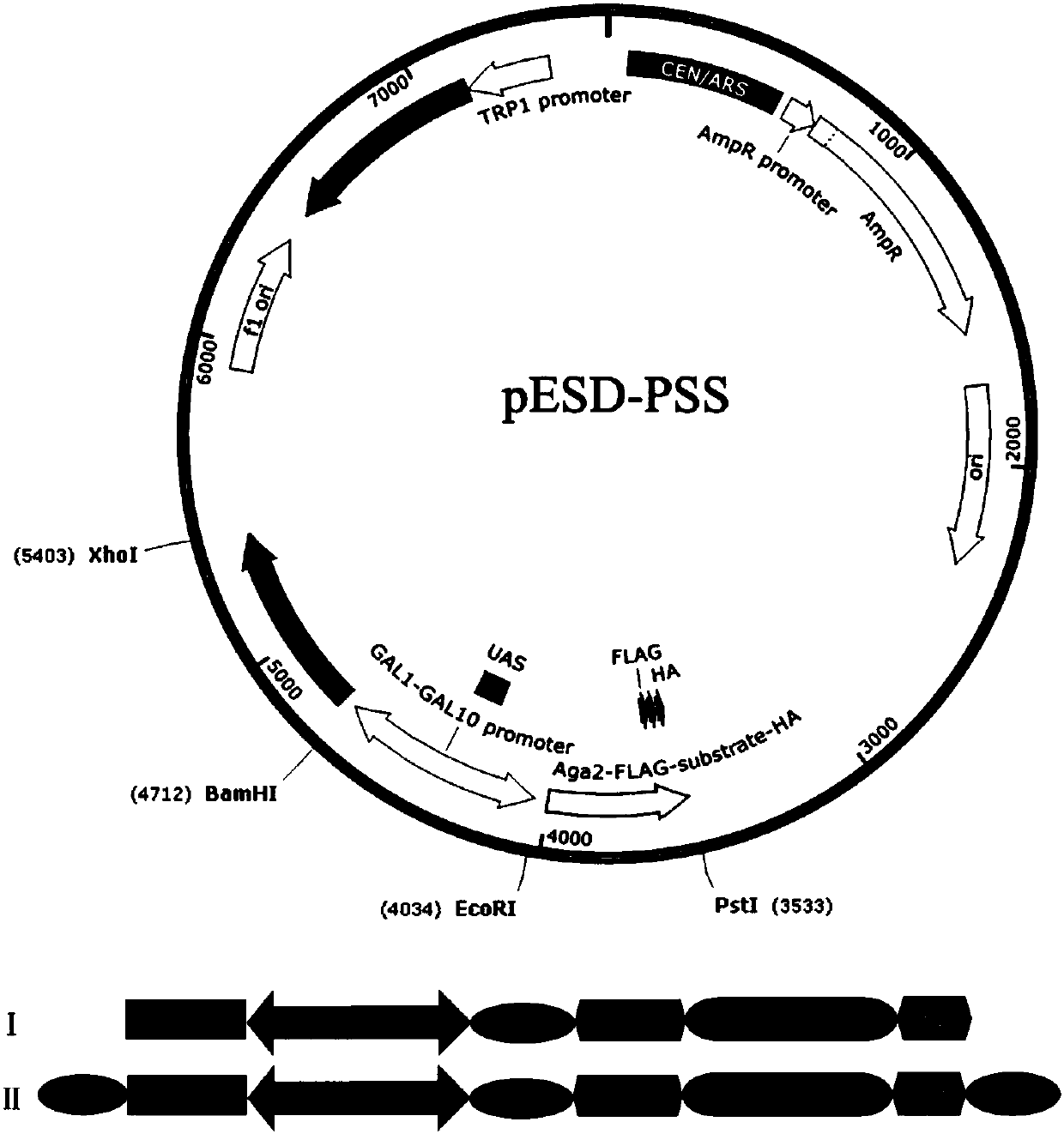
The invention discloses a method for constructing a split-TEV-Fast system based on saccharomyces cerevisiae and an application of the split-TEV-Fast system in detecting a protein interaction. The method comprises the following steps: 1) constructing a vector pESD-PPI, wherein the vector comprises a forward promoter and a bidirectional promoter induced by galactose, the forward promoter is used forexpressing a TEV-Fast protease substrate as well as FLAG and HA tag sequences, and the bidirectional promoter is used for expressing resolving TEV-Fast protease and a to-be-detected target protein; 2) simultaneously inducing the promoters via the galactose, and inducing equivalent expression of a downstream gene; 3) marking cells via fluorescent antibodies which recognize the FLAG and HA tag sequences; and 4) detecting fluorescence signals on the surfaces of the cells via a flow cytometry, and judging the intensity of the protein interaction in accordance with the single and double fluorescence signals. The method provided by the invention, by adopting endoplasmic reticulum retention signal peptide differing in intensity at -COOH terminals of the TEV-Fast protease and the substrate thereof, can widen a range of detecting the protein interaction; and the intensity of the protein interaction can be analyzed depending on a finally detected proportion of single and double fluorescence signal intensities.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
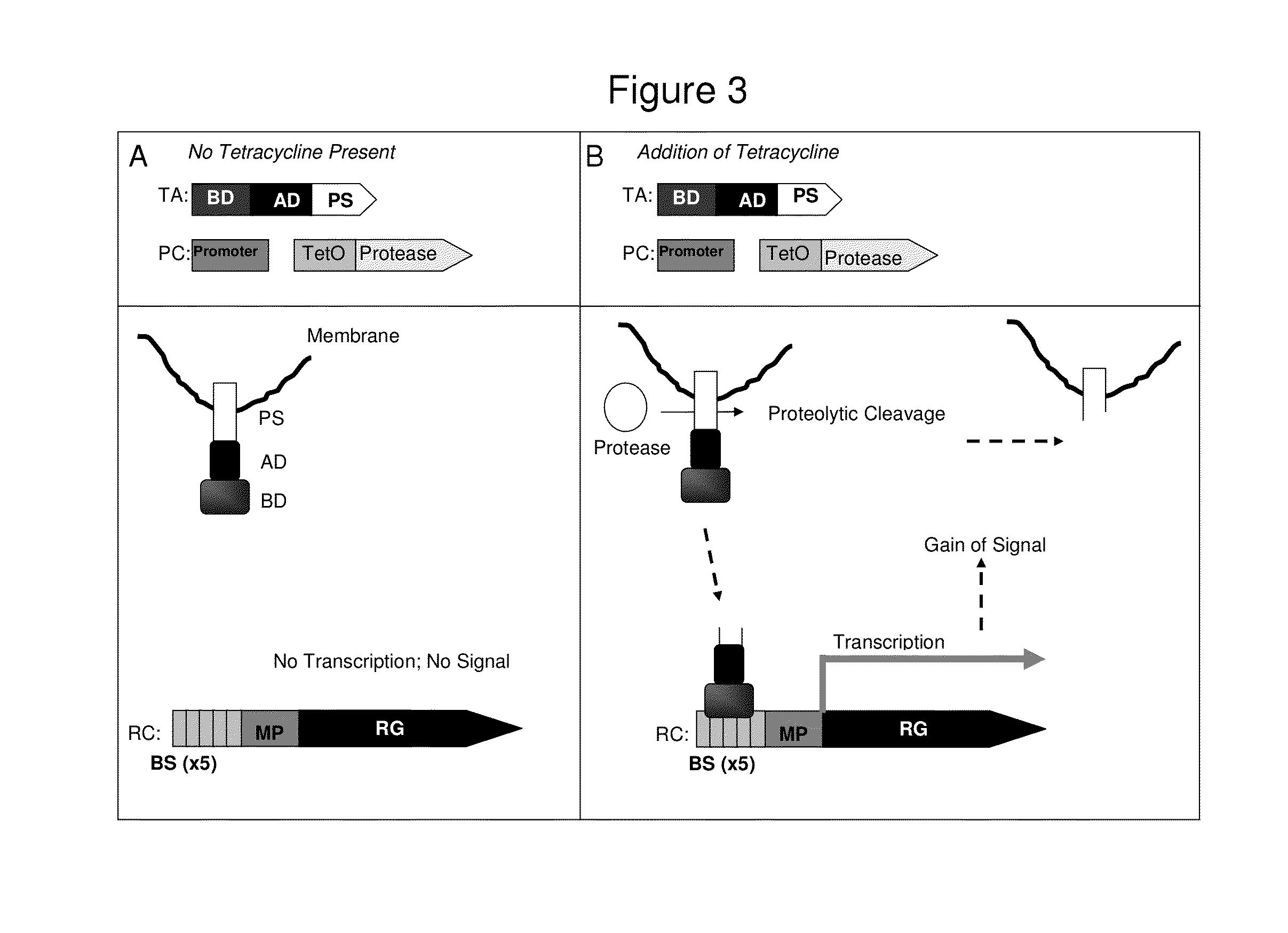
Method for identification of protease activity inhibitors and assaying the presence of protease activity
ActiveUS20140017697A1Microbiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionBinding siteBinding domain
A system for the identification of proteases and protease inhibitors is provided. The system has at least two components. The first component is a reporter construct with at least one binding site, a transcriptional promoter, an inducible promoter region, and at least one reporter gene, all functionally connected for expression of the reporter gene(s) in functional coordination with a transcriptional activation agent. The second component is a transcriptional activation agent comprising a nucleic acid binding domain, at least one protease substrate domain, and at least one transcriptional activation domain for an inducible promoter. The system allows detection and evaluation of agents affecting protease activity directed to the protease substrate domain. The system also allows for the detection of the presence of proteases in environmental samples.
Owner:IPSEN PHARMA SAS
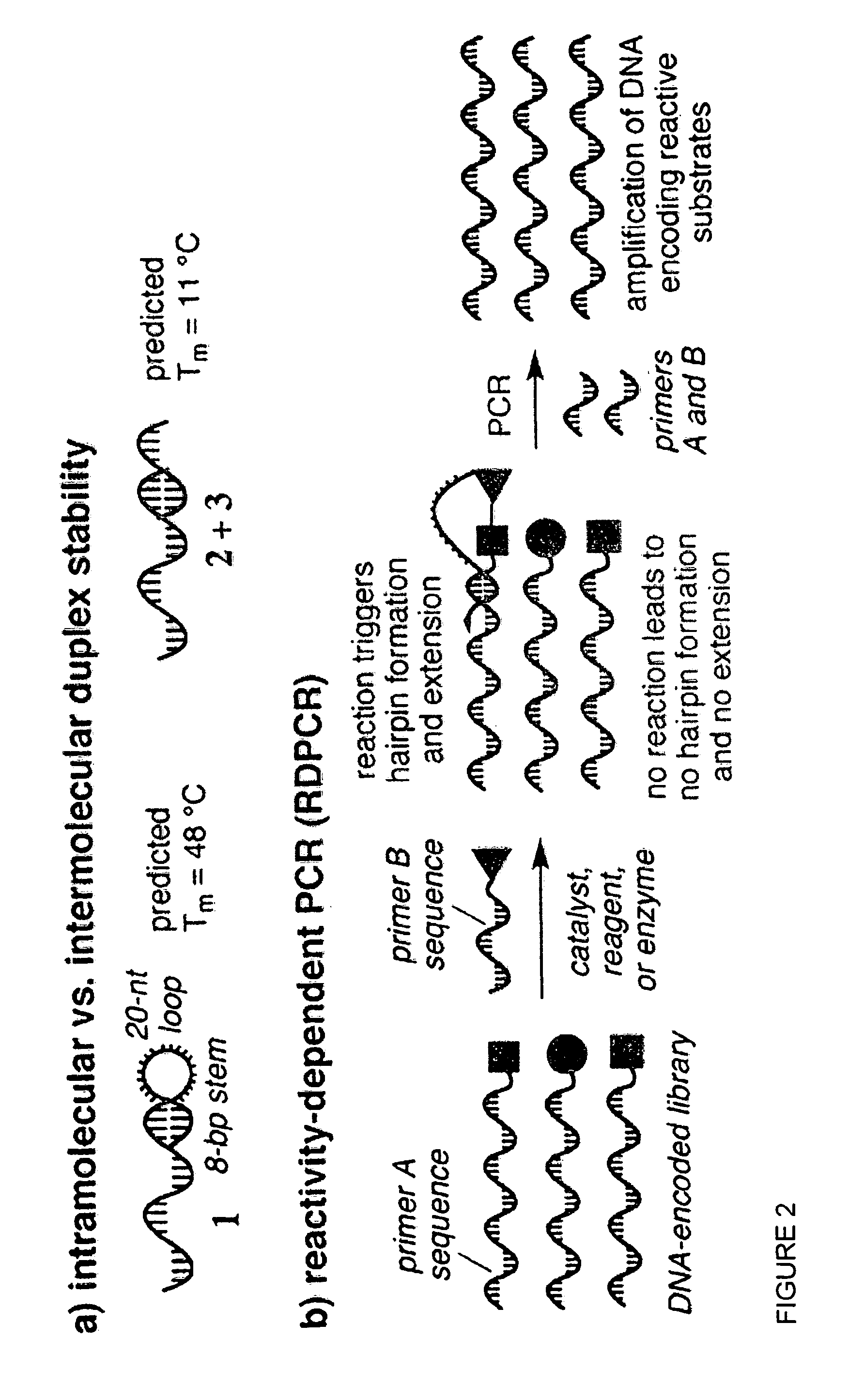
Reactivity-dependent and interaction-dependent PCR
Methods, reagents, compositions, and kits for reactivity-dependent polymerase chain reaction (RD-PCR) and interaction-dependent polymerase chain reaction (ID-PCR) are provided herein. RD-PCR is a technique useful for determining whether a reactive moiety can form a covalent bond to a target reactive moiety, for example, in screening a library of candidate reactive moieties for reactivity with a target reactive moiety, and in identifying an enzyme substrate, for example, in protease substrate profiling. ID-PCR is a technique useful for determining whether a ligand can non-covalently bind to a target molecule, for example, in screening a library of candidate ligands for non-covalent interaction with a target molecule. RD-PCR and ID-PCR are also useful in detecting the presence of an analyte or an environmental condition.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
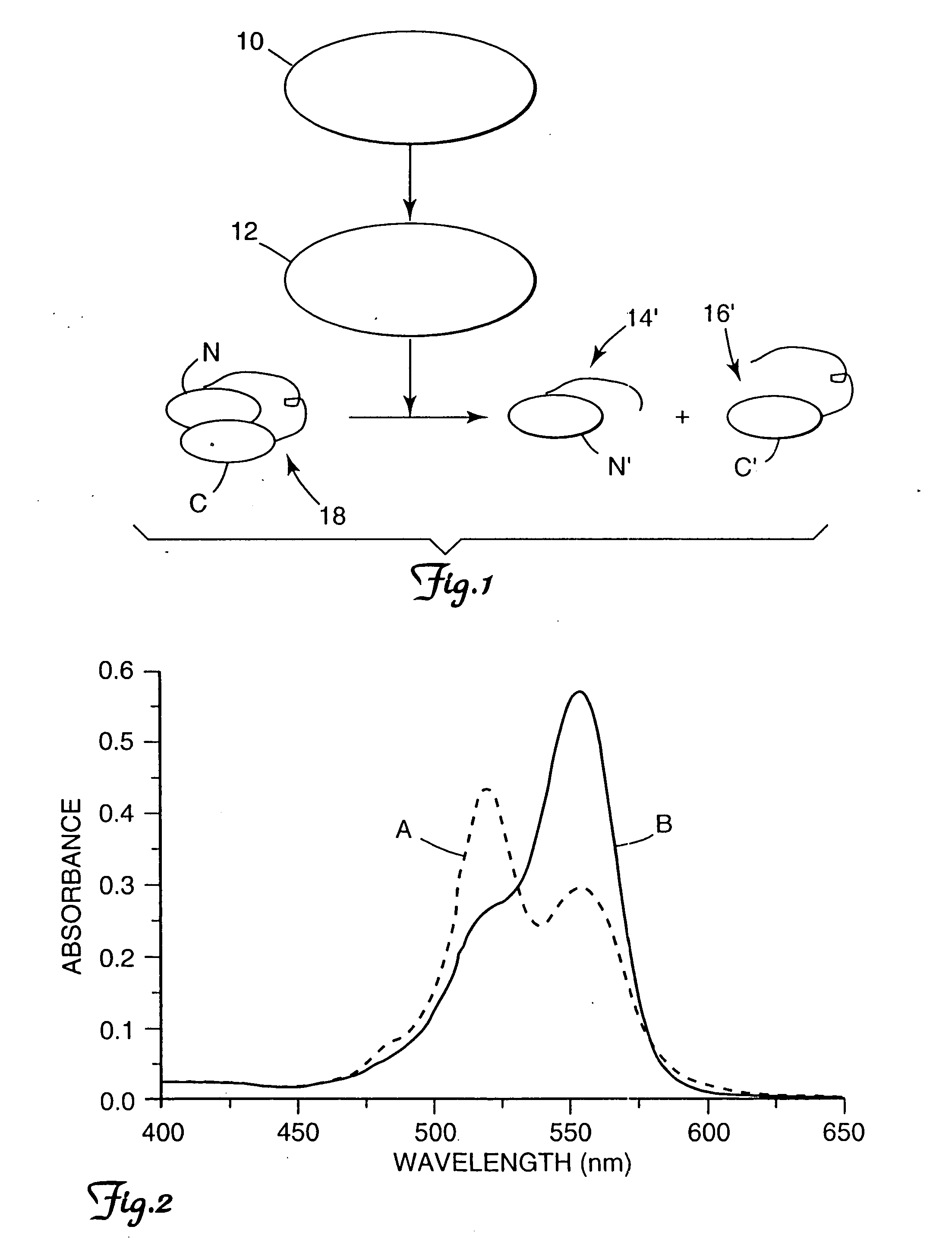
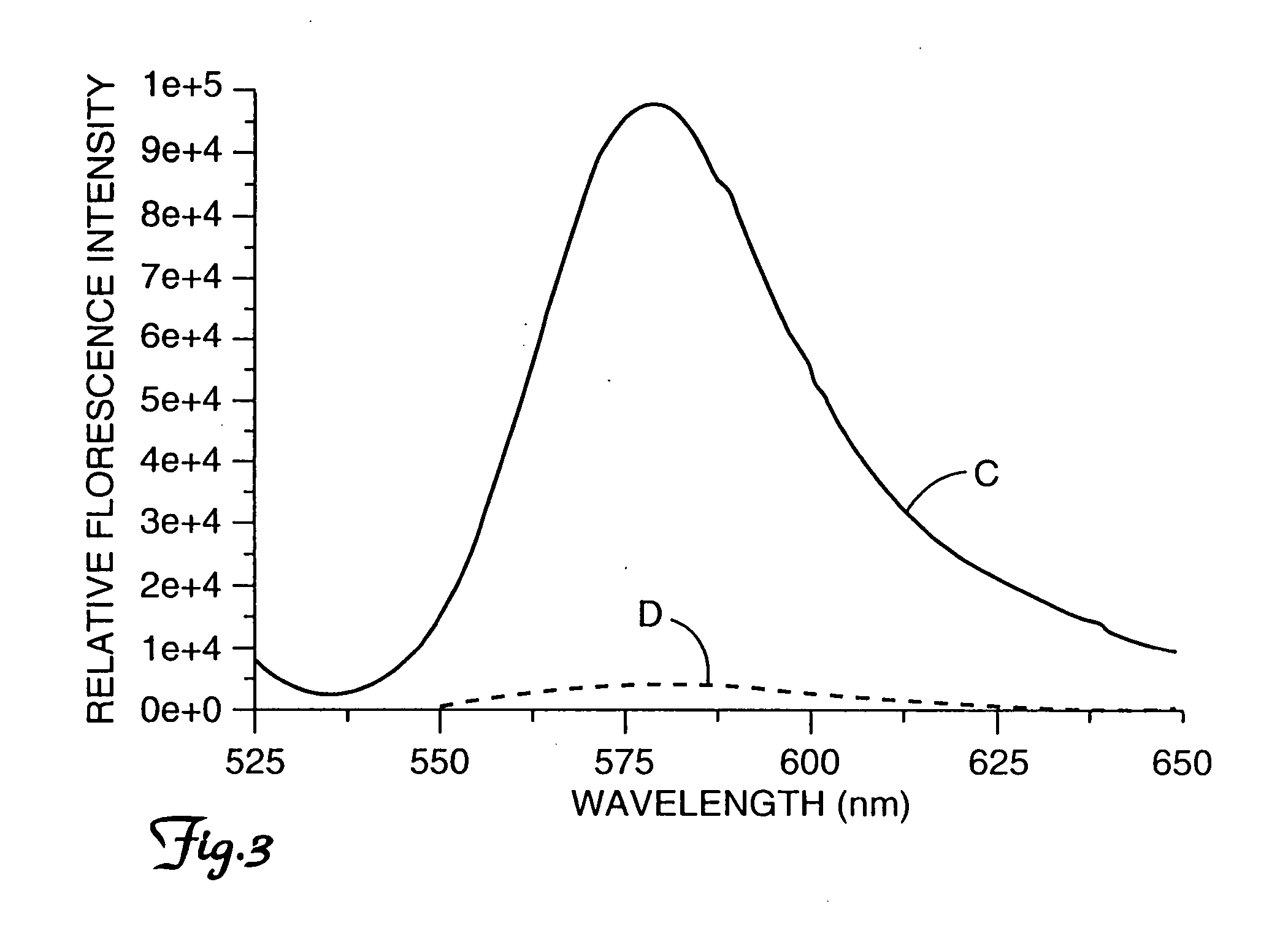
Fluorogenic protease substrates based on dye-dimerization
InactiveUS7256012B2High fluorescence intensityEasy to observePeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismImmuno assay
A method of biological assay comprises the steps of providing an enzyme substrate comprising two fluorescence dye groups bound to a flexible peptide, the dye groups being of proximity sufficiently close so as to allow free energy attractions to draw the dyes together to essentially self-quench fluorescence of the dye groups, wherein self quenching of fluorescence of the dye groups is effected by dye dimerization or stacking, and enzymatically cleaving the peptide to release the fluorescence dye groups from dye dimerization or stacking, thereby producing an increase in fluorescence intensity. A protease substrate for use in the method of the invention is also disclosed. This invention finds use in detection and identification of microorganisms, sterilization assurance, pharmaceutical discovery, enzyme assays, immunoassays, and other biological assays.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Genetic selection system to identify proteases, protease substrates and protease inhibitors
The present invention concerns a tester protein for identifying and / or monitoring protease activity in a cellular assay suitable for high throughput screenings by growth selection, wherein the tester polypeptide is a non-regulatory protein carrying a protease cleavage sequence. Upon co-expression of the protease recognizing said cleavage sequence the tester protein is inactivated, which influences the growth and / or survival of the host cells under the chosen conditions. However, in the presence of protease inhibitor the growth phenotype is reversed. The system can be used to identify proteases, protease inhibitors, and protease cleavage sites.
Owner:ONCALIS
Synthetic protease substrates, assay methods using such substrates and kits for practicing the assay
InactiveUS20110319293A1Strong specificityImprove solubilityPeptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementOrganic chemistryProteasome
Owner:LIFESENSORS INC
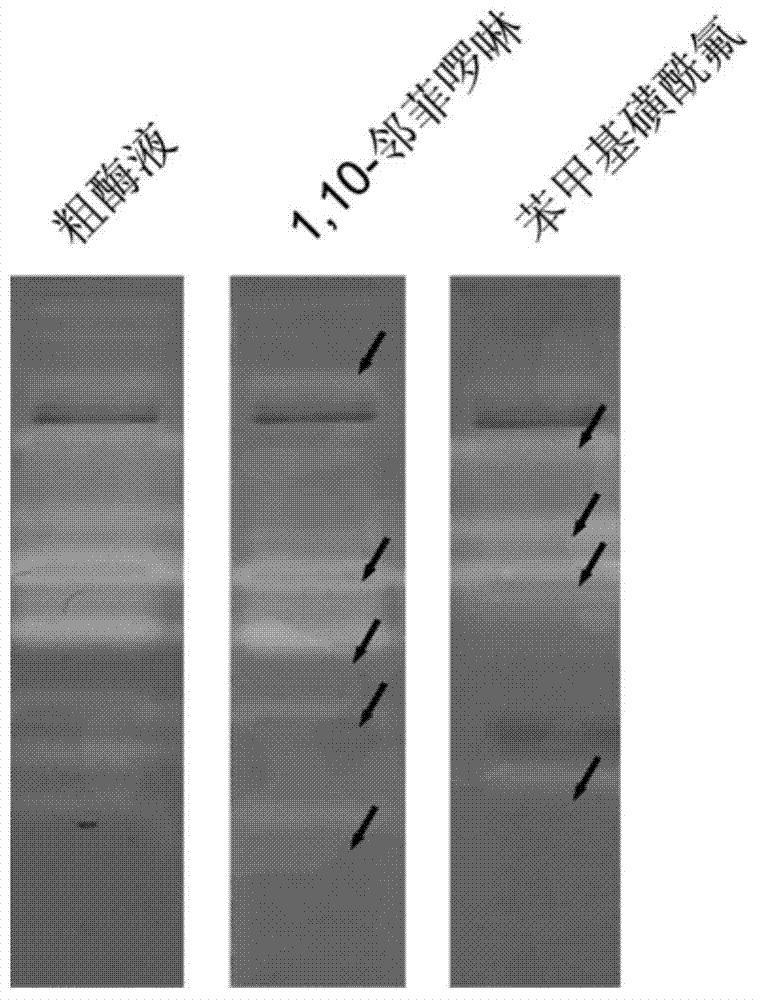
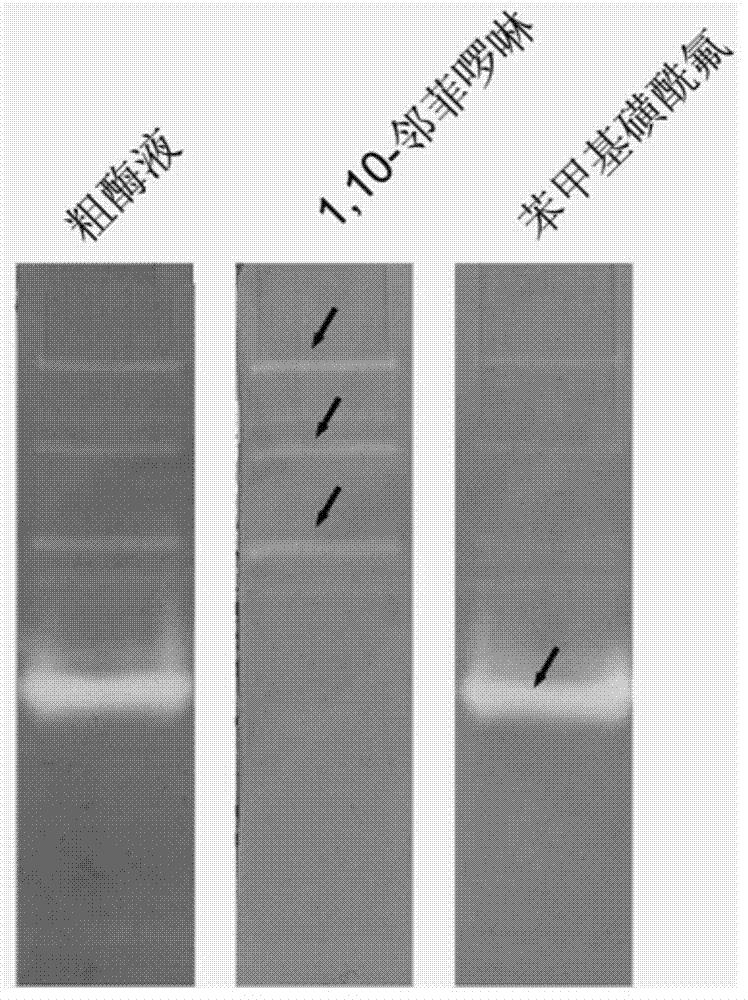
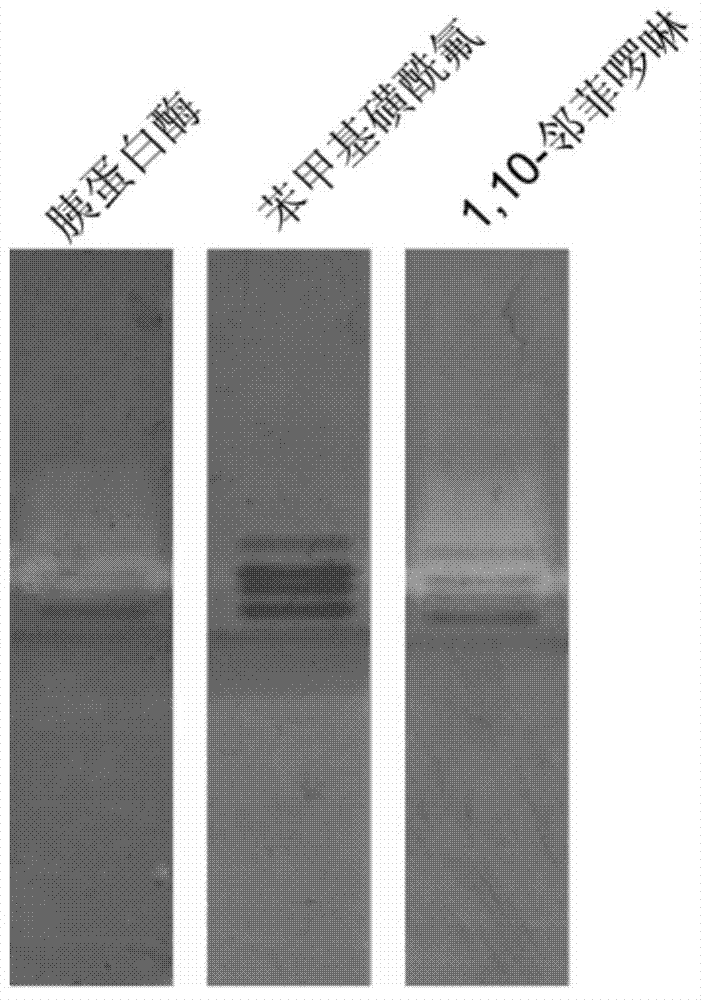
Application of protease graph electrophoresis detection method to rapid identification of extracellaluar protease variety of bacteria
ActiveCN104122317AConfirm the typeReduce cumbersome stepsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansWater bathsElectrophoresis
The invention discloses application of a protease graph electrophoresis detection method to rapid identification of extracellaluar protease variety of bacteria. The application is implemented by the following steps: a, preparing SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate) polyacrylamide gel containing no a protease substrate; b, evenly mixing a protease sample with a loading buffer solution containing no beta-mercaptoethanol and then loading the sample without heating in boiling water bath; c, carrying out electrophoresis; d, washing the gel; e, soaking the gel in a substrate solution containing different protease inhibitors; and f, reacting and developing. The protease graph electrophoresis detection method is capable of determining the natures of different proteases and obviously shortened in time in contrast with a traditional method; complex steps of separating and purifying the proteases are omitted; the method is good in repeatability, high in sensitivity and accurate in active stripe measurement, thus being highly advantageous for subsequent protease identification and purposeful purification operation; the method can be applied to detection of various types of proteases and has wide use space.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Synthetic substrates and inhibitors with enhanced specificity
InactiveUS20080070804A1Preserve proteolytic susceptibility of SR-peptideIncrease profitCompound screeningApoptosis detectionArthritisProtease binding
Novel synthetic enzyme substrates with improved enzymatic specificity are disclosed. These synthetic enzyme substrates consist of a substrate peptide that has had its specificity further improved by additional synthetic moieties, selected by combinatorial chemistry techniques, that act to sterically block non-target enzymes. These “steric restrictor” moieties may be labeled to produce a detectable signal upon enzymatic reaction. These novel substrates are particularly useful for improved enzyme substrate microarrays. Specific applications for improved protease substrate microarrays are discussed. A variety of applications for these improved protease substrate microarrays are also disclosed, including proteomics research, protease discovery, protease binding site characterization, diagnosis of the protease composition of biological samples, monitoring the angiogenic status of a tumor, monitoring the status of arthritis and other inflammatory diseases, and the discovery and optimization of novel drugs that modify or inhibit protease activity. The same techniques may also be used to design improved enzyme inhibitors.
Owner:ZWEIG STEPHEN ELIOT
Cleavage efficiency enhanced substrate mutant of HRV (Human Rhinovirus) 3C protease and application thereof
ActiveCN107602706AAdvantages and Notable ImprovementsSignificant progressBacteriaMicroorganism based processesYeastReticulum cell
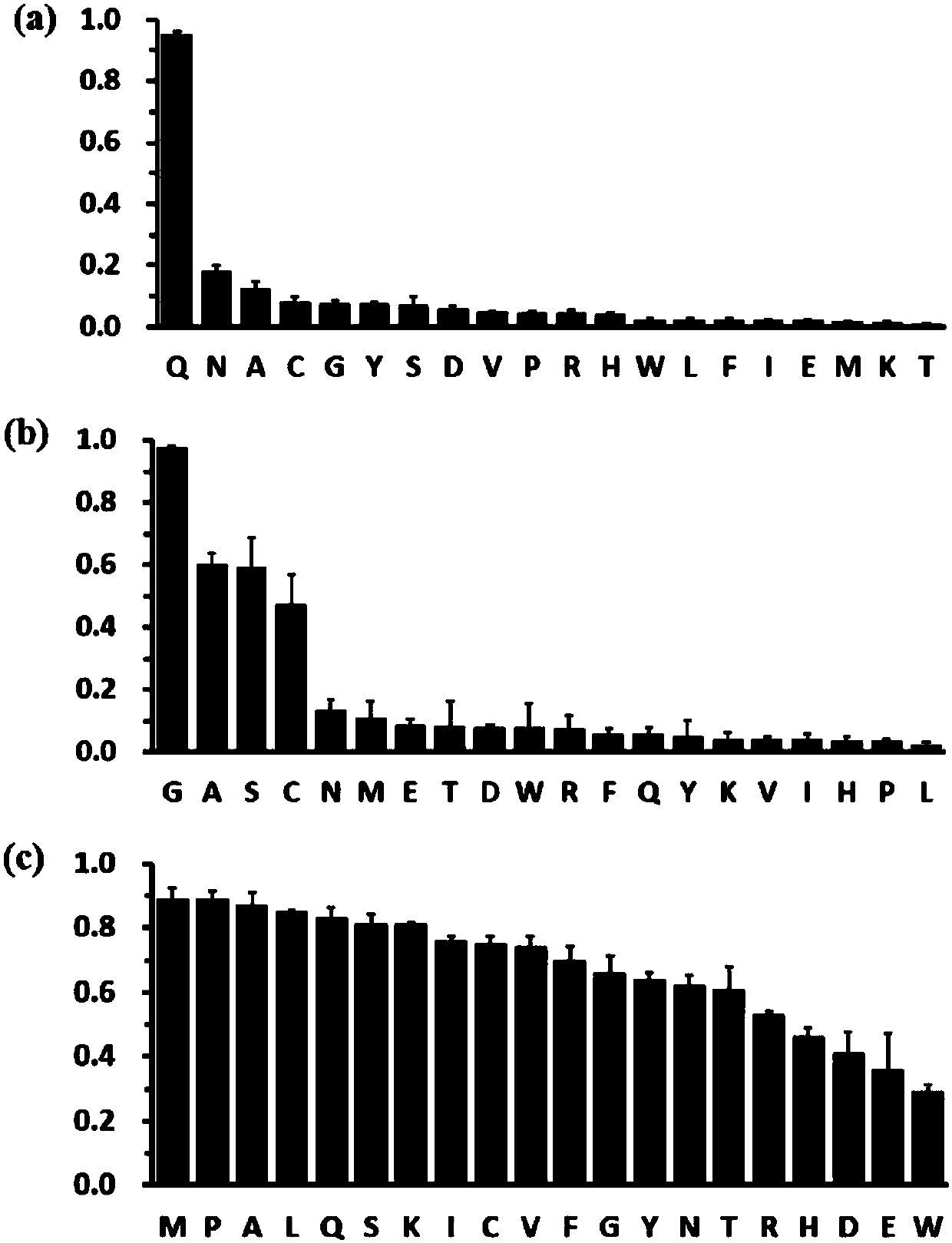
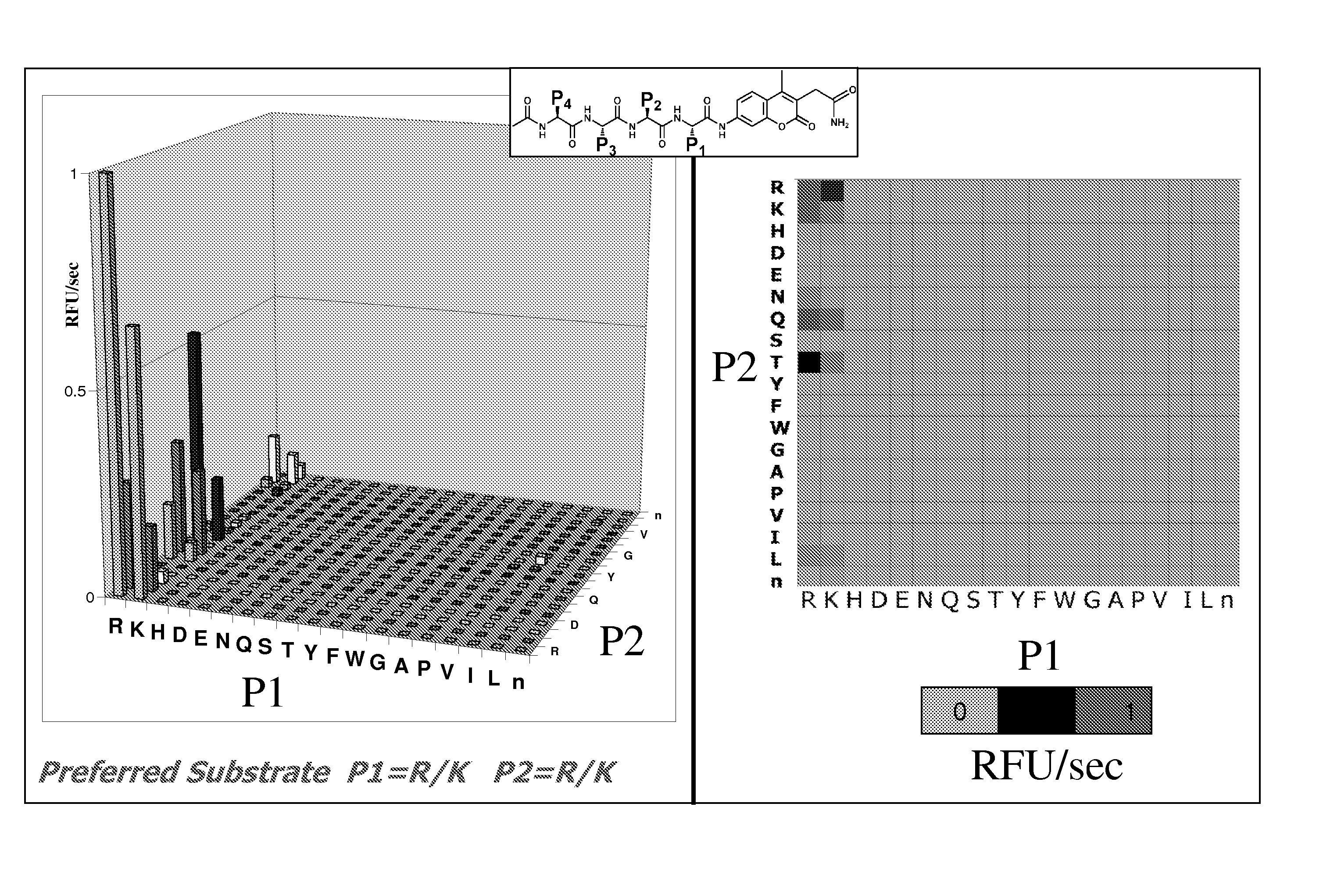
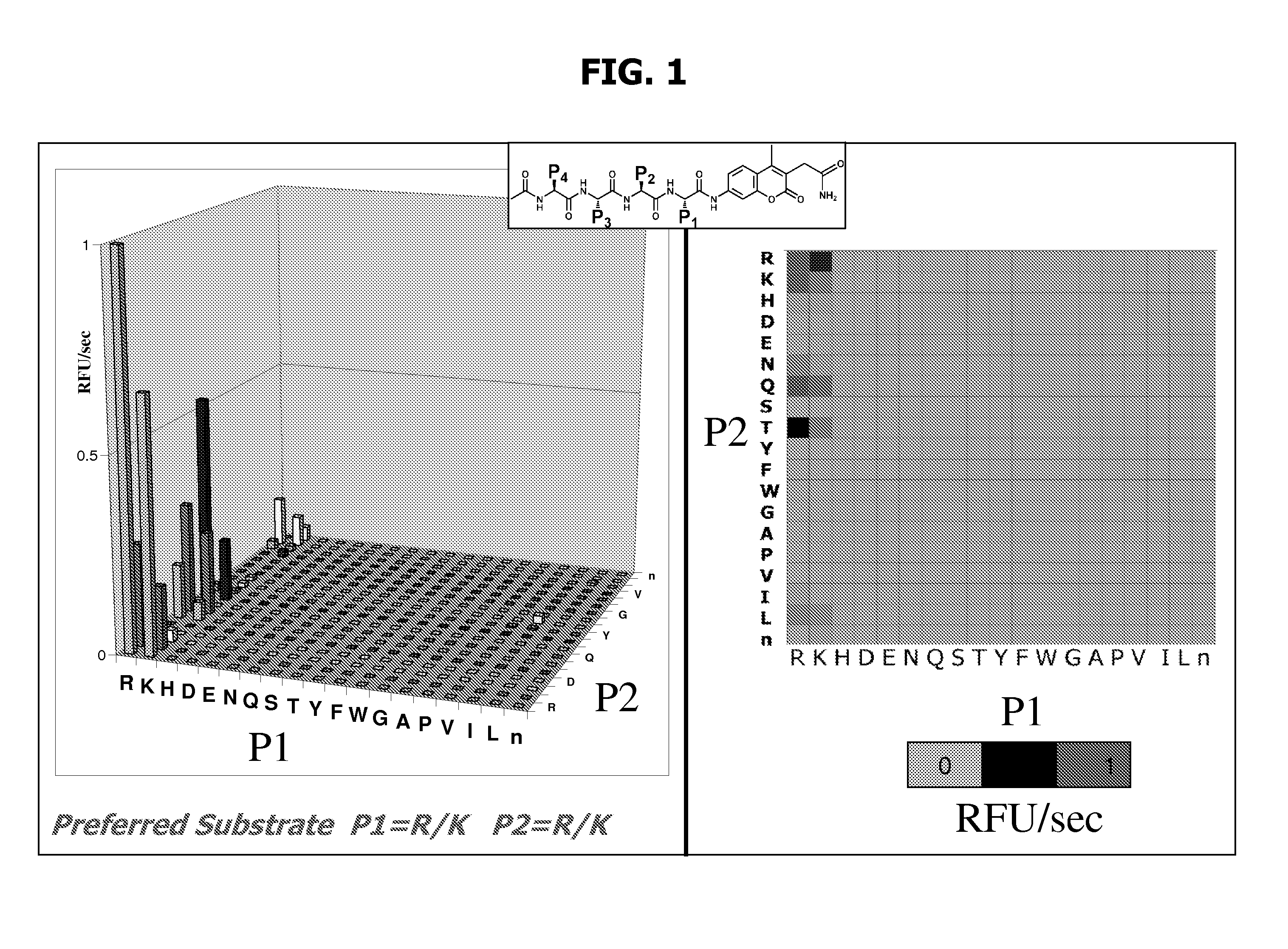
The invention utilizes a yeast endoplasmic reticulum sequestration screening system (YESS) to quickly analyze the specificity of a cleavage site of a substrate of protease, and finally provides a cleavage efficiency enhanced substrate sequence mutant of HRV (Human Rhinovirus) 3C protease and application thereof. The substrate mutant includes an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 in a sequence table, and has a better practical application advantage in the removal of a purification tag in a protein purification process, and therefore, the further application and research of the HRV 3C protease are facilitated.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Flavivirus protease substrates and inhibitors
InactiveUS20080032917A1Decrease protease activityBiocideCompound screeningProteinase activitySubstrate specificity
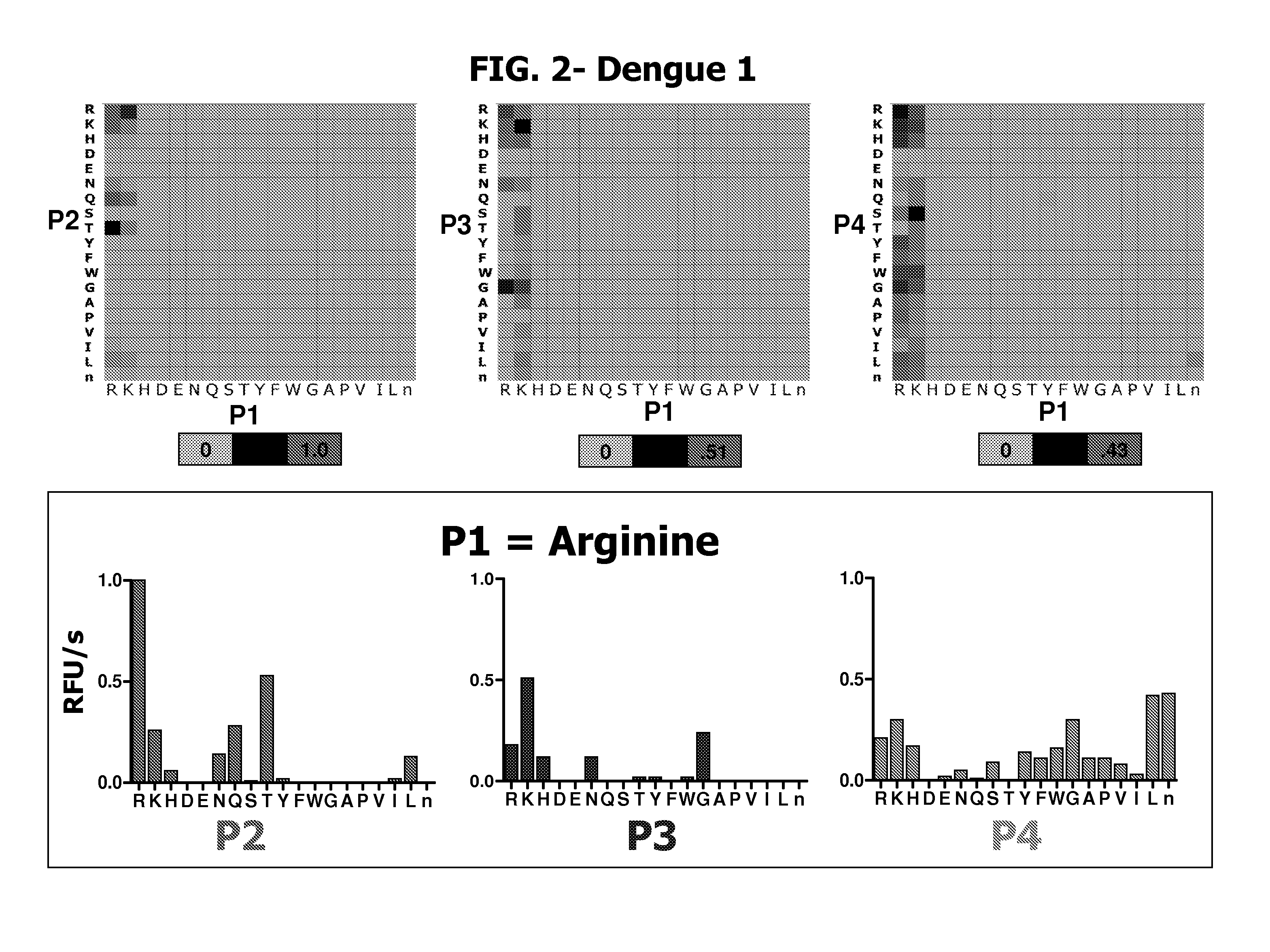
The invention provides substrate specificity profiles for flaviviral proteases (e.g., dengue proteases or West Nile protease). Optimal flaviviral protease substrate sequences, both to the prime side and non-prime side of the flaviviral protease recognition site, are disclosed herein. The flaviviral protease substrate sequences are used in designing substrates, inhibitors, and prodrugs. Flaviviral protease inhibitors based on substrate specificity are also provided.
Owner:IRM
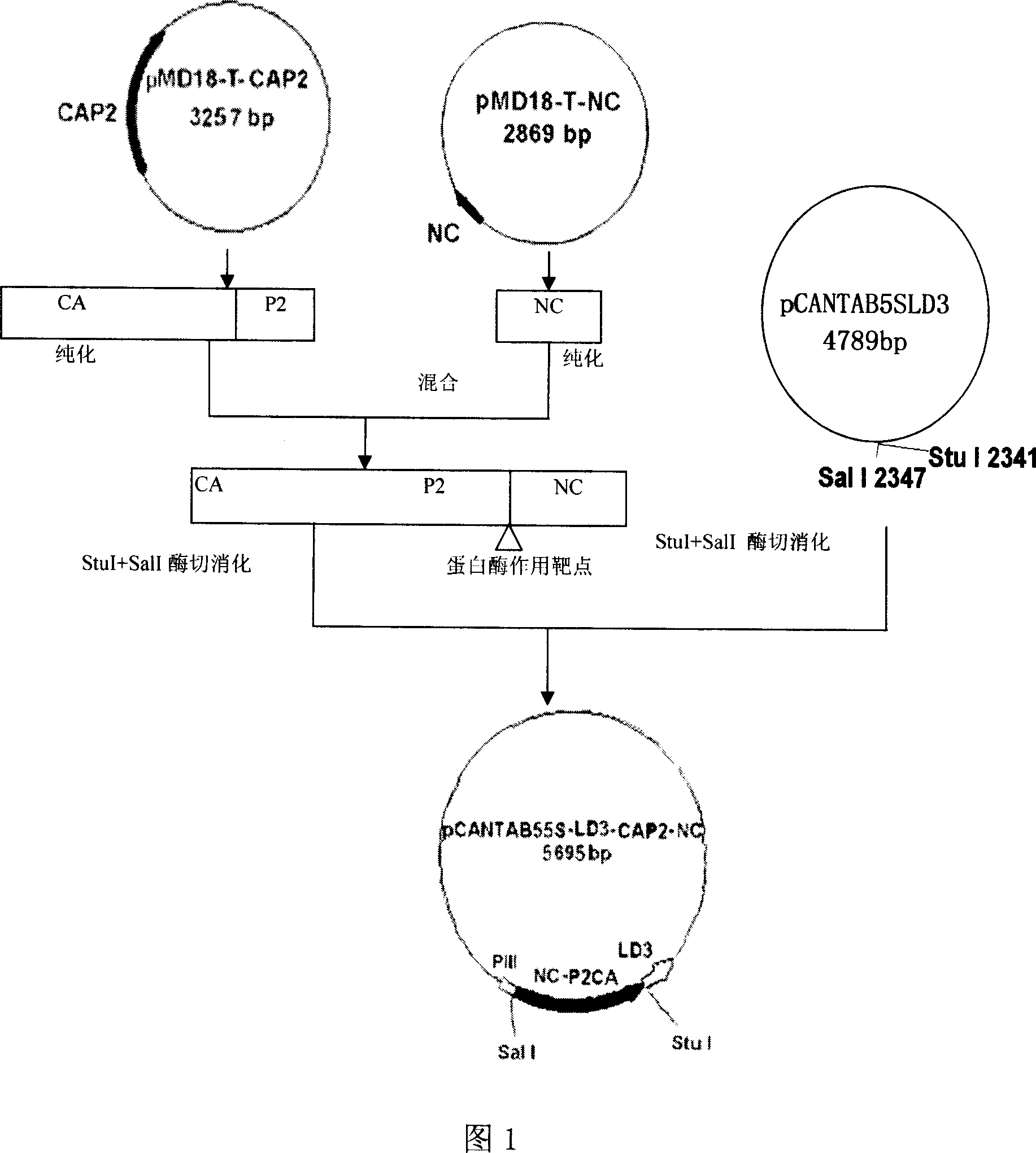
HIV protease substrate molecular with evolution immune globulin binding molecular, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101045748AHigh positive rateImprove screening efficiencyBacteriaVirus peptidesBiologyAmino acid
This invention relates to system construction, preparation method and application of a new type of HIV proteolytic enzyme cutting model. This invention discloses a recomposed HIV proteolytic enzyme substrate molecule that carry with evolution immunoglobulin binding molecule, it is the protein which amino acid sequential showed as SEQ ID NO: 1 or has conservatism variation. This invention also discloses the preparation method and application of above protein, and the preparation method and application of its bacteriophage. This HIV proteolytic enzyme cutting model be able to used in judging HIV proteinase activity, judging sensibility of HIV proteolytic enzyme to proteolytic enzyme depressor drug, and screening HIV proteolytic enzyme depressor drug.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
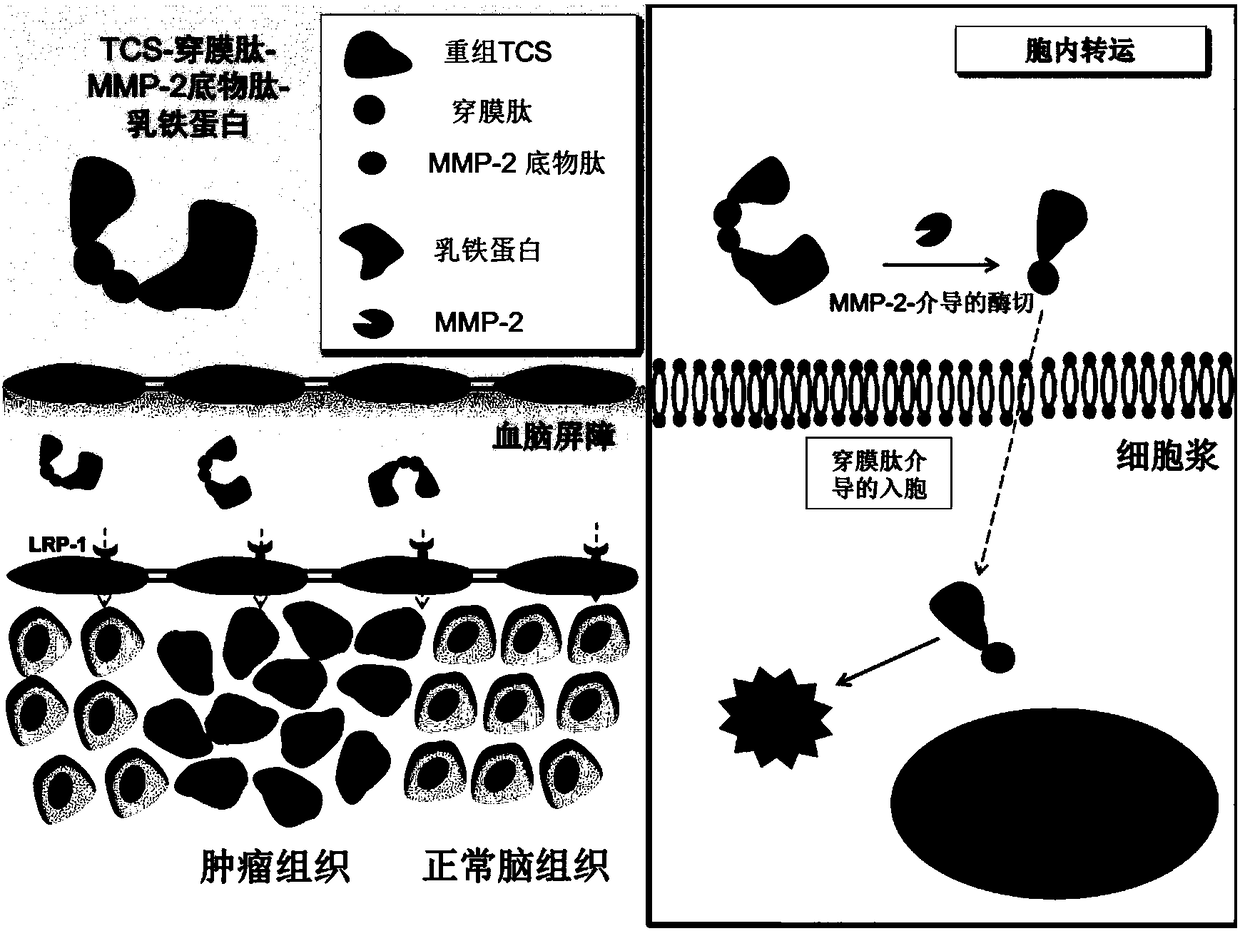
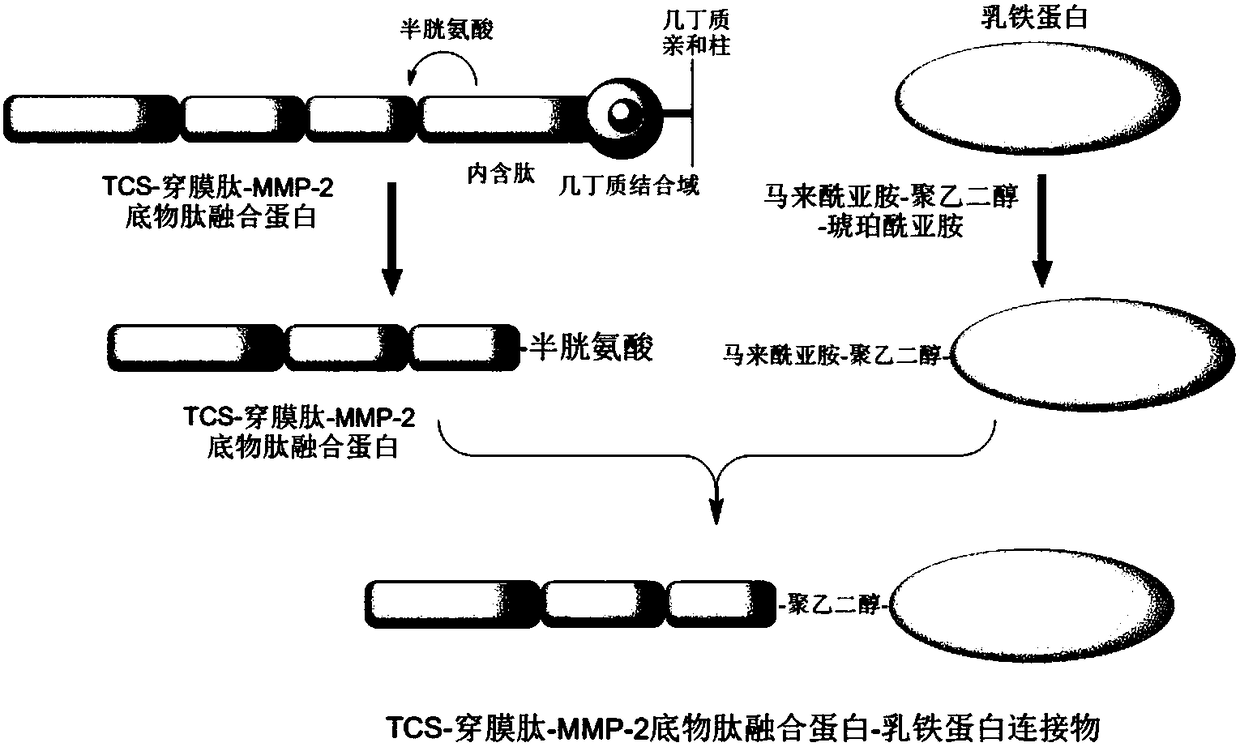
TCS-cell penetrating peptide-tumor protease substrate peptide fusion protein, preparation method and uses thereof
ActiveCN108456254AHigh molecular weightLower metabolismPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsCytotoxicityWilms' tumor
The invention relates to a TCS-cell penetrating peptide-tumor protease substrate peptide fusion protein and a preparation method thereof, further provides a TCS-cell penetrating peptide-tumor proteasesubstrate peptide fusion protein-lactoferrin linker and a preparation method thereof, and further relates to uses of the linker in preparation of drugs for treatment of tumors. According to the present invention, the TCS-cell penetrating peptide-tumor protease substrate peptide fusion protein can increase the cytotoxicity of Trichosanthin on tumor cells, and is used for the treatment of malignanttumors; and the linker can penetrate through the blood-brain barrier and can be accumulated in brain tumors, and can responsively and selectively kill tumor cells with high matrix metalloproteinase-2expression due to the high matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression in tumor cells so as to inhibit the growth of tumors and prolong survival period.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Visualization and quantitiation of cellular cytotoxicity using cell-permeable fluorogenic protease substrates and caspase activity indicator markers
InactiveUS20090263830A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingApoptosis pathwaysT lymphocyte
This invention provides a non-radioactive assay to monitor and quantify the target-cell killing activities mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). This assay is predicated on the discovery that apoptosis pathway activation and, in particular, caspase activity, provides a measure of cytotoxic effector cell activity. In one embodiment, measurement of CTL-induced caspase activation in target cells is achieved through detection of the specific cleavage of fluorogenic caspase substrates. This assay reliably detects antigen-specific CTL killing of target cells, and provides a more sensitive, more informative and safer alternative to the standard 51Cr-release assay most often used to quantify CTL responses. The assay can be used to study CTL-mediated killing of primary host target cells of different cell lineages, and enables the study of antigen-specific cellular immune responses in real time at the single-cell level. As such, the assay can provide a valuable tool for studies of infectious disease pathogenesis and development of new vaccines and immunotherapies.
Owner:ONCOIMMUNIN
Measurement Of Protease Activity In Post-Mortem Meat Samples
InactiveUS20100209943A1Improve accuracyInexpensive meat tenderness determinationElectrolysis componentsMicrobiological testing/measurementPresent methodLiquid medium
The present methods and systems relate to the placement on meat surfaces of a dye-linked protease substrate bonded in a defined location to a solid, porous support. Proteases in the meat hydrolyze the substrate, which then releases the dye, which diffuses away so that the extent of diffusion can be determined by imaging. Alternatively, the amount of dye released can be determined by its mobilization into a liquid medium. The present methods and systems also relates to determining the amount of hydrolyzed protein that is present in post-mortem meat samples. Agents which bond to hydrolyzed proteins, but not to unhydrolyzed proteins, are generated, wherein such agents comprise antibodies or aptamers. Such agents are then used in quantitative assays comprising ELISA tests or lateral flow tests.
Owner:GOLDBERG DAVID +1
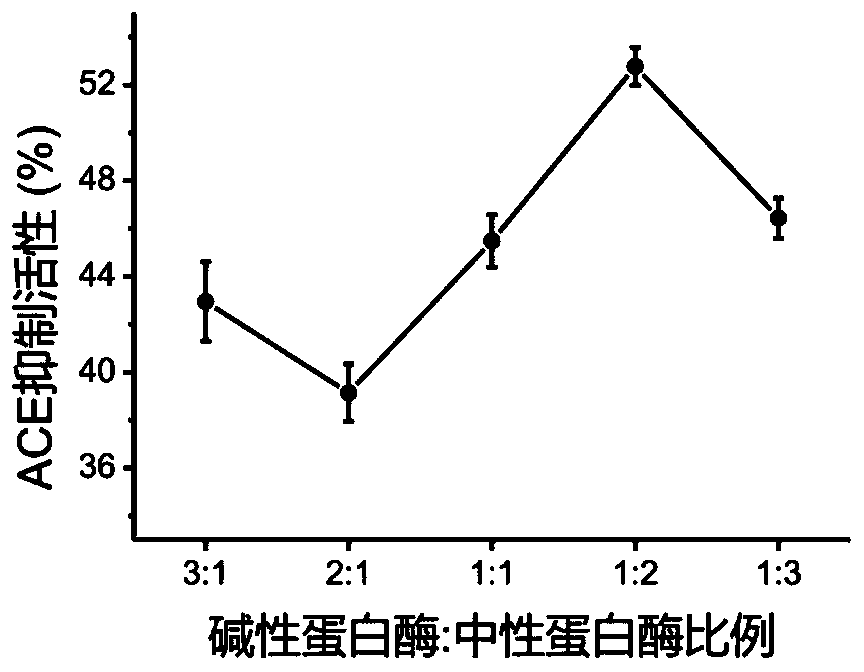
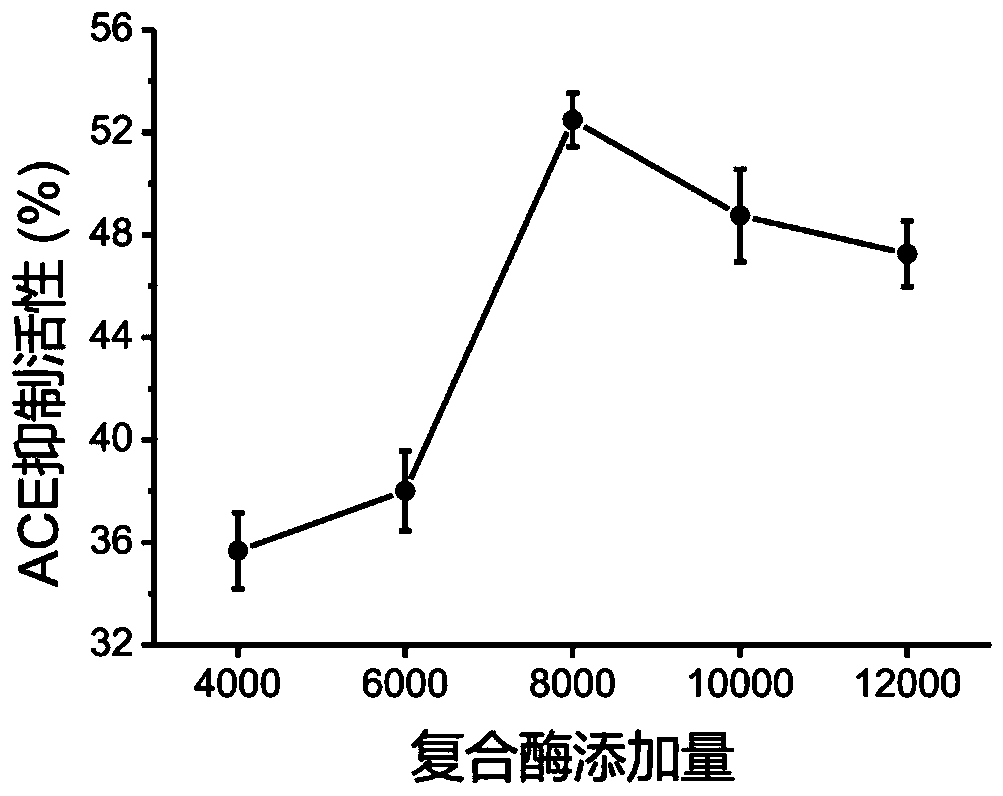
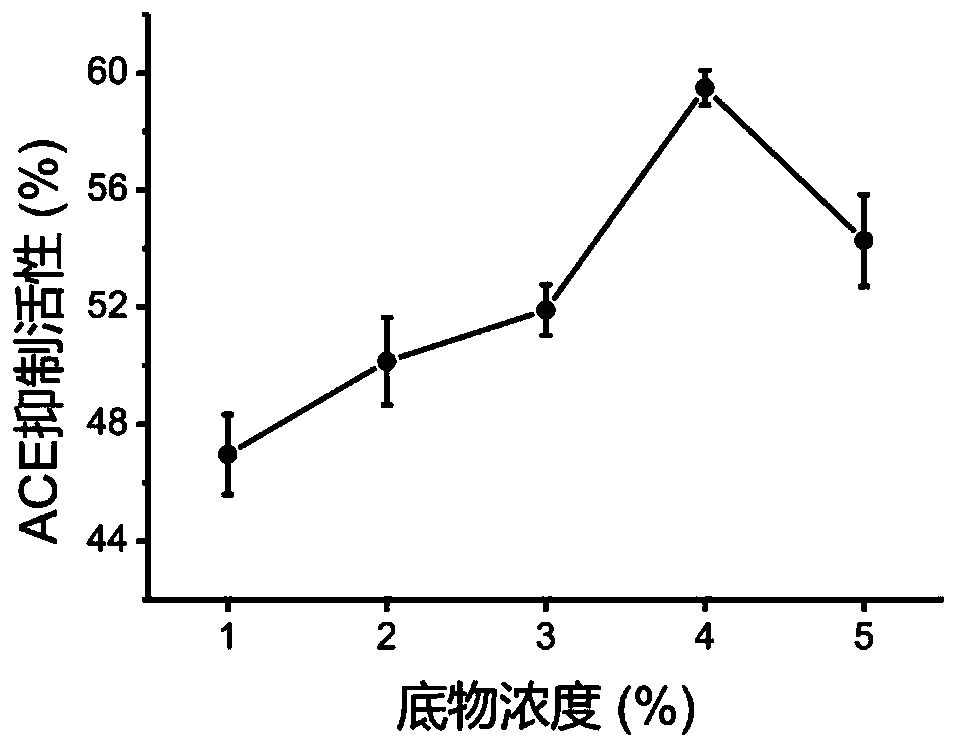
Method for preparing antihypertensive peptide by enzymolysis of walnut meal with compound protease
The invention discloses a method for preparing antihypertensive peptide by enzymolysis of walnut meal with compound protease, which belong to the technical field of food-borne protein deep processing.The protease preparation is screened and compounded, and enzymolysis process conditions are optimized, so that the walnut protein source antihypertensive peptide with high activity is prepared. The optimal process conditions for enzymolysis of walnut protein are as follows: the ratio of compound enzyme is 1: 2 (alkaline protease: neutral protease), the substrate concentration is 4%, the enzymolysis temperature is 45 DEG C, a pH value is 8.0, the enzyme addition amount is 8000U / g, and the enzymolysis time is 60min. The properties of polypeptide products are compared and analyzed, the relativemolecular mass of the products is mainly concentrated within a range of 0-2 kDa, good normal-temperature storage stability and in-vitro digestion stability are achieved, and a theoretical basis is provided for industrial production and practical application of the products.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Fluorogenic protease substrates based on dye-dimerization
InactiveUS20050089946A1Rapid and convenient homogeneous approachImprove accuracyPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme assayQuenching
A method of biological assay comprises the steps of providing an enzyme substrate comprising two fluorescence dye groups bound to a flexible peptide, the dye groups being of proximity sufficiently close so as to allow free energy attractions to draw the dyes together to essentially self-quench fluorescence of the dye groups, wherein self quenching of fluorescence of the dye groups is effected by dye dimerization or stacking, and enzymatically cleaving the peptide to release the fluorescence dye groups from dye dimerization or stacking, thereby producing an increase in fluorescence intensity. A protease substrate for use in the method of the invention is also disclosed. This invention finds use in detection and identification of microorganisms, sterilization assurance, pharmaceutical discovery, enzyme assays, immunoassays, and other biological assays.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Sterility indicating biological compositions, articles and methods
InactiveUS20140370535A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSporeProteinase activity
A sterility indicating composition comprising a plurality of sterilization process resistant spores which contain an active protease during germination and initial outgrowth of the spores; and a germination medium comprising at least one labeled protease substrate and at least one nutrient for germination of the spores; wherein the medium is essentially free of a) any active protease other than the active protease contained by the plurality of spores and b) any protease substrate other than the at least one labeled protease substrate, other than any protease substrate originating from the plurality of spores, and other than any protease substrate which does not compete with the labeled protease substrate for the active protease; and wherein the at least one labeled protease substrate comprises a peptide which can be cleaved by the active protease and which is labeled with one or more dye groups, at least one of which undergoes a detectable change when the peptide is cleaved by the active protease, and wherein the labeled protease substrate is stable at least at a temperature for incubating the spores, a sterilization process indicator comprising the composition, and a method of determining the effectiveness of a sterilization process using the composition and indicator are disclosed.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com