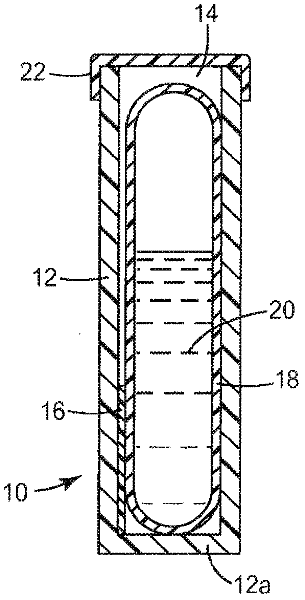
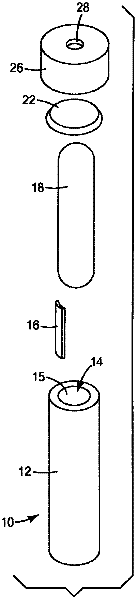
Sterility indicating biological compositions, articles and methods
A technology of sterilization indication and composition, which is applied in the fields of biochemical equipment and methods, enzyme production/bioreactor, and microorganism determination/inspection, etc., and can solve problems such as excessive time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0171] Spore suspension
example 1
[0174] Protease detection
[0175] Dilutions of the spore suspension of G. stearothermophilus were made in sterile rinse water (Baxter, Deerfield, IL). The resulting diluted spore preparation (1 μL) was diluted with 1×10 6 spores, 1×10 5 spores, 1×10 4 spores, 1×10 3 The final population of 0 and 0 spores was assayed in a plate reader as described below. The spores were dried for 20 minutes in a 37°C incubator. The spores were then rehydrated in 100 uL of medium consisting of: 50 uL of GFK (1 mg / mL glucose, 1 mg / mL fructose, 3.3 mg / mL potassium chloride), 25 uL of Tris buffer (containing 0.2 mM CaCl) and 25 uL of 4 mg / mL labeled protease substrate (Calbiochem, casein labeled with N-(resorufin-4-carbonyl)piperidine-4-carbonic acid, protease substrate (EMD Chemicals, Gibbstown, NJ) ). Each resulting mixture was added to the wells of the plate. Plates were then placed in a preheated Synergy 4 plate reader (BioTech, Winooski, VT) at 50°C and incubated for 480 minutes. D...
example 2
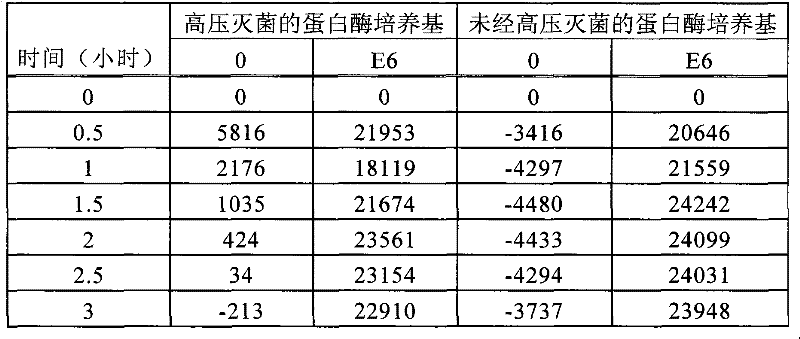
[0180] Stability of Labeled Protease Substrates to Exposure to Sterilization Temperatures
[0181] Dilutions of the spore suspension of G. stearothermophilus were made in sterile rinse water (Baxter, Deerfield, IL). The resulting diluted spore preparation (1 μL) was diluted with 1×10 6 The final populations of spores and 0 spores were tested. The spores were dried for 20 minutes in a 37°C incubator. The spores were then rehydrated in 100 uL of medium consisting of: 50 uL of GFK (1 mg / mL glucose, 1 mg / mL fructose, 3.3 mg / mL potassium chloride), 25 uL of Tris buffer (containing 0.2 mM CaCl) and 25uL of the 4mg / mL labeled protease substrate as in Example 1, the culture medium was previously carried out at 121° C. for 15 minutes in an AMSCO Scientific SG-120 Eagle / Century Series steam sterilizer (Steris, Mentor, OH). (250°F) vacuum assisted circulation. At the same time, a culture medium not subjected to sterilization conditions (non-autoclaved protease medium) was tested as...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com