Application of protease graph electrophoresis detection method to rapid identification of extracellaluar protease variety of bacteria
A detection method, protease technology, applied in the field of identification of protease species, can solve problems such as unintuitive results, and achieve the effect of saving cumbersome steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
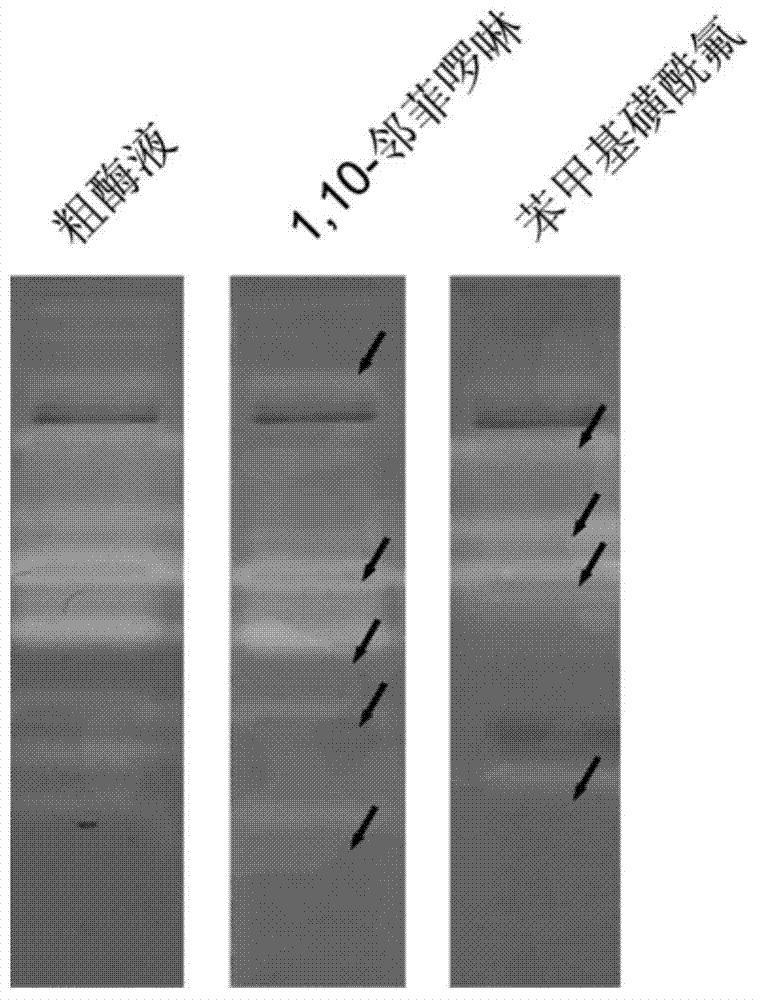
[0042]Example 1: Using the method of the present invention to detect the extracellular protease of Pseudoalteromonas sp. SJN2. Pseudoalteromonas sp. SJN2 is a strain isolated from sea sand in the intertidal zone of Haikou Holiday Beach in our laboratory.
[0043] Proceed as follows:
[0044] (1) Streak-inoculate Pseudoalteromonas on solid medium, activate and culture at 18°C for 48h, then inoculate in 5ml liquid LB medium, shake and culture at 18°C and 200rpm for 24h, then press 5% (v / v) inoculum was inoculated into 100ml of fermentation medium, cultured with shaking at 18°C and 200rpm for 4 days, and centrifuged at 10000rpm to obtain a fermentation broth;
[0045] The above-mentioned solid medium components are as follows, all in parts by weight:
[0046] 1 part of peptone, 0.5 parts of yeast powder, 1.5 parts of agar, 100 parts of distilled water, pH 7.5-8.0;
[0047] The components of LB medium are as follows, all in parts by weight:
[0048] 1 part of peptone, 0....
Embodiment 2
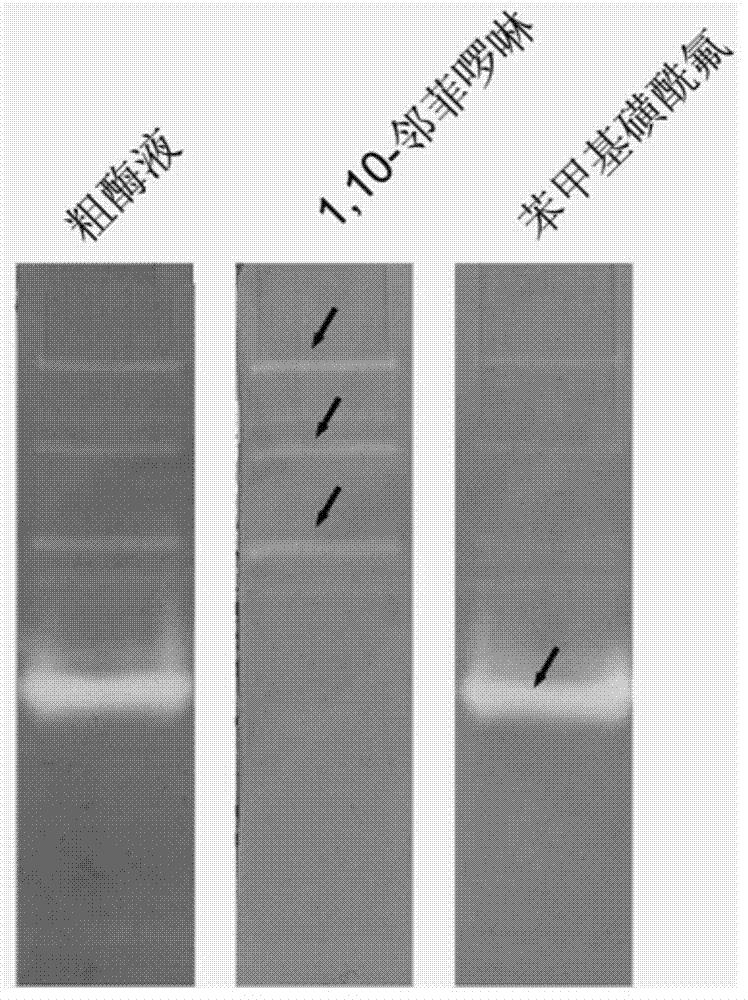
[0055] Example 2: The steps of detecting the extracellular protease of marine bacteria (Bacillus sp.SQN6-1) by the method of the present invention are the same as in Example 1, and the fermentation and cultivation time is 72 hours. Marine Bacillus sp.SQN6-1 is a strain isolated from Haikou Holiday Beach seawater in our laboratory. Step is with embodiment 1. Protease bands such as figure 2 shown. OP specifically binds divalent metal ions and can inhibit the activity of metalloproteases. PMSF is a serine protease inhibitor, so it can be obtained from figure 2 It is clearly seen in the figure that 3 of them are serine protease bands, because the active bands disappear after adding PMSF, and 1 is a metalloprotease, and the degradation band disappears on the active electrophoresis map containing OP, indicating that it is strongly inhibited by OP , loss of enzymatic activity.
Embodiment 3
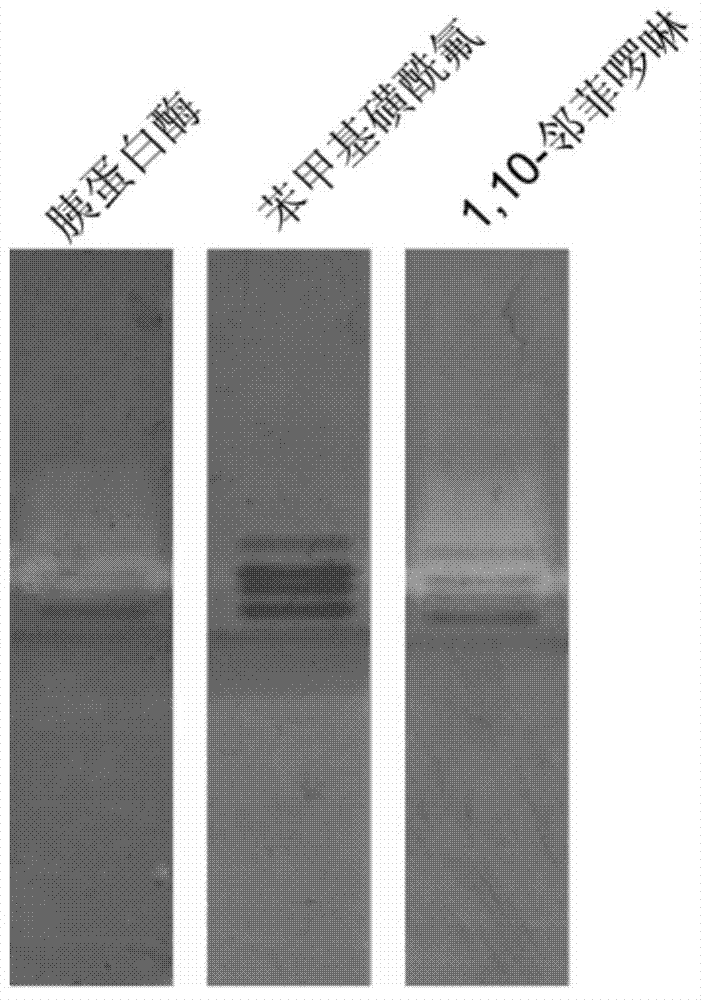
[0056] Embodiment 3: The operation steps of using the method of the present invention to detect trypsin Trypsin are the same as in Example 1, except that the commercial enzyme preparation purchased by Shanghai Sangong, trypsin Trypsin, is used. The purpose of this experiment is to establish an experimental method. Protease is a typical serine protease, which can be inhibited by PMSF inhibitor, but inhibitor OP has no effect on its enzyme activity. Trypsin bands such as image 3 shown. Trypsin is a typical serine protease. When the substrate solution is added with PMSF, its active bands completely disappear after incubation, while the degradation bands on the active electrophoresis spectrum containing OP do not change.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com