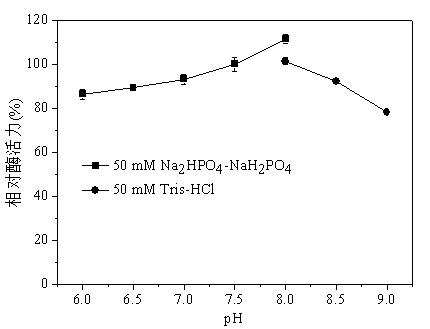
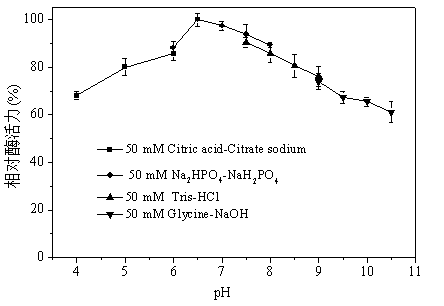
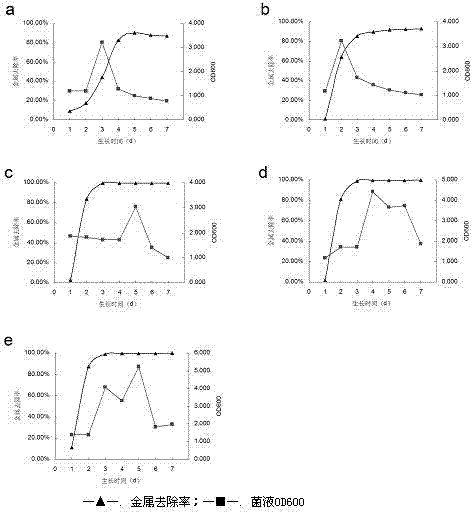
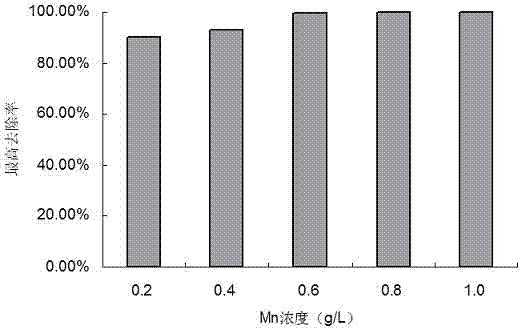
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
80 results about "Achromobacter xylosoxidans" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
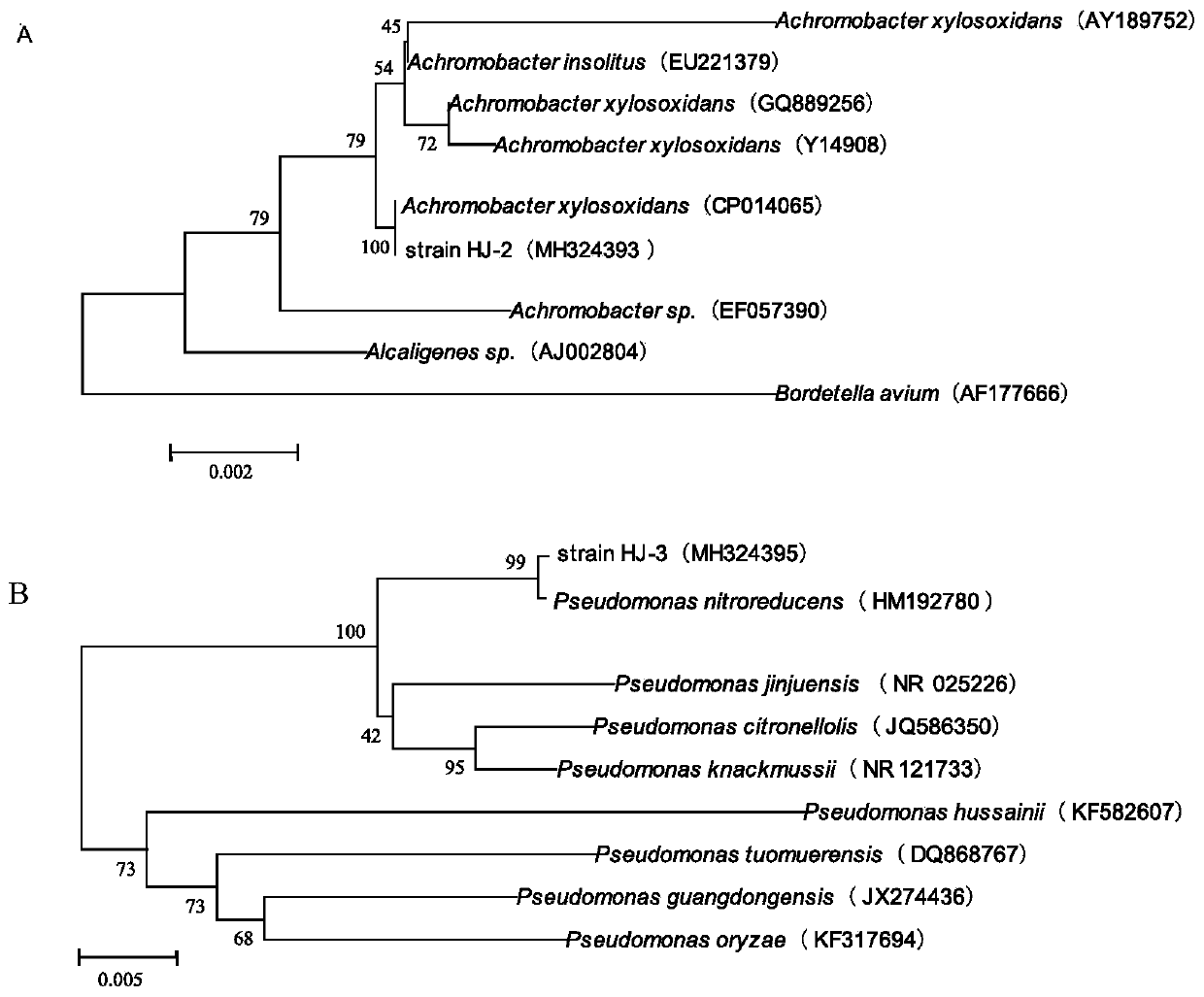
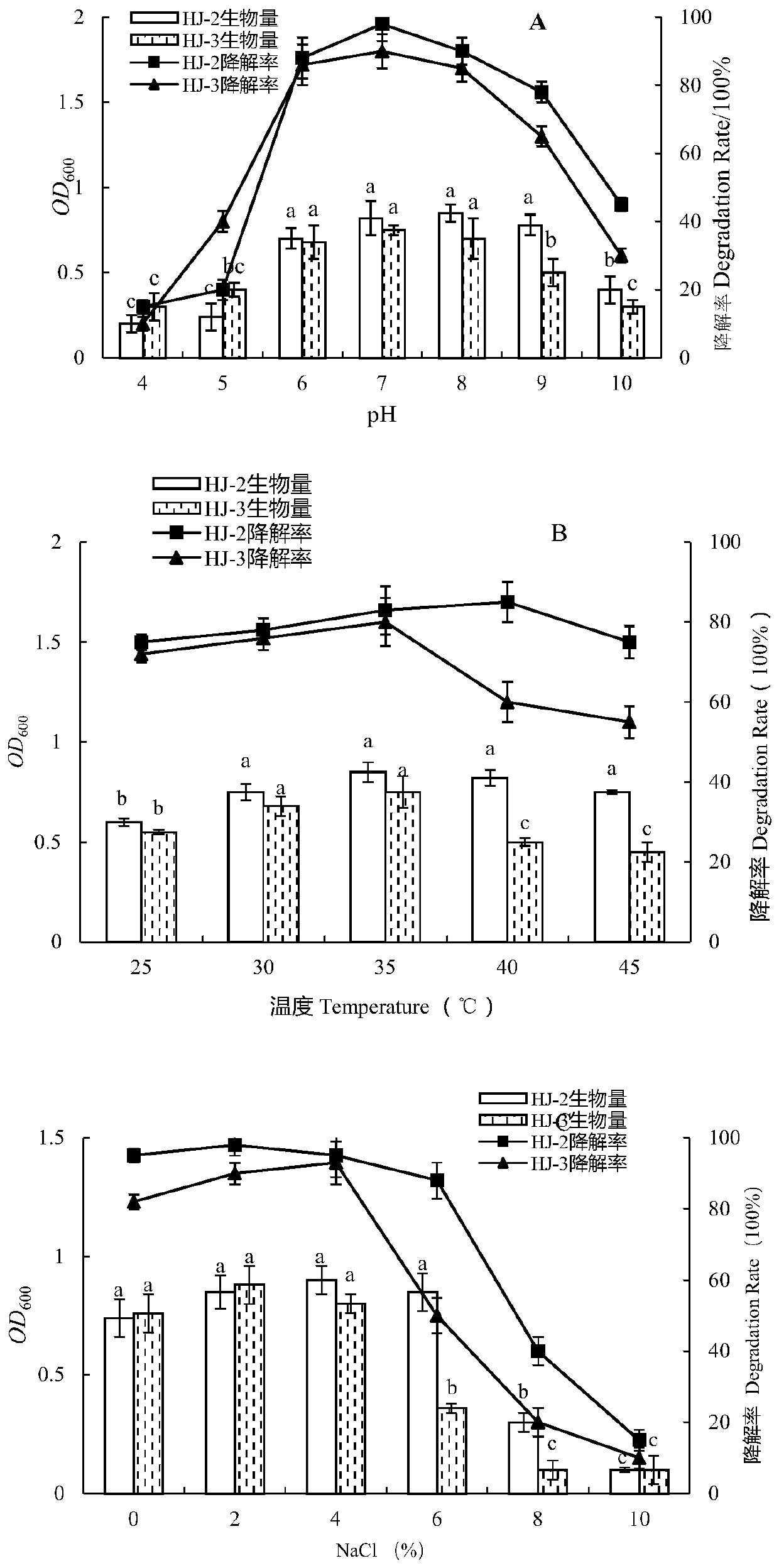
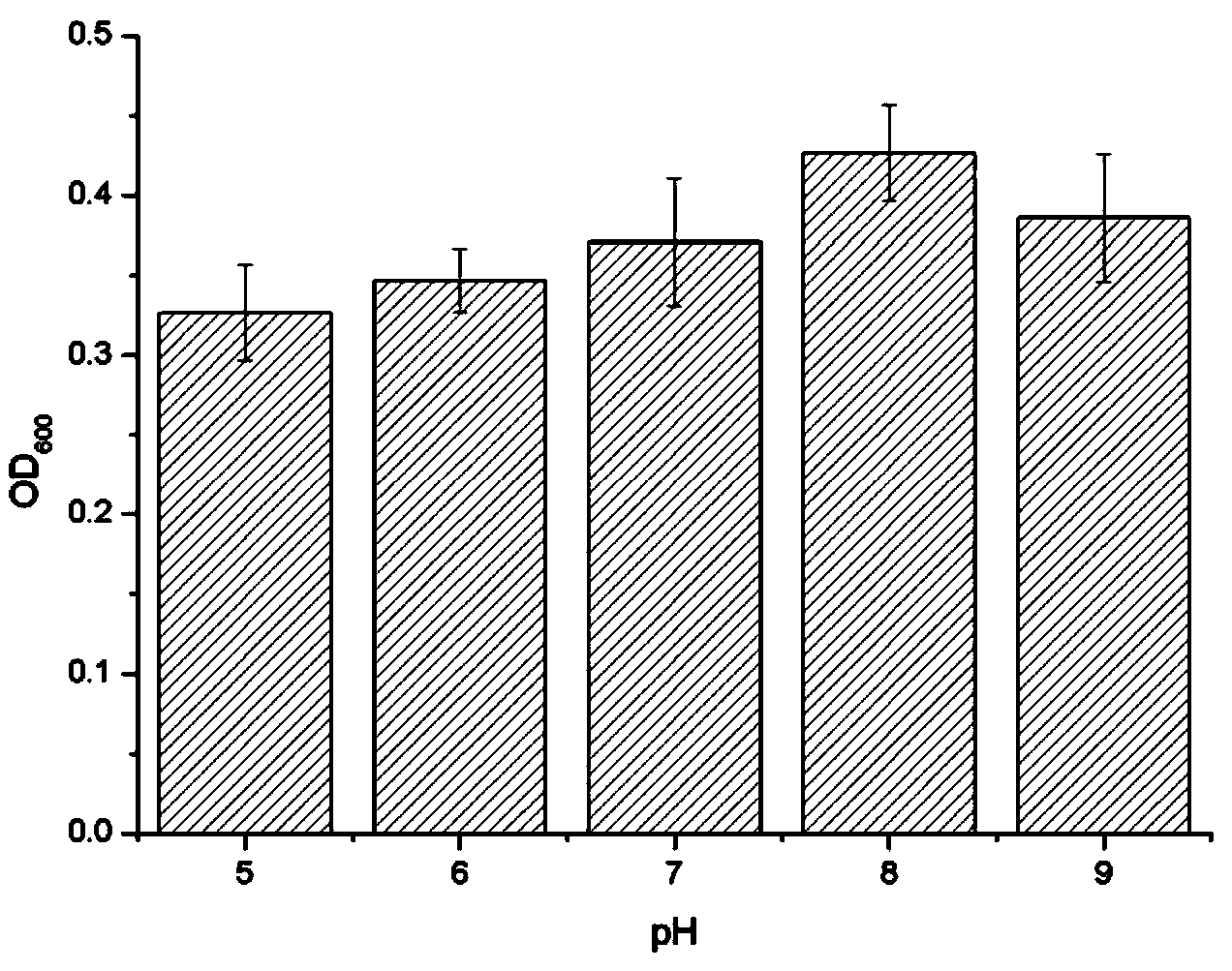
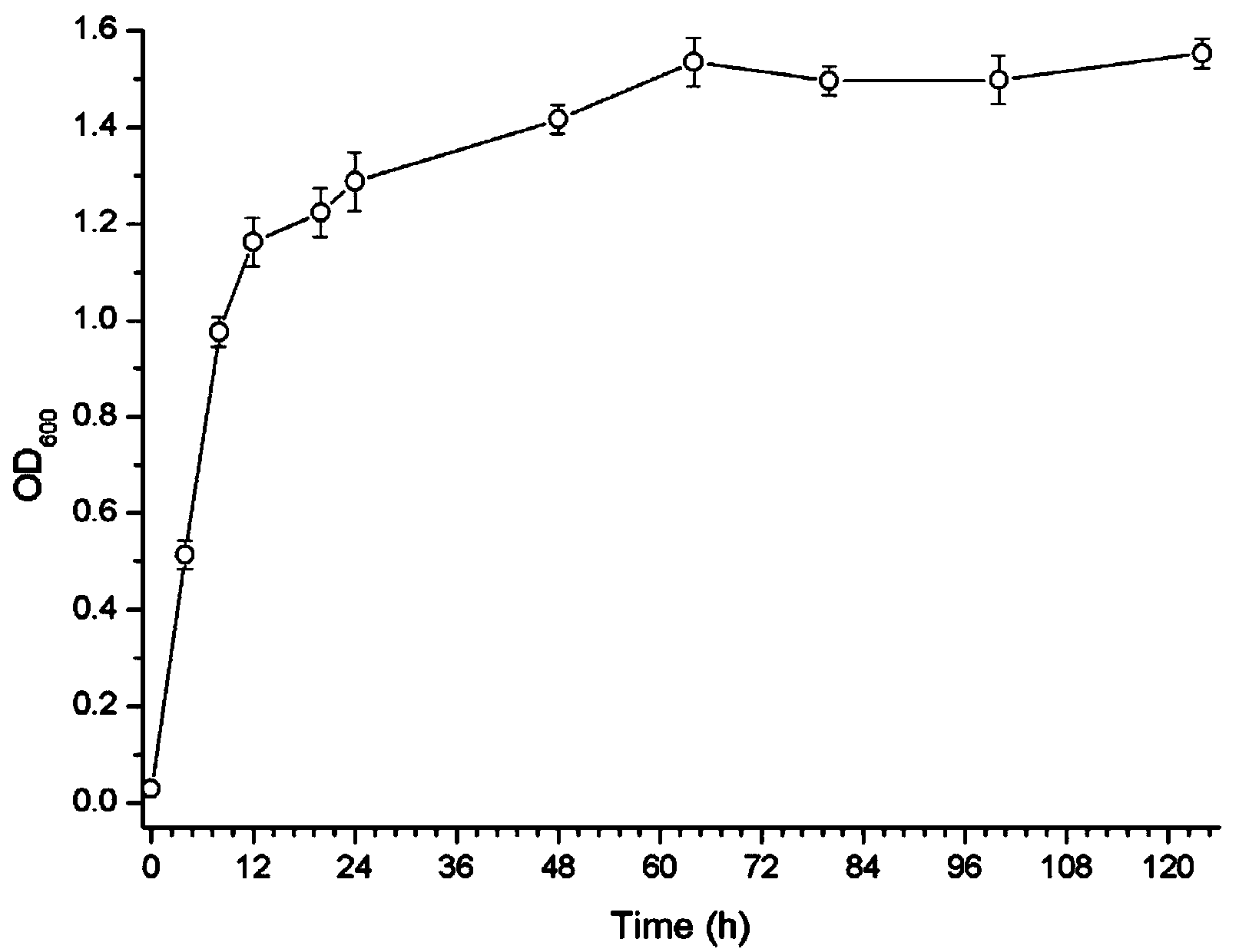
Achromobacter xylosoxidans (formerly Alcaligenes xylosoxidans) is a Gram-negative, aerobic, oxidase and catalase-positive, motile bacterium with peritrichous flagella, from the genus Achromobacter. It is generally found in wet environments. Achromobacter xylosoxidans can cause infections such as bacteremia, especially in patients with cystic fibrosis. In 2013, the complete genome of an A. xylosoxidans strain from a patient with cystic fibrosis was sequenced.
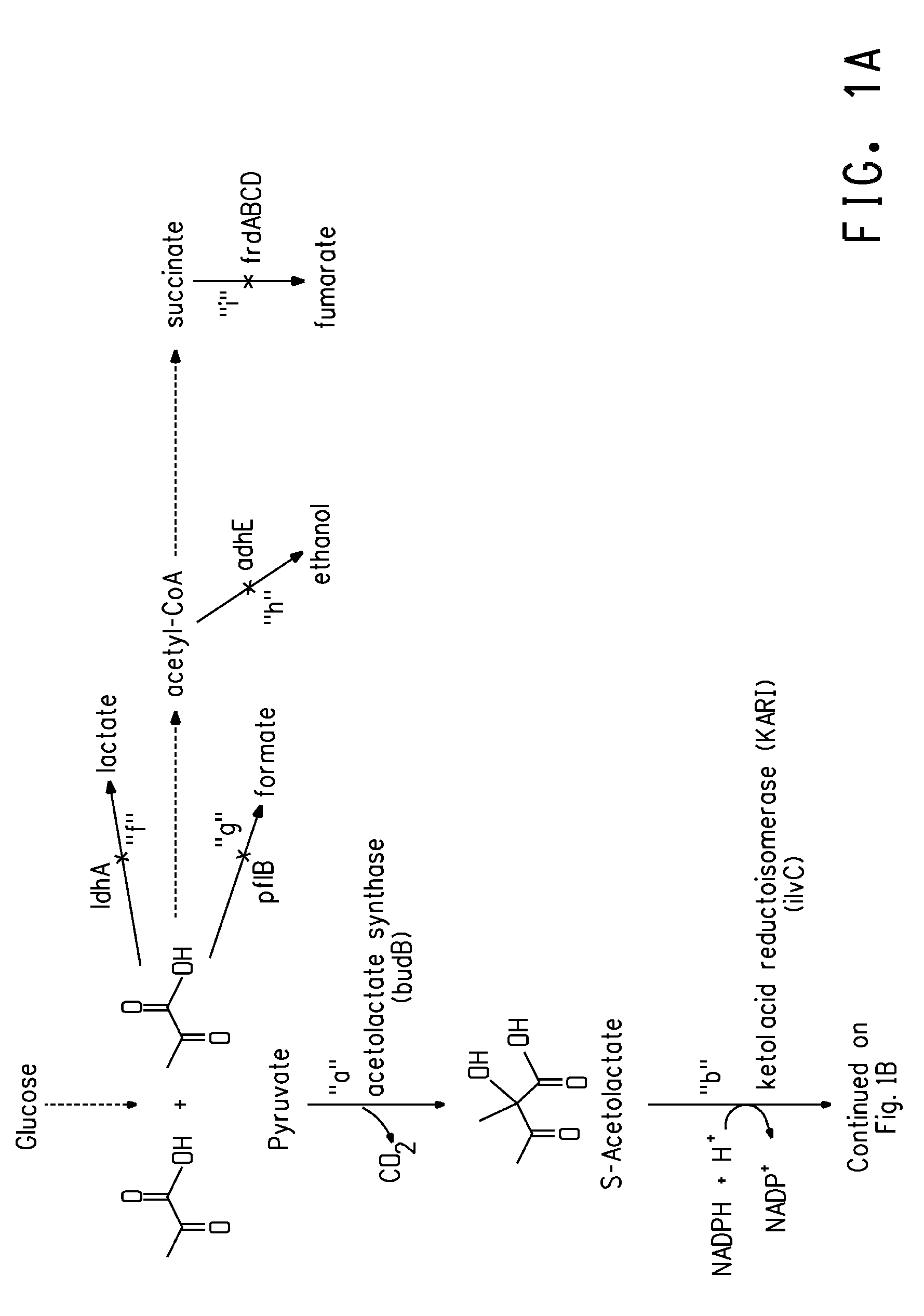
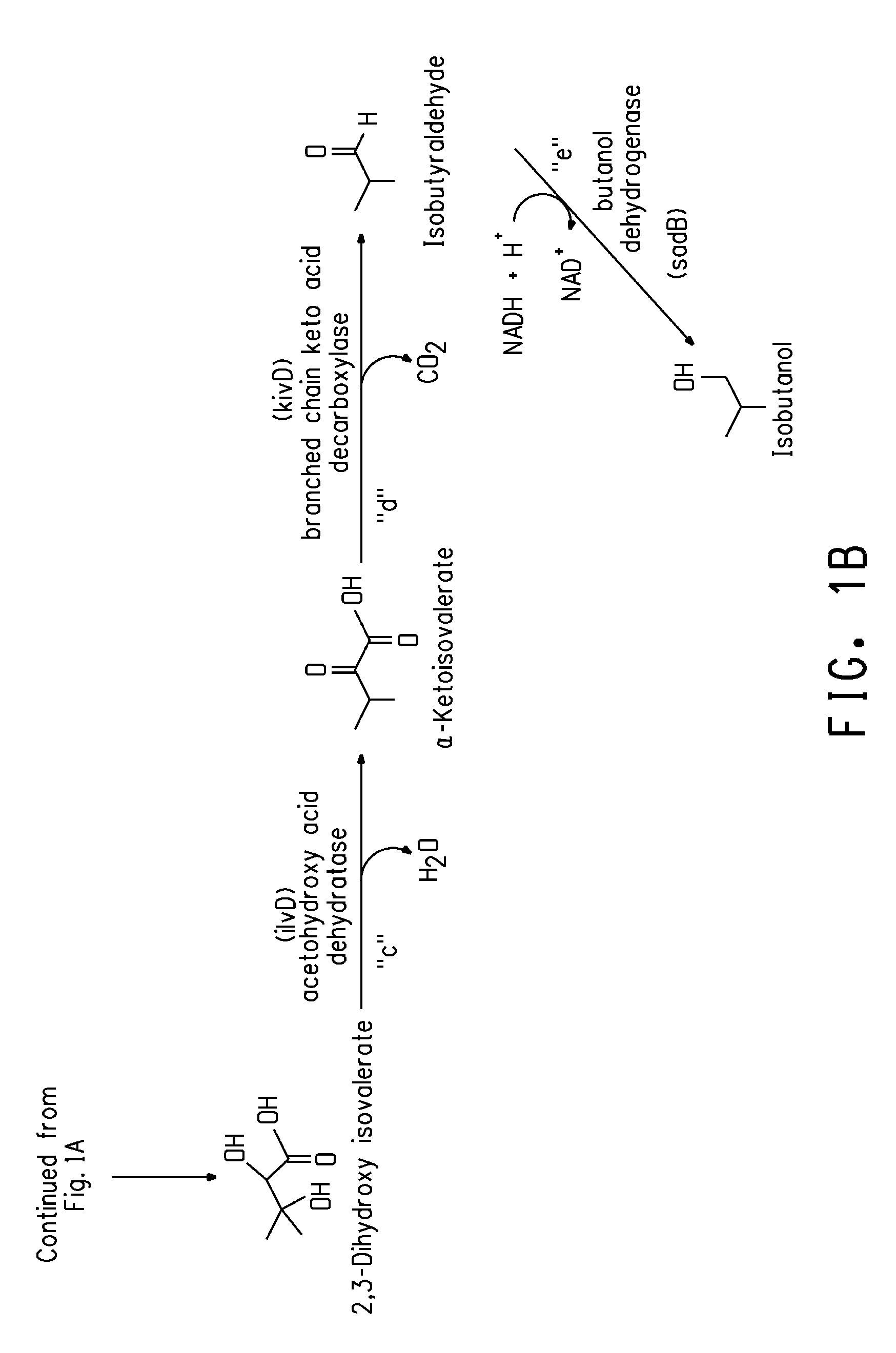
Deletion mutants for the production of isobutanol
An E. coli host strain was engineered wherein genes adhE, IdhA, frdB, and pfIB were disrupted and novel butanol dehydrogenase gene, sadB, from Achromobacter xylosoxidans, was added to produce the isobutanol production host.
Owner:BUTAMAXTM ADVANCED BIOFUELS
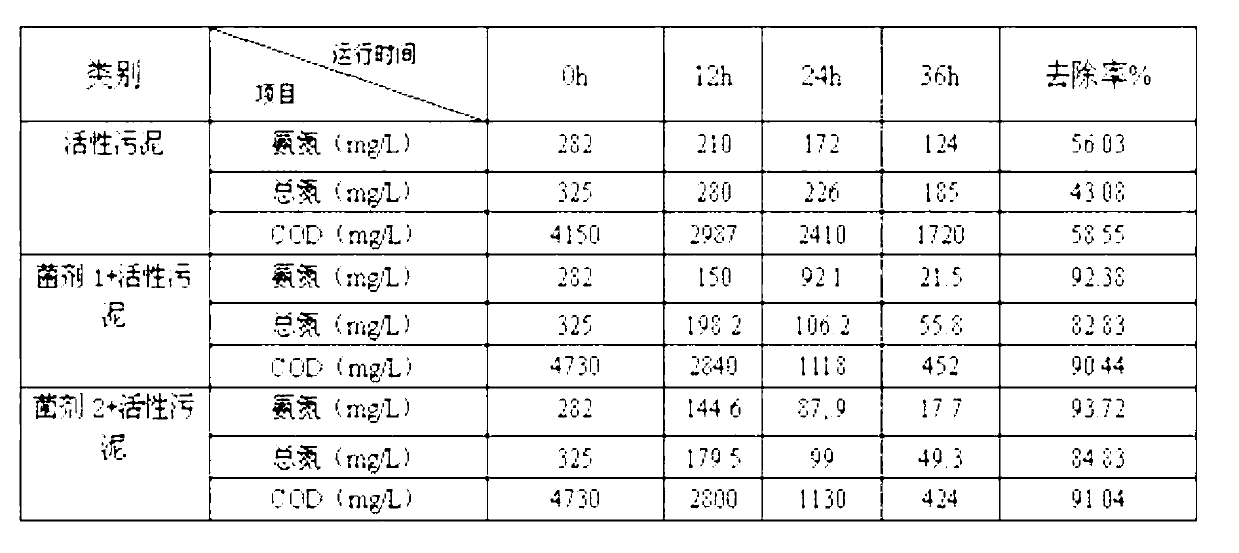
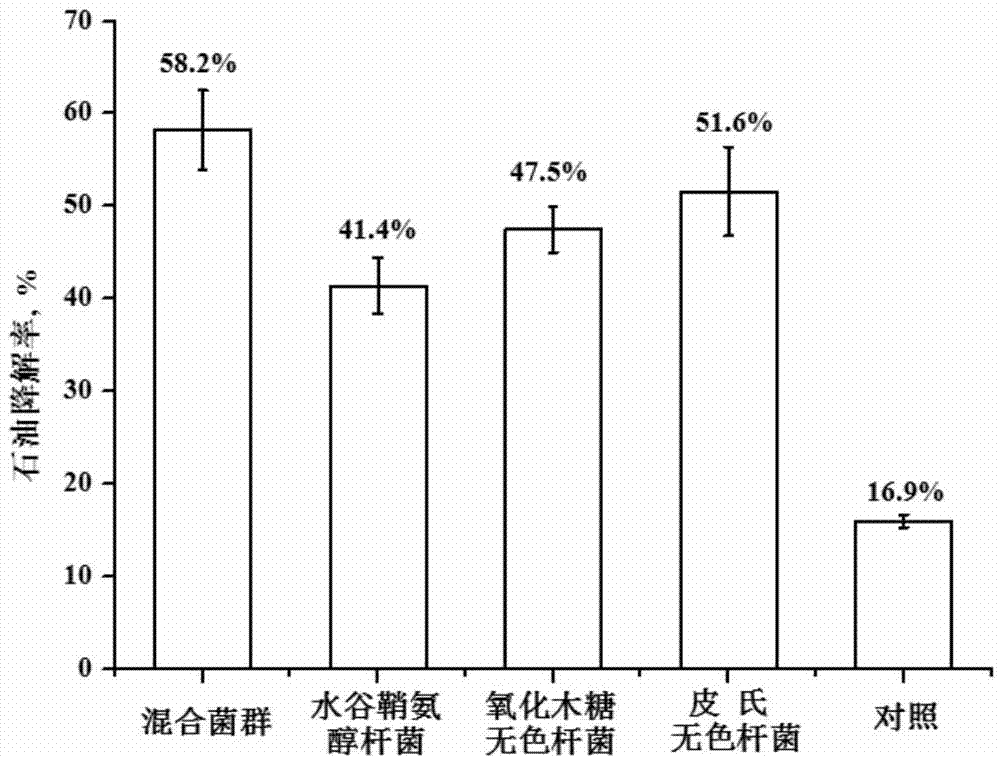
Microorganism composite bacterial agent for restoration of saline alkali soil polluted by petroleum
InactiveCN102453678ANo secondary pollutionPollution fitBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationAlkali soilBacillus megaterium
The invention relates to a microorganism composite bacterial agent applicable to the restoration of saline alkali soil polluted by petroleum, and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of environment protection. The bacterial agent mainly comprises the following 3 components: composite microorganism bacterial liquid, nutrients, and a surfactant. The composite microorganism bacterial liquid is obtained by performing liquid culture of 3 petroleum hydrocarbon degrading bacteria of bacillus megaterium P9 strains (with a preservation number of CGMCC No. 4270), pseudomonas sp. P4 strains (with a preservation number of CGMCC No. 4269), and achromobacter xylosoxidans P2 strains (with a preservation number of CGMCC No. 4268) to obtain microorganism bacterial strains, and mixing the strains with the nutrients. The bacterial strains are preserved at China microorganism strain preservation management committee general microbiological center. The composite microorganism bacterial liquid, the nutrients and the surfactant are mixed according to a ratio of 30-200:1-2:0.2-0.5 so as to obtain the microorganism composite bacterial agent. The microorganism composite bacterial agent prepared by the invention has high removing efficiency for petroleum pollution in saline alkali soil, can both reduce the pH value of the saline alkali soil, and improve soil physical and chemical properties.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
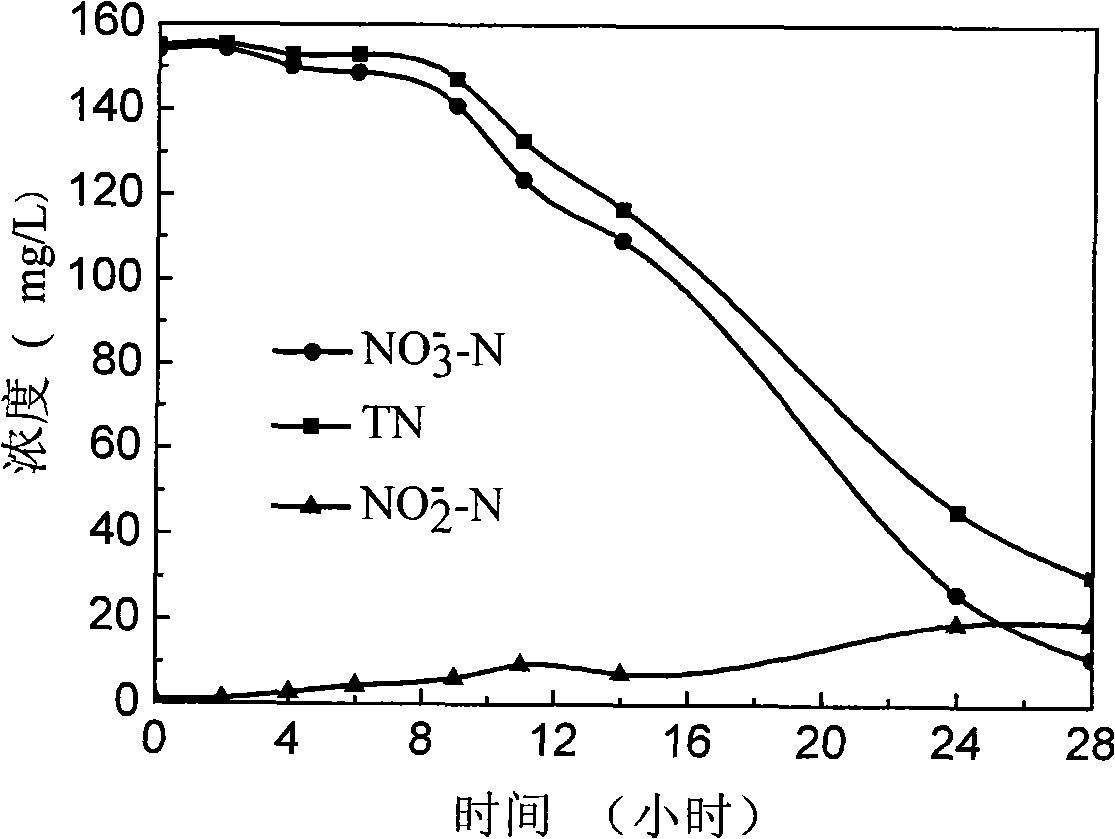
Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain for biological denitrificaion and application thereof
InactiveCN101560486ASimple processLow costBacteriaWater contaminantsAchromobacterMicrobiological culture
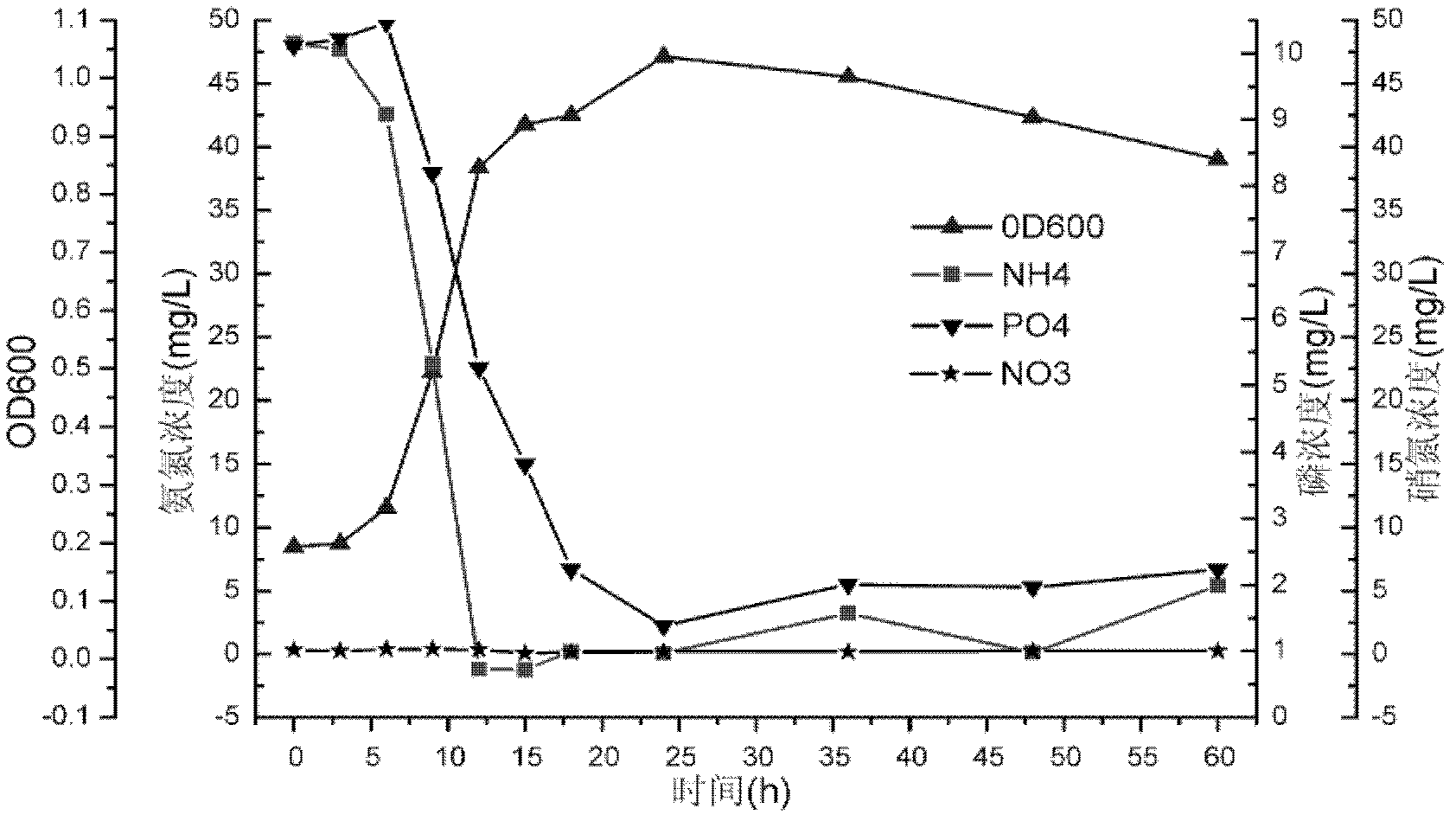
The invention discloses an achromobacter xylosoxidans strain for biological denitrificaion and application thereof. The achromobacter xylosoxidans strain GAD3 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC for short) with preservation number CGMCC No. 2964 in March 19th, 2009. The strain is added to nitrogenous effluent with 2 to 6mg / L of dissolved oxygen to realize biological denitrificaion. The strain not only has the capability of heterotrophic nitrification, but also has the capability of aerobic denitrification. In the process of treating the nitrogenous effluent, only one aerobic stage is needed, the denitrification efficiency is high, and the operation is convenient and quick; and compared with the conventional biological denitrification process, the application has huge economic benefits.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
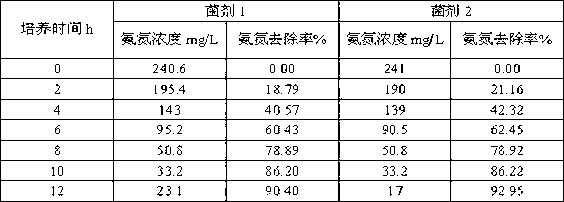
Achromobacter xylosoxidans subsp.xylosoxidans LH-N25 and heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification microorganism bactericide and preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN103122332ASolve the difficult removal of total nitrogenFacilitate large-scale production applicationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesToxic materialTotal nitrogen
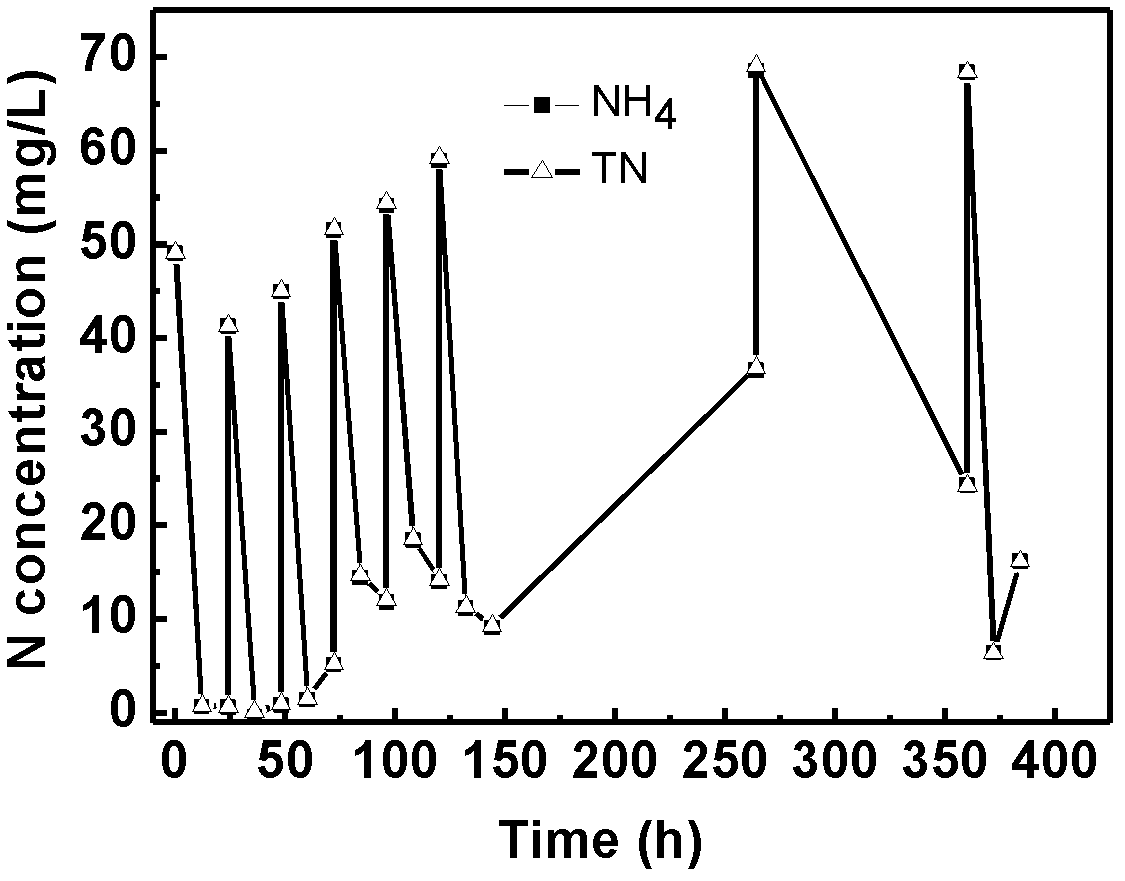
The invention discloses achromobacter xylosoxidans subsp.xylosoxidans LH-N25 with CGMCC No.6972. The invention also discloses a heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification microorganism bactericide. The microorganism bactericide comprises achromobacter xylosoxidans subsp.xylosoxidans LH-N25 or also comprises paracoccus aminovorans LH-N40; and the strains are combined according to any ratio. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the microorganism bactericide. The microorganism bactericide disclosed by the invention not only can solve the problem that total nitrogen cannot be easily removed in the traditional reactor, but also can effectively remove ammonia nitrogen and total nitrogen in a water body in the same reactor, and has tolerance and degradation ability on the toxic substances such as phenols, amines, hetercyclics, cyanogens and polyaromatic hydrocarbon in the wastewater at the same time. The microorganism bactericide is especially suitable for chemical wastewater containing nitrogen, is simple in treatment process, stable in effect, and resistant to impact of environmental toxic substances, and has a wide application prospect in treatment of chemical wastewater containing nitrogen.
Owner:BLUESTAR LEHIGH ENG INST CO LTD
Autotrophic and allotrophic symbiosis ammonia oxidation bacterial agent as well as culture method and application thereof
ActiveCN101831392AConversion efficiency is not affectedPromote growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAchromobacter xylosoxidansAmmonia
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental organisms and particularly relates to an autotrophic and allotrophic symbiosis ammonia oxidation bacterial agent for treating ammonia-nitrogen wastewater as well as a culture method and application thereof. The autotrophic and allotrophic symbiosis ammonia oxidation bacterial agent is prepared by mixing culturing nitrosomonas Nitrosomonas sp.N-1, pseudomonas Pseudomonas sp.He-X, thermomonas Thermomonas haemolytica D-2 and achromobacter Achromobacter xylosoxidans C-1 and is used for treating ammonia-nitrogen wastewater. The invention has the advantages of wide adaptation range, strong stability, environmental and toxic impact resistance and the like.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
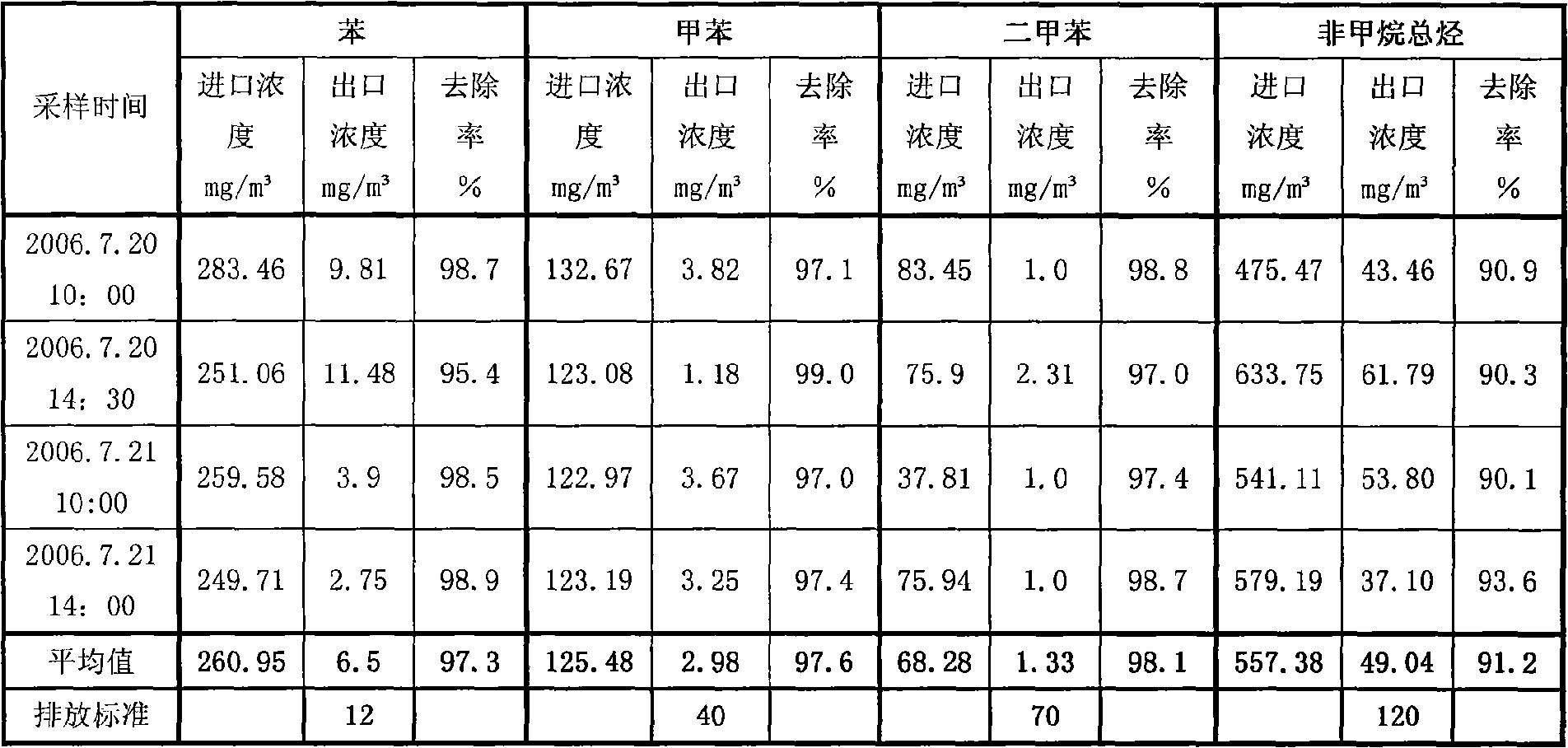
Culture method of biological cleaning strains in low-concentration volatile mixed organic waste gas
The invention relates to a culture method of biological cleaning strains in low-concentration volatile mixed organic waste gas. The method comprises the following steps: a), culturing a first strain; b), carrying out the combined inoculation of the first strain and a second strain and using tap water to prepare the sludge concentration of the mixed strains; and c), using mixed organic matter in the waste gas as a substrate to be cast into an insition culture medium so as to culture and train insitions. The first strain is prepared by culturing and training from activated mud taken from a printing and dyeing sewage treatment plant and is a mixed strain of flavobacterium and Bacillus cereus, and the second strain is prepared by collecting activated mud collected from a secondary sedimentation tank of a petrochemical sewage treatment plant and is a mixed strain comprising the flavobacterium, the Bacillus cereus, xylose oxidase Achromobacter and Pseudomonas stutzeri. The method facilitates the balanced growth of various cultured microorganisms and can simultaneously decompound various target configuration compounds at high efficiency.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HUANFA ENVIRONMENTAL ENG CO LTD
Straw-decomposition composite microbial preparation and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103194407AAccelerate the rate of decayIncrease productionFungiAgriculture tools and machinesBacillus megateriumDecomposition
The invention relates to a straw-decomposition composite microbial preparation and a preparation method thereof. The straw-decomposition composite microbial preparation disclosed by the invention is prepared by mixing bacillus weihenstephanensis, bacillus amyloliquefaciens, bacillus megaterium, staphylococci, achromobacter xylosoxidans and aspergillus niger according to certain mass percent, is suitable for directly returning all rice straws to the field, can outstandingly accelerate the decomposition speed of straws, is favorable to transferring the transplanting stubble, can increase the organic content, enhance the soil enzyme activity, improve the soil physicochemical property and enhance the rice yield in a next season, and can also improve the soil, enhance the water and fertilizer utilization ratio, reduce the fertilizer, increase the efficiency, reduce the pollution of straw incineration on the environment and achieve the outstanding integrated benefit.
Owner:南昌市亿隆达生物科技开发有限公司
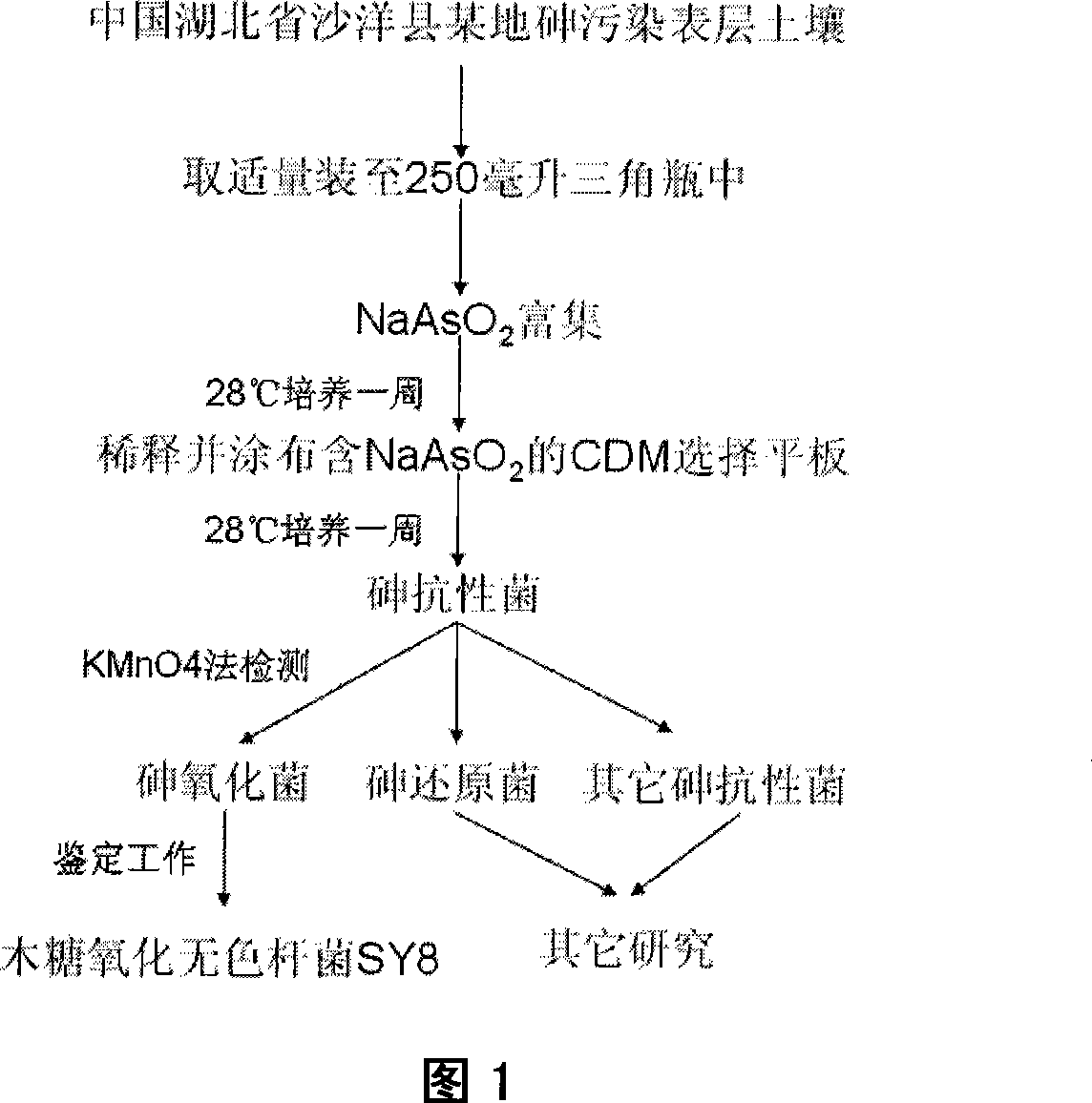
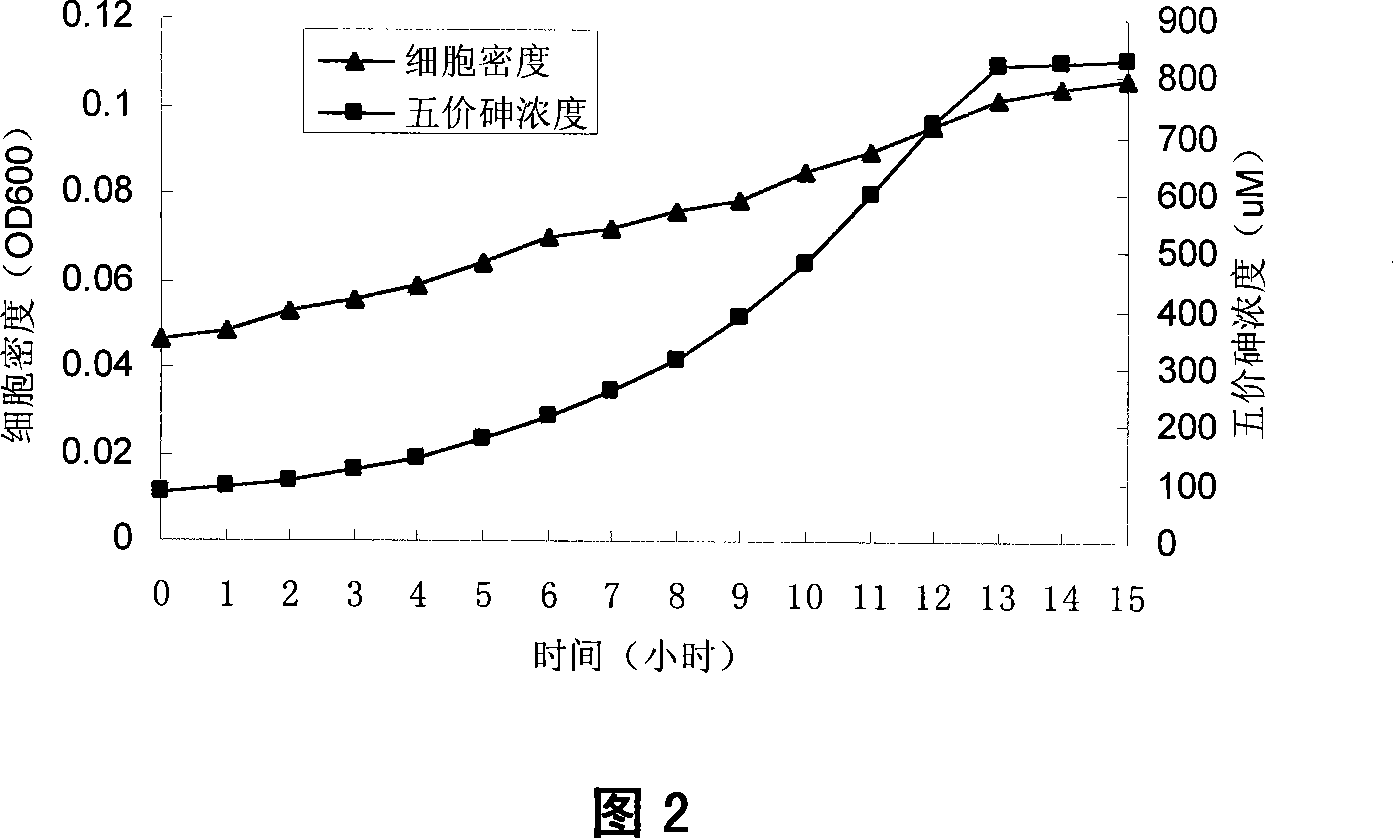
Xylose oxidation achromatous bacillus SY8 for purifying arsenic contamination and usage thereof
InactiveCN101063097AHarm reductionHighly toxicBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationBacteroidesMicroorganism
The invention discloses a wood sugar oxidation achromobacter SY8 and appliance in purifying arsenic contamination aspect in environmental microbiology technical domain, which is characterized by the following: separating a wood sugar oxidation achromobacter SY8 from arsenic contamination soil; possessing oxidation for inorganic tervalence arsenic; oxidizing inorganic tervalence arsenic to inorganic pentavalent arsenic in arsenic environmental pollution; decreasing toxicity of arsenic in environment; decreasing adsorbing removing property of arsenic; setting the preserved number as CCTCC NO: M207048. This strain possesses better applying prospect in arsenic pollution aspect.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Comamonas testosteroni LH-N5 and heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification microbial inoculum, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103146604AFacilitate large-scale production applicationSolve the problem of difficult removal of total nitrogenBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSynechococcusTotal nitrogen
The invention discloses a Comamonas testosteroni LH-N5 CGMCC No.6975. The invention also discloses a heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification microbial inoculum which comprises the Comamonas testosteroni LH-N5, or one or both of Achromobacter xylosoxidans subtype xylosoxidans LH-N25 and Paracoccus aminovorans LH-N40; and the strains are combined in any proportion. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the microbial inoculum. The microbial inoculum disclosed by the invention can solve the problem of difficulty in removing total nitrogen in the traditional reactor, can effectively remove ammonia nitrogen and total nitrogen in the water body in one reactor, has tolerance or degradation capability for phenols, amines, heterocycles, cyanides, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and other toxic substances in wastewater, is especially applicable to nitrogenous chemical wastewater, has the advantages of simple treatment process, stable effect and environmental toxicant impact resistance, and has very wide application prospects in various actual nitrogenous chemical wastewater treatment processes.
Owner:BLUESTAR LEHIGH ENG INST CO LTD
Complex microbial agent for restoring coastline with heavy oil pollution, as well as preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN104745511AImprove salt toleranceStrong competitive advantageBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationAchromobacter xylosoxidansSalt resistance
The invention relates to a complex microbial agent for restoring coastline with heavy oil pollution, as well as a preparation method and applications thereof. The complex microbial agent comprises Sphingobacterium mizutaii, Achromobacter xylosoxidans and Achromobacter piechaudii, furthermore, the collection number of the Sphingobacterium mizutaii is CGMCC No.800; the collection number of the Achromobacter xylosoxidans is CGMCC No.8022; and the collection number of Achromobacter piechaudii is CGMCC No.8021. The complex microbial agent is good in salt resistance property, prominent in competitive advantages, and has a high-efficiency restoration effect on the crude oil pollution of coastline, especially refractory heavy oil contamination through the synergistic effect of the three bacteria, and can also be applied to restoration of saline alkali soil with overflow oil contamination.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
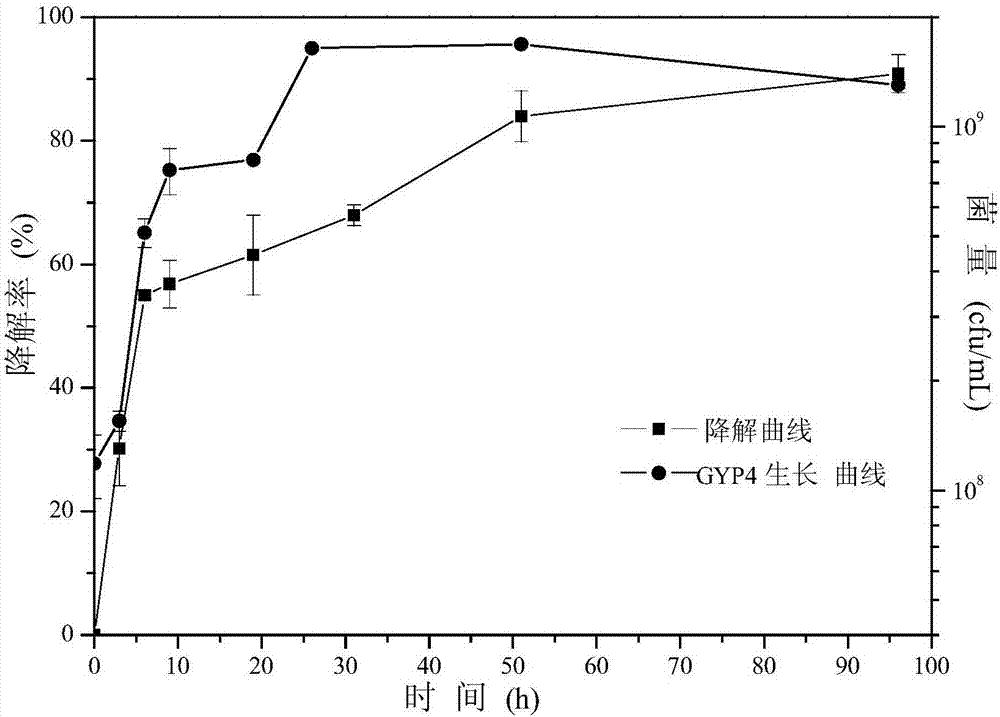
Achromobacter xylosoxidans GYP4, and application of same to degradation of brominated fire retardants
ActiveCN106939293APromote degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsDiphenyl etherAchromobacter xylosoxidans
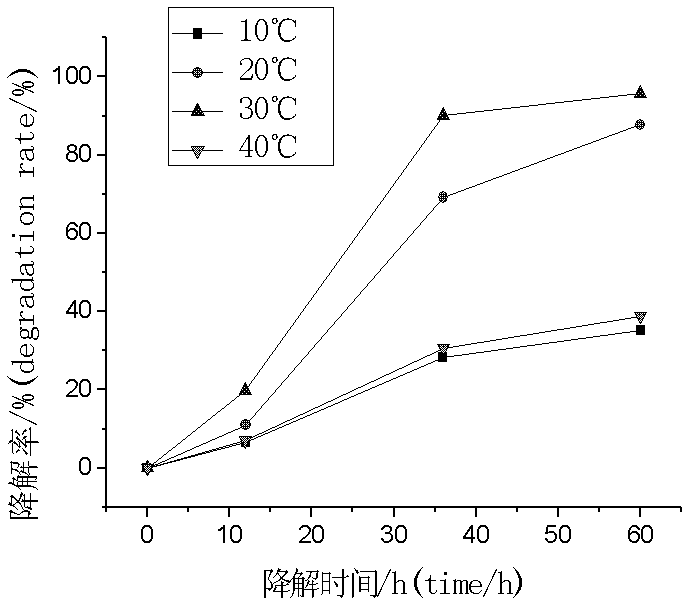
The invention discloses Achromobacter xylosoxidans GYP4, and application of the same to degradation of brominated fire retardants, belonging to the field of biological treatment technologies for environmental pollutants. The Achromobacter xylosoxidans GYP4 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on March 9th, 2017, with an accession number of CCTCC No. M2017104. After a strain of Achromobacter xylosoxidans GYP4 is subjected to shake cultivation under the conditions of a pH value of 3.0 to 7.0, a temperature of 25 to 35 DEG C and a shaking speed of 150 r / min for 4 days, the strain can degrade 80% or more of 2,2',4,4'-tetrabromodiphenyl ether with an initial concentration of 1 mg / L. The strain of Achromobacter xylosoxidans GYP4 is applicable to bioremediation of water bodies and soil contaminated by polybrominated diphenyl ethers.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
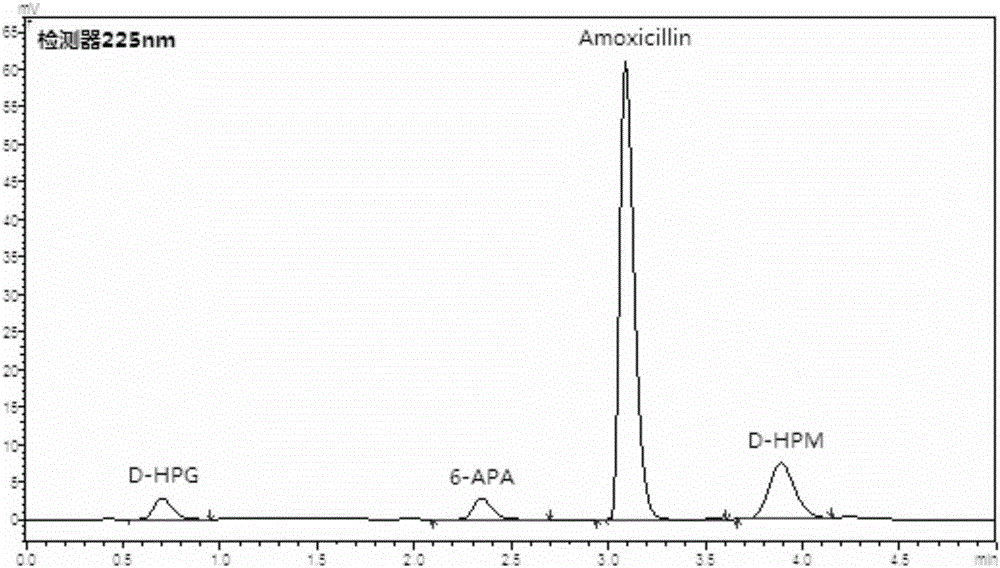
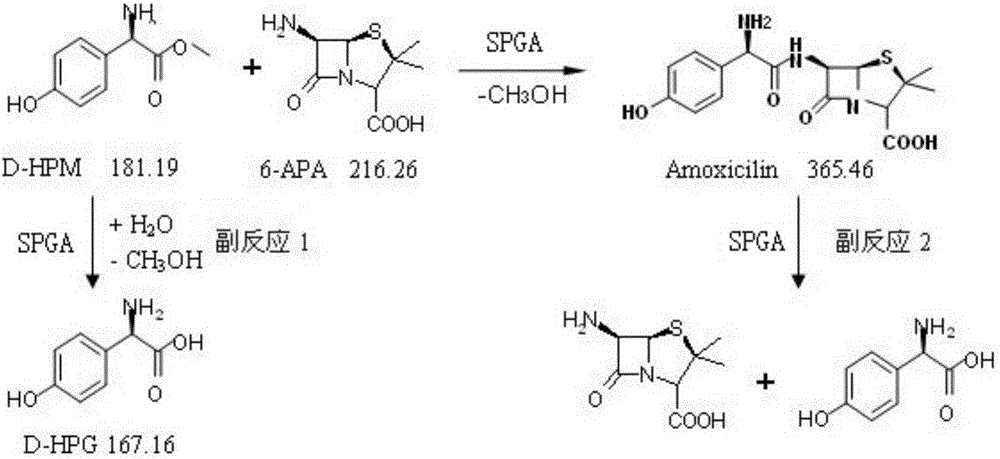
Penicillin G acylase mutant for synthesis and application thereof in preparation of amoxicillin
ActiveCN105274082ASynthetic activity is goodImprove stabilityHydrolasesFermentationContinuous useOrthogenesis
The invention provides a penicillin G acylase mutant for synthesis and an application thereof in the preparation of amoxicillin. Penicillin G acylase of Achromobacter xylosoxidans origin is mutated by computer aided design in connection with semi-rational design of site-saturation mutagenesis technique and enzyme engineering modification of orthogenesis, thus acquiring the penicillin G acylase mutant lower in hydrolytic activity, better in synthetic activity, higher in synthesis-hydrolysis ratio (S / H), higher in acid resistance and better in stability, and amoxicillin can be catalytically synthesized more effectively and quickly. Immobilized enzyme hydrolytic activity of the mutant SPGA-4 obtained is decreased by 8.7 times, synthetic activity is increased by 5.6 times, the S / H ratio is increased by 8 times, the activity remains at 79% for 60 min under the condition of pH 2.0, amoxicillin is catalytically synthesized by a solid method at 10 DEG C or 20 DEG C, substrates 6-APA and D-HPM are directly charged in a solid form without dissolving, reaction pH need not be controlled, substrate conversion rate is higher than 99%, continuous use is available in more than 300 batches, and good operational stability is given.
Owner:HUNAN FLAG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Achromobacter xylosoxidans with denitrification and dephosphorization function and application of Achromobacter xylosoxidans
ActiveCN102533623ARealize synchronous removalSolve bottlenecksBacteriaTreatment using aerobic processesPhosphateInorganic phosphorus
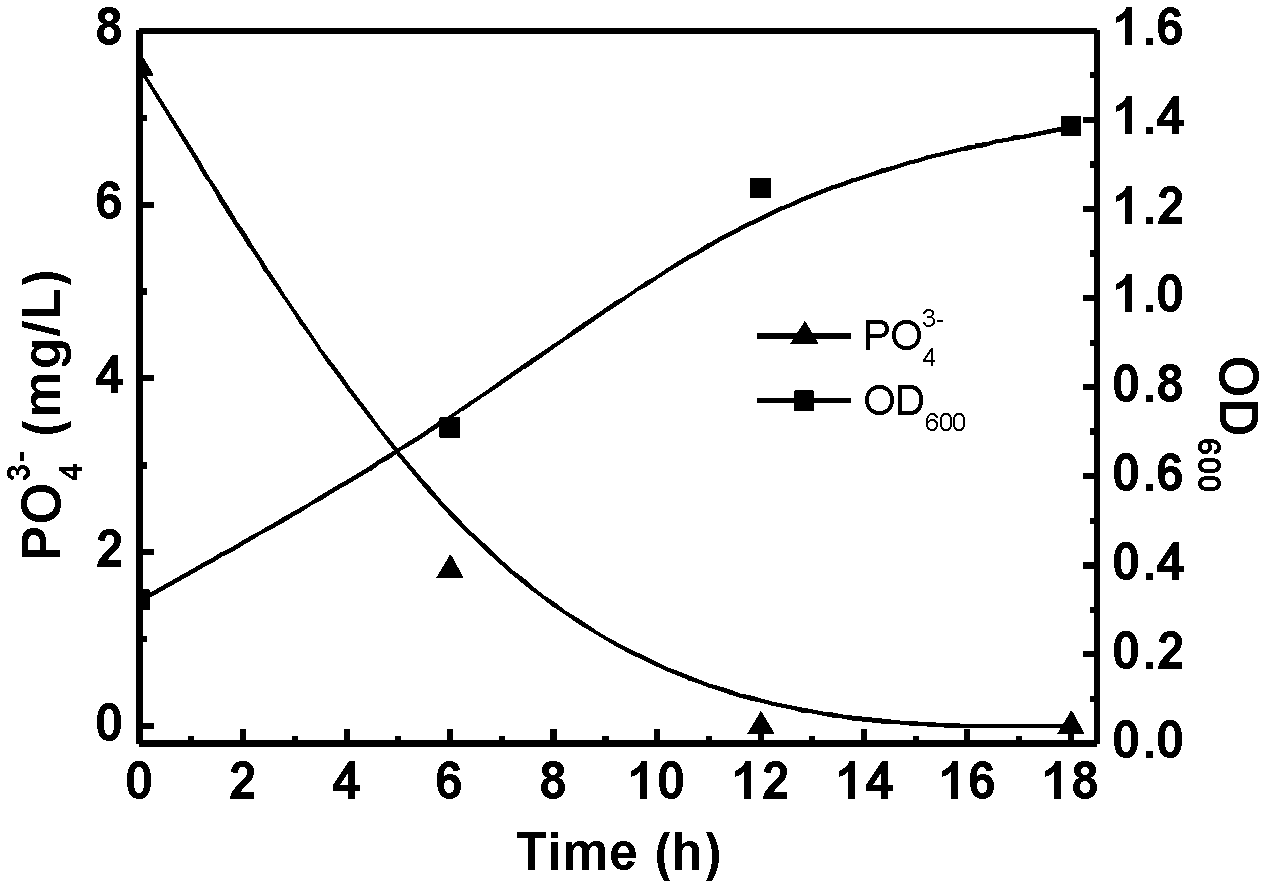
The invention relates to application of Achromobacter xylosoxidans with a heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification and dephosphorization function in wastewater treatment. The Achromobacter xylosoxidans can metabolize by using organic carbon as a unique carbon source and using ammonia nitrogen as a unique nitrogen source and can directly convert the ammonia nitrogen into gas products through the action of heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification so as to achieve the aim of denitrification, can also take nitrate nitrogen as a unique nitrogen source and convert the nitrate nitrogen into gas products through the action of aerobic denitrification, and can further ingest inorganic phosphorus and convert the inorganic phosphorus into a tissue of the Achromobacter xylosoxidans under an aerobic condition so as to achieve the aim of removing phosphorus from wastewater. The Achromobacter xylosoxidans are applied to the wastewater treatment, the simultaneous removal of nitrogen and phosphorus can be achieved under the single aerobic condition, and the difficult problem that the biological denitrification and dephosphorization in the traditional wastewater treatment need to adopt the segmented treatments of anaerobic phosphate release, anoxic denitrification and aerobic nitrification and phosphorus absorption, is better solved, so that the Achromobacter xylosoxidans have broad application prospects.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Application of microbial agent to malodorous gas pollution regulation
ActiveCN103432900AGood governanceEfficient removalDispersed particle separationAir quality improvementToxicantSulfur containing
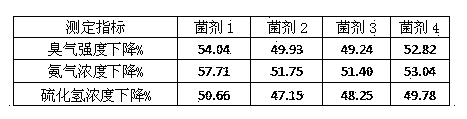
The invention relates to application of a microbial agent to malodorous gas pollution regulation. Malodorous gas is nitrogen-containing or sulfur-containing inorganic / organic malodorous gas or volatile heterocyclic organic gas, and the microbial agent is formed by comamonas testosteroni LH-N5, achromobacter xylosoxidans subsp. xylosoxidans LH-N25CGMCC No.6972 and Paracoccus aminovorans LH-N40CGMCC No.6971 in any proportion. The microbial agent has a remarkable deodorization effect, can tolerate or degrade organic and toxic pollutants, is particularly suitable for deodorization and purification of nitrogen-containing or sulfur-containing inorganic / organic waste gas, is suitable for regulation of volatile heterocyclic toxic organic malodorous gas, has a simple treatment process and stable effects, is resistant to environmental toxicant impact, and has wide application prospect in malodorous gas pollution control.
Owner:BLUESTAR LEHIGH ENG INST CO LTD
Achromobacter xylosoxidans and application of Achromobacter xylosoxidans in heavy metal ion removing
ActiveCN103937704AEfficient removalNo secondary pollutionBacteriaWater contaminantsAchromobacter xylosoxidansScreening method
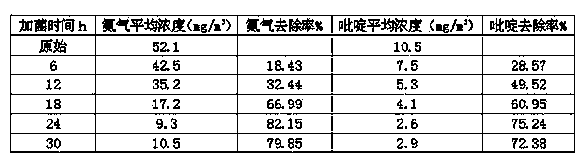
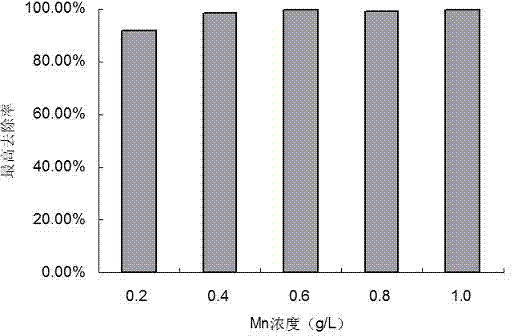
The present invention discloses a strain of Achromobacter xylosoxidans M2, and an application of the Achromobacter xylosoxidans M2 in heavy metal ion removing, wherein the Achromobacter xylosoxidans M2 provides a heavy metal ion Mn<2+> removing effect. The method for screening Achromobacter xylosoxidans providing a heavy metal ion Mn<2+> removing effect from soil and water comprises: a, preparing a metal selective culture medium; b, carrying out enrichment acclimatization on a heavy metal resistance strain; c, screening and re-screening the heavy metal resistance strain; and d, detecting the heavy metal removing capability of the strain. According to the present invention, with the detection test on the heavy metal removing capability of the strain obtained by carrying out enrichment acclimatization on the heavy metal resistance strain with the metal ion-containing culture medium and purification, the reasonable and effective screening method for the heavy metal removing strain is established so as to obtain the strain suitable for requirements; and with application of the Achromobacter xylosoxidans M2 in the heavy metal pollution treatment, advantages of no secondary pollution, high treatment efficiency, wide application range, low cost and the like are provided.
Owner:润桐(苏州)技术服务有限公司
A strain of Achromobacter xylosoxidans and use thereof for depredating clomazone
InactiveCN101463337AEfficient degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsAchromobacter xylosoxidansHigh concentration
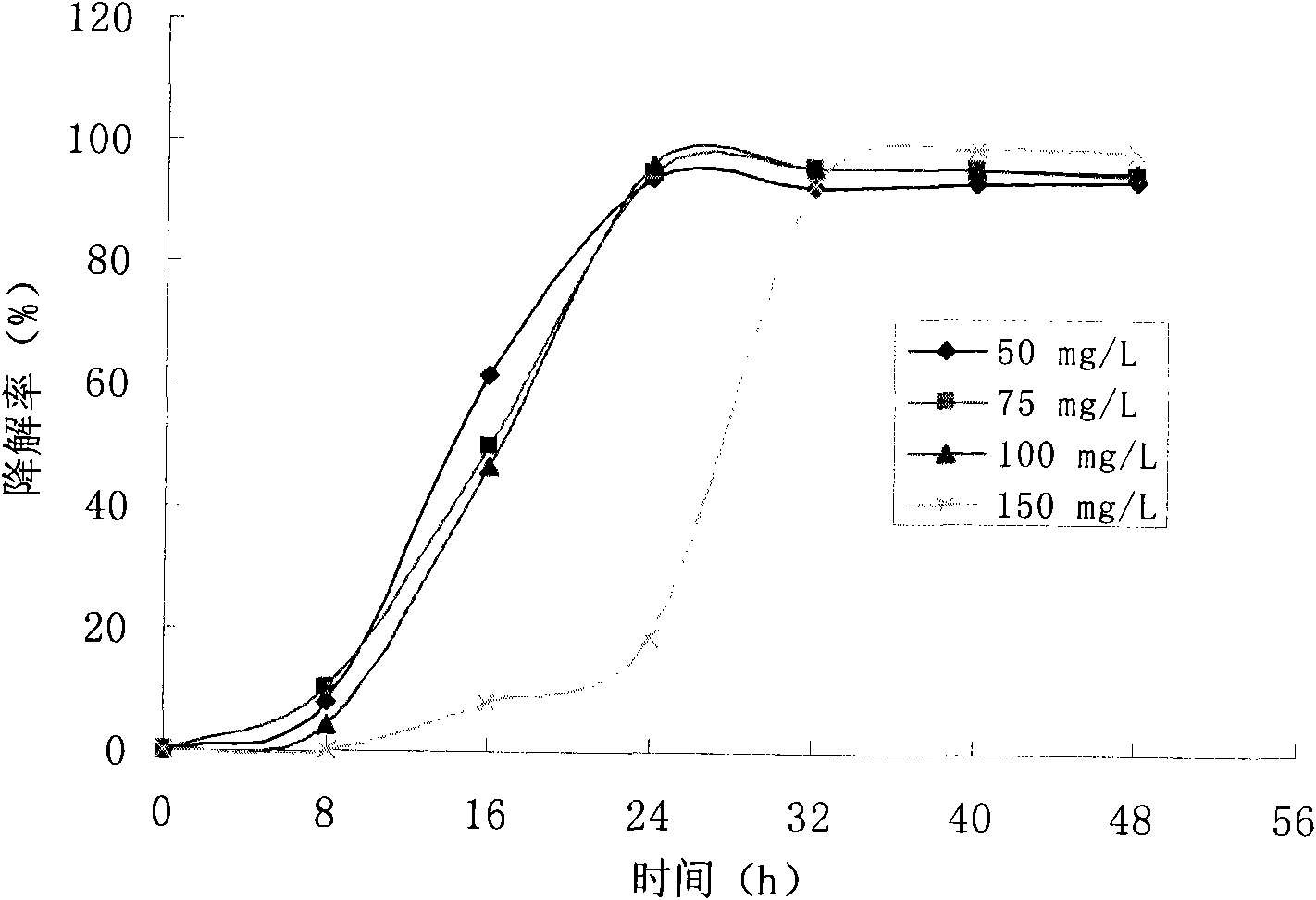
The invention discloses an achromobacter xylosoxidans and the application thereof in the degradation of clomazone. The achromobacter xylosoxidans is achromobacter xylosoxidans CGMCC No. 2773. The bacterial strain can grow in the environment of high concentration clomazone, and can degrade the clomazone with high efficiency, so as to provide important foundation for the study of micro-biological degradation of residual weedicide clomazone, thus being applied to biological purification of the water body and soil which are polluted by the clomazone.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Complex bactericide for efficiently purifying sewage anaerobic outlet water of pig farm and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105176868ACompatibility is reasonableEasy synergismBacteriaWaste water treatment from animal husbandryAchromobacter xylosoxidansPig farms
The invention discloses complex bactericide for efficiently purifying sewage anaerobic outlet water of a pig farm and a preparation method and an application thereof. The complex bactericide is formed by mixing rhodopseudomonas palustris, bacillus subtillis, nevskia, microbacterium esteraromaticum, paracoccus and xylose oxidized achromobacter. The complex bactericide has unique purifying effect on the sewage anaerobic outlet water of the pig farm, also has a good purifying effect for artificial synthetic sewage and has a popularization application value.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF MICROBIOLOGY
Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain and application thereof
InactiveCN101914467AEfficient degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsAchromobacter xylosoxidansWastewater
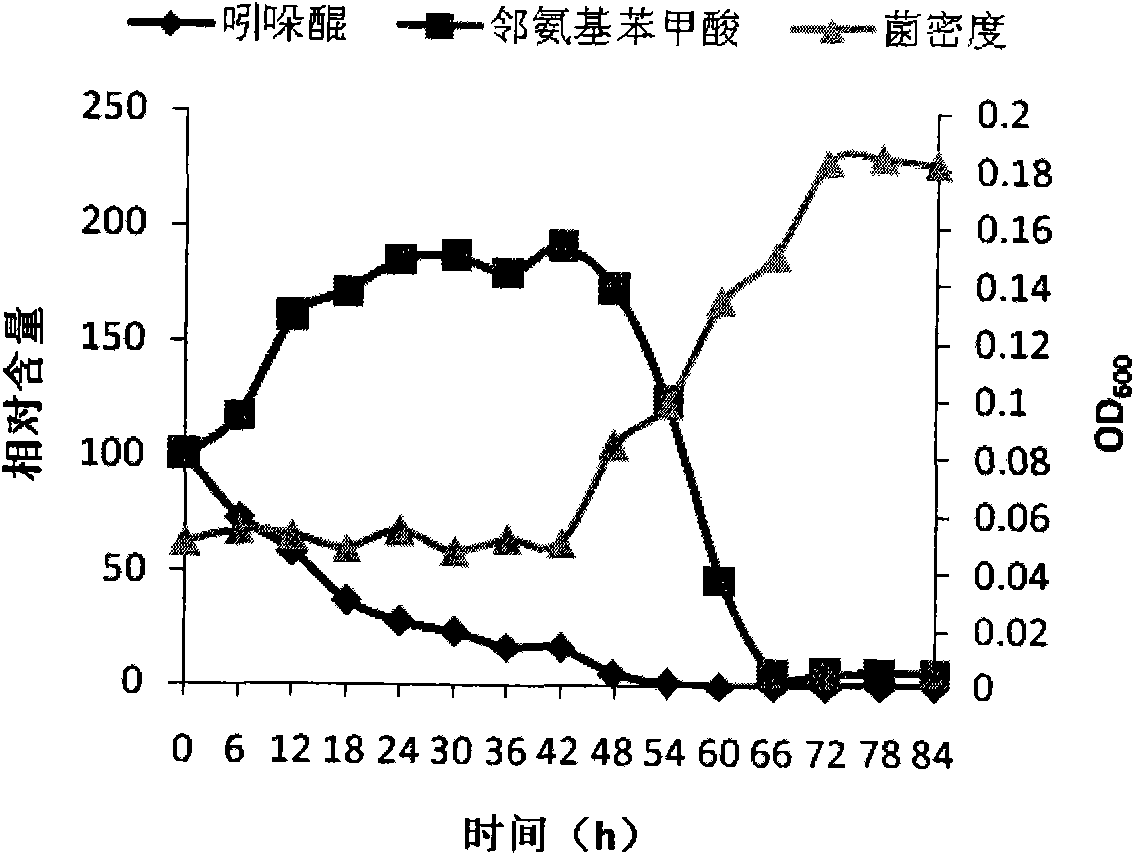
The invention discloses an Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain and application thereof. The strain is Achromobacter xylosoxidans N4 with the collection number of CGMCC No.3632. The Achromobacter xylosoxidans N4 GCMCC No.3632 can quickly and efficiently degrade isatin and o-aminobenzoic acid, and can be used for biologically treating calico printing wastewater.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Application of arsenic oxidizing bacterium in repairing pollution of trivalent arsenic in paddy field
ActiveCN107974415AIncreased toxicityEasy to moveBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationAchromobacter xylosoxidansMicroorganism
The invention provides arsenic oxidizing bacterium and application thereof in repairing pollution of trivalent arsenic in a paddy field. The arsenic oxidizing bacterium is (Achromobacter xylosoxidans)YYS001, and was preserved into Common Microorganism Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on August 31th, 2017, and the collection number is CGMCC NO.14583. The arsenic oxidizing bacterium has the advantages that the toxicity of the high-toxicity trivalent arsenic in the soil of the paddy field is obviously decreased, and the better application prospect is realized inthe field of repairing of pollution of trivalent arsenic in the paddy field.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Penicillin acylase, as well as high-yield strain and application thereof
InactiveCN103184182AIncrease vitalityIncreased substrate specificityBacteriaHydrolasesAchromobacter xylosoxidansPenicillin
The invention provides penicillin acylase, as well as a high-yield strain and an application thereof, belonging to the field of bio-pharmaceuticals. The strain is Achromobacter xylosoxidans K18 with the collection number of CCTCC NO: M2012541. The penicillin acylase is obtained by fermenting the strain K18. The amino acid sequence of the penicillin acylase is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, and the gene sequence of the penicillin acylase is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention further provides the application of the penicillin acylase in synthesis of beta-lactam type antibiotics. The strain K18 is the high-yield strain of the penicillin acylase, and when fermentation is performed through a culture medium containing an inducing agent, the yield of the penicillin acylase can be above 200U / L. The penicillin acylase produced by the strain K18 has the advantages of high temperature resistance, capability of keeping higher activity under an acidic environment, higher specificity of a substrate, strong organic solvent tolerance and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Achromobacter strain with monomethylamine degradation ability and application thereof
ActiveCN107904188AHas the ability to degrade monomethylamineBacteriaWater contaminantsColony morphologyAchromobacter xylosoxidans
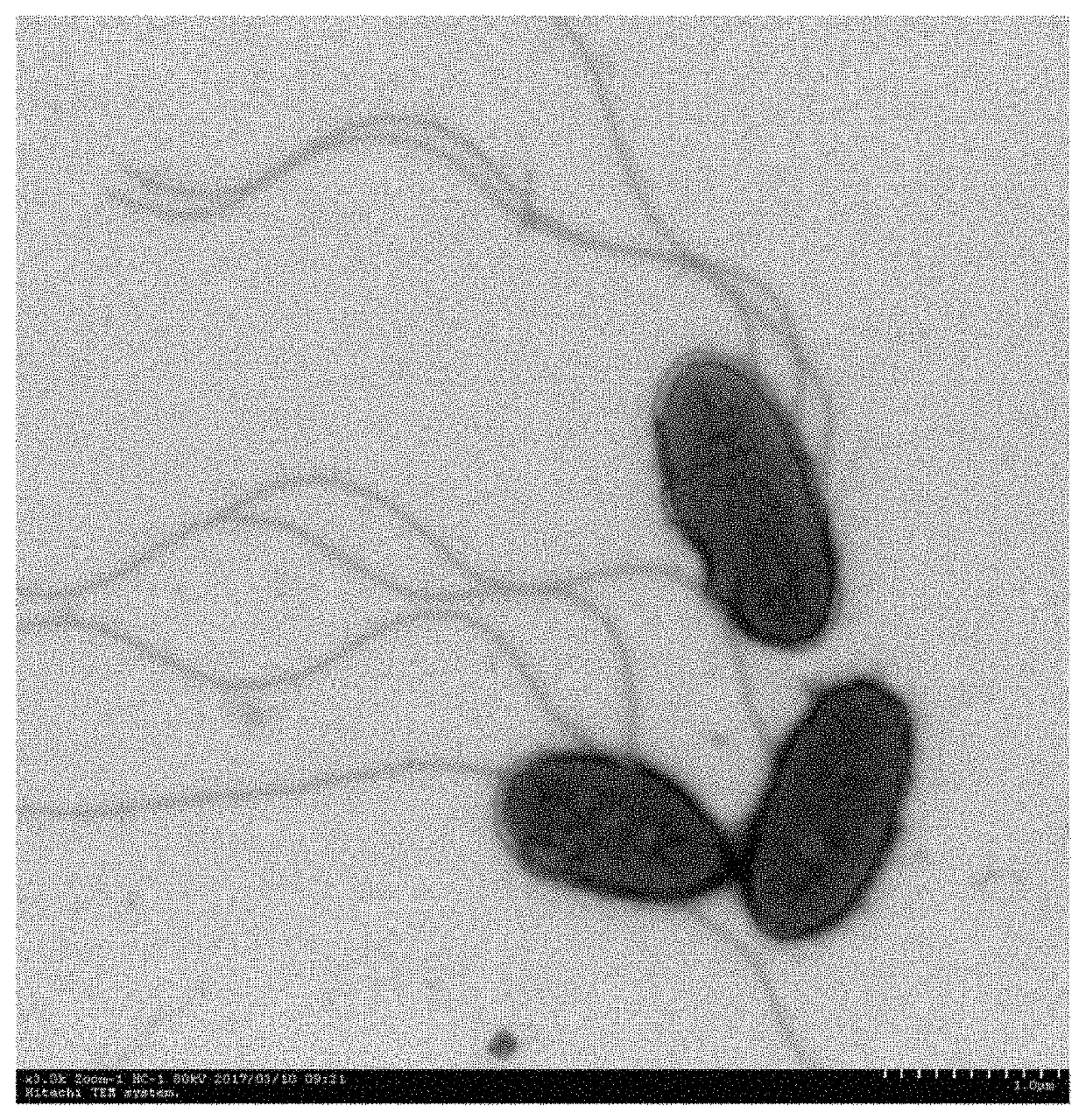
The invention discloses an achromobacter strain with monomethylamine degradation ability and application thereof. The name of the strain is Achromobacter xylosoxidans GDUTAN5 which is preserved in theChina Center for Type Culture Collection at Wuhan University, No. 299, Bayi Road, Wuchang District, Wuhan, Hubei Province, China. The preservation number is CCTCC NO:M 2017285. The preservation dateis May 24, 2017. The Achromobacter xylosoxidans GDUTAN5 is Gram-negative and rod-shaped, has a round colony morphology, is light yellow and opaque, and has a smooth surface and a colony diameter of 1-2 mm. The Achromobacter xylosoxidans GDUTAN5 can be applied to environmental remediation for degradation of monomethylamine in the environment and has a high degradation rate. When the substrate concentration is 5 mg / L, the degradation rate can reach 92.3% after 96 h of degradation.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Composite fungicide for remediating lead-containing wastewater
InactiveCN107032505AStrong adhesionReduce outputWater contaminantsBiological water/sewage treatmentSludgeBacillus cereus
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbes and discloses a composite fungicide for remediating lead-containing wastewater. The composite fungicide is prepared from a compound bacterium solution and an adsorption carrier and is characterized in that the compound bacterium solution is prepared from marsh rhodop seudanonas palustris, bacillus stearothermophilus, arthrobacter crystallopoietes, acinetobacter calcoaceticus, achromobacter xylosoxidans fermentation liquor and bacillus cereus. The composite fungicide can effectively remediate lead polluted wastewater, and sludge production amount is small.
Owner:蒋瑞忠
Serratia marcescens M7a and application of Serratia marcescens M7a in heavy metal ion removing
ActiveCN103937703AEfficient removalNo secondary pollutionBacteriaWater contaminantsScreening methodAchromobacter
The present invention discloses a strain of Serratia marcescens M7a, and an application of the Serratia marcescens M7a in heavy metal ion removing, wherein the Serratia marcescens M7a provides a heavy metal ion Mn<2+> removing effect. The method for screening Achromobacter xylosoxidans providing a heavy metal ion Mn<2+> removing effect from soil and water comprises: a, preparing a metal selective culture medium; b, carrying out enrichment acclimatization on a heavy metal resistance strain; c, screening and re-screening the heavy metal resistance strain; and d, detecting the heavy metal removing capability of the strain. According to the present invention, with the detection test on the heavy metal removing capability of the strain obtained by carrying out enrichment acclimatization on the heavy metal resistance strain with the metal ion-containing culture medium and purification, the reasonable and effective screening method for the heavy metal removing strain is established so as to obtain the strain suitable for requirements; and with application of the Serratia marcescens M7a in the heavy metal pollution treatment, advantages of no secondary pollution, high treatment efficiency, wide application range, low cost and the like are provided.
Owner:润桐(苏州)技术服务有限公司
Degradative bacteria capable of degrading allelochemicals in plant root exudates and application of degradative bacteria
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms and provides degradative bacteria capable of degrading allelochemicals in plant root exudates and an application of the degradative bacteria. The degradative bacteria are classified and named Achromobacter xylosoxidans and Pseudomonas nitroreducens, and strain preservation numbers are CGMCC NO.14517 and CGMCC NO.14518 respectively. The degradative bacteria for the allelochemicals can degrade the allelochemicals in multiple degraded plant root exudates.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain for producing carboxymethyl cellulase
ActiveCN104232522AGrow fastBroaden your optionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesSequence analysis
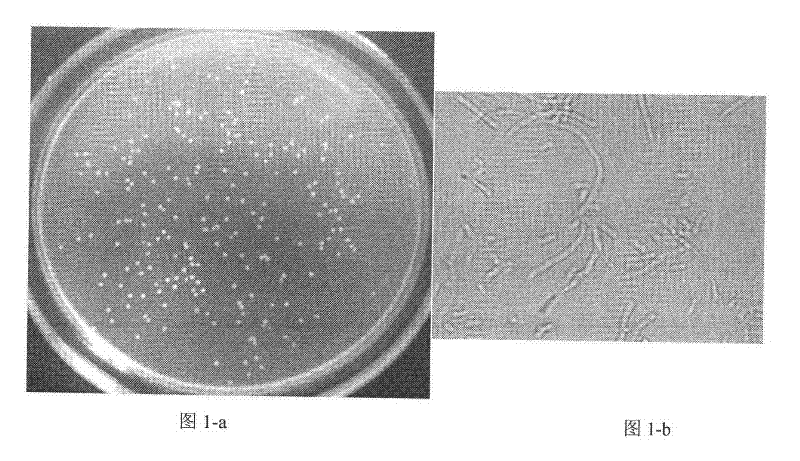
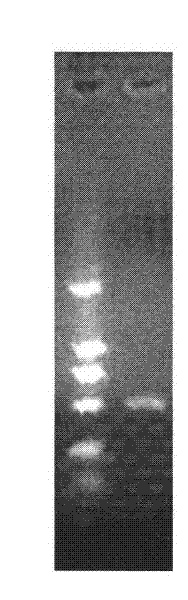
The invention discloses a bacterium 7B capable of producing cellulase separated and screened from stockpile manure. The bacterium is collected by China Center for Type Culture Collection, and the collection number is CCTCC NO:M2013365. The strain 7B is Gram-negative bacilli, and forms a smooth, wet, lustrous, offwhite bacterial colony with regular edge, of which the diameter is 0.5-1mm, on the LB (Langmuir-Blodgett) culture medium. A BIOLOG microorganism identification system and 16s rDNA sequence analysis are utilized to identify that the strain is Achromobacter xylosoxidans. A CMC (carboxymethyl cellulose) fermentation culture medium is used for culturing to obtain the 0.183U / mL carboxymethyl cellulase activity, and the Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain is hopeful to be used for cellulase production.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Fermentation inoculum for producing cellulase and hemicellulase
The invention discloses a microbial inoculum for producing cellulase and hemicellulase by a natural lignocellulose material. The microbial inoculum for producing the cellulase and the hemicellulase comprises the following active ingredients: Achromobacter xylosoxidans, Alcaligenes faecalis, Fusarium sporotrichioides and Fusarium poae. In the invention, microbes in the microbial inoculum for producing the cellulase and the hemicellulase have a strong synergistic effect so that a stable ecological system can be formed in an autologous mode. The microbial inoculum is especially developed for an energy crop-Panicum virgatum but is not limited to production of the cellulase and the hemicellulase by use of the Panicum virgatum, and meanwhile the inoculum can be also used for producing the cellulase and the hemicellulase by waste crop straw.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Achromobacter xylosoxidans MG1 strain and application thereof
InactiveCN102181379AStrong decolorization efficiencyHigh decolorization rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesMalachite green stain
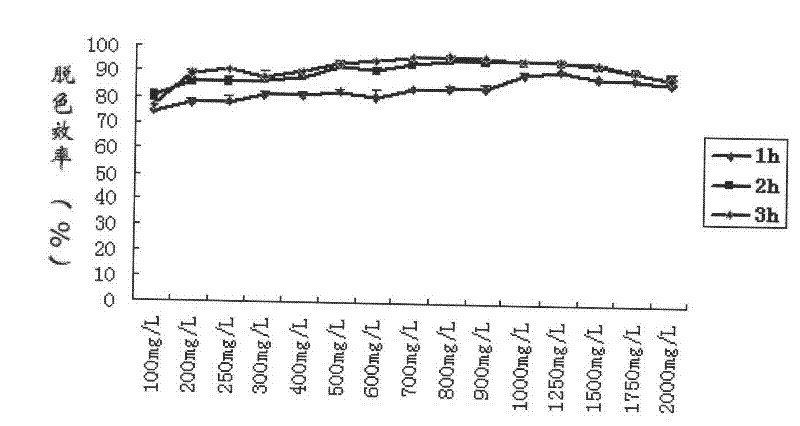
The invention relates to an achromobacter xylosoxidans MG1 strain and application thereof, and belongs to the field of environmental application of microorganisms. The achromobacter xylosoxidans MG1 strain is prepared by screening bacteria obtained by separating printing and dyeing wastewater by the conventional method, and was collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on December 15, 2010; and the collection number is CGMCC NO.4476. The achromobacter xylosoxidans MG1 strain has ultrastrong efficiency of decoloration on malachite green in triphenylmethane dyes, and the decolorization rate at 1 hour is up to 86+ / -1 percent when the concentration of the malachite green is up to 2,000mg / L. In addition, the MG1 strain also has a better effect of decolorizing crystalviolet, and can be applied to the preparation of biological decoloring agents. The achromobacter xylosoxidans MG1 strain has the advantages that: the range of strains which can degrade dyes can be broadened, so that an additional artificial degradation way is provided for the malachite green and the crystal violet in the environment, and the treatment cost for environmental pollution is reduced.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
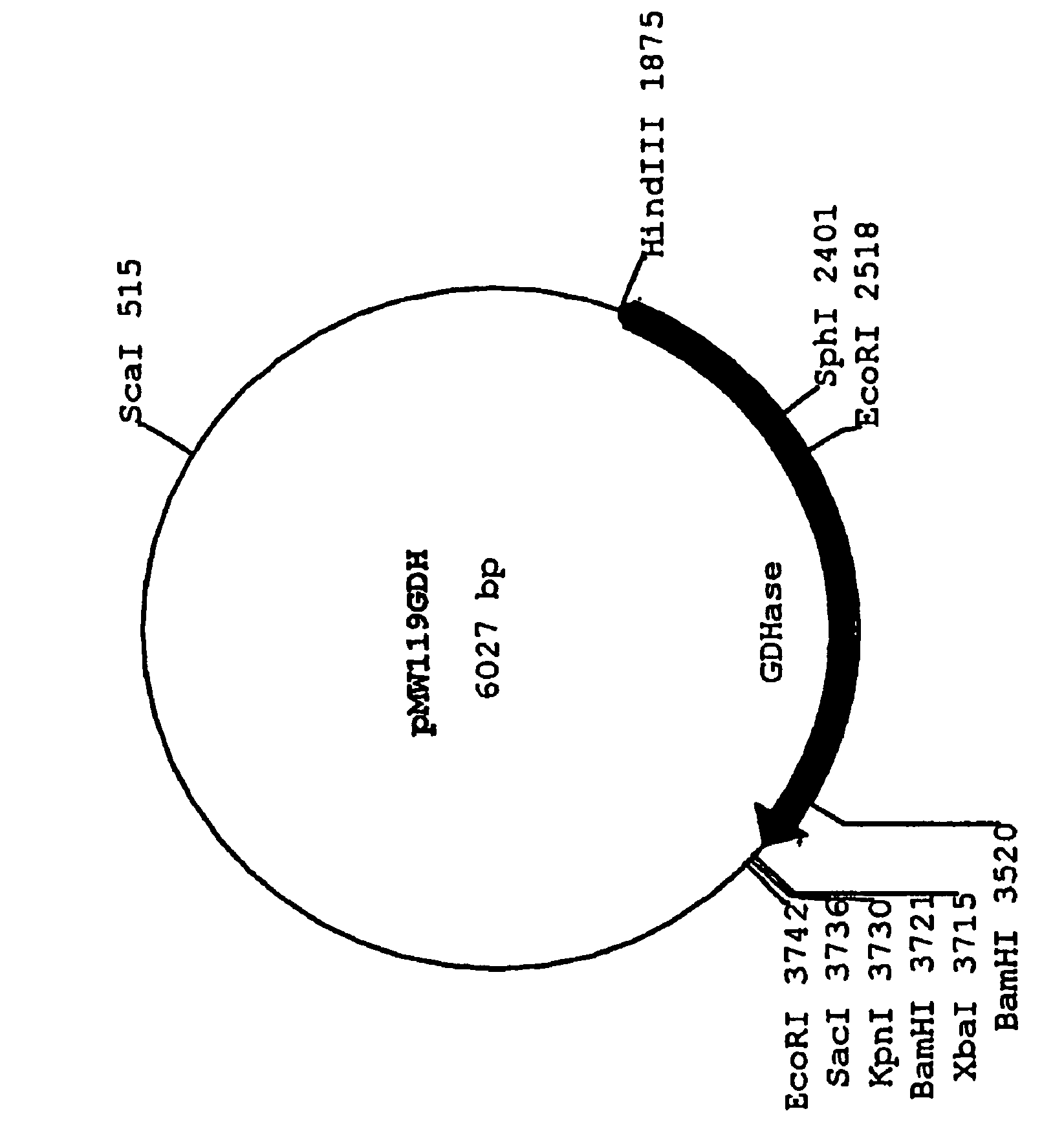
Gluconate dehydratase
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Achromobacter xylosoxidans with monomethylamine degradability and application thereof
PendingUS20210371808A1Promote degradationImprove degradation efficiencyBacteriaWater contaminantsAchromobacter xylosoxidansMicrobiology
The present invention discloses a strain of Achromobacter xylosoxidans with monomethylamine degradability and the application thereof. This strain, named Achromobacter xylosoxidans GDUTAN5, was deposited on May 24, 2017 in the China Center for Type Culture Collection in Wuhan University (No. 299 Bayi Road, Wuchang District, Wuhan City, Hubei Province) with a deposit number of CCTCC NO: M 2017285. This Achromobacter xylosoxidans GDUTAN5 was Gram-negative and rod-shaped, and the colony appeared to be round, light yellow, opaque and smooth, having a diameter of 1-2 mm. The Achromobacter xylosoxidans GDUTAN5 of the present invention can be applied to environmental restoration, degrading monomethylamine in the environment at a high degradation efficiency. When it degraded monomethylamine for 96 h at a substrate concentration of 5 mg / L, the degradation efficiency could reach 92.3%.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Achromobacter xylosoxidans and application thereof to degradation of isoquinoline
The invention discloses Achromobacter xylosoxidans and application thereof to degradation of isoquinoline. The conservation registration number of the Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain which is named Y-4 is CCTCC No. M2011308, and the Genbank accession number of the strain 16SrDNA is JN381516. The Achromobacter xylosoxidans Y-4 has unique degradationeffect on the isoquinoline, the maximum tolerance concentration (MTC) for the isoquinoline can reach 1000mg / L, and the isoquinoline with the concentration of not more than 500mg / L can be fully degraded in 36 hours, the optimal degradation temperature is 25-35 DEG C, the pH value is 4-8; meanwhile the Achromobacter xylosoxidans Y-4 also has better degradation effect on naphthalene, pyridine and quinoline, and has obvious effect particularly for the isoquinoline in biological purified coking wastewater. According to the Achromobacter xylosoxidans and application thereof disclosed by the invention, an important basis is provided for research on micro-biological degradation of the isoquinoline in the coking wastewater, and an important role can be played in practice of quinoline industrial wastewater treatment.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com