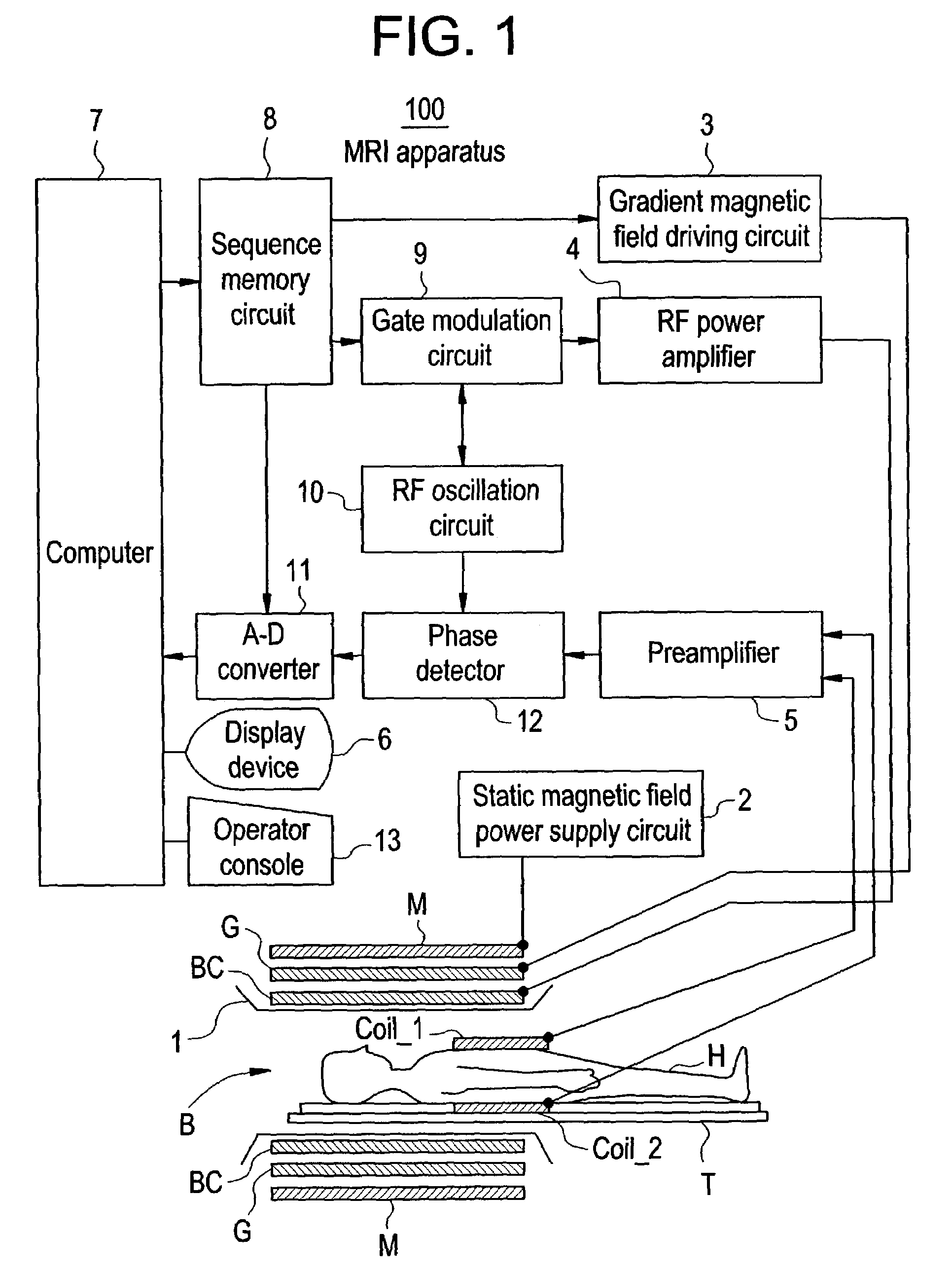
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41 results about "Sensitivity encoding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sensitivity Encoding. (SENSE™) A MRI technique for relevant scan time reduction. The spatial information related to the coils of a receiver array are utilized for reducing conventional Fourier encoding.
Superresolution parallel magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20090285463A1Increase spatio-temporal resolutionReduce acquisition timeGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionVoxelReceiver coil
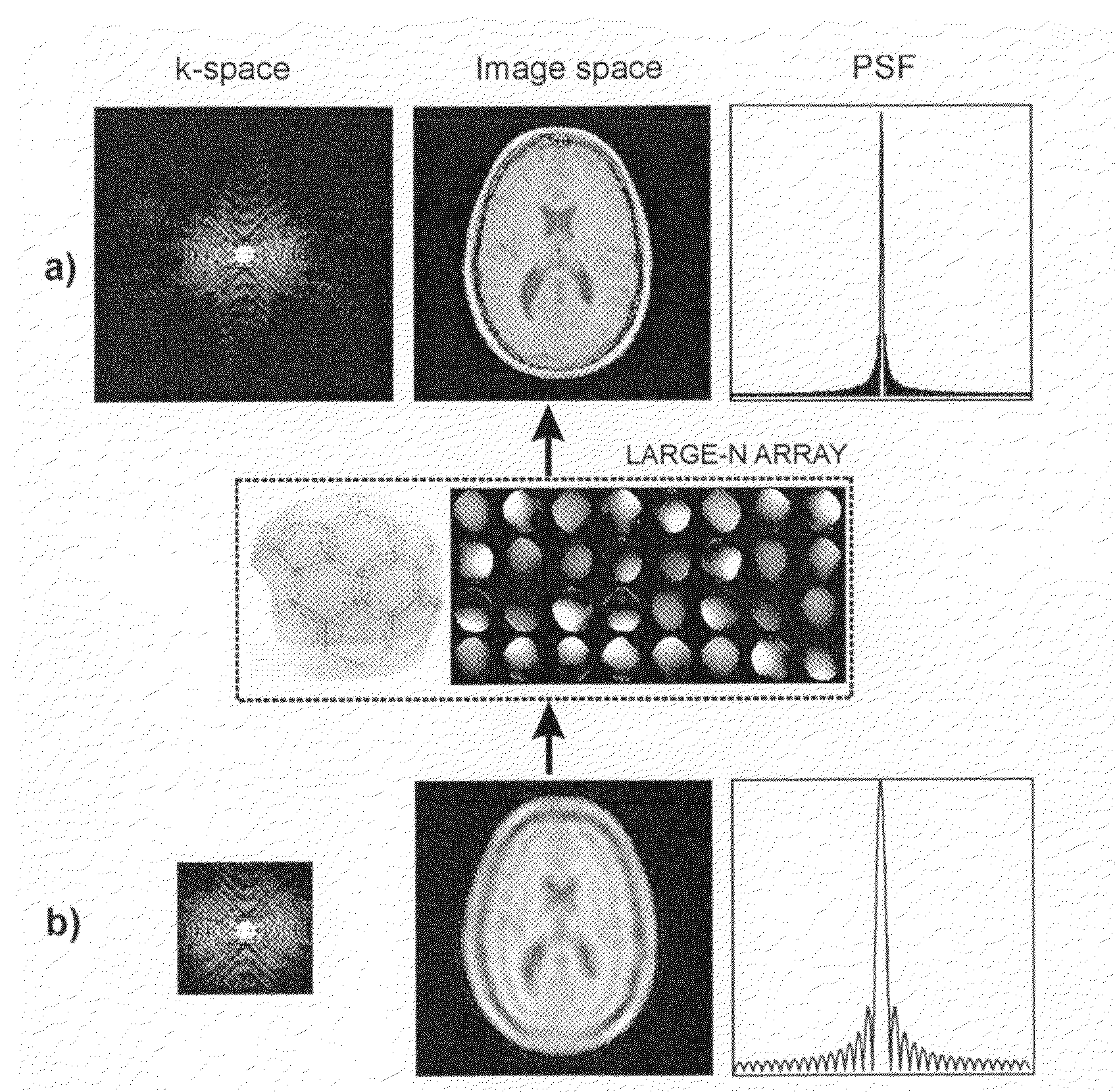
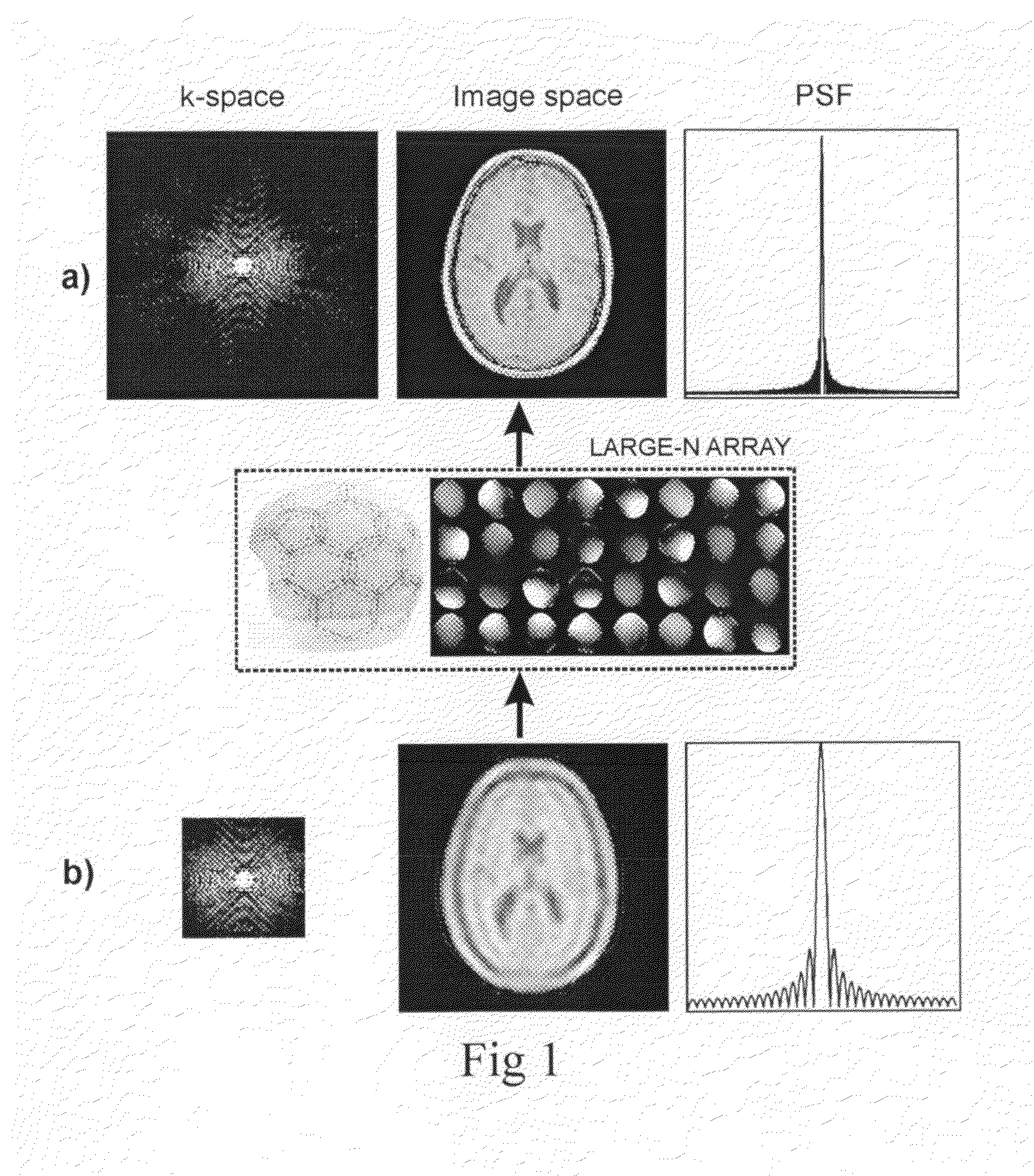
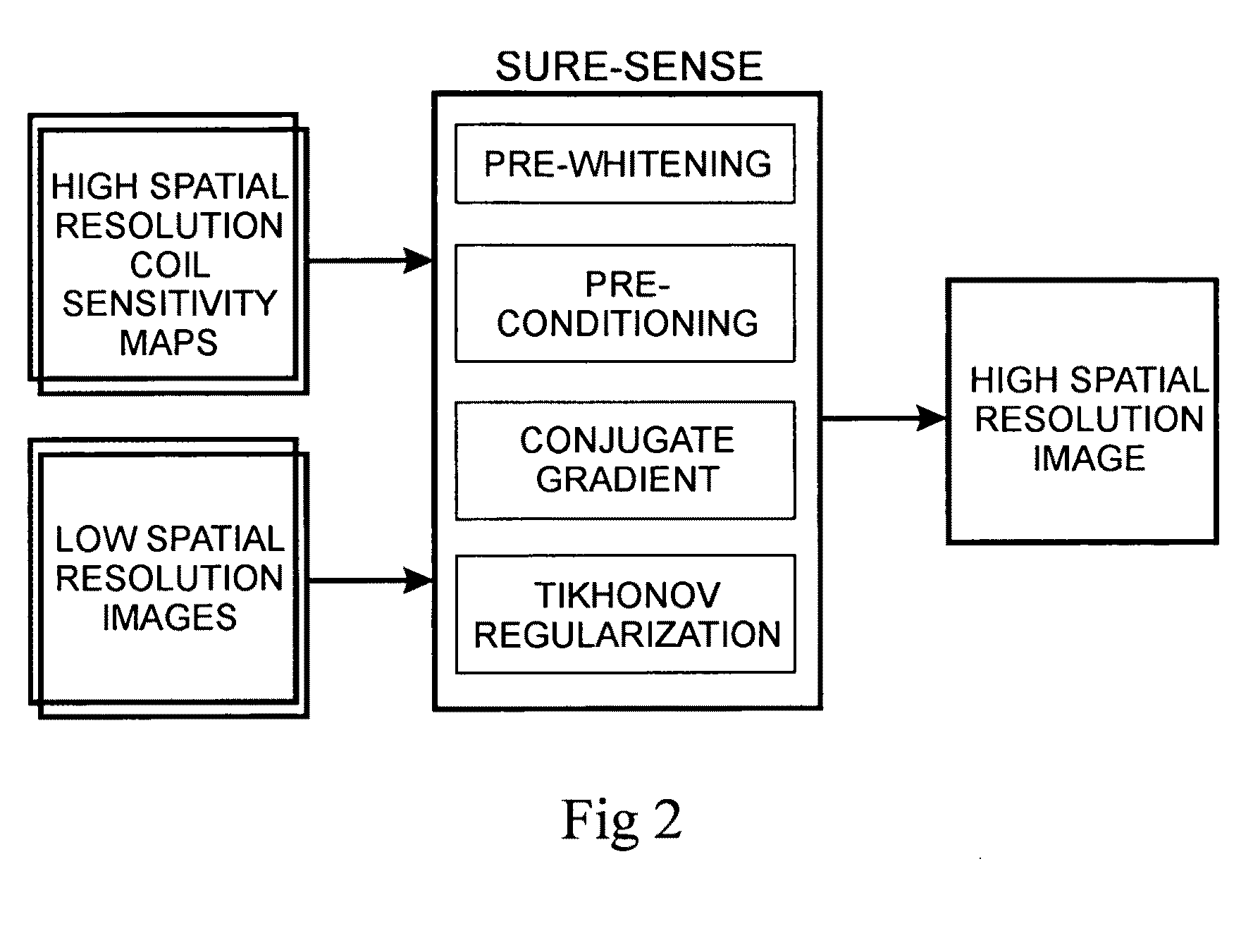
The present invention includes a method for parallel magnetic resonance imaging termed Superresolution Sensitivity Encoding (SURE-SENSE) and its application to functional and spectroscopic magnetic resonance imaging. SURE-SENSE acceleration is performed by acquiring only the central region of k-space instead of increasing the sampling distance over the complete k-space matrix and reconstruction is explicitly based on intra-voxel coil sensitivity variation. SURE-SENSE image reconstruction is formulated as a superresolution imaging problem where a collection of low resolution images acquired with multiple receiver coils are combined into a single image with higher spatial resolution using coil sensitivity maps acquired with high spatial resolution. The effective acceleration of conventional gradient encoding is given by the gain in spatial resolution Since SURE-SENSE is an ill-posed inverse problem, Tikhonov regularization is employed to control noise amplification. Unlike standard SENSE, SURE-SENSE allows acceleration along all encoding directions.
Owner:OTAZO RICARDO +1
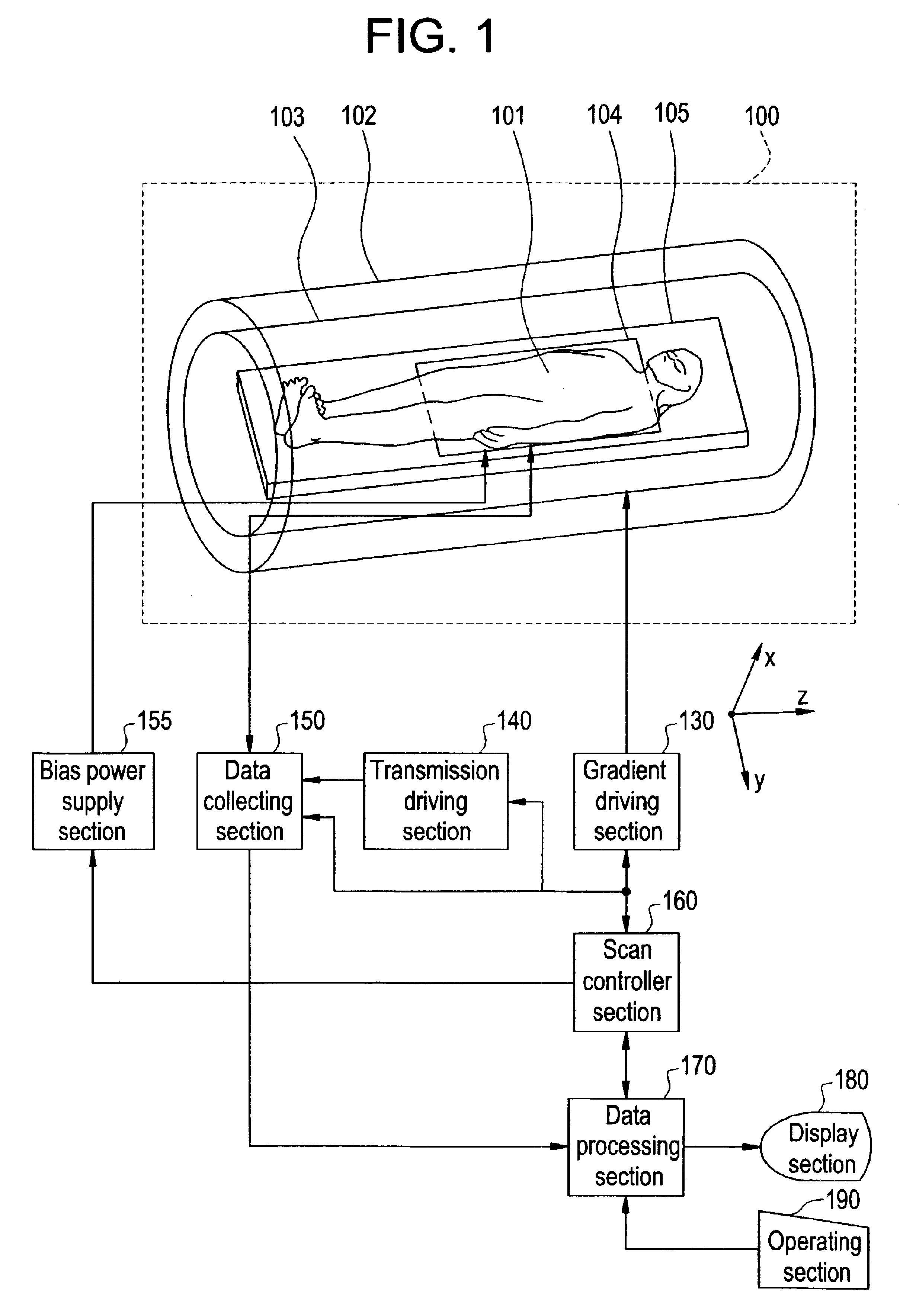
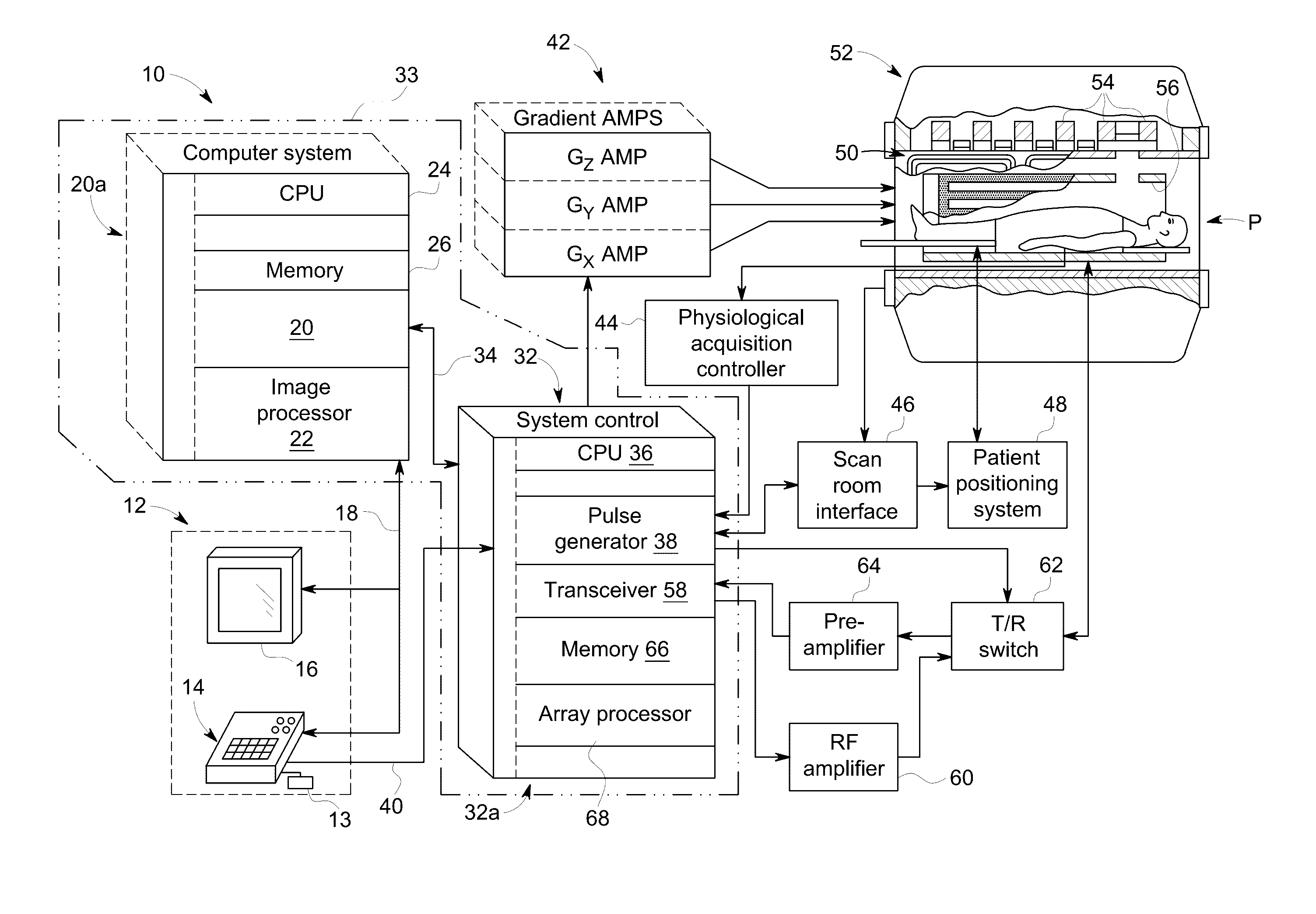
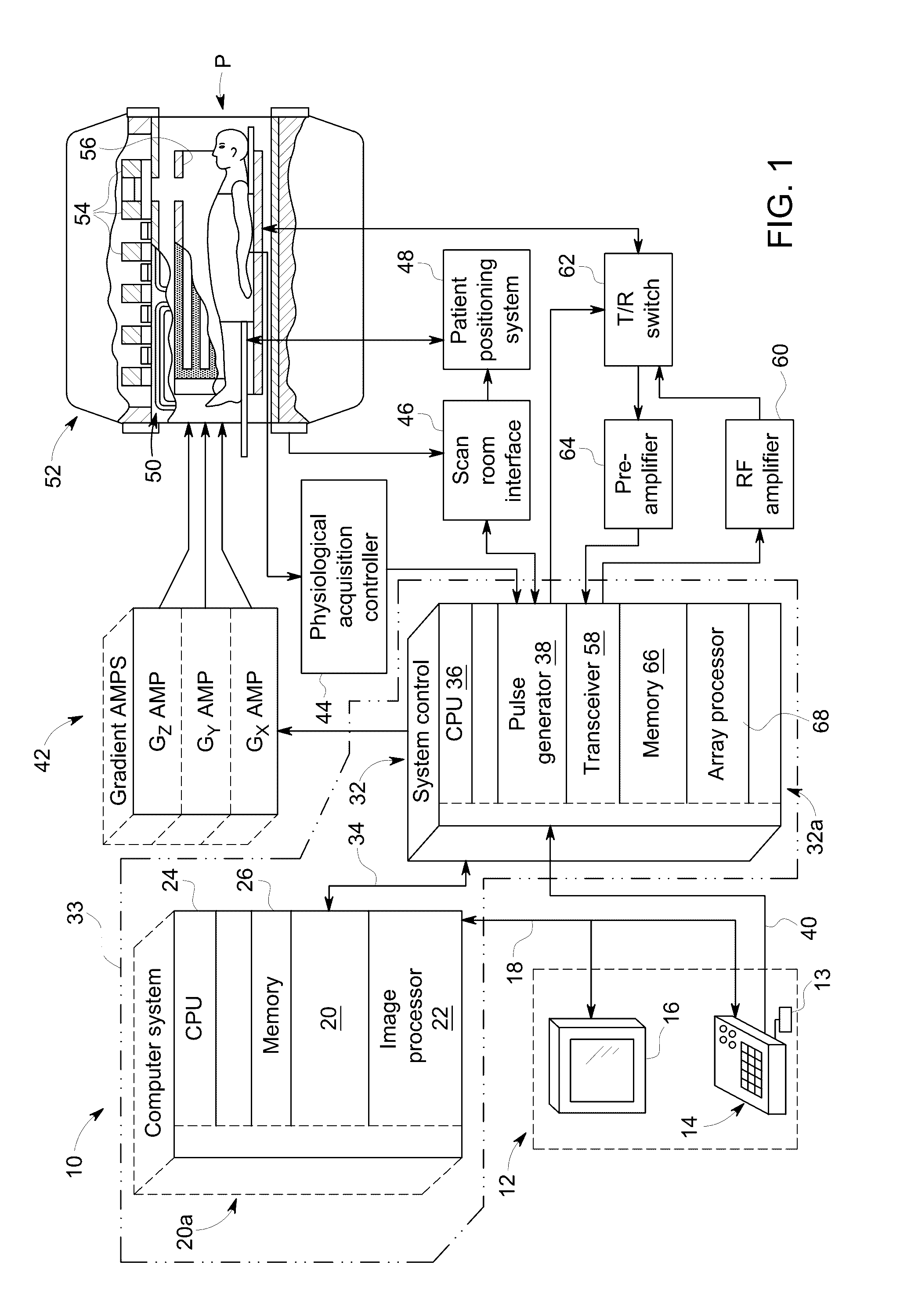
Methods & apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS6980001B2Shorten Image Acquisition TimeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetizationPhysical entity
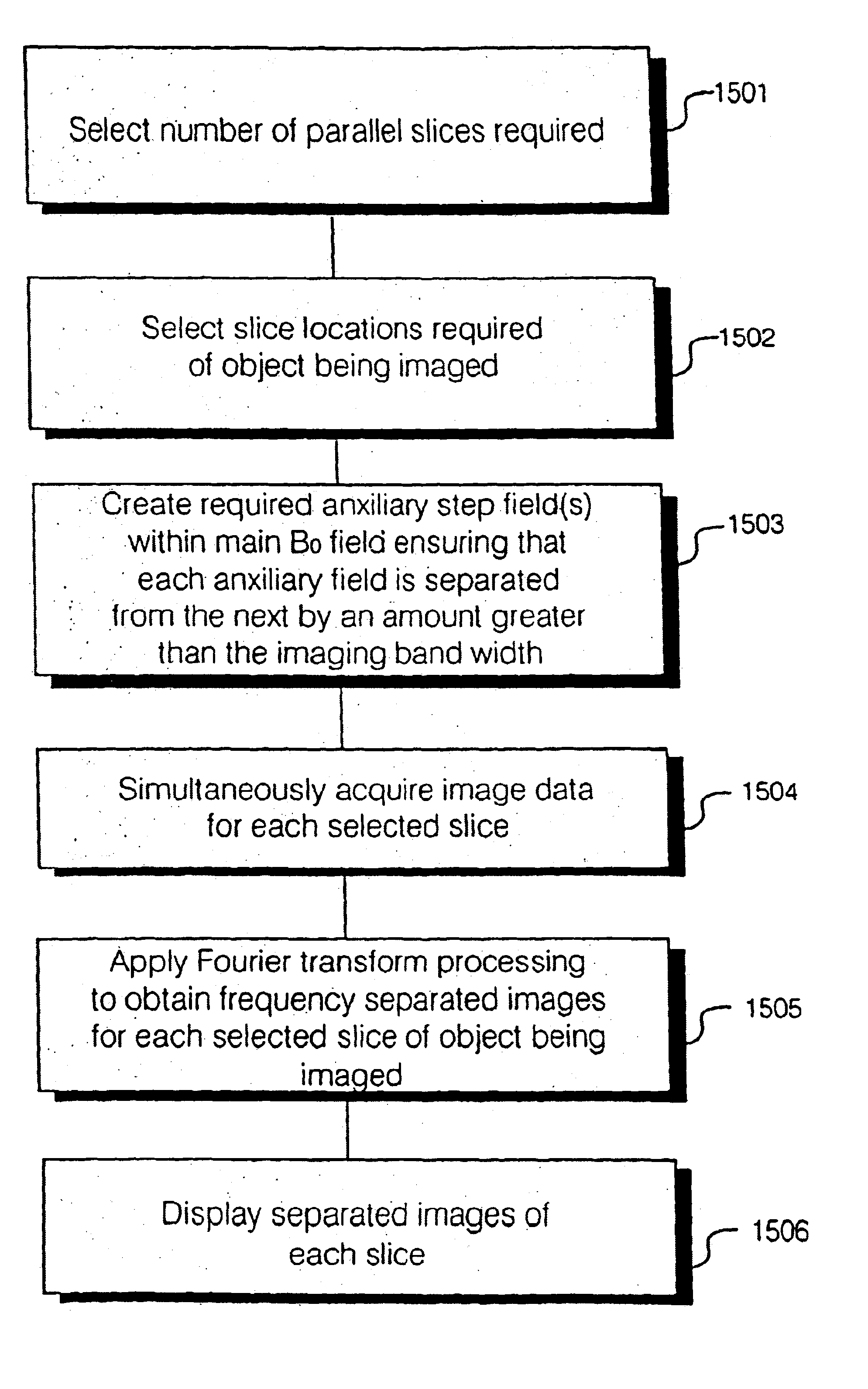
A parallel magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus configurable to image a physical entity comprises:a main magnetic flux source for providing a uniform fixed magnetic field, B0;an RF array system comprising a plurality of RF coils and receivers, said RF system configured for:generating rotating RF excitation magnetic fields B1; andreceiving RF signals due to precessing nuclear magnetization on multiple spatially distinct radio frequency coils and associated receiver channels, said RF system being configured to operate in accordance with a B1 sensitivity encoding technique;a control processor for controlling imaging functionality, collecting image data and effecting data processing of the captured image data the control processor being configured with post processing capability for the B1 sensitivity encoding technique;an image display means for displaying processed image data as resultant images; andan auxiliary magnetic field means capable of producing at least one auxiliary uniform B0 step magnetic field imaging region within the main B0 magnetic field;wherein:the auxiliary magnetic field, means is configured to operate in combination with the RF coil system and the B1 sensitivity encoding technique, the imaging apparatus thereby providing faster image acquisition than that attributed to the speed up factor provided solely by the B1 sensitivity encoding technique.The invention also includes a method of imaging using this apparatus.Furthermore, the invention also includes a method and apparatus for three-dimensional MR imaging using a 1D Multiple Acquisition Micro B0 array coupled with a 2D Multiple Acquisition Micro B0 array.
Owner:UNIV OF SHEFFIELD AT WESTERN BANK THE
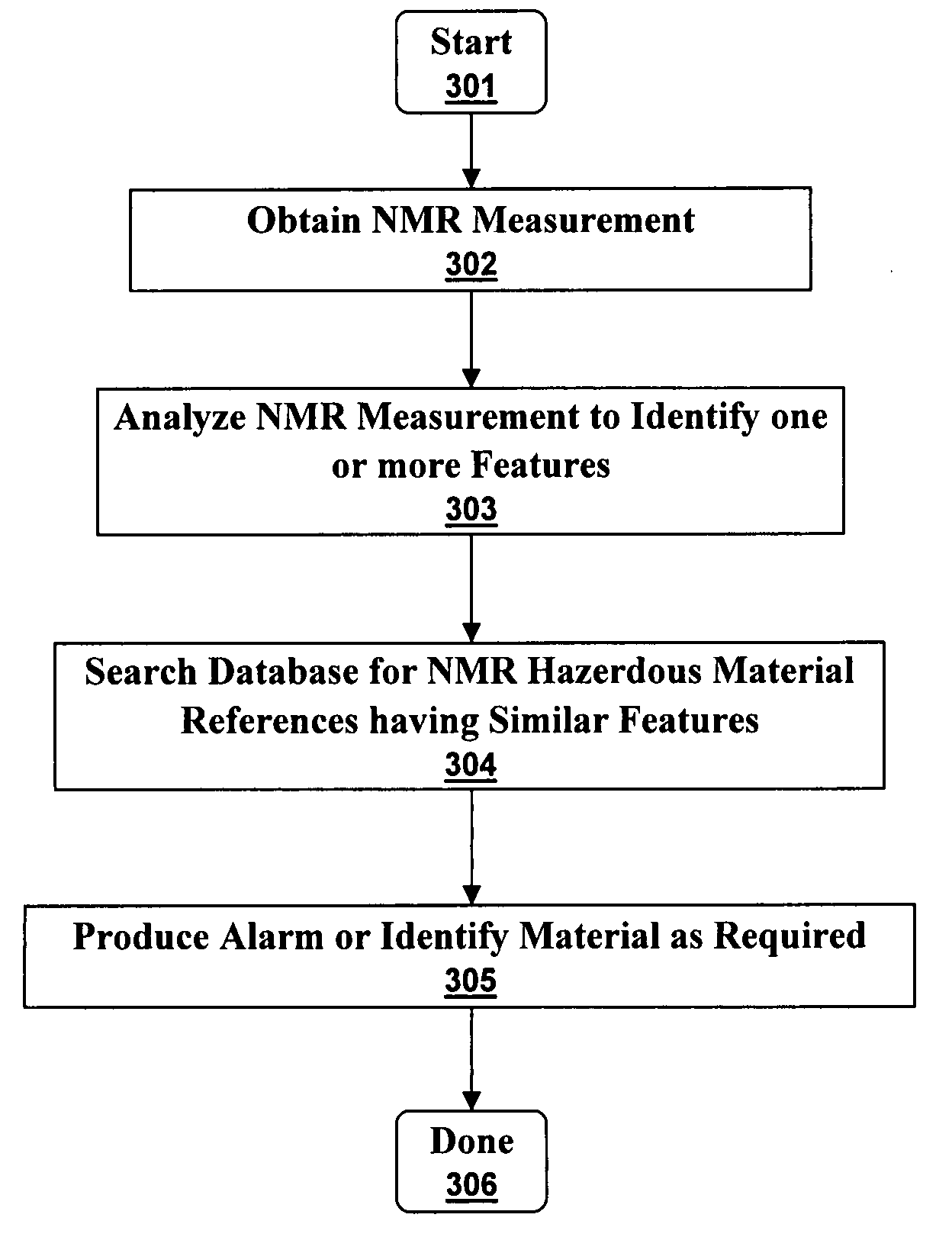
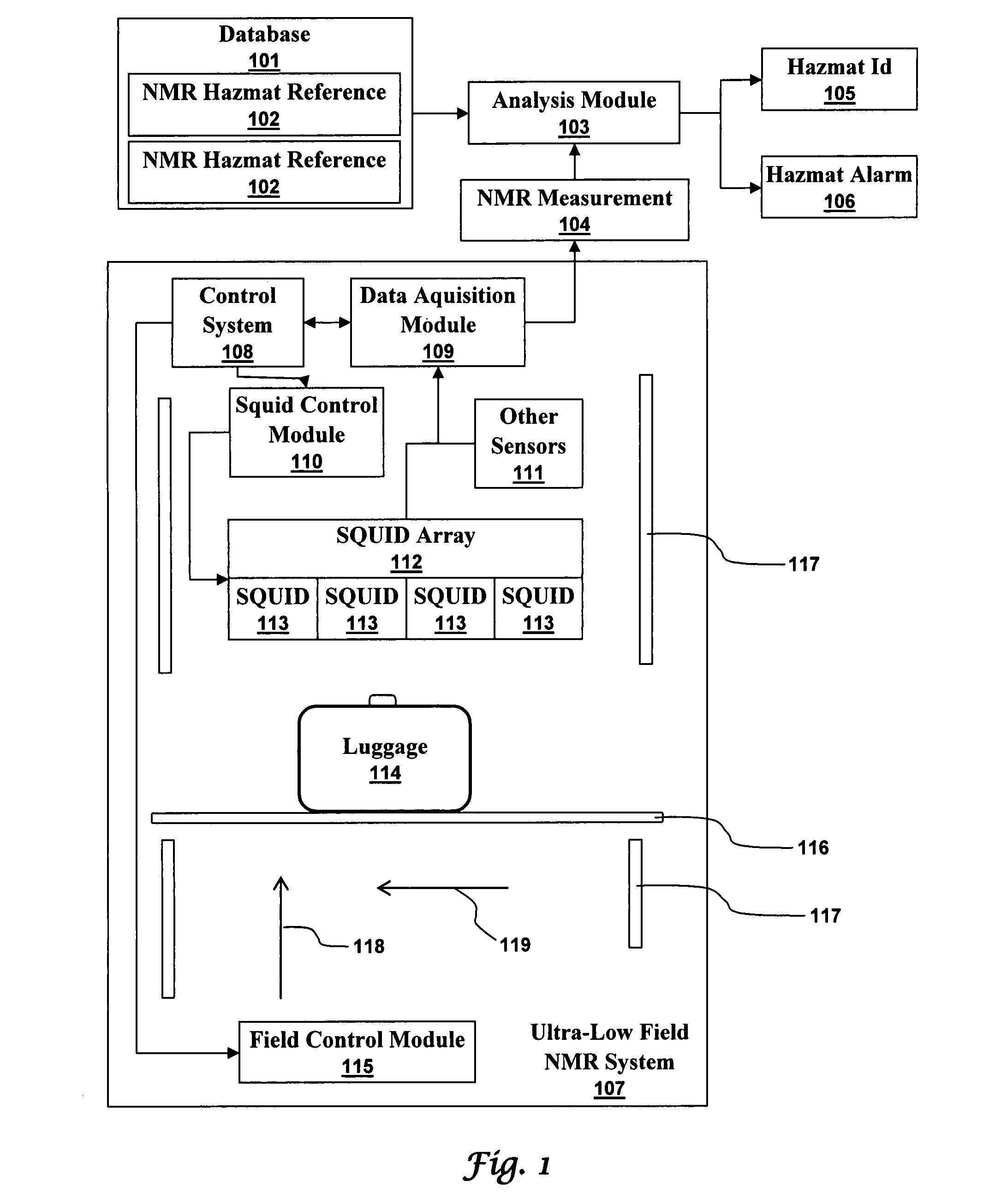
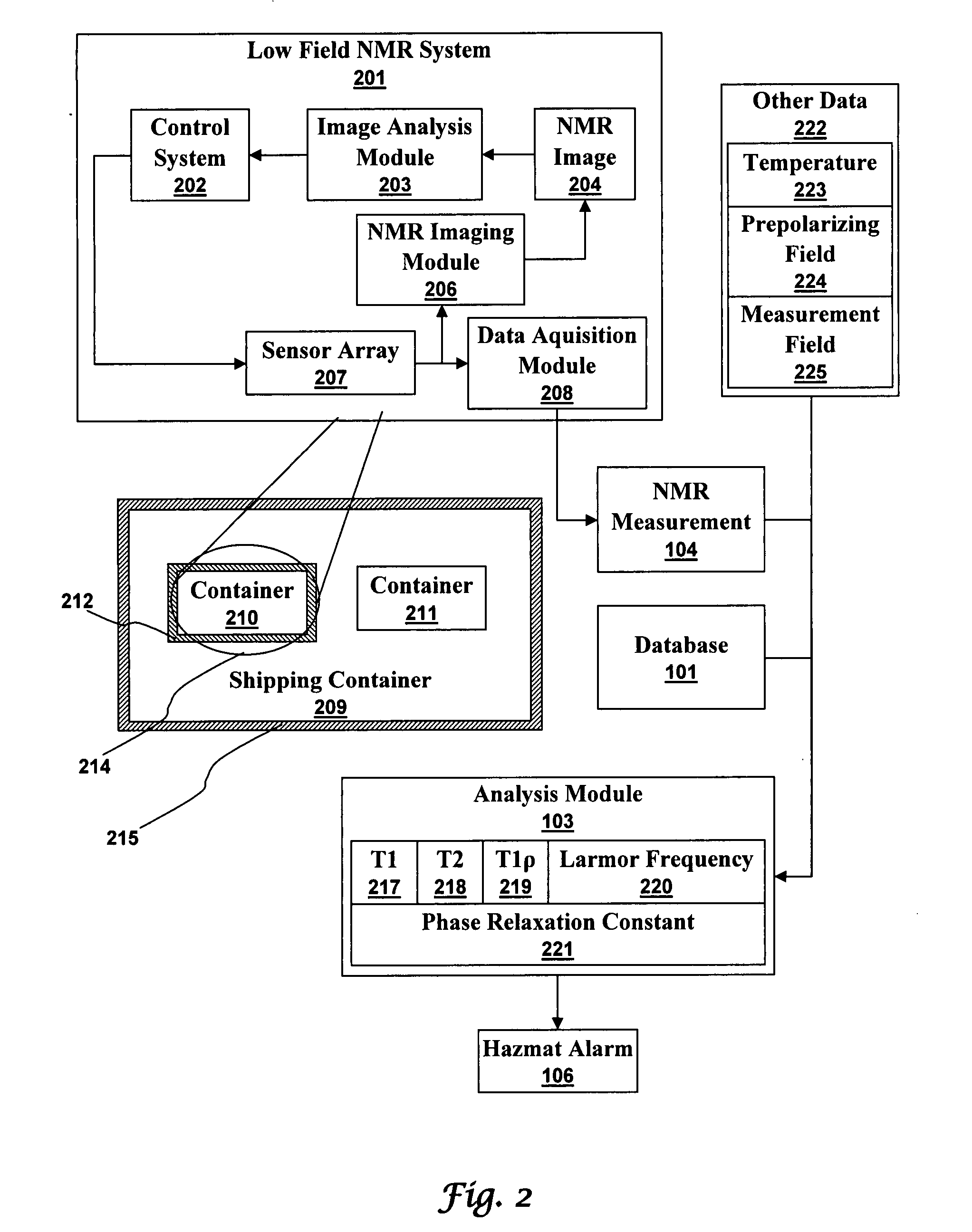
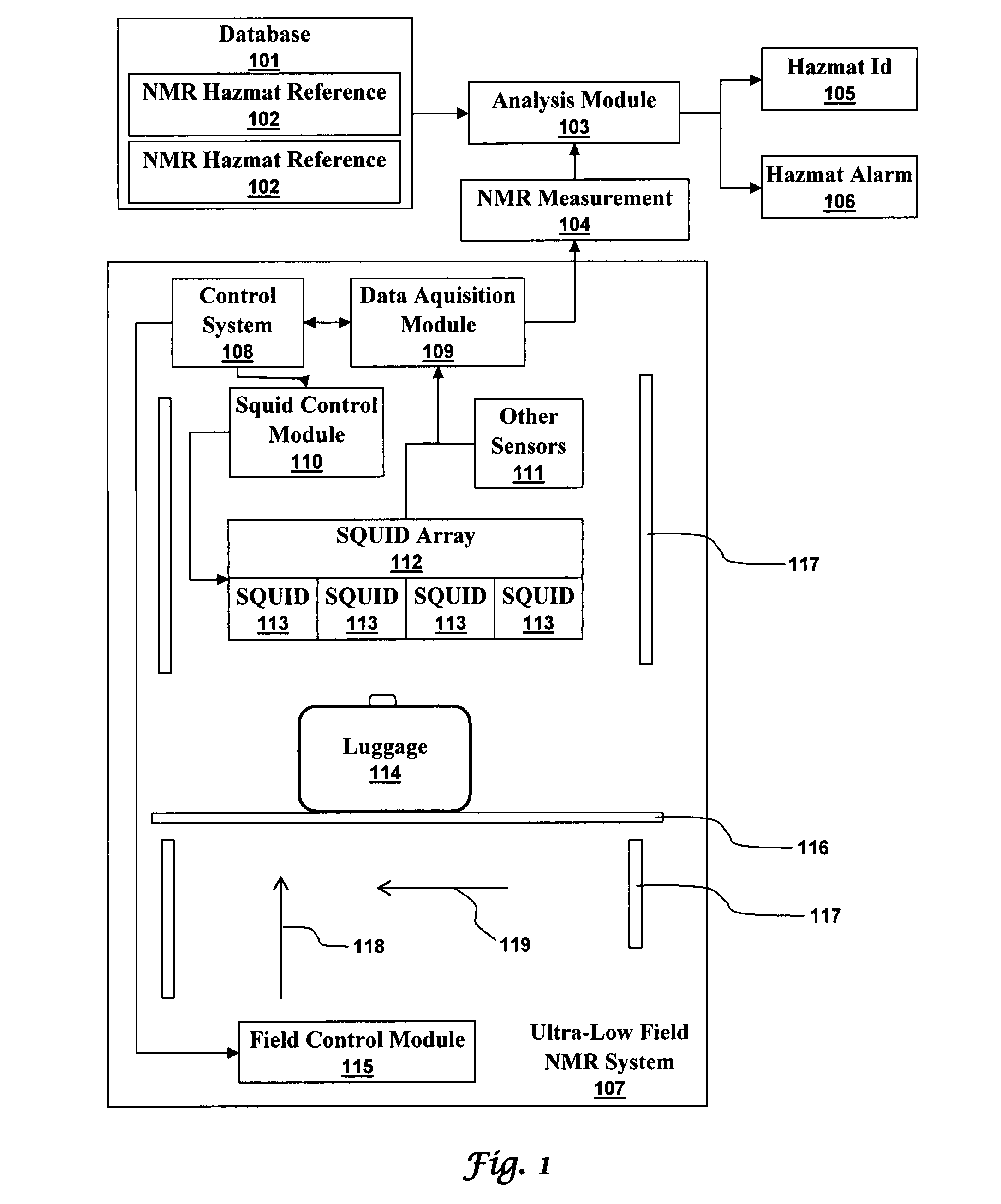
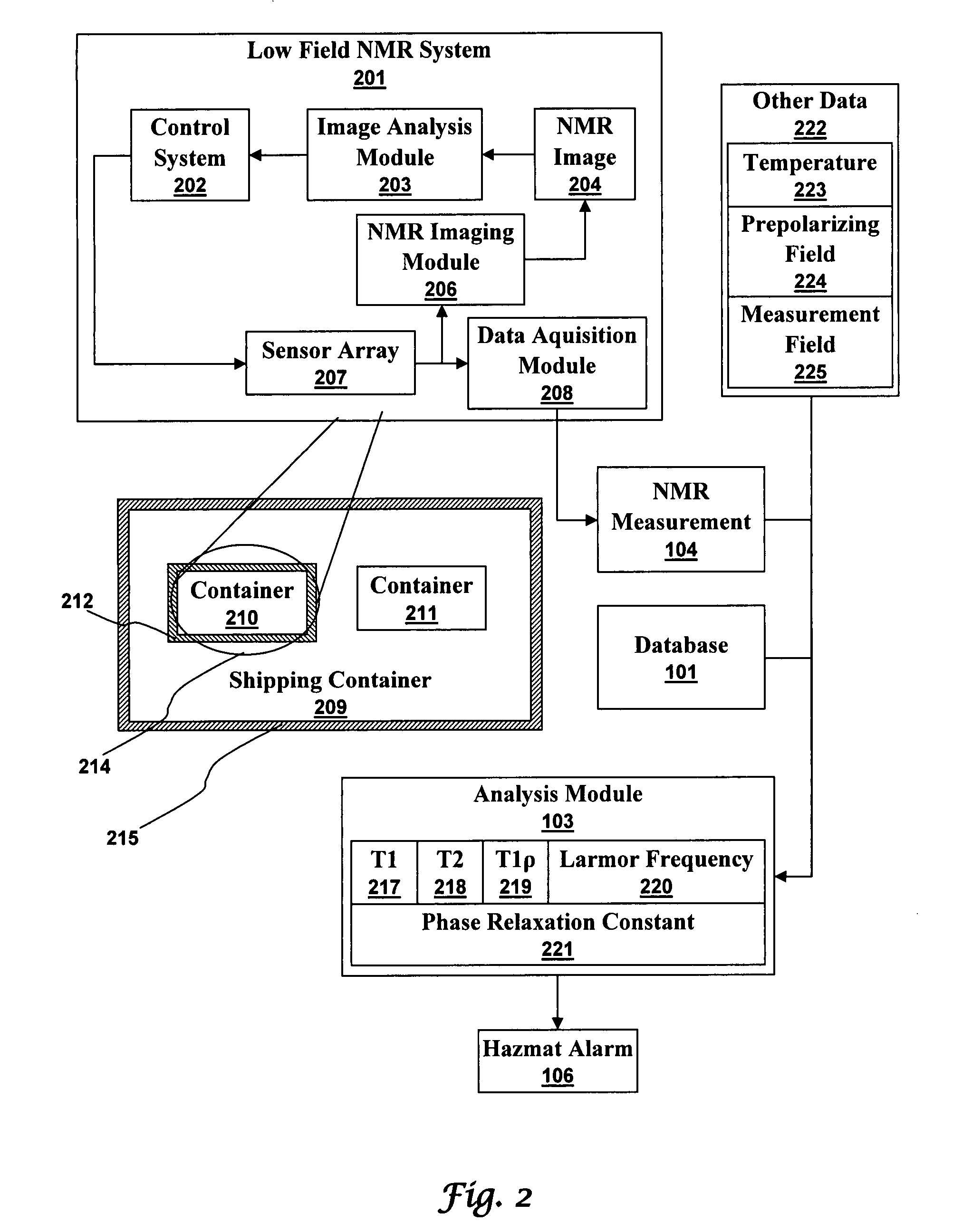
Ultra-low field nuclear magnetic resonance and magnetic resonance imaging to discriminate and identify materials
InactiveUS20080284433A1Increased signal noiseMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceLow field nuclear magnetic resonanceProton NMR
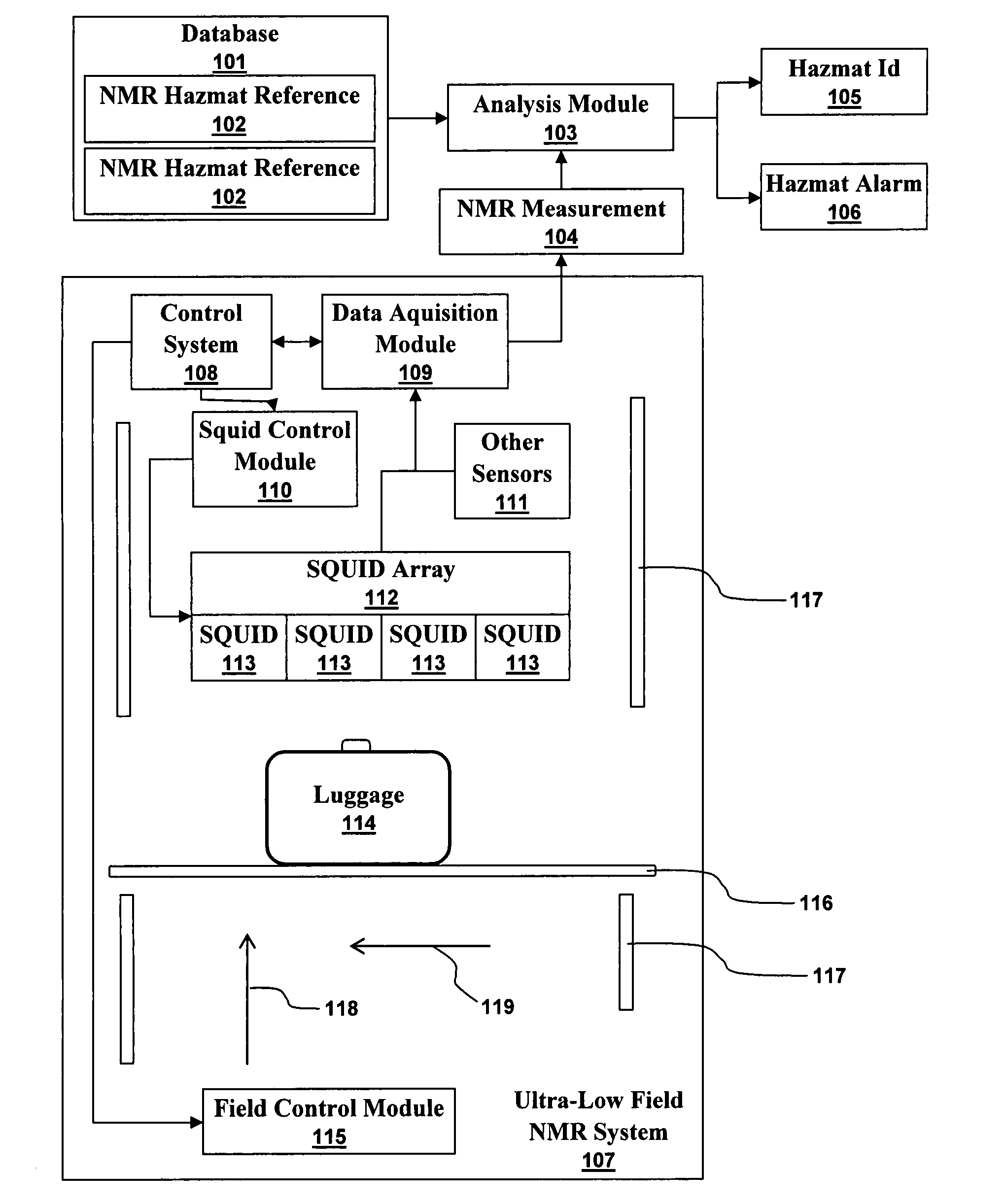
An ultra-low magnetic field NMR system can non-invasively examine containers. Database matching techniques can then identify hazardous materials within the containers. Ultra-low field NMR systems are ideal for this purpose because they do not require large powerful magnets and because they can examine materials enclosed in conductive shells such as lead shells. The NMR examination technique can be combined with ultra-low field NMR imaging, where an NMR image is obtained and analyzed to identify target volumes. Spatial sensitivity encoding can also be used to identify target volumes. After the target volumes are identified the NMR measurement technique can be used to identify their contents.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
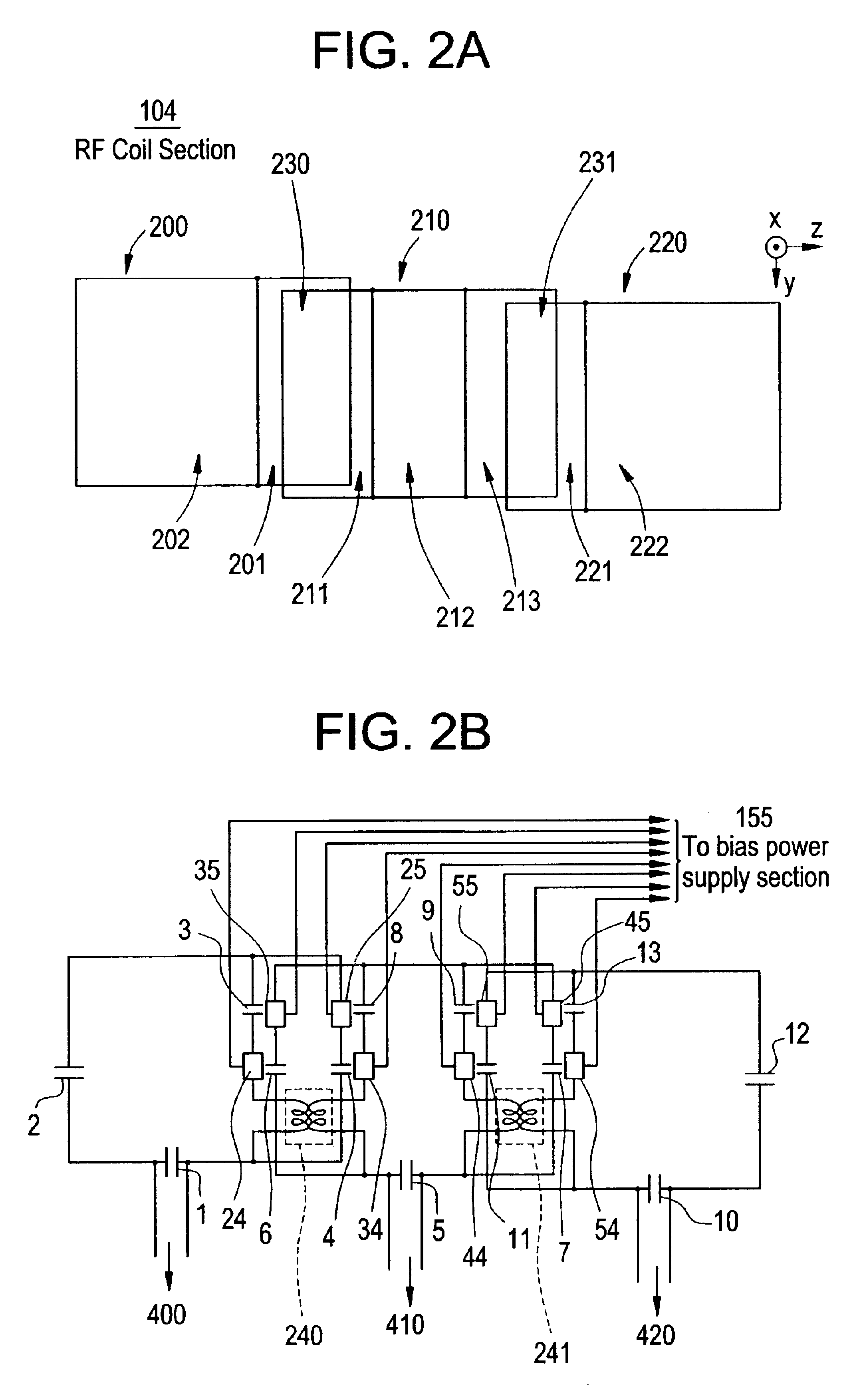
RF coil and magnetic resonance imaging apparatus
InactiveUS6879159B2High sensitivityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectronic switchEngineering
For the purpose of changing the geometry of and spacing between loop coils incorporated into an RF coil without moving the RF coil, a first plurality of loops having a geometry optimized for a square sum method employing a phased array, and a second plurality of small loops having a geometry optimized for a sensitivity encoding method are switched by switching elements for an open / close operation using a diode, and at the same time, a first decoupling means and a second decoupling means are switched. Thus, an operator is not required to replace the RF coil positioned on a cradle, and the first plurality of loops for the square sum method employing a phased array and the second plurality of small loops for the sensitivity encoding method can be switched by electronic switching and can be used as RF coils.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
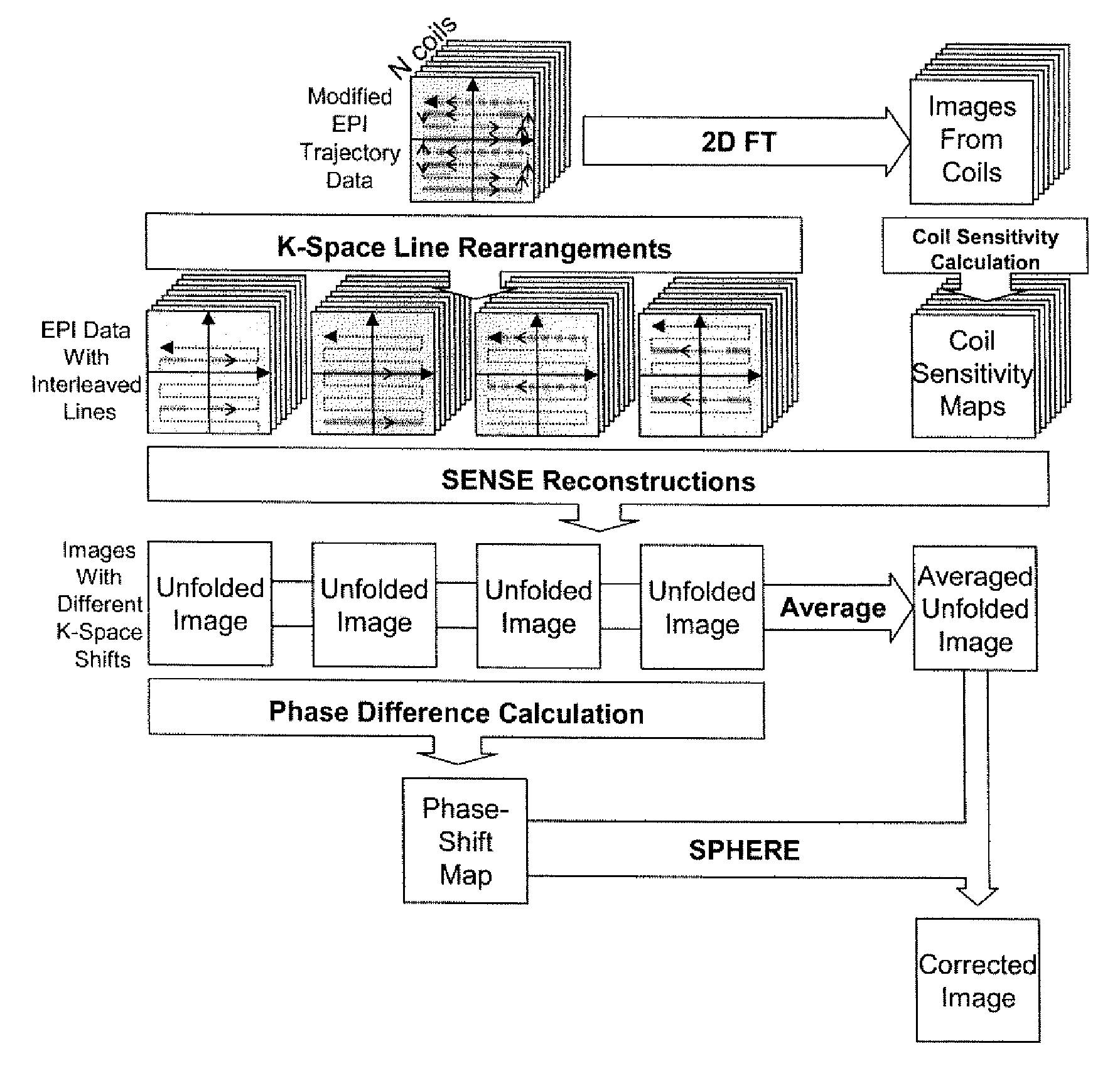
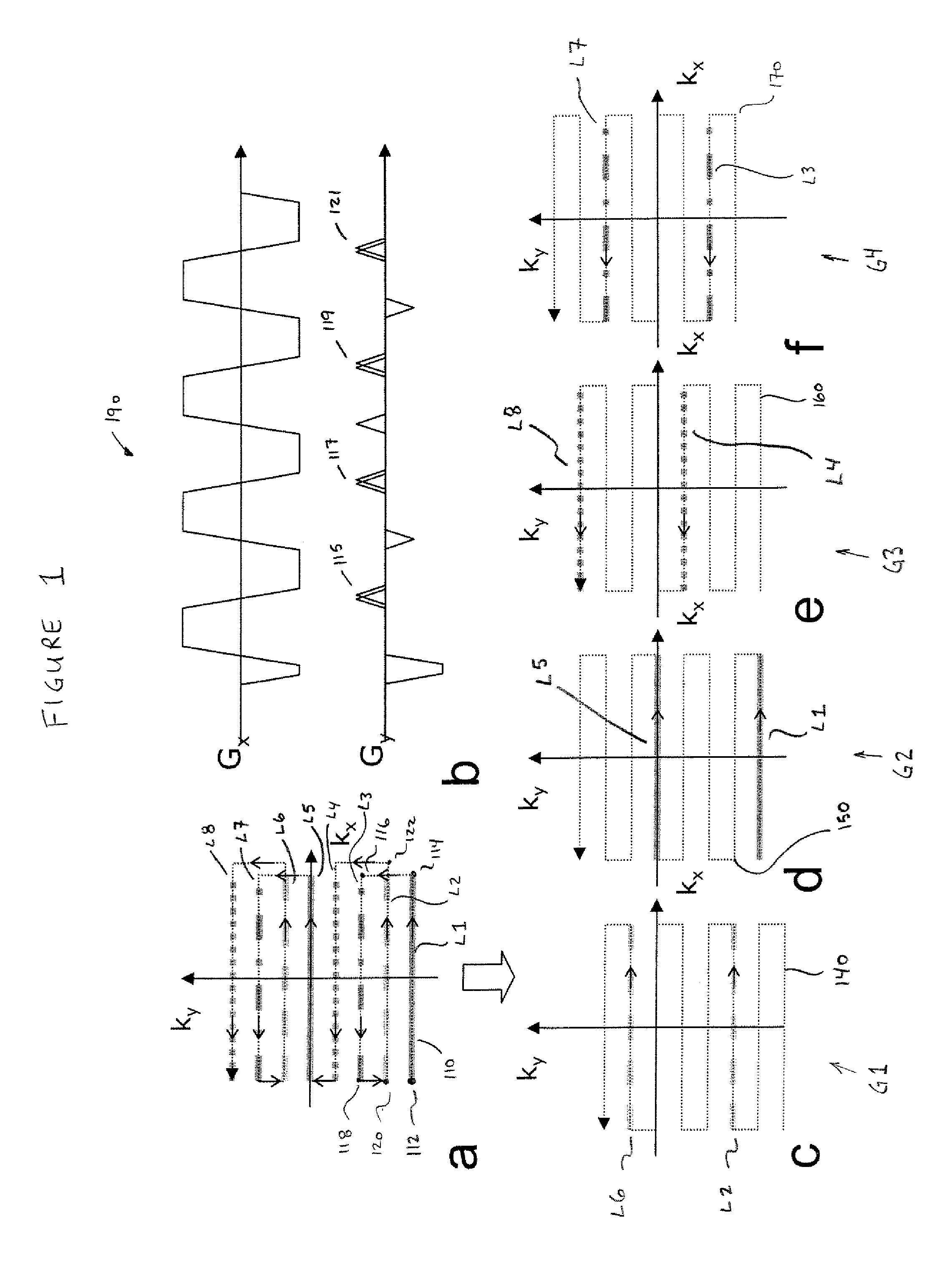
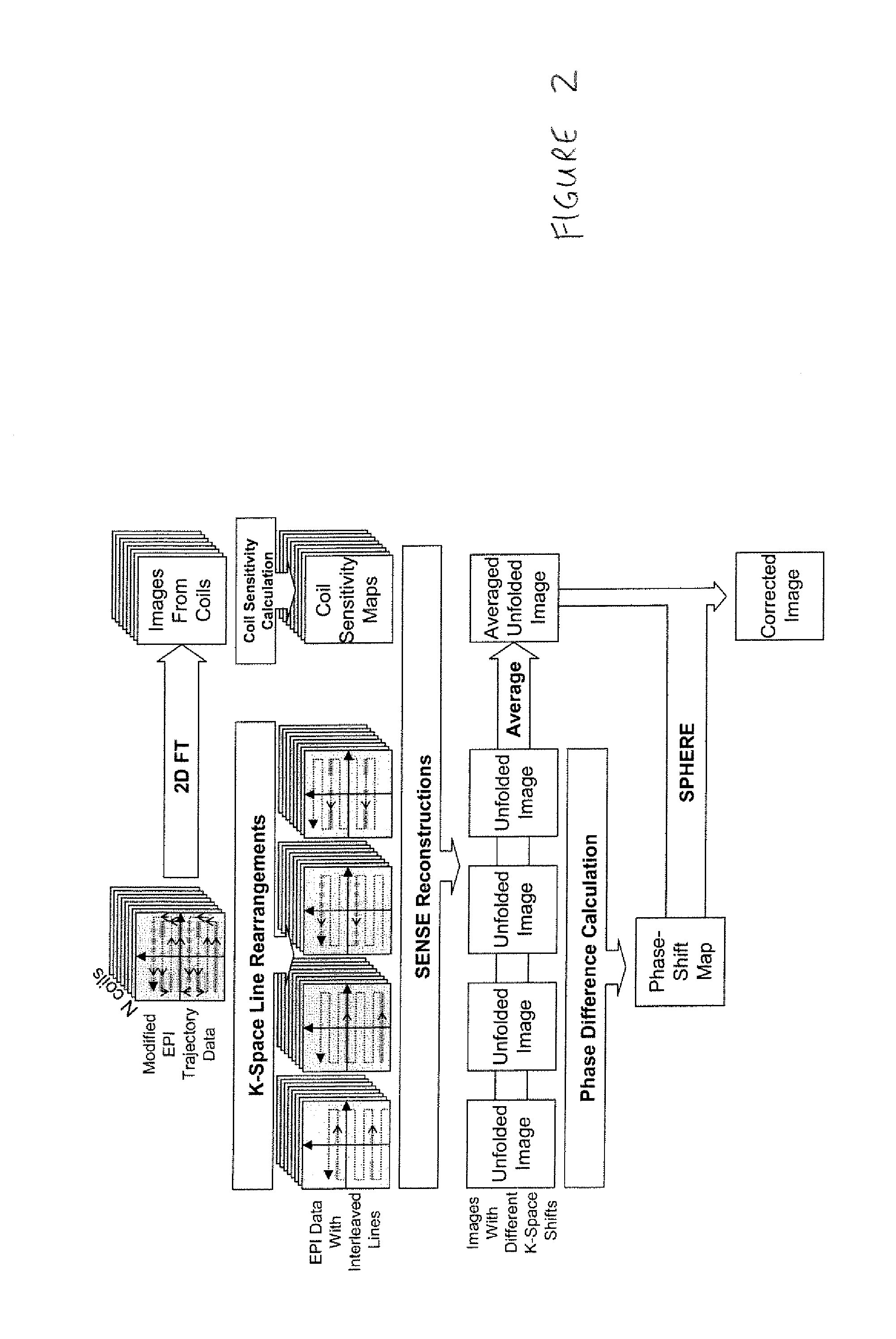
Phase labeling using sensitivity encoding: data acquisition and image reconstruction for geometric distortion correction in epi
InactiveUS20110260726A1Easy to pass to SPHERE calculationReduce artifactsMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionPhase shiftedData acquisition
A phase labeling using sensitivity encoding system and method for correcting geometric distortion caused by magnetic field inhomogeneity in echo planar imaging (EPI) uses local phase shifts derived directly from the EPI measurement itself, without the need for extra field map scans or coil sensitivity maps. The system and method employs parallel imaging and k-space trajectory modification to produce multiple images from a single acquisition. The EPI measurement is also used to derive sensitivity maps for parallel imaging reconstruction. The derived phase shifts are retrospectively applied to the EPI measurement for correction of geometric distortion in the measurement itself.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Methods & apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20040044280A1Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsData displayMagnetization
A parallel magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus configurable to image a physical entity comprises: a main magnetic flux source for providing a uniform fixed magnetic field, Balpha; an RF array system comprising a plurality of RF coils and receivers, said RF system configured for: generating rotating RF excitation magnetic fields B1; and receiving RF signals due to precessing nuclear magnetization on multiple spatially distinct radio frequency coils and associated receiver channels, said RF system being configured to operate in accordance with a B1 sensitivity encoding technique; a control processor for controlling imaging functionality, collecting image data and effecting data processing of the captured image data the control processor being configured with post processing capability for the B1 sensitivity encoding technique; an image display means for displaying processed image data as resultant images; and an auxiliary magnetic field means capable of producing at least one auxiliary uniform Bo step magnetic field imaging region within the main B0 magnetic field; wherein: the auxiliary magnetic field, means is configured to operate in combination with the RF coil system and the B1 sensitivity encoding technique, the imaging apparatus thereby providing faster image acquisition than that attributed to the speed up factor provided solely by the B1 sensitivity encoding technique. The invention also includes a method of imaging using this apparatus. Furthermore, the invention also includes a method and apparatus for three-dimensional MR imaging using a 1D Multiple Acquisition Micro Bo array coupled with a 2D Multiple Acquisition Micro Bo array.
Owner:UNIV OF SHEFFIELD AT WESTERN BANK THE
Magnetic resonance parallel imaging method with K-space sensitivity encoding
ActiveUS20060208731A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce Image ArtifactsMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Resonance
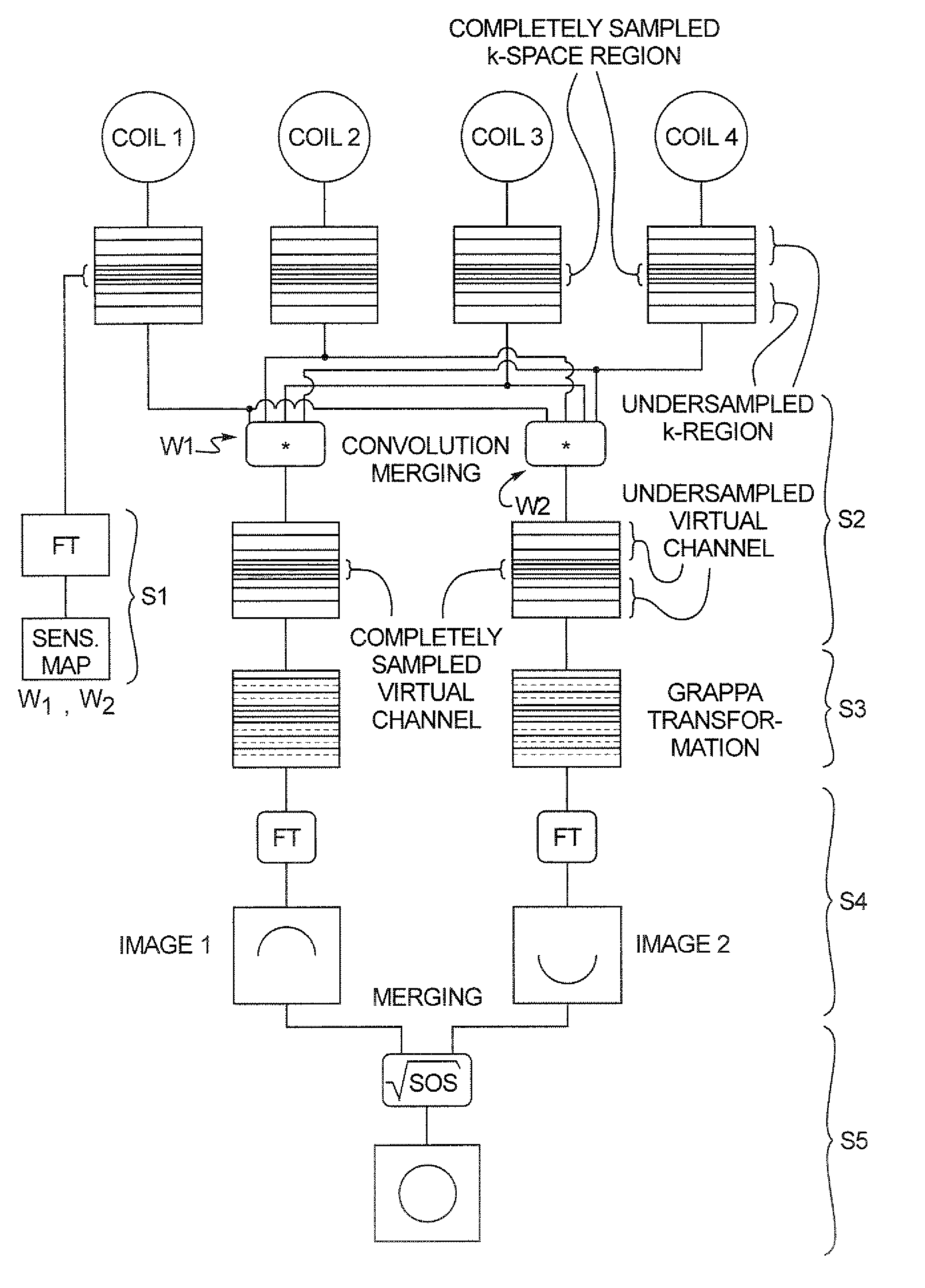
In a K-space SENSitivity Encoding (KSENSE) magnetic resonance parallel imaging method the sensitivity distribution of MR reception coils; is calculated and based on the sensitivity of the coils, signals from the respective coil merging channels are merged. The merged data are used to perform k-space data fitting and optimal fitting parameters are found. The fitting parameters are used to remove artifacts in the reconstructed image. The KSENSE method, compared to SENSE, mSENSE and GRAPPA, has the advantages of the image reconstructed by KSENSE having an optimized signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) that is superior to that of an image reconstructed by GRAPPA under the same conditions and approximates that when mSENSE is used, and an image reconstructed by KSENSE has relatively low residual artifacts and an artifact intensity, as a whole, that is superior to that of an image reconstructed by SENSE or the like under the same conditions and equivalent to that when GRAPPA is used, and, compared to GRAPPA that also performs operations in k-space, KSENSE has a higher reconstruction speed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
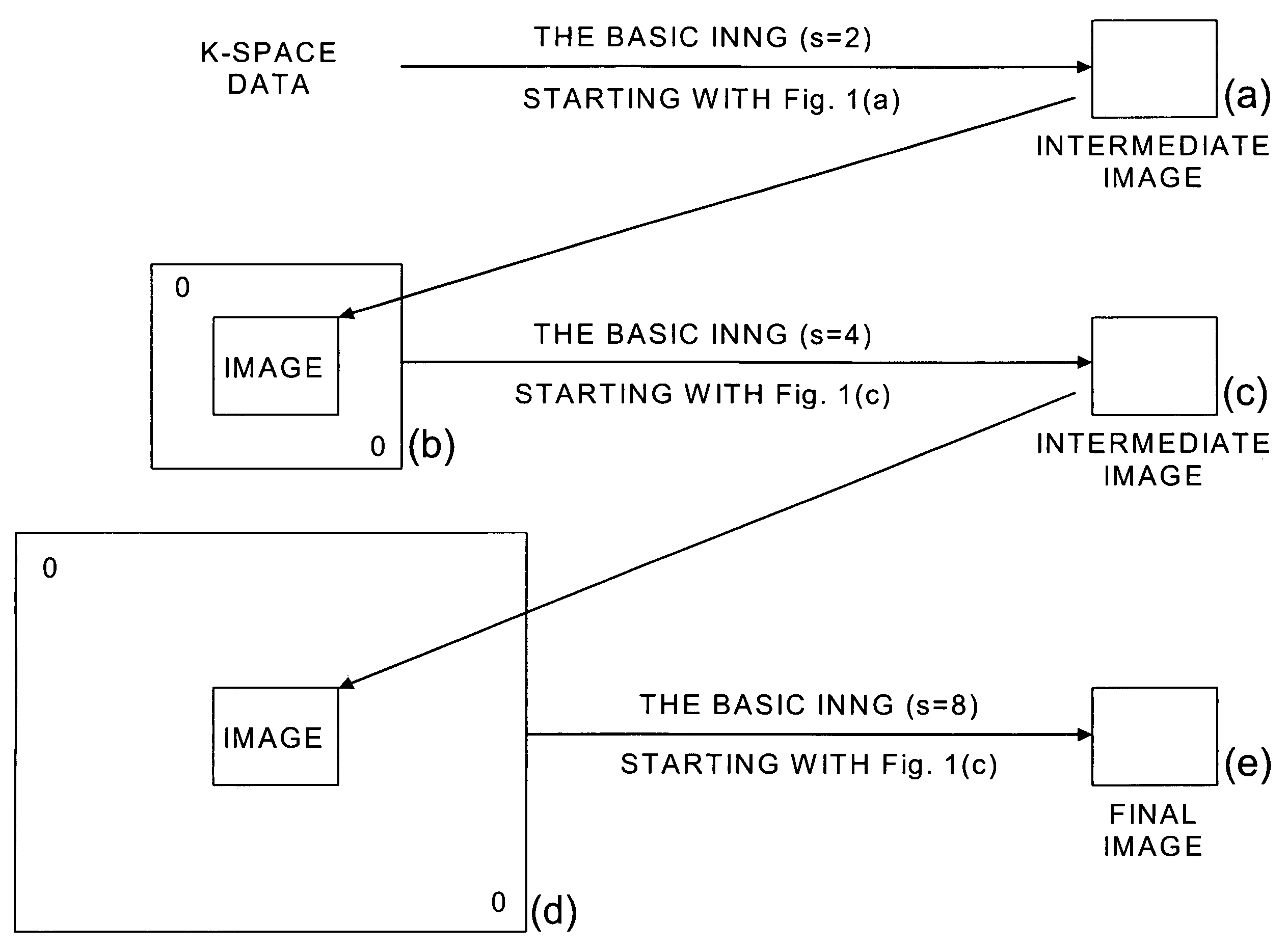
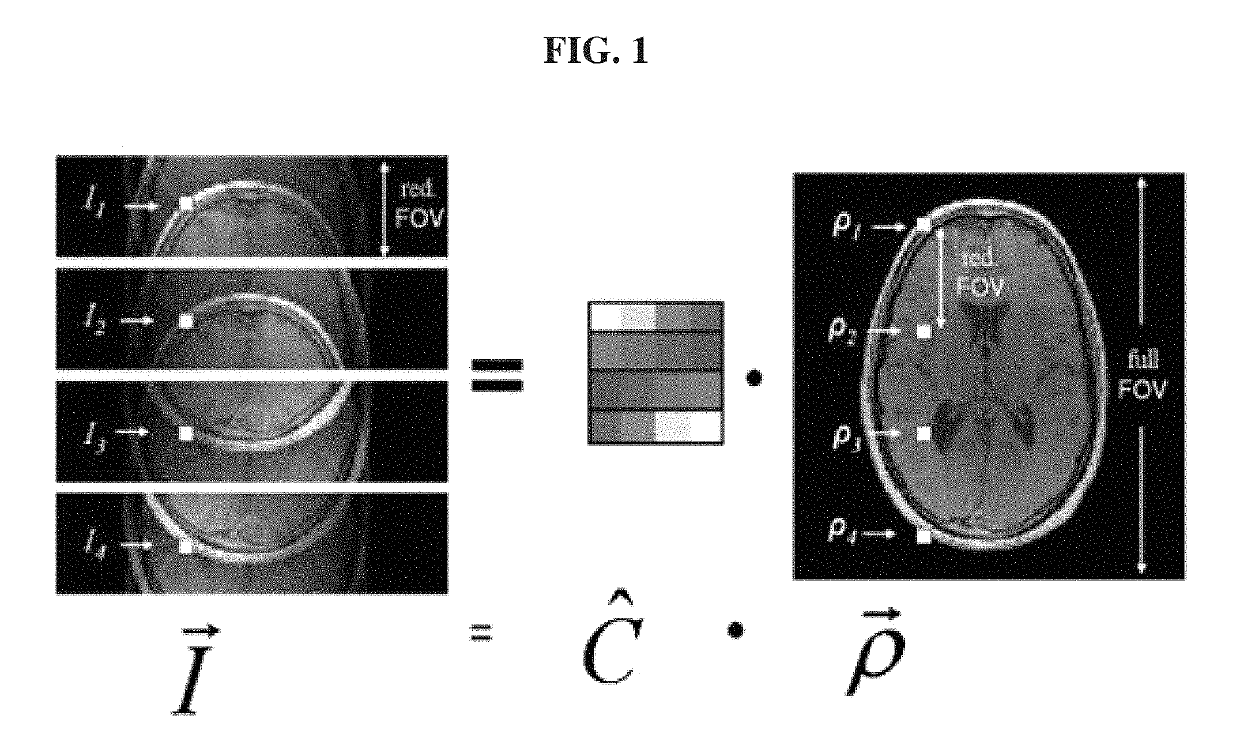
Efficient method for MR image reconstruction using coil sensitivity encoding
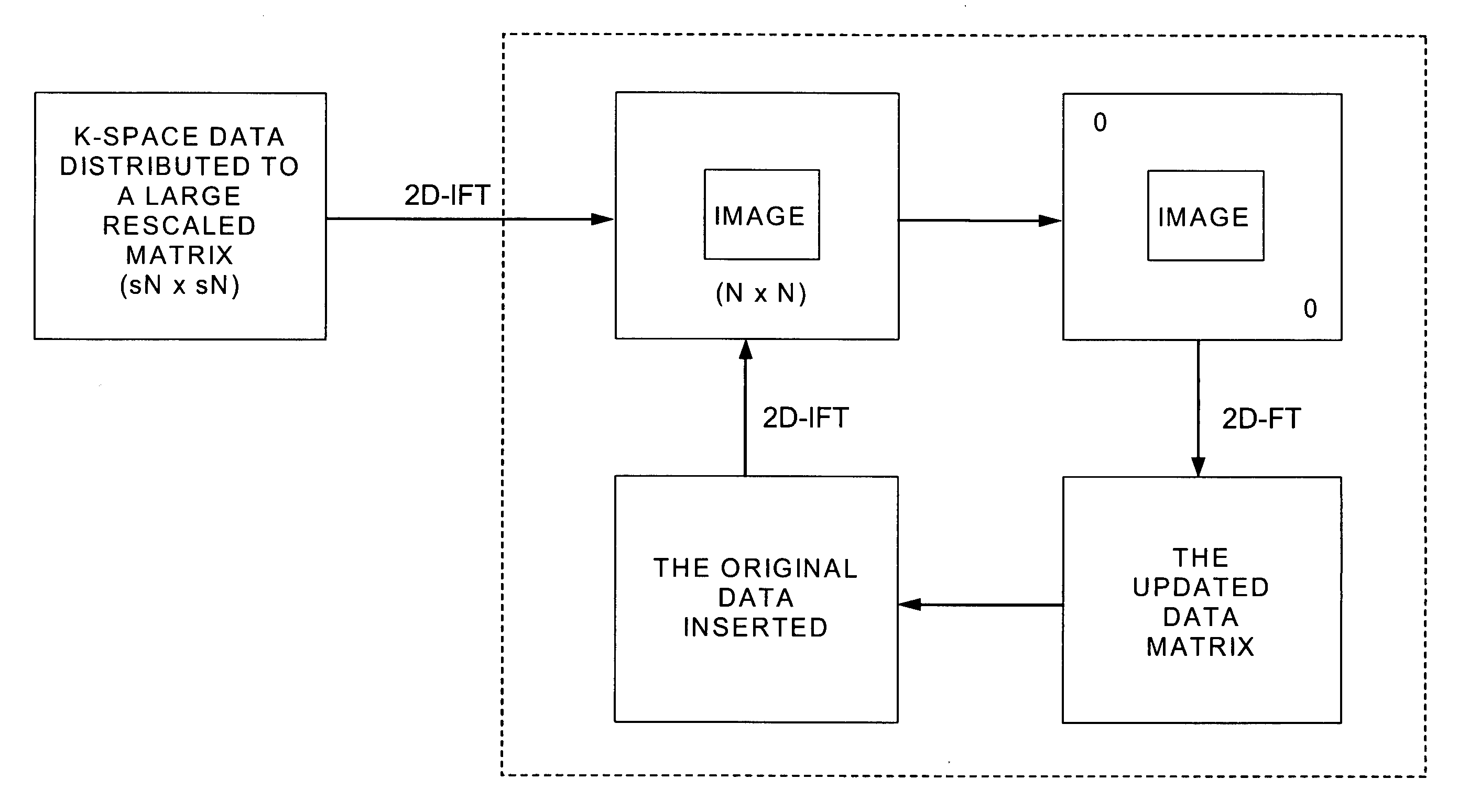
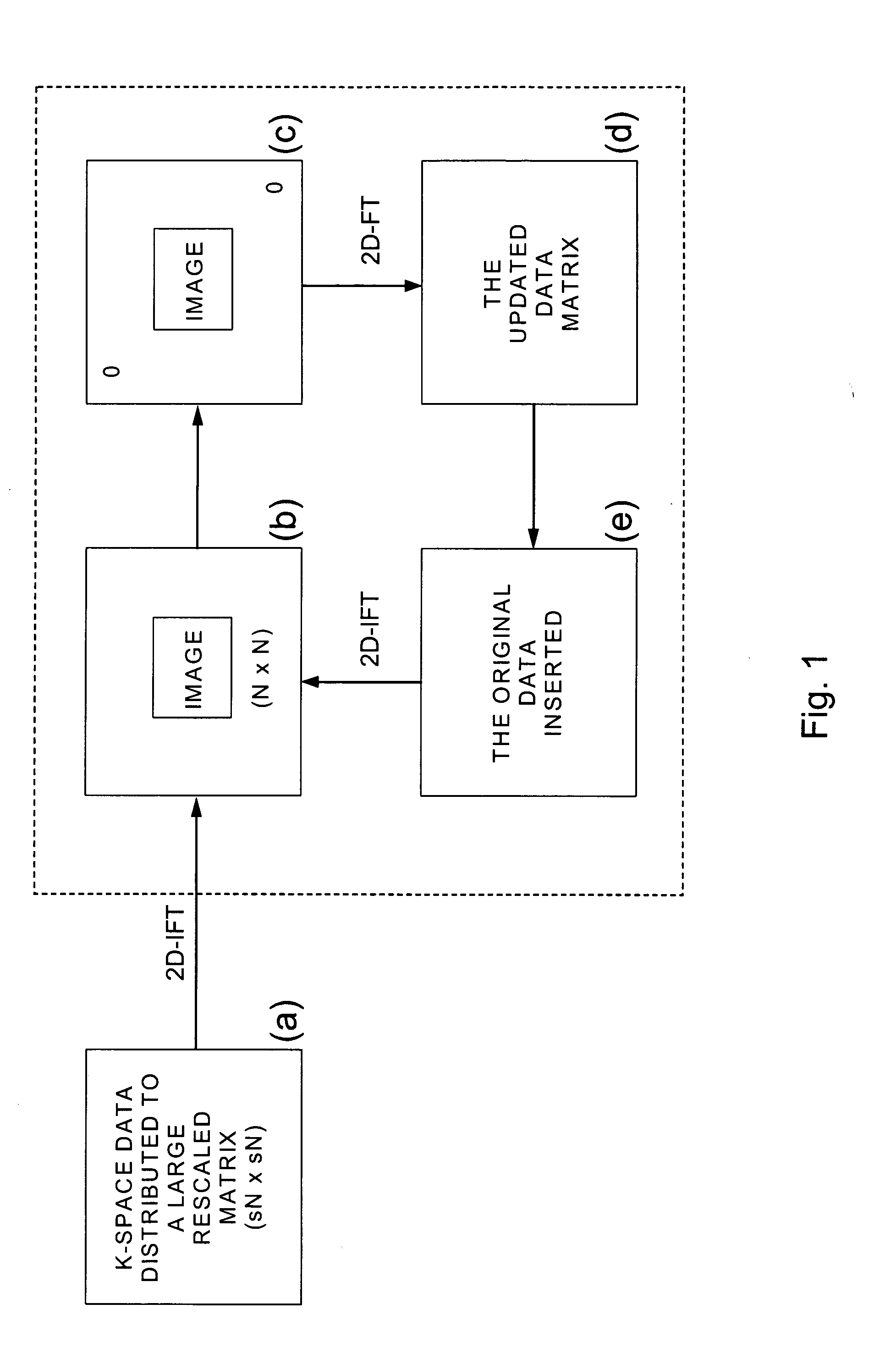
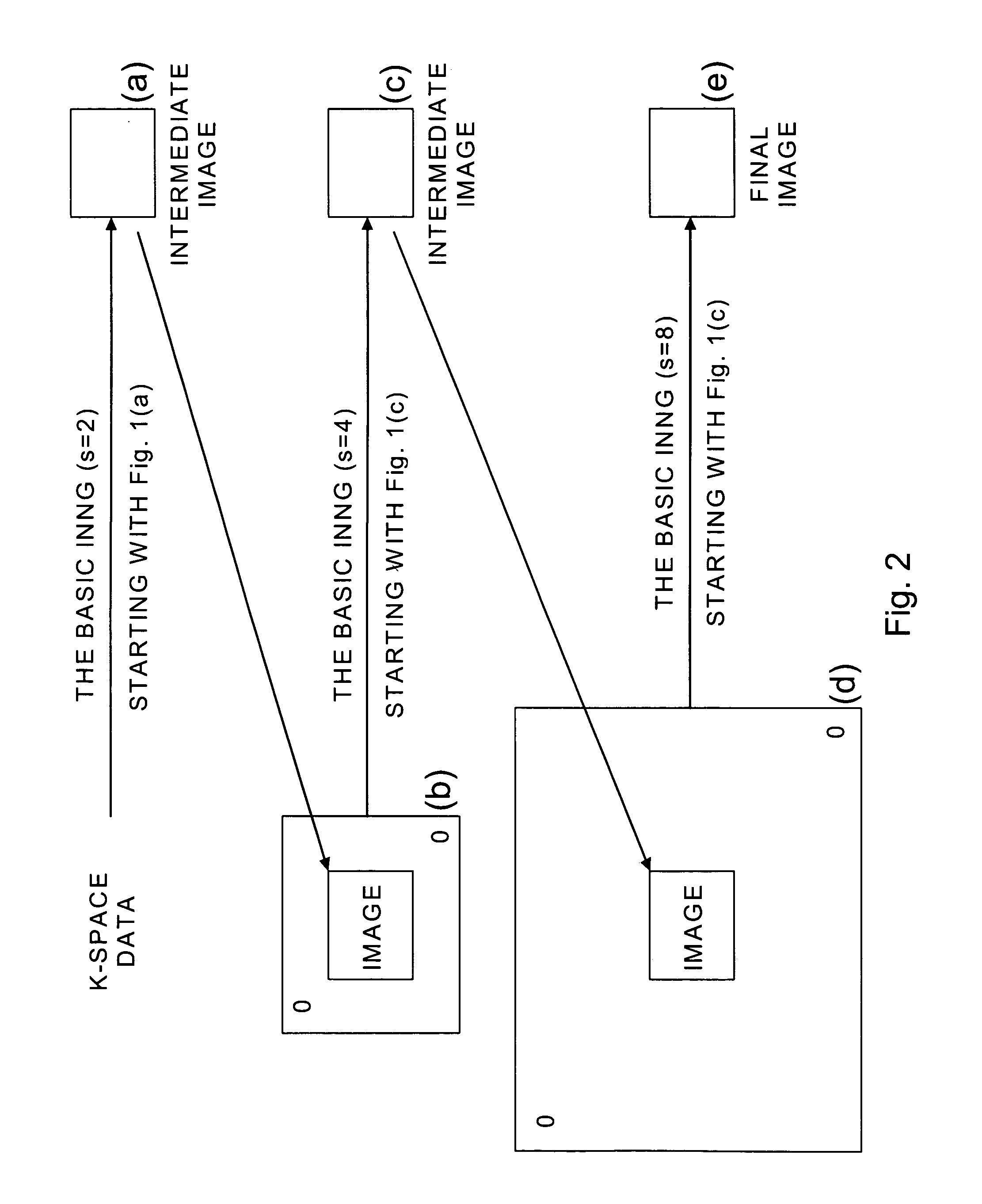
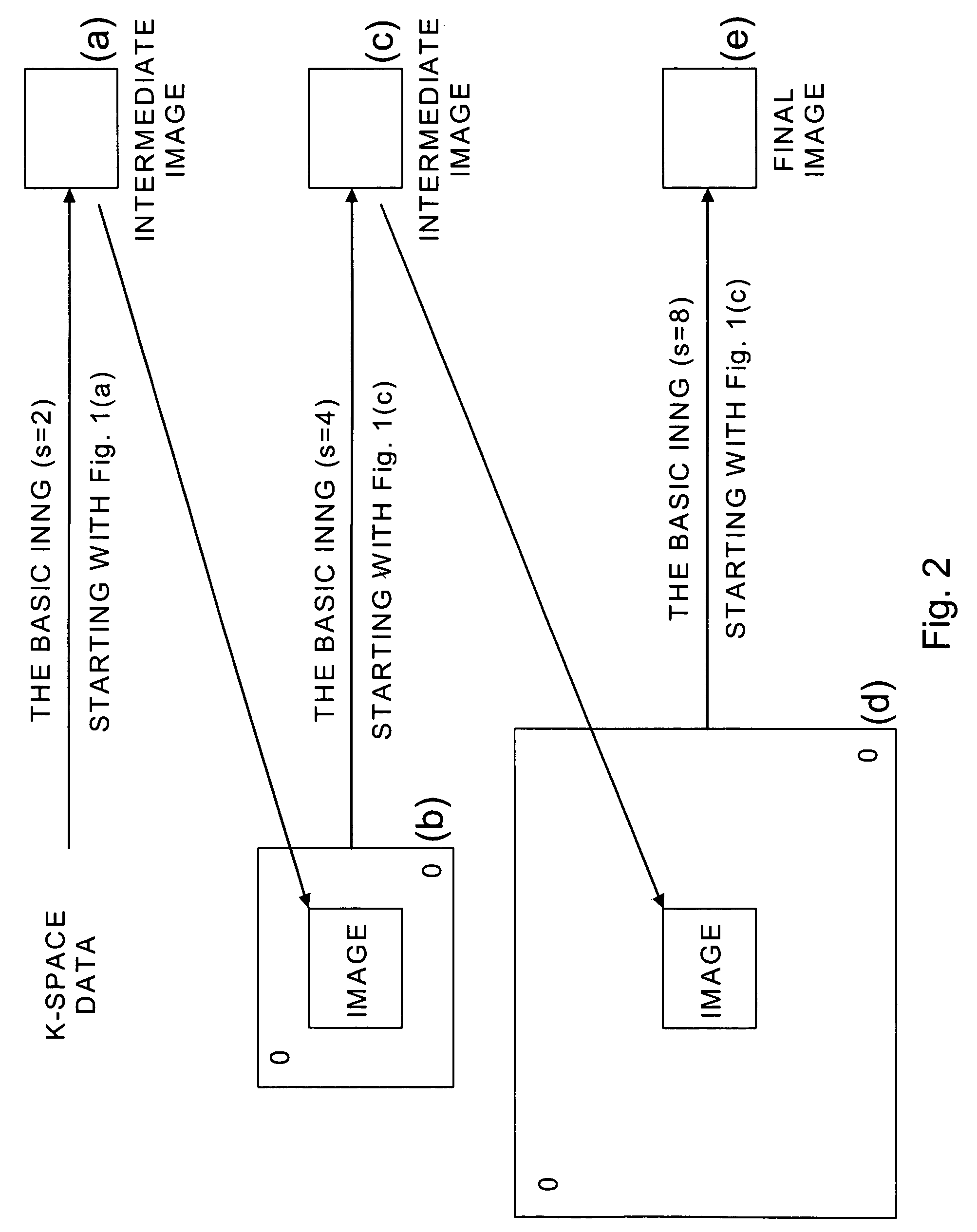
SENSitivity Encoding (SENSE) has demonstrated potential for significant scan time reduction using multiple receiver channels. SENSE reconstruction algorithms for non-uniformly sampled data proposed to date require relatively high computational demands. A Projection Onto Convex Sets (POCS)-based SENSE reconstruction method (POCSENSE) has been recently proposed as an efficient reconstruction technique in rectilinear sampling schemes. POCSENSE is an iterative algorithm with a few constraints imposed on the acquired data sets at each iteration. Although POCSENSE can be readily performed on rectilinearly acquired k-space data, it is difficult to apply to non-uniformly acquired k-space data. Iterative Next Neighbor re-Gridding (INNG) algorithm is a recently proposed new reconstruction method for non-uniformly sampled k-space data. The POCSENSE algorithm can be extended to non-rectilinear sampling schemes by using the INNG algorithm. The resulting algorithm (POCSENSINNG) is an efficient SENSE reconstruction algorithm for non-uniformly sampled k-space data, taking into account coil sensitivities.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Ultra-low field nuclear magnetic resonance and magnetic resonance imaging to discriminate and identify materials
InactiveUS7688069B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsMaterial analysis by using resonanceHazardous substanceLow field nuclear magnetic resonance
An ultra-low magnetic field NMR system can non-invasively examine containers. Database matching techniques can then identify hazardous materials within the containers. Ultra-low field NMR systems are ideal for this purpose because they do not require large powerful magnets and because they can examine materials enclosed in conductive shells such as lead shells. The NMR examination technique can be combined with ultra-low field NMR imaging, where an NMR image is obtained and analyzed to identify target volumes. Spatial sensitivity encoding can also be used to identify target volumes. After the target volumes are identified the NMR measurement technique can be used to identify their contents.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Efficient method for MR image reconstruction using coil sensitivity encoding
SENSitivity Encoding (SENSE) has demonstrated potential for significant scan time reduction using multiple receiver channels. SENSE reconstruction algorithms for non-uniformly sampled data proposed to date require relatively high computational demands. A Projection Onto Convex Sets (POCS)-based SENSE reconstruction method (POCSENSE) has been recently proposed as an efficient reconstruction technique in rectilinear sampling schemes. POCSENSE is an iterative algorithm with a few constraints imposed on the acquired data sets at each iteration. Although POCSENSE can be readily performed on rectilinearly acquired k-space data, it is difficult to apply to non-uniformly acquired k-space data. Iterative Next Neighbor re-Gridding (INNG) algorithm is a recently proposed new reconstruction method for non-uniformly sampled k-space data. The POCSENSE algorithm can be extended to non-rectilinear sampling schemes by using the INNG algorithm. The resulting algorithm (POCSENSINNG) is an efficient SENSE reconstruction algorithm for non-uniformly sampled k-space data, taking into account coil sensitivities.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
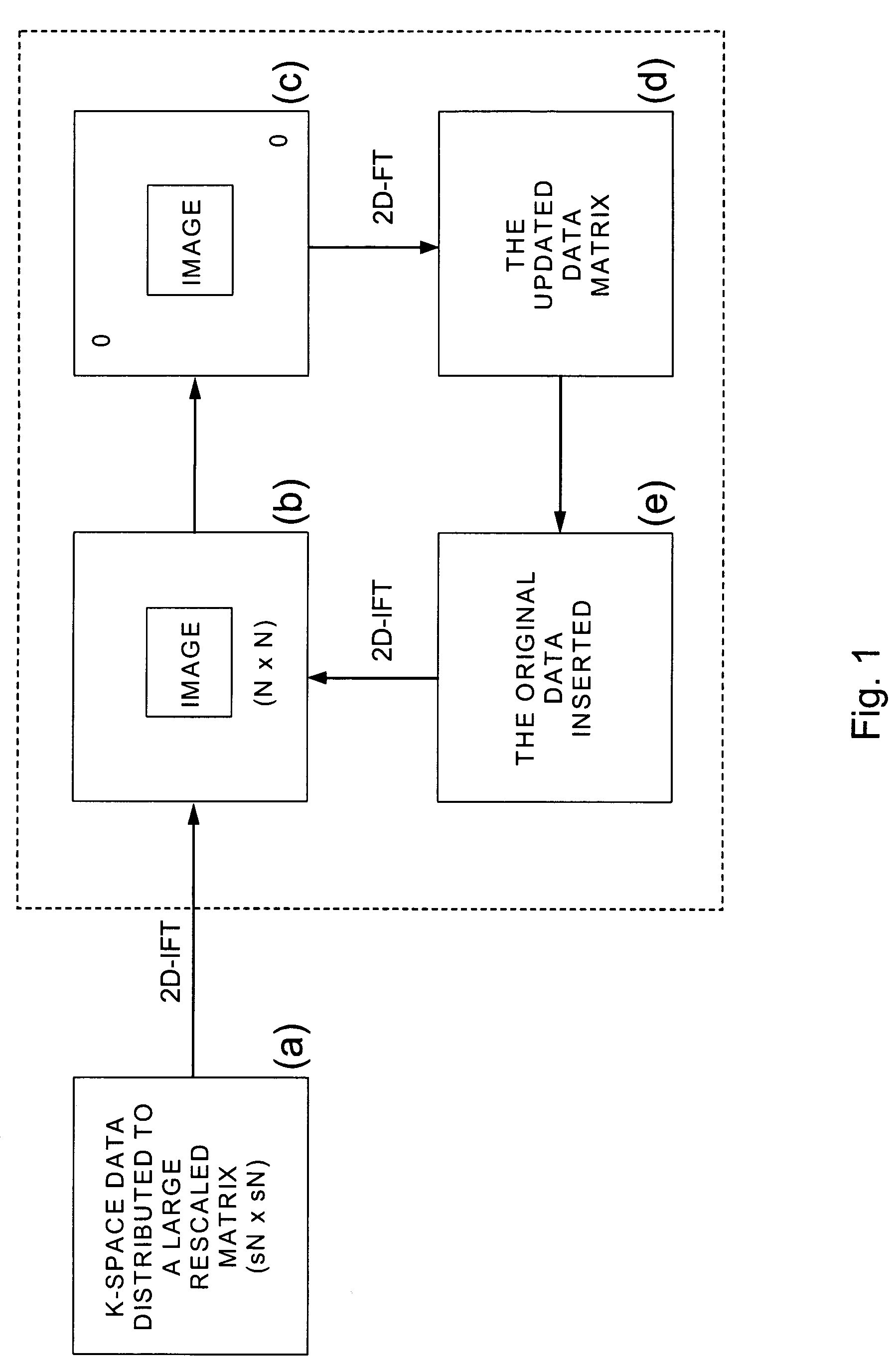
Fast self-calibrating radial sensitivity encoded image reconstruction using rescaling and preconditioning
InactiveUS20080144900A1Remove complexityFast convergenceMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmReduction factor
In a magnetic resonance imaging method and apparatus, sensitivity encoding (SENSE) with radial sampling trajectories combines the gridding principle with conjugate-gradient least-squares (CGLS) iterative reconstruction. Radial k-space is mapped to a larger matrix by a resealing factor to eliminate the computational complexity of conventional gridding and density compensation. To improve convergence rate of high spatial frequency signals in CGLS iteration, a spatially invariant de-blurring k-space filter uses the impulse response of the system. This filter is incorporated into the SENSE reconstruction as preconditioning. The optimal number of iterations represents a tradeoff between image accuracy and noise over several reduction factors.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
System and Method for Mode Mixing in Magnetic Resonance Imaging
ActiveUS20100289494A1Reduce in quantityEasy to detectElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRSignal compressionSensitivity encoding
The present invention provides a system and method for using a hardware-based compression of signals acquired with an magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system. This allows a first multi-channel MR signal to be compressed to a second multi-channel MR signal having fewer channels than the first MR signal. This system and method reduces the number of RF receivers needed to achieve the sensitivity encoding benefits associated with highly parallel detection in MRI. Furthermore, the system and method reduces bottlenecks connection an MRI system's RF receiver and reconstruction computer and reduces the computational burden of image reconstruction.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Magnetic resonance parallel imaging method with K-space sensitivity encoding
ActiveUS7202666B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce Image ArtifactsMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Resonance
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and method for variable mode-mixing in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS8581589B2Reduce in quantitySensitivity and encodingElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceEngineeringSensitivity encoding
The present invention provides a system and method for using a hardware-based compression of signals acquired with an magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system. This allows a first multi-channel MR signal to be compressed to a second multi-channel MR signal having fewer channels than the first MR signal. This system and method reduces the number of RF receivers needed to achieve the sensitivity encoding benefits associated with highly parallel detection in MRI. Furthermore, the system and method reduces bottlenecks connection an MRI system's RF receiver and reconstruction computer and reduces the computational burden of image reconstruction.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
PPI joint reconstruction method of multi-contrast magnetic resonance images
The invention relates to the field of reconstruction of magnetic resonance images, for the purpose of providing a PPI joint reconstruction method of multi-contrast magnetic resonance images. The PPI joint reconstruction method of the multi-contrast magnetic resonance images comprises the following process: obtaining the multi-contrast magnetic resonance images needing image reconstruction, reconstructing the acquired images by use of a space sensitivity encoding technology, performing the image reconstruction by use of a model, and finally obtaining reconstructed images through calculation. According to the invention, a rapid and highly efficient reconstruction algorithm is designed through establishment of a reasonable mathematical model and is applied to the problem of joint reconstruction of the magnetic resonance image, such that the purposes of shortening the scanning time, improving the imaging quality and reducing the pain of patients and the treatment cost can be effectively realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DE IMAGE SOLUTIONS CO LTD
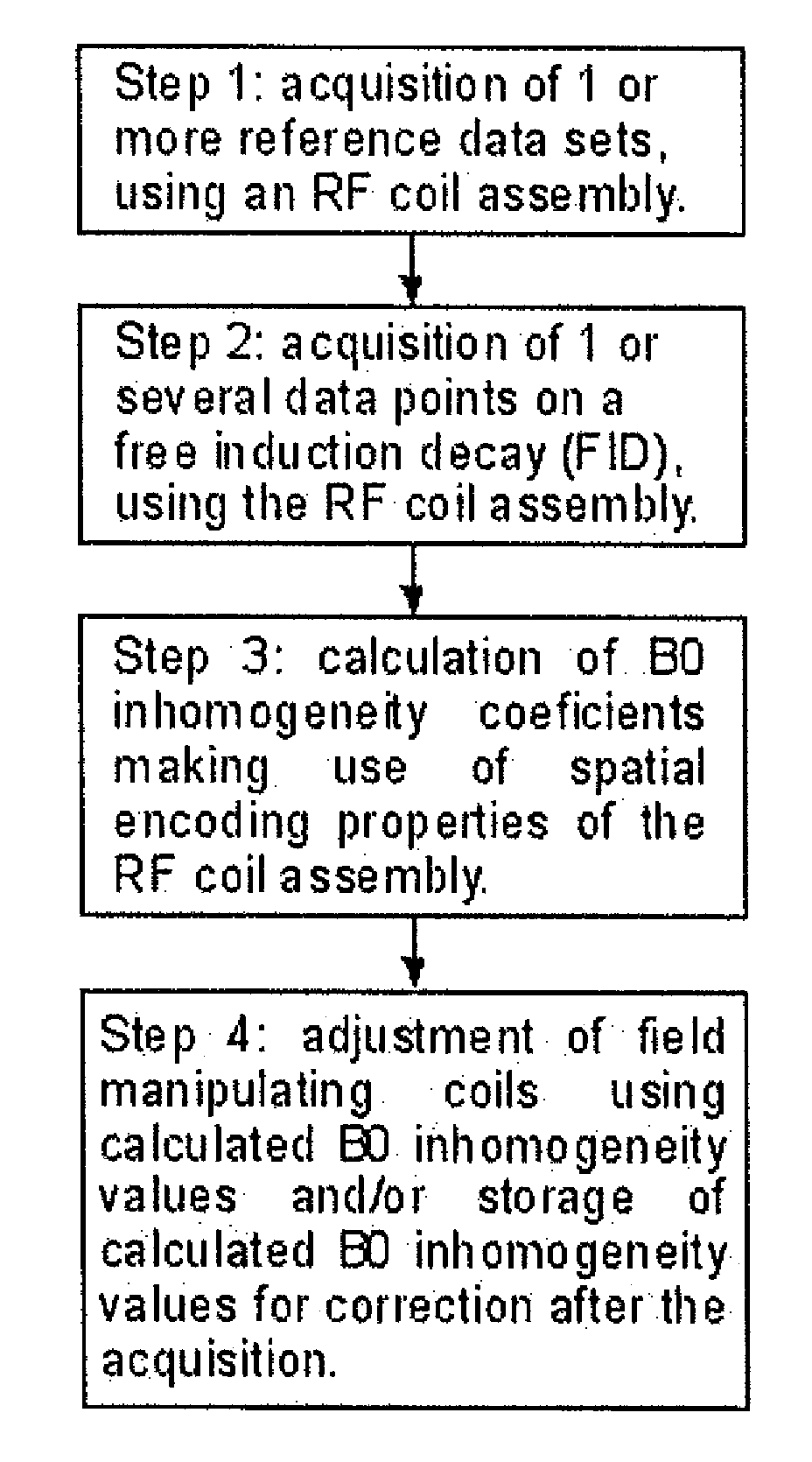
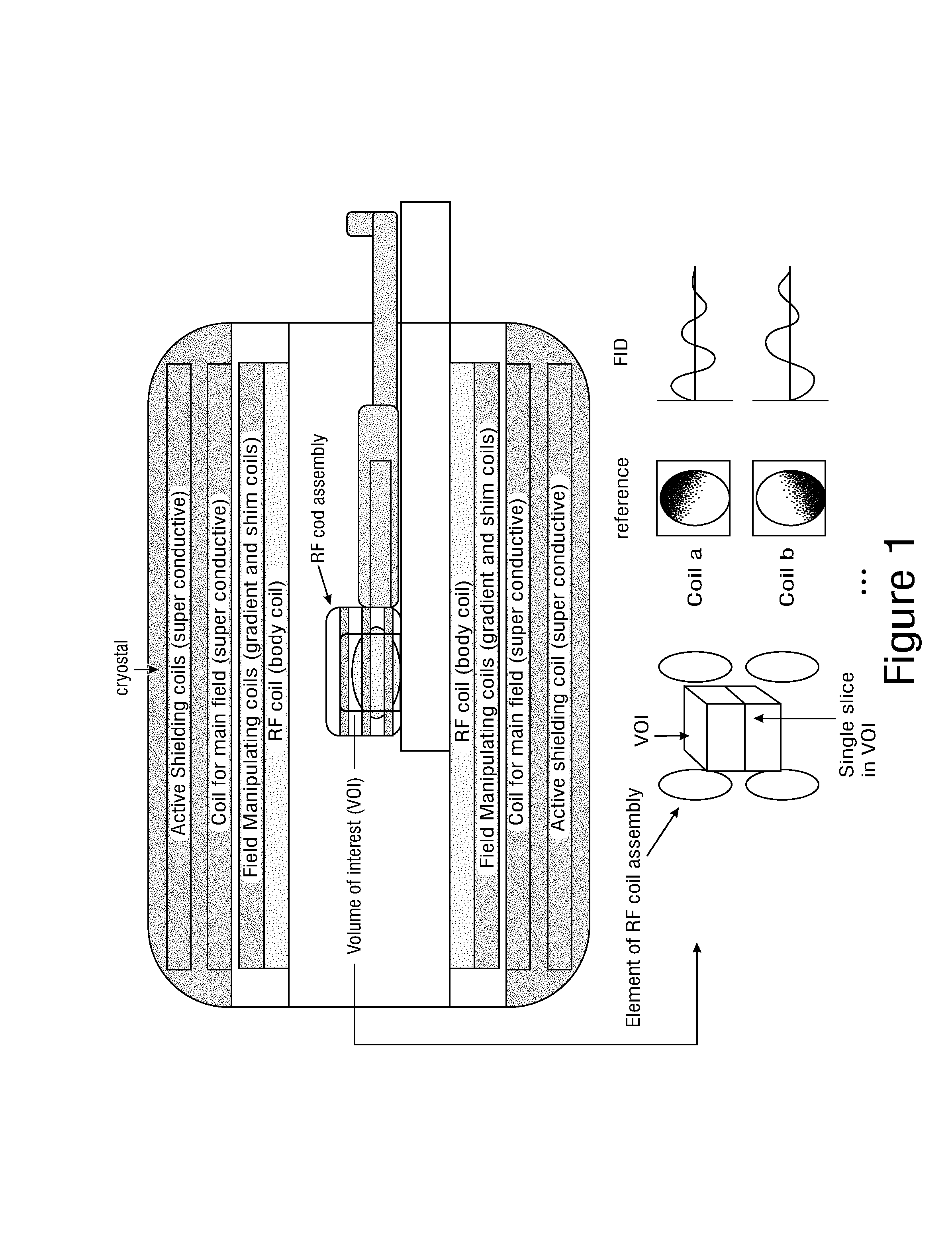
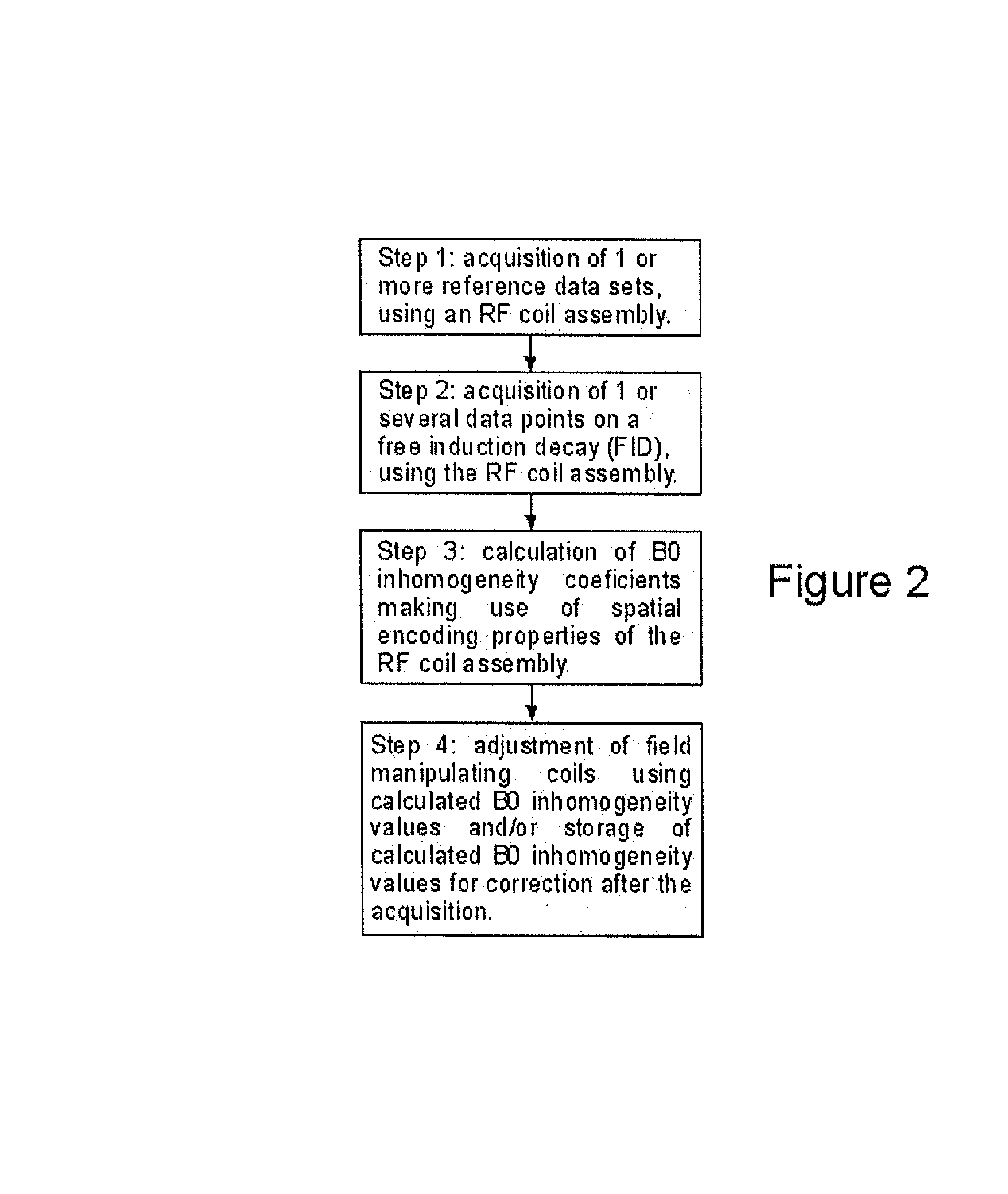
Sense Shimming (SSH): a fast approach for determining B0 field inhomogeneities using sensitivity encoding
InactiveUS20100102819A1Quick checkQuick correctionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionCoil arrayData acquisition
The pursuit for ever higher field strengths and faster data acquisitions has led to the construction of coil arrays with high numbers of elements. With the SENSE technique it has been shown, how the sensitivity of those elements can be used for spatial image encoding. A method in accordance with the present invention, largely abstains from using encoding gradients. The resulting sensitivity encoded free induction decay (FID) data is then not used for imaging, but for determining field inhomogeneity distribution. The method has therefore been termed SSH for Sense SHimming.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
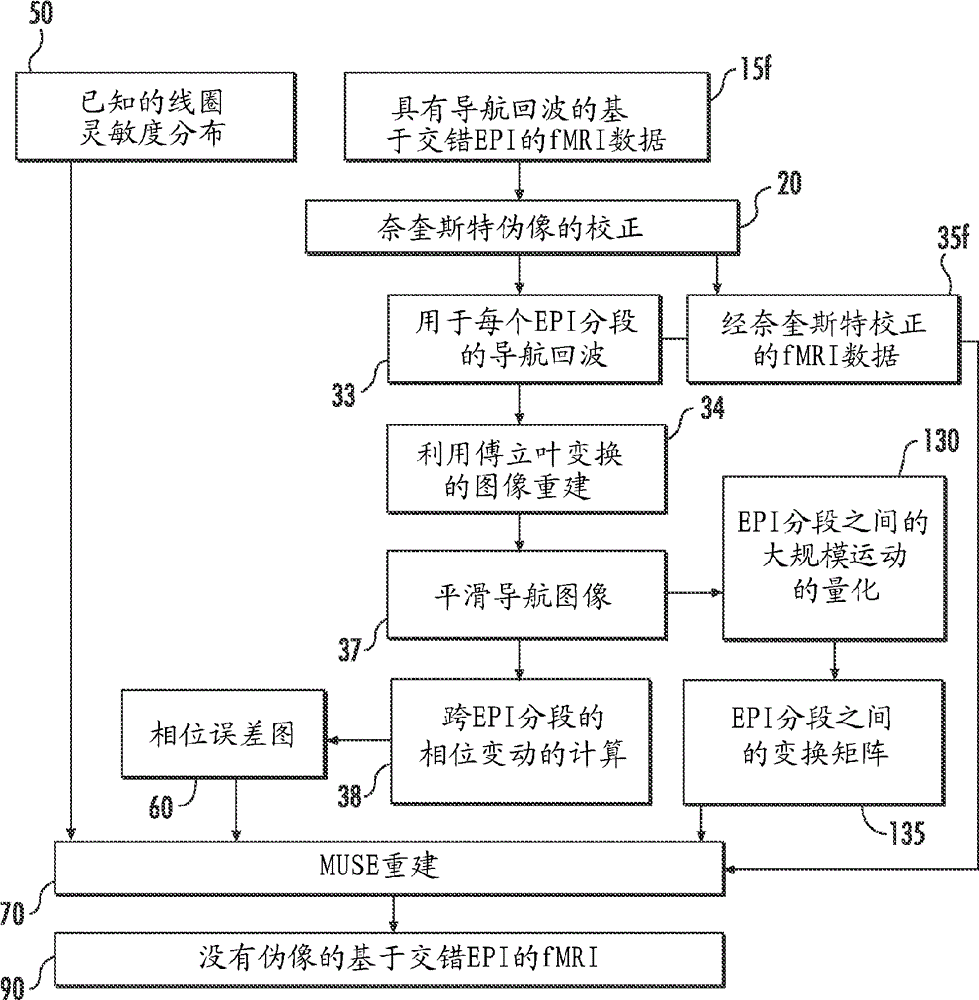
Multi-shot scan protocols for high-resolution mri incorporating multiplexed sensitivity-encoding (muse)
Diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) using a new technique, termed multiplexed sensitivity encoding with inherent phase correction, is proposed and implemented to effectively and reliably provide high-resolution segmented DWI and DTI, where shot-to-shot phase variations are inherently corrected, with high quality and SNR yet without relying on reference and navigator echoes. The performance and consistency of the new technique in enabling high-quality DWI and DTI are confirmed experimentally in healthy adult volunteers on 3 Tesla MRI systems. This newly developed technique should be broadly applicable in neuroscience investigations of brain structure and function.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
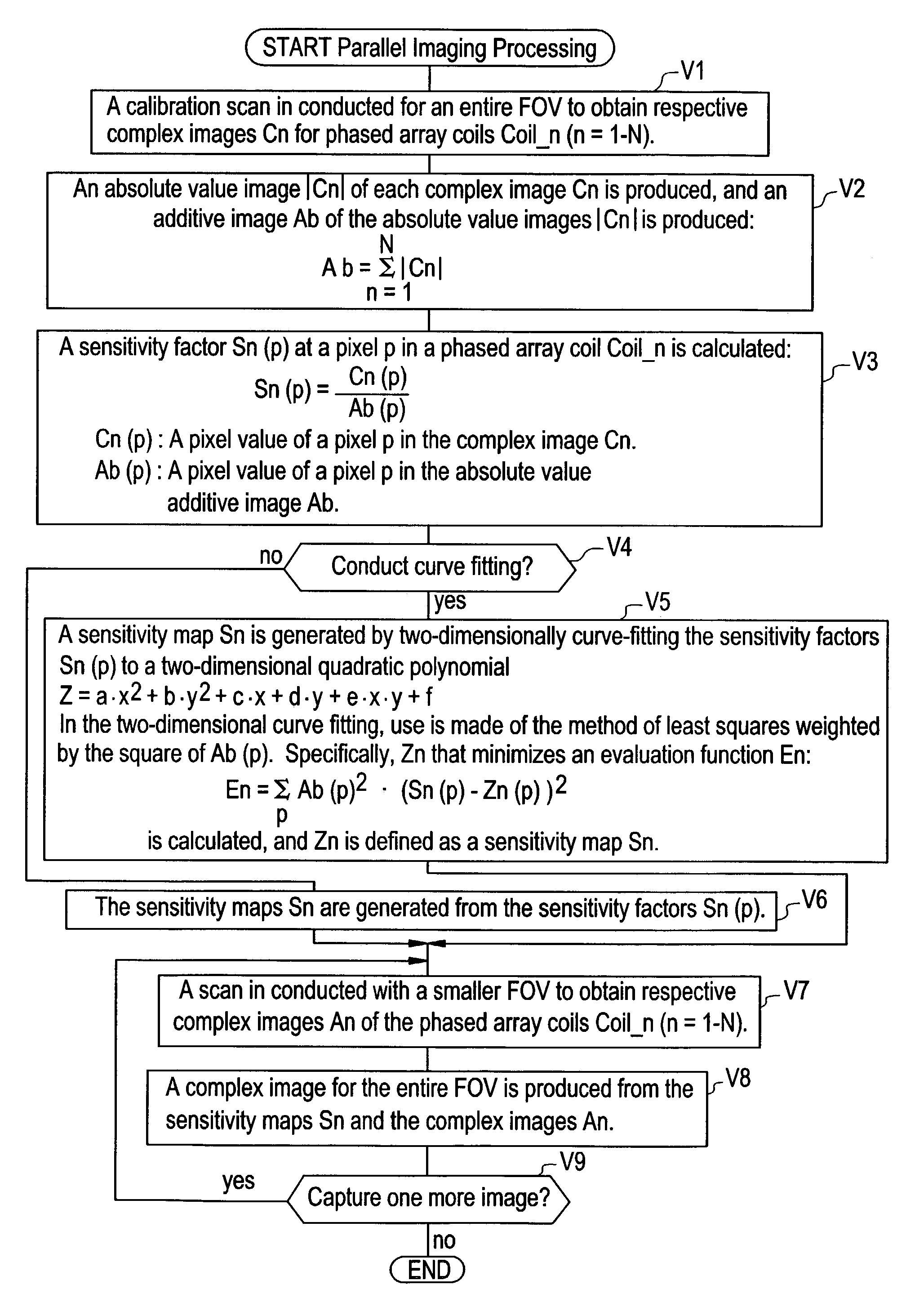
Coil sensitivity map generating method, parallel imaging method, and MRI apparatus
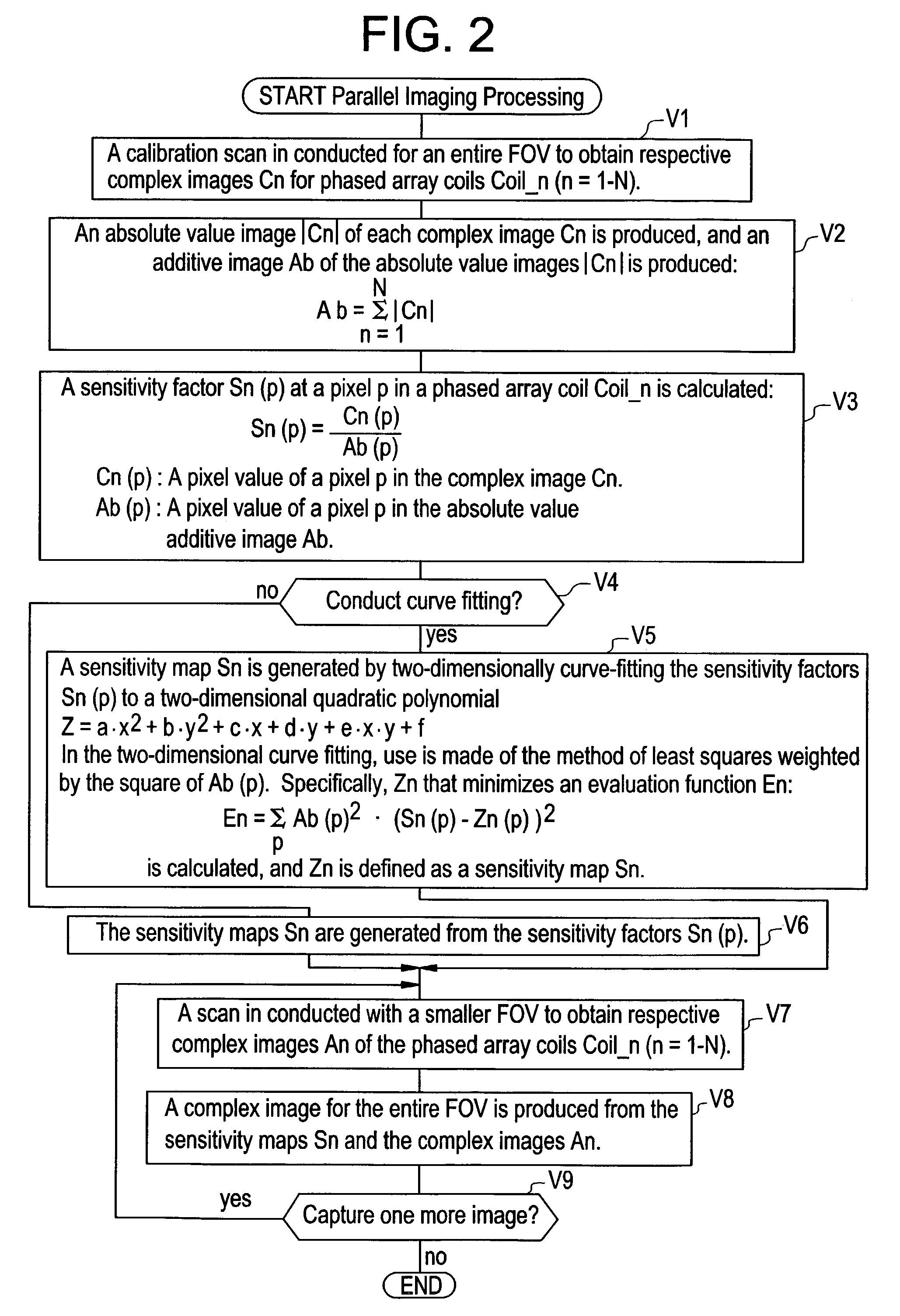
InactiveUS7187791B2Improve homogeneityCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringCurve fittingComputer vision
For a purpose of improving homogeneity of an image obtained in a self-calibration by a parallel imaging method generally referred to as SENSE (SENSitivity Encoding), sensitivity factors Sn(p) are calculated using an additive image Ab=Σ|Cn| of complex images Cn obtained by conducting a calibration scan of an entire FOV for phased array coils Coil_n (n=1–N, N≧2) (Steps V2, V3). Moreover, sensitivity maps Sn are generated by conducting curve fitting by the method of least squares weighted by the square of a pixel value Ab(p) of the absolute value additive image Ab (Step V4).
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Magnetic resonance imaging method and device
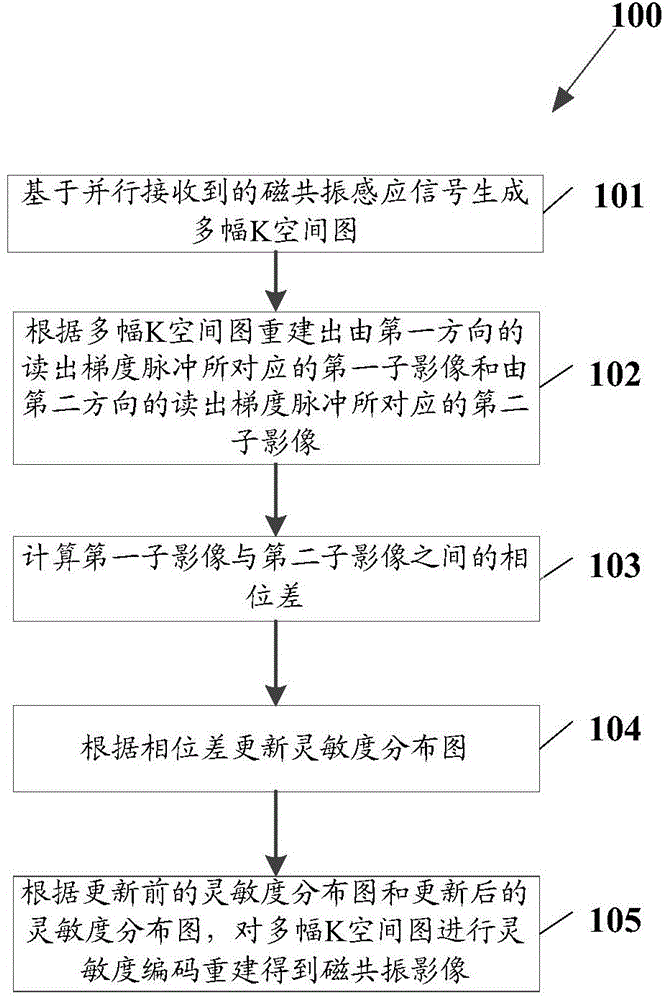
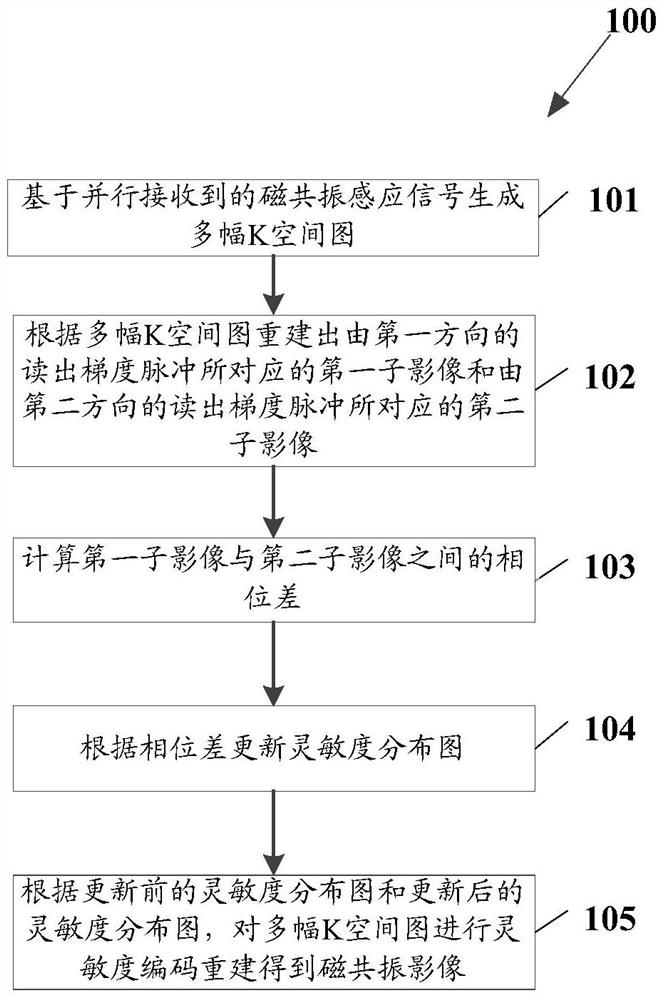
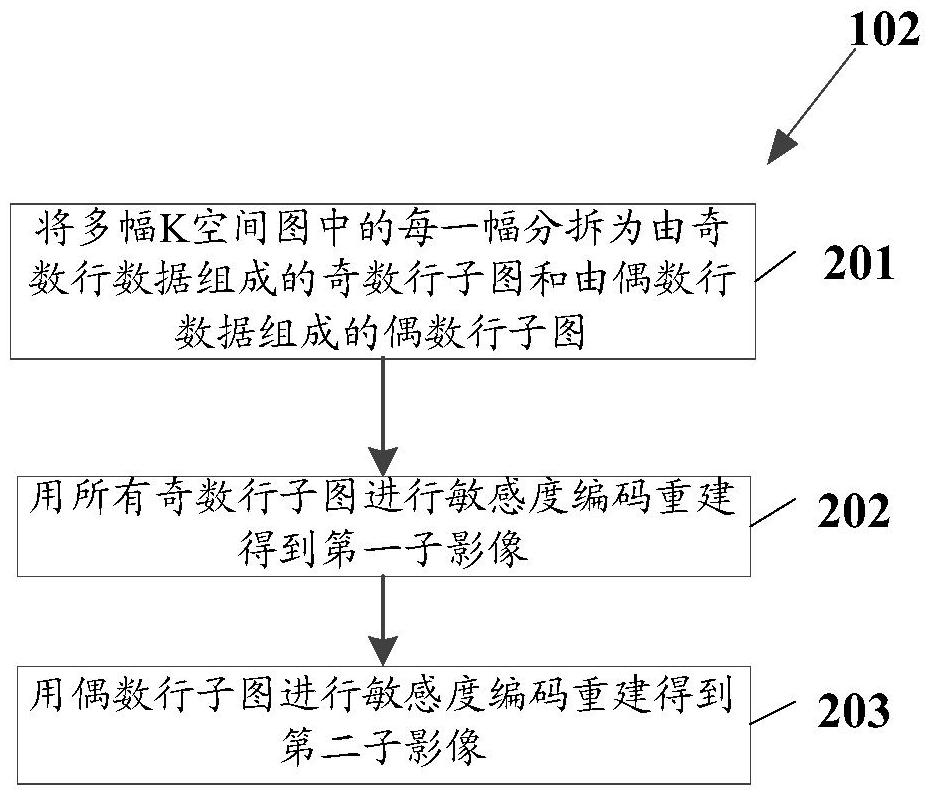
ActiveCN106137198AEfficient removalReduced imaging timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonancePhase difference
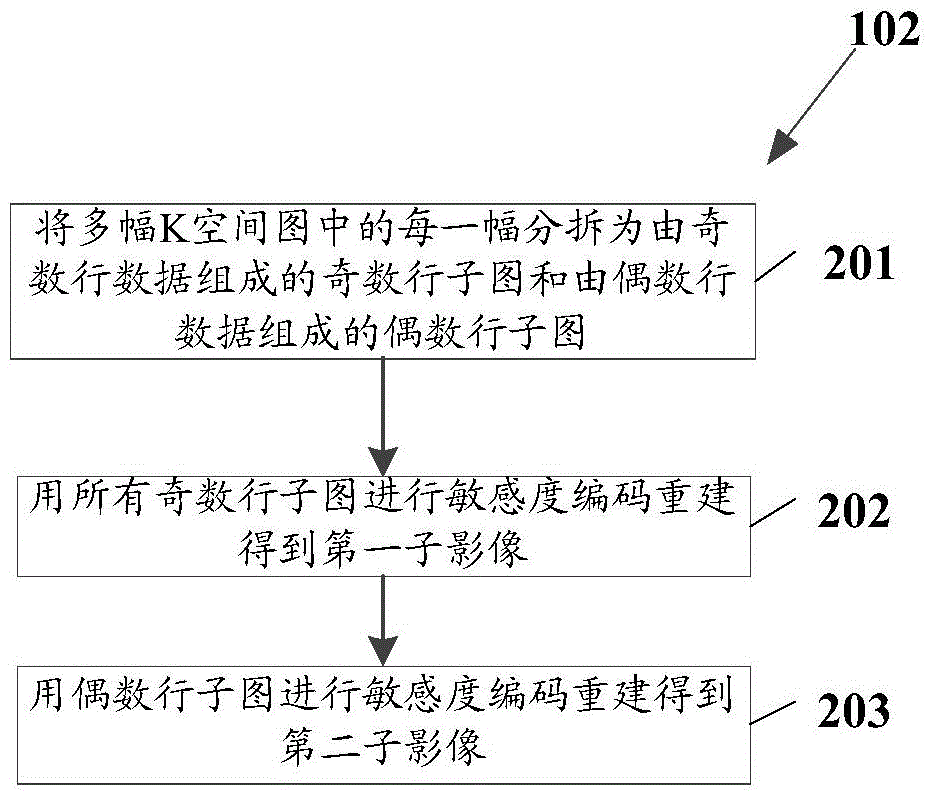
The invention relates to a magnetic resonance imaging method and a magnetic resonance imaging device. The magnetic resonance imaging method comprises the following steps: generating a plurality of K space diagrams on the basis of magnetic resonance sensation signals which are arranged in a parallel manner; according to the plurality of K space diagrams, reconstructing a first sub-image corresponding to a reading gradient pulse in a first direction, and a second sub-image corresponding to a reading gradient pulse in a second direction; calculating the phase difference between the first sub-image and the second sub-image; updating a sensitivity distribution diagram according to the phase difference; according to a sensitivity distribution diagram before updating and a sensitivity distribution diagram after updating, performing sensitivity encoding reconstruction on the plurality of K space diagrams, thereby obtaining magnetic resonance images.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
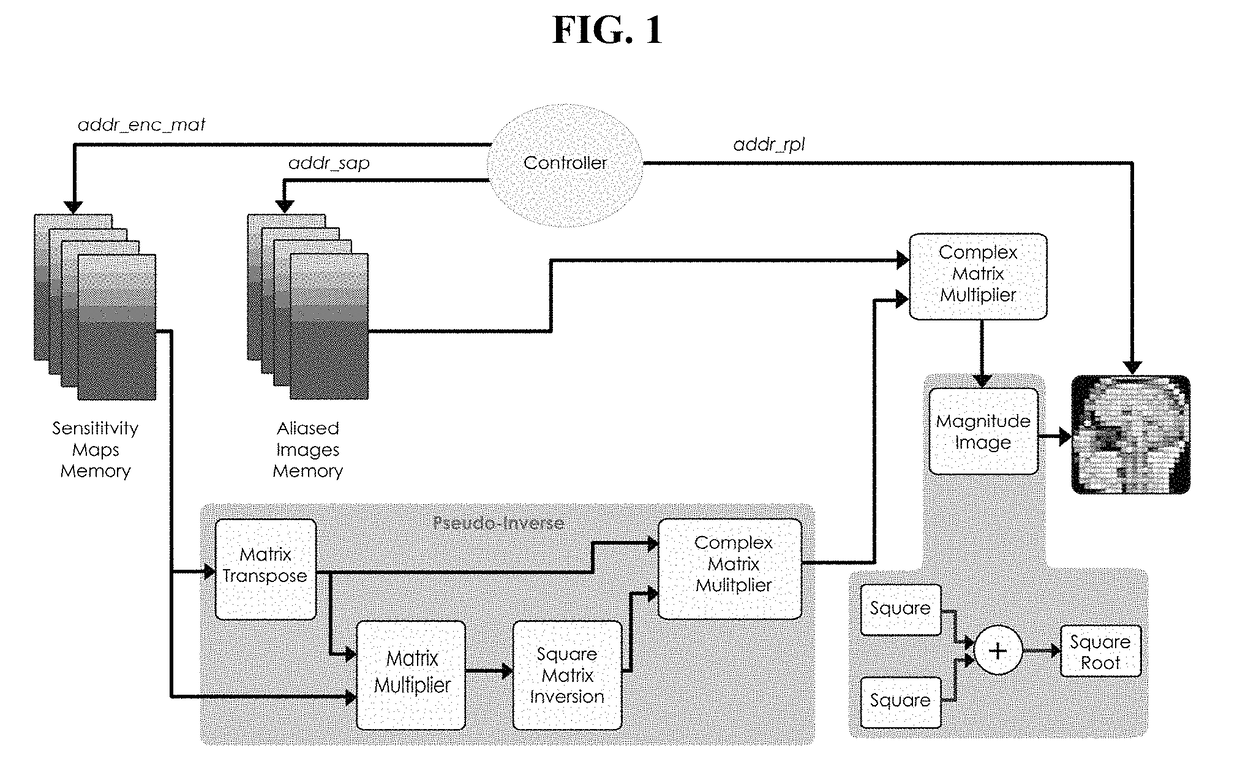
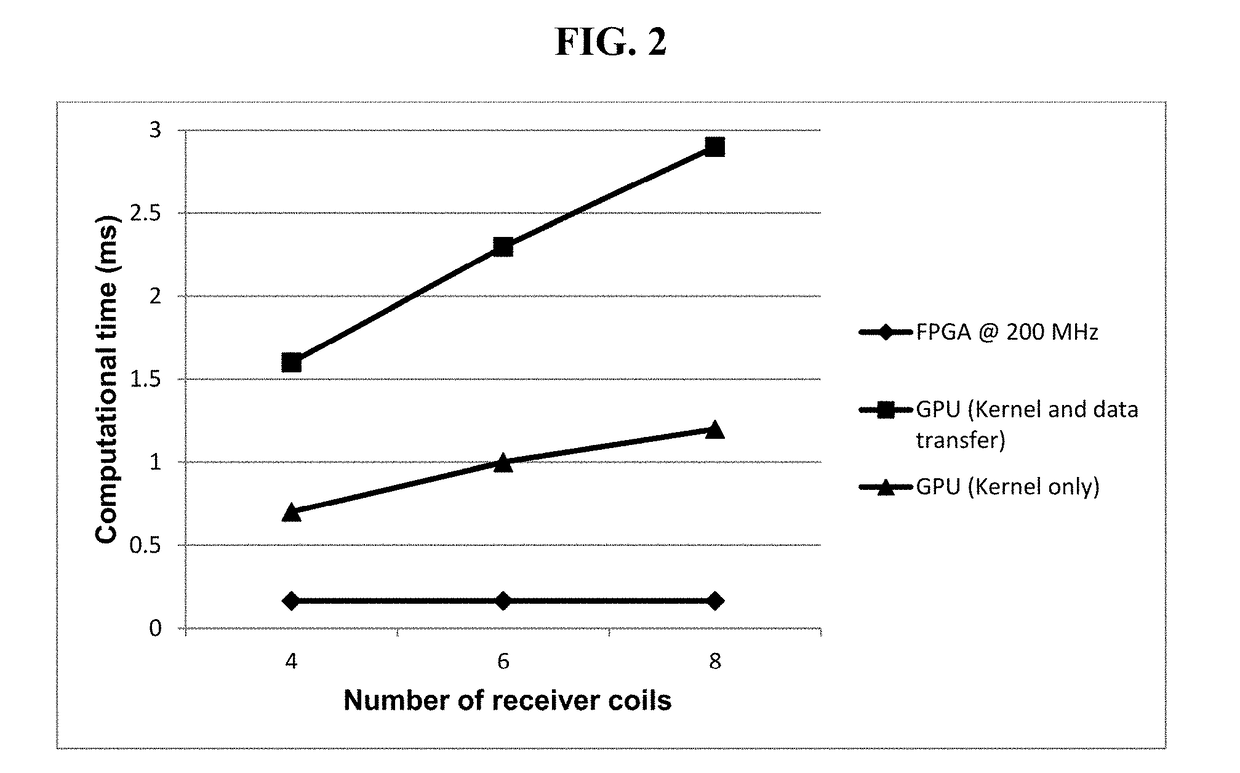
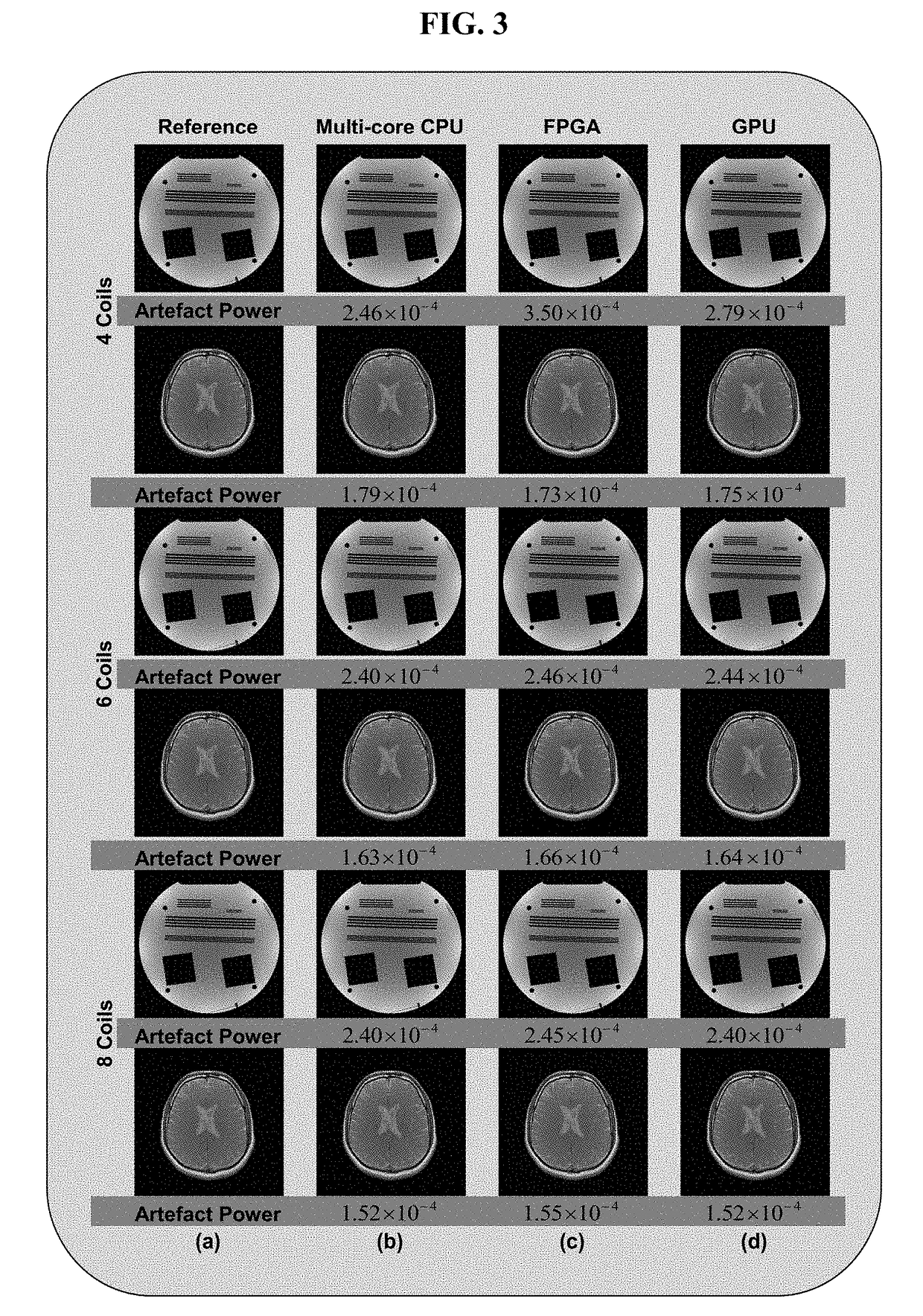
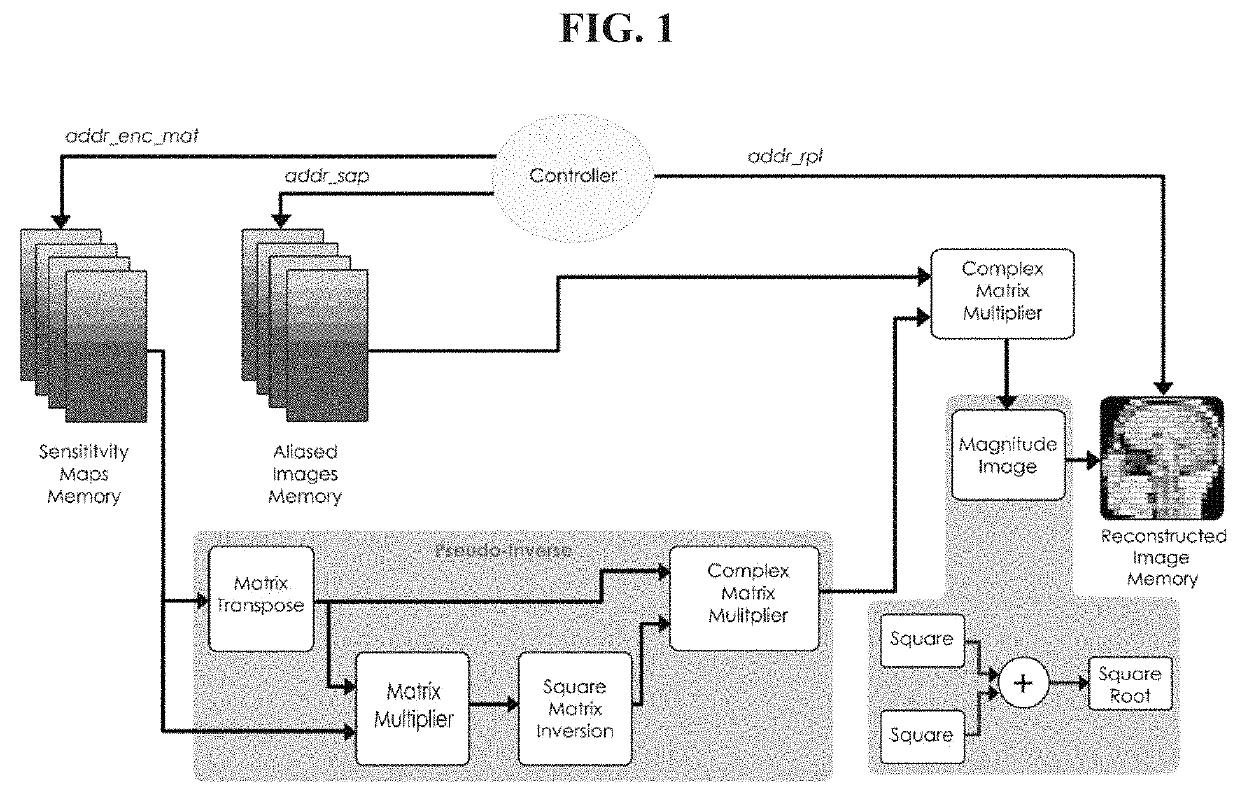
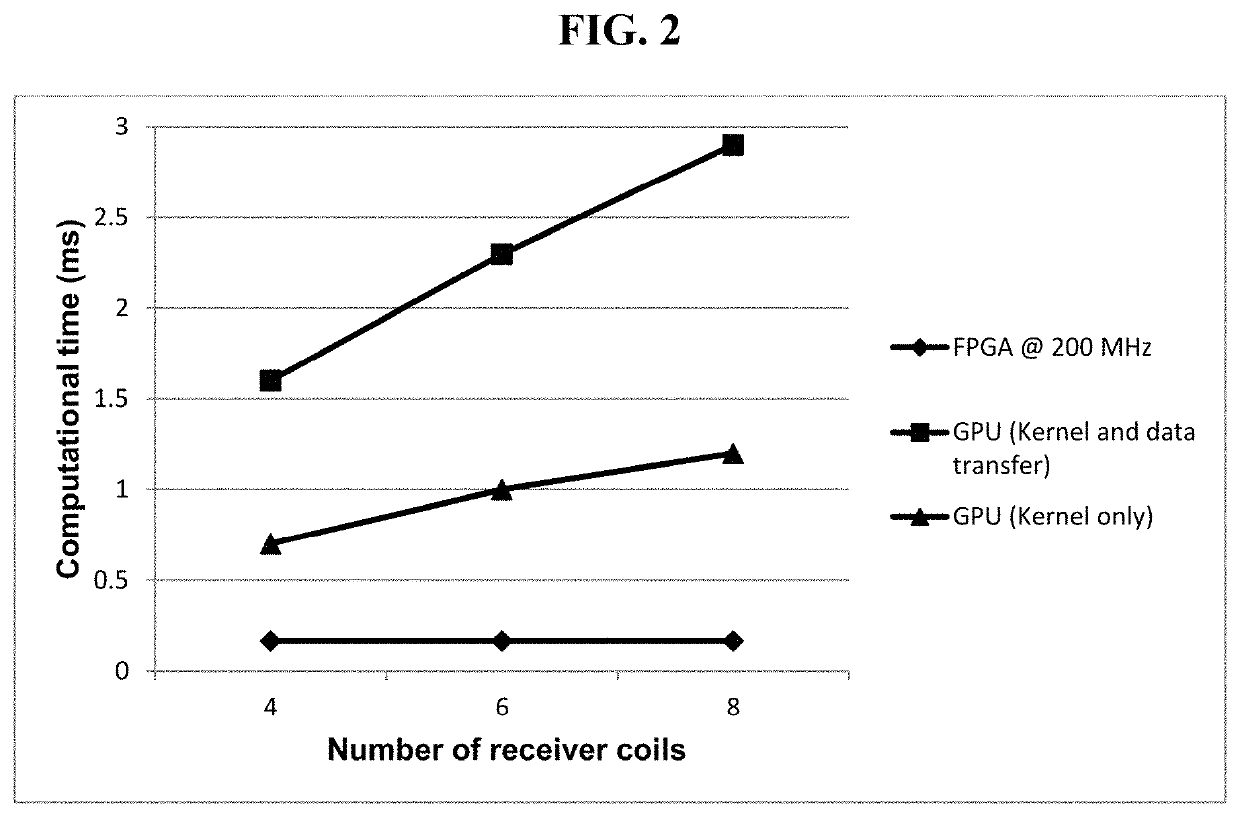
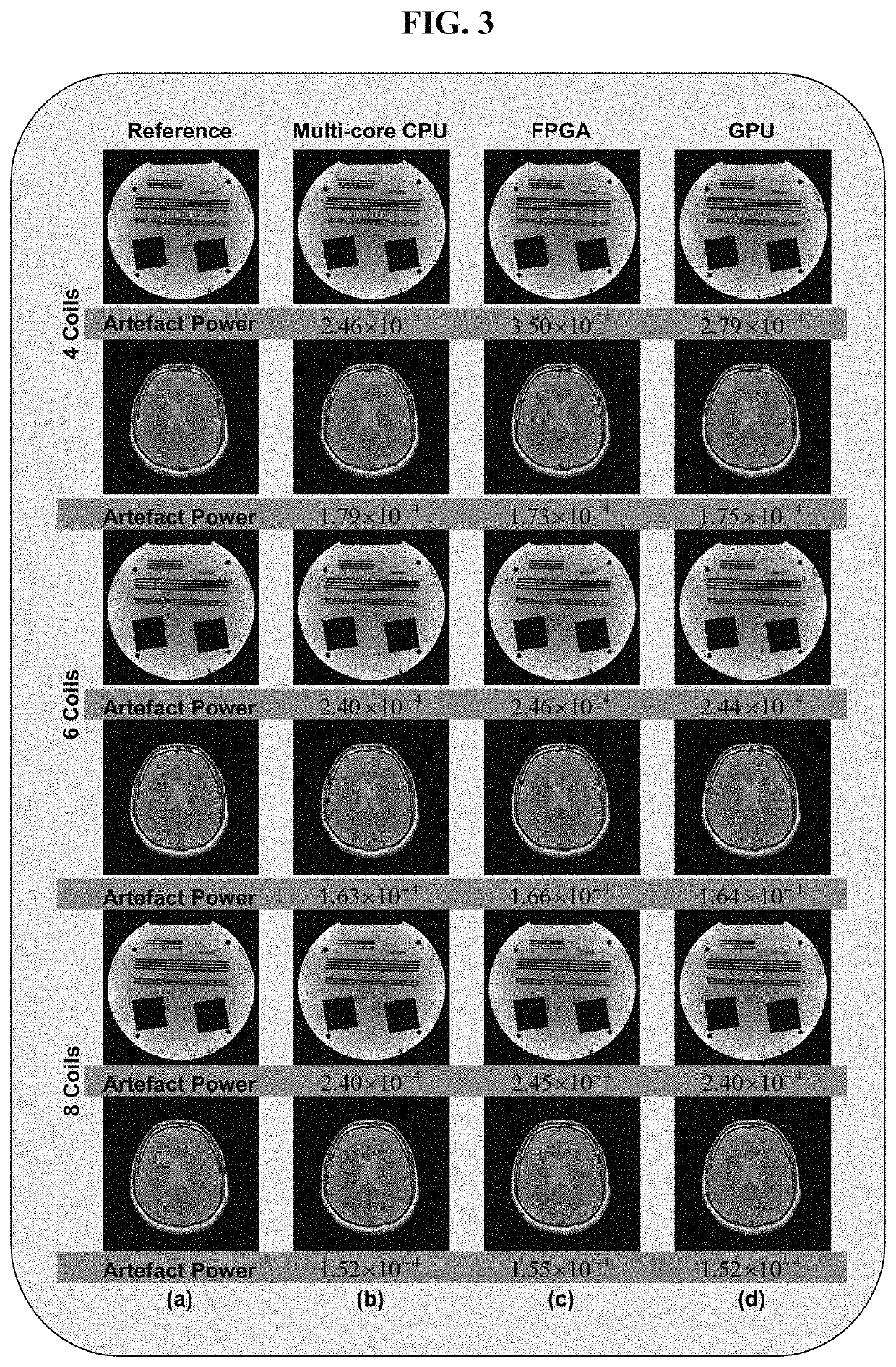
FPGA implementation of a real-time parallel MRI reconstruction
A system for parameterized FPGA (Field Programable Gate Array) implementation of real-time SENSE (SENSitivity Encoding) reconstruction including: a sensitivity maps memory configured to store sensitivity map data; an aliased image memory configured to store aliased image data acquired from a scanner; a reconstructed image memory configured to store reconstructed image data; a parameterized complex matrix multiplier; a pseudo-inverse calculator; a magnitude image block; and a controller; wherein sensitivity map data from the sensitivity maps memory is transferred to the pseudo-inverse calculator; wherein data from the pseudo-inverse calculator and the aliased image data from the aliased image memory is transferred to the complex matrix multiplier; wherein data from the complex matrix multiplier is transferred to the magnitude image block; wherein the controller is configured to generate an address of the sensitivity map memory and an address of the aliased image memory to access the encoding matrix and corresponding aliased image data and also configured to generate an address of the reconstructed image memory to store the reconstructed image data.
Owner:COMSATS INST OF INFORMATION TECH
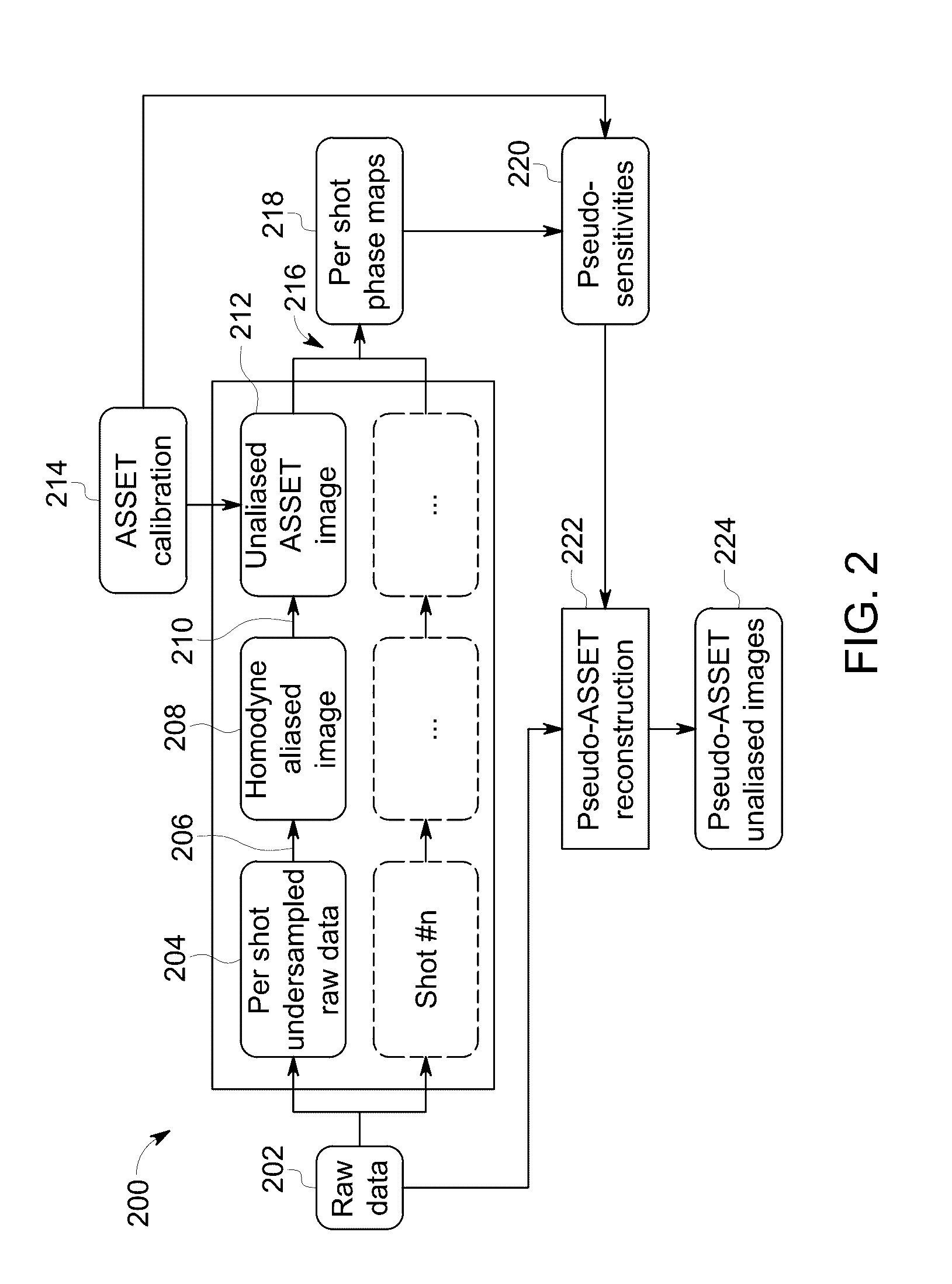
Apparatus and method for multishot diffusion weighted imaging with array spatial pseudo-sensitivity encoding technique
A method for magnetic resonance imaging includes unwrapping a calibration image based on coil sensitivity data obtained according to an array spatial sensitivity encoding technique and acquiring raw scan data of a plurality of MRI scan shots. The method further includes reconstructing an aliased image for each of the MRI scan shots, reconstructing an unaliased image for each of the MRI scan shots, according to the calibration image, recovering a plurality of pseudo-sensitivity maps from the plurality of unaliased images and from the calibration image, and unwrapping at least one final unaliased image from the plurality of aliased images, according to the plurality of pseudo-sensitivity maps.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Sense shimming (SSH): a fast approach for determining B0 field inhomogeneities using sensitivity encoding
InactiveUS8018230B2Reduce amountReduce acquisition timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionData acquisitionSpatial image
The pursuit for ever higher field strengths and faster data acquisitions has led to the construction of coil arrays with high numbers of elements. With the SENSE technique it has been shown, how the sensitivity of those elements can be used for spatial image encoding. A method in accordance with the present invention, largely abstains from using encoding gradients. The resulting sensitivity encoded free induction decay (FID) data is then not used for imaging, but for determining field inhomogeneity distribution. The method has therefore been termed SSH for Sense SHimming.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
CEST (Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer) image reconstruction method and device based on variable acceleration sensitivity encoding
ActiveCN109839607AEliminate artifacts2D-image generationDiagnostic recording/measuringAcceleration factorVoxel
The invention discloses a chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging method and device based on a variable acceleration sensitivity encoding method, and belongs to the field of magnetic resonance imaging. In the method, Fourier transform is carried out on K-space data formed by a measured object in CEST imaging to obtain image space folding data of each voxel, wherein the image space folding data includes at least one undersampled frame accurate image with the acceleration factor R1 being greater than or equal to 1 and a plurality of other to-be-reconstructed undersampled frame images with the acceleration factor being not less than R1; and then image reconstruction is carried out on the to-be-reconstructed undersampled frame images with the acceleration factor being R2. The sensitivity map of the traditional SENSE method can be modified by using undersampled frames. The reconstruction error of the method is basically the same as that of the traditional SNESE method which applies a low acceleration factor in a CEST source image, but the speed of the method is twice or more the speed of the traditional SENSE method. Since it is unnecessary to adopt fully sampled frames, the method is particularly applicable to three-dimensional (3D) CEST imaging.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method of fast imaging of nmr parameters with variably-accelerated sensitivity encoding
ActiveUS20190101603A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceData set
A method of spatially imaging a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)parameter whose measurement requires the acquisition of spatially localized NMR signals in a sample includes placing the sample in an MRI apparatus with a plurality of MRI detectors each having a spatial sensitivity map; and applying MRI sequences adjusted to be sensitive to the NMR parameter. At least one of the MRI sequences is adjusted so as to substantially fully sample an image k-space of the sample. The remainder of the MRI sequences is adjusted to under-sample the image k-space. The method further includes acquiring image k-space NMR signal datasets; estimating a sensitivity map of each of the MRI detectors using a strategy to suppress unfolding artefacts; and applying the estimated sensitivity maps to at least one of the image k-space NMR signal data sets to reconstruct a spatial image of NMR signals that are sensitive to the NMR parameter.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
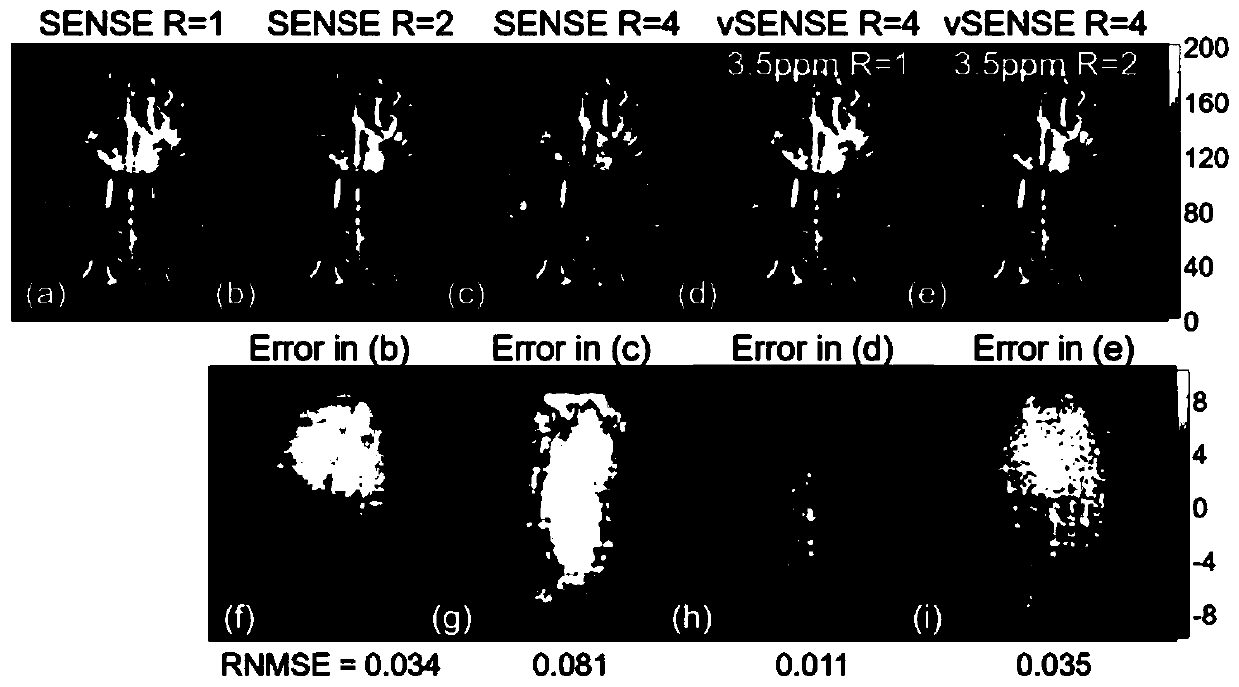
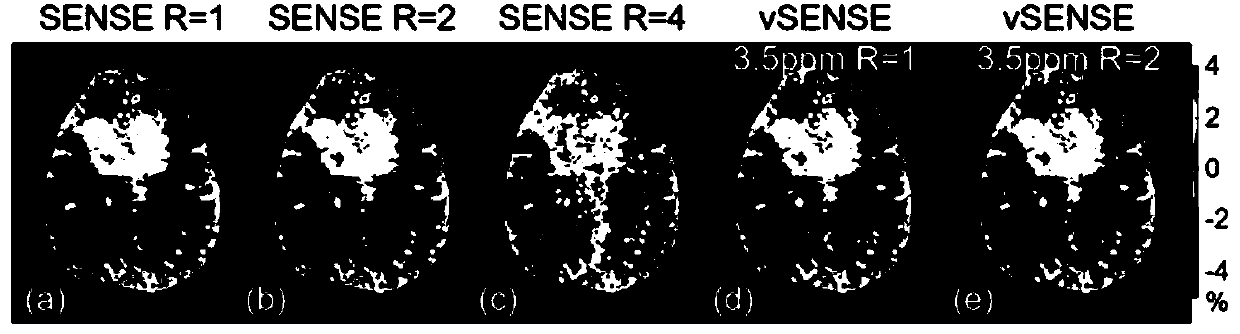
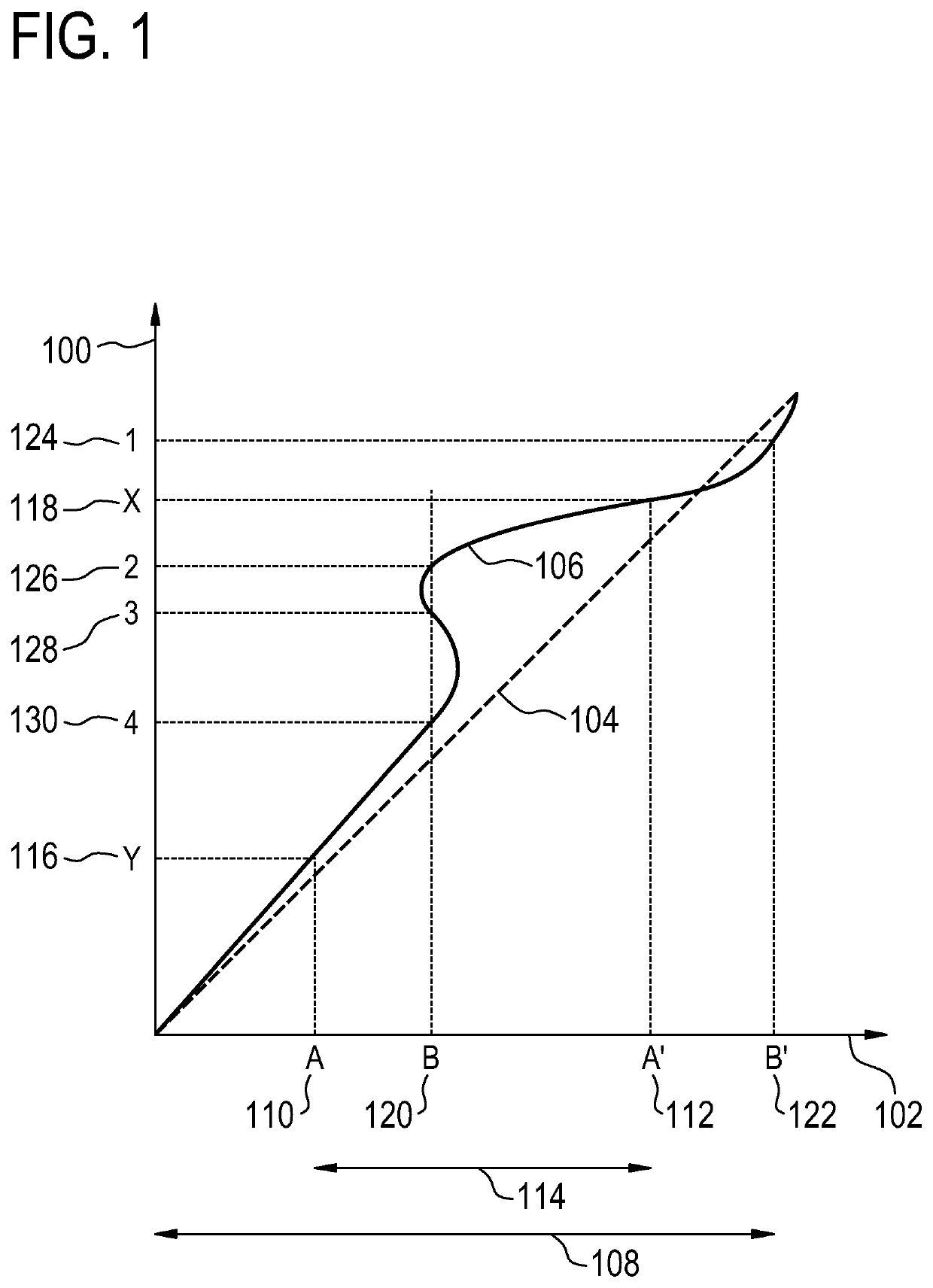
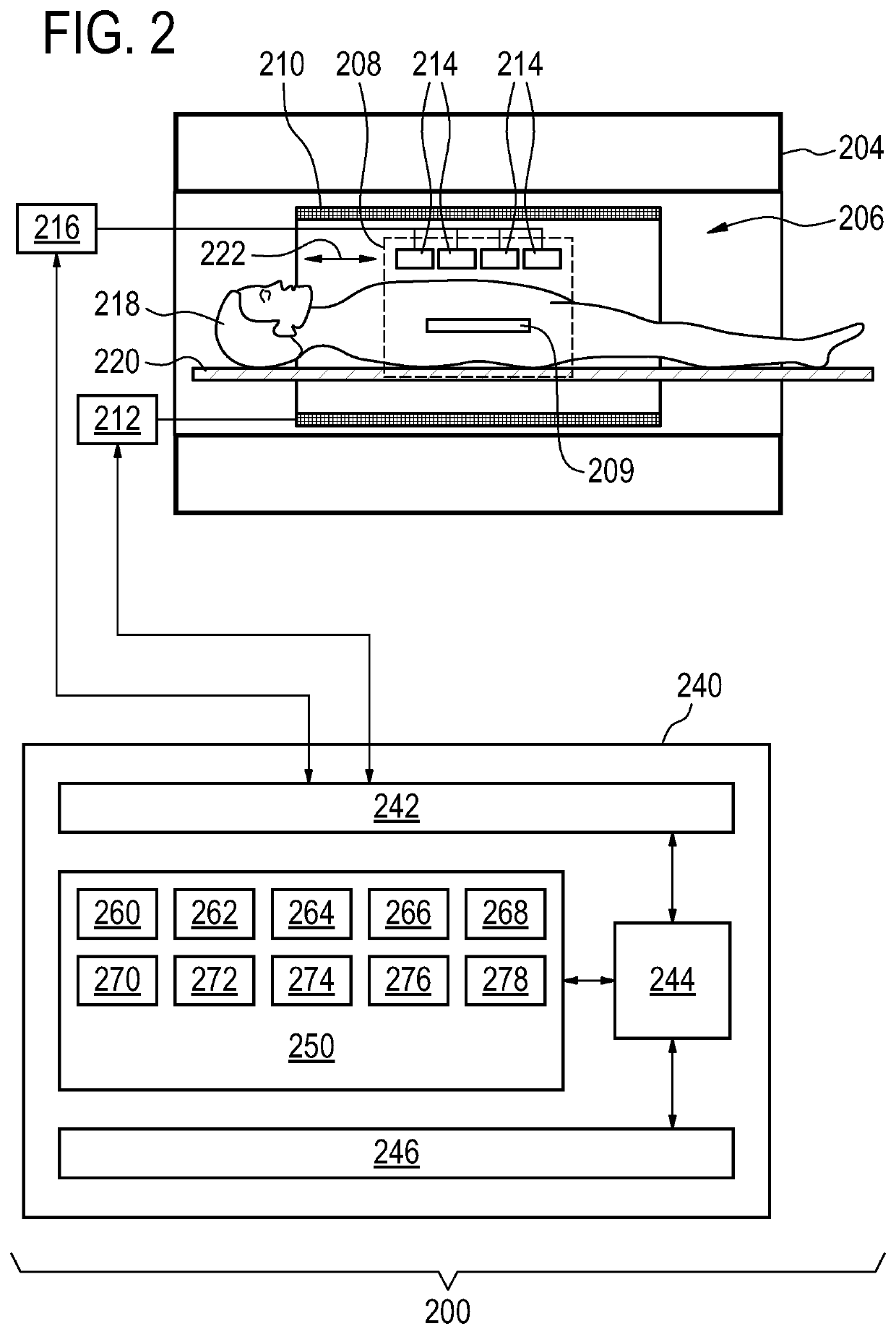
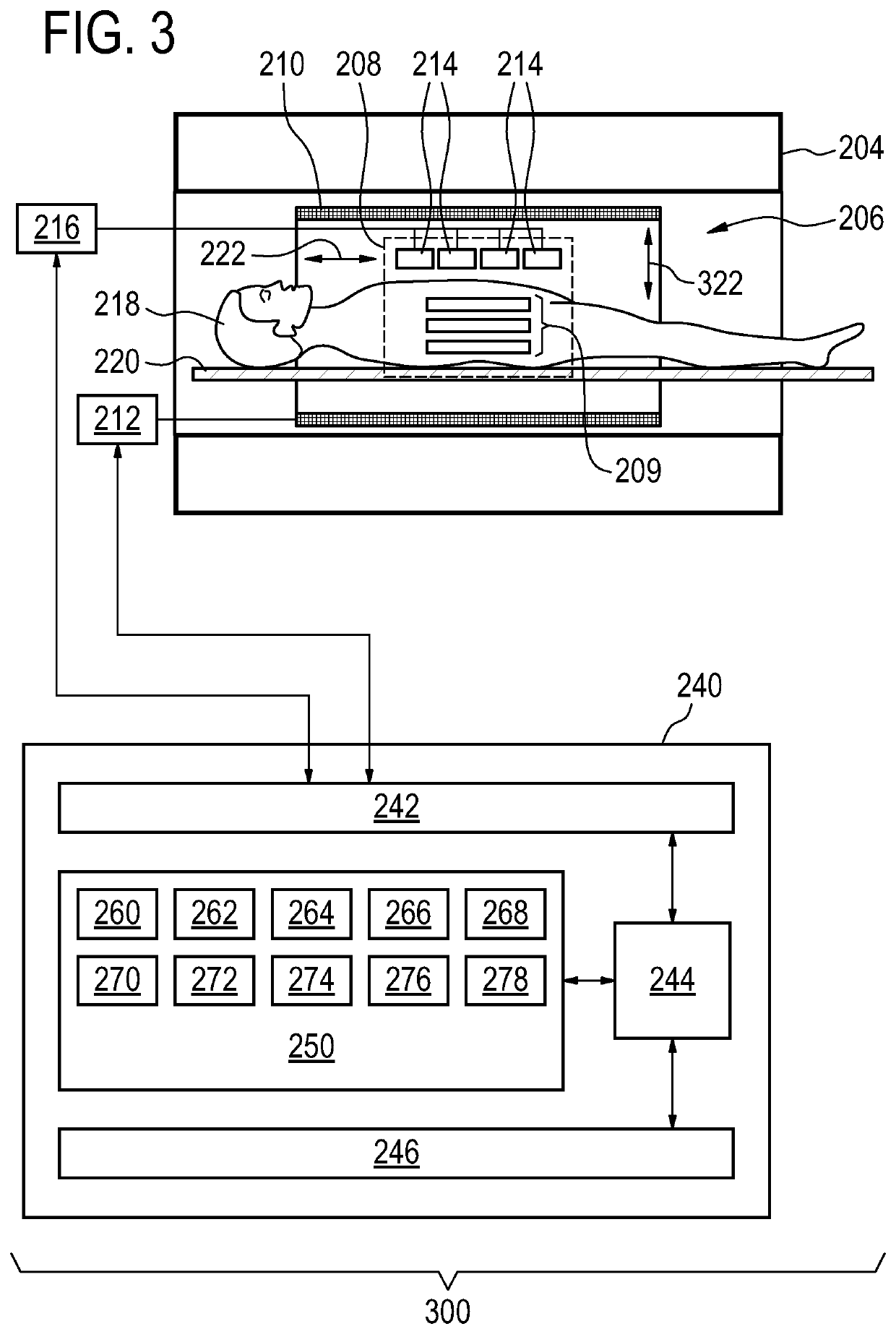
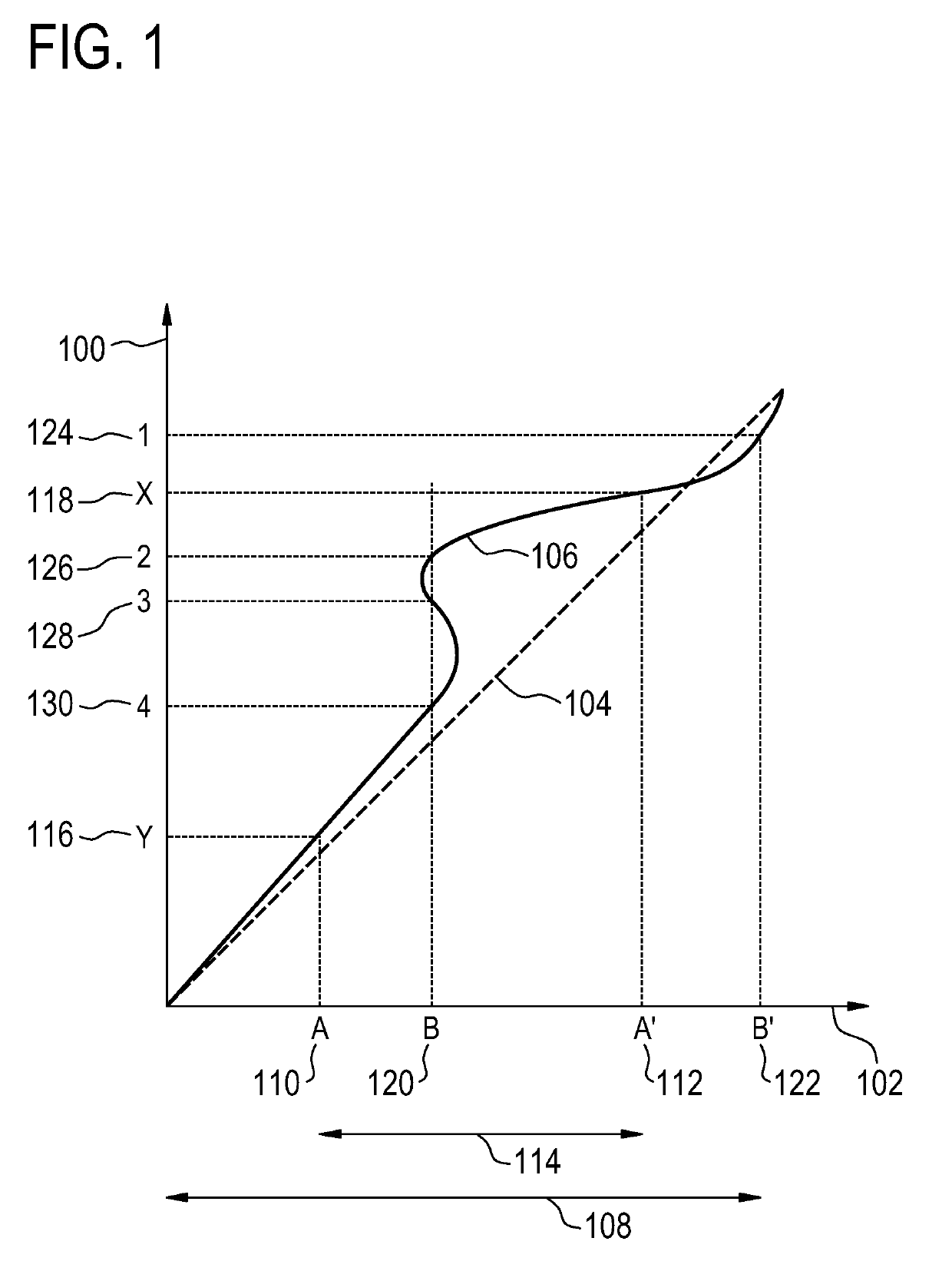
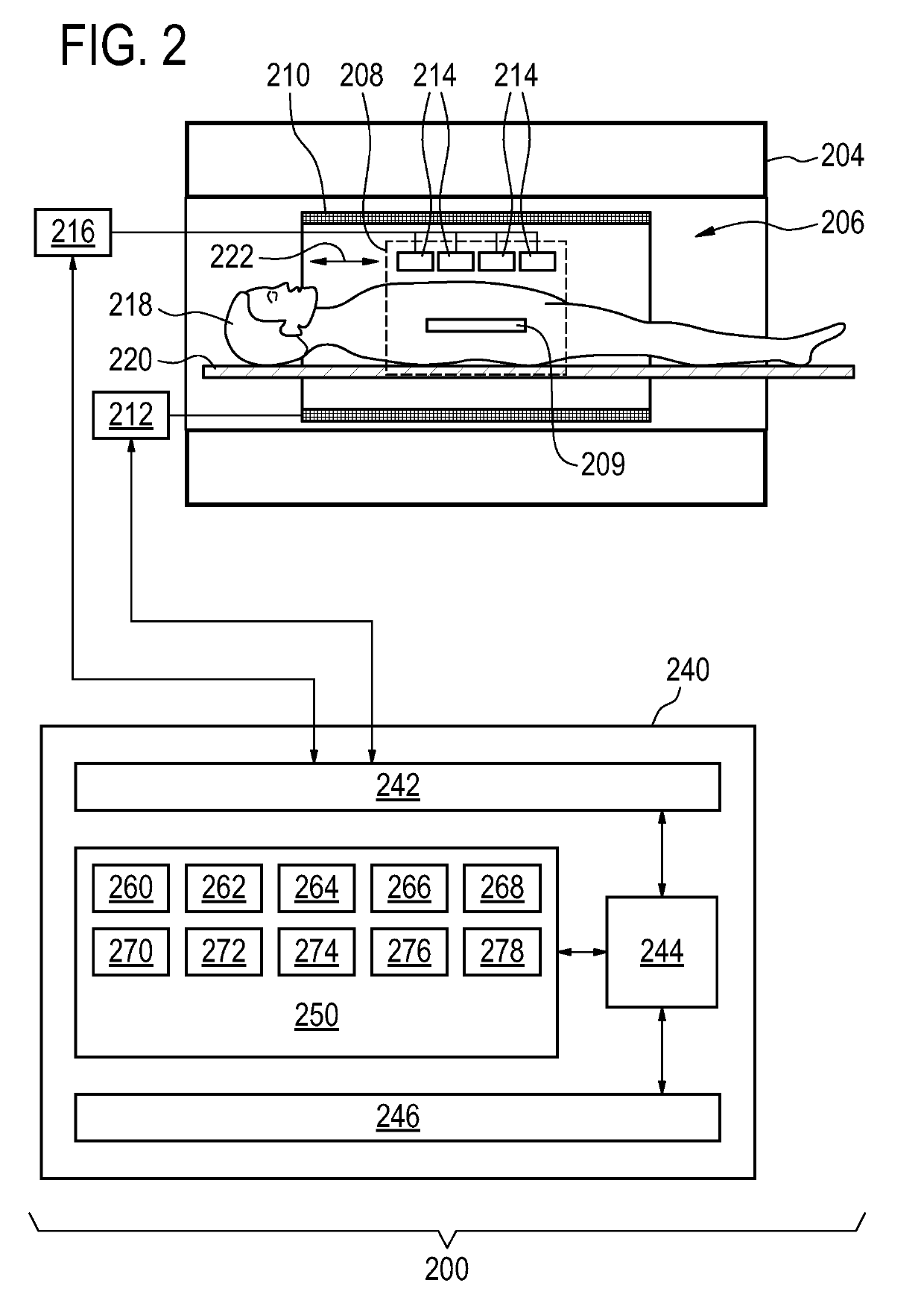
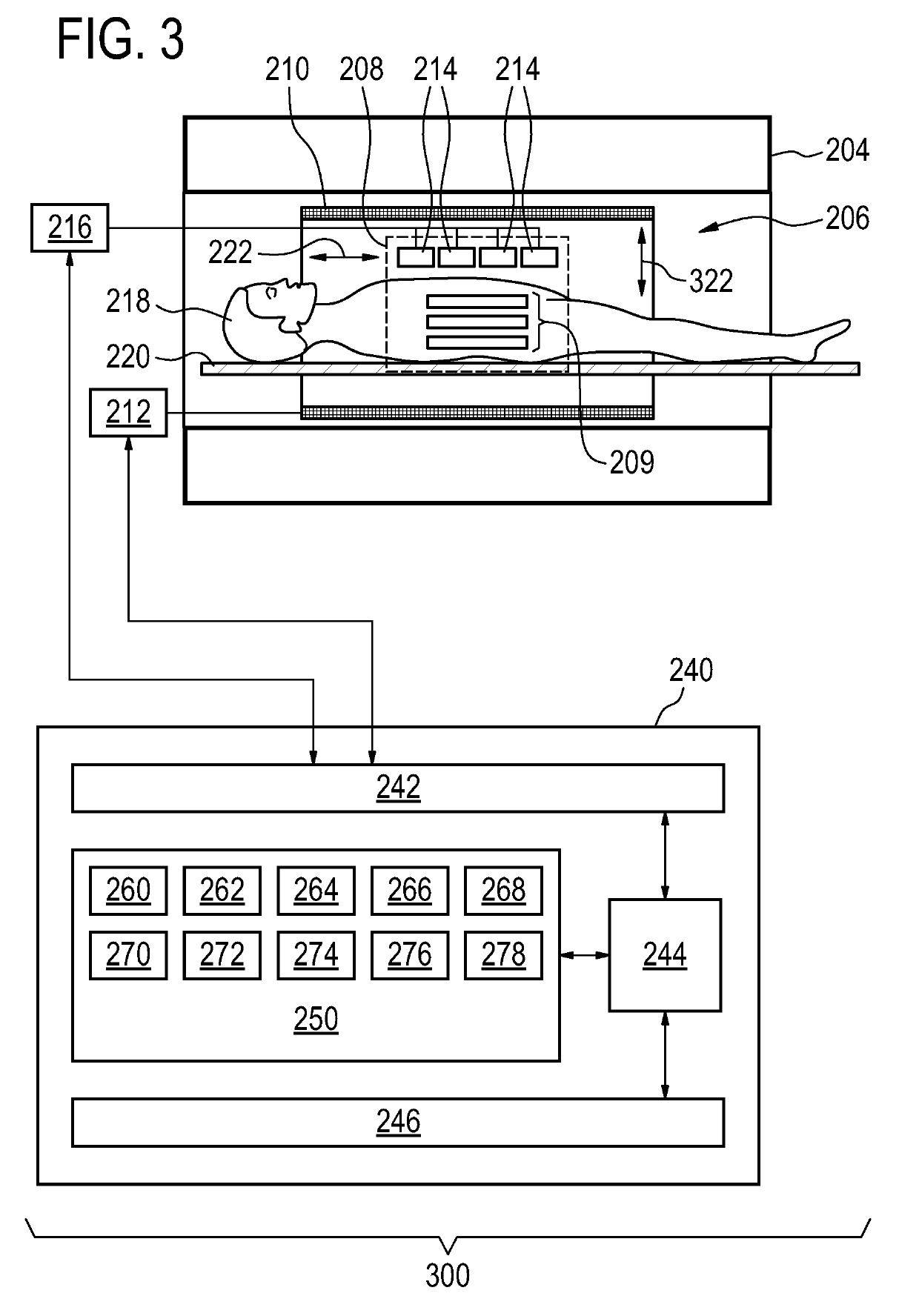
BO-corrected sensitivity encoding magnetic resonance imaging
A magnetic resonance imaging system (200, 300, 400) includes a radio-frequency system (216, 214) with multiple coil elements (214) for acquiring magnetic resonance data (264) and a memory (250) for storing machine executable instructions (260) and pulse sequence commands (262). The pulse sequence commands are configured for controlling the magnetic resonance imaging system to acquire the magnetic resonance data according to a SENSE imaging protocol. Execution of the machine executable instructions causes a processor (244) to: control (500) the magnetic resonance imaging system to acquire the magnetic resonance data using the pulse sequence commands; reconstruct (502) a set of folded magnetic resonance images (266) from the magnetic resonance data; calculate (504) a voxel deformation map (270) from a magnetic field inhomogeneity map; and calculate (506) a set of unfolding matrices (274) using a least partially a coil sensitivity matrix (272) for the multiple coil elements, wherein the set of unfolding matrices includes at least one modified unfolding matrix which is calculated at least partially using the a coil sensitivity matrix and the voxel deformation map. Undistorted magnetic resonance image data (276) is calculated (508) using the set of folded magnetic resonance images and the set of unfolding matrices.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Bo-corrected sensitivity encoding magnetic resonance imaging
The invention provides for a magnetic resonance imaging system (200, 300, 400) comprising a radio-frequency system (216, 214) comprising multiple coil elements (214) for acquiring magnetic resonance data (264). The magnetic resonance imaging system further comprises a memory (250) for storing machine executable instructions (260) and pulse sequence commands (262). The pulse sequence commands are configured for controlling the magnetic resonance imaging system to acquire the magnetic resonance data according to a SENSE imaging protocol. The magnetic resonance imaging system further comprises a processor (244) for controlling the magnetic resonance imaging system. Execution of the machine executable instructions causes the processor to: control (500) the magnetic resonance imaging system to acquire the magnetic resonance data using the pulse sequence commands; reconstruct (502) a set of folded magnetic resonance images (266) from the magnetic resonance data; calculate (504) a voxel deformation map (270) from a static magnetic field (B0) inhomogeneity map; calculate (506) a set of unfolding matrices (274) using a least partially a coil sensitivity matrix (272) for the multiple coil elements, wherein the set of unfolding matrices comprises at least one modified unfolding matrix, wherein the at least one modified unfolding matrix is calculated at least partially using the a coil sensitivity matrix and the voxel deformation map; and calculate (508) undistorted magnetic resonance image data (276) using the set of folded magnetic resonance images and the set of unfolding matrices.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
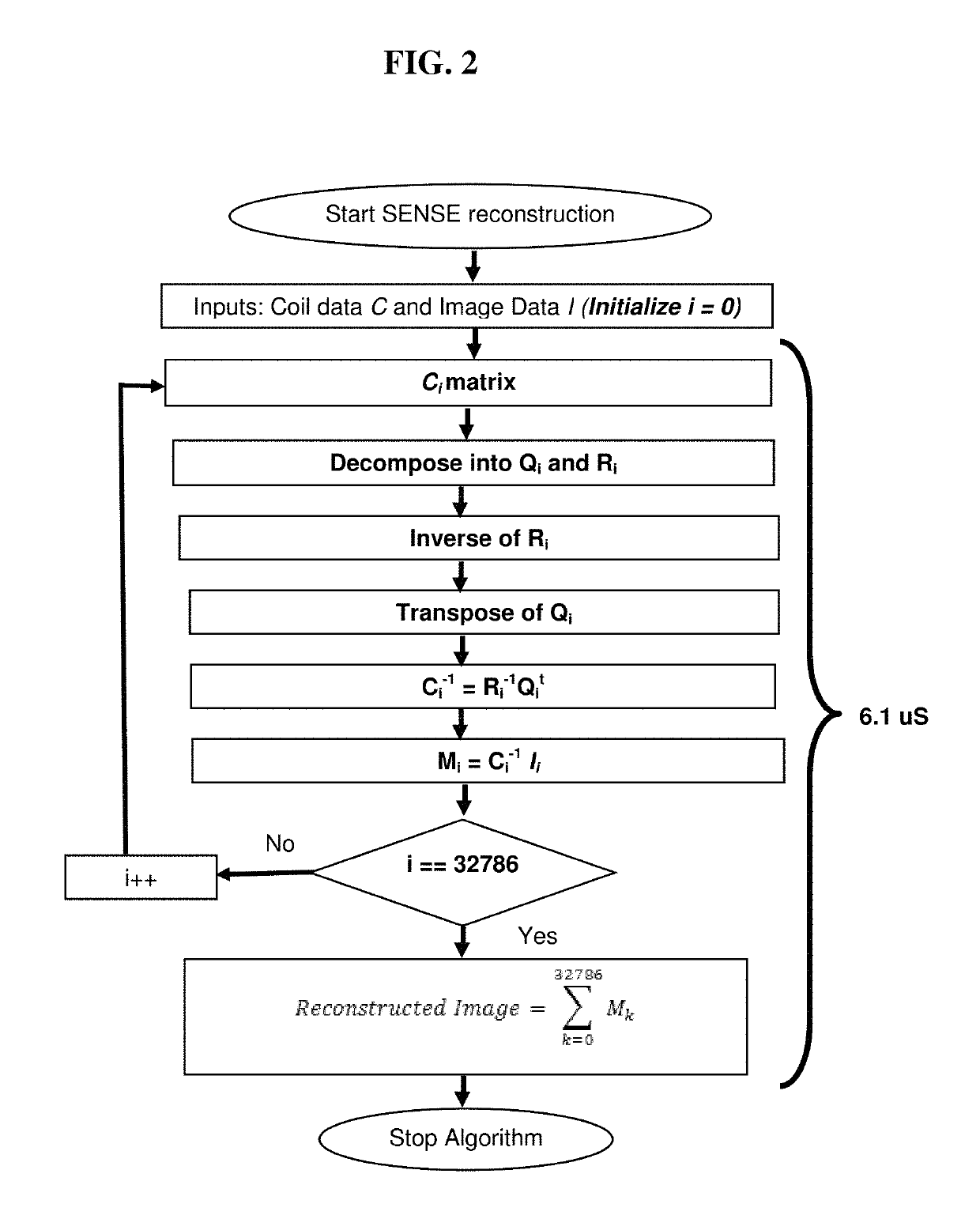
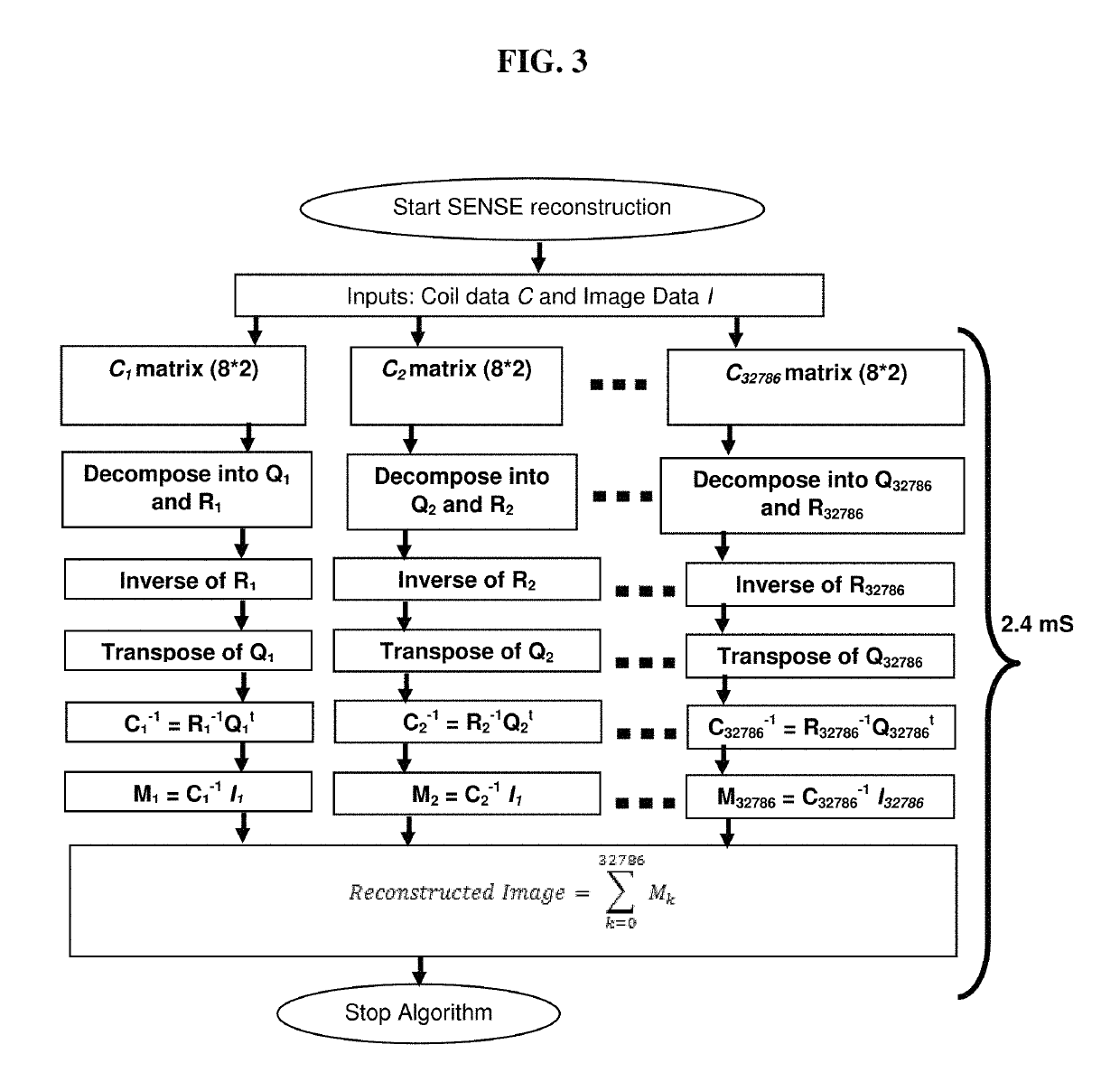
GPU based implementation of SENSE (a parallel MRI algorithm) using QR decomposition
A method of SENSE reconstruction including: constructing a coil sensitivity encoding matrix; inversing of the coil sensitivity encoding matrix using a QR decomposition algorithm; and multiplying an inverse of the receiver coil sensitivity encoding matrix with an under-sampled data using a central processing unit (CPU) and using a GPU residing on a host computer to further decrease computation time.
Owner:COMSATS INST OF INFORMATION TECH
A magnetic resonance imaging method and device
ActiveCN106137198BEfficient removalReduced imaging timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSensitivity distributionSensitivity encoding
The invention relates to a magnetic resonance imaging method and device. The method includes: generating multiple K-space images based on the magnetic resonance induction signals received in parallel; reconstructing the first sub-image corresponding to the readout gradient pulse in the first direction and the first sub-image corresponding to the readout gradient pulse in the second direction according to the multiple K-space images. Reading out the second sub-image corresponding to the gradient pulse; calculating the phase difference between the first sub-image and the second sub-image; updating the sensitivity distribution map according to the phase difference; and according to the sensitivity distribution map before updating and the sensitivity distribution after updating Figure, MRI images obtained by performing sensitivity encoding reconstruction on multiple K-space images.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Parameterized FPGA implementation of a real-time sensitivity encoding reconstruction
A system for parameterized FPGA (Field Programable Gate Array) implementation of real-time SENSE (SENSitivity Encoding) reconstruction including: a sensitivity maps memory configured to store sensitivity map data; an aliased image memory configured to store aliased image data acquired from a scanner; a reconstructed image memory configured to store reconstructed image data; a parameterized complex matrix multiplier; a pseudo-inverse calculator; a magnitude image block; and a controller; wherein sensitivity map data from the sensitivity maps memory is transferred to the pseudo-inverse calculator; wherein data from the pseudo-inverse calculator and the aliased image data from the aliased image memory is transferred to the complex matrix multiplier; wherein data from the complex matrix multiplier is transferred to the magnitude image block; wherein the controller is configured to generate an address of the sensitivity map memory and an address of the aliased image memory to access the encoding matrix and corresponding aliased image data and also configured to generate an address of the reconstructed image memory to store the reconstructed image data.
Owner:COMSATS INST OF INFORMATION TECH
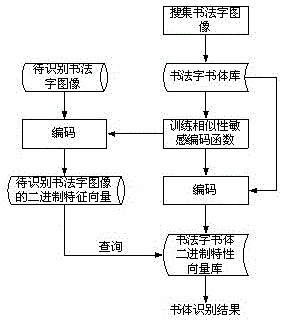
Calligraphic character recognition method based on similarity-sensitive coding
ActiveCN103186795BOvercome the disadvantage that features are difficult to defineEasy to identifyCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorFeature extraction
The invention discloses a calligraphy character writing style identification method based on similarity sensitivity encoding. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, collecting calligraphy character images, forming a calligraphy character writing style library according to the writing style types, then, training a similarity sensitivity encoding function by the calligraphy character writing style library, encoding each calligraphy character in the writing style library, and converting the calligraphy character into a binary feature vector; when identifying the writing style, extracting features of the to-be-identified calligraphy character image, and then encoding the features to get the binary feature vector of the to-be-identified calligraphy character image, then, matching the binary feature vector with the encoded writing style library, and taking the writing style represented by the writing style library most similar as the to-be-identified calligraphy character as the identification result. The method solves the defect that the calligraphy character writing style is difficult to define, and provides an effective method capable of identifying the writing style of the calligraphy character better.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com