Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
190 results about "High spatial frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
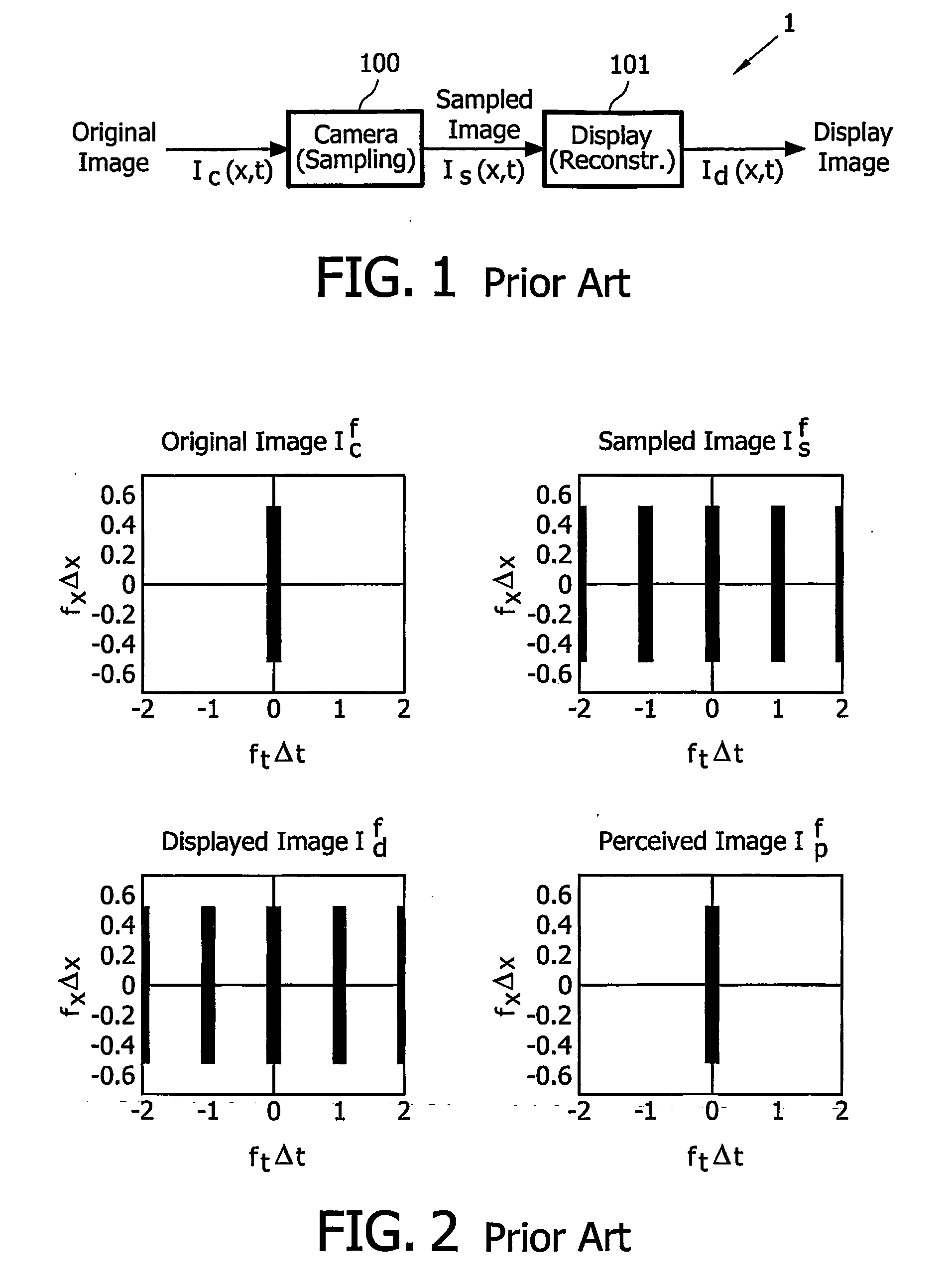
High spatial frequencies represent abrupt spatial changes in the image, such as edges, and generally correspond to configural information and fine detail. Low spatial frequencies, on the other hand, represent global information about the shape, such as general orientation and proportions.
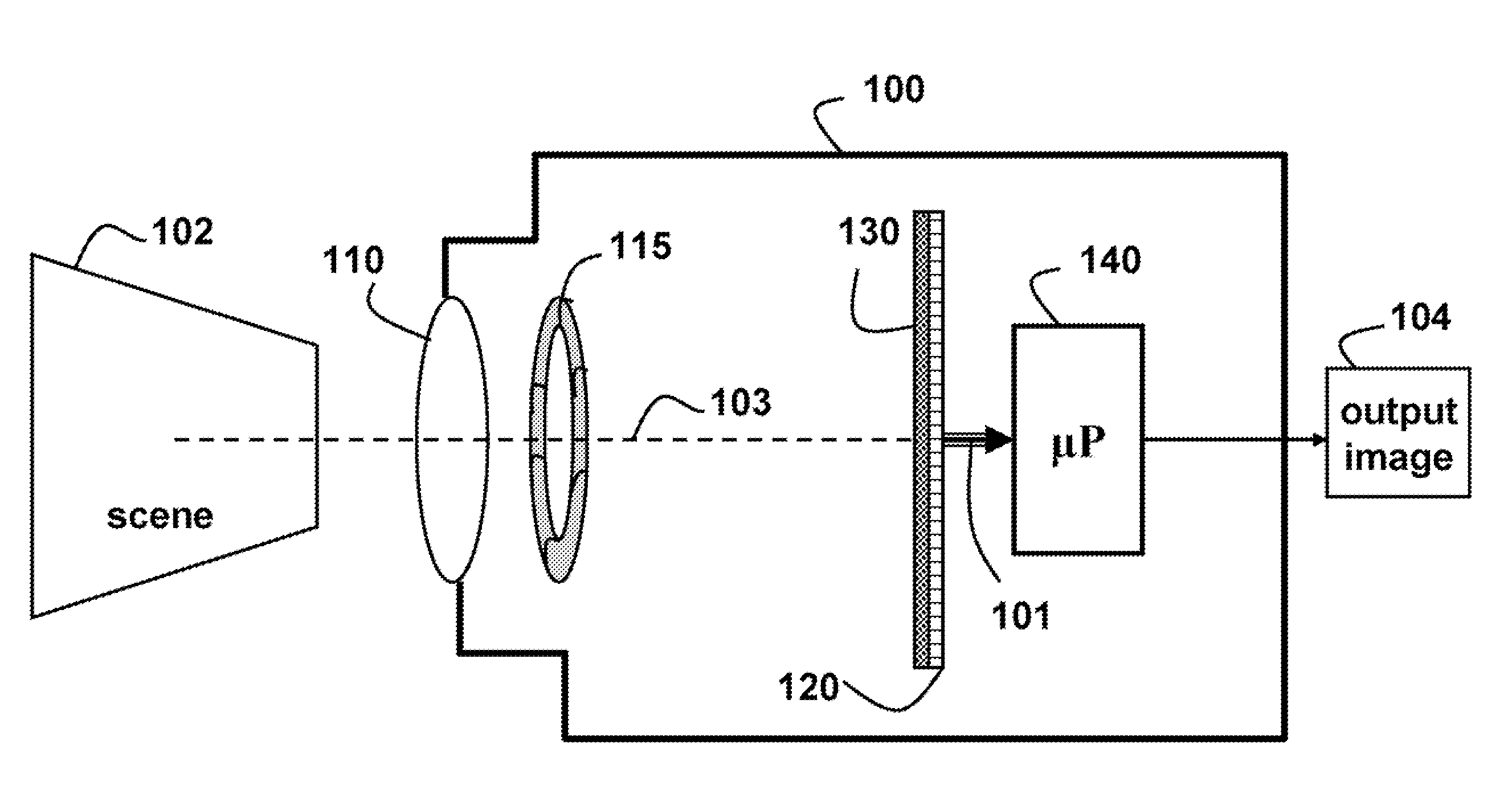
4D light field cameras
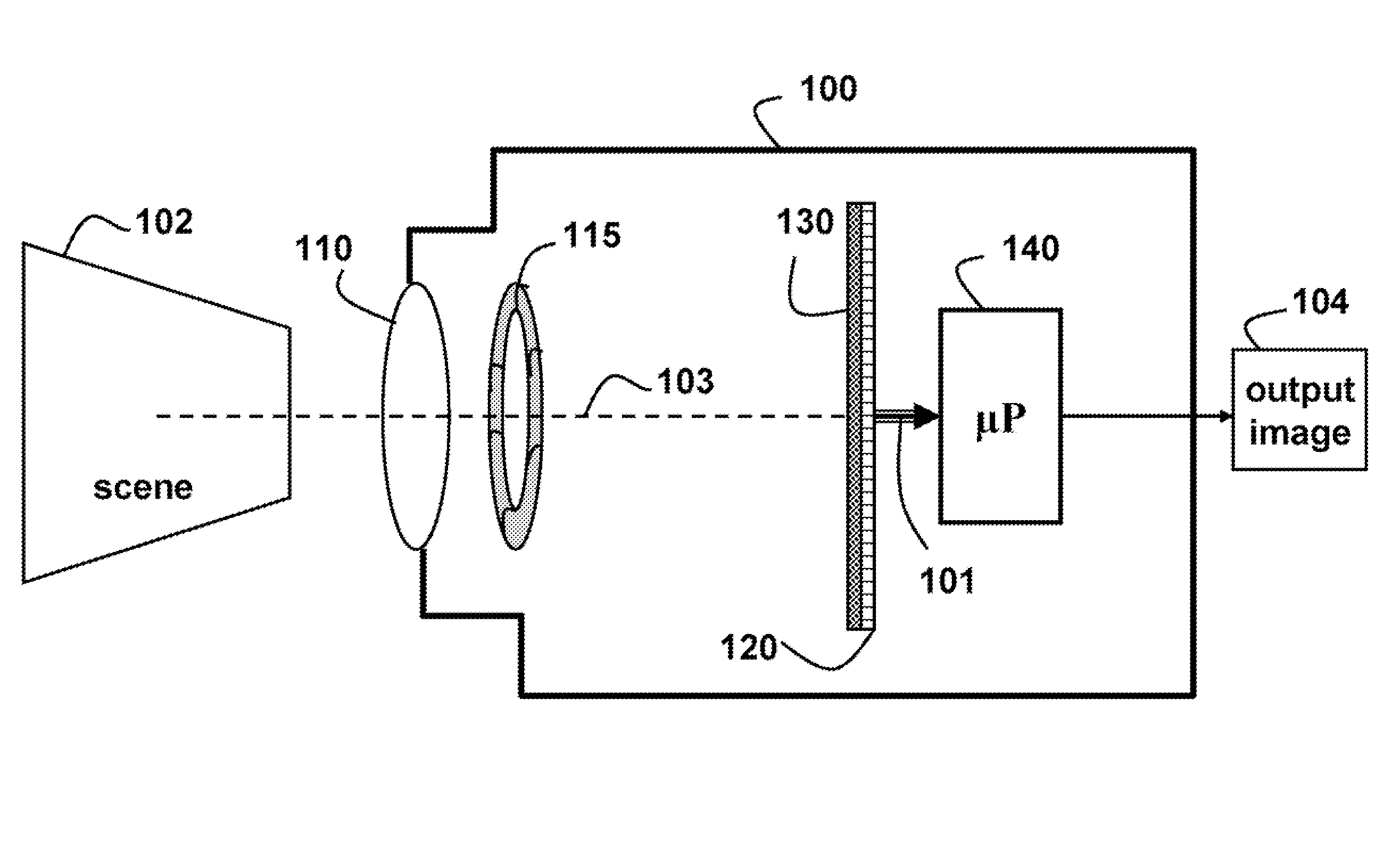
InactiveUS20080187305A1Simple attenuating maskSuppress unwanted occludersProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementCamera lensUltrasound attenuation
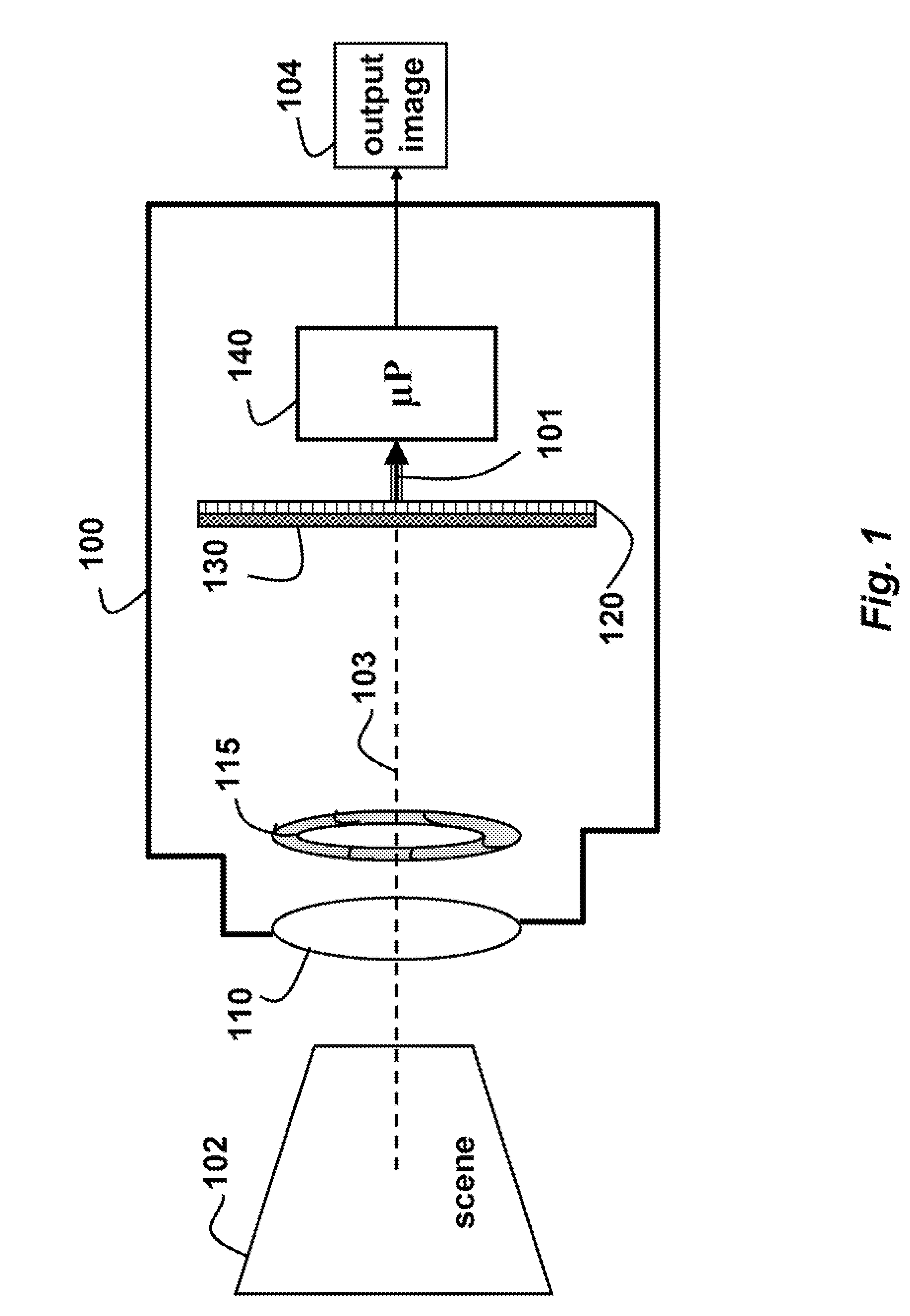
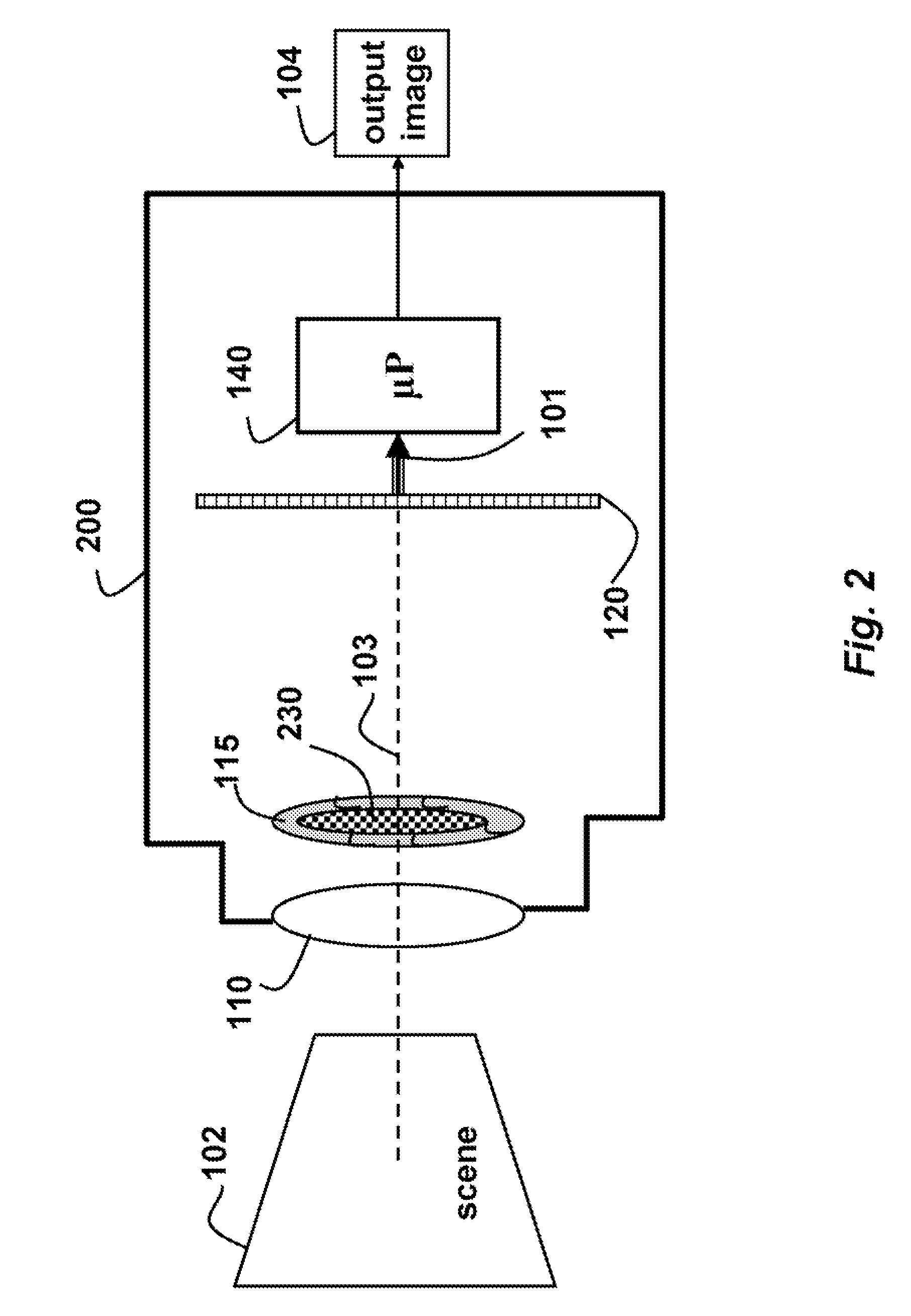
A camera acquires a 4D light field of a scene. The camera includes a lens and sensor. A mask is arranged in a straight optical path between the lens and the sensor. The mask including an attenuation pattern to spatially modulate the 4D light field acquired of the scene by the sensor. The pattern has a low spatial frequency when the mask is arranged near the lens, and a high spatial frequency when the mask is arranged near the sensor.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
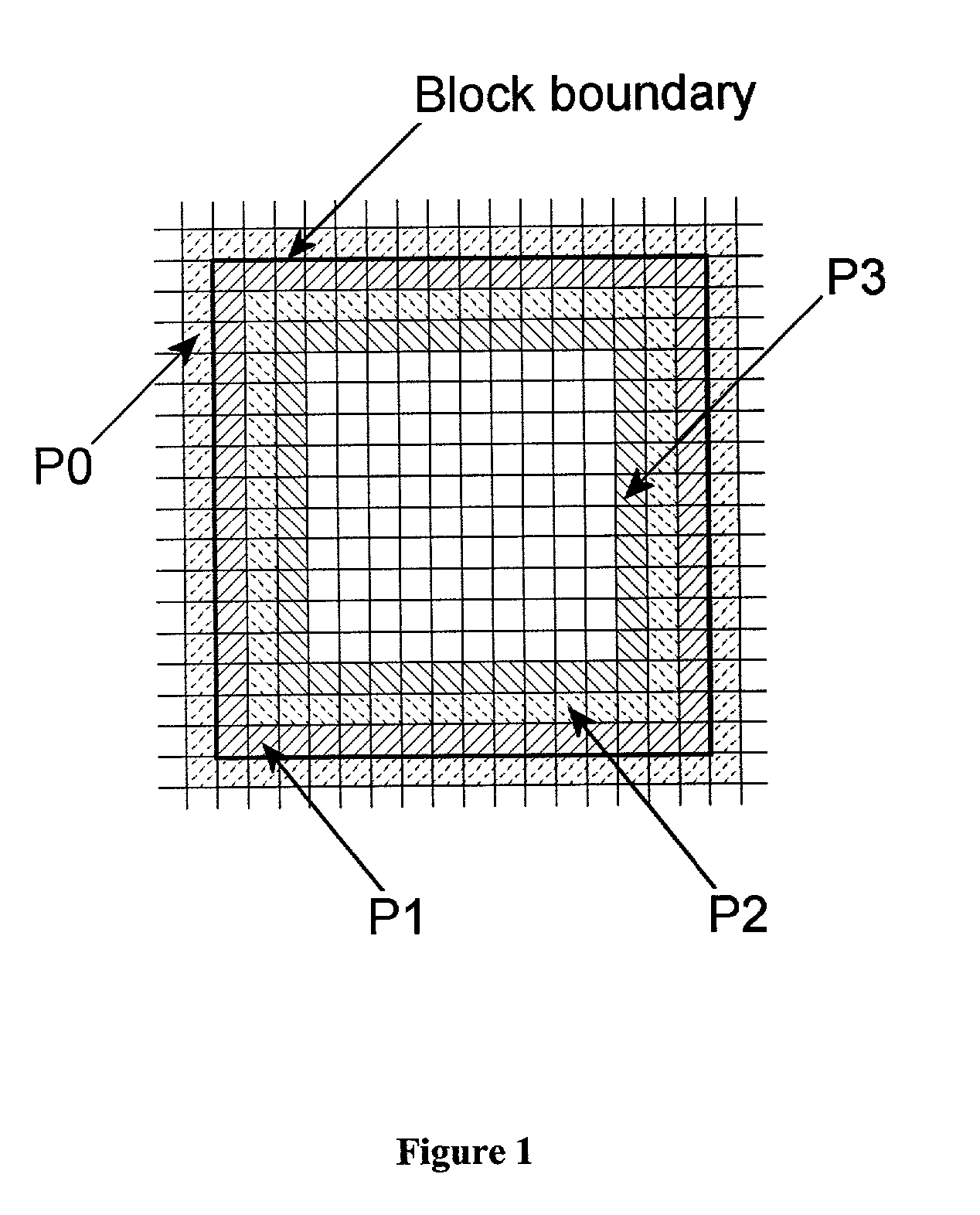
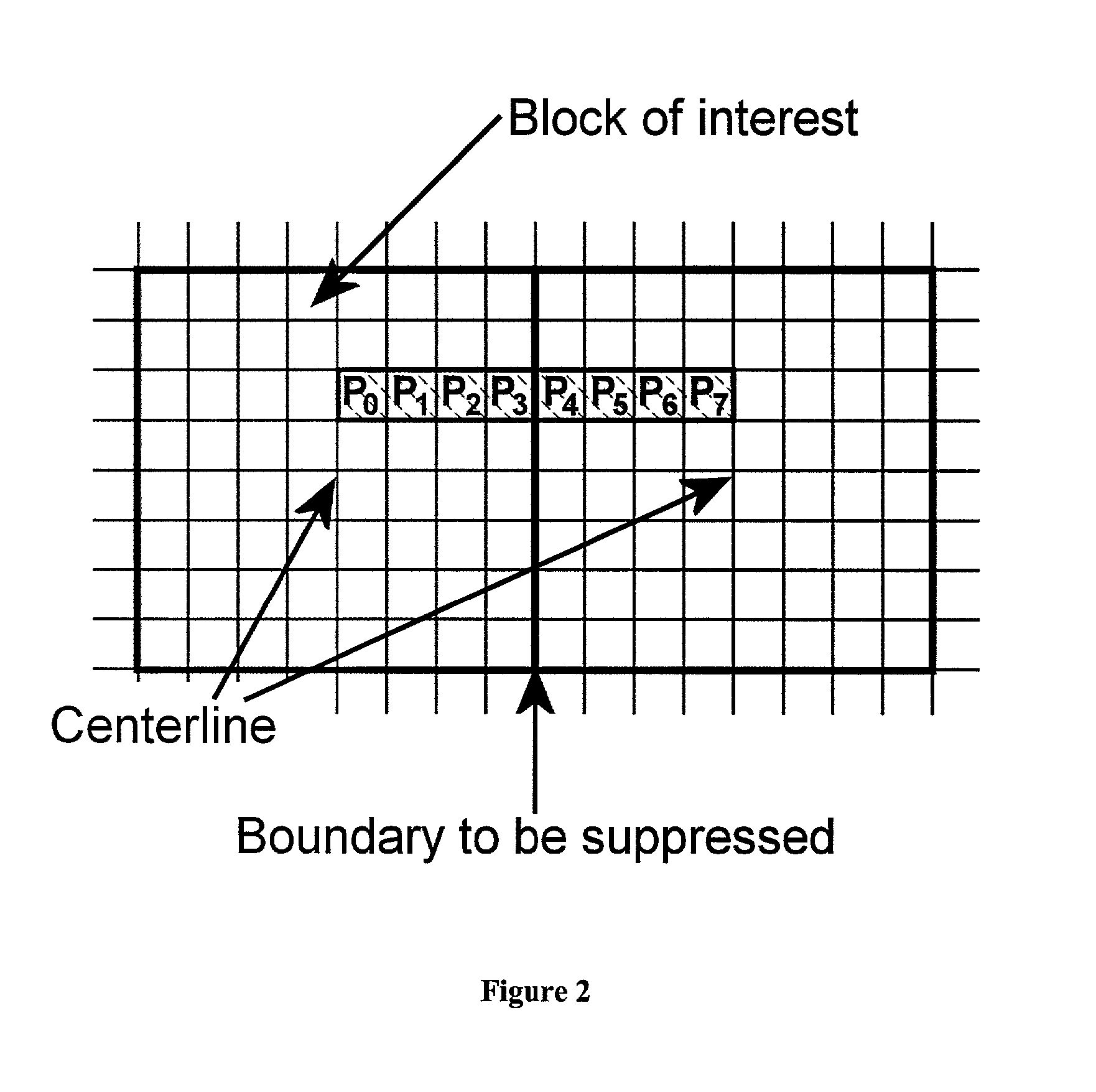
Removal of block encoding artifacts
InactiveUS7003174B2Reduce artifactsAccessImage enhancementPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVisibilityPattern recognition
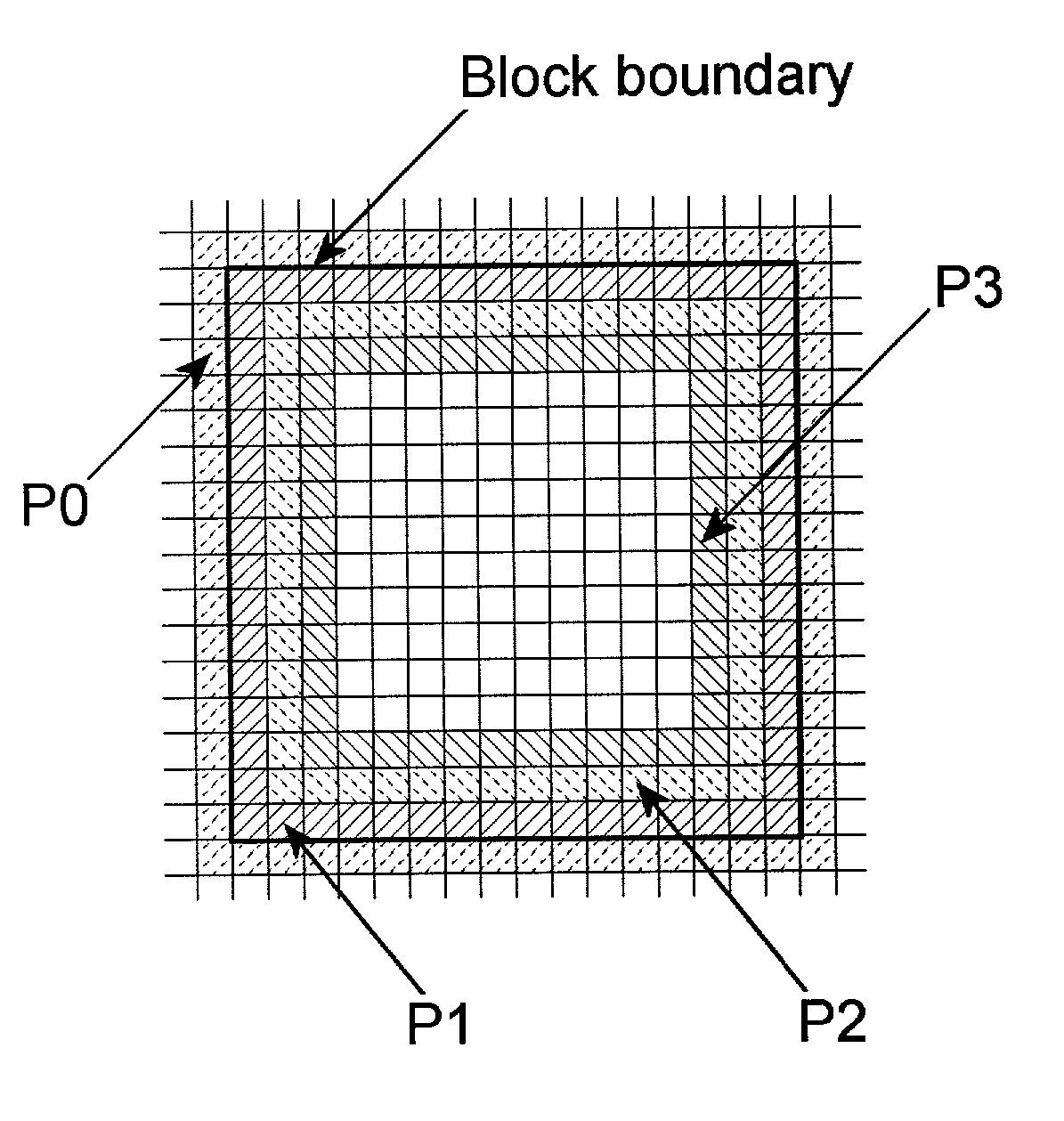
A method of reducing artifacts in an image previously processed by block transform encoding may comprise the steps of:determining block boundaries;determining an approximate metric of artifact visibility;optionally interpolating across block boundaries;adaptively filtering luminance;optionally adaptively filtering chrominance;adaptively adjusting local saturation variation; andadaptively simulating high spatial frequency image detail;wherein the adaptive steps are executed to an extent or in an amount depending on the metric or standard or measurement of artifact visibility.
Owner:COREL CORP +1
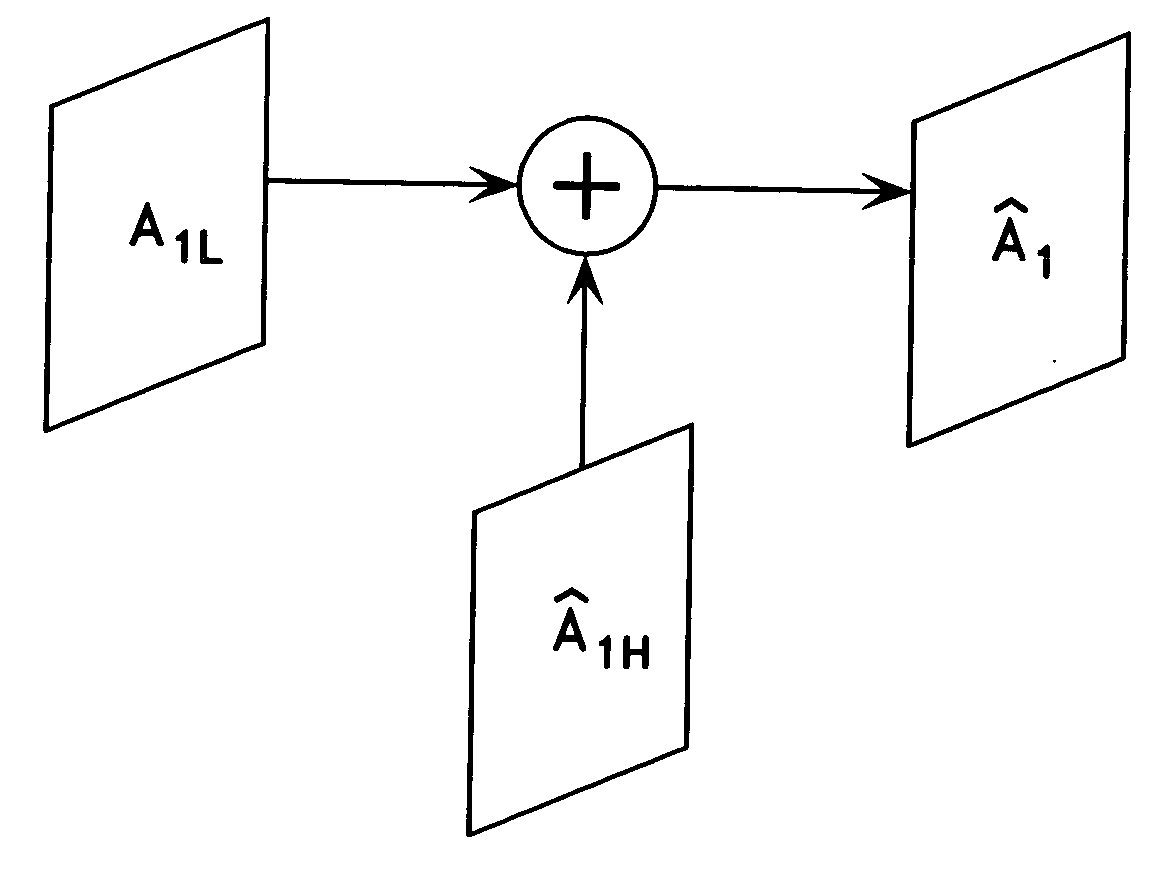
High resolution image reconstruction
ActiveUS20050013509A1Image enhancementGeometric image transformationImage resolutionHigh resolution image
A technique of reconstructing a high resolution image from at least one image sequence of temporally related high and low resolution image frames wherein each of said high resolution image frames includes a low spatial frequency component and a high spatial frequency component is described. The high-resolution image reconstruction technique uses spatial interpolation to generate a low spatial frequency component from a low-resolution image frame of the image sequence. The technique is adapted to generate a high spatial frequency component from at least one high resolution image frame of the image sequence which is closely related to the low resolution image frame, and to remap the high spatial frequency component to a motion-compensated high spatial frequency component estimate of the low resolution image frame. The motion-compensated high spatial frequency component estimate is added to the generated low spatial frequency component to form a reconstructed high-resolution image of the low-resolution image frame.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
4D light field cameras
InactiveUS7792423B2Suppress unwanted occludersProjector focusing arrangementPhotometryCamera lensUltrasound attenuation
A camera acquires a 4D light field of a scene. The camera includes a lens and sensor. A mask is arranged in a straight optical path between the lens and the sensor. The mask including an attenuation pattern to spatially modulate the 4D light field acquired of the scene by the sensor. The pattern has a low spatial frequency when the mask is arranged near the lens, and a high spatial frequency when the mask is arranged near the sensor.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Methods and arrangements employing mixed-domain displays
ActiveUS8331724B2Small distortionTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingDisplay device
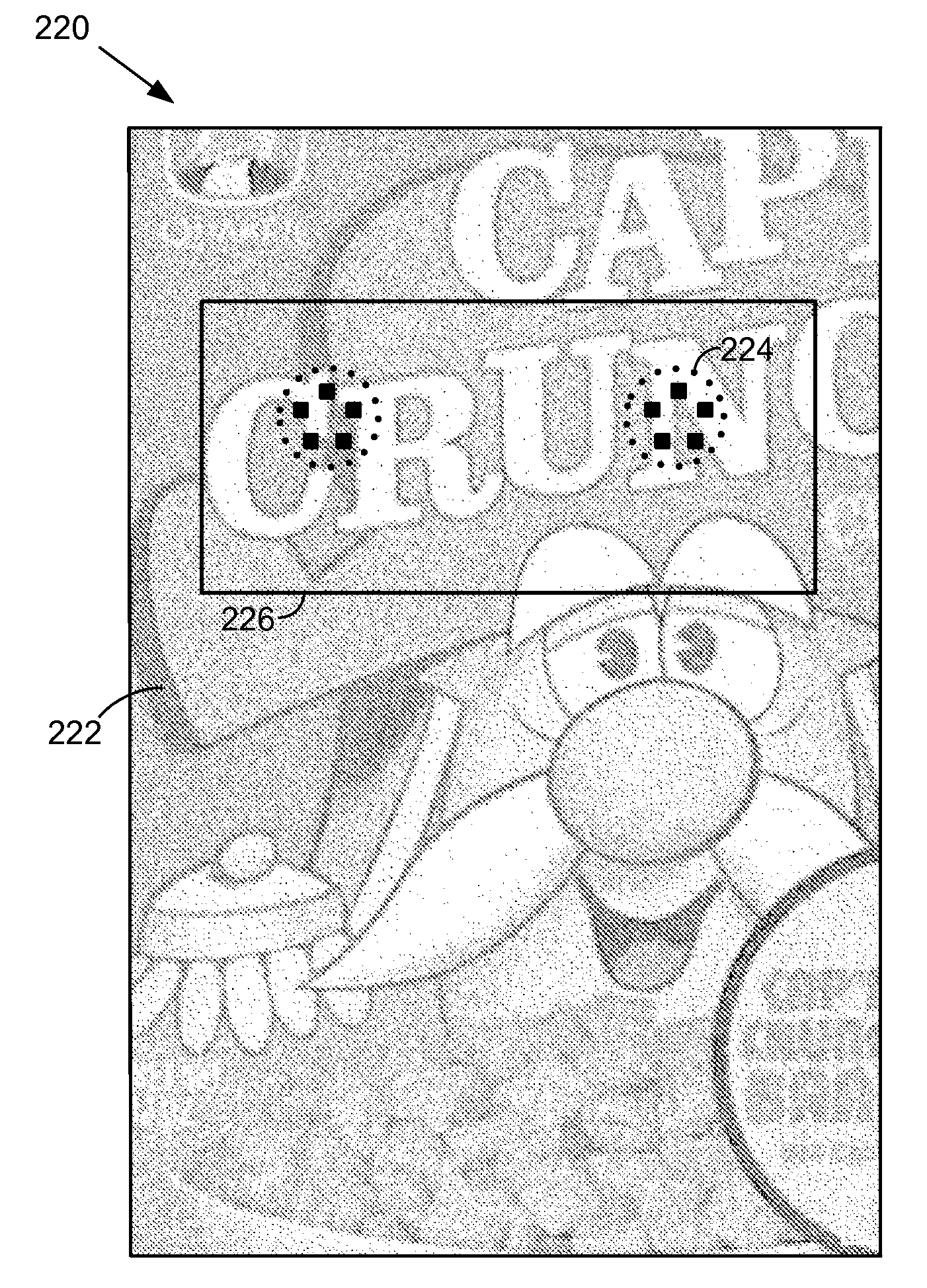
An image is encoded to define one or more spatial regions that can be sensed by a suitably-equipped mobile device (e.g., a smartphone), but are imperceptible to humans. When such a mobile device senses one of these regions, it takes an action in response (e.g., rendering an associated tone, playing linked video, etc.). The regions may overlap in layered fashion. One form of encoding employs modification of the color content of the image at higher spatial frequencies, where human vision is not acute. In a particular embodiment, the encoding comprises altering a transform domain representation of the image by adding signal energy in a first chrominance channel, where the added signal energy falls primarily within a segmented arc region in a transform domain space. In another arrangement, a smartphone display presents both image data captured from a scene, and a transform representation of the image data (e.g., in the Fourier domain). This latter information can aid a user in positioning the phone, e.g., to enhance decoding of a steganographic digital watermark. In still another arrangement, foveal filtering is applied to of smartphone-captured image data in connection with other image processing.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
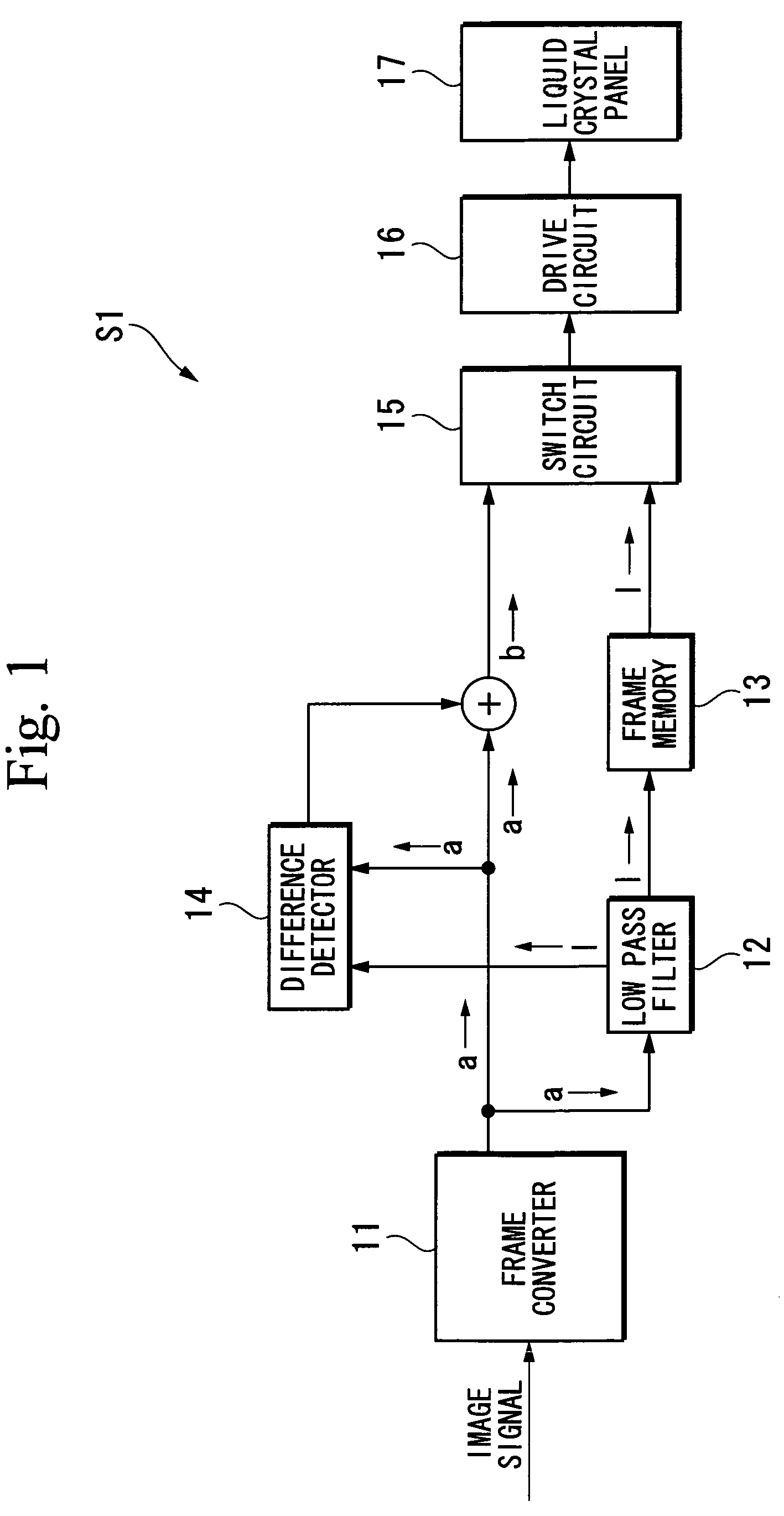
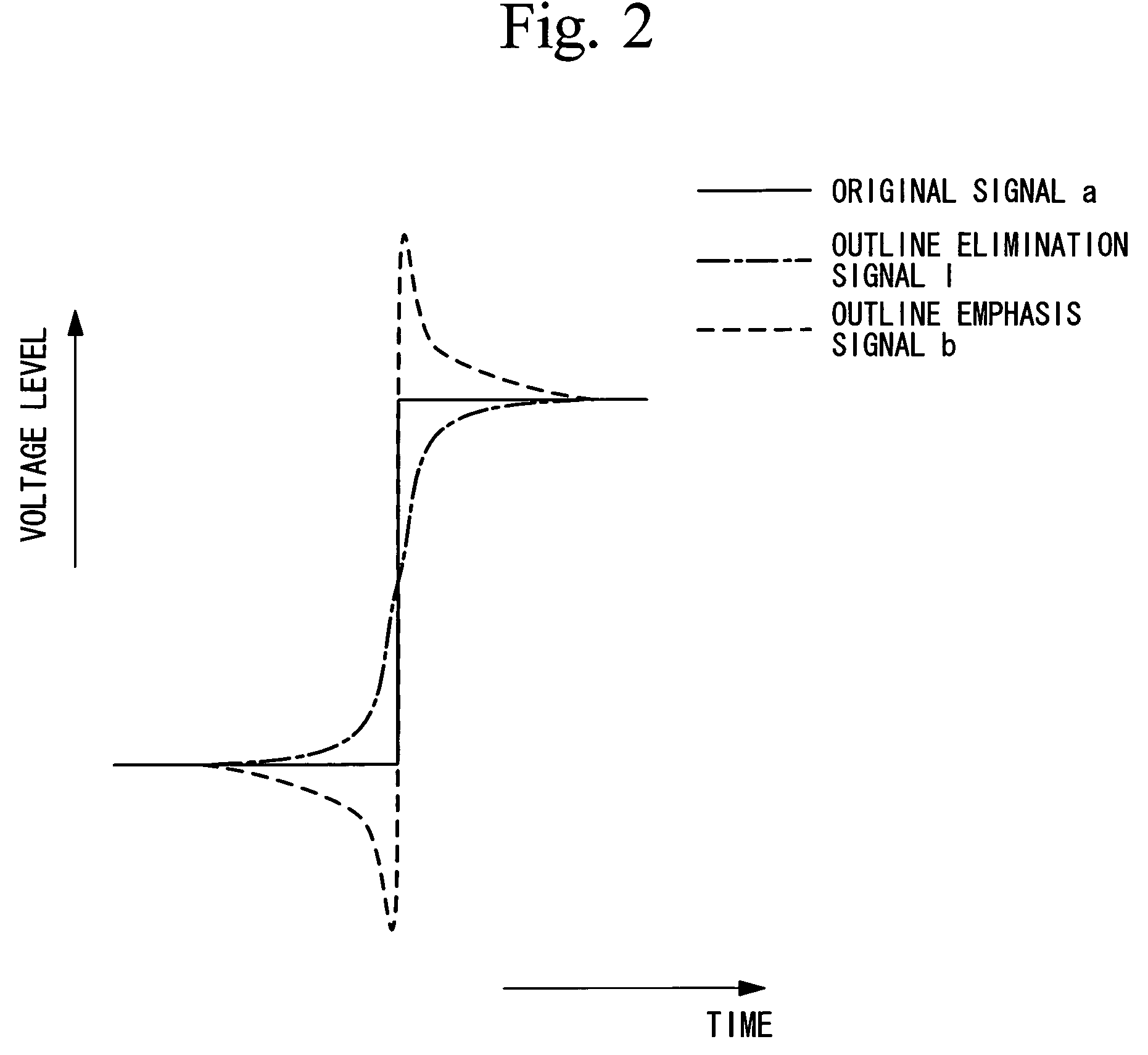
Image display method, image display device, and projector
ActiveUS20060119617A1Reduce signaling processing loadSuppress blurCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Image signal
An image display method includes dividing one frame into a plurality of sub-frames by multiplying a frame frequency of an input image signal, reducing a high-spatial frequency component of an image signal which is used for image display in at least one predetermined sub-frame among the plurality of sub-frames in comparison with that of an image signal which is used for image display in another sub-frame, and displaying an image in each sub-frame.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Infrared resolution and contrast enhancement with fusion
ActiveUS20110261207A1Without losing clarity and interpretabilityEasy to analyzeImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage resolutionContrast enhancement
The present disclosure relates to combination of images. A method according to an embodiment comprises: receiving a visual image and an infrared (IR) image of a scene; extracting high spatial frequency content from said visual image; and combining said extracted high spatial frequency content from said visual image with said IR image, wherein a resolution for the visual image and the IR image are substantially the same, to generate a combined image.
Owner:FLIR SYST AB
Semi-active optical tracking system
A system and method for tracking an airborne target including an illumination source (e.g., a diode laser array) is used to enhance a target signature and a detector (e.g., a passive high-speed camera) is used to detect to electromagnetic radiation (e.g., infrared radiation) reflected off the target. The received electromagnetic radiation may be processed by a digital computer and passed through a spatial filter that implements a band limited edge detection operation in the frequency domain. The filter may remove low spatial frequencies that attenuate soft edged clutter such as clouds and smoke as well as filter out artifacts and attenuated medium to high spatial frequencies to inhibit speckle noise from the detector as well as speckle from the laser return off the target.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
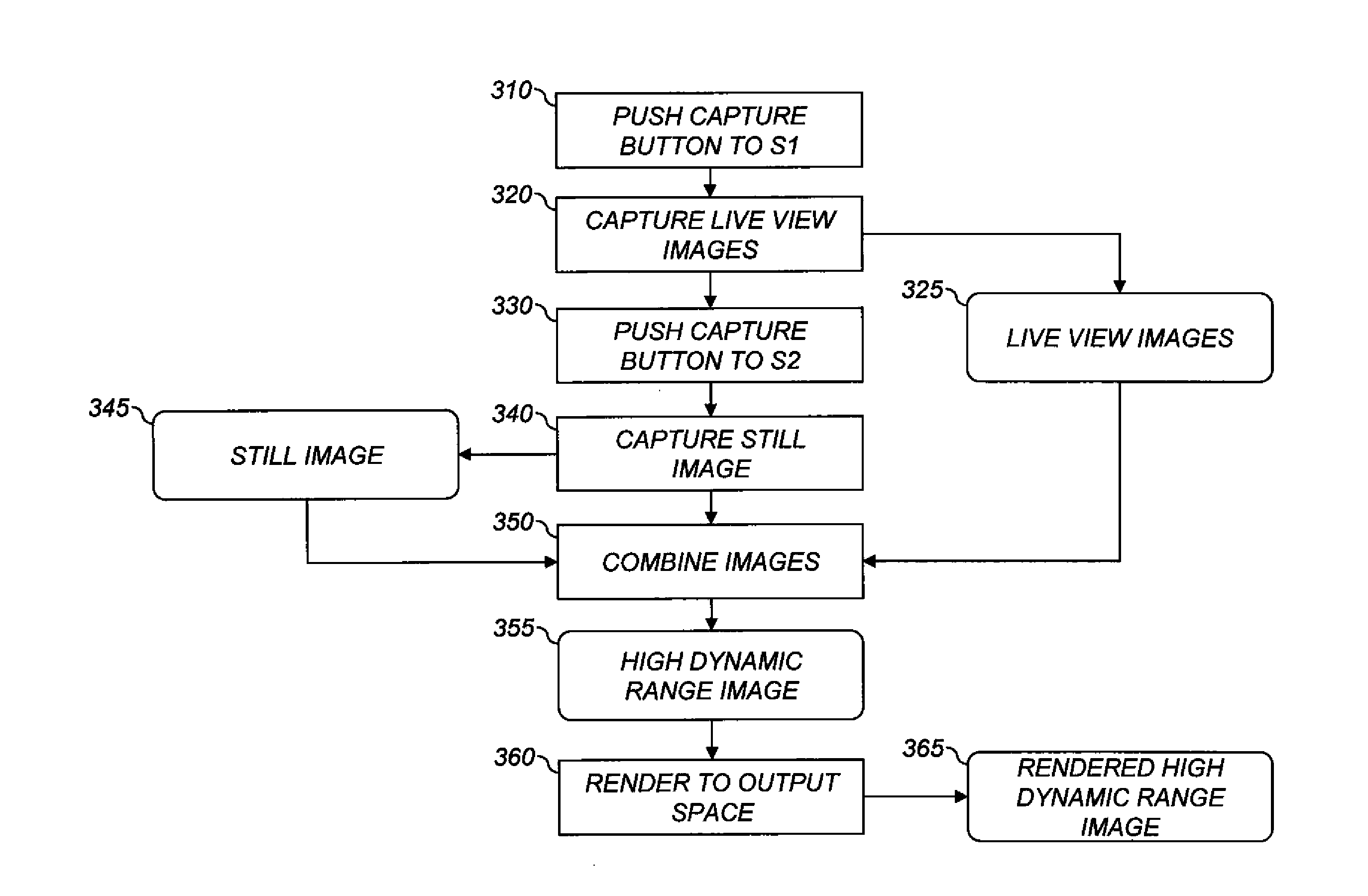
Method for producing high dynamic range images
ActiveUS20120105681A1Improve dynamic rangeSacrificing performanceImage enhancementTelevision system detailsComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
A method for producing a high-dynamic-range image, comprising: receiving a low-resolution image of a scene having a first resolution and captured at a first exposure level; receiving a first high-resolution image of the scene having a second resolution and captured at a second exposure level different from the first exposure level, the second resolution being greater than the first resolution; forming a residual image corresponding to high spatial frequency content in the first high-resolution image; forming a second high-resolution image having the second resolution and the first exposure level by combining the low-resolution image and the residual image; producing the high-dynamic-range image by combining the first high-resolution image and the second high-resolution image; and storing the high-dynamic-range image in a processor accessible memory.
Owner:KODAK ALARIS INC
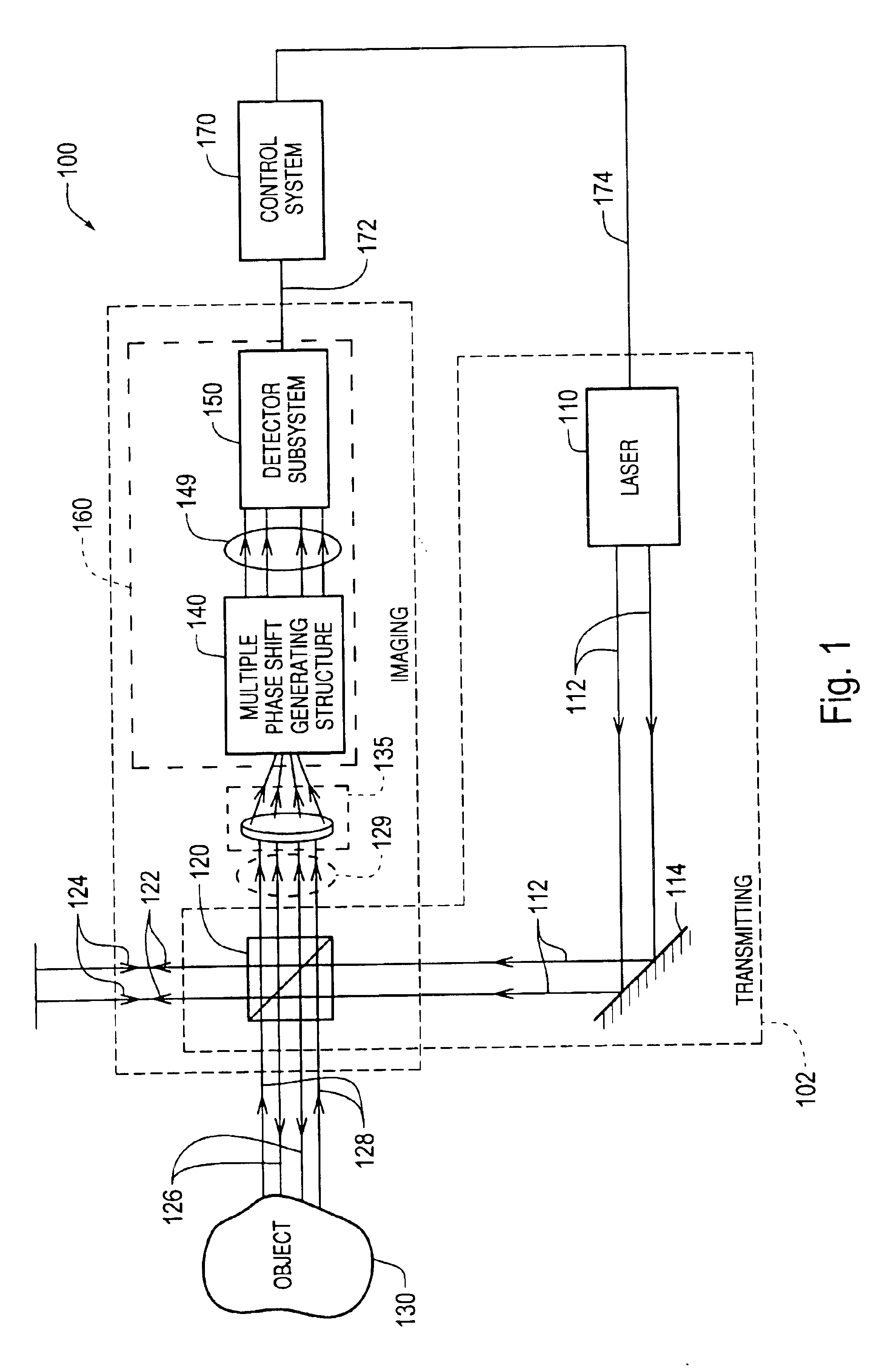
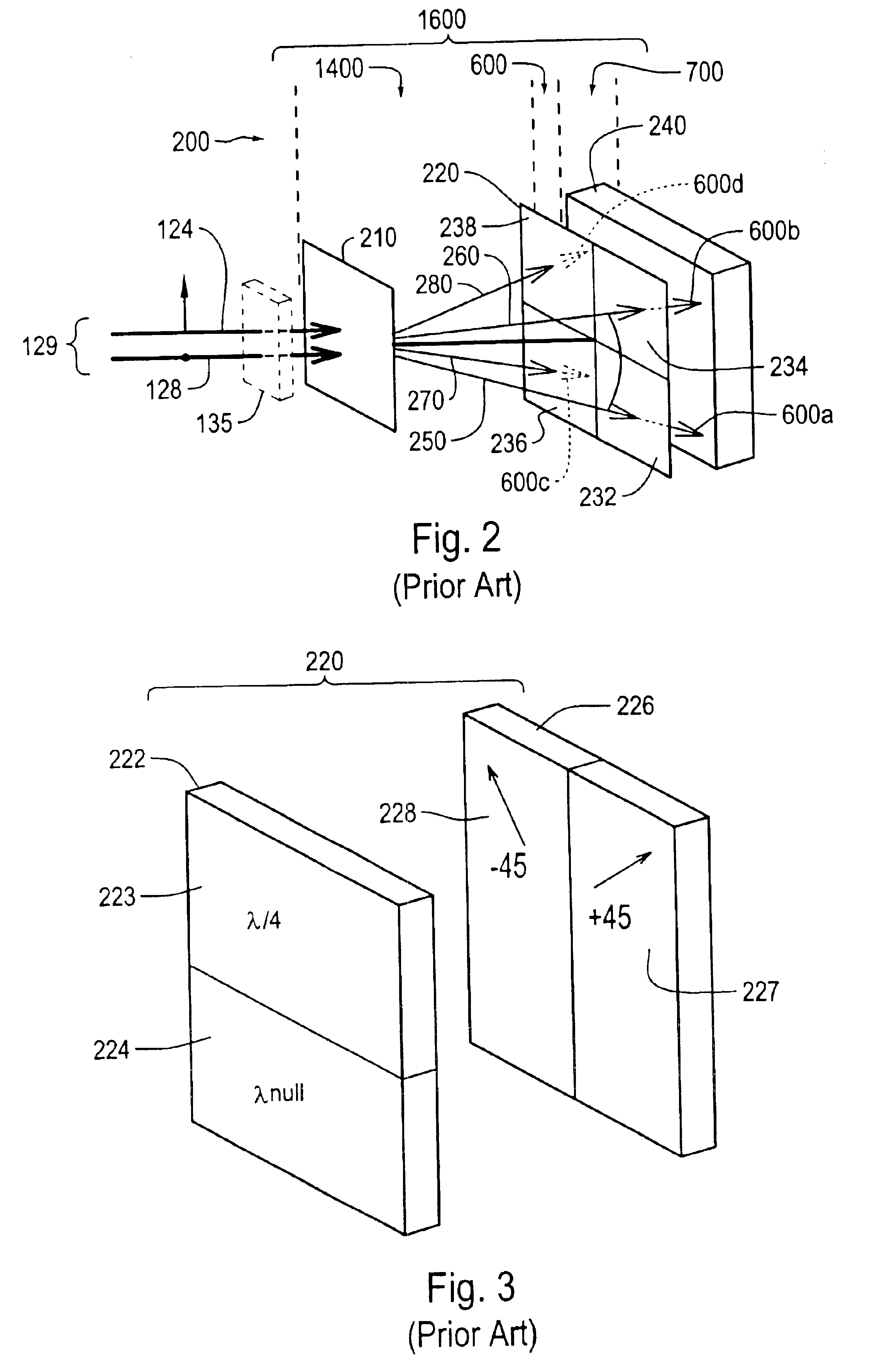
Interferometer using integrated imaging array and high-density phase-shifting array
An integrated imaging element for an interferometer generates at least one interference image that includes multiple interference portions with different relative phase shifts interleaved in a pattern having a high spatial frequency in the image. The interleaved pattern is at least partially determined by the pattern of a high density relative retarder array used in the integrated imaging element. In various embodiments, the multiple interference portions are interleaved in a checkerboard-like pattern across the entire surface of a detector device. As a result, various non-common mode errors present in various interferometers that generate separate non-interleaved images for each relative phase are reduced or eliminated.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
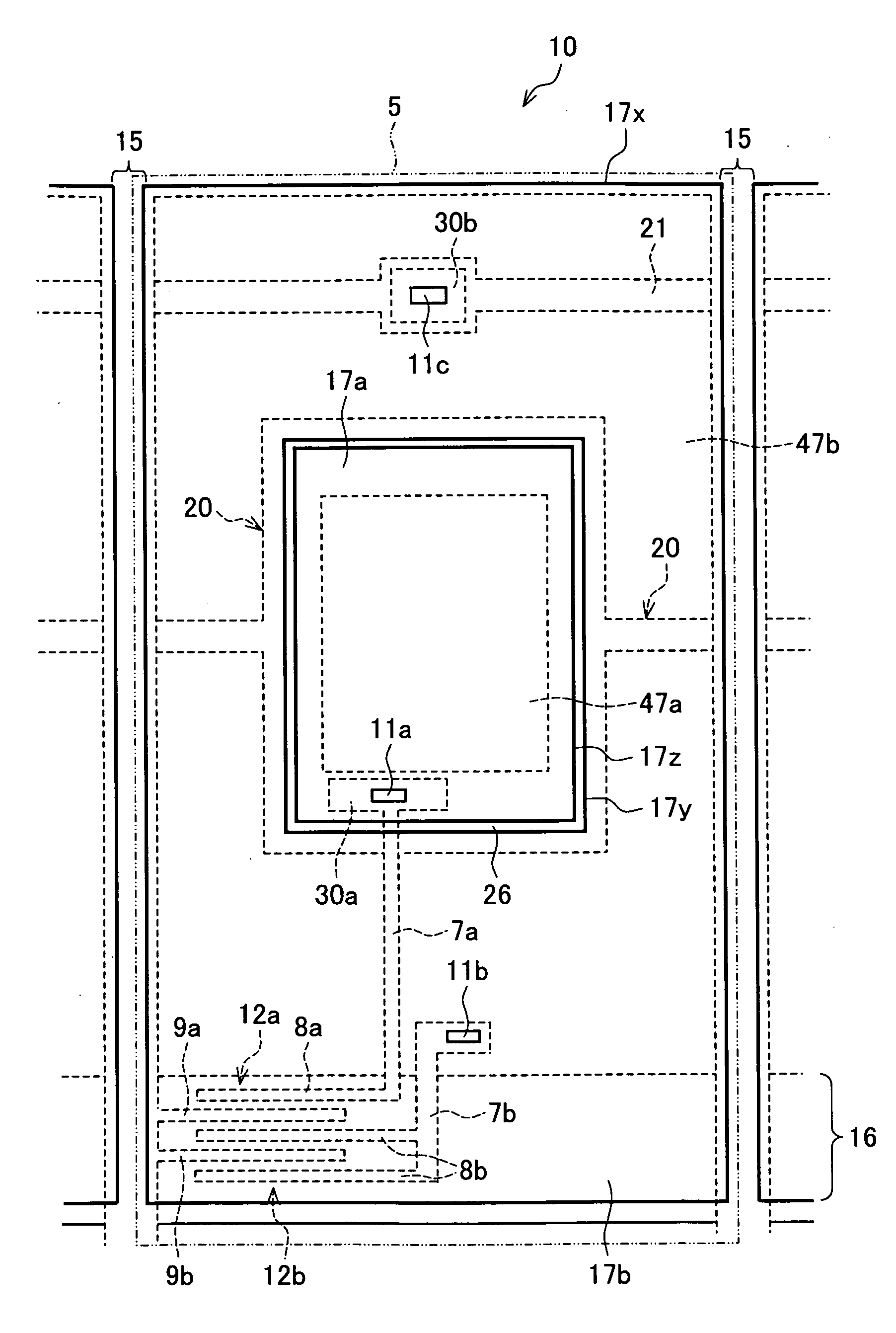
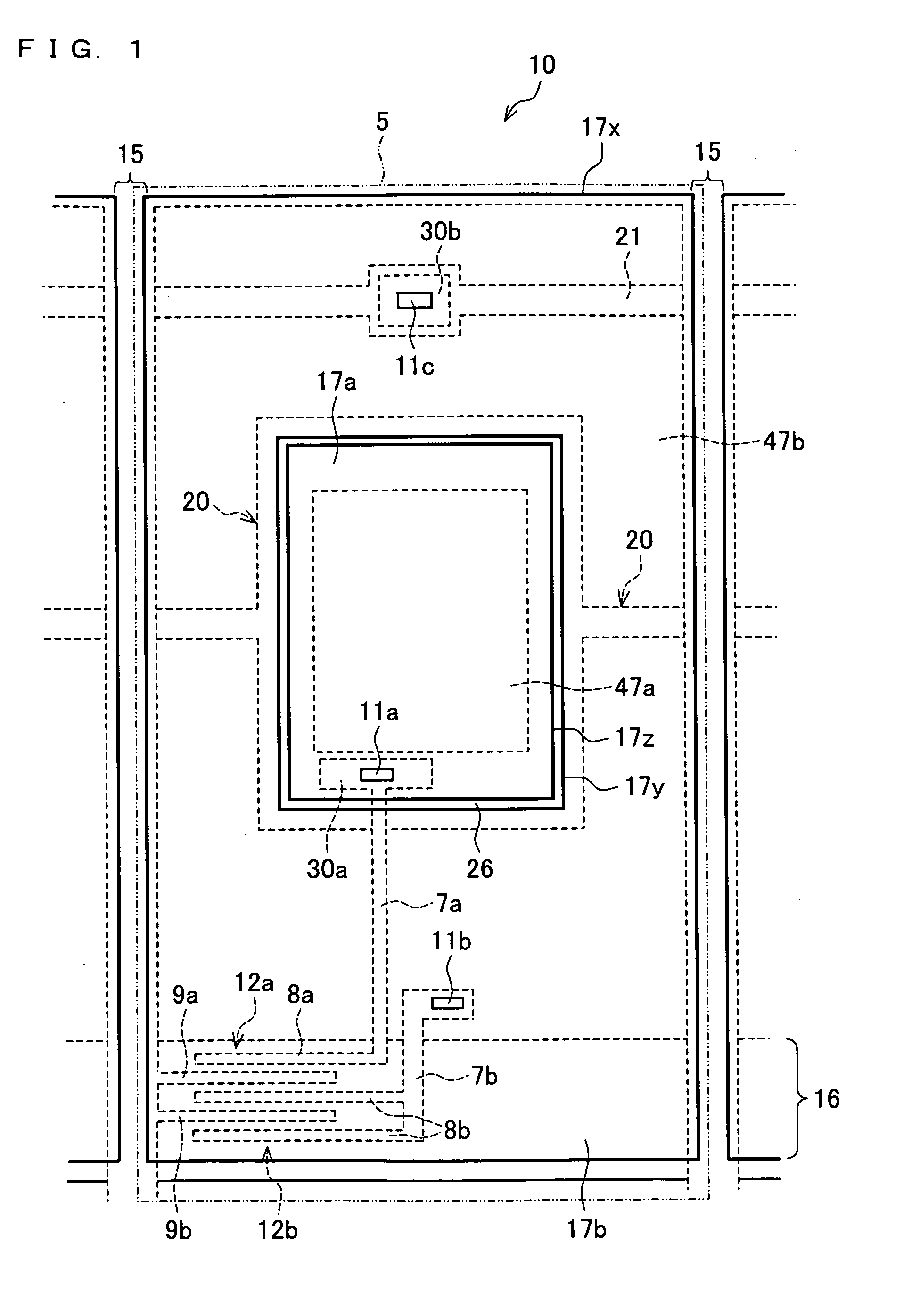
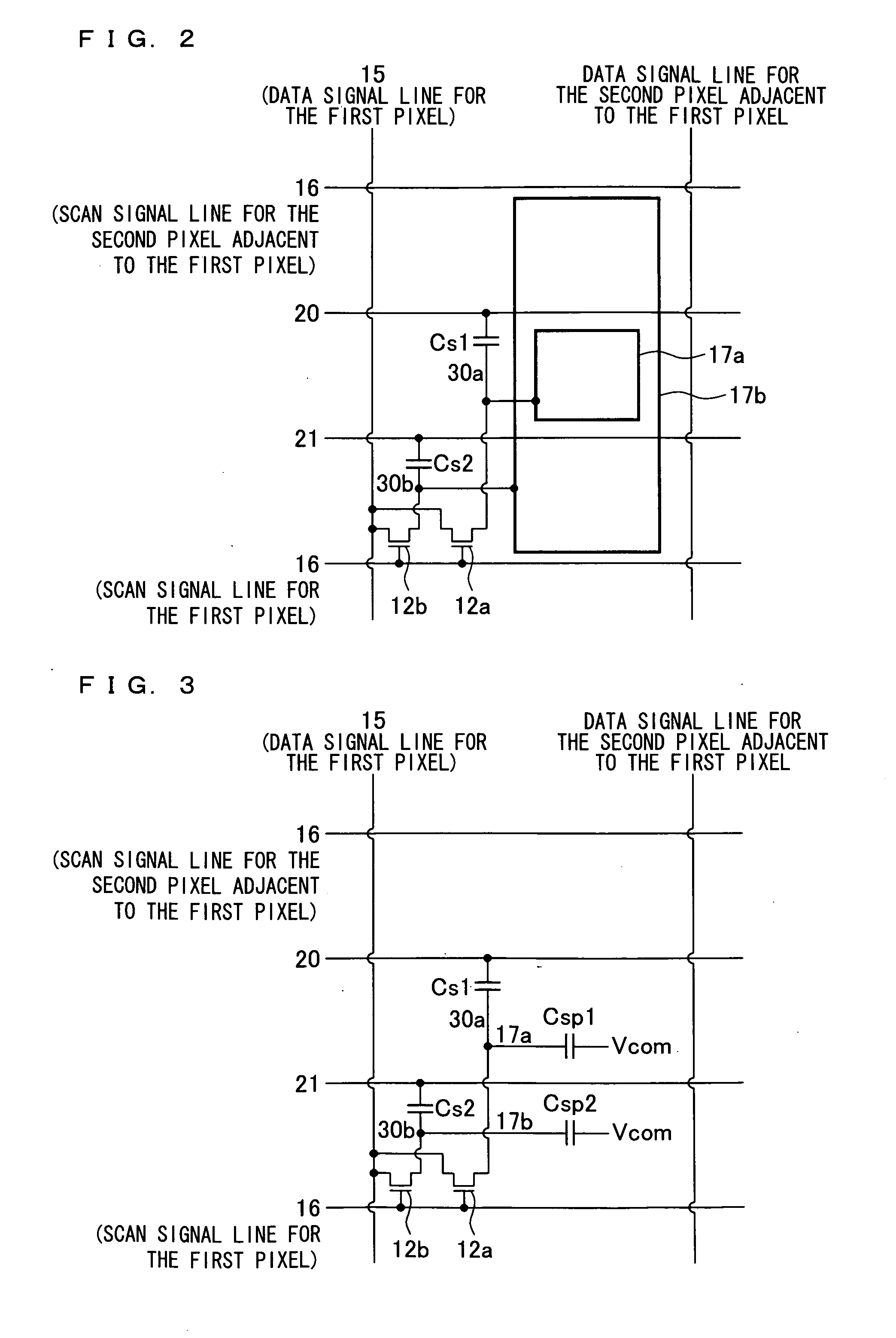
Display device, active matrix substrate, liquid crystald display device and television receiver
InactiveUS20090009449A1Lower areaHigh luminance areaStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayTelevision receivers
In one embodiment of a display device, pixels are arranged in matrix, and a first luminance area (high luminance area) and a second luminance area (low luminance area) which surrounds the first luminance area and has a luminance lower than that of the first luminance area can be formed in each pixel. The display device which can clearly display an image having a high spatial frequency and an active matrix substrate to be used for the display device are provided.
Owner:SHARP KK
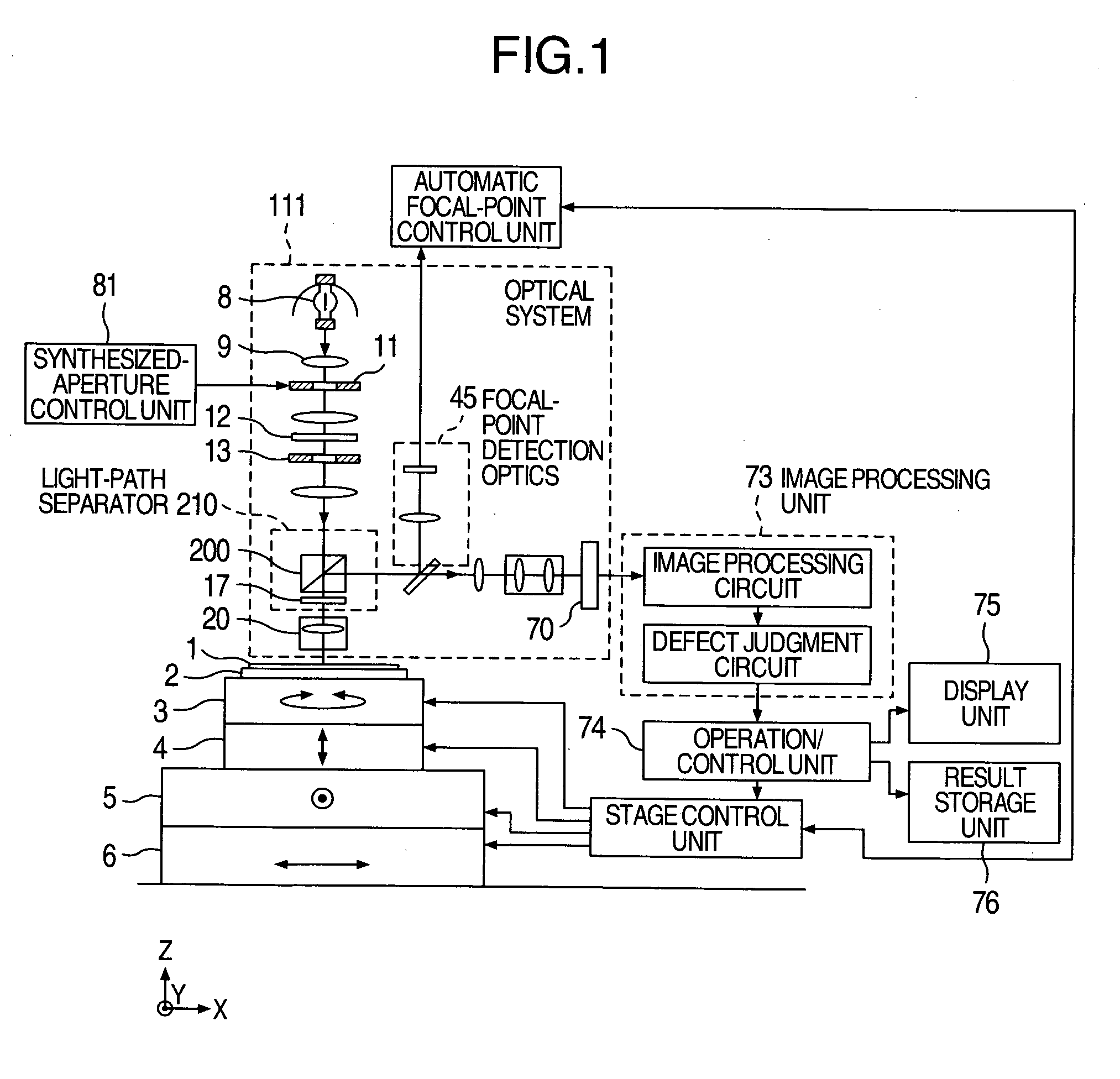
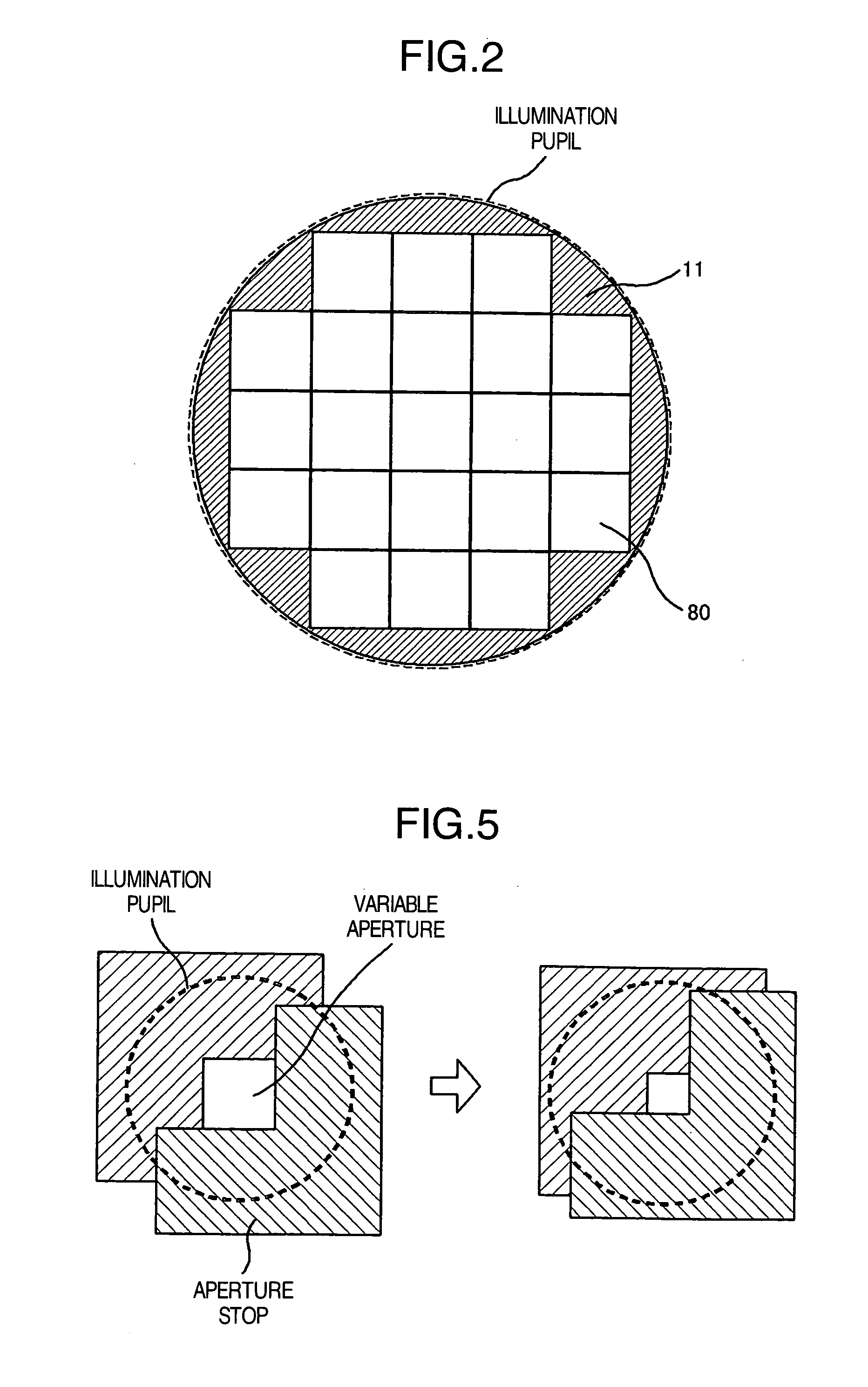
Apparatus and method for defect inspection
InactiveUS20060262297A1High sensitivitySharp contrastOptically investigating flaws/contaminationEngineeringPupil
In the conventional methods for enhancing defect detection sensitivity by improving the resolving power, if a microscopic pattern, which is a high spatial-frequency structure as is the case with a microscopic defect, has become the brightest portion, the gray-scale contrast of the microscopic defect will be enhanced. At the same time, however, the gray-scale contrast of the microscopic pattern will also be enhanced simultaneously. Consequently, there has existed a problem that it is impossible to enhance the microscopic-defect detection sensitivity further than that. In the present invention, an aperture stop which is divided into a plurality of small apertures is located on an illumination pupil plane. Then, light-shield / light-transmission for each small aperture is controlled independently of each other. This control allows an inspection-target object to be illuminated at only an incident angle at which the gray-scale contrast of the microscopic defect will be emphasized more sharply.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Dual function detector device
A dual function detector device operates in either a normal operating mode or in an EMI correction mode to suppress effects of EMI within the detector. The detector device may be a flat panel x-ray detectors used in x-ray imaging systems. The device has a pixel architecture and panel read-out technique that enables real-time, high spatial frequency measurement of noise induced by electromagnetic radiation on a digital x-ray detector. The measurement can be used to calibrate the detector in real-time to attain artifact-free imaging in all environments, including those that contain temporally and spatially changing electromagnetic fields.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
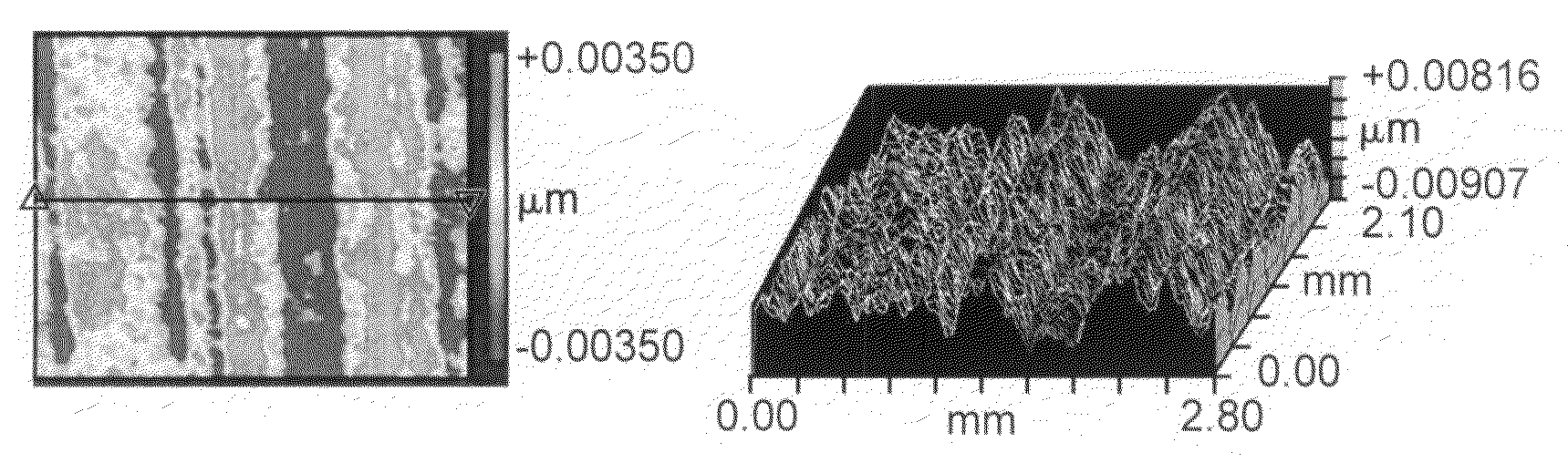
Method for accurate high-resolution measurements of aspheric surfaces
ActiveUS20060221350A1High measurement accuracyReduce impactOptical measurementsUsing optical meansWavefrontMetrology
A system comprising a plurality of methods for measuring surfaces or wavefronts from a test part with greatly improved accuracy, particularly the higher spatial frequencies on aspheres. These methods involve multiple measurements of a test part. One of the methods involves calibration and control of the focusing components of a metrology gauge in order to avoid loss of resolution and accuracy when the test part is repositioned with respect to the gauge. Other methods extend conventional averaging methods for suppressing the higher spatial-frequency structure in the gauge's inherent slope-dependent inhomogeneous bias. One of these methods involve averages that suppress the part's higher spatial-frequency structure so that the gauge's bias can be disambiguated; another method directly suppresses the gauge's bias within the measurements. All of the methods can be used in conjunction in a variety of configurations that are tailored to specific geometries and tasks.
Owner:QED TECH INT
Deformable mirror with passive and active actuators
InactiveUS20040027632A1Aberration correctionMirrorsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionEngineeringDeformable mirror
A combination of active and passive force actuators provide adjustments to the shape of an optical element to reduce or compensate for aberrations in an optical system. Passive actuators at a high spatial frequency are capable of correcting higher order steady state components of shape error while dynamic corrections of higher frequency, operationally dependent is provided allowing the number of active actuators and the power supplied to each active actuator to be reduced; reducing heating of the optical element by the active actuators and increasing stability of the system. Compound actuators including a combination of an active actuator portion with a passive actuator portion (which provides a mechanical force bias to the active actuator portion) allows increased spatial flexibility of application of forces to the optical element and other advantages.
Owner:NIKON CORP
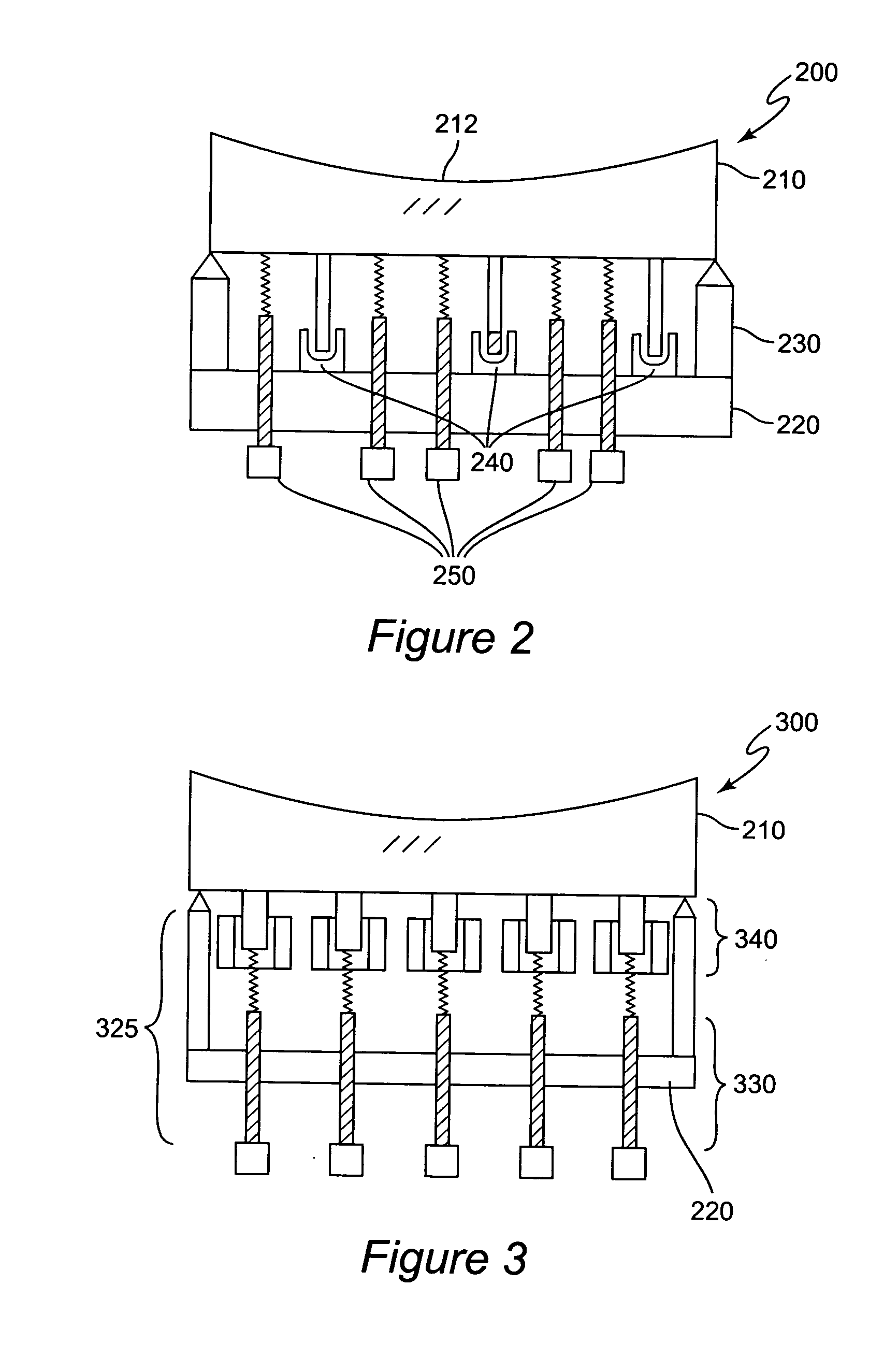
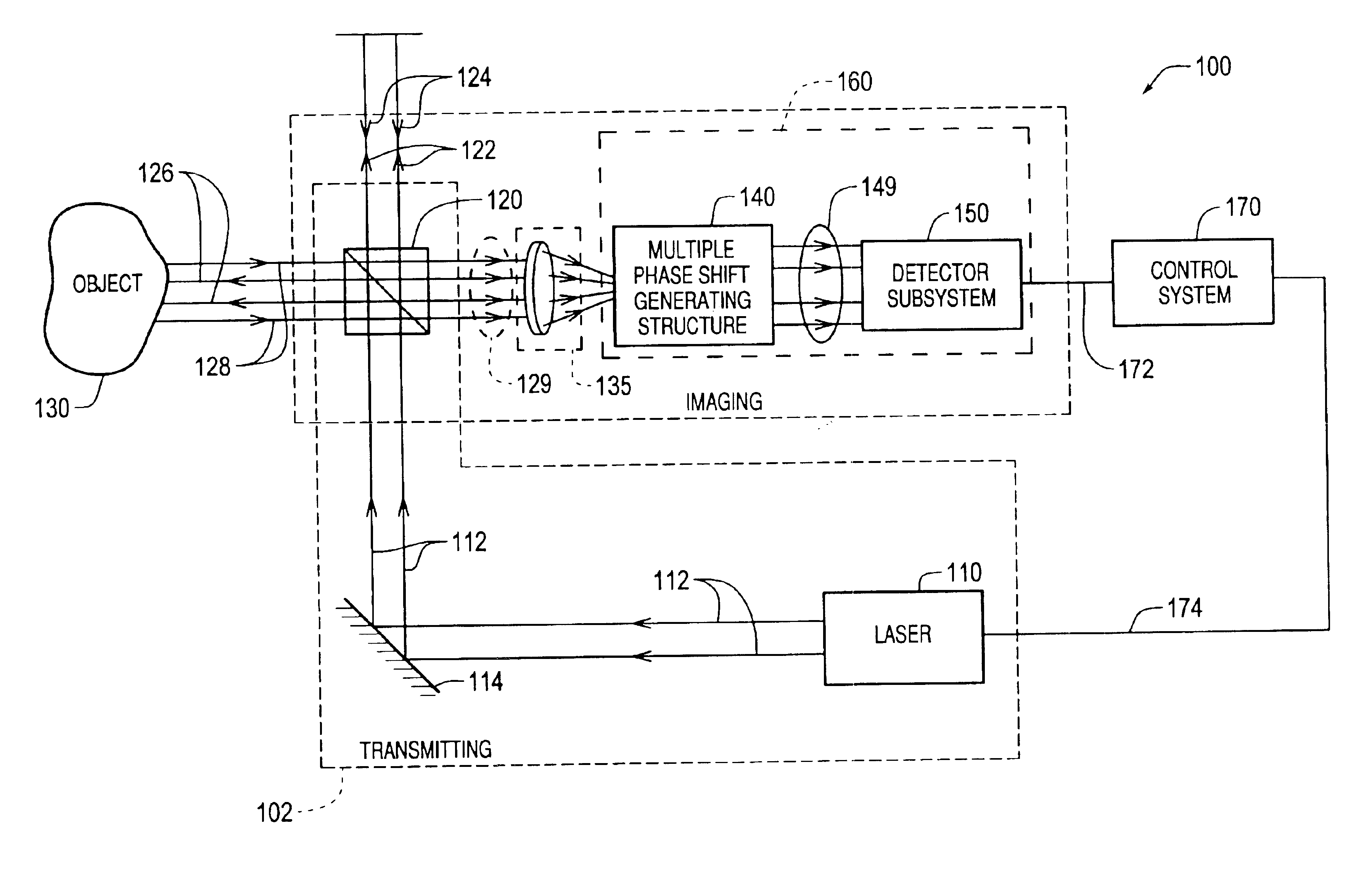
Interference projection exposure system and method of using same
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention provides an interference projection exposure system comprising a beam-providing subsystem and an objective lens subsystem that can provide a plurality of light beams which intersect and interfere at an image plane to produce a high spatial frequency periodic optical-intensity distribution. The interference projection system can further comprise a pattern mask that can alter the periodic optical-intensity distribution so as to incorporate functional elements within the periodic optical-intensity distribution. The beam providing subsystem can comprise a beam generating subsystem, a beam conditioning subsystem and a beam directing subsystem. Another exemplary embodiment of the present invention provides for a method of producing a high spatial frequency periodic optical-intensity distribution using a interference projection exposure system.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
System and method for projection lithography with immersed image-aligned diffractive element
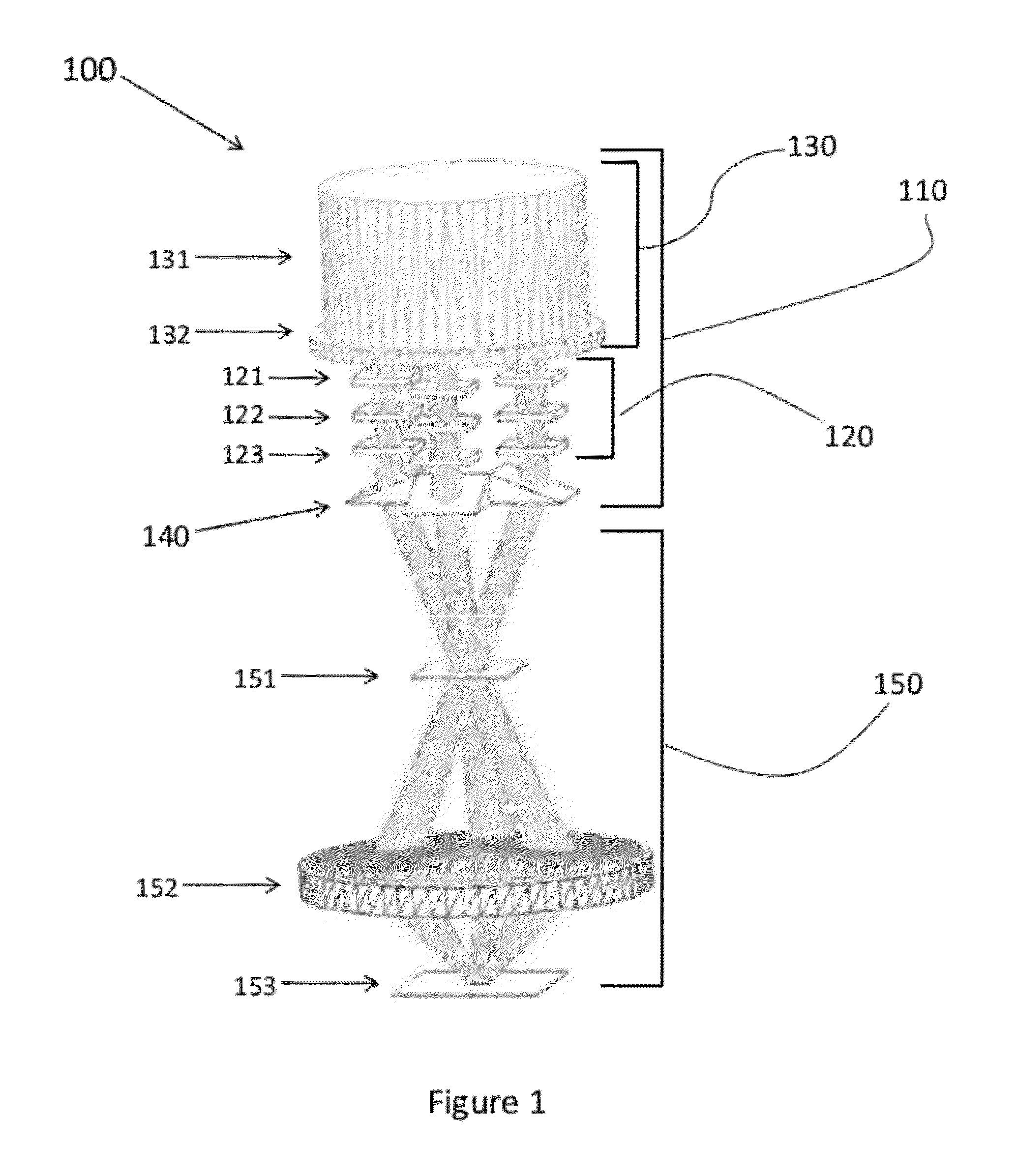
InactiveUS20100003605A1High sensitivityAvoid contactHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesPhotomechanical apparatusPersonalizationResist
A novel system and method and computer program product for exposing a photoresist film with patterns of finer resolution than can physically be projected onto the film in an ordinary image formed at the same wavelength. A hologram structure containing a set of resolvable spatial frequencies is first formed above the photoresist film. If necessary the photoresist is then sensitized. An illuminating wavefront containing a second set of resolvable spatial frequencies is projected through the hologram, forming a new set of transmitted spatial frequencies that expose the photoresist. The transmitted spatial frequencies include sum frequencies of higher frequency than is present in the hologram or illuminating wavefront, increasing the resolution of the exposing pattern. These high spatial frequency transmitted waves can be evanescent, or they can propagate at a steeper obliquity in a higher index medium than is possible in a projected image. A further method is described for designing lithographic masks to fabricate the hologram and to project the illuminating wavefront. In other embodiments, a simple personalization based on Talbot fringes and plasmonic interference is performed.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
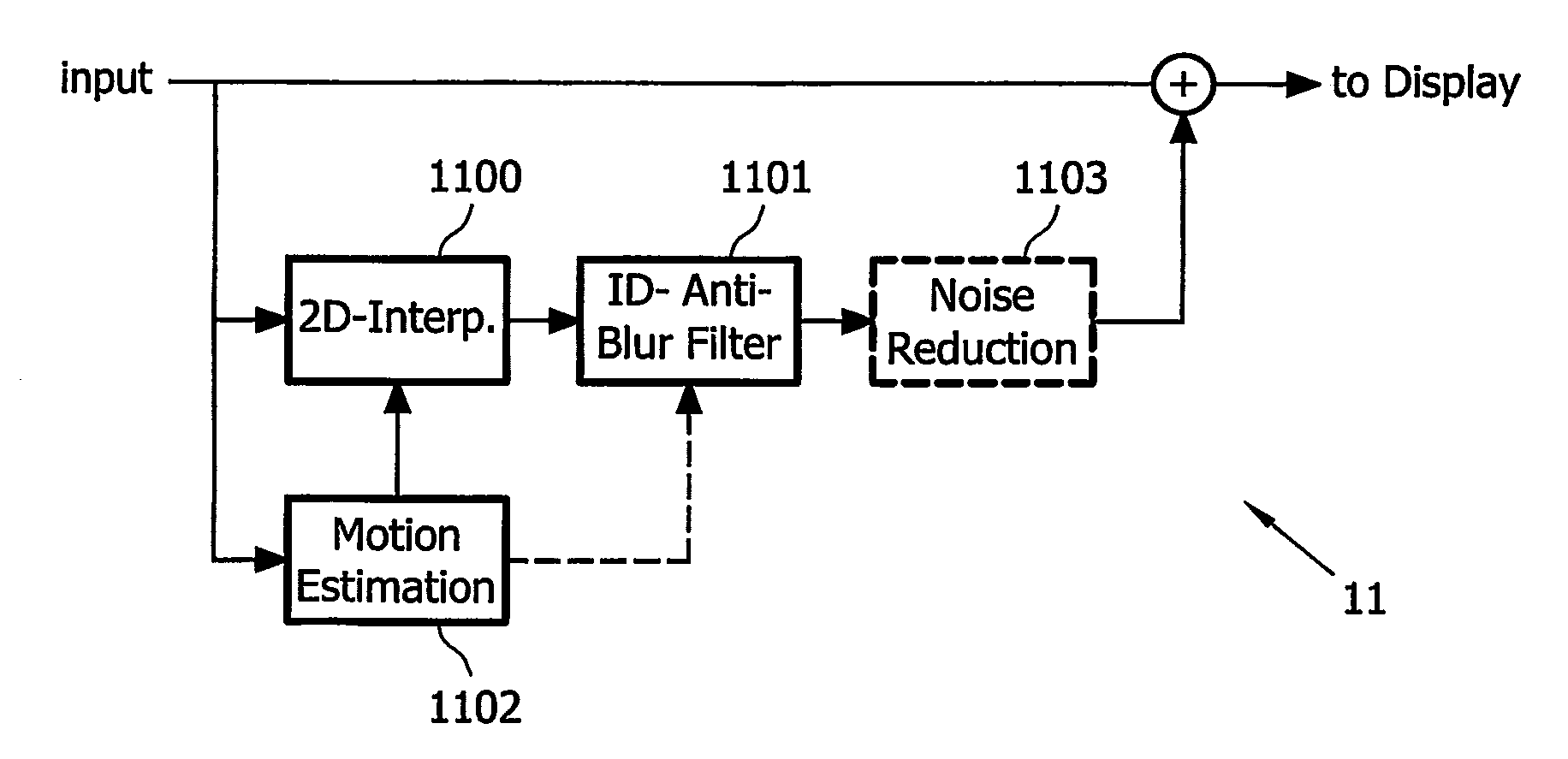
Motion-compensated inverse filtering with band-pass filters for motion blur reduction
InactiveUS20070126928A1Reduce motion blurReduce relative motionTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesBandpass filteringMotion vector
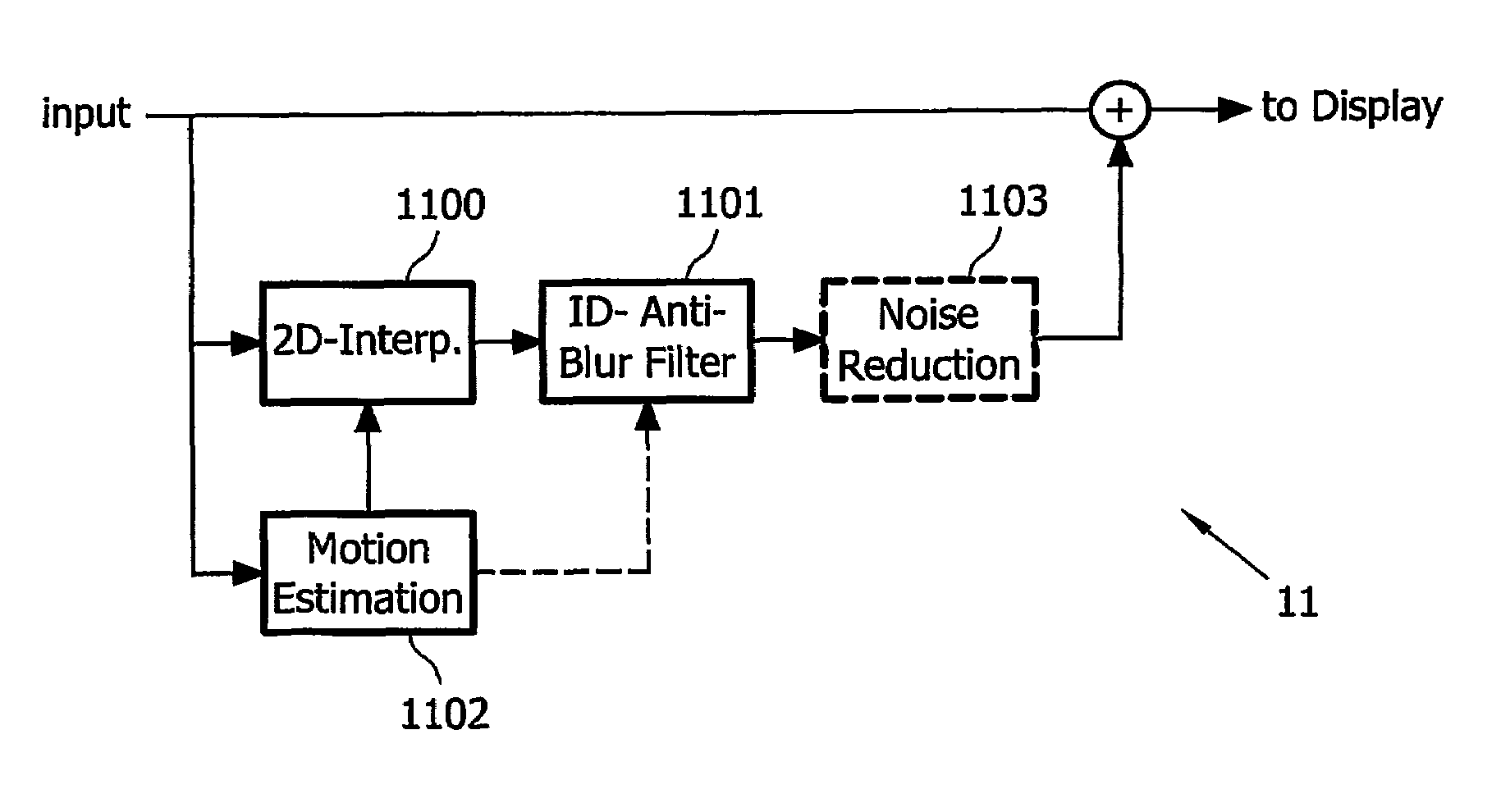
This invention relates to a method, a computer program, a computer program product, and a device for reducing motion blur of images of a video signal shown on a hold-type display (101), comprising estimating (1102) motion vectors of moving components in said images of said video signal; band-pass filtering (1100, 1101) said video signal with respect to a spatial frequency domain, wherein said band-pass filtering at least partially depends on said estimated motion vectors, and wherein with increasing length of said estimated motion vectors, the passband of said band-pass filtering adaptively shifts from high spatial frequencies to medium spatial frequencies; and combining (1104) said video signal and said band-pass filtered video signal to produce an input video signal for said hold-type display.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Deformable mirror with passive and active actuators
InactiveUS6840638B2MirrorsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionDeformable mirrorControl theory
A combination of active and passive force actuators provide adjustments to the shape of an optical element to reduce or compensate for aberrations in an optical system. Passive actuators at a high spatial frequency are capable of correcting higher order steady state components of shape error while dynamic corrections of higher frequency, operationally dependent is provided allowing the number of active actuators and the power supplied to each active actuator to be reduced; reducing heating of the optical element by the active actuators and increasing stability of the system. Compound actuators including a combination of an active actuator portion with a passive actuator portion (which provides a mechanical force bias to the active actuator portion) allows increased spatial flexibility of application of forces to the optical element and other advantages.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Image display method, image display device, and projector
ActiveUS7542619B2Increase loadSuppress blurCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Display device
An image display method includes dividing one frame into a plurality of sub-frames by multiplying a frame frequency of an input image signal, reducing a high-spatial frequency component of an image signal which is used for image display in at least one predetermined sub-frame among the plurality of sub-frames in comparison with that of an image signal which is used for image display in another sub-frame, and displaying an image in each sub-frame.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
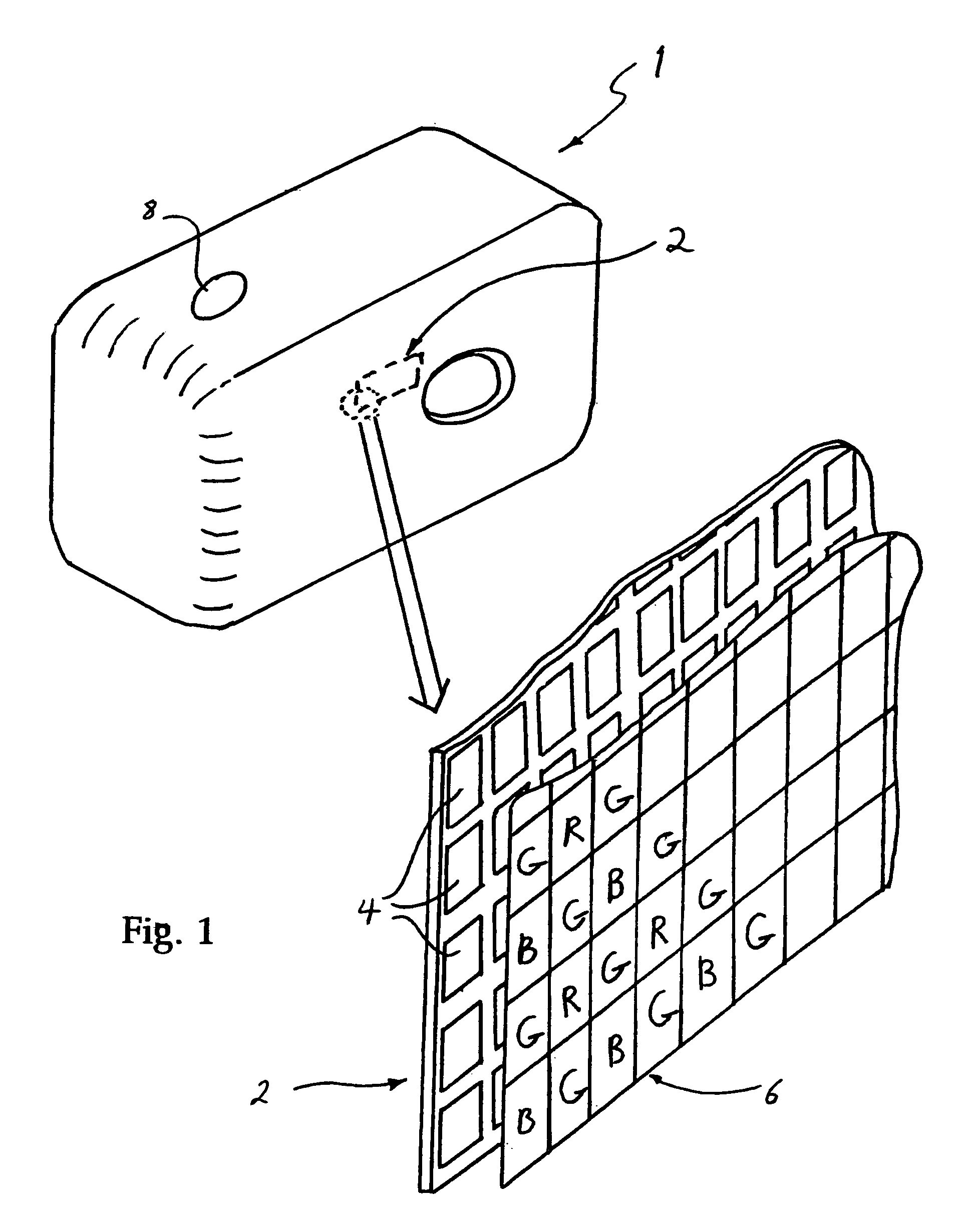
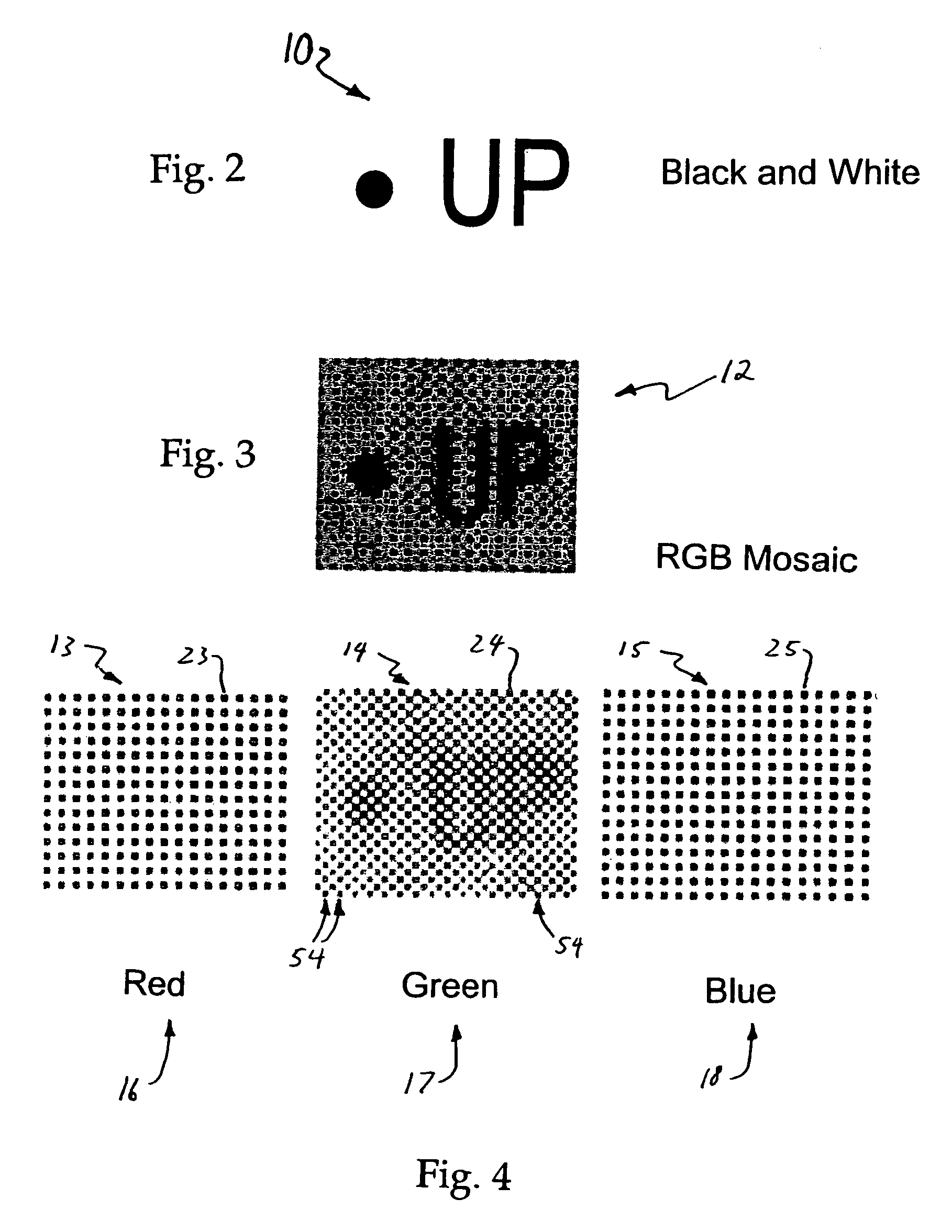
Image mosaic data reconstruction
InactiveUS7006686B2Eliminate the effects ofLow implementation costTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsComputer graphics (images)Radiology
This invention relates to the reconstruction of a full colour image from an image mosaic composed of a plurality of image pixels that have one of at least three colour values. The pixels are interleaved in rows and columns across the mosaic with pixels of different colour values to form the mosaic in such a way that each row and column contains pixels of at least two colours. A high spatial frequency luminance image is generated from the mosaic that extends across all pixel locations of the image mosaic. The luminance values of pixels in the high frequency image are adjusted to reduce zippering effects. The adjustment is performed on pixels generated from a particular colour value at least in a first row and / or a first column of the high frequency luminance image according to the luminance values for said pixels and the luminance values of pixels generated from another colour value. A low spatial frequency luminance image is generated from the mosaic for each colour value. After the luminance adjustment the high frequency luminance pixels are combined with each of the low frequency luminance images in order to generate a de-mosaiced image for each of the colour values corresponding to said low frequency luminance images.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Imaging system using a negative index of refraction lens
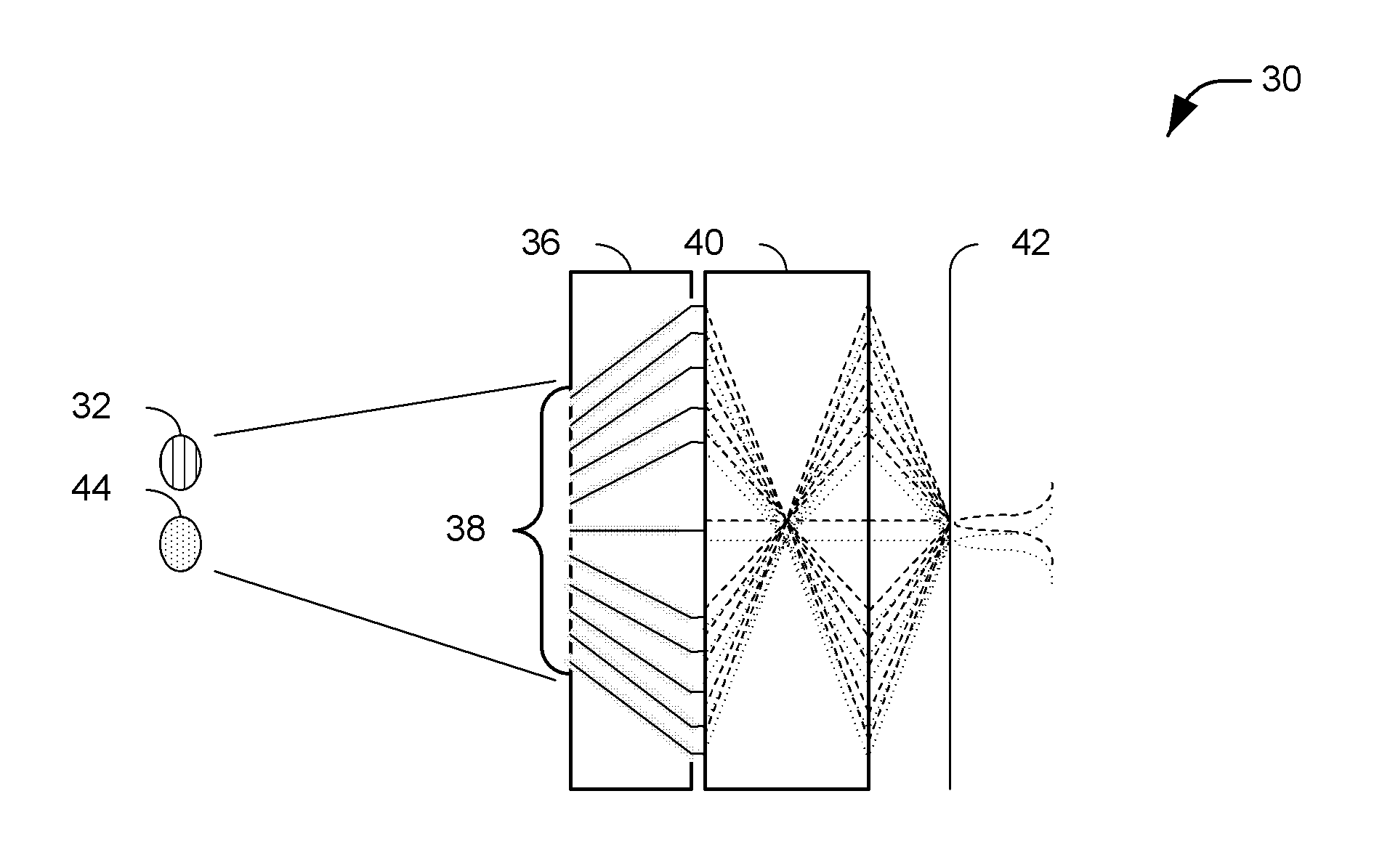
InactiveUS8017894B2High resolutionPhotometry using reference valueInstruments for comonautical navigationImage resolutionPhotodetector
Owner:YAHOO INC +1
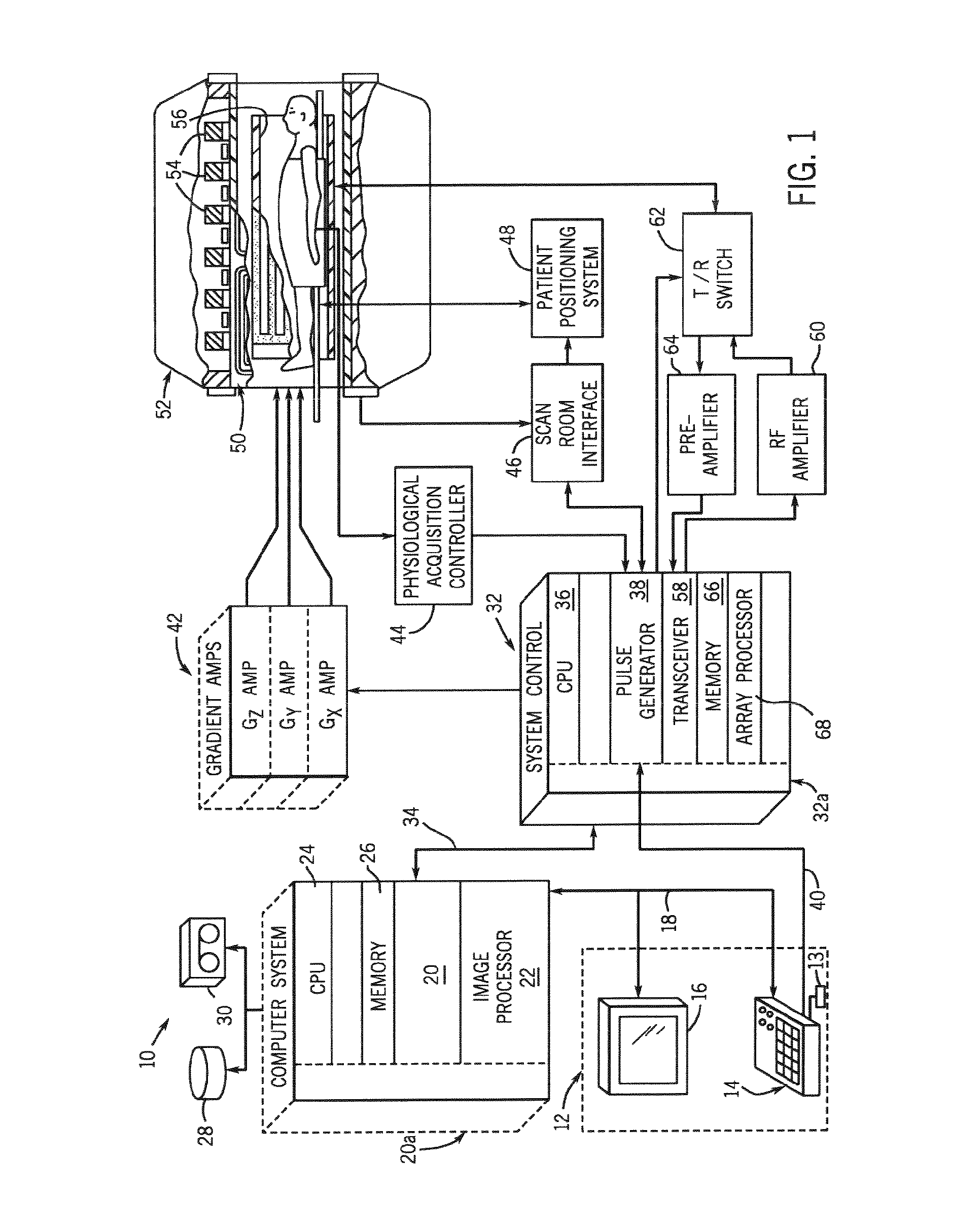
Method and apparatus for breath-held mr data acquisition using interleaved acquisition
InactiveUS20100222666A1Minimizes k-space transition artifactT weightingDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsVentricular volumeCardiac cycle
A method and apparatus are presented for acquiring MR cardiac images in a time equivalent to a single breath-hold. MR data acquisition is segmented across multiple cardiac cycles. MR data acquisition is interleaved from each phase of a first cardiac cycle with MR data from each phase of a subsequent cardiac cycle. Preferably, low spatial frequency data are interleaved between multiple cardiac cycles, and the subsequent cardiac cycle acquisition includes sequential acquisition of high spatial frequency data towards the end of the acquisition window. An MR image can then be reconstructed with data acquired from each of the acquisitions that reduce ghosting and artifacts. Volume images of the heart can be produced within a single breath-hold. Images can be acquired throughout the cardiac cycle to measure ventricular volumes and ejection fractions. Single phase volume acquisitions can also be performed to assess myocardial infarction.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Double wave front calibrator self-adaptive optical system
ActiveCN1664650AReduce production difficulty requirementsQuality improvementConverting sensor output opticallyOptical elementsWavefront sensorLight beam
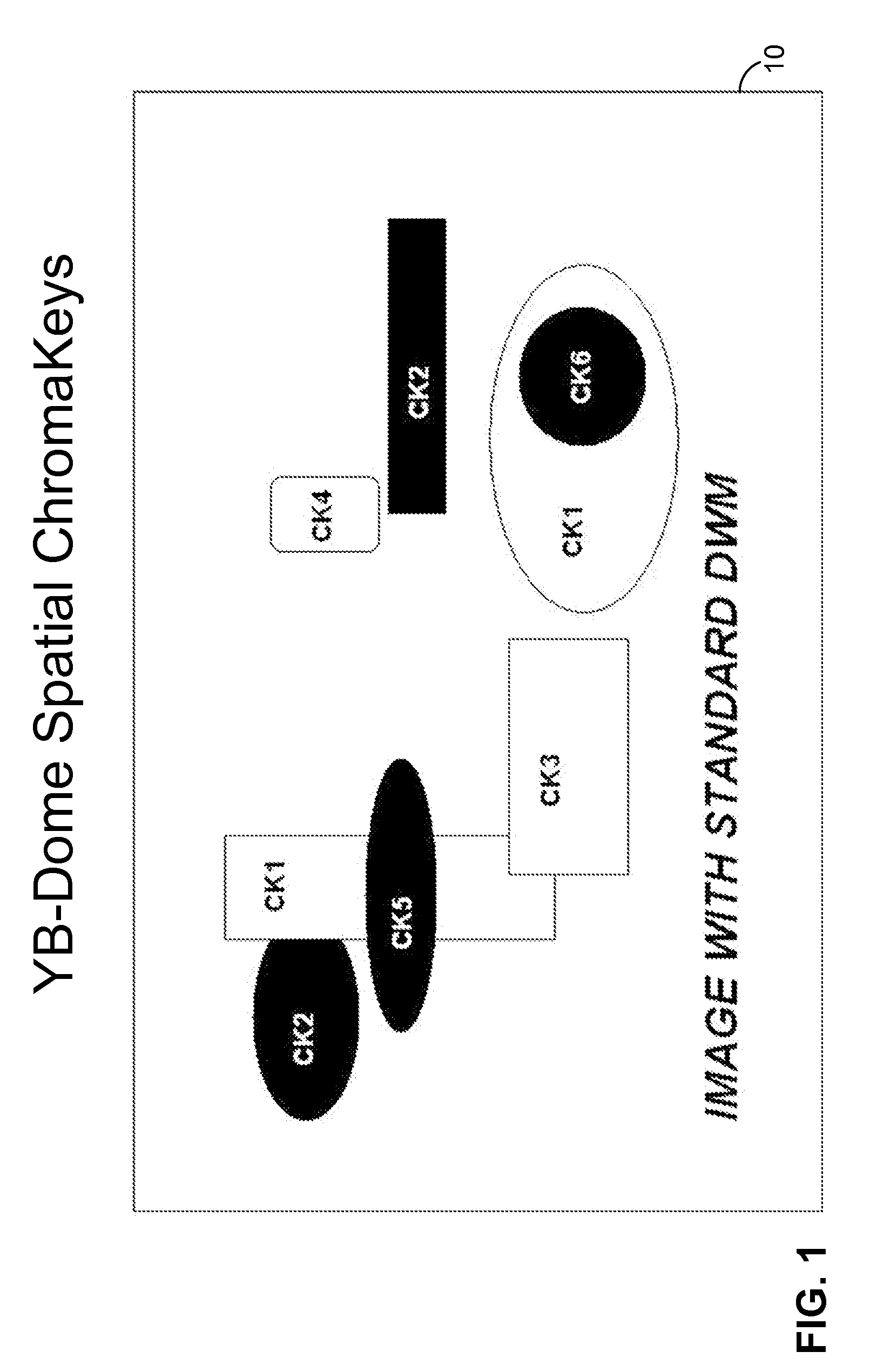
This invention relates to double wave pre-corrector self-adapting optical system, which comprises incline reflection lens, two before wave correctors, before wave sensor, splitter lens, before wave processor, two before wave correctors, which separately realize the low and high picture difference correction as needed. The before wave corrector needs large journey to correct the low picture difference and the before wave corrector has larger space frequency.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
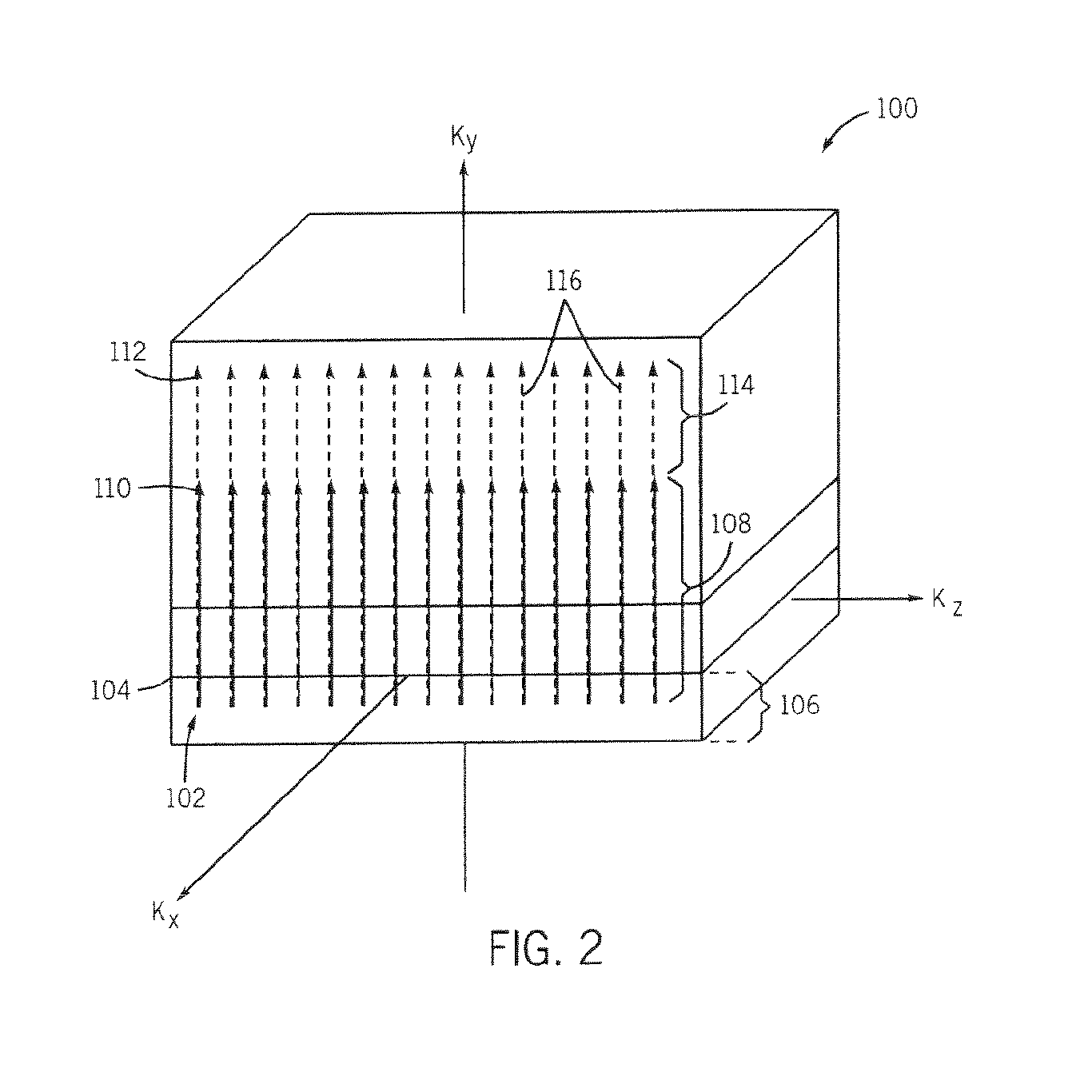
Dynamic sampling
ActiveUS8446530B2Increase chanceIncrease the number ofTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsHigh rateComputer graphics (images)
A sampling system adapts the sampling rate for sampling analog signals and / or the stored number of samples to the fixed or video image content, such that a higher rate, and equivalently a larger number of samples, are acquired for an image or video segment containing higher spatial frequencies while a lower number of samples (lower sampling rate) are retained for image or video segments containing lower spatial frequencies. The Nyquist theorem may still be satisfied for each individual image segment, while information necessary for edge enhancement is retained.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
Interferometer using integrated imaging array and high-density phase-shifting array
An integrated imaging element for an interferometer generates at least one interference image that includes multiple interference portions with different relative phase shifts interleaved in a pattern having a high spatial frequency in the image. The interleaved pattern is at least partially determined by the pattern of a high density relative retarder array used in the integrated imaging element. In various embodiments, the multiple interference portions are interleaved in a checkerboard-like pattern across the entire surface of a detector device. As a result, various non-common mode errors present in various interferometers that generate separate non-interleaved images for each relative phase are reduced or eliminated.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Defect mitigation in display panels
Defect mitigation in display panels. Defects in a display panel are mapped, and the defect information is associated with the display system or associated with the panel. During panel operation, the values of pixels neighboring defective pixels are altered to minimize their visibility to the observer. In a first model, luminance error caused by a defect is compensated by adjust neighboring pixels. In a second model, Error in luminance and one of the two chrominance channels is compensated by adjusting neighboring pixels. The defect mitigation methods seek to shift the errors introduced by defective pixels into high spatial frequency elements and chromatic elements, which the human eye is not sensitive to.
Owner:WISTRON CORP
Polishing method for extreme ultraviolet optical elements and elements produced using the method
InactiveUS20080132150A1Optical surface grinding machinesRadiation/particle handlingThermal expansionExtreme ultraviolet
The invention is directed to polished glass substrates suitable for extreme ultraviolet lithography. The elements are silica-titania glass elements having a coefficient of thermal expansion of 0±30×10−9 / ° C. or less, and containing 5-10 wt. % titania. The polished elements have a mid-spatial frequency peak-to-valley roughness of <10 nm and a high-spatial frequency roughness of <0.20 nm average roughness. The invention is further directed to a method of for producing optical elements suitable for extreme ultraviolet lithography (“EUVL”), the method having at least the steps of providing a glass substrate in the shape of the desired optical element and polishing the shaped substrate using a high abrasive slurry flow rate of >2.0 ml / cm2 / min. Generally the flow rates are in the range of 2.0-10 ml / cm2 / min. Glass substrates suitable for extreme ultraviolet lithography element have a coefficient of thermal expansion of 0±30×10−9 / ° C. or less. A particular glass suitable for EUVL use is silica-titania glass containing 5-10 wt. % titania.
Owner:CORNING INC
Motion-compensated inverse filtering with band-pass filters for motion blur reduction
InactiveUS7693343B2Reduce motion blurTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesBandpass filteringMotion vector
This invention relates to a method, a computer program, a computer program product, and a device for reducing motion blur of images of a video signal shown on a hold-type display (101), comprising estimating (1102) motion vectors of moving components in said images of said video signal; band-pass filtering (1100, 1101) said video signal with respect to a spatial frequency domain, wherein said band-pass filtering at least partially depends on said estimated motion vectors, and wherein with increasing length of said estimated motion vectors, the passband of said band-pass filtering adaptively shifts from high spatial frequencies to medium spatial frequencies; and combining (1104) said video signal and said band-pass filtered video signal to produce an input video signal for said hold-type display.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
High resolution image reconstruction
ActiveUS7596284B2Image enhancementGeometric image transformationImage resolutionHigh resolution image
A technique of reconstructing a high resolution image from at least one image sequence of temporally related high and low resolution image frames wherein each of said high resolution image frames includes a low spatial frequency component and a high spatial frequency component is described. The high-resolution image reconstruction technique uses spatial interpolation to generate a low spatial frequency component from a low-resolution image frame of the image sequence. The technique is adapted to generate a high spatial frequency component from at least one high resolution image frame of the image sequence which is closely related to the low resolution image frame, and to remap the high spatial frequency component to a motion-compensated high spatial frequency component estimate of the low resolution image frame. The motion-compensated high spatial frequency component estimate is added to the generated low spatial frequency component to form a reconstructed high-resolution image of the low-resolution image frame.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com