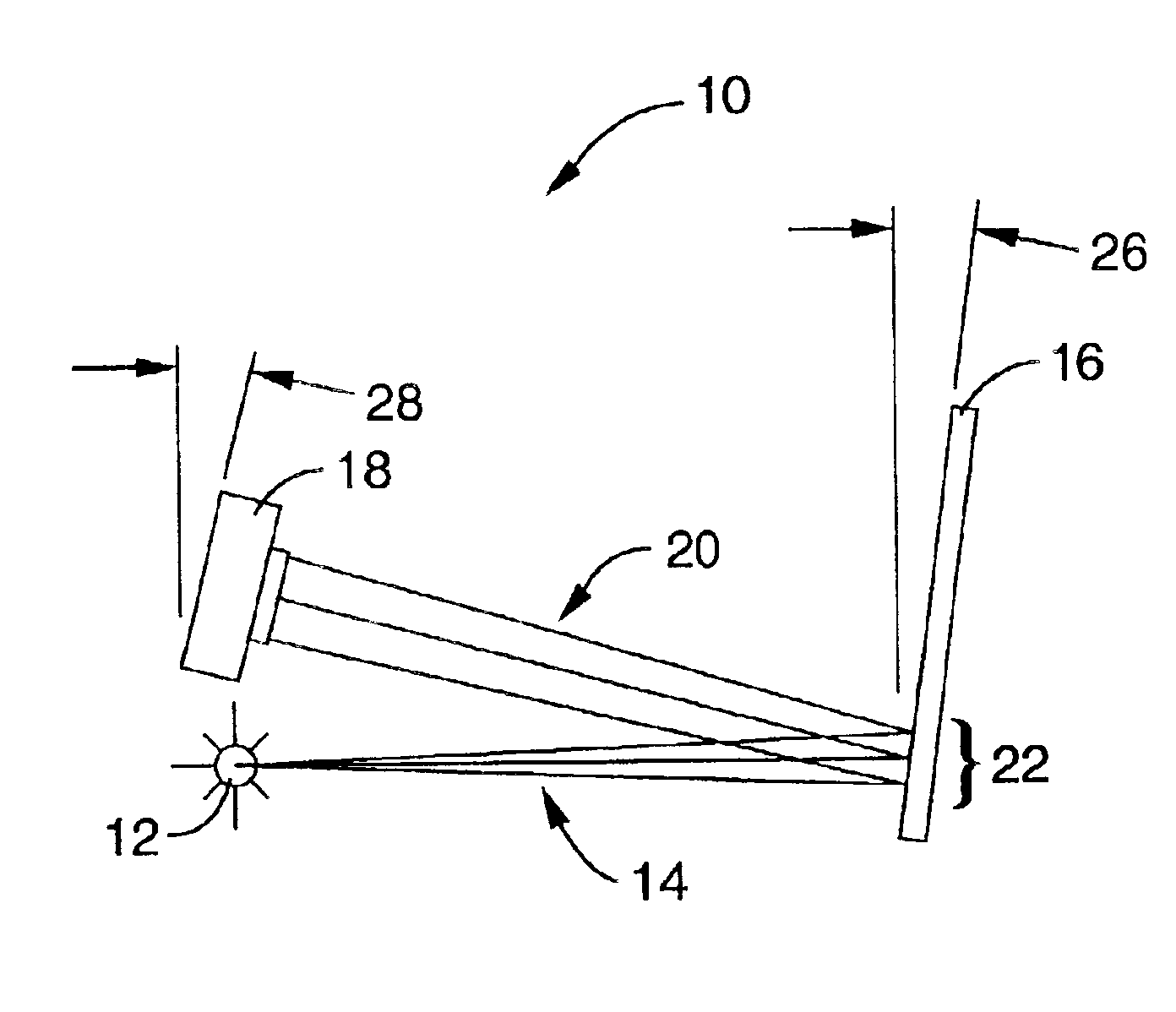
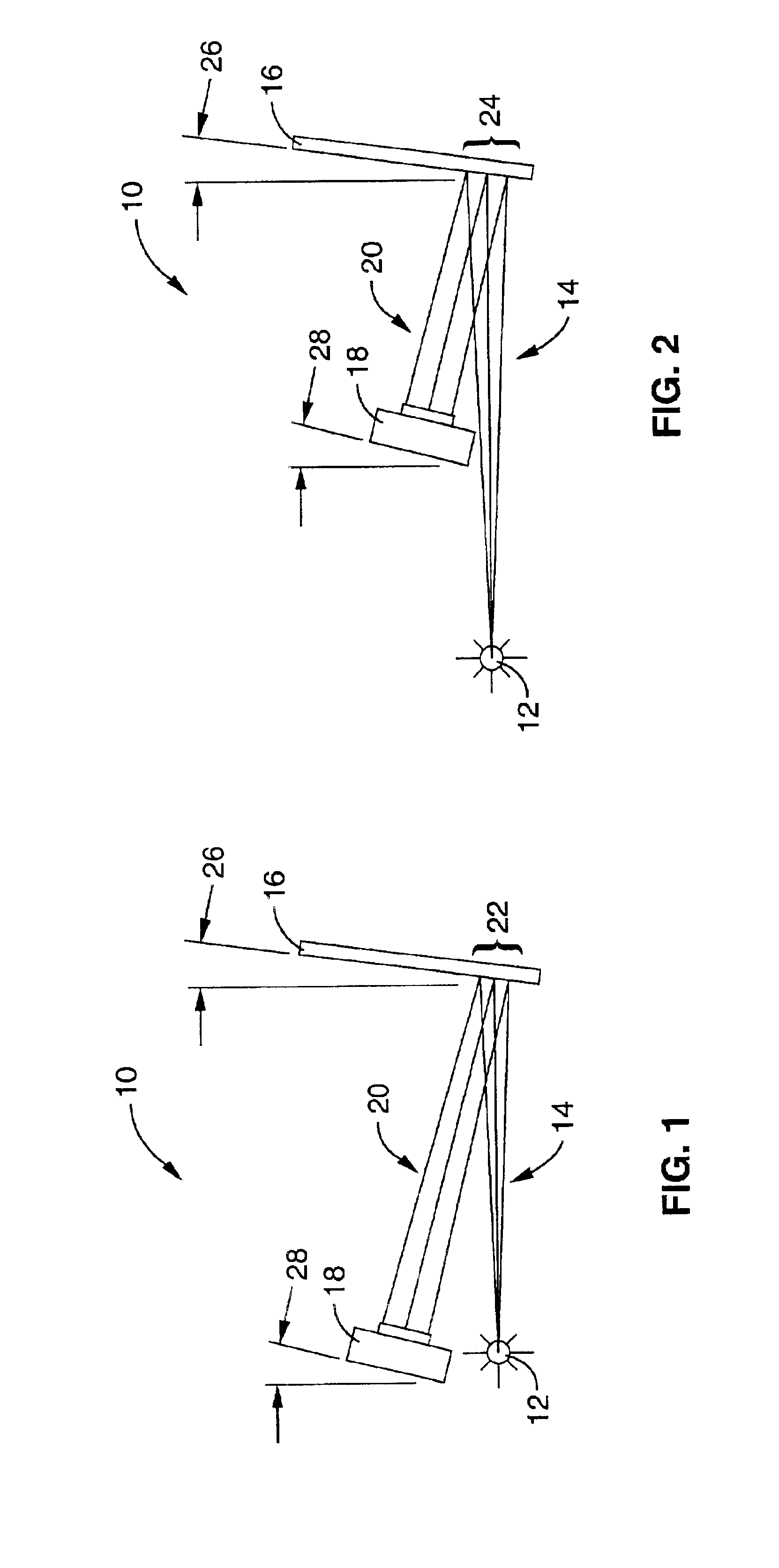
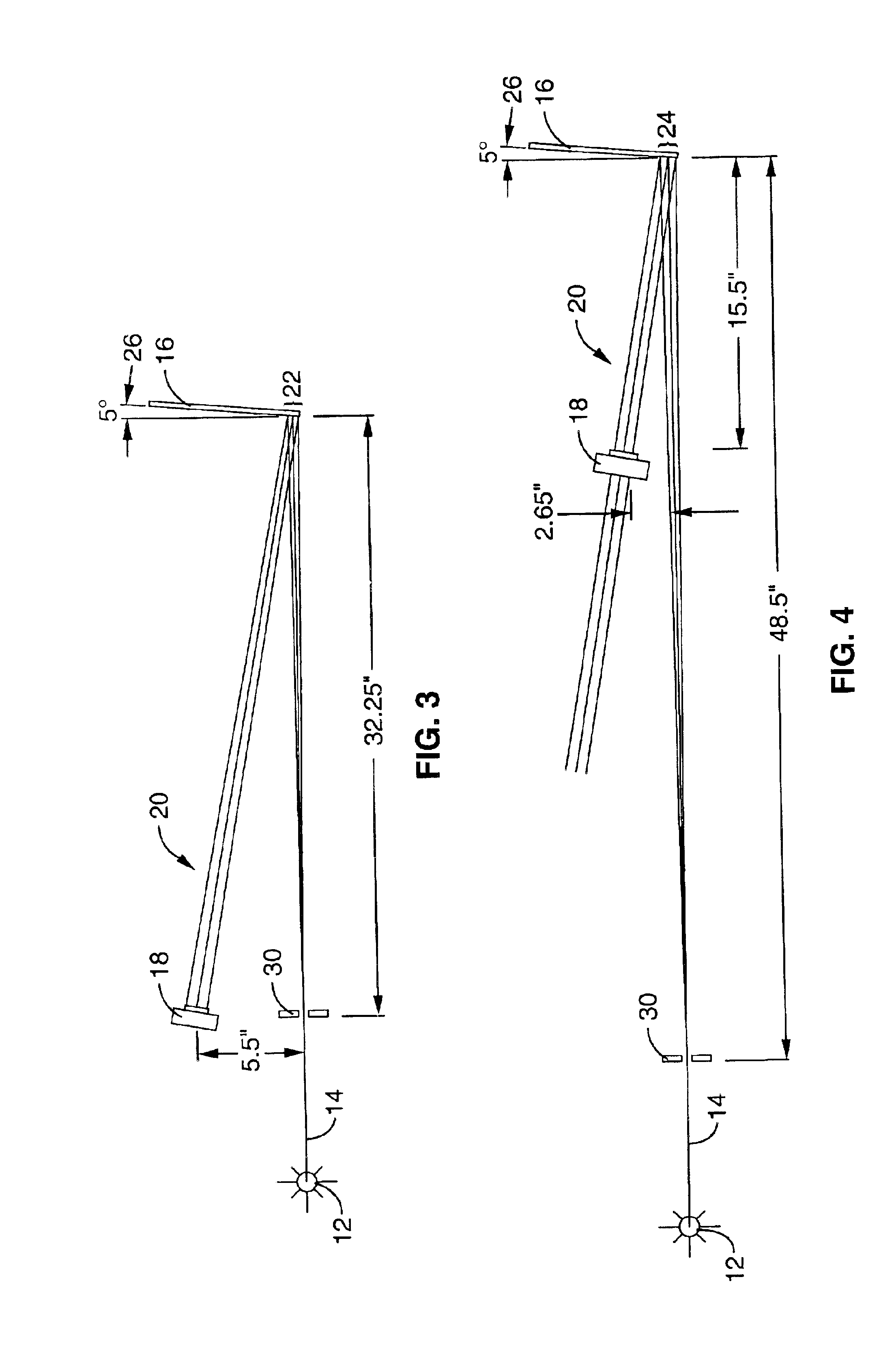
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
97 results about "Low spatial frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
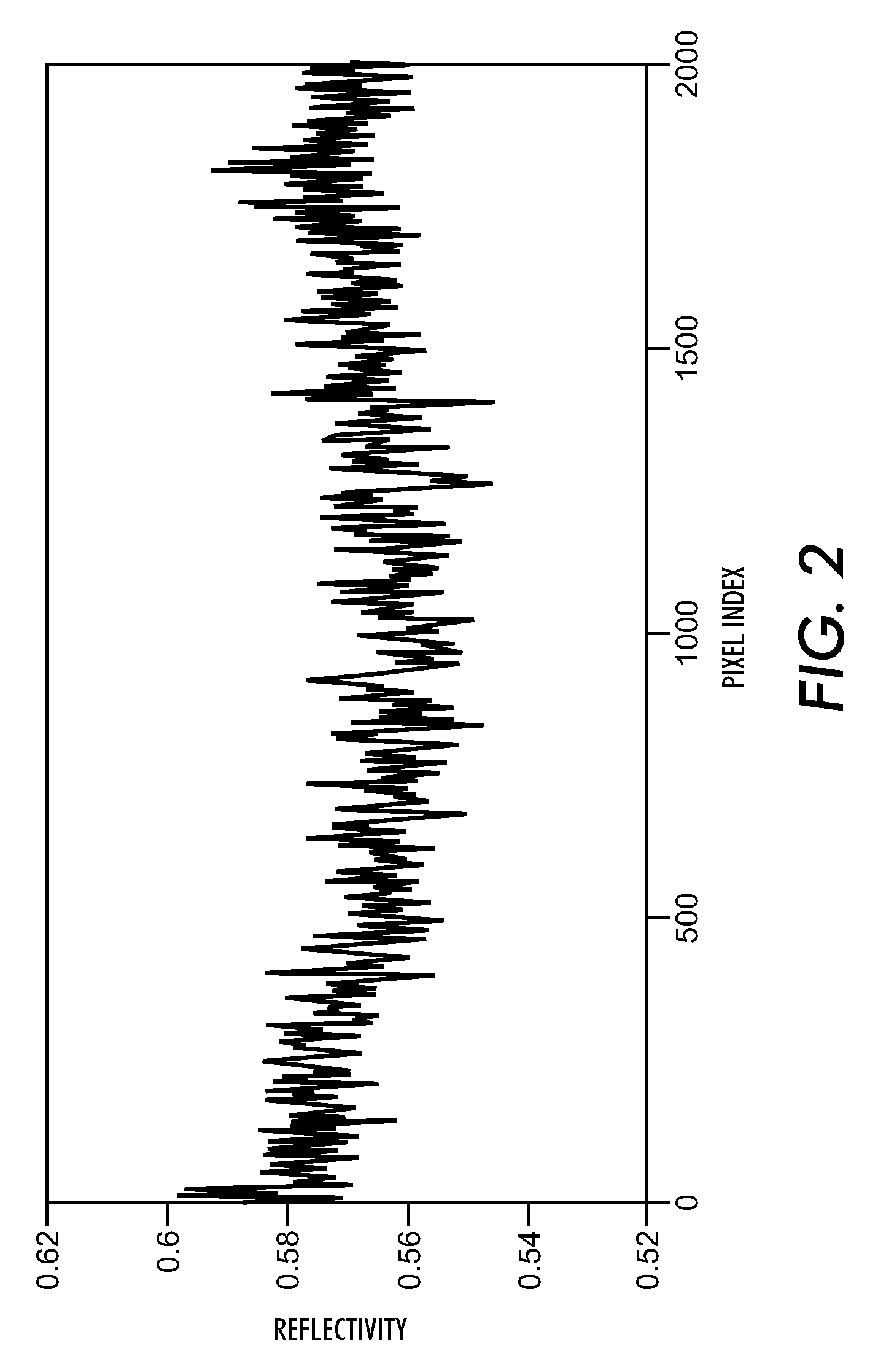
Spatial frequency In remote sensing, the frequency of change per unit distance across an image. High spatial frequencies include those changes which occur in very close proximity, such as fine lines, low spatial frequencies include those changes which occur over greater distances, such as broad bands.
4D light field cameras
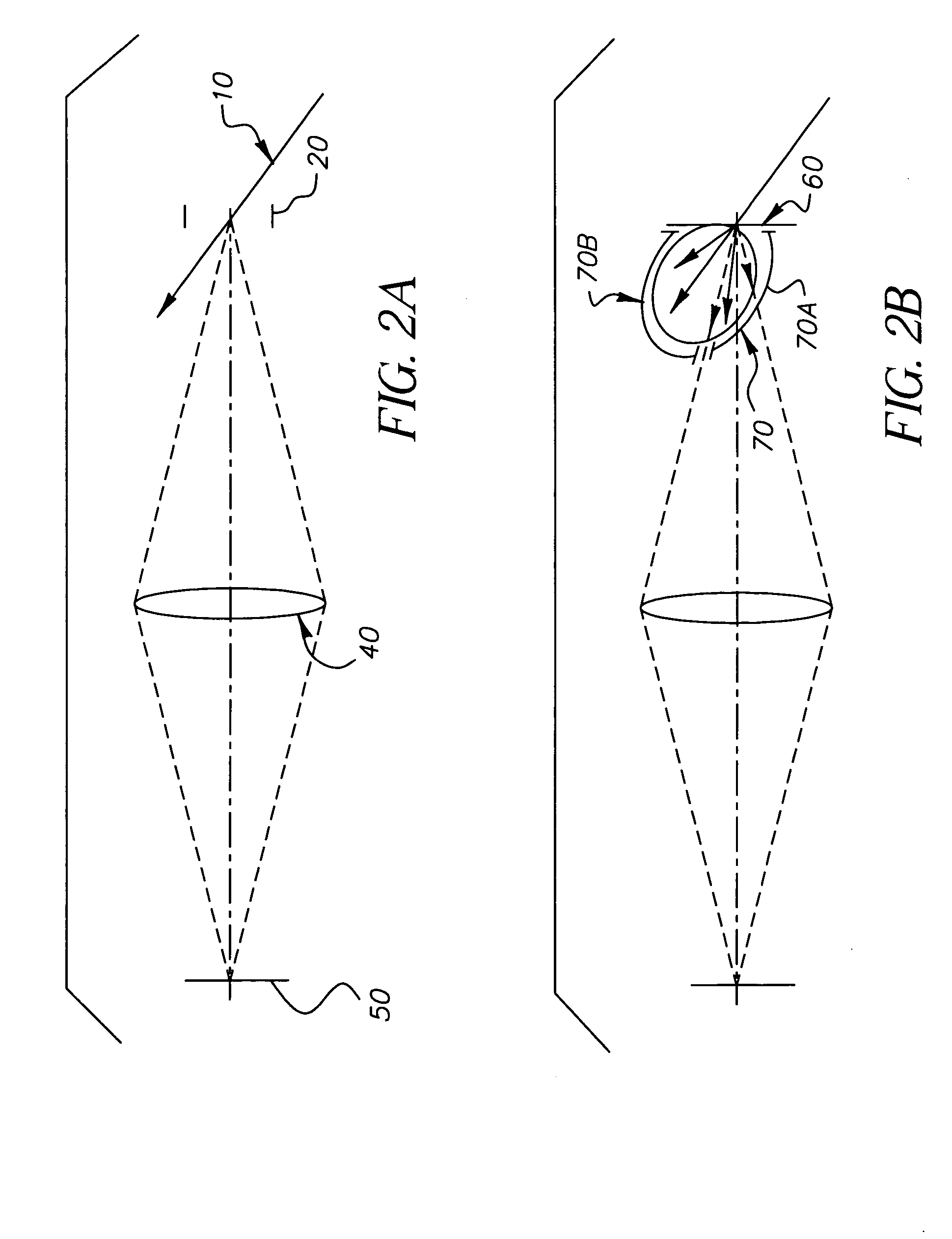
InactiveUS20080187305A1Simple attenuating maskSuppress unwanted occludersProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementCamera lensUltrasound attenuation
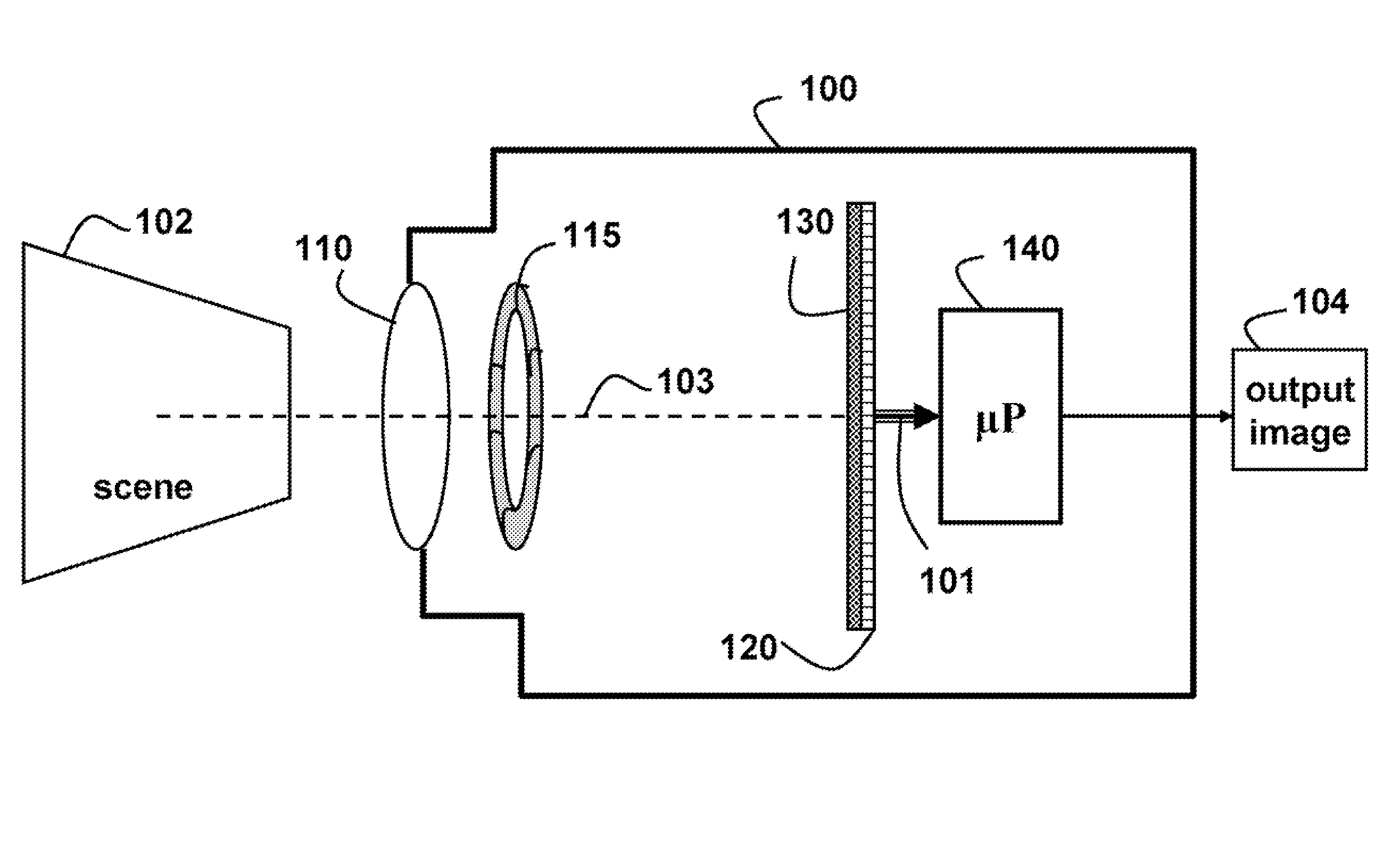
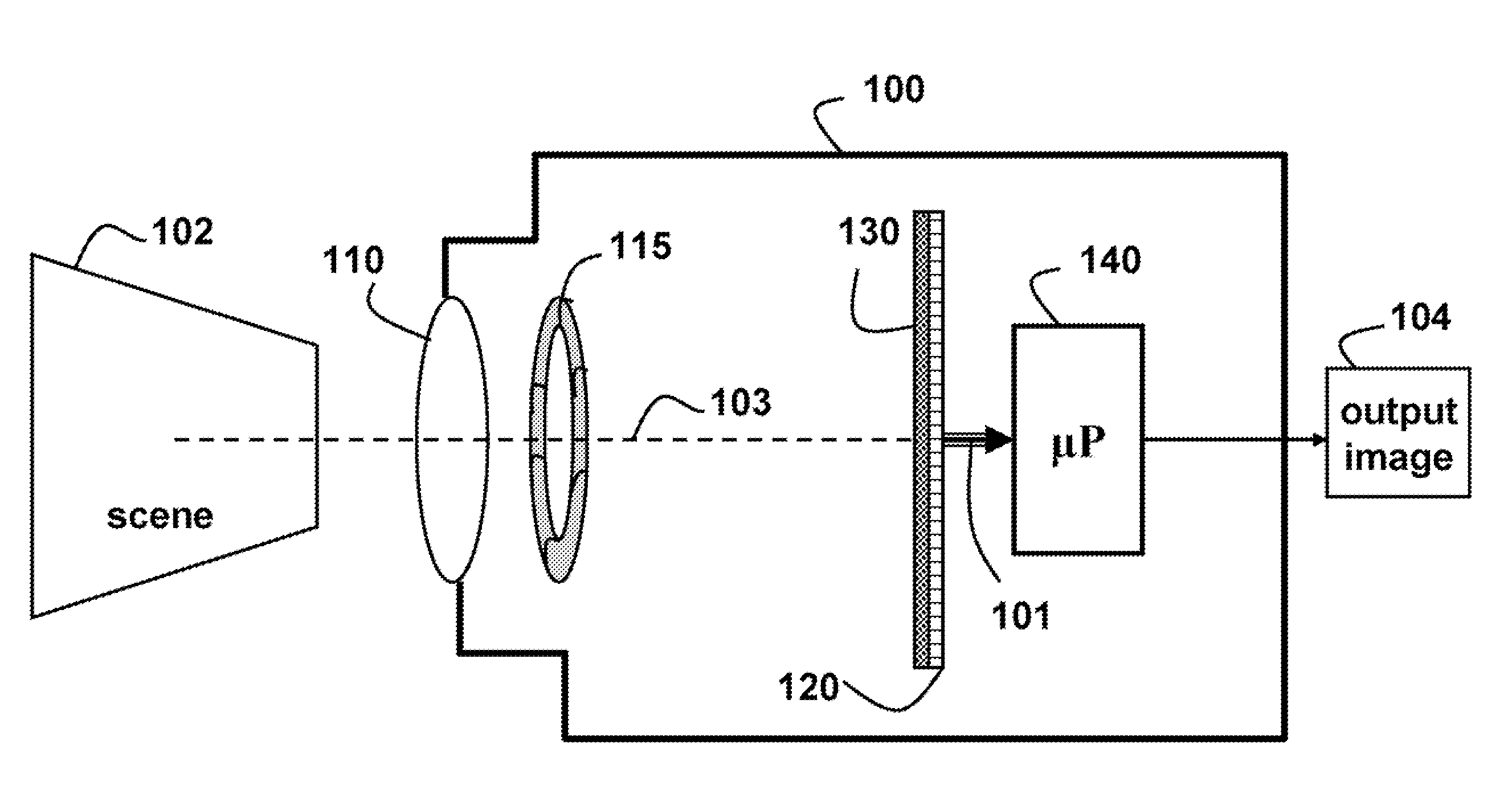
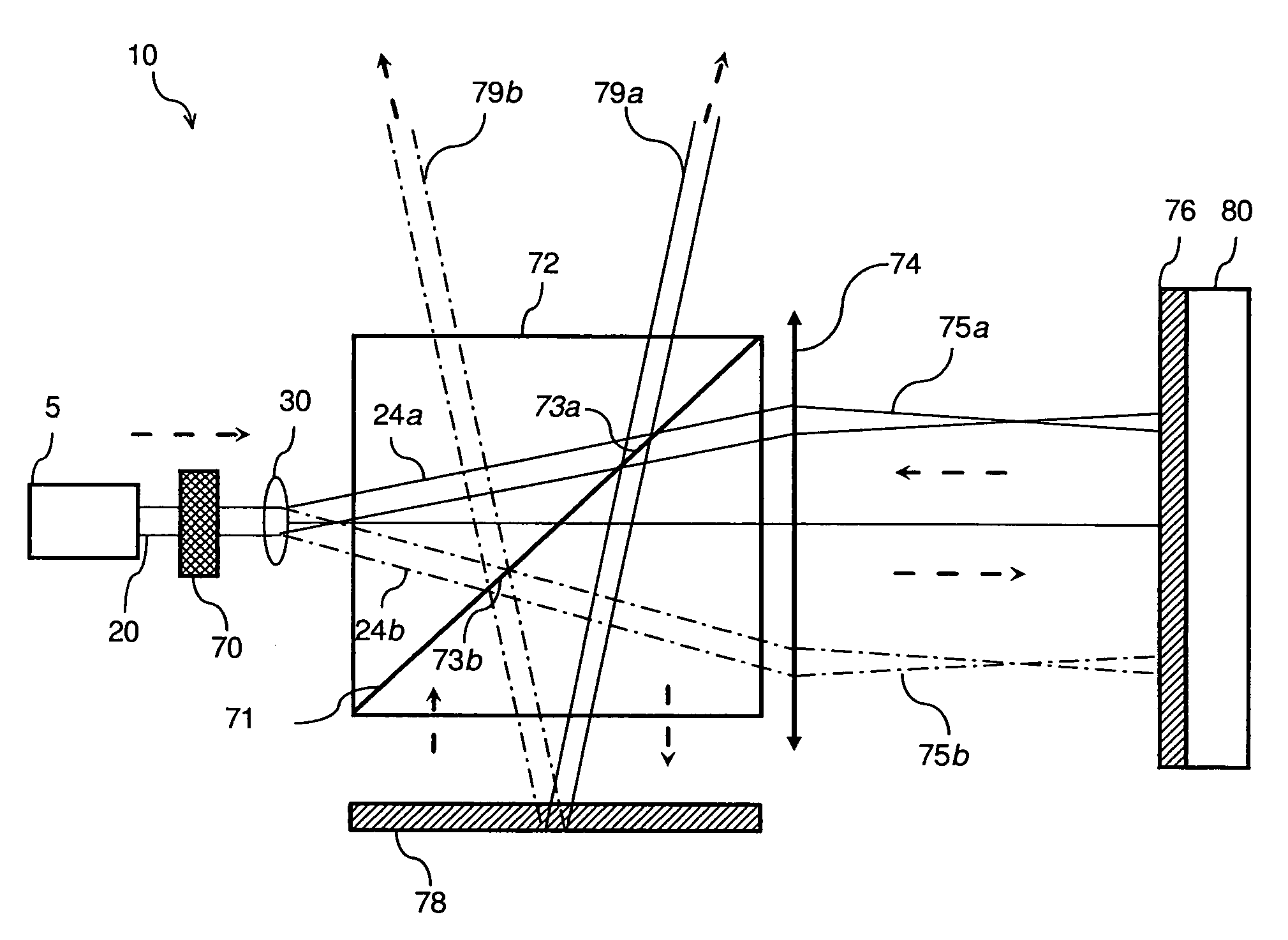
A camera acquires a 4D light field of a scene. The camera includes a lens and sensor. A mask is arranged in a straight optical path between the lens and the sensor. The mask including an attenuation pattern to spatially modulate the 4D light field acquired of the scene by the sensor. The pattern has a low spatial frequency when the mask is arranged near the lens, and a high spatial frequency when the mask is arranged near the sensor.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
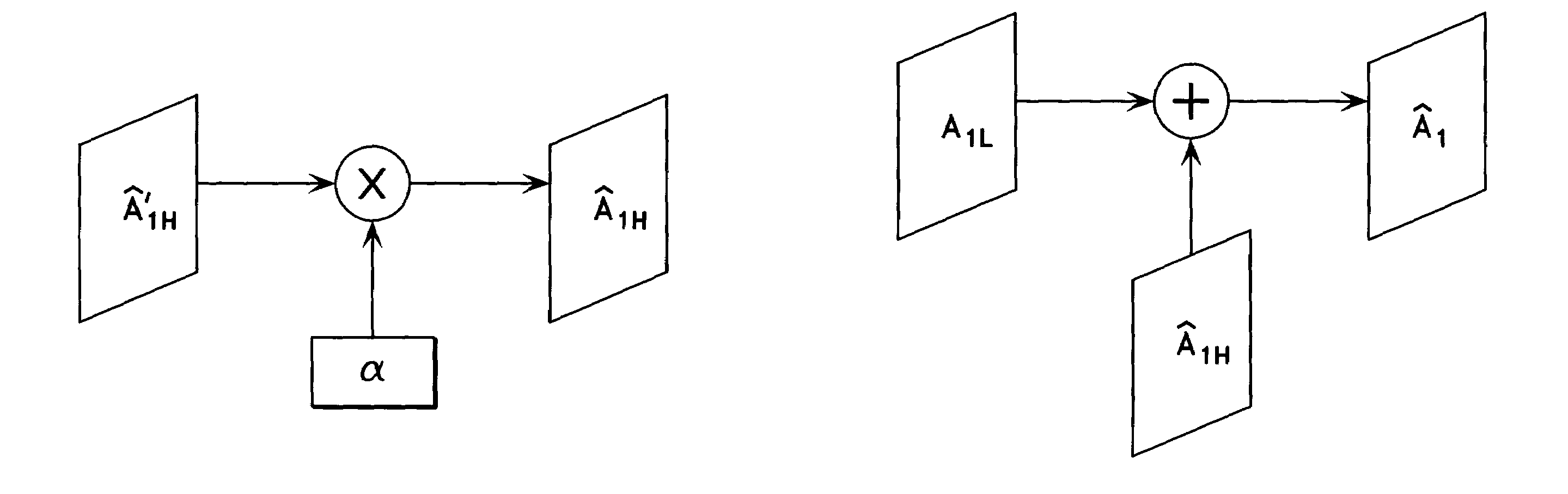
High resolution image reconstruction
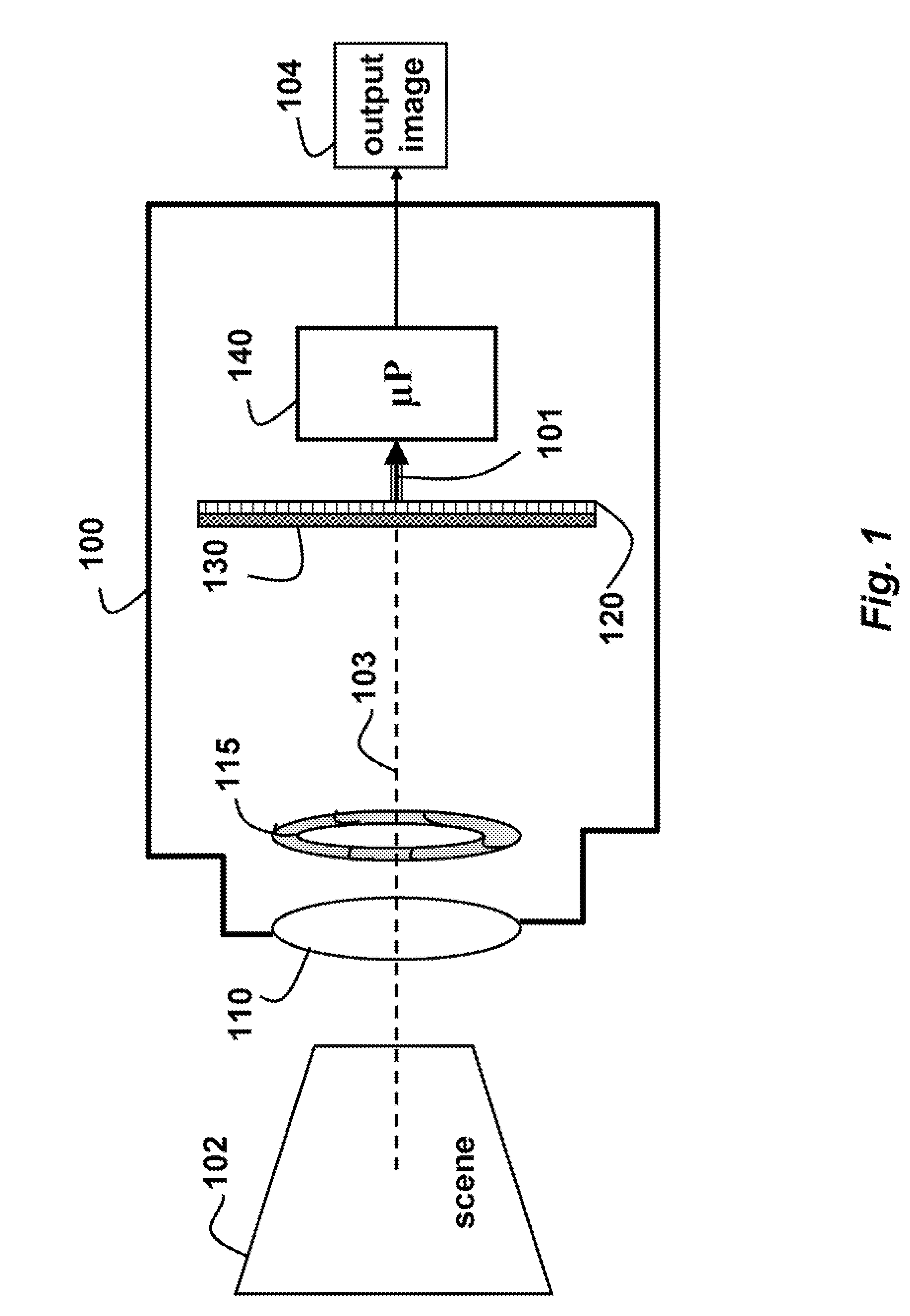
ActiveUS20050013509A1Image enhancementGeometric image transformationImage resolutionHigh resolution image
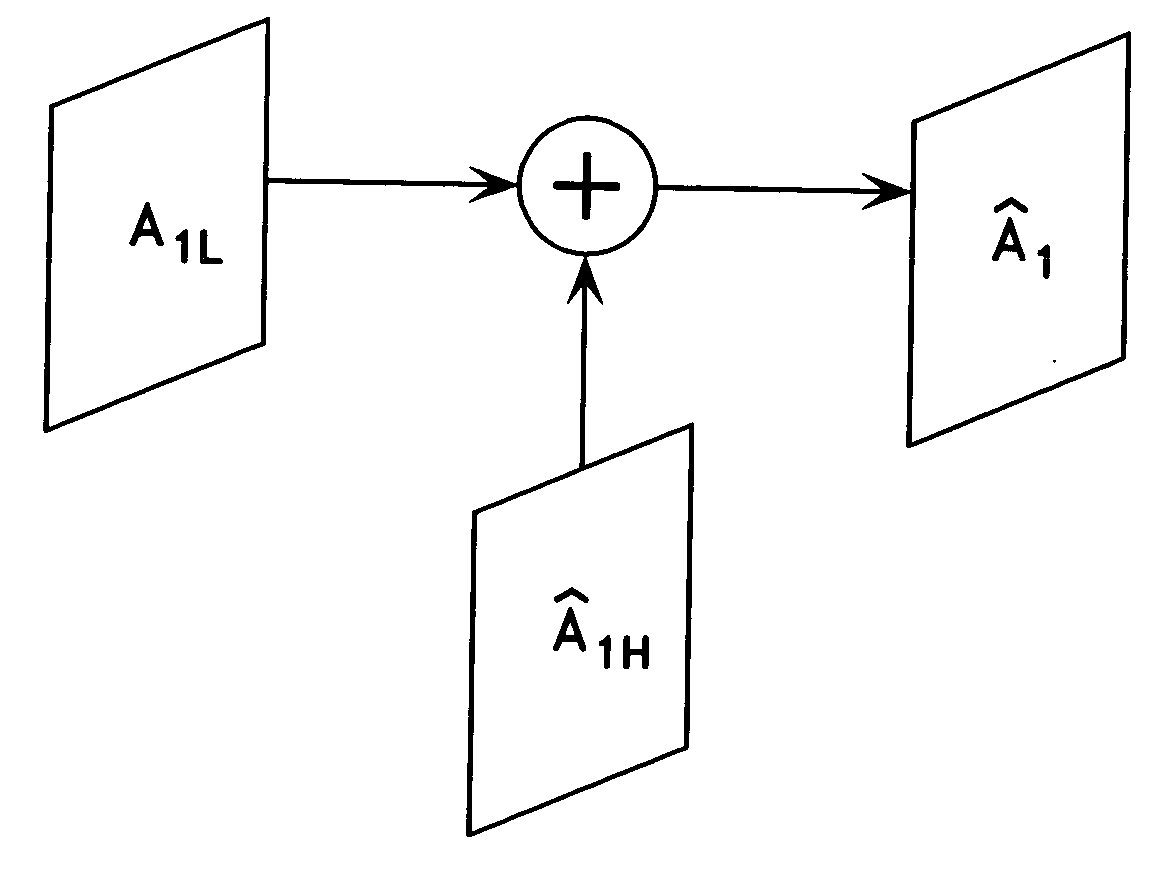
A technique of reconstructing a high resolution image from at least one image sequence of temporally related high and low resolution image frames wherein each of said high resolution image frames includes a low spatial frequency component and a high spatial frequency component is described. The high-resolution image reconstruction technique uses spatial interpolation to generate a low spatial frequency component from a low-resolution image frame of the image sequence. The technique is adapted to generate a high spatial frequency component from at least one high resolution image frame of the image sequence which is closely related to the low resolution image frame, and to remap the high spatial frequency component to a motion-compensated high spatial frequency component estimate of the low resolution image frame. The motion-compensated high spatial frequency component estimate is added to the generated low spatial frequency component to form a reconstructed high-resolution image of the low-resolution image frame.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
4D light field cameras
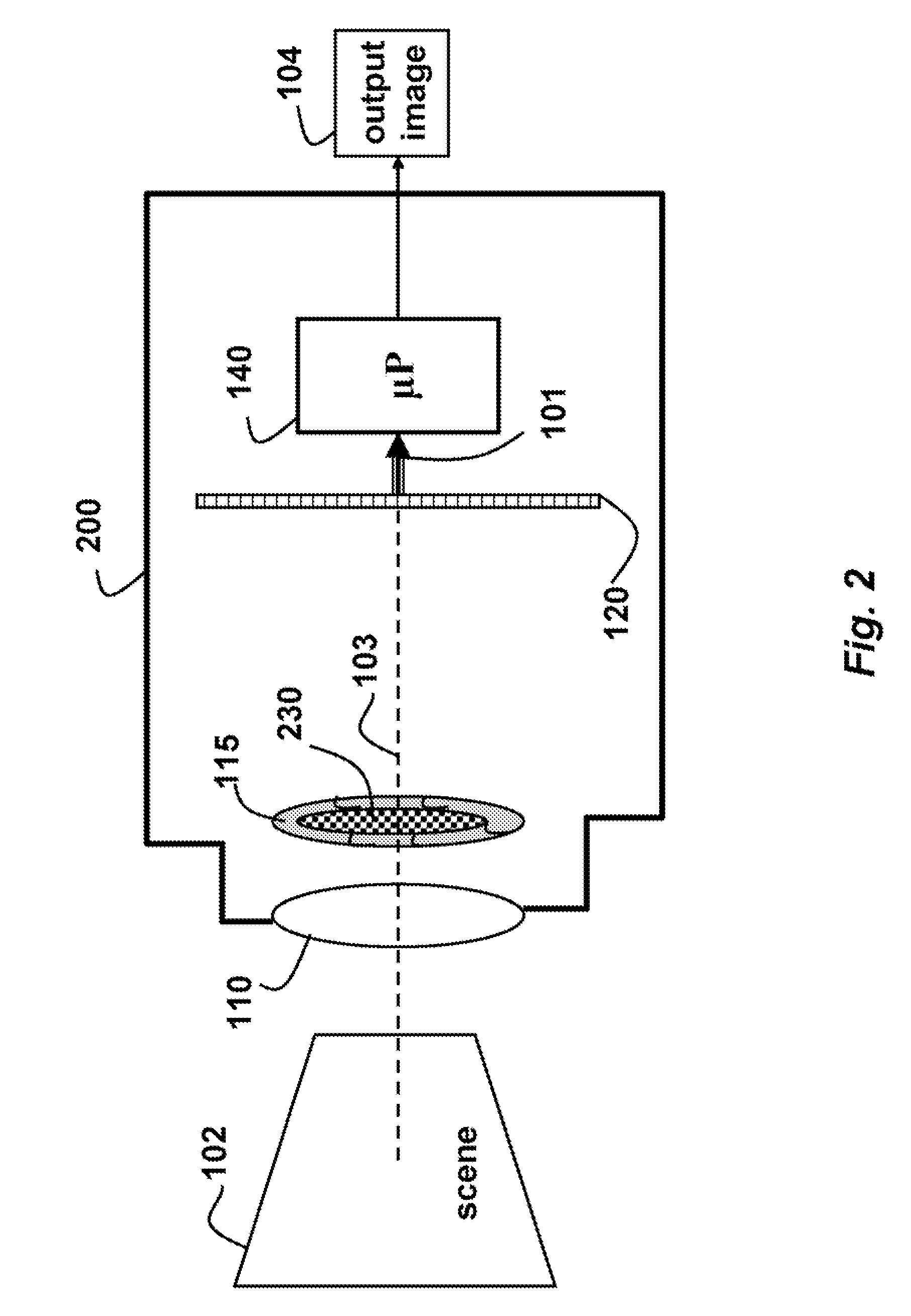
InactiveUS7792423B2Suppress unwanted occludersProjector focusing arrangementPhotometryCamera lensUltrasound attenuation
A camera acquires a 4D light field of a scene. The camera includes a lens and sensor. A mask is arranged in a straight optical path between the lens and the sensor. The mask including an attenuation pattern to spatially modulate the 4D light field acquired of the scene by the sensor. The pattern has a low spatial frequency when the mask is arranged near the lens, and a high spatial frequency when the mask is arranged near the sensor.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
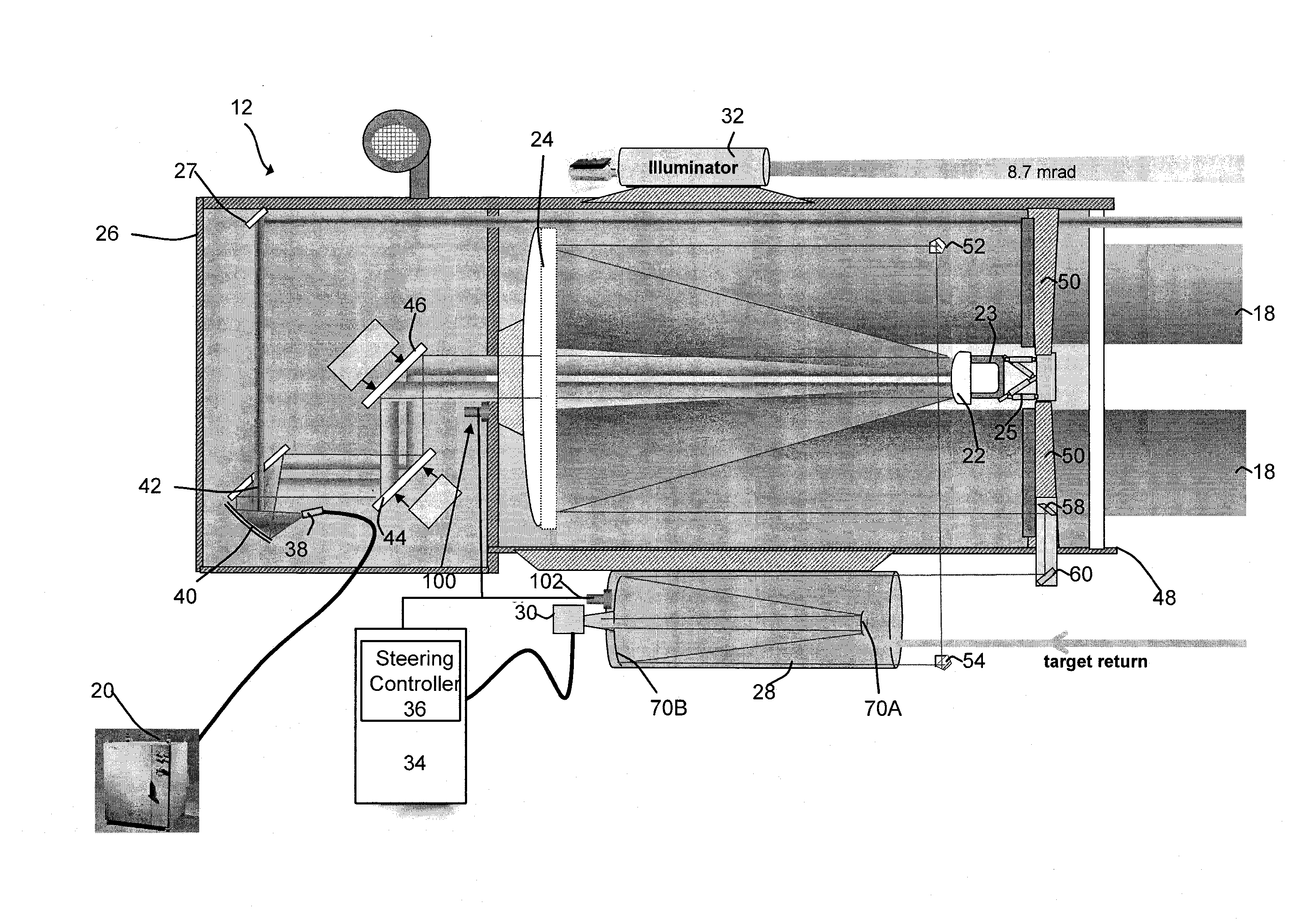
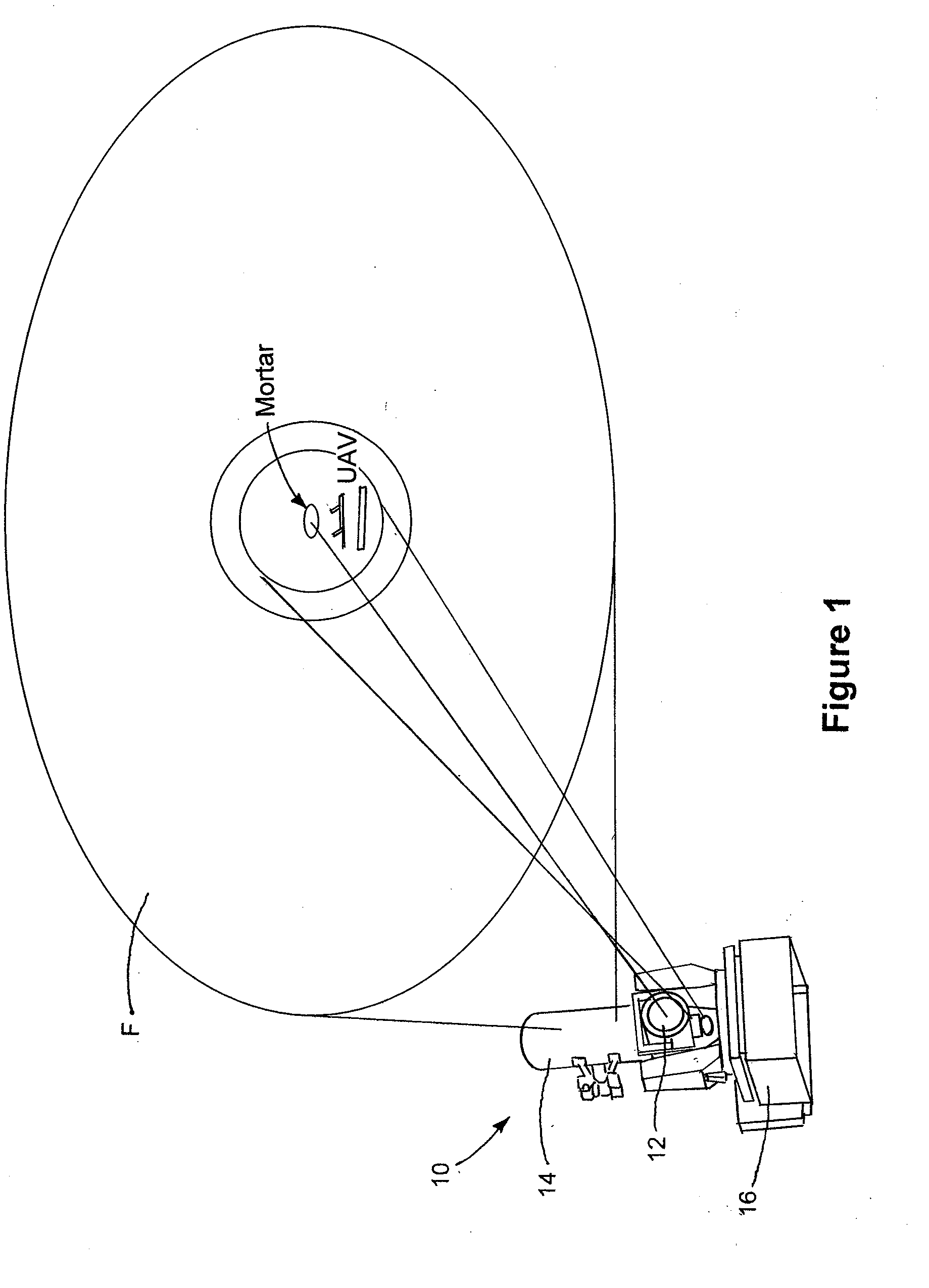
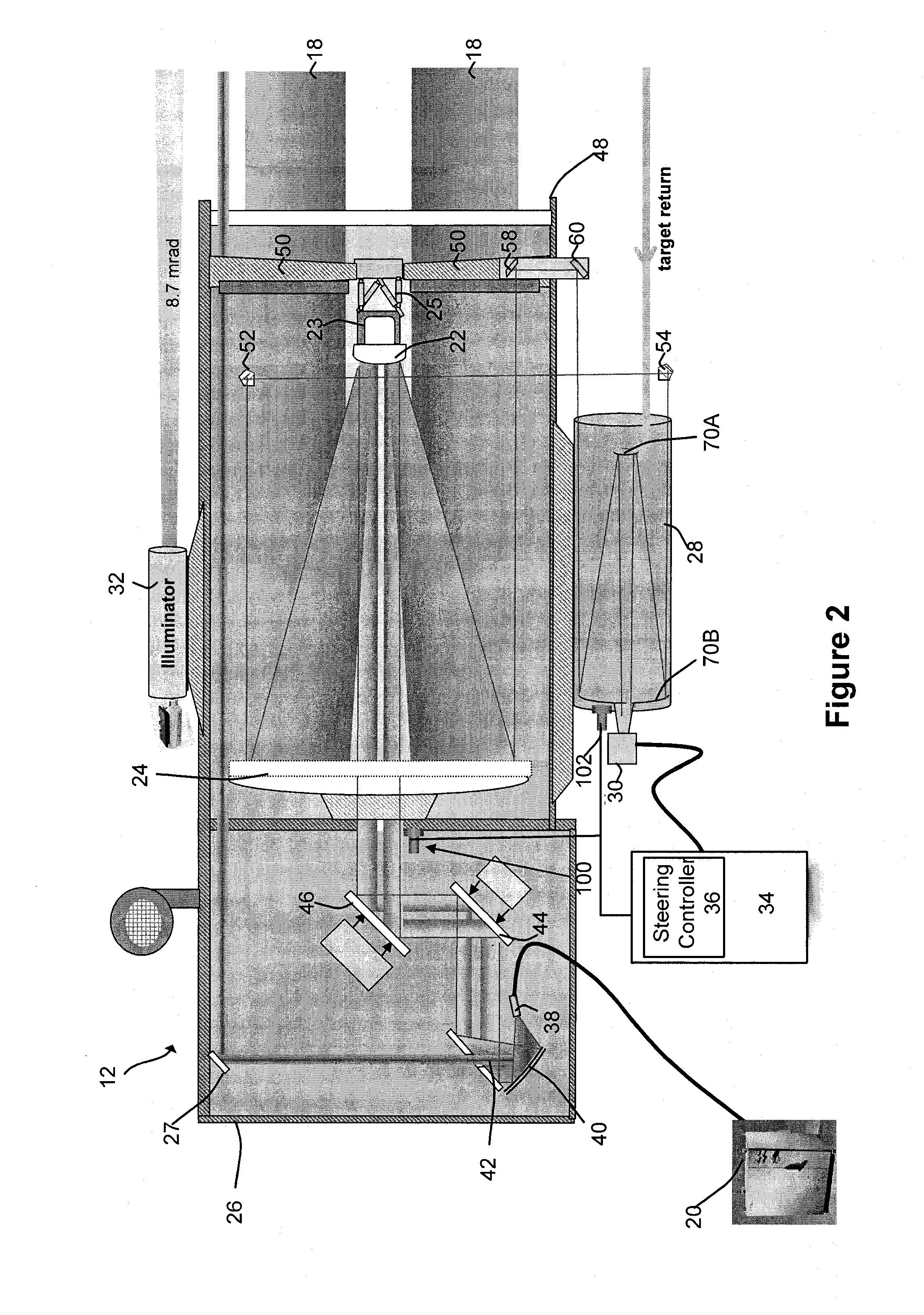
Semi-active optical tracking system
A system and method for tracking an airborne target including an illumination source (e.g., a diode laser array) is used to enhance a target signature and a detector (e.g., a passive high-speed camera) is used to detect to electromagnetic radiation (e.g., infrared radiation) reflected off the target. The received electromagnetic radiation may be processed by a digital computer and passed through a spatial filter that implements a band limited edge detection operation in the frequency domain. The filter may remove low spatial frequencies that attenuate soft edged clutter such as clouds and smoke as well as filter out artifacts and attenuated medium to high spatial frequencies to inhibit speckle noise from the detector as well as speckle from the laser return off the target.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
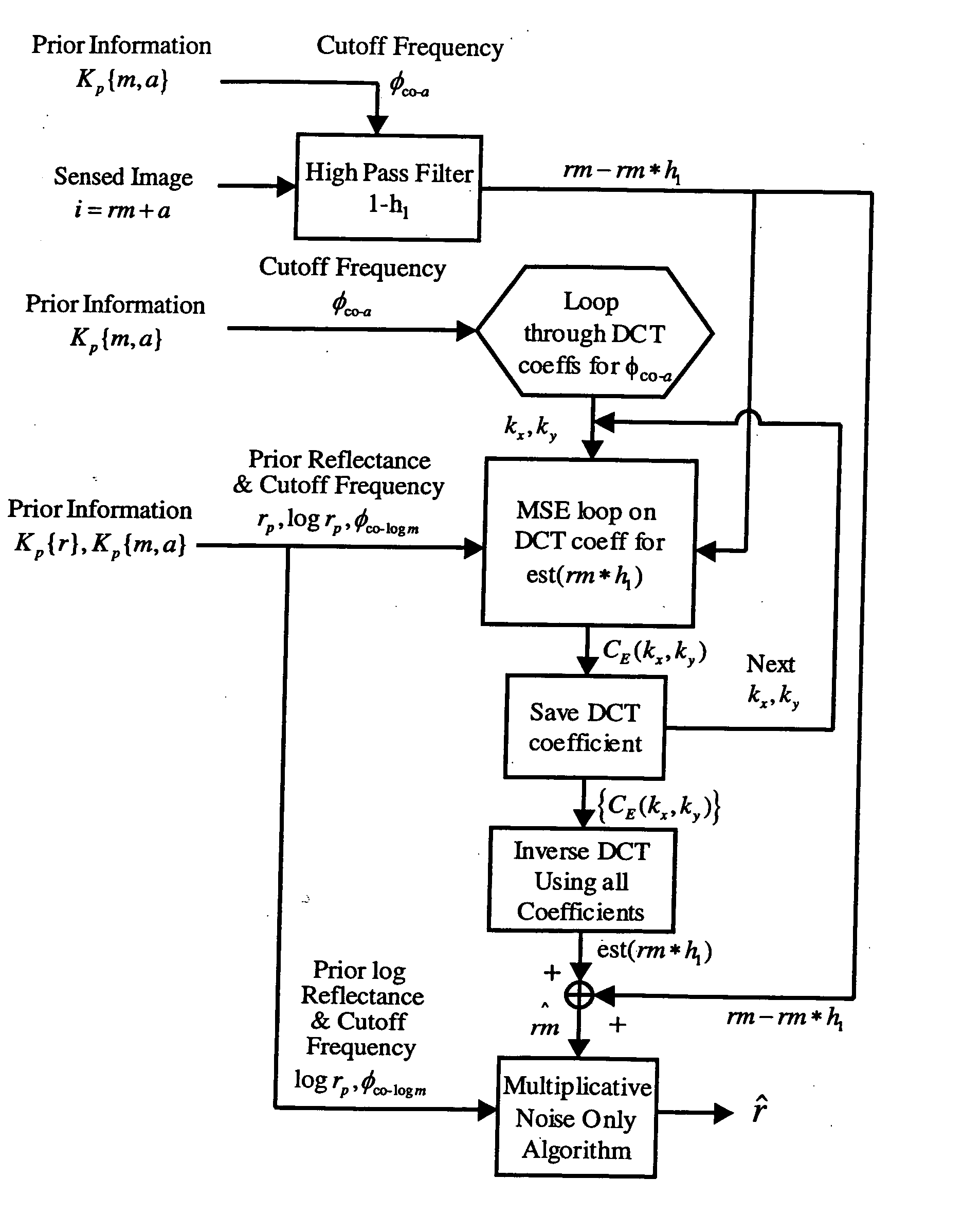
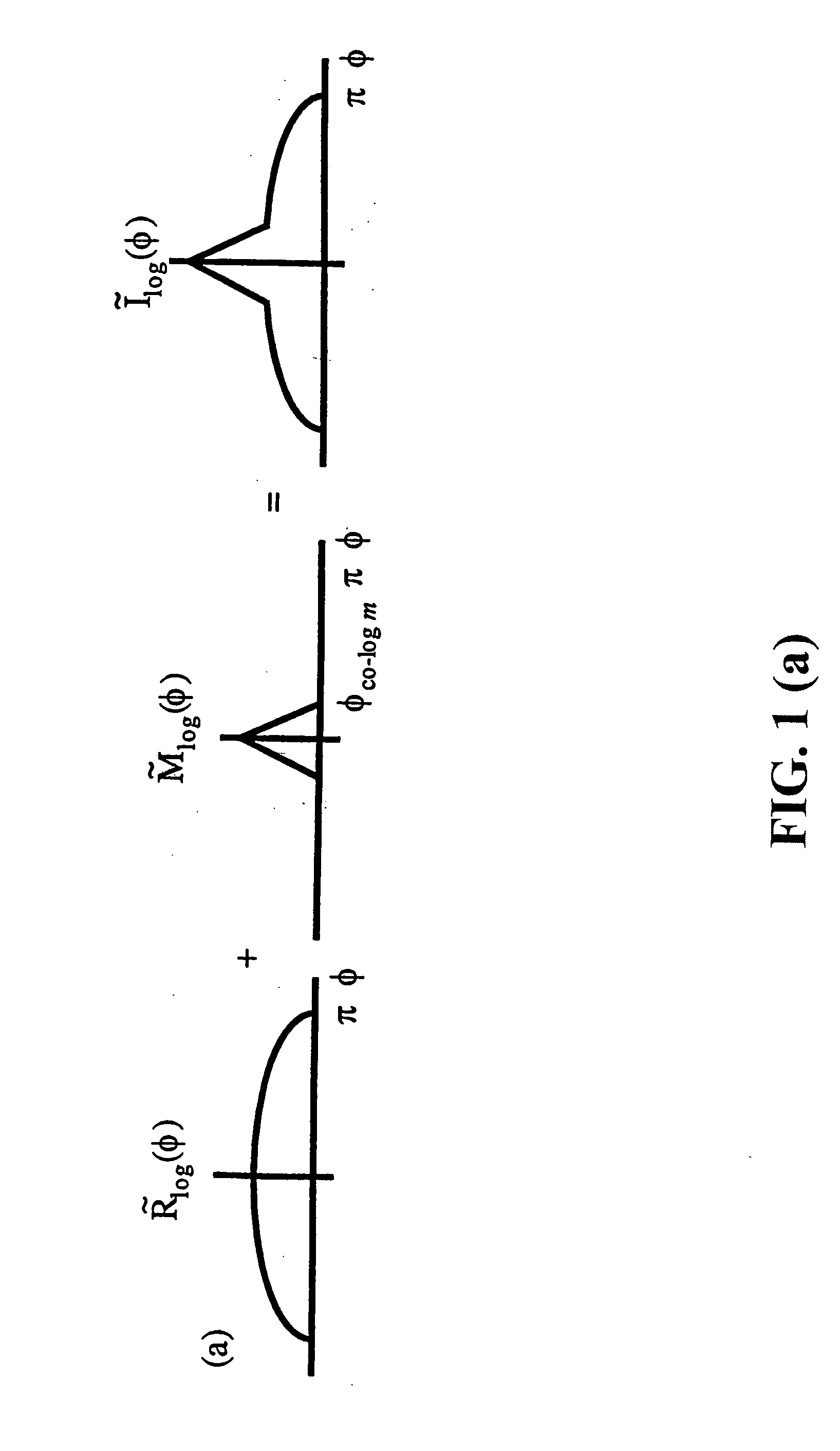
Spatial surface prior information reflectance estimation (SPIRE) algorithms
InactiveUS20050036661A1Remove additive noiseScattering properties measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionGround truthAtmospherics
A new class of algorithms has been developed to estimate spectral reflectance in remote sensing imagery. These algorithms are called Surface Prior Information Reflectance Estimation (SPIRE) algorithms and estimate surface spectral reflectance using prior spatial and spectral information about the surface reflectance. This paper describes SPIRE algorithms that employ spatial processing of single channel data to estimate local changes in spectral reflectance under spatially and spectrally varying multiplicative and additive noise caused by variations in illumination and atmospheric effects. Rather than modeling the physics of the atmosphere and illumination (using a physics-based code such as ATREM), or using ground truth spectra at known locations to compensate for these effects (using the Empirical Line Method), prior information about the low spatial frequency content of the scene in each spectral channel is used instead. HYDICE VNIR-SWIR hyperspectral data were used to compare the performance of SPIRE, ATREM, and ELM atmospheric compensation algorithms. The Spatial SPIRE algorithm performance was found to be nearly identical to the ELM ground-truth based results, while Spatial SPIRE performed better than ATREM overall, and significantly better under high clouds and haze.
Owner:AIR FORCE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE
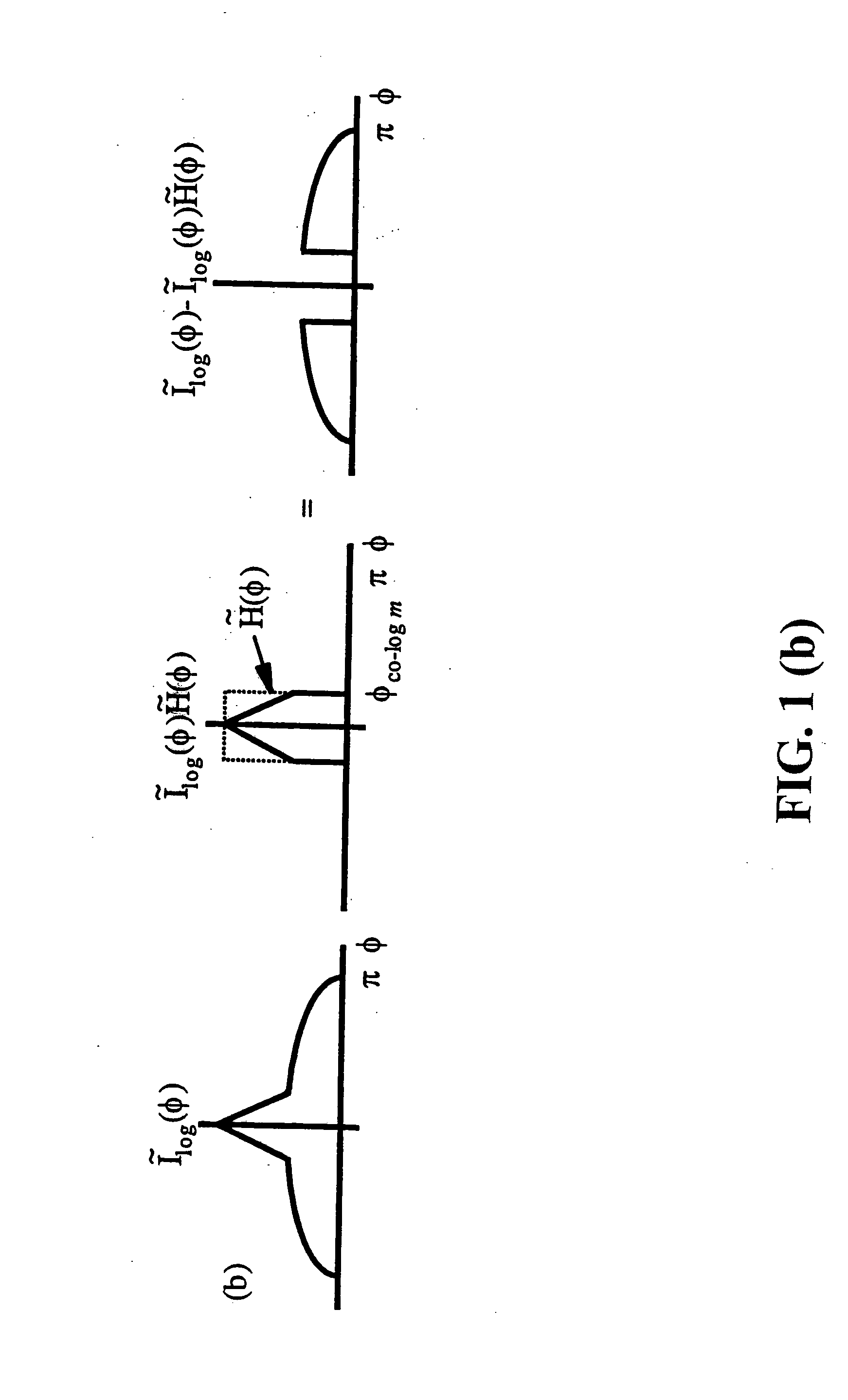
Image mosaic data reconstruction
InactiveUS7006686B2Eliminate the effects ofLow implementation costTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsComputer graphics (images)Radiology
This invention relates to the reconstruction of a full colour image from an image mosaic composed of a plurality of image pixels that have one of at least three colour values. The pixels are interleaved in rows and columns across the mosaic with pixels of different colour values to form the mosaic in such a way that each row and column contains pixels of at least two colours. A high spatial frequency luminance image is generated from the mosaic that extends across all pixel locations of the image mosaic. The luminance values of pixels in the high frequency image are adjusted to reduce zippering effects. The adjustment is performed on pixels generated from a particular colour value at least in a first row and / or a first column of the high frequency luminance image according to the luminance values for said pixels and the luminance values of pixels generated from another colour value. A low spatial frequency luminance image is generated from the mosaic for each colour value. After the luminance adjustment the high frequency luminance pixels are combined with each of the low frequency luminance images in order to generate a de-mosaiced image for each of the colour values corresponding to said low frequency luminance images.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
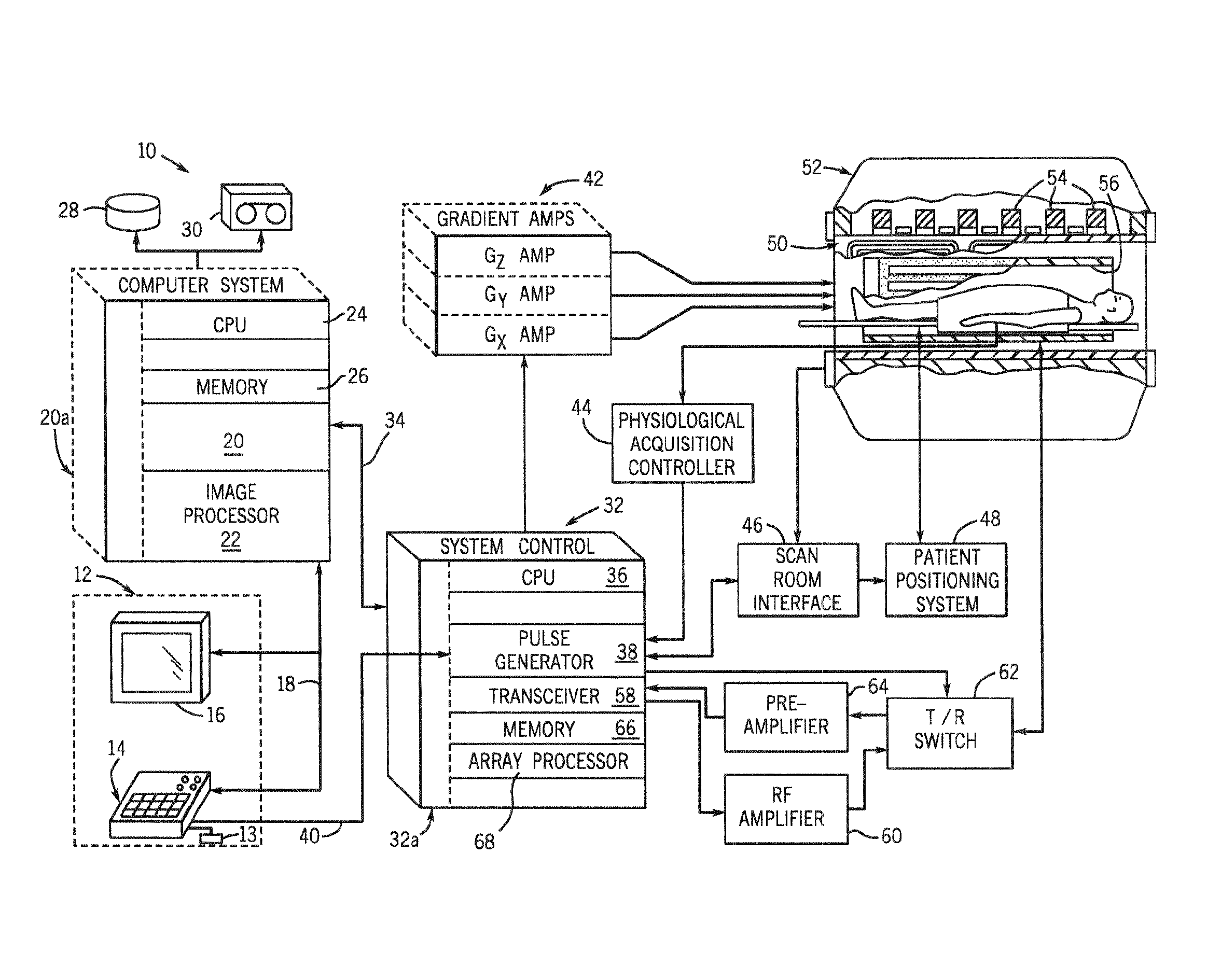
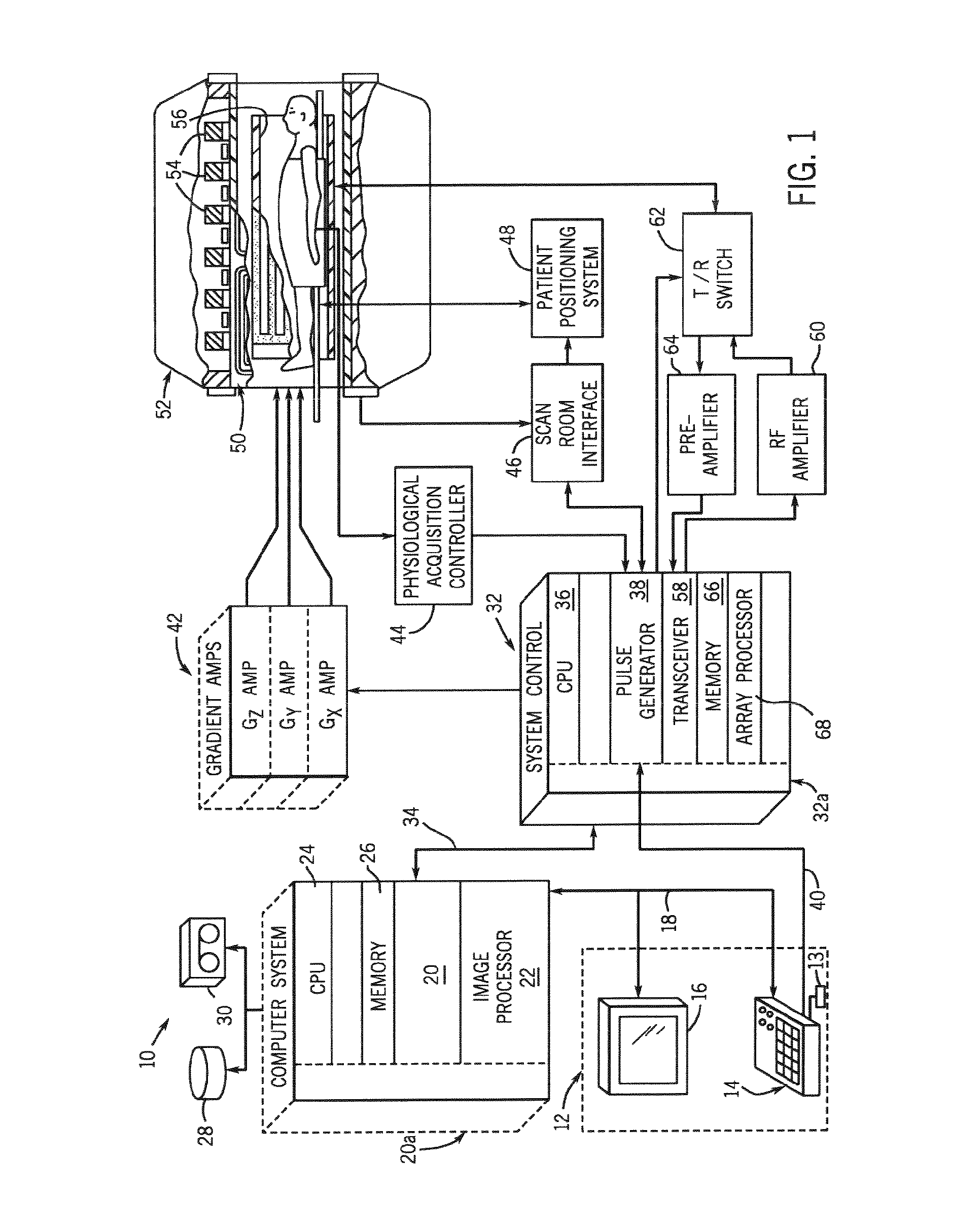
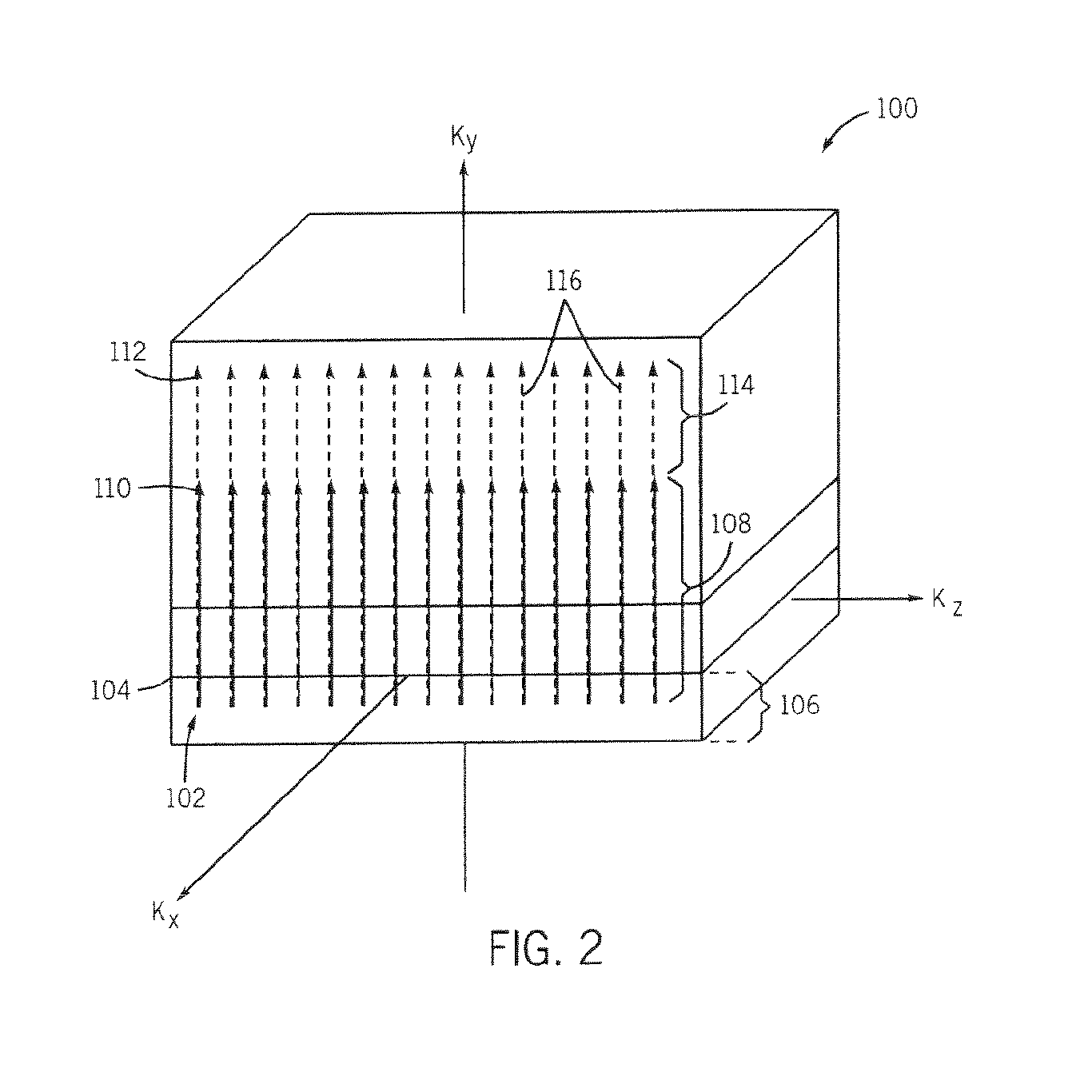
Method and apparatus for breath-held mr data acquisition using interleaved acquisition
InactiveUS20100222666A1Minimizes k-space transition artifactT weightingDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsVentricular volumeCardiac cycle
A method and apparatus are presented for acquiring MR cardiac images in a time equivalent to a single breath-hold. MR data acquisition is segmented across multiple cardiac cycles. MR data acquisition is interleaved from each phase of a first cardiac cycle with MR data from each phase of a subsequent cardiac cycle. Preferably, low spatial frequency data are interleaved between multiple cardiac cycles, and the subsequent cardiac cycle acquisition includes sequential acquisition of high spatial frequency data towards the end of the acquisition window. An MR image can then be reconstructed with data acquired from each of the acquisitions that reduce ghosting and artifacts. Volume images of the heart can be produced within a single breath-hold. Images can be acquired throughout the cardiac cycle to measure ventricular volumes and ejection fractions. Single phase volume acquisitions can also be performed to assess myocardial infarction.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
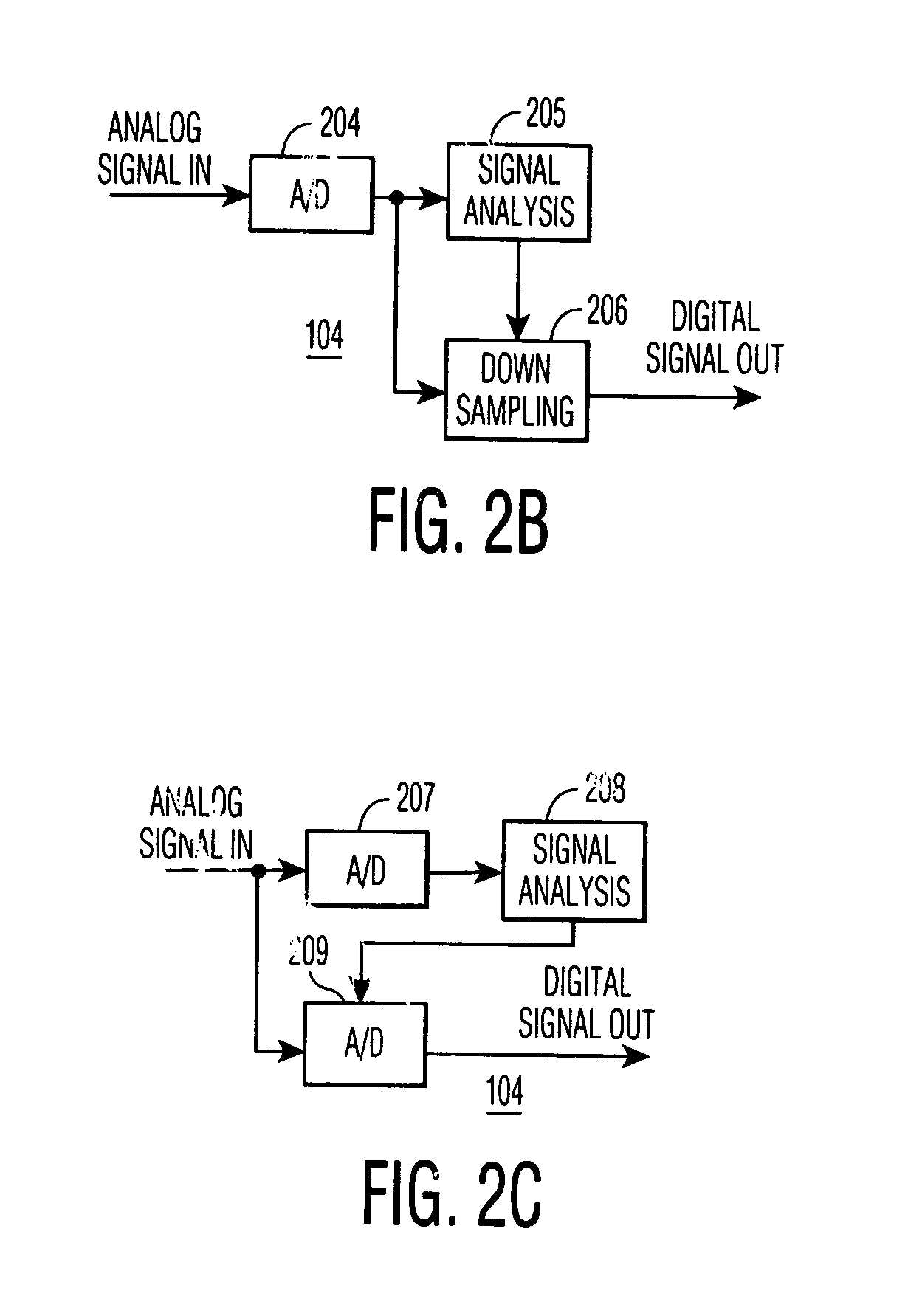
Dynamic sampling
ActiveUS8446530B2Increase chanceIncrease the number ofTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsHigh rateComputer graphics (images)
A sampling system adapts the sampling rate for sampling analog signals and / or the stored number of samples to the fixed or video image content, such that a higher rate, and equivalently a larger number of samples, are acquired for an image or video segment containing higher spatial frequencies while a lower number of samples (lower sampling rate) are retained for image or video segments containing lower spatial frequencies. The Nyquist theorem may still be satisfied for each individual image segment, while information necessary for edge enhancement is retained.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
System and method for robust multi-frame demosaicing and color super-resolution
ActiveUS7412107B2Quality improvementBlur artifactImage enhancementImage analysisMulti inputImage fusion algorithm
An integrated method for both super-resolution and multi-frame demosaicing includes an image fusion followed by simultaneous deblurring and interpolation. For the case of color super-resolution, the first step involves application of recursive image fusion separately on the three different color layers. The second step is based on minimizing a maximum a posteriori (MAP) cost function. In one embodiment, the MAP cost function is composed of several terms: a data fidelity penalty term that penalizes dissimilarity between the raw data and the super-resolved estimate, a luminance penalty term that favors sharp edges in the luminance component of the image, a chrominance penalty term that favors low spatial frequency changes in the chrominance component of the image, and an orientation penalty term that favors similar edge orientations across the color channels. The method is also applicable to color super-resolution (without demosaicing), where the low-quality input images are already demosaiced. In addition, for translational motion, the method may be used in a very fast image fusion algorithm to facilitate the implementation of dynamic, multi-input / multi-output color super-resolution / demosaicing.
Owner:UNIV OF CALIFORNIA SANTA CRUZ
High resolution image reconstruction
ActiveUS7596284B2Image enhancementGeometric image transformationImage resolutionHigh resolution image
A technique of reconstructing a high resolution image from at least one image sequence of temporally related high and low resolution image frames wherein each of said high resolution image frames includes a low spatial frequency component and a high spatial frequency component is described. The high-resolution image reconstruction technique uses spatial interpolation to generate a low spatial frequency component from a low-resolution image frame of the image sequence. The technique is adapted to generate a high spatial frequency component from at least one high resolution image frame of the image sequence which is closely related to the low resolution image frame, and to remap the high spatial frequency component to a motion-compensated high spatial frequency component estimate of the low resolution image frame. The motion-compensated high spatial frequency component estimate is added to the generated low spatial frequency component to form a reconstructed high-resolution image of the low-resolution image frame.
Owner:DOLBY INT AB
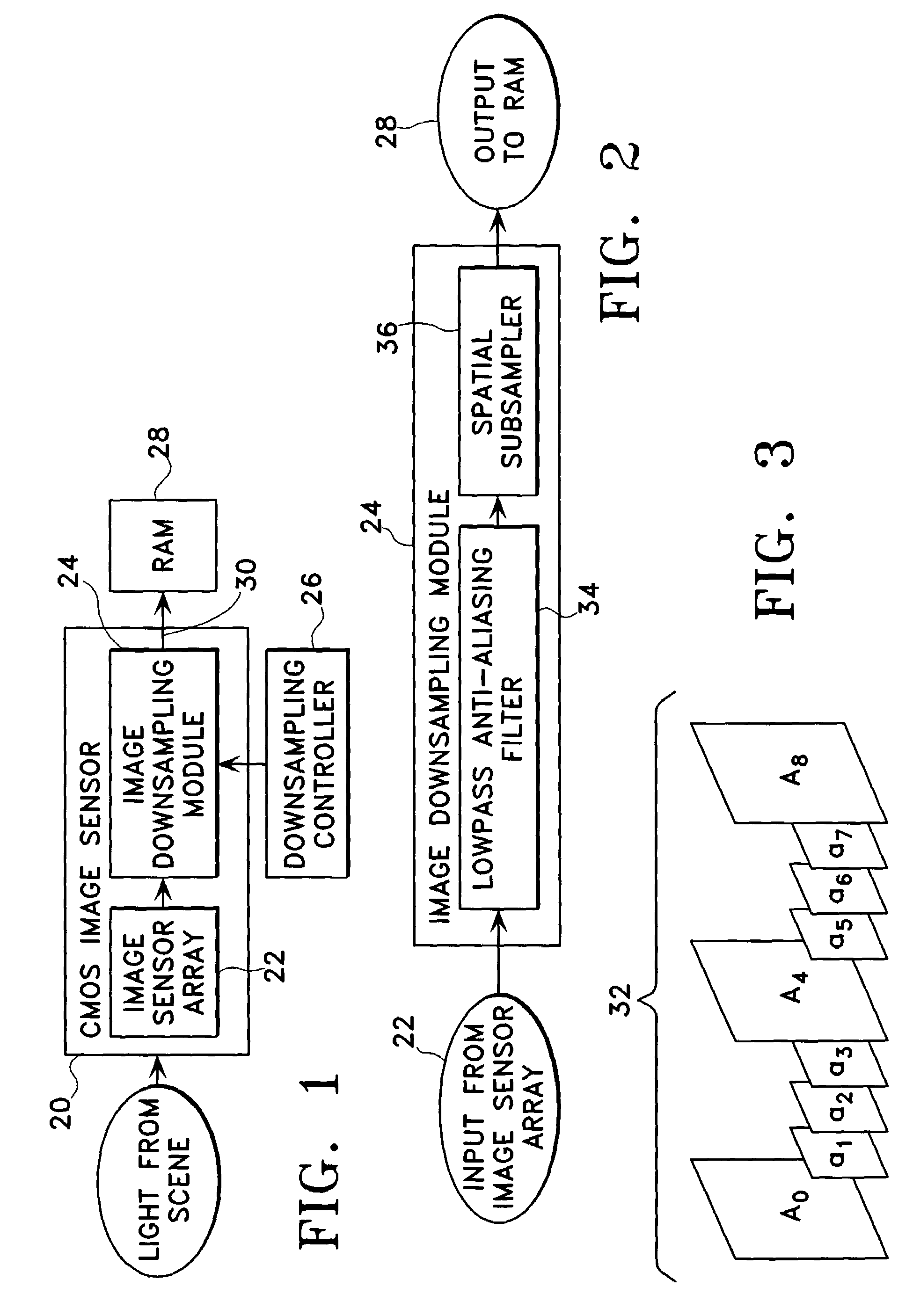
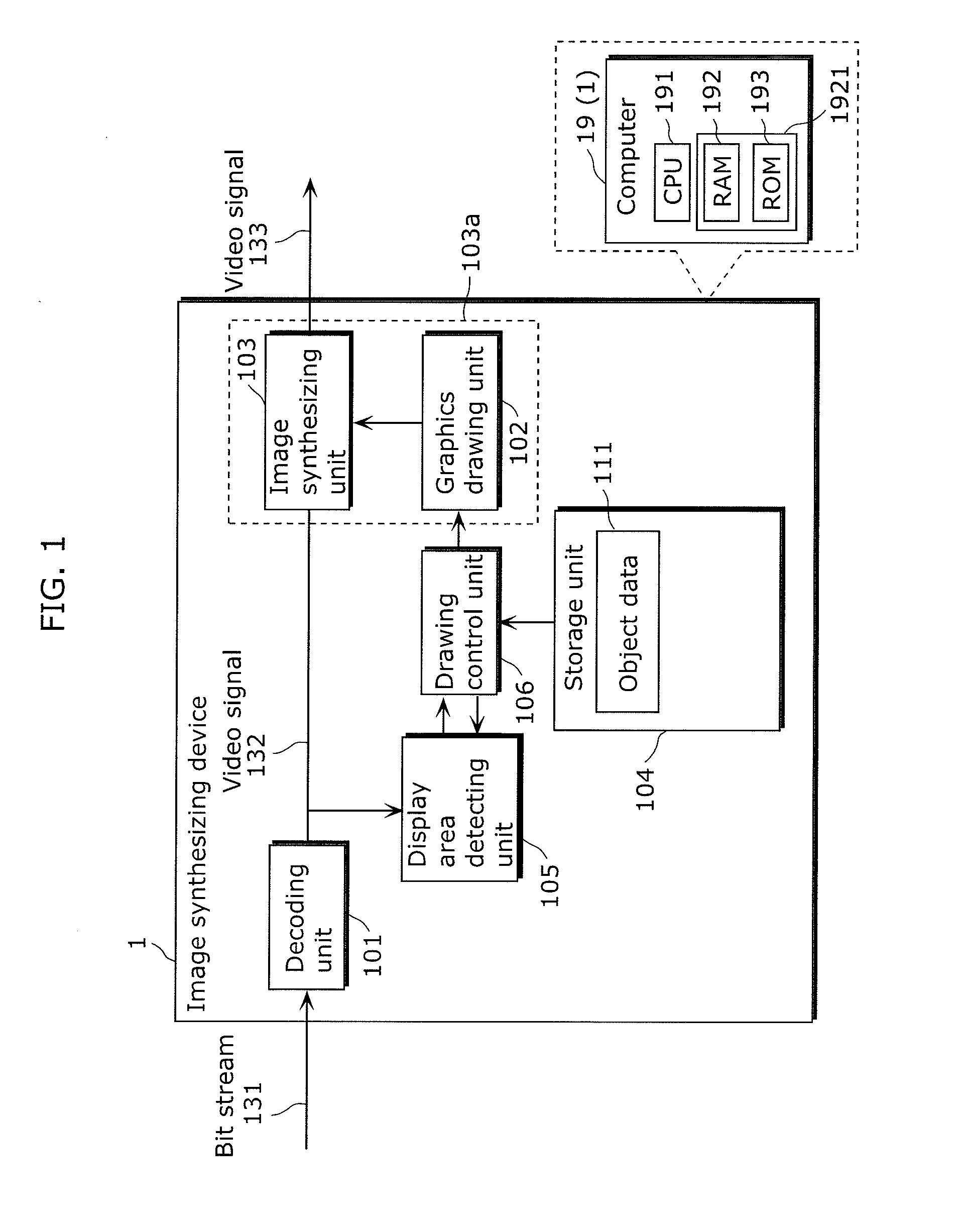
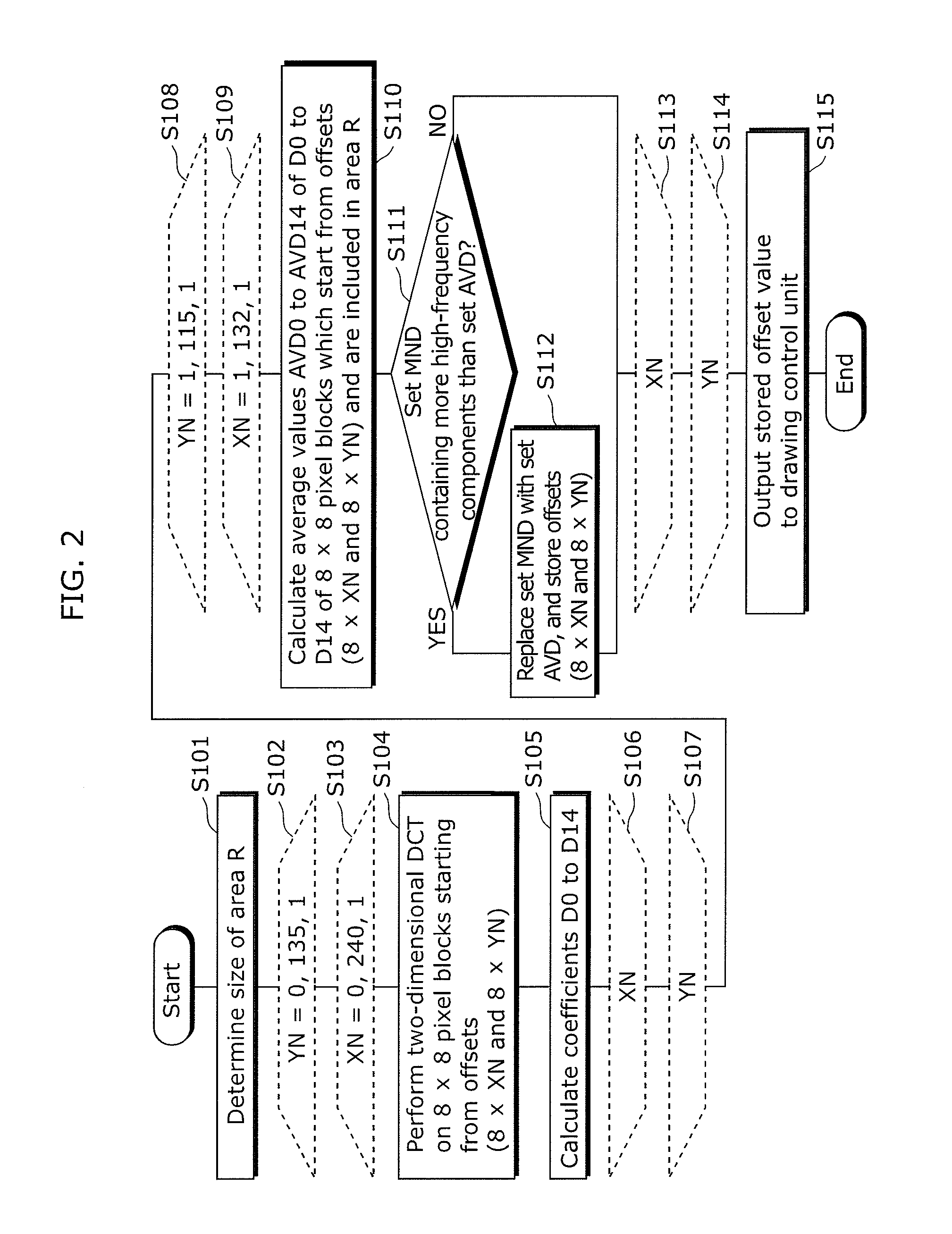
Image synthesizing device, coding device, program, and recording medium
ActiveUS20120120312A1Easy to synthesizeAvoid obstructionTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesGraphicsComputer science
In order to prevent obstruction of a view of a subtitle due to synthesis of the subtitle onto an object area such as a person and display of the synthesized subtitle, an image synthesizing device includes: an image synthesizing unit which synthesizes a graphics object onto an image; and a display area detecting unit which outputs a display position of an area having the lowest spatial frequency; and a drawing control unit which causes the graphics object to be drawn at the display position.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
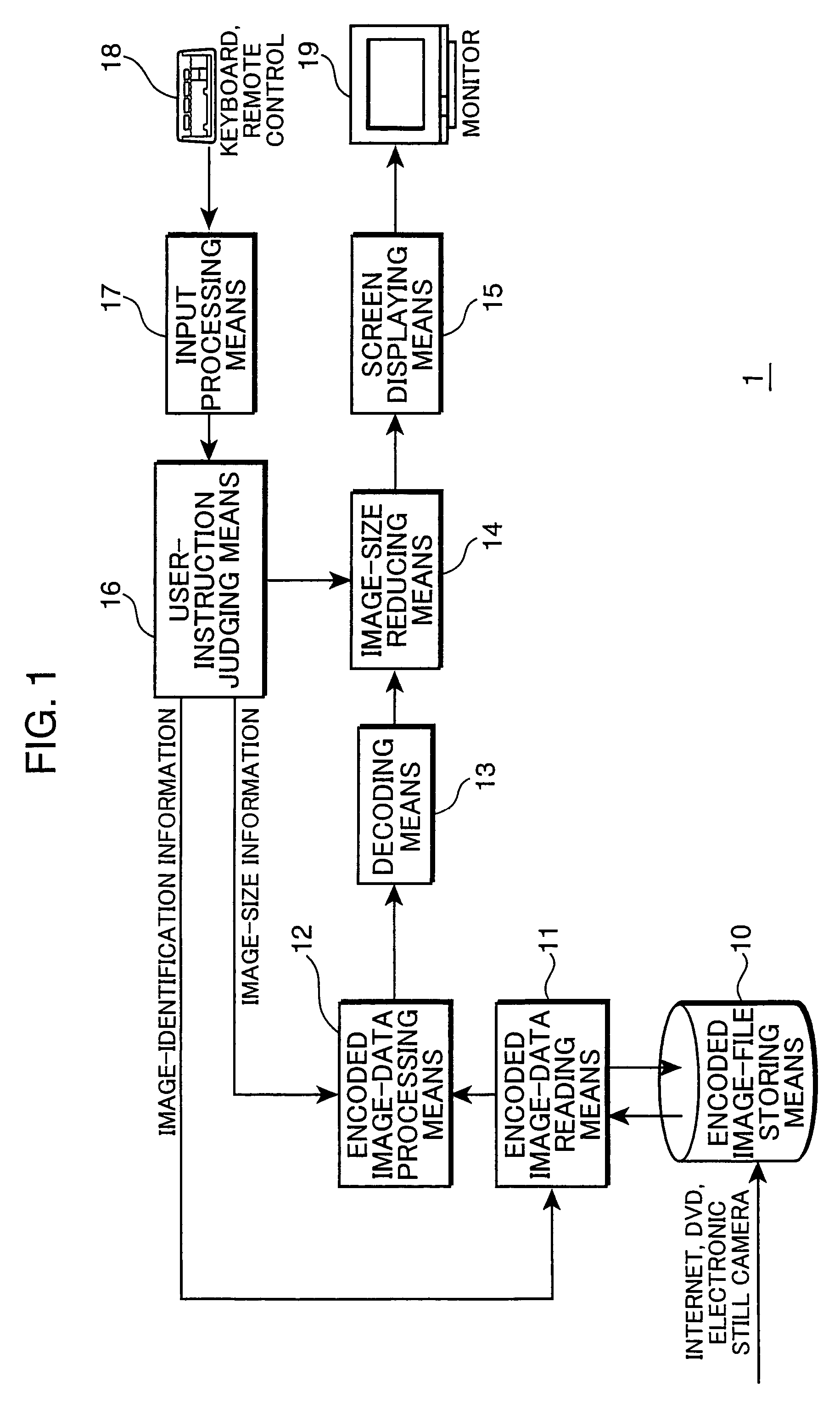
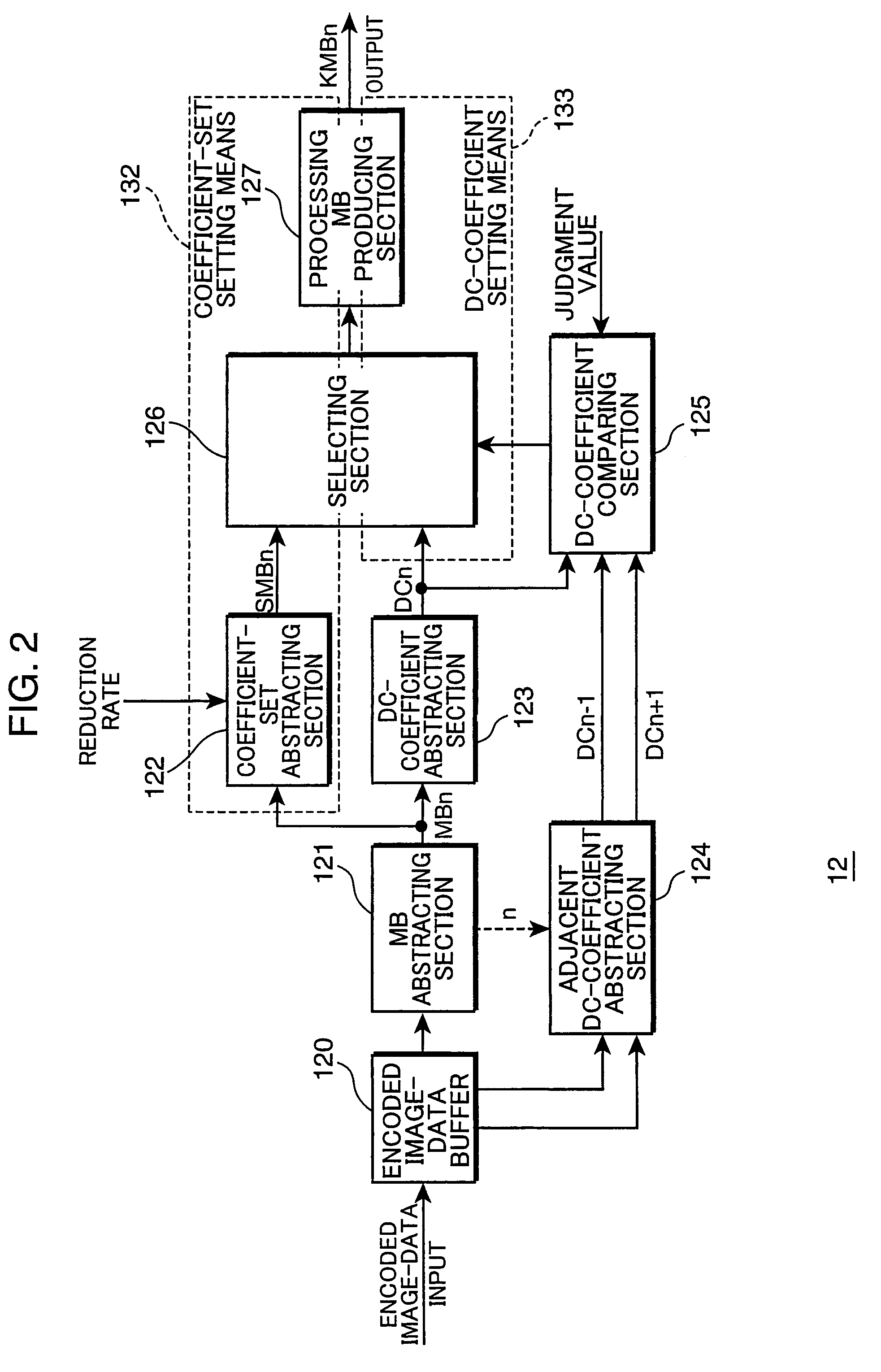
Image-data processing device, image-data processing method, image-data distributing device and image-data transmitting system
InactiveUS20040151393A1Reduce image qualityQuality improvementColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionReduction rateComputer graphics (images)
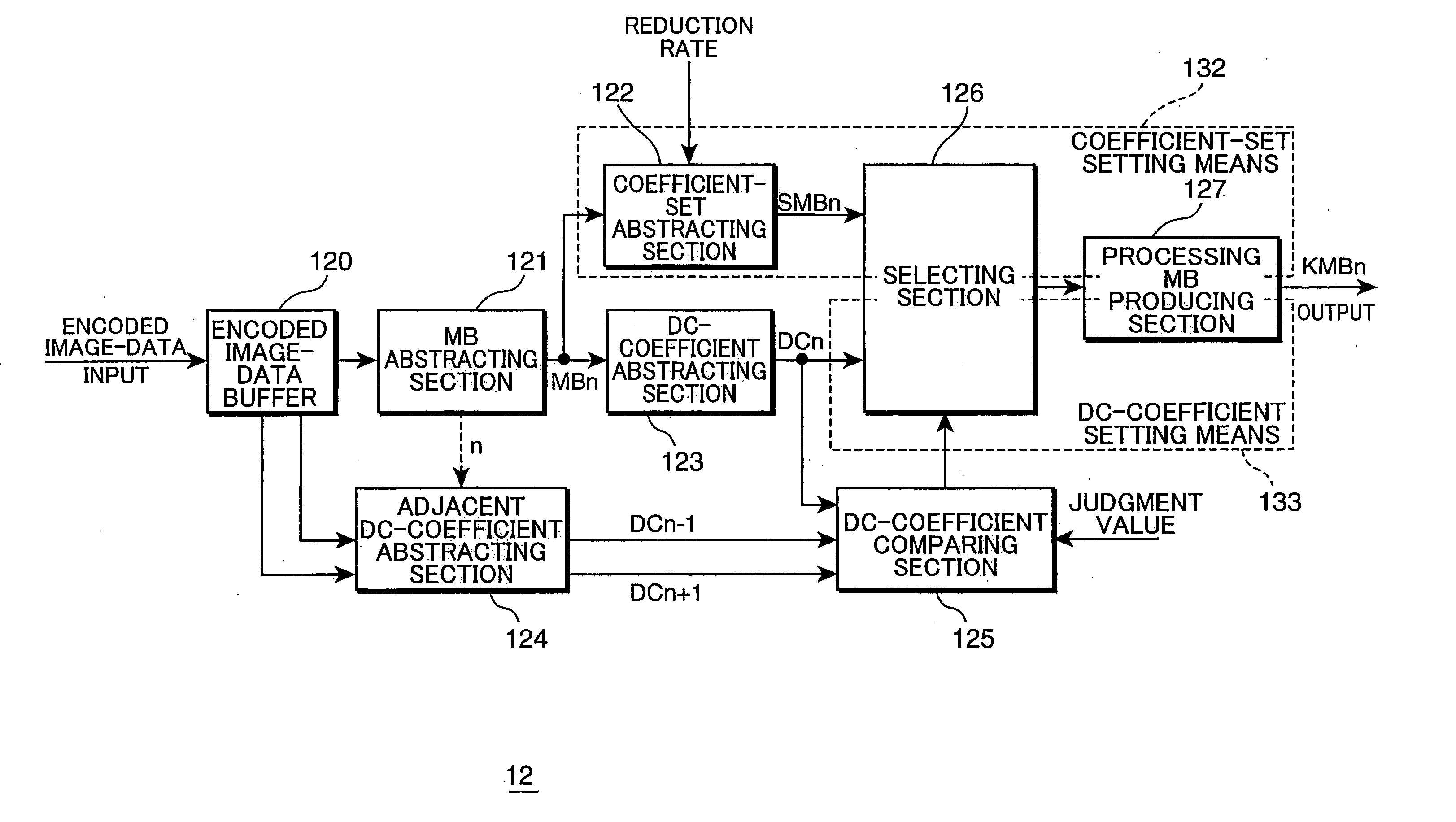
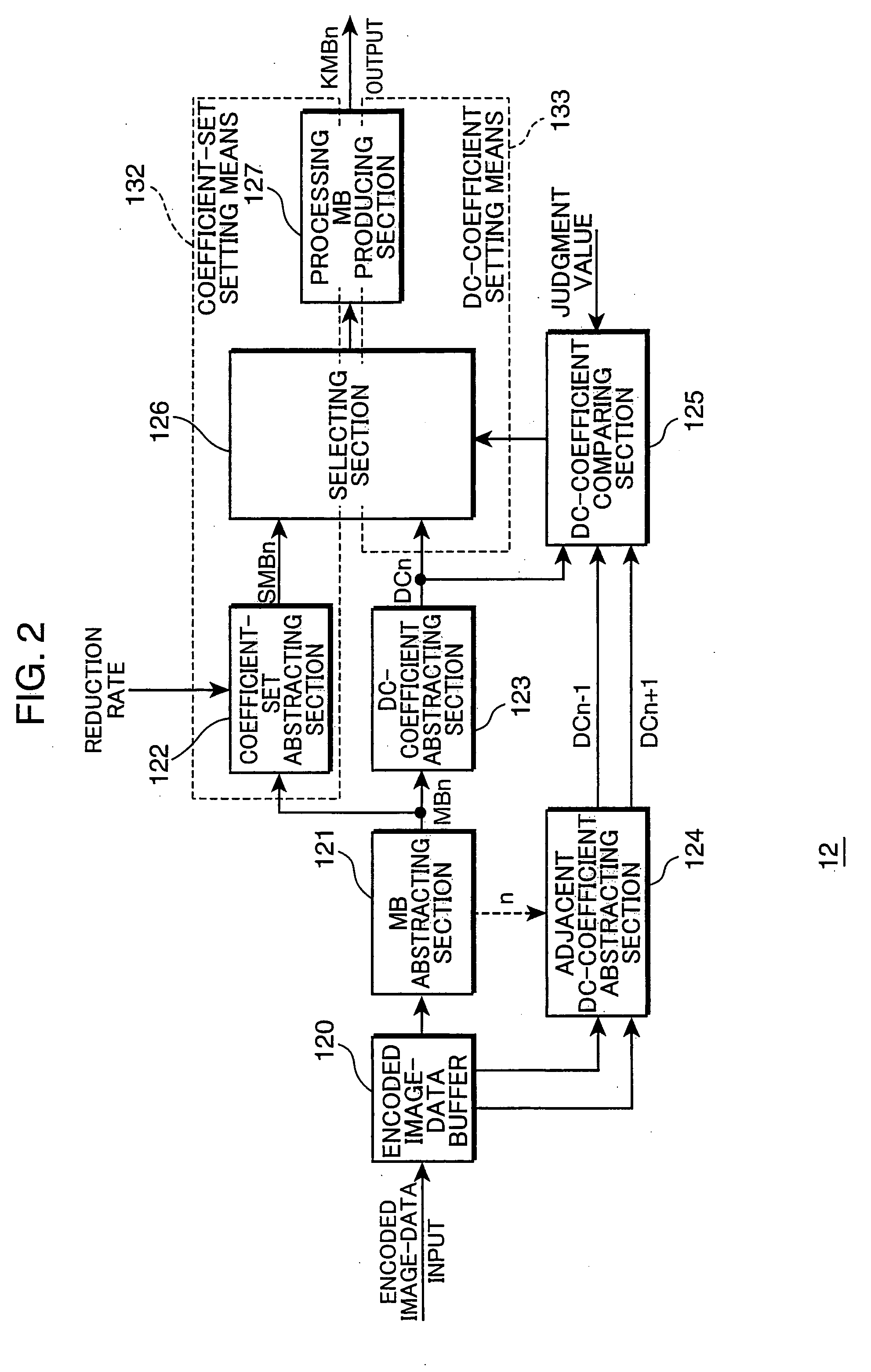
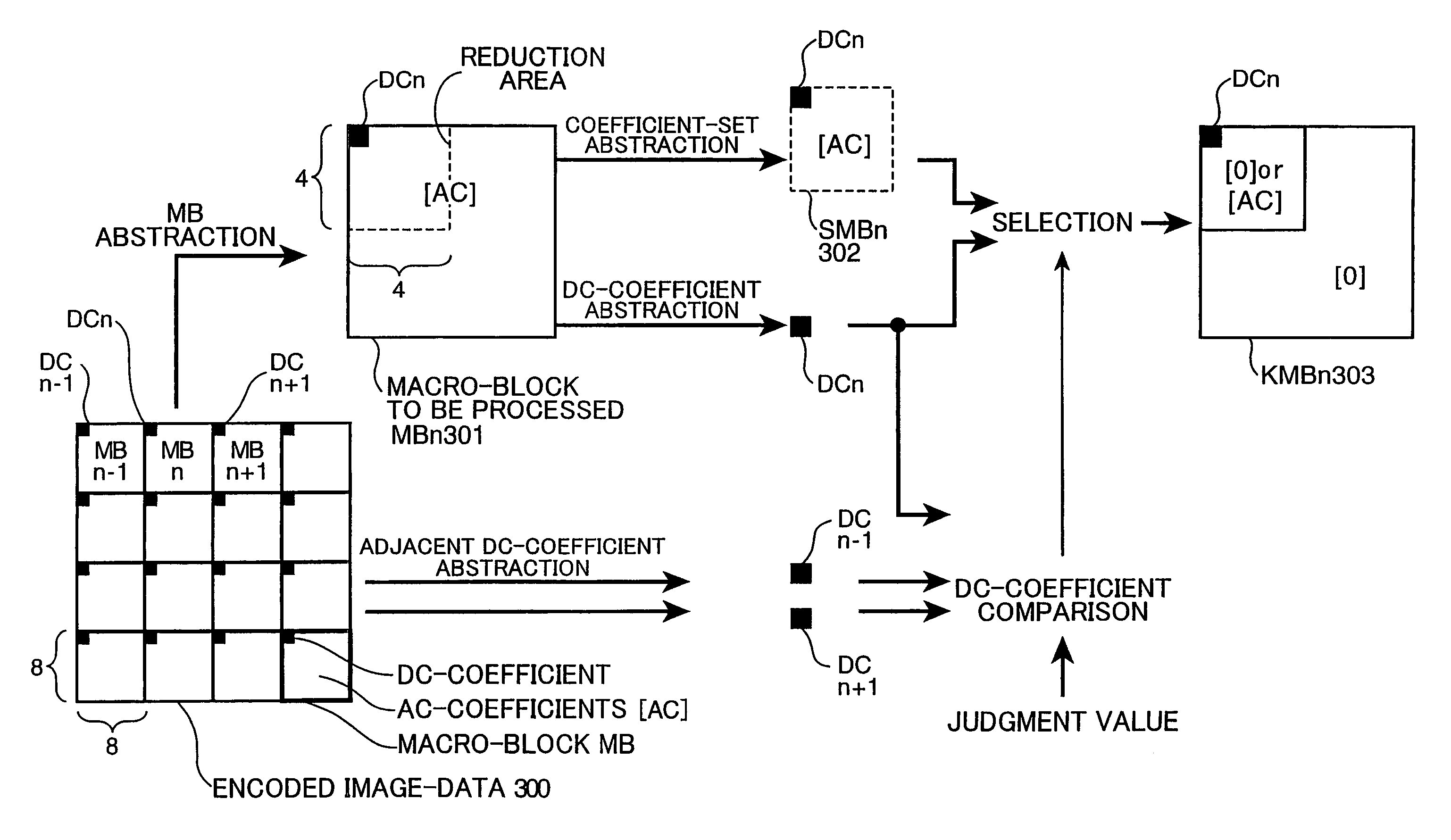
An original image is divided into a plurality of blocks that are made up of a plurality of picture elements, and in each block, from encoded image-data which is obtained by encoding a spatial-frequency component of the block as a plurality of spatial-frequency coefficients, reduced encoded image-data is produced which is encoded data on a reduced image that is obtained by reducing the original image to a given reduction rate. If the block in the encoded image-data of the original image is in an area where the value of the function is small due to gentle change in brightness or color of the image, for example, only the direct-current component coefficient of is used for the block. On the other hand, if the block is in a area where the value of the function is large because the area is a boundary area, for example, such as an outline in the image, limited number of lower spatial frequency-coefficients are used for the block. The number is based on the reduction rate of the image.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
Systems and methods for speckle reduction
A laser projection system including a system controller, a visible light source, and a light disrupting element is provided. The visible light source includes at least one laser and the laser projection system is programmed to scan a scanned optical signal of the visible light source across a plurality of image pixels. The scanned optical signal comprises a low spatial frequency beam and a high spatial frequency beam, and the low spatial frequency beam generates a low spatial frequency image having spatial frequencies below a spatial frequency threshold, the high spatial frequency beam generates a high spatial frequency image having spatial frequencies that are above the spatial frequency threshold, and the scanned laser image is a sum of the high spatial frequency image and the low spatial frequency image. The low spatial frequency beam is altered by an out of focus light disrupting element.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method of correcting streaks using exposure modulation and spatially varying trcs
Systems and methods are provided for compensating for streak defects in images formed by an image forming device, such as a digital printer. The systems and methods include using both modulation of a raster output scanner (ROS actuation) and spatially varying tone reproduction curve (STRC actuation) in a common control system for improving streak correction. Low spatial frequency large amplitude streak defects are corrected using ROS actuation and high spatial frequency streak defects, as well as any residual low frequency defects, are corrected using STRC actuation.
Owner:XEROX CORP
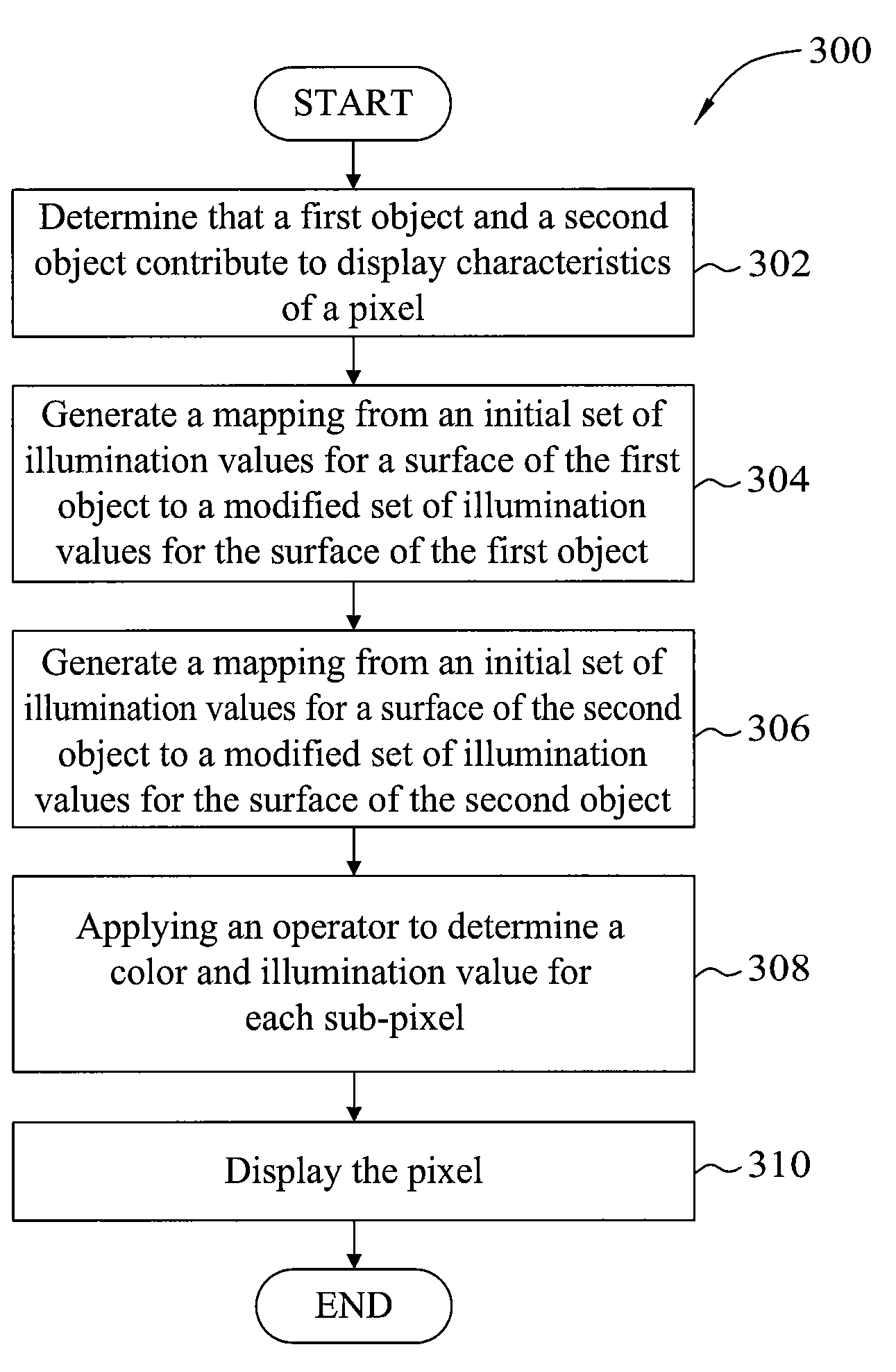
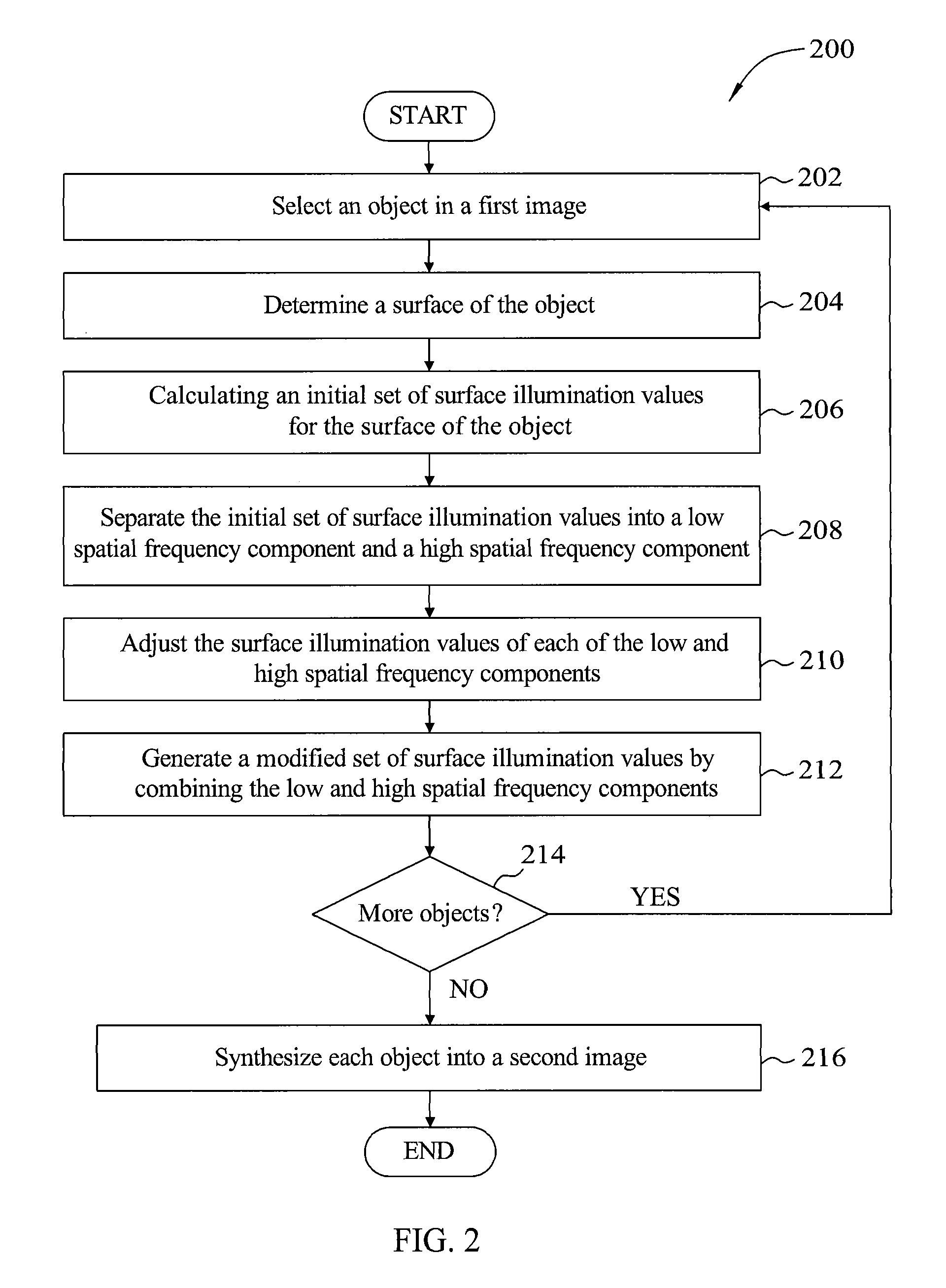
Tone mapping for motion pictures
ActiveUS8237730B1Reduce artifactsLow-frequency effectTexturing/coloringCharacter and pattern recognitionTone mappingComputer graphics (images)
A method for rendering an image including objects defined by surfaces. A rendering application selects an object in a first image and determines a surface of the object. An initial set of illumination values is calculated and is separated into low and high spatial frequency components associated with the surface of the object. The rendering application independently adjusts the illumination values of the low and high spatial frequency components based lighting information in the first image, and generates a modified set of illumination values by combining the adjusted low and high spatial frequency components. The surface of the object is then rendered using the modified set of illumination values. Advantageously, embodiments of the invention provide techniques for rendering an object without introducing halo effects around the object. Additionally, embodiments of the invention provide for rendering a sequence of frames without introducing fluctuations in the low frequency components from across frame.
Owner:PIXAR ANIMATION
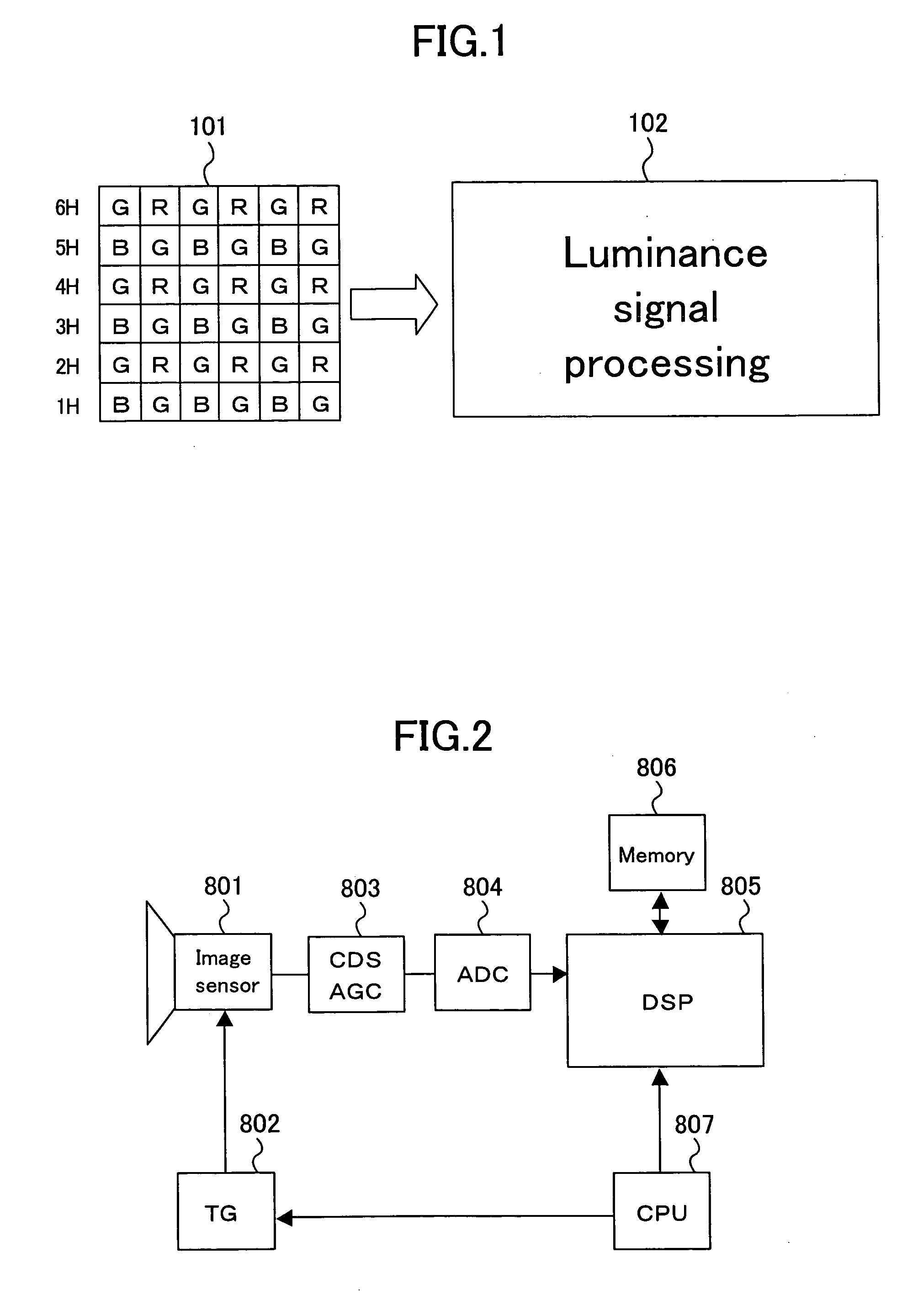
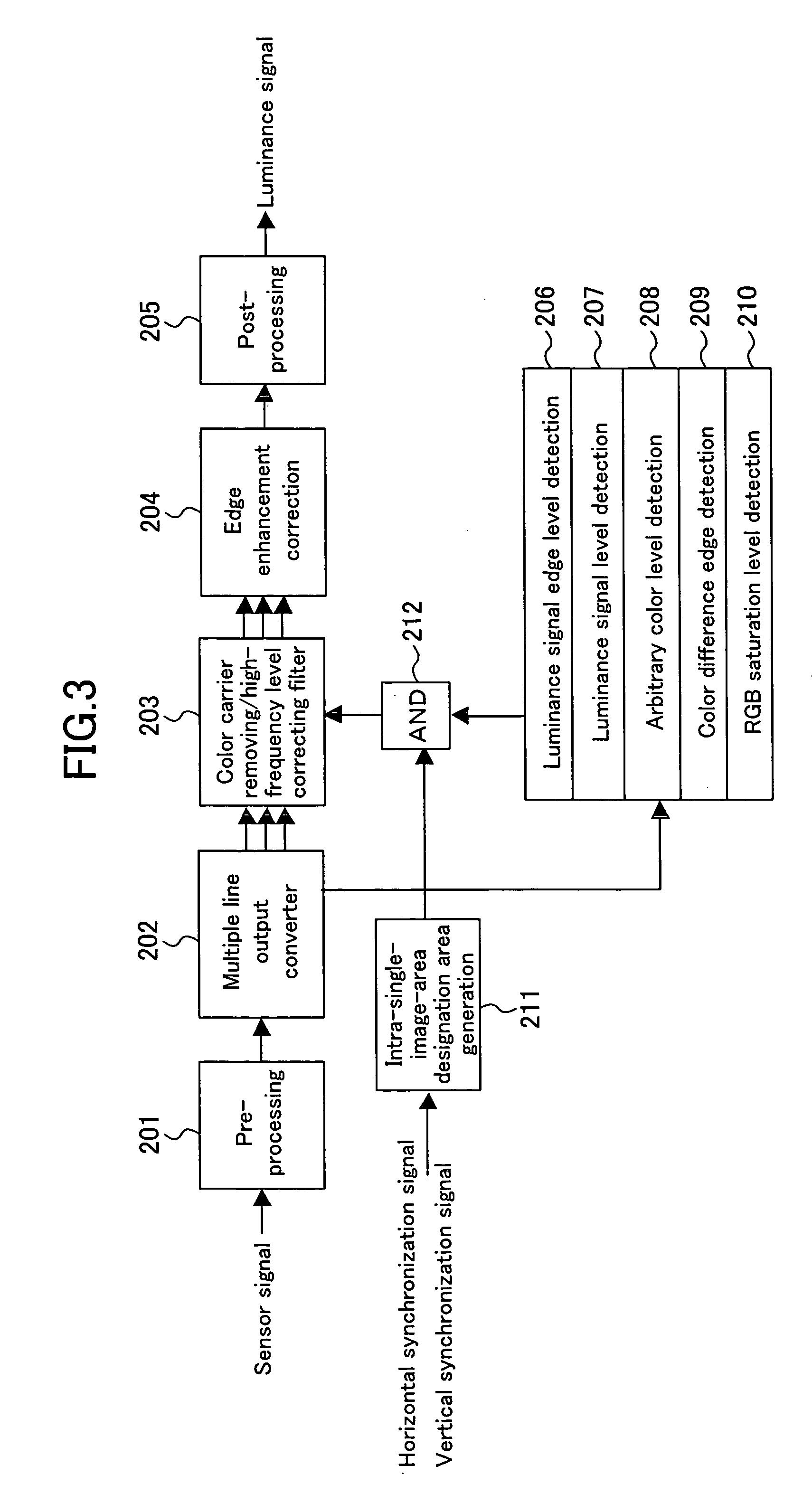
Luminance signal processing device
InactiveUS20060256217A1High resolutionInhibitionTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsColor imageSignal edge
A filter section performs color carrier component removal and high-frequency level correction according to color image signal data, and a correction section performs edge enhancement correction. By these operations, luminance signal data is obtained. The characteristics of the filter section are established adaptively in accordance with the luminance signal level of low spatial frequency components in the color image signal data, the luminance signal edge level in the color image signal data, whether or not a predetermined color is exhibited in the color image signal data, a color difference edge level in the color image signal data, or whether or not the RGB data reaches the saturation level in the color image signal data.
Owner:COLLABO INNOVATIONS INC
Method and apparatus for interferometric measurement of components with large aspect ratios
Methods and apparatus that combine the techniques of reversal (or self-calibration) to provide a low spatial frequency measurement of a part shape, independent of systematic errors in the staging used to move the part and small aperture interferometry to provide high spatial frequency information on a large part. The low spatial frequency is used to establish the rigid body motions (e.g., tip, tilt, and piston for a plano object) to be applied to the individual sub-apertures of interferometric data in stitching them together to give a full map at high resolution of the whole part. No overlap between sub-apertures is required.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
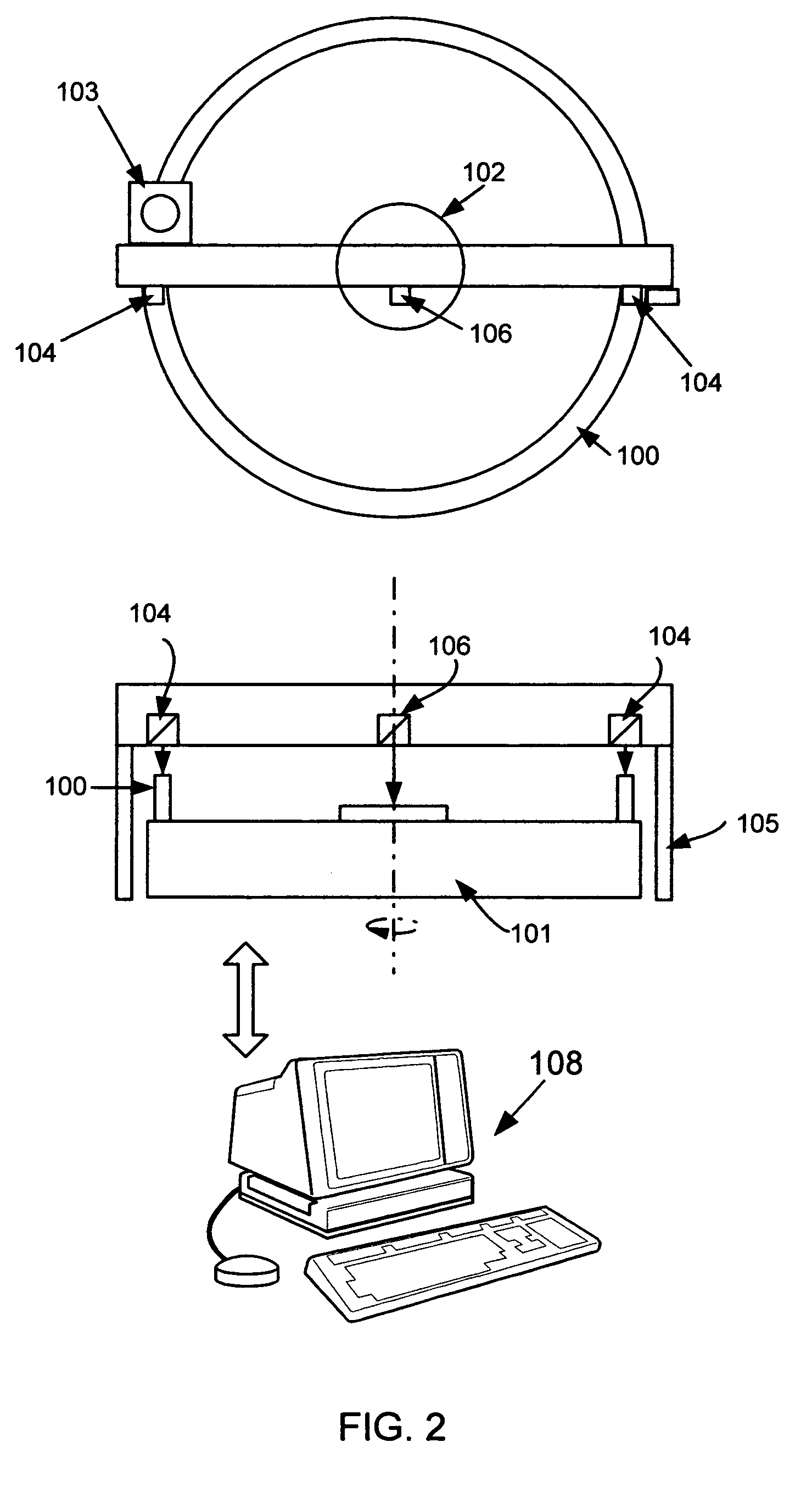
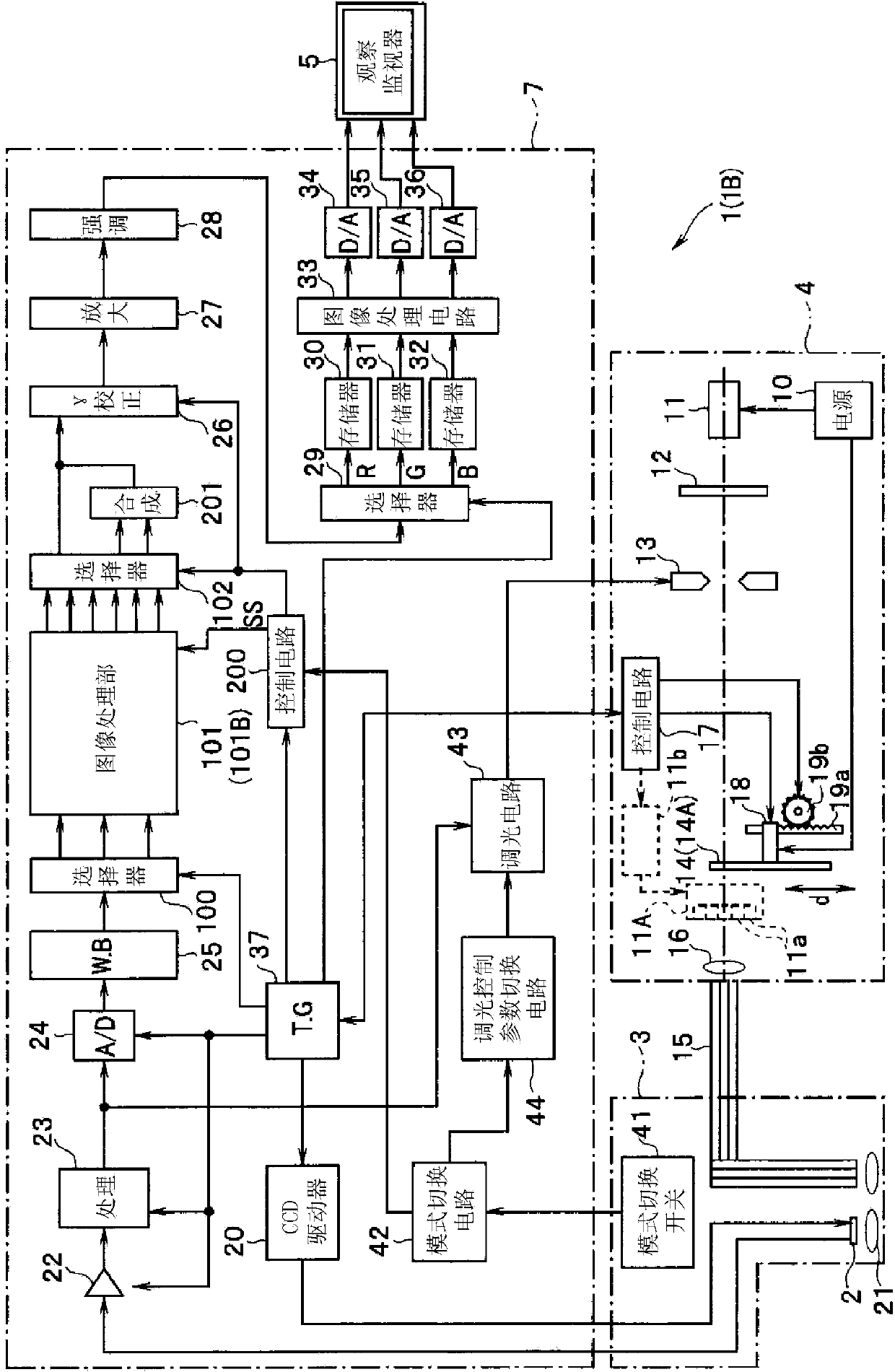
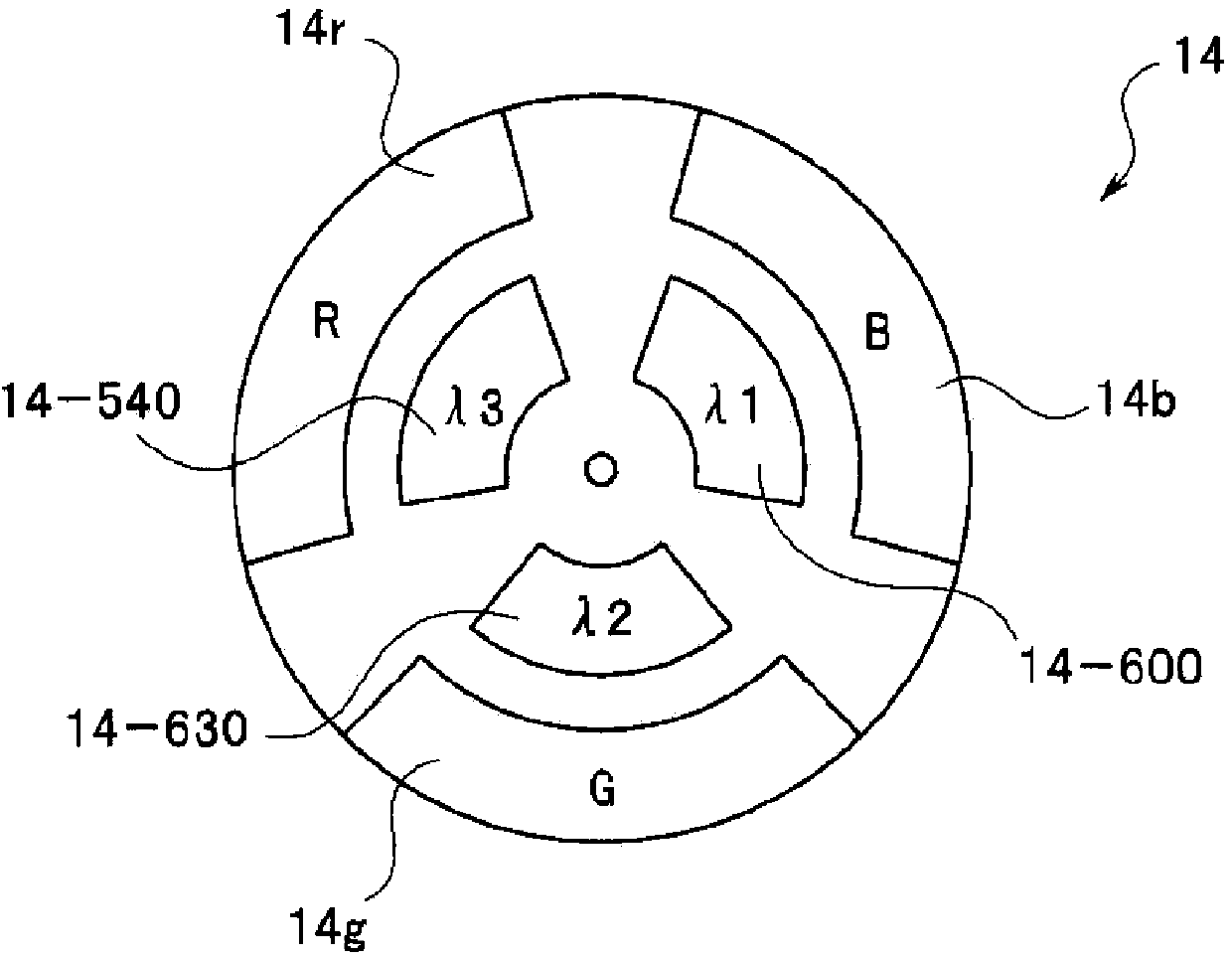
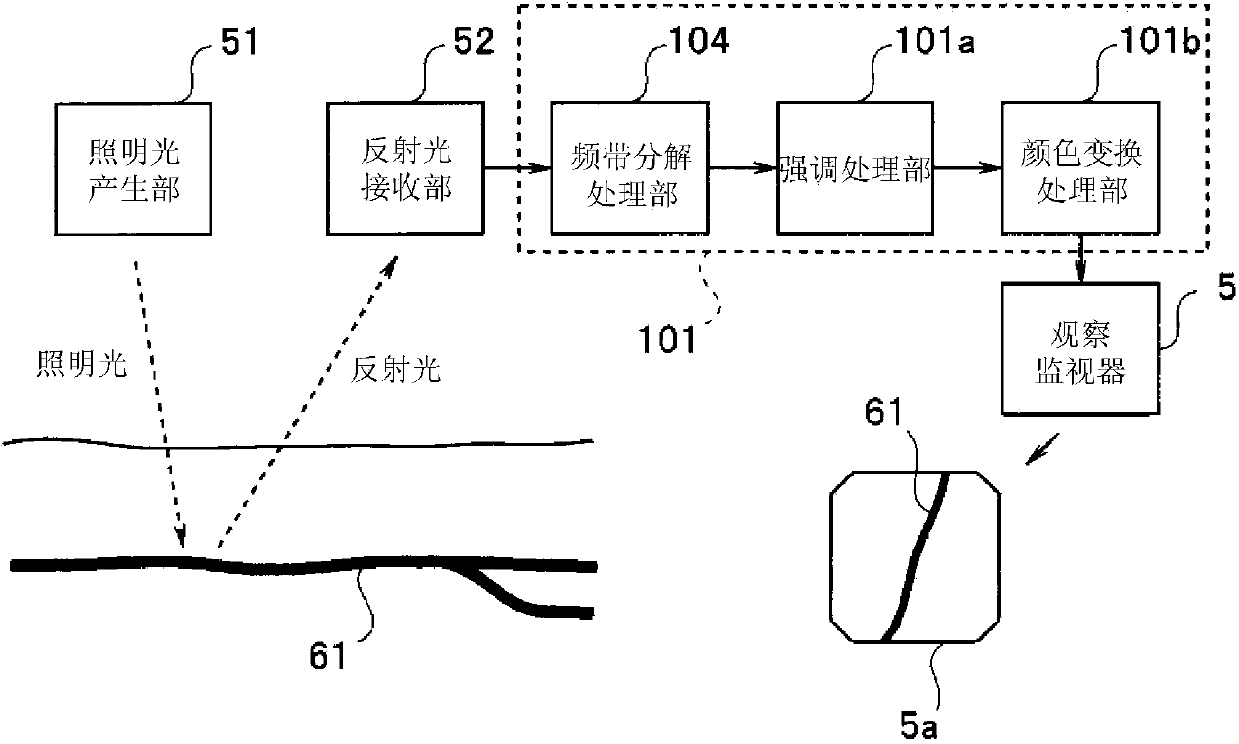
Endoscopic device
An endoscope apparatus includes: a light source device radiating at least one or more illumination lights having a predetermined wavelength band to a subject, and an image pickup device picking up an image of a return light from the subject. A band decomposition processing section of a video processor performs processing for decomposition into multiple spatial frequency bands, for a first image signal having a peak wavelength of spectral characteristic, between a wavelength band including a maximum value and a wavelength band at a minimum value with regard to an absorption characteristic of living tissue after image pickup by the image pickup device. An emphasis processing section of the video processor performs emphasis processing on the basis of a band image signal with a lowest spatial frequency among multiple band image signals obtained by the decomposition processing to generate an emphasis-corrected image signal.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Method for spatial up-scaling of video frames
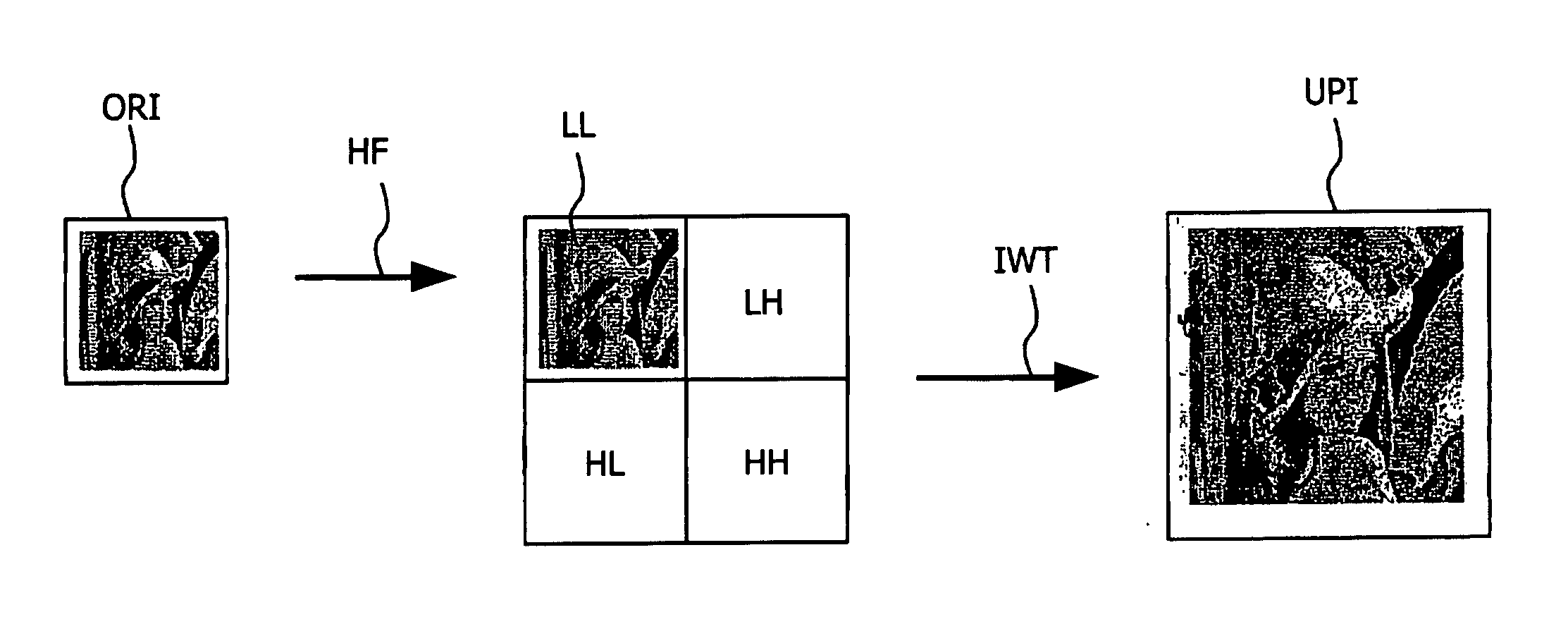
InactiveUS20060284891A1Improve picture qualityGeometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsWavelet transformLow spatial frequency
The present invention relates to method for spatial up-scaling of an original video frame comprising p rows and q colums of pixels, where p and q are integers. Said up-scaling method comprises a step of constructing high-low (HL), low-high (LH), and high-high (HH) virtual spatial frequency subbands comprising p rows and q colums of pixels from the use of high-pass filtering of the original video frame, considered as a low-low spatial frequency subband (LL), in horizontal, vertical, and both directions, respectively. Said up-scaling method further comprises a step of applying an inverse wavelet transform (IWT) to the constructed subbands and to the original video frame in such a way that an up-sampled version of the original image is obtained.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
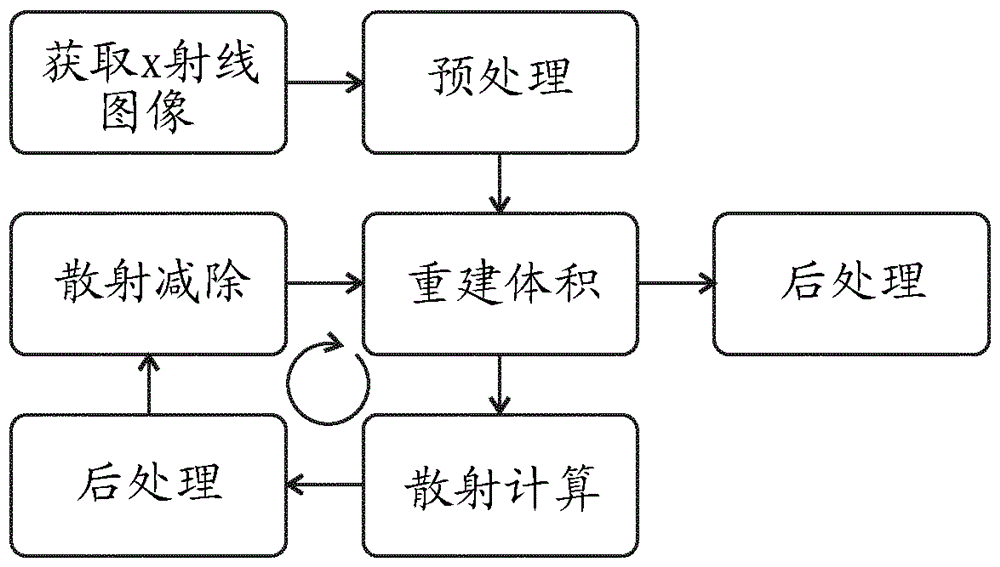
Target-specific dose & scatter estimation in CT images
Scatter correction of the projection images used to reconstruct volume CT images is a computationally intensive process that cannot at present be done in real time. We note, however, that although scatter is non-uniform, it varies smoothly - i.e. with a low spatial frequency. Existing Monte-Carlo estimation methods need to run over a large number of iterations in order to eliminate the mainly high-frequency artefacts that are present initially, but this process can be cut short and a low-pass filter applied instead thereby substantially reducing the computational load. By applying the same principle in the spatial domain and interpolating some scatter images from adjacent and surrounding scatter images, the computational load can be reduced still further. Applying these techniques in an iterative process on graphics-processor-quality computational hardware enables real-time scatter correction and reconstruction of CT volume images.
Owner:ELEKTA AB +1
Method and apparatus for inspecting an EUV mask blank
InactiveUS6963395B2Quick testIncrease the areaMaterial analysis by optical meansOriginals for photomechanical treatmentReference sampleLength wave
An apparatus and method for at-wavelength EUV mask-blank characterization for inspection of moderate and low spatial frequency coating uniformity using a synchrotron or other source of EUV light. The apparatus provides for rapid, non-destruction, non-contact, at-wavelength qualification of large mask areas, and can be self-calibrating or be calibrated to well-characterized reference samples. It can further check for spatial variation of mask reflectivity or for global differences among masks. The apparatus and method is particularly suited for inspection of coating uniformity and quality and can detect defects in the order of 50 μm and above.
Owner:EUV
Image-data processing device, image-data processing method, image-data distributing device and image-data transmitting system
InactiveUS7369706B2Increase speedQuality improvementColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionReduction rateImaging processing
An image processing device for processing an original image divided into a plurality of blocks that are made up of a plurality of picture elements from encoded image-data which is obtained by encoding a spatial-frequency component of the block as a plurality of spatial-frequency coefficients, and producing reduced encoded image-data which is encoded data on a reduced image that is obtained by reducing the original image to a given reduction rate. If the block in the encoded image-data of the original image is in an area where the value of the function is small due to gentle change in brightness or color of the image, for example, only the direct-current component coefficient of is used for the block. On the other hand, if the block is in a area where the value of the function is large because the area is a boundary area, for example, such as an outline in the image, limited number of lower spatial frequency-coefficients are used for the block. The number is based on the reduction rate of the image.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
Image processing system and method
ActiveUS7796297B2Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImaging processingFrequency spectrum
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
High resolution ct scanner
InactiveUS20050152490A1Improve imaging resolutionHigh resolutionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationCt scannersX-ray
CT scanner is disclosed for providing an image of a region comprising: at least one X-ray cone beam for illuminating mthe region with X-rays; a plurality of rows of X-ray detectors that generate signals responsive to line attenuation of X-rays from the at least one controller that controls providing an image of a region comprising: at least one X-ray cone beam for illuminating the region with X-rays; a plurality of rows of X-ray detectors that generate signals responsive to line attenuation of X-rays from the at least one X-ray source that pass through the region; a controller that controls the at least one X-ray cone beam to acquire line attenuation data for the region for different view angles of the region; and a processor that receives the signals and: a) determines low spatial frequency components of the image from the data; b) generates a first spatial image of the region from the low high spatial frequency components of the image from the data; d) generates a second spatial image of the region from the high frequency components; and e) combines the first and second images to generate the image.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Semi-active optical tracking system
A system and method for tracking an airborne target including an illumination source (e.g., a diode laser array) is used to enhance a target signature and a detector (e.g., a passive high-speed camera) is used to detect to electromagnetic radiation (e.g., infrared radiation) reflected off the target. The received electromagnetic radiation may be processed by a digital computer and passed through a spatial filter that implements a band limited edge detection operation in the frequency domain. The filter may remove low spatial frequencies that attenuate soft edged clutter such as clouds and smoke as well as filter out artifacts and attenuated medium to high spatial frequencies to inhibit speckle noise from the detector as well as speckle from the laser return off the target.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
High resolution CT scanner
InactiveUS7027552B2Improve imaging resolutionHigh resolutionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationCt scannersX-ray
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Process for the stabilization of the images of a scene correcting offsets in grey levels, detection of mobile objects and harmonization of two snapshot capturing apparatuses based on the stabilization of the images
A process for the electronic stabilization of the images of a scene of a snapshot capturing apparatus of an imaging system in which, in a terrestrial reference frame, the images of the scene captured by the apparatus are filtered in a low-pass filter, so as to retain only the low spatial frequencies thereof, and the optical flow equation is solved to determine the rotations to be imposed on the images in order to stabilize them with regard to the previous images is provided. The invention also relates to a process for correcting offsets in grey levels of a snapshot capturing apparatus of an imaging system whose images are stabilized according to the process of the invention, where the calculation of the offsets is deduced from the steps of the stabilization process.
Owner:SAGEM DEFENSE SECURITE SA
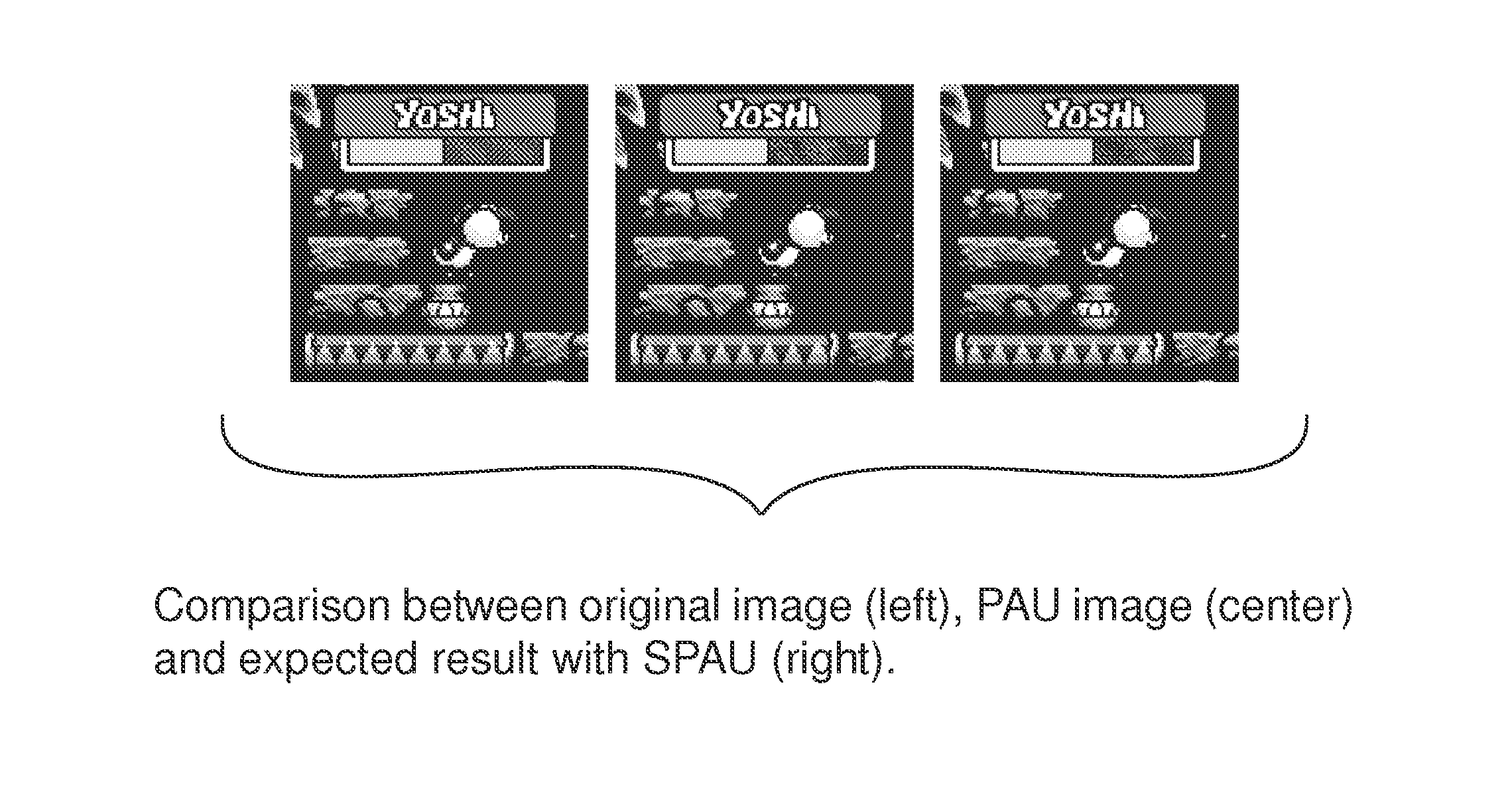
Brightness-compensating safe pixel art upscaler
ActiveUS20160148347A1Reducing and removing staircase effectMade sharperGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionFrequency spectrumVisual perception
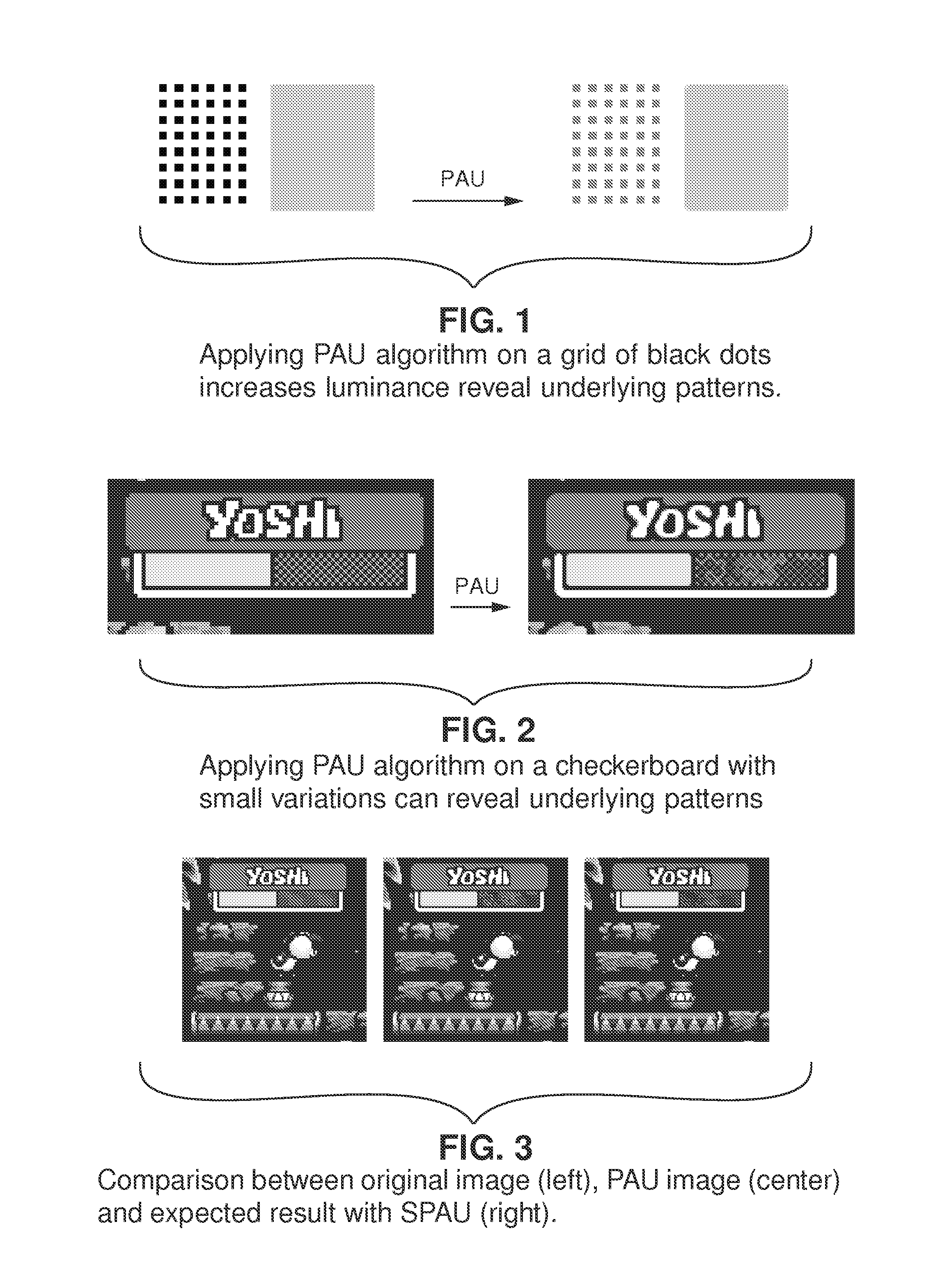
Low spatial frequencies of an original image and an upscaled filtered image are analyzed. Differences will be observed in the low frequency components of the two images in the general case since the pixel art upscaler filter as a side effect introduces low frequency changes. A modification to images produced by the PAU is applied to attempt to match the brightness of the original images in the low frequency spectrum. From a viewer perspective (e.g., based on typical blurring visual effects), the original image and the modified filtered image will look the same—demonstrating that there is no low frequency brightness creep or resulting increased photosensitivity concerns.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
Calibration arrangement for a scanner
InactiveUS20050063026A1Easy to optimizeCancel noisePictoral communicationCalibration resultLow spatial frequency
The present invention relates to a low spatial frequency calibration arrangement for scanning systems. In the method and system of the present invention, calibration is performed to compensate for non-uniformities introduced when light scattering media is scanned. This calibration results in a non-uniformity mapping at each scanning pixel location.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Magnetic resonance imaging device and synchronous imaging method
InactiveCN102238909AShorten the recording timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImage contrastBody movement
The time required for capturing an image in synchronization with cyclic body movement information relating to an examinee having a cyclic body movement can be reduced while maintaining a desired image contrast. In a synchronous measurement of an echo signal synchronized with trigger information detected from the cyclic body movement information relating to the examinee, a first period is providedbefore the measurement period of the echo signal or a second period is provided after the measurement period of the echo signal. A K-space is divided into a plurality of partial regions. At least oneof the first period and the second period is made different between the echo signal measurement corresponding to the partial region of the low spatial frequency side and the echo signal measurement corresponding to the partial region of the high spatial frequency side.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com