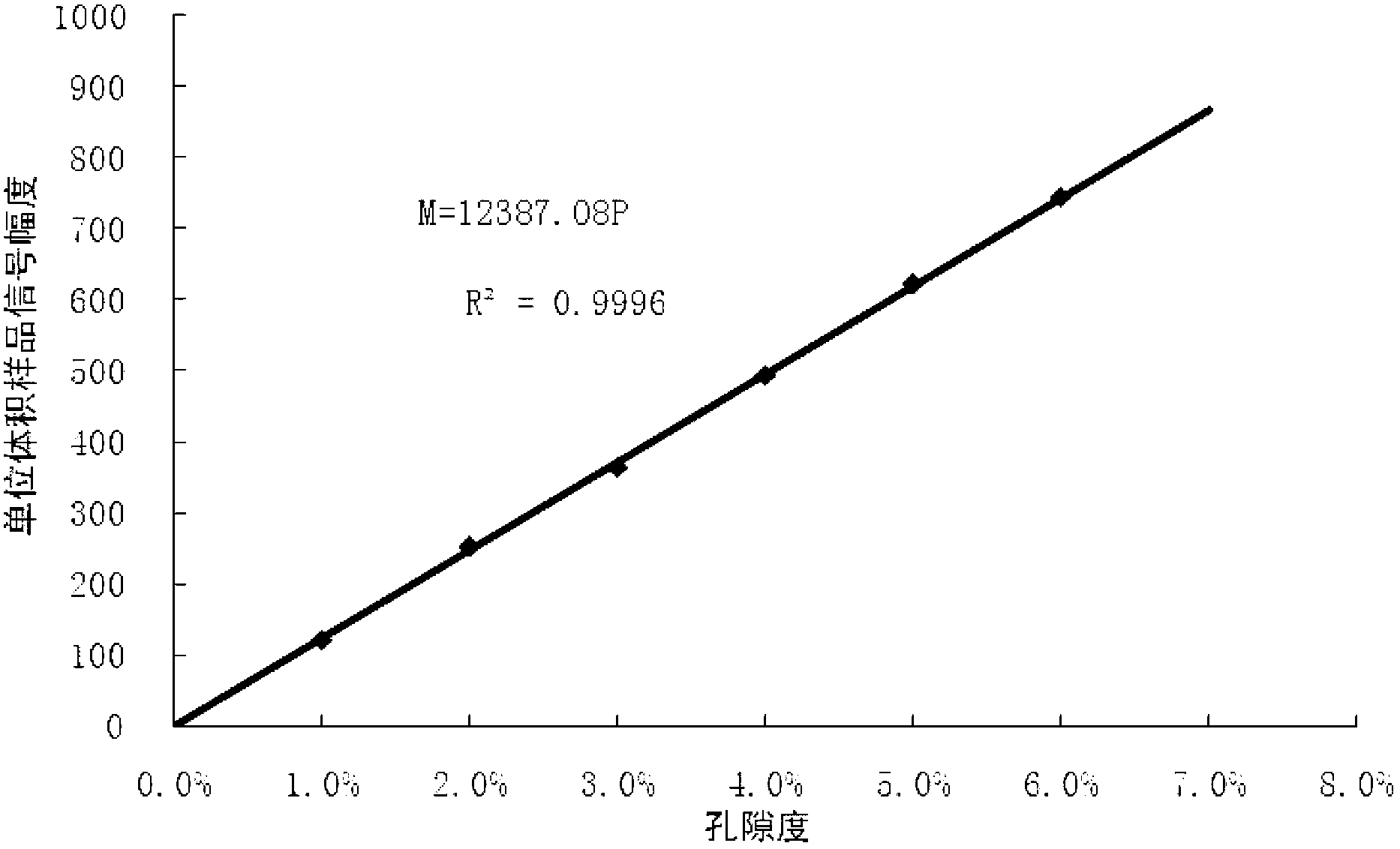Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
334 results about "Low field nuclear magnetic resonance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
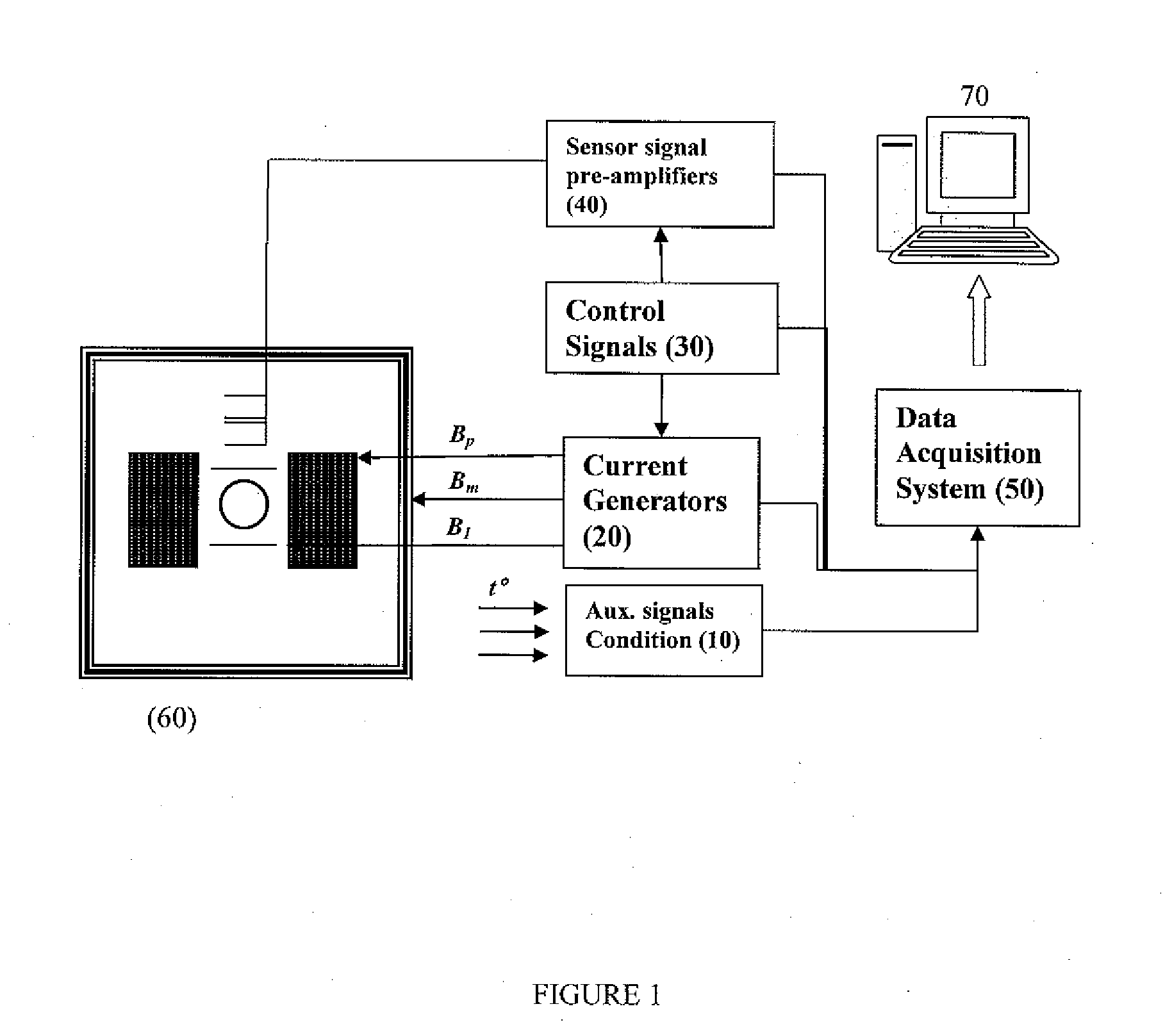
Low field NMR spans a range of different nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) modalities, going from NMR conducted in permanent magnets, supporting magnetic fields of a few T, all the way down to zero field NMR, where the Earth's field is carefully shielded such that magnetic fields of nT are achieved where nuclear spin precession is close to zero. In a broad sense, "Low-field NMR" is the branch of nuclear magnetic resonance that is NOT conducted in superconducting high-field magnets. Low field NMR also includes Earth's field NMR where simply the Earth's field is exploited to cause nuclear spin-precession which is detected. With magnetic fields on the order of μT and below magnetometers such as SQUIDs or atomic magnetometers (among others) are used as detectors. "Normal" high field NMR relies on the detection of spin-precession with inductive detection with a simple coil. However, this detection modality becomes less sensitive as the magnetic field and the associated frequencies decrease. Hence the push toward alternative detection methods at very low fields.
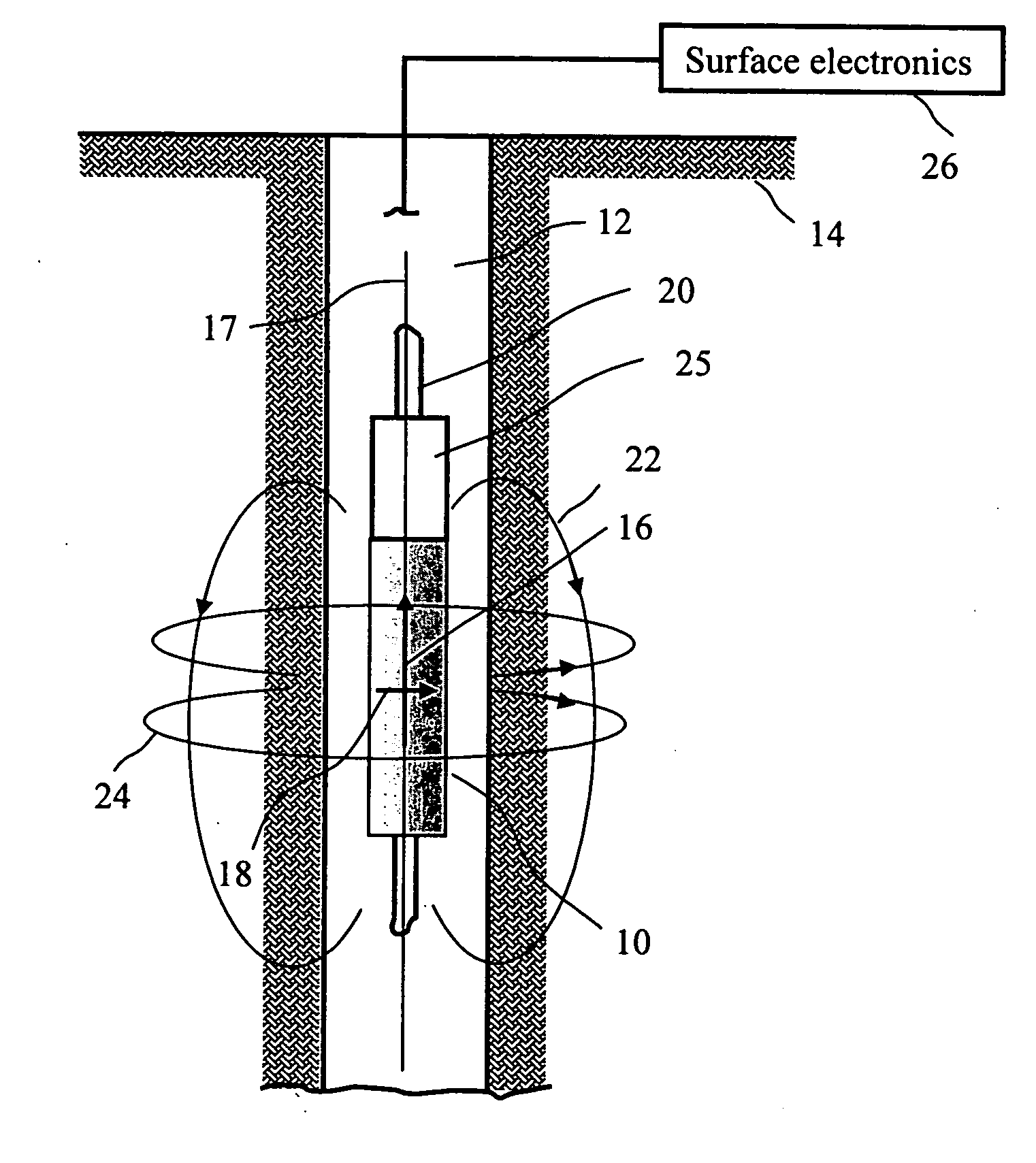
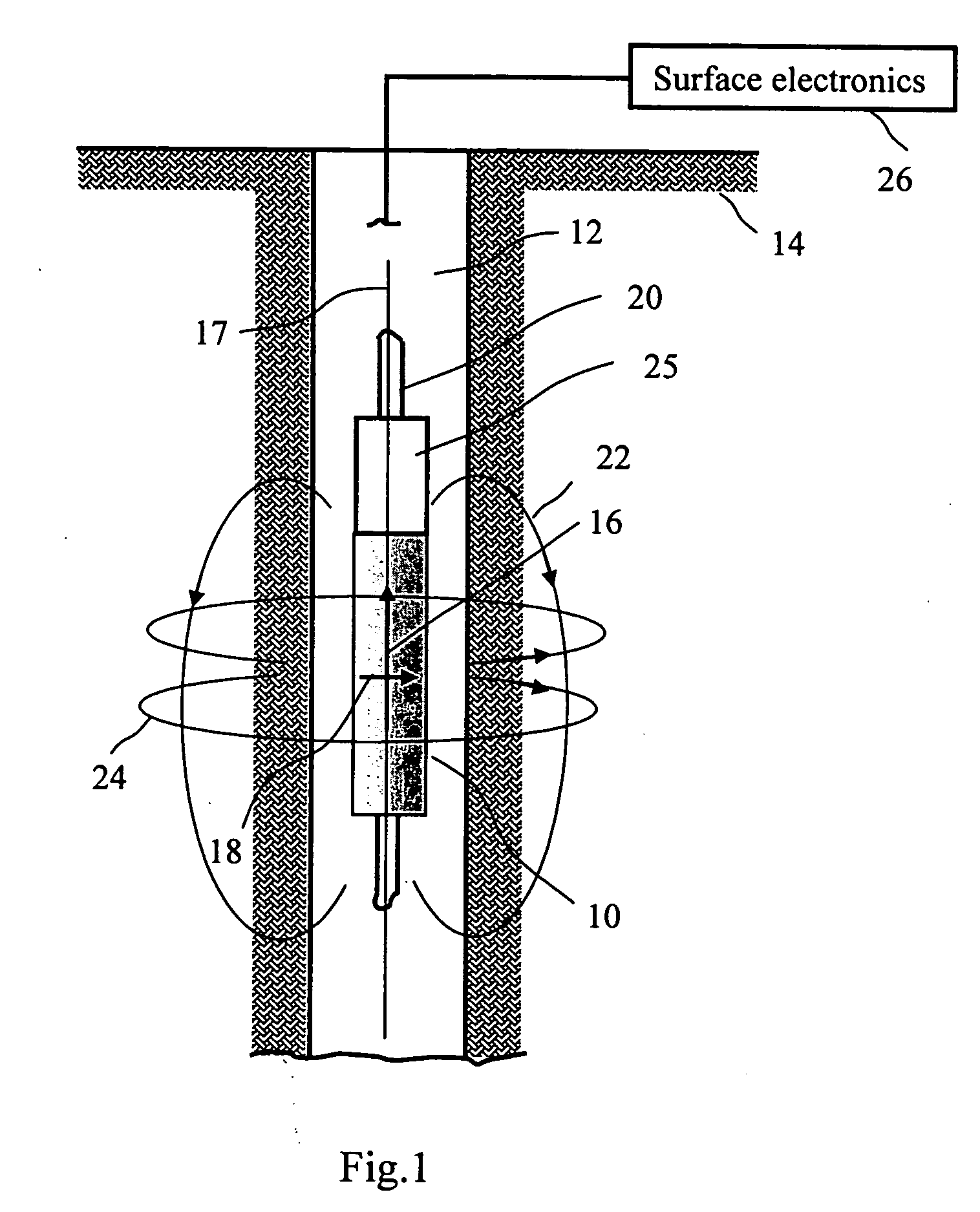
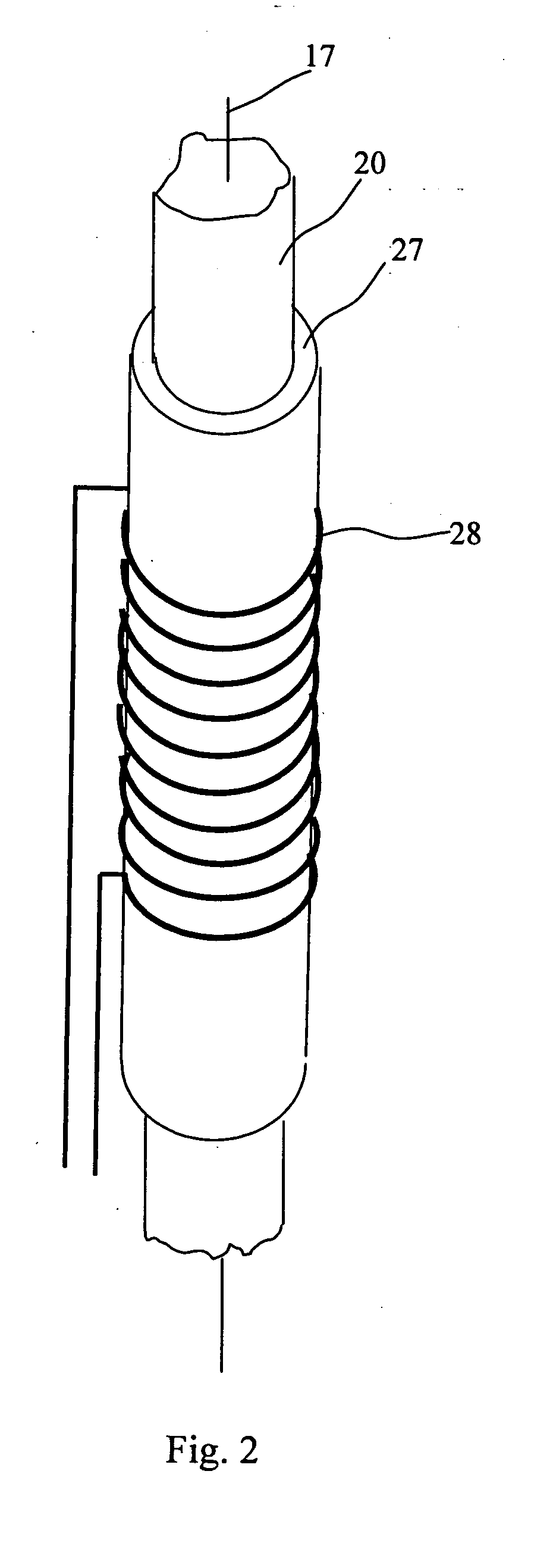
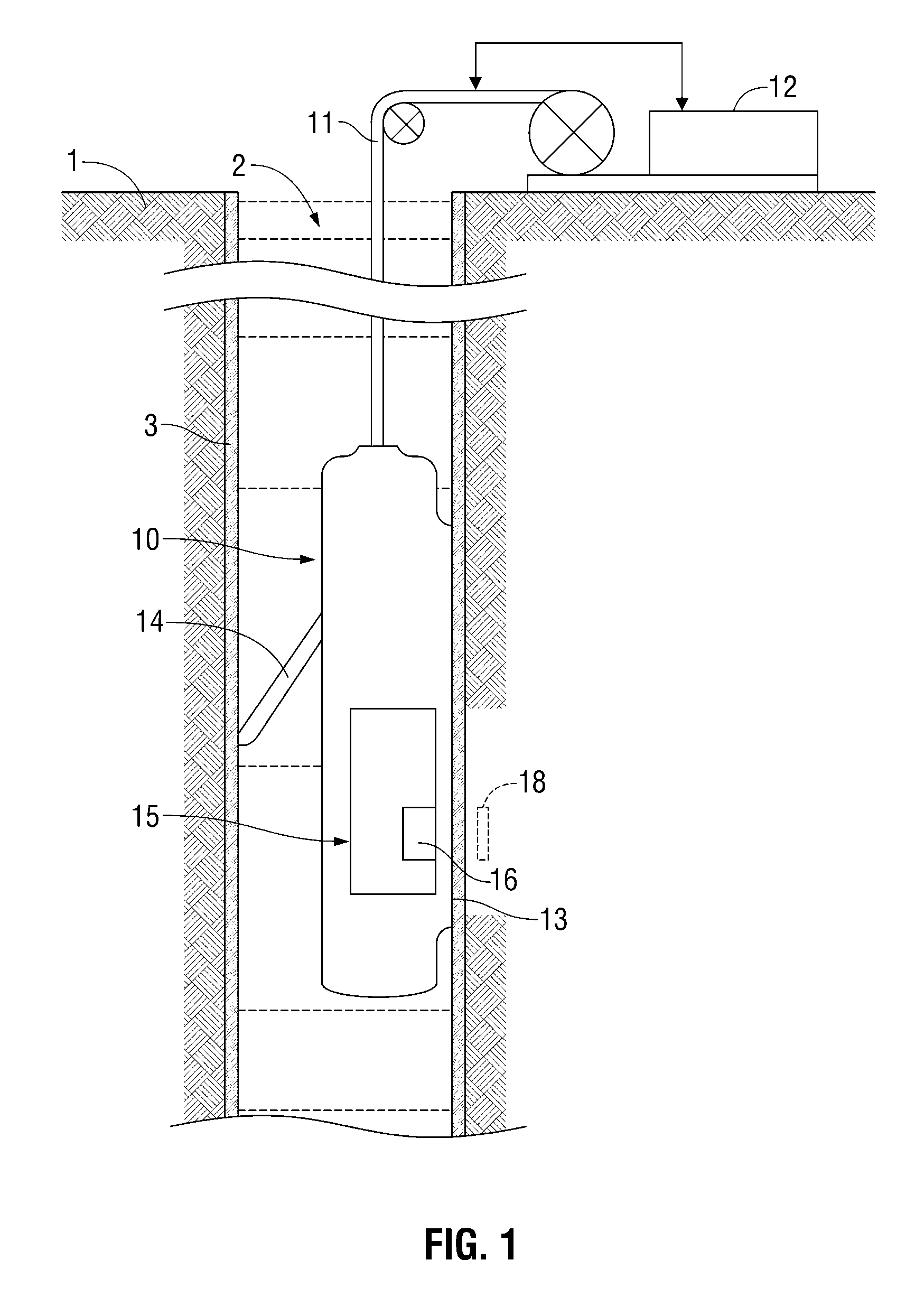
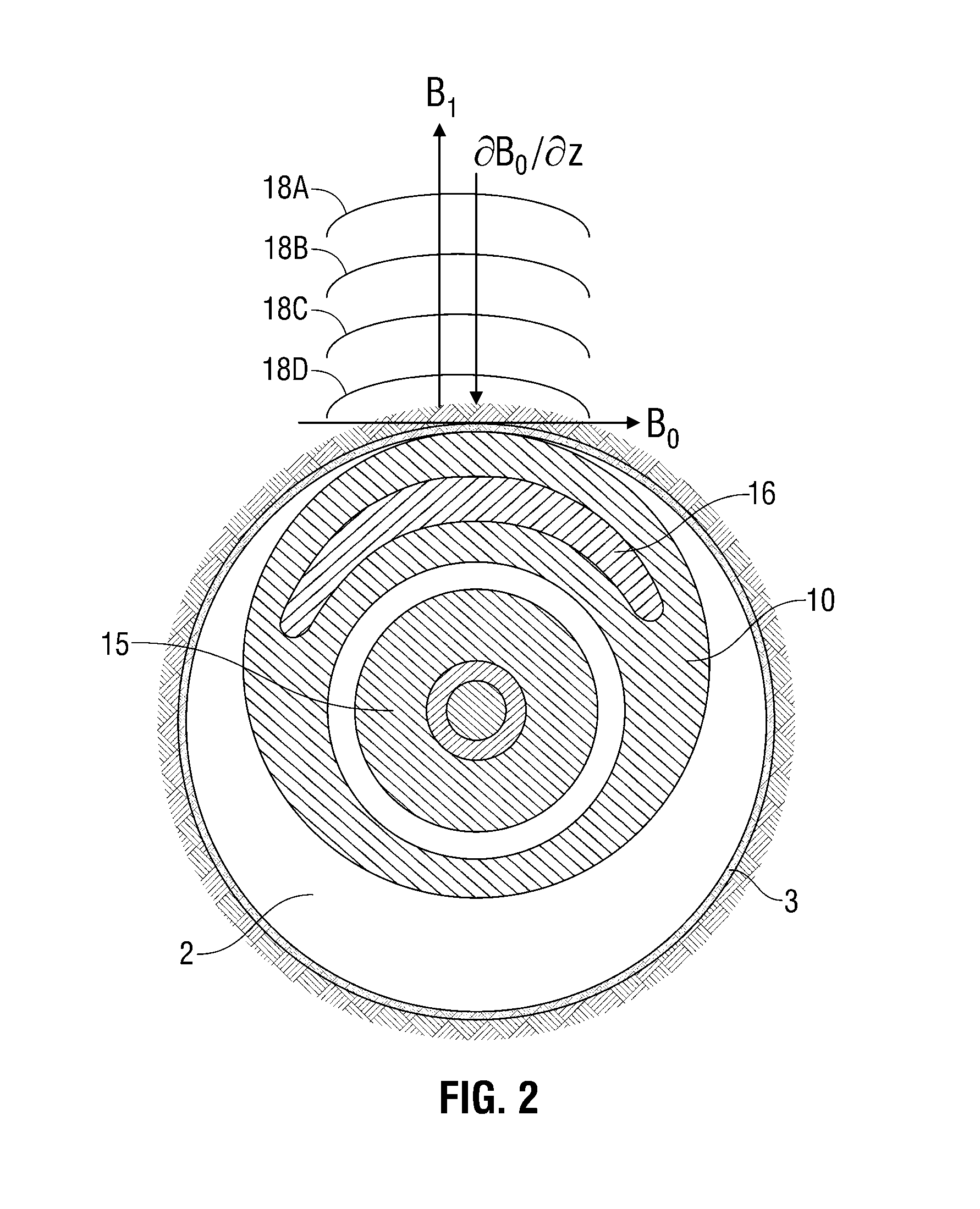
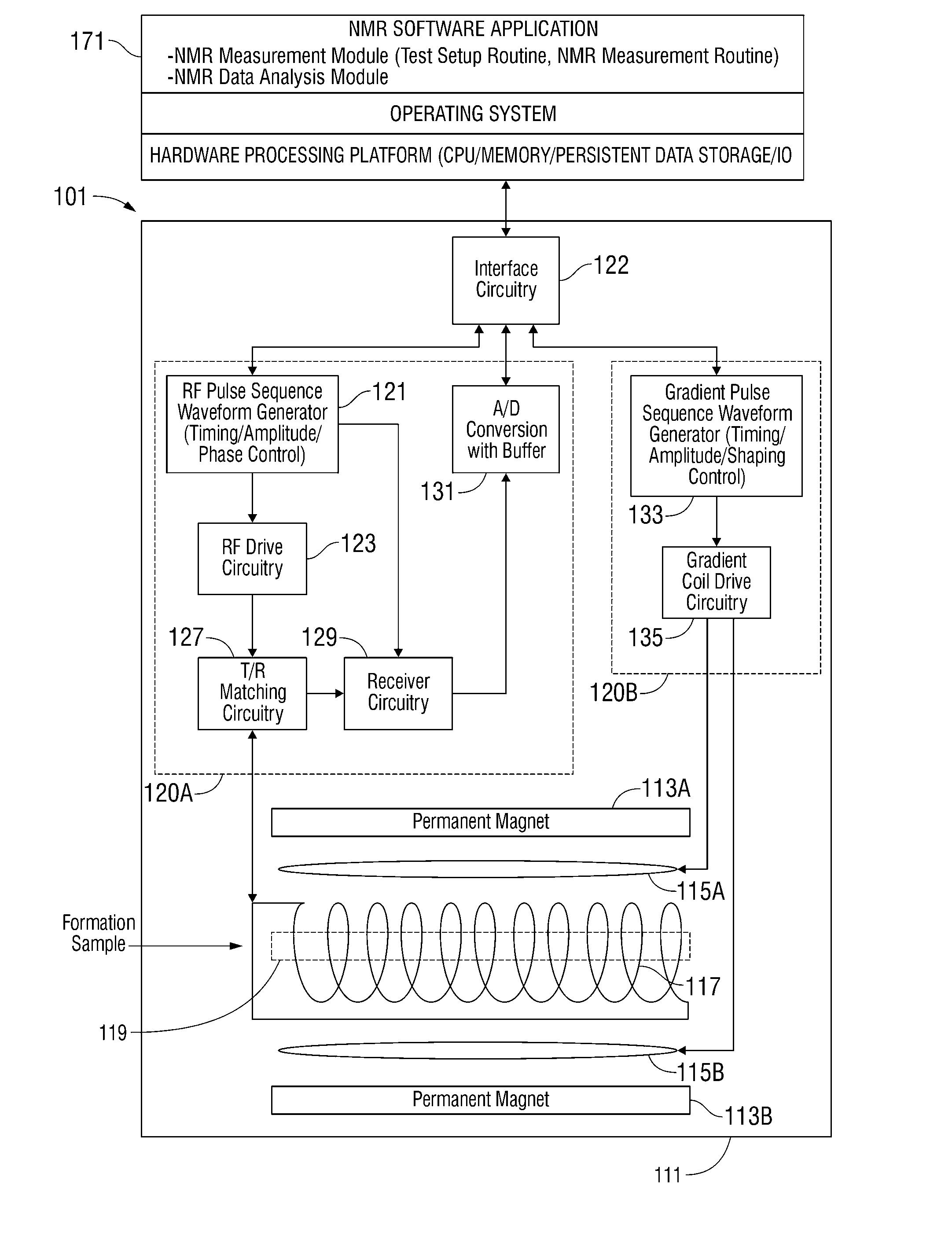
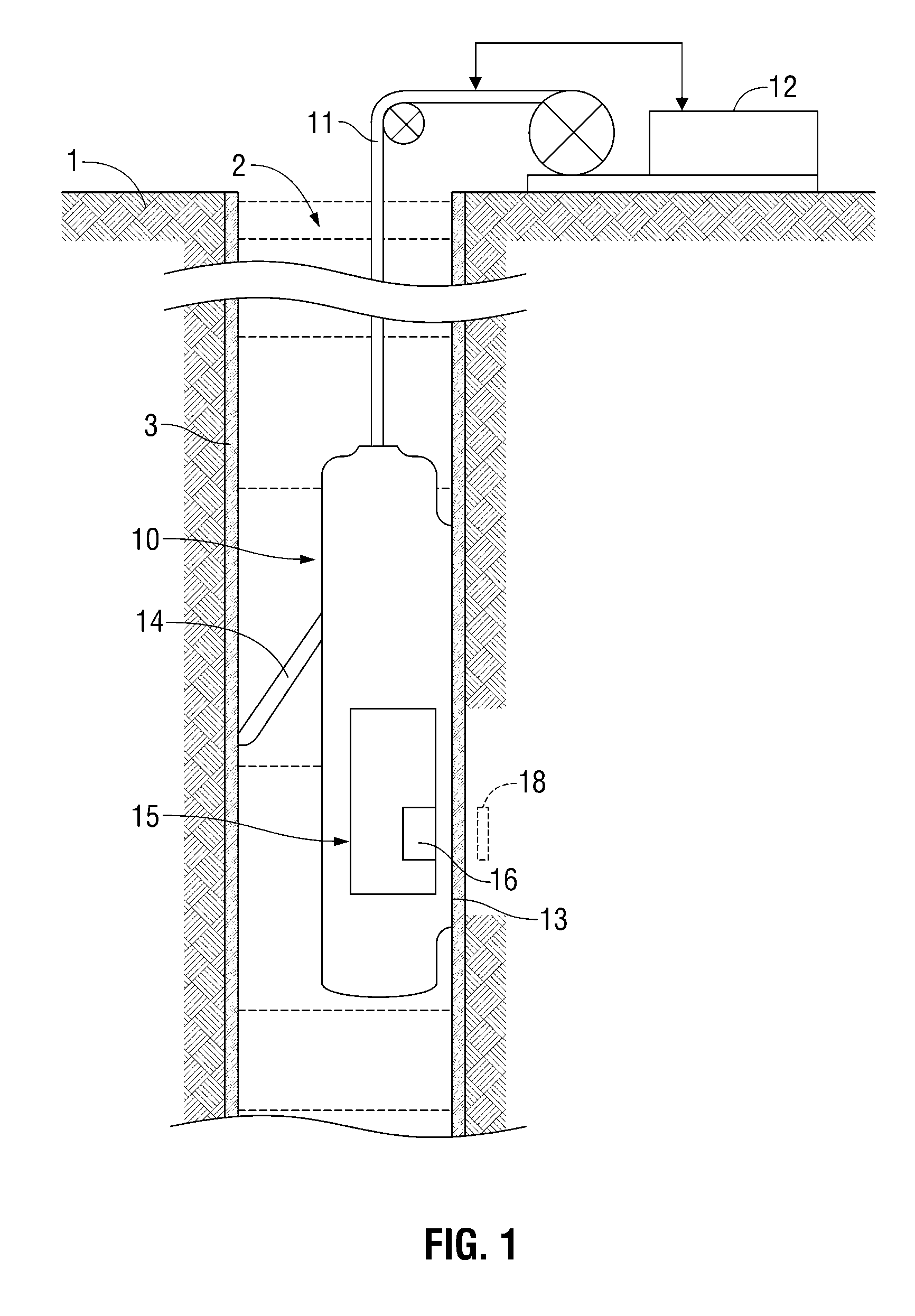
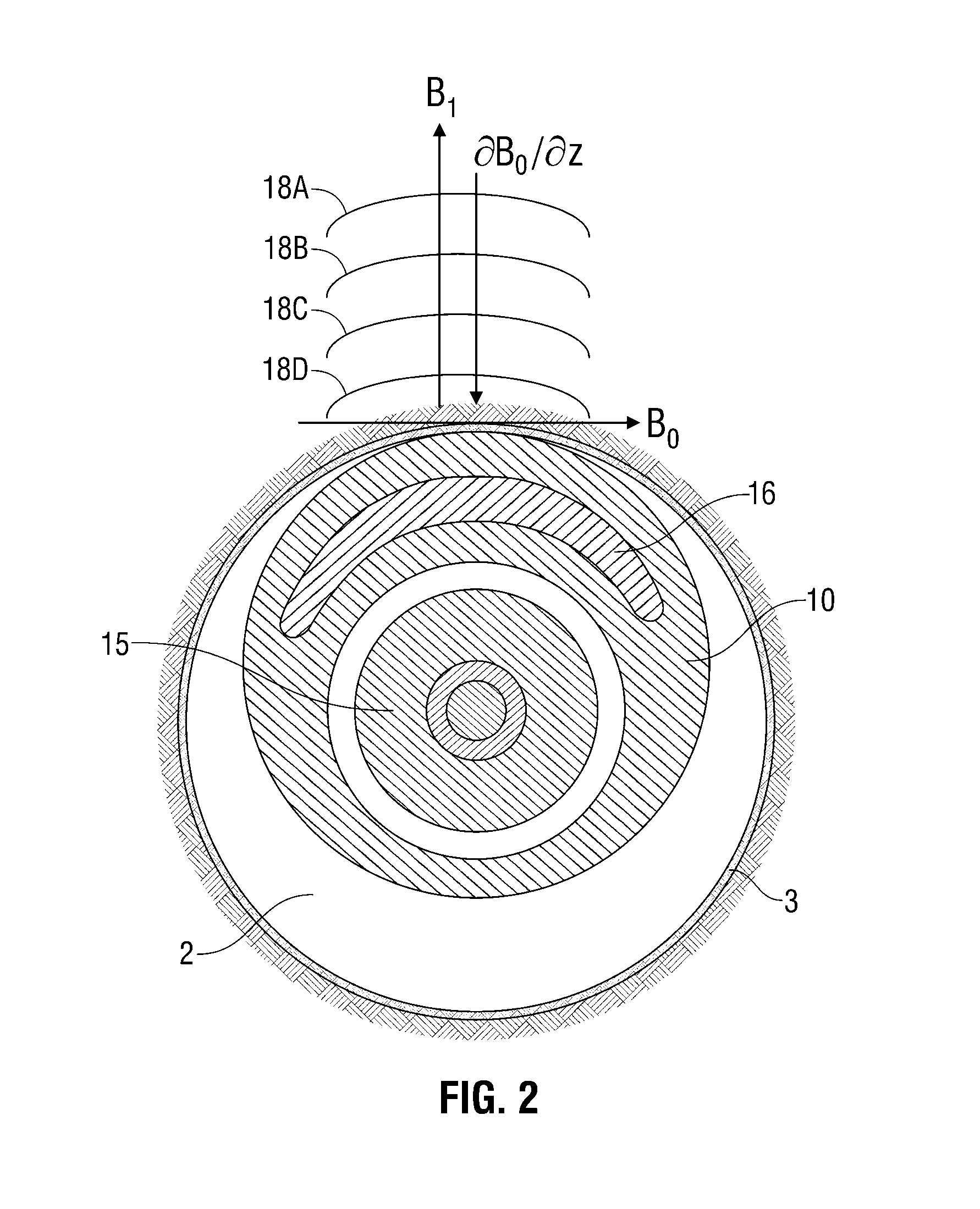
Nuclear magnetic resonance tool using switchable source of static magnetic field
ActiveUS20060255799A1Effective permeability of magneticElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceSpin magnetic moment
A nuclear magnetic resonance sensing apparatus and method for operating in an earth borehole comprises a source of switchable magnetic field to polarize nuclei in the region of interest, said source comprising a coil wound on a magnetic core having controllable residual magnetization. Maintaining the magnetization of the core during a polarization interval does not require steady current in the coil. Switching intensity and polarity of magnetization of the core causes precession of spin magnetic moments of the nuclei; the precession induces a signal indicative of nuclear magnetic resonance properties of earth formations.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
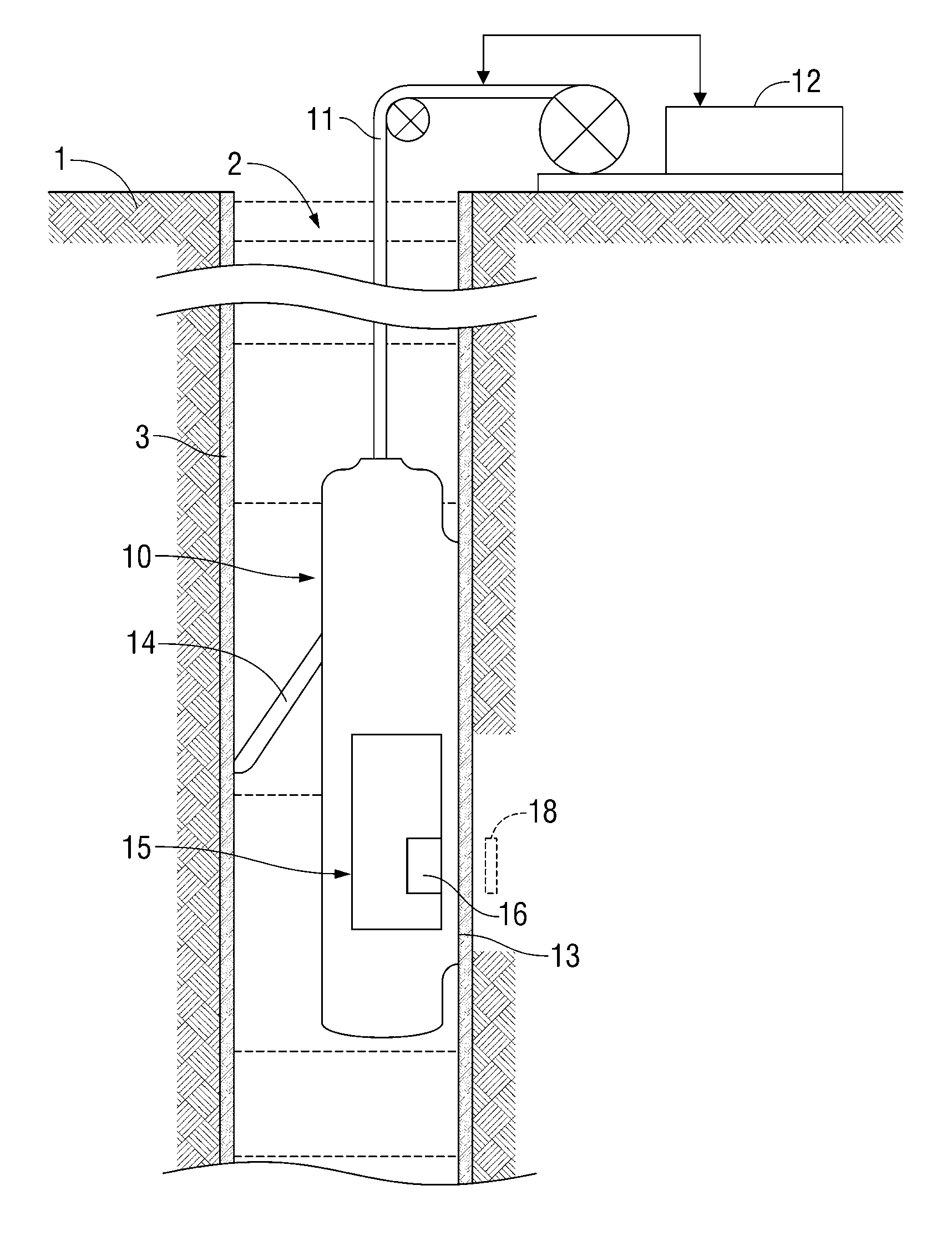
System and method for emulating nuclear magnetic resonance well logging tool diffusion editing measurements on a bench-top nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer for laboratory-scale rock core analysis
InactiveUS20110234220A1Increase displacementPromote recoveryElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsWell loggingLaboratory scale
A laboratory NMR methodology (and corresponding laboratory apparatus) defines a sample volume. The method stores downhole tool data corresponding to a hydrocarbon-bearing sample collected from a given subsurface formation. The downhole tool data includes parameters pertaining to magnetic fields used by a downhole tool during a suite of NMR measurements of the given subsurface formation. The sample is positioned in the sample volume of the laboratory apparatus, which applies a static magnetic field in the sample volume. Furthermore, the laboratory apparatus applies a suite of NMR measurements to the sample volume to thereby determine a property of the sample. The NMR measurements of the suite each include a pulse sequence of oscillating magnetic field in conjunction with a pulsed-mode gradient field. The pulsed-mode gradient field is based on the stored downhole tool data corresponding to the sample. A laboratory NMR methodology for optimizing downhole NMR measurements is also described.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
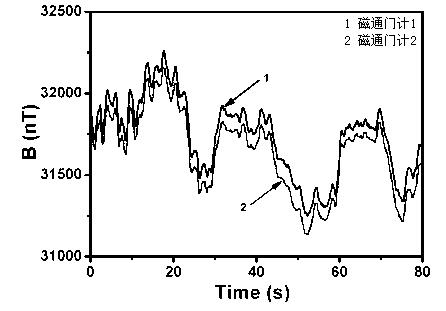
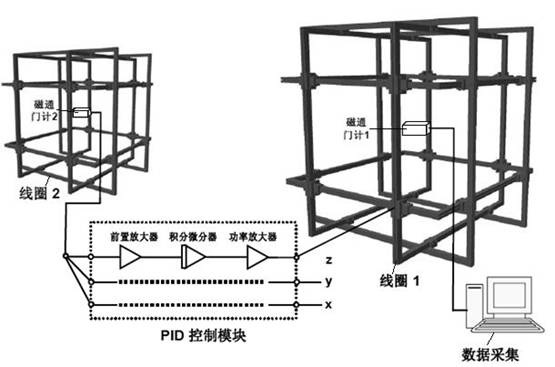
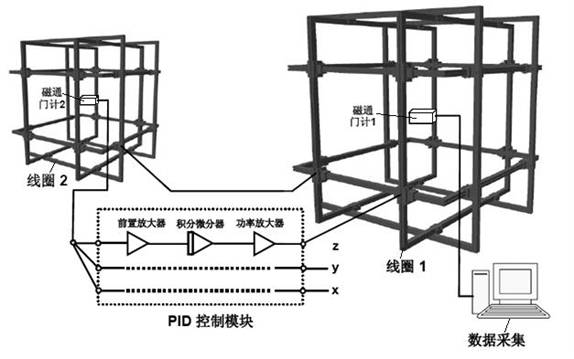
Magnetic-field dynamic compensation system and methods based on spatial correlation
ActiveCN101893693AEliminate the effects ofEasy to buildMagnetic measurementsHelmholtz coilCompensation effect
The invention relates to a magnetic-field dynamic compensation system and methods based on spatial correlation, wherein the system can realize the dynamic compensation of environment magnetic fields at the directions of three axles through a large set and a small set of Helmholtz coil racks and two fluxgate meters based on the spatial correlation of a PID (Proportion Integration Differentiation) negative feedback electronic circuit and the fluctuation of the environment magnetic fields. The invention further discloses three methods using the system, including (1) a proportioning type magnetic-field dynamic compensation method, (2) a series type integral magnetic-field dynamic compensation method, and (3) a parallel integral type magnetic-field dynamic compensation method. The system of the invention is easy to construct, has low cost and simple operation, and can achieve excellent dynamic compensation effect, and simultaneously, the methods can maximally eliminate the affects of the fluxgate meters to other magnetic detectors at the centers of coils, and have great application prospect in extremely-low field nuclear magnetic resonance, imaging thereof and other biological magnetic researches based on an SQUID (Superconducting Quantum Interference Device).
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
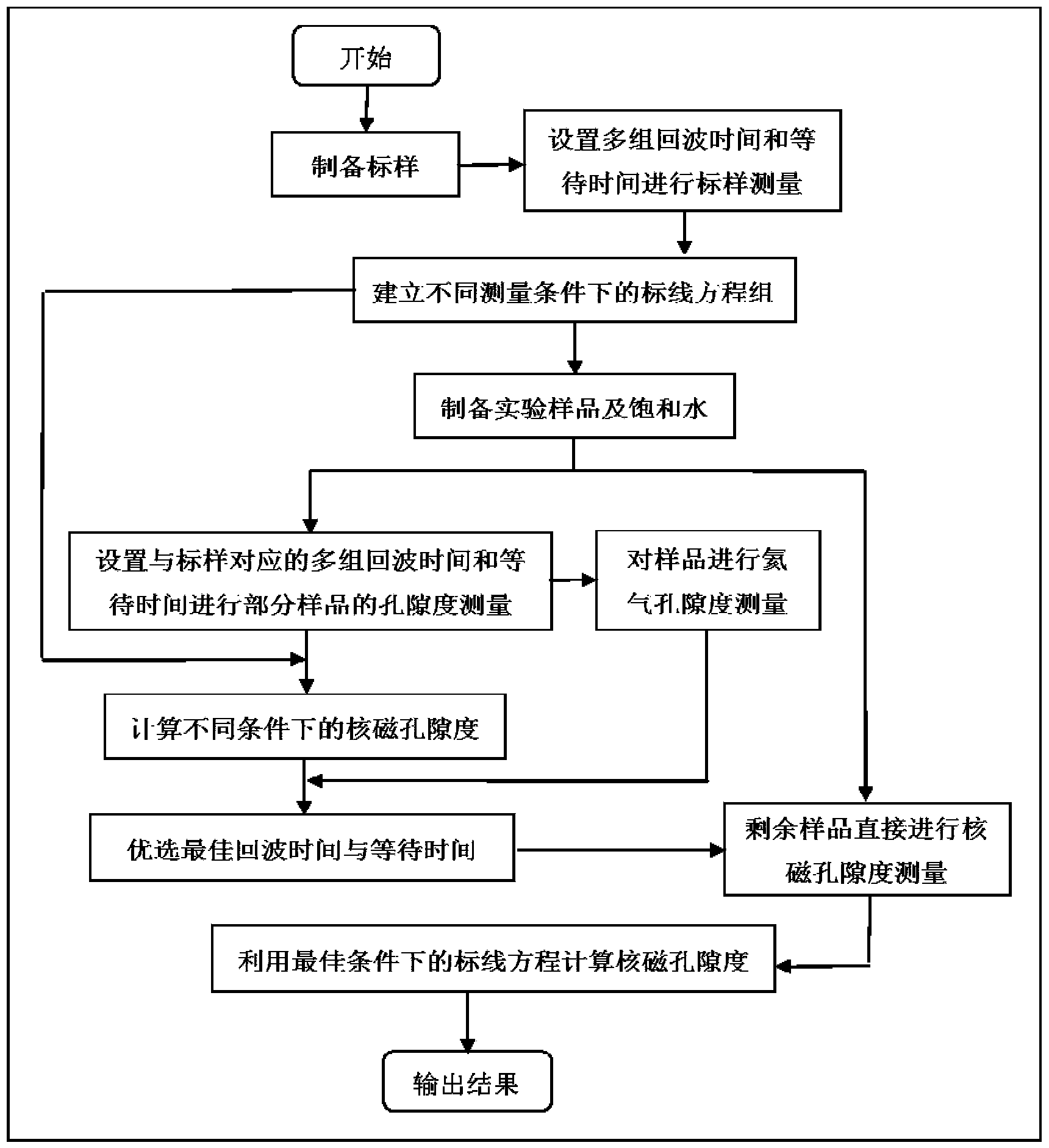
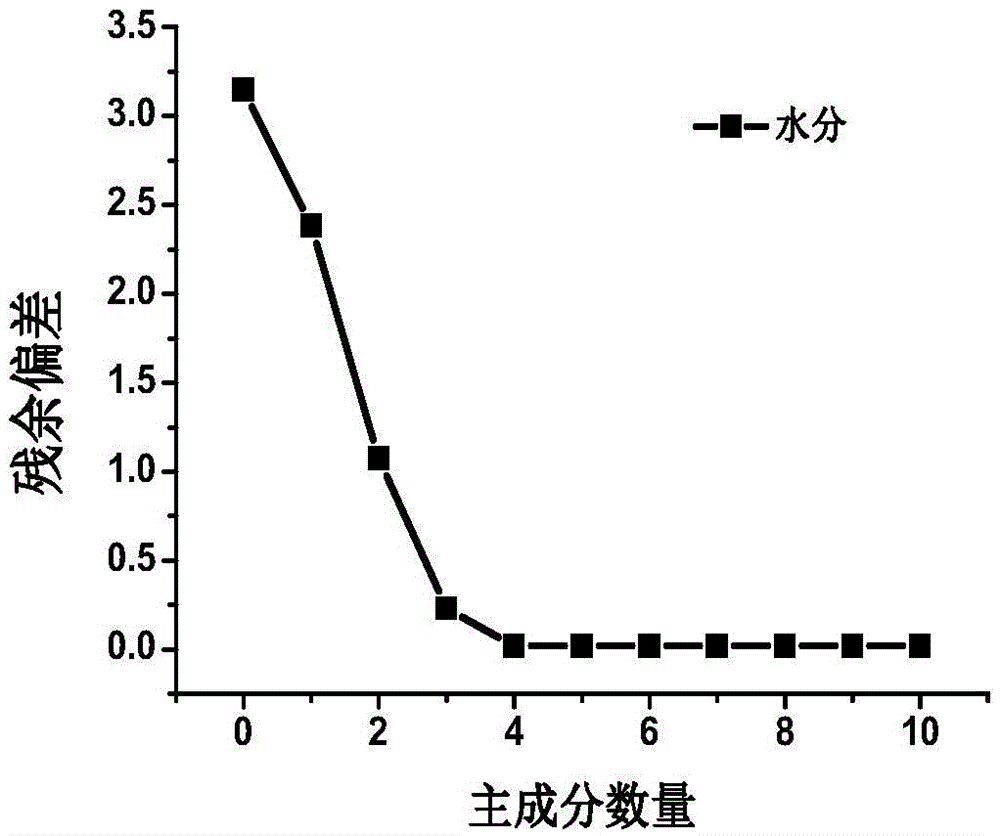
Method for accurately measuring shale porosity by adopting low-field nuclear magnetic resonance
InactiveCN104075974ATest accurateQuick testAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePermeability/surface area analysisSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonancePorosity
The invention discloses a method for accurately measuring shale porosity by adopting the low-field nuclear magnetic resonance. The method comprises the following steps: as for a saturated water column-shaped shale sample, conducting nuclear magnetic porosity measurement in different echo time and waiting time; conducting helium porosity measurement; comprehensively comparing and analyzing the porosity results of the two methods; optimizing the optimal echo time and waiting time for testing to facilitate the accurate testing of follow-up samples. The method solves the problems of how to set reasonable parameters to measure the shale porosity by adopting the low-field nuclear magnetic resonance, and solves the problem that in the actual testing, the nuclear magnetic porosity obtained in different echo time and waiting time is in great disparity, and the comparability of the nuclear magnetic porosity and the helium porosity is relatively poor; compared with the prior art, by adopting the method, the shale porosity can be quickly and nondestructively measured, the accuracy and precision of the shale porosity measurement can be improved, and the operation is convenient.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Low-field nuclear magnetic resonance multi-probe quantitative test system and method special for hydrate
PendingCN107807143ARealize the integration of testing and analysisRealize integrationAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceWater resource assessmentPore fluidLow field nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a low-field nuclear magnetic resonance multi-probe quantitative test system and a low-field nuclear magnetic resonance multi-probe quantitative test method special for hydrate.The test system comprises a low-field nuclear magnetic resonance analyzer, a confining pressure-adding low-temperature high-pressure probe, a confining pressure-free low-temperature high-pressure probe, a confining pressure-free normal-temperature normal-pressure probe, a temperature confining pressure control module, a pore fluid supply module and an industrial personal computer. Through combined use of the confining pressure-adding low-temperature high-pressure probe, the confining pressure-free low-temperature high-pressure probe and the confining pressure-free normal-temperature normal-pressure probe and the improved design of the structure as well as by adoption of a multi-probe combined use mode, research on integration of hydrate-containing deposit low-field nuclear magnetic resonance measuring signal quantitative calibration and hydrate-containing deposit pore scale behavior measuring analysis is realized, research on the hydrate-containing deposit pore scale behavior featureis facilitated, and foundation is laid for discussion on hydrate-containing deposit basic physical property parameter change micromechanism.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF MARINE GEOLOGY
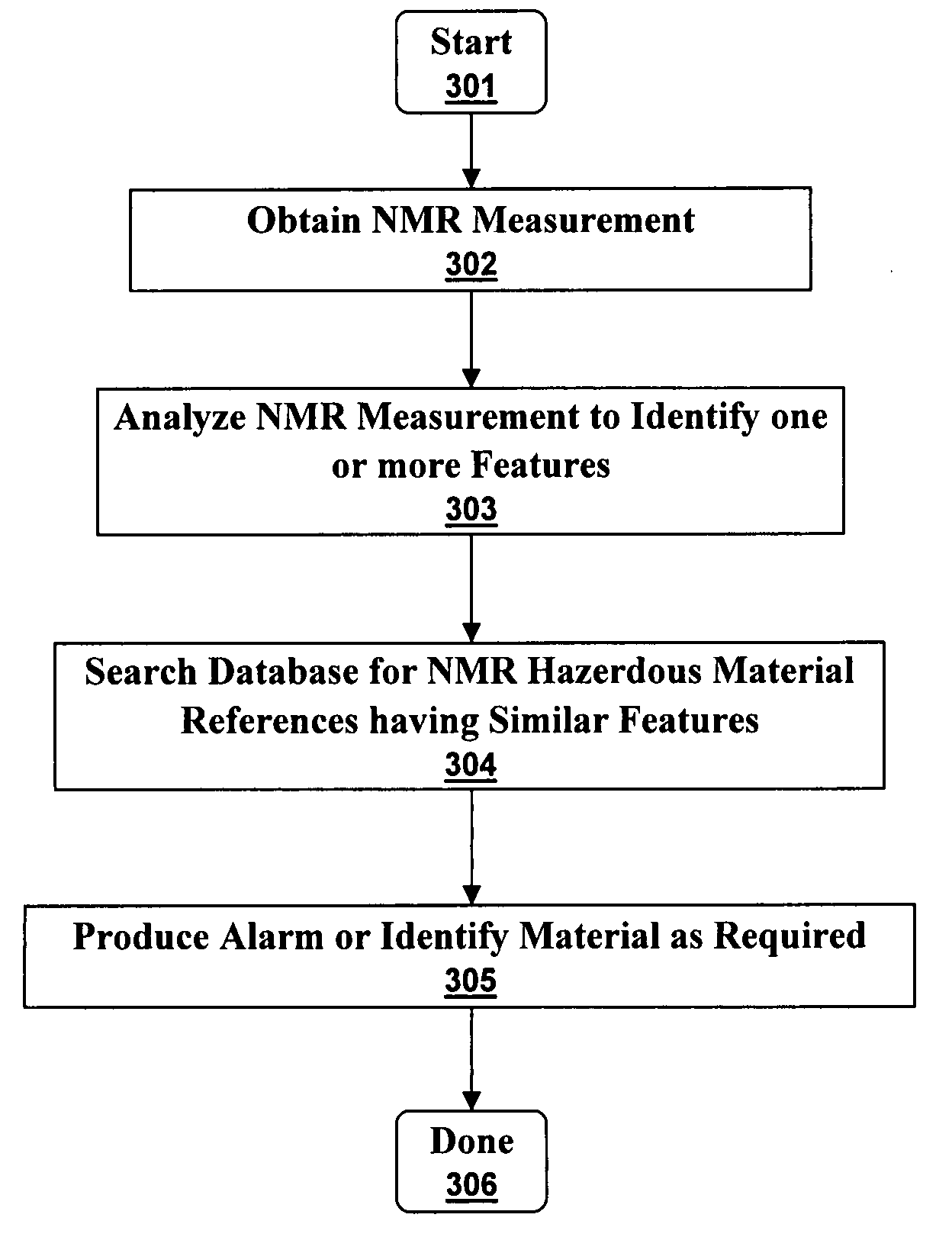
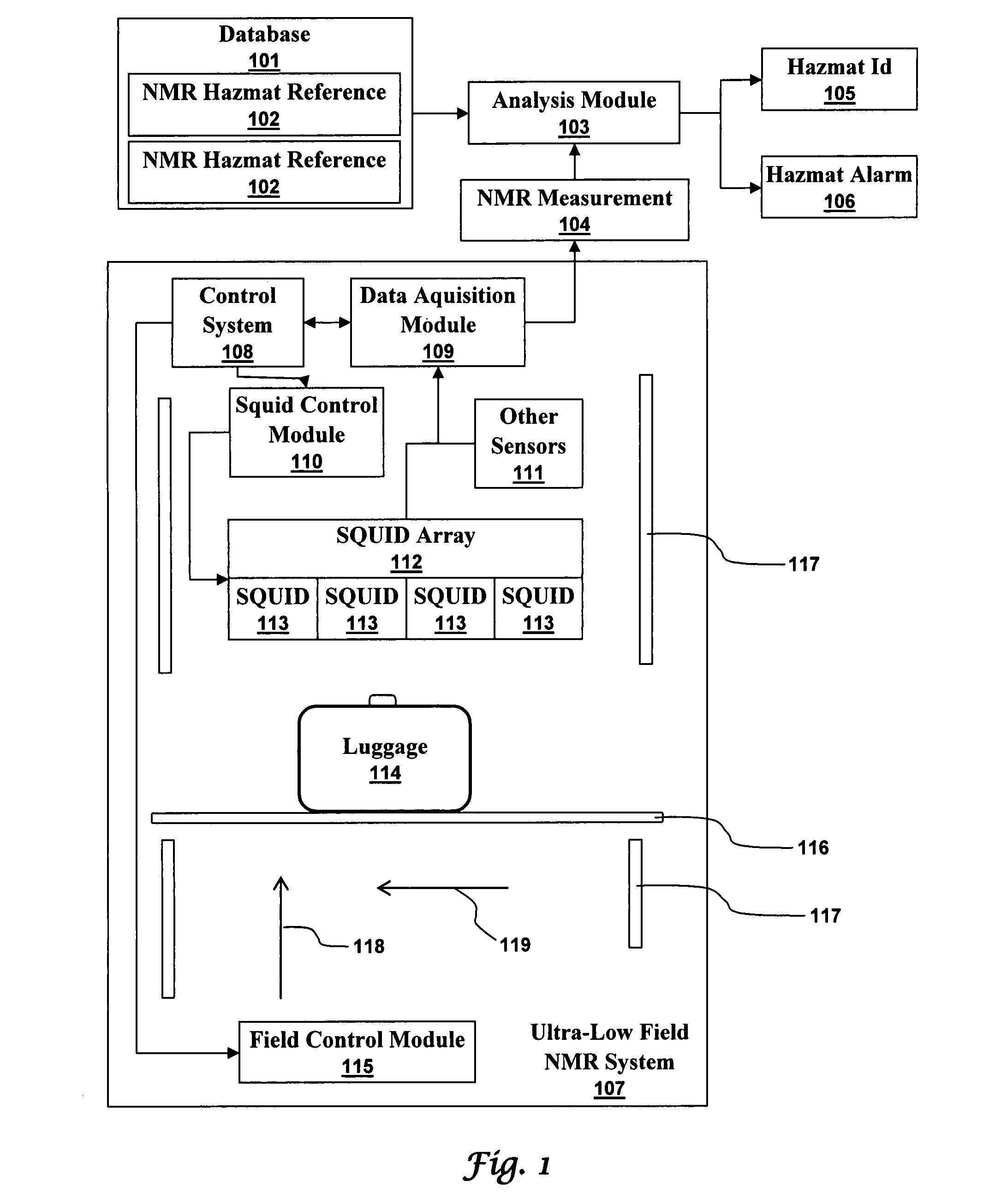
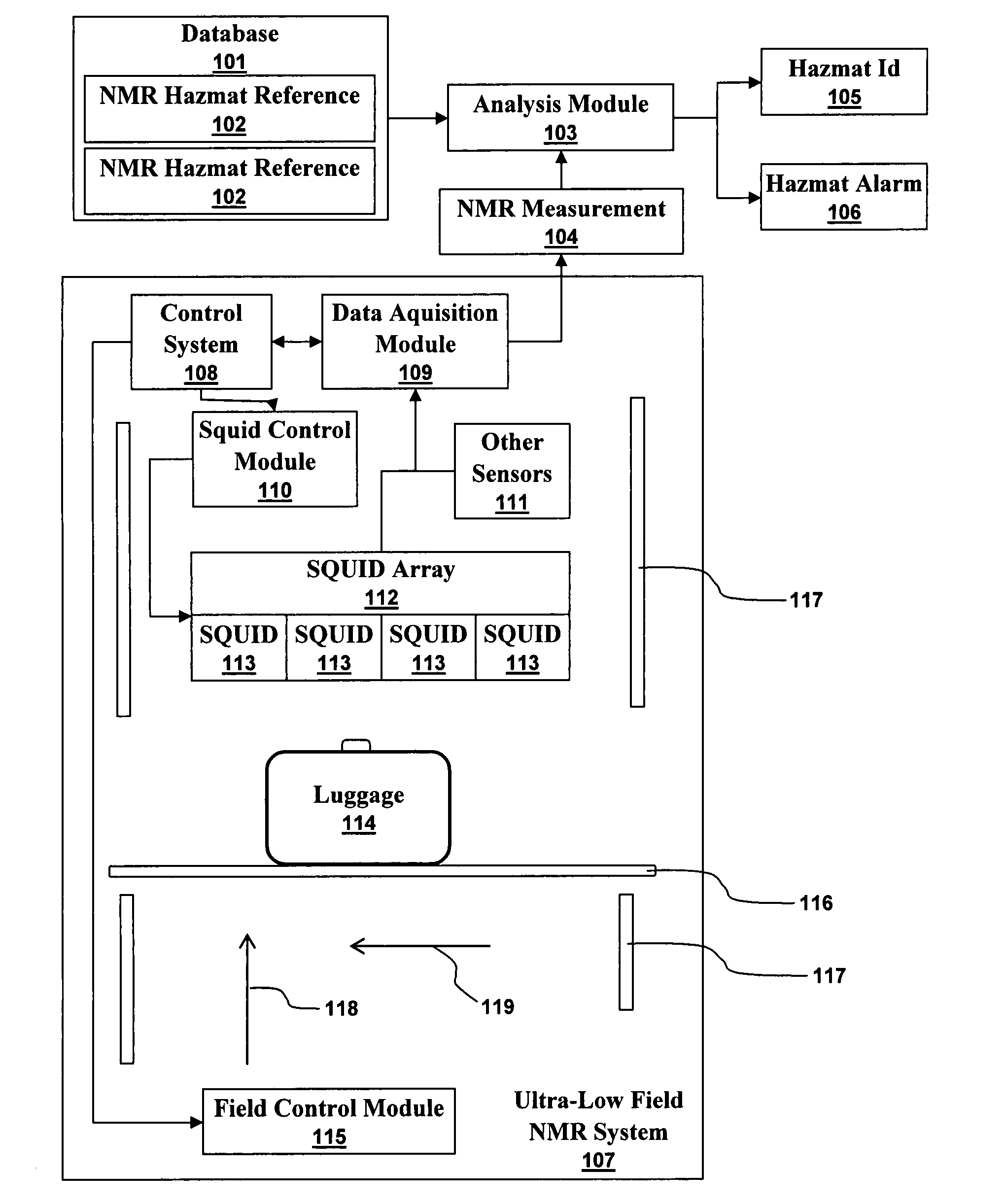
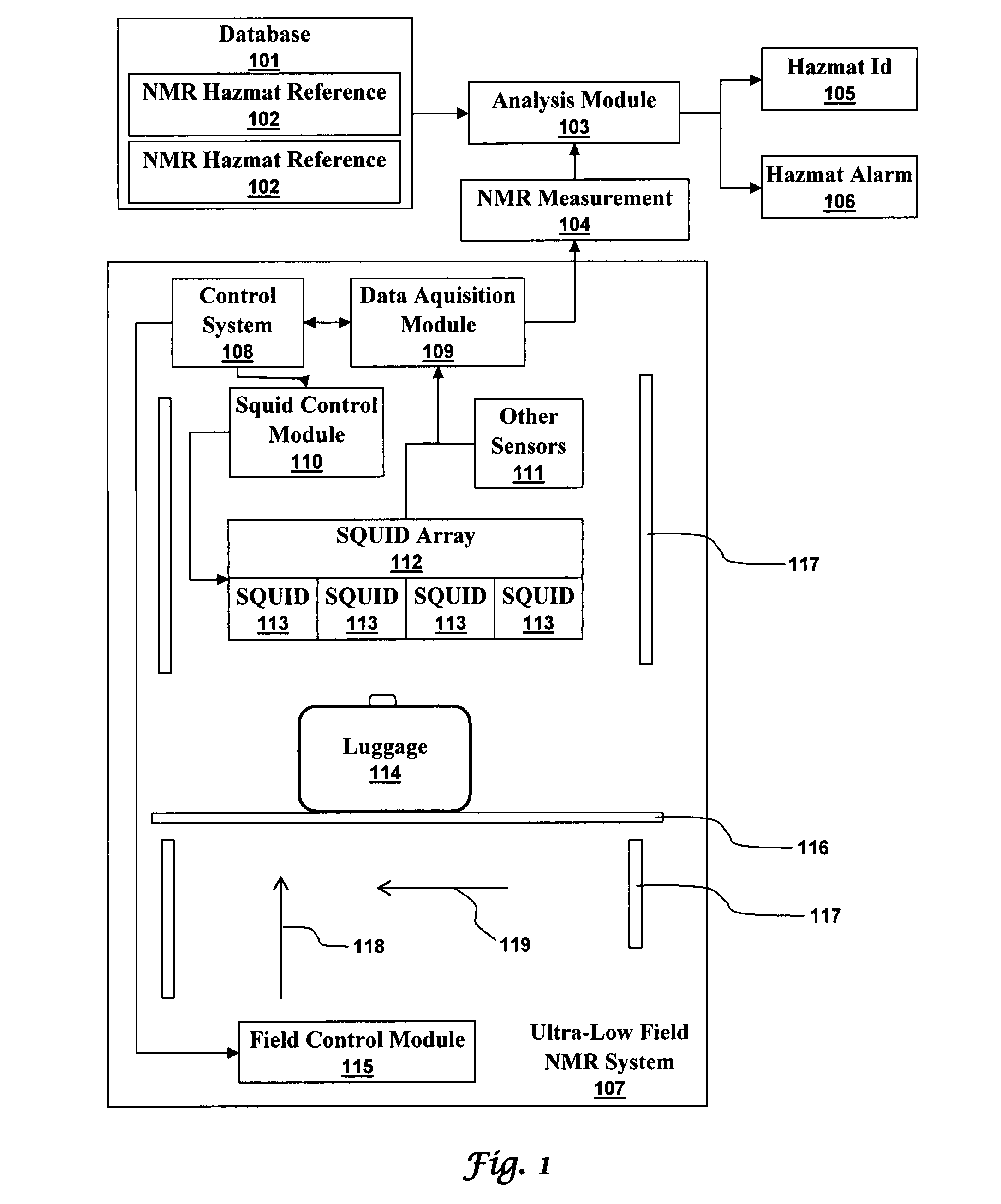
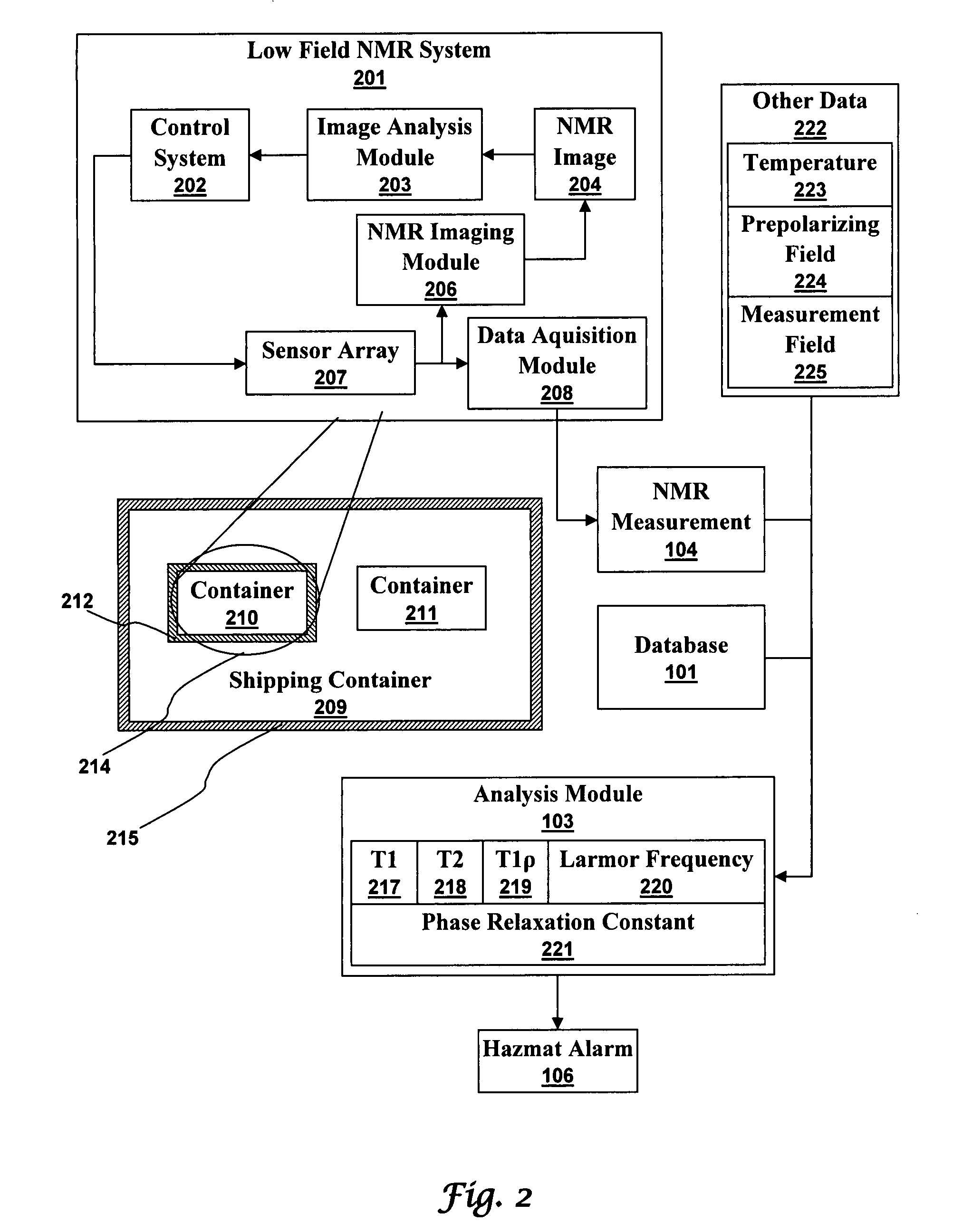
Ultra-low field nuclear magnetic resonance and magnetic resonance imaging to discriminate and identify materials
InactiveUS20080284433A1Increased signal noiseMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceLow field nuclear magnetic resonanceProton NMR
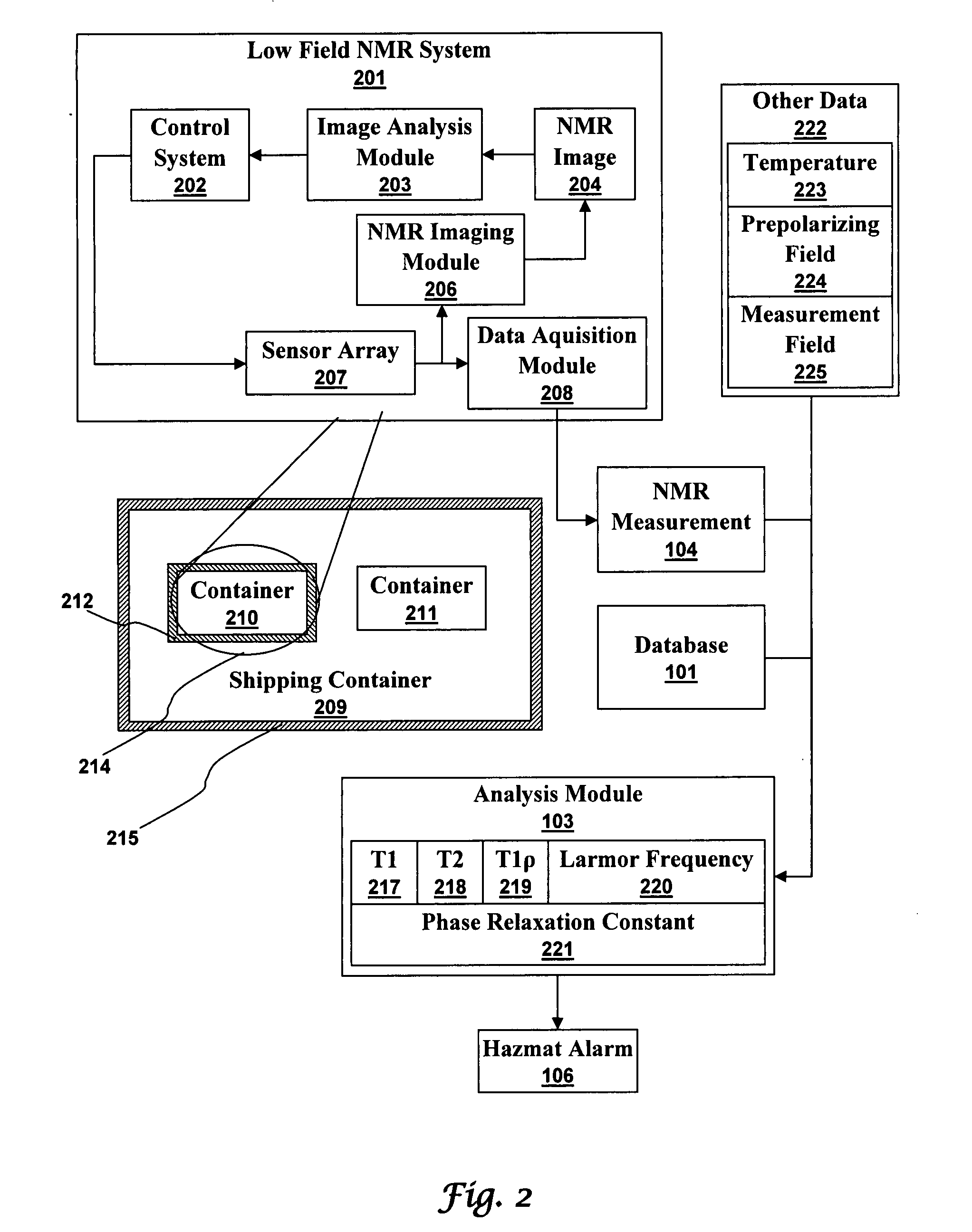
An ultra-low magnetic field NMR system can non-invasively examine containers. Database matching techniques can then identify hazardous materials within the containers. Ultra-low field NMR systems are ideal for this purpose because they do not require large powerful magnets and because they can examine materials enclosed in conductive shells such as lead shells. The NMR examination technique can be combined with ultra-low field NMR imaging, where an NMR image is obtained and analyzed to identify target volumes. Spatial sensitivity encoding can also be used to identify target volumes. After the target volumes are identified the NMR measurement technique can be used to identify their contents.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy using light with orbital angular momemtum
InactiveUS20100327866A1Less noisyHigh resolutionLaser detailsAnalysis using optical pumpingTwo-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopySpectroscopy
The present invention relates to a device capable of producing a high resolution chemical analysis of a sample, such as fluid, based upon nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, where the nuclear magnetic polarizations of the sample are generated by sequentially illuminating the sample with a focused beam of light carrying angular orbital angular momentum (OAM) and possibly momentum (spin). Unlike in usual NMR used for magnetic nuclear resonance imaging (MRI) or spectroscopy, the invention does not make use of a strong magnet.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
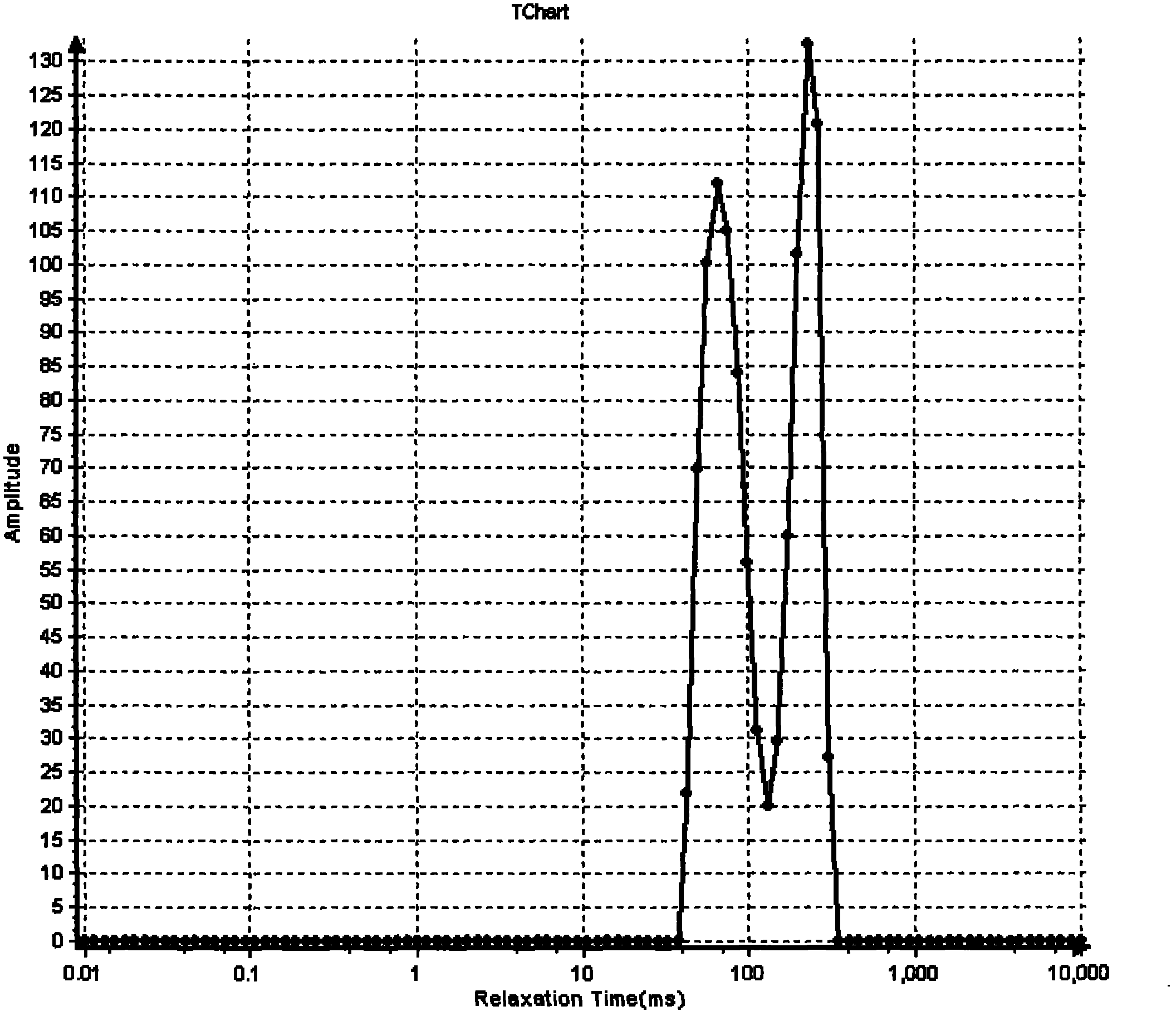
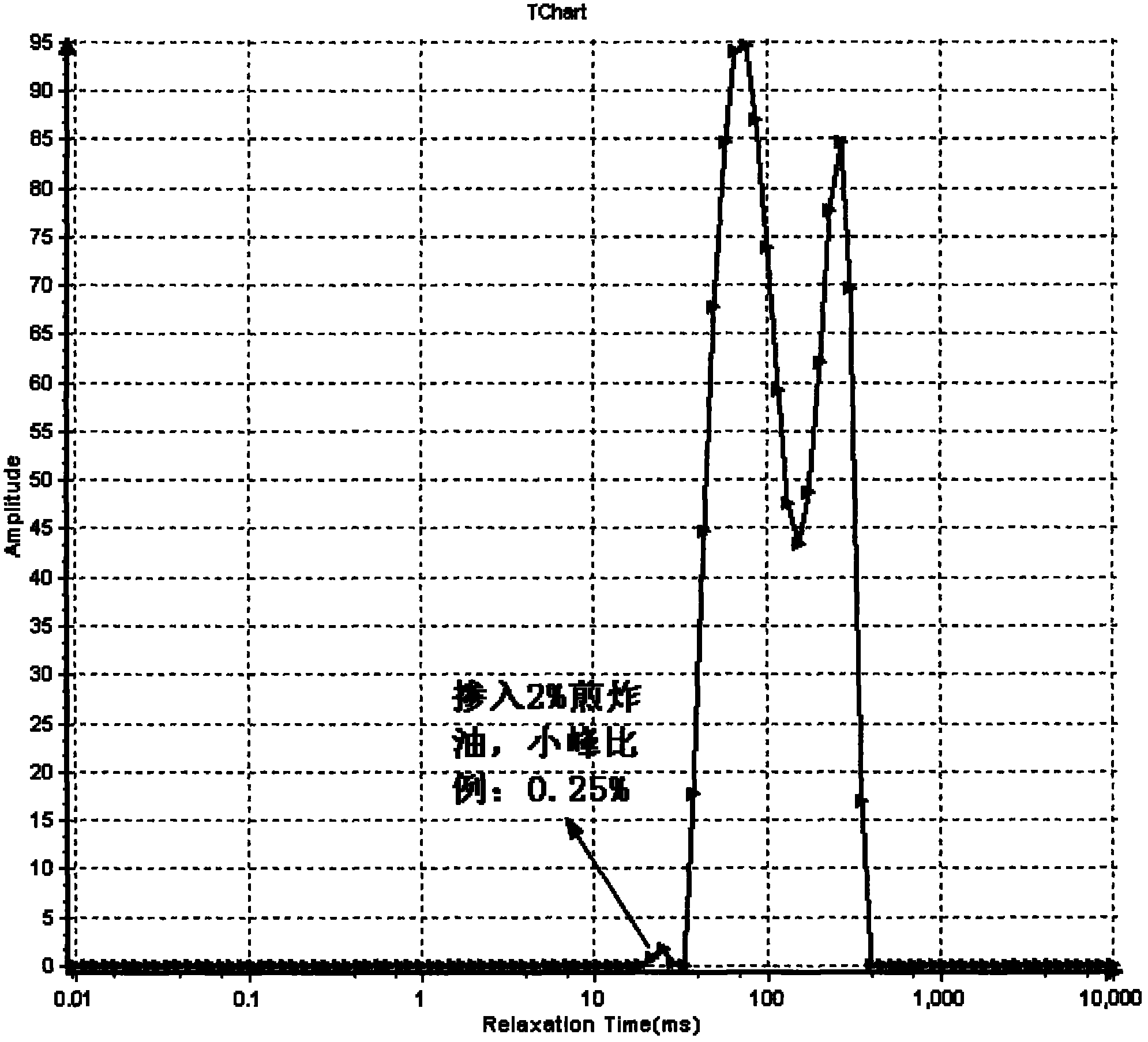
Method for identifying quality of edible oil with low-field NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance)
ActiveCN101975788ARapid identificationAccurate identificationAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceLow field nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a method for identifying the quality of edible oil with low-field NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance), suitable for identifying and measuring genuine edible oil and inferior drainage oil. The method rapidly and accurately identifies the genuine edible oil and the inferior drainage oil by using the difference between the relaxation time map data of the genuine edible oil and the inferior drainage oil as a main identification reference, using NMR signals of the genuine edible oil and the inferior drainage oil as main observation objects and using the comparison and the analysis of the transversal relaxation time map data of the genuine edible oil and the inferior drainage oil as main measures. The method of the invention has high measuring result accuracy, good repetition and stability, short duration, and the like, is beneficial to the realization of the one-site identification of the qualities of various kinds of edible oil and provides reliable oil quality information for detecting the qualities of various kinds of edible oil.
Owner:SUZHOU NIUMAG ELECTRONICS TECH +2
Method for measuring oil content of drilling fluid through low-field NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance)
ActiveCN101943669AAccurate analysisAccurate Analysis TestAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceLow field nuclear magnetic resonanceCorrelation analysis
The invention discloses a method for measuring the oil content of drilling fluid through low-field NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance), suitable for measuring the content of crude oil with different densities in the drilling fluid. The method comprises the step of measuring the oil content of the drilling fluid by using the transverse relaxation time of the crude oil and the drilling fluid and different diffusion coefficients as main identification criteria, using the signal strength of NMR of the crude oil and the drilling fluid as a main observation object and using the transverse relaxation analysis of the drilling fluid and the correlation analysis of the diffusion coefficients and transverse relaxation as main measures. The method of the invention has the advantages of high measuring result accuracy, good stability, short time consumption, and the like, is easy to realize the online measurement of the oil content of the drilling fluid and provides reliable storage information of an oil layer for logging operation.
Owner:SUZHOU NIUMAG ELECTRONICS TECH
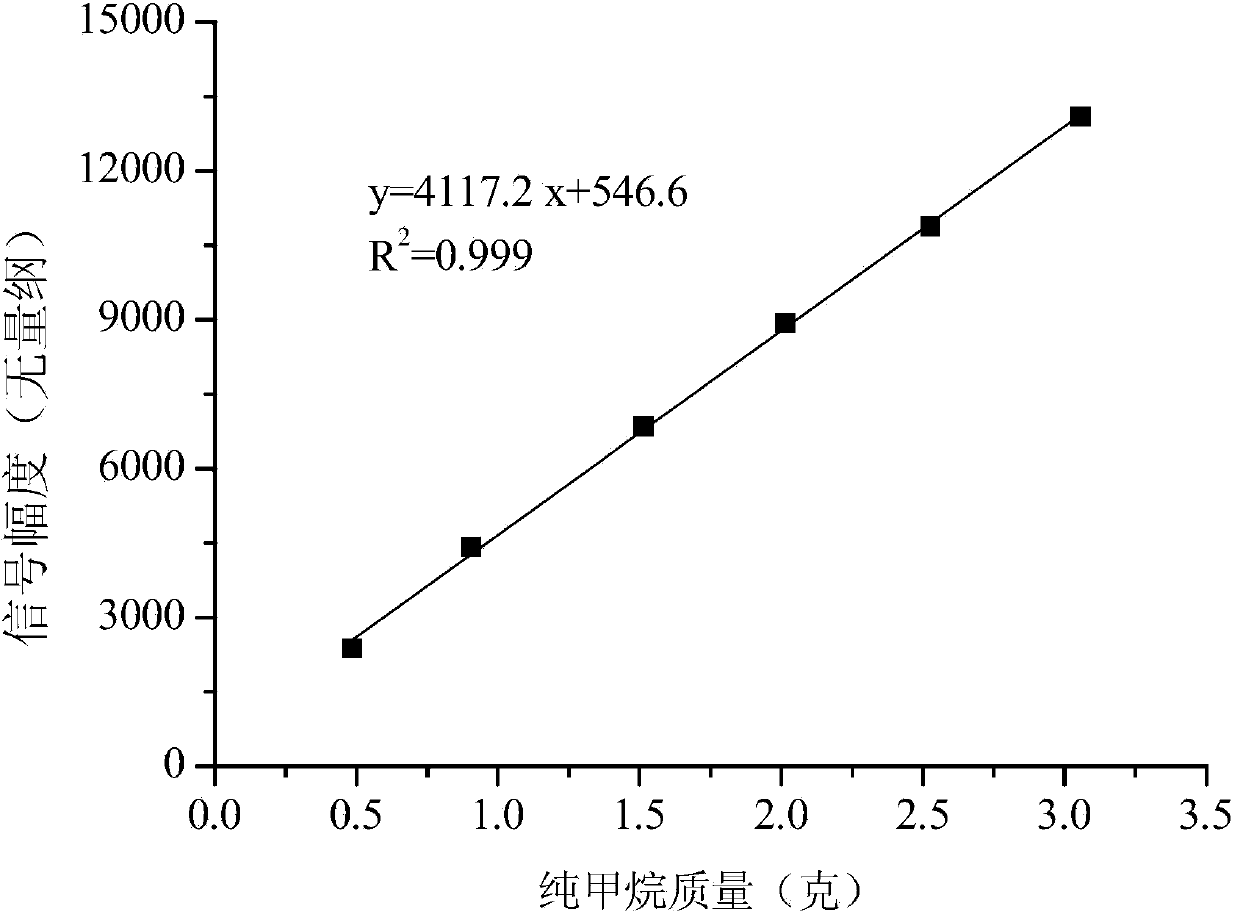
Method for measuring coal sample methane adsorbing capacity through low-field nuclear magnetic resonance
ActiveCN103424421AShort measurement timeHigh speedAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceUnit massLow field nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a method for measuring coal sample methane adsorbing capacity through low-field nuclear magnetic resonance. According to the method, selected measuring parameters are used for carrying out low-field nuclear magnetic resonance measurement on powder coal samples after methane adsorption balance under set pressure, the nuclear magnetism T2 spectrum of methane in the coal samples is obtained, then signal amplitude integrals of the first spectrum peak (in the range of 0.1-4ms spectrum) on the left of the T2 spectrum are substituted to a hydrogen content index reticle equation of methane under the standard condition built through an experiment, the standard condition size of methane adsorbed by the coal samples is obtained, and therefore the methane adsorbing capacity of unit mass of coal under the set pressure is obtained. According to the method, the scale relation of methane mass and nuclear magnetic resonance 1H nuclear signals is built, the quantitative assay of methane adsorbing capacity under the same temperature and different pressures is achieved, and the novel method can be used for measuring coal methane absorbing capacity in a real-time, home-position and dynamic mode.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
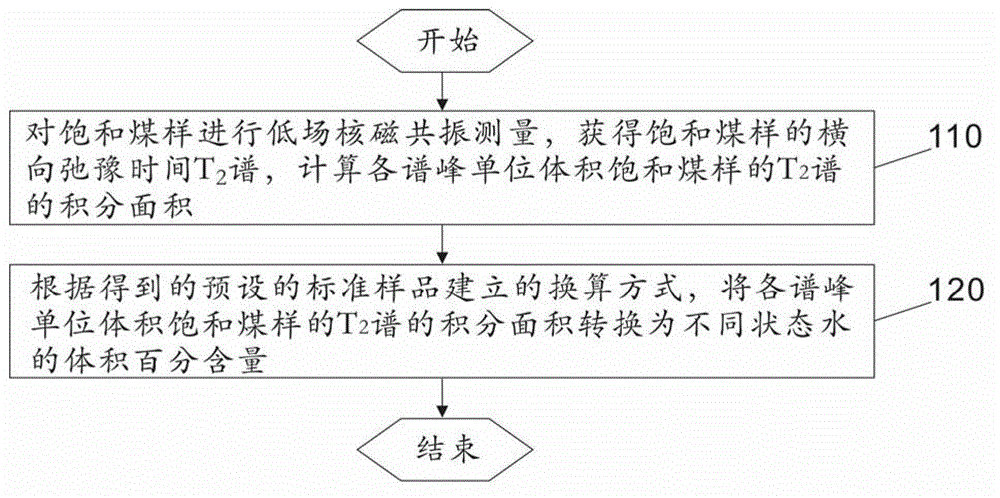
Method for measuring content of different state water in coal
InactiveCN102944571AQuick measurementNon-destructive measurementAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceLow field nuclear magnetic resonanceStandard samples
The invention discloses a method for measuring the content of different state water in coal. The method comprises the steps of performing low field nuclear magnetic resonance measurement on a saturated coal sample to obtain a transverse relaxation time T2 spectrum of the saturated coal sample, calculating integral areas of the T2 spectrum of each spectral unit volume saturated coal sample; and conversing the integral areas of the T2 spectrum of each spectral unit volume saturated coal sample to the volume percent of the different state water according to obtained conversion modes established by preset standard samples. The method solves the problem that how to measure the content of different state water in the coal.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
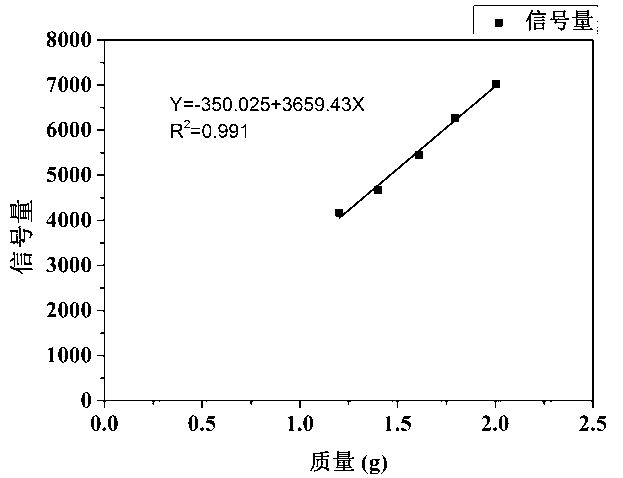
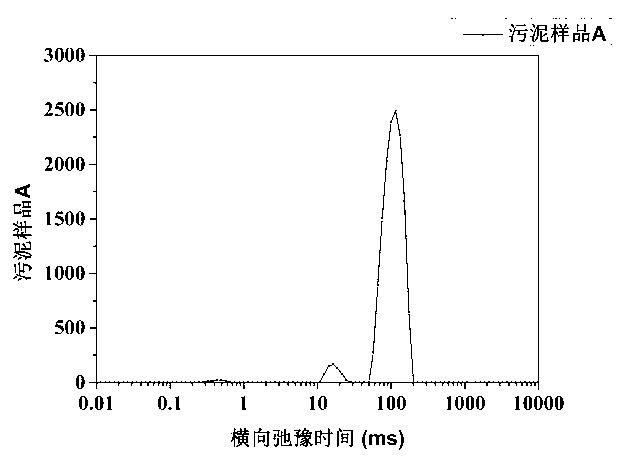
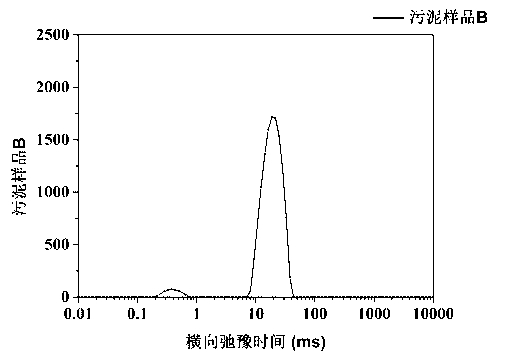
Quick measurement method for different forms of water in sludge
ActiveCN103308543ASimple and fast operationQuick measurementAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceInterstitial waterActivated sludge
The invention discloses a quick measurement method for different forms of water in sludge. The quick measurement method comprises the following steps of: (1) performing low-field nuclear magnetic resonance measurement on the sludge to obtain a transverse relaxation time T2 spectrum of different forms of water in the sludge; (2) stewing and settling activated sludge, preparing a standard sample by supernatant liquid at equal mass interval, and constructing a standard curve; (3) according to the obtained standard curve, matrixing the low-field nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation time of the sludge to obtain three different forms of water, namely free water mass, interstitial water mass and surface combined water mass in the sludge; and (4) drying the sludge to be measured until the weight is balanced, subtracting the final mass from the initial mass, and calculating the fourth form of water in the sludge, namely the internal combined water mass. Compared with the conventional method, the quick measurement method for measuring the content of different forms of water in the sludge by a nuclear magnetic resonance technology has the advantages of short experiment time, harmlessness to experiment samples, precision of measurement and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
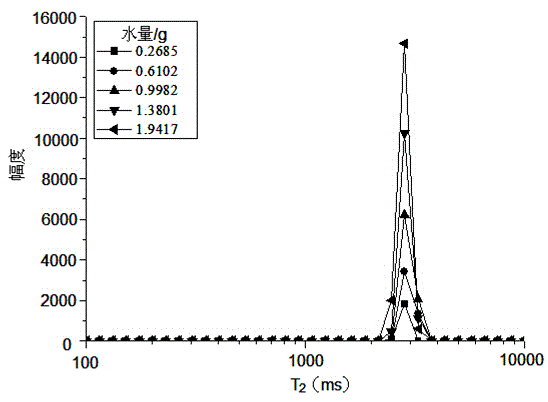
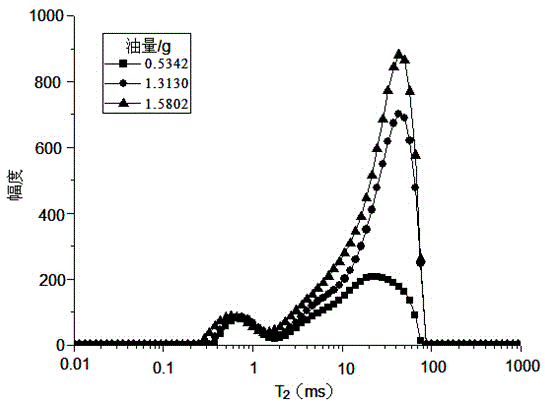
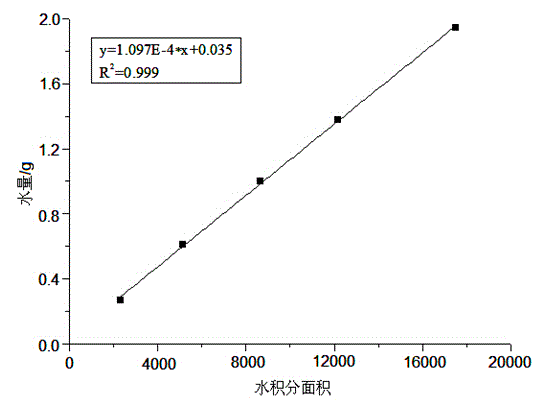
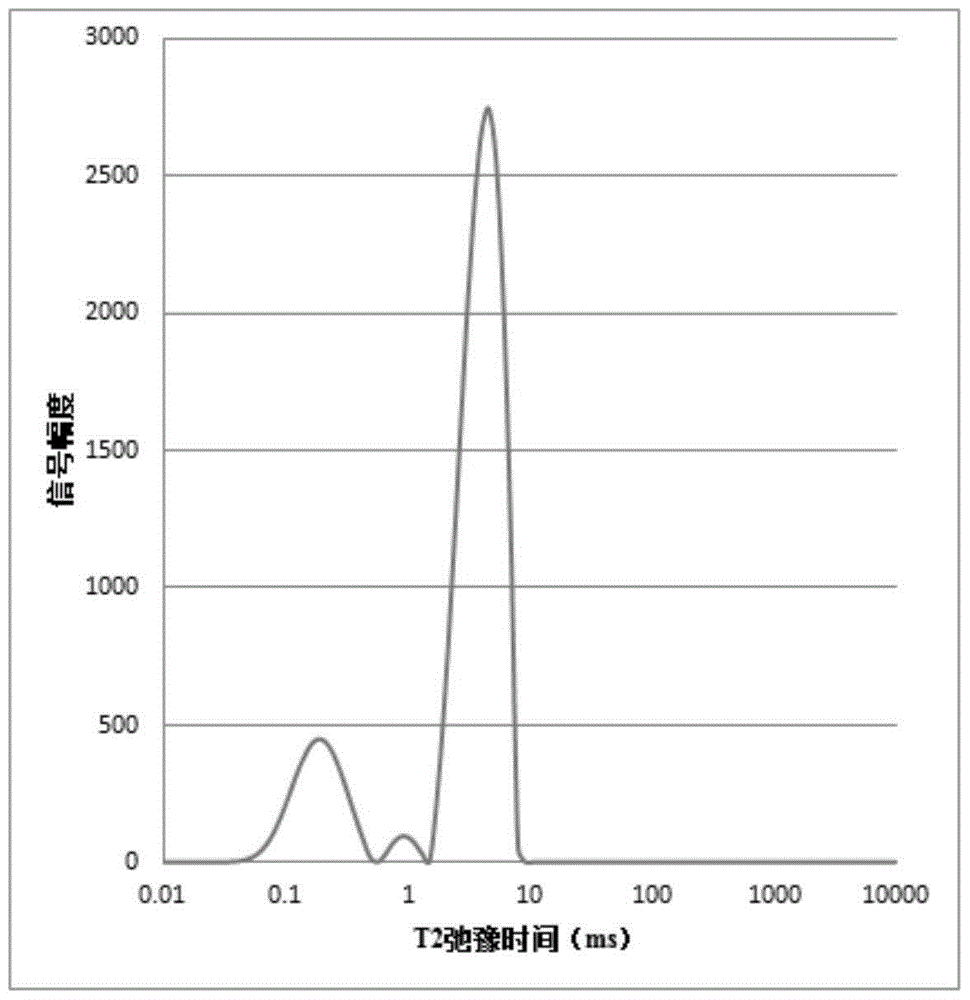
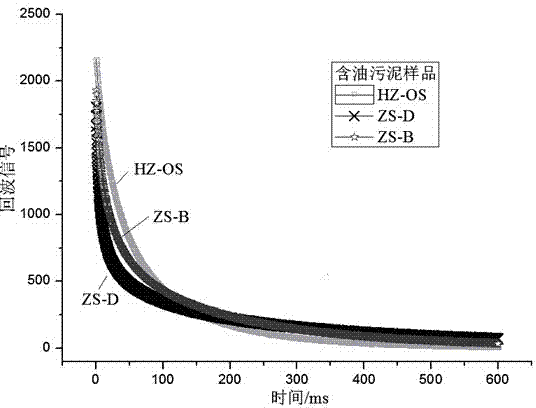
Method for simultaneously quantitatively analyzing water and oil in oily sludge through low-field NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance)
InactiveCN104807847AFast testThe test result is accurateAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceCorrection algorithmSludge
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously quantitatively analyzing water and oil in oily sludge through low-field NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance). The method comprises steps as follows: deionized water and crude oil are taken as standard samples to perform low-field NMR measurement, and calibration curves of water and oil are established; a to-be-measured sample which is uniformly stirred is divided into two parts and put in containers respectively, a reagent capable of realizing signal partition of oil and water is added to one part, and the mixture is uniformly stirred to form a sample a; the other part keeps unchanged and is taken as a sample b; the two samples are subjected to low-field NMR measurement to obtain an echo attenuation curve, and transverse relaxation time T2 curves of the two samples are obtained through inversion with a joint iterative correction algorithm; the transverse relaxation time T2 curves of the two samples are subjected to area integration and calculation to obtain integral areas of a water peak and an oil peak, and the calibration curves of water and oil are substituted to calculate water content and oil content of the to-be-measured sample b. The method can be suitable for measurement of content of water and oil in various kinds of oily sludge, and the measurement result is high in accuracy and good in repeatability and consumes short time.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
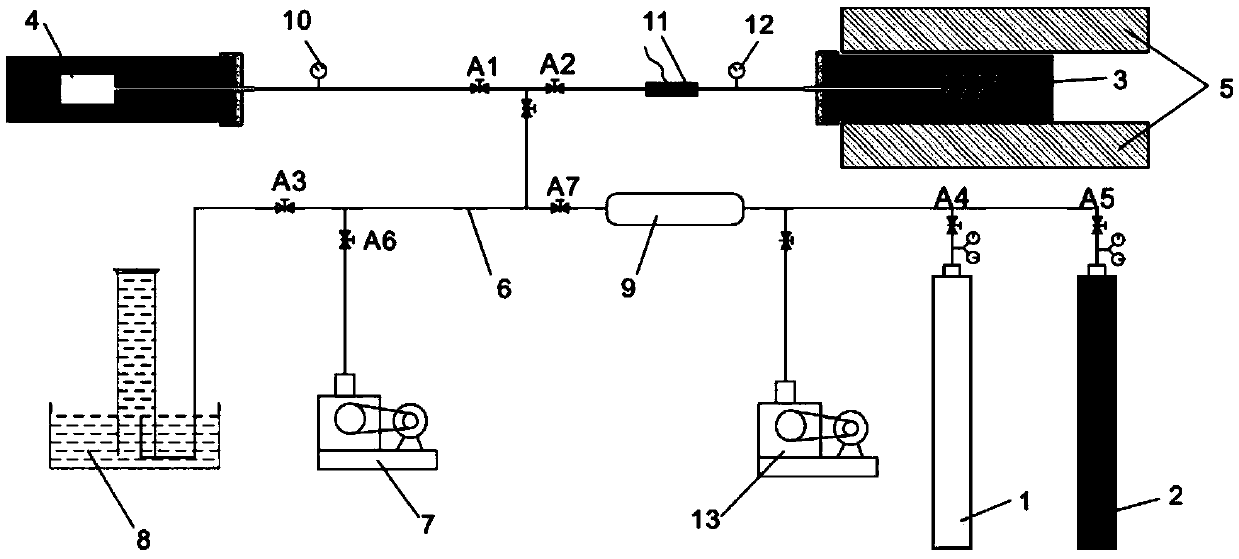
Nuclear magnetic resonance experiment device and method for multi-phase fluid flow characteristic in dense core porous media
InactiveCN109444201AAccurate Realistic Fluid Flow Study ResultsWater resource assessmentAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePorous mediumLow field nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance experiment device and method for multi-phase fluid flow characteristic in dense core porous media, and belongs to the field of petroleum engineering and fluid research. The device consists of a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer system, a magnet system, a radio frequency system and a core displacement system. At present, a core displacement experiment in a laboratory only can calculate the oil discharge amount of a terminal, and a distribution state in the core and the pore throat utilization degree of different apertures cannot be obtained. According to the device, a low-field nuclear magnetic resonance technology is adopted to research fluid flow characteristics in the dense core porous media, the core displacement experiment andan online nuclear magnetic resonance technology are combined through a nuclear magnetic resonance T2 spectrum analysis technology, the change characteristics of a fluid signal in the porous media canbe obtained through the online detection of the T2 spectrum so as to make the utilization characteristics of crude oil in the porous media clear, and an accurate and true research result of fluid flow in the dense core porous media is obtained.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Method for measuring oil content and water content in drilling fluid through low-field nuclear magnetic resonance
ActiveCN105223221AAccurate Analysis TestRapid analysis testAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceManganeseLow field nuclear magnetic resonance
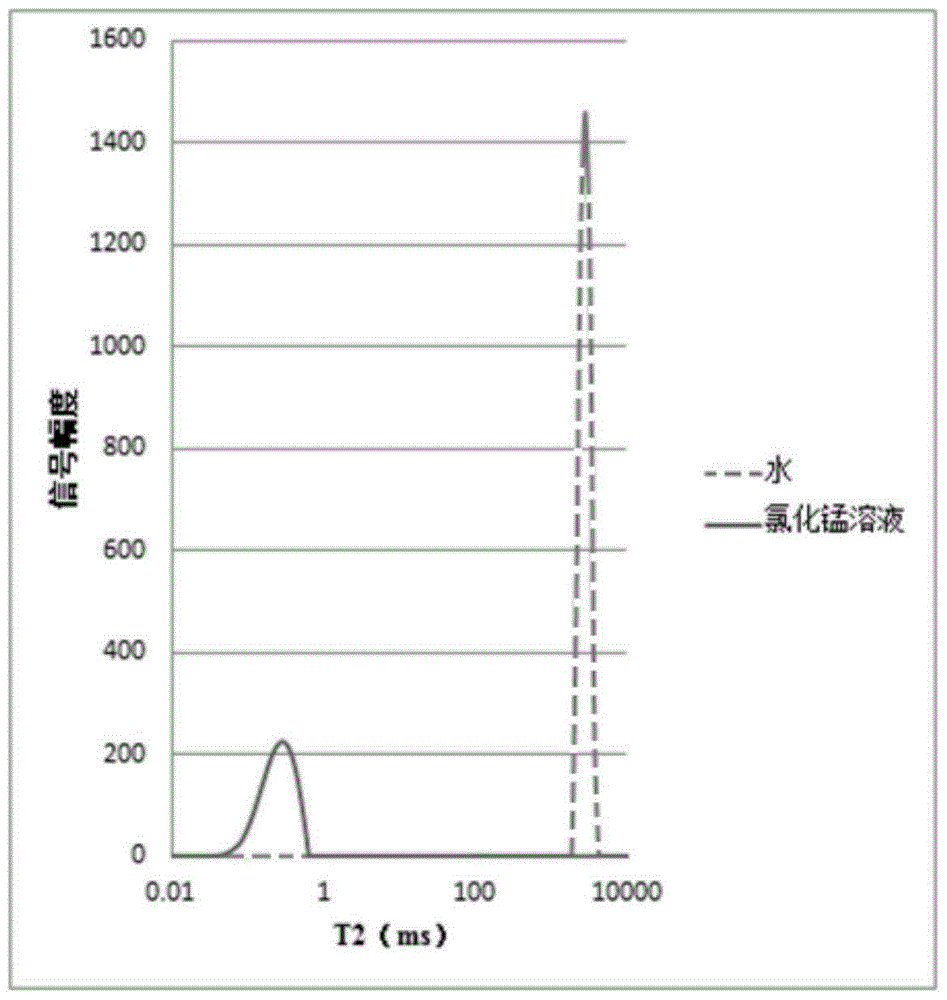
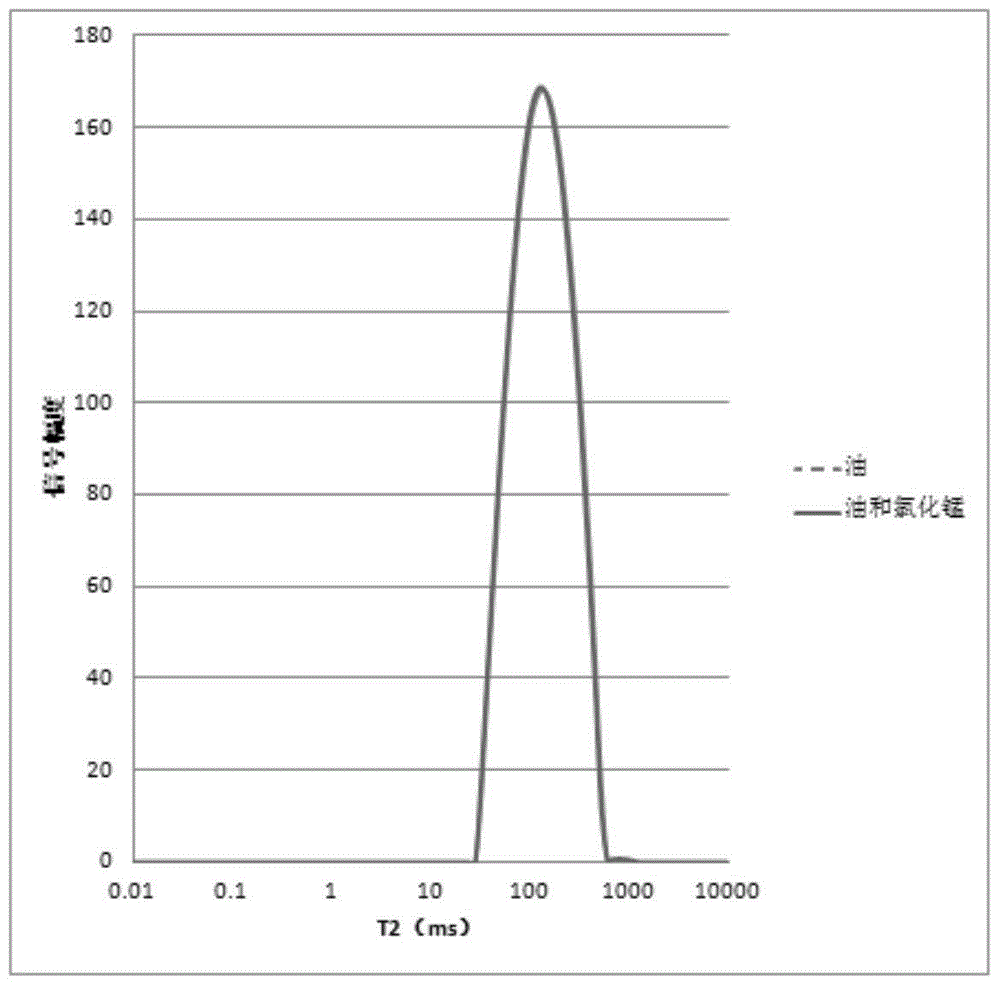
The invention discloses a method for measuring the oil content and the water content in drilling fluid through low-field nuclear magnetic resonance. Manganese chloride is used so that the relaxation time of water can be shortened, however, the relaxation time of oil is not affected, hence, the oil and the water in the drilling fluid can be distinguished, and quantitative testing of the oil content and the water content in the drilling fluid is achieved. The method includes the steps that nuclear magnetic resonance analysis is conducted on an original sample of the drilling fluid first, and the T2 relaxation spectrum of the original sample of the drilling fluid is tested; then a manganese chloride solution is added into the original sample of the drilling fluid to be fully stirred; afterwards, nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of the manganese-saturated drilling fluid is performed; the peak area of crude oil is the peak area of the manganese-saturated drilling fluid after the relaxation time is 1 ms, the peak area of the water in the drilling fluid is the difference between the peak area before manganese saturation and the peak area of the crude oil, and the peak area of the crude oil and the peak area of the water in the drilling fluid are introduced into corresponding working curve equations so that the oil content and the water content in the drilling fluid can be obtained; at last, the oil content and the water content of the drilling fluid can be obtained by combining the mass of the drilling fluid.
Owner:SUZHOU NIUMAG ELECTRONICS TECH
Low-field nmr device for measuring the water content of solids and slurries
InactiveUS20130154644A1Extends measurement volumeSmall and cost-effectiveWater resource assessmentAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceElectrical resistance and conductanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) apparatus and method for measuring the water content of samples has a device to produce a main magnetic field; a sample receiving space within a main magnetic field; a device to excite a measurable RF magnetization to a sample placed into the sample receiving space at an operating frequency defined by the main magnetic field; a device to measure the RF signal produced by the excited sample; and a device to determine the water content in the sample based on the RF signal. The sample receiving space is capable of accommodating a sample having a volume of at least 0.5 dm3, and the device to produce a main magnetic field has a resistive electromagnet which is adapted to produce a main magnetic field corresponding to an operating frequency of 400-2000 kHz.
Owner:METSO AUTOMATION OY
Ultra-low field nuclear magnetic resonance method to discriminate and identify materials
InactiveUS20120001631A1Easy to changeHigh sensitivityMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceRapid identification
An ultra-low field (ULF) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and / or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system can be used for rapid identification and discrimination of materials, e.g., liquid in opaque containers and / or materials in or on human bodies. The system utilizes the ability of ULF NMR / MRI to measure NMR parameters in magnetic fields that can be easily changed in field strength and orientation.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
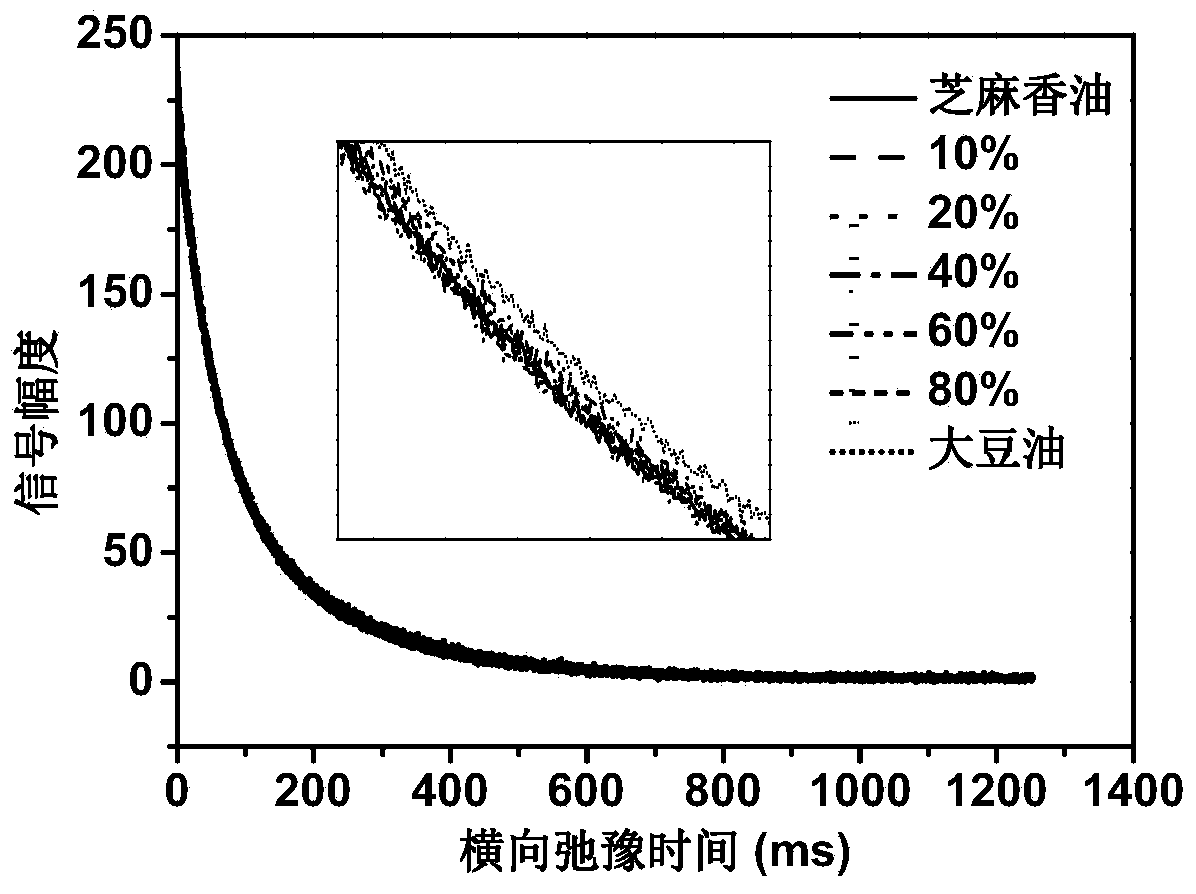
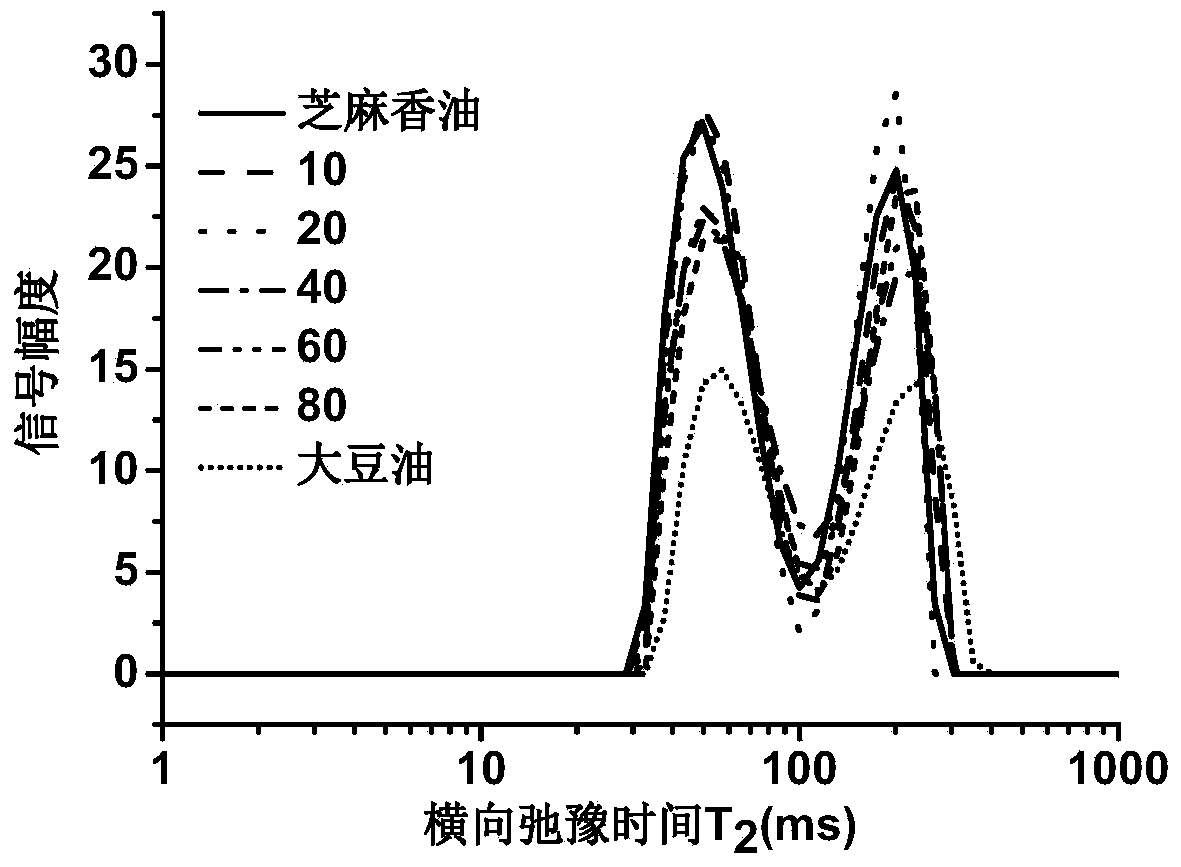
Method for true and false identification and content determination of sesame oil
InactiveCN104198518ARapid identificationQuick checkAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceLow field nuclear magnetic resonanceContent determination
The invention provides a method for true and false identification and content determination of sesame oil. The method utilizes a low-field nuclear magnetic resonance technique to identify and determine the content of the sesame oil. The method mainly comprises the operation steps that 1, a mixed oil sample is prepared; 2, a detection sample is prepared; 3, relaxation signals of pure sesame oil, pure soybean oil and mixed oil are quickly determined by the low-field nuclear magnetic resonance technique; and 4, signal data is analyzed and processed. The method is easy and simple to operate and good in effect, can achieve quick detection of the content of the sesame oil in the sesame oil and soybean oil mixed sample, is applicable to the field of quality control of the pure sesame oil, and lays a foundation for quality detection work of the sesame oil.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for measuring content of moisture of tobaccos through low-field nuclear magnetic resonance
ActiveCN103837560ANo form requirementsNo lossAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceLow field nuclear magnetic resonance
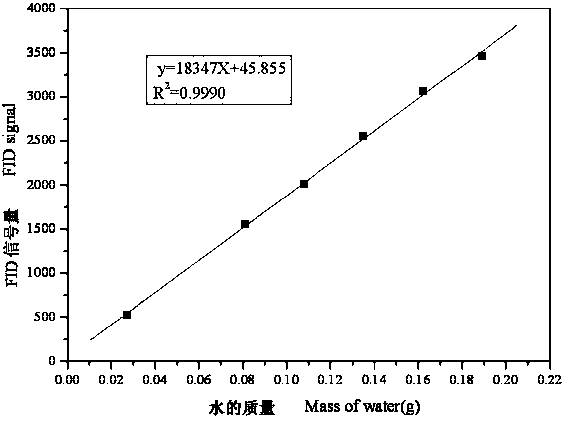
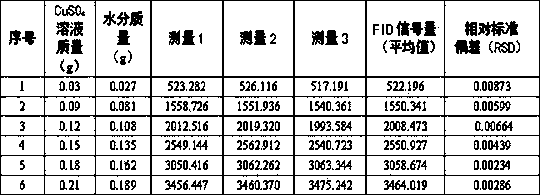
The invention discloses a method for measuring the content of moisture of tobaccos through low-field nuclear magnetic resonance. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: measuring nuclear magnetic resonance FID signals of a series of CuSO4 solution samples containing different moisture masses, and fitting a standard measurement curve according to the FID signal amount and the corresponding moisture mass of each CuSO4 solution; performing the rapid and accurate measurement on a tobacco sample with the unknown content of the moisture, and converting the FID signal amount of the sample into the moisture mass according to the standard measurement curve, wherein the ratio of the moisture mass to the mass of the tobacco sample is the moisture of a tested sample. The method has the beneficial effects that compared with a conventional testing method, the method is high in testing speed and accurate in testing result, the sample pretreatment process and the sample shape requirement in the testing process are avoided, a solvent is not required to be consumed, the sample loss is avoided, and the environment-friendly testing concept is fully reflected.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC +1
Ultra-low field nuclear magnetic resonance and magnetic resonance imaging to discriminate and identify materials
InactiveUS7688069B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsMaterial analysis by using resonanceHazardous substanceLow field nuclear magnetic resonance
An ultra-low magnetic field NMR system can non-invasively examine containers. Database matching techniques can then identify hazardous materials within the containers. Ultra-low field NMR systems are ideal for this purpose because they do not require large powerful magnets and because they can examine materials enclosed in conductive shells such as lead shells. The NMR examination technique can be combined with ultra-low field NMR imaging, where an NMR image is obtained and analyzed to identify target volumes. Spatial sensitivity encoding can also be used to identify target volumes. After the target volumes are identified the NMR measurement technique can be used to identify their contents.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
United detection method for determinming freshness of prepared aquatic product at low temperature shelf life
ActiveCN106324011AImprove forecast accuracyReduce forecast errorAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceTesting foodSmall sampleLow field nuclear magnetic resonance
A united detection method for determinming freshness of prepared aquatic product at low temperature shelf life belongs to the technical field of food preservation. This invention is based on low field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) combined with the electronic nose as the main measurement tools, on the basis of regulating RBF neural network model which is eatablished among the relaxation time data, flavor changing data and volatile base nitrogen (TVB- N) data of aquatic products and based on regulating nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and electronic nose signal in the process of low temperature storage of aquatic products as the main target of observation, through the analysis of relaxation time data and the flavor changing data of aquatic products in the process of low temperature storage, and makes the judgement to regulate shelf life limits of aquatic products. This invention has the advantages of simple analysis process, small sample usage quantity, and high accuracy, short time-consuming, low cost and easy popularization. By adopting the similar method of the invention, the corresponding database and the prediction model can be established for other meat products, and the accurate prediction for the limit value of the shelf life during the storage process can be realized.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
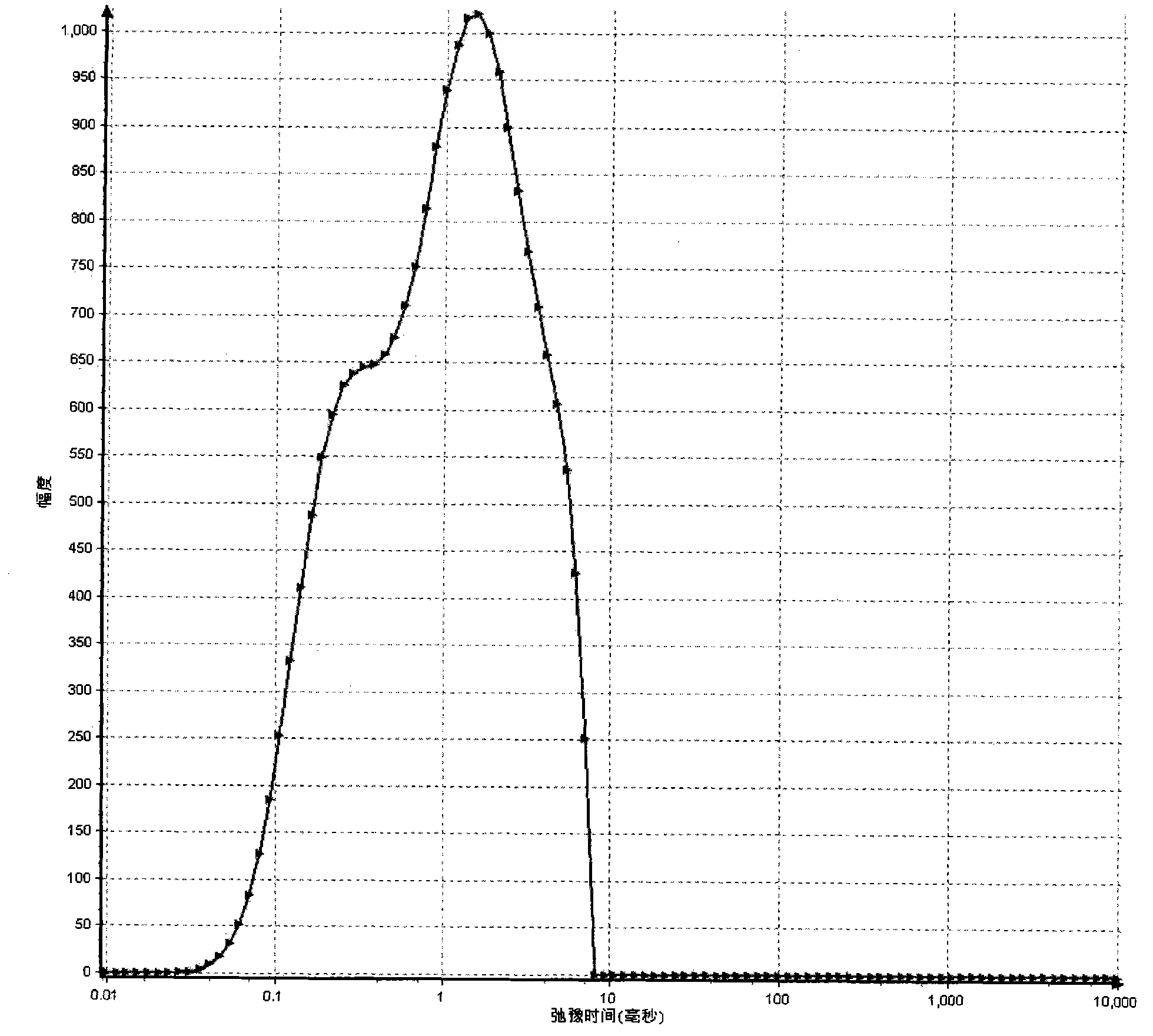
Method for measuring porosity of coal core
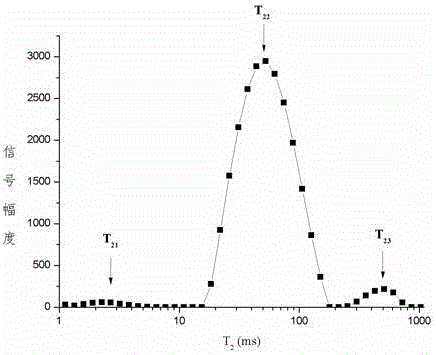
ActiveCN103018148AImprove detection accuracyShort time consumingPermeability/surface area analysisSurface moisturePorosity
The invention discloses a method for measuring the porosity of a coal core. The method comprises the following steps of setting echo of measuring parameters of a low-field nuclear magnetic resonance instrument to be 0.10 microseconds; carrying out low-field nuclear magnetic resonance measurement on the saturated coal core after surface moisture is removed so as to obtain a spectrum T2 of transverse relaxation time of the saturated coal core; calculating an integral area of the spectrum T2of the saturated coal core in unit volume; and calculating to obtain a porosity value of the coal core through the integral area of the spectrum T2of the saturated coal core in the unit volume according to conversion relation established by an obtained preset standard sample. With the adoption of the method provided by the invention, the porosity of a core hole is reflected by a signal generated by moisture in a sample hole in a low-field nuclear magnetic resonance manner, so that the detection precision is high, and the consumed time is short.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
Method of simultaneously measuring water content and oil content of oily sludge
InactiveCN104730099AImprove accuracyGood repeatabilityAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMetrologySludge
The invention relates to a method of simultaneously measuring water content and oil content of oily sludge. The method includes: collecting oily sludge samples from different sources from different batches; measuring water content and oil content of each sample with a modified Dean-Stark device, as modeling reference values; subjecting each sample to low-field nuclear magnetic resonance analysis to obtain an echo attenuation curve, and performing inversion to obtain a transverse relaxation time T2 curve of the sample; correlating the echo attenuation curve data of the samples and corresponding water content and oil content, and performing fitting with chemometrics software to establish a water content model and an oil content model; calling established models of water content and oil content calibration sets to analyze the echo attenuation curves of the samples to be measured, so as to obtain the corresponding water content and oil content values. The method has the advantages such as high result accuracy, good repeatability, low time consumption, no consumption of organic reagents and no need for pre-processing of samples; by the method, the water content and oil content of the samples can be measured simultaneously.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Low field nuclear magnetic resonance probe based on printed circuit board helmholtz coil
InactiveCN103645451AUniform RF fieldEasy to makeMeasurements using magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceHelmholtz coil
The invention discloses a low field nuclear magnetic resonance probe based on a printed circuit board helmholtz coil. A PCB substrate is taken as a substrate. An upper surface of the PCB substrate is provided with a first bonding pad, a second bonding pad, an upper portion lead wire and an upper portion plane coil. A lower surface of the PCB substrate is provided with a lower portion lead wire and a lower portion plane coil. An outer end of the upper portion plane coil is connected with the first bonding pad through the upper portion lead wire. An outer end of the lower portion plane coil is connected with the lower portion lead wire. An inner end of the upper portion plane coil and an inner end of the lower portion plane coil are connected through a first metalized through hole. The second bonding pad and the lower portion lead wire are connected through a second metalized through hole. A central section of the PCB substrate is provided with a sample through hole which passes through up and down. The nuclear magnetic resonance probe based on PCB helmholtz coil provided in the invention adopts a PCB technology and possesses the following advantages that manufacturing is simple; cost is low; a period is short; mass production can be realized and so on. And a radio-frequency field which is relatively uniform can be generated.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
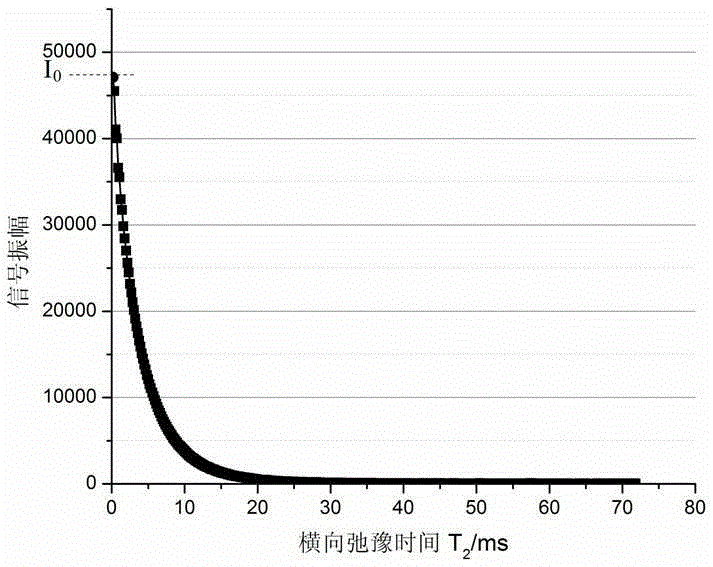
Method for representing cement hydration degrees by means of low-field nuclear magnetic resonance technology
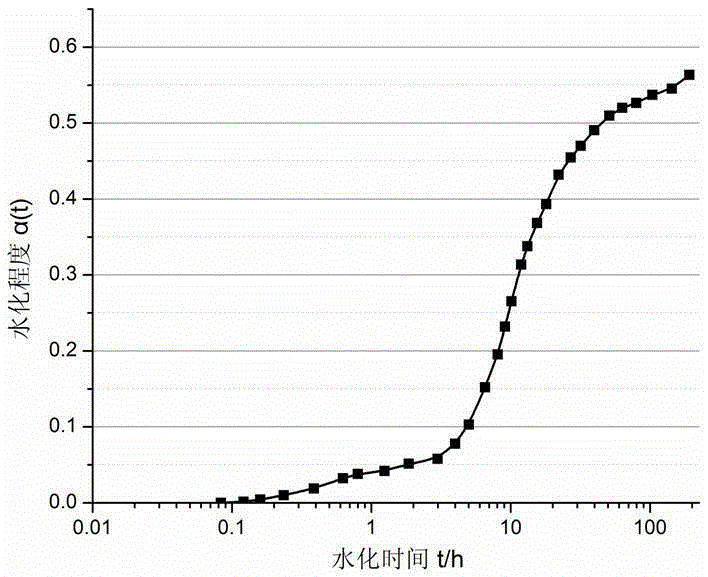
InactiveCN105259200AAvoid damageDoes not damage the microstructureAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceTransverse relaxation
The invention belongs to the field of building materials, and particularly relates to a method for rapidly and continuously representing cement hydration degrees by means of a low-field nuclear magnetic resonance technology. The method comprises the following steps that 1, slurry is prepared, weighing is conducted, the water content m<0> and the cement content m<c> in the cement slurry are calculated, the slurry is rapidly put in a low-field nuclear magnetic resonance instrument, and test is conducted after system parameters and sampling interval time are set; 2, a CPMG impulse sequence is adopted to collect nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation decay signals at t moments in different hydration time; 3, first echo peak amplitudes I(t) of a decay curve at the t moments in the different hydration time are automatically collected, and an amplitude I<0> of a first collection point is recorded; 4, physical combined water amounts m(t) at the hydration t moments are determined through the specific value of the I(t) to the I<0>, and hydration degrees alpha(t) at the hydration t moments are obtained according to the formula in the specification; 5, a relation curve of the alpha(t) and t is drawn, and the hydration degrees at any hydration t moment can be read. According to the method for rapidly and continuously representing the cement hydration degrees by means of the low-field nuclear magnetic resonance technology, drying or stopping of hydration to samples is not needed, and in-situ detection and continuous monitoring to the cement hydration degrees can be achieved.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Object discrimination method using ultra-low magnetic field nuclear magnetic resonance and an object discrimination apparatus of the same
ActiveUS20140232400A1Analysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceLow field nuclear magnetic resonance
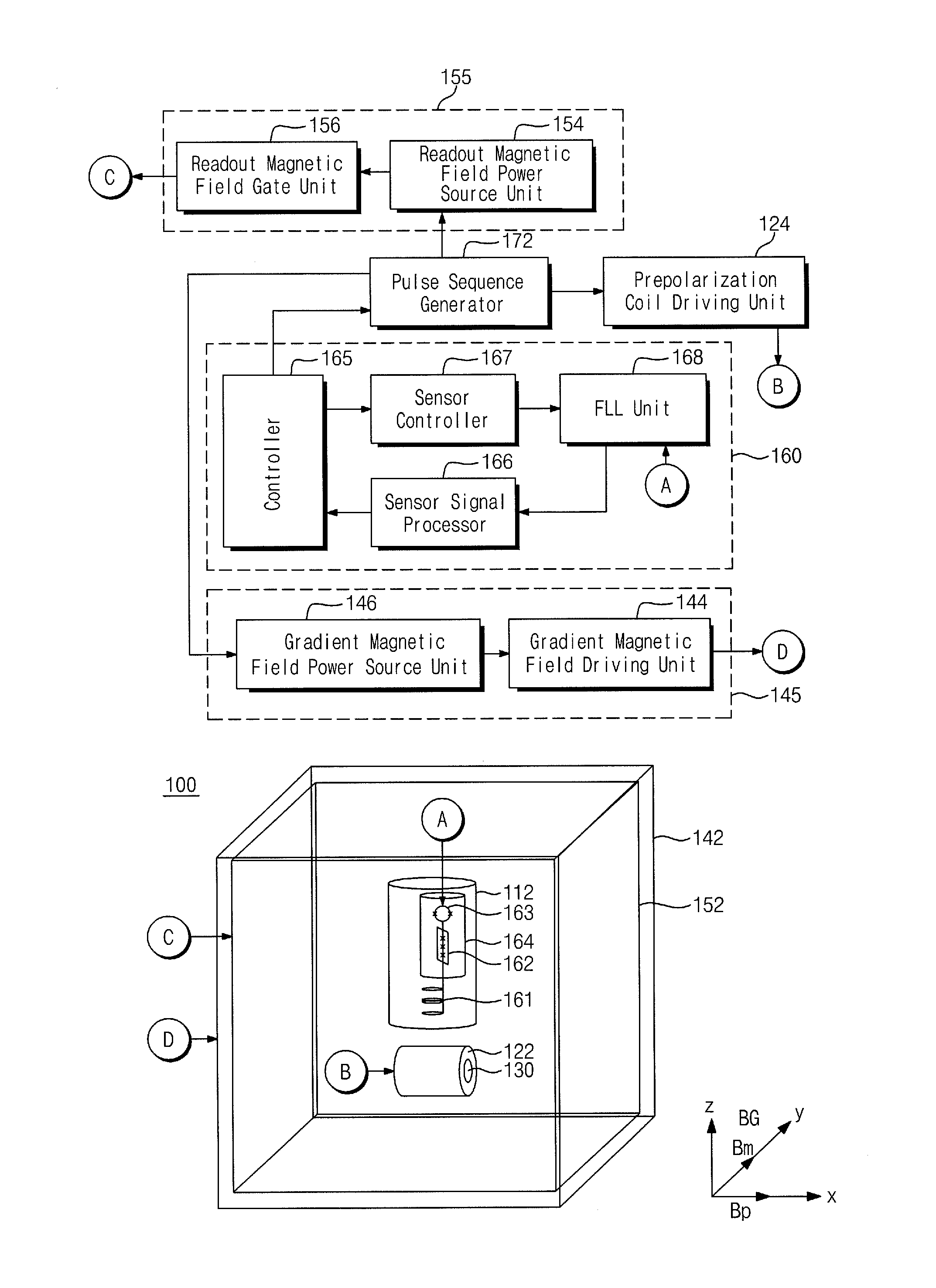
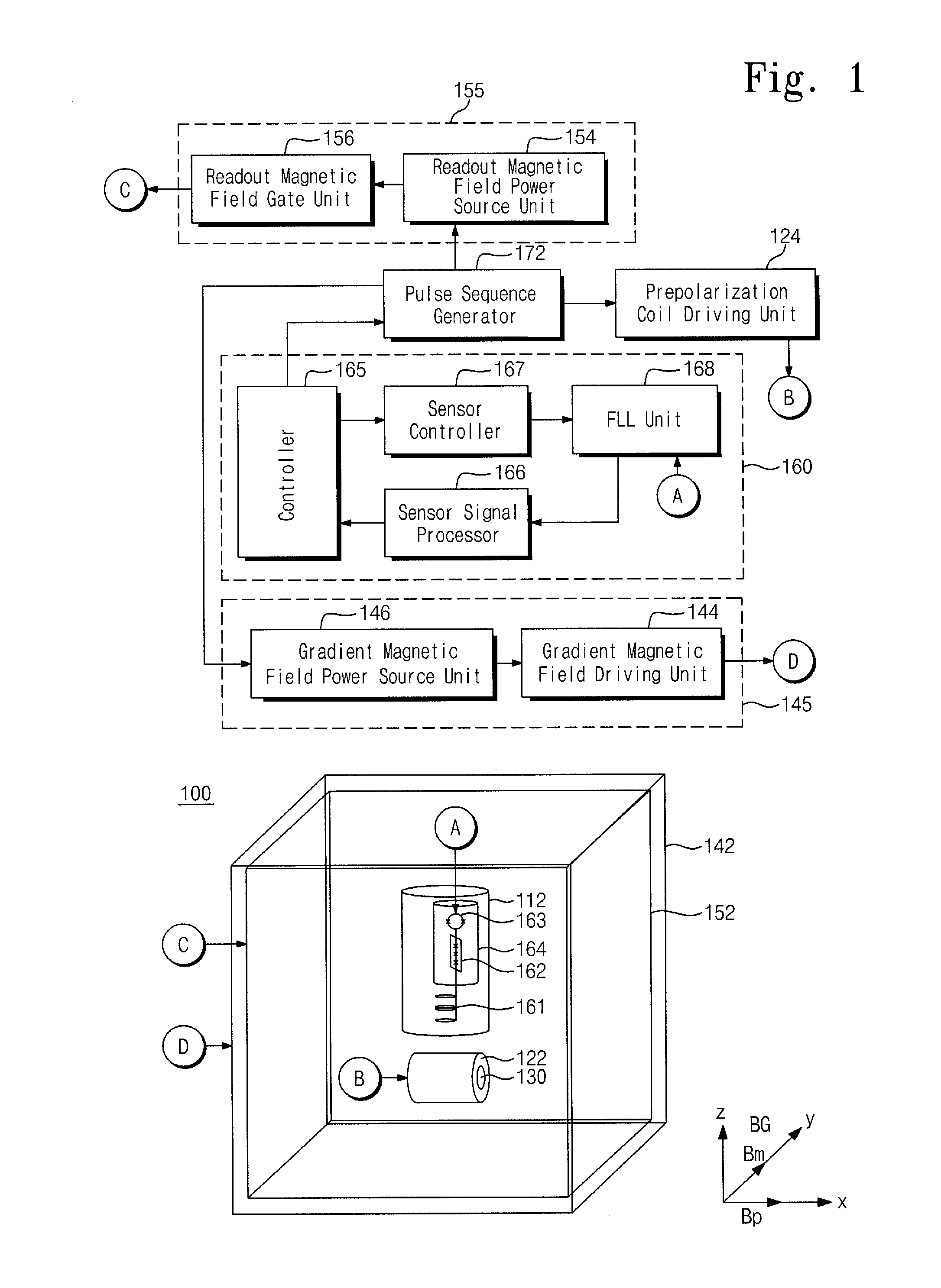
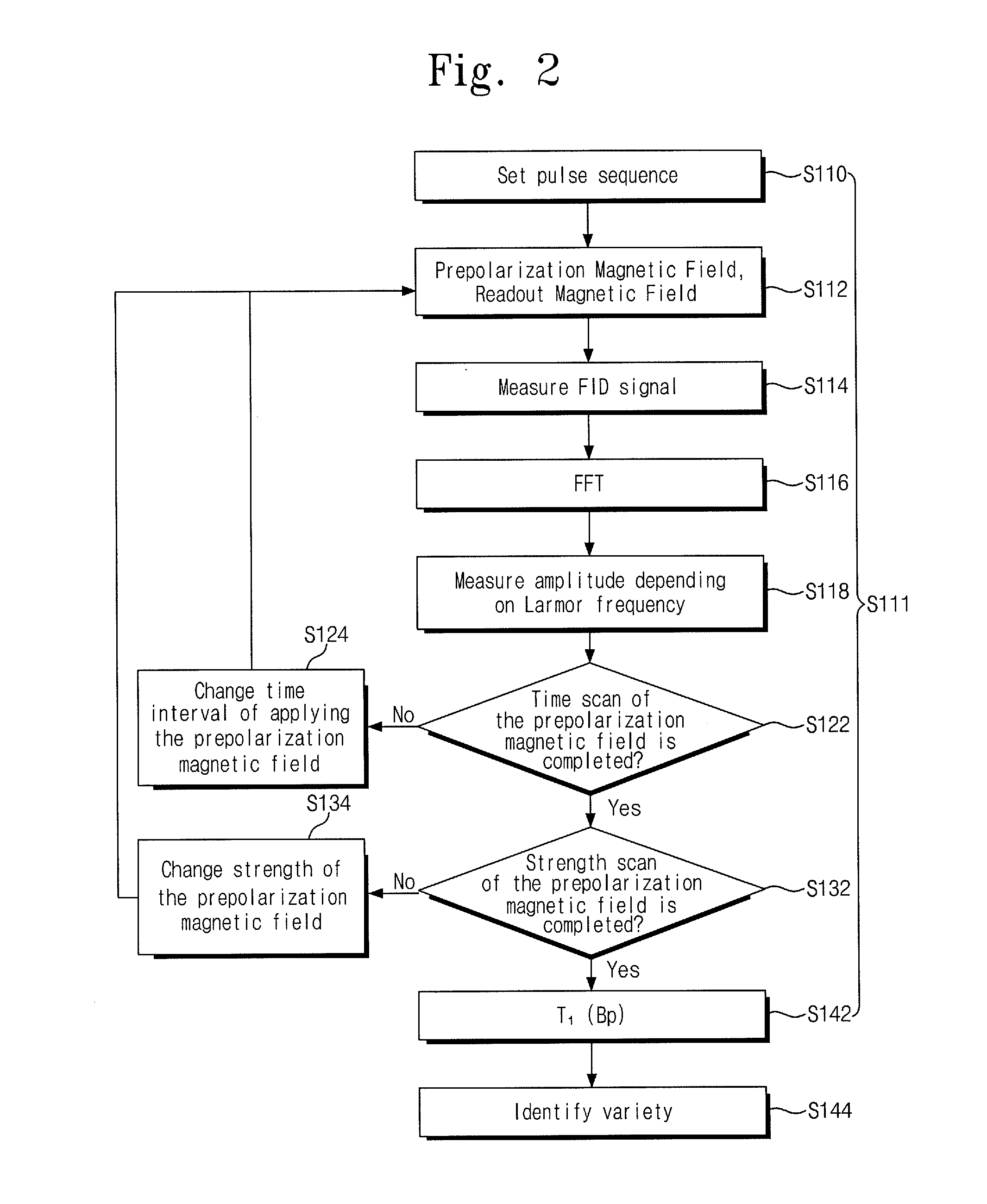
Provided are an object discrimination method and an object discrimination apparatus using an ultra-low magnetic field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). The method includes measuring the respective spin-lattice relaxation times at a plurality of strengths of prepolarization magnetic fields with respect to a measurement target and classifying the measurement target using the spin-lattice relaxation times.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Movable low-field nuclear magnetic resonance imaging system
ActiveCN101869479ALimited timeRestricted locationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsWhole bodyLow field nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a movable low-field nuclear magnetic resonance imaging system which comprises a movable spectrometer, a magnet, a computer, a radio frequency amplifier, a gradient power amplifier and a coil, as well as a movable magnet frame, wherein the magnet is a rotatable low-field magnet arranged on the movable magnet frame, and a shield is embedded in the low-field magnet. The movable low-field nuclear magnetic resonance imaging system combines the low-field magnet with the movable magnet frame, has small equipment volume and light weight and can carry out fast and timely medical examination in emergencies, rescue scenes, playgrounds, countrysides and other special occasions without being limited by time and place; the low-field magnet can realize omni-directional rotation on the magnet frame, adjust the height of a magnetic field according to needs, carry out accurate examination and diagnosis on a patient in any posture and body position and further reduce the motion of the patient; the adoption of the low magnetic permanent magnet has low maintenance cost and low cost and reduce the production cost; and the movable low-field nuclear magnetic resonance imaging system has good openness, can not cause the oppression to the patient, is applicable to local examination or interventional therapy of the head, the limbs and the like, and is particularly applicable to thorough examination of infants.
Owner:SUZHOU NIUMAG ELECTRONICS TECH
Method for detecting water content and fat content in abalone through low-field nuclear magnetic resonance technology
ActiveCN105606637AEasy to operateMeet the needs of rapid analysisAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceLow field nuclear magnetic resonanceFat content
The invention provides a method for detecting the water content and fat content in abalone through a low-field nuclear magnetic resonance technology. The method comprises the following first step of collecting samples, the second step of carrying out low-field nuclear magnetic analysis on the sample, the third step of measuring the samples, the fourth step of establishing a model, the fifth step of evaluating the model, and the sixth step of measuring the water content and the fat content of the samples to be detected. By means of the method, the water content and fat content in abalone can be measured at the same time, detection is rapid and accurate and free of the influence of the surface feature of abalone, and abalone is not damaged in the measuring process.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
System and method for emulating nuclear magnetic resonance well logging tool diffusion editing measurements on a bench-top nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer for laboratory-scale rock core analysis
InactiveUS8427145B2Spin dynamics are simplifiedImprove signal-to-noise ratioElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsWell loggingLaboratory scale
A laboratory NMR methodology (and corresponding laboratory apparatus) defines a sample volume. The method stores downhole tool data corresponding to a hydrocarbon-bearing sample collected from a given subsurface formation. The downhole tool data includes parameters pertaining to magnetic fields used by a downhole tool during a suite of NMR measurements of the given subsurface formation. The sample is positioned in the sample volume of the laboratory apparatus, which applies a static magnetic field in the sample volume. Furthermore, the laboratory apparatus applies a suite of NMR measurements to the sample volume to thereby determine a property of the sample. The NMR measurements of the suite each include a pulse sequence of oscillating magnetic field in conjunction with a pulsed-mode gradient field. The pulsed-mode gradient field is based on the stored downhole tool data corresponding to the sample. A laboratory NMR methodology for optimizing downhole NMR measurements is also described.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method for nondestructive detection of water and fat contents of yellow croaker
InactiveCN105548234AQuick checkAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceTransverse relaxationResearch Object
The invention provides a method for nondestructive detection of water and fat contents of yellow croaker. The method comprises 1, yellow croaker sample detection: acquiring a transverse relaxation signal through a CPMG sequence so that a yellow croaker sample transverse relaxation spectrum is obtained, 2, determination of yellow croaker water and fat contents, 3, building of yellow croaker water and fat content prediction models: building prediction models through the T2 relaxation spectrum as an independent variable and water and fast contents as dependent variables, and 4, signal data analysis and processing. The method researches correlation of the spectrum and ingredients, utilizes yellow croaker low field nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation data as a research object and yellow croaker water and fast contents as indexes to build the yellow croaker water and fat content PCR and PLSR prediction models and realizes fast detection of water and fat contents of the yellow croaker.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com