Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46results about "Analysis using optical pumping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
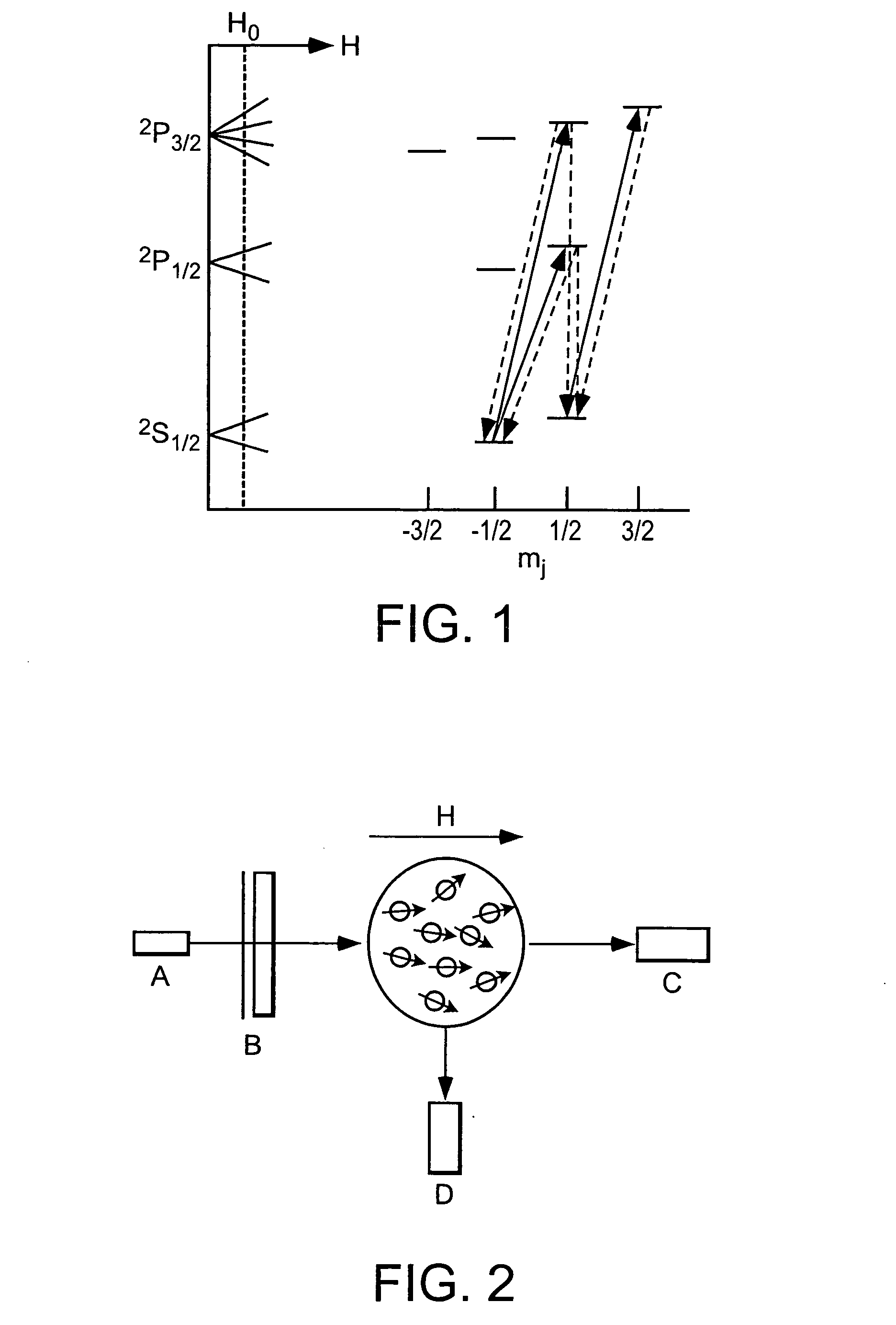
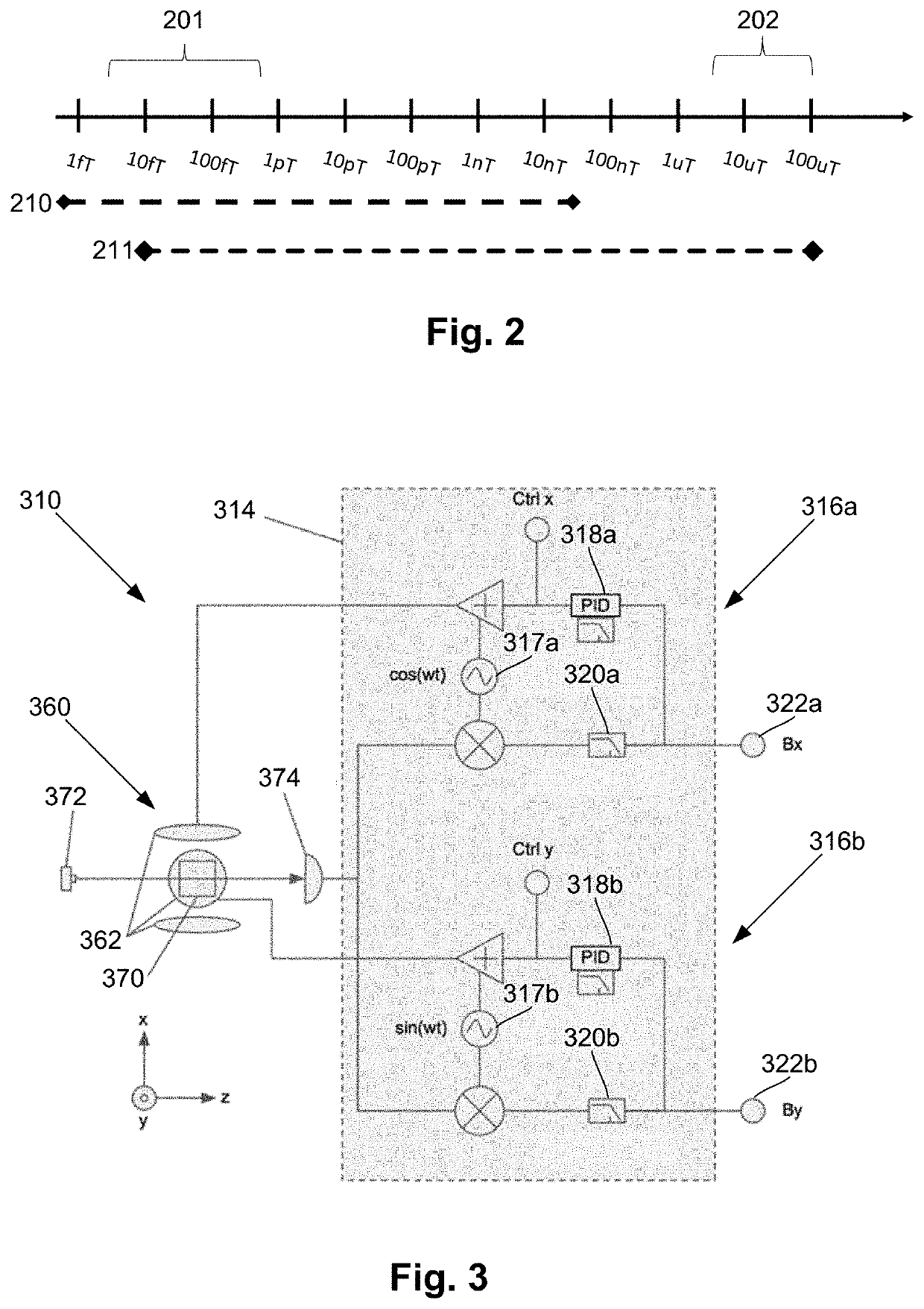
System for detecting zero-field resonance
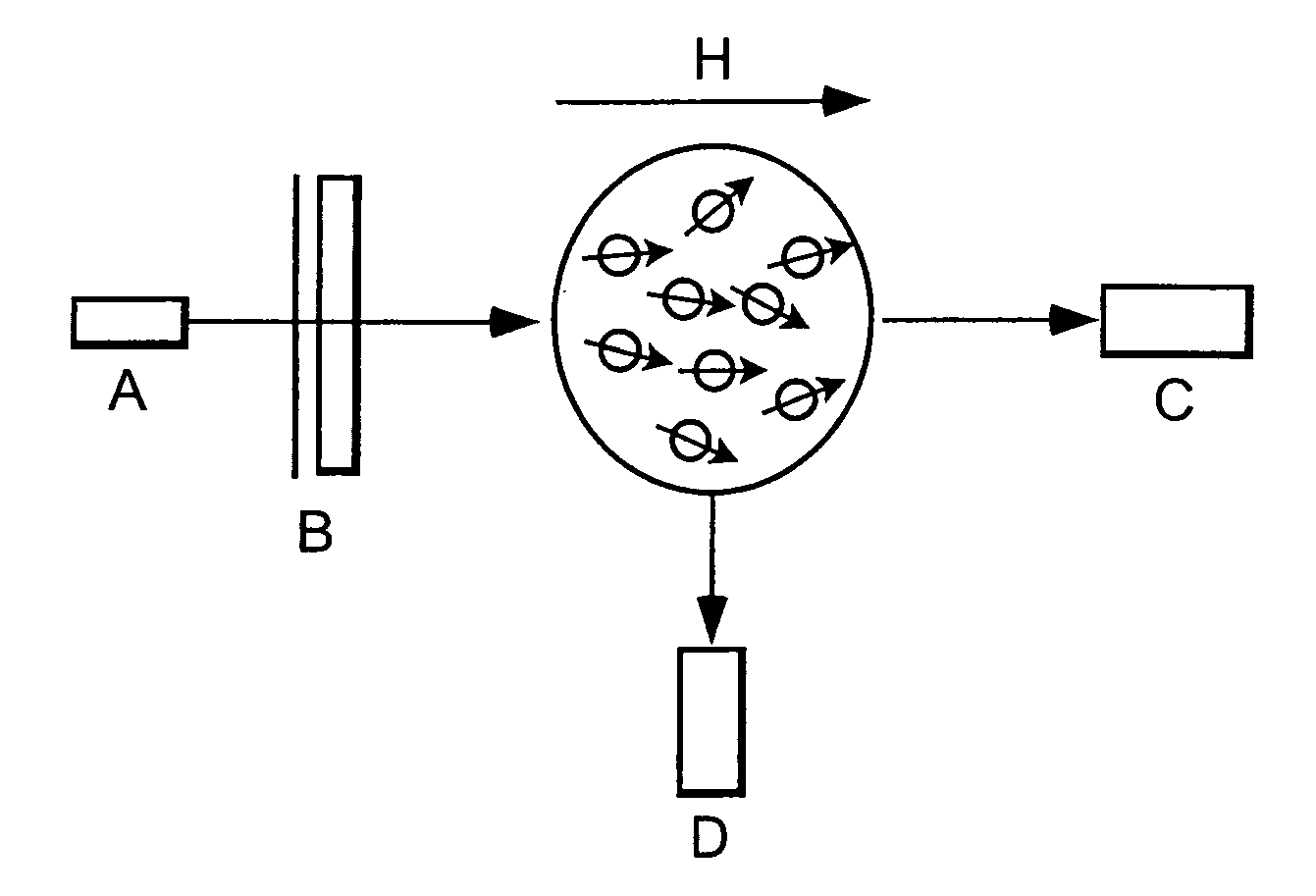
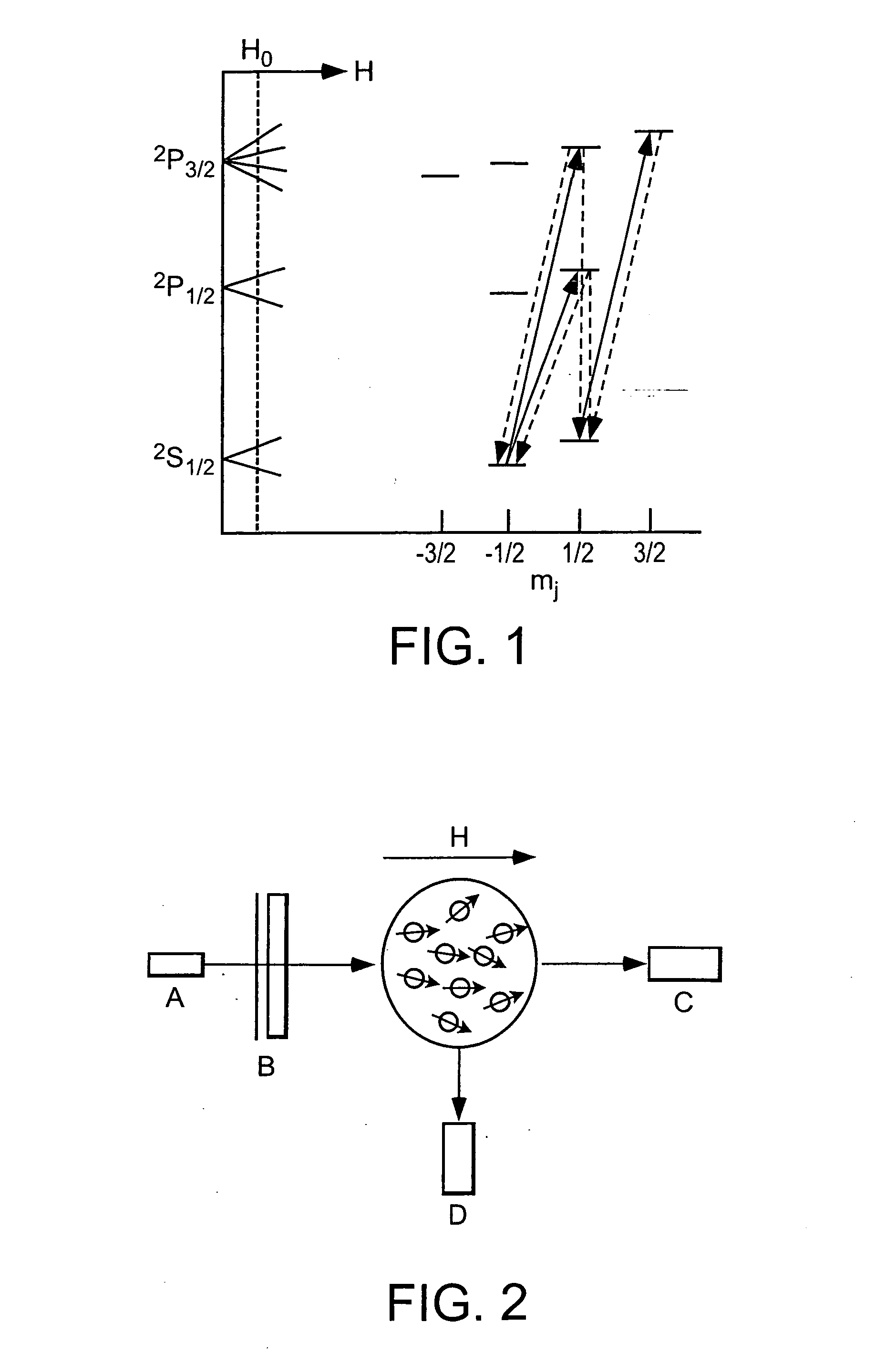
ActiveUS20160223627A1Width minimizedImprove maximizationAnalysis using optical pumpingAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceResonanceBias field
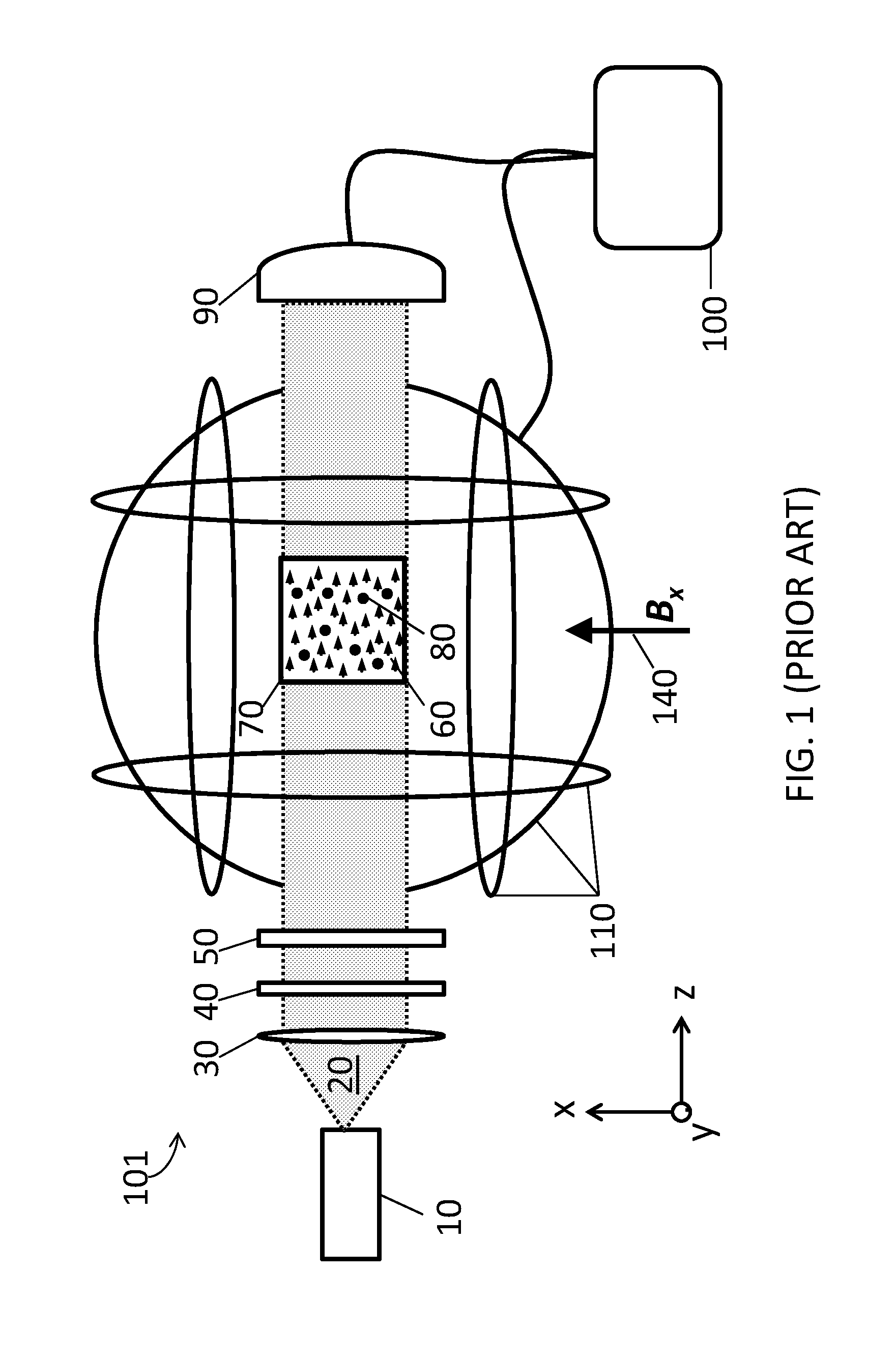
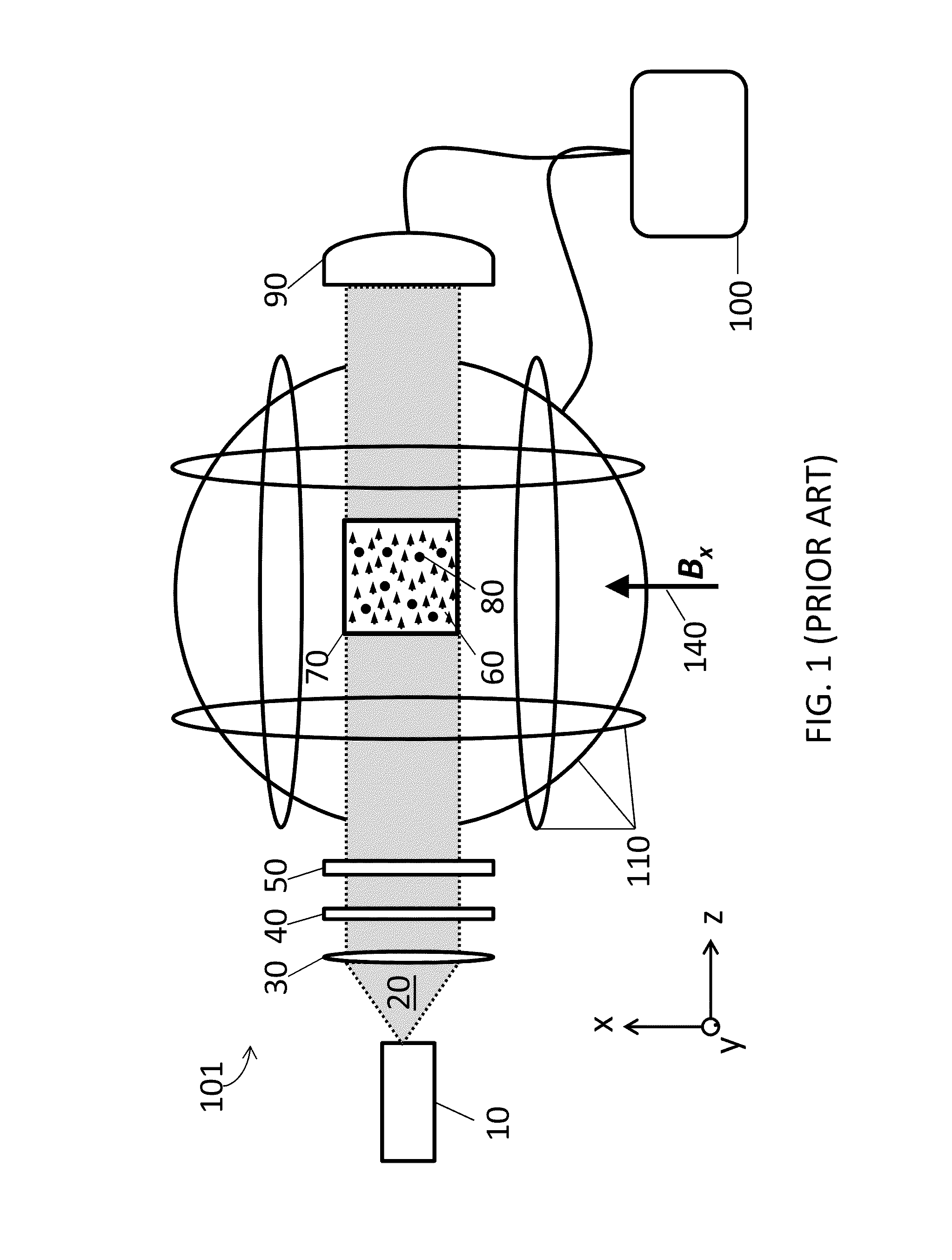
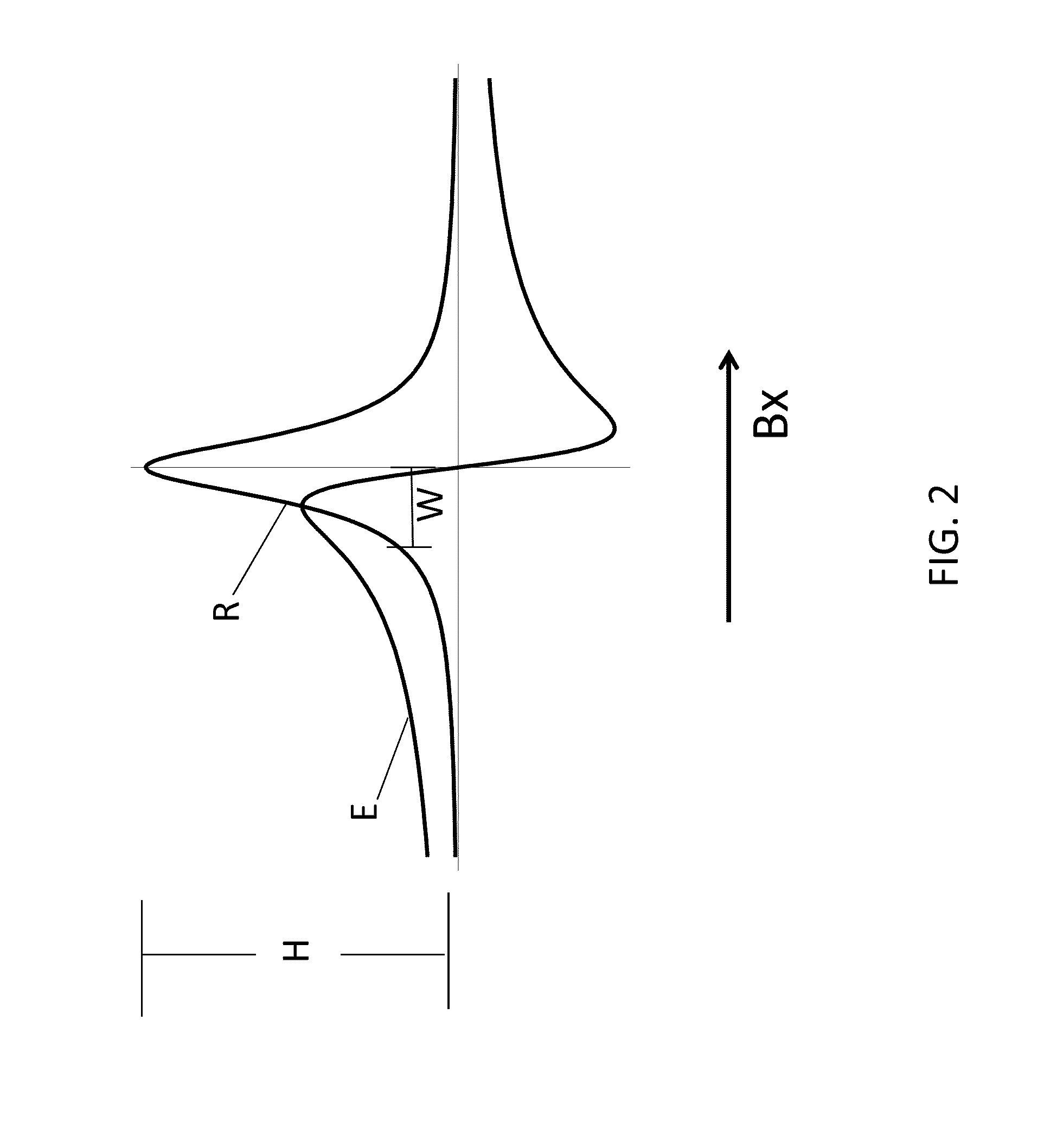
A zero-field paramagnetic resonance magnetometer (ZF-PRM) system and method for quickly and efficiently finding and optimizing the zero-field (ZF) resonance is described. In this system and method a magnetic coil is used to apply a magnetic bias field in the direction of the pump beam to artificially broaden the width and maximize the strength of the ZF resonance. By making the ZF resonance easy to detect, the ZF resonance may be found quickly found without the use of additional components and complex algorithms. Once the ZF resonance is found, a compensating magnetic field can be applied to null the magnetic field in the vicinity of the vapor cell in the ZF-PRM, thereby initializing it for operation.
Owner:QUSPIN
Method for detecting zero-field resonance
ActiveUS9116201B2Width minimizedImprove maximizationAnalysis using optical pumpingAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceResonanceBias field
A zero-field paramagnetic resonance magnetometer (ZF-PRM) system and method for quickly and efficiently finding and optimizing the zero-field (ZF) resonance is described. In this system and method a magnetic coil is used to apply a magnetic bias field in the direction of the pump beam to artificially broaden the width and maximize the strength of the ZF resonance. By making the ZF resonance easy to detect, the ZF resonance may be found quickly found without the use of additional components and complex algorithms. Once the ZF resonance is found, a compensating magnetic field can be applied to null the magnetic field in the vicinity of the vapor cell in the ZF-PRM, thereby initializing it for operation.
Owner:QUSPIN
Detection with evanescent wave probe
InactiveUS20070090836A1Improve spatial resolutionReduce background noiseMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceAnalysis using optical pumpingSpatially resolvedResonance
Methods and systems for spatially resolved spin resonance detection in a sample of material are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods and systems for spatially resolved impedance measurements in a sample of material. The disclosed methods and samples can be used in screening of plurality of biological, chemical and material samples.
Owner:INTEMATIX
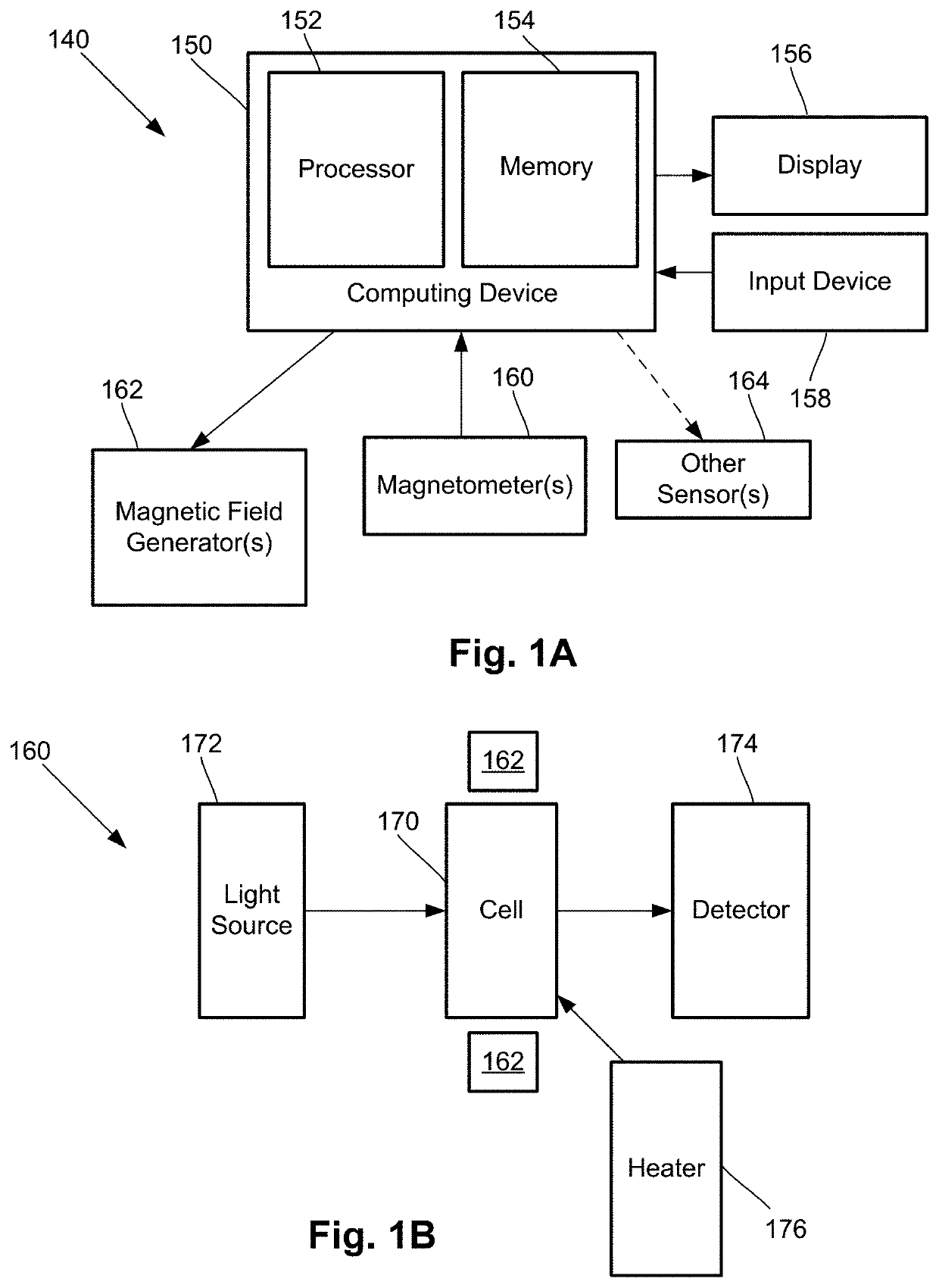
Integrated magnetometer arrays for magnetoencephalography (MEG) detection systems and methods
ActiveUS20200309873A1Analysis using optical pumpingDiagnostic recording/measuringWaferingEngineering
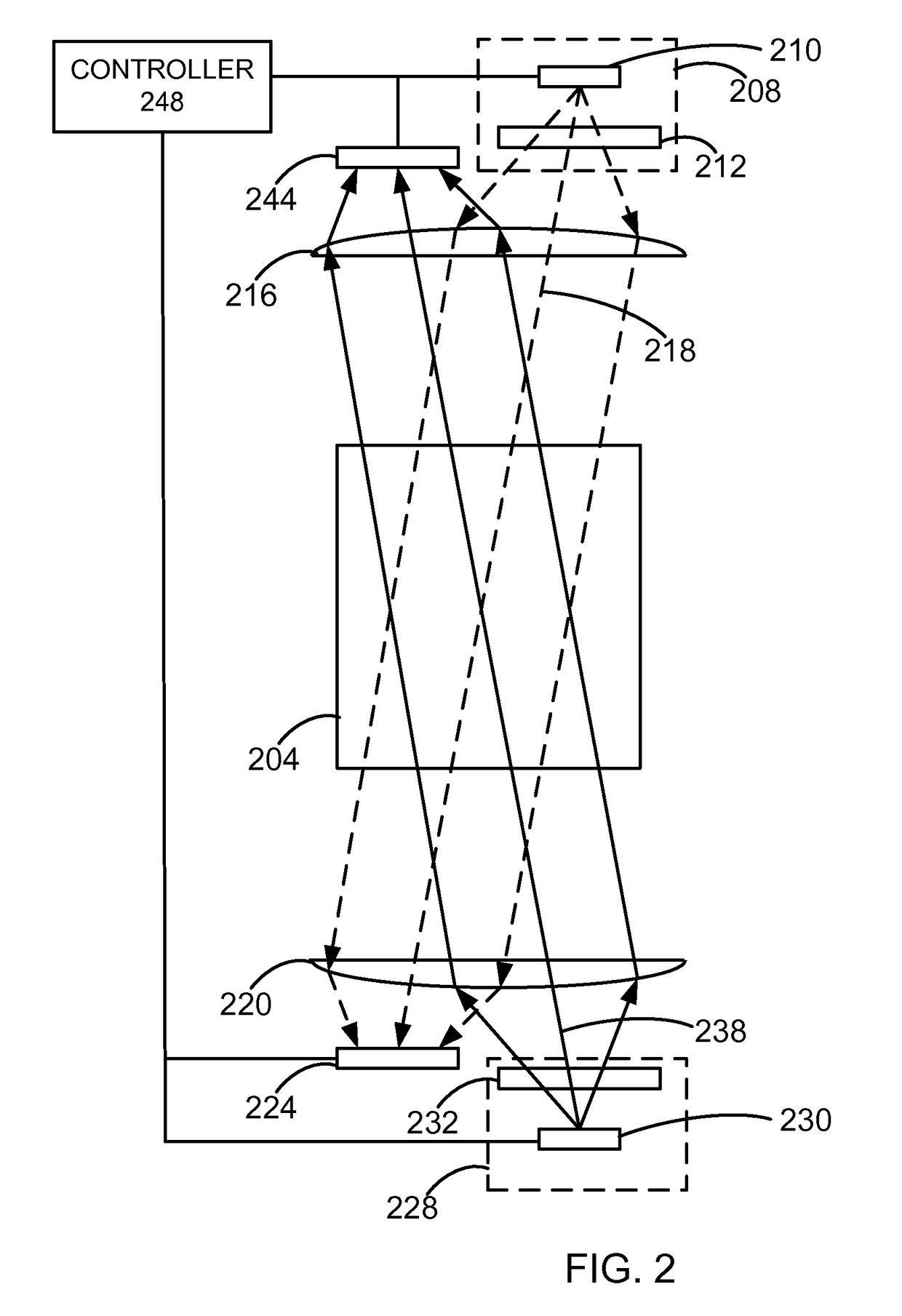
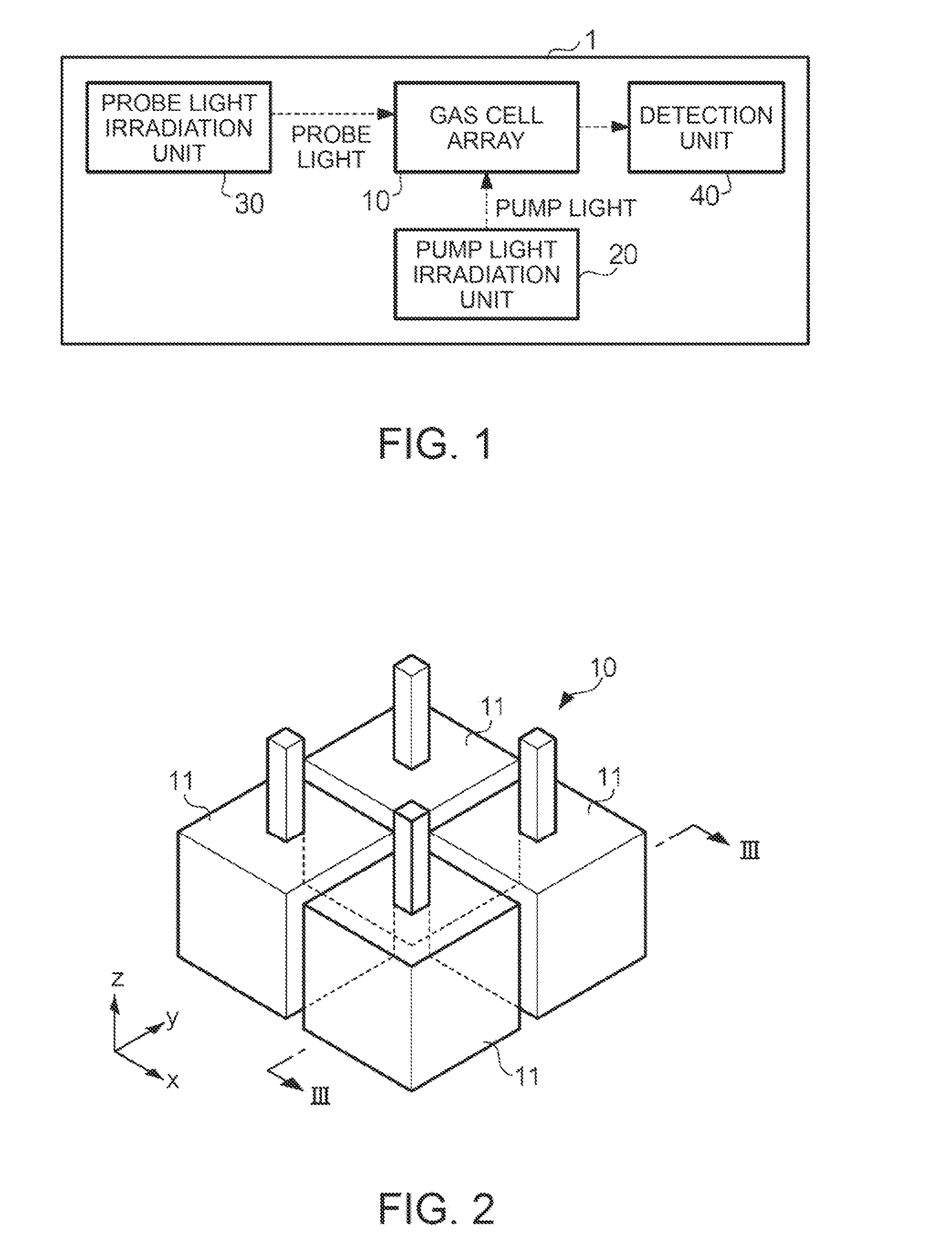
An array of optically pumped magnetometers includes a vapor cell arrangement having a wafer defining one or more cavities and alkali metal atoms disposed in the cavities to provide an alkali metal vapor; an array of light sources, each of the light sources arranged to illuminate a different portion of the one or more cavities of the vapor cell arrangement with light; at least one mirror arranged to reflect the light from the array of light sources after the light passes through the one or more cavities of the vapor cell arrangement; and an array of detectors to receive light reflected by the at least one mirror, wherein each of the detectors is arranged to receive light originating from one of the light sources.
Owner:HI LLC
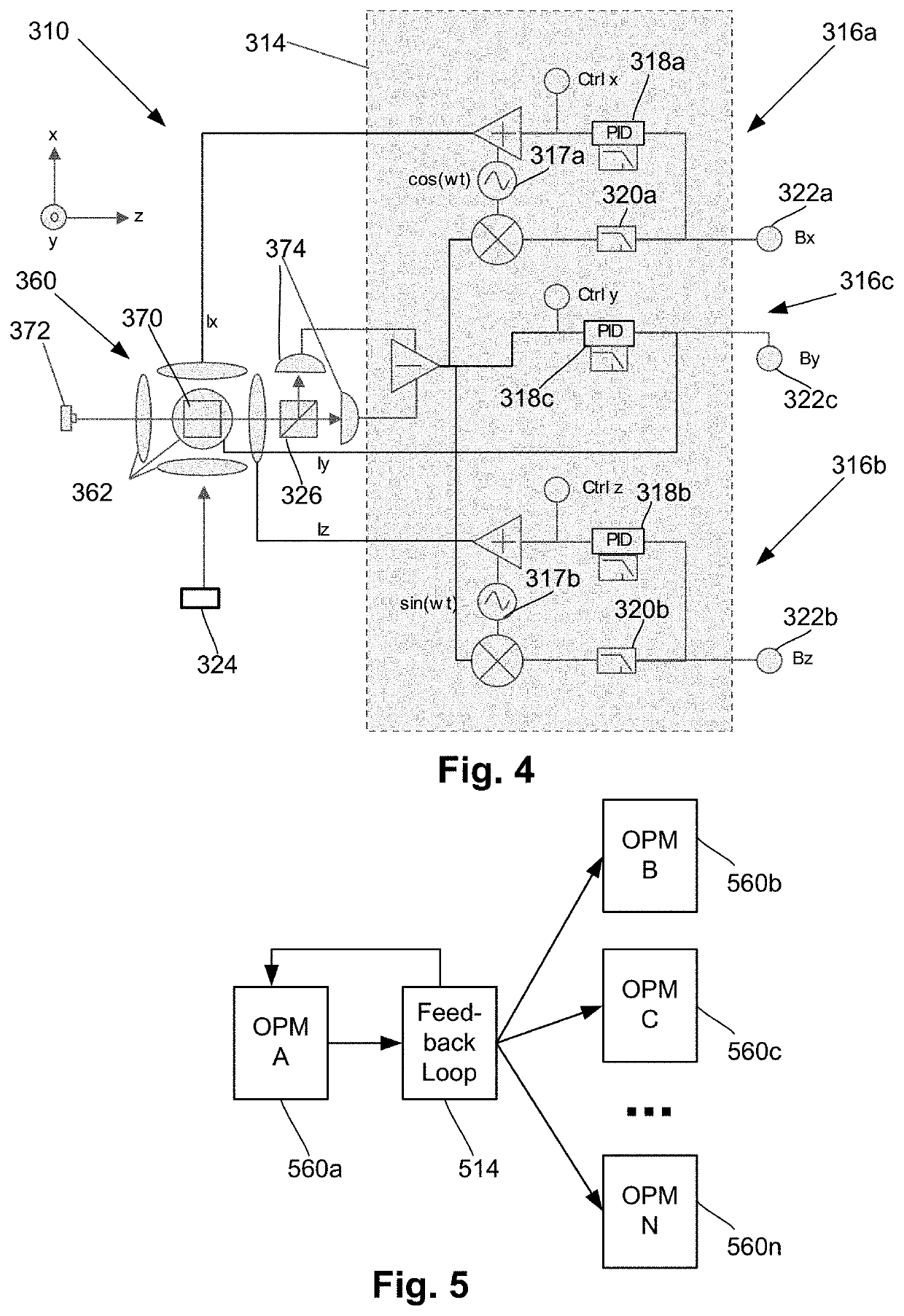
Neural feedback loop filters for enhanced dynamic range magnetoencephalography (MEG) systems and methods
ActiveUS20200256929A1Analysis using optical pumpingDiagnostic recording/measuringLow-pass filterSoftware engineering
One embodiment is a magnetic field measurement system that includes at least one magnetometer having a vapor cell, a light source to direct light through the vapor cell, and a detector to receive light directed through the vapor cell; at least one magnetic field generator disposed adjacent the vapor cell; and a feedback circuit coupled to the at least one magnetic field generator and the detector of the at least one magnetometer. The feedback circuit includes at least one feedback loop that includes a first low pass filter with a first cutoff frequency. The feedback circuit is configured to compensate for magnetic field variations having a frequency lower than the first cutoff frequency. The first low pass filter rejects magnetic field variations having a frequency higher than the first cutoff frequency and provides the rejected magnetic field variations for measurement as an output of the feedback circuit.
Owner:HI LLC
Quantum mechanical measurement device
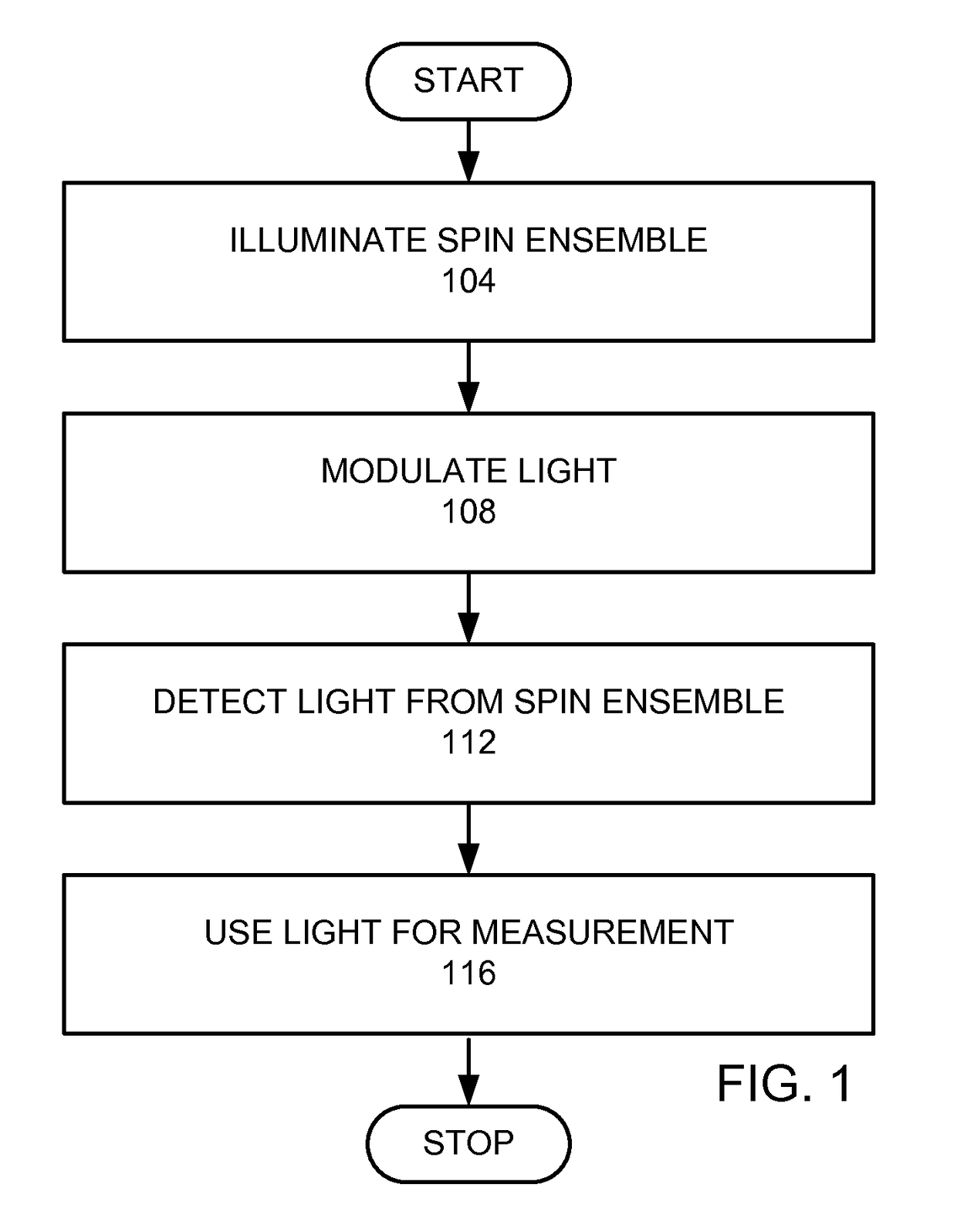
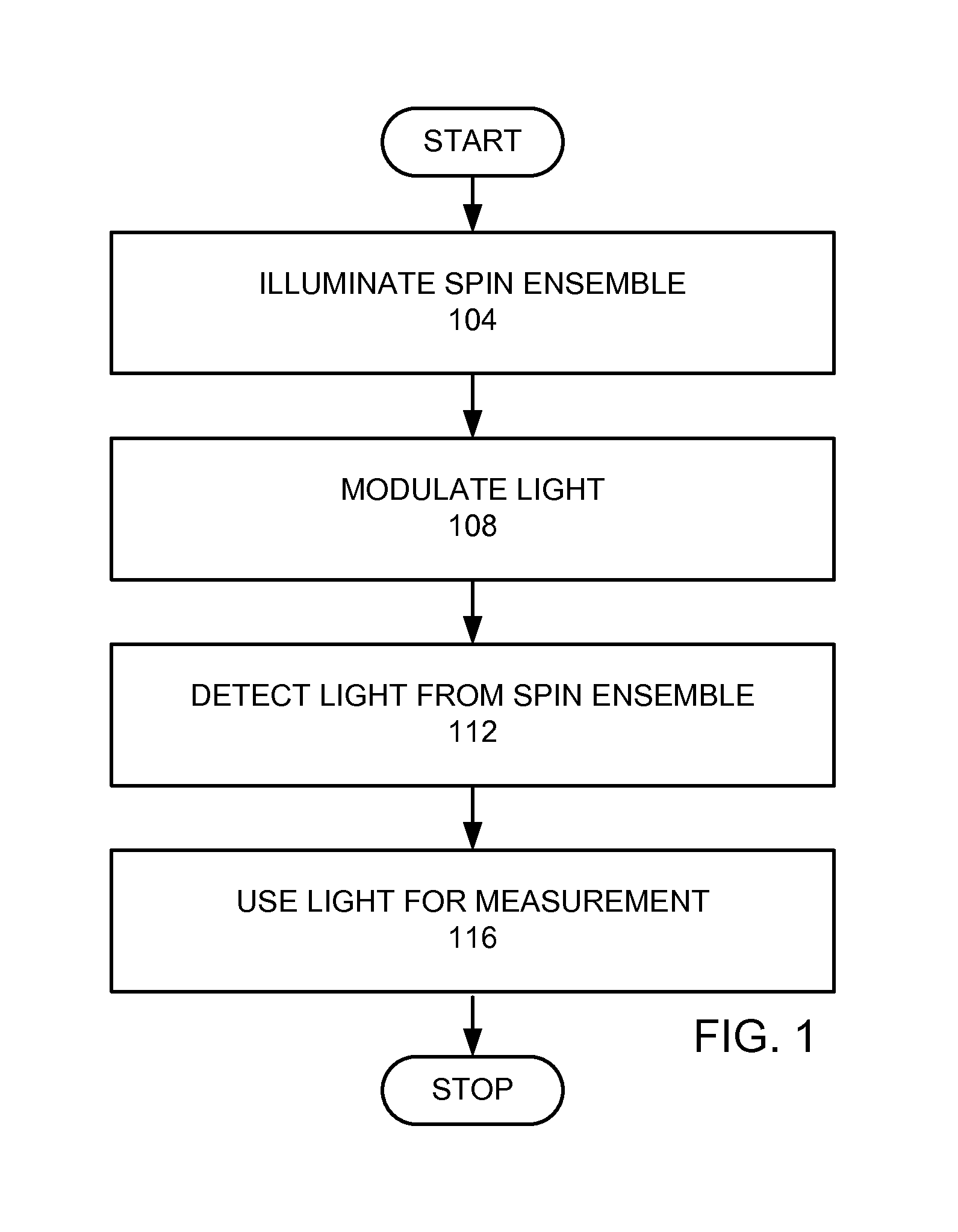
A quantum mechanical measurement device is provided. A spin ensemble is provided. A first light source provides a first light at a first wavelength, wherein the first light source is positioned to provide light into the spin ensemble. A detector is positioned to detect light from the spin ensemble. A modulator modulates absorption of the first light from the first light source by the spin ensemble at a frequency greater than a Larmor frequency of the spin ensemble.
Owner:GEOMETRICS
Method for the hyperpolarisation of nuclear spin in a diamond via a long-range interaction
ActiveUS20160061914A1Narrow line widthEfficient transferQuantum computersNanoinformaticsColour centreOptical pumping
The invention concerns a method for the hyperpolarisation of 13C nuclear spin in a diamond, comprising an optical pumping step, in which colour centre electron spins in the diamond are optically pumped. The method further comprises a transfer step in which the polarisation of a long-lived state of the colour centre electron spins is transferred to 13C nuclear spins in the diamond via a long-range interaction.
Owner:UNIV ULM
Methods and systems for fast field zeroing for magnetoencephalography (MEG)
PendingUS20210063510A1Easy to operateMagnetic field offset compensationAnalysis using optical pumpingLight beamParticle physics
A method of operating an optically pumped magnetometer (OPM) includes directing a light beam through a vapor cell of the OPM including a vapor of atoms; applying RF excitation to cause spins of the atoms to precess; measuring a frequency of the precession; for each of a plurality of different axes relative to the vapor cell, directing a light beam through the vapor cell, applying a magnetic field through the vapor cell along the axis, applying RF excitation to cause spins of the atoms to precess, and measuring a frequency of the precession in the applied magnetic field; determining magnitude and components of an ambient background magnetic field along the axes using the measured frequencies; and applying a magnetic field based on the components around the vapor cell to counteract the ambient background magnetic field to facilitate operation of the OPM in a spin exchange relaxation free (SERF) mode.
Owner:HI LLC
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy using light with orbital angular momemtum
InactiveUS20100327866A1Less noisyHigh resolutionLaser detailsAnalysis using optical pumpingTwo-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopySpectroscopy
The present invention relates to a device capable of producing a high resolution chemical analysis of a sample, such as fluid, based upon nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, where the nuclear magnetic polarizations of the sample are generated by sequentially illuminating the sample with a focused beam of light carrying angular orbital angular momentum (OAM) and possibly momentum (spin). Unlike in usual NMR used for magnetic nuclear resonance imaging (MRI) or spectroscopy, the invention does not make use of a strong magnet.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Magnetic sensor
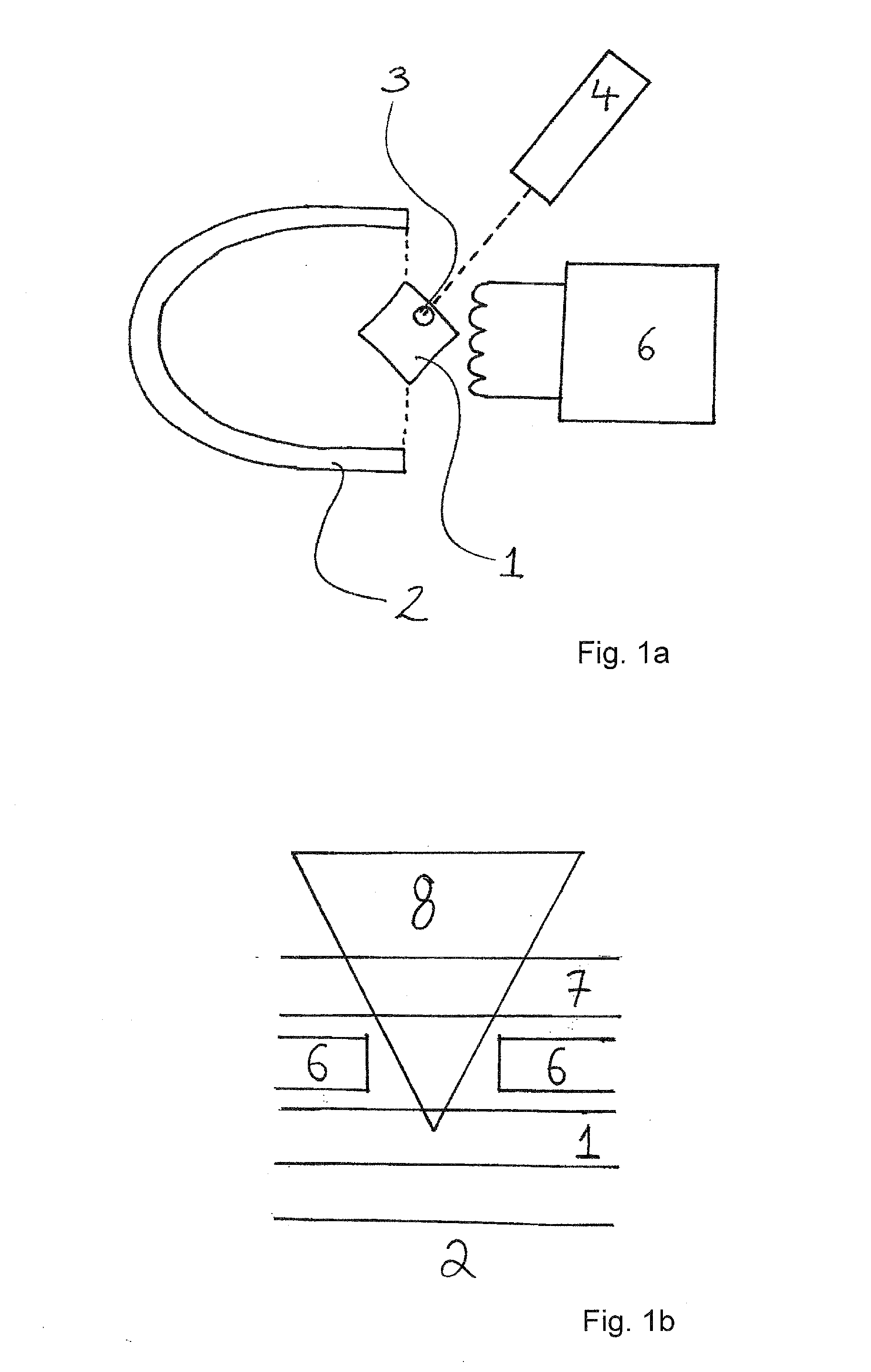
ActiveUS20100327865A1Simple device structureEasy to set upAnalysis using optical pumpingElectric/magnetic detectionOptical pumpingValence electron
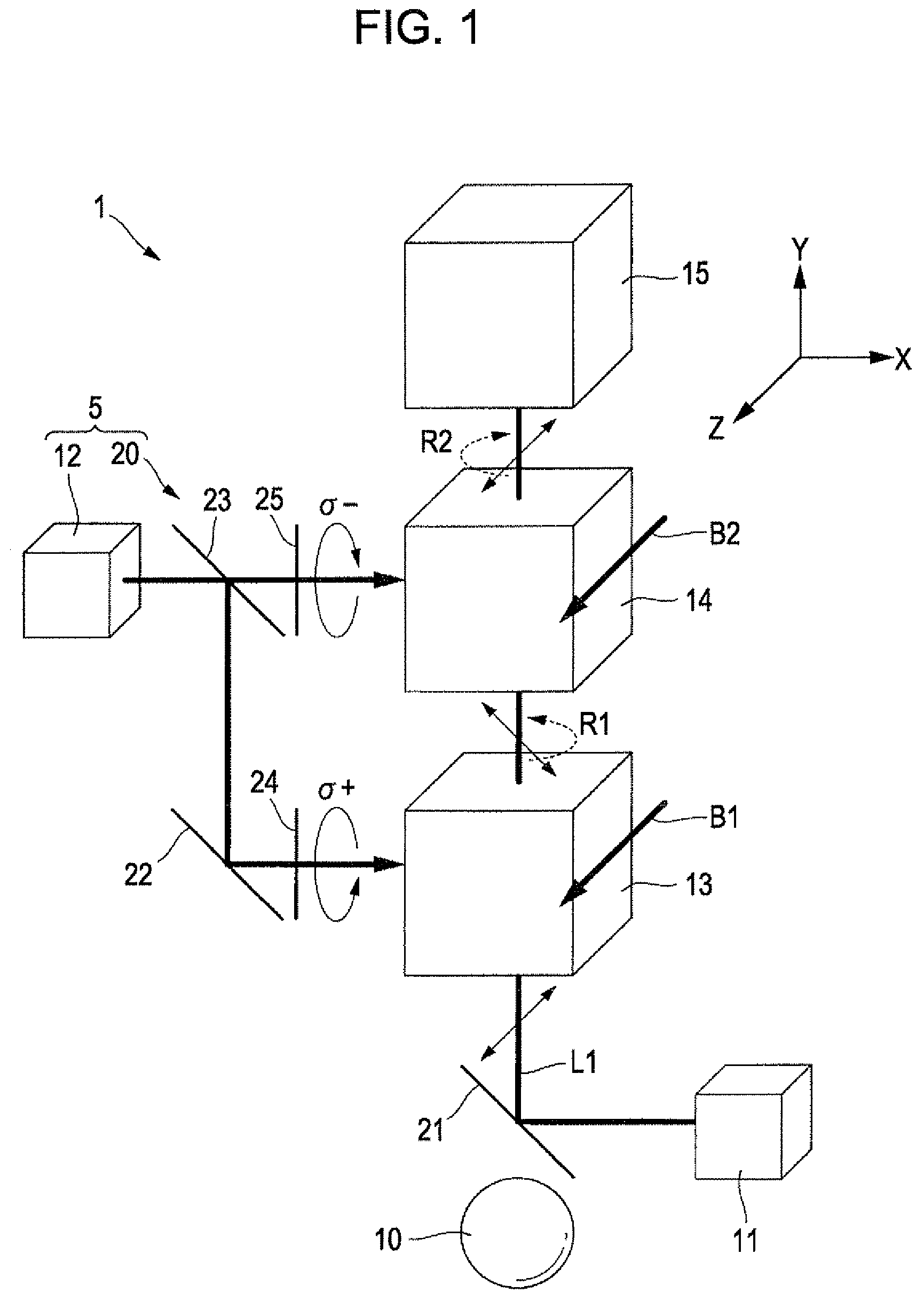
A magnetic sensor for measuring a magnetic field using an optical pumping method includes a first gas in which a valence electron is composed of an odd number of atoms or ions, a probe light incidence device which causes first probe light including straight polarized light to be incident on the first gas, a second gas in which a valence electron arranged on an optical path of second probe light that is the first probe light transmitted through the first gas is composed of an odd number of atoms or ions, a pumping light incidence device which causes first pumping light including first circular polarized light to be incident on the first gas and second pumping light including second circular polarized light to be incident on the second gas, and a detector which detects a rotation angle of a polarization plane of the first probe light and a polarization plane of third probe light that is the second probe light transmitted through the second gas.
Owner:COLUMBIA PEAK VENTURES LLC
Scalar atomic magnetometer with heading error suppression
ActiveUS10274549B1Analysis using optical pumpingMeasurements using magnetic resonanceAtomic vaporLaser beams
An atomic magnetometer includes a vapor cell, one or more pumping lasers, a probe laser, and a sensor. The one or more pumping lasers are disposed to direct one or more laser beams though the vapor cell to interact with atoms of an atomic vapor in the vapor cell. The atomic vapor periodically absorbs light of alternating circular polarization from the one or more laser beams. The probe laser is disposed to direct polarized light to pass through the vapor cell. The sensor is disposed to intersect the polarized light from the probe laser after passing through the vapor cell.
Owner:AOSENSE
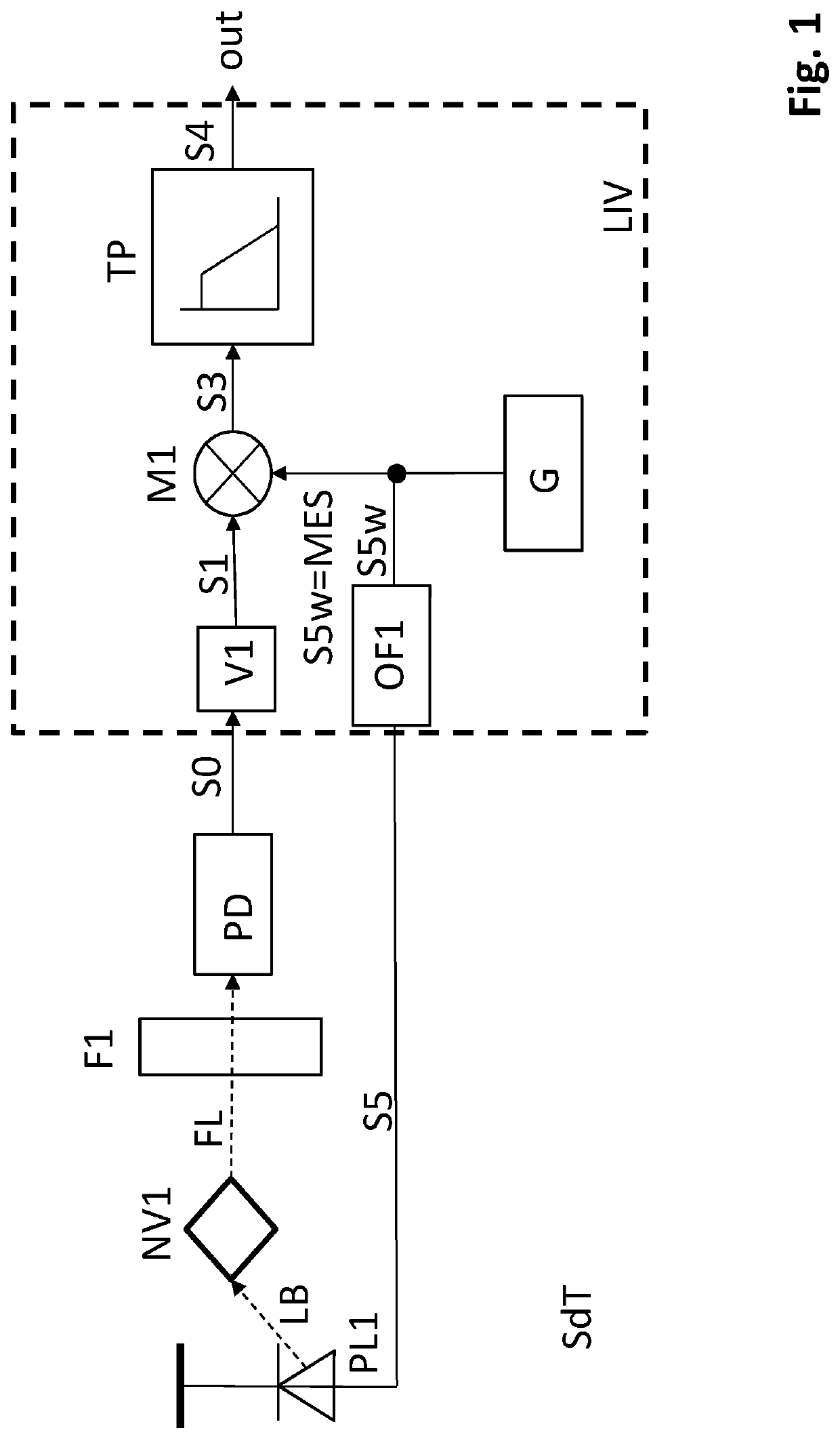
Magnetic field measurement device
ActiveUS20160146909A1Reduce noiseGuaranteed uptimeLaser detailsAnalysis using optical pumpingMeasurement deviceMagnetic measurements
A magnetic measurement device has a magnetic sensor including a glass cell having alkali metal gas encapsulated therein that is configured to detect a magnetic field using a magneto-optical characteristic of spin-polarized alkali metal. A laser light source is configured to generate pump light introduced into the magnetic sensor and a coil provided in the same magnetically shielded space as the magnetic sensor is configured to apply a static magnetic field and a RF magnetic field to the magnetic sensor. A signal processor is configured to perform lock-in detection of a light detection signal transmitted through the glass cell of the magnetic sensor, control an intensity of the static magnetic field and a frequency of the RF magnetic field generated by the coil according to a lock-in detection output, and obtain a measurement signal reflecting a magnetic field intensity of an object to be measured in the magnetically shielded space.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy using light with orbital angular momentum
InactiveCN101939638AHigh sensitivityReduce noiseAnalysis using optical pumpingMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyTwo-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopySpectroscopy
The present invention relates to a device capable of producing a high resolution chemical analysis of asample, such as fluid, based uponnuclear magneticresonance (NMR) spectroscopy, where the nuclear magnetic polarizations of the sample are generated by sequentiallyilluminating the sample with a focused beam of lightcarrying angular orbital angular momentum(OAM) and possiblymomentum (spin). Unlike in usual NMR used for (10) magneticnuclear resonance imaging (MRI) or spectroscopy, the invention does not make use of a strong magnet.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Magnetic sensor
ActiveUS8362768B2Improve accuracySimple structureAnalysis using optical pumpingElectric/magnetic detectionValence electronOptical pumping
A magnetic sensor for measuring a magnetic field using an optical pumping method includes a first gas in which a valence electron is composed of an odd number of atoms or ions, a probe light incidence device which causes first probe light including straight polarized light to be incident on the first gas, a second gas in which a valence electron arranged on an optical path of second probe light that is the first probe light transmitted through the first gas is composed of an odd number of atoms or ions, a pumping light incidence device which causes first pumping light including first circular polarized light to be incident on the first gas and second pumping light including second circular polarized light to be incident on the second gas, and a detector which detects a rotation angle of a polarization plane of the first probe light and a polarization plane of third probe light that is the second probe light transmitted through the second gas.
Owner:COLUMBIA PEAK VENTURES LLC
Gas Cell
InactiveUS20150369427A1Inhibition of relaxationInhibitionContainer filling methodsAnalysis using optical pumpingInterior spaceHydrogen
A gas cell includes a cell main body having an internal space defined by inner walls, a gas of alkali metal or hydrogen sealed in the internal space, and a coating layer formed at least on part of the inner walls using a material having a long-chain molecule structure, wherein molecules more than half of molecules forming the coating layer are perpendicularly oriented with respect to the inner walls.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
A magnetometer using optically active defects in a solid state material
ActiveUS20200158798A1Improve efficiencyEnhanced responsivityMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceAnalysis using optical pumpingOptical cavityFluorescence
The present invention relates to a magnetometer (100) using optically detected magnetic resonance (ODMR), where a solid state material (10), such as diamond, with an ensemble of paramagnetic defects, such as nitrogen vacancies centers NV, is applied. An optical cavity (20) is optically excited by an irradiation laser (25) arranged therefore. A coupling structure (30) causes a microwave excitation (Ω) of the paramagnetic defects, and a permanent magnetic field (40, B_C) causes a Zeeman splitting of the energy levels in the paramagnetic defects. A probing volume (PV) in the solid state material is thereby defined by the spatially overlapping volume of the optical excitation by the irradiation laser (25), the coupling structure (30) also exciting the defects, and the constant magnetic field. The magnetometer then measures an unknown magnetic field by detecting emission (27), e.g. fluorescence, from the defects in the probing volume (PV) from the double excitation of the defects by the irradiation laser, and the coupling structure exciting these defects.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
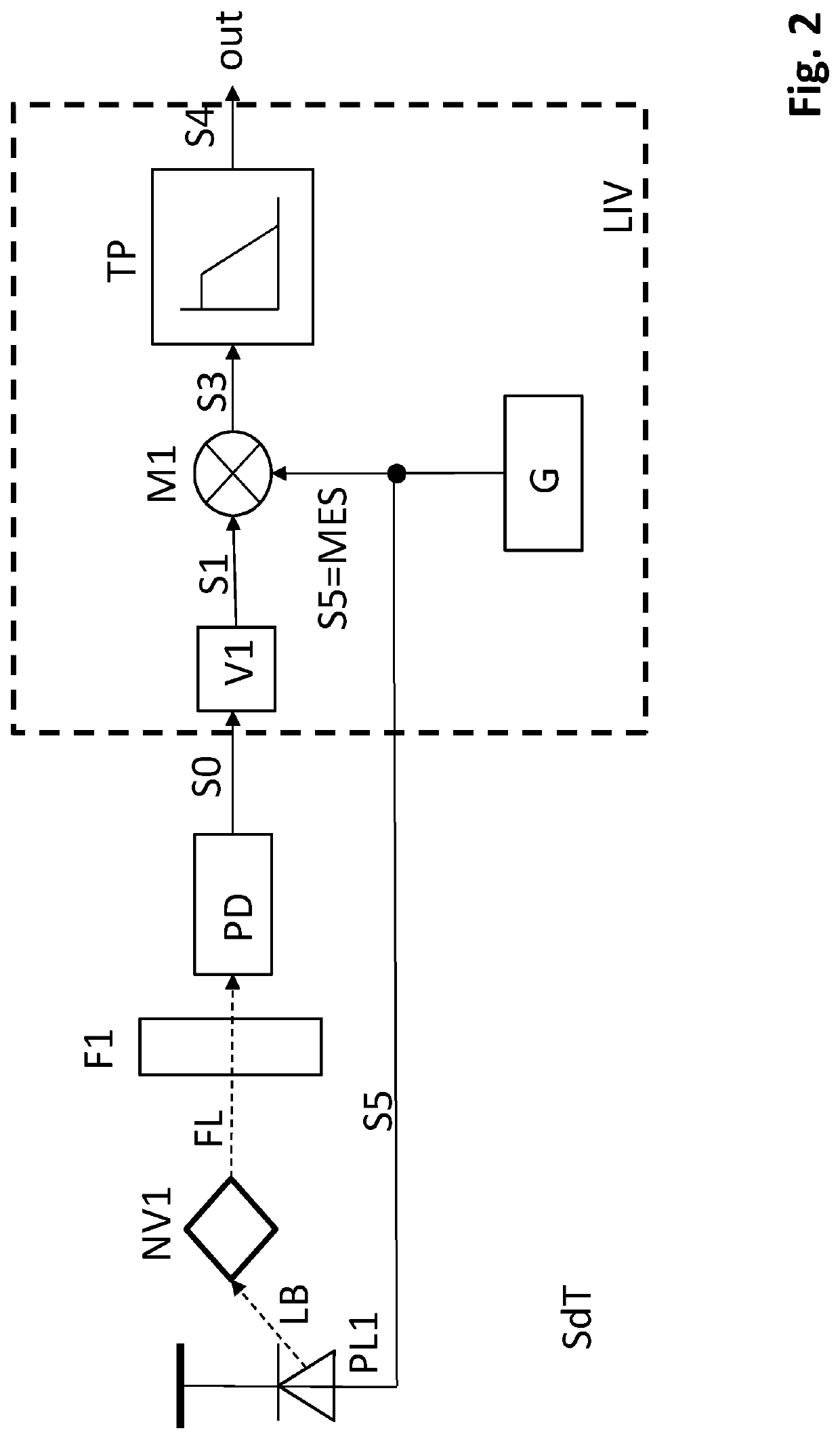
Magnetic field measurement device
ActiveUS10162021B2Reduce noiseGuaranteed uptimeLaser detailsAnalysis using optical pumpingMeasurement deviceMagnetic measurements
A magnetic measurement device has a magnetic sensor including a glass cell having alkali metal gas encapsulated therein that is configured to detect a magnetic field using a magneto-optical characteristic of spin-polarized alkali metal. A laser light source is configured to generate pump light introduced into the magnetic sensor and a coil provided in the same magnetically shielded space as the magnetic sensor is configured to apply a static magnetic field and a RF magnetic field to the magnetic sensor. A signal processor is configured to perform lock-in detection of a light detection signal transmitted through the glass cell of the magnetic sensor, control an intensity of the static magnetic field and a frequency of the RF magnetic field generated by the coil according to a lock-in detection output, and obtain a measurement signal reflecting a magnetic field intensity of an object to be measured in the magnetically shielded space.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Sensors and methods of identifying a gas, and levitated spin-optomechanical systems
ActiveUS20180059039A1Analysis using optical pumpingAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceMicrowaveSpins
Sensors and methods are provided that include a diamond material containing a nitrogen vacancy center, the diamond material being configured to be exposed to an environment comprising one or more gases, an optical light source configured to excite the nitrogen vacancy center of the diamond material with an optical light beam produced therefrom, a detector configured to detect a signal originating from the diamond material in response to the optical light beam exciting the nitrogen vacancy center, and the capability of analyzing the signal to identify a specific gas in the environment. Also included are levitated spin-optomechanical systems capable of elevating in a vacuum a diamond material containing a nitrogen vacancy center, applying microwave radiation to the diamond material for controlling and flipping the electron spin of the nitrogen vacancy center, and monitoring electron spin of the nitrogen vacancy center.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Quantum mechanical measurement device
ActiveUS20130214780A1Analysis using optical pumpingElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurement deviceSpins
A quantum mechanical measurement device is provided. A spin ensemble is provided. A first light source provides a first light at a first wavelength, wherein the first light source is positioned to provide light into the spin ensemble. A detector is positioned to detect light from the spin ensemble. A modulator modulates absorption of the first light from the first light source by the spin ensemble at a frequency greater than a Larmor frequency of the spin ensemble.
Owner:GEOMETRICS
Hyperpolarisation device using photons with orbital angular momentum
A magnetic resonance examination system comprises an RF-system for inducing resonance in polarised dipoles and receiving magnetic resonance signals from an object to be examined and an photonic-based hyperpolarisation device. The an electromagnetic source for emitting photonic radiation: - a mode converter to impart orbital angular momentum to the electromagnetic radiation; a spatial filter to select from the mode converter a diffracted or refracted photonic beam endowed with orbital angular momentum for polarising the dipoles via transferred orbital angular momentum; - a beam controller to apply the photonic beam endowed with orbital angular momentum over an extended target zone.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Detection with evanescent wave probe
InactiveUS20070085541A1Improve spatial resolutionReduce background noiseMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceAnalysis using optical pumpingSpatially resolvedResonance
Methods and systems for spatially resolved spin resonance detection in a sample of material are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods and systems for spatially resolved impedance measurements in a sample of material. The disclosed methods and samples can be used in screening of plurality of biological, chemical and material samples.
Owner:INTEMATIX
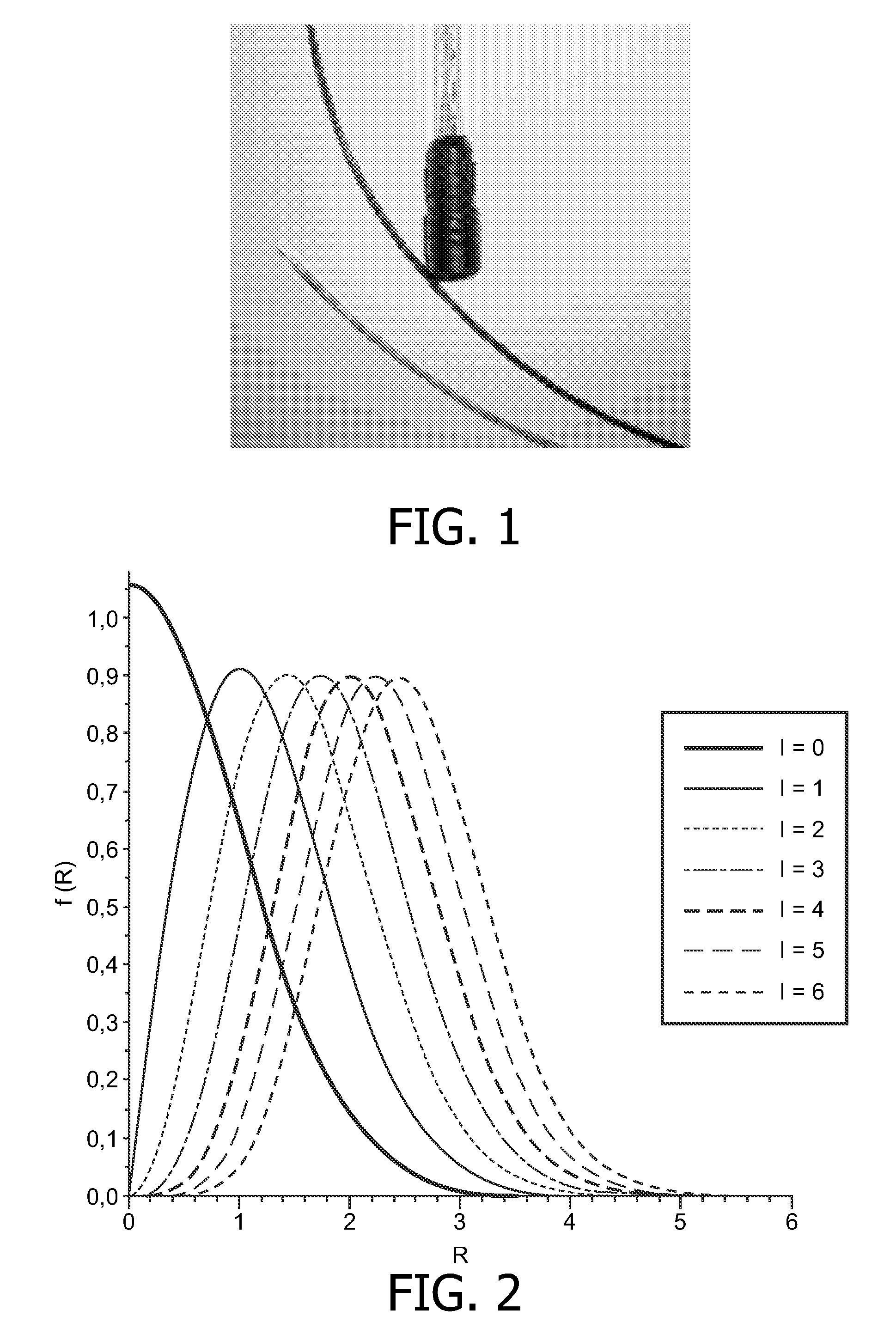
Experimental device for detecting ODMR spectrum of diamond NV color center based on DAC device
The invention discloses an experimental device for detecting an ODMR spectrum of a diamond NV color center based on a DAC device. A beam expanding lens, a second reflecting mirror, a first reflectingmirror, a focusing lens, ruby and the diamond NV color center are sequentially installed on a light path emitted by a laser device. A focusing lens, a filter lens, a collimating lens and a photoelectric detector are sequentially arranged on a light path of fluorescence emitted by the ruby and diamond NV color center, and the photoelectric detector is connected with a signal collector. The microwave generator is sequentially connected with the power amplifier and the copper wires through SMA port connecting wires; two ends of the platinum wire are connected with copper wires; and the diamond NVcolor center is picked up to be close to the platinum wire. The experimental device for detecting the ODMR spectrum of the diamond NV color center based on the DAC device is simple in structure, anda new choice is provided for detection of the superconducting phenomenon and the like.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy using light with orbital angular momentum
InactiveUS8508222B2Less noisyHigh measurement sensitivityLaser detailsMasersTwo-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopySpectroscopy
A device capable of producing a high resolution chemical analysis of a sample, such as fluid, is based upon nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The nuclear magnetic polarizations of the sample are generated by sequentially illuminating the sample with a focused beam of light carrying angular orbital angular momentum (OAM) and possibly momentum (spin). Unlike in a typical NMR used for magnetic nuclear resonance imaging (MRI) or spectroscopy, the present device does not make use of a strong magnet.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Nv-center-based microwave-free quantum sensor and uses and characteristics thereof
PendingUS20220307997A1Low densityIncrease productionDiamondAnalysis using optical pumpingQuantum sensorHigh density
A sensor system is based on diamonds with a high density of NV centers. The description includes a) methods for producing the necessary diamonds of high NV center density, b) characteristics of such diamonds, c) sensing elements for utilizing the fluorescence radiation of such diamonds, d) sensing elements for utilizing the photocurrent of such diamonds, e) systems for evaluating these quantities, f) reduced noise systems for evaluating these systems, g) enclosures for using such systems in automatic placement equipment, g) methods for testing these systems, and h) a musical instrument as an example of an ultimate application of all these devices and methods.
Owner:QUANTUM TECH UG GMBH
Systems and methods for multimodal pose and motion tracking for magnetic field measurement or recording systems
PendingUS20210369201A1Analysis using optical pumpingDiagnostic recording/measuringData streamMedicine
A magnetic field recording system includes a headgear to be placed on a user; optically pumped magnetometers (OPMs) disposed in or on the headgear to detect magnetic fields; at least two sensing modalities selected from the following: i) a magnetic sensing modality, ii) an optical sensing modality, or iii) an inertial sensing modality; and a tracking unit configured to receive, from each of the at least two sensing modalities, a corresponding magnetic data stream, optical data stream, or inertial data stream and to track a position or orientation of the headgear or user; and a system controller configured to control operation of the OPMs and to receive, from the tracking unit, the position or orientation of the headgear or user.
Owner:HI LLC
Neural feedback loop filters for enhanced dynamic range magnetoencephalography (MEG) systems and methods
ActiveUS11022658B2Analysis using optical pumpingDiagnostic recording/measuringLow-pass filterSoftware engineering
One embodiment is a magnetic field measurement system that includes at least one magnetometer having a vapor cell, a light source to direct light through the vapor cell, and a detector to receive light directed through the vapor cell; at least one magnetic field generator disposed adjacent the vapor cell; and a feedback circuit coupled to the at least one magnetic field generator and the detector of the at least one magnetometer. The feedback circuit includes at least one feedback loop that includes a first low pass filter with a first cutoff frequency. The feedback circuit is configured to compensate for magnetic field variations having a frequency lower than the first cutoff frequency. The first low pass filter rejects magnetic field variations having a frequency higher than the first cutoff frequency and provides the rejected magnetic field variations for measurement as an output of the feedback circuit.
Owner:HI LLC
Microwave Resonator Readout of an Ensemble Solid State Spin Sensor
InactiveUS20210255258A1Enhanced interactionMagnetic field offset compensationMagnetic property measurementsFluorescenceParticle physics
Microwave resonator readout of the cavity-spin interaction between a spin defect center ensemble and a microwave resonator yields fidelities that are orders of magnitude higher than is possible with optical readouts. In microwave resonator readout, microwave photons probe a microwave resonator coupled to a spin defect center ensemble subjected to a physical parameter to be measured. The physical parameter shifts the spin defect centers' resonances, which in turn change the dispersion and / or absorption of the microwave resonator. The microwave photons probe these dispersion and / or absorption changes, yielding a measurement with higher visibility, lower shot noise, better sensitivity, and higher signal-to-noise ratio than a comparable fluorescence measurement. In addition, microwave resonator readout enables coherent averaging of spin defect center ensembles and is compatible with spin systems other than nitrogen vacancies in diamond.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Microwave resonator readout of an ensemble solid state spin sensor
ActiveUS10962611B2Enhanced interactionMagnetic field offset compensationMagnetic property measurementsFluorescenceParticle physics
Microwave resonator readout of the cavity-spin interaction between a spin defect center ensemble and a microwave resonator yields fidelities that are orders of magnitude higher than is possible with optical readouts. In microwave resonator readout, microwave photons probe a microwave resonator coupled to a spin defect center ensemble subjected to a physical parameter to be measured. The physical parameter shifts the spin defect centers' resonances, which in turn change the dispersion and / or absorption of the microwave resonator. The microwave photons probe these dispersion and / or absorption changes, yielding a measurement with higher visibility, lower shot noise, better sensitivity, and higher signal-to-noise ratio than a comparable fluorescence measurement. In addition, microwave resonator readout enables coherent averaging of spin defect center ensembles and is compatible with spin systems other than nitrogen vacancies in diamond.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Caesium optical pump detector specially used for buried corrosive pipelines
ActiveCN108426906AImprove detection efficiencyImprove detection accuracyAnalysis using optical pumpingMeasurements using magnetic resonanceOptical ModuleResonance
The invention discloses a caesium optical pump detector specially used for buried corrosive pipelines. The caesium optical pump detector comprises a pumping light generation module, a first optical module, a magnetic resonance module, a photoelectric detection module, a signal processing module, and a terminal control module; the signal processing module is connected with the photoelectric detection module; the single processing module comprises a frequency waveband selection unit; the terminal control module comprises a buried pipeline database; the frequency waveband selection unit is used for selecting different working wave bands based on the data from the buried pipeline database, so that monitoring efficiency and precision are increased.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for the hyperpolarisation of nuclear spin in a diamond via a long-range interaction
ActiveUS10345400B2Narrow line widthEfficient transferQuantum computersNanoinformaticsColour centreOptical pumping
The invention concerns a method for the hyperpolarisation of 13C nuclear spin in a diamond, comprising an optical pumping step, in which colour centre electron spins in the diamond are optically pumped. The method further comprises a transfer step in which the polarisation of a long-lived state of the colour centre electron spins is transferred to 13C nuclear spins in the diamond via a long-range interaction.
Owner:UNIV ULM
Popular searches
Acoustic wave reradiation Analysis using nuclear magnetic resonance Sensors Magnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devices Magnetic sensor arrays Electrodynamic magnetometers Stray field compensation Measurements using NMR imaging systems Analysis using double resonance Magnetic variable regulation
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com