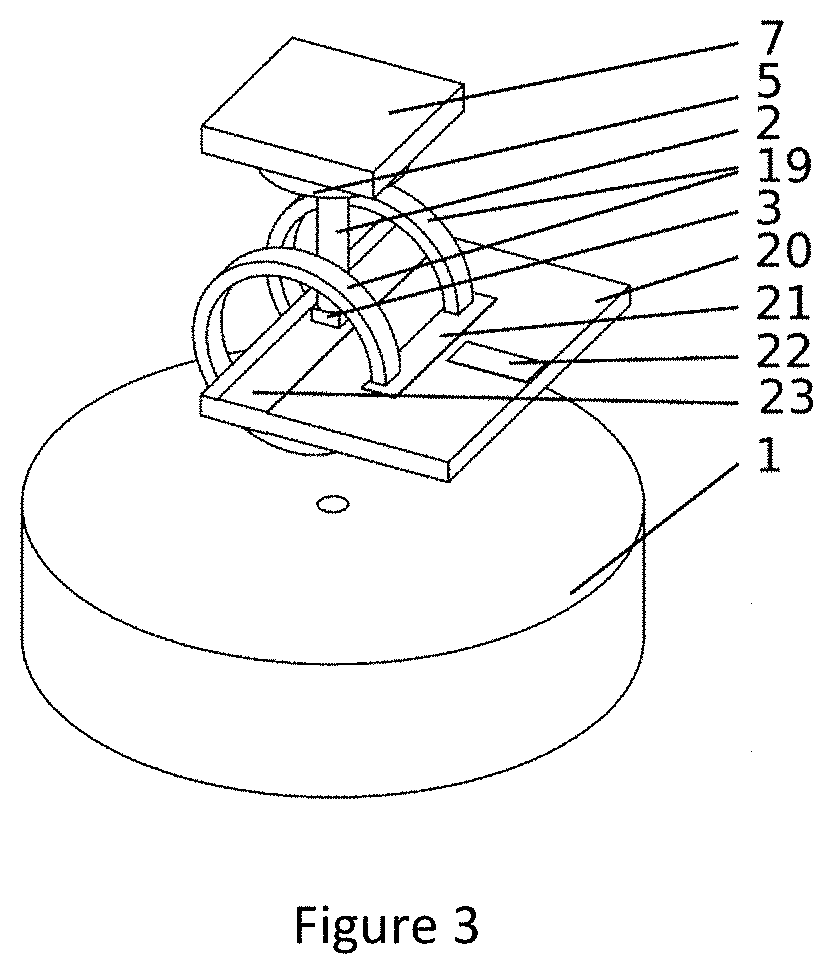
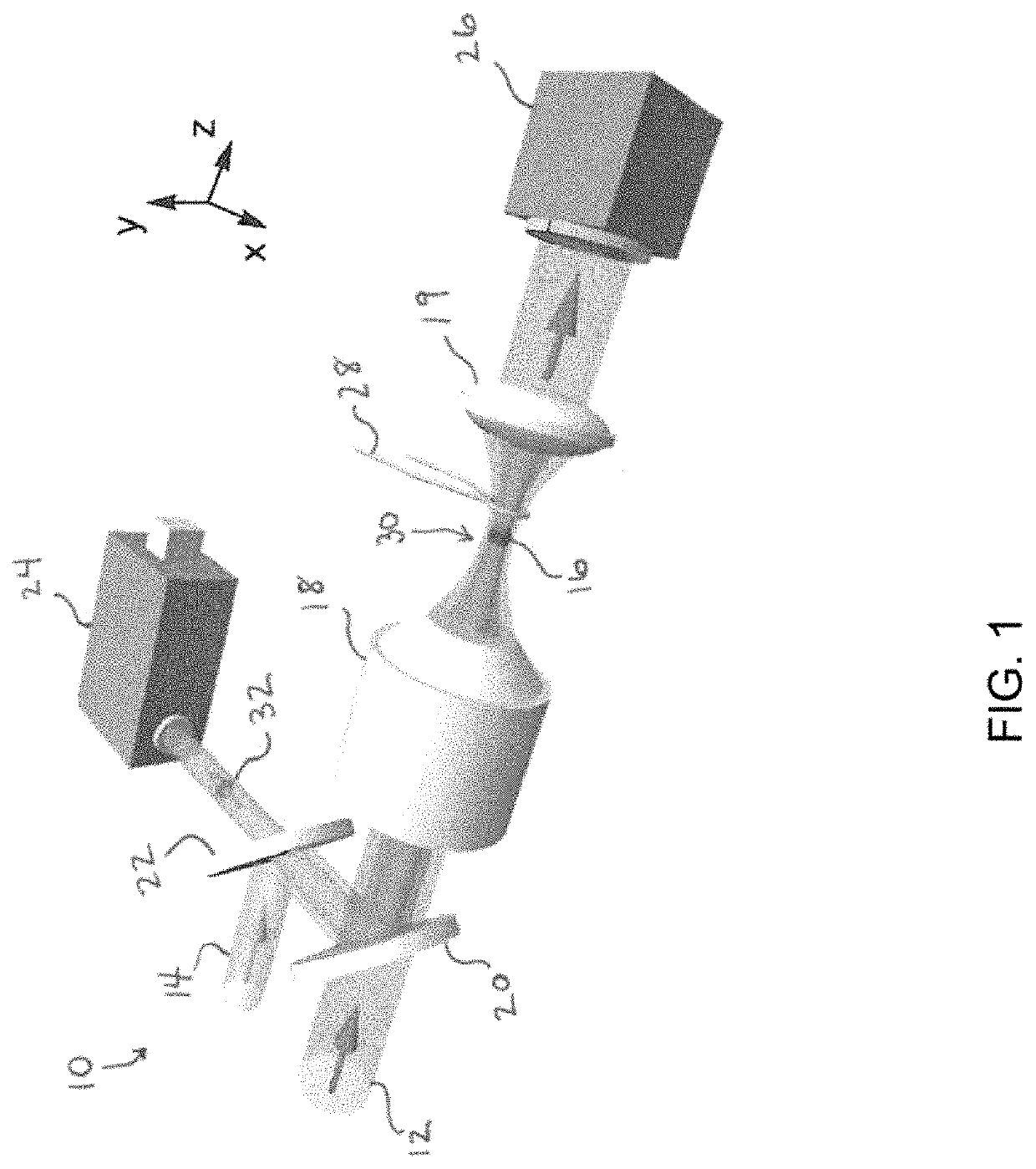
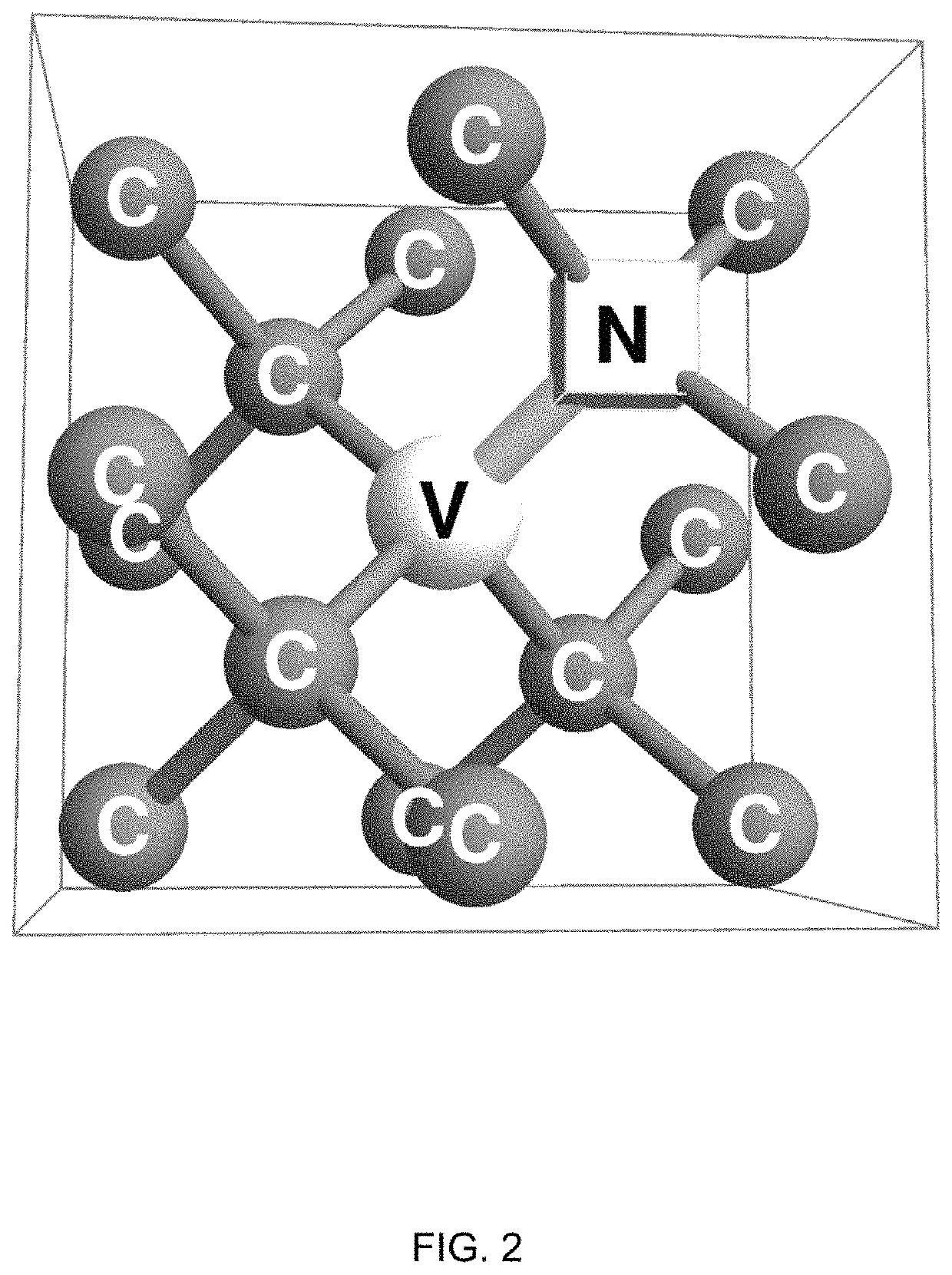
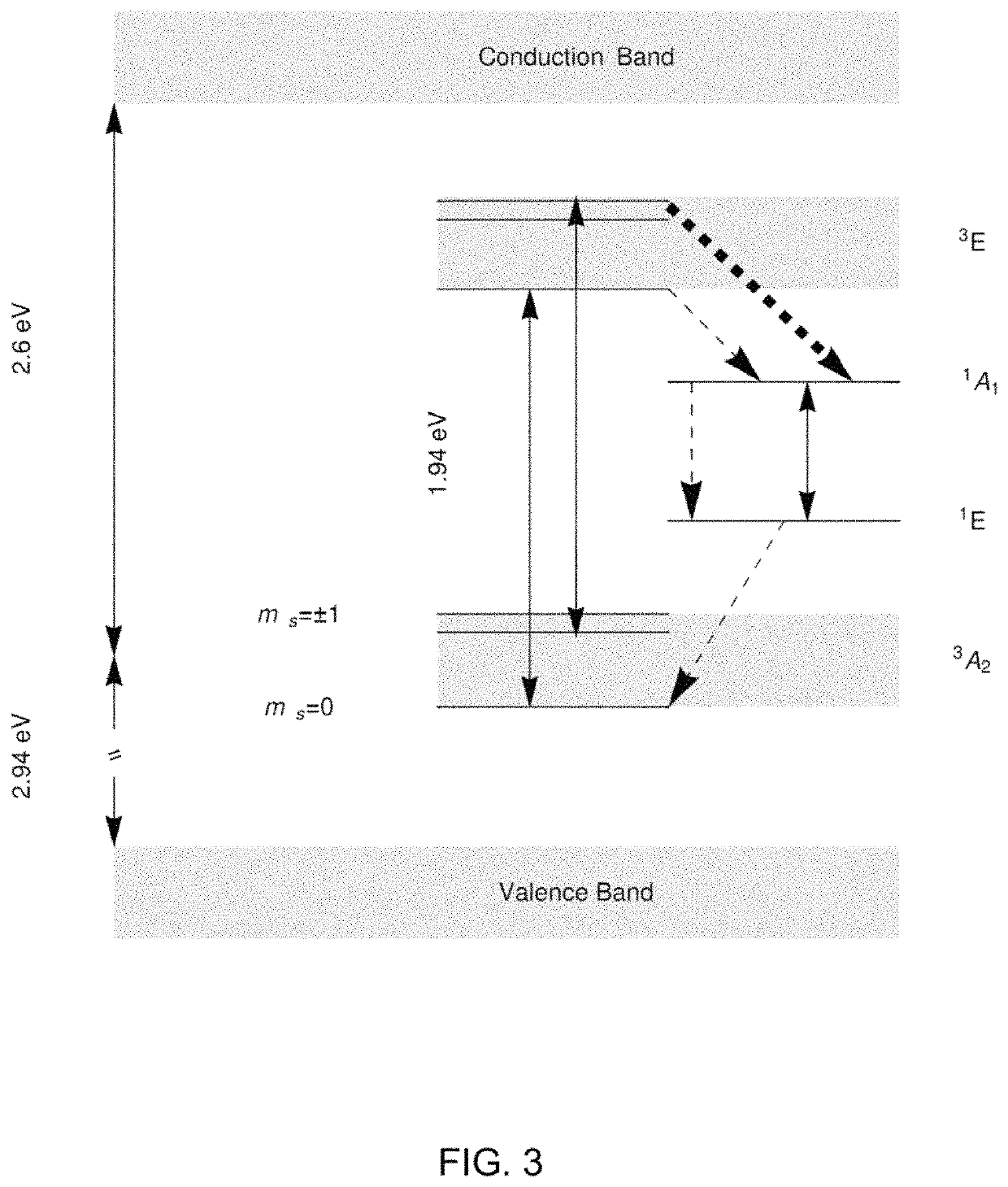
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Nitrogen-vacancy center" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
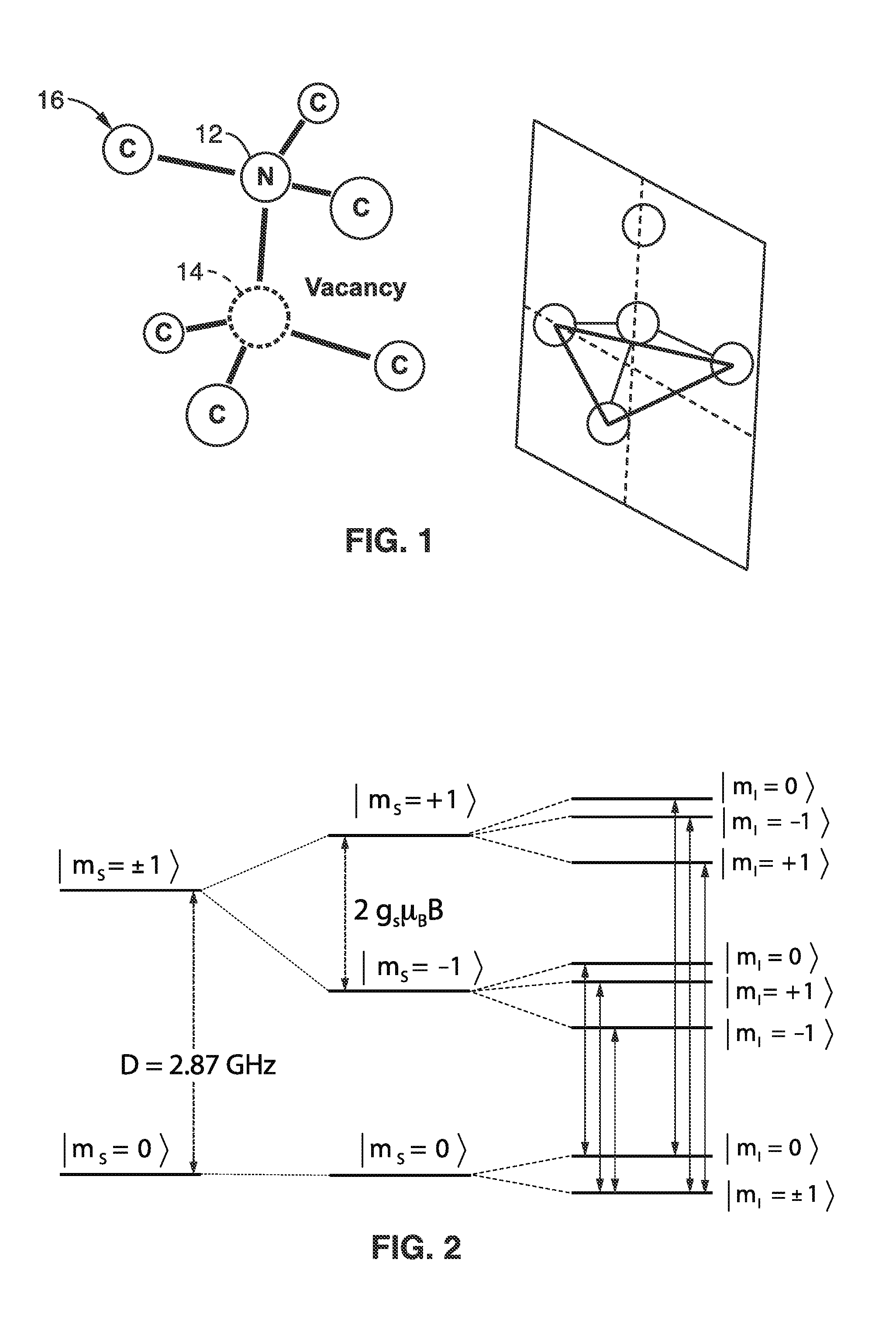
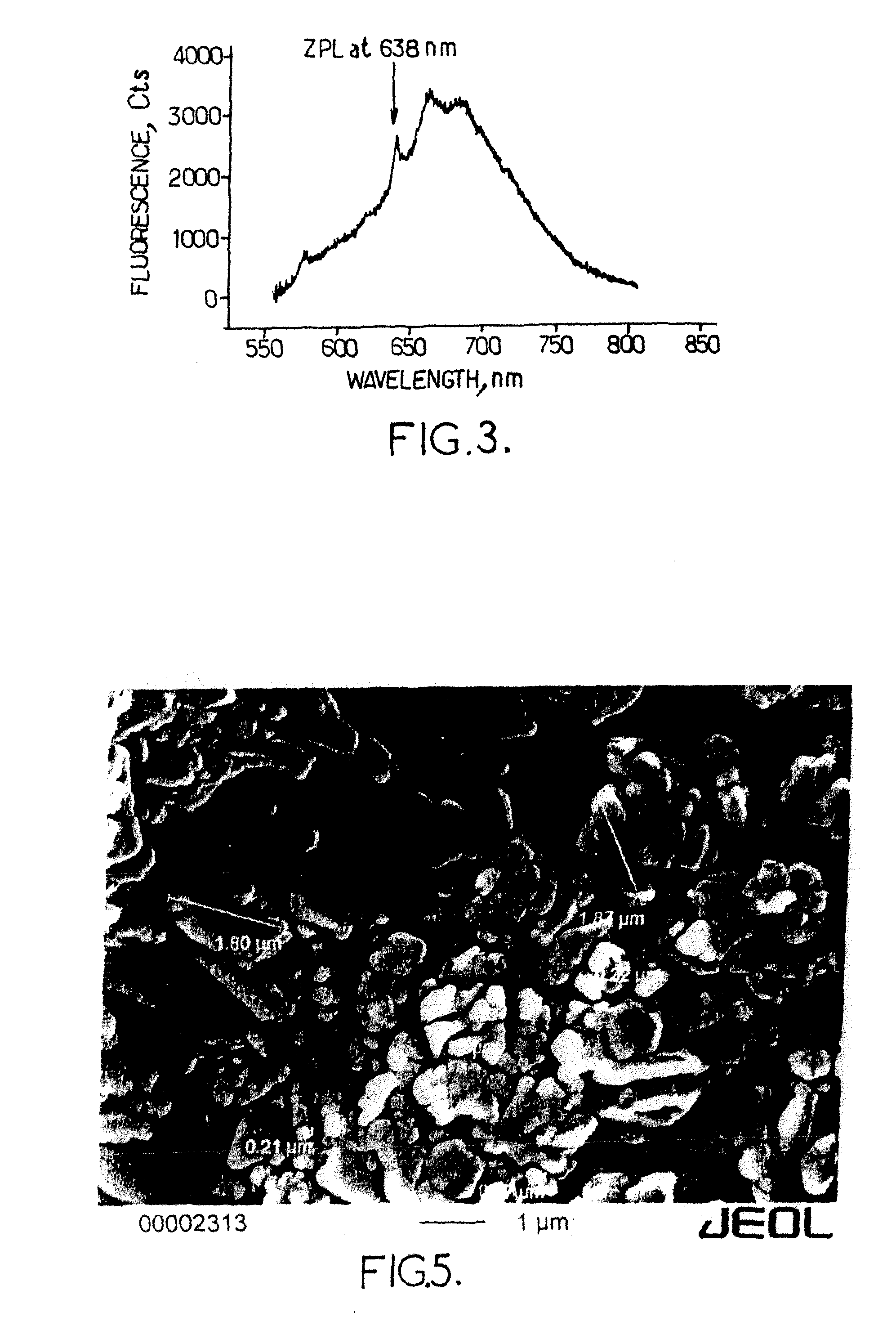
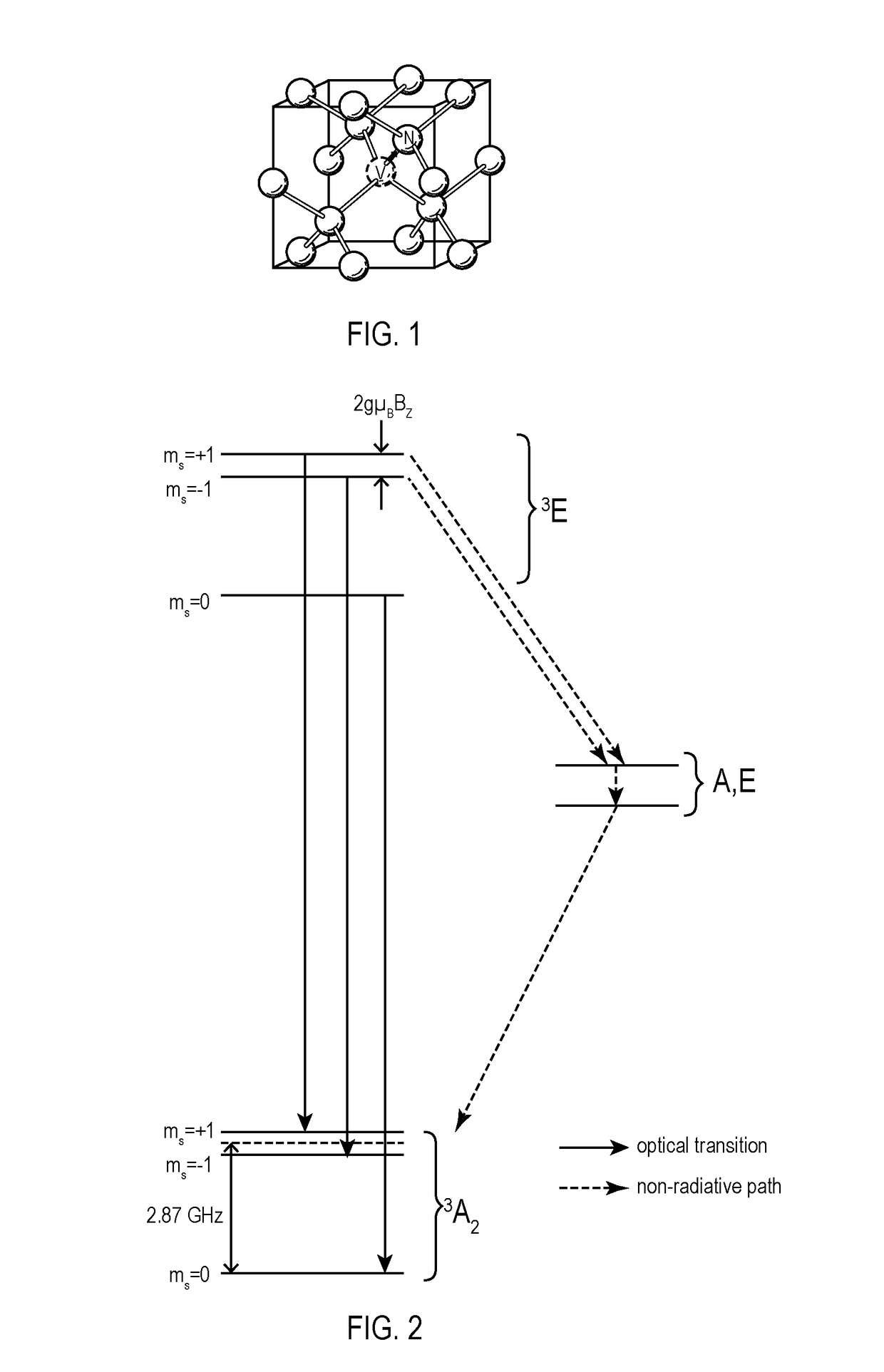
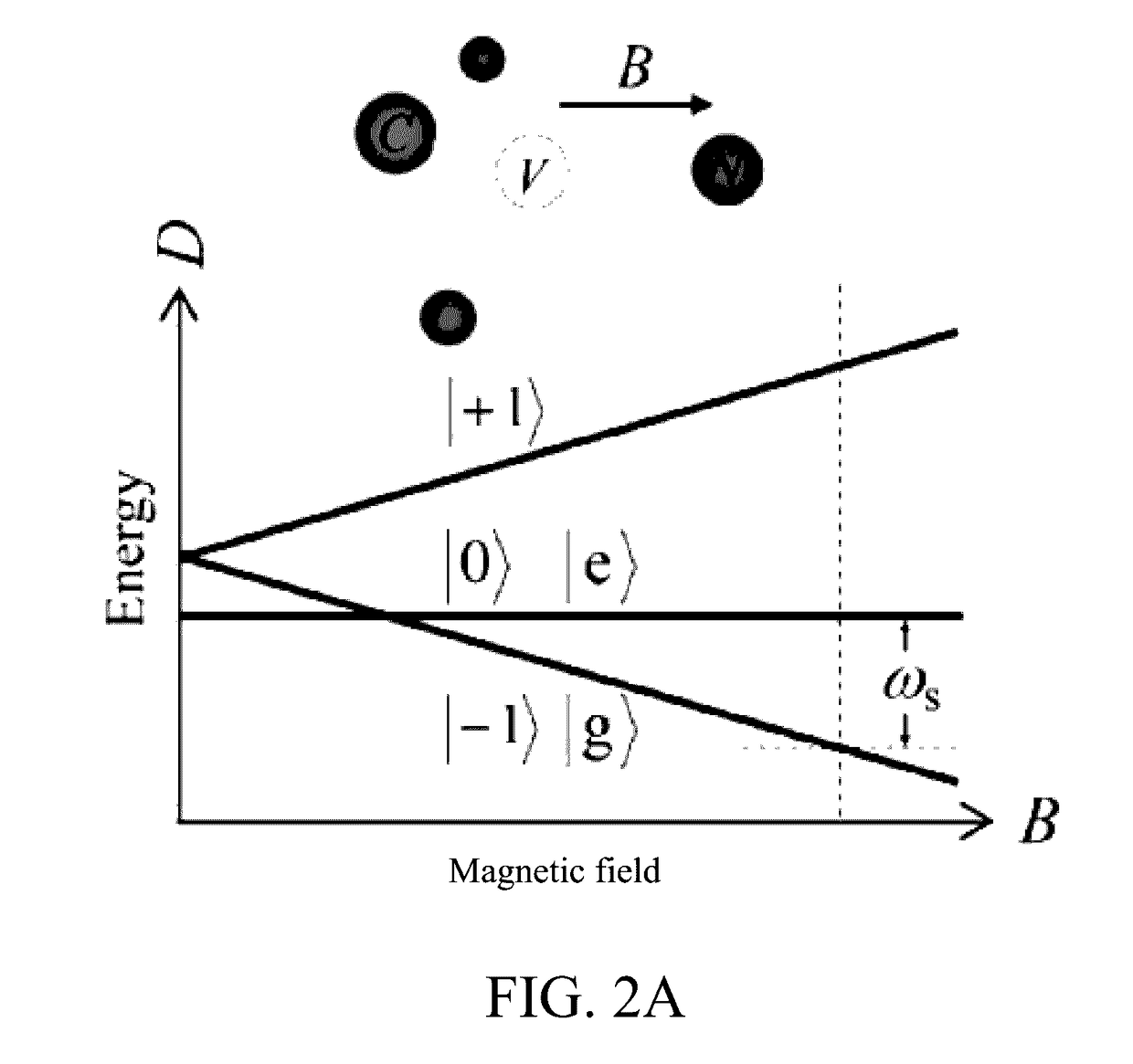
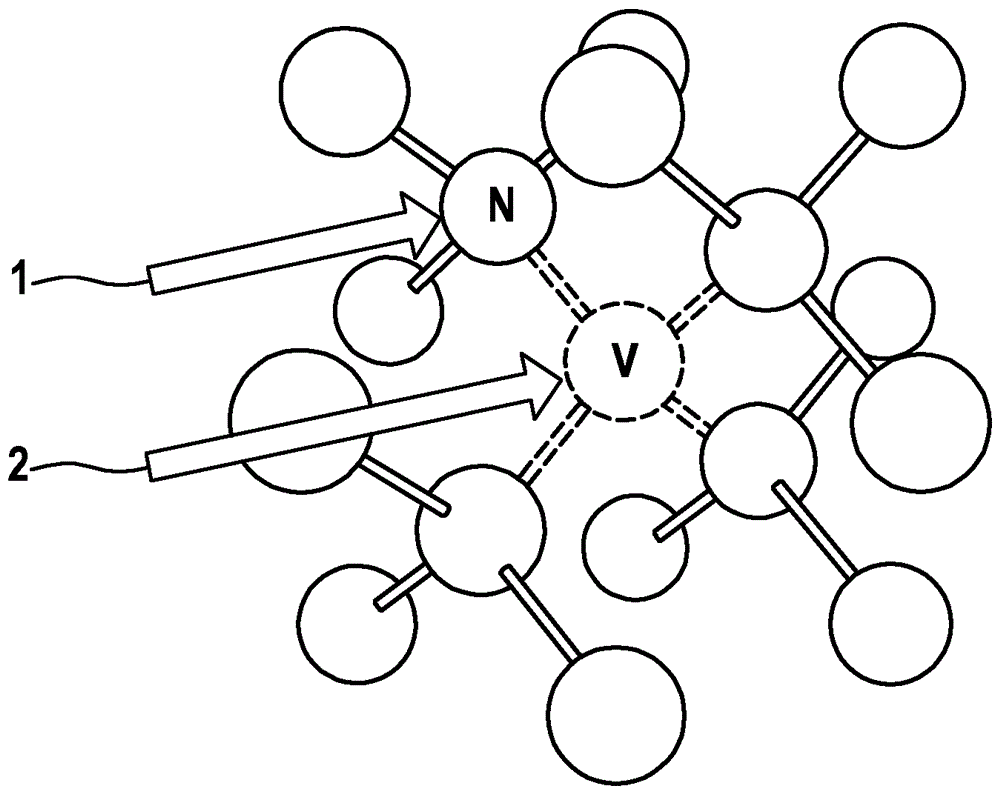
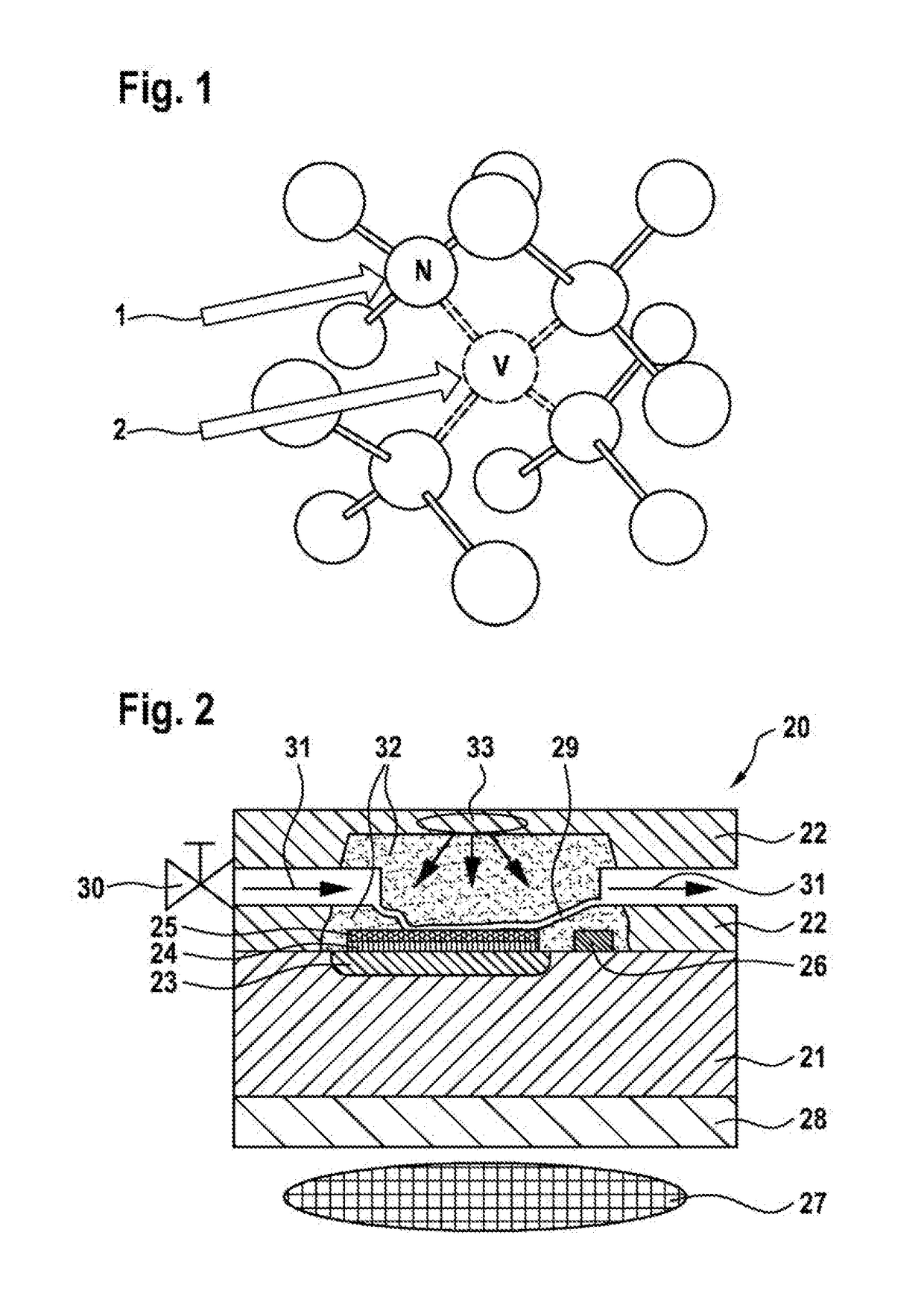
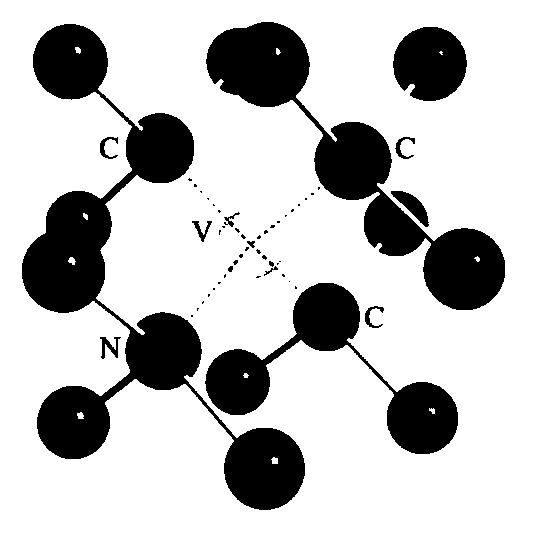
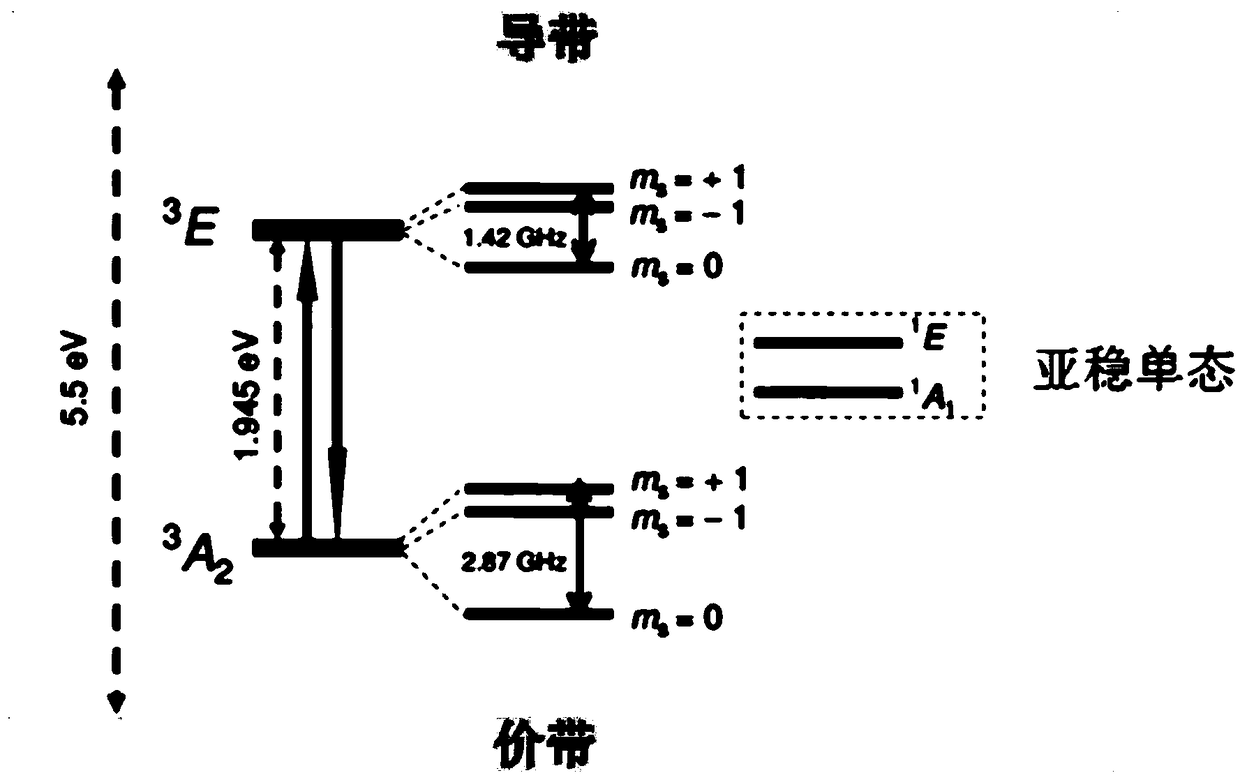
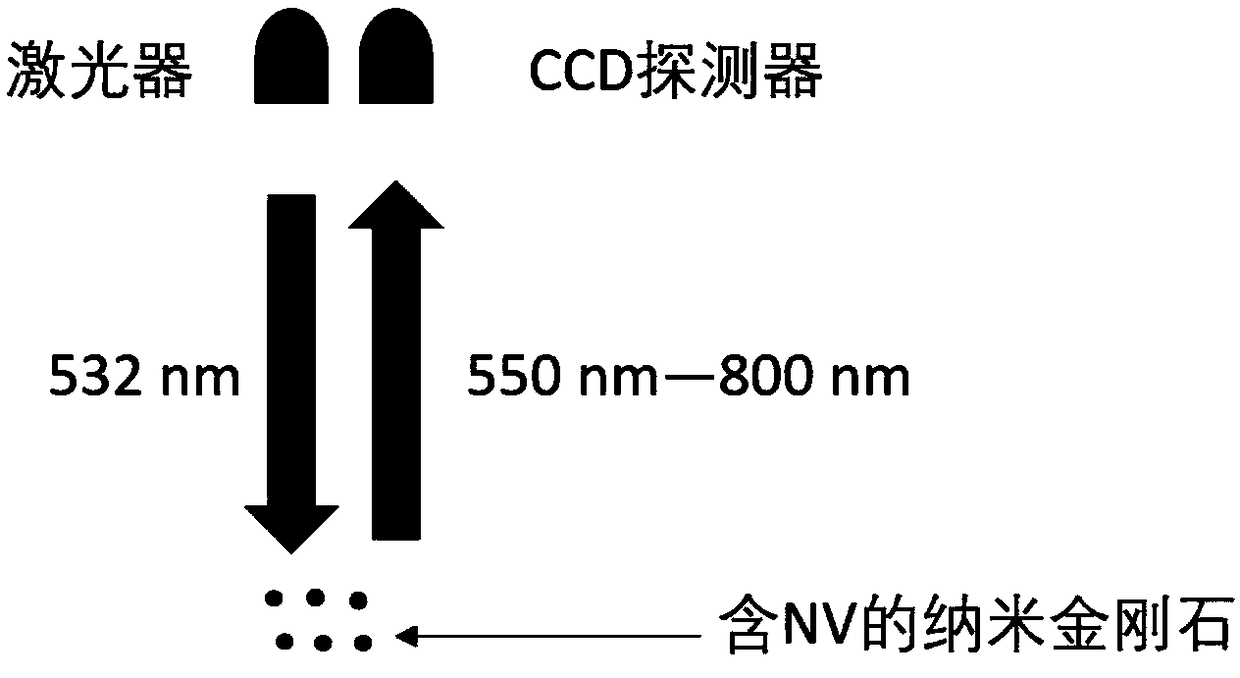
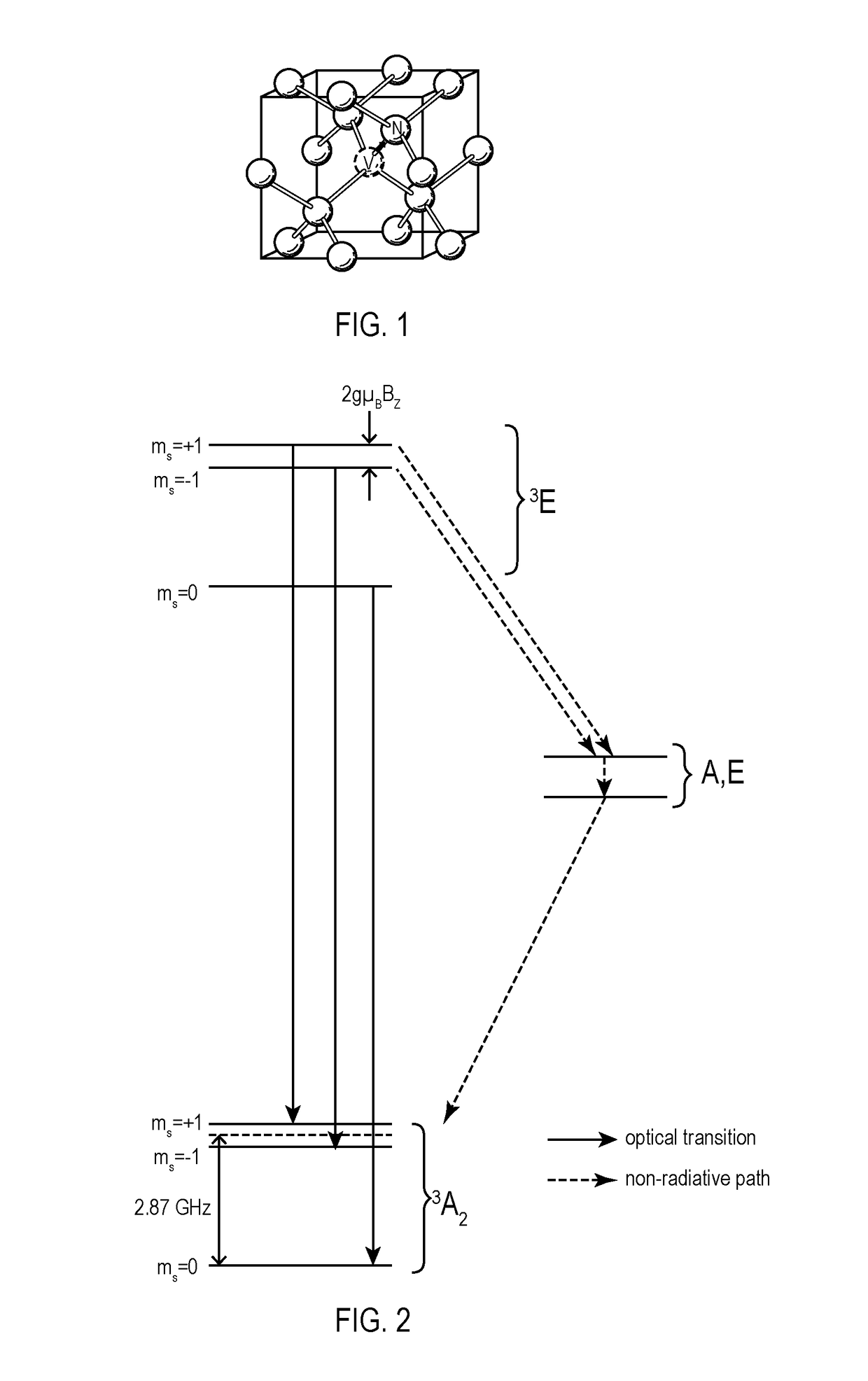
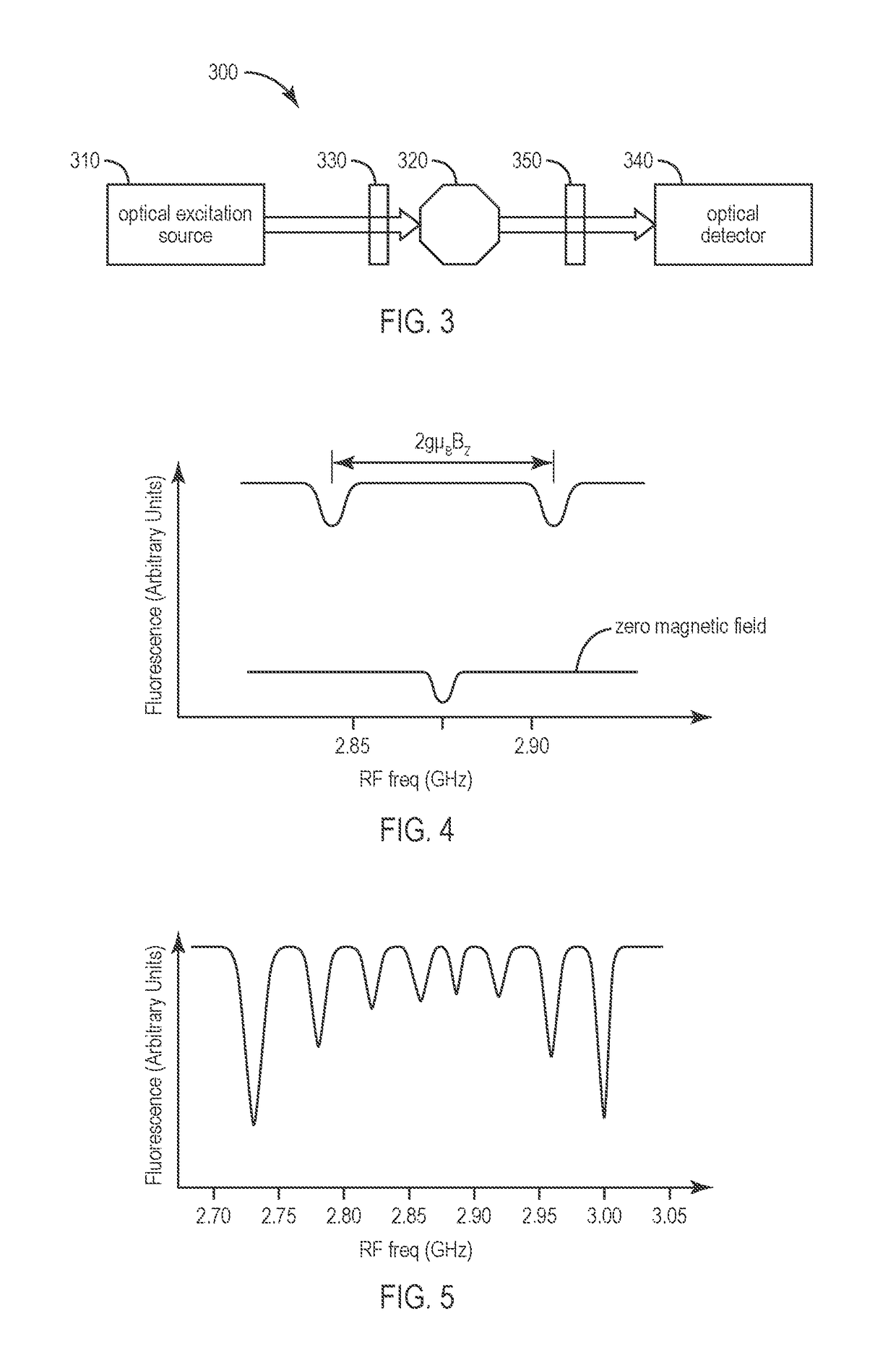
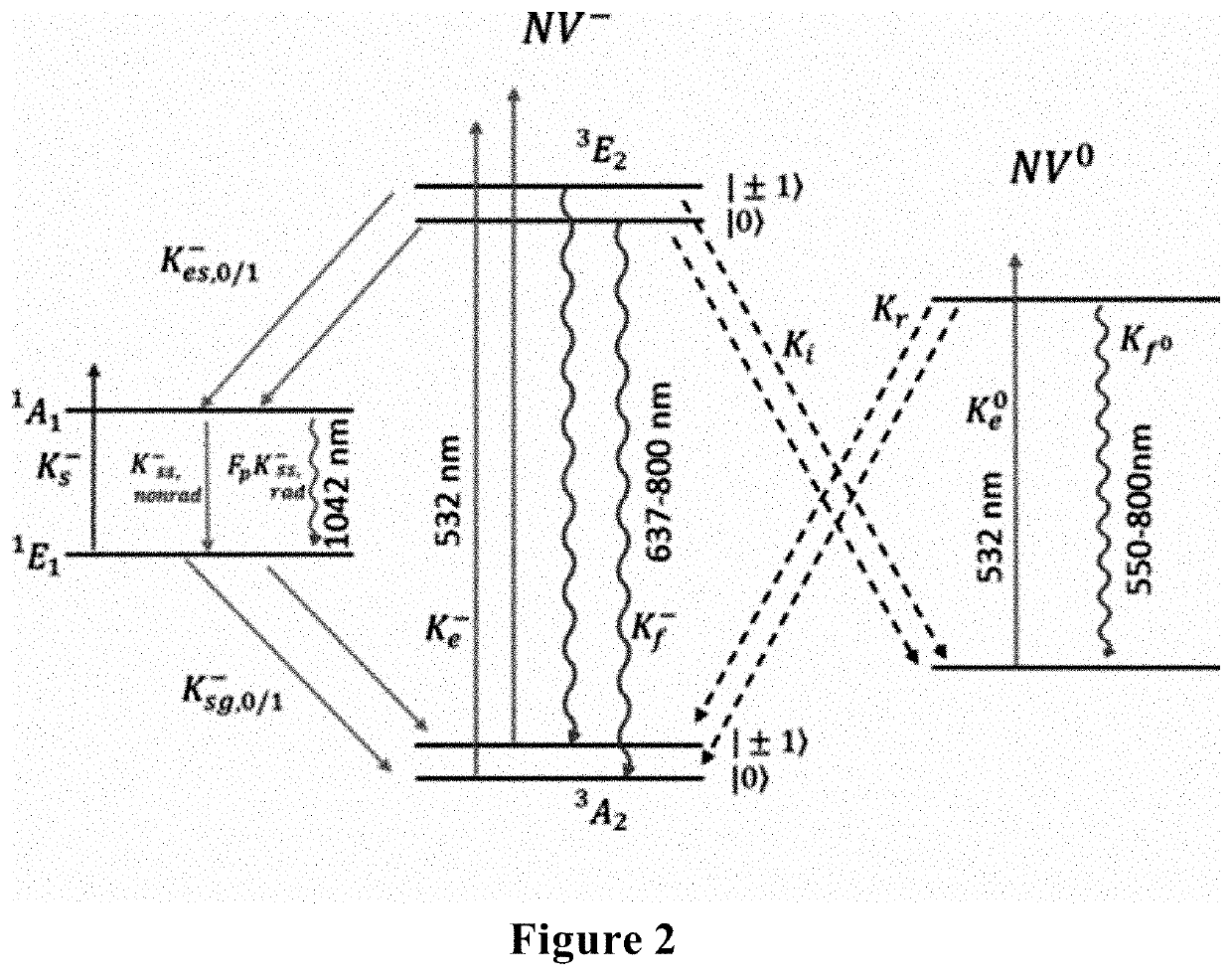
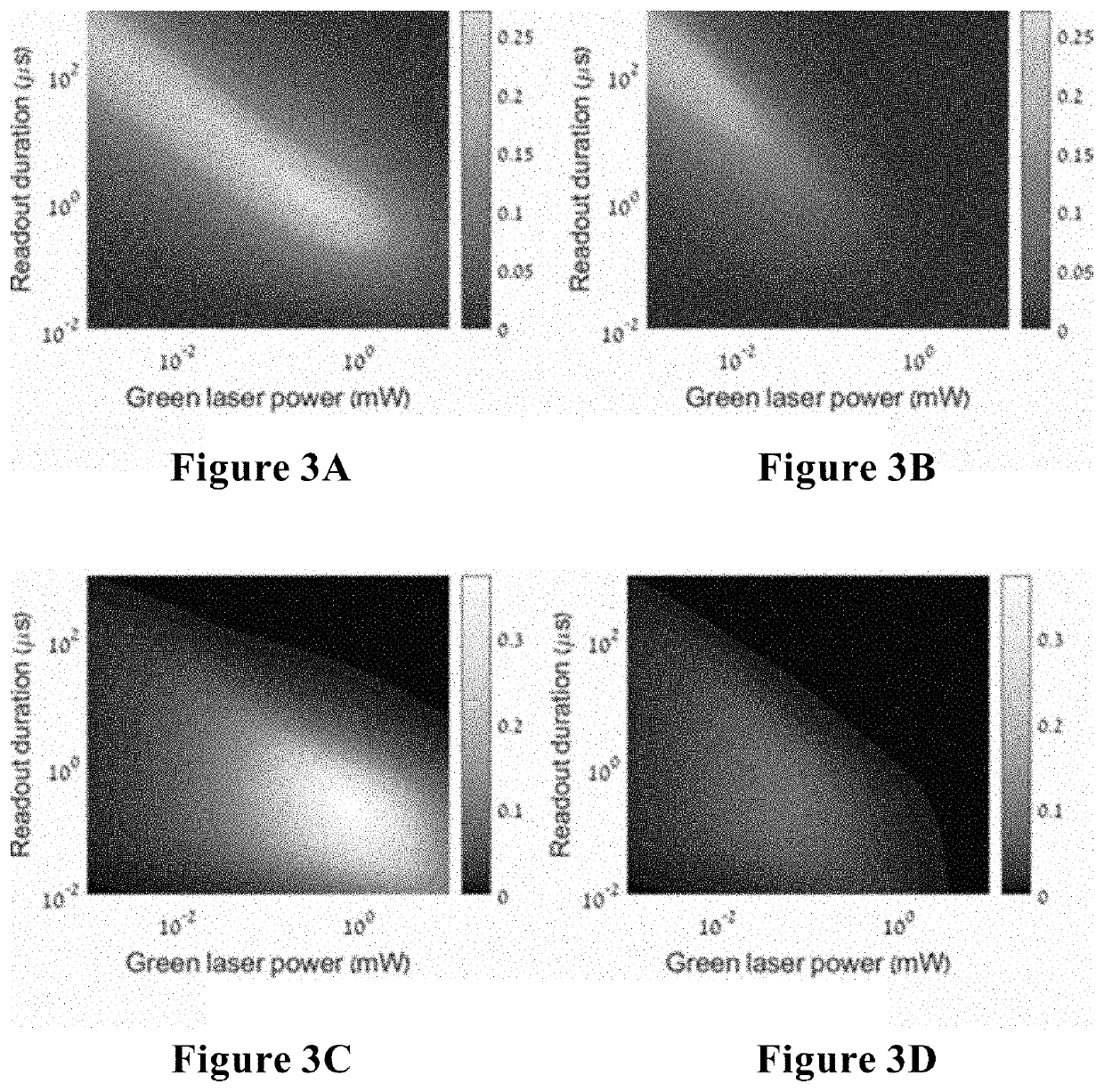
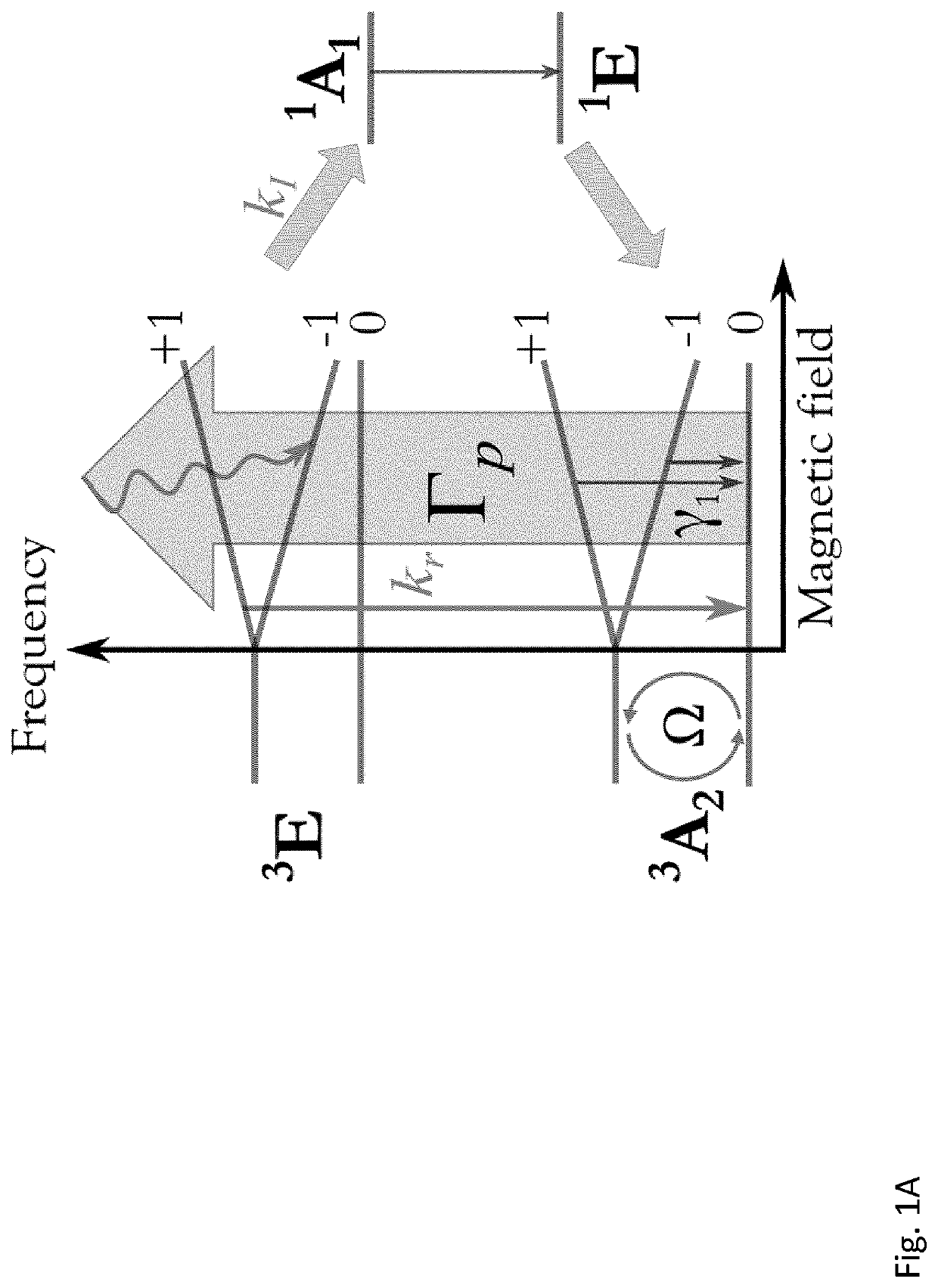
A nitrogen-vacancy center (N-V center) is one of numerous point defects in diamond. Its most explored and useful property is photoluminescence, which can be easily detected from an individual N-V center, especially those in the negative charge state (N-V⁻). Electron spins at N-V centers, localized at atomic scales, can be manipulated at room temperature by applying a magnetic field, electric field, microwave radiation or light, or a combination, resulting in sharp resonances in the intensity and wavelength of the photoluminescence. These resonances can be explained in terms of electron spin related phenomena such as quantum entanglement, spin-orbit interaction and Rabi oscillations, and analysed using advanced quantum optics theory. An individual N-V center can be viewed as a basic unit of a quantum computer, and it has potential applications in novel, more efficient fields of electronics and computational science including quantum cryptography, spintronics and masers.
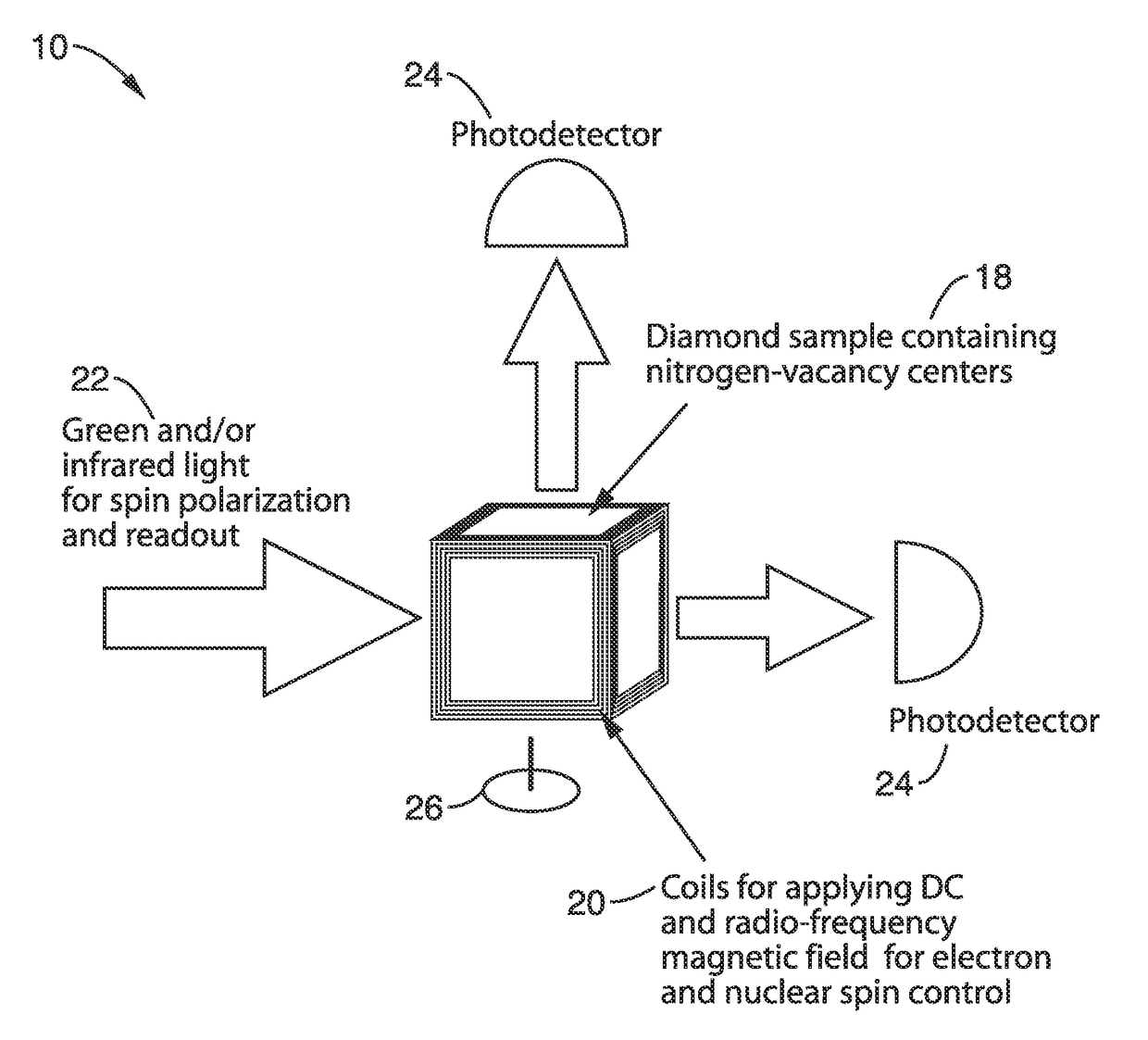
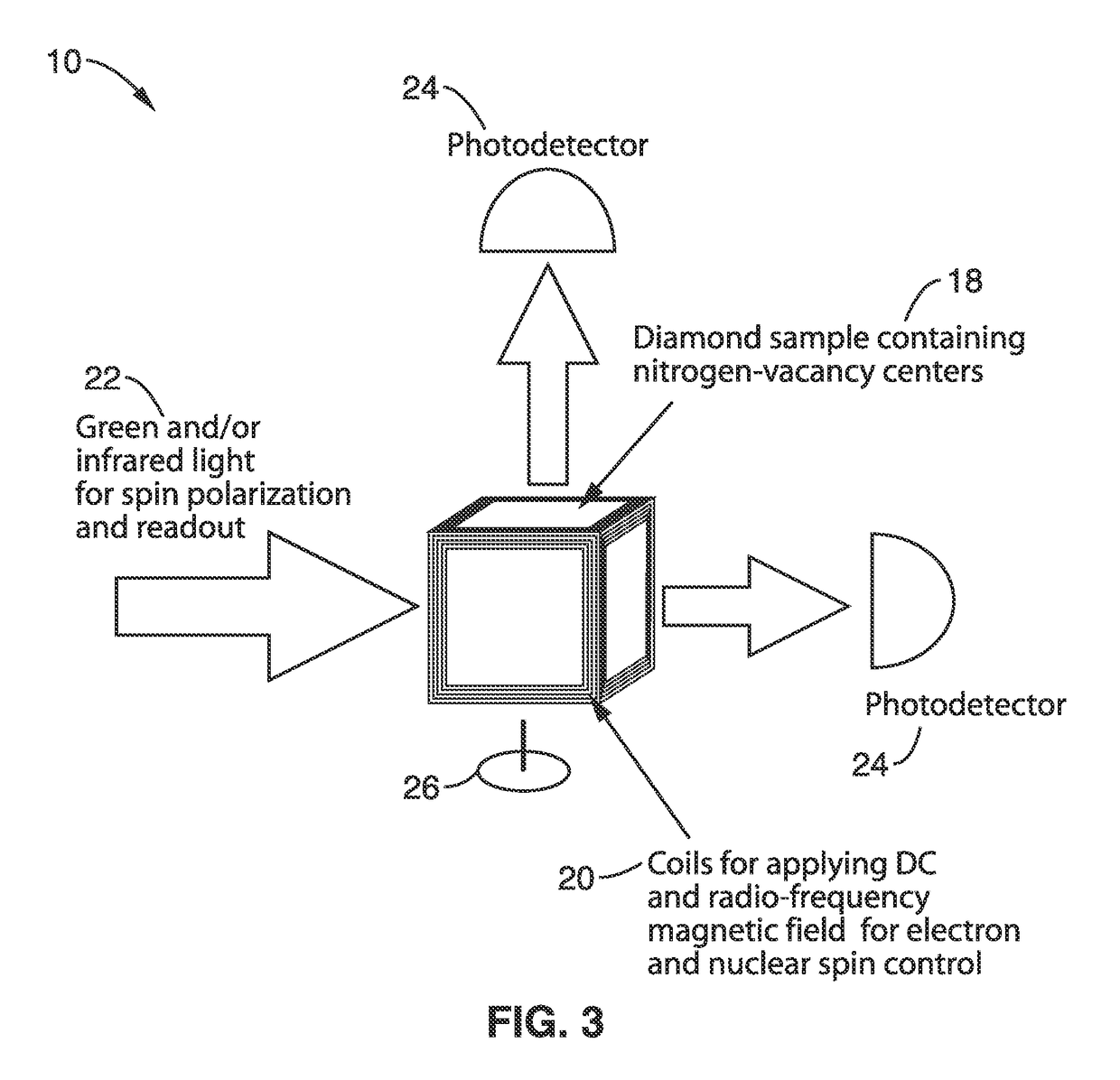
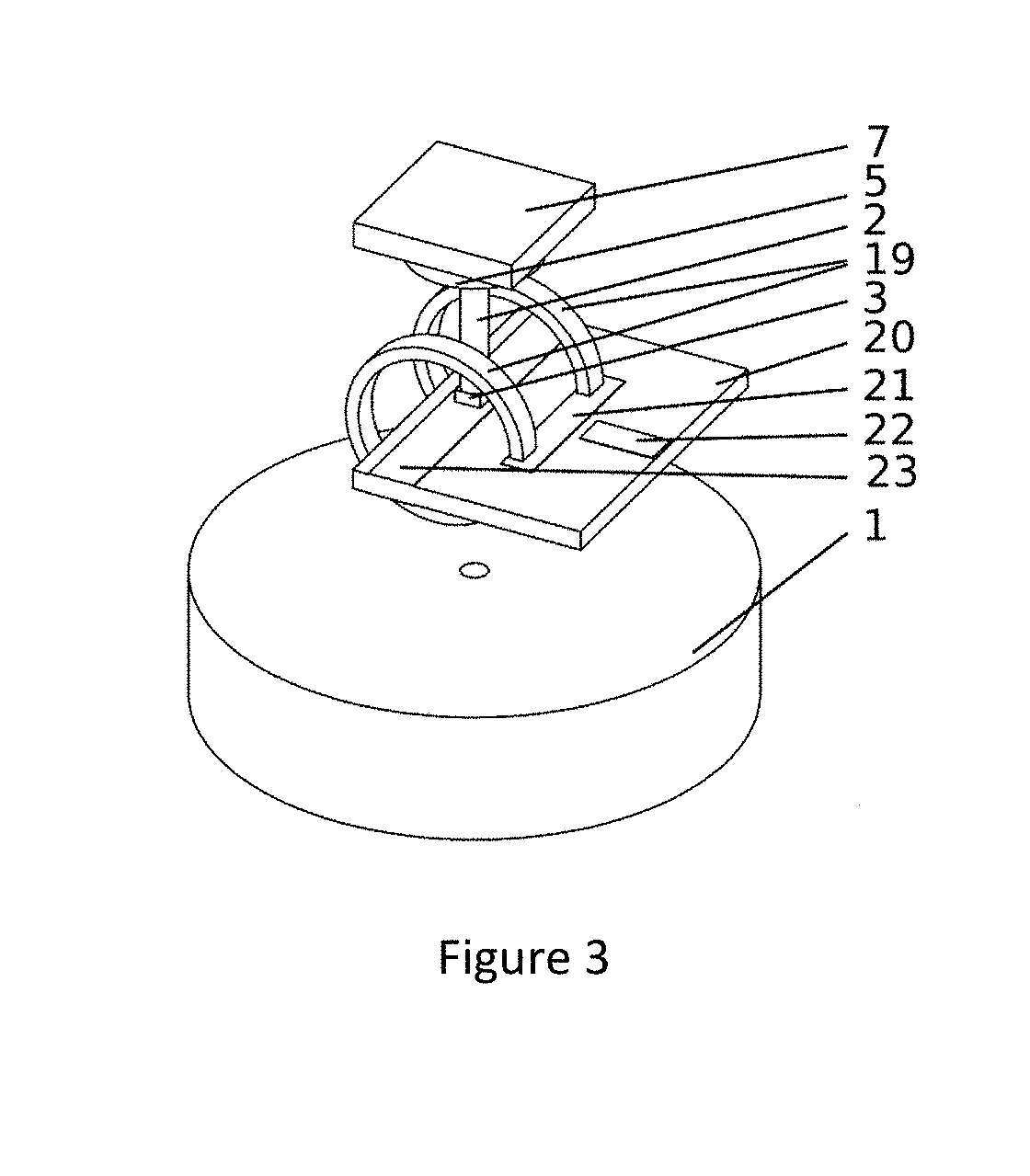
Gyroscopes based on nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond
ActiveUS20150090033A1Small dimensionThermal robustnessAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopePhase shifted
A solid-state gyroscope apparatus based on ensembles of negatively charged nitrogen-vacancy (NV−) centers in diamond and methods of detection are provided. In one method, rotation of the NV− symmetry axis will induce Berry phase shifts in the NV− electronic ground-state coherences proportional to the solid angle subtended by the symmetry axis. A second method uses a modified Ramsey scheme where Berry phase shifts in the 14N hyperfine sublevels are employed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method to produce light-emitting nano-particles of diamond
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
Gyroscopes based on nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond
ActiveUS9689679B2Small dimensionThermal robustnessMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyTurn-sensitive devicesGyroscopePhase shifted
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Diamond nitrogen vacancy sensed ferro-fluid hydrophone
ActiveUS20170211947A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSeismologyHydrophoneNitrogen
Systems and apparatuses are disclosed for a hydrophone using a nitrogen vacancy center diamond magnetic sensor.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Diamond maser and microwave amplifier
Masers and microwave amplifiers that can function in the continuous-wave mode at room temperature are provided. The maser system can include a diamond gain medium having nitrogen-vacancy centers, and a resonator can be disposed around the gain medium. The resonator can be disposed in a cavity box, and radiation (e.g., visible light) can be provided to the gain medium to cause emission of microwave radiation.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Method And System For Magnetic Resonance Imaging Using Nitrogen-Vacancy Centers
InactiveUS20170038411A1Measurements using double resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic field gradientElectronic spin
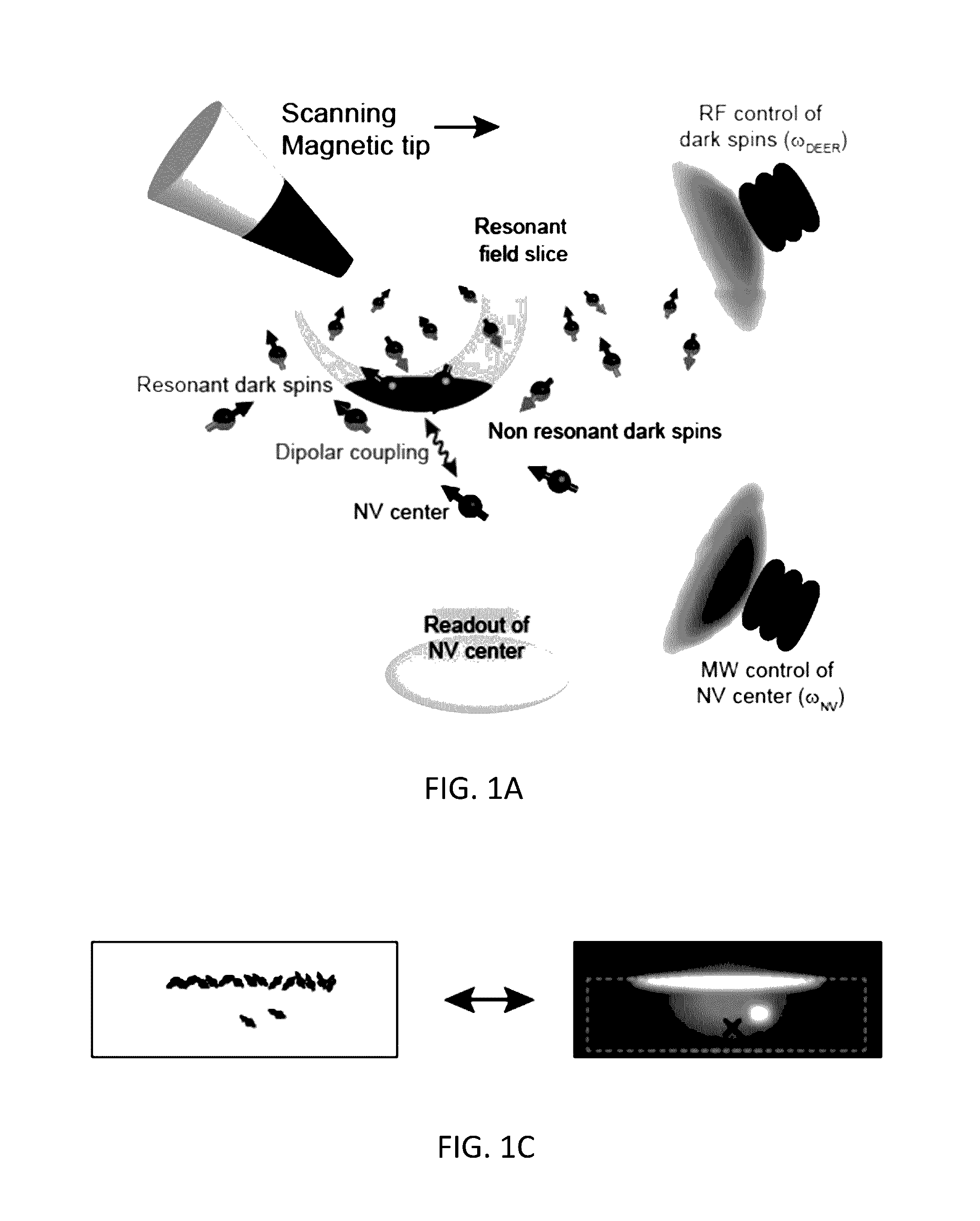
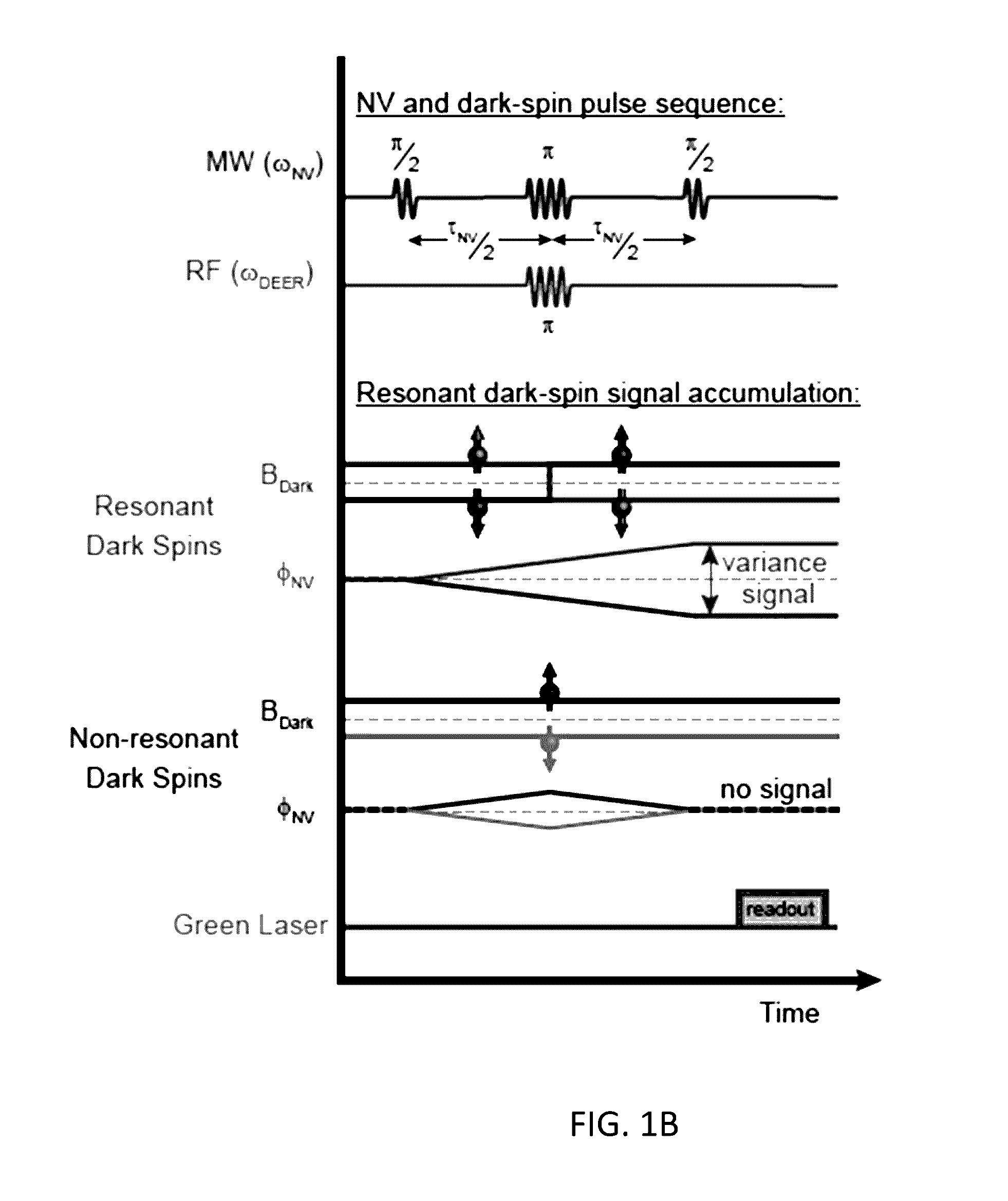
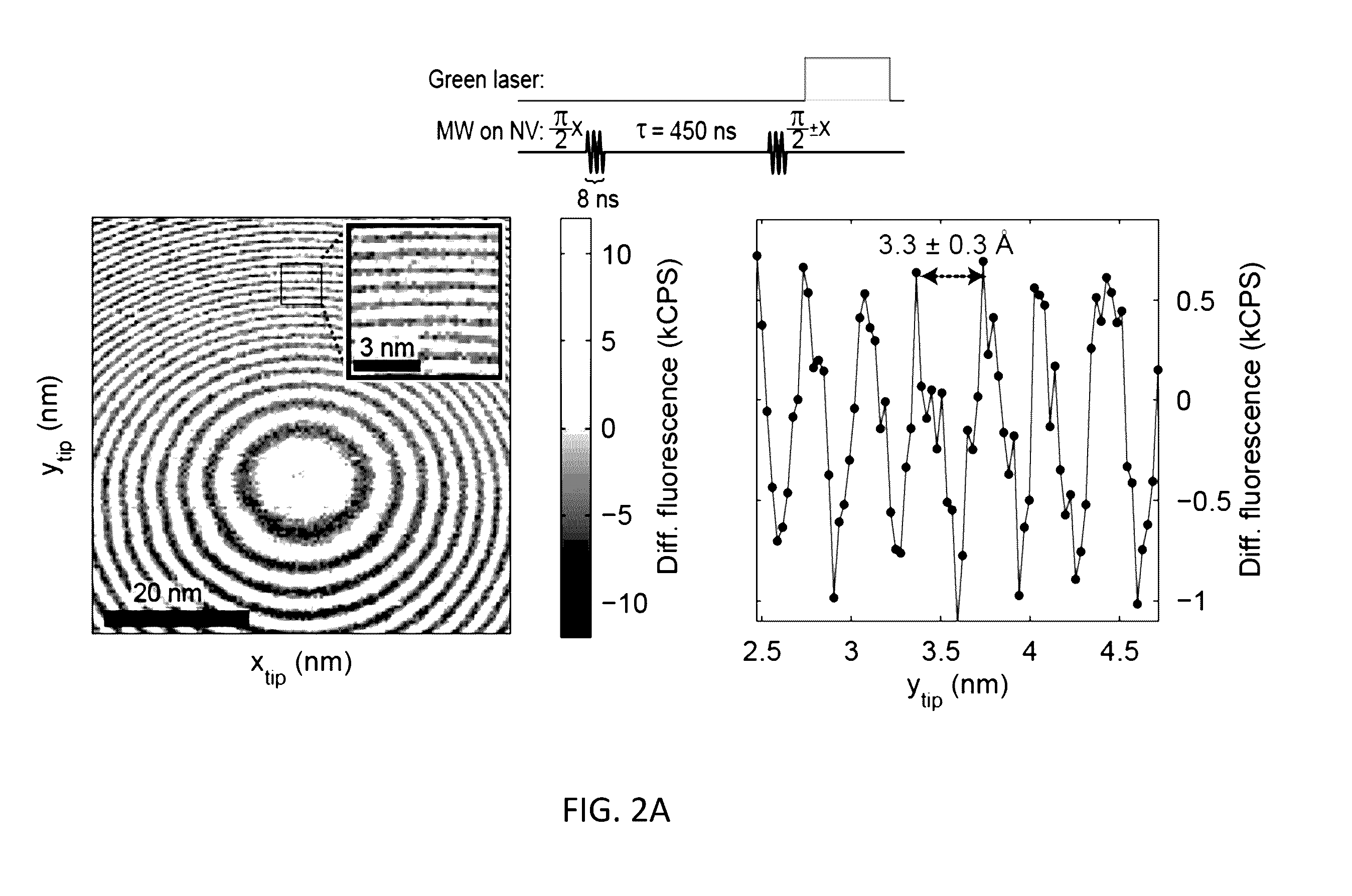
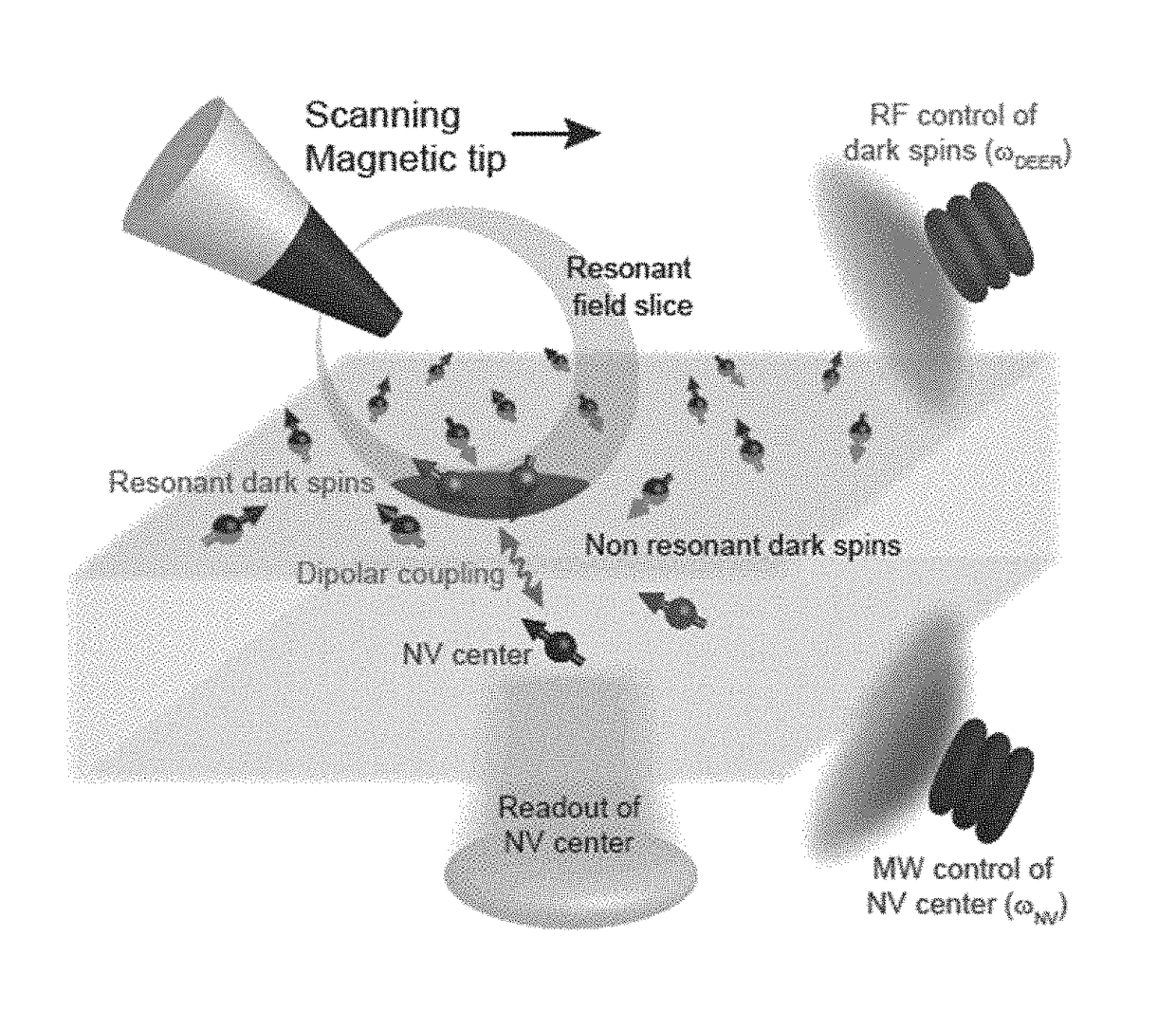
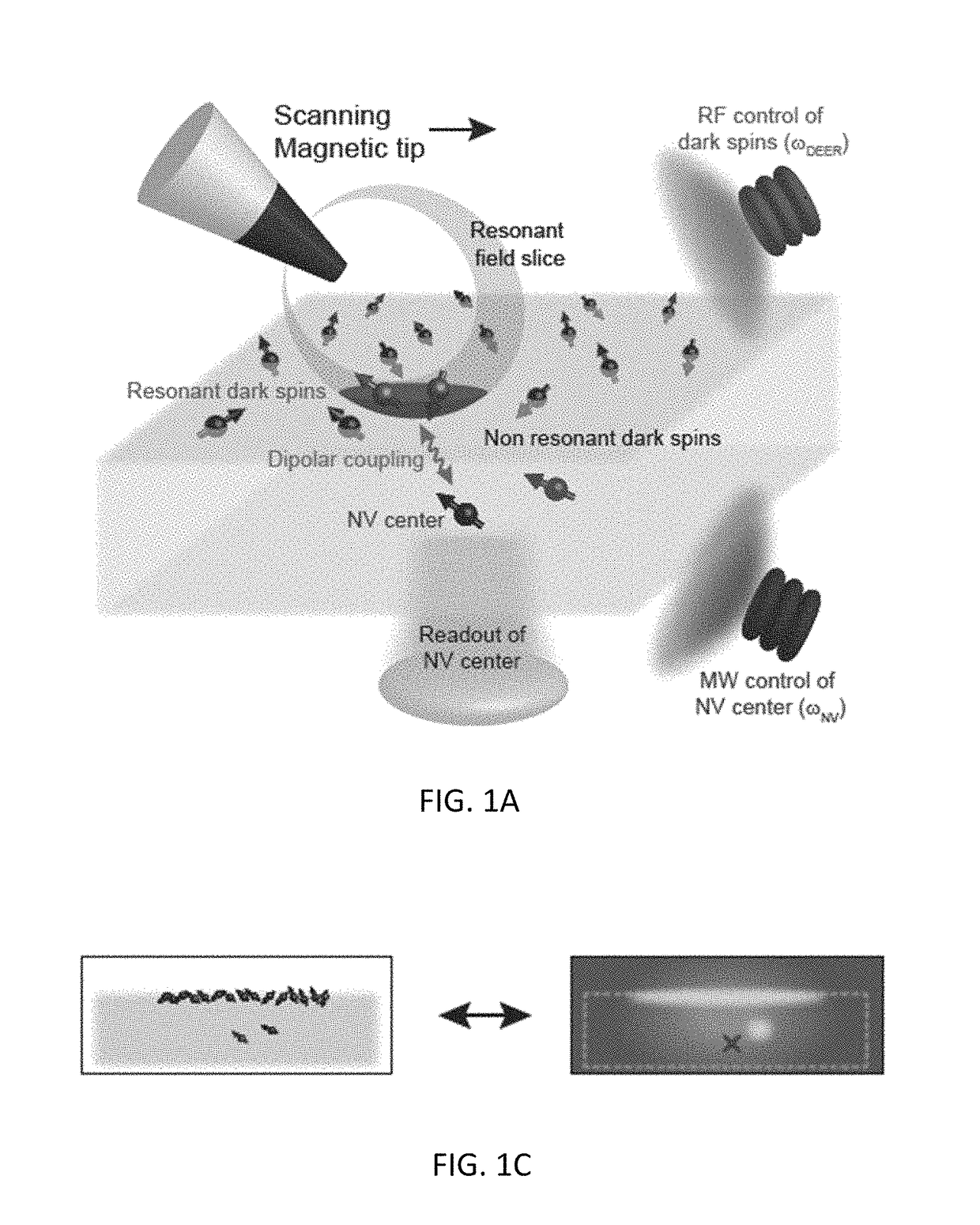
A method for performing sub-nanometer three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging of a sample under ambient conditions using a diamond having at least one shallowly planted nitrogen-vacancy (NV) center. A driving radio-frequency (RF) signal and a microwave signal are applied to provide independent control of the NV spin and the target dark spins. A magnetic-field gradient is applied to the sample with a scanning magnetic tip to provide a narrow spatial volume in which the target dark electronic spins are on resonance with the driving RF field. The sample is controllably scanned by moving the magnetic tip to systematically bring non-resonant target dark spins into resonance with RF signal. The dark spins are measured and mapped by detecting magnetic resonance of said nitrogen-vacancy center at each of said different magnetic tip positions. The dark-spin point-spread-function for imaging the dark spins is directly measured by the NV center.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Novel nitrogen-vacancy center diamond scanning magnetometer
ActiveCN105137126ARemove restrictionsHigh measurement sensitivityScanning probe microscopyUltra-high vacuumFeedback control
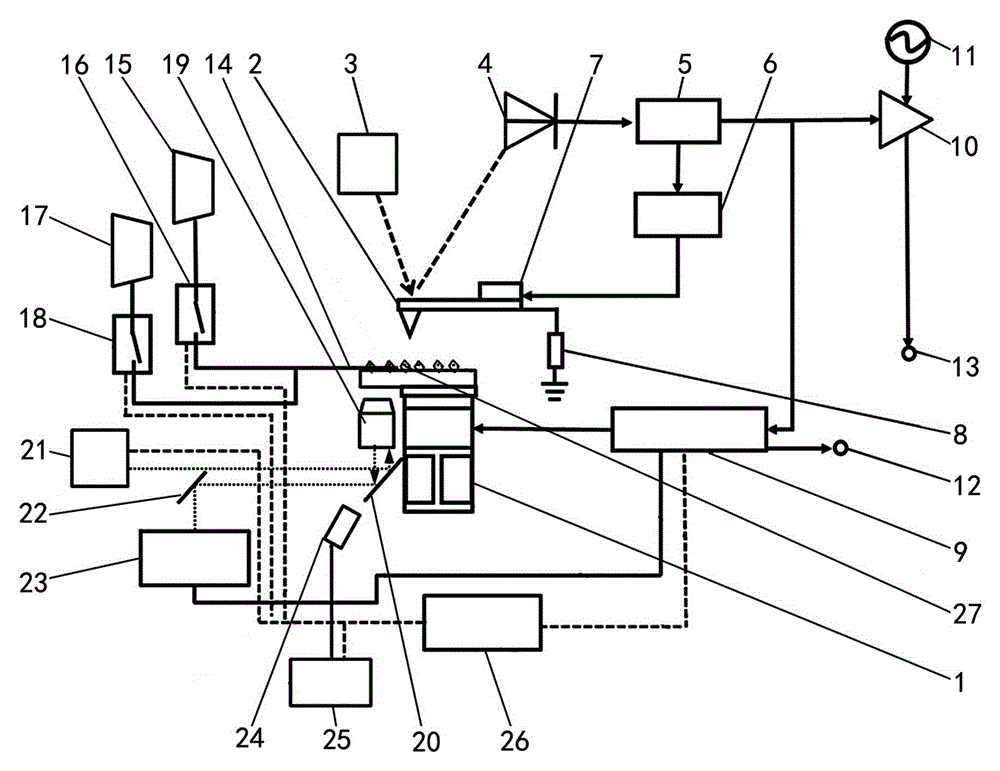
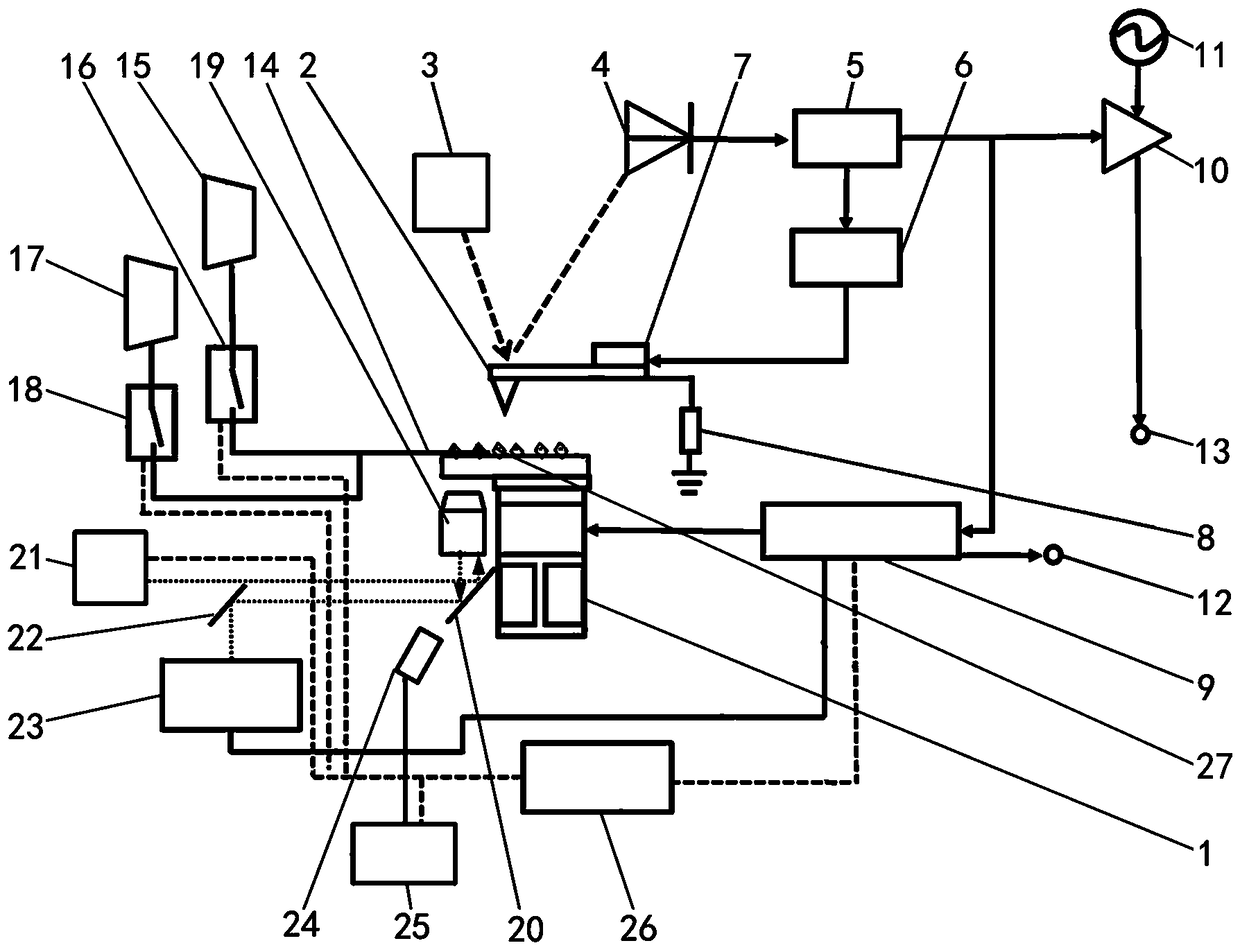
The invention relates to a weak magnetic field measurement technique, in particular, a novel nitrogen-vacancy center diamond scanning magnetometer. With the novel nitrogen-vacancy center diamond scanning magnetometer adopted, the problems of low sensitivity and limited application range of existing weak magnetic field information measuring tools can be solved. The novel nitrogen-vacancy center diamond scanning magnetometer of the nitrogen-vacancy center diamond includes an atomic force microscope system and an optical detection magnetic information system; and the atomic force microscope system includes an ultra-high vacuum chamber, a scanning tube, a nitrogen-vacancy center diamond probe, a 670nm-wavelength laser, a four-quadrant photodiode detector, a phase-locked loop, an automatic gain control loop, piezoelectric ceramic, a 50-ohm resistor, a feedback control loop, a lock-in amplifier, a carrier, a surface topography information output port and a magnetic information output port. The novel nitrogen-vacancy center diamond scanning magnetometer of the invention is suitable for weak magnetic field information measurement.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Titanium nitride based metamaterial
ActiveUS20150285953A1Good dispersionImprove efficiencyRadiation/particle handlingElectrode and associated part arrangementsSharp interfaceTantalum nitride
A titanium nitride-based metamaterial, and method for producing the same, is disclosed, consisting of ultrathin, smooth, and alternating layers of a plasmonic titanium nitride (TiN) material and a dielectric material, grown on a substrate to form a superlattice. The dielectric material is made of A1-xScxN, where ‘x’ ranges in value from 0.2 to 0.4. The layers of alternating material have sharp interfaces, and each layer can range from 1-20 nanometers in thickness. Metamaterials based on titanium TiN, a novel plasmonic building block, have many applications including, but not ‘limited to emission enhancers, computer security, etc. The use of nitrogen vacancy centers in diamond, and light emitting diode (LED) efficiency enhancement is of particular interest.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Optical fiber magnetic field sensor and preparation method thereof
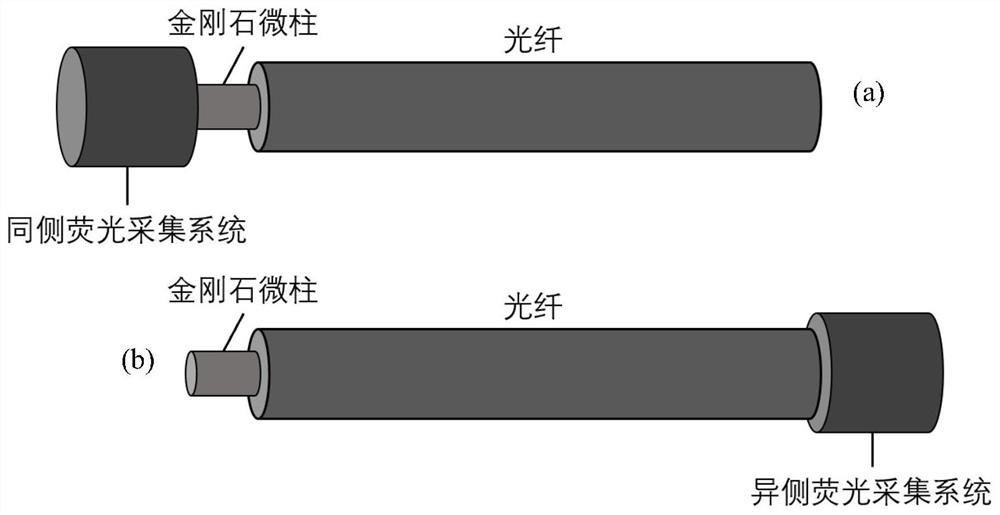
ActiveCN110554332AHigh sensitivityImprove fluorescence collection efficiencyMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesColour centreFluorescence
The invention discloses an optical fiber magnetic field sensor and a preparation method thereof. The optical fiber magnetic field sensor comprises an optical fiber and a plurality of diamond micro-columns, the plurality of diamond micro-columns are positioned at one end in the optical fiber; each diamond micro-column contains a nitrogen-vacancy center; when the optical fiber magnetic field sensoris used for measuring a magnetic field, one end, containing the diamond micro-column, of the optical fiber is placed in an environment of the magnetic field to be measured, and laser with a preset wavelength is emitted from the other end of the optical fiber, so that the the nitrogen-vacancy center is excited to emit fluorescence; and steps of transmitting a sweep frequency signal in a preset frequency range to one end, containing the diamond micro-column, of the optical fiber, collecting fluorescence, and determining the size of the magnetic field to be measured by analyzing the change rule of the intensity of the fluorescence along with the frequency of the sweep frequency signal are carried out. According to the invention, more nitrogen-vacancy centers can be integrated at an optical fiber port, the sensitivity is related to the number of the nitrogen-vacancy centers in the sample, and a magnetometer with higher sensitivity can be obtained through the diamond micro-column sample with higher nitrogen-vacancy center color center density.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
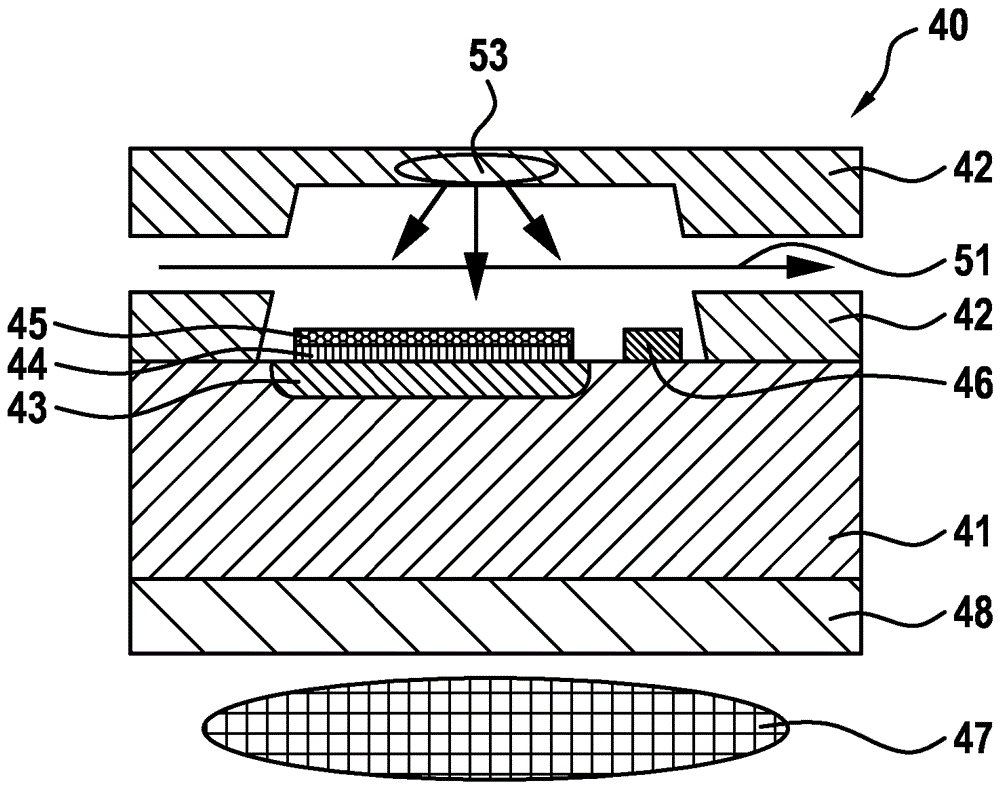
A magnetometer using optically active defects in a solid state material
ActiveUS20200158798A1Improve efficiencyEnhanced responsivityMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceAnalysis using optical pumpingOptical cavityFluorescence
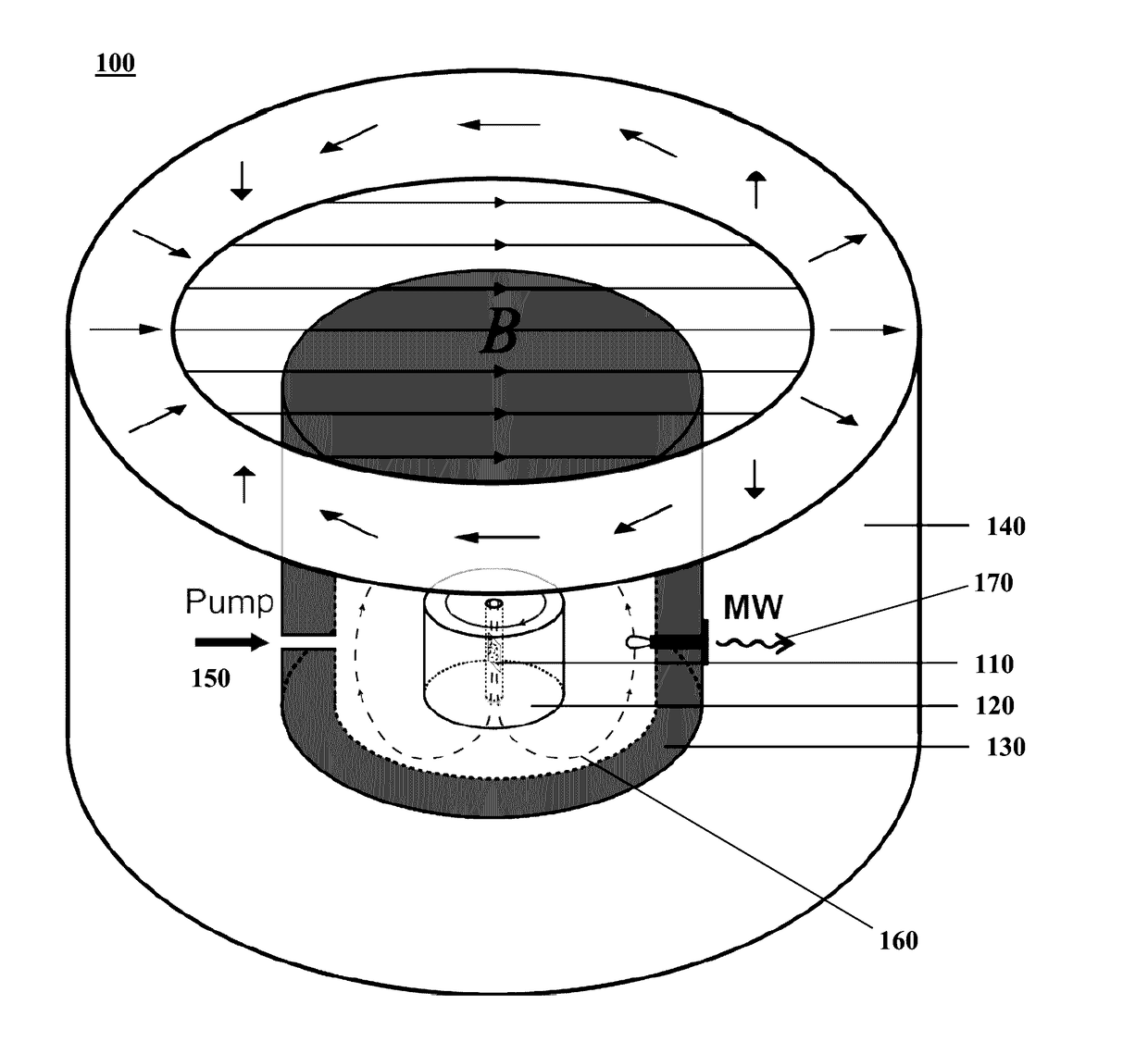
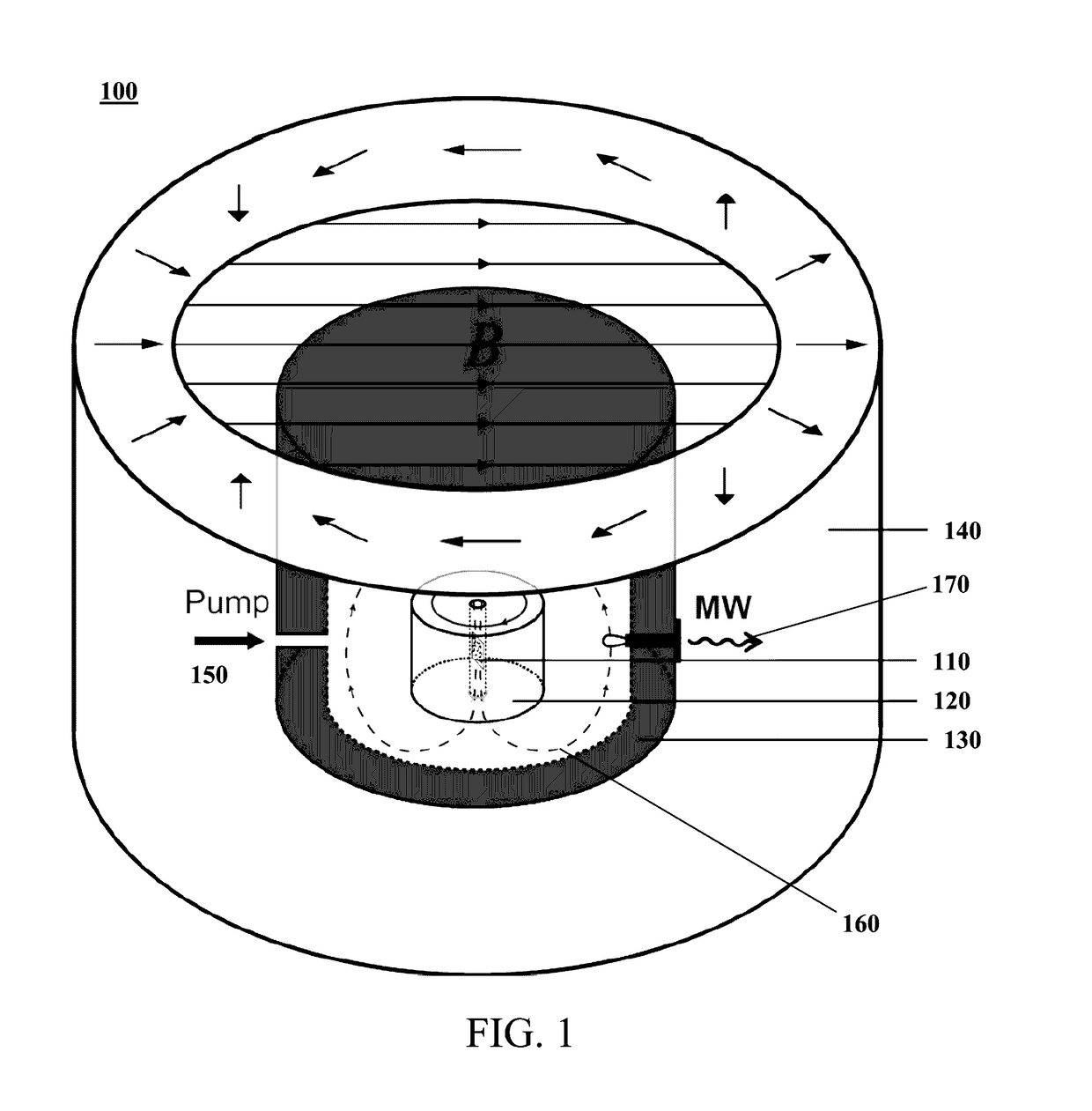
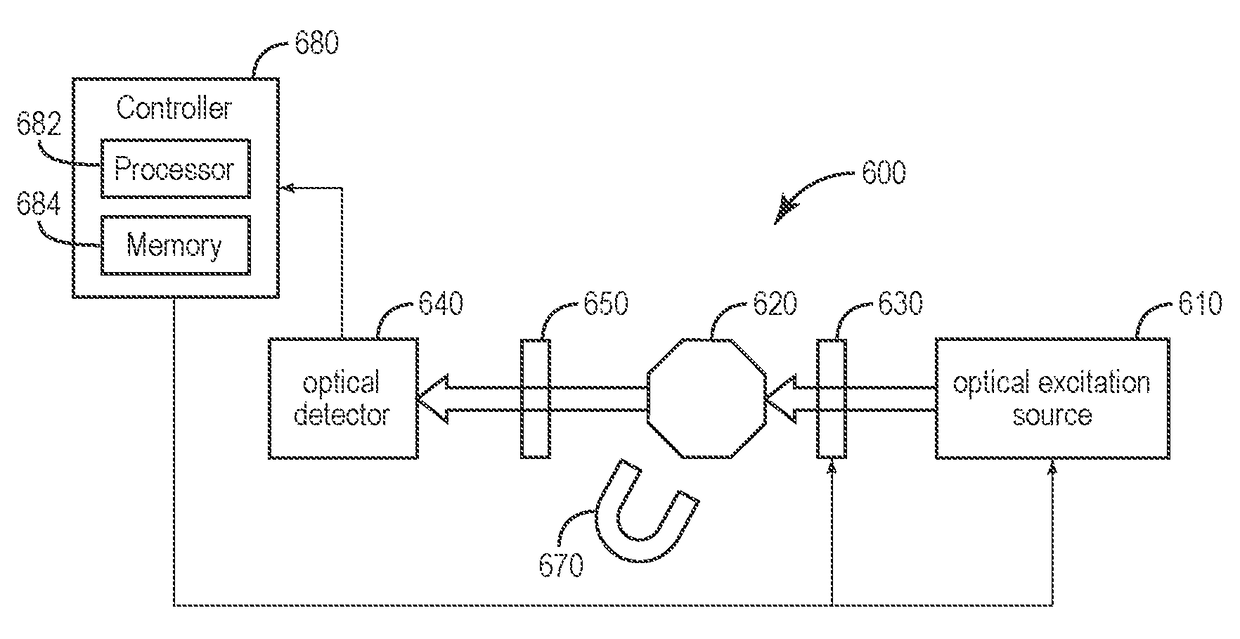
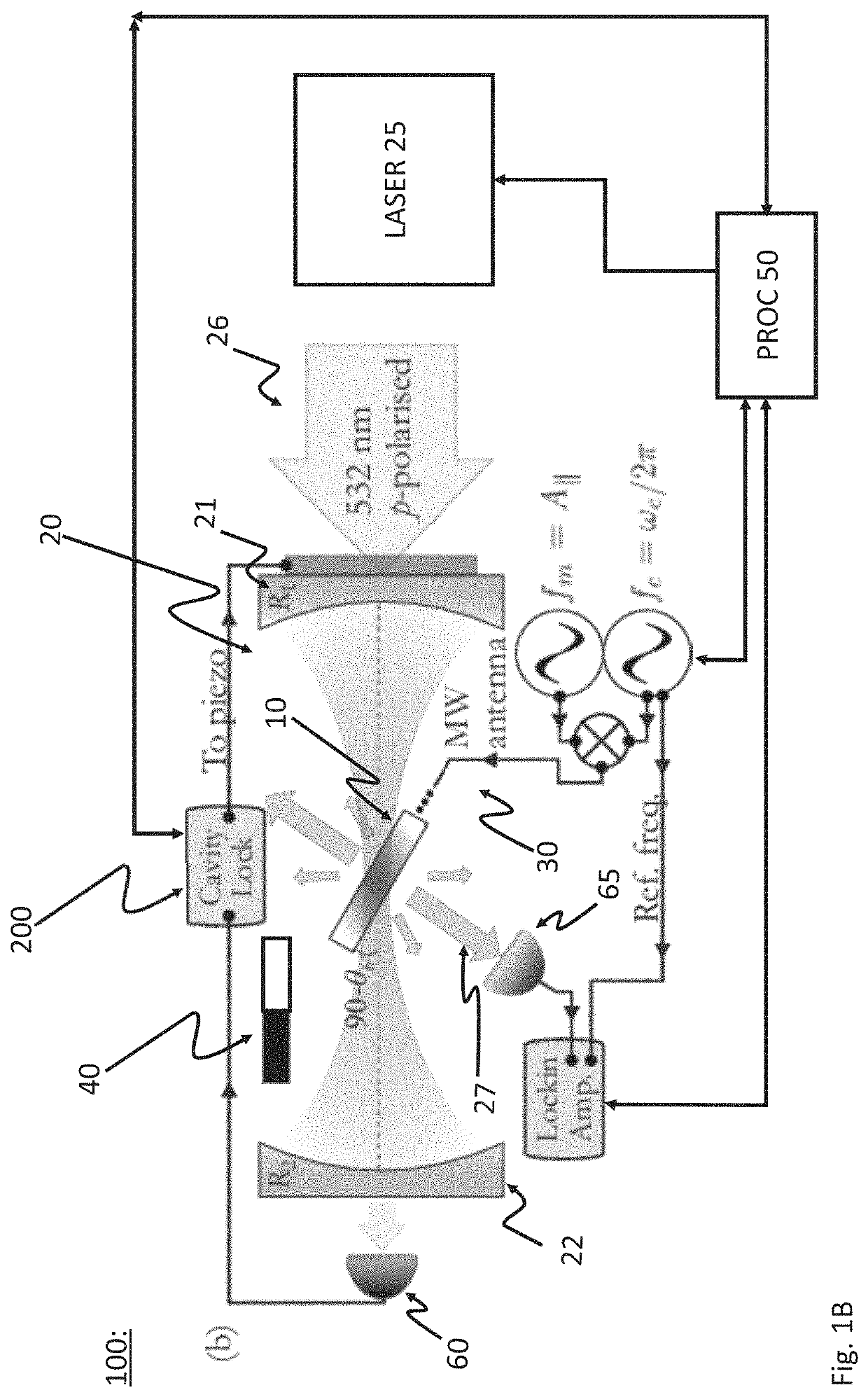
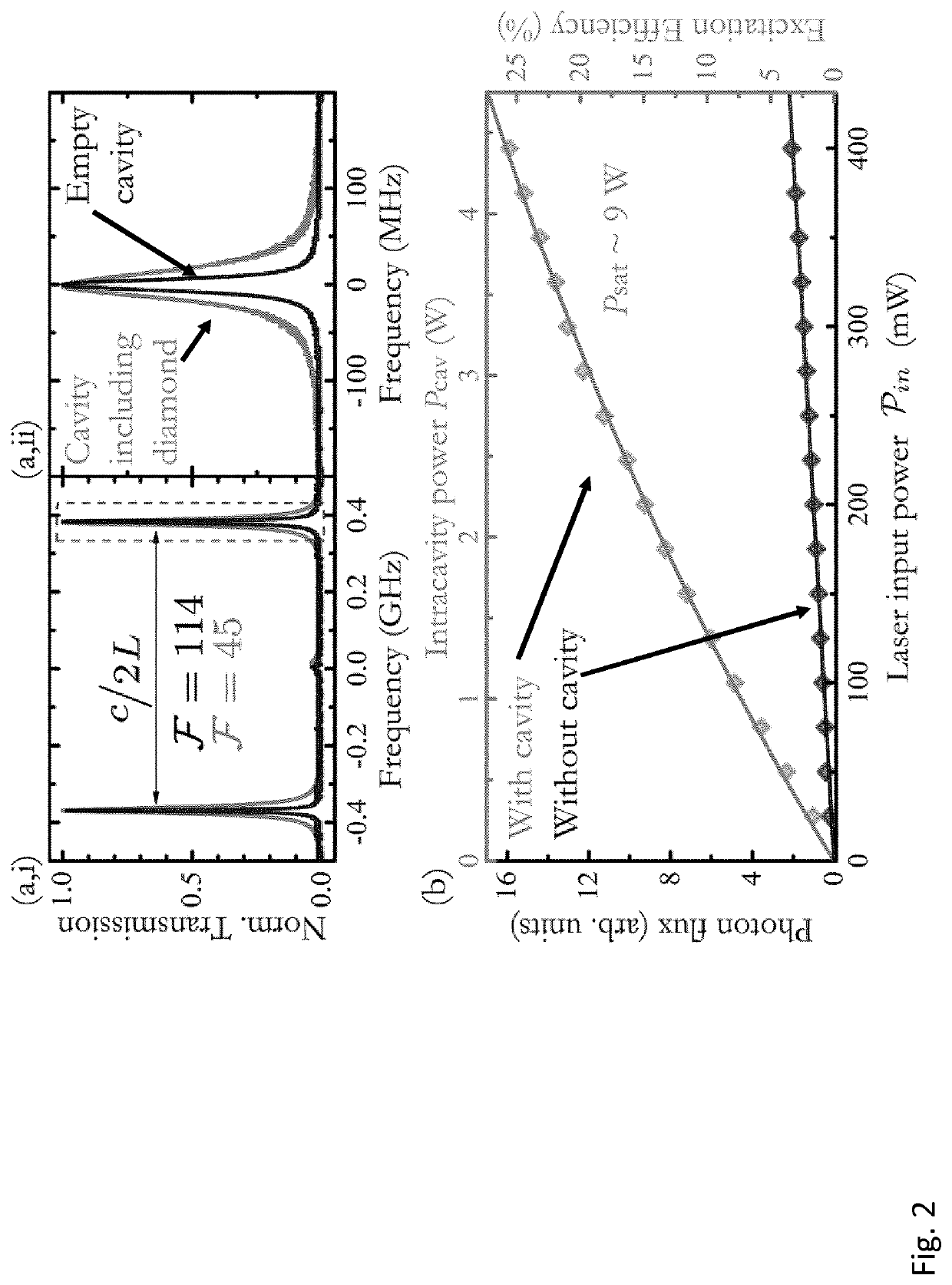
The present invention relates to a magnetometer (100) using optically detected magnetic resonance (ODMR), where a solid state material (10), such as diamond, with an ensemble of paramagnetic defects, such as nitrogen vacancies centers NV, is applied. An optical cavity (20) is optically excited by an irradiation laser (25) arranged therefore. A coupling structure (30) causes a microwave excitation (Ω) of the paramagnetic defects, and a permanent magnetic field (40, B_C) causes a Zeeman splitting of the energy levels in the paramagnetic defects. A probing volume (PV) in the solid state material is thereby defined by the spatially overlapping volume of the optical excitation by the irradiation laser (25), the coupling structure (30) also exciting the defects, and the constant magnetic field. The magnetometer then measures an unknown magnetic field by detecting emission (27), e.g. fluorescence, from the defects in the probing volume (PV) from the double excitation of the defects by the irradiation laser, and the coupling structure exciting these defects.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Gyrocope based on nitrogen vacancy centers in diamond
ActiveUS20190293425A1Eliminating externally induced unwanted componentReduce impactRotary gyroscopesTurn-sensitive devicesGyroscopeFluorescence
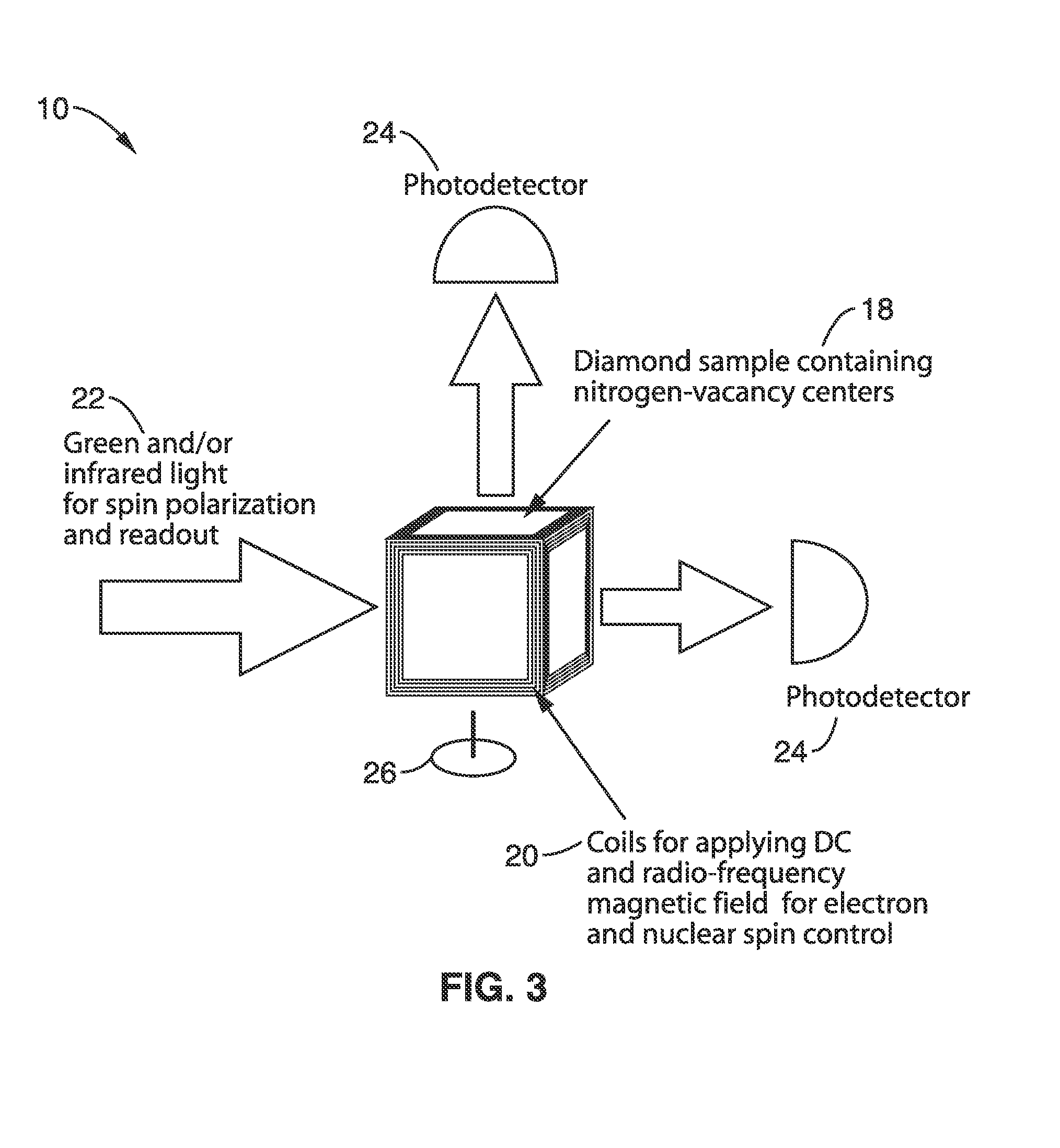
The invention pertains to the field of gyroscopes, in particular—to quantum gyroscopes. The invention provides a gyroscope employing an ensemble of NV-centers in diamond, which includes a diamond plate, a source of green light, an optical system for directing the green light to the diamond plate, a photodetector for registering fluorescence of the color centers in the diamond plate, optical elements that direct the fluorescence from the diamond plate to the photodetector, a source of microwave radiation, a source of radiofrequency radiation, and a source of constant magnetic field, the gyroscope being different from the prior art in that it comprises an energy-efficient antenna that creates a strong longitudinal homogeneous field in the entire volume of the diamond plate with the possibility of frequency adjustment, as well as a system for locking the frequency of the microwave field to that of the transition in the color centers. The invention allows to reduce the volume of the sensing element, provides high relative spectral sensitivity, and allows to create a hybrid device that comprises a 3-axis gyroscope, a magnetometer, and a temperature sensor.
Owner:LLC SENSOR SPIN TECH
Sensors and methods of identifying a gas, and levitated spin-optomechanical systems
ActiveUS20180059039A1Analysis using optical pumpingAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceMicrowaveSpins
Sensors and methods are provided that include a diamond material containing a nitrogen vacancy center, the diamond material being configured to be exposed to an environment comprising one or more gases, an optical light source configured to excite the nitrogen vacancy center of the diamond material with an optical light beam produced therefrom, a detector configured to detect a signal originating from the diamond material in response to the optical light beam exciting the nitrogen vacancy center, and the capability of analyzing the signal to identify a specific gas in the environment. Also included are levitated spin-optomechanical systems capable of elevating in a vacuum a diamond material containing a nitrogen vacancy center, applying microwave radiation to the diamond material for controlling and flipping the electron spin of the nitrogen vacancy center, and monitoring electron spin of the nitrogen vacancy center.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
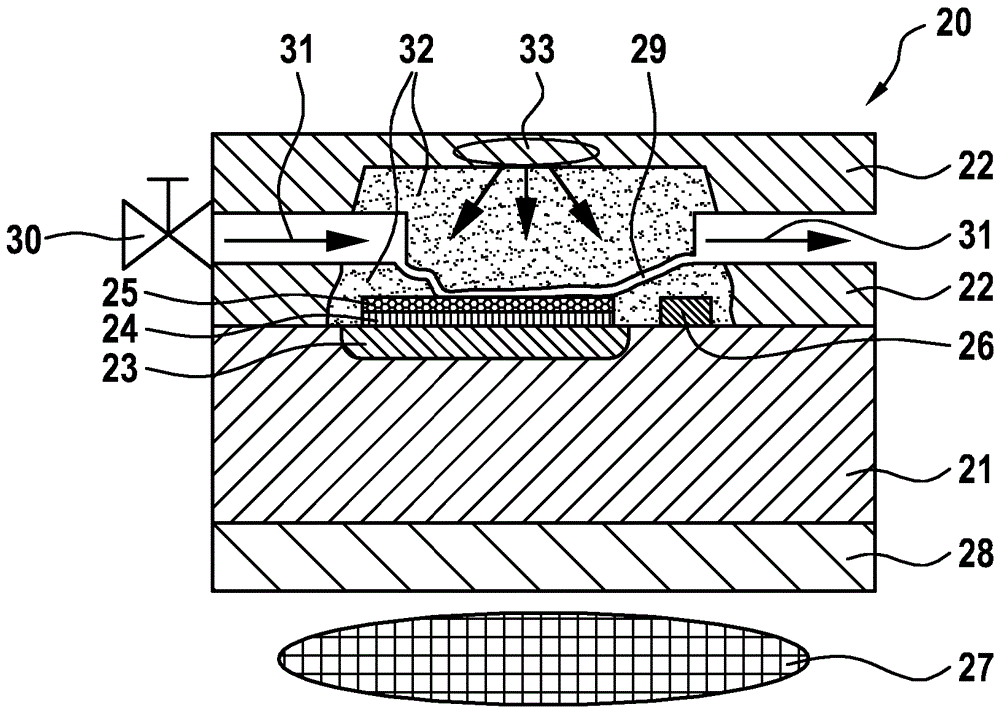
Device for the nmr analysis of substances in a sample, respiratory gas analysis device, fuel sensor and method
ActiveCN106687035AFuel testingMaterial analysis by optical meansGas analysisNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
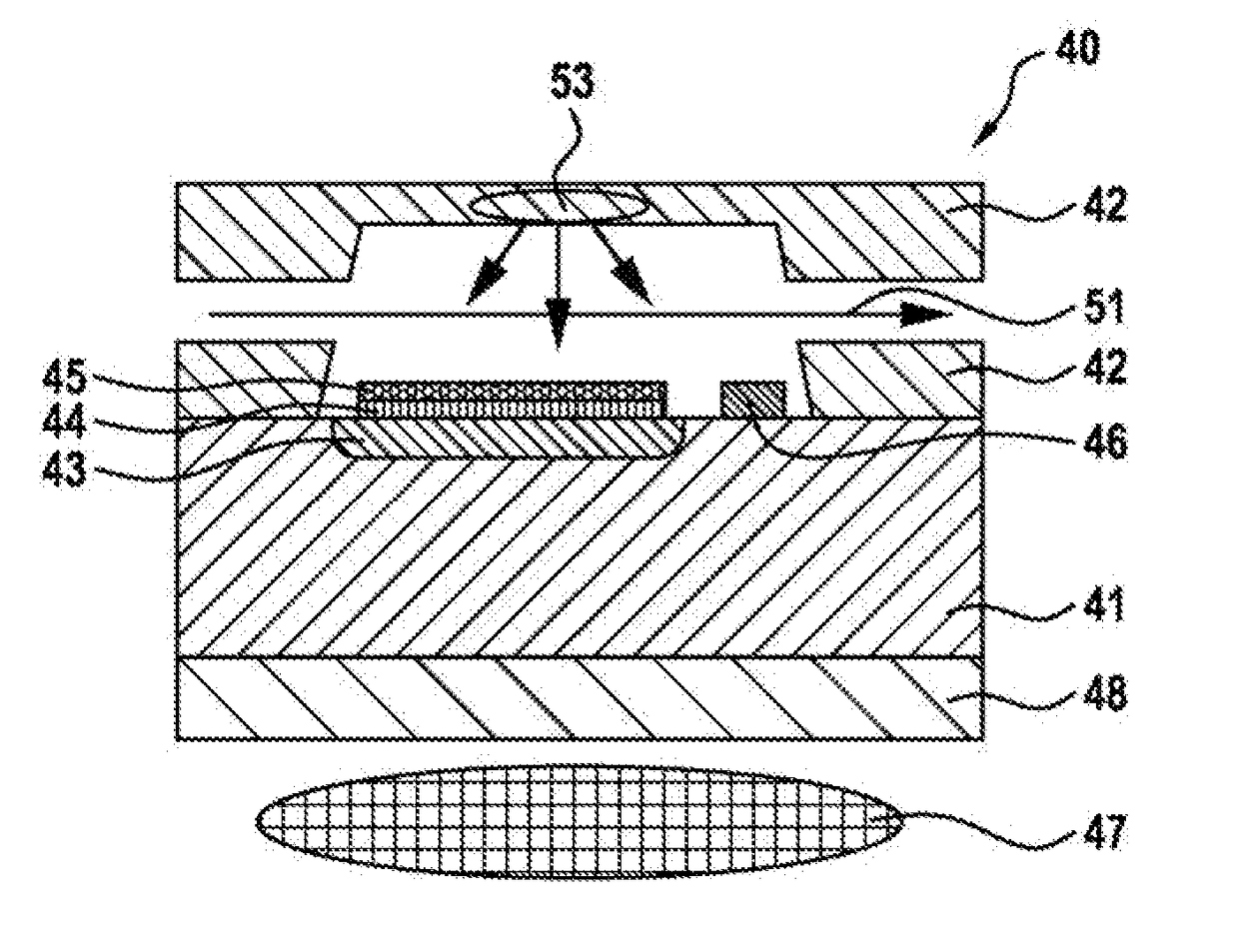
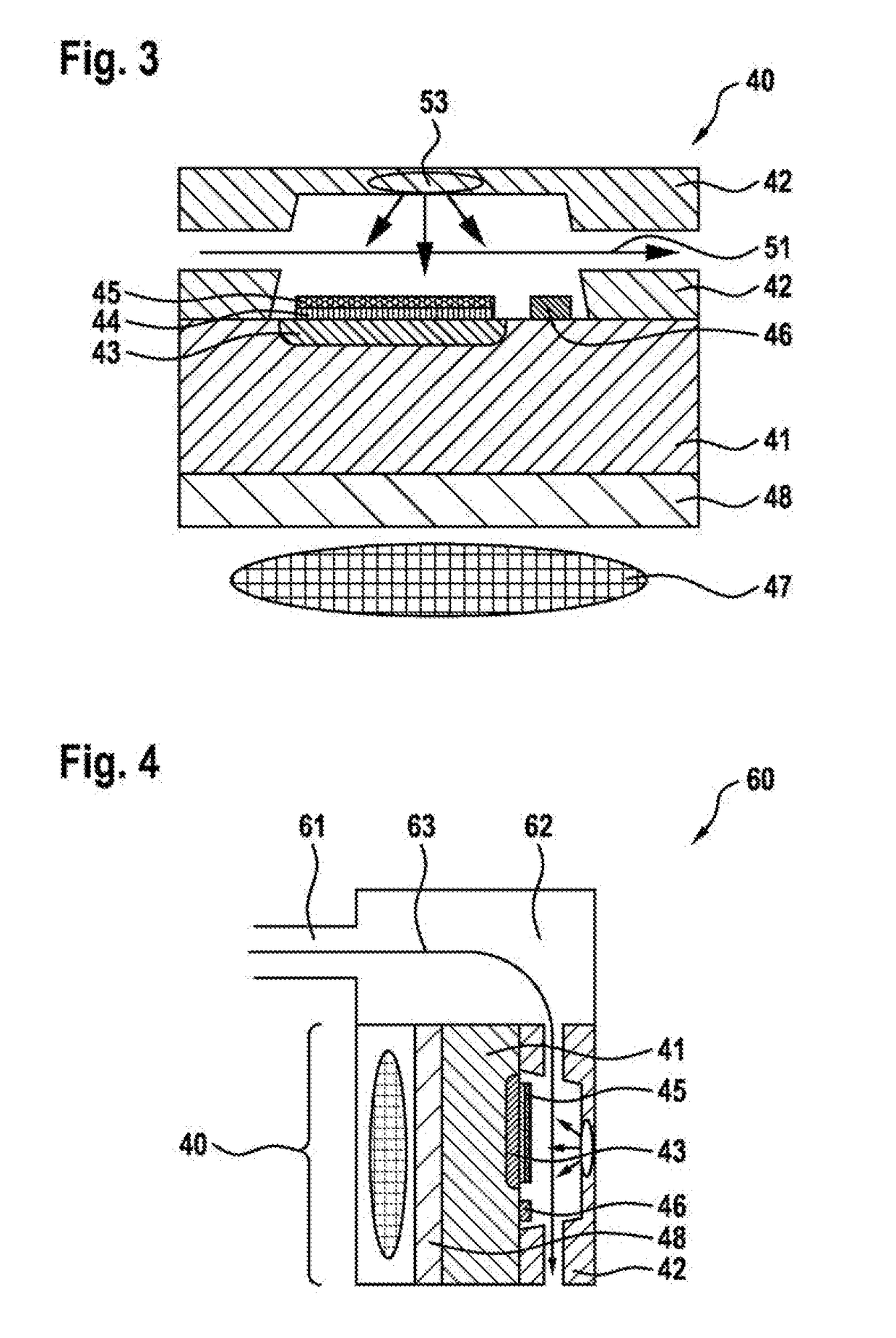
In a device (40) for analysing substances in a sample on the basis of a measurement of nuclear magnetic resonances, the device comprises means (47) for generating a magnetic field. The device (40) is characterized in that, in order to detect magnetic resonances induced in the sample by the generation of the magnetic field, provision is made of at least one magnetic field sensor which comprises at least one sensitive component (45) with diamond structures, wherein the diamond structures have nitrogen vacancy centres.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Device for the NMR Analysis of Substances in a Sample, Respiratory Gas Analysis Device, Fuel Sensor and Method
ActiveUS20180202952A1Fuel testingRespiratory organ evaluationGas analysisNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A device for analyzing substances in a sample on the basis of a measurement of nuclear magnetic resonances including a magnetic field device configured to generate a magnetic field. The device is configured such that, in order to detect magnetic resonances induced in the sample by the generation of the magnetic field, provision is made of at least one magnetic field sensor which comprises at least one sensitive component with diamond structures. The diamond structures have nitrogen vacancy centers.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Nano-diamond-based anti-counterfeiting method, corresponding medicine, anti-counterfeiting ink and application thereof
InactiveCN108918485ARealize anti-counterfeitingNovel anti-counterfeiting methodInksFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceLength wave
The invention discloses a nano-diamond-based anti-counterfeiting method, a corresponding medicine, anti-counterfeiting ink and an application thereof. The nano-diamond-based anti-counterfeiting methodcomprises: coating the surface of the article to be subjected to anti-counterfeiting treatment with nano-diamond particles or adding nano-diamond particles into the article to be subjected to anti-counterfeiting treatment. The nano-diamond particle contains nitrogen-vacancy center NV<-> in a negatively charged state and produces fluorescence emitted by the excitation light at the wavelength of 400 nm to 600 nm so that anti-counterfeiting effects are obtained. Under control of the internal structure of the key nano-diamond material, through fluorescence produced by the nano-diamond material containing nitrogen-vacancy center NV<-> in a negatively charged state under excitation light at the wavelength of 400 nm to 600 nm, the anti-counterfeiting effects are effectively achieved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
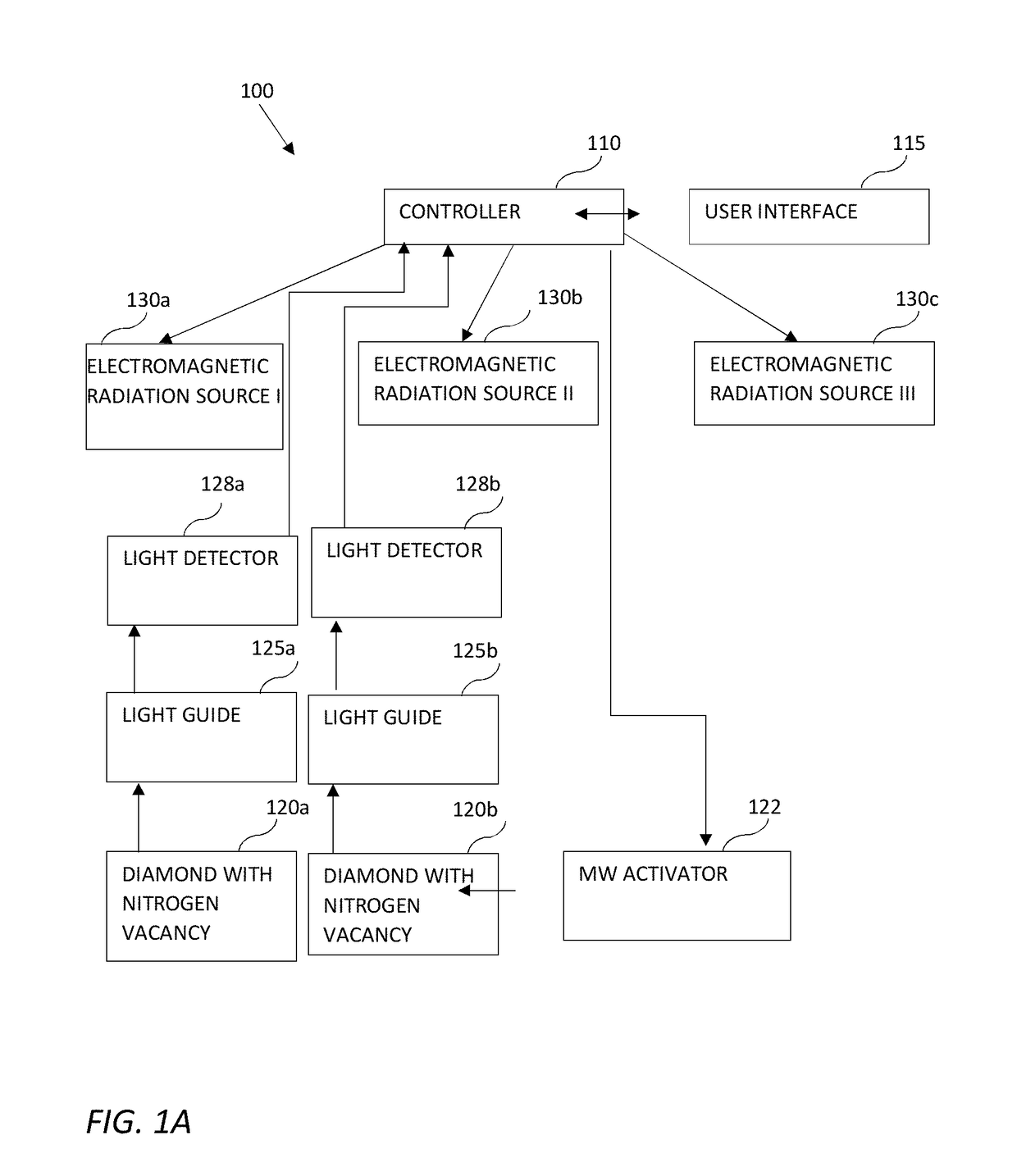
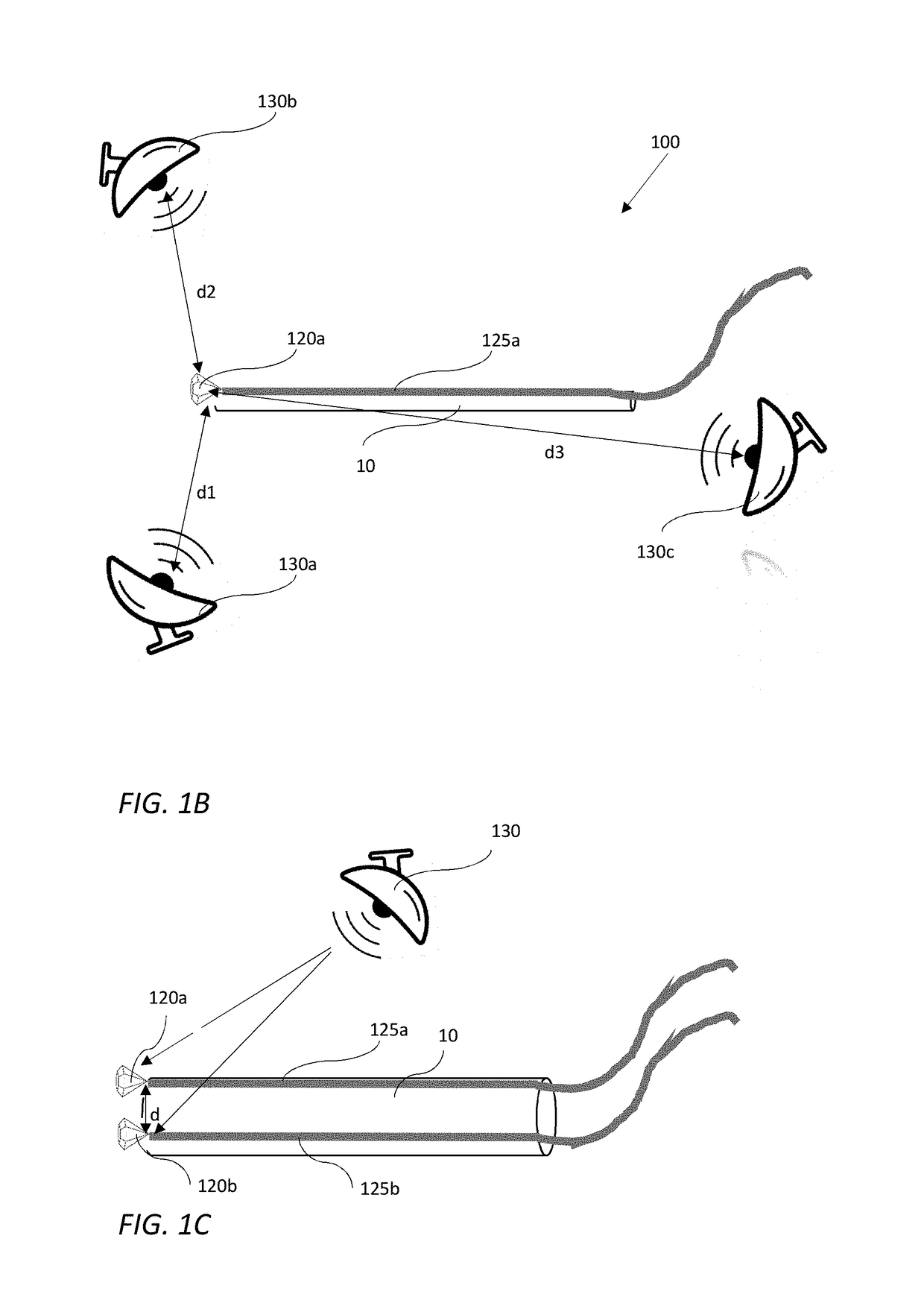
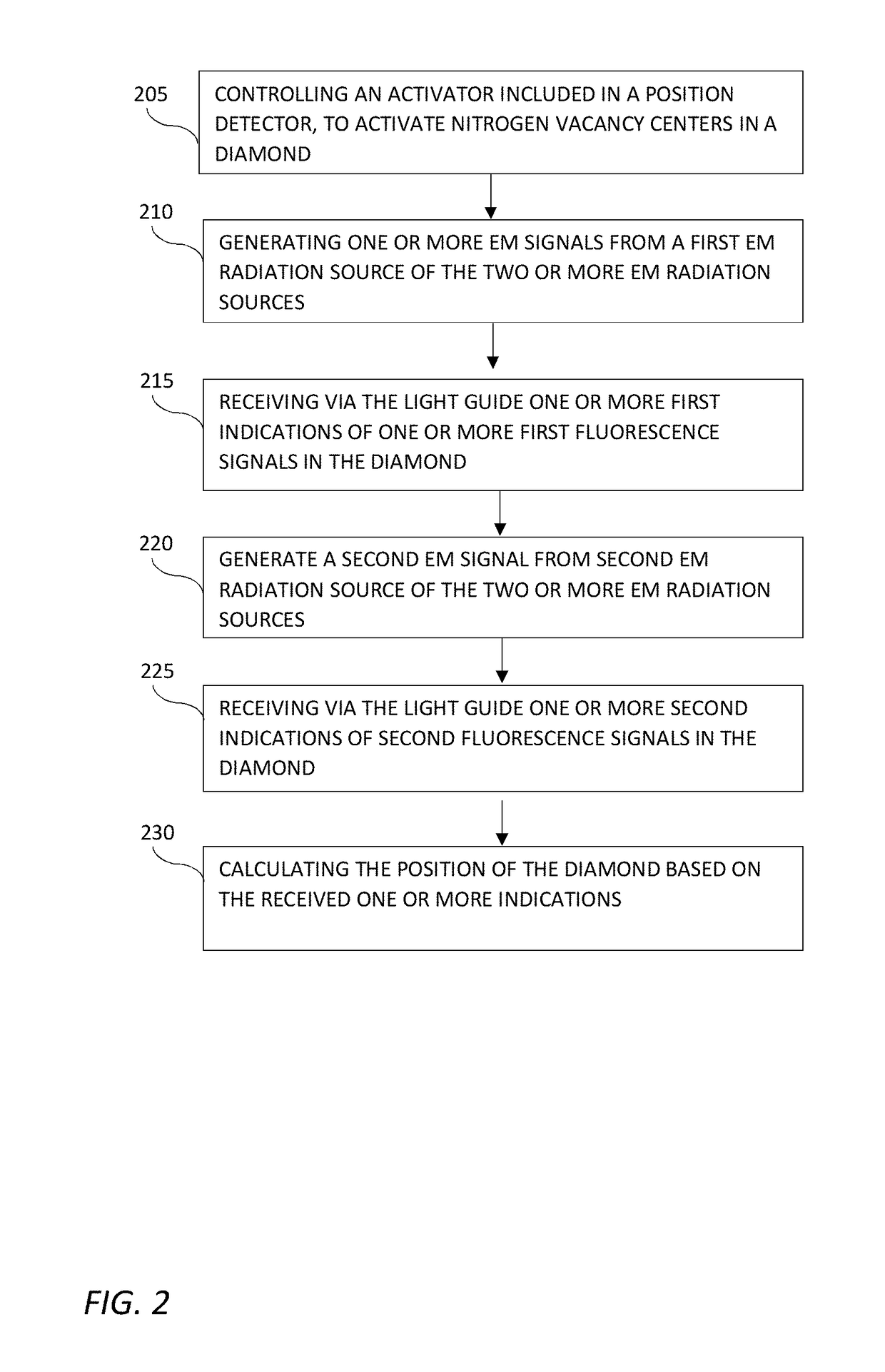
Position detectors for in-vivo devices and methods of controlling same
The position detector disclosed may include: a diamond with nitrogen vacancy centers; an activator configured to activate the nitrogen vacancy centers in the diamond to emit fluorescence signals; a sensor configured to detect the fluorescence signals emitted from the diamond, and a controller configured to control components of the position detector. The controller may be configured to: control the activator to activate the nitrogen vacancy centers in the diamond; control a first EM radiation source to generate one or more EM signals; receive via the sensor one or more first indications of one or more first fluorescence signals; control a second EM radiation source to generate one or more EM signals; receive via the sensor one or more second indications of one or more second fluorescence signals; and calculate the position of the diamond based on the received indications. The position detector has utility in detecting a medical tool in the body of a subject, for example
Owner:DIAMSENSE LTD
Extensible quantum information processing system and method
ActiveCN110766162AAchieving quantum entanglementAchieve indirect couplingQuantum computersInformation processingData acquisition
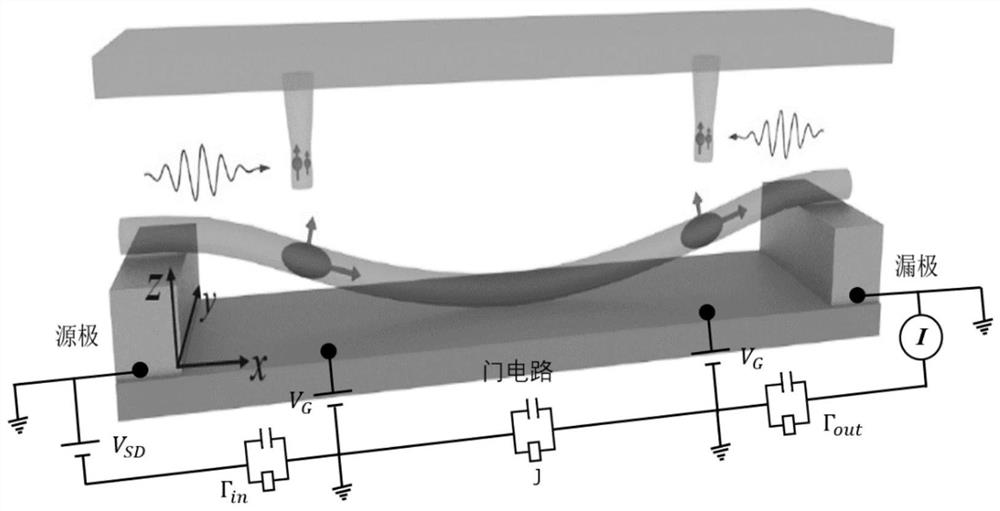
The invention discloses an extensible quantum information processing system and method, and relates to the technical field of quantum computing. The structure of the extensible quantum information processing system comprises a columnar diamond sample, an optical system, a microwave system, a magnetic field system, a carbon nanotube double-quantum-dot sample, a low-temperature system, a data acquisition system and an electric control system. The invention provides a carbon nanotube-spinning hybrid quantum system, wherein microwave signals and a magnetic field are applied to an area where each group of nitrogen vacancy centers and quantum dots are located, and magnetic dipole-dipole interaction exists between electrons of each group of nitrogen vacancy centers and the quantum dots; and by controlling a magnetic field and a microwave signal, indirect coupling between two nitrogen-vacancy centers which are spaced by a micron dimension can be realized through the action of the carbon nano tube, and quantum entanglement between the two nitrogen-vacancy centers in a long distance is realized, so that an extensible quantum information processing method is provided.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Diamond nitrogen vacancy sensed ferro-fluid hydrophone
ActiveUS10088336B2Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSeismologyHydrophoneNitrogen
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Titanium nitride based metamaterial
ActiveUS9784888B2Good dispersionImprove efficiencyLayered productsSolid-state devicesSharp interfaceTantalum nitride
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Diamond maser and microwave amplifier
Masers and microwave amplifiers that can function in the continuous-wave mode at room temperature are provided. The maser system can include a diamond gain medium having nitrogen-vacancy centers, and a resonator can be disposed around the gain medium. The resonator can be disposed in a cavity box, and radiation (e.g., visible light) can be provided to the gain medium to cause emission of microwave radiation.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Method and system for magnetic resonance imaging using nitrogen-vacancy centers
InactiveUS9702900B2Measurements using double resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsRf fieldMagnetic field gradient
A method for performing sub-nanometer three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging of a sample under ambient conditions using a diamond having at least one shallowly planted nitrogen-vacancy (NV) center. A driving radio-frequency (RF) signal and a microwave signal are applied to provide independent control of the NV spin and the target dark spins. A magnetic-field gradient is applied to the sample with a scanning magnetic tip to provide a narrow spatial volume in which the target dark electronic spins are on resonance with the driving RF field. The sample is controllably scanned by moving the magnetic tip to systematically bring non-resonant target dark spins into resonance with RF signal. The dark spins are measured and mapped by detecting magnetic resonance of said nitrogen-vacancy center at each of said different magnetic tip positions. The dark-spin point-spread-function for imaging the dark spins is directly measured by the NV center.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
A Scanning Magnetometer of Nitrogen-Vacancy Color Center Diamond
ActiveCN105137126BRemove restrictionsHigh measurement sensitivityScanning probe microscopyUltra-high vacuumFeedback control
The invention relates to a weak magnetic field measurement technique, in particular, a novel nitrogen-vacancy center diamond scanning magnetometer. With the novel nitrogen-vacancy center diamond scanning magnetometer adopted, the problems of low sensitivity and limited application range of existing weak magnetic field information measuring tools can be solved. The novel nitrogen-vacancy center diamond scanning magnetometer of the nitrogen-vacancy center diamond includes an atomic force microscope system and an optical detection magnetic information system; and the atomic force microscope system includes an ultra-high vacuum chamber, a scanning tube, a nitrogen-vacancy center diamond probe, a 670nm-wavelength laser, a four-quadrant photodiode detector, a phase-locked loop, an automatic gain control loop, piezoelectric ceramic, a 50-ohm resistor, a feedback control loop, a lock-in amplifier, a carrier, a surface topography information output port and a magnetic information output port. The novel nitrogen-vacancy center diamond scanning magnetometer of the invention is suitable for weak magnetic field information measurement.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
A scalable quantum information processing system and method
ActiveCN110766162BAchieving quantum entanglementAchieve indirect couplingQuantum computersInformation processingParticle physics
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Quantum diamond precision magnetic measurement system based on single spin
PendingCN114594075AEnabling Multimodal ImagingHigh resolutionInvestigating jewelsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceFluorescenceParticle physics
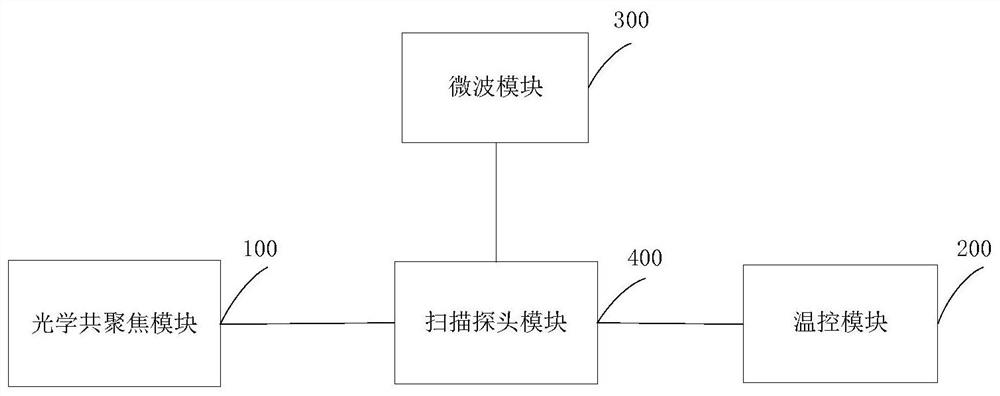
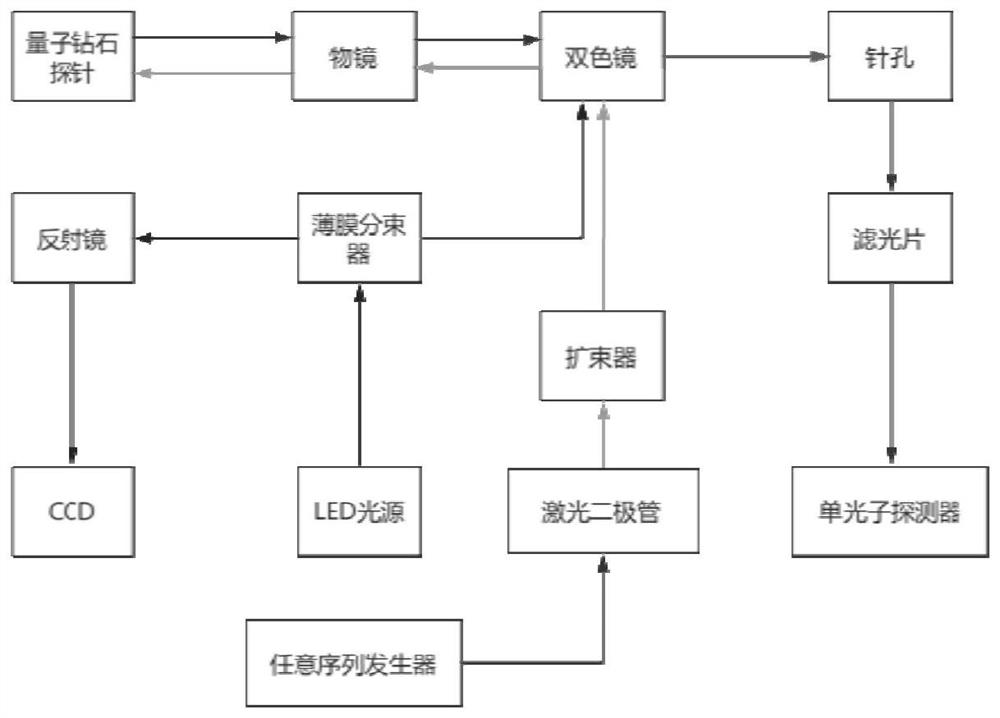
The invention discloses a quantum diamond precision magnetic measurement system based on single spin, and the system comprises an optical confocal module which is used for generating laser with a preset wavelength, irradiating the laser on a probe, integrating a nitrogen-vacancy center in the probe, and collecting and filtering fluorescence emitted by an NV color center in the probe due to energy level transition; the temperature control module is used for maintaining the temperature environment of the system; the microwave module is used for generating microwaves, accurately radiating the microwaves to the sample and reducing the microwaves radiated to the microwave amplifier so as to reduce the damage to the microwave amplifier; and the scanning probe module is used for realizing alignment of a probe and an objective lens and realizing barrier type scanning imaging of a sample. The system realizes room-temperature atmosphere, multi-mode, quantitative microscopic magnetic property and lossless imaging, and greatly meets the experimental requirements of multiple important fields such as topological magnetic structure, superconducting magnetic imaging and life science in-situ imaging.
Owner:CHINAINSTRU & QUANTUMTECH (HEFEI) CO LTD
A kind of optical fiber magnetic field sensor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110554332BHigh sensitivityImprove fluorescence collection efficiencyMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesFluorescenceStimulated emission
The invention discloses an optical fiber magnetic field sensor and a preparation method thereof. The optical fiber magnetic field sensor comprises an optical fiber and a plurality of diamond micro-columns, the plurality of diamond micro-columns are positioned at one end in the optical fiber; each diamond micro-column contains a nitrogen-vacancy center; when the optical fiber magnetic field sensoris used for measuring a magnetic field, one end, containing the diamond micro-column, of the optical fiber is placed in an environment of the magnetic field to be measured, and laser with a preset wavelength is emitted from the other end of the optical fiber, so that the the nitrogen-vacancy center is excited to emit fluorescence; and steps of transmitting a sweep frequency signal in a preset frequency range to one end, containing the diamond micro-column, of the optical fiber, collecting fluorescence, and determining the size of the magnetic field to be measured by analyzing the change rule of the intensity of the fluorescence along with the frequency of the sweep frequency signal are carried out. According to the invention, more nitrogen-vacancy centers can be integrated at an optical fiber port, the sensitivity is related to the number of the nitrogen-vacancy centers in the sample, and a magnetometer with higher sensitivity can be obtained through the diamond micro-column sample with higher nitrogen-vacancy center color center density.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Device and method based on diamond nv centers
PendingUS20210263116A1Improve performanceEfficient optical controlQuantum computersMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesParticle physicsMaterials science
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Gyrocope based on nitrogen vacancy centers in diamond
ActiveUS10890448B2Eliminating externally induced unwanted componentReduce impactRotary gyroscopesTurn-sensitive devicesUniform fieldGyroscope
The invention pertains to the field of gyroscopes, in particular—to quantum gyroscopes. The invention provides a gyroscope employing an ensemble of NV-centers in diamond, which includes a diamond plate, a source of green light, an optical system for directing the green light to the diamond plate, a photodetector for registering fluorescence of the color centers in the diamond plate, optical elements that direct the fluorescence from the diamond plate to the photodetector, a source of microwave radiation, a source of radiofrequency radiation, and a source of constant magnetic field, the gyroscope being different from the prior art in that it comprises an energy-efficient antenna that creates a strong longitudinal homogeneous field in the entire volume of the diamond plate with the possibility of frequency adjustment, as well as a system for locking the frequency of the microwave field to that of the transition in the color centers. The invention allows to reduce the volume of the sensing element, provides high relative spectral sensitivity, and allows to create a hybrid device that comprises a 3-axis gyroscope, a magnetometer, and a temperature sensor.
Owner:LLC SENSOR SPIN TECH
Sensors and methods of identifying a gas, and levitated spin-optomechanical systems
ActiveUS10690604B2Analysis using optical pumpingAnalysis using electron paramagnetic resonanaceLight beamParticle physics
Sensors and methods are provided that include a diamond material containing a nitrogen vacancy center, the diamond material being configured to be exposed to an environment comprising one or more gases, an optical light source configured to excite the nitrogen vacancy center of the diamond material with an optical light beam produced therefrom, a detector configured to detect a signal originating from the diamond material in response to the optical light beam exciting the nitrogen vacancy center, and the capability of analyzing the signal to identify a specific gas in the environment. Also included are levitated spin-optomechanical systems capable of elevating in a vacuum a diamond material containing a nitrogen vacancy center, applying microwave radiation to the diamond material for controlling and flipping the electron spin of the nitrogen vacancy center, and monitoring electron spin of the nitrogen vacancy center.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Polariton-Stabilized Solid-State Spin Clock
ActiveUS20220197225A1Better-than-millihertz stabilityImprovement in fractional frequency stabilityPulse automatic controlApparatus using atomic clocksAnalytic modelParticle physics
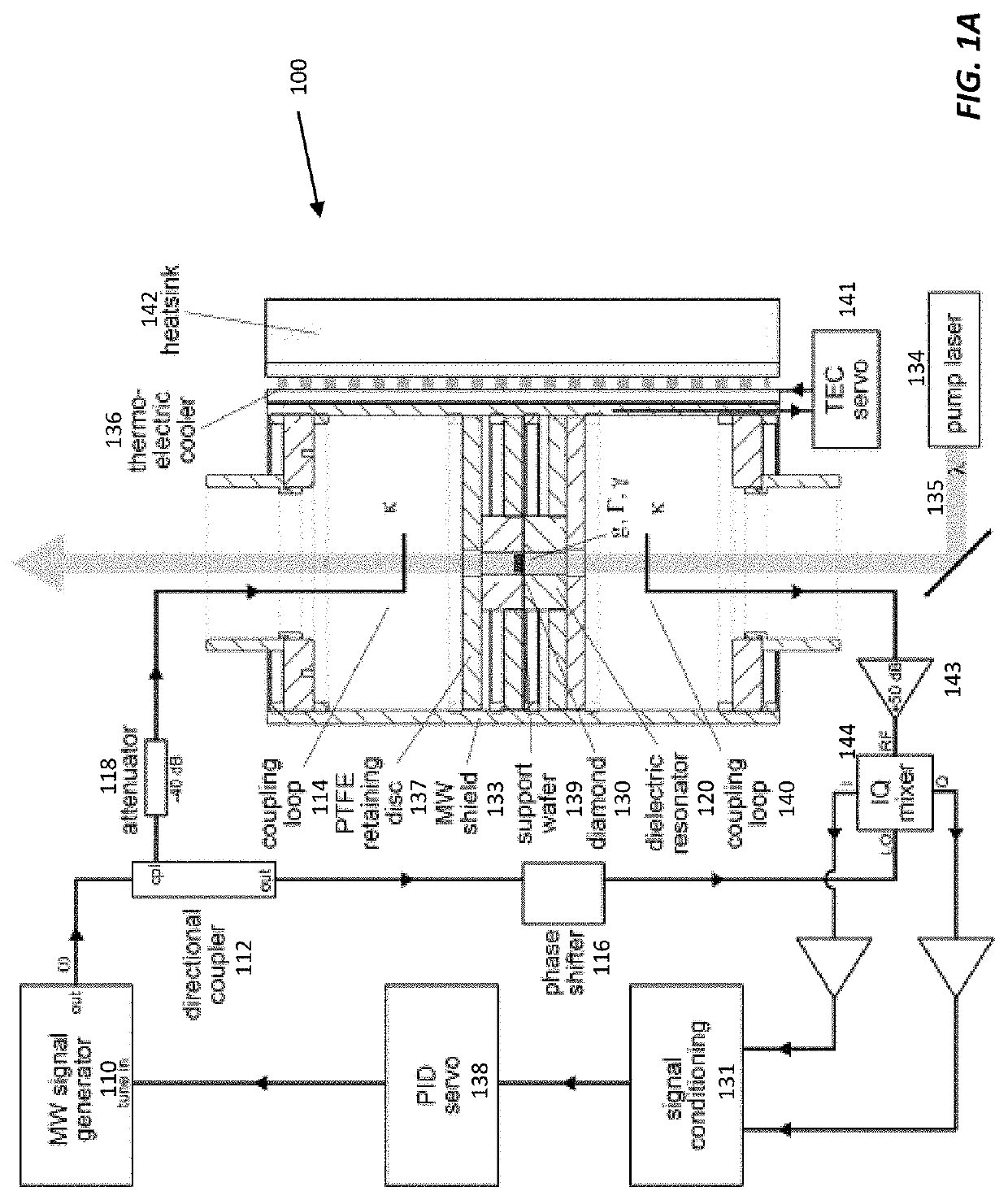
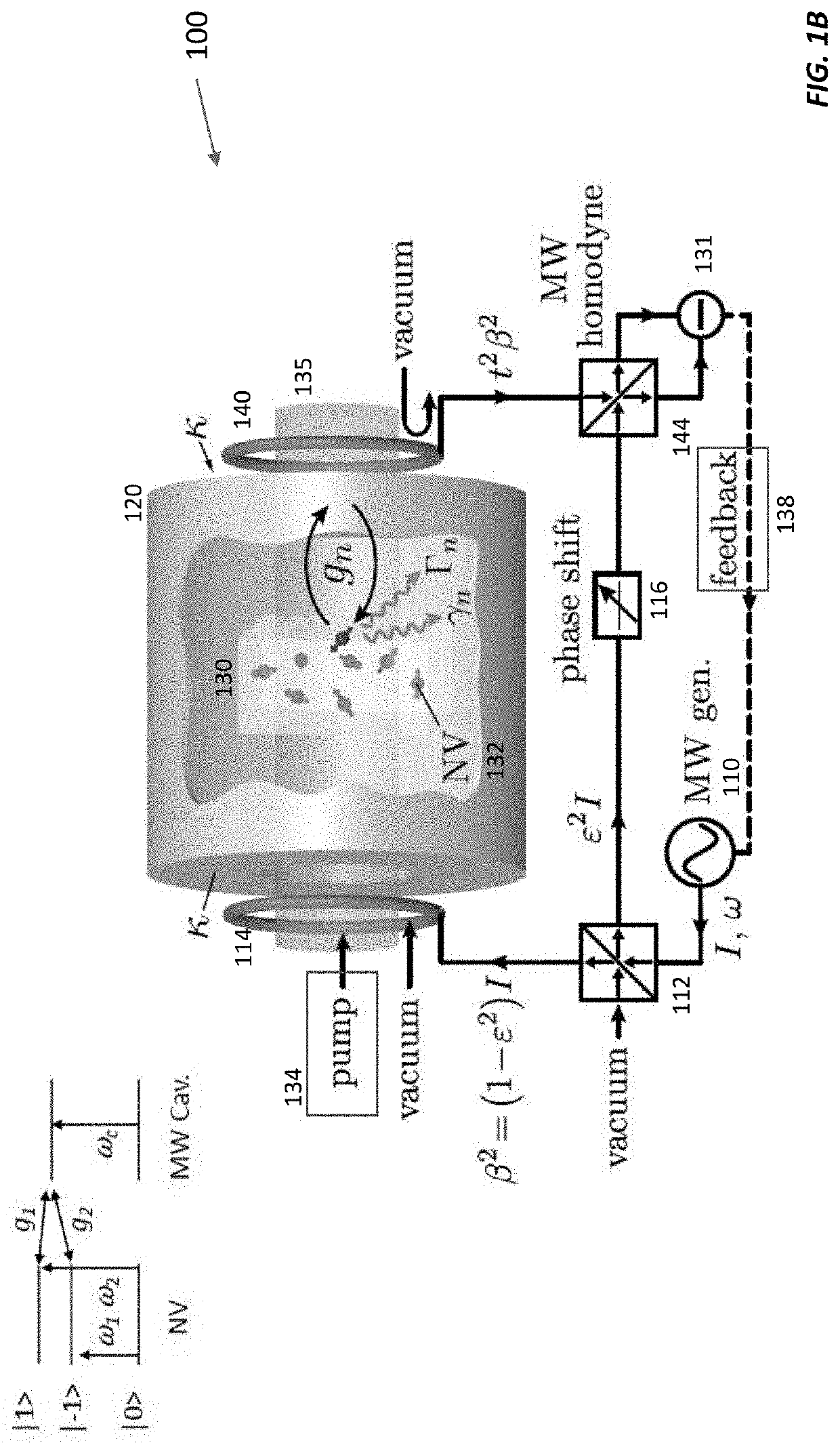
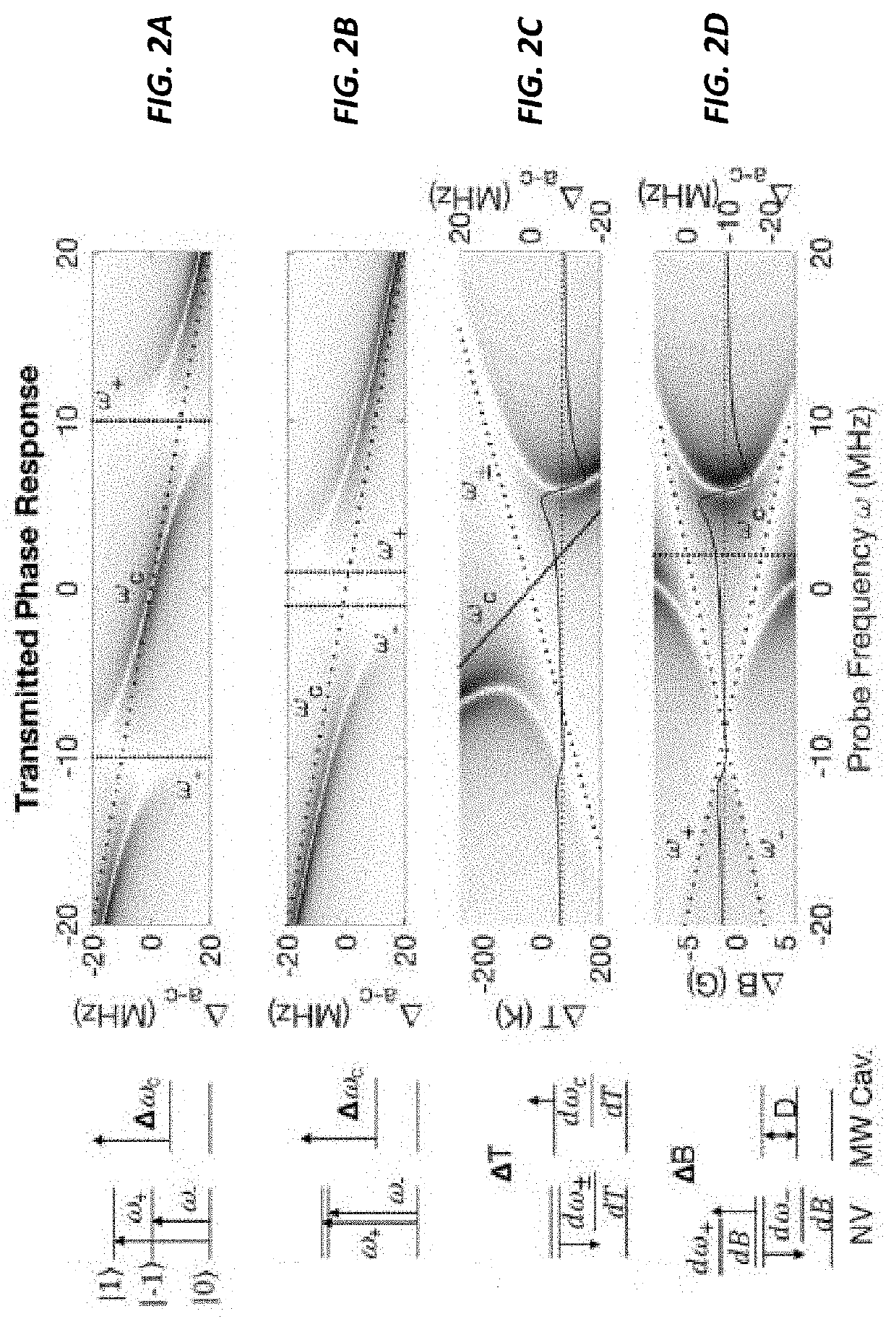
An ensemble of spin defect centers or other atom-like quantum systems in a solid-state host can be used as a compact alternative for an atomic clock thanks to an architecture that overcomes magnetic and temperature-induced systematics. A polariton-stabilized solid-state spin clock hybridizes a microwave resonator with a magnetic-field-insensitive spin transition within the ground state of a spin defect center (e.g., a nitrogen vacancy center in diamond). Detailed numerical and analytical modeling of this polariton-stabilized solid-state spin clock indicates a potential fractional frequency instability below 10-13 over a 1-second measurement time, assuming present-day experimental parameters. This stability is a significant improvement over the state-of-the-art in miniaturized atomic vapor clocks.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY +1
Magnetometer for measuring an unknown external magnetic field
ActiveUS11340320B2Improve efficiencyEnhanced responsivityMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceAnalysis using optical pumpingOptical cavityFluorescence
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com