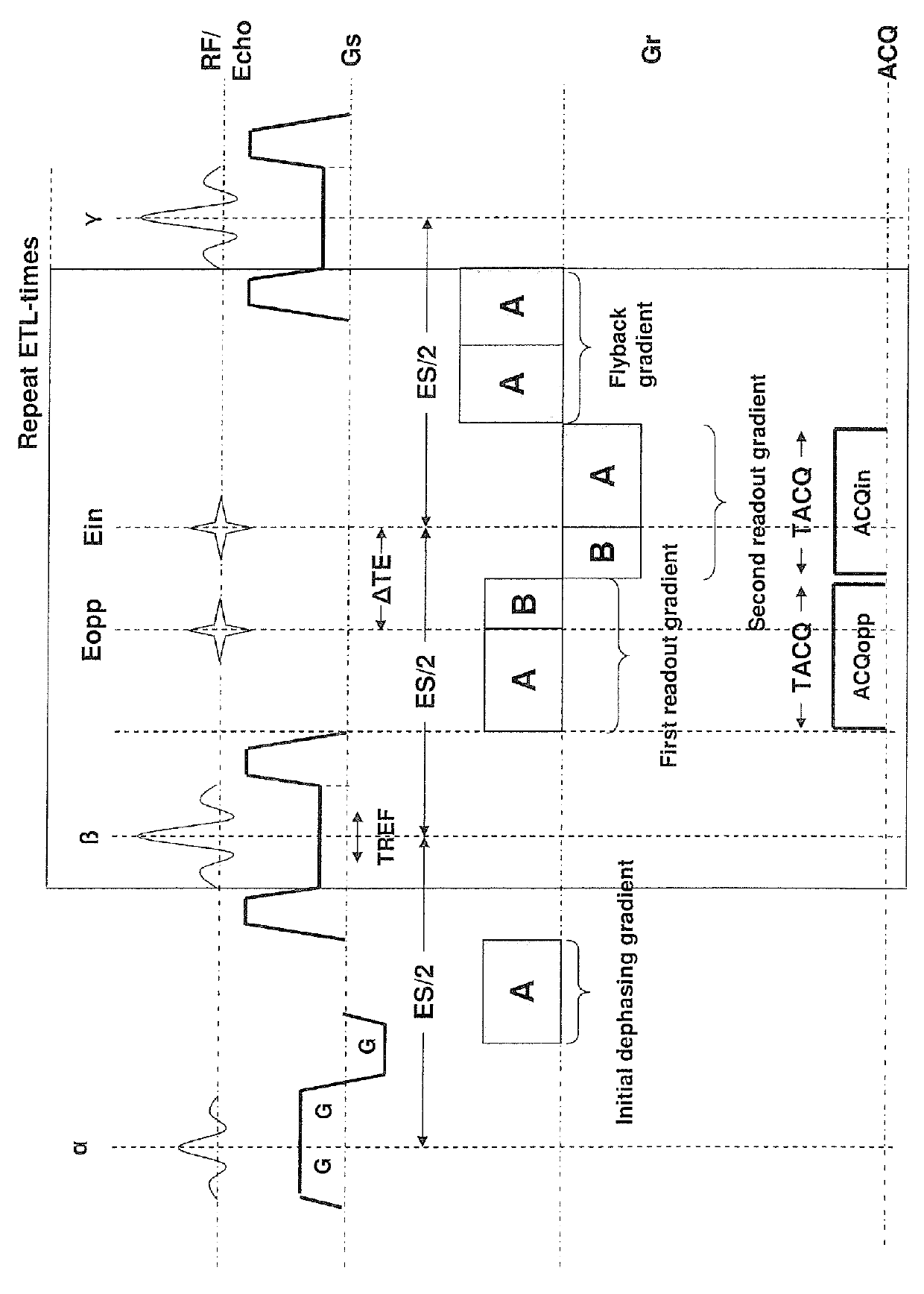
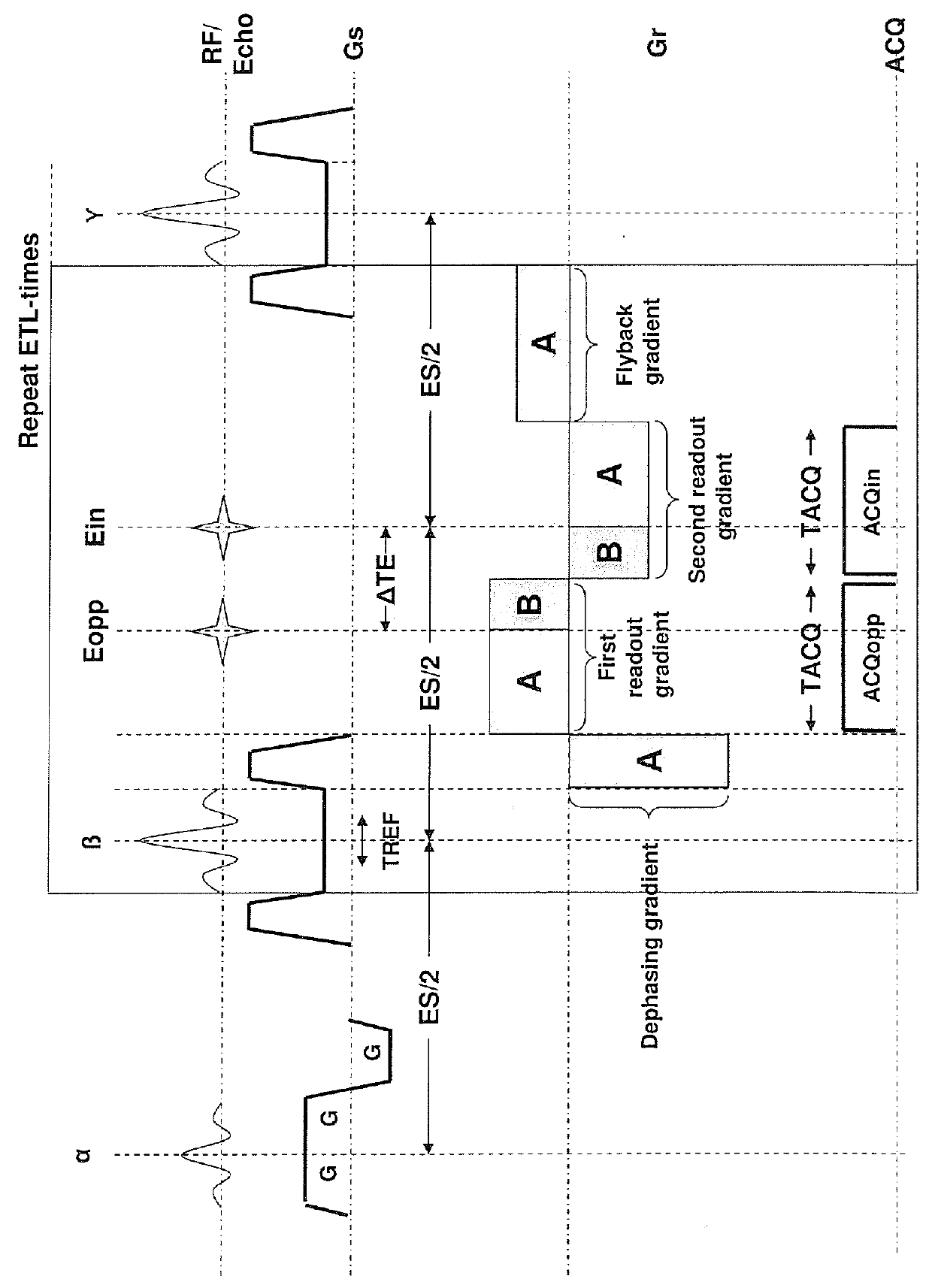
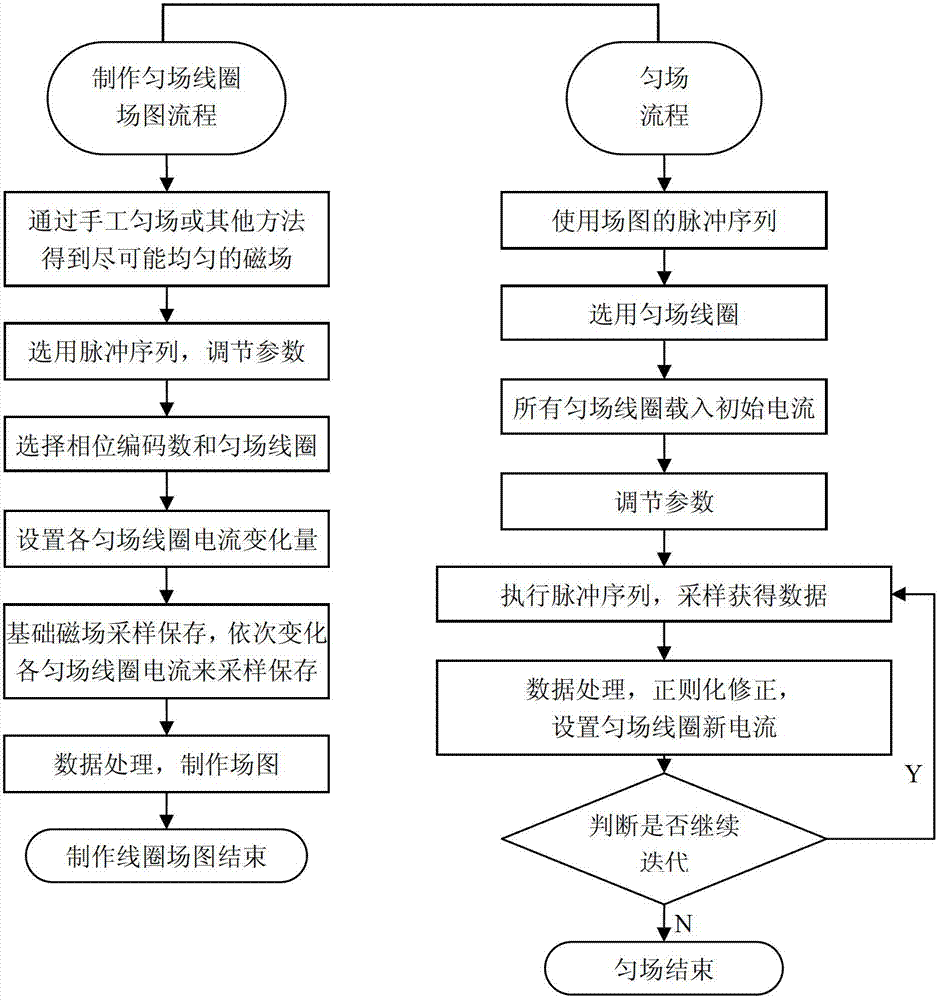
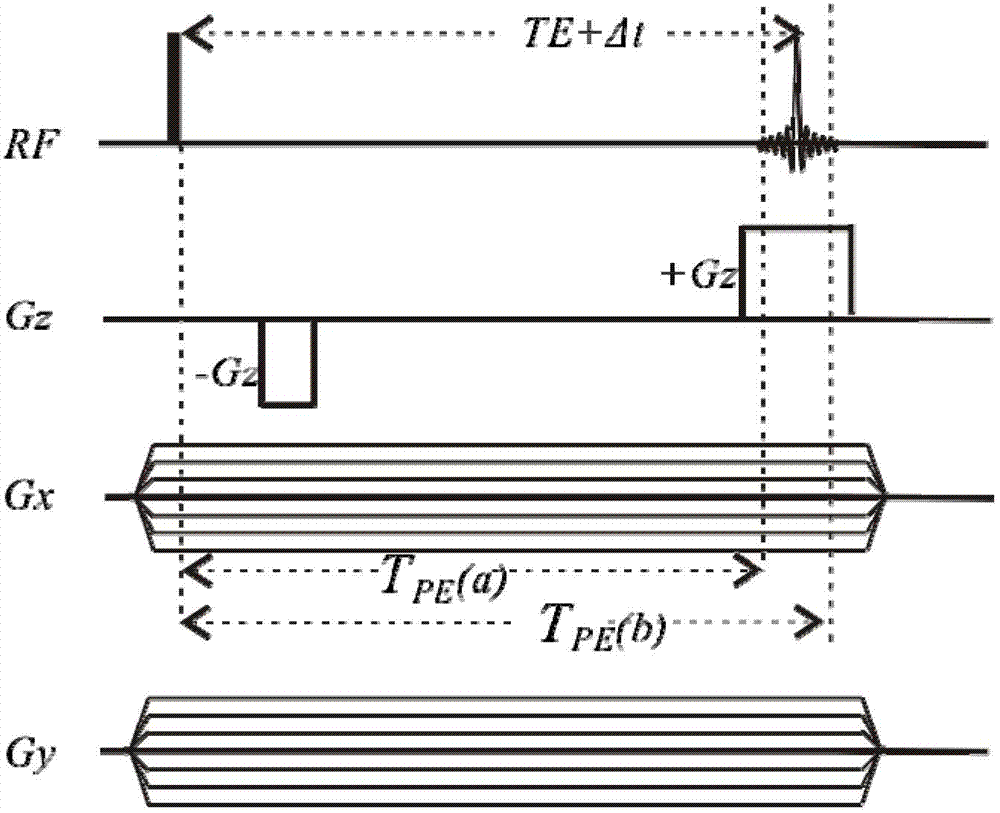
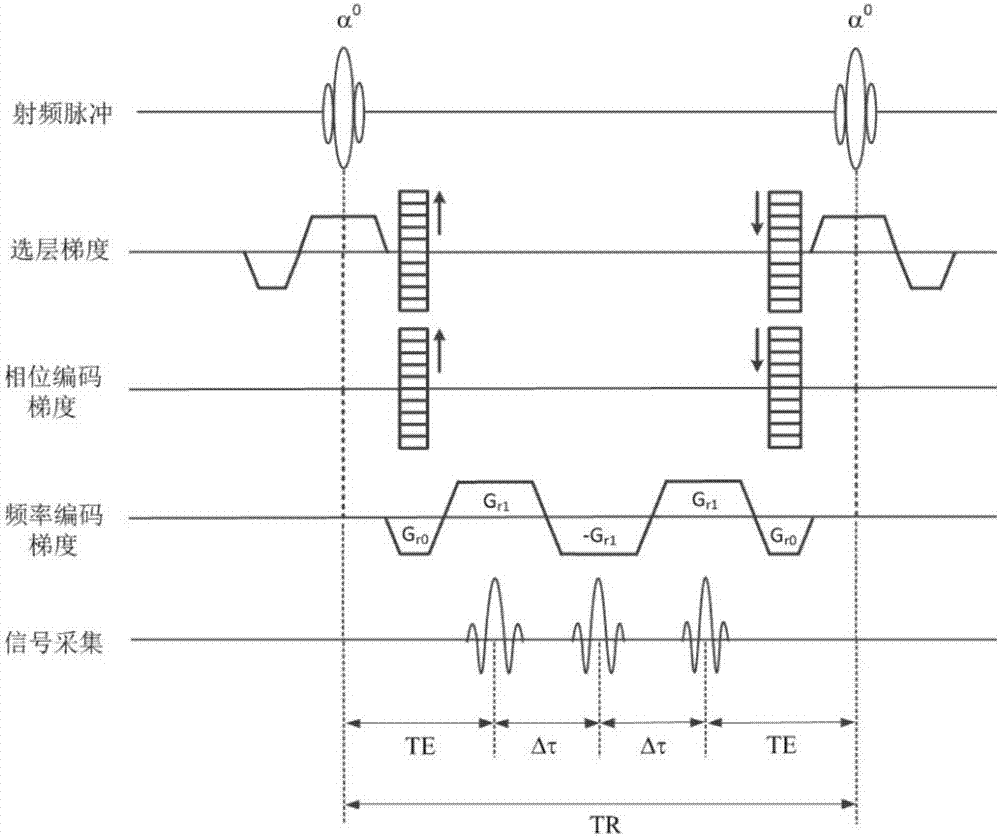
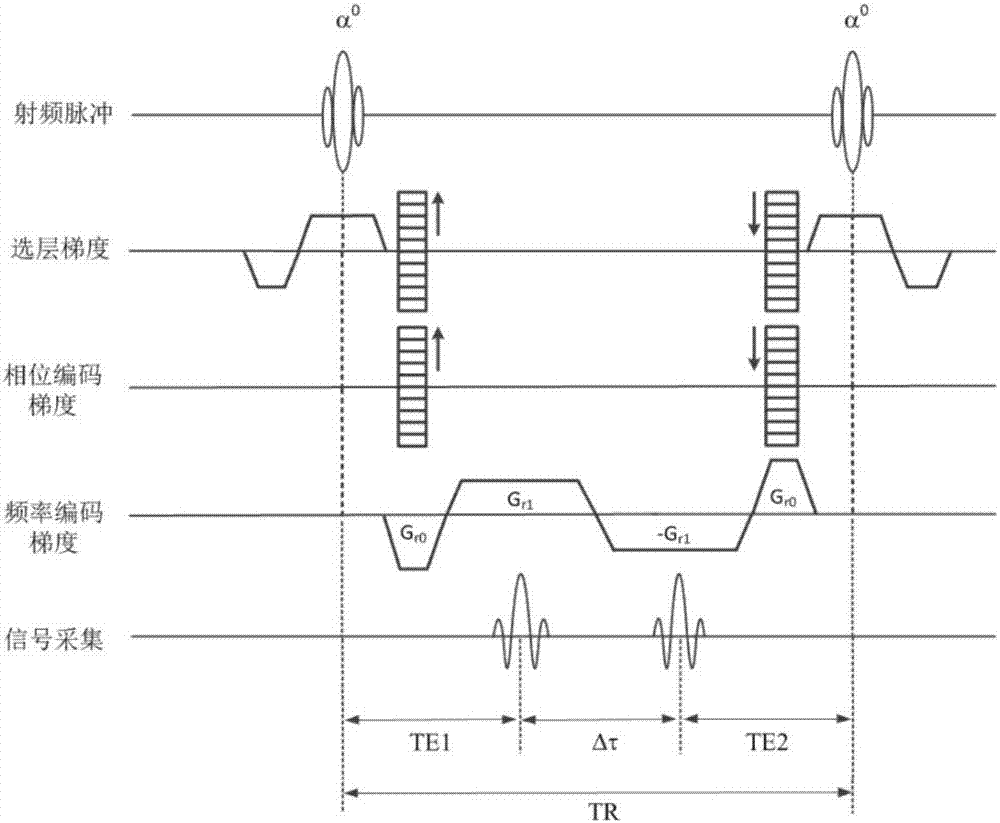
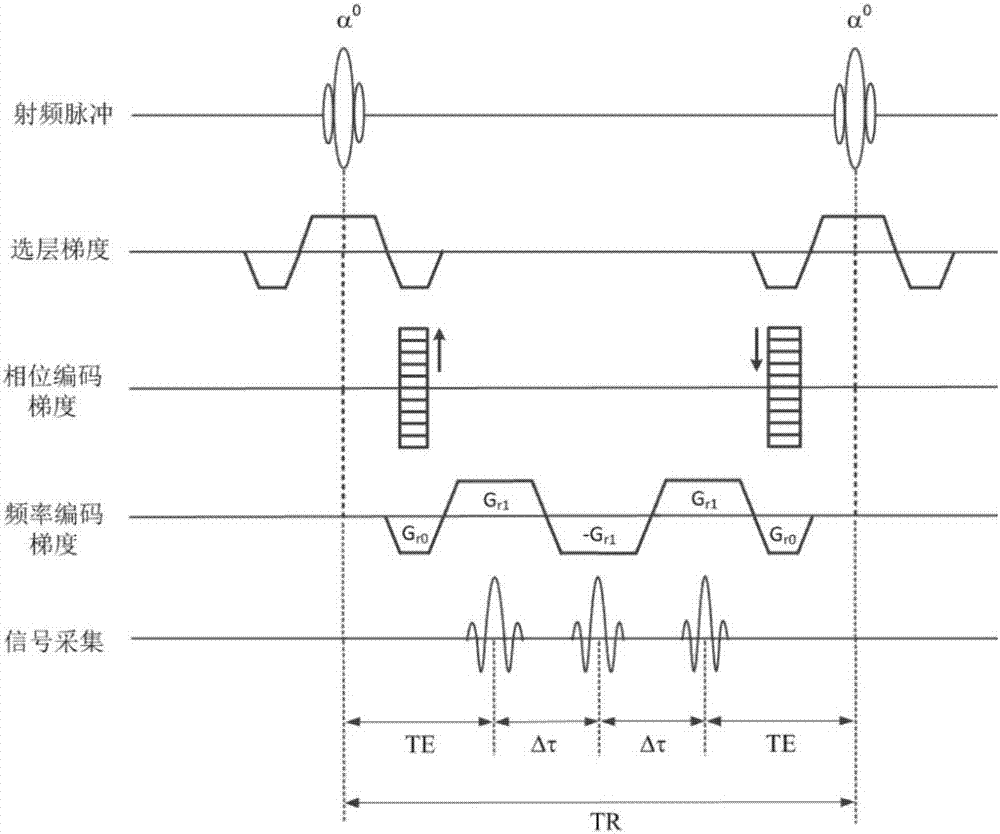
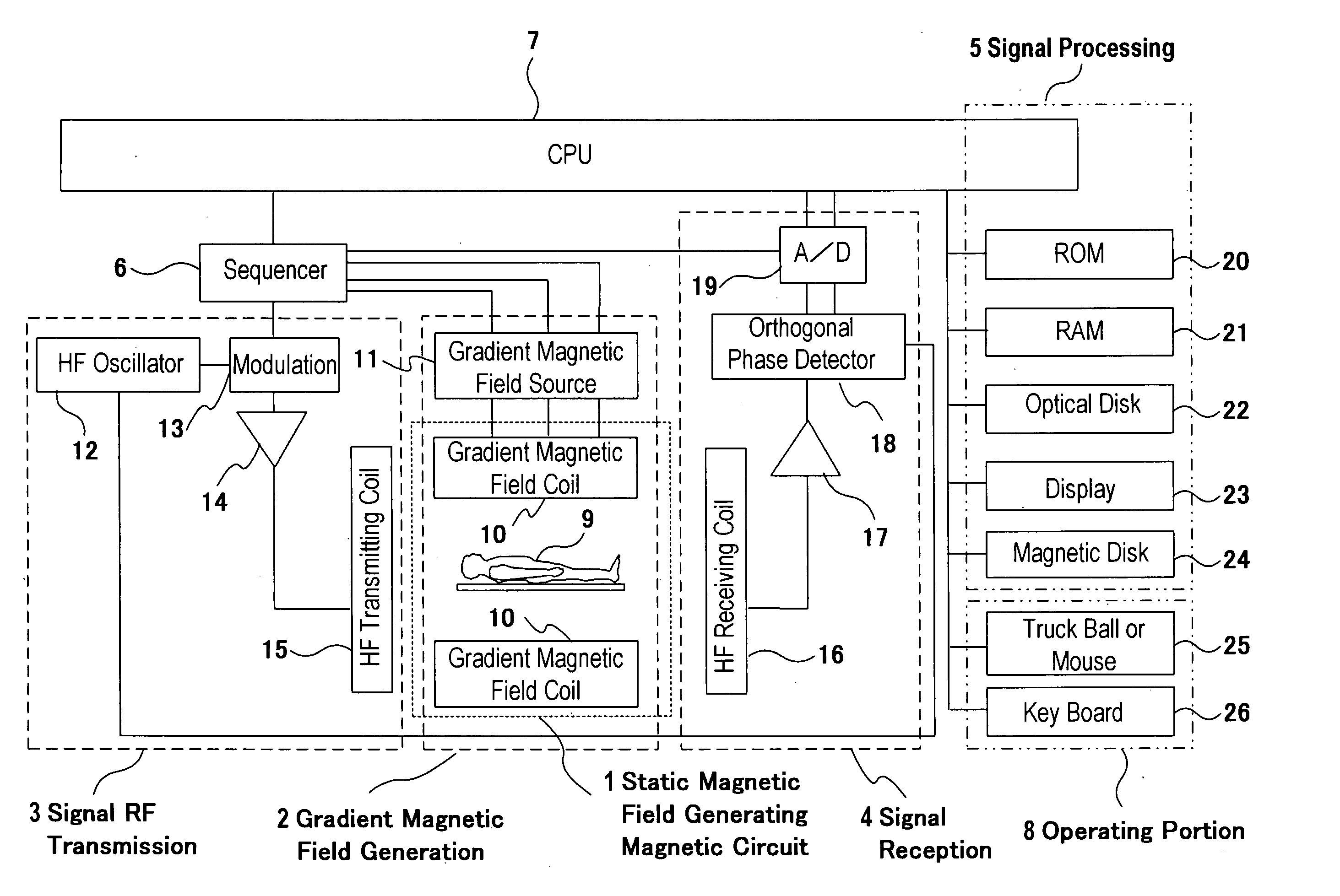
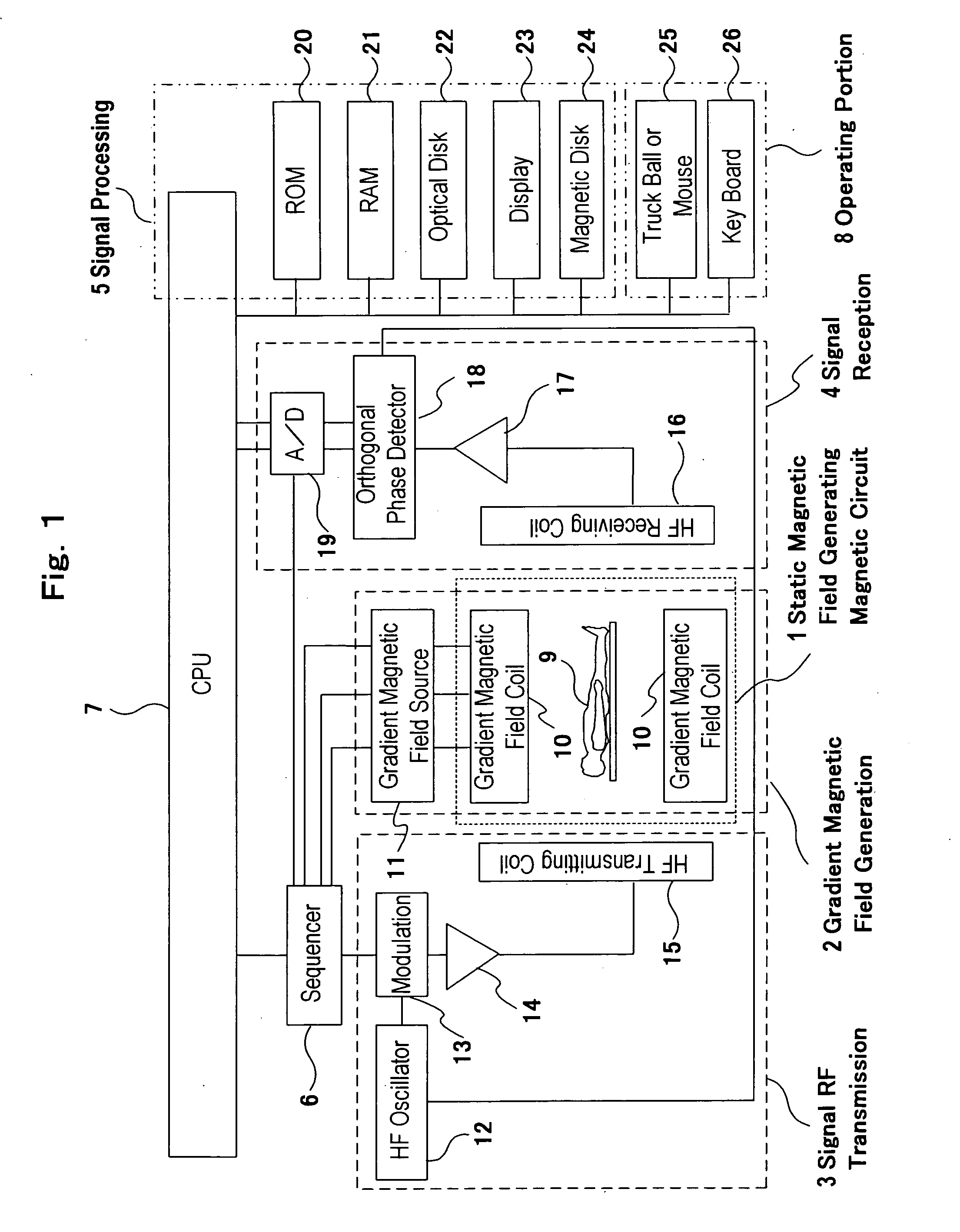
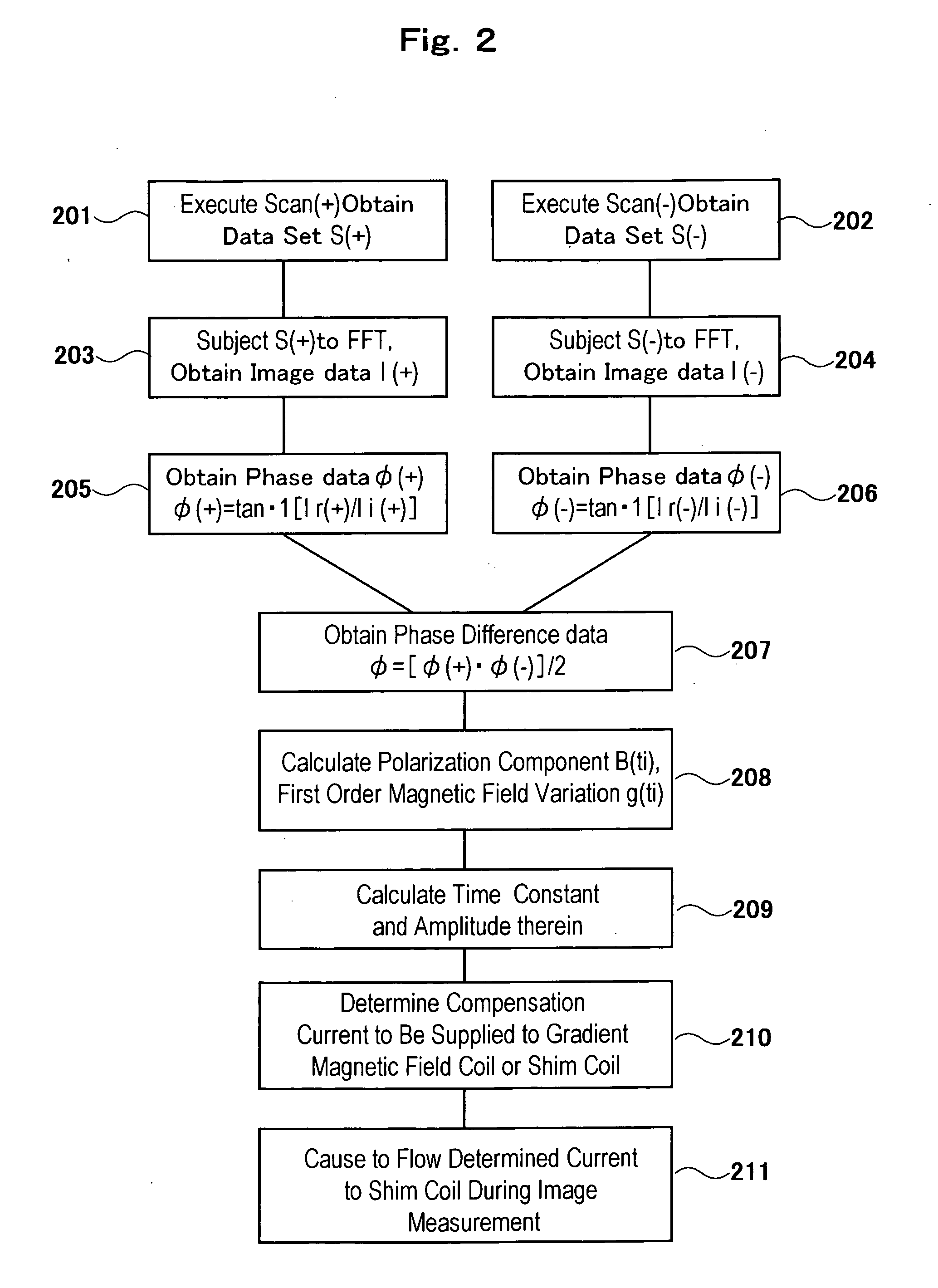
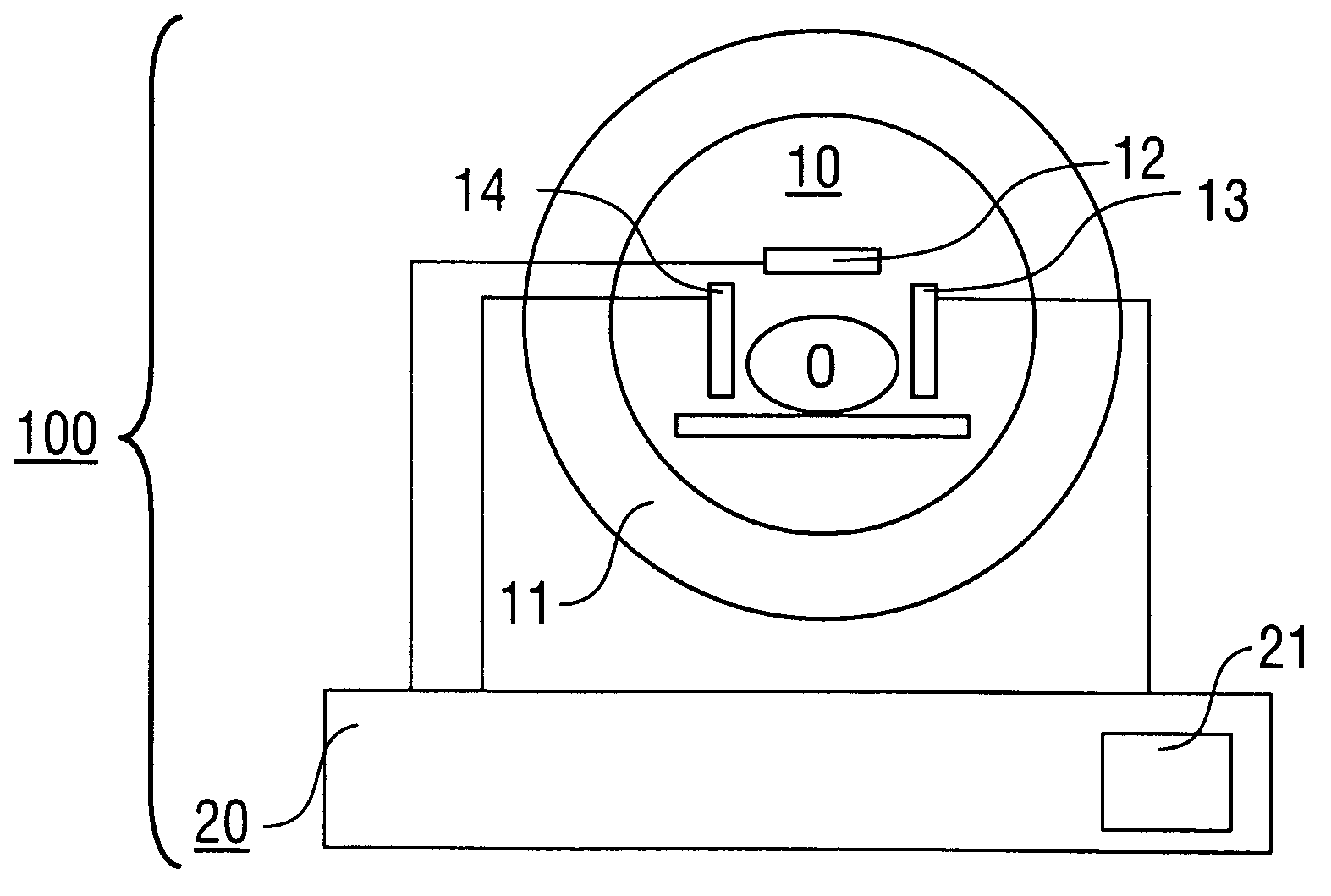
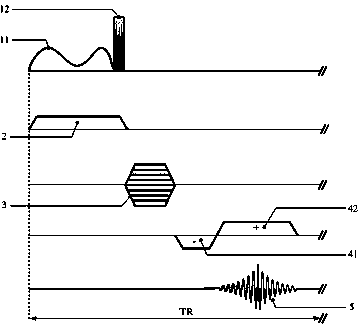
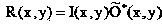Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
211 results about "Gradient echo" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A gradient echo (GRE) is simply a clever manipulation of the FID signal that begins by applying an external dephasing gradient field across the specimen or tissue.
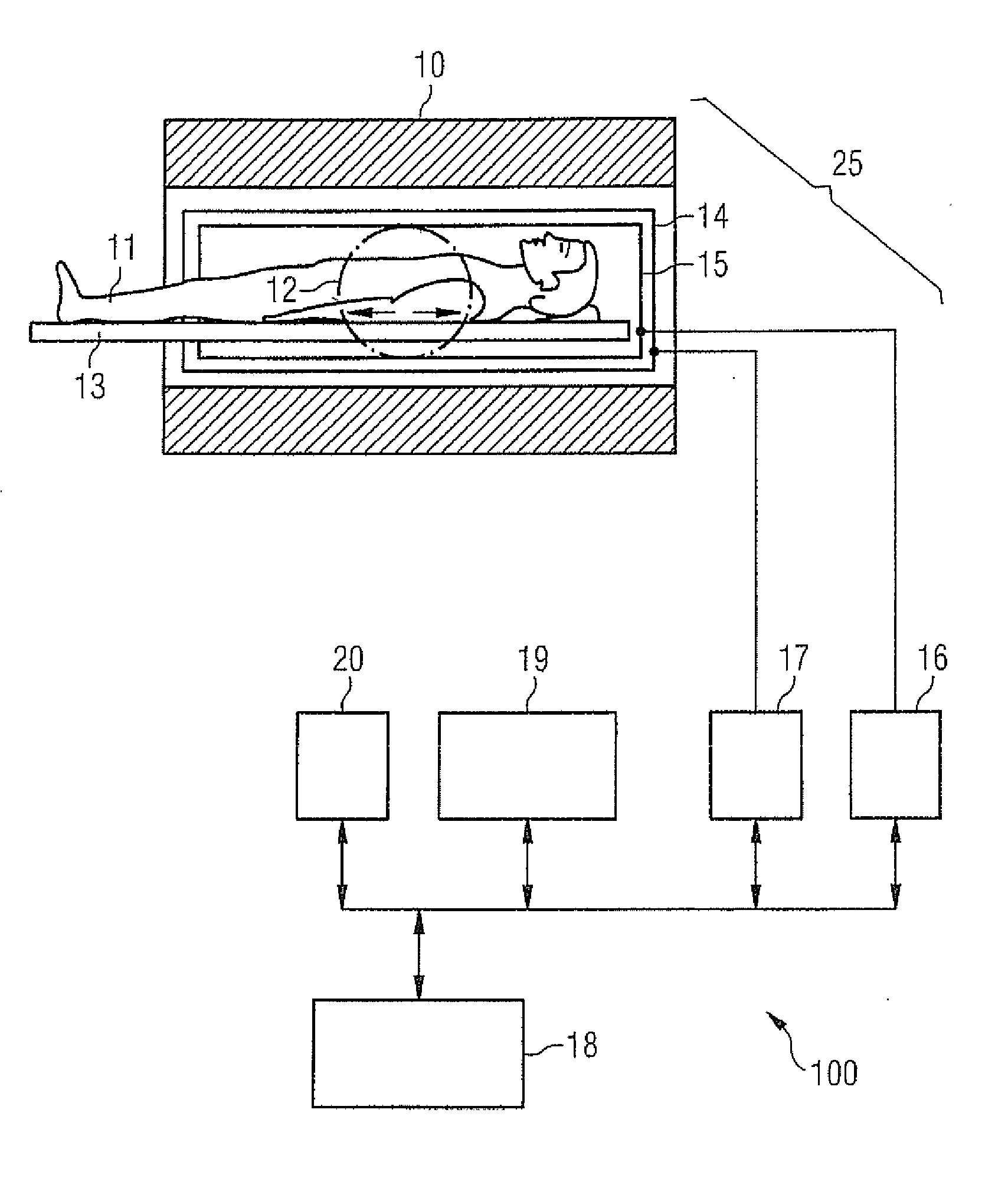
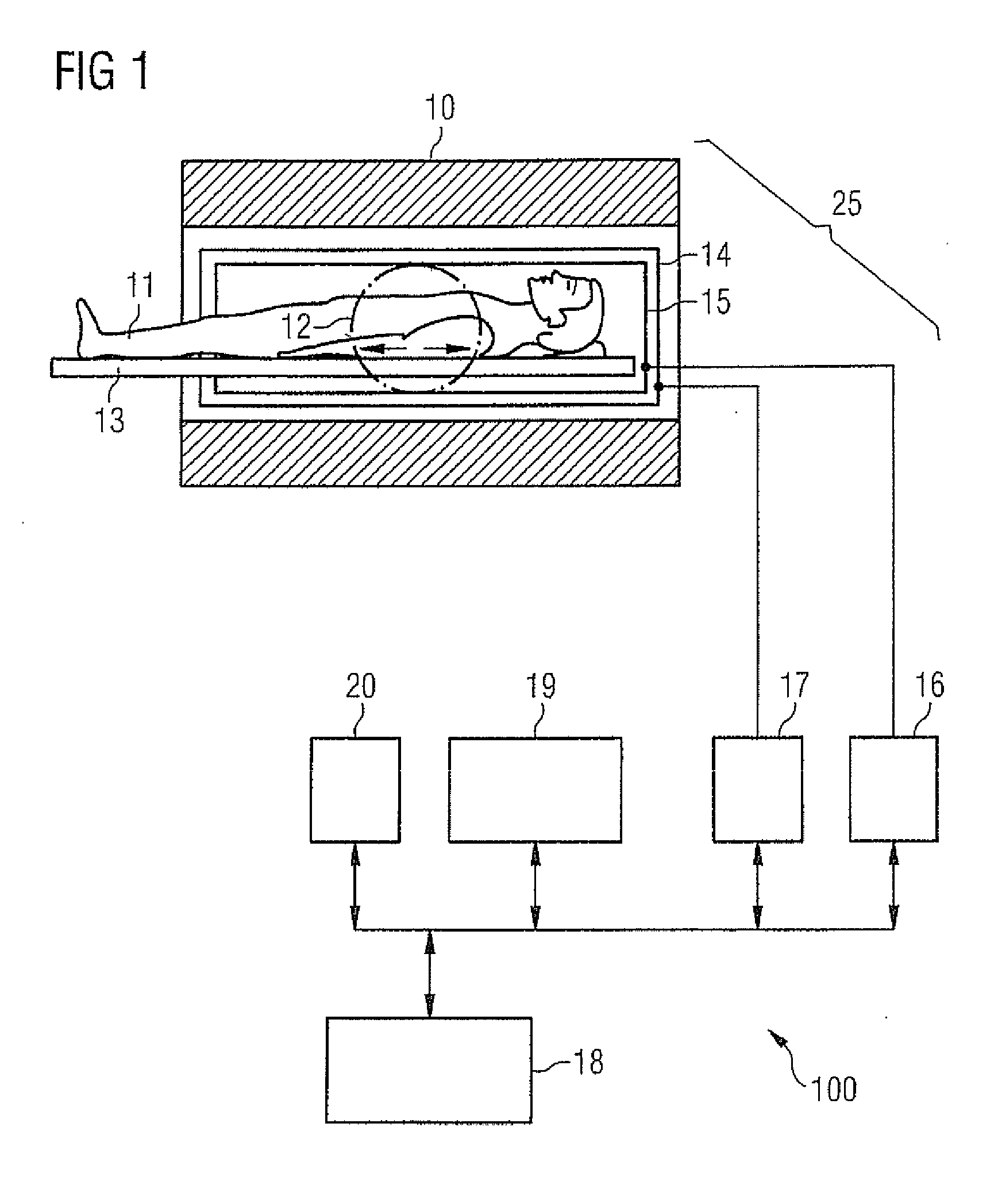
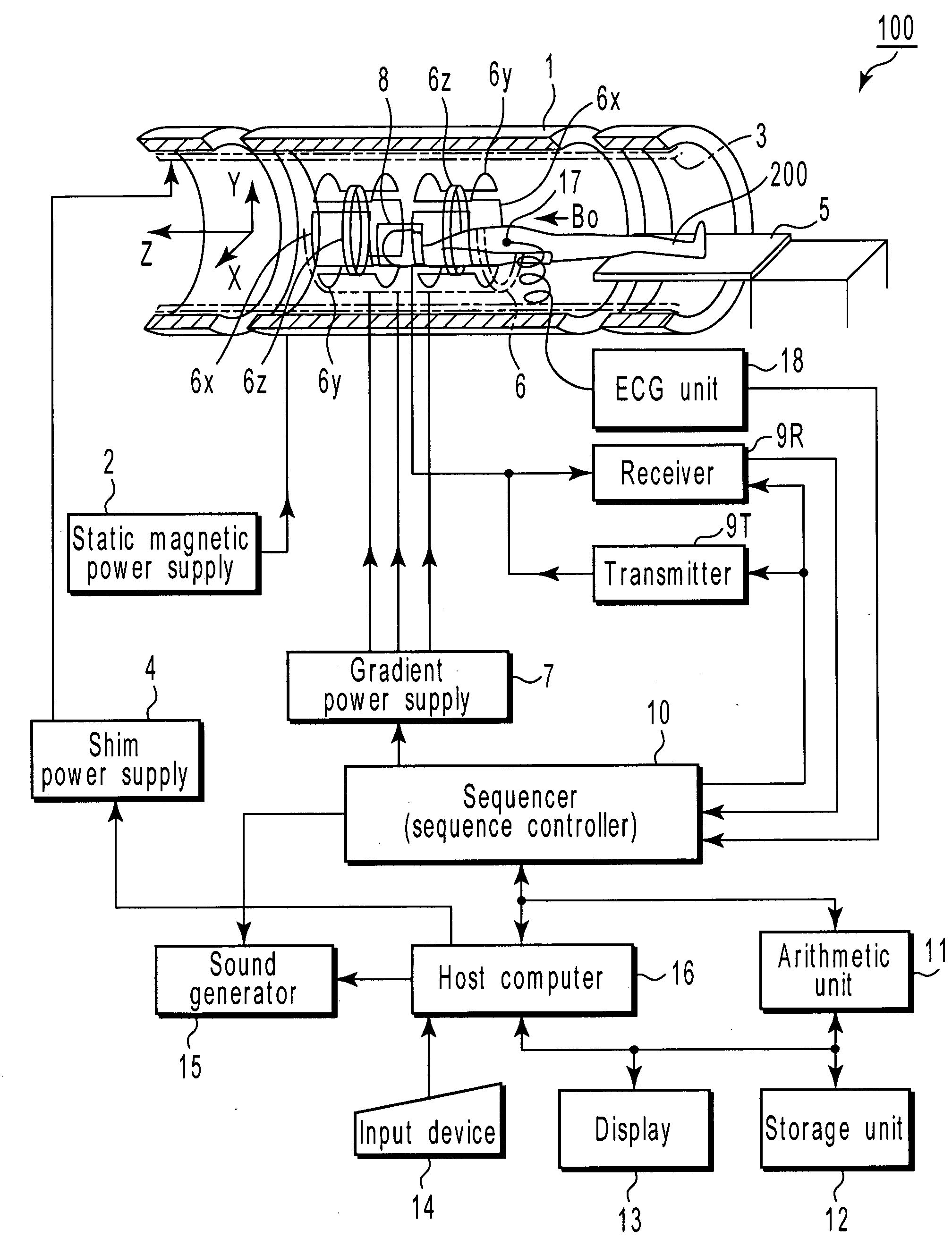
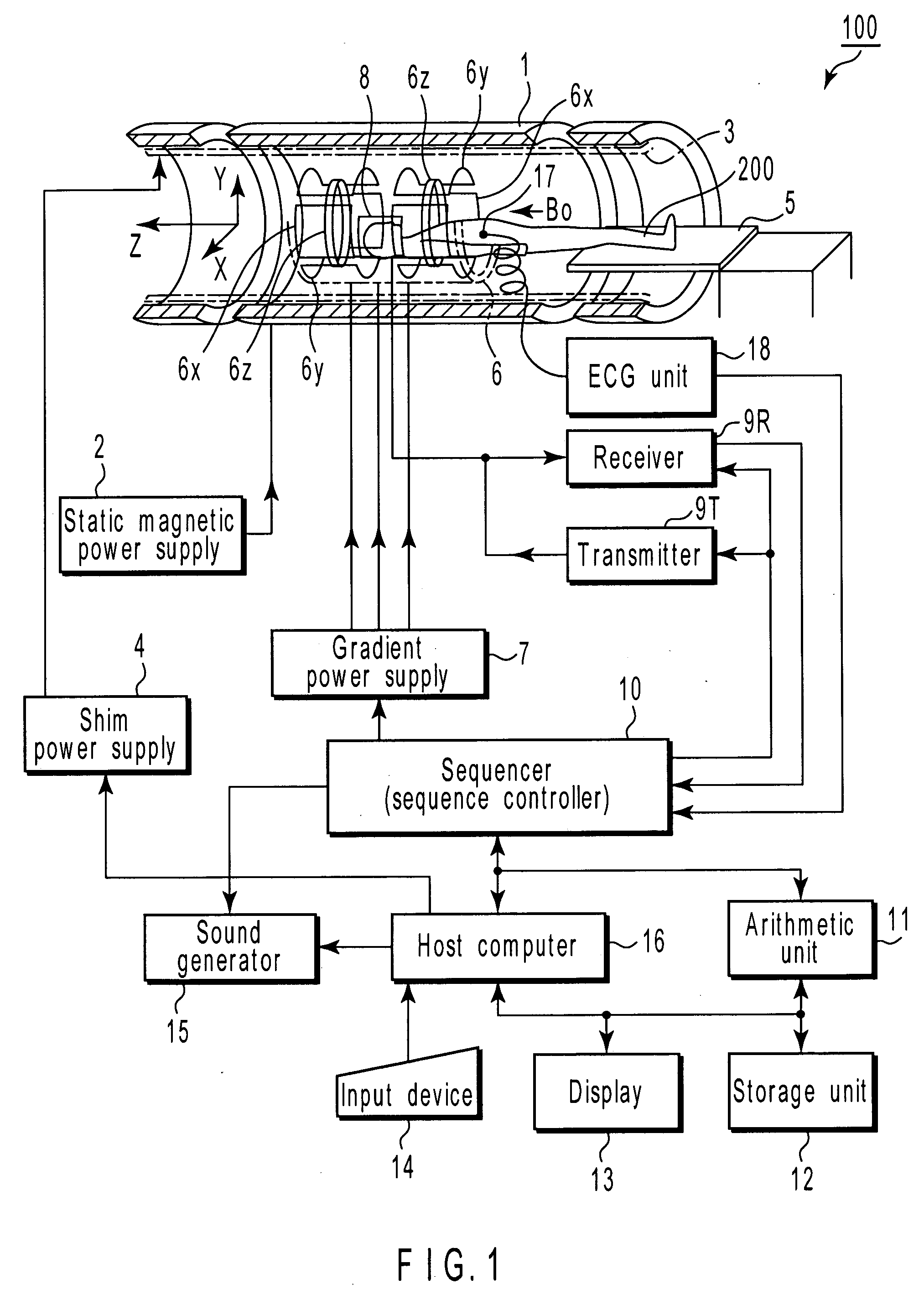
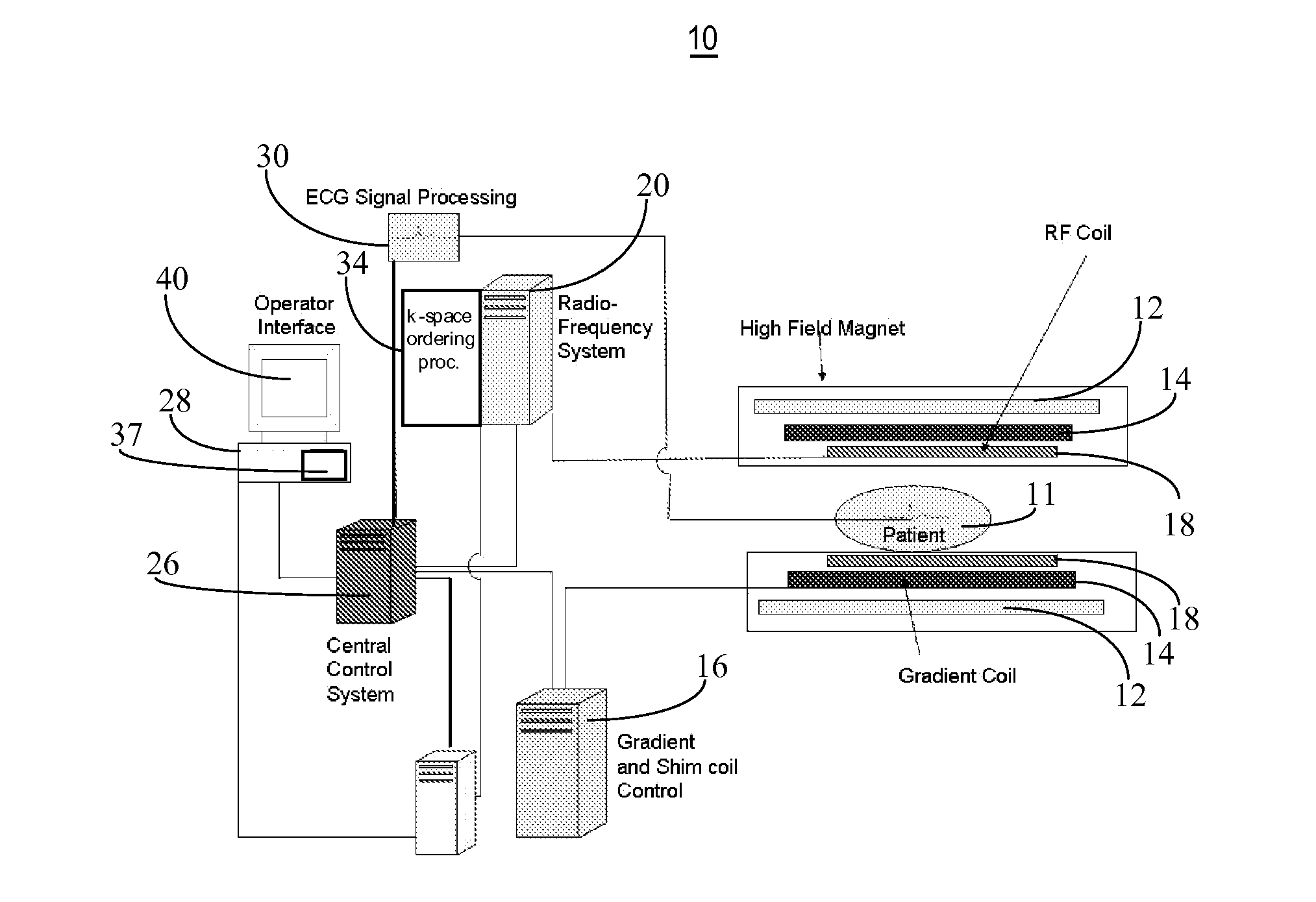
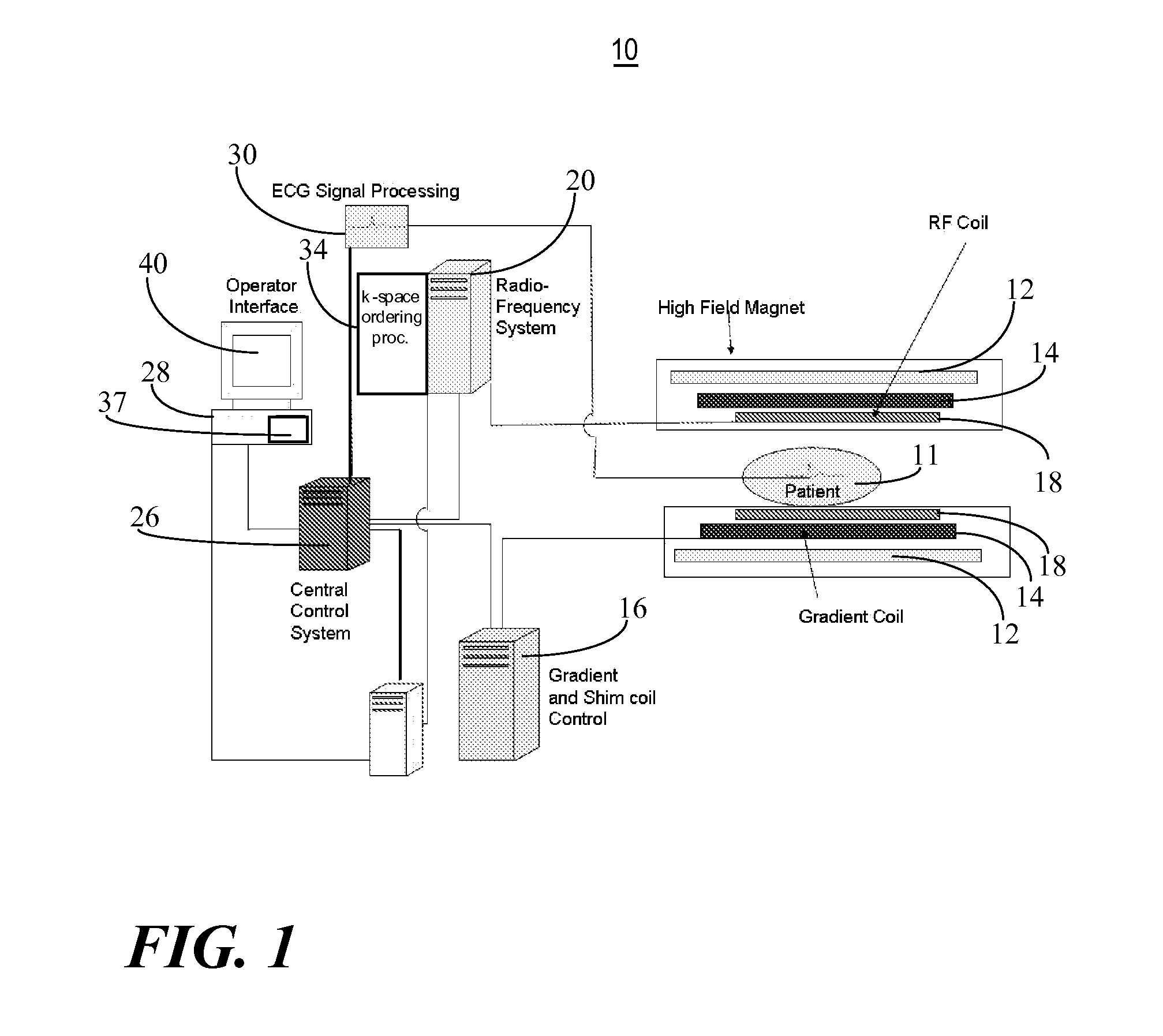
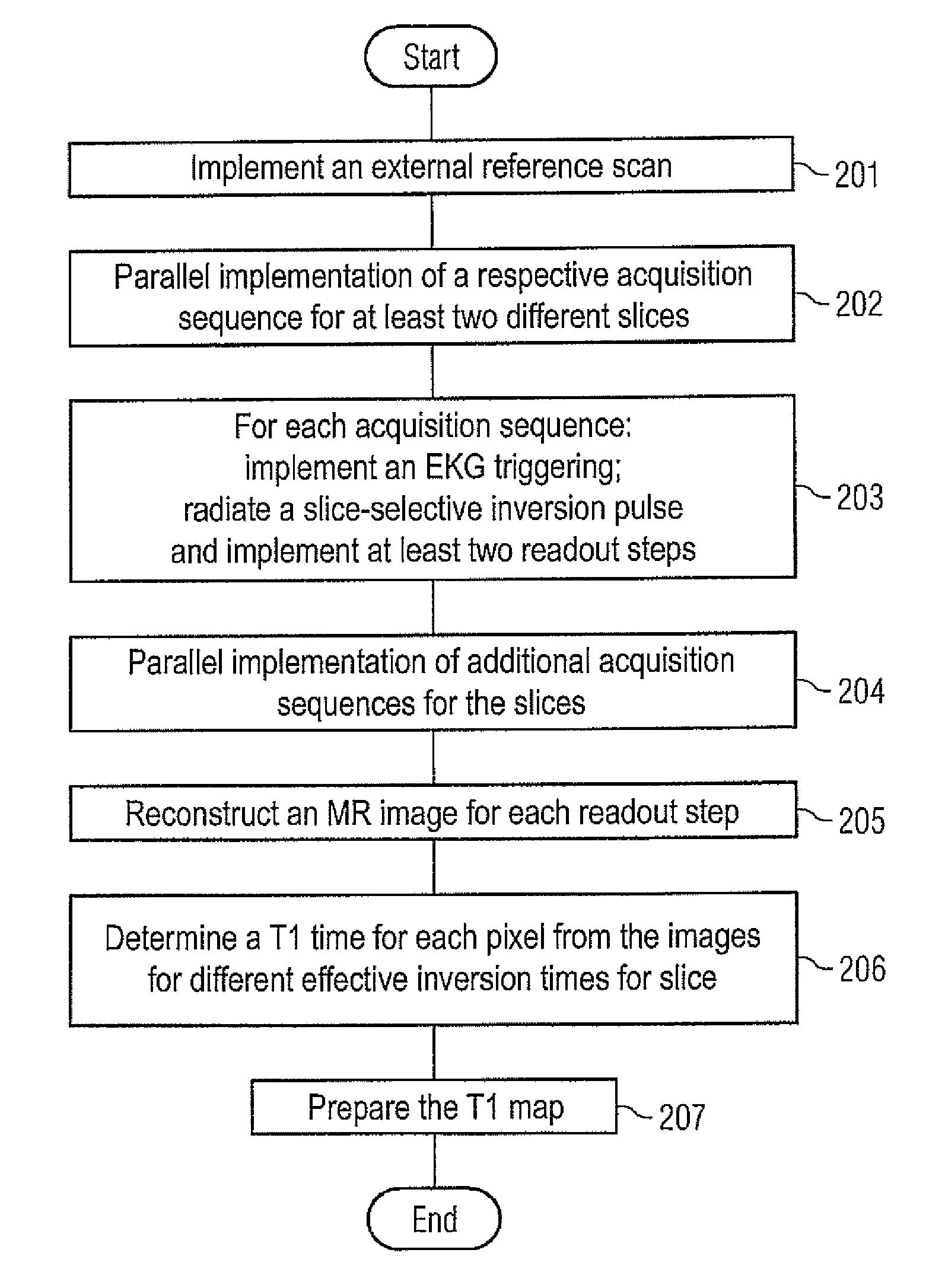
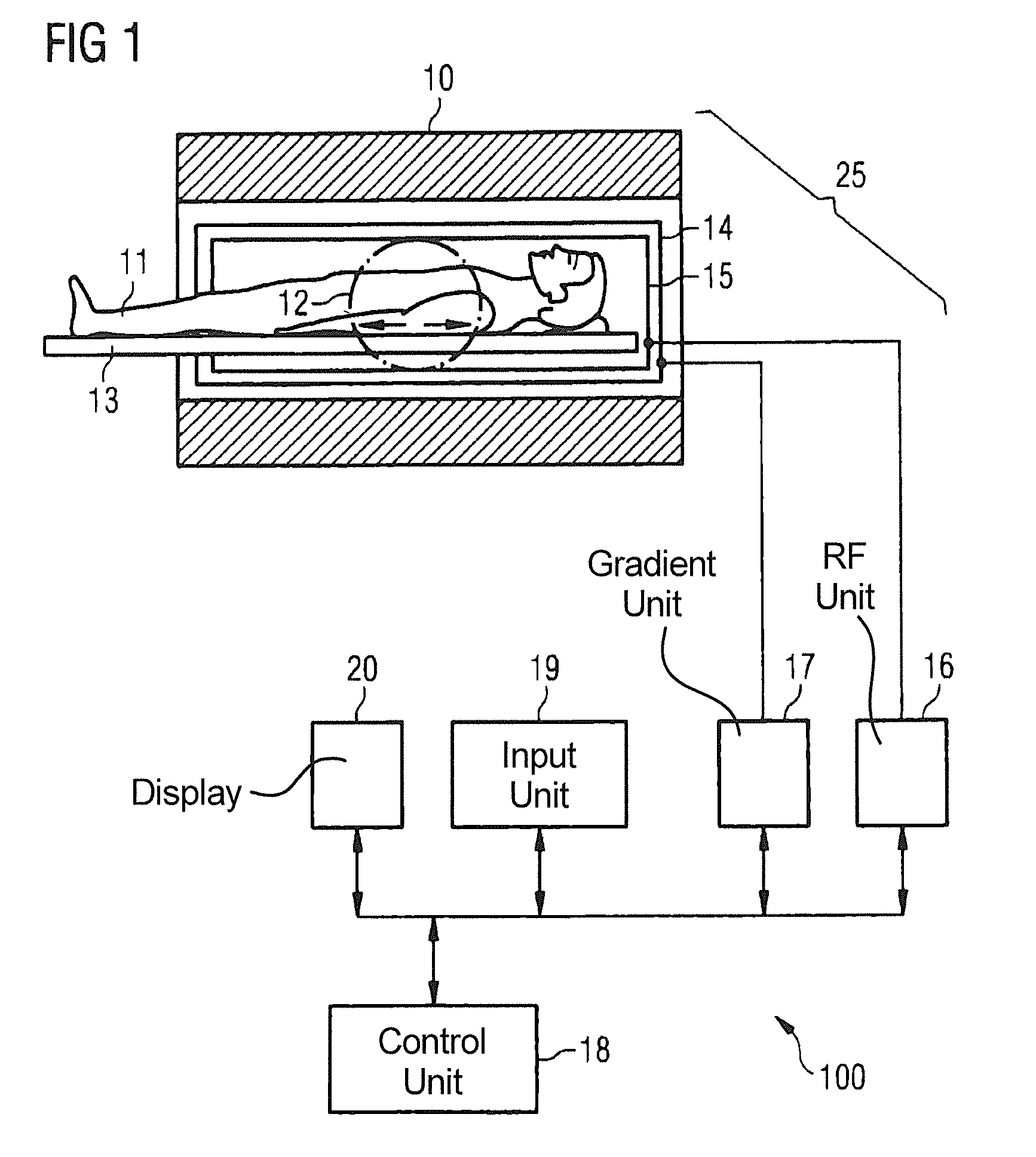
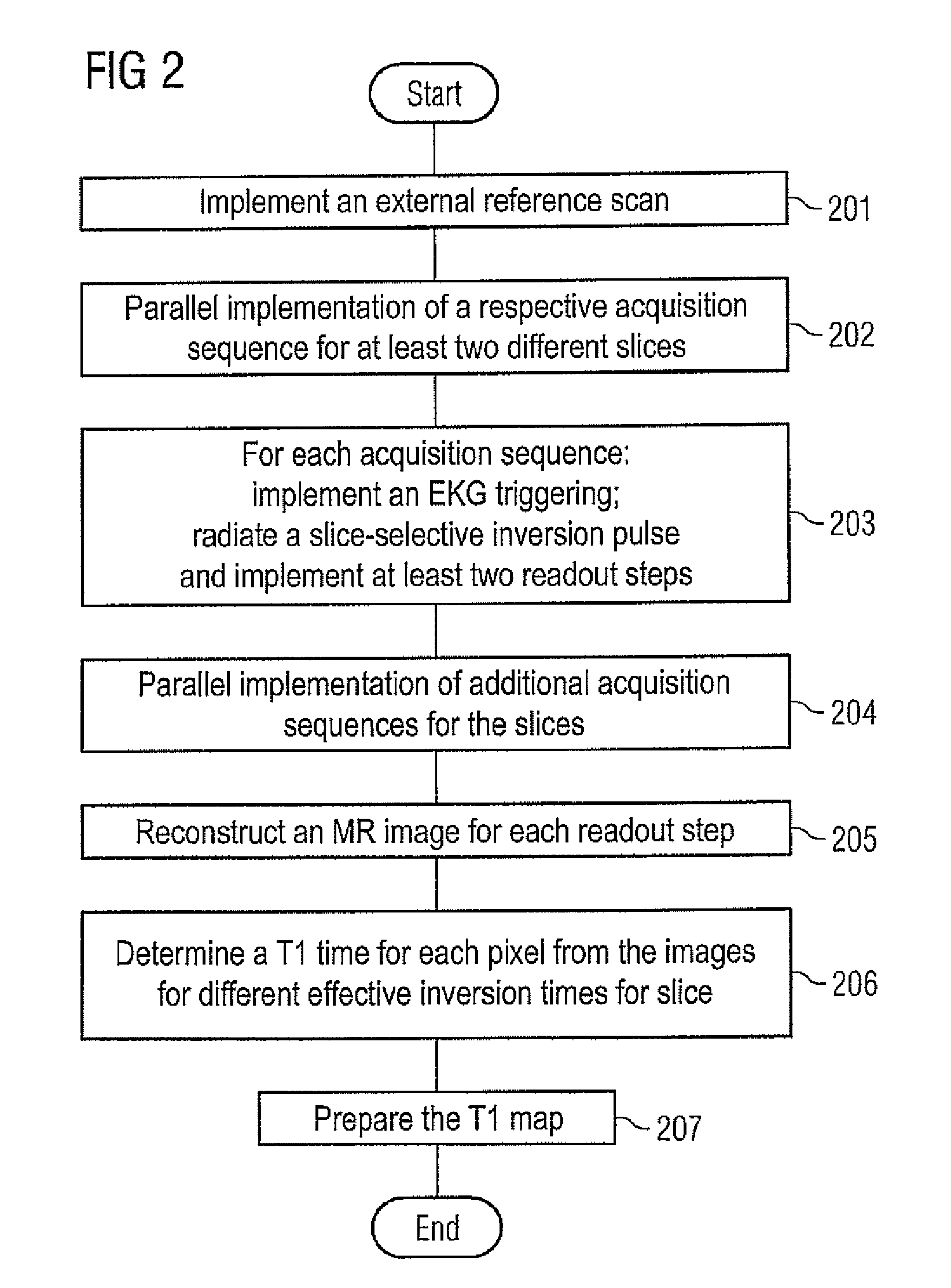
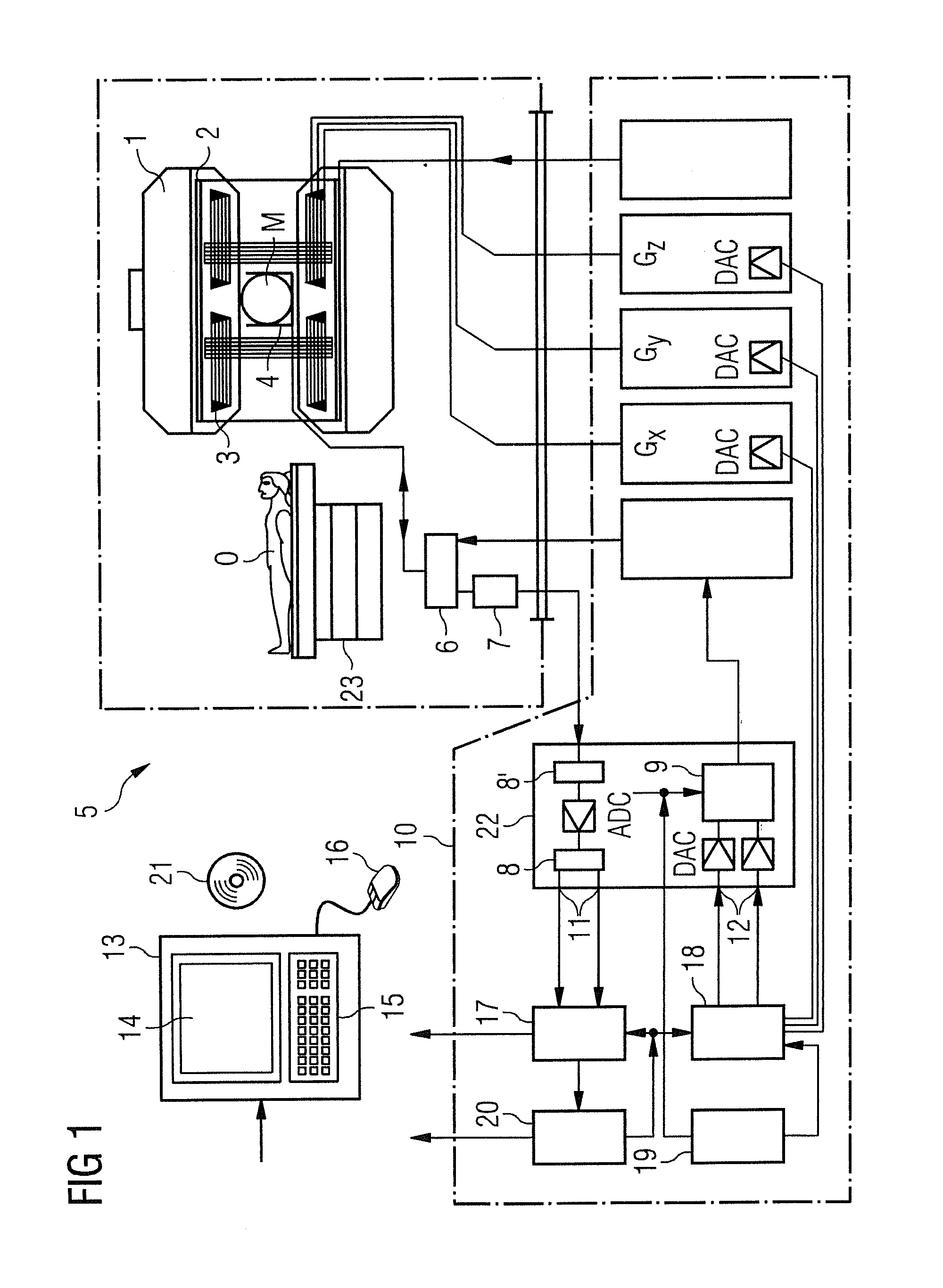
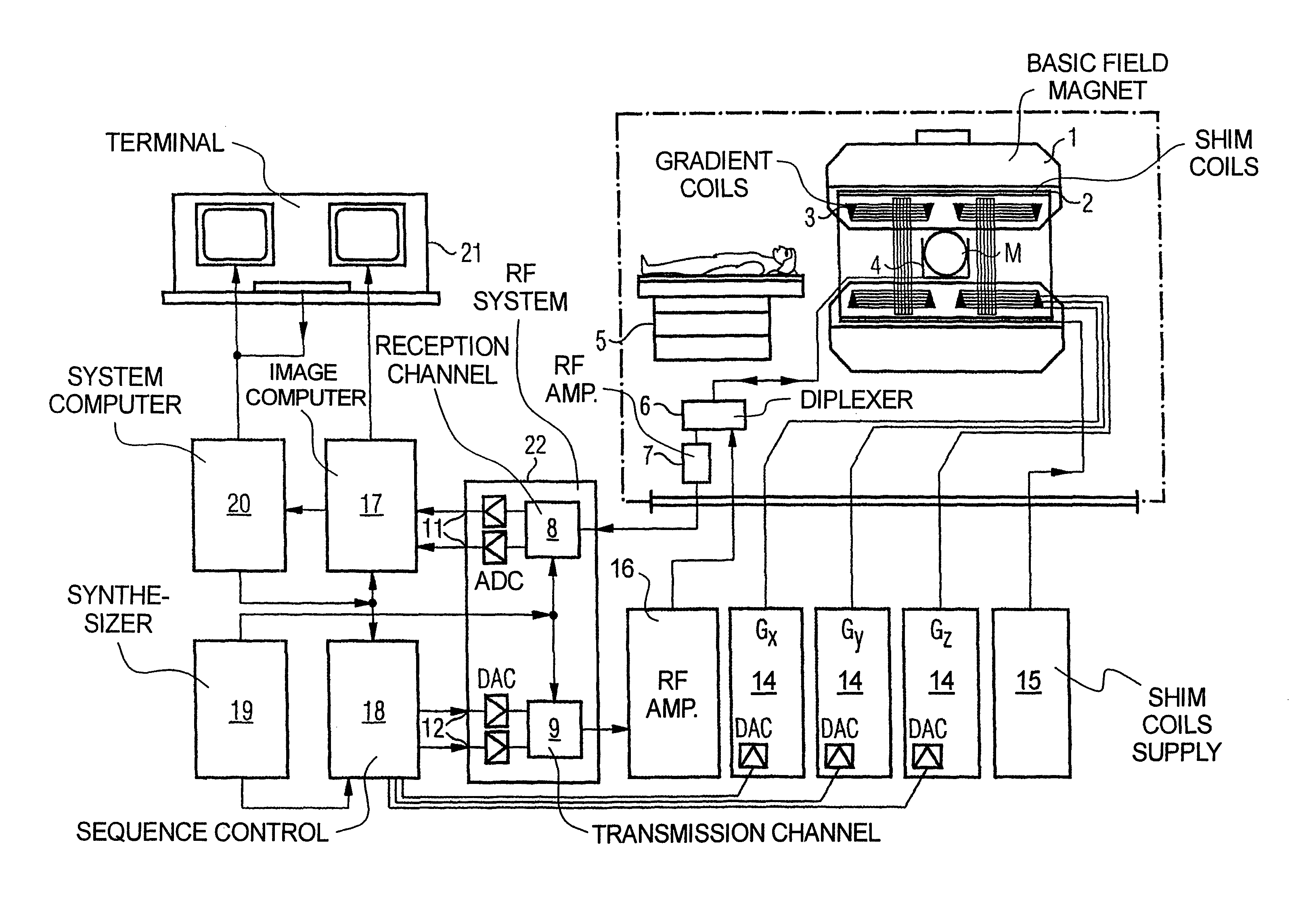
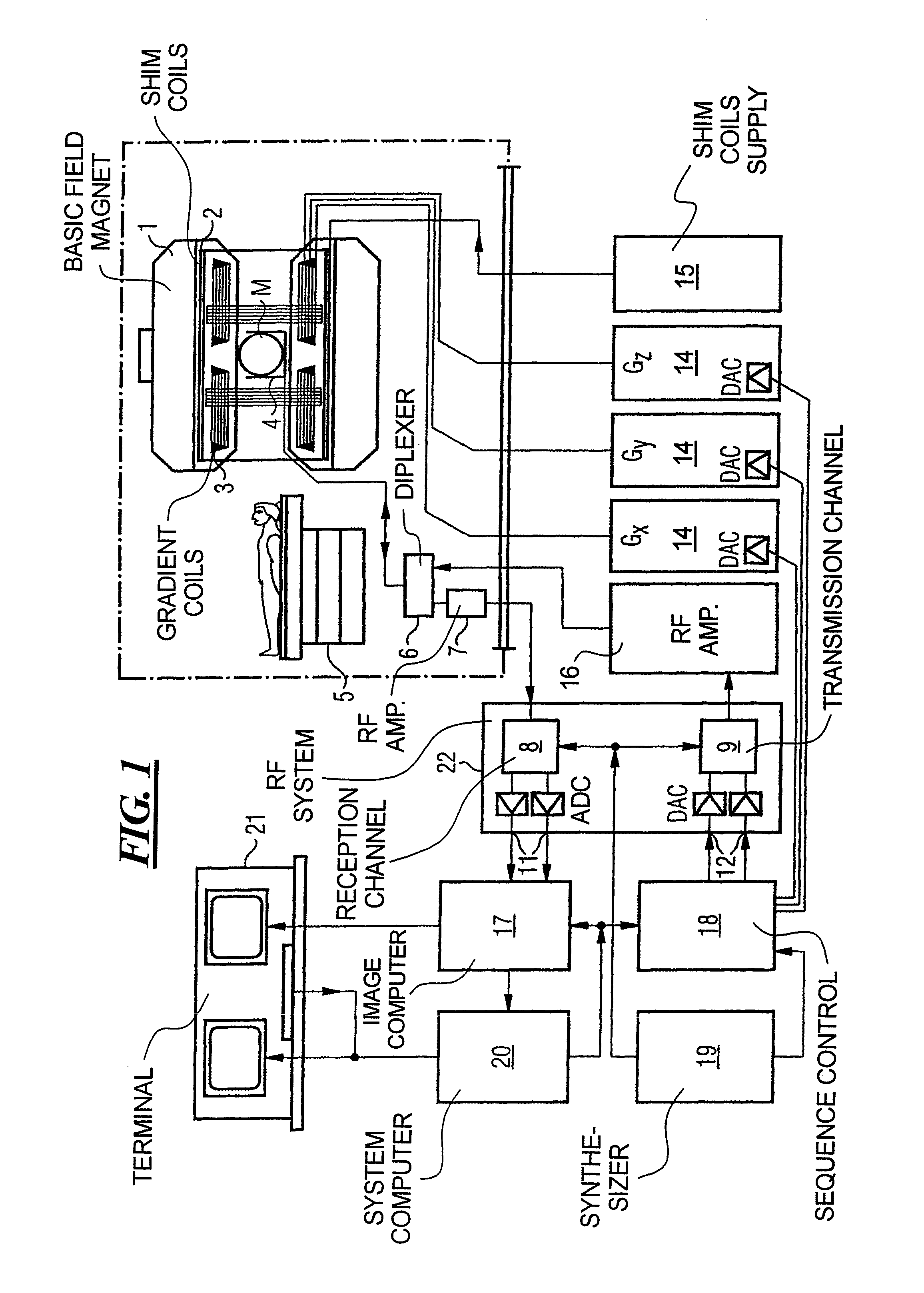
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging to create t1 maps
ActiveUS20110181285A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSpatially resolvedProton magnetic resonance
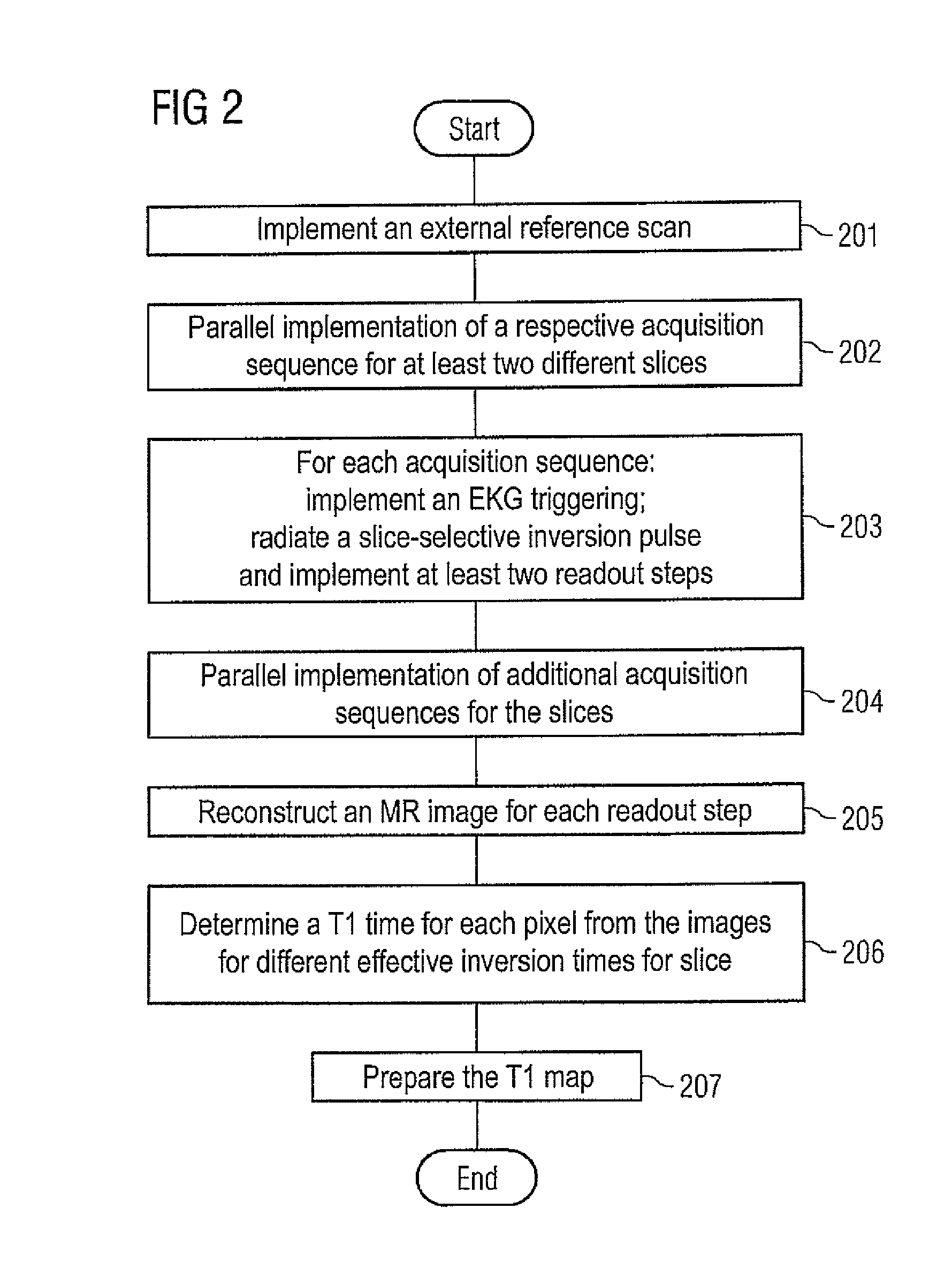
In a method and apparatus for MR imaging, a data acquisition sequence is executed wherein at least two slices of an examination subject are imaged in parallel with a gradient echo method for spatially resolved quantification of the T1 relaxation time.At least one first acquisition sequence is implemented to acquire MR data from a first slice of the examination subject and at least one second acquisition sequence is implemented to acquire MR data from a second slice of the examination subject. The acquisition sequences each include an inversion pulse and at least two successive readout steps. The first and second acquisition sequences are temporally offset from one another such that they at least partially overlap.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
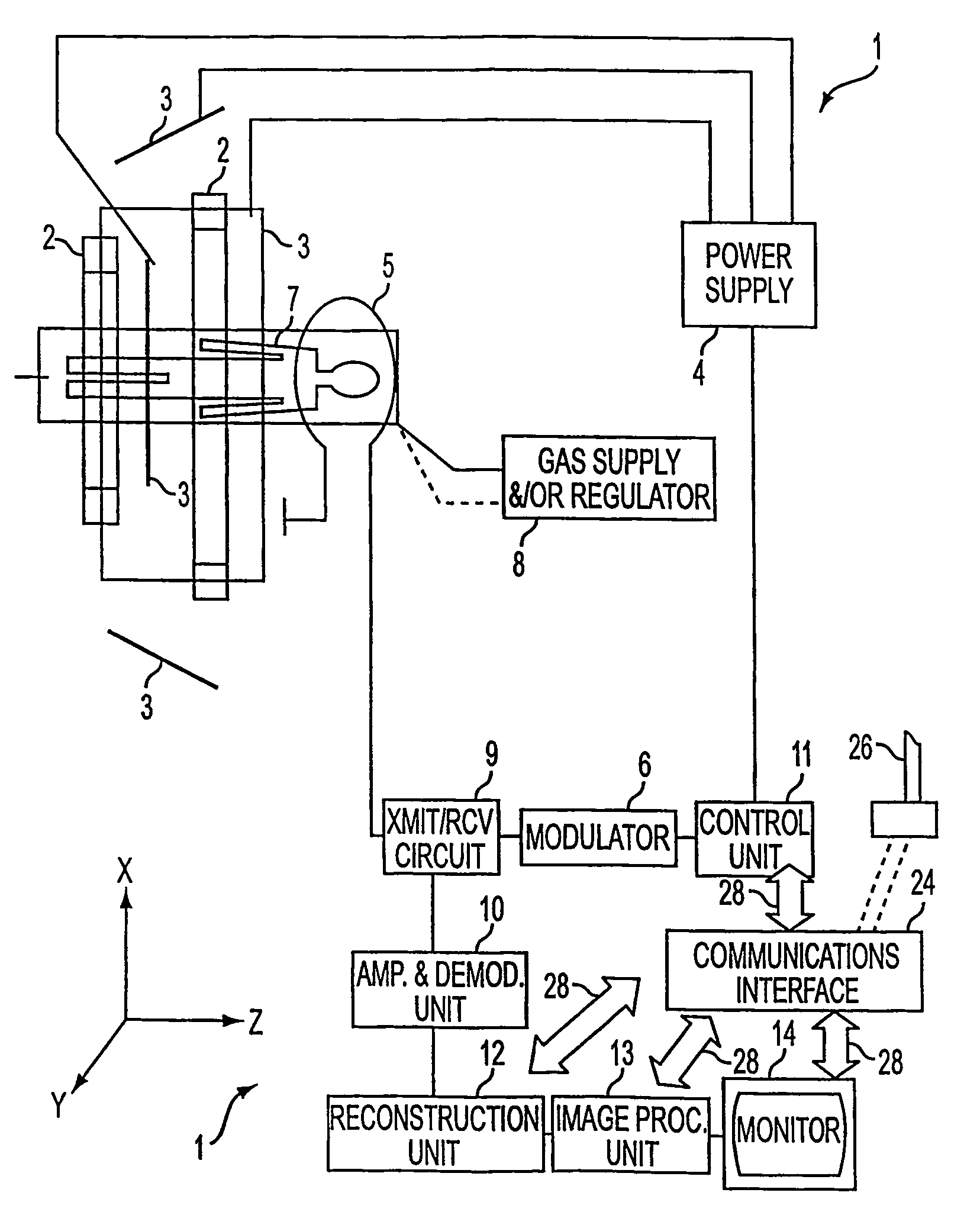
Method and device for magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging
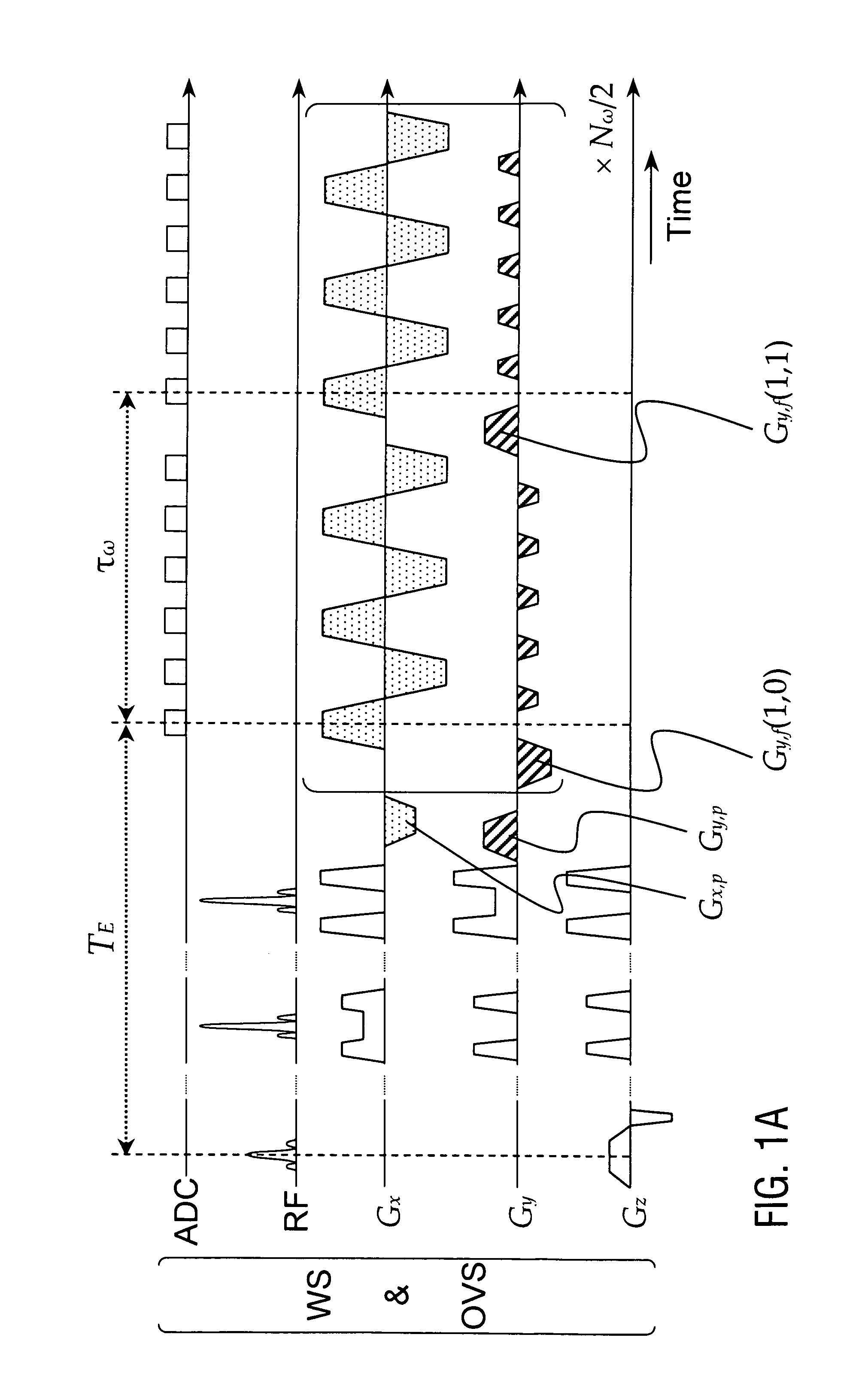
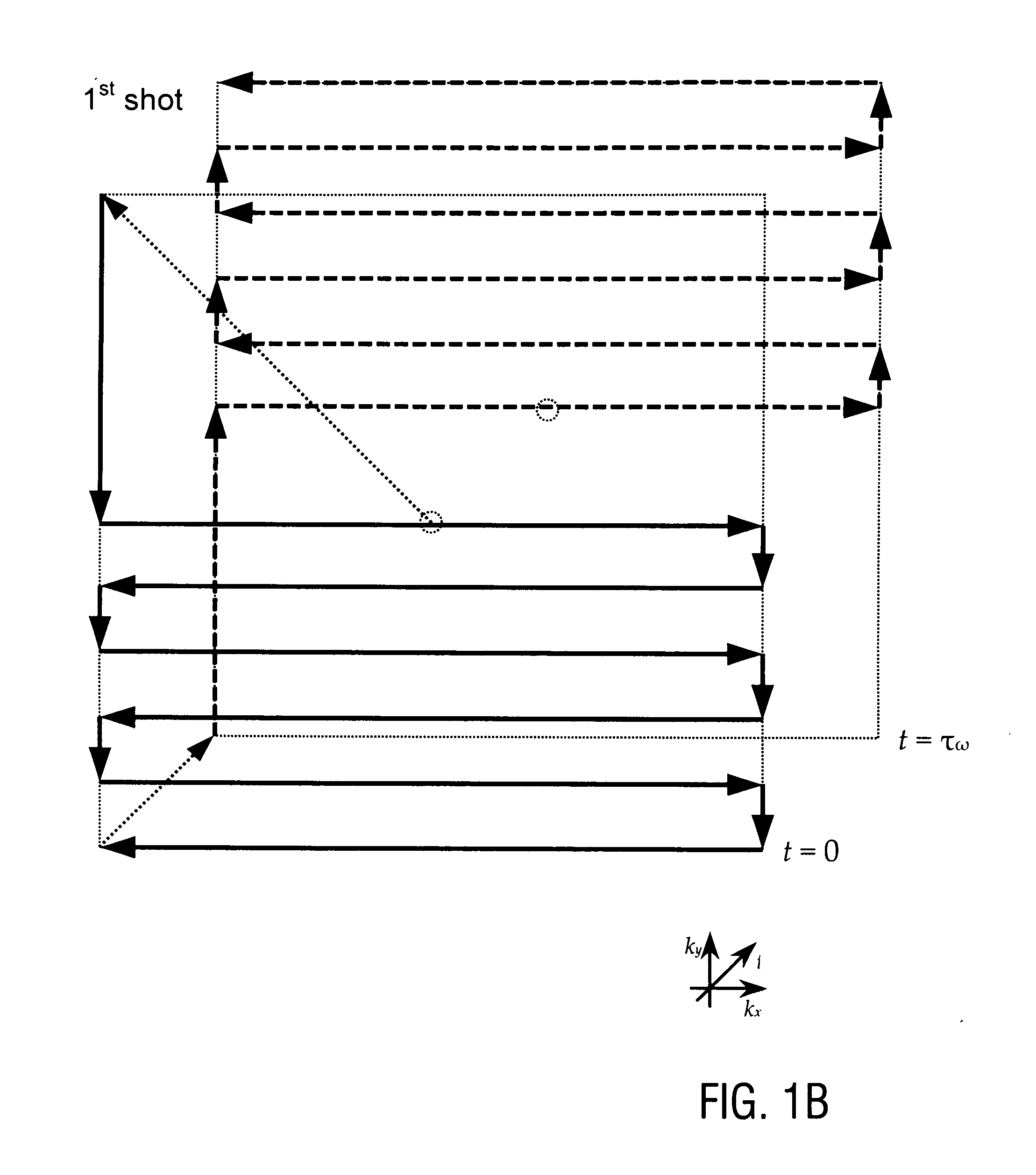
InactiveUS20120313641A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioAvoid disadvantagesMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionChemical speciesMirror image
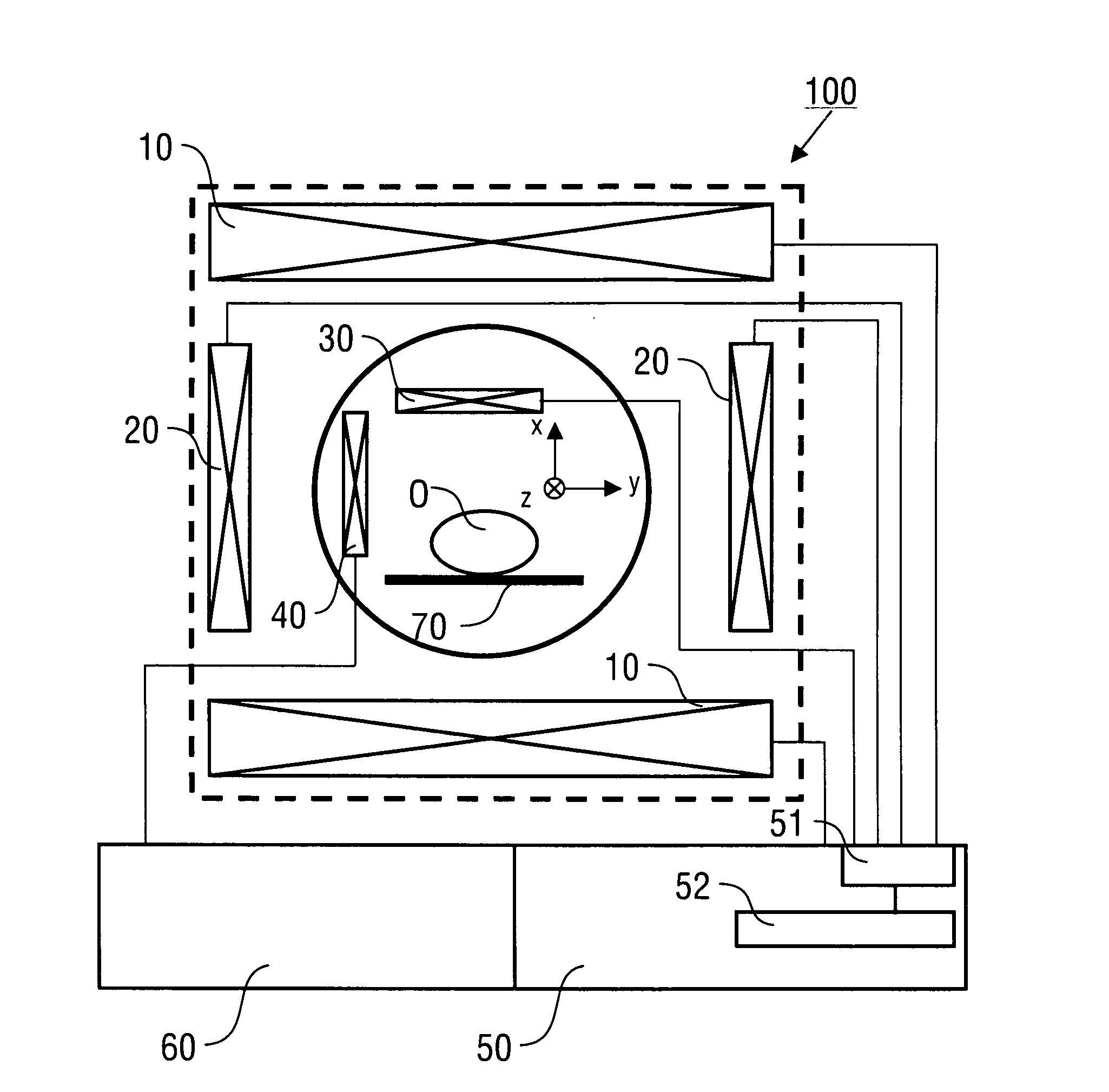
A method of magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging of an object (O) including at least one chemical species to be imaged, comprising sampling of the k-space such that a plurality of Nω first sampling trajectories through at least one k-space segment of the k-space is formed along a phase-encoding direction, each of said first sampling trajectories beginning in a central k-space region and continuing to a k-space border of the at least one k-space segment and having a duration equal to or below a spectral dwell time corresponding to the reciprocal spectral bandwidth, collecting at least one first set of gradient-echo signals obtained along said first sampling trajectories, collecting at least one second set of gradient-echo signals obtained along a plurality of Nω second sampling trajectories, said Nω second sampling trajectories and said Nω first sampling trajectories being mutually mirrored relative to a predetermined k-space line in the central k-space region.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Dynamic shimming method of multi-order harmonics for magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveCN102508182AImprove uniformityAccurate analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsUniform fieldPower flow
The invention discloses a method for carrying out dynamic and real-time shimming on any multi-order harmonic component in a selected area for magnetic resonance imaging, and the method can be used for improving the uniformity degree of a main magnetic field in an imaging area through cancelling out non-uniform harmonic items. According to the method provided by the invention, the weight distribution of any-order harmonic of the main magnetic field in the selected area can be analyzed once through phase information of images which are acquired by a three-dimensional gradient echo sequence twice, wherein a series of technical means of carrying out water-fat phase synchronization, eliminating low-signal noise pollution by virtue of an amplitude template and unwinding a three-dimensional phase are adopted, so that the weight component coefficient of any-order harmonic in the selected imaging area can be accurately and rapidly analyzed; a reversed compensating current is added into a corresponding harmonic shimming coil so as to accurately cancel out non-uniform high-order harmonics and only reserve zero-order harmonics, namely a uniform field; and the method provided by the invention has the advantage of maximally improving the uniformity degree of the main magnetic field by combining owned hardware conditions.
Owner:SUZHOU LONWIN MEDICAL SYST
Magnetic-resonance image diagnostic apparatus and method of controlling the same
ActiveUS20080071167A1Improve accuracyImprove abilitiesMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringPulse sequenceImaging diagnostic
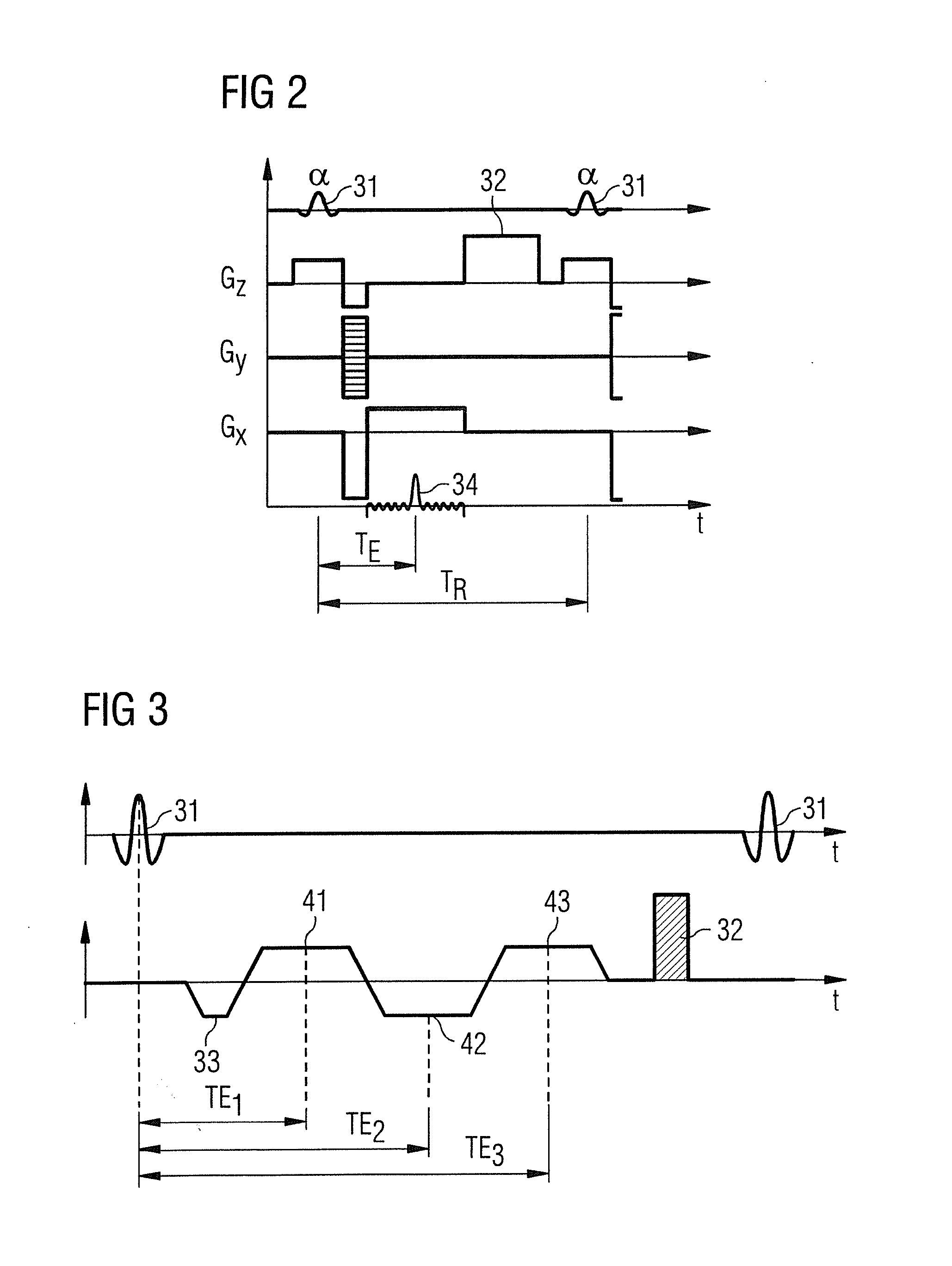
A magnetic resonance imaging diagnostic apparatus includes a generating unit which generates a slice gradient magnetic field, a phase-encode gradient magnetic field and a read-out gradient magnetic field that extend in a slice axis, a phase-encode axis and a read-out axis, respectively, a setting unit which sets a dephase amount for weighting a signal-level decrease resulting from flows in the arteries and veins present in a region of interest of a subject, with respect to at least one axis selected form the slice axis, phase-encode axis and read-out axes, and a control unit which controls the generating unit by using a pulse sequence for a gradient echo system, which includes a dephase gradient-magnetic-field pulse that corresponds to the dephase amount set by the setting unit for the at least one axis.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and imaging method
InactiveUS6169398B1Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic susceptibilityProton magnetic resonance
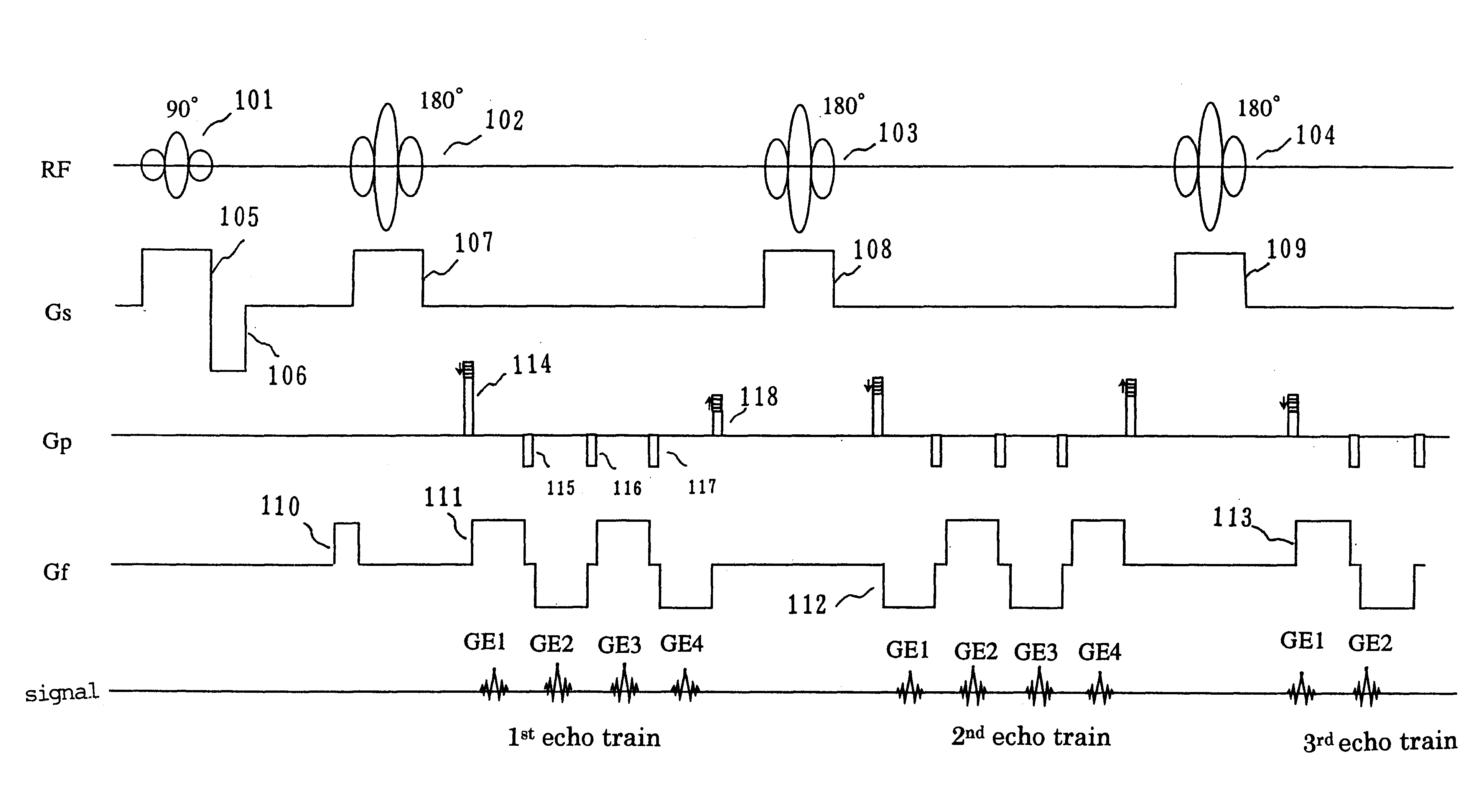
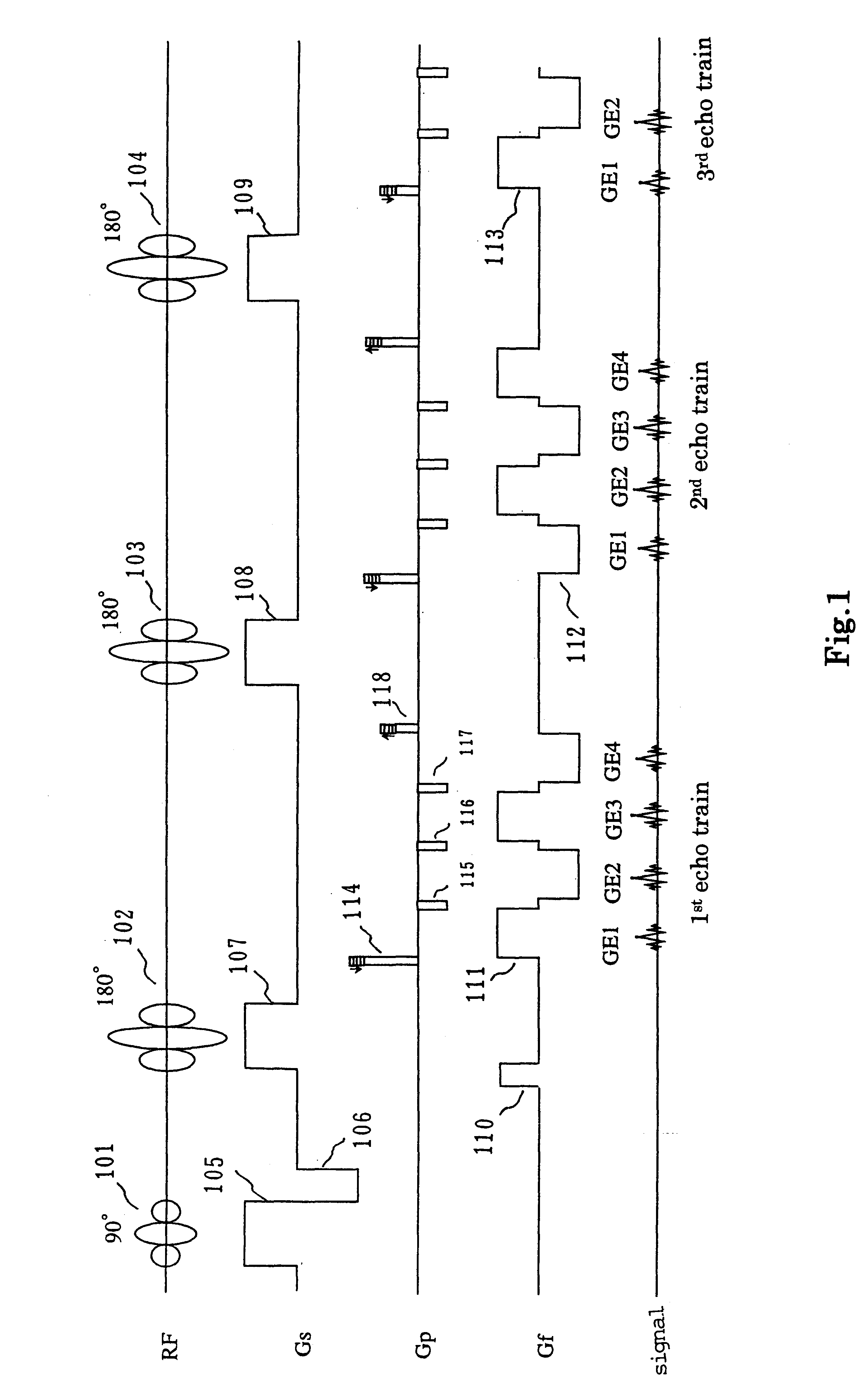
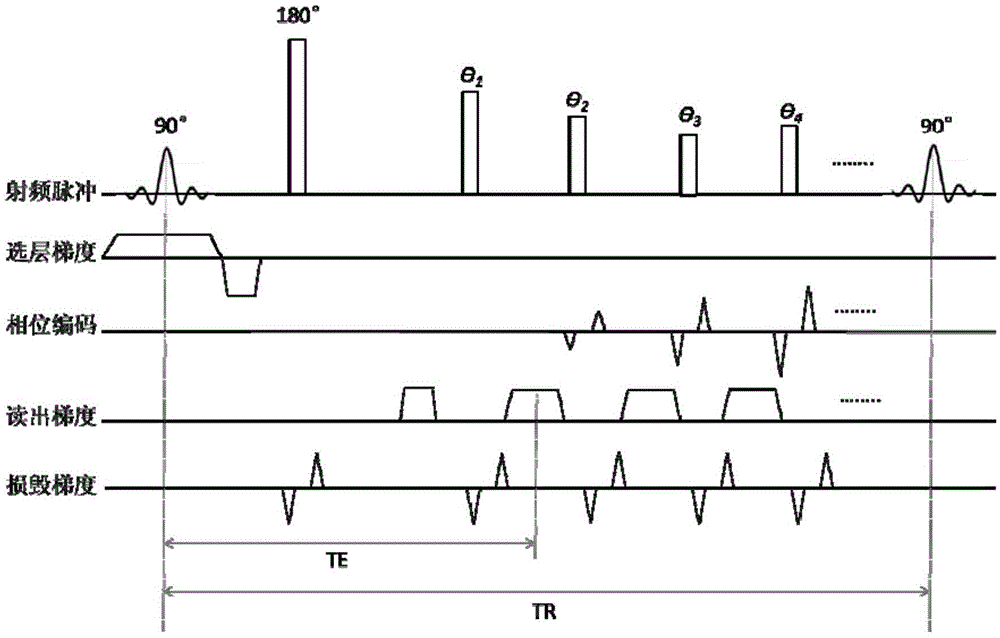
The MRI apparatus of the present invention performs a pulse sequence for applying successively 180° pulses 102, 103 . . . after application of a 90° pulse 101 at constant intervals and applying readout magnetic fields 111 during the interval between pairs of 180° pulses while the polarity of the magnetic field 111 is inverted several times to collect a plurality of gradient echo signals that are phase encoded differently. Here, the application of the readout gradient magnetic field is controlled such that generation of the gradient echo signals does ot coincide with generation of the spin echo signal. The image reconstruction is performed by using only T2* weighted gradient echo signals to obtain images reflecting difference in magnetic susceptibility and inhomogeneities in local magnetic fields.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
Characterization of respiratory motion in the abdomen using a 4d MRI technique with 3D radial sampling and respiratory self-gating
ActiveUS20160324500A1Magnetic measurementsOrgan movement/changes detectionRespiratory phaseAnesthesia
In some embodiments, the present application discloses utilizing a continuous spoiled gradient echo sequence with 3D radial trajectory and 1D self-gating for respiratory motion detection. In certain embodiments, data acquired are retrospectively sorted into different respiratory phases based on their temporal locations within a respiratory cycle, and each phase is reconstructed via a self-calibrating CG-SENSE program.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Spin locked balanced steady-state free precession (slssfp)
ActiveUS20100264920A1Improve contrast ratioShorten Image Acquisition TimeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionGradient echoOff resonance
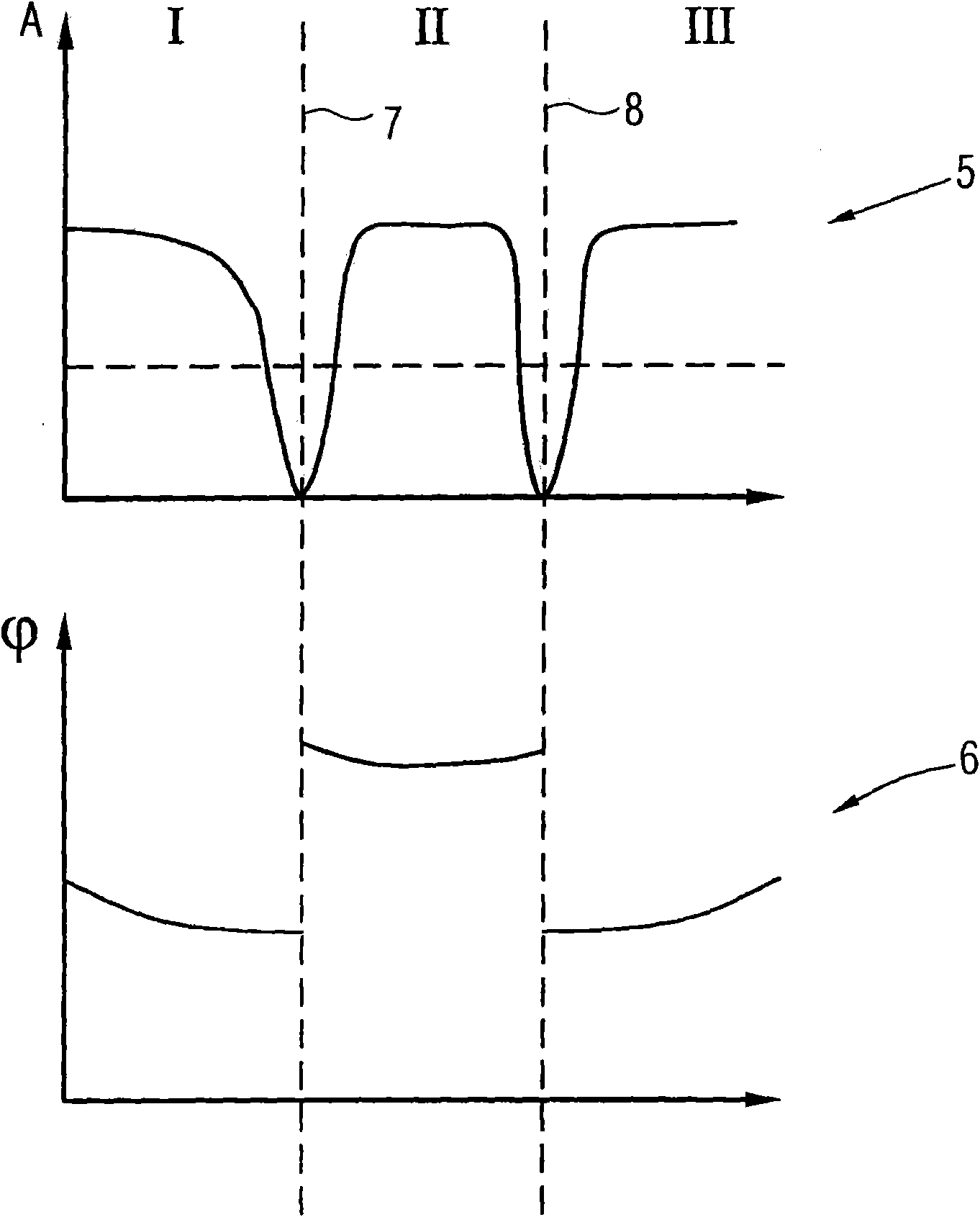
A spin locked balanced steady-state free precession (slSSFP) pulse sequence combines a balanced gradient echo acquisition with an off-resonance spin lock pulse for fast MRI. The transient and steady-state magnetization trajectory is solved numerically using the Bloch equations and is shown to be similar to balanced steady-state free precession (bSSFP) for a range of T2 / T1 and flip angles, although the slSSFP steady-state could be maintained with considerably lower RF power. In both simulations and brain scans performed at 7 T, slSSFP is shown to exhibit similar contrast and SNR efficiency to bSSFP, but with significantly lower power.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
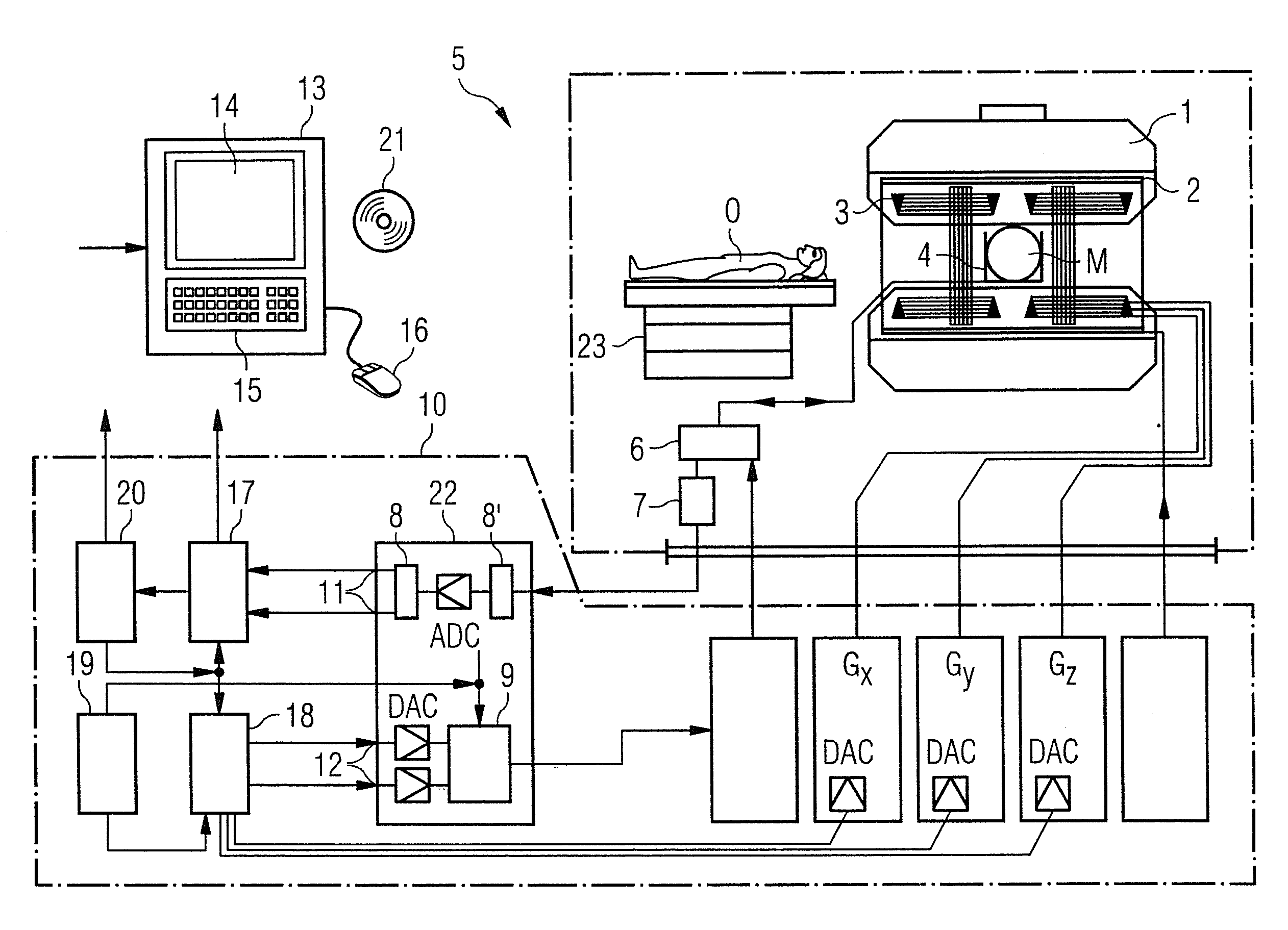
Method and device for reconstructing a sequence of magnetic resonance images
ActiveUS20110234222A1Degree of reductionEasy access to dataAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsOriginal dataResonance
A method for reconstructing a sequence of magnetic resonance (MR) images of an object under investigation, includes the steps of (a) providing a series of sets of image raw data including an image content of the MR images to be reconstructed, the image raw data being collected with the use of at least one radiofrequency receiver coil of a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) device, wherein each set of image raw data includes a plurality of data samples being generated with a gradient-echo sequence, in particular a FLASH sequence, that spatially encodes an MRI signal received with the at least one radiofrequency receiver coil using a non-Cartesian k-space trajectory, each set of image raw data includes a set of homogeneously distributed lines in k-space with equivalent spatial frequency content, the lines of each set of image raw data cross the center of k-space and cover a continuous range of spatial frequencies, and the positions of the lines of each set of image raw data differ in successive sets of image raw data, and (b) subjecting the sets of image raw data to a regularized nonlinear inverse reconstruction process to provide the sequence of MR images, wherein each of the MR images is created by a simultaneous estimation of a sensitivity of the at least one receiver coil and the image content and in dependency on a difference between a current estimation of the sensitivity of the at least one receiver coil and the image content and a preceding estimation of the sensitivity of the at least one receiver coil and the image content.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
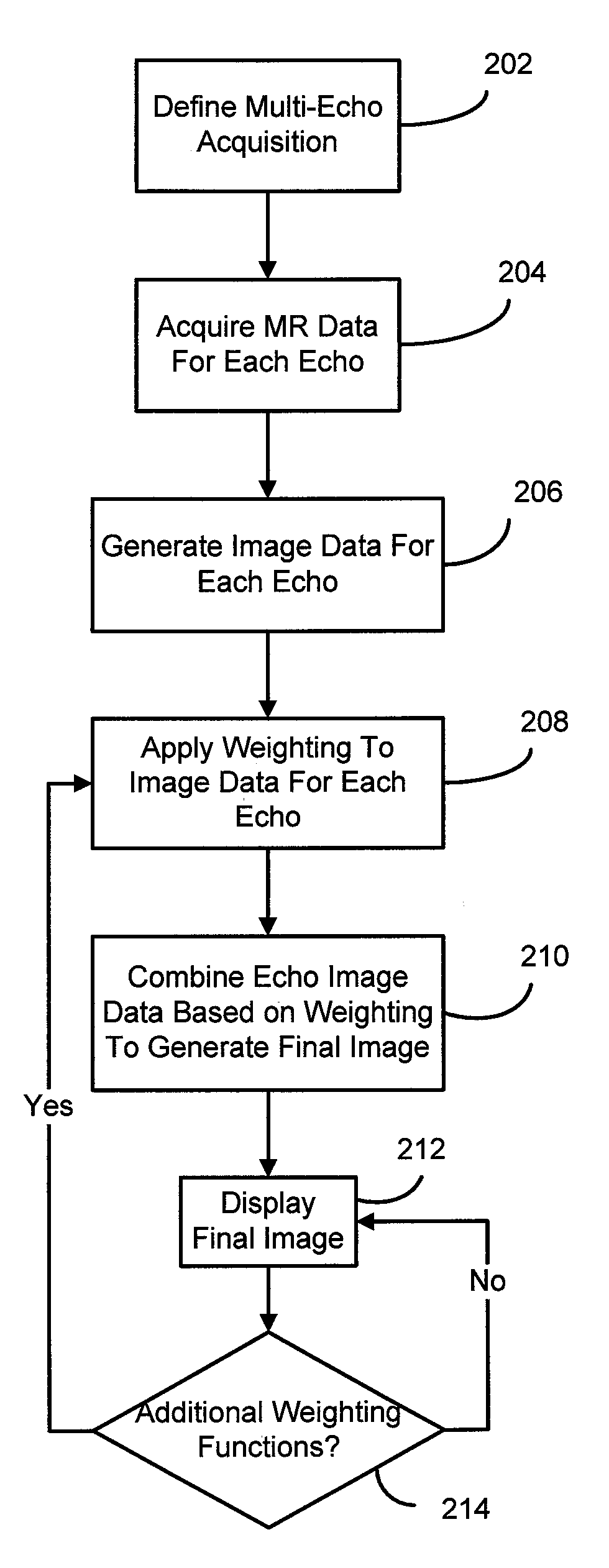
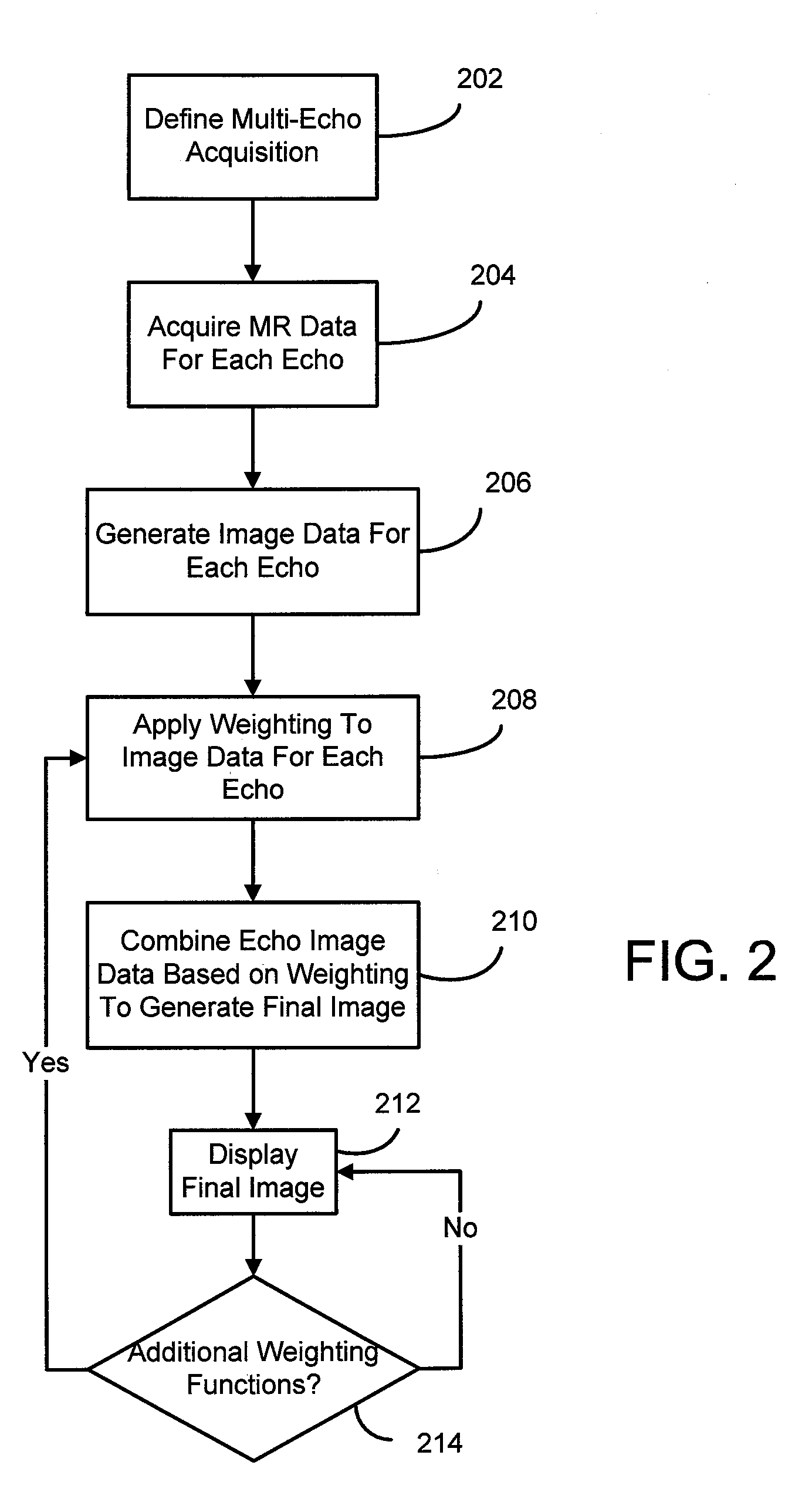
Method and apparatus for generating t2* weighted magnetic resonance images
ActiveUS20090251140A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic susceptibilityResonance
A method for generating a susceptibility (or T2*) weighted magnetic resonance (MR) image includes defining a pulse sequence having a plurality of gradient echoes and acquiring MR data for each of the plurality of gradient echoes. A weighting function is applied to image data for each gradient echo such as MR data (e.g., k-space data) or magnitude images associated with each gradient echo. A susceptibility weighted image is generated by combining the image data for each gradient echo based on at least the application of the weighting function.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and device for reconstructing a sequence of magnetic resonance images
ActiveUS8384383B2Degree of reductionReduce in quantityAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsOriginal dataResonance
A method for reconstructing a sequence of magnetic resonance (MR) images of an object under investigation, includes the steps of (a) providing a series of sets of image raw data including an image content of the MR images to be reconstructed, the image raw data being collected with the use of at least one radiofrequency receiver coil of a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) device, wherein each set of image raw data includes a plurality of data samples being generated with a gradient-echo sequence, in particular a FLASH sequence, that spatially encodes an MRI signal received with the at least one radiofrequency receiver coil using a non-Cartesian k-space trajectory, each set of image raw data includes a set of homogeneously distributed lines in k-space with equivalent spatial frequency content, the lines of each set of image raw data cross the center of k-space and cover a continuous range of spatial frequencies, and the positions of the lines of each set of image raw data differ in successive sets of image raw data, and (b) subjecting the sets of image raw data to a regularized nonlinear inverse reconstruction process to provide the sequence of MR images, wherein each of the MR images is created by a simultaneous estimation of a sensitivity of the at least one receiver coil and the image content and in dependency on a difference between a current estimation of the sensitivity of the at least one receiver coil and the image content and a preceding estimation of the sensitivity of the at least one receiver coil and the image content.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Method and apparatus for acquiring magnetic resonance data
ActiveUS20160033605A1High resolutionShort acquisition timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionPhase shiftedResonance
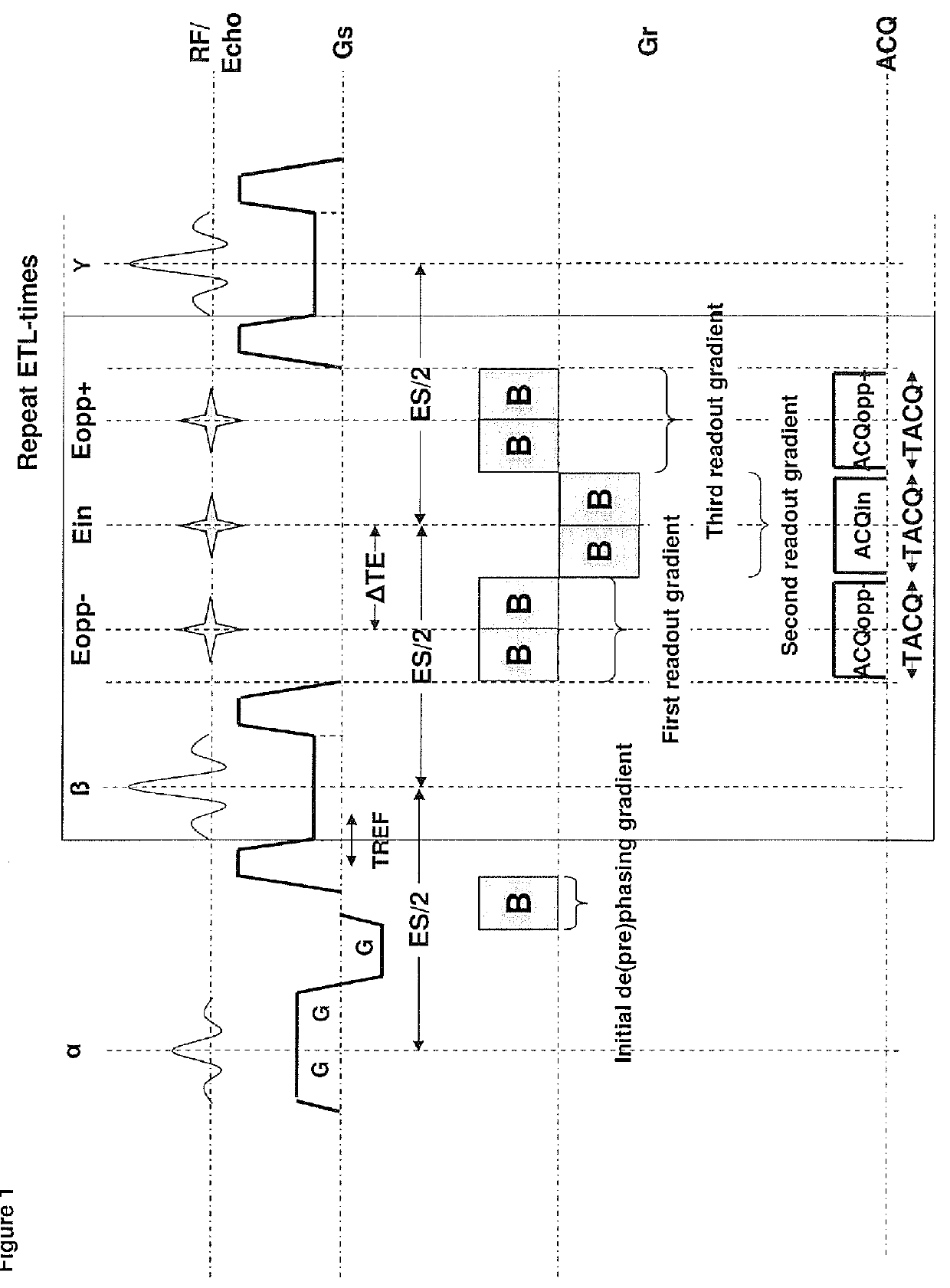
In a method and apparatus for acquiring magnetic resonance (MR) data from a subject, excitation pulses and at least two refocusing pulses are applied to the subject in an MR scanner, and the MR scanner is operated to activate gradients in a readout direction that cause at least two gradient echoes to be formed between the at least two successive refocusing pulses, with a temporal distance between the at least two gradient echoes that produces a predetermined phase shift between a signal acquired from a first nuclei in the subject and a signal acquired from a second nuclei in the subject at times of the respective gradient echoes, and that include readout gradients associated respectively with a first and a last gradient echo, among said at least two gradient echoes, the readout gradients being asymmetrical.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Rapid three-dimensional gradient shimming method for reducing phase encoding number on nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer
InactiveCN102768347AAvoid mutual interferenceGet rid of dependenceMeasurements using magnetic resonanceHydrogenSelective excitation
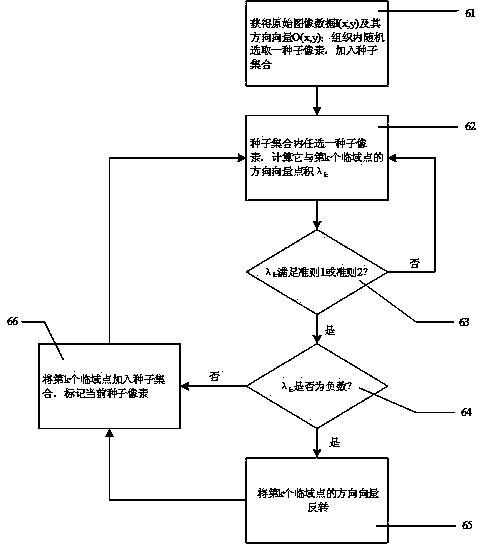
The invention discloses a rapid three-dimensional gradient shimming method for reducing phase encoding number on a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, which relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer. A method of shimming coils is selected according to the phase encoding number, X and Y high-order shimming coils are deducted, on this basis, a proper revised regularization method can be added to the calculation, a good shimming effect can still be achieved when the phase encoding number can be reduced to be 3*3 or 2*2. These few 2*2 and 3*3 phase codes are widely applied to all three-dimensional gradient shimming pulse sequences of the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, such as a three-dimensional gradient echo pulse sequence, a tilt three-dimensional gradient echo pulse sequence, and a pulse gradient field excitation echo pulse sequence. The mutual interference of multiple spectral peaks with farer chemical shifts can be overcome in the phase measurement. The three-dimensional gradient shimming in which the hydrogen nuclear is selectively excited enable the shimming method to get rid of the dependence on deuterium reagent, brings speed increase in cooperation with few phase encoding number and small-angle excitation, and has wide application range.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
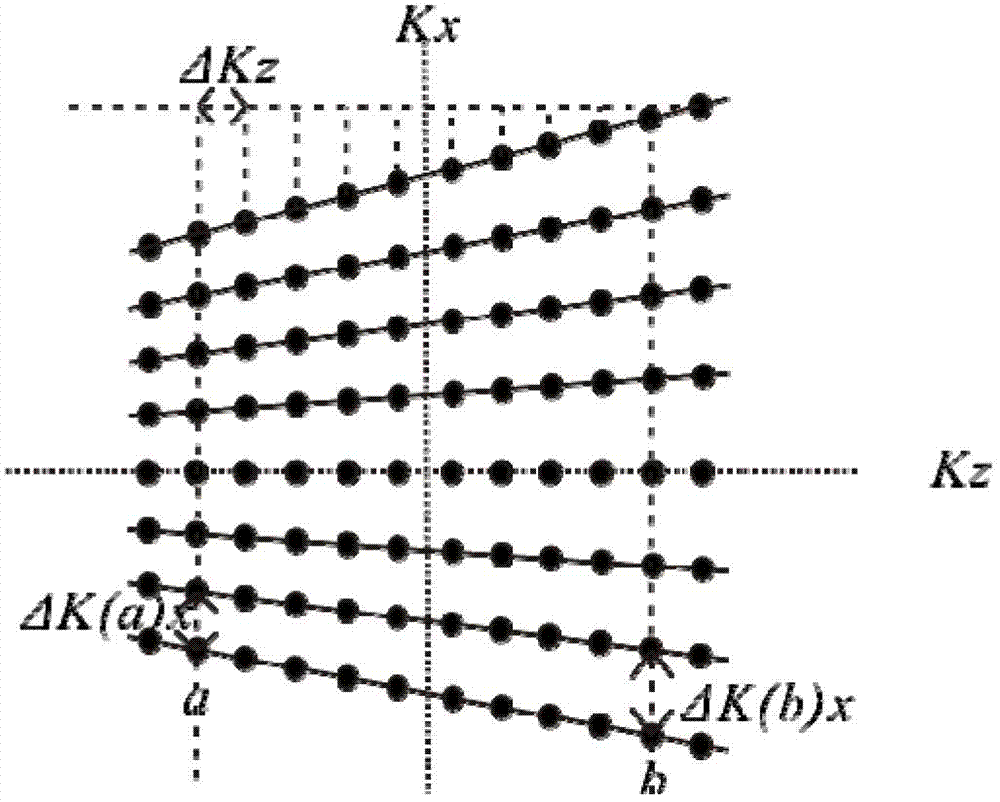
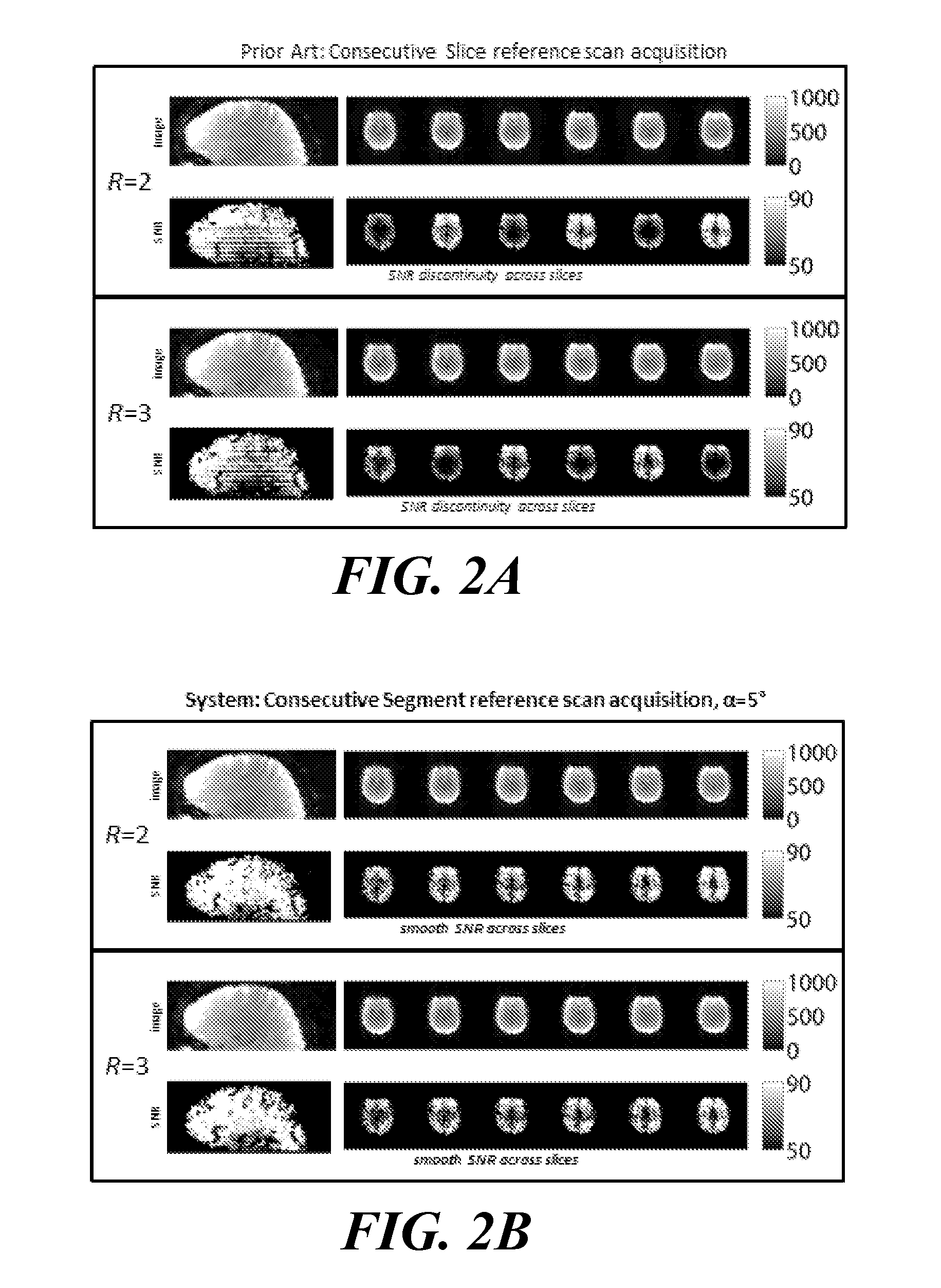
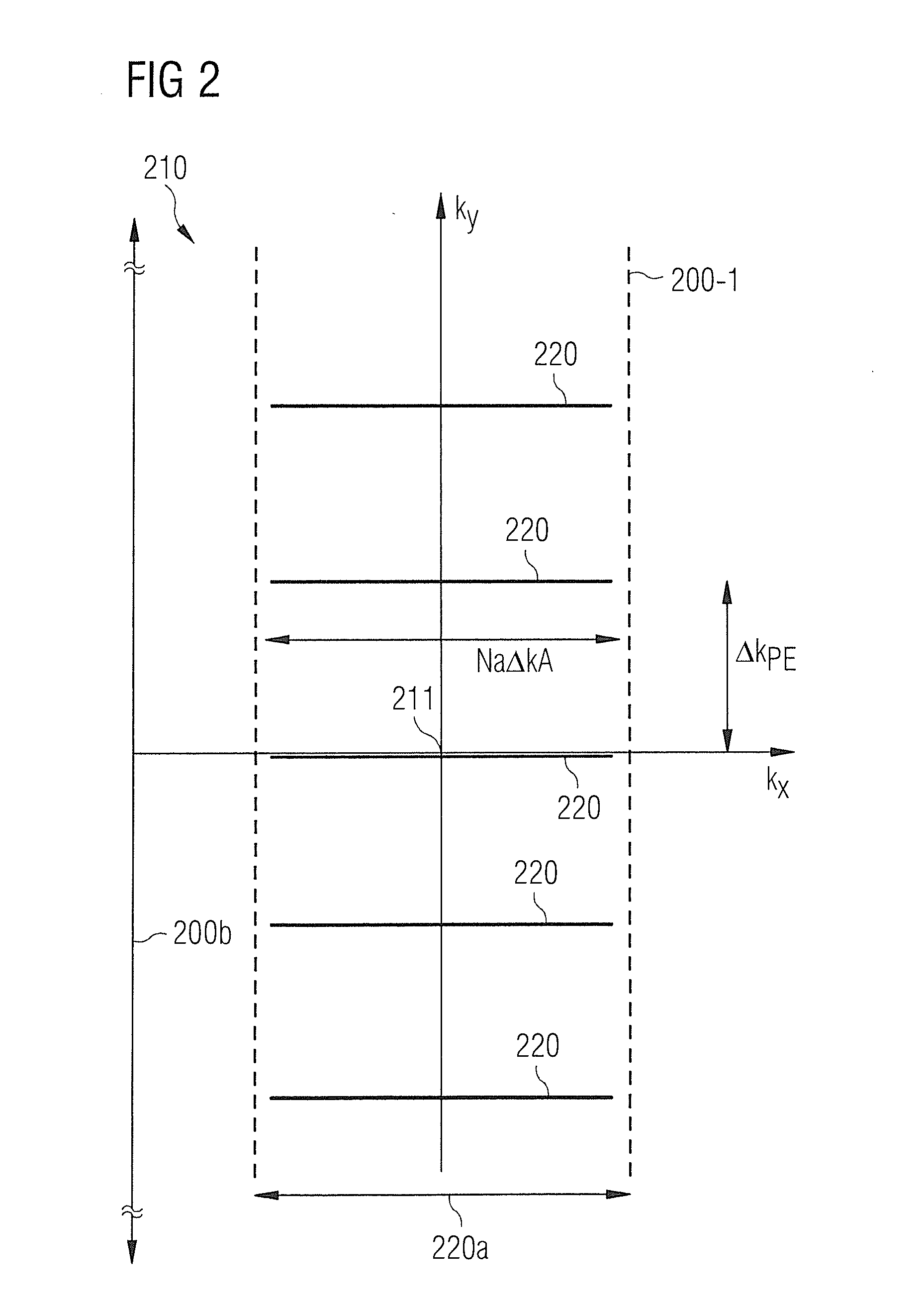
System for Accelerated Segmented MR Image Data Acquisition
ActiveUS20140037171A1Accelerates segmented magnetic resonance (MR) image data acquisitionReconstruction from projectionMagnetic measurementsMagnetic field gradientResonance
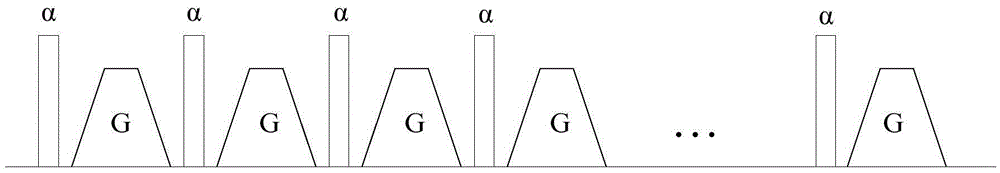
A system for accelerated segmented magnetic resonance (MR) image data acquisition includes an RF (Radio Frequency) signal generator and a magnetic field gradient generator. The RF signal generator generates RF excitation pulses in anatomy and enabling subsequent acquisition of associated RF echo data. The magnetic field gradient generator generates magnetic field gradients for anatomical volume selection, phase encoding, and readout RF data acquisition in a three dimensional (3D) anatomical volume. The RF signal generator and the magnetic field gradient generator acquire consecutive segments of k-space line data representative of an individual image slice in a gradient echo method by adaptively varying RF excitation pulse flip angle between acquisition of the consecutive segments.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH +1
Methods for fat signal suppression in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20080218169A1Shorten the timeReduce acquisition timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionData setFat suppression
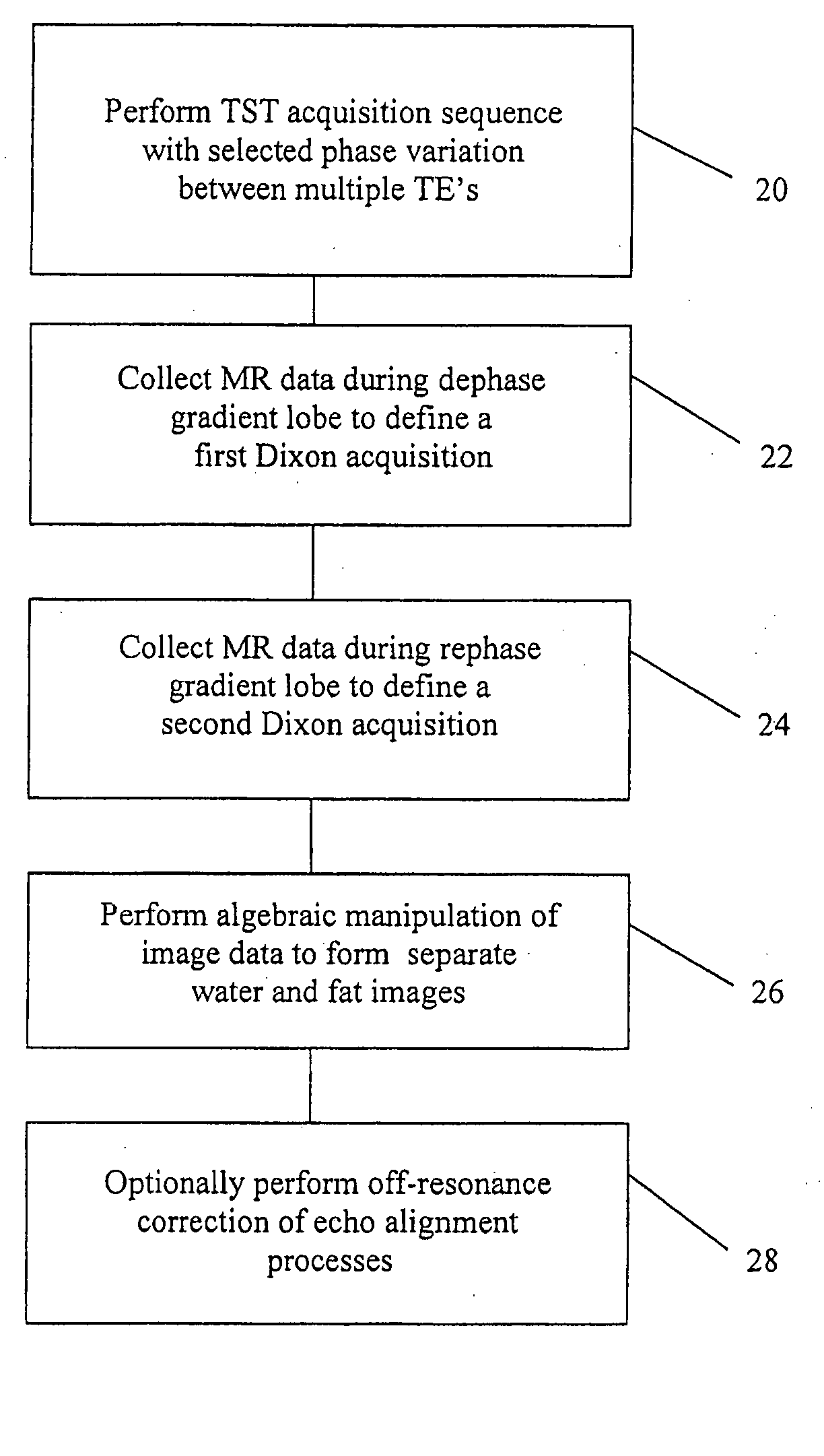
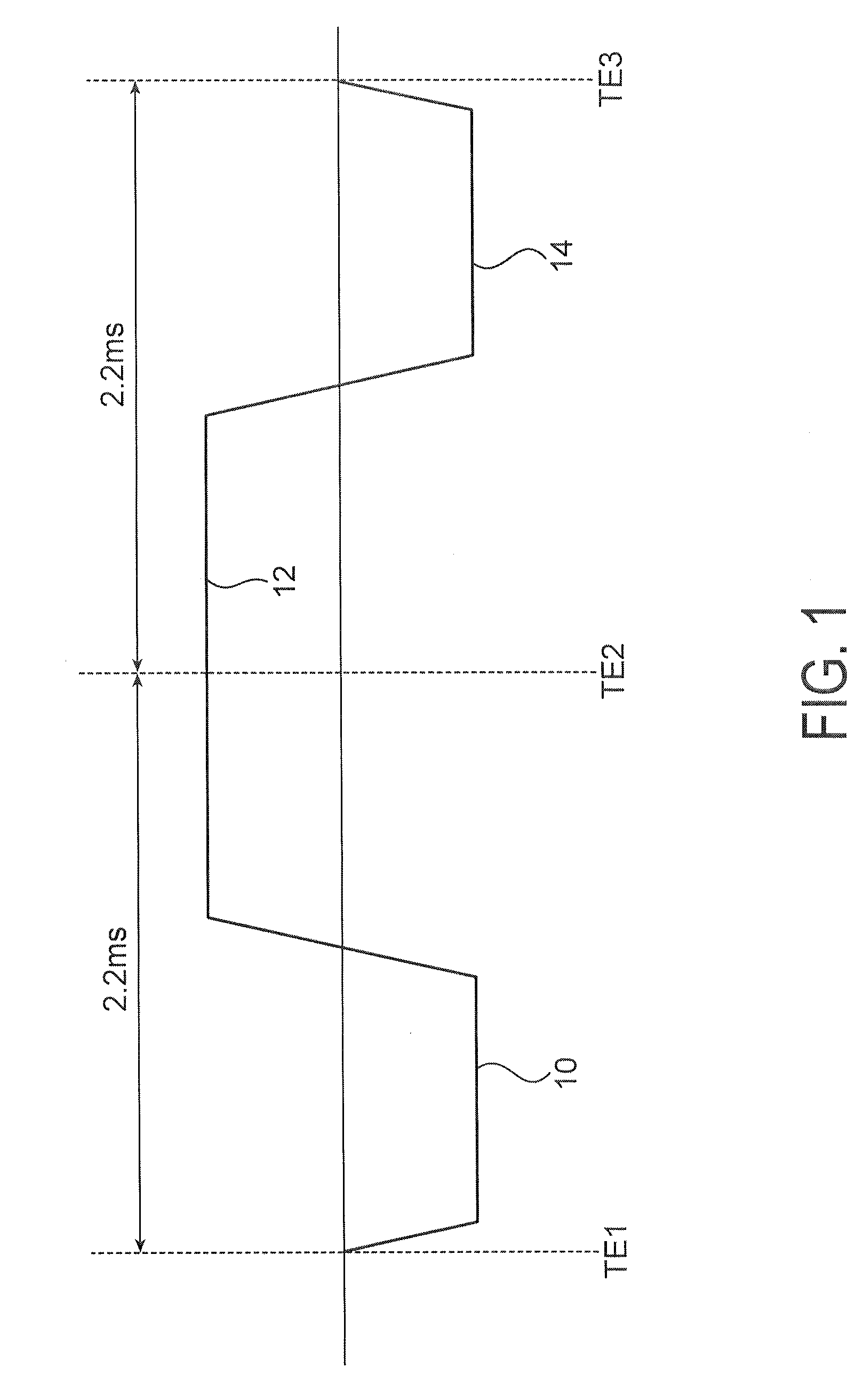
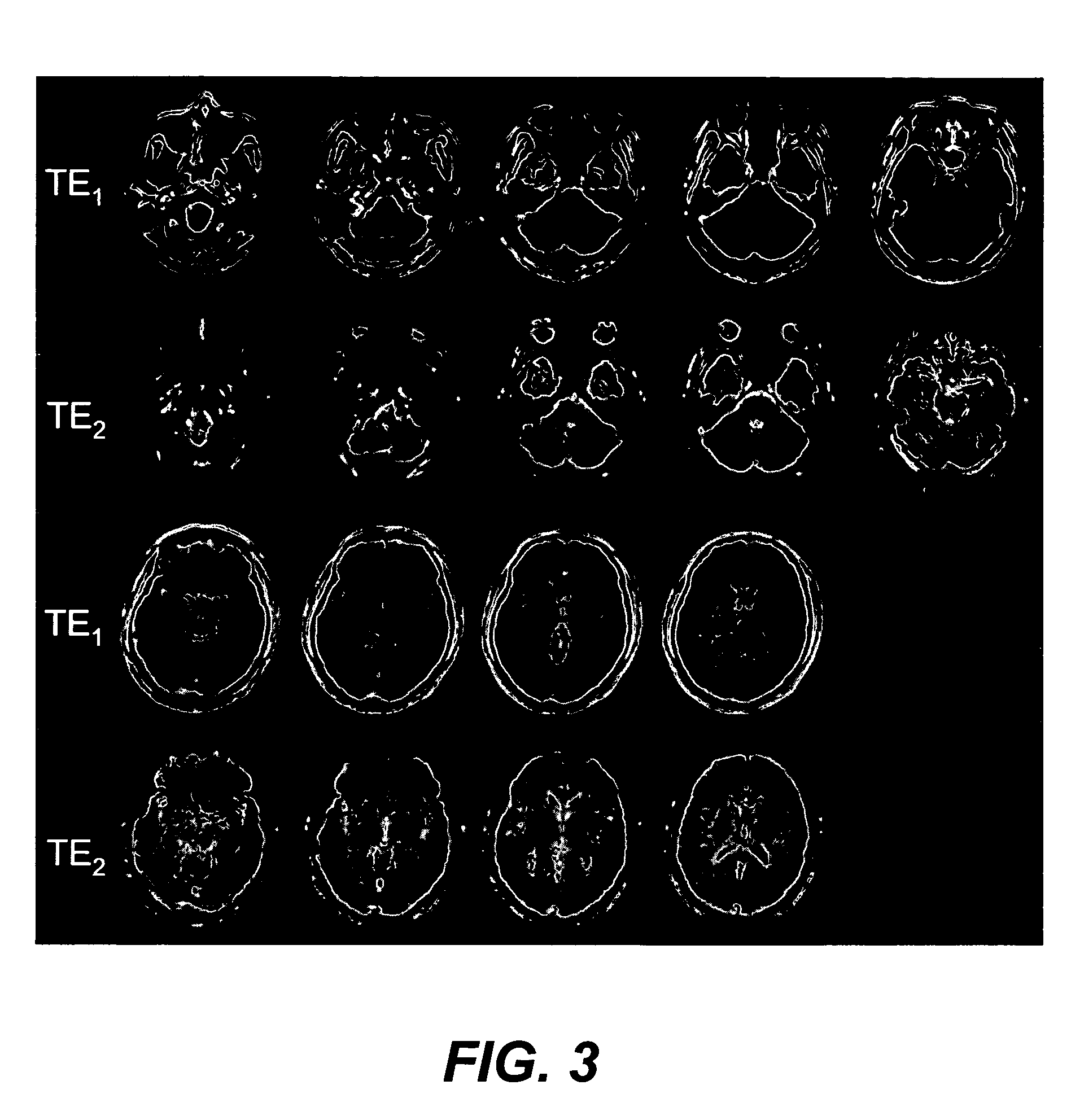
The present invention is directed to methods for chemical species signal suppression in magnetic resonance imaging procedures, wherein Dixon techniques are enhanced by continuously sampling techniques. In the invention, k-space data is acquired during the entire period of read gradient associated with a gradient echo pulse acquisition scheme. The invention utilizes a total sampling time (TST) acquisition during the entire read gradient, using three echoes of a TST data set to achieve chemical species separation in both homogenous fields as well as areas of field inhomogeneity. As an example, a continuously sampled rectilinearly FLASH pulse sequence is modified such that the time between echoes was configured to be 2.2 milliseconds, with TE selected to allow 180° phase variation in the fat magnetization between each of the three TE's (TE1, TE2, and TE3). Data collected during the dephase and rephase gradient lobes are defined as a first Dixon acquisition, with data collected by the read gradient lobe being defined as a second Dixon acquisition. Two point Dixon reconstruction techniques are used to form images for each chemical species, such as for generating water and fat images of the scanned object region. Other corrections, such as off-resonance correction may be applied on the image data.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
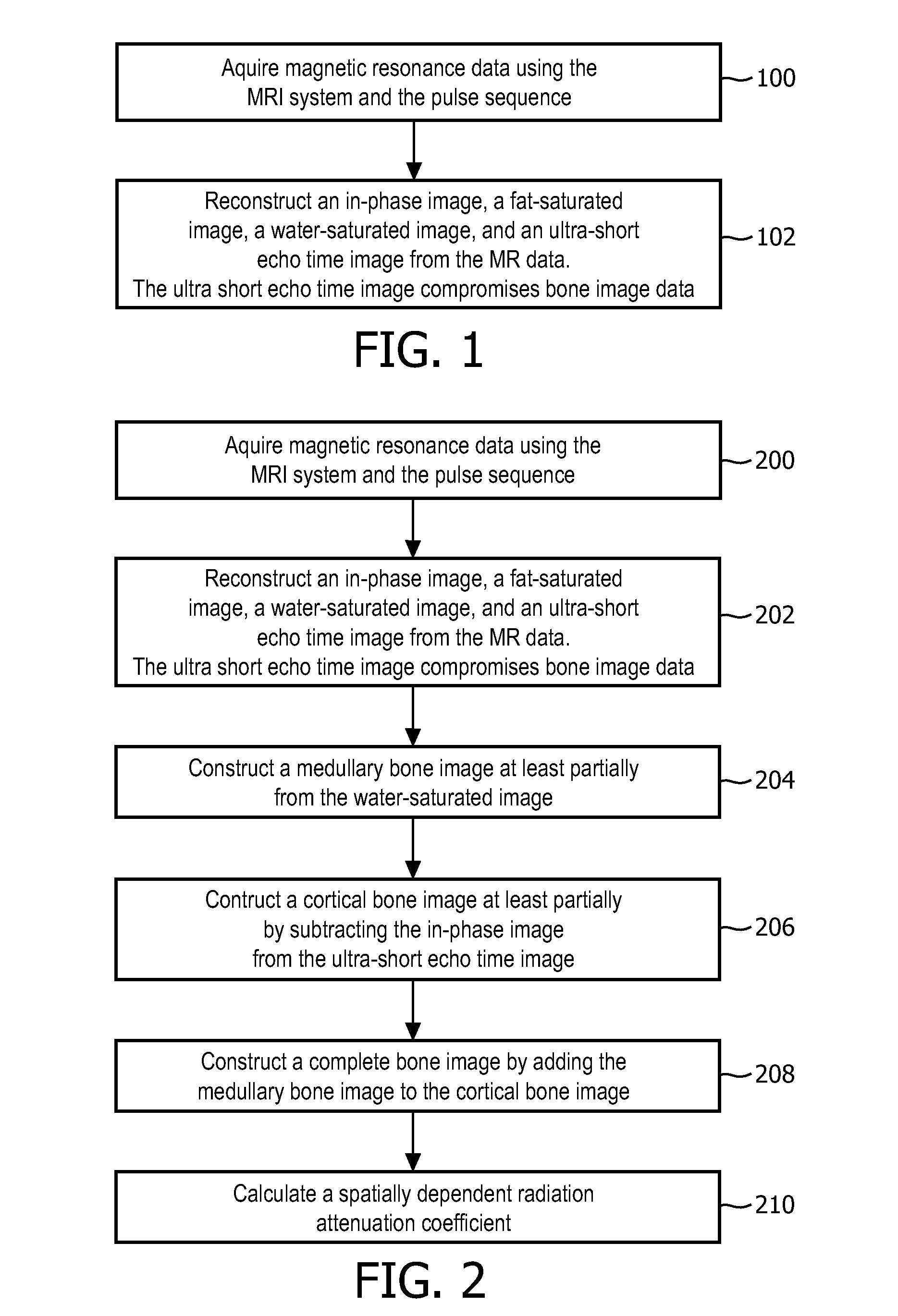
Method and system using magnetic resonance imaging for tissue classification and bulk-density assignment
InactiveUS20140296696A1Reliable identificationEasy to separateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPatient positioning for diagnosticsResonanceVolumetric density
An apparatus includes a magnetic resonance imaging system, a processor for controlling the apparatus, and a memory containing machine executable instructions and a pulse sequence. The machine executable instructions and pulse sequence cause the processor to control the apparatus to: acquire magnetic resonance data from an imaging volume, wherein the magnetic resonance data includes gradient echo data; segment the magnetic resonance data into a plurality of segments, the segments including a fat segment, a water segment, a cortical bone segment, and an air segment; and create a bulk density map of the imaging volume from the segments.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method and magnetic resonance system to generate multiple magnetic resonance images
ActiveUS20140285195A1Achieve effectImprove spatial resolutionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionGradient echoRadio frequency
In a method and magnetic resonance system to determine multiple magnetic resonance images for respective different echo points in time, k-space is scanned on a segment-by-segment basis with at least two rectangular k-space segments, these being scanned line by line with respective k-space lines oriented parallel to one another. A short side of the rectangular k-space segments is oriented parallel to the k-space lines. First and second gradient echoes are respectively produced by a radio-frequency pulse radiated for each k-space line.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Steady-state procession gradient multi-echo water and grease separation imaging method
ActiveCN107153169AHigh precisionSuppresses Motion ArtifactsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRadio frequencyImage sequence
The invention discloses a steady-state procession gradient multi-echo water and grease separation imaging method. The steady-state procession gradient multi-echo water and grease separation imaging method comprises the following steps of on the basis of a steady-state procession imaging sequence for conventional scanning on a magnetic resonance imaging system, repeatedly exciting the imaging area by a radio frequency pulse at the interval of 10ms magnitude or smaller short cycle TR; setting a pulse flip angle into +alpha / 2 in a first sequence repetition cycle, and eliminating the sampling period; alternatively setting the pulse flip angle into +alpha and -alpha in the subsequent sequence repetition cycle; using the layer selection gradient, phase encoding gradient and frequency encoding gradient to perform three-dimensional encoding, wherein the sum of integral areas of gradients in each bearing is zero, and the proton magnetizing vector procession is approximate to the steady state; enabling the magnetizing vectors to form three or two gradient echoes under the action of three or two positive and negative alternating frequency encoding gradients in each TR period, wherein the integral area of gradients in the frequency encoding direction is zero; performing direct phase encoding on the three or two echoes according to echo peak interval and water and grease chemical displacement difference value.
Owner:谱影医疗科技(苏州)有限公司
Magnetic resonance imaging device
InactiveUS20050218894A1Keep for a long timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionData setPhase difference
An MRI apparatus having a calibration pulse sequence, wherein a group of pulse sequences for applying test gradient magnetic fields are established from a basic pulse sequence by a gradient echo method of short TR, a group of pulse sequences not applying test gradient fields are established from the basic pulse sequence, a set of three- or four-dimensional data including a time variable is created by using echo signals collected by at least one of the groups, two data sets are created as a whole by inverting the polarity of the test gradient magnetic field, the difference between phase images thereof is determined, the magnitude and time constant of eddy current induced at the fall or rise of the gradient magnetic field are determined from the phase difference image, and the variation of the magnetic field due to eddy current induced at the rise and / or fall of the gradient magnetic field can be measured in a relatively short time with a desired time resolution even if the magnetic field variation is of a very long time constant.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and device for reconstructing a sequence of mr images using a regularized nonlinear inverse reconstruction process
A method for reconstructing a sequence of magnetic resonance (MR) images of an object under investigation, comprises the steps of (a) providing a series of sets of image raw data including an image content of the MR images to be reconstructed, said image raw data being collected with the use of at least one radiofrequency receiver coil of a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) device, wherein each set of image raw data includes a plurality of data sampies being generated with a gradient-echo sequence, in particular a FLASH sequence, that spatially encodes an MRl signal received with the at least one radiofrequency receiver coil using a non-Cartesian k-space trajectory, each set of image raw data comprises a set of homogeneously distributed lines in k-space with equivalent spatial frequency content,; the lines of each set of image raw data cross the center of k-space and cover a continuous range of spatial frequencies, and the positions of the lines of each set of image raw data differ in successive sets of image raw data, and (b) subjecting the sets of image raw data to a regularized nonlinear inverse reconstruction process to provide the sequence of MR images, wherein each of the MR images is created by a simultaneous estimation of a sensitivity of the at least one receiver coil and the image content and in dependency on a difference between a current estimation of the sensitivity of the at least one receiver coil and the image content and a preceding estimation of the sensitivity of the at least one receiver coil and the image content.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Imaging method for MRI contrast enhancement
ActiveCN104161517ASolve the scan time is too longReduce usageDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsInversion recoveryPhase sensitive
The invention discloses an imaging method for MRI contrast enhancement. Optimized inversion pulses are utilized to replace inversion pulses of a conventional inversion recovery sequence in MRI and to restore delay time, under the precise control of the optimized pluses, spin of different tissue will be evolved towards the trend of maximization of longitudinal magnetic moment differences, and the maximum longitudinal magnetic moment difference is obtained at the end moment of the pluses; on that basis, 90-degree excitation read pluses are applied to enable the maximized magnetic moment difference among the tissue to be turned over to a transverse plane, gradient echo signals are collected to form k spatial data, and the purpose of contrast enhancement among the tissue can be finally achieved through improvement on a phase sensitive image reconstruction method. According to the imaging method, the problem of too long scanning time of the conventional inversion recovery sequence is solved, the advantages of flexibility of optimized pulse waveforms and flexibility of the phase sensitive image reconstruction method are fully utilized, use of expensive magnetic resonance contrast media can be avoided, and the imaging method is superior to an existing MRI contrast enhancement method both in performance and in cost.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
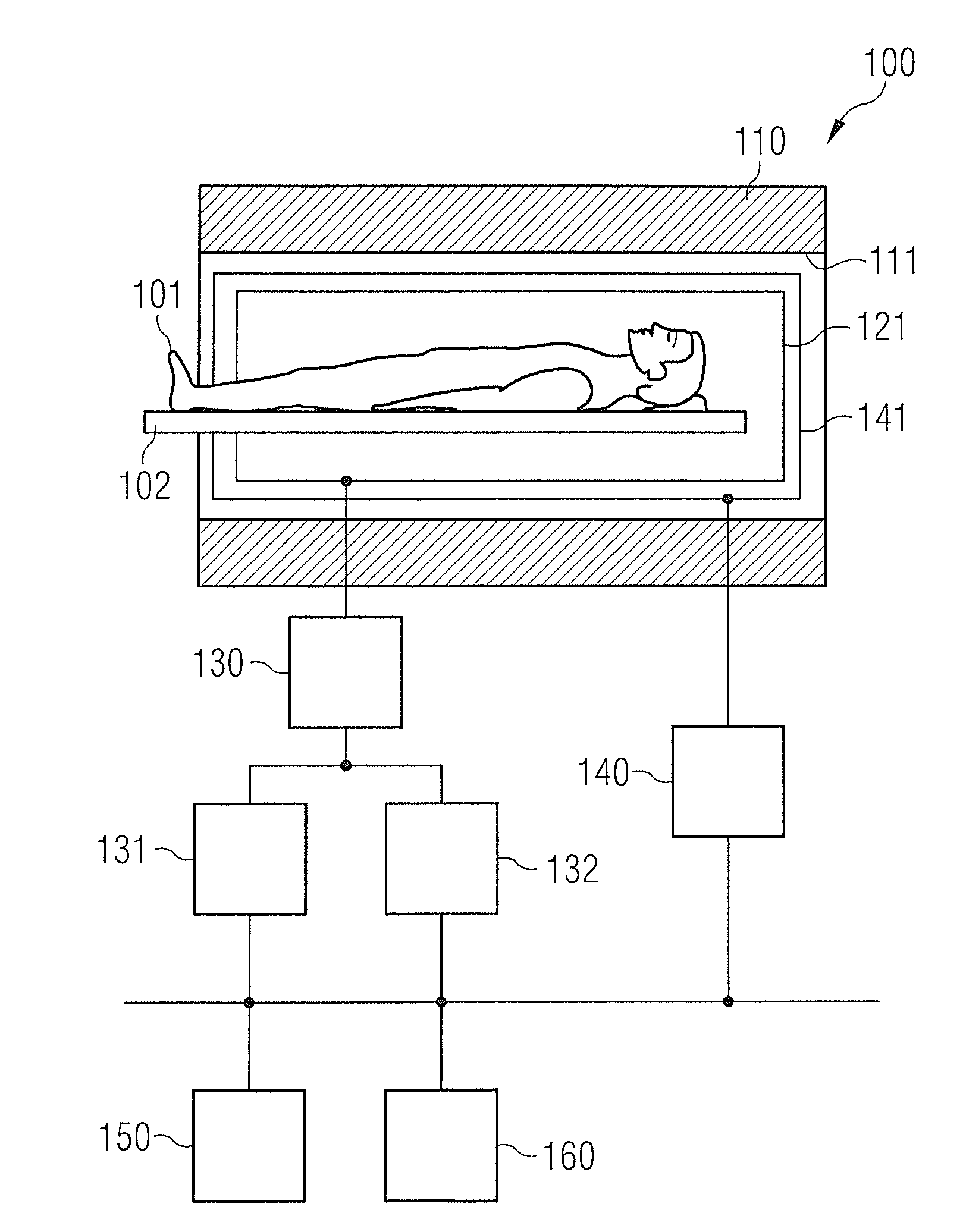
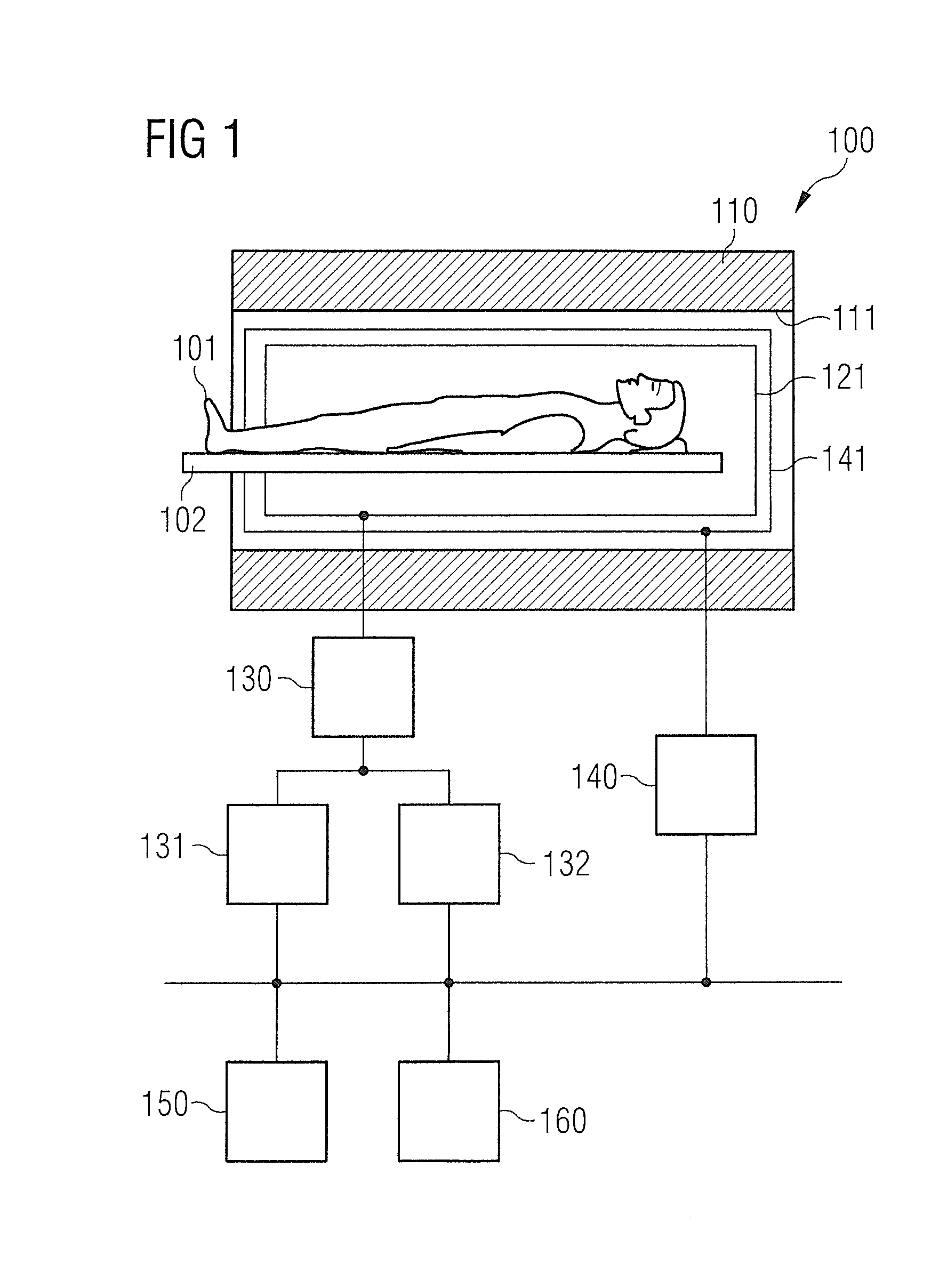
Method for determining an attenuation map and homogeneity information relating to the magnetic resonance magnetic field
ActiveCN101658422AReliable determinationSure easyDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsVoxelPhase difference
A method is disclosed for determining an attenuation map for use in positron emission tomography and for the use of homogeneity information relating to the magnetic resonance magnetic field, in particular for the purpose of determining shim settings, within the scope of a single magnetic resonance image recording. In at least one embodiment of the method, a first and a second image data record are firstly recorded with a three-dimensional gradient echo sequence during a first and a second echo time, respectively, with the phase difference between the water and the fat signal amounting to zeroduring the first echo time and amounting to 180 degrees during the second echo time. The attenuation map is determined from fat / water ratios obtained from the image data records by way of a Dixon technology, in particular a 2-point Dixon technology. In at least one embodiment, all voxels with a signal intensity below a first threshold value are excluded at least for the second image data record by using a mask and only the non excluded voxels of the first and second image data record are taken into consideration in order to determine the homogeneity information from the phase differences of adjacent voxels.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
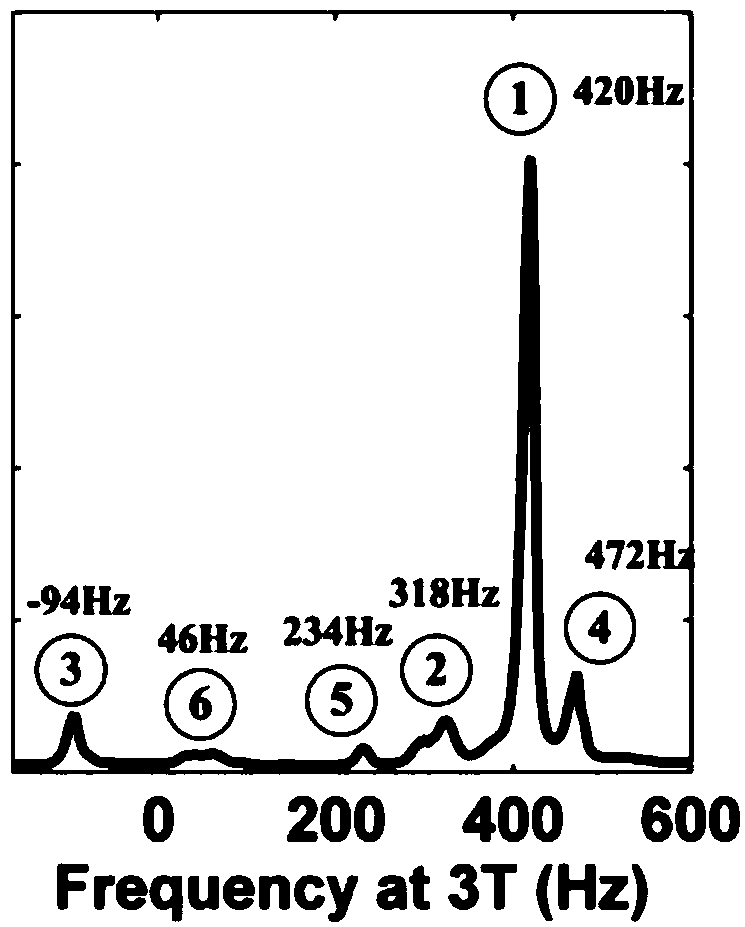
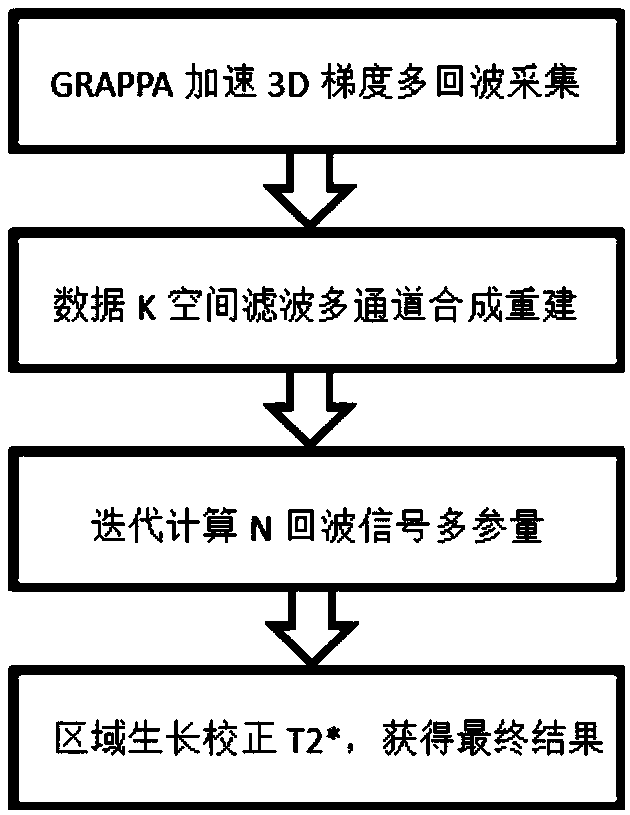
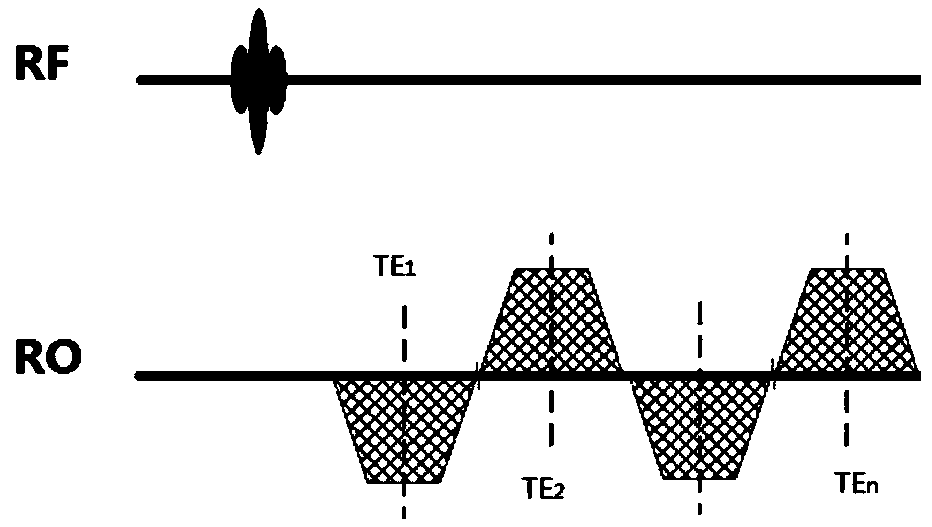
Gradient-echo multi-echo water and fat separation method and magnetic resonance imaging system using method
ActiveCN108720834AFast scanningQuick correctionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImage domainPhase coding
The invention discloses a gradient-echo multi-echo water and fat separation method. The method includes the following steps of 1, using a three-dimensional gradient-echo N echo sequence for conductingimaging scanning on a magnetic resonance imaging region, collecting N pieces of echo data, and using a GRAPPA technology for accelerating data collection during collection, wherein N is greater thanor equal to 4; 2, using the GRAPPA technology for fitting and restoring to-be-collected phase encoding data of the N pieces of echo data within respective K spaces, and then conducting preliminary data processing to obtain complete image domain data of N echoes; 3, substituting the image domain data of the N echoes into a water and fat separation algorithm of a multi-peak water-fat model, introducing T2* variables, conducting iterative calculation, obtaining a T2* distribution map of an imaged object, and meanwhile obtaining water and fat images through calculation. According to the method, the T2* distribution can be accurately estimated, the signal attenuation between the echoes is effectively corrected, and phase changes caused by inhomogeneity of a magnetic field are reduced, so that results of the quantitative analysis images are more accurate and stable. A magnetic resonance imaging system using the method is also provided.
Owner:SUZHOU LONWIN MEDICAL SYST
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging to create T1 maps
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and system for rapid magnetic resonance imaging of gases with reduced diffusion-induced signal loss
InactiveUS7034533B2Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceNoble gasTemporal resolution
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Method and magnetic resonance system to determine the t1 time of water and the t1 time of fat
ActiveUS20150042334A1Accurate measurementAccurately determineMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientVoxel
In a method and a magnetic resonance system to determine the T1 time of water and the T1 time of fat in a predetermined volume segment of an examination subject, magnetic field gradients are activated to generate multiple gradient echoes. First echoes are acquired at at least two different echo times based on RF pulses with a first flip angle. A first water magnetization and a first fat magnetization are determined for each voxel of the volume segment from the first echoes, according to the Dixon method. Second echoes are acquired at at least two different echo times based on RF pulses with a second flip angle. A second water magnetization and a second fat magnetization are determined for each voxel of the volume segment depending on the second echoes according to the Dixon method. The T1 time of water and the T1 time of fat for each voxel are determined depending on the first water magnetization of the respective voxel, the first fat magnetization of the respective voxel, the first flip angle, the second water magnetization of the respective voxel, the second fat magnetization of the respective voxel, and the second flip angle.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging on the basis of a gradient echo sequence
ActiveUS8165657B2Sharp contrastMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringImage contrastResonance
In a method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging on the basis of a gradient echo sequence by excitation of nuclear spins and measurement of radio-frequency signals arising from the excited nuclear spins:(a) the magnetization of the spins is prepared by an inversion pulse;(b) a number of steps for spin excitation are implemented as well as acquisition of an RF response signal for a first image contrast, with the measurement data being acquired along a first two-dimensional slice, and this first two-dimensional slice being parallel to a plane spanned by two coordinate axes x, y standing orthogonal to one another;(c) implementation of a number of steps for spin excitation as well as acquisition of an RF response signal for a second image contrast, with the measurement data being acquired along the first two-dimensional slice that exist in (b); and(d) repetition of steps (a) through (c) for further two-dimensional slices that are offset parallel to the first two-dimensional slice along a third coordinate axis z that is orthogonal to the first two coordinate axes x and y.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and device for magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging
InactiveUS9234953B2Avoid disadvantagesIncrease contrastMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionChemical speciesGradient echo
A method of magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging of an object (O) including at least one chemical species to be imaged, comprising sampling of the k-space such that a plurality of Nω first sampling trajectories through at least one k-space segment of the k-space is formed along a phase-encoding direction, each of said first sampling trajectories beginning in a central k-space region and continuing to a k-space border of the at least one k-space segment and having a duration equal to or below a spectral dwell time corresponding to the reciprocal spectral bandwidth, collecting at least one first set of gradient-echo signals obtained along the first sampling trajectories, collecting at least one second set of gradient-echo signals obtained along a plurality of Nω second sampling trajectories, the Nω second sampling trajectories and the Nω first sampling trajectories being mutually mirrored relative to a predetermined k-space line in the central k-space region.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Methods and systems relating to high resolution magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20160018489A1Easy to assembleImprove usabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsShape optimizationSingle shot
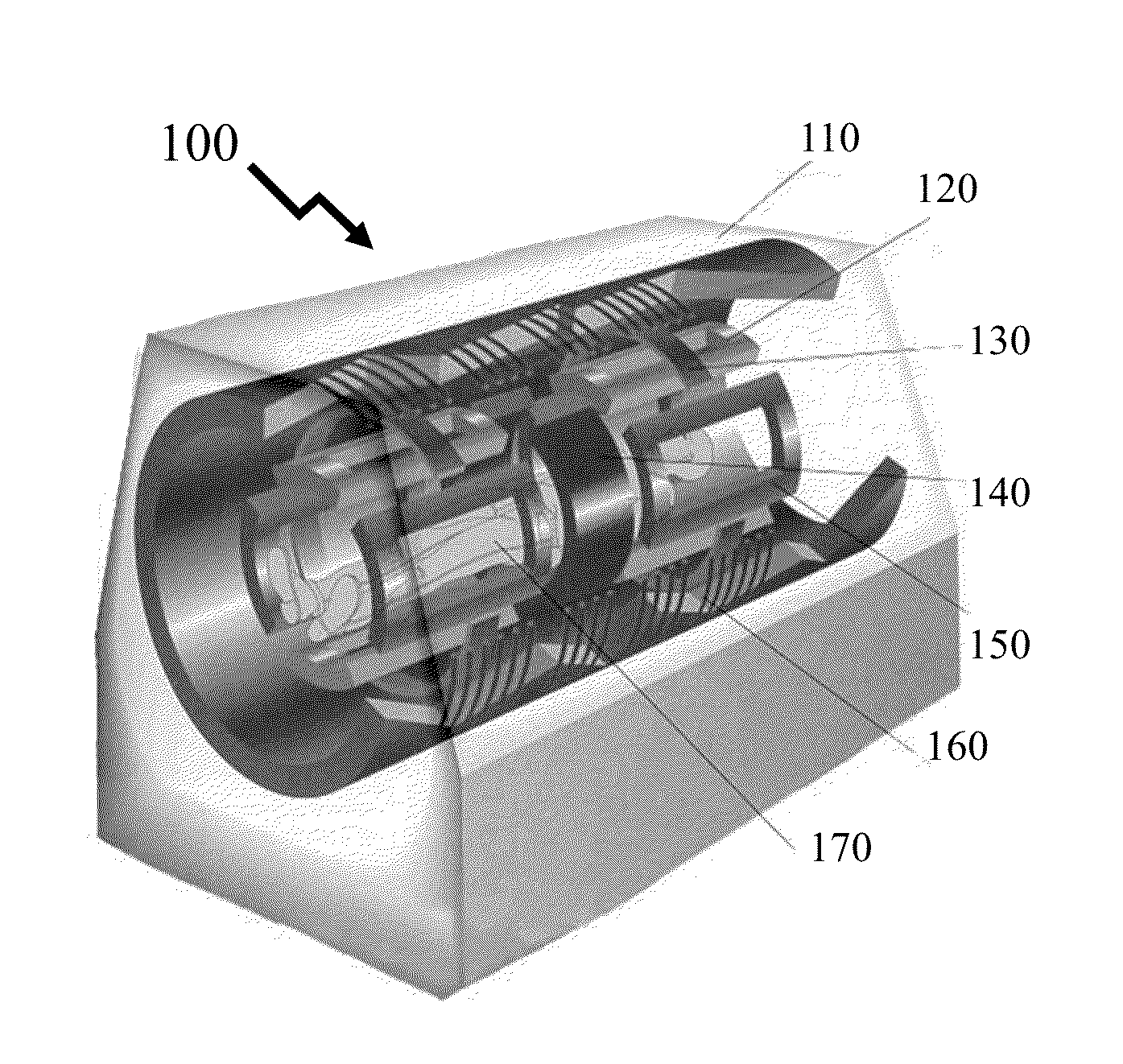
The inventors have established design principles for phased-array MRI coils from the considerations of the target region of the anatomy being evaluated and physical anatomy of the patients. Accordingly, the inventors have demonstrated shape-optimized phased array coils with dense packing of 32 channels for posterior-head imaging exhibiting the SNR gains required to realize not only sub-millimeter fMRI BOLD imaging but also allowing single-shot Gradient Echo-EPI imaging to be performed upon general 3 T MRI instruments. At the same time the design techniques address ergonomic considerations of the patient and designing shape-optimized phased-array MRI coils and patient supports that account for variations within the human population arising from factors such as race, gender, etc.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Dual gradient echo pulse sequence using interleaved spiral-out spiral-in k-space trajectories
ActiveUS20060062731A1Avoids saturation effectMore sensitivityMagnetic measurementsNMR/MRI constrast preparationsMagnetic susceptibilityBlood flow
Measurements of functional, hemographic, and blood flow parameters use a multiple echo or spin echo gradient pulse sequence whereby an early echo is acquired near the beginning of the pulse sequence which avoids saturation effects and a later echo near the end of the pulse sequence which can provide information with more sensitivity to a contrast agent for a susceptibility weighted image.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Lower limb deep venous thrombus magnetic resonance imaging method and device
The invention provides a lower limb deep venous thrombus magnetic resonance imaging method and device. On the premise that no contrast media are used, injuries to a patient are avoided, and meanwhile the imaging effect is improved. The method includes the steps that blood flow signals of lower limb deep veins are suppressed, blood vessel wall and thrombus signals of the lower limb deep veins are retained, and preprocessed signals of the lower limb deep veins are obtained; the preprocessed signals of the lower limb deep veins are sampled through a variable-turning-angle spin echo sequence or a fast small-angle gradient echo sequence; according to sampled data, a lower limb deep venous thrombus magnetic resonance image is acquired. By means of the technical scheme, on one hand, blood vessel walls, blood flow and thrombi of the lower limb deep veins can be accurately differentiated, and whether thrombi exist in blood vessels or not can be visually displayed; on the other hand, the lower limb deep venous thrombus magnetic resonance image obtained through the method and device can display whether thrombi exist in the lower limb deep veins or not and the distribution positions of the thrombi, the thrombi can be preliminarily staged, and practical and effective information is provided for clinical treatment.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com