Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3119 results about "Transverse plane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
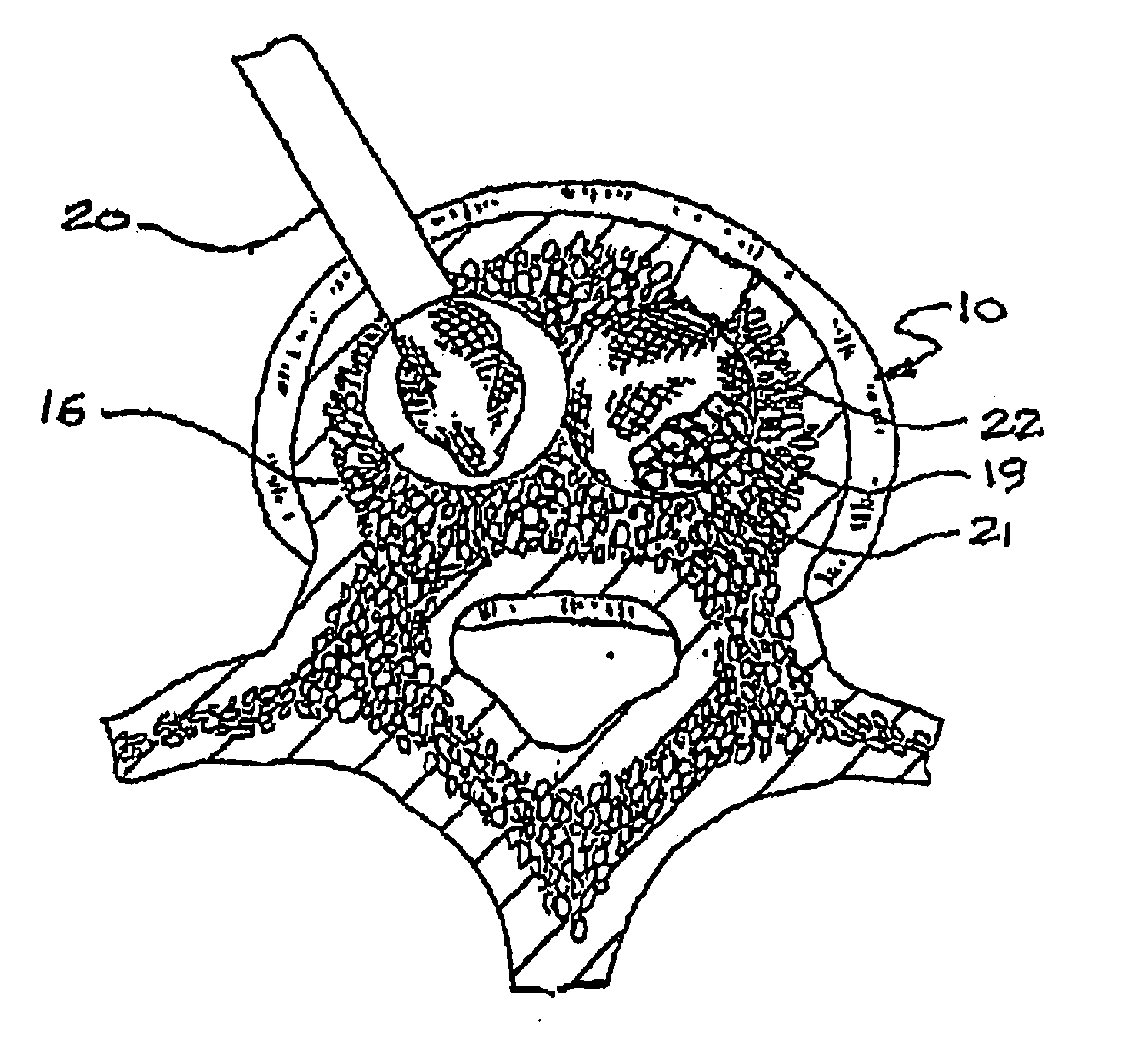
The transverse plane or axial plane (also called the horizontal plane or transaxial plane) is an imaginary plane that divides the body into superior and inferior parts. It is perpendicular to the coronal plane and sagittal plane.
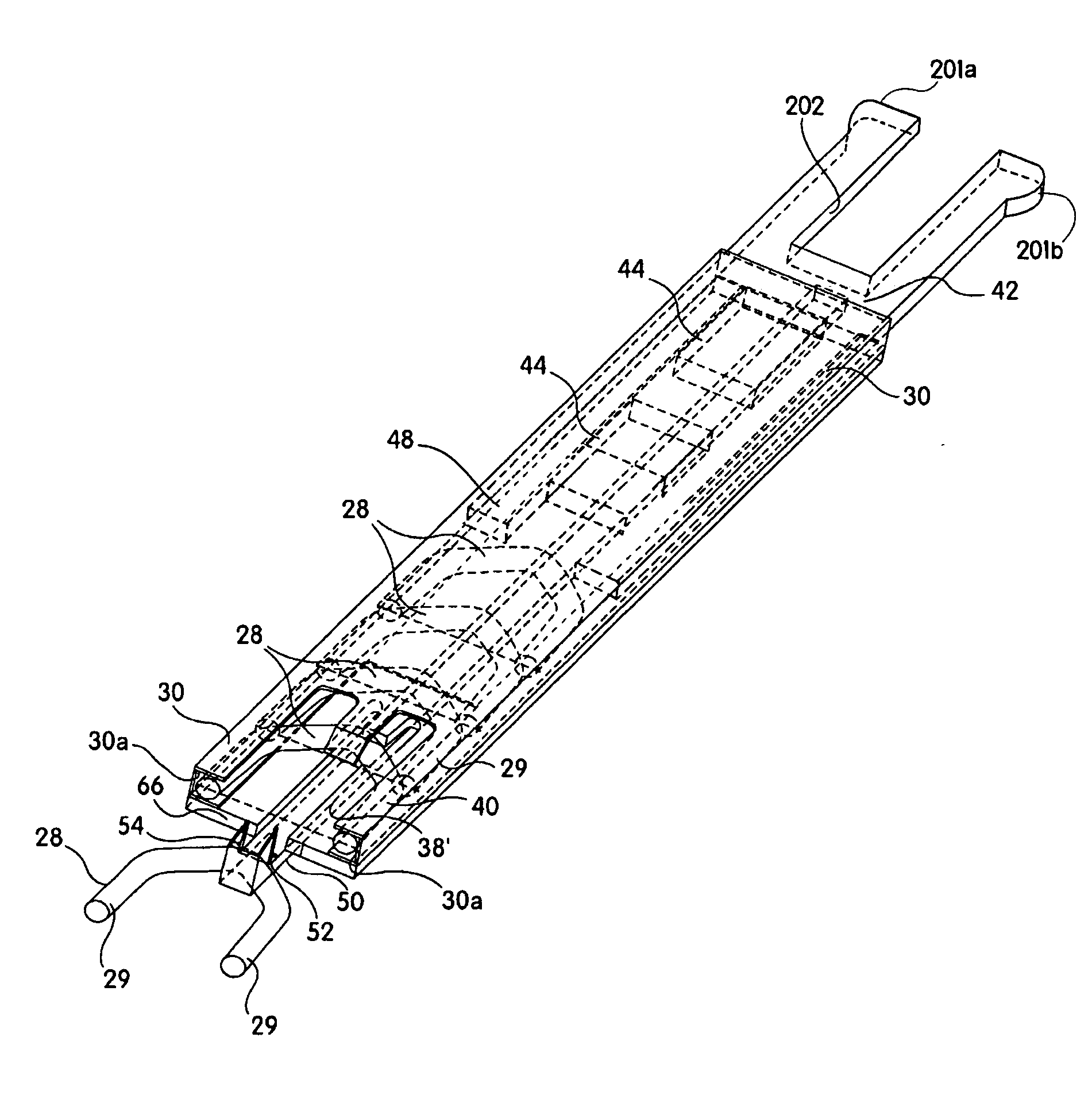
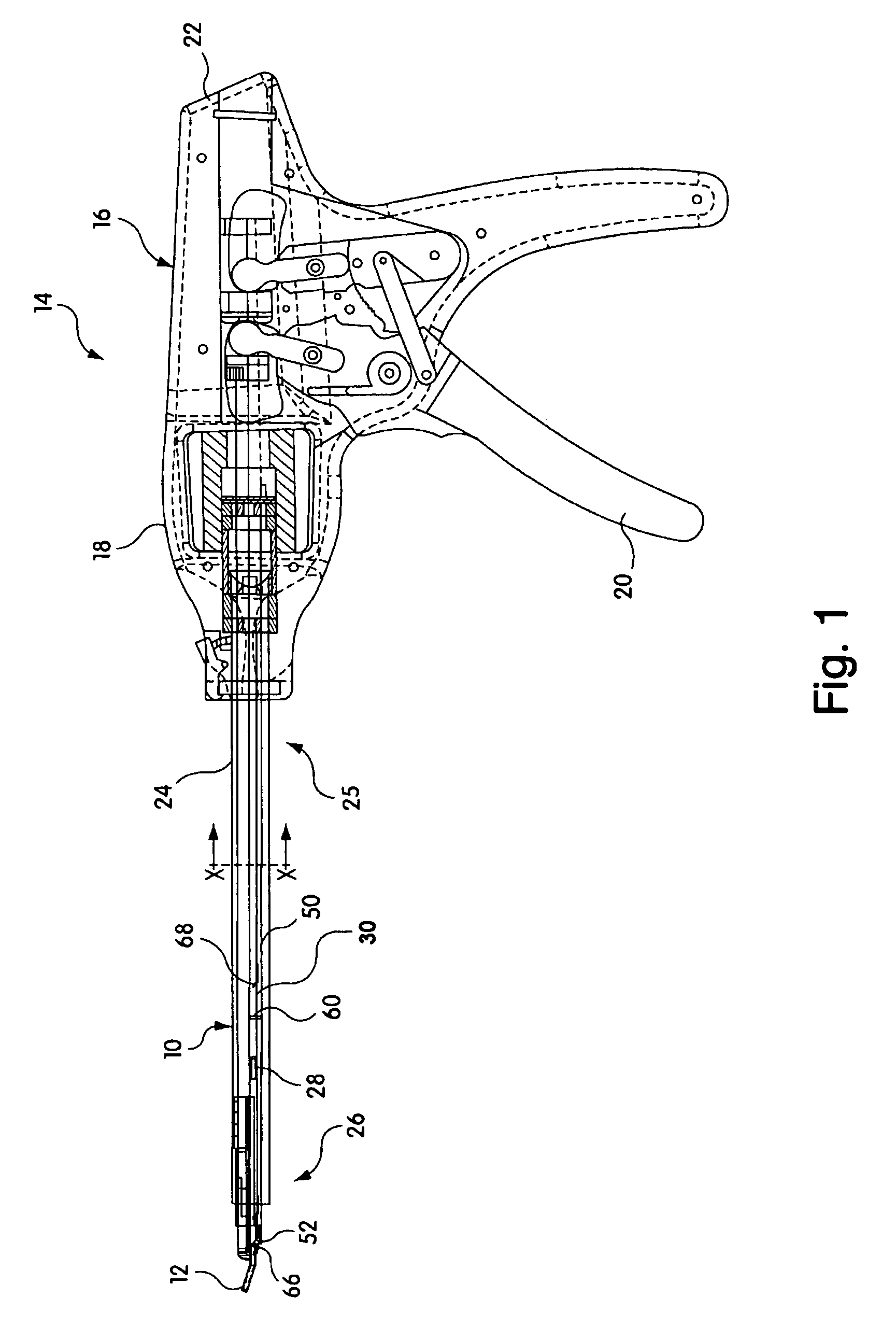
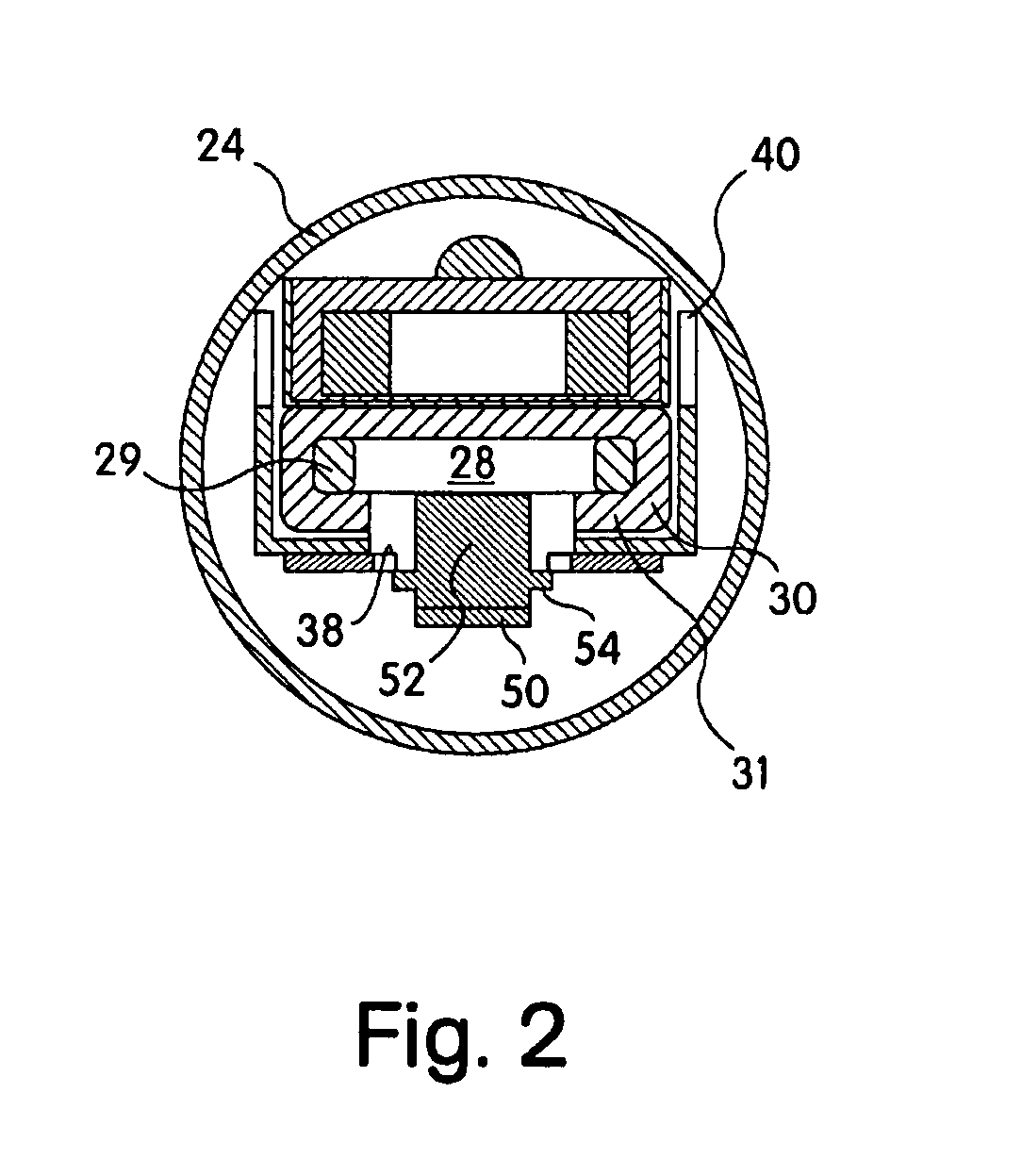
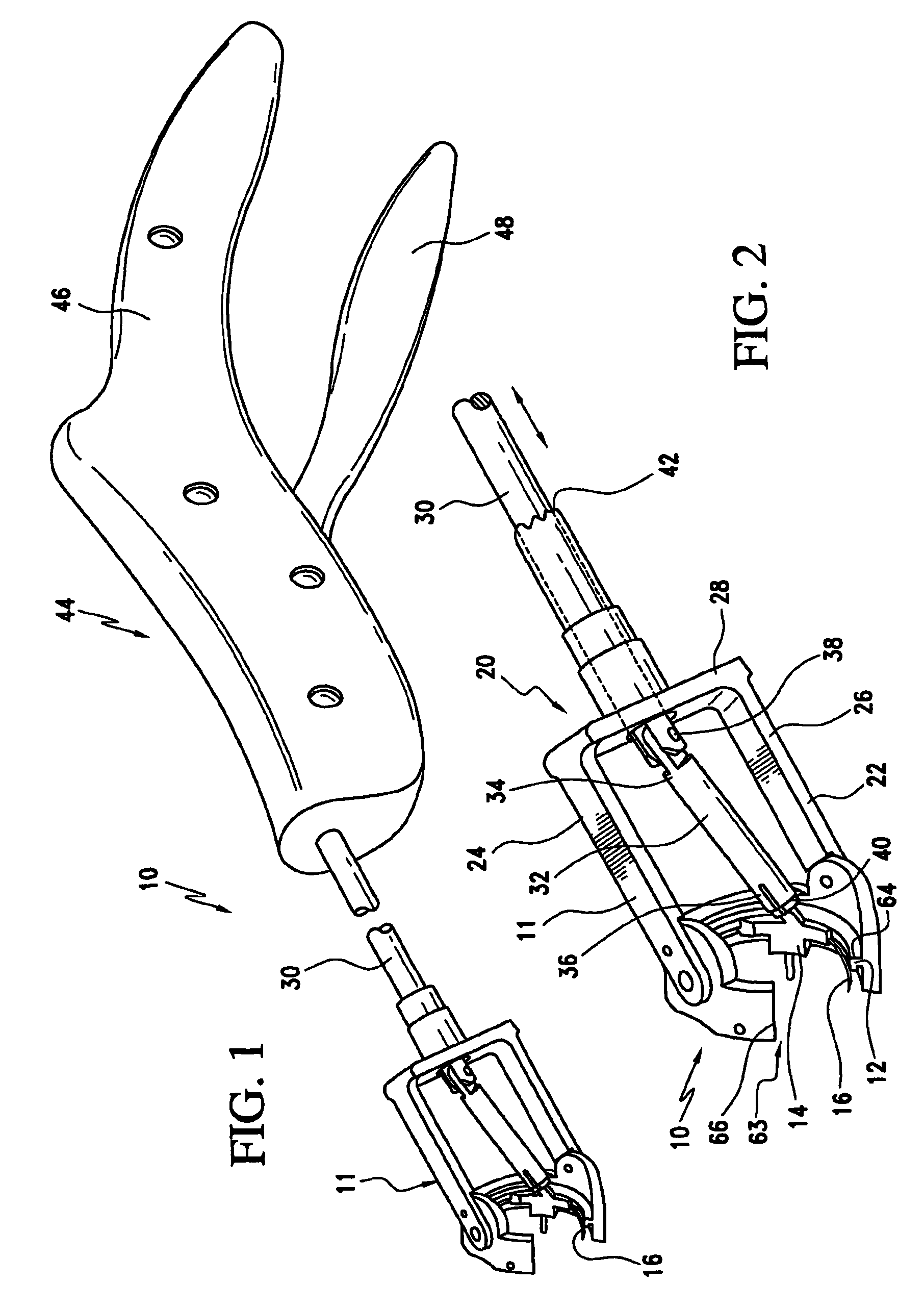
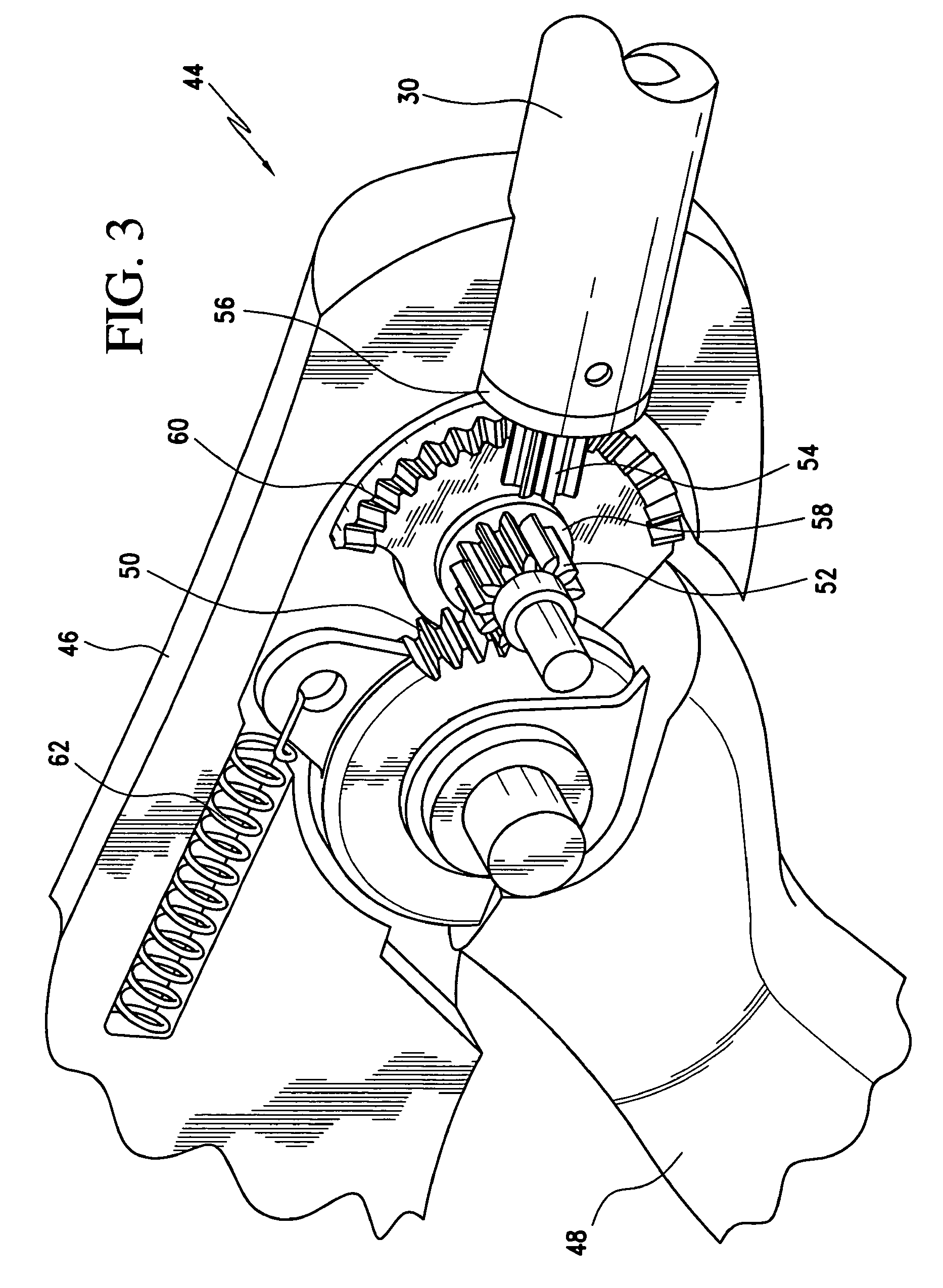
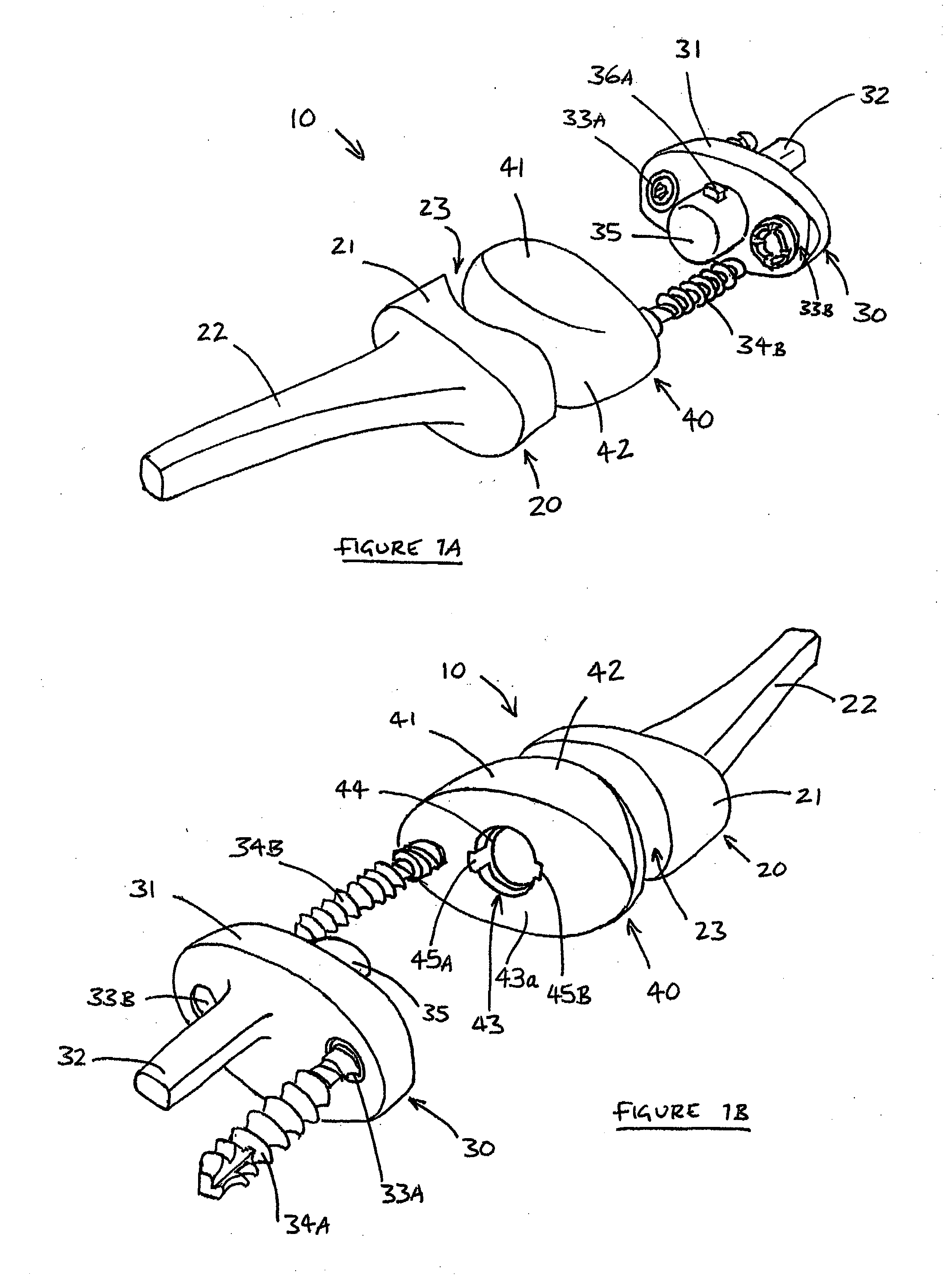
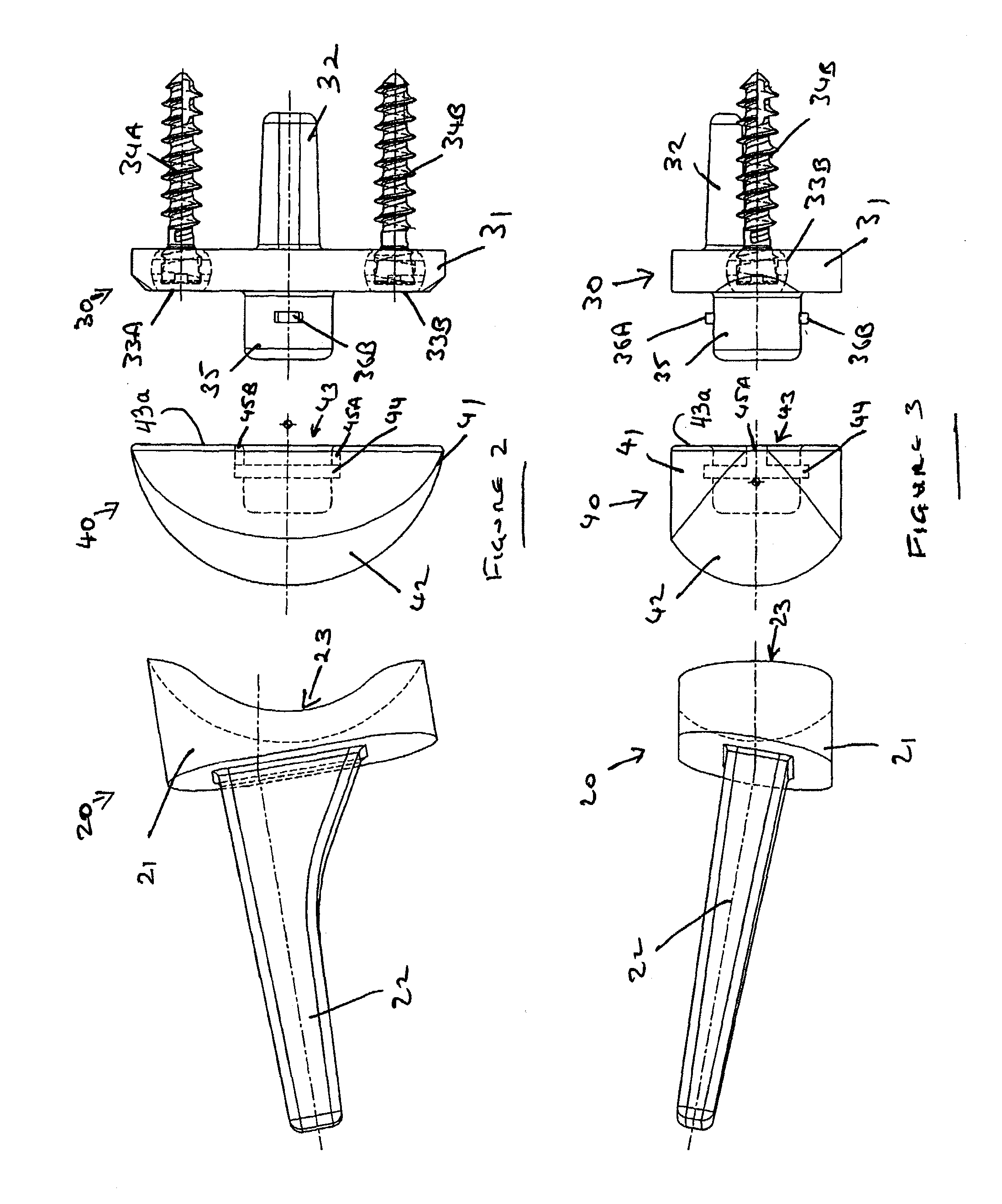
Medical clip feeding mechanism
InactiveUS20070185504A1Appropriate resistanceSurgical staplesWound clampsTransverse planeSurgical Staplers
A ladder for use with a clip applying device may include first and second protrusions extending from an end of the ladder along a lateral plane generally coplanar with the ladder or an orthogonal plane generally orthogonal to the ladder, in which the ladder may serially urge a clip outward from the surgical stapler, and the first and second protrusions may abut a cartridge in which the ladder is disposed.
Owner:MICROLINE PENTAX
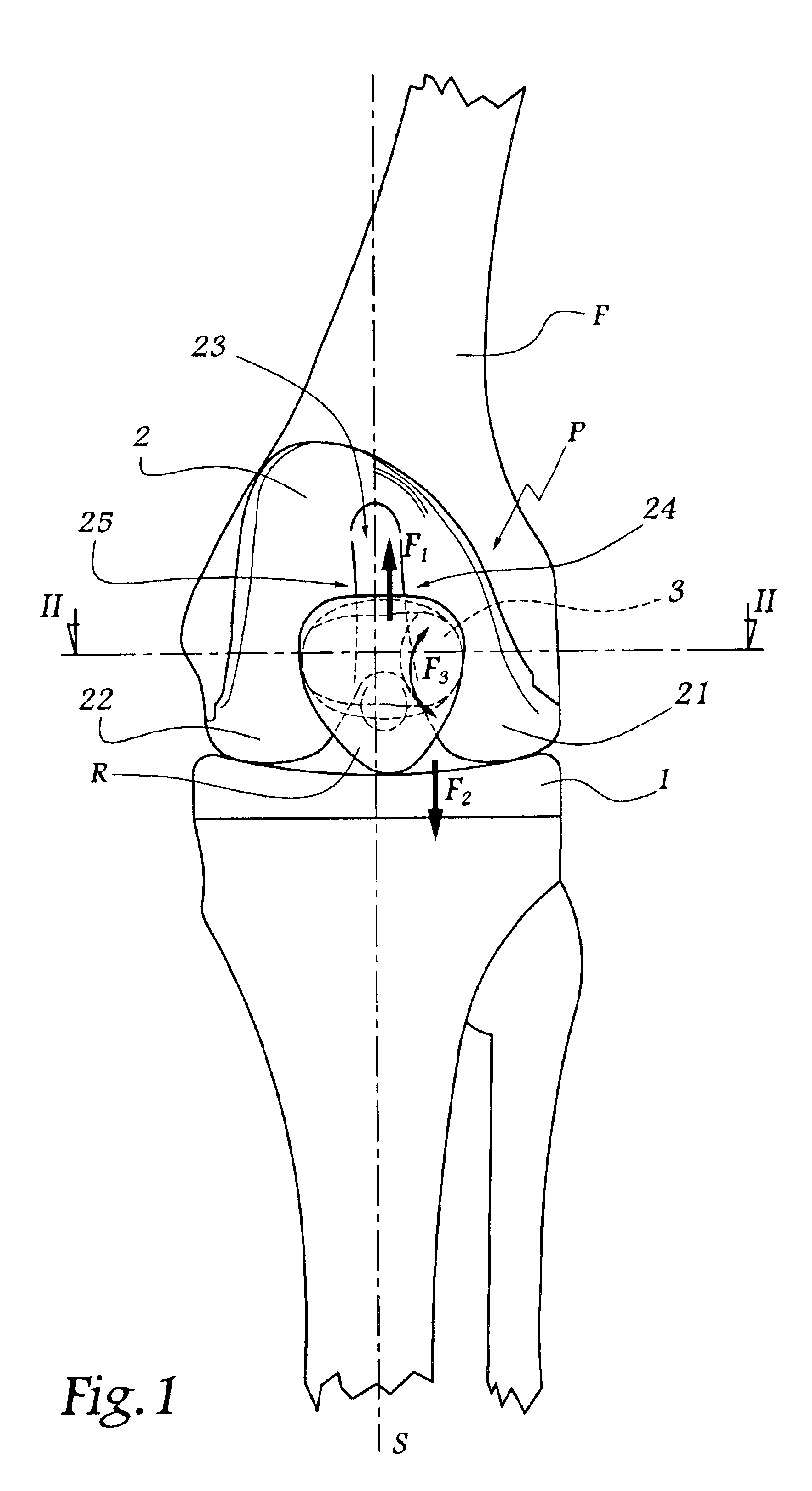
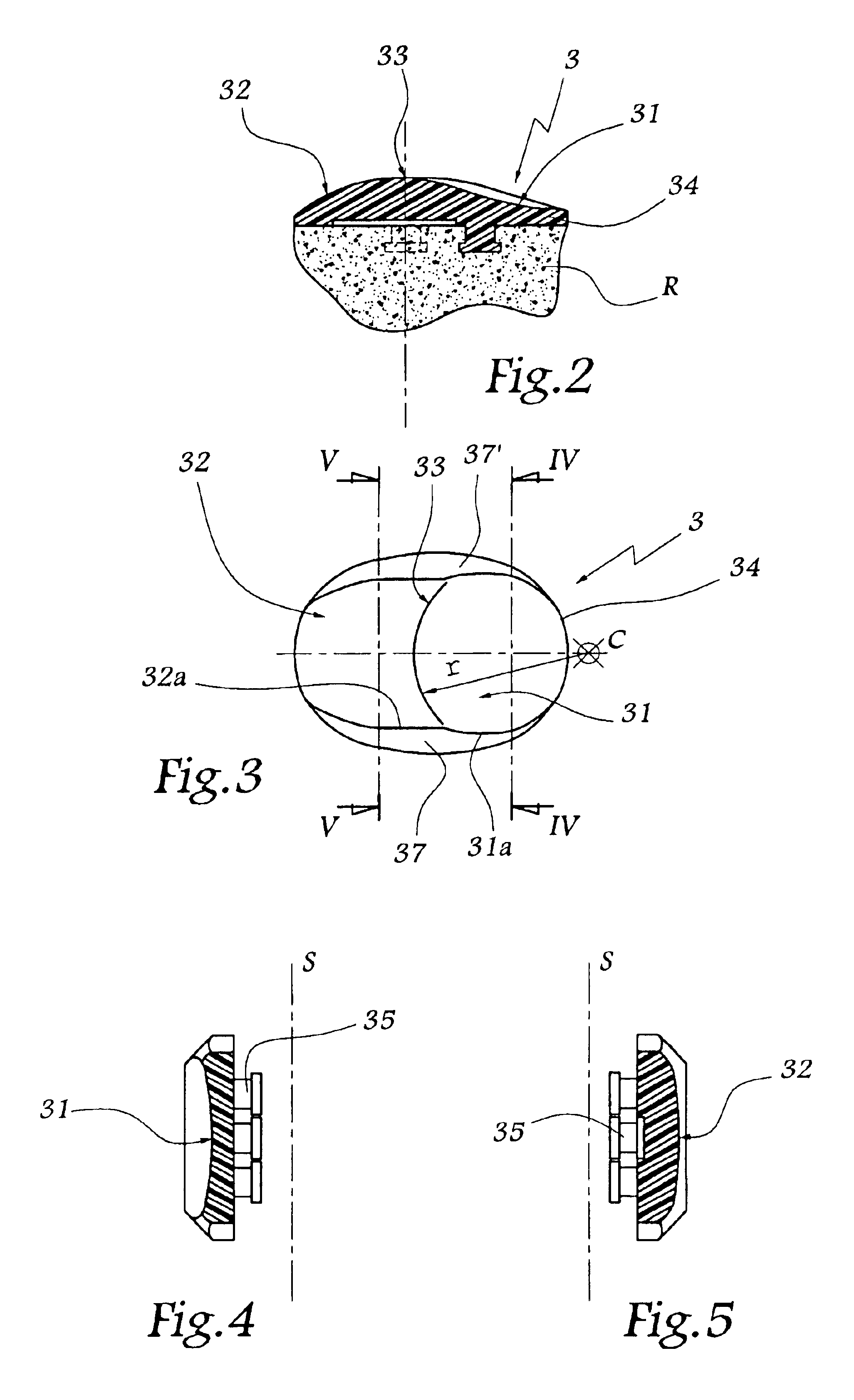
Patellar implant and knee prosthesis incorporating such an implant
InactiveUS6802864B2Improve contact stabilityReduce wearJoint implantsKnee jointsArticular surfacesArticular surface
A patellar implant for total or partial prosthesis of the knee joint incorporates an outer articular surface and an inner articular surface provided to cooperate respectively with an outer side and an inner side of a femoral trochlea or of a femoral prosthetic component. The inner and outer articular surfaces are separated by a transition ridge which is curved, as viewed from a front of the implant, so as to be concave facing the outer articular surface. The outer articular surface is concave in a plane parallel to a sagittal plane and in a transverse plane of the knee joint.
Owner:CORIN
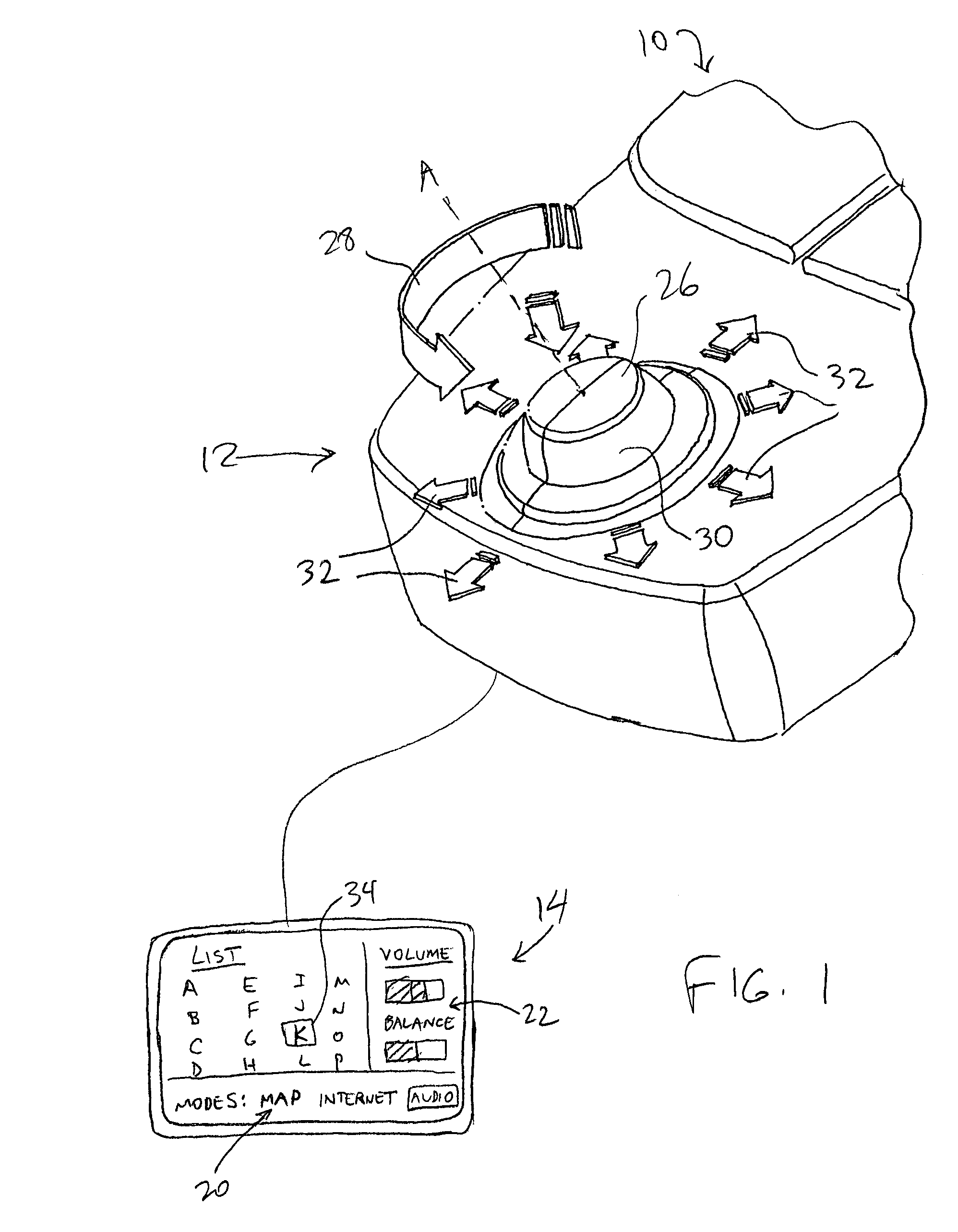
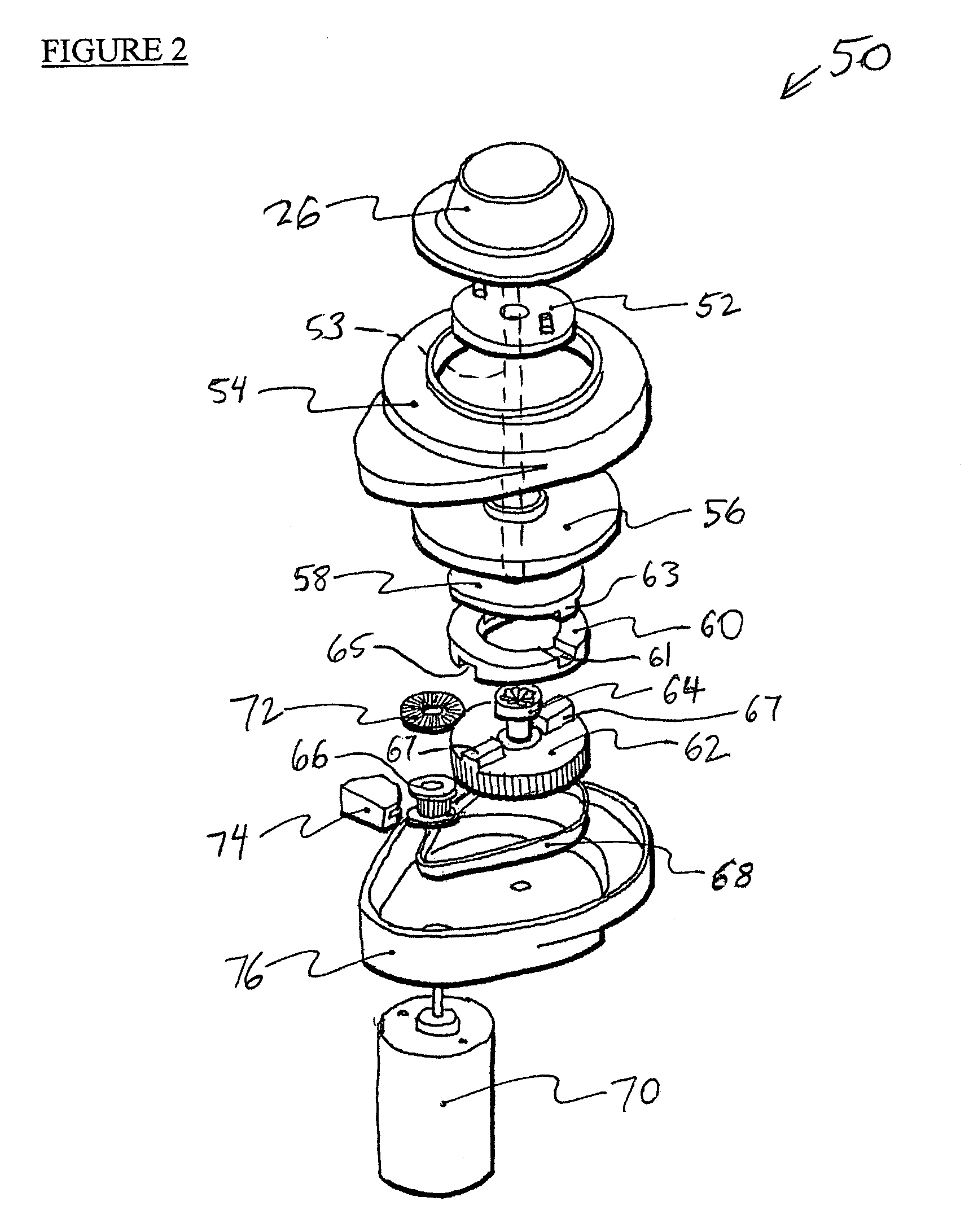
Mechanisms for control knobs and other interface devices
InactiveUS7038667B1Strong control functionGreat easeCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectrical haptic/tactile feedbackRotational axisLinear motion
Mechanisms for a control knob or other interface device providing additional degrees of freedom for the knob. One embodiment provides a rotatable knob moveable also in a lateral plane approximately perpendicular to the axis of rotation. A mechanism providing the lateral motion can include a gate member and a plunger member that engages grooves in the gate member. A rotational sensor detects a rotational position and a lateral sensor can detect a lateral position of the knob. Another embodiment provides an actuator that includes a shaft that is coaxial with the axis of rotation and which can be moved linearly along the axis of rotation with respect to actuator housing to accommodate linear motion of the knob. In another embodiment, a gear assembly including two interlocked gears is provided to transmit rotational motion from the knob to the sensor, and the interlocked gears translate with respect to each other when the knob is translated along the rotational axis.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
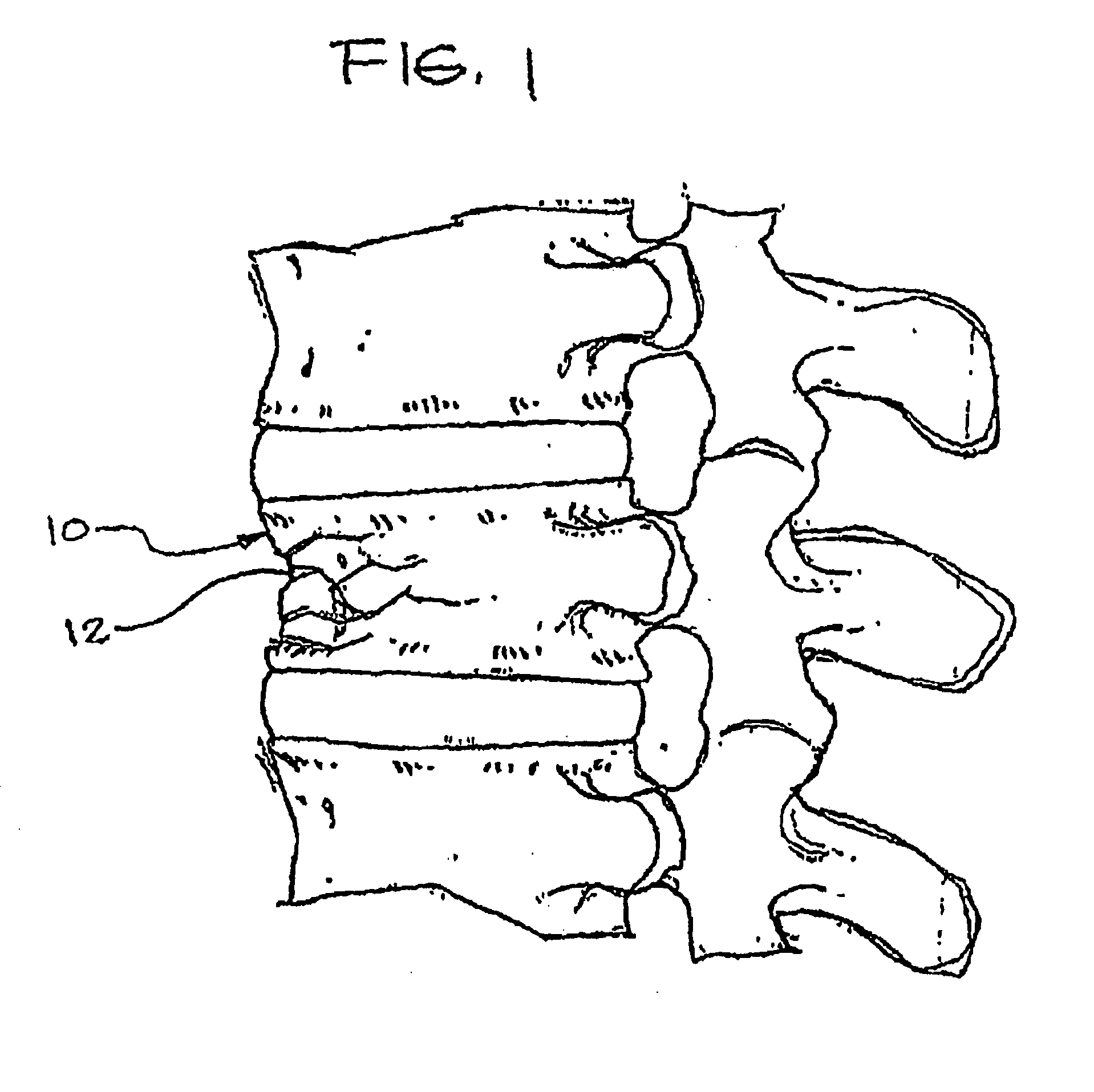
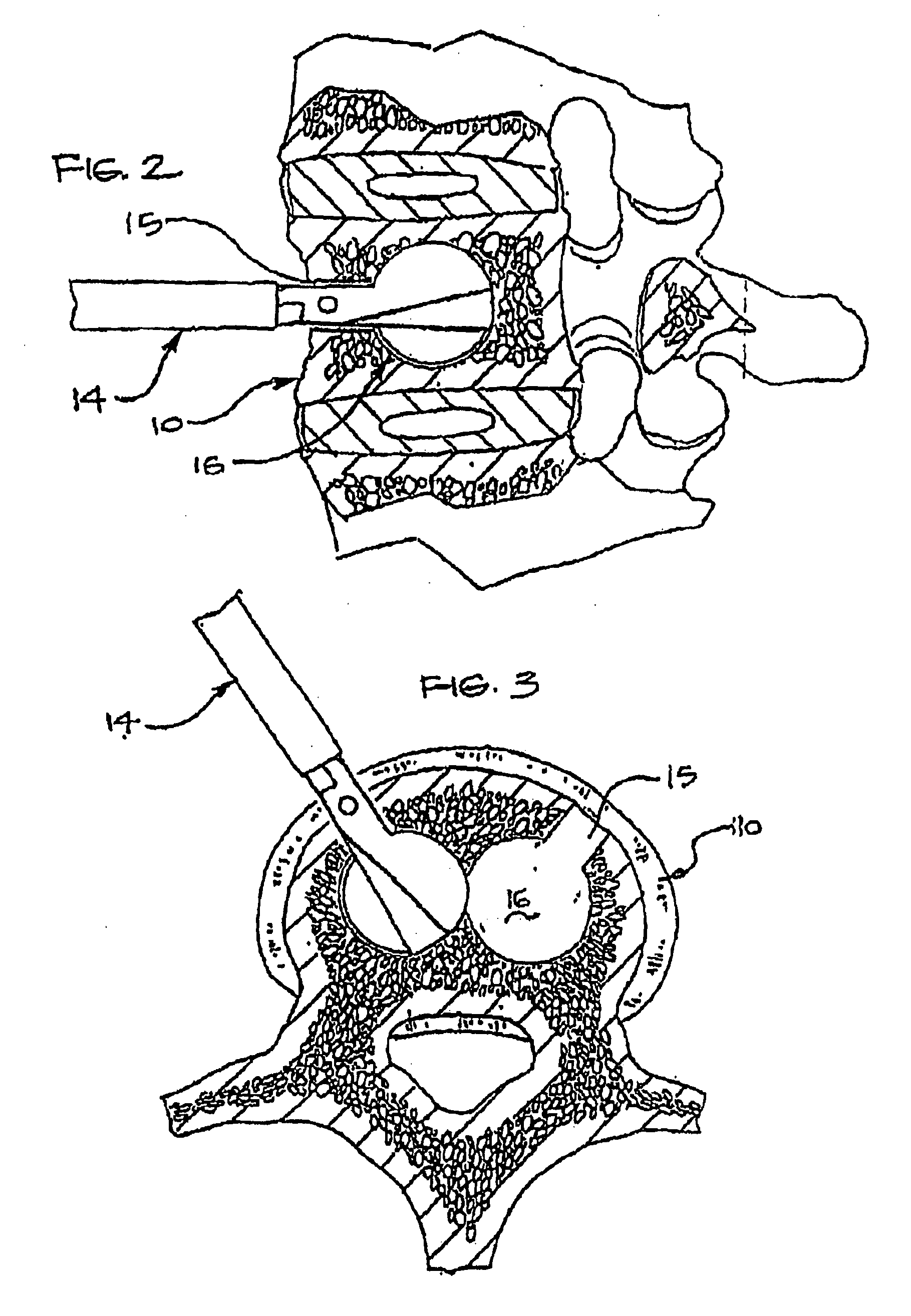
Expandable porous mesh bag device and methods of use for reduction, filling, fixation and supporting of bone
InactiveUS20080086133A1Less fear of punctureAvoid breakingInternal osteosythesisBone implantTransverse planeBiomedical engineering
A method of treating a compression fracture in a bone comprising the steps of forming a transverse cavity within said bone defined by at least one substantially flat surface lying substantially in a transverse plane formed by and communicating with said transverse cavity, the transverse cavity having a substantially uniform transverse extent and a maximum height, the maximum height being less than said transverse extent and applying a force within said transverse cavity generally normal to said surface to displace said surface and restore said bone to its substantially normal anatomic position.
Owner:SPINEOLOGY
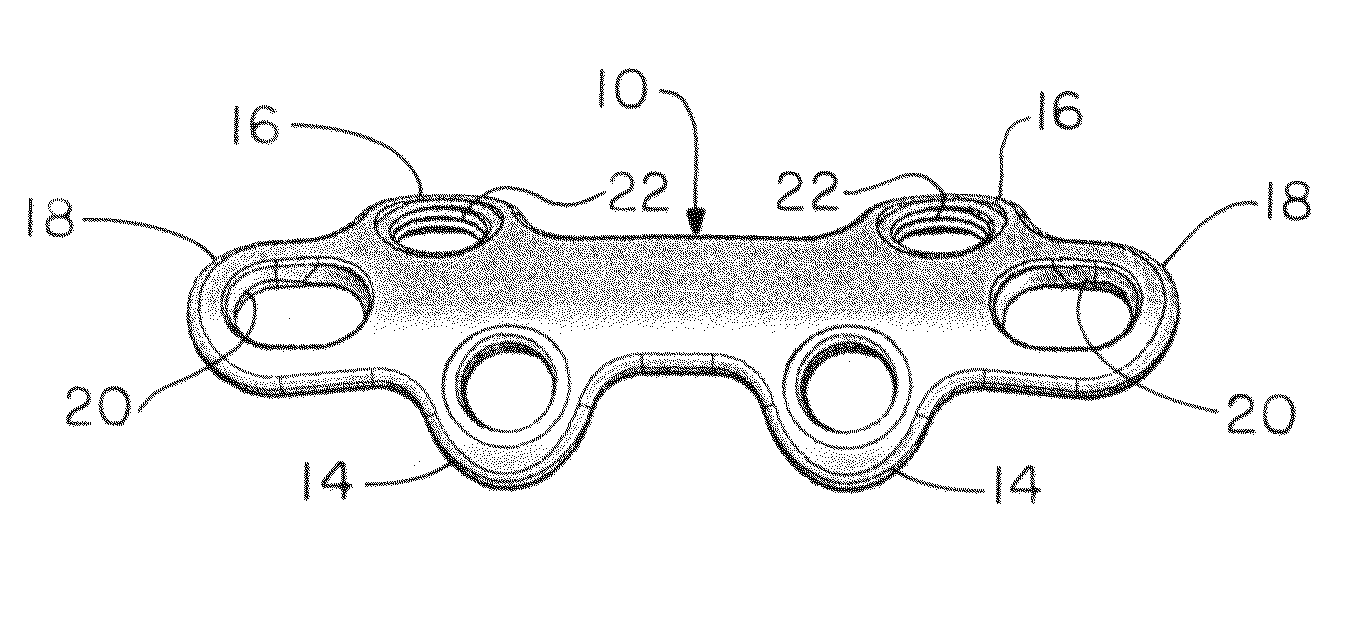
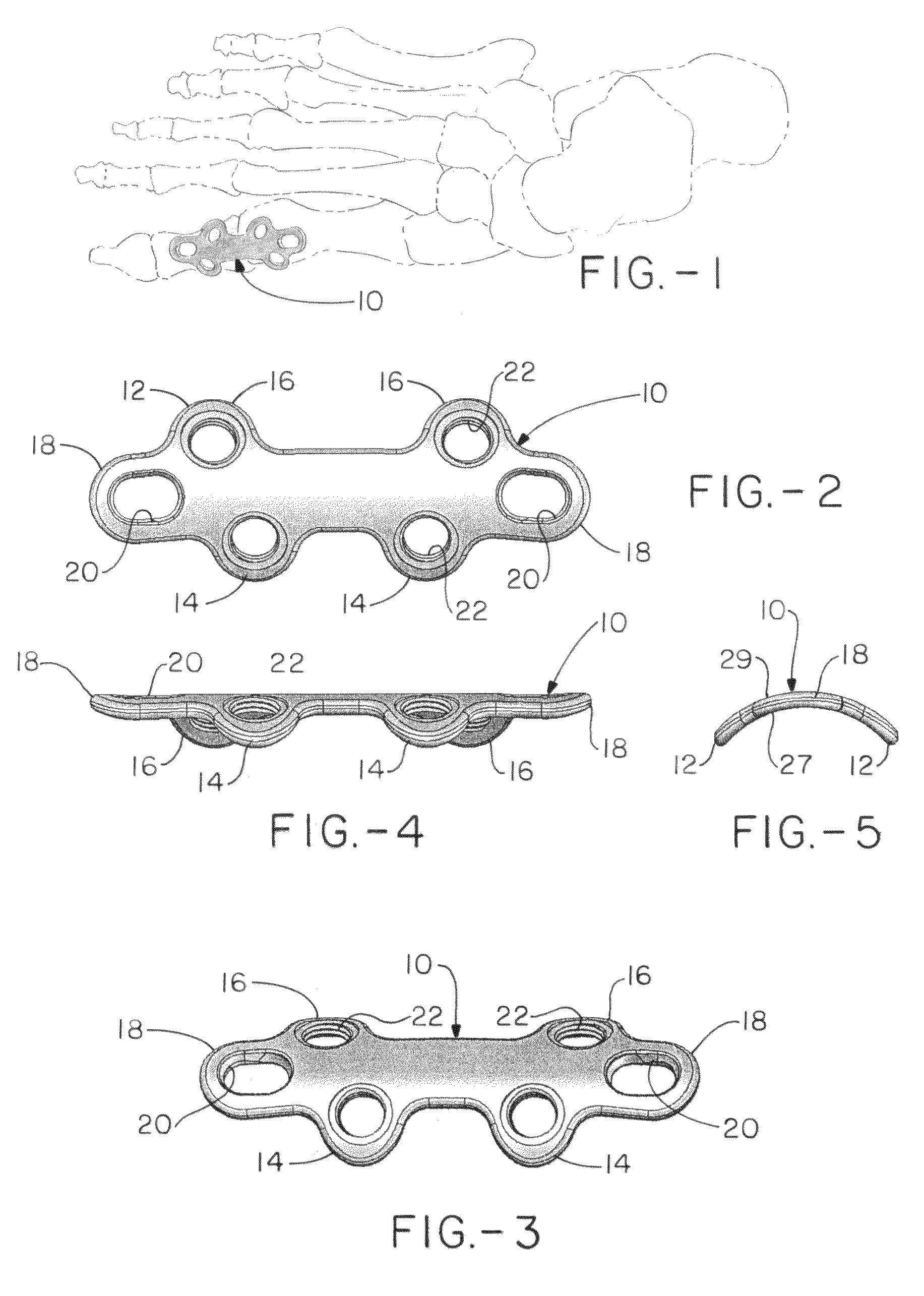
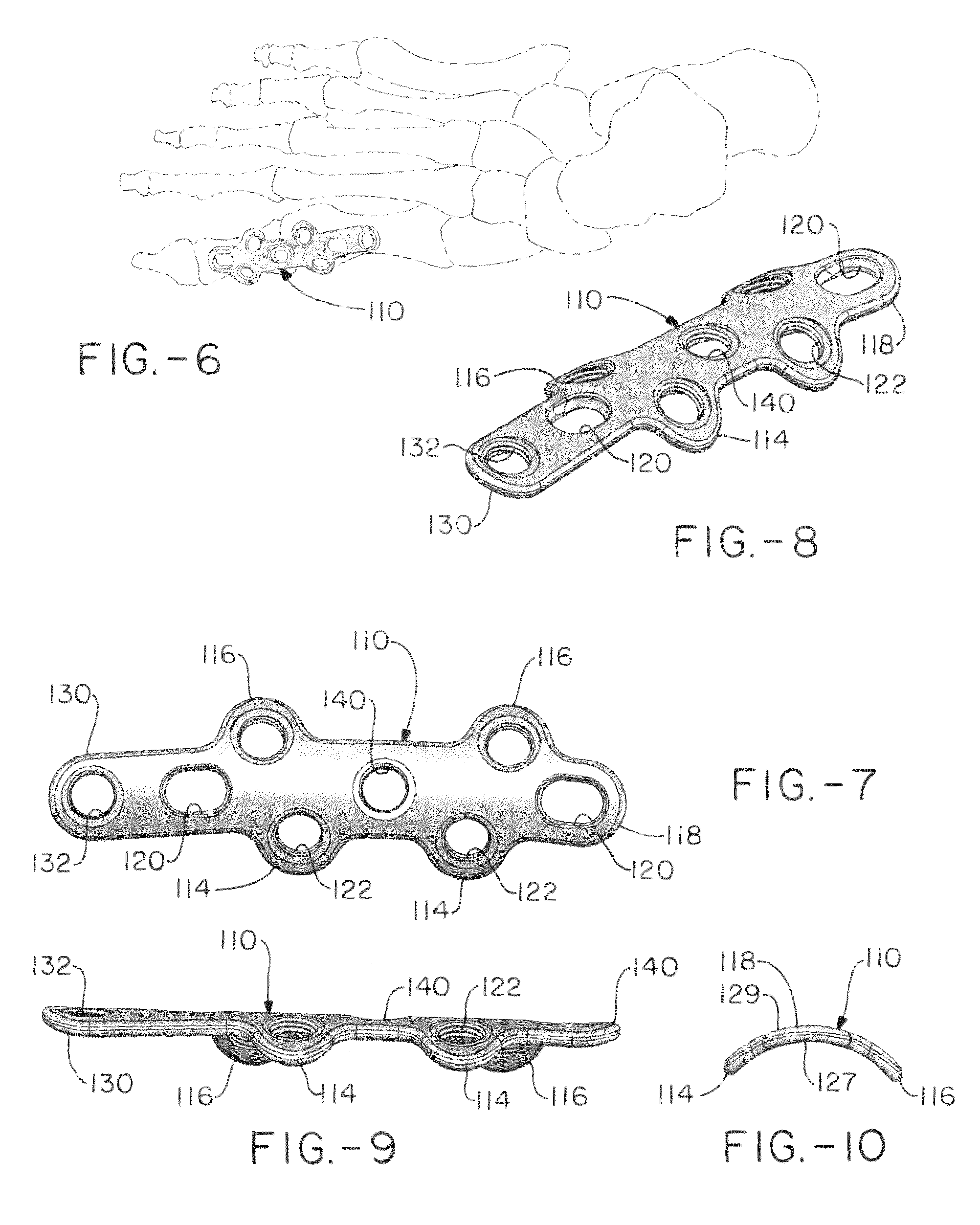
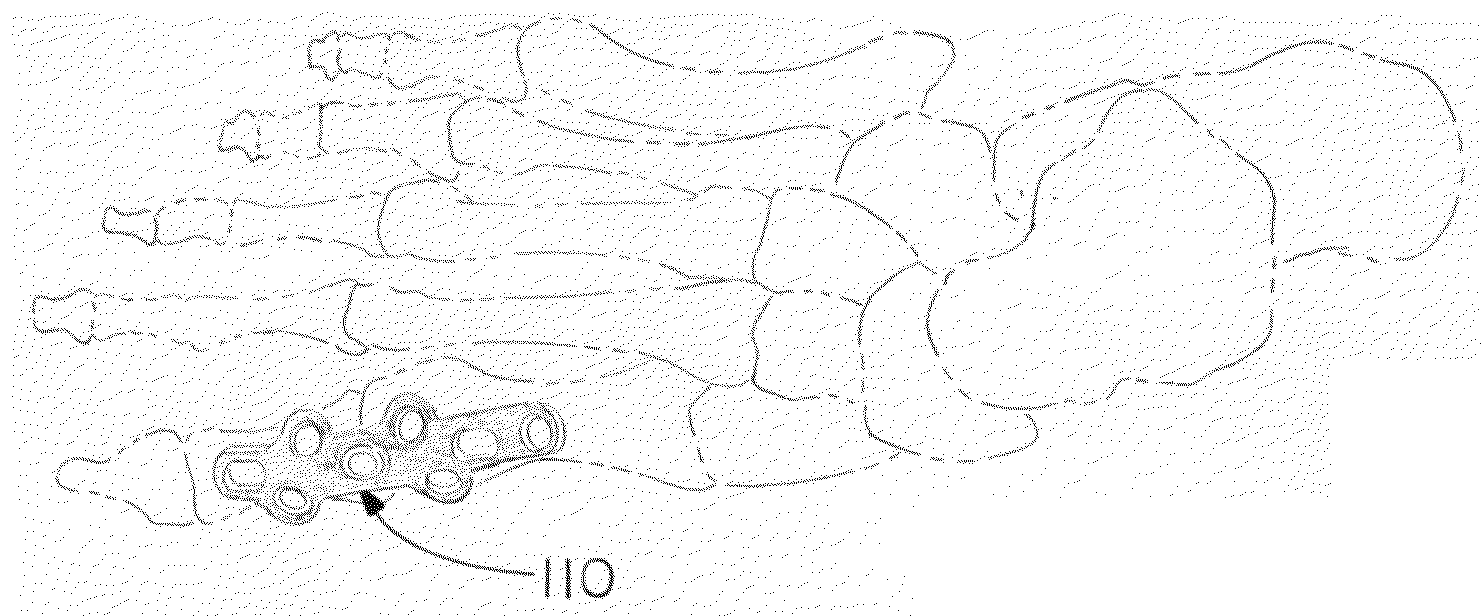
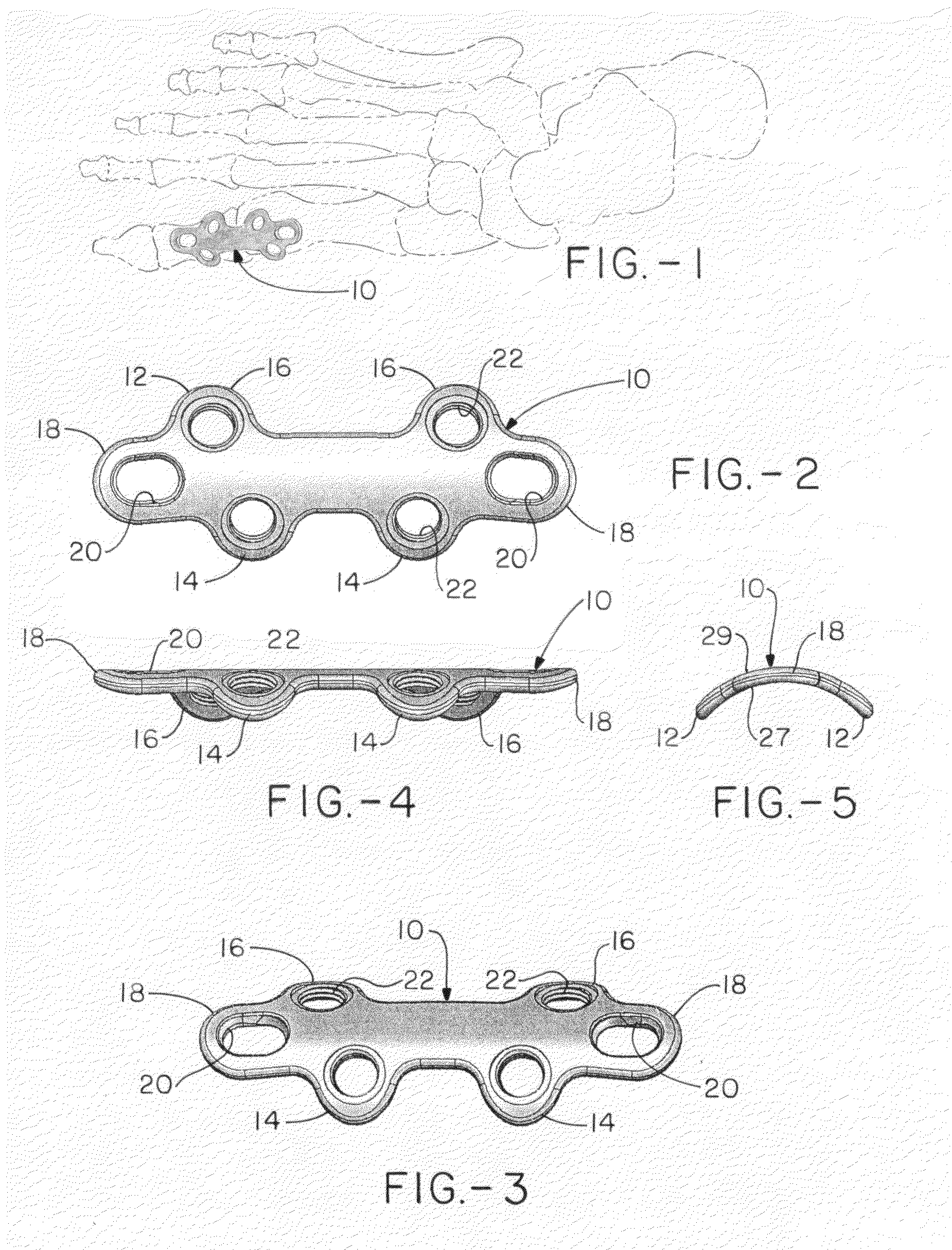
Orthopedic plate for use in the MTP joint
The present invention is a MTP plate that has a first embodiment with a profile having bilateral mirror symmetry of the about a transverse plane with an angle of about 5° for dorsiflexion and an angle of about 10° for valgus. Both ends of the plate include a central arm having a slot for compression and two offset arms having offset ears with locking screw holes that provide for multiplanar compressive fixation. The bone contacting surface of the plate is radiused to allow the plate to be in snug contact with the bone. In a second embodiment of the plate for revision surgery, the proximal end of the plate includes a metatarsal extension and the plate has a central locking hole for securing bone graft.
Owner:ORTHOHELIX SURGICAL DESIGNS
Suturing device with angled head
A suturing apparatus for the continuous application of a suture includes a suturing head shaped and dimensioned for attachment to a distal end of a support member. The suturing head includes a track shaped and dimensioned for receiving a needle for movement about the track. A support arm includes first and second lateral arms connected by a central connecting member supporting the track. The support arm includes a longitudinal axis and the track lies in a transverse plane. Angular orientation of the support arm relative to the track is achieved by positioning the transverse plane of the track at an oblique angle relative to the longitudinal axis of the support arm such that operators are provided with improved access to the surgical site. A drive assembly is coupled to the needle for controlled movement about the track.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
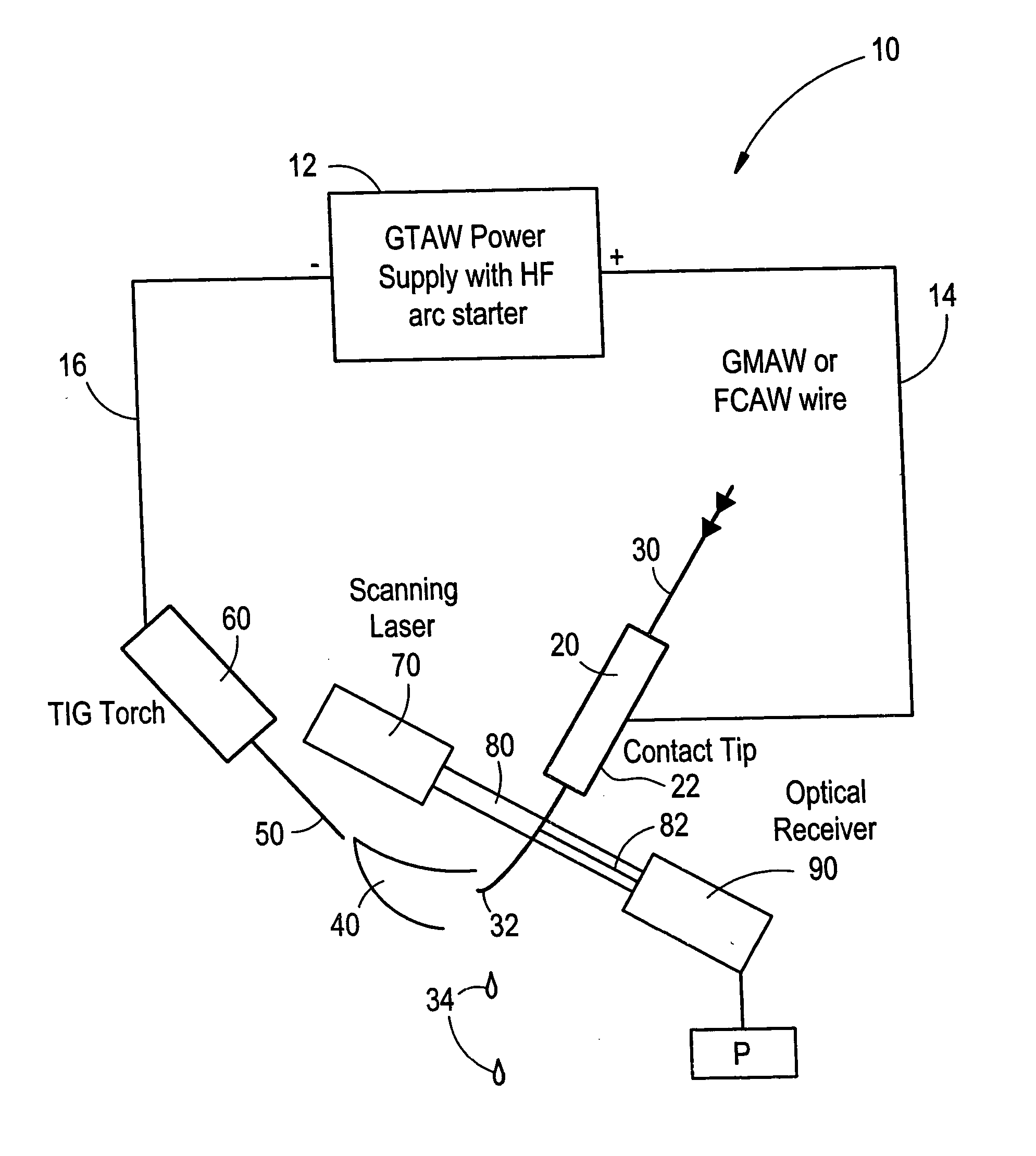
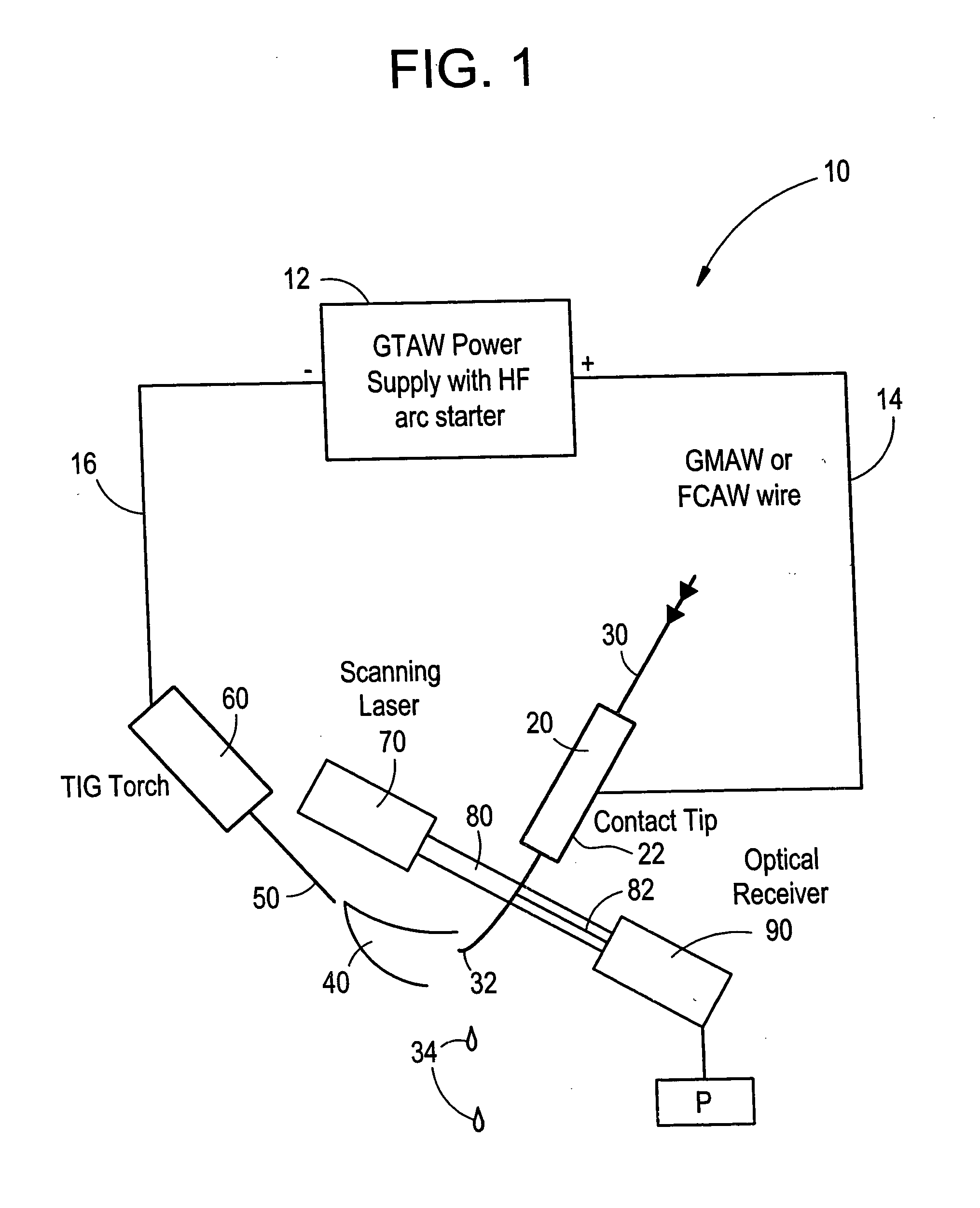
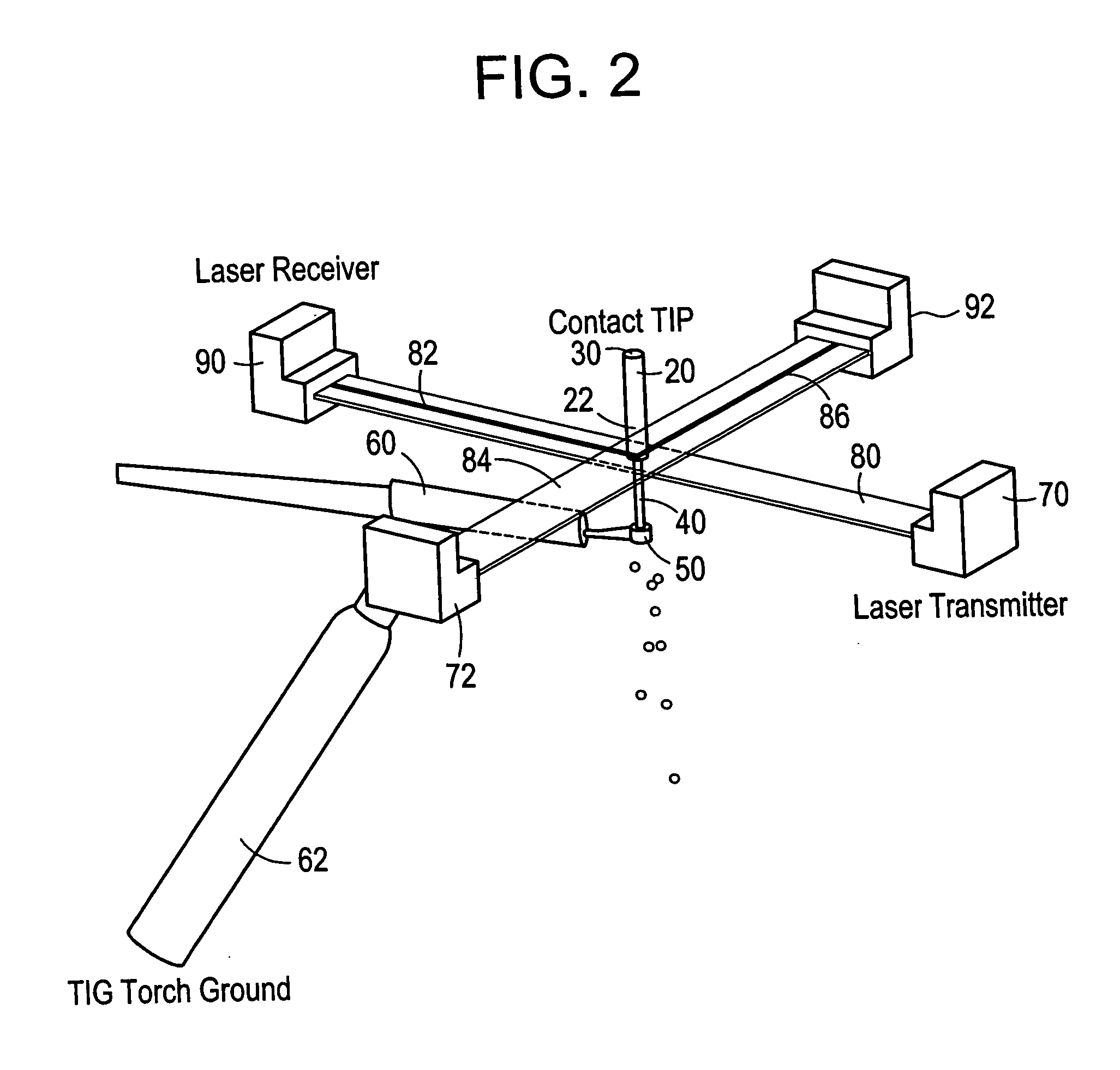
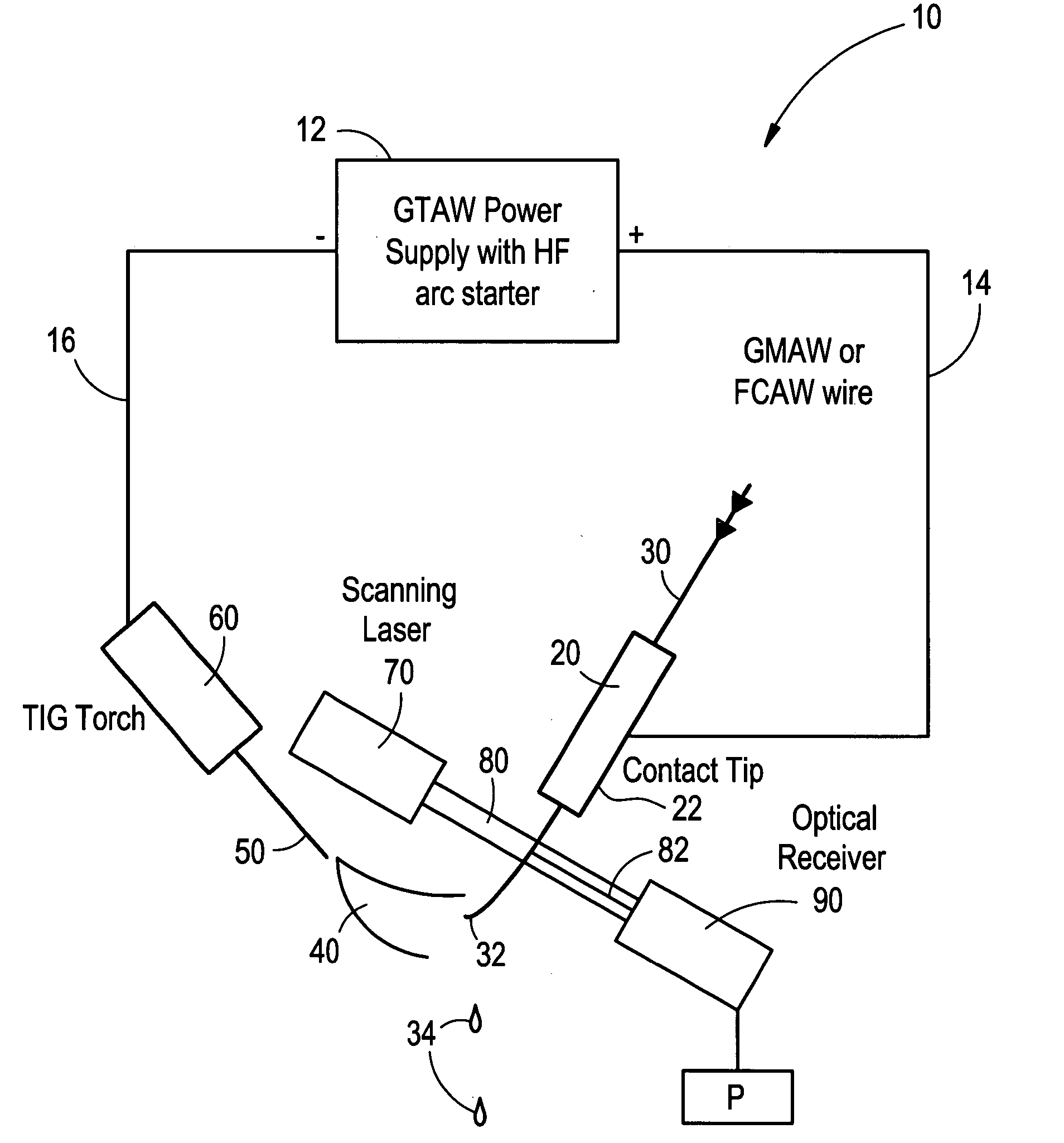
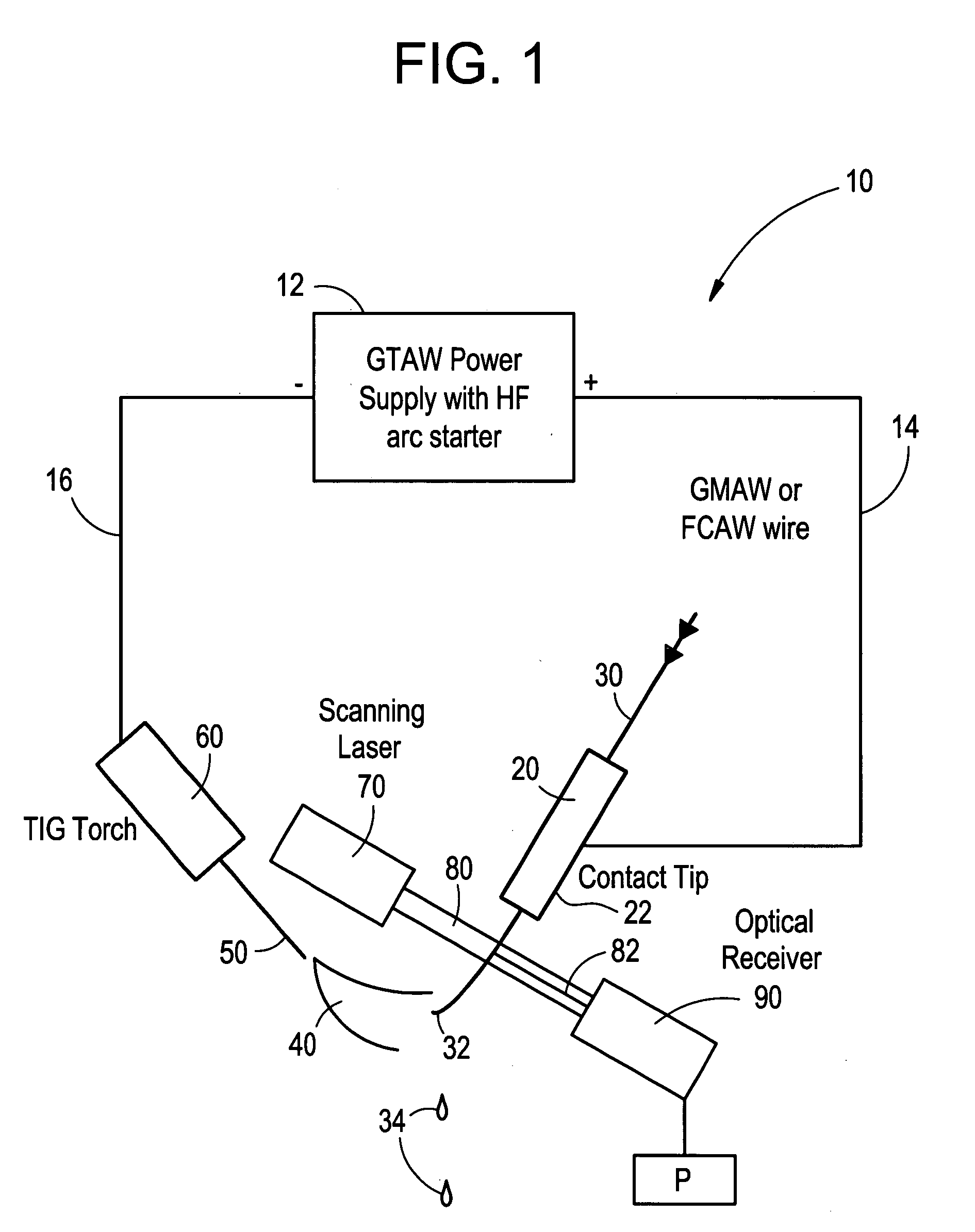
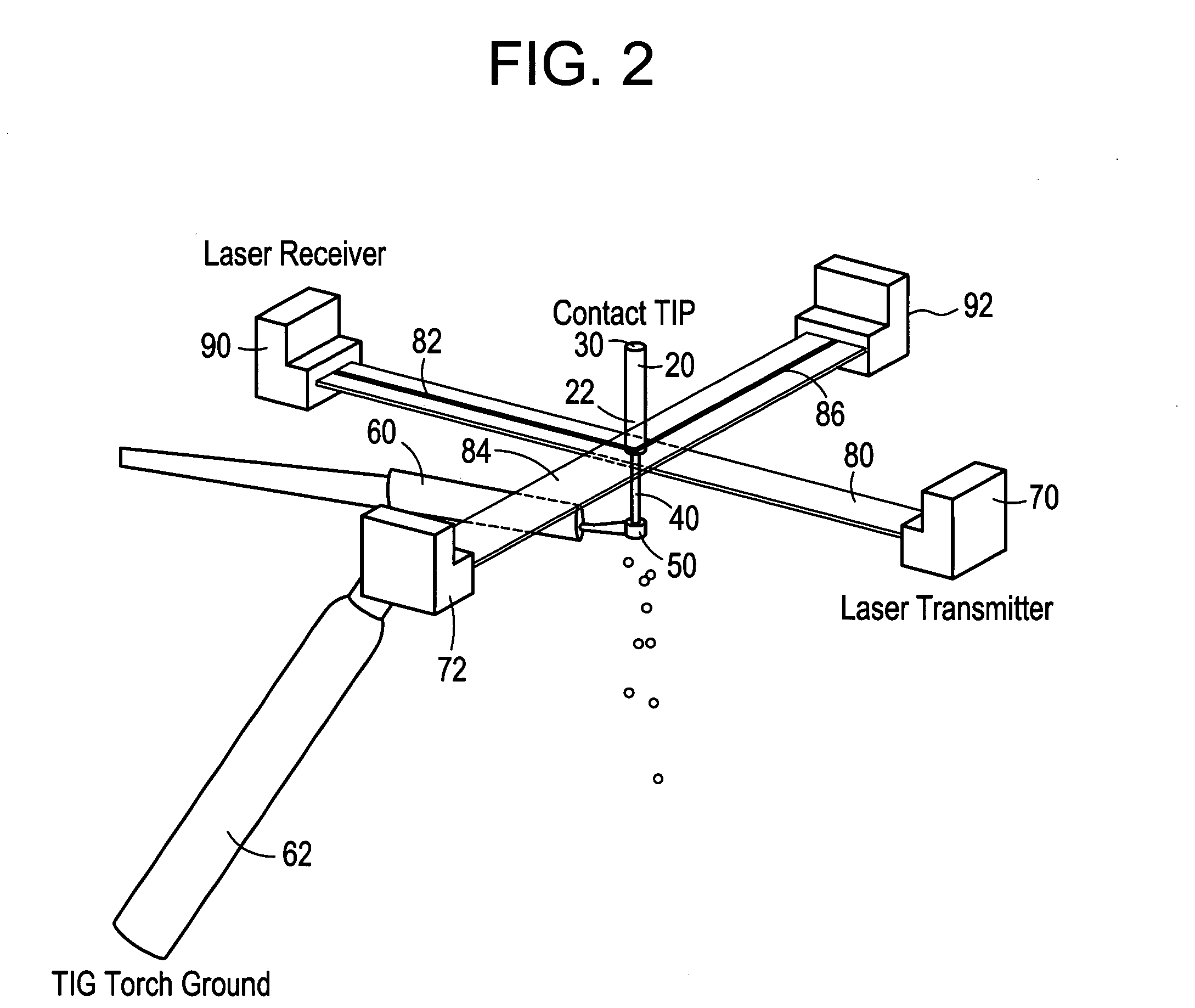
Welding wire positioning system
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
Welding wire positioning system
InactiveUS20050006363A1Minimize wire movementMinimize impactConveyorsArc welding apparatusTransverse planeEngineering
An electrode position detection system for a welder having a laser that is projected in a lateral plane to laterally cross a welding wire at a location below a contact tip of a welding gun and a receiver that receive the laser bean after crossing the welding wire, and a measuring device that determines one or more parameter of the welding wire based on the received laser beam. Arc voltage measurements can also be used to determine one or more parameter of the welding wire.
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
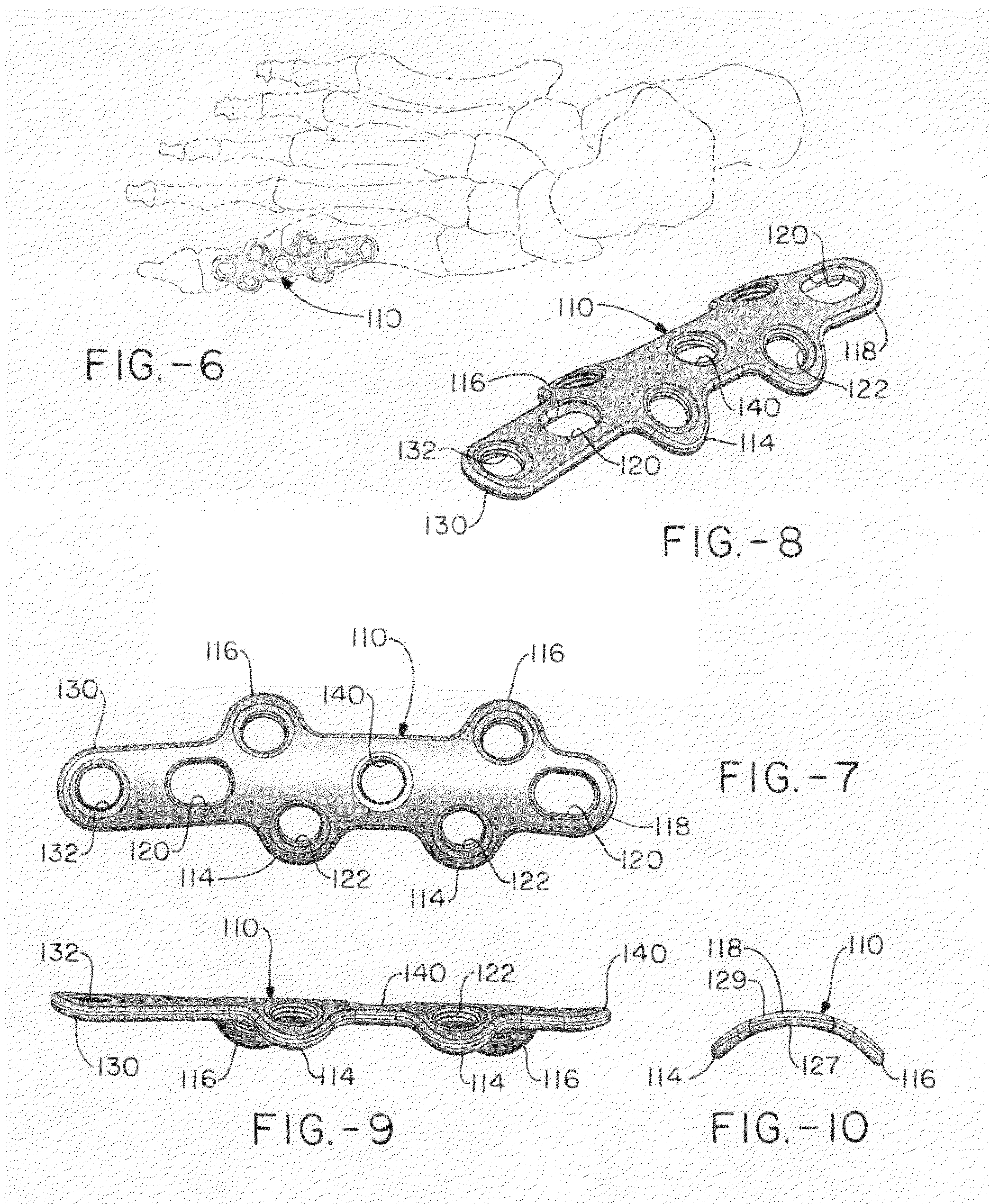
Orthopedic plate for use in the MTP joint
The present invention is a MTP plate that has a first embodiment with a profile having bilateral mirror symmetry of the about a transverse plane with an angle of about 5° for dorsiflexion and an angle of about 10° for valgus. Both ends of the plate include a central arm having a slot for compression and two offset arms having offset ears with locking screw holes that provide for multiplanar compressive fixation. The bone contacting surface of the plate is radiused to allow the plate to be in snug contact with the bone. In a second embodiment of the plate for revision surgery, the proximal end of the plate includes a metatarsal extension and the plate has a central locking hole for securing bone graft.
Owner:ORTHOHELIX SURGICAL DESIGNS
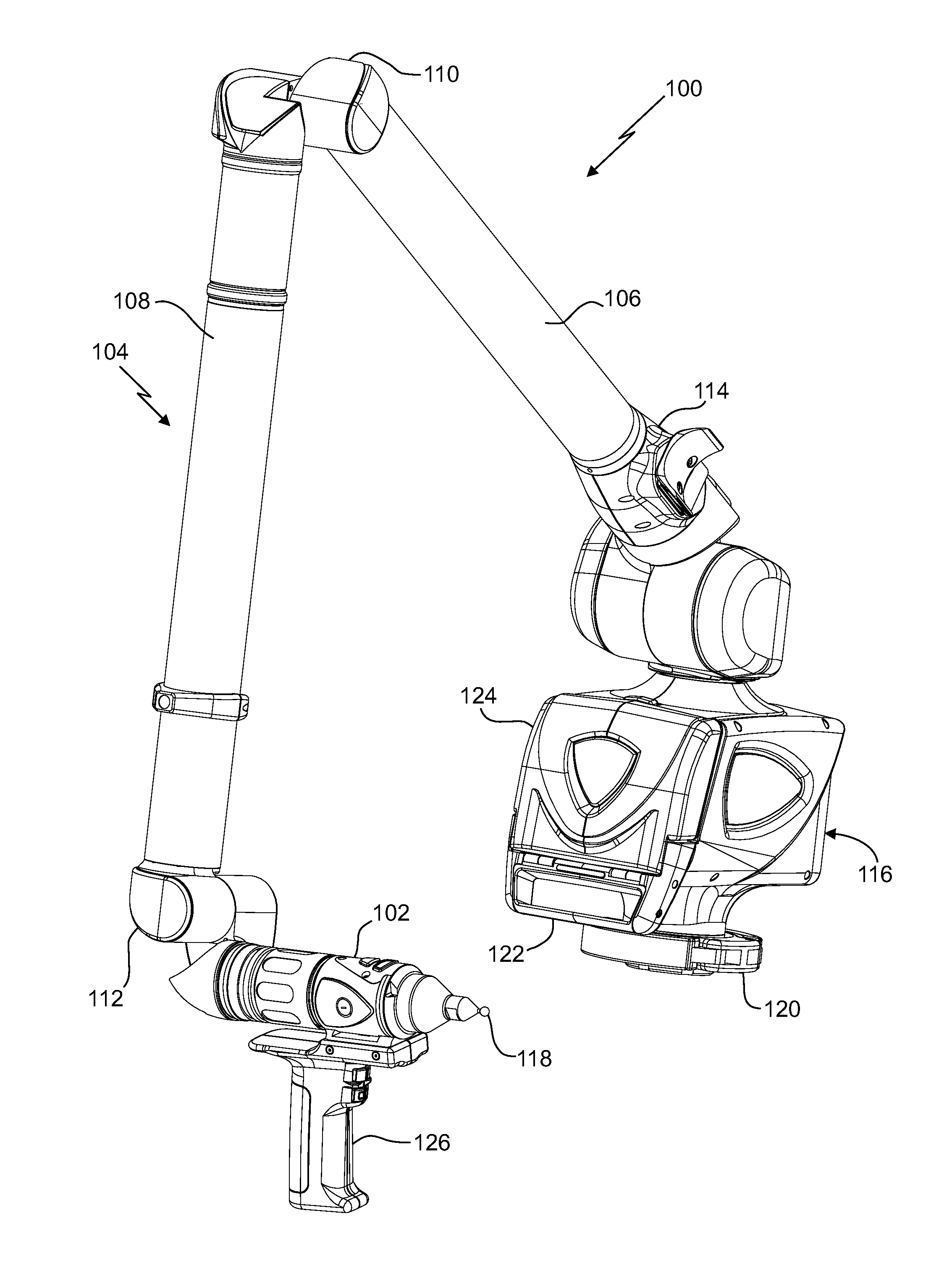
Embedded arm strain sensors
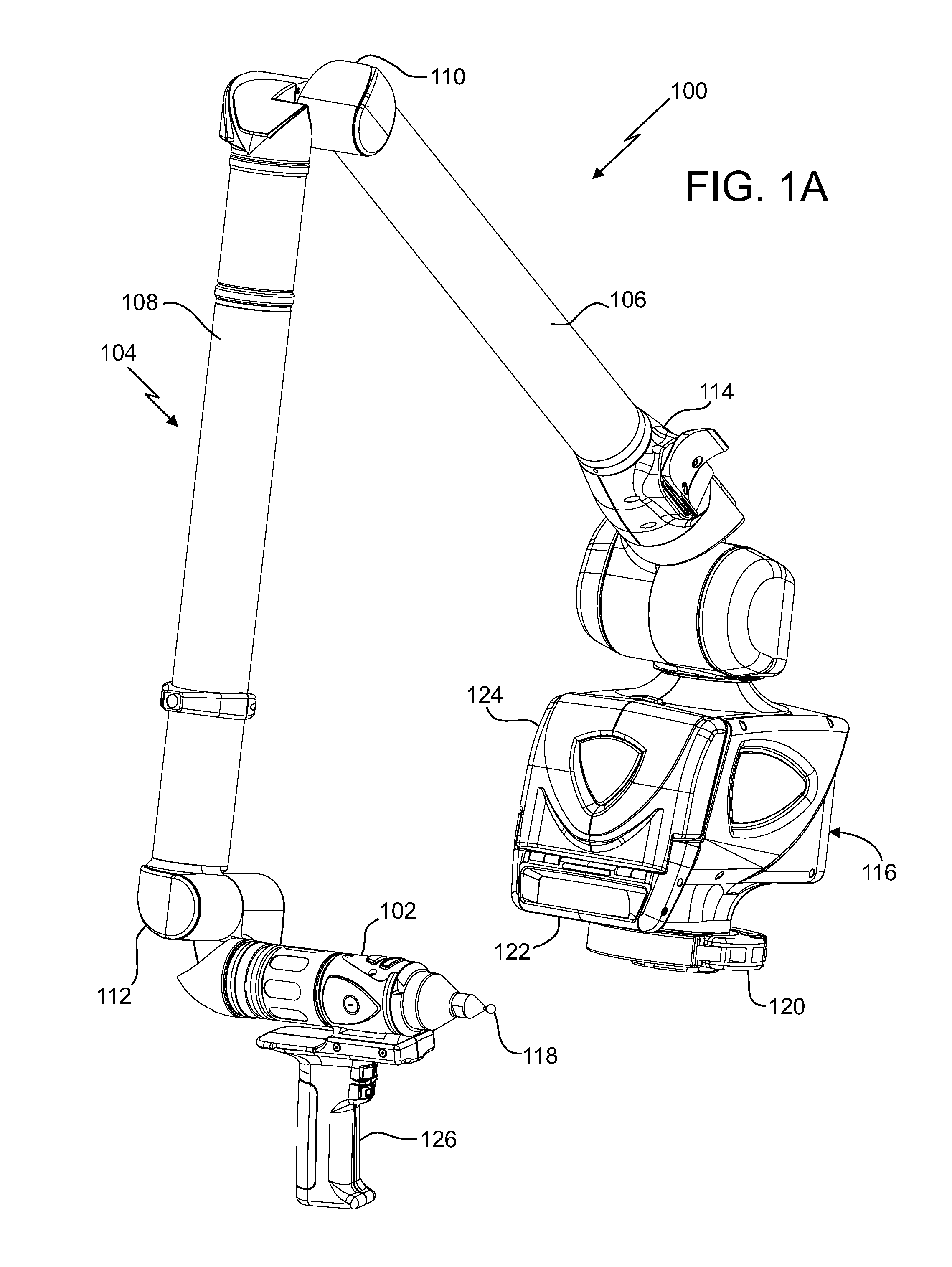
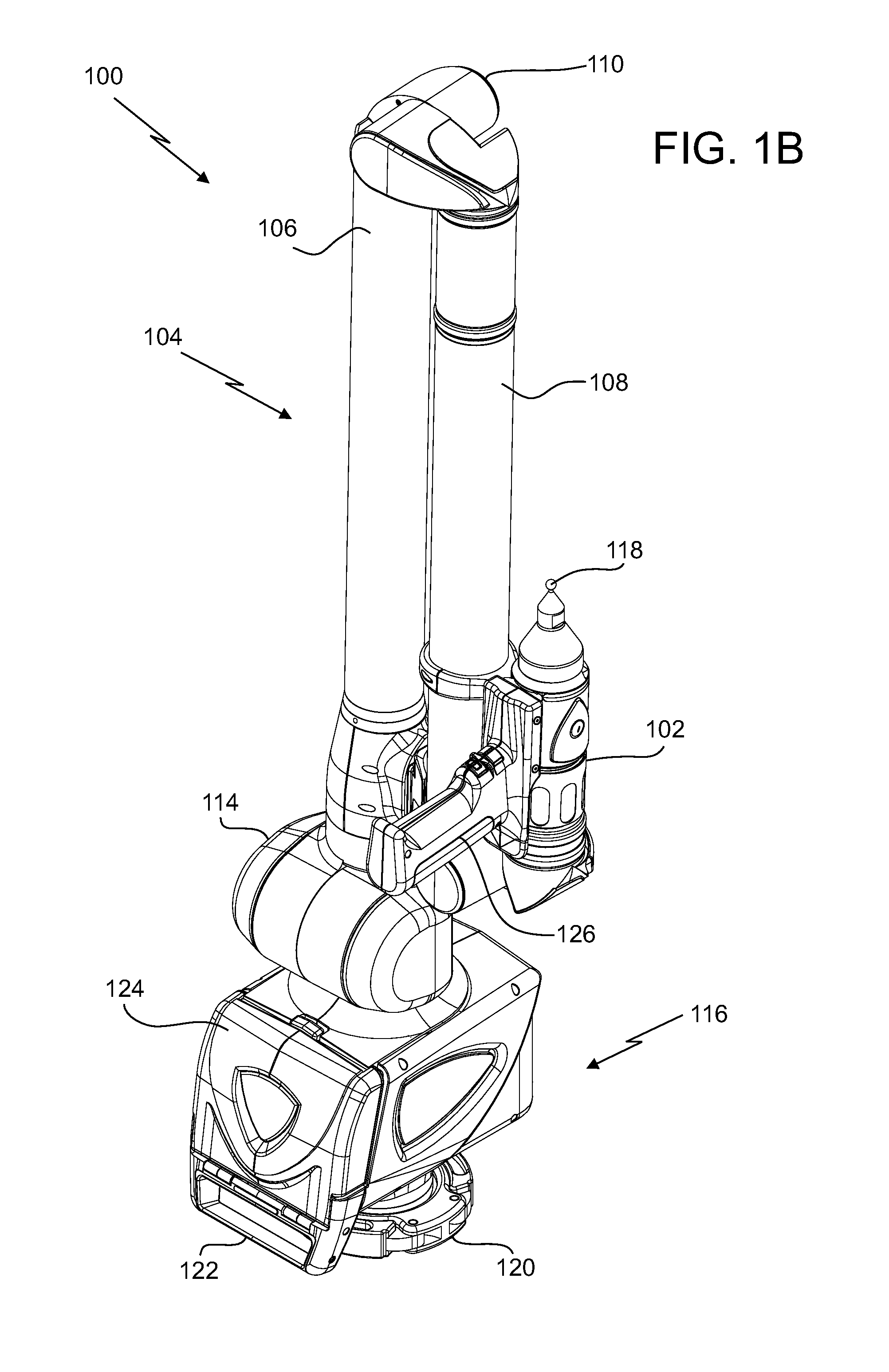
InactiveUS20110175745A1Programme controlTesting/monitoring control systemsMeasurement deviceTransverse plane
A portable articulated arm coordinate measurement machine (AACMM) can include a manually positionable articulated arm portion, a measurement device attached to the first end, a structural component of the AACMM, wherein the structural component has an axial direction, at least three strain gage sensors, each having a sensitive axis, coupled to the structural component, wherein the sensitive axis of each strain gage sensor is oriented approximately parallel to the axial direction, each strain gage sensor is approximately intersected by a transverse plane perpendicular to the axial direction, each strain gage sensor produces an analog strain gage signal, and the strain gage sensors are disposed to provide data sufficient to determine a bending strain at any point residing on both the structural component and the transverse plane and an electronic circuit that receives the position signal and provides data corresponding to a position of the measurement device.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
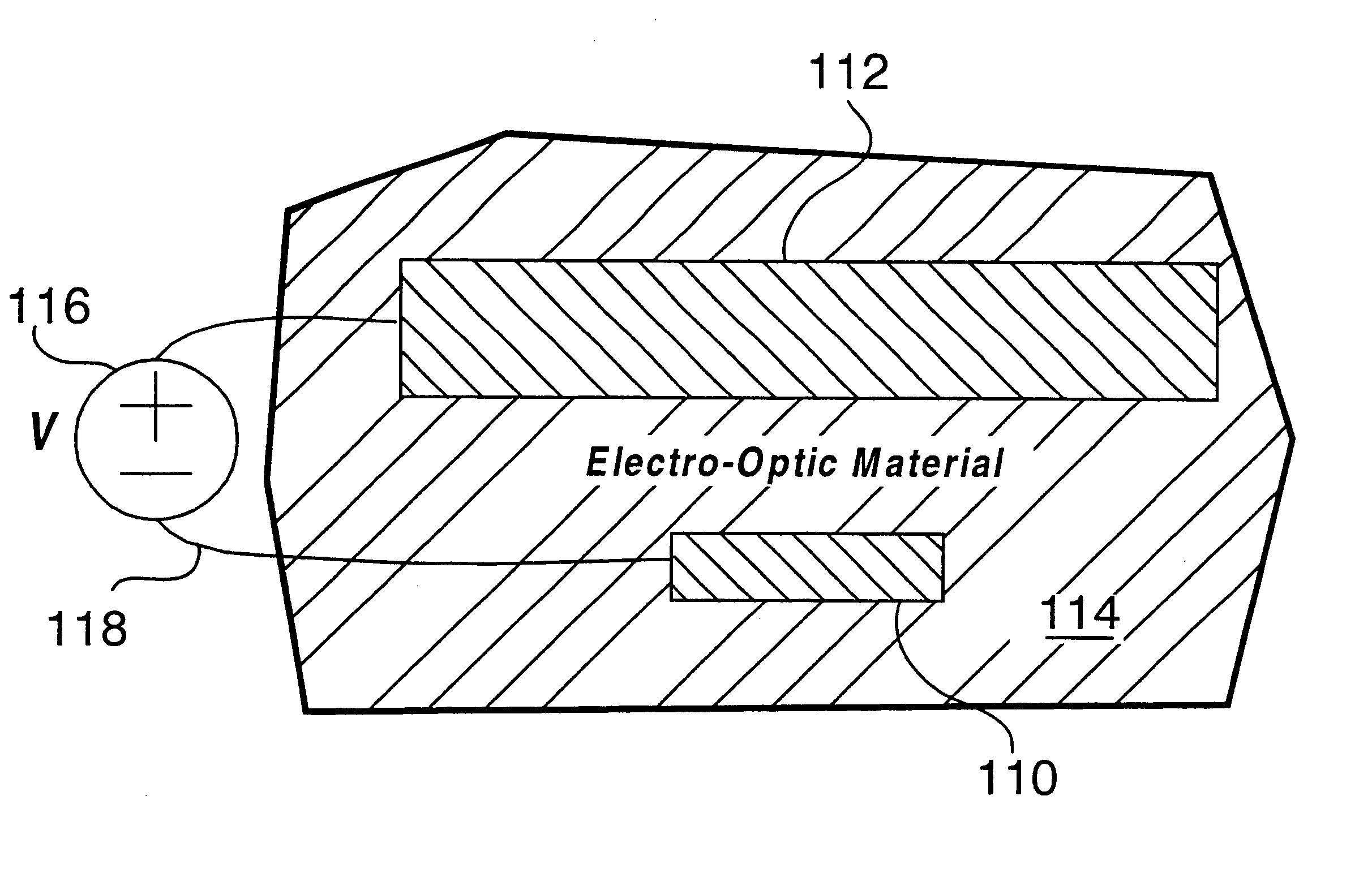
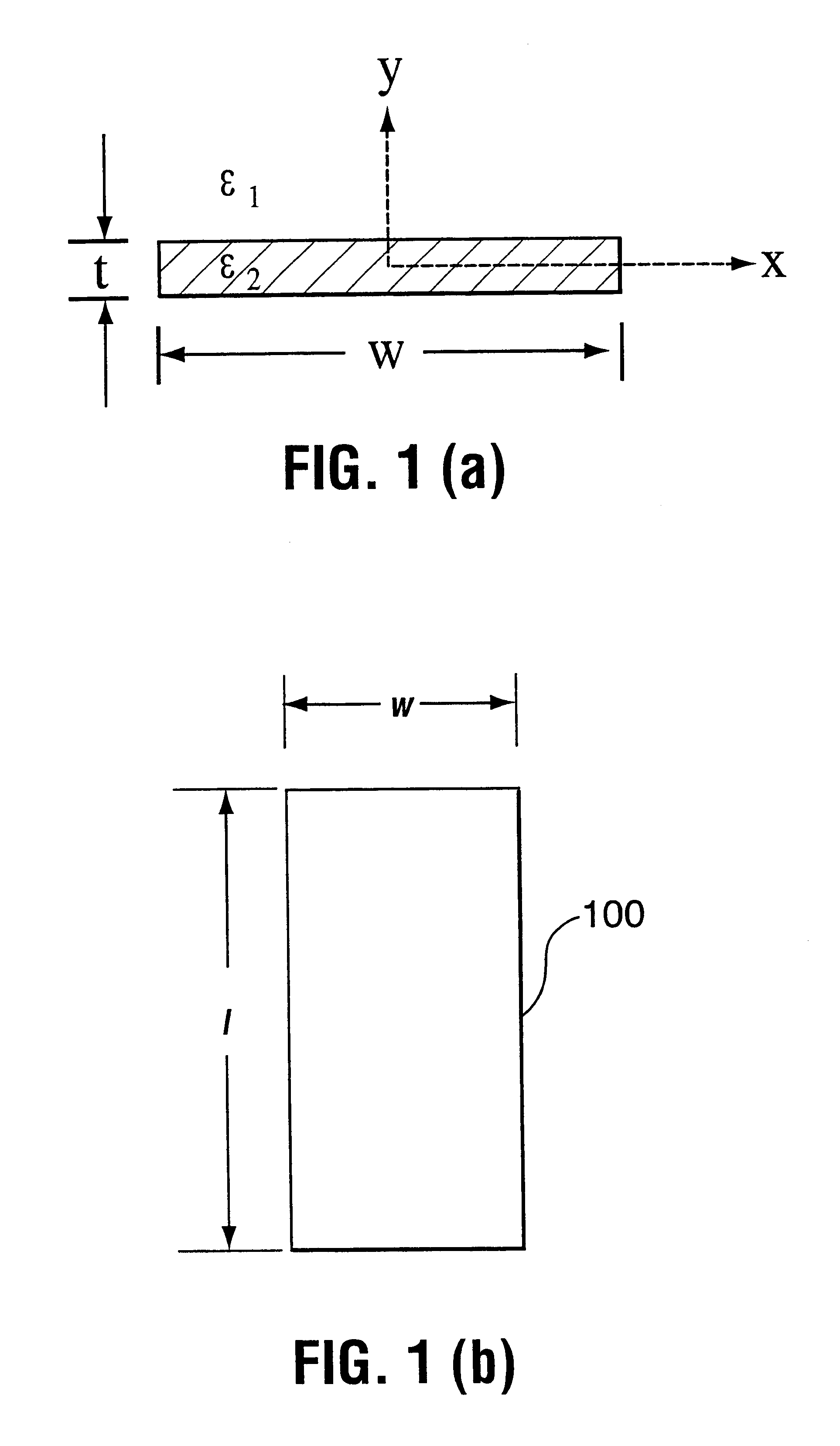
Optical waveguide structures
InactiveUS6614960B2Optical resonator shape and constructionRecord information storageUltrasound attenuationElectricity
Waveguide structures comprising a thin lossy metal film of finite width embedded in an infinite homogeneous dielectric support purely bound electromagnetic modes of propagation low mode power attenuation in the neighbourhood of 10 to 0.1 dB / cm is achievable at optical communications wavelengths, with even lower values being possible. Carefully selecting the film's thickness and width can make this mode the only long-ranging one supported. In addition, the mode can have a field distribution that renders it excitable using an end-fire approach. The finite-width metal film waveguide may be used for applications requiring short propagation distances and 2-D field confinement in the transverse plane, enabling various devices to be constructed, such as couplers, splitters, modulators, interferometers, switches and periodic structures. Under certain conditions, an asymmetric structure can support a long-ranging mode having a field distribution that is suitable to excitation using an end-fire technique.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA
Multi-angled duckbill seal assembly
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
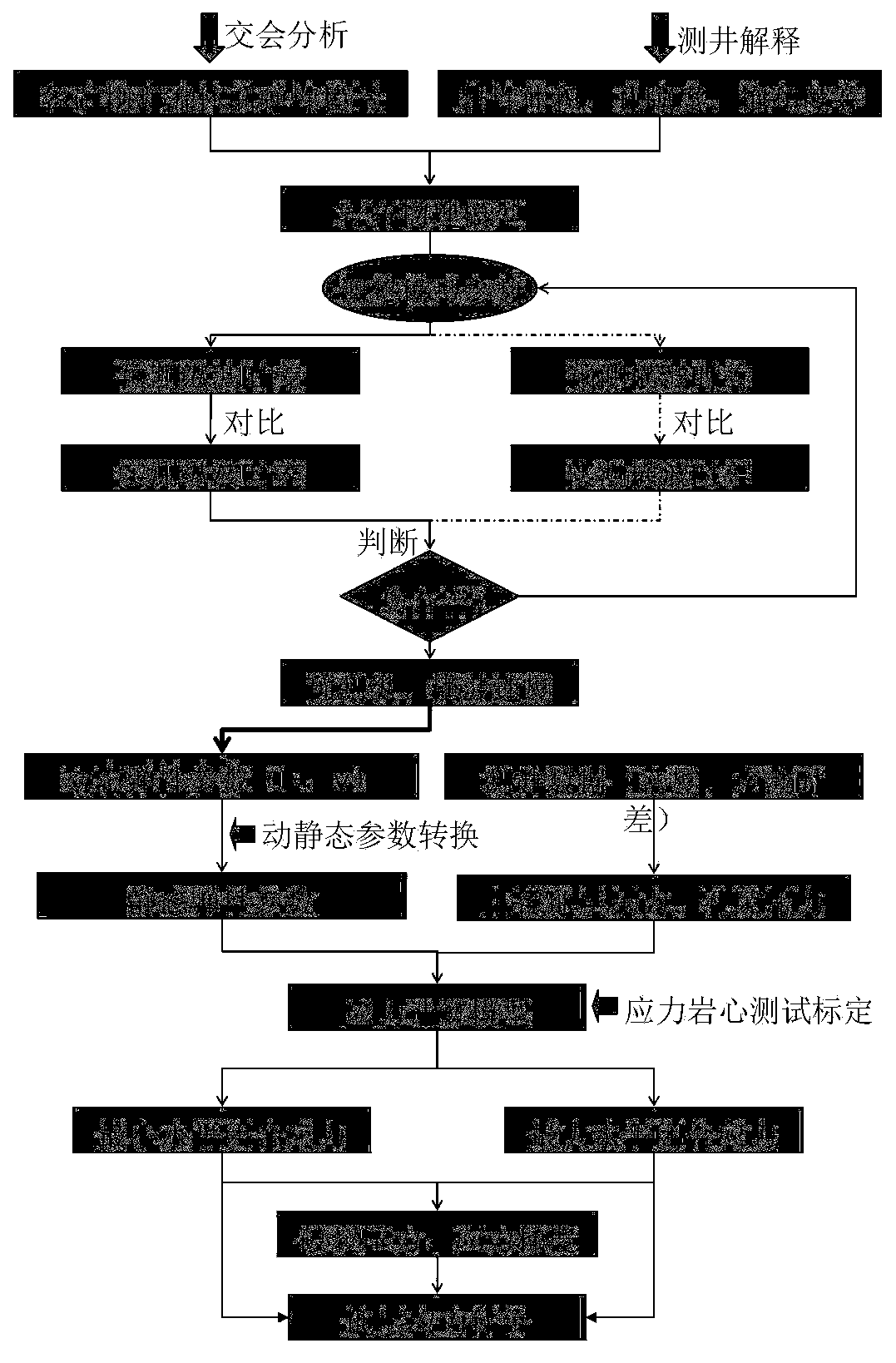
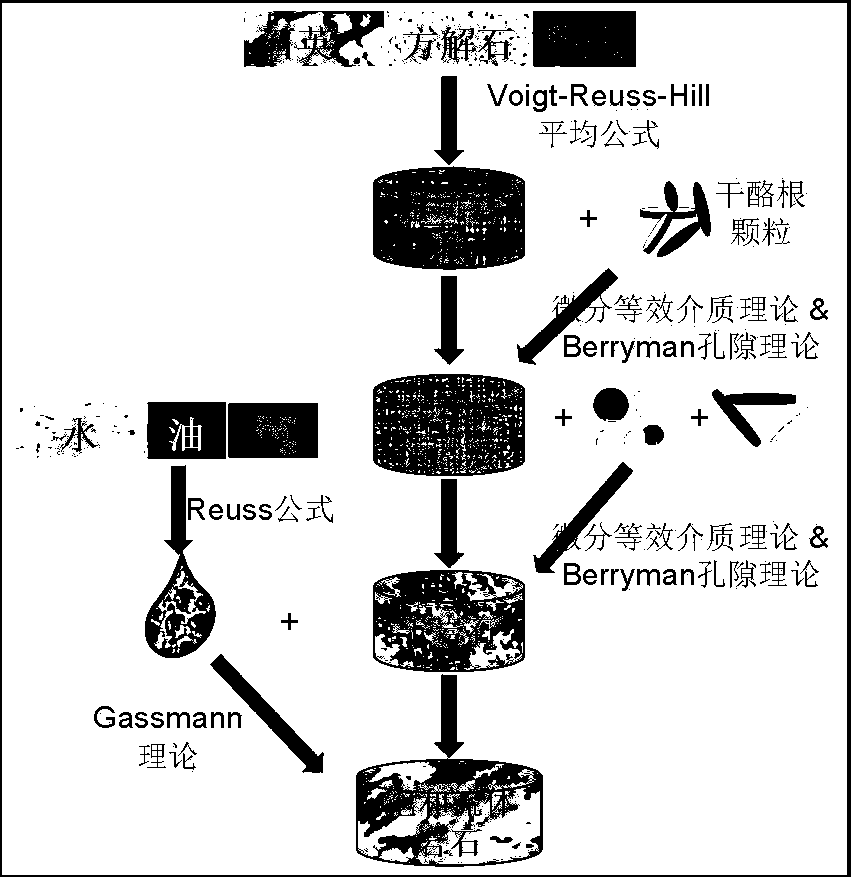
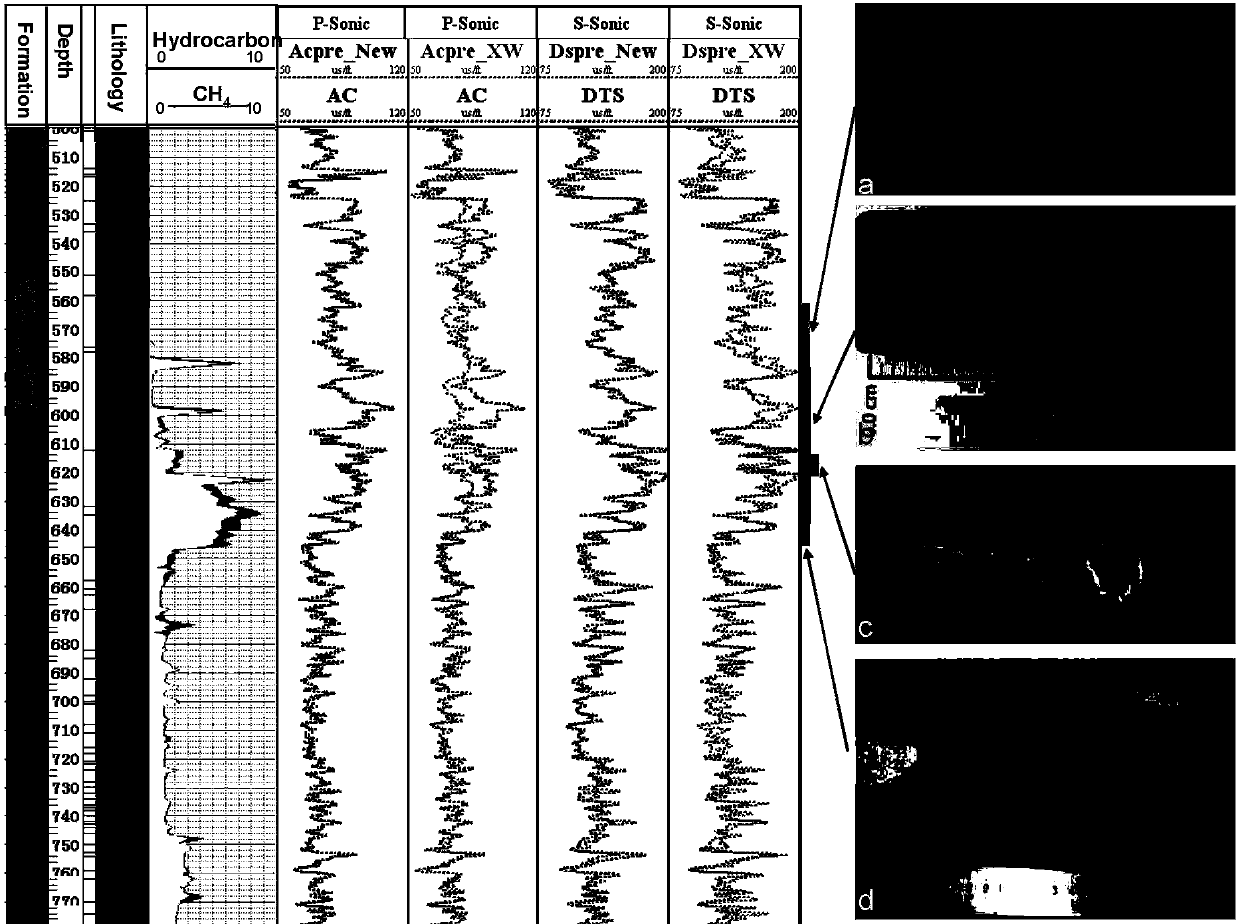
Shale gas reservoir crustal stress logging prediction method based on rock physics model
The present invention relates to a shale gas reservoir crustal stress logging prediction method based on a rock physics model. According to the method, a shale gas reservoir rock physics model which takes kerogen particles into consideration is established, so as to predict a longitudinal and transverse wave velocity of the logging; based on the above, a maximum and minimum horizontal principal stress and a fracture pressure of the reservoir are calculated; and an accurate stress assessment of a shale gas reservoir is carried out while a transverse wave logging is not provided. The beneficial effects of the invention are that: the rock physics model in line with characteristics of the shale gas reservoir is established to improve precision of the prediction velocity; and based on the rock physical model, the maximum and minimum horizontal principal stress and the fracture pressure are obtained, so that while the measured transverse wave logging data are not provided, the underground stress can be predicted on the basis of a conventional logging curve, and the prediction result is high in accuracy.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Total wrist prosthesis
InactiveUS20070225820A1Reduce chanceReliable connectorWrist jointsAnkle jointsTransverse planeLigament structure
Total wrist prosthesis comprising a radial component with a stem for fixation into the radius, a carpal component with one or more stems for fixation into the capitate and an intermediate bearing component which articulates with the radial component and allows rotational movement of the carpal component relative to the radial component plus hinged movement in two transverse planes. The radial component body may have a concave or convex surface to articulate with a matching surface on the intermediate bearing component. The carpal body may have a projection which is received in a recess in a base surface of the intermediate bearing component, and which has a pair of lugs that are received in an annular groove in the recess for an axially secure connection that allows small relative rotational movement as permitted by tendons and ligaments of the wrist.
Owner:ASCENSION ORTHOPEDICS
Adhesive Wafer
An adhesive wafer for an ostomy faceplate or wound dressing comprising a backing layer, said backing layer having one surface facing the skin, said surface comprising a first and a second adhesive zone being separated from each others by a void volume, said void volume being defined by the backing layer, the first and the second adhesive zones and the skin surface and wherein the first and the second adhesive zones are capable of moving independently of each others with respect to the lateral plane of the backing layer.
Owner:COLOPLAST AS
Solids strainer system for a hydraulic choke
InactiveUS20050006150A1Improve liquidityDrilling rodsValve members for absorbing fluid energyTransverse planeEngineering
The invention contemplates a strainer based upon a four-way, two-position rotary cylindrical plug valve having a hollow plug. The normal entry port for the sealing plug of the plug valve is a circular radial hole passing from the exterior of the plug into the interior cavity of the plug. The normal exit port for the sealing plug is a regular array of small holes across from and coaxial with the normal entry hole. The ports for the valve body are in two pairs positioned at 90° from each other, with the axes of the ports lying in the same transverse plane as the ports of the valve plug.
Owner:EXPRO AMERICAS
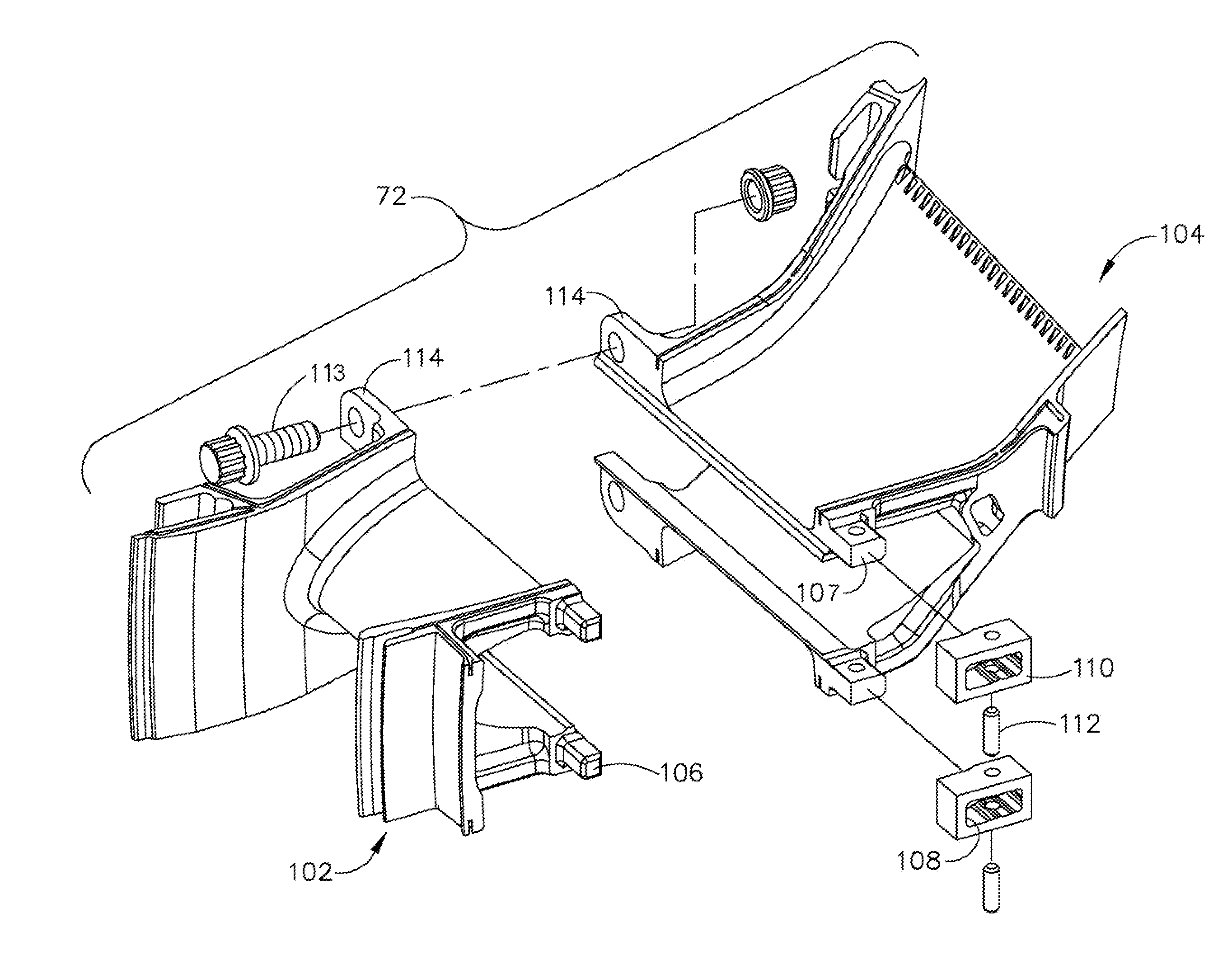
Split fairing for a gas turbine engine
A fairing for a structural strut in a gas turbine engine includes: (a) an inner band; (b) an outer band; (c) a hollow, airfoil-shaped vane extending between the inner and outer bands; (d) wherein the fairing is split along a generally transverse plane passing through the inner band, outer band and vane, so as to define a nose piece and a tail piece; and (e) complementary structures carried by the nose piece and the tail piece adapted to secure the nose piece and the tail piece to each other.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
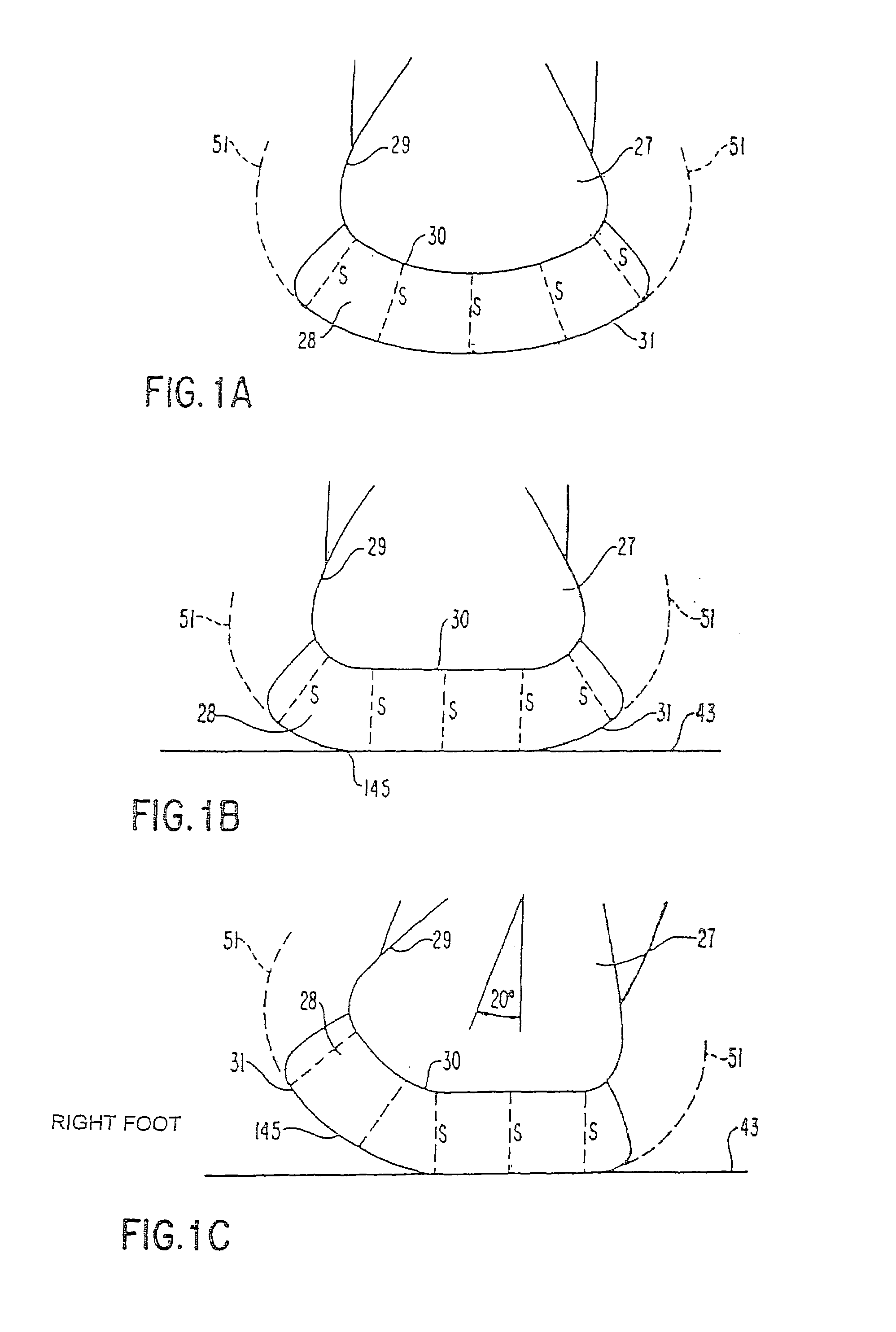
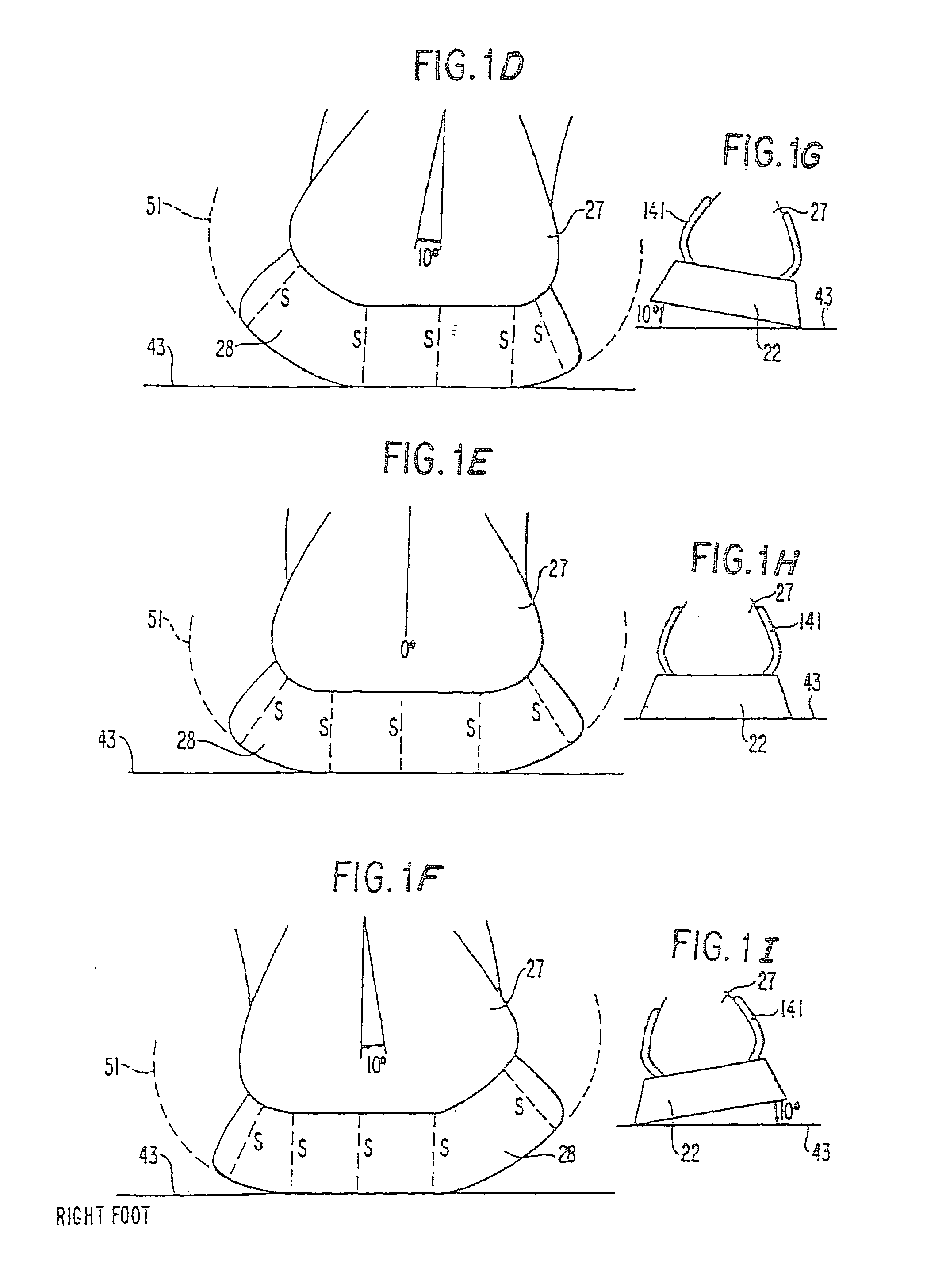
Shoes sole structures
In its simplest conceptual form, the applicant's invention is the structure of a conventional shoe sole that has been modified by having its sides bent up so that their inner surface conforms to a shape nearly identical but slightly smaller than the shape of the outer surface of the sides of the foot sole of the wearer (instead of the shoe sole sides conforming to the ground by paralleling it, as is conventional). The shoe sole sides are sufficiently flexible to bend out easily when the shoes are put on the wearer's feet and therefore the shoe soles gently hold the sides of the wearer's foot sole when on, providing the equivalent of custom fit in a mass-produced shoe sole. This invention can be applied to shoe sole structures based on a theoretically ideal stability plane as a basic concept, especially including structures exceeding that plane. The theoretically ideal stability plane is defined as the plane of the surface of the bottom of the shoe sole, wherein the shoe sole conforms to the natural shape of the wearer's foot sole, particularly its sides, and has a constant thickness in frontal or transverse plane cross sections.
Owner:ANATOMIC RES
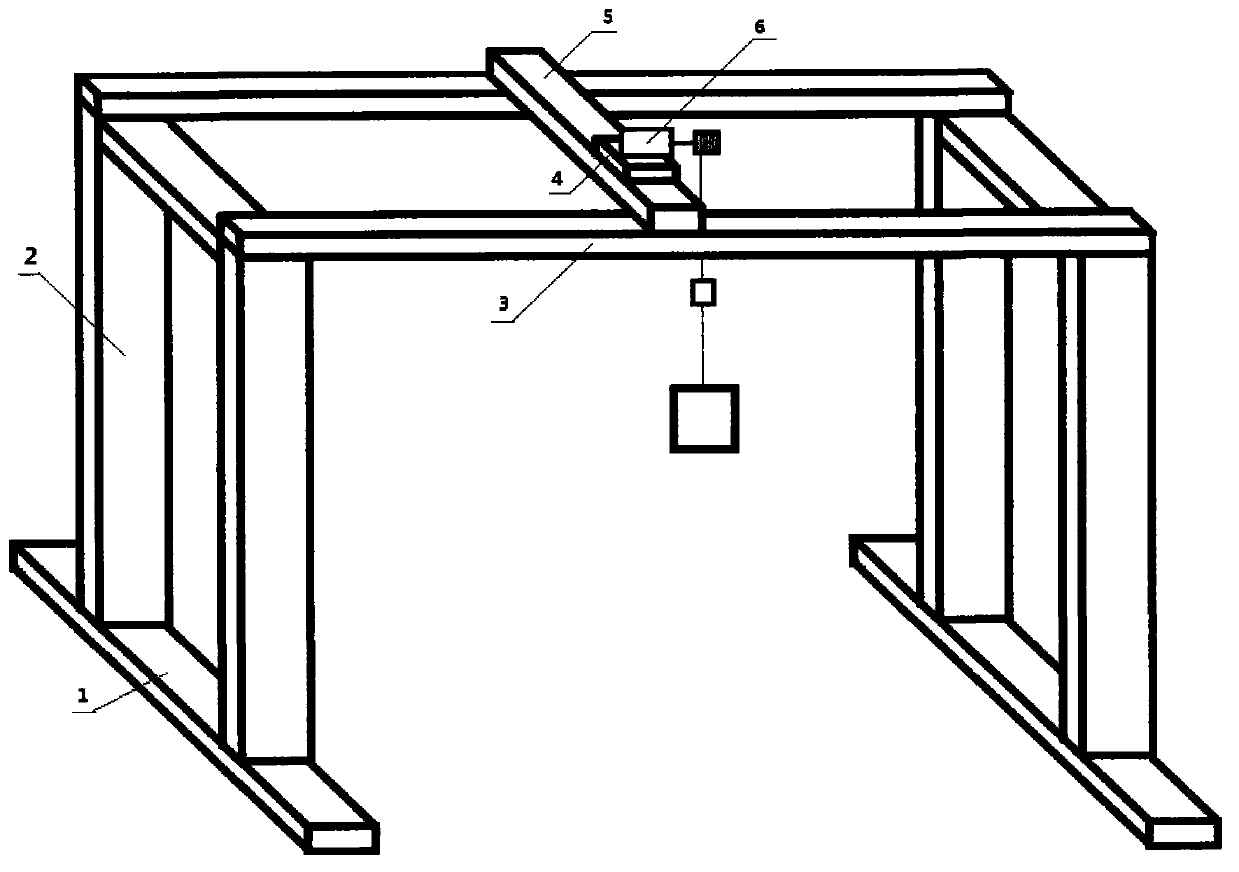
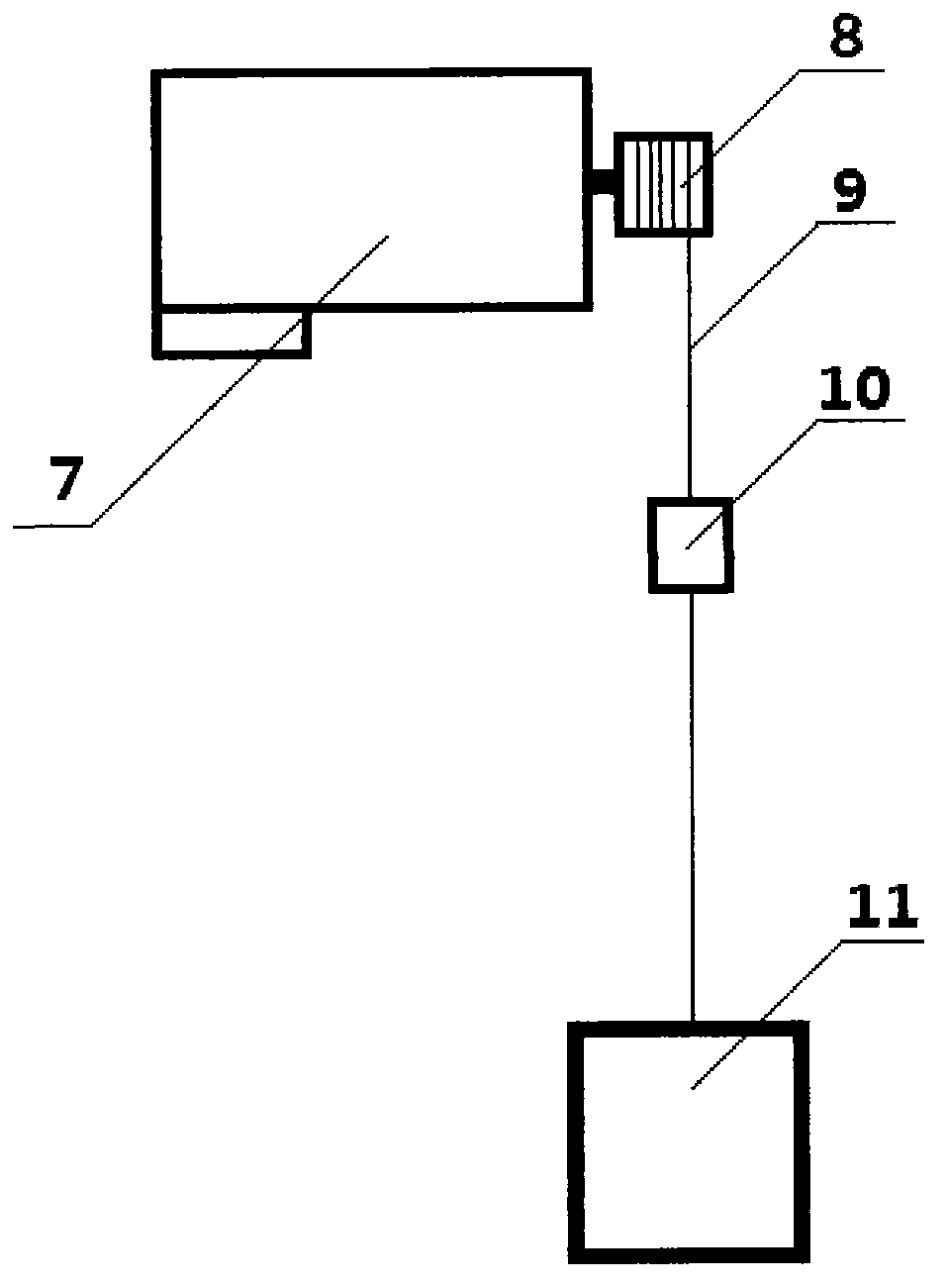
Space microgravity environment ground simulation experiment device
ActiveCN103466109ASimple structureImprove realismCosmonautic condition simulationsControl systemTransverse plane
The invention relates to a space microgravity environment ground simulation experiment device. The device comprises a foundation, two support posts, a transverse air floating guide rail, a longitudinal air floating guide rail, a slide trolley and a weightless simulation control system. Two support posts are respectively mounted on the foundation horizontally, the transverse air floating guide rail is mounted on the two support posts, the longitudinal air floating guide rail is mounted on the transverse air floating guide rail, the slide trolley is mounted on the longitudinal air floating guide rail, weightless simulation control system is mounted on the slide trolley, and a controller is mounted on the slide trolley. The weightless simulation control system comprises a servo motor, a coiling wheel, a hang spring, a force sensor and an aircraft, the servo motor is connected with the coiling wheel, the coiling wheel is connected with the hang spring, the hang spring is connected with the force sensor, the force sensor is connected with the aircraft, and the controller is respectively connected with the force sensor and the servo motor in an electrical signal manner. The device is simple in structure, high in vividness, convenient to operate, easy to achieve, low in cost, and unlimited in experiment time.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Bottle made of plastic material having a gripping portion
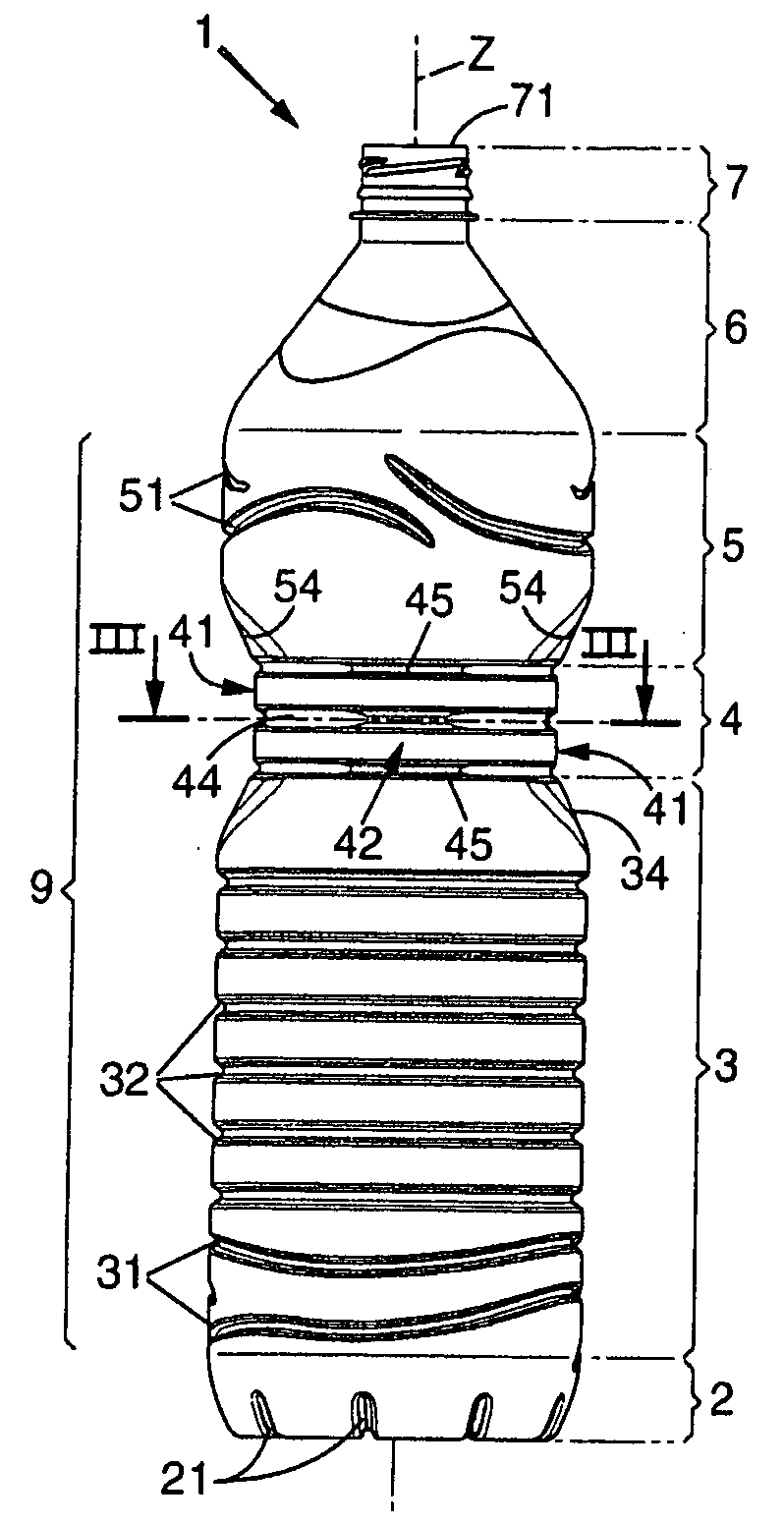
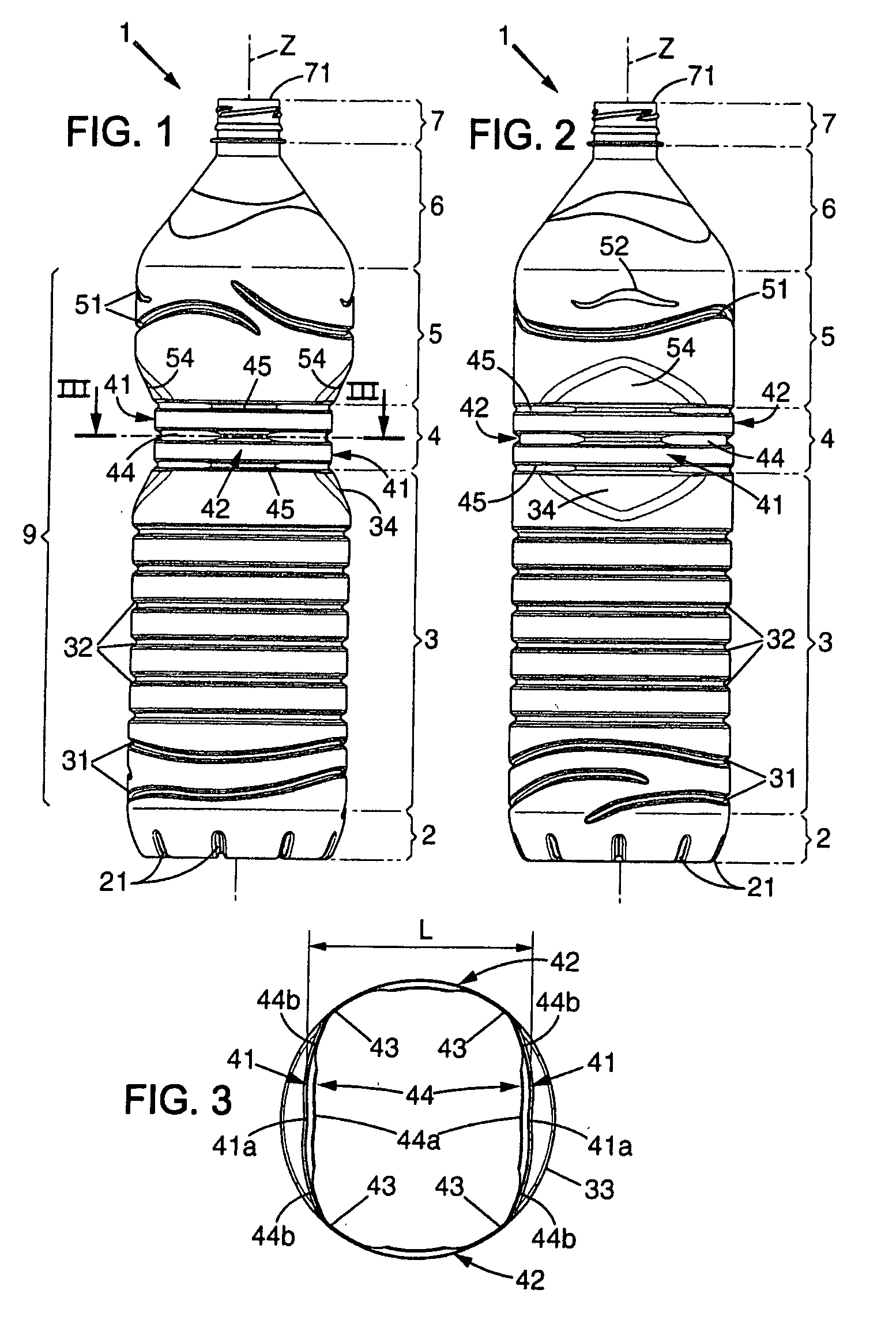
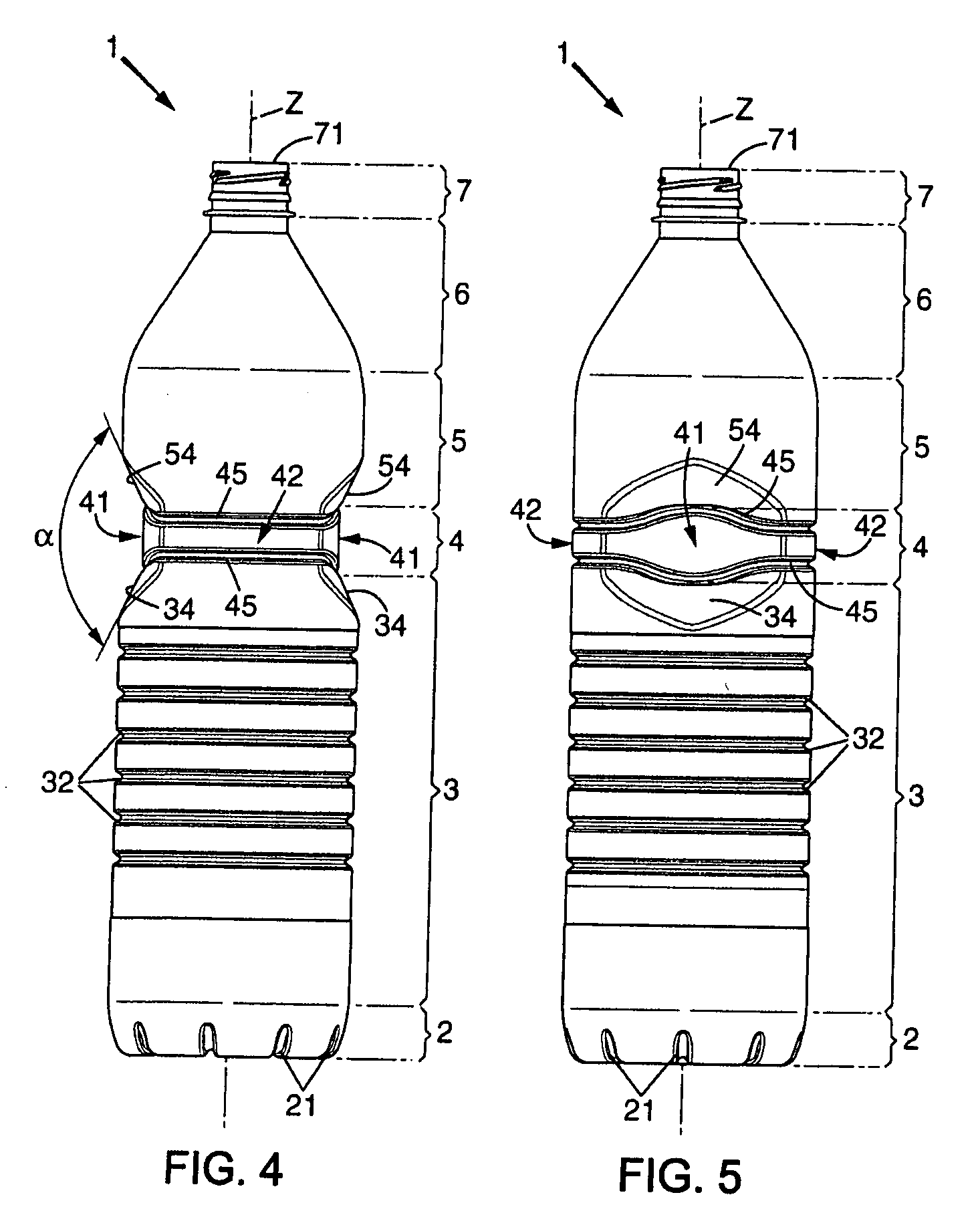
InactiveUS20070257003A1Easy to shapeReduce weightBottlesLarge containersPlastic materialsTransverse plane
A bottle made of plastic material having a body extending along a central axis which comprises:a lower portion having a cross section with an essentially constant profile, followed bya gripping portion, and ending inan upper portion having a section with an essentially constant profile arranged in alignment with the profile of the section of the lower portion.The gripping portion comprises two globally plane gripping panels arranged parallel to one another and in relation to the central axis at a distance which is adapted for a hand taking. These panels have at least one reinforcing relief which extends in a transverse plane and are interconnected by connecting panels extending in continuation of the lower and upper portions by means of rounded corners located at the circumferential ends of the panels.
Owner:DES EAUX MINERALES DEVIAN
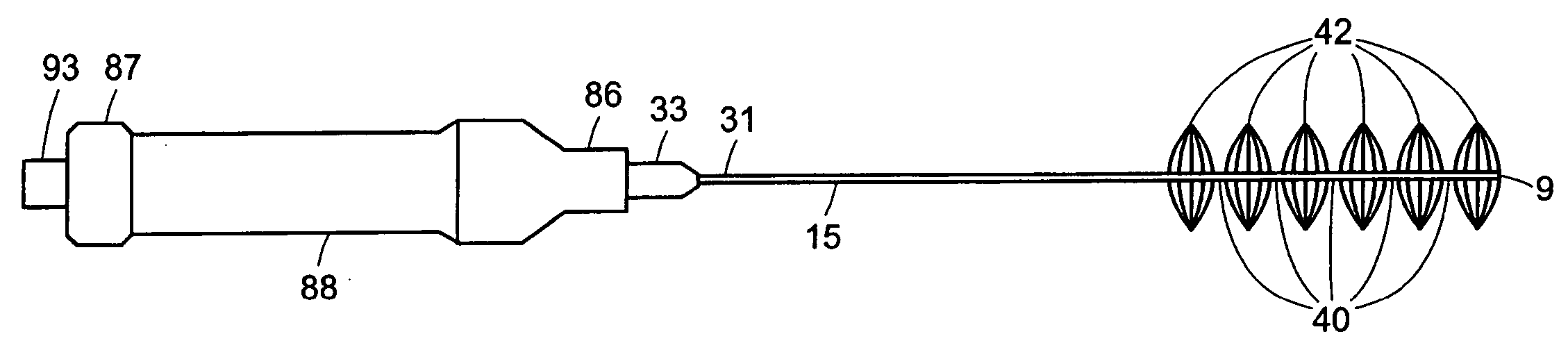
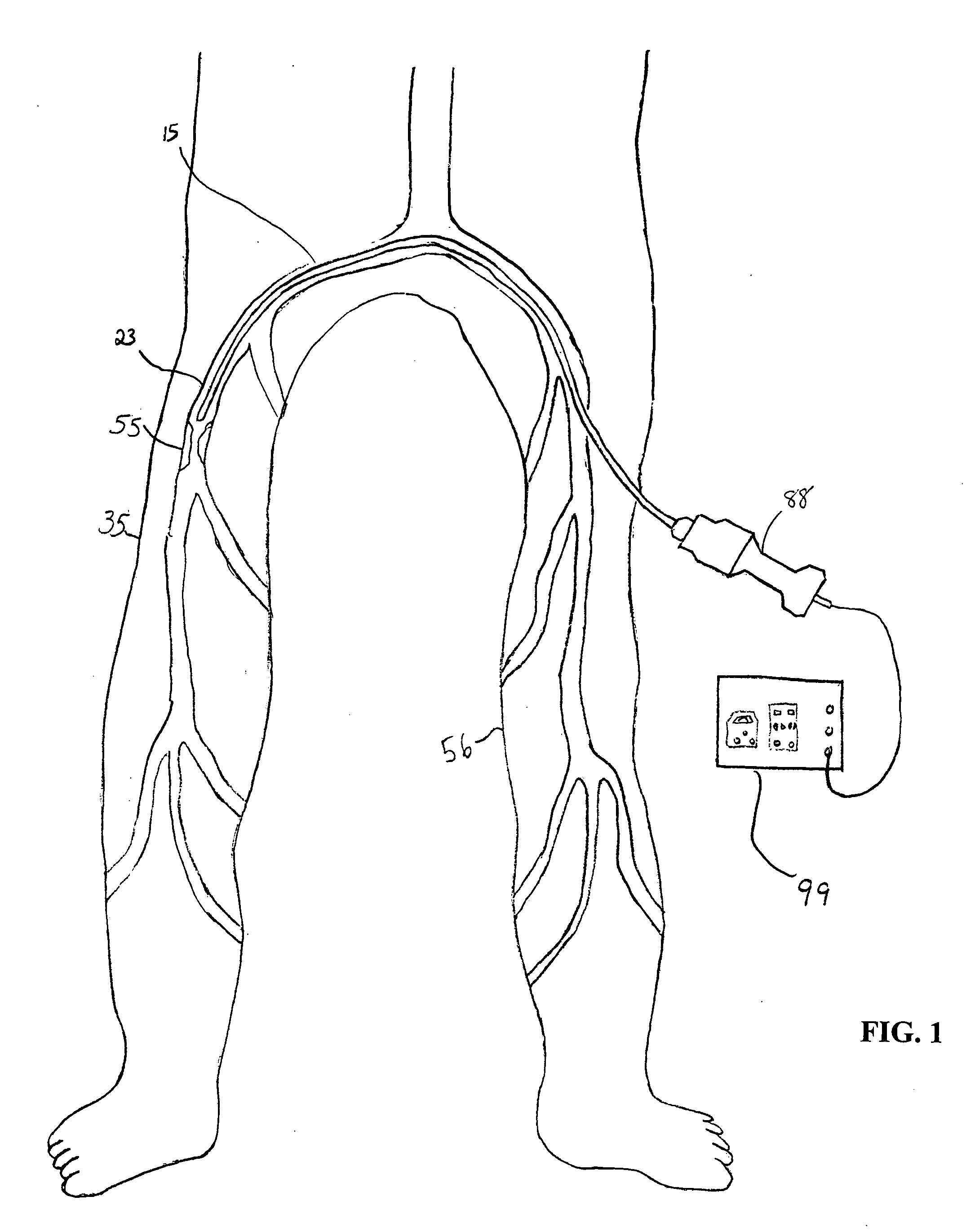
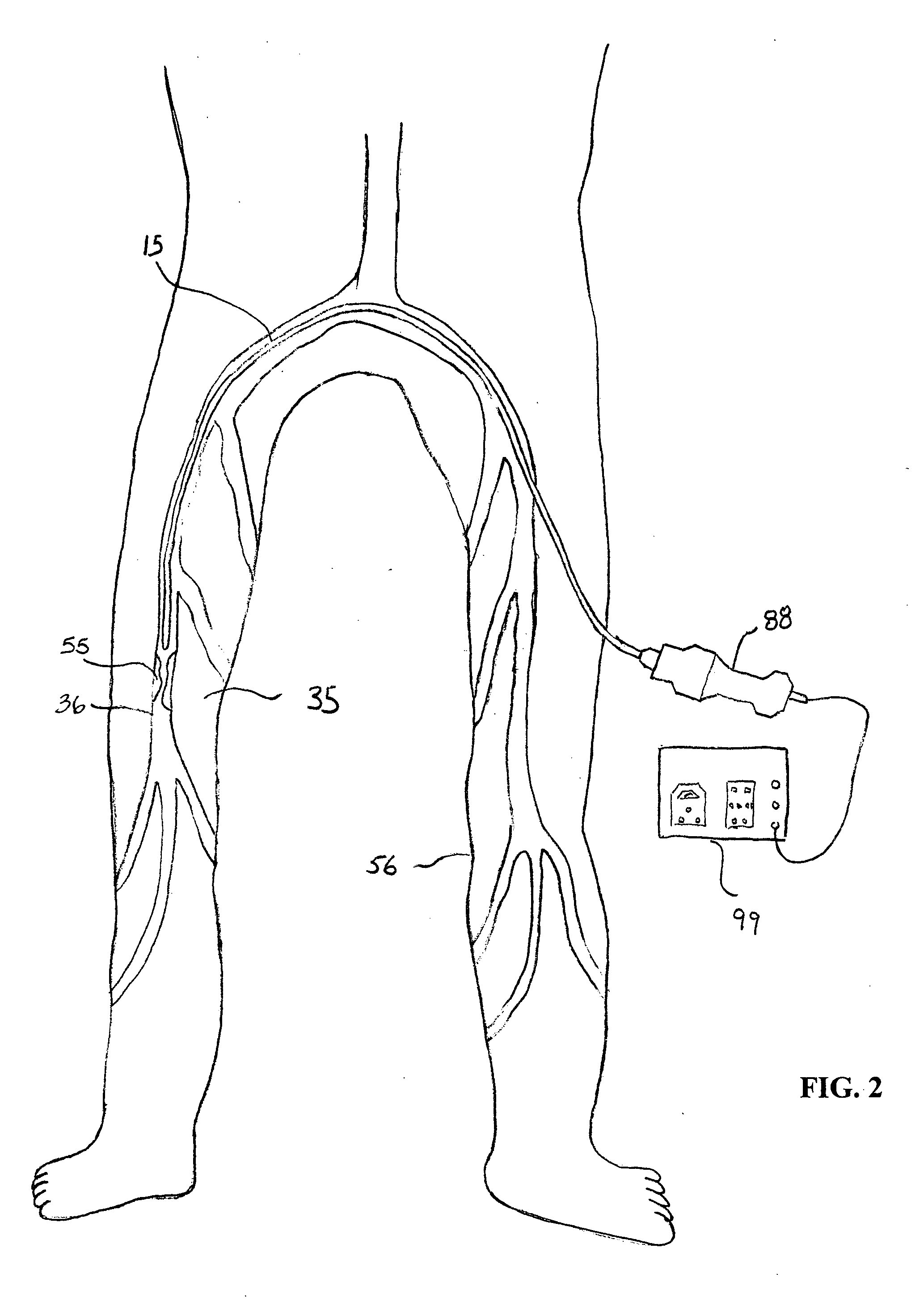
Apparatus and method for an ultrasonic medical device to treat peripheral artery disease
InactiveUS20050043753A1Effective timeSimple, user-friendlyUltrasound therapyCannulasCavitationTransverse plane
An apparatus and method for an ultrasonic medical device to treat peripheral artery disease. The ultrasonic medical device comprises an ultrasonic probe having a proximal end, a distal end and a longitudinal axis therebetween. The ultrasonic probe is inserted into an insertion point in a leg opposite the leg having an occlusional deposit and is moved adjacent to the occlusional deposit. An ultrasonic energy source is activated to generate a transverse ultrasonic vibration along at least a portion of the longitudinal axis of the ultrasonic probe. The transverse ultrasonic vibration creates a plurality of transverse nodes and a plurality of transverse anti-nodes along the longitudinal axis of the ultrasonic probe, generating cavitation in a medium surrounding the ultrasonic probe to ablate the occlusional deposit causing peripheral artery disease.
Owner:CYBERSONICS
Feed pipe coupling for a pressurised fluid system
The invention proposes a feed pipe coupling for a pressurised fluid system, characterised in that the branch of the spring clip which includes the locking portion is configured generally as a hairpin having a radially internal, locking, first branch portion of which the locking portion is a part, together with a radially external, connecting, second branch portion which is connected at each of its ends, firstly to the operational locking branch portion through a bent connecting portion, and, secondly to the central connecting branch of the spring clip, in such a way as to give the locking branch a capacity for elastic deformation in the general transverse plane of the spring clip.
Owner:VALEO EMBRAYAGES SAS
Solid state lighting apparatus utilizing axial thermal dissipation
InactiveUS7740380B2Improve cooling effectHeat dissipationPoint-like light sourceLighting support devicesLight equipmentHighly oriented pyrolytic graphite
A solid state lighting apparatus characterized by its compact, predominately axial form factor, utilizes an axial thermal transfer member constructed of Highly Oriented Pyrolytic Graphite (HOPG) to aid in the dissipation of waste heat generated during its operation. The lighting apparatus is chiefly comprised of a Light Emitting Diode (LED) die array and circuit structure assembly affixed to one end of the axial thermal transfer member and further includes a transversely mounted heat sink structure, running the length of, and being affixed to, opposite sides of the axial member. The axial member serves to distribute waste heat down its length, and simultaneously, into a transverse plane where the waste heat is dissipated into the transversely mounted heat sink structure. A fan may be utilized to evacuate the waste heat out of the lighting apparatus and into the ambient environment.
Owner:THRAILKILL JOHN E
Optical waveguide structures
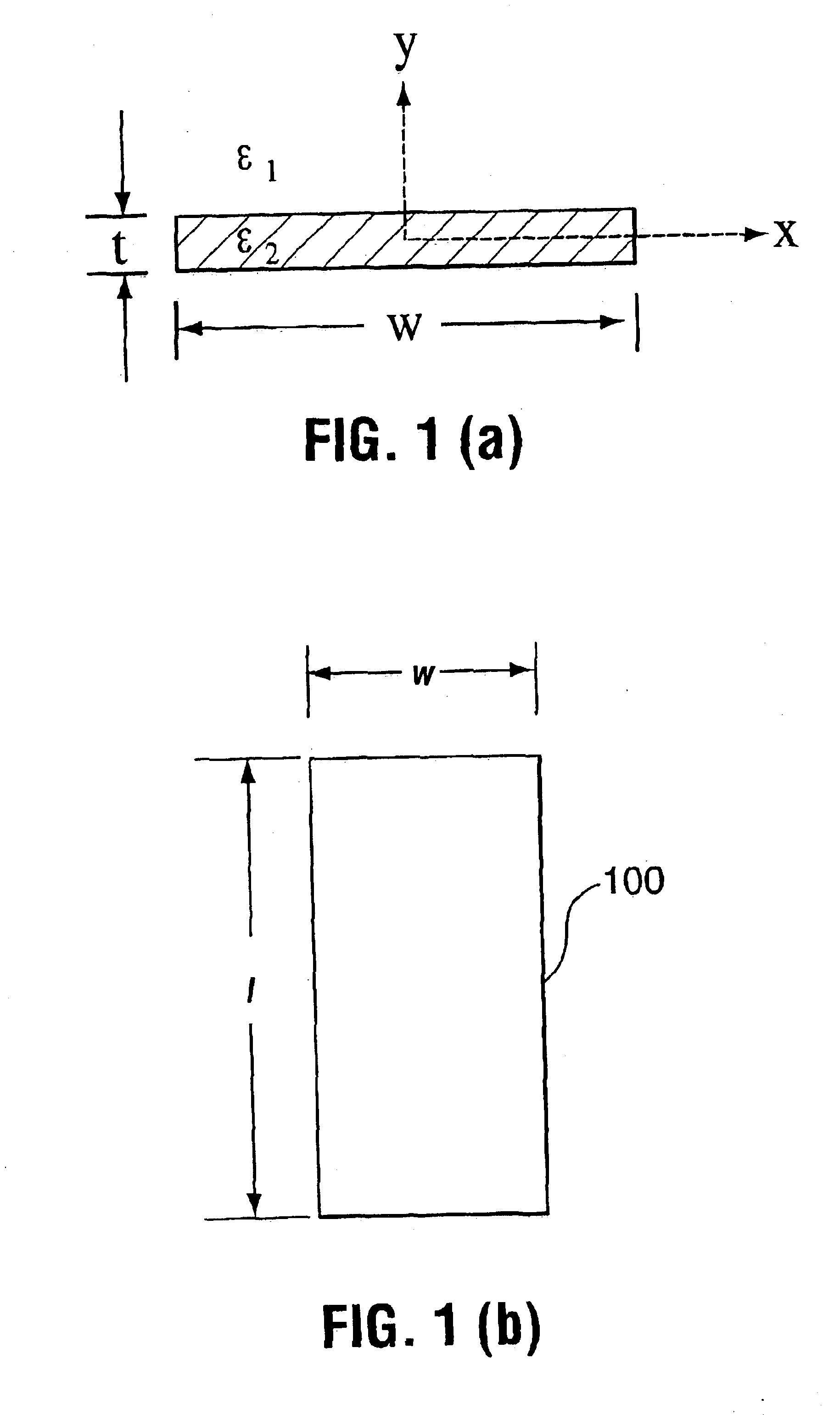
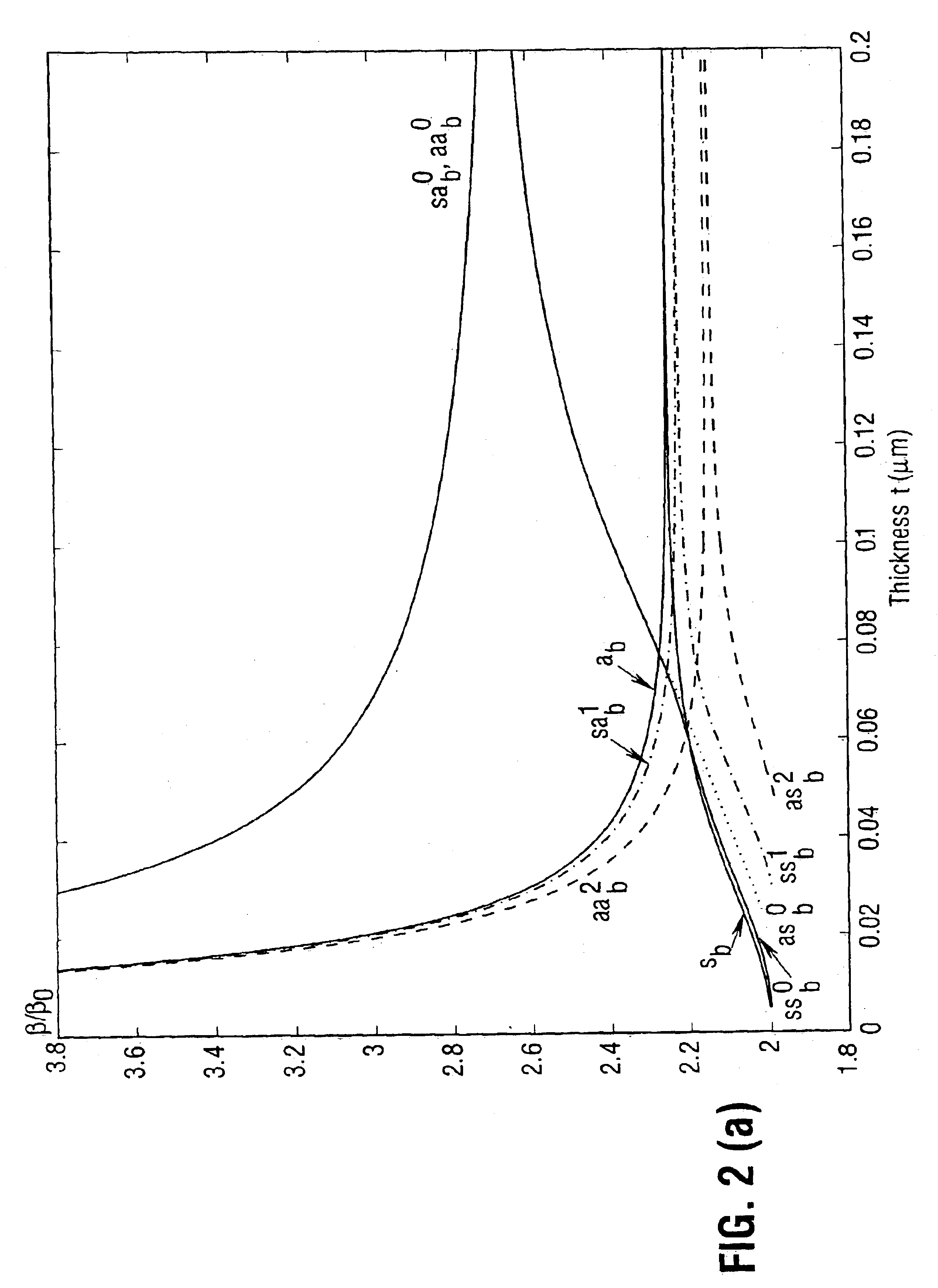
The purely bound electromagnetic modes of propagation supported by waveguide structures comprised of a thin lossy metal film of finite width embedded in an infinite homogeneous dielectric have been characterized at optical wavelengths. One of the fundamental modes supported by the structure exhibits very interesting characteristics and is potentially quite useful. It evolves with decreasing film thickness and width towards the TEM wave supported by the background (an evolution similar to that exhibited by the sb mode in symmetric metal film slab waveguides), its losses and phase constant tending asymptotically towards those of the TEM wave. Attenuation values can be well below those of the sb mode supported by the corresponding metal film slab waveguide. Low mode power attenuation in the neighbourhood of 10 to 0.1 dB / cm is achievable at optical communications wavelengths, with even lower values being possible. Carefully selecting the film's thickness and width can make this mode the only long-ranging one supported. In addition, the mode can have a field distribution that renders it excitable using an end-fire approach. The existence of this mode renders the finite-width metal film waveguide attractive for applications requiring short propagation distances and 2-D field confinement in the transverse plane, enabling various devices to be constructed, such as couplers, splitters, modulators, interferometers, switches and periodic structures. Under certain conditions, an asymmetric structure can support a long-ranging mode having a field distribution that is suitable to excitation using an end-fire technique. Like asymmetric slab waveguides. The attenuation of the long-ranging mode near cutoff decreases very rapidly, much more so than the attenuation related to the long-ranging mode in a similar symmetric structure. The cutoff thickness of a long-ranging mode in an asymmetric finite-width structure is larger than the cutoff thickness of the sb mode in a similar asymmetric slab waveguide. This implies that the long-ranging mode supported by an asymmetric finite-width structure is more sensitive to the asymmetry in the structure compared to the sb mode supported by a similar slab waveguide. This result is interesting and potentially useful in that the propagation of such a mode can be affected by a smaller change in the dielectric constant of the substrate or superstrate compared with similar slab structures.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA
Hybrid vertical-cavity laser
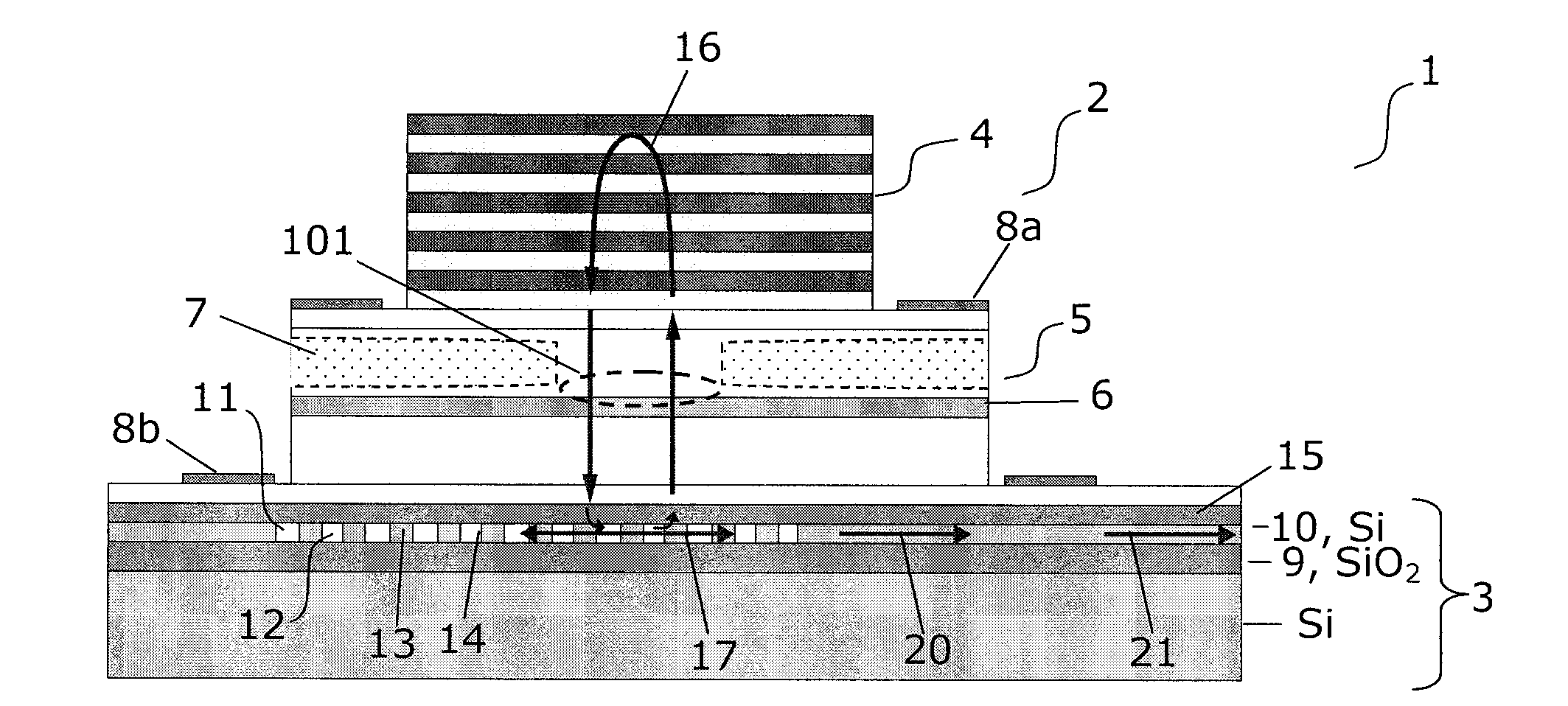
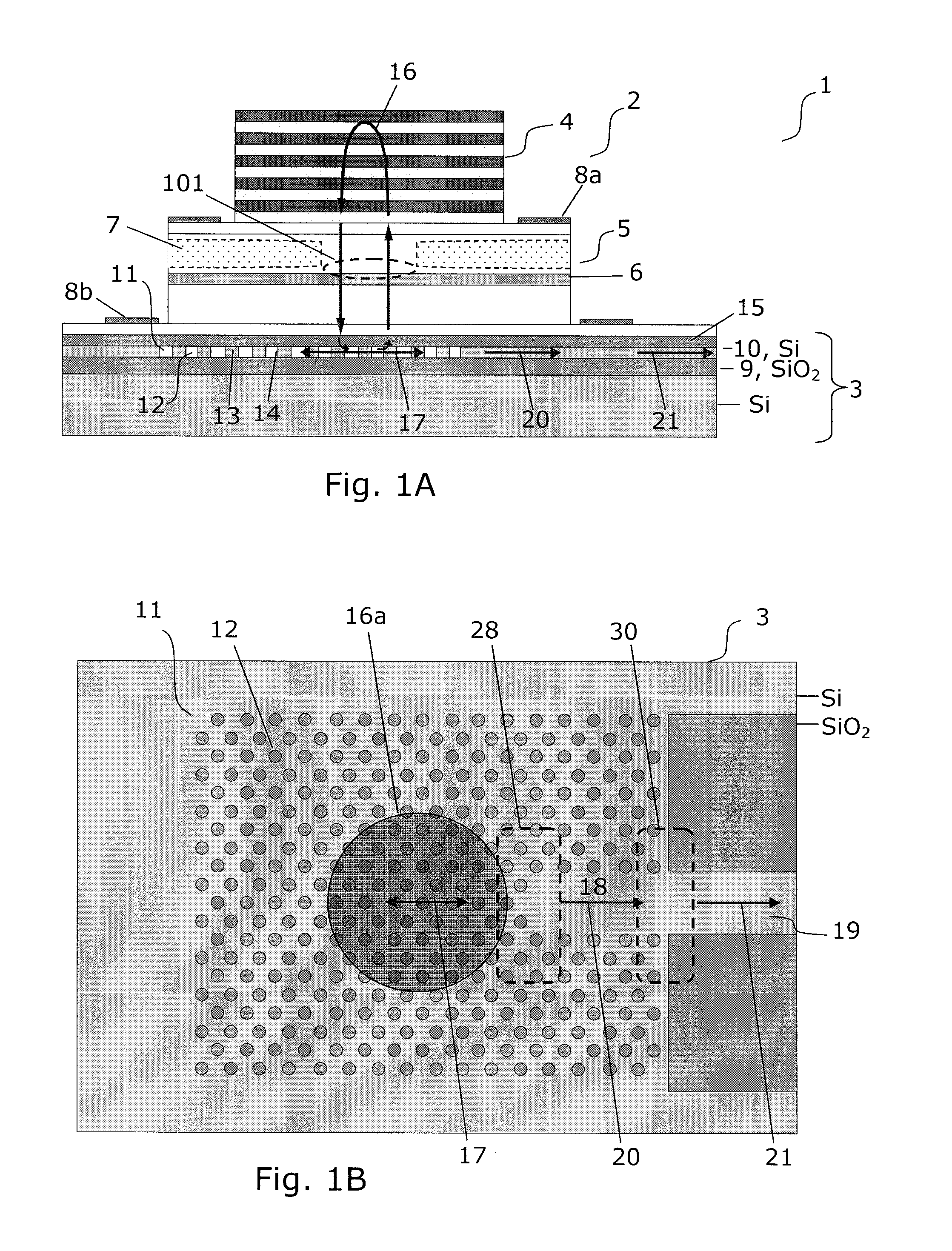
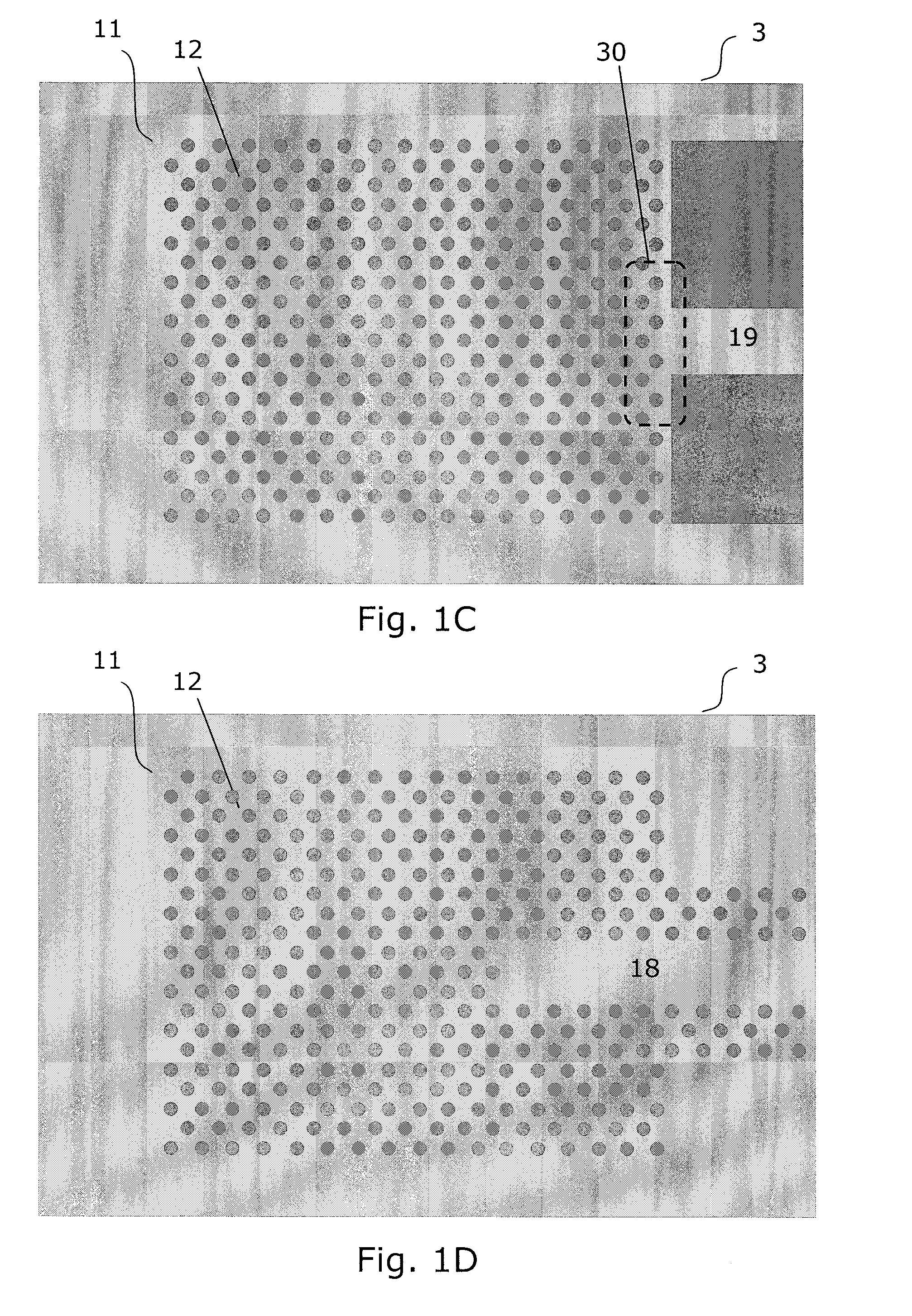
InactiveUS20120008658A1Decrease unwanted scattering lossImprove routing efficiencyLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionIn planeCMOS
The present invention provides a light source (2) for light circuits on a silicon platform (3). A vertical laser cavity is formed by a gain region (101) arranged between a top mirror (4) and a bottom grating-mirror (12) in a grating region (11) in a silicon layer (10) on a substrate. A waveguide (18, 19) for receiving light from the grating region (11) is formed within or to be connected to the grating region, and functions as an 5 output coupler for the VCL. Thereby, vertical lasing modes (16) are coupled to lateral in-plane modes (17, 20) of the in-plane waveguide formed in the silicon layer, and light can be provided to e.g. photonic circuits on a SOI or CMOS substrate in the silicon.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Collapsible steering column assembly
InactiveUS20090256342A1Increase sliding frictionIncrease in sliding frictional forceSteering columnsSteering columnTransverse plane
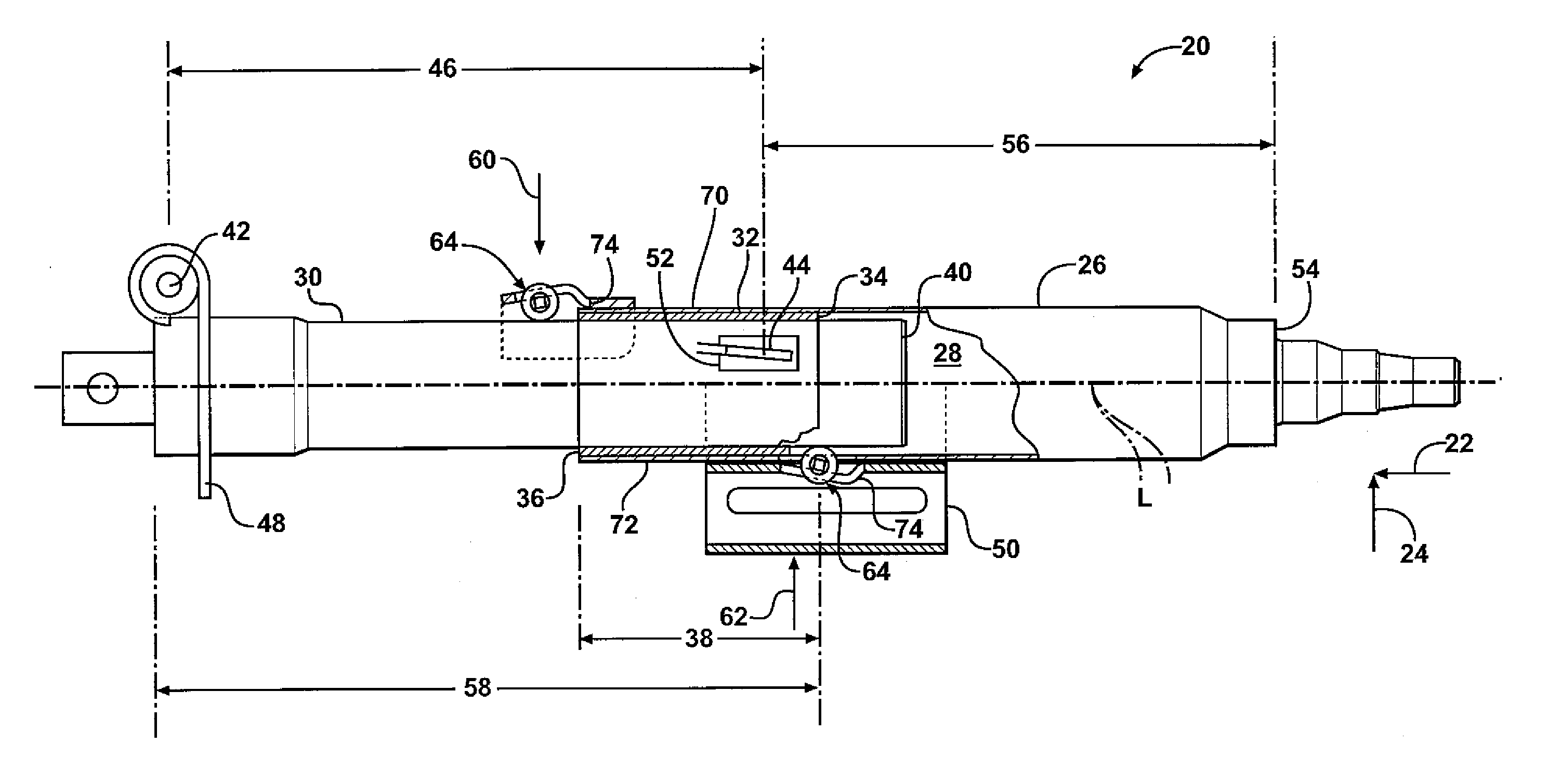
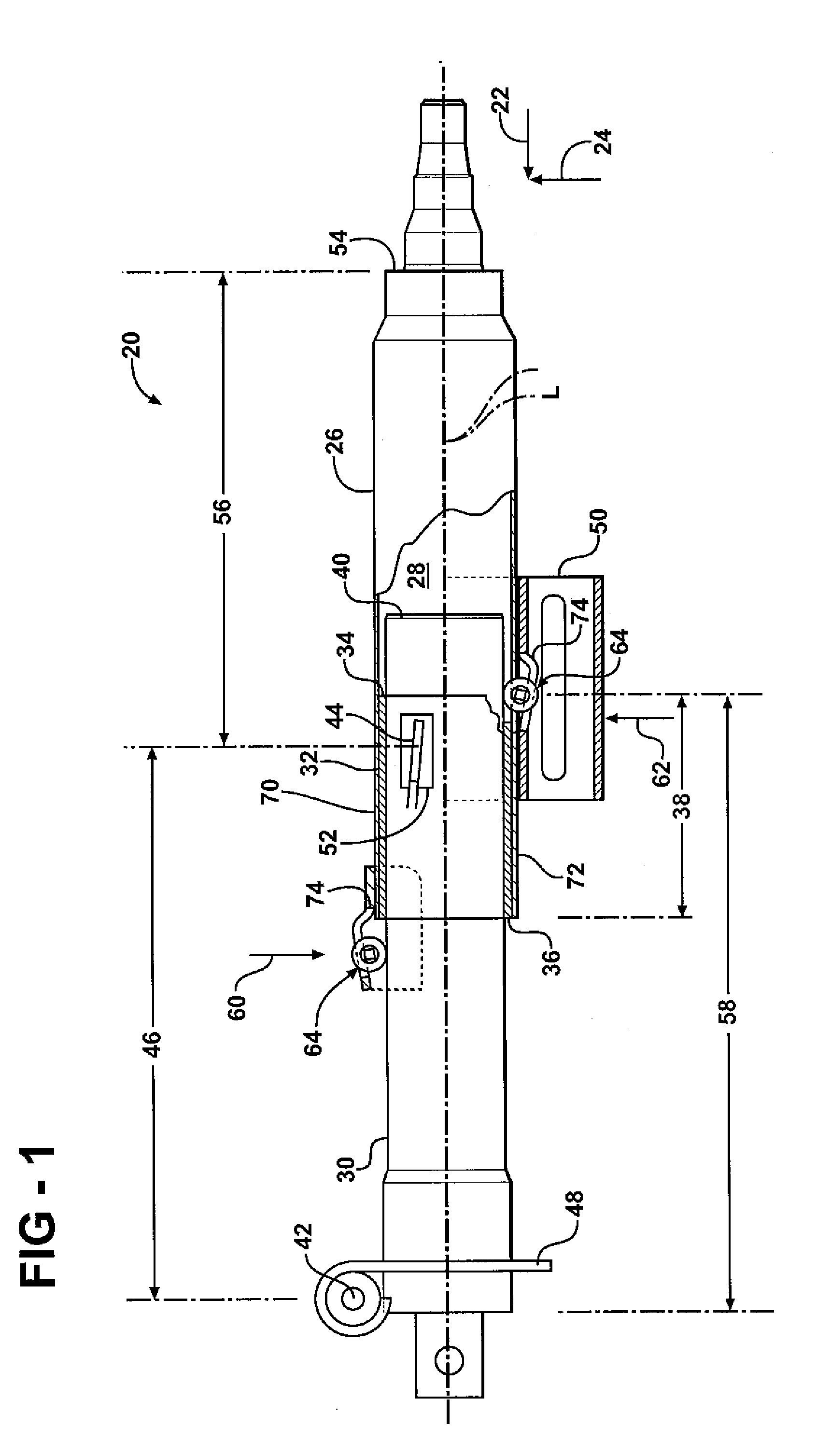
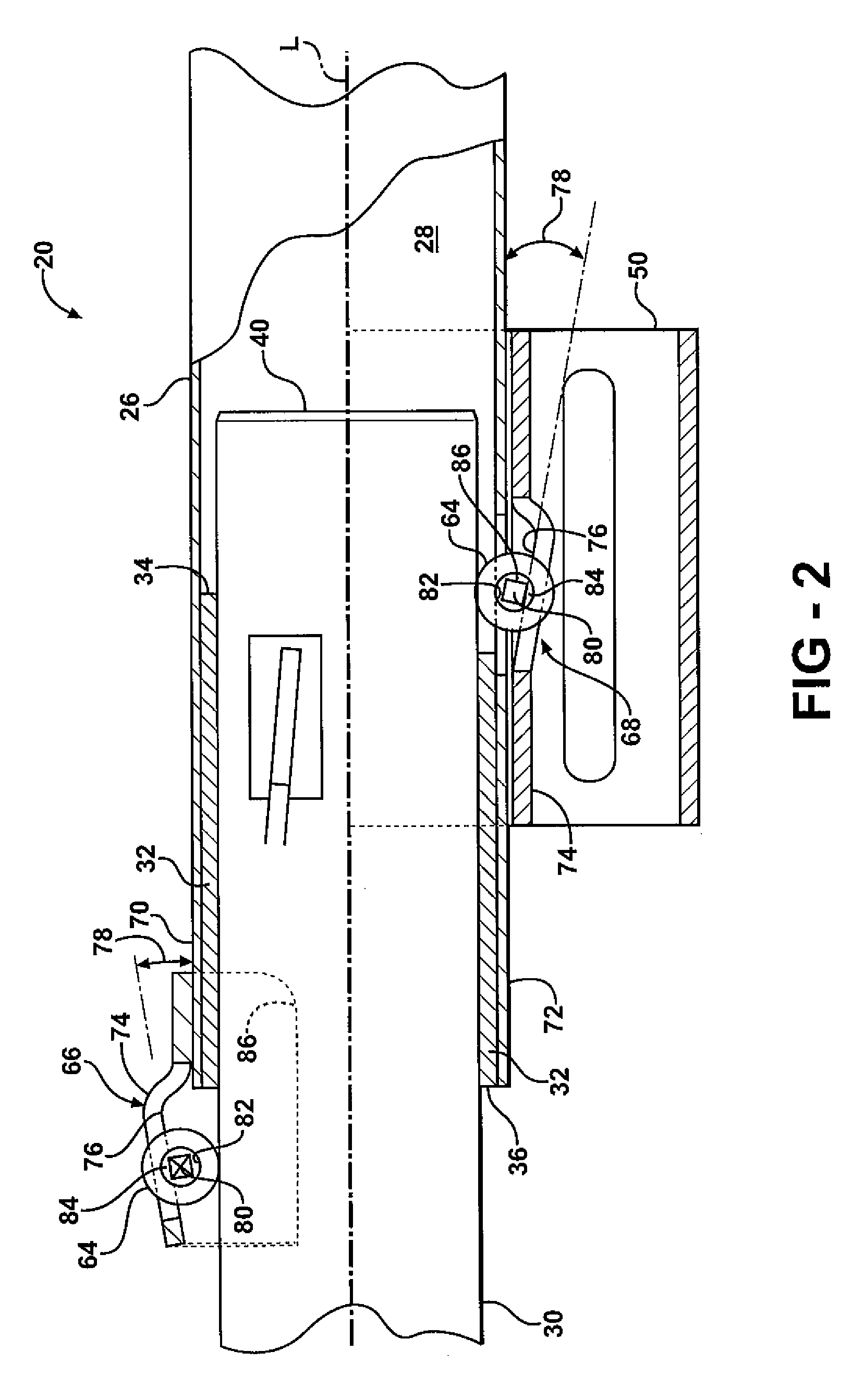
A steering column assembly includes an upper jacket and a lower jacket partially disposed within said upper jacket. A bushing is disposed between the upper jacket and the lower jacket. The upper jacket and the lower jacket are collapsible along a longitudinal axis in response to a collision event. A first roller mechanism and a second roller mechanism are mounted to the upper jacket near a forward end and a rearward end of the bushing respectively for engaging the lower jacket in rolling engagement. The first and second roller mechanisms resist a resultant force caused by a bending moment created by a transverse load applied to a distal end of the upper jacket to minimize an increase in a sliding frictional force between the bushing and the lower jacket.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC +1
Device and method for indicating scheduled doses
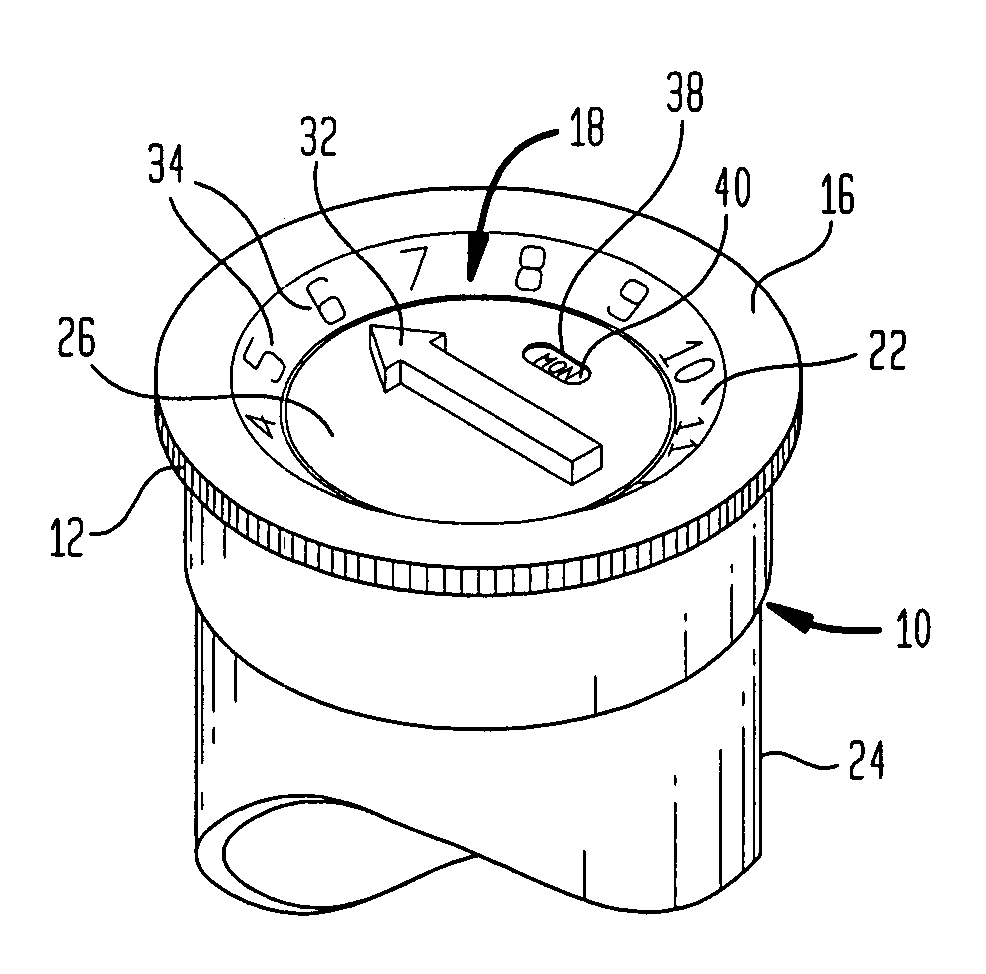
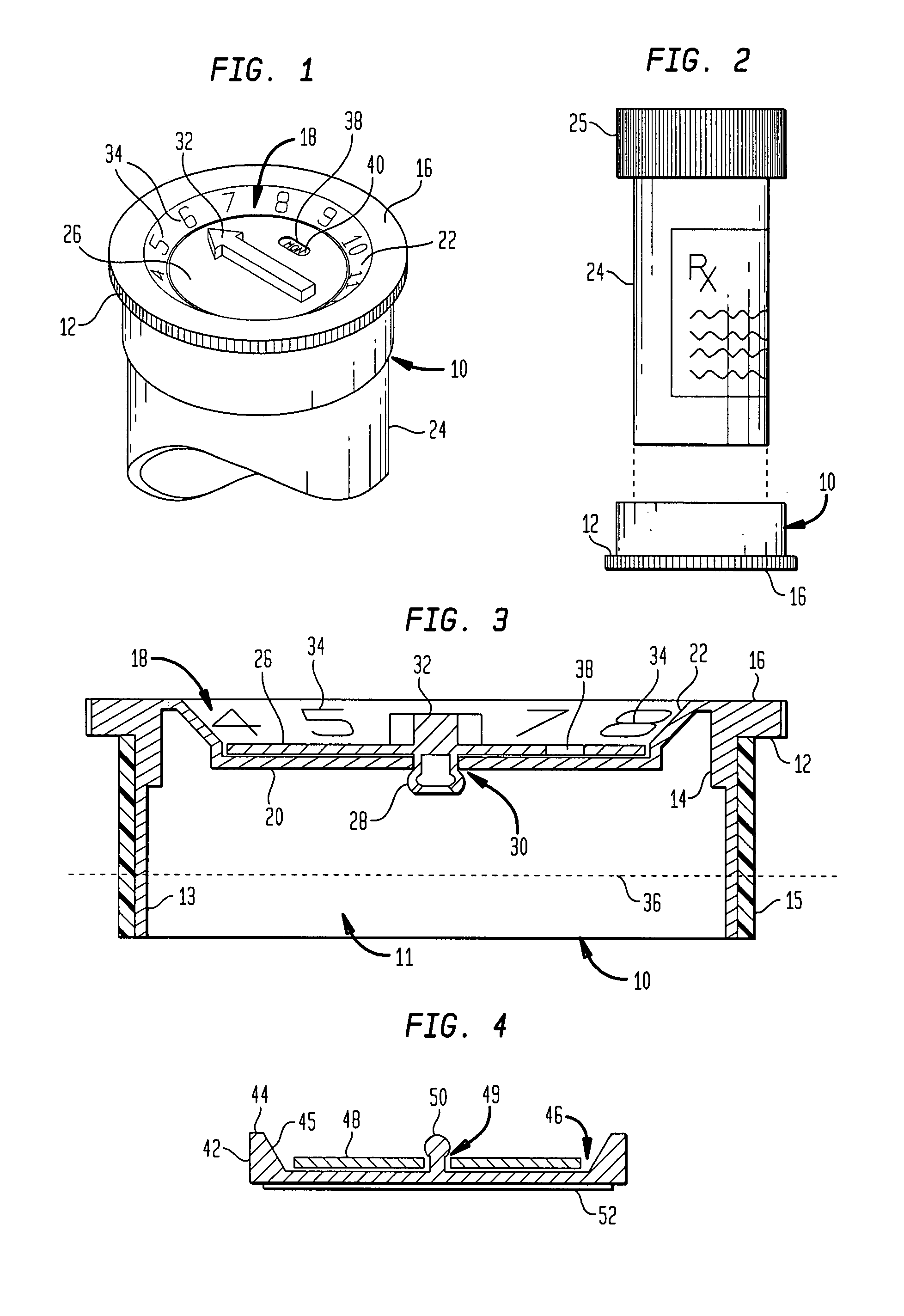
InactiveUS7222736B1Prevent tippingAvoid interferenceSmall article dispensingCapsTransverse planeEngineering
A reminder device can be attached to the bottom of a medicine container that has a cap. The reminder device has an indicator rotatably mounted on a base in order to rotate and indicate a scheduled event. The base adhesively or frictionally engages the bottom of the container opposite the cap. The base may have an opening for engaging the bottom of the medicine container. Along some transverse plane within the opening, the opening may be shaped to engage the container along most of its periphery. A user can adjust the indicator on the base to indicate a scheduled event when medicine is ingested.
Owner:SEIJAS JAMES
Lifting device
ActiveUS7284744B1Longer expected lifetimeWork lessWinding mechanismsLoad-engaging elementsLongitudinal planeTransverse plane
Owner:HANS KUENZ GMBH +1
Optical waveguide structures
The purely bound electromagnetic modes of propagation supported by waveguide structures comprised of a thin lossy metal film of finite width embedded in an infinite homogeneous dielectric have been characterized at optical wavelengths. One of the fundamental modes supported by the structure exhibits very interesting characteristics and is potentially quite useful. It evolves with decreasing film thickness and width towards the TEM wave supported by the background (an evolution similar to that exhibited by the sb mode in symmetric metal film slab waveguides), its losses and phase constant tending asymptotically towards those of the TEM wave. Attenuation values can be well below those of the sb mode supported by the corresponding metal film slab waveguide. Low mode power attenuation in the neighborhood of 10 to 0.1 dB / cm is achievable at optical communications wavelengths, with even lower values being possible. Carefully selecting the film's thickness and width can make this mode the only long-ranging one supported. In addition, the mode can have a field distribution that renders it excitable using an end-fire approach. The existence of this mode renders the finite-width metal film waveguide attractive for applications requiring short propagation distances and 2-D field confinement in the transverse plane, enabling various devices to be constructed, such as couplers, splitters, modulators, interferometers, switches and periodic structures. Under certain conditions, an asymmetric structure can support a long-ranging mode having a field distribution that is suitable to excitation using an end-fire technique. Like asymmetric slab waveguides. The attenuation of the long-ranging mode near cutoff decreases very rapidly, much more so than the attenuation related to the long-ranging mode in a similar symmetric structure. The cutoff thickness of a long-ranging mode in an asymmetric finite-width structure is larger than the cutoff thickness of the sb mode in a similar asymmetric slab waveguide. This implies that the long-ranging mode supported by an asymmetric finite-width structure is more sensitive to the asymmetry in the structure compared to the sb mode supported by a similar slab waveguide. This result is interesting and potentially useful in that the propagation of such a mode can be affected by a smaller change in the dielectric constant of the substrate or superstrate compared with similar slab structures.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA
Solid marine seismic cable
InactiveUS6853604B2Enhance total acoustic signal receivedGood effectSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSeismic signal receiversFlexible circuitsAdhesive
A support structure for piezoelectric elements in a marine seismic cable is provided. The support structure comprises upper and lower cylindrical halves, each with channels formed therein. Two axial channels are adapted to retain three piezoelectric elements each. A third axial channel, positioned between the sensor element channels, is adapted to retain a flexible circuit. Transverse channels between the sensor element channels and the circuit channels accommodate extension from the flexible circuit. The piezoelectric elements are mounted within their respective channels with a resilient pad with adhesive on both sides. The piezoelectric elements are graded so that any group of three piezoelectric elements exhibits approximately the same sensitivity as any of the other three groups of piezoelectric elements on the support structure.
Owner:SERCEL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com