Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
709 results about "Sagittal plane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
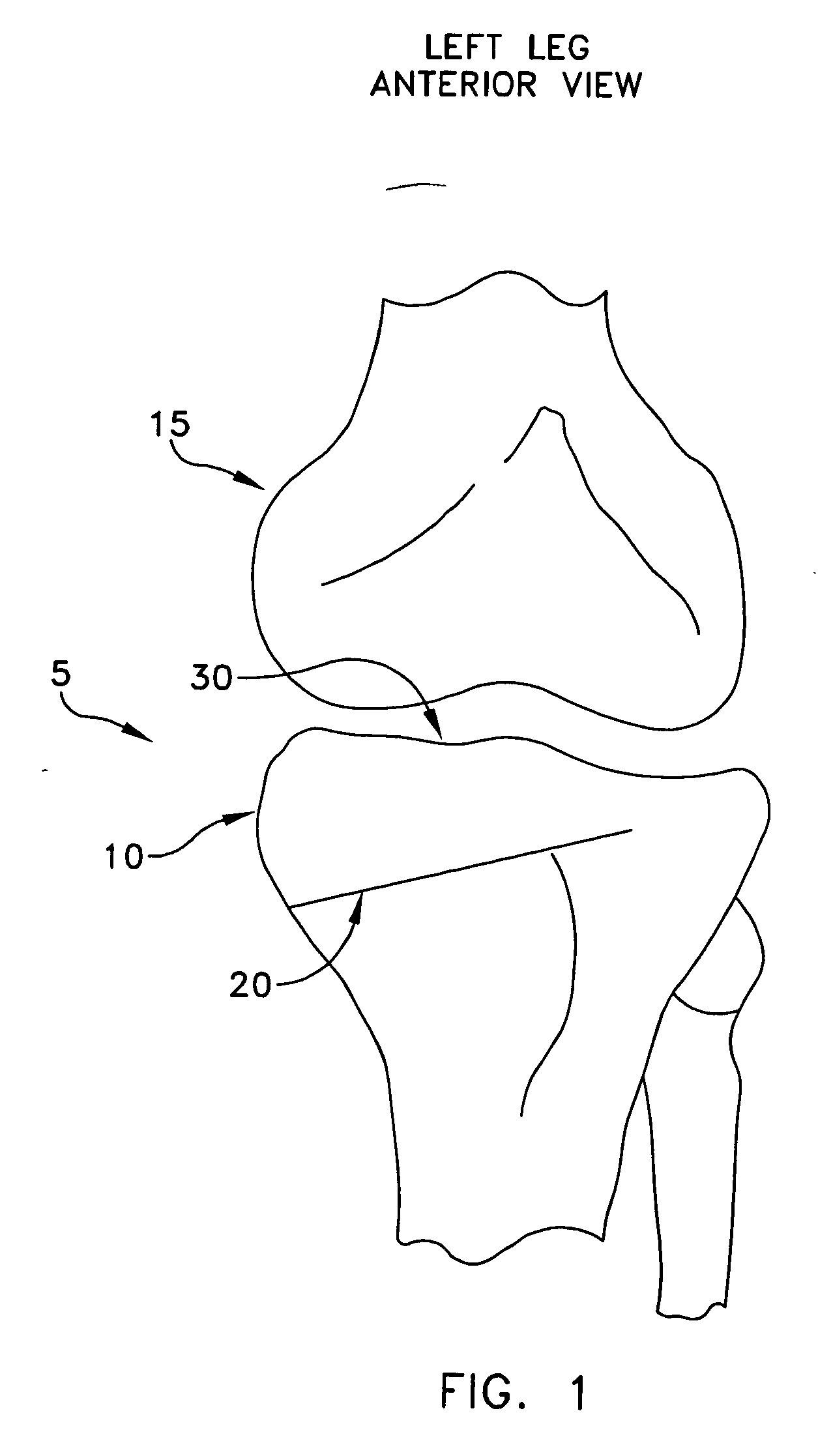
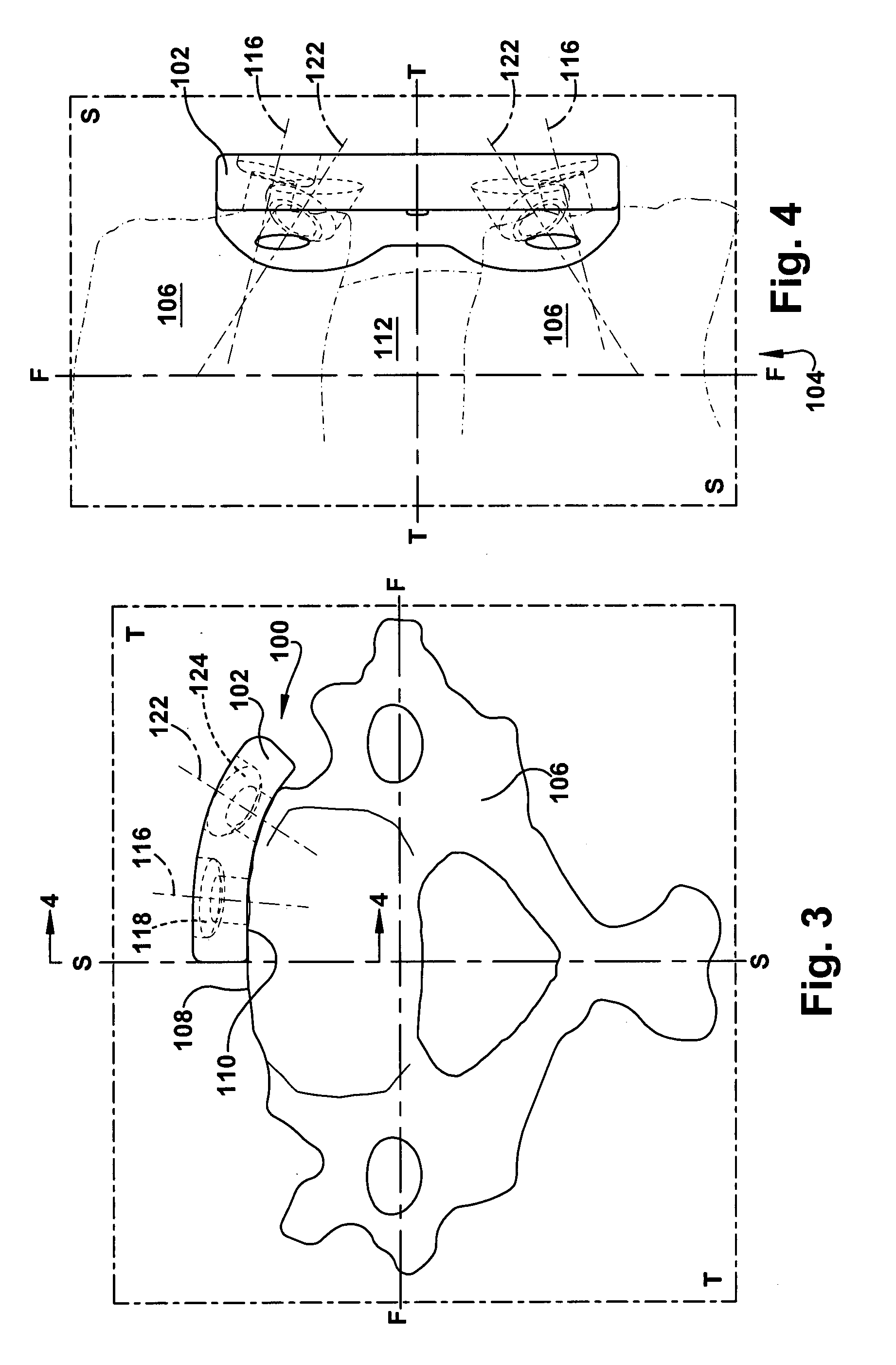
A sagittal plane (/ˈsædʒɪtəl/), or longitudinal plane, is an anatomical plane which divides the body into right and left parts. The plane may be in the center of the body and split it into two halves (mid-sagittal) or away from the midline and split it into unequal parts (para-sagittal).The anatomical term sagittal was coined by Gerard of Cremona.
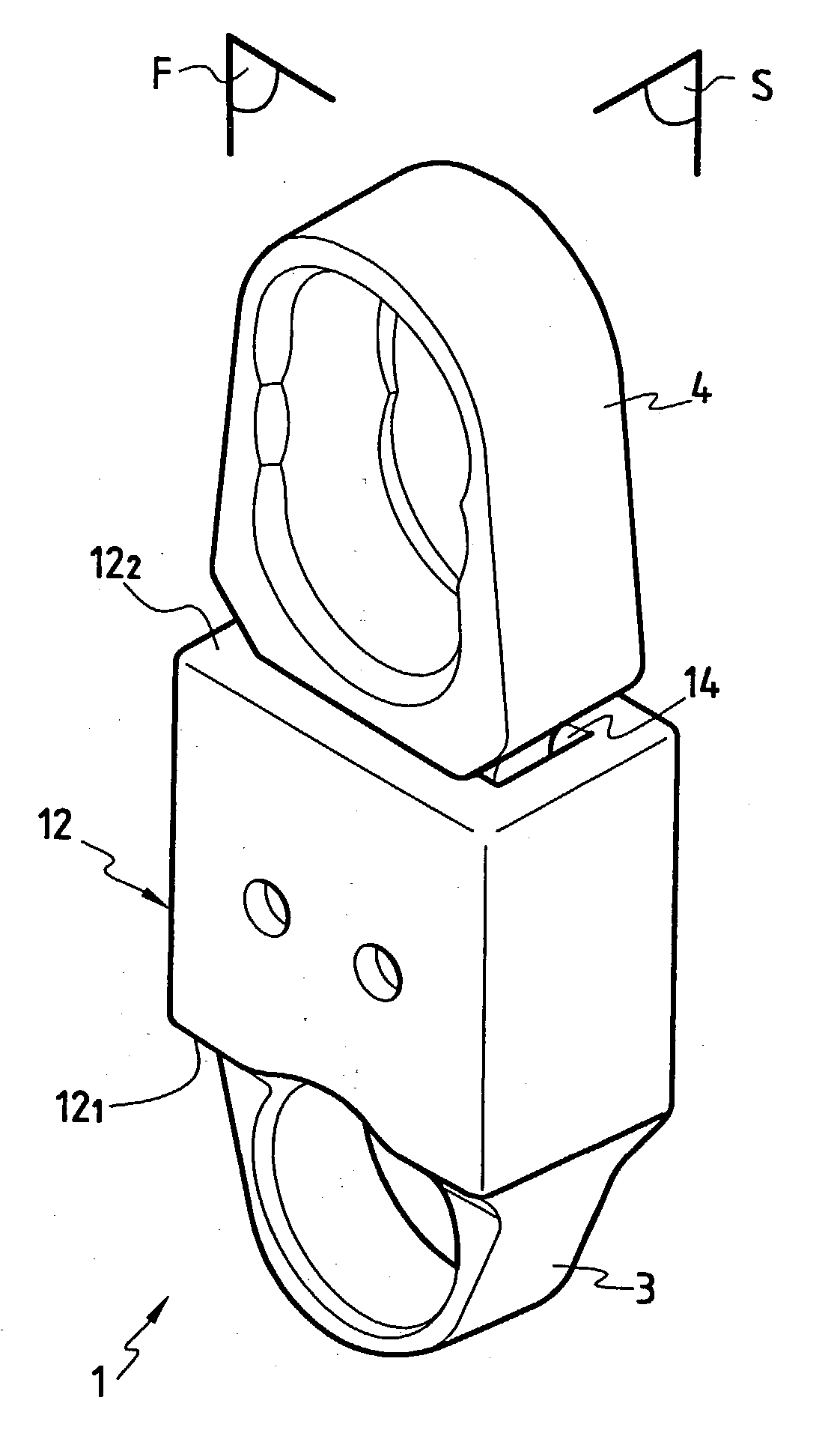
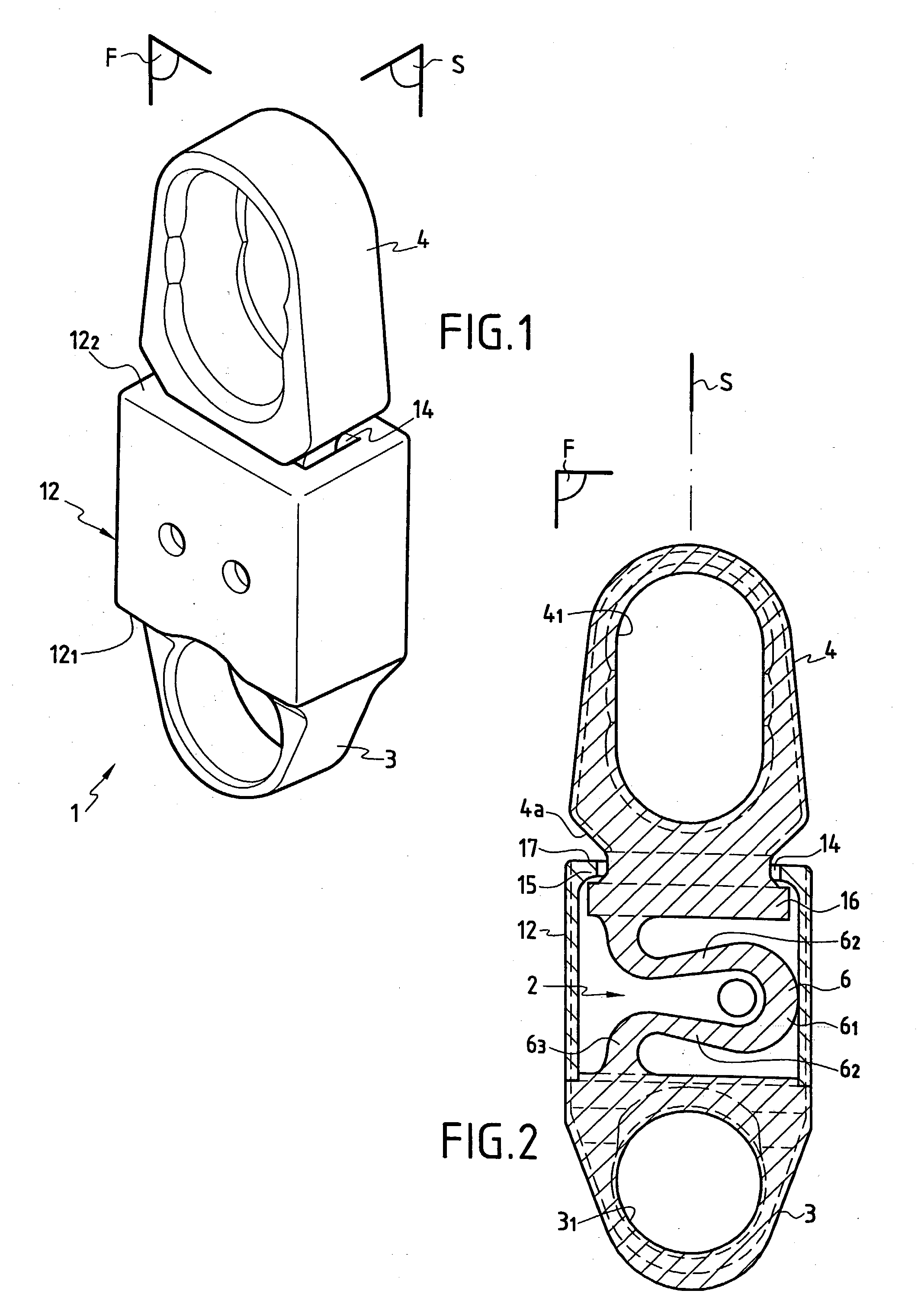
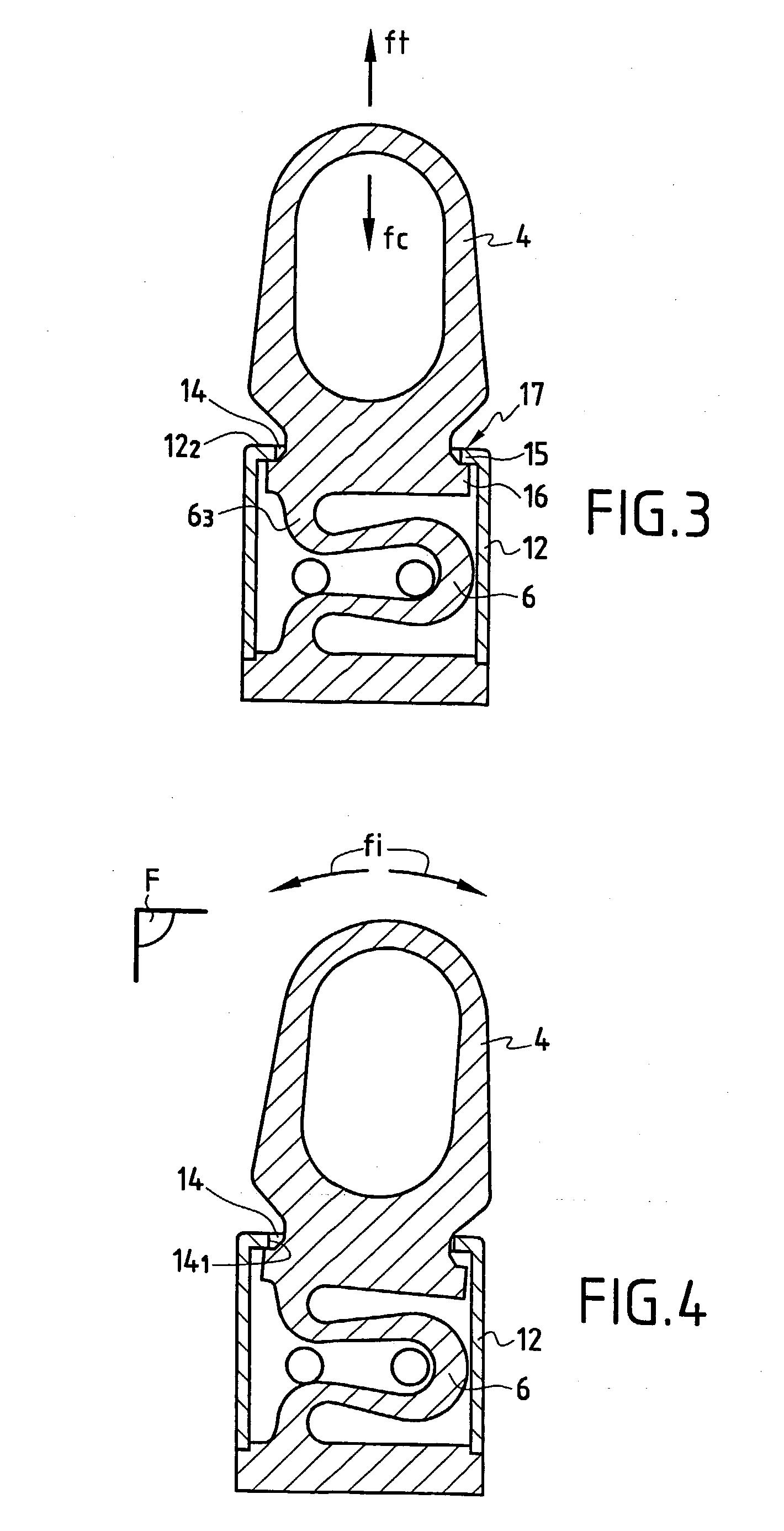
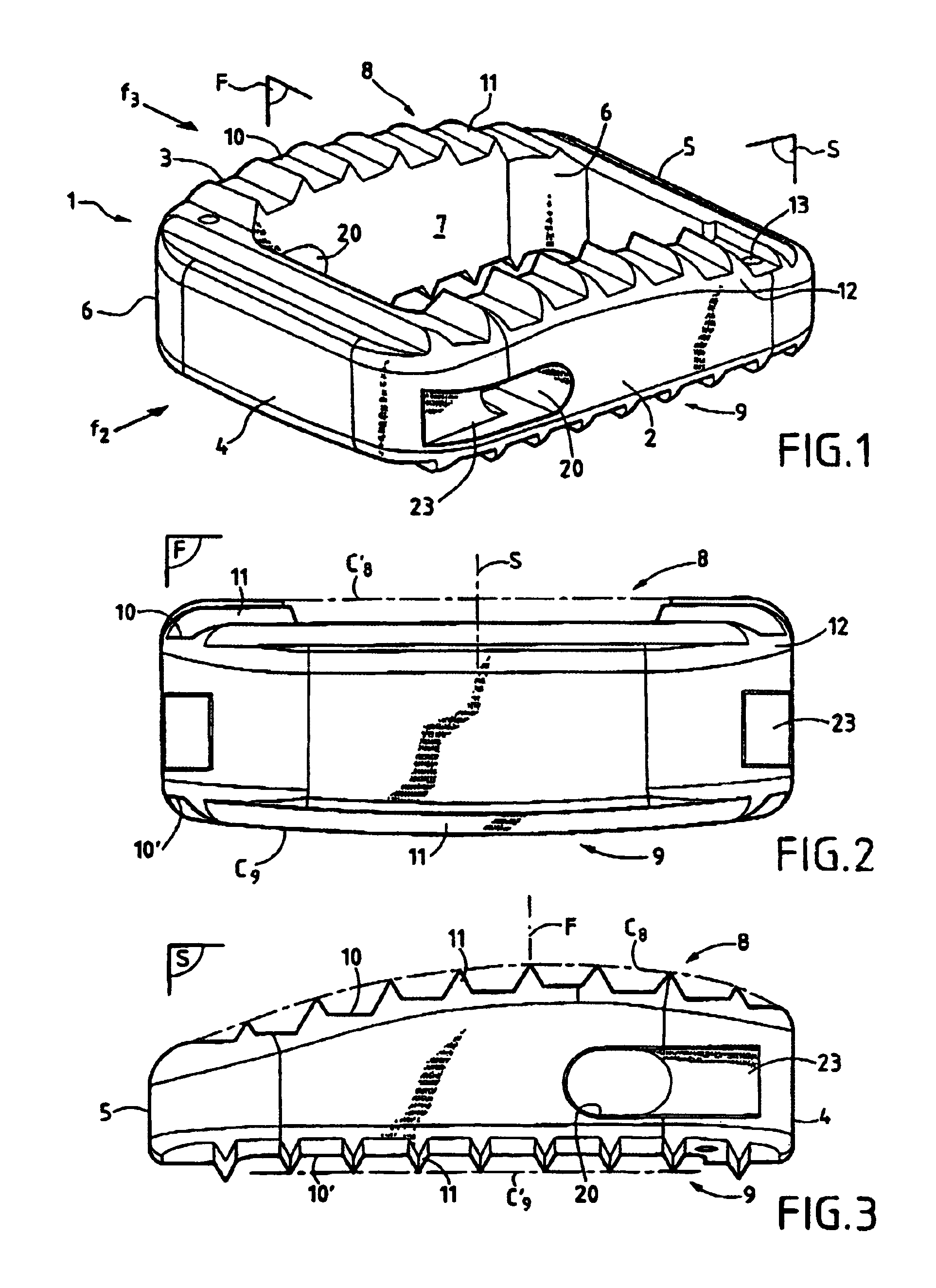
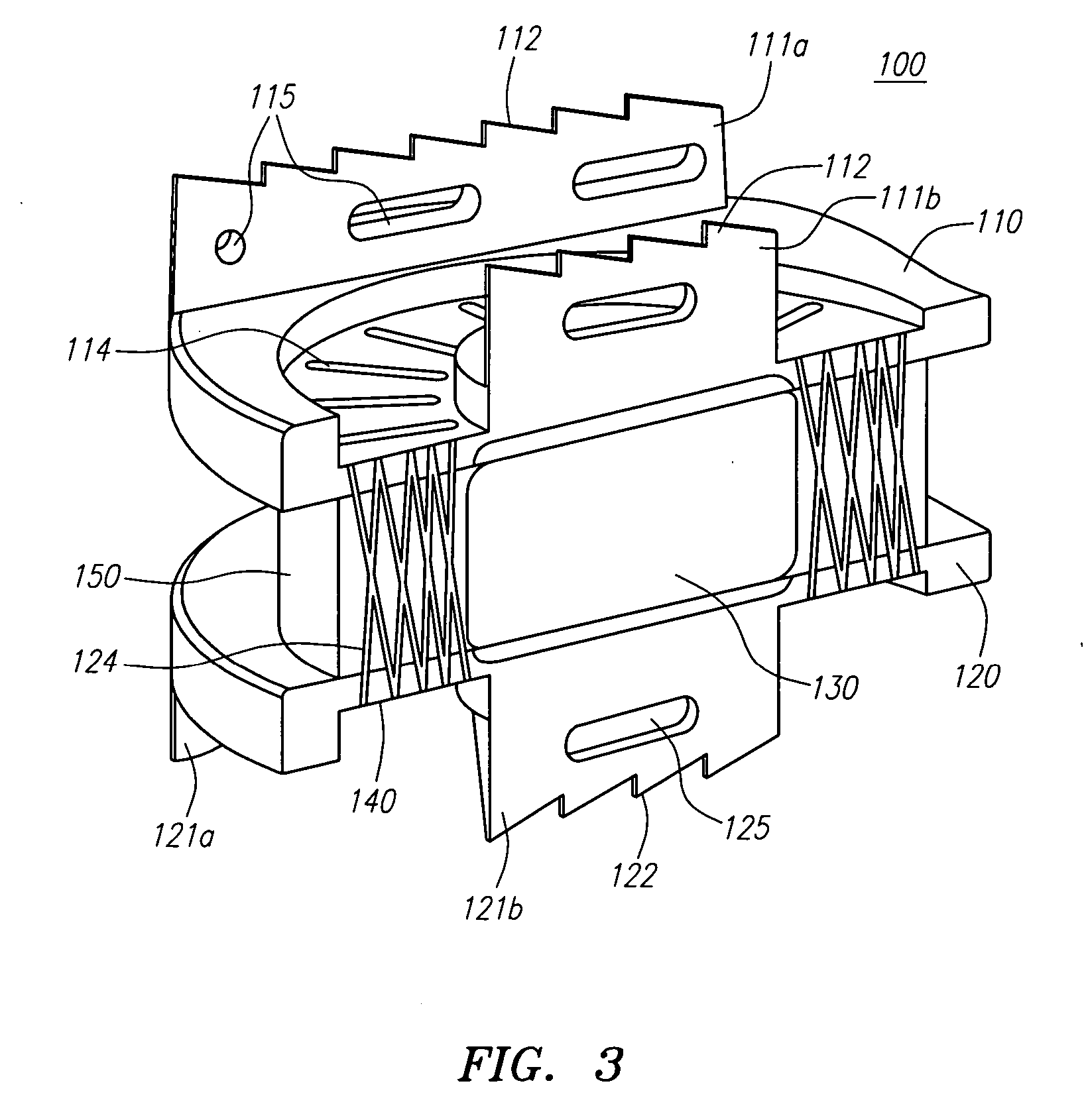
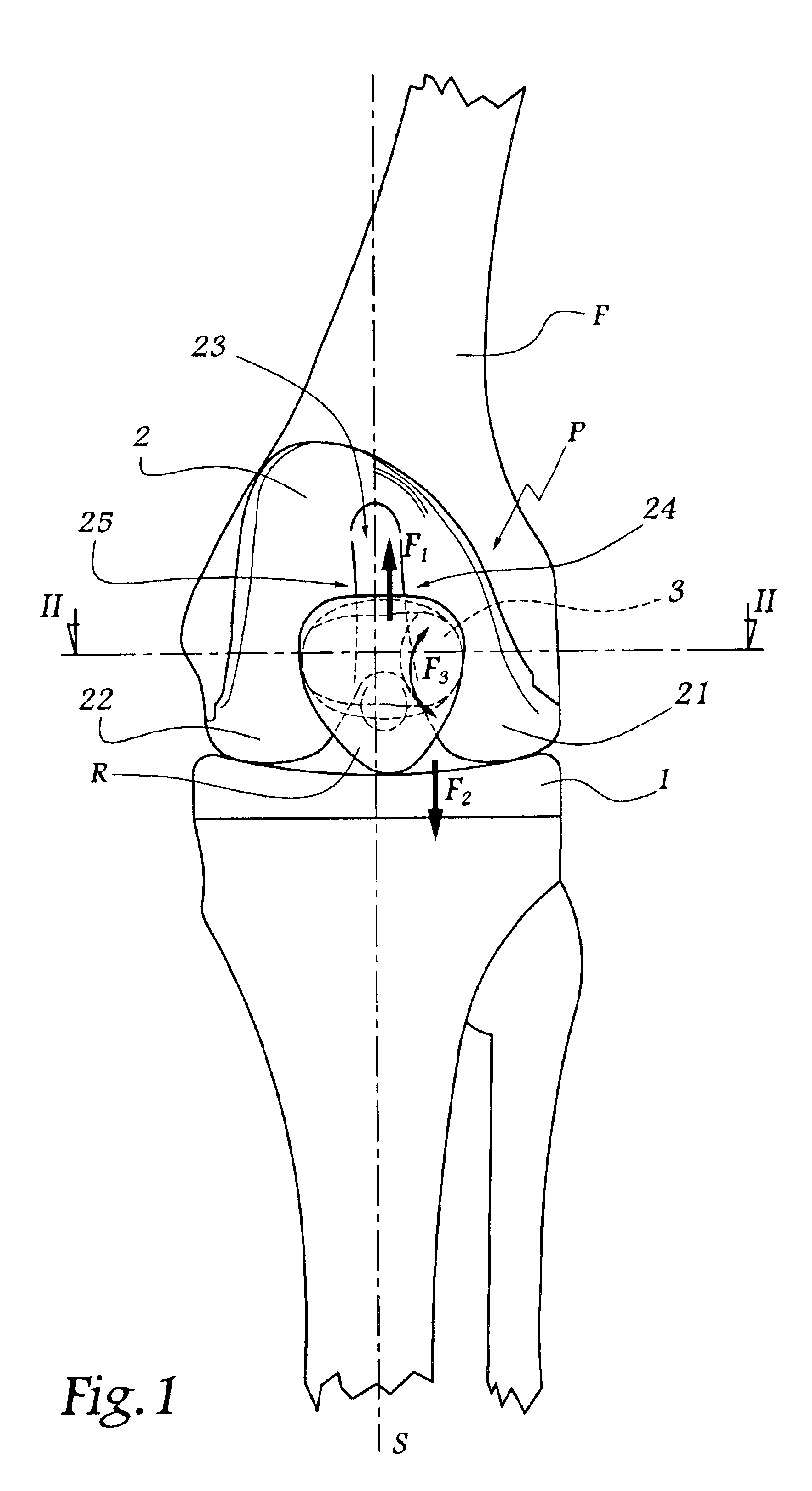
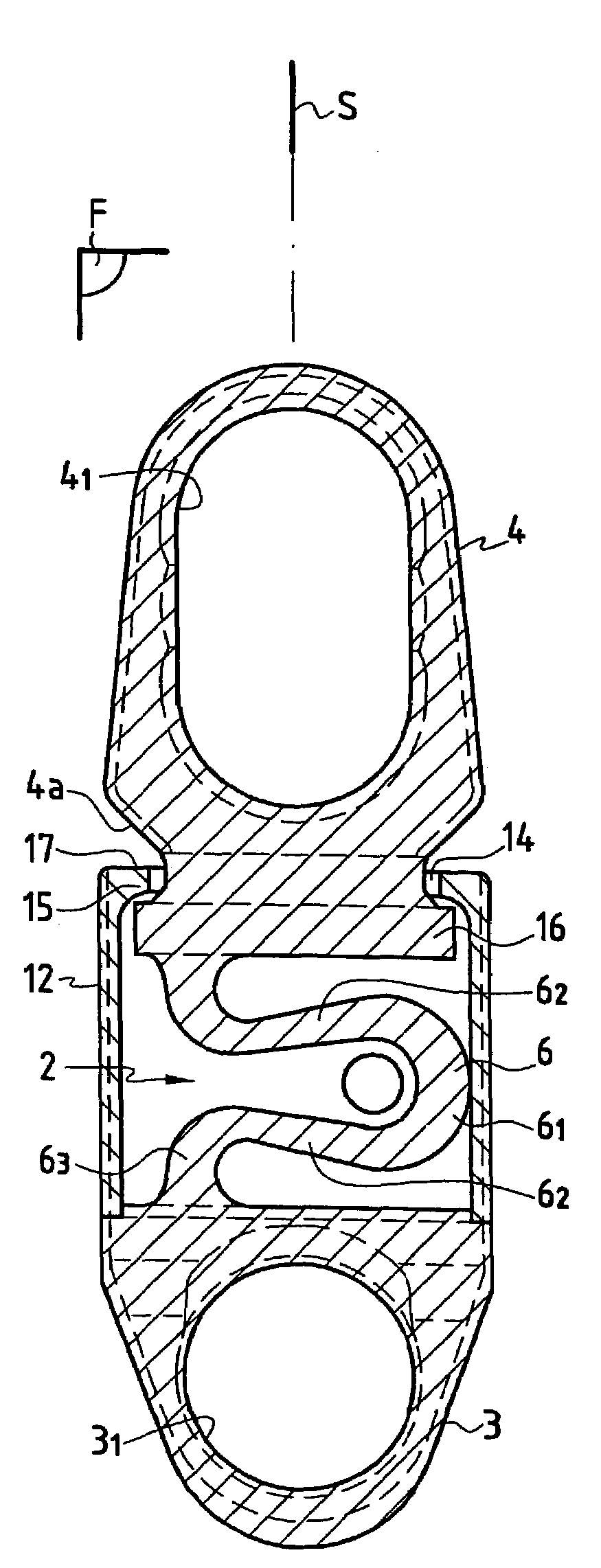
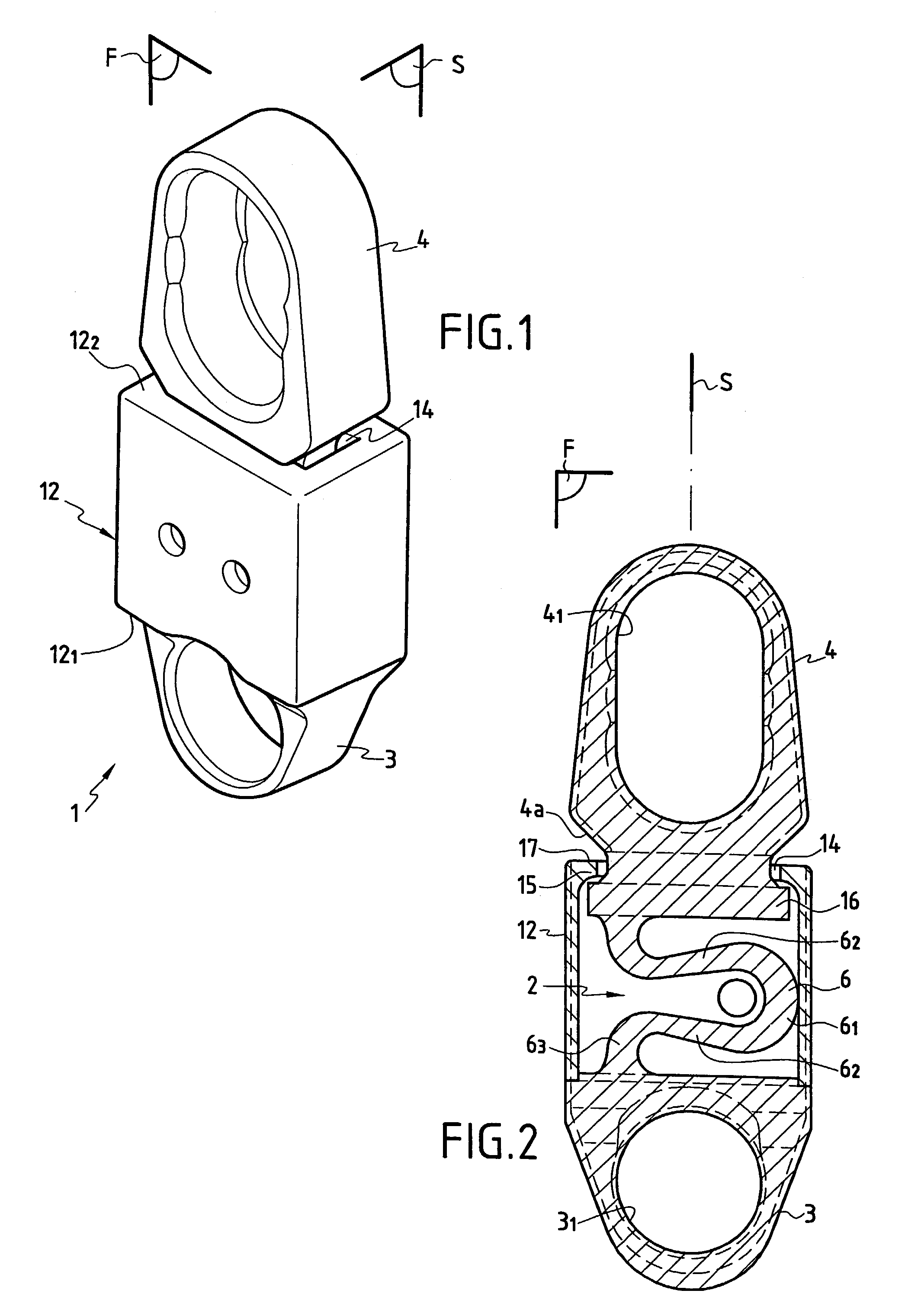
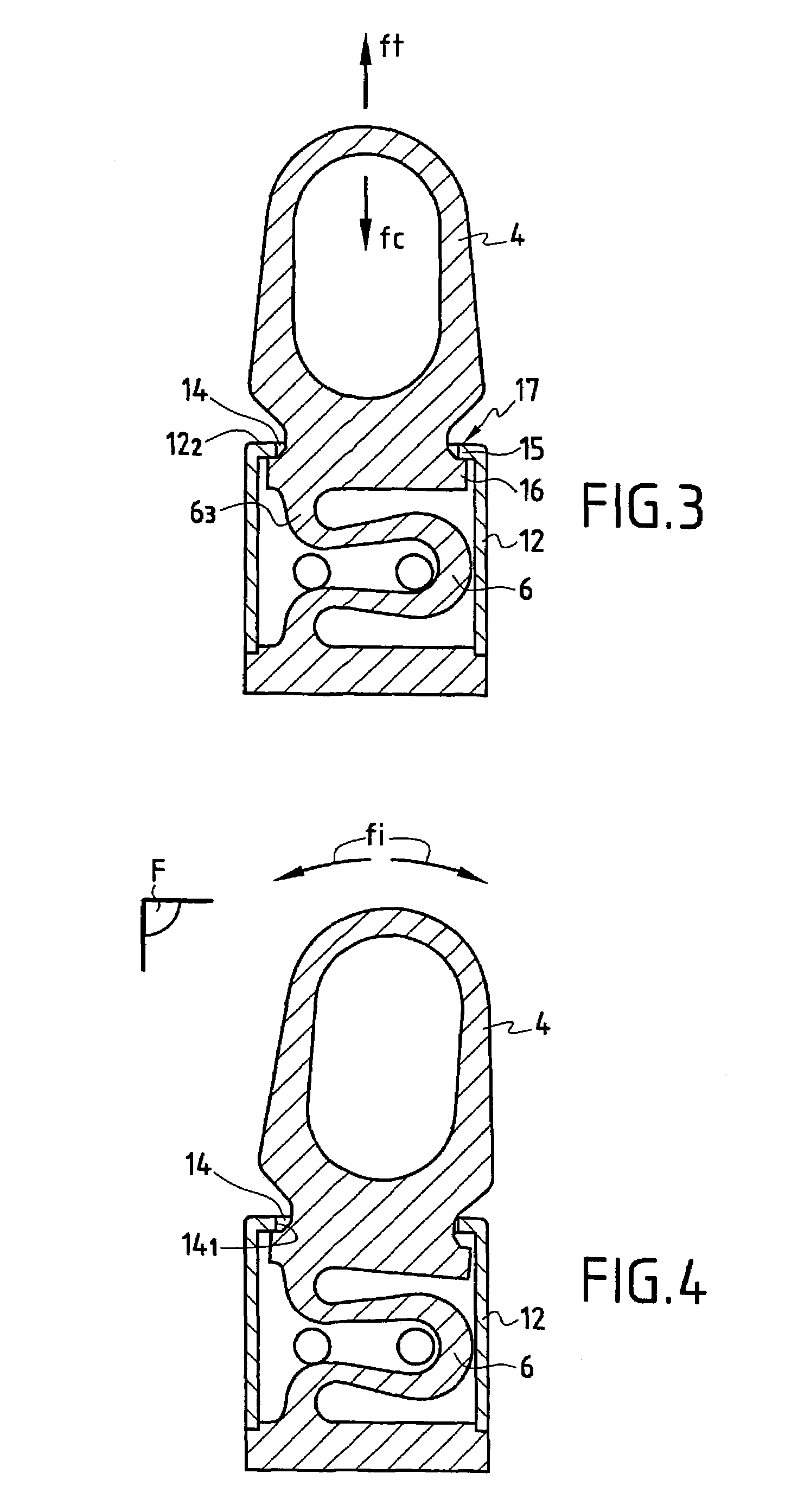
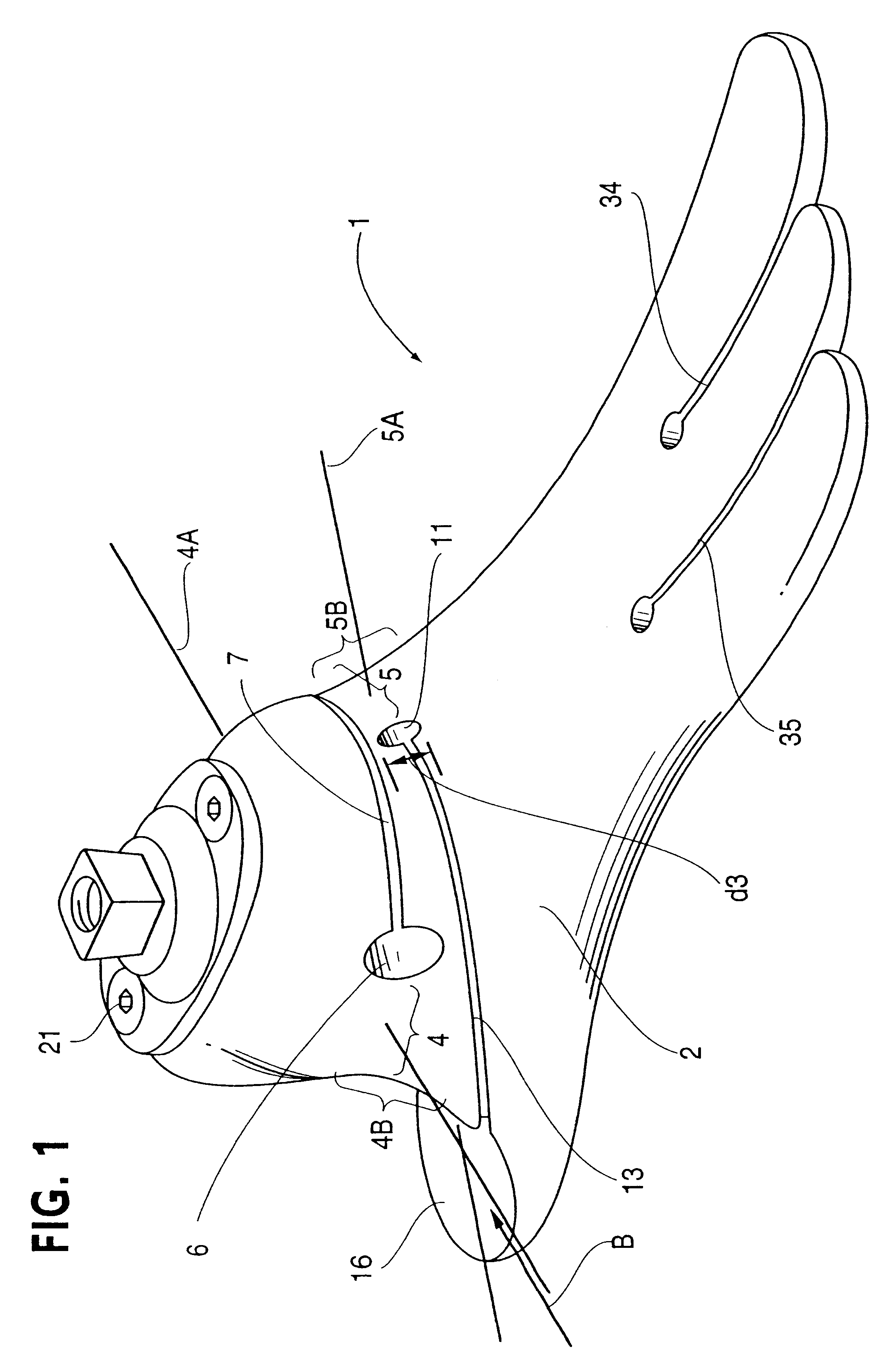
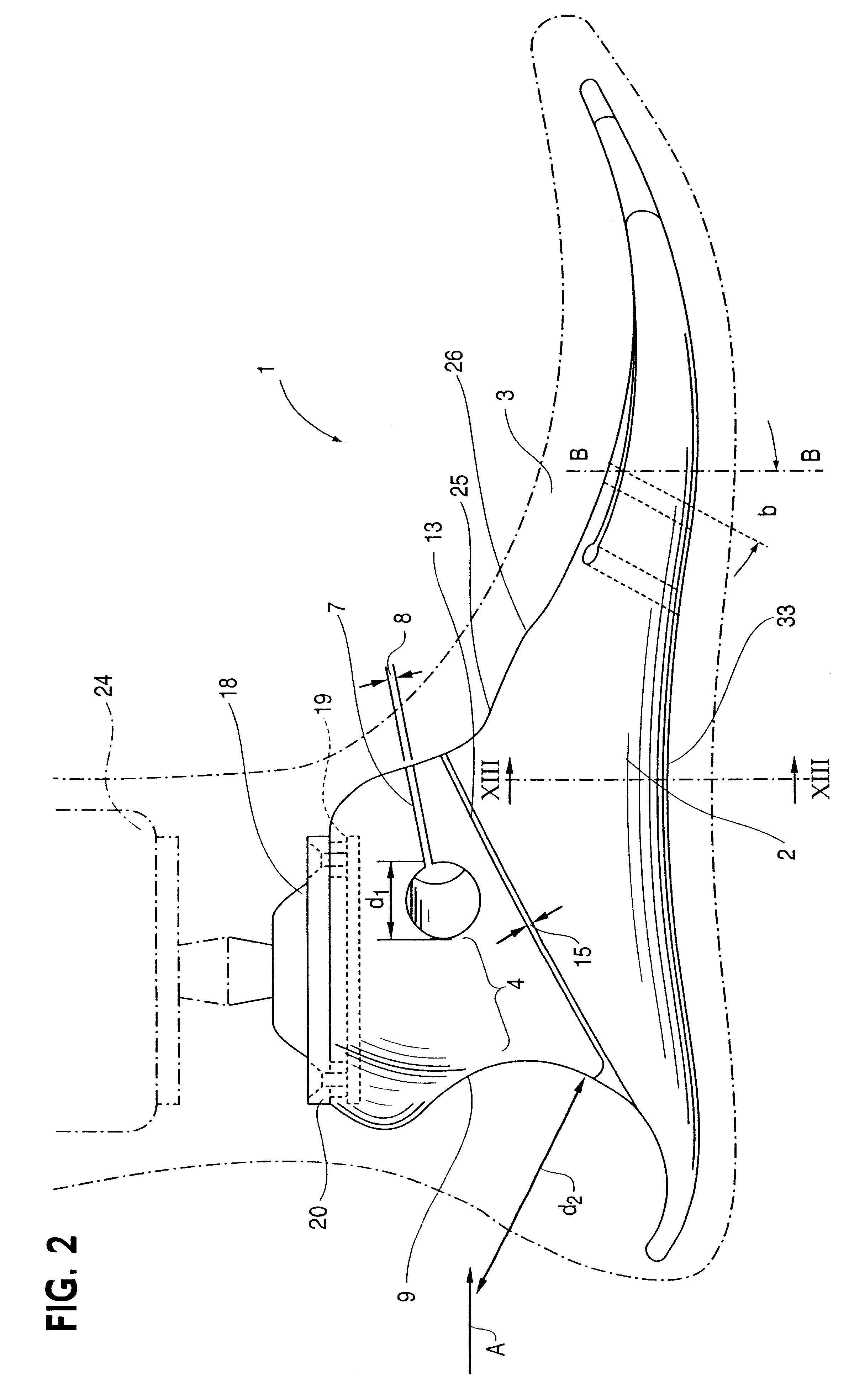
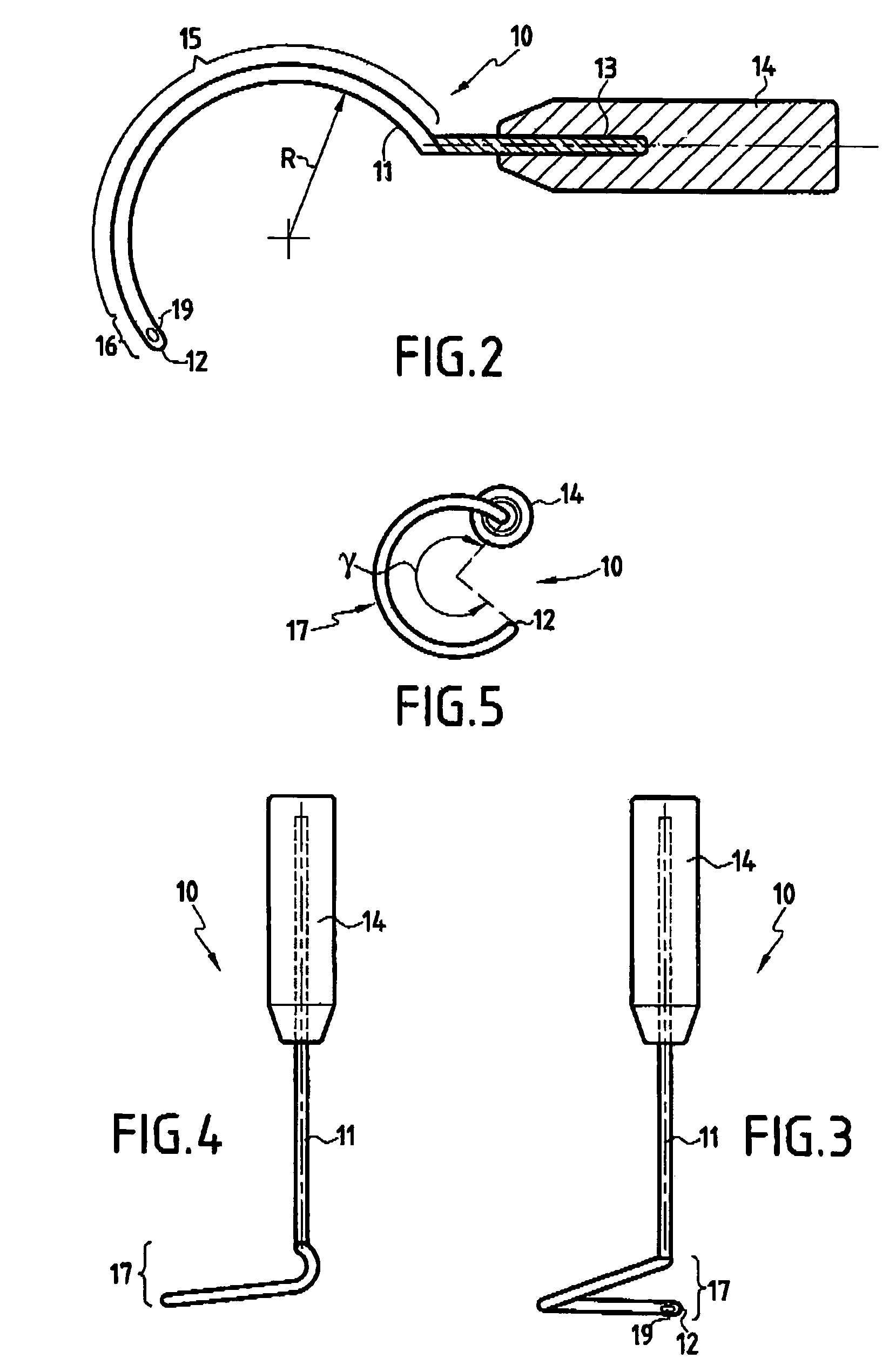
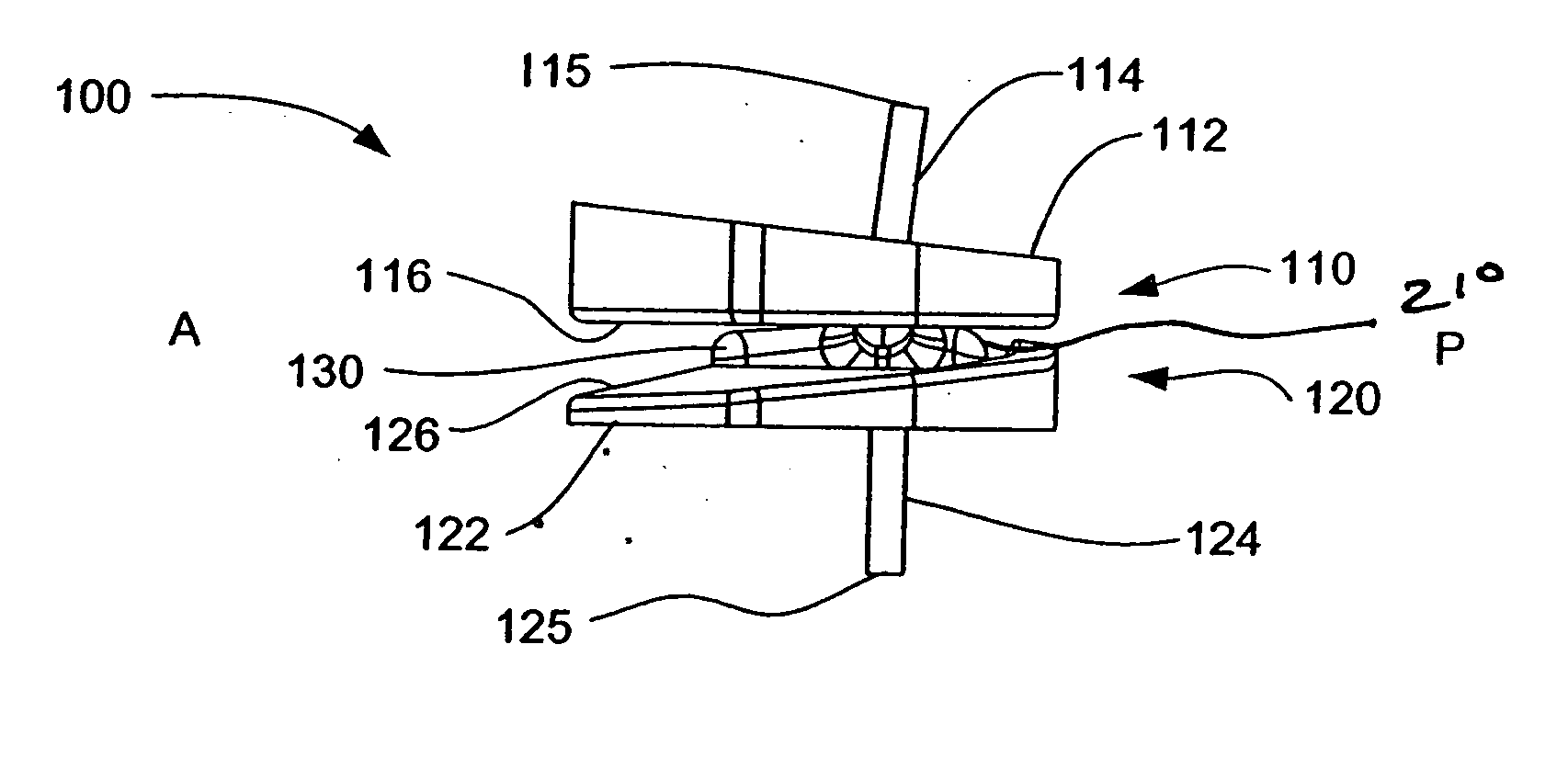
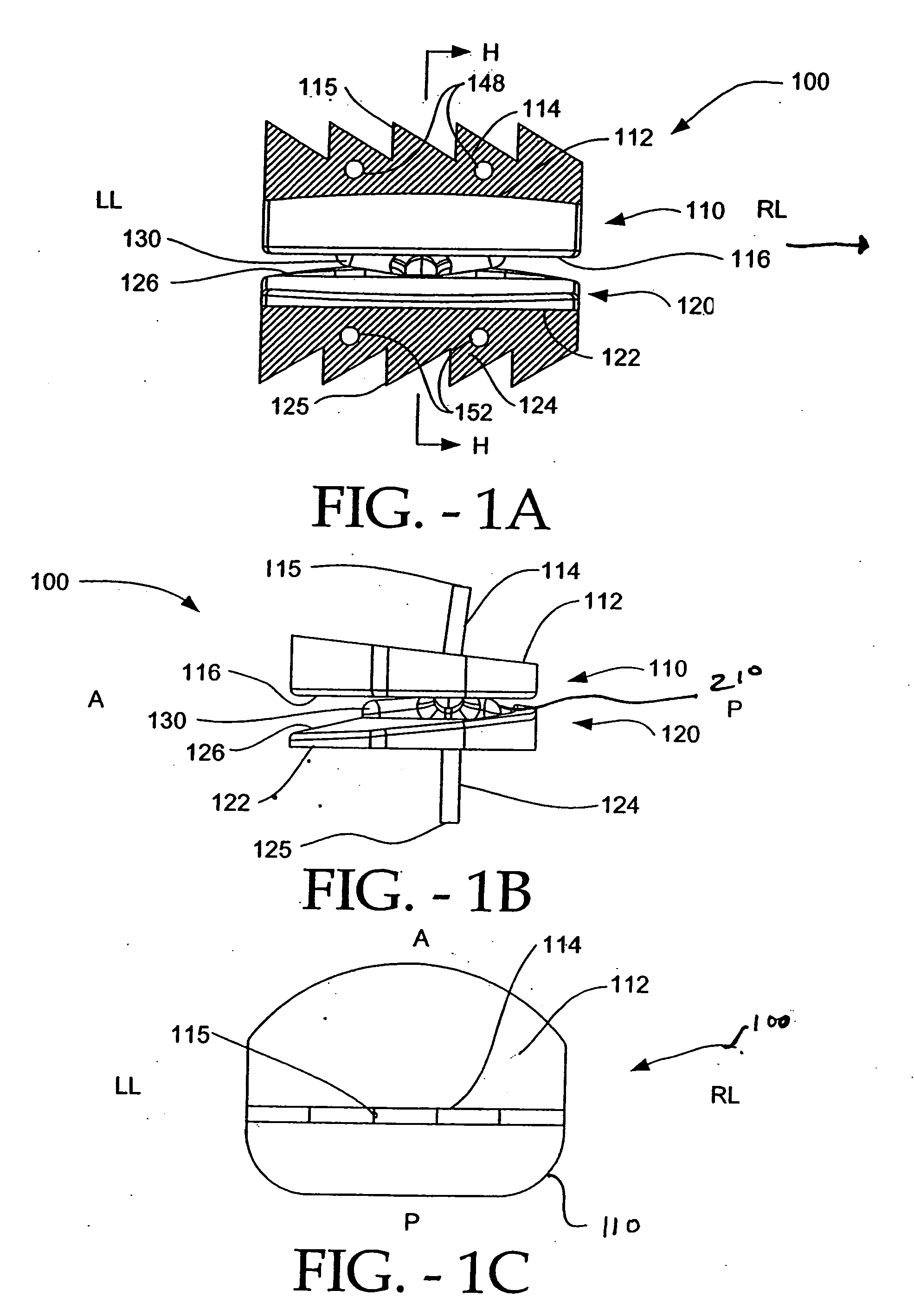
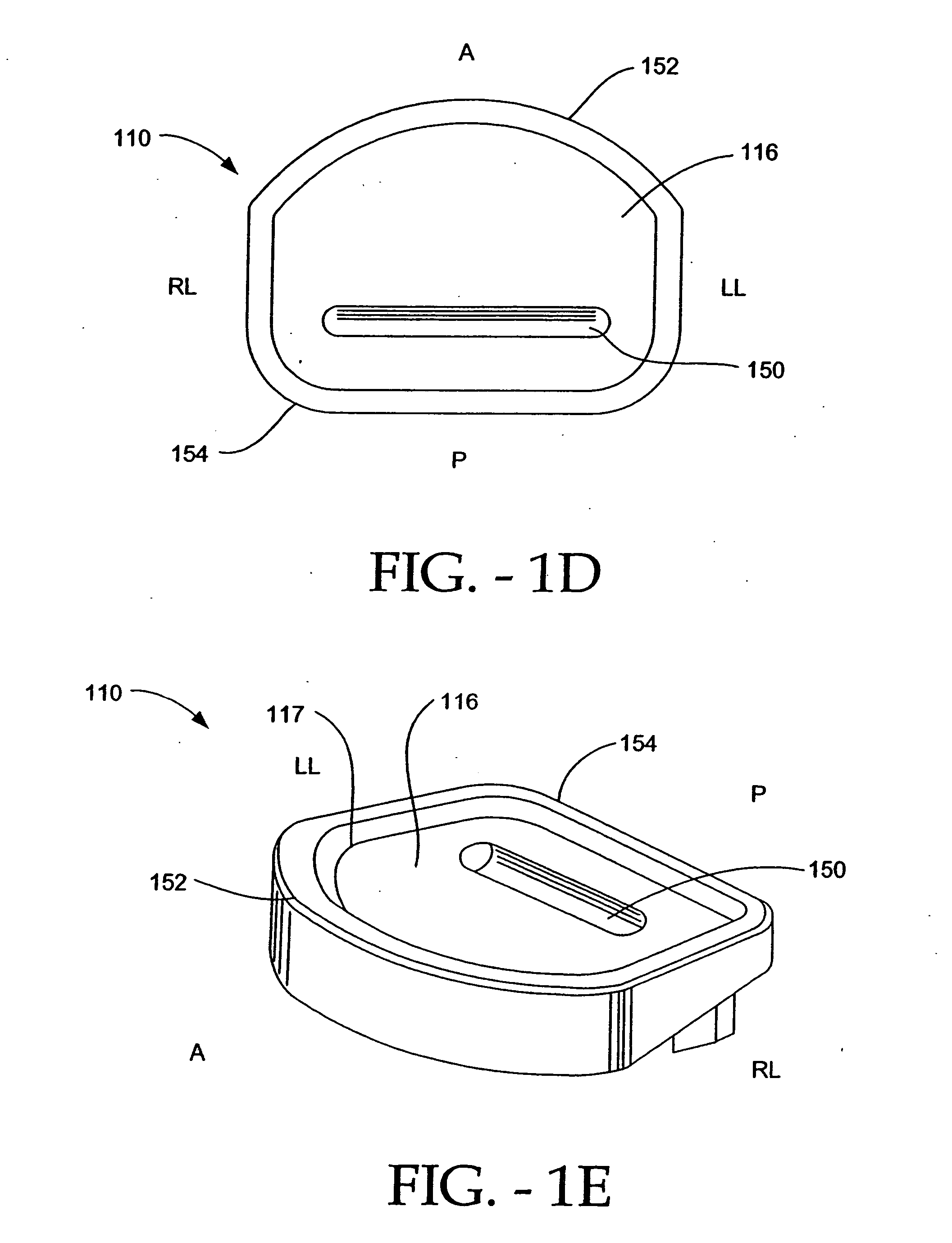
Dynamic intervertebral connection device with controlled multidirectional deflection
In the osteosynthesis device of the invention, the elastically deformable connection system comprises: a deformable connection member presenting: in a "sagittal" plane, determined stiffness for exerting a return force on flexion-extension movements between the fixing portions; in a "frontal" plane perpendicular to the sagittal plane, determined stiffness for exerting a return force on lateral inflexion movements between the fixing portions, the stiffness of the deformable connection member in the frontal plane being less than its stiffness in the sagittal plane; and along an axis defined by the intersection between the sagittal and frontal planes, determined stiffness for exerting a return force on traction-compression movements between the fixing portions; and means for limiting flexion-extension, traction-compression, and lateral inflexion movements between the fixing portions.
Owner:SCIENTX
Anatomical interbody implant and gripper for same
The invention relates to an intersomatic implant designed to be inserted in the disk space defined between two adjacent vertebrae, namely an overlying vertebra and an underlying vertebra, for the purpose of reestablishing the anatomic space between the vertebrae, the implant being in the form of a cage (1) that is generally in the shape of a rectangular block having at least two sagittal walls (2, 3) interconnected at least by an anterior transverse wall (4) and by a posterior transverse wall (5), the walls (2 to 5) presenting rims (10) extending on one surface to define a first transverse face (8) and on the other side to define a second transverse face (9).According to the invention, the implant comprises:a first transverse face (8) presenting in the sagittal plane a convex profile congruent with the sagittal anatomic profile of an overlying vertebra; anda second transverse face presenting in the frontal plane a convex profile congruent with the frontal anatomic profile of an overlying vertebra.
Owner:SCIENTX
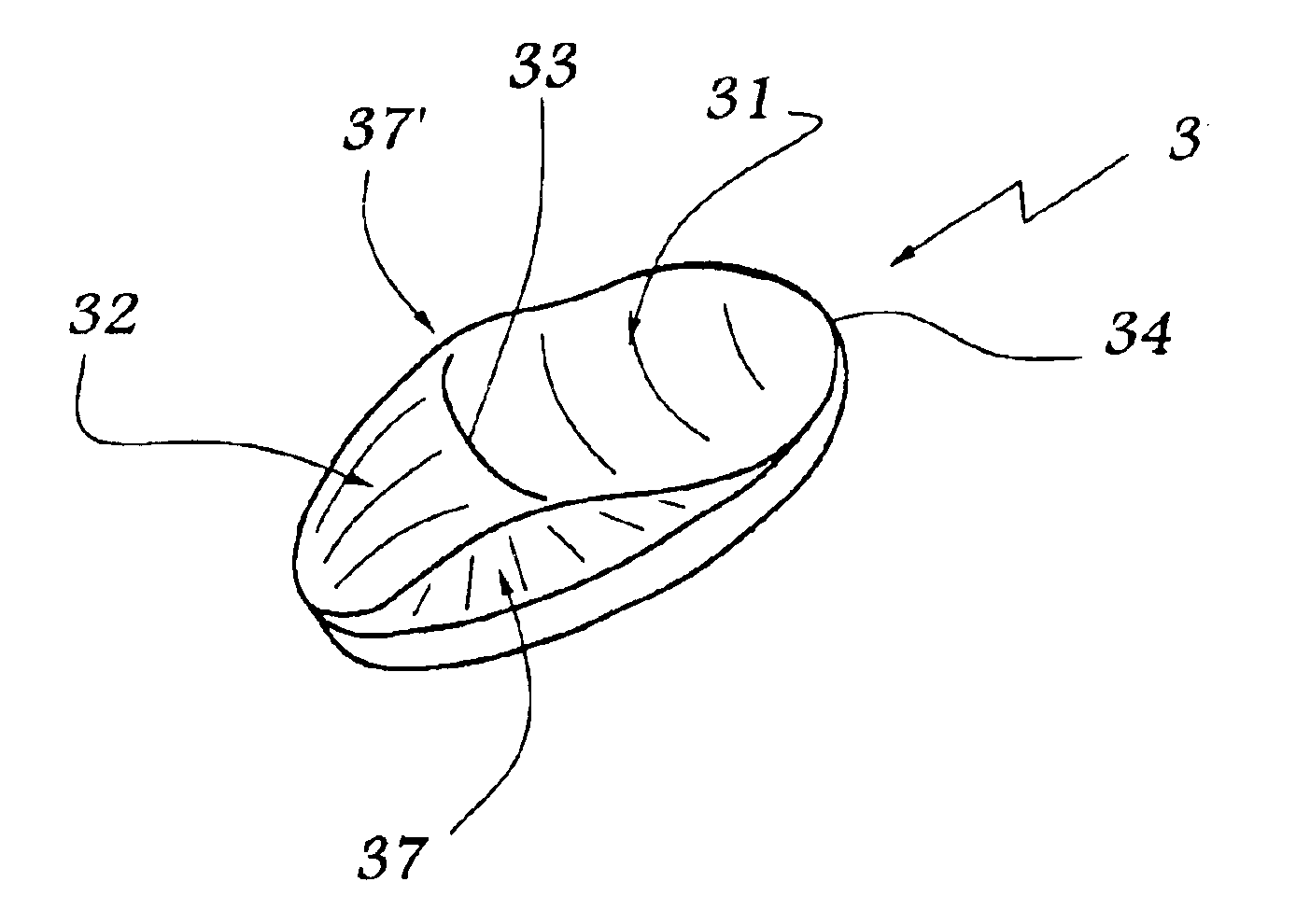
Prosthetic intervertebral discs
Prosthetic intervertebral discs, systems including such prosthetic intervertebral discs, and methods for using the same are described. The subject prosthetic discs include upper and lower endplates separated by a compressible core member. The subject prosthetic discs exhibit stiffness in the vertical direction, torsional stiffness, bending stiffness in the saggital plane, and bending stiffness in the front plane, where the degree of these features can be controlled independently by adjusting the components, construction, and other features of the discs.
Owner:SPINAL KINETICS
Anterior spinal implant
InactiveUS20050149188A1Resists migrationIncrease contact areaBone implantJoint implantsSagittal planeSurgery
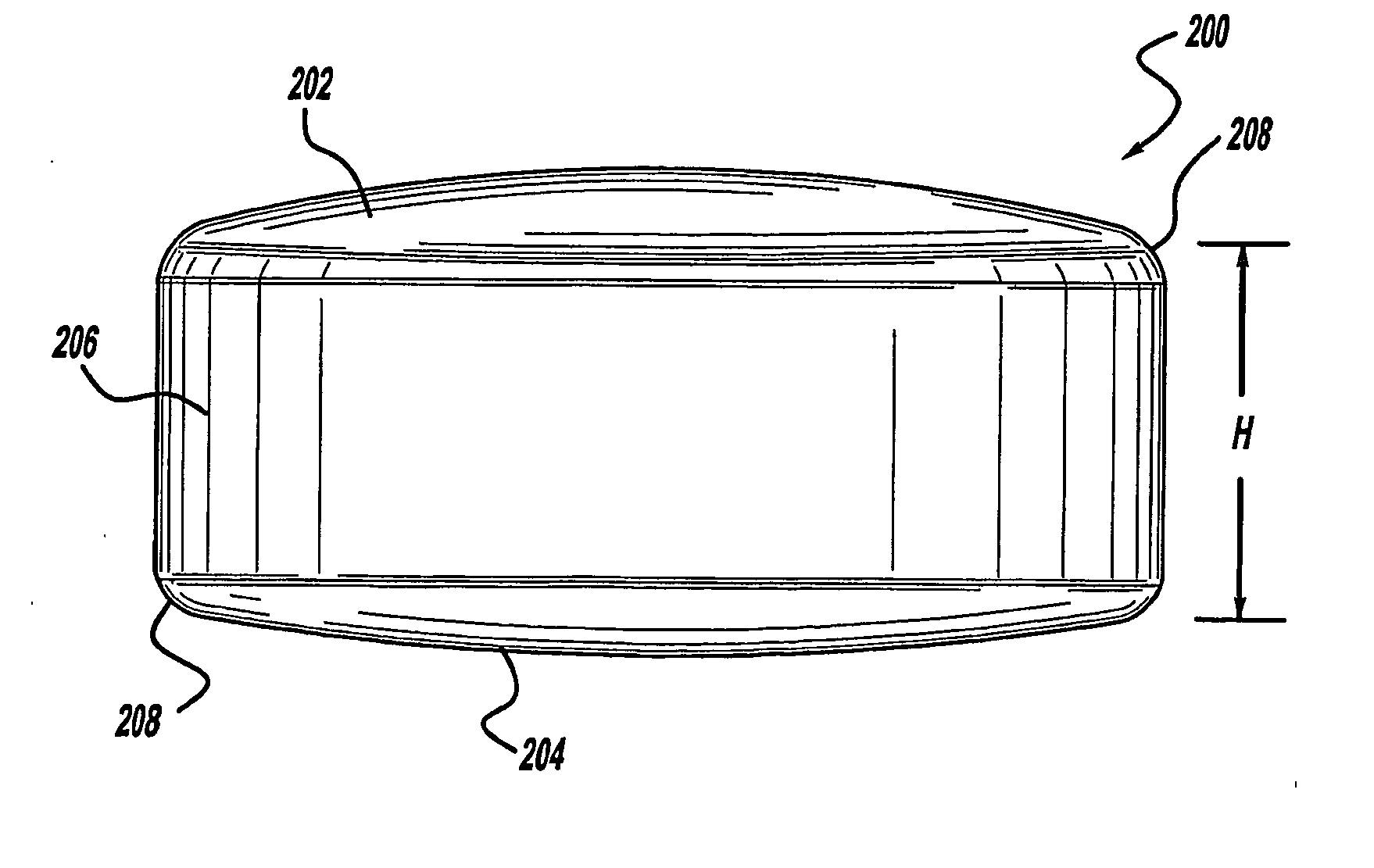
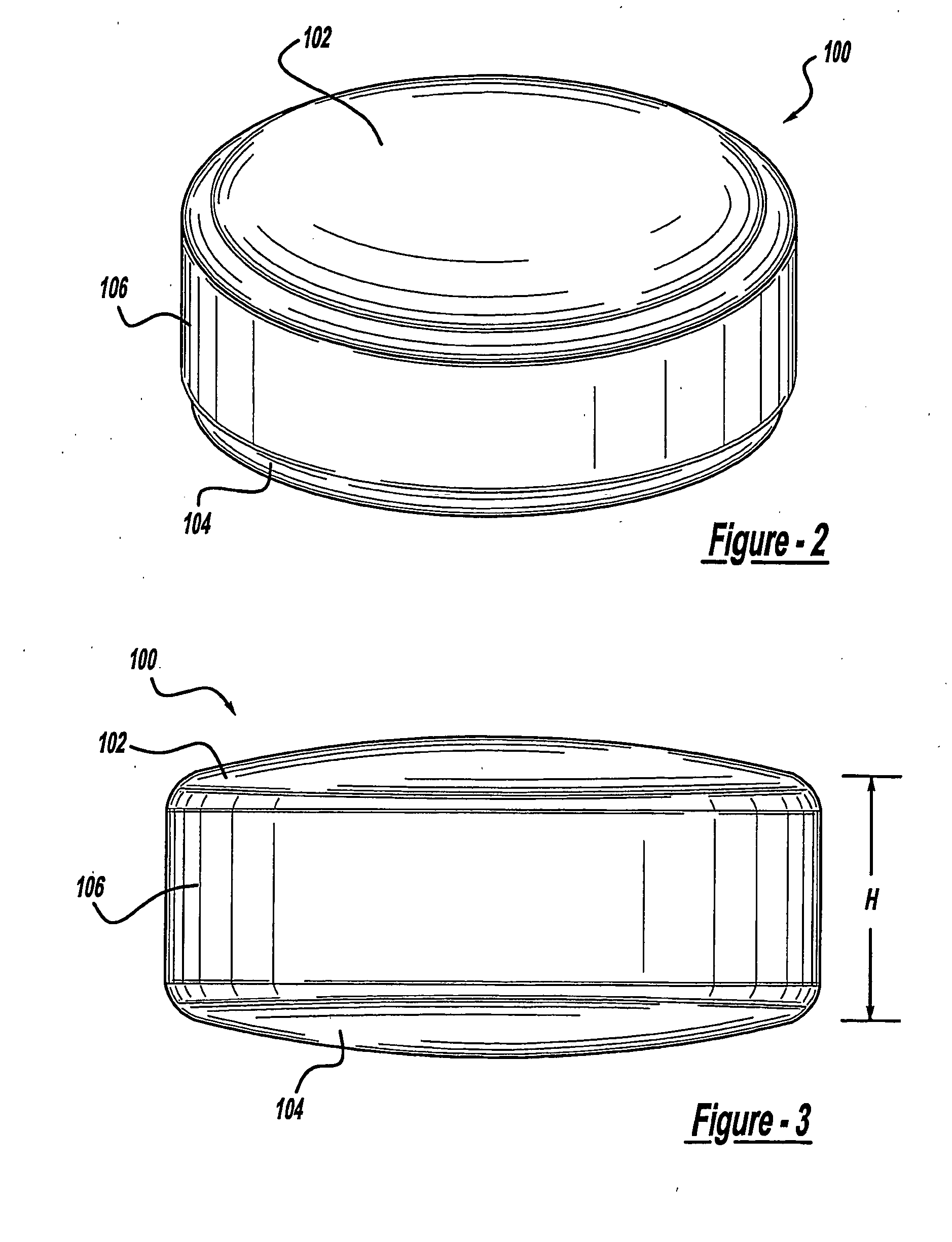
An anterior spinal implant includes a superior end face, an inferior end face and a sidewall extending between the superior end face and the inferior end face. The superior end face and the inferior end face are convex. In one application, the superior and inferior end faces are convex. The sidewall includes a convexly curved leading portion, a convexly curved trailing portion and a pair of substantially planar side portions. The superior and inferior end faces transition in a sagittal plane from a first radius of curvature to a second radius of curvature. The first radius of curvature is smaller than the second radius of curvature. The apexes of the superior and inferior end faces are offset from a center of the implant.
Owner:EUROPEAN BIOINFORMATICS INSTITUTE
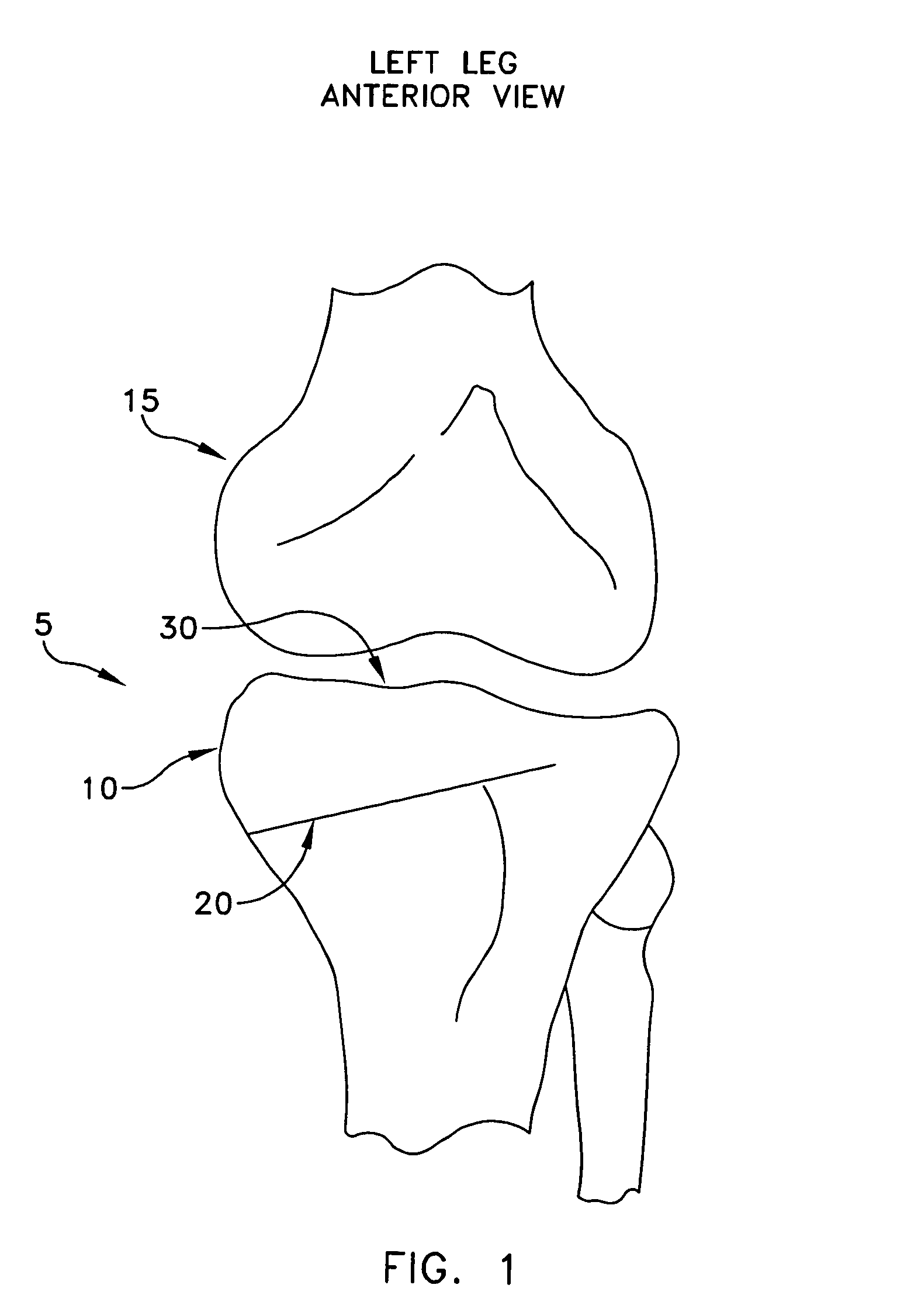
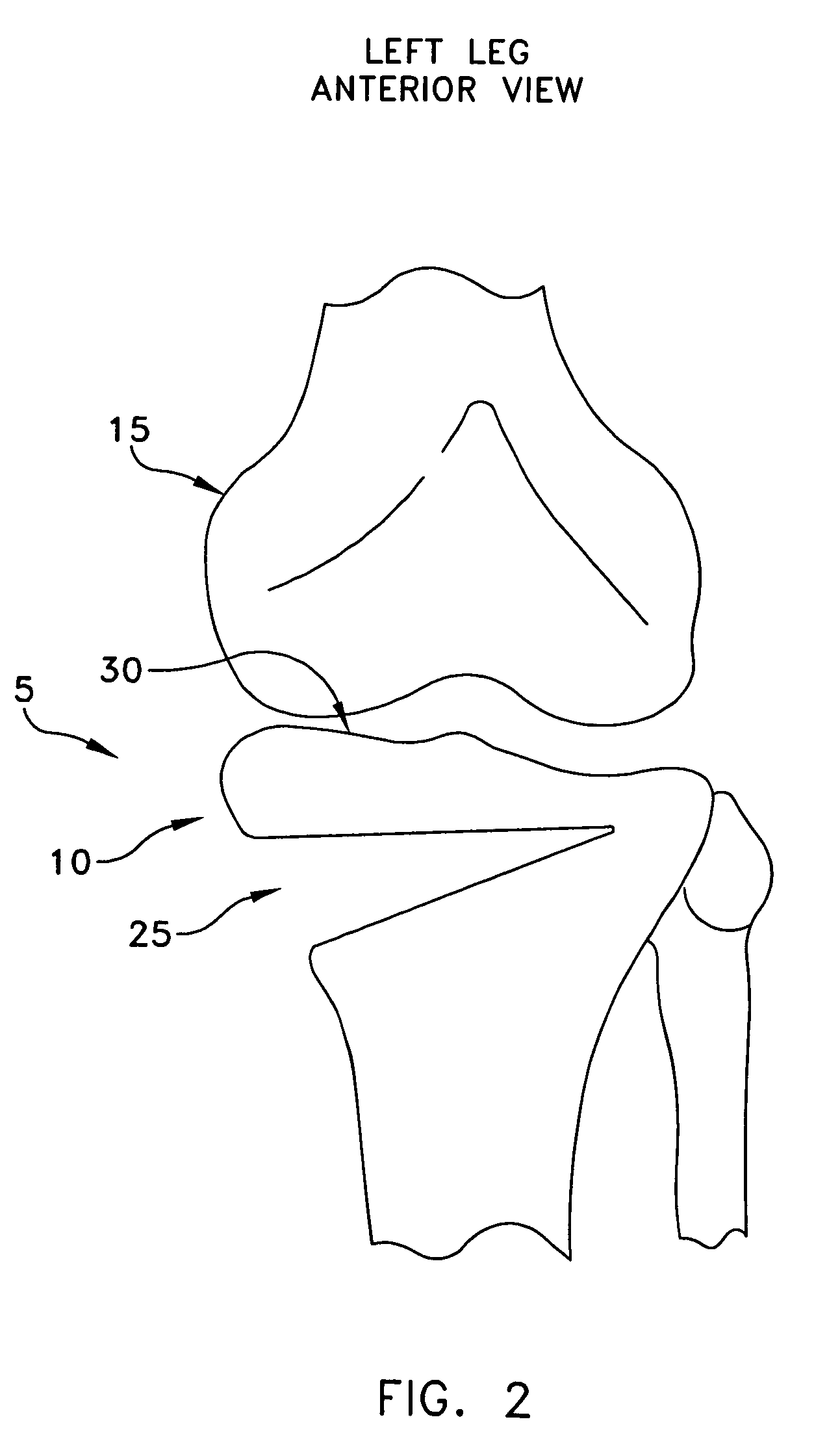
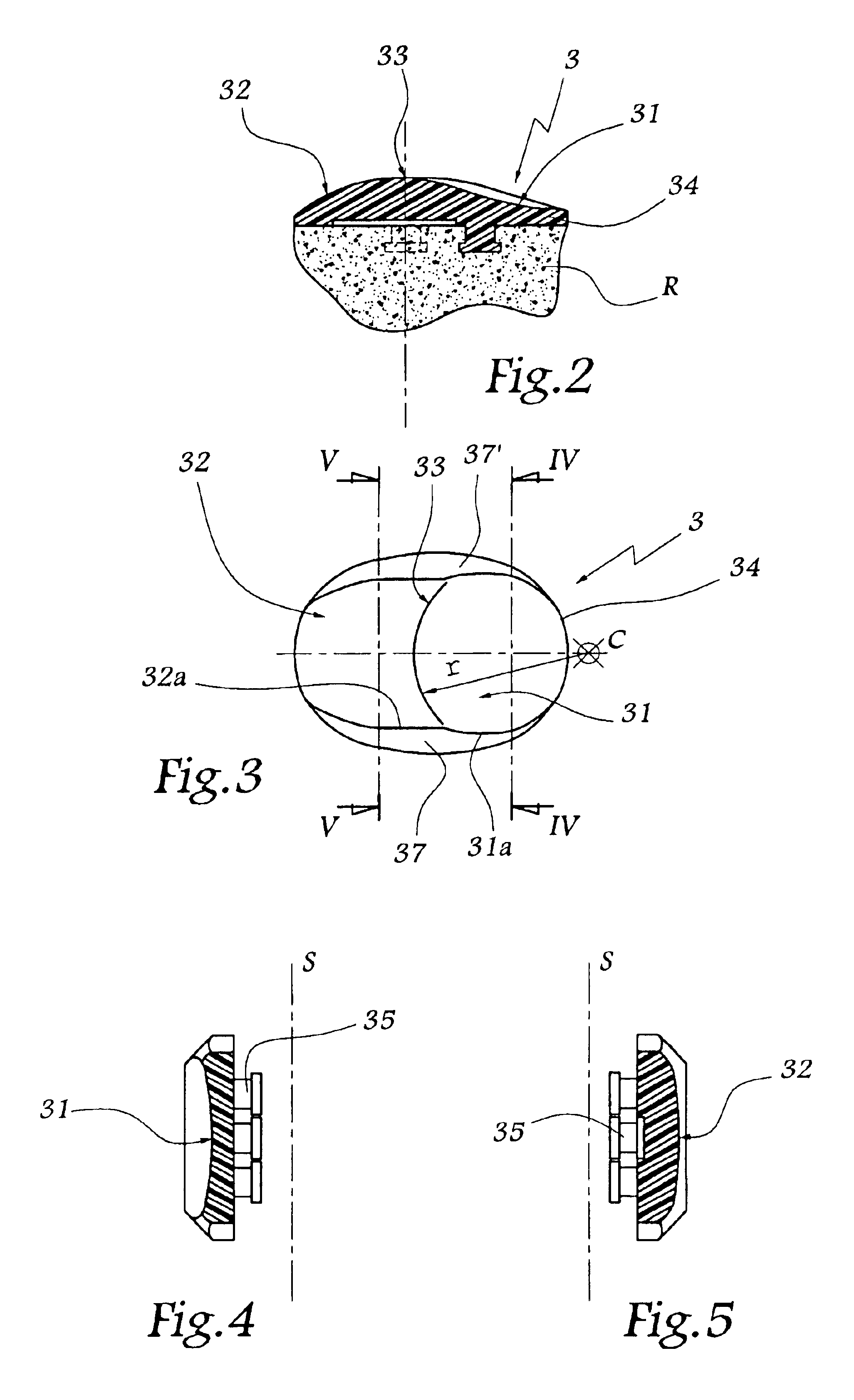
Knee prosthesis
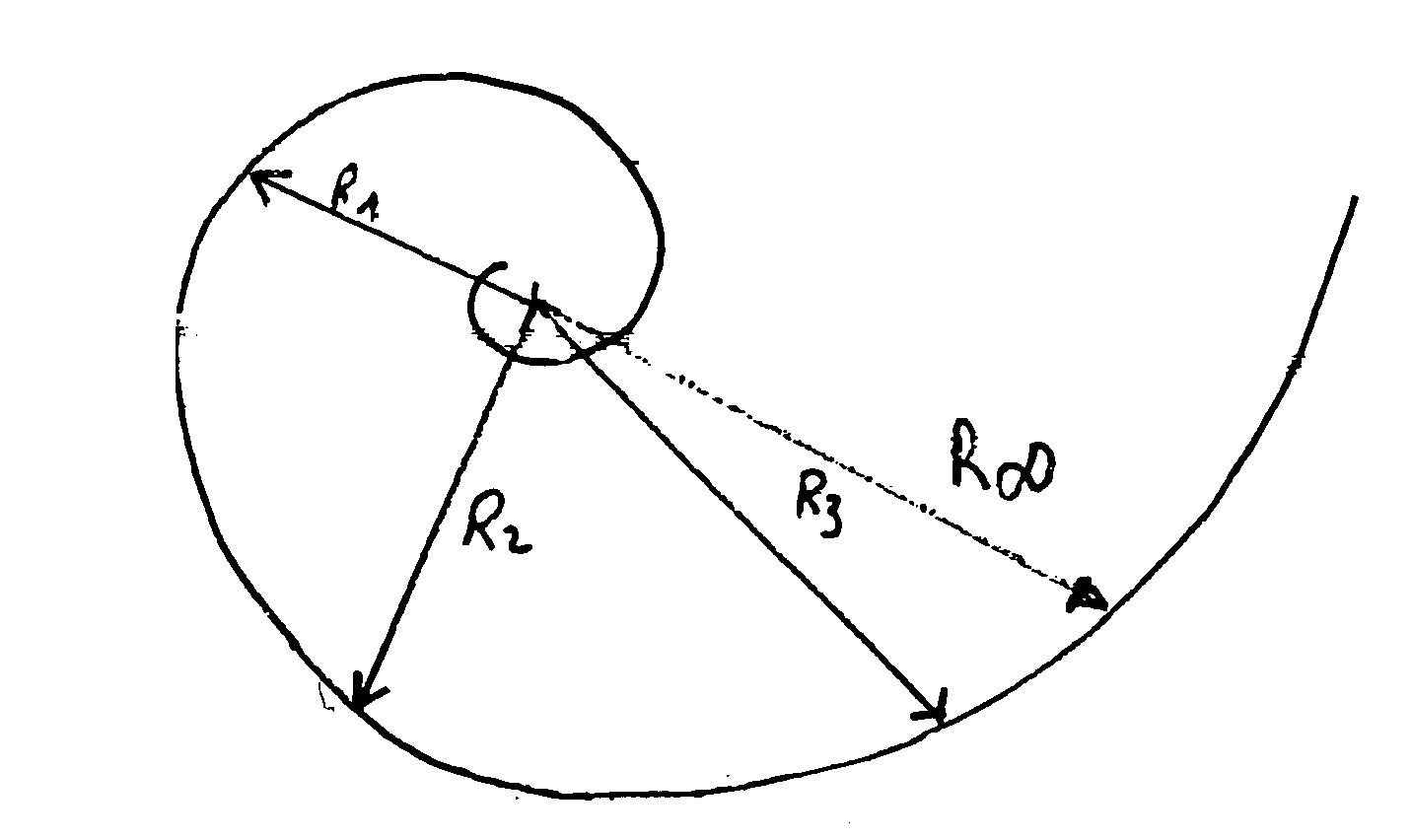
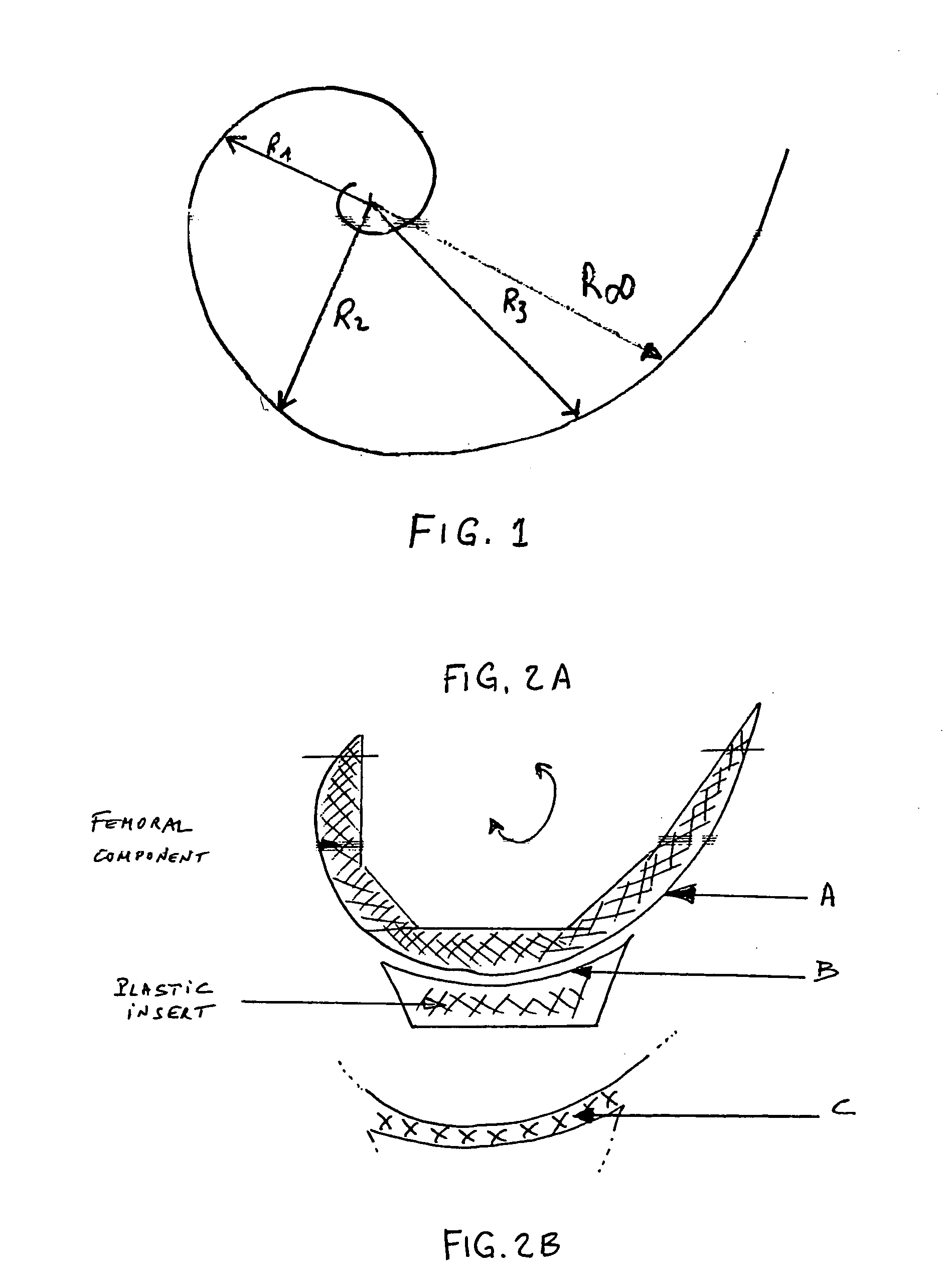
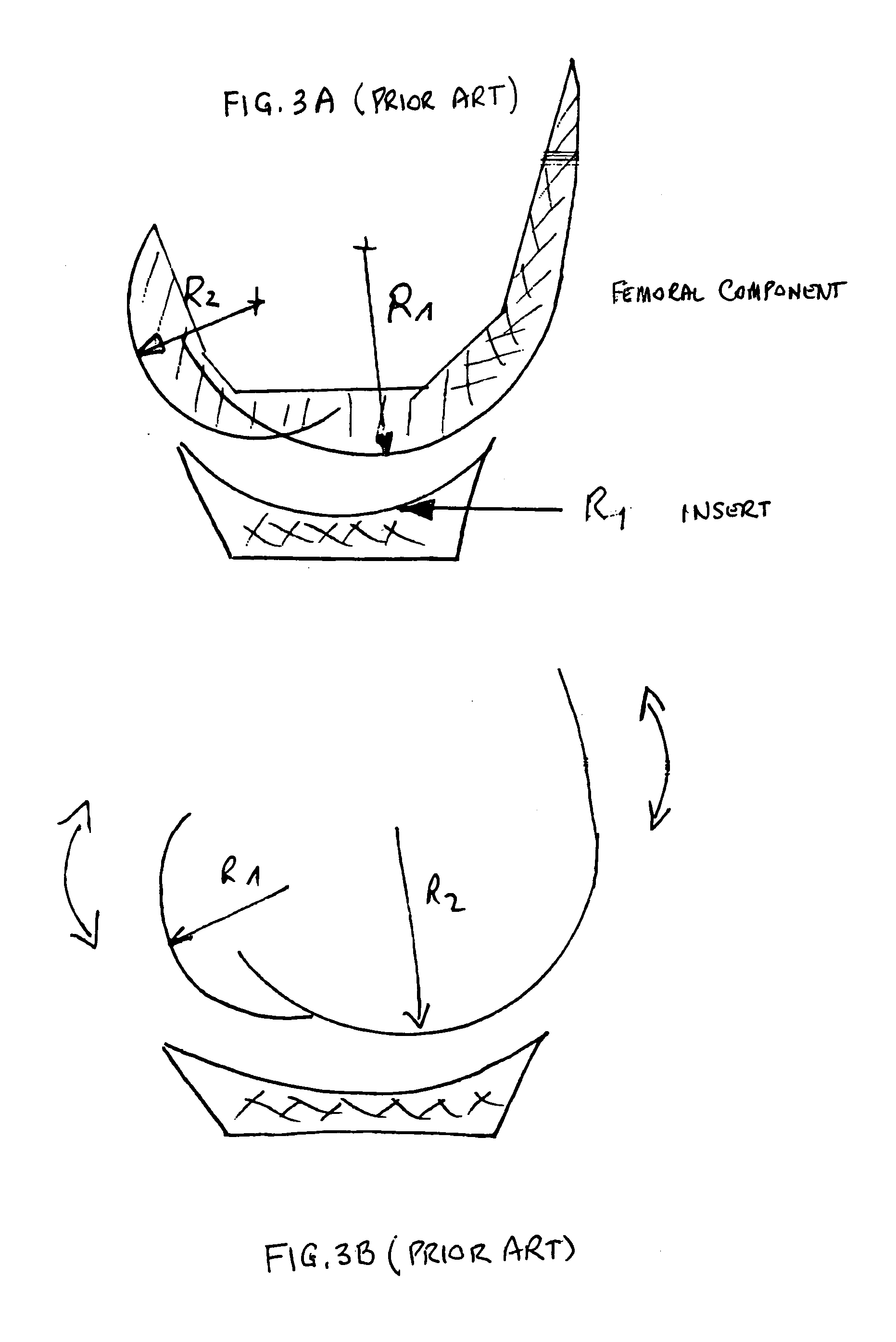
The invention concerns a prosthesis wherein the contact surfaces of the femoral part (i), the insert (3) and the knee joint are defined by the combination of two curves, a spiral-type curve in the saggital plane following an undulating curve (sinusoidal) in the frontal plane. The latter comprises two concave lateral parts and a central dome-shaped convex part, the three parts being connected without any angulation, protuberance, or flat parts or bends and providing continuous medio-lateral contact on the three zones, from complete extension to complete bending, and a concave-convex nesting in the central zone.
Owner:BERCOVY MICHEL
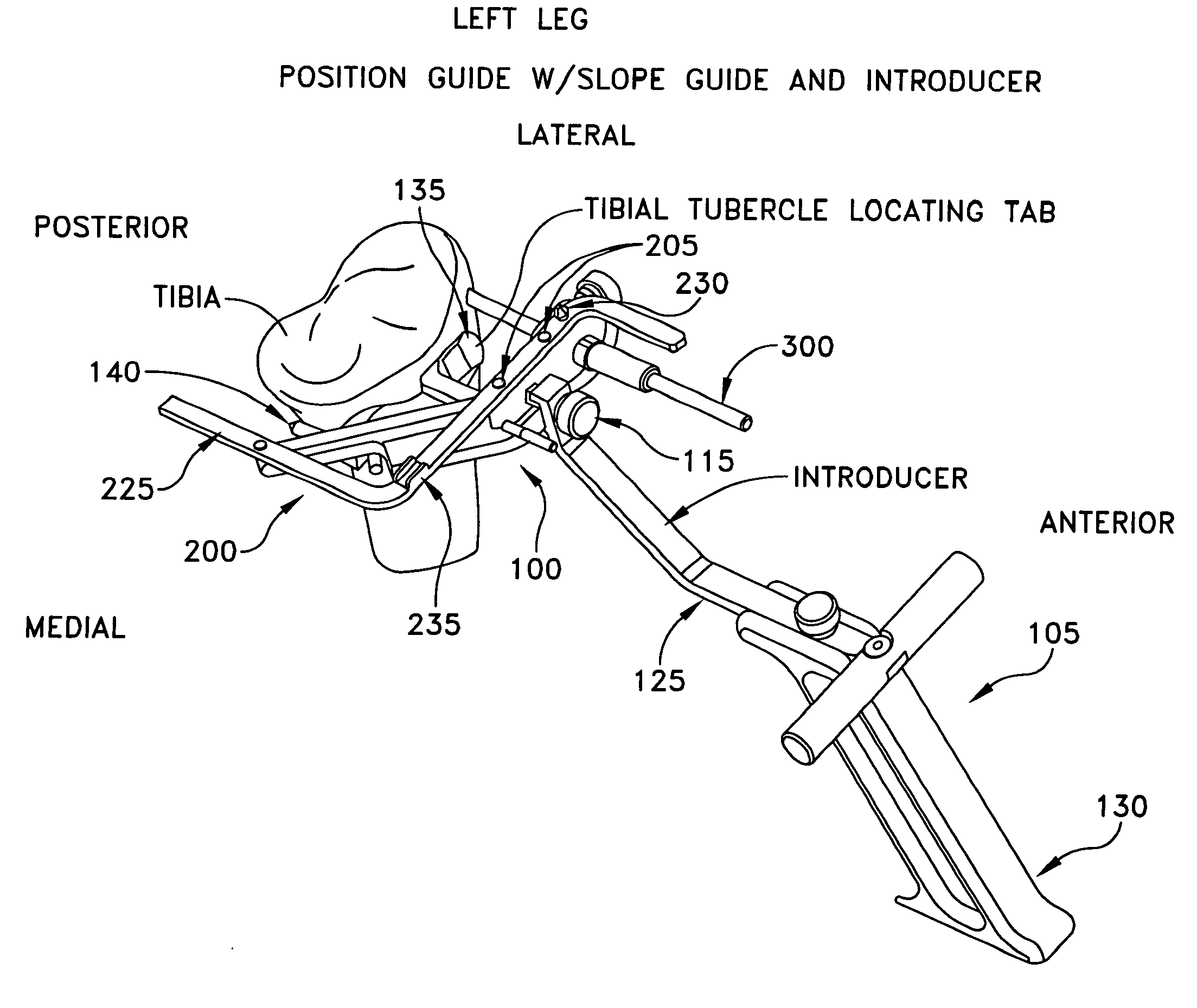
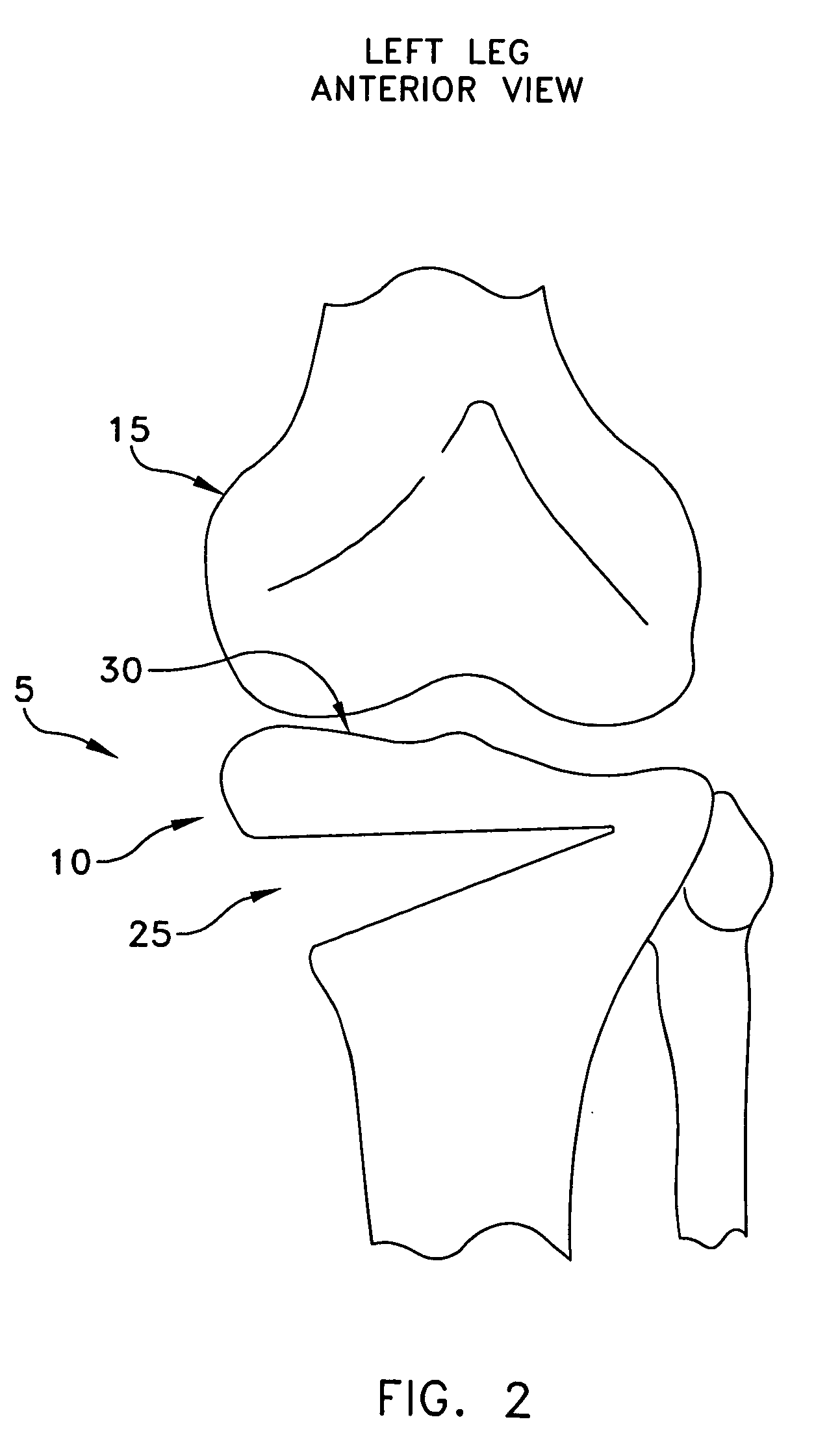
Method and apparatus for performing an open wedge, high tibial osteotomy
Apparatus for performing an open wedge, high tibial osteotomy, the apparatus comprising:cutting apparatus for forming an osteotomy cut in the tibia, the cutting apparatus comprising:targeting apparatus for identifying a cutting plane through the tibia and a boundary line for terminating a cut made along the cutting plane, wherein the boundary line is located within the tibia, parallel to the anterior-posterior slope of the tibia and parallel to the sagittal plane of the patient.A method for performing an open wedge, high tibial osteotomy, the method comprising:positioning targeting apparatus for identifying a cutting plane through the tibia and a boundary line for terminating a cut made along the cutting plane, wherein the boundary line is located within the tibia, parallel to the anterior-posterior slope of the tibia and parallel to the sagittal plane of the patient;cutting the bone along the cutting plane, with the cut terminating at the boundary line;moving the bone on either side of the cut apart so as to form the wedge-like opening in the bone; andstabilizing the bone.
Owner:ARTHREX
Patellar implant and knee prosthesis incorporating such an implant
InactiveUS6802864B2Improve contact stabilityReduce wearJoint implantsKnee jointsArticular surfacesArticular surface
A patellar implant for total or partial prosthesis of the knee joint incorporates an outer articular surface and an inner articular surface provided to cooperate respectively with an outer side and an inner side of a femoral trochlea or of a femoral prosthetic component. The inner and outer articular surfaces are separated by a transition ridge which is curved, as viewed from a front of the implant, so as to be concave facing the outer articular surface. The outer articular surface is concave in a plane parallel to a sagittal plane and in a transverse plane of the knee joint.
Owner:CORIN
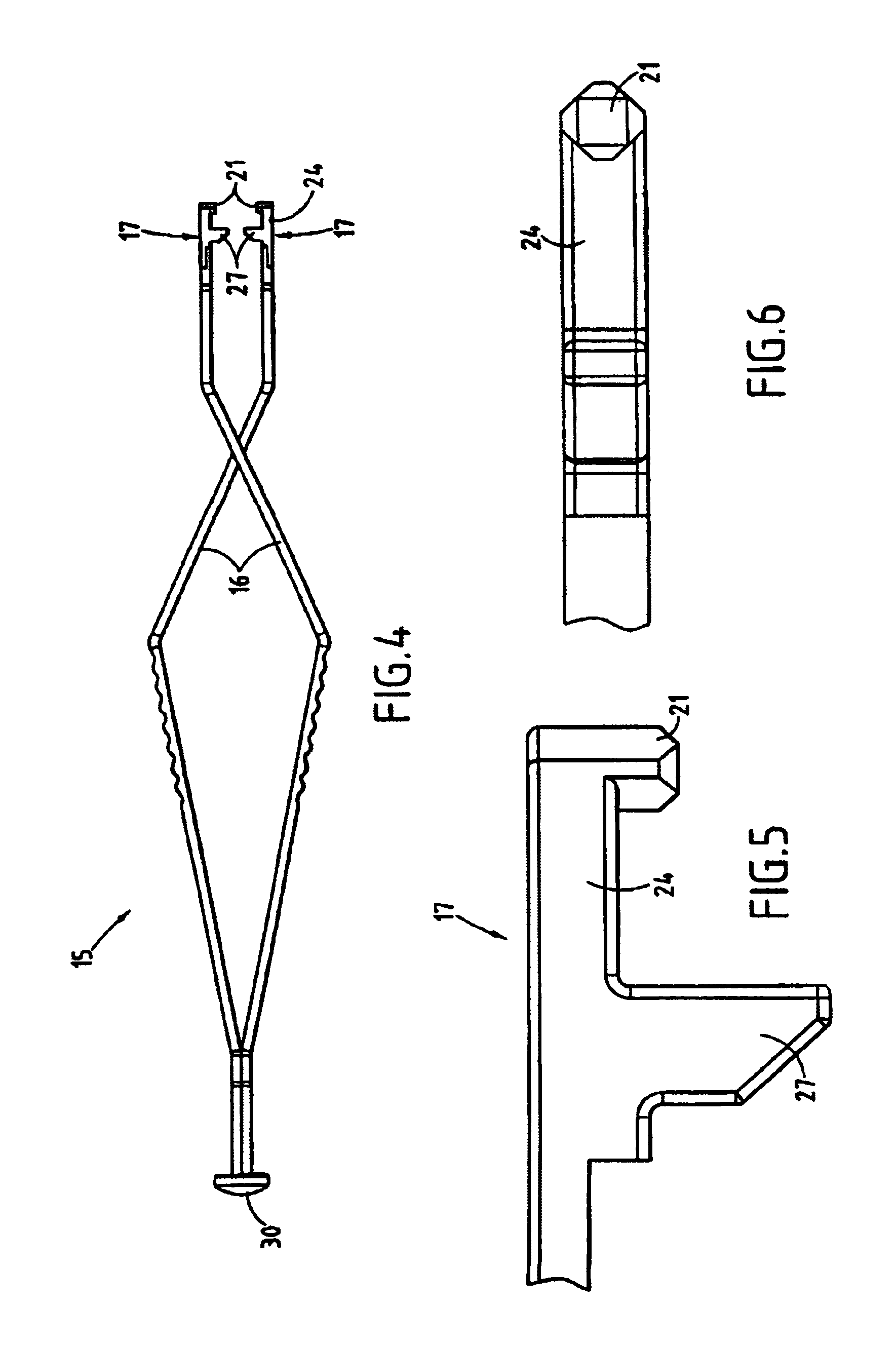
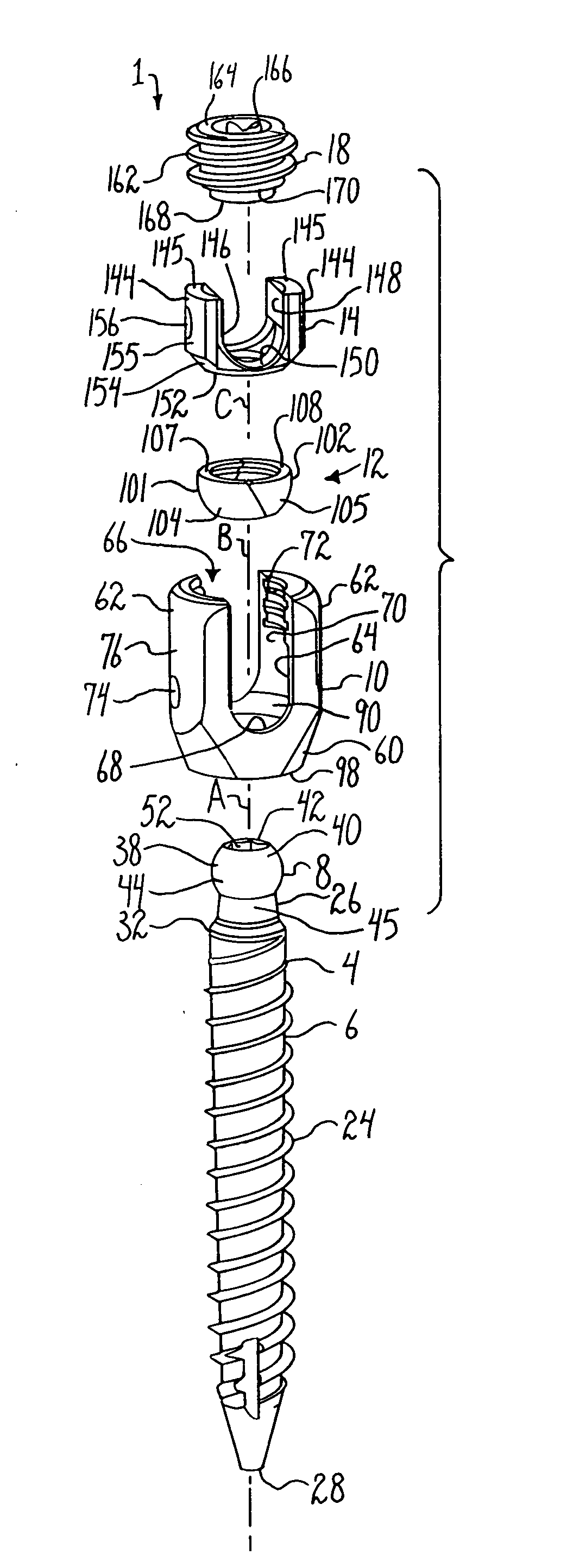
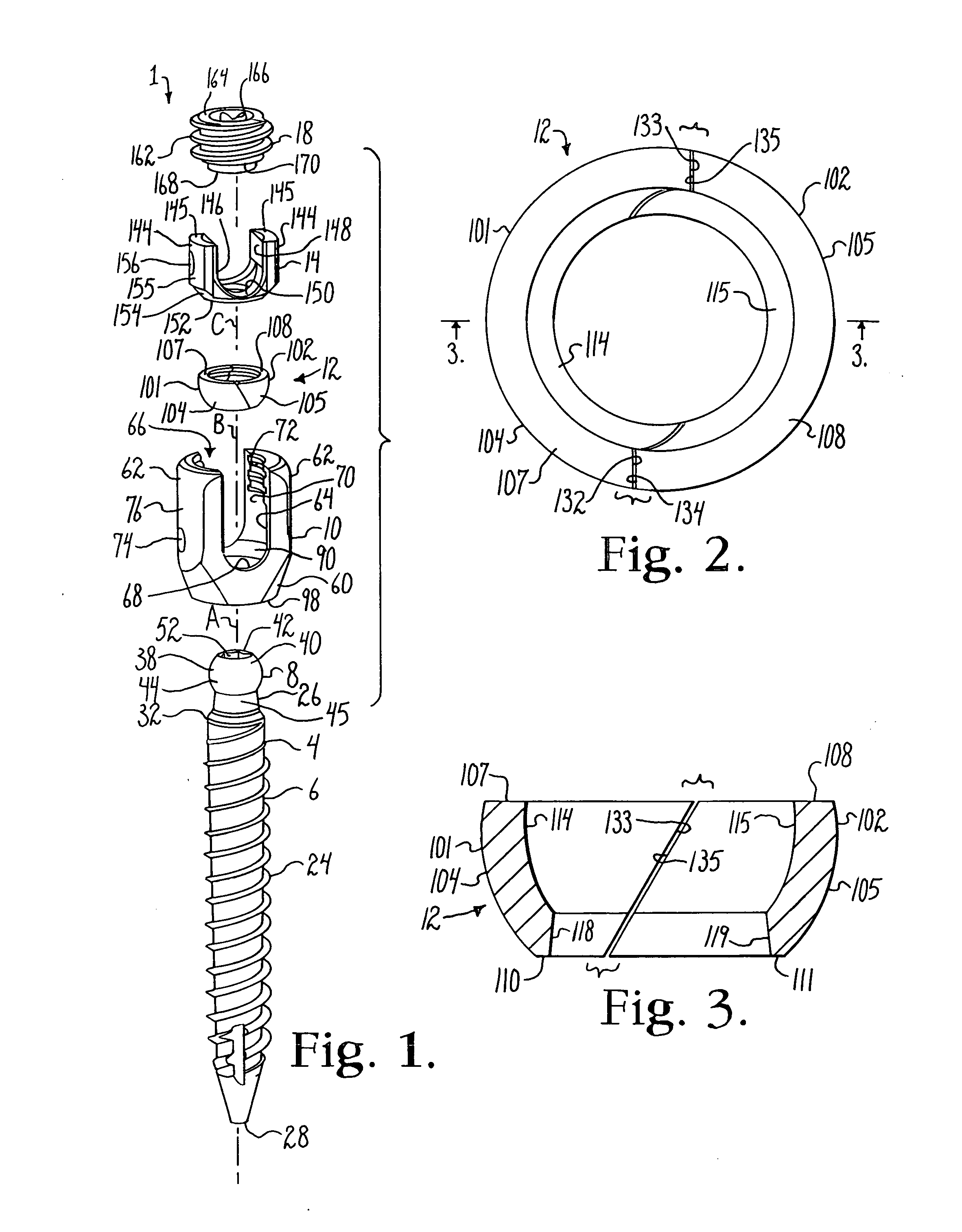
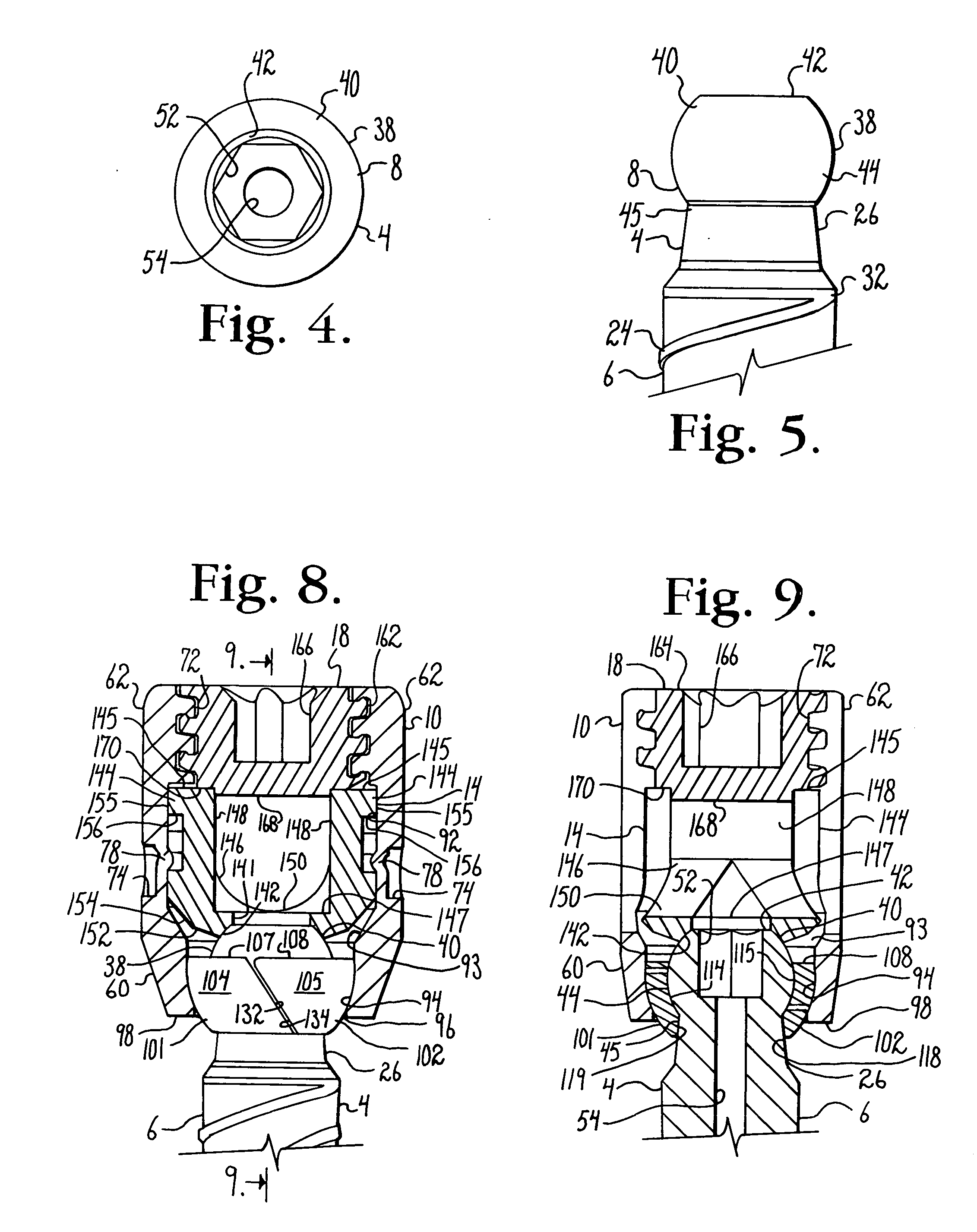
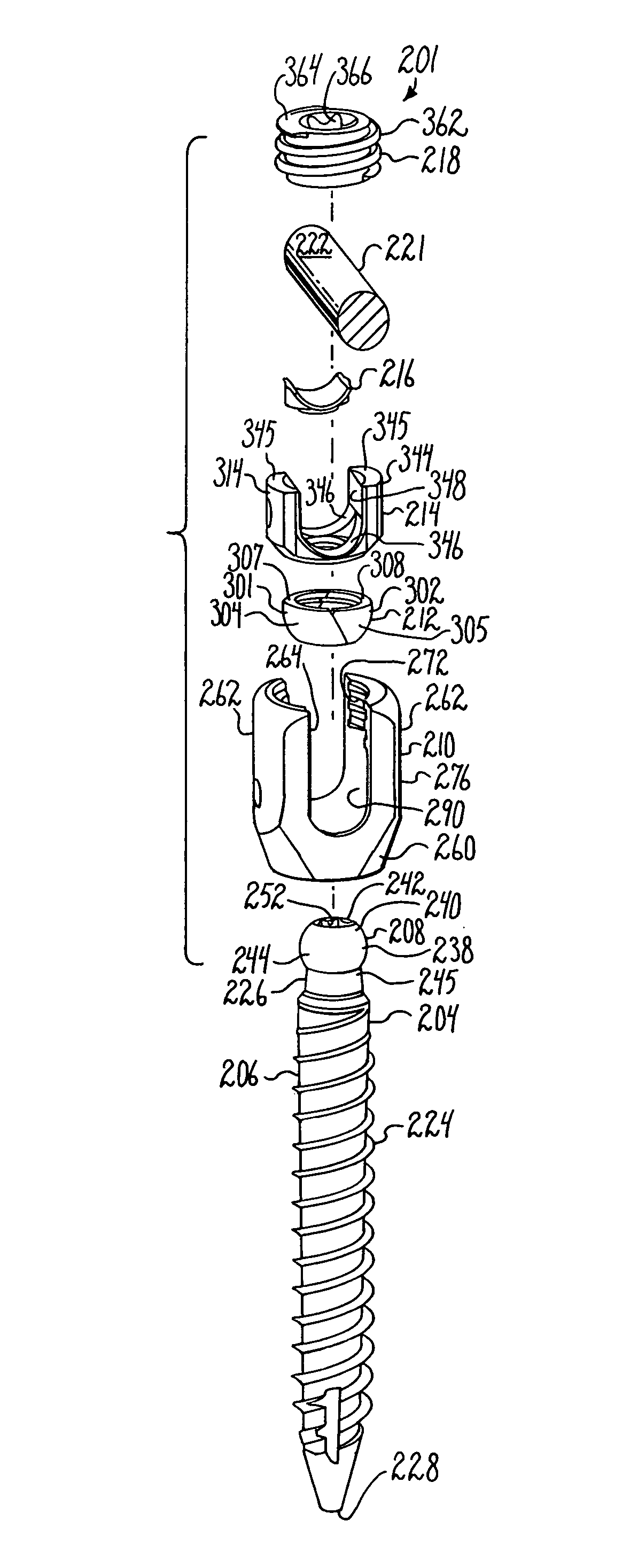
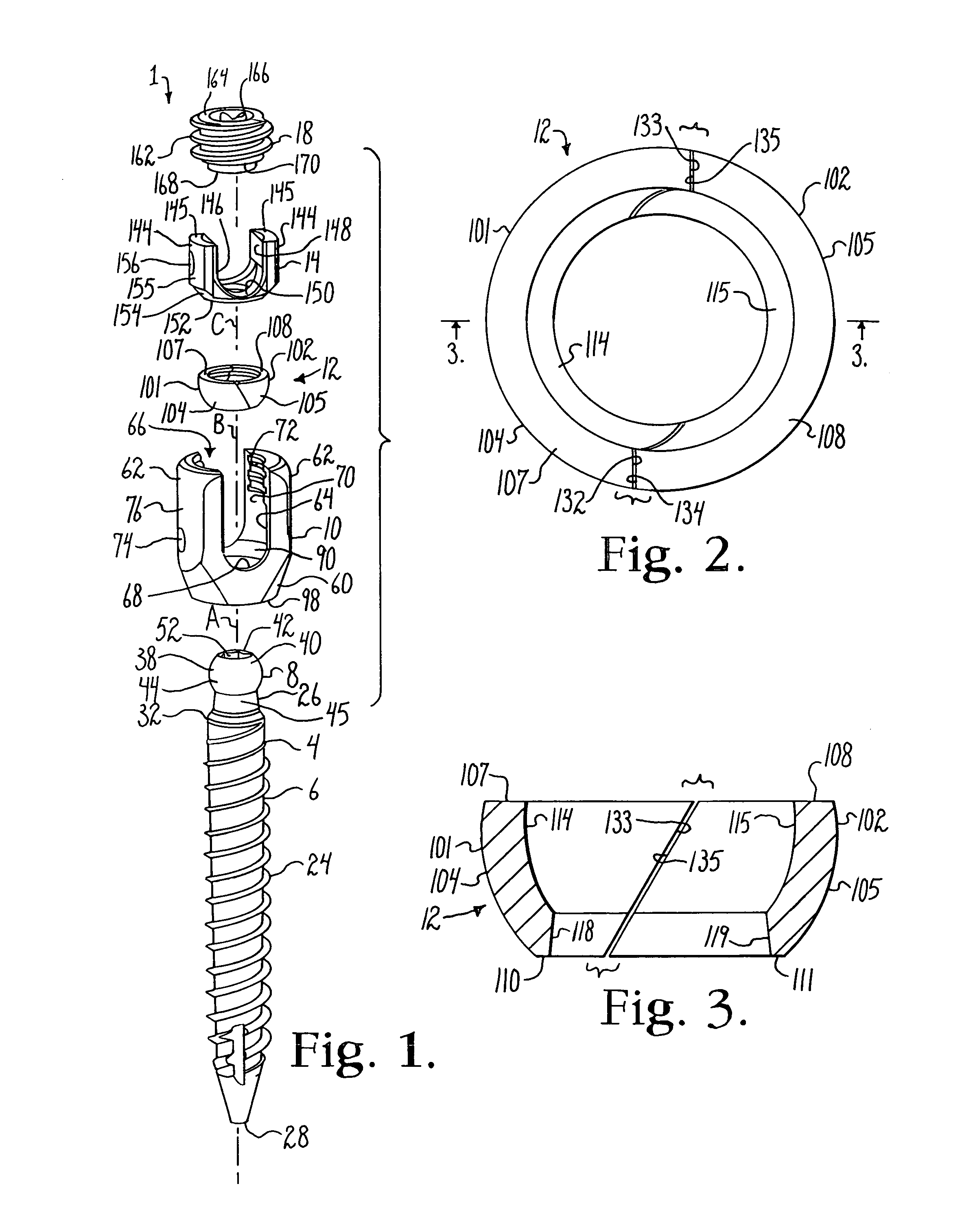
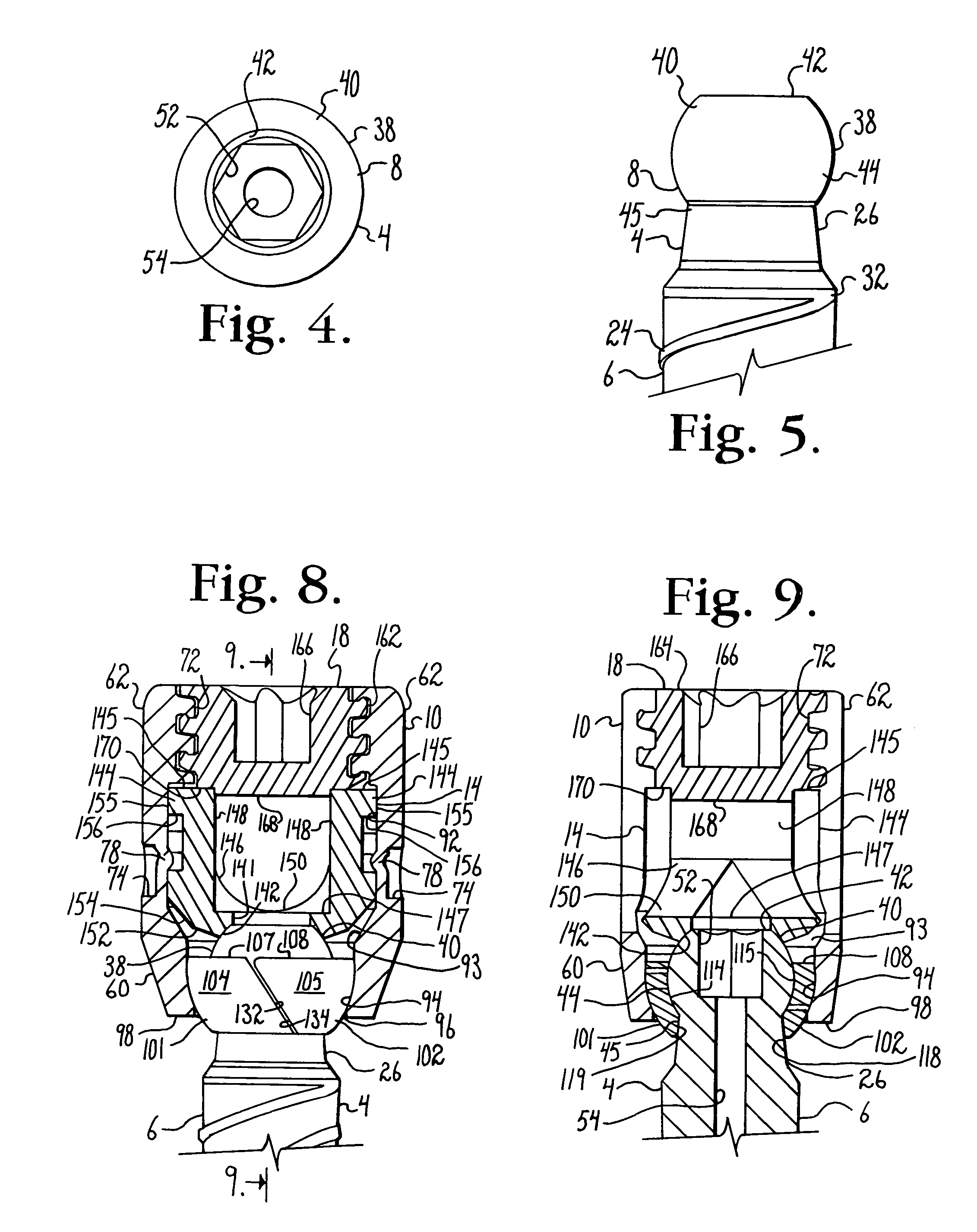
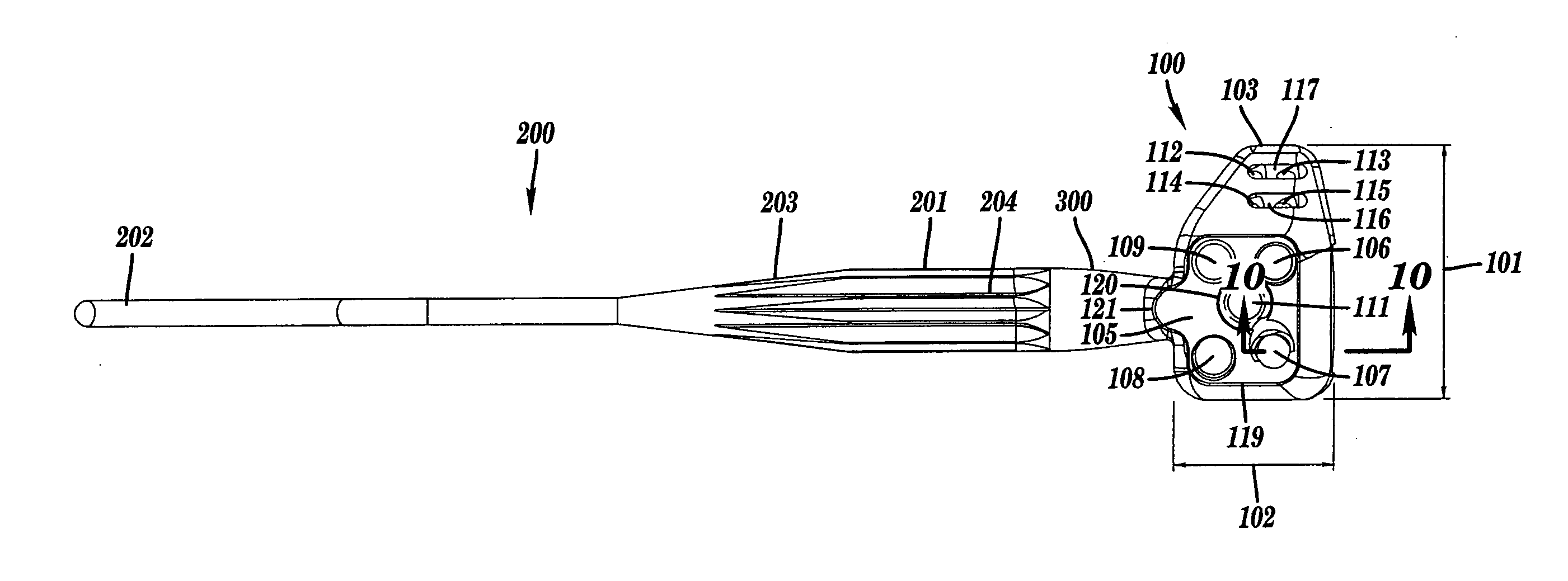
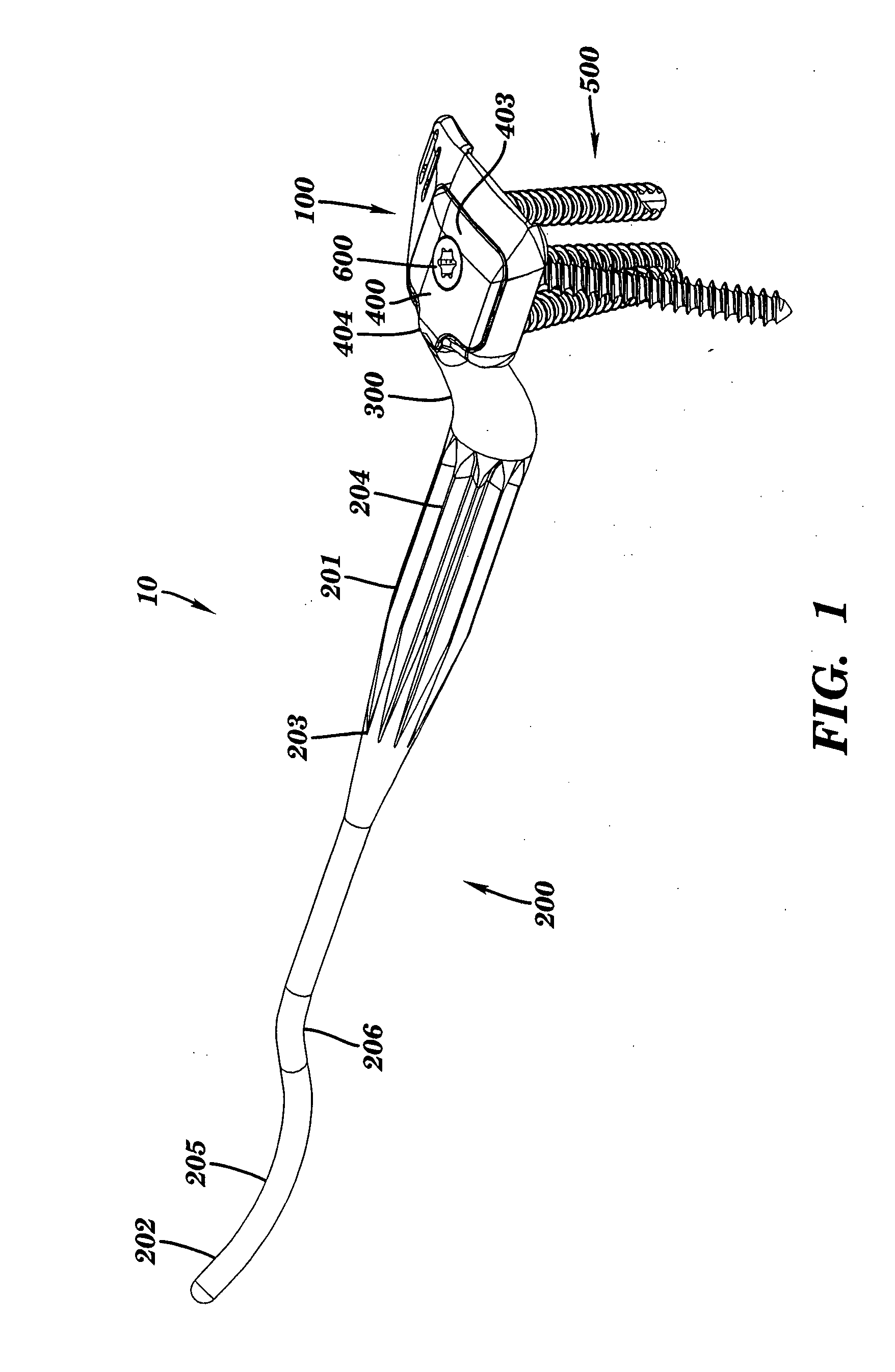
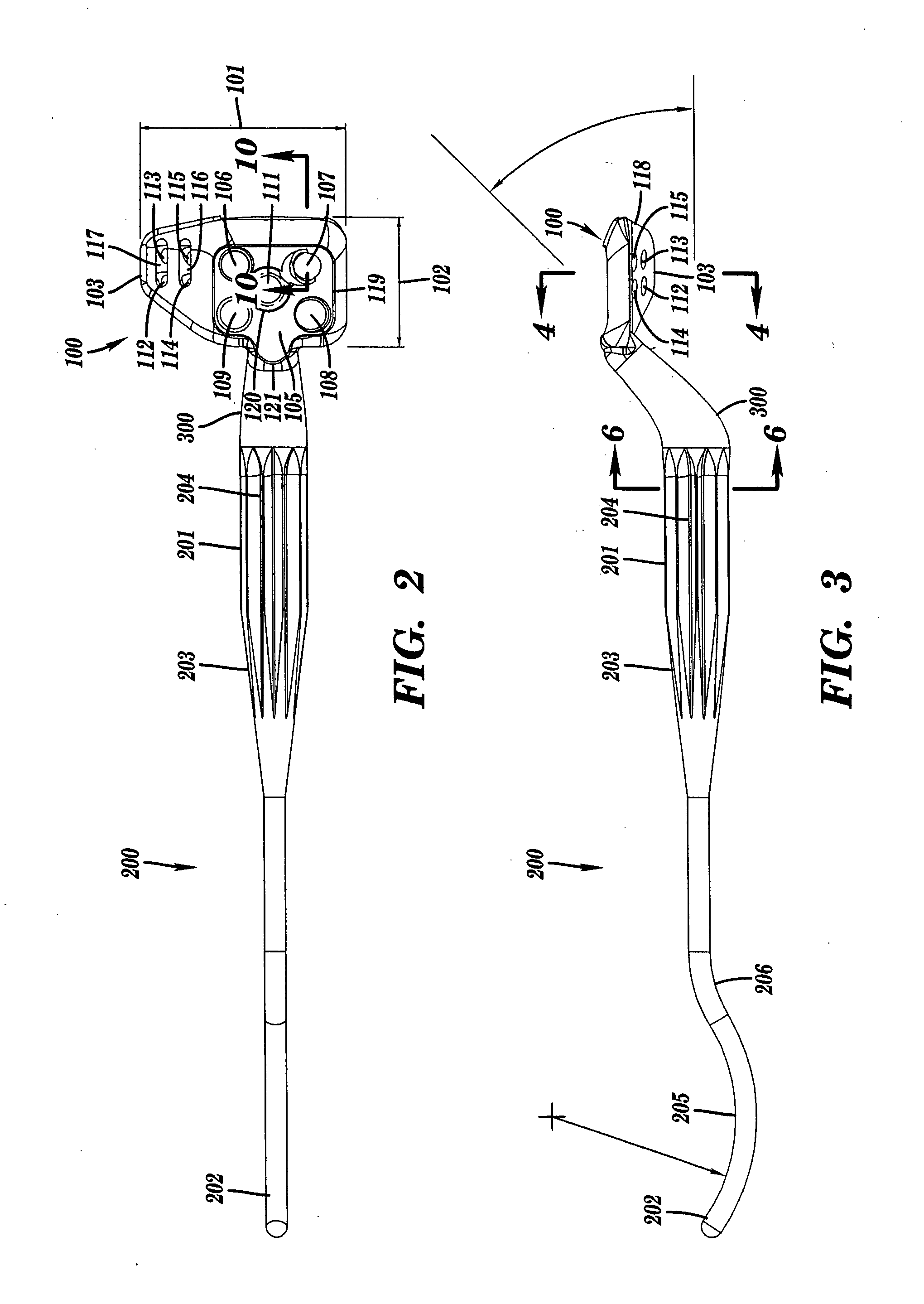
Bone anchors with longitudinal connecting member engaging inserts and closures for fixation and optional angulation
ActiveUS20100298891A1Easy to useLow production costSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSagittal planePlastic materials
Polyaxial bone anchors include a retainer for holding a shank within a receiver, the retainer being in at least two discrete pieces and cooperating with a variety of inserts, some of which independently lock the polyaxial mechanism. Polyaxial and mono-axial bone anchor assemblies include pivot and / or pressure inserts or pads that cooperate with longitudinal connecting members to provide a desired degree of continued control of angulation of the longitudinal connecting member in the sagittal plane or to hold the connecting member in place. Pressure pads for deformable rods may also be made from a deformable plastic material.
Owner:JACKSON
Dynamic intervertebral connection device with controlled multidirectional deflection
InactiveUS7335200B2Simple designInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSagittal planeMechanical engineering
Owner:SCIENTX
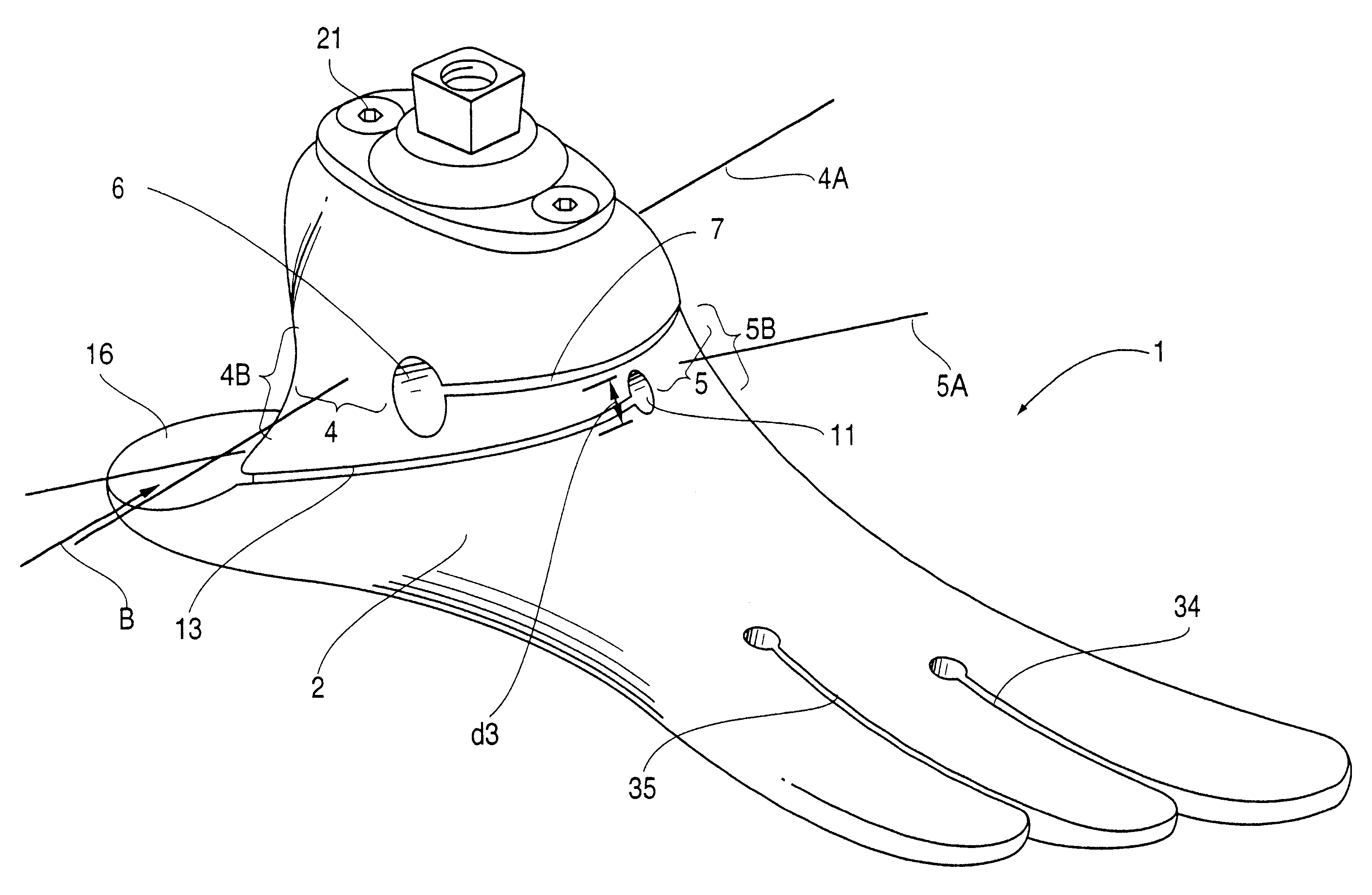
Prosthetic foot
InactiveUS6443995B1Improve the quality of lifeImproves footArtificial legsSagittal planePlantar surface
An ankle joint and a subtalar joint provided in a hindfoot permit closed kinetic chain motion of the foot. The ankle and subtalar joints are preferably formed integrally with the hindfoot by respective struts of resilient material of the hindfoot. An arch in the midfoot creates frontal and sagittal plane motion capabilities. The forefoot includes at least one expansion joint hole extending therethrough between dorsal and plantar surfaces. An expansion joint extends forward from the hole to the anterior edge of the forefoot to form plural expansion struts that create improved biplanar motion capability of the forefoot. Concavities and convexities on the surface of the hindfoot, midfoot and forefoot encourage desired motions and motion directions so that the foot functions and feels like a normal foot to the amputee.
Owner:BIOQUEST PROSTHETICS
Method and apparatus for performing an open wedge, high tibial osteotomy
Apparatus for performing an open wedge, high tibial osteotomy, the apparatus comprising:cutting apparatus for forming an osteotomy cut in the tibia, the cutting apparatus comprising:targeting apparatus for identifying a cutting plane through the tibia and a boundary line for terminating a cut made along the cutting plane, wherein the boundary line is located within the tibia, parallel to the anterior-posterior slope of the tibia and parallel to the sagittal plane of the patient.A method for performing an open wedge, high tibial osteotomy, the method comprising:positioning targeting apparatus for identifying a cutting plane through the tibia and a boundary line for terminating a cut made along the cutting plane, wherein the boundary line is located within the tibia, parallel to the anterior-posterior slope of the tibia and parallel to the sagittal plane of the patient;cutting the bone along the cutting plane, with the cut terminating at the boundary line;moving the bone on either-side of the cut apart so as to form the wedge-like opening in the bone; andstabilizing the bone.
Owner:ARTHREX
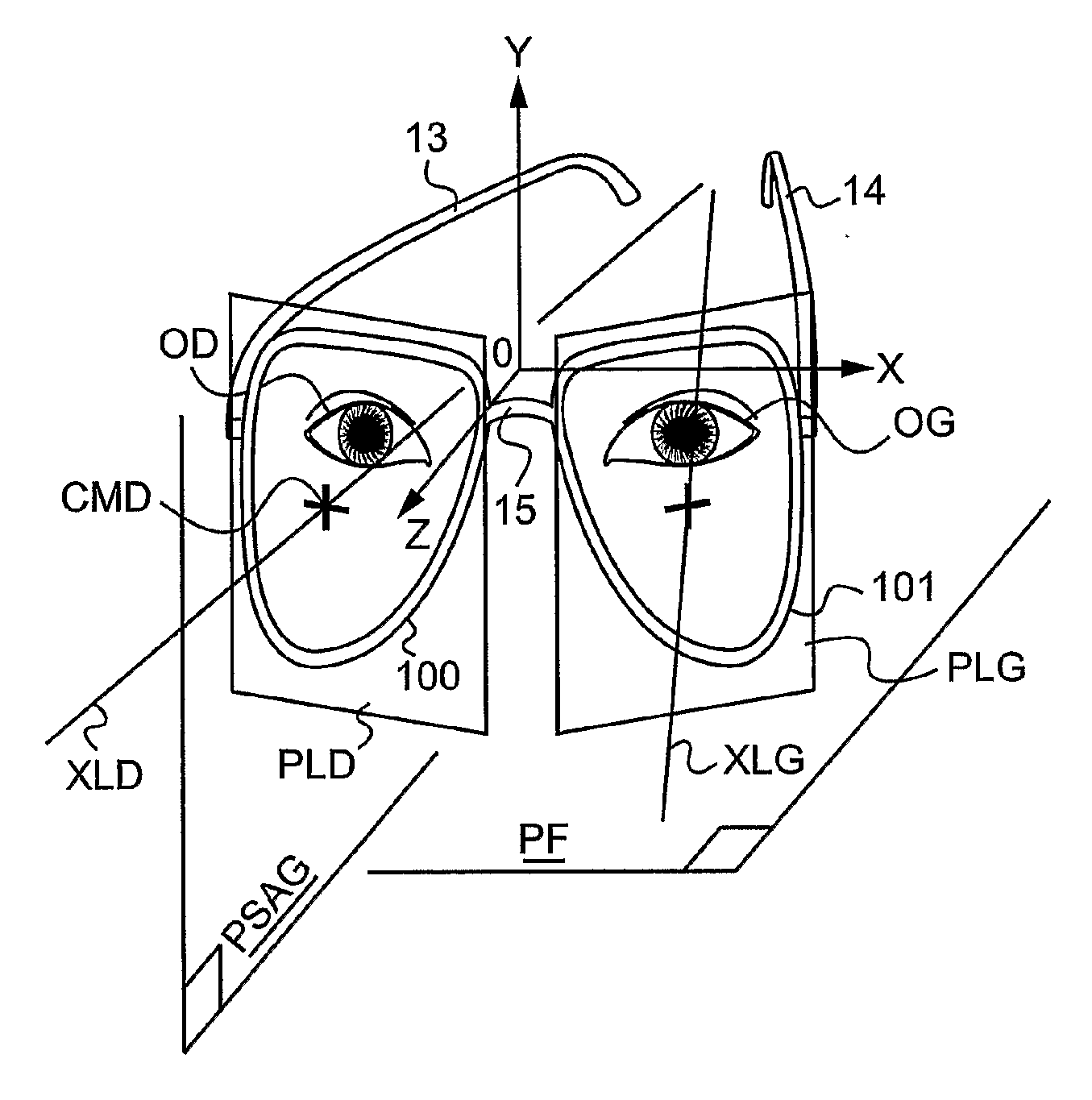
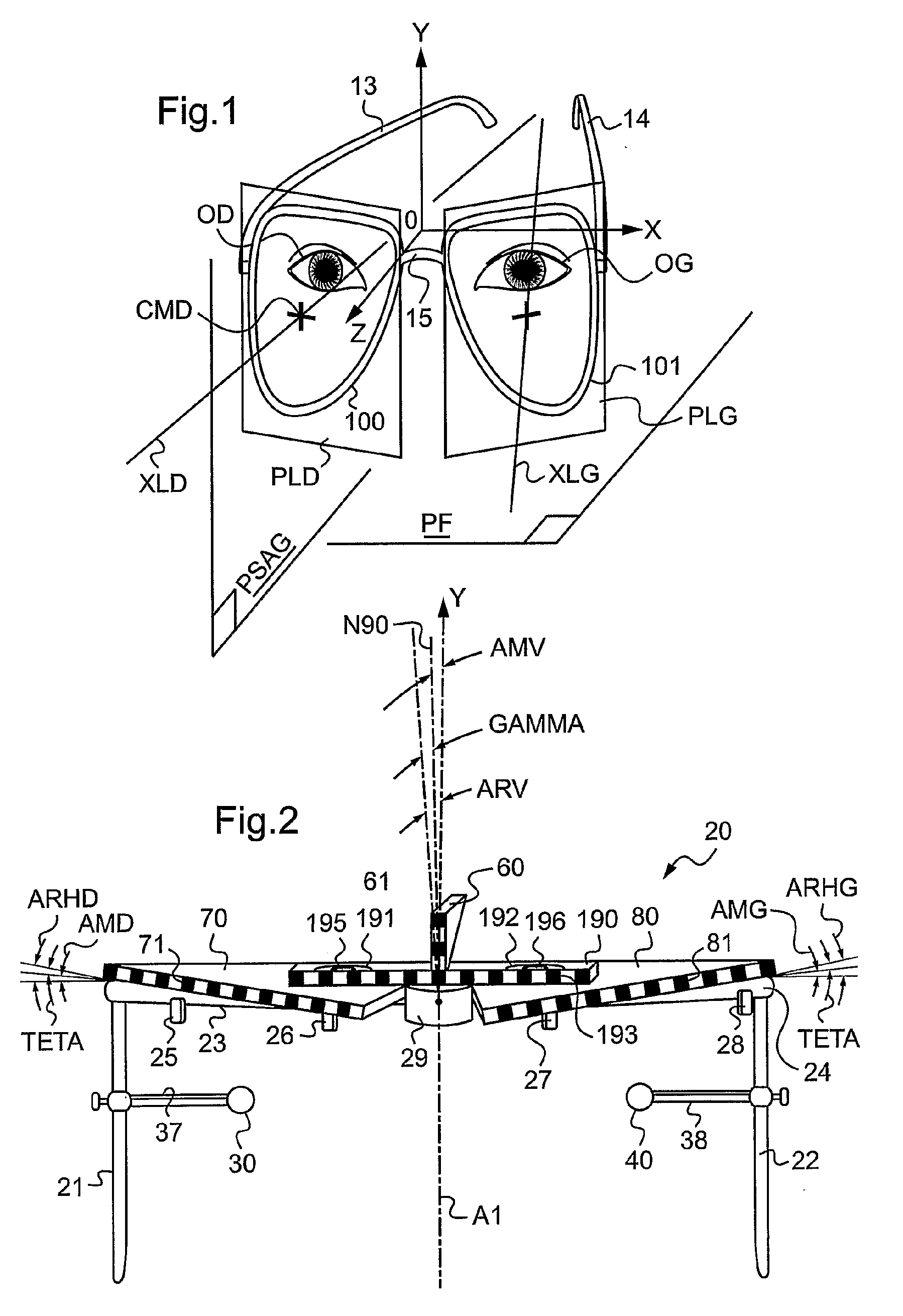
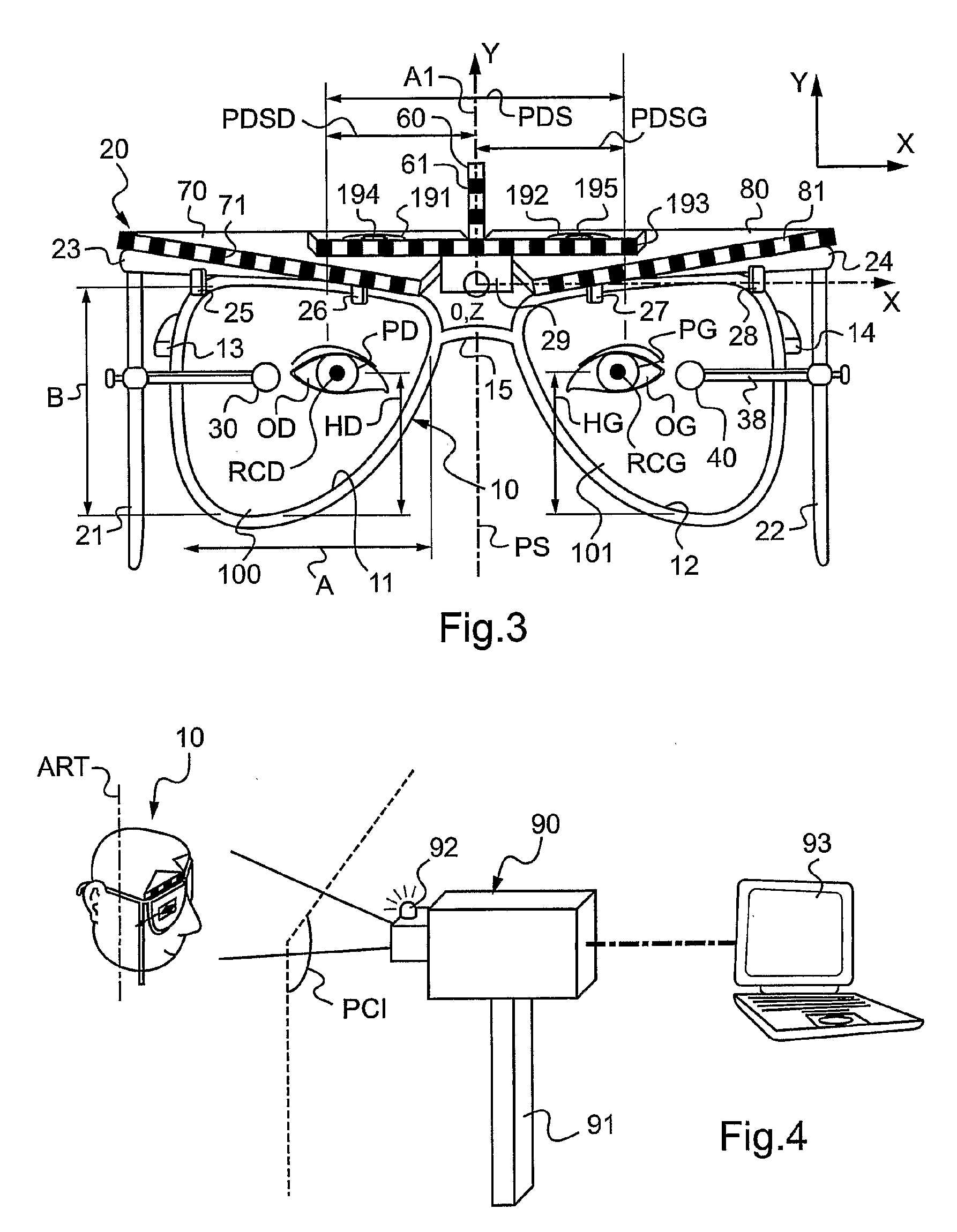
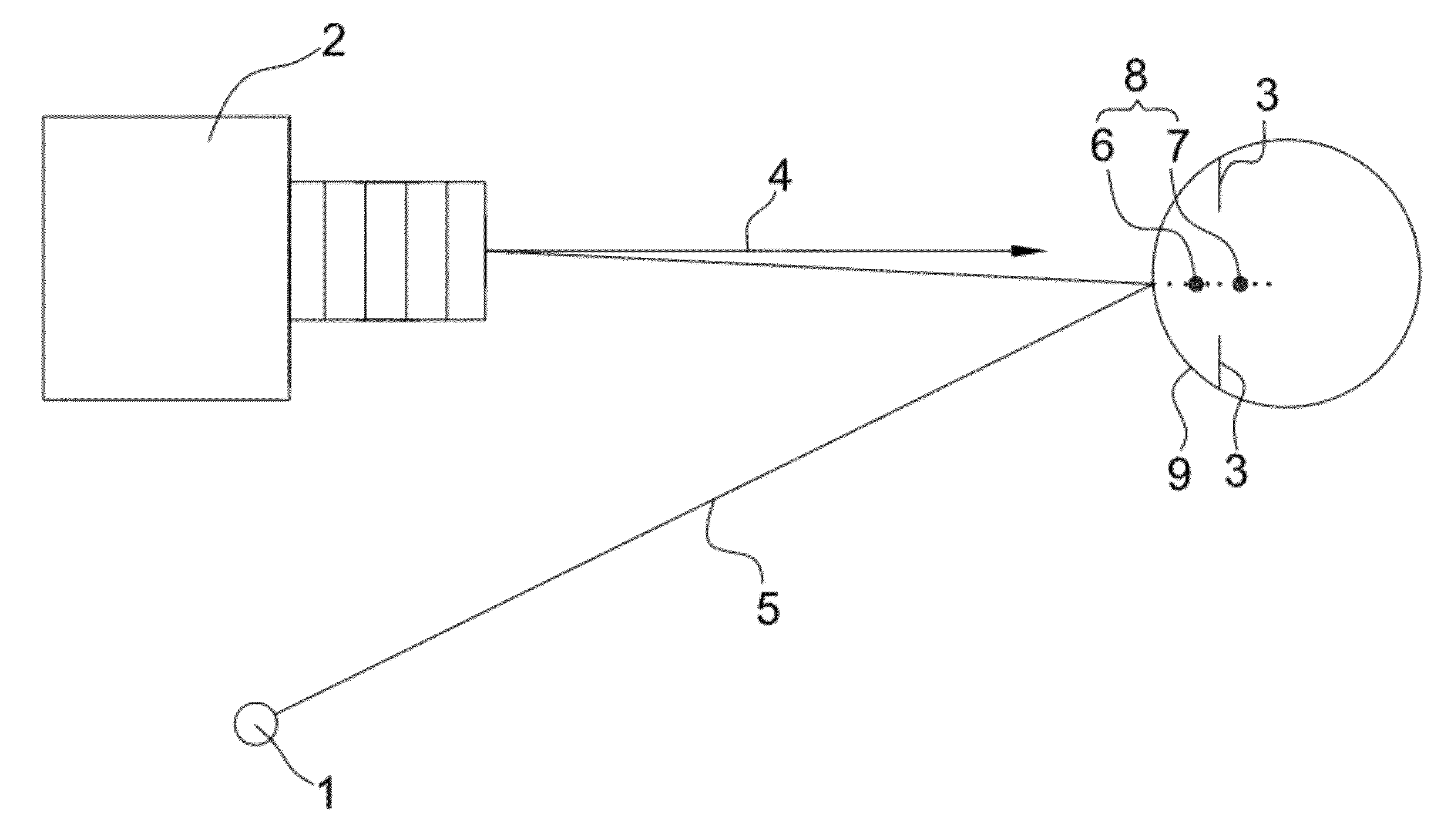
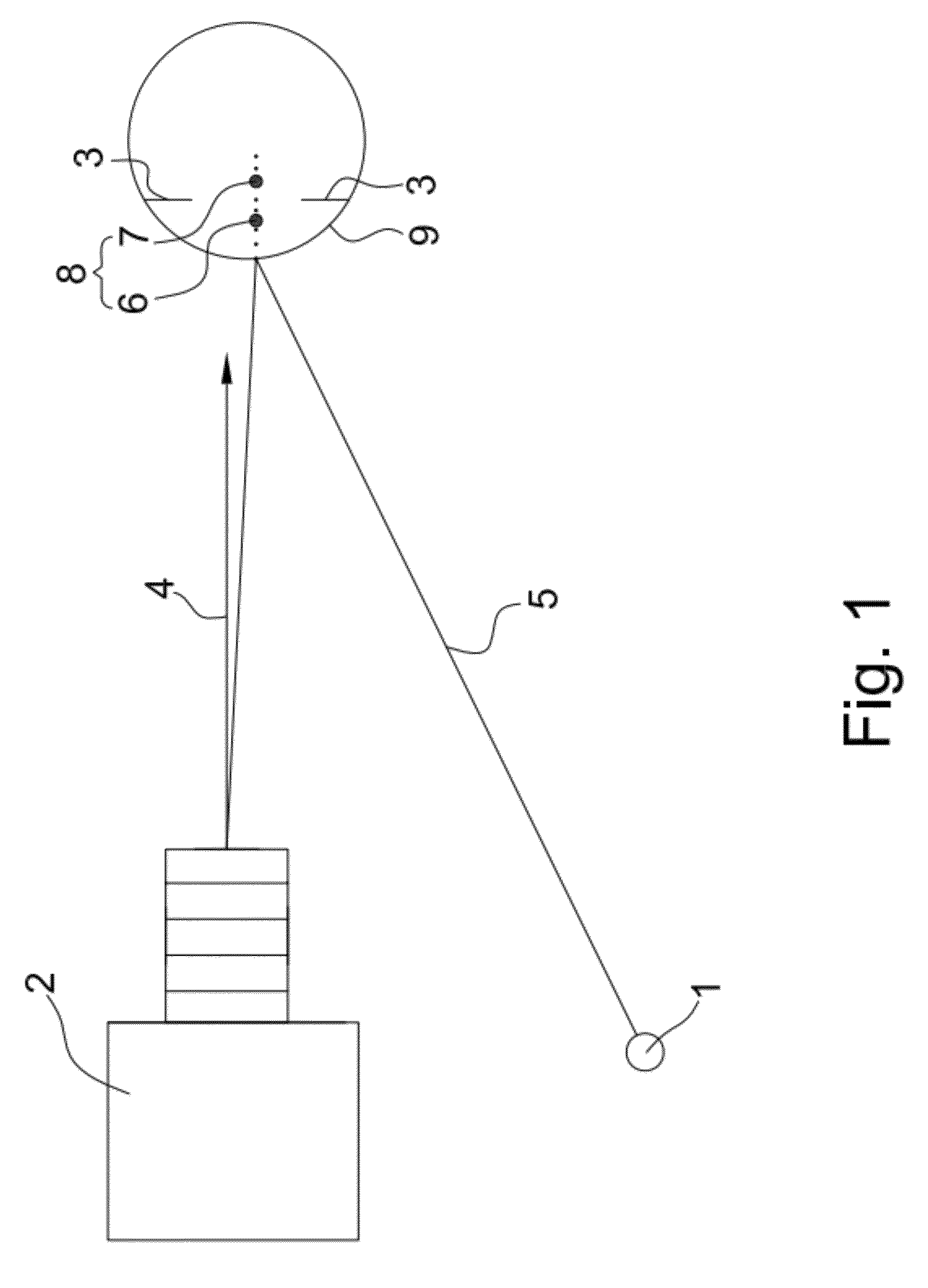
Method of measuring the position, in a horizontal direction in the sagittal plane, of a remarkable point of an eye of a subject
ActiveUS20100128220A1Speed andSpectales/gogglesAcquiring/recognising eyesSagittal planeComputer vision
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
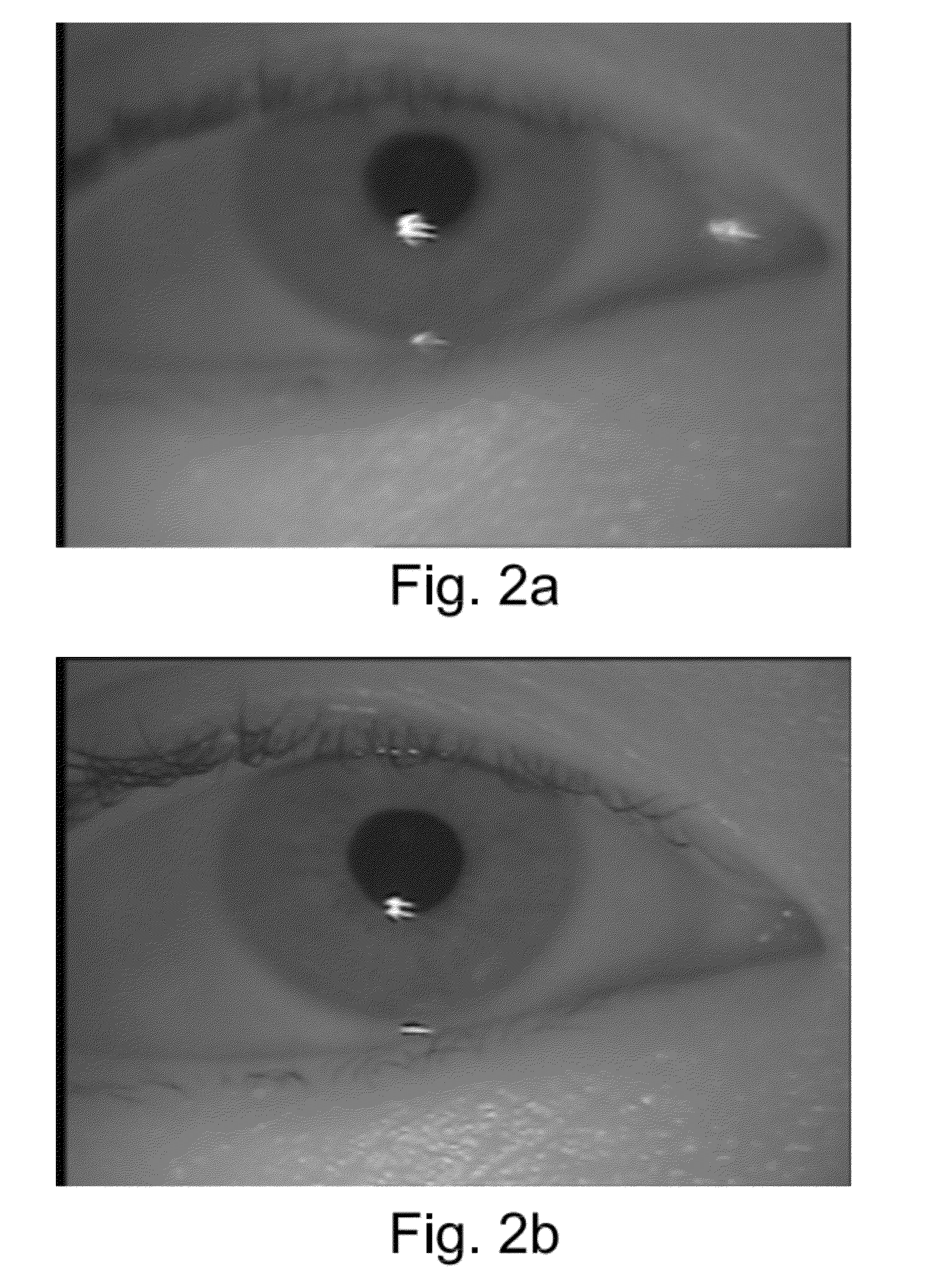
Iris image definition estimation system using the astigmatism of the corneal reflection of a non-coaxial light source
An iris image definition estimation system using the astigmatism of the corneal reflection of a non-coaxial light source to assess both the resolution of the iris patterns and the direction of focus adjustment. The corneal reflection results in two virtual images on the meridional and the sagittal planes. These virtual images are formed behind the cornea and close to the iris. Yet, both are projected onto the same location and result in a composite glint area. In addition, the shape of the glint area of a non-coaxial light source varies with different camera focus settings. Furthermore, due to the high intensity of the glint area, the shape can be easily observed, and the size and the shape of the glint area can be used to determine the resolution of the iris image and the direction of focus adjustment, respectively.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Bone anchors with longitudinal connecting member engaging inserts and closures for fixation and optional angulation
ActiveUS8308782B2Easy to useLow production costSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSagittal planePlastic materials
Polyaxial bone anchors include a retainer for holding a shank within a receiver, the retainer being in at least two discrete pieces and cooperating with a variety of inserts, some of which independently lock the polyaxial mechanism. Polyaxial and mono-axial bone anchor assemblies include pivot and / or pressure inserts or pads that cooperate with longitudinal connecting members to provide a desired degree of continued control of angulation of the longitudinal connecting member in the sagittal plane or to hold the connecting member in place. Pressure pads for deformable rods may also be made from a deformable plastic material.
Owner:JACKSON
Implant for treating rectocele and a device for putting said implant into place
InactiveUS7588598B2Good stability of implantationMinimize traumaAnti-incontinence devicesSurgical needlesFiberPolyester
An implant for treating rectocele and / or prolapsus of the vaginal fornix is thin and flexible and includes a support body from which there extend at least two upper suspension stabilizers disposed on either side of a sagittal plane and two lower suspension stabilizers disposed on either side of the sagittal plane. The implant may be constructed from a suitable biocompatible material such as a woven synthetic material, or a knitted material of polypropylene or polyester fibers.
Owner:COLOPLAST AS
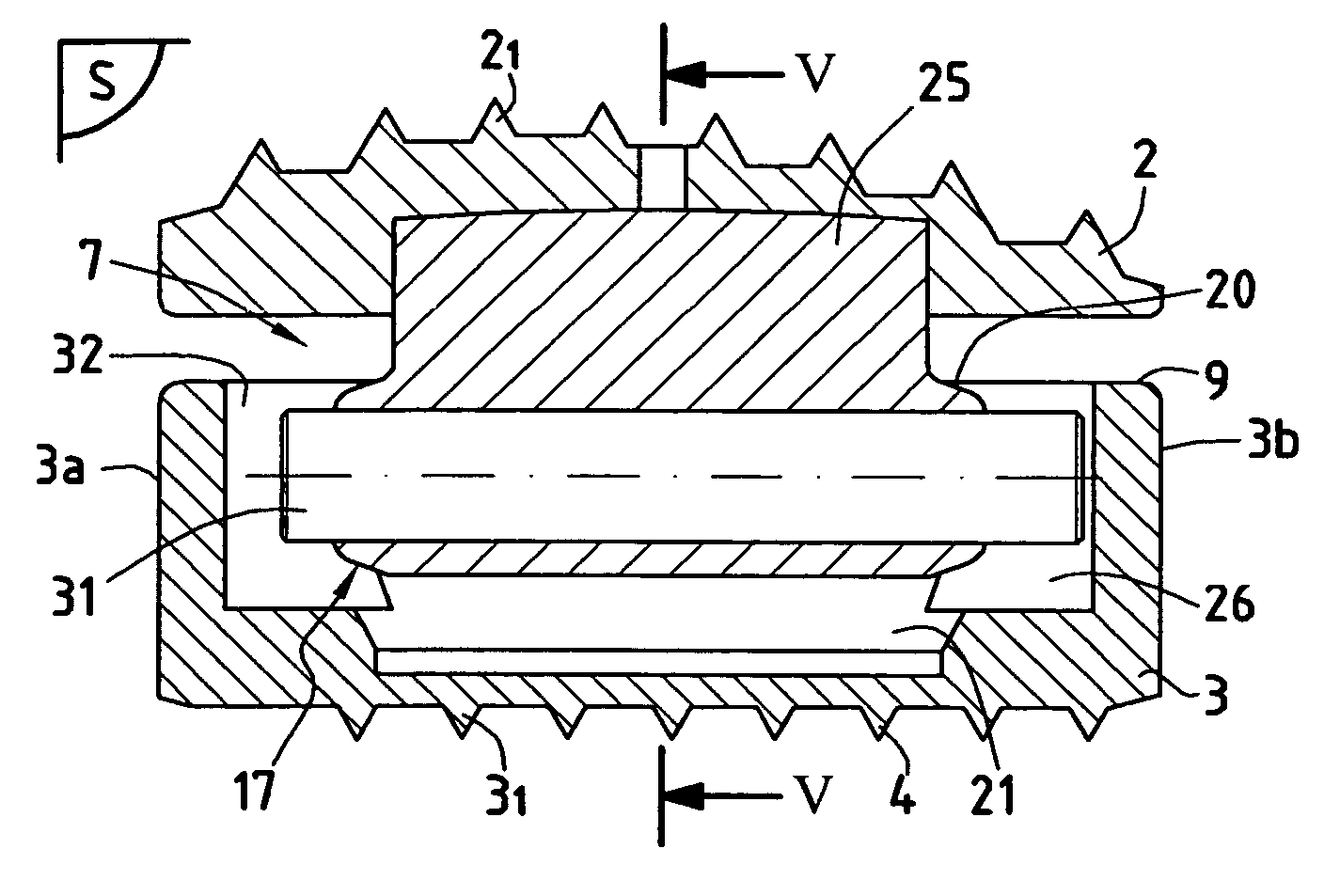
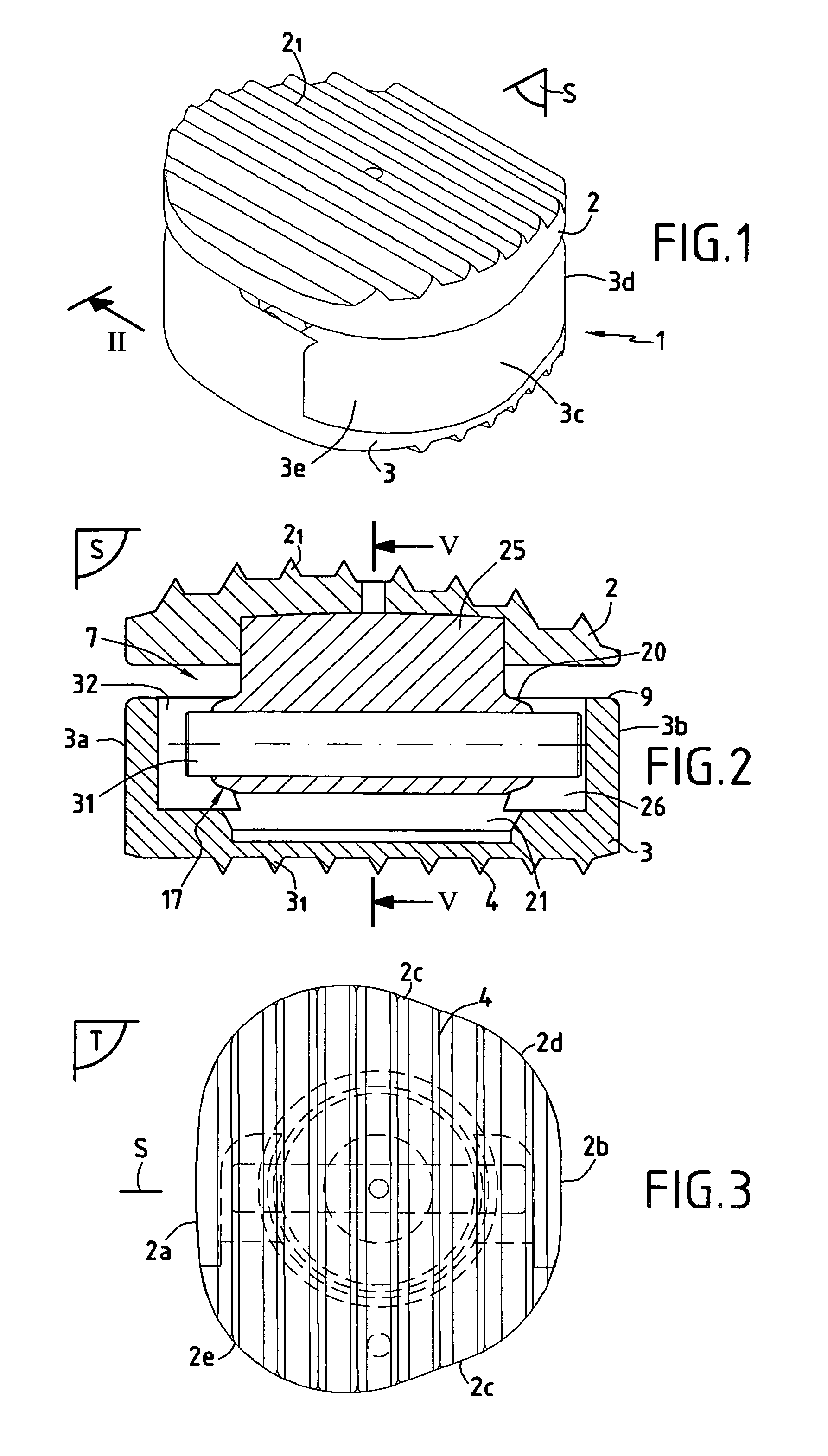
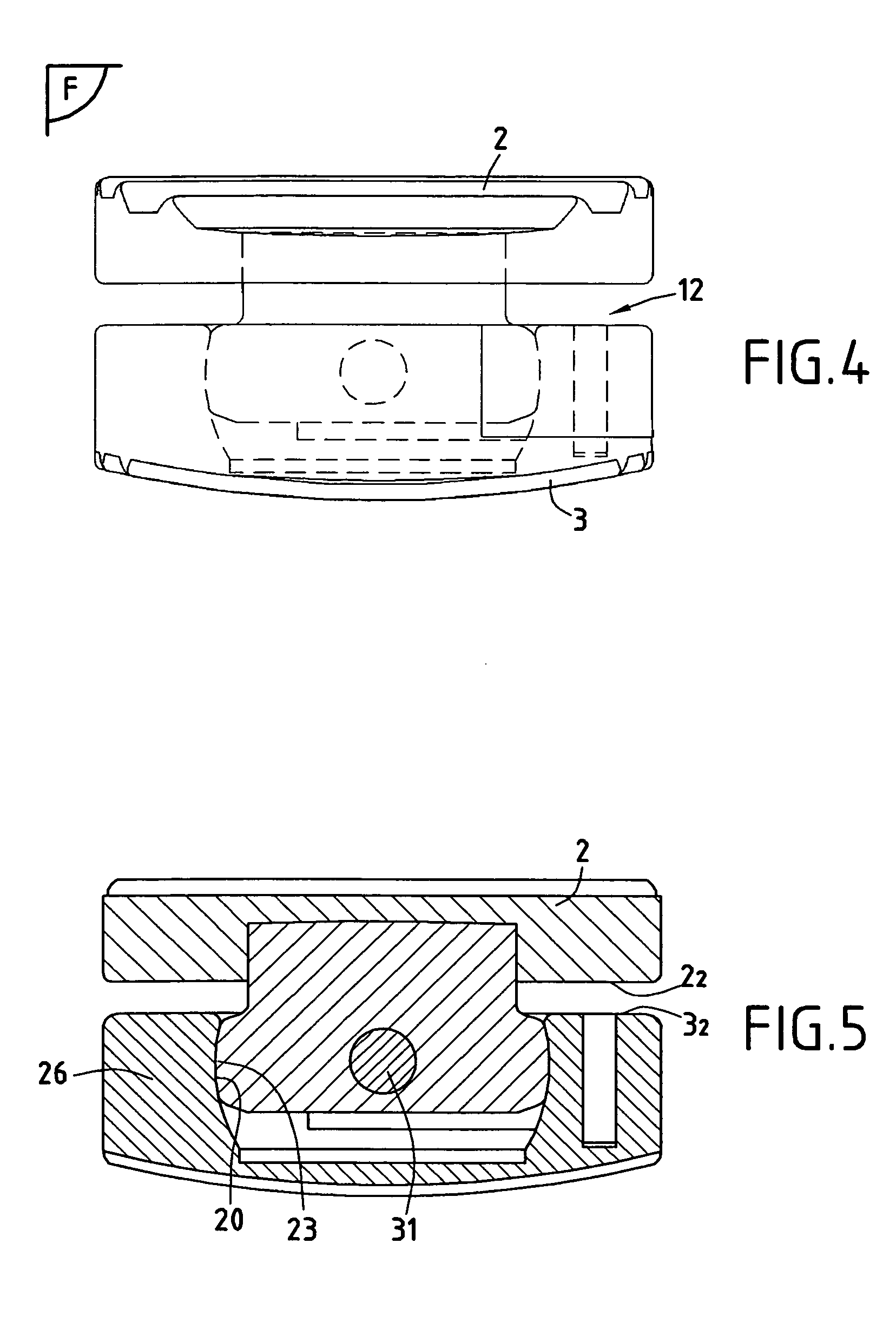
Disk prosthesis for cervical vertebrae with controlled clearance
A disk prosthesis includes first and second plates (2, 3) to be fixed on neighboring cervical vertebrae and an articulation arrangement (7) inserted between the two plates in a superposed position. The articulation arrangement allows for flexion-tension movements in a sagittal plane (S) according to a limited clearance, lateral inflexion movements in a plane perpendicular to the sagittal plane (S) according to limited angular clearance, and relative rotation movements between the first and second plates according to a limited angular clearance. The first and second plates are assembled to form a prosthesis of a single piece.
Owner:SCIENTX
Laterally insertable artificial vertebral disk replacement implant with crossbar spacer
The present invention is directed to an implant that can be placed between two adjacent vertebral bodies using a lateral insertion method. The implant is characterized as having a first end plate and a second end plate which a crossbar spacer therebetween. The crossbar spacer preferably fits within a channel on the inner surfaces of the first end plate and the second end plate, whereby the crossbar spacer allows pivots, twisting and / or rotational movement of the spine. The first end plate and the second end plate include a keel extending therefrom, whereby the keel traverses longitudinally between a first lateral side and a second opposed lateral side and is substantially perpendicular to the sagittal plane of the patient's spine.
Owner:KYPHON
Detection and localization of vascular occlusion from angiography data
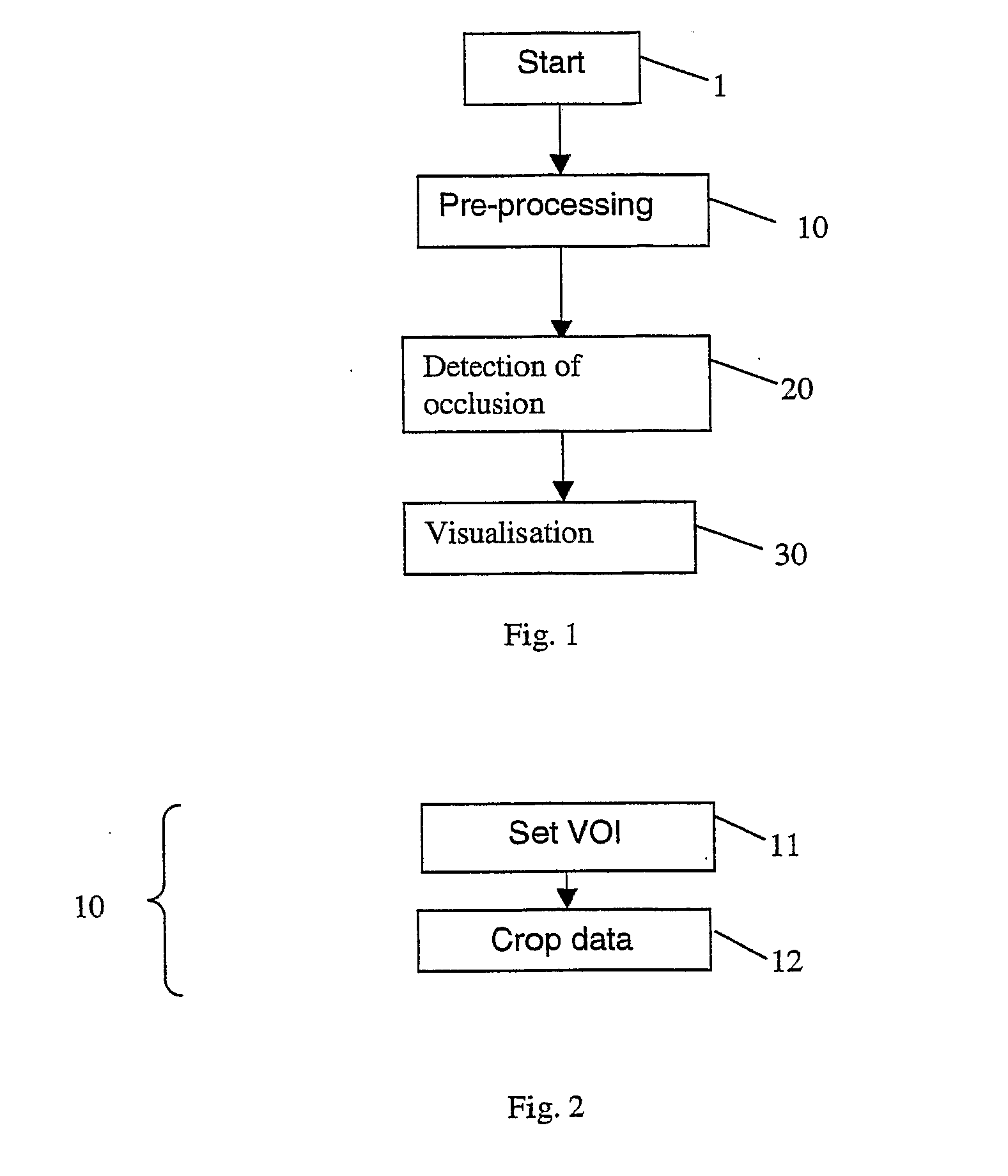
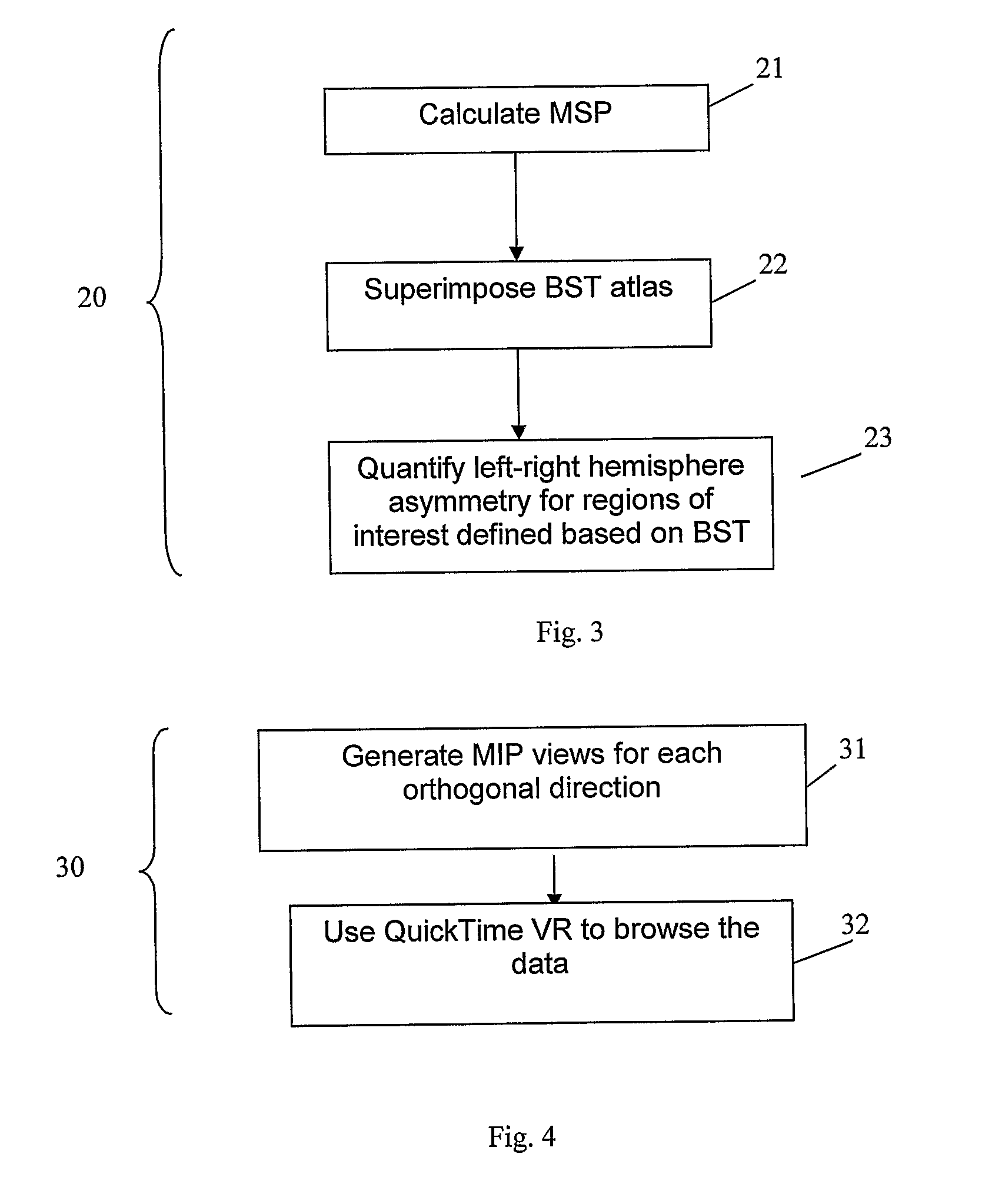
A technique for detecting and localising vascular occlusions in the brain of a patient is presented. The technique uses volumetric angiographic data of the brain. A mid-sagittal plane and / or lines is / are identified within the set of angiographic data. Optionally, the asymmetry of the hemispheres is measured, thereby obtaining an initial indication of whether an occlusion might be present. The angiographic data is mapped to pre-existing atlas of blood supply territories, thereby obtaining the portion of the angiographic data corresponding to each of the blood supply territories. For each territory (including any sub-territories), the asymmetry of the corresponding portion of the angiographic data about the mid-sagittal plane / lines is measured, thereby detecting any of the blood supply territory including an occlusion. The angiographic data for any such territory is displayed by a three-dimensional imaging technique.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Method and apparatus for determining symmetry in 2d and 3d images
InactiveUS20040240753A1Accurate and fast determinationMaximizing modified local symmetry indexImage enhancementImage analysisSagittal plane3d image
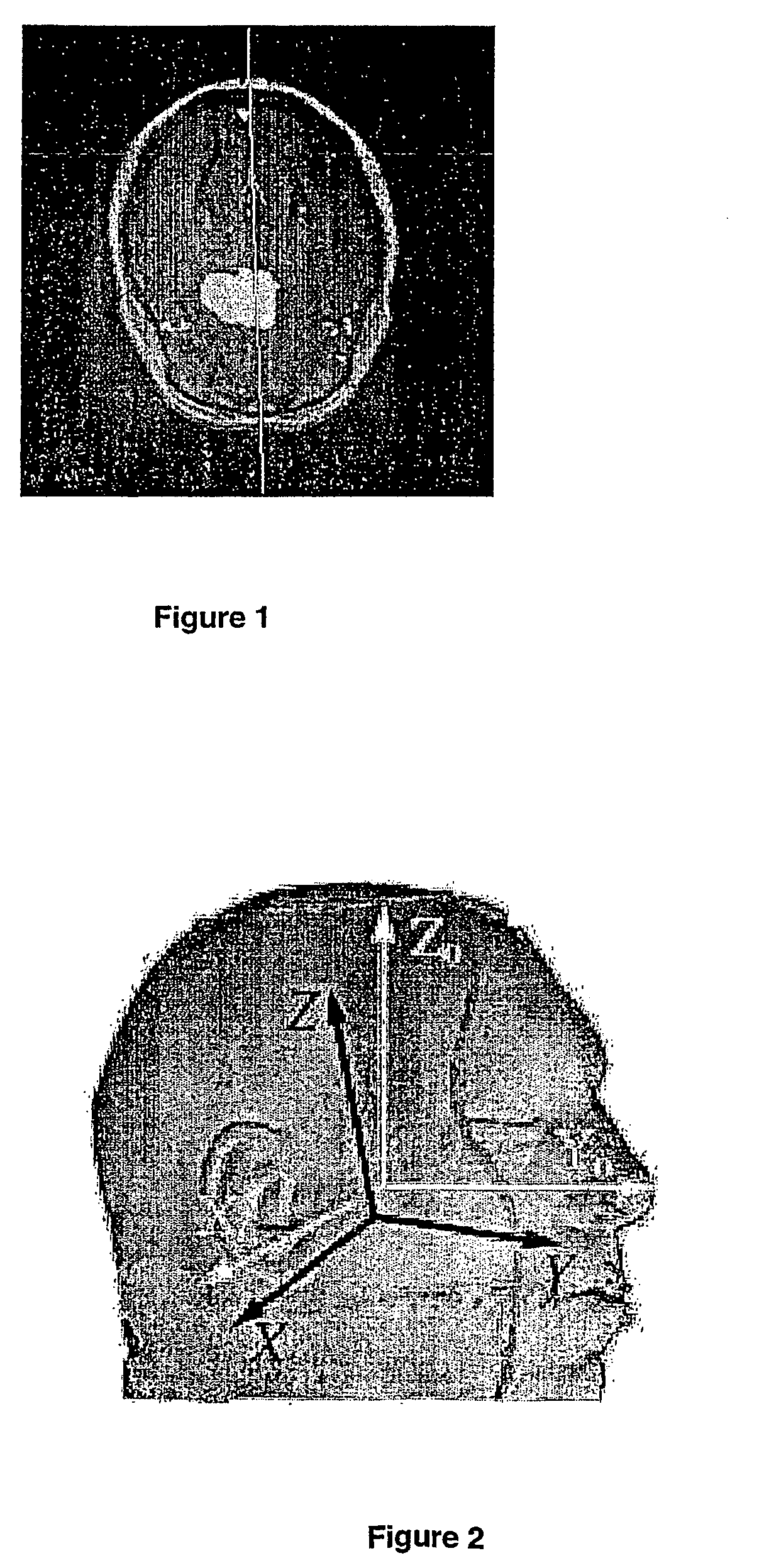
The present invention is suitable for use in determining symmetry in images, namely 2D images or 3D images, which comprise 2D images slices. In a preferred form, a method is disclosed for extracting a midsagittal plane MSP of human brains from radiological images. The method includes the steps of: 1) determining axial slices to be processed from said radiological images; 2) analysing said axial slices to determine fissure line segments; and 3) calculating plane equation of MSP from said fissure line segments.
Owner:KENT RIDGE DIGITAL LABS
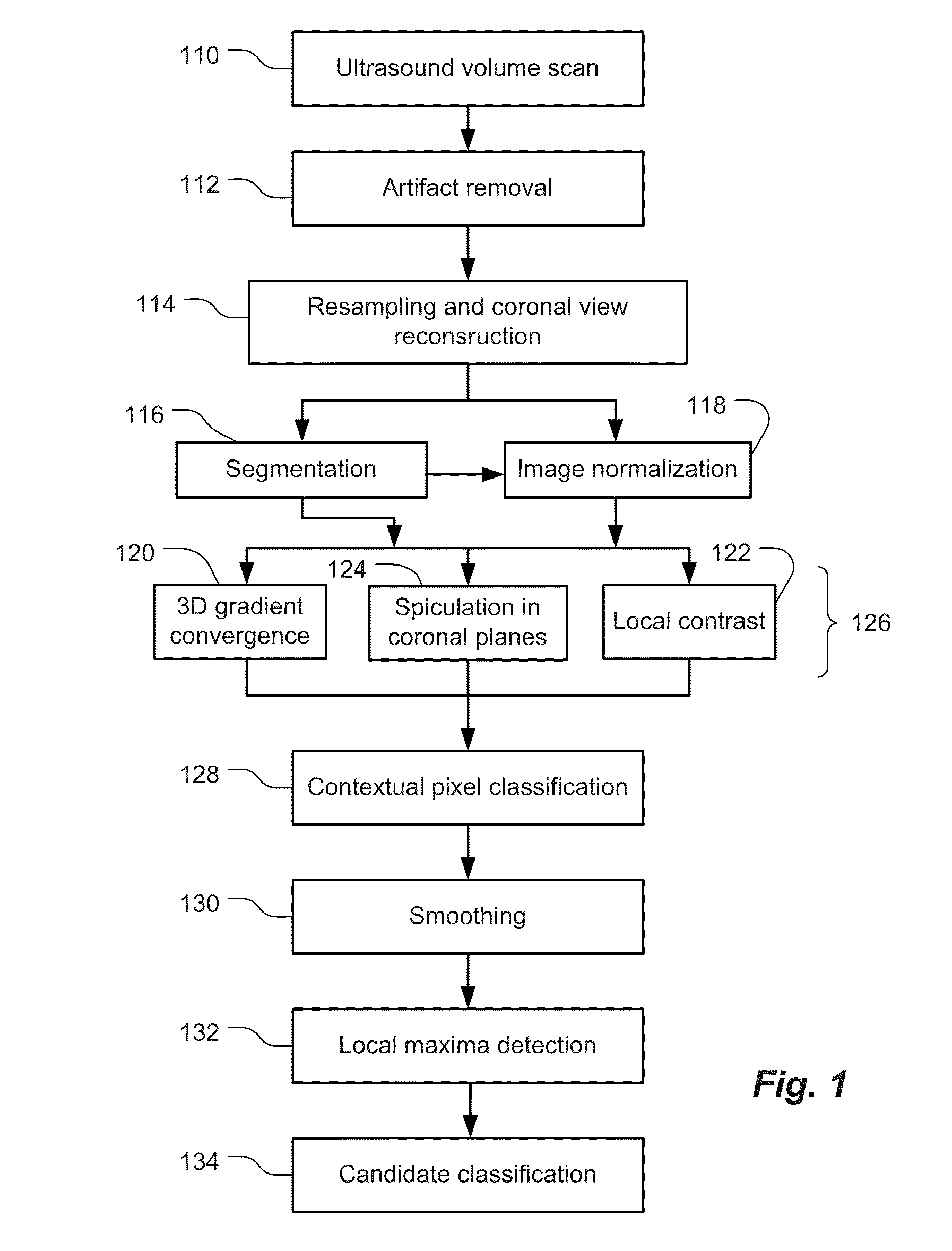
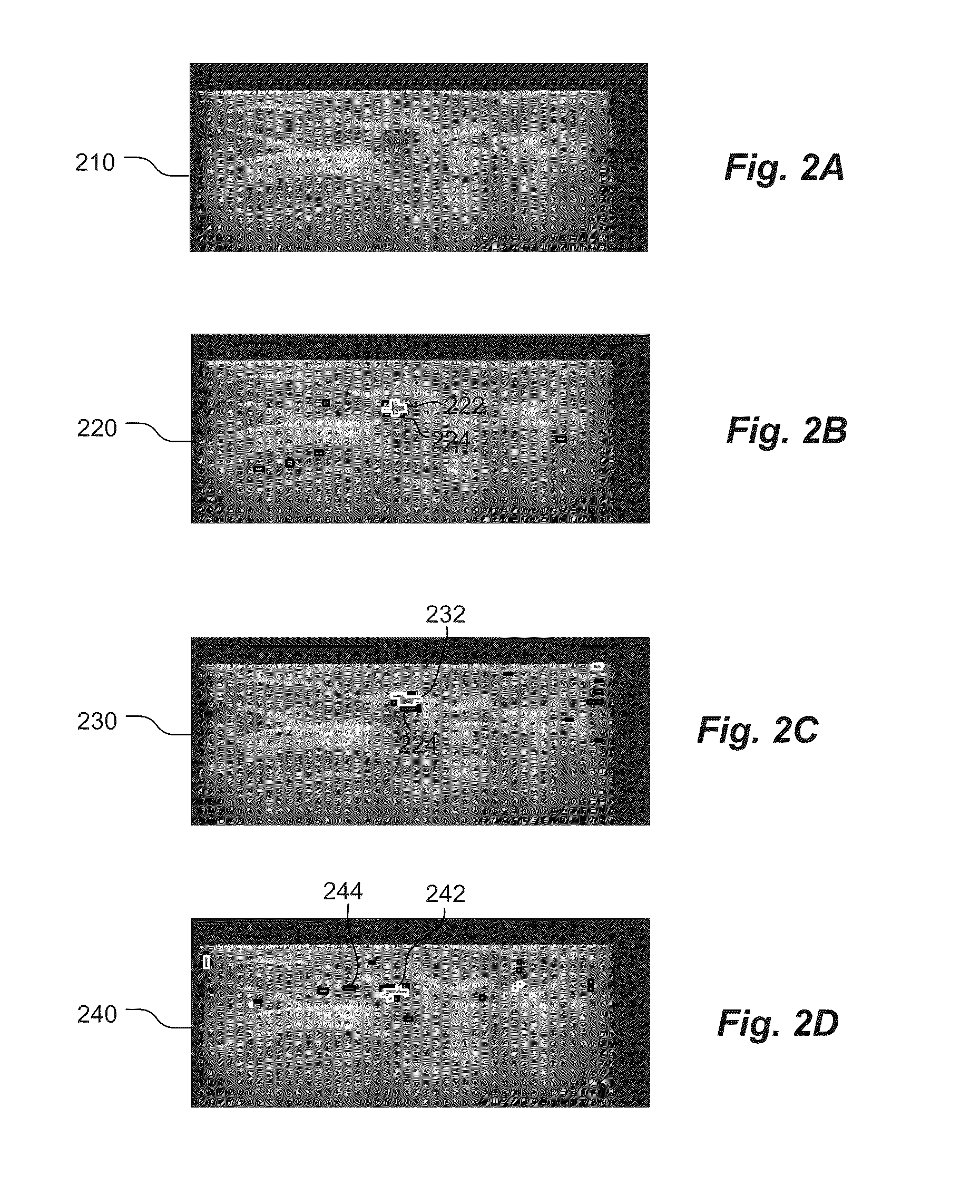
Computer Aided Detection Of Abnormalities In Volumetric Breast Ultrasound Scans And User Interface
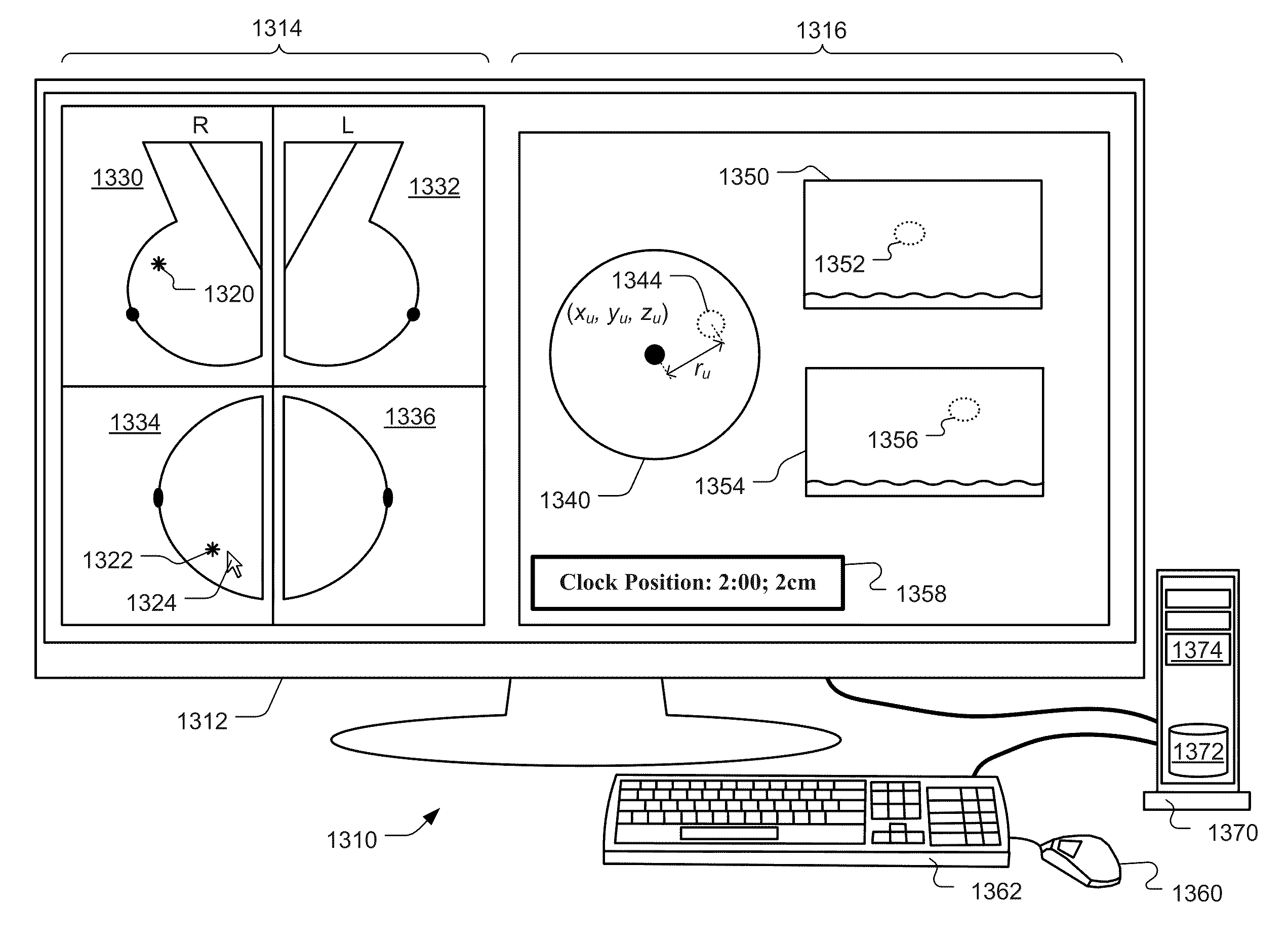
Methods and related systems are described for detection of breast cancer in 3D ultrasound imaging data. Volumetric ultrasound images are obtained by an automated breast ultrasound scanning (ABUS) device. In ABUS images breast cancers appear as dark lesions. When viewed in transversal and sagittal planes, lesions and normal tissue appear similar as in traditional 2D ultrasound. However, architectural distortion and spiculation are frequently seen in the coronal views, and these are strong indicators of the presence of cancer. The described computerized detection (CAD) system combines a dark lesion detector operating in 3D with a detector for spiculation and architectural distortion operating on 2D coronal slices. In this way a sensitive detection method is obtained. Techniques are also described for correlating regions of interest in ultrasound images from different scans such in different scans of the same breast, scans of a patient's right versus left breast, and scans taken at different times. Techniques are also described for correlating regions of interest in ultrasound images and mammography images. Interactive user interfaces are also described for displaying CAD results and for displaying corresponding locations on different images.
Owner:QVIEW MEDICAL
Cervical fusion apparatus and method for use
In an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, a method of implanting a fusion plate, having at least two primary fastener openings, into a patient is described. According to the inventive method, a throat of the patient is dissected, providing access through the throat dissection to a spinal column of the patient. The fusion plate is inserted into the throat dissection, and the fusion plate is then positioned in an asymmetrical relationship with a sagittal plane of the spinal column. A first primary fastener is inserted through a first primary fastener opening of the fusion plate and into the first vertebra. A second primary fastener is inserted through a second primary fastener opening of the fusion plate and into the second vertebra. A cervical fusion apparatus is also disclosed.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Intramedullary bone plate with sheath
InactiveUS20070083202A1Enhance bone fixationImprove fixation stabilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFluteSagittal plane
An intramedullary bone plate with sheath having an intramedullary stem, a bone plate head and a neck that connects the intramedullary stem to the bone plate head in a manner where the stem and head are offset from each other longitudinally and axially in the sagittal plane. The bone plate head includes a sheath recess wherein non-threaded bone screw holes and a threaded sheath screw hole are located. Bone screws are inserted through the sheath recess and oriented at set angles allowing for bone fragment fixation and fracture reduction. A sheath element is placed within the boundaries of the sheath recess and secured with the sheath screw. The intramedullary stem includes longitudinal flutes in its distal portion and a bi-arced geometry in its proximal portion providing for stabilization of the implanted device. The bone plate head configuration provides for more complete fracture capture and multiple fixation modalities.
Owner:TORNIER INC
Prosthetic Intervertebral Discs
Prosthetic intervertebral discs, systems including such prosthetic intervertebral discs, and methods for using the same are described. The subject prosthetic discs include upper and lower endplates separated by a compressible core member. The subject prosthetic discs exhibit stiffness in the vertical direction, torsional stiffness, bending stiffness in the sagittal plane, and bending stiffness in the front plane, where the degree of these features can be controlled independently by adjusting the components, construction, and other features of the discs.
Owner:SPINAL KINETICS
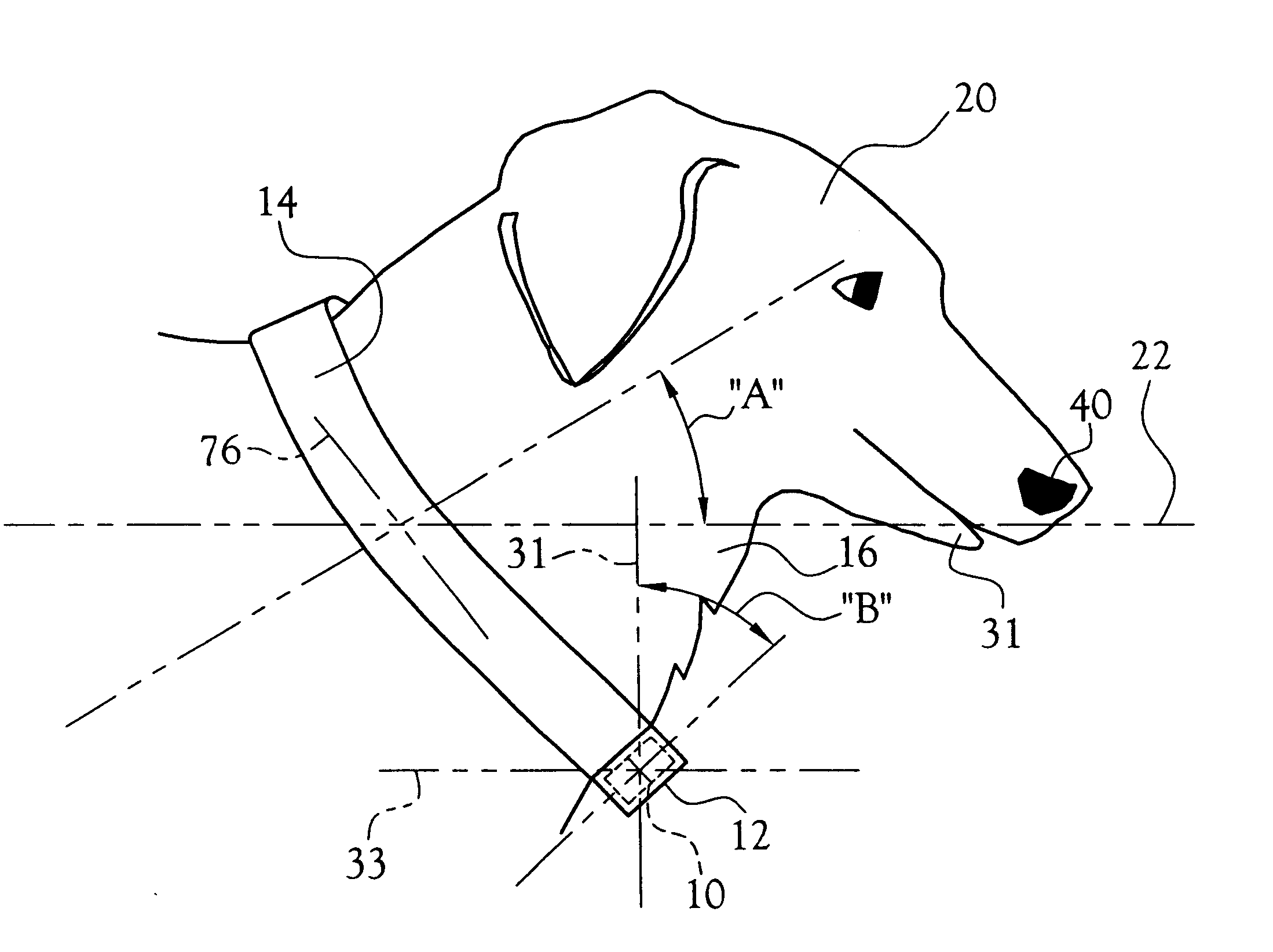
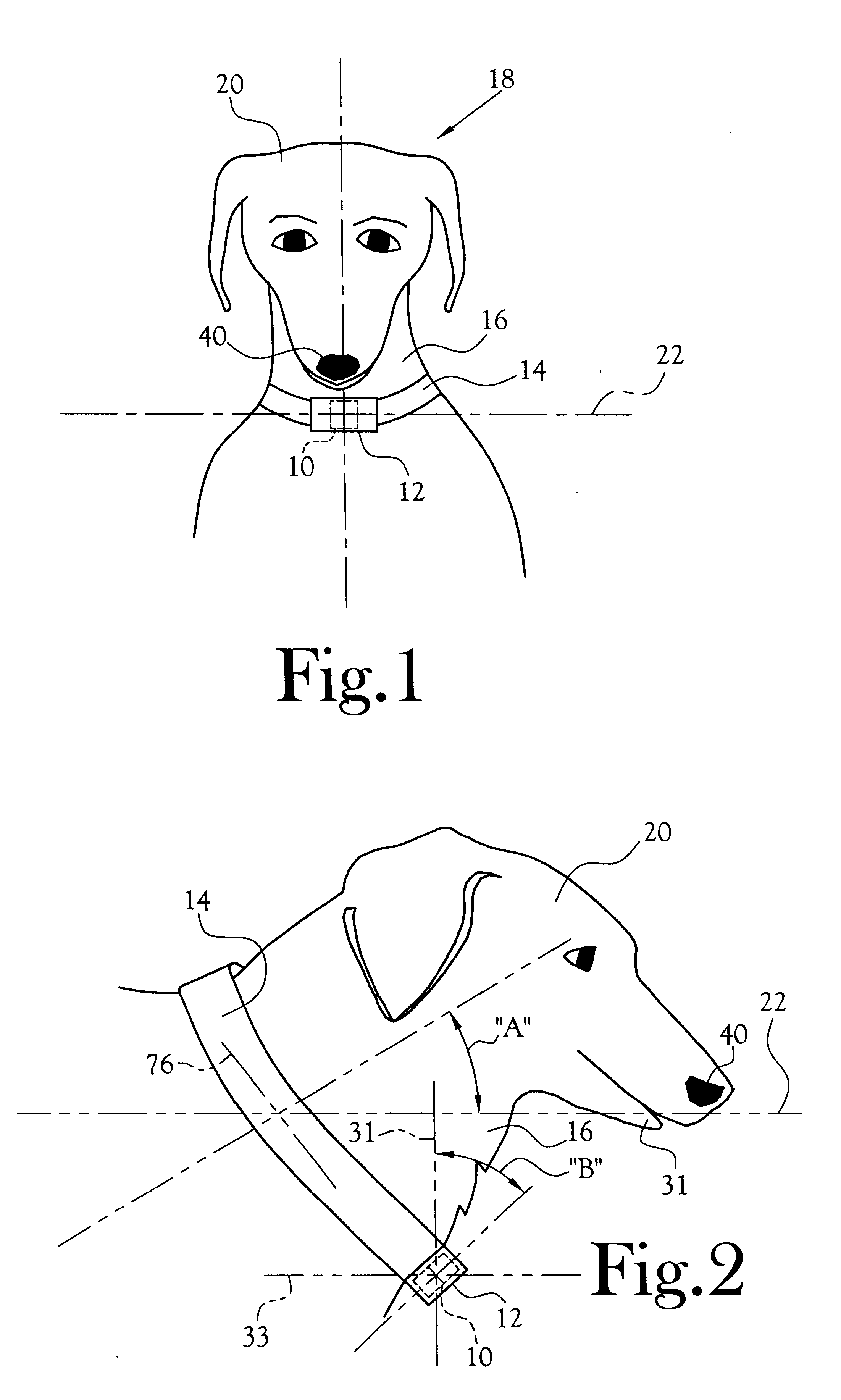
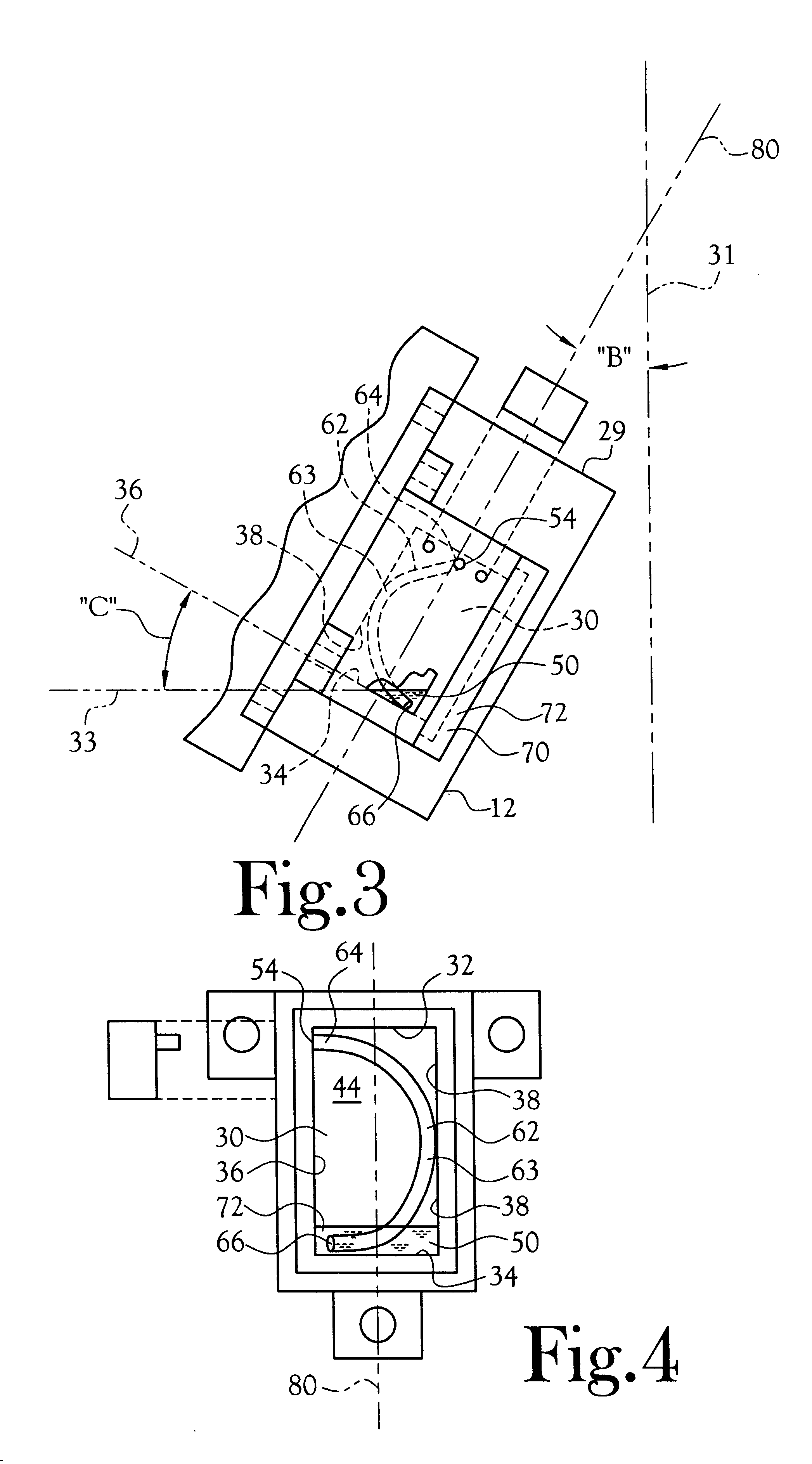
Appliance for dissuasion of a dog from barking
In a device adapted to dissuade a dog from barking, there is provided a reservoir of spray material associated with a collar which encircles the dog's neck. The reservoir includes at least one wall member defining an interior volume for the receipt of spray material therein. The reservoir includes a first dimension (i.e., a centerline) which lies within the median sagittal plane of an erect dog which is facing forward, thereby orienting one portion of the interior of the reservoir vertically lowermost. An exit port is provided for the transport of spray material from the interior to the exterior of the reservoir. A semi-rigid, lengthwise substantially non-compressible, conduit having a first end thereof connected in fluid flow communication with the exit port, extends from the exit port and terminates at its opposite and open end at the vertically lowermost interior portion of the reservoir when the present appliance is mounted at a location on the collar beneath the lower jaw of the dog. The length of the conduit is chosen to exceed the straight-line distance between the exit port and the vertically lowermost portion of the reservoir by an amount sufficient to provide for wedging of the conduit against at least one interior wall of the reservoir opposite the exit port and preferably opposite to terminal open end of the conduit.
Owner:RADIO SYST CORP
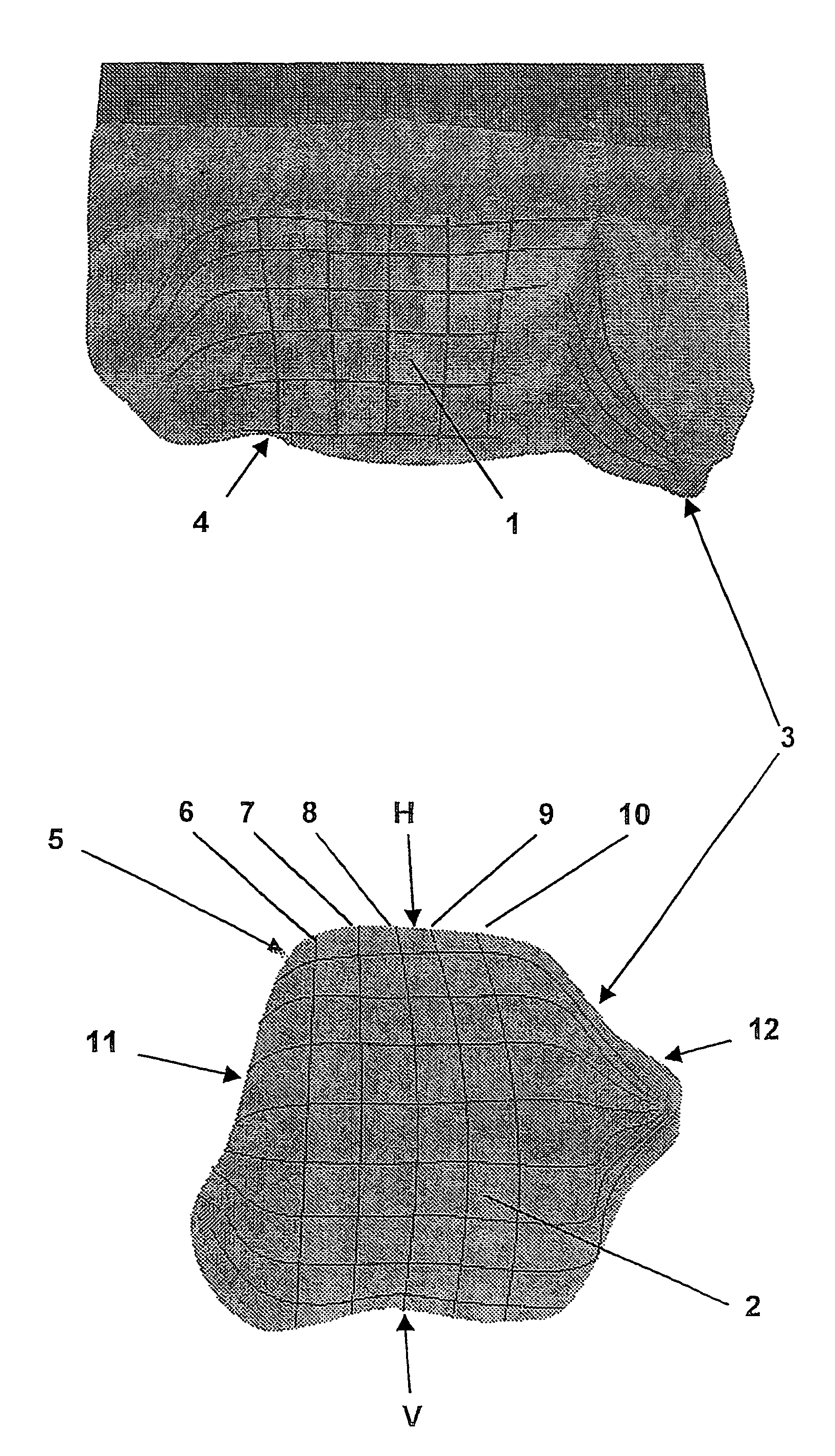
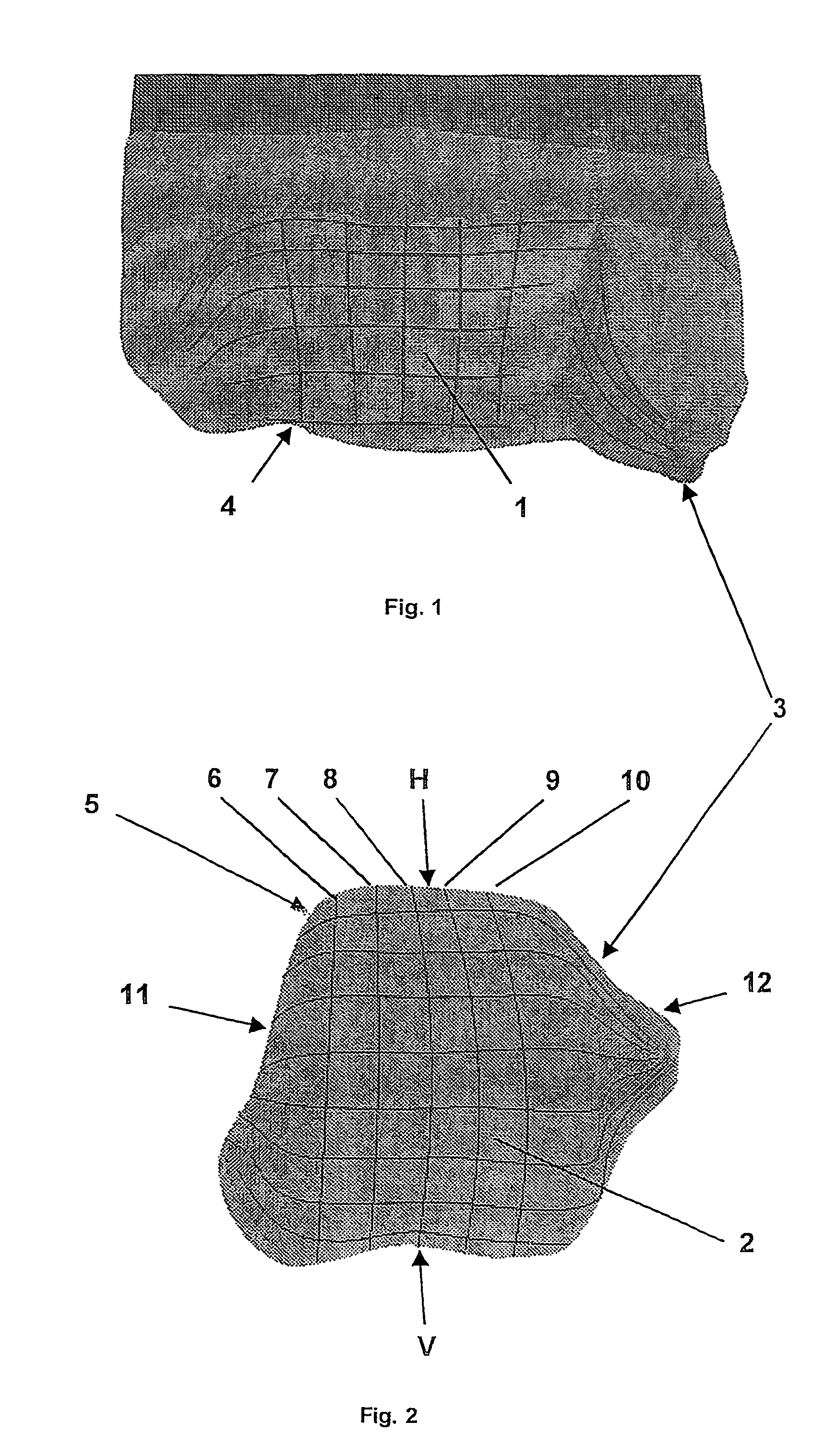
Artificial joint
InactiveUS7615082B2Improve mobilityIncreased durabilityAnkle jointsJoint implantsTibiaArticular surfaces
An artificial joint (3), particularly for replacing a talocrural joint, including a first primary joint surface (1) that forms an articular fossa (4) particularly for replacing the tibia composed of concave curvatures extending parallel to a primary function plane of the joint (3), which corresponds to the sagittal plane, and a second primary joint surface (2) which cooperates with the first primary joint surface (1) as a component of a condoyle (5) that replaces the talus and has convex curvatures (7, 8, 9, 10) on the primary function plane that are adapted to the first primary joint surface (1). To achieve high stress resistance and optimal joint mobility, depending on the position of the joint, the radii of the curvatures (7, 8, 9, 10) are calculated such that the differential amounts arising between the corresponding radii of the first and second primary joint surfaces (1, 2) in an ascending angular position (V) relative to a descending angular position and also simultaneously between a medial face (11) and a lateral face (12) of the joint (3) deviate from one another.
Owner:HJS GELENK SYST
Spinous process implant spacer and method of use therefor
InactiveUS20100131009A1Easy to implantSmall diameterInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSagittal planeBiomedical engineering
A spinous process implant, and a method therefor can be positioned with its longitudinal axis substantially perpendicular to the median sagittal plane of the patient, between an upper and an adjacent lower spinous process. The implant comprises, as spacers, upper support means, and lower support means, which, in each case, are applied with a recess saddle against the upper or lower spinous process. The support means can be spread apart in each case by means of clamping means, which are arranged between the support means in the longitudinal direction.
Owner:ROEBLING CHRISTIAN +1
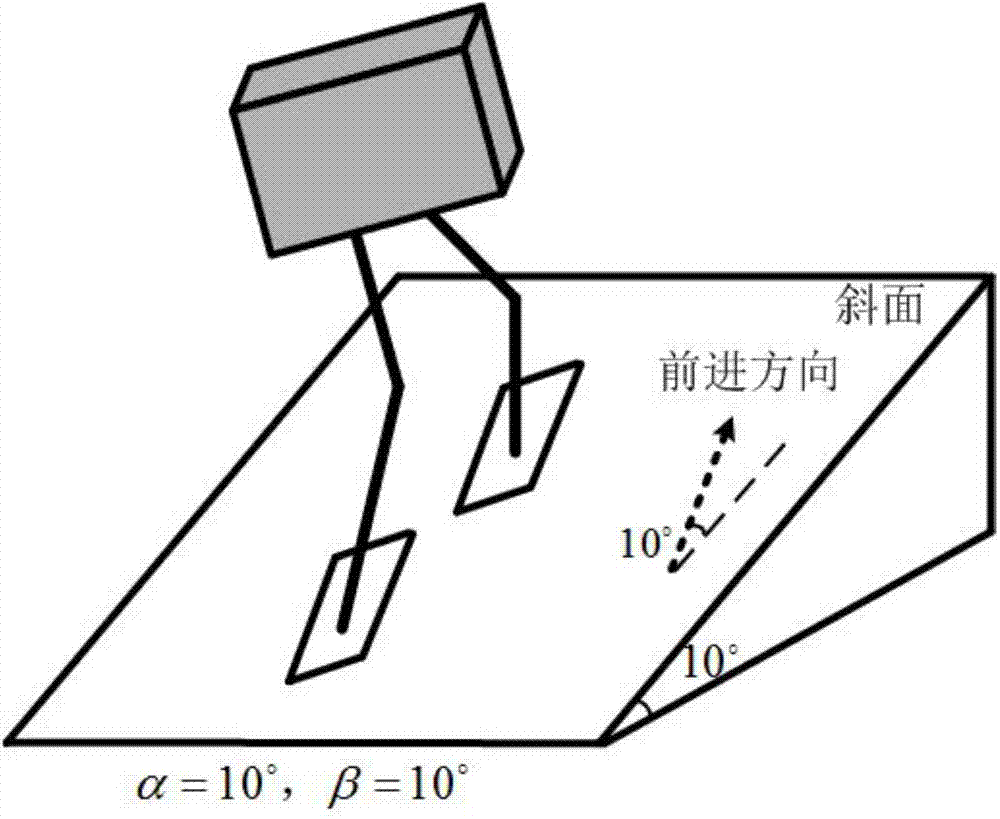
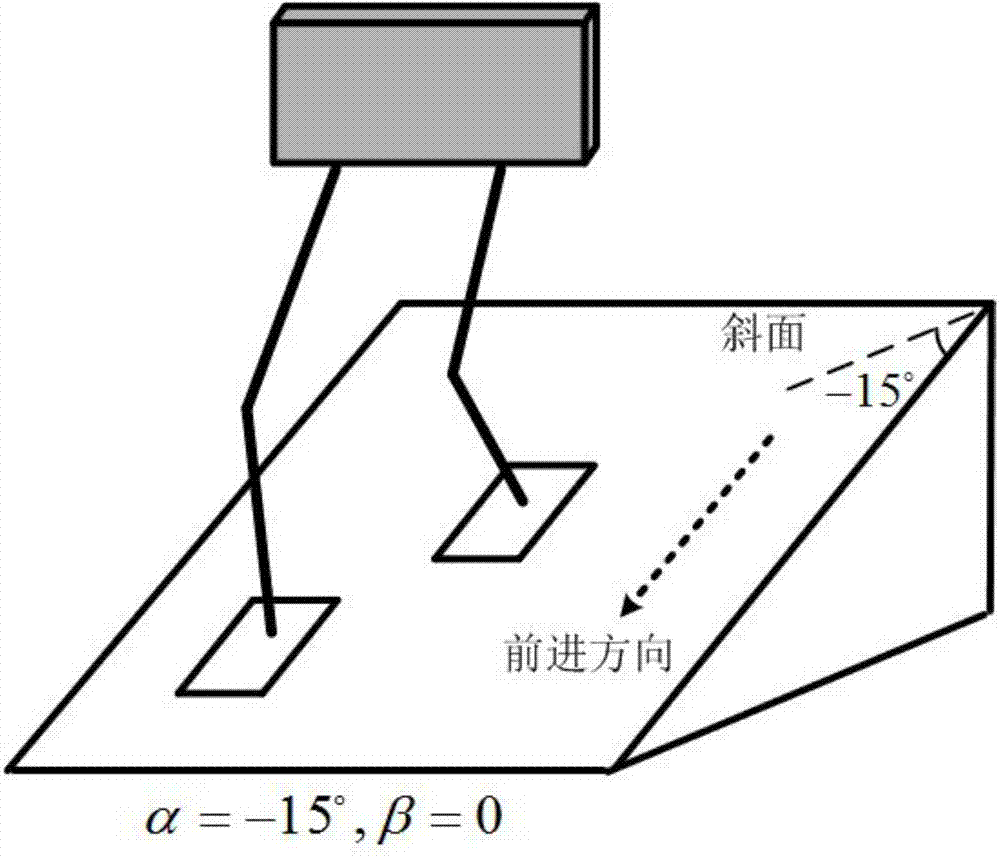
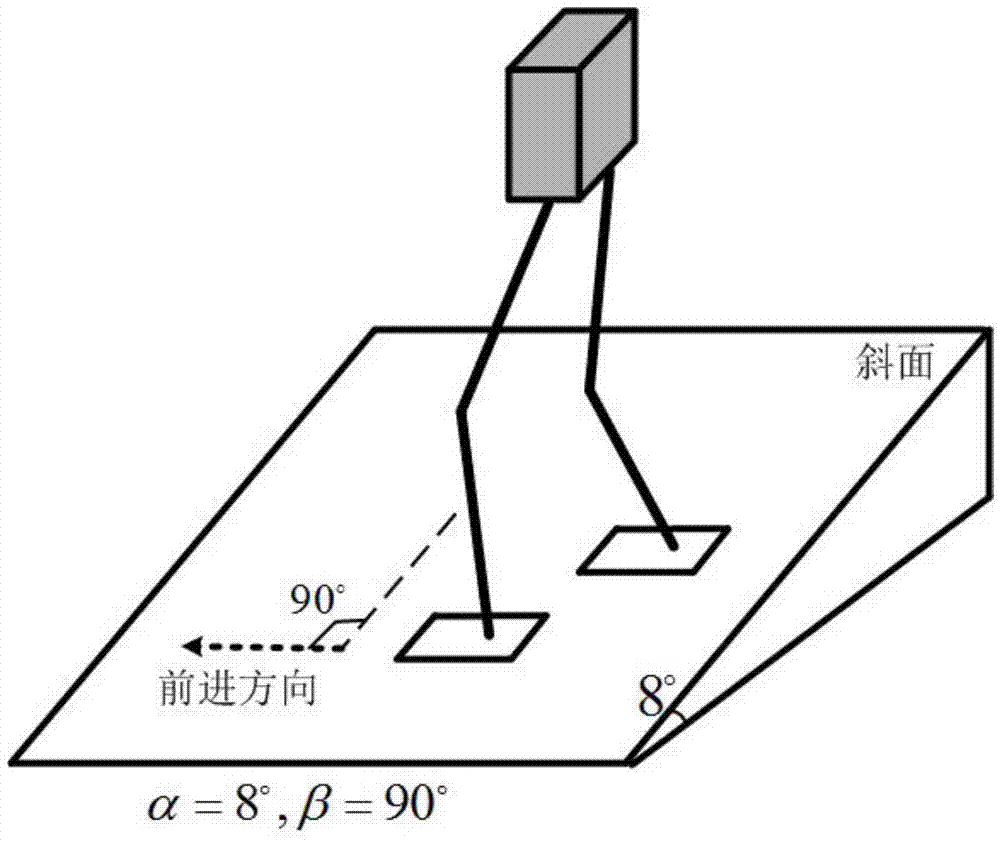
Gait planning method for walking of biped robot along slope
ActiveCN104331081AImprove environmental adaptabilityMovement coordination and natureAttitude controlCoronal planeDecomposition
The invention discloses a gait planning method for walking of a biped robot along a slope, and belongs to the technical field of robots. The method contains two core theories, namely, non-orthogonal decomposition and synthesis of a three-dimensional linear inverted pendulum and gait planning based on a biped long linear inverted pendulum. The method comprises the steps of gait parameter configuration, non-orthogonal decomposition of a three-dimensional linear inverted pendulum, foot trajectory planning based on three times of spline interpolation, centroid trajectory planning of a sagittal plane and a coronal plane based on a biped long linear inverted pendulum, non-orthogonal synthesis of the centroid trajectories of the sagittal plane and the coronal plane, and solving of joint trajectories of a robot based on inverse kinematics. By adopting the method of the invention, stable walking of a biped robot along all directions of a slope can be effectively achieved. The method is universal, simple in algorithm and high in practicality.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
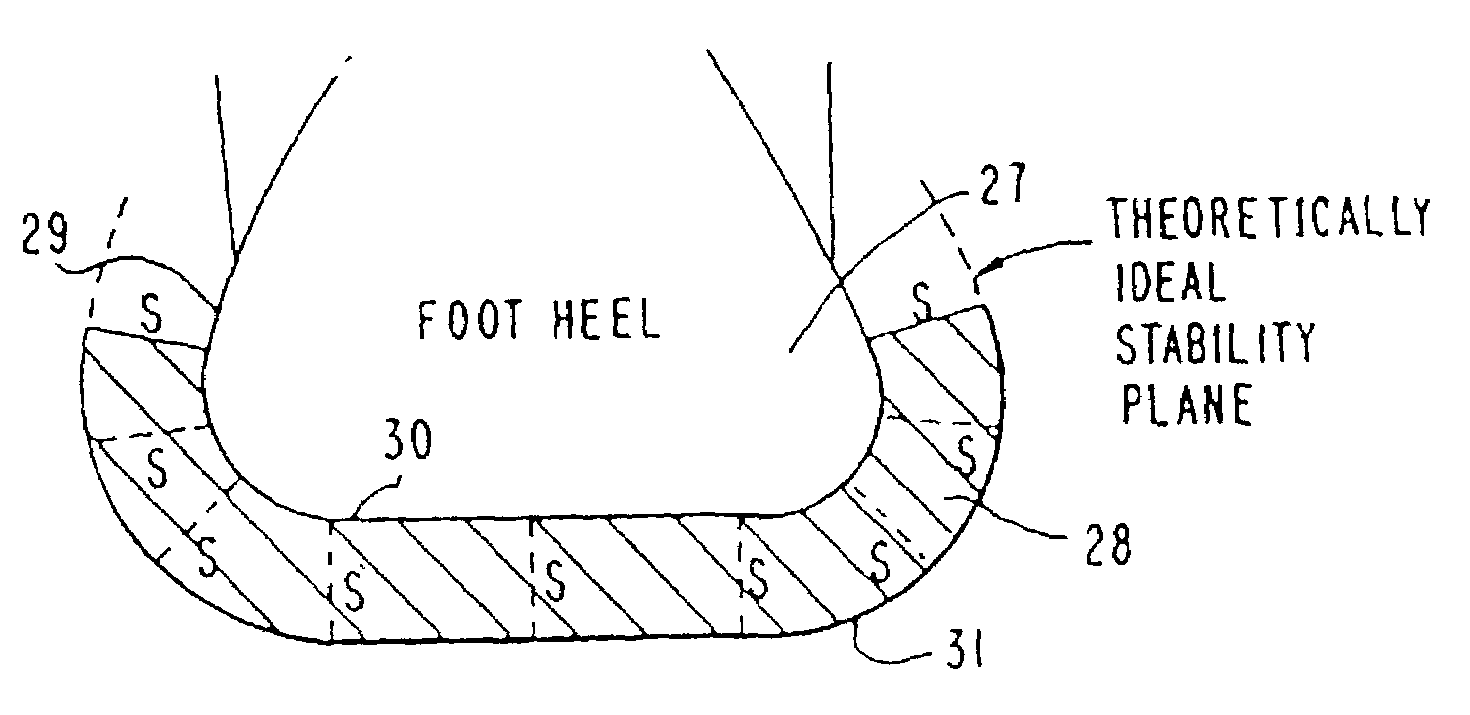
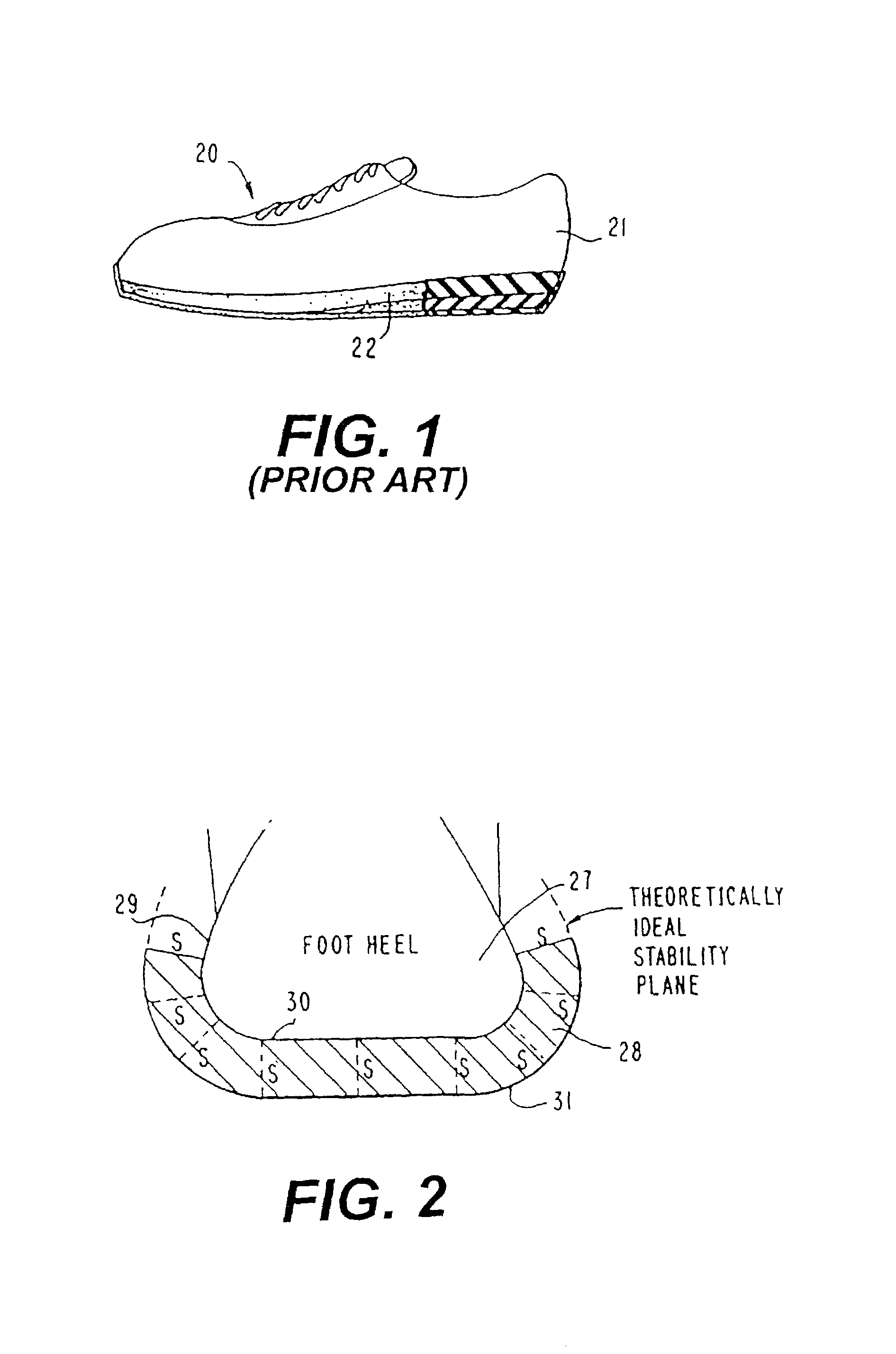
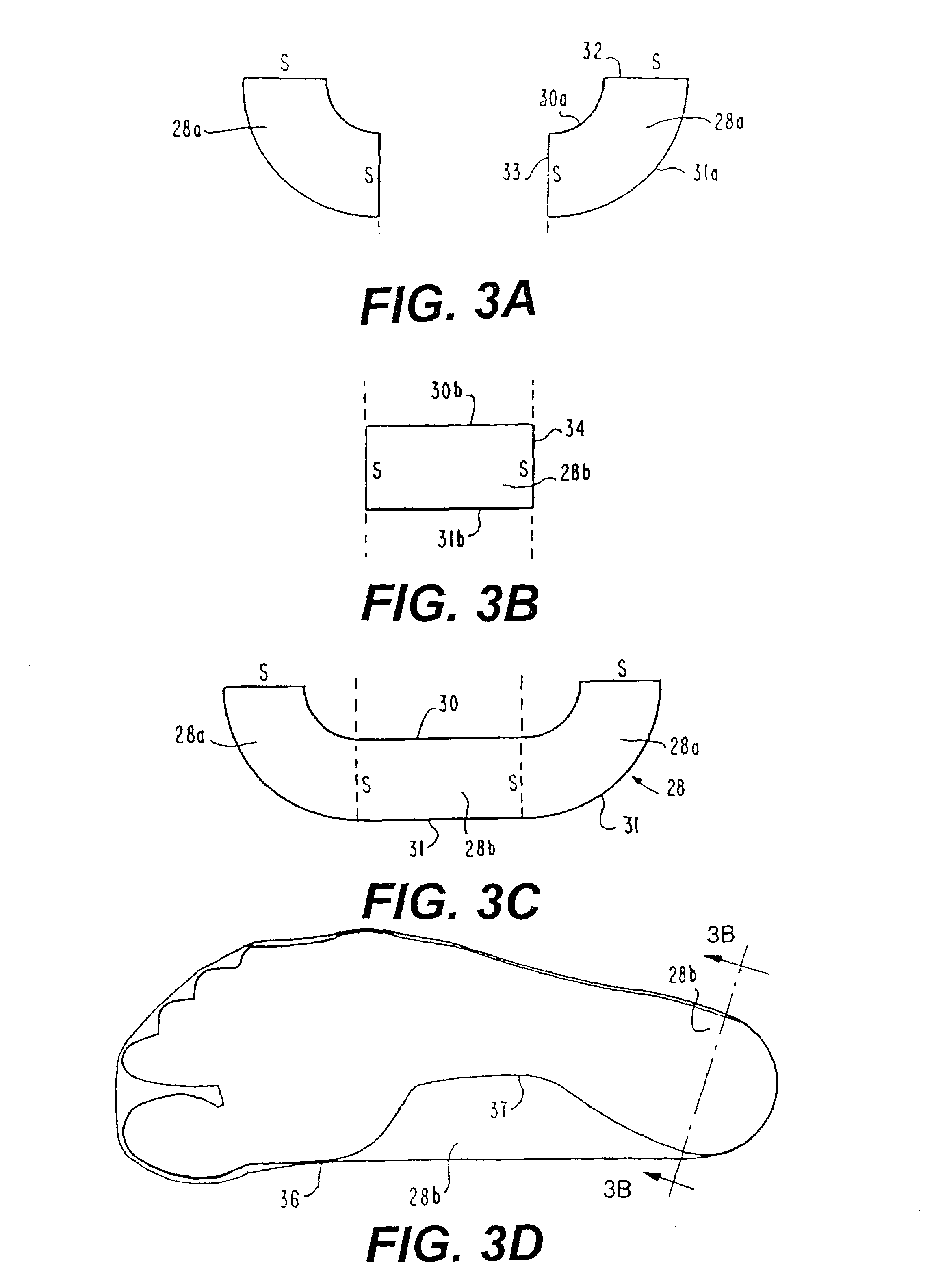
Shoe sole with rounded inner and outer side surfaces
An athletic shoe sole for a shoe has side portions with concavely rounded inner and outer surfaces, as viewed in at least a heel area and a midtarsal area of the shoe sole. The rounded surfaces increasing at least one of lateral and medial stability of the sole. The concavely rounded portion of the sole outer surface located at the heel area extends substantially continuously through a sidemost part of the sole side. The rounded portion of the sole outer surface located at the midtarsal area extends up the sole side to at least a level corresponding to a lowest point of the sole inner surface. A midsole component of the shoe sole extends into the sidemost section of the sole side and also extends up the sole side to above a level corresponding to a lowest point of the sole inner surface. The concavely rounded portions of the sole midtarsal area are located at least at the sole lateral side. The sole outer surface of at least part of the midtarsal area is substantially convexly rounded, as viewed in a shoe sole sagittal plane.
Owner:ANATOMIC RES
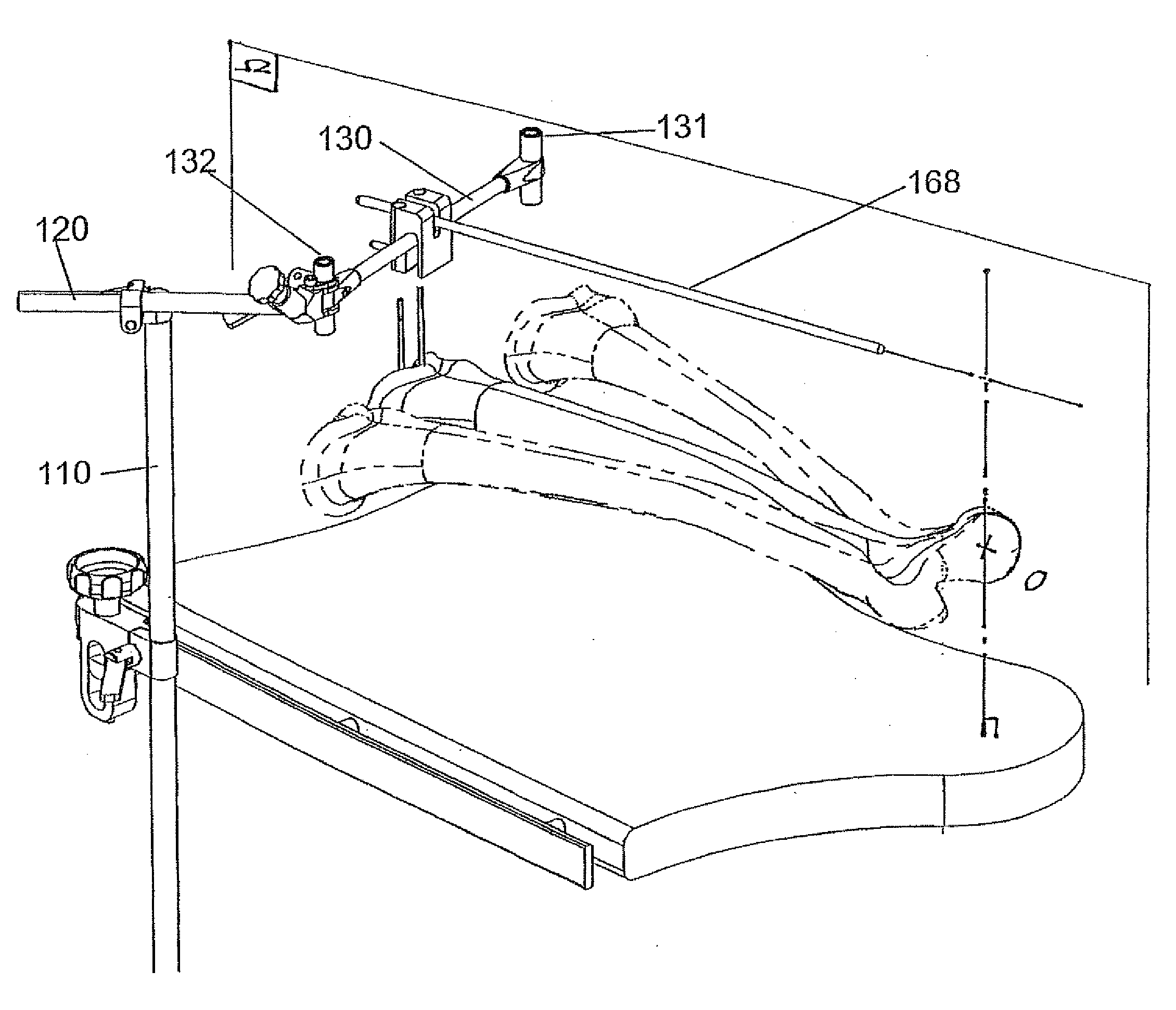
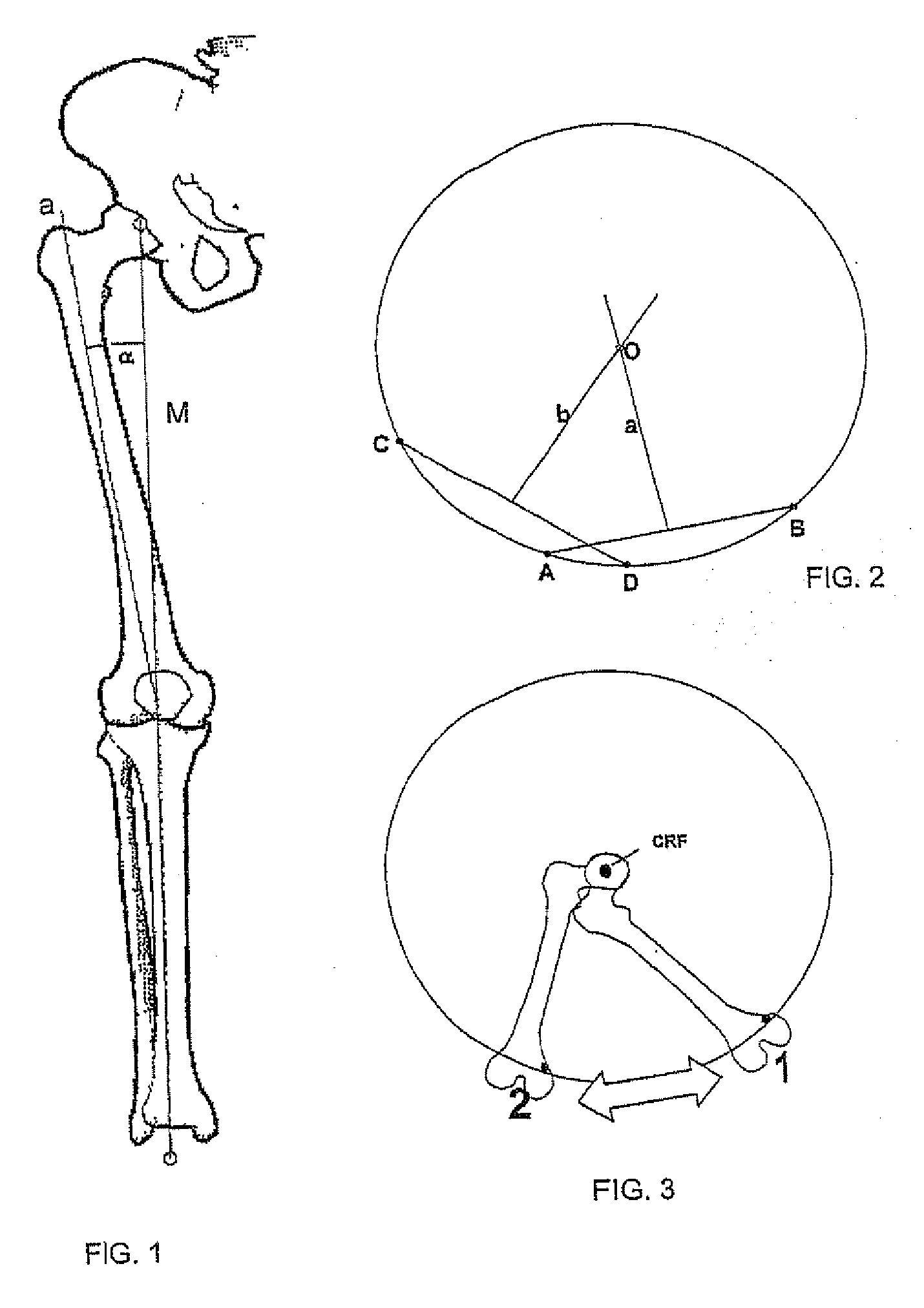
Sighting instrument for determining the mechanical axis of the femur
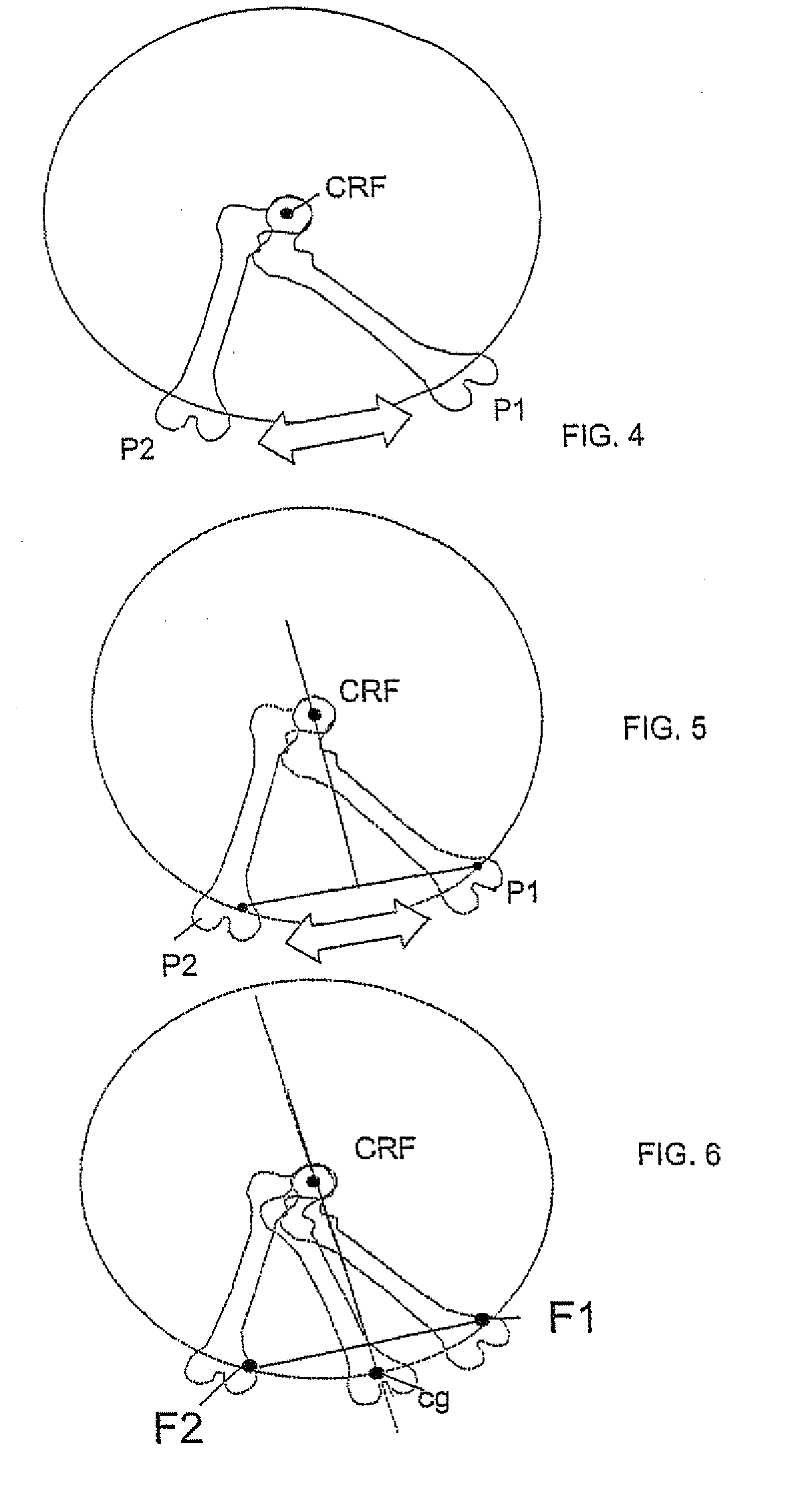
ActiveUS20090216247A1Simple fast and less-costlyGood precisionMeasurement devicesOperating tablesRight femoral headSagittal plane
A device for the determination of a plane containing the mechanical axis of the femur includes a mechanical member of articulated and or / sliding elements for the determination and memorization of two positions in space (F1 and F2) of the same point (F) of the knee, freely selected, when the knee is in position P1 and P2, relative to a referential system. These positions are obtained by rotation of the inferior limb from position P1 to position P2, about the centre of the femoral head. The orientation of an omega plan perpendicular to the frontal or sagittal plane containing the centre of the femoral head and the centre of the knee can be materialized by a rod contained in this plane, which rod is fixed perpendicularly and in the middle of the arm having at the ends two localization elements for points F1 and F2.
Owner:BREVEXCO S P R L
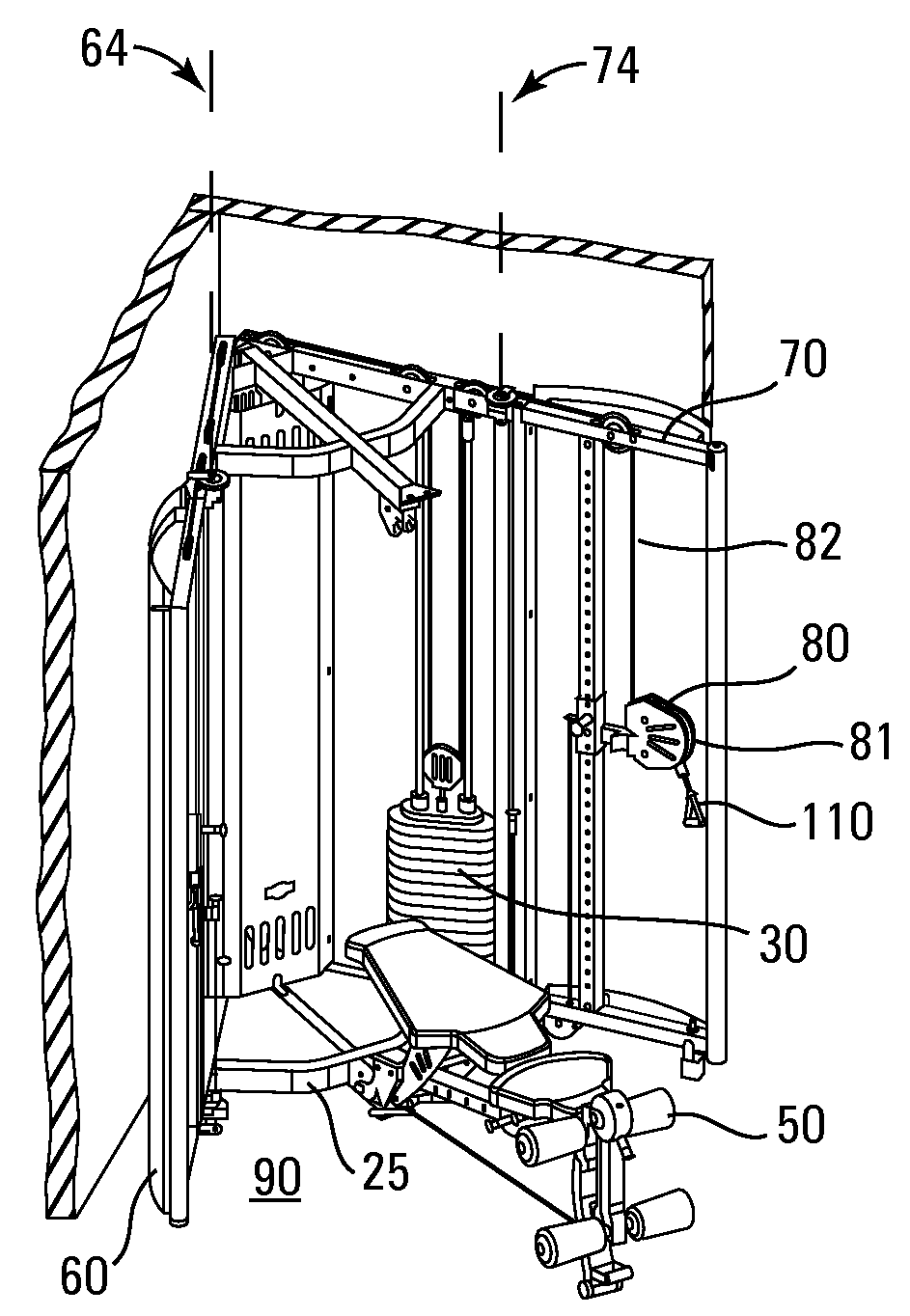
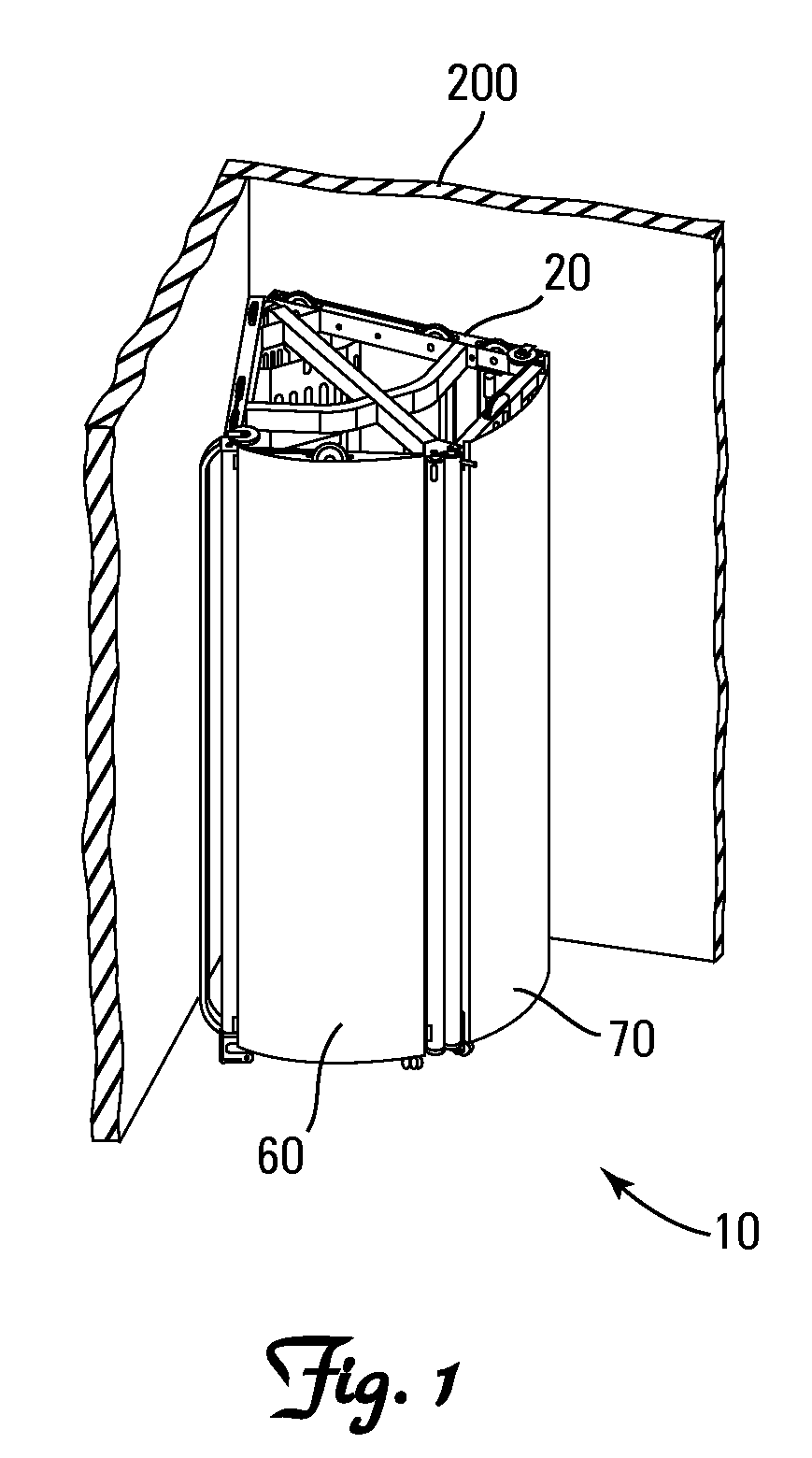
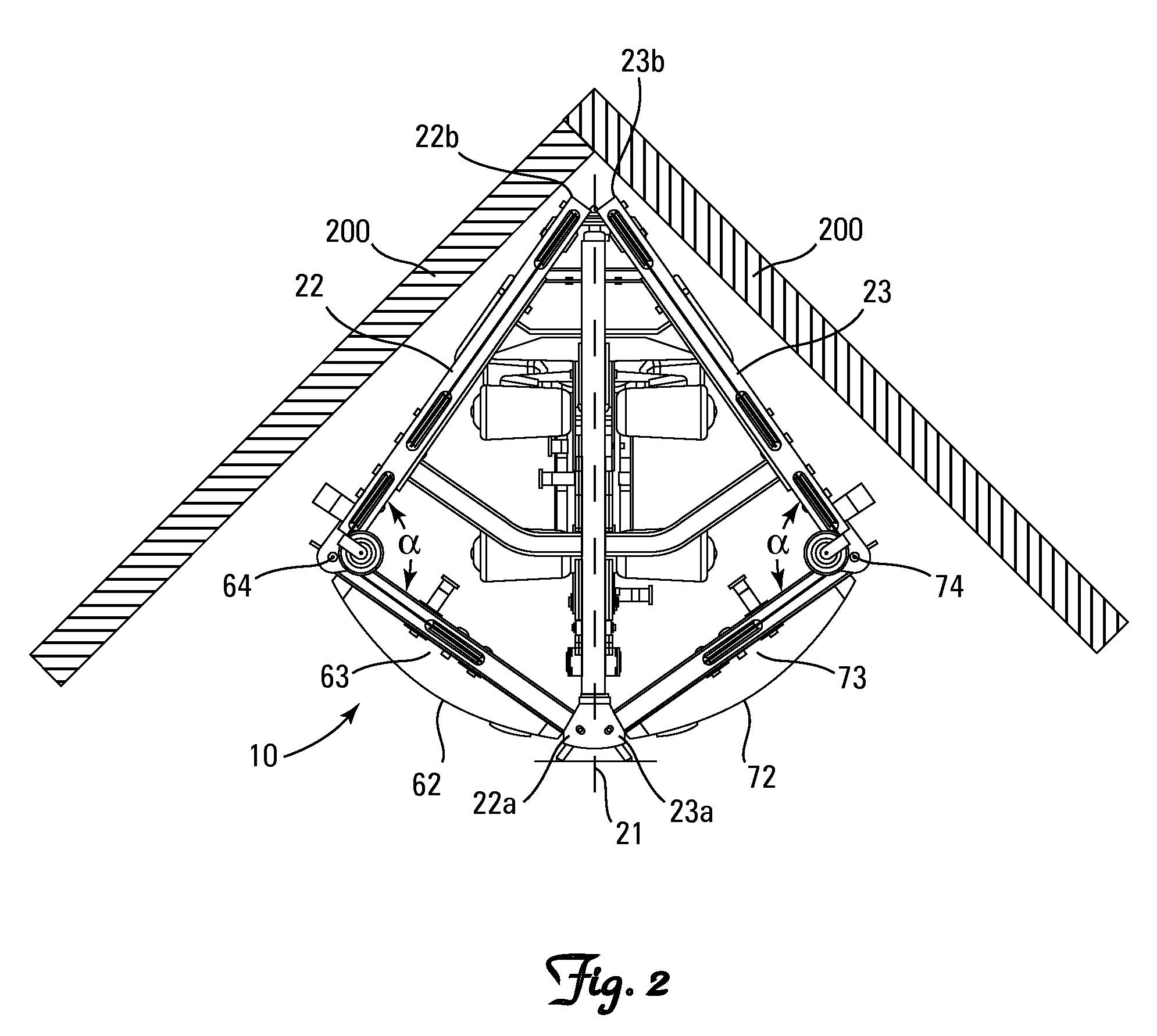
Freestanding exercise apparatus
A freestanding exercise apparatus comprises a frame, a right door, a left door, and an exercise resistance source. The frame defines a sagittal plane dividing the frame into a left half and a right half with anterior and posterior ends. The right door is pivotally attached to the right half of the frame proximate the anterior end of the frame for pivoting about a right pivot axis. The left door is pivotally attached to the left half of the frame proximate the anterior end of the frame for pivoting about a left pivot axis. The exercise resistance source is connected to the frame. The frame, right pivot axis, and left pivot axis are configured and arranged such that the angle formed at the intersection of a first plane defined by the right pivot axis and the posterior end of the right half of the frame and a second plane defined by the left pivot axis and the posterior end of the left half of the frame is less than 90°.
Owner:TORQUE FITNESS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com