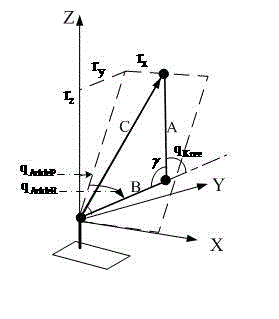
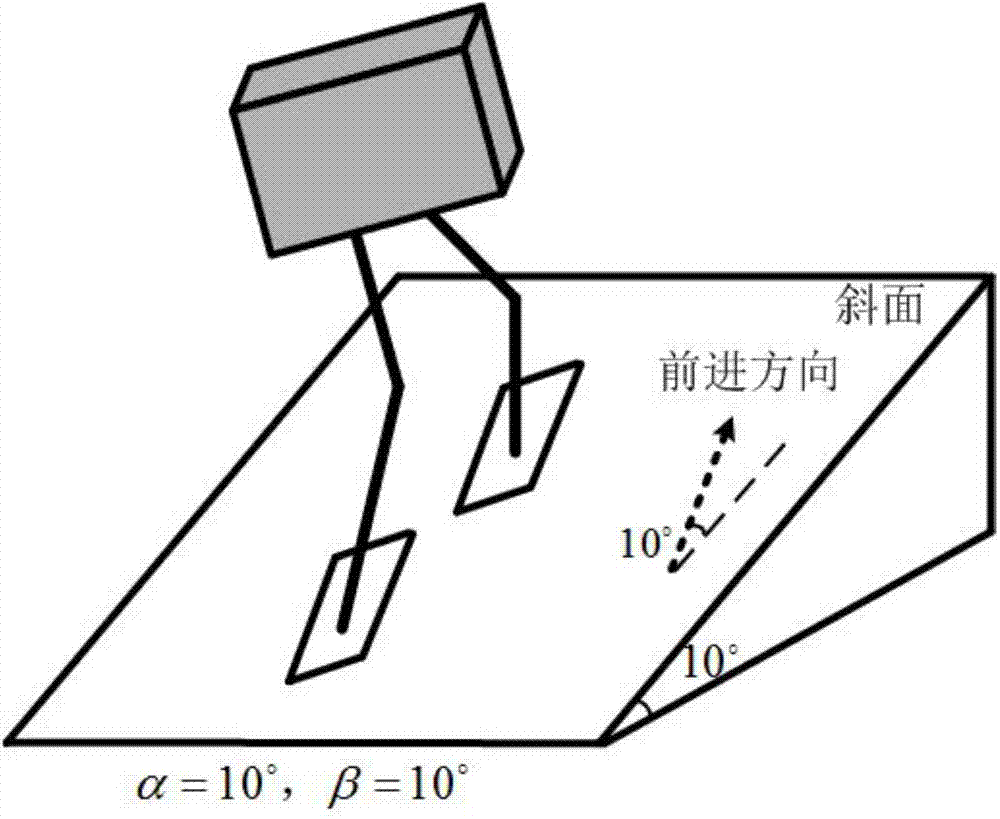
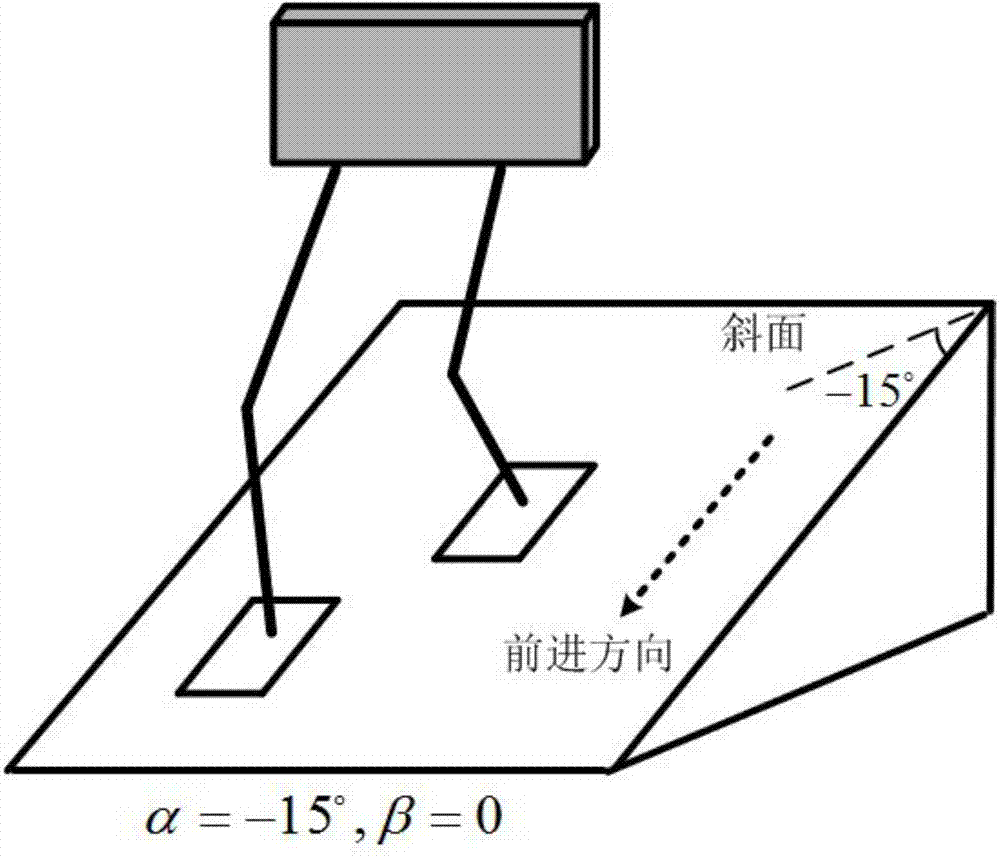
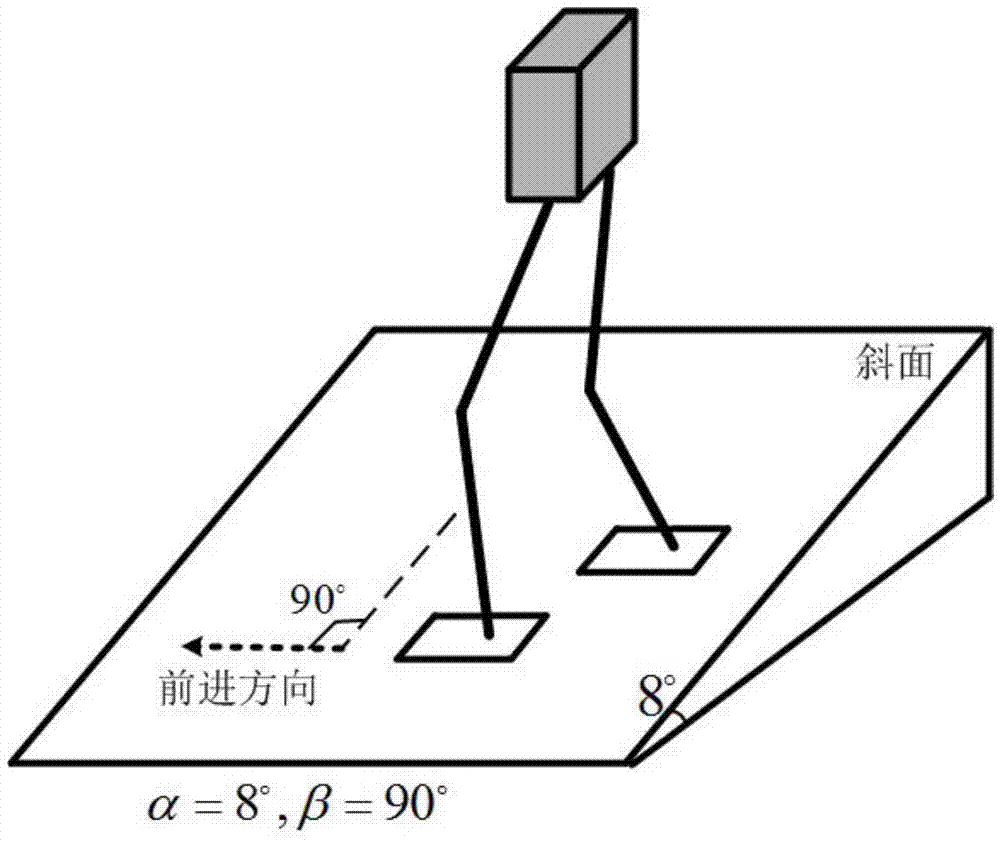
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
310 results about "Inverted pendulum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An inverted pendulum is a pendulum that has its center of mass above its pivot point. It is unstable and without additional help will fall over. It can be suspended stably in this inverted position by using a control system to monitor the angle of the pole and move the pivot point horizontally back under the center of mass when it starts to fall over, keeping it balanced. The inverted pendulum is a classic problem in dynamics and control theory and is used as a benchmark for testing control strategies. It is often implemented with the pivot point mounted on a cart that can move horizontally under control of an electronic servo system as shown in the photo; this is called a cart and pole apparatus. Most applications limit the pendulum to 1 degree of freedom by affixing the pole to an axis of rotation. Whereas a normal pendulum is stable when hanging downwards, an inverted pendulum is inherently unstable, and must be actively balanced in order to remain upright; this can be done either by applying a torque at the pivot point, by moving the pivot point horizontally as part of a feedback system, changing the rate of rotation of a mass mounted on the pendulum on an axis parallel to the pivot axis and thereby generating a net torque on the pendulum, or by oscillating the pivot point vertically. A simple demonstration of moving the pivot point in a feedback system is achieved by balancing an upturned broomstick on the end of one's finger.
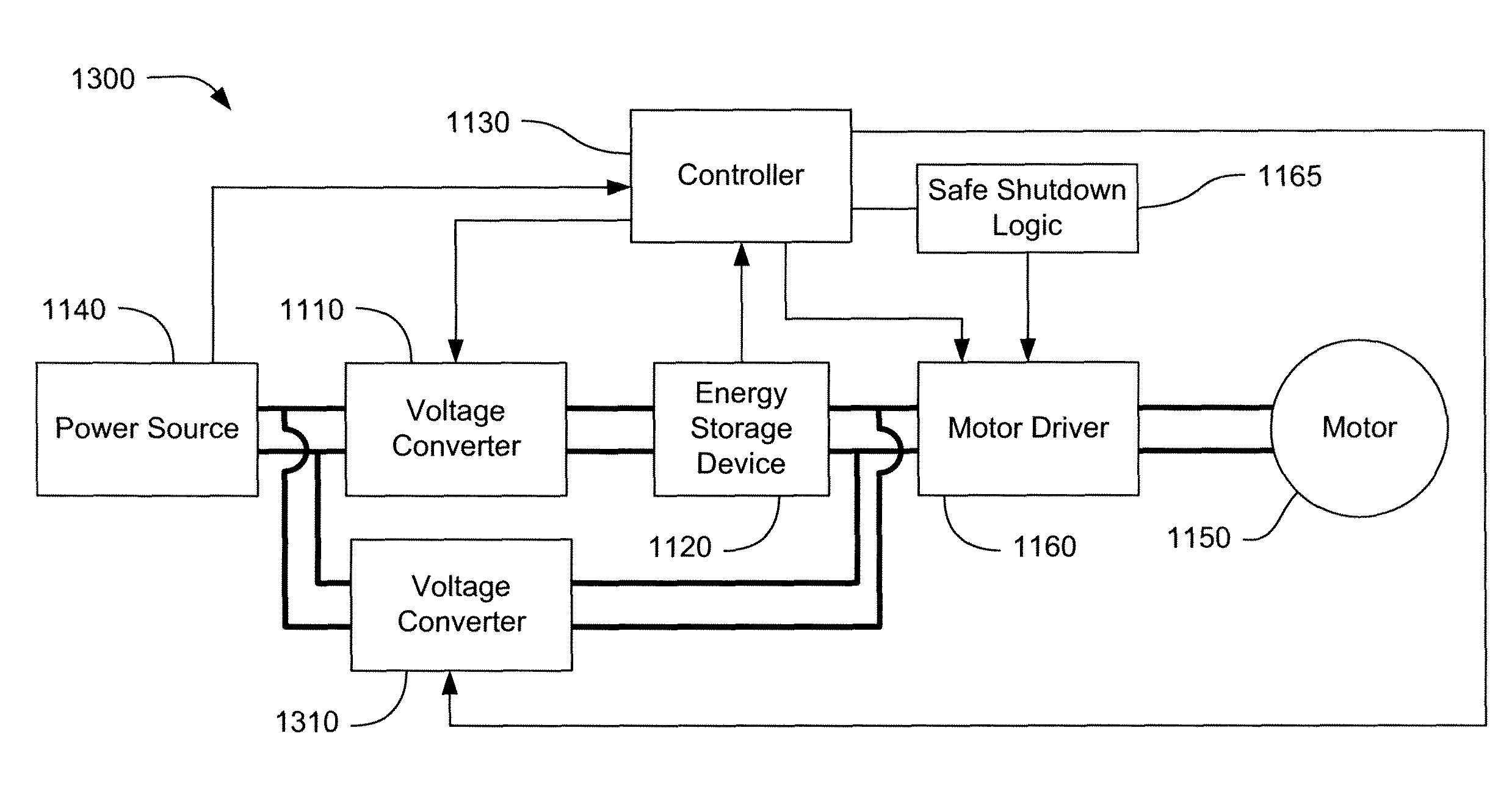
Self-balancing robot including an ultracapacitor power source
ActiveUS8041456B1Maintain balanceProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorElectric power systemEngineering
A power system is provided for robotic systems such as dynamically balancing robots, including inverted pendulum robots, robots that balance on two legs, and dynamically balancing robotic personal vehicles. Under normal operation, the power system provides operating power from a power source such as an internal battery system or an external AC power supply. The power system includes an energy storage device, such as an ultracapacitor assembly, that can provide emergency power sufficient to power components of the robotic system to a stable shutdown configuration in the event of a deleterious power event.
Owner:ANYBOTS 2 0
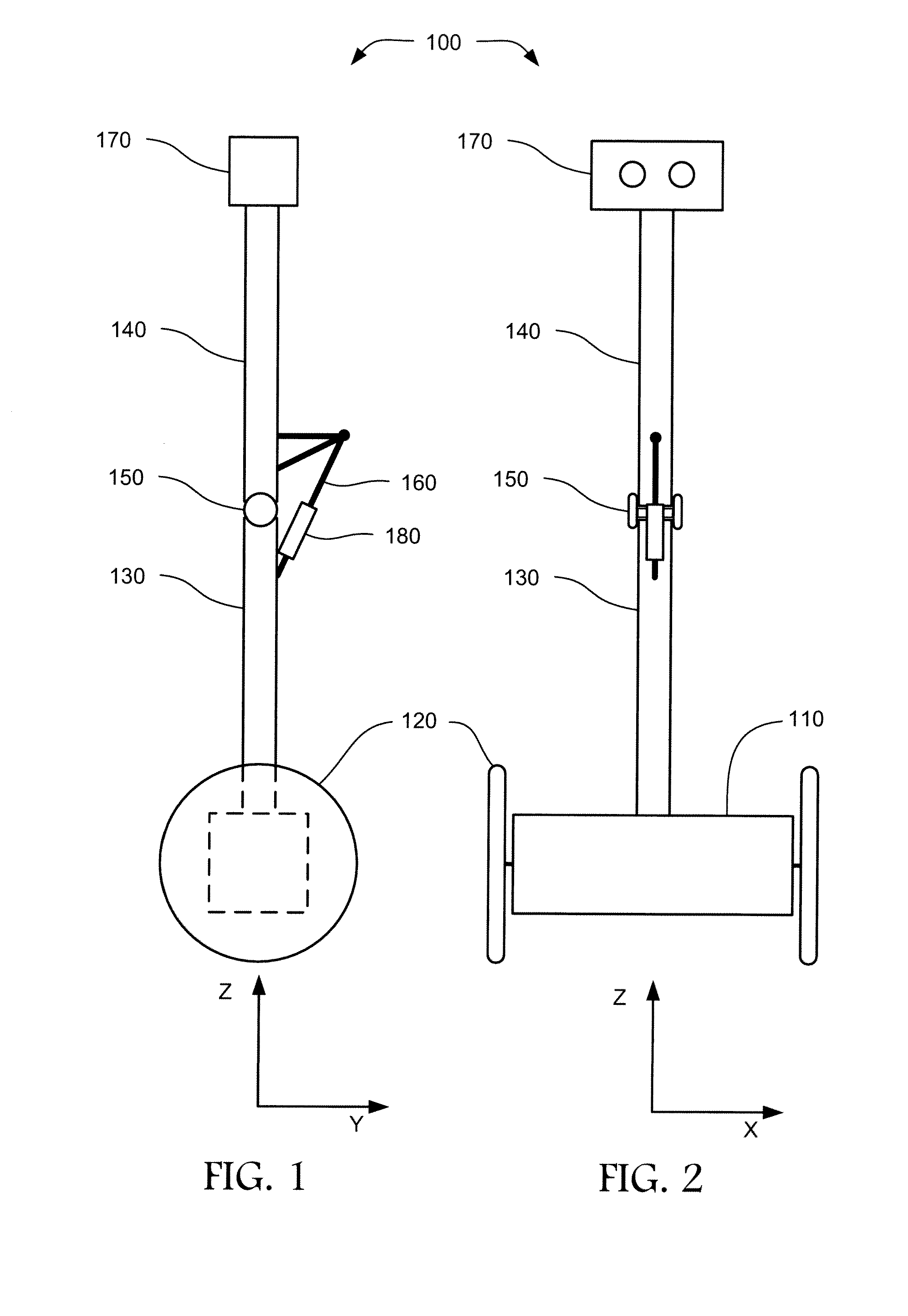
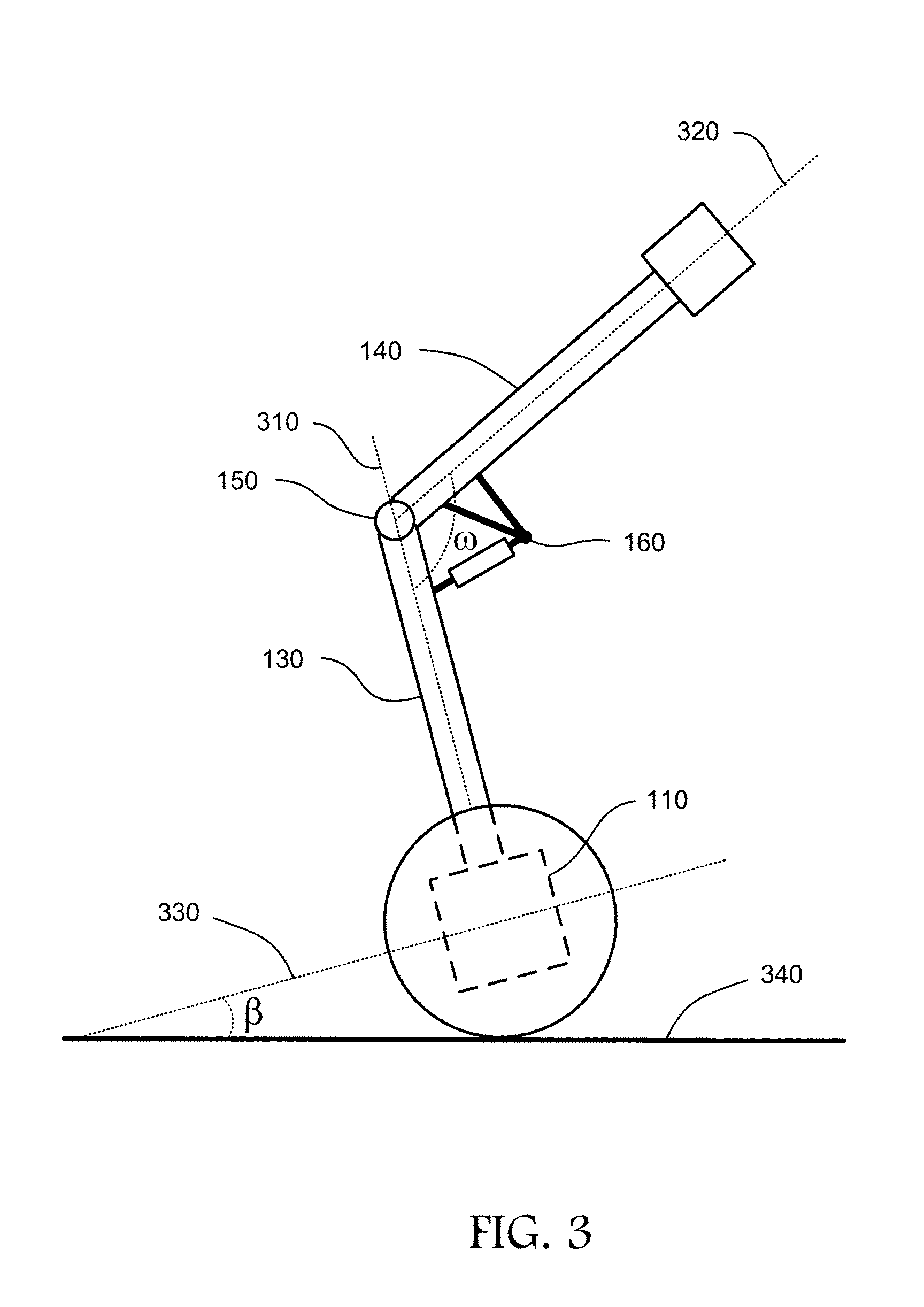
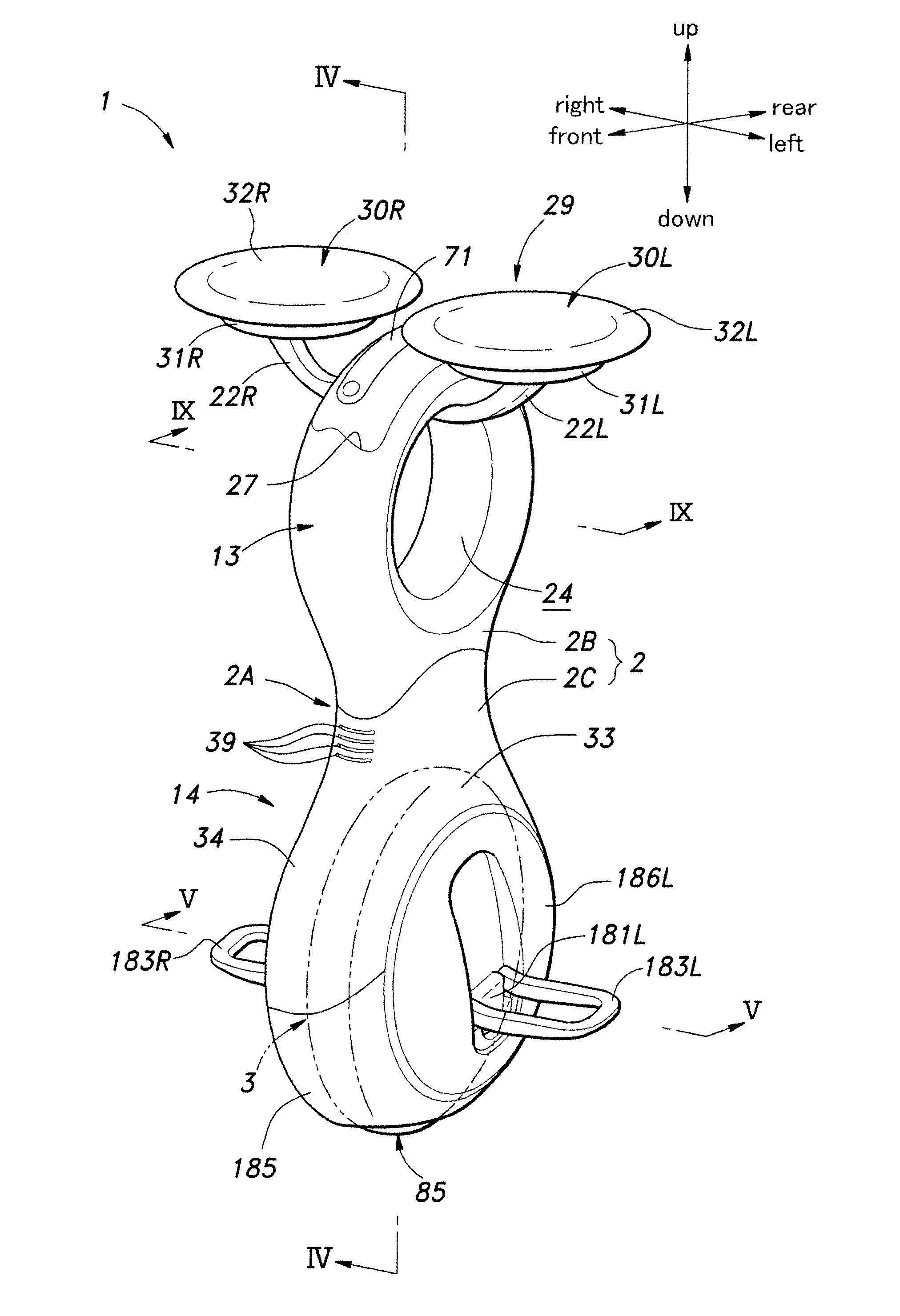
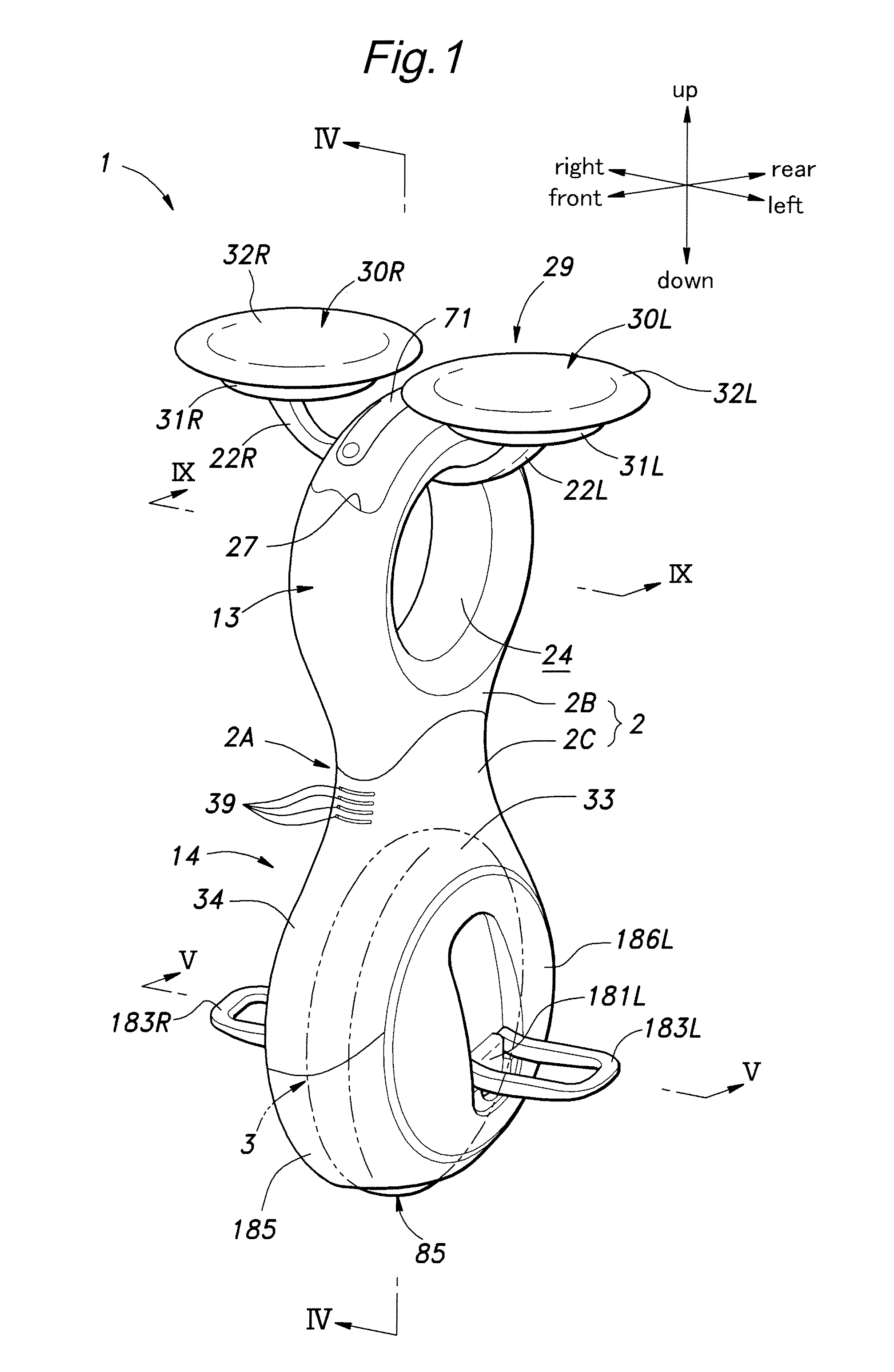
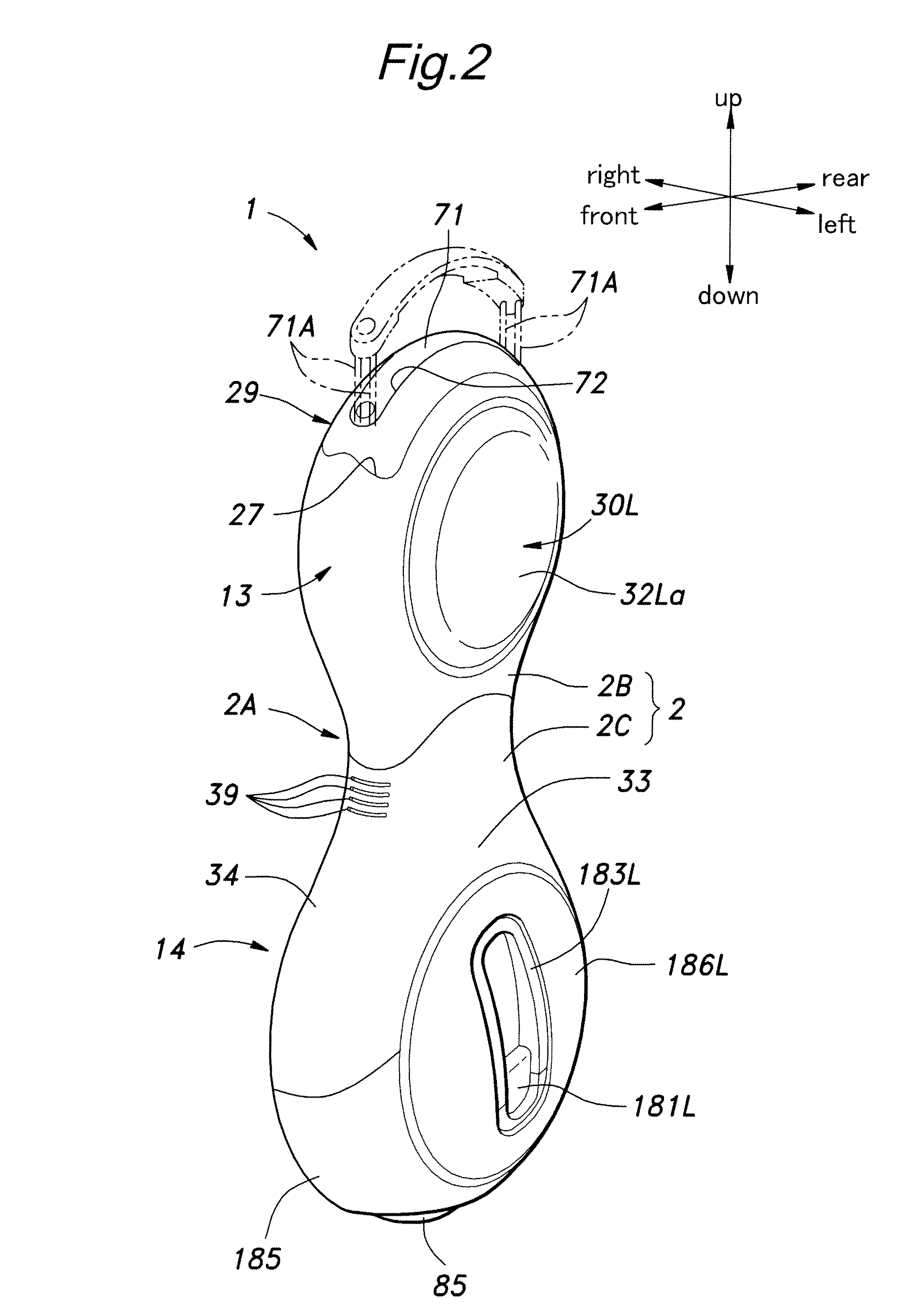
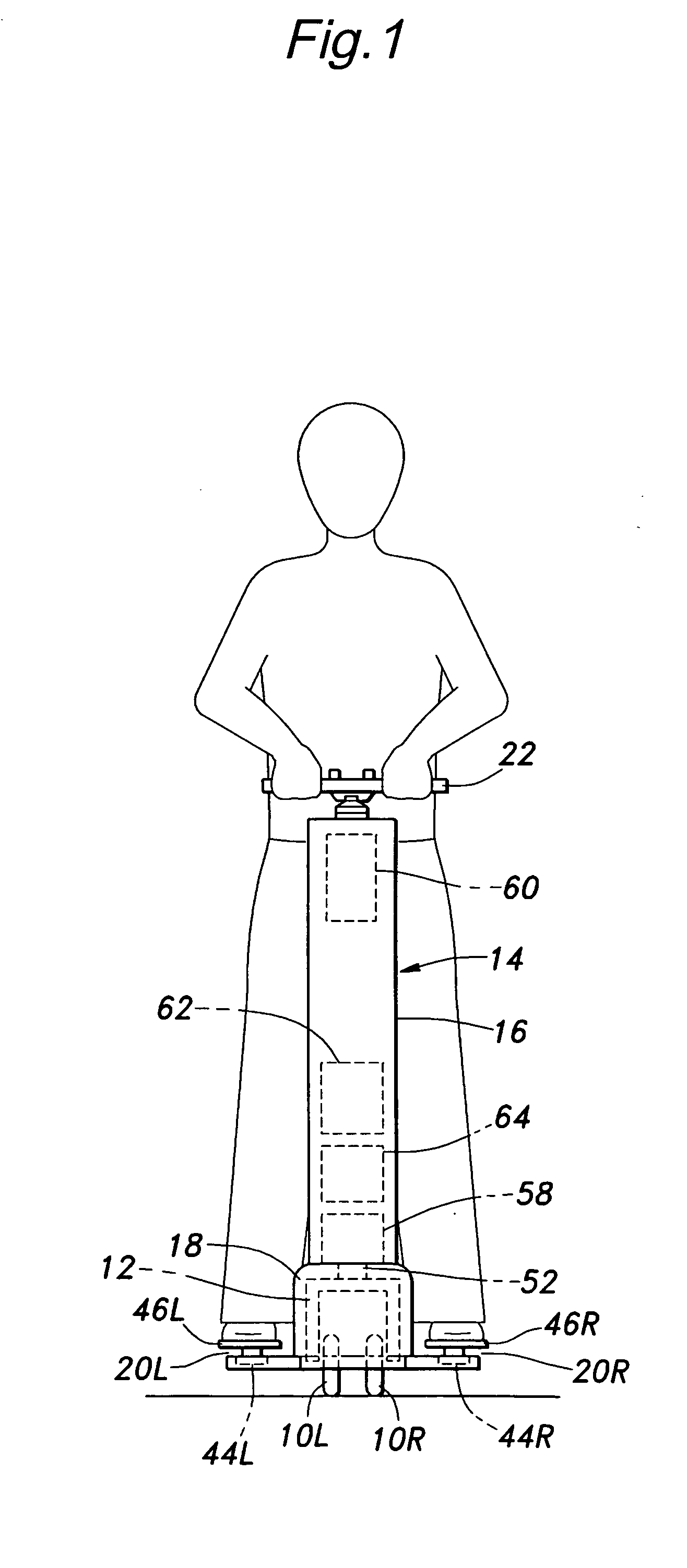
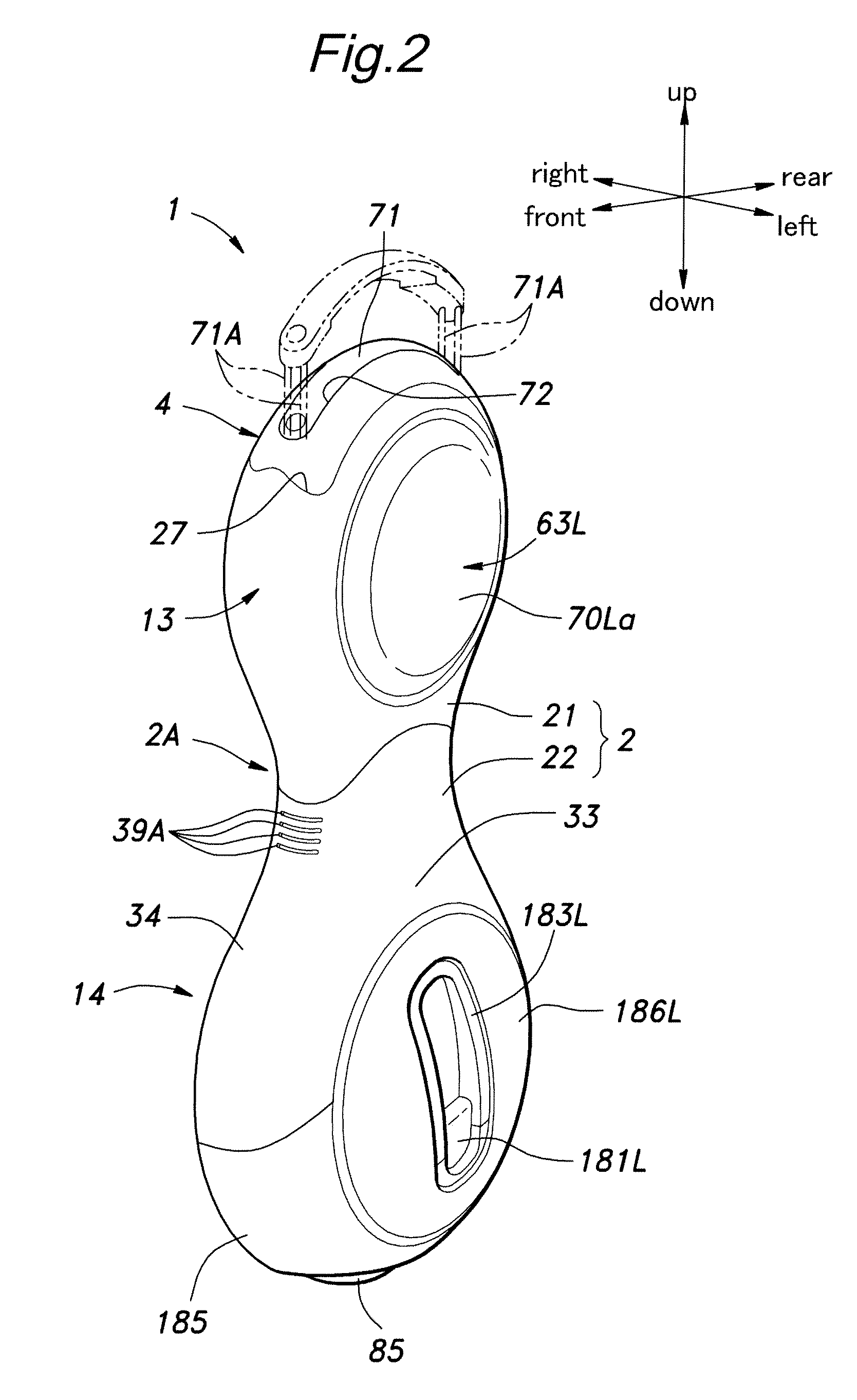
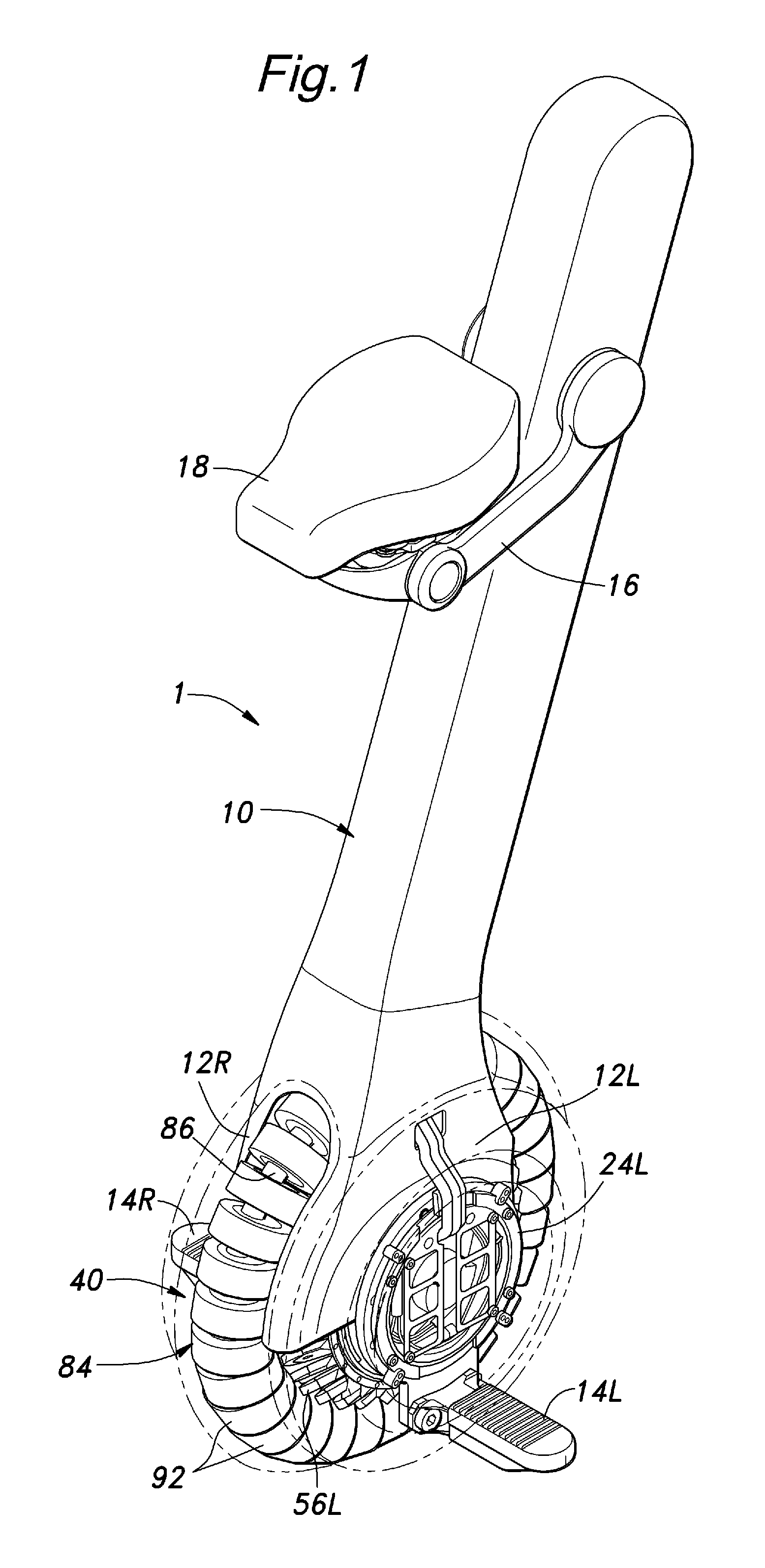
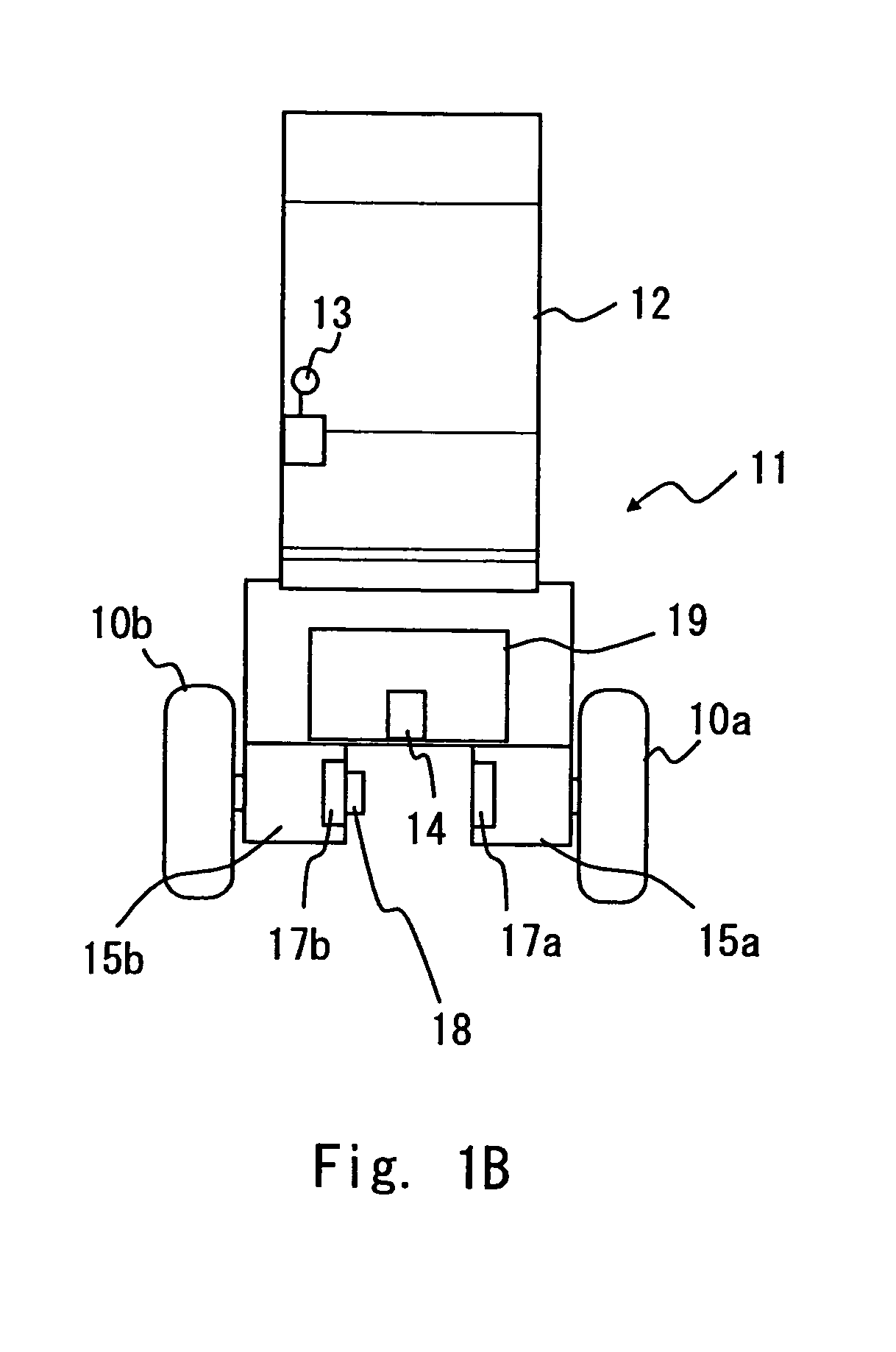
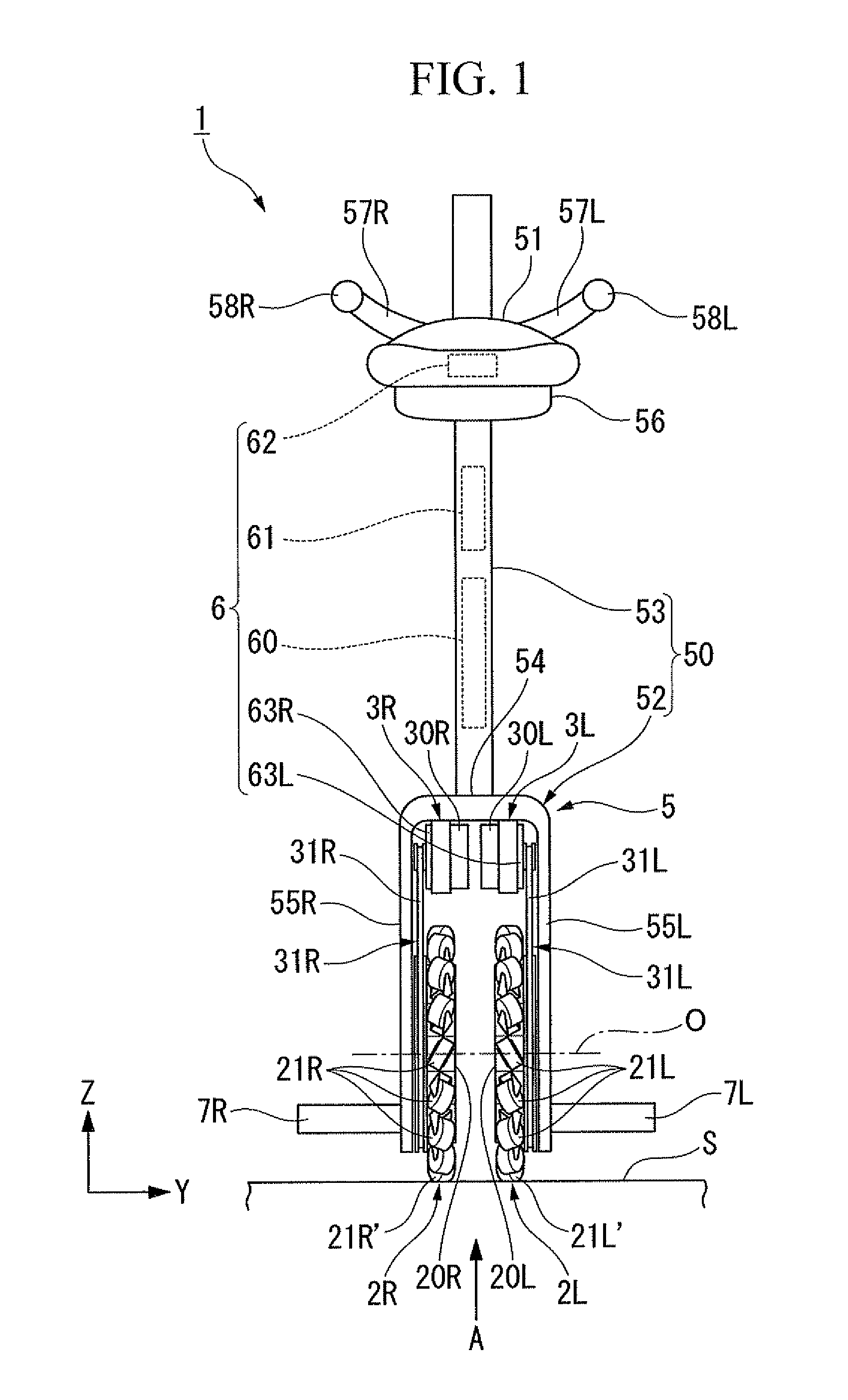
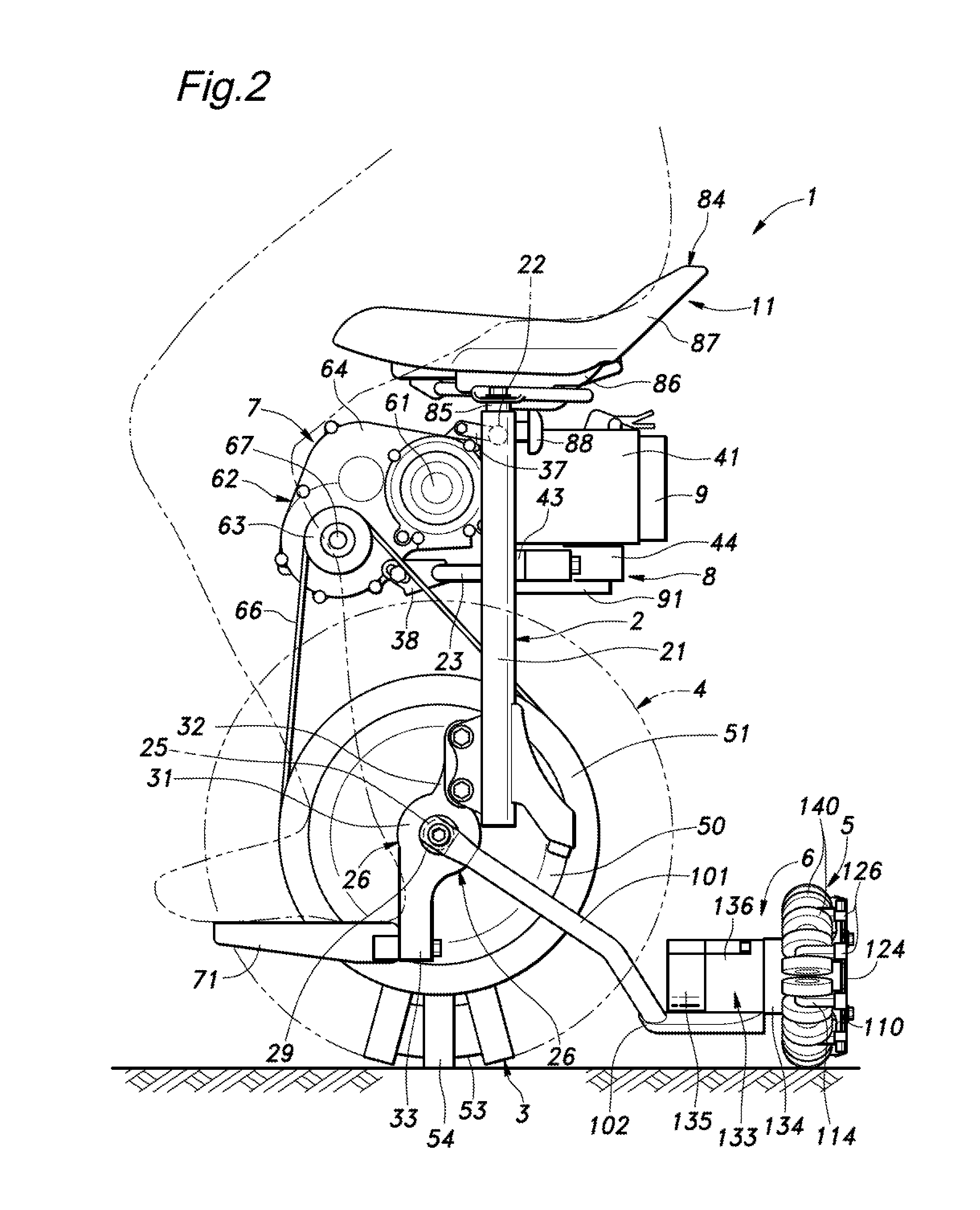
Inverted pendulum mobile vehicle
ActiveUS8225891B2Small radiusIncreased complexityOperating modesVehicle position/course/altitude controlMobile vehicleVehicle frame
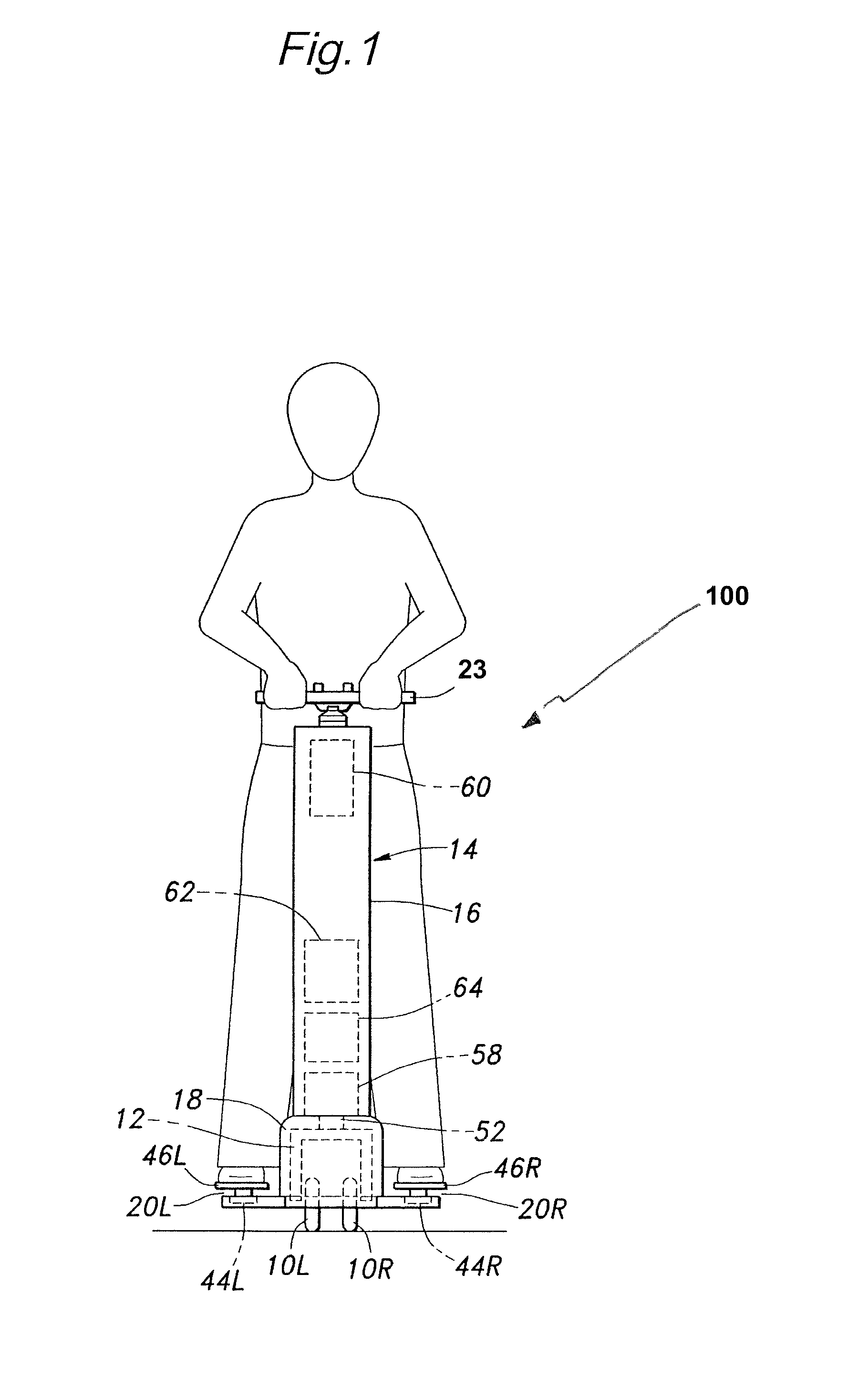
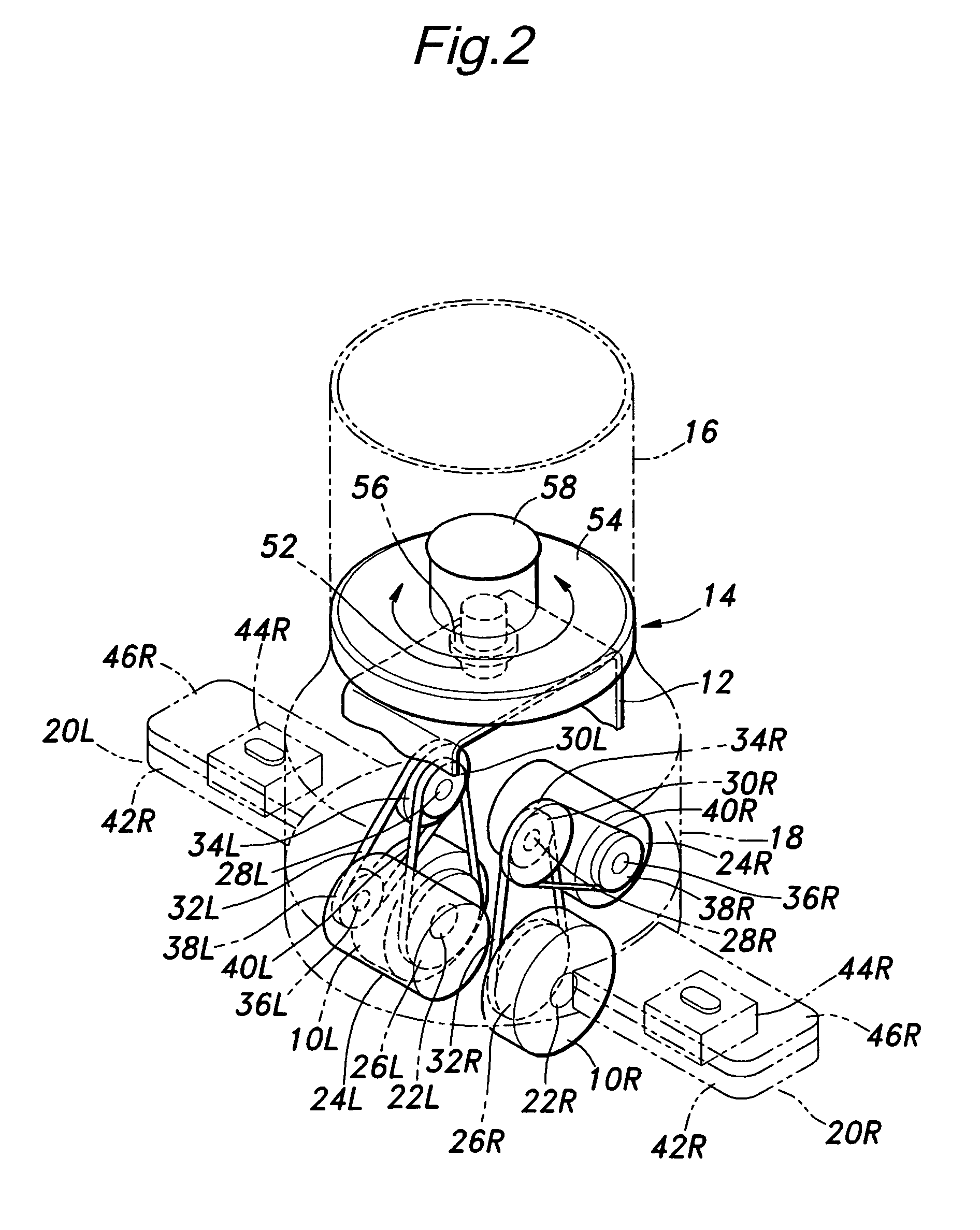
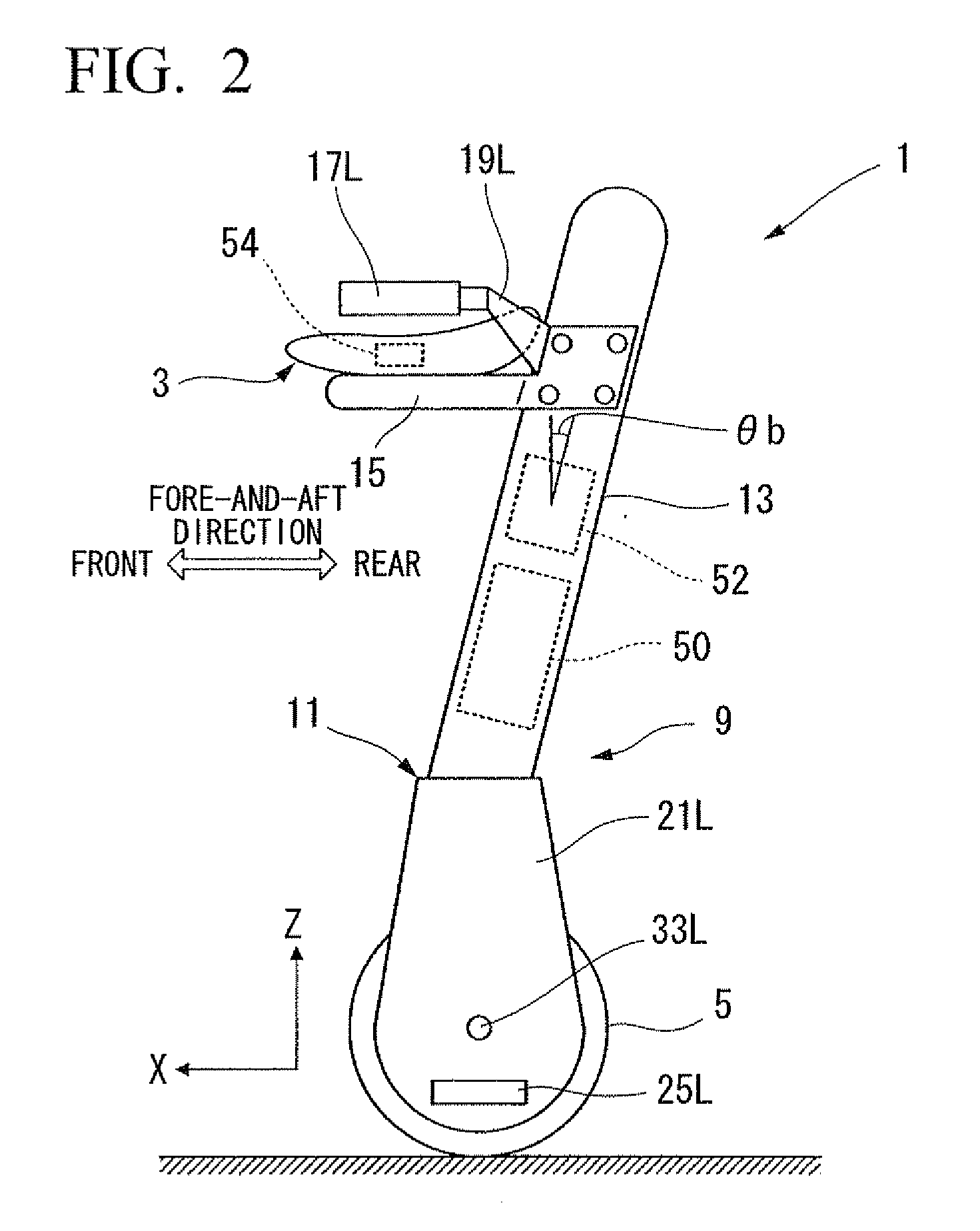
Provided is an inverted pendulum mobile vehicle such as a single-passenger coaxial two-wheel vehicle which is capable of turning with a small turning radius without causing discomfort to a rider or a vehicle occupant or causing a cargo or the like on the vehicle from shifting or falling off from the vehicle. The vehicle comprises a wheel supporting frame (12), a body frame (12) supported by the wheel supporting frame so as to be rotatable around a vertical axial line and carry a rider and or a cargo and a body coupler (52, 78, 70) that couples the body frame relative to the wheel supporting frame in a prescribed dynamic positional relationship. Thereby, even when the wheel supporting frame undergoes a rapid yaw movement either while traveling in a fore-and-aft direction or remaining stationary, the body frame that carries a vehicle occupant or a cargo is allowed to follow the yaw movement of the wheel supporting frame at a slower angular speed and / or acceleration / deceleration so that the vehicle occupant is prevented from experiencing discomfort and the cargo is prevented from shifting on the body frame or falling off from the vehicle.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
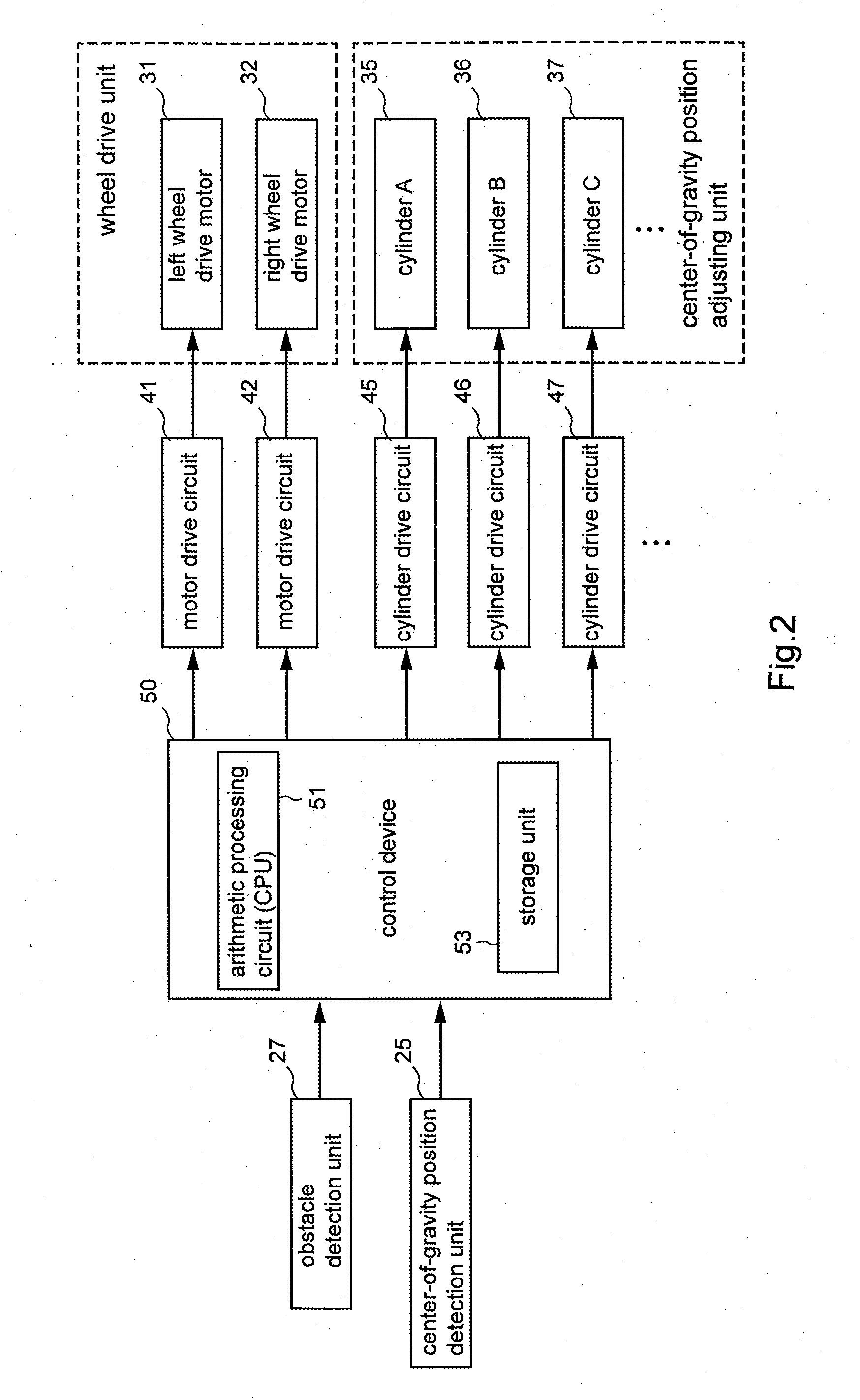
Inverted pendulum type moving body
InactiveUS20120166048A1Less discomfortAvoid overall overturningDigital data processing detailsPower-operated mechanismOperation modeInverted pendulum
An inverted pendulum type moving body subject to a traveling control in response to a traveling instruction based on an intention of a rider while keeping a balance, a manipulation mode is performed based on the intention of the rider and an automatic operation mode is performed without being based on the intention of the rider.The inverted pendulum type moving body includes a center-of-gravity position adjusting unit for adjusting a center-of-gravity position of the rider in accordance with a manipulation signal outputted from a control device. When an instruction for switching a control mode to an automatic operation mode, where a predetermined traveling control is performed without being based on intention of the rider, is generated, and controls a wheel drive unit in accordance with a traveling instruction based on the center-of-gravity position.
Owner:BOSCH CORP
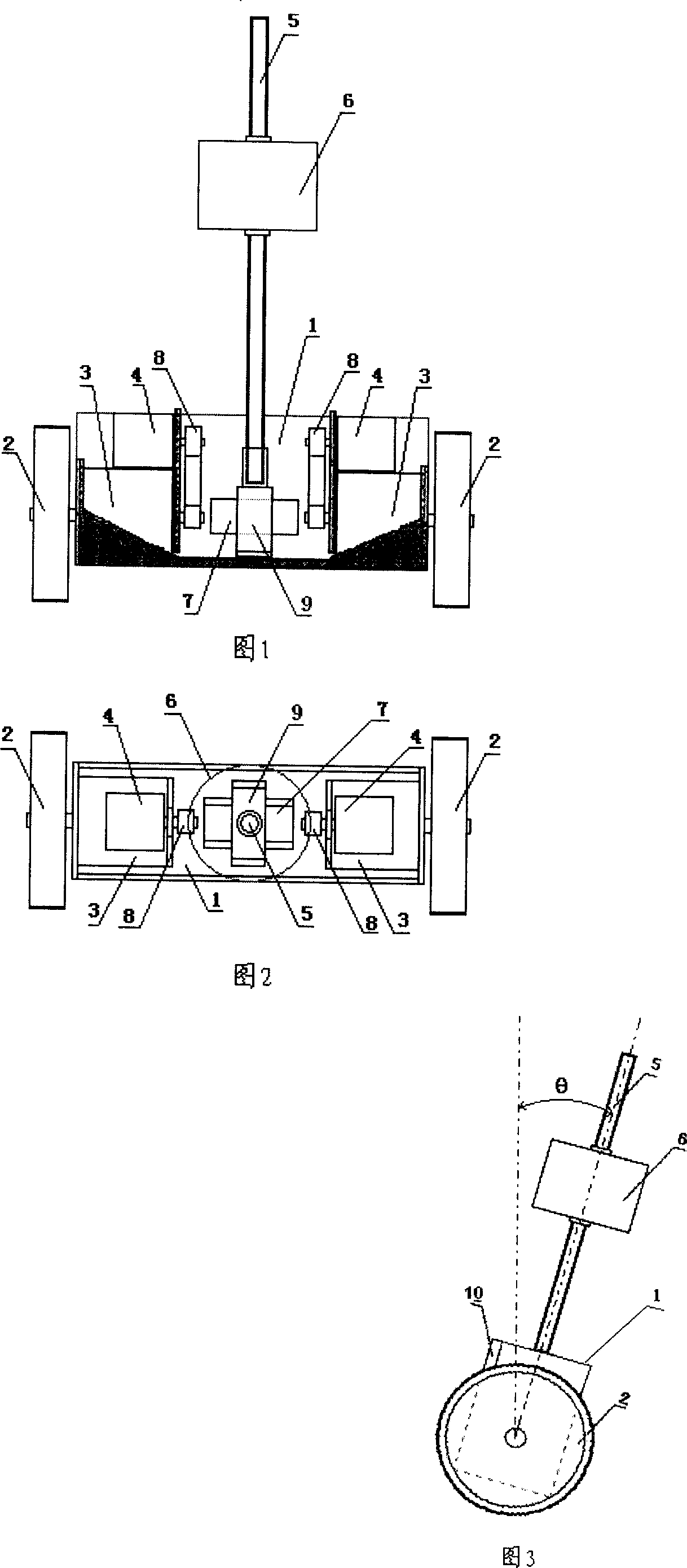
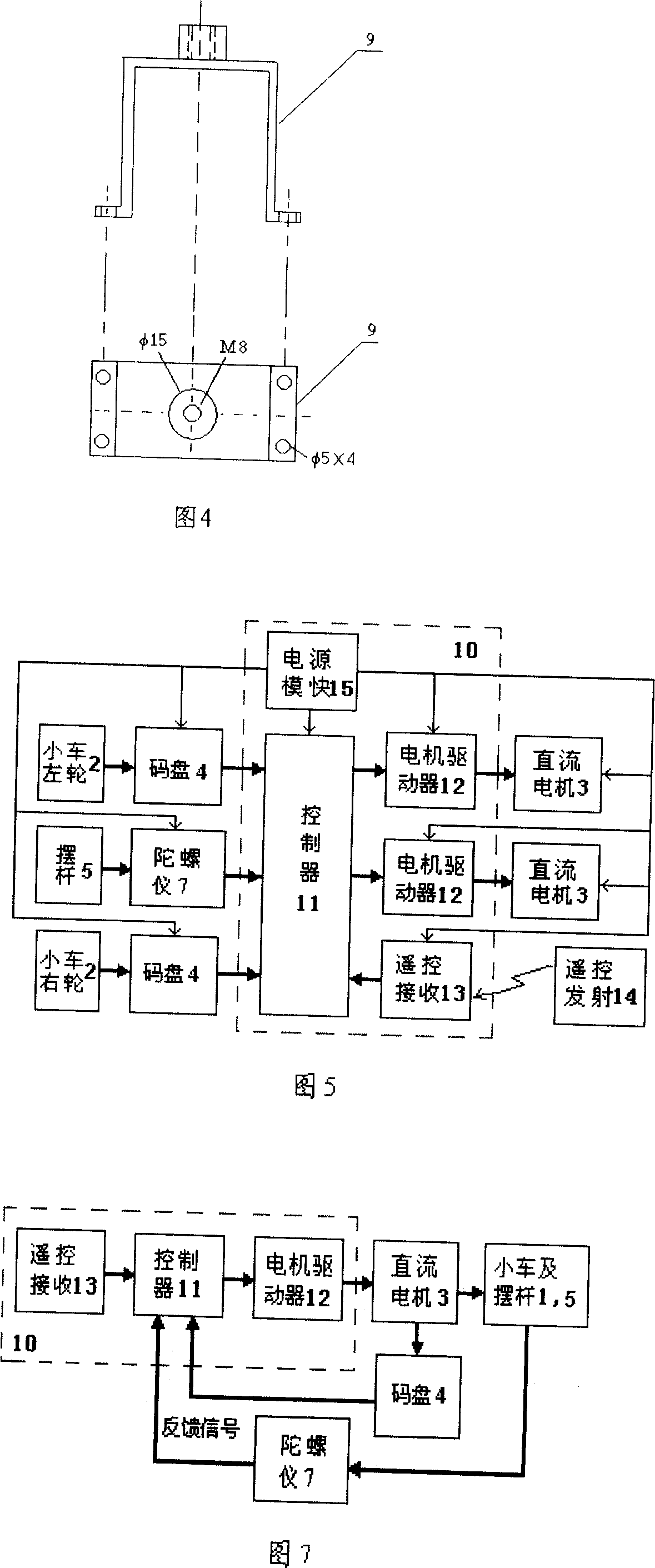
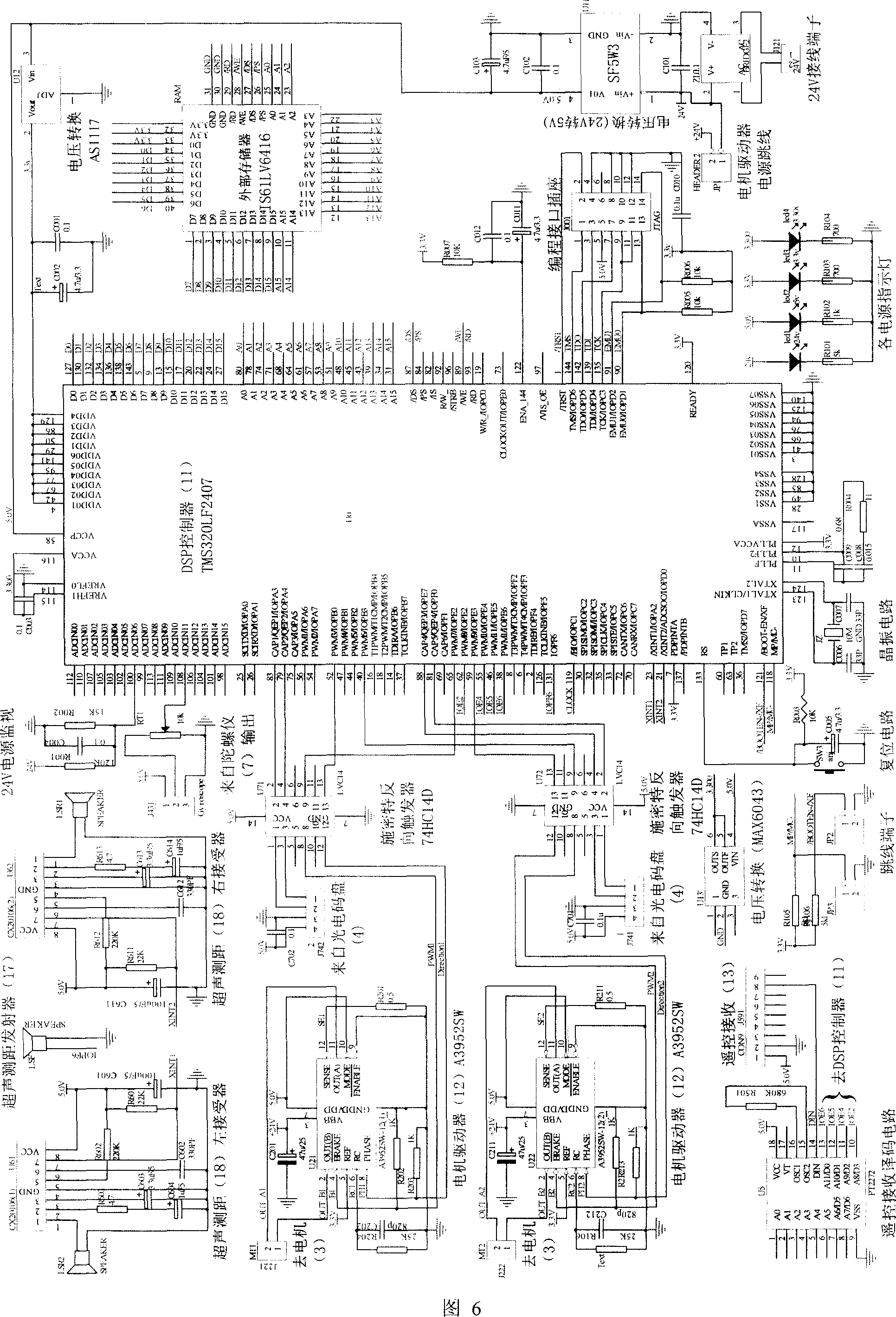
Inverted pendulum of remote car with two wheels and balance control method thereof
InactiveCN1952996ADifficult to controlRich control meansComputer controlControl using feedbackGyroscopeElectric machine
This invention relates to two remote trolley swing and its balance control method, which is characterized by the following: fixing the two direct motors onto car with one end of motor axis connected to wheel and with other end connected to code disc axis; the two axis middle position is fixed with gyroscope with swing bar, controller, remote receiver, power conversion module and motor driver welded on circuit board; the circuit board and direct power are fixed on car. The balance control method comprises automatically parts voltage judging, float correcting and noise measuring for filtering.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Closed-loop control-based humanoid robot omnidirectional walking method
The invention provides a closed-loop control-based humanoid robot omnidirectional walking method, which comprises foot stance planning, robot body movement track, foot space track planning, joint angle calculation and feedback control policy. The method comprises the following steps of planning the stances of the feet of the robot in a two-dimensional space, and calculating a zero moment point (ZMP) value of the robot; establishing a bilinear inverted pendulum model with prediction control according to the ZMP value, and obtaining a reference pose of the robot body; performing cubic spline interpolation on the planned stances to obtain the best moving track of every two stances in a three-dimensional space so as to obtain a foot stance pose; and calculating angles of joints of the robot according to the reference poses of the body and the feet by using inverse kinematics knowledge. In the walking process of the humanoid robot, the omnidirectional walking of the robot is realized through closed-loop control. Compared with the prior art, the robot walking method has the advantages of high robustness and high stability.
Owner:DEEPBLUE ROBOTICS (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Gait planning method for walking of biped robot along slope
ActiveCN104331081AImprove environmental adaptabilityMovement coordination and natureAttitude controlCoronal planeDecomposition
The invention discloses a gait planning method for walking of a biped robot along a slope, and belongs to the technical field of robots. The method contains two core theories, namely, non-orthogonal decomposition and synthesis of a three-dimensional linear inverted pendulum and gait planning based on a biped long linear inverted pendulum. The method comprises the steps of gait parameter configuration, non-orthogonal decomposition of a three-dimensional linear inverted pendulum, foot trajectory planning based on three times of spline interpolation, centroid trajectory planning of a sagittal plane and a coronal plane based on a biped long linear inverted pendulum, non-orthogonal synthesis of the centroid trajectories of the sagittal plane and the coronal plane, and solving of joint trajectories of a robot based on inverse kinematics. By adopting the method of the invention, stable walking of a biped robot along all directions of a slope can be effectively achieved. The method is universal, simple in algorithm and high in practicality.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
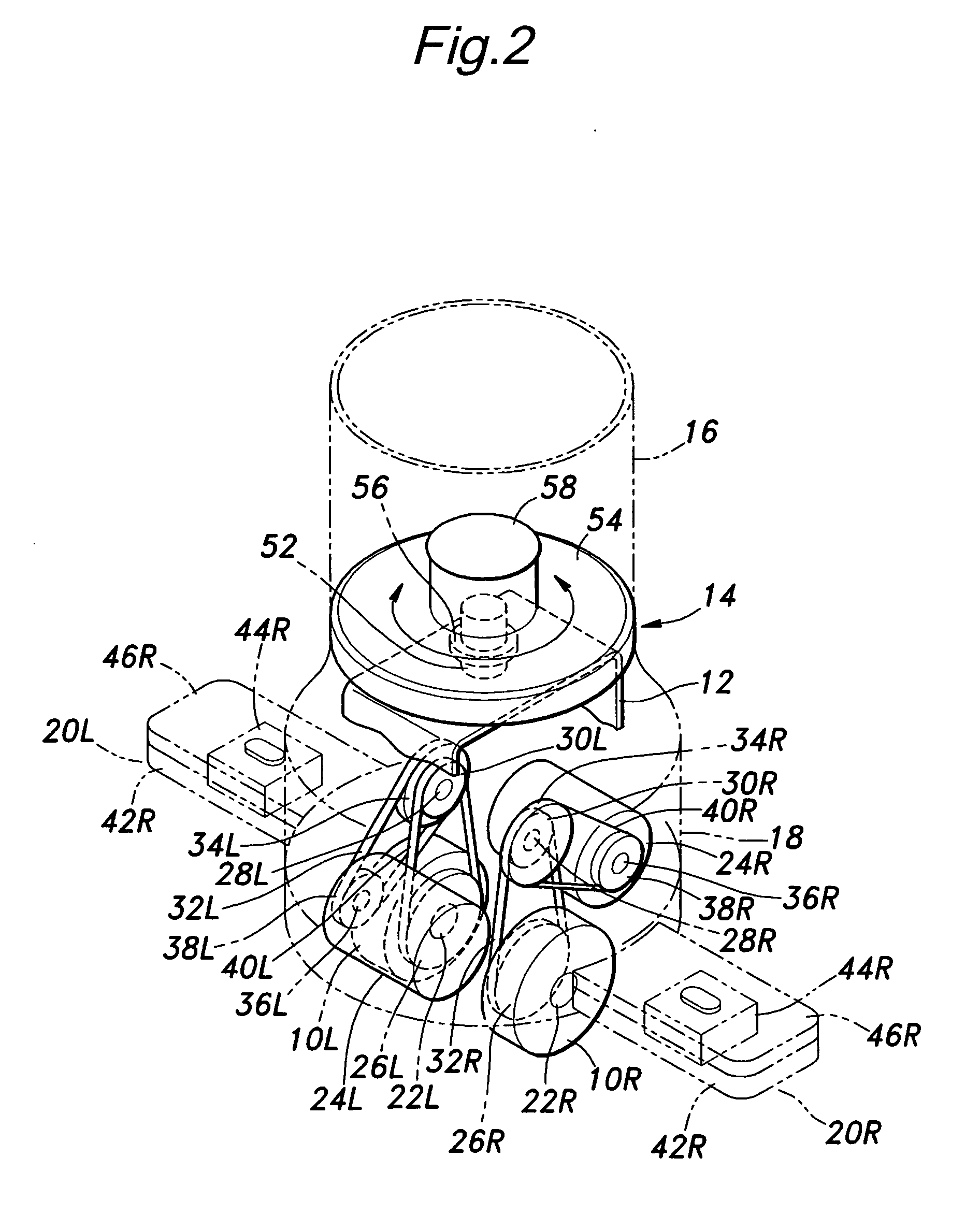
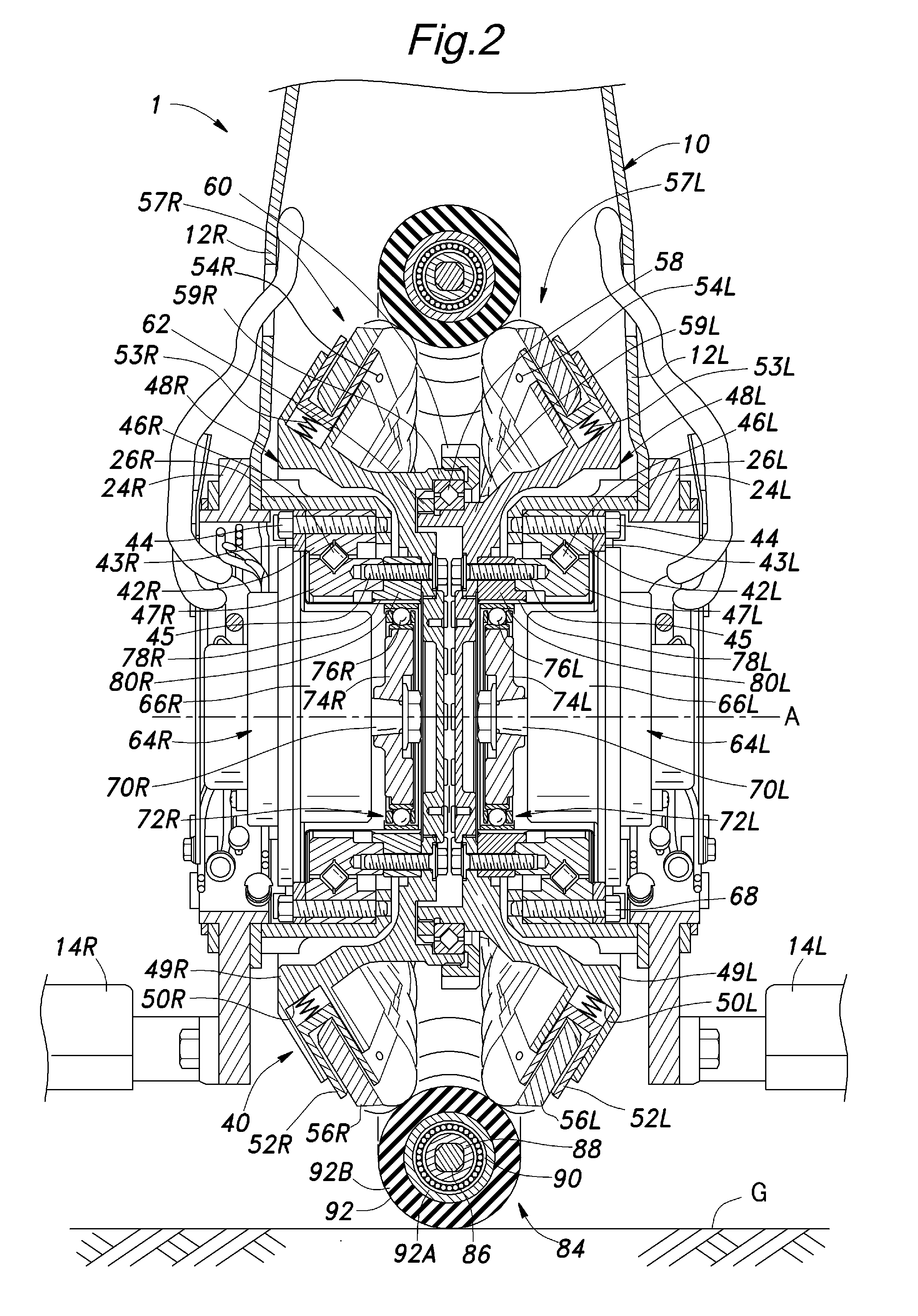
Frictional drive device and inverted pendulum type vehicle using the same
ActiveUS20110067937A1Reduce frictionImprove driving efficiencyUnicyclesPower to auxillary motorsEngineeringActuator
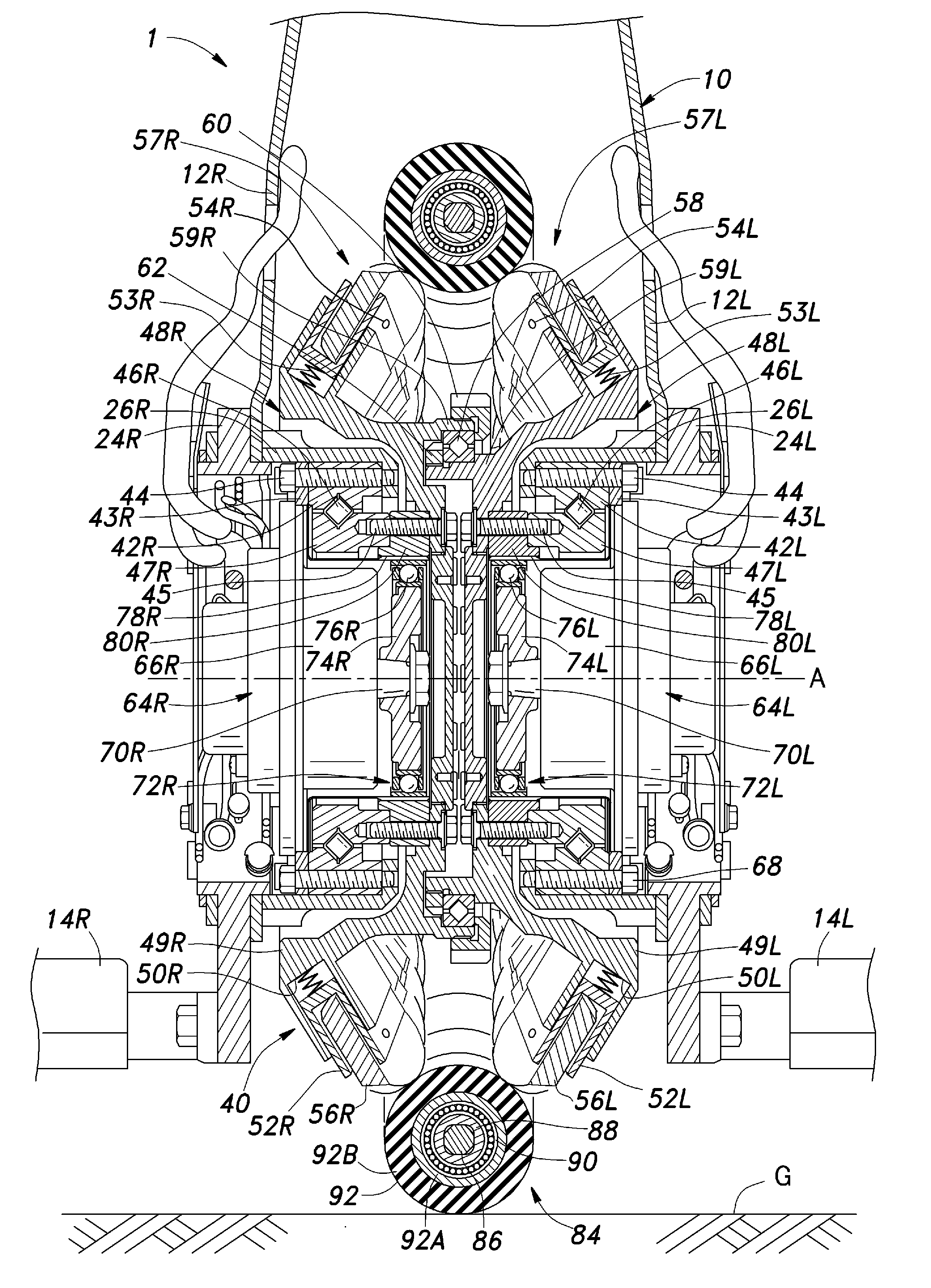
A frictional drive device comprises a pair of drive disks (48) each rotatably supported by a frame (2, 42) around a central axial line (A) in a mutually opposing relationship, and a pair of actuators (64) supported by the frame for individually rotatively actuating the drive disks and coaxially disposed with respect to the corresponding drive disks, a plurality of drive rollers (56) arranged along an outer periphery of each drive disk and each having a rotational center line so as to be rotatable along a plane which is neither parallel nor perpendicular to the central axial line, and an annular main wheel (85) disposed approximately coaxially with respect to the central axial line and engaged by the drive rollers of the drive disks, the main wheel comprising an annular member (86) and a plurality of driven rollers (92) supported along the annular member so as to be rotatable around a tangential line of the annular member. A speed reduction unit (72, 100) may be interposed between each actuator and the corresponding drive disk all in a coaxial relationship.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Inverted pendulum mobile vehicle
ActiveUS20090288900A1Small radiusIncreased complexityUnicyclesOperating modesMobile vehicleVehicle frame
Provided is an inverted pendulum mobile vehicle such as a single-passenger coaxial two-wheel vehicle which is capable of turning with a small turning radius without causing discomfort to a rider or a vehicle occupant or causing a cargo or the like on the vehicle from shifting or falling off from the vehicle. The vehicle comprises a wheel supporting frame (12), a body frame (12) supported by the wheel supporting frame so as to be rotatable around a vertical axial line and carry a rider and or a cargo and a body coupler (52, 78, 70) that couples the body frame relative to the wheel supporting frame in a prescribed dynamic positional relationship. Thereby, even when the wheel supporting frame undergoes a rapid yaw movement either while traveling in a fore-and-aft direction or remaining stationary, the body frame that carries a vehicle occupant or a cargo is allowed to follow the yaw movement of the wheel supporting frame at a slower angular speed and / or acceleration / deceleration so that the vehicle occupant is prevented from experiencing discomfort and the cargo is prevented from shifting on the body frame or falling off from the vehicle.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Elliptical exercise machine with adjustable stride length
An elliptical exercise machine and methods for using the machine where the horizontal length of the stride of the ellipse can be adjusted by the user without the user having to alter the vertical dimension of the ellipse by an equivalent amount. The machine provides for alteration using an inverted pendulum arm which is driven by rotation of a rail and which in turn drives a footskate on the rail. The position for the driving of the inverted pendulum arm by the rail and the driving of the footskate by the inverted pendulum arm are adjustable relative to each other so as to provide for multiple different stride lengths in exercising. The machine may allow for this adjustment to occur during the performance of an exercise routine.
Owner:TRUE FITNESS TECH
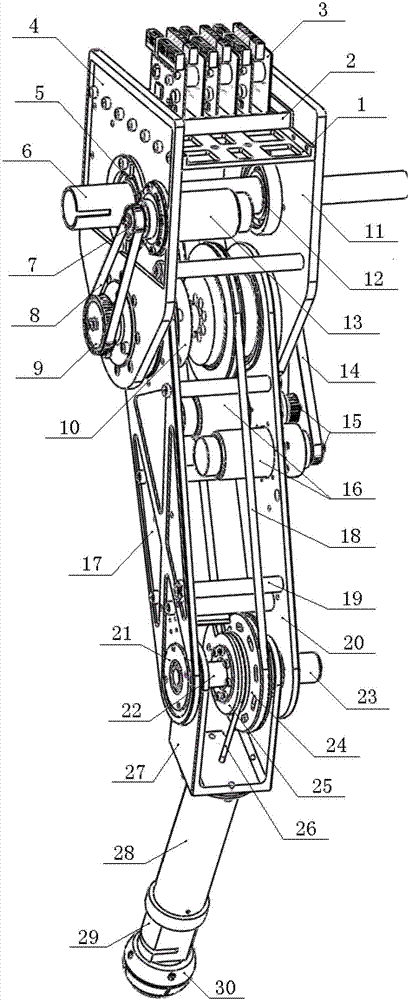
Hopping robot mechanism
The invention discloses a hopping robot mechanism which comprises a body, a thigh and a shank which are connected through a hip joint and a knee joint respectively. First harmonic reducers and second harmonic reducers of the hip joint and the knee joint are all mounted on the hip, and driving motors are mounted at a position close to the hip, so that a robot is close to an ideal inverted pendulum model to reduce controlling difficulty; the knee joint drives through a thigh steel wire rope which adopts an inclined plane mechanism and a slider adjusting mechanism to realize adjustment of tensioning degree of the steel wire rope; and the knee joint when bent compresses a spring, so that force of gravity is transformed into potential energy of the spring to accumulate energy for stretching. A force sensor is mounted on the pelma of the hopping robot and used for sensing grounding information, and a pelma rubber pad buffers grounding impact. By rationally distributing force of gravity and serially connecting spring energy storage mechanism, improvement of flexibility, compliance and effectiveness of motion of the robot is facilitated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
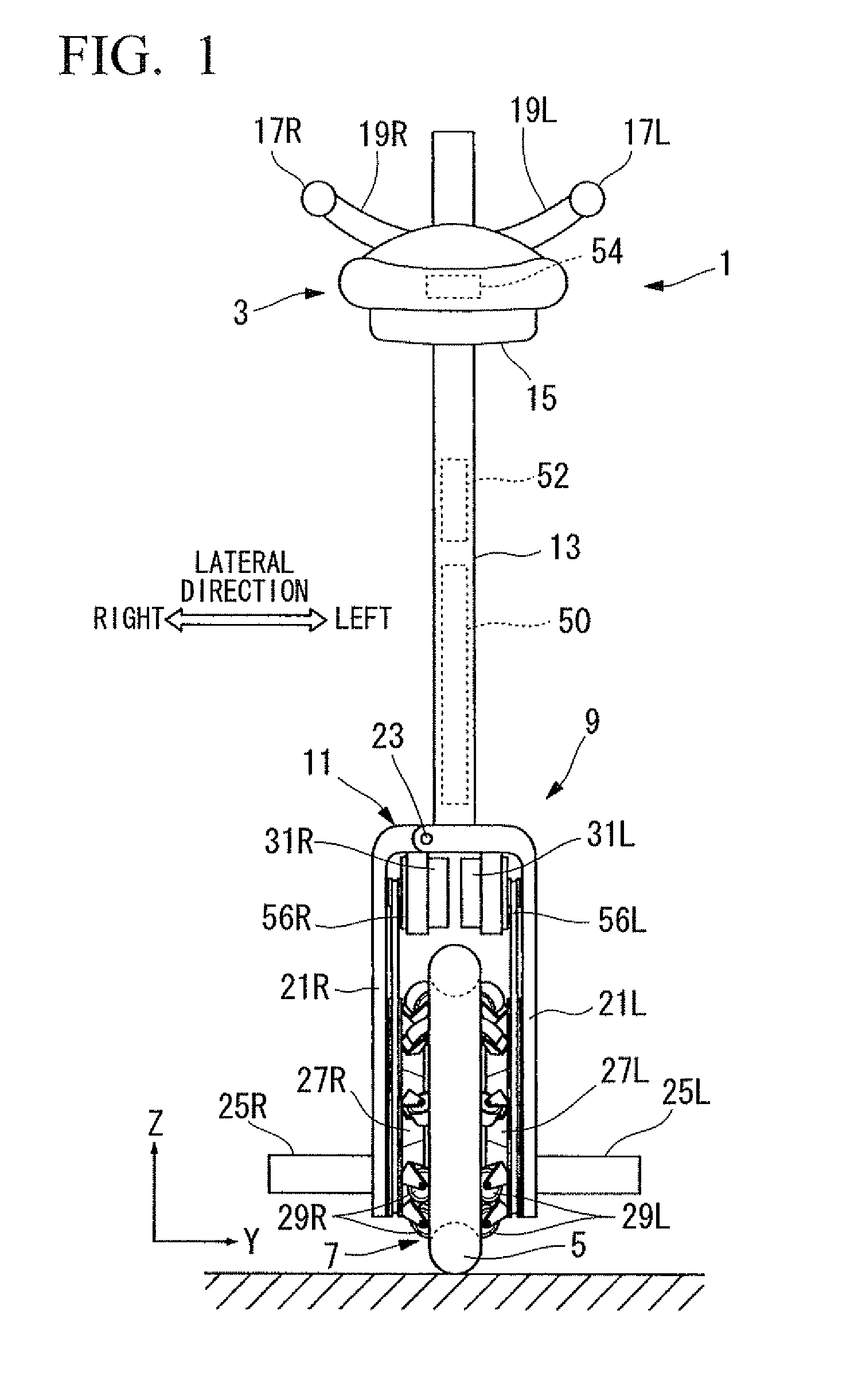
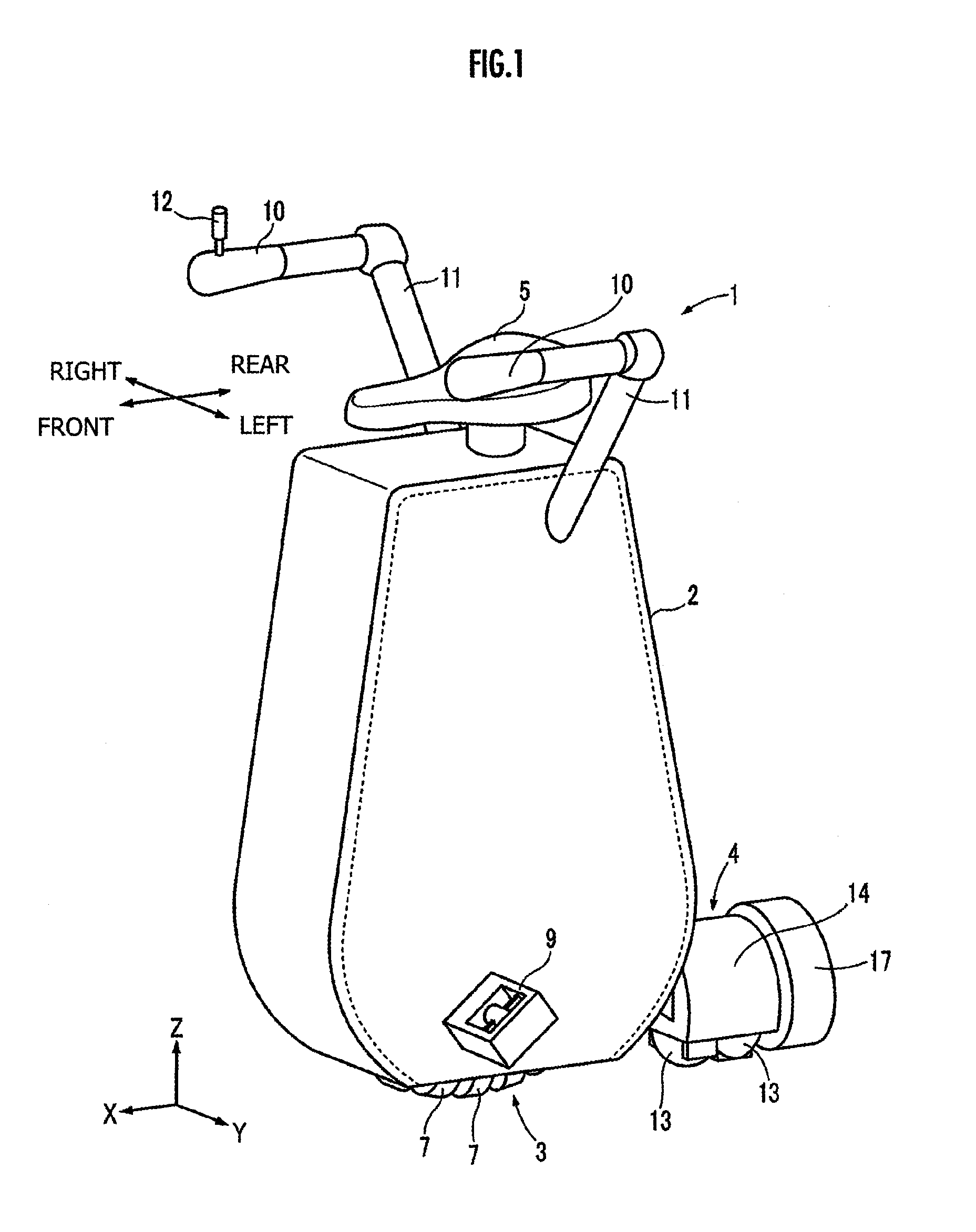
Vehicle
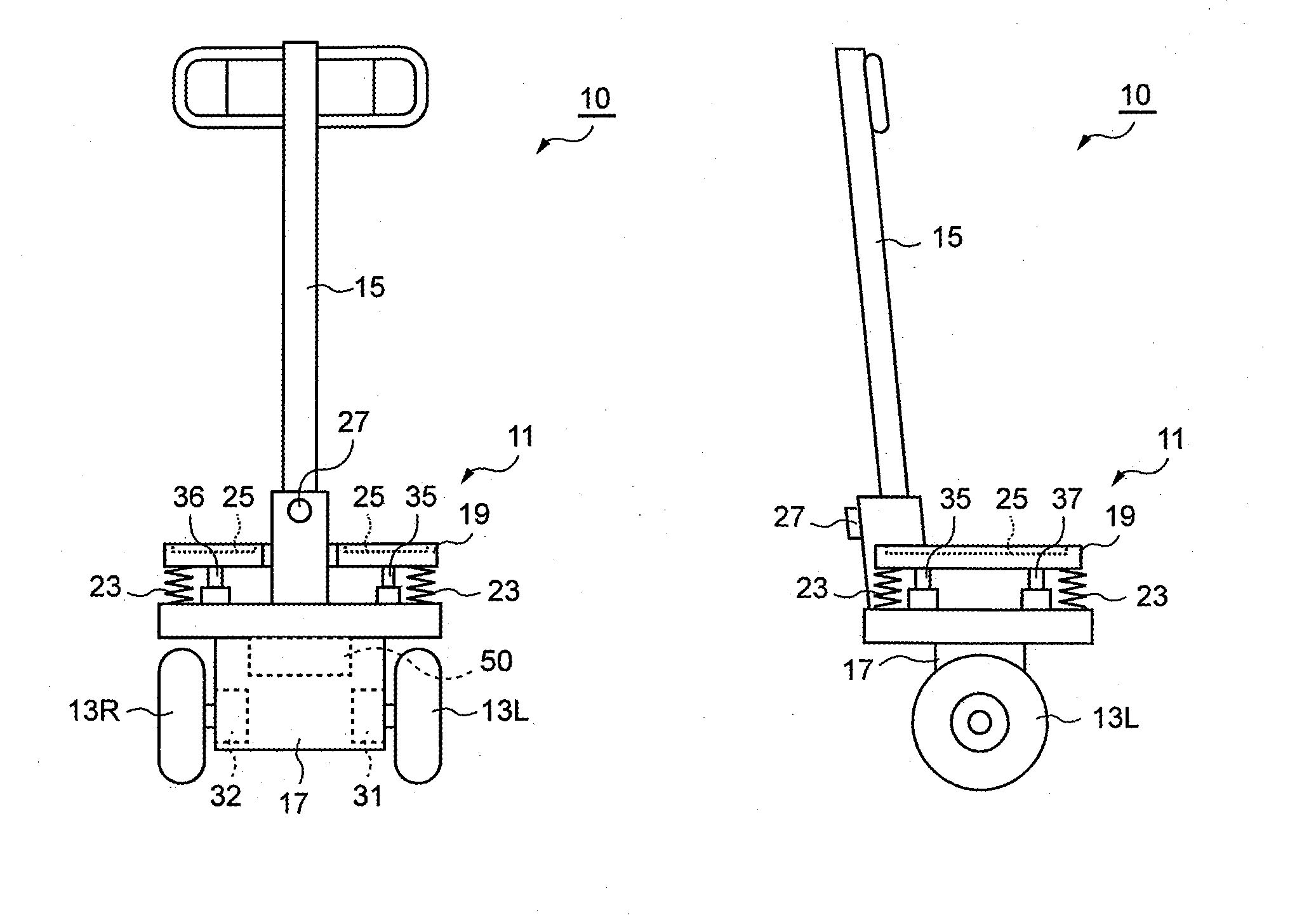
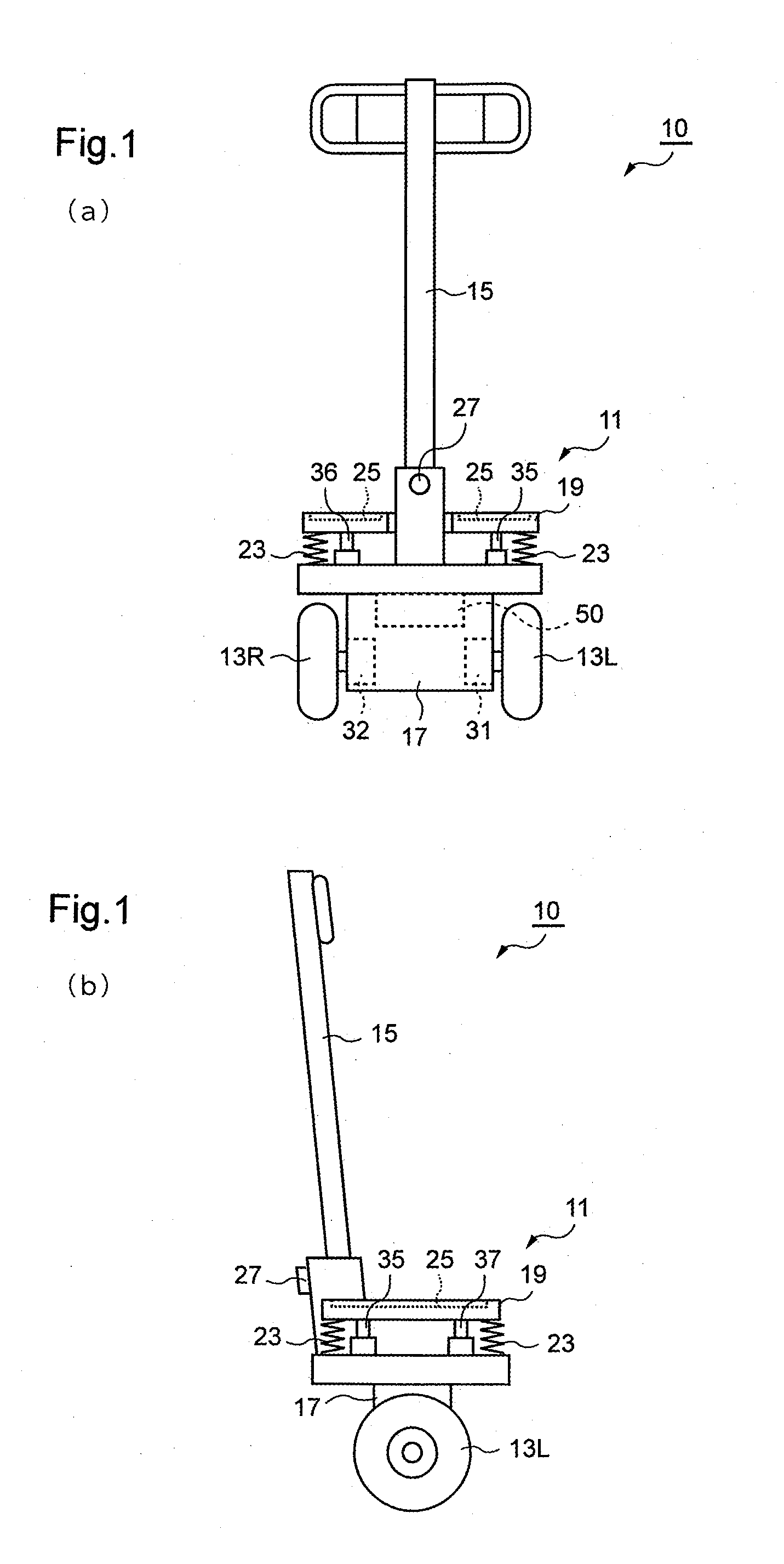
An inverted pendulum type vehicle provided with a body, a pair of wheels and that is attached to the pertinent body and that is arranged in parallel, drive mechanisms and that separately rotate the pertinent pair of wheels and around wheel axes, and a control member that controls the drive mechanisms and, wherein: the body is provided with a base to which the pair of wheels and is attached, a column disposed upright from the base, and a load-supporting part that is attached to the column and that sustains a payload; the column is joined to the base via a shaft that extends in a non-parallel direction relative to the wheel axes, and is provided so as to be capable of sliding around the shaft; and the shaft is provided with an actuator which imparts torque to the column that slides around the shaft with an orientation that is the reverse of the sliding direction of the column.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Inverted pendulum type moving body and method of controlling the same
ActiveUS20090107240A1Improve responseImprove accuracyDigital data processing detailsWheelchairs/patient conveyanceDrive wheelMovement control
An inverted pendulum type moving body according to the present invention includes: first actuators that rotationally drive wheels each disposed on an axle; and a turning motion control portion that controls the first actuators when the inverted pendulum type moving body comes into contact with an obstacle so as to allow the inverted pendulum type moving body to perform a turning motion.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
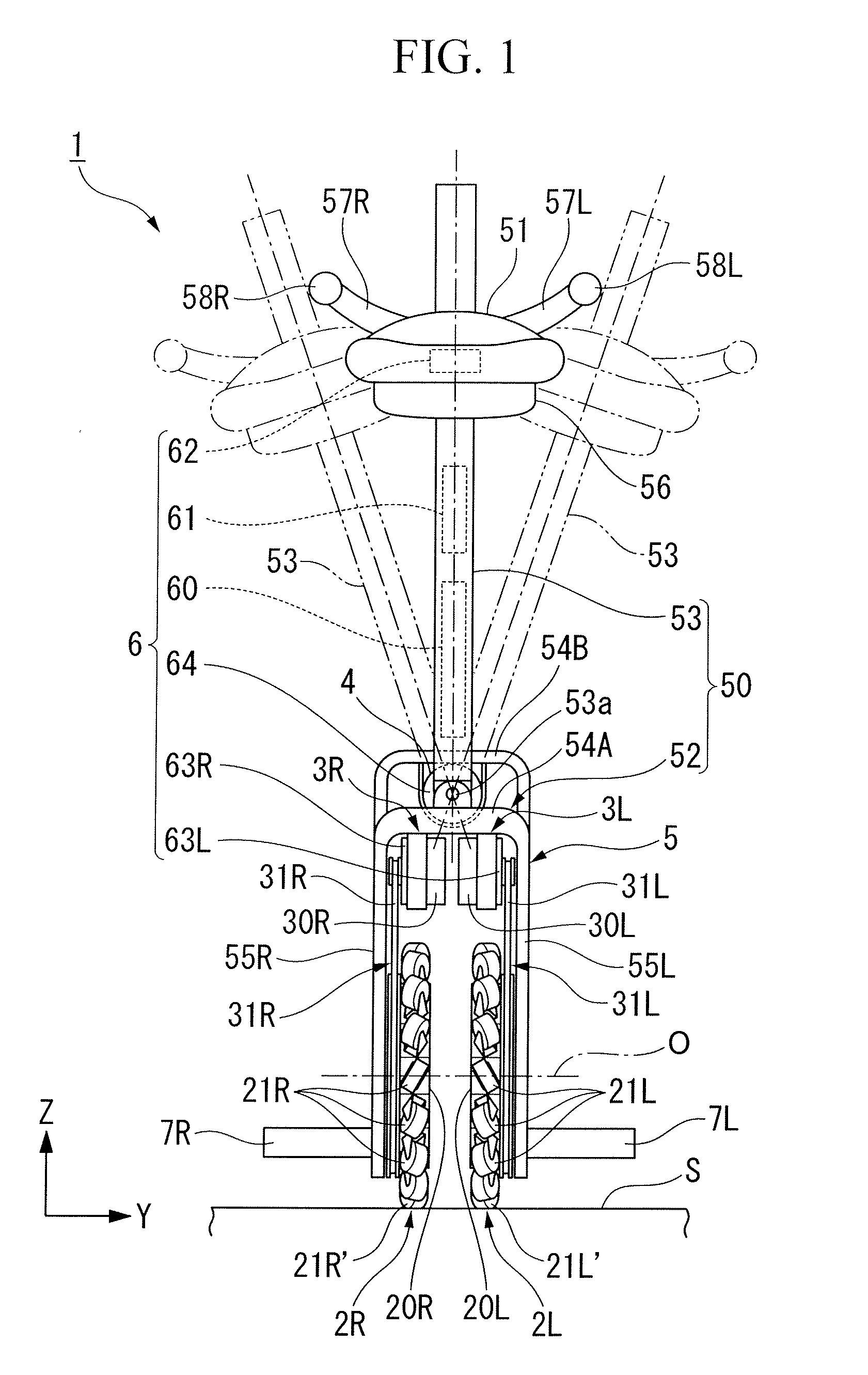
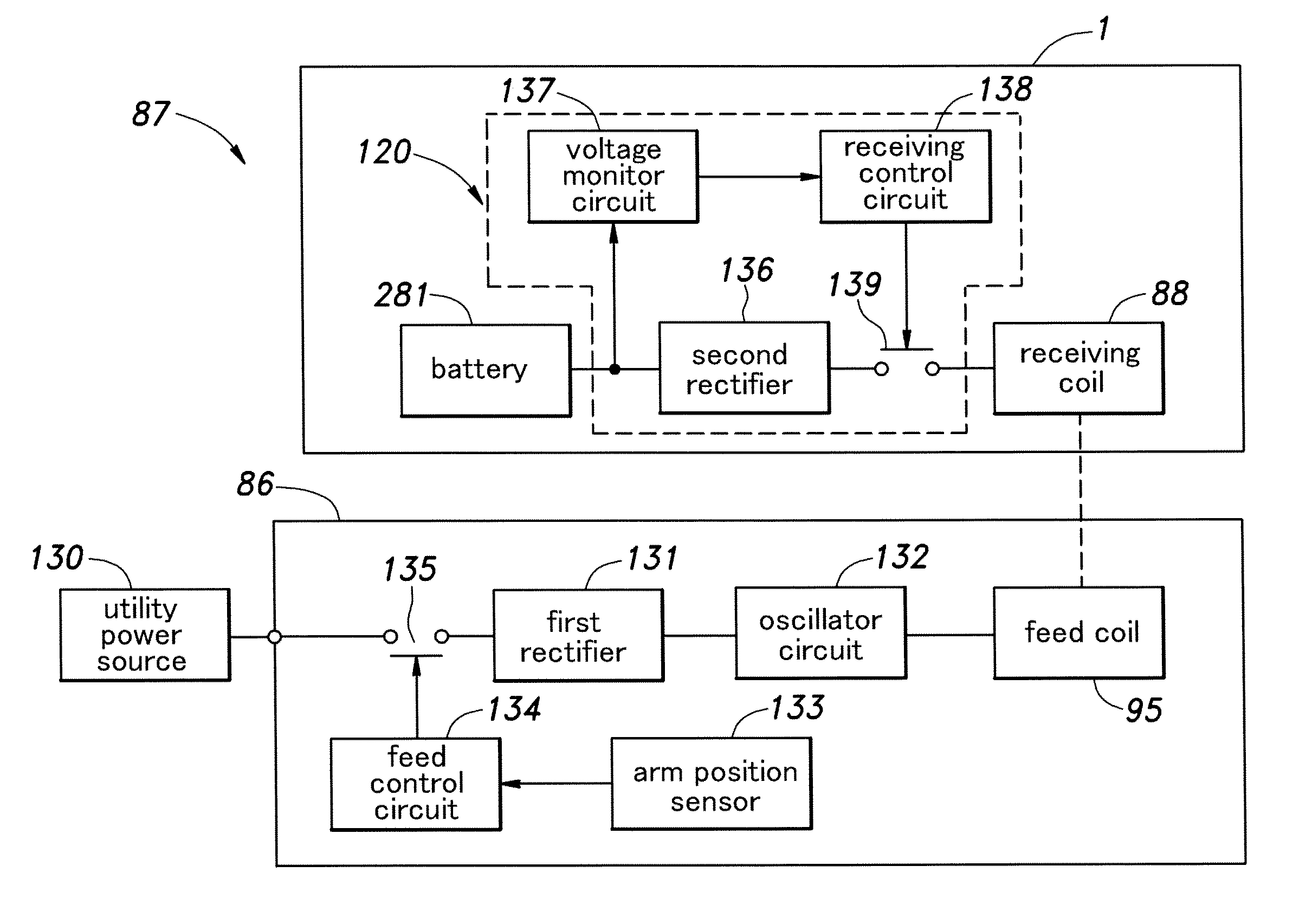
Recharging system for a rechargeable battery of an inverted pendulum type vehicle
ActiveUS20110068738A1Minimize powerPower Loss MinimizationBatteries circuit arrangementsUnicyclesElectricityElectrical battery
A recharging system for a rechargeable battery (281) of an inverted pendulum type vehicle (1) comprises a stand (86) for holding the vehicle in a substantially upright posture by using a supporting member (91, 96) that engages a prescribed part of the vehicle, a power feed device (95, 152) is provided on the stand, and a power take device (88, 151) provided on the vehicle. The power take device is positioned so as to couple with the power feed device when the prescribed part of the vehicle is engaged by the supporting member of the stand. The stand allows the vehicle to be placed in an upright posture simply leaning the vehicle against a part of the supporting member, and the electric connection between the rechargeable battery of the vehicle and the power source can be established at the same time without requiring any extra effort.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Vehicle
An inverted pendulum type vehicle provided with a body, a pair of wheels and that is attached to the pertinent body and that is arranged in parallel, drive mechanisms and that separately rotate the pertinent pair of wheels and around wheel axes, and a control member that controls the drive mechanisms and, wherein: the body is provided with a base to which the pair of wheels and is attached, a column disposed upright from the base, and a load-supporting part that is attached to the column and that sustains a payload; the column is joined to the base via a shaft that extends in a non-parallel direction relative to the wheel axes, and is provided so as to be capable of sliding around the shaft; and the shaft is provided with an actuator which imparts torque to the column that slides around the shaft with an orientation that is the reverse of the sliding direction of the column.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Heavy load precision damper and vibration reduction system formed thereby
InactiveCN101398052AMany degrees of freedomMulti-subwooferGas based dampersVibration suppression adjustmentsEngineeringActuator
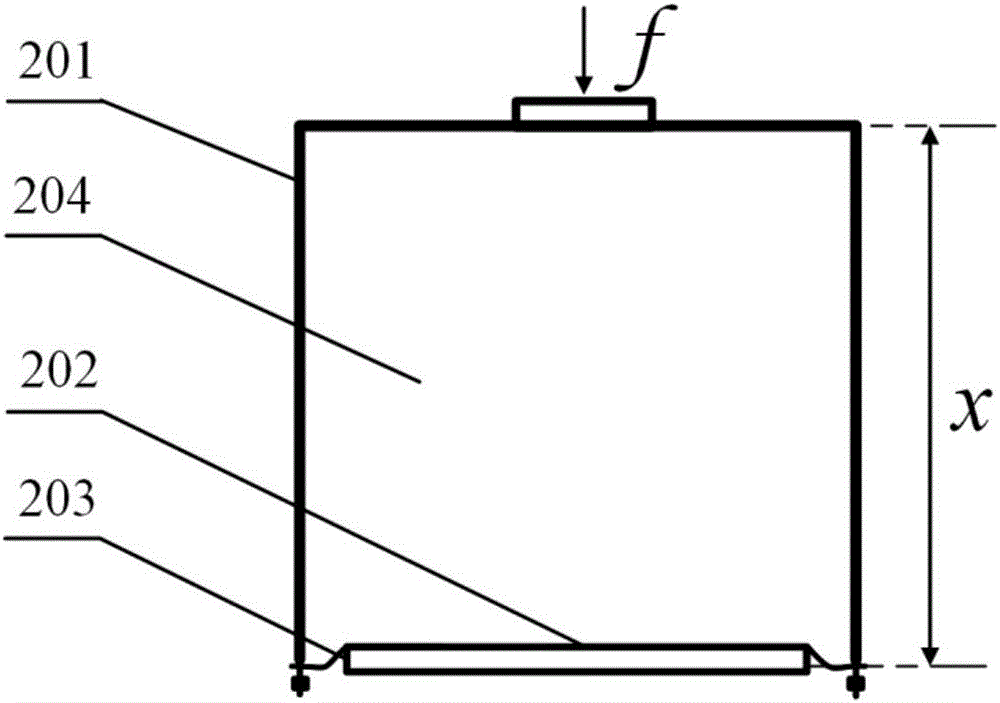
The invention pertains to the technical field of precision damping, and is a heavy-load precision damper and a damping system comprising thereof. The damper comprises a low-rigidity air spring with variable damp, an inverted-pendulum structure with low horizontal rigidity and a group of three-degree-of-freedom active damping actuators. The structure of the air spring is external-internal annularity double air chambers communicated with a throttling hole; the inverted-pendulum structure comprises a main supporting rod and at least two flexible swing rods and is located in an annular air chamber; and the active damping actuator comprises three linear motors arranged in an orthogonal manner. The heavy-load precision damper vertically generates large bearing force by the air spring, respectively separates vertical and horizontal vibration transmission by the air spring and the inverted-pendulum structure, and actively controls the damp vibration by acting force of the vertical and horizontal linear motors. The damping system comprises at least three heavy-load precision dampers arranged in the shape of a polygon, and realizes six-degree-of-freedom precision damping of a vibration-isolation device by the mutual action of every heavy-load precision dampers.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
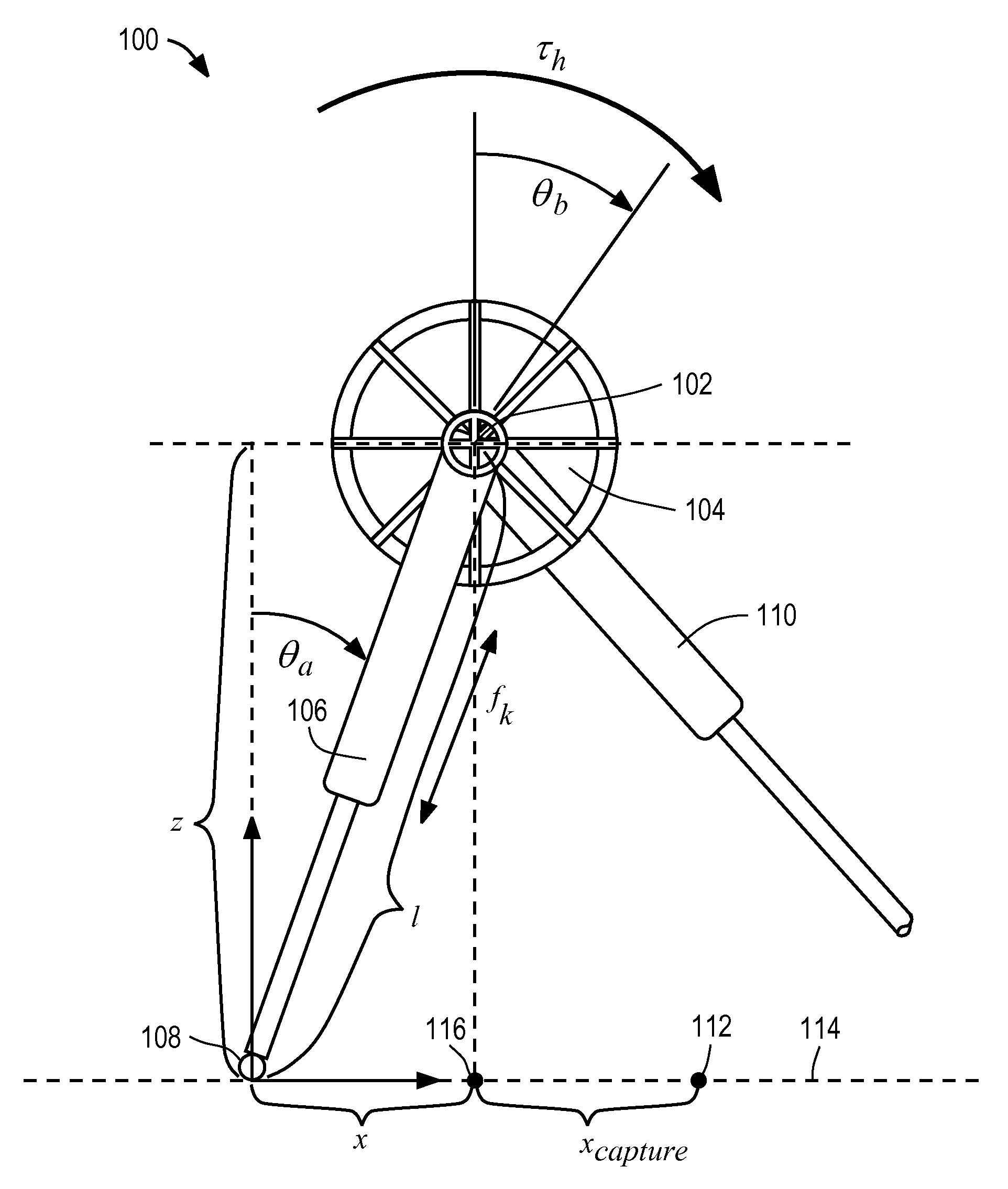
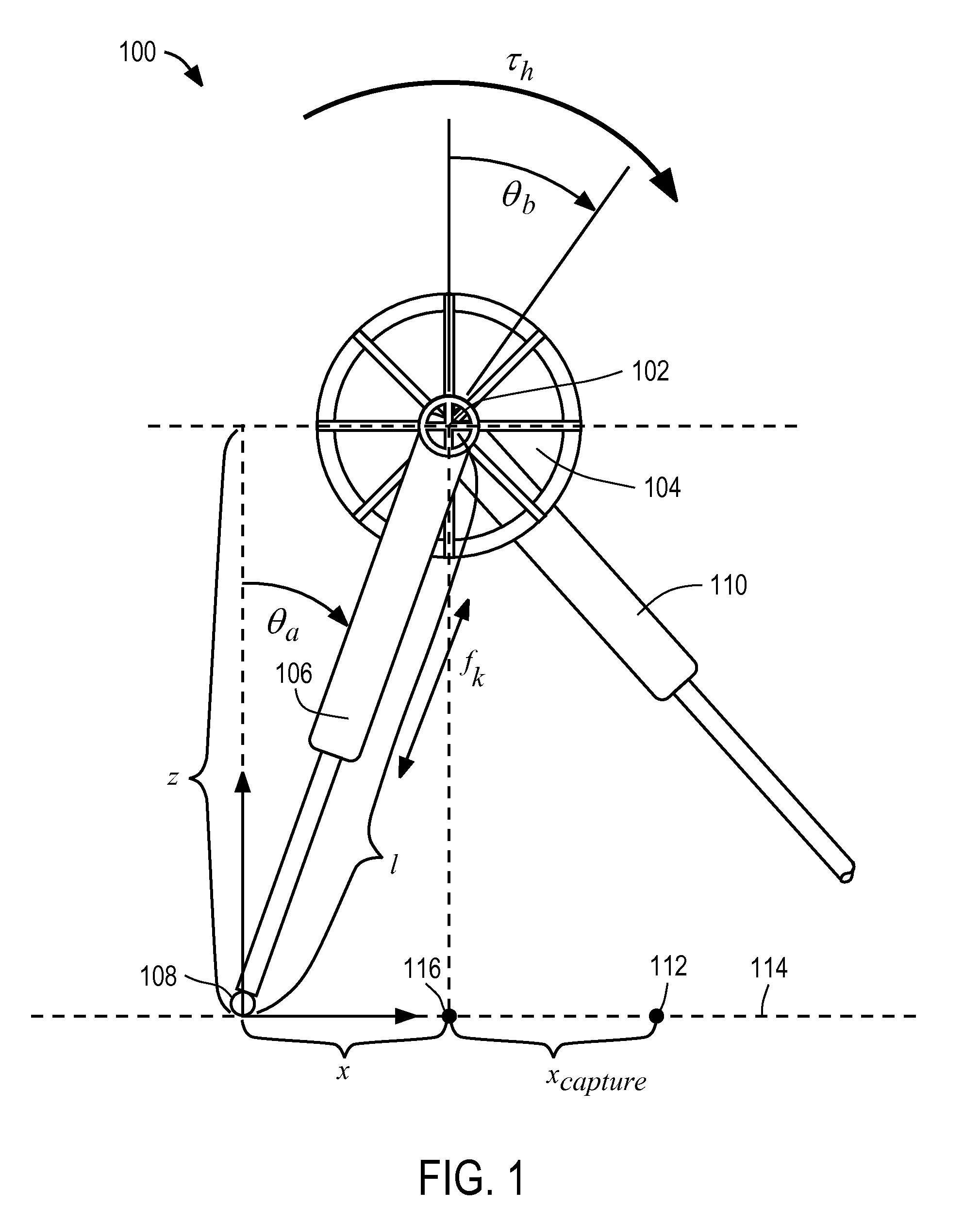
Determination of foot placement for humanoid push recovery
InactiveUS7949430B2Programme-controlled manipulatorProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersLegged robotEngineering
Owner:FLORIDA INST FOR HUMAN & MACHINE COGNITION +1
Frictional drive device and inverted pendulum type vehicle using the same
InactiveUS20110070997A1Improve efficiencyIncrease torqueElectric machinesWheel manufactureCentre of rotationInverted pendulum
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Inverted pendulum type moving body
ActiveUS20110071752A1Reduce external forceReduces gain coefficientSpeed controllerUnicyclesInformation controlEngineering
An inverted pendulum type moving body moving over a floor surface in a self standing manner, the inverted pendulum type moving body comprising: an information acquisition unit obtaining a state information indicating a current state of an another moving body; and a movement control unit controlling a movement of a self moving body, based on the state information, so that a state of the self moving body with respect to the current state of the another moving body satisfies a predetermined condition established so that the self moving body and the another moving body moves in alignment.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Active-passive combined vibration isolator based on positive-stiffness and negative-stiffness parallel connection
ActiveCN106321719AHigh static stiffnessRaise the natural frequencyMagnetic springsGas based dampersAir springNegative stiffness
The invention discloses an active-passive combined vibration isolator based on positive-stiffness and negative-stiffness parallel connection. The active-passive combined vibration isolator based on positive-stiffness and negative-stiffness parallel connection comprises a basic platform (10), a load-bearing platform (30), a passive vibration isolation unit and an active vibration isolation unit, wherein the passive vibration isolation unit is provided with a positive-stiffness air spring (20) and a magnetic negative-stiffness mechanism (28) with adjustable negative stiffness in the first direction, so that the inherent frequency in the first direction is decreased, and the passive vibration isolation unit is provided with a stiffness-adjustable positive-stiffness leaf spring and a negative-stiffness inverted pendulum in the second direction, so that the inherent frequency in the second direction is decreased; the active vibration isolation unit is arranged at the outer side of the passive vibration isolation unit, the upper end of the active vibration isolation unit is linked with the load-bearing platform (30), and the lower end of the active vibration isolation unit is linked with the basic platform (10); and the active vibration isolation unit comprises displacement sensors, speed sensors, a proportional pressure valve and a voice coil motor, and the voice coil motor is used for fine adjustment of the load-bearing platform, so that vibration is further isolated. The active-passive combined vibration isolator based on positive-stiffness and negative-stiffness parallel connection has high bearing capacity, and active and passive vibration isolation of two degrees of freedom is achieved at the same time.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
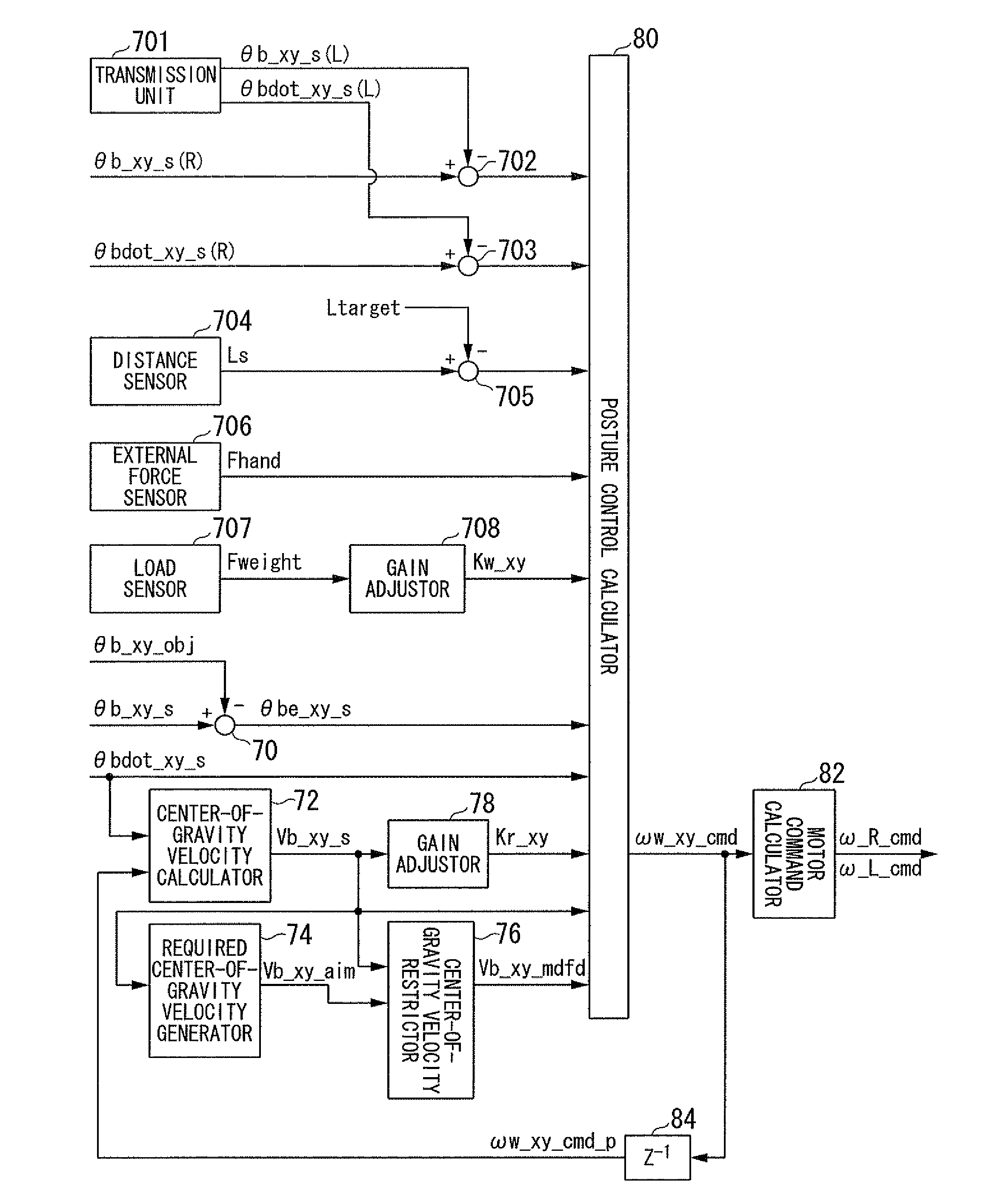
Mobile unit and control method of mobile unit
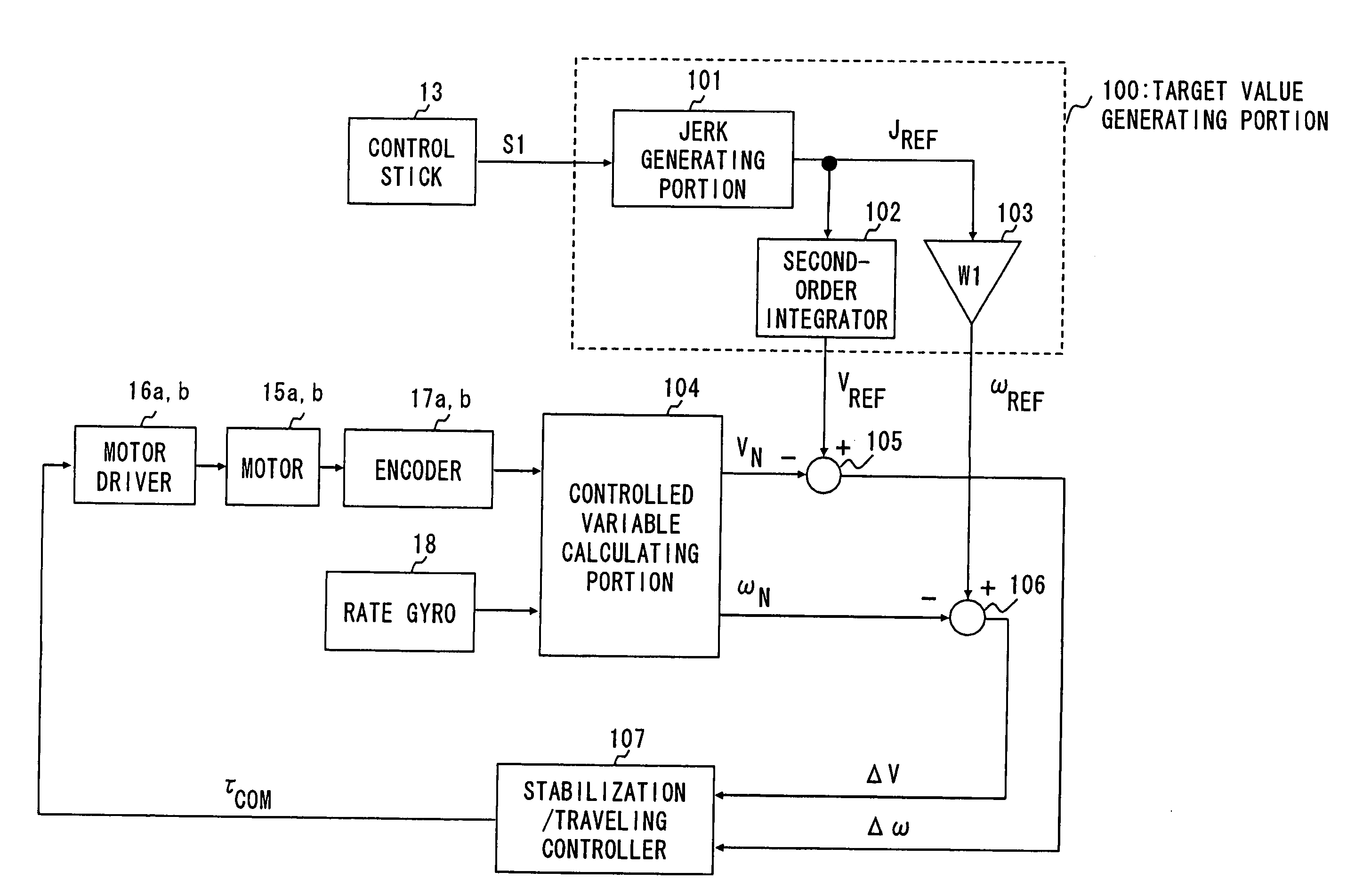
InactiveUS8050837B2Smooth changeSpeed controllerAnalogue computers for trafficStabilization controlGravity center
In an inverted pendulum type mobile unit that performs inverted pendulum stabilization control and traveling control based on a velocity target value as an input variable, a change in tilt angle of a vehicle body occurring during traveling is smoothed. The target value generating portion in the inverted pendulum type mobile unit generates the velocity target value VREF of the mobile unit and the tilt angular rate target value ωREF of the vehicle body so that a second-order time derivative of VREF is continuous and ωREF is continuous with respect to time. The controller in the inverted pendulum type mobile unit calculates a torque command value Tcom for the motor drivers using VREF and ωREF as a control target to allow the mobile unit to travel at VREF while maintaining the state where the gravity center of the vehicle body or the gravity center of total mass of the vehicle body and a subject supported on the vehicle body is located above the rotation center of the wheels.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
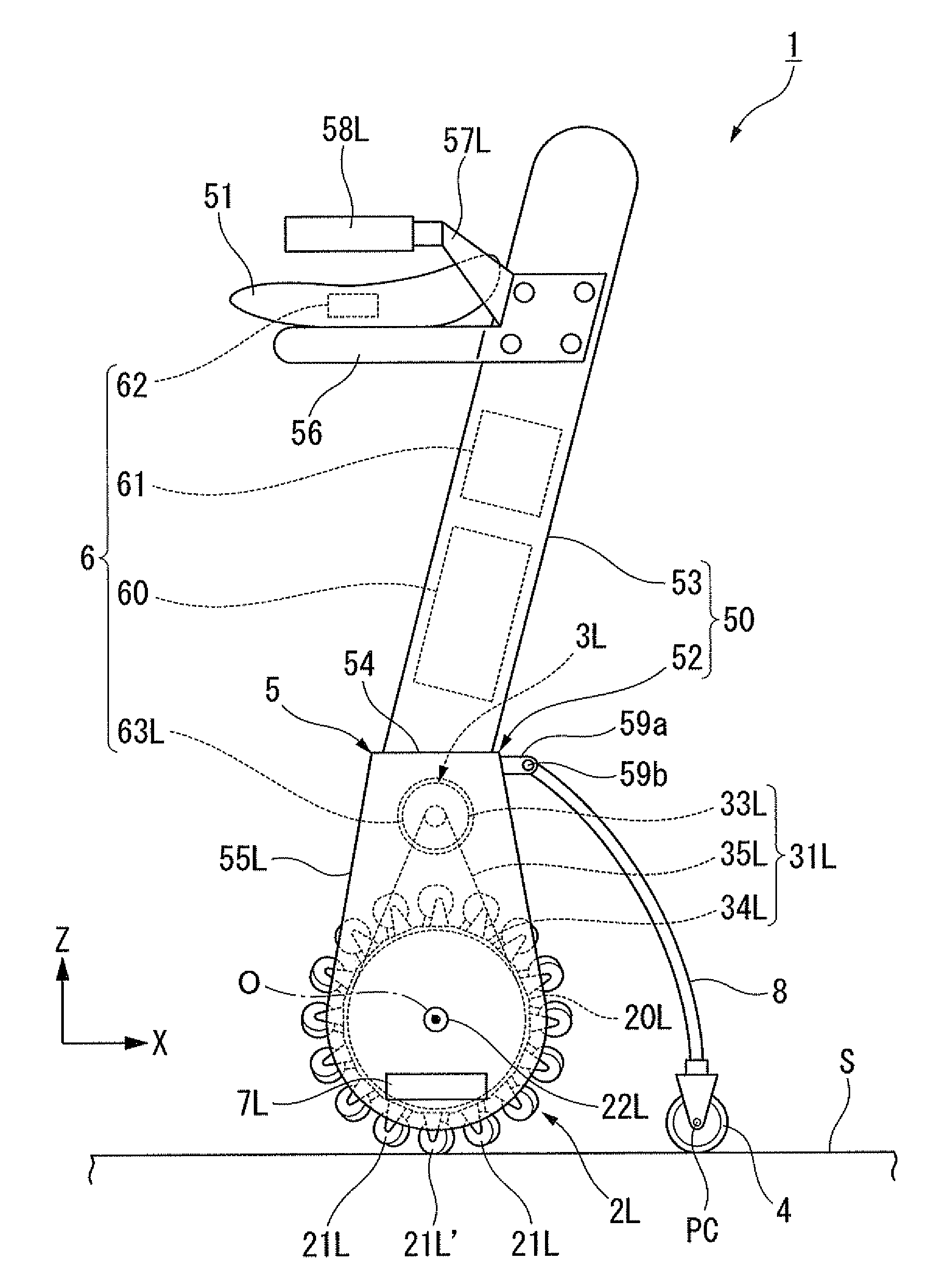
Inverted pendulum type vehicle
ActiveUS8862301B2Turn easilyImprove controllabilityUnicyclesDigital data processing detailsAngular velocityActuator
An inverted pendulum type vehicle includes a control device which sets a target turning angular velocity ωz_cmd to a nonzero value not only when a predetermined steering operation is performed but also at least in an external force application state in which an external force for turning the vehicle about a yaw axis is applied to the vehicle. The control device controls a first actuator device and a second actuator device such that a second moving operation unit has a different velocity from a first moving operation unit in a left-right direction. Such an inverted pendulum type vehicle makes it possible to turn the vehicle easily even in a state in which no steering operation is performed.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Inverted pendulum balancing control system based on flywheel
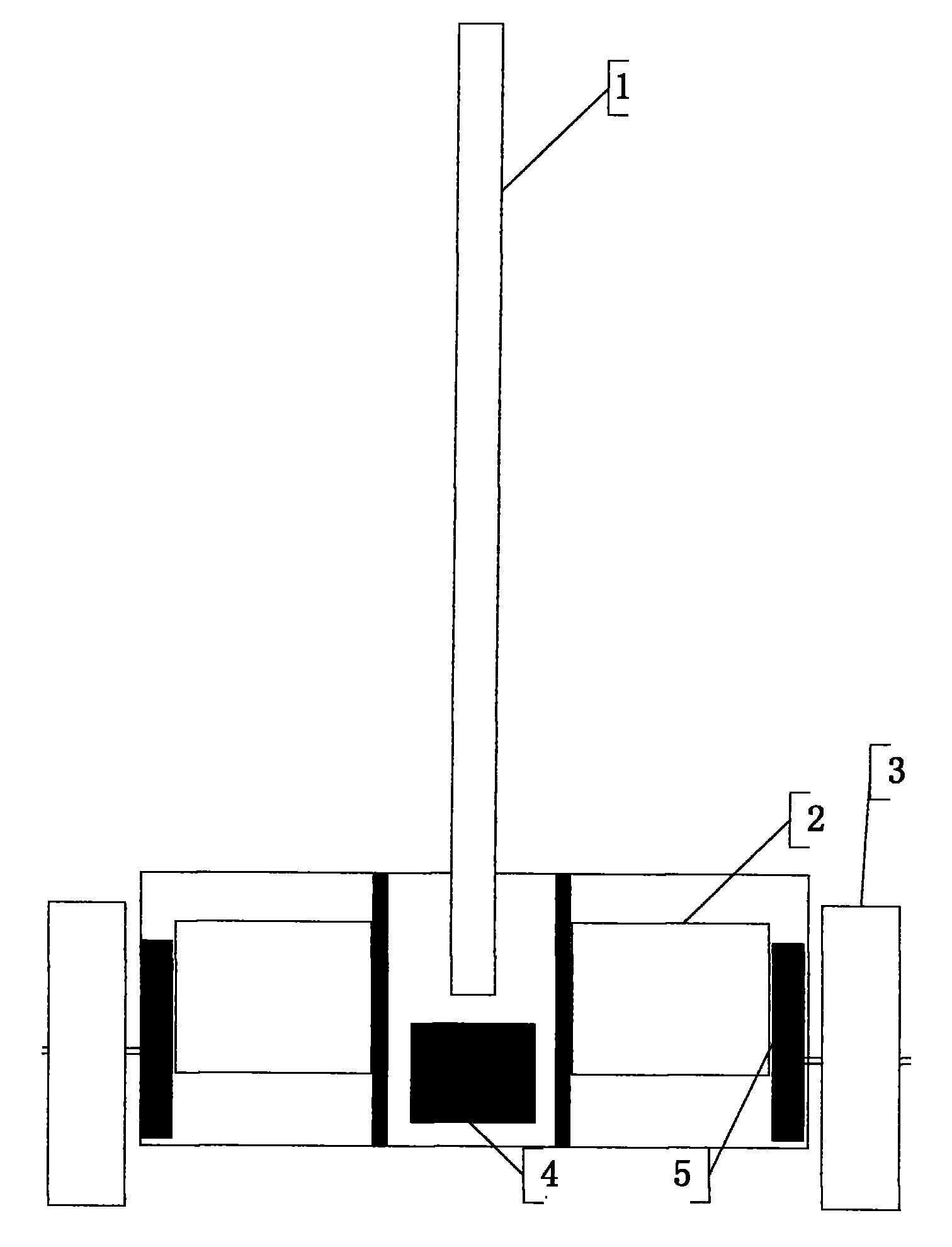
The invention belongs to the category of intelligent robots, in particular to a static unbalanced robot capable of the self-control of balancing. The system controls a flywheel to rotate along the vertical direction with a DC servo motor so as to realize the balancing of the left and the right directions. In detection, in order to realize the posture self-detection of a pendulum bar in a swing process, an inertial navigation system based on an MEMS technology and an inclinometer are adopted to obtain the motion information of the pendulum bar. In safety, both sides of the pendulum bar are provided with pendulum bar side supports capable of conveniently adjusting the maximum angle of the pendulum bar, thereby not only protecting components in the system but also satisfying various control requirements in experiments. In order to reduce the control difficulty, some electronic devices, such as a power supply, a motion controller, a servo driver, a power adapter board and the like are arranged on a base, thereby reducing the pendulum bar control difficulty and improving the stability of the system. In mobility, casters with the brake function are arranged on the four corners of the base, thereby facilitating the debugging of the system in different places.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Omnidirectional vehicle
ActiveUS20110067940A1Improve steering stabilityImprove ride qualityFrictional rollers based transmissionUnicyclesGround contactEngineering
An inverted pendulum type omnidirectional vehicle includes: a pair of wheels; a drive mechanism; a control apparatus; an auxiliary wheel; and a vehicle body. Each of the wheels includes: a rotation member capable of rotating about the wheel axis; a plurality of free rollers which are disposed all around an outer circumference of the rotation member, and each of which is brought into contact with a road surface at a lowest position of the rotation member and is rotatable about a rotation axis diagonal with respect to the wheel axis. The free rollers on both sides in contact with the road surface at ground contact portions each have the rotation axis extending in parallel with the road surface, and are arranged in an orientation in which a distance between the rotation axes of the free rollers is shorter toward a side of the auxiliary wheel.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
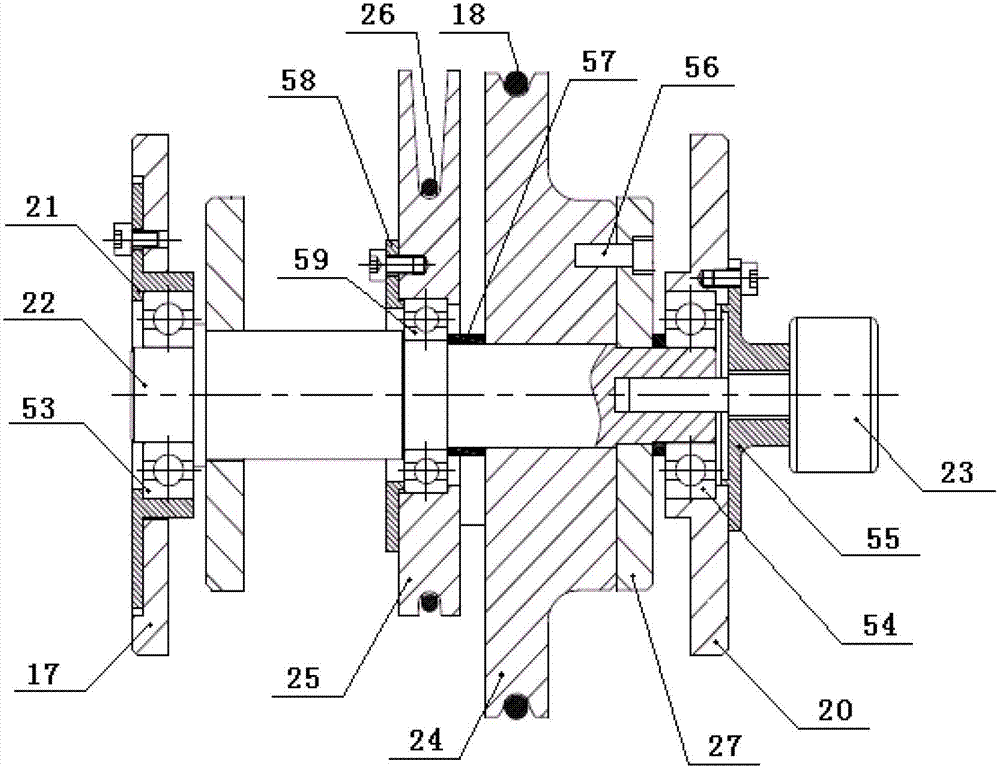
Wheel, wheel device and inverted pendulum type vehicle
ActiveUS20150129327A1Gap minimizationIncrease the number ofUnicyclesElectric propulsion mountingCentre of rotationEngineering
An omni-wheel of a highly compact and light-weight is provided. The omni-wheel includes a disk-shaped hub member (110), a plurality of support arms (114) extending axially from the peripheral part of the hub member and arranged along a circle concentric to a rotational center line of the hub member at a regular interval, and a free roller (140) rotatably supported by a free end of each support arm around a rotational center line extending tangentially to a circle concentric to the rotational center line of the hub member and passing through a center of the free roller. The present invention also provides a wheel device incorporated with such a wheel and an inverted pendulum type vehicle using such a wheel device as a tail wheel unit.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Determination of Foot Placement for Humanoid Push Recovery
InactiveUS20080133053A1Maintain balanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlLegged robotMoment of inertia
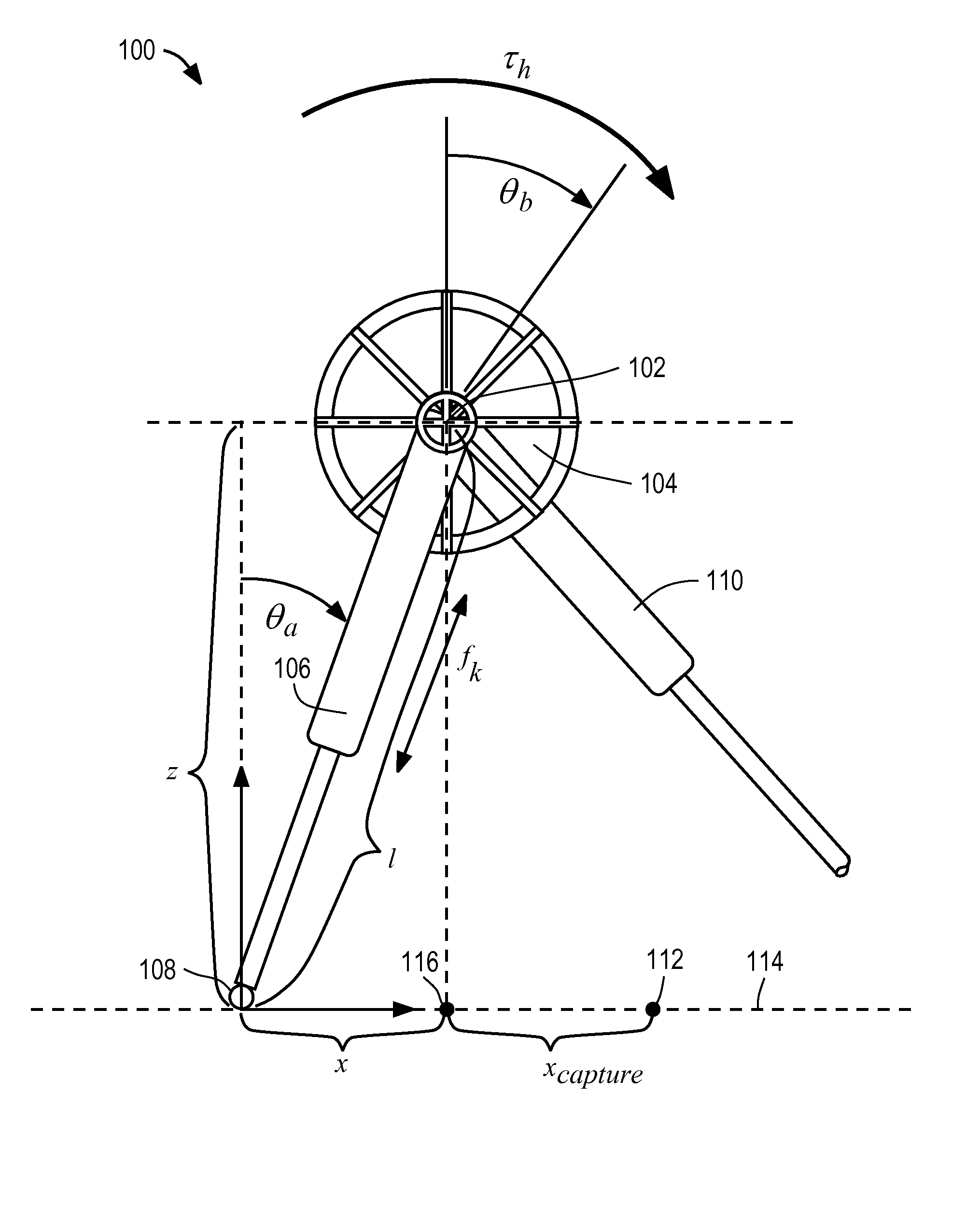
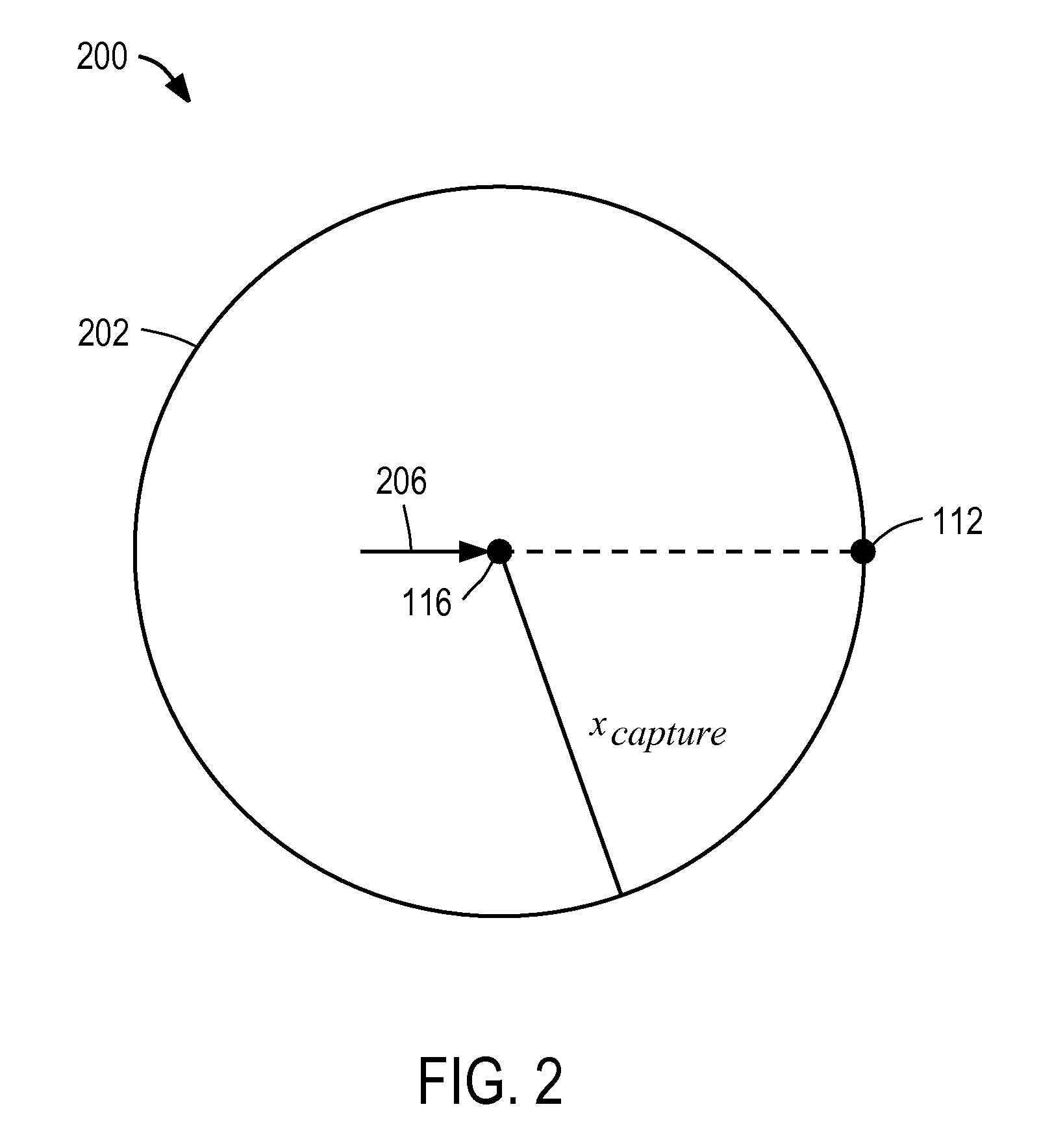
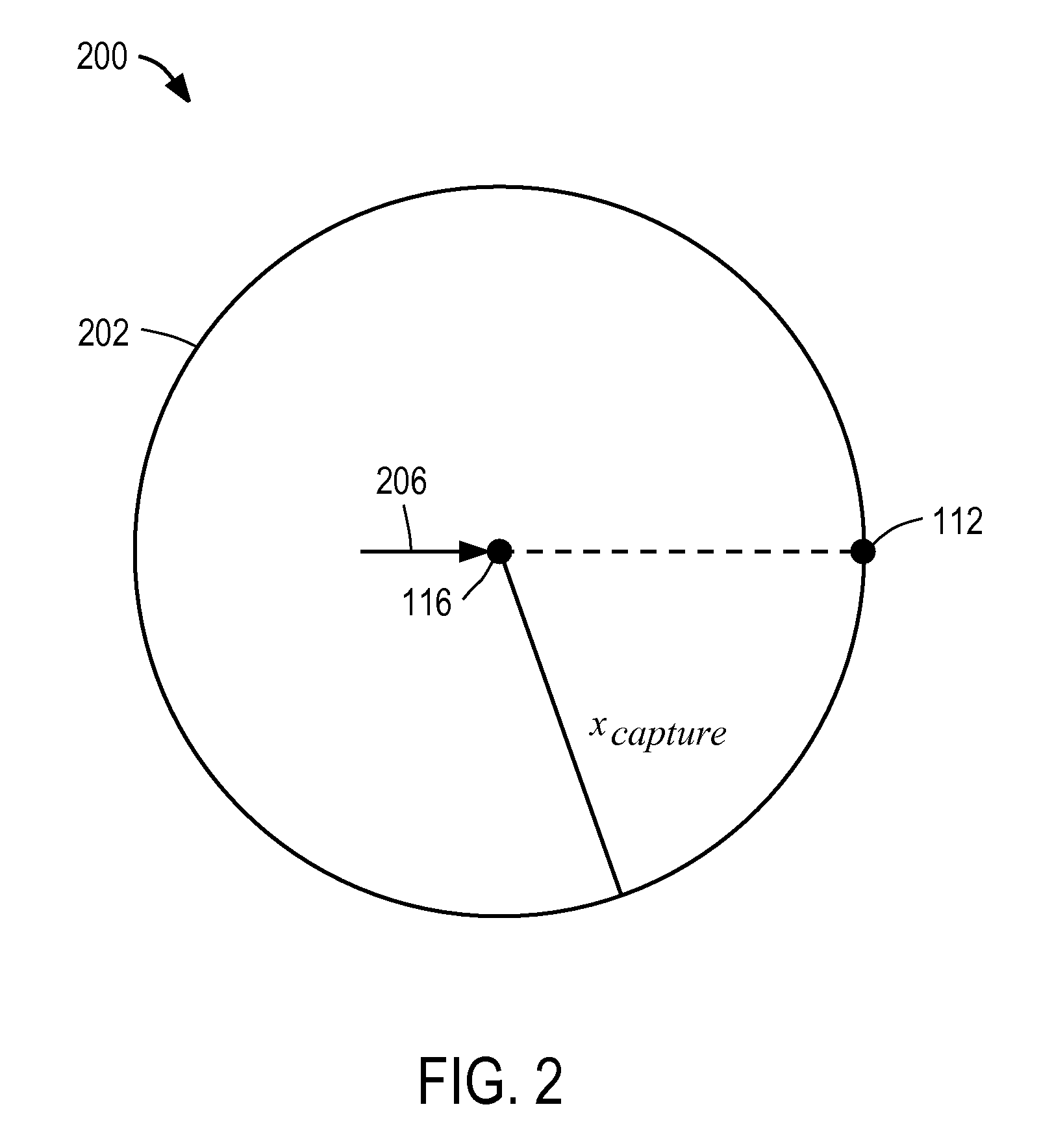
A legged robot subjected to a force is controlled by determining an instantaneous capture point where the robot will step with a swing leg to reach a balanced home position, the balanced home position being a state in which the Center of Mass remains substantially over the Center of Pressure and the robot is able to maintain its balance indefinitely. The capture point can be determined using a Linear Inverted Pendulum Plus Flywheel (LIPPF) model of the robot. The LIPPF model includes a flywheel with a mass and a rotational inertia, and a variable length leg link. A torque profile is applied to the flywheel and a set of capture points is determined based on this torque profile An experimentally determined error value can be added to a capture point that is determined based on the model to account for differences between an actual robot and the model.
Owner:FLORIDA INST FOR HUMAN & MACHINE COGNITION +1
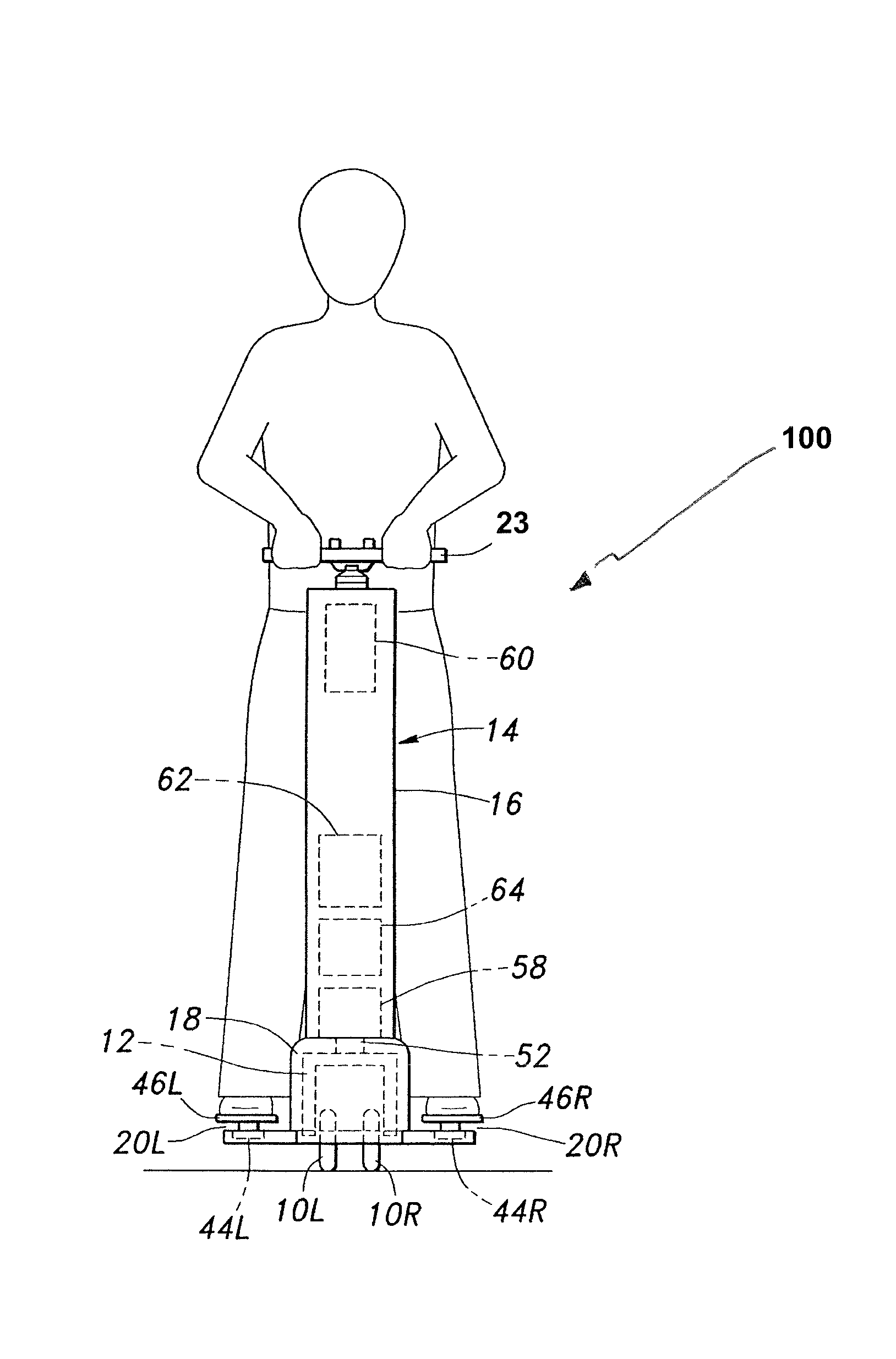
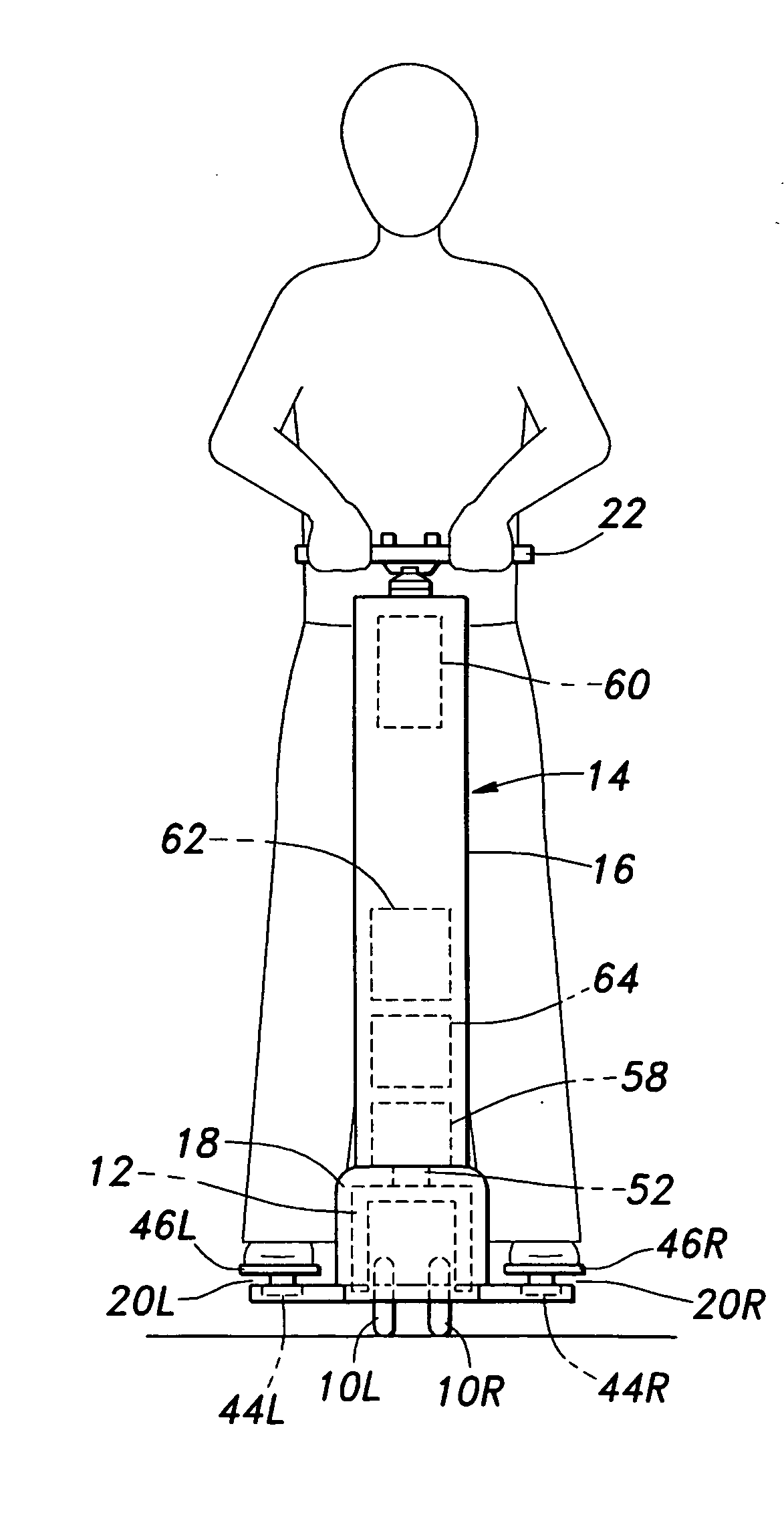
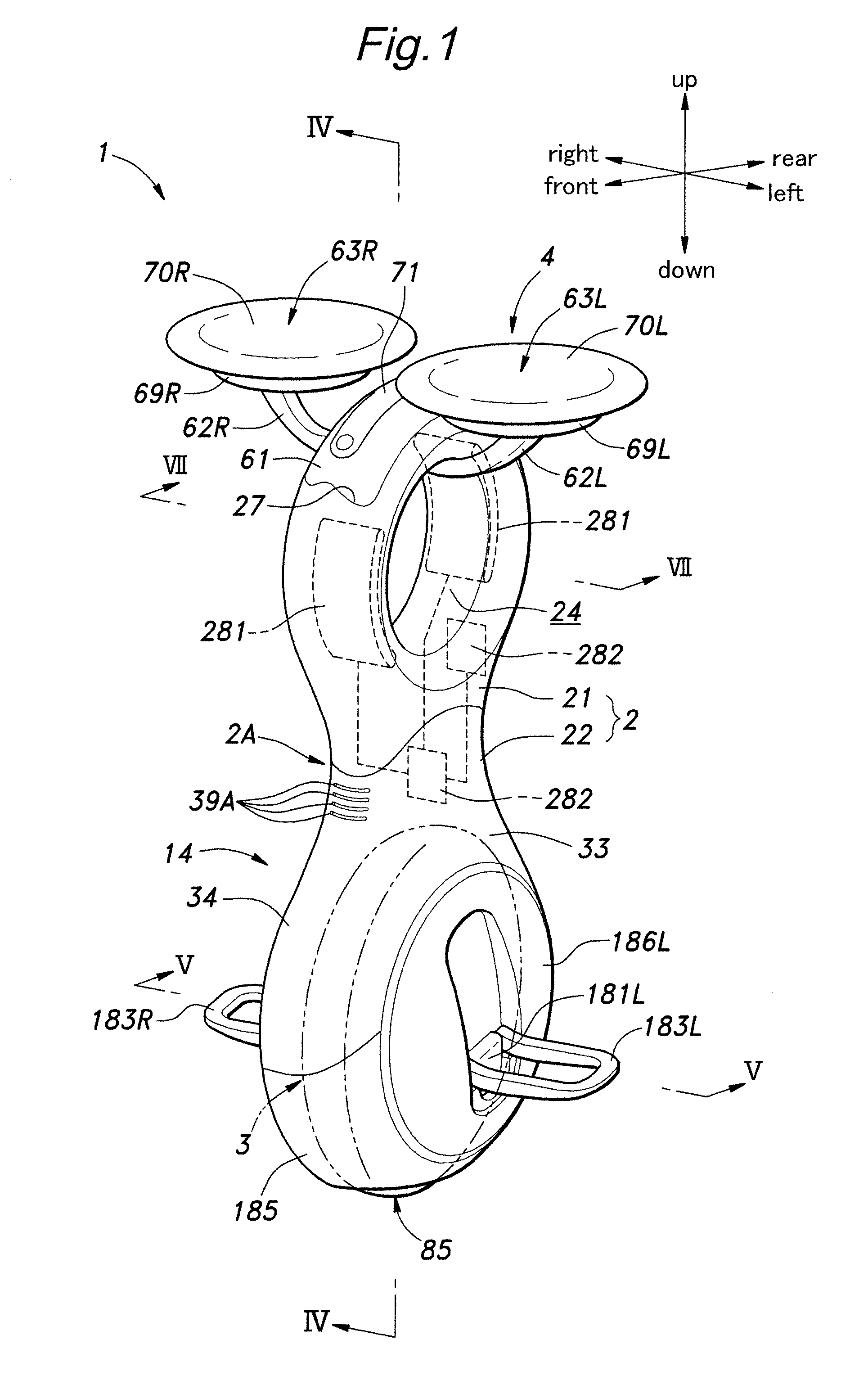
Inverted pendulum type vehicle
ActiveUS20110067938A1Easy to separateEnsure accessibilityUnicyclesOperating modesSmall footInverted pendulum
In an inverted pendulum type vehicle having a lower frame (22) and an upper frame (21) detachably joined to an upper end of the lower frame, the lower and upper frames each defining a hollow interior, a drive unit (3) is incorporated in the lower frame, and a battery unit (10) is received in the upper frame and configured to supply electric power to the drive unit via an electric unit (11) received in a narrow section intermediate between the upper and lower frames. Thereby, the vehicle may be of a compact and small foot print design. In particular, when this structure is applied to a vehicle using a main wheel having a relatively small width, by matching the upper part of the vehicle to have a corresponding small width, the overall profile of the vehicle may have a highly small width. Furthermore, the total weight of the vehicle can be relatively evenly distributed between the upper and lower parts for easy handling and control.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
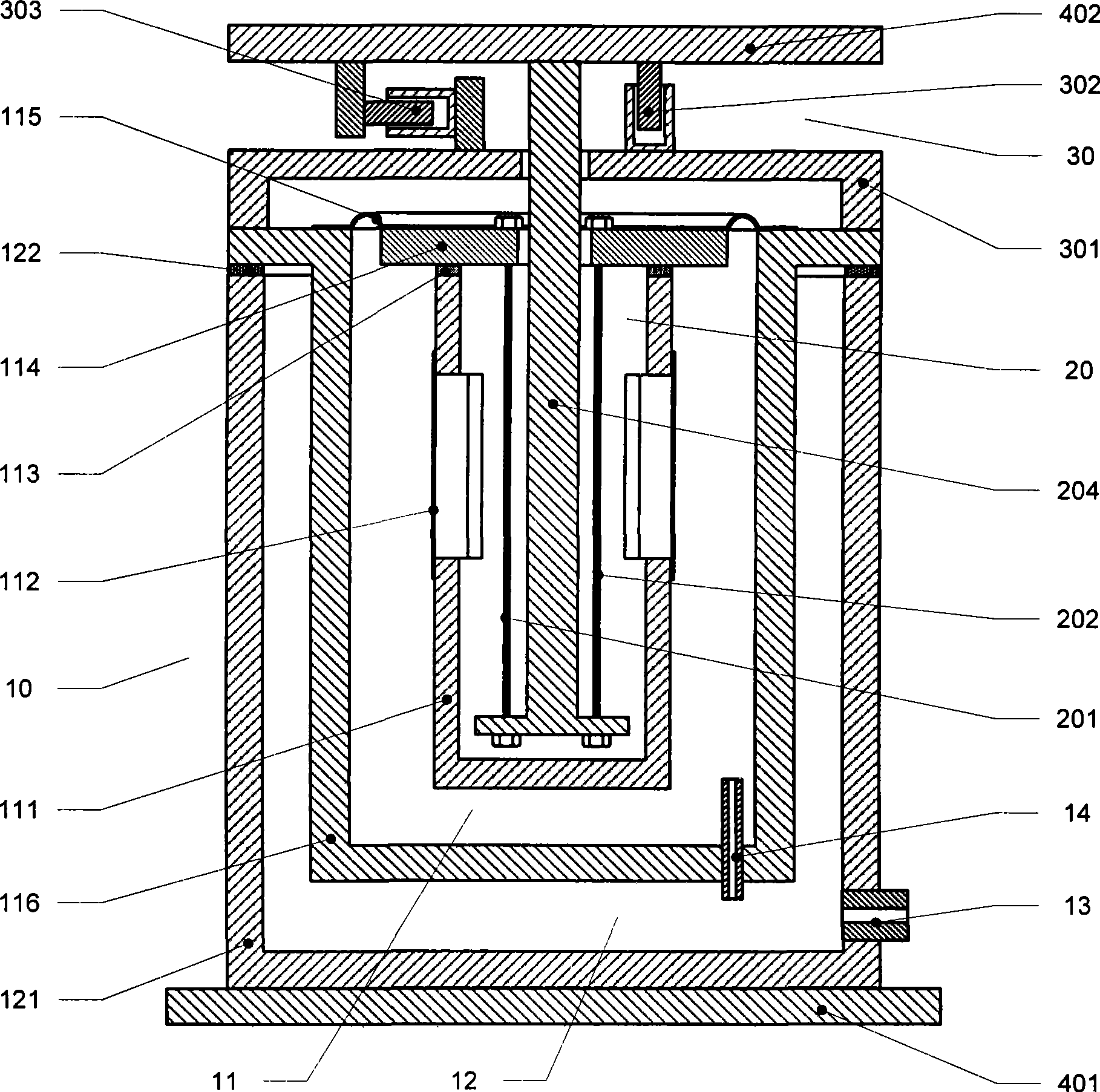
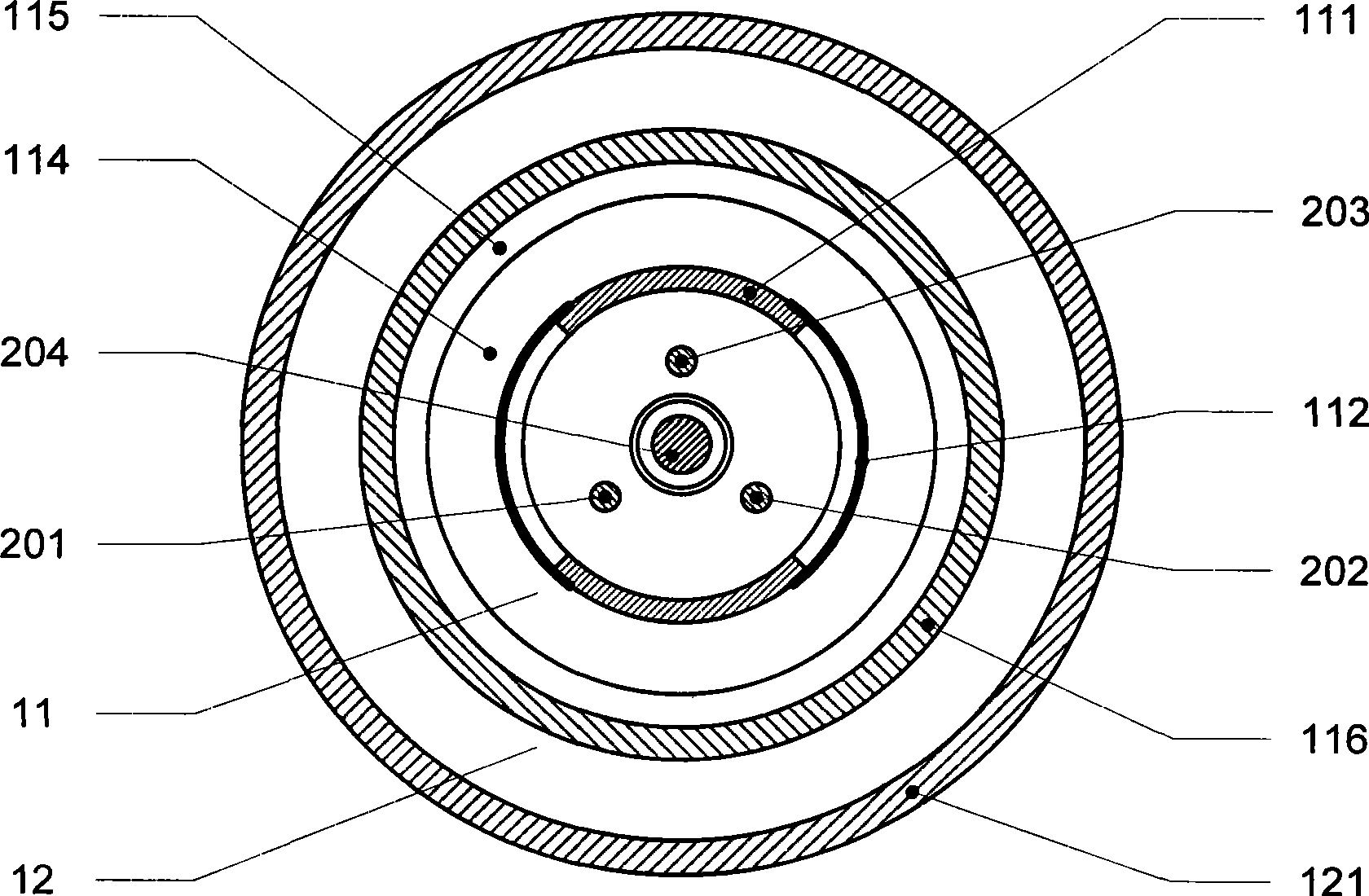
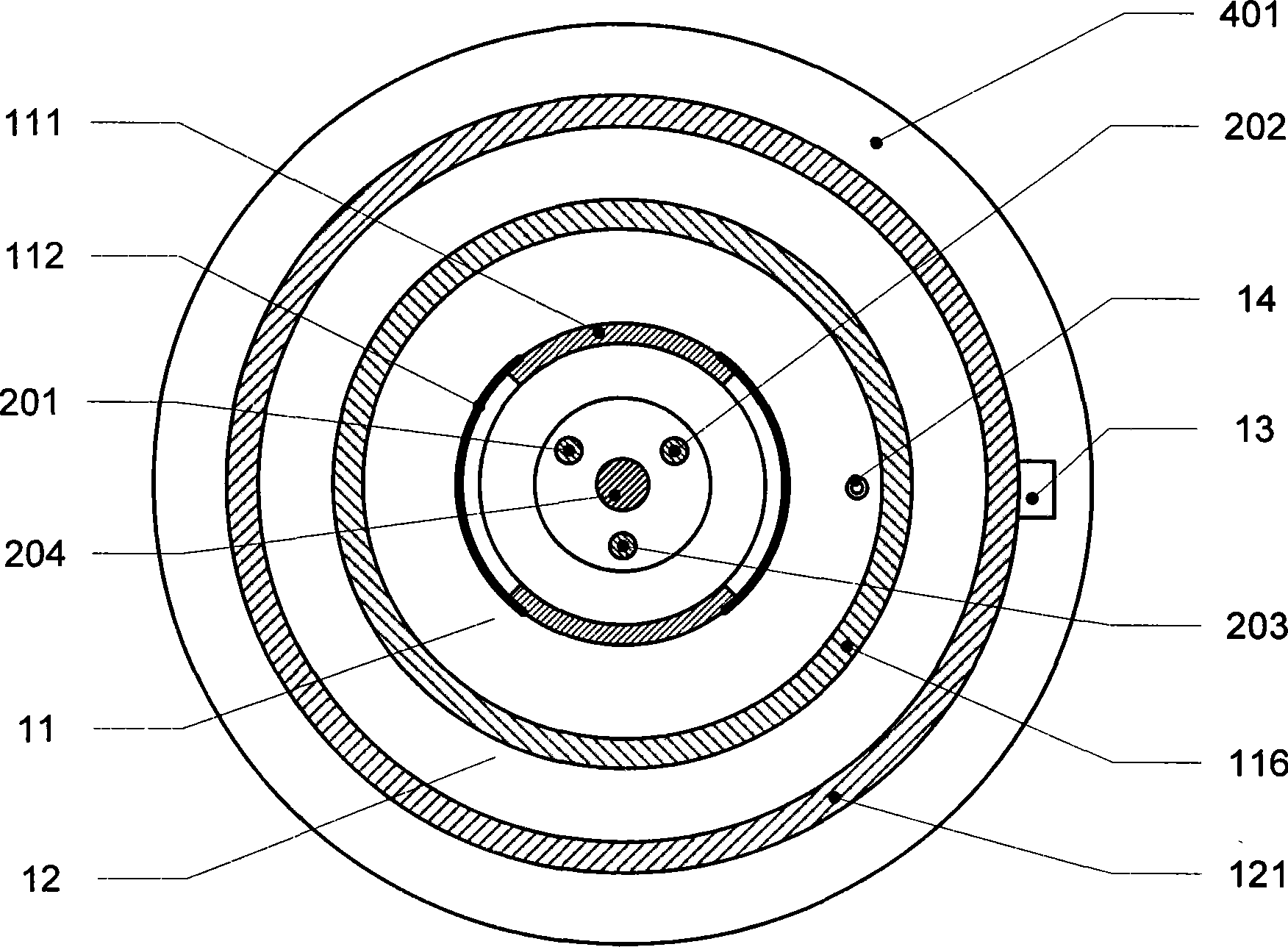
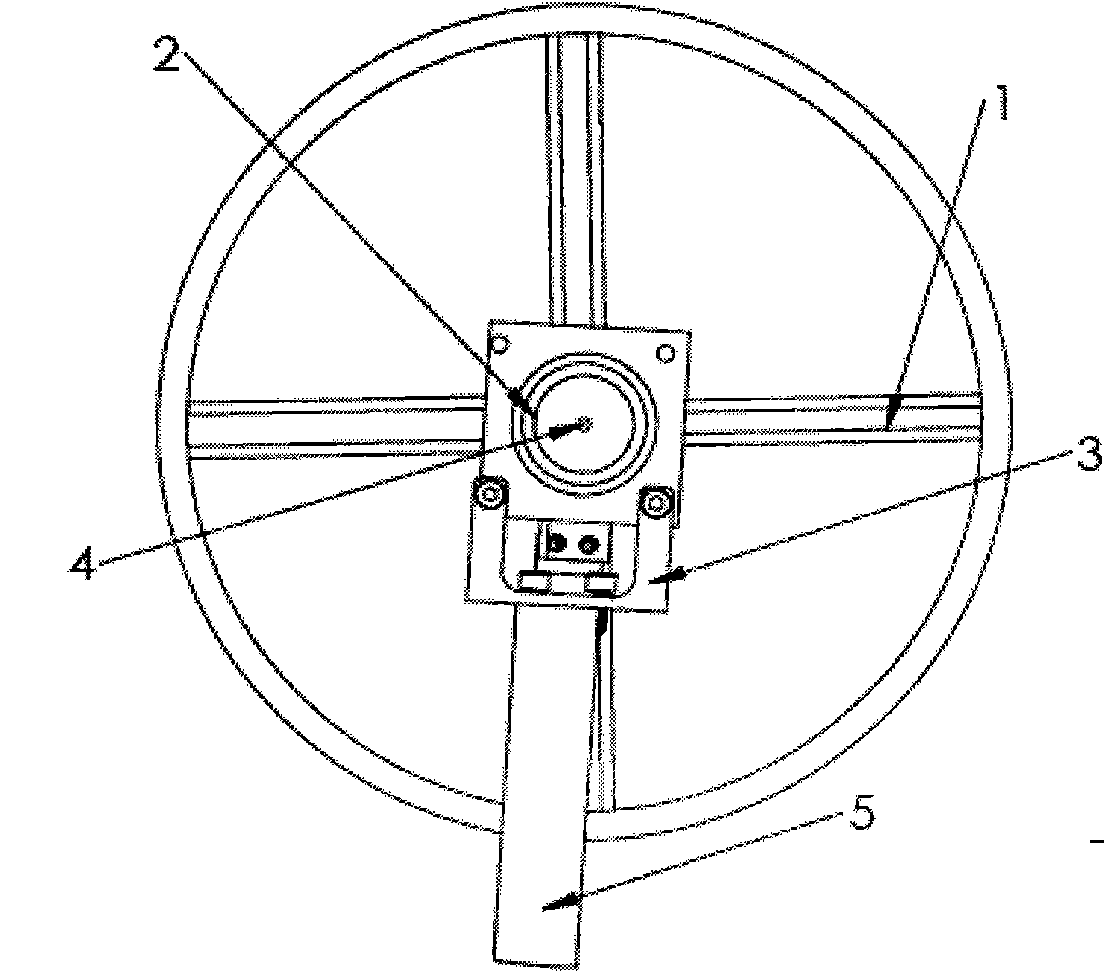
Sensor processing and balancing control algorithm of wheeled inverted pendulum
ActiveCN101823485AImprove stabilityImprove reliabilityVehicle position/course/altitude controlAutomatic controlElectric machine
The invention relates to sensor processing and balancing control algorithm of a wheeled inverted pendulum, which relates to the technical field of automatic control. The algorithm comprises sensor processing algorithm, balancing control algorithm, over-speed protection algorithm and emergency processing algorithm; the wheeled inverted pendulum comprises a swing link (1), a driving motor (2) with a controller, a wheel (3), the controller and a sensor (4), and a speed measurement device (5); and the sensor processing and balancing control algorithm of the wheeled inverted pendulum can improve the work stability and reliability of the inverted pendulum and takes a plurality of protective measures under the circumstance of keeping the inverted pendulum balanced, so that the whole inverted pendulum system works more stably and more reliably in the complicated external environment.
Owner:张明铭
Vehicle
ActiveUS20080164083A1Simplify attitude controlImprove performanceAuxillary drivesUnicyclesAttitude controlAngular acceleration
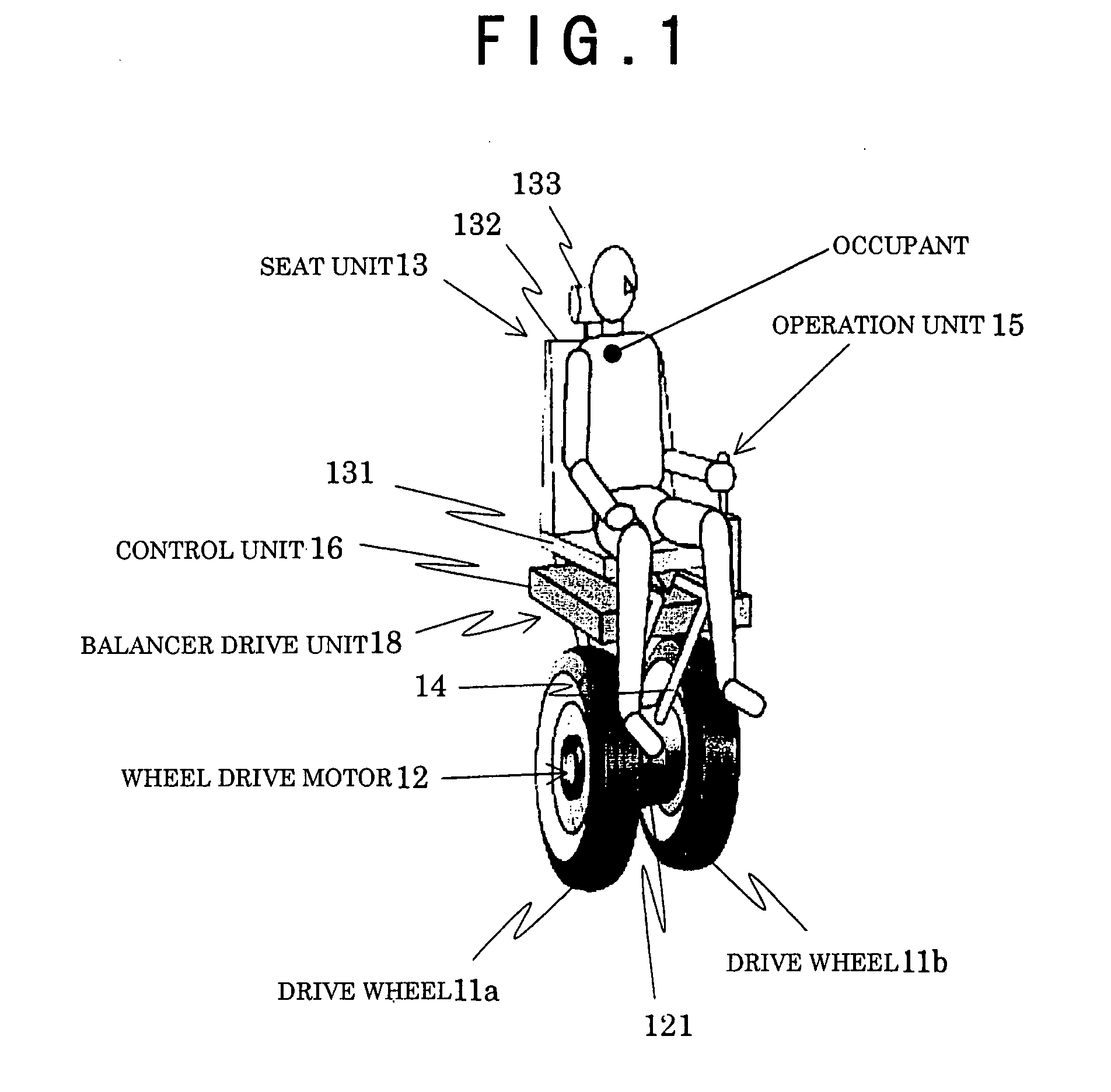
A vehicle utilizing the attitude control of an inverted pendulum, wherein the attitude of the vehicle is dynamically controlled by moving a balancer. The inclination of a vehicle body is detected by a gyro-sensor, a torque T1 against the inclination of a boarding part is calculated by using the angular acceleration of the vehicle body, and a torque T2 for returning the boarding part in the opposite direction of an inclination direction by canceling that torque is generated by moving the balancer (B). Namely, a reaction torque T3 against the torque T2 is allowed to act on the boarding part by driving the balancer with the torque T2(>T1) in the inclination direction. The boarding part is pushed back in the opposite direction of the first inclination direction by the reaction torque T3. Since the boarding part is pushed back in the opposite direction, the angular acceleration of the vehicle body when the boarding part is tilted to the opposite side of a vertical line is detected by the gyro sensor, and the balancer is moved again in the opposite direction with the torque T2 corresponding to the angular acceleration.
Owner:EQUOS RES
Inverted pendulum type vehicle
ActiveUS20110067943A1Equally distributedVehicle seatsUnicyclesHorizontal orientationInverted pendulum
In a vehicle (1) including a frame (2) incorporated with a drive unit (3) for enabling the frame to travel in a prescribed direction and a seat assembly (4) supported by the frame and including a pair of saddle members (63) defining a pair of seat surfaces (70A), respectively, configured to jointly support buttocks of a vehicle occupant, the saddle members are resiliently supported by the frame in such a manner that the seat surface of each saddle member is in an approximately horizontal orientation but is progressively tilted inward with a downward movement of the saddle member under a load of a vehicle occupant. Thus, one of the saddle members receiving a greater load than the other tilts downward toward the center of the vehicle, and this causes the vehicle occupant to be urged toward the saddle member receiving a smaller load so that the vehicle occupant is automatically urged toward the center of the vehicle, and hence the gravitational center of the vehicle occupant may be placed in the center of the vehicle at all times.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Two-degree-of-freedom ultralow-frequency vibration isolator
ActiveCN106321707ARealization of ultra-low frequency vibration isolation with degrees of freedomVibration isolation achievedNon-rotating vibration suppressionSprings/dampers functional characteristicsMarine engineeringAir spring
The invention discloses a two-degree-of-freedom ultralow-frequency vibration isolator. The two-degree-of-freedom ultralow-frequency vibration isolator comprises a basic platform (10) and a load-bearing platform (30), and the basic platform (10) and the load-bearing platform (30) are connected through supporting rods. The two-degree-of-freedom ultralow-frequency vibration isolator is characterized in that the vibration isolator further comprises a positive-stiffness air spring (20) and a magnetic negative-stiffness mechanism (28) with adjustable negative stiffness, and the positive-stiffness air spring (20) and the magnetic negative-stiffness mechanism (28) form a parallel mechanism in the direction of the center axes of the basic platform and the load-bearing platform, so that the inherent frequency in the direction of the center axes of the basic platform and the load-bearing platform is decreased; and a stiffness-adjustable positive-stiffness leaf spring and a negative-stiffness inverted pendulum are arranged in the direction perpendicular to the center axes of the basic platform and the load-bearing platform and form a negative-stiffness parallel mechanism, so that the inherent frequency in the direction perpendicular to the center axes of the basic platform and the load-bearing platform is decreased. According to the vibration isolator, positive-stiffness and negative-stiffness parallel type passive structures are adopted both in the direction of the center axes of the basic platform and the load-bearing platform and in the direction perpendicular to the center axes of the basic platform and the load-bearing platform, and thus vibration of two degrees of freedom is achieved at the same time.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com