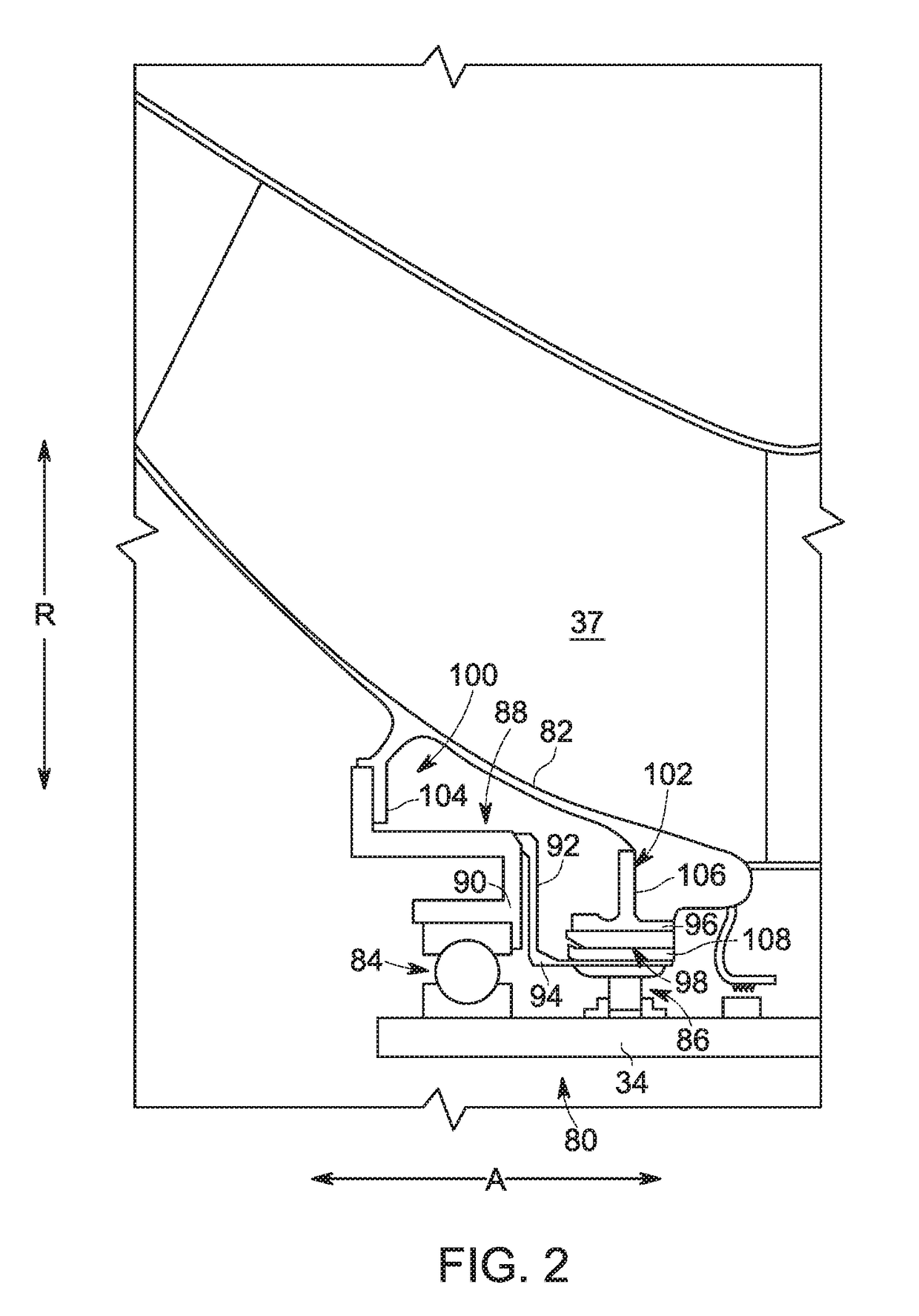
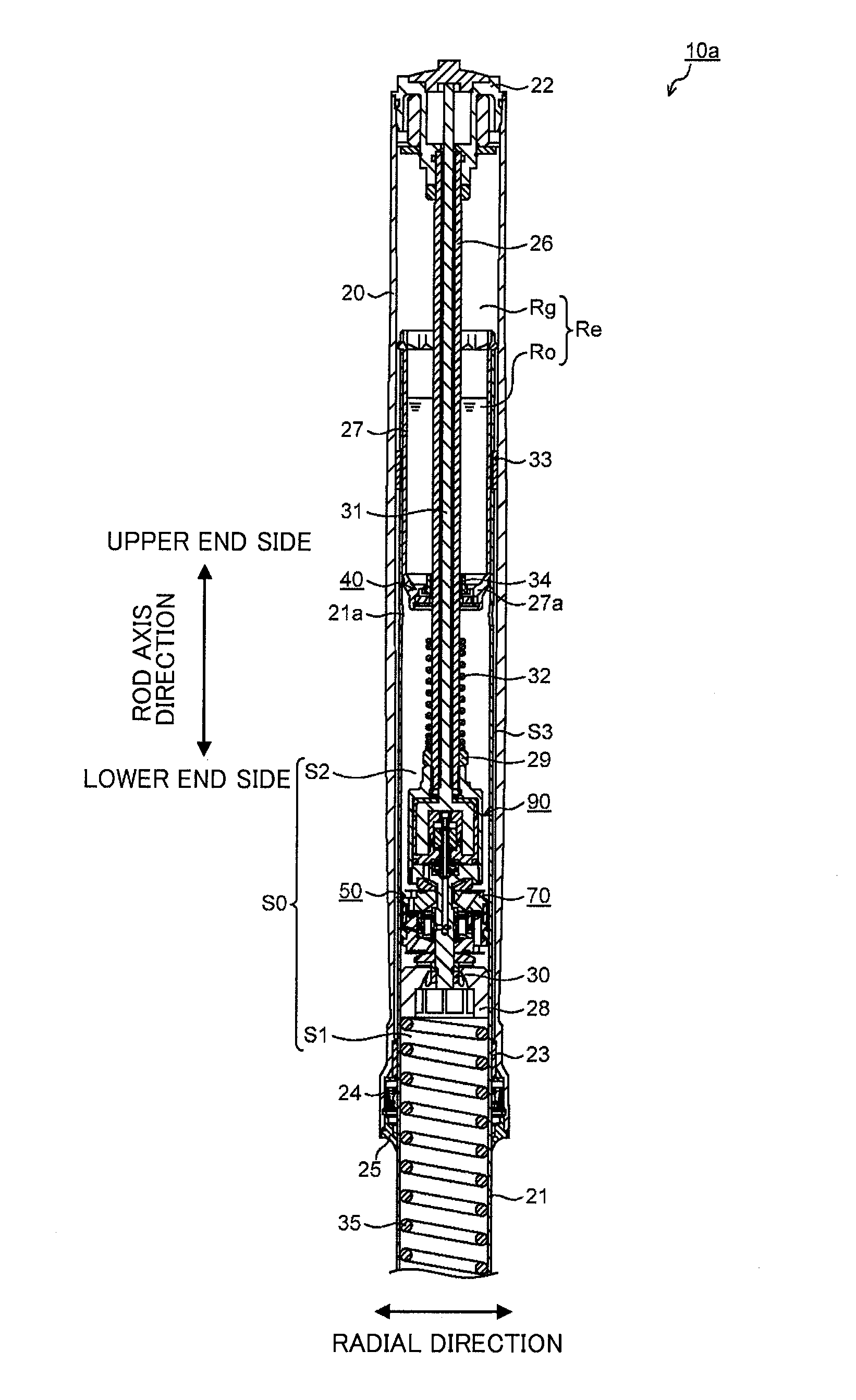
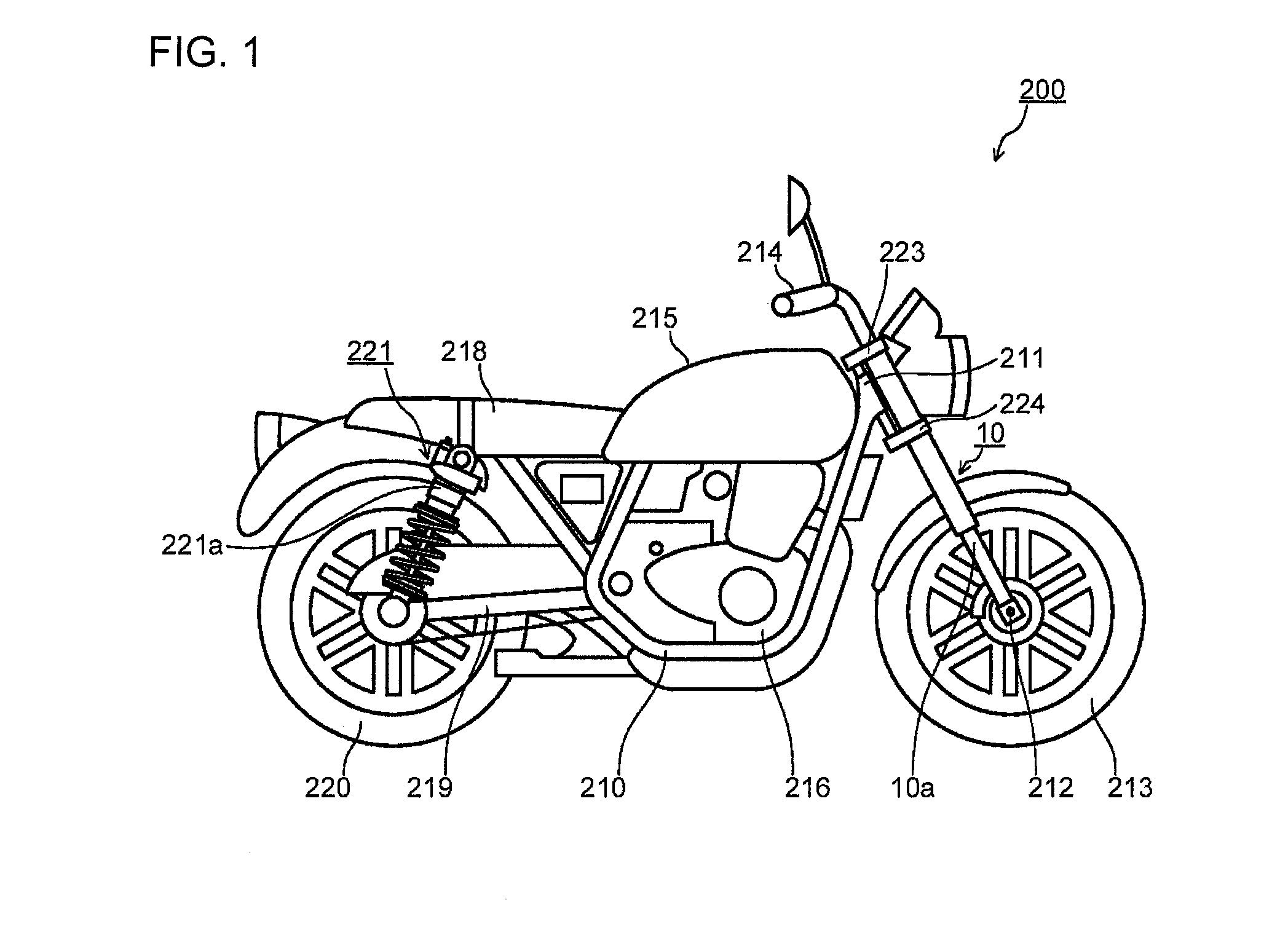
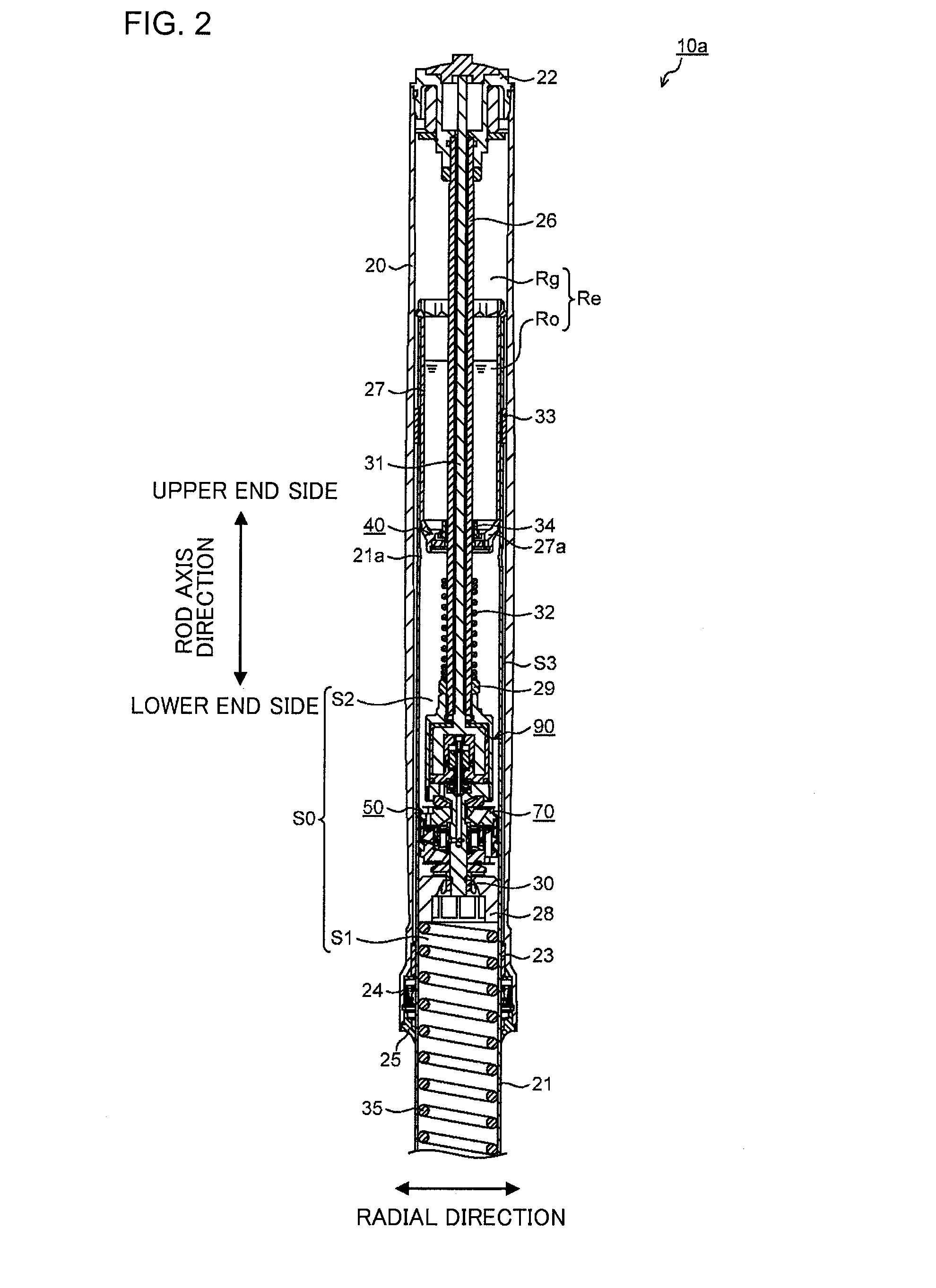
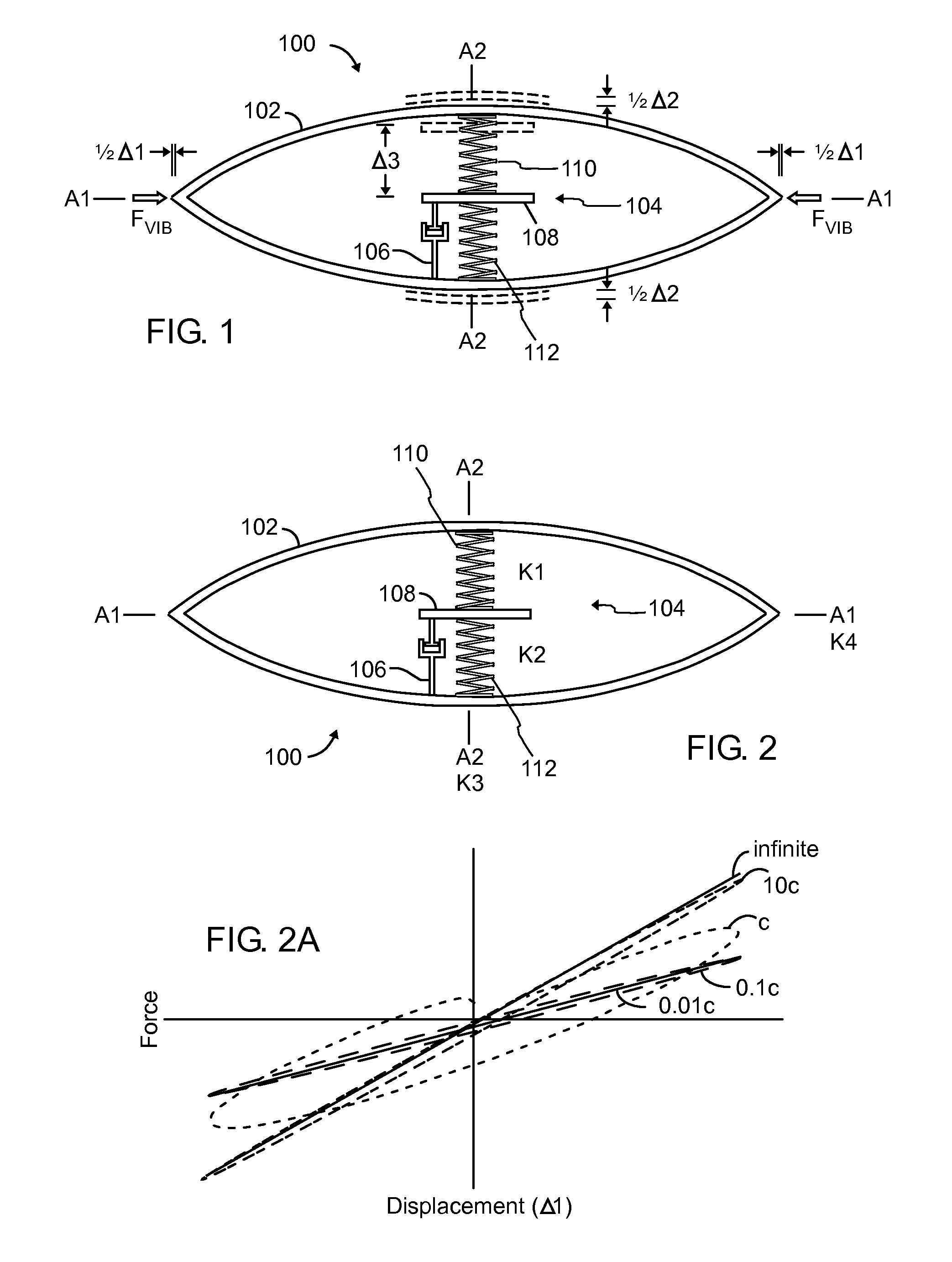
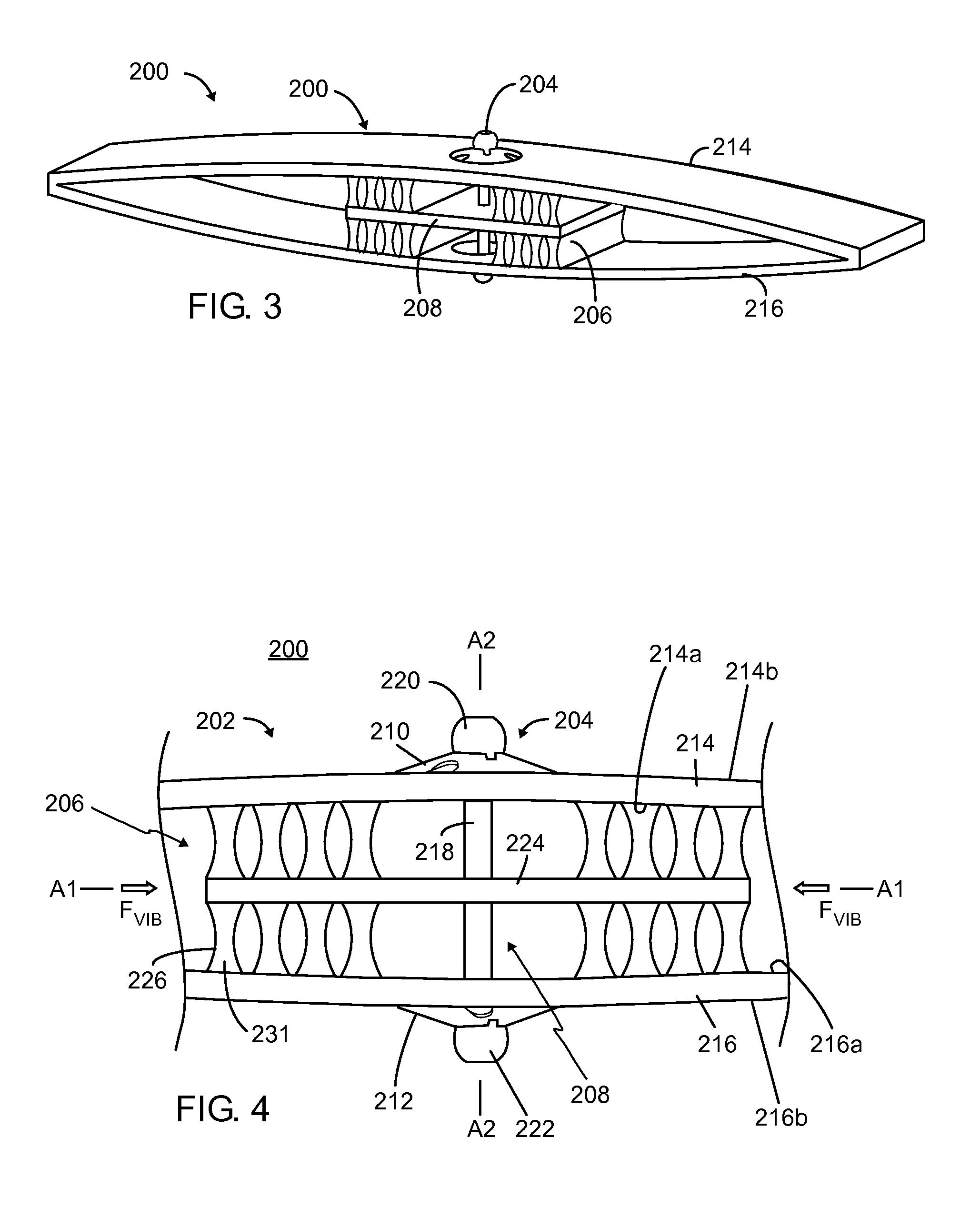
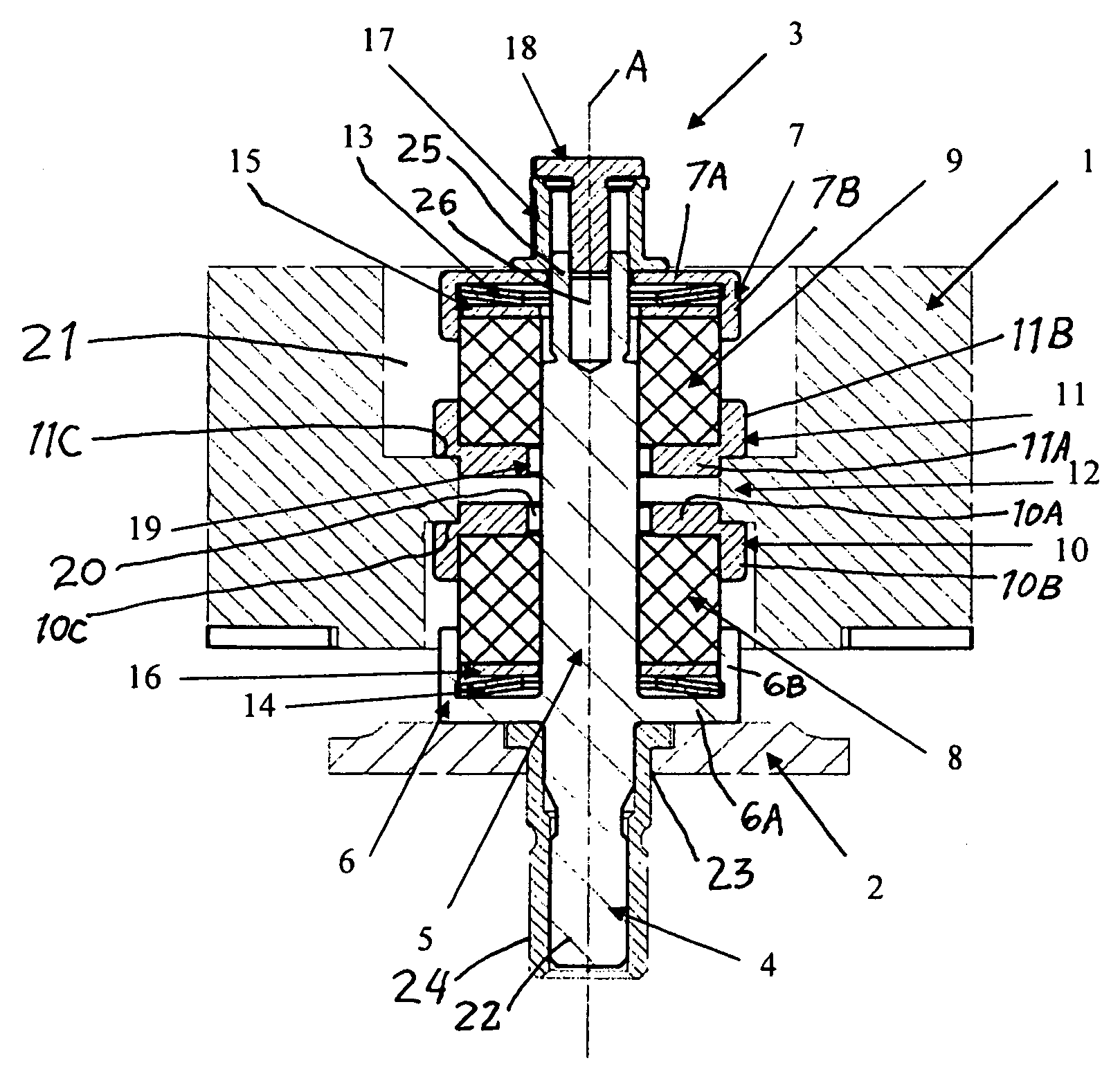
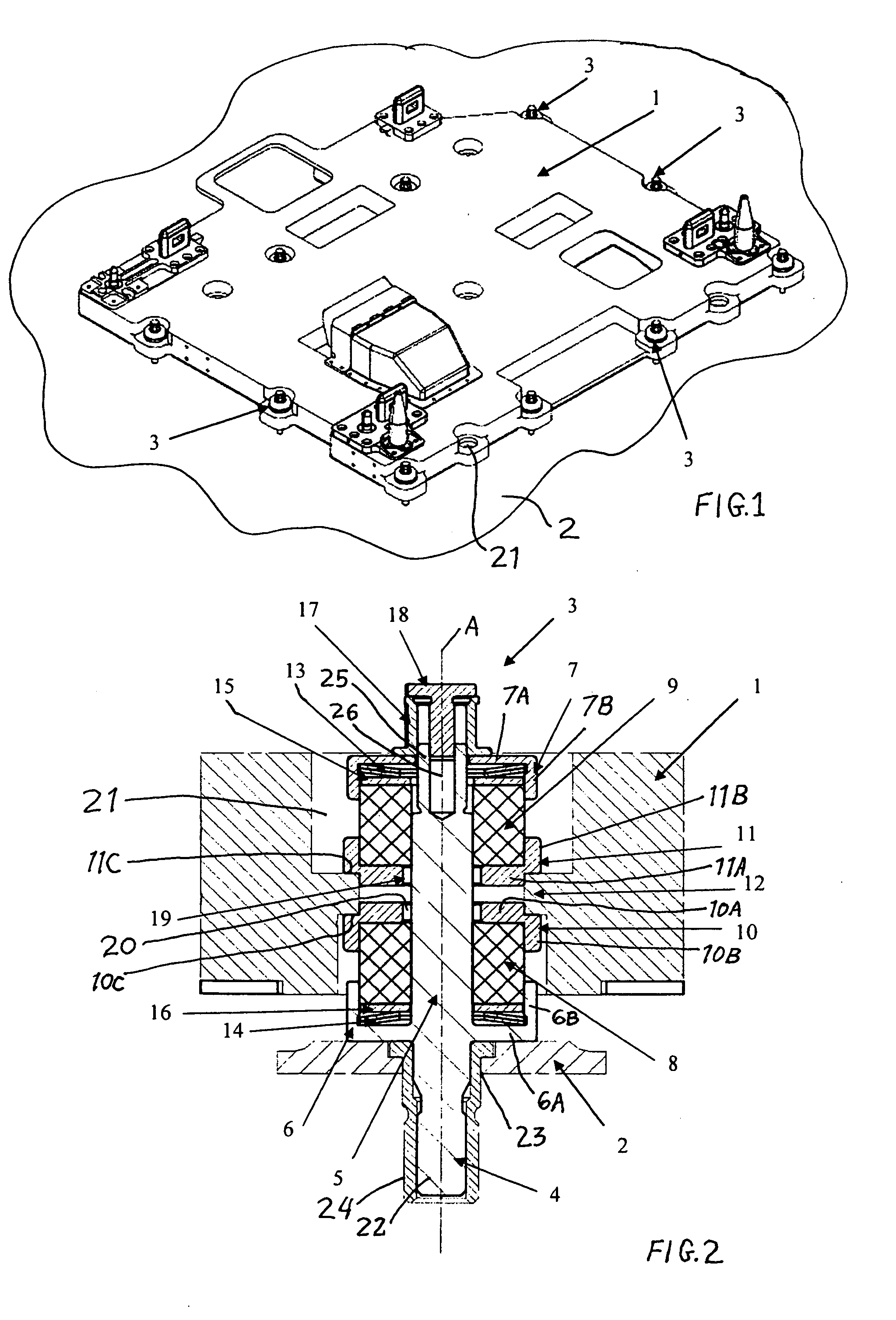
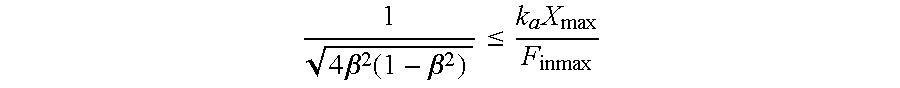Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1646results about "Springs/dampers functional characteristics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
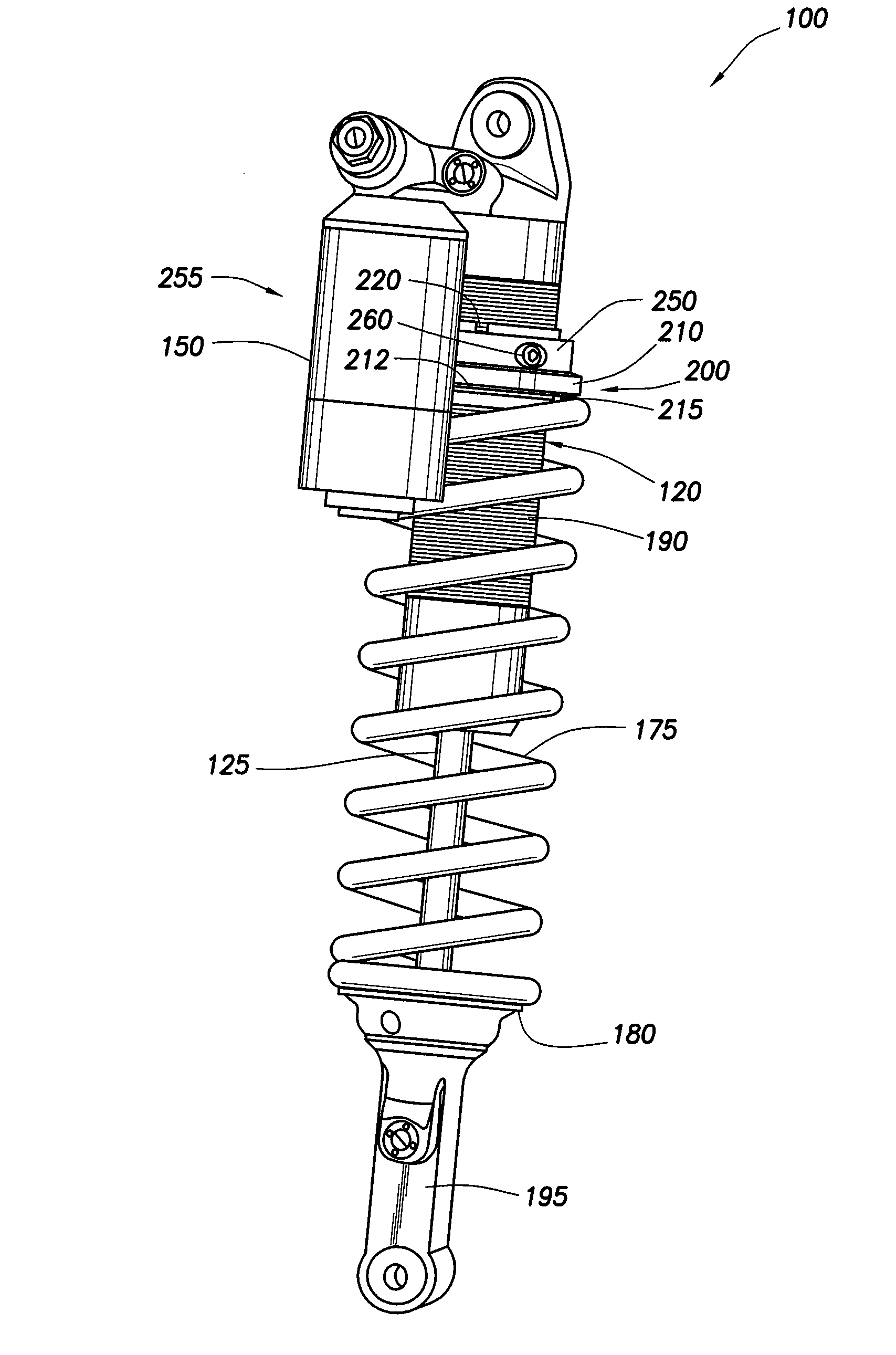
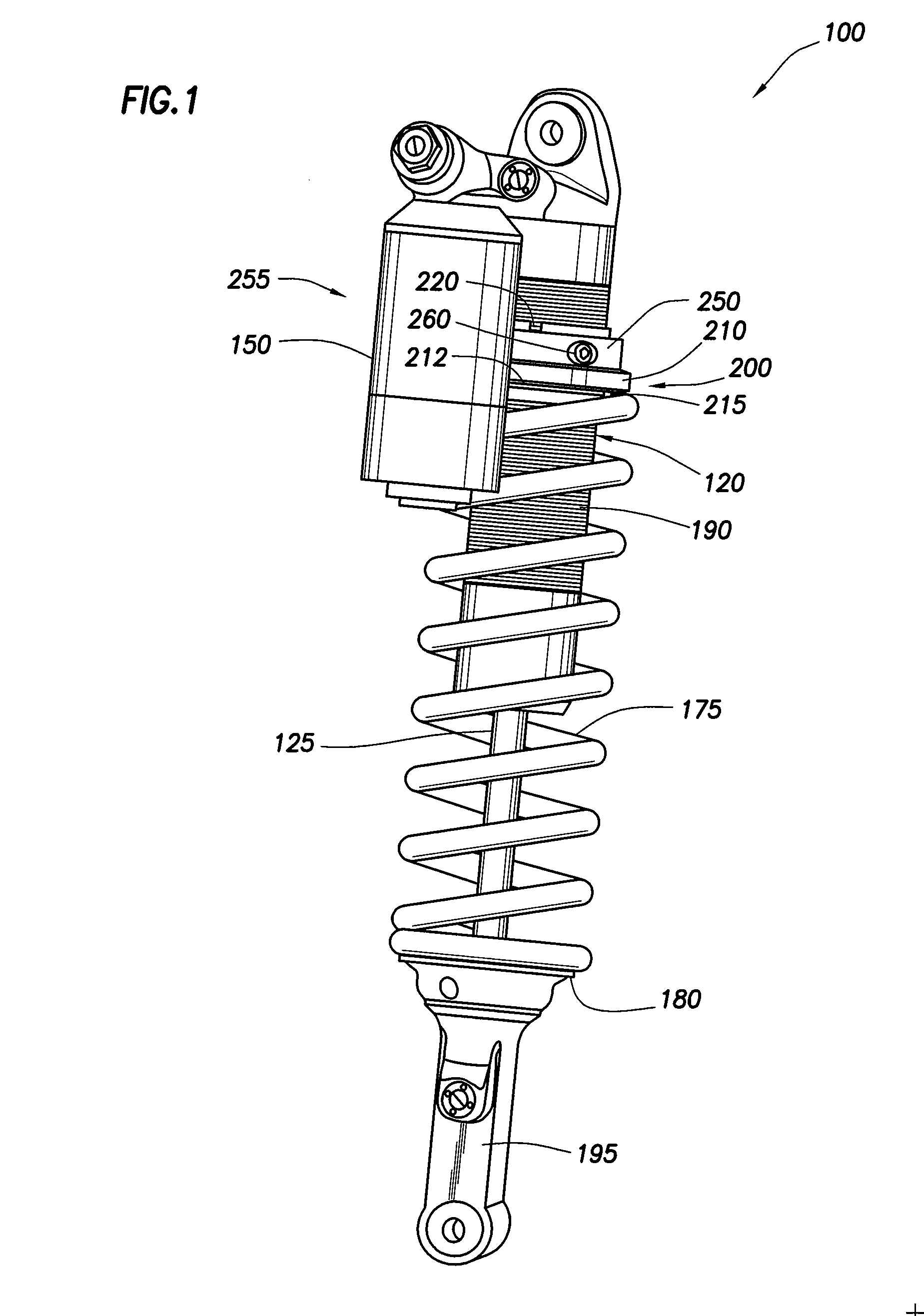
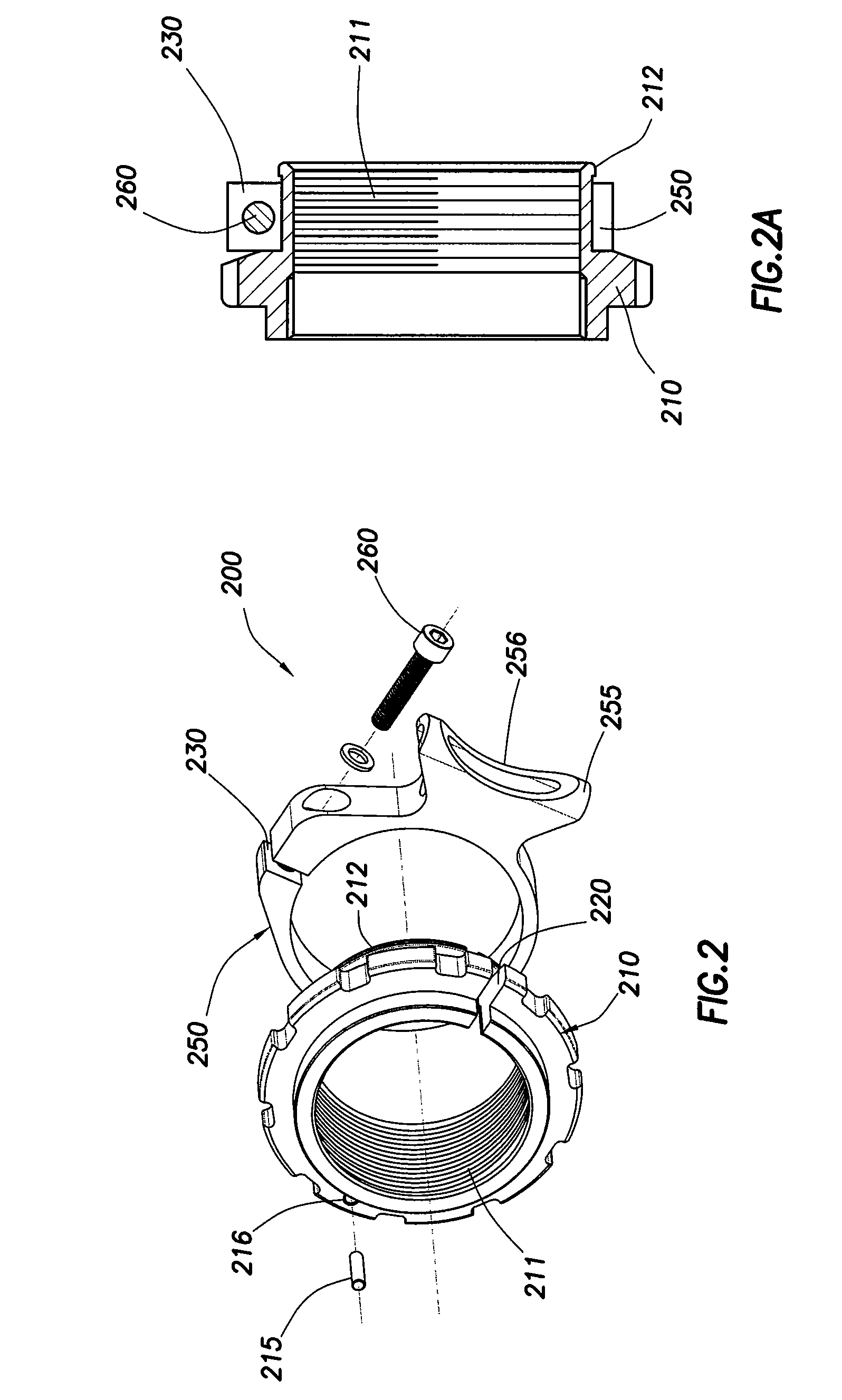
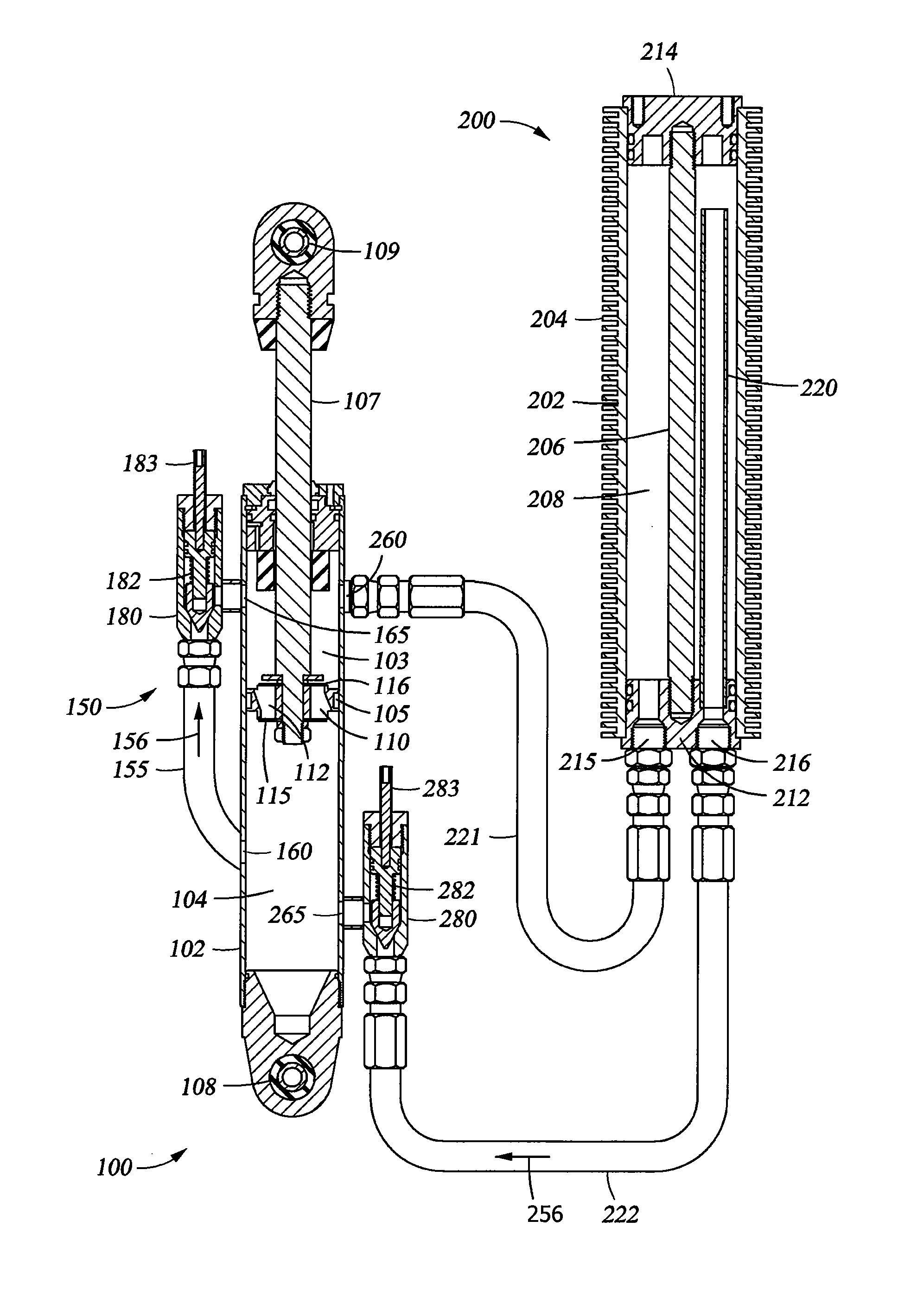
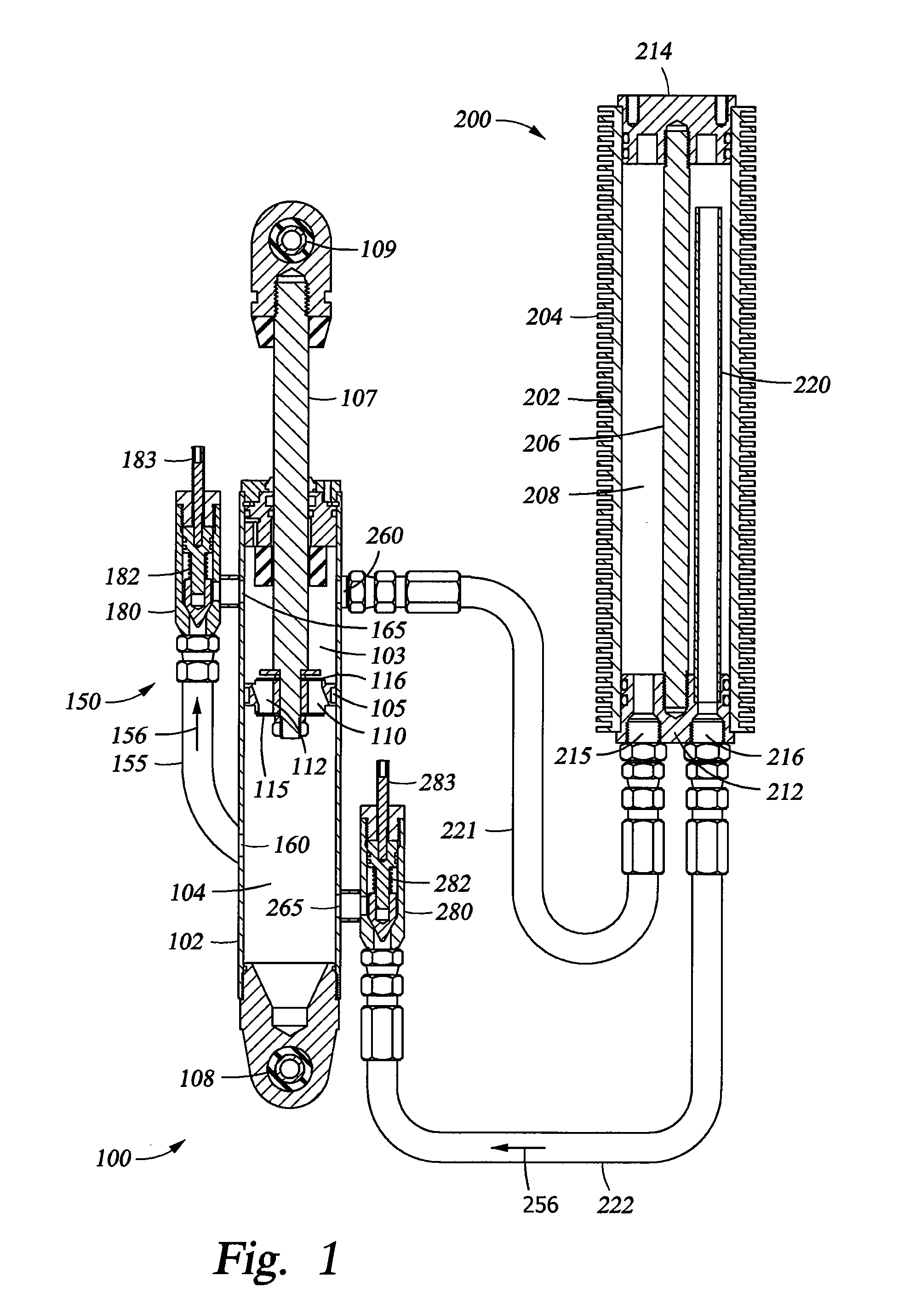
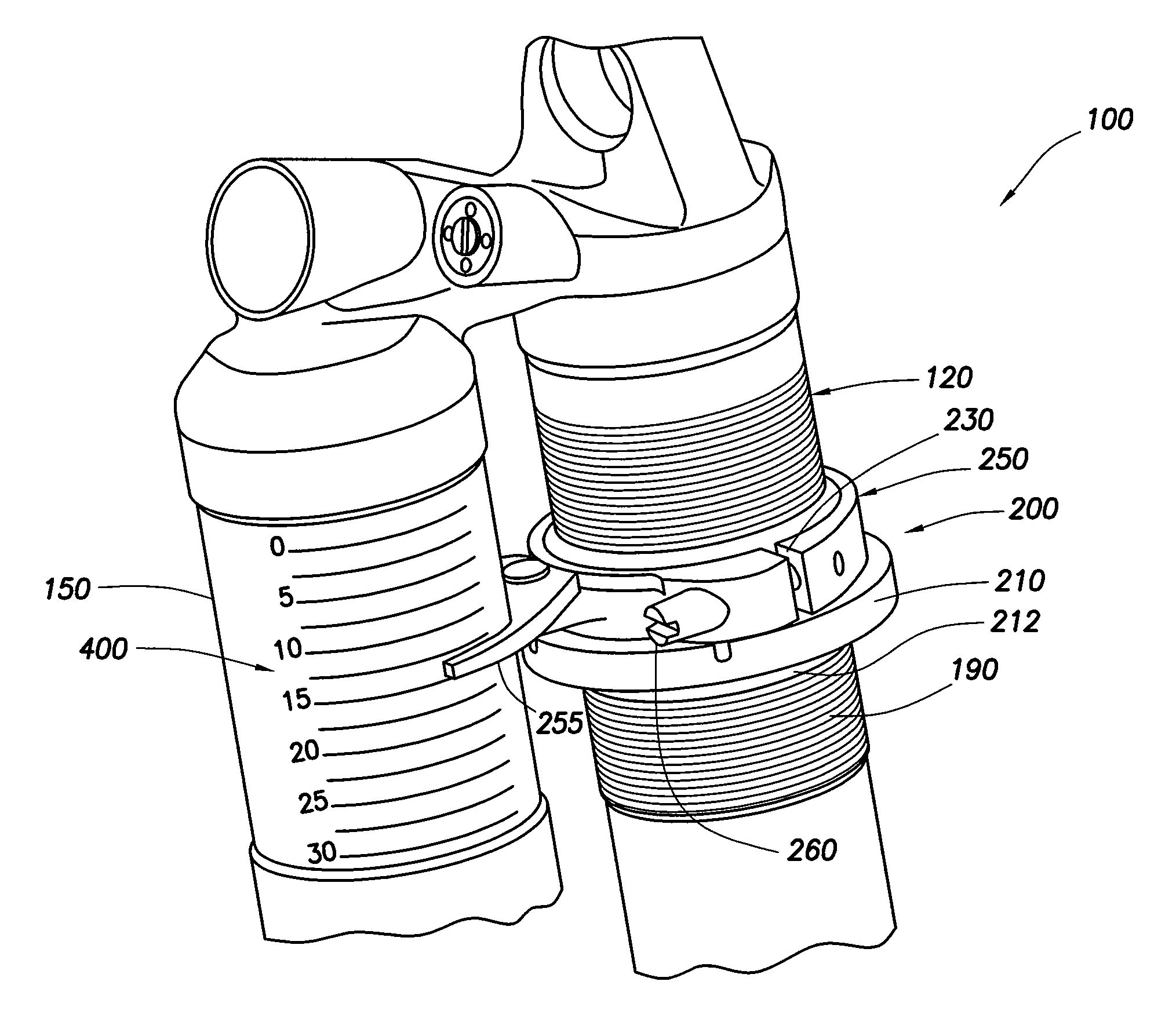
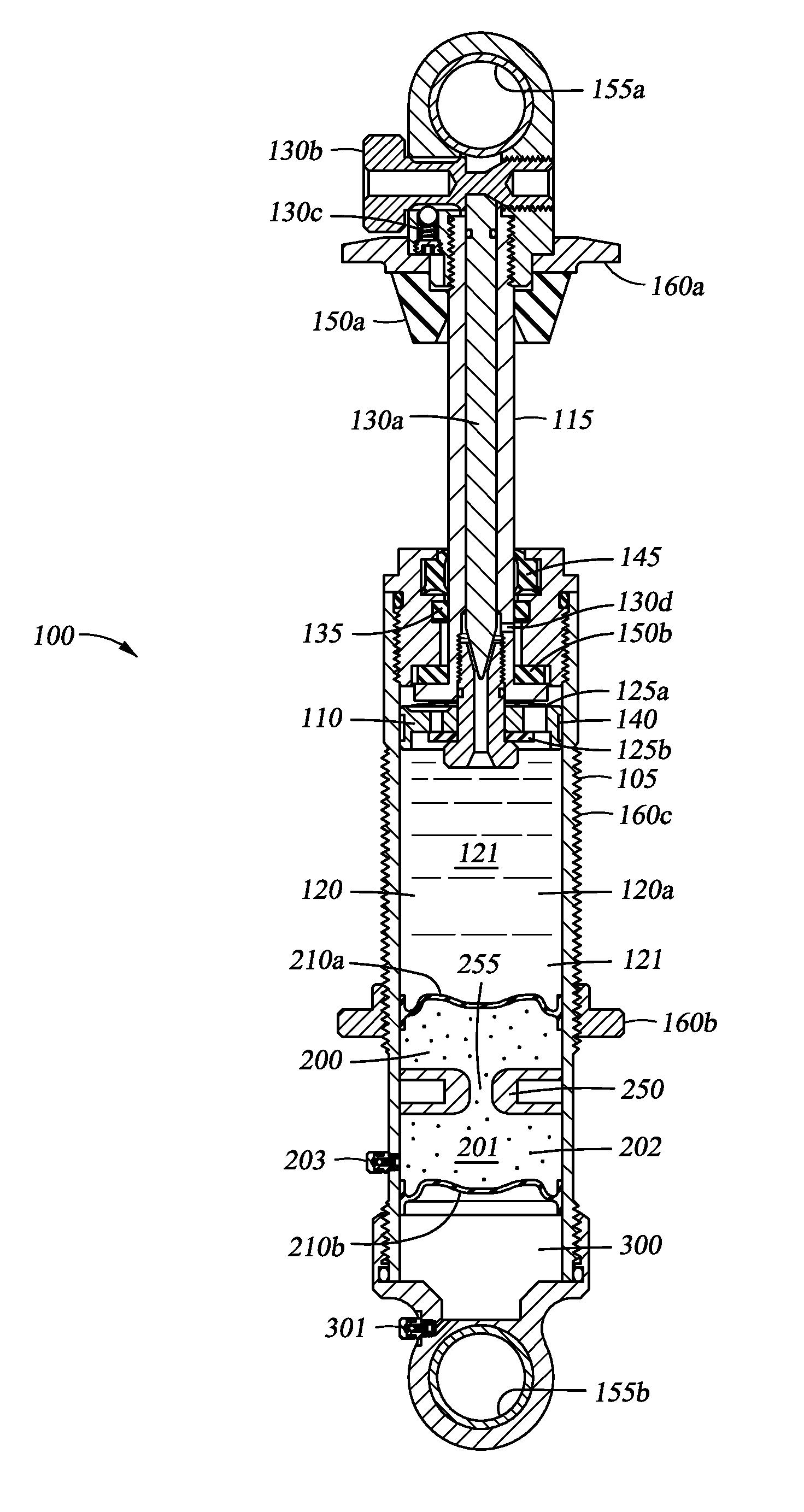
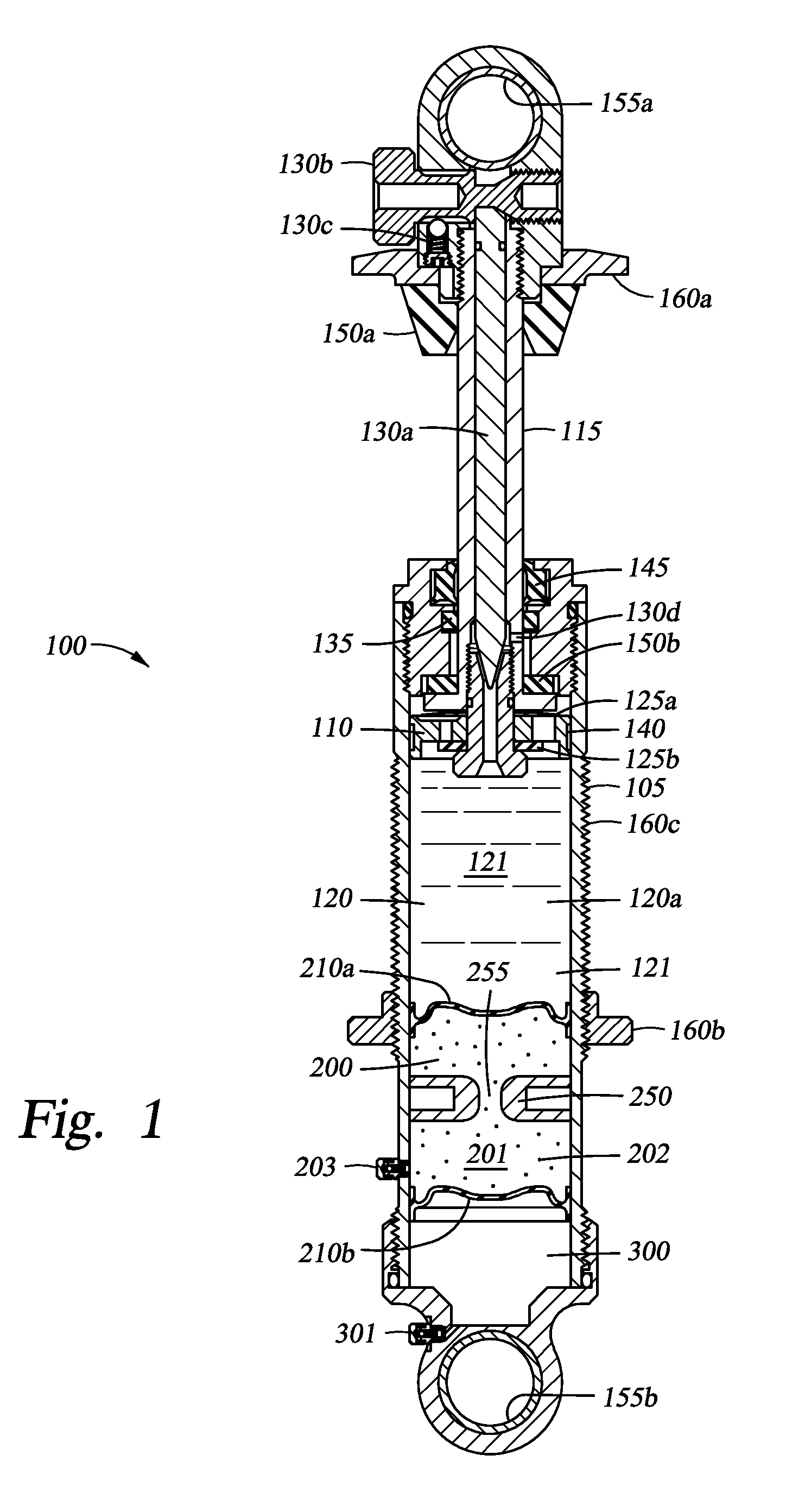
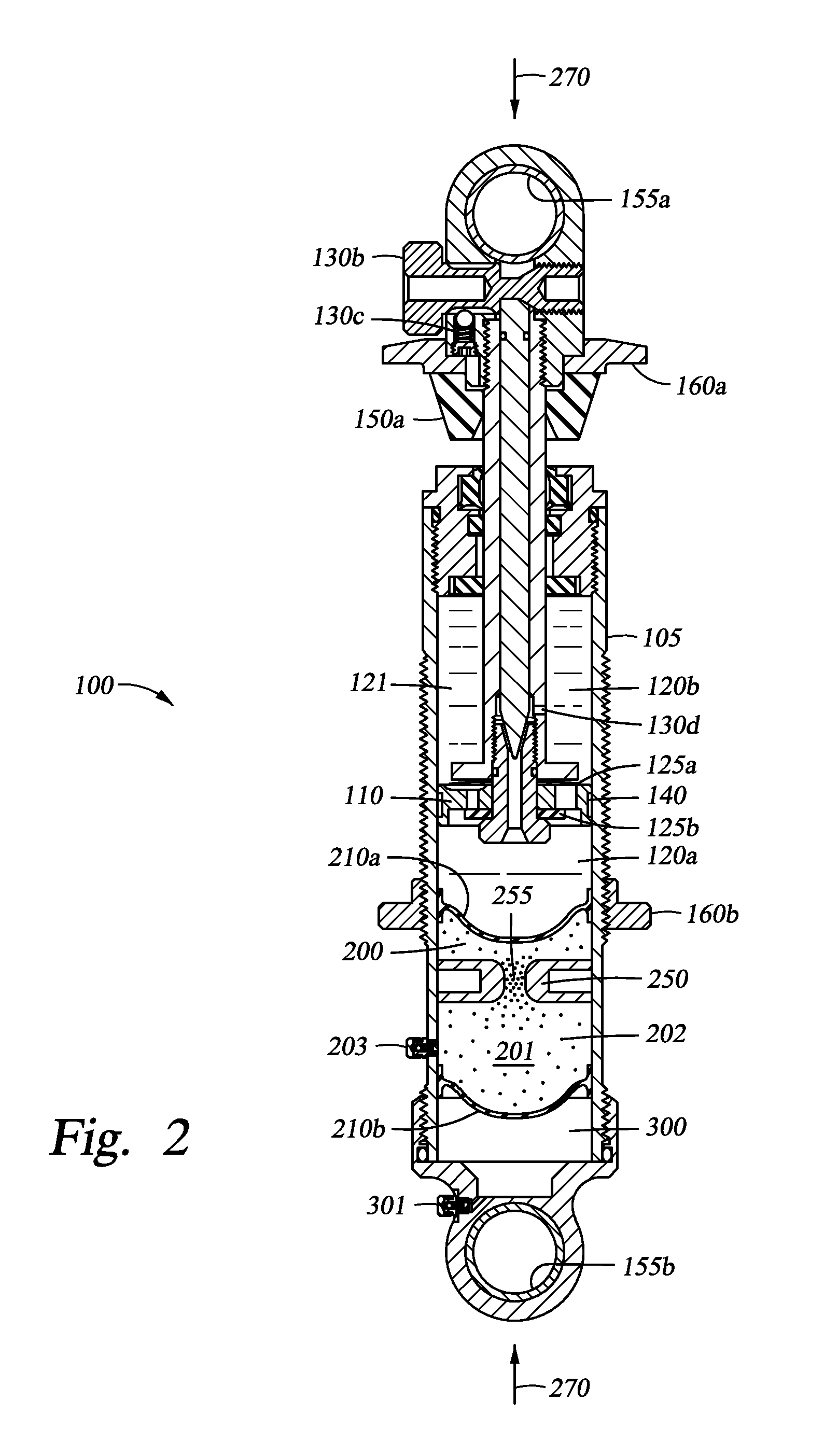
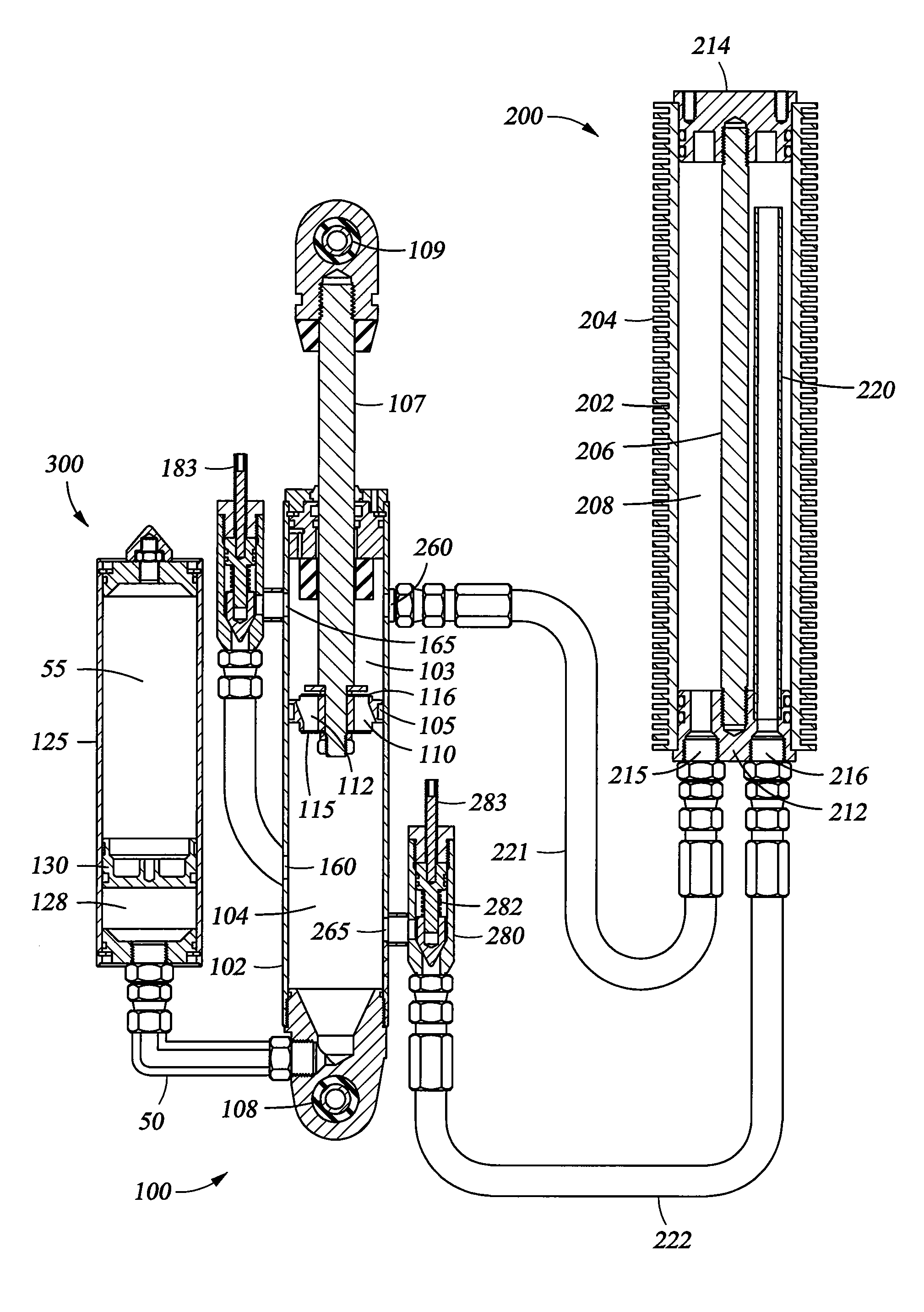
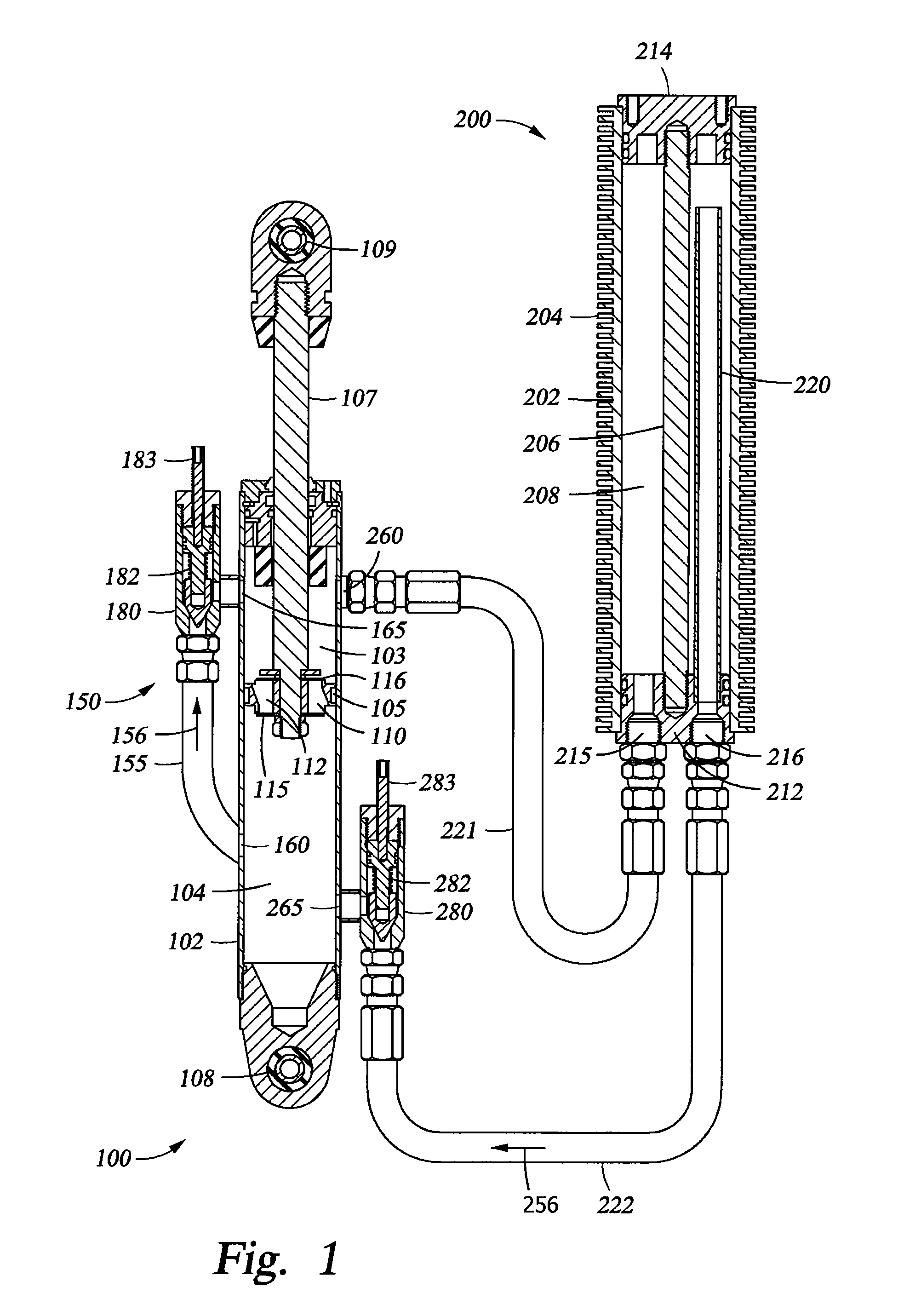
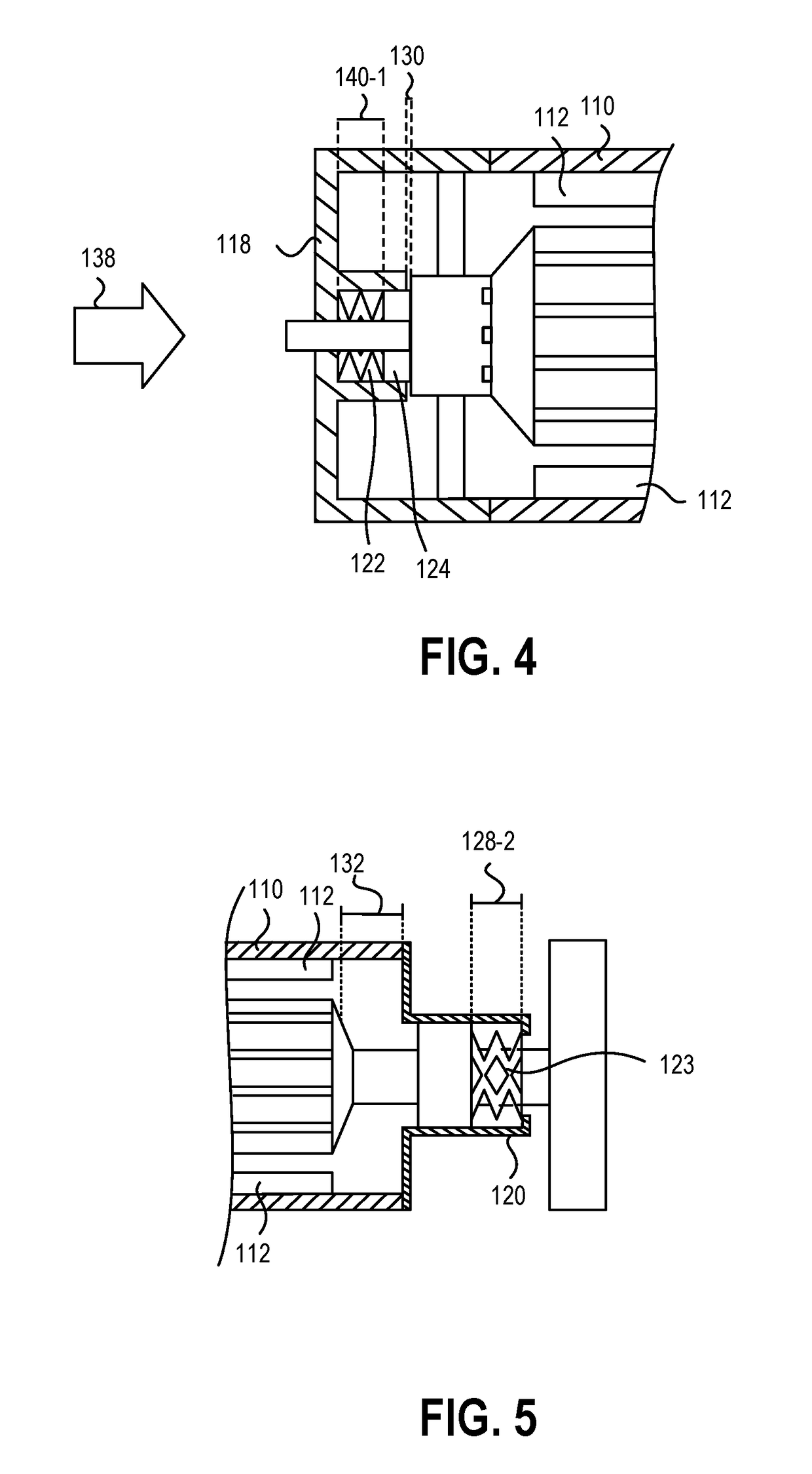
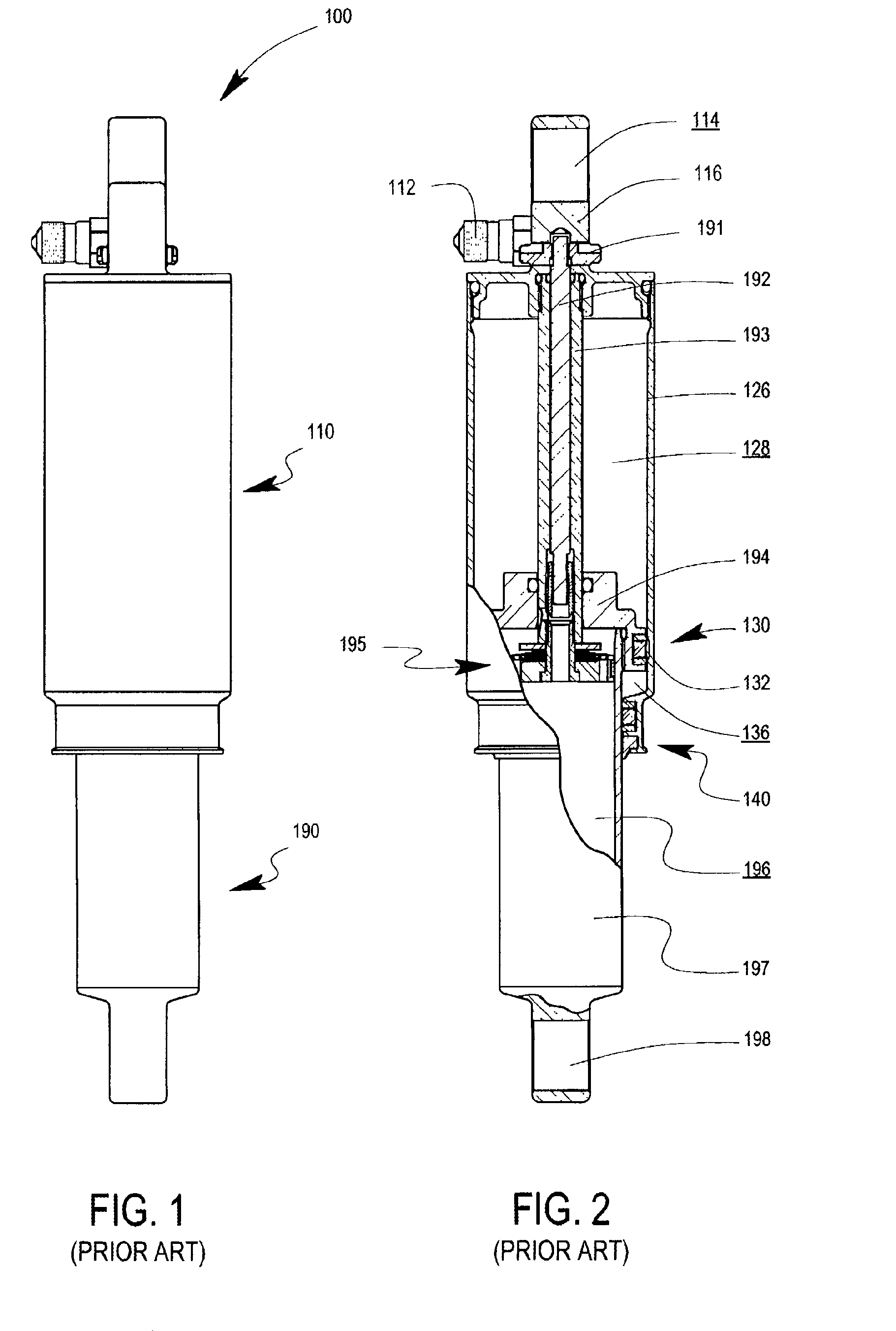
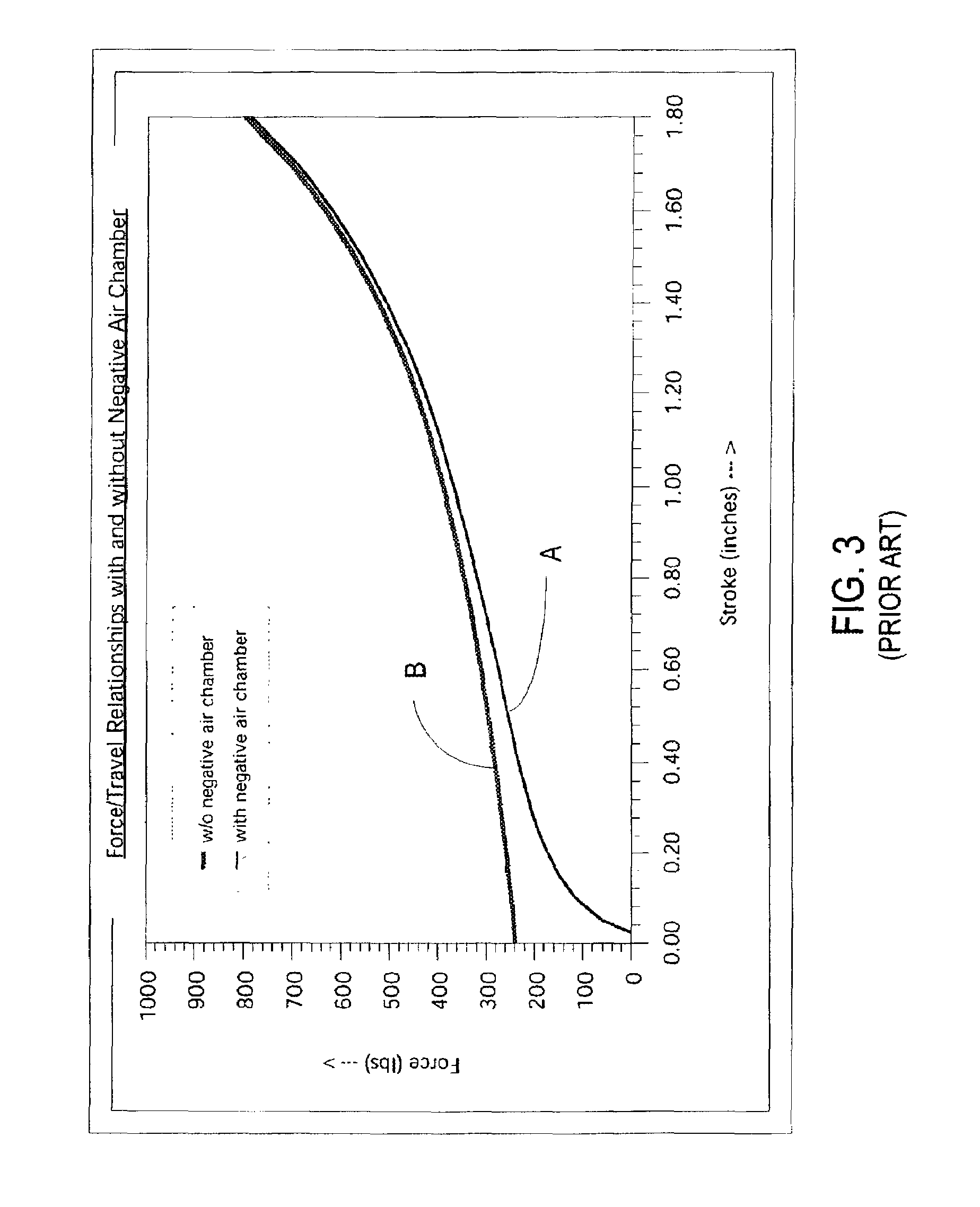
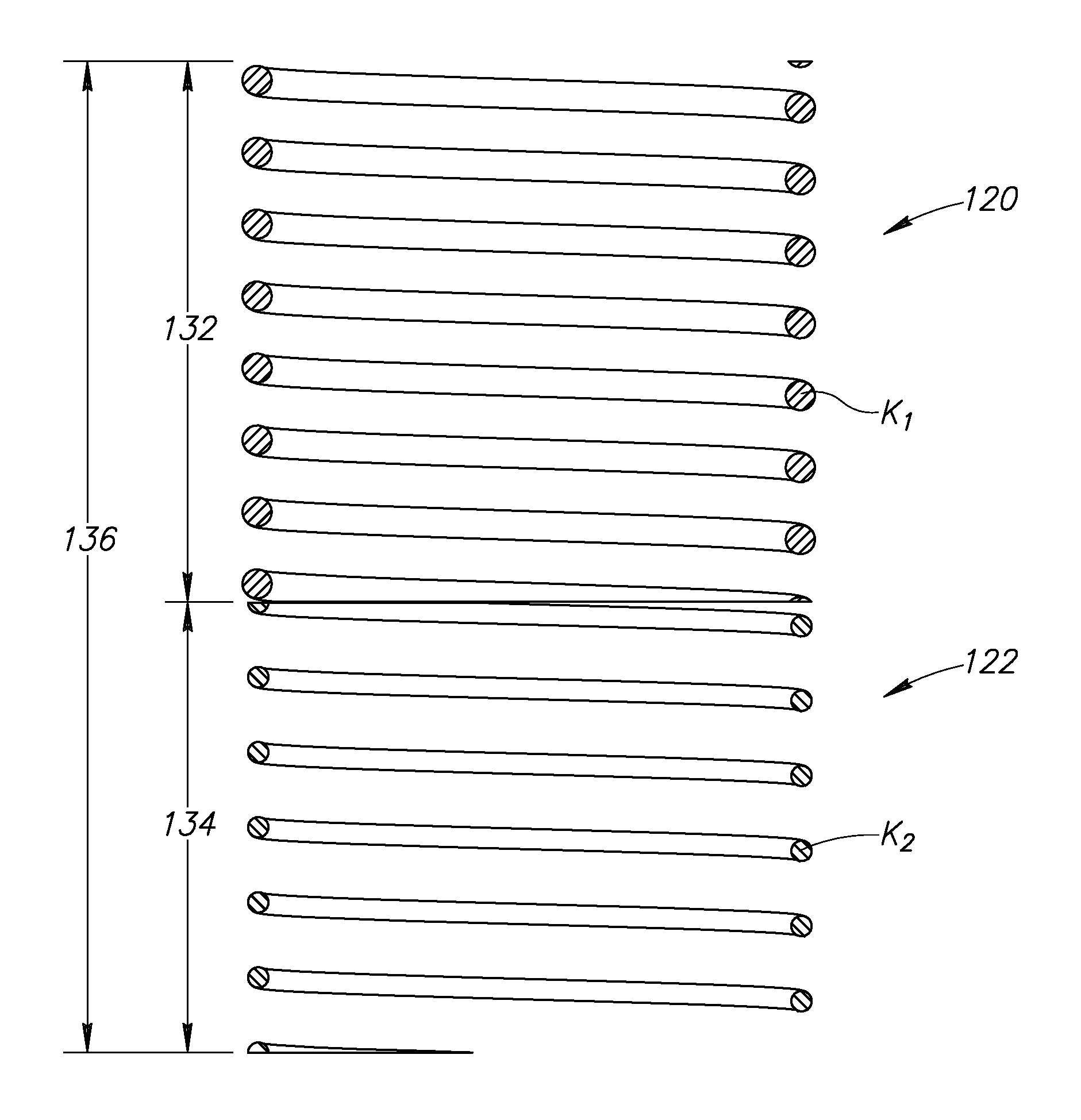
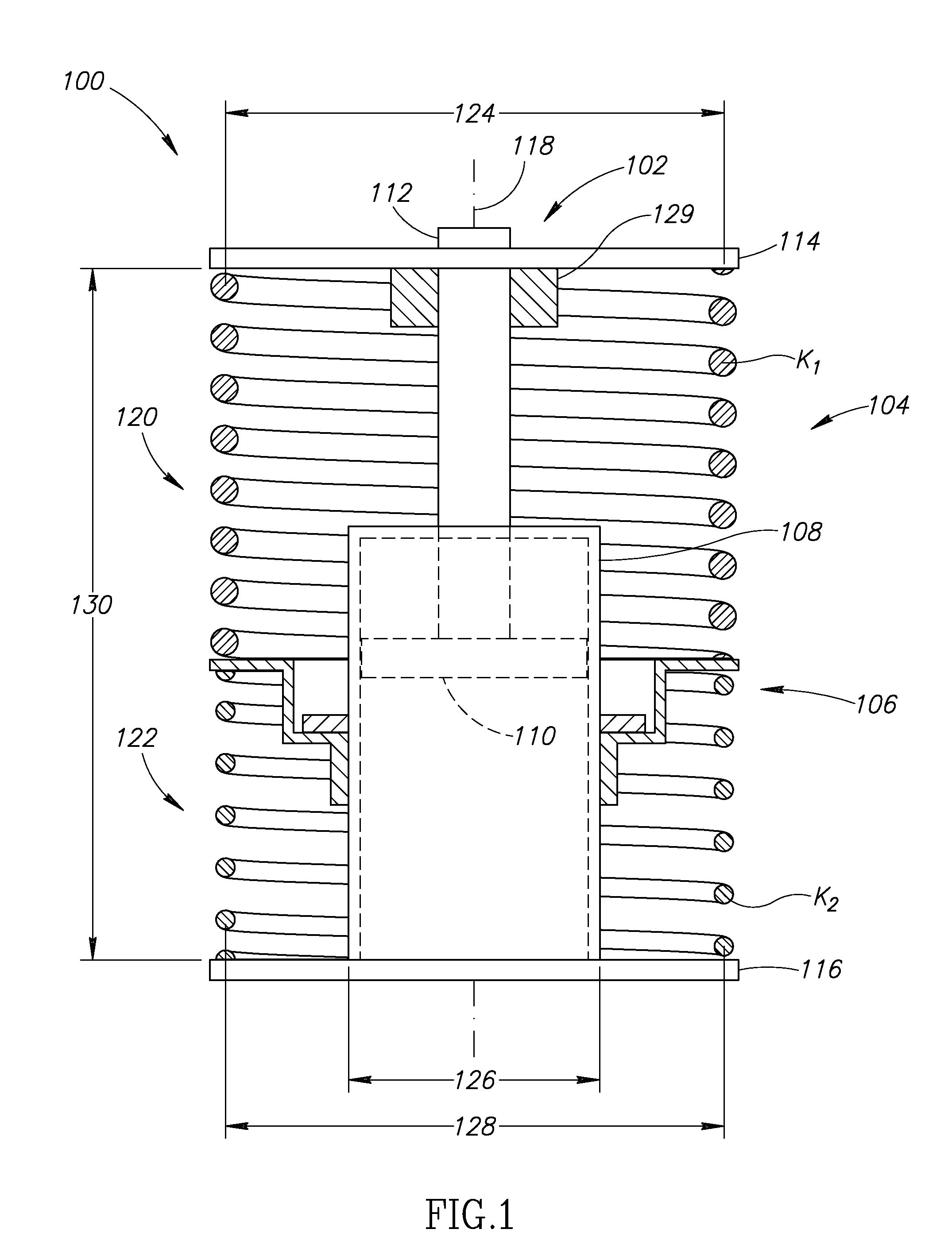
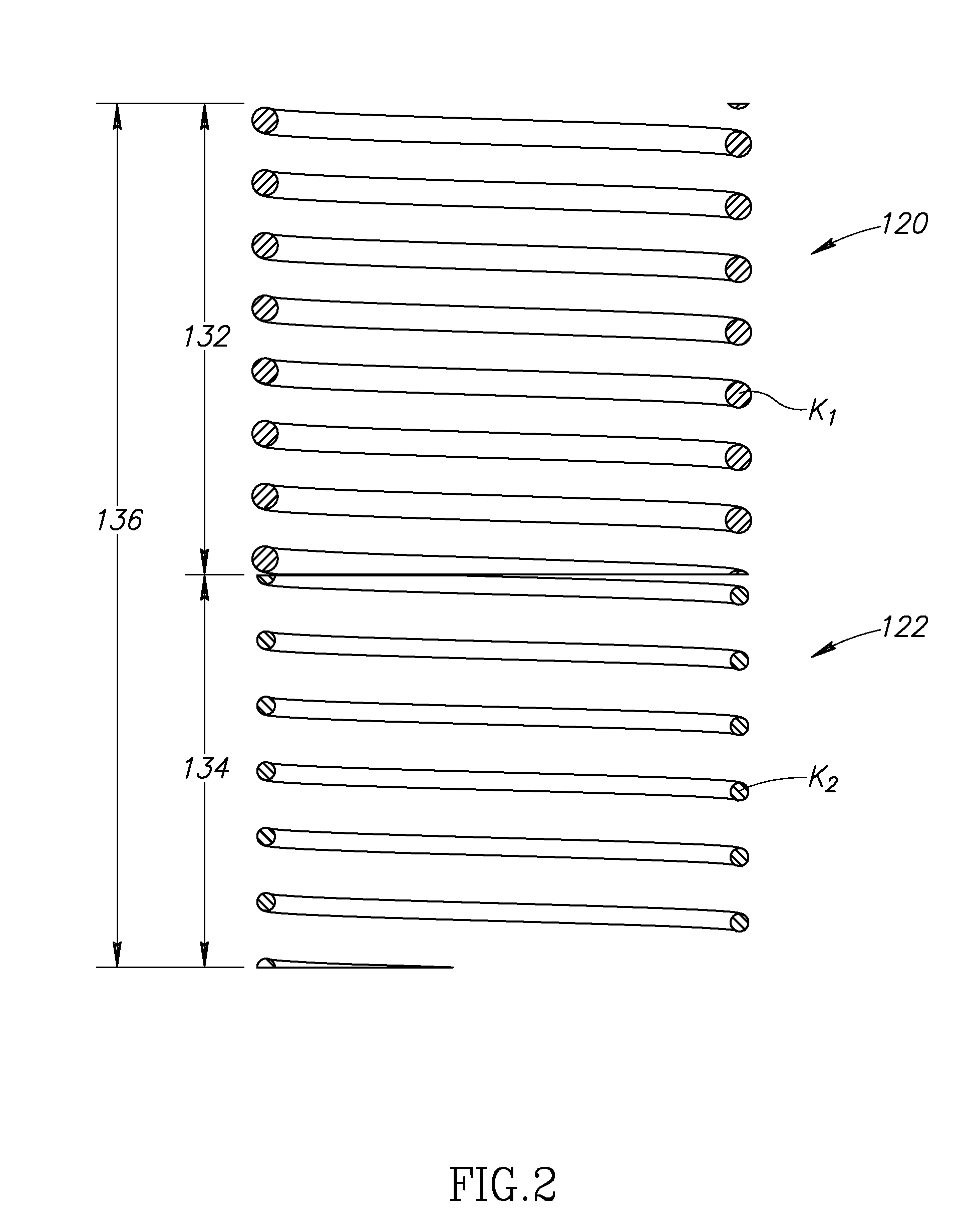
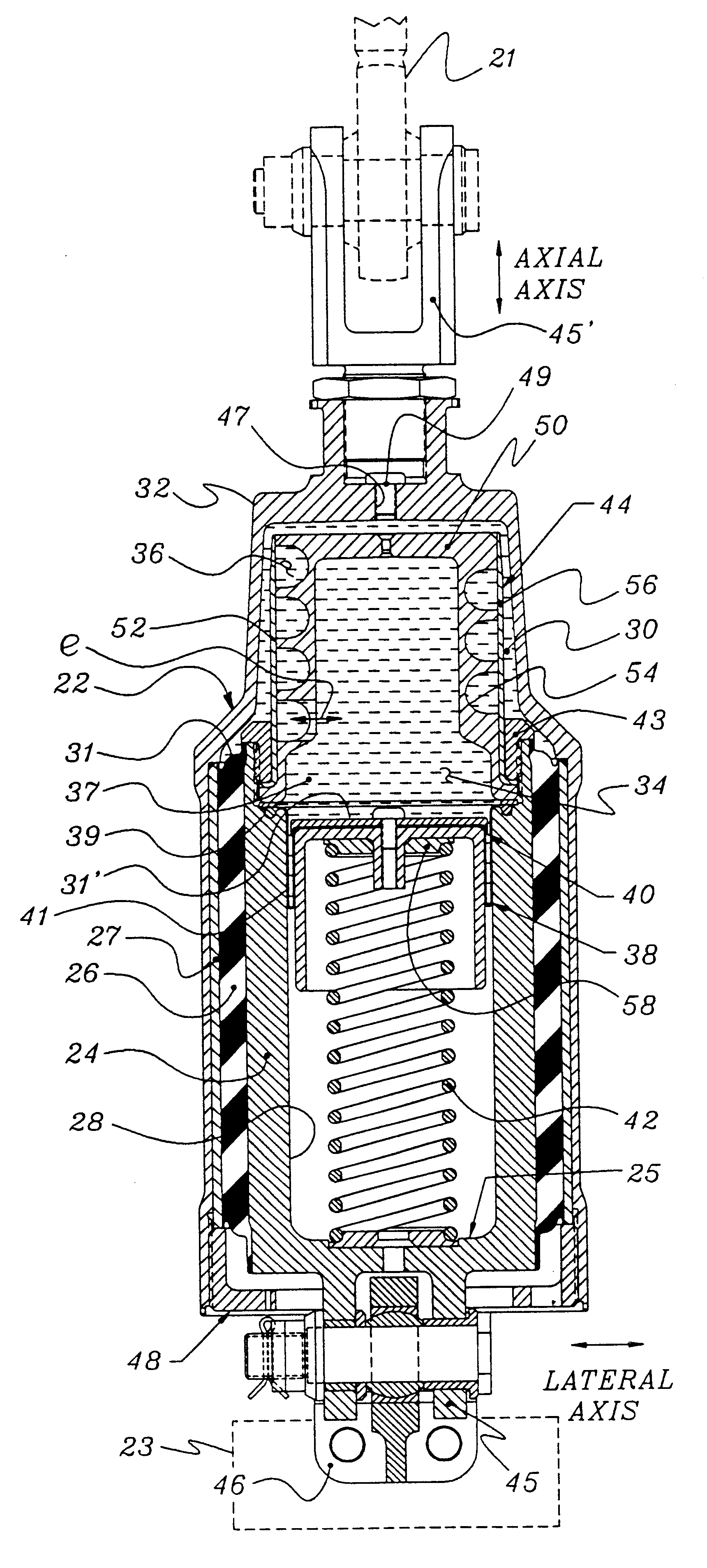
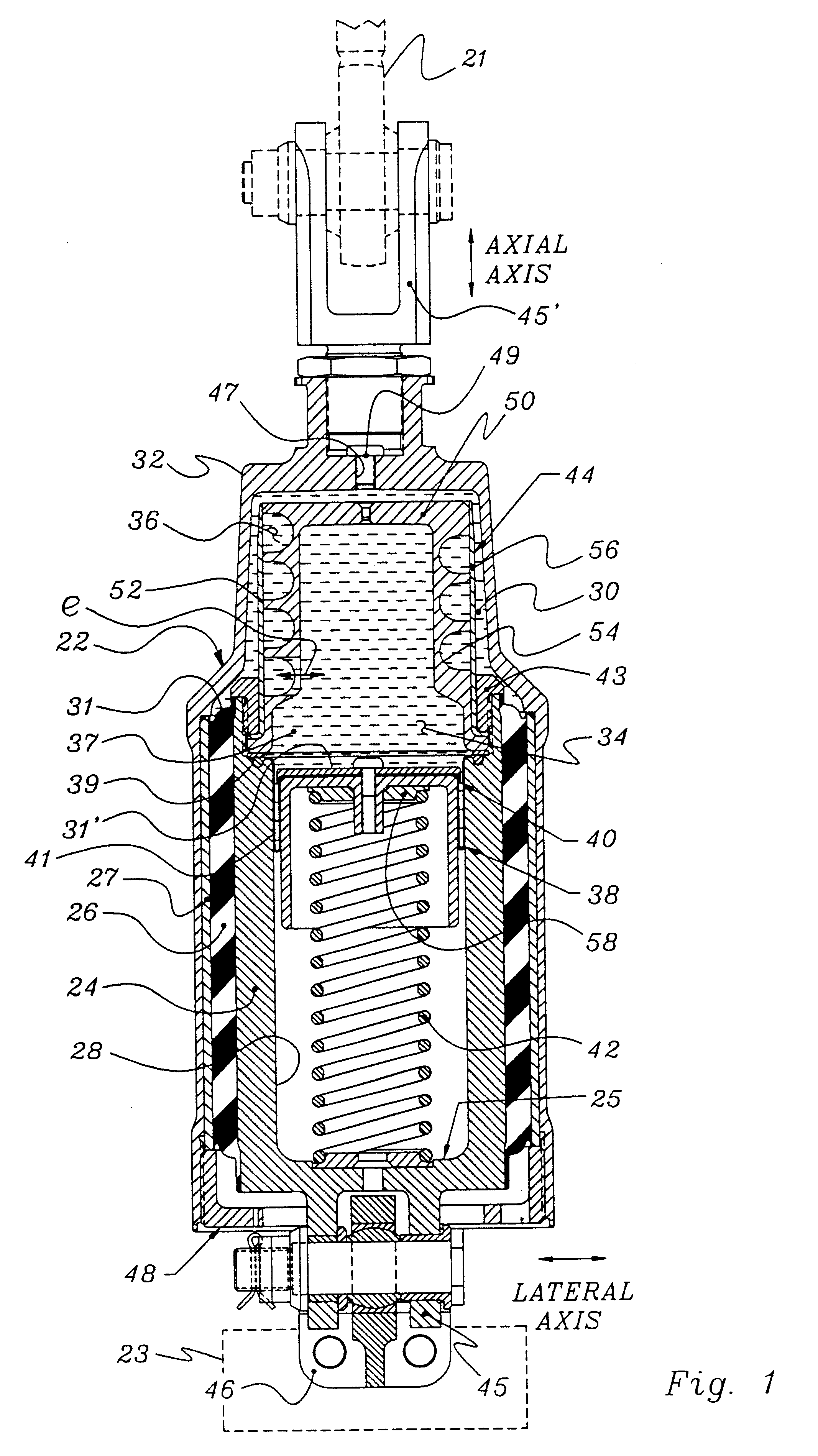
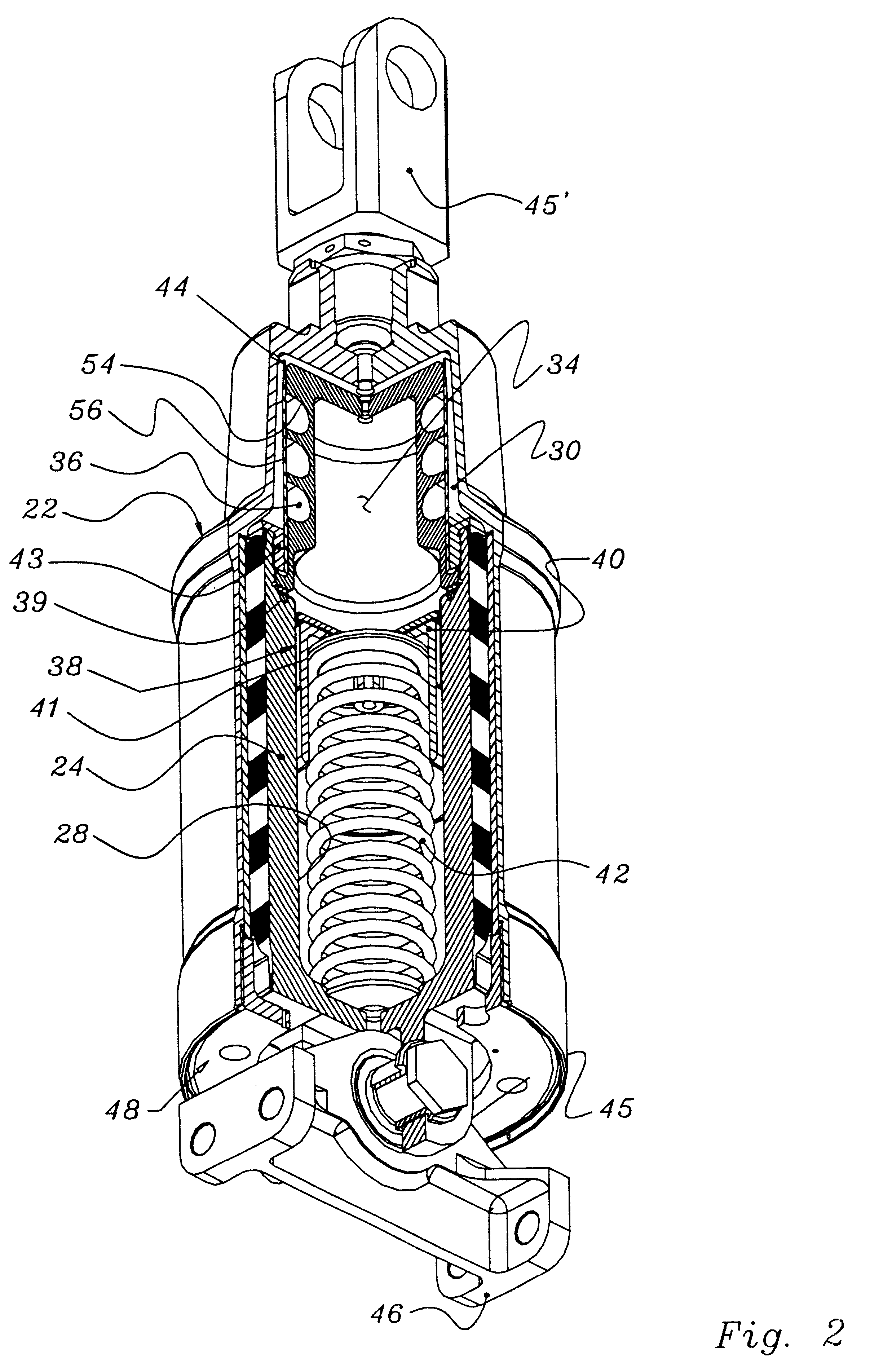
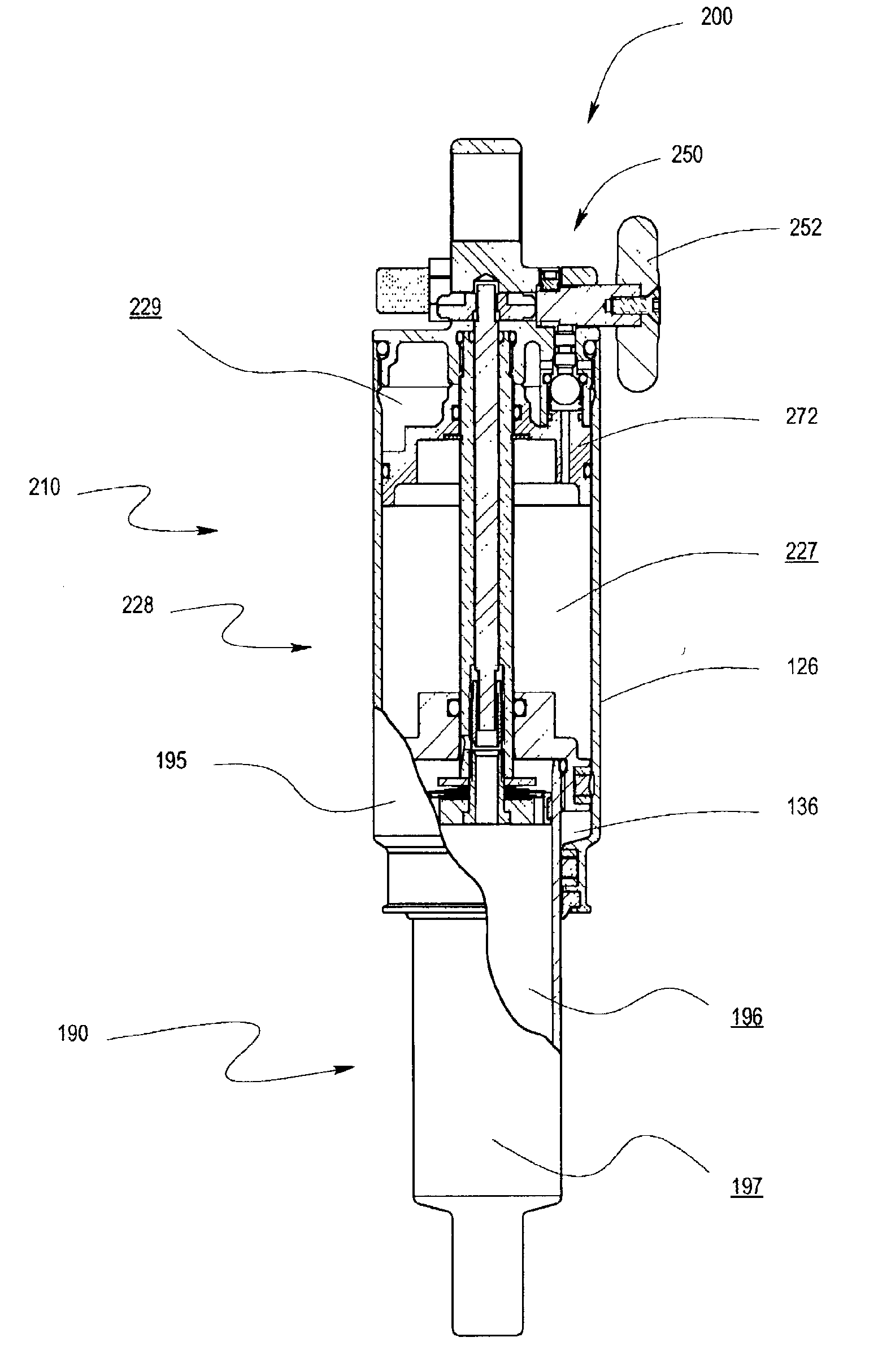
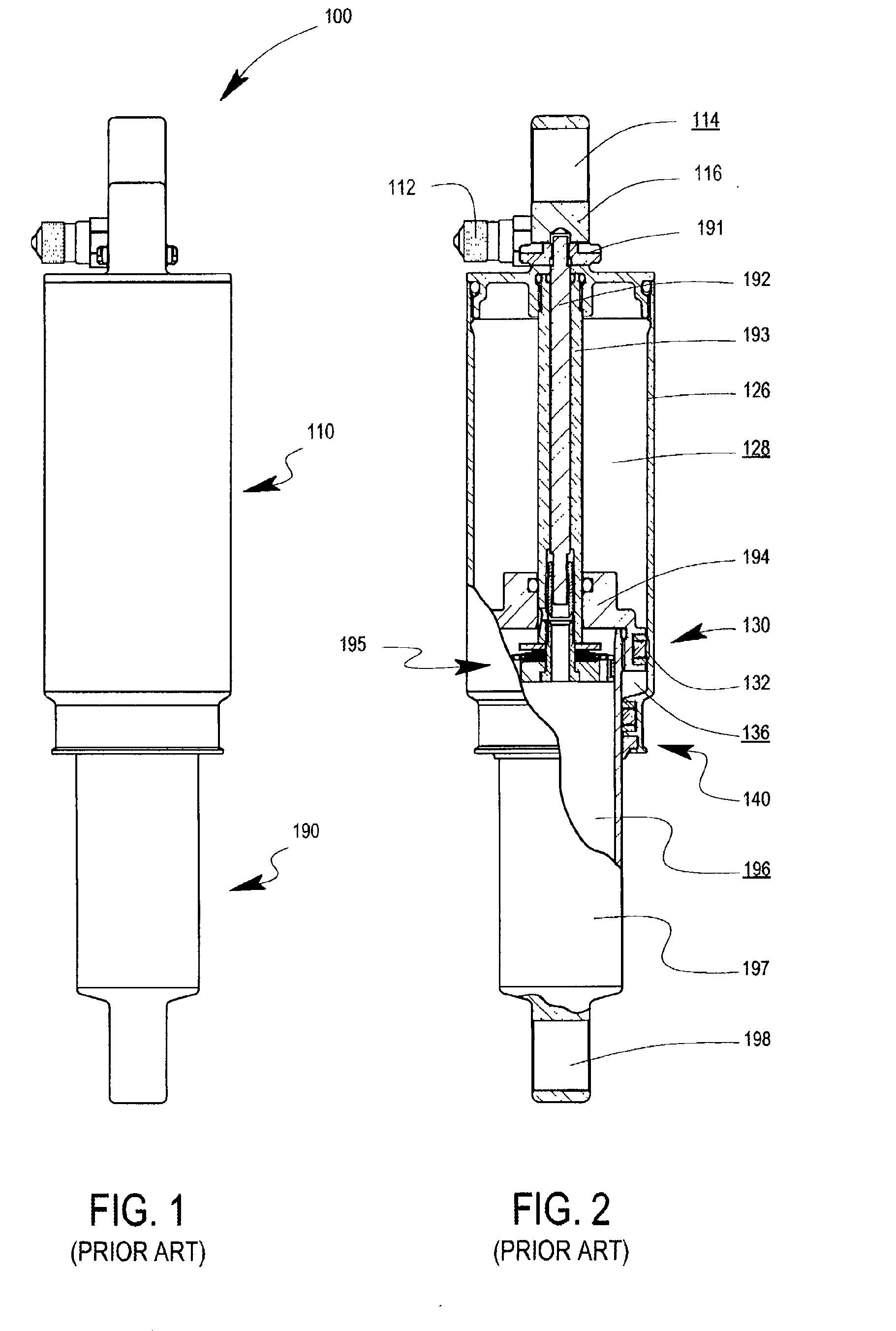
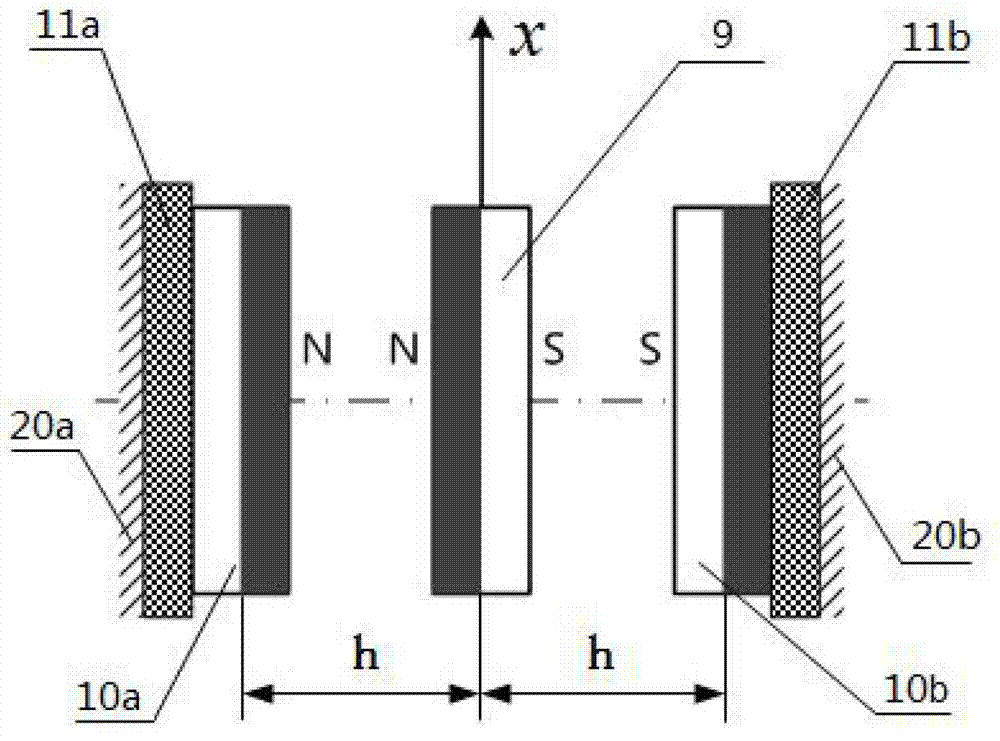
Methods and apparatus for selective spring pre-load adjustment
ActiveUS20100252972A1Springs/dampers functional characteristicsResilient suspensionsEngineeringPiston
A method and apparatus for a suspension comprising a spring having a threaded member at a first end for providing axial movement to the spring as the spring is rotated and the threaded member moves relative to a second component. In one embodiment, the system includes a damper for metering fluid through a piston and a rotatable spring member coaxially disposed around the damper and rotatable relative to the damper.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
Cooler for a suspension damper
ActiveUS20120222927A1Not to damageSpringsSprings/dampers functional characteristicsElectronic controllerEngineering
A method and apparatus are disclosed for cooling damping fluid in a vehicle suspension damper unit. A damping unit includes a piston mounted in a fluid cylinder. A bypass fluid circuit having an integrated cooling assembly disposed therein is fluidly coupled to the fluid cylinder at axial locations that, at least at one point in the piston stroke, are located on opposite sides of the piston. The cooling assembly may include a cylinder having cooling fins thermally coupled to an exterior surface of the cylinder and made of a thermally conductive material. The bypass channel may include a check valve that permits fluid flow in only one direction through the bypass channel. The check valve may be remotely operated, either manually or automatically by an electronic controller. A vehicle suspension system may implement one or more damper units throughout the vehicle, controlled separately or collectively, automatically or manually.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
Methods and apparatus for suspension adjustment
ActiveUS10036443B2SpringsSprings/dampers functional characteristicsUser interfaceAutomotive engineering
Methods and apparatus of a system for vehicles comprising a vehicle suspension, a sensor operable to measure an operational characteristic of the vehicle suspension, and a processor in communication with the sensor that is operable to suggest an operational setting of the vehicle suspension in response to an input from the sensor corresponding to the operational characteristic. A method for adjusting a suspension of a vehicle may comprise receiving suspension data with a processor, calculating a suspension setting suggestion with the processor, communicating the suspension setting suggestion to a user interface device, and adjusting the suspension based on the suspension setting suggestion.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
Methods and apparatus for selective spring pre-load adjustment
ActiveUS9140325B2Springs/dampers functional characteristicsResilient suspensionsPistonShock absorber
Owner:FOX FACTORY
Methods and apparatus for controlling a fluid damper
A method and apparatus for a fluid damper comprising a first fluid-filled chamber, a second chamber filled with a fluid having variable flow characteristics and at least partially displaceable by the first fluid, and a gas chamber, the gas chamber compressible due to the displacement of the second chamber. In one embodiment, the fluid in the second chamber is a variable rheology fluid.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
Cooler for a suspension damper
ActiveUS8763770B2Not to damageSpringsSprings/dampers functional characteristicsElectronic controllerEngineering
A method and apparatus are disclosed for cooling damping fluid in a vehicle suspension damper unit. A damping unit includes a piston mounted in a fluid cylinder. A bypass fluid circuit having an integrated cooling assembly disposed therein is fluidly coupled to the fluid cylinder at axial locations that, at least at one point in the piston stroke, are located on opposite sides of the piston. The cooling assembly may include a cylinder having cooling fins thermally coupled to an exterior surface of the cylinder and made of a thermally conductive material. The bypass channel may include a check valve that permits fluid flow in only one direction through the bypass channel. The check valve may be remotely operated, either manually or automatically by an electronic controller. A vehicle suspension system may implement one or more damper units throughout the vehicle, controlled separately or collectively, automatically or manually.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
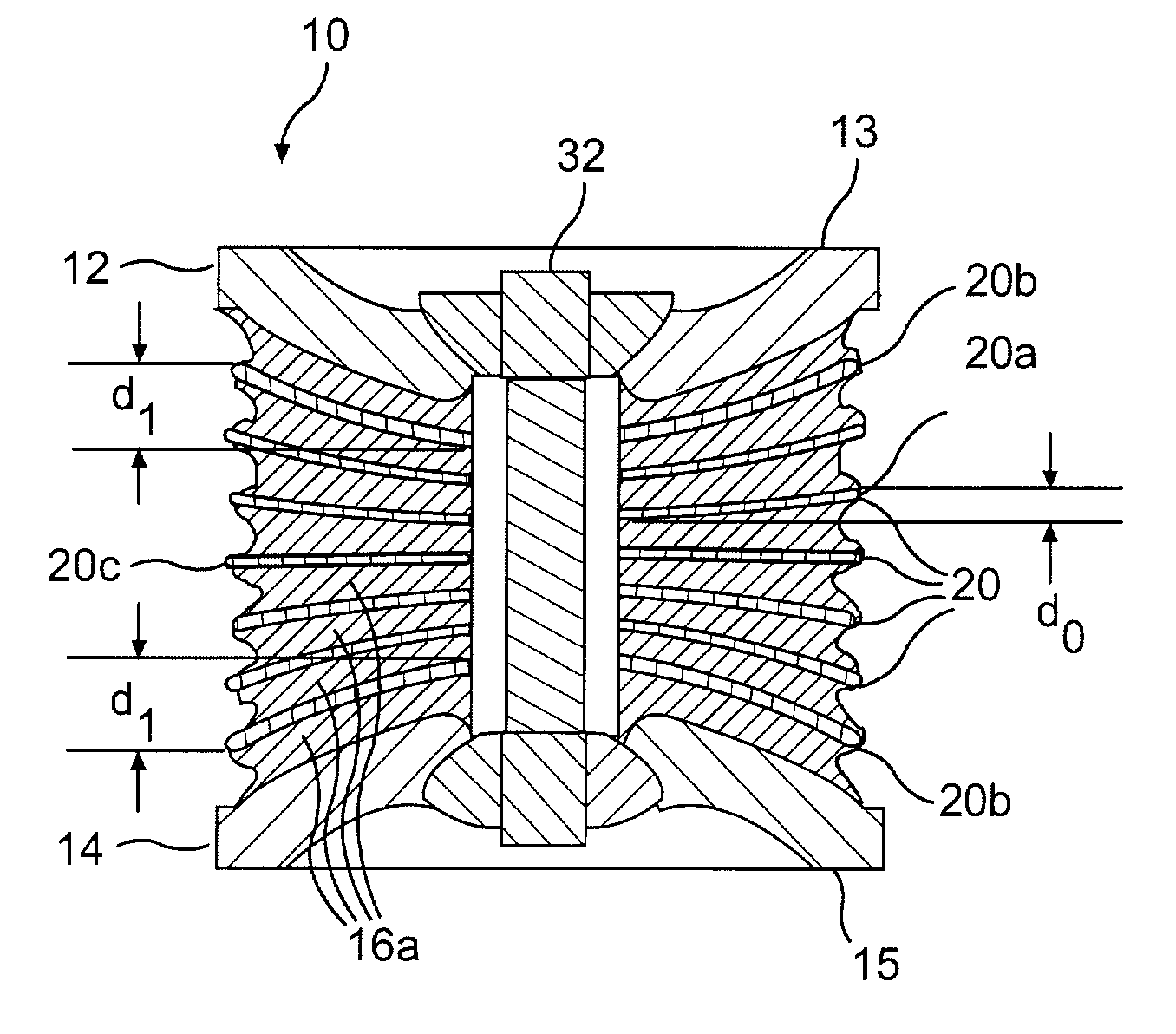
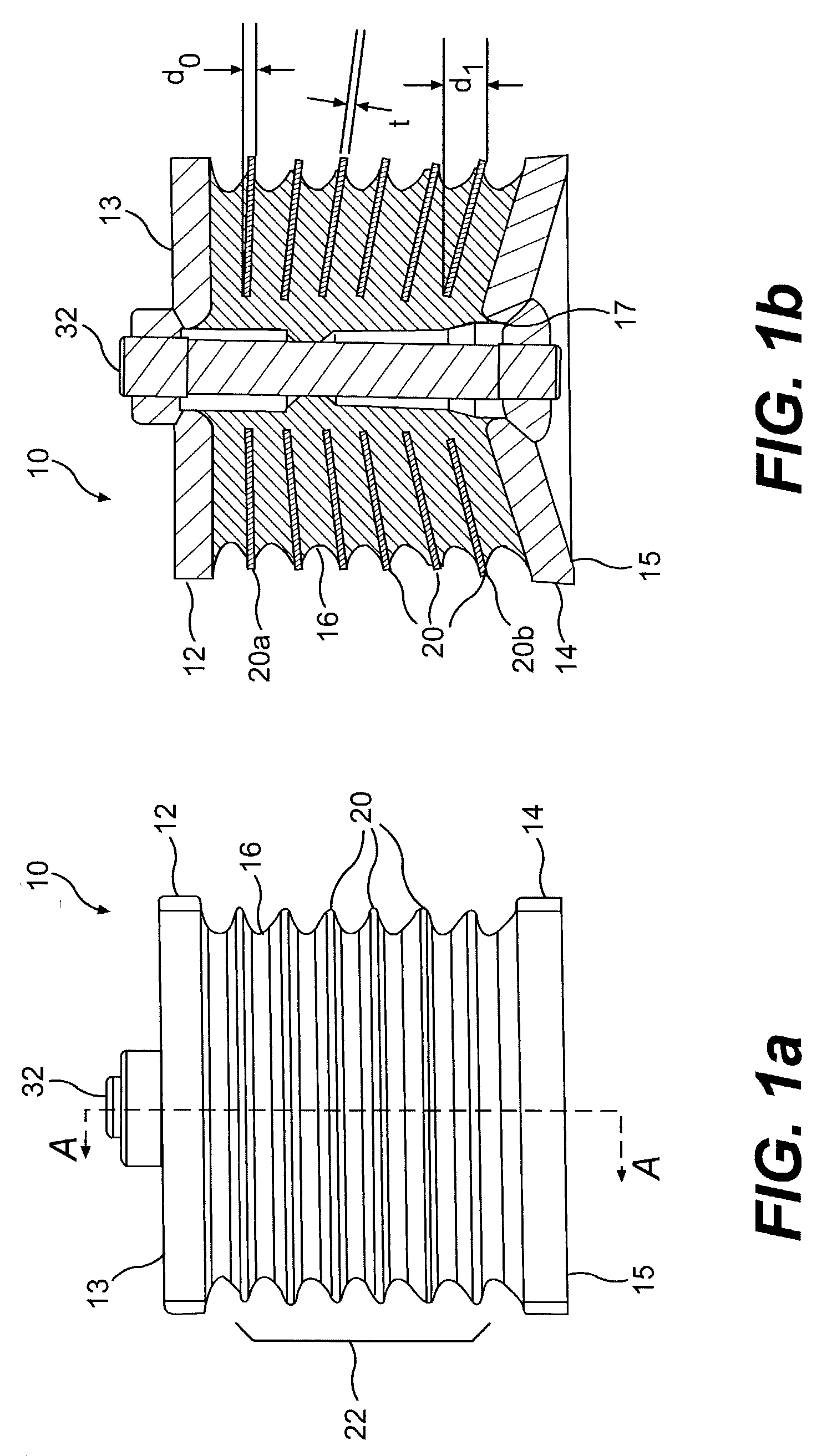
Load-bearing resilient mount
ActiveUS7201367B2Springs/dampers functional characteristicsResilient suspensionsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A resilient mount including a first mounting member and a second mounting member is provided. The mount may include a first plurality of stiffening elements located between the first and second mounting members. At least a first stiffening element may be non-parallel to a second stiffening element. The mount may also include a resilient material located between and coupled to adjacent stiffening elements of the first plurality of stiffening elements.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Hydraulically prestressed elastomer spring element and the use thereof in wind turbine bearings
ActiveUS20080308980A1Advantageous, stable and completePortable framesMachines/enginesElastomerPre stress
The invention relates to spring elements and bearings which contain these spring elements, the spring stiffness of the bearings and spring elements being individually adjustable by deformable elastomer bodies or elastomer layers by prestressing. The deformation of the elastomer layers and hence of the spring elements is achieved by an appropriately designed hydraulic device. The leak-tightness of the spring elements and bearing elements according to the invention is achieved through special hydraulically prestressed sealing elements, use of a pressure membrane and special structural features of the elastomer elements.
Owner:FM ENERGIE GMBH& CO KG
Systems and methods for axial impact resistance in electric motors
ActiveUS20190058370A1Well formedBelleville-type springsNon-rotating vibration suppressionEngineeringMechanical engineering
A system for providing torque includes a stator, a rotor, an axle, an endcap, an endbell, and a compliant member. The stator has a first end and a second end opposite the first end with a chamber therein. The rotor is at least partially positioned in the chamber and rotatable relative to the stator about a longitudinal axis. The axle has a first end, a second end opposite the first end, and supports the rotor. The endcap is located at a first end of the stator and adjacent to the first end of the axle, and the endbell is located at the second end of the stator and adjacent to the second end of the axle. The compliant member is positioned relative to the axle between a portion of the rotor and one of the endbell and the endcap.
Owner:IFIT INC
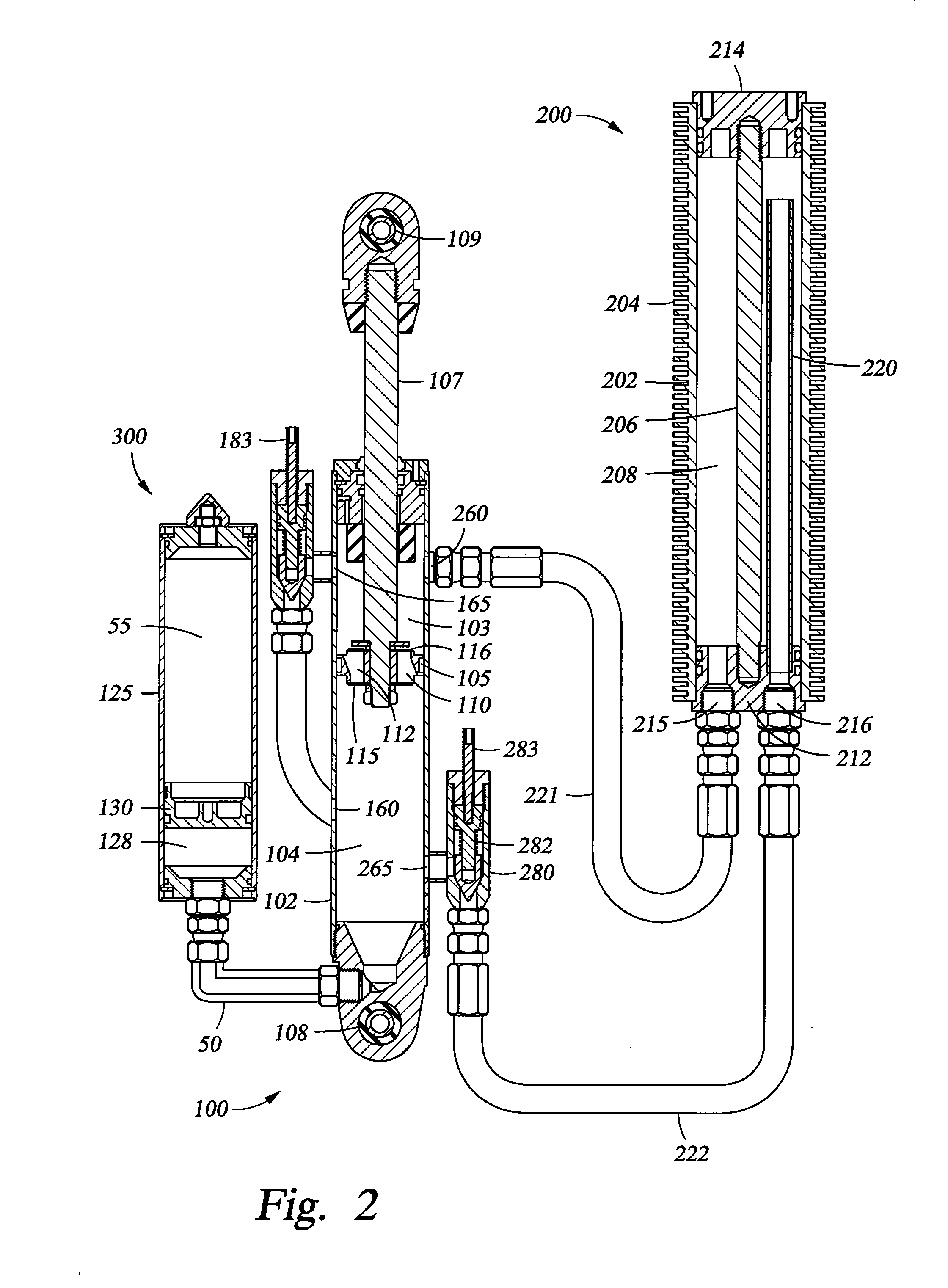
Integrated and self-contained suspension assembly having an on-the-fly adjustable air spring
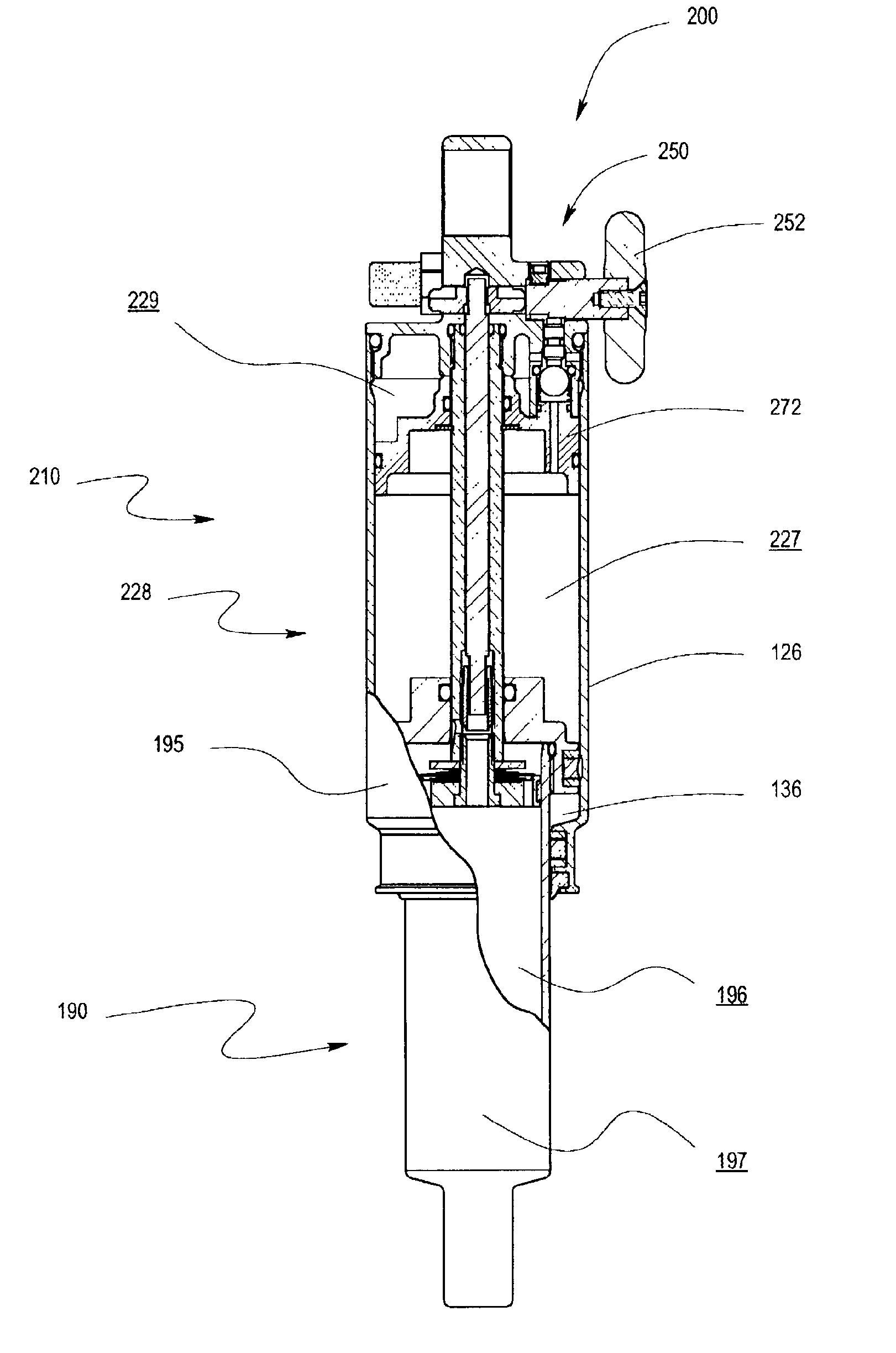
InactiveUS7641028B2The process is convenient and fastThe process is simple and fastCycle springsSprings/dampers functional characteristicsElectricityGas cylinder
An integrated and self-contained suspension assembly having a gas spring integrated with a shock absorber (damper) is described. The rigid gas cylinder of the air spring is divided into a first gas chamber and a second gas chamber. A flow port connects the first and second gas chambers, and can be manually opened or closed by valve and a simple one-quarter turn rotation of an external knob to instantly switch the gas spring between two different spring rates. The different spring rates are functions of the separate or combined volumes of the two gas chambers. The integrated suspension assembly is compactly packaged and self-contained, i.e., does not require any externalities, such as gas sources or electricity, to operate.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
Sine wave spring
InactiveUS20120073884A1Prevents undesirable recoilLess forceVehicle seatsPortable framesA wave amplitudeStable state
A spring is formed of a relatively thin sheet of spring material which is constricted and held in place at each end forming a bell curve being located between two substantially planar members. As additional compressive force is applied in the vertical direction, the curve then compresses and starts to form sine waves. The greater the force, progressively higher the wave frequency with lower amplitude would form. When the force is removed, the flexible material returns to its original shape. The force needed to shift the curve (increase the number of waveform) increases at an exponential rate, as opposed to the linear rate of most normal springs. The maintenance force of new stable state is considerable less than the threshold force. Such a relatively flat spring with an exponential spring rate and self dampening through phase change has a number of useful applications for automotive and industrial use.
Owner:GUTHRIE WALKER LEE
A fitness equipment spring counterweights banlancer
InactiveUS20160332020A1OptimizationReduce equipment investmentFriction gearingsMuscle exercising devicesBlock and tackleEngineering
A fitness equipment spring counterweights balancer, comprising hand wheel, lead screw, upper and lower frame beams, upper and lower pulley blocks, spring guiding pillar, upper and lower spring seats, at least one spring, vortex track, big wheel, steel wire rope connecting the pulley block and the vortex track, steel wire rope which connects both the big wheel and fitness equipment. The springs are arranged between upper and lower spring seats. After the spring guiding pillar passes through the springs and the upper and lower spring seats, the both ends of the spring guiding pillar are connected with the upper and lower frame beams. One end of the steel wire rope connecting the pulley block and the vortex track is mounted on one side of the lower pulley block. One end of the steel wire rope connecting the big wheel and fitness equipment is mounted on the big wheel.
Owner:CHEN JIAJIA
Spring strut for vehicles
InactiveUS6076814AEasy to combineBelleville-type springsSprings/dampers functional characteristicsMobile vehicleMotorized vehicle
The invention is directed to a spring strut for motor vehicles comprising a hydropneumatic vibration damper and a supporting spring. The vibration damper has a piston rod connected with a piston and is axially guided in a piston rod guide at the end of a container. The piston rod is outwardly sealed by a piston rod seal. The piston rod guide comprises a damping valve acted upon by external forces, such as the force of the supporting spring arranged between a structural component part connected with the vehicle and a spring carrier surrounding the container of the spring strut. The spring carrier acts on the damping valve with a contact surface. The supporting spring and / or the spring carrier cooperates with at least one auxiliary device exerting a force. The auxiliary device is supported at the container by a structural component part that is fixed with respect to the container or at a vehicle part which is connected with the container.
Owner:MANNESMANN SACHS AG
Negative stiffness adjustable zero stiffness vibration isolation device and application method thereof
PendingCN110388408AAvoid failureFlexible adjustment of positive stiffnessNon-rotating vibration suppressionSprings/dampers functional characteristicsDynamic stiffnessEngineering
The invention discloses a negative stiffness adjustable zero stiffness vibration isolation device and an application method thereof, wherein the negative stiffness adjustable zero stiffness vibrationisolation device comprises a bearing table, a positive stiffness mechanism is arranged at the lower side of the bearing table, a plurality of adjustable negative stiffness mechanisms which are centrosymmetrically arranged are connected around the bearing table, the positive stiffness mechanism comprises a vertical elastic element for supporting the bearing table, and the adjustable negative stiffness mechanism comprises a horizontal elastic element for applying horizontal acting force to the bearing table; and the application method comprises the steps of installing a bearing object on the bearing table and then adjusting each height adjusting mechanism to enable the horizontal elastic element to be horizontal. The negative stiffness adjustable zero stiffness vibration isolation device canflexibly adjust the negative stiffness according to the bearing at any time, so that the negative stiffness can be adjusted according to the actual situation after bearing, the negative stiffness adjustable zero stiffness vibration isolation device can be adjusted to ensure that the negative stiffness adjustable zero stiffness vibration isolation device is in an ideal state that the dynamic stiffness is close to zero in a static load state after field installation, the failure of a vibration isolation system can be avoided, and the negative stiffness adjustable zero stiffness vibration isolation device has the advantages of simple structure, easiness in processing, convenience in loading and unloading, reasonable design and easiness in adjustment.
Owner:STATE GRID HUNAN ELECTRIC POWER +2
Preloaded dual-spring assembly
InactiveUS20110291338A1High rebound rateHigh occurrenceSprings/dampers functional characteristicsResilient suspensionsAbsorbed energyTorsion spring
The present invention relates to dual-spring assembly that may be employed in cooperation with a damper unit to form a shock absorber. The spring rate of at least one of the springs is adjustable with a preload mechanism, which in turn is movable relative to the damper unit. Further, the dual-spring assembly includes two compression springs arranged in series and each having selected, but different spring rates. The first spring primarily absorbs the energy of applied loads that are below a first amplitude or threshold of applied load. Once the applied loads exceed the first amplitude of applied load, the dual-spring assembly operates with an effective spring rate to absorb the energy of applied loads that exceed the first amplitude of applied load. After a second spring of the dual-spring assembly achieves a desired amount of deflection, the first spring continues to absorb energy from the applied loads.
Owner:RENTON COIL SPRING
Support assembly having variable stiffness member
A support assembly for a load-bearing unit, a gas turbine engine including the support assembly, and a method of operation of the support assembly are provided. The support assembly includes a support element, a damper, and a variable stiffness member. The support element supports the load-bearing unit. The damper supports the support element and is configured to provide dampening of the load-bearing unit. The variable stiffness member is positioned between the damper and the load-bearing unit. The variable stiffness member is configured to provide a serial dampening of the load-bearing unit with the damper. The variable stiffness member includes a shape memory alloy.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Damping force variable shock absorber
InactiveUS20160369862A1SpringsSprings/dampers functional characteristicsInternal pressureEngineering
There is provided a compact damping force variable shock absorber capable of implementing different adjustments for a compression-side stroke and an extension-side stroke as initial settings. A damping force variable device in one embodiment includes: a main valve that opens and closes to control flow of oil caused by sliding of a piston in a cylinder, thereby generating damping force; a pilot chamber into which a portion of the flow of the oil is introduced so that internal pressure is applied to the main valve in a valve-closing direction; a pilot valve that opens and closes to adjust the internal pressure of the pilot chamber; and a communication passage that communicates the pilot chamber with a rod-side oil chamber or a piston-side fluid chamber.
Owner:SHOWA CORP
SMA spring-STF viscous damper
InactiveCN109404477AGood shock absorptionGood reset functionSprings/dampers functional characteristicsSprings/dampers design characteristicsControl theoryPiston rod
The invention provides an SMA spring-STF viscous damper which comprises a first connecting component, a piston rod, a left end cover, a first damping cavity, a damping cylinder, a piston, a second damping cavity, two SMA springs, a right end cover and a second connecting component, wherein the left end cover is arranged at one end of the damping cylinder; the right end cover is arranged at the other end of the damping cylinder; the interior of the damping cylinder is divided by the piston into the first damping cavity and the second damping cavity; the SMA springs which sleeve the piston rod are correspondingly arranged in the first damping cavity and the second damping cavity; the first damping cavity and the second damping cavity are filled with an STF shearing thickener; when the pistonmoves towards one side, the SMA spring on one side is compressed, and the SMA spring on the other side is restored towards the trend of the original length; and due to the different expansion and contraction degrees of the SMA springs on both sides, the resistance difference is produced, and the damping force is provided for the viscous damper. The SMA spring-STF viscous damper provided by the invention has the effects of improving the energy consumption under low-frequency loads and causing limiting resistance to the structural excessive displacement; furthermore, the self-resetting effect can be achieved after unloading; and the SMA spring-STF viscous damper has the advantages that the structure is simple and the space is saved.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
Fluid and elastomer apparatus
Owner:LORD CORP
Shock absorber with frequency-dependent damping
InactiveUS7395907B2Increase volumeMinimum volumeSpringsSprings/dampers functional characteristicsPistonEngineering
Shock absorber containing a flow channel (16), provided with a valve assembly, made in the piston section. This valve assembly is designed to be actuated hydraulically. To this end there is an auxiliary chamber (22, 42) which on one side is eliminated by a movable valve body (18). This valve body is provided with an inlet for oil from the flow channel to the auxiliary chamber. There is an outlet (21, 41) (that can be closed off). The surface area of the valve body acting on the valve seat (19) is less than the surface area of the valve body in the auxiliary chamber, so that fluid flowing through the inlet of the valve body results in an increase in the volume of the auxiliary chamber and thus in closing movement of the valve body. Because filing of the auxiliary chamber takes some time, a frequenncy-dependend closing characteristic of the flow channel is obtained.
Owner:KONI BV
Negative stiffness device and method
ActiveUS20130118098A1Negative stiffnessReduce demandSprings/dampers functional characteristicsBuilding repairsSeismic protectionSpring force
A negative stiffness device and method for seismic protection of a structure is described. In one embodiment, the device has an anchor frame and a movement frame laterally translatable relative to the anchor frame. The anchor frame and movement frame have respective extension portions. A linkage is pivotably connected to the extension portion of the anchor frame. A compressed spring has a first end is attached to the extension portion of the movement frame and a second end attached to the linkage. The compressed spring has a spring force. In a rest state, the compressed spring does not apply a lateral force to the movement frame. In an engaged state, the compressed spring is configured to apply a lateral force to displace the movement frame in a lateral direction of a seismic load. The spring force is amplified by the linkage when the movement frame is laterally displaced to an amplification point.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +2
Integrated and self-contained suspension assembly having an on-the-fly adjustable air spring
InactiveUS20080179795A1The process is convenient and fastThe process is simple and fastCycle springsSprings/dampers functional characteristicsElectricityAir spring
An integrated and self-contained suspension assembly having a gas spring integrated with a shock absorber (damper) is described. The rigid gas cylinder of the air spring is divided into a first gas chamber and a second gas chamber. A flow port connects the first and second gas chambers, and can be manually opened or closed by valve and a simple one-quarter turn rotation of an external knob to instantly switch the gas spring between two different spring rates. The different spring rates are functions of the separate or combined volumes of the two gas chambers. The integrated suspension assembly is compactly packaged and self-contained, i.e., does not require any externalities, such as gas sources or electricity, to operate.
Owner:FOX FACTORY
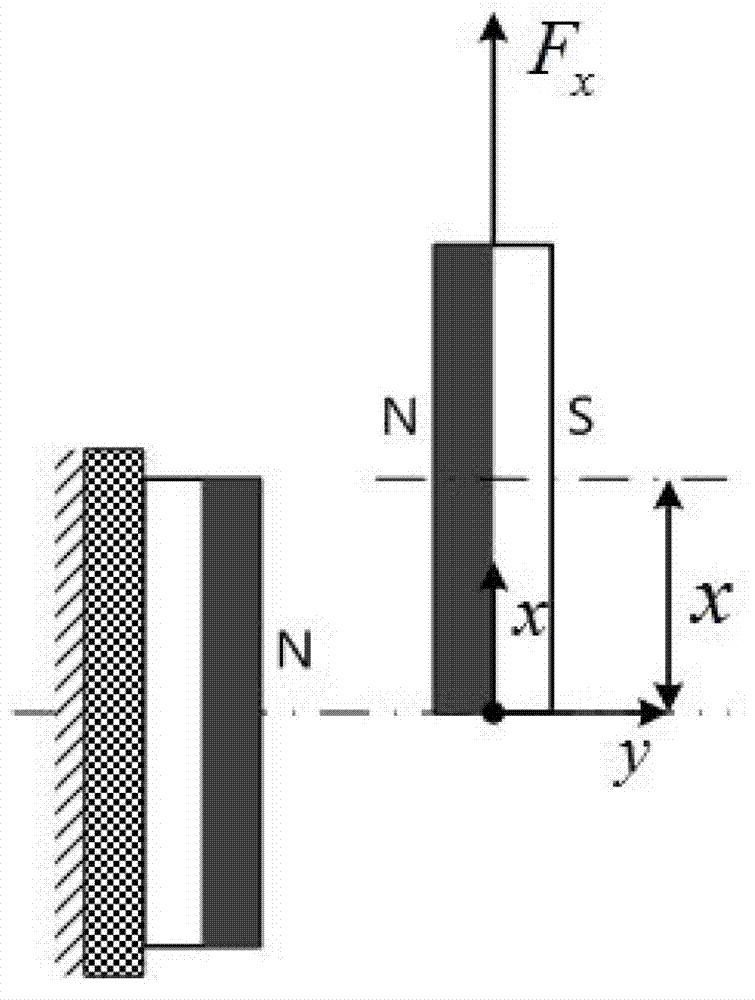
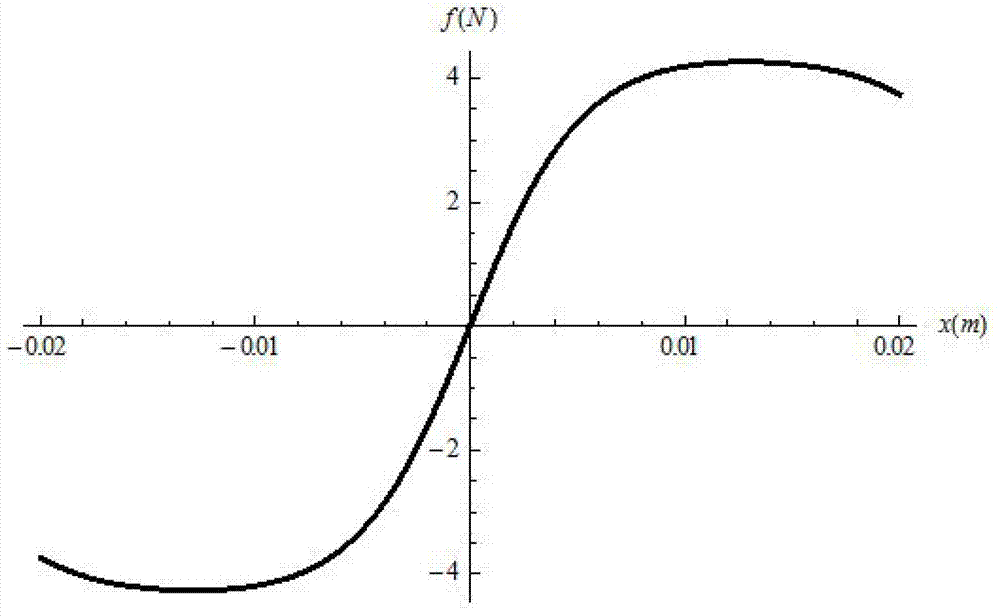
Magnetic negative stiffness mechanism
ActiveCN102808883AOvercome the impossibleOvercome the shortcoming that it is difficult to achieve ultra-low frequency vibration reductionSprings/dampers functional characteristicsMagnetic springsDynamic stiffnessEngineering
The invention provides a magnetic negative stiffness mechanism with a compact structure, and belongs to the field of ultra-precise vibration damping. The magnetic negative stiffness mechanism includes a frame part, a negative stiffness adjusting part, a flexible guiding part and a moving part. The negative stiffness mechanism utilizes the reverse repelling action of the magnet to form the negative stiffness characteristic, and the size of the negative stiffness can be adjusted through the negative stiffness adjusting part. As the ultra-low frequency vibration damper formed by combining the magnetic negative stiffness mechanism and the positive stiffness spring has extremely low dynamic stiffness, the inherent frequency of the ultra-low frequency vibration damper is greatly reduced, as a result, the vibration damper not only has excellent vibration isolation effect towards the high-frequency vibration interference, but also can effectively isolate the ultra-low frequency vibration, and the magnetic negative stiffness mechanism is applicable to the ultra-precise machining and measuring equipment sensitive to the vibration.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
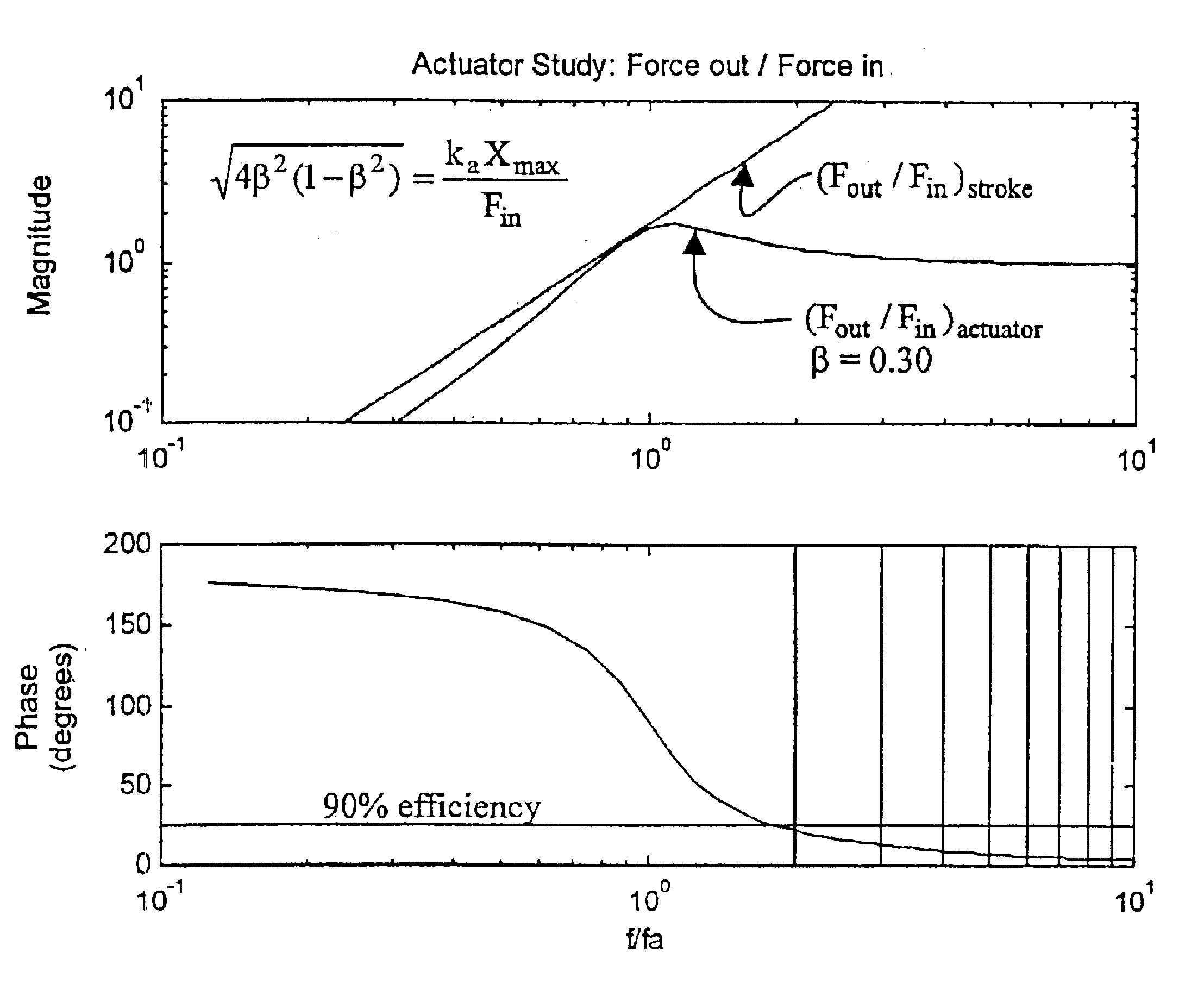
Active floor vibration control system
An active vibration control system for controlling excessive or unwanted vibrations in floors or other structures. The system has three main components: (1) velocity sensor w / signal conditioner; (2) feedback controller; and (3) proof-mass actuator. This system works by creating a feedback loop that generates a control force proportional to the velocity, thus adding damping to the controlled modes of floor vibration. In other words, the feedback loop makes the moving mass of the actuator move to counteract the motion of the floor. The system is optimized such that the motor can be driven with a sinusoidal force where the peak force is at or near the full motor capacity at any frequency without exceeding the stroke while maintaining a simple and cost effective feedback controller. Additionally, a relationship between the fundamental natural frequency of the floor system and actuator is established to provide efficient and stable control.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
High stiffness vibration damping apparatus, methods and systems
ActiveUS9194452B2Springs/dampers functional characteristicsHigh internal friction springsHigh stiffnessEngineering
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
Multi-axis spring damping system for a payload in a spacecraft
InactiveUS20090278292A1Simple structural arrangementEasy to implementPortable framesSpringsMulti axisControl theory
A multi-axis spring damping element includes two spring damping cushion members received between caps on a bolt shaft, and an axial adjustment mechanism at a free end of the bolt shaft. The other end of the bolt shaft is connected to a support structure, and a load to be supported in a vibration-damped manner is carried by intermediate caps between the two spring damping cushion members. A plurality of such spring damping elements forms a spring damping system, for example for supporting a payload-carrying pallet on a load platform of a spacecraft.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
Quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator applicable to isolation of micro-amplitude and low-frequency vibration and realization method of quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator
InactiveCN105864339AReduce the vibration isolation start frequencyImprove performanceSpringsSprings/dampers functional characteristicsLow frequency vibrationFixed frame
The invention relates to a quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator applicable to isolation of micro-amplitude and low-frequency vibration and a realization method of the quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator and relates to the field of an isolation vibration device. The quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator comprises a base, wherein an elastic hoisting mechanism is arranged in the middle of the base; an object carrying platform is arranged at the upper end of the elastic hoisting mechanism; and the two sides of the object carrying platform are connected with negative rigidity mechanisms arranged at the two side parts of the base respectively. The realization method comprises the steps: an object subjected to vibration isolation and having a certain weight is put on the object carrying platform to compress a spring; the object carrying platform moves downwards and drives a connecting rod; the connecting rod pushes a shaft rod to slide horizontally in a transverse groove of a fixed frame; a shearing and forking mechanism extends downwards and a resetting spring is compressed; the connecting rod moves on a horizontal position so that the vibration isolator is located at a balanced position; when external vibration and excitation act on the base, the vibration is transmitted onto the vibration isolator; and then the vibration isolator starts to work to isolate the micro-amplitude and low-frequency vibration. The vibration isolator provided by the invention not only can guarantee certain bearing capability and extremely low rigidity, but also has a stroke amplification effect; and meanwhile, the realization method is simple and convenient.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
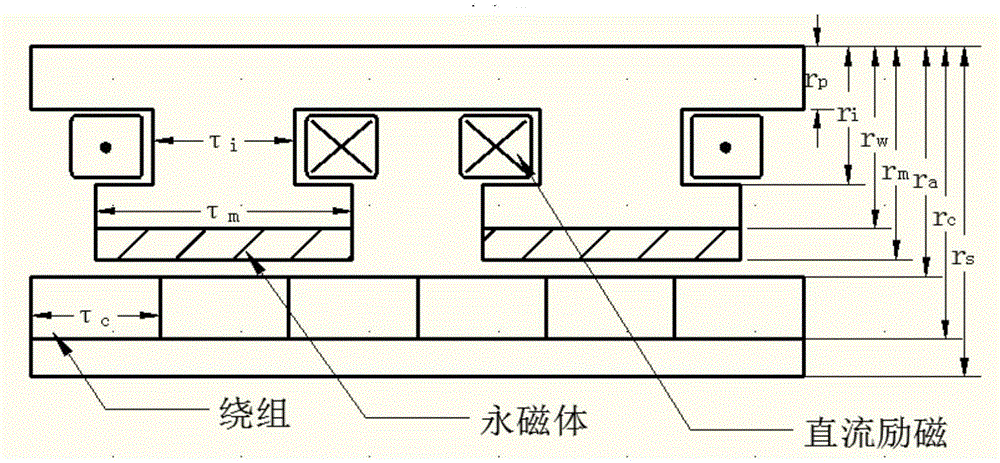
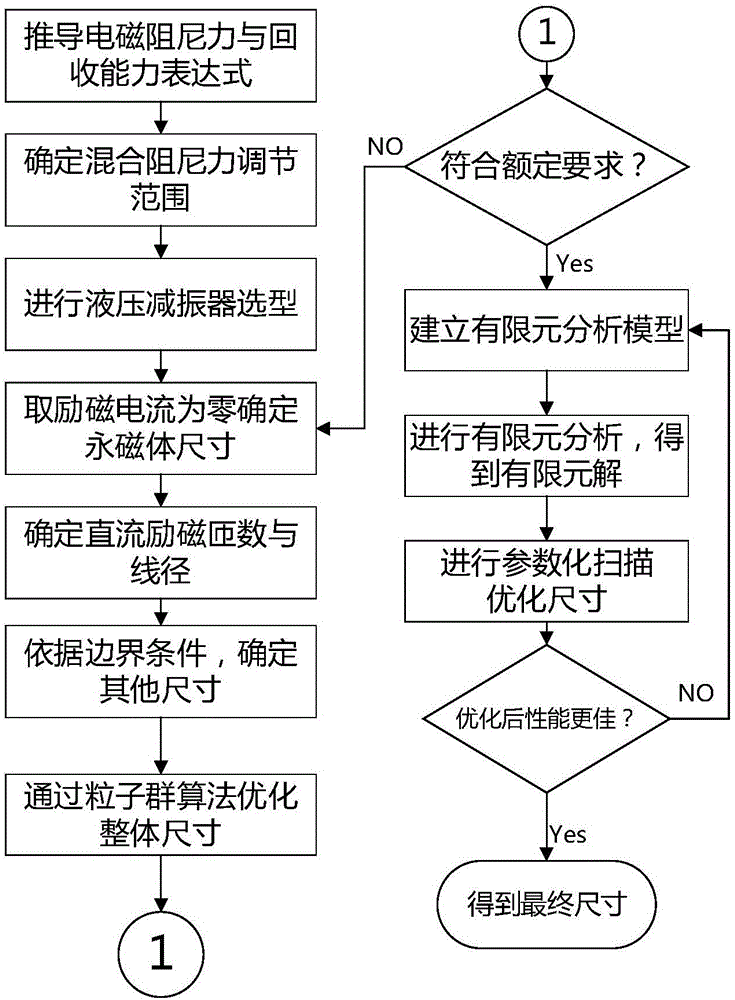
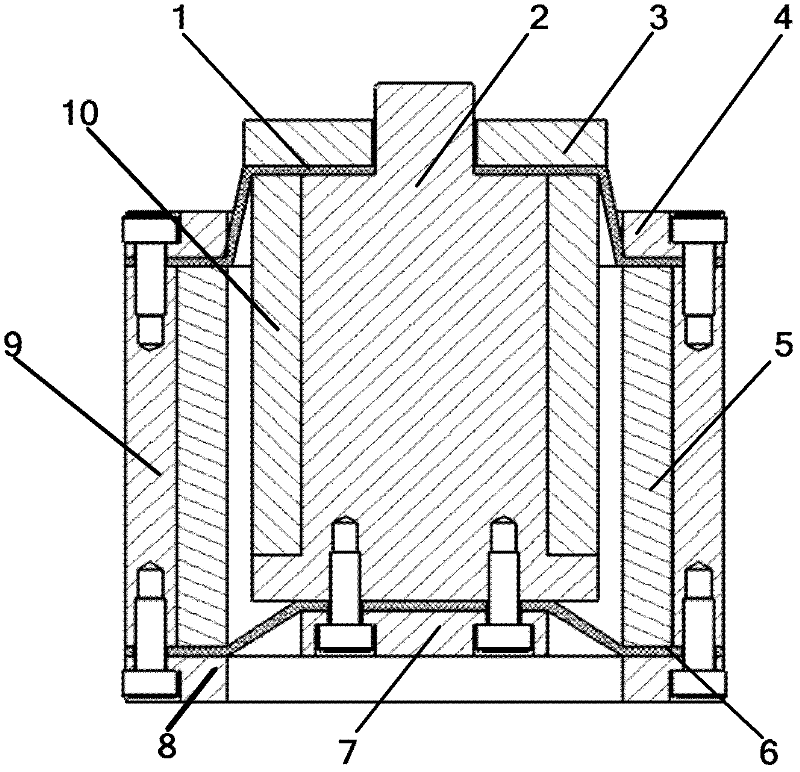
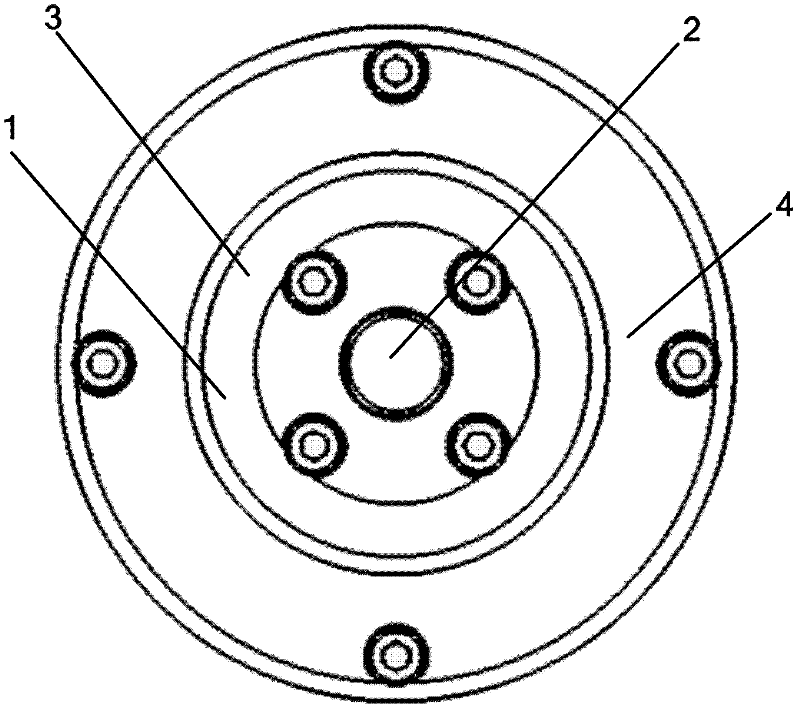
Semi-active energy regenerative suspension shock absorber based on mixed excitation and size determining method of shock absorber
ActiveCN106224425AAdjustable damping forceGood vibration isolationGeometric CADAuxillary drivesViscous dampingSemi active
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Permanent magnet low frequency single-degree-of-freedom vibration isolation mechanism based on negative stiffness theory
ActiveCN102506110AGood vibration isolationSimple structureSprings/dampers functional characteristicsMagnetic springsThree degrees of freedomSingle degree of freedom
The invention discloses an annular permanent magnet low frequency vibration isolation mechanism based on a negative stiffness theory. The mechanism comprises an upper rubber sheet, an inner annular permanent magnet fixing mandrel, an upper rubber sheet upper pressing ring, an upper rubber sheet outer pressing ring, an outer annular permanent magnet, a lower rubber sheet, a lower rubber sheet inner pressing sheet, a lower rubber sheet outer pressing ring, an outer annular permanent magnet fixing sleeve and an inner annular permanent magnet, wherein the inner annular permanent magnet is magnetized axially; the outer annular permanent magnet is radially magnetized; a positive stiffness system consists of the inner annular permanent magnet and the outer annular permanent magnet; a negative stiffness system consists of the upper rubber sheet and the lower rubber sheet; and the positive stiffness system and the negative stiffness system are used in parallel to form the low frequency vibration isolation mechanism. Three or four single-degree-of-freedom vibration isolation mechanisms are used in parallel to realize three-degree-of-freedom low frequency vibration isolation. When the vibration isolation mechanism has the largest magnetic force, the stiffness of the vibration isolation mechanism approximates to zero. Without an outside air source, the vibration isolation mechanism has a prospect of being used in vacuum, has the characteristics of simple structure and low cost, is easy to process, and can be applied to the fields of optics, acoustics, biologics, semiconductor manufacturing, precise measurement and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Two-degree-of-freedom ultralow-frequency vibration isolator
ActiveCN106321707ARealization of ultra-low frequency vibration isolation with degrees of freedomVibration isolation achievedNon-rotating vibration suppressionSprings/dampers functional characteristicsMarine engineeringAir spring
The invention discloses a two-degree-of-freedom ultralow-frequency vibration isolator. The two-degree-of-freedom ultralow-frequency vibration isolator comprises a basic platform (10) and a load-bearing platform (30), and the basic platform (10) and the load-bearing platform (30) are connected through supporting rods. The two-degree-of-freedom ultralow-frequency vibration isolator is characterized in that the vibration isolator further comprises a positive-stiffness air spring (20) and a magnetic negative-stiffness mechanism (28) with adjustable negative stiffness, and the positive-stiffness air spring (20) and the magnetic negative-stiffness mechanism (28) form a parallel mechanism in the direction of the center axes of the basic platform and the load-bearing platform, so that the inherent frequency in the direction of the center axes of the basic platform and the load-bearing platform is decreased; and a stiffness-adjustable positive-stiffness leaf spring and a negative-stiffness inverted pendulum are arranged in the direction perpendicular to the center axes of the basic platform and the load-bearing platform and form a negative-stiffness parallel mechanism, so that the inherent frequency in the direction perpendicular to the center axes of the basic platform and the load-bearing platform is decreased. According to the vibration isolator, positive-stiffness and negative-stiffness parallel type passive structures are adopted both in the direction of the center axes of the basic platform and the load-bearing platform and in the direction perpendicular to the center axes of the basic platform and the load-bearing platform, and thus vibration of two degrees of freedom is achieved at the same time.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com