Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
740 results about "Variable stiffness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
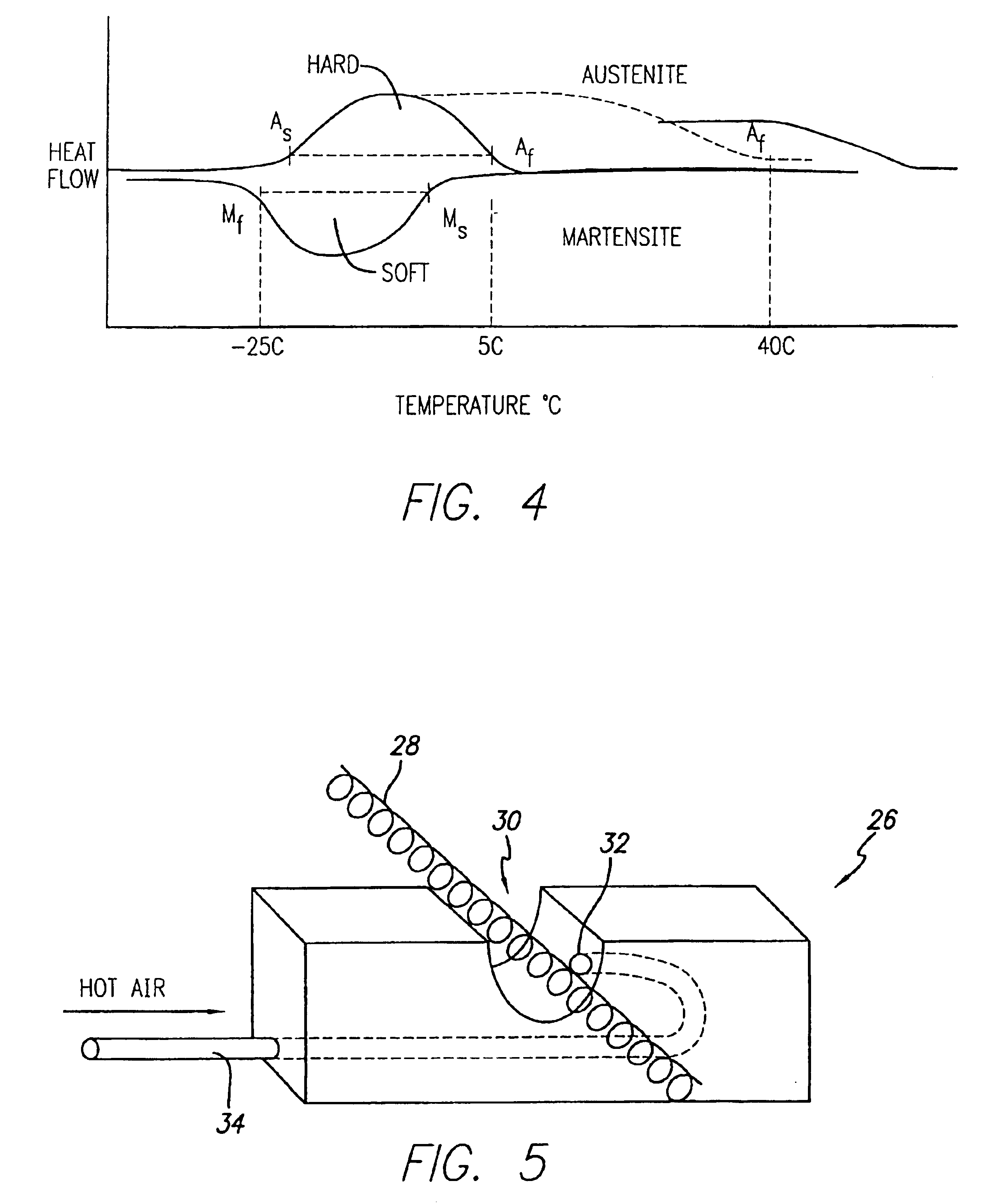
One of the more subtle ones is the variable stiffness of your joints. In technical terms, stiffness refers to the ability to resist a load. Delicately manipulating an artist’s paint brush, for example, doesn’t require much load resistance, but does require fine control.
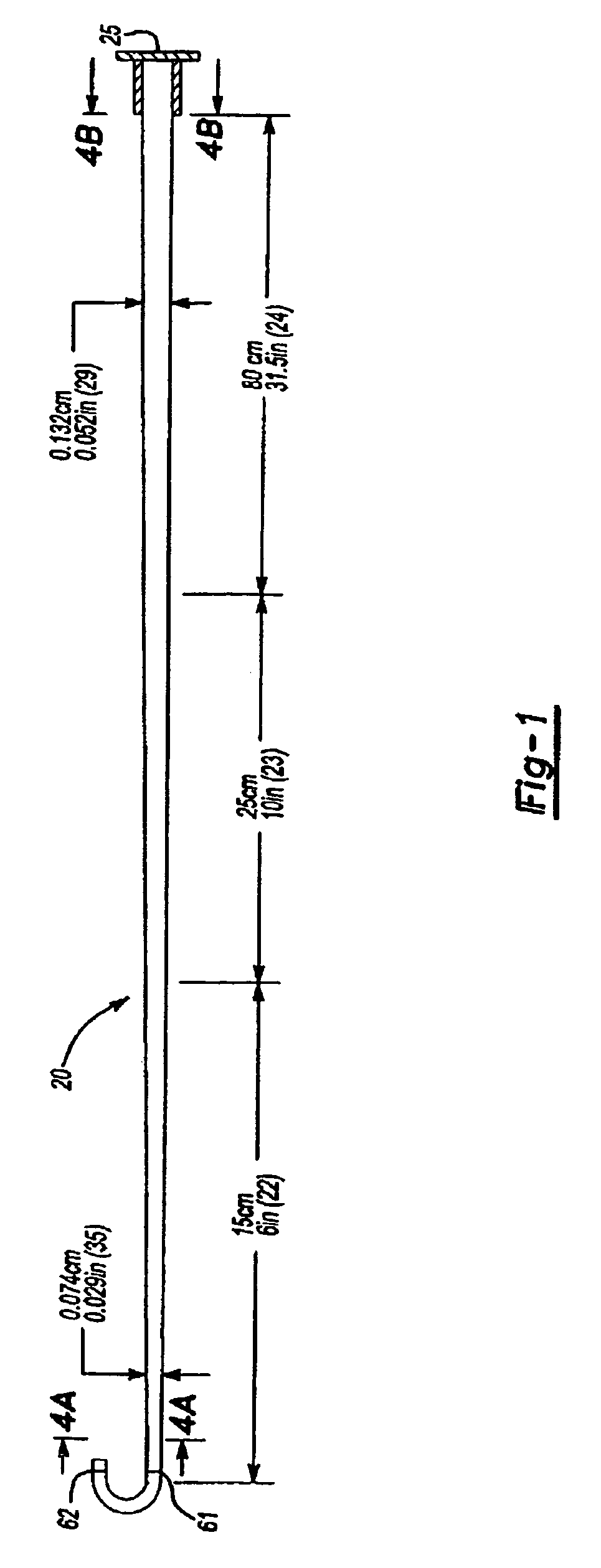
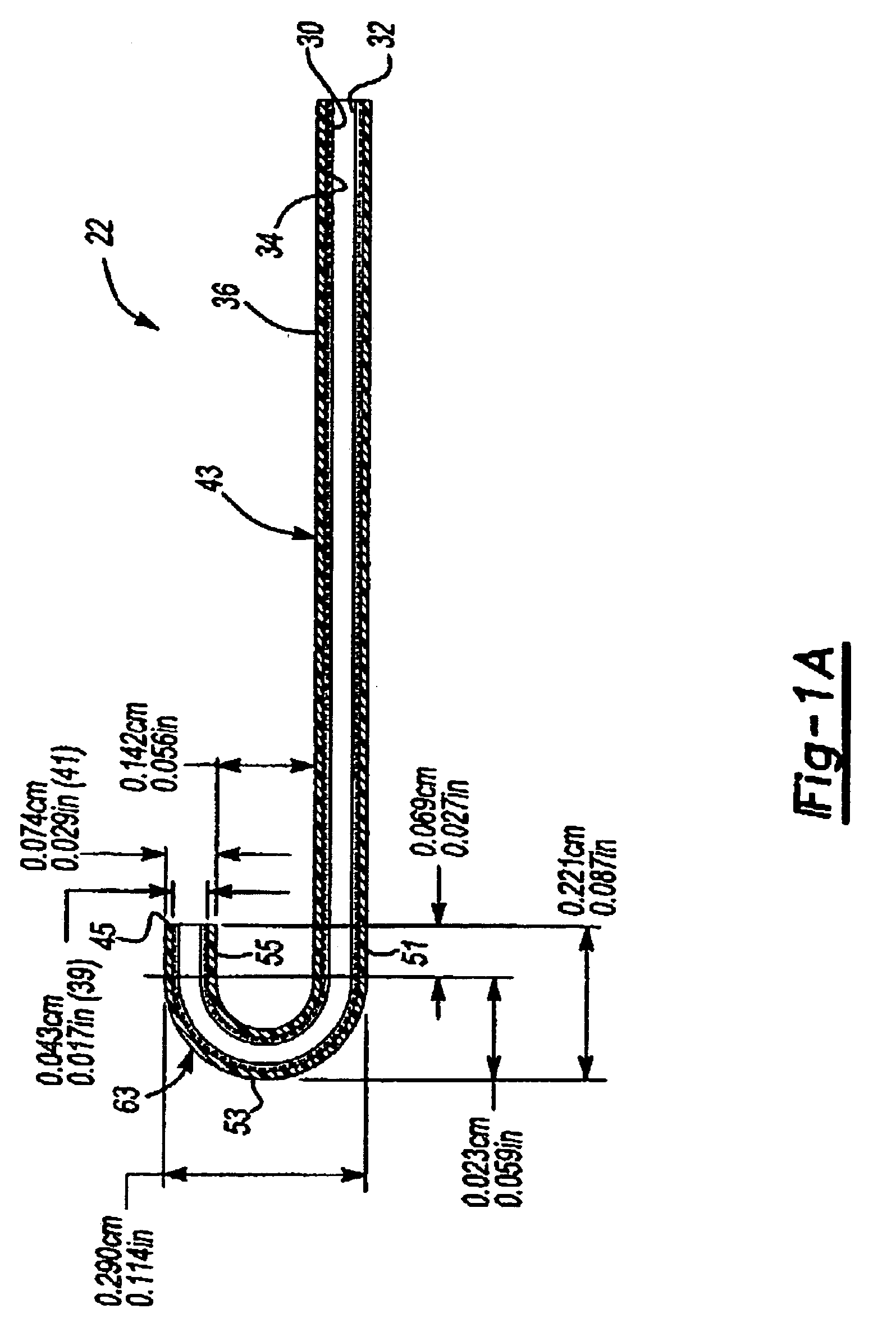
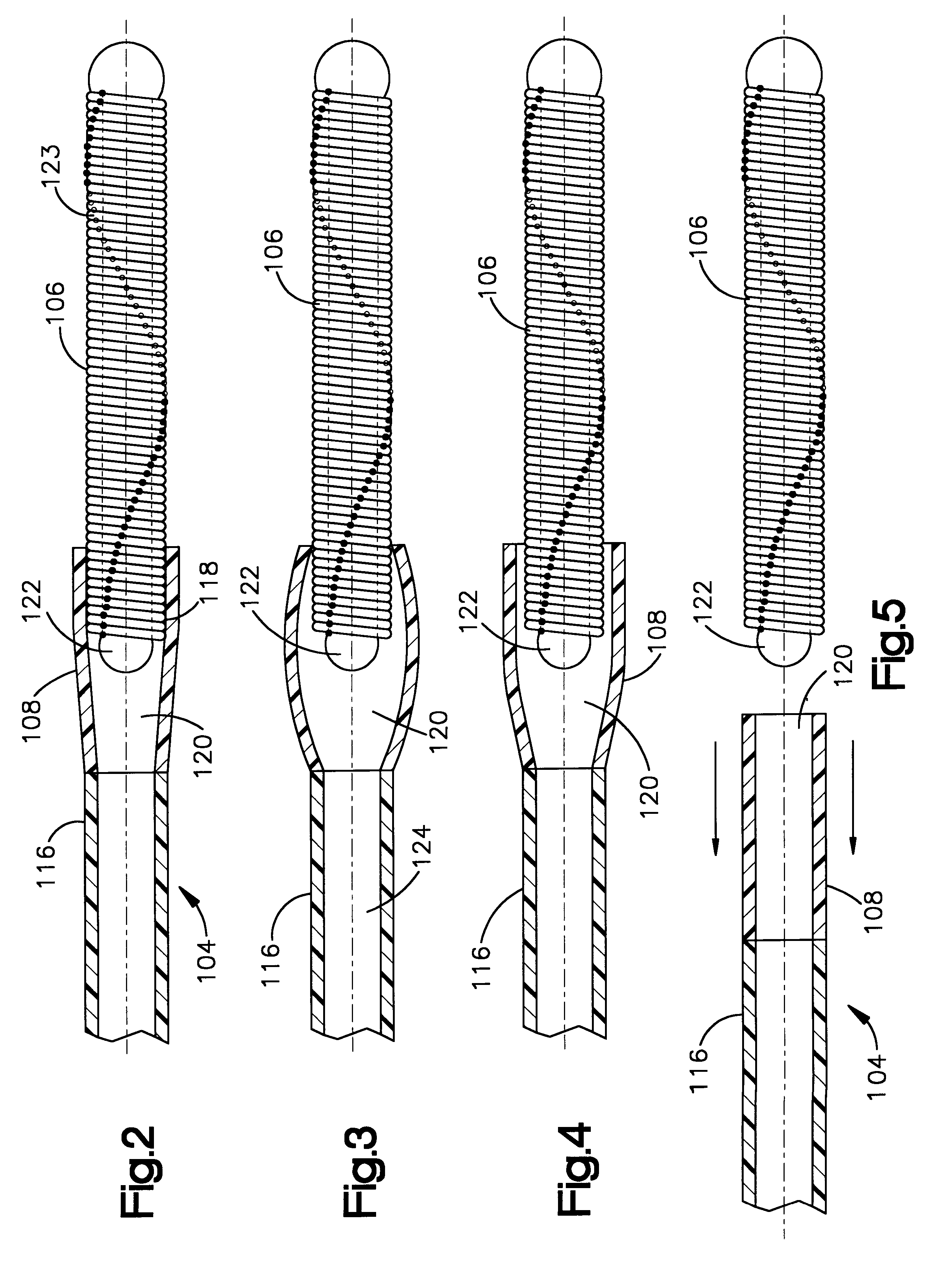
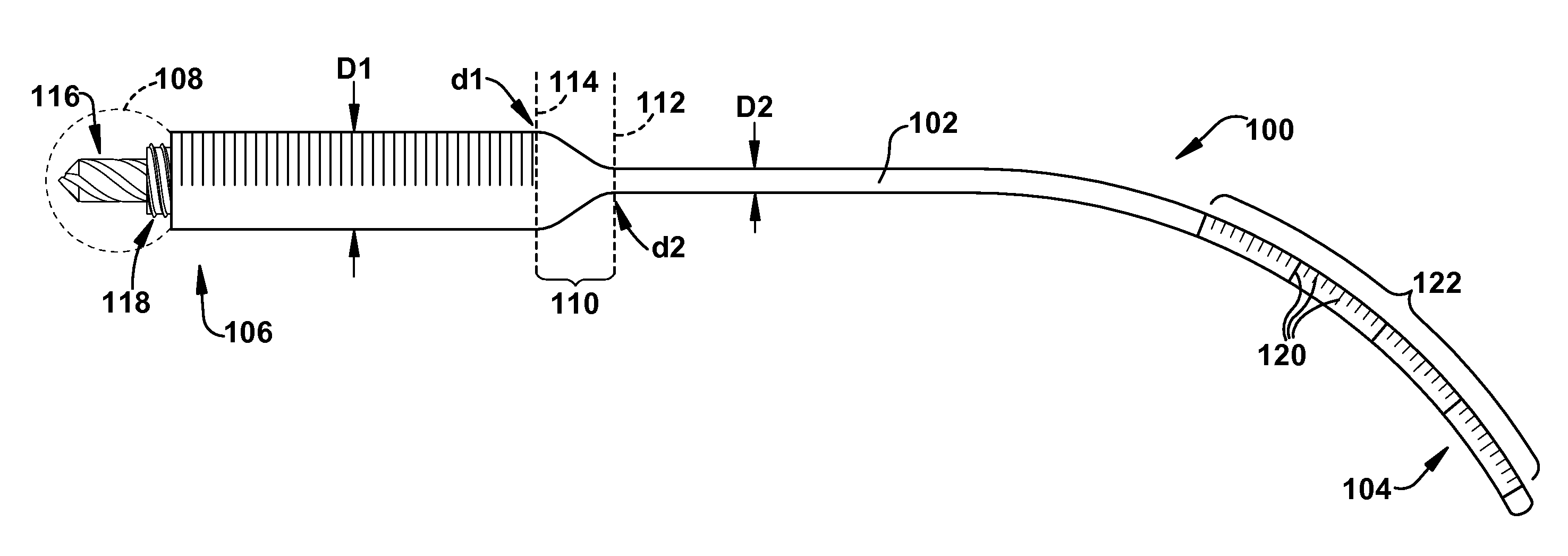
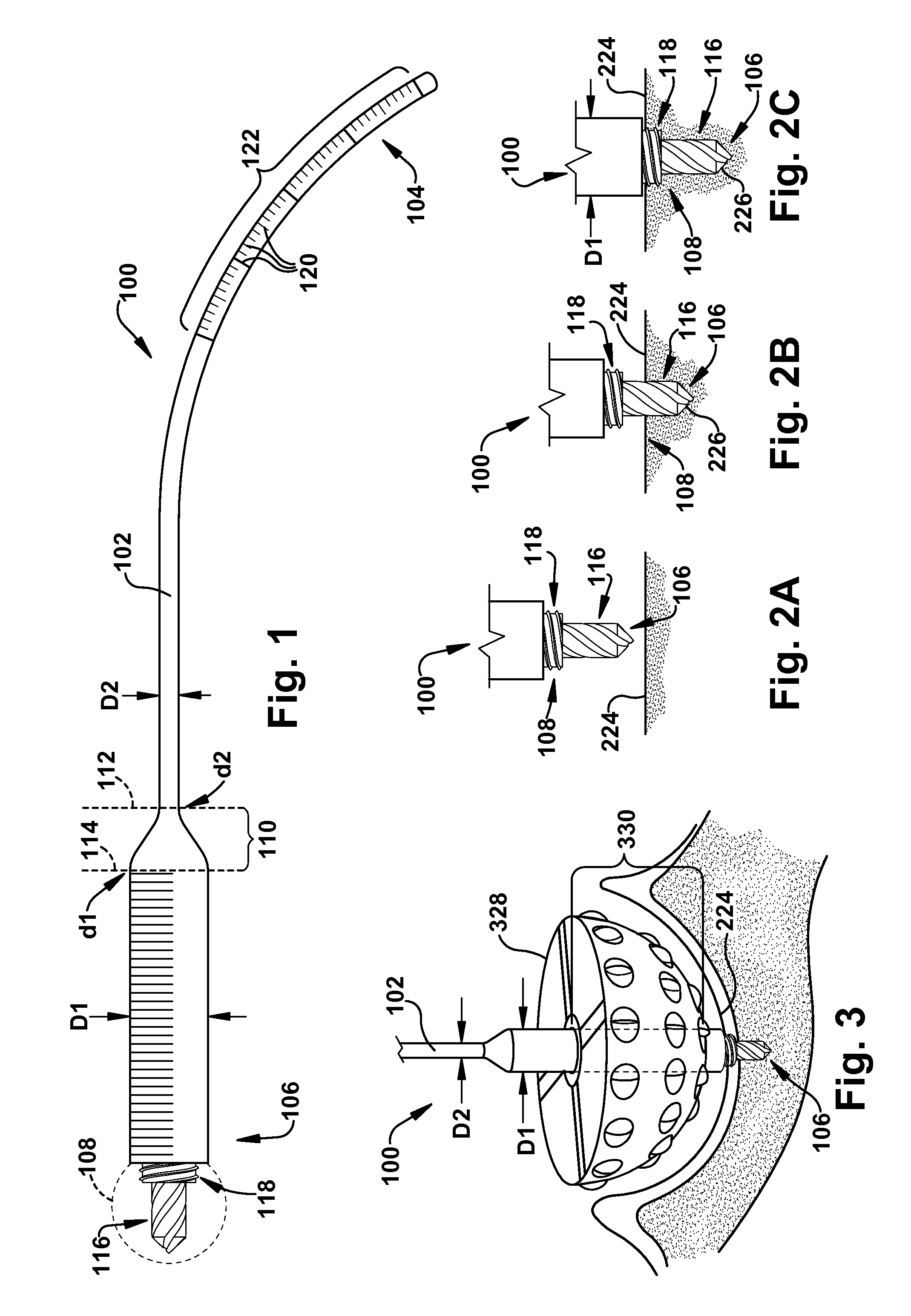
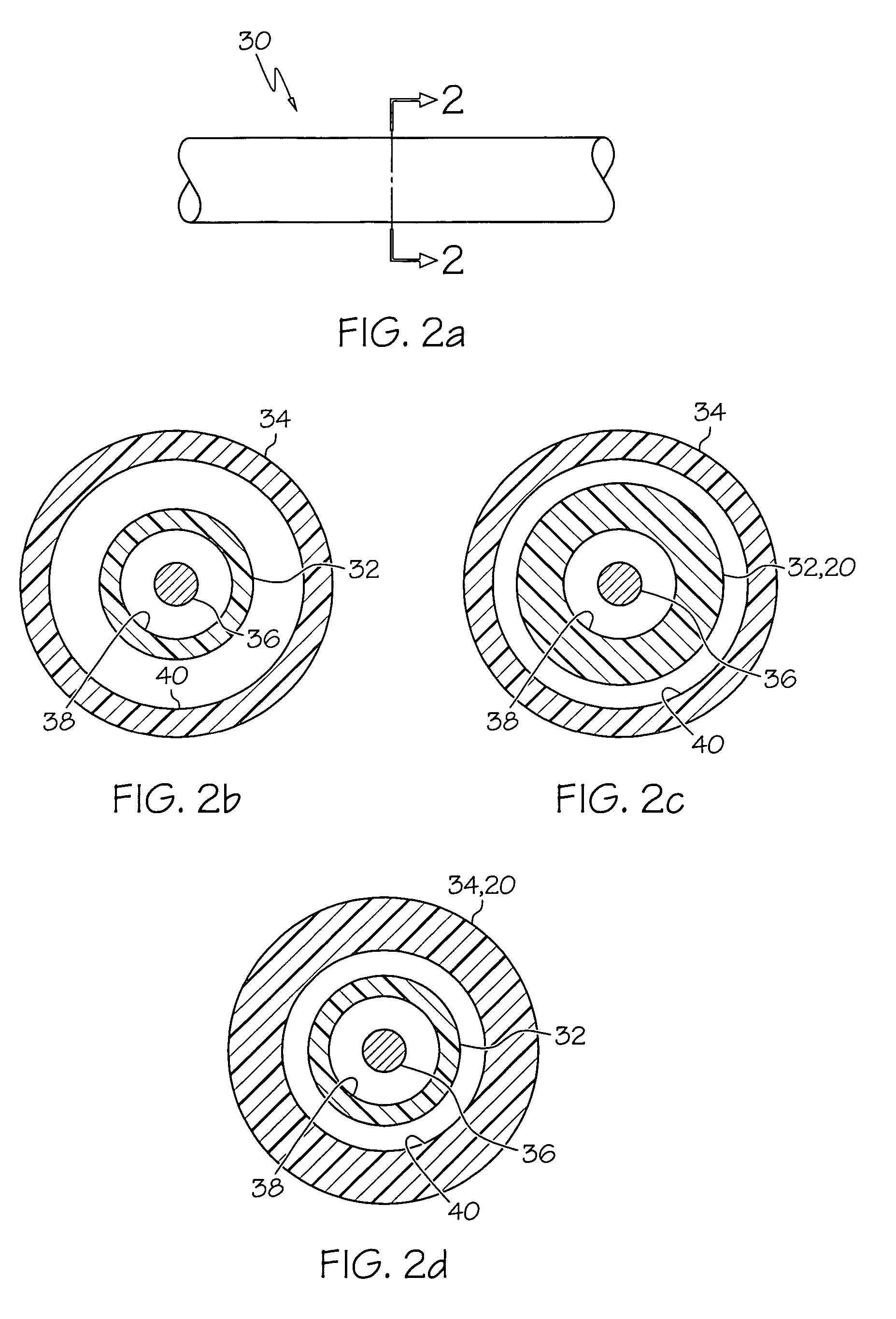
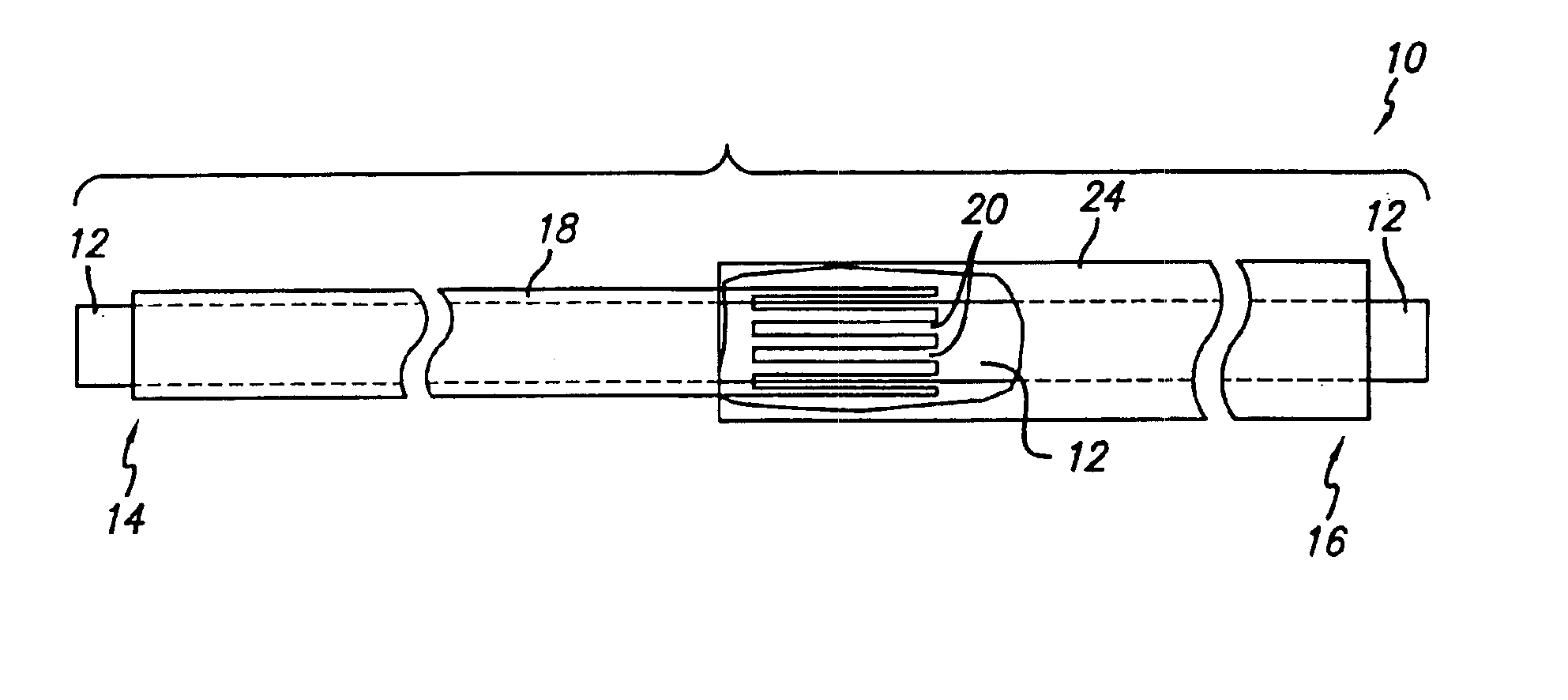
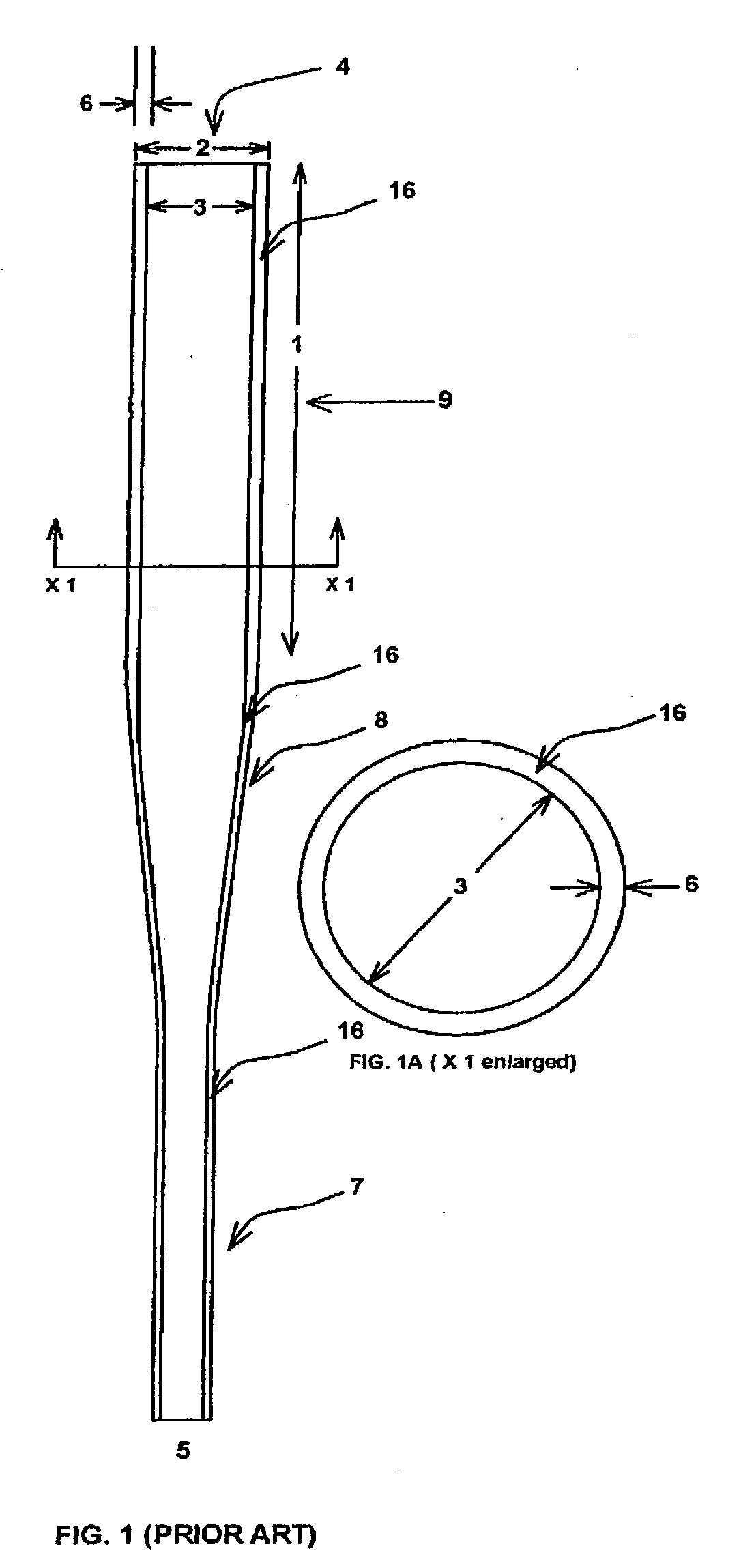
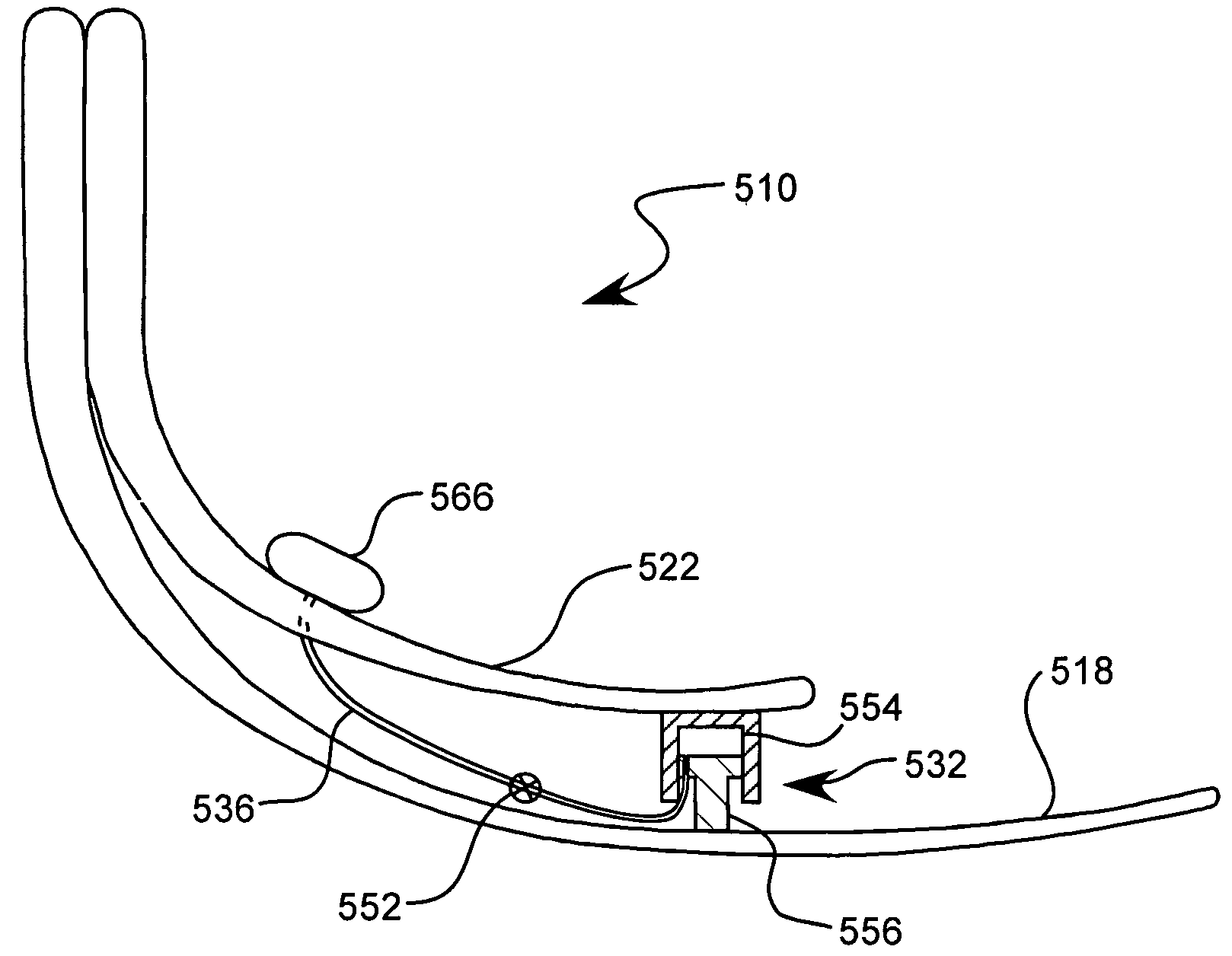
Variable stiffness shaft
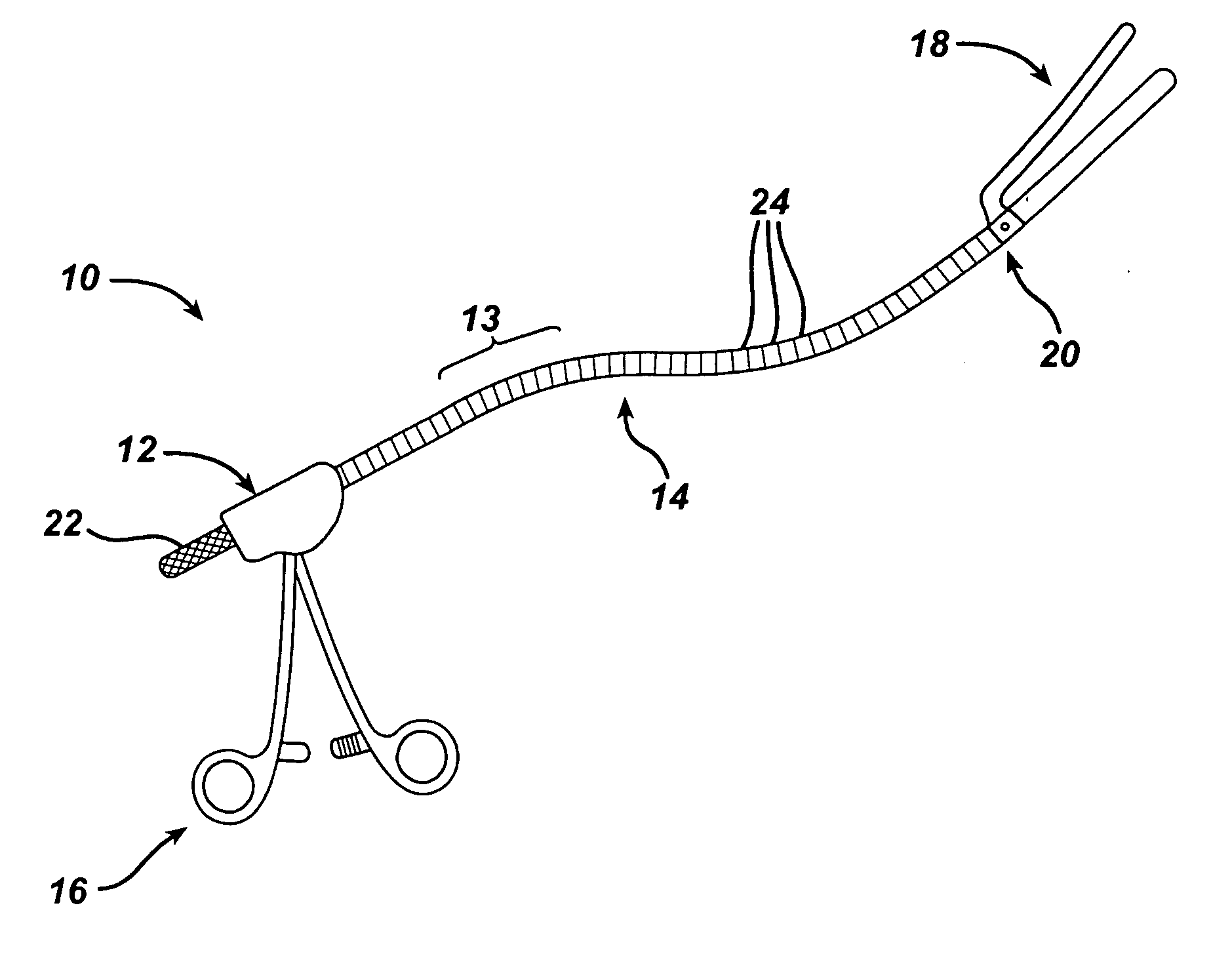
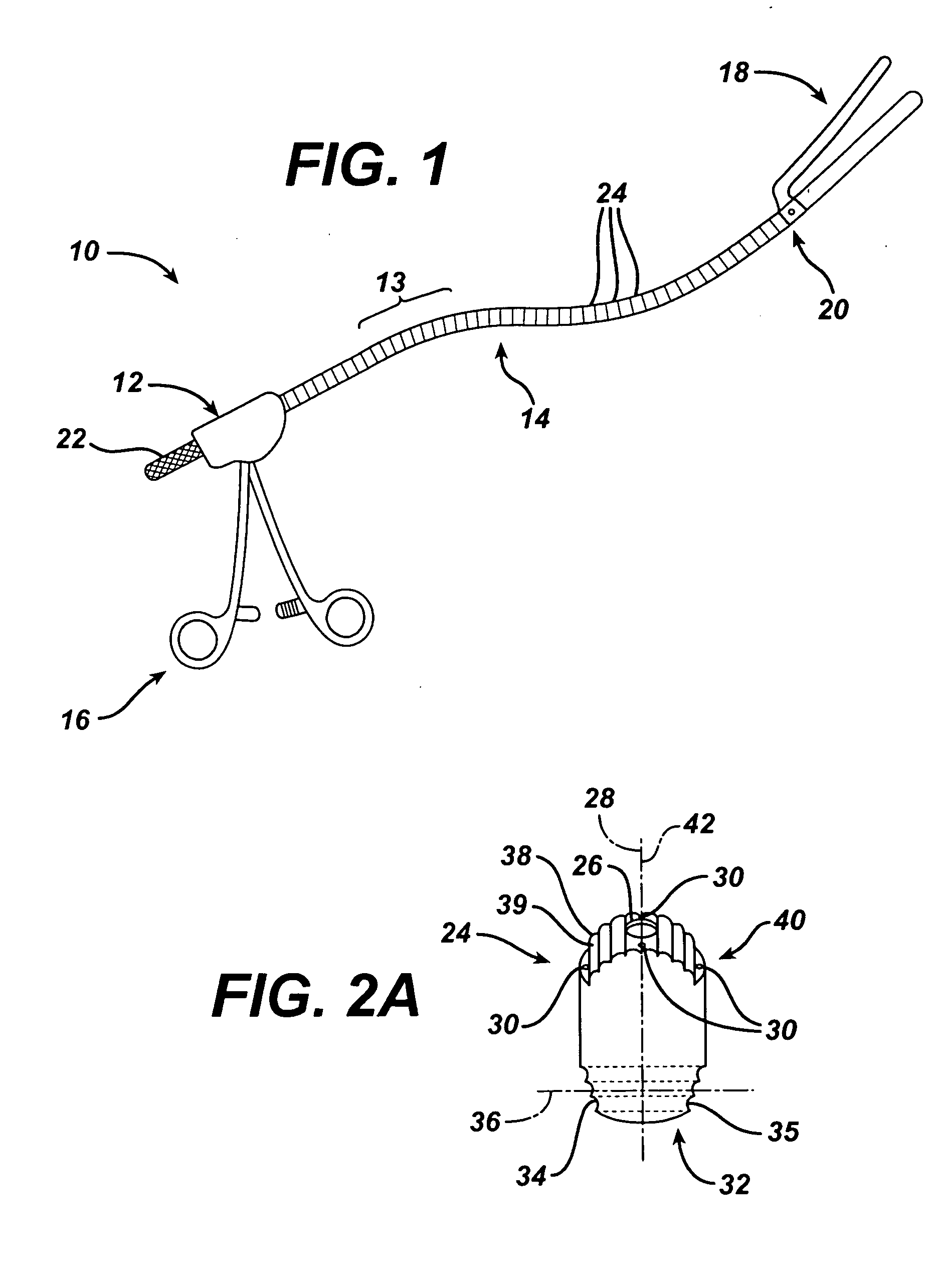
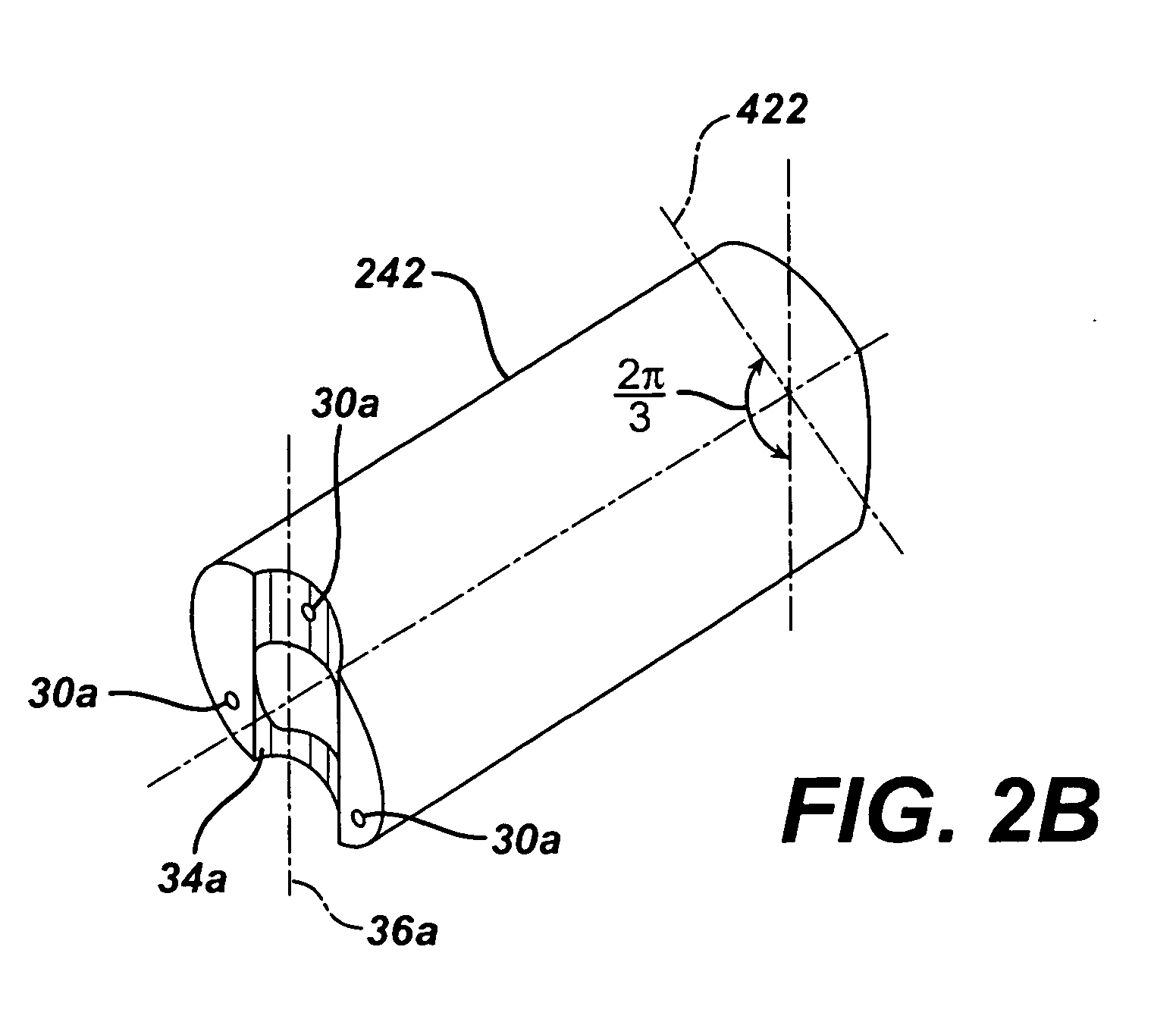
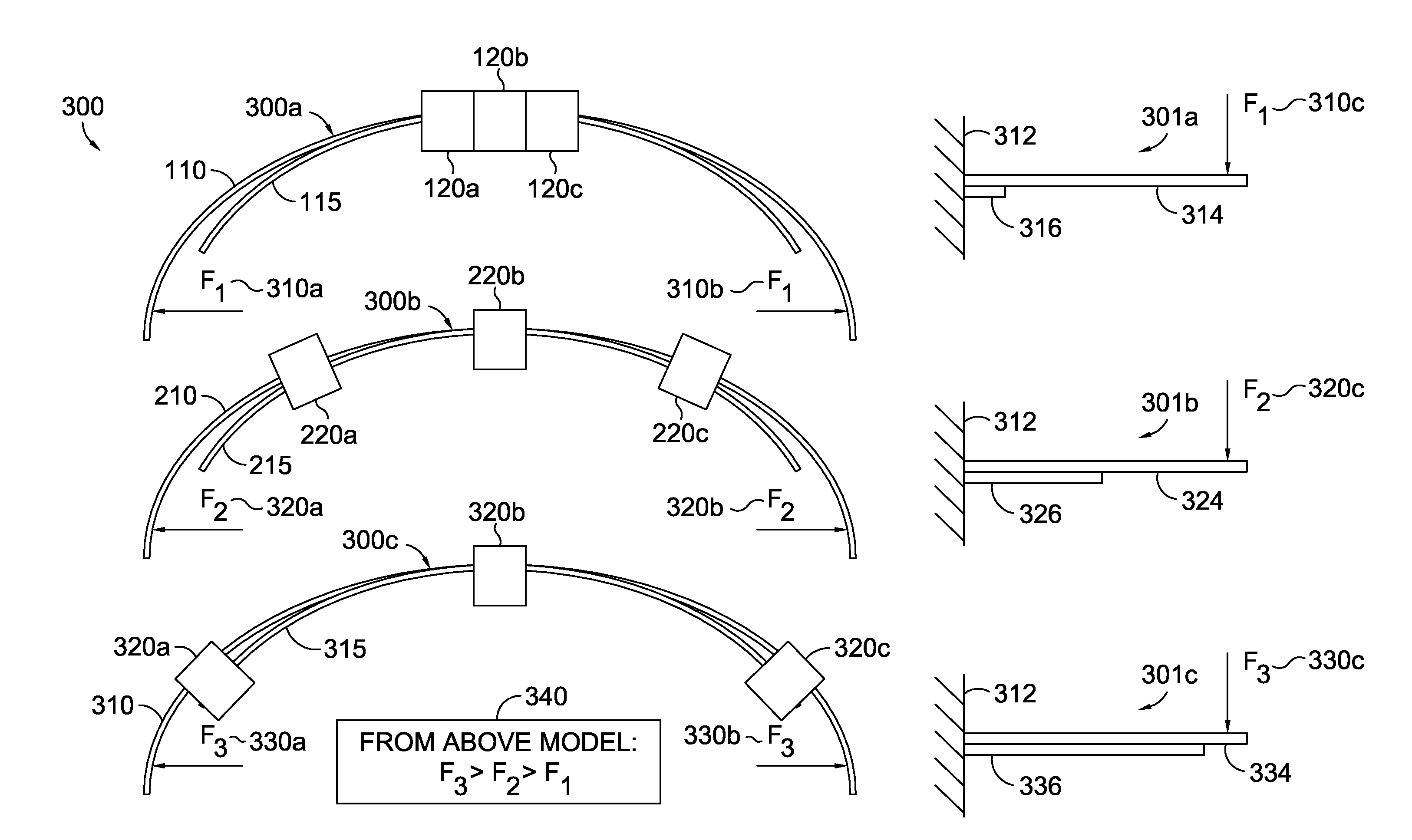
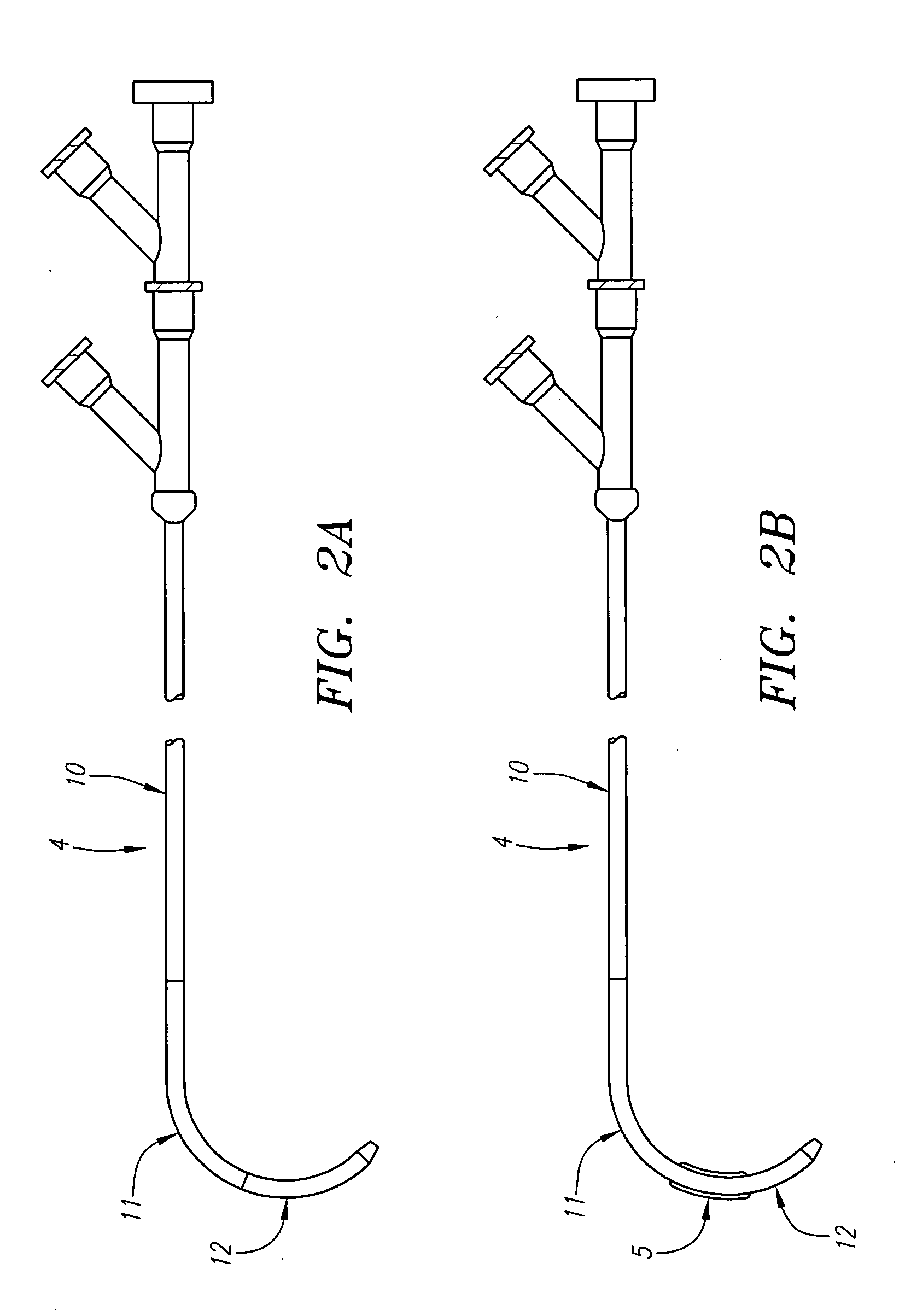
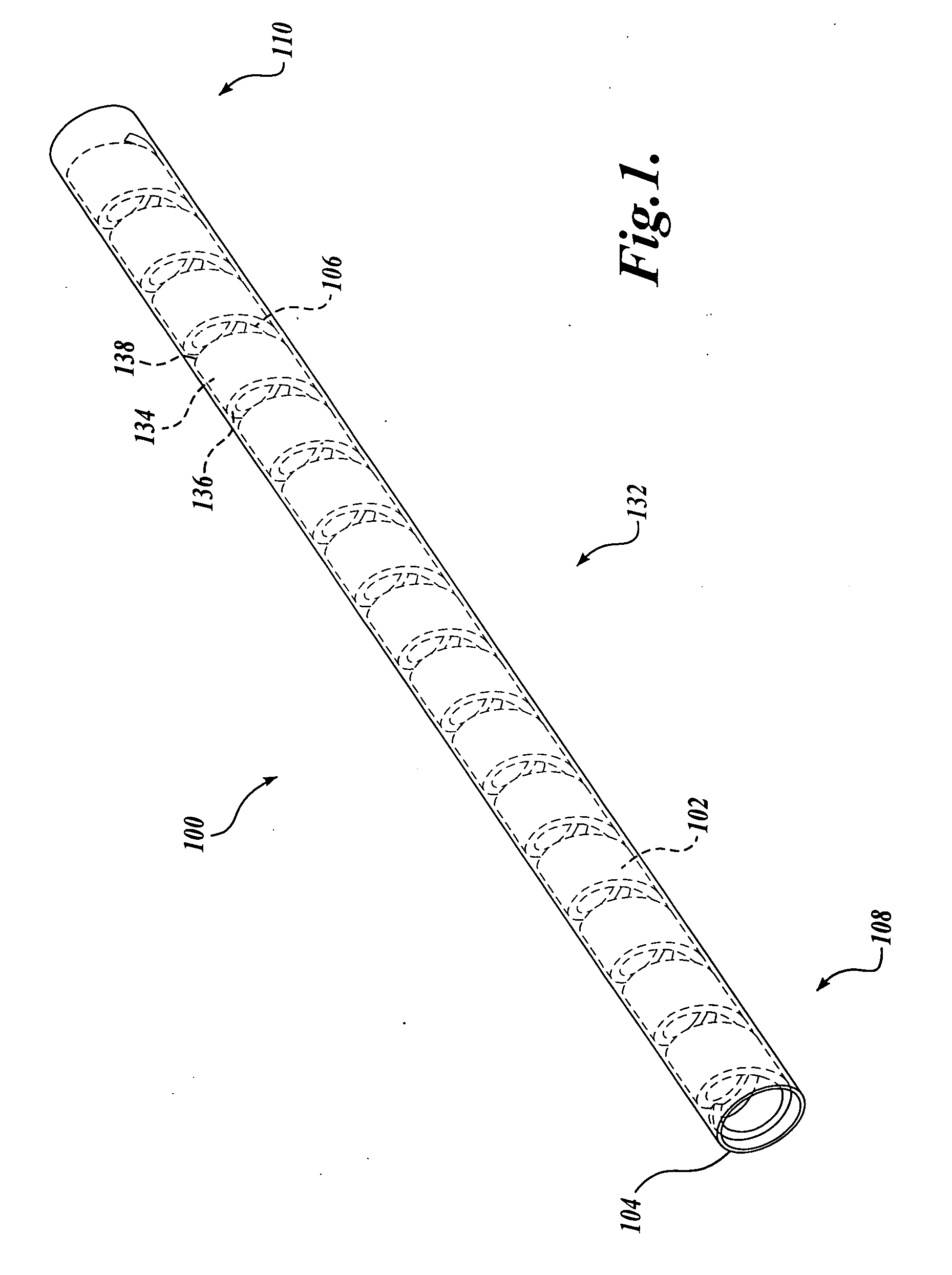
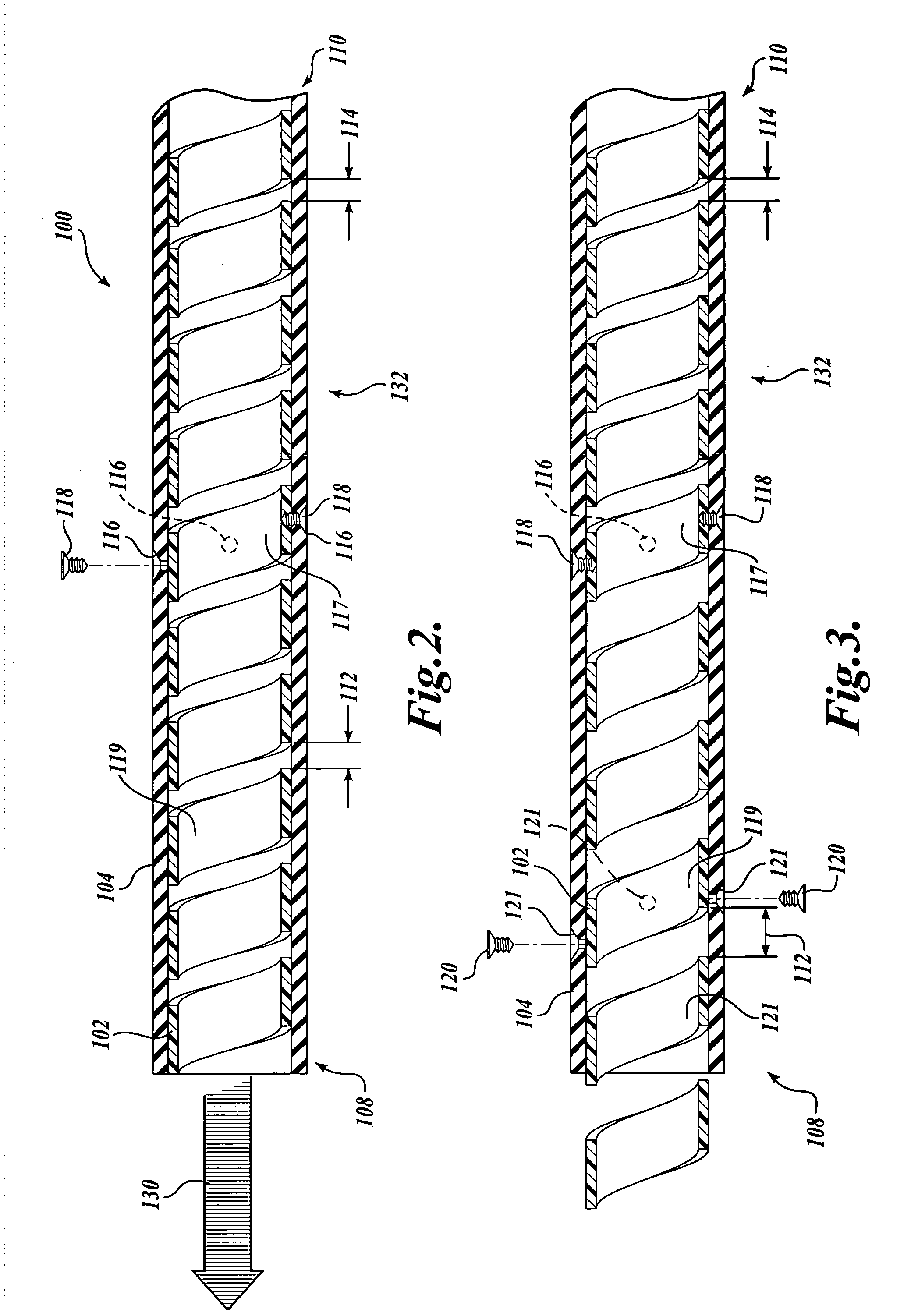
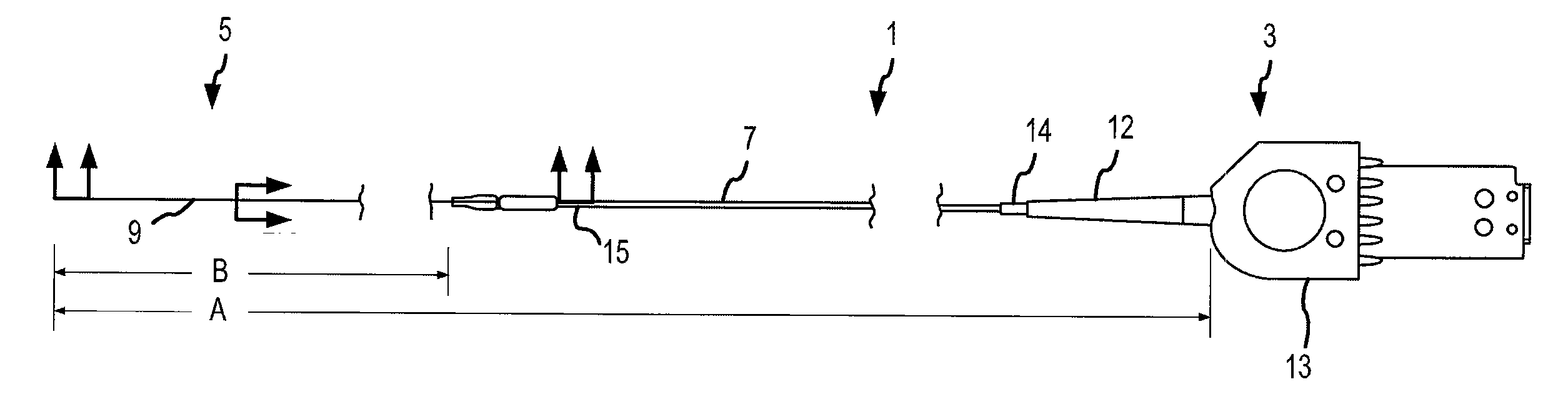
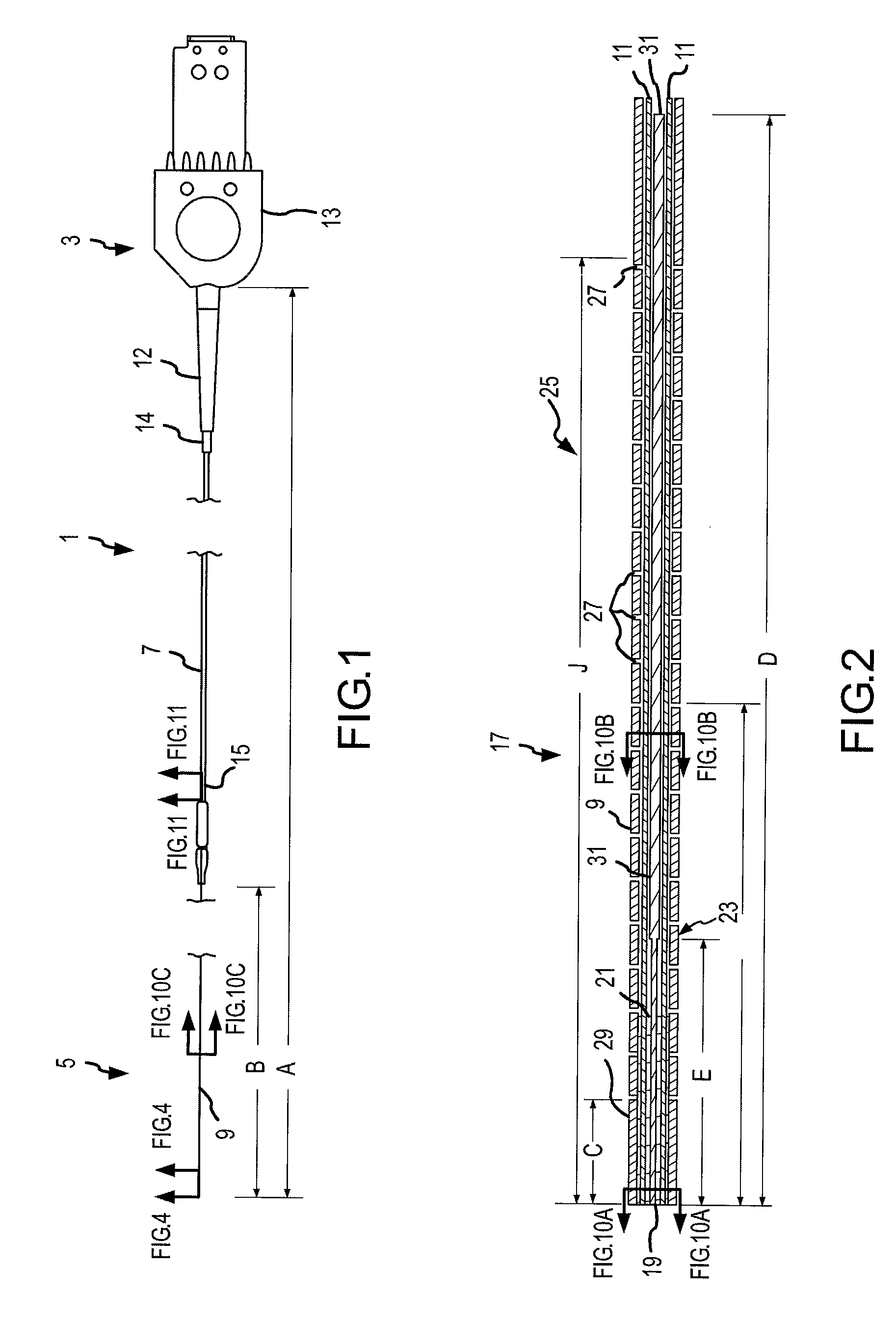
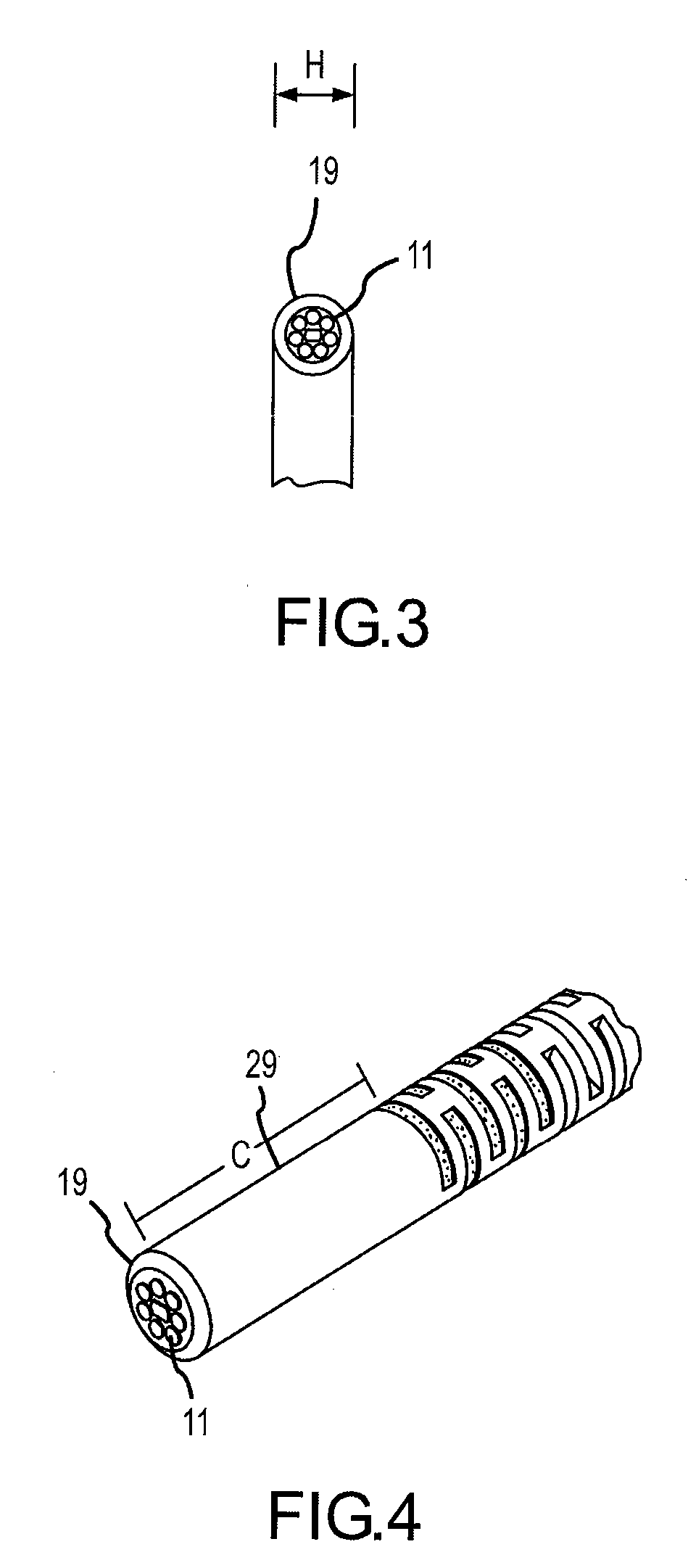
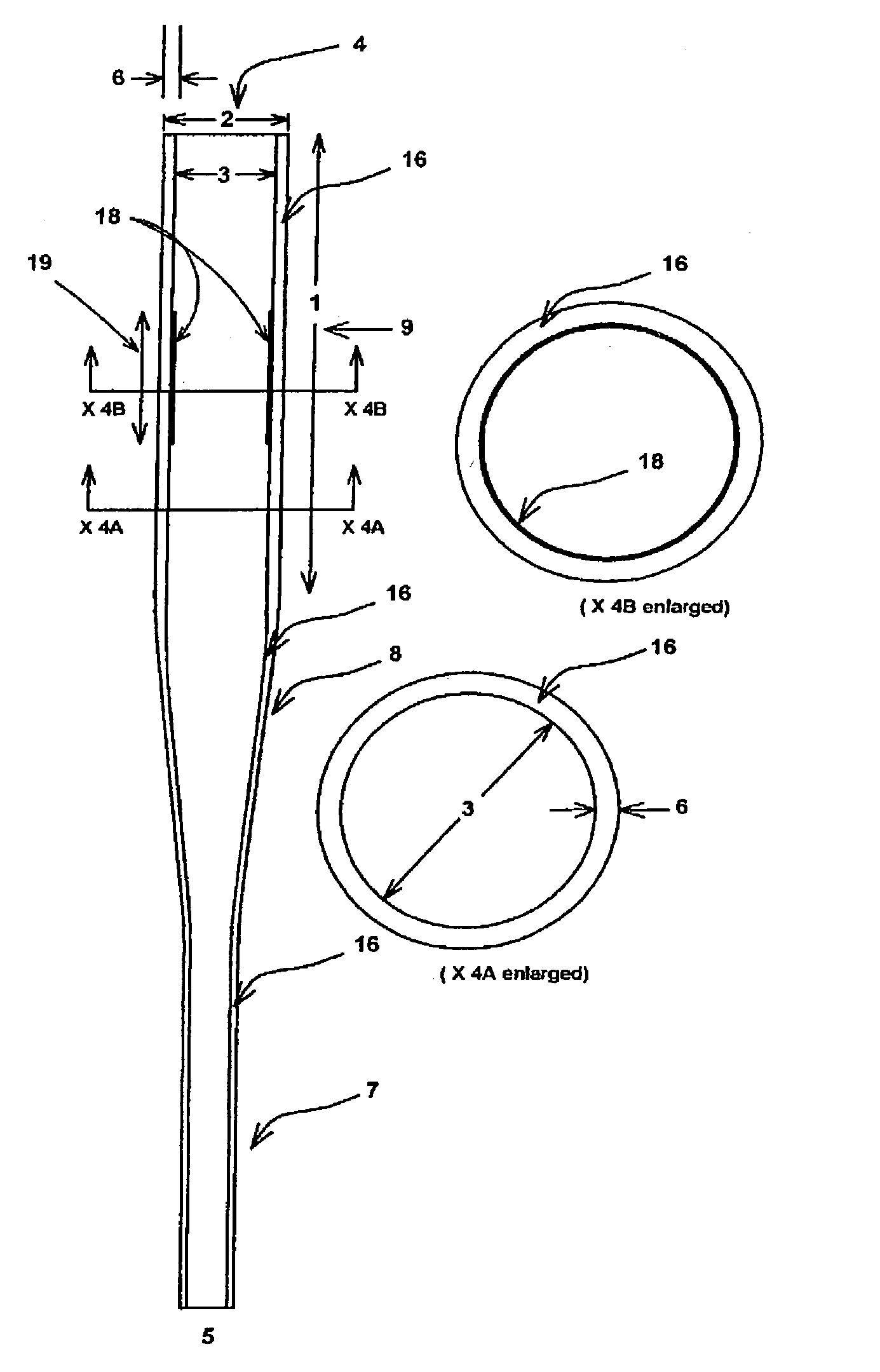
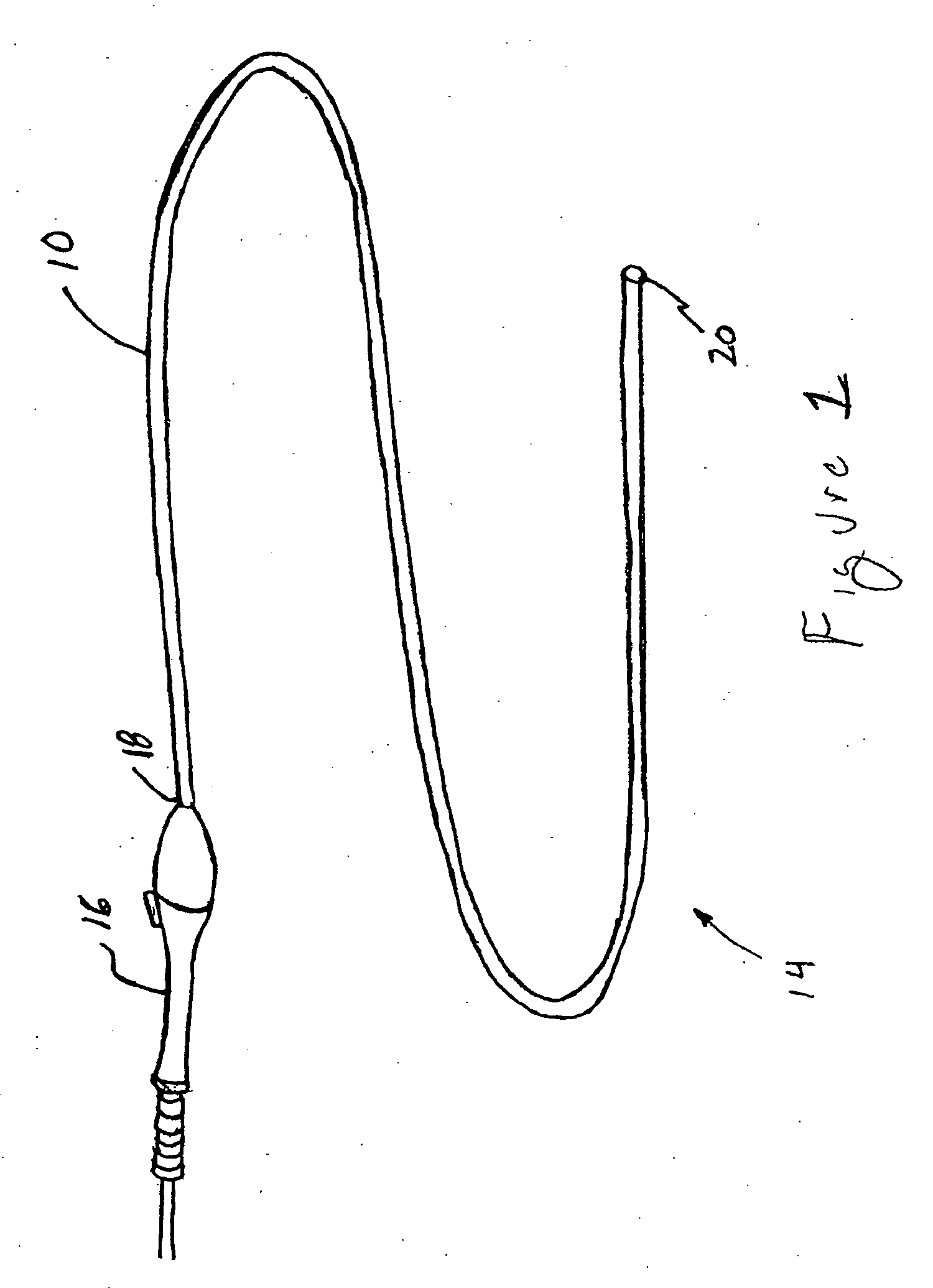
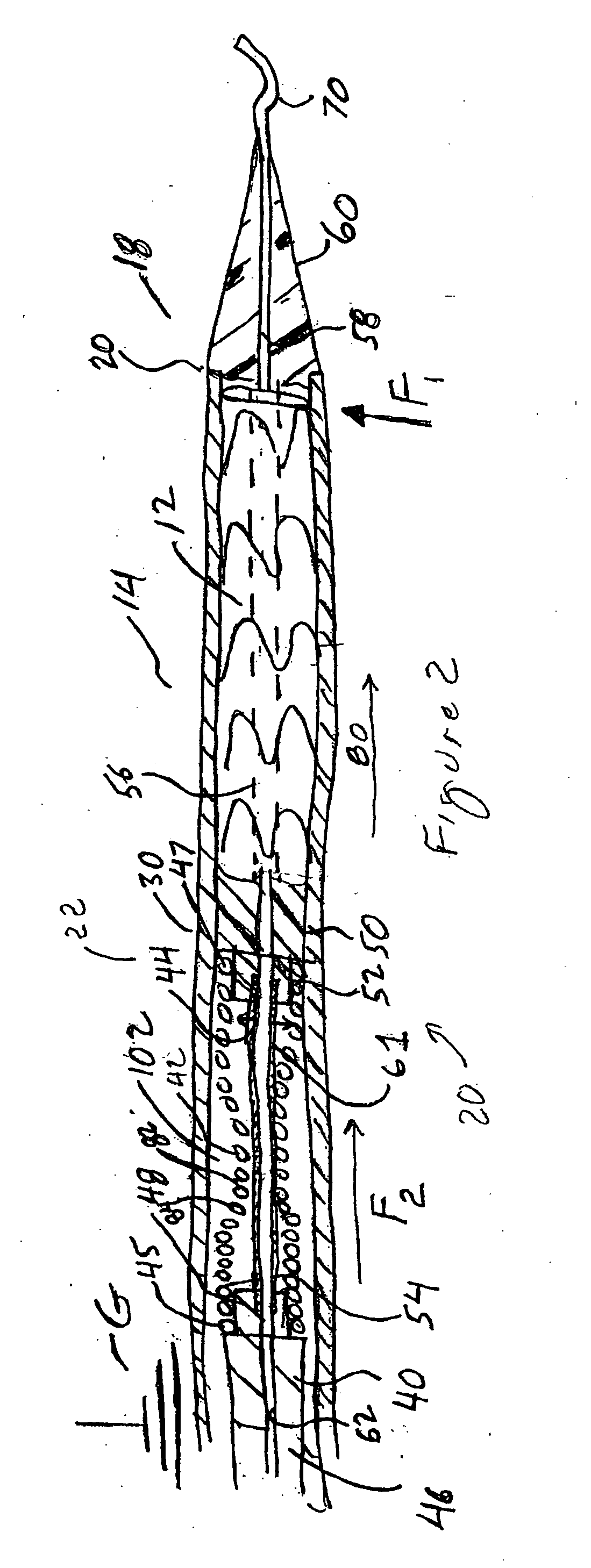
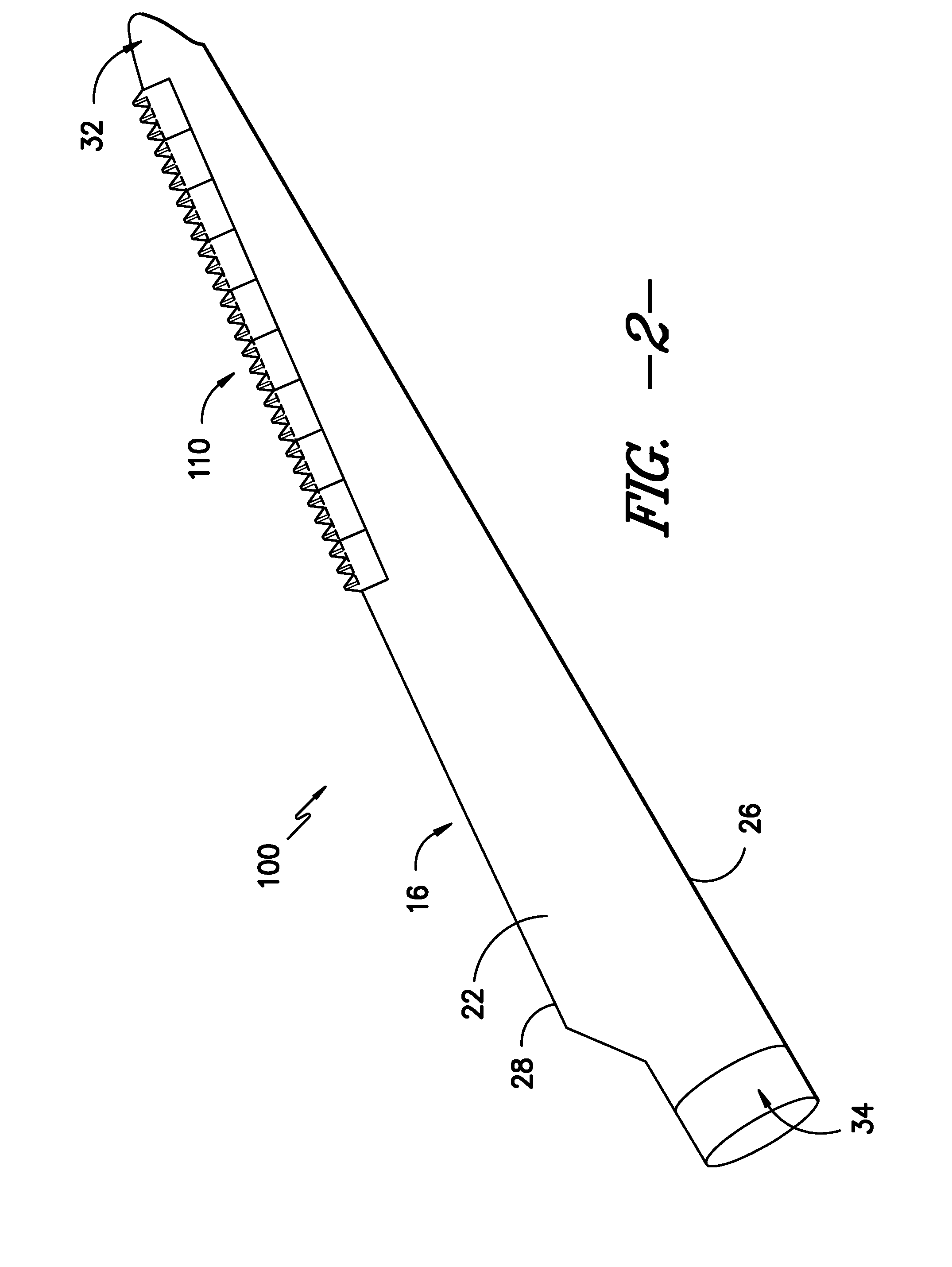
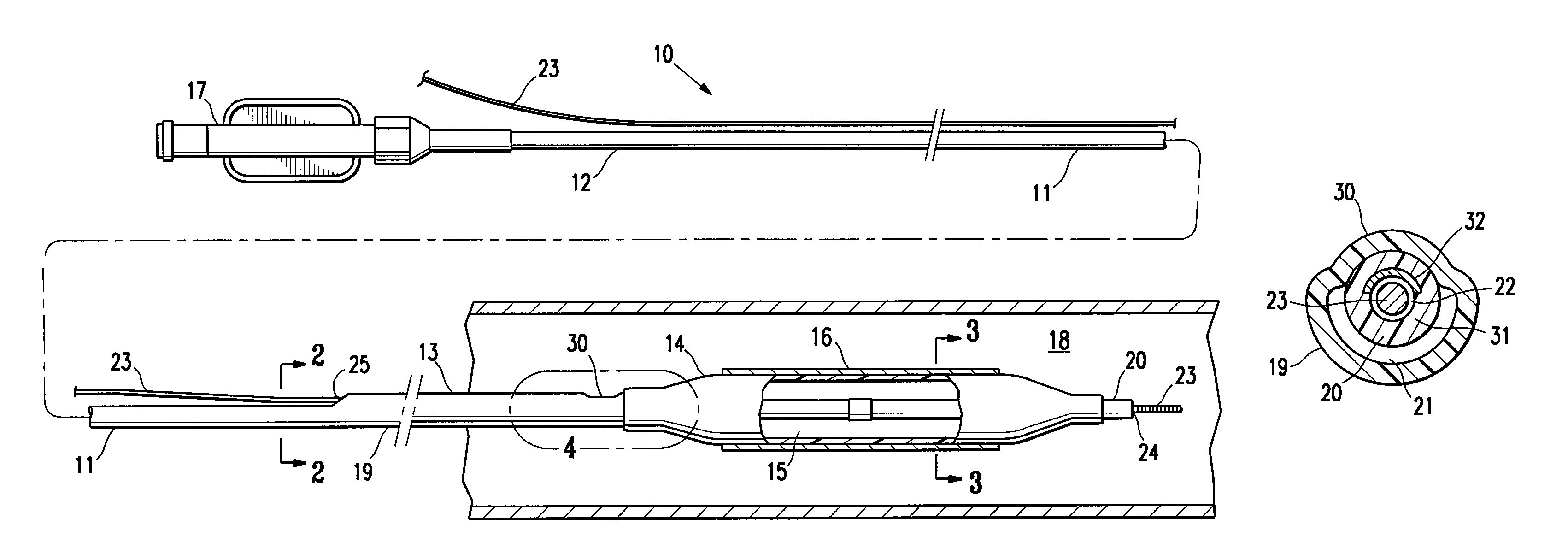
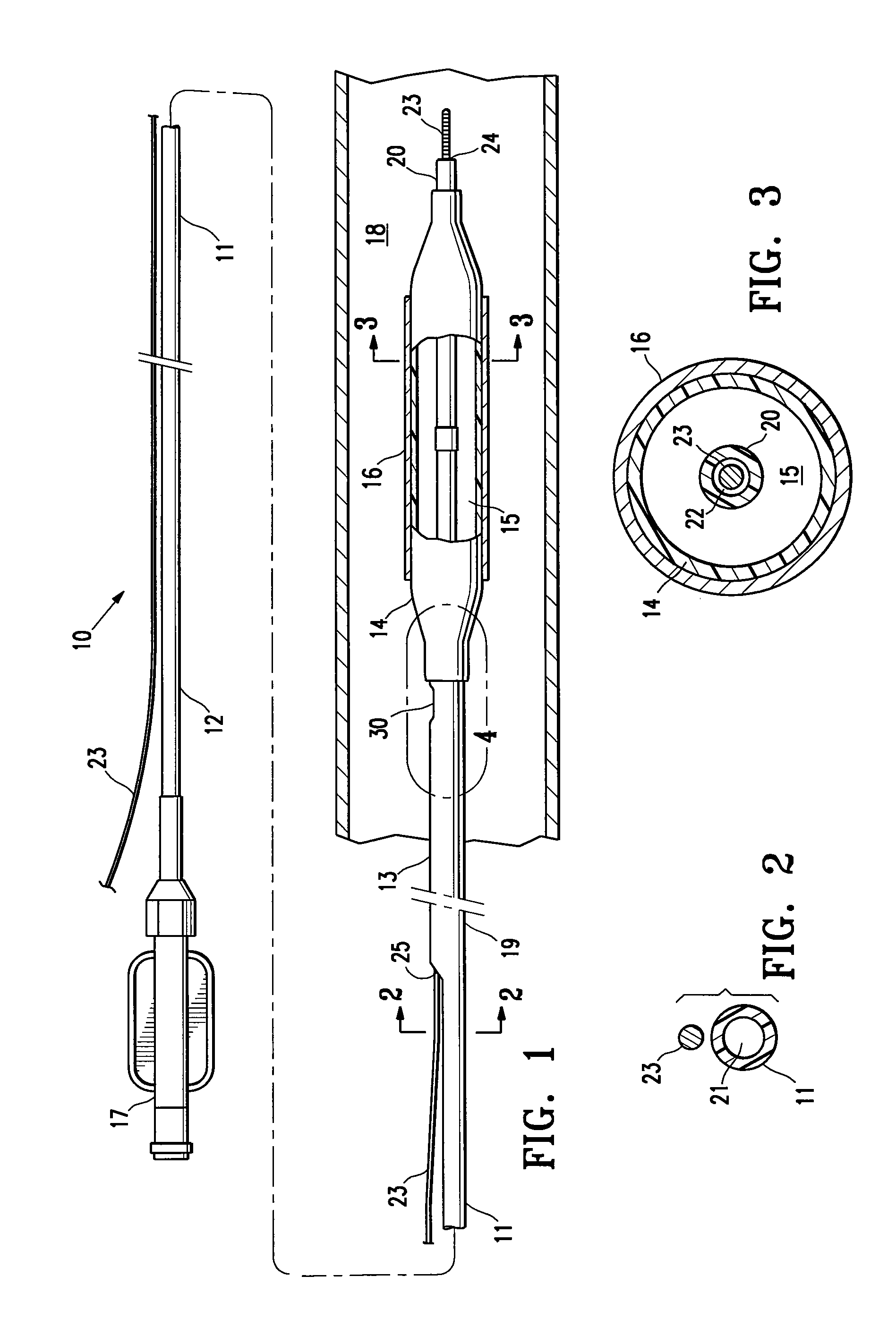
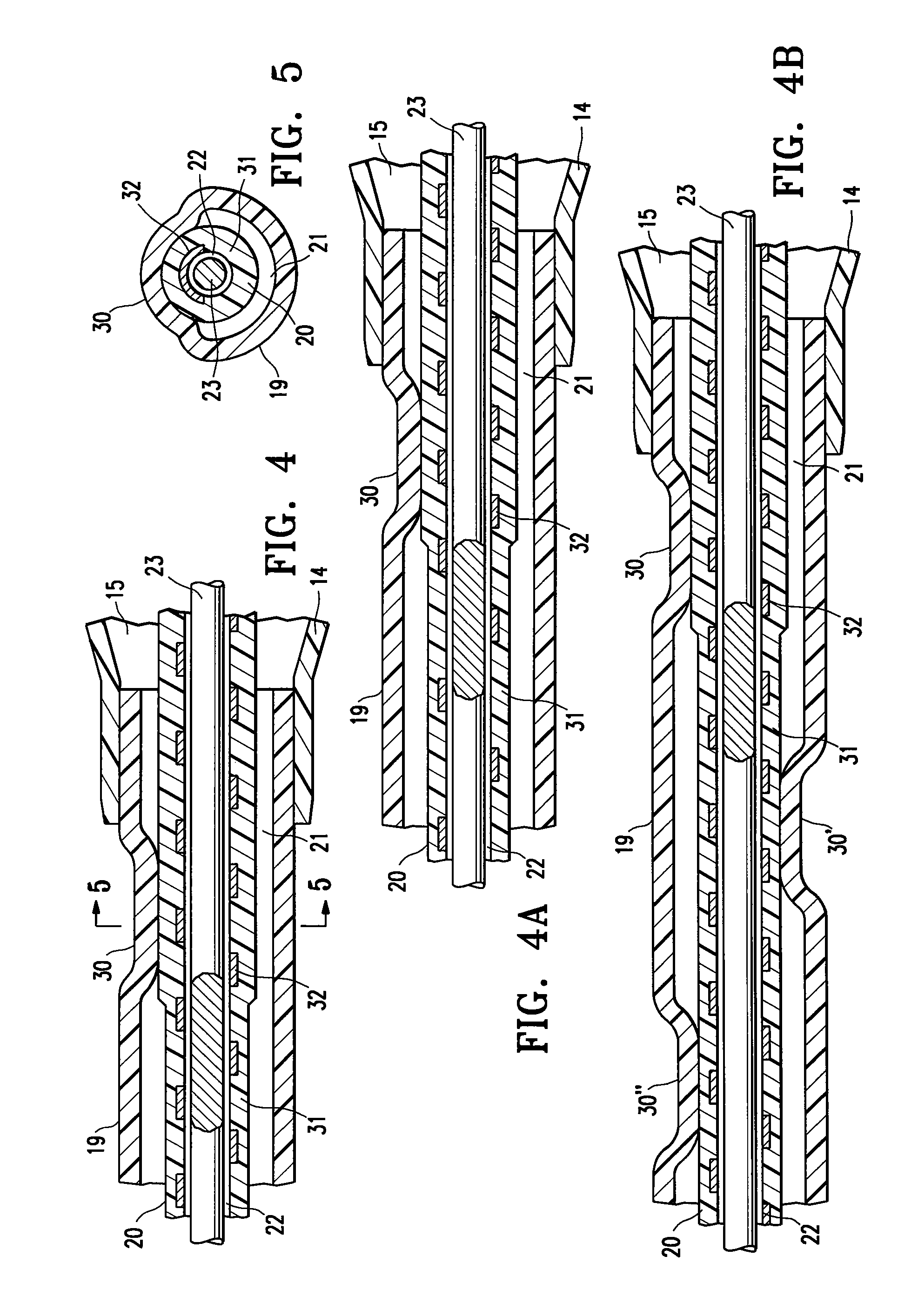
A flexible malleable shaft is made up of a plurality of prismatic shaft elements adjacent one another. A recess is formed in a proximal end of each shaft element, the recess defined along a transverse axis. A protrusion is formed in a distal end of each shaft element, the protrusion defined along a transverse axis. The transverse axes are oriented to one another such that adjacent like shaft elements are aligned with one another when a protrusion of one shaft element is aligned with a recess in an adjacent shaft element. A tension element secured to a distal end of the malleable shaft is in communication with a proximal end of the malleable shaft via an axial through hole. Additionally, a variable stiffness malleable shaft can accommodate the differential lengths of tension elements when applying force to transition the shaft.
Owner:ETHICON INC
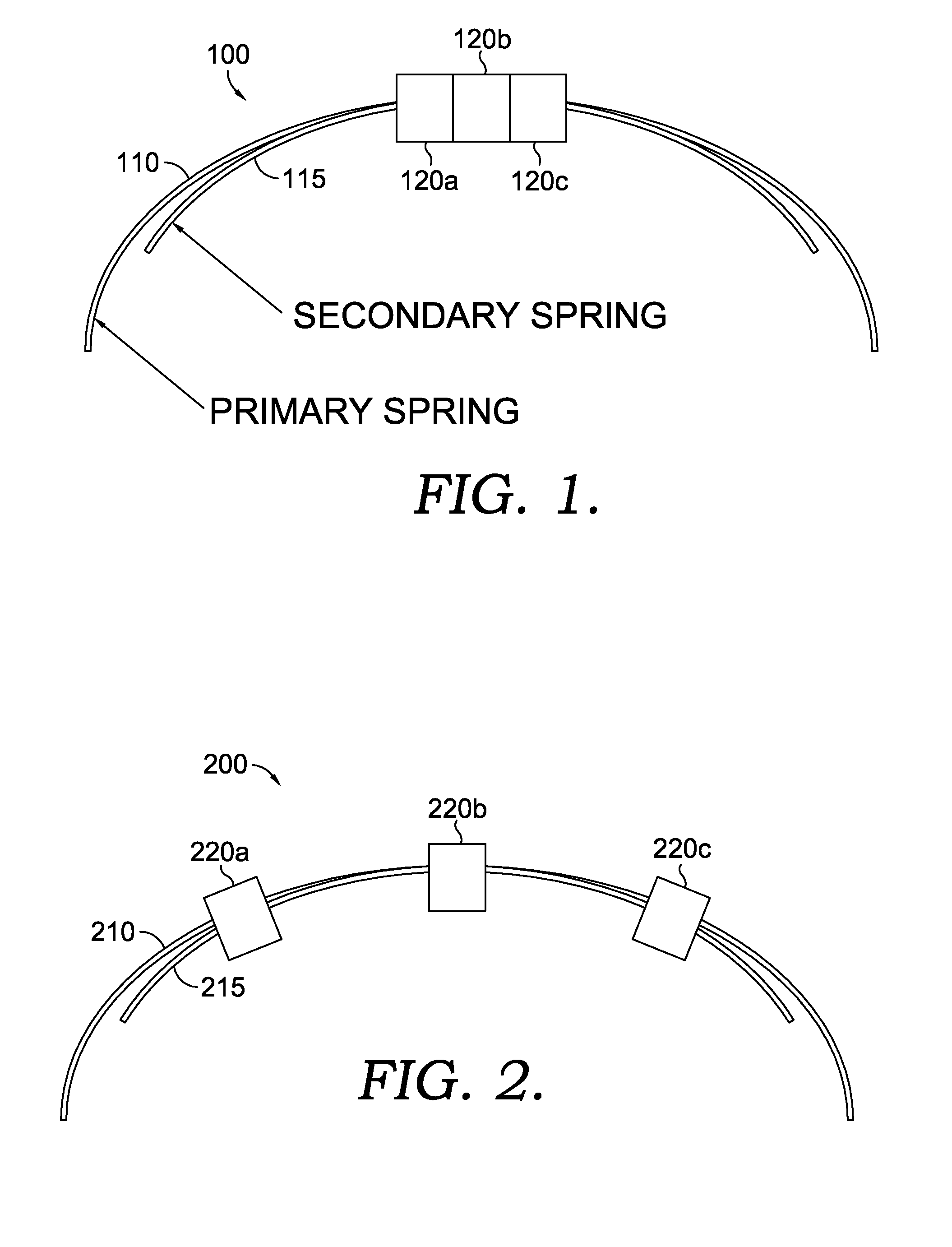
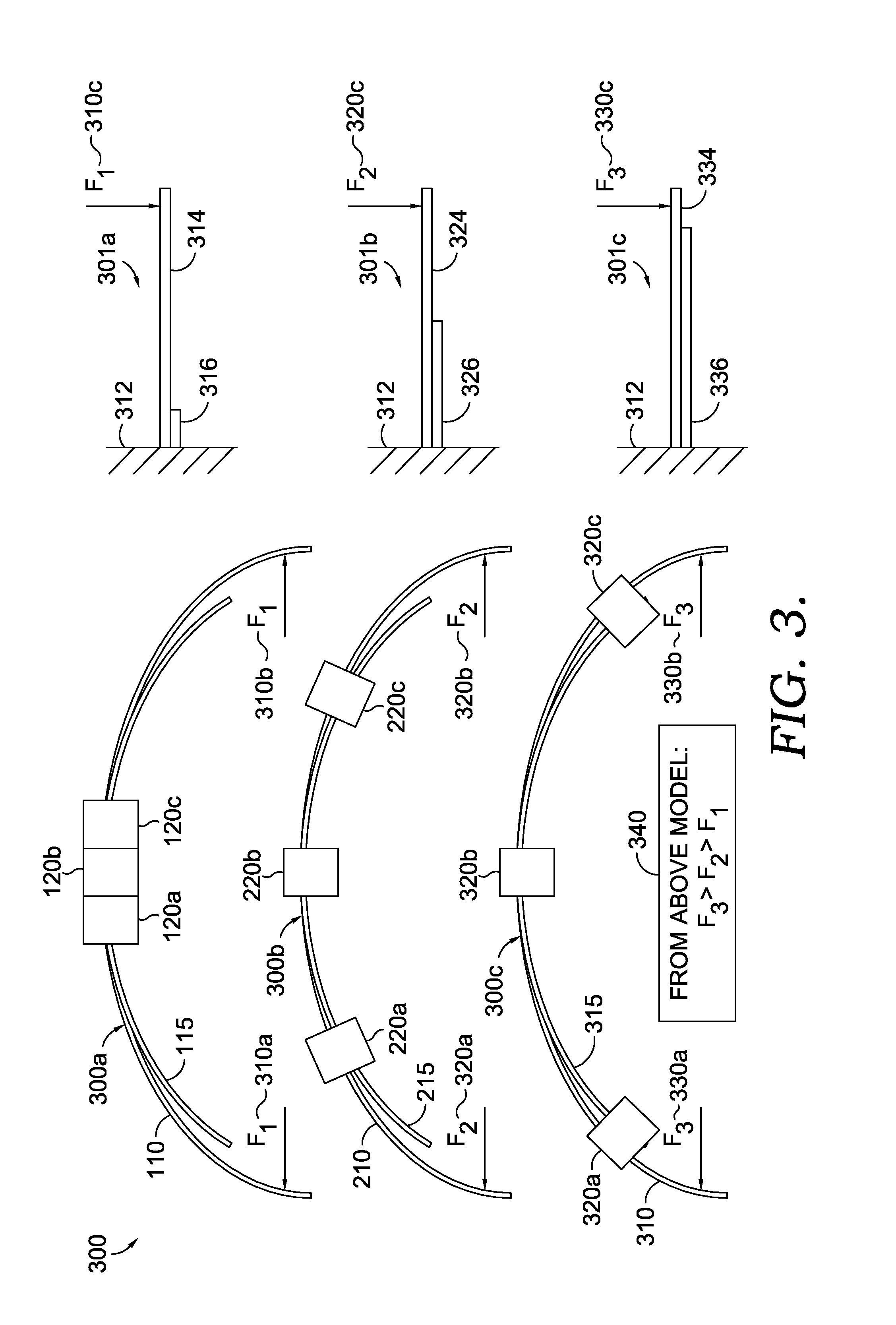
Headband variable stiffness
A method and apparatus are provided for allowing a user to change the stiffness of their headband, thus changing the clamping force of the headset. The section properties of the headband equivalent spring, which is a cantilevered beam, are changed by engaging a secondary spring, which is also a shorter cantilevered beam. The change is achieved by manipulating the effective length of the secondary spring, which can be accomplished with a set of clamps. Thus, the stiffness of the headband can be modified to the desire of the user.
Owner:VOCOLLECT
Methods and apparatus for localized and semi-localized drug delivery
InactiveUS20050059931A1Turn easilyEasy to navigateStentsBalloon catheterVariable stiffnessThree vessels
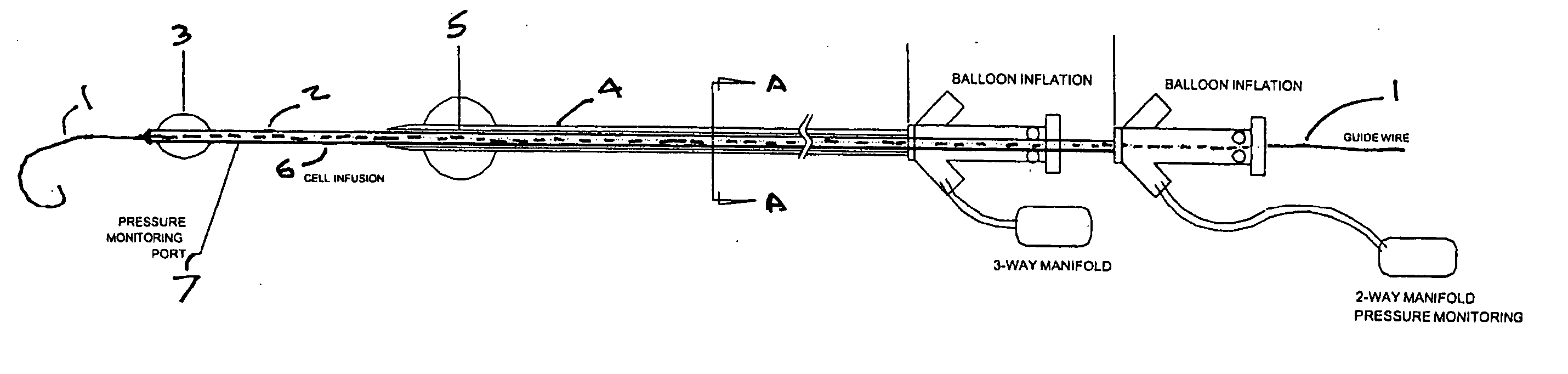
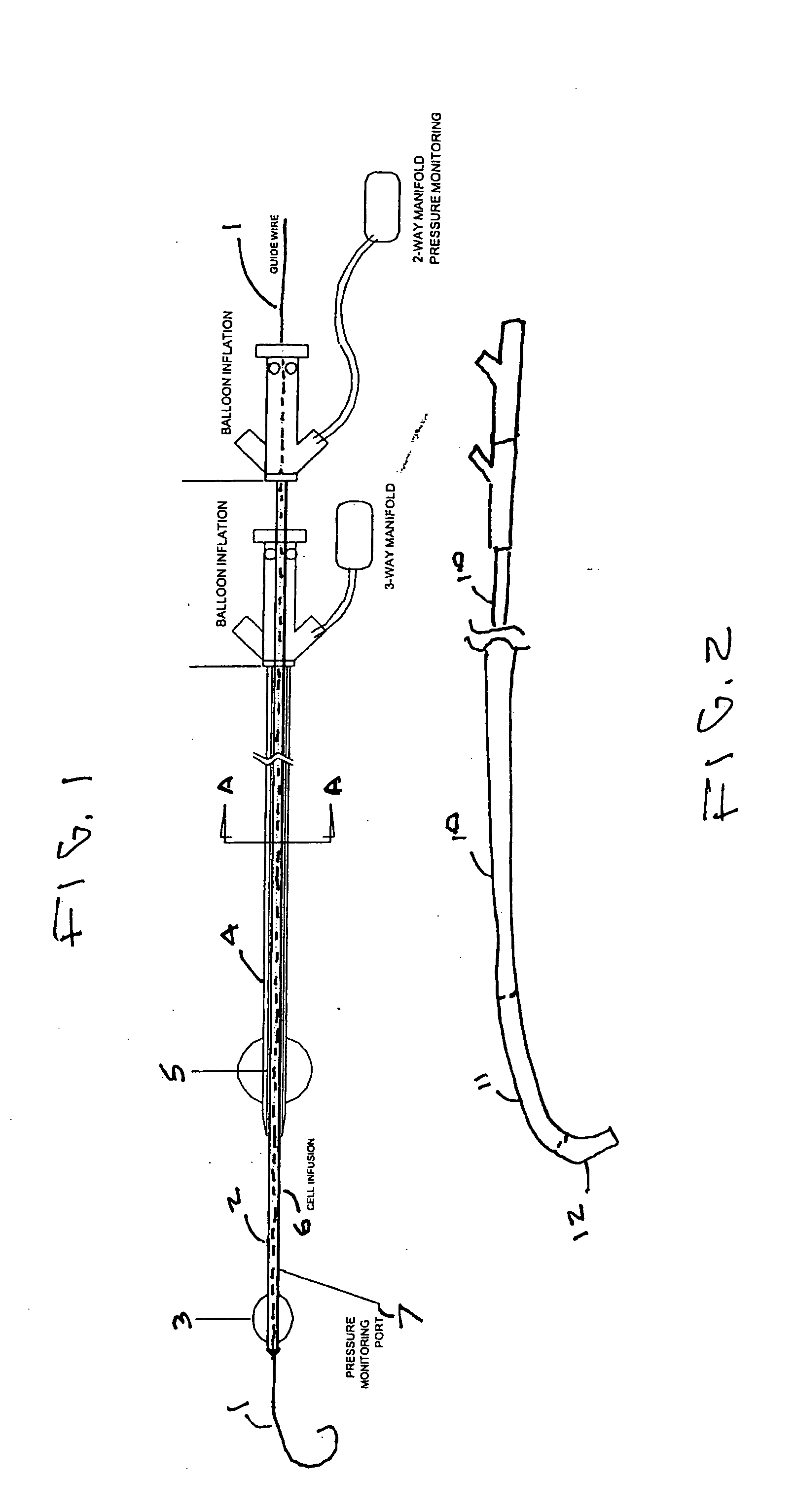
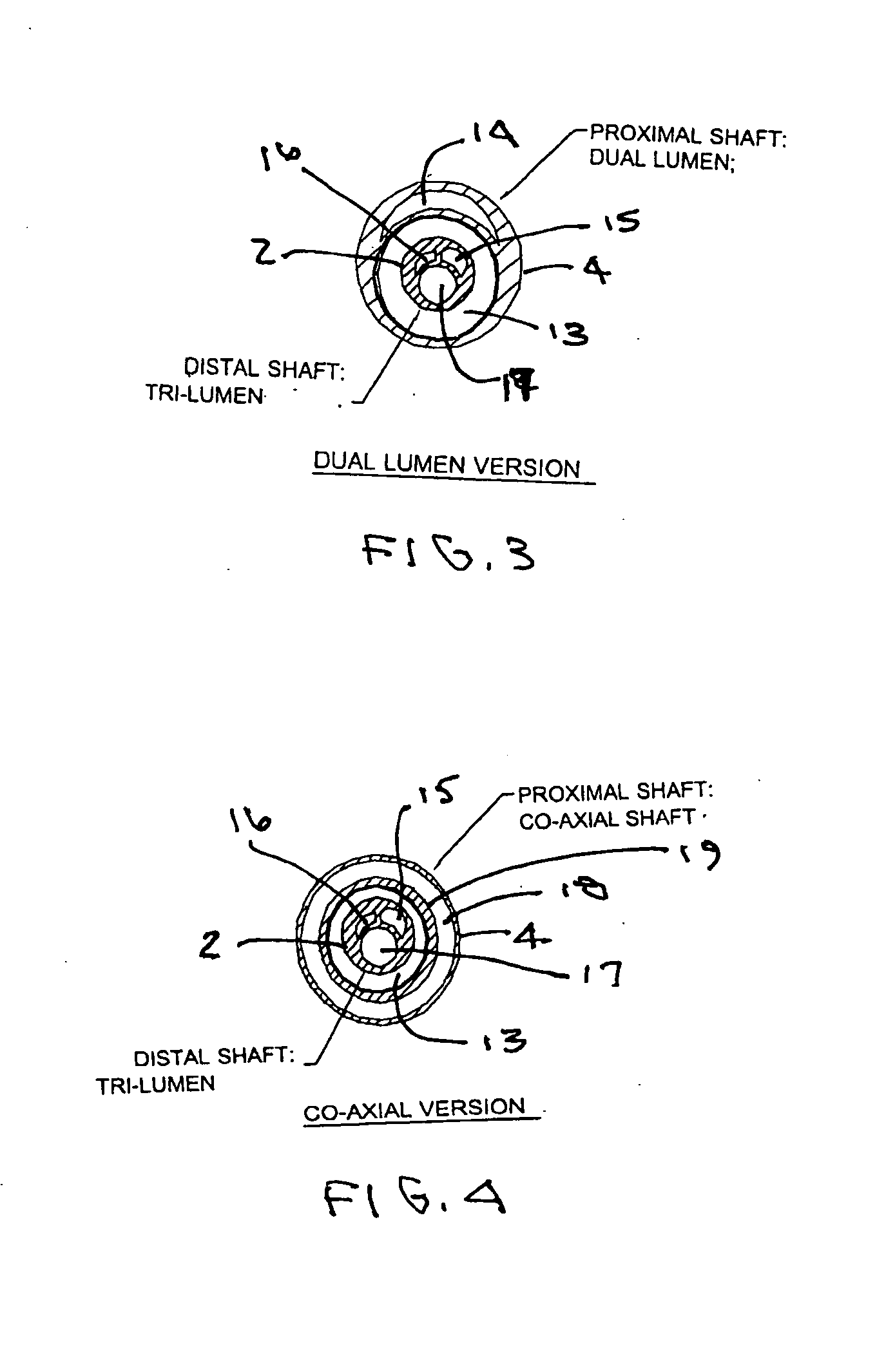
A catheter system for localized or semi-localized administration of agents through the wall of a blood vessel is provided. Various catheter system constructions which use at least one expandable occluding device to create an isolated region are provided. Constructions using one catheter and one occlusion device are provided, along with constructions using two catheters and multiple occlusion devices. The catheter system may include a catheter with a variable stiffness along its length. The catheter system may also include a guide wire integrated with an inner catheter. The catheter can infuse the agent into the blood vessel in a pressure regulated manner. Methods for delivery and infusion of the agent within a blood vessel are also provided.
Owner:VENOMATRIX
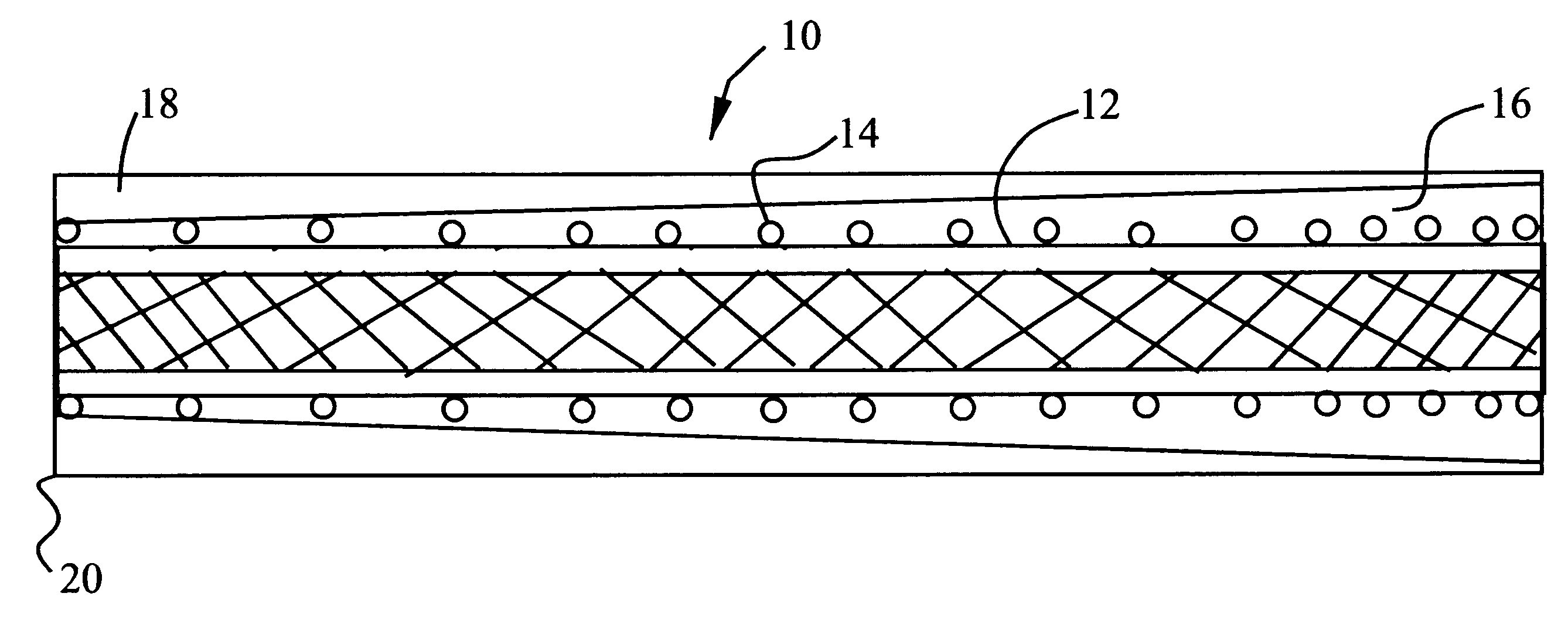
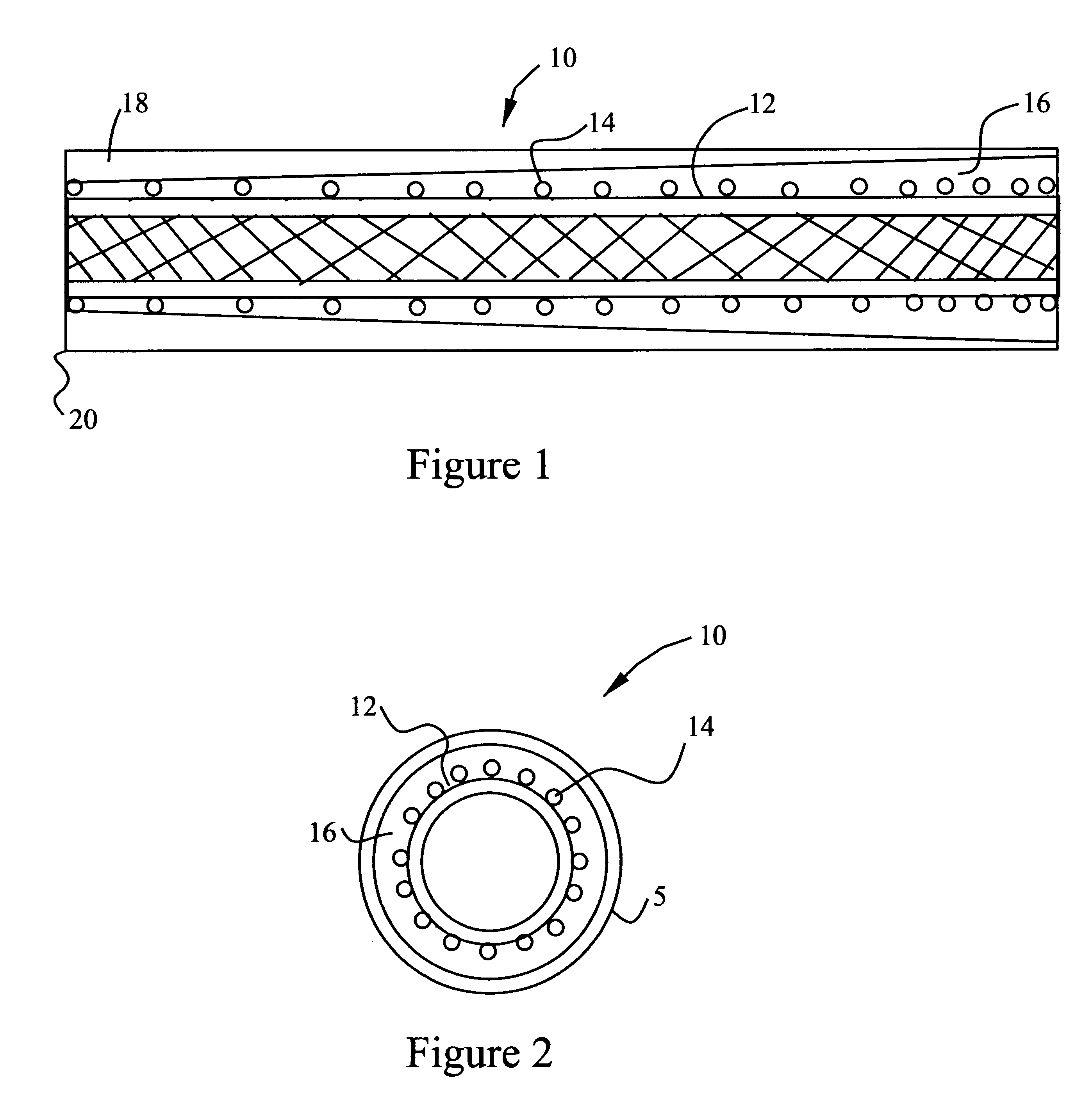
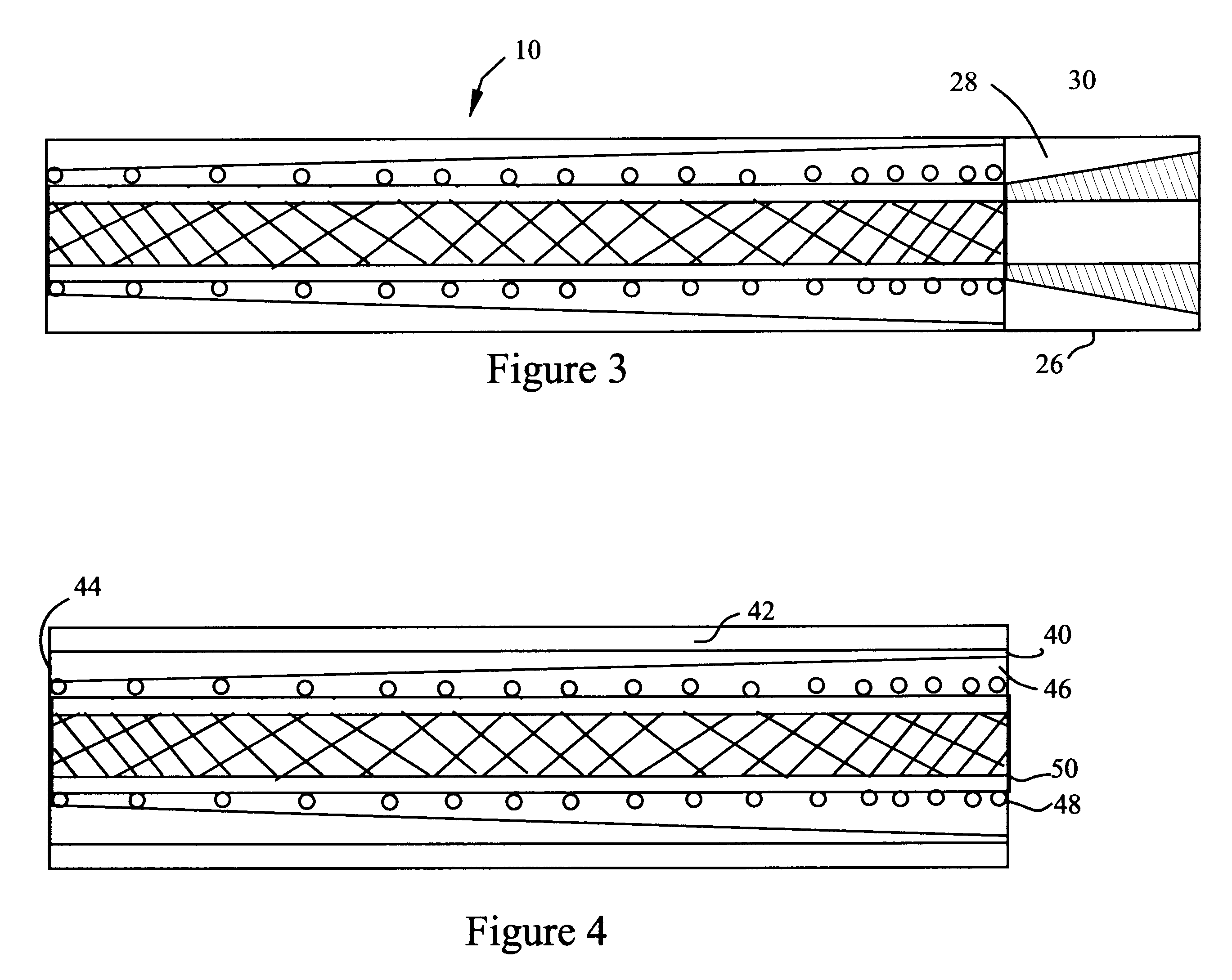
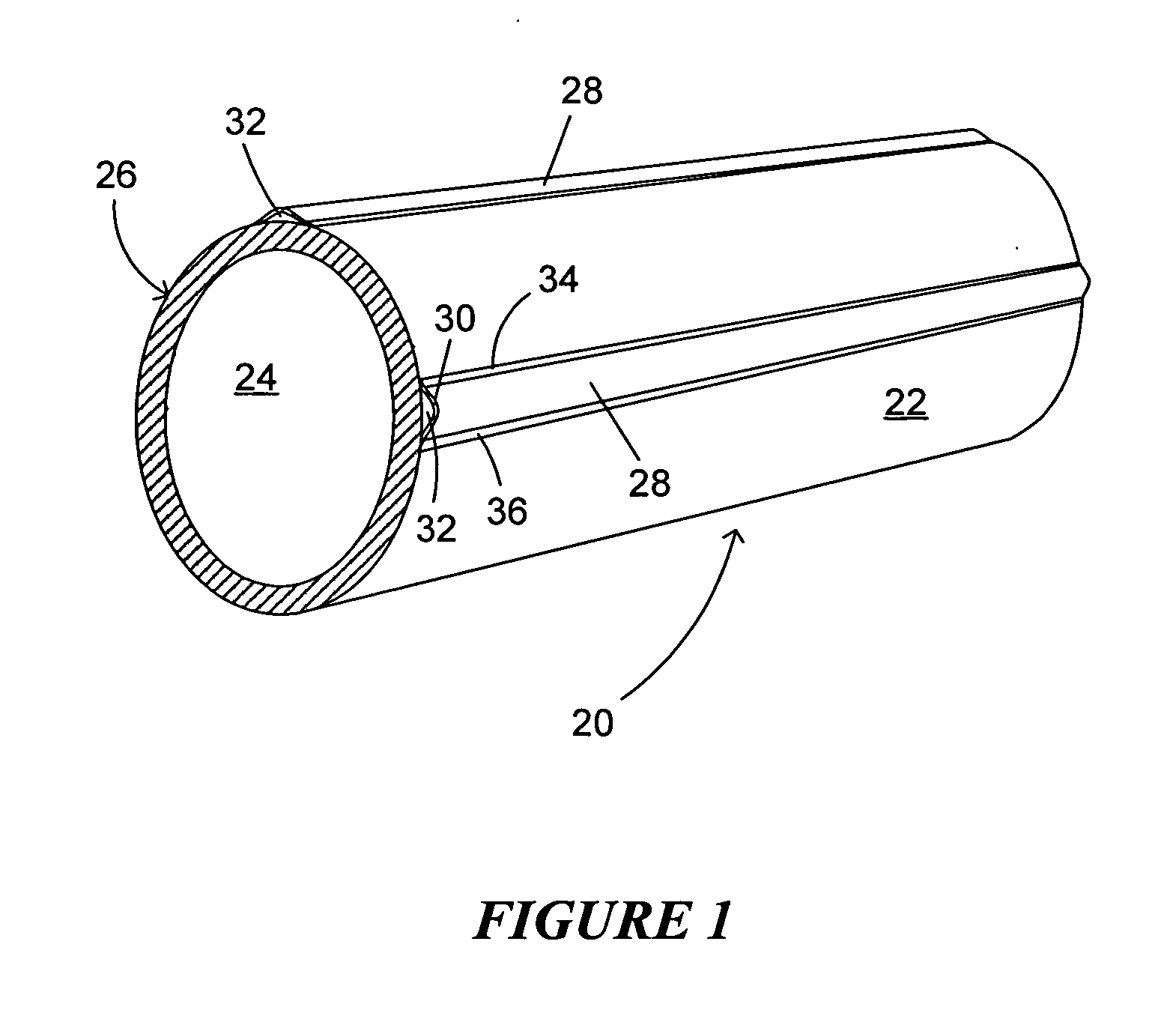
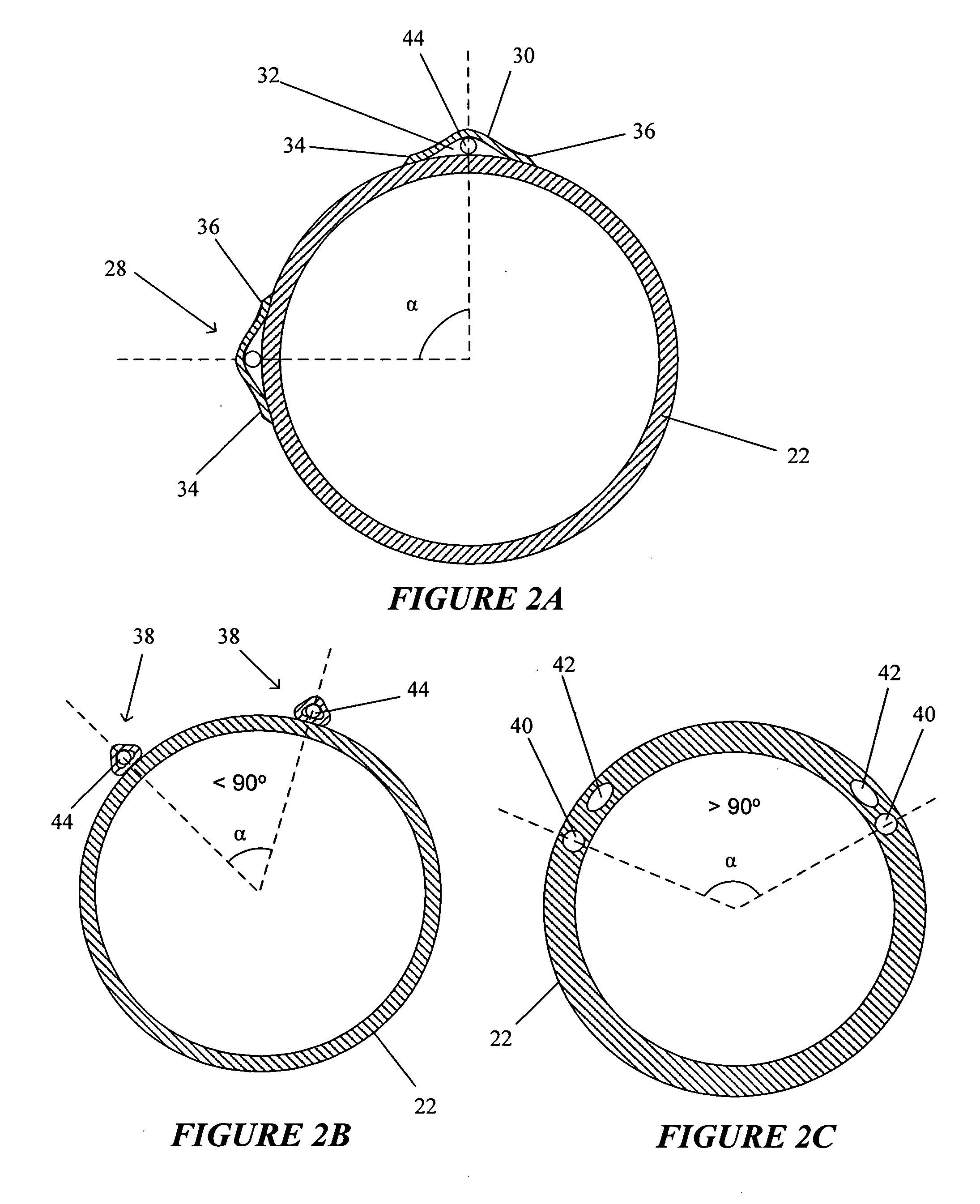
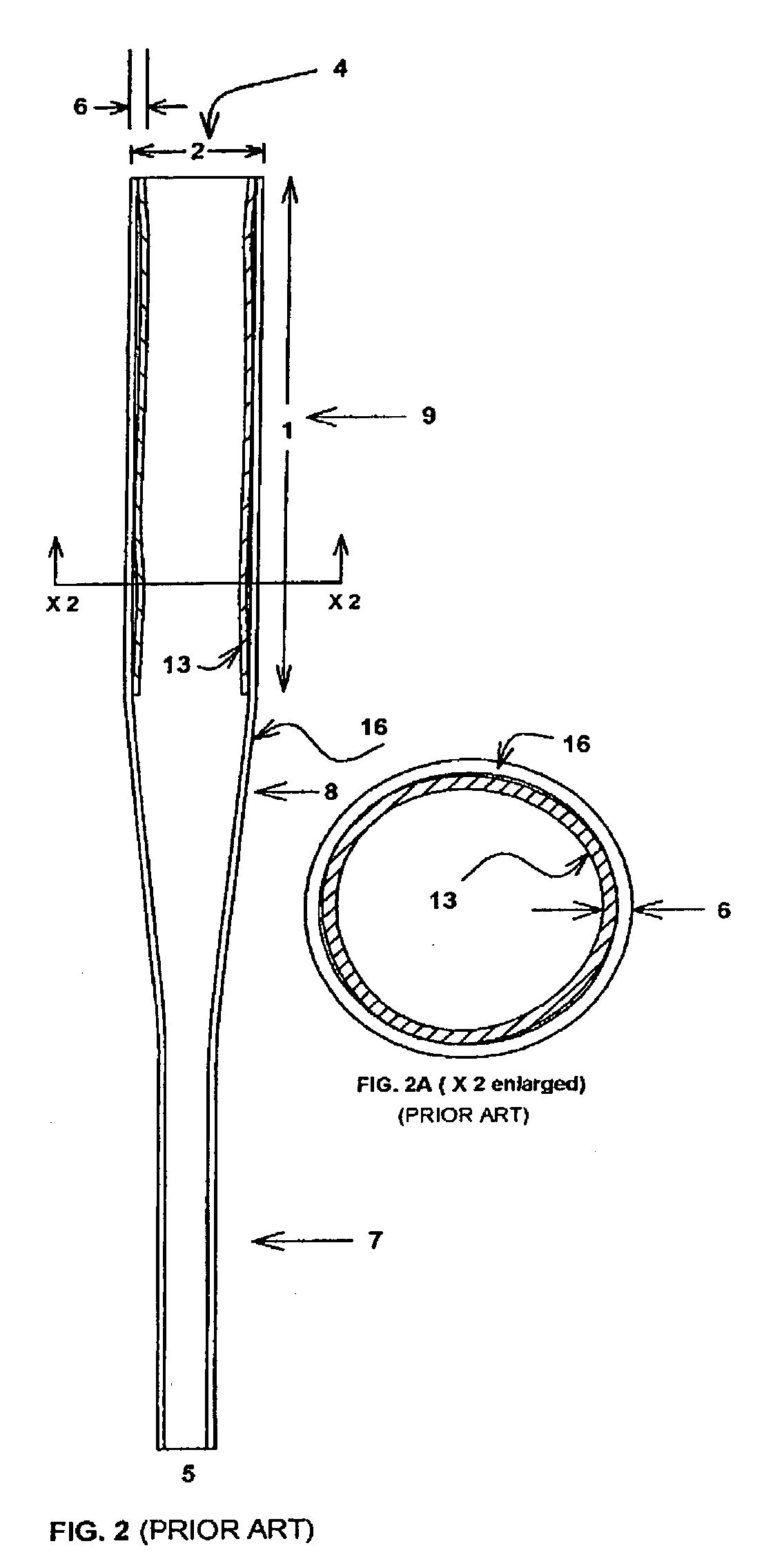
Reinforced variable stiffness tubing
A reinforced catheter having a multi-layered structure suitable for medical uses comprising an inner liner, a braided reinforced layer adjacent to the inner liner, a first resin adjacent to the braided layer, and a harder second resin overlaying the first resin; wherein, the first resin and second resin taper inversely to one another along the length of the catheter, thereby forming a co-tapered soft tip that reduces body trauma.
Owner:COHEN MARK
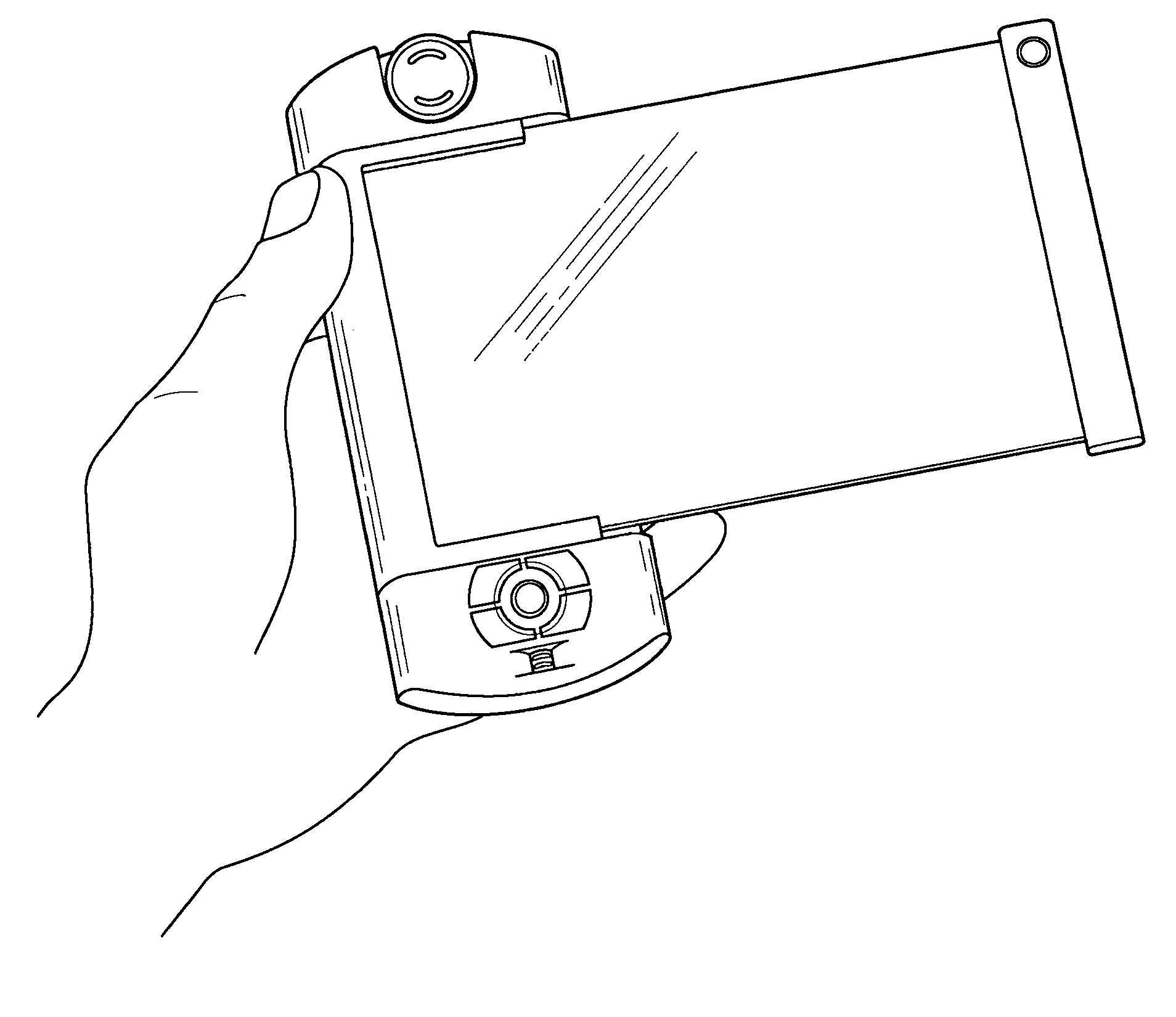
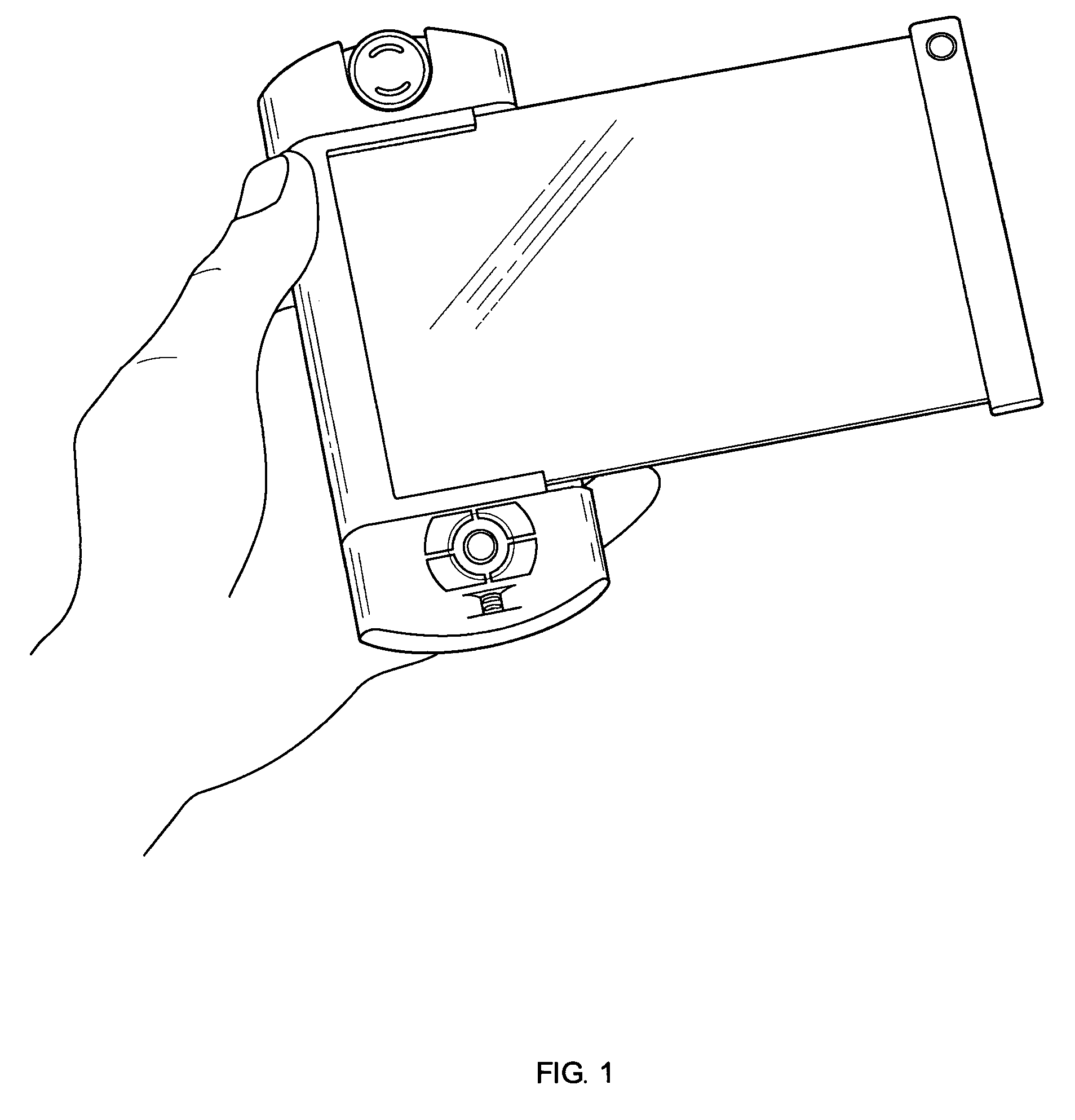
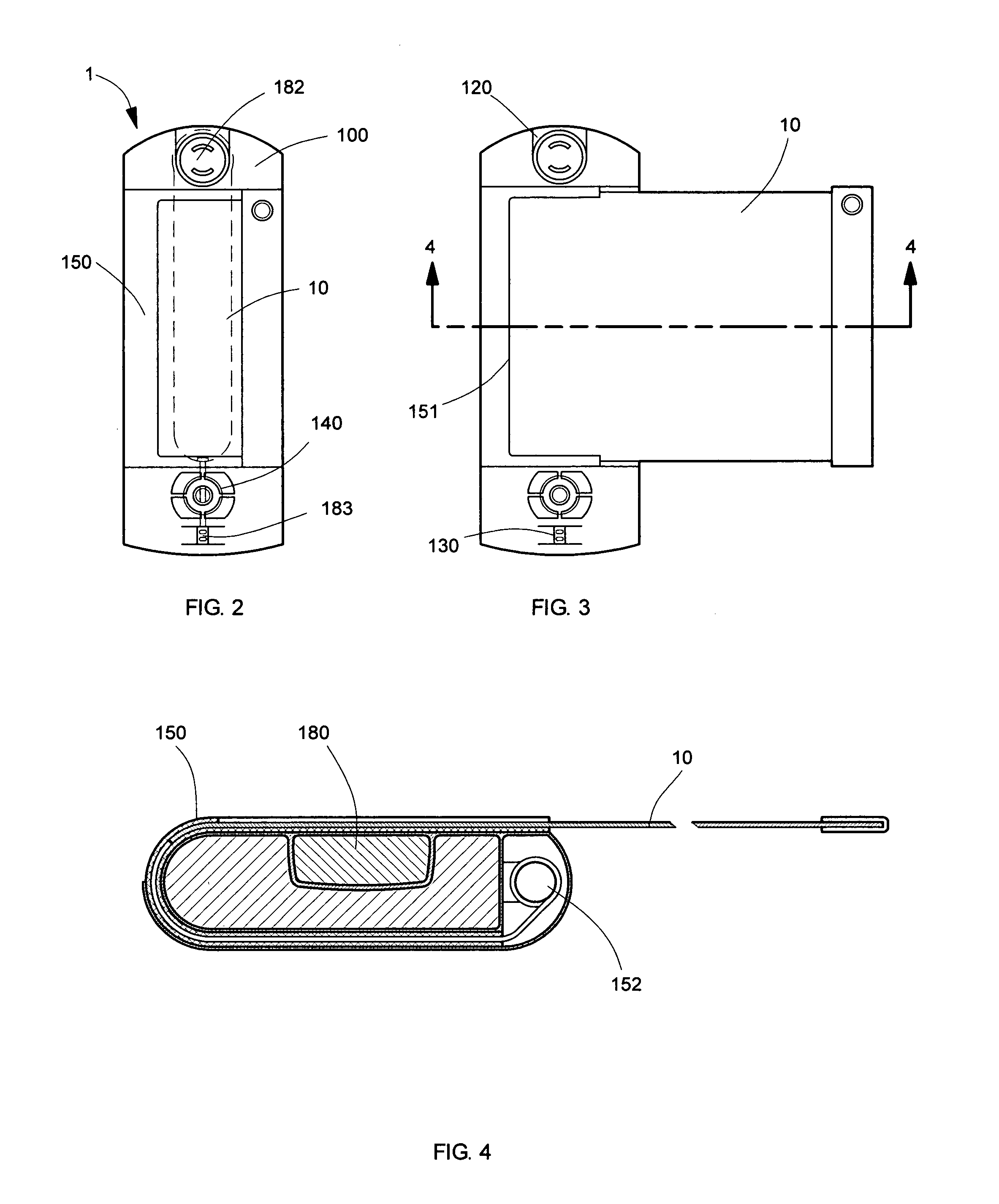
Personal digital device with adjustable interface
InactiveUS7558057B1High trafficPrecise and quick and comfortable mannerDetails for portable computersSubstation equipmentGraphicsVariable stiffness
A personal digital device comprises a variable stiffness screen capable of varying its display size by managing its stiffness, and a body carrying means for wireless communication and for storing and processing information. The functional flexibility of the screen allows for creating an adjustable visual interface between the user and the device: with the screen inside the device for compact storage, and with the screen extended to display high-quality graphics and images. In some particular embodiments the device incorporates a detachable audio unit allowing configuration of the user audio interface depending on the specifics of usage.
Owner:NAKSEN ALEX +1
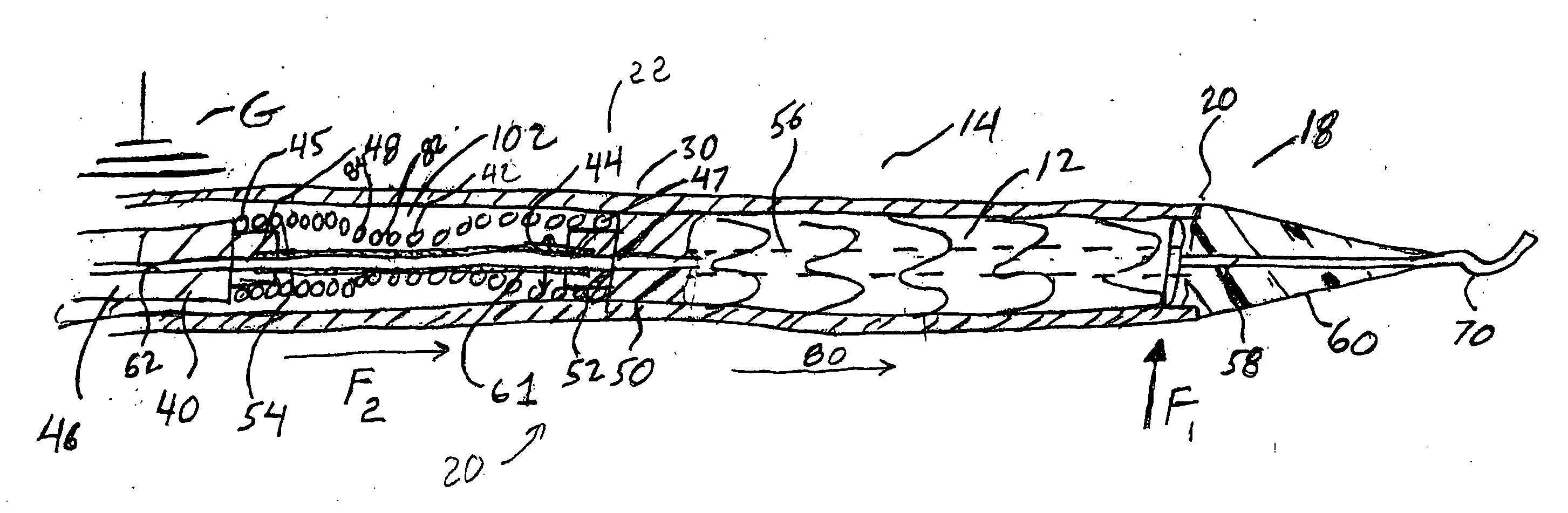
Catheter with flexible tip and shape retention
ActiveUS7115134B2Reduce the possibilitySimple designEar treatmentGuide wiresVariable stiffnessAcute angle
An improved apparatus and method to catheterize passages is disclosed. The present invention provides a catheter having a soft flexible pre-formed distal tip, that when used in combination with commercially available guidewires of variable stiffness, results in the ability to control the direction and angle of wire advancement allowing cannulation of body passages, including those that arise at acute angles. The catheter can have a longitudinal axis, a proximal section and a distal section having a soft flexible pre-formed tip having a curvature of ninety degrees or greater and shape retention. The catheter can have an inner wall that defines a lumen that runs along said longitudinal axis forming a single continuous tube, a reinforcement braid disposed over the inner wall, and an outside covering disposed over the reinforcement braid. A spacer can be added between said wall liner and said reinforcement braid in the proximal end.
Owner:CHAMBERS TECH INC
Stretch resistant embolic coil with variable stiffness
Owner:CODMAN & SHURTLEFF INC
Variable stiffness catheter assembly
InactiveUS20070250036A1Variable stiffnessIncrease thrustStentsMulti-lumen catheterVariable stiffnessActive polymer
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method and apparatus for providing a relative location indication during a surgical procedure
An orthopedic guidewire includes an elongate guidewire body having longitudinally spaced proximal and distal guidewire ends. An engaging feature is located at the distal guidewire end and is configured to selectively engage a bone surface. At least one of a variable diameter and a variable stiffness are along a portion of the guidewire body spaced apart from the engaging feature. A method of providing a relative location indication during a surgical procedure utilizing the orthopedic guidewire is also included.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Variable stiffness catheter assembly
InactiveUS7766896B2Variable stiffnessIncrease thrustStentsMulti-lumen catheterVariable stiffnessCatheter
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Variable stiffness screen
InactiveUS20060038745A1High trafficStatic indicating devicesDigital data processing detailsVariable stiffnessDisplay device
A variable stiffness screen for wearable electronic devices provides a viewable area that can be adjusted by managing the screen's physical properties. The screen incorporates a flexible electronic display, attached to a structural system, in which the physical properties can be changed from a flexible state to a rigid one to control the stiffness of the display.
Owner:NAKSEN ALEX +1
Method and apparatus for localized drug delivery
InactiveUS20050059930A1Easy to manufactureAccurate measurementStentsBalloon catheterVariable stiffnessSystem construction
A catheter system for localized administration of agents through the wall of a blood vessel is provided. Various catheter system constructions which use at least two expandable occluding elements to create the localized site are provided. The catheter system may include a catheter with a variable stiffness along its length. The catheter system may also include a hollow guide wire which is coupled to an expandable occluding element.
Owner:GARRISON MICHI +2
Catheters having stiffening mechanisms
InactiveUS20060264907A1Solve the lack of flexibilitySufficient pushabilityCatheterVariable stiffnessShape change
Catheters having selectively insertable or selectively activatable and releasable stiffening mechanisms are provided. In general, the catheter is inserted, navigated and withdrawn from a subject in a relaxed, flexible condition and stiffening mechanisms are deployed to prevent the catheter from shifting during placement or operation of an accessory device or tool through the catheter. Stiffening members(s) may be inserted into and removed from one or more longitudinal channel(s) provided in proximity to the catheter wall and generally coaxial with the primary catheter lumen to change the stiffness properties of the catheter. The properties, configuration and size of the stiffening members and channels may be varied to vary the stiffness properties of the catheter and stiffening members may be constructed from materials having shape change properties or materials that change conformation or stiffness with application of heat, current or electrical field. Stiffening mechanisms may also employ energy absorbing and viscoelastic polymer materials having variable stiffness properties depending on ambient conditions.
Owner:PULSAR VASCULAR
Variable stiffness heating catheter
InactiveUS6887235B2Variable stiffnessEasy to trackElectrotherapyCatheterVariable stiffnessEngineering
The variable stiffness heating catheter includes a heating catheter shaft including at least one electrically conductive member, a reinforcing tube with apertures formed around the surface of the reinforcing tube, and at least one coaxial outer layer of a polymer, metal, or both for providing desired variations in stiffness along at least a portion of the length of the shaft. The apertures can be formed as axial or helical slits in the surface of the reinforcing tube, and the reinforcing tube can also be formed to be tapered at the point where the apertures are formed in the reinforcing tube to provide a heating catheter that is torqueable and pushable at the proximal end, yet soft and flexible at the distal end.
Owner:MICRUS CORP
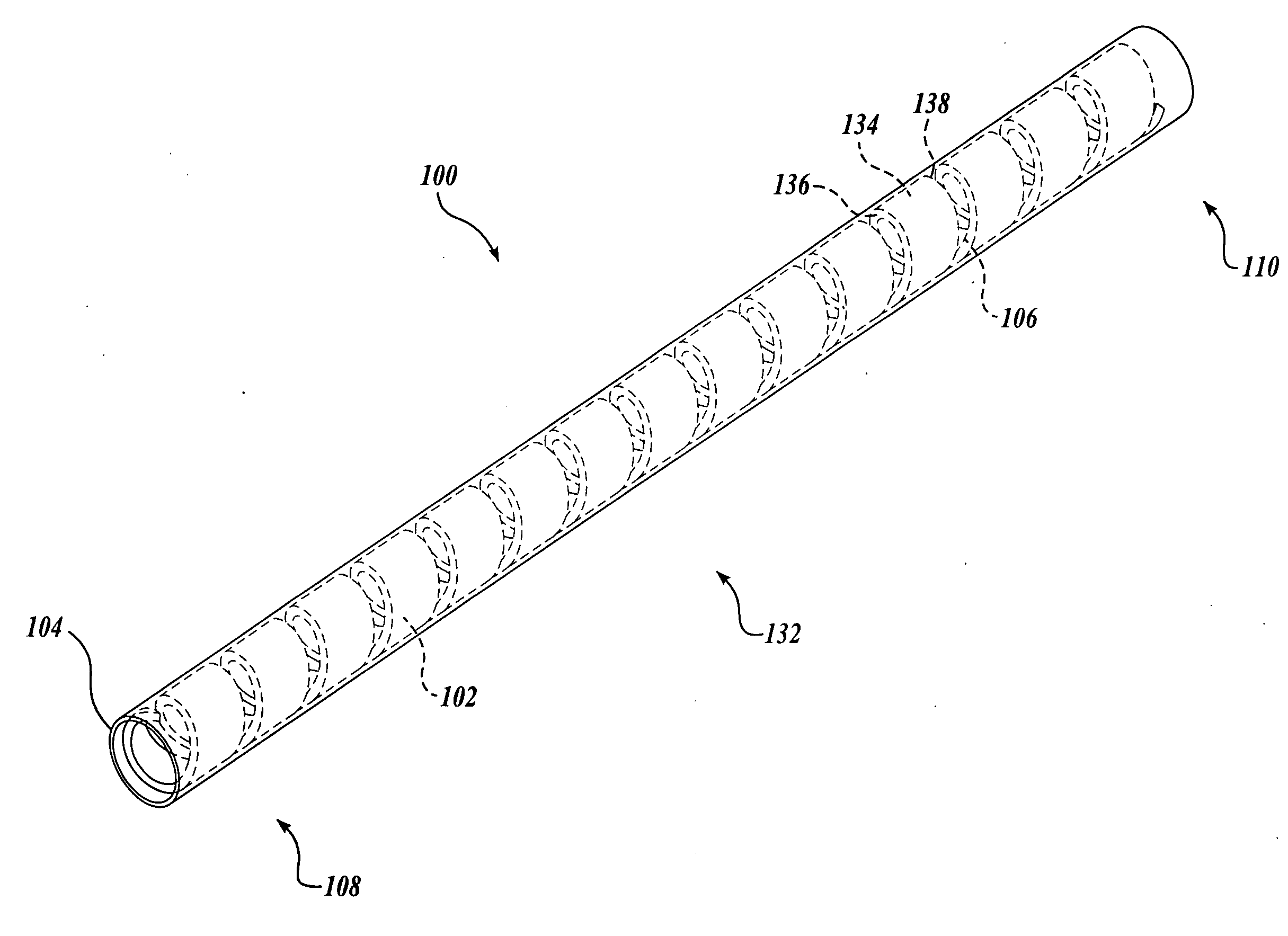
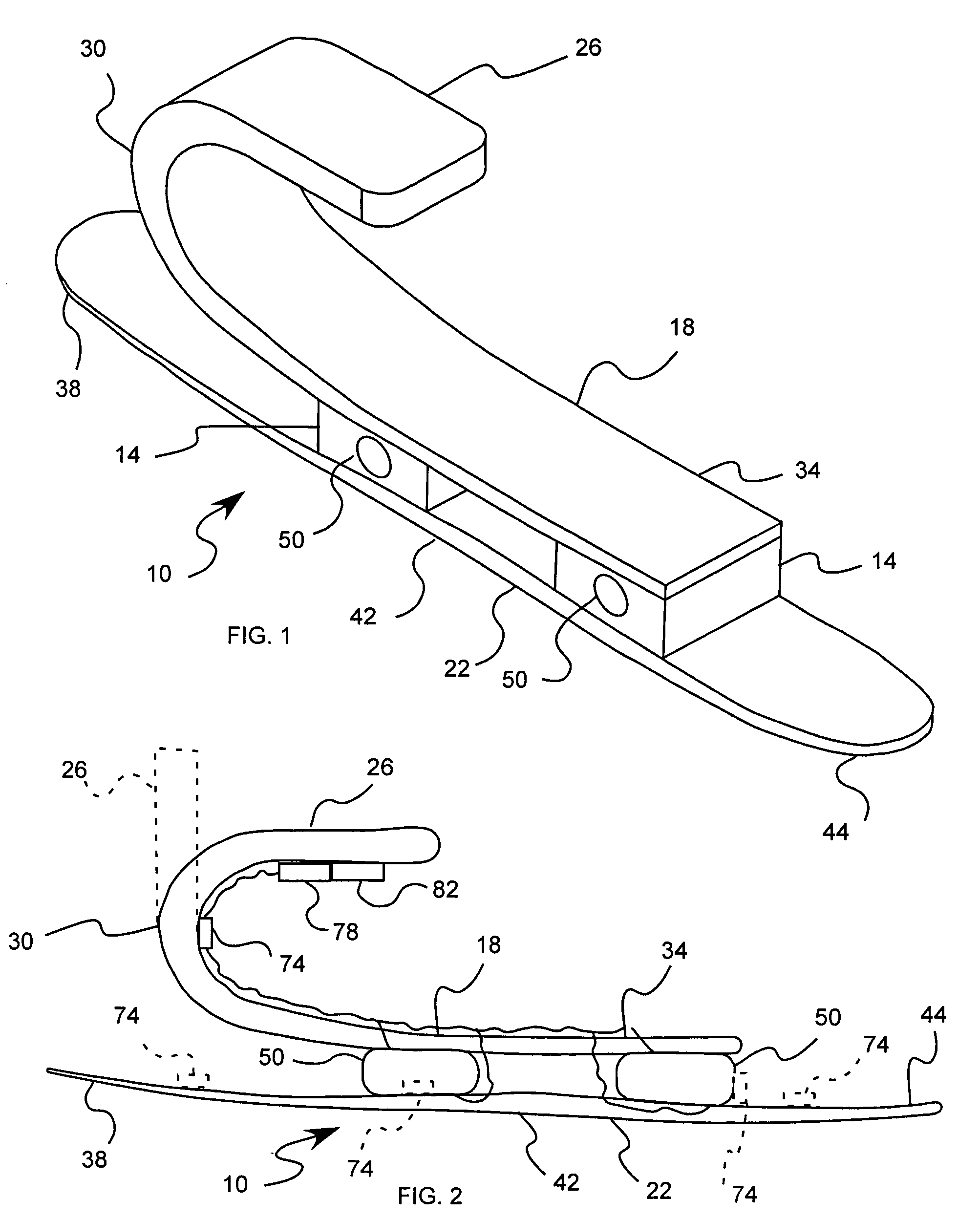
Flexible endoscope with variable stiffness shaft
A shaft for a medical device includes an outer sheath and a flexible spiral wrap therein. The flexibility of the spiral wrap is modified by changing the width of the wraps of a spiral, the thickness of the wraps of a spiral, or the gap spacing of the spiral. The spacing between wraps is maintained by attaching the spiral wrap to the cover sheath that surrounds the spiral wrap at two or more locations.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
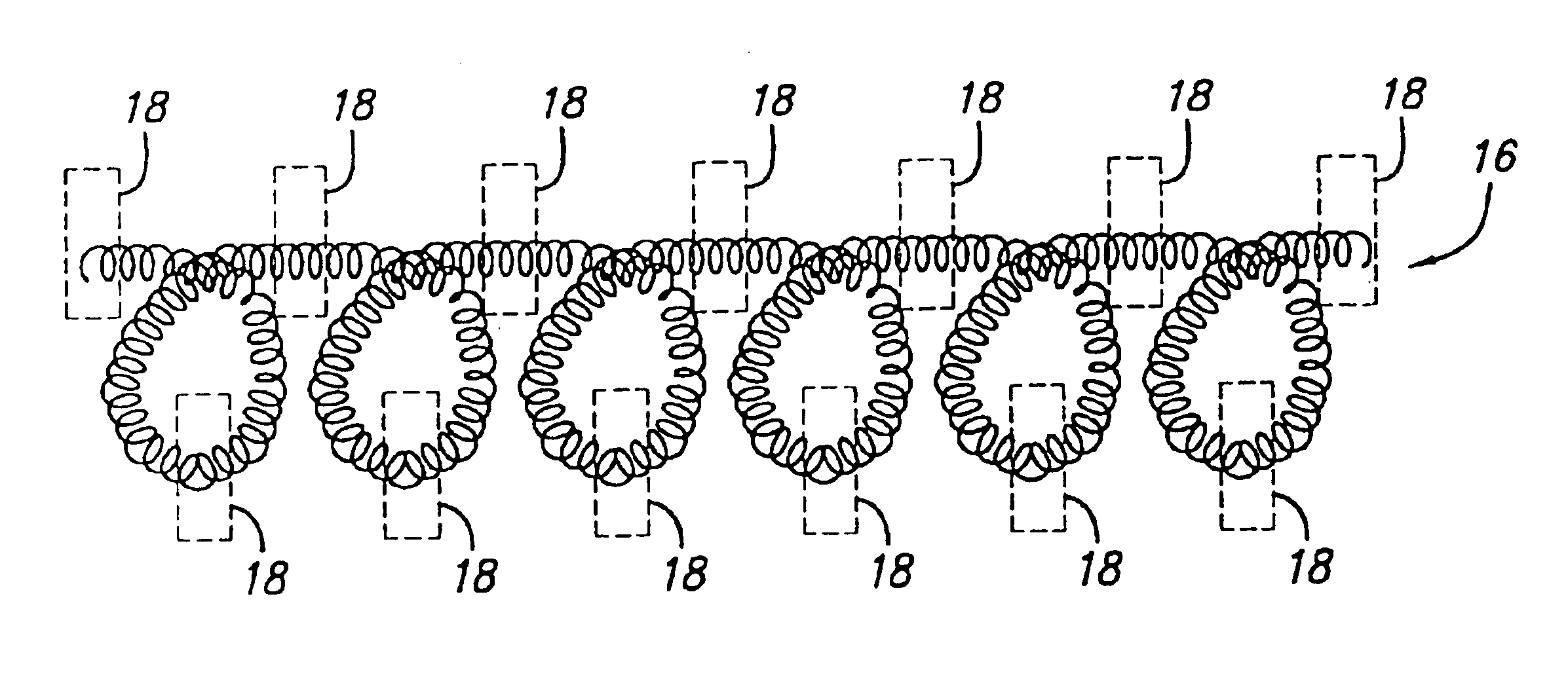
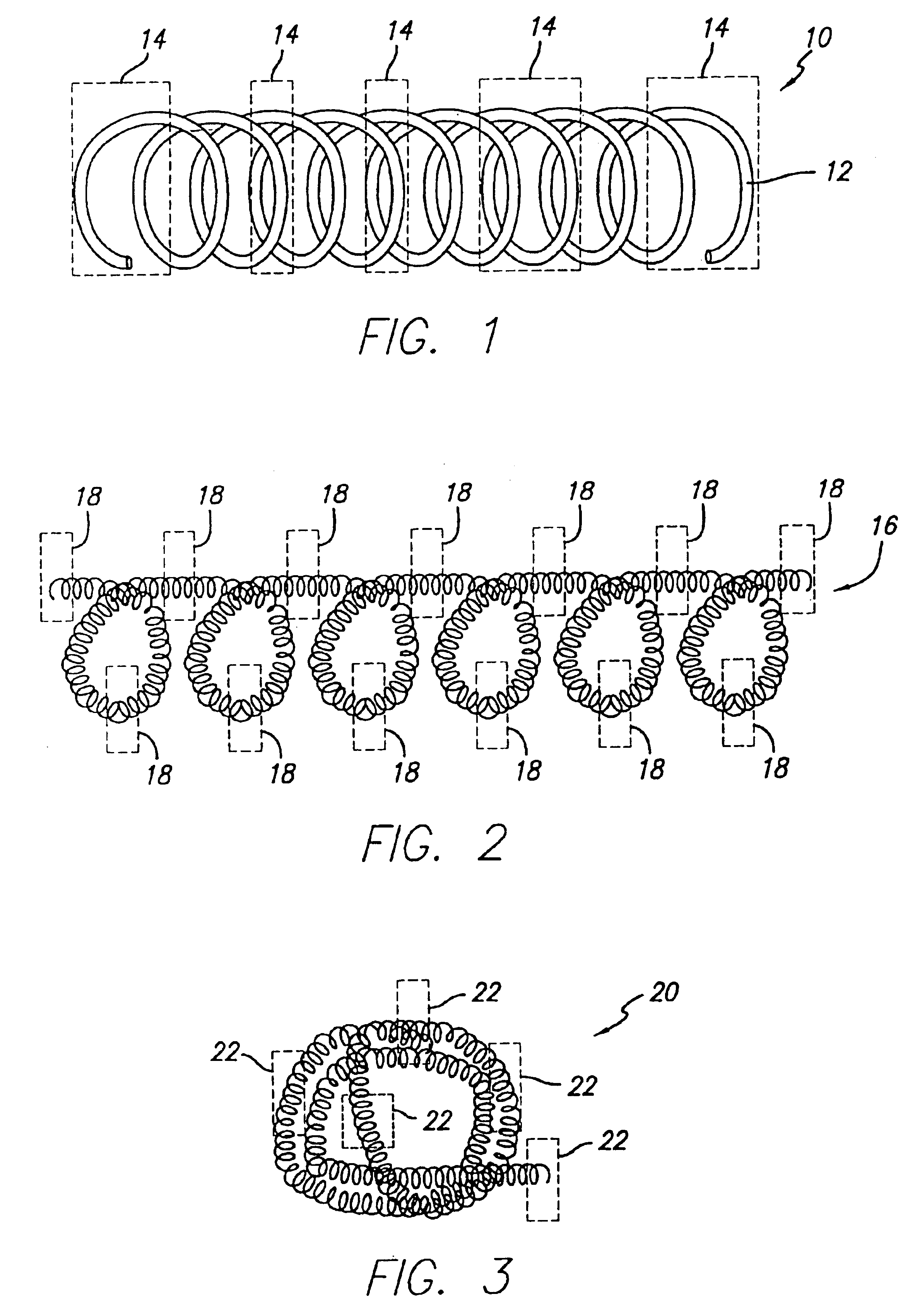
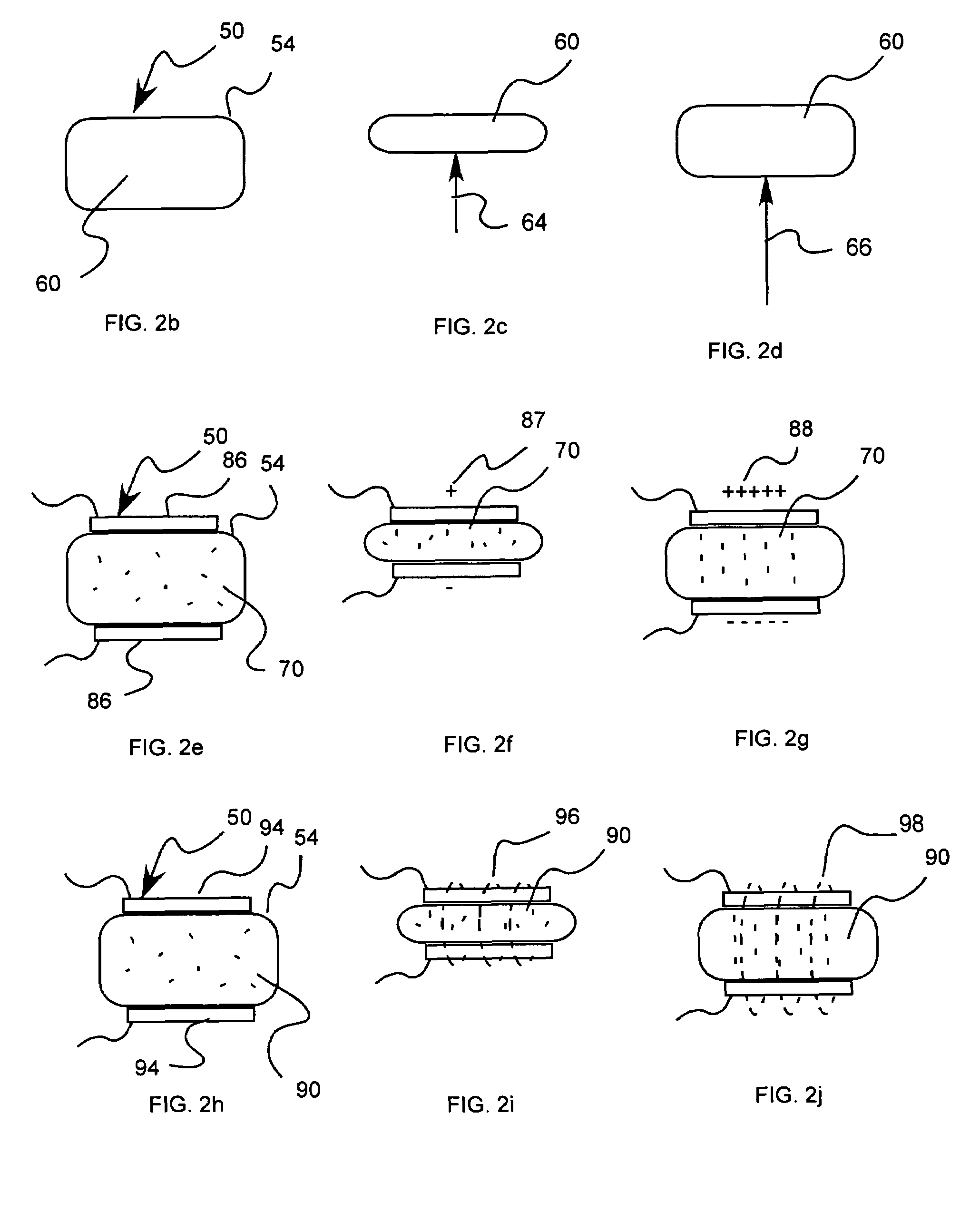
Variable stiffness coil for vasoocclusive devices
InactiveUS6872218B2Variable stiffnessSofter, more deformable, or less traumaticDilatorsDiagnostic markersVariable stiffnessEngineering
The variable stiffness vasoocclusive coil is given variable stiffness along the length of the coil by selectively heat treating certain segments of a primary or secondary coil. The primary coil can be selectively heat treated to form soft or deformable segments along the length of the coil, and can then be shaped into a secondary shape that is set by a heat treatment process. Distal regions of the coil can also be heat treated to make the distal ends of the coil softer, more deformable, or less traumatic.
Owner:MICRUS CORP
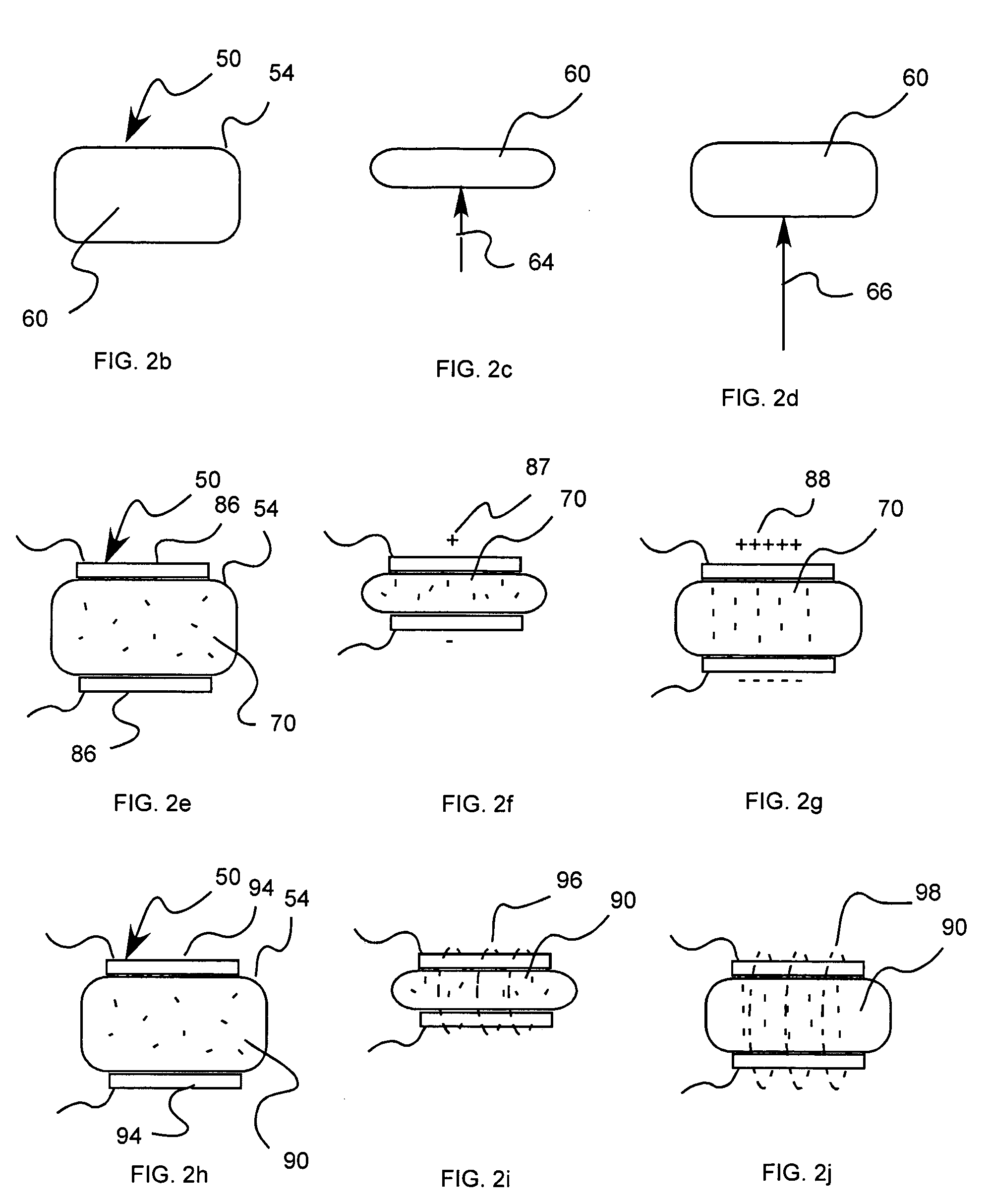
Deformable variable-stiffness cellular structures
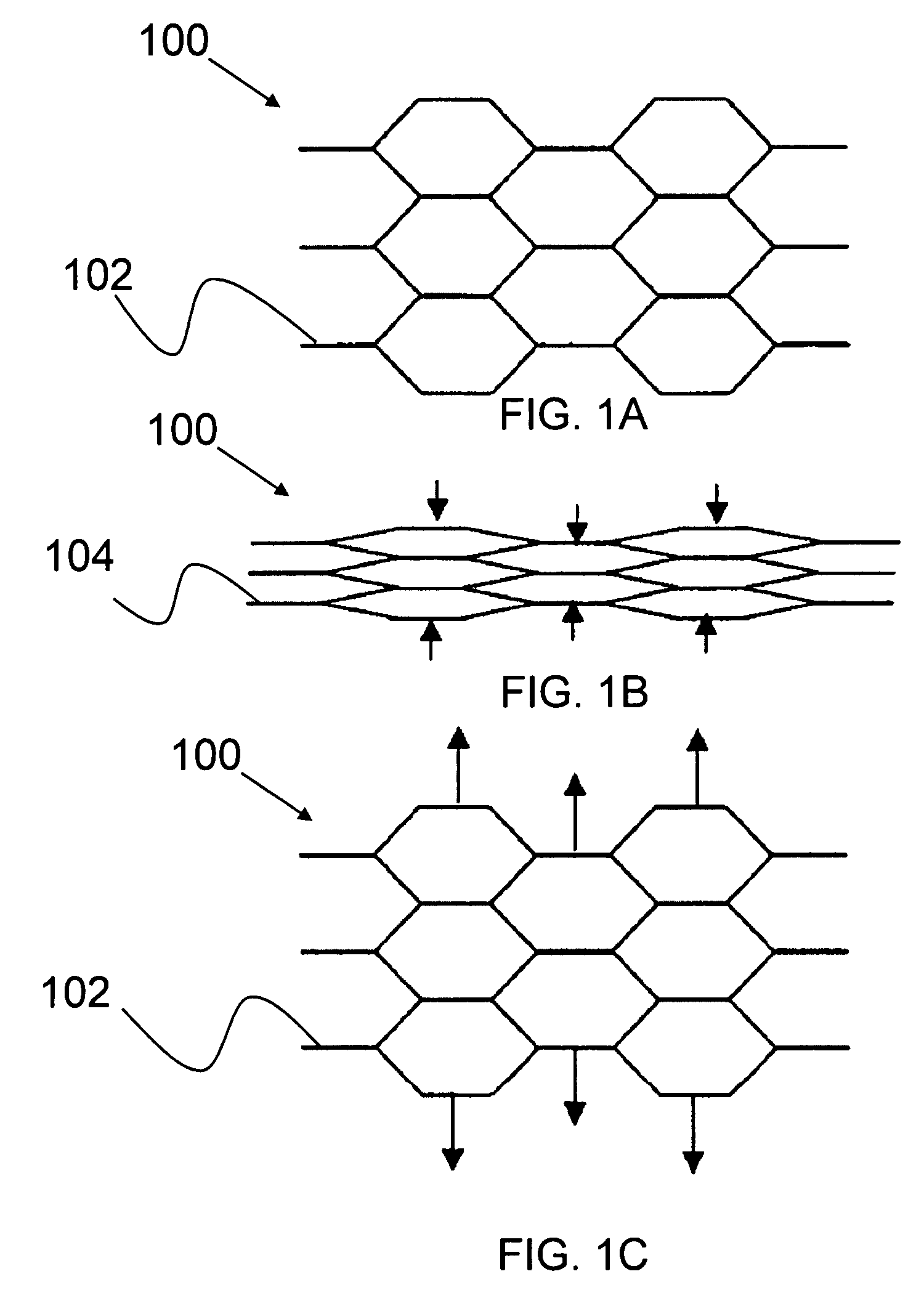
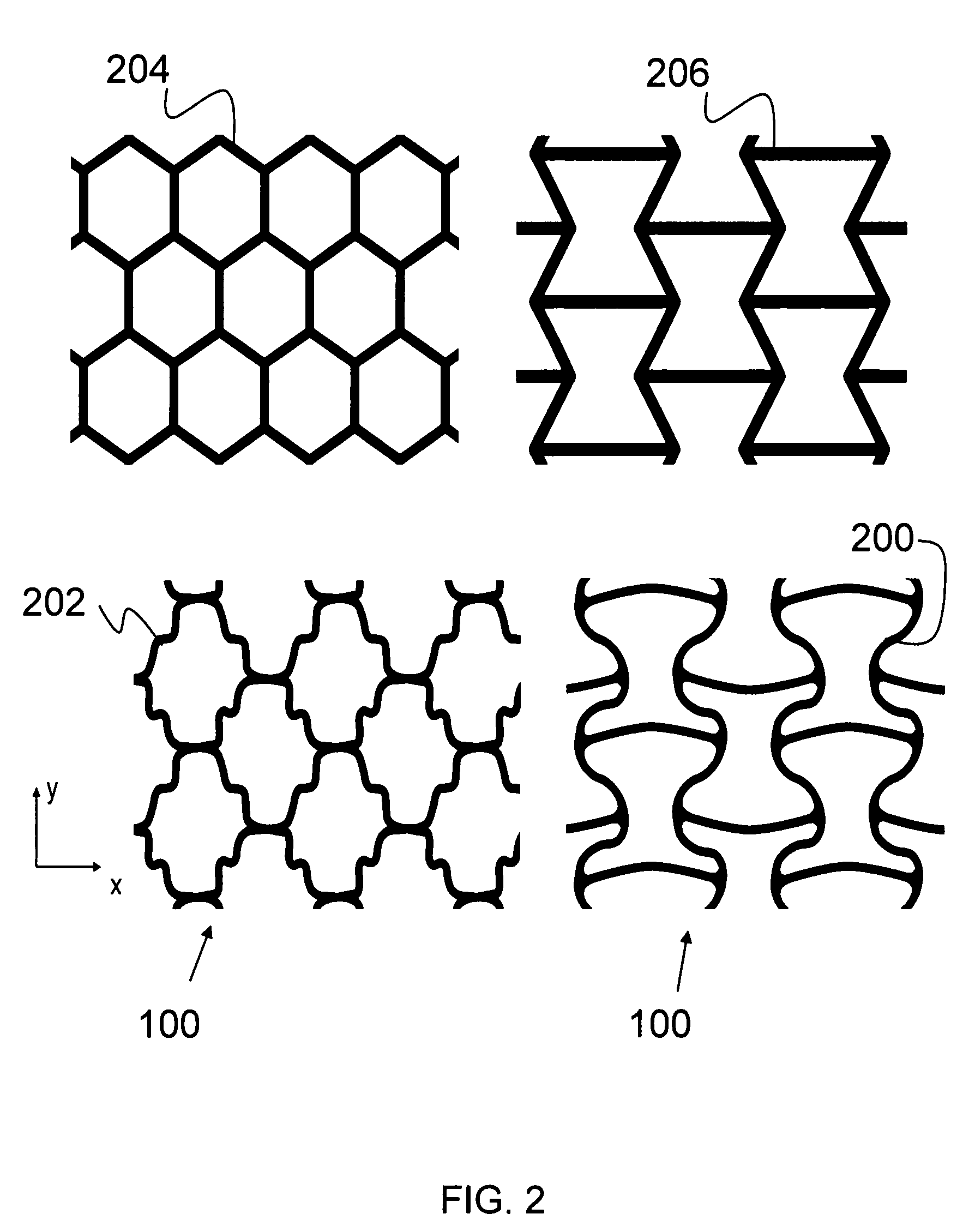
ActiveUS7678440B1Assist shapeAssist strainLayered productsCeramic shaping apparatusVariable stiffnessHoneycomb structure
Described is a deformable, variable-stiffness cellular structure. The cellular structure a group of unit cells with each unit cell having a cellular geometry. The group of unit cells are formed of a variable-stiffness composite material (VSM). The VSM has a first stiffness state and a second stiffness state. Additionally, the cellular structure has a first shape and a second shape, with a gradation of shapes between the first shape and second shape. The transition from the first shape to the second shape occurs through using an actuation signal to actuate the VSM to change the stiffness of the cellular structure, thereby allowing the cellular structure to be deformed from the first shape to the second shape, and any shape therebetween. The cellular structure can be locked in the second shape through actuating the VSM from the second stiffness state to the first stiffness state.
Owner:HRL LAB
Laser-assisted guidewire having a variable stiffness shaft
Embodiments of the present invention comprise a fiber optic guidewire having a hypotube with a plurality of openings that provide variable stiffness and tracking characteristics between at least one proximal segment and one distal segment of the guidewire. In some embodiments, the guidewire further comprises a mandrel disposed within the hypotube, the mandrel cooperating with the optical fibers to permit the distal end of the hypotube to be shaped as desired by a user. Methods of manufacturing and using the guidewire are also disclosed.
Owner:SPECTRANETICS
Tubular baseball bats with variable stiffened barrels
Tubular baseball bats comprised of an elongated handle portion and a striking or barrel portion wherein the barrel portion has variable stiffness along its length. One such bat has a circumferential low cost, low weight stiffener generally located in the sweetspot area designed to increase radial stiffness in a controlled manner which results in decreasing the bat performance to meet a changed bat performance standard and can be applied at low cost to both used field returned bats and bats being newly manufactured. Further, new tubular polymer composite bats can be designed with increased radial stiffness generally located in the sweetspot area or with radial stiffness graduated from highest, generally in the sweetspot area, to lowest at the barrel ends. All bats of the present invention result in calculated bat performance to meet applicable regulatory standards while also increasing the sweetspot size.
Owner:CE COMPOSITES BASEBALL
Squeeze film damper with variable support stiffness
A squeeze film damper assembly having a variable stiffness and damping control. The squeeze film damper includes a damper chamber formed by two flexible bellows chambers of the sides. A first pressure source is applied to the damper chamber to regulate the damping. A second pressure source is applied to the flexible bellows chambers to vary the stiffness of the damper. The flexible bellows chambers are secured between an outer member and an inner member of the damper assembly and form the sealed damper chamber. A pressure ratio between the bellows chambers and the damper chamber can vary to control the stiffness of the squeeze film damper.
Owner:FLORIDA TURBINE TECH
Laser-assisted guidewire having a variable stiffness shaft
Owner:SPECTRANETICS
Prosthetic foot with energy transfer including variable orifice
A prosthetic foot device with variable stiffness response includes a variable energy transfer mechanism or variable resistance cell disposed between first and second foot members to transfer a variable amount of energy from the second member to the first member during use. The energy transfer mechanism or variable resistance cell includes a variable orifice with variable size to variably resist flow of fluid therethrough, and thus variably transfers energy between the first and second members to vary stiffness of the prosthetic foot device.
Owner:FREEDOM INNOVATIONS INC
Intravascular deployment device with improved deployment capability
An intravascular delivery catheter includes a middle member or manipulator to ameliorate the effect of buckling of the graft cover during the tracking or positioning of the delivery device within a body flow lumen to deploy an exclusion device, such a stent graft. The delivery device / catheter includes a region or regions of lower resistance to bending than other portions of the delivery device, which are positioned, within the delivery device, to preferentially bend the delivery system at locations where buckling will have minimal effect upon the deployment of the exclusion device from the delivery system. The preferential bending is accomplished, by providing a middle member / manipulator that is a rod with laterally oriented slots, having different depth and spacing configurations, or by using a wire coil as a portion of the middle member where the variable stiffness is created either by providing a variable / multiple coil diameter or by using a wire having a variable diameter along its length while the wire coil diameter is relatively uniform.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
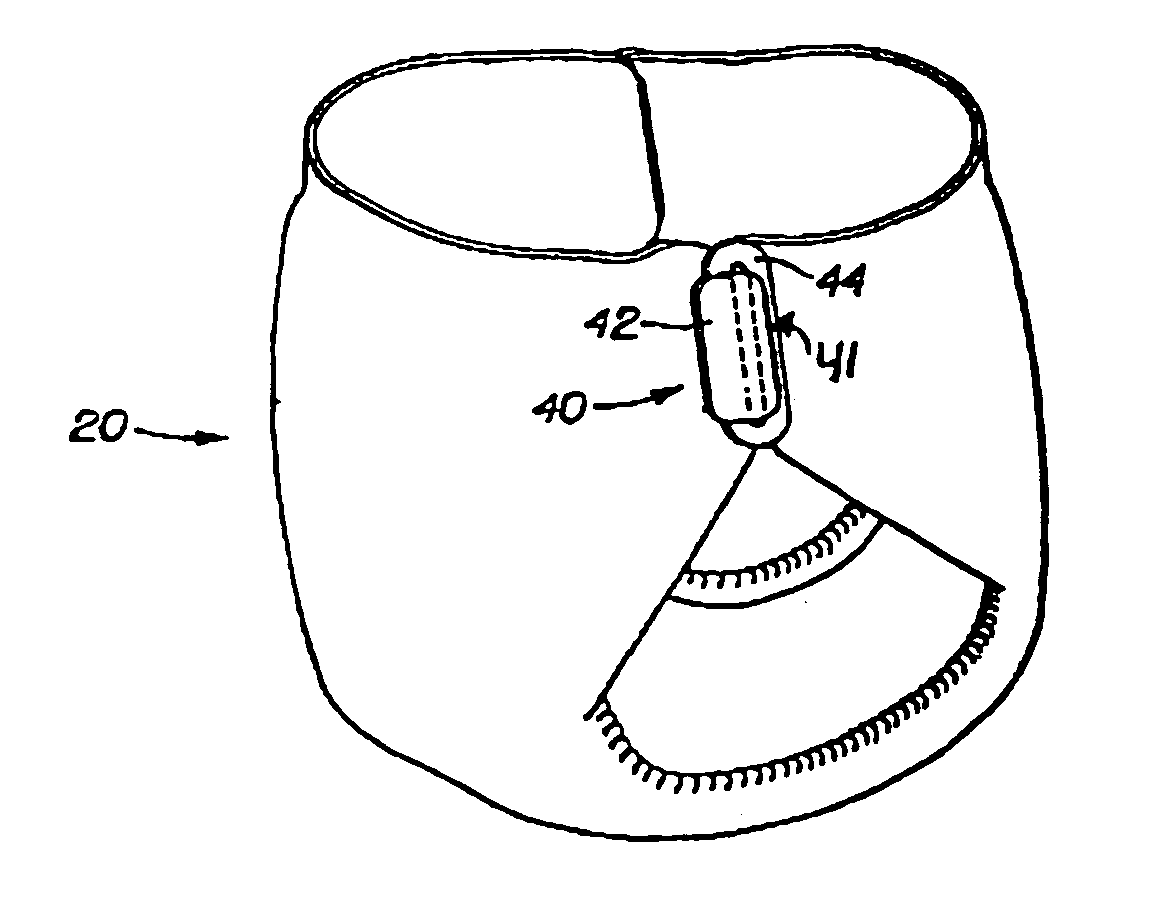
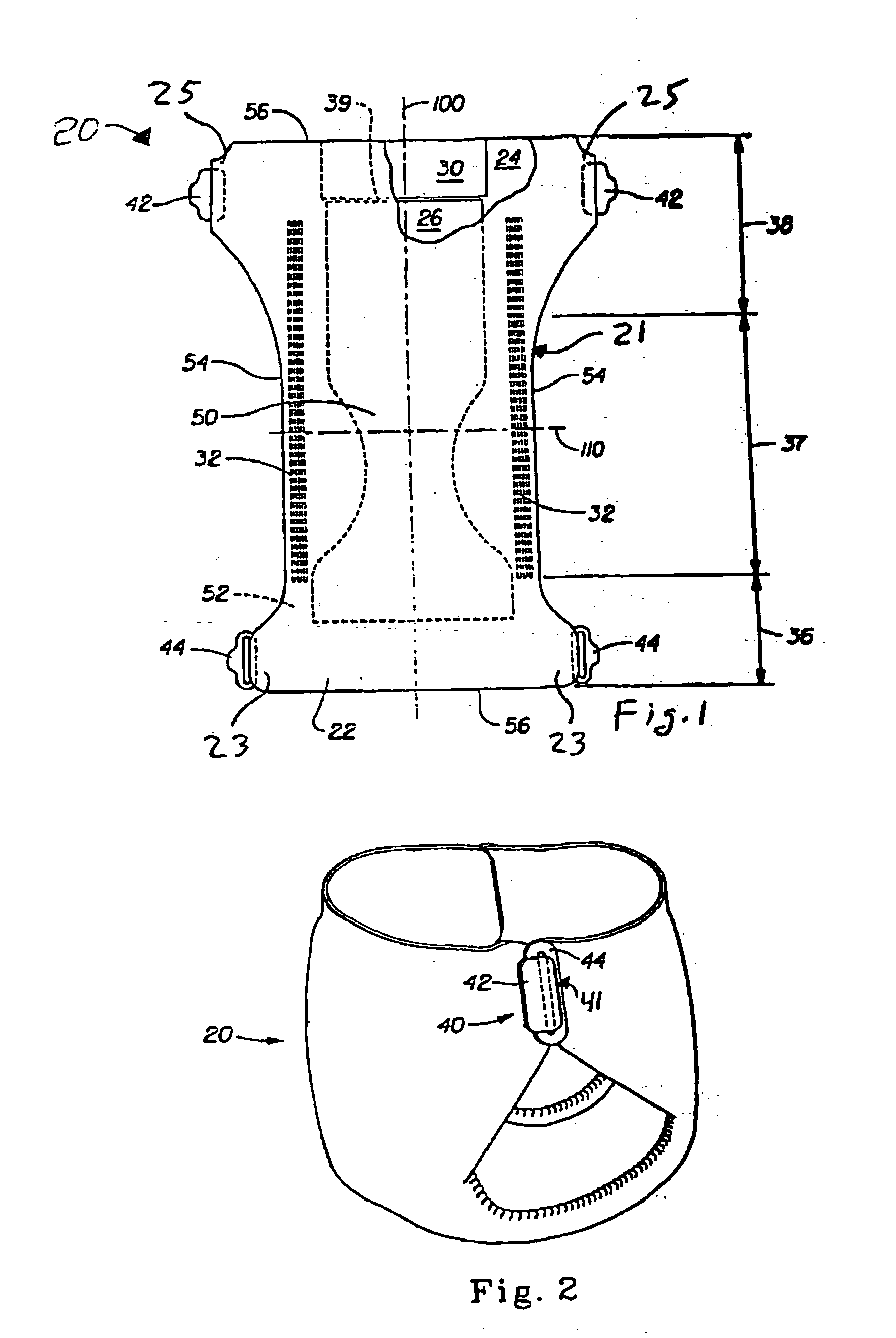
Absorbent article fastening device having stiffness changing characteristics
The present invention relates to a disposable absorbent article comprising a chassis defining a front waist region, a back waist region, and a crotch region disposed between the front waist region and back waist region. The article includes a fastening system that includes one or more fastening devices, each having at least one tab member configured to releasably connect to a slot member when, for instance, fastening the article to the body of the wearer. A variable stiffness member is associated with at least a portion of the fastening device that, in response to a predetermined external stimulus, reduces its stiffness to correspondingly reduce the stiffness of the fastening device.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Vibration-based power generator
InactiveUS8222754B1Minimizing velocityHigh bandwidthPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMachines/enginesVariable stiffnessInertial mass
A vibration-based power generator has a variable stiffness oscillator connected to a base. The oscillator comprises an inertial mass moving relative to the base in response to vibrations. The oscillator has a neutral position corresponding to a position of the oscillator when no vibrations are transmitted to the base. The oscillator has a first position where the mass is at a first distance and a second position where the inertial mass is at a second distance from a position of the mass when the oscillator is in neutral position. The second distance is greater than the first distance. A stiffness of the oscillator at the second position is greater than a stiffness of the oscillator at the first position. A transducer generating electric power in response to movement of the inertial mass is associated with the oscillator. A method of optimizing a vibration-based power generator is also presented.
Owner:SOUNDS ENERGY SYST
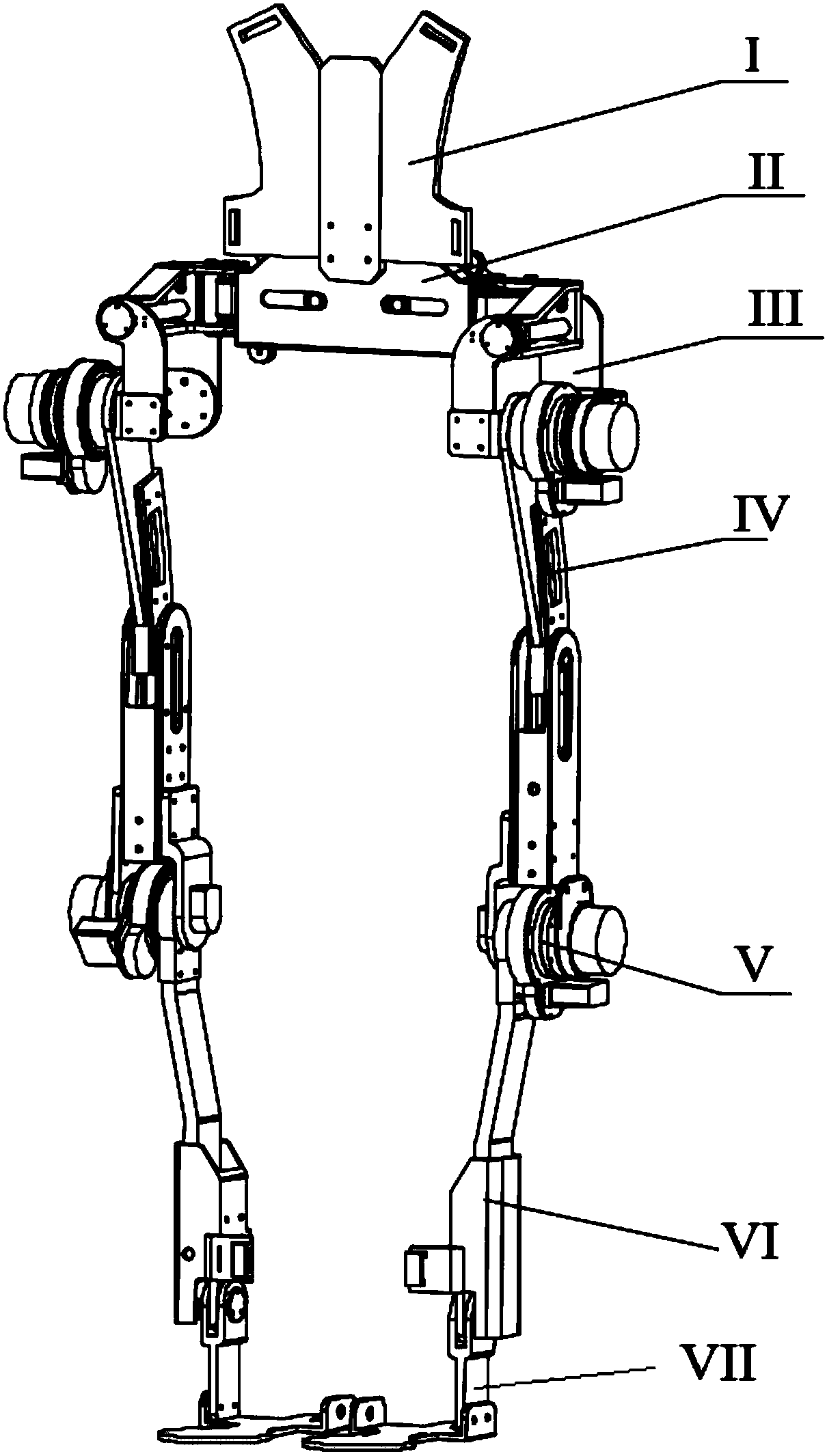
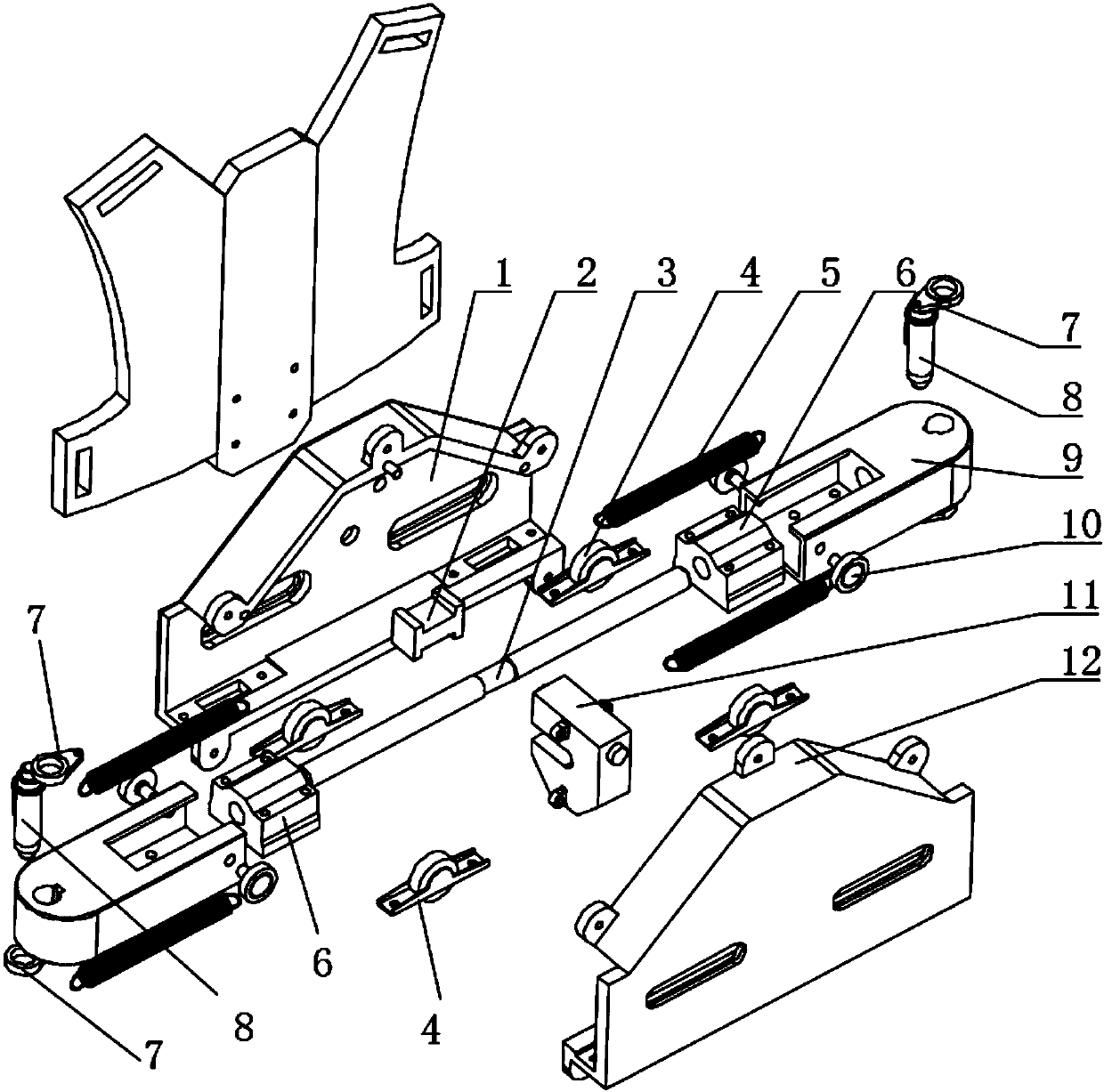
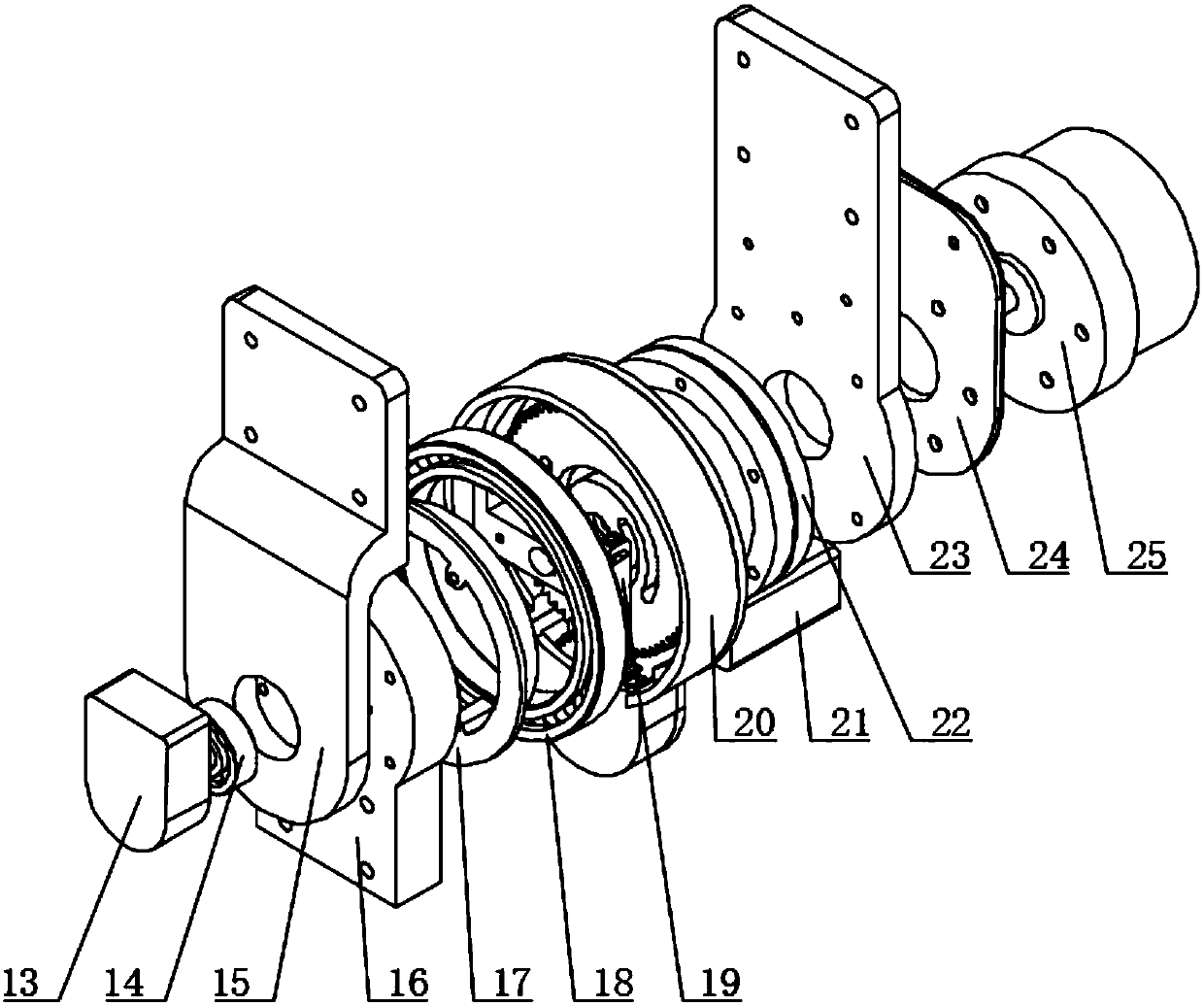
Variable stiffness lower limb external skeleton robot
ActiveCN107773384ASmooth movementAdaptableProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesVariable stiffnessThigh
The invention discloses a variable stiffness lower limb external skeleton robot which comprised a back plate, a flexible waist adjusting mechanism, hip joint mechanisms, thighs, knee joint mechanisms,shanks, ankle joint mechanisms, two driving degrees of freedom and three driven degrees of freedom. A driving control system is arranged on the back plate, the flexible waist adjusting mechanism is fixed with the back plate and connected with the thighs through the hip joint mechanisms, and the thighs are connected with the shanks and the ankle joint mechanisms through the knee joint mechanisms.According to the variable stiffness lower limb external skeleton robot, driving is performed by the aid of a variable stiffness driver, so that the robot is smooth in movement and high in safety, physical structures of lower limbs of human bodies can be effectively fitted by the aid of the two driving degrees of freedom and the three driven degrees of freedom, length adjusting mechanisms are arranged at the waists, the thighs and the shanks, so that the robot can adapt to physical sizes of different users, and the robot is wearable and has flexibility in the movement by the aid of the flexiblewaist adjusting mechanism. The robot can be applied and popularized in aspects of rehabilitation training, boosting and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Prosthetic foot with energy transfer
A prosthetic foot device with variable stiffness response includes a variable energy transfer mechanism disposed between first and second foot members to transfer a variable amount of energy between the members during use. A chamber is associated with one of the first and second foot members, and a piston is associated with another of the first and second foot members and is movable in the chamber. At least one aperture is formed between the piston and the chamber. A variable viscosity fluid is disposed in the chamber and displaceable through the at least one aperture between the piston and the chamber to allow fluid to flow within the chamber between opposite sides of the piston. The variable viscosity fluid has a viscosity that is variable to vary an ability of the variable viscosity fluid to flow through the at least one aperture.
Owner:FREEDOM INNOVATIONS INC
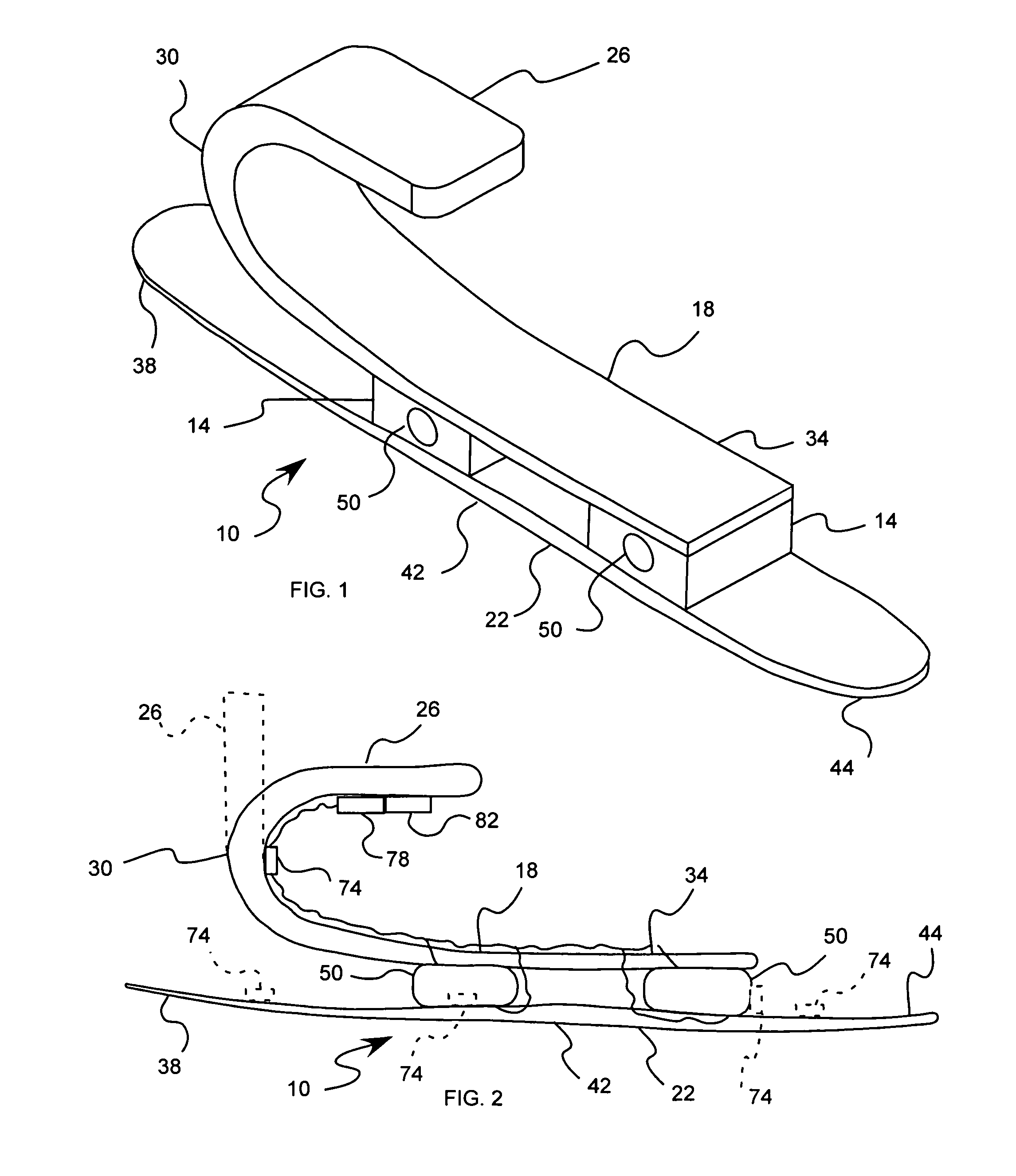
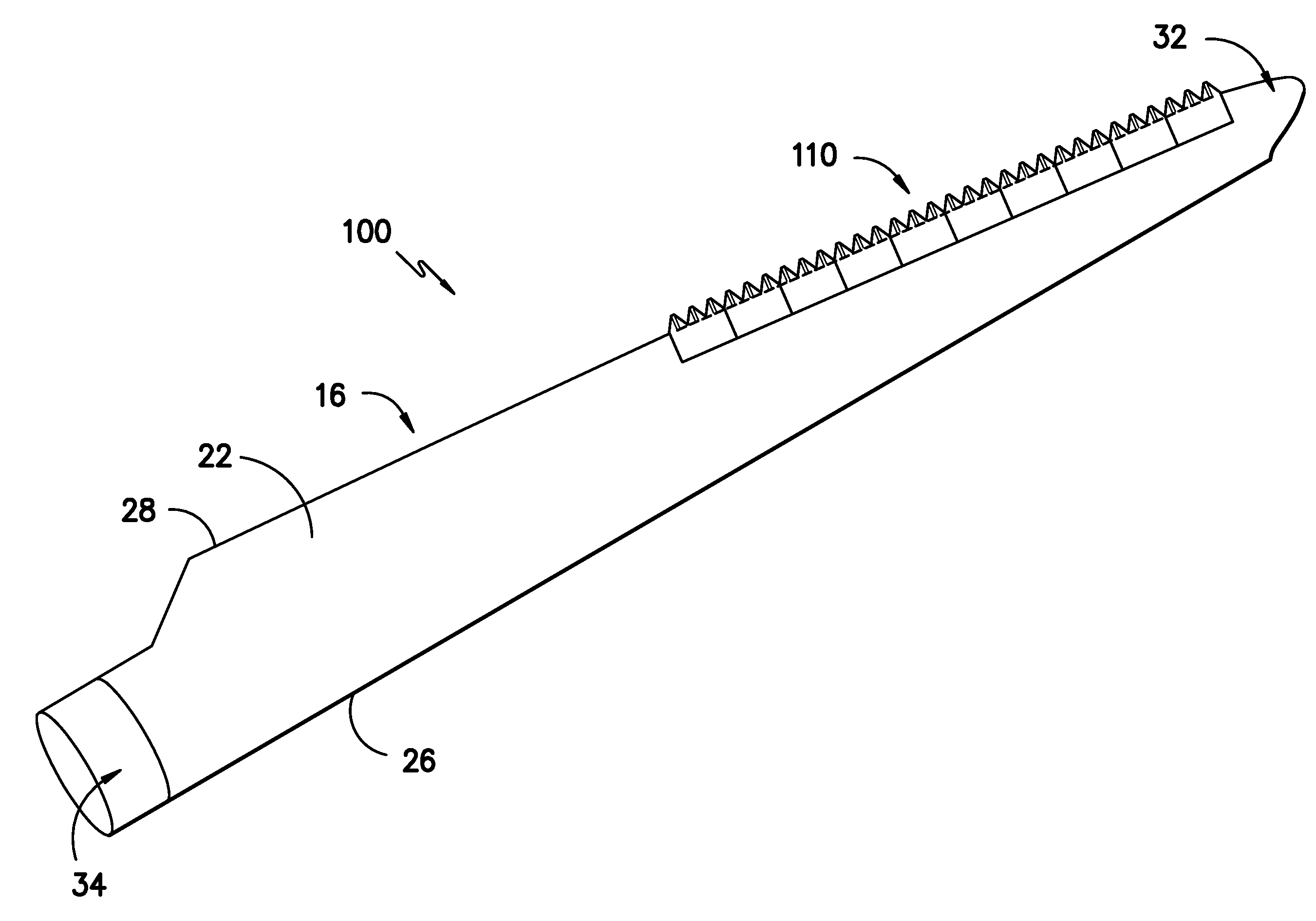
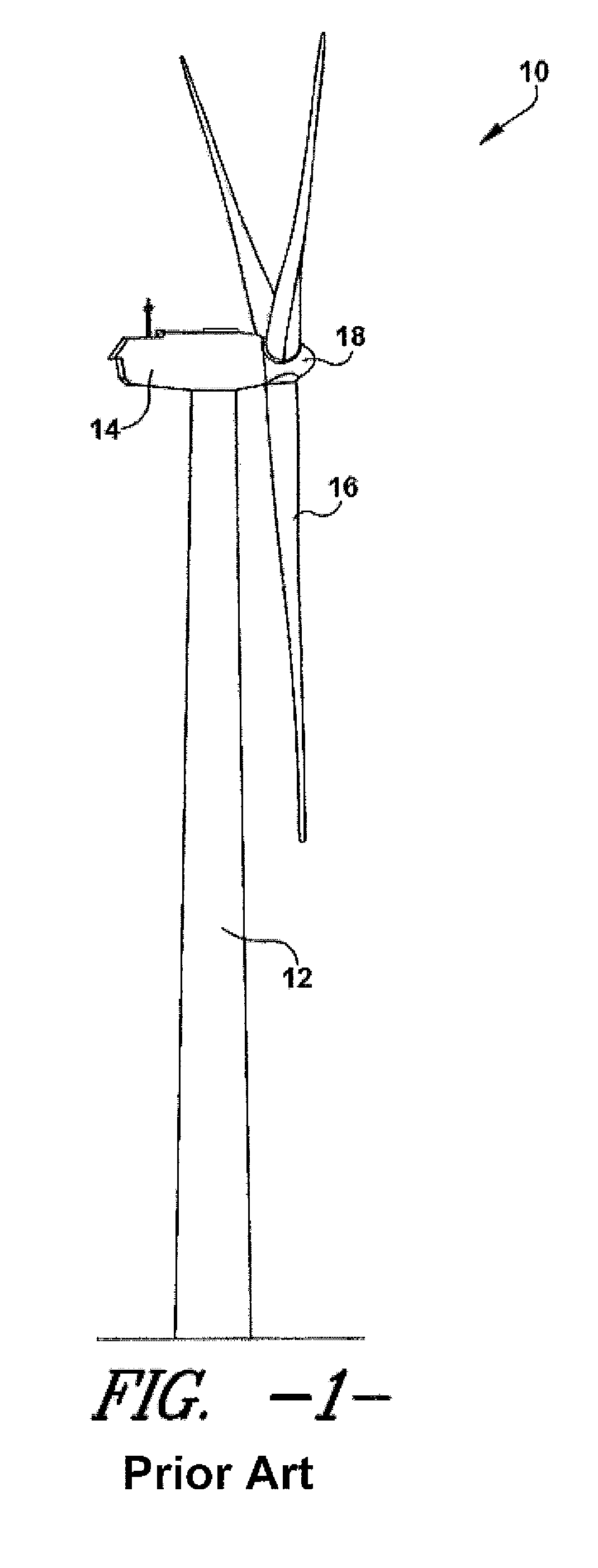
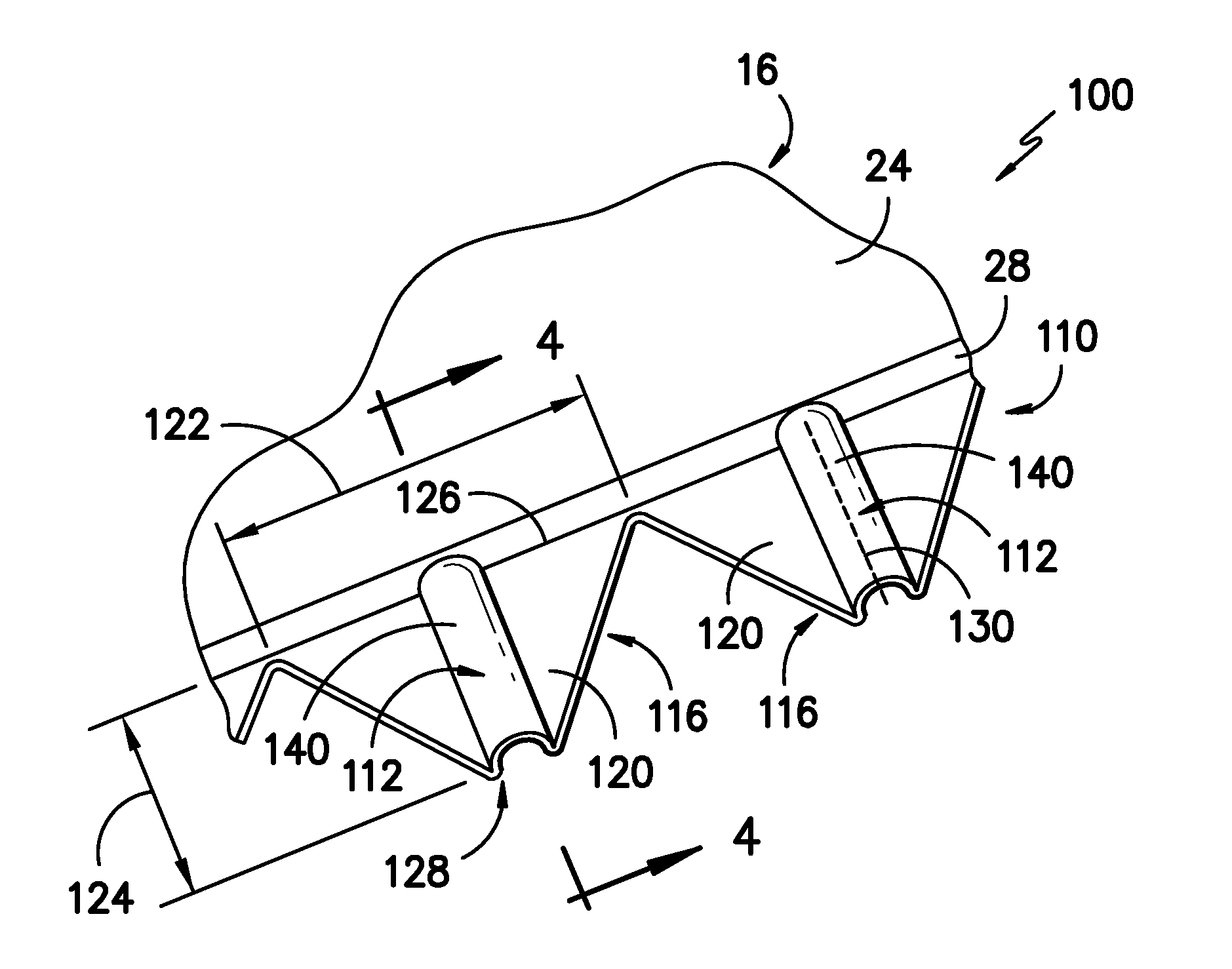
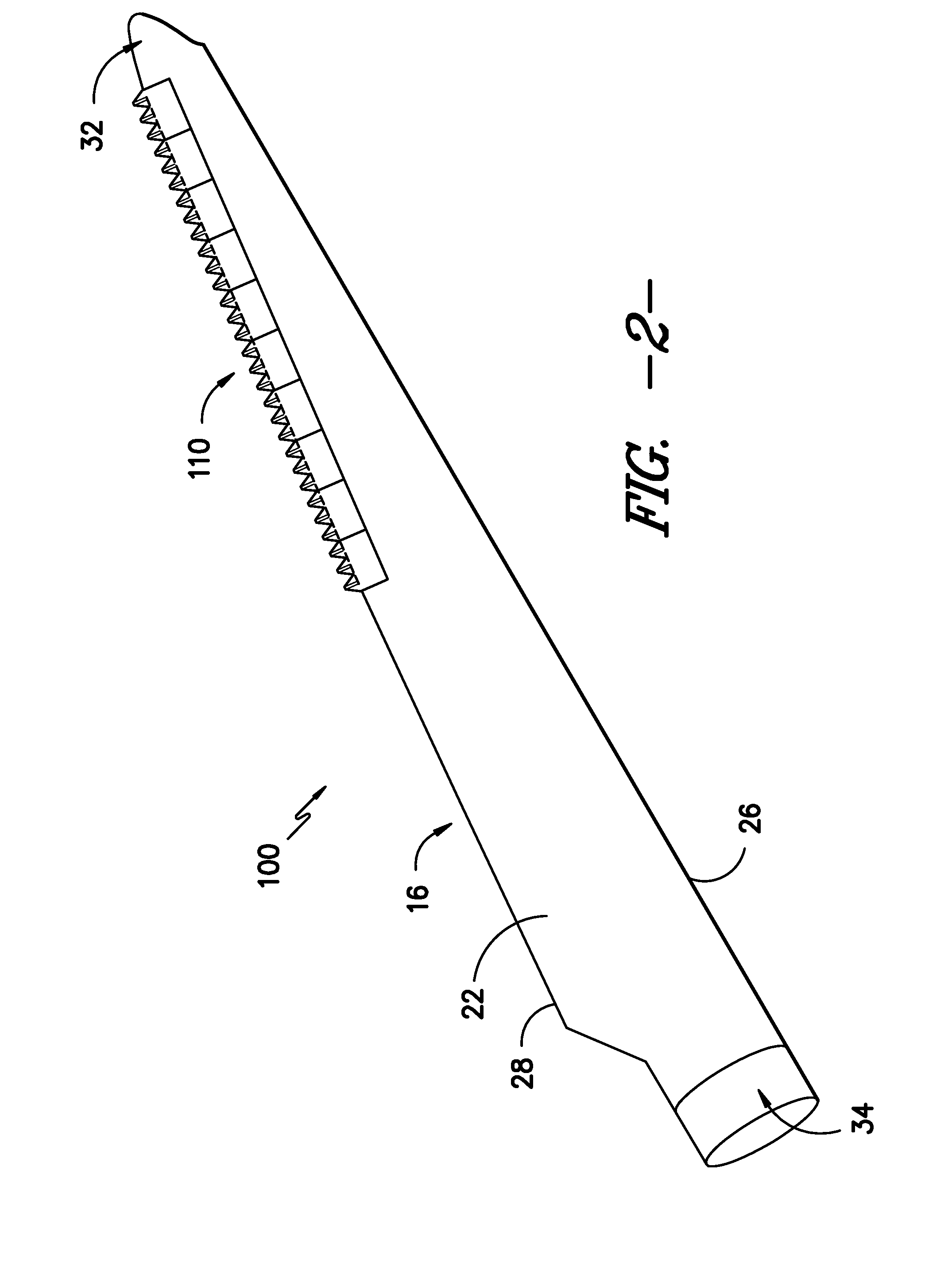
Noise reducer for rotor blade in wind turbine
A rotor blade assembly for a wind turbine is disclosed. The rotor blade assembly includes a rotor blade having surfaces defining a pressure side, a suction side, a leading edge, and a trailing edge extending between a tip and a root. The rotor blade assembly further includes a noise reducer configured on a surface of the rotor blade. The noise reducer includes a plurality of reinforcing members and a plurality of noise reduction features. Each of the plurality of reinforcing members extends outwardly with respect to the rotor blade. Each of the plurality of noise reduction features is connected to one of the plurality of reinforcing members and defines a width. Each of the plurality of reinforcing members causes the connected noise reduction feature to have a variable stiffness throughout at least a portion of the width of the connected noise reduction feature.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Balloon catheter having a shaft with a variable stiffness inner tubular member
ActiveUS7273485B2Reduce wall thicknessIncrease wall thicknessStentsBalloon catheterVariable stiffnessAxial compression
A catheter having an elongated shaft and a balloon on a distal shaft section, the elongated shaft comprising an outer tubular member, and an inner tubular member which has a bonded portion along which an outer surface of the inner tubular member is bonded to an inner surface of the outer tubular member. The inner tubular member has a proximal portion proximal to the bonded portion, and a distal portion distal to the bonded portion with higher axial compression stiffness and column strength than the proximal portion thereof. The catheter has improved traceability, axial collapse resistance, pushability, and crossability, for improved ability to position the balloon at a desired location in a patient's body lumen.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Noise reducer for rotor blade in wind turbine
A rotor blade assembly for a wind turbine is disclosed. The rotor blade assembly includes a rotor blade having surfaces defining a pressure side, a suction side, a leading edge, and a trailing edge extending between a tip and a root. The rotor blade assembly further includes a noise reducer configured on a surface of the rotor blade. The noise reducer includes a plurality of reinforcing members and a plurality of noise reduction features. Each of the plurality of reinforcing members extends outwardly with respect to the rotor blade. Each of the plurality of noise reduction features is connected to one of the plurality of reinforcing members and defines a width. Each of the plurality of reinforcing members causes the connected noise reduction feature to have a variable stiffness throughout at least a portion of the width of the connected noise reduction feature.
Owner:LM WIND POWER US TECH APS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com